Patents
Literature
385results about How to "Reduce repair" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Device and method for forming hands of randomly arranged cards
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for moving playing cards from a first group of cards into plural hands of cards, wherein each of the hands contains a random arrangement of the same quantity of cards. The apparatus comprises a card receiver for receiving the first group of cards, a single stack of card-receiving compartments generally adjacent to the card receiver, the stack generally vertically movable, an elevator for moving the stack, a card-moving mechanism between the card receiver and the stack, and a microprocessor that controls the card-moving mechanism and the elevator so that an individual card is moved into an identified compartment. The number of compartments receiving cards and the number of cards moved to each compartment may be selected.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
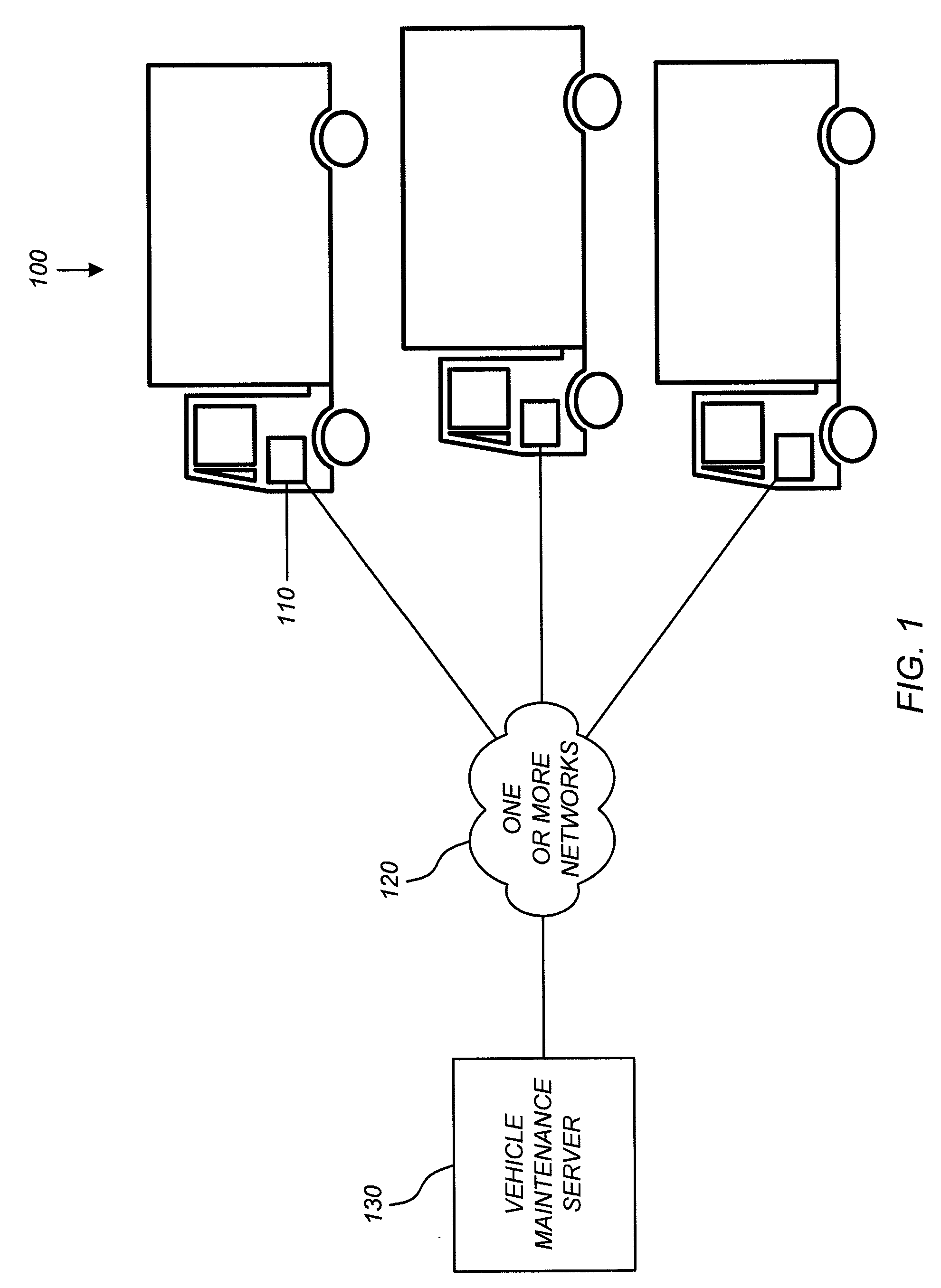
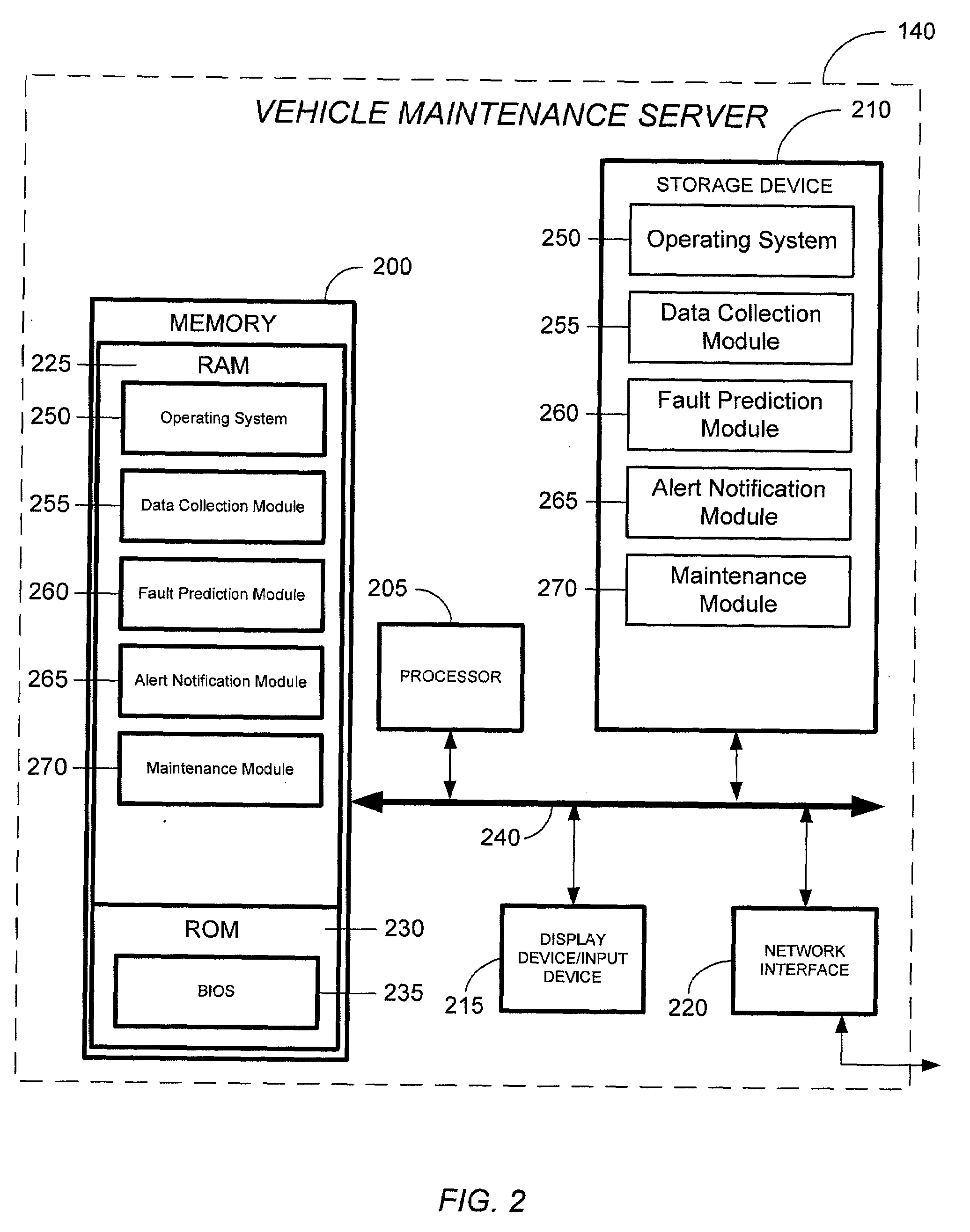
Vehicle maintenance systems and methods
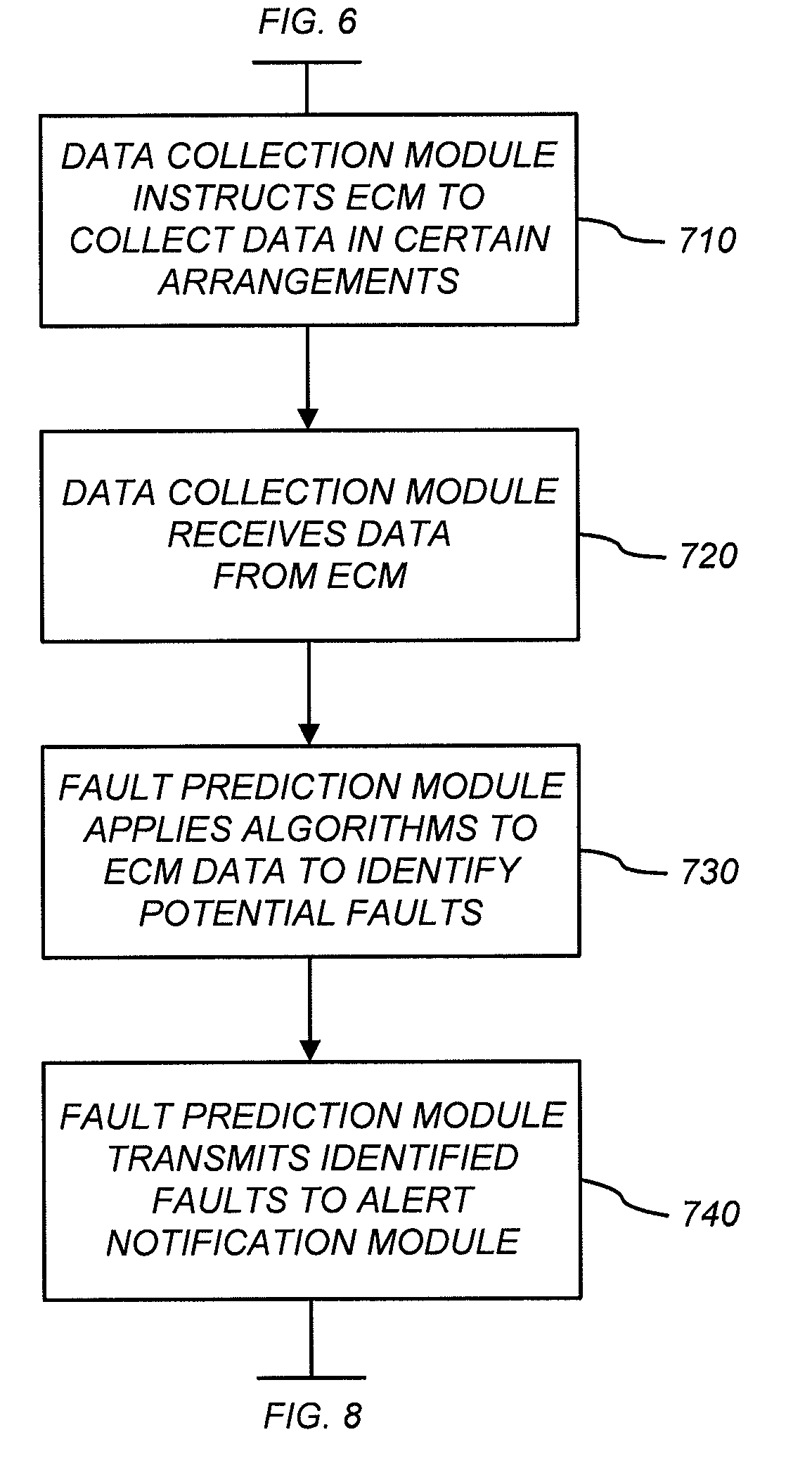
ActiveUS20090254240A1Reduce in quantityImprove performanceVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDriver/operatorIn vehicle
A system that enables a fleet of vehicles to be maintained is provided. The disclosed system allows a fleet operator to review the history of the vehicles in the fleet along with vehicle sensor data to identify earmarks in the vehicle sensor data that are predictive of faults that the vehicles have experienced. The operator develops statistical algorithms that can detect an earmark in vehicle sensor data. The system then collects vehicle sensor data and applies the statistical algorithms the vehicle data to determine if a potential fault is going to occur in a vehicle. In response to determining that a potential fault is going to occur, the disclosed system automatically alerts the vehicle driver, automatically schedule a maintenance visit, automatically check the fleet inventory for components required for a maintenance visit and order unavailable components, and automatically dispatch the components to the mechanic.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
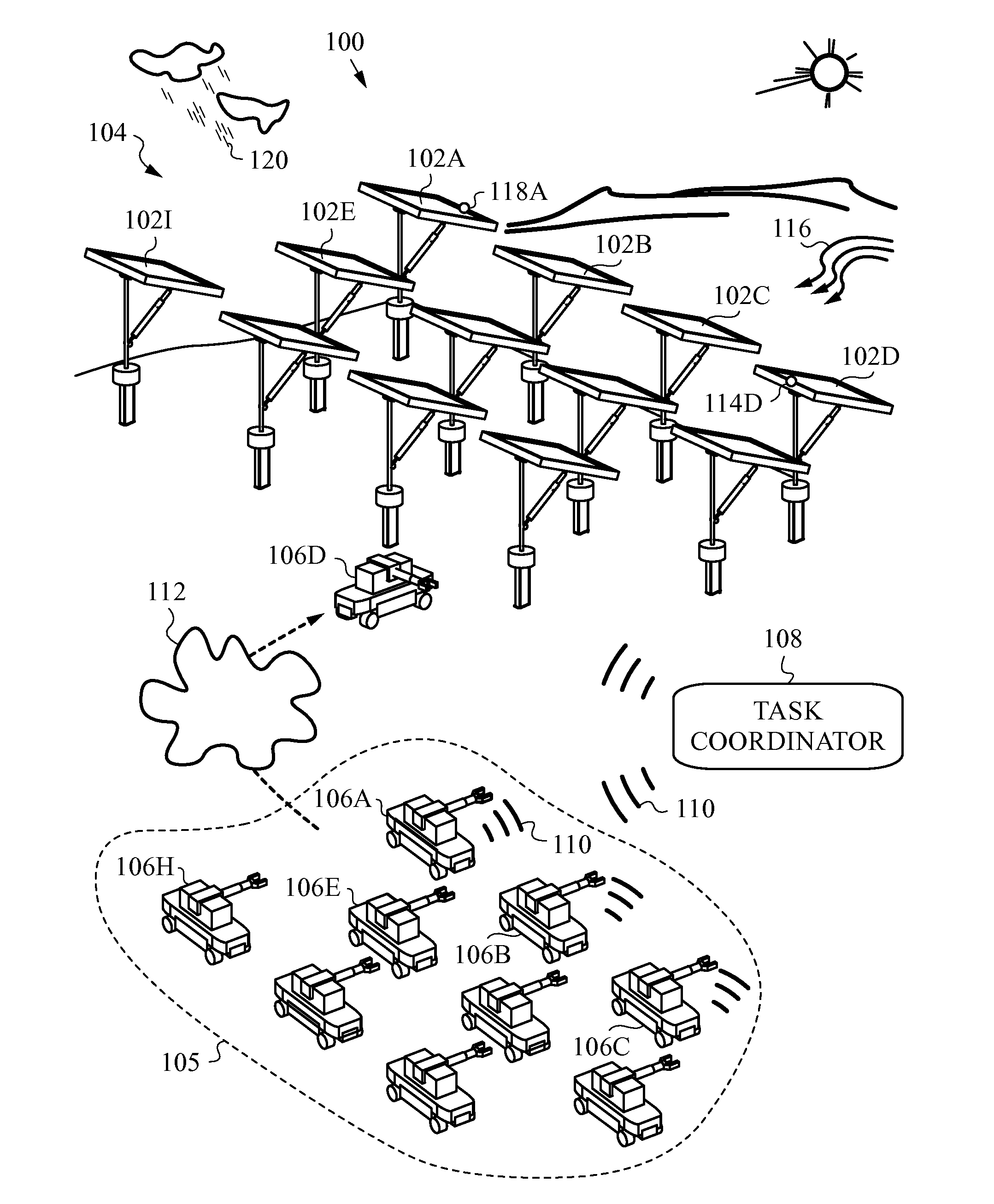
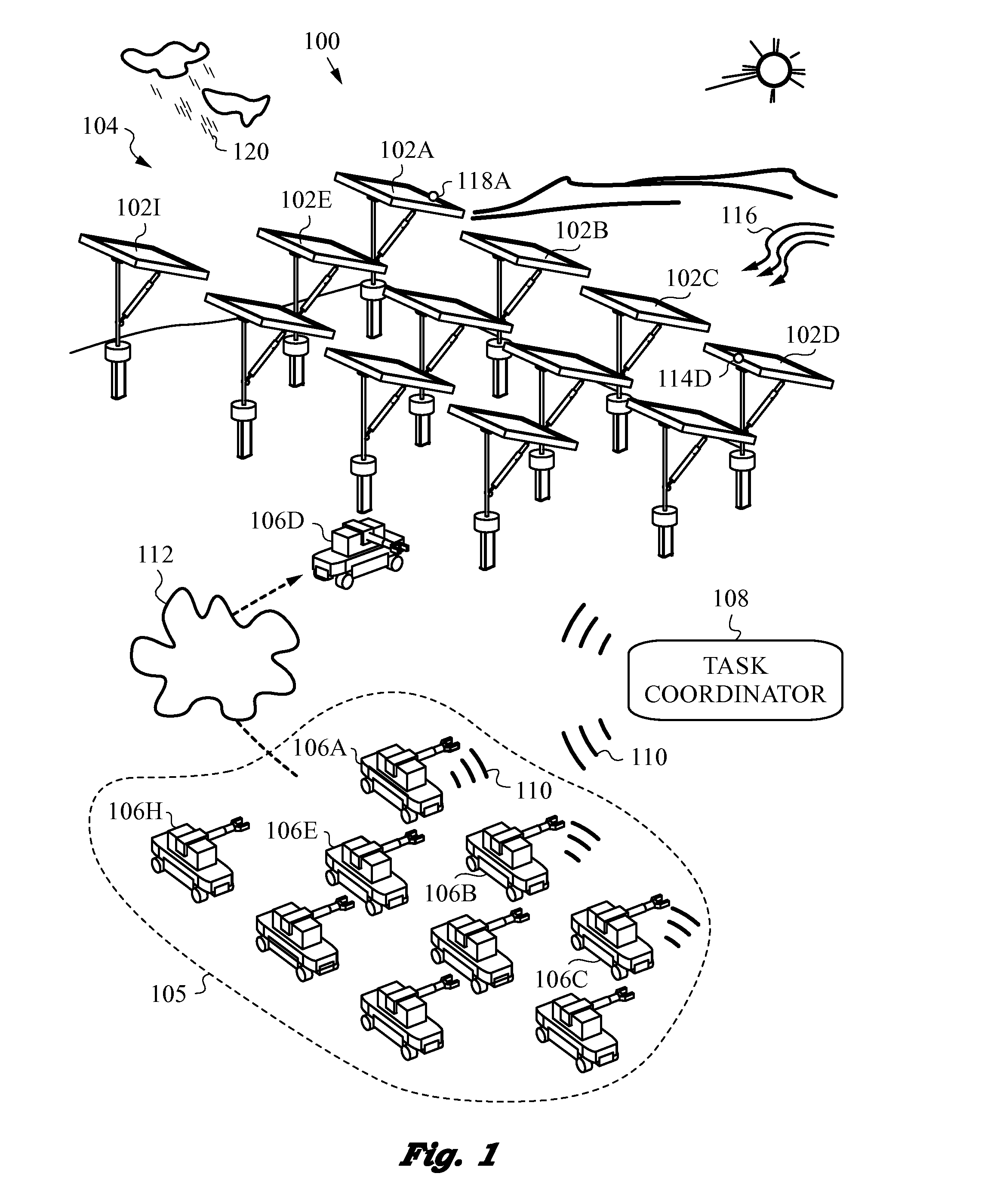
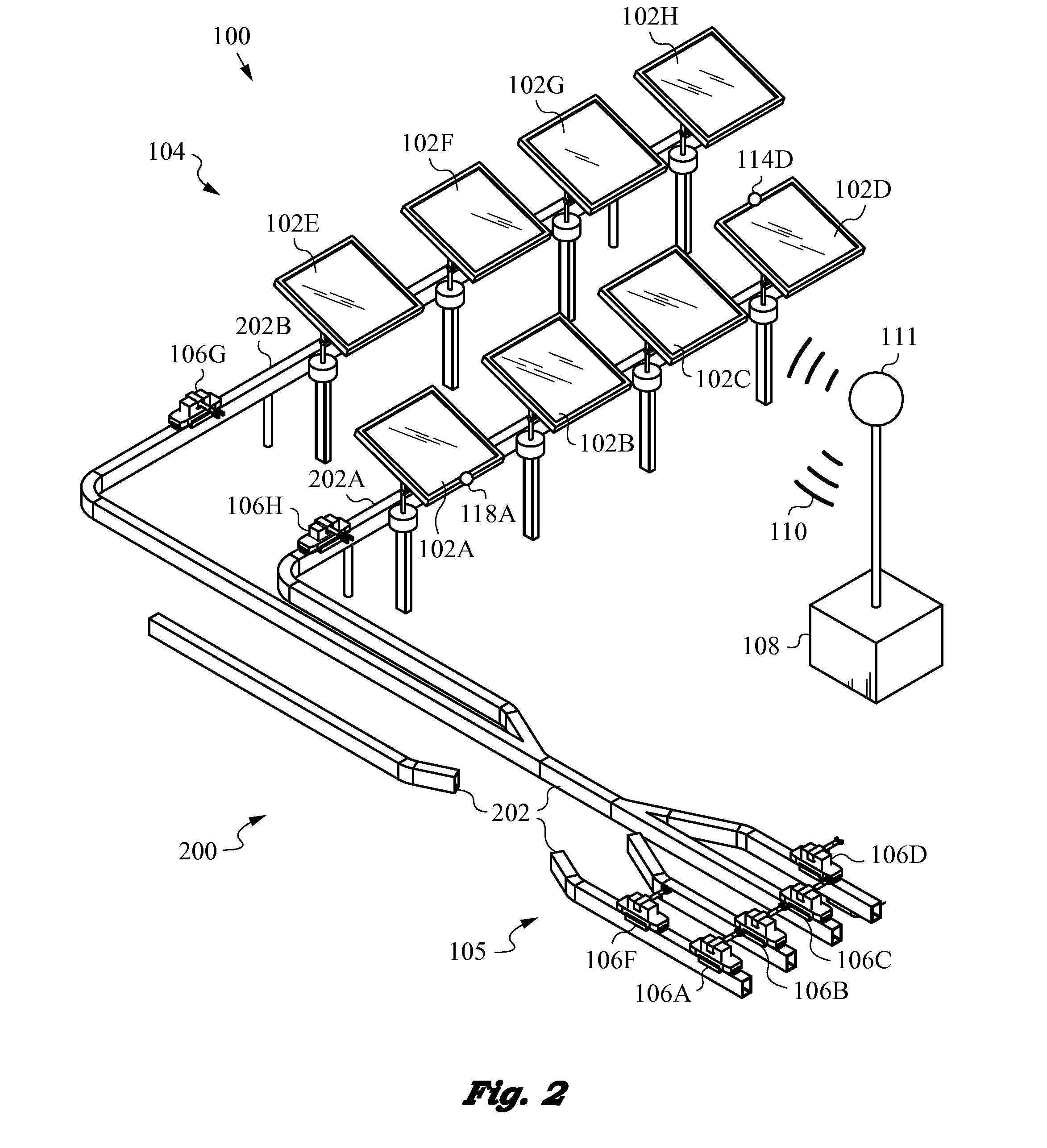
Solar Tracking System Employing Multiple Mobile Robots
ActiveUS20150073594A1Highly-available, reliable and fault-tolerantLow costSolar heating energyProgramme-controlled manipulatorMobile robotEngineering
The present invention relates to a highly-available and fault-tolerant solar tracking system and the process required to manage such a system. A fleet of multiple, redundant mobile robots managed by a task coordinator is deployed to track solar panels in a solar farm in alignment with the sun. Each robot has a control unit for engaging with a coupler connected to one or multiple solar panels and adjusting their orientation, as well as communicating with the task coordinator to receive tasks. The task coordinator senses various events such as robot failure / deterioration, as well as various environmental conditions, and sends tasks reconciled with event types. The system is highly-available and fault-tolerant as it remains operational as long as there is one operational robot. The task coordinator assigns tasks to the mobile robots so as to optimize battery life or other factors, such as, e.g., overall maintenance costs across the fleet.
