Patents
Literature
493 results about "Parallel communication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In data transmission, parallel communication is a method of conveying multiple binary digits (bits) simultaneously. It contrasts with serial communication, which conveys only a single bit at a time; this distinction is one way of characterizing a communications link.
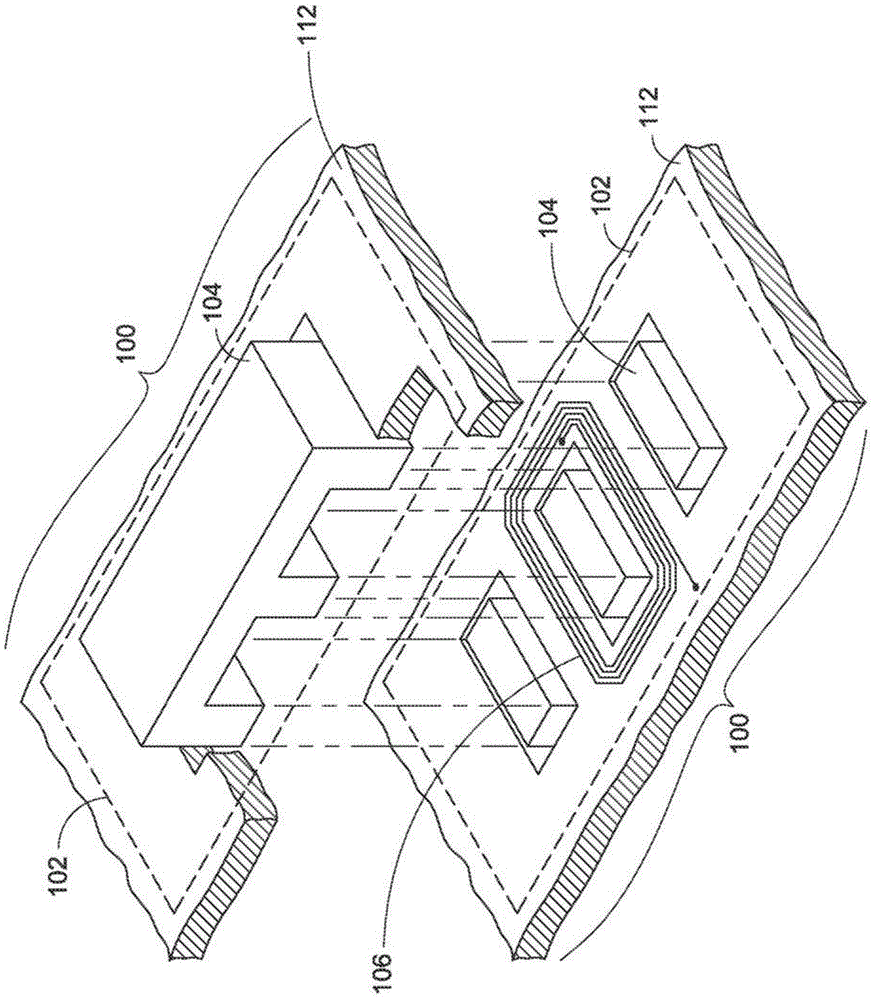
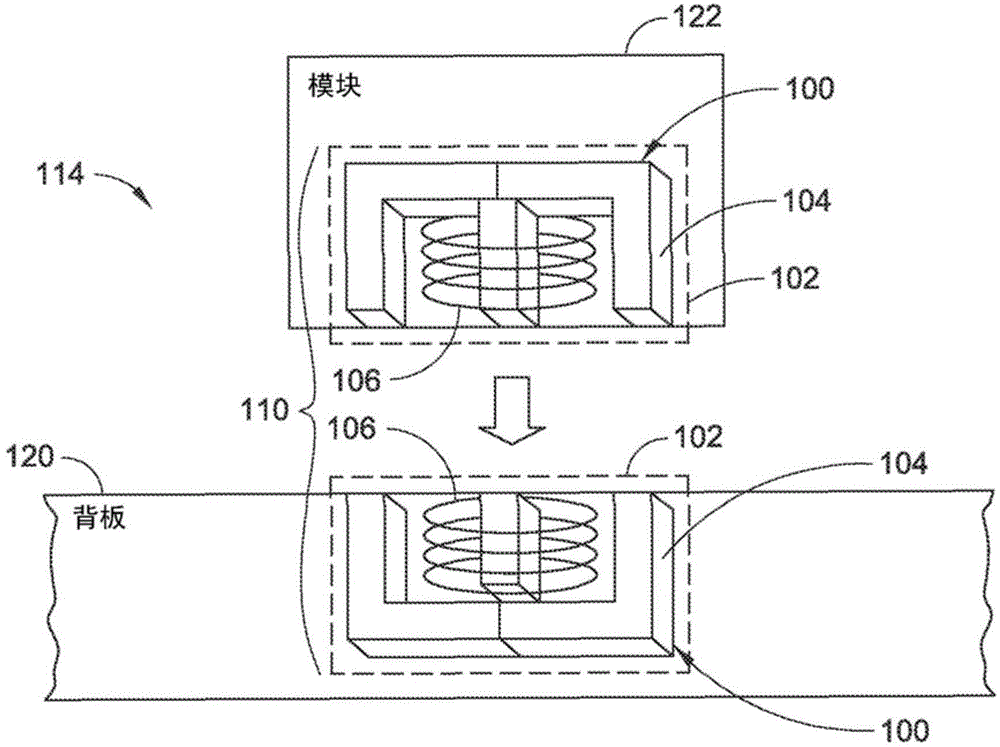
Transaction verification system
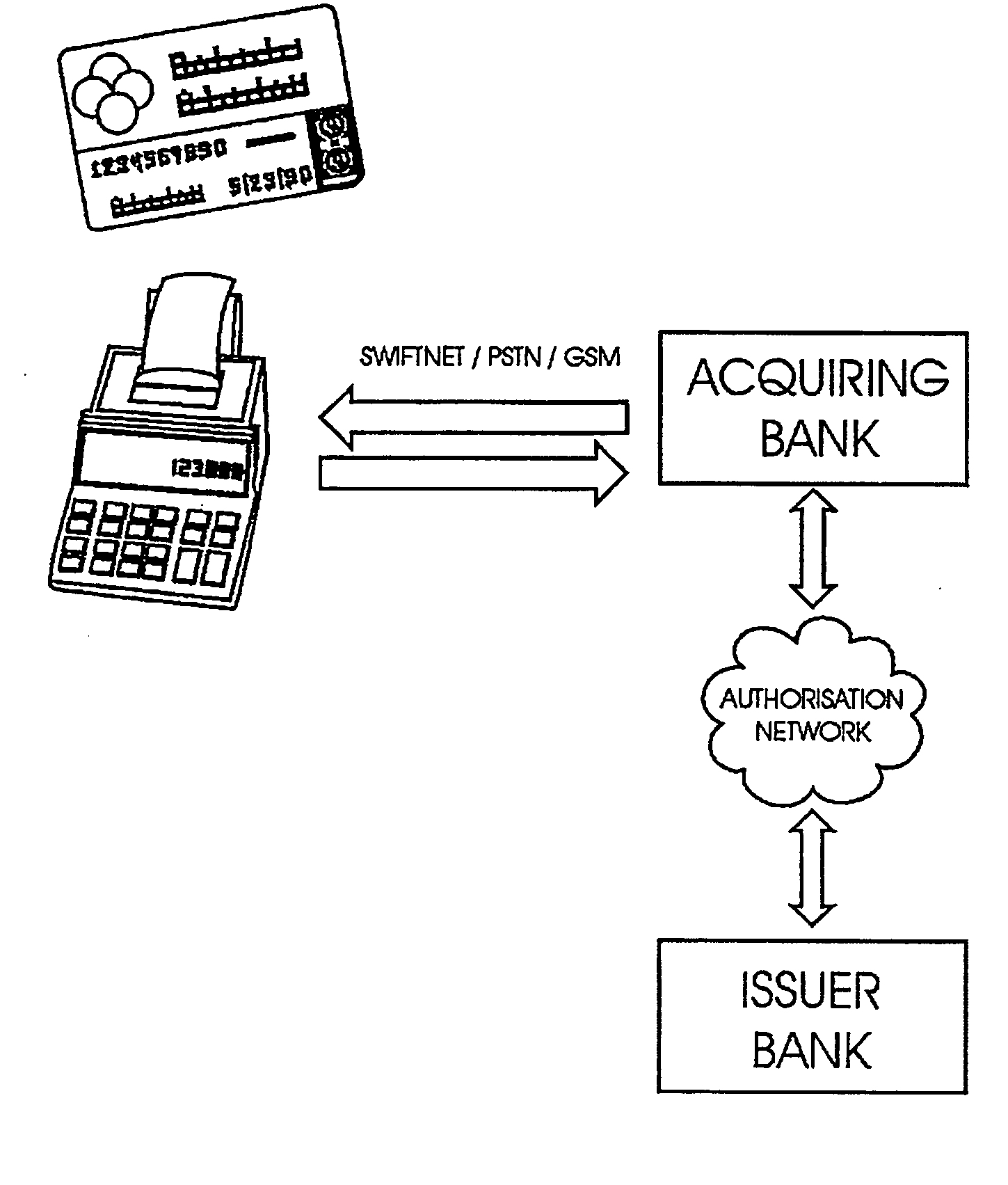
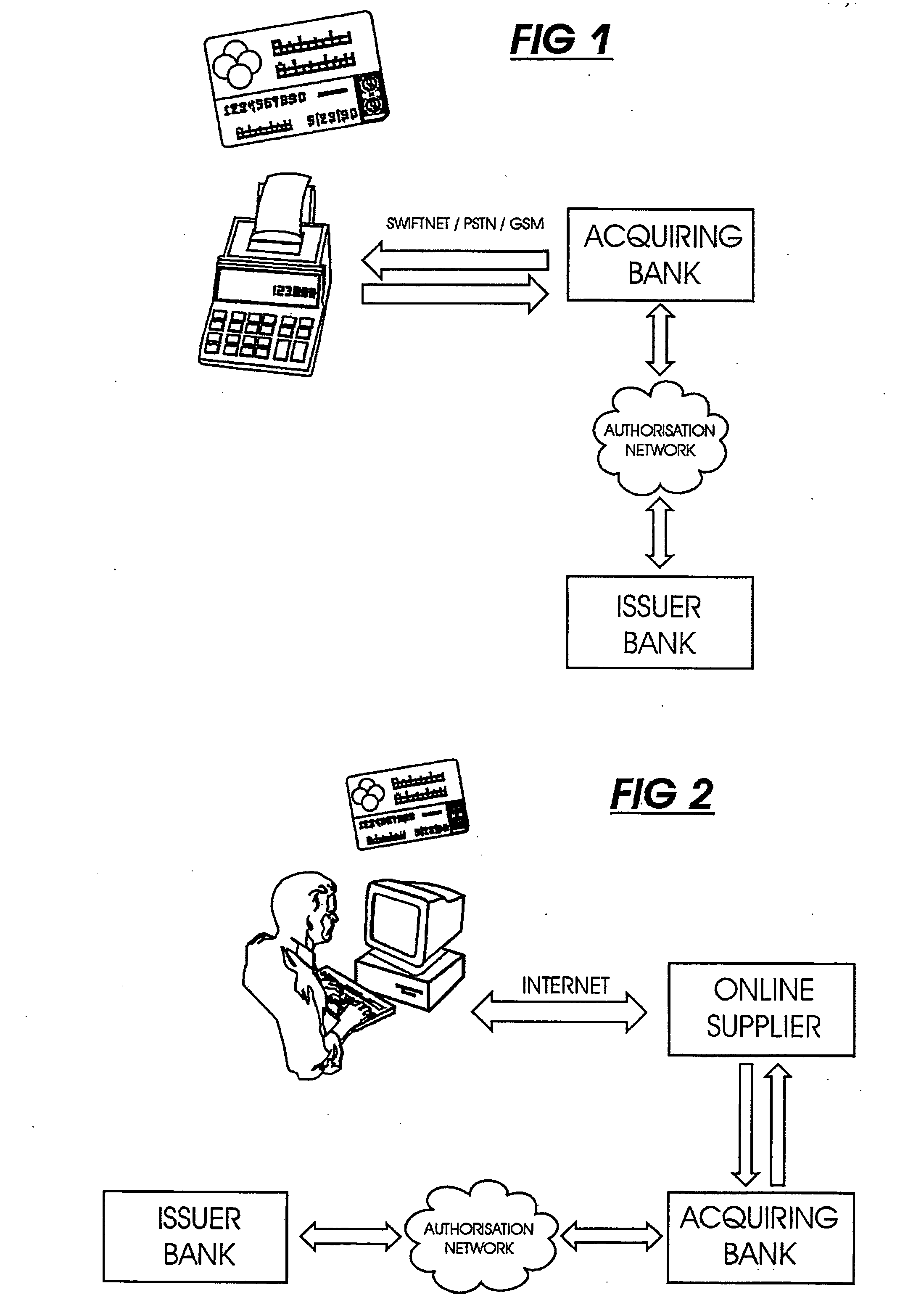
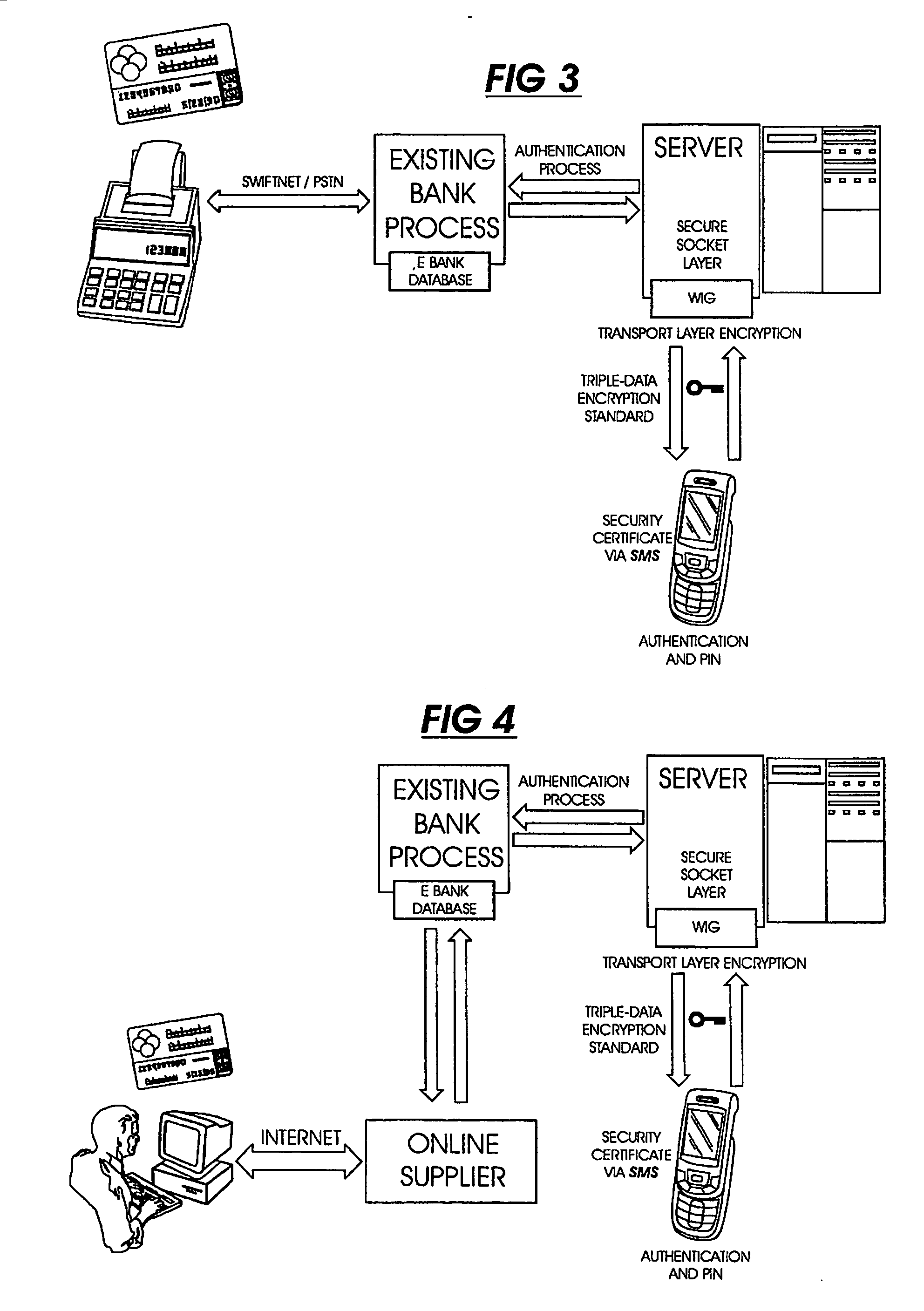
This invention uses separate, parallel communication channels to authorise and authenticate a transaction. A primary data channel (PSTN, radio or the like) is used to communicate between the merchant terminal and the bank, and a parallel data channel (a mobile phone network for instance) is used for the authentication process. In the example, the transaction is initiated (on a primary data channel), using a POS terminal as a transaction processing client. The transaction processing server and financial services provider fulfill their normal functions. At this point, the process loops into a transaction authorisation component using the parallel data channel, that requires authentication of the transaction initiator (the card holder). In the example, communications on the parallel data channel are by way of SMS. In the authorisation process, the card holder receives an SMS requesting authorisation of the transaction. If the card holder is not the transaction initiator, the card holder can cancel the transaction. If the transaction can be authorised, an authentication process is initiated in which the mobile phone is programmed to require the entry of a normally secret code (such as a personal identification number (PIN)) that serves to authenticate the card holder and to give final authorisation of the transaction.
Owner:NARAINSAMY SELVANATHAN
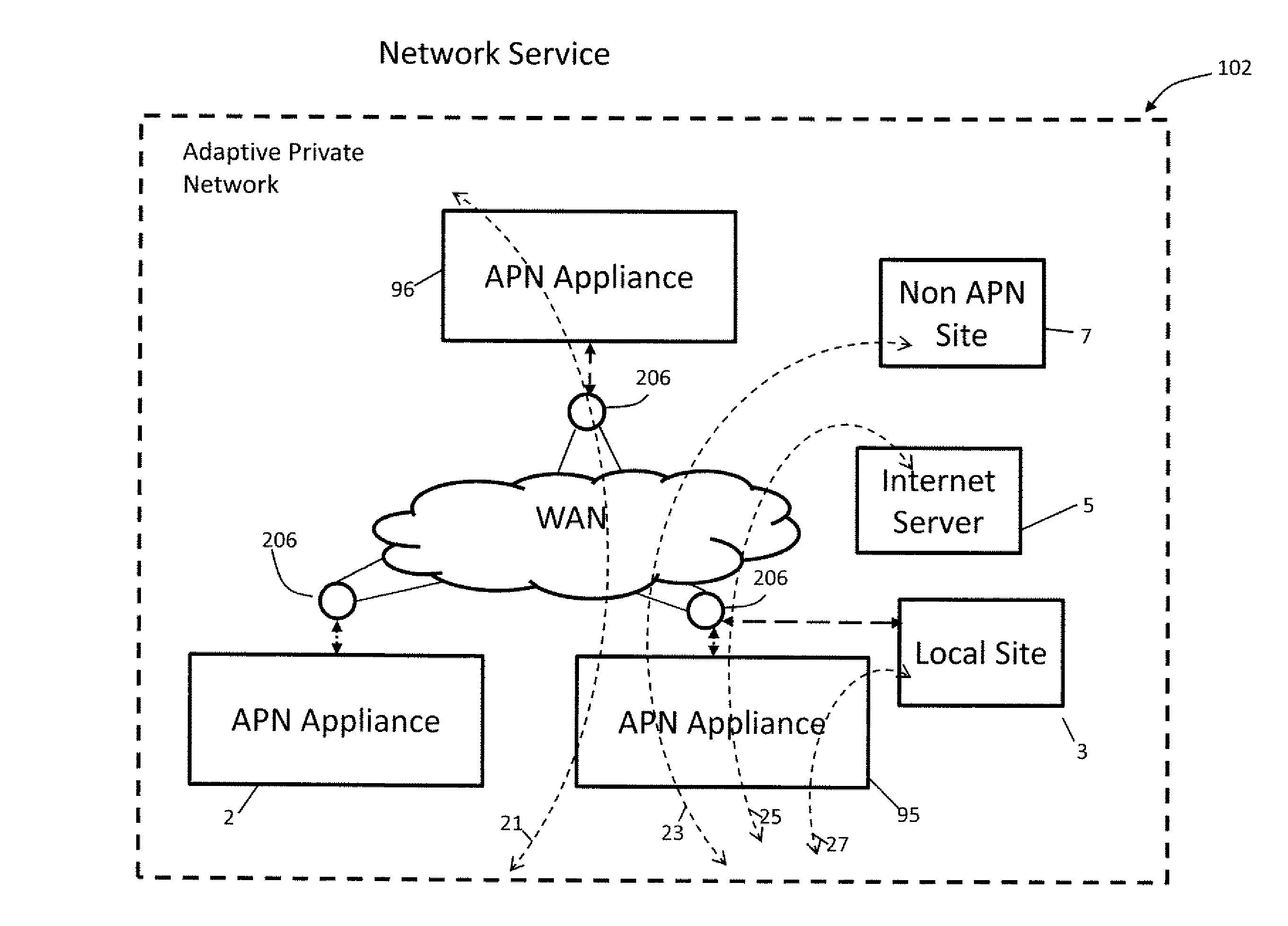
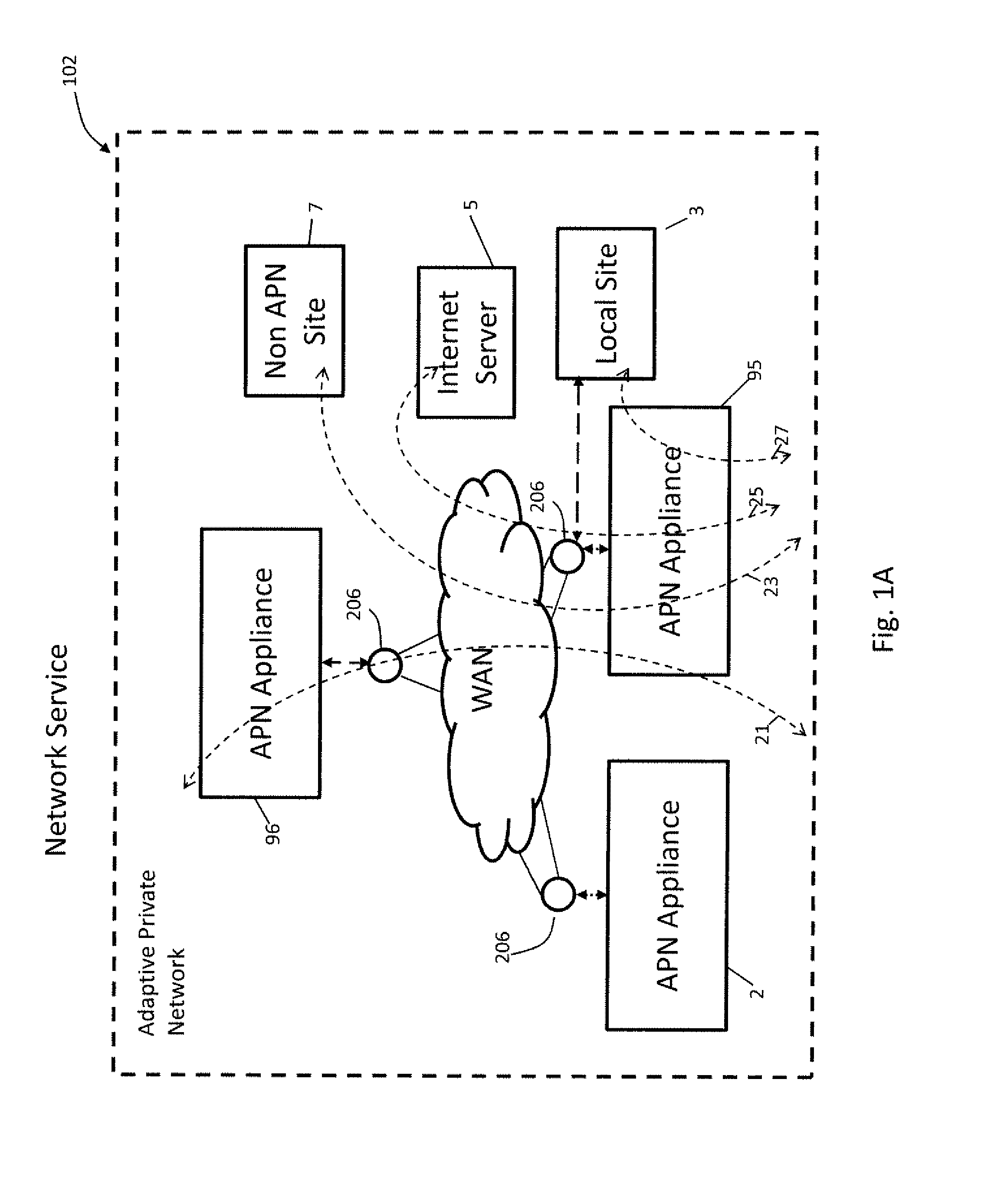
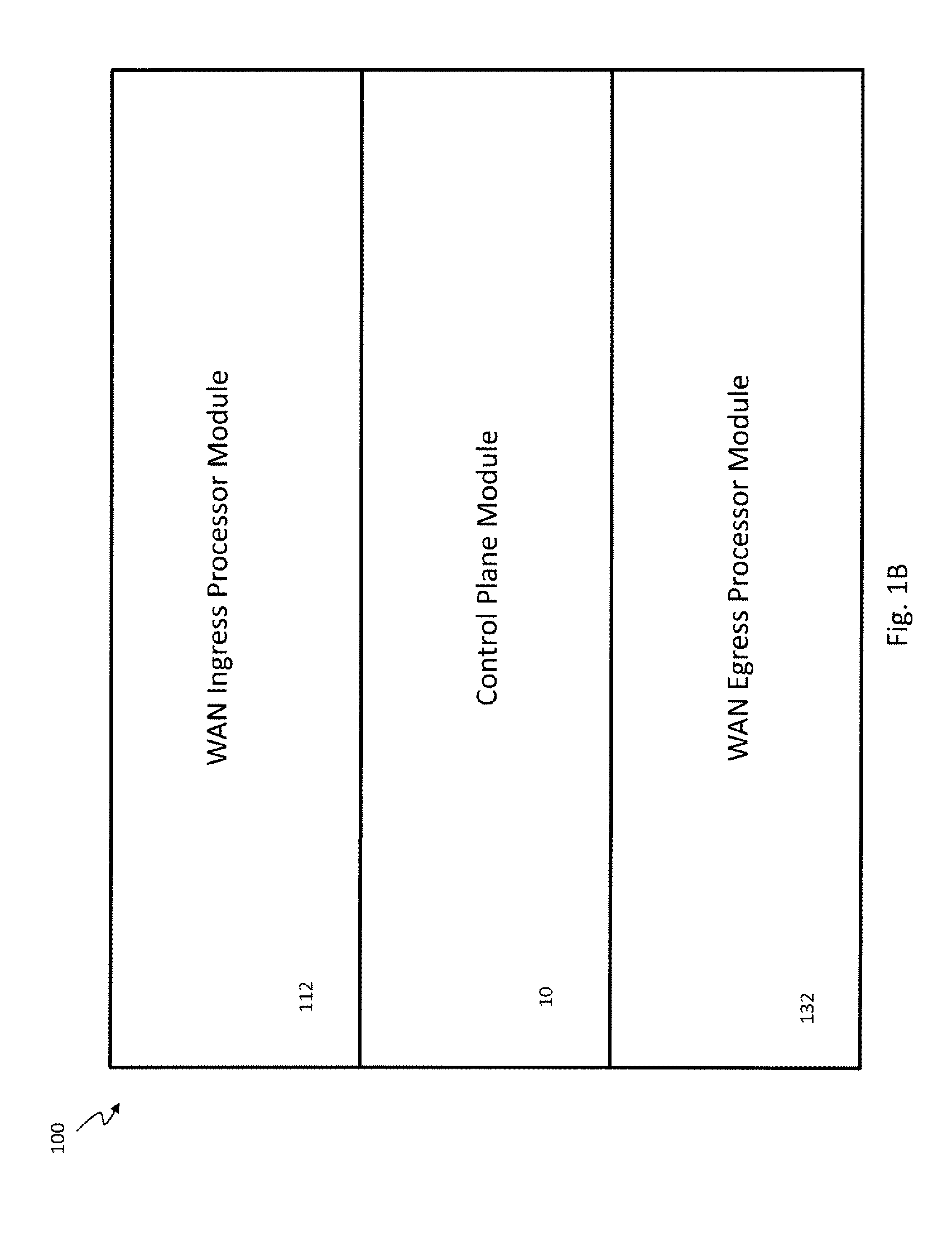
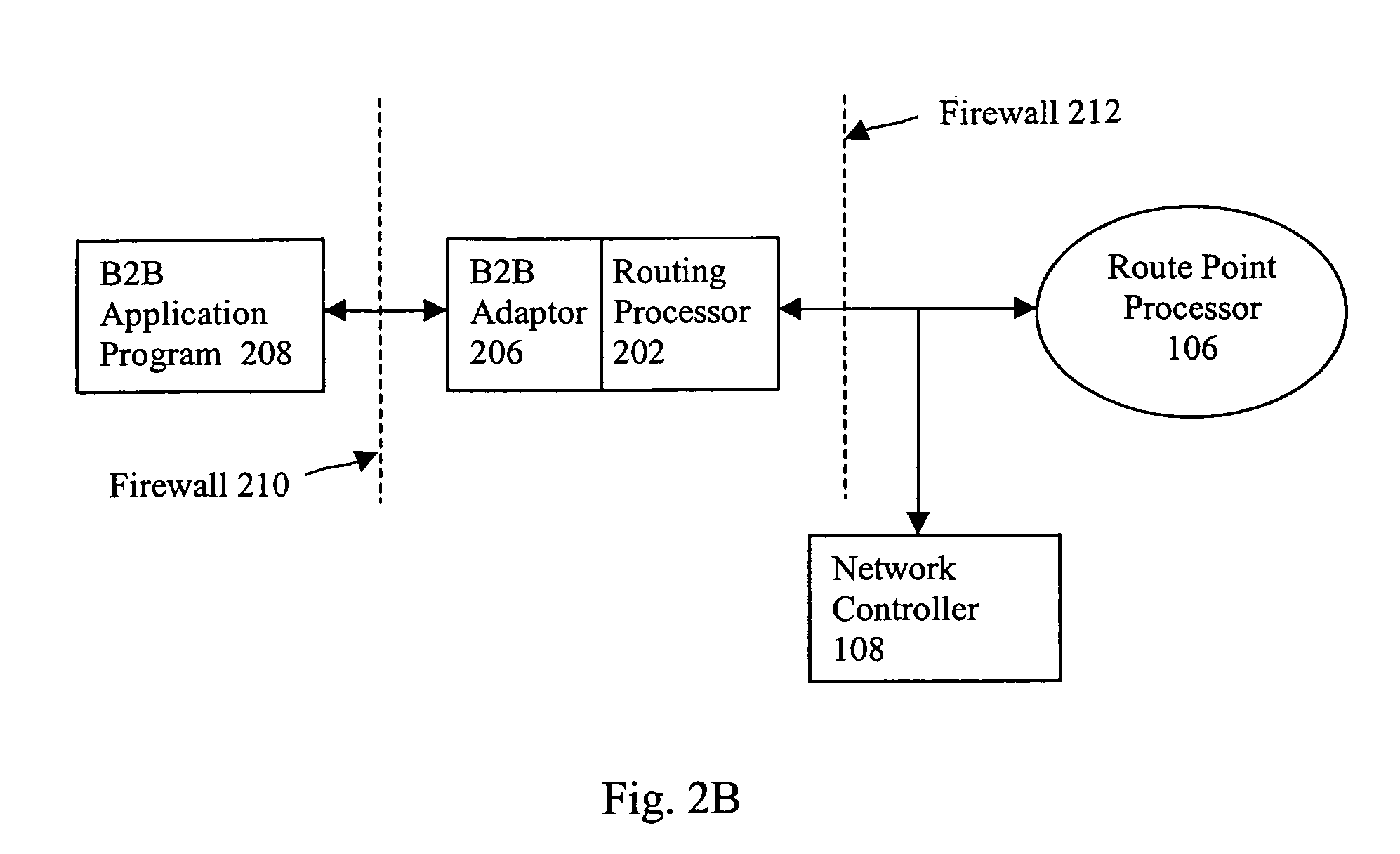
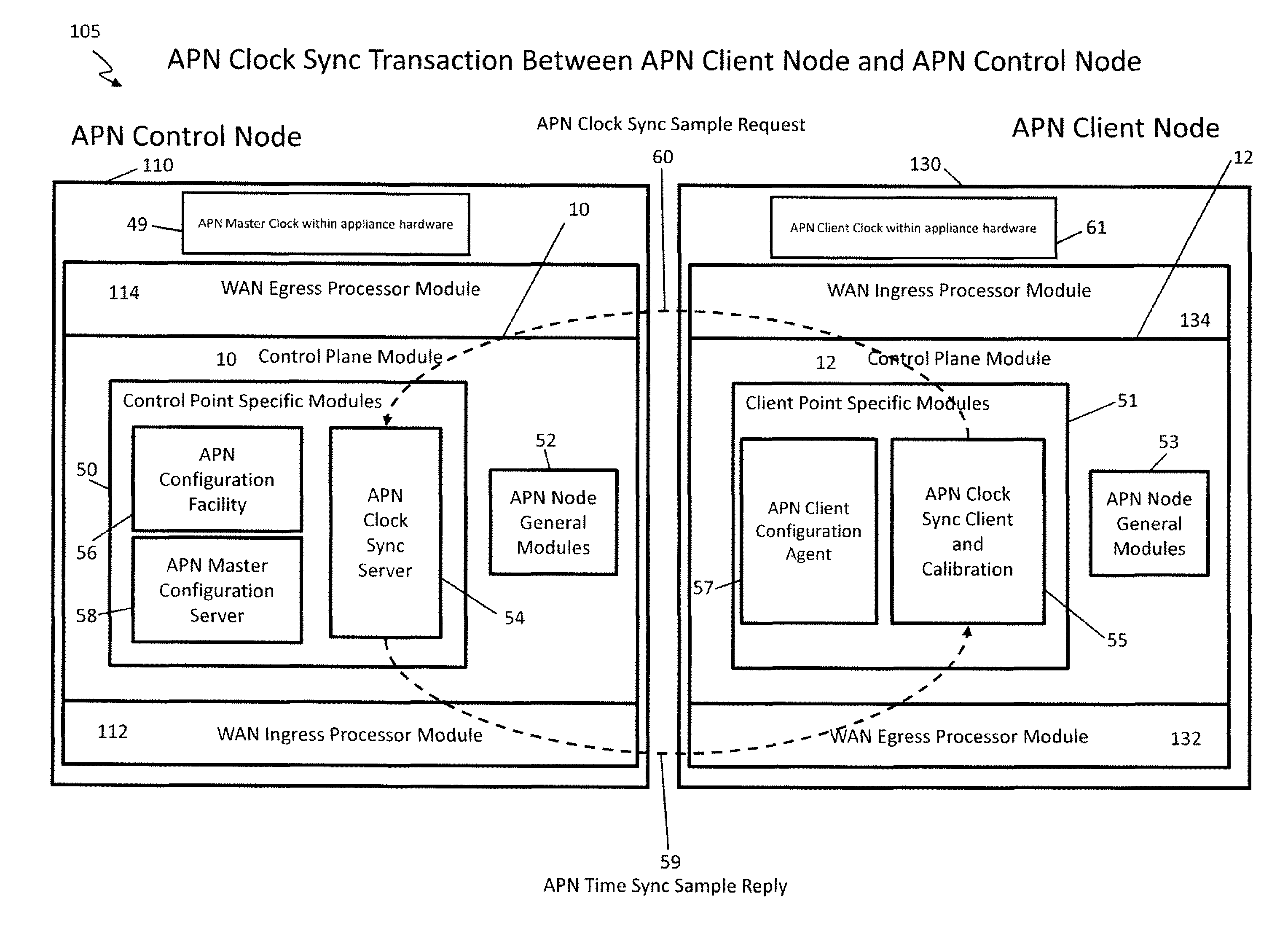
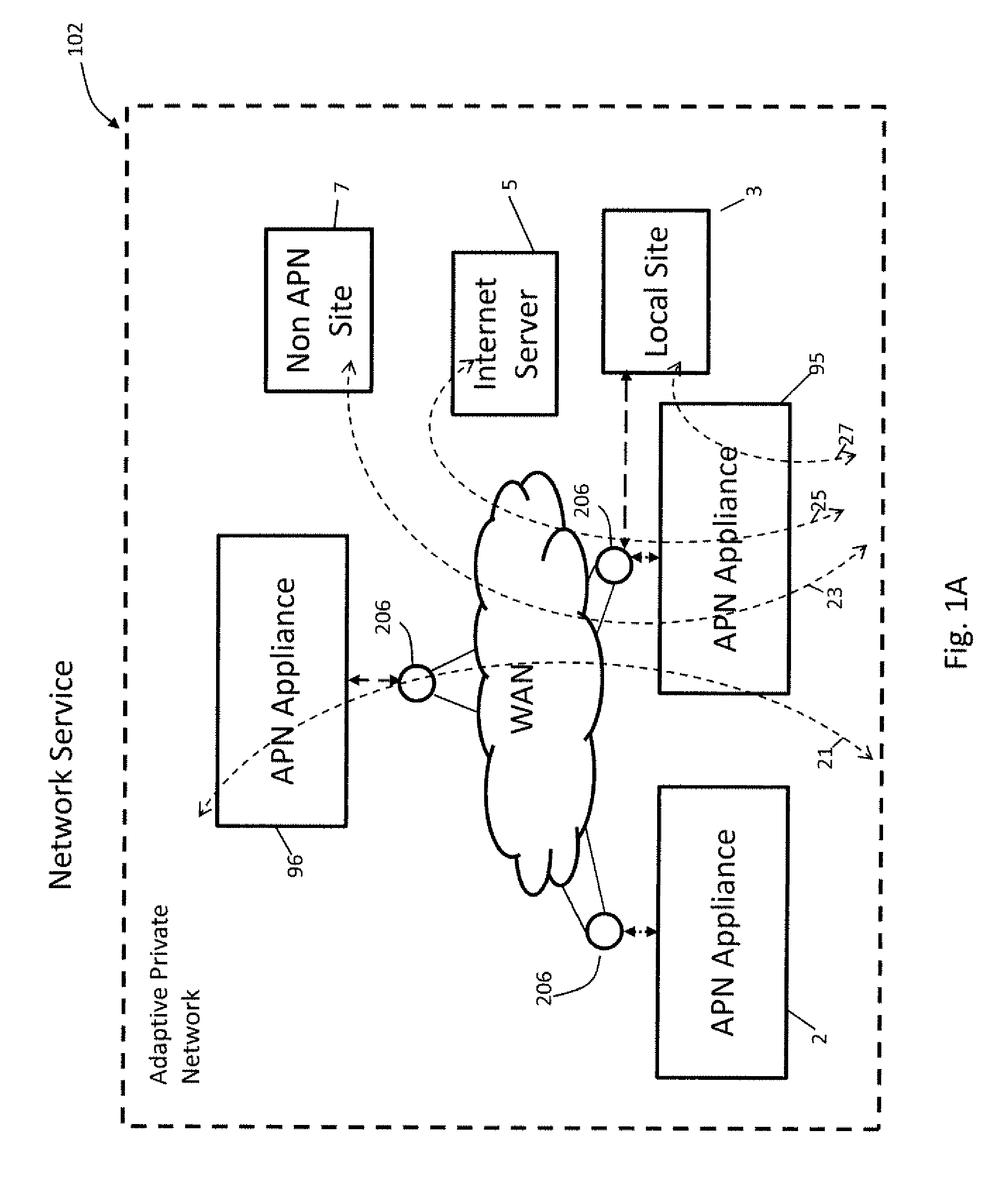
Flow-Based Adaptive Private Network with Multiple Wan-Paths
ActiveUS20090310485A1Improve performance and reliability and predictabilityError preventionTransmission systemsPrivate networkByte
Systems and techniques are described which improve performance, reliability, and predictability of networks without having costly hardware upgrades or replacement of existing network equipment. An adaptive communication controller provides WAN performance and utilization measurements to another network node over multiple parallel communication paths across disparate asymmetric networks which vary in behavior frequently over time. An egress processor module receives communication path quality reports and tagged path packet data and generates accurate arrival times, send times, sequence numbers and unutilized byte counts for the tagged packets. A control module generates path quality reports describing performance of the multiple parallel communication paths based on the received information and generates heartbeat packets for transmission on the multiple parallel communication paths if no other tagged data has been received in a predetermined period of time to ensure performance is continually monitored. An ingress processor module transmits the generated path quality reports and heartbeat packets.
