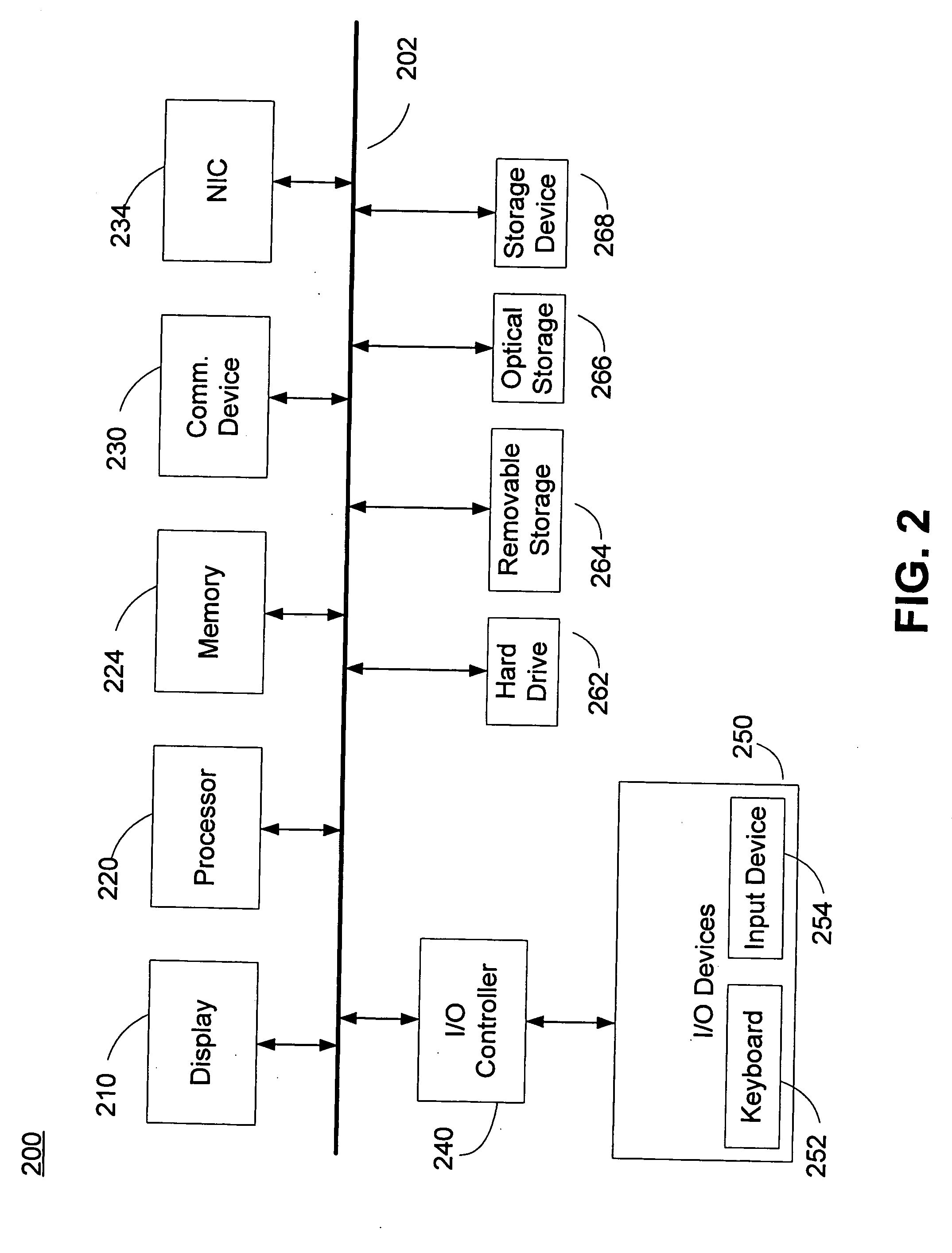
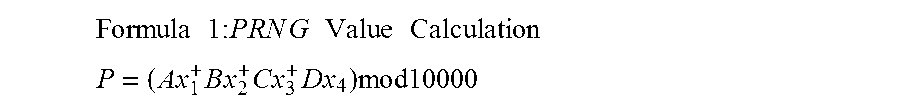Patents
Literature
824 results about "Personal identification number" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
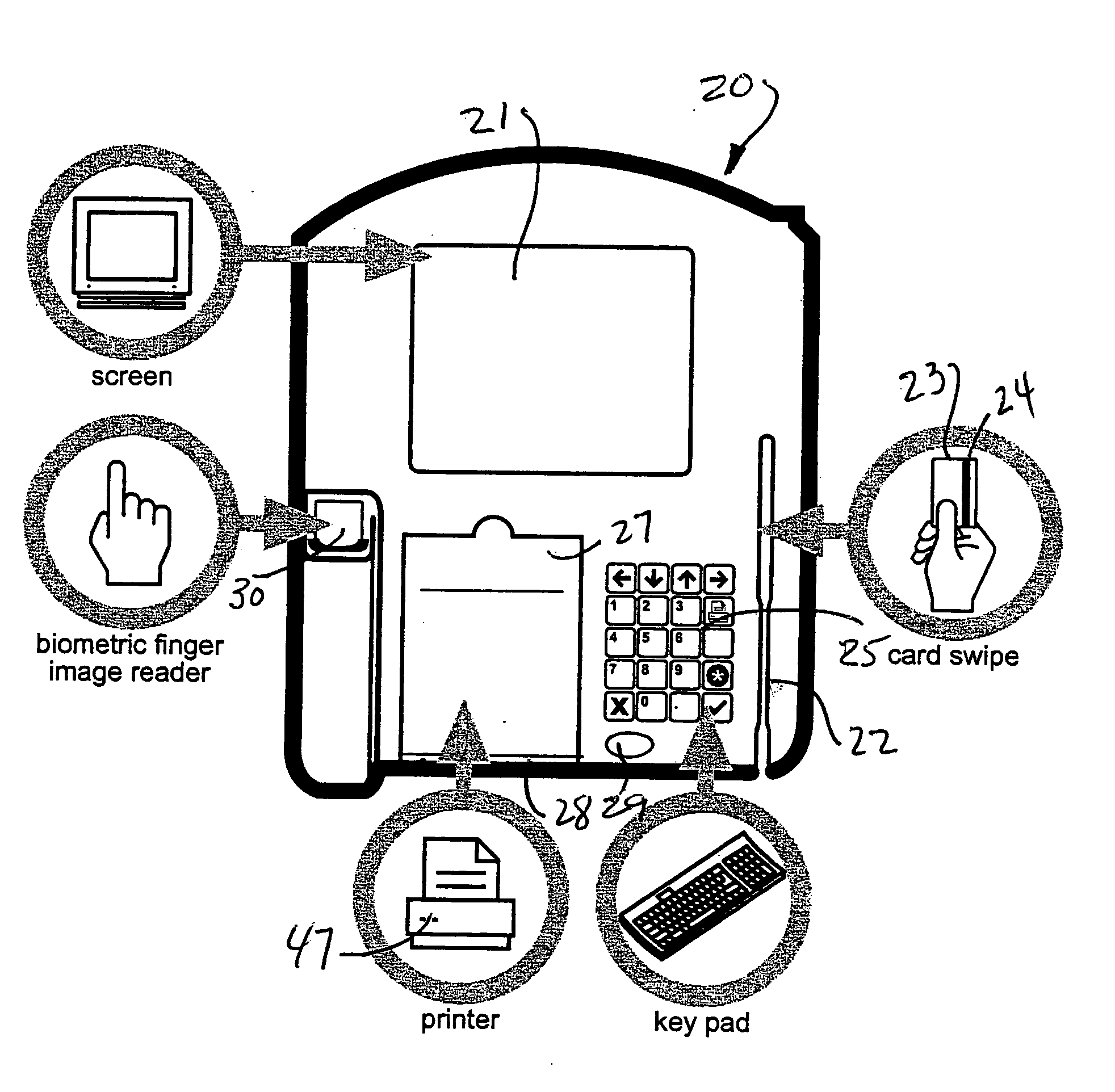
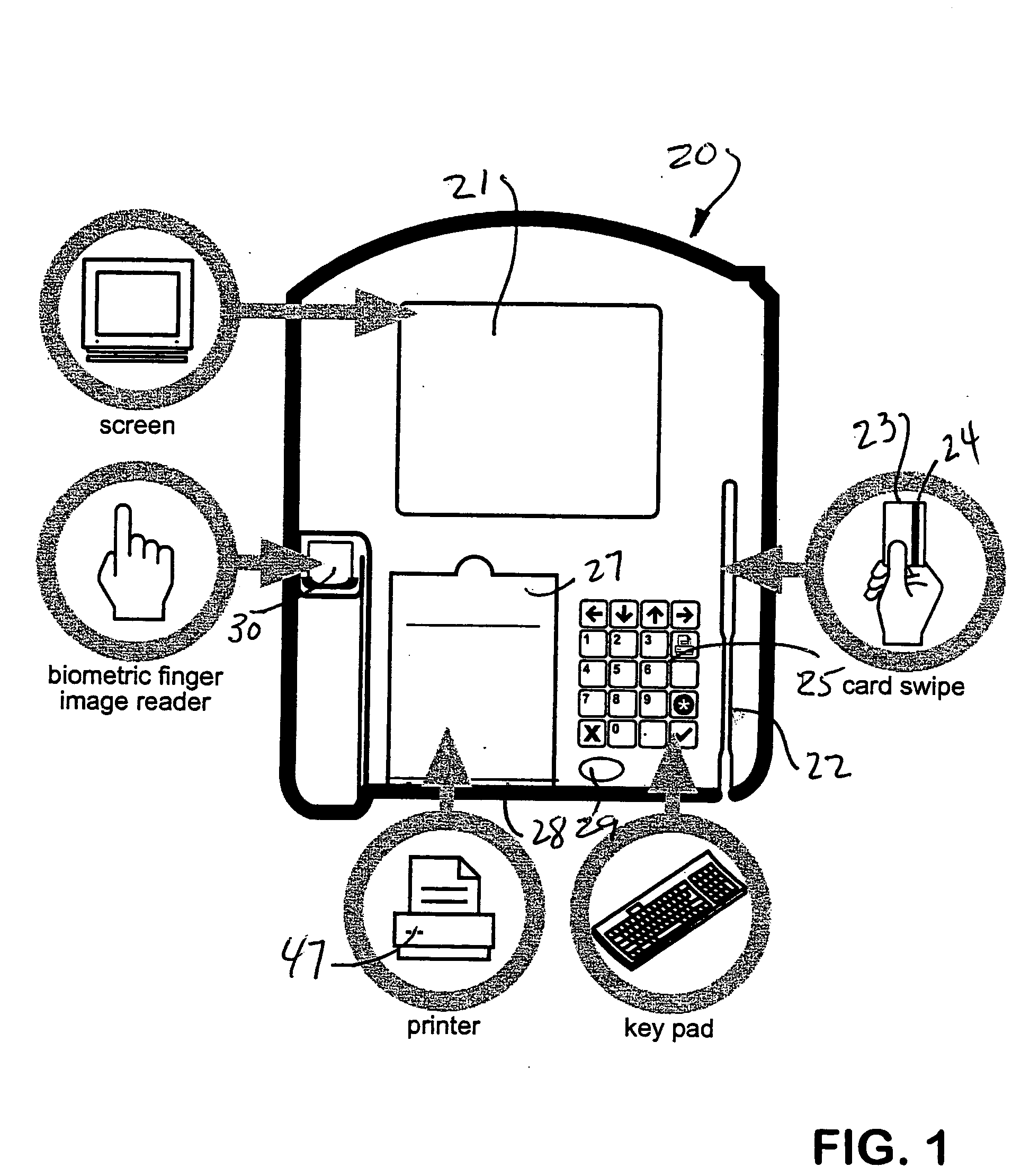
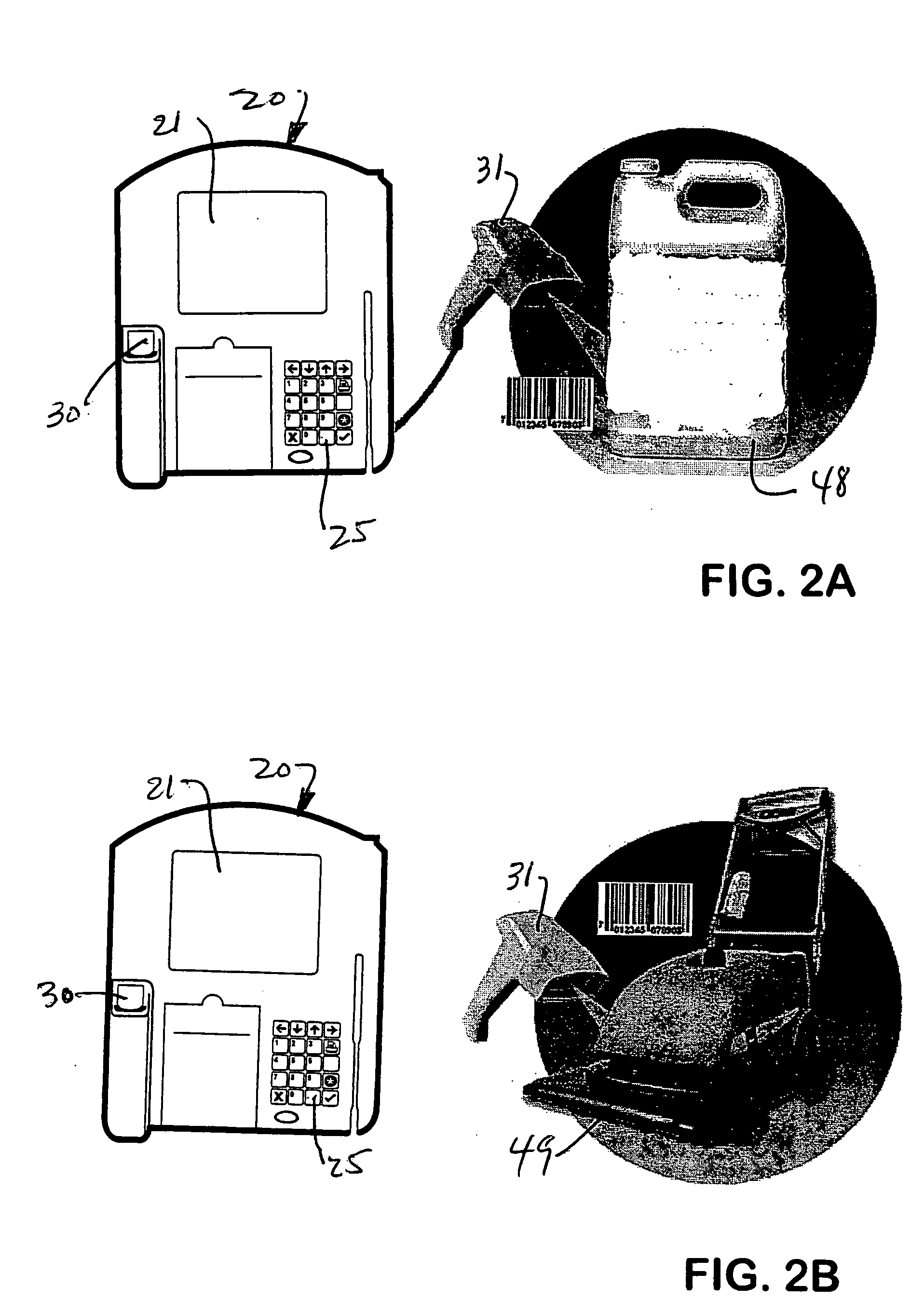
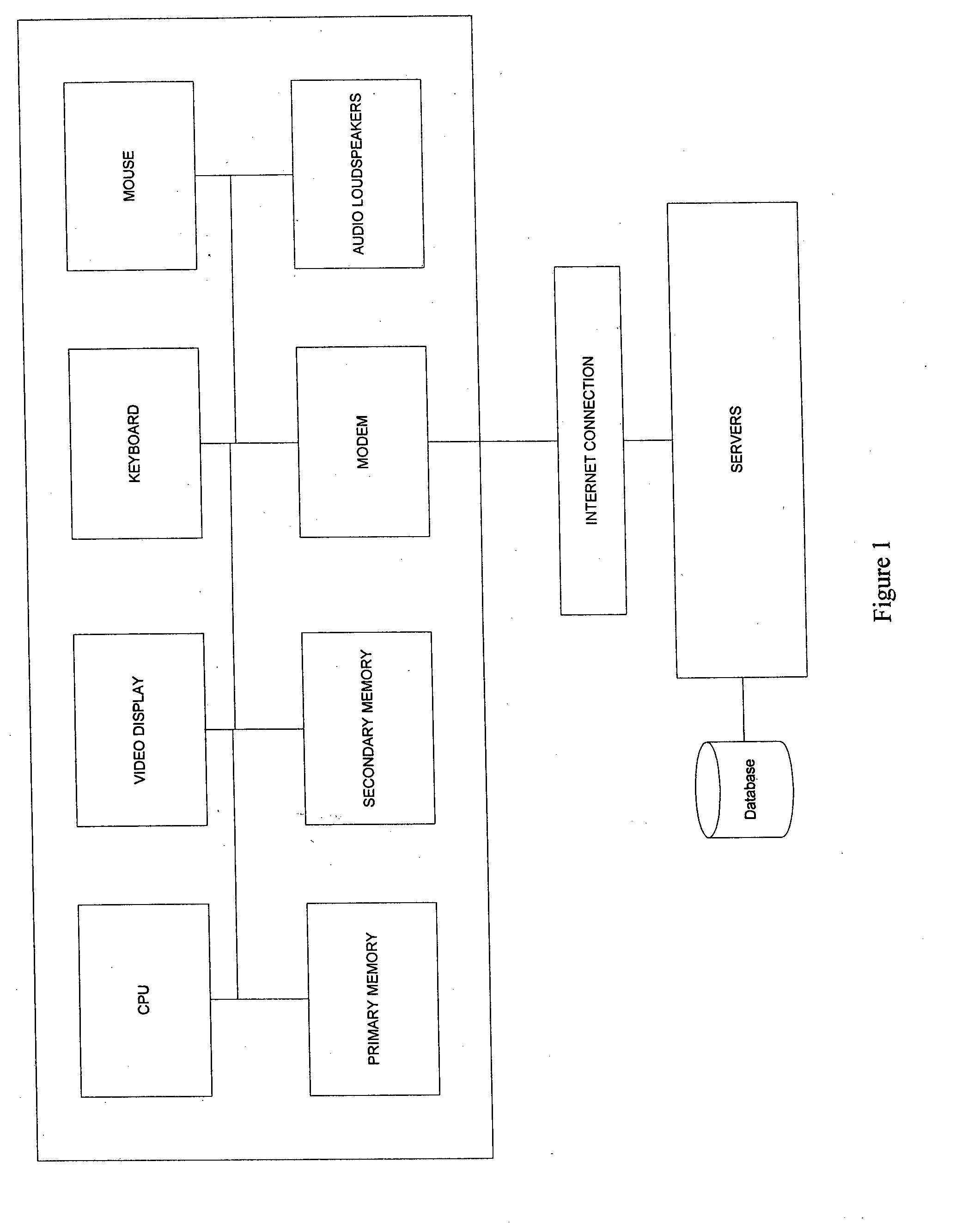
A personal identification number (PIN), or sometimes redundantly a PIN number, is a numeric or alpha-numeric password used in the process of authenticating a user accessing a system. The personal identification number has been the key to flourishing the exchange of private data between different data-processing centers in computer networks for financial institutions, governments, and enterprises. PINs may be used to authenticate banking systems with cardholders, governments with citizens, enterprises with employees, and computers with users, among other uses.
Electronic educational game set having communicating elements with a radio-frequency tag
InactiveUS20060246403A1Short response timeLower average response timeBoard gamesInput/output processes for data processingEducational gamePersonal identification number
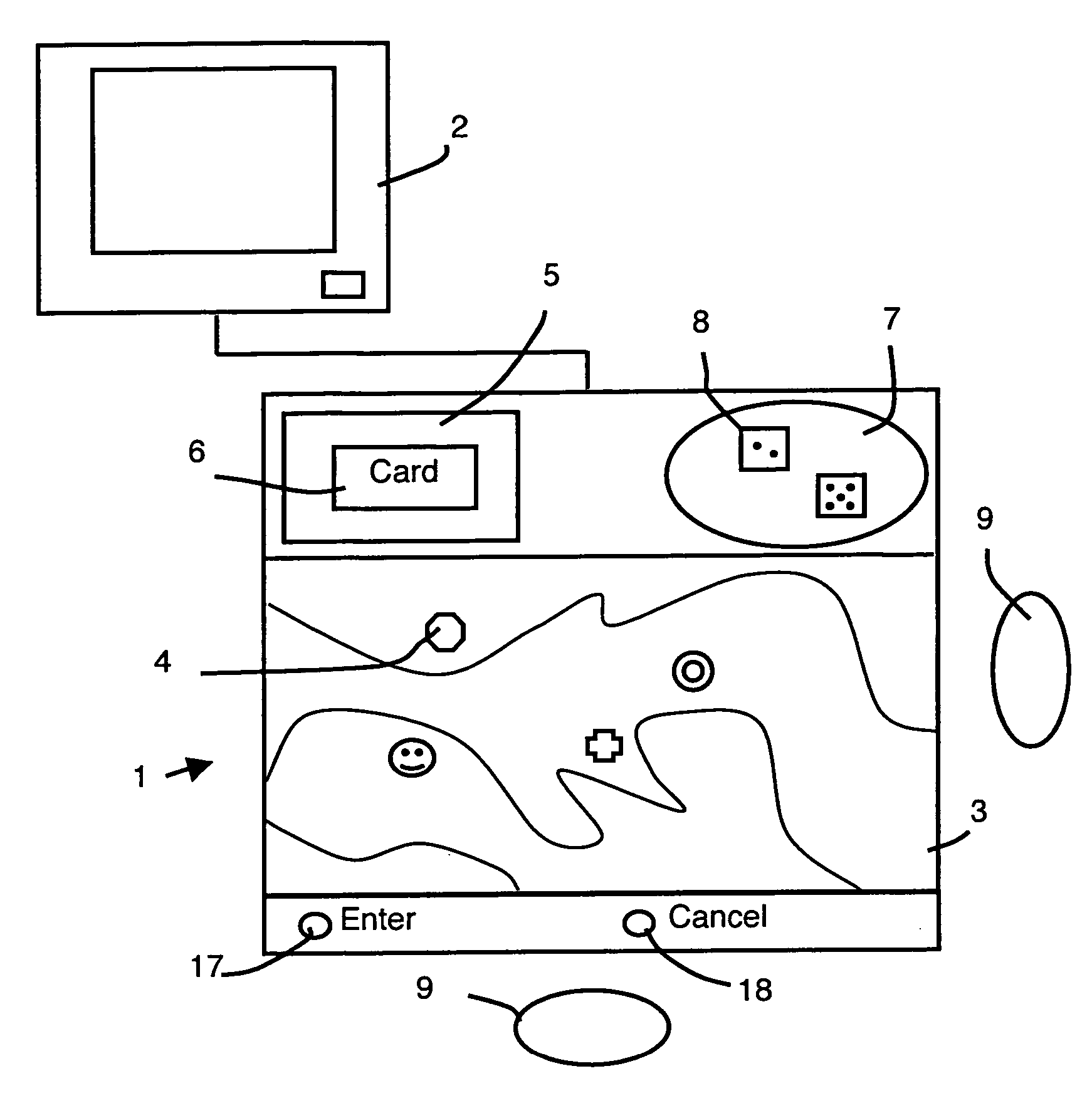
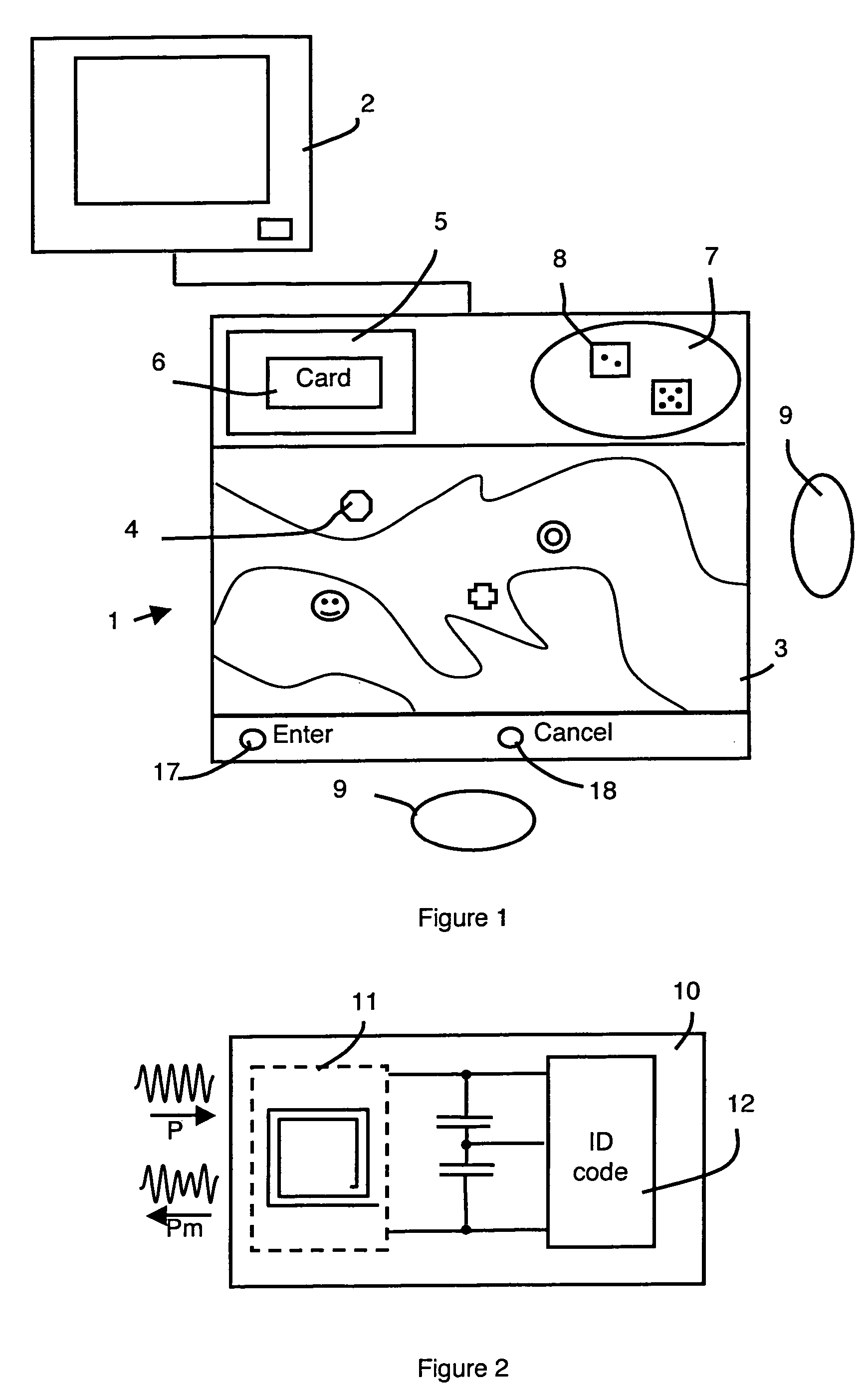
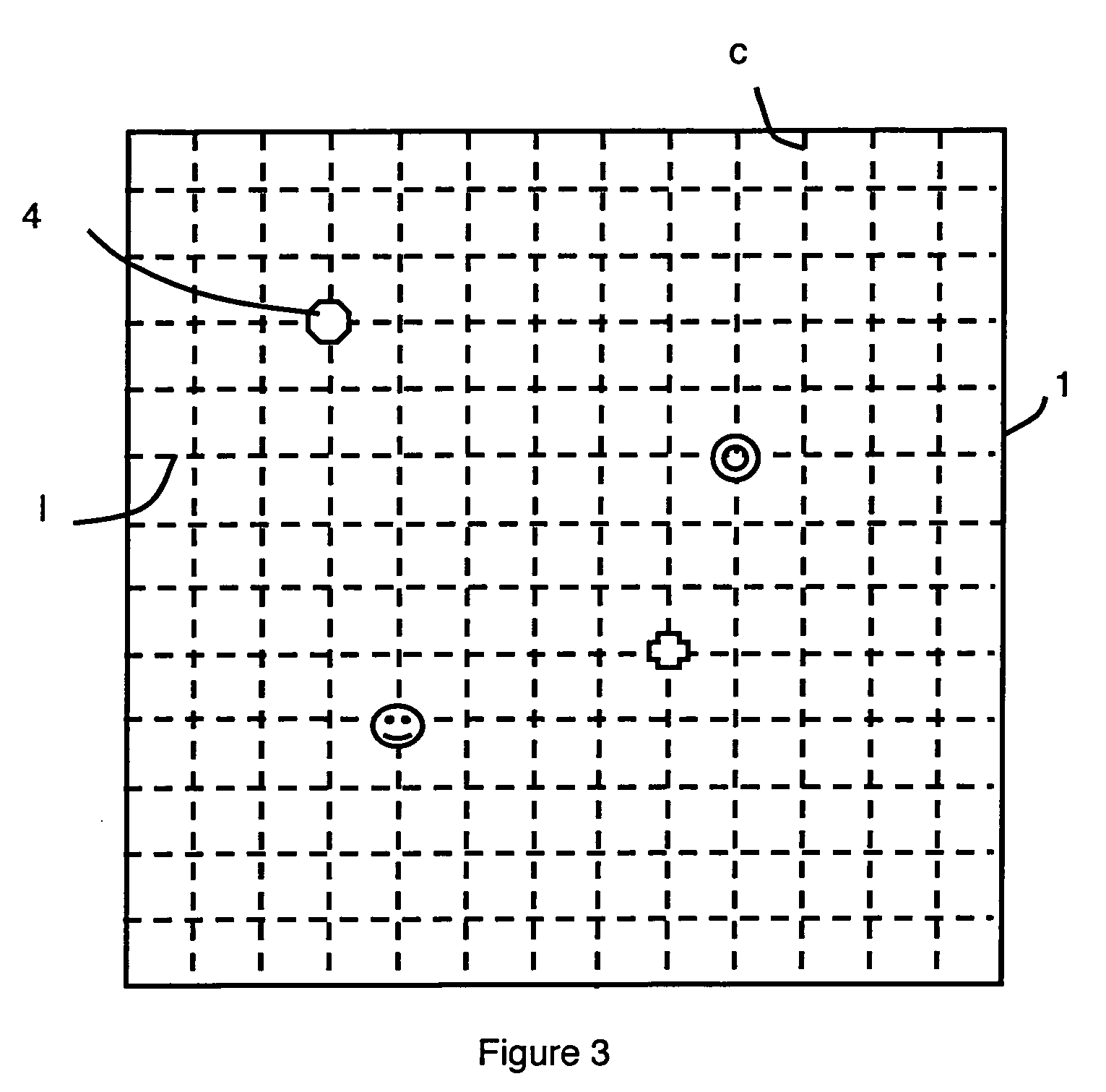
The invention relates to a game set which comprises communicating elements, in the form of pieces, figurines, cards or dice, each having a radio-frequency tag provided with an individual identification code. A game board comprises a digital processing circuit which is connected to a plurality of antennas, arranged such as to form a sensor matrix, for detecting the presence, type and position of the communicating elements. Radio-frequency readers are respectively connected to m corresponding input / output terminals of the digital processing circuit. Each radio-frequency reader is connected to an associated group of antennas, preferably by means of a corresponding multiplexer. The game board may consist of a removable assembly of basic boards, each comprising a basic digital processing circuit which is connected to the antennas of the corresponding basic board.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
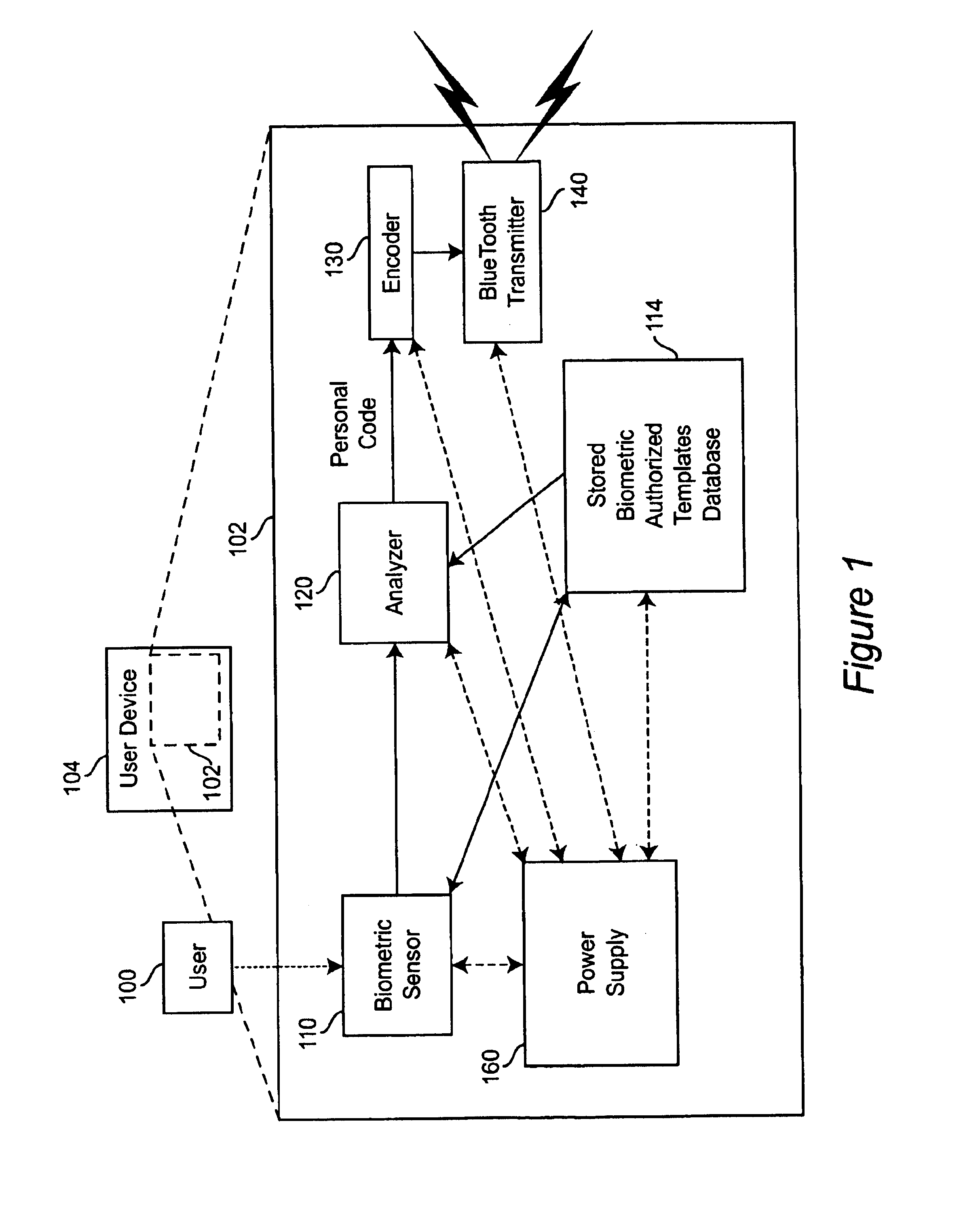
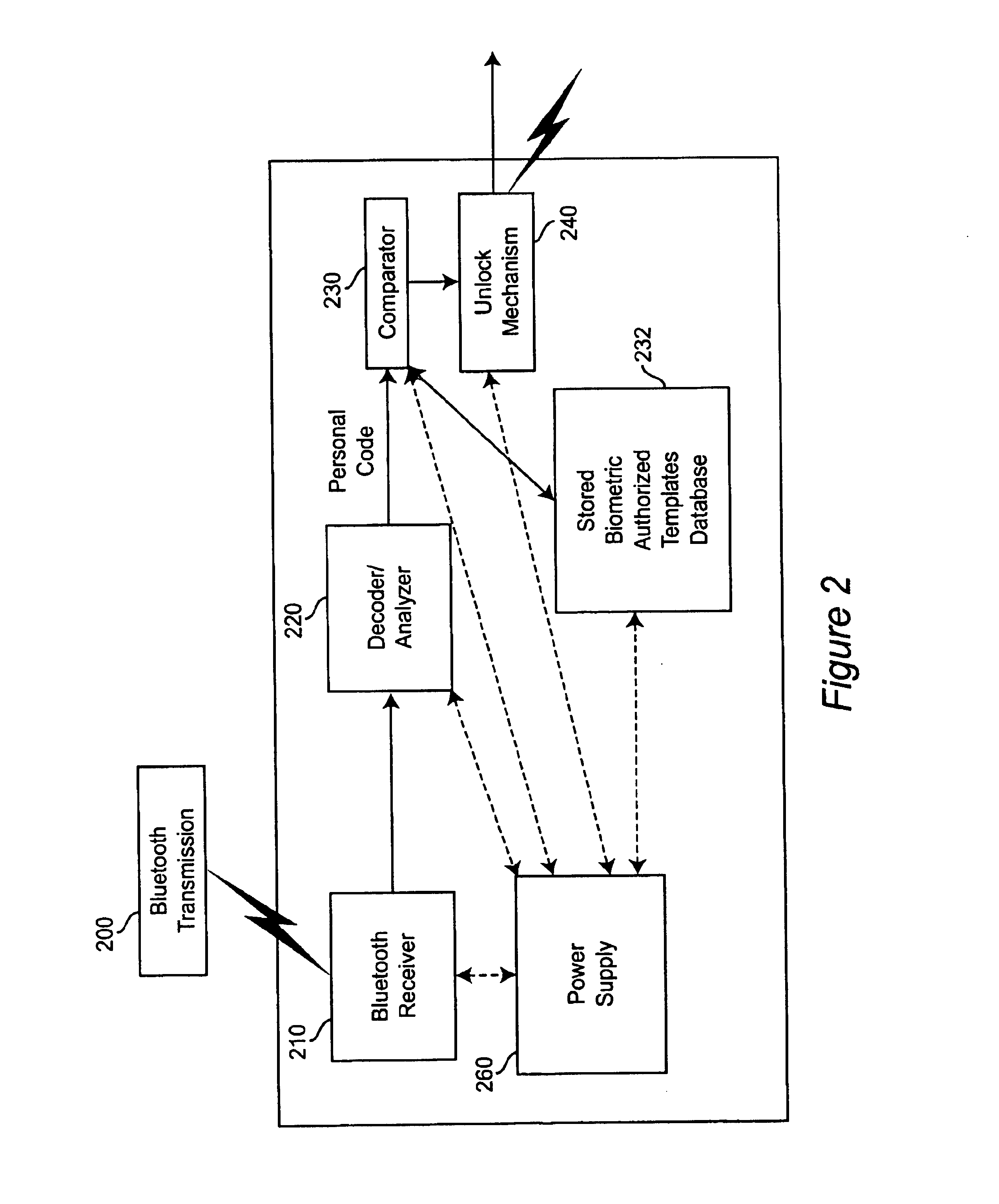
Personal biometric key
InactiveUS6850147B2Reliable resultsEasy to compressElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisComputer hardwareCommunications system
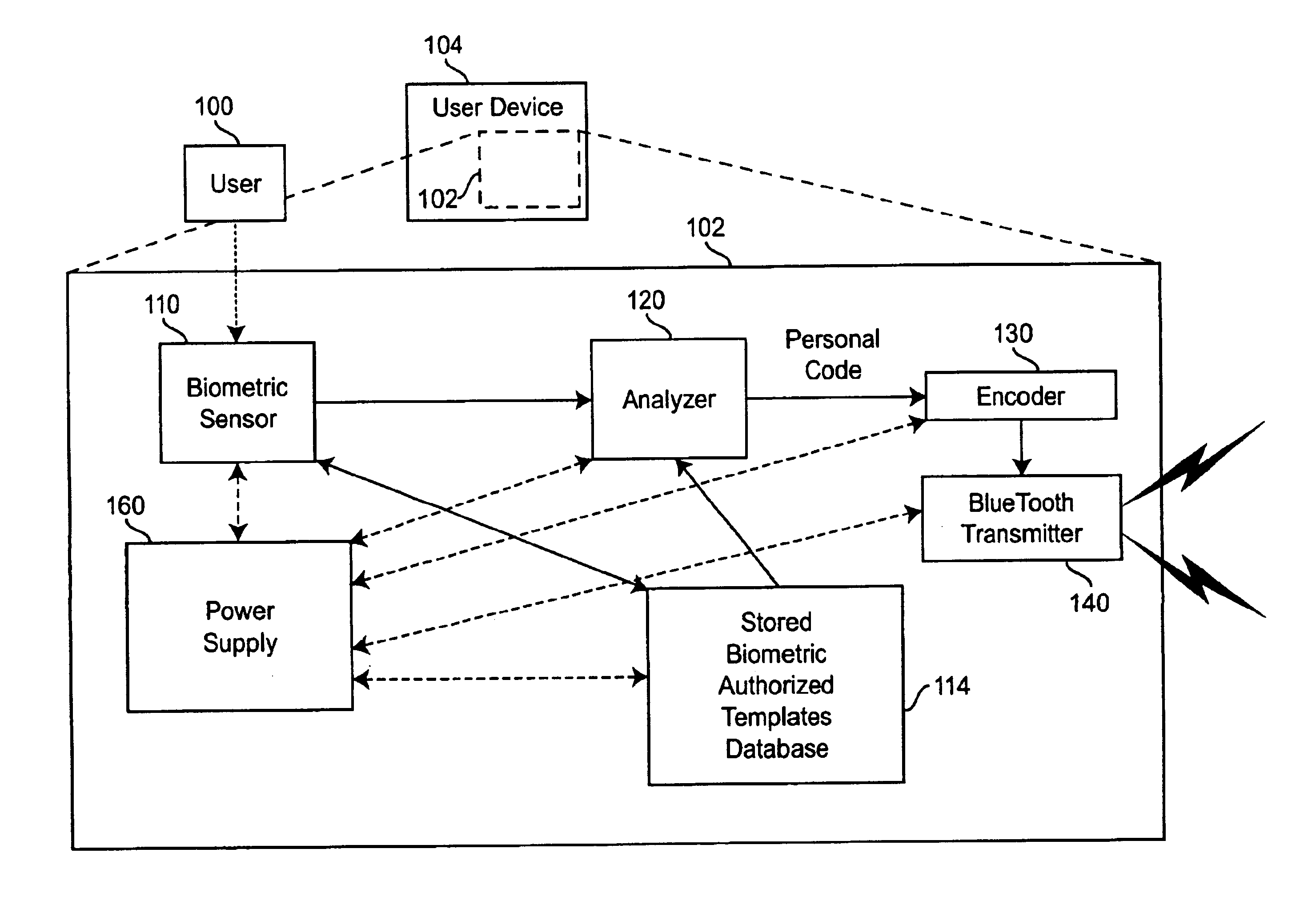
A personal biometric key system uses a personal identity code transmitted to a universal biometric electronic lock via a communication system and using a clock or GPS chip and allows a person to select one or more personal biometric methods and to be personally responsible for the maintenance of the sensor and its availability. The selection can be tailored to the particular needs and circumstances of the person using the key. The person can also change the personal biometric sensor when needs and circumstances change. The organization being accessed by the key can set minimum levels for what type sensor data they will accept and for level of services they will provide for a given type sensor.