Owner:TESLA INC
Method and apparatus for dermatological treatment
ActiveUS7331953B2Easy to processSimple to useSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyWound healingTissue remodeling
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
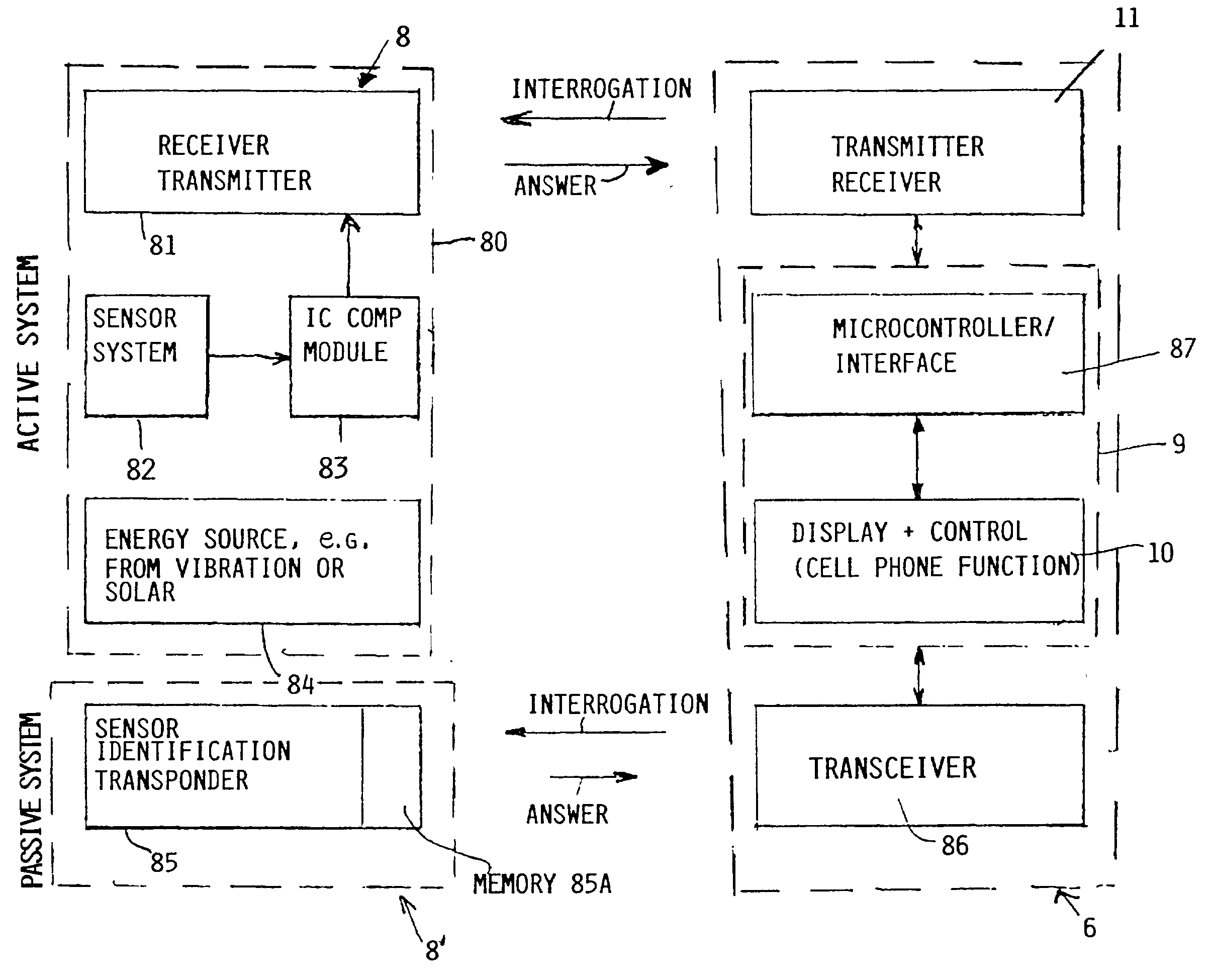
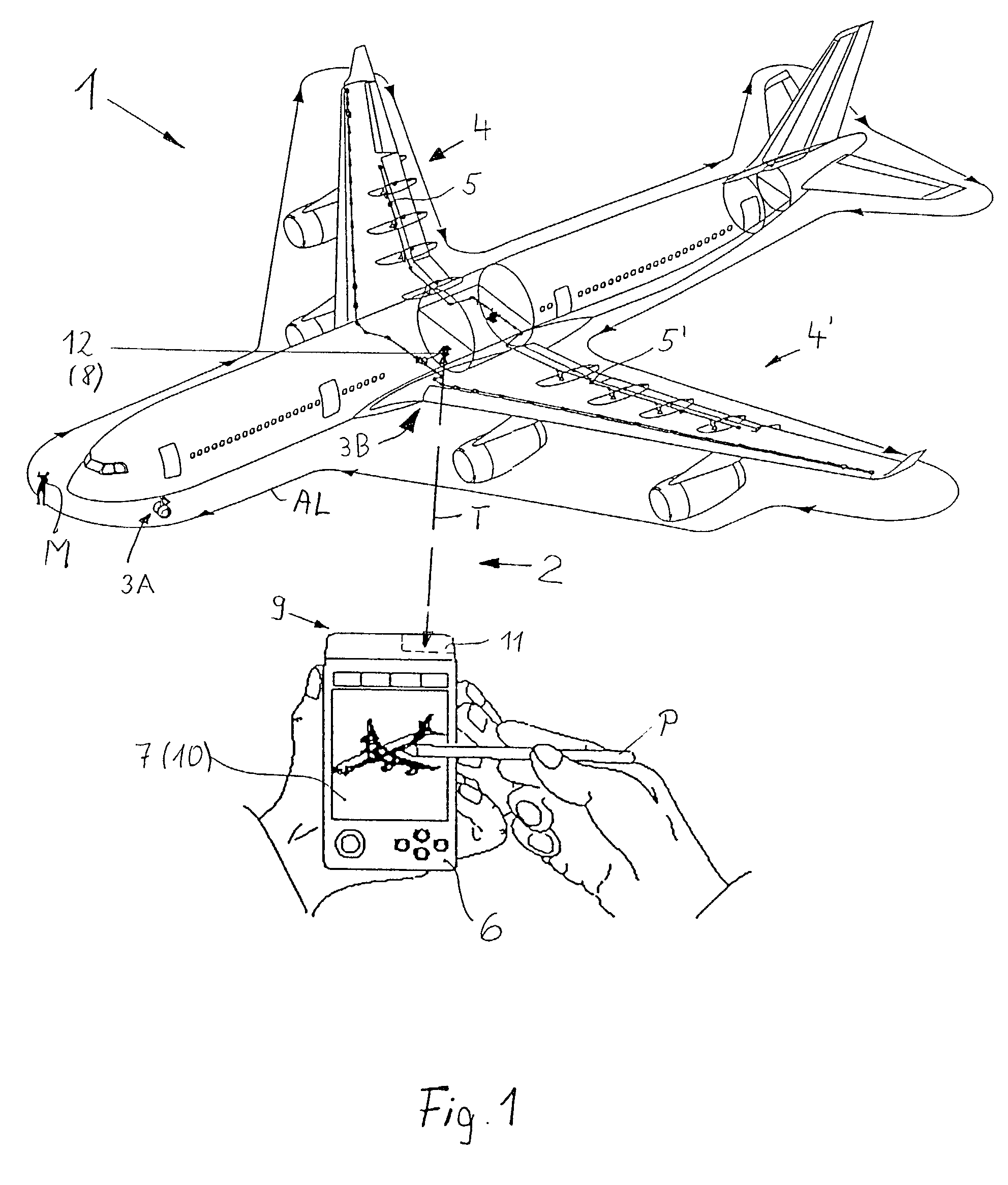
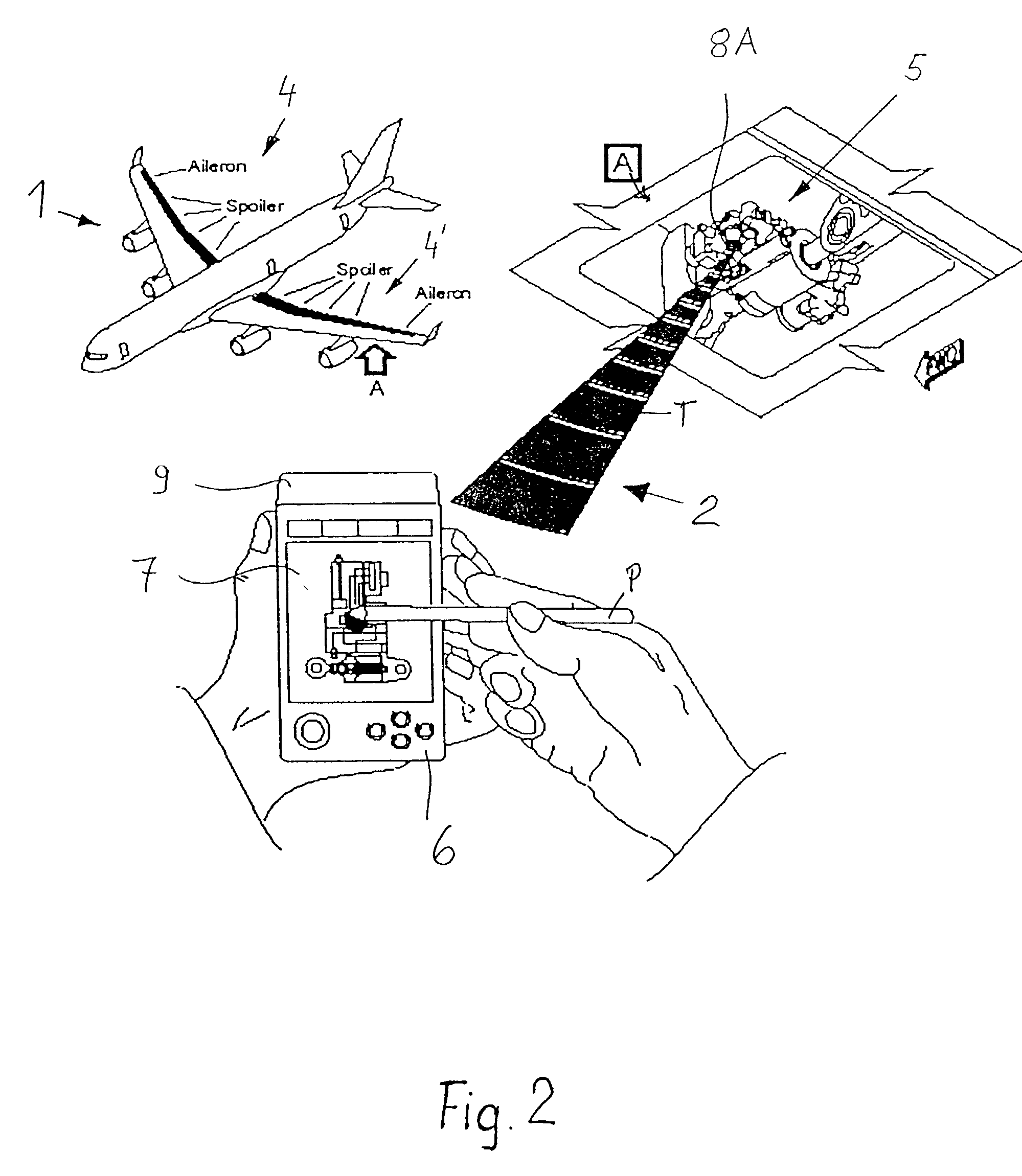
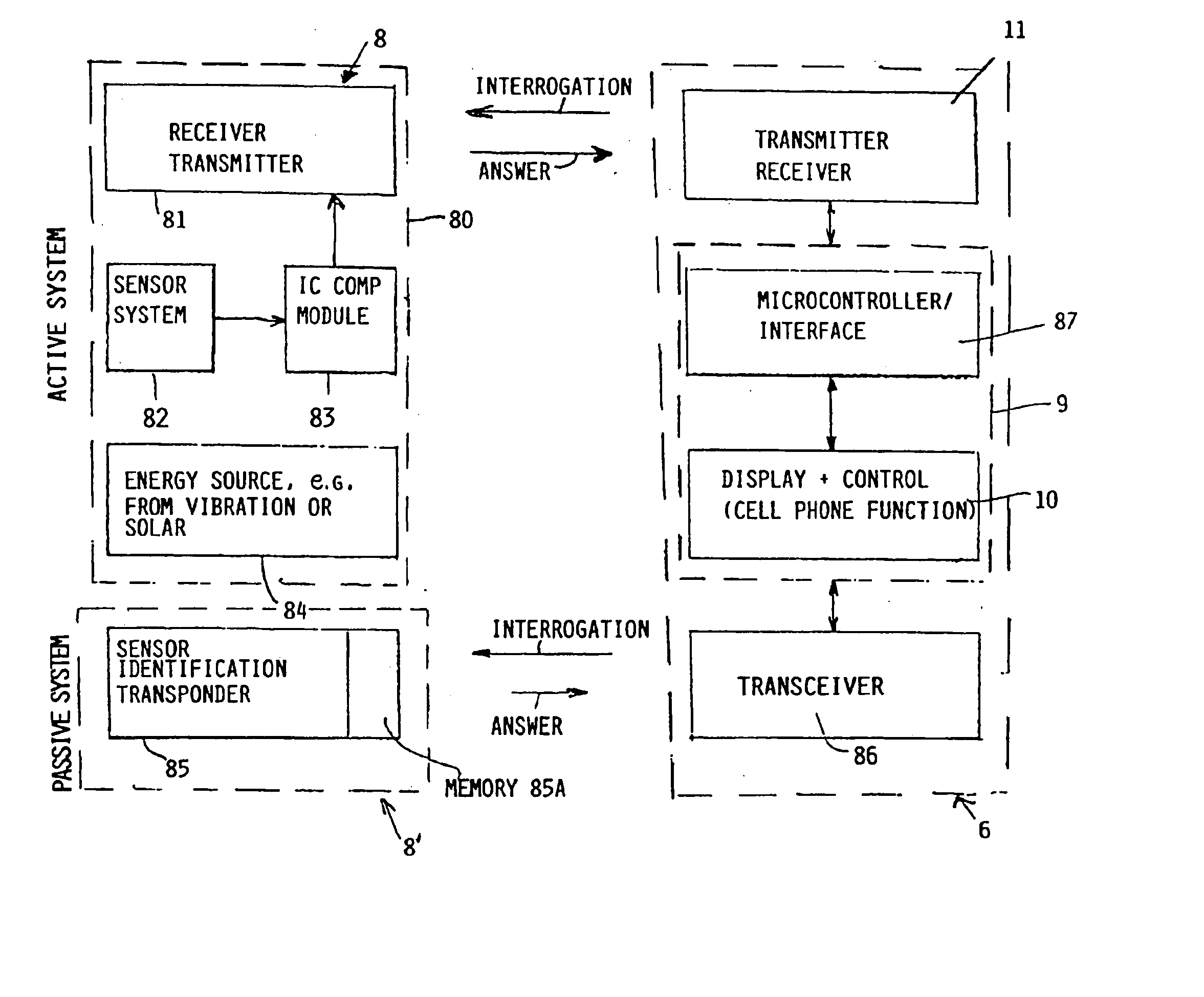
System and method for diagnosing aircraft components for maintenance purposes
InactiveUS20030083794A1Easy maintenanceAvoid replacementVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic systemSignal processing
Aircraft maintenance and repair work is facilitated, especially for a commercial aircraft, by a diagnostic system and method, wherein an aircraft component or assembly of components is monitored by at least one sensor which produces and preferably also stores component status information. Respective status information signals are transmitted, preferably in a wireless manner, from a transmitter of the sensor to a receiver of a signal processing unit which provides status information on a display screen. The status information signals are preferably processed and evaluated with reference to rated maintenance and repair reference information to provide instructions as to what needs to be done where and when for a maintenance or repair. The sensor or sensors may operate during flight and the respective stored information is then processed and used on the ground.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
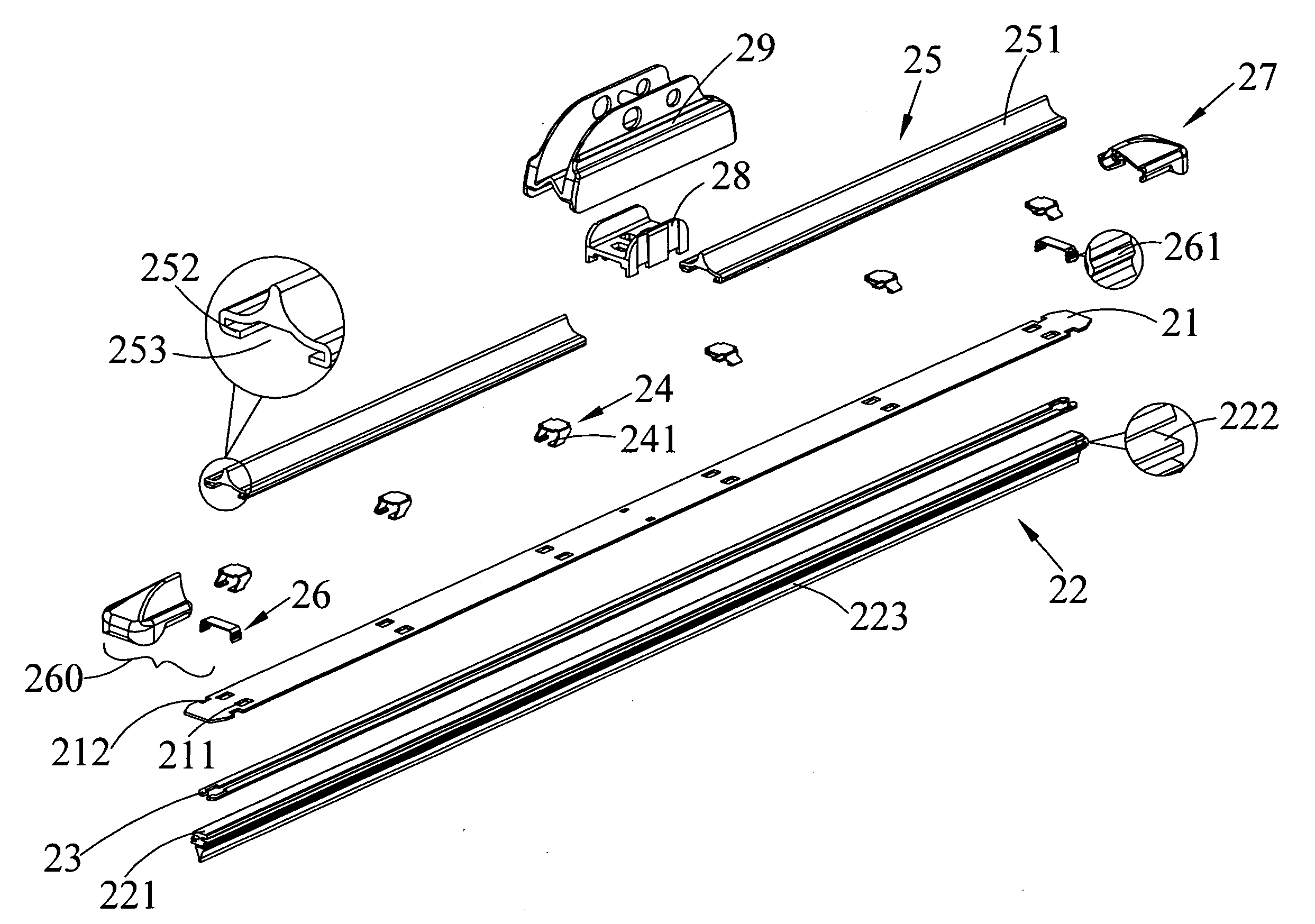
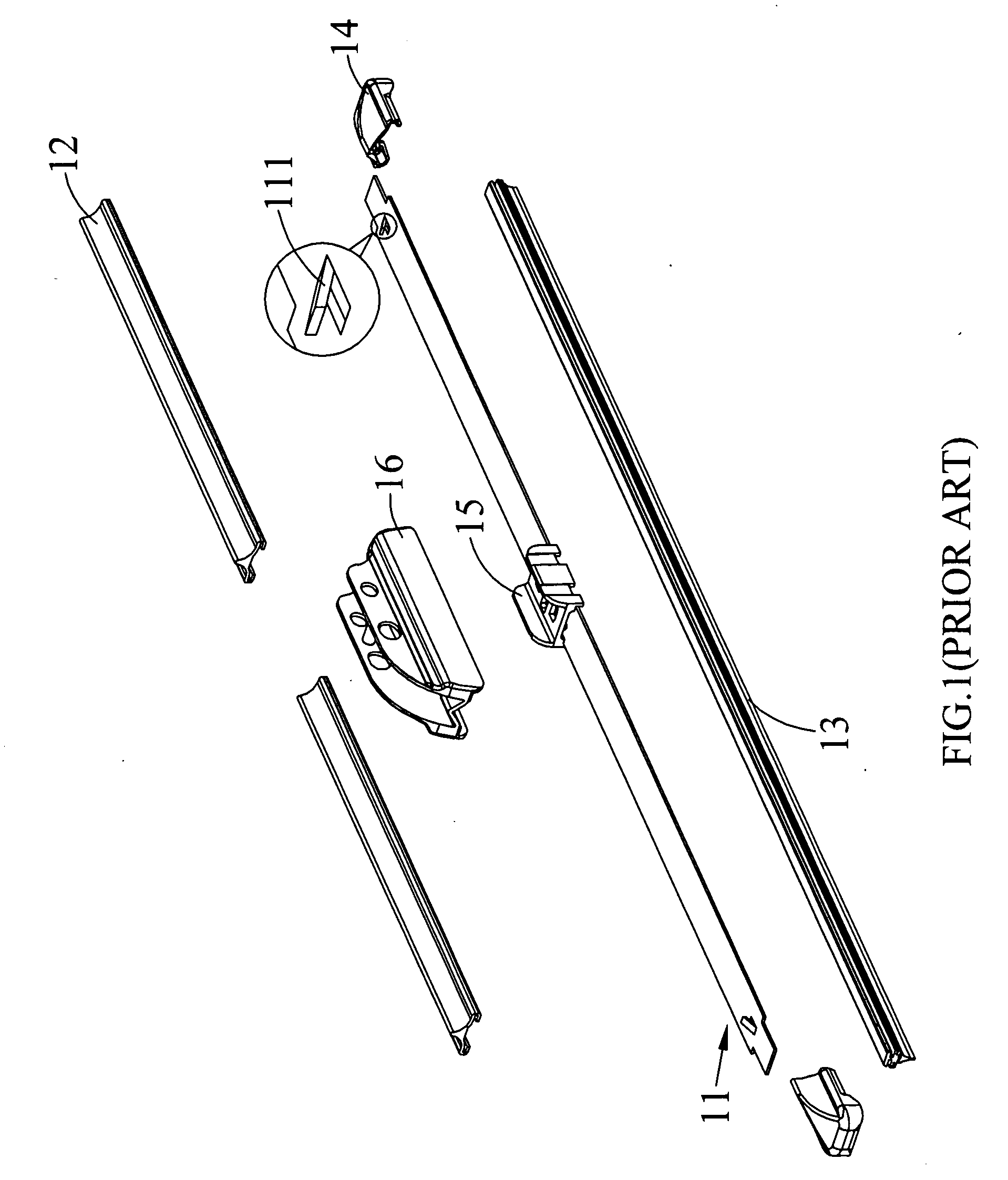
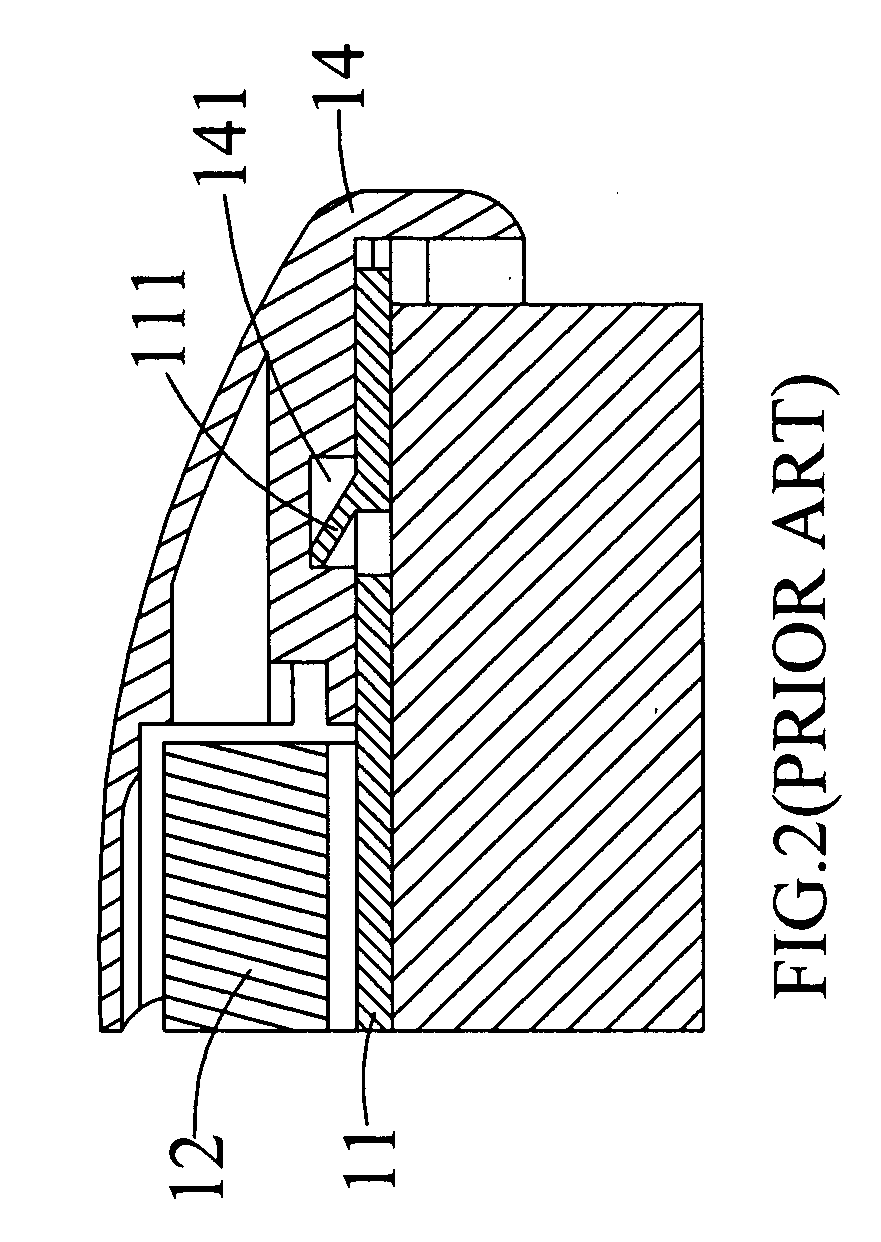
Windshield wiper blade structure
InactiveUS20100242204A1Easy to disassembleReduce maintenanceWindow cleanersVehicle cleaningEngineeringWindshield
A windshield wiper blade structure includes a support strip, a wiper strip disposed below the support strip, two flexible strips set on two sides of the wiper strip, a set of clamping elements downward extended through holes formed on the support strip to clamp the support strip, the flexible strips and the wiper strip together, two wind deflector strips disposed on a top of the support strip, two elastic locking elements each including two elastic arms separately fitted near two opposite ends of the support strip, and two end caps detachably connected to the two ends of the support strip and each internally provided with two notches engaged with the elastic arms. By compressing the elastic arms toward each other to disengage them from the notches, the end caps can be removed from the support strip to allow replacement of the wiper strip with a new one.