Owner:TALARI NETWORKS
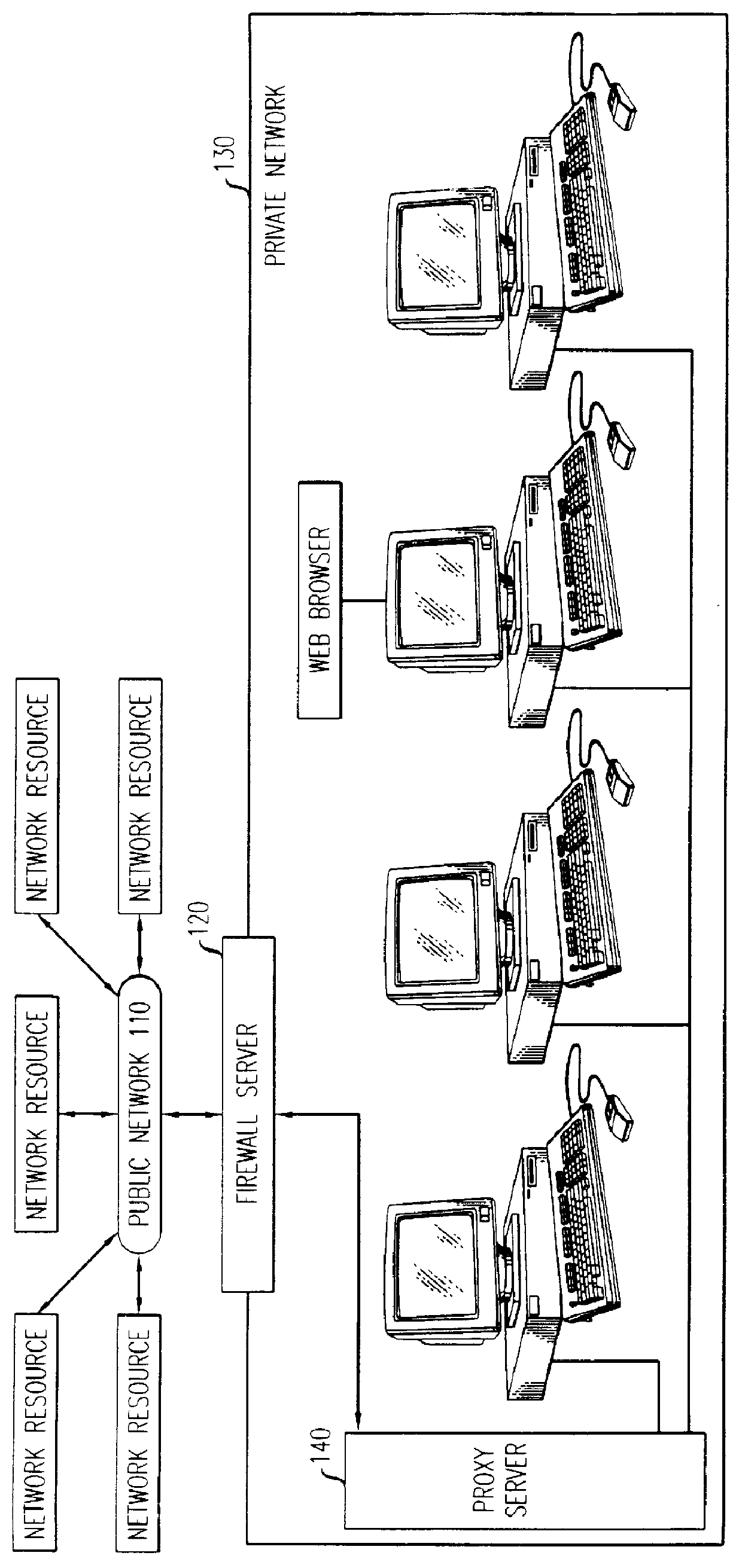
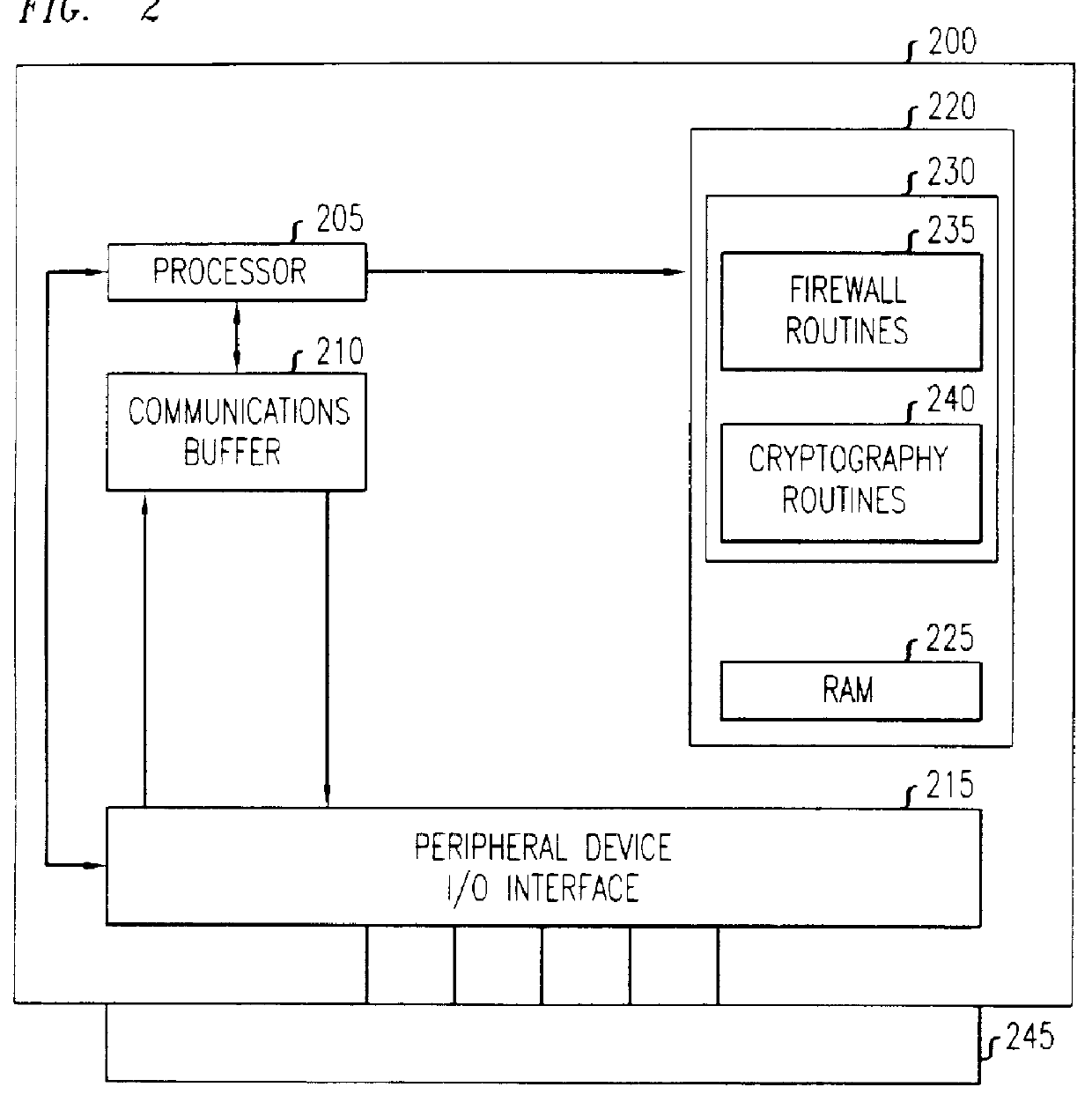
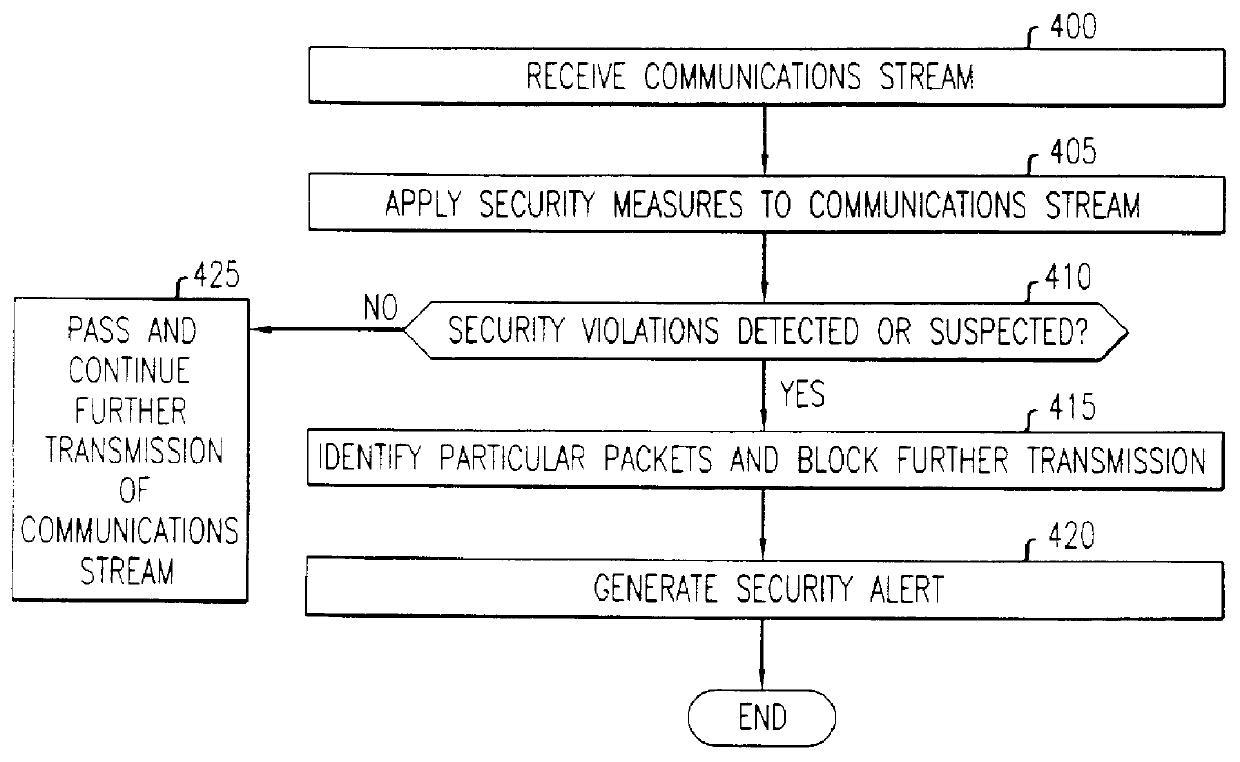
Firewall security method and apparatus
InactiveUSH1944H1Reduce riskUnauthorized memory use protectionMultiple digital computer combinationsSecurity MeasurePersonal computer
A technique for the delivering a client-based firewall. A firewall security device is configured for connecting to individual clients, e.g., personal computers, for providing firewall security measures directly to the client. The firewall security device is configured as a electronic dongle which is attached to an external communications port of the client, e.g., the parallel communications port. The incoming communications stream to the client from, e.g., public networks, is passed through the firewall security device. In this way, the firewall security device applies and delivers a set of standard network security measures thereby protecting the client from security breaches triggered by the communications stream received from the public network. Advantageously, the firewall is delivered directly by the client without intervention, use, or connection to a separate firewall server.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
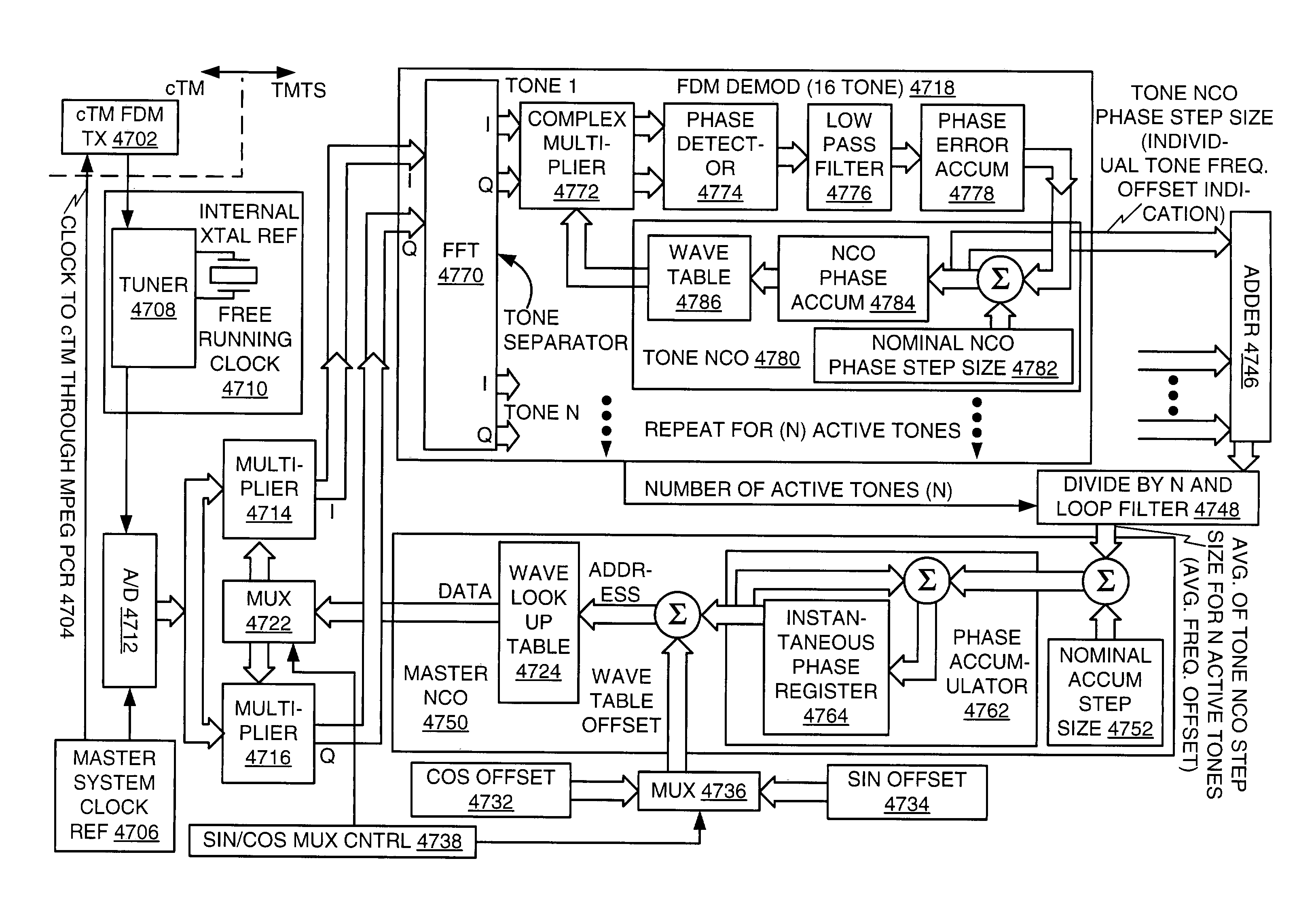
Automatic frequency control of multiple channels
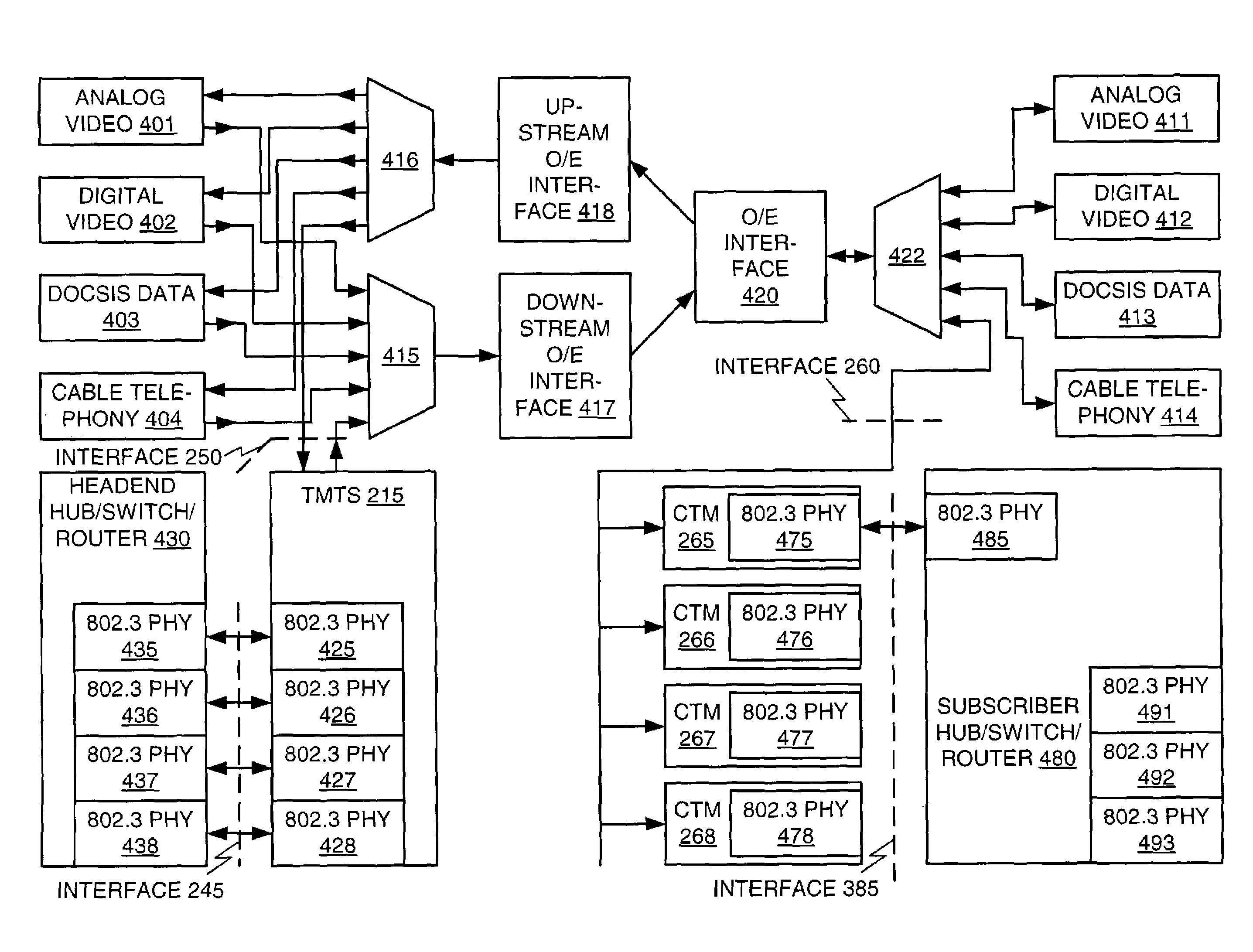
ActiveUS7218901B1Broadband local area networksHybrid switching systemsCable transmissionMultiplexing
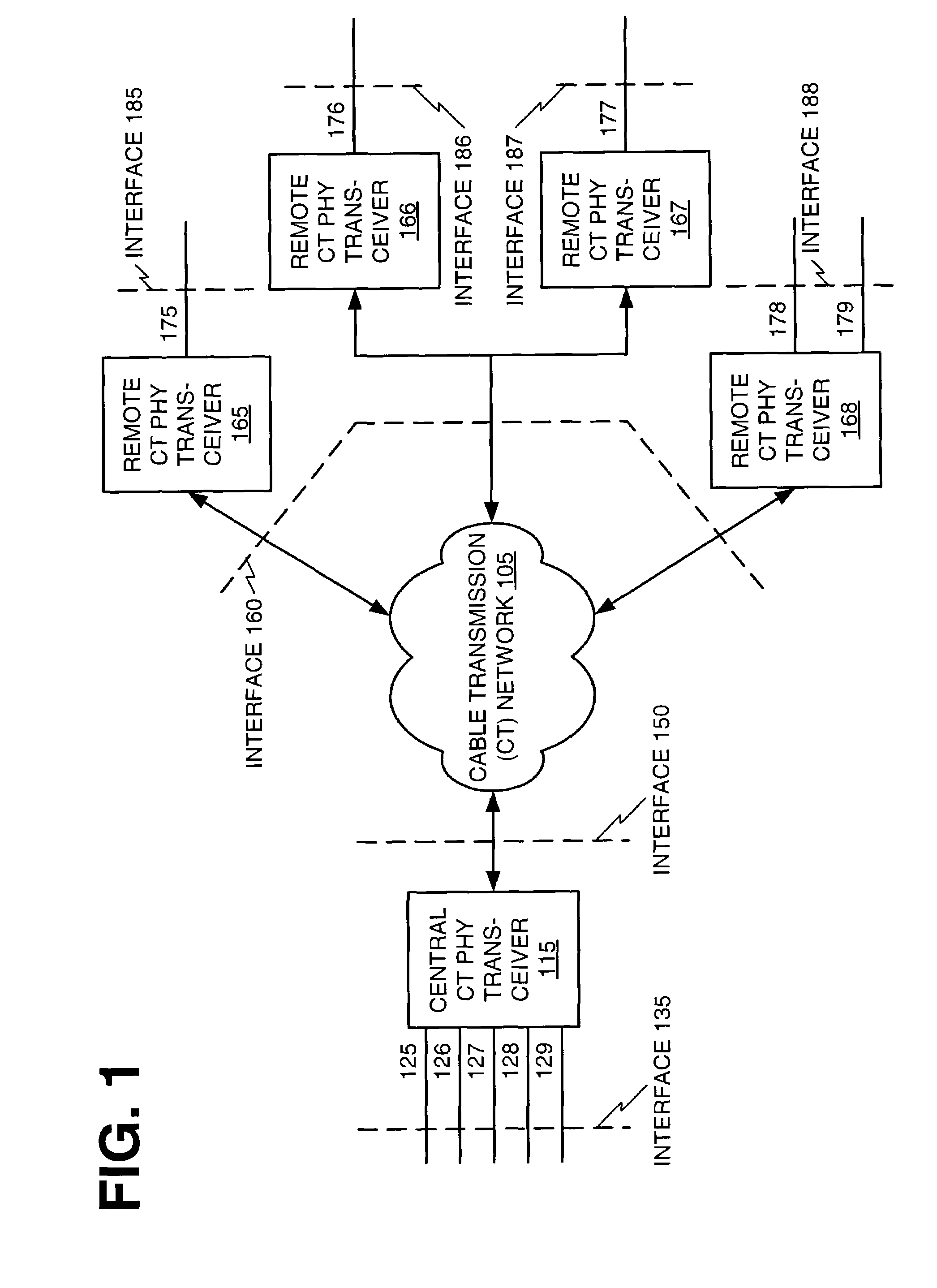
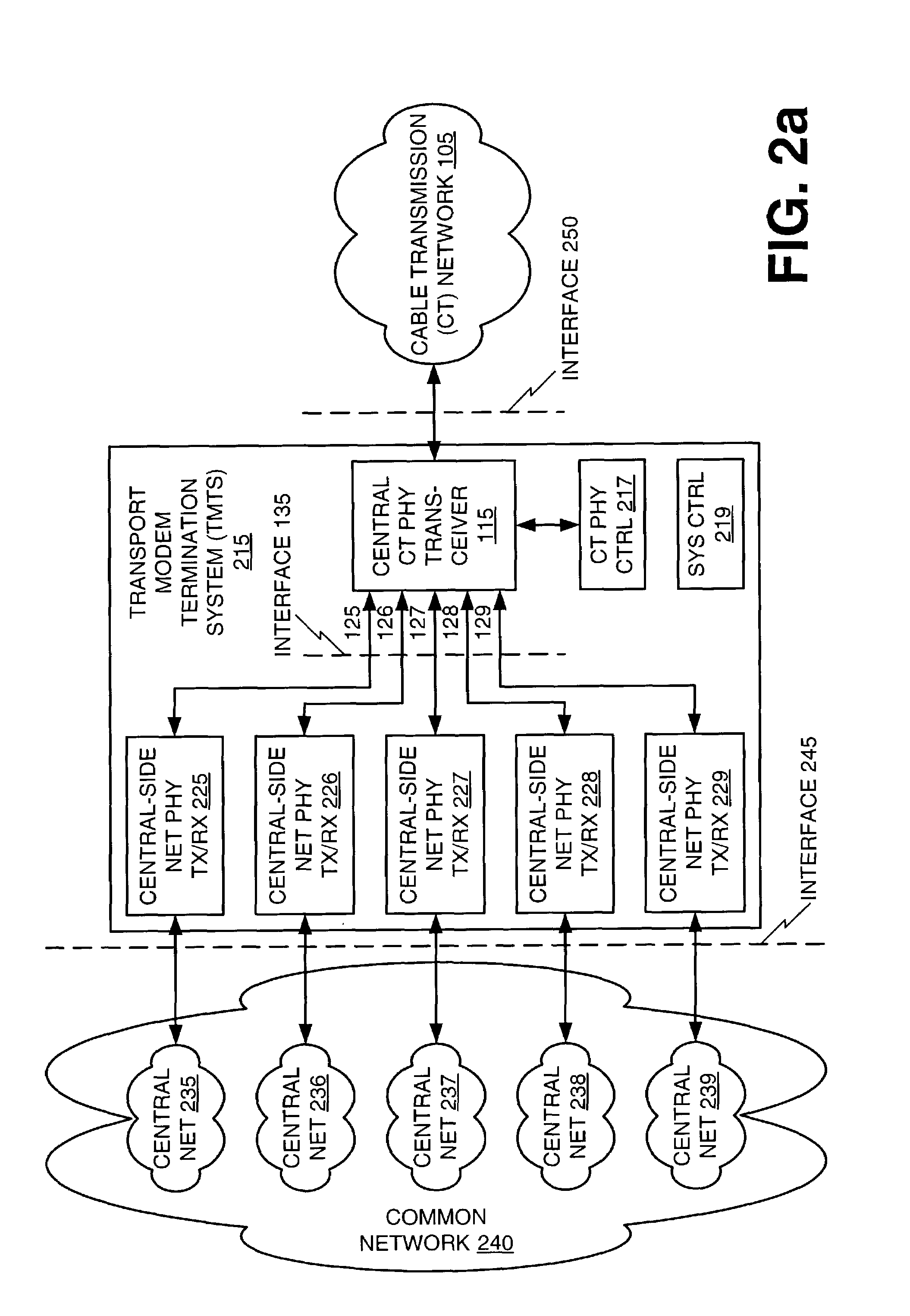
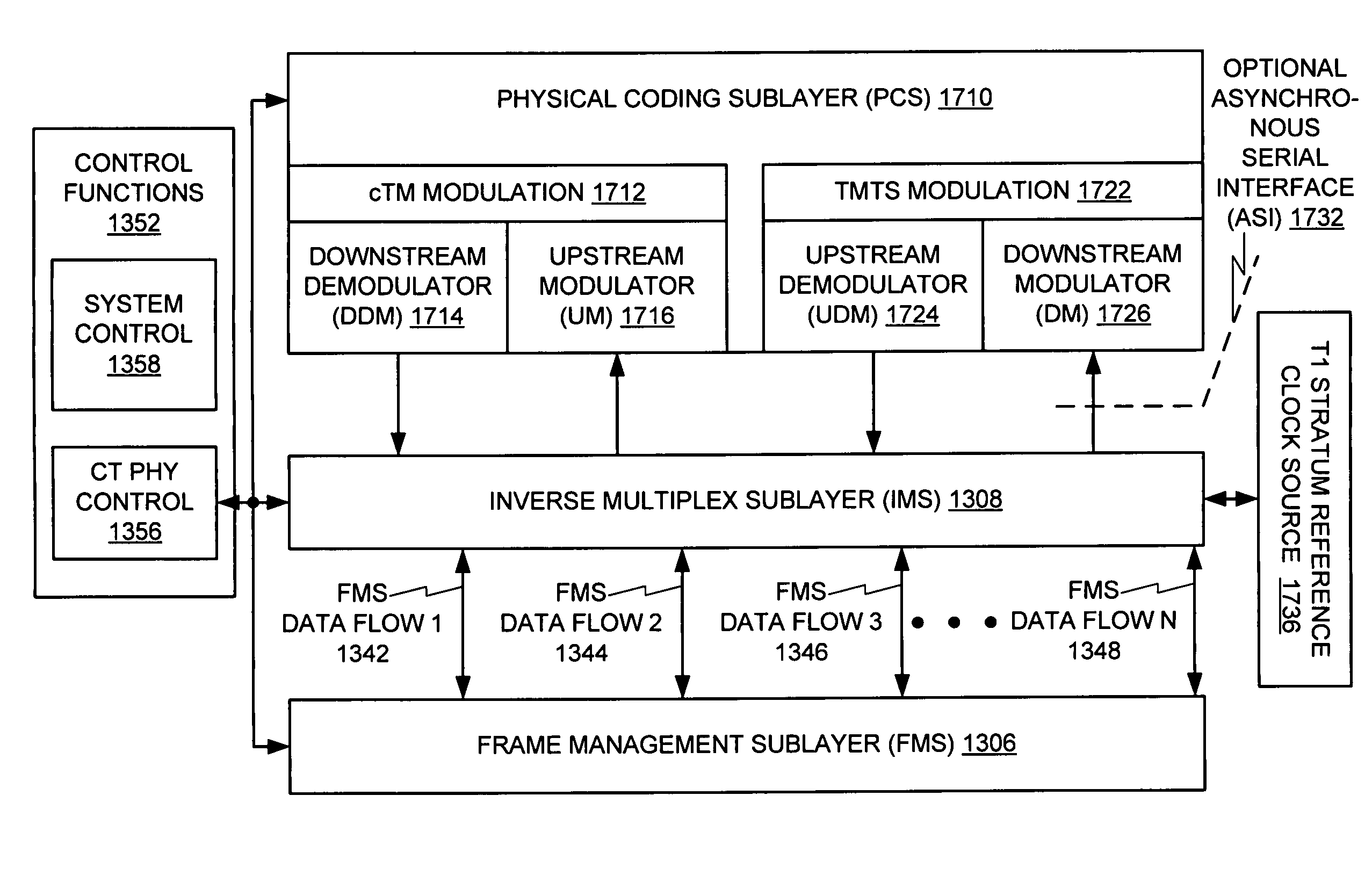
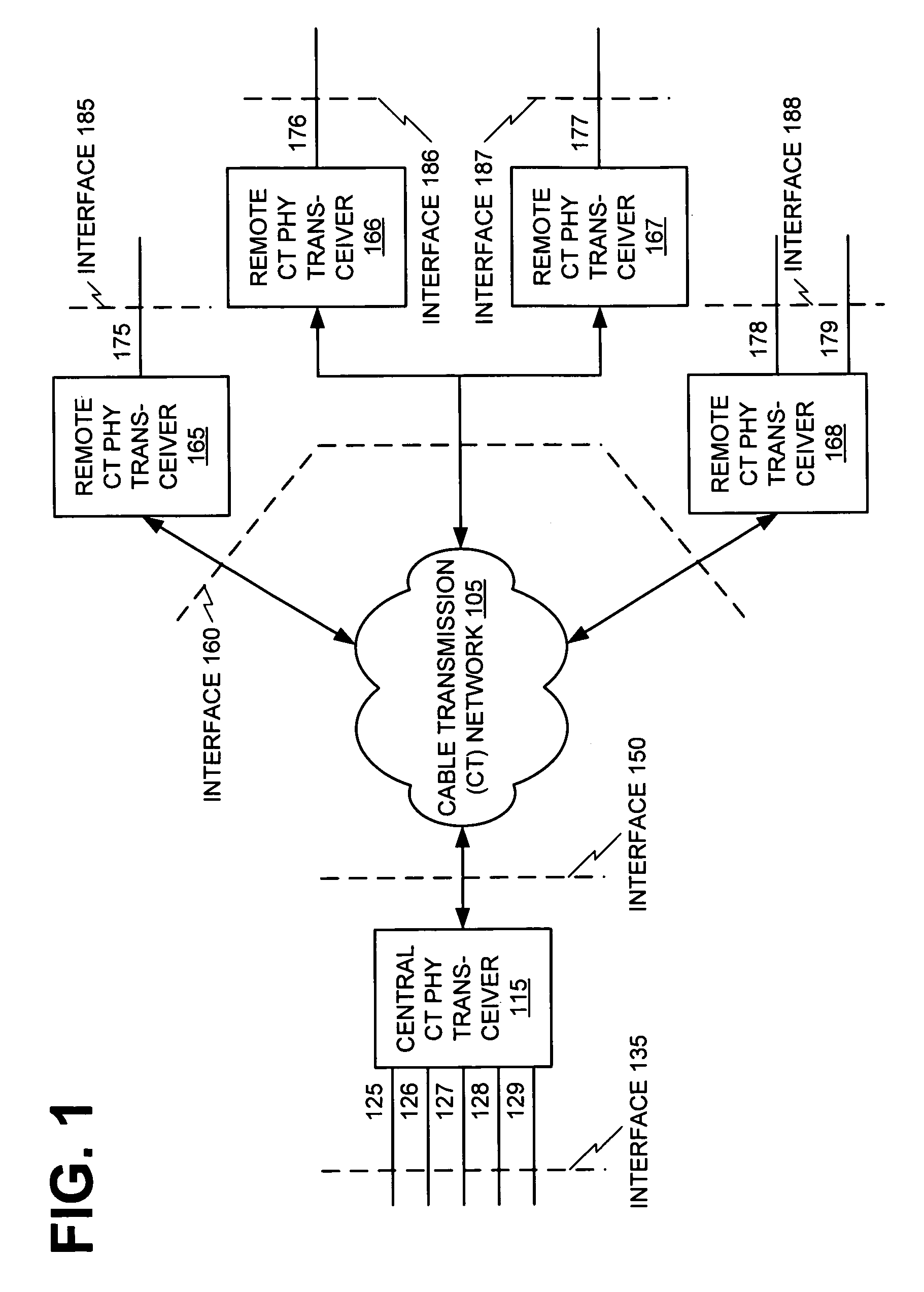
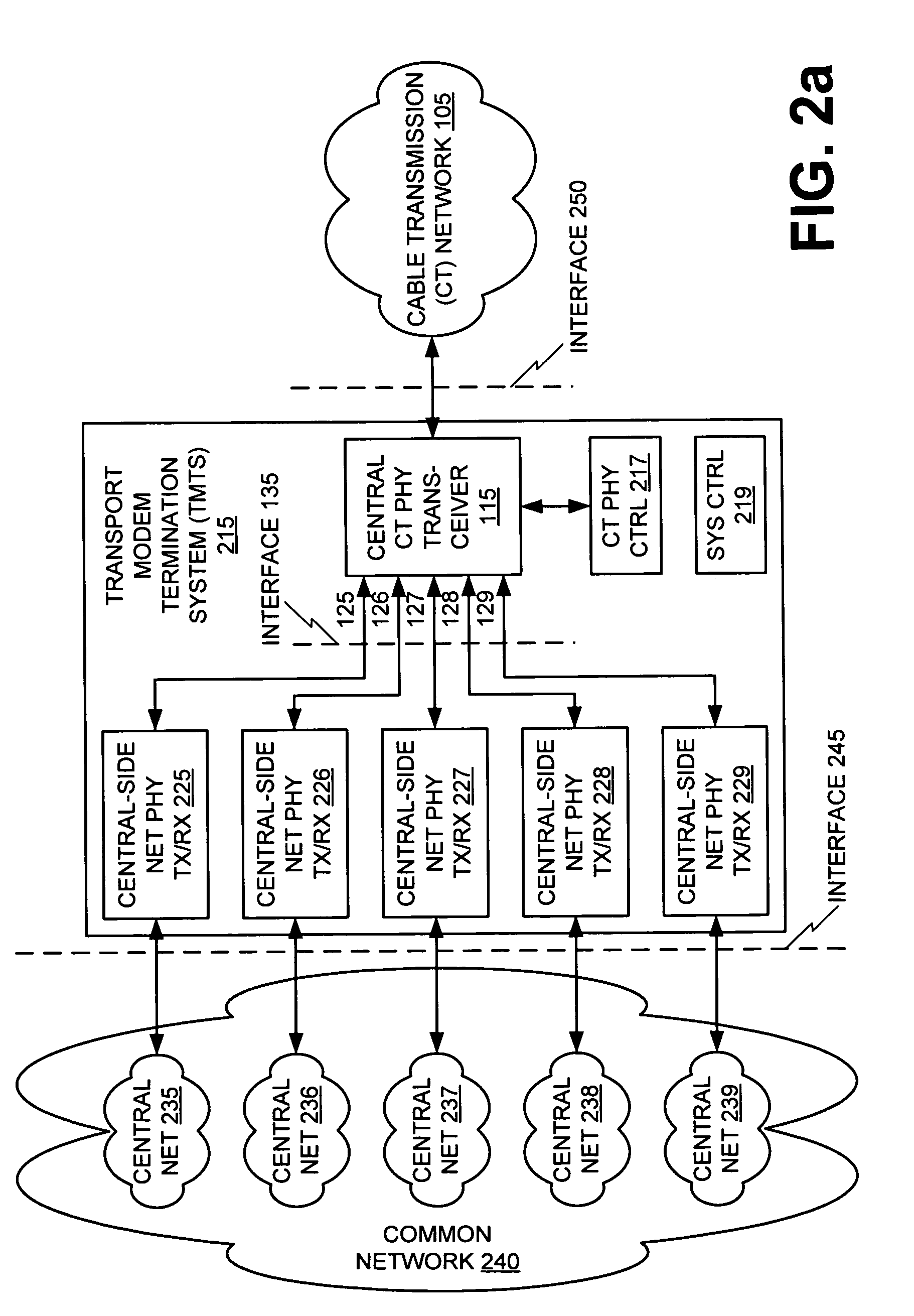
An architecture for providing high-speed access over frequency-division multiplexed (FDM) channels allows transmission of ethernet frames and / or other data across a cable transmission network or other form of FDM transport. The architecture involves downstream and upstream FDM multiplexing techniques to allow contemporaneous, parallel communications across a plurality of frequency channels. Moreover, an automatic frequency control resolves some issues of a free-running clock in an upstream tuner of the central concentrator by performing adjustments based on the average frequency error of a number of active upstream tones. In the preferred embodiments of the present invention, the automatic frequency control (AFC) utilizes a feedback loop for at least each active upstream tone. Also, the average of the active upstream tones is determined and is utilized in providing feedback to adjust the automatic frequency control (AFC).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
High-speed memory system
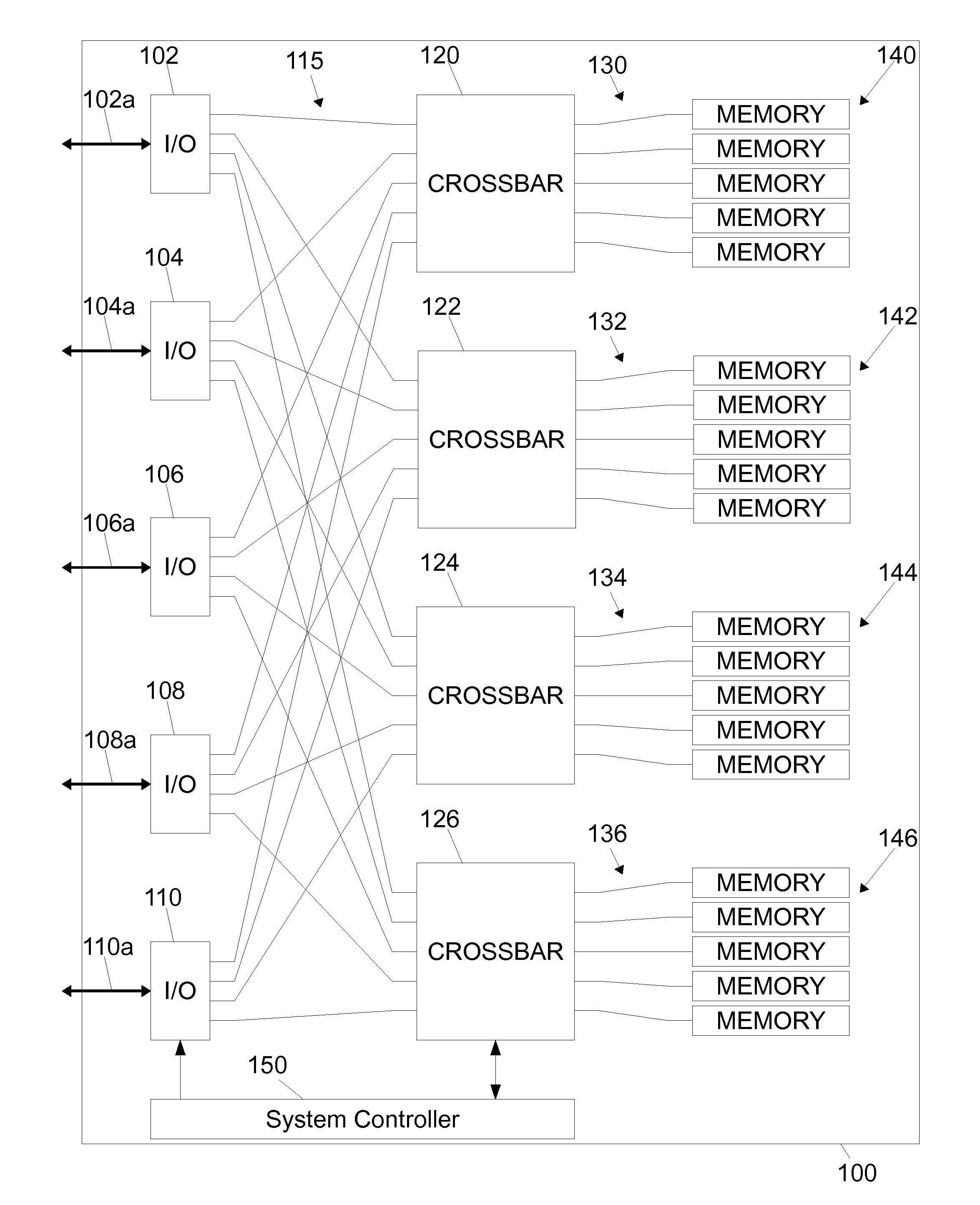
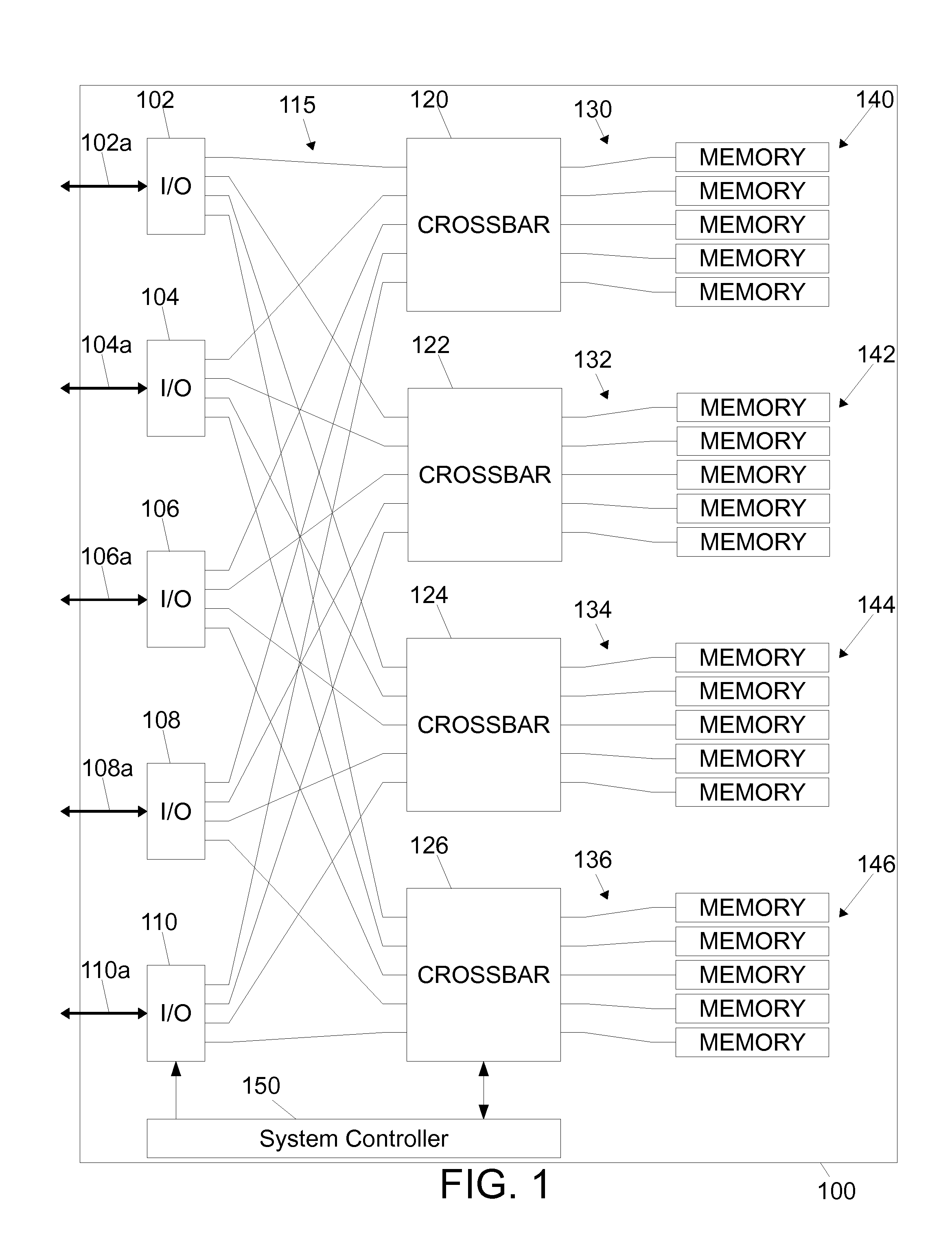
InactiveUS20120079352A1Effective and efficient and optimalMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital storageTelecommunications linkHigh speed memory
