Patents
Literature
311 results about "Solar tracking system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
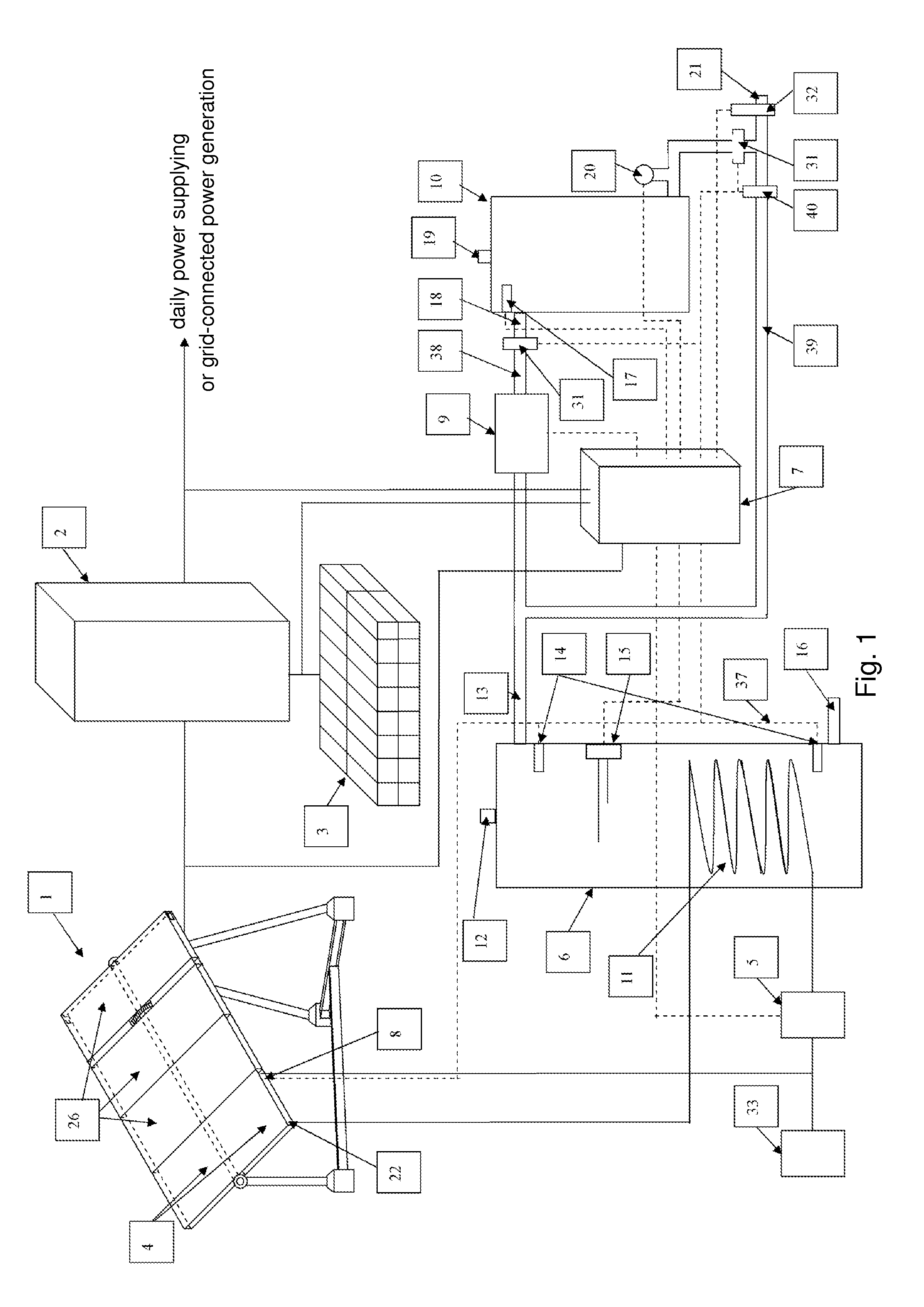
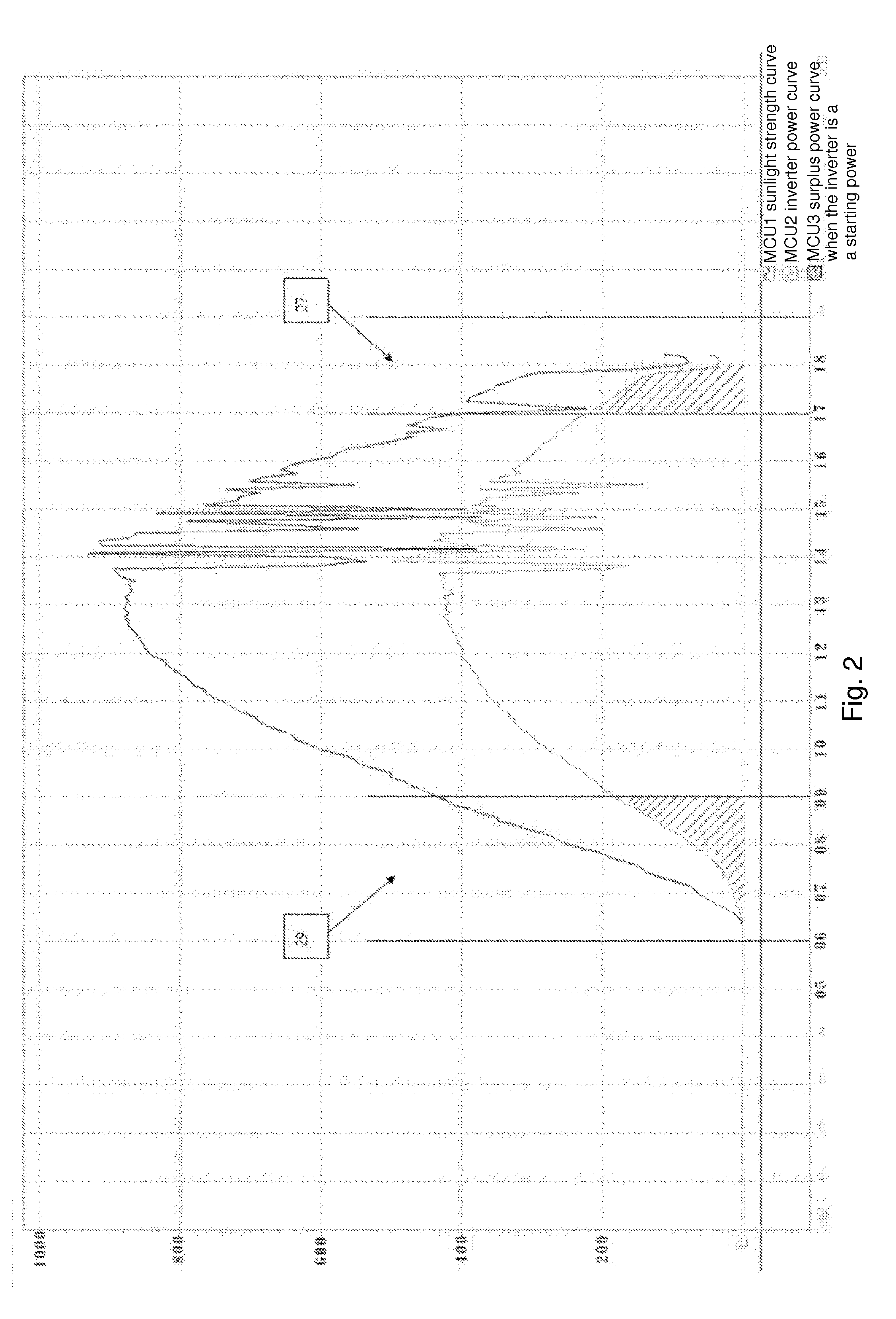
High-performance solar photovoltaic ( PV) energy conversion system
InactiveUS20070236187A1Stable DC voltage VdSimple designEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPerturbation and observationPower factor
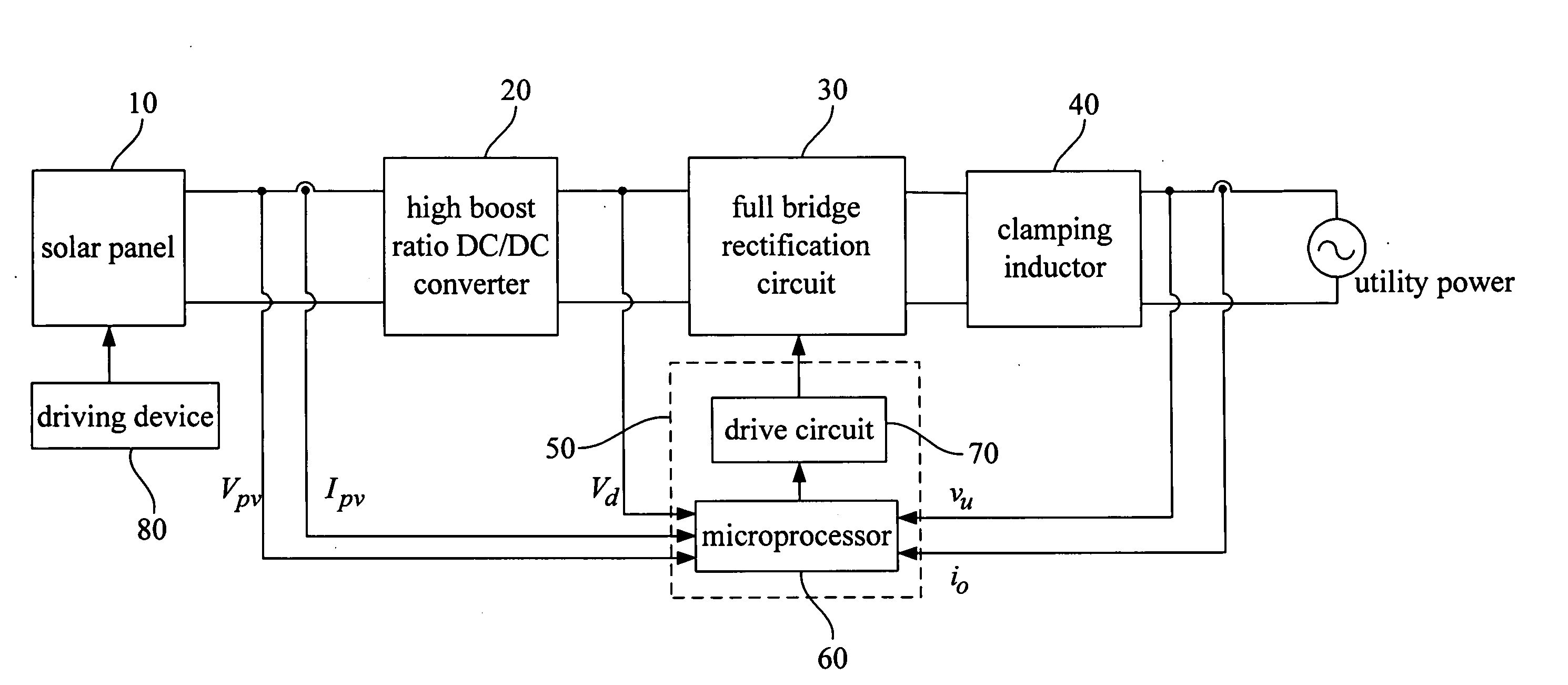
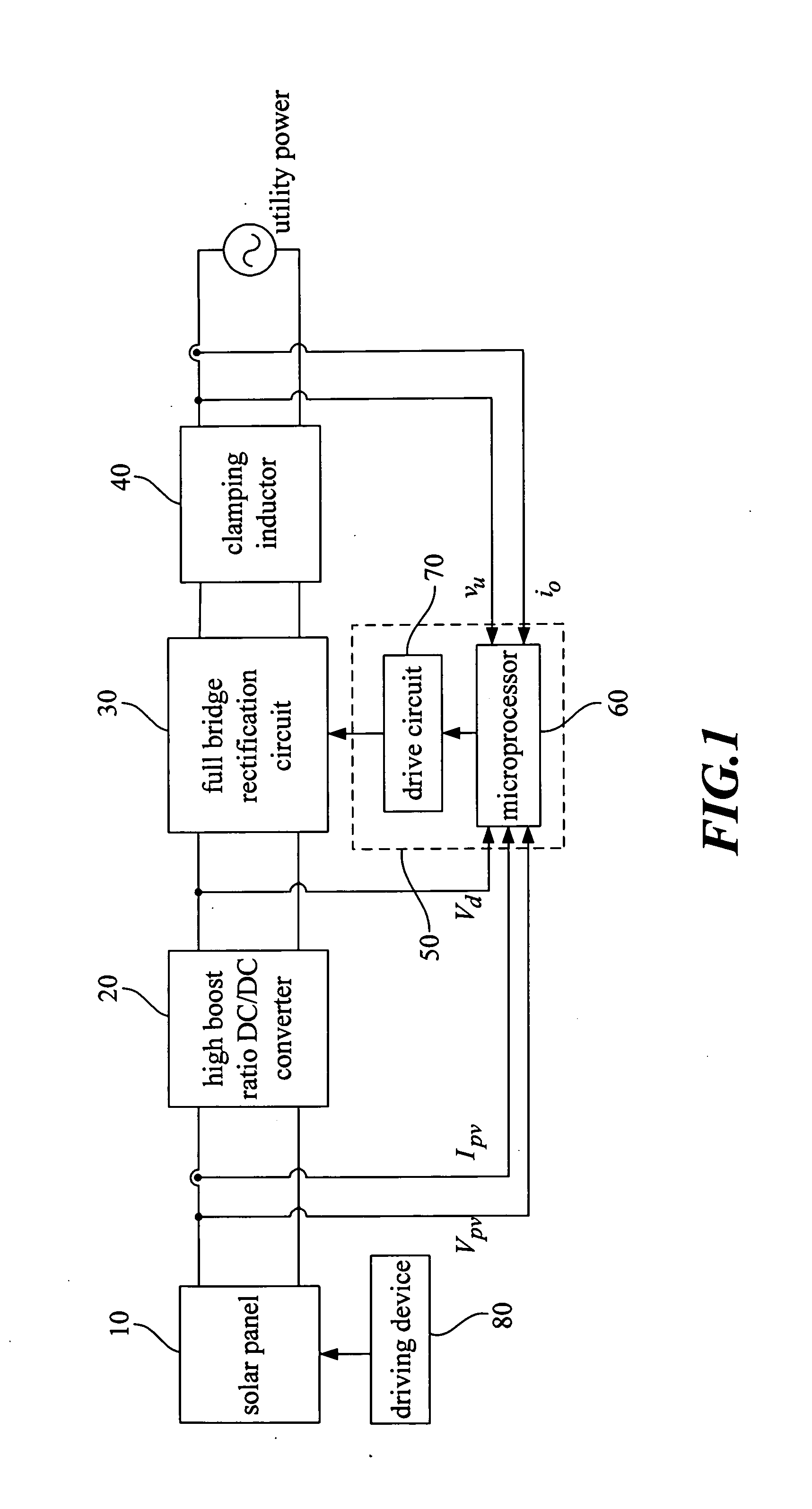
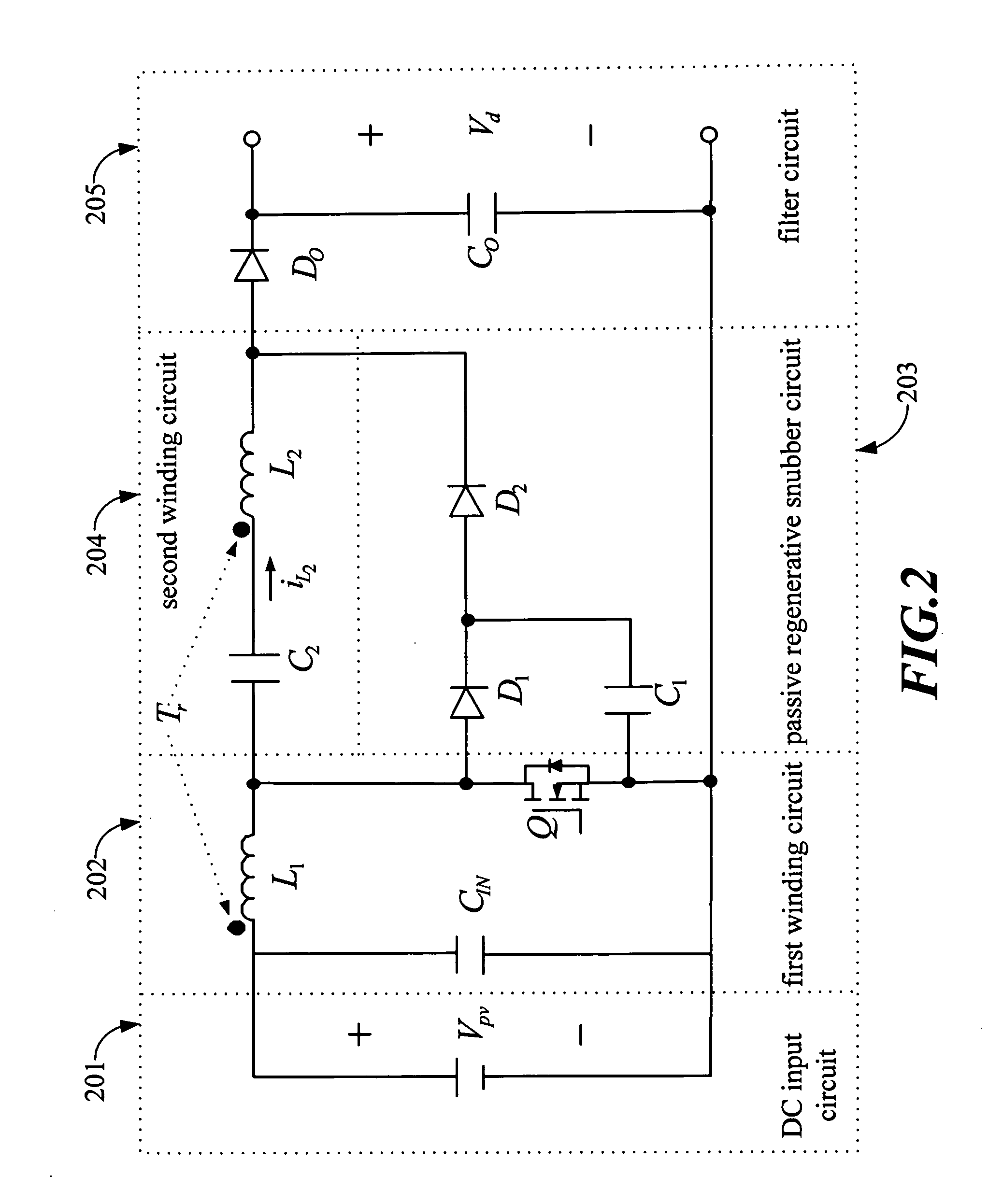
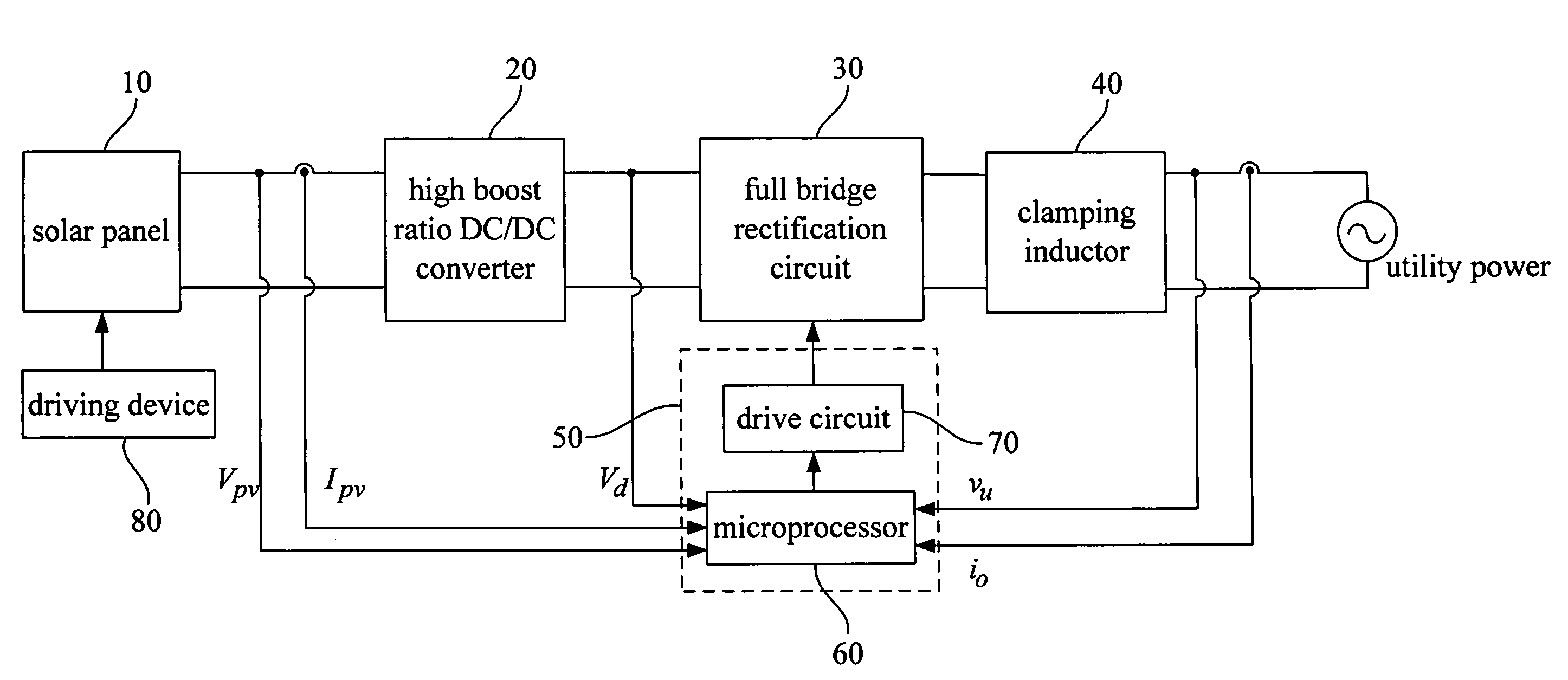
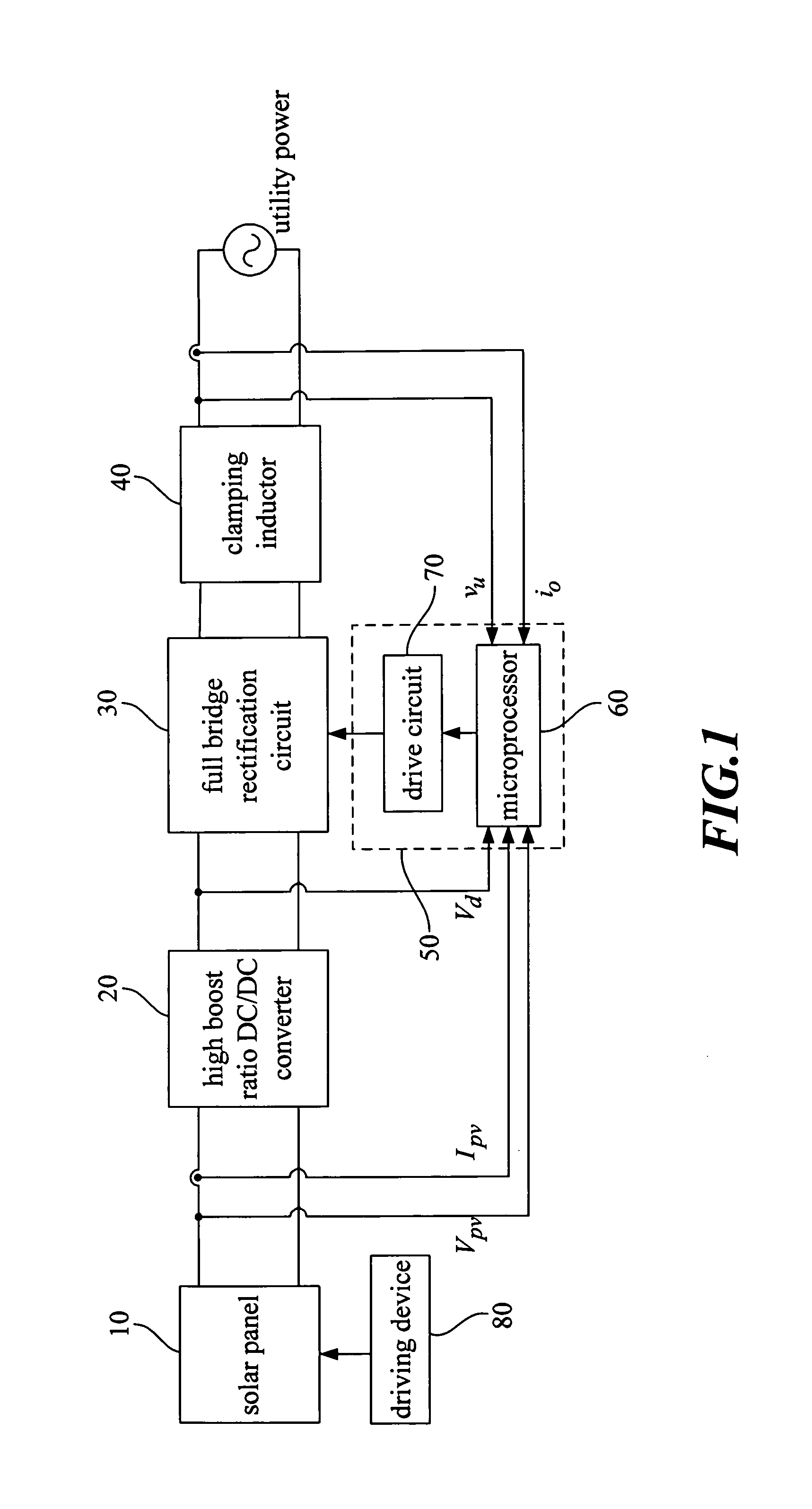
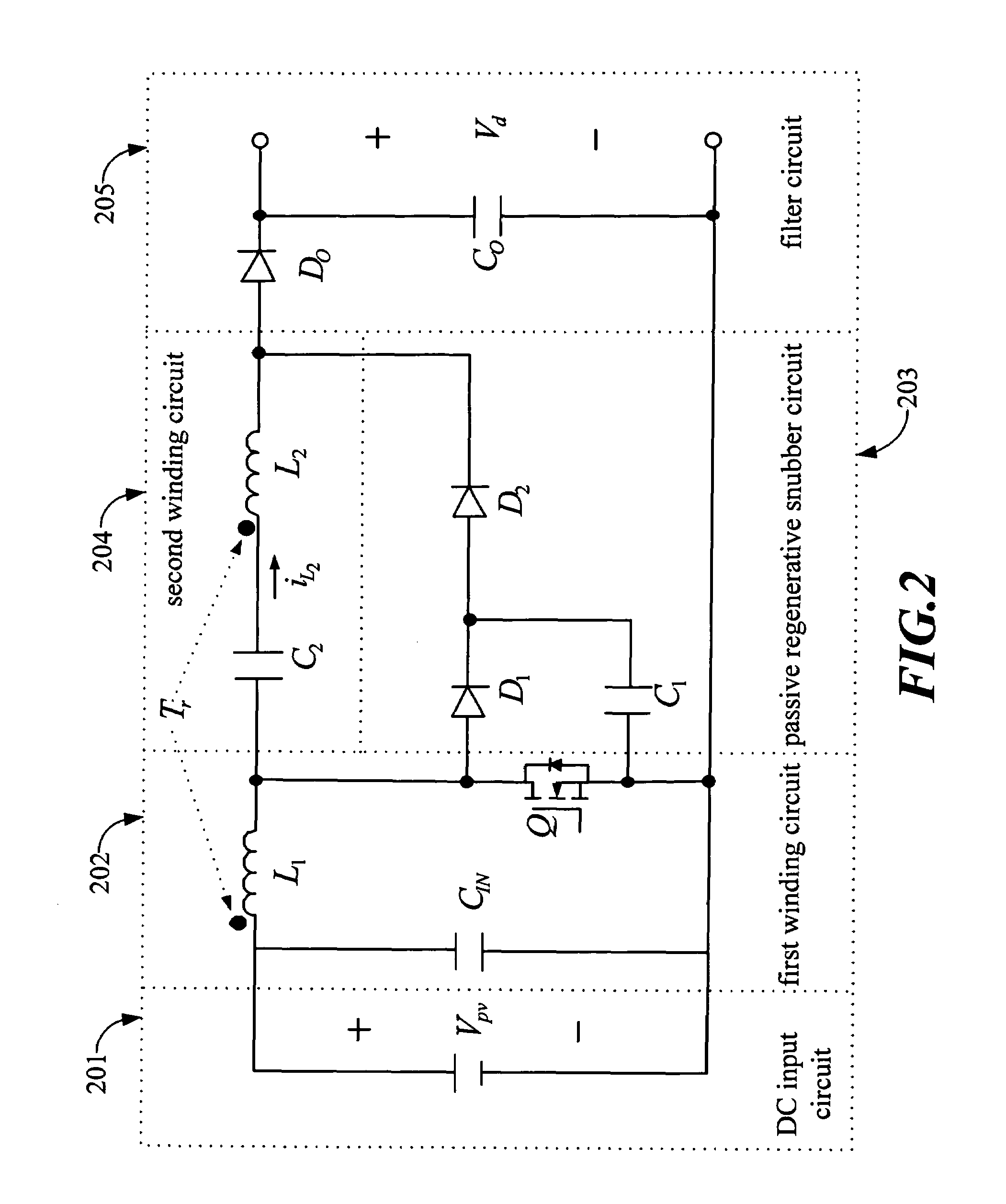
The present invention focuses on the development of a high-performance solar photovoltaic (PV) energy conversion system. The power circuit of the invention is made of a two-stage circuit, connecting a step-up DC-DC converter and a full-bridge inverter in serial. The present invention uses an adaptive perturbation and observation method to increase tracking speed of maximum power position and at the same time reduces energy loss. In addition, the full-bridge inverter's output has to have the same phase with the utility power in order to achieve unit power factor and increase the system efficiency. The present invention uses voltage type current control full-bridge inverter to achieve the goal of merging into utility grid. The present invention provides an active Sun tracking system, by utilizing the character of changing in open circuit output voltage with Sun radiation strength to follow the Sun, and decreases the system cost and increases system effectiveness.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
High-performance solar photovoltaic (PV) energy conversion system
InactiveUS7479774B2Simple designHigh boost ratioEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFull bridgePower factor