Owner:UNIPOINT ELECTRIC MANUFACTURING CO LTD
Method and apparatus for dermatological treatment
ActiveUS20050222555A1Treatment safetyRepair and alleviates skin defectSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyWound healingTissue remodeling
The present invention provides improved methods and apparatus for skin treatment. The apparatus includes multiple sources of optical energy or several blades that are scanned along a region of skin to form micro-line patterns of damaged tissue. The micro-lines are small in at least one dimension, having a width of less than about 1 mm, and the wounded regions promote beneficial results by stimulation of wound healing and tissue remodeling.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and apparatus for dermatological treatment
ActiveUS20080058784A1Easy to processSimple to useSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyWound healingTissue remodeling
The present invention provides improved methods and apparatus for skin treatment. The apparatus includes multiple sources of optical energy or several blades that are scanned along a region of skin to form micro-line patterns of damaged tissue. The micro-lines are small in at least one dimension, having a width of less than about 1 mm, and the wounded regions promote beneficial results by stimulation of wound healing and tissue remodeling.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
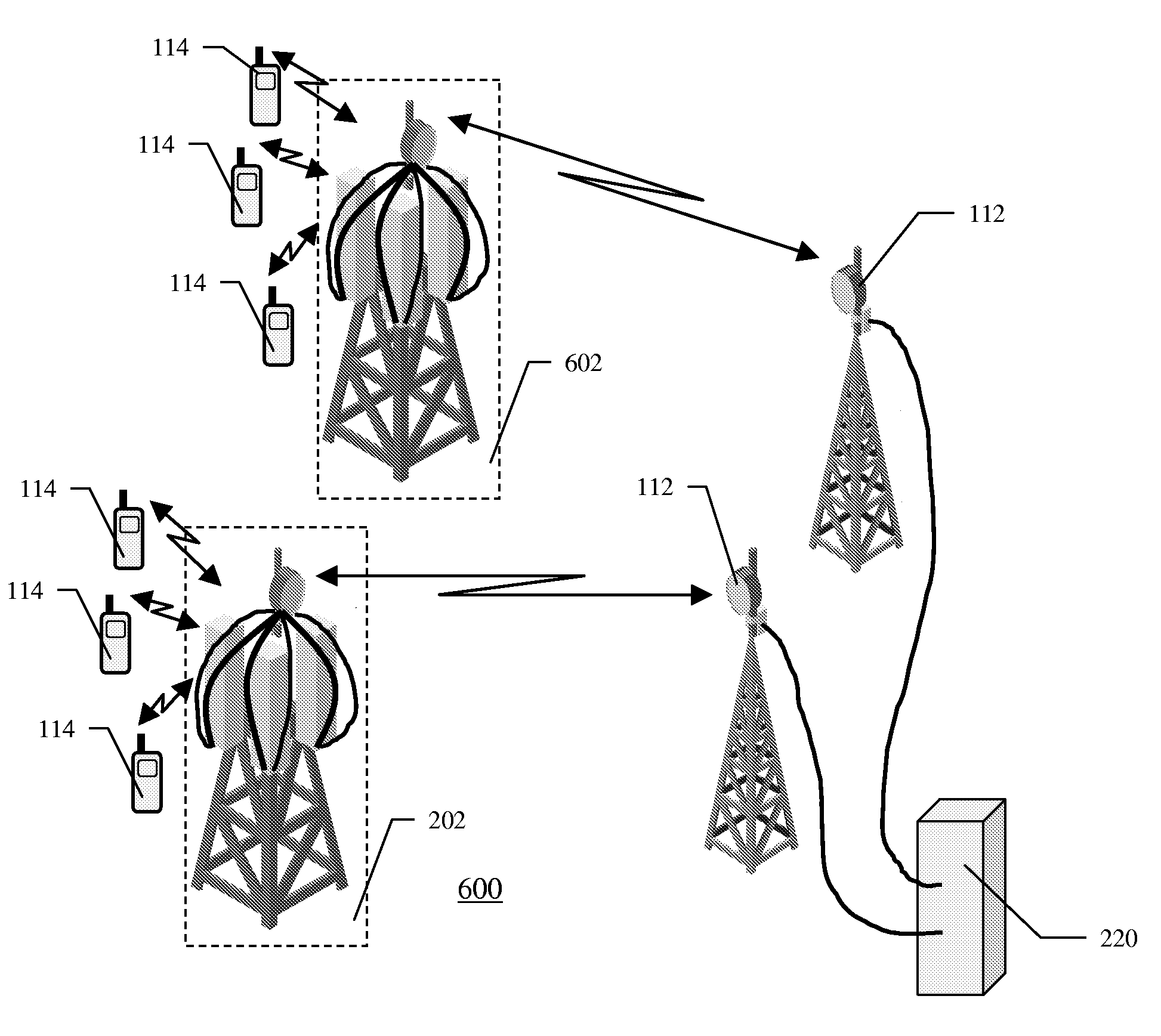
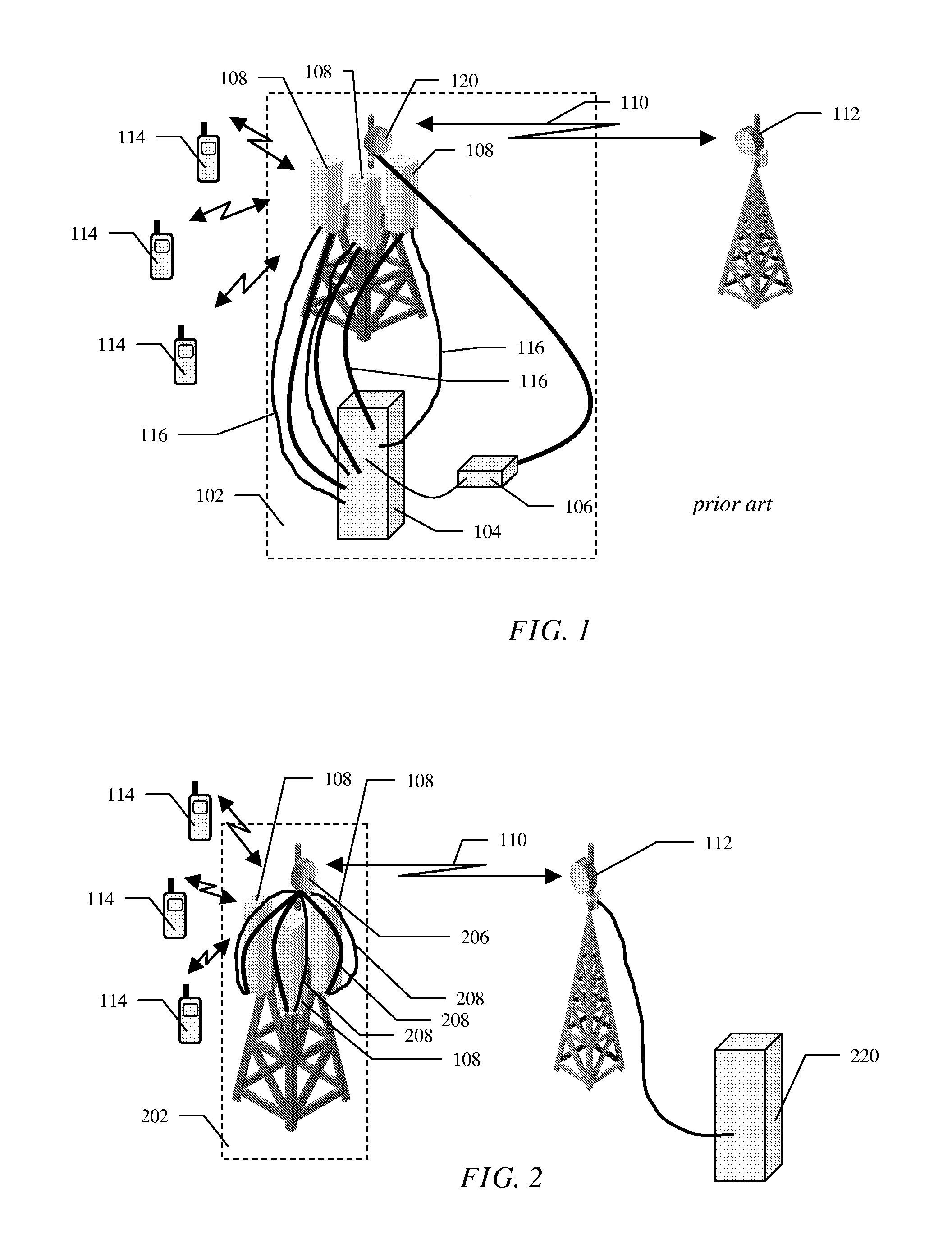
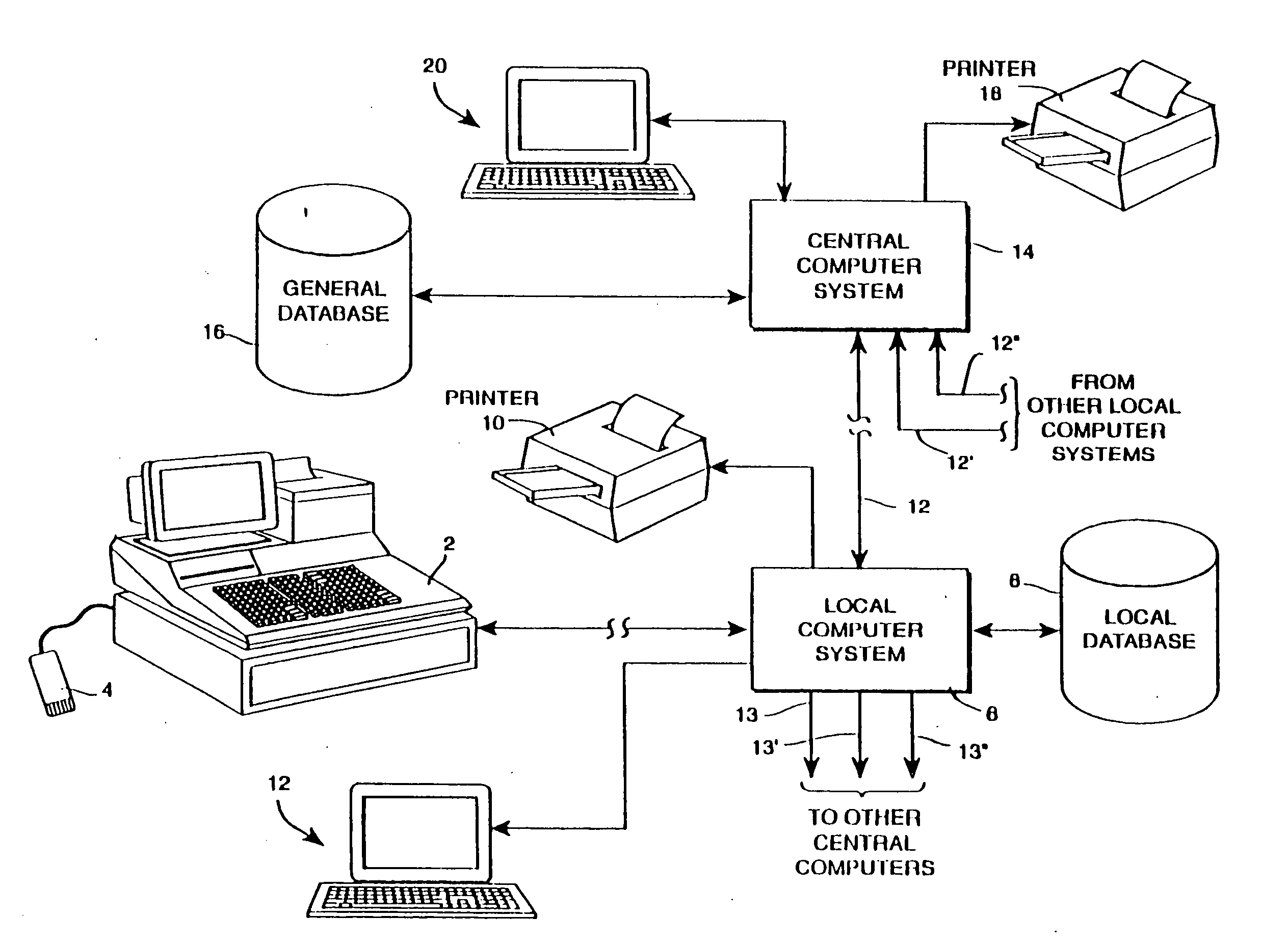
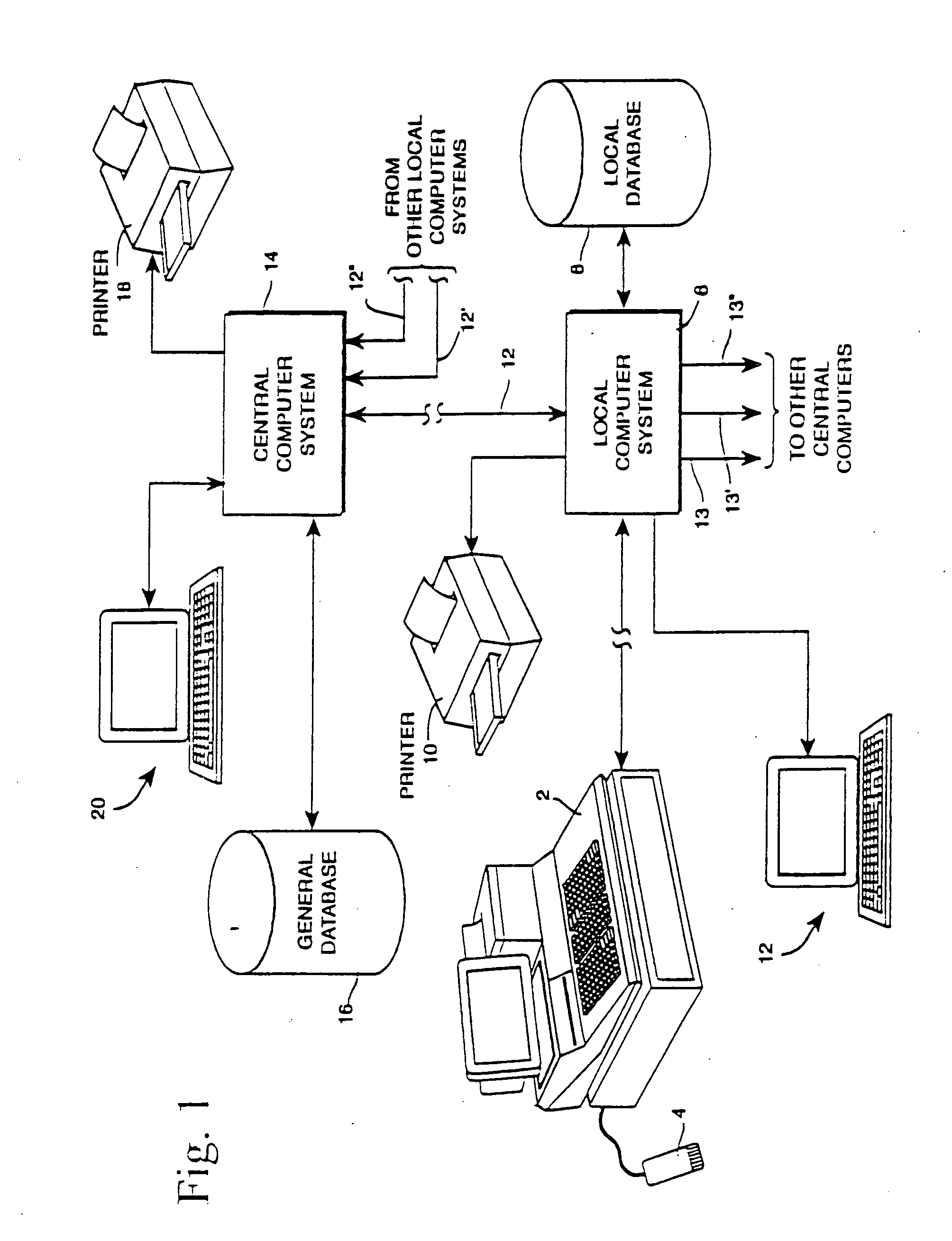
Base transceiver stations and method of operating thereof
InactiveUS20100056205A1Lower capital expenditureMitigate, alleviate or eliminate oneSubstation equipmentTransmissionTransceiverEngineering
A base transceiver station (202) for use in a wireless telecommunications system comprising at least one radio transceiver of a first type connected to an antenna of a first type (108) for providing wireless access for remote subscriber units (114) and a radio transceiver of a second type connected to an antenna of a second type (206). The radio transceivers of the first type are operably connected via cables (208), in an intermediate 10 frequency domain, to the transceiver of the second type.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
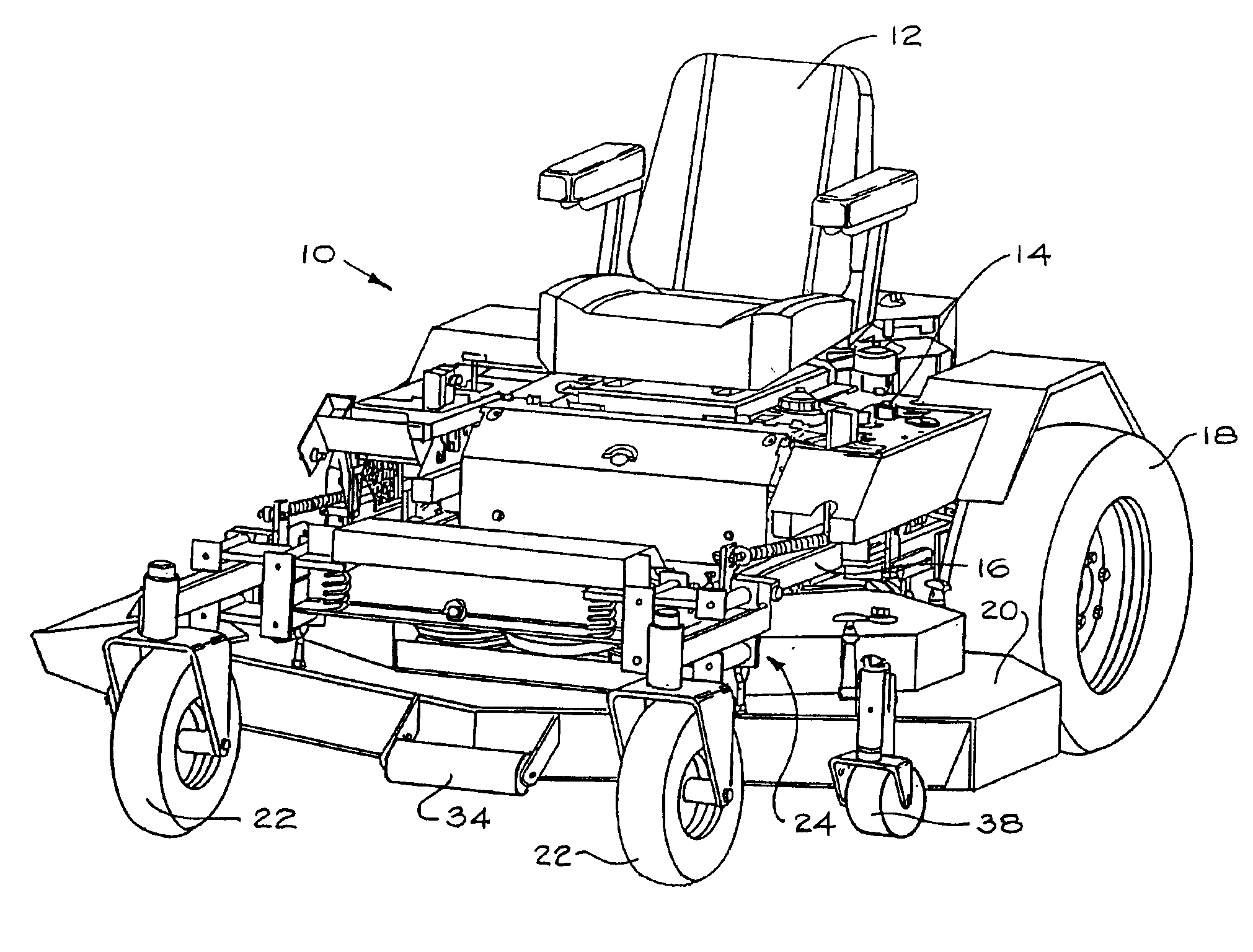
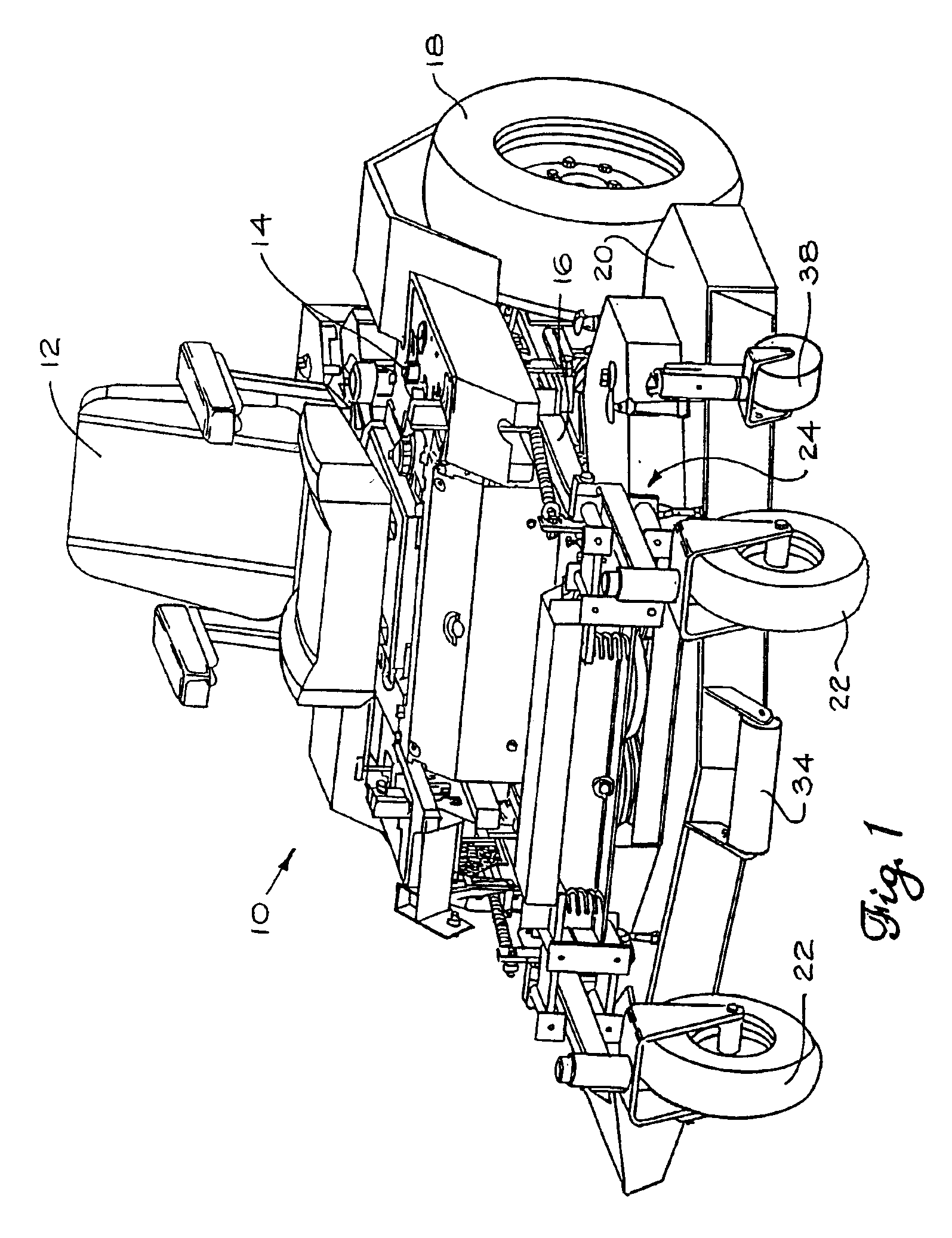
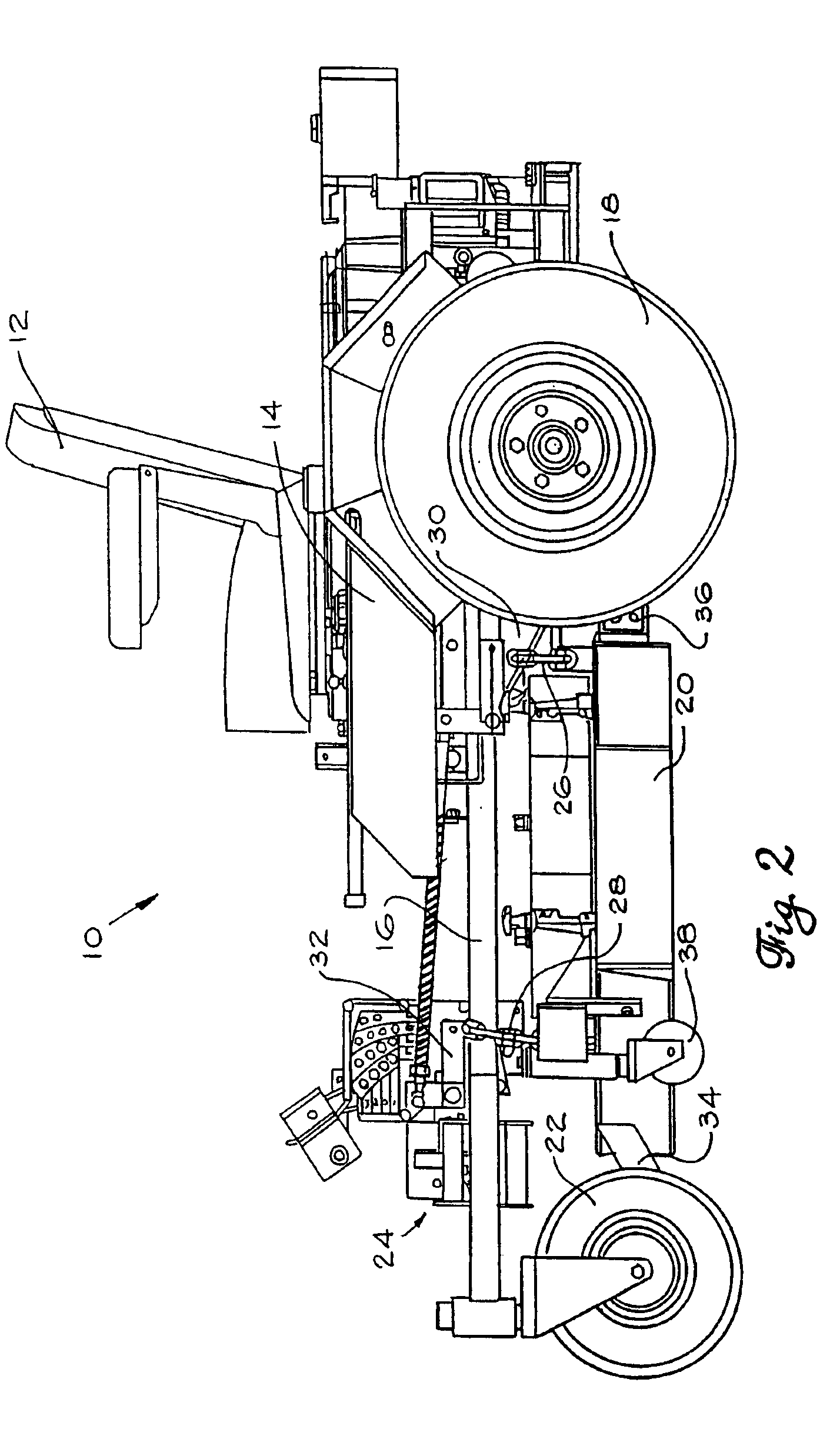
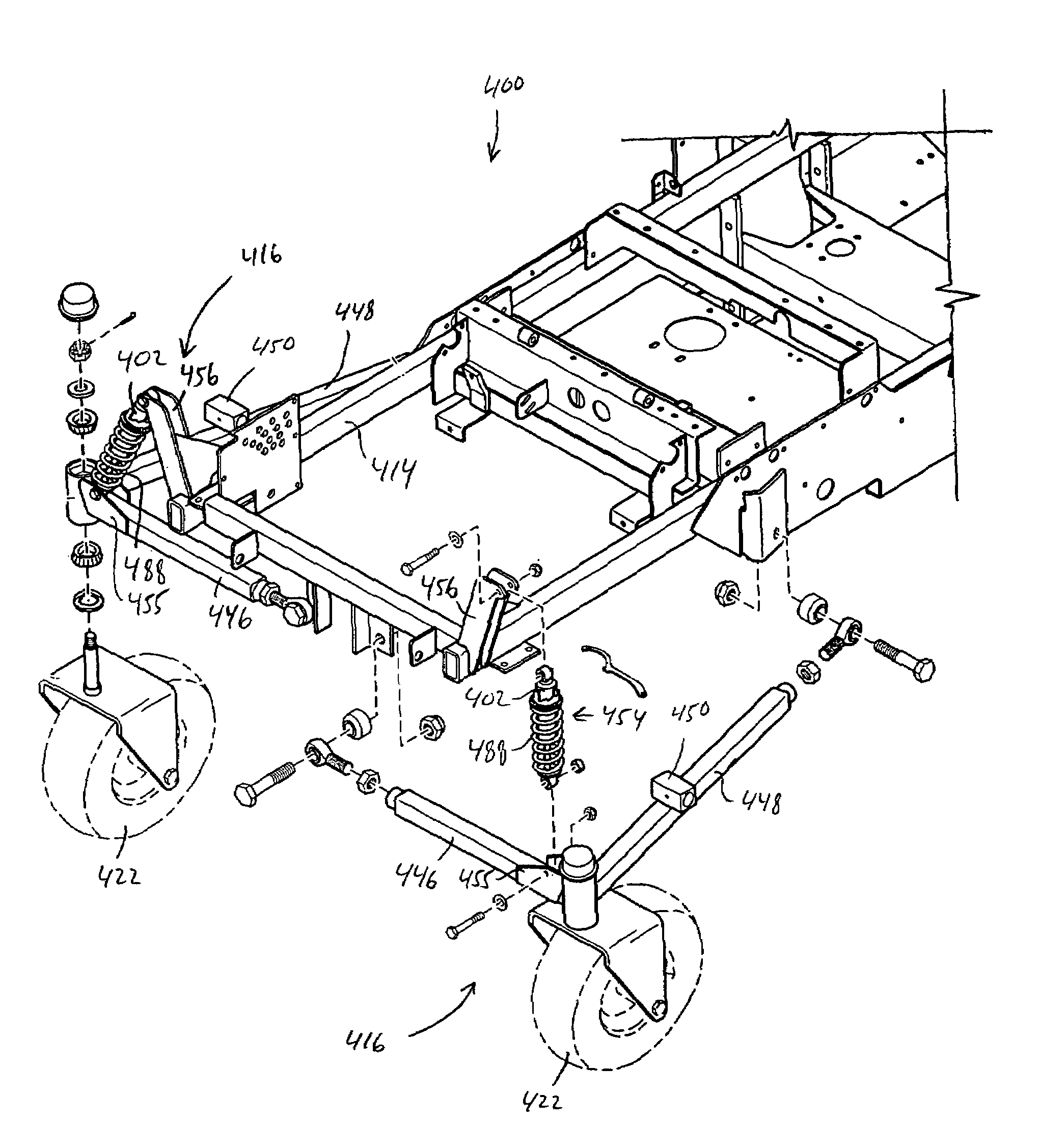
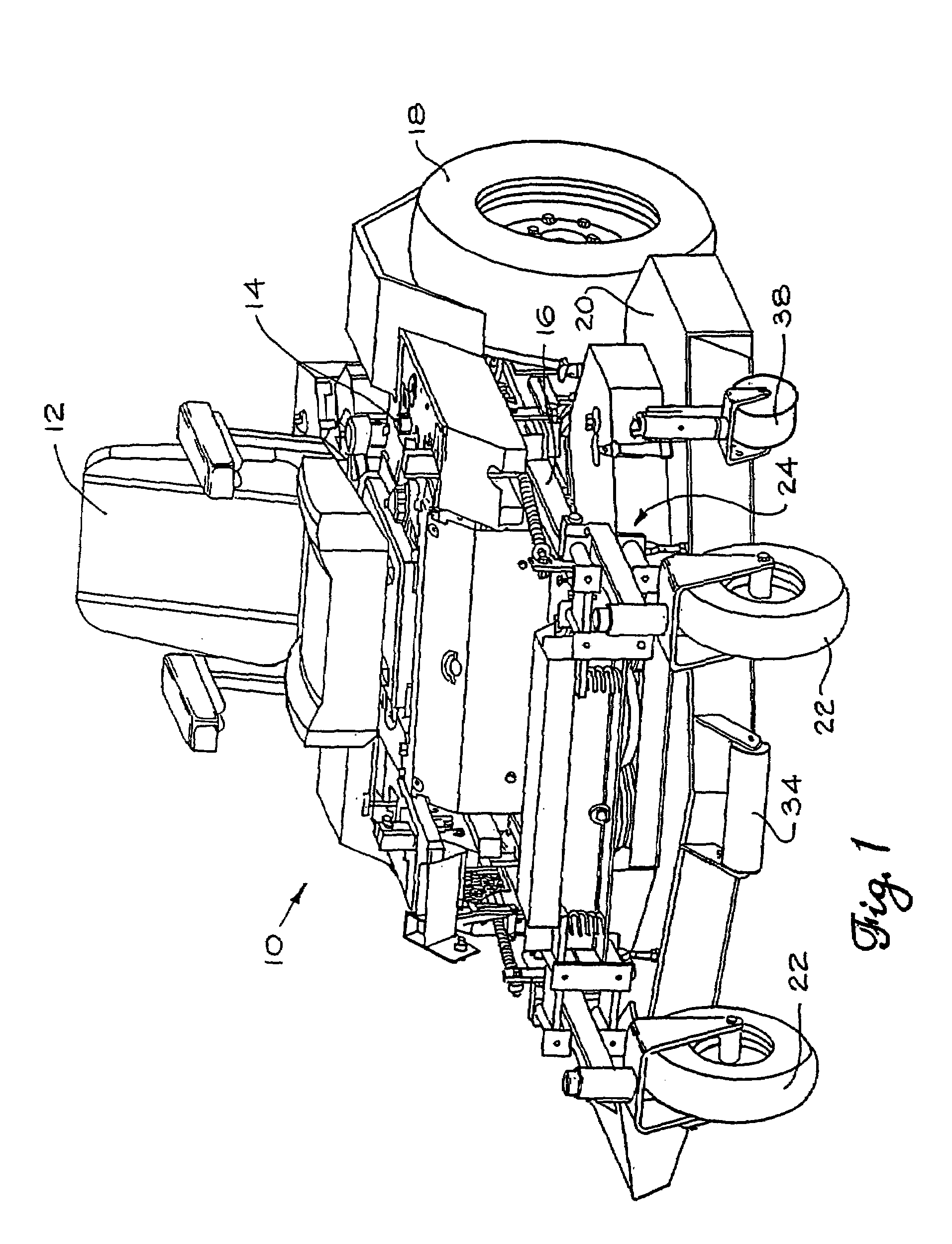
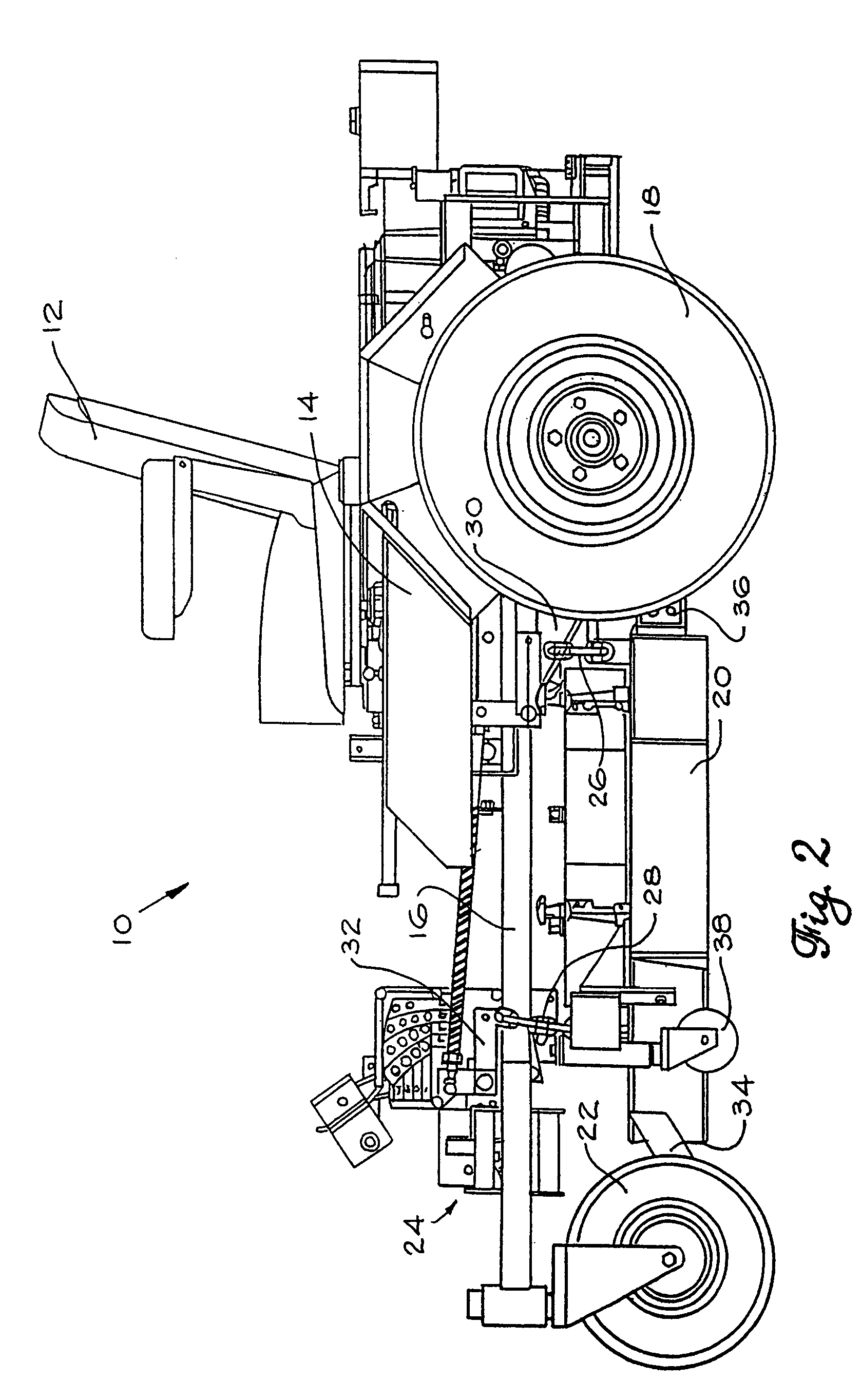
Mower suspension system and method
InactiveUS6857254B2Good suspensionImproved cutter deck movementHigh internal friction springsCastorsEngineeringCantilever
The mower front independent suspension assembly in some embodiments of the present invention includes a first suspension arm connected to the front of the lawn mower frame and a second suspension arm connected to the side of the lawn mower frame. In some embodiments, the first suspension arm is connected to the front of the frame at or near the longitudinal center of the frame, while the second suspension arm is connected to the side of the frame a distance from the front of the frame. Also, in some embodiments the cutter deck of the lawn mower is connected to the front independent suspension assemblies for movement therewith.