The disclosed embodiments relate to a Flash-based memory module having high-speed serial communication. The Flash-based memory module comprises, among other things, a plurality of I / O modules, each configured to communicate with an external device over one or more external communication links, a plurality of Flash-based memory cards, each comprising a plurality of Flash memory devices, and a plurality of crossbar switching elements, each being connected to a respective one of the Flash-based memory cards and configured to allow each one of the I / O modules to communicate with the respective one of the Flash-based memory cards. Each I / O module is connected to each crossbar switching element by a high-speed serial communication link, and each crossbar switching element is connected to the respective one of the Flash-based memory cards by a plurality of parallel communication links.
Owner:IBM CORP
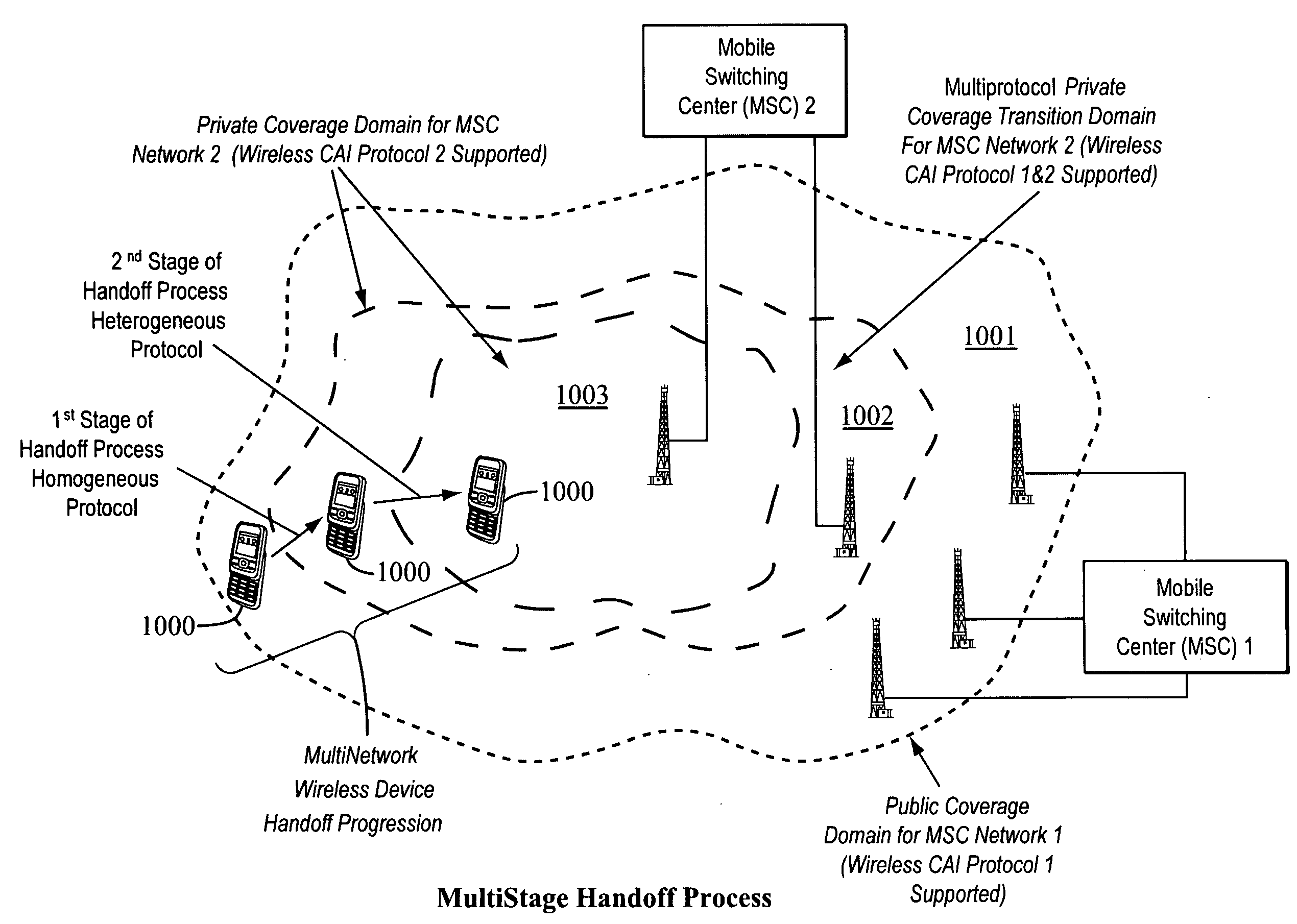
Seamless multistage handoff algorithm to facilitate handoffs between hetergeneous wireless networks
InactiveUS20080310371A1Facilitate seamless multistage handoffFacilitate a seamless multistage handoffSpecial service for subscribersConnection managementMulti protocolClient-side
A method for automatically adapting a multi-protocol wireless device to facilitate a seamless multistage handoff according to various embodiments can include initiating a seamless multistage handoff process using a multi-protocol wireless device when the multi-protocol wireless device crosses a boundary area into an overlapping region where the multi-protocol wireless device is capable of simultaneously accessing a plurality of networks; and implementing the seamless multistage handoff process by performing at least a two-stage handoff process comprising a homogeneous handoff and a heterogeneous handoff without interrupting a communication call session conducted using the multi-protocol wireless device. A multi-network client device according to various embodiments can include a controller configured to support multiple independent call sessions, wherein the independent call sessions are concurrently conducted on a single wireless device through the use of parallel communication sessions and simultaneously connect the wireless device to a plurality of different networks hosting different content services.
Owner:INCNETWORKS
System for handling information and information transfers in a computer network
InactiveUS7032005B2Improve latencySpecial service provision for substationMultiple digital computer combinationsThe InternetNetwork control
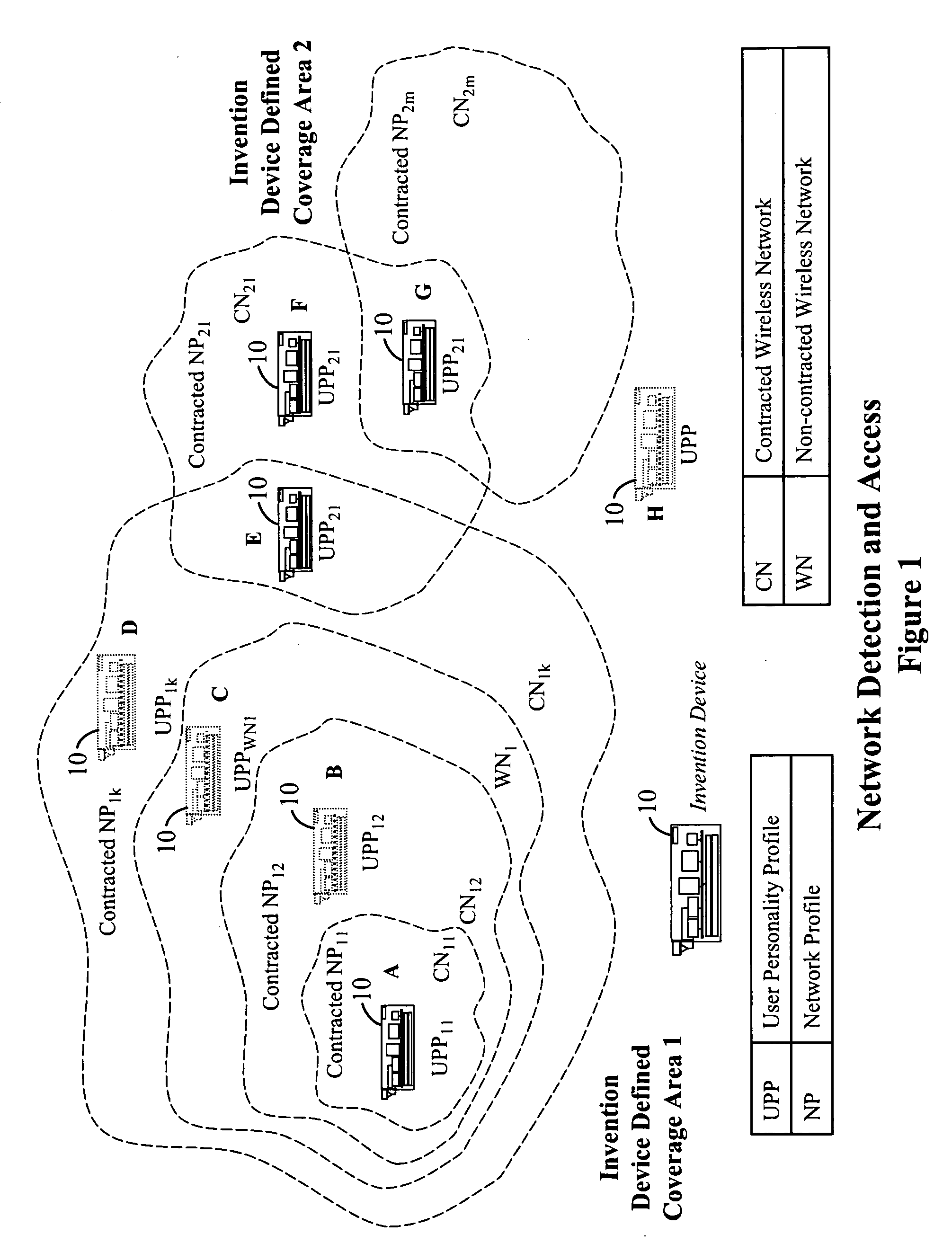
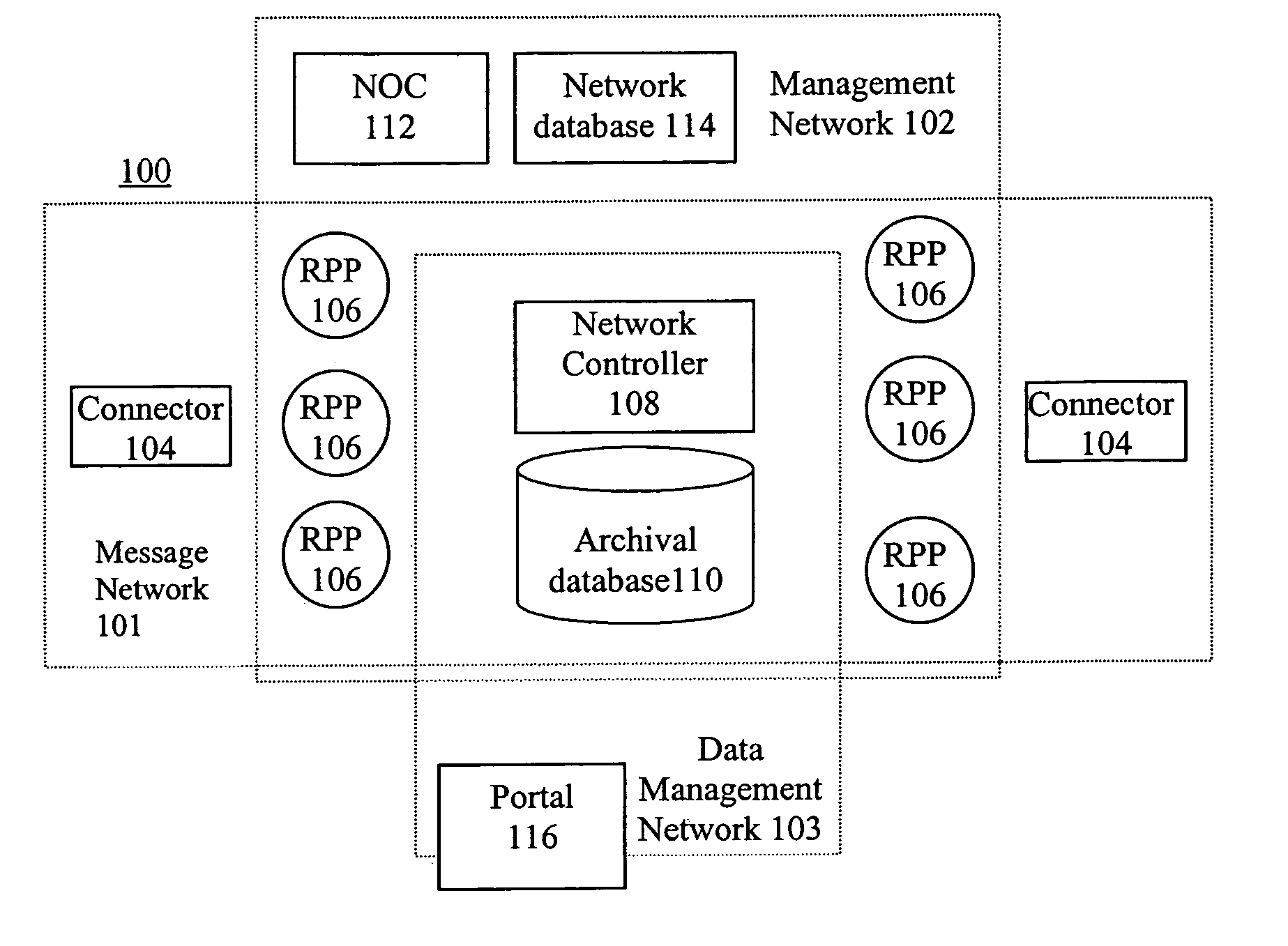
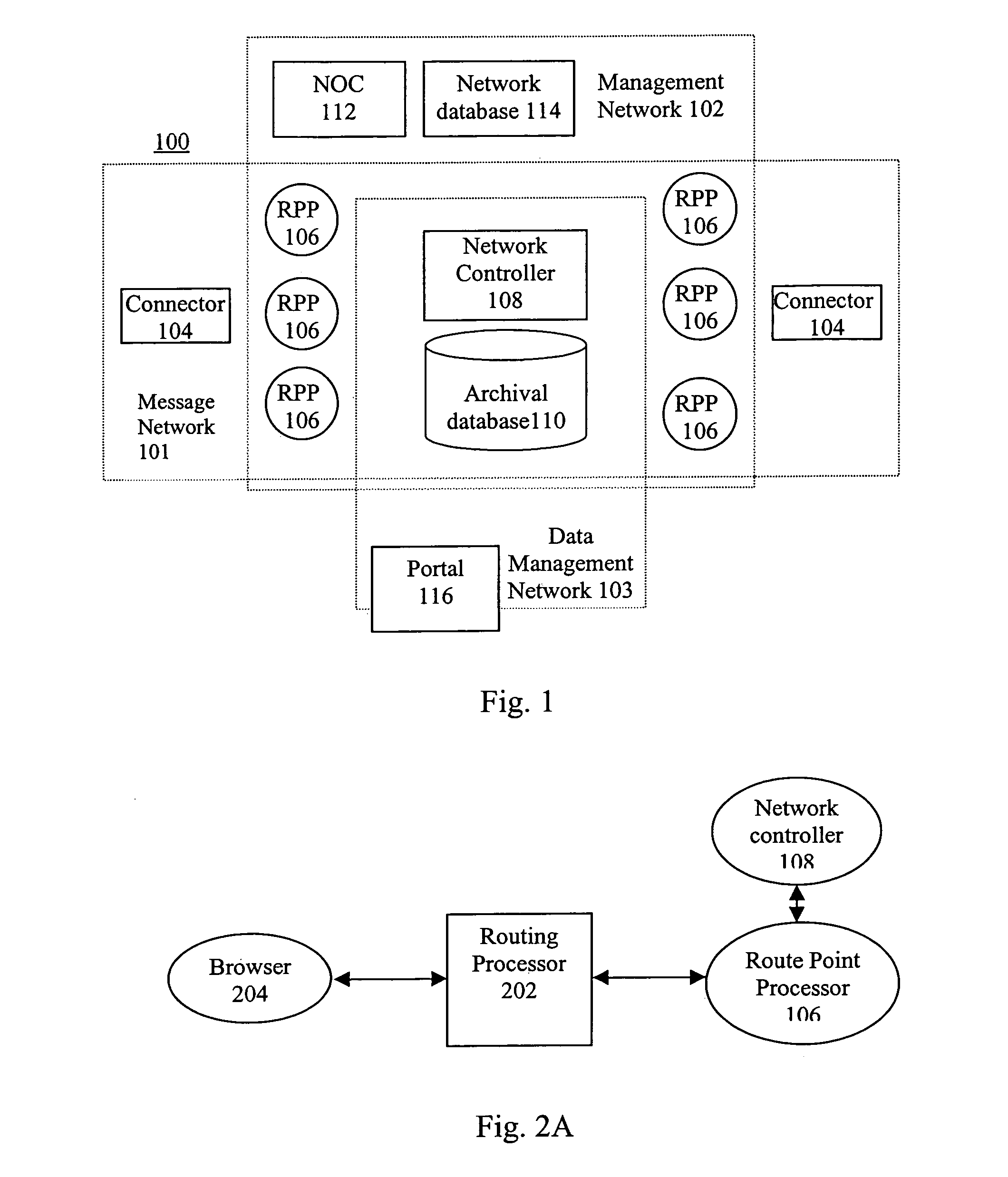
The present invention relates to relates to the efficient and secure transfer of information over a distributed computer network such as the Internet. The system provides parallel communication paths between the source and destination. Each path includes a dedicated route point to eliminate intermediate ISPs. Each source is associated with an archive and each route point is coupled to the archive. Upon receipt of the message at a route point the message is copied to the archive and then transmitted to the destination. Message archival and storage of transmission-related information enables data-mining features not presently available using email or a point-and-click browser. Since two messages are transmitted from the source to the common destination across separate and distinct communication paths, message latency is improved and the chance of lost messages is reduced or even eliminated. A network controller monitors transmission results and dynamically re-configures the network to balance loading across the route points and to avoid failures or other bottlenecks in the system.