Owner:MIKOS
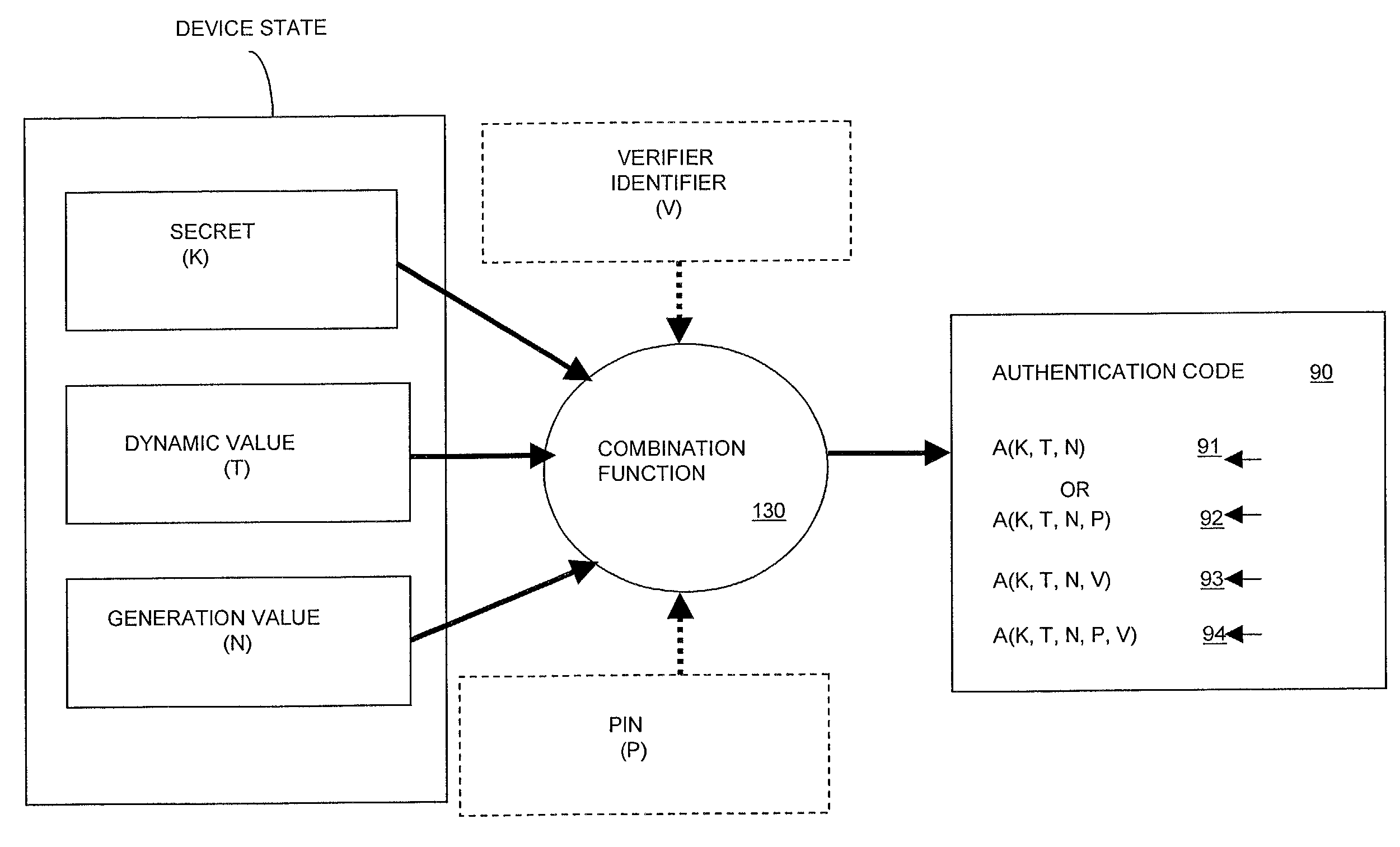
Method and apparatus for performing enhanced time-based authentication
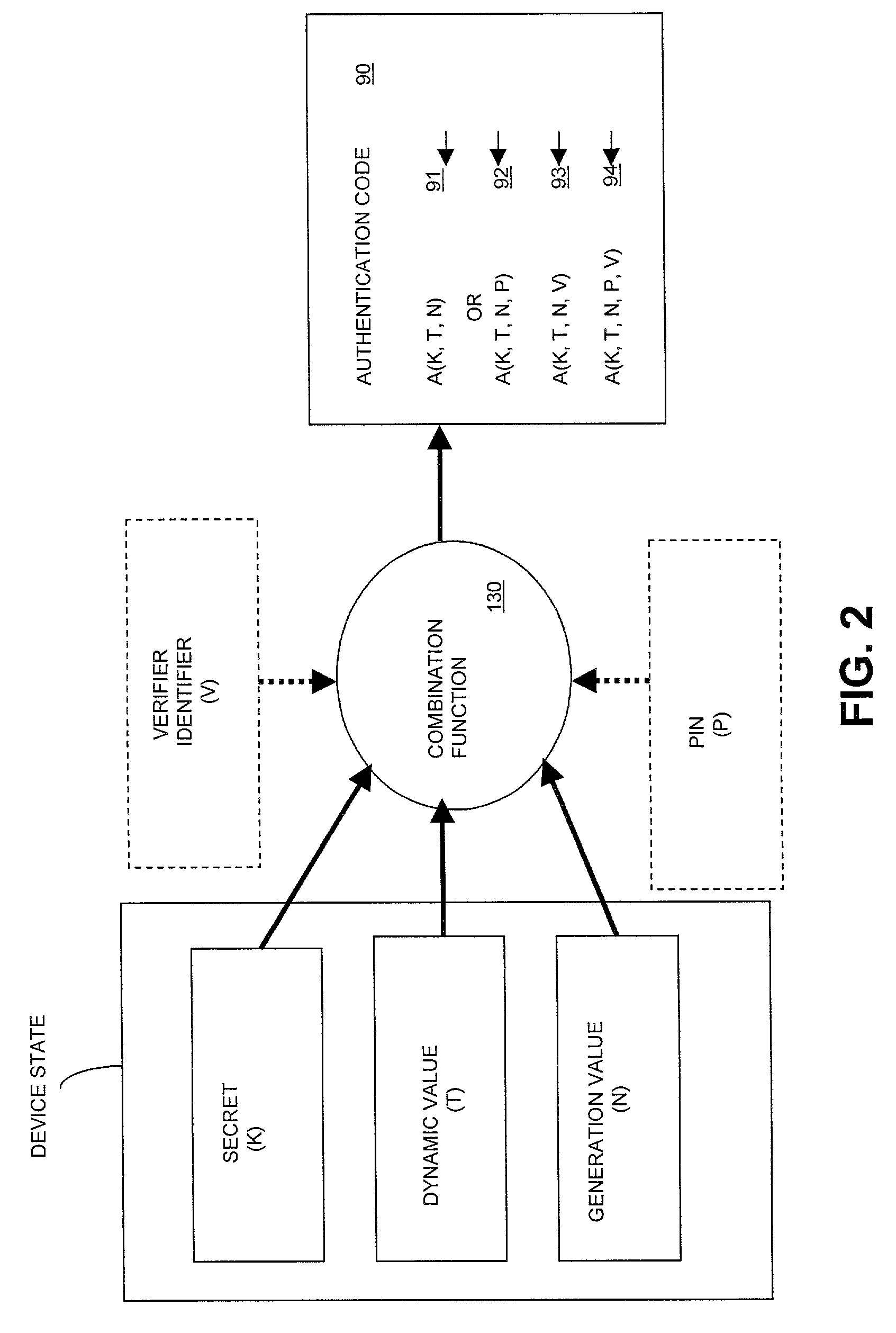
ActiveUS7363494B2Resist attackDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwarePersonal identification number
A time-based method for generating an authentication code associated with an entity uses an authentication code generated from a secret, a dynamic, time-varying variable, and the number of previous authentication code generations within the particular time interval. Other information such as a personal identification number (PIN) and a verifier identifier can also be combined into the authentication code.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method for generating customer one-time unique purchase order numbers
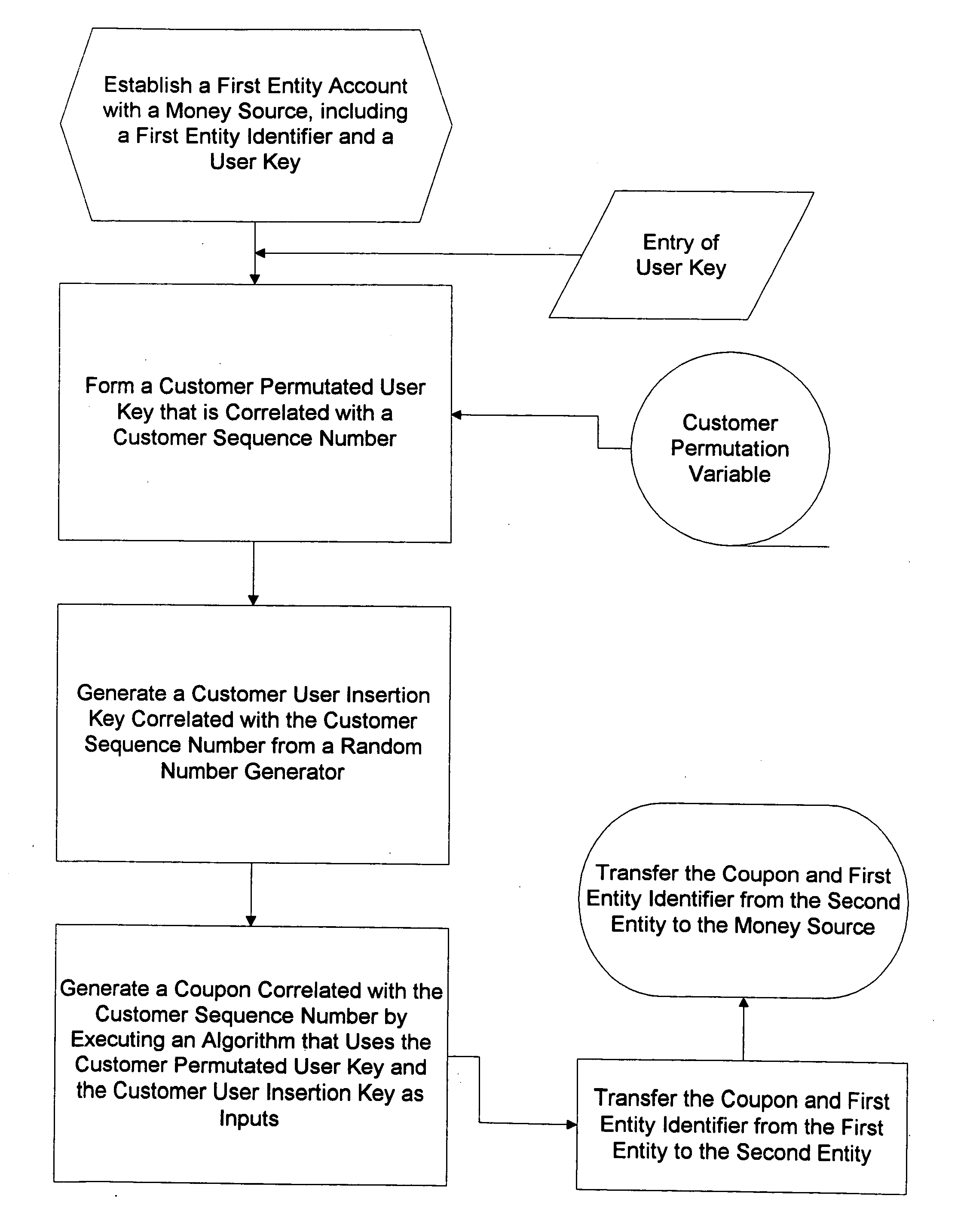
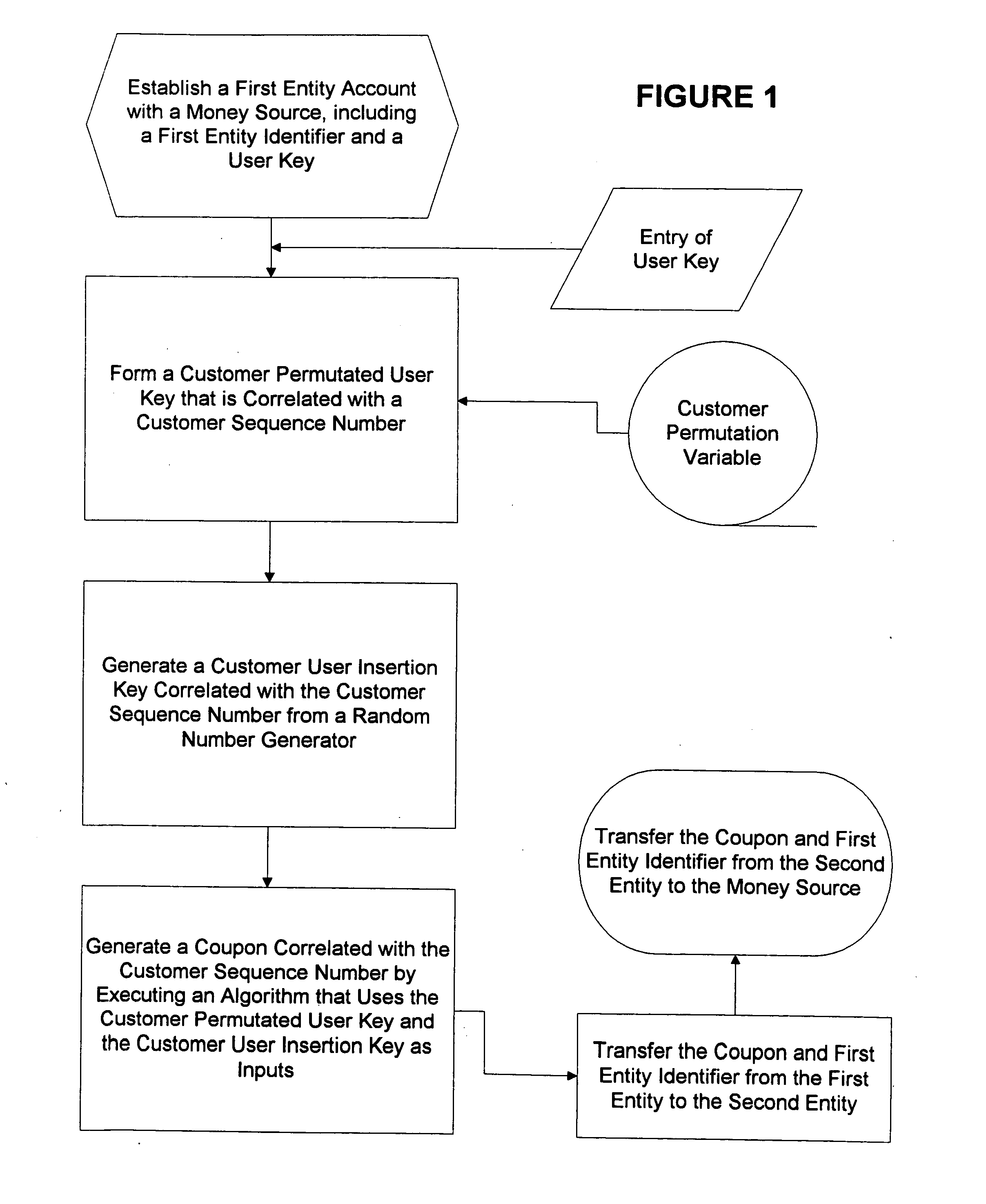
InactiveUS20050080747A1Anonymous user systemsRecord carriers used with machinesCredit cardPersonal identification number
Multiple secure transactions are provided through use of a method that uses customer one-time unique purchase order numbers (“Coupons”) generated by an algorithm that uses a permutated user key and a user insertion key as input variables. A user key (such as a Personal Identification Number, or “PIN”) is combined with a permutation variable that is correlated with a customer sequence number to create the permutated user key. A random number generator is used to generate the user insertion key correlated with the customer sequence number. The algorithm can insert the permutated user key into a user account number through use of the user insertion key. A Coupon is validated by confirming that it is contained in a set of money source Coupons generated by a money source using the user key and a random number generator that is synchronized with the random number used to generate Coupons. Once a Coupon is validated, the matching money source Coupon and all earlier generated money source Coupons are deleted from the set, and a new set is generated. If a preselected number of Coupons are not validated for a chosen entity, an invalid user account number will be set. Coupons can be used for credit card or bank card transactions, and they can be generated without changing fixed digits of traditional twenty digit account numbers.
Owner:PRIVASYS
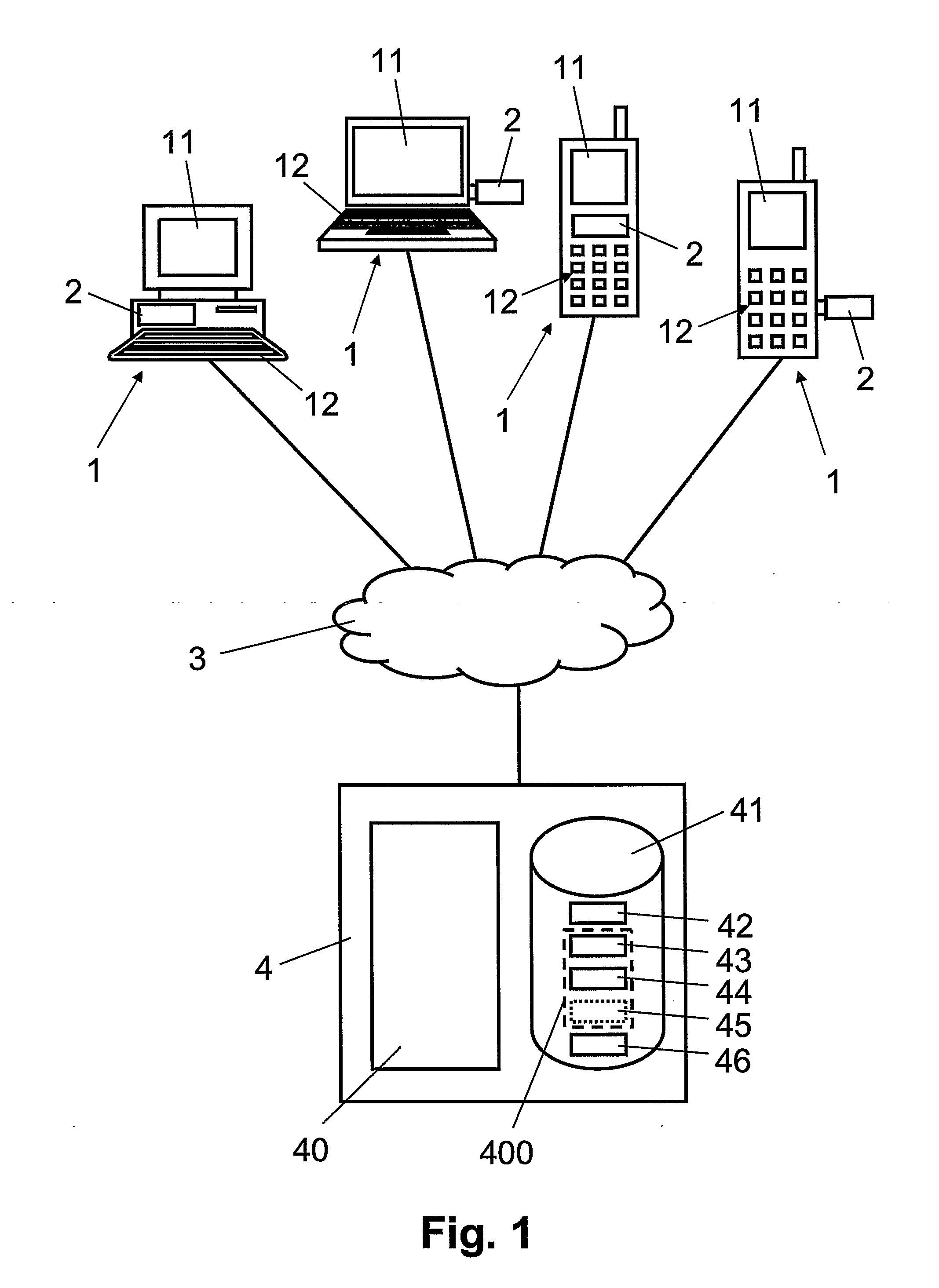
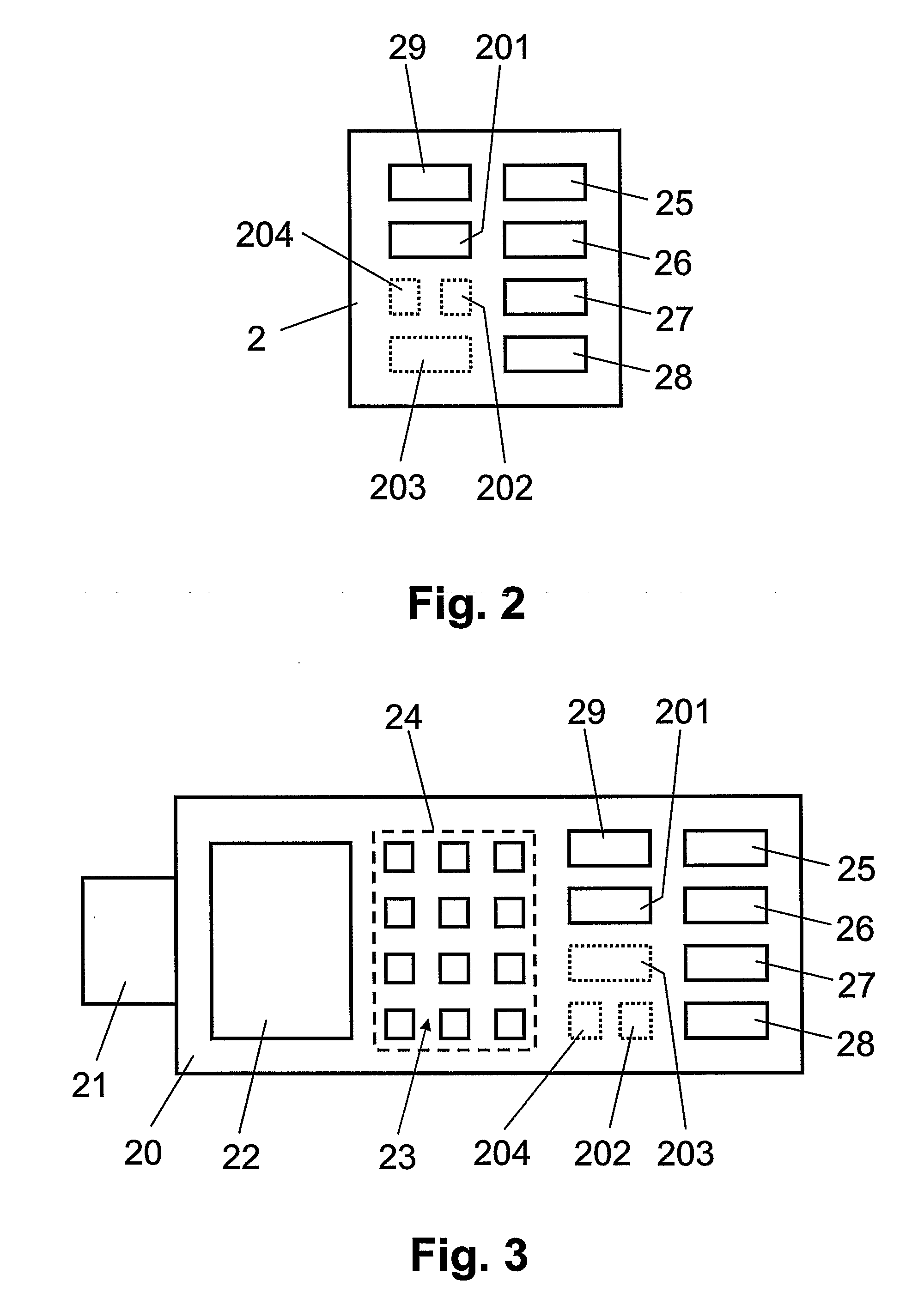
Secure money transfer between hand-held devices
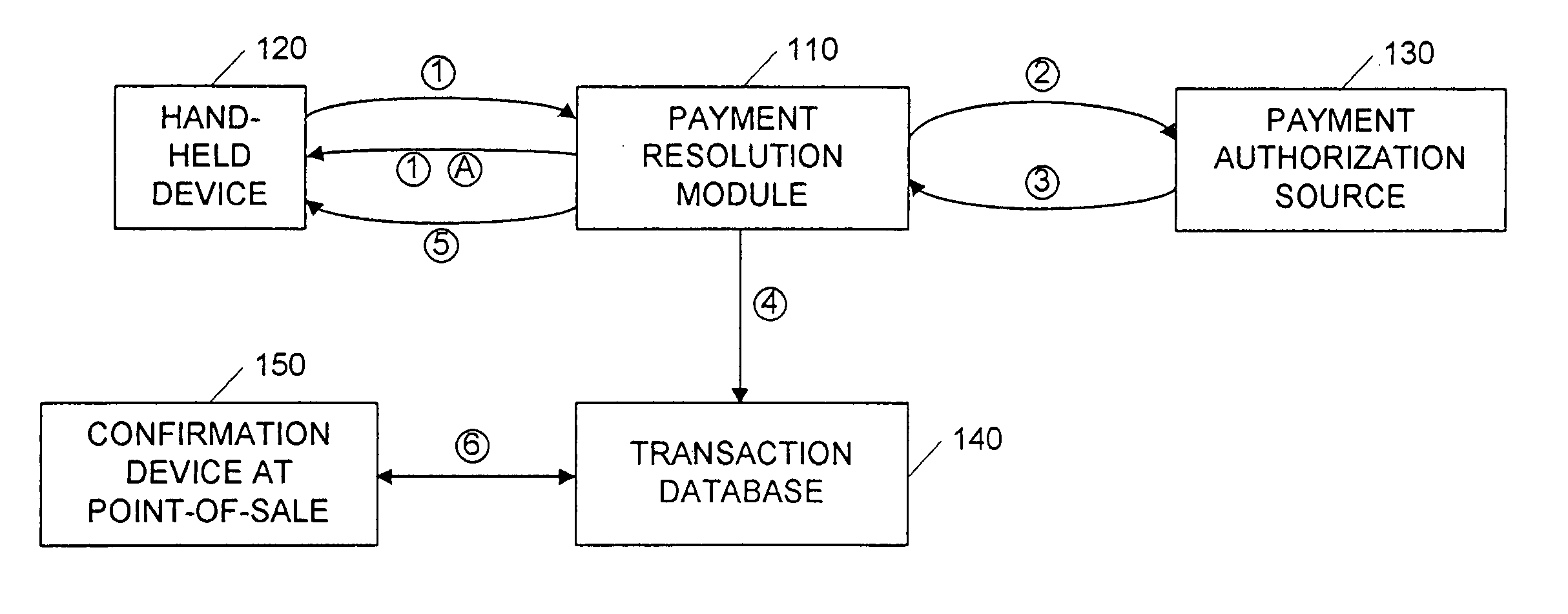
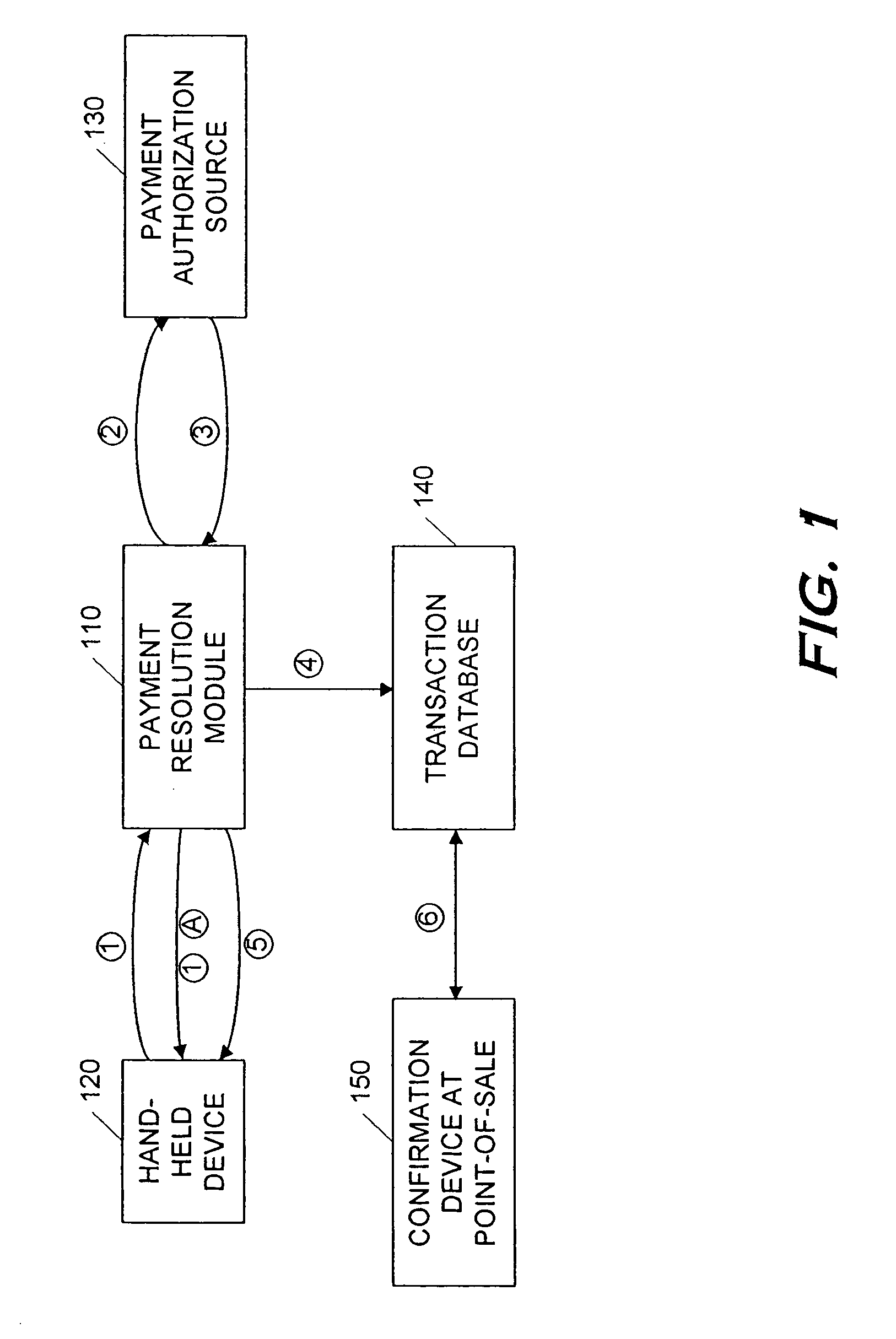
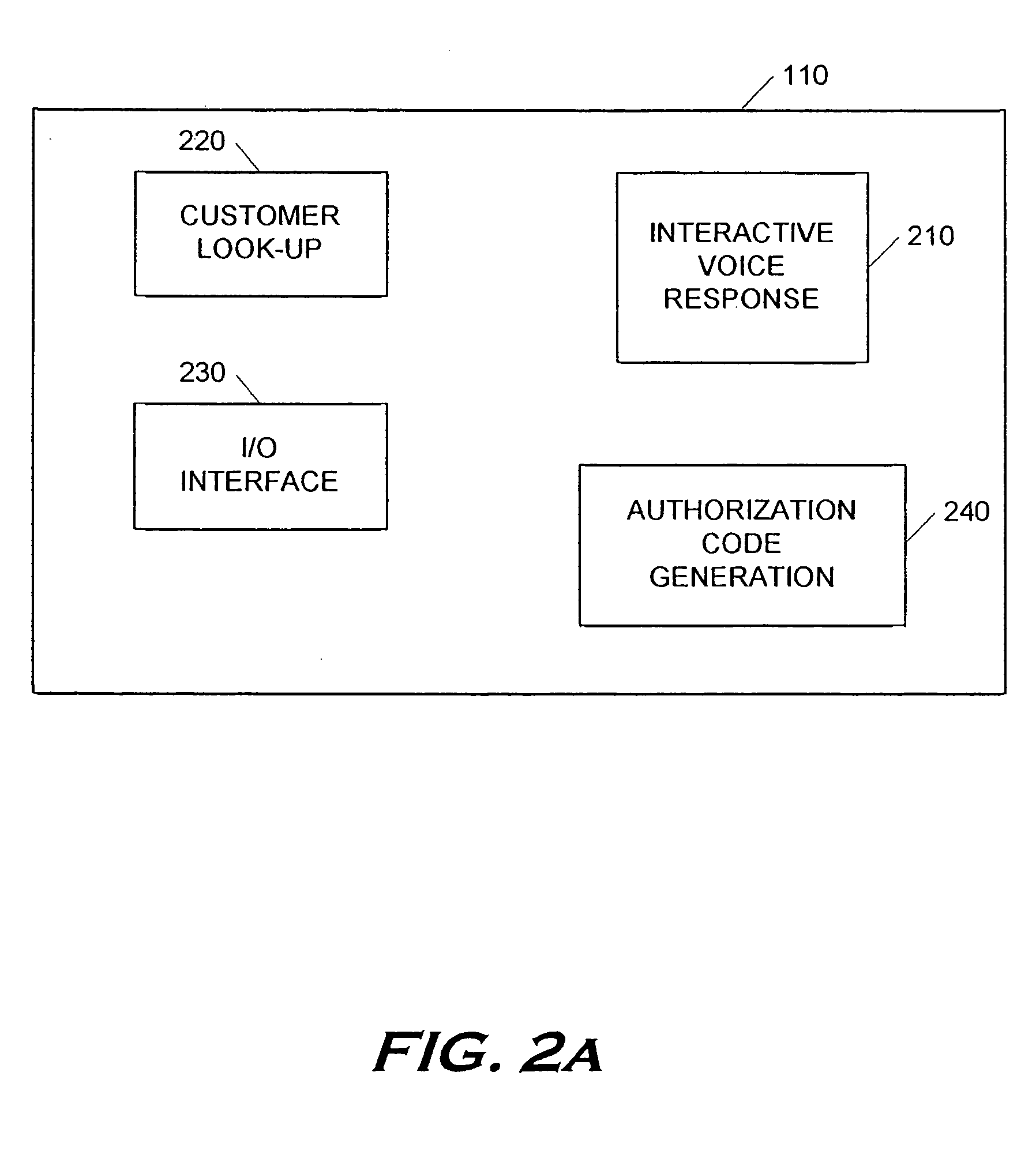
A payment resolution module is configured to communicate with hand-held devices (such as mobile phones, PDA's, or computers) to allow secure transfer of funds between financial accounts associated with each of the hand-held devices. A user of a paying device may be identified as the owner of the device either by having the option to enter a personal identification code, or by using a biometric to identify himself, for example. Accordingly, only an authorized user of the hand-held device may use the hand-held device to transfer funds. A user of the recipient device may be identified by an identification code or a telephone number, for example, which is associated with a recipient financial account. After the payment resolution module receives authorization for a payment request to the recipient account, a payment transfer module transmits the requested amount from a payment source associated with the identified owner of the paying device to the recipient account.