The present invention focuses on the development of a high-performance solar photovoltaic (PV) energy conversion system. The power circuit of the invention is made of a two-stage circuit, connecting a step-up DC-DC converter and a full-bridge inverter in serial. The present invention uses an adaptive perturbation and observation method to increase tracking speed of maximum power position and at the same time reduces energy loss. In addition, the full-bridge inverter's output has to have the same phase with the utility power in order to achieve unit power factor and increase the system efficiency. The present invention uses voltage type current control full-bridge inverter to achieve the goal of merging into utility grid. The present invention provides an active Sun tracking system, by utilizing the character of changing in open circuit output voltage with Sun radiation strength to follow the Sun, and decreases the system cost and increases system effectiveness.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
Single axis solar tracking system
ActiveUS8459249B2Performance maximizationEasy to installPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyShadowingsTerrain
Owner:ARRAY TECH
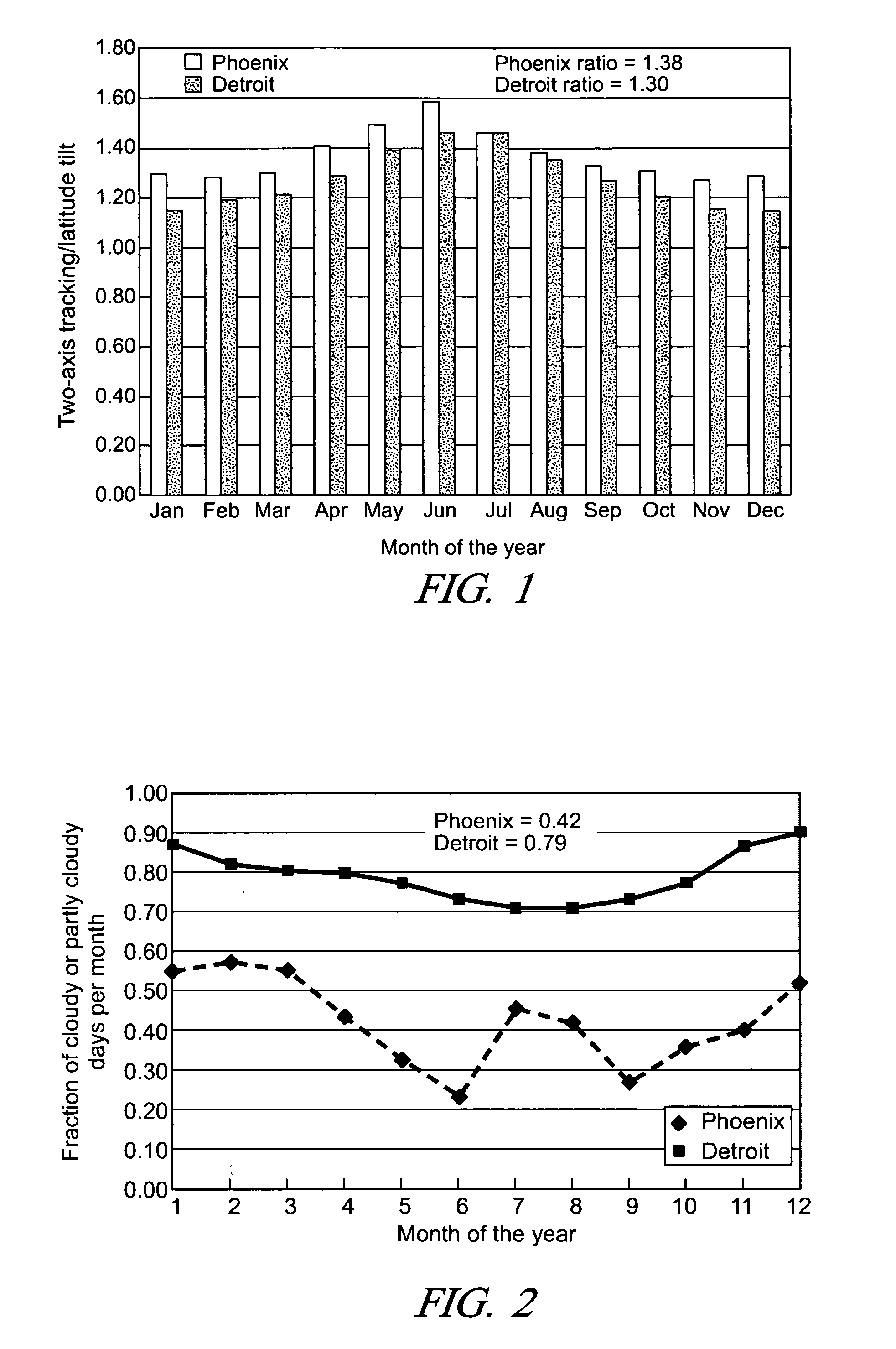
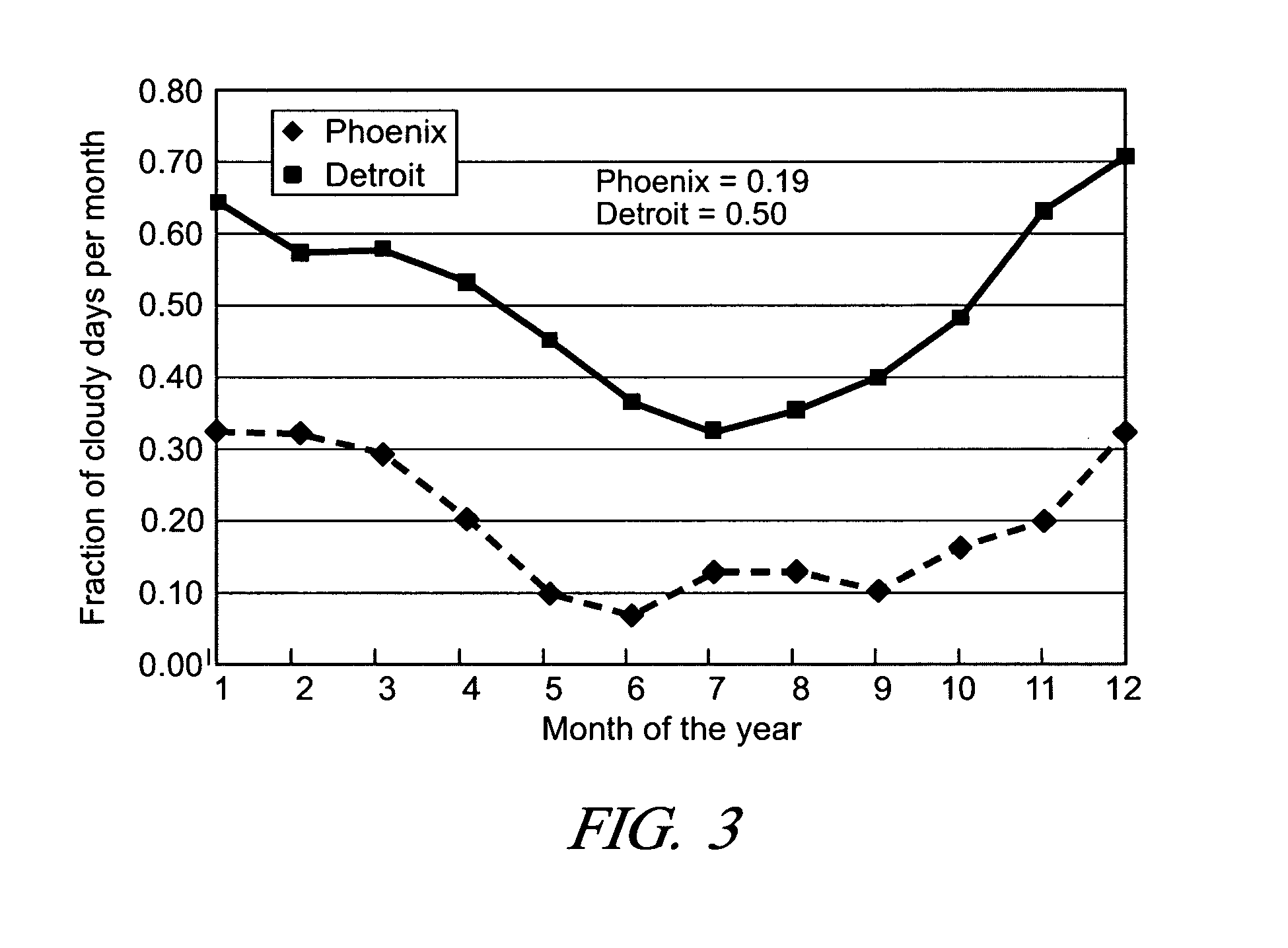
Solar photovoltaic output for cloudy conditions with a solar tracking system
ActiveUS20070084502A1Maximize its energy outputEasy to usePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyIlluminanceEngineering
An array of solar powered photovoltaic modules is optimally oriented and operated to provide more electrical energy for uses such as powering an electrolyzer system for hydrogen production. The array is positioned with its light receiving surface at an optimal angle, preferably a continually changing angle determined by two-axis solar tracking, when continually measured solar irradiance indicates suitable sunlight, and at a horizontal position when measured solar irradiance indicates excessive atmospheric cloudiness.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and Method for Solar Tracking