Owner:FERRIS IND
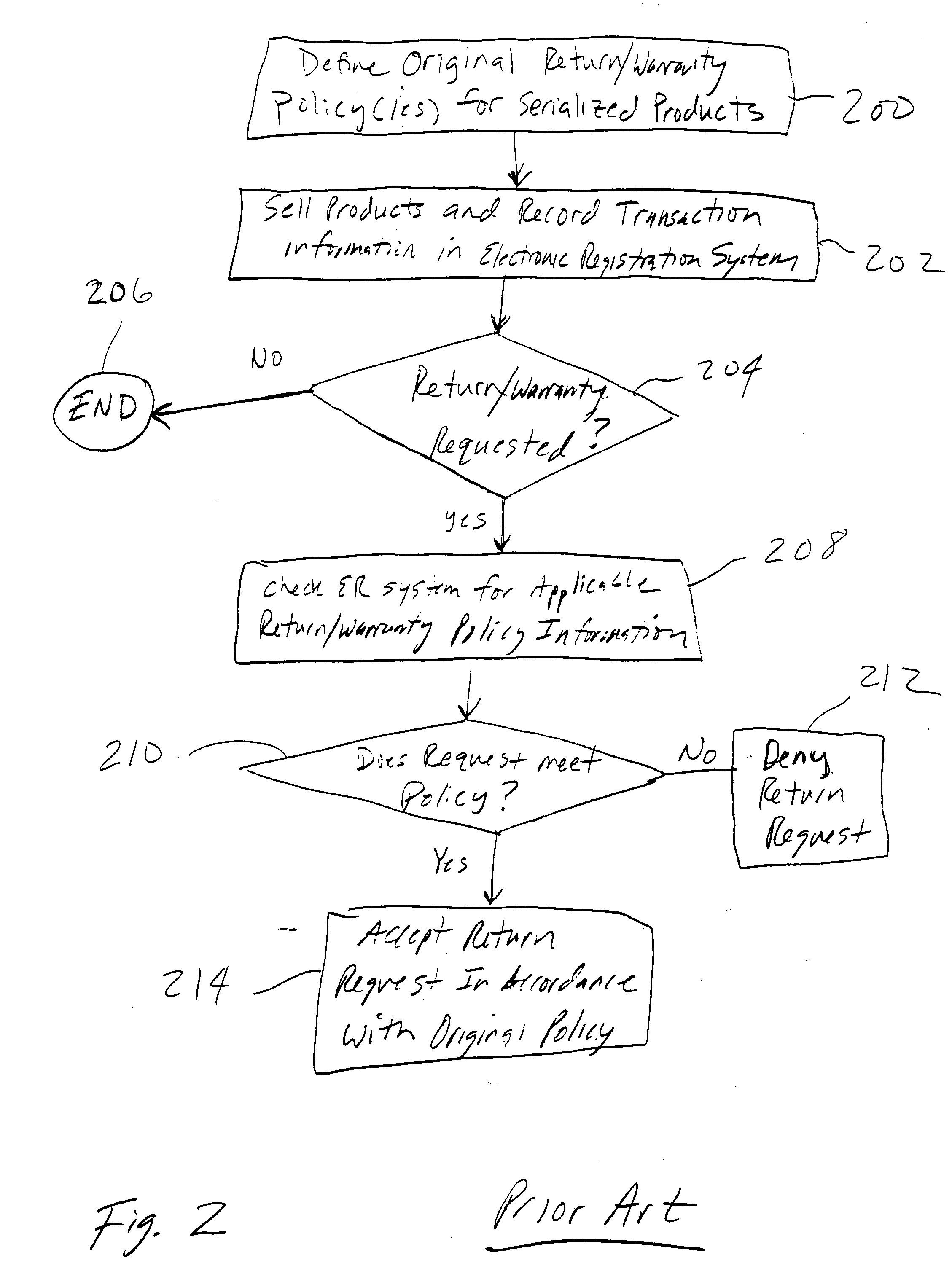
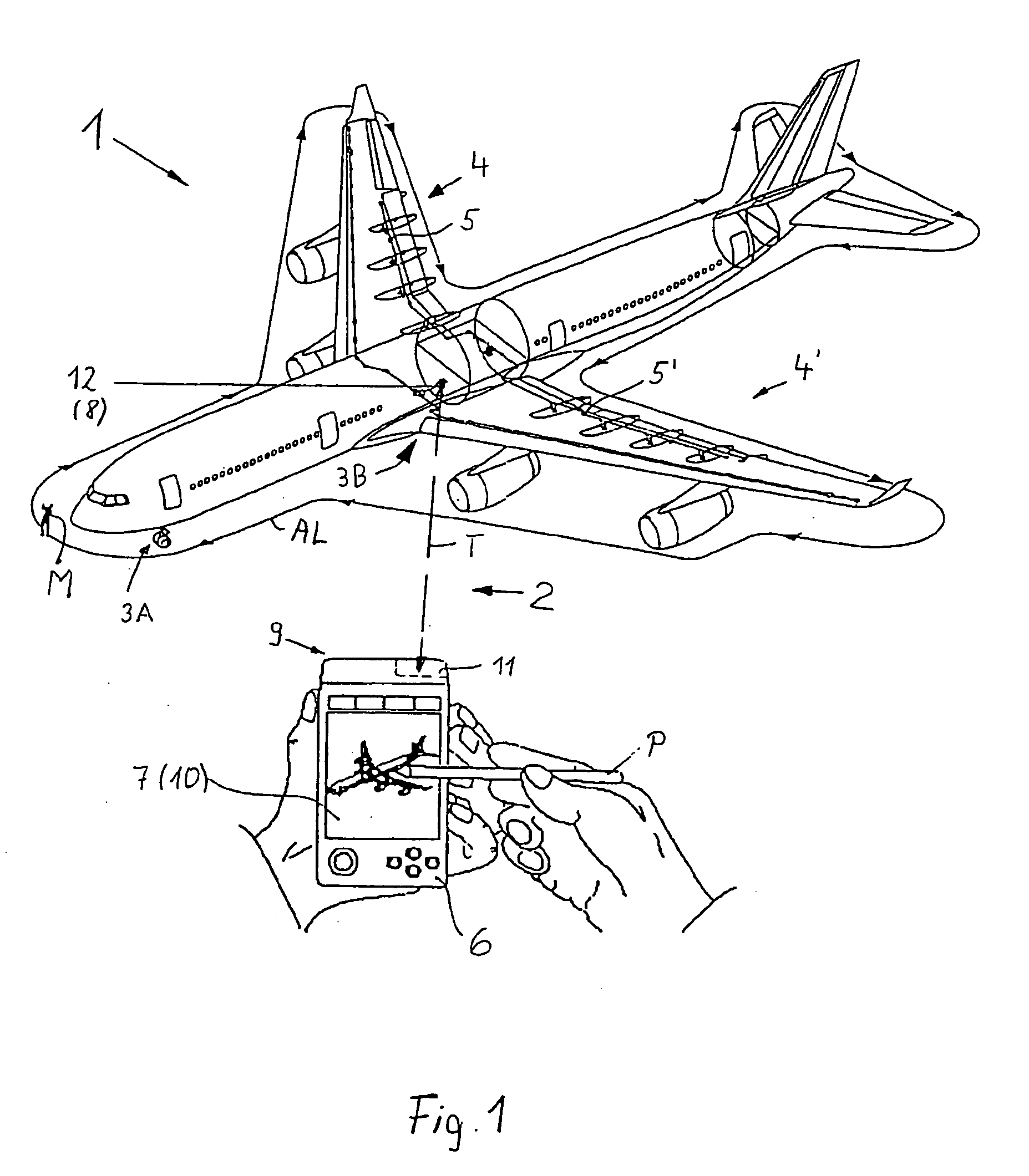
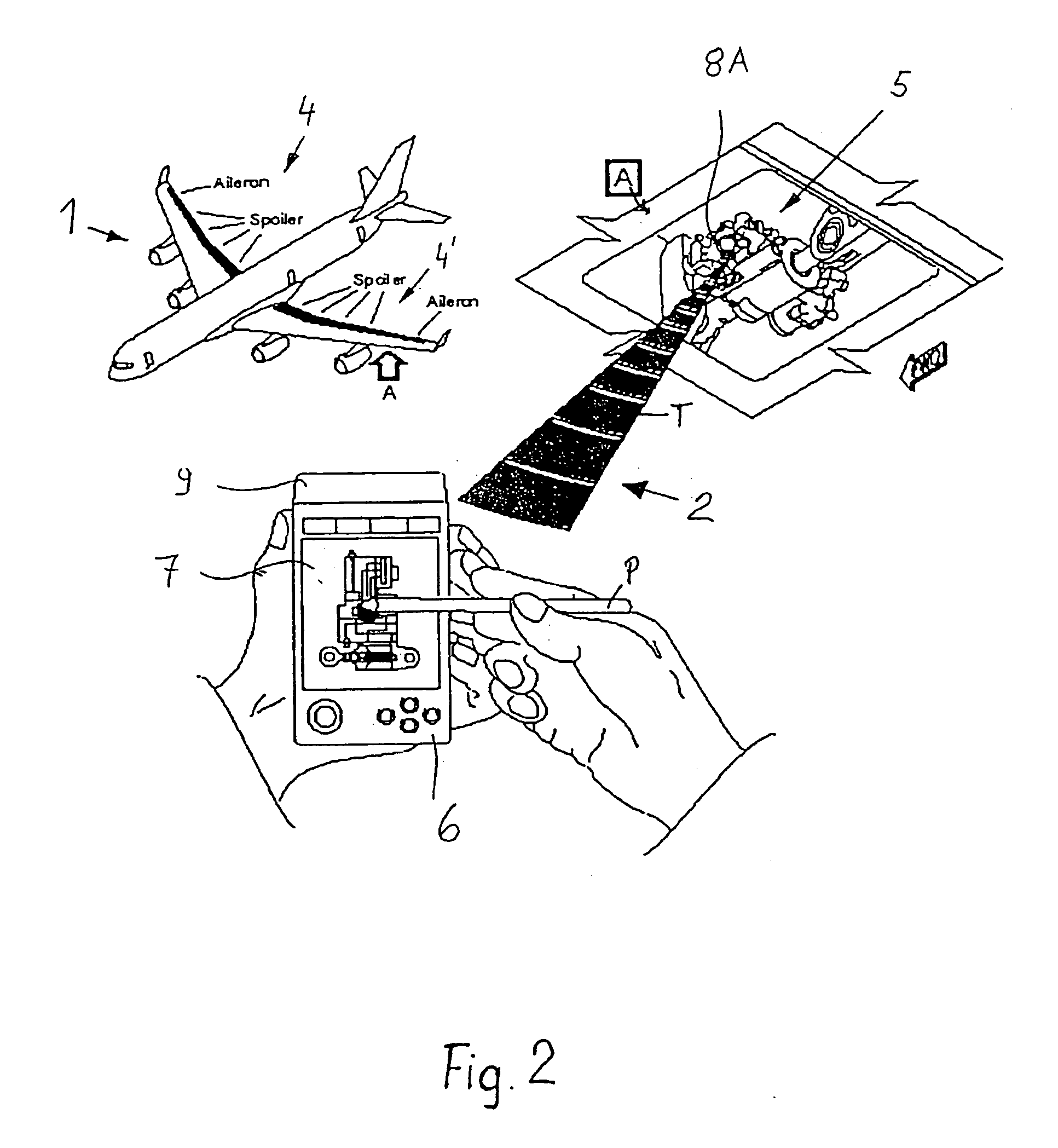
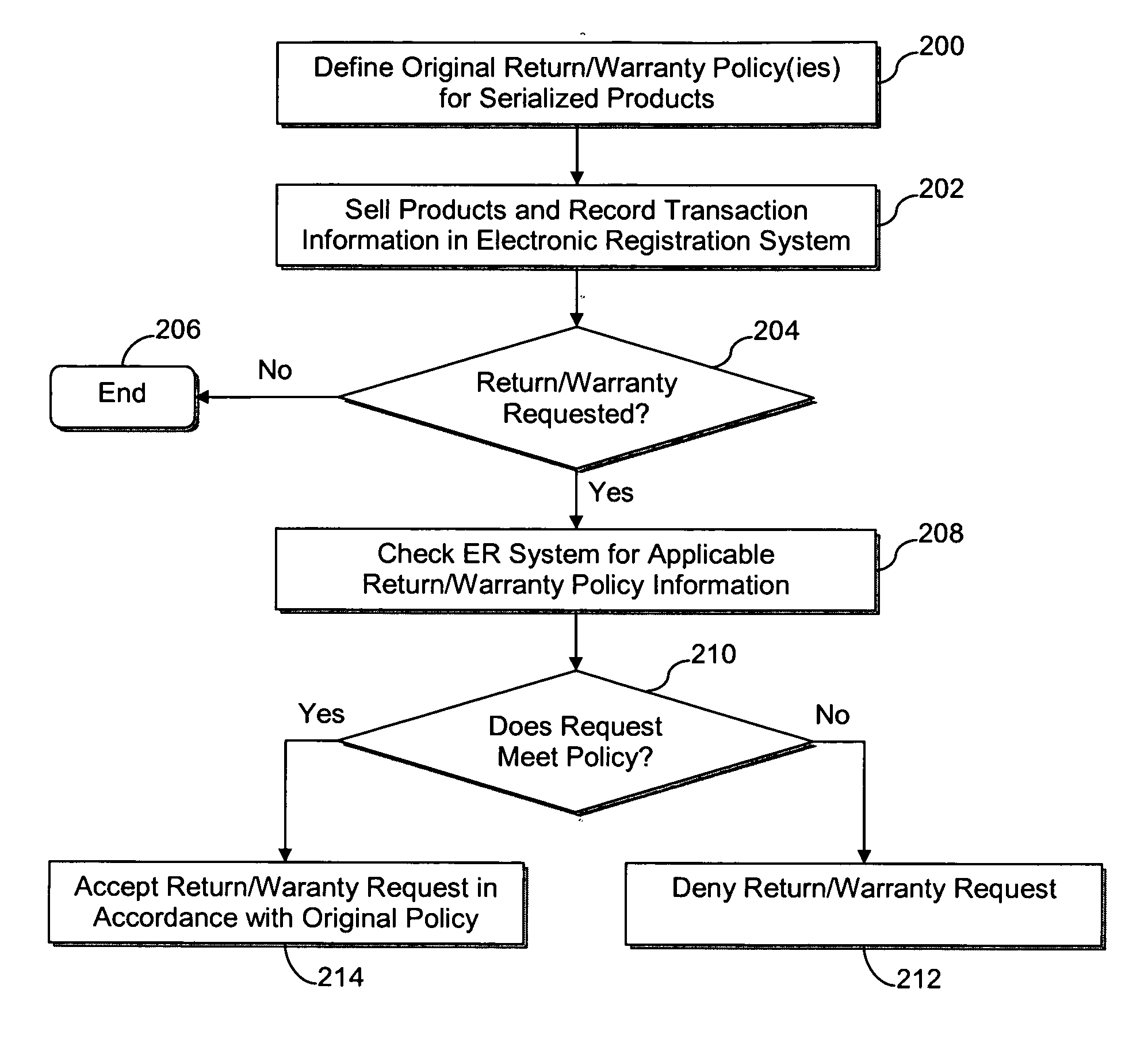
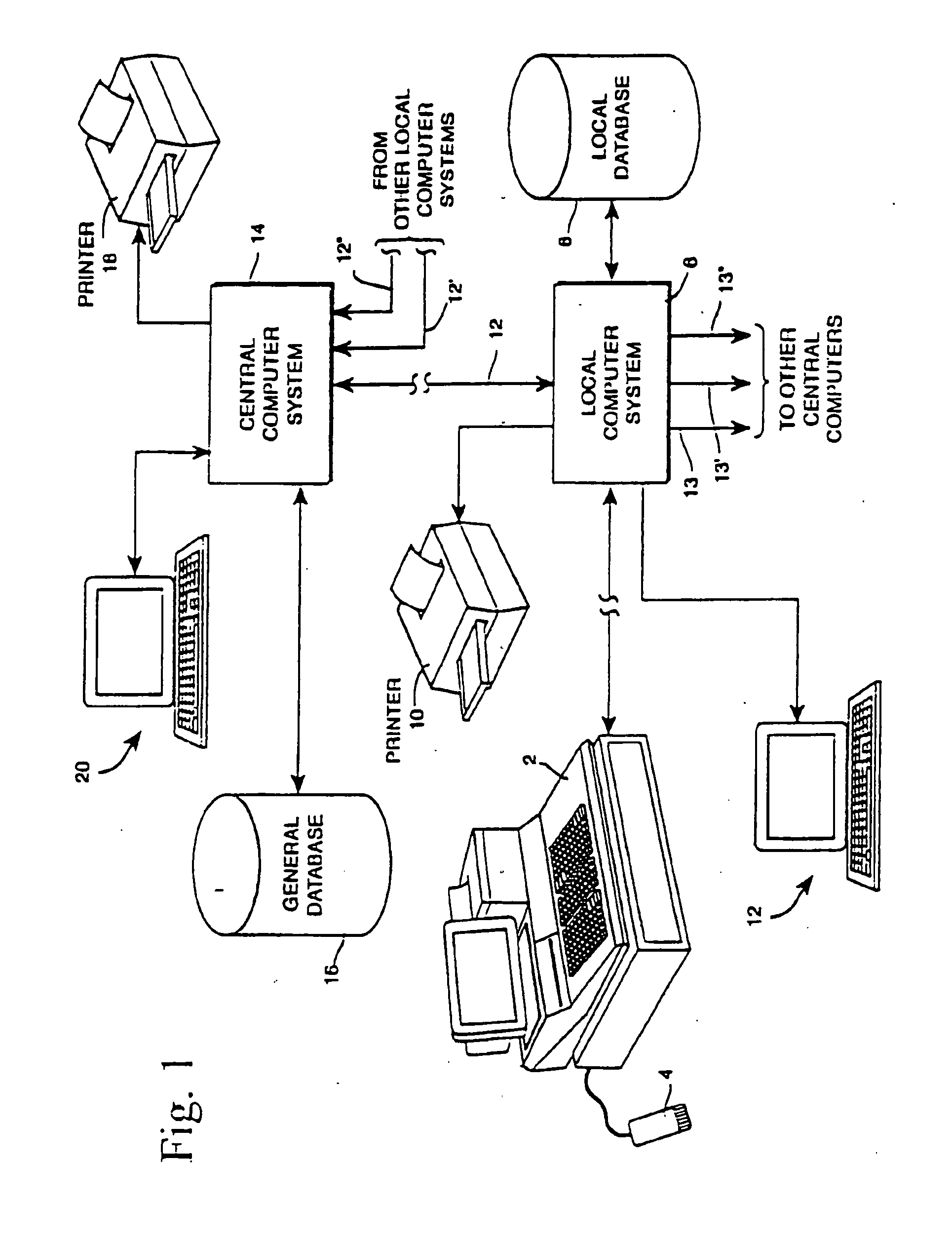
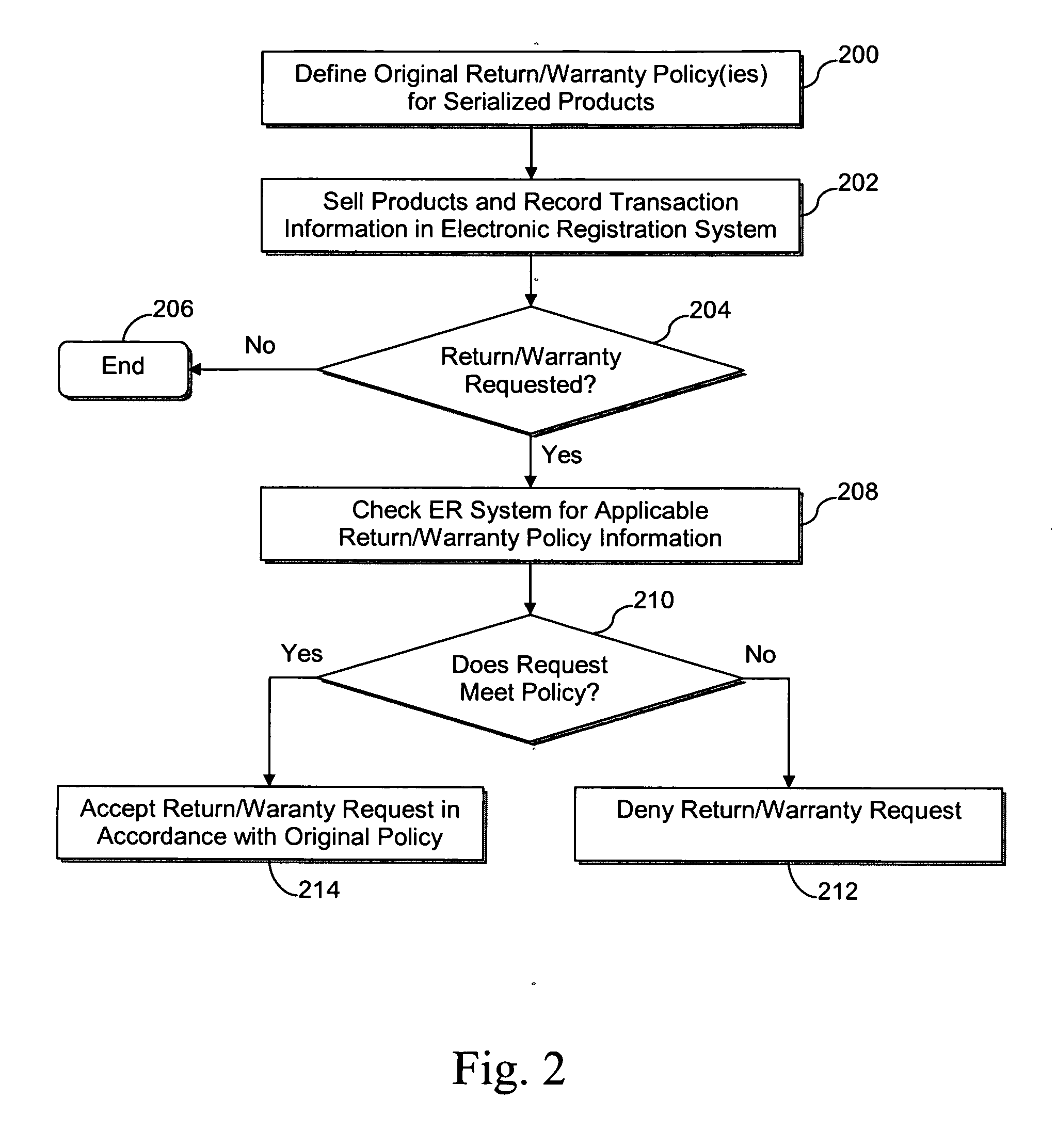
Systems and methods for product authentication and warranty verification for online auction houses
InactiveUS20080052184A1Reduce repairAccurate determinationCommerceRegistration systemProduct Approvals
The example embodiments herein relate to the field of electronic registration (ER) of purchased products and, more particularly, to an improved electronic registration system which enables online buyers and sellers (e.g. those participating in online auctions) to take advantage of the benefits associated with ER systems. The ER techniques enable buyers to determine whether the product for sale, for example, has been purchased through authorized channels, was stolen, is covered under a warranty, etc. Such techniques may be used with existing brick-and-mortar stores as well as online stores. Value may be added for buyers, sellers, auction houses, manufacturers, and / or contract service partners.
Owner:E2INTERACTIVE INC D B A E2INTERACTIVE
Door handle apparatus
InactiveUS7062945B2Easy constructionLow costWing handlesDoors/windowsBack doorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A door handle apparatus having a door handle 12 which is provided on a back door of an automobile in such a manner as to oscillate freely and a cover member 20 for covering the door handle 12, wherein a detection sensor 30 for detecting the approach of an operator toward the door handle 12 is provided between the door handle 12 and the cover member 20.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
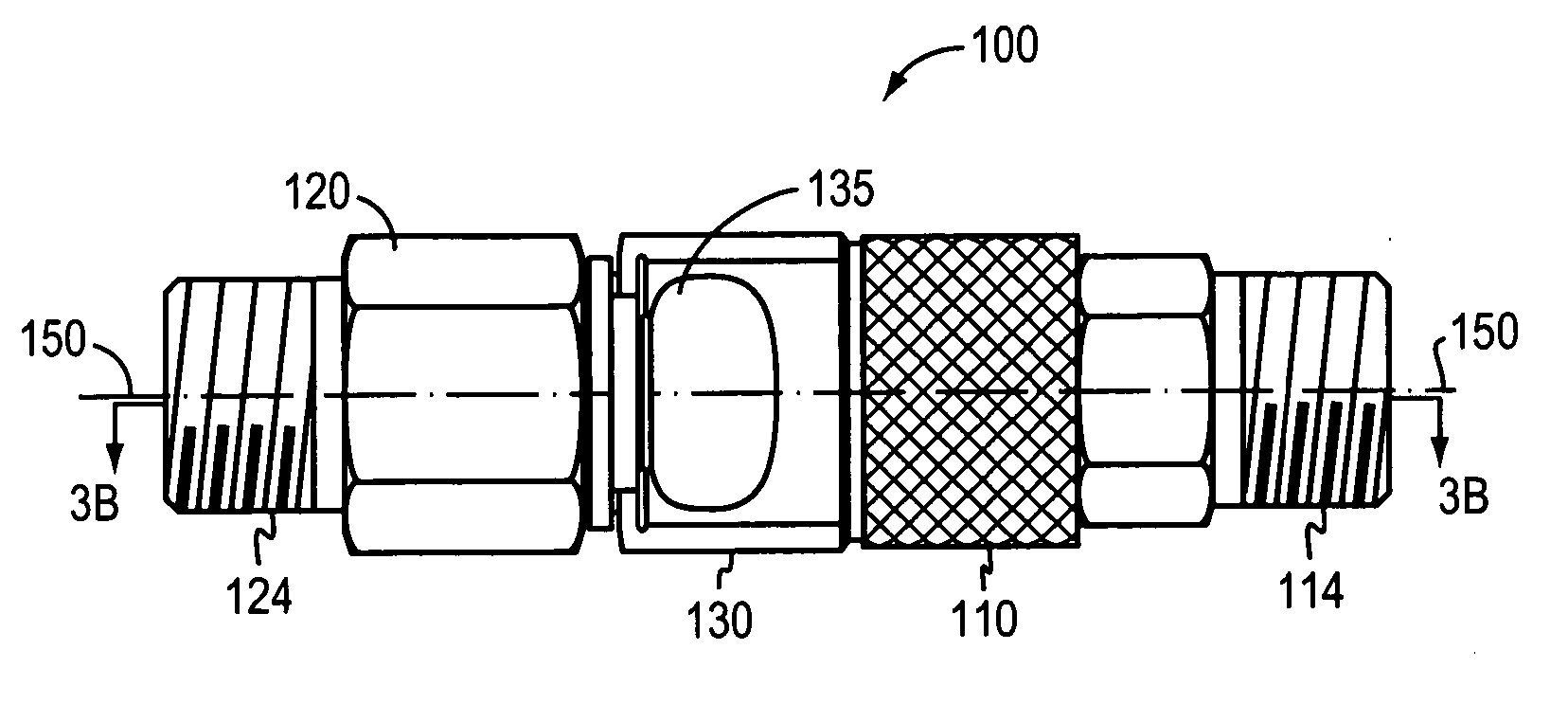
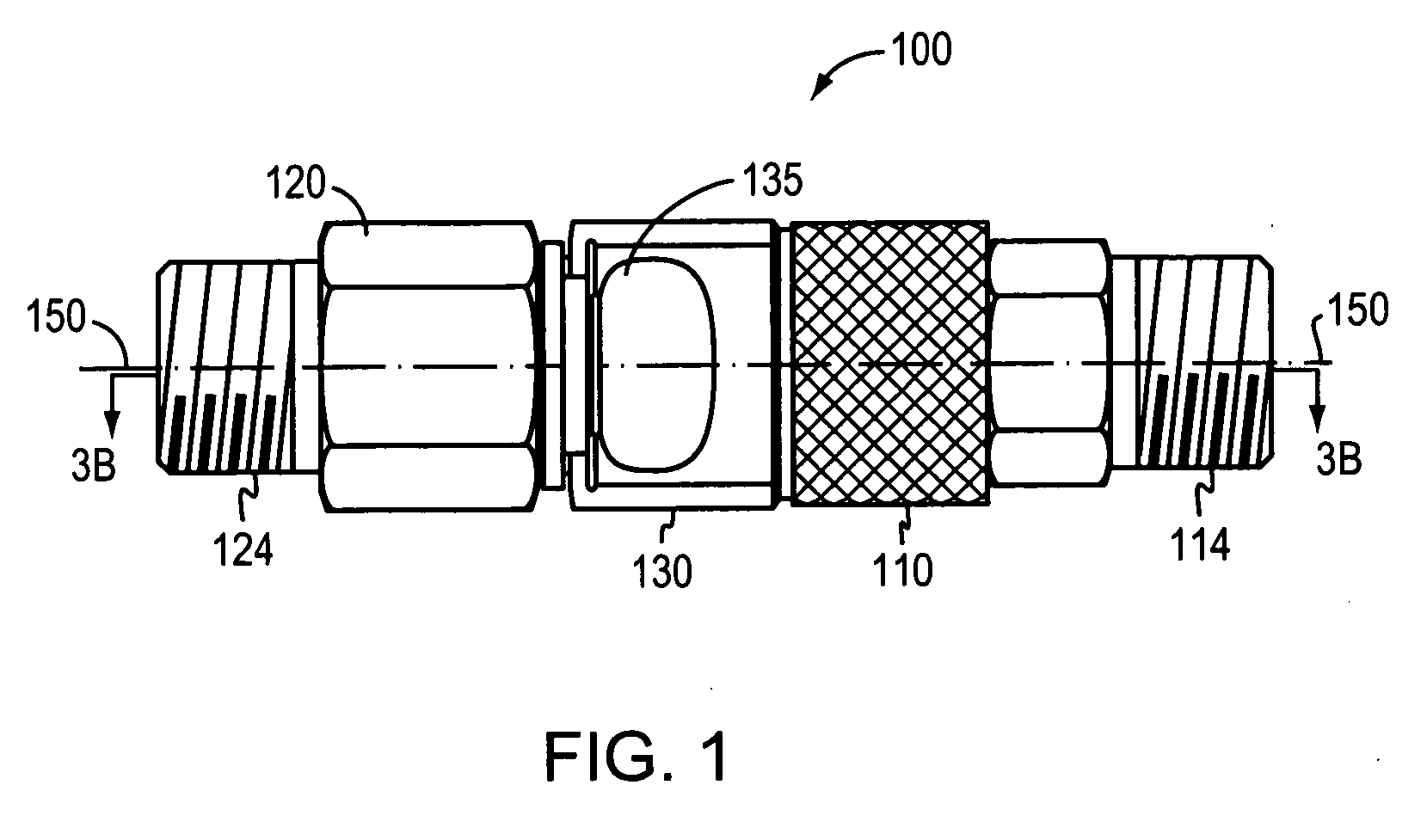
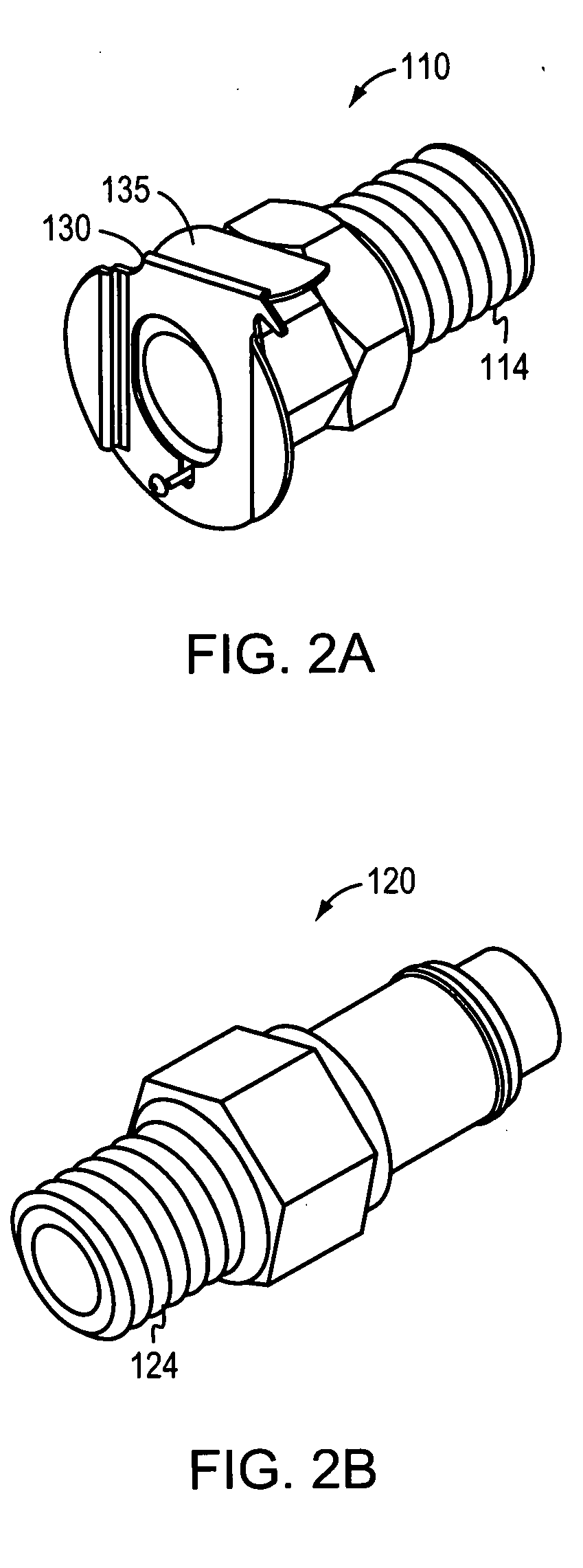
One-touch connection and disconnection method and apparatus
InactiveUS20070082533A1Easy to useShorten the timeCoupling device detailsPlasma techniqueEngineeringLinearity
A first connector is disposed on a first end of a lead in a lead set for use with a plasma arc torch. The first connector is capable of engaging a second connector by causing a compression force in a second connector. The second connector compression force is caused by application of a translational force along a longitudinal axis. The second connector causes, upon application of a depression force along the longitudinal axis, disengagement of the first connector. The second causes disengagement of the first connector upon application of a linear force applied along the longitudinal axis to at least one of the first connector and the second connector. The second end of the lead may also be connected to a power supply. Methods for connecting and disconnecting a lead are also disclosed.