Owner:XILIDEV
System and method for detecting card fraud
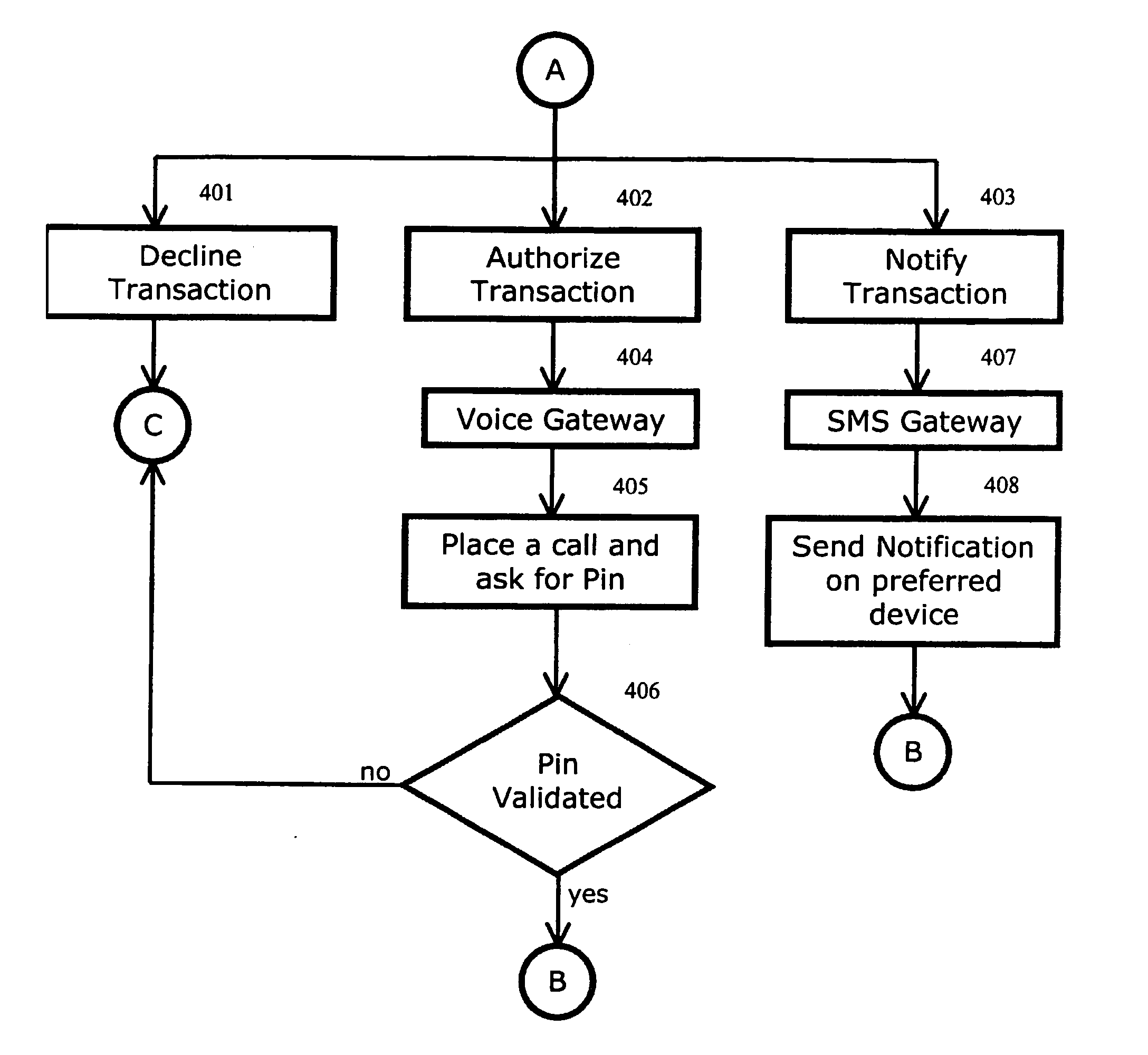
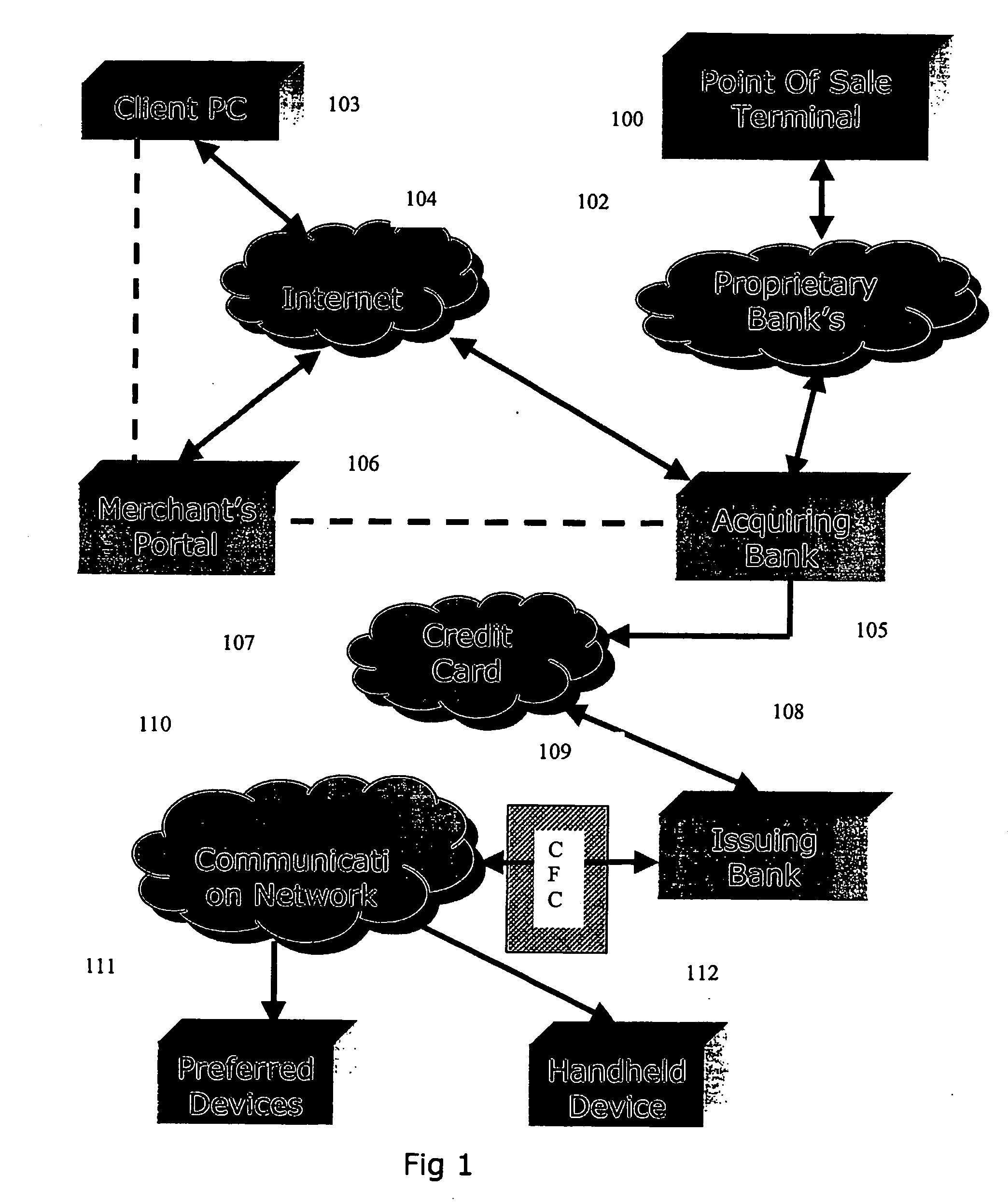
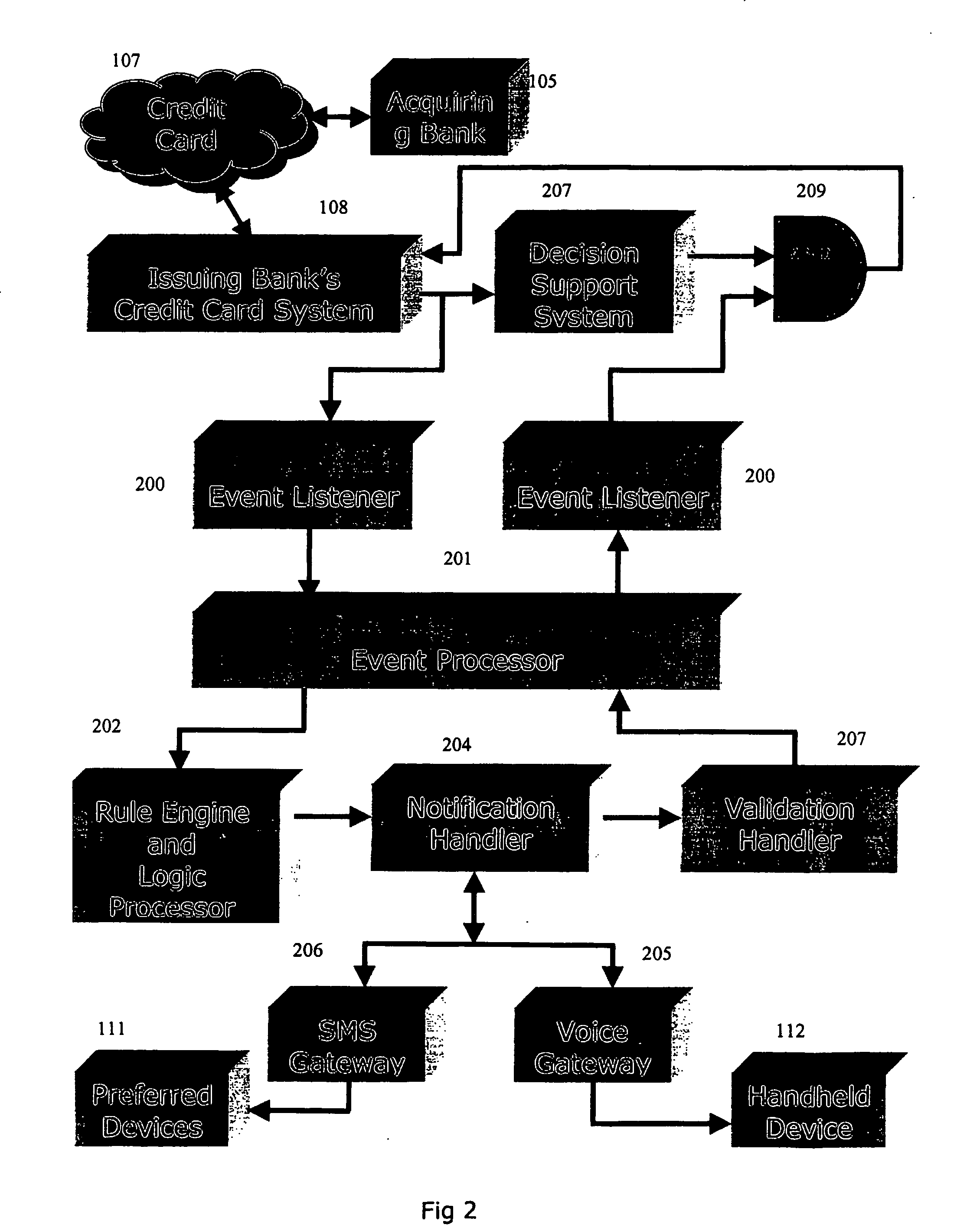
The invention discloses a system and method for notifying and authorizing card transaction by a user. The notifying and authorizing a card is done by a card fraud control system. The card user is notified on his hand held device by a short message service that a card transaction is taking place. The card user can also authorize the credit card transaction by keying in a personal identification number from his hand held device. The system also enables the user to change the rule-based system for a credit card transaction using voice and text inputs from a hand held device.
Owner:MADHOK AJAY +2
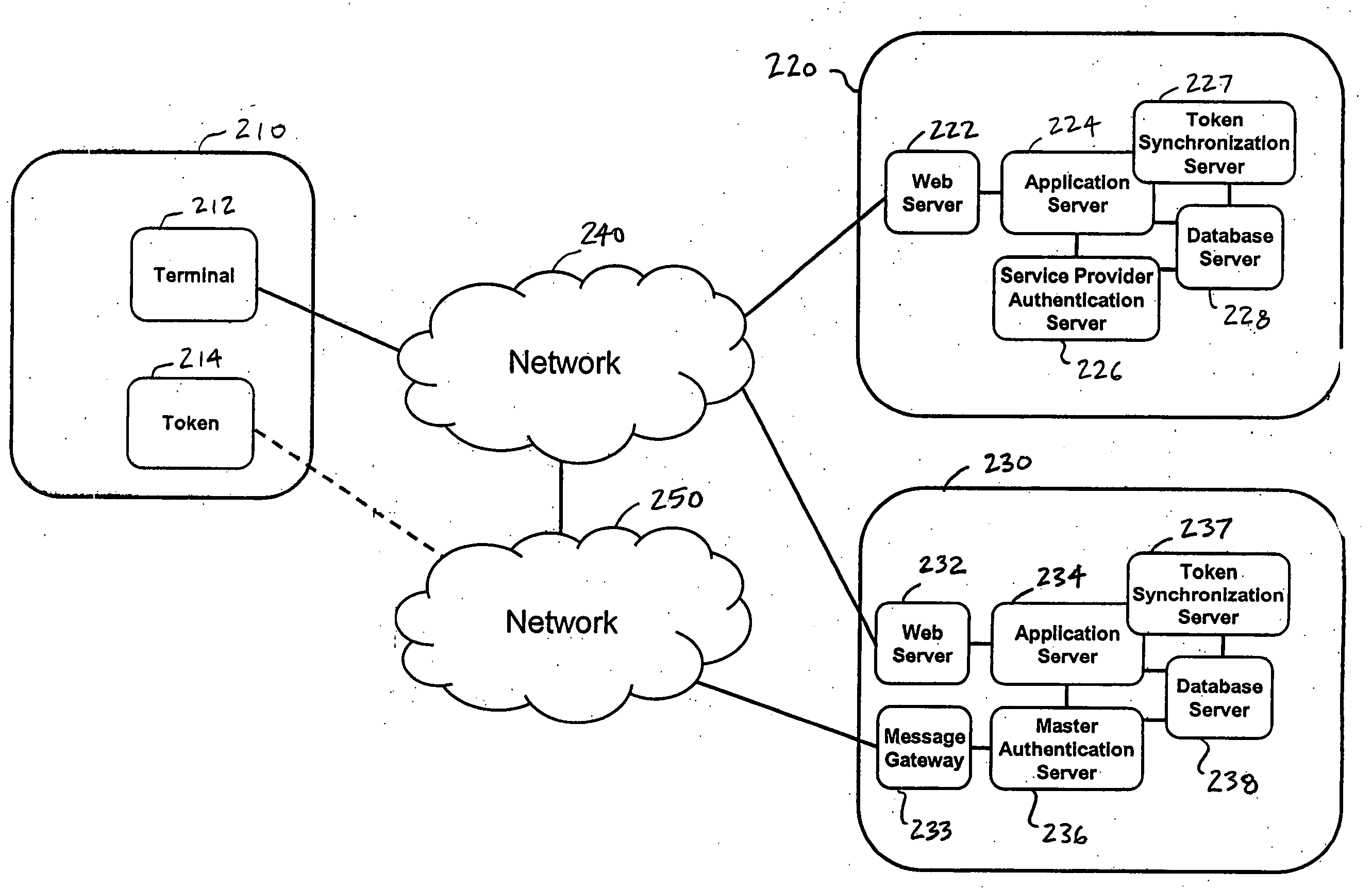
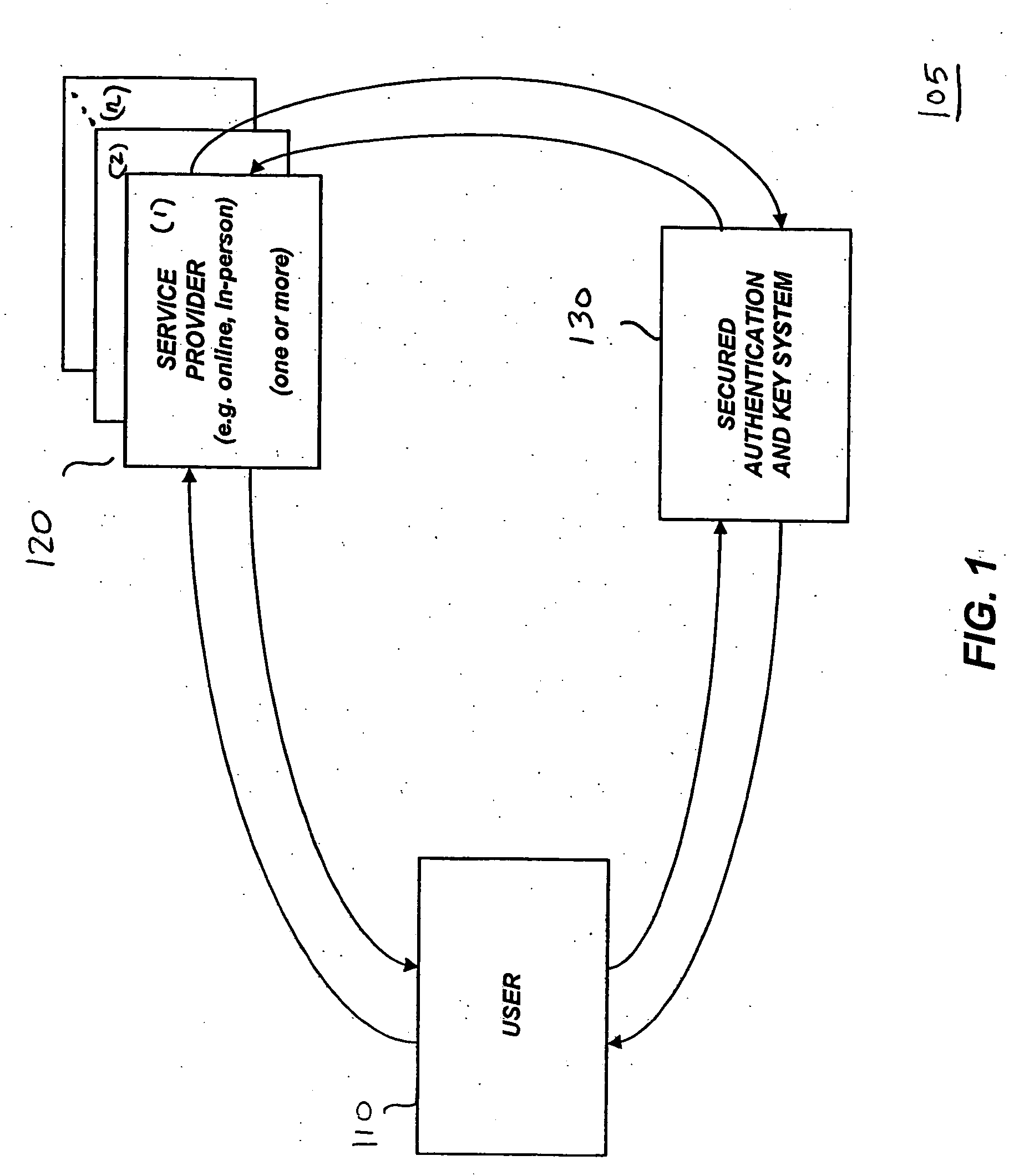
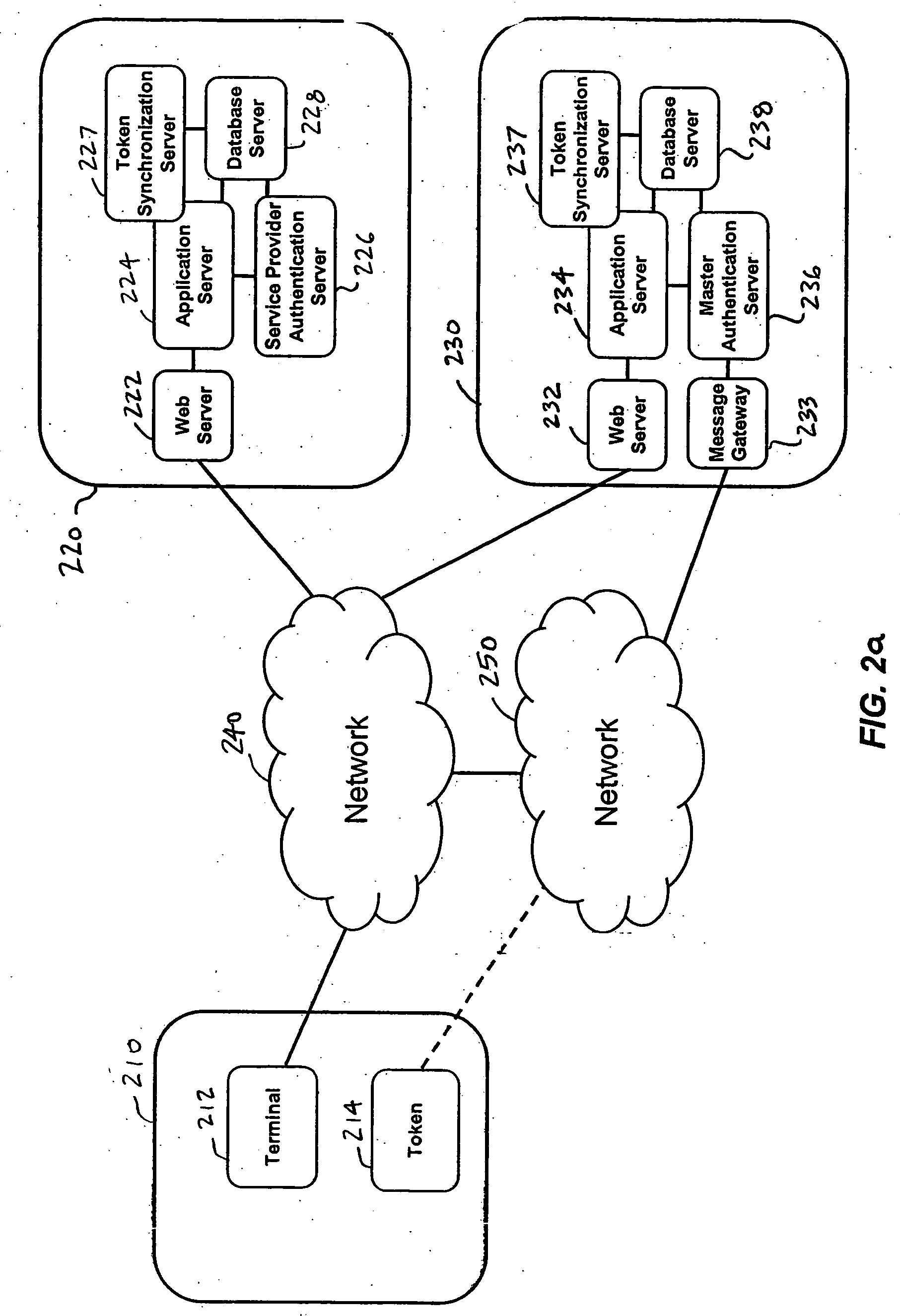
Single one-time password token with single PIN for access to multiple providers
InactiveUS20070130463A1Centralized managementEasy to useUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationThird partyPersonal identification number
A system and a method are disclosed that includes a first party with a terminal and a one-time password token, one or more second parties, each with a host application system and a service provider authentication server, and a third party with a host application system and a master authentication server. The first party uses a single one-time password token with a single personal identification number (PIN) to access the one or more second parties. A third party issues the token to the first party and synchronizes token secrets and parameters with the one or more second parties. This offloads token management from the second parties and allows the second parties to directly authenticate the first party. The authentication of the first party by the second party does not involve the third party.
Owner:BONCLE
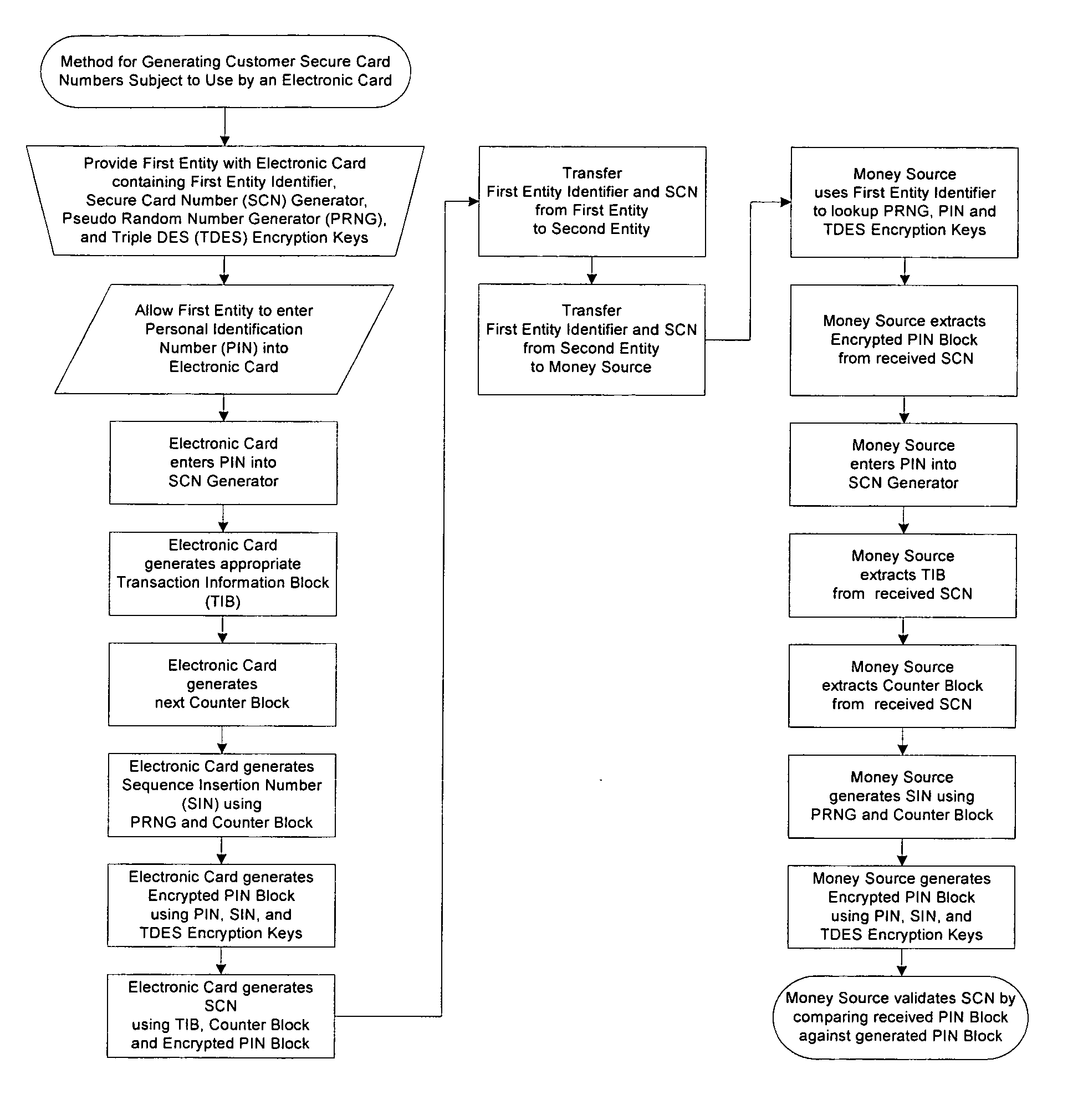
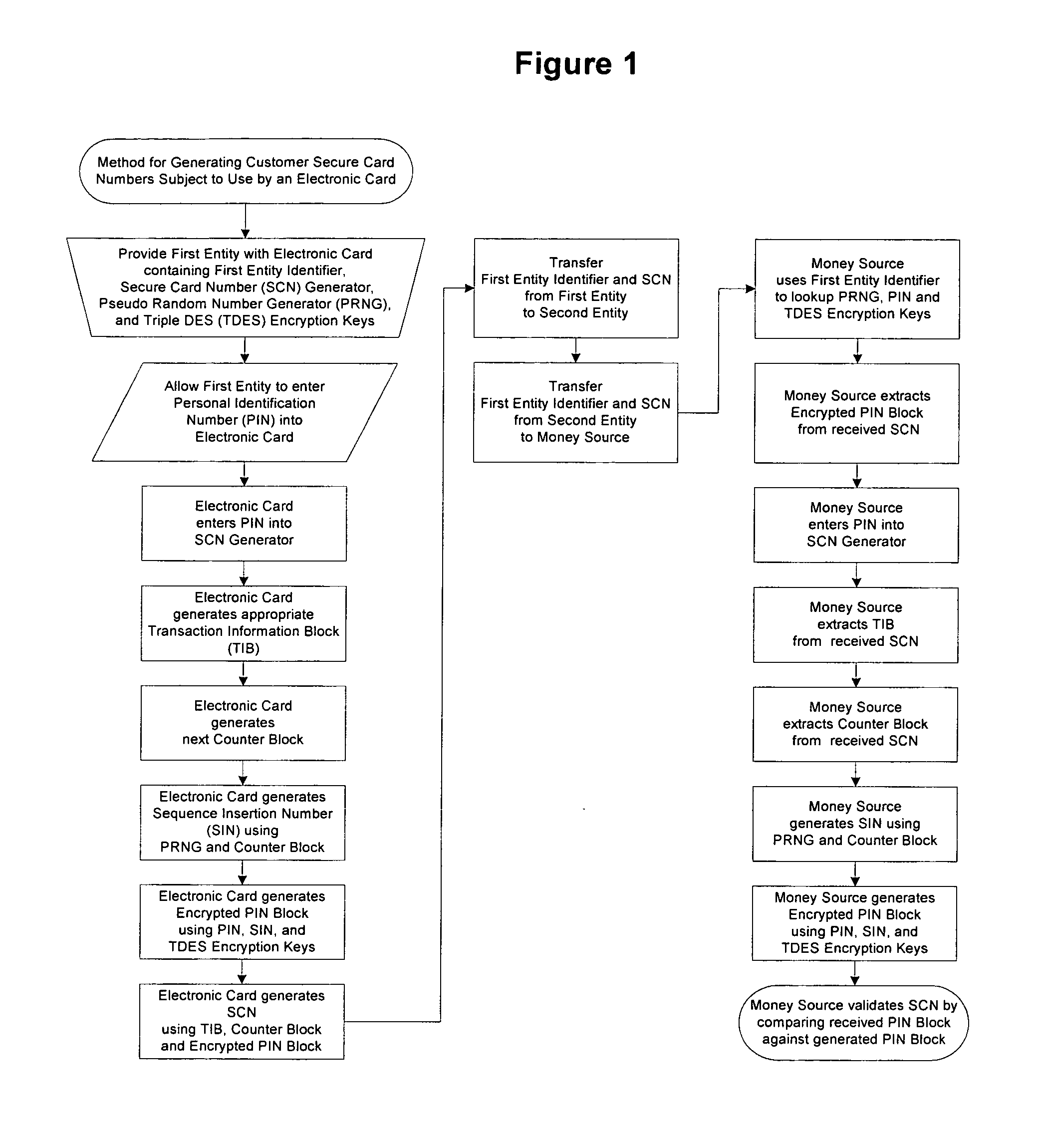
Method for generating customer secure card numbers
A method for providing secure transactions generates a Secure Card Number (“SCN”) for a first entity that is transferred with a first entity identifier to a second entity and then to a money source that verifies that the transaction is valid by use of the first entity identifier and the SCN. The SCN includes a 0Transaction Information Block (“TIB”), a Counter Block, and an encrypted Personal Identification Number (“PIN”) Block. The SCN is transferred to the money source in an account number or a non-account data field. The money source can use the TIB to determine whether the SCN should be used once or multiple times or to identify one of several physical devices, all of which are issued to the first entity, used to generate the SCN. The money source validates the SCN by duplicating the encryption process used to create an encrypted PIN Block and comparing the result to the encrypted PIN Block received with the transaction. A Triple Data Encryption Standard algorithm encrypts a PIN Block generated from a PIN, a Sequence Insertion Number (“SIN”) and a known starting value. The SIN can be a combination of three seed values and a random value generated by a Pseudo Random Number Generator (“PRNG”) initialized with the seed values. A Counter value is associated with the Counter Block and the seed values.