InactiveUS20090050191A1Easy to installStable and cost-effective designSolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueRange of motionComputer module
Owner:SOLFOCUS
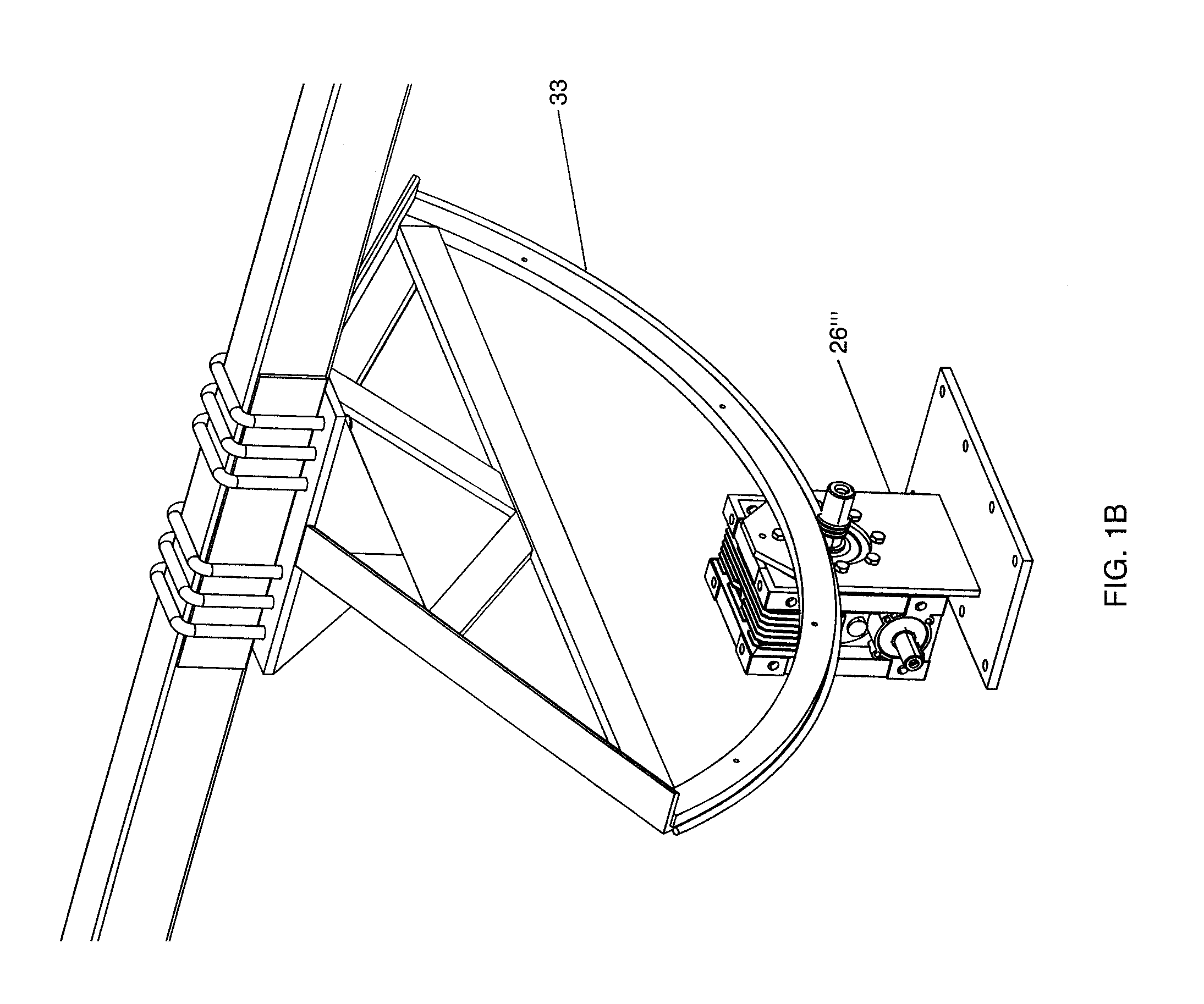
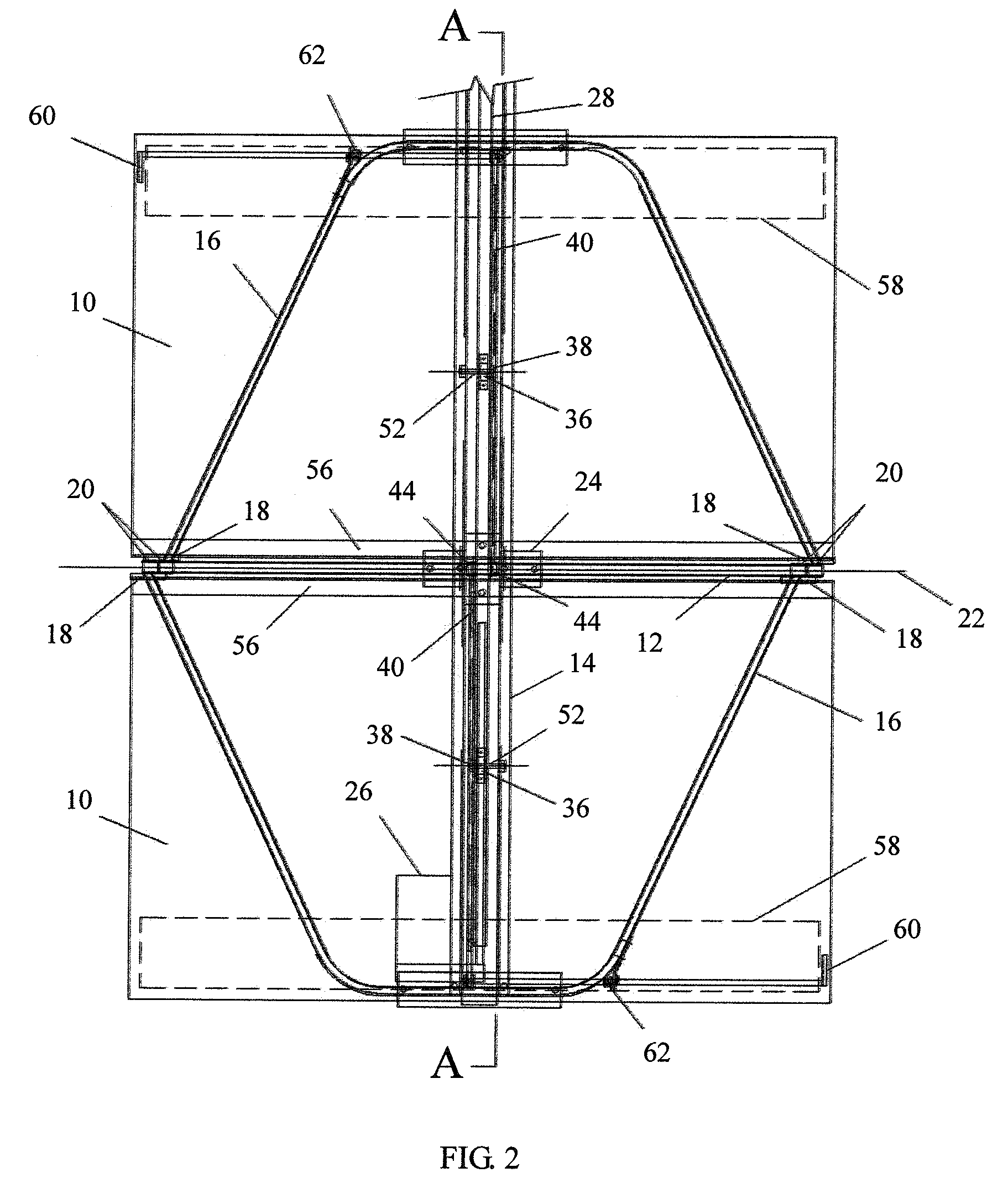
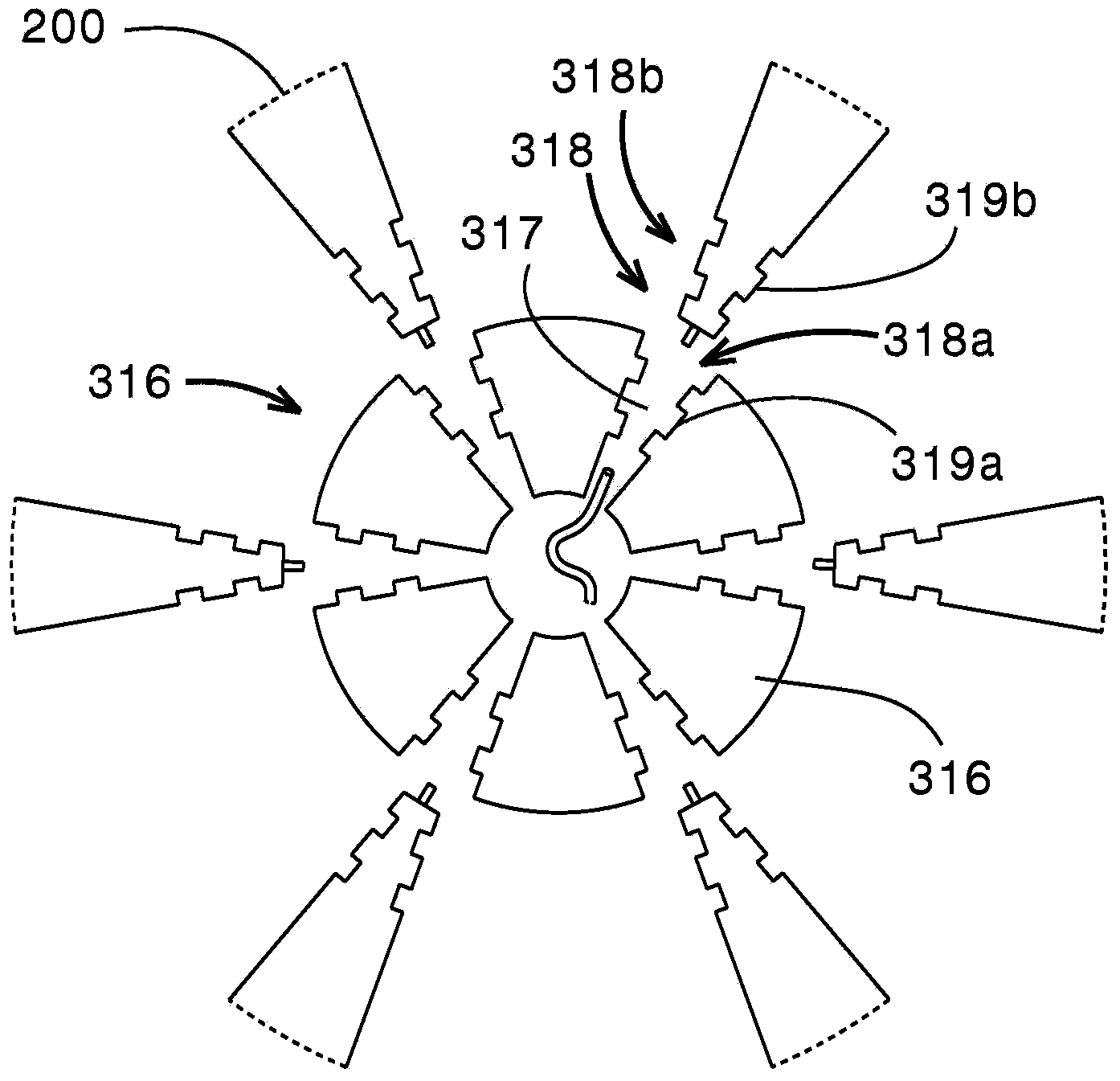
Solar tracking system
InactiveUS7109461B2More sensitiveSolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueSolar tracking systemInstrumentation
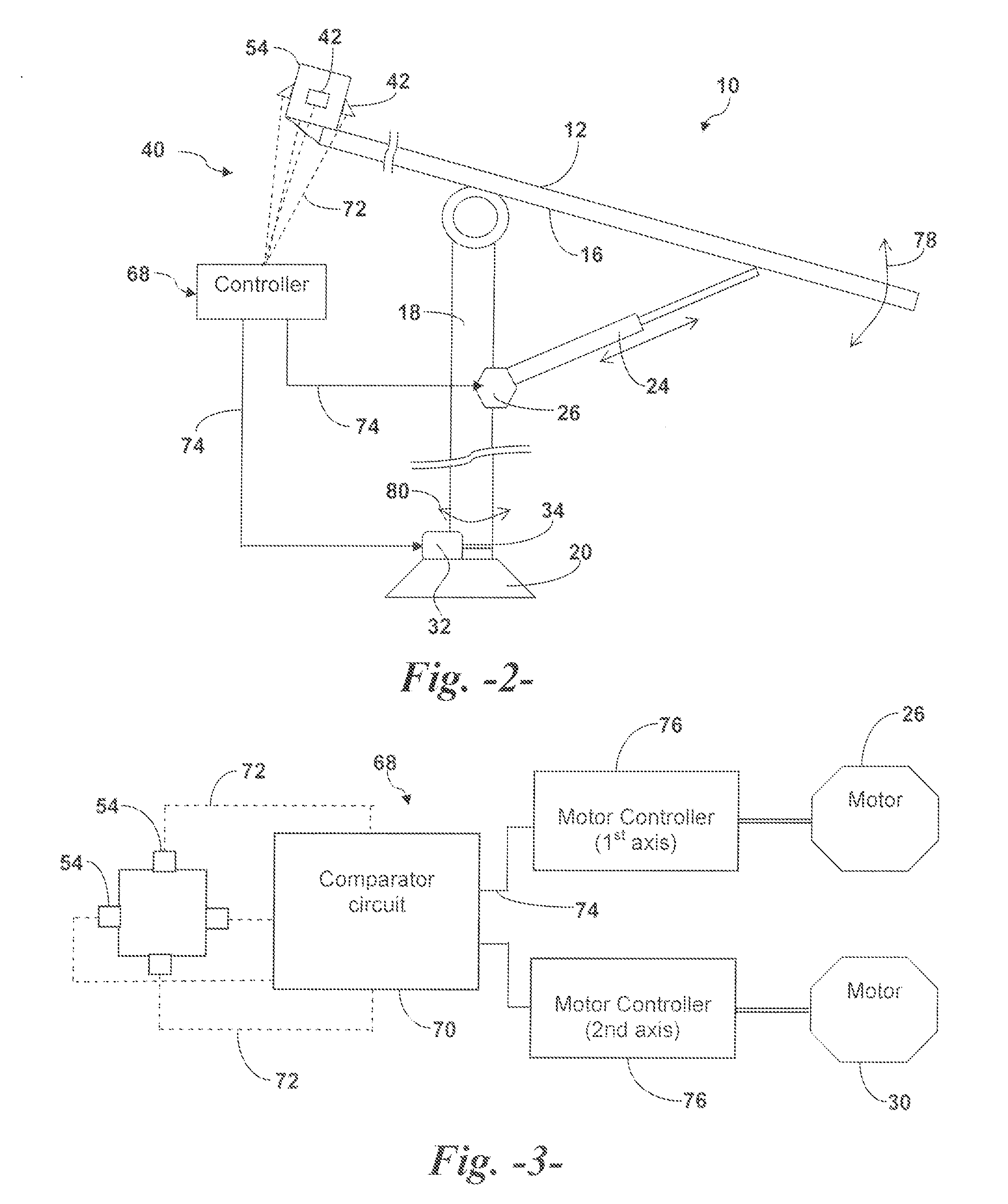
The invention provides a solar tracking system for controlling the alignment of an instrument with respect to the sun, the instrument having a solar radiation receiver and a solar radiation collector for collecting solar radiation and directing the radiation towards the receiver, the system having: at least first and second detectors locatable so as to move with the receiver and receive radiation from the collector, for generating respective first and second output signals according to their respective exposure to solar radiation from the collector; a comparison means for comparing the first and second outputs and producing a comparison signal indicative thereof; and control means for controlling the alignment of the instrument according to the comparison signal.
Owner:SOLAR SYST PTY LTD
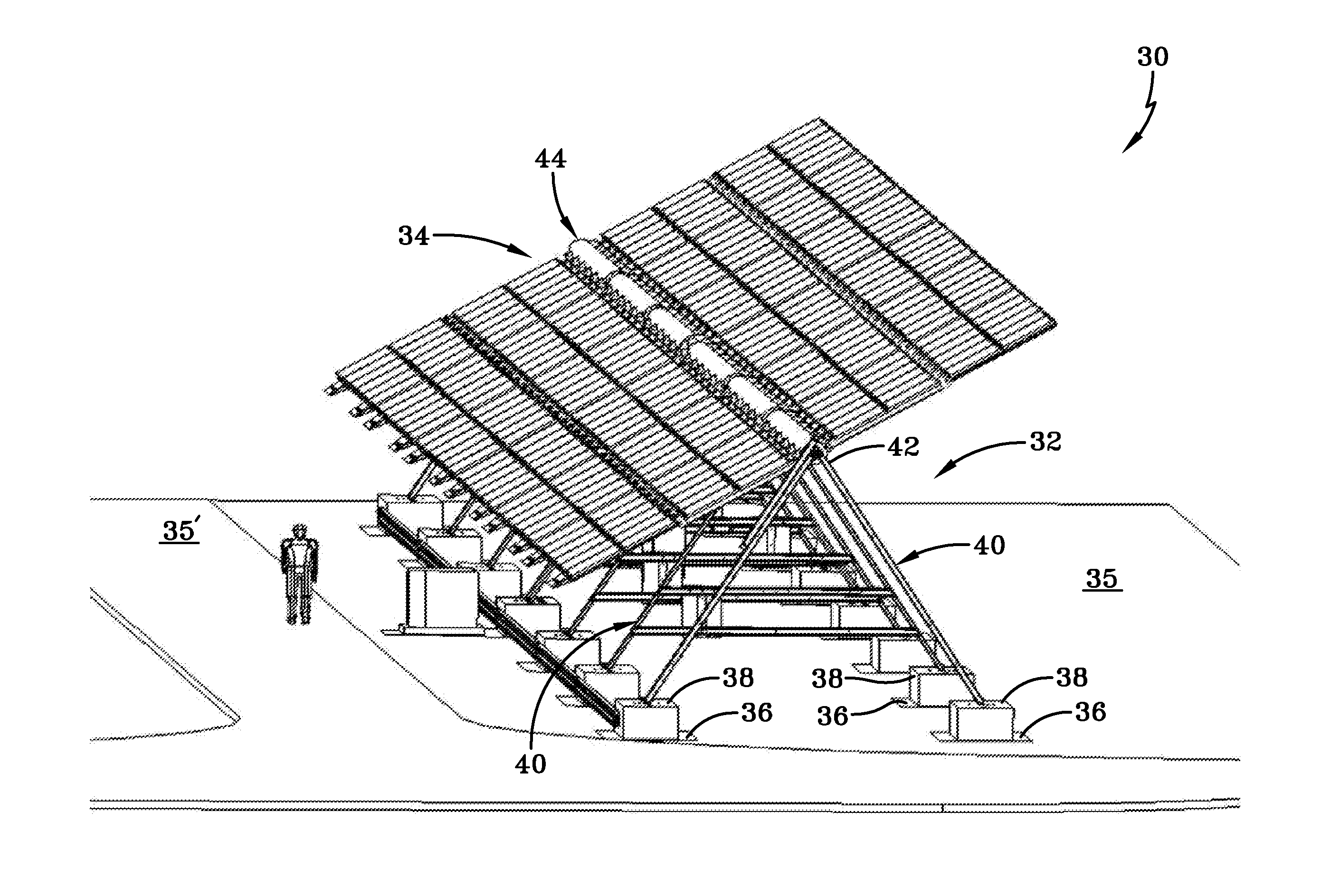
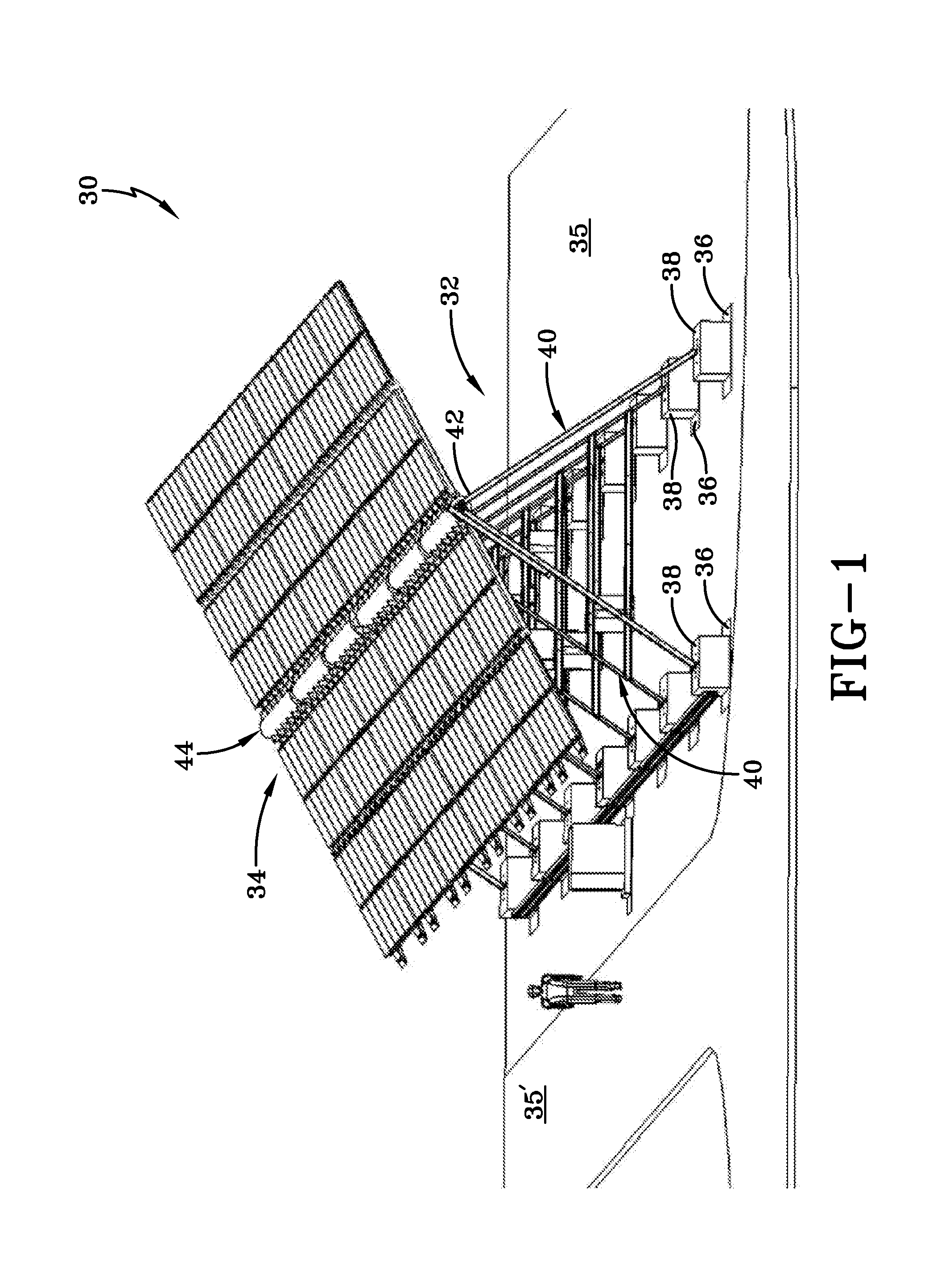
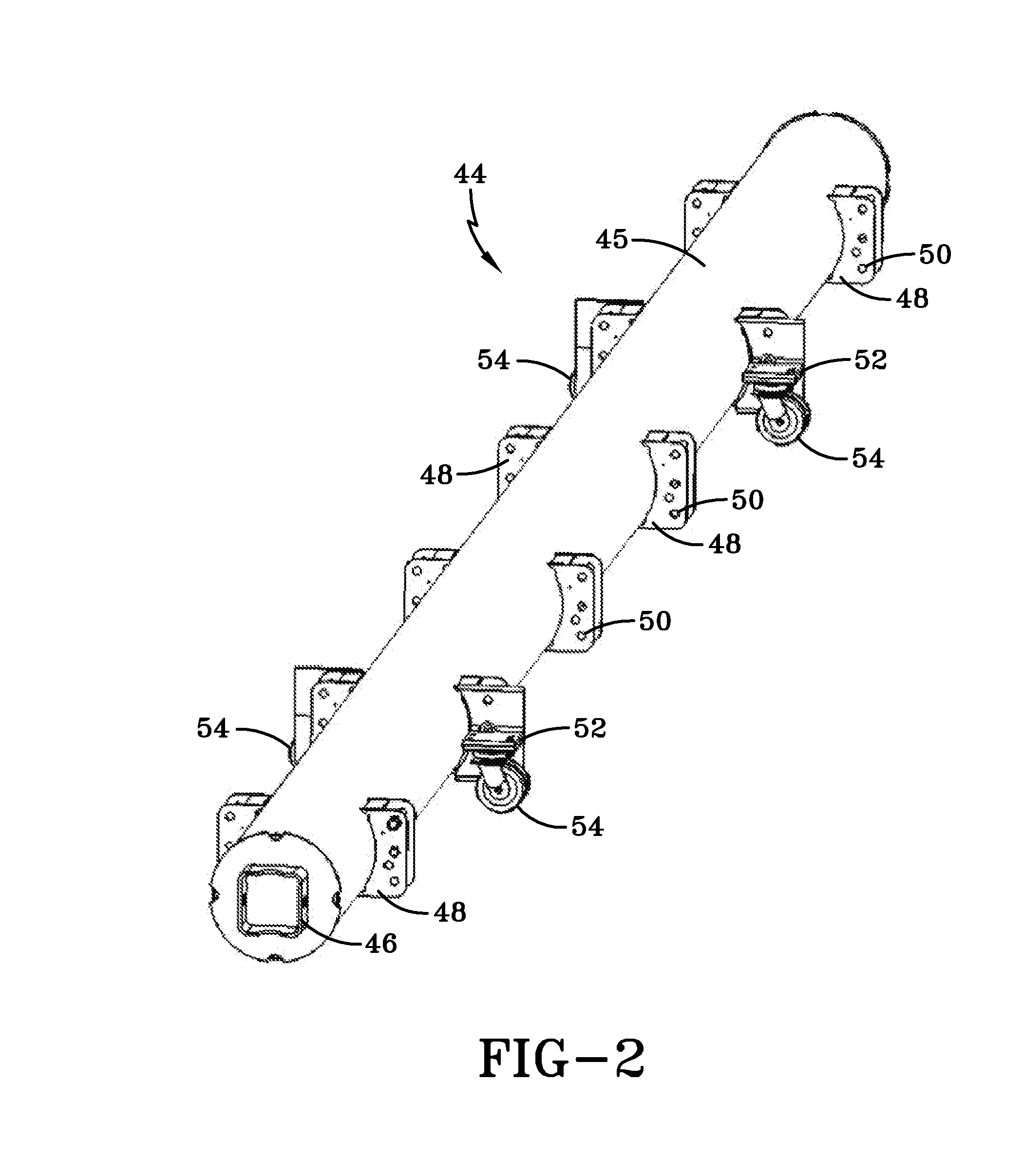
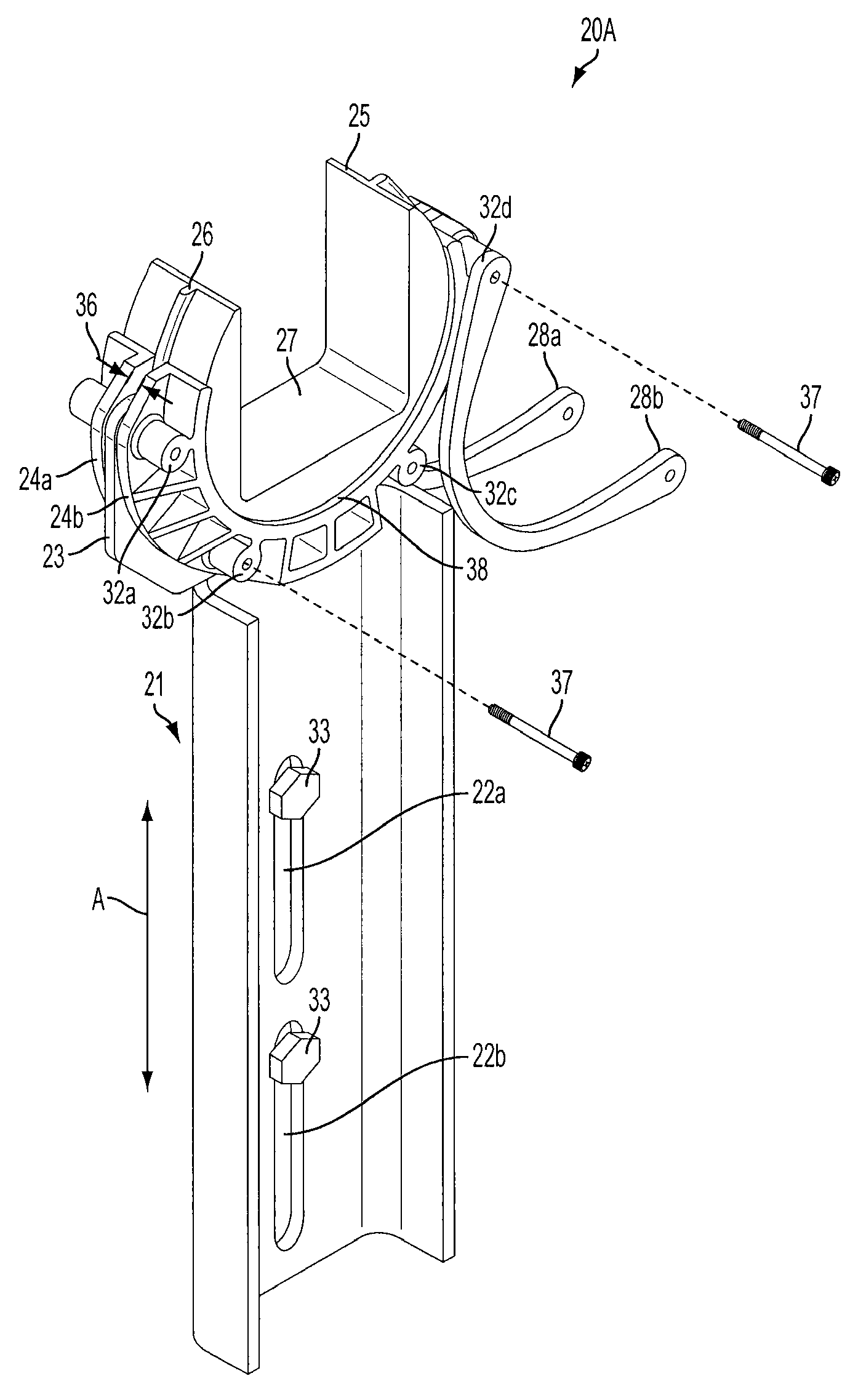
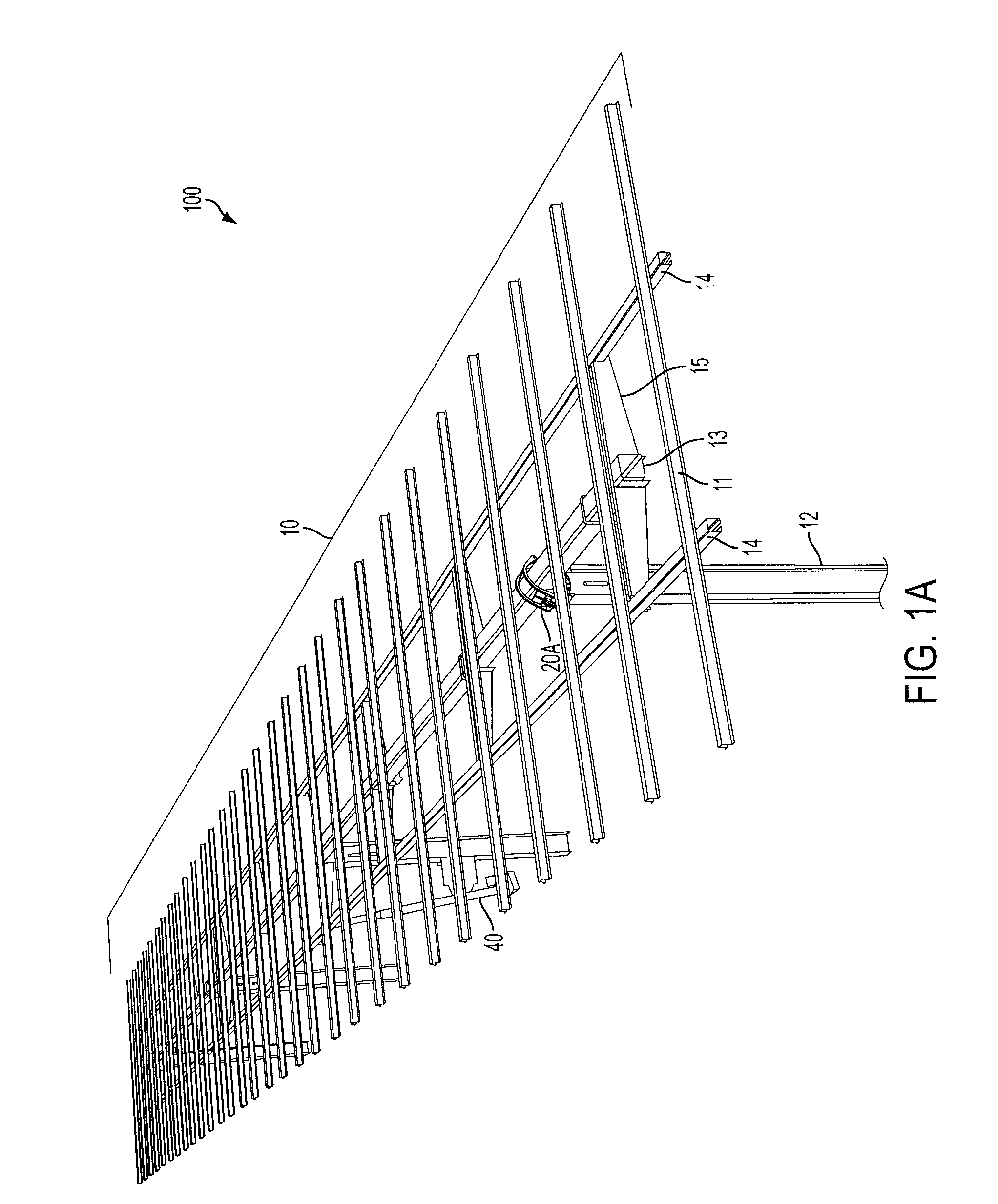
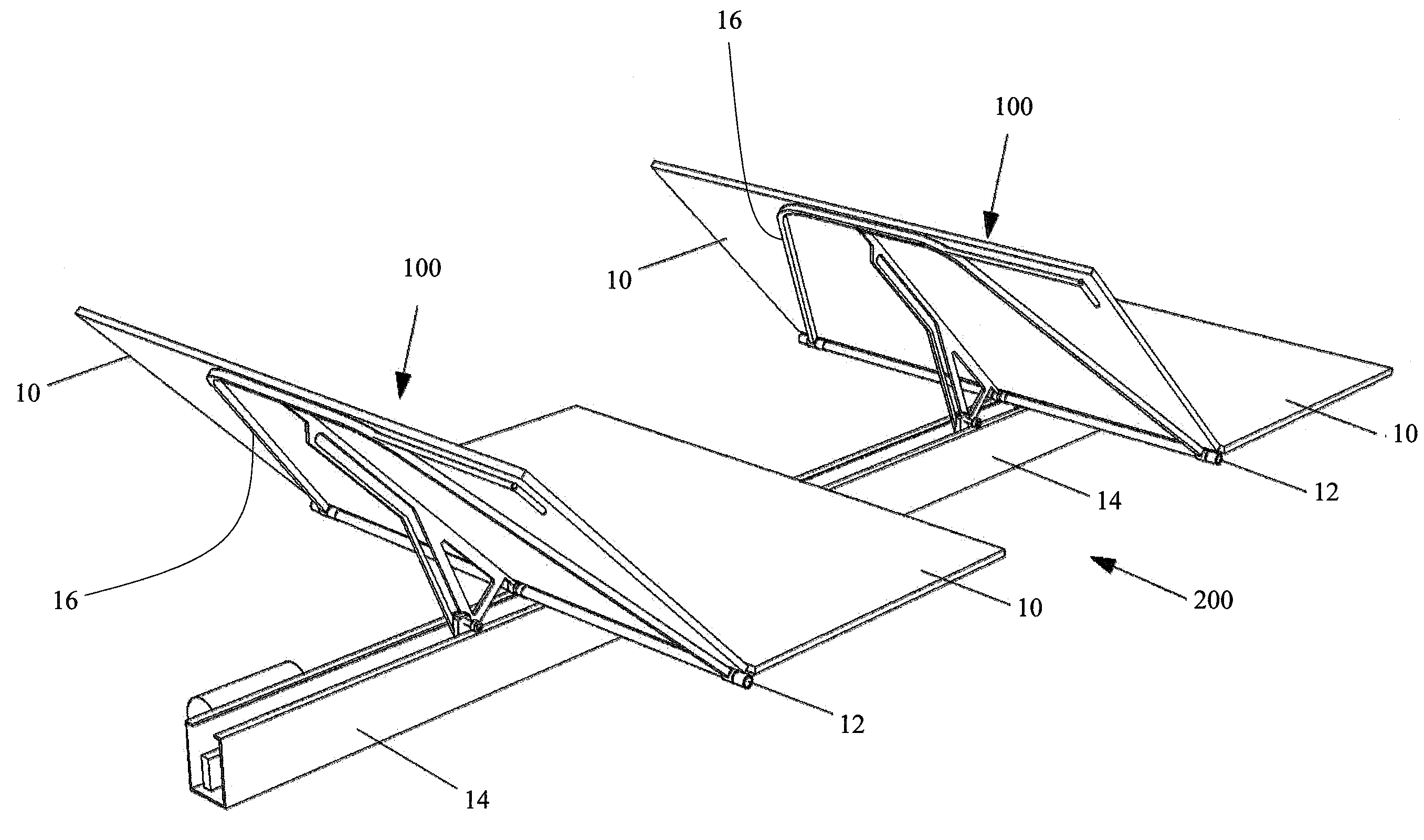
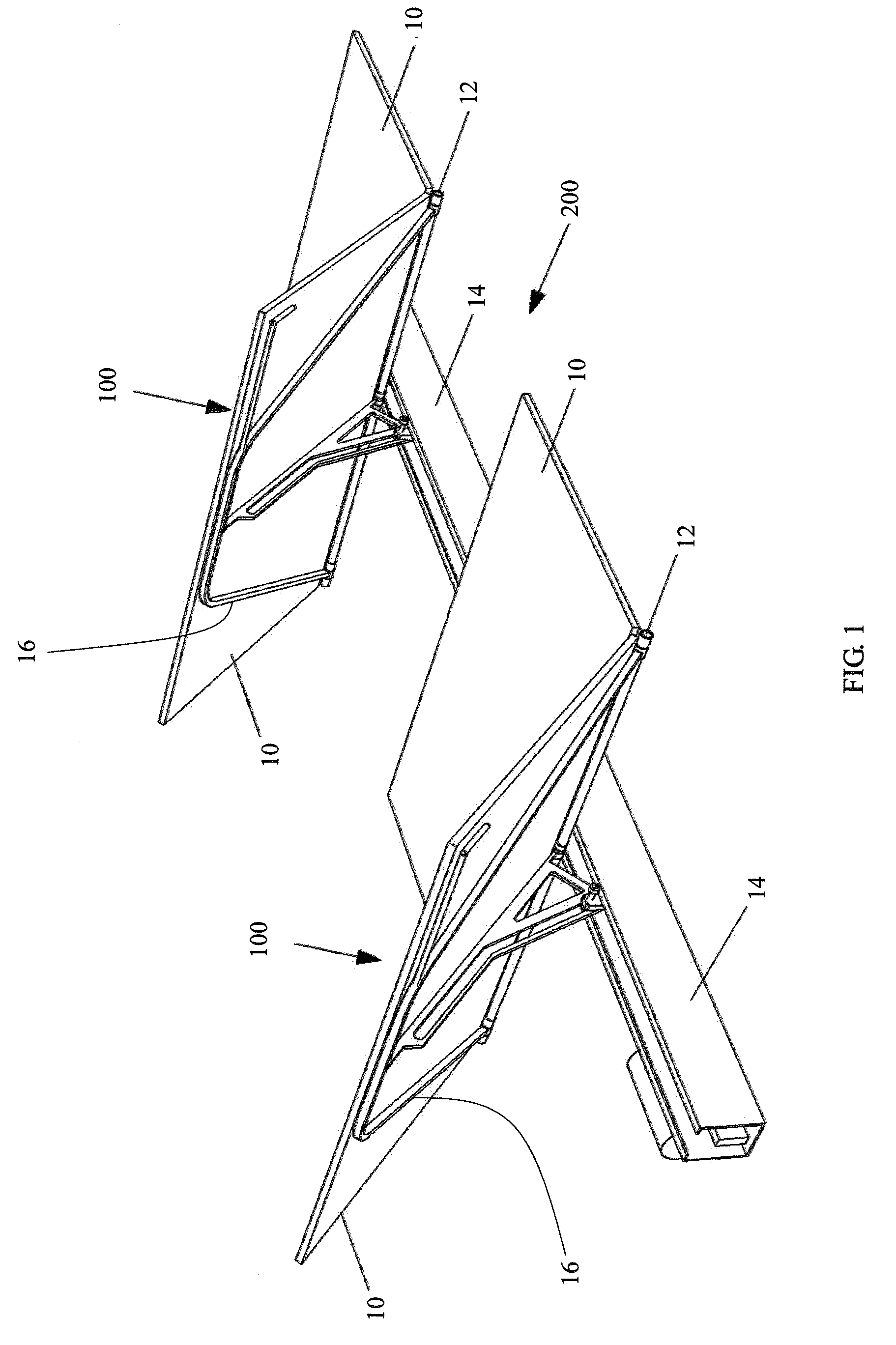
Foldable solar tracking system, assembly and method for assembly, shipping and installation of the same
ActiveUS20130340807A1Compact transportPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringSolar tracking system