Owner:HYPERTHERM INC
System and method for diagnosing aircraft components for maintenance purposes
InactiveUS20040162651A1Easy maintenanceAvoid replacementVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic systemSignal processing
Aircraft maintenance and repair work is facilitated, especially for a commercial aircraft, by a diagnostic system and method, wherein an aircraft component or assembly of components is monitored by at least one sensor which produces and preferably also stores component status information. Respective status information signals are transmitted, preferably in a wireless manner, from a transmitter of the sensor to a receiver of a signal processing unit which provides status information on a display screen. The status information signals are preferably processed and evaluated with reference to rated maintenance and repair reference information to provide instructions as to what needs to be done where and when for a maintenance or repair. The sensor or sensors may operate during flight and the respective stored information is then processed and used on the ground.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
System and/or method for handling returns involving products tied to post-paid subscriptions/services
ActiveUS20110066514A1Reduce repairAccurate determinationComplete banking machinesHand manipulated computer devicesRegistration systemService provider
The exemplary embodiments described herein relate to the field of electronic registration (ER) of purchased products and, more particularly, to an improved electronic registration system that enables unique item-level tracking from an initial point-of-sale (POS) transaction involving a post-paid service / subscription and related device or product, to any cancellations in service and returns to the store or service provider. Certain exemplary embodiments thus advantageously “close the gap” between retailers and service providers, e.g., in connection with subscriptions / post-paid service agreements and related devices or products. In certain exemplary embodiments, an “interest” may be taken and charged in the event that the customer does not return the device when or after an associated service has been cancelled.
Owner:E2INTERACTIVE INC D B A E2INTERACTIVE
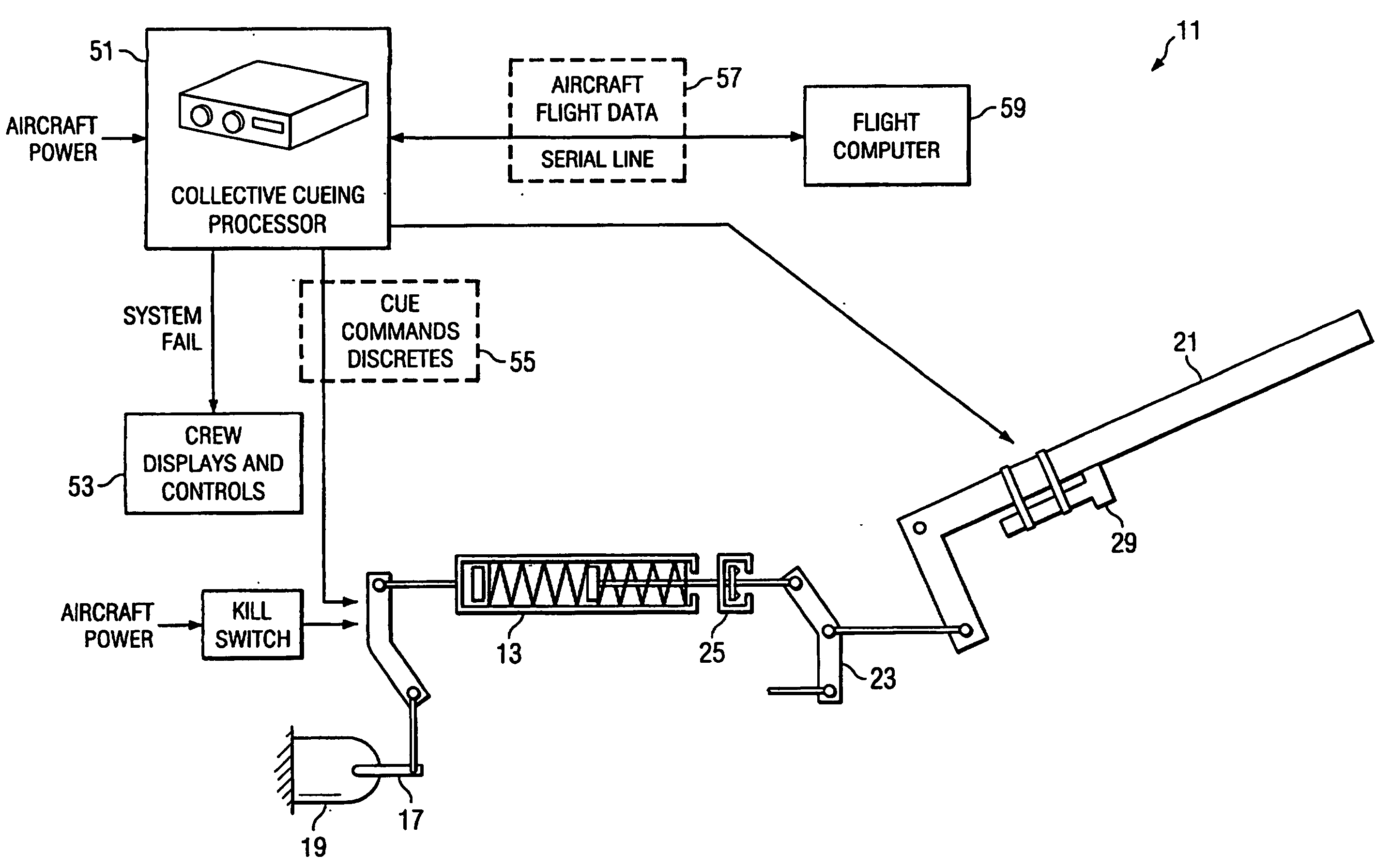
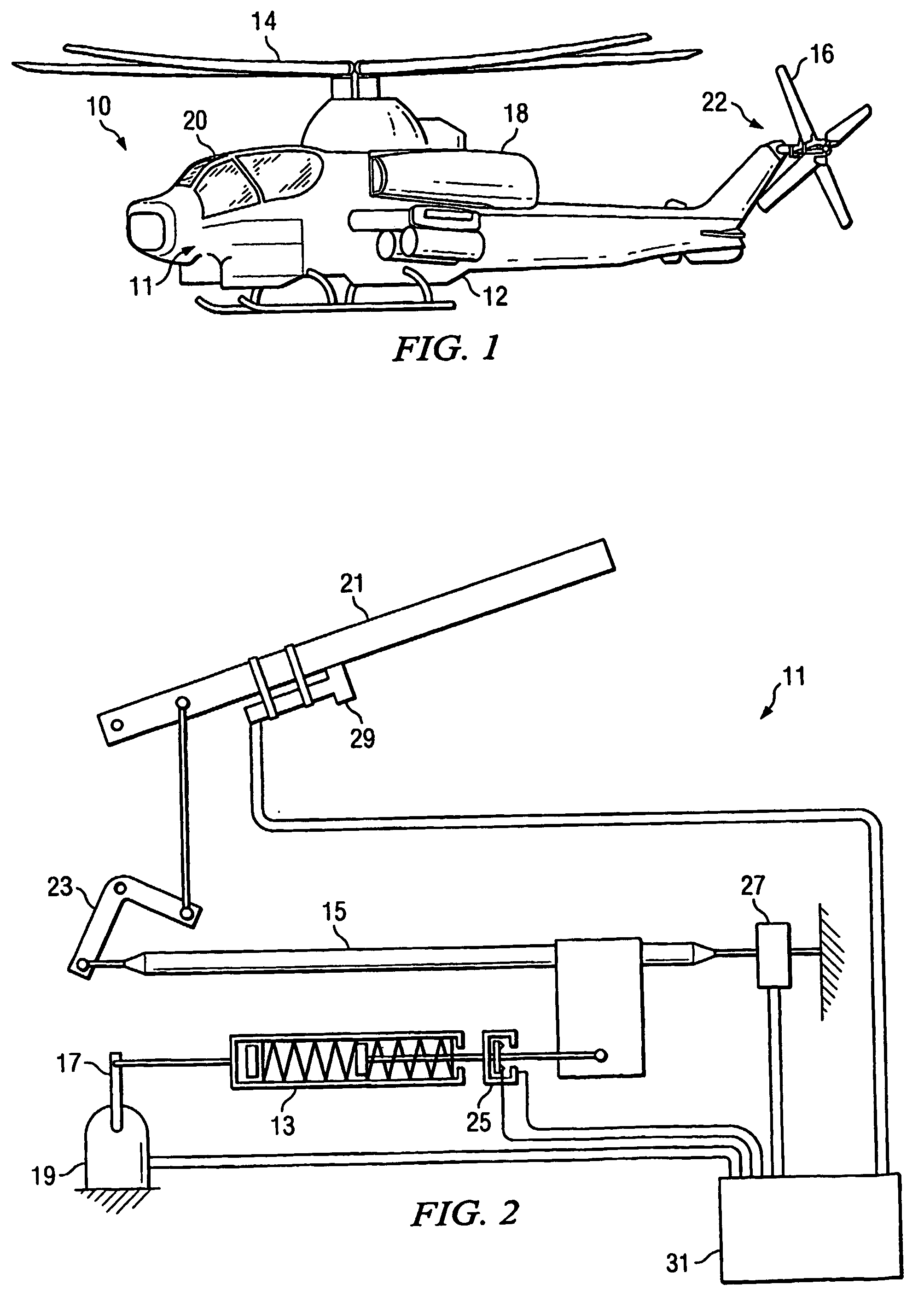
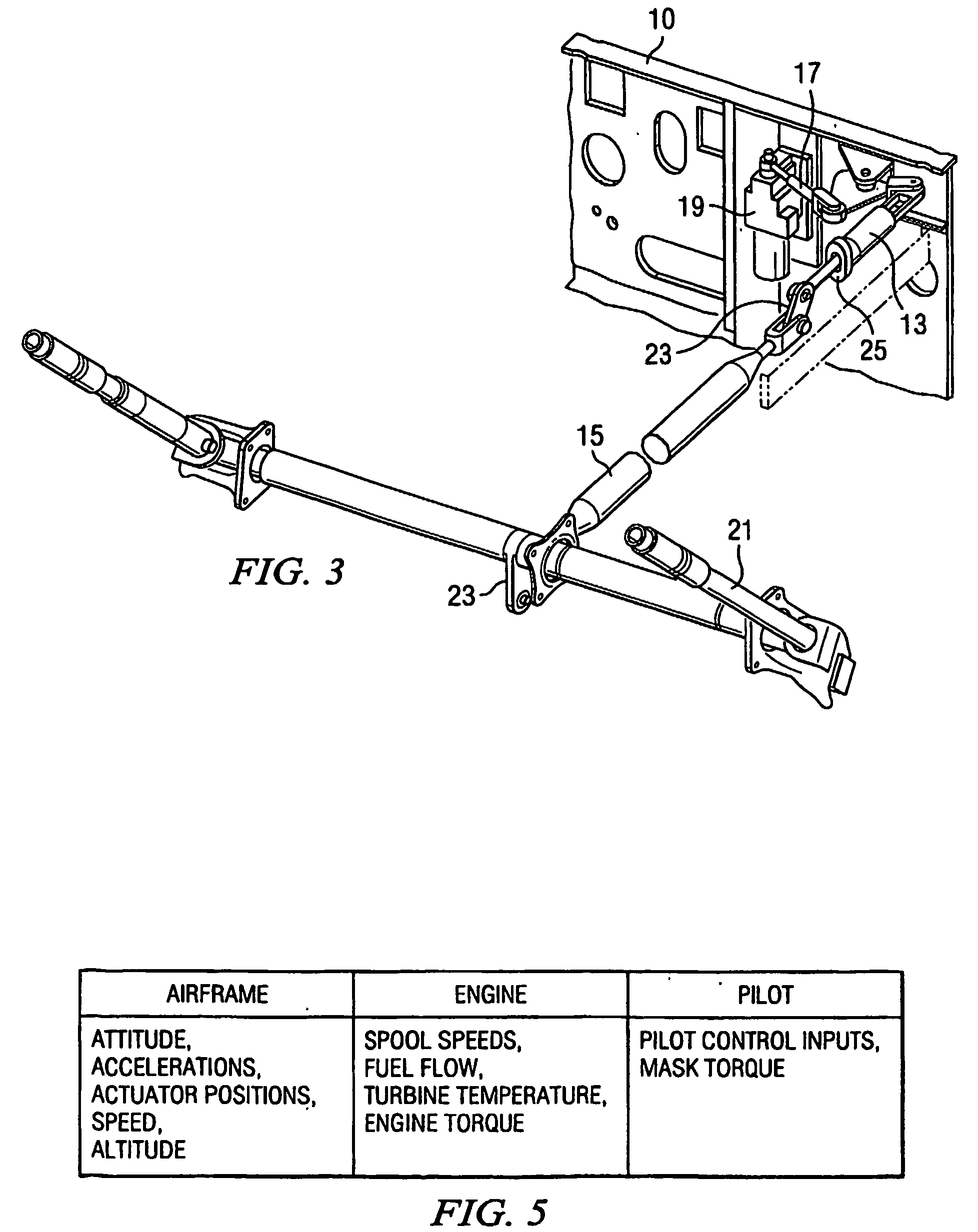
Method and apparatus for tactile cueing of aircraft controls
InactiveUS20050151672A1Less complexMore reliabilityWith power amplificationActuated personallyTouch PerceptionAdded resistance
A method and apparatus for tactile cueing of aircraft controls (21) is disclosed. The apparatus of the present invention warns pilots of approaching limits on certain aircraft performance parameters. The most common warnings are for rotor speed exceeding a moving limit. The present invention uses tactile cueing through the collective stick (21). Tactile cueing means that the pilot does not need to scan the intruments to ascertain proximity to the aforementioned limits. Instead, the pilot can operate the aircraft within proper limits by touch, while maintaining situational awareness outside of the cockpit (20). The method and apparatus of the present invention provides customary friction resistance up to a limit position that is continuously updated. According to the present invention, continued motion of the collective (21) in a direction beyond that limit position results in a breakout force and an increasing resistive force.
Owner:BELL HELICOPTER TEXTRON INC
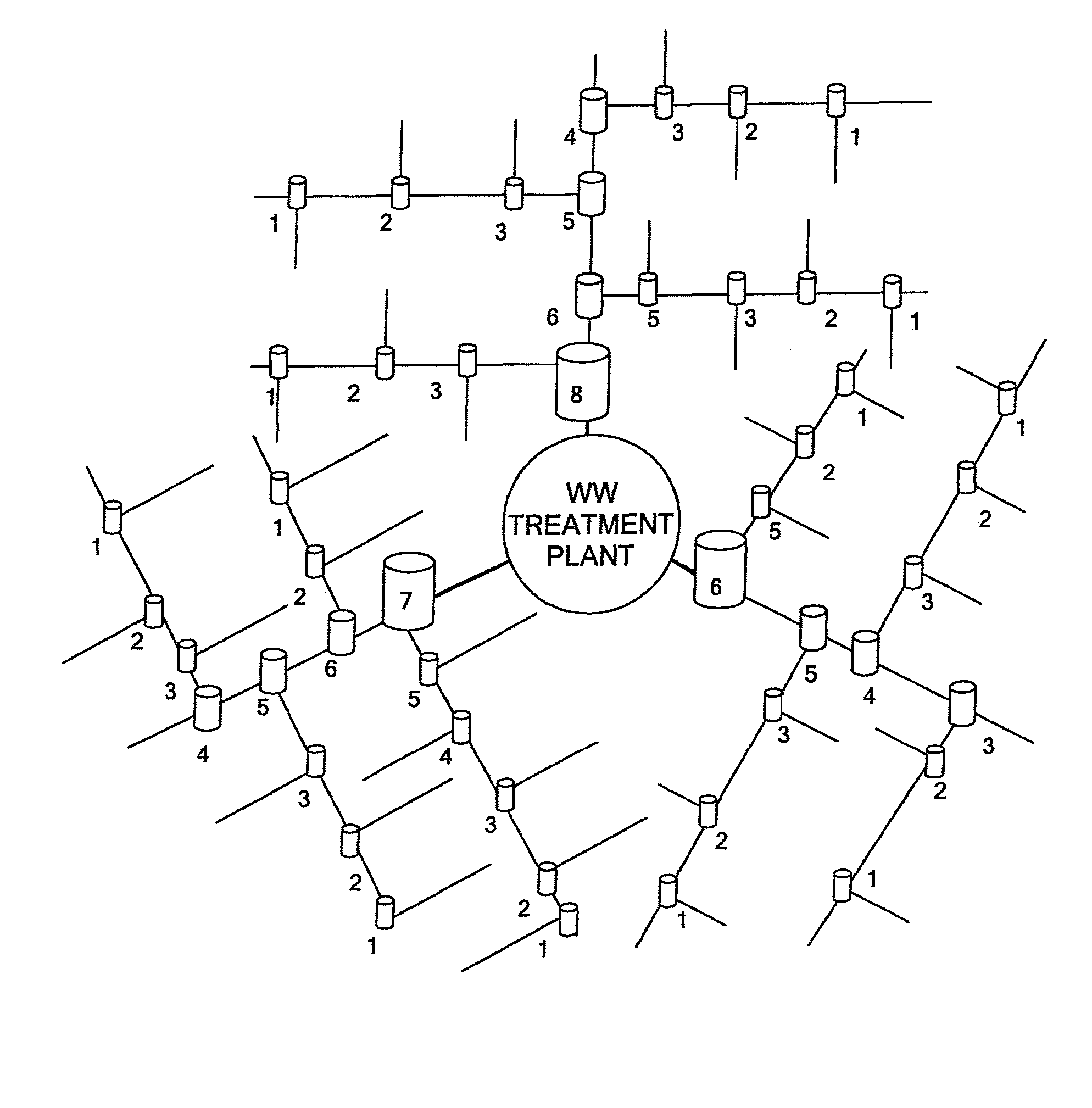
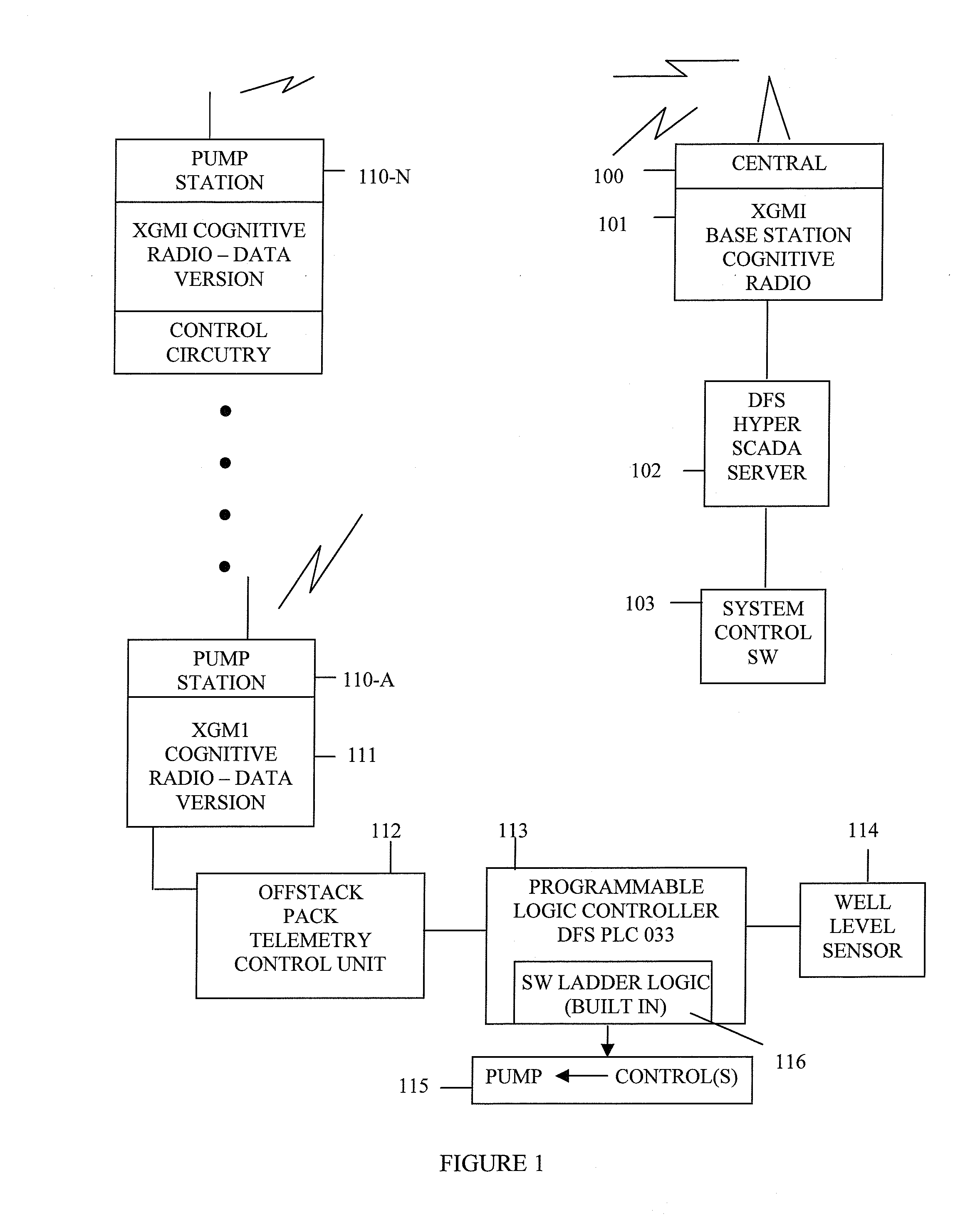
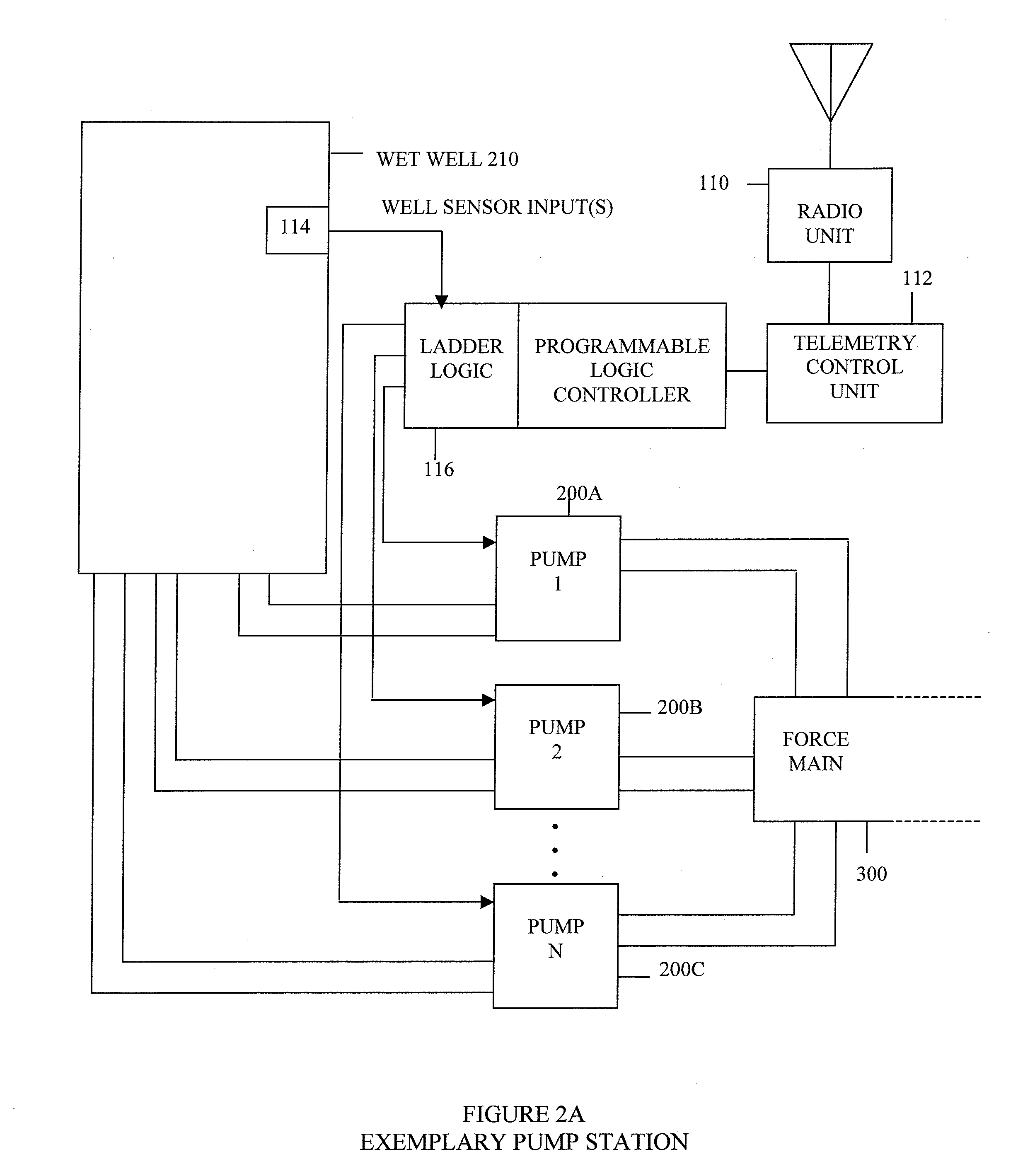
Wastewater collection flow management system and techniques
ActiveUS8594851B1Reduce maintenanceIncrease threshold level of activationFuel supply regulationLevel controlPeak valueEnergy expenditure
Reductions in energy consumption and maintenance requirements for operating a wastewater treatment plant are achieved by controlling the operation of pumps at pump stations along a force main in a systematic fashion. The operation of the pumps is controlled to manage the flow of wastewater along the force main to minimize energy consumption, to eliminate sediment, to manage peak pressures encountered by smaller pumps and to avoid septic conditions.