Owner:PRIVASYS
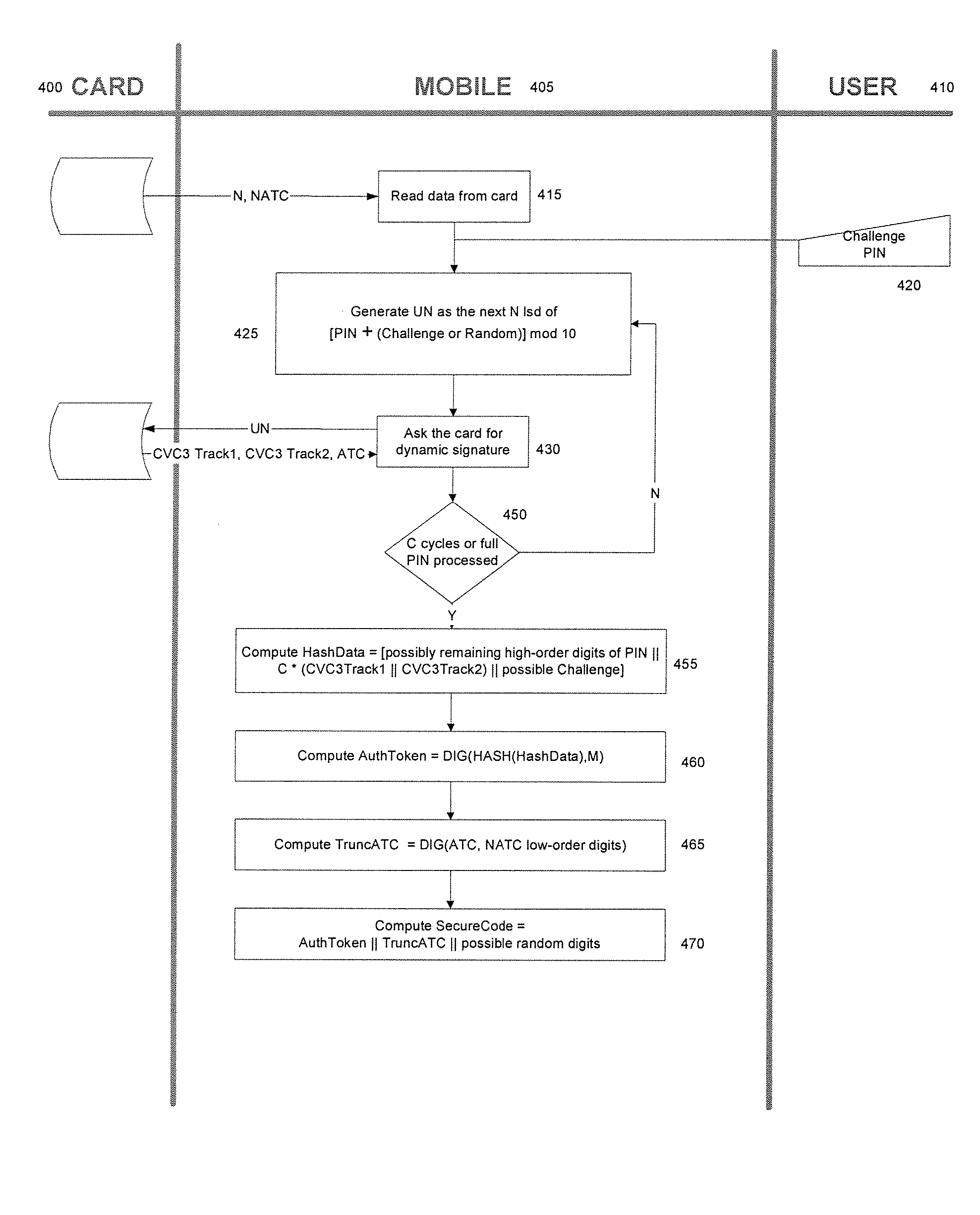
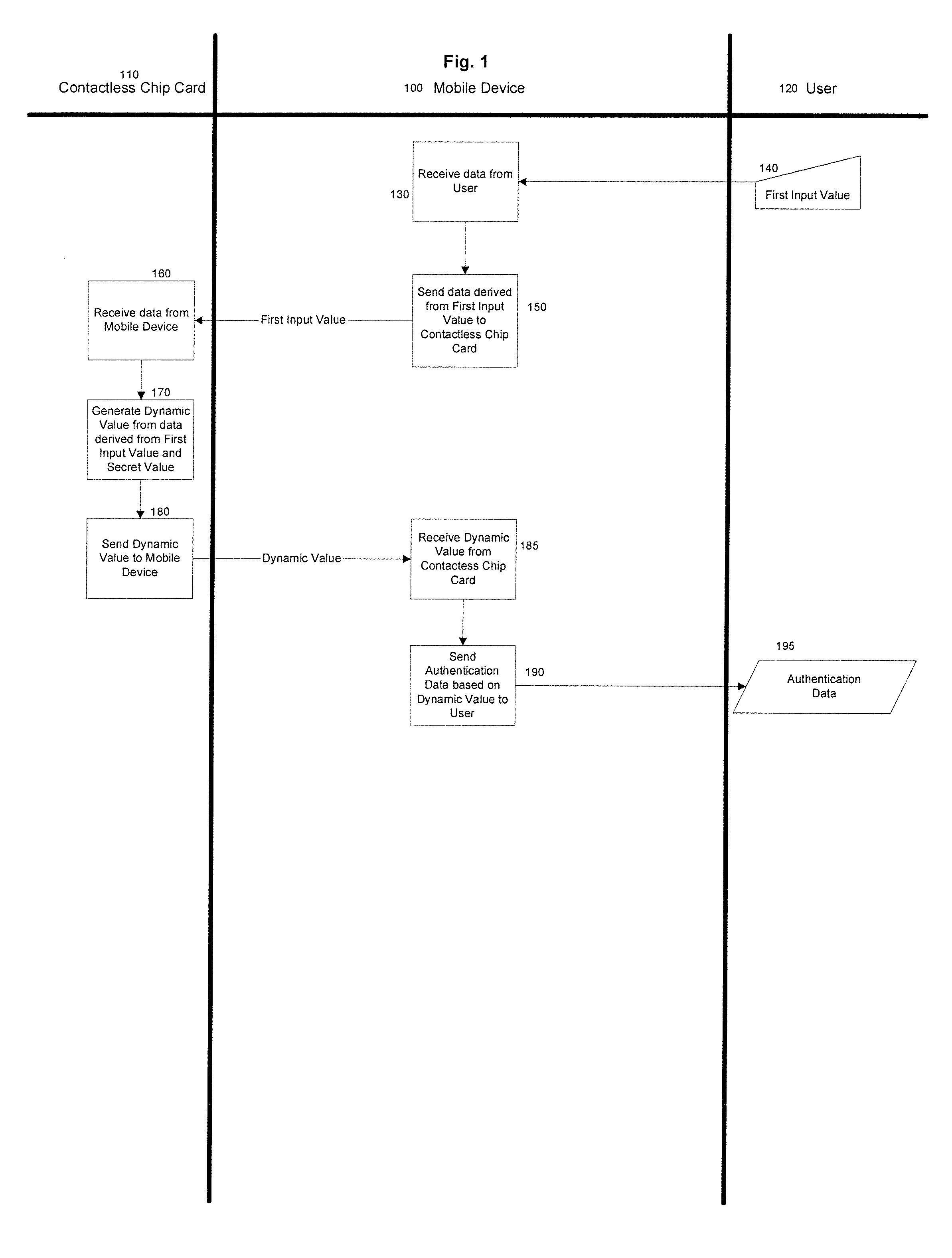
Methods and Systems for Two-Factor Authentication Using Contactless Chip Cards or Devices and Mobile Devices or Dedicated Personal Readers
Generating authentication data for use in a transaction by providing a contactless payment device or smart card configured to communicate with a mobile device, placing the contactless chip card in a proximity to the mobile device to instantiate communication between the contactless chip card and the mobile device, inputting a first input value into the mobile device, communicating data derived from the first input value from the mobile device to the contactless chip card, the contactless chip card converting a set of conversion data, including the first input value, into at least one dynamic value based at least in part on a secret value, communicating the dynamic value from the contactless chip card to the mobile device, and communicating authentication data based at least in part on the dynamic value to a user. In some embodiments the first input value is a Personal Identification Number (PIN), a challenge, or both a PIN and a challenge.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
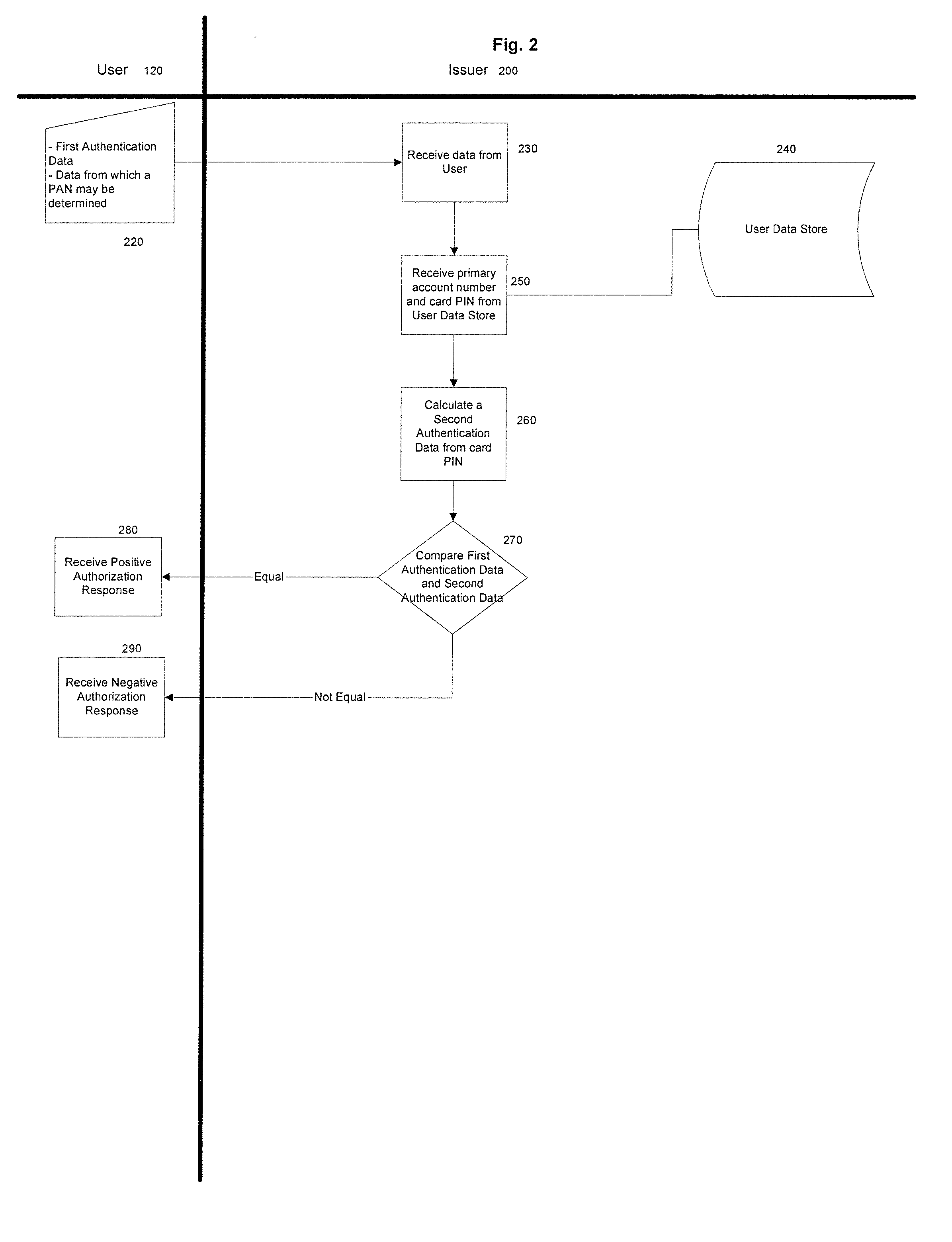
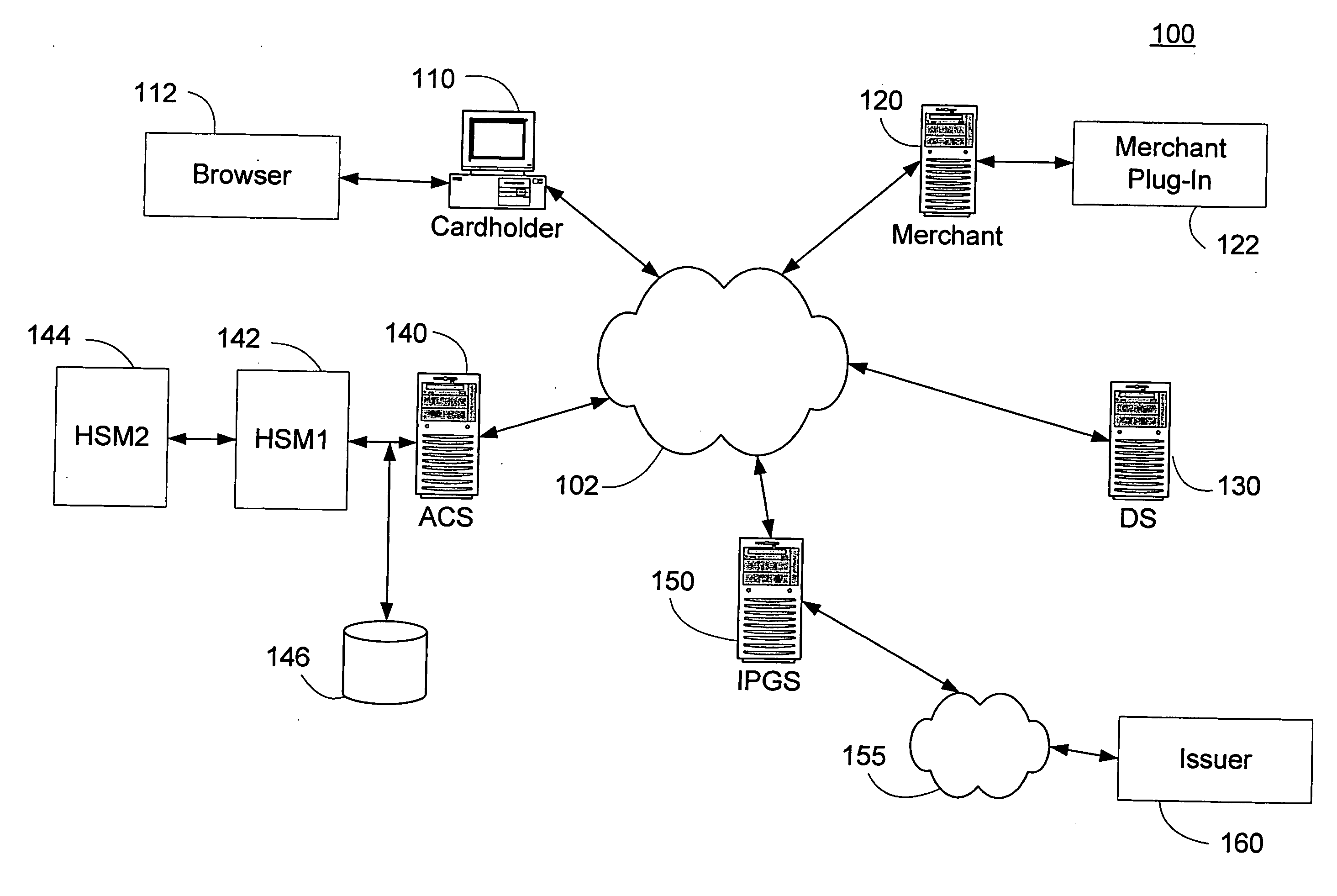
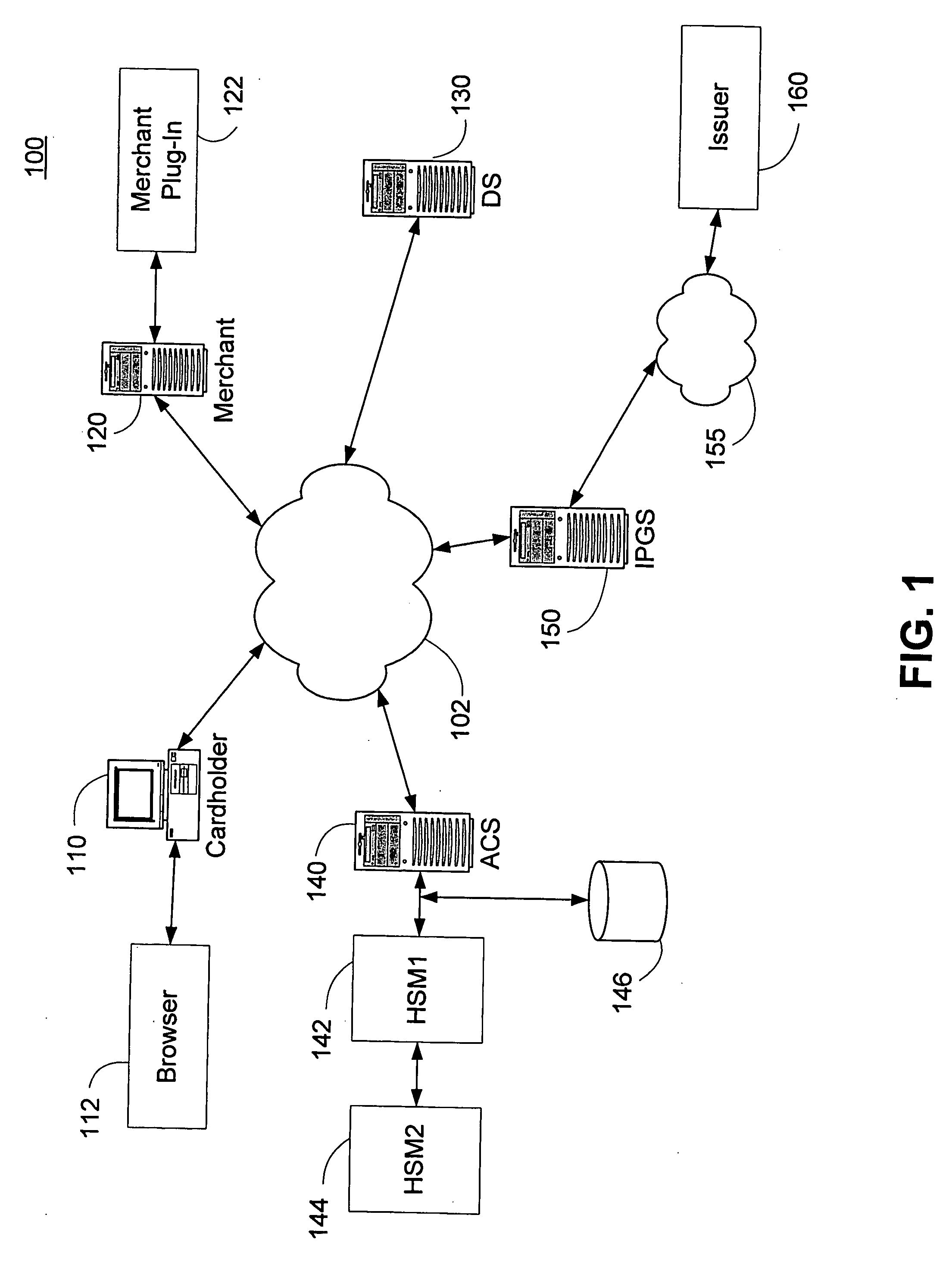
Method and system for secure authentication
ActiveUS20050036611A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPaymentTelecommunications link
A system and method configured to provide secure Personal Identification Number (PIN) based authentication is disclosed. A passcode or PIN associated with a customer value card can be securely authenticated by an issuer prior to authorizing payment. An Access Control Server (ACS) can receive the PIN or passcode from a customer via a secure connection over a public network. The ACS can generate an encrypted PIN and can communicate the encrypted PIN to a remote issuer for authentication. The ACS can use one or more hardware security modules to generate the encrypted PIN. The hardware security modules can be emulated in software or implemented in hardware. The system can be configured such that the PIN is not exposed in an unencrypted form in a communication link or in hardware other than the originating customer terminal.
Owner:VISA USA INC (US)
System and method for controlling financial transactions over a wireless network
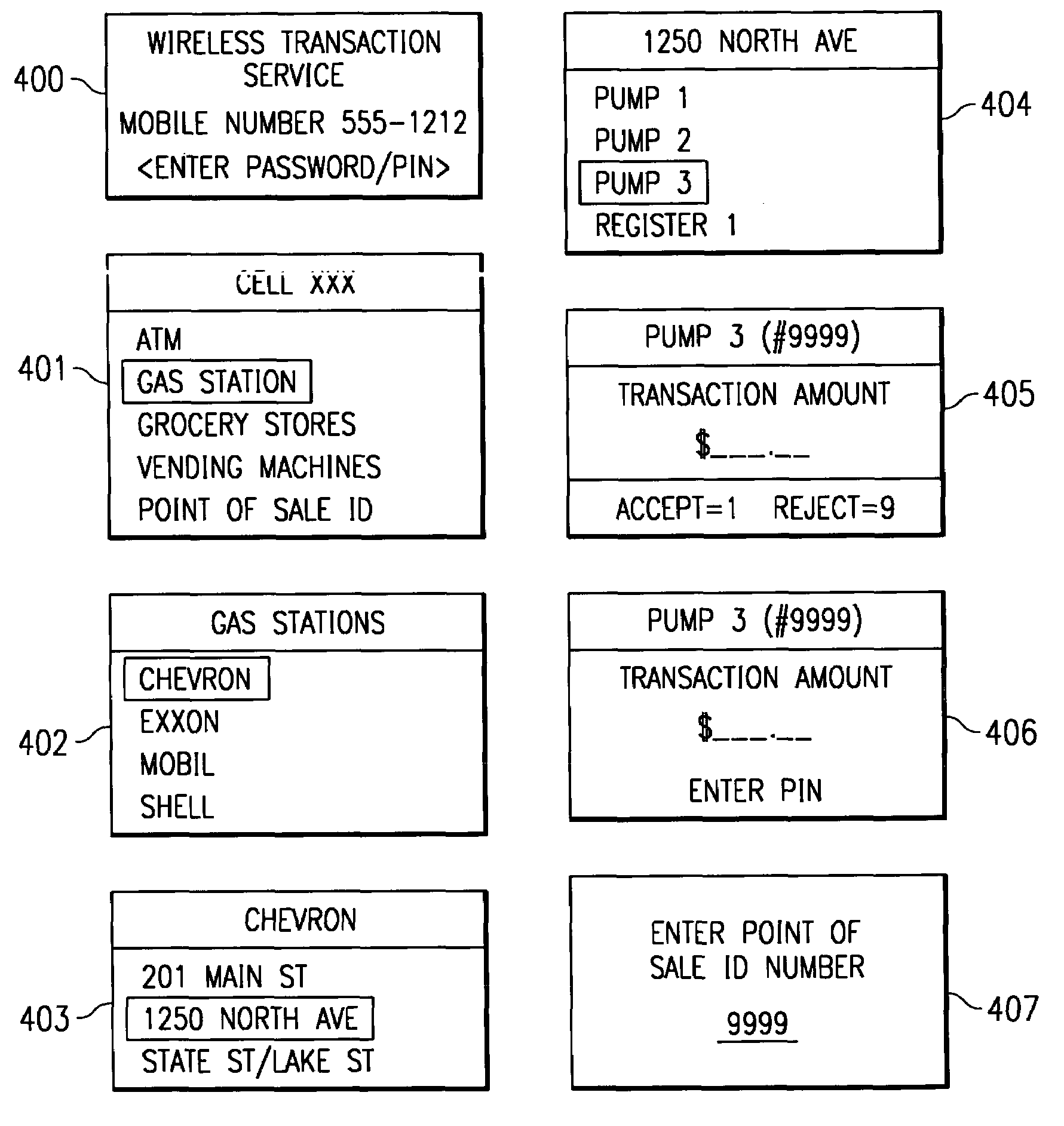
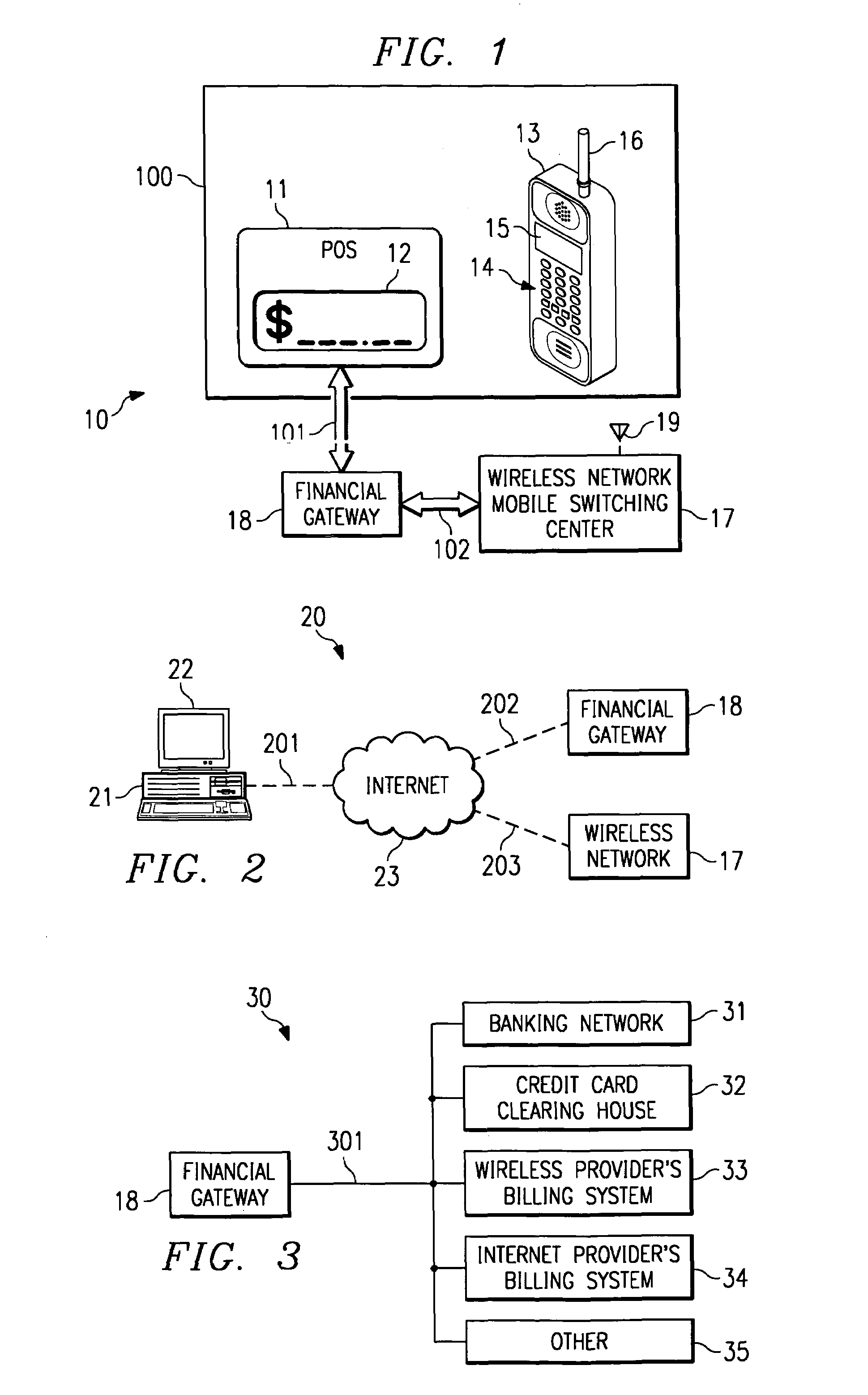
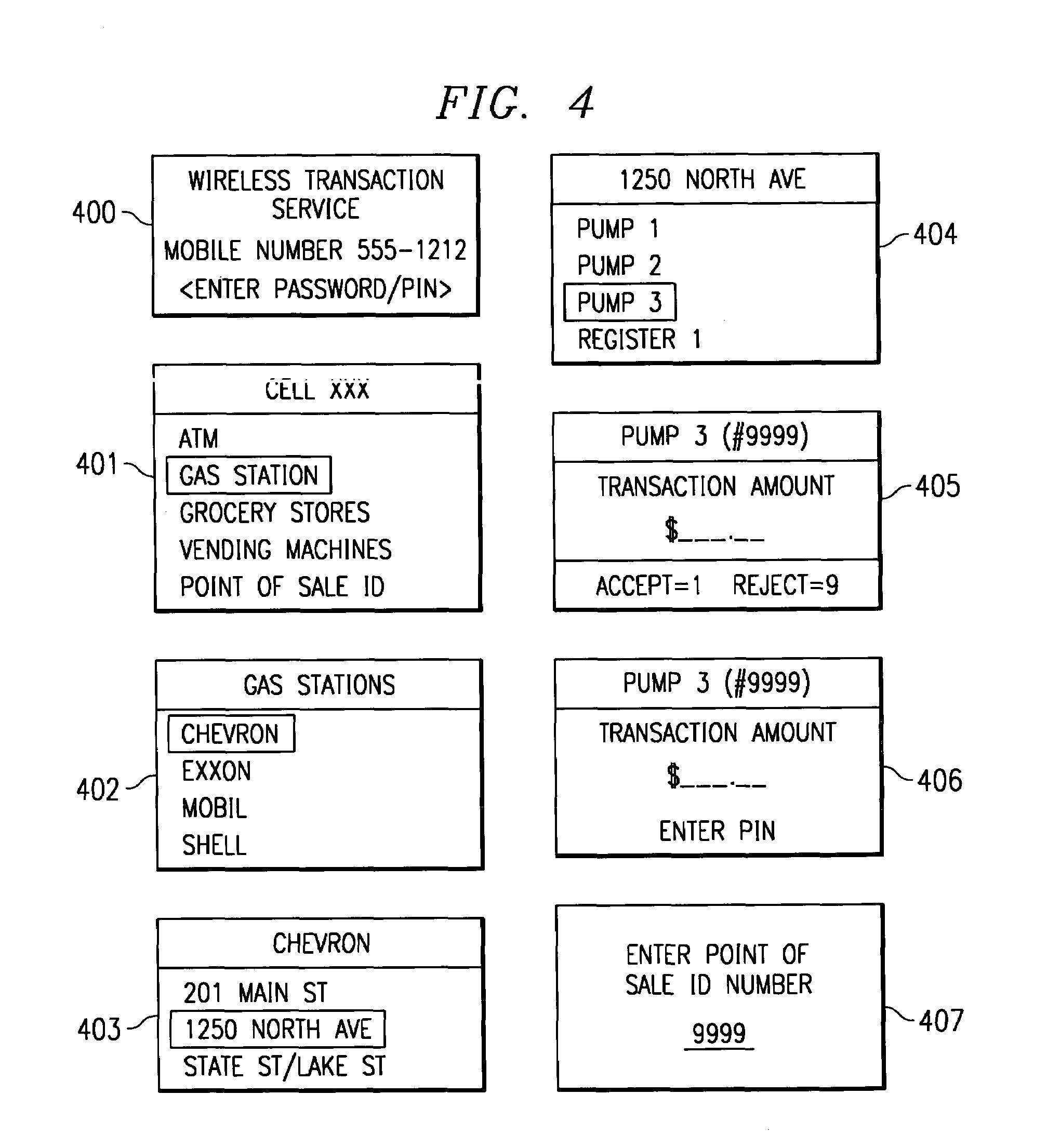
InactiveUS7167711B1Hand manipulated computer devicesFrequency-division multiplex detailsCredit cardPersonal identification number
A system and method for controlling financial transactions is disclosed. A customer, using a wireless device, identifies a point of sale and the amount of a transaction at that point of sale is first communicated to a central service and then transmitted to the wireless device for display at the wireless device. The customer can either accept the transaction amount to complete the transaction or reject the amount to cancel the transaction. The customer may have to enter a password or personal identification number to verify the authorization to use the wireless financial system. The customer is billed for the transaction via credit, debit, ATM or other methods, such as the wireless carrier or an internet provider.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
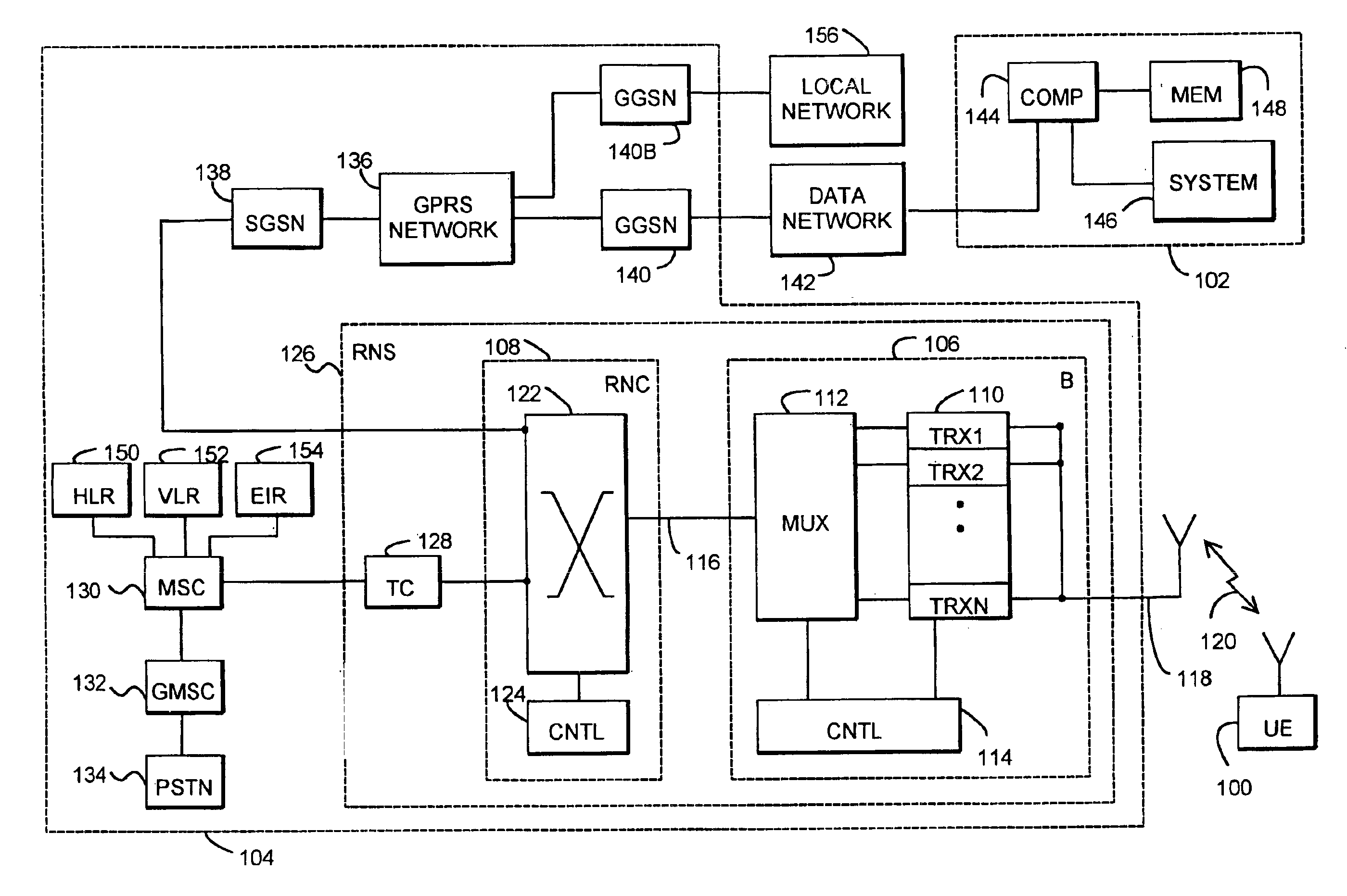
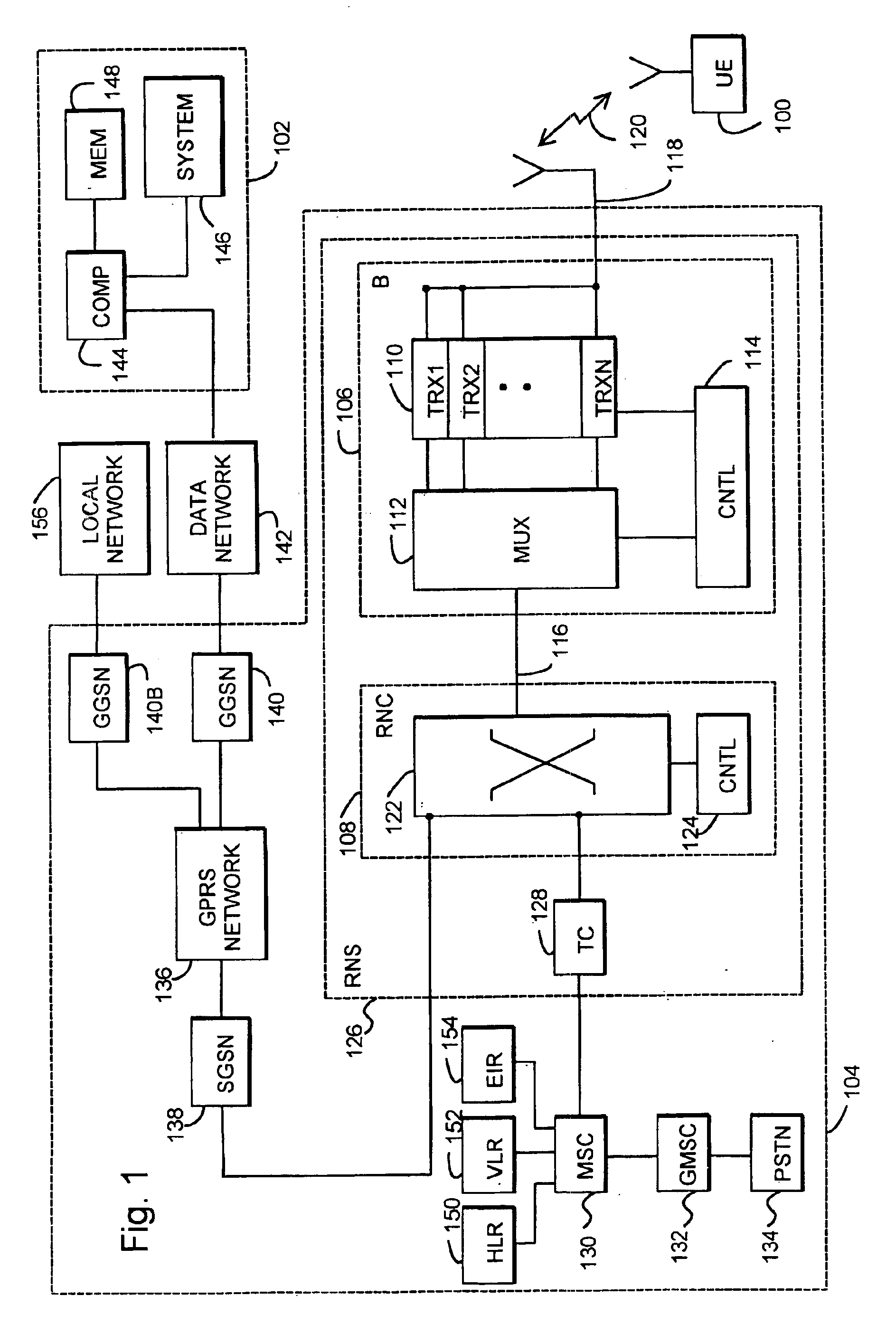
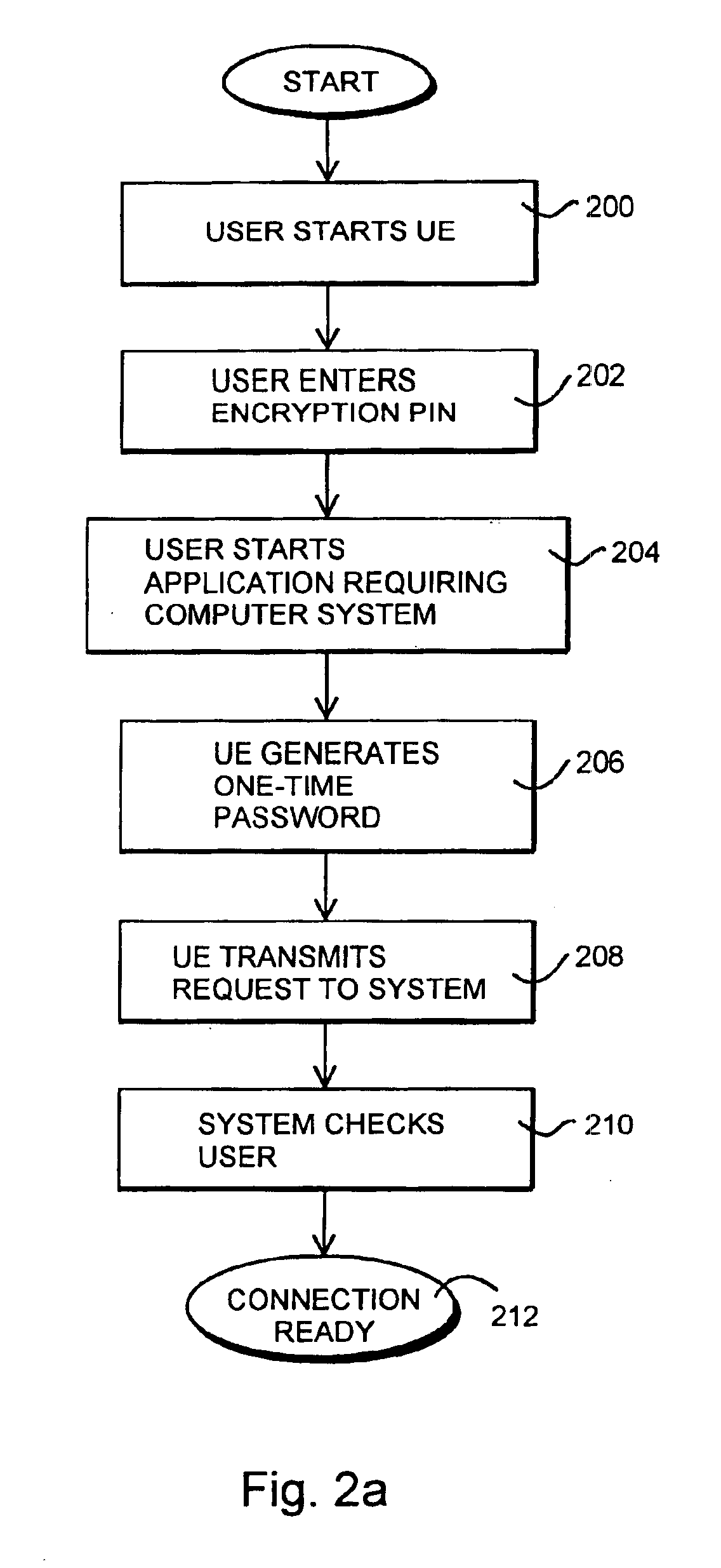
Method and arrangement for reliably identifying a user in a computer system
InactiveUS6928558B1Avoid disadvantagesReliable identificationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPersonal identification numberComputerized system
The invention relates to an arrangement and a method for reliably identifying a user in a computer system. The method utilizes a mobile station for communicating with the system. The method comprises generating a first one-time password in the mobile station by utilizing a known algorithm on the basis of the identification number of the user, subscriber-specific identifier, device-specific identifier of the mobile station, and time. The password obtained and the subscriber-specific identifier of the user are encoded and transmitted to an authentication server of the computer system, comprising identifying the user on the basis of the subscriber-specific identifier, searching a database for the personal identifier number of the user and the device-specific identifier of the mobile station associated with the user, generating a second password at the authentication server by utilizing the same predetermined algorithm on the basis of the personal identification number of the user, subscriber-specific identifier, device-specific identifier of the mobile station and time, comparing the first and the second passwords with each other at the authentication server, and if the passwords match, enabling the telecommunication connection between the mobile station and the computer system.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
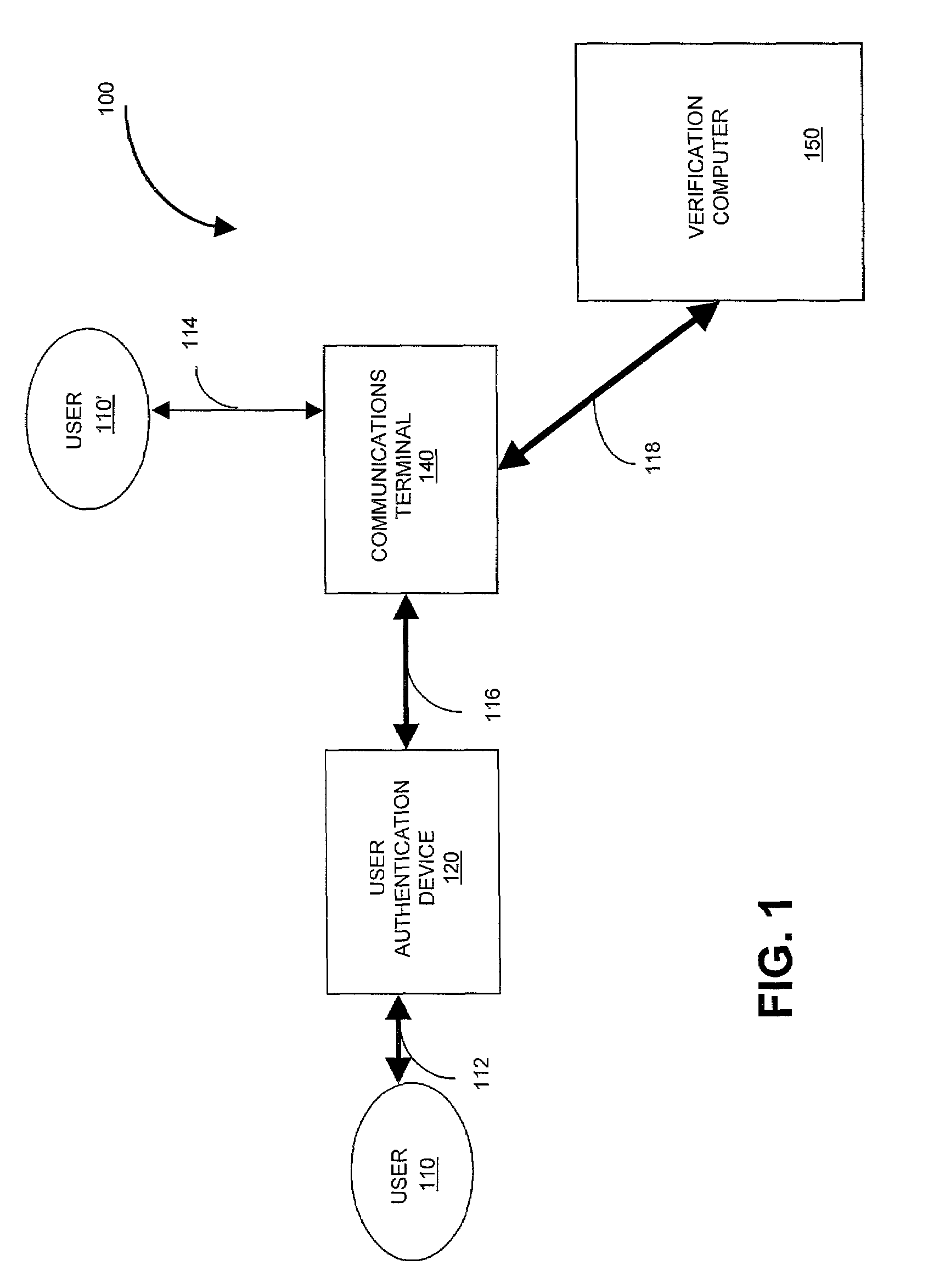
Method and Devices For User Authentication
InactiveUS20080212771A1Effective protectionSecurity of the proposed method is not particularly underminedAcutation objectsDigital data processing detailsMan-in-the-middle attackData set
For authenticating a user using a communication terminal (1) to access a server (4) via a telecommunications network, a personal identification code is received from the user From secure session establishment protocol messages exchanged (S1, S2, S3) between the communication terminal (1) and the server (4), a data set is generated (S4). Based on the data set, a transaction authentication number is generated (S52) using the personal identification code. The transaction authentication number is transmitted (S54) from the communication terminal (1) to the server (4). In the server (4), the transaction authentication number received is verified (S20) based on the secure session establishment protocol messages exchanged with the communication terminal (1). The transaction authentication number enables session aware user authentication that protects online users against real-time man-in-the-middle attacks.