A solar tracking assembly includes a spine and a plurality of paired brackets connected to the spine. The brackets are positioned on opposite sides of the spine and at least one of the paired brackets includes wheels to allow rolling movement of the spine. An array arm is attached to each bracket and is moveable from a shipping position to a deployed position, and at least one solar array panel is secured to each array arm. A method of installing a solar panel assembly includes assembling in a secondary automated process at least one solar panel assembly in an offsite location, loading the solar panel assembly in the shipping position on a truck, transporting the truck to a deployment site, and off-loading the solar panel assembly from said truck.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Single axis solar tracking system
ActiveUS20140338659A1Performance maximizationTight and efficient connectionPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyHigh torqueControl theory
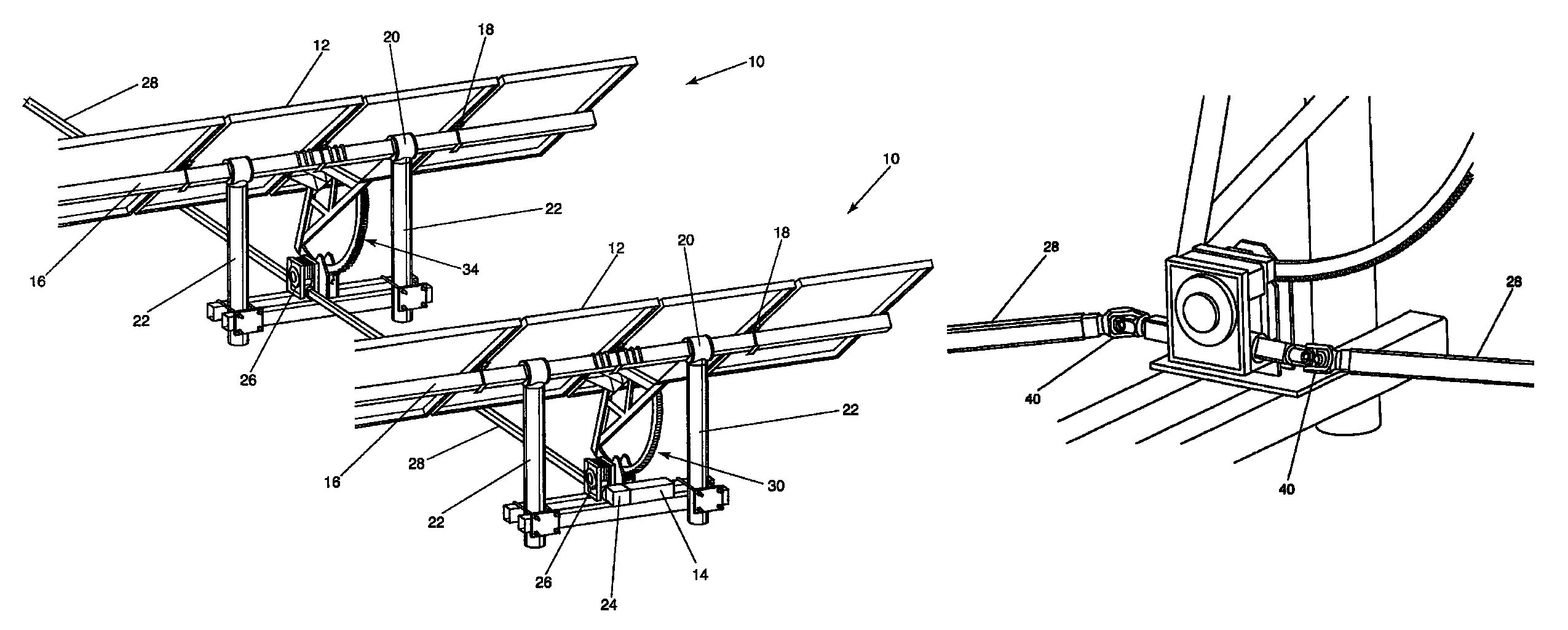
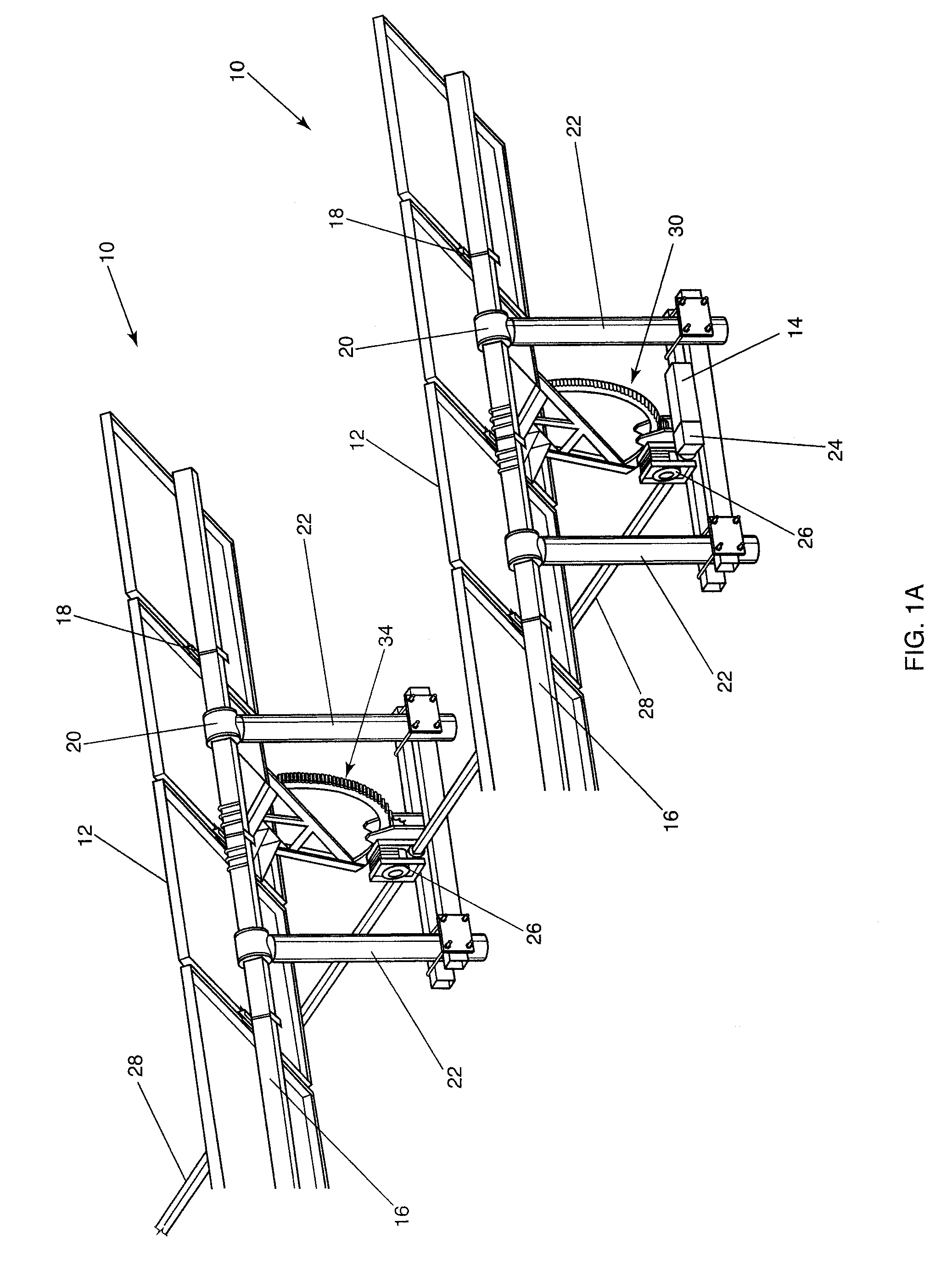
A solar tracking system with a plurality of tracking assemblies moved by a single motor. A method and system that prevents overloading the motor or tripping a circuit breaker due to an obstructed or impeded tracker includes sensing movement of the tracker assemblies and entering into obstruction clearing modes. Obstruction clearing mode 1 (OCM1) is a high frequency adjustable mode that prompts movement for an adjustable period of time. If movement commences, the system returns to a normal mode. If there is no movement, the system enters into an obstruction clearing mode 2 (OCM2) with is an adjustable lower frequency series of attempts. If there is no movement, no further attempts are made. Each of these steps are monitored and controlled remotely. There are two types of secure connections for drivelines, torque tubes or affixing driveline linkages for high torque conditions.