Owner:CLOUDPRIME
Hybrid interface for serial and parallel communication
ActiveUS20110196997A1Improve reliabilityReduced pin countPulse automatic controlTransmissionSerial portParallel communication
Embodiments of the invention are generally directed to a hybrid interface for serial and parallel communication. An embodiment of a method includes initializing a first apparatus for transmission of data to or reception of data from a second apparatus, switching an interface for the first apparatus to a first mode for a parallel interface, the parallel interface including a first plurality of pins, and transmitting or receiving parallel data in the first mode via the first plurality of pins. The method further includes switching the interface of the first apparatus to a second mode for a serial interface, the serial interface including a second plurality of pins, the first plurality of pins and the second plurality of pins both including an overlapping set of pins, and transmitting or receiving serial data in the second mode via the second plurality of pins.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Flow-based adaptive private network with multiple WAN-paths
ActiveUS8125907B2Improve performance and reliability and predictabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPrivate networkArrival time
Systems and techniques are described which improve performance, reliability, and predictability of networks without having costly hardware upgrades or replacement of existing network equipment. An adaptive communication controller provides WAN performance and utilization measurements to another network node over multiple parallel communication paths across disparate asymmetric networks which vary in behavior frequently over time. An egress processor module receives communication path quality reports and tagged path packet data and generates accurate arrival times, send times, sequence numbers and unutilized byte counts for the tagged packets. A control module generates path quality reports describing performance of the multiple parallel communication paths based on the received information and generates heartbeat packets for transmission on the multiple parallel communication paths if no other tagged data has been received in a predetermined period of time to ensure performance is continually monitored. An ingress processor module transmits the generated path quality reports and heartbeat packets.
Owner:TALARI NETWORKS
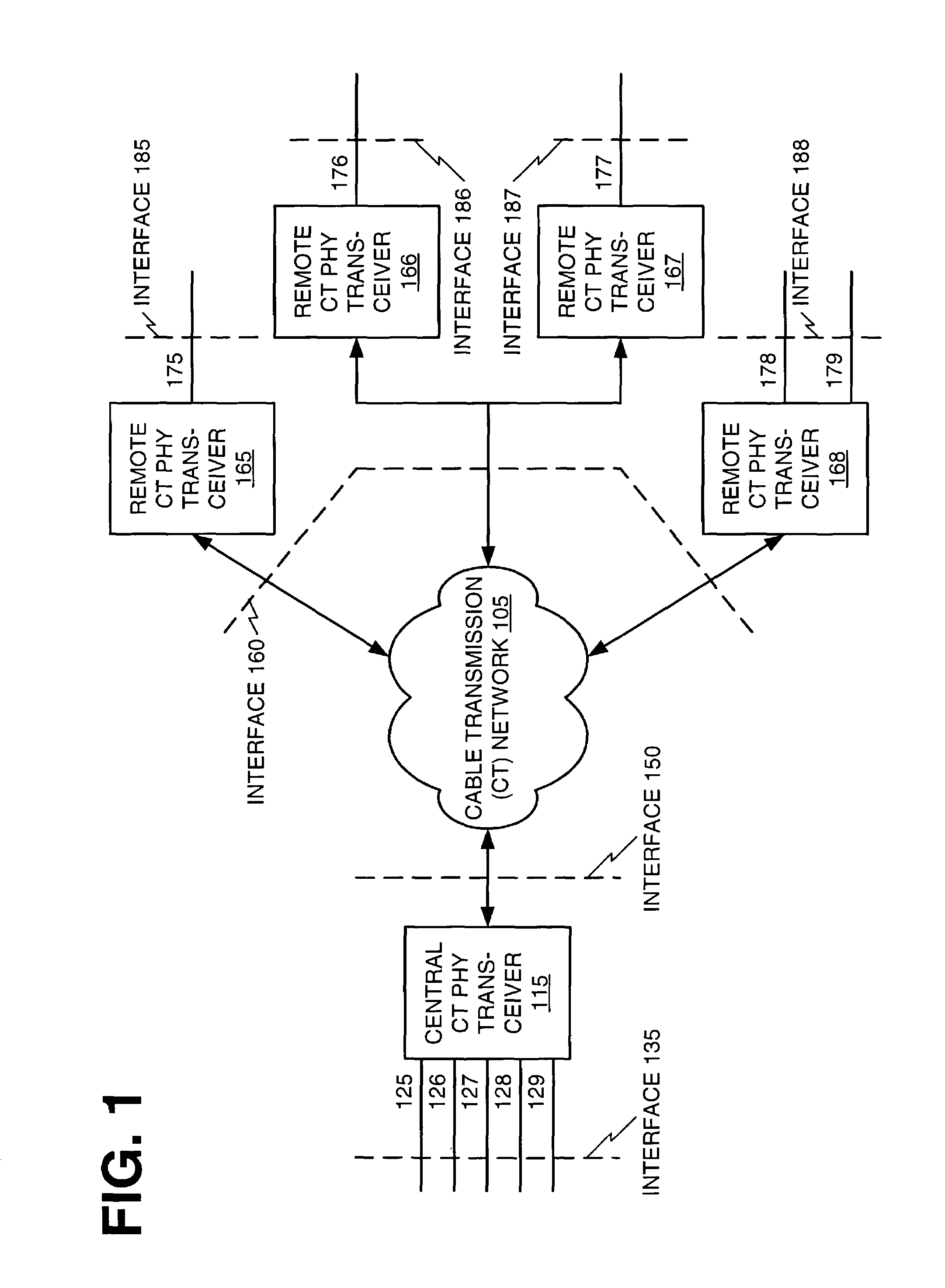
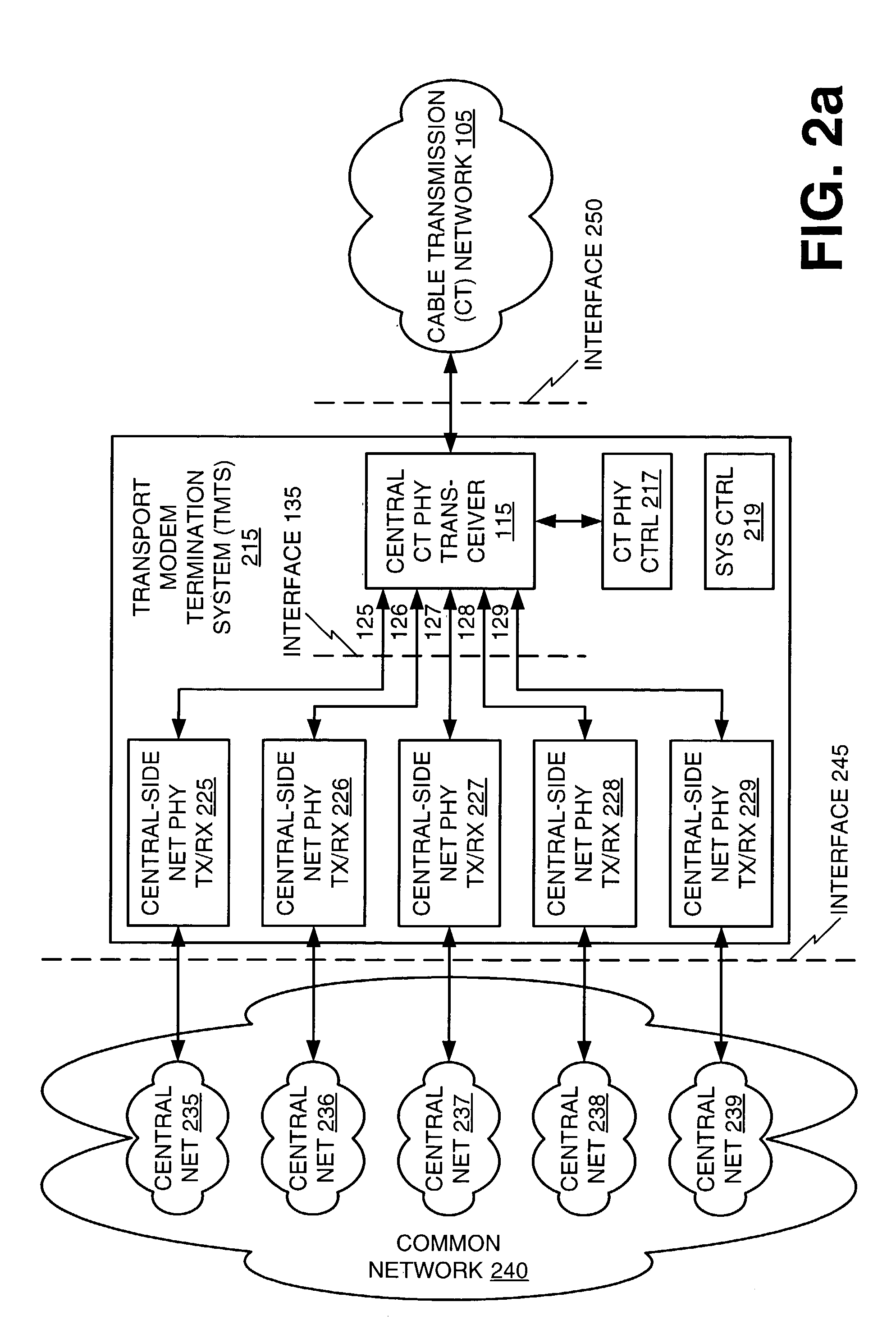
Multi-carrier frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) architecture for high speed digital service
An architecture for providing high-speed access over frequency-division multiplexed (FDM) channels allows transmission of ethernet frames and / or other data across a cable transmission network or other form of FDM transport. The architecture involves downstream and upstream FDM multiplexing techniques to allow contemporaneous, parallel communications across a plurality of frequency channels. Furthermore, the architecture allows a central concentrator to support a plurality of remote devices that each have guaranteed bandwidth through connection-oriented allocations of bi-directional data flows. The upstream and downstream bandwidth allocation can support symmetrical bandwidth as well as asymmetrical bandwidth in either direction. The architecture generally can be used to support connection-oriented physical layer connectivity between a remote device and the central concentrator. Furthermore, the architecture may be integrated into other higher level devices such as, but not limited to, bridges, switches, routers, and / or gateways. The architecture generally may peacefully coexist with other services commonly-found in cable distribution networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for controlling data reading and writing of multi-channel solid-state disc
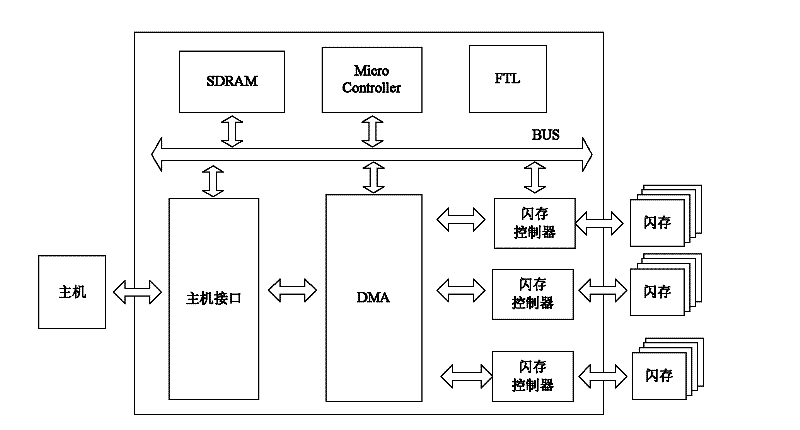
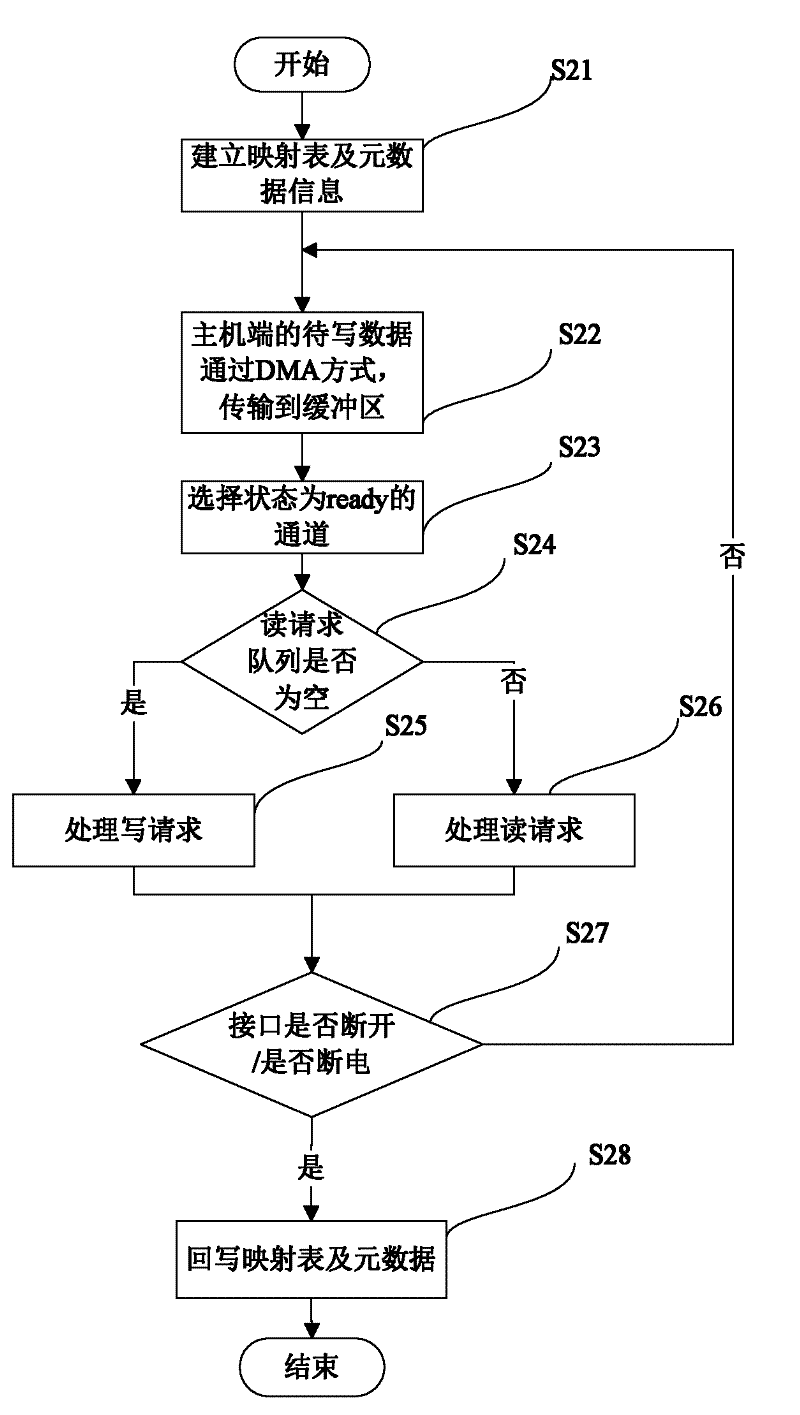
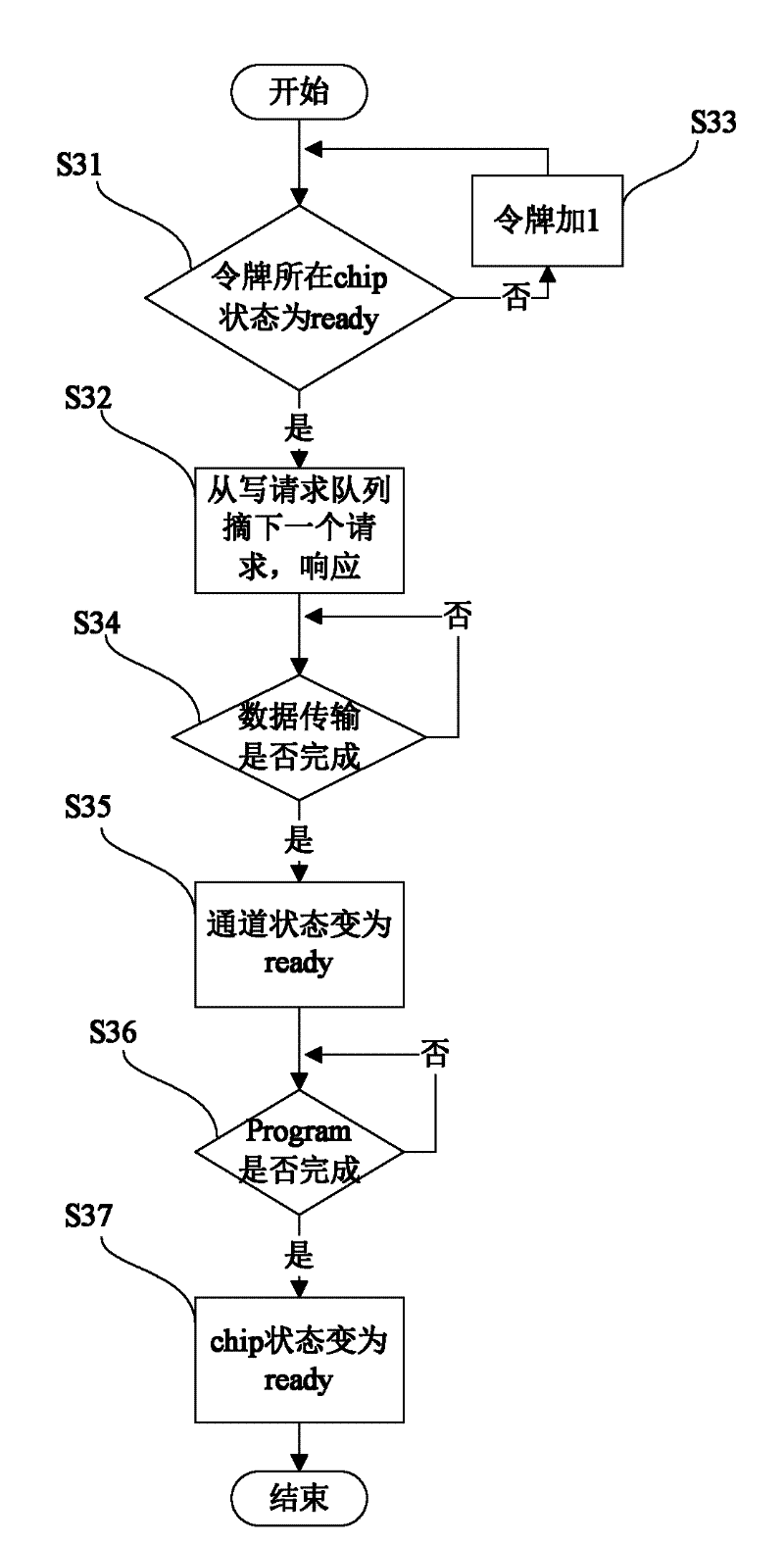
ActiveCN102567257AFast transferUniform wearInput/output to record carriersDirect memory accessComputer science
The invention discloses a method for controlling data reading and writing of a multi-channel solid-state disc, comprising the steps of: (1) building a mapping table to store a mapping relationship of a solid-state disc logic address and a physical address, (2) transmitting a data to be written of a host terminal to a buffer area of a channel controller through a DMA (Direct Memory Access), (3) selecting a channel of which a channel state is ready, (4) finding out a reading request in a chip state which is ready from a reading request queue of the channel of which the state is ready and serving the reading request, (5) finding out a writing request in the chip state which is ready from a writing request queue if the reading request queue is null, writing the data of the buffer area into a free page of the chip, and then modifying corresponding relationship between a corresponding logic address and a physical address in the mapping table so as to finish writing operation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, fast transfer of an interface data is realized, and parallel communication among the channels and serial pipeline operation inside the channels are also realized. Abrasions among all the chips of SSD (solid state disks) are also uniform due to mode adoption of a token ring.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
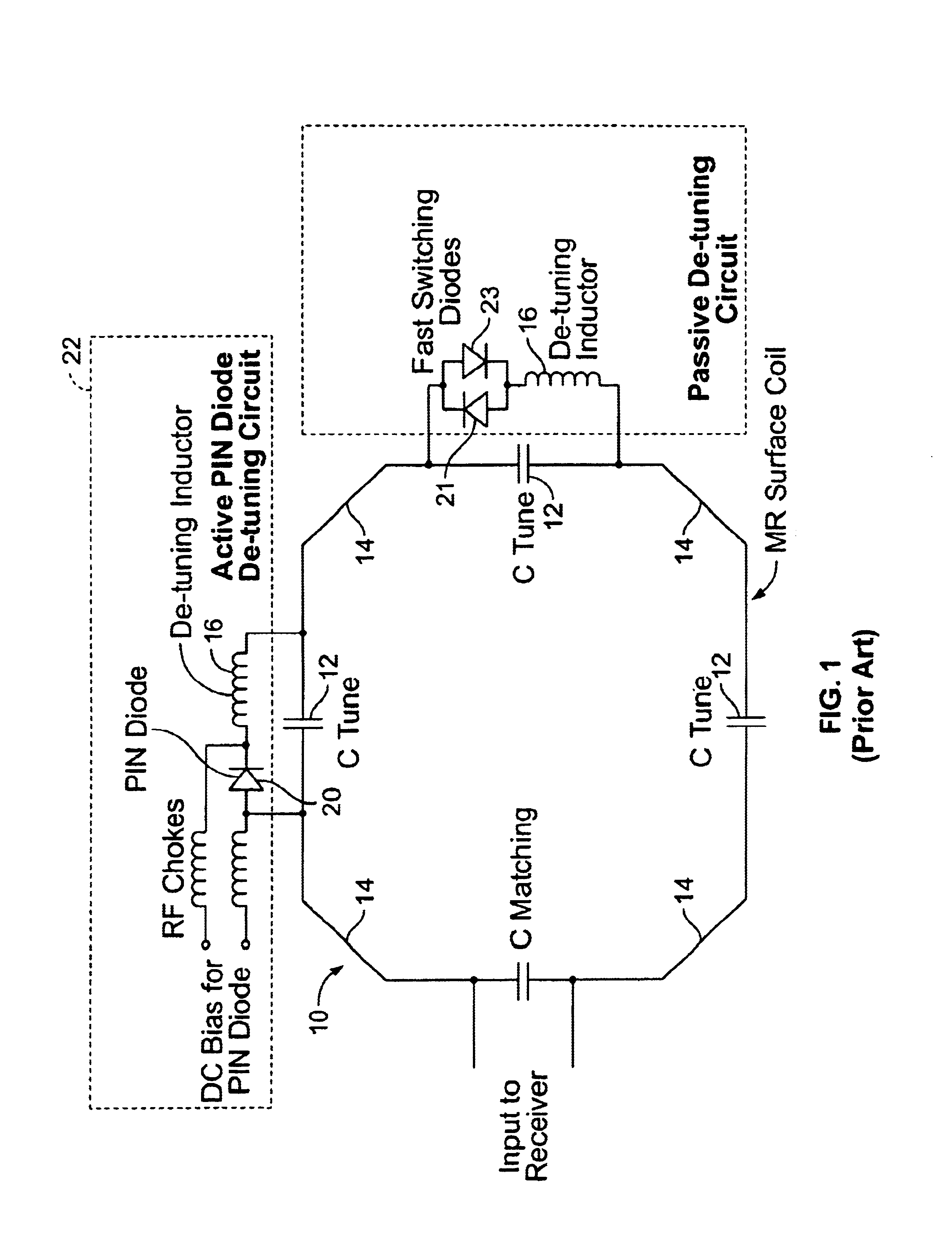
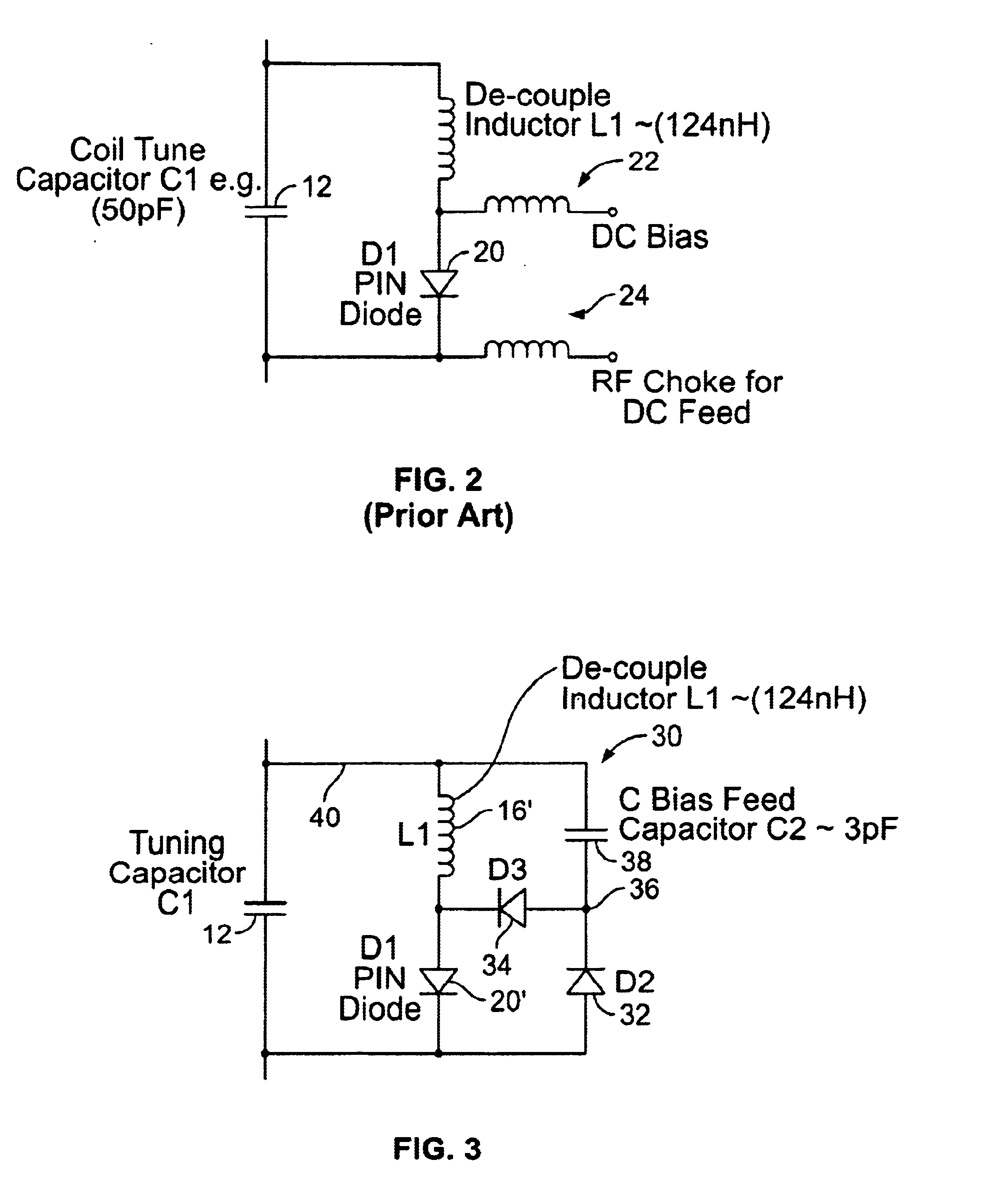
Transmit mode coil detuning for MRI systems
InactiveUS6850067B1Reduces “ blocking ” impedanceCreates heatElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceElectricityElectrical polarity
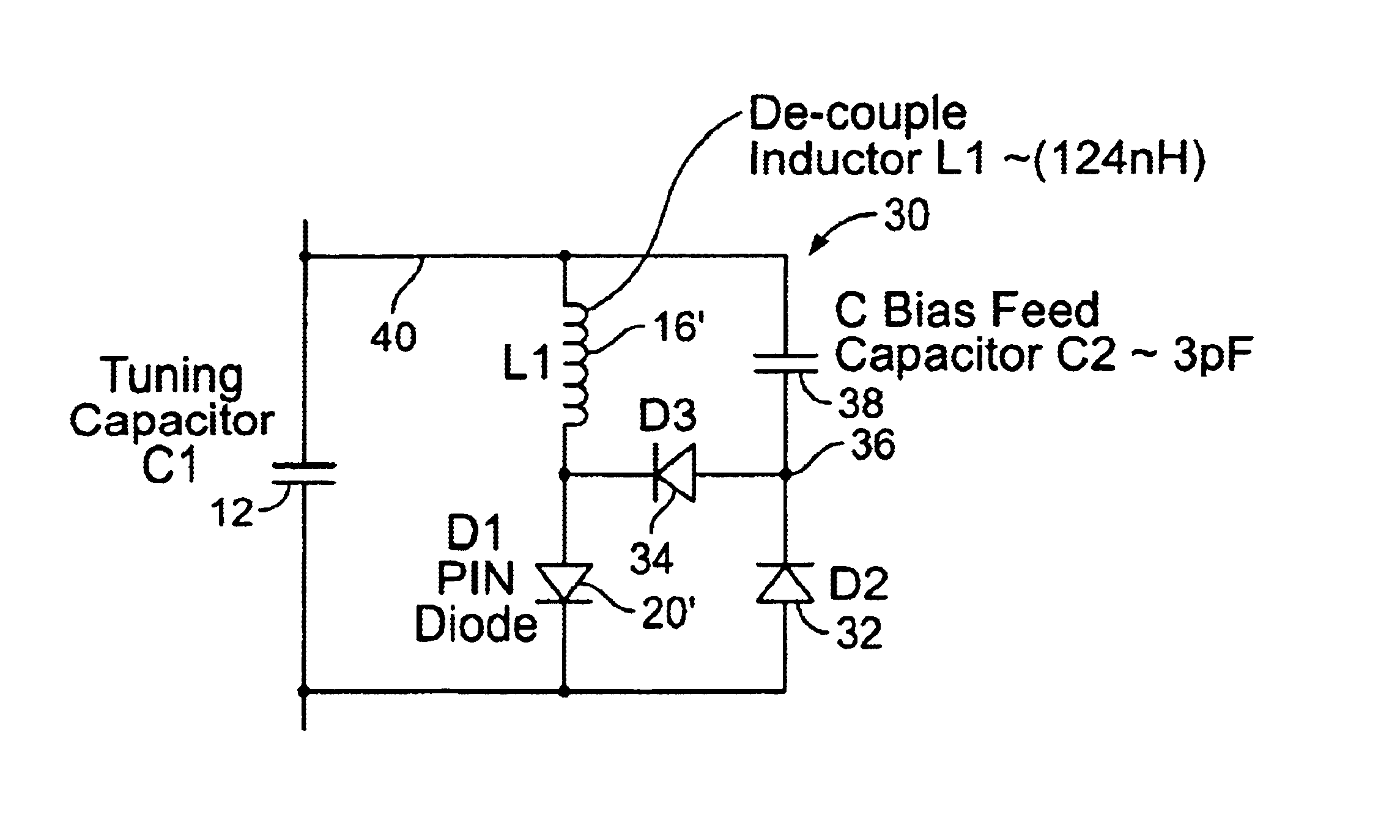
A detuning circuit for an MRI coil having a series tuning capacitor includes: a detuning inductor and a PIN diode in parallel communication with the tuning capacitor, where the tuning capacitor has a tuning inductor node and a PIN diode node; a first diode and a second diode in parallel communication with the PIN diode, where the first, second and PIN diodes are arranged with the same serial polarity and the first and second diodes have a common node; and a reactance in communication between the common node and the tuning inductor node. The circuit detunes the MRI coil in response to an MRI transmit pulse. A detuning circuit for an MRI coil having a series tuning capacitor includes a detuning inductor; and a detuning switch in parallel combination with a secondary tuning capacitor, the detuning inductor and the parallel combination being in parallel communication with the series tuning capacitor. The secondary tuning capacitor acts to reduce current during detuning of the MRI coil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Tunnel construction information monitoring system based on three-dimensional scanning point cloud
ActiveCN104680579AQuick scanFast transferData processing applications3D modellingVertical planeStructure of Management Information
The invention relates to a tunnel construction information monitoring system based on three-dimensional scanning point cloud. The system comprises the following realization steps: acquiring coordinate information, intensity information, grey information, pixel information and the like of a tunnel full-section spatial structure by adopting a three-dimensional scanning point cloud measuring technology, performing automatic filtering processing and point cloud data automatic splicing and generating a tunnel two-dimensional plane model and a three-dimensional space model; realizing the continuous real-time transmission of monitoring data and data flow by adopting a '5S' parallel communication method; introducing a time, motion and rotation multi-dimensional coordinate axis, describing the change posture in a plane, the change posture of a vertical plane and the change posture along with time, performing data filtering and data analysis and realizing seamless butt joint between a monitoring and analysis structure and project construction information; based on an internet of things technology, by adopting a B / S framework and a three-layer system mode as well as seven-level security management, realizing the data monitoring as well as advanced forecasting and construction information real-time processing, update, inquiry, browsing, three-stage early warning and forecasting and three-level risk management.