Owner:PRIVASPHERE AG
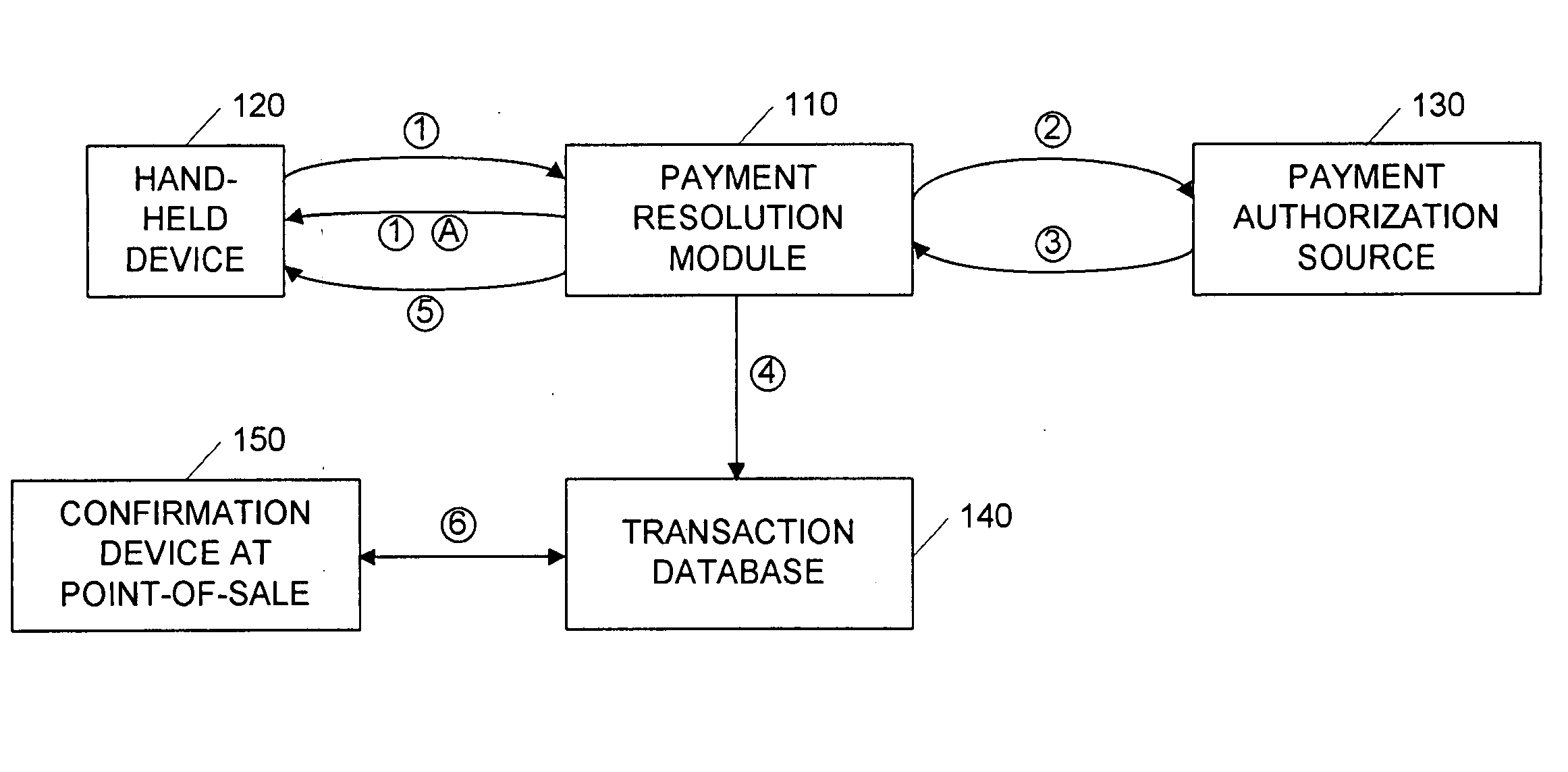
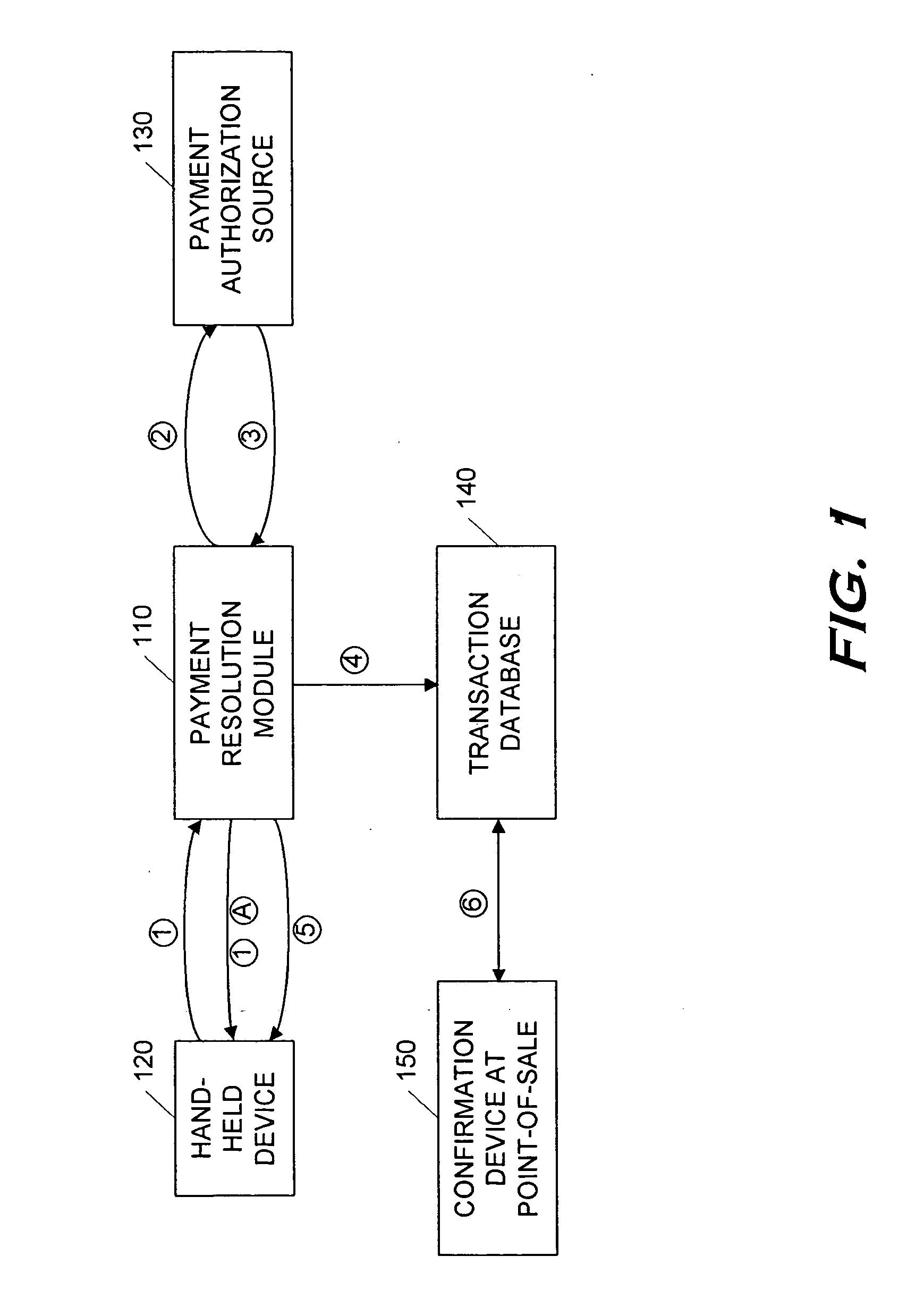
Point-of-sale billing via hand-held devices
InactiveUS20050109838A1Reduce fraudComplete banking machinesFinancePaymentPersonal identification number
A payment resolution module is configured to communicate with hand-held devices (such as mobile phones, PDA's, or computers) to allow purchase of products using the hand-held devices, without requiring the user of the hand-held device to enter payment information for each transaction. The user of the hand-held device may be identified as the owner of the device either by having the option to enter a personal identification code, or by using a biometric to identify himself, for example. Accordingly, only an authorized user of the hand-held device may use the hand-held device to purchase products. After the payment resolution module receives authorization for payment, an authorization code is transmitted to the mobile device. The user may be required to present the authorization code at the point of sale, such as by entering the code into a computing device at the point-of-sale, prior to completion of the transaction.
Owner:XILIDEV
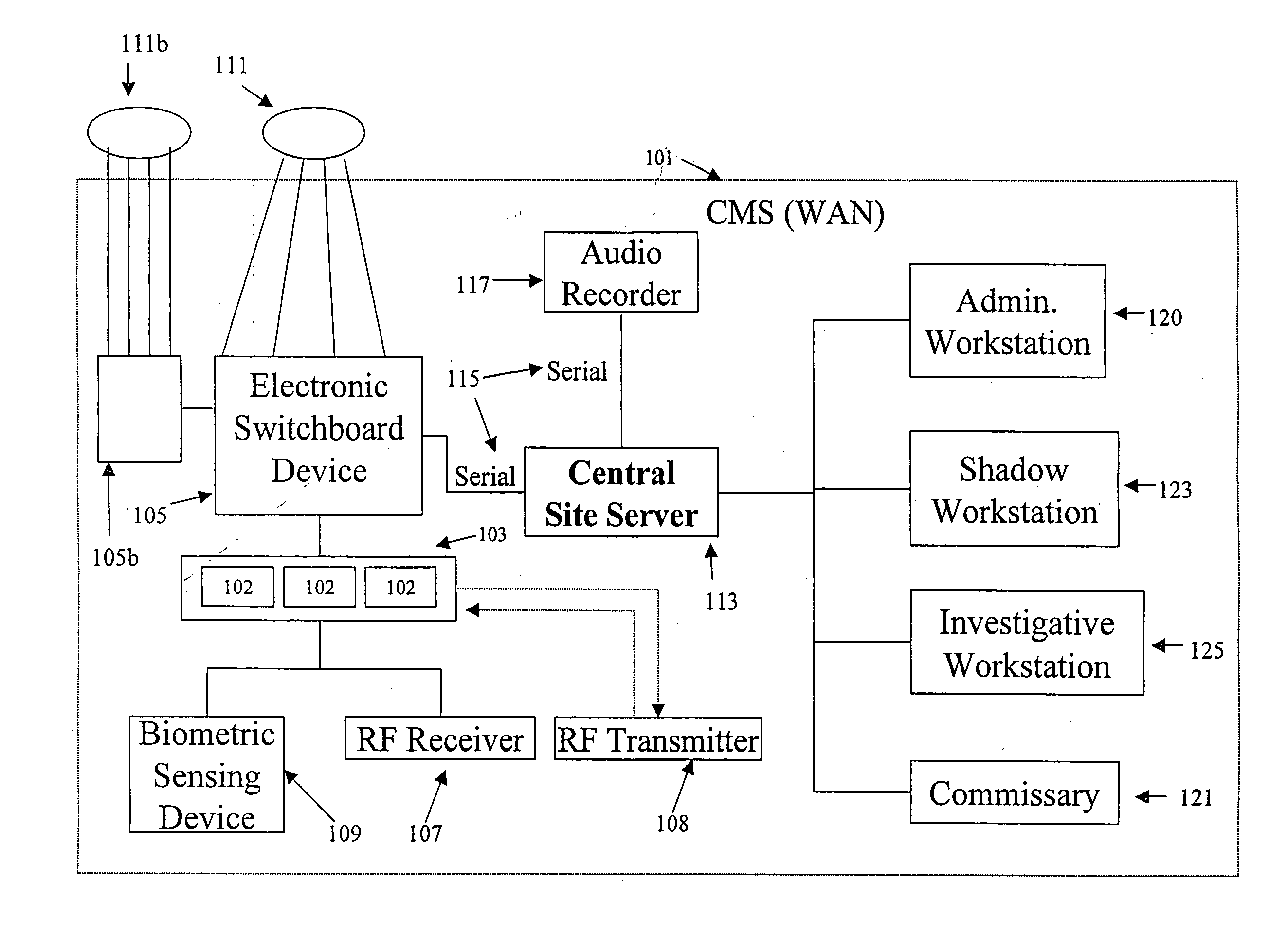
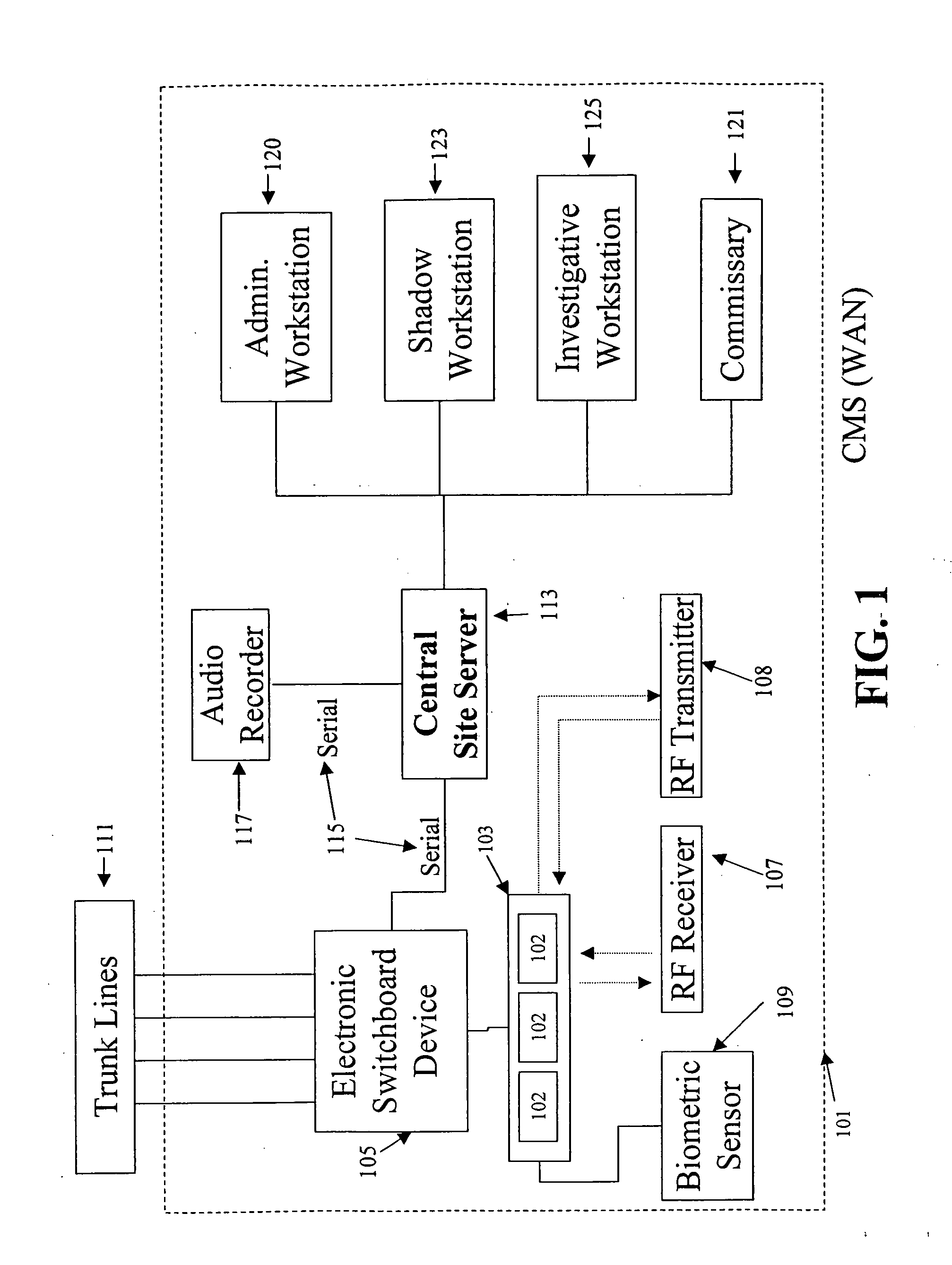
Interactive audio/video system and device for use in a secure facility
ActiveUS20120262271A1Electric signal transmission systemsImage analysisDisplay deviceMessage passing
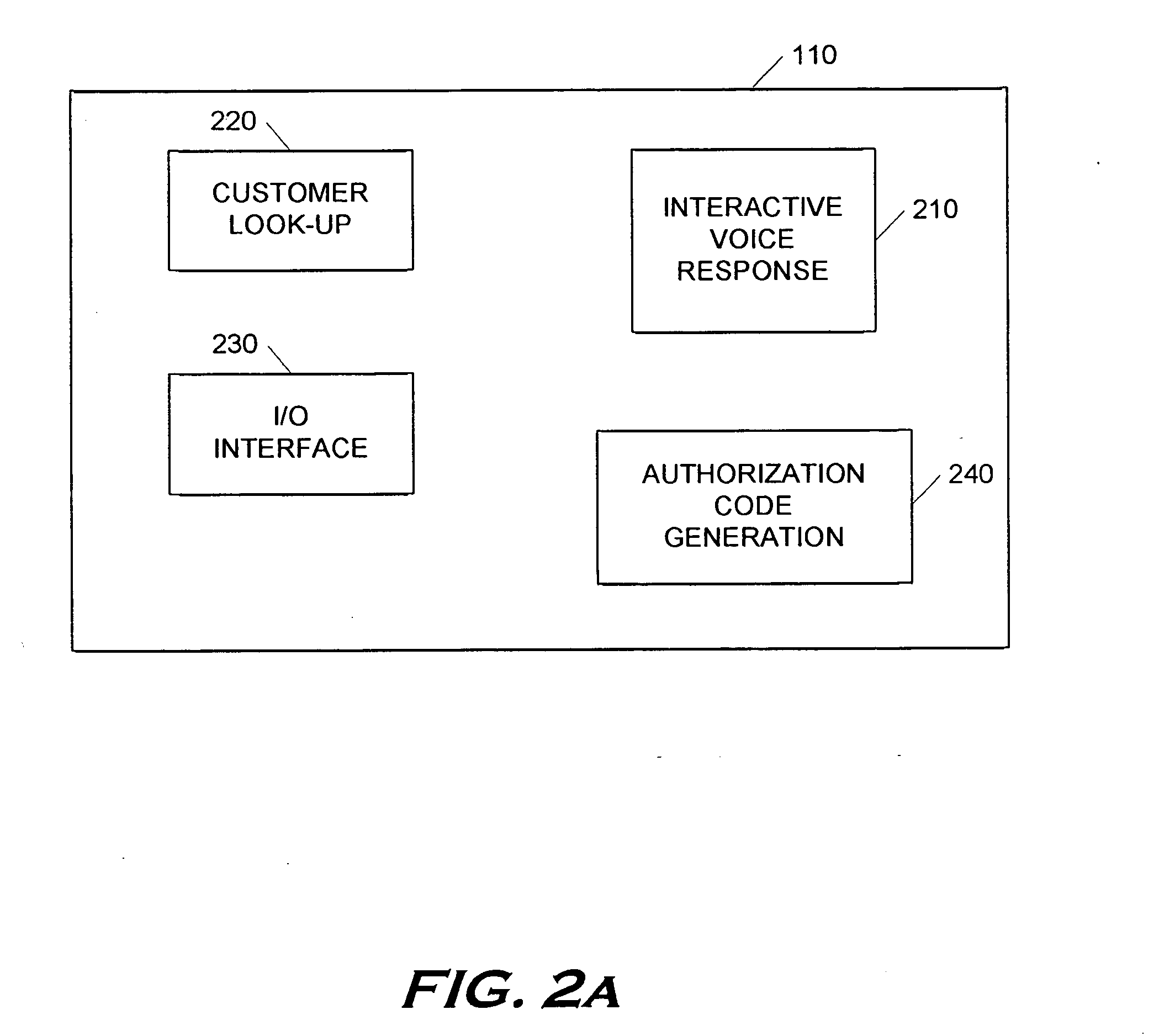
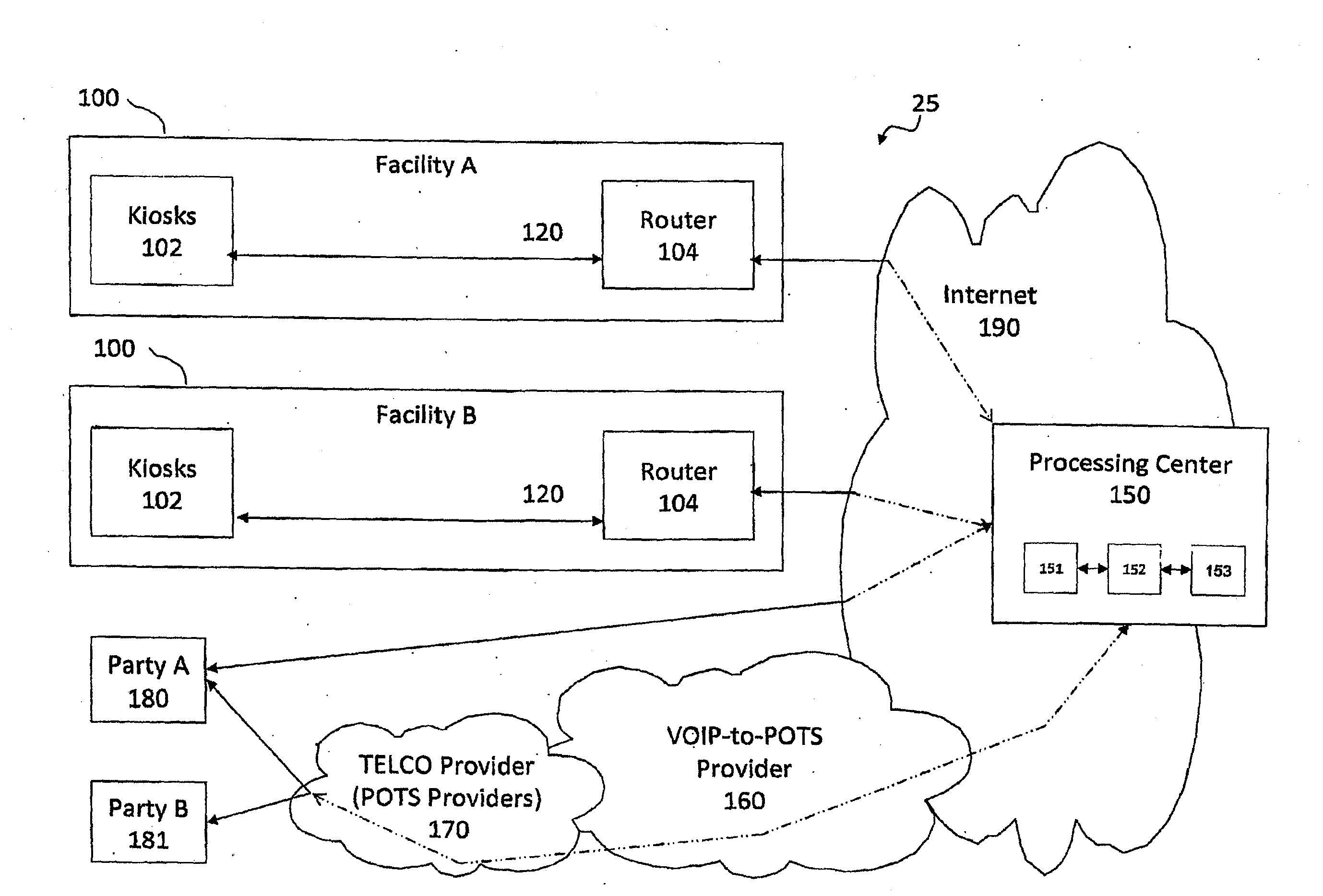
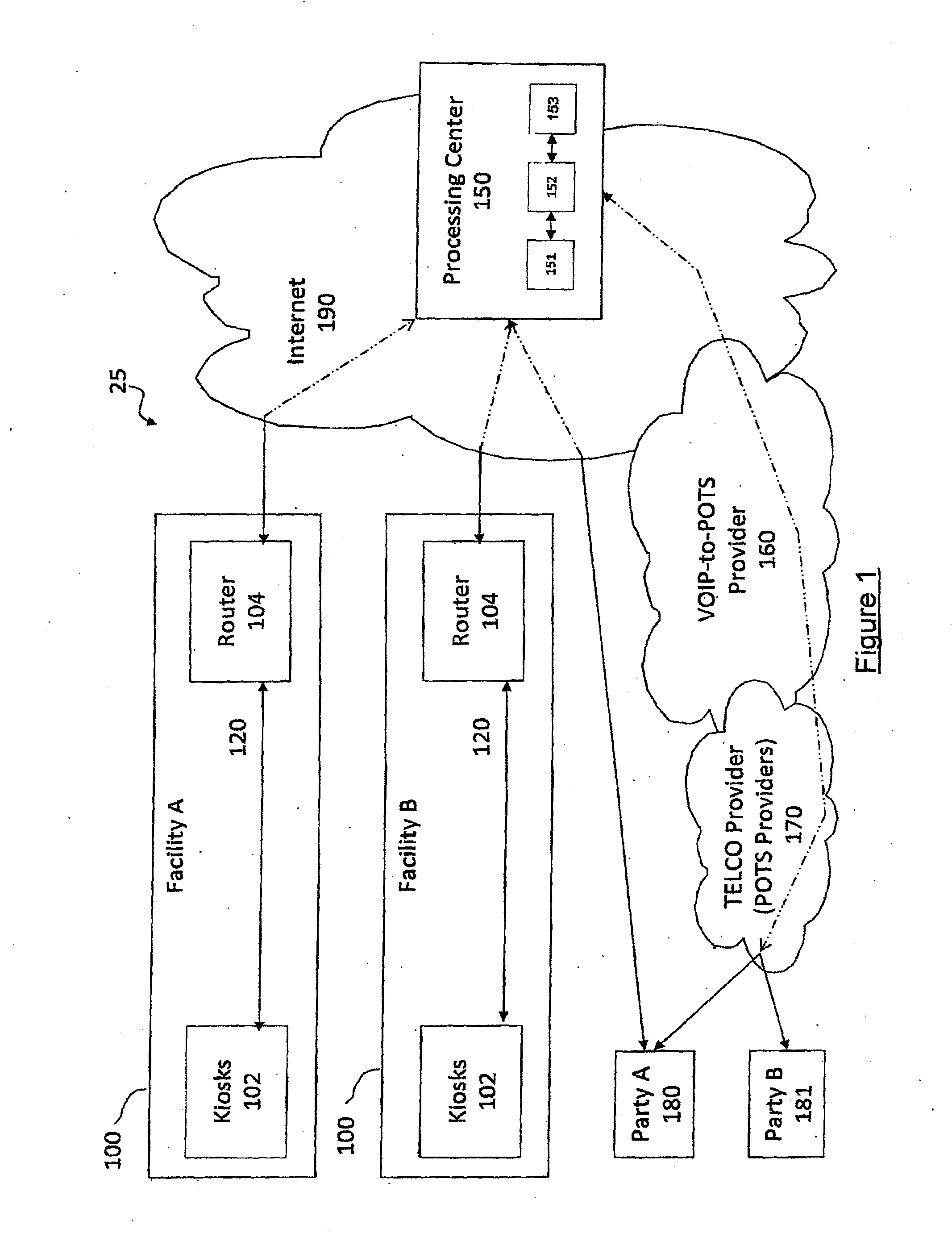
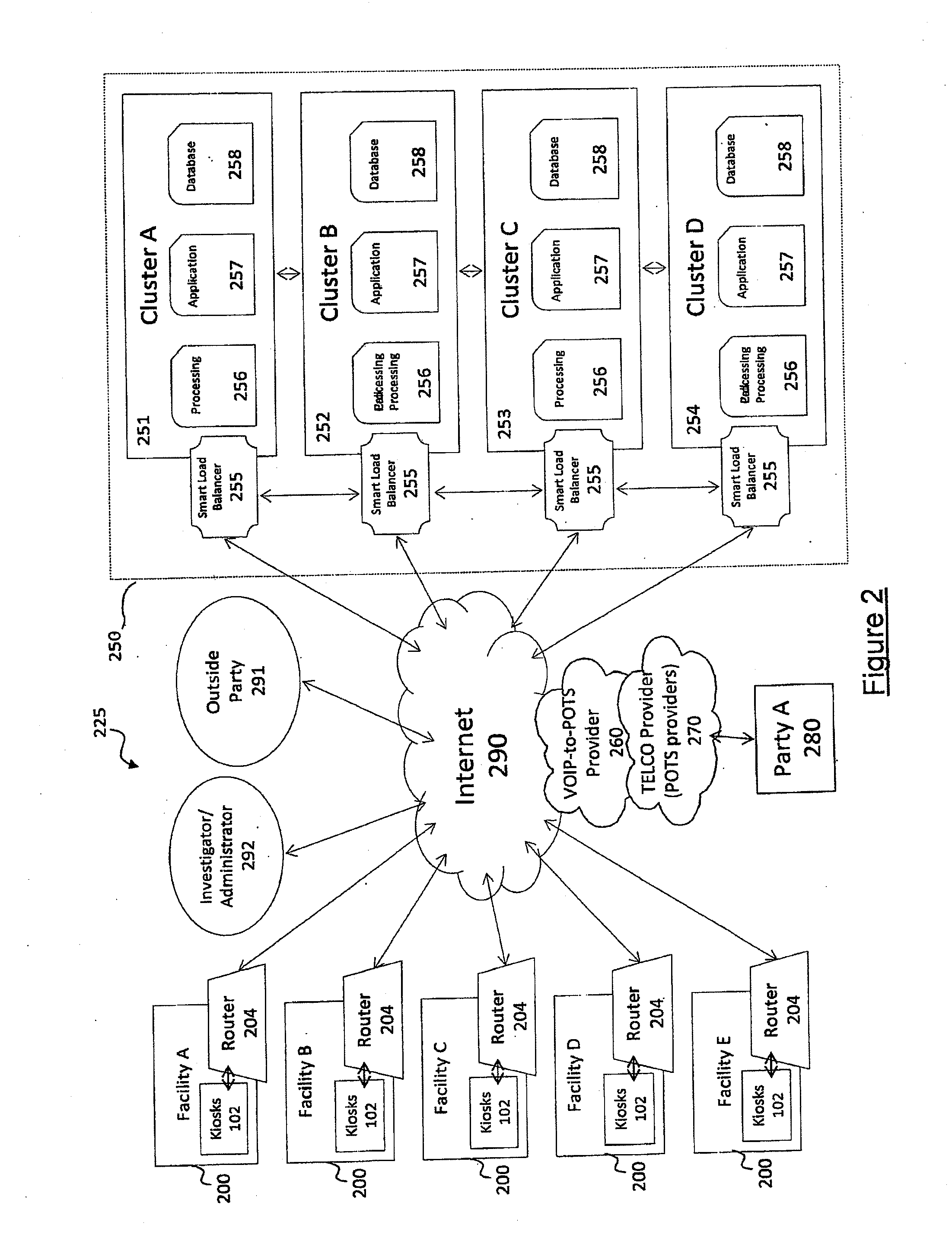
A system and device for providing services to a secure facility. The system includes a kiosk with a processor, display, speaker, microphone, and a camera, and the kiosk communicates with a server that includes a server processor, a network interface unit, and a computer memory. The kiosk receives communications and transmits audio and video of the communications to the server via an internet connection, and the server records the audio and video and transmits the audio and video to a destination. The kiosk is configured to authenticate the identity of a user by verifying a personal identification number entered by the user and also performing one or more of a facial recognition via the camera or a biometric voice recognition via the microphone. The kiosk provides access to services including internet services, text-based messaging, tele-medical services, religious and educational materials, commissary ordering, and entertainment.
Owner:GLOBAL TELLINK
Biometric multi-purpose terminal, payroll and work management system and related methods
InactiveUS20050109836A1Efficient use ofAssist in managementRegistering/indicating time of eventsFinancePersonal identification numberBank account
Employees gain access to a payroll and work management system by authentication at a multi-purpose terminal with a bankcard encoded with a unique account number and a personal identification number (PIN). The terminal may then be used to check-in and checkout of work, to receive new work instructions or assignments, to review payroll details, to print a payroll stub, to execute financial transactions, to print a receipt of financial transactions or to review or to upload the results of work quality audits. The invention also includes systems and methods that utilize such multi-purpose terminals to calculate the payroll and deductions for each employee and to issue electronic fund transfers from the employer's bank account to deposit the net pay in a bank account associated with each employee's bankcard so that the pay is immediately accessible by each employee, such as by withdrawal of cash at an ATM or by purchases at a point of sale. Electronic payrolls may be processed and employee's accounts credited with pay on a daily basis, or on any preset period of time, including hourly.
Owner:AMERICAN EPS
System and method for generating a strong multi factor personalized server key from a simple user password
ActiveUS20130124292A1Method securityEfficient consumptionPayment architectureDigital data authenticationPersonalizationPersonal identification number
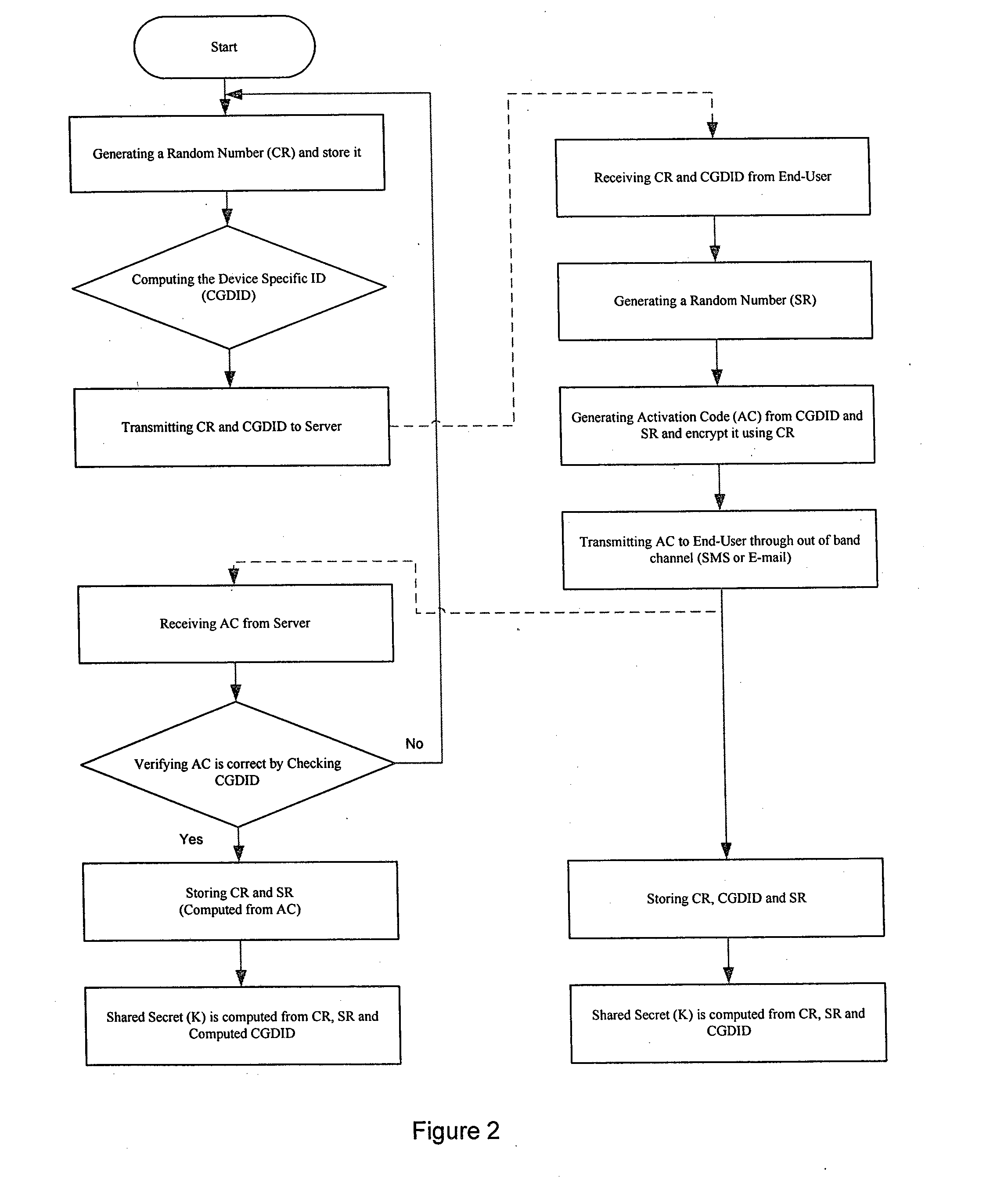
The present invention relates to a method of generating a multi-factor encryption key using a simple password in order to access control over information stored at a second entity from a first entity via at least one communication network. In one embodiment this is accomplished by, requesting to receive an application at the first entity from the second entity via the communication network, activating the first entity to generate a shared secret key, wherein the shared secret key is computed from a first entity specific ID and a random number generated at the first and second entity and allowing the user to register with the application of the second entity by the first entity, wherein the registration include entry of a personal PIN (personal identification number), a personal message etc.