Owner:ARRAY TECH
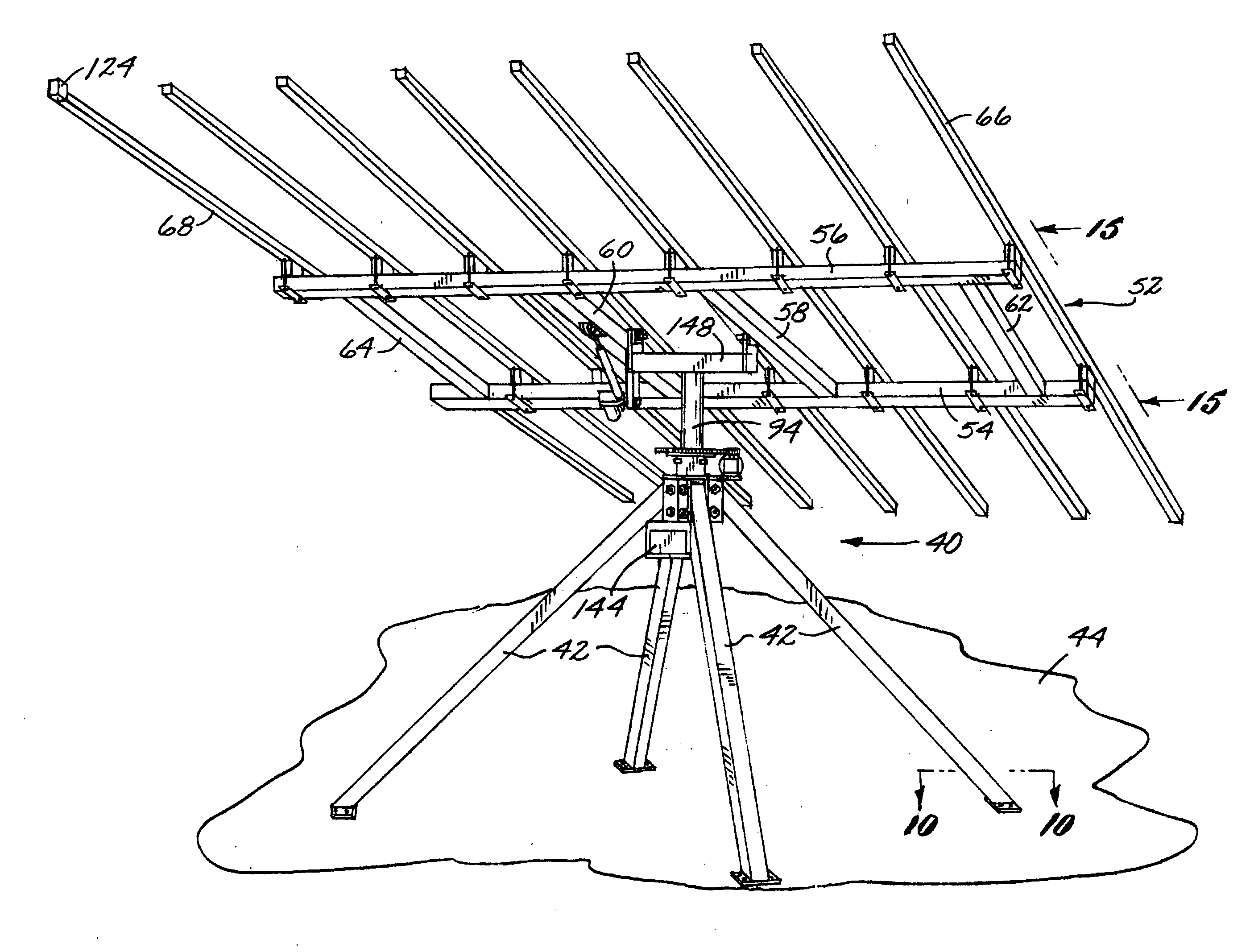
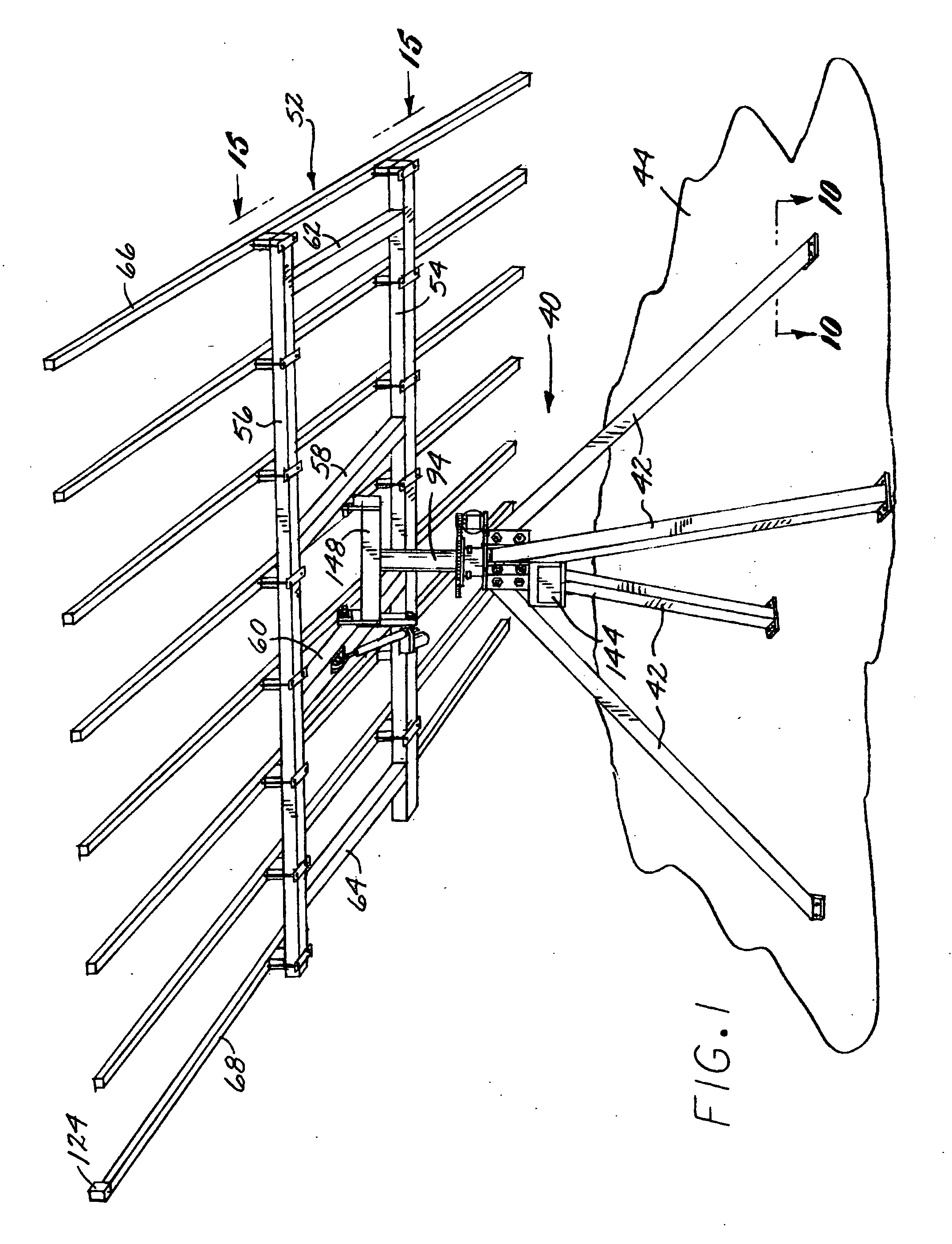
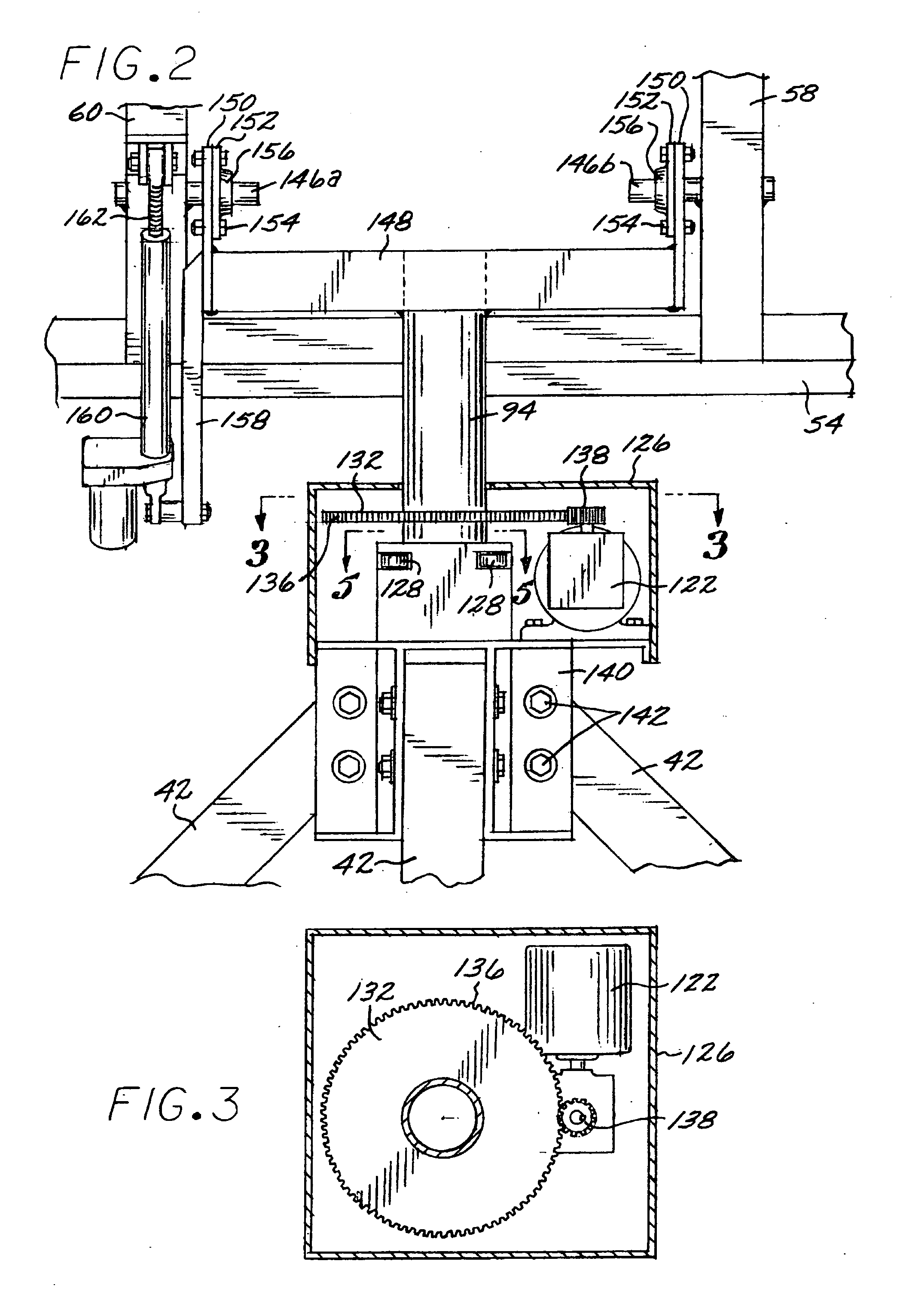
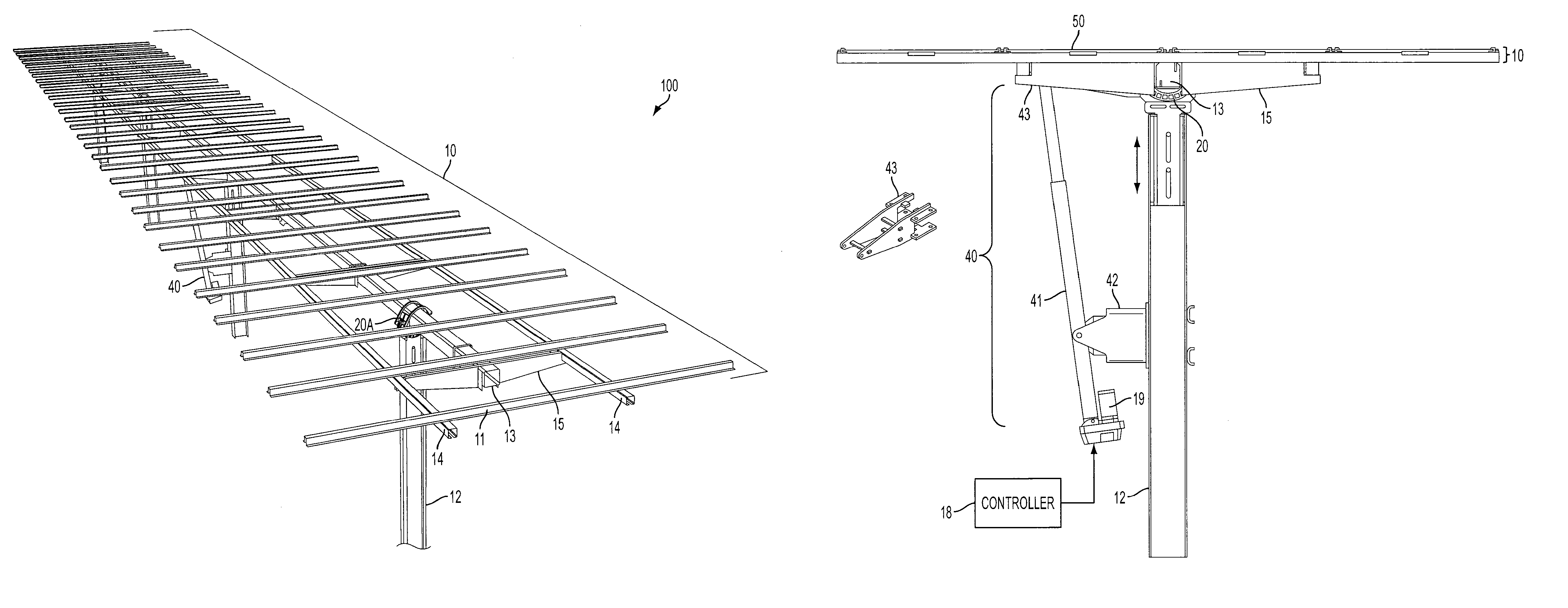
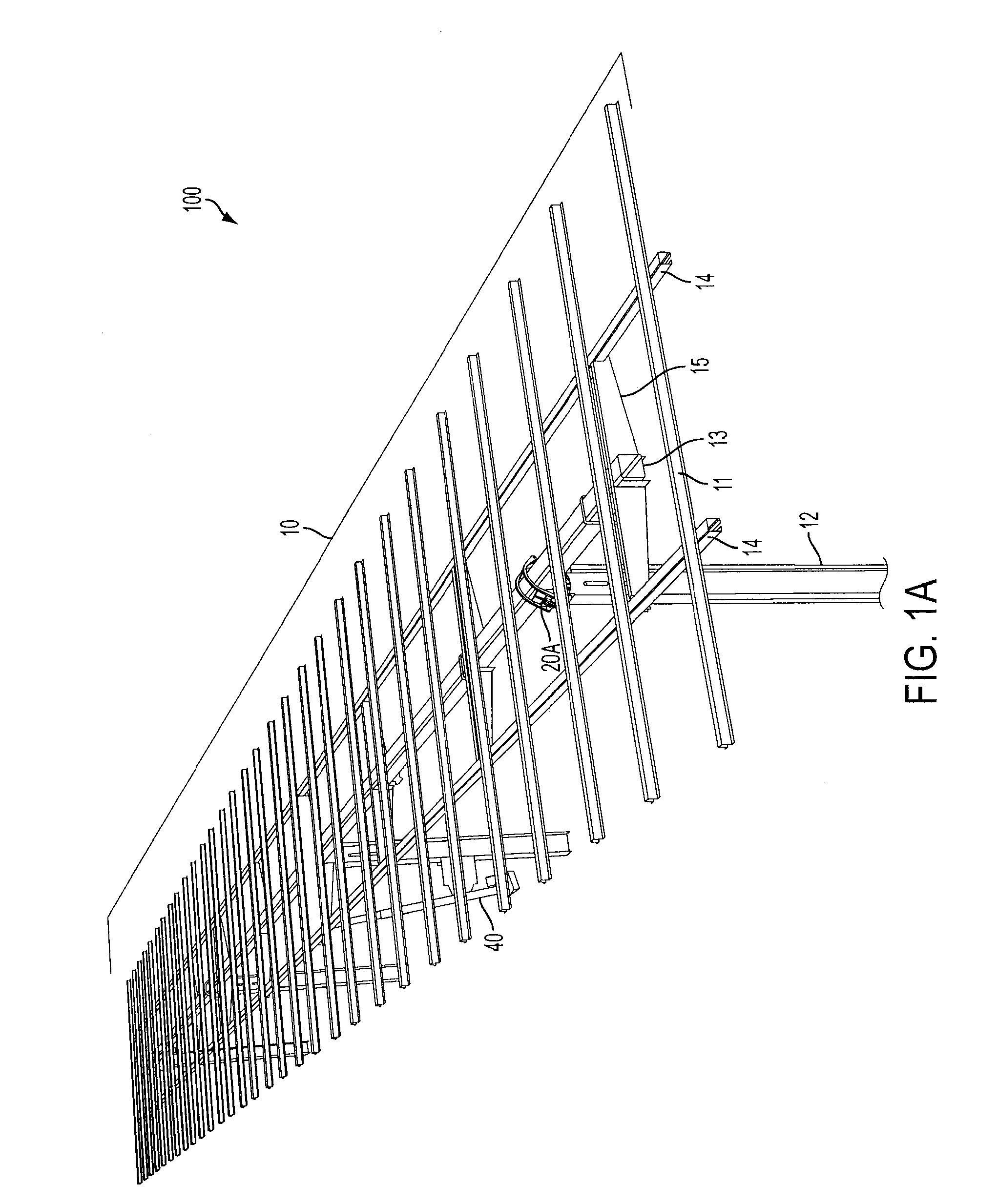
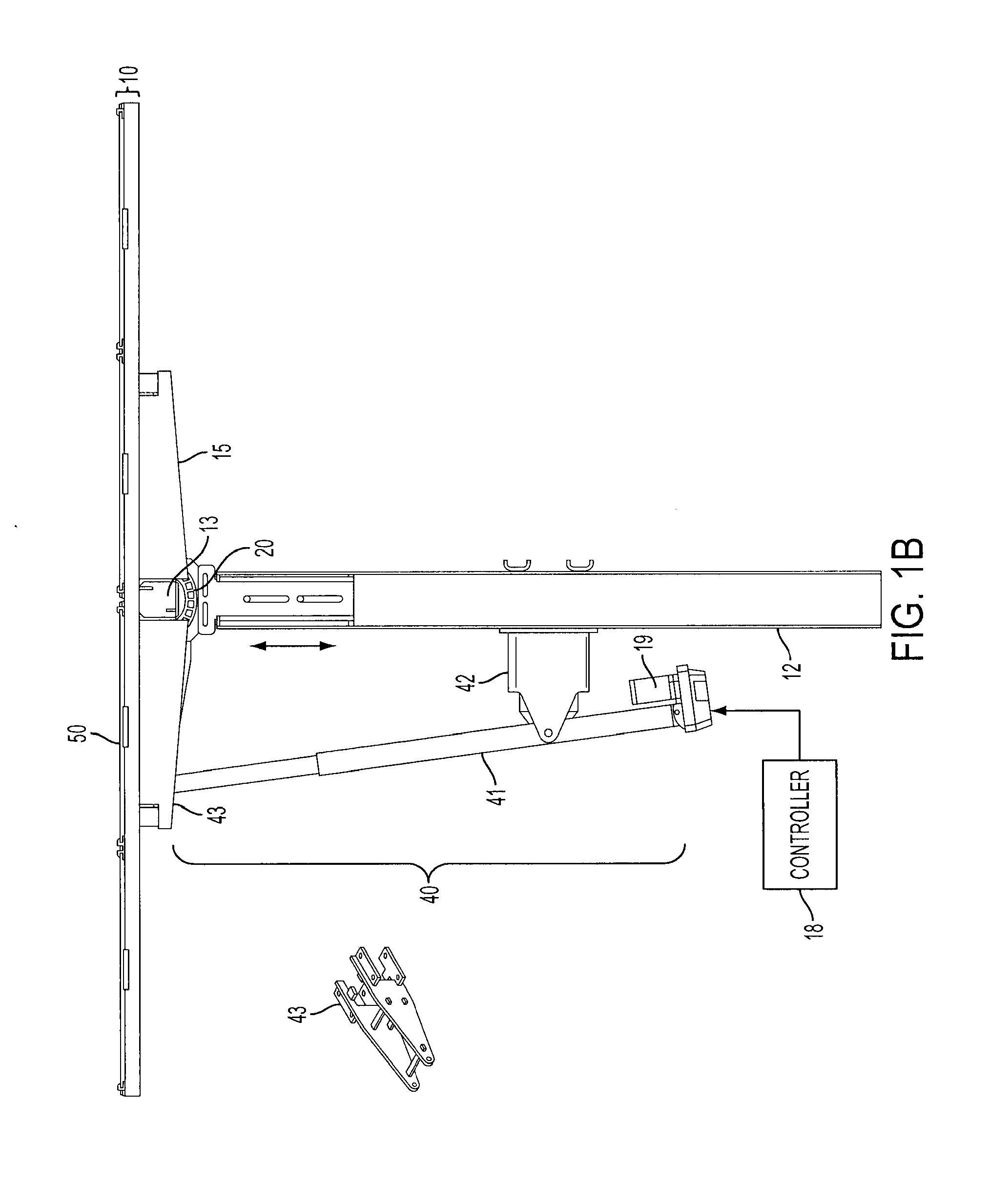
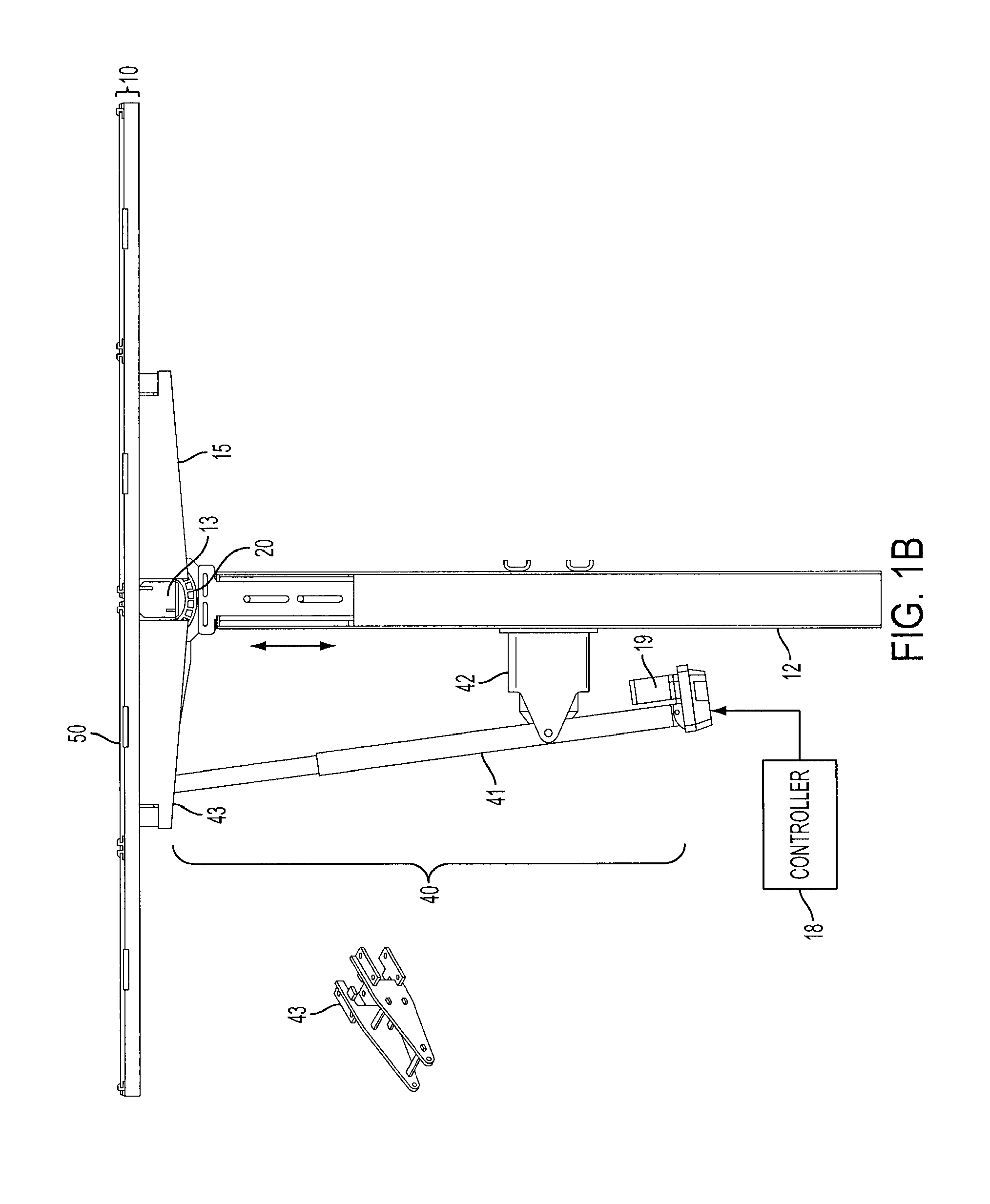
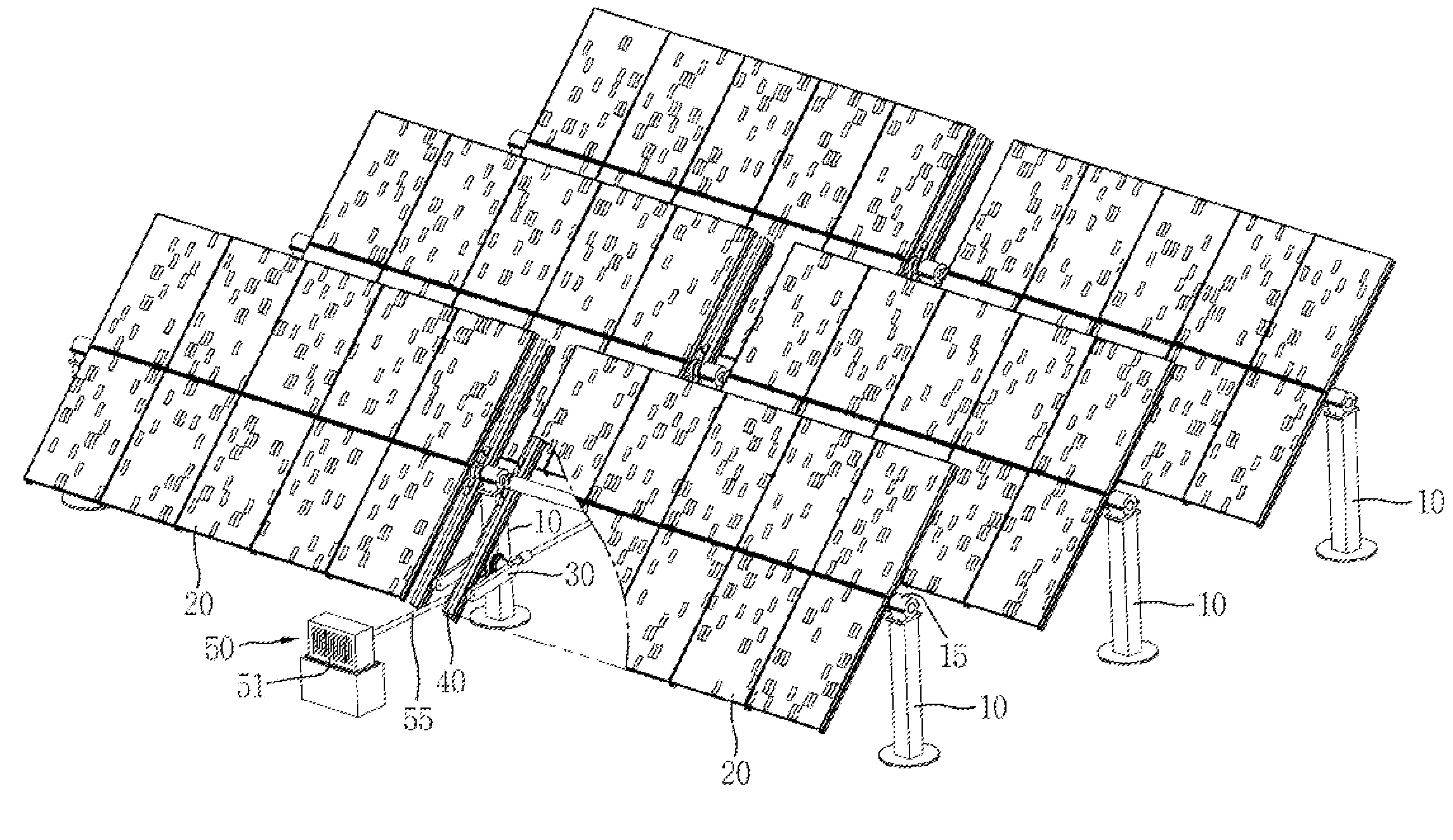
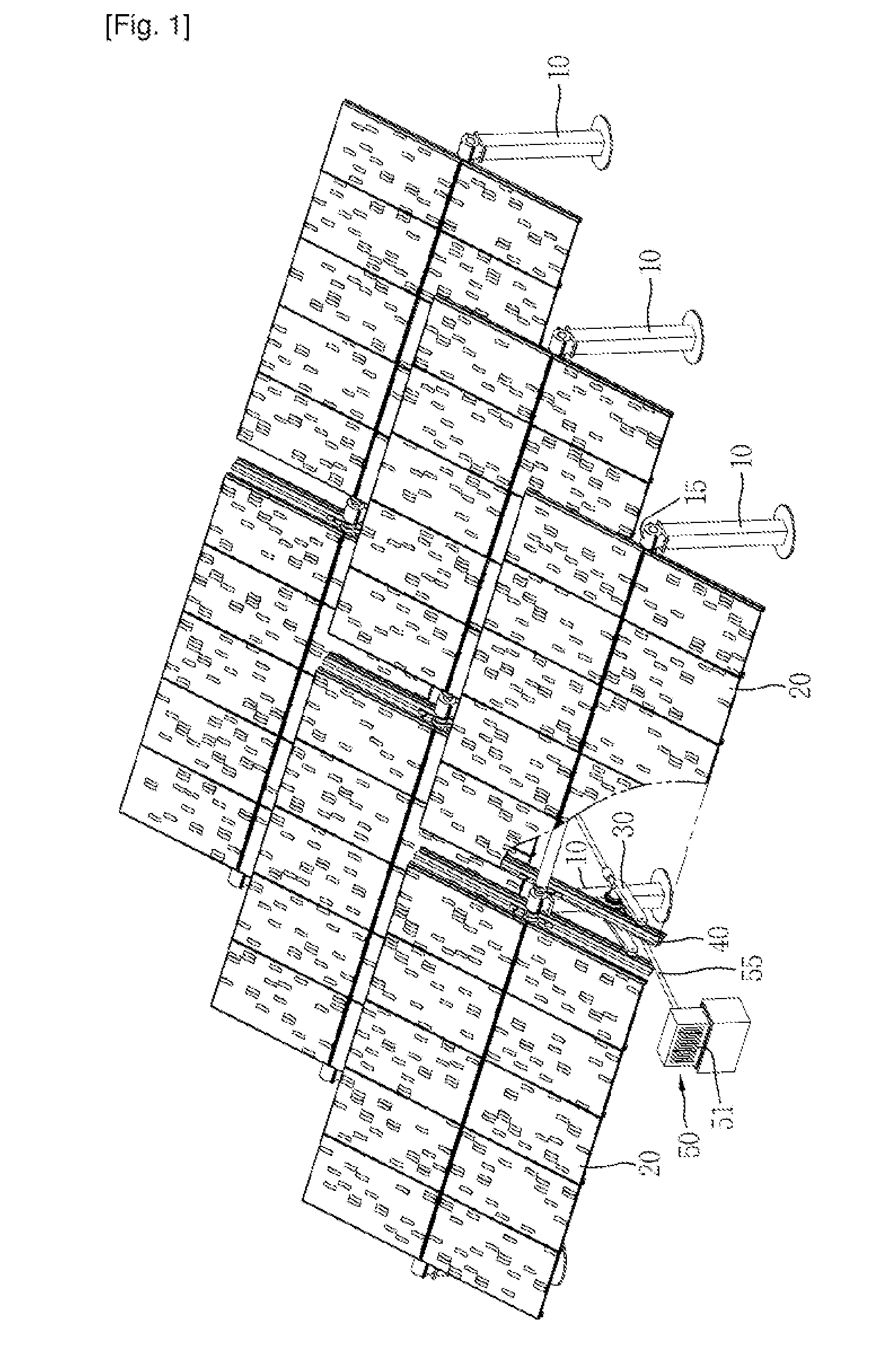
Solar Panel Array Sun Tracking System
InactiveUS20080251115A1Eliminates large side loadReduce the force requiredPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyDual beamEngineering
A solar panel tracking system that can simultaneously rotate large arrays of solar panels position in multiple rows utilizing a single drive system. The drive system comprises a single actuation device that drives multiple rotational translation stages at each solar array row for tilting the panels to the correct position. A dual beam structure within each row insure appropriate panel support during rotation and provide the framework for simplified installation and maintenance.
Owner:THOMPSON TECH IND
Solar Roof Tracker
A solar tracking system for mounting on a roof having one or more rooftop planar surfaces includes an array of solar tracking assemblies for at least one of the one or more rooftop planar surfaces, each array of solar tracking assemblies mountable at substantially the same orientation on the rooftop planar surface, each solar tracking assembly including a mounting structure, a steering mechanism, and one or more energy converting units that convert solar energy into electrical energy, the steering mechanism supported at least in part by the mounting structure and the one or more energy converting units steered by the steering mechanism; a drive mechanism that drives multiple steering mechanisms of the array of solar tracking assemblies; and a control processor that controls the drive mechanism so that the one or more energy converting units follow the sun.