Owner:武汉岩石科技有限公司
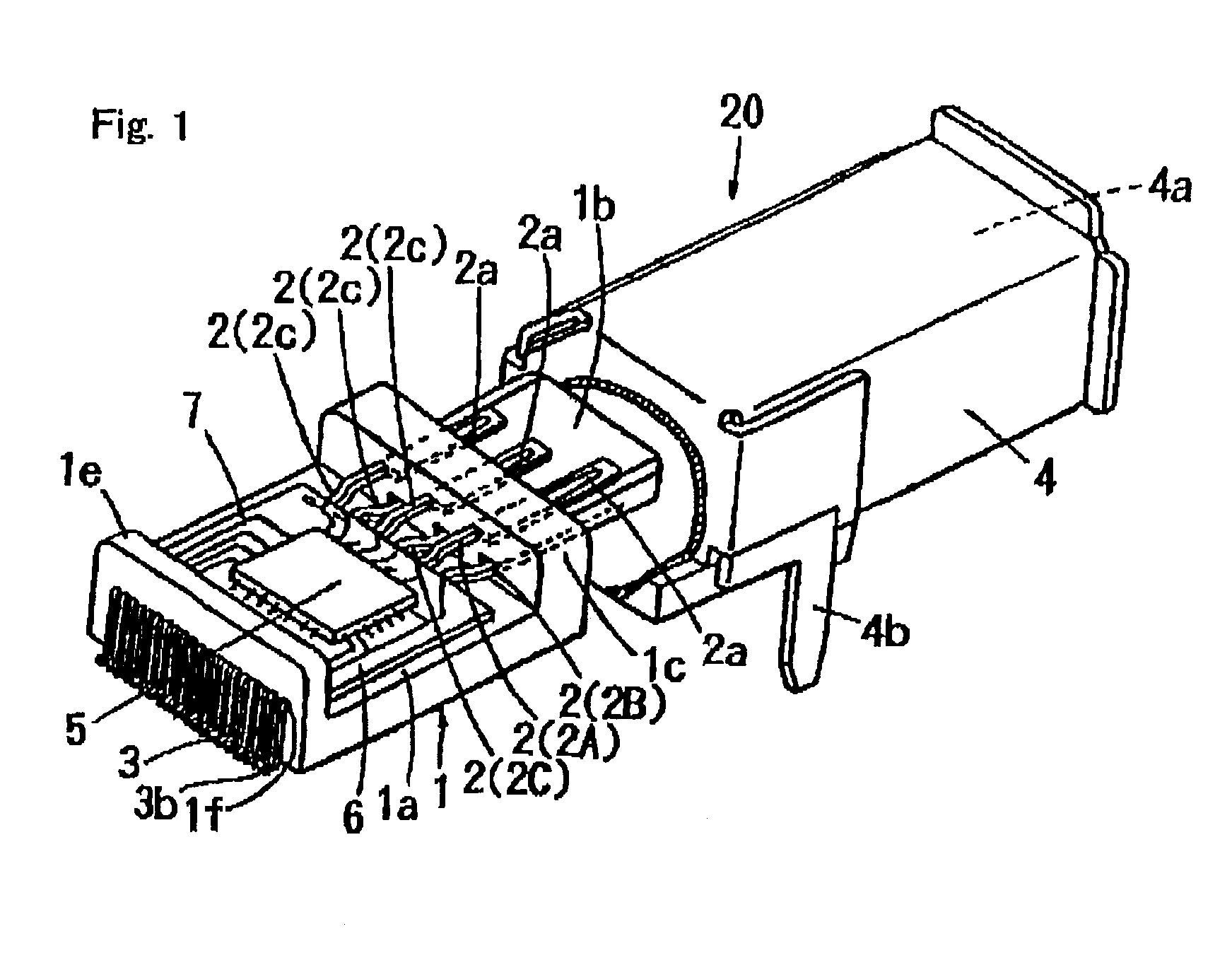
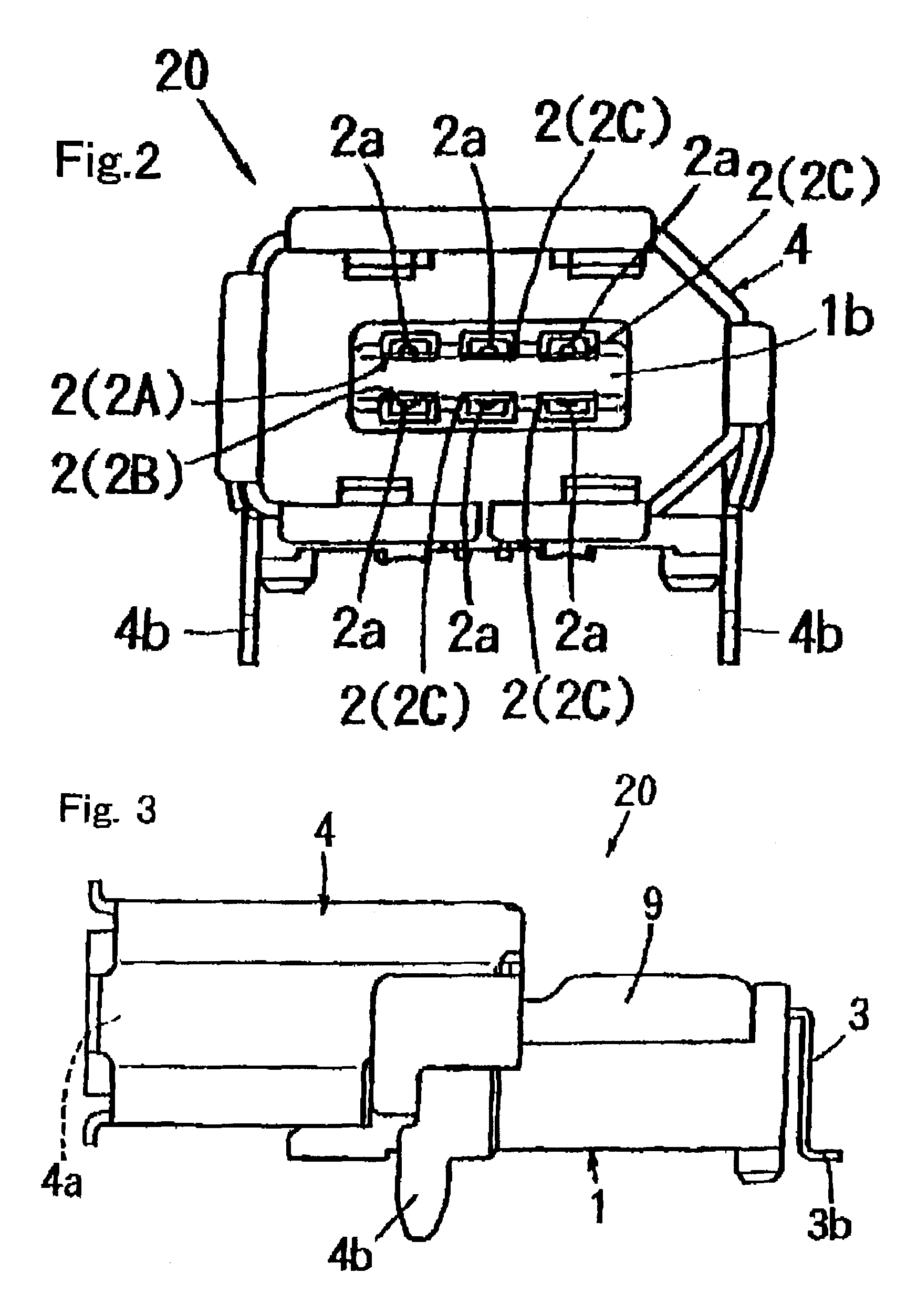
Connector receptacle
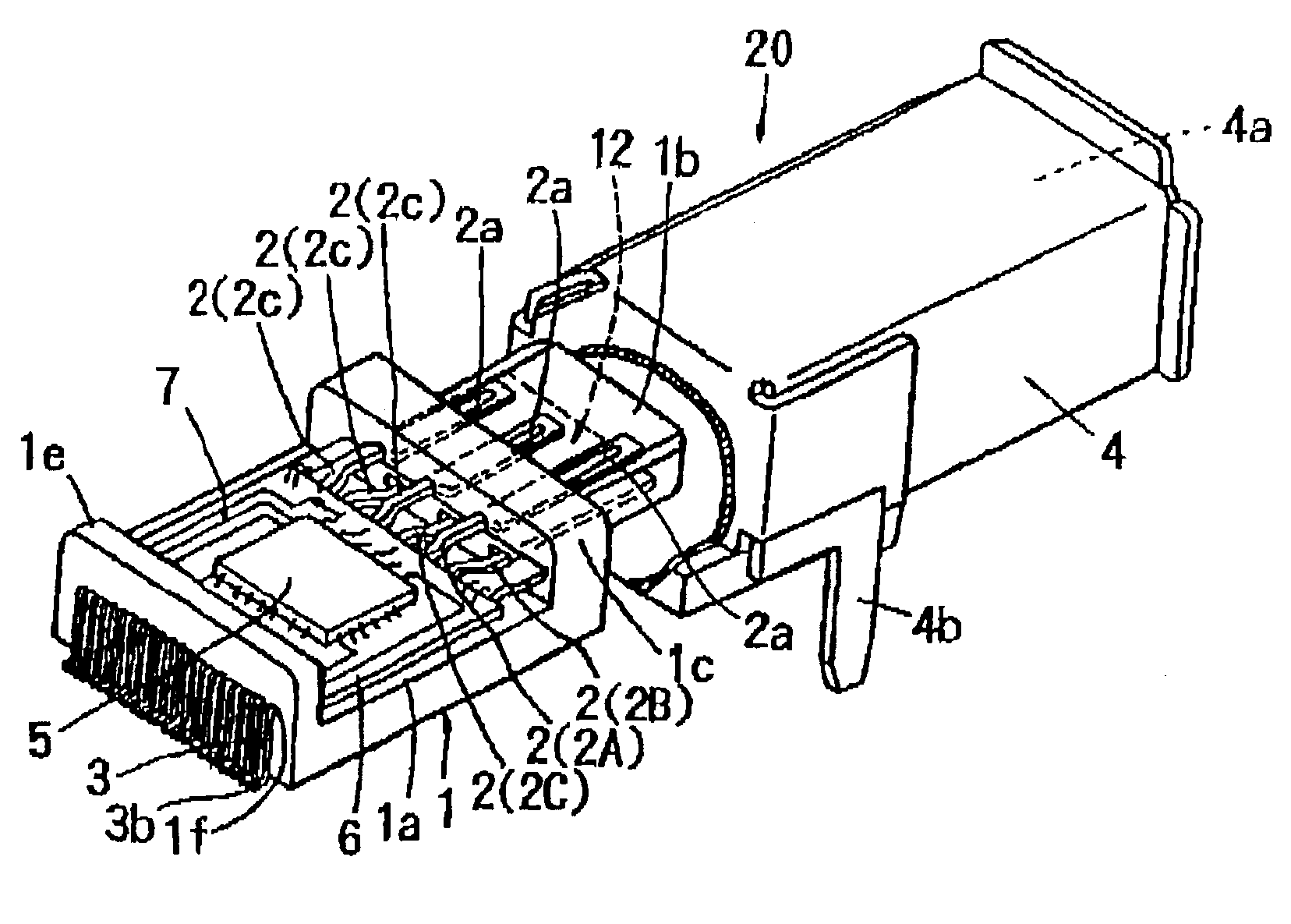
InactiveUS6902433B1Reduce the number of partsReduce in quantityCoupling device detailsPrinted circuits structural associationsPhysical layerData signal
A connector receptacle (20) is constituted by a contact (2) to which a data signal is serially communicated through a connector plug and a physical layer basic circuit (5) provided inside the connector receptacle (20) and adapted to perform specified processings so that the data signal is parallel communicated between the basic circuit and a link layer circuit for the communication. As a result, the distance between the contact (2) and the physical layer basic circuit (5) is short. Therefore, it is not necessary to pay so much attention as in conventional cases in designing a pattern layout (7) so as to prevent influence on the EMI and transmission characteristics, and it is easy to design the layout of the pattern constituting the transmission line for the data.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Information transmitting system for use in factory
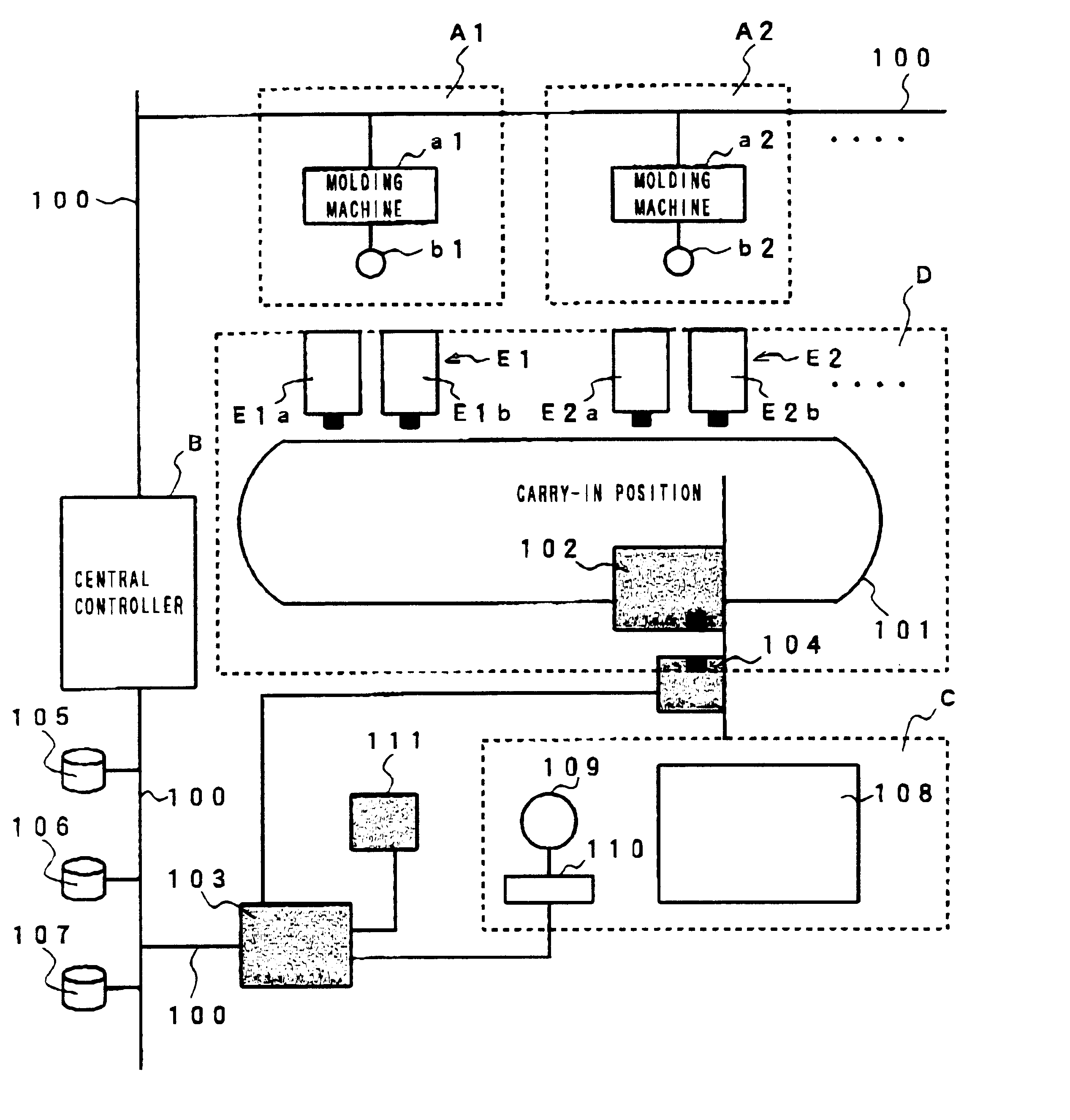
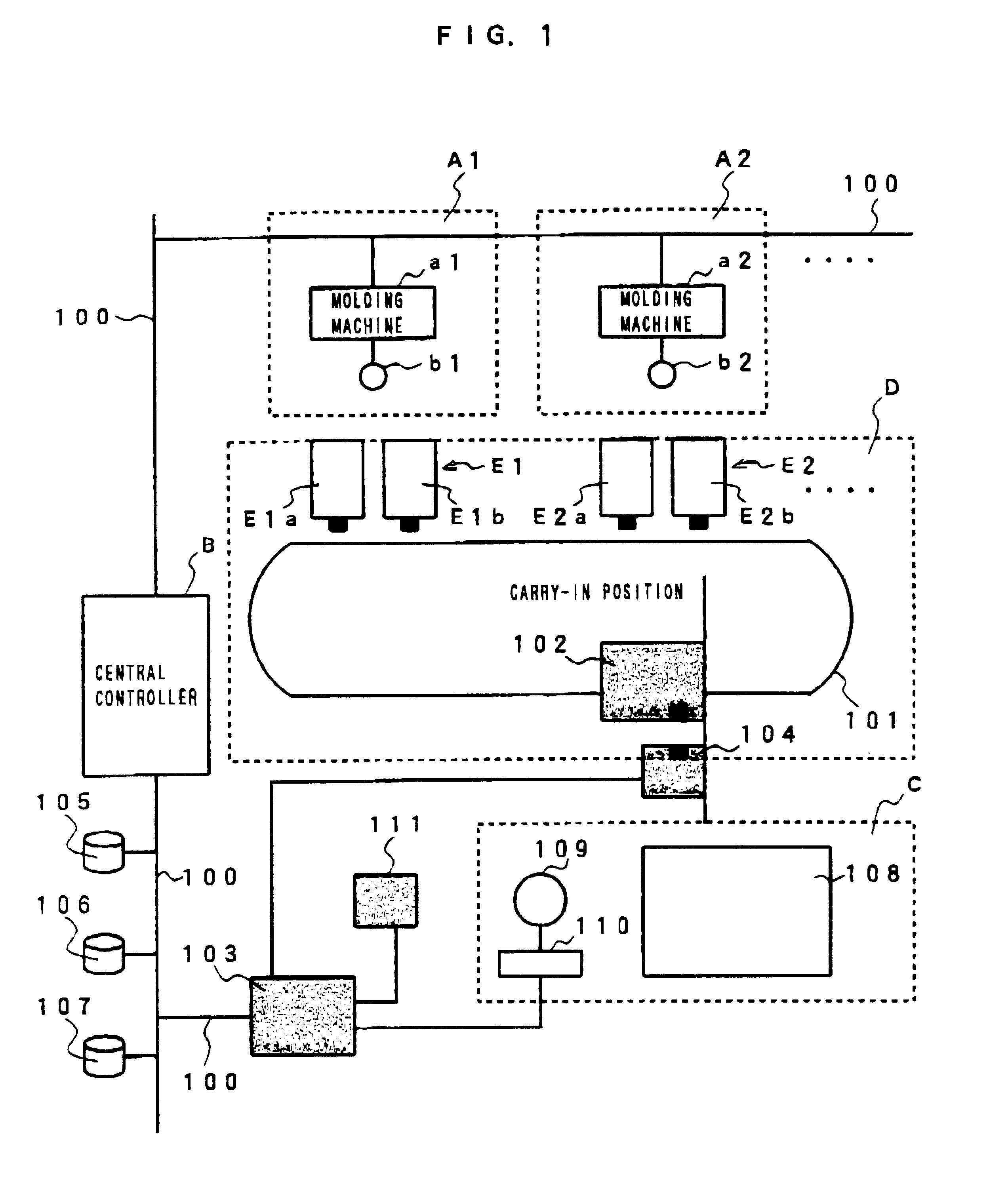
InactiveUS6516234B2Low costAvoid makingDigital data processing detailsAssembly machinesEngineeringEthernet
An information transmitting system for use in a factory, which is capable of transmitting information among controllers simply without the complicated lead-around of a communication line nor the need of complicated communication protocol. A controller for every molding cell Ai, where i=1,2 . . . max and max is a maximum number of molding cells, a conveyance controller to control an automatic conveyor, a stock cell and a centralized controller are connected to each other via an Ethernet line to provide a common information storage unit, and information is transmitted among the controllers through the common information storage unit. Since there is no need of parallel communication lines between the controllers, an I / O port or a communication line may be prevented from increasing in number and the lead-around of the communication line is prevented from being complicated, resulting in a reduction of cost required for setting up the devices.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Link aggregation
ActiveUS7414985B1Improve uptimeImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTError preventionLink aggregationNetwork topology
A method and system for aggregating a plurality of parallel communications links transmitting data between adjacent nodes in a network is provided. The method simplifies network topology by replacing multiple parallel communications links between nodes in the network with a single aggregated link. The method advertises the available bandwidth of each aggregated link to the network, the available bandwidth being the maximum bandwidth available for any one of the parallel links in the aggregate. The method permits each aggregated link to select which of the parallel links in the aggregate is to be used to transfer data from one node to the other. Aggregating links can be automatic and based on one or more predetermined criteria, such as the service class supported by the parallel links.
Owner:CIENA
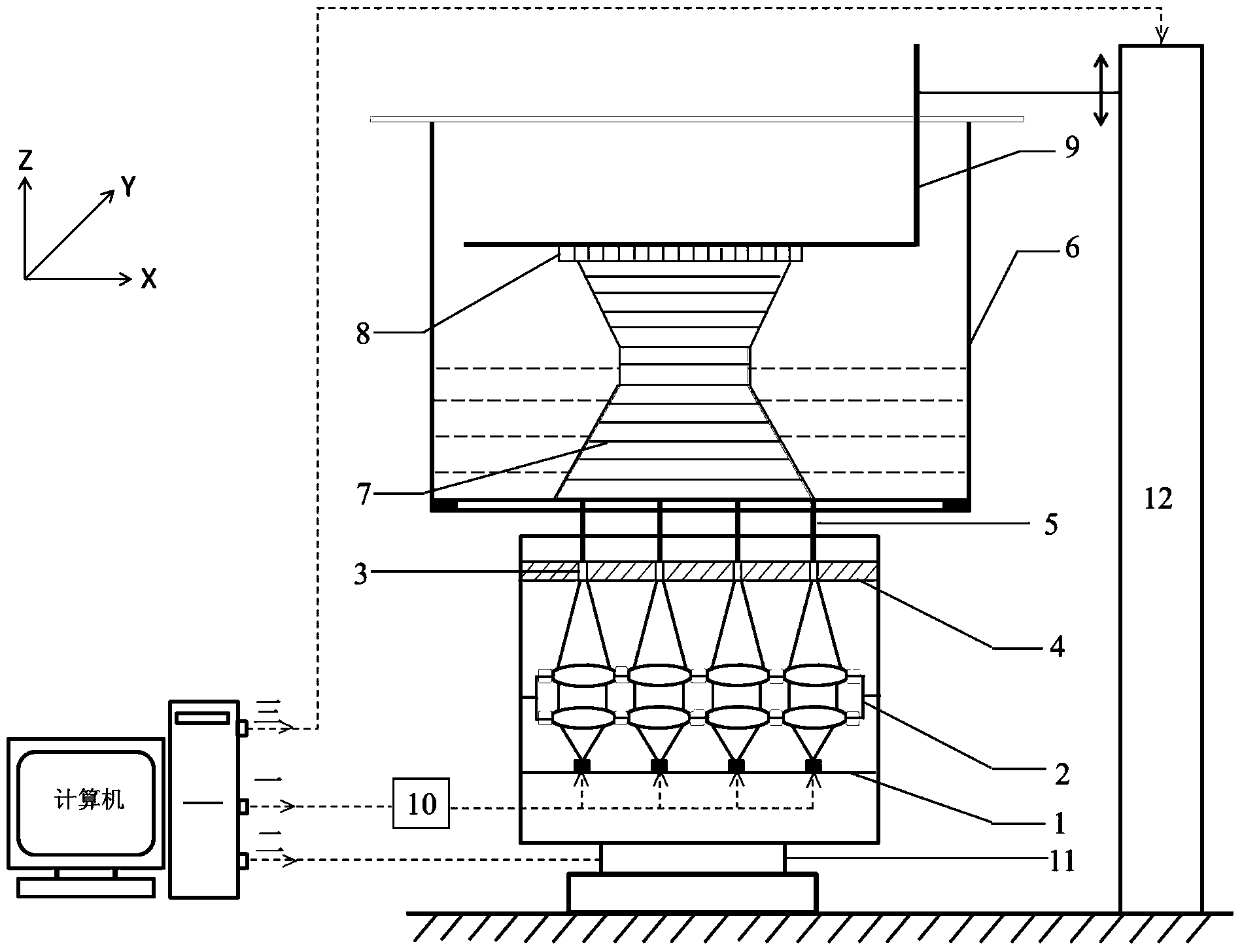
Photo-curing 3D forming system adopting LED array micro-projection light source
The invention provides a photo-curing 3D forming system adopting an LED array micro-projection light source. LEDs in the LED array light source are equidistantly distributed in the y direction and equidistantly staggered in the x direction. Lower LED array light sources are gathered to form a micro-projection beam array with dense distribution through a lens array group and a photomask plate to facilitate quick scanning and curing of a part model with small structural size. Moreover, single LEDs in the LED array light source are independently controlled through computer-single chip microcomputer parallel communication, the number of LEDs needing to be driven in the LED array light source is regulated in real time through a computer according to two-dimensional section information of each layer in the scanning process, and the scanning and curing are finished with an X-Y mobile platform controlling the micro-projection beam array to move in the X-Y horizontal direction. By taking original photo-curing 3D forming equipment as an application basis, the photo-curing forming system can improve the manufacturing efficiency and reduce the cost while guaranteeing the prototype manufacturing accuracy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
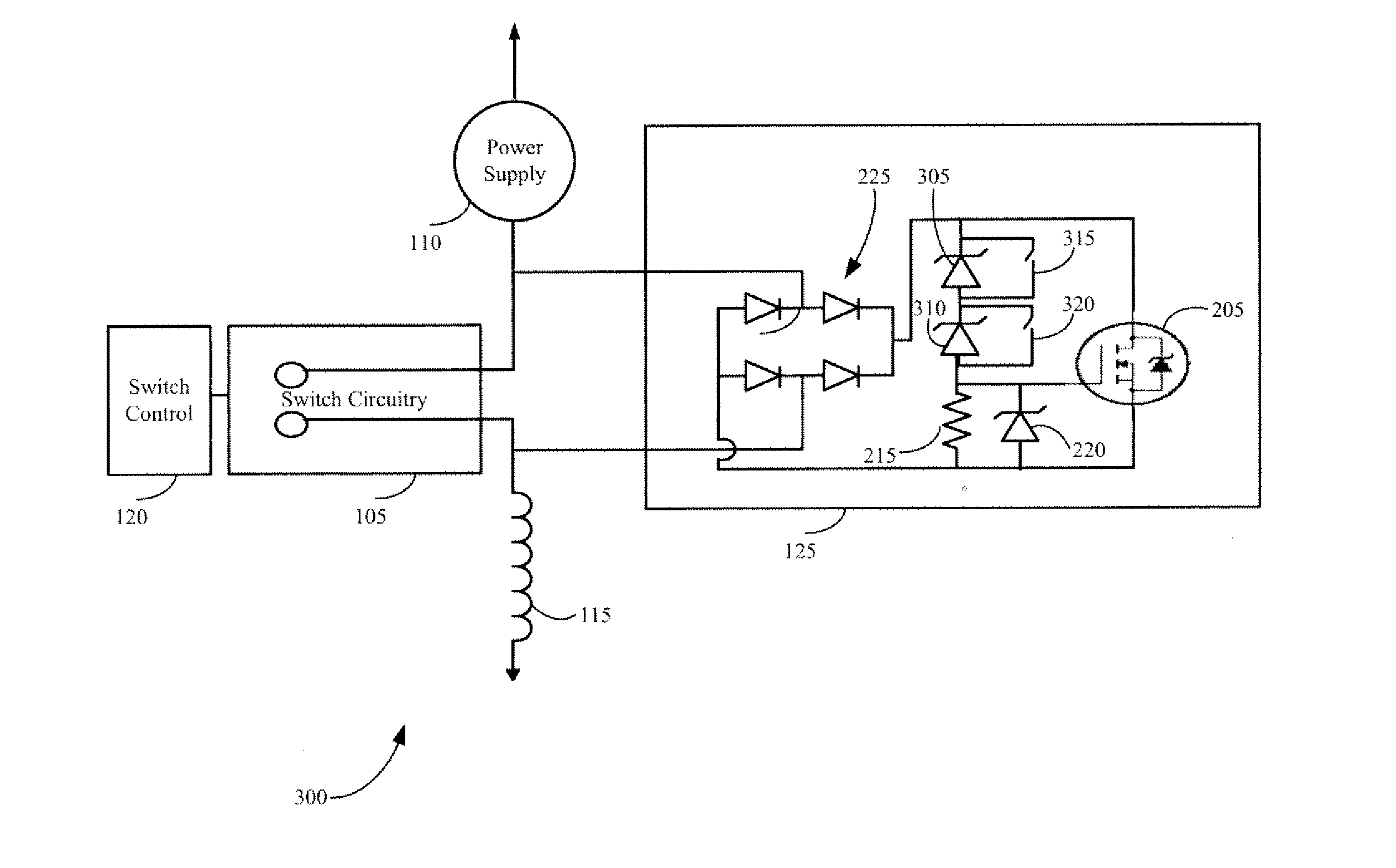
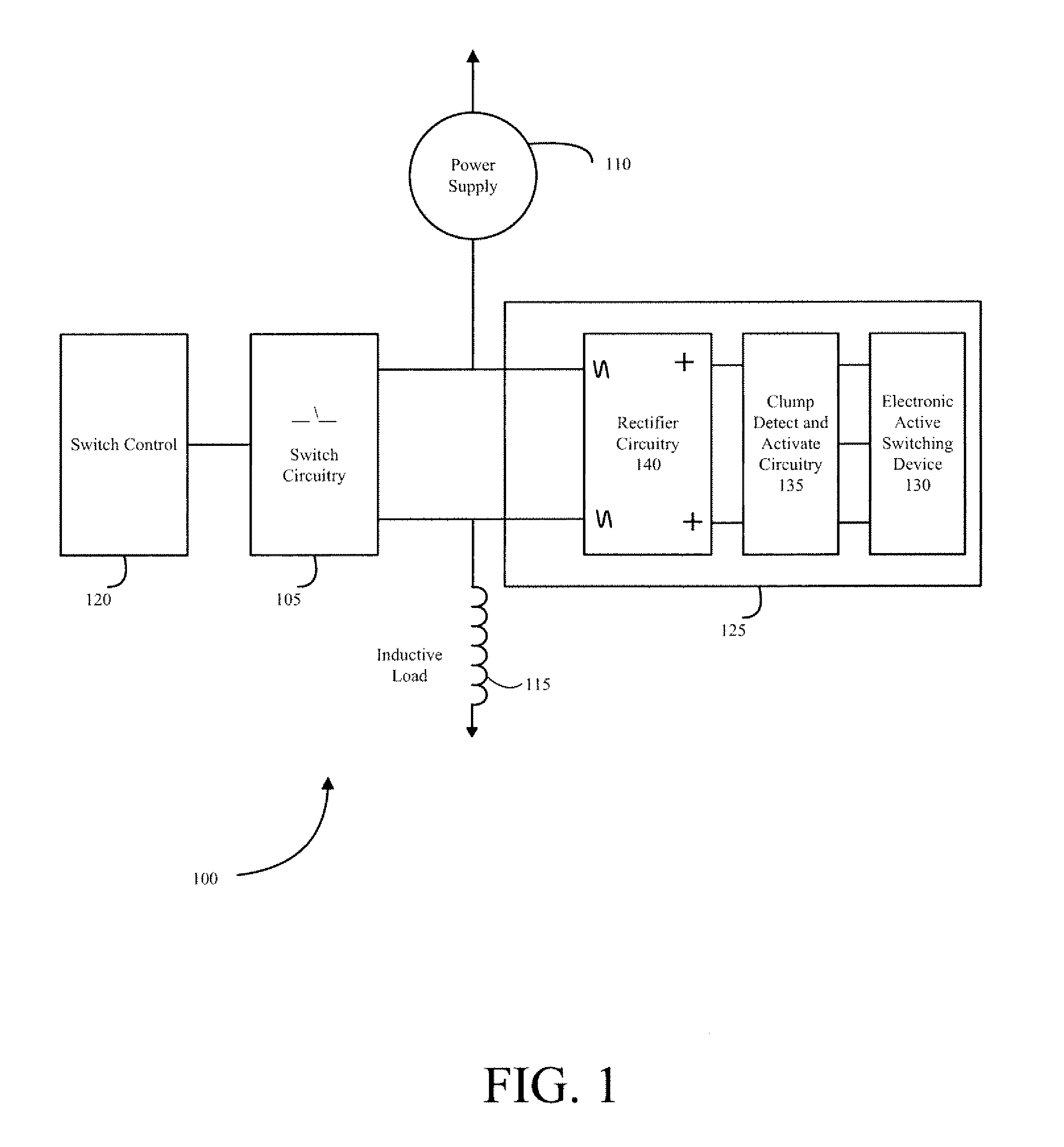
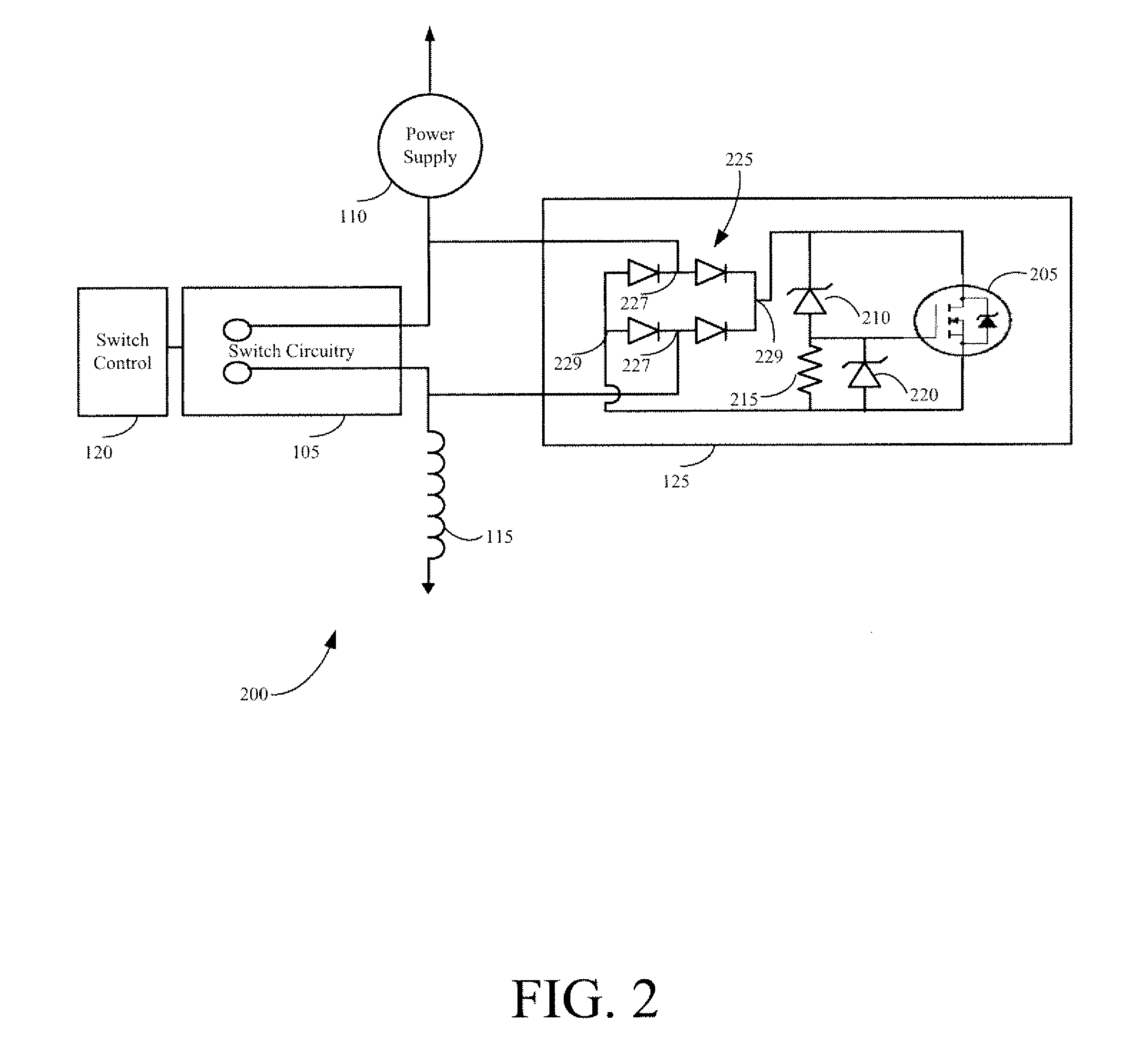
Systems, Methods, and Apparatus for Limiting Voltage Across a Switch
ActiveUS20120026632A1Switching is limitedAvoid flowElectronic switchingEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentZener diodeEngineering
Systems, methods, and apparatus for limiting voltage across a switch utilizing voltage clamping circuitry are provided. The voltage clamping circuitry may include a rectifier circuit comprising inputs and outputs, the inputs in parallel communication across operational circuitry; an electronic active switching device in parallel communication with the outputs of the rectifier circuit; and at least one Zener diode in parallel communication with the electronic active switching device. When voltage across the electronic active switching device and the Zener diode meets or exceeds a predetermined value, the current will flow through the electronic active switching device and limit voltage across the operational circuitry to within a voltage clamping circuitry voltage limit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus to support parallel communication for multiple subscriber identities in a wireless communication device
Apparatus and methods to support parallel communication using multiple subscriber identities in a wireless communication device via multiple subscriber identity modules (SIMs) are disclosed. A representative method includes establishing a connection with a first wireless network via a first wireless cellular protocol software stack for a first subscriber identity associated with a first subscriber identity module; registering with a second wireless network via a second wireless cellular protocol software stack for a second subscriber identity associated with a second subscriber identity module; and receiving radio frequency signals from the second wireless network via the second wireless cellular protocol software stack in parallel with communicating with the first wireless network via the first wireless cellular protocol software stack. The first and second wireless cellular protocol software stacks share at least a portion of radio frequency wireless circuitry for communicating with the first and second wireless network respectively.