Owner:JUTHANI NIRMAL
Telecommunication call management and monitoring system with voiceprint verification
InactiveUS20050043014A1Accurate verificationEliminating system overloadTelevision system detailsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionPersonal identification numberMonitoring system
Disclosed is a secure telephone call management system for authenticating users of a telephone system in an institutional facility. Authentication of the users is accomplished by using a personal identification number, preferably in conjunction with speaker independent voice recognition and speaker dependent voice identification. When a user first enters the system, the user speaks his or her name which is used as a sample voice print. During each subsequent use of the system, the user is required to speak his or her name. Voice identification software is used to verify that the provided speech matches the sample voice print. The secure system includes accounting software to limit access based on funds in a user's account or other related limitations. Management software implements widespread or local changes to the system and can modify or set any number of user account parameters.
Owner:GLOBAL TELLINK
Usage monitoring HVAC control system
InactiveUS6741915B2Cost effectiveOverhead energy costProgramme controlSampled-variable control systemsPersonal identification numberOn board
Systems and methods are described for a usage monitoring HVAC control system. A method, includes: providing a usage monitoring heating ventilation and air conditioning control system, the usage monitoring heating ventilation and air conditioning control system including a programmable digital thermostat with an on board memory, issuing personal identification numbers to each of a plurality of system users; associating each of the plurality of system users with at least one of a plurality of user types; storing the personal identification numbers in a first data structure in the on board memory; and linking each one of a plurality of entries in the first data structure by reference to at least one of a plurality of entries in a second data structure in the on board memory, the second data structure including a list of user types. A method, includes regulating user access to an interactive user interface of a programmable thermostat, each user identified by a personal identification number associated with a user type such as, for example, building owners, maintenance personnel, building tenants, and manufacturers.
Owner:MMI CONTROLS
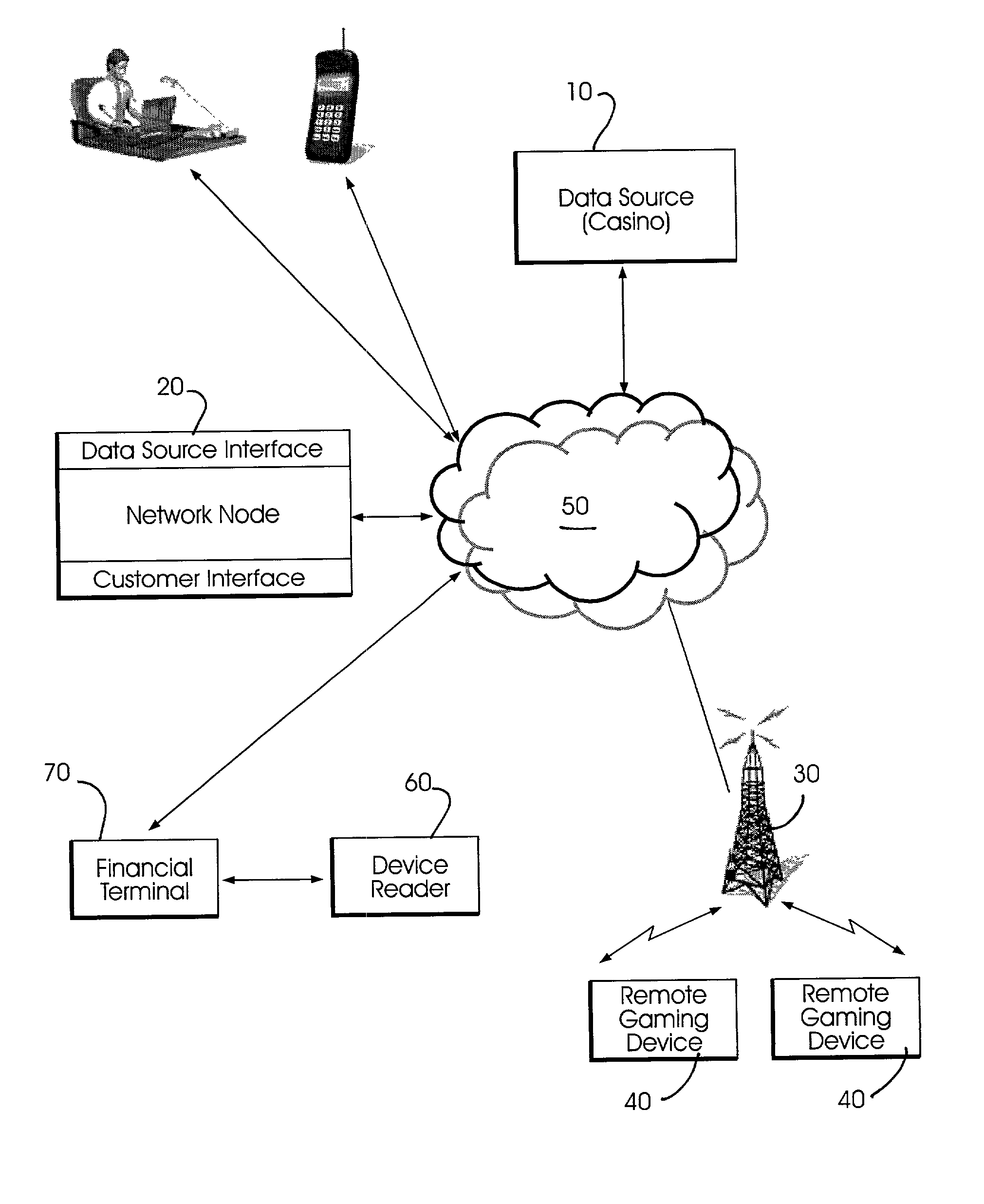
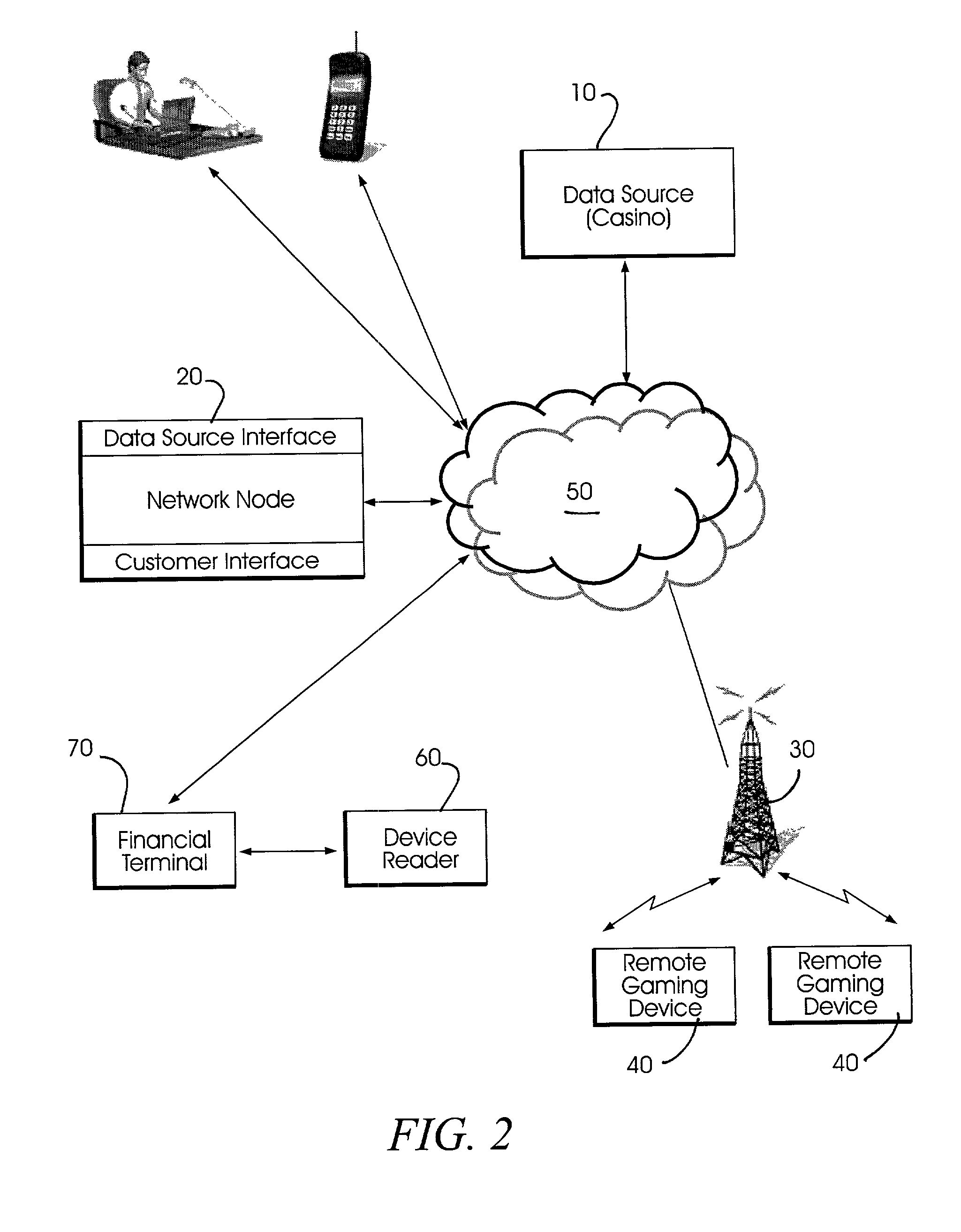
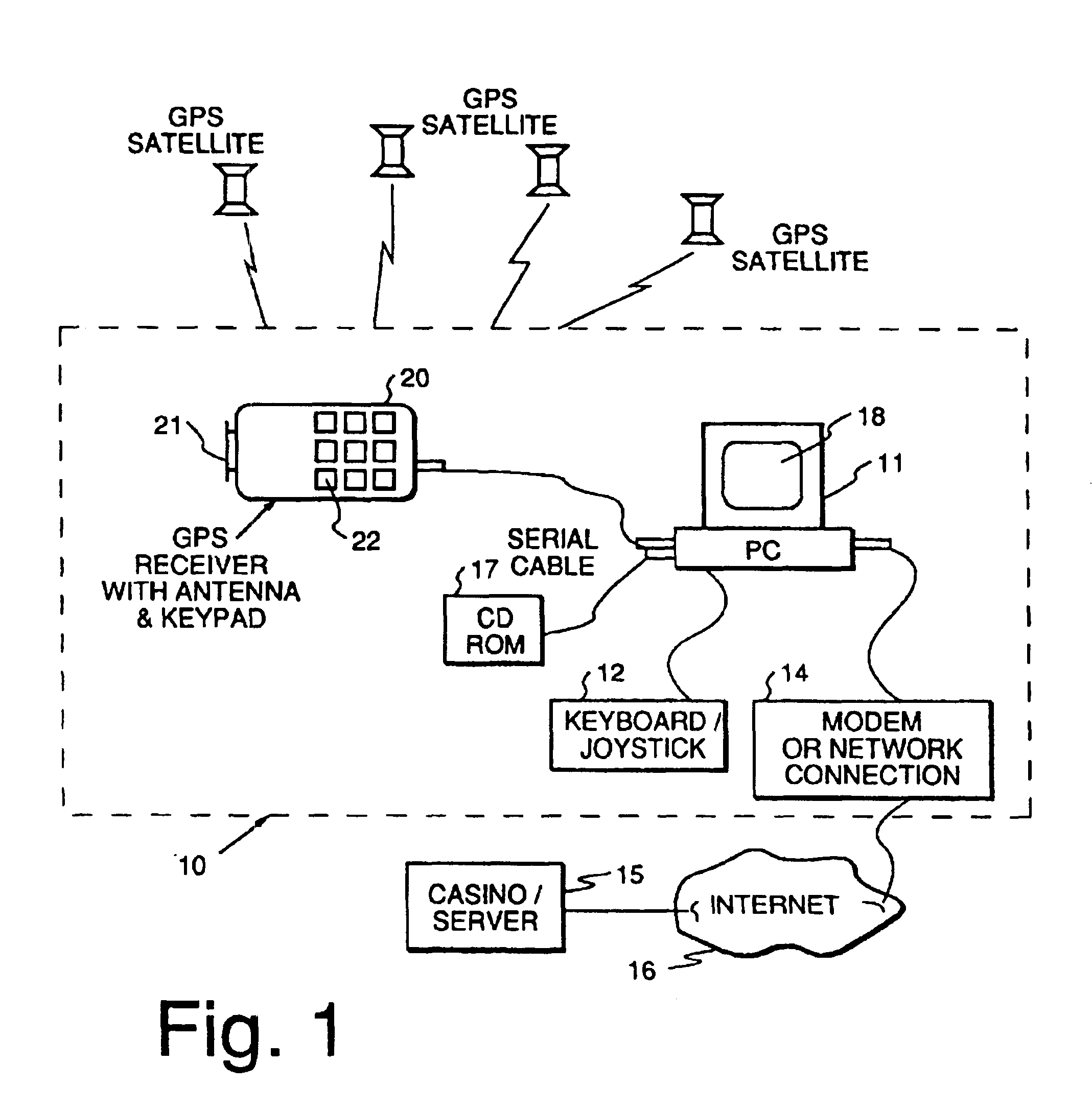
Method and apparatus using geographical position to provide authenticated, secure, radio frequency communication between a gaming host and a remote gaming device
InactiveUS7460863B2Broadcast information characterisationResource management arrangementsTriangulationGeolocation
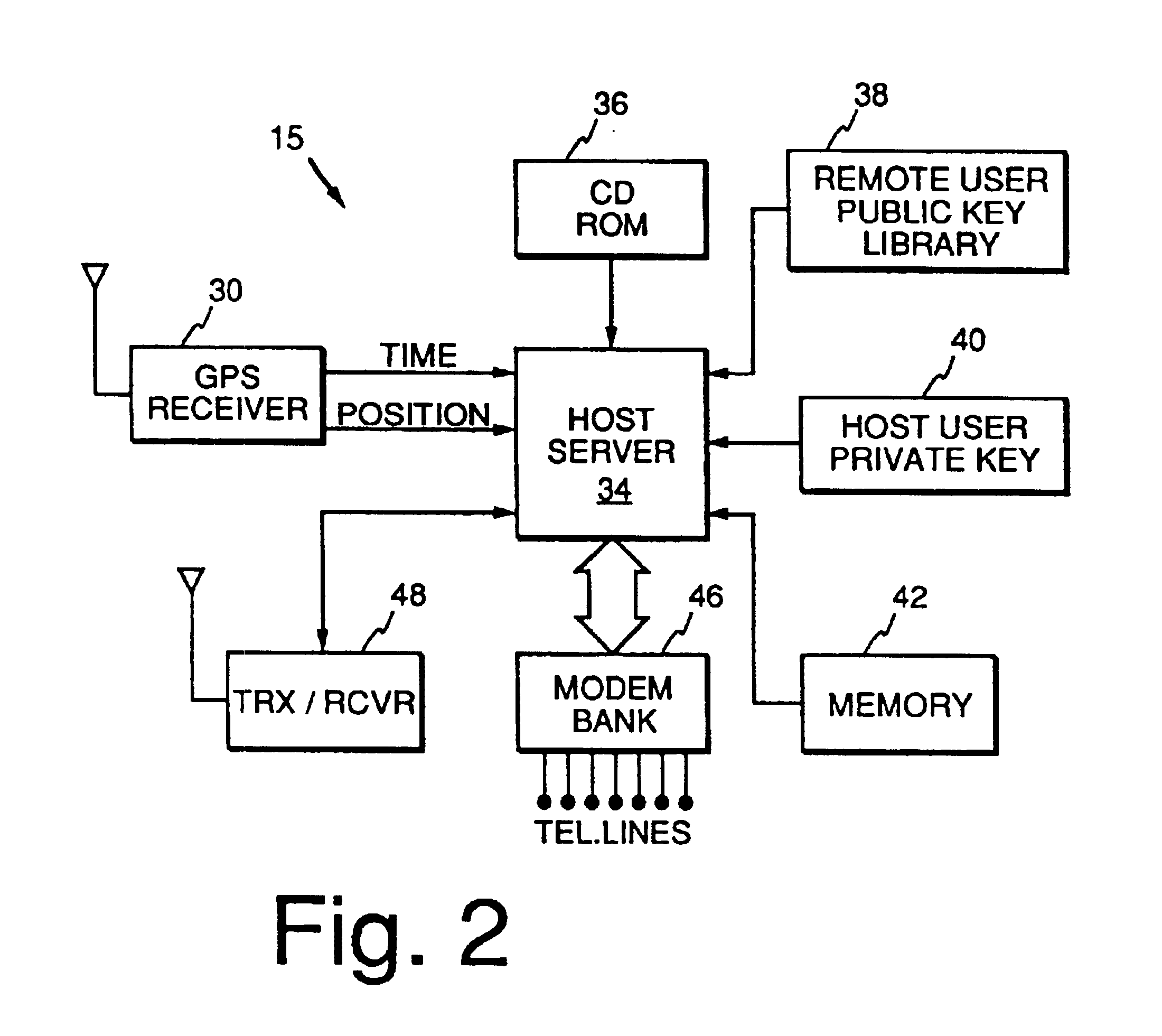
Method and apparatus for providing authenticated, secure, communication between a gaming host communicating via radio frequency (RF) subcarriers to a remote user device in another location. Location of the remote user device and the host server are determined by accessing signals generated by either Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites, or by terrestrial radio broadcast stations, through a process known as radio frequency triangulation telemetry tracking (RF-3T). Player authentication (identity verification) is determined by use of a personal identification number (PIN). A remote user device may be implemented as a stand alone or self-contained single unit that is portable and can receive communications via radio frequency, or may be implemented as one or more discreet components adapted to be used with a laptop, a personal digital assistant (PDA), or desktop personal computer (PC).
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
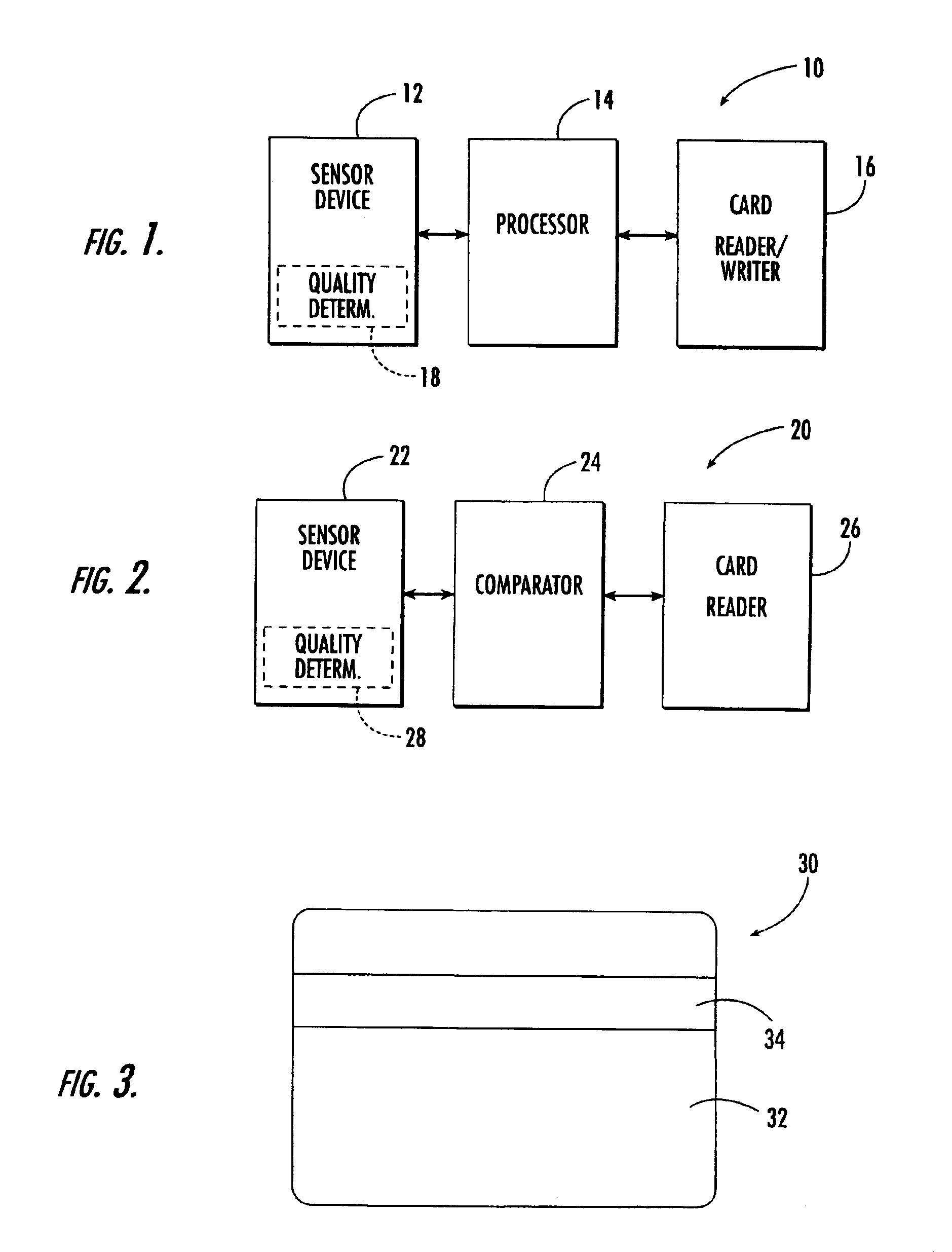
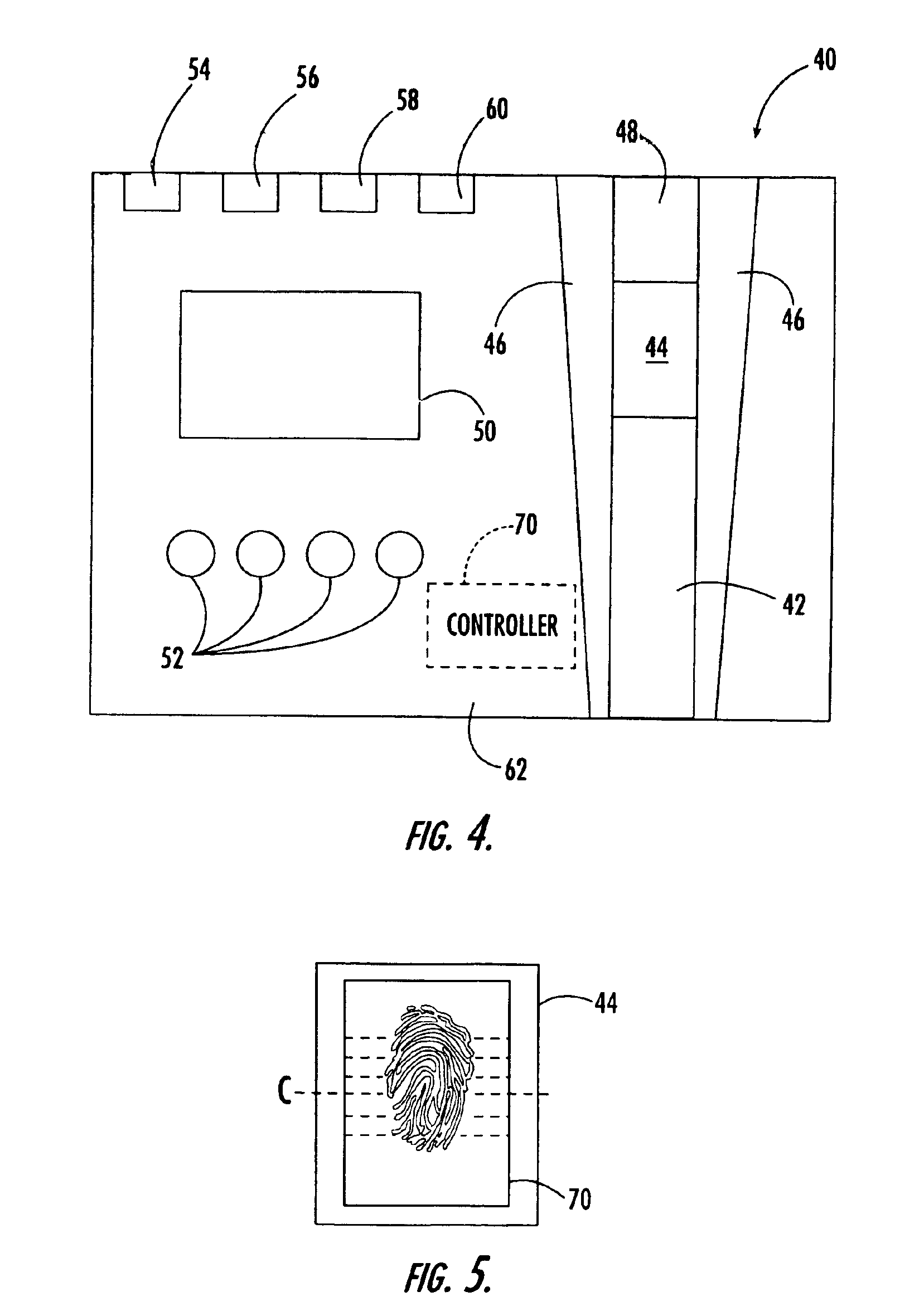
Biometric identification system using biometric images and personal identification number stored on a magnetic stripe and associated methods
InactiveUS6959874B2Digital data authenticationBiometric pattern recognitionPersonal identification numberBiometric data
The system and method store biometric information and a personal identification number (PIN) on a token having a magnetic storage medium. A biometric image is captured, biometric data is produced and a PIN is provided by an authorized user. The biometric data and PIN are stored on the magnetic storage medium of the token for subsequent use in verifying an authorized user of the token.
Owner:III HLDG 1
Method and apparatus using geographical position and universal time determination means to provide authenticated, secure, on-line communication between remote gaming locations
InactiveUSRE39644E1Facilitates denialAccurately determineSecret communicationApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingGeolocationThe Internet
Method and apparatus for providing authenticated, secure, on-line communication between remote locations including a user terminal adapted to enable a player in one location to remotely communicate via a communications medium such as the Internet with a gaming host in another location. Location of the remote user terminal, the host server and universal time are determined using means for accessing signals generated by geostationary navigational transmitters, such as in the global positioning satellite (GPS) system. Player authentication (identity verification) is determined by use of a personal identification number (PIN) and an electronic signature verification service. Security of communication is accomplished through use of a public-key / private-key encryption system. The remote user terminal may be comprised of one or more discreet components adapted to be used with a laptop or desktop personal computer (PC), or may be embodied in a stand alone or self-contained single unit that is portable and communicates via radio waves, telephone lines or the Internet to a host server.