Owner:DATA FLOW SYST
Dentifrice compositions containing calcium silicate and a basic amino acid
ActiveUS20120141588A1Reduce and inhibit formationPromote remineralizationAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsCalcium silicateMedicine
An oral care composition includes an effective amount of a basic amino acid in free or salt form; and an effective amount of calcium silicate particles. The calcium silicate particles have an average diameter of less than about 5 microns, such that they can occlude dentinal tubules of the teeth. An oral care method includes applying the composition to an oral cavity of a subject to reduce or inhibit hypersensitivity of the teeth and to achieve other benefits.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
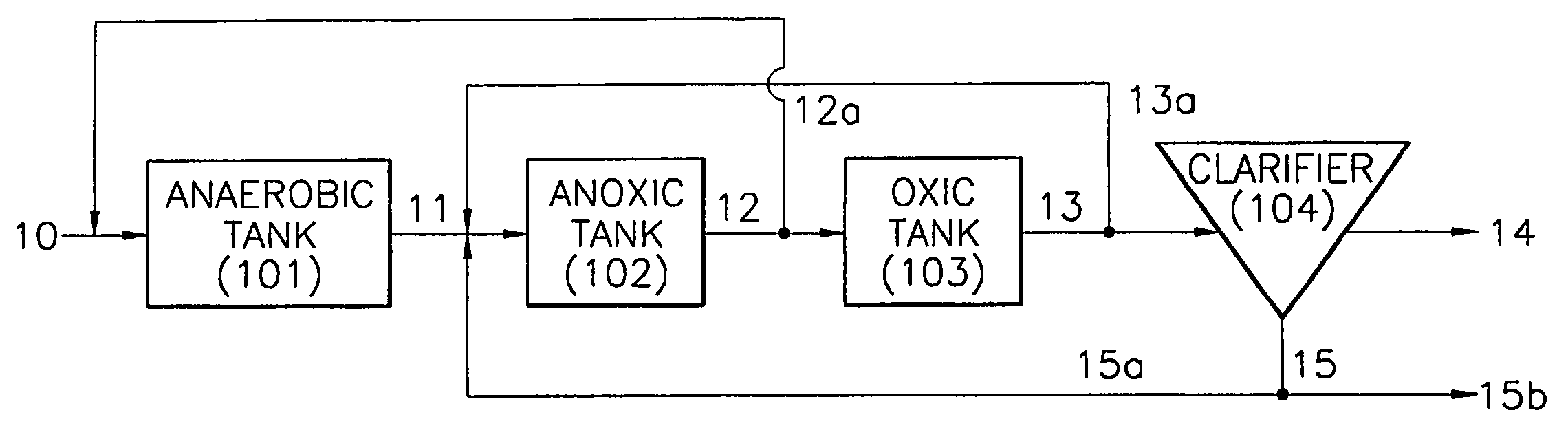
Wastewater treatment apparatus and method for removing nitrogen and phosphorus
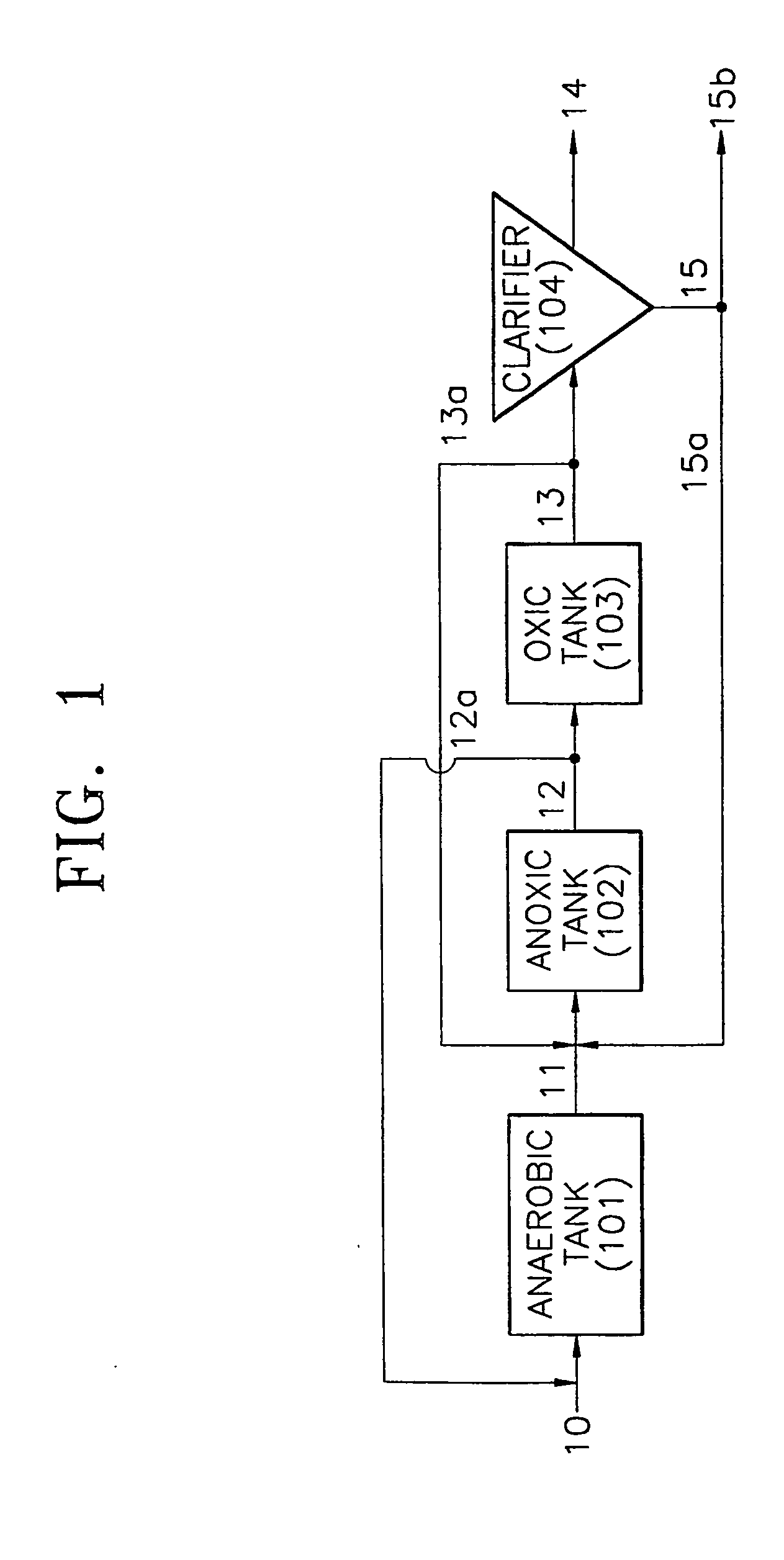
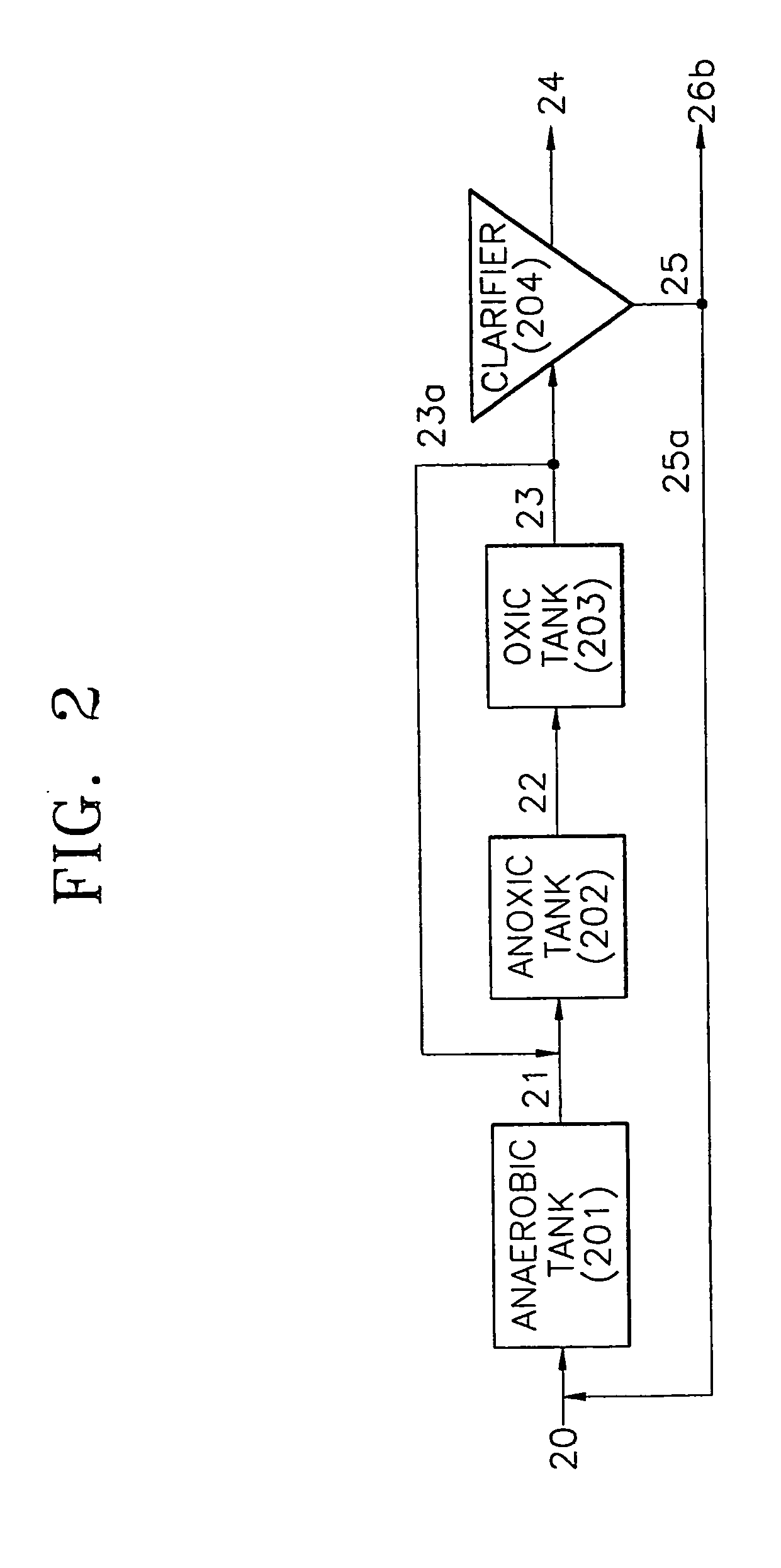
InactiveUS20050087480A1Reduce maintenanceReduce repairTreatment using aerobic processesIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic matterOxygen
Provided is a wastewater treatment apparatus for removing nitrogen and phosphorus having an anaerobic tank, an anoxic tank, an aerobic tank and a clarifier, wherein the aerobic tank includes has a baffle installed at one side thereof to form a dissolved oxygen reducing zone for reducing the concentration of dissolved oxygen contained in internally recycled wastewater returned from a dissolved oxygen reducing zone while increasing the concentration of dissolved oxygen contained in treated effluent supplied from a part other than the dissolved oxygen reducing zone of the aerobic tank to a clarifier in a subsequent stage. Since organic matter present in wastewater is effectively used, the efficiency of removing nitrogen and phosphorus can be increased and the amounts of oxygen required throughout the treatment process and organic matter required for denitrification can be reduced. Also, synthesis of cells of microorganisms is suppressed. Therefore, the repair and maintenance costs can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ENGINEERING CO LTD
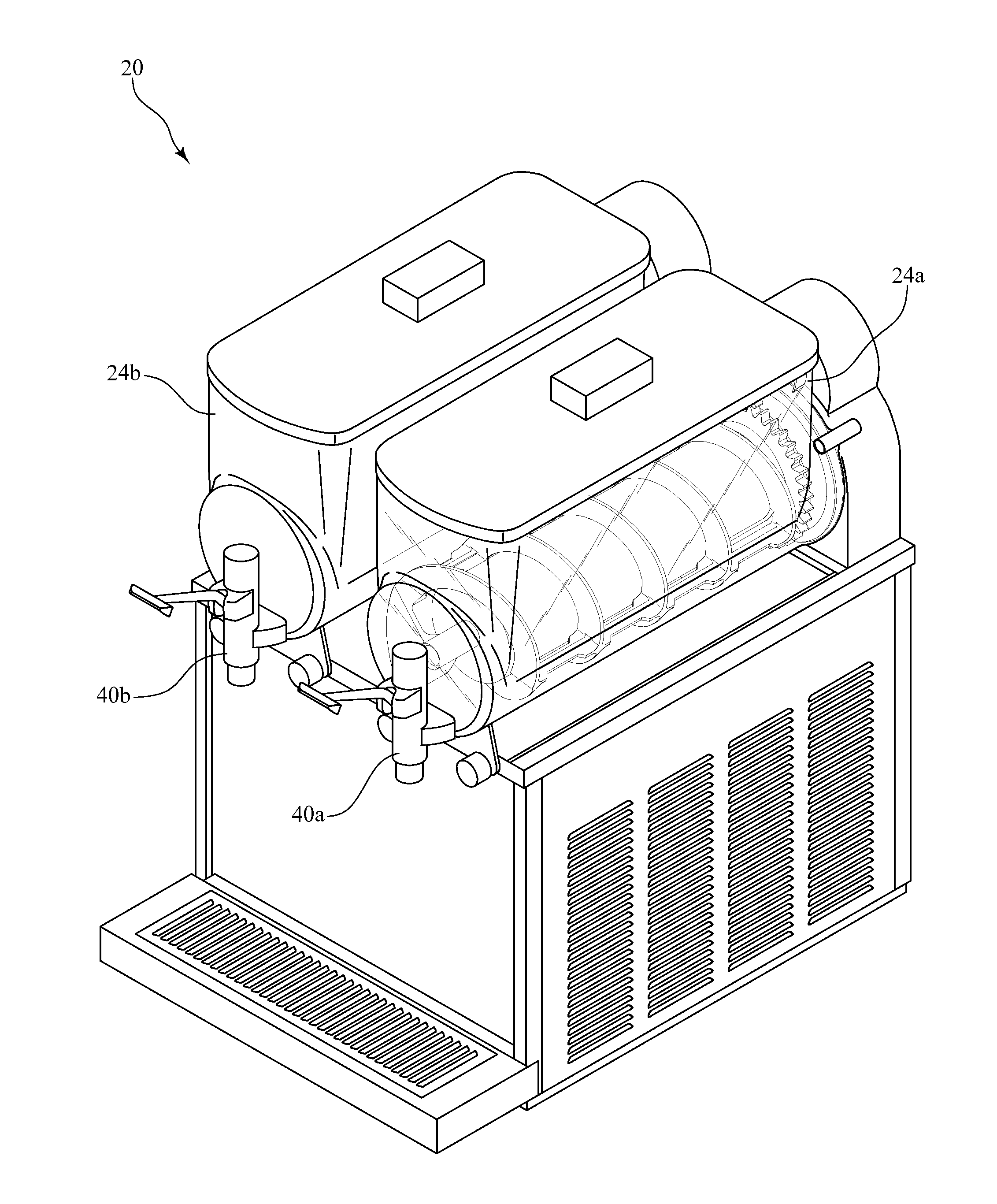
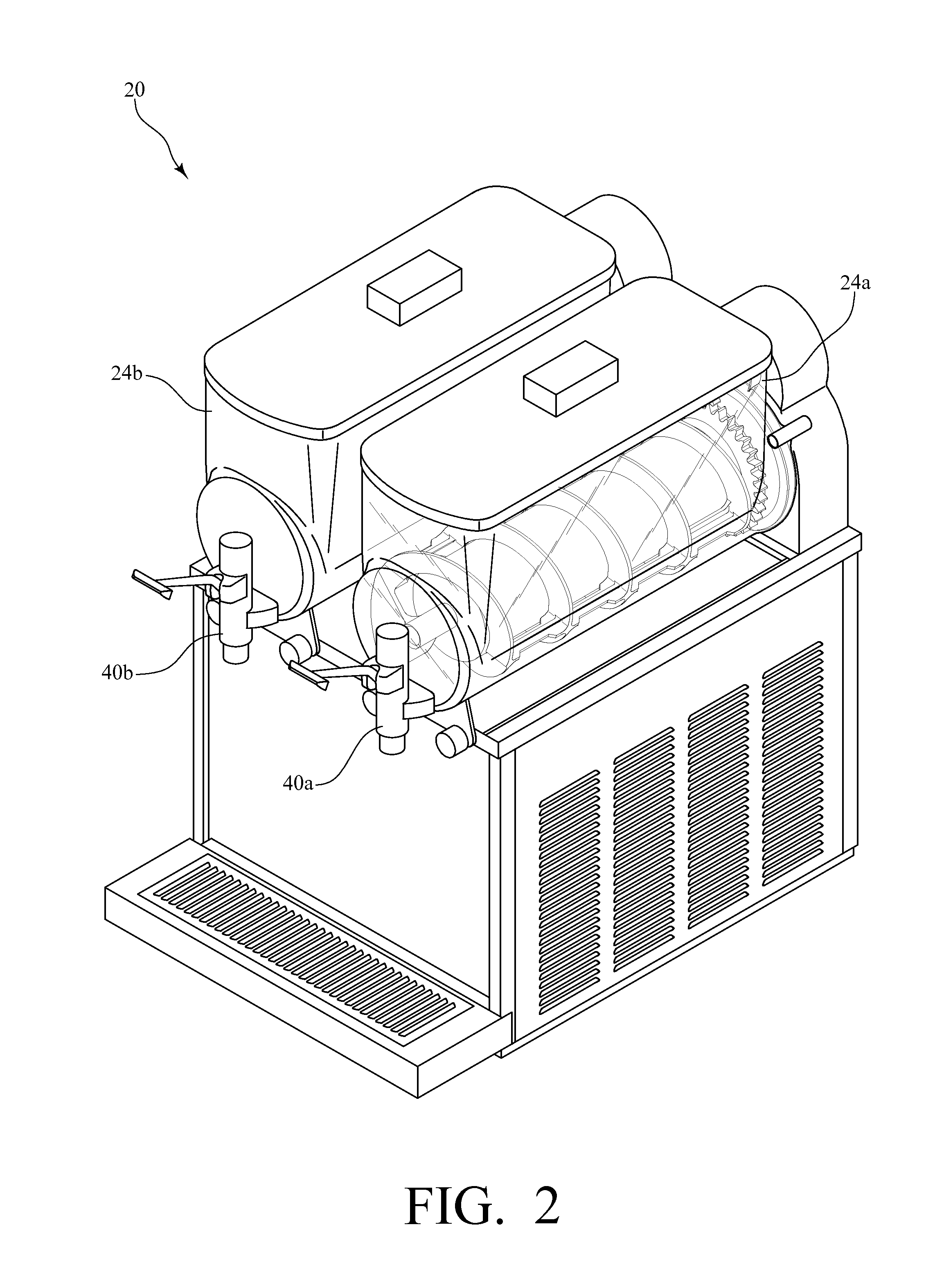
Beverage dispenser for partially frozen beverages with an improved drive and sealing system
InactiveUS20120055189A1Easy to cleanMinimizes problemMovable measuring chambersFrozen sweetsEvaporatorEngineering
A beverage dispenser for partially frozen beverages includes at least one bowl for storing a beverage product, with a freezing cylinder positioned in the bowl and housing evaporator coils. The beverage dispenser further includes a cooling system for supplying a cooling medium through the evaporator coils to cool the beverage product when stored in the bowl. The beverage dispenser further includes a dispenser assembly for dispensing the beverage product from the bowl. Finally, the beverage dispenser includes an auger which rotates about the freezing cylinder, the auger including a first end positioned near a front of the beverage dispenser and a second end positioned near a rear of the beverage dispenser. The auger has a ring gear positioned at its second end, and a drive system that includes a belt and pulley arrangement rotates the auger by driving the ring gear.
Owner:GRINDMASTER CORP
Mower suspension system and method
InactiveUS7107746B2Reduce scalping and uneven cuttingReduce exerciseCastorsLawn-mowersEngineeringLawn mower
A mower including a frame having a front portion, a rear portion, and at least one central longitudinal beam. The at least one beam is parallel with a longitudinal axis passing from the front portion to the rear portion of the frame. First and second wheels are positioned on opposite sides of the front portion of the frame and are spaced to define a track width of the mower, with the track width being a distance between a center portion of each of the first and second wheels. The first and second wheels pivot about a first longitudinal pivot axis and a second longitudinal pivot axis, respectively. The first and second longitudinal pivot axes are laterally spaced from the longitudinal axis between about 0% and about 20% of the track width.
Owner:FERRIS A DIV OF SIMPLICITY MFG
Waterless vacuum toilet system for aircraft
InactiveUS20040010843A1Reduces and eliminates adhesionIncrease surface areaWater closetsDispersed particle filtrationWaste collectionEngineering
A waterless vacuum toilet system for an aircraft includes a toilet bowl connected via a suction valve and a waste collection pipe to a waste collection tank. Waste-contacting surfaces that come into contact with urine and fecal waste are coated with an adhesion-inhibiting or adhesion-reducing nanocoating. The adhesion of waste is significantly reduced, and the need for flushing water is completely eliminated. Instead, an air jet arrangement preferably including an annular ring nozzle or annular air gap directs an airflow into the toilet bowl and along the nanocoated waste-contacting surface thereof, to "air flush" the waste material from these surfaces. The flushing airflow may be induced through the air jet arrangement into the toilet bowl by the suction applied through the suction valve. The "air flushed" toilet system substantially reduces the total system weight and eliminates the need for toilet flushing water to be carried in the aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
System and method for diagnosing aircraft components for maintenance purposes
InactiveUS6941204B2Maintenance costLow costVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDiagnostic systemSignal processing
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Waterless vacuum toilet system for aircraft
InactiveUS6977005B2Reduces and eliminates adhesionIncrease surface areaWater closetsDispersed particle filtrationWaste collectionFlush toilet
A waterless vacuum toilet system for an aircraft includes a toilet bowl connected via a suction valve and a waste collection pipe to a waste collection tank. Waste-contacting surfaces that come into contact with urine and fecal waste are coated with an adhesion-inhibiting or adhesion-reducing nanocoating. The adhesion of waste is significantly reduced, and the need for flushing water is completely eliminated. Instead, an air jet arrangement preferably including an annular ring nozzle or annular air gap directs an airflow into the toilet bowl and along the nanocoated waste-contacting surface thereof, to “air flush” the waste material from these surfaces. The flushing airflow may be induced through the air jet arrangement into the toilet bowl by the suction applied through the suction valve. The “air flushed” toilet system substantially reduces the total system weight and eliminates the need for toilet flushing water to be carried in the aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
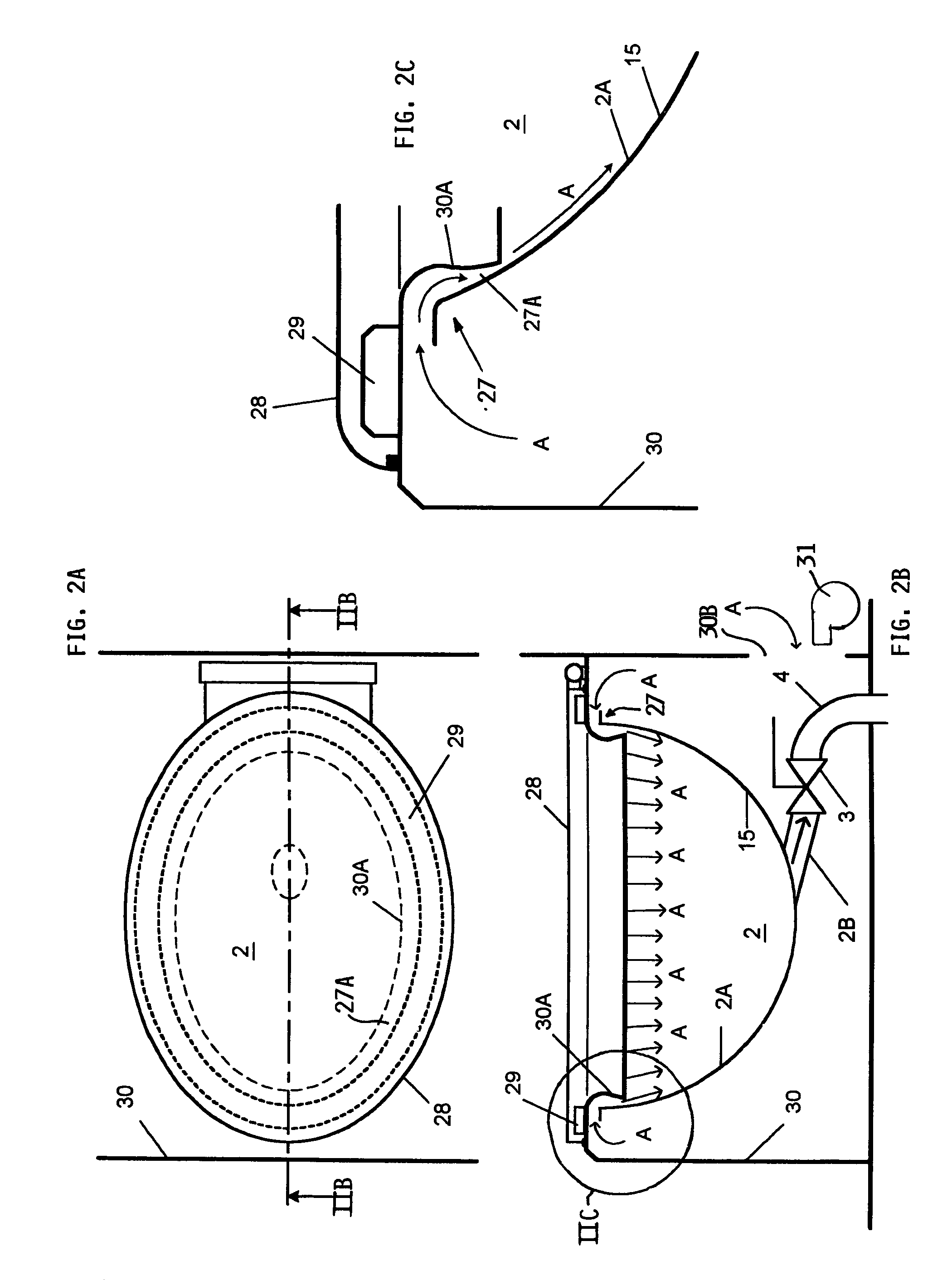
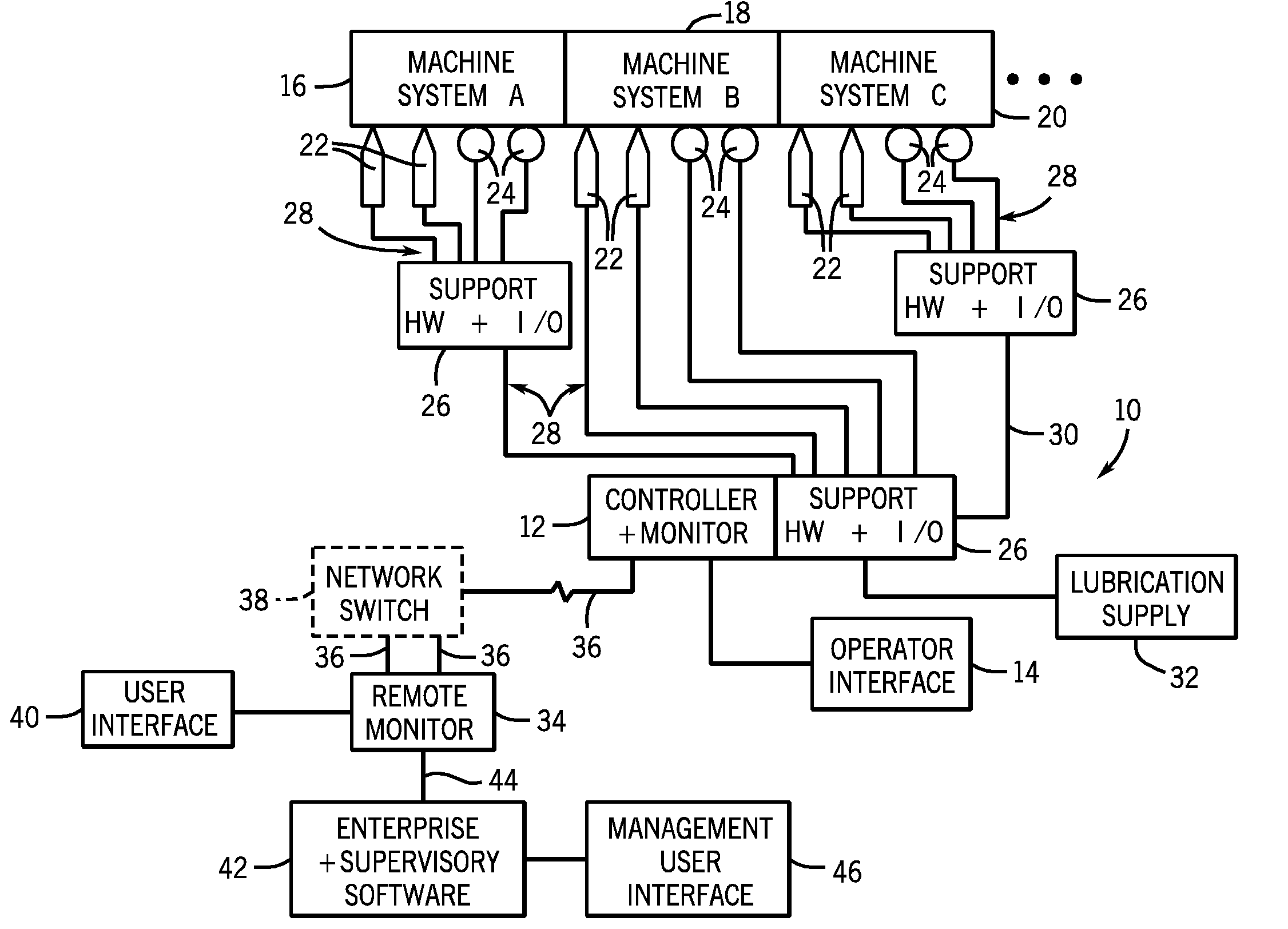
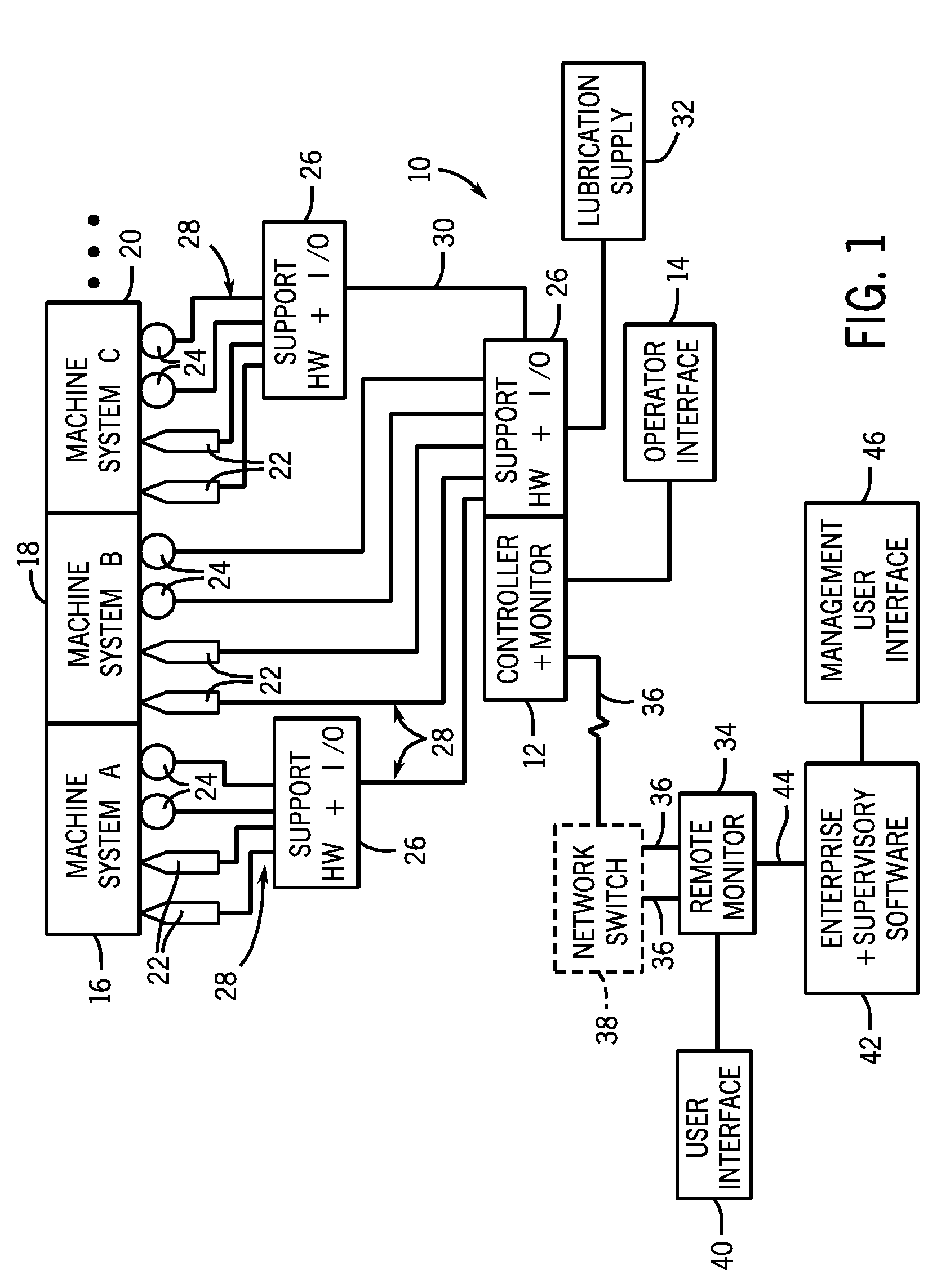
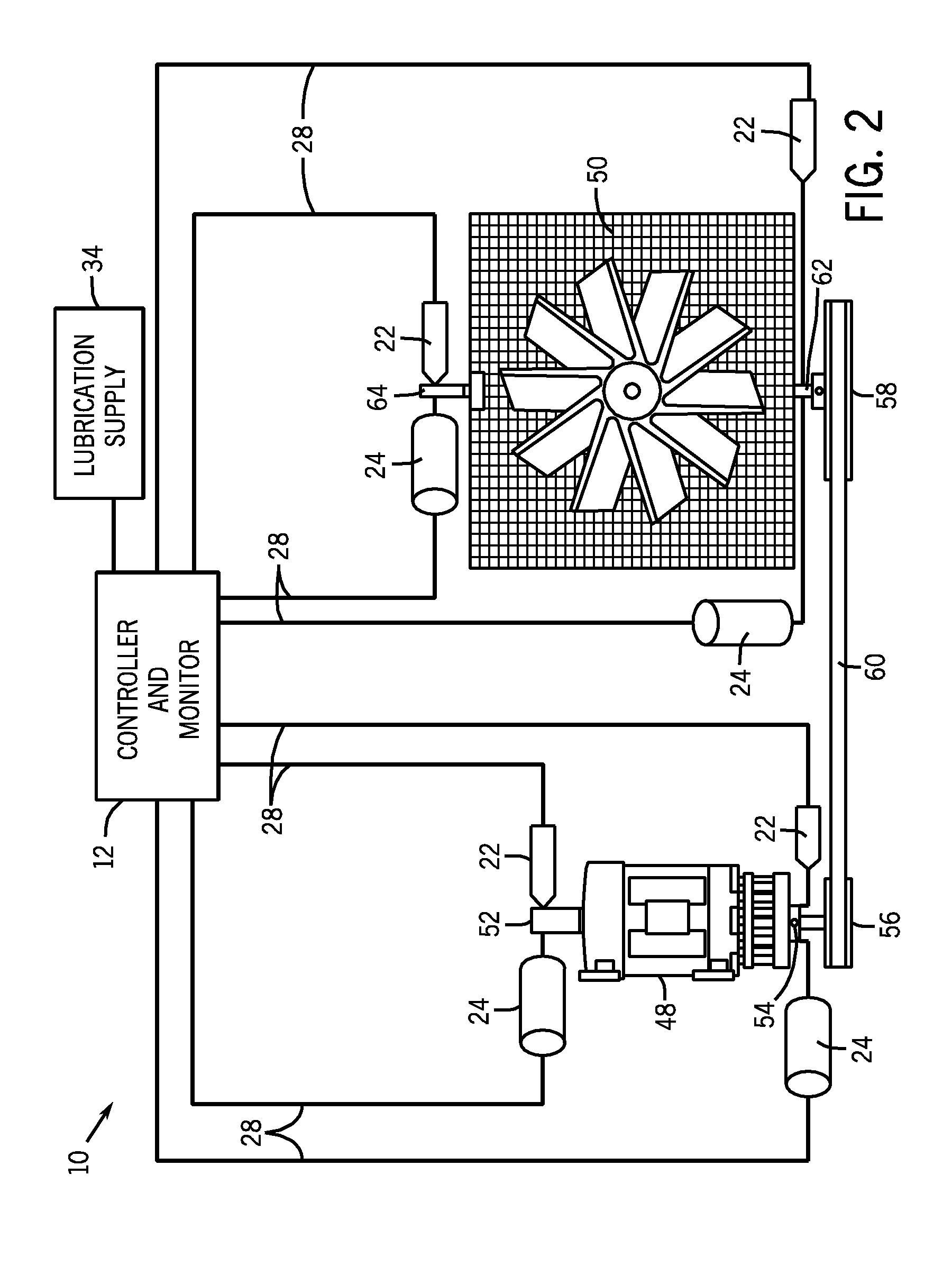
Machine conditioning monitoring closed loop lubrication system and method
ActiveUS20100147627A1Improve machine lifeReduce maintenanceVibration measurement in solidsProportioning devicesAccelerometerClosed loop
In one embodiment, the disclosed method for lubricating a machine bearing system includes monitoring a bearing system using a vibration sensor, such as an accelerometer, receiving a signal from the vibration sensor, calculating a parameter based on the signal; and adding a lubricant to the bearing system based upon the parameter. In another embodiment, a system may include a vibration sensor, a monitor configured to receive a signal from the vibration sensor and calculate a spike energy value, and a lubrication device configured to add a lubricant to a bearing system based on the spike energy value. The system and method help reduce maintenance and repair costs, while prolonging the life of the machine system components being monitored.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Mower Suspension System and Method
InactiveUS20110197419A1Reduce scalping and uneven cuttingReduce exerciseAssembly machinesLawn-mowersEngineeringMower
In some embodiments, the present invention provides a mower including a frame having a front portion and a rear portion, at least one front wheel coupled to the front portion of the frame, and two drive wheels on substantially opposite sides of the rear portion of the frame. Each drive wheel is coupled to the frame by a first link pivotably coupled at one end to the front portion of the frame and at an opposite end to the drive wheel, and a second link pivotably coupled at one end to the rear portion of the frame and at an opposite end to the drive wheel. The mower also includes at least one spring positioned to bias the drive wheels in a downward direction. Each of the drive wheels are movable upward and downward relative to the frame.