Owner:APPLE INC
Clock synchronization in a bidirectional network
InactiveUS8363679B2Broadband local area networksHybrid switching systemsCable transmissionMultiplexing
An architecture for providing high-speed access over frequency-division multiplexed (FDM) channels allows transmission of Ethernet frames and / or other data across a cable transmission network or other form of FDM transport. The architecture involves downstream and upstream FDM multiplexing techniques to allow contemporaneous, parallel communications across a plurality of frequency channels. Furthermore, the architecture allows a central concentrator to support a plurality of remote devices that each has guaranteed bandwidth through connection-oriented allocations of bi-directional data flows. The upstream and downstream bandwidth allocation can support symmetrical bandwidth as well as asymmetrical bandwidth in either direction. As a local network, the architecture supports guaranteed bandwidth for delivery of data flows to a plurality of host devices.
Owner:SCI ATLANTA LLC
Electromagnetic connector and communications/control system/switch fabric with serial and parallel communications interfaces
ActiveCN104025387AEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionControl systemEngineering
An electromagnetic connector is disclosed that is configured to form a first magnetic circuit portion comprising a first core member and a first coil disposed of the first core member. The electromagnetic connector is configured to mate with a second electromagnetic connector. A communications control system / switch fabric is disclosed that includes a serial communications interface and a parallel communications interface (e.g., for coupling input / output modules with a control module). The serial communications interface is configured for connecting input / output modules / slave devices to a control module / master device in parallel, and the parallel communications interface is configured for separately connecting the input / output modules / slave devices to the control module / master device.
Owner:BEDROCK AUTOMATION PLATFORMS
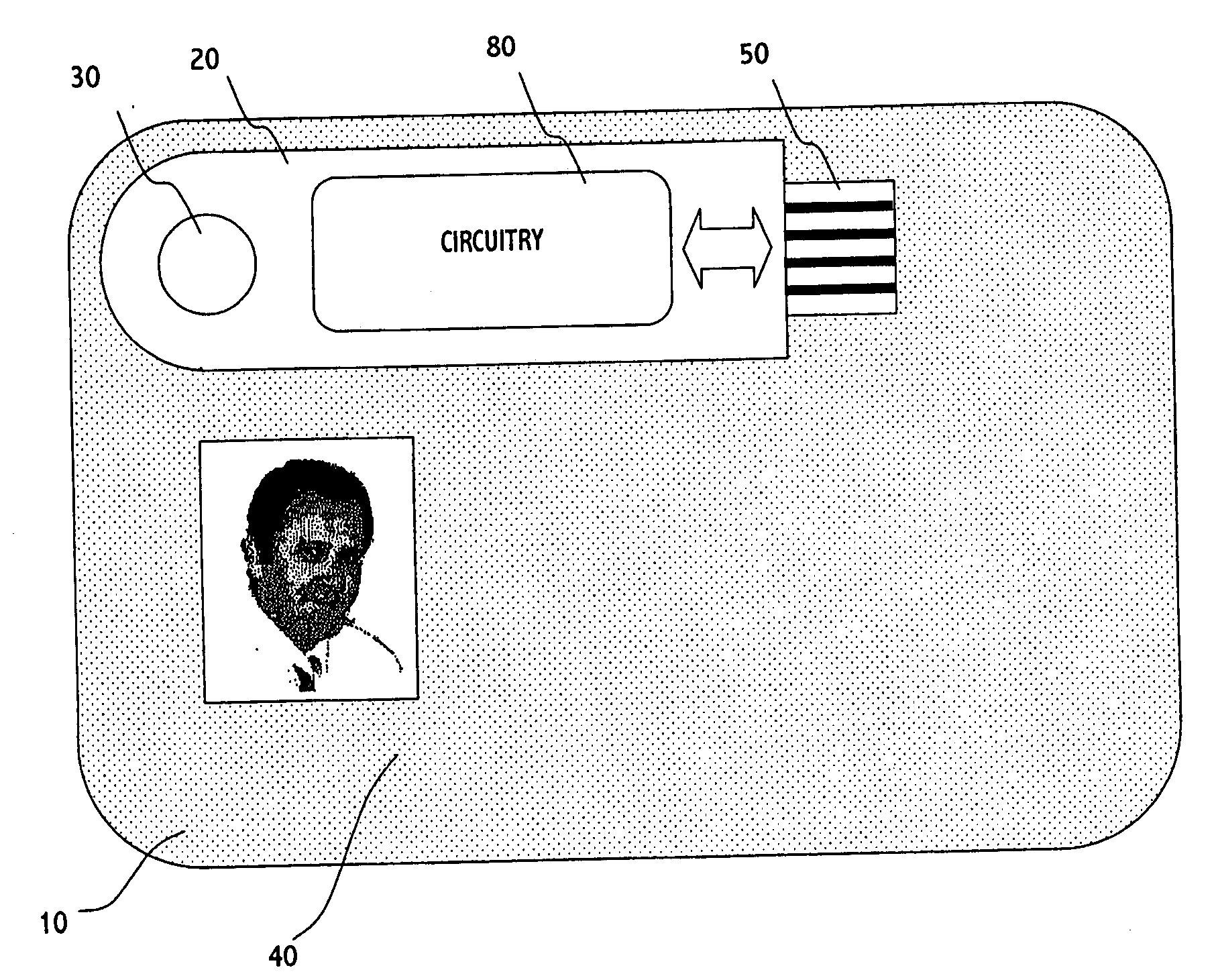
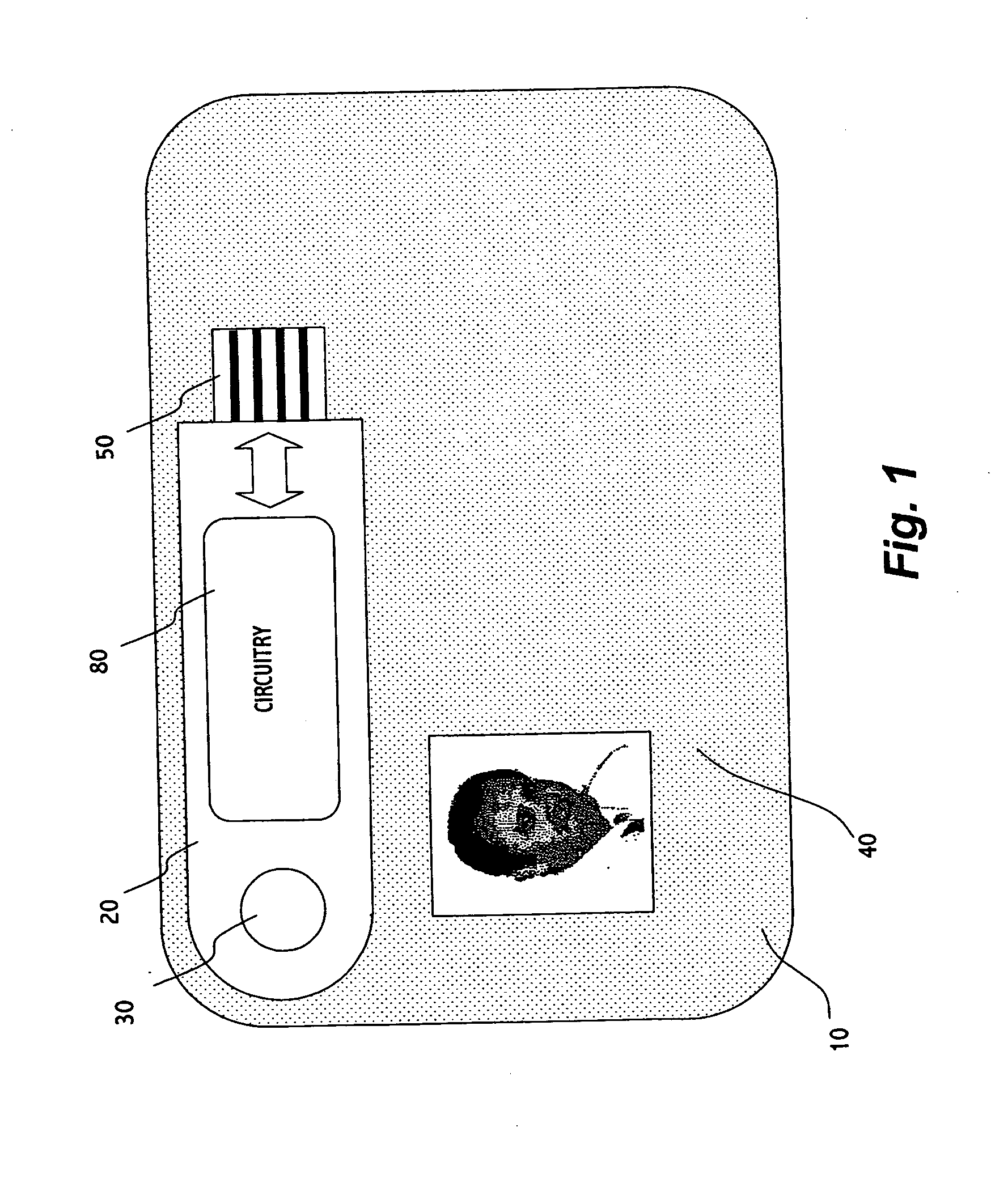
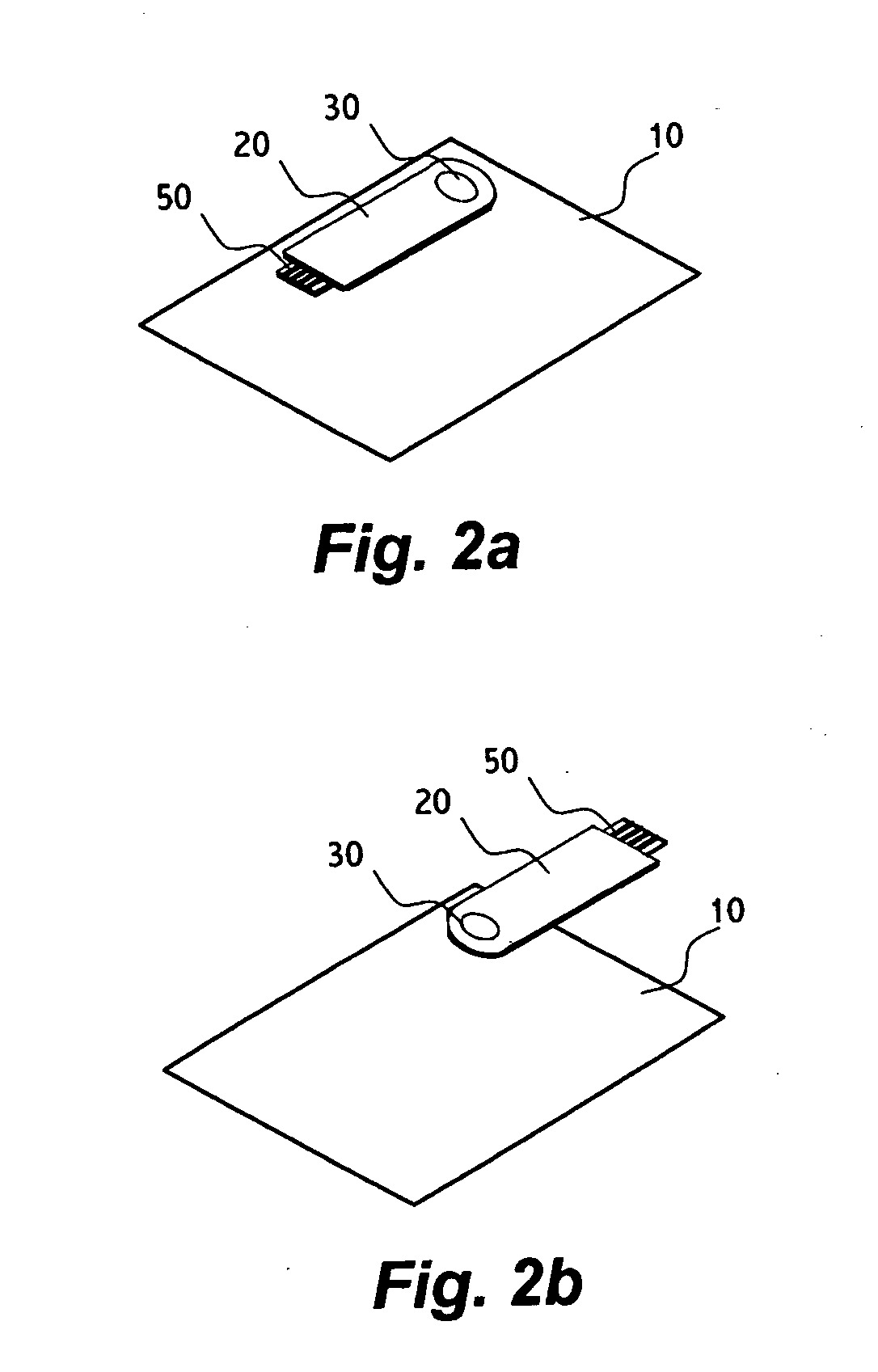
Security card apparatus
The present invention is directed to a security card apparatus, comprising: a portable device coupled with a wired communication interface (e.g. USB, FireWire, RS232, parallel communication interface, serial communication interface); a substrate of a typical credit card or typical smart card format; and a shaft for connecting the portable device to the substrate such that the portable device can be rotated around the shaft for creating a state where the portable device can be connected to a host, and a state where the security card apparatus can be stored within a typical case for storing credit cards in a wallet. The substrate may comprise a figure of a user thereof.
Owner:MARGALIT YANKI +1
Method, system and equipment for connection establishment
InactiveCN104980980AAvoid interruptionImprove transmission efficiencyWireless communicationPerformance indexData transmission
Embodiments of the invention relate to the field of wireless communication technologies, in particular to a method, a system and equipment for connection establishment, which are used for solving the problem of a strong impact on a maximum jitter performance index of data transmission delay due to data transmission interruption during hard handover of UE (User Equipment) in the prior art. According to the embodiments of the invention, the method comprises the following steps that the user equipment reports target cell information which conforms to establishment conditions of a second link to a serving base station through a first link; and the user equipment receives a second link resource, which is sent by the serving base station and is allocated to the user equipment by a target base station, establishes a connection with the target base station according to the second link resource and does not disconnect the first link with the serving base station. The user equipment is capable of simultaneously carrying out parallel communication with two base stations through the two links, and the two base stations are interactive, so that data transmission interruption during hard handover is avoided, and the impact on the maximum jitter performance index of data transmission delay during hard handover is reduced.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TELECOMM TECH
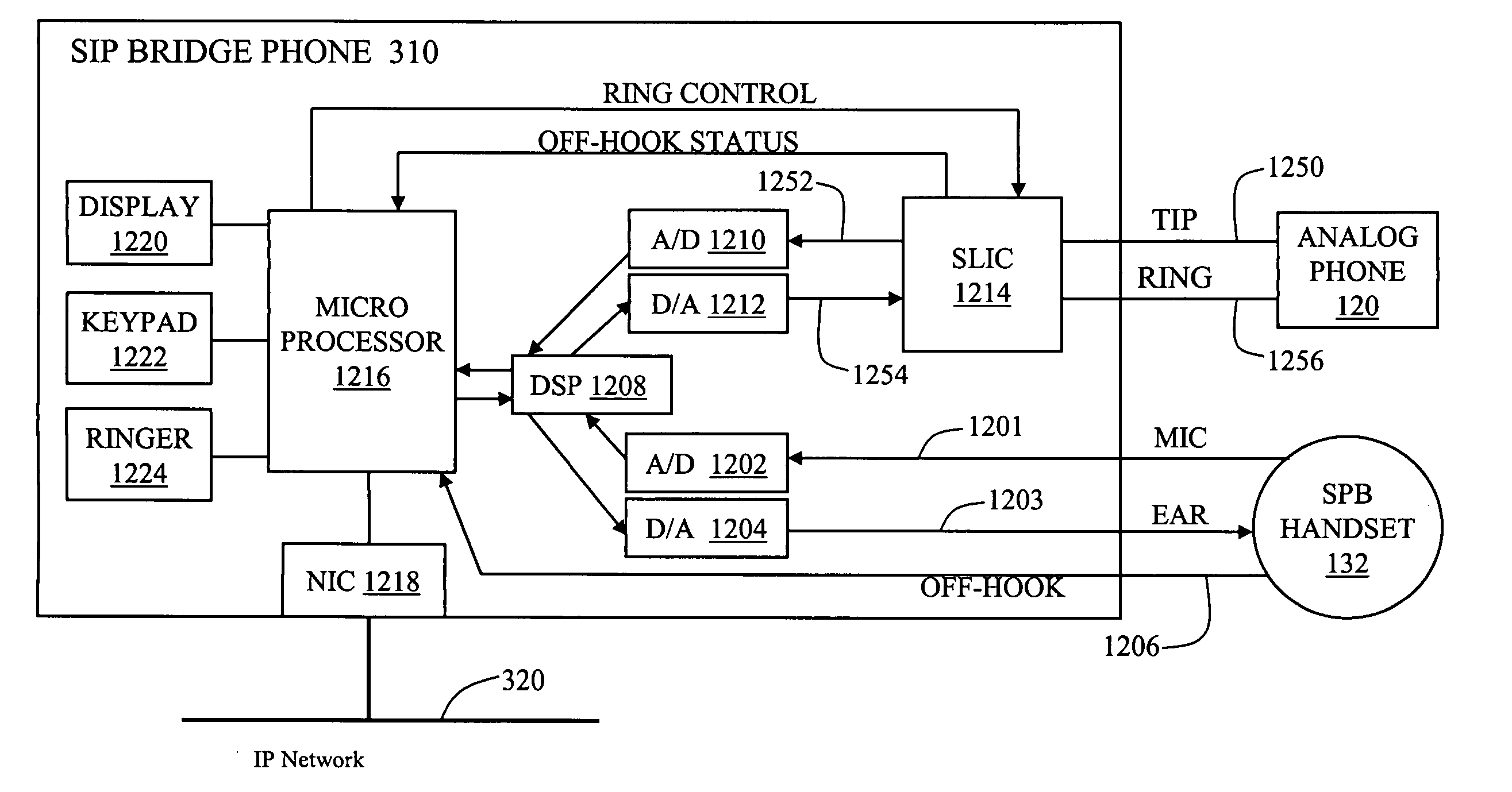
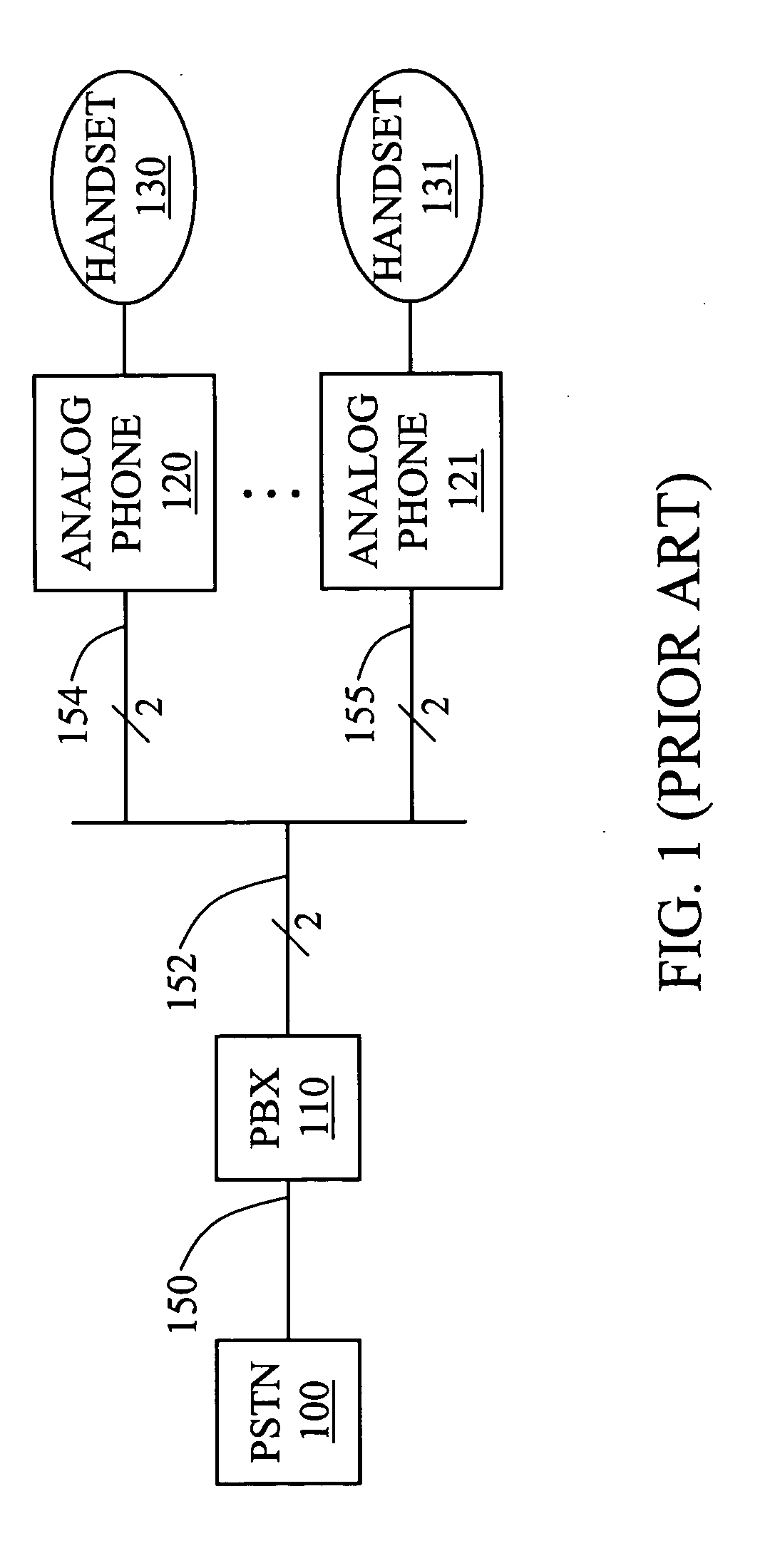
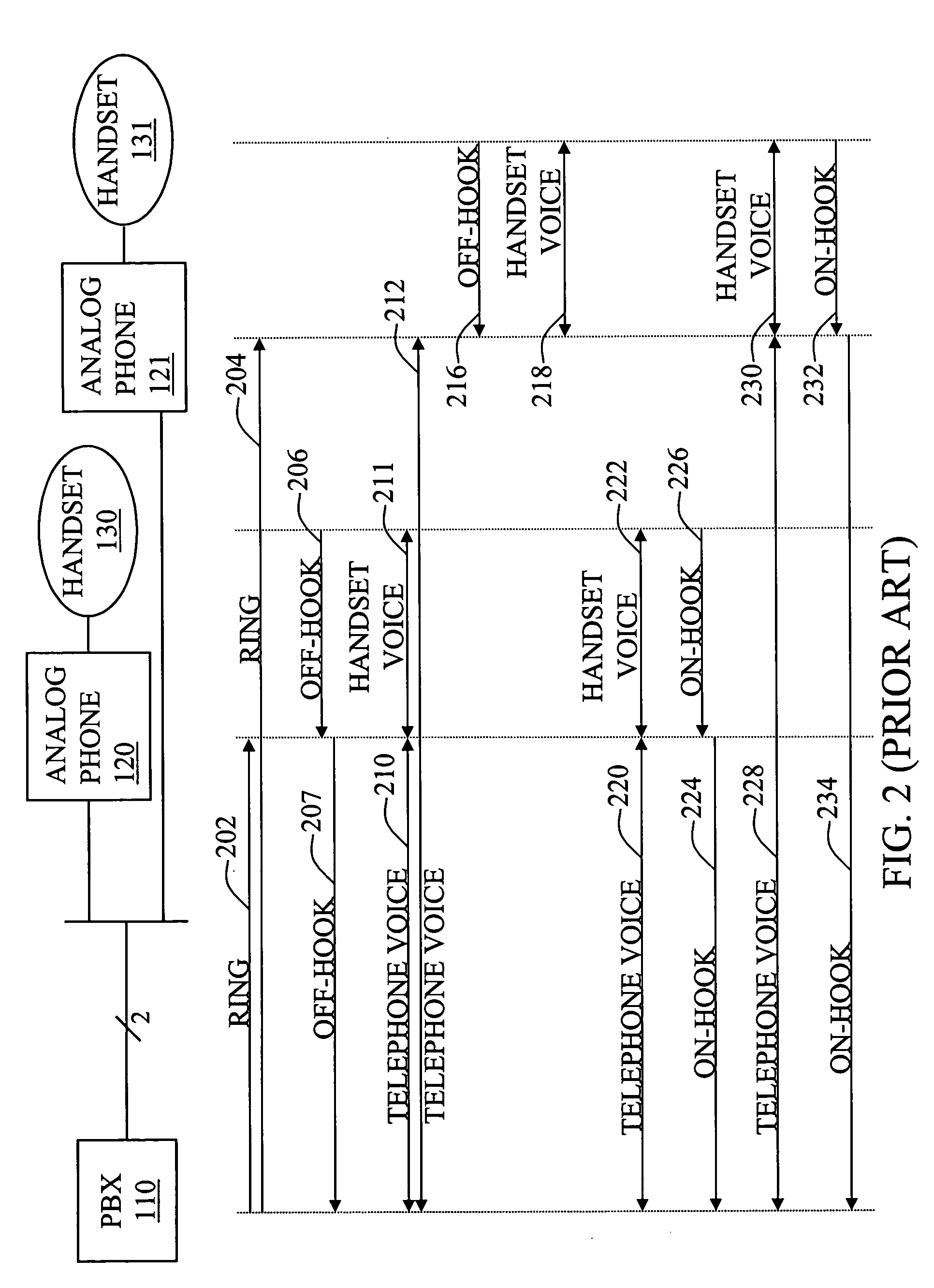
Methods and devices for achieving parallel operation between IP and analog phones
An IP bridge phone for operatively coupling one or more analog phones to a digital communications network to support parallel communications is disclosed. The IP bridge phone includes a phone handset interface adapted to connect to a phone handset, an analog phone interface, and a network interface. A mixing module is adapted to receive a first voice signal from the handset interface, a second voice signal from the analog phone, and a third voice signal from the data communications network; generate a plurality of combined signals from the first voice signal, the second voice signal, and the third voice signal; and transmit each of the plurality of combined signals to one of the plurality of interfaces. The plurality of combined signals provide parallel communications between the phone handset, the analog phone, and the remote calling party.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
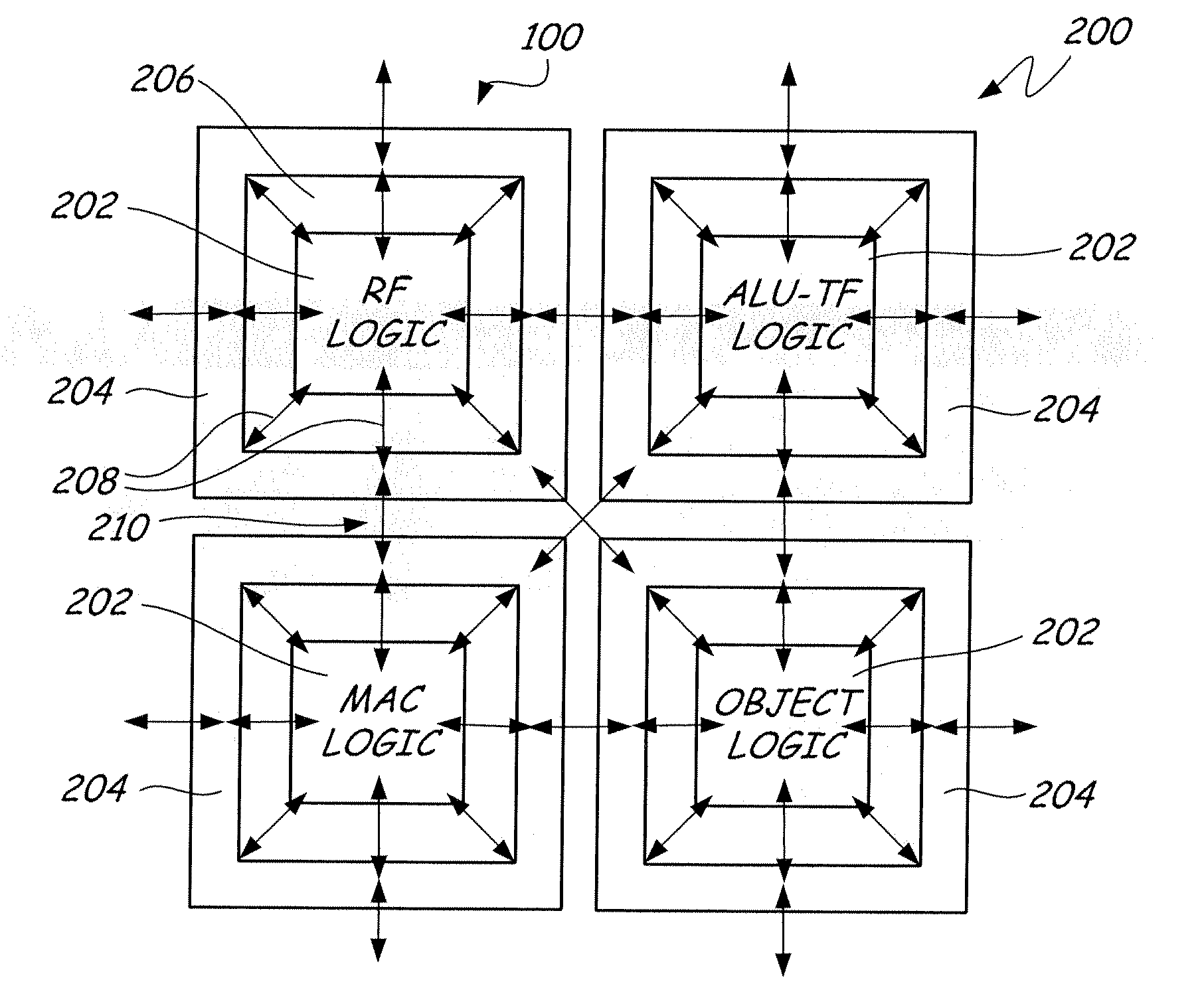
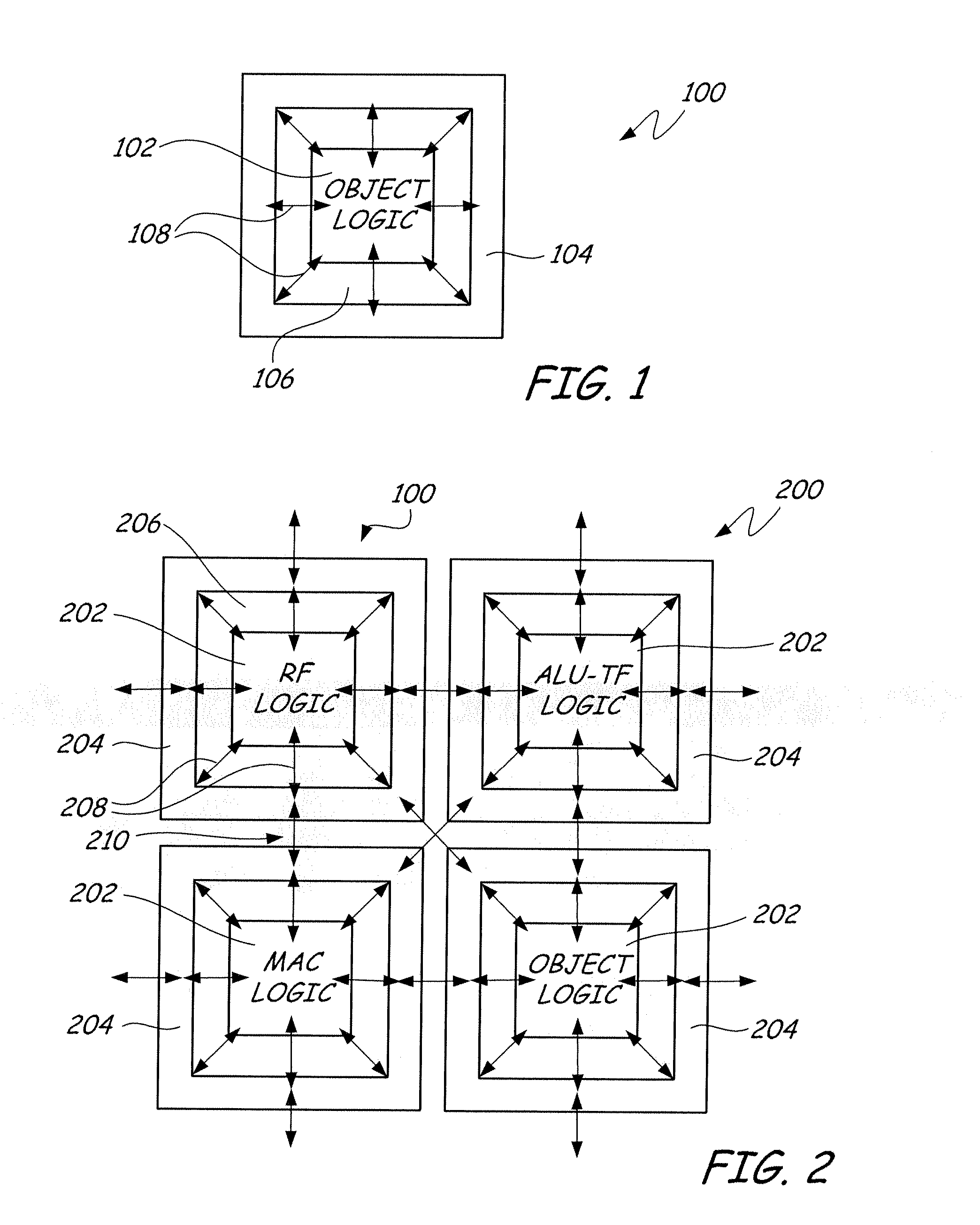
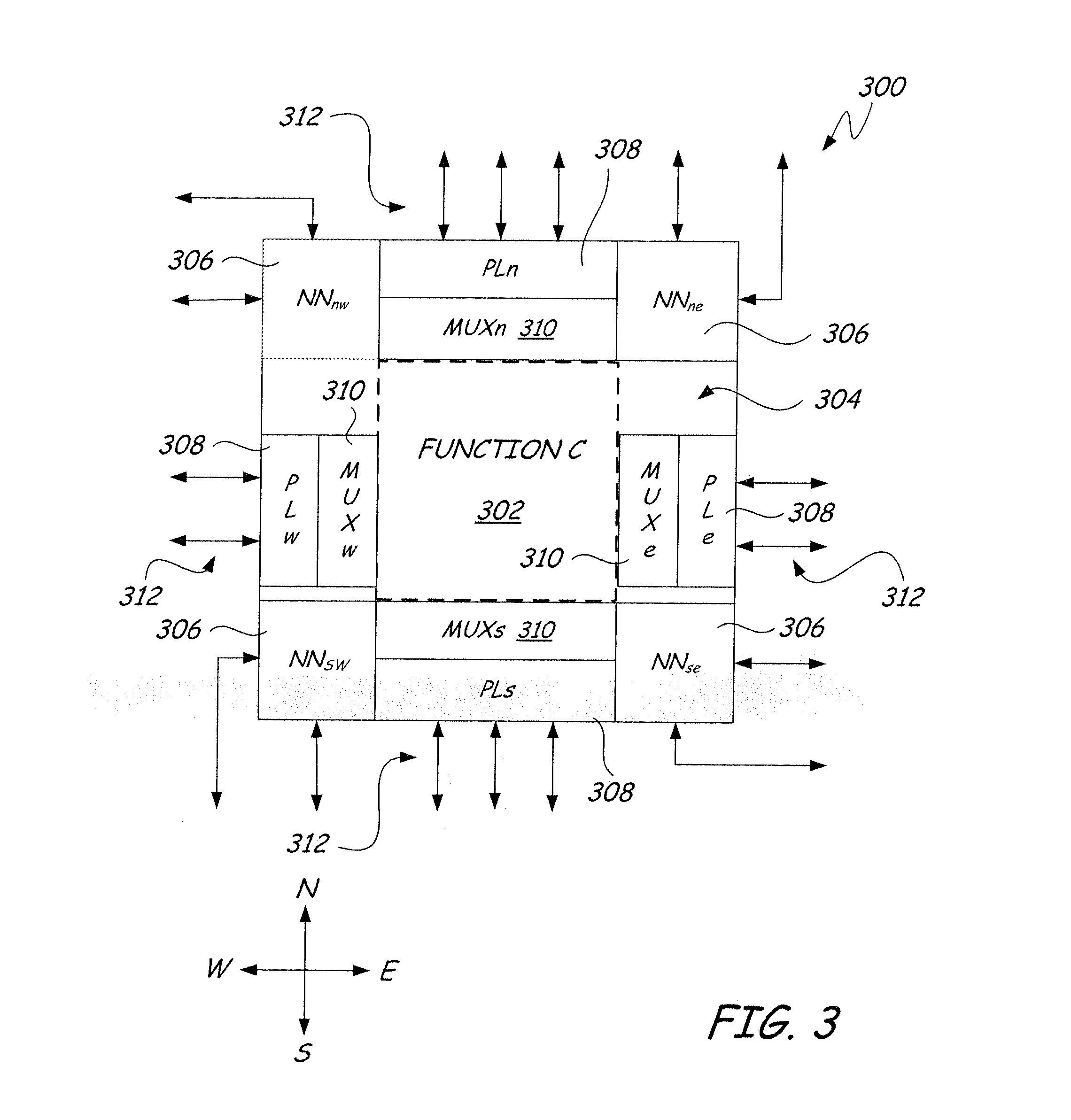
Field programmable semiconductor object array integrated circuit
InactiveUS20070247189A1Facilitating rapid designEasy to implementSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsField-programmable object arrayEngineering
A field-programmable object array integrated circuit employs a course gain architecture comprising a core array of highly optimized silicon objects that are individually programmed and synchronously connected via high performance parallel communications structures permitting the user to configure the device to implement a variety of very high performance algorithms. The high level functions available in the objects combined with the unique interconnect structures enables performance superior to existing field programmable solutions while maintaining and enhancing the flexibility. A consistent peripheral “donut” structure around the core of each object makes them interchangeable to build up complex circuits without redesign of standard objects.