Owner:IGT
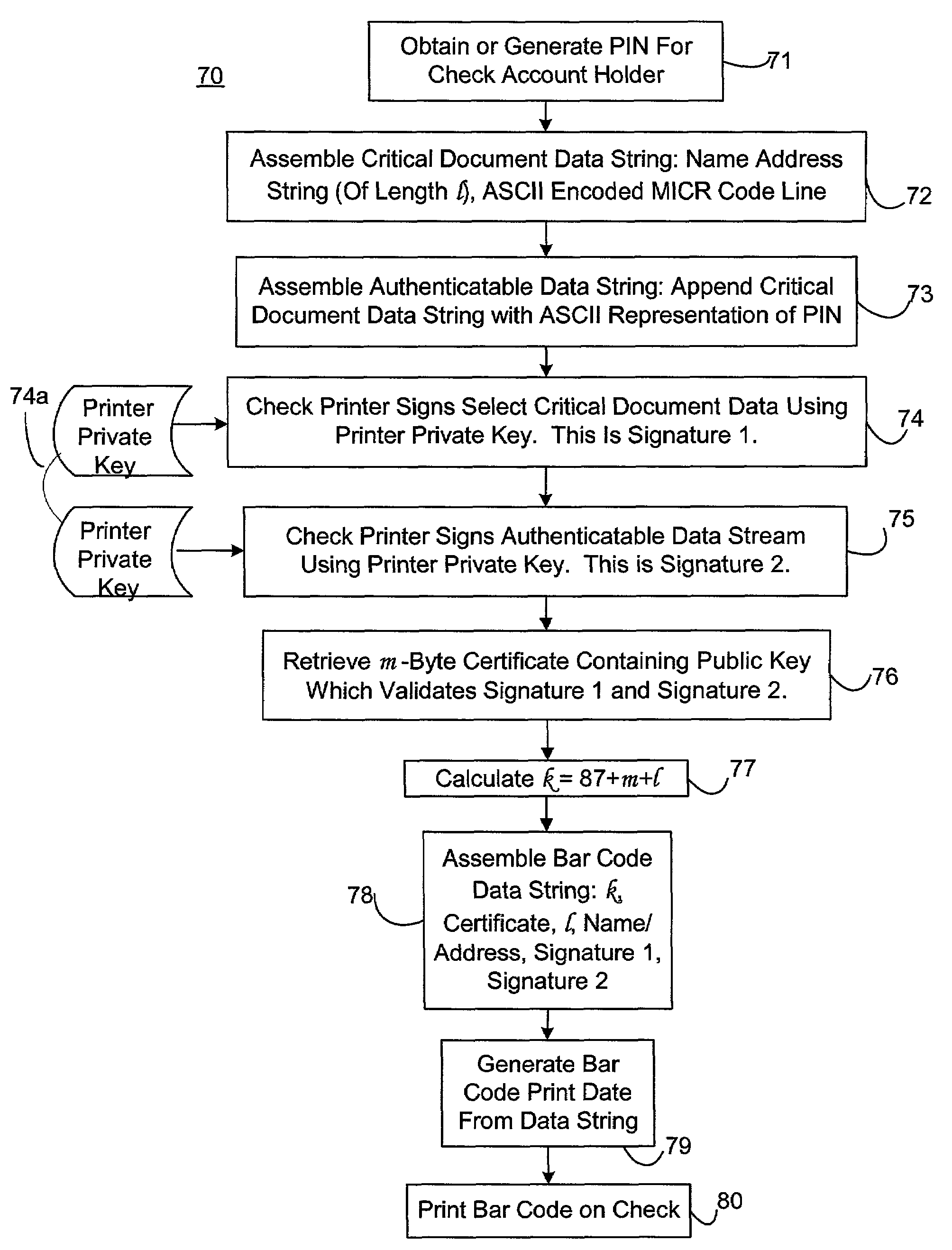
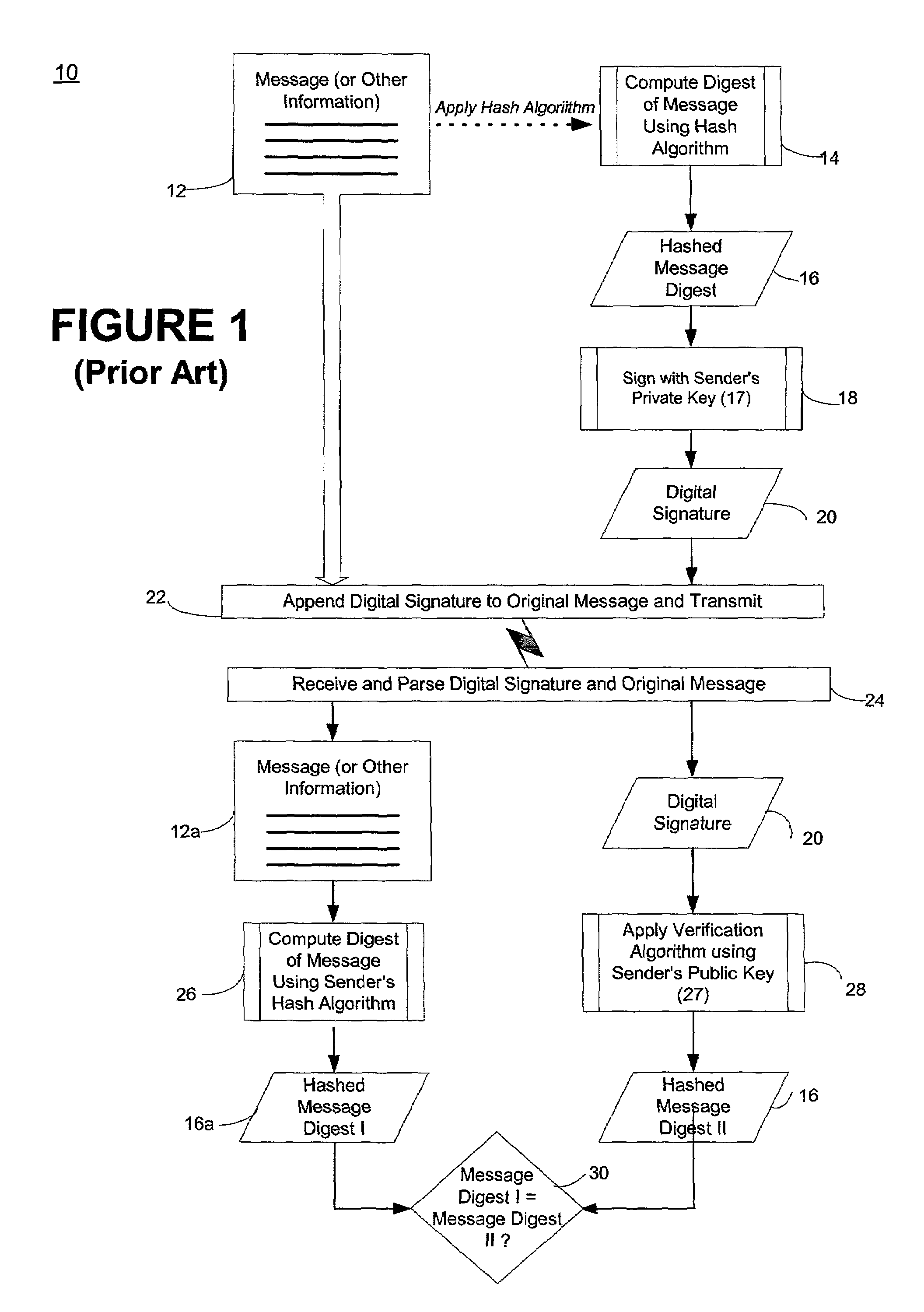
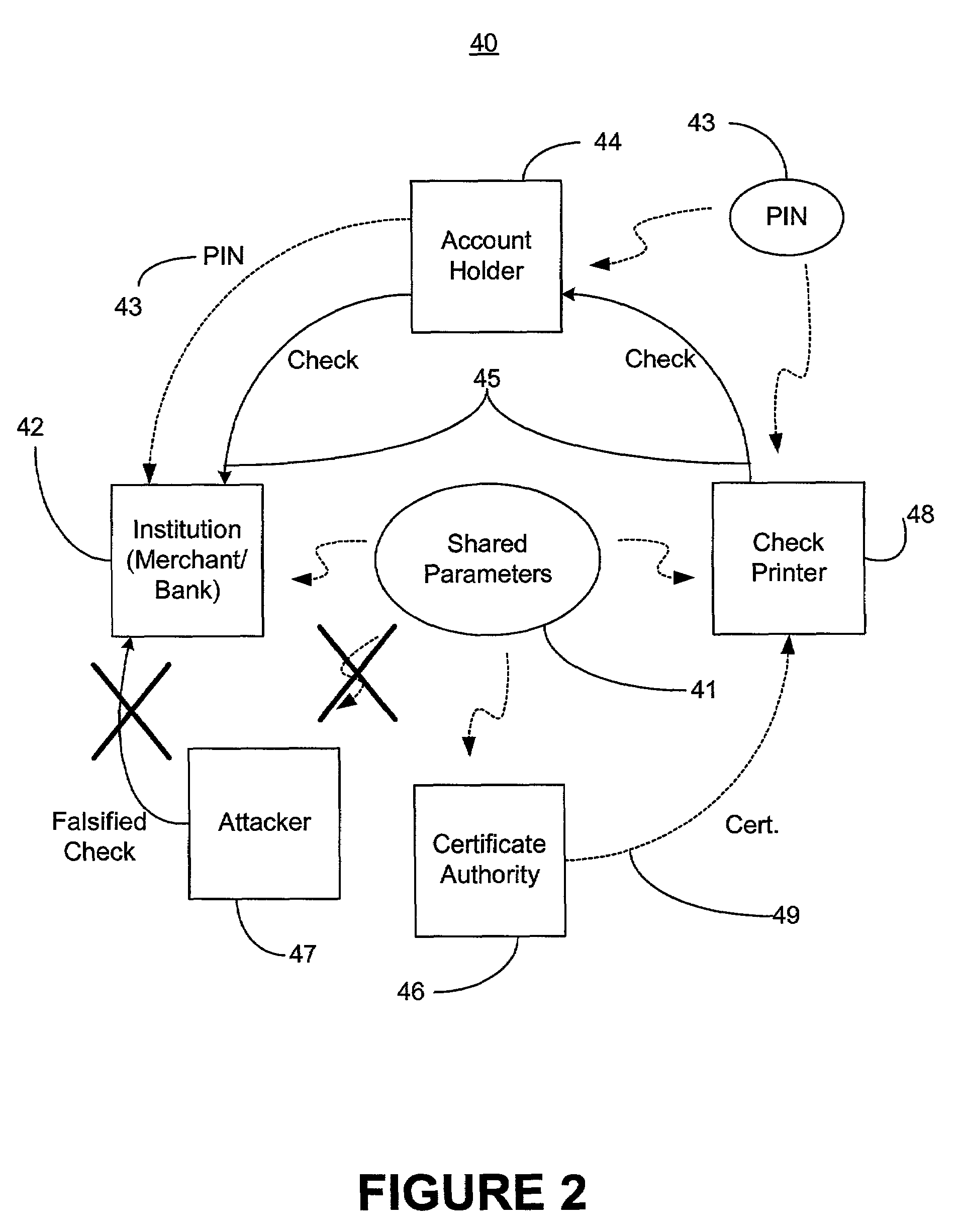
Methods for authenticating self-authenticating documents
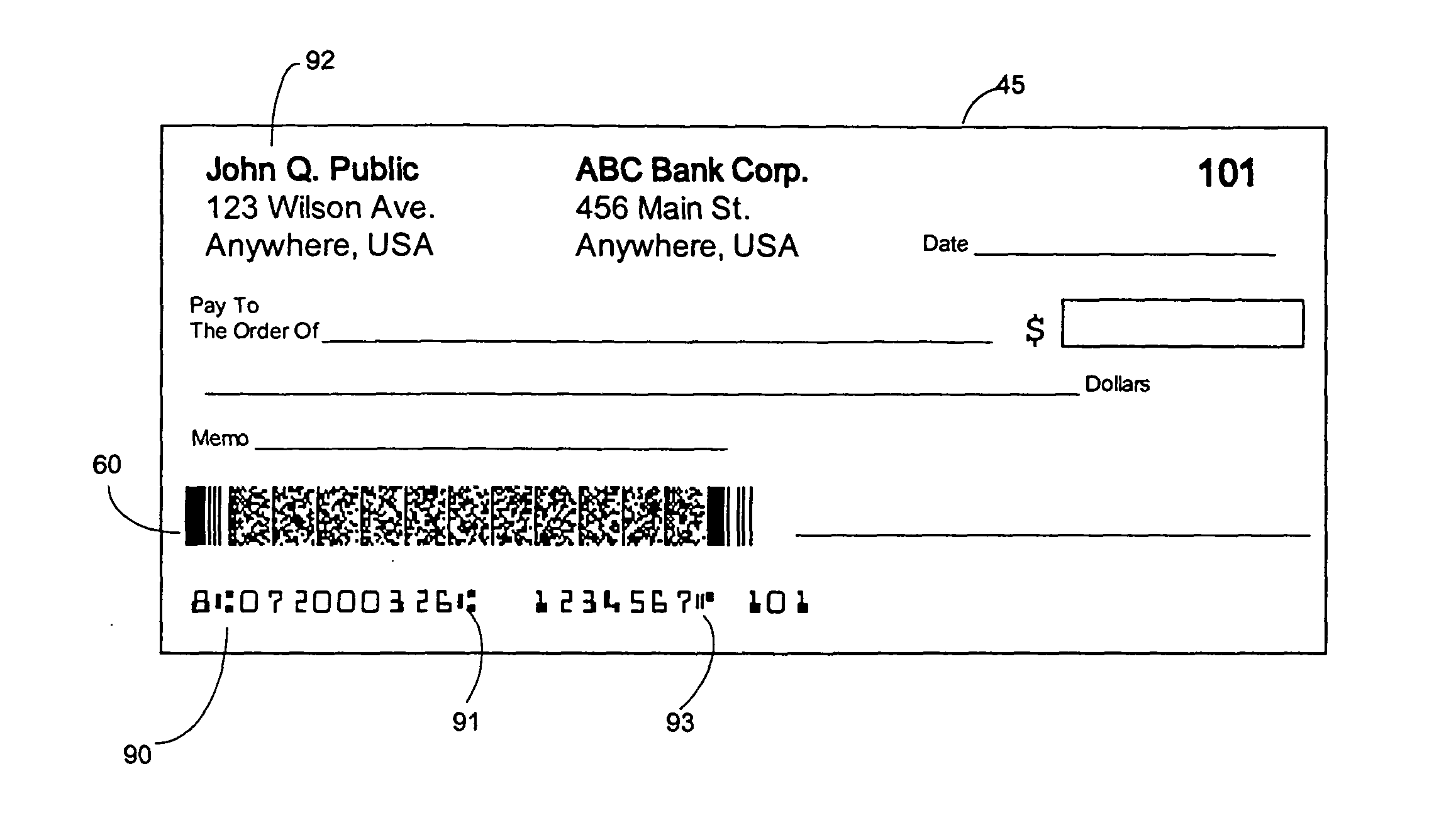
InactiveUS20050038754A1Low costImprove reliabilityUser identity/authority verificationPayment architecturePersonal identification numberDigital signature
Methods of authenticating self-authenticating documents presented at a point of purchase or financial institution. Data contained on the value document may be signed with a first digital signature and authenticated with a public key certificate. A unique personal identification number (PIN) may be included in the document data that is signed by a second digital signature. The signed data and a public key certificate are stored on the value document. At a point of purchase, a merchant or teller can scan and read the stored data and together with the PIN the customer provides, can authenticate the value document thus presented using the second digital signature. Alternatively, if the customer is not present, the document may be verified using a PIN-generating algorithm. The first digital signature alone may be used to authenticate the document even when the PIN is not available.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
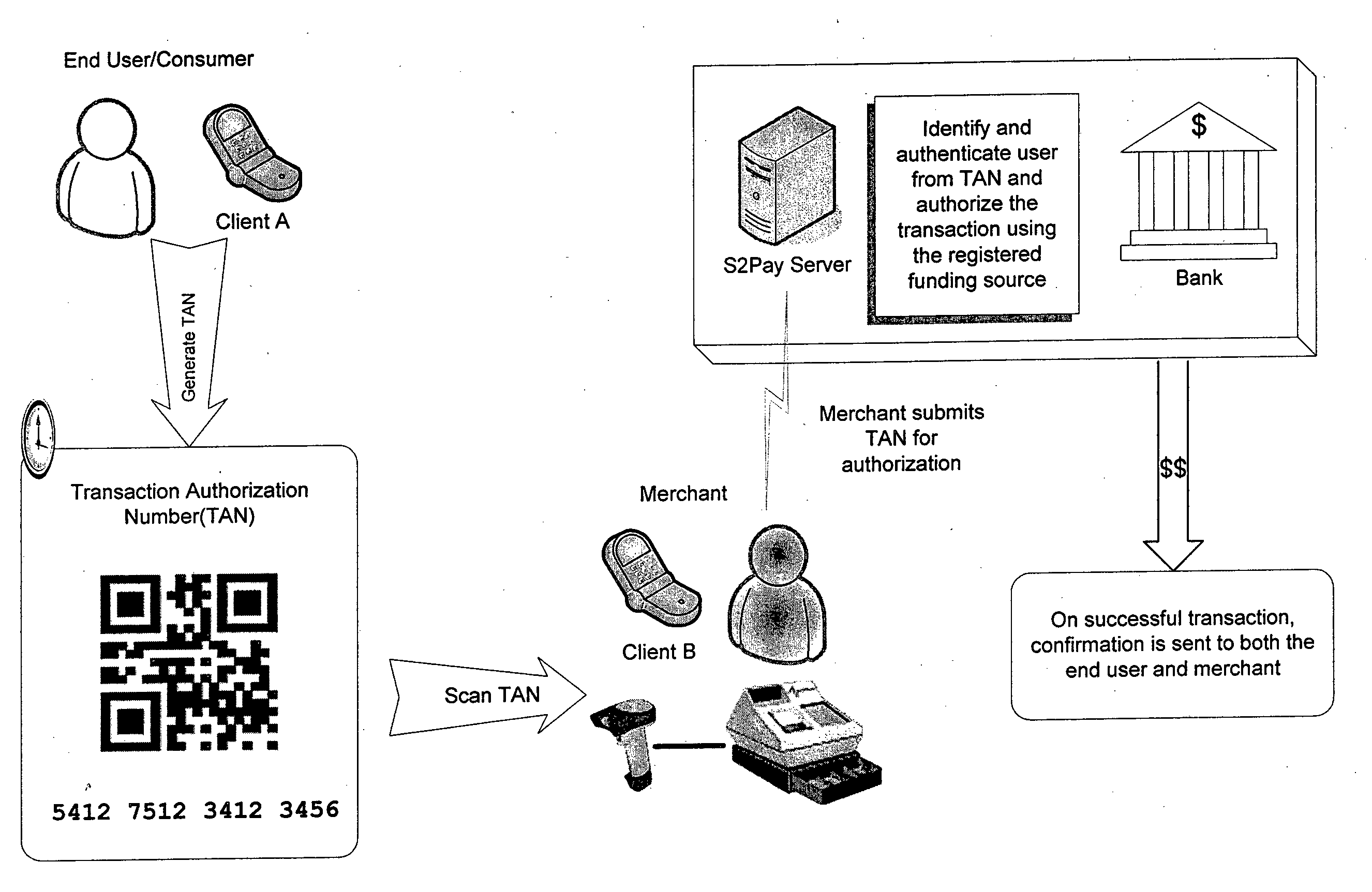
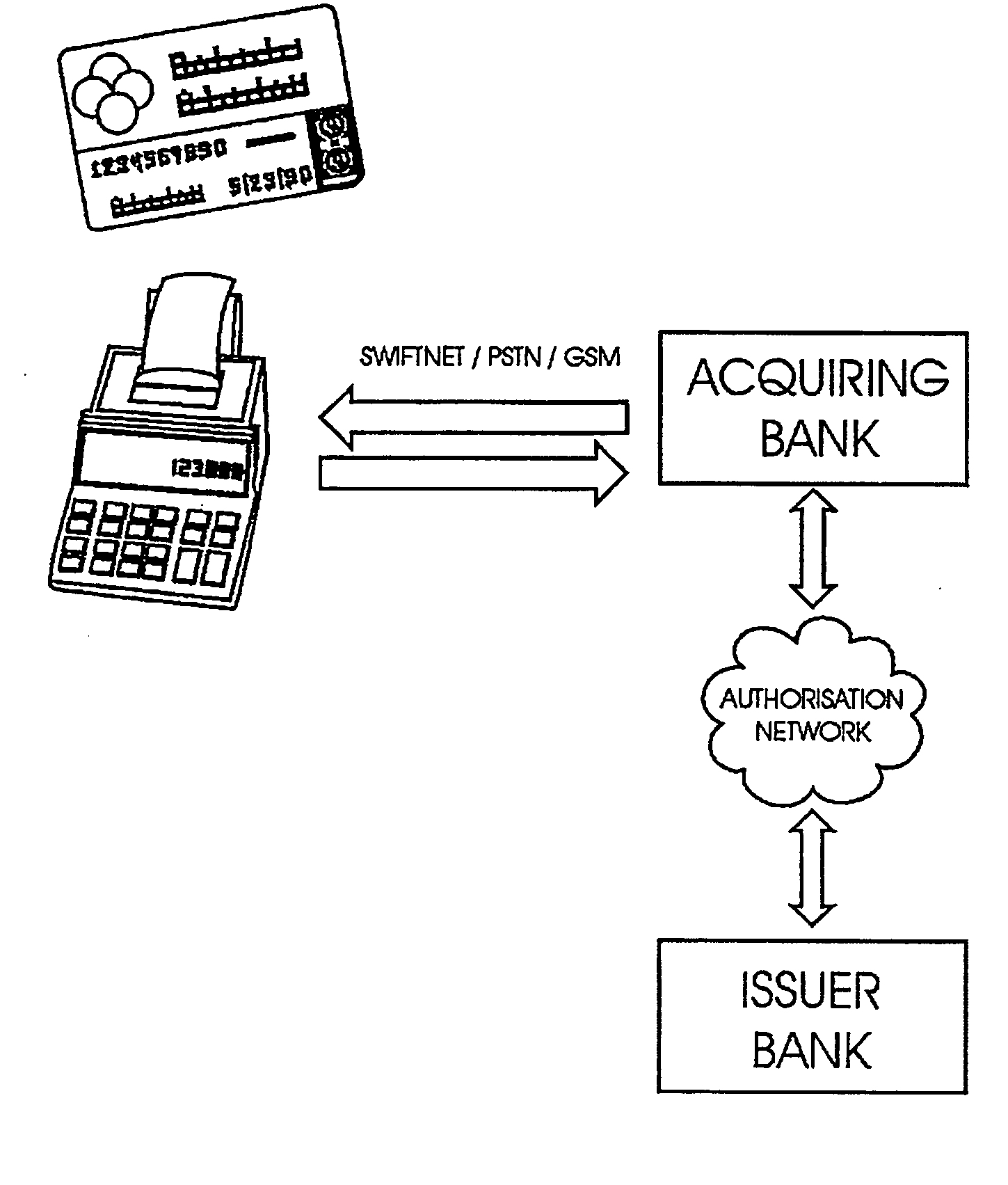
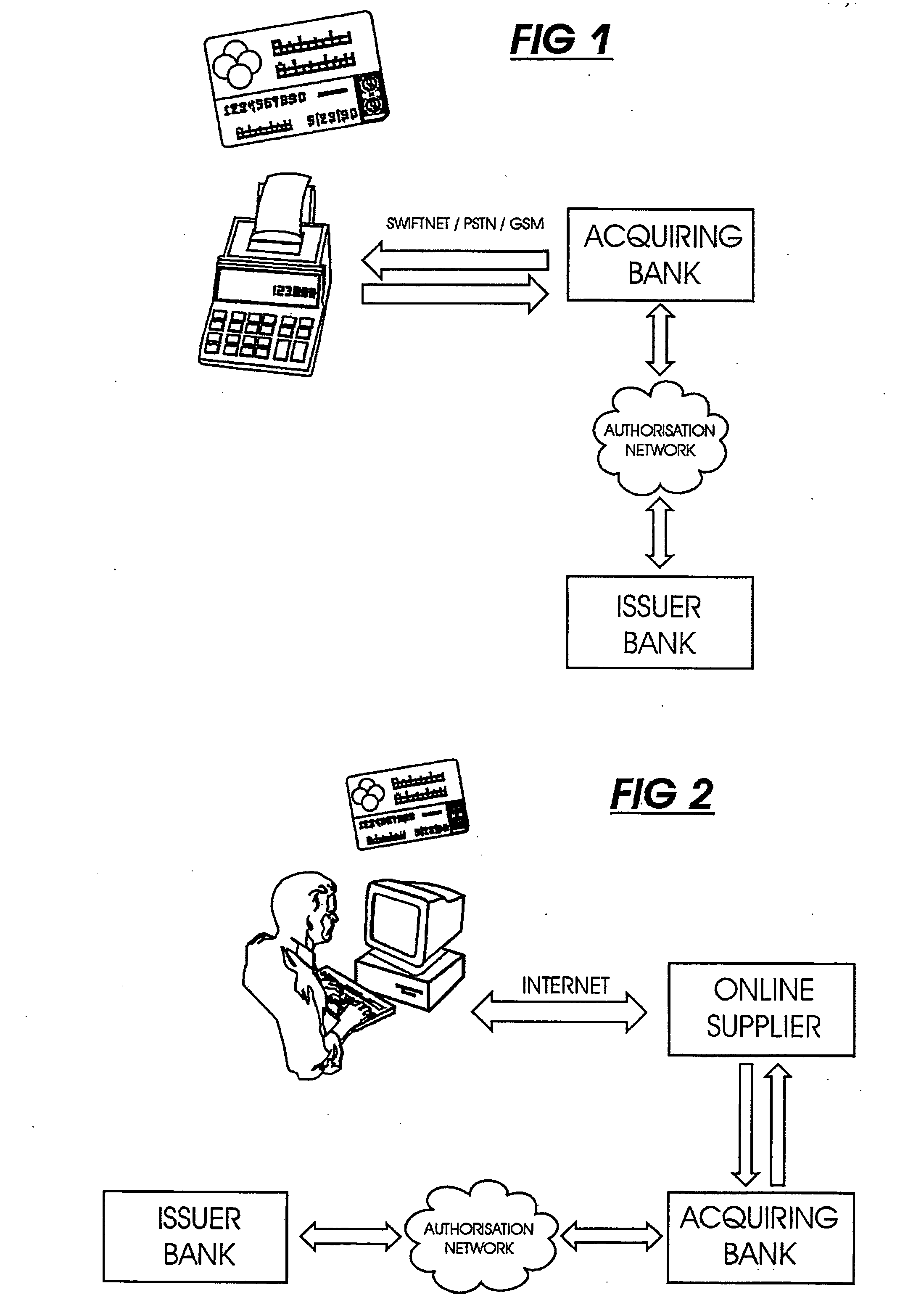
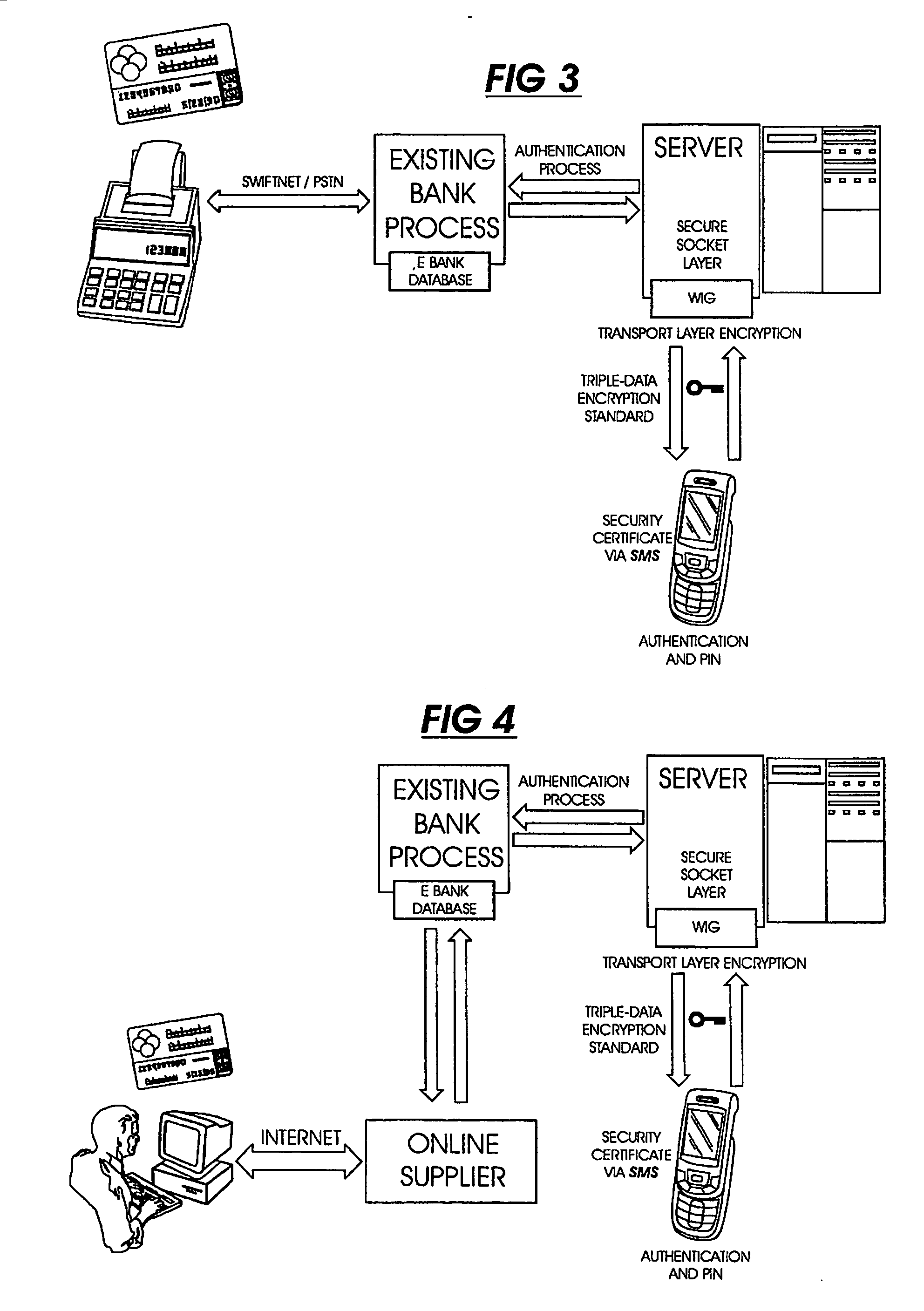
Transaction verification system
This invention uses separate, parallel communication channels to authorise and authenticate a transaction. A primary data channel (PSTN, radio or the like) is used to communicate between the merchant terminal and the bank, and a parallel data channel (a mobile phone network for instance) is used for the authentication process. In the example, the transaction is initiated (on a primary data channel), using a POS terminal as a transaction processing client. The transaction processing server and financial services provider fulfill their normal functions. At this point, the process loops into a transaction authorisation component using the parallel data channel, that requires authentication of the transaction initiator (the card holder). In the example, communications on the parallel data channel are by way of SMS. In the authorisation process, the card holder receives an SMS requesting authorisation of the transaction. If the card holder is not the transaction initiator, the card holder can cancel the transaction. If the transaction can be authorised, an authentication process is initiated in which the mobile phone is programmed to require the entry of a normally secret code (such as a personal identification number (PIN)) that serves to authenticate the card holder and to give final authorisation of the transaction.
Owner:NARAINSAMY SELVANATHAN
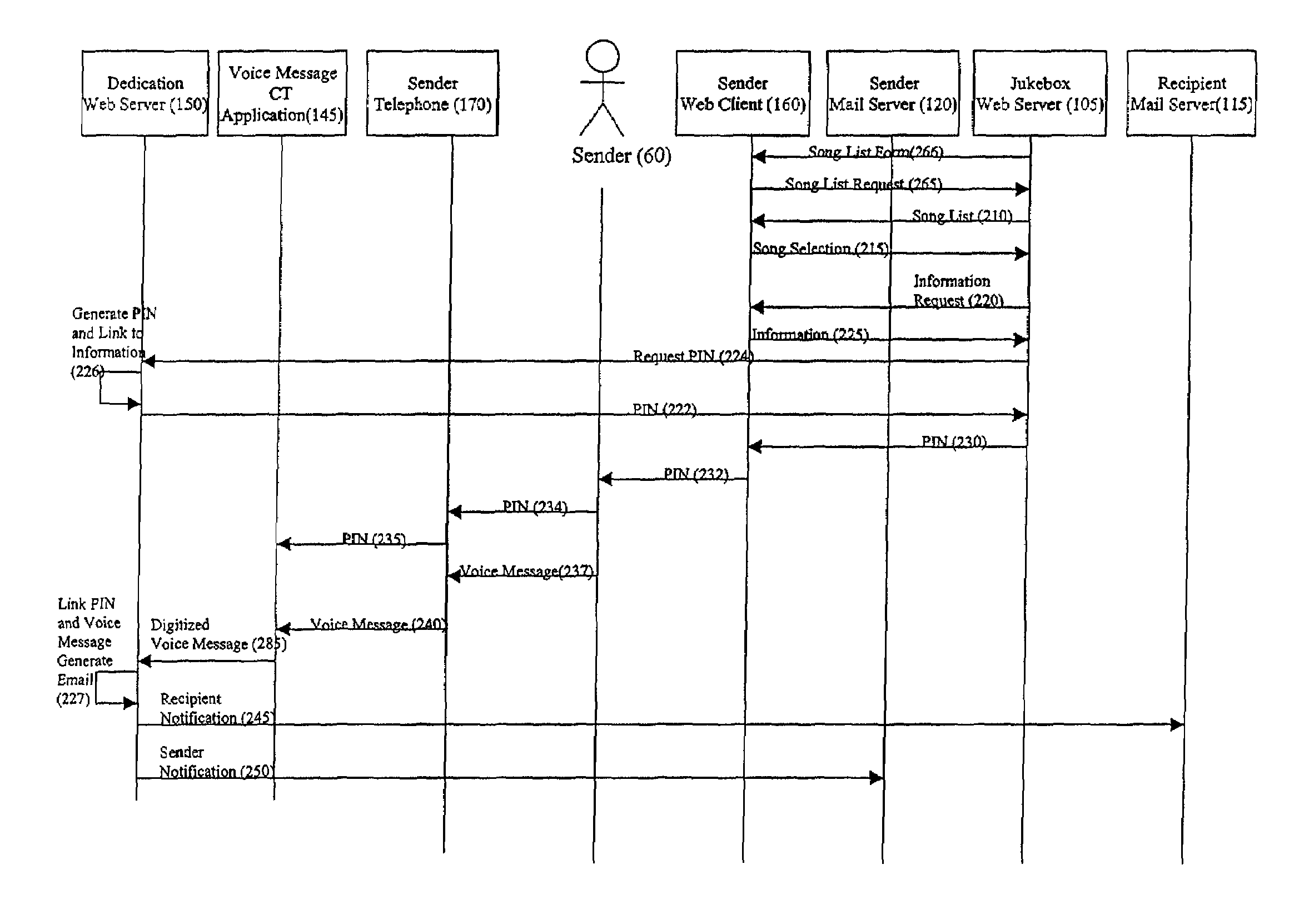
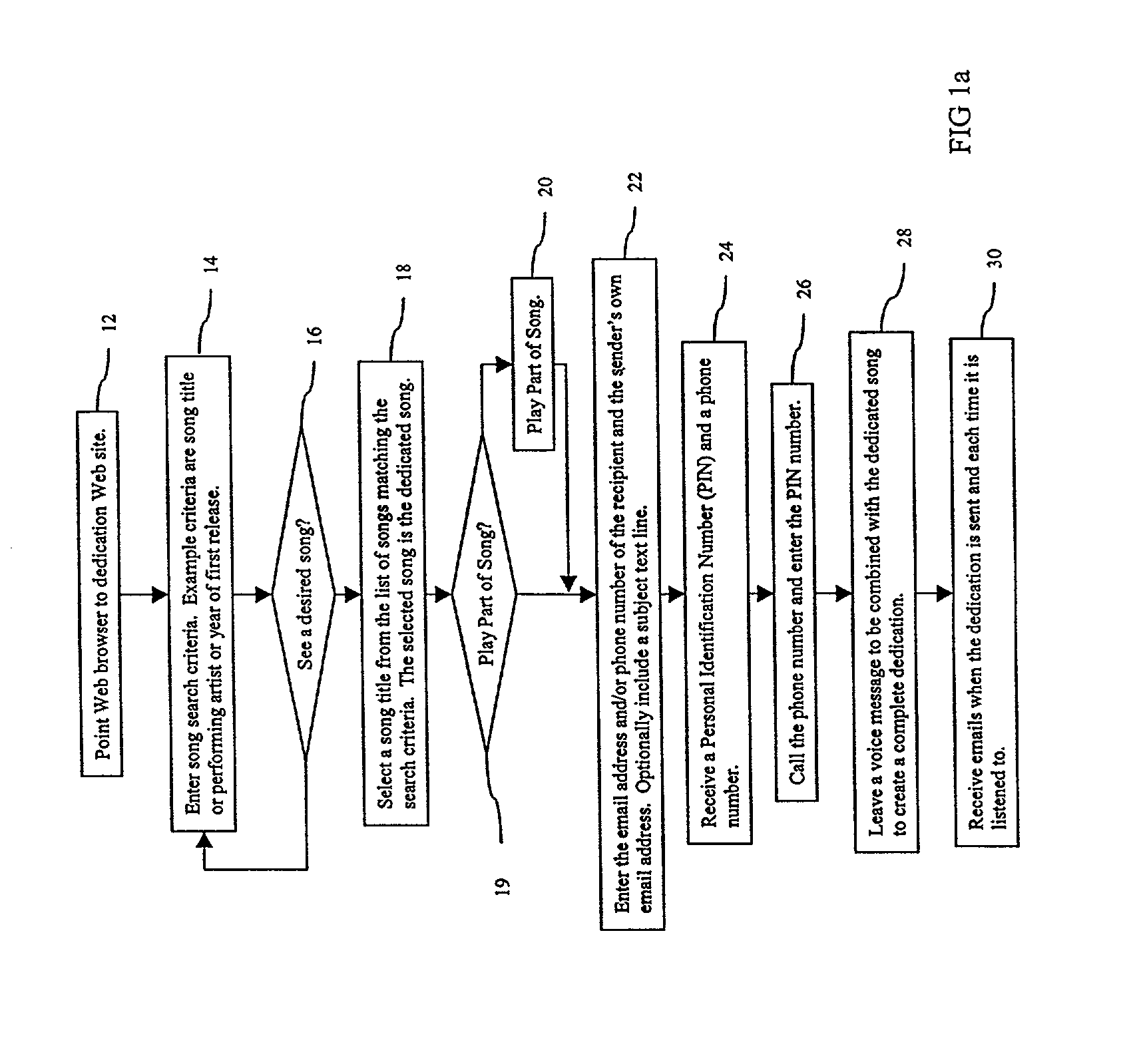
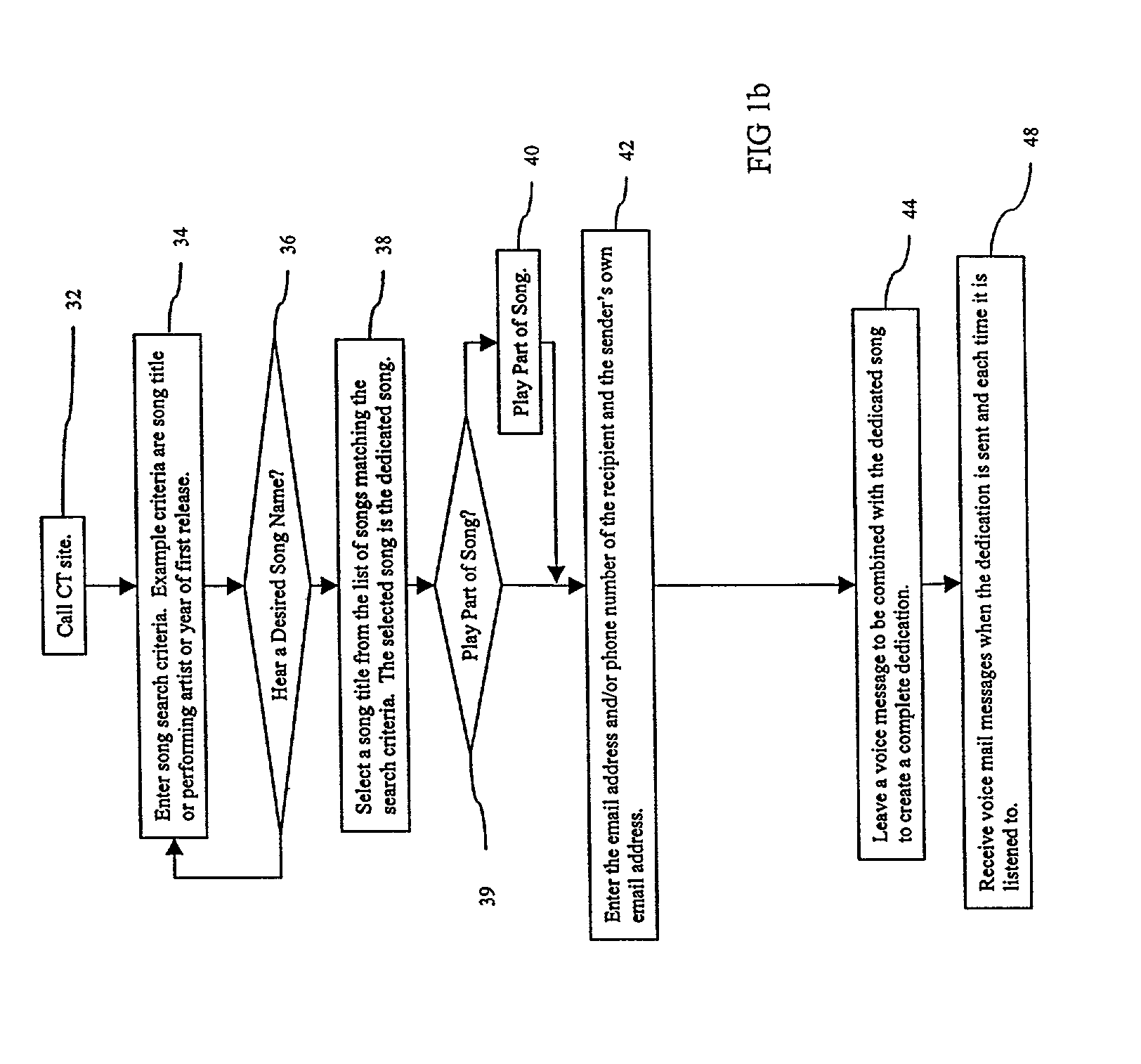
Method and system for electronic song dedication
InactiveUS7082469B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb siteEmail address
A system and method to send dedications of popular songs through a communications medium such as the Internet. A sender contacts a musical jukebox Web site and selects a song to dedicate and enters a recipient's electronic mail (email) address. The sender is given a phone number and Personal Identification Number (PIN). The sender calls the phone number, enters the PIN, and leaves a voice message to introduce the dedication. An email is sent to the recipient's email address containing a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) as a link to a dedication Web page. Retrieval of the dedication Web page causes retrieval of a dedication file containing URLs pointing to the voice dedication and the dedicated song. The URLs are extracted from the dedication file and used to play back the voice dedication and the dedicated song.
Owner:GOLD MUSTACHE PUBLISHING
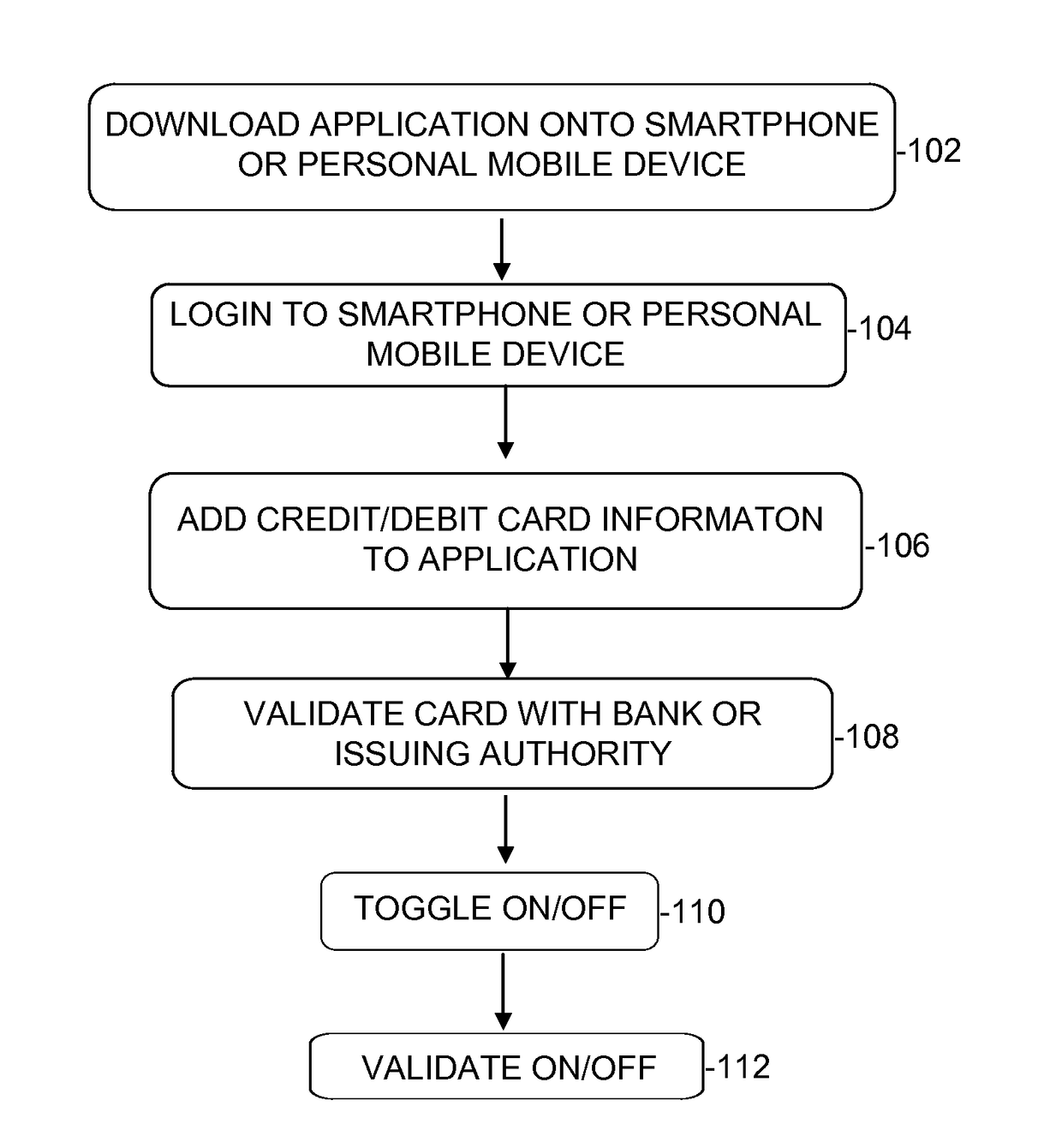
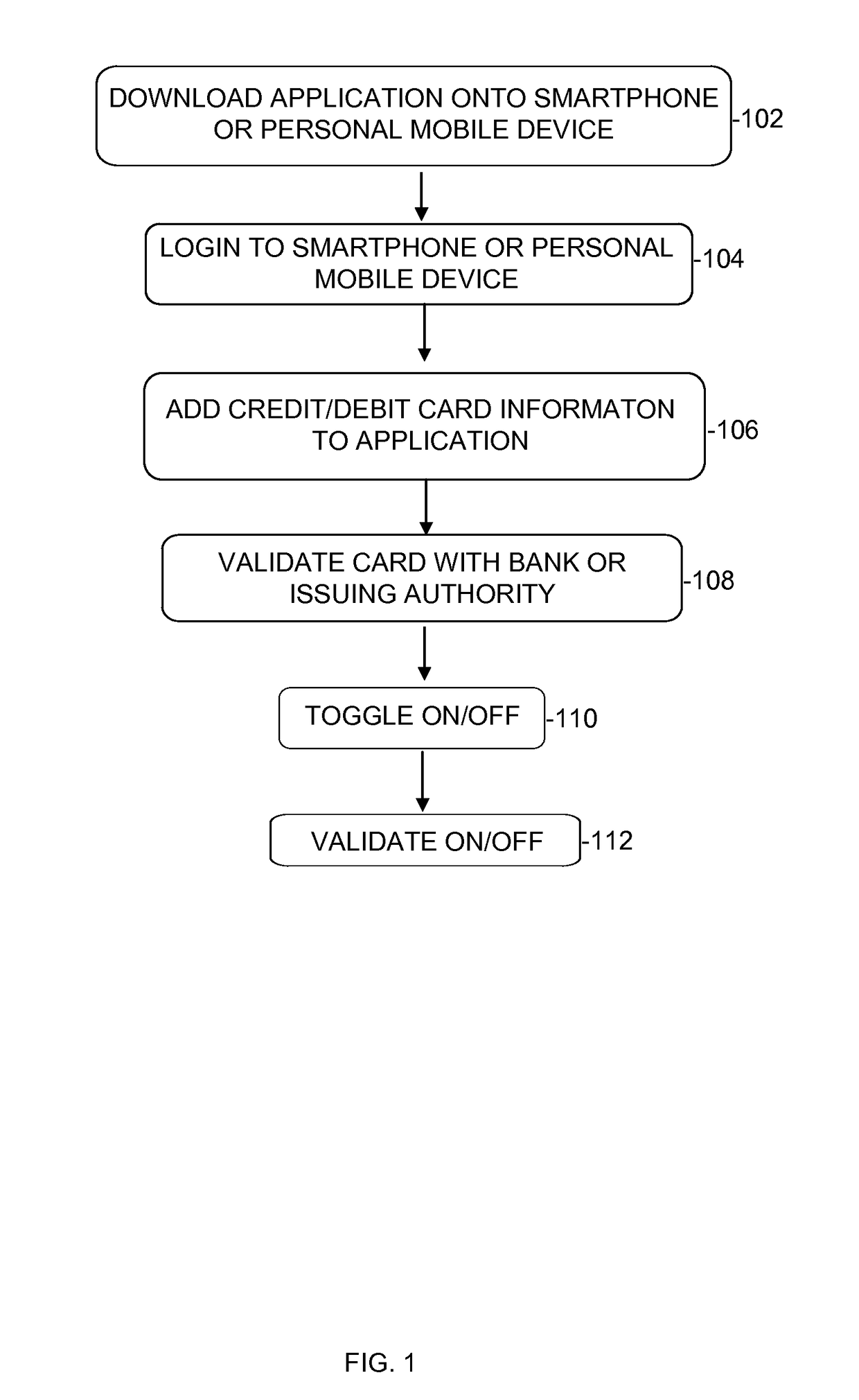
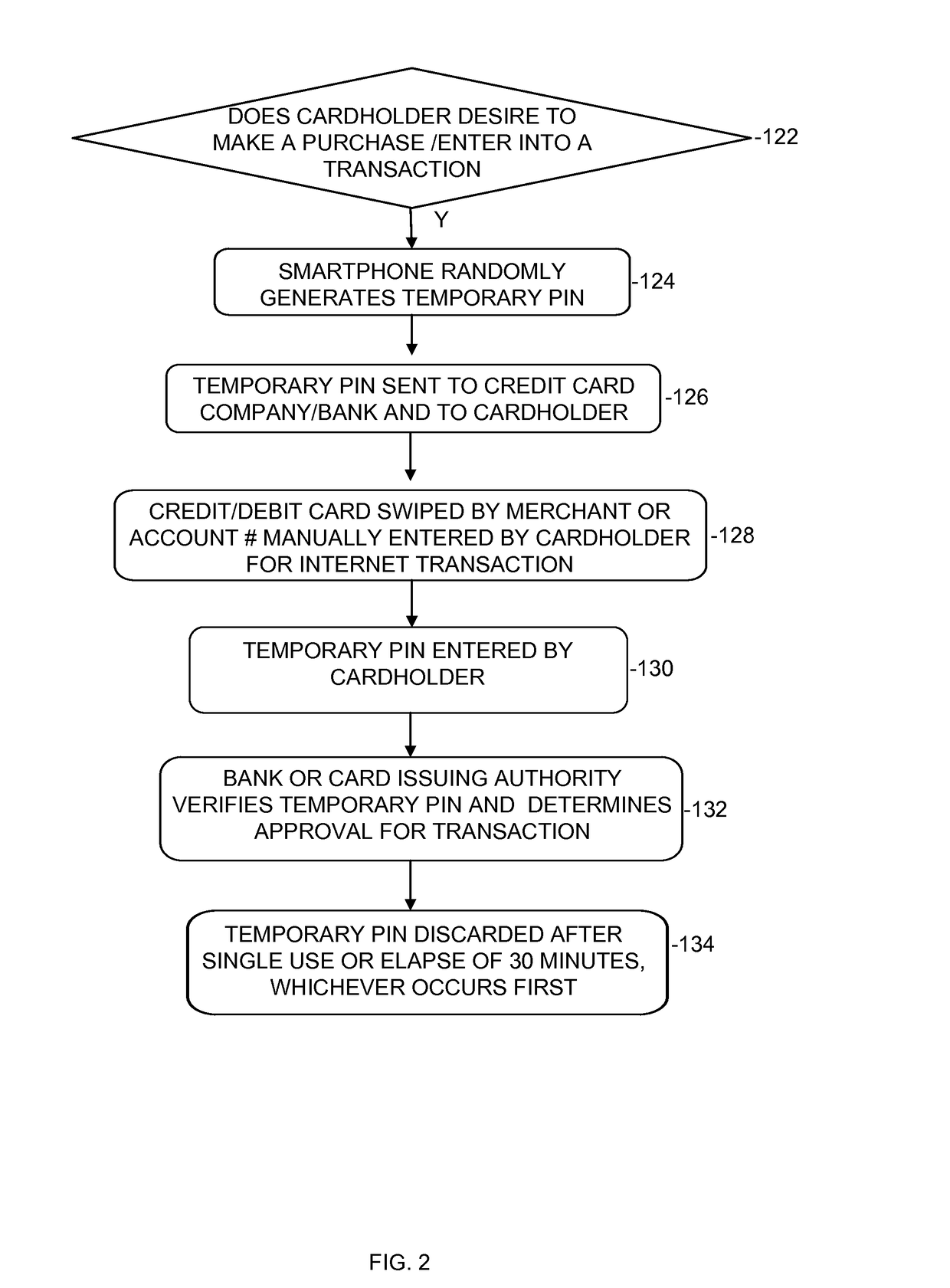
Credit card randomly generated pin
InactiveUS20170140379A1Acutation objectsProtocol authorisationComputer hardwarePersonal identification number
The present invention relates to systems and methods of randomly generating a Personal Identification Number (“PIN”) for a credit or debit card. A smart phone or other mobile device generates the PIN. The PIN number is required to be generated before a credit or debit card transaction is approved by the issuing authority.