Owner:COLLINS KENNETH D +1
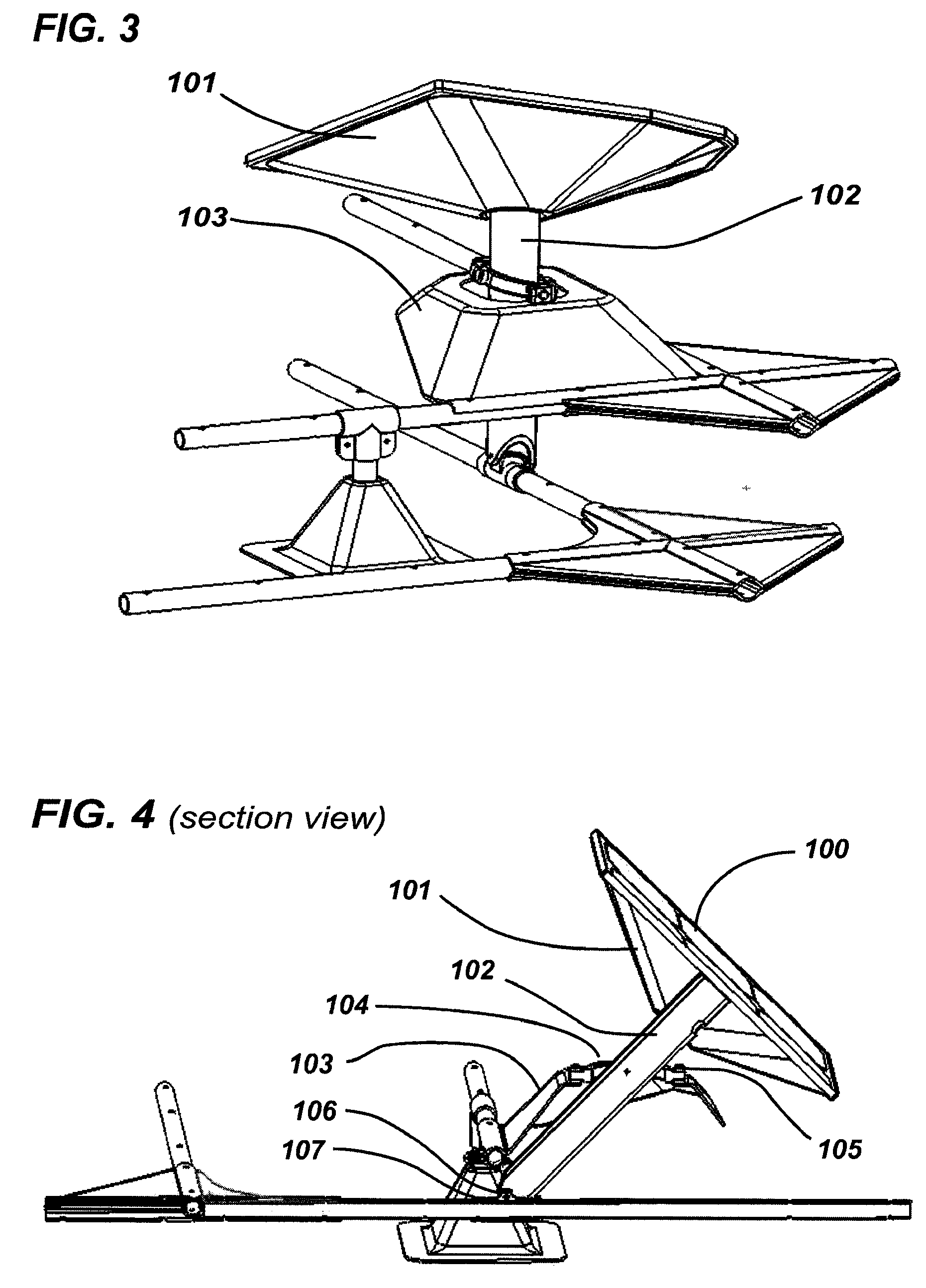
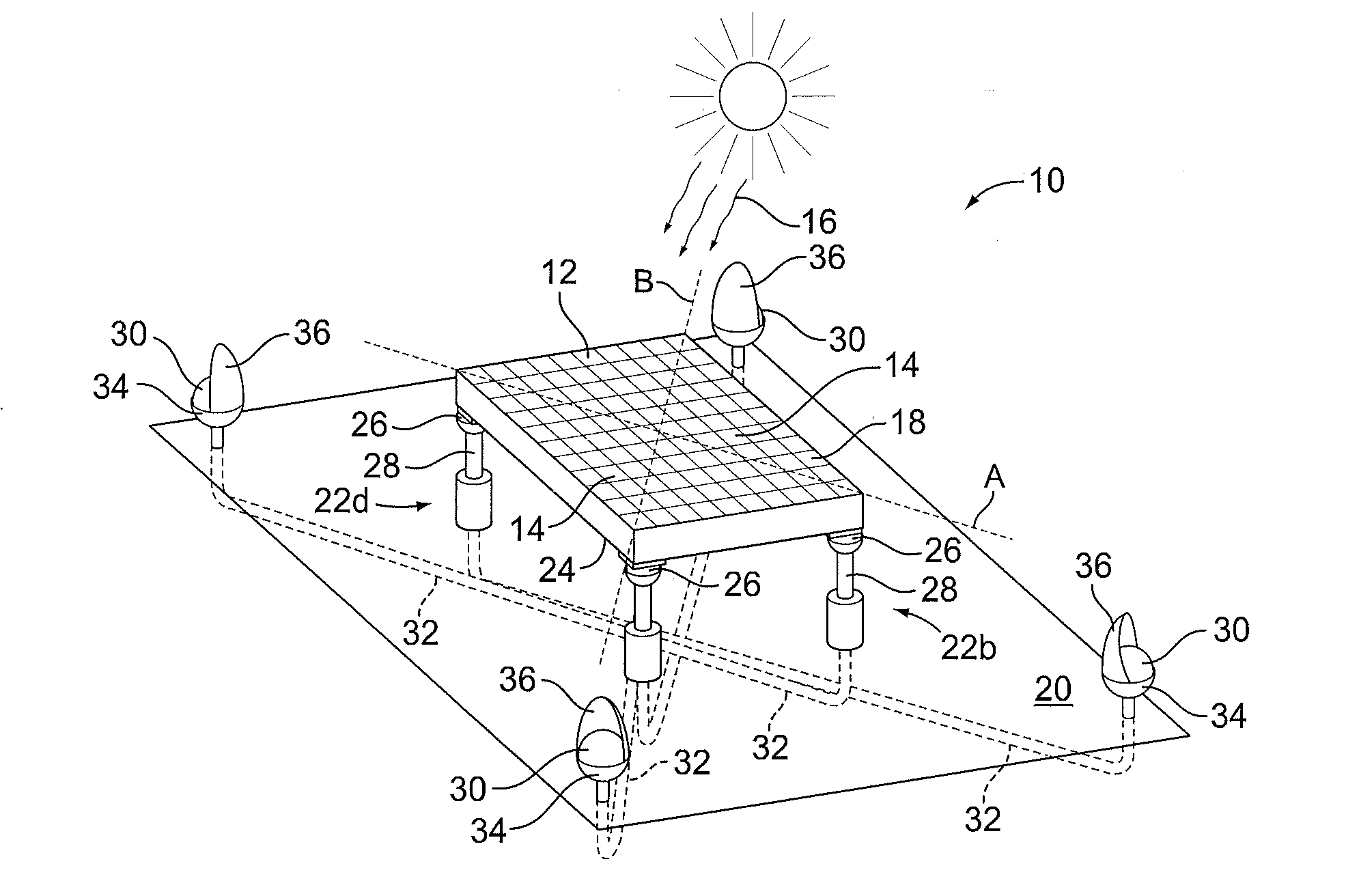
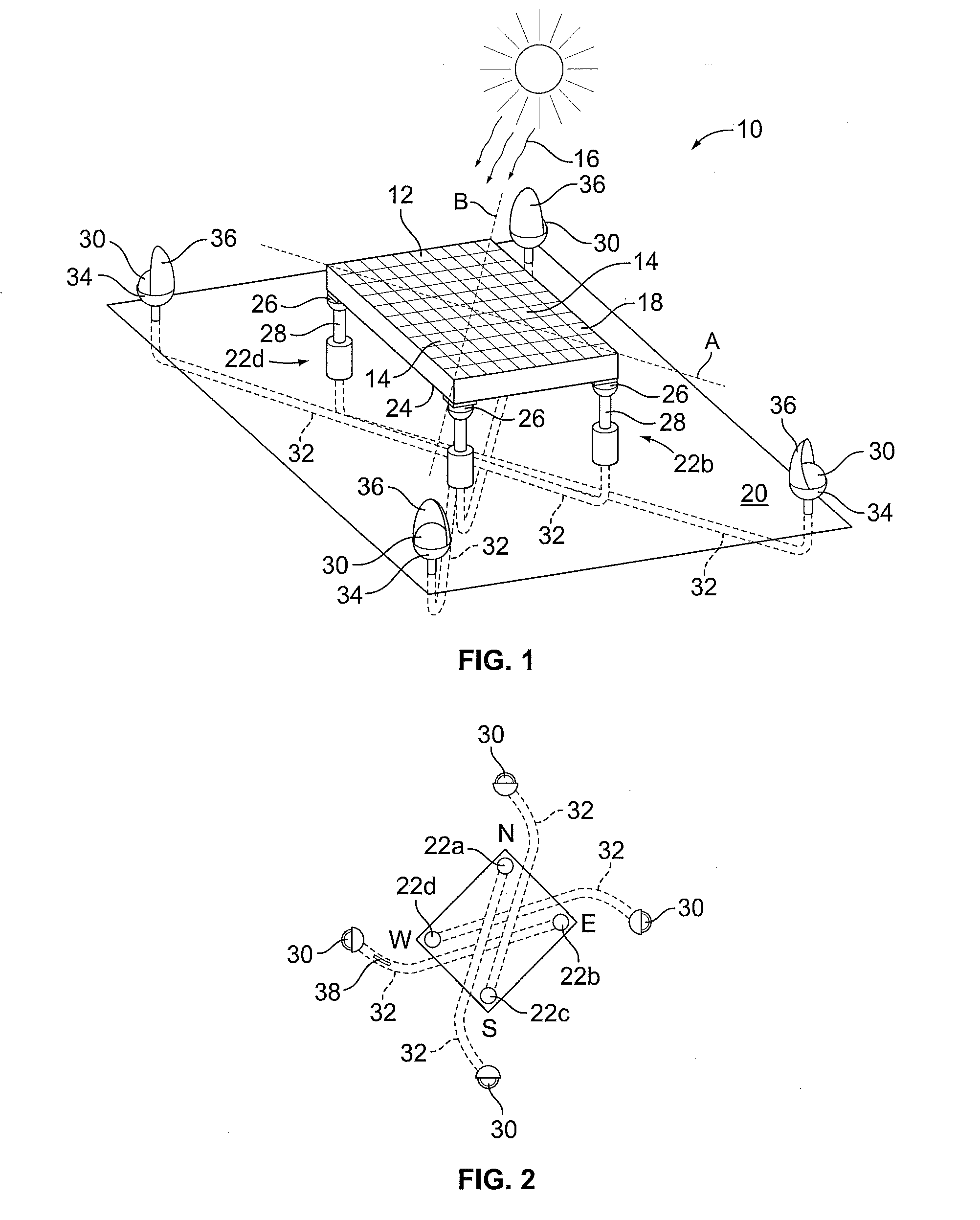
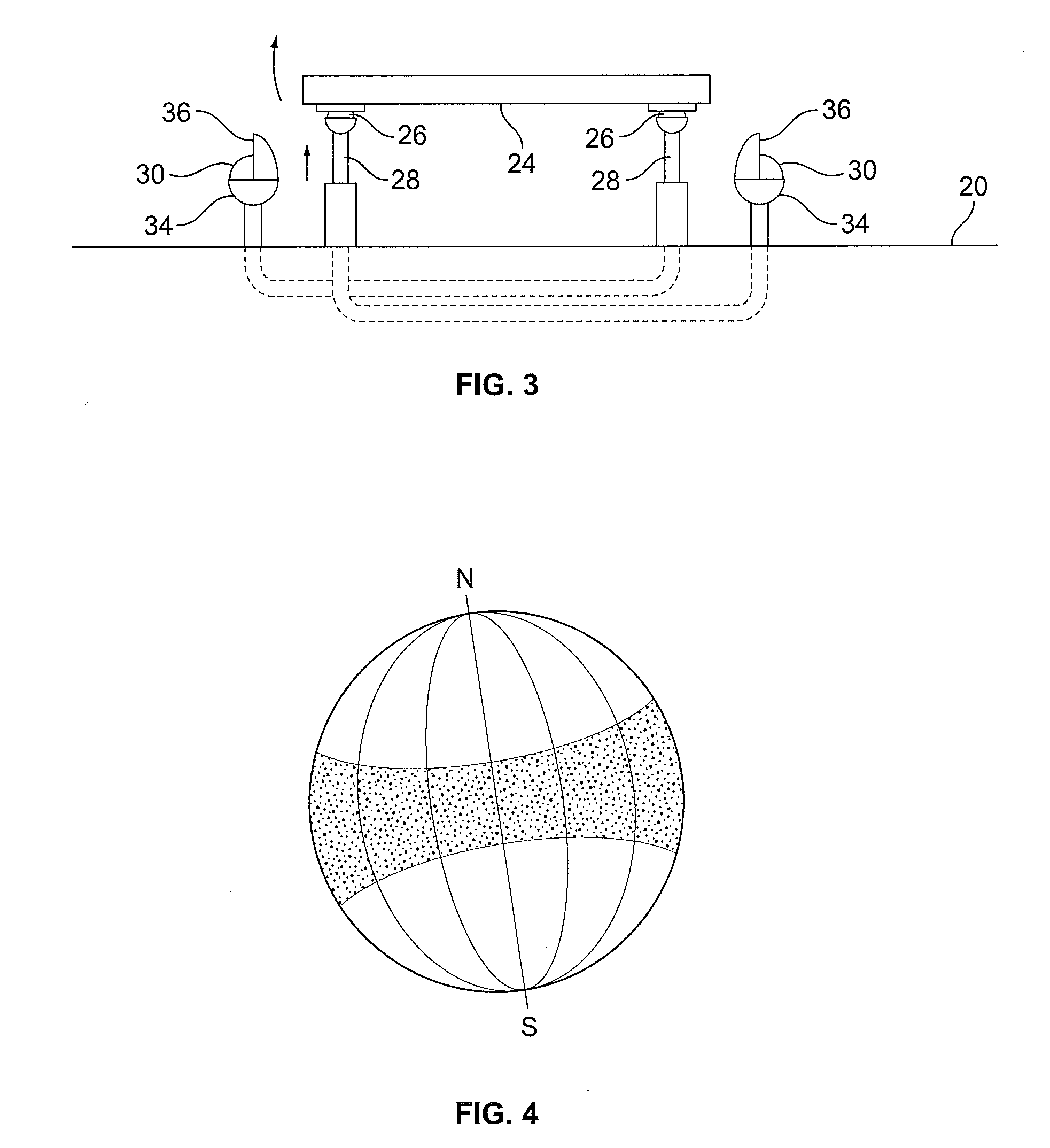
Balanced support and solar tracking system for panels of photovoltaic cells
A solar tracking mechanism and mounting platform for solar panels is mounted with three or four legs attachable to a concrete pad and includes a substantially vertically disposed axle and a substantially horizontally disposed axle to which a plurality of panel support members are mounted to form a panel support assembly. The vertically disposed axle allows at least 240 degree rotation of the panel support assembly to follow the daily East-West travel of the Sun in the sky. The substantially horizontally disposed axle allows declining or tilting of the panel support assembly for the North-South adjustment of the panel support assembly to correspond to the geographic latitude of the location where the solar tracking mechanism and platform is used. The substantially horizontally disposed axle is placed on the centroid or substantially on the centroid location relative to the panel support members, including solar panels so that, as a result, the assembly is completely or substantially balanced and can be placed horizontally or in any inclined position without the weight of the assembly, including solar panels mounted thereon, causing it to precipitously drop or fall.
Owner:SUN A RAY
Solar tracking bearing and solar tracking system employing same
An solar tracker bearing comprising a pair of stationary outer bearing races attached on either side of a bearing support element and a rotatable inner bearing race held by the pair of outer bearing races, the rotatable inner bearing race having an beam slot for seating a torque tube beam therein.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Sun tracking system for a solar panel
InactiveUS20090056700A1Solar heating energySolar heat collector controllersEngineeringSolar tracking system
A sun tracking system includes a first, and a second photo sensors, separately mounted on a solar panel on two positions apart from one another and symmetrical with respect to a center of the panel. A first sleeve surrounds the first photosensor; a second sleeve surrounds the second photosensor. Each of the sleeves has an inclined opening with reference to the surface of the panel.
Owner:LIN JEFFREY +2
Solar panel tracking system and associated tracking sensor
InactiveUS20120048340A1Photovoltaic supportsSolar heating energySolar irradianceSolar tracking system
A solar tracking system for active tracking of a solar panel array relative to the sun's position includes at least two photovoltaic (PV) sensors disposed along a common axis at opposite cardinal headings. A shadow structure is configured with the PV sensors, wherein the PV sensors are oriented relative to the shadow structure such that one of the sensors lies at least partially in a shadow cast by the shadow structure at tilt angles of the sensor on either side of a null position of the PV sensors, with the null position defined when the PV sensors are exposed to equal solar irradiance.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Two-axes solar tracking system and device for solar panels