Owner:MATHSTAR +1
Hash-based packet distribution in a computer system
A method for distributing packets across multiple parallel interfaces between a first instruction executing device and a second instruction executing device may include: the first instruction executing device receiving a stream of data packets, each data packet including header information regarding that data packet; and for each data packet, the first instruction executing device executing instructions to identify one or more particular information elements in the data packet; execute a hash function to the one or more particular information elements to calculate a hash value for the data packet; select a particular one of the multiple parallel communication interfaces based on the calculated hash value for the data packet; and forward the data packet to the second instruction executing device via the selected communication interface. Such method may provide traffic load balancing across the multiple parallel interfaces.
Owner:BREAKINGPOINT SYST
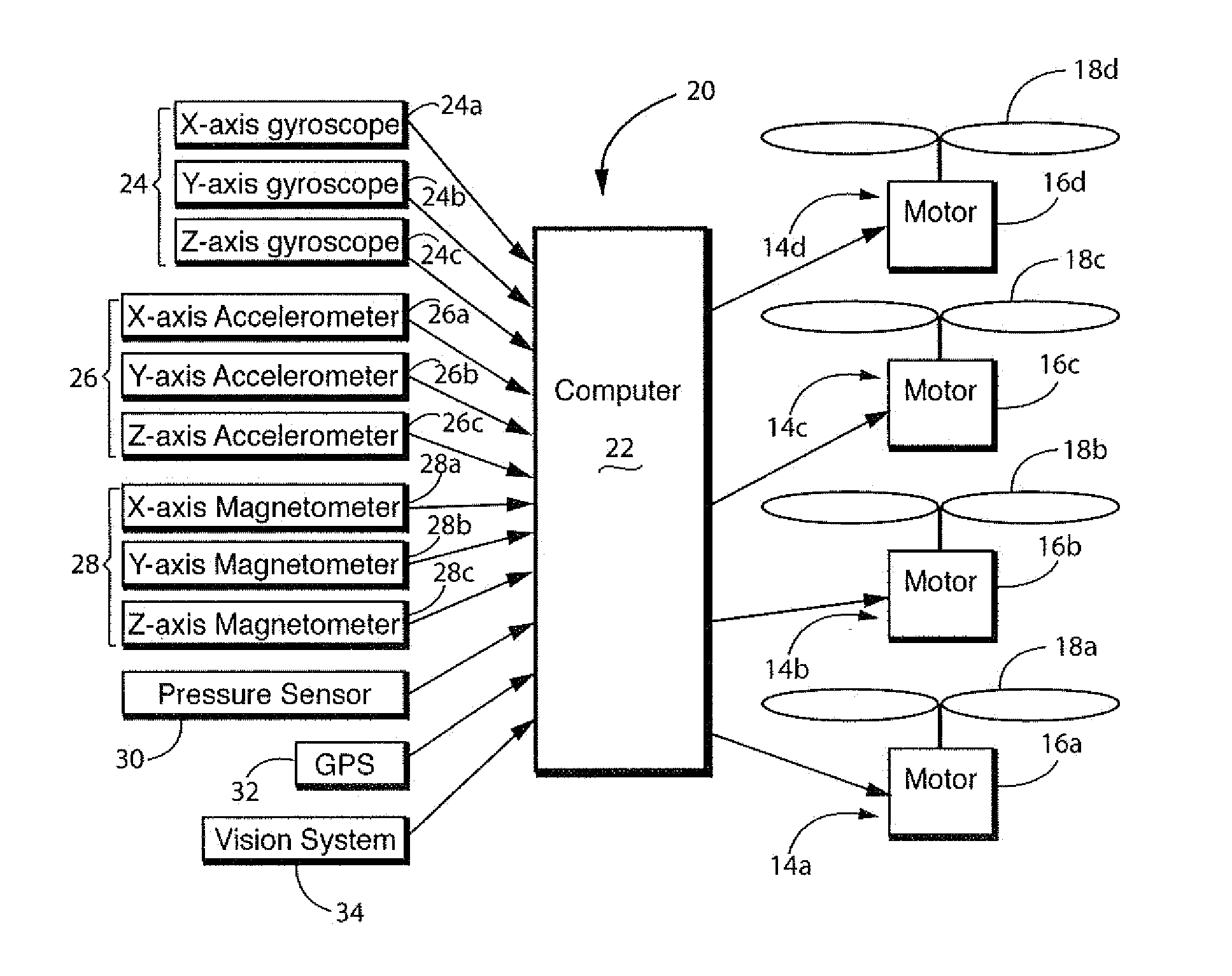
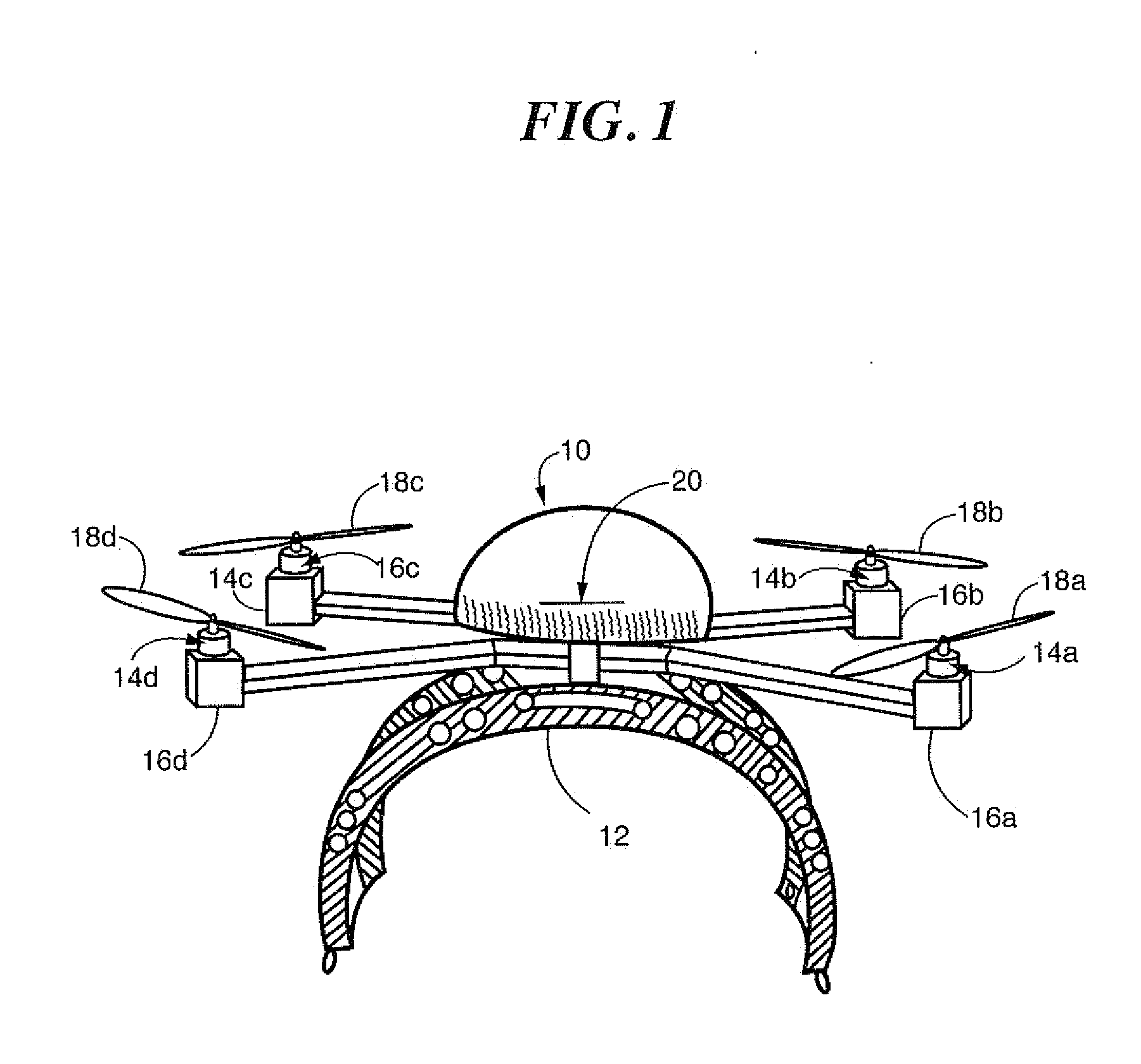
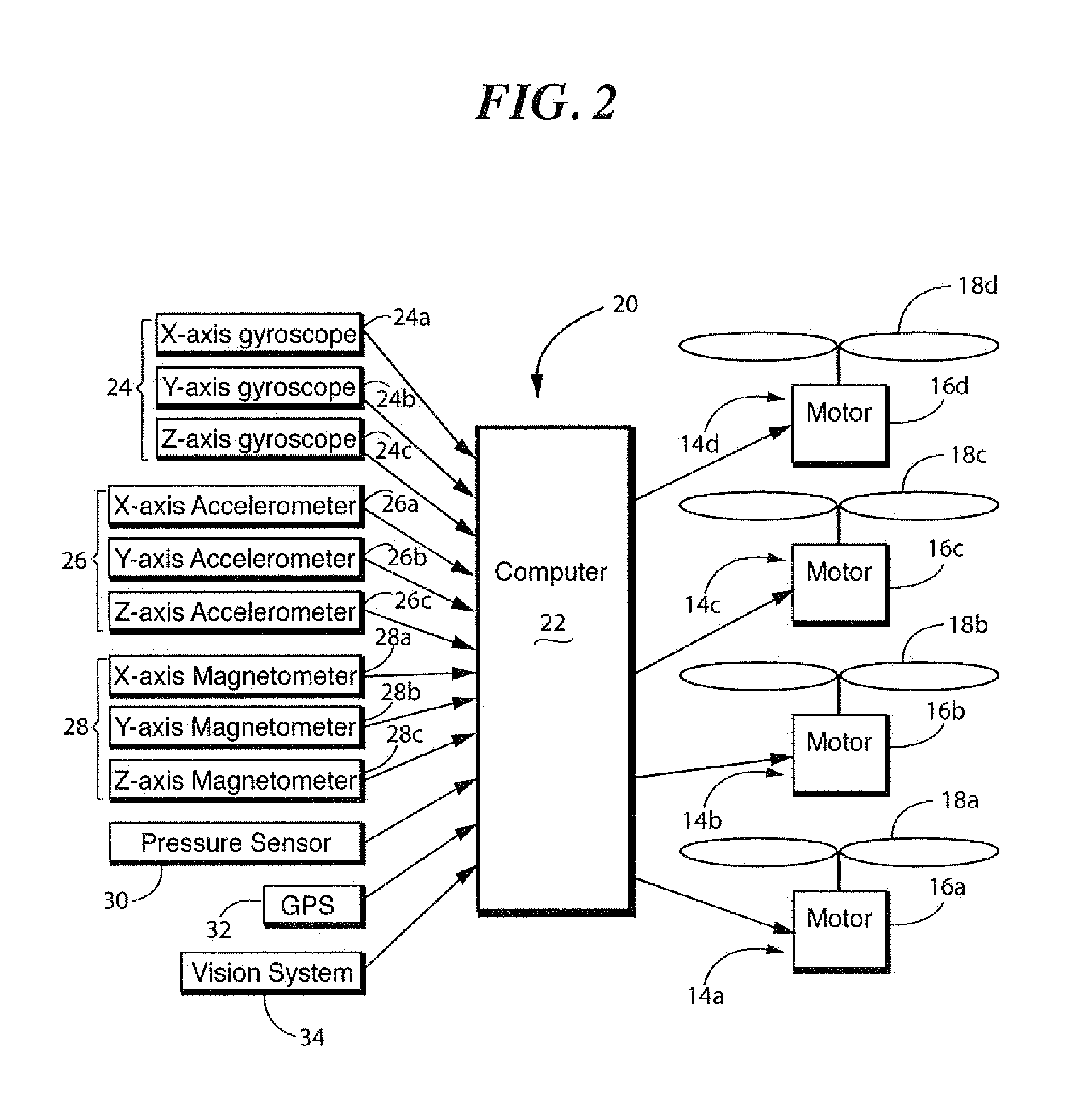
Control system for unmanned aerial vehicle utilizing parallel processing architecture
ActiveUS20130110325A1Autonomous decision making processDigital data processing detailsDistribution controlControl signal
A UAV has two rotors. First and second sensors sense a first and second type of input respectively. The second type of input is different than the first type, the first sensor providing a first sensor output and the second sensor providing a second sensor output. The first sensor output is input to a first computer and the second sensor output is input to a second computer. The first and second computer communicate in parallel to process the first and second sensor outputs to create a control signal having a predetermined number of variables therein, each variable having an exclusive position within the signal. The first computer outputs a first variable and the second computer outputs a second variable, each output being assigned an exclusive position within the control signal. At least one of the first and second computers outputting the control signal to the rotors.
Owner:HOVERFLY TECH INC
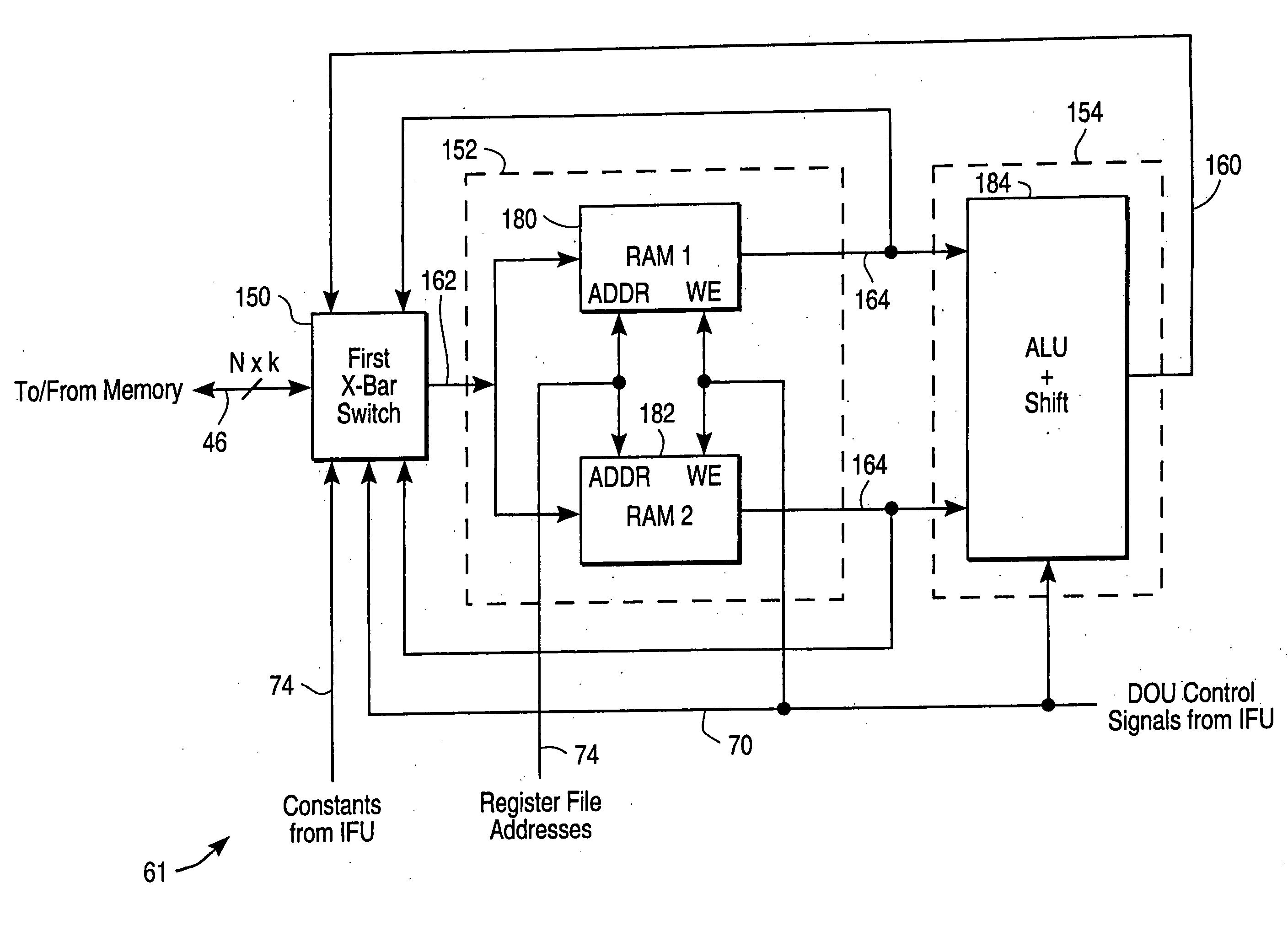
Meta-address architecture for parallel, dynamically reconfigurable computing
InactiveUS20050268070A1More communication bandwidthIrregular scalabilityProgram control using stored programsConcurrent instruction executionPublic interfaceData set
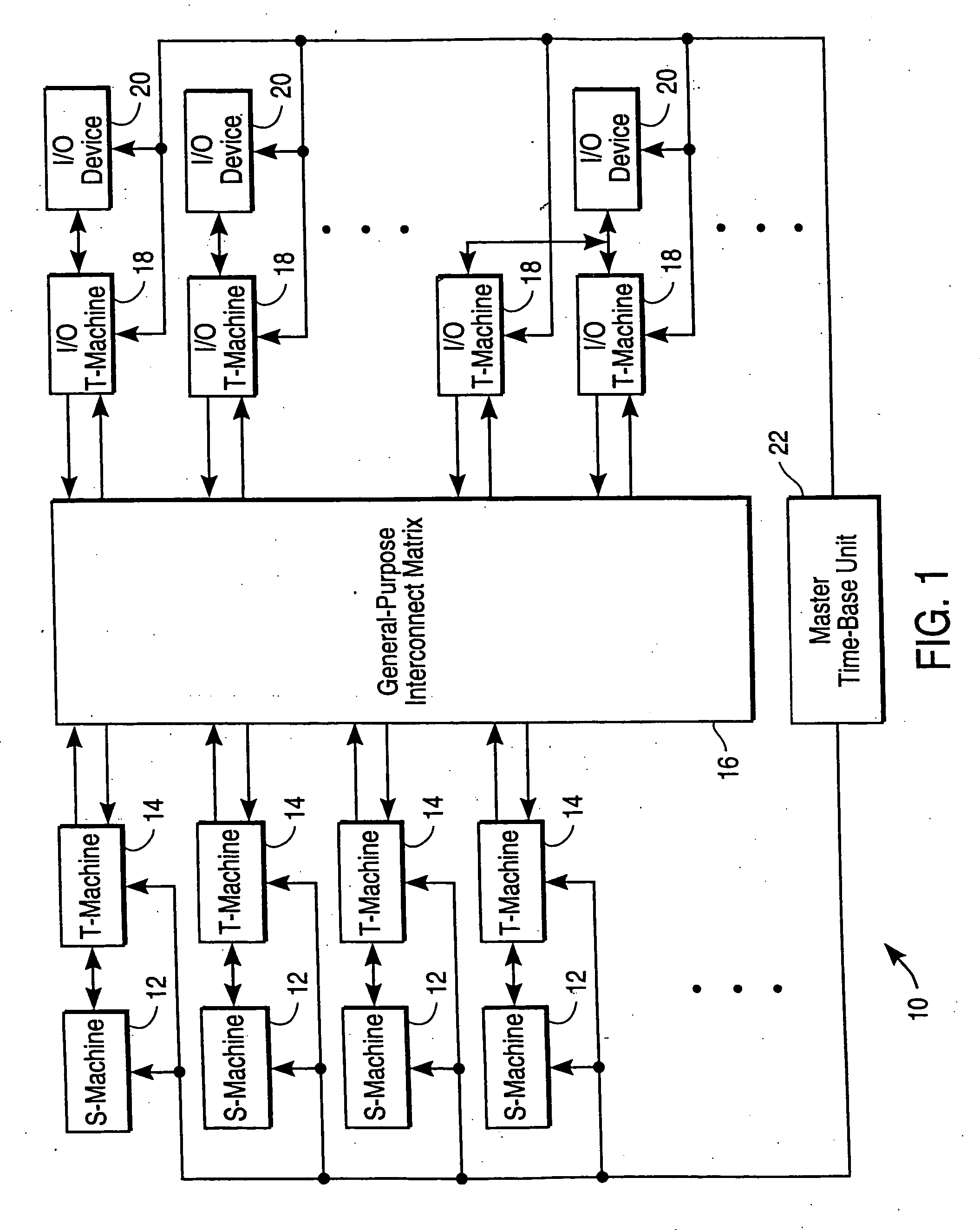
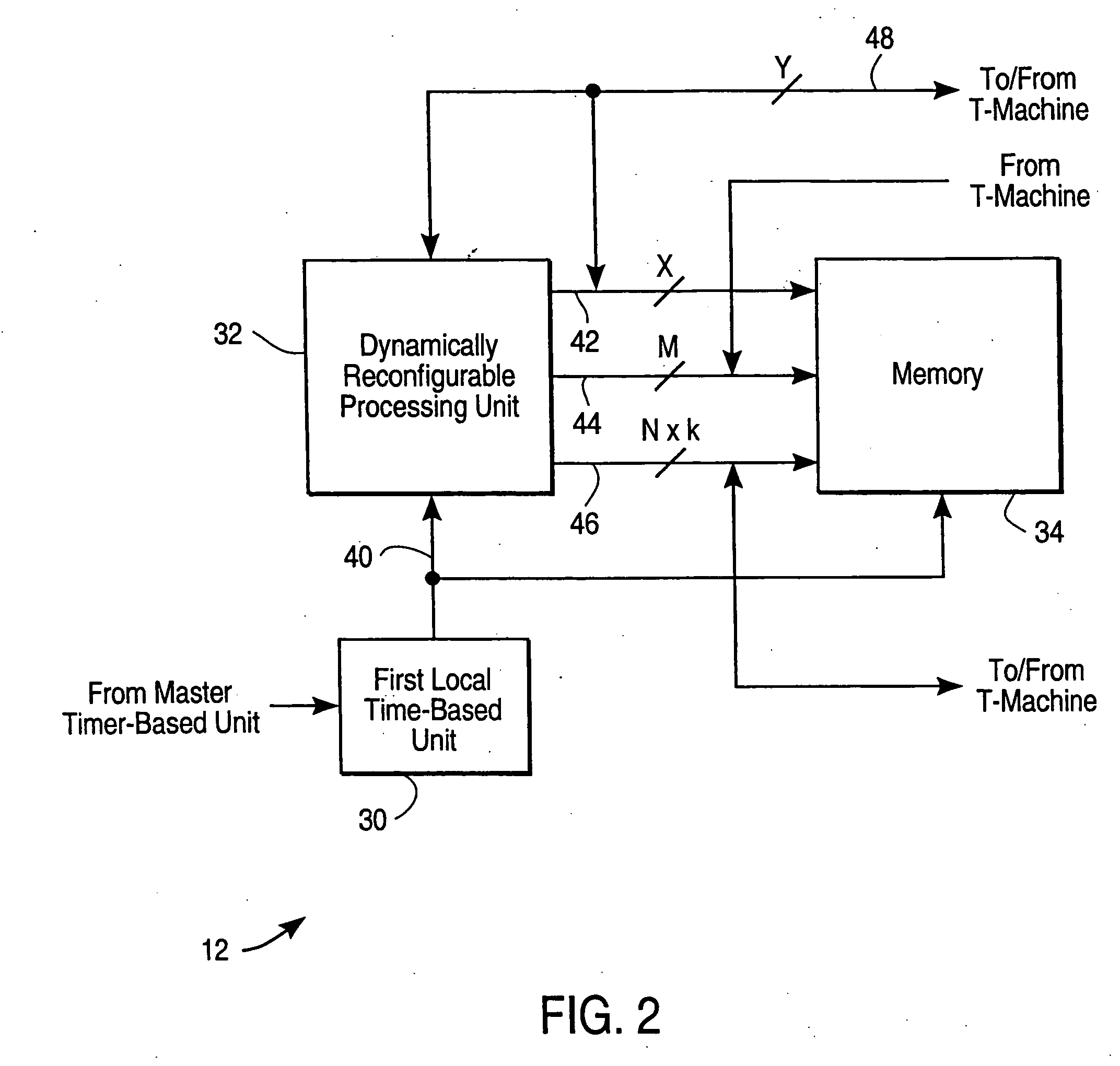
A set of S-machines, a T-machine corresponding to each S-machine, a General Purpose Interconnect Matrix (GPIM), a set of I / O T-machines, a set of I / O devices, and a master time-base unit form a system for scalable, parallel, dynamically reconfigurable computing. Each S-machine is a dynamically reconfigurable computer having a memory, a first local time-base unit, and a Dynamically Reconfigurable Processing Unit (DRPU). The DRPU is implemented using a reprogrammable logic device configured as an suction Fetch Unit (IFU), a Data Operate Unit (DOU), and an Address Operate Unit (AOU), each of which are selectively reconfigured during program execution in response to a reconfiguration interrupt or the selection of a reconfiguration directive embedded within a set of program instructions. Each reconfiguration interrupt and each reconfiguration directive references a configuration data set specifying a DRPU hardware organization optimized for the implementation of a particular Instruction Set Architecture (ISA). The IFU directs reconfiguration operations, instruction fetch and decode operations, memory access