Owner:DECK BRUCE D
Self-authentication of value documents using digital signatures
ActiveUS7051206B1Low costImprove reliabilityKey distribution for secure communicationPaper-money testing devicesCredit cardPublic key certificate
An encryption-free technique for enabling the self-authentication of value documents (including personal and commercial checks) presented at a point of purchase or financial institution. Certain data contained on the value document may be signed with a first digital signature and authenticated with a public key certificate issued from a trusted certificate authority. The signed data and public key certificate are stored on the value document, preferably in a two-dimensional bar code data format. In the case of certain personal value documents (such as checks, credit cards, passports, birth certificates, Social Security cards, etc.), a unique personal identification number (PIN) also may be included in the document data that is signed by a second digital signature. At a point of purchase, a merchant or teller can scan and read the data stored in the two-dimensional bar code and other magnetically recorded information, and together with the PIN the customer provides, can authenticate the value document thus presented using the second digital signature. Alternatively, if the customer is not present, if the personal value document contains the second digital signature, the document may be verified using a PIN-generating algorithm or other method that generates all permutations of PINs. The first digital signature alone may be used to authenticate selected data within the personal value document even when the PIN is not available. Similarly, in the case of a commercial value documents, authentication of pre-printed data may be based entirely upon only the first digital signature.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
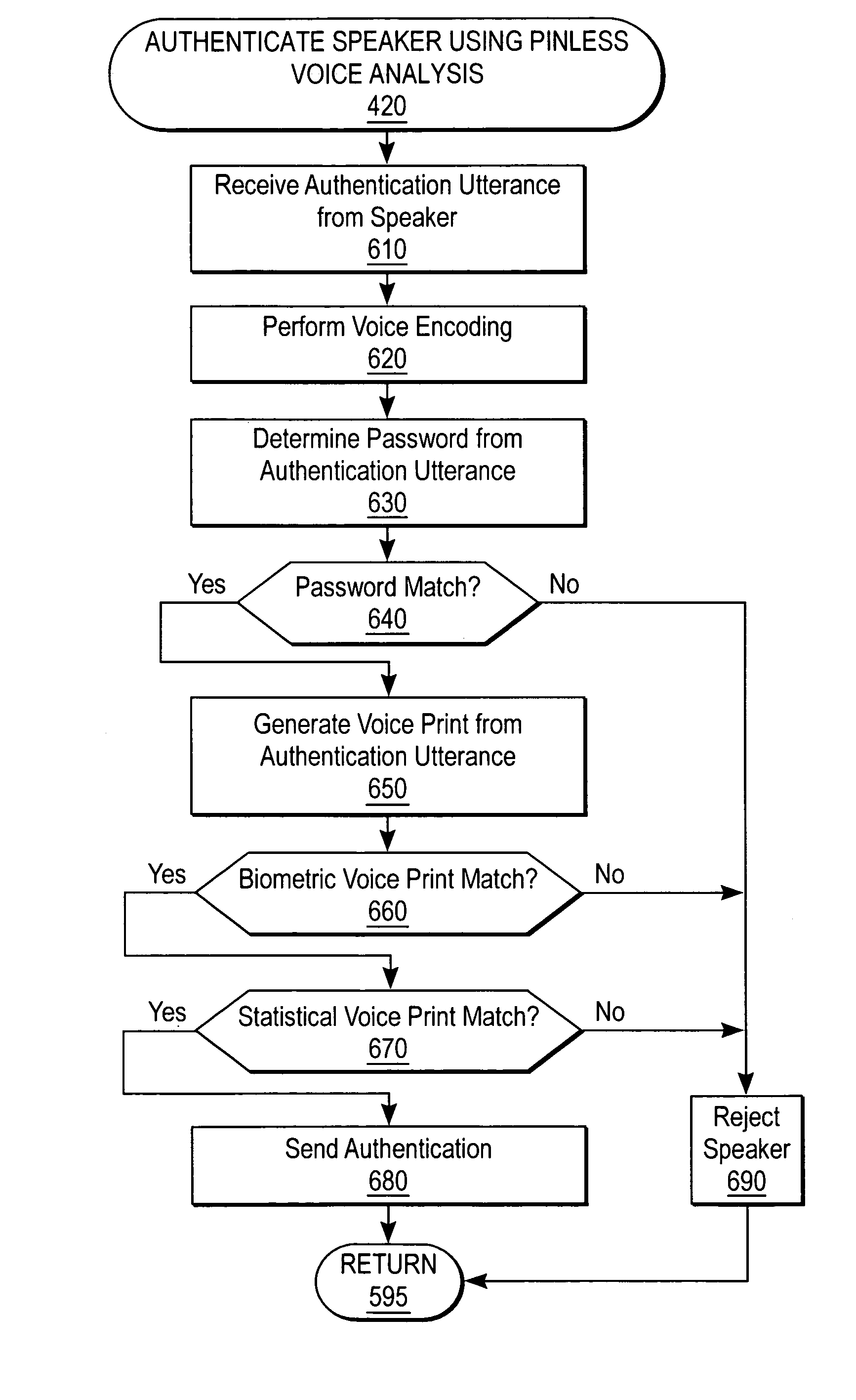
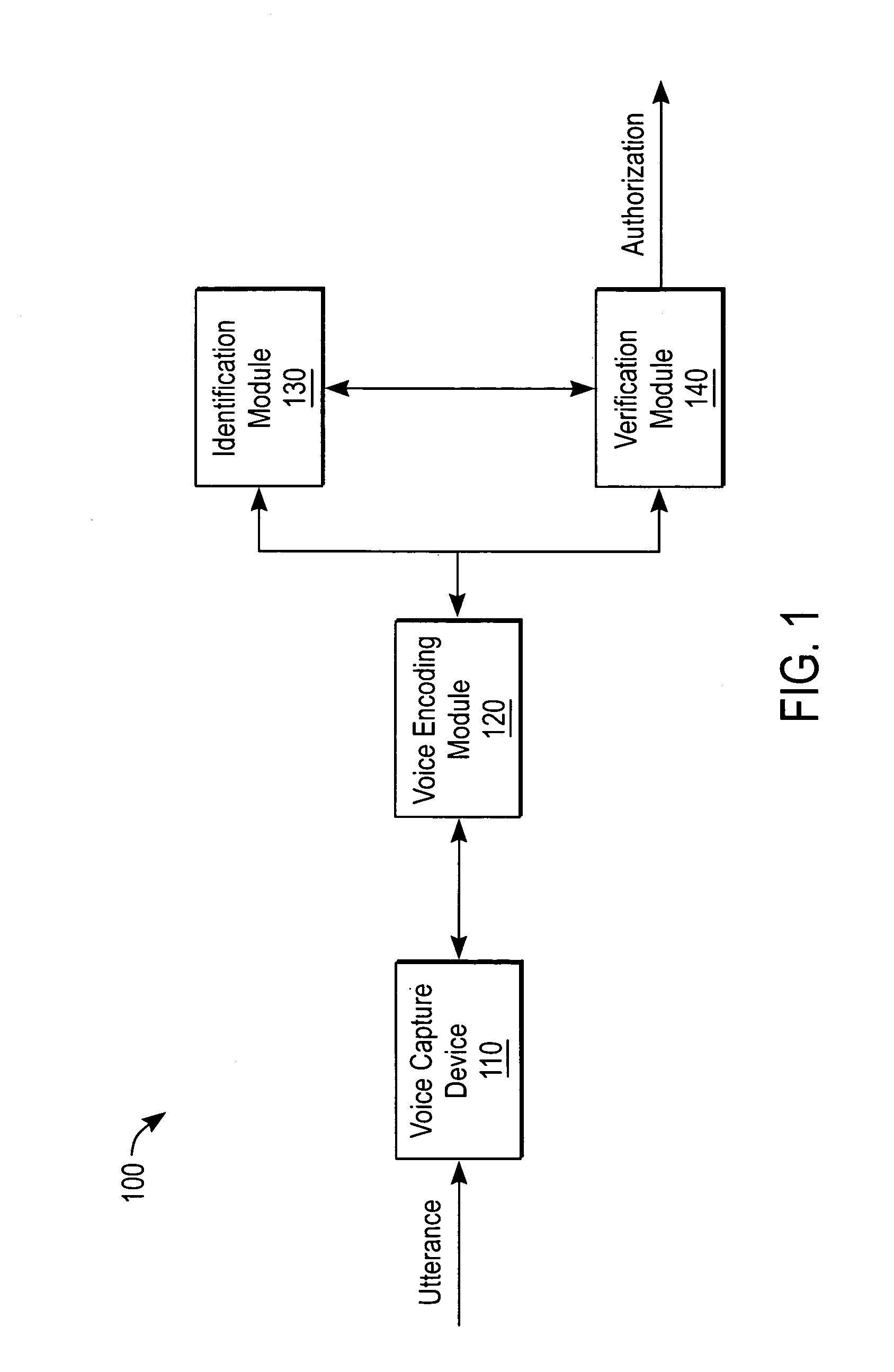
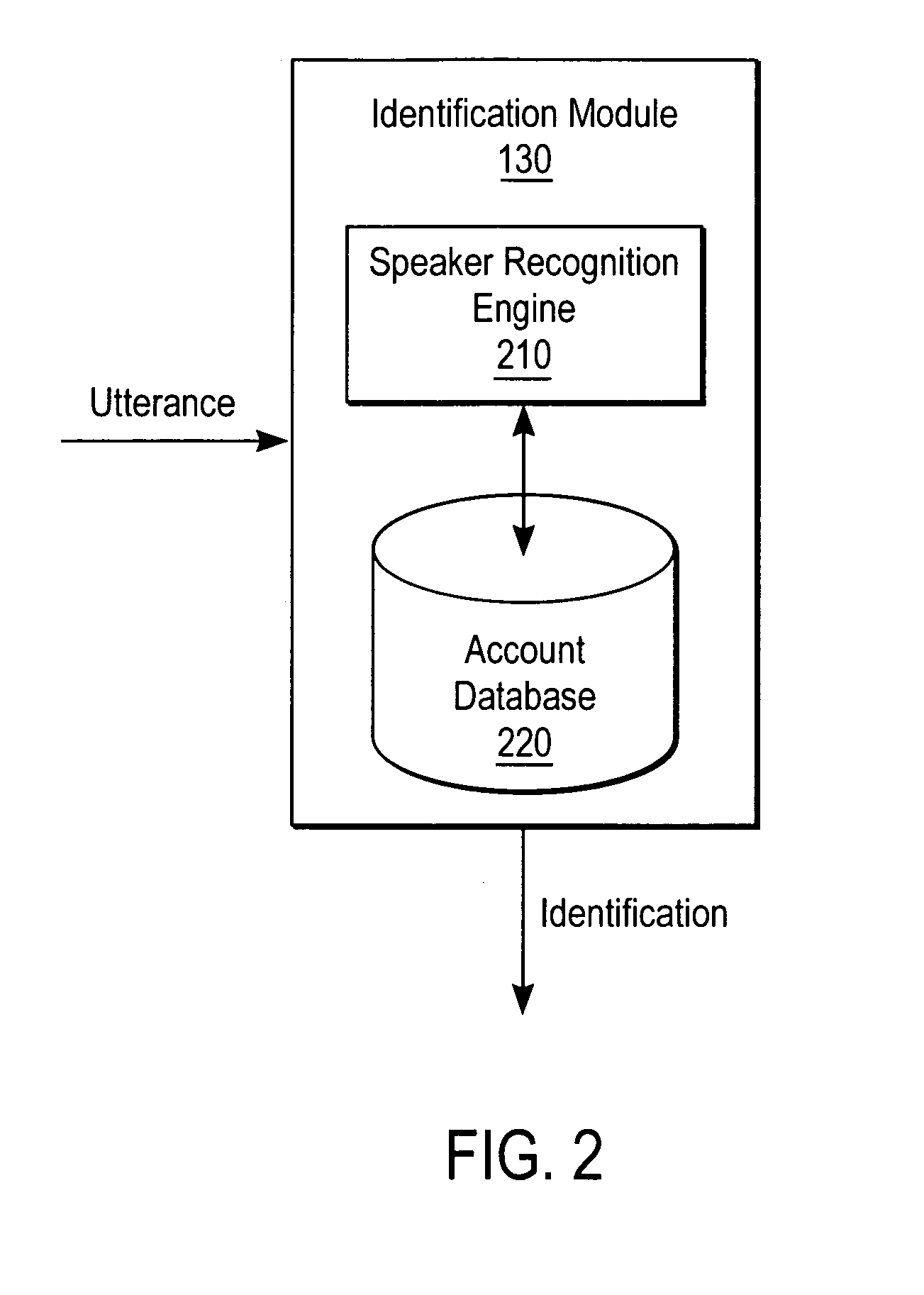
Biometric voice authentication
ActiveUS7386448B1Reducing user complexityReduce complexityAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingAutomatic exchangesBiometric dataPersonal identification number
A system and method enrolls a speaker with an enrollment utterance and authenticates a user with a biometric analysis of an authentication utterance, without the need for a PIN (Personal Identification Number). During authentication, the system uses the same authentication utterance to identify who a speaker claims to be with speaker recognition, and verify whether is the speaker is actually the claimed person. Thus, it is not necessary for the speaker to identify biometric data using a PIN. The biometric analysis includes a neural tree network to determine unique aspects of the authentication utterances for comparison to the enrollment authentication. The biometric analysis leverages a statistical analysis using Hidden Markov Models to before authorizing the speaker.
Owner:SECURUS TECH LLC
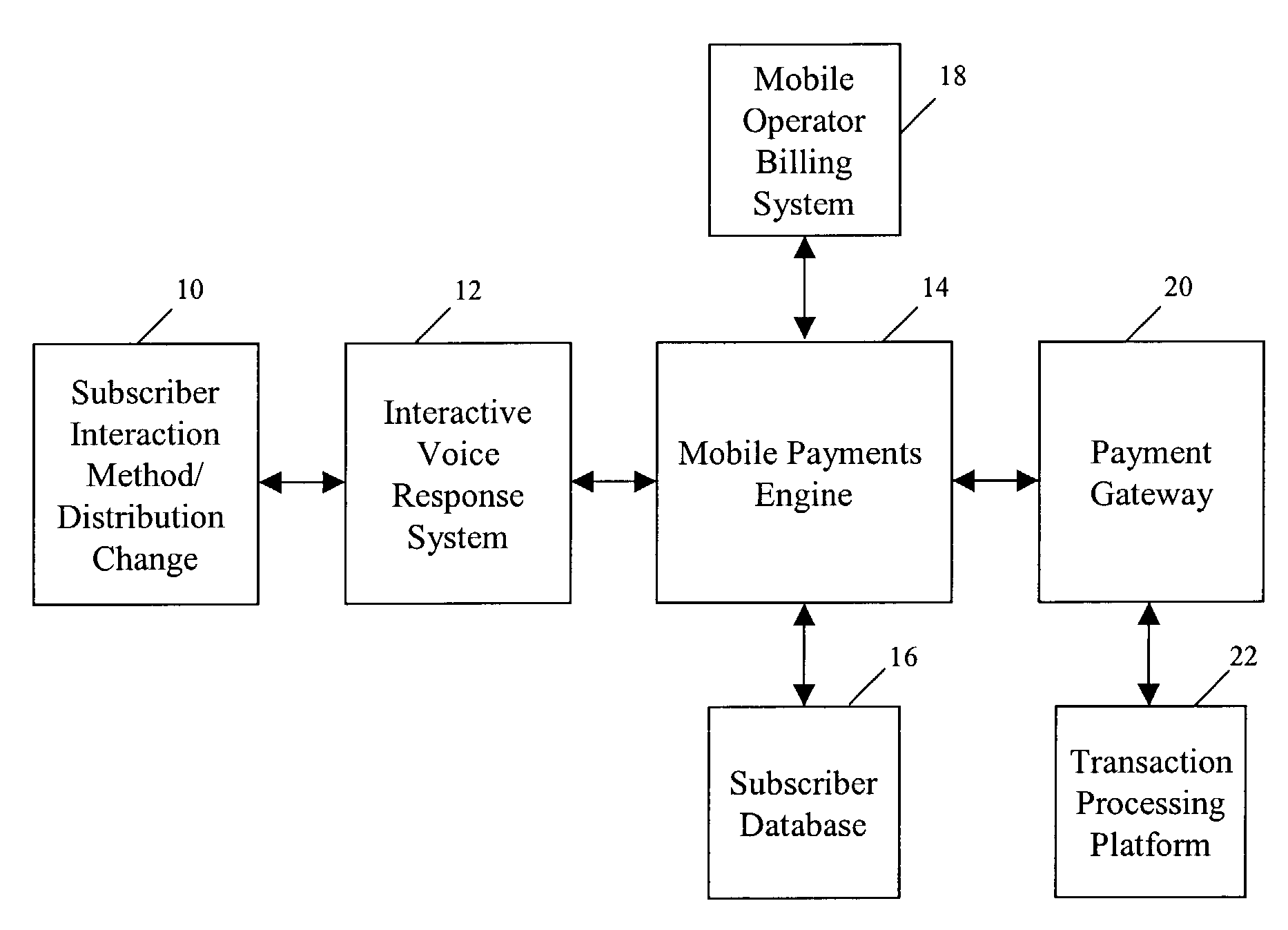
Method and system for data management in electronic payments transactions
ActiveUS7024174B2Reduces charge-backsEliminate the problemUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsPayment transactionThe Internet
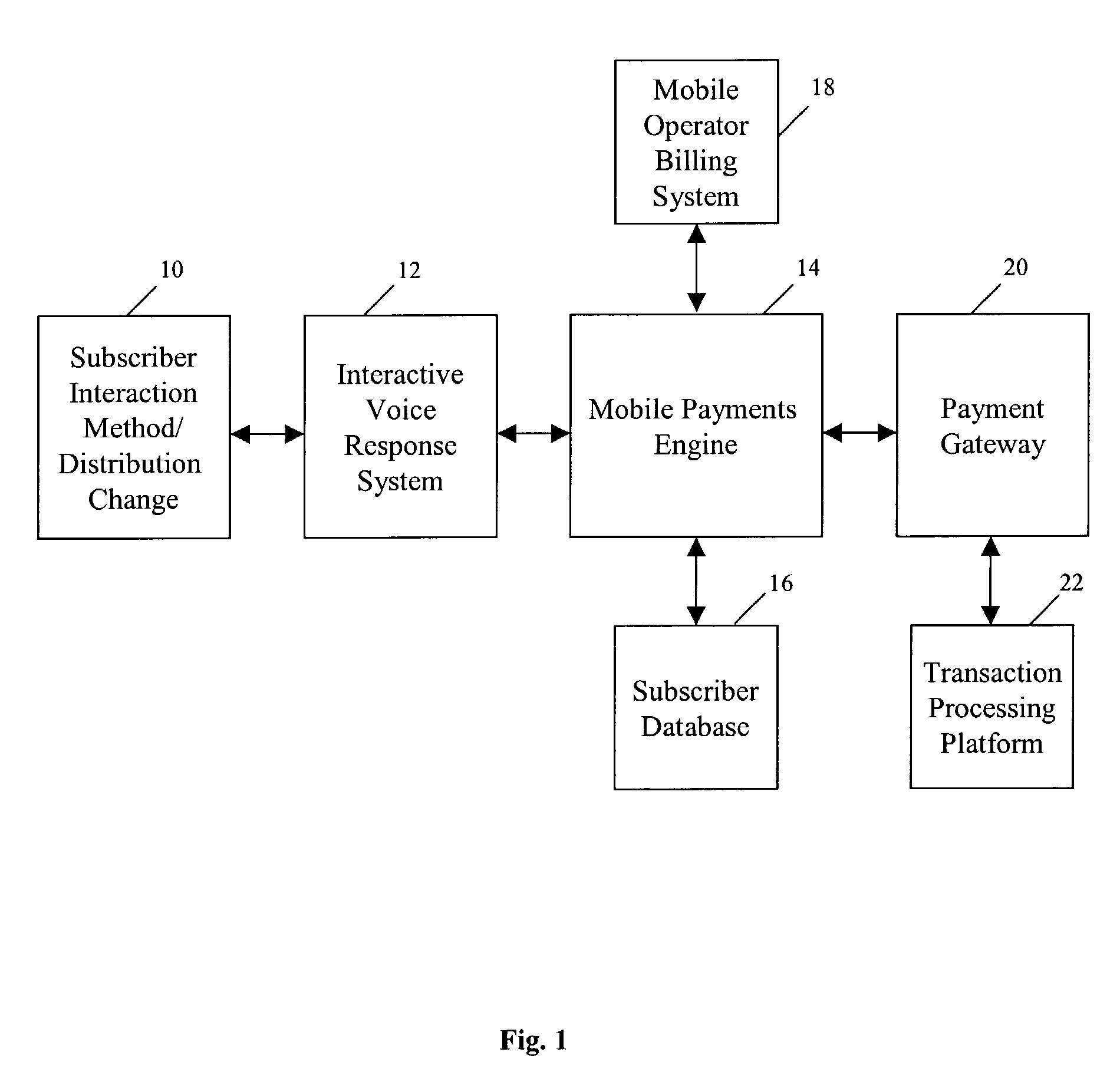
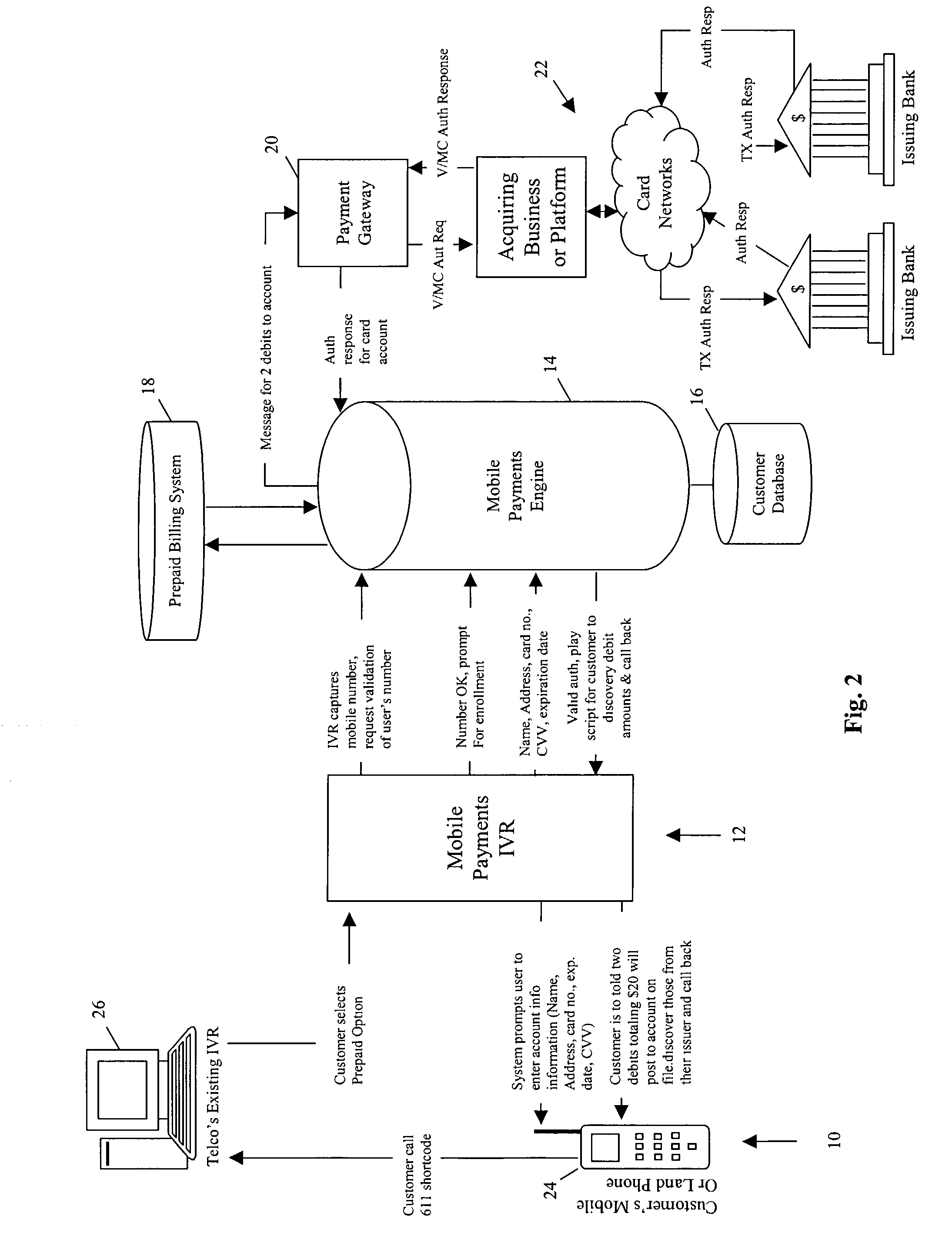
A method and system for prepaying wireless telecommunications charges utilizes computer hardware and software including, for example, a user's mobile phone, a mobile operator's interactive voice response unit, a mobile payments interactive voice response unit, SMS, test messaging, email, ATM, kiosk, the Internet, and / or WAP or the like, a mobile payments engine, a mobile operator's prepaid billing system, a subscriber database, a payment gateway, and a transaction processing platform. The mobile payments engine receives information identifying a user's wireless telecommunication device via the mobile payments interactive voice response unit, passes the information to the mobile operator's billing system with a request for validation of a mobile account for the user, and if validation is received, the mobile payments engine receives financial source account and user identity verification information from the user, assigns a mobile personal identification number for the user, and arranges a credit from the source account to the user's mobile account.
Owner:CITIBANK
System and method for gaming terminal with account funding
ActiveUS20080153583A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesPersonal identification numberBank account
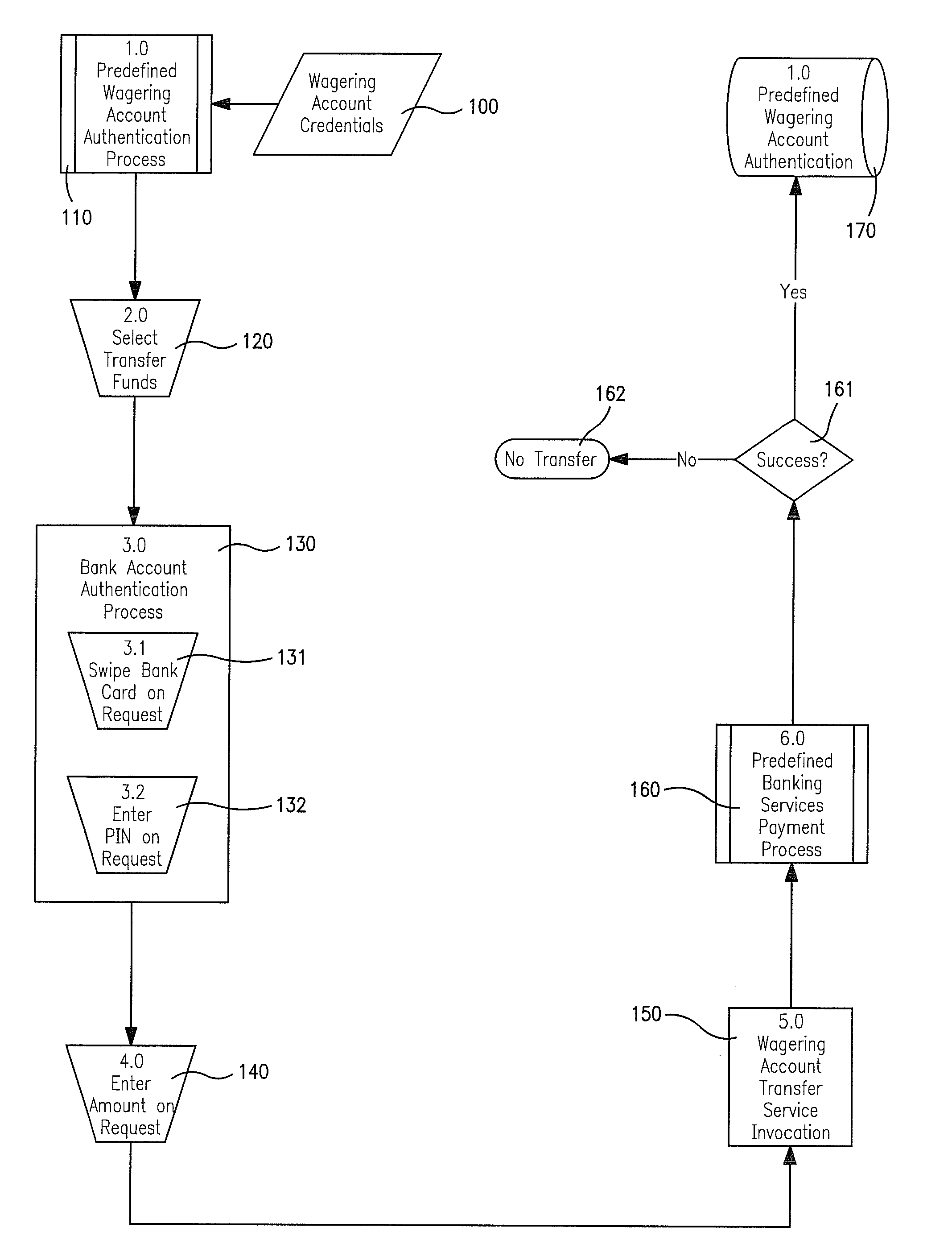
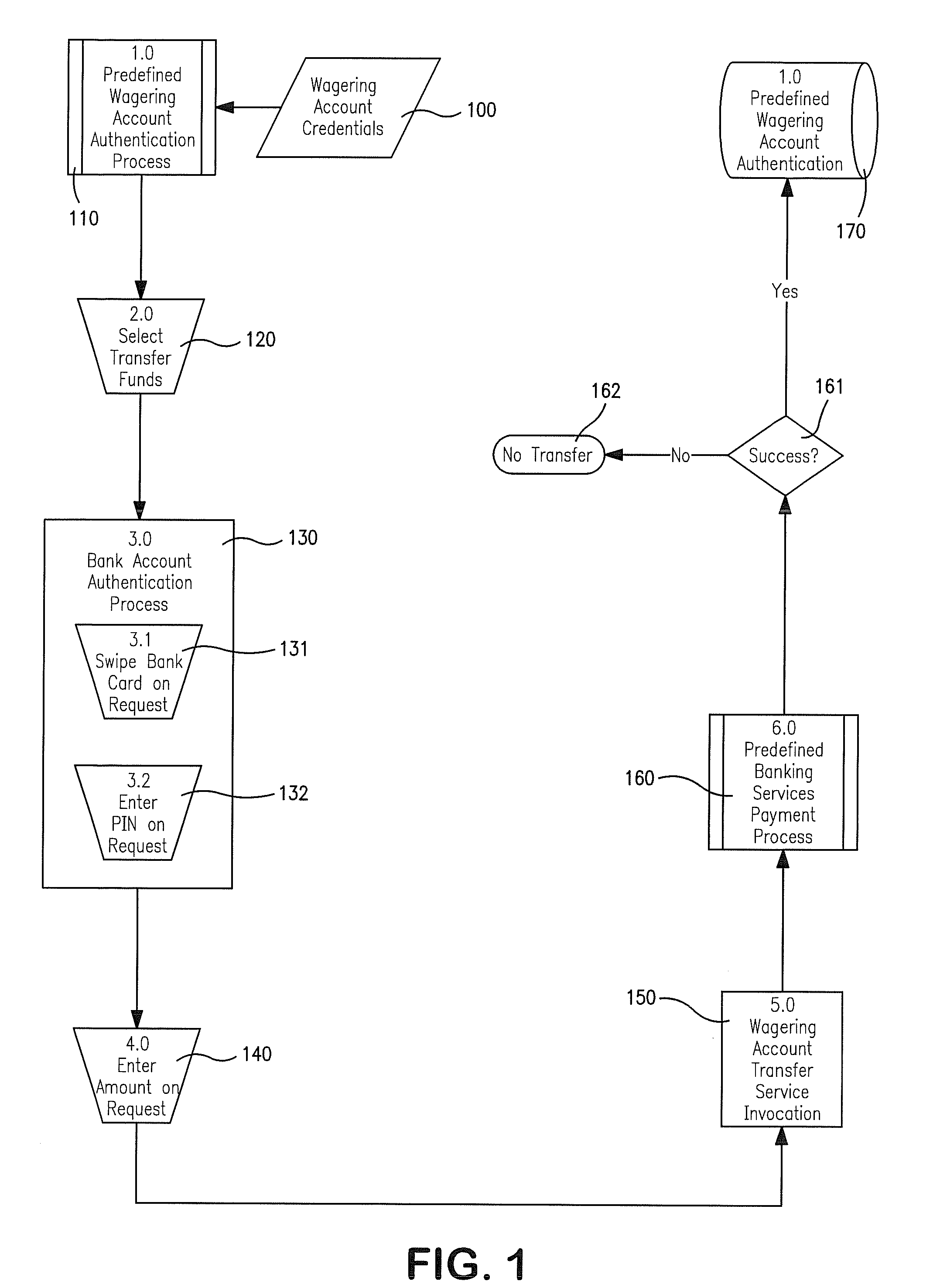
A system and method for providing a terminal with account funding is described. In one exemplary aspect of the invention, a system is provided having an interface whereby a player can interact with the gaming system. The interface allows the player to request a transfer of funds from the player's bank account to a wagering account. The system prompts the player to provide for reading the player's bank card such as by swiping the card. The system receives the player's entry of a personal identification code and sends information concerning the player's request for a transfer to a bank. The system then reports the bank's response to the player's request and, if allowed, credits that player's wagering account with the requested transfer of funds.
Owner:SCI GAMES LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com