Owner:BRIGGS & STRATTON
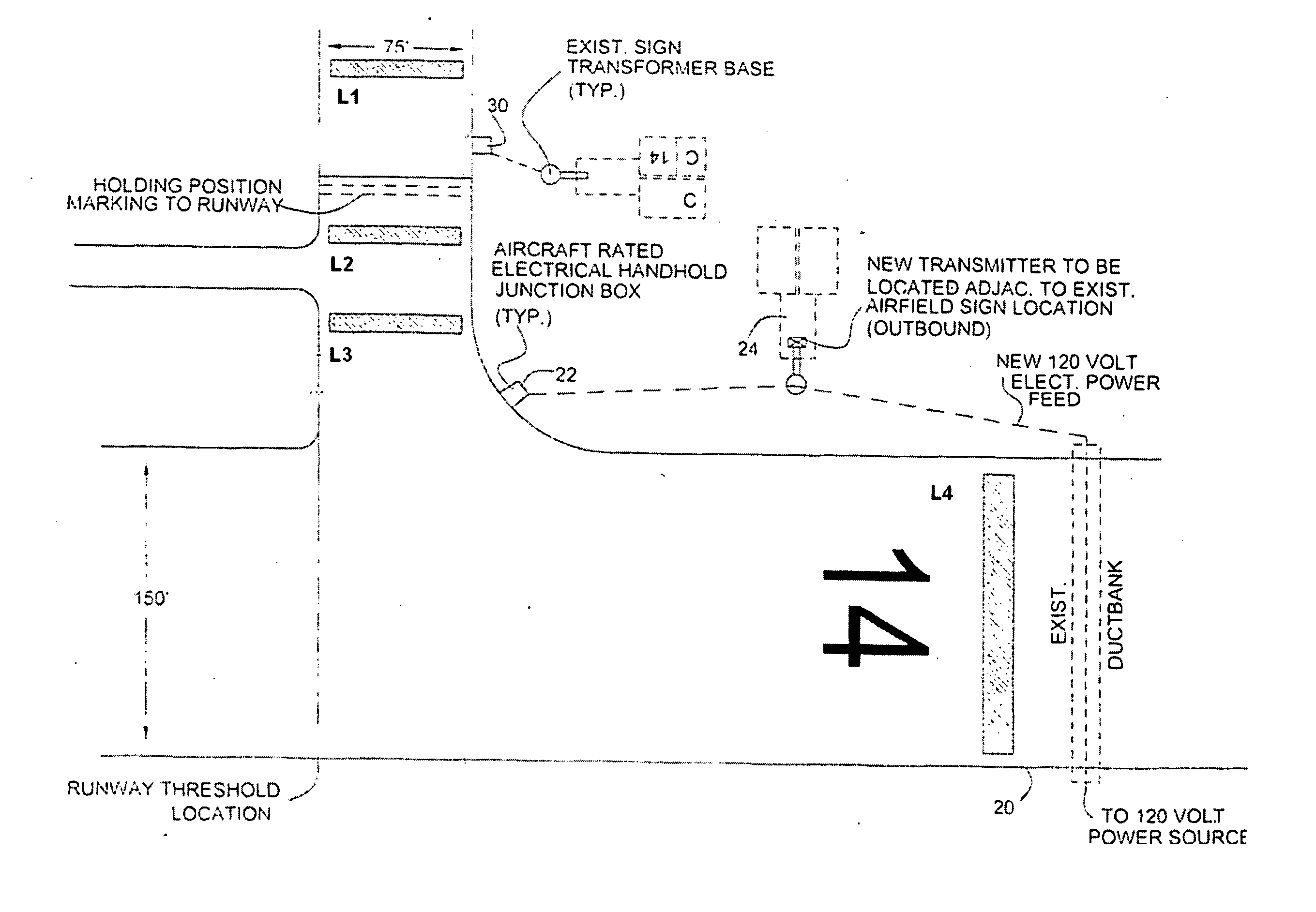
System for monitoring vehicle and airplane traffic on airport runways
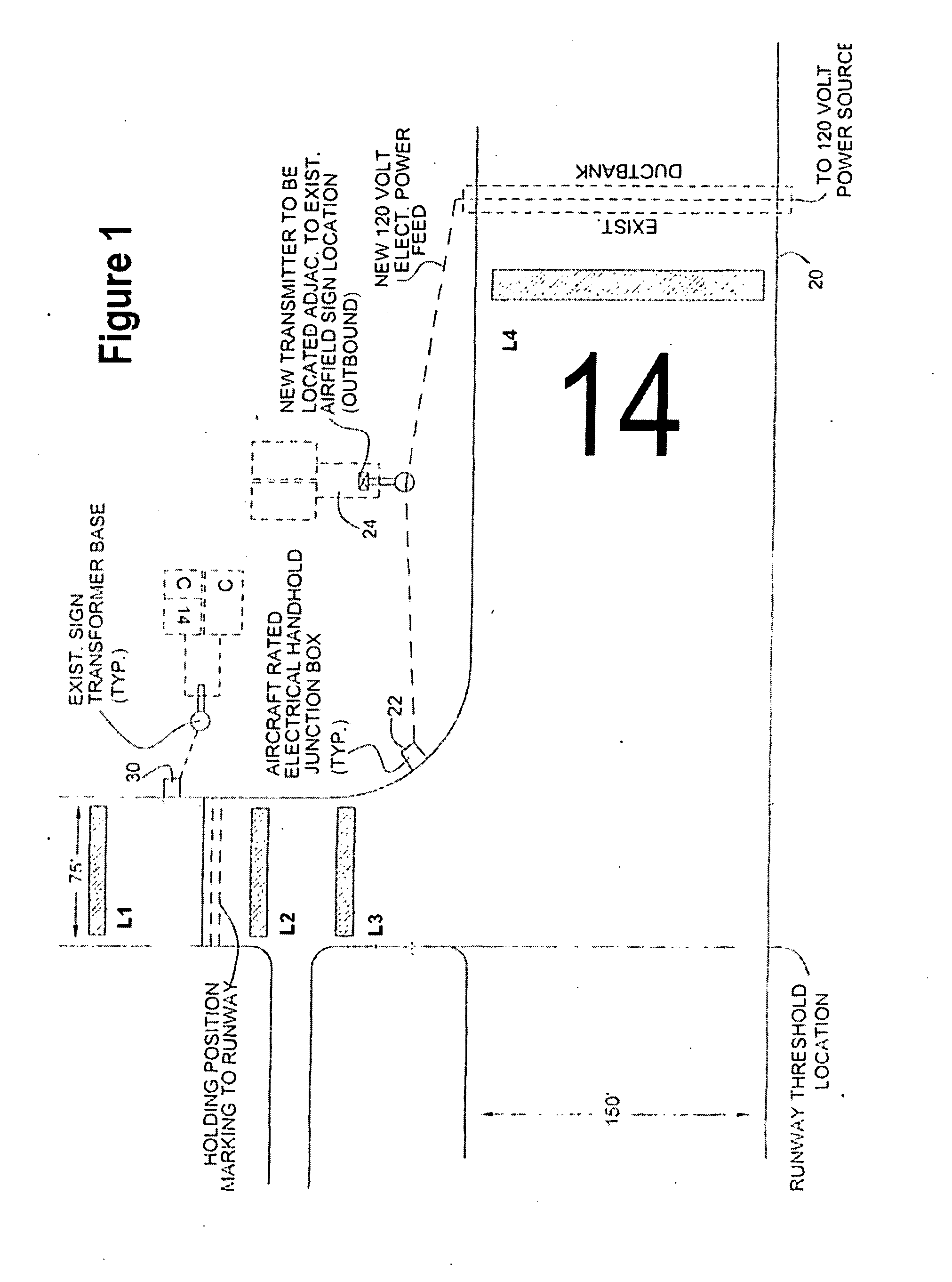
InactiveUS20060259232A1Reduce maintenanceReduce repairAnalogue computers for vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficJet aeroplaneCommunications system
An airfield runway occupancy warning system includes inductive loops buried in a runway proximate to an intersection of said runway and a taxiway. Other inductive loops are buried in a taxiway proximate an intersection of the taxiway and a runway. A communication system receives data from each of the inductive loops and transmits the data to at least one monitoring device.
Owner:PATRIOT TECH
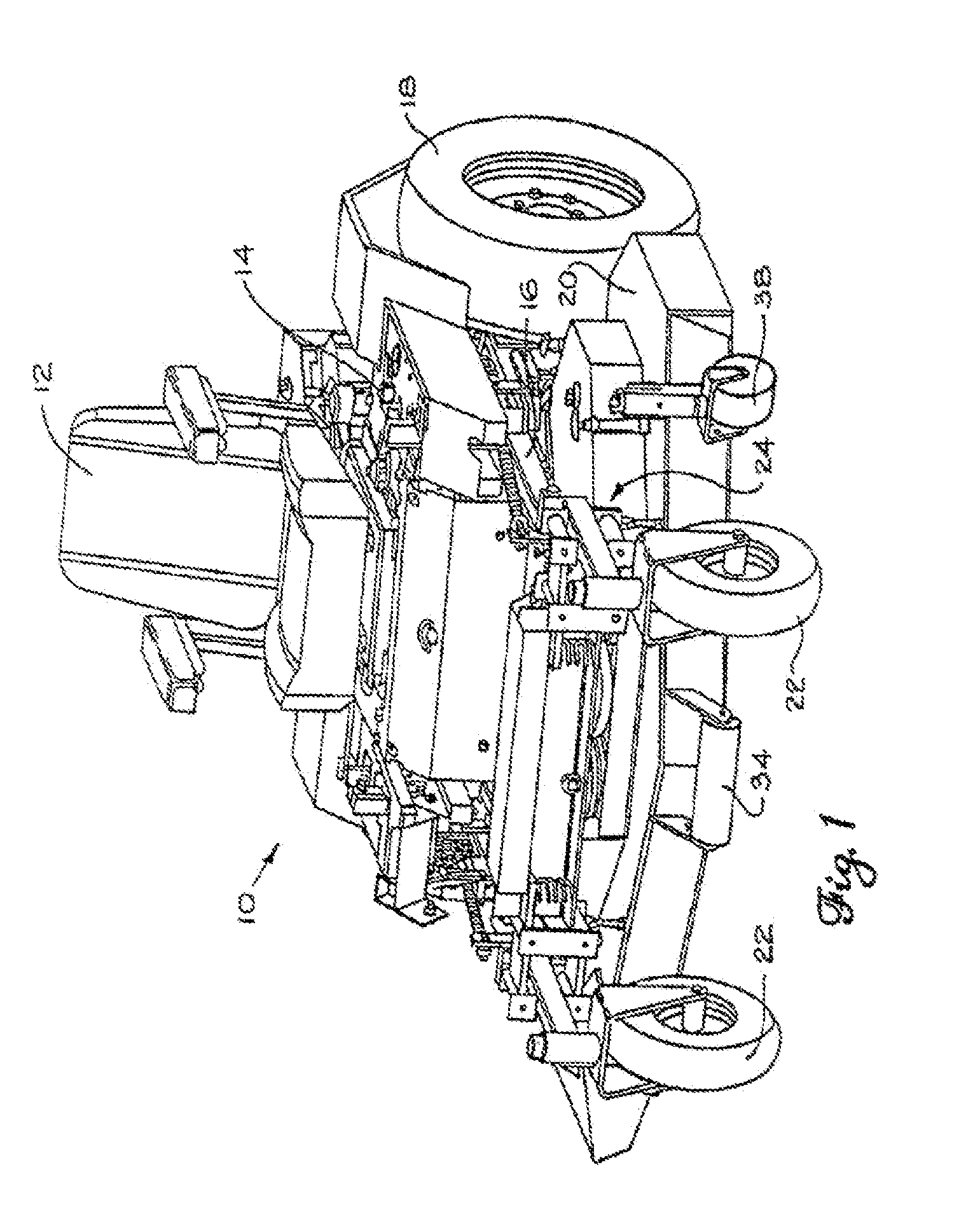
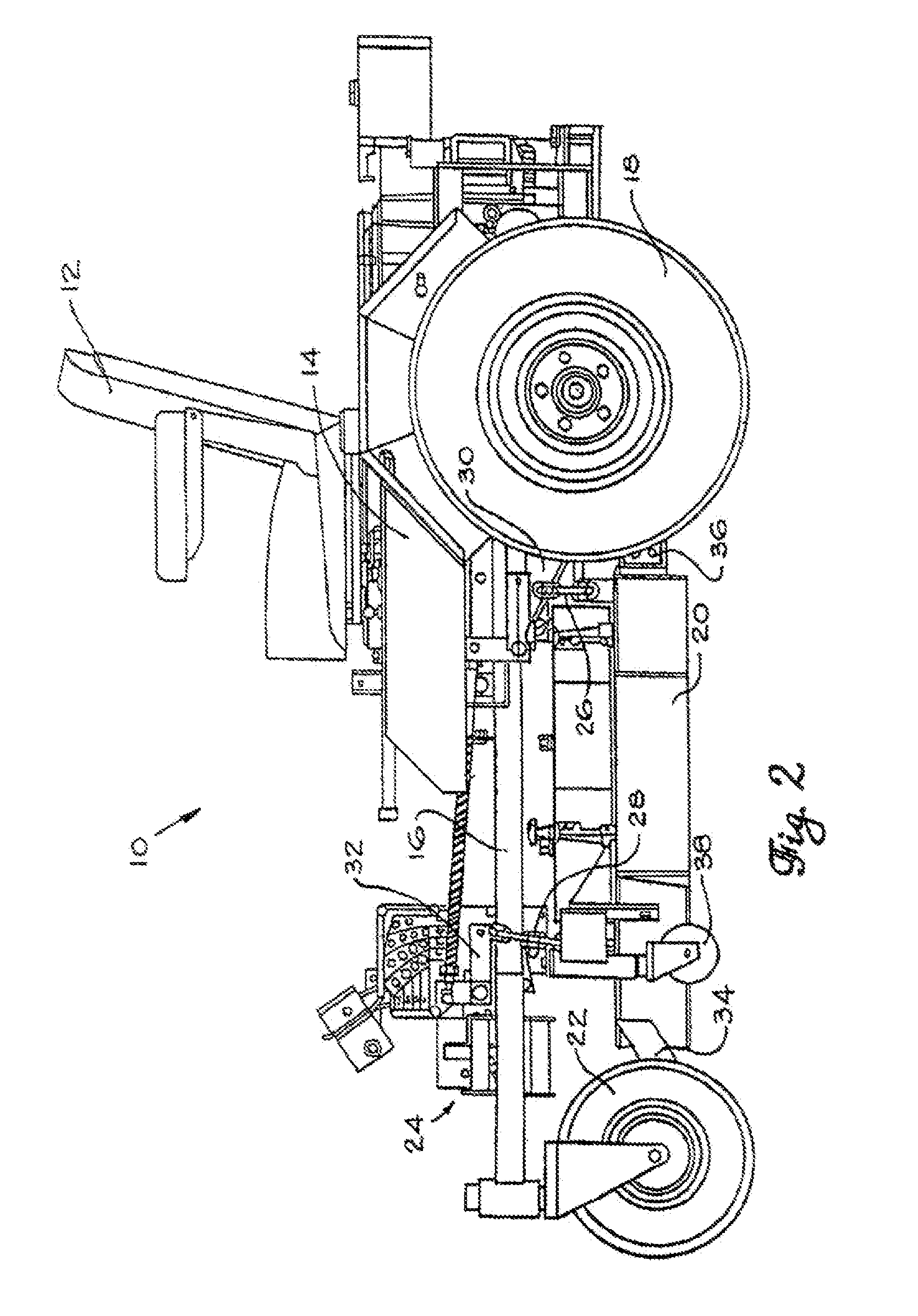
Tandem disk with finishing reel
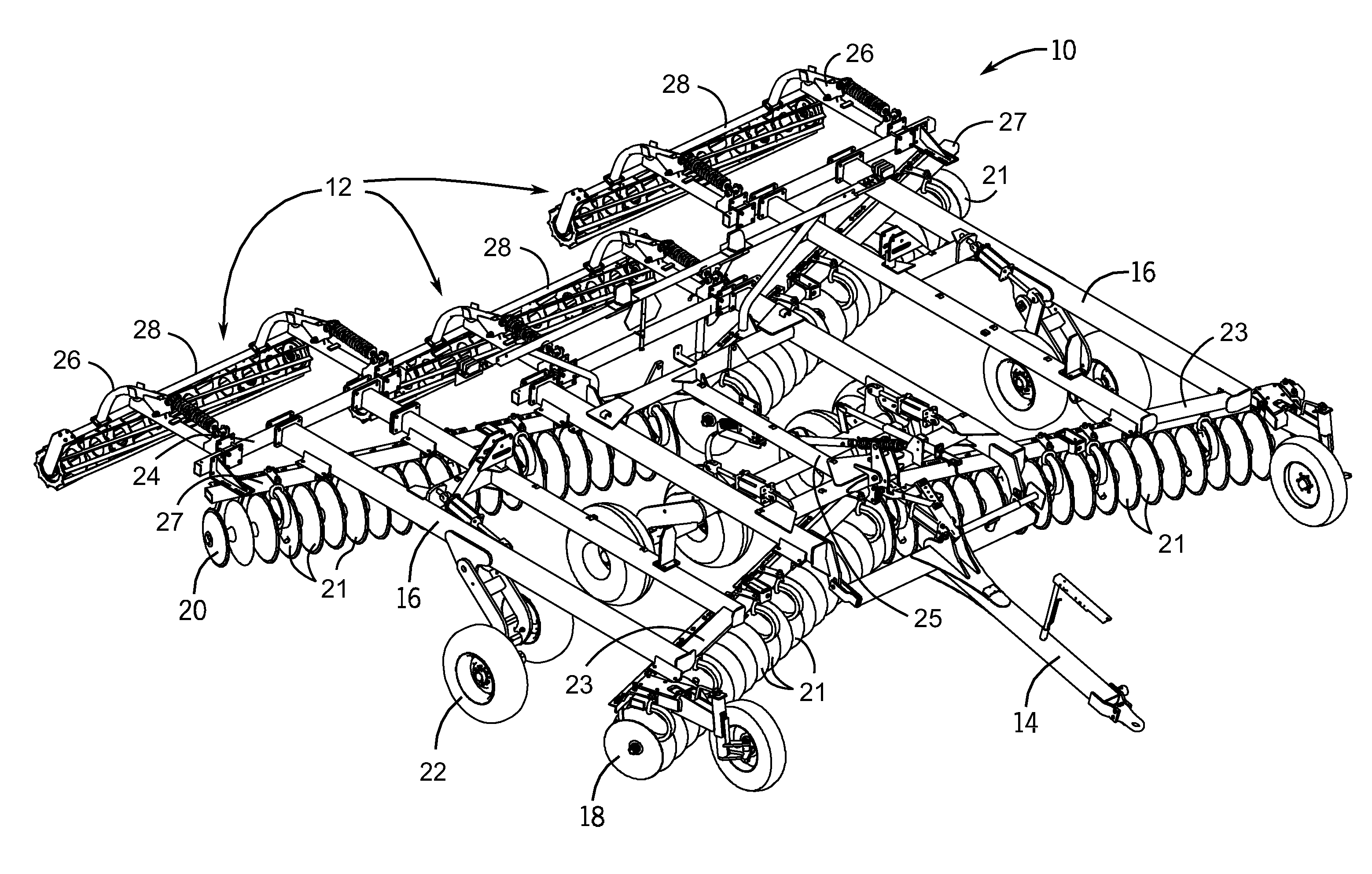
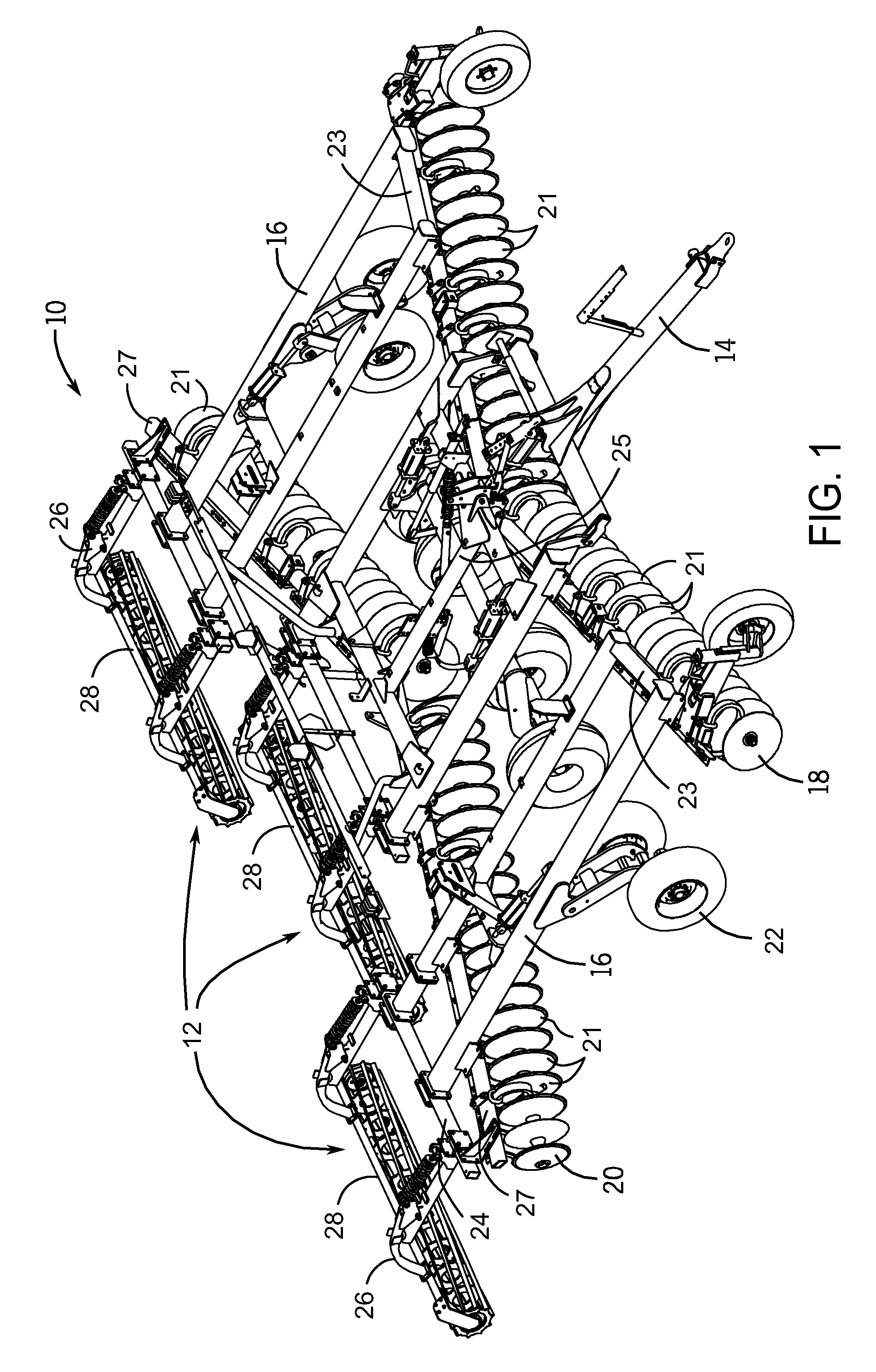
InactiveUS20100084148A1Reduce in quantityReduce maintenanceSpadesHarrowsGerminationAgricultural engineering
Embodiments of the present invention provide a novel configuration for agricultural tandem disk systems that feature soil finishing systems. This configuration of the finishing system features finishing reels that provide a robust assembly that will require less frequent repair and maintenance. The finishing system also features support arms that allow the user to adjust the position of finishing reels and the downward force applied to the reels. In an exemplary embodiment, the soil finishing reels are located behind two rows of ground breaking disk blades. After the soil is opened by the disks, the finishing reel may be used to break up or split large soil clods created by the disks. The soil finishing system allows the user to have the soil in an optimized state for germination after one pass of the agricultural system, reducing the number of passes needed to prepare the field.