InactiveCN101997453ANo need to expend strengthExtend your lifePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyGravity centerEngineering
The present invention relates to a simplified and lower cost two-axes tracker for solar PV (photovoltaic) or CPV (concentrated photovoltaic) solar panel, as well as heliostat solar reflectors and solar Stirling engine. In particular, the disclosure addresses a simplified and gravity centered tracker structure with low cost single or dual linear actuators mounted on the side of ground post which is easier for replacement and maintenance at lower cost.
Owner:廖恒俊
Solar tracking bearing and solar tracking system employing same
An solar tracker bearing comprising a pair of stationary outer bearing races attached on either side of a bearing support element and a rotatable inner bearing race held by the pair of outer bearing races, the rotatable inner bearing race having an beam slot for seating a torque tube beam therein.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Method and apparatus for solar panel tracking
InactiveUS20110094503A1Improve and refine tracking abilityImprove accuracyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringDaylight
A method for tracking the movement of the sun from East to West across the sky during daylight hours to enable solar photovoltaic (PV) panels or arrays of such panels to capture significantly more solar energy than fixed solar panels. Readily-available sun position data (taken from ephemeris or celestial navigation tables) can be programmed into read-only memory (ROM) chips. Date and time of day information can also be programmed into ROM chips powered by long-life, rechargeable batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries. Using such ROM chip data, a solar panel or an array of solar panels can track the sun position provided that during installation (with the panels aimed longitudinally towards the South), the solar panels are positioned upwards towards the noontime sun position to establish a starting point. This enables the sun tracking system of the present invention to track the sun without requiring a solar sensing device. Sun tracking provides an increase of from about 20% to 50% increased solar energy capture compared with fixed, non-tracking solar panels. Experimental data is also provided to illustrate the effectiveness of the present invention.
Owner:JONES DALE G +1
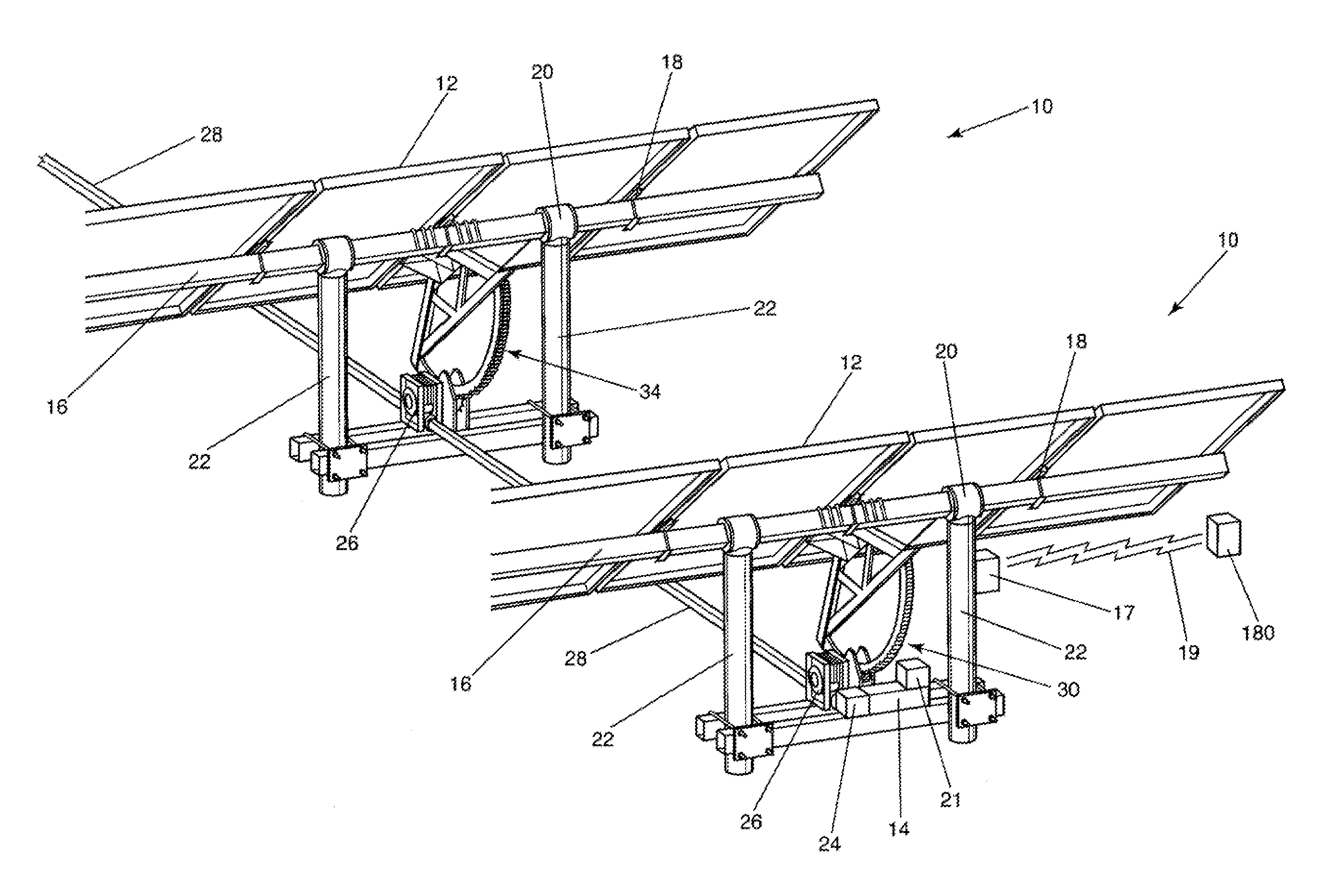
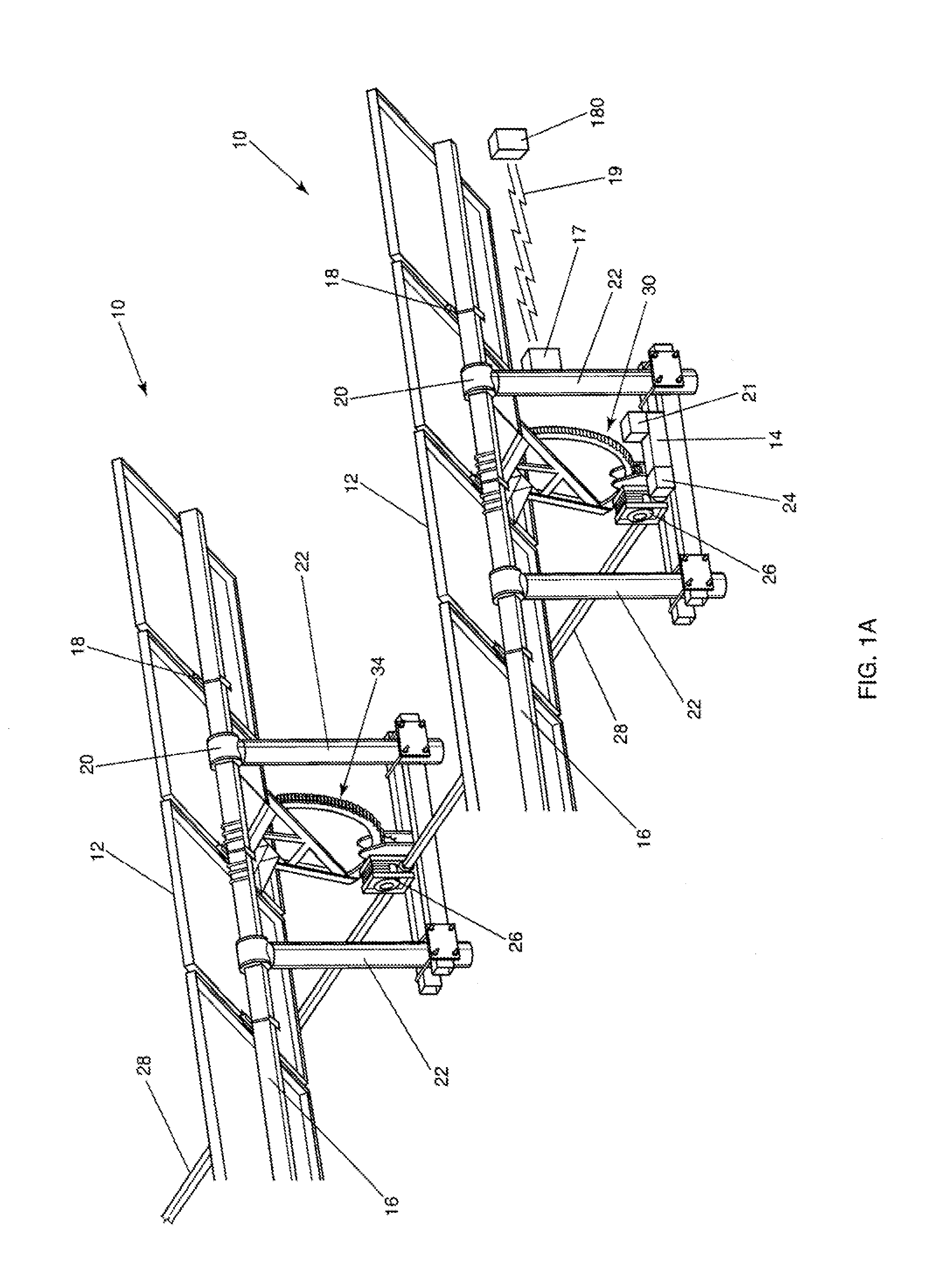
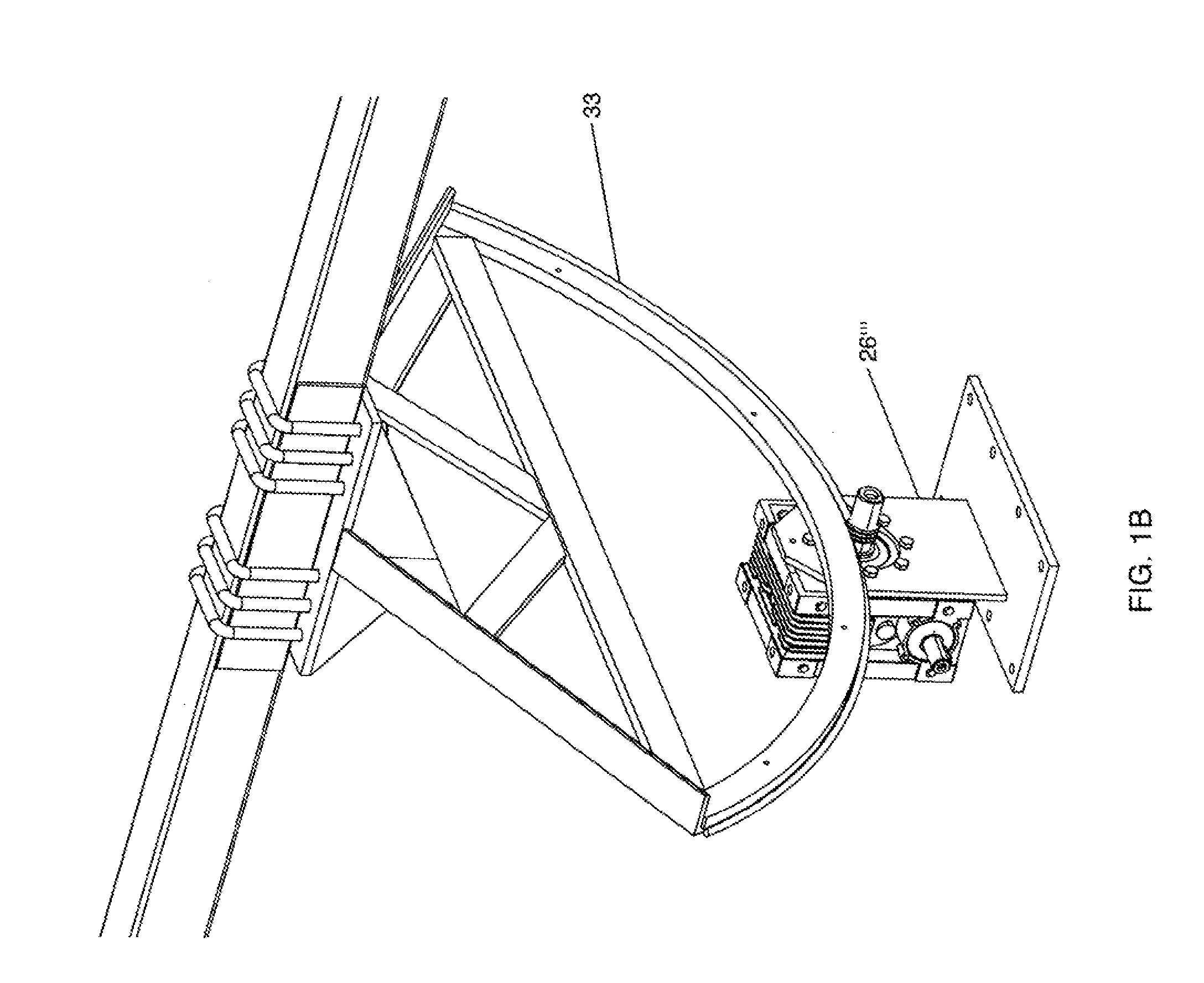
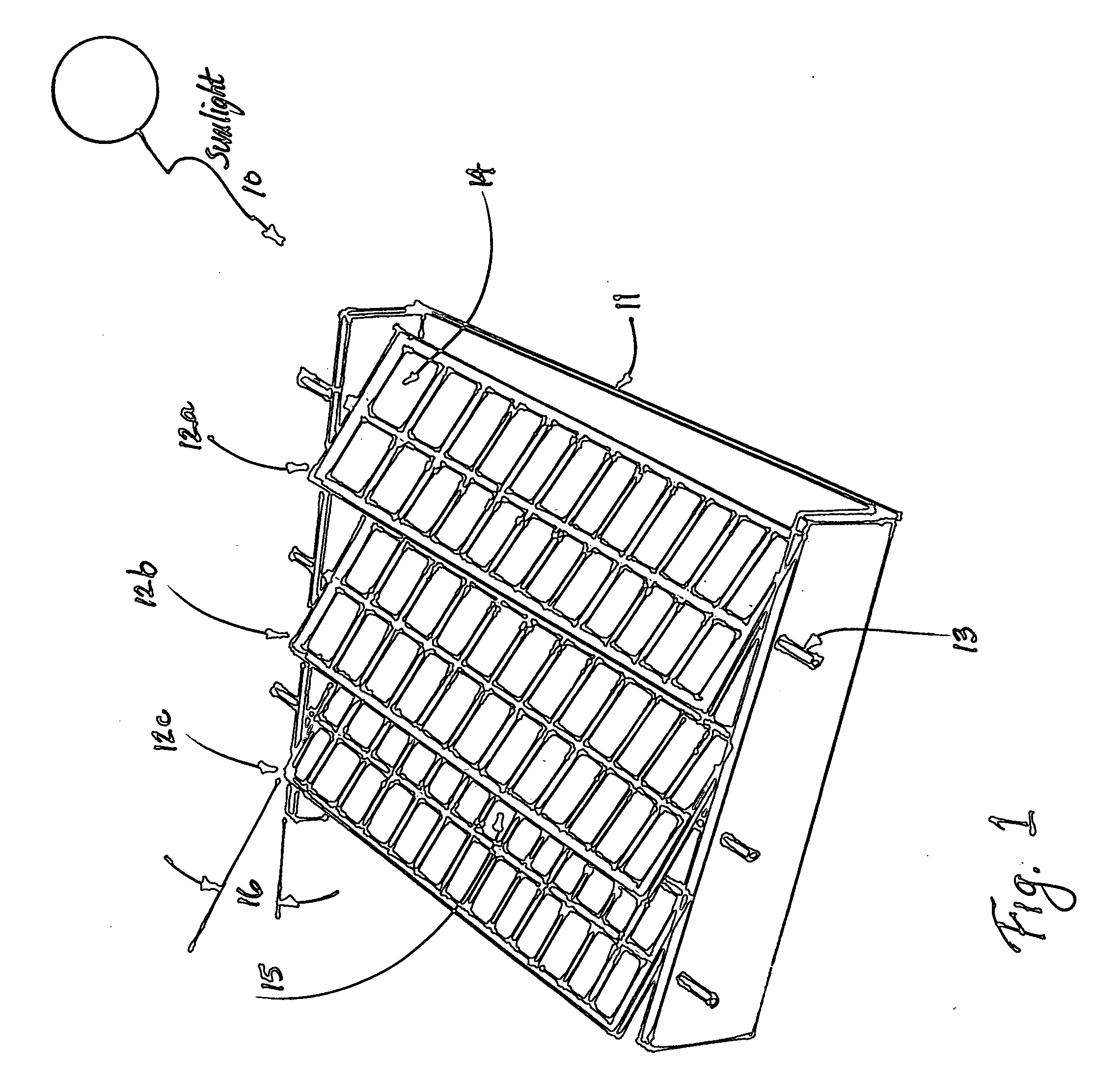
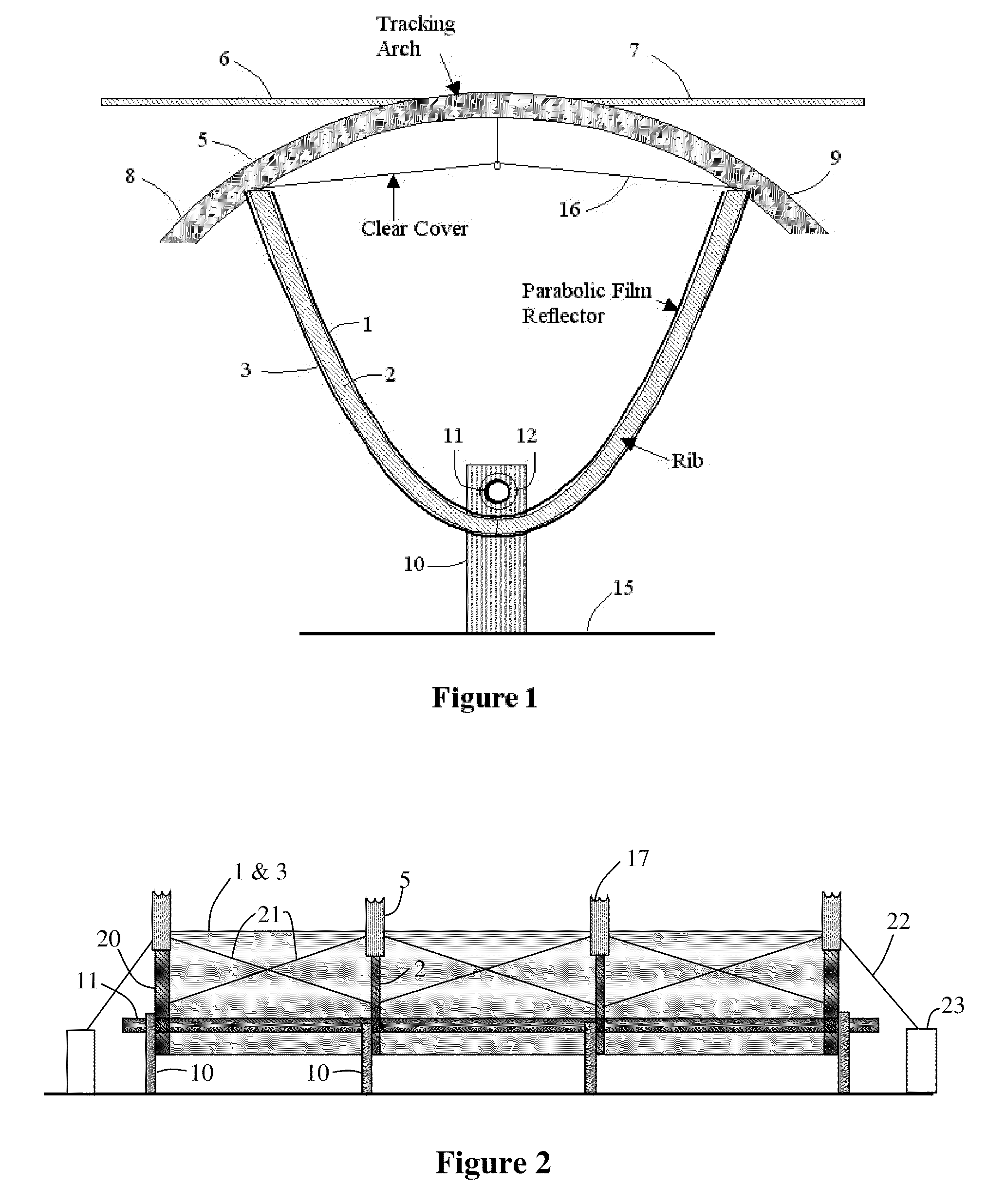
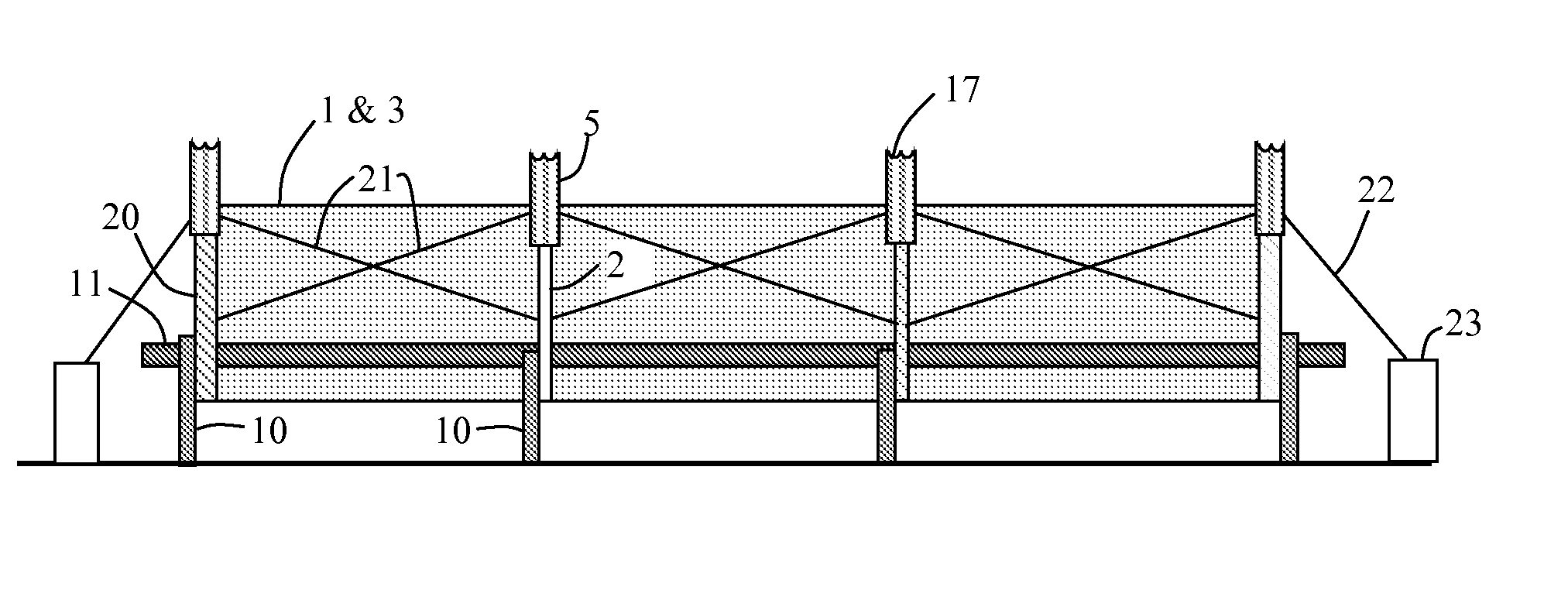
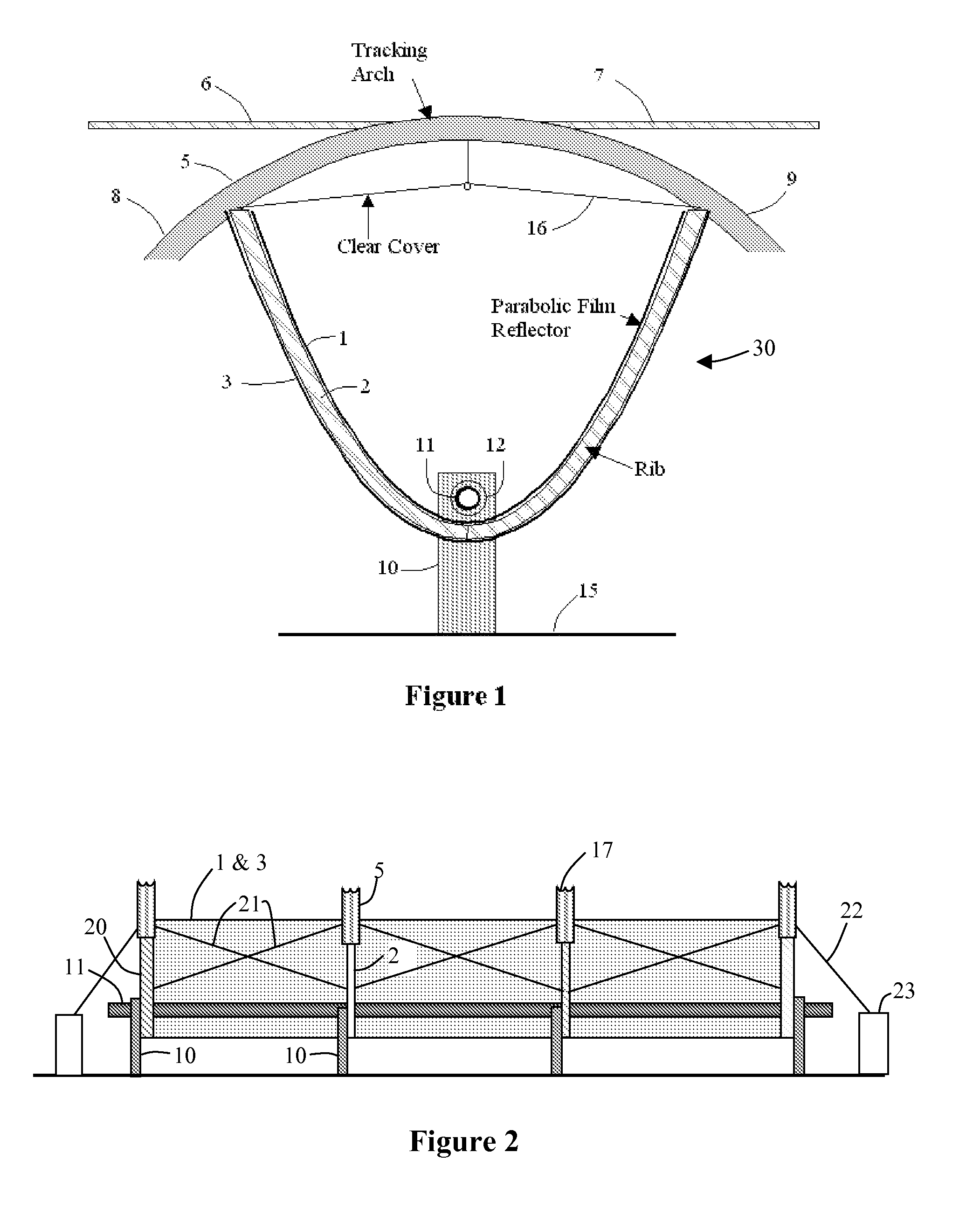
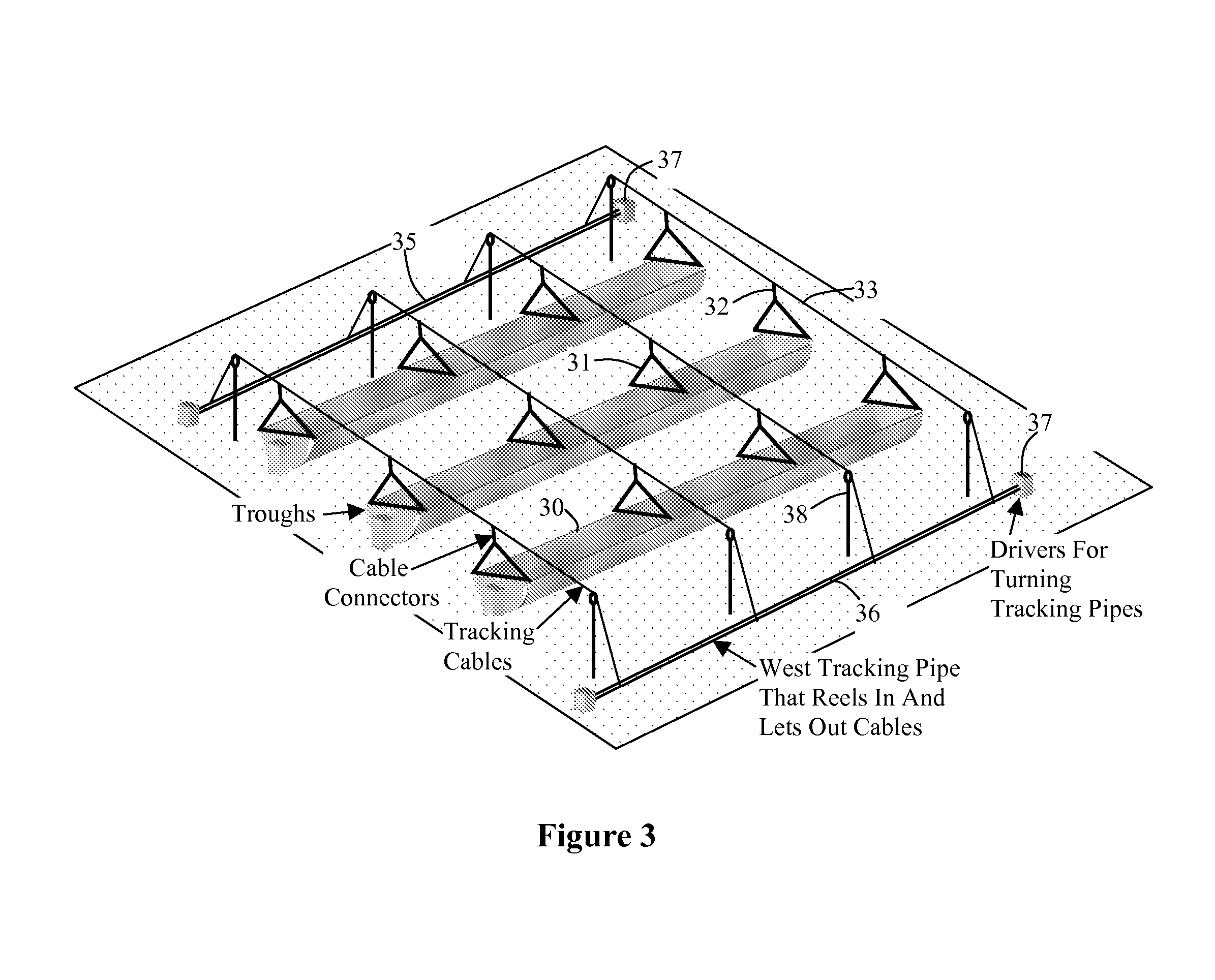
High leverage trough solar collector
InactiveUS7975686B2Avoid entanglementInexpensively moldedSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersEngineeringSolar energy harvesting