operations, and issues control signals to the DOU and the AOU to facilitate instruction execution. The DOU performs data computations, and the AOU performs address computations. Each T-machine is a data transfer device having a common interface and control unit, one or more interconnect I / O units, and a second local time-base unit. The GPIM is a scalable interconnect network that facilitates parallel communication between T-machines. The set of T-machines and the GPIM facilitate parallel communication between S-machines. The T-machines also control the transfer of data between S-machines in the network, and provide the addressing operations required. A meta-address is used to provide scalable bit-addressable capability to every S-Machine.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
System and method for allocating identifier to multi-bms
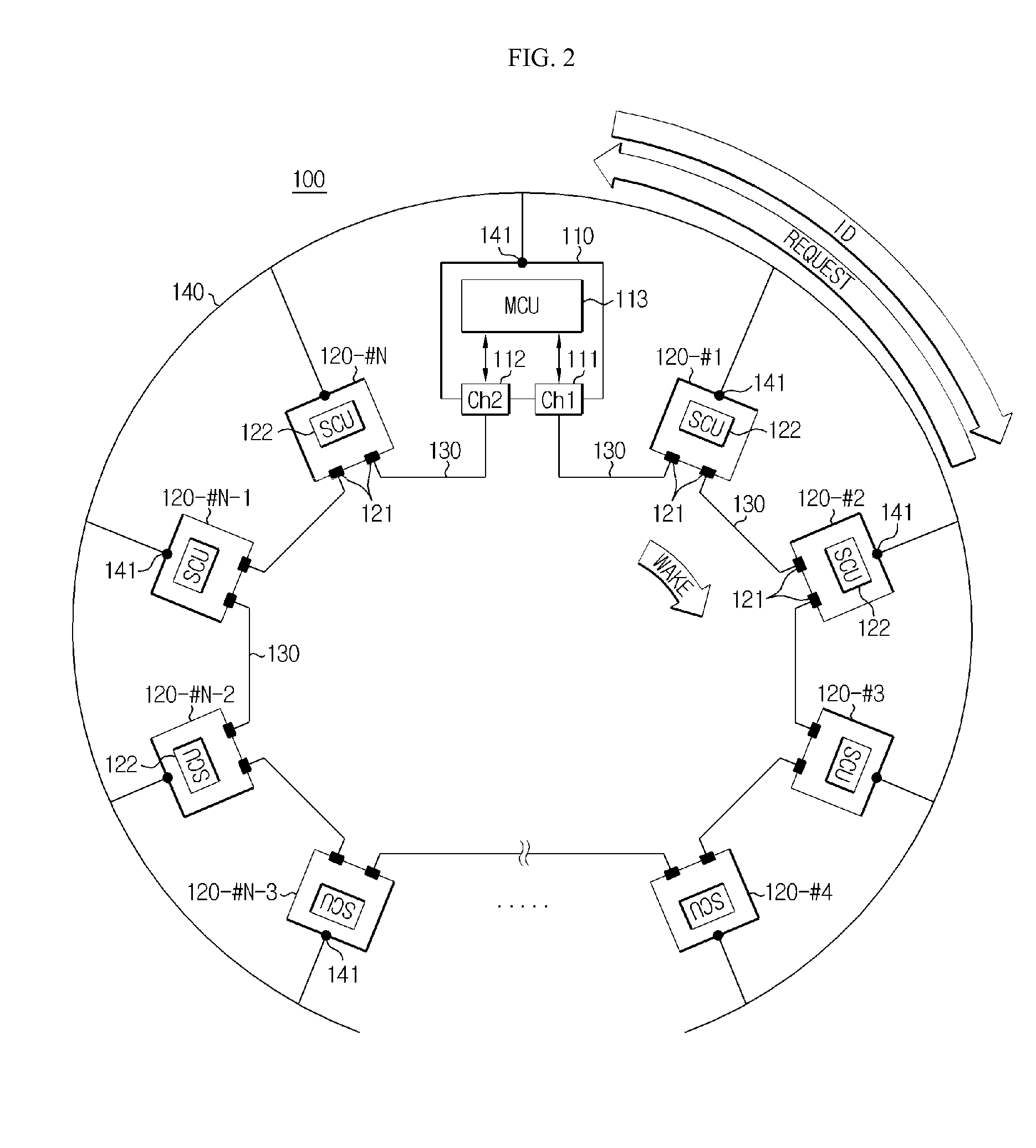
ActiveUS20140091770A1Automatic detectionSolve the real problemWired architecture usageElectrical testingCommunication interfaceUser identifier
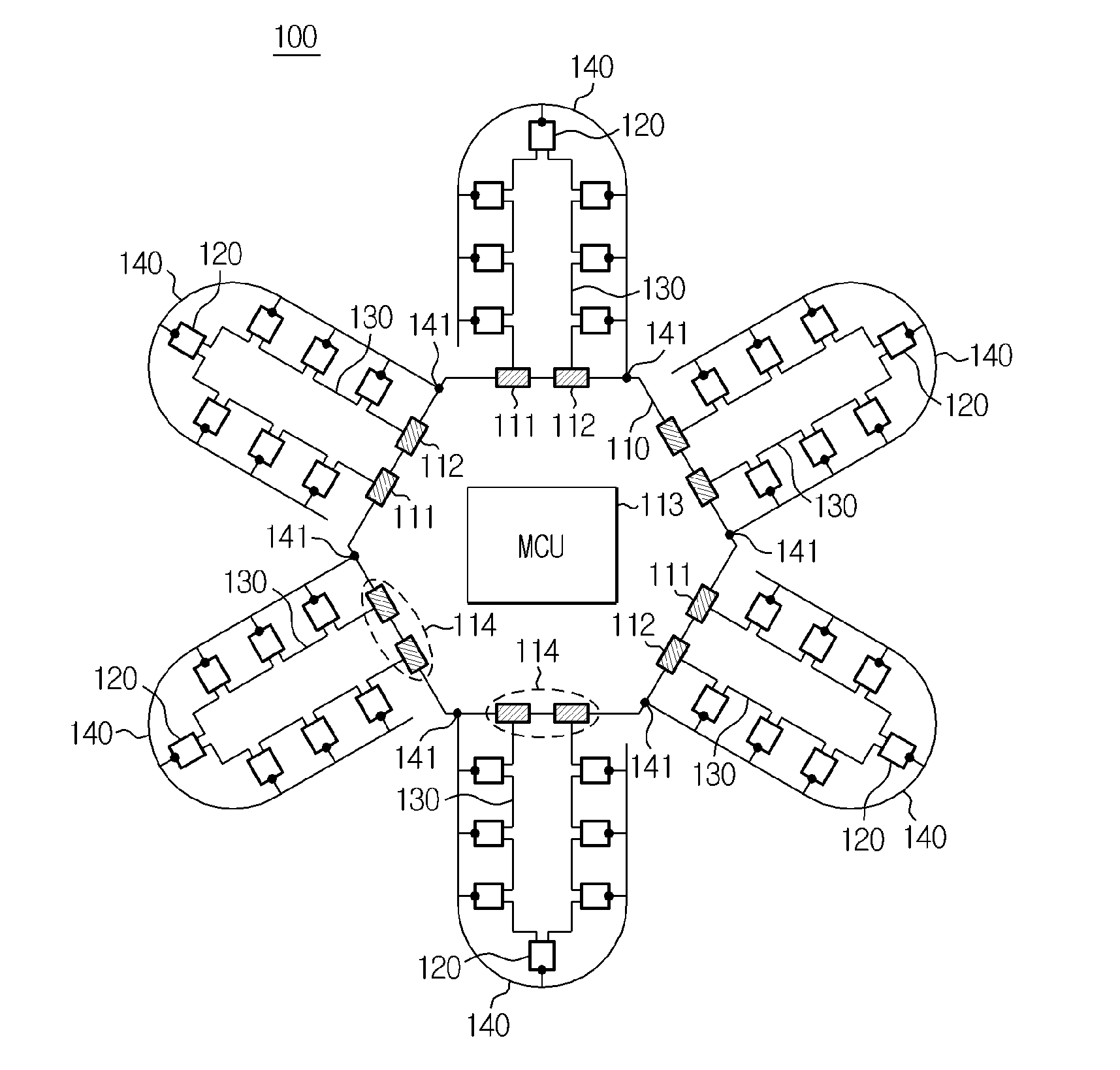
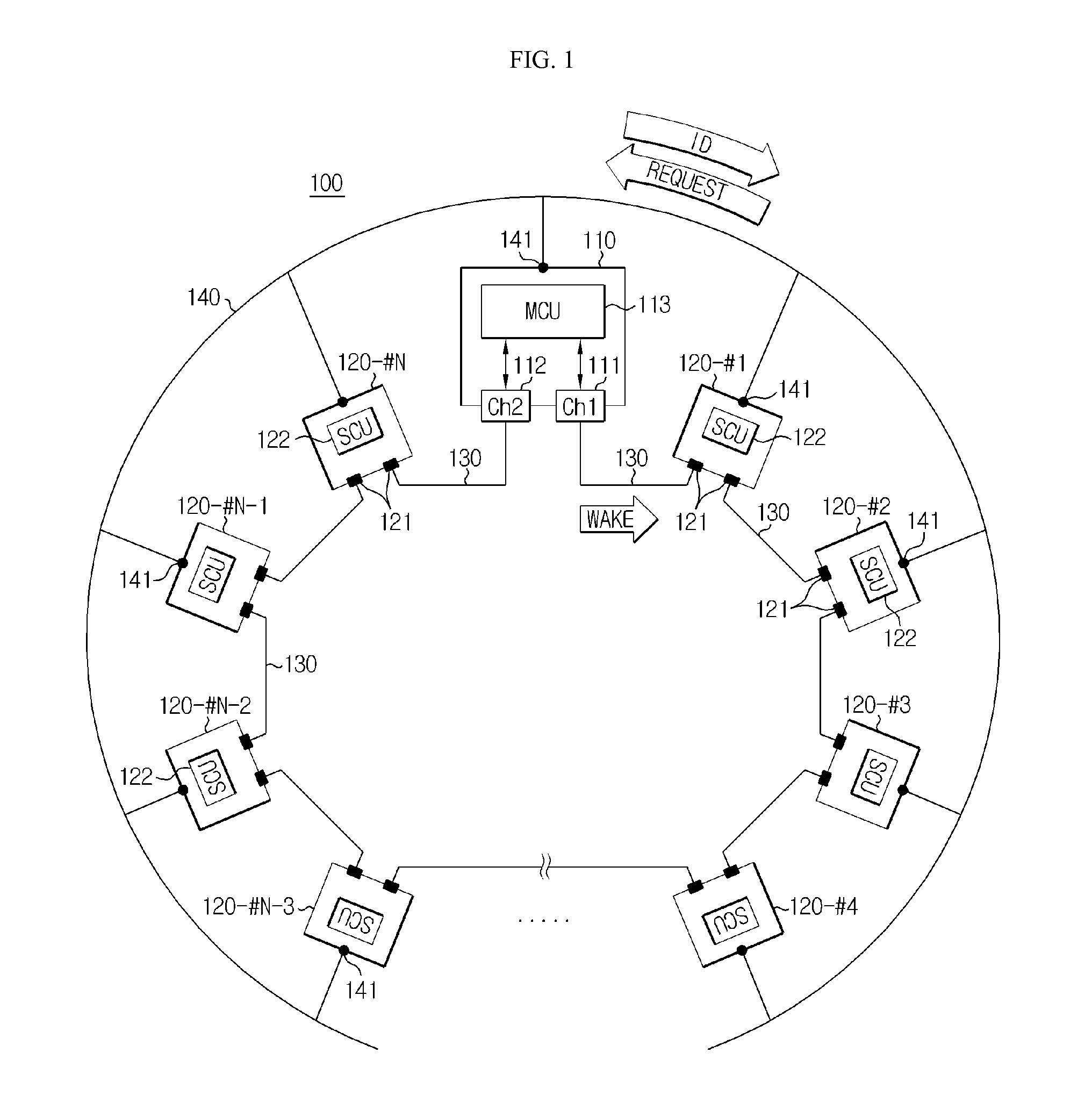
Disclosed is a multi-BMS identifier allocation system. The multi-BMS identifier allocation system according to the present invention comprises a master BMS and N slave BMSs (N is an integer greater than or equal to 2) which are connected to a series communication network and a parallel communication network, wherein the master BMS comprises at least two first and second master communication channels which form a communication interface with the series communication network and selectively output a forward or backward enabling signal and allocates unique communication identifiers to the slave BMSs through the parallel communication network, and the first to Nth slave BMSs start enabling in response to the forward or backward enabling signal received through the series communication network, are allocated the identifiers from the master BMS through the parallel communication network, and output an enabling signal to an adjacent slave BMS along a transmission direction of the enabling signal.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
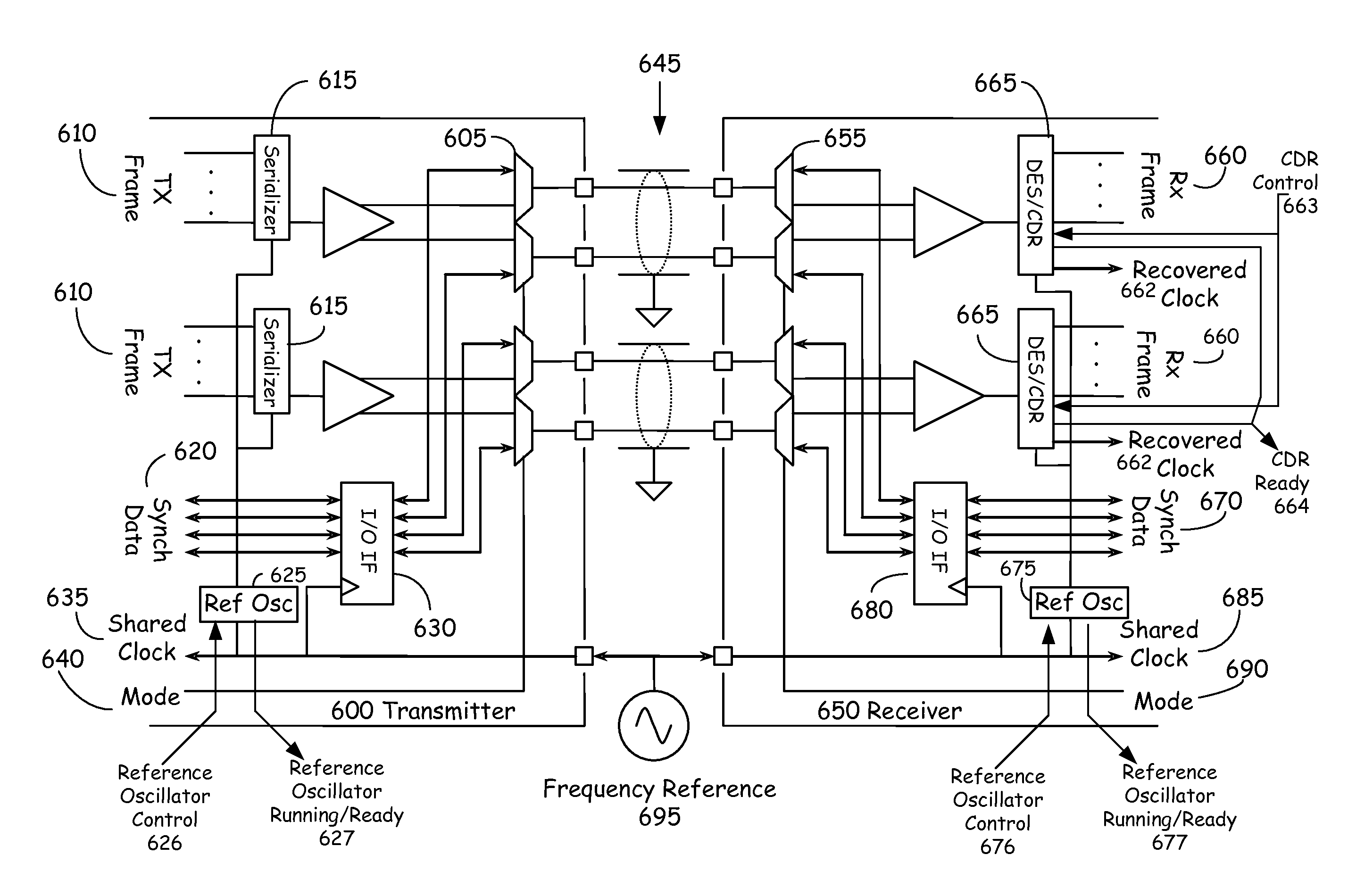
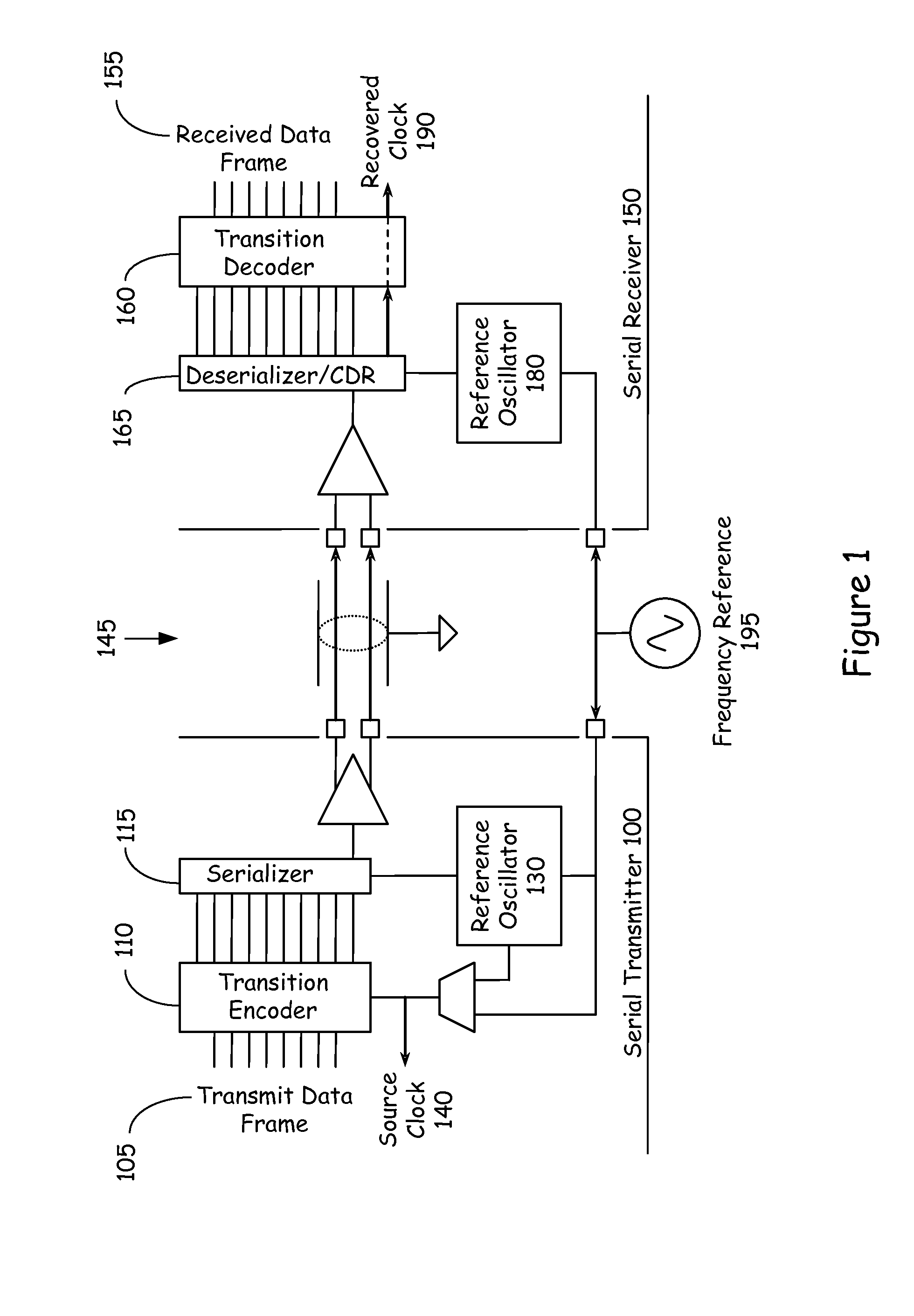
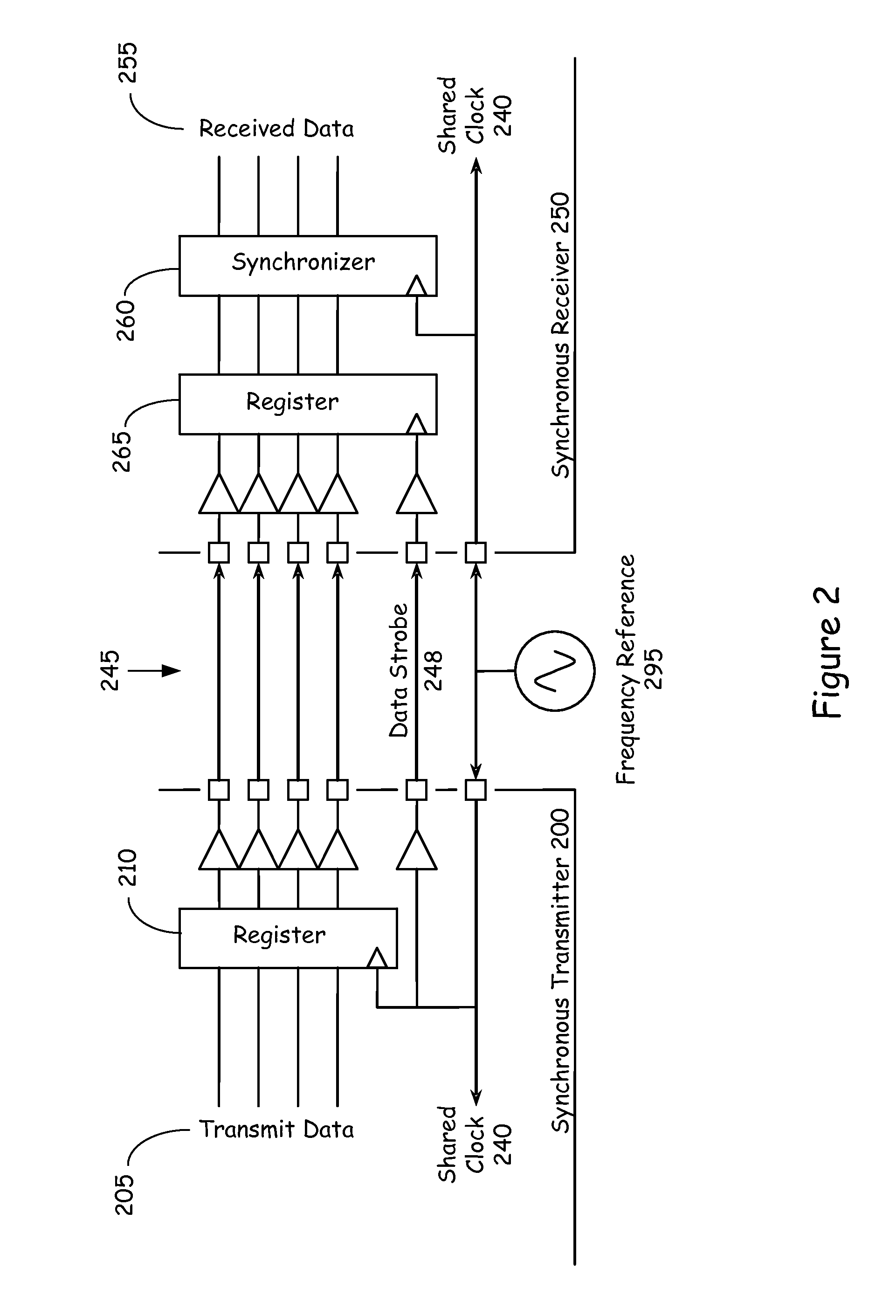
Parallel data communication having skew intolerant data groups
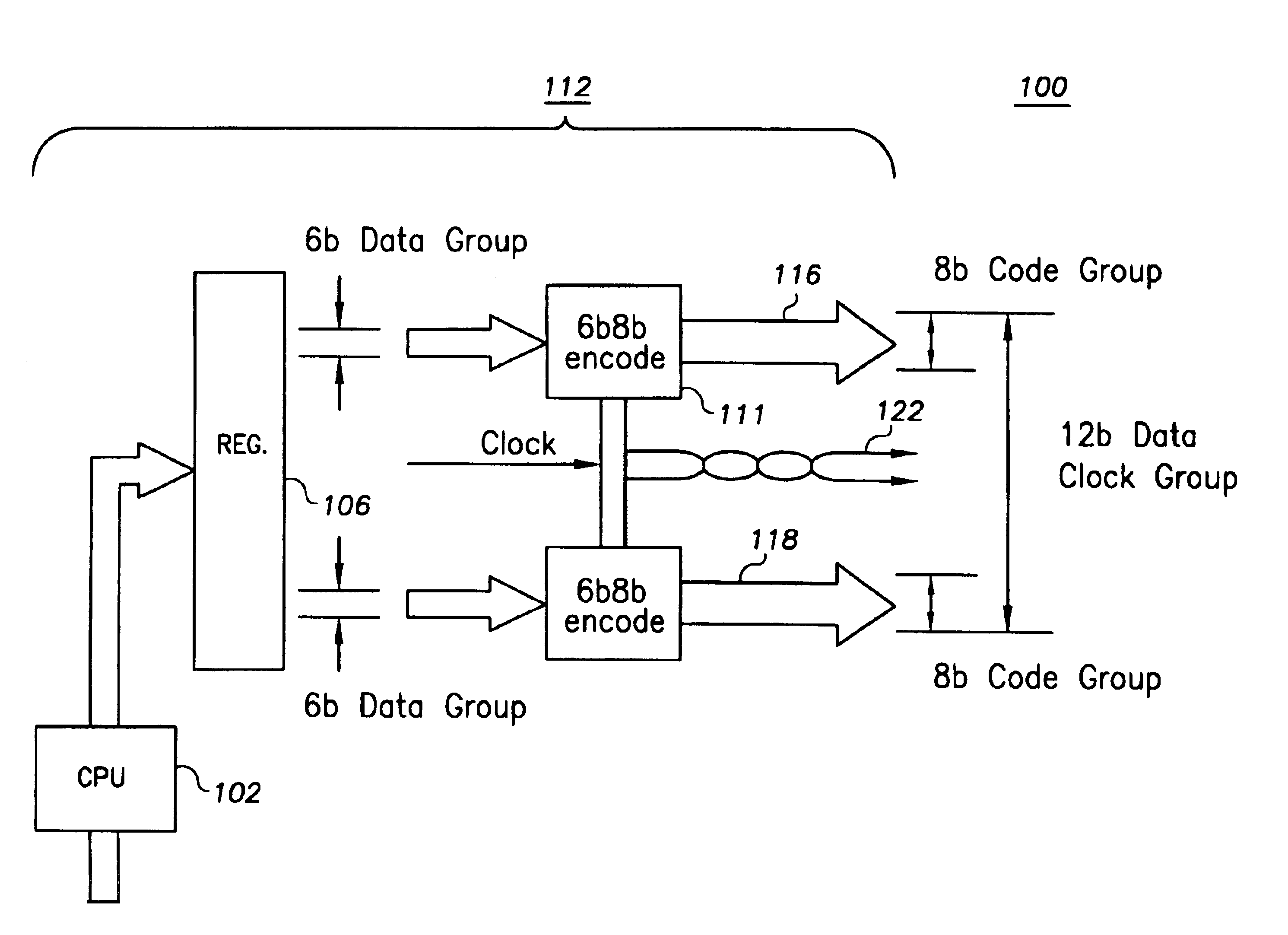
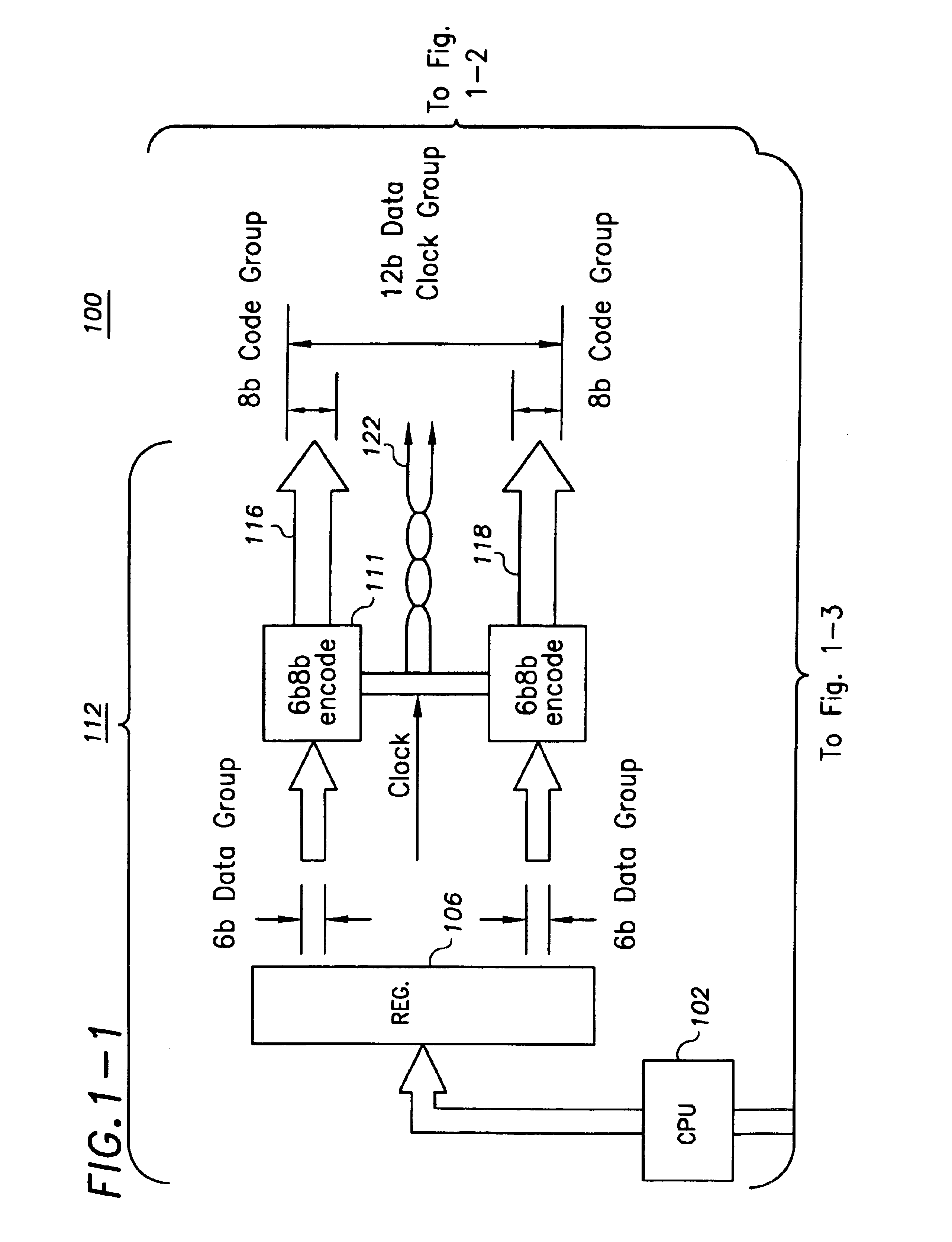
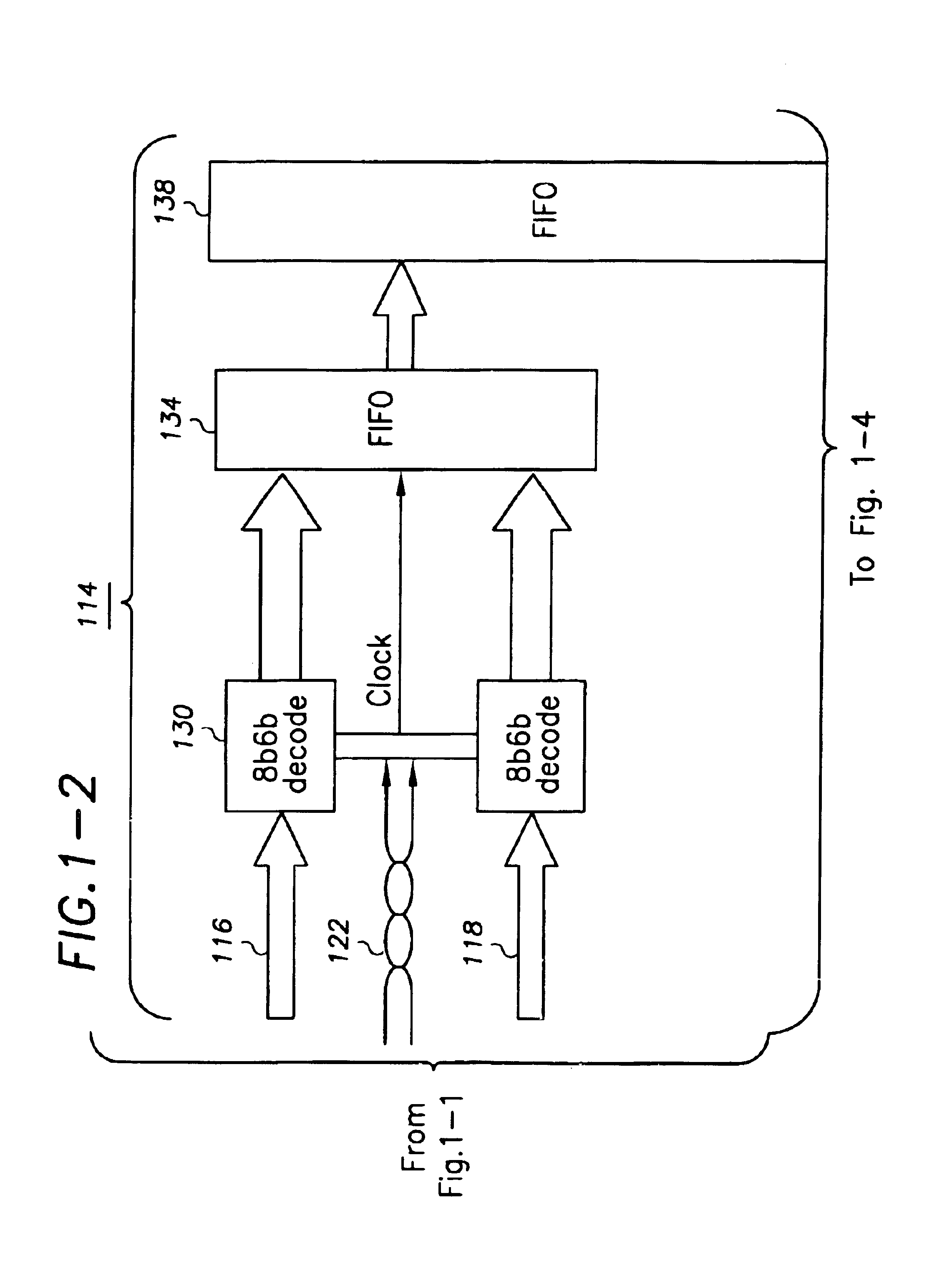
InactiveUS6839862B2Small degreeOvercomes more significant skew-caused misalignmentsChannel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsDigital dataComputer module
In one example embodiment, a high-speed parallel-data communication approach transfers digital data in parallel from a first module to a second module over a communication channel including a plurality of parallel data-carrying lines and a clock path. The parallel bus lines are arranged in a plurality of groups, each of the groups including a plurality of data-carrying lines and a clock path adapted to carry a clock signal for synchronizing digital data carried from the first module to the second module. The sets of data are concurrently transferred using the groups of lines of the parallel bus, and at the second module and for each group, the transferred digital data is synchronously collected via the clock signal for the group. At the second module, the data collected for each group is aligned. By grouping the bus lines in groups with each group having its own clock domain, skew across clock-domain groups is tolerated and overcome by processing the data and the skew first within each clock domain group, and then between groups.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com