Owner:CNH IND AMERICA LLC
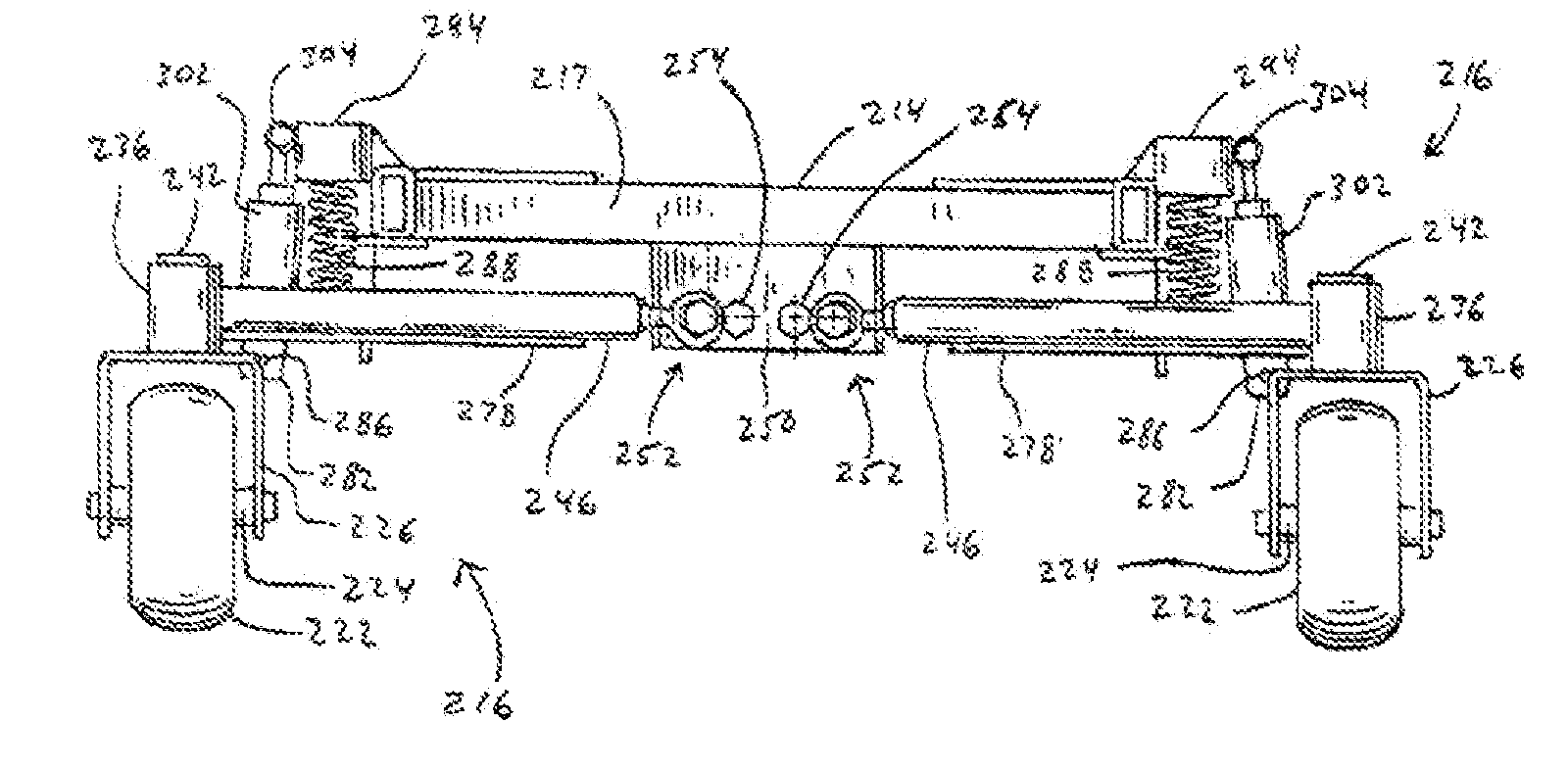
Cryogenic probehead cooler in a nuclear magnetic resonance apparatus
ActiveUS20120242335A1Lower energy requirementsLess cooling energyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceNuclear engineering
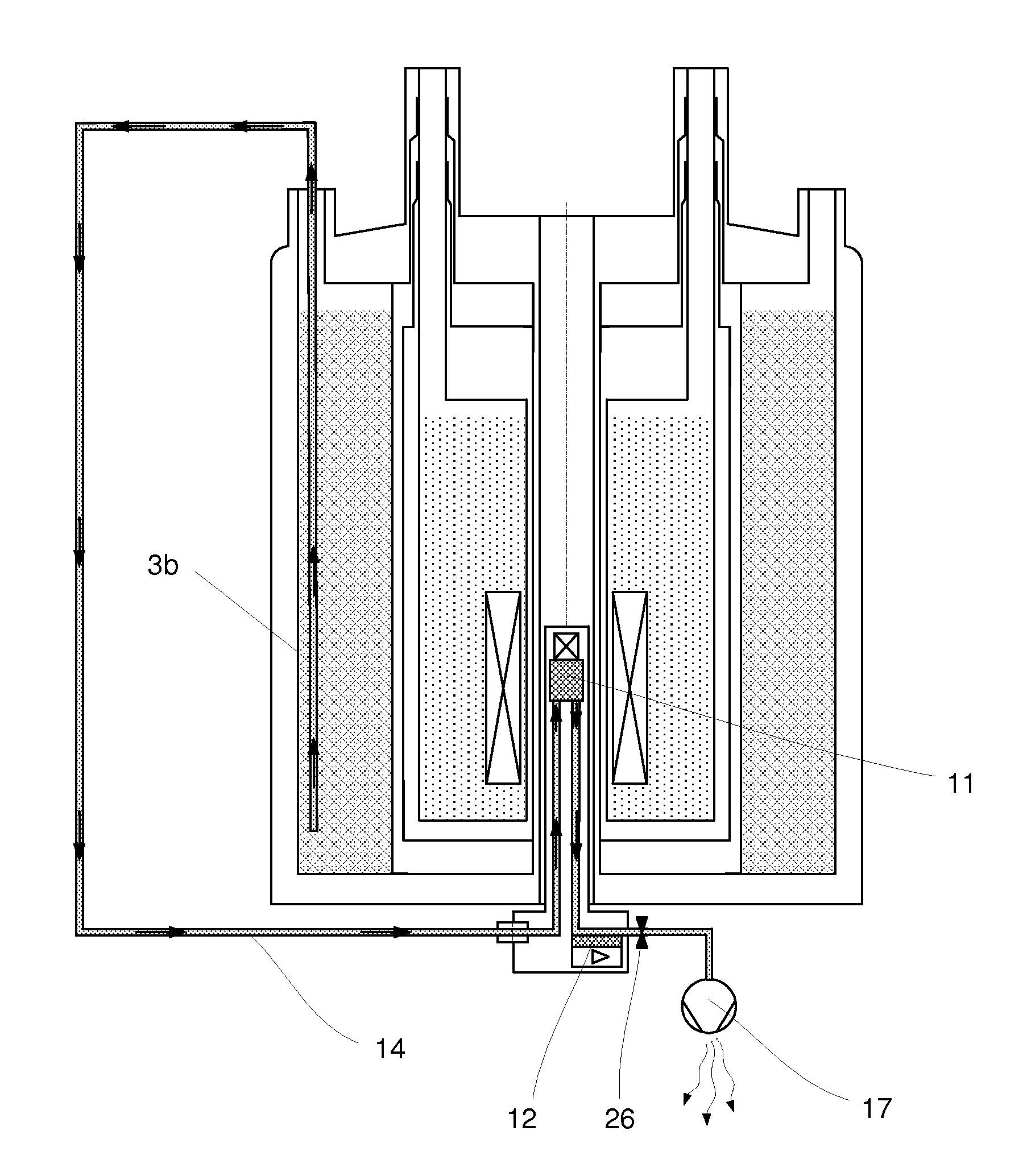
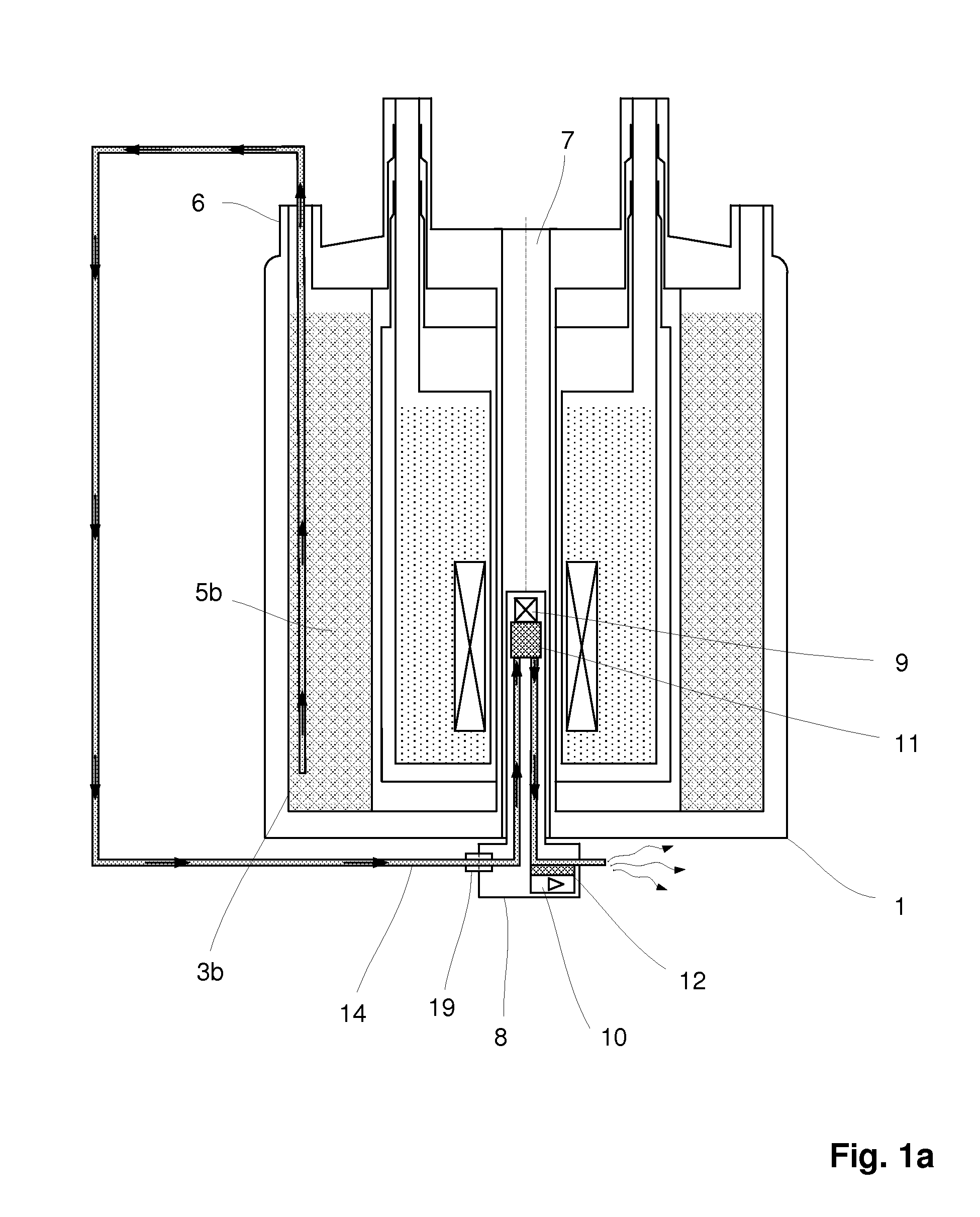
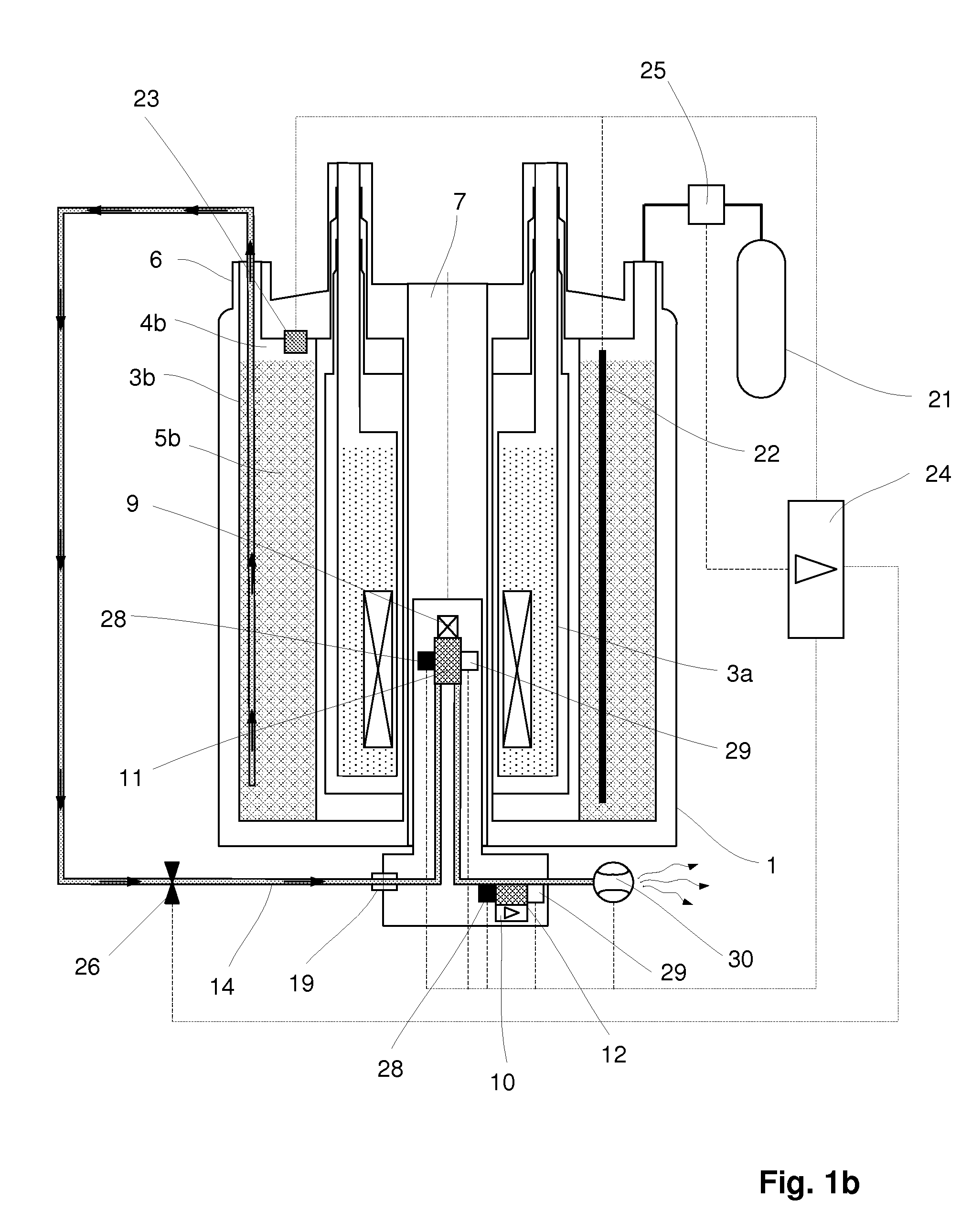
An NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) apparatus has a magnet system disposed in a cryostat (1), the cryostat having at least one nitrogen tank (3b) for receiving liquid nitrogen (5b) and a room temperature bore (7) for receiving an NMR probehead (8), wherein part(s) of the probehead or the overall probehead can be cooled to cryogenic temperatures by supplying liquid nitrogen (5b) via a supply line (14). The nitrogen tank (3b) of the cryostat (1) is connected to the NMR probehead (8) by means of a supply line (14) in such a fashion that liquid nitrogen (5b) is removed from the nitrogen tank (3b) and guided to the NMR probehead (8). The overall apparatus is therefore more compact, the operating comfort of the apparatus is increased, and the costs for acquisition, operation and maintenance are considerably reduced compared to previous comparable devices.
Owner:BRUKER SWITZERLAND AG
System and method for allocating identifier to multi-bms
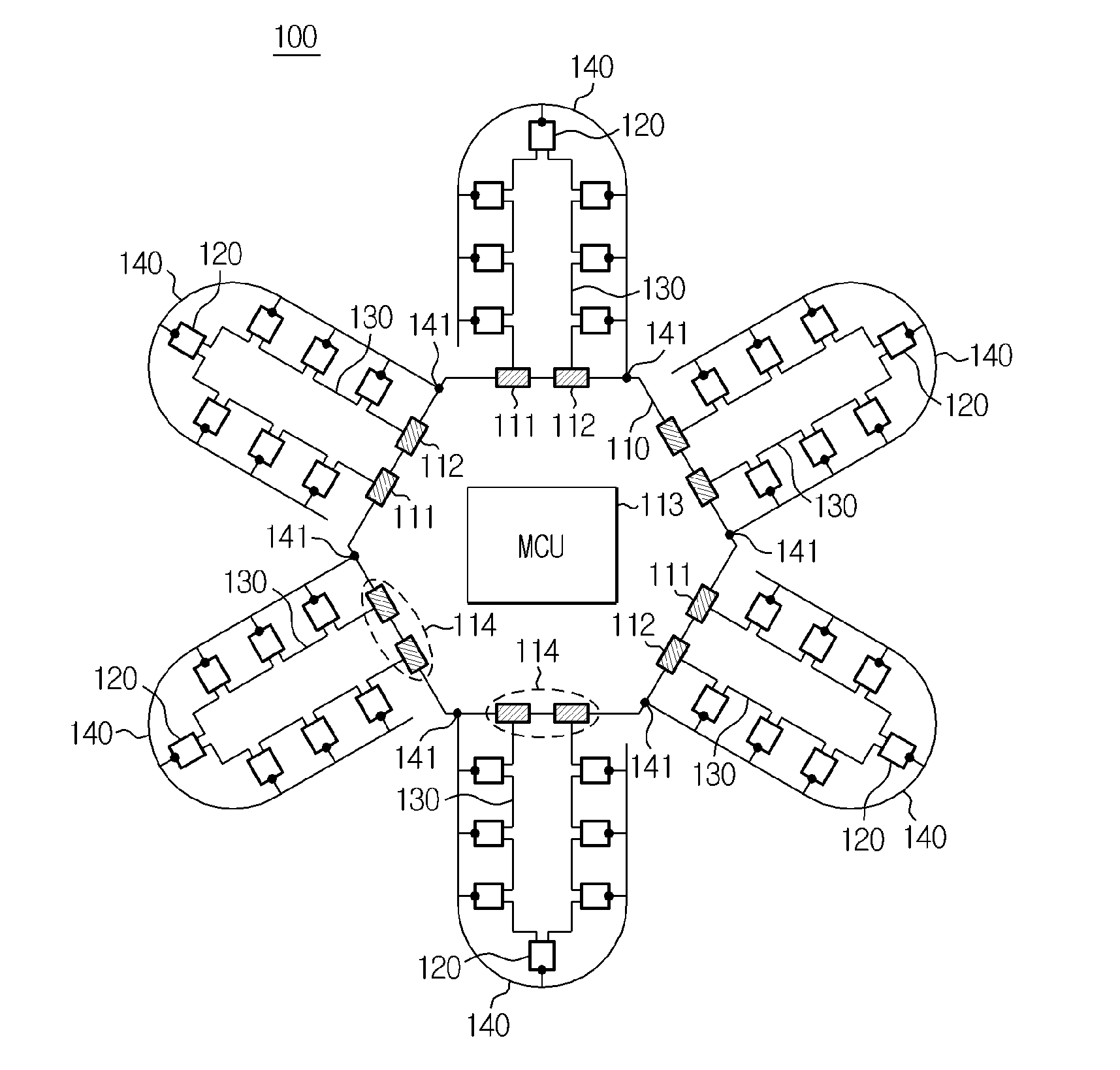
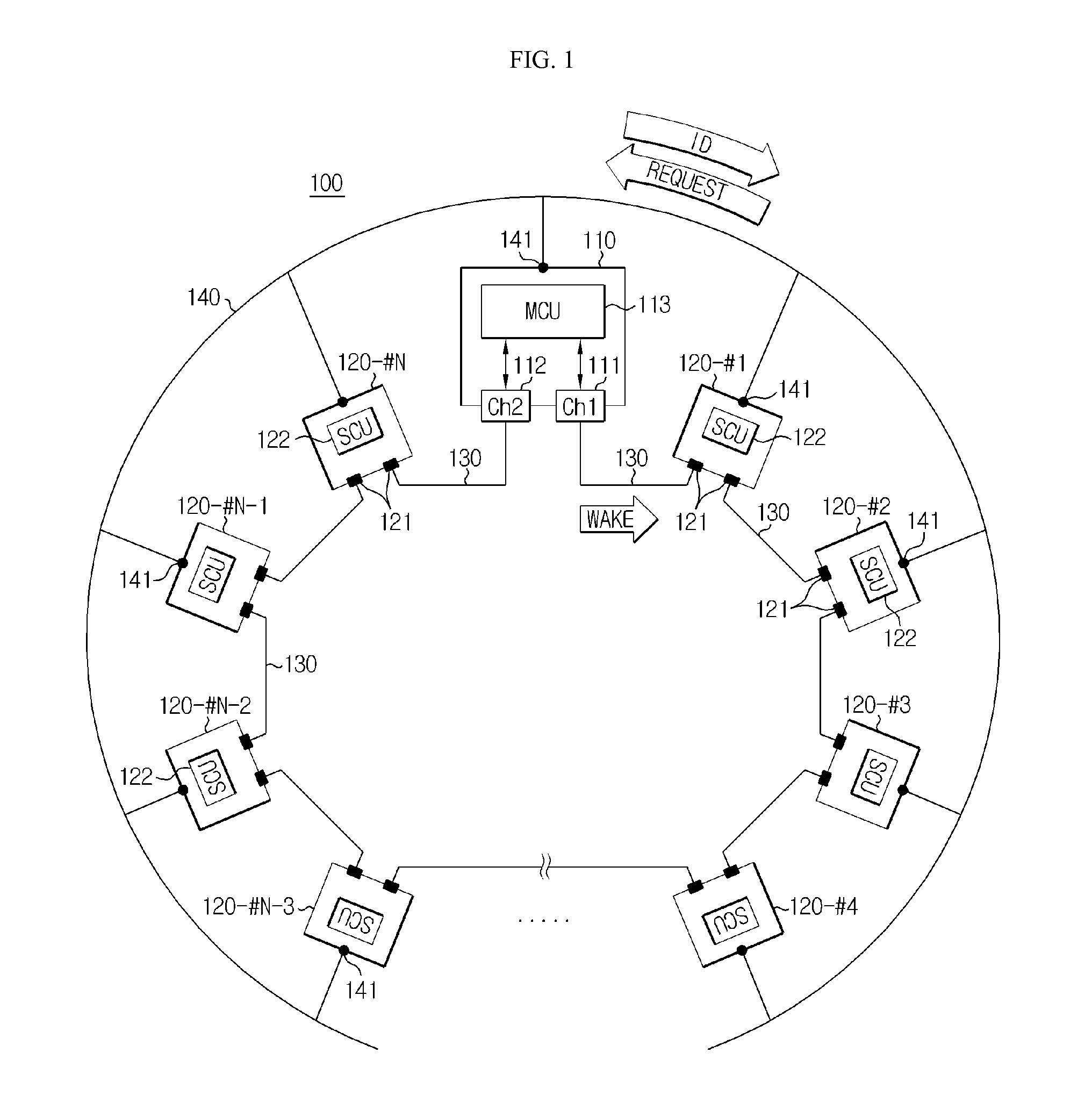
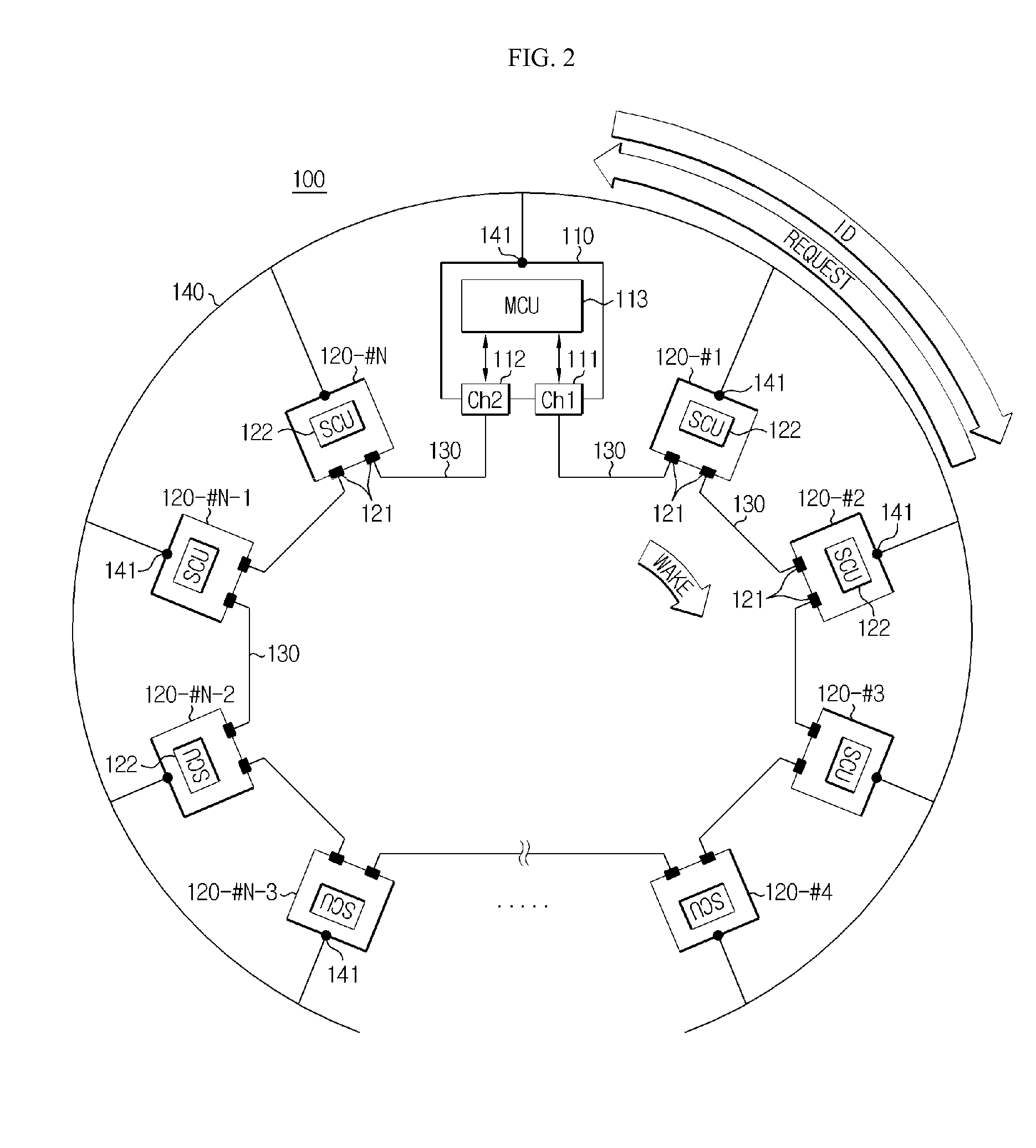
ActiveUS20140091770A1Automatic detectionSolve the real problemWired architecture usageElectrical testingCommunication interfaceUser identifier
Disclosed is a multi-BMS identifier allocation system. The multi-BMS identifier allocation system according to the present invention comprises a master BMS and N slave BMSs (N is an integer greater than or equal to 2) which are connected to a series communication network and a parallel communication network, wherein the master BMS comprises at least two first and second master communication channels which form a communication interface with the series communication network and selectively output a forward or backward enabling signal and allocates unique communication identifiers to the slave BMSs through the parallel communication network, and the first to Nth slave BMSs start enabling in response to the forward or backward enabling signal received through the series communication network, are allocated the identifiers from the master BMS through the parallel communication network, and output an enabling signal to an adjacent slave BMS along a transmission direction of the enabling signal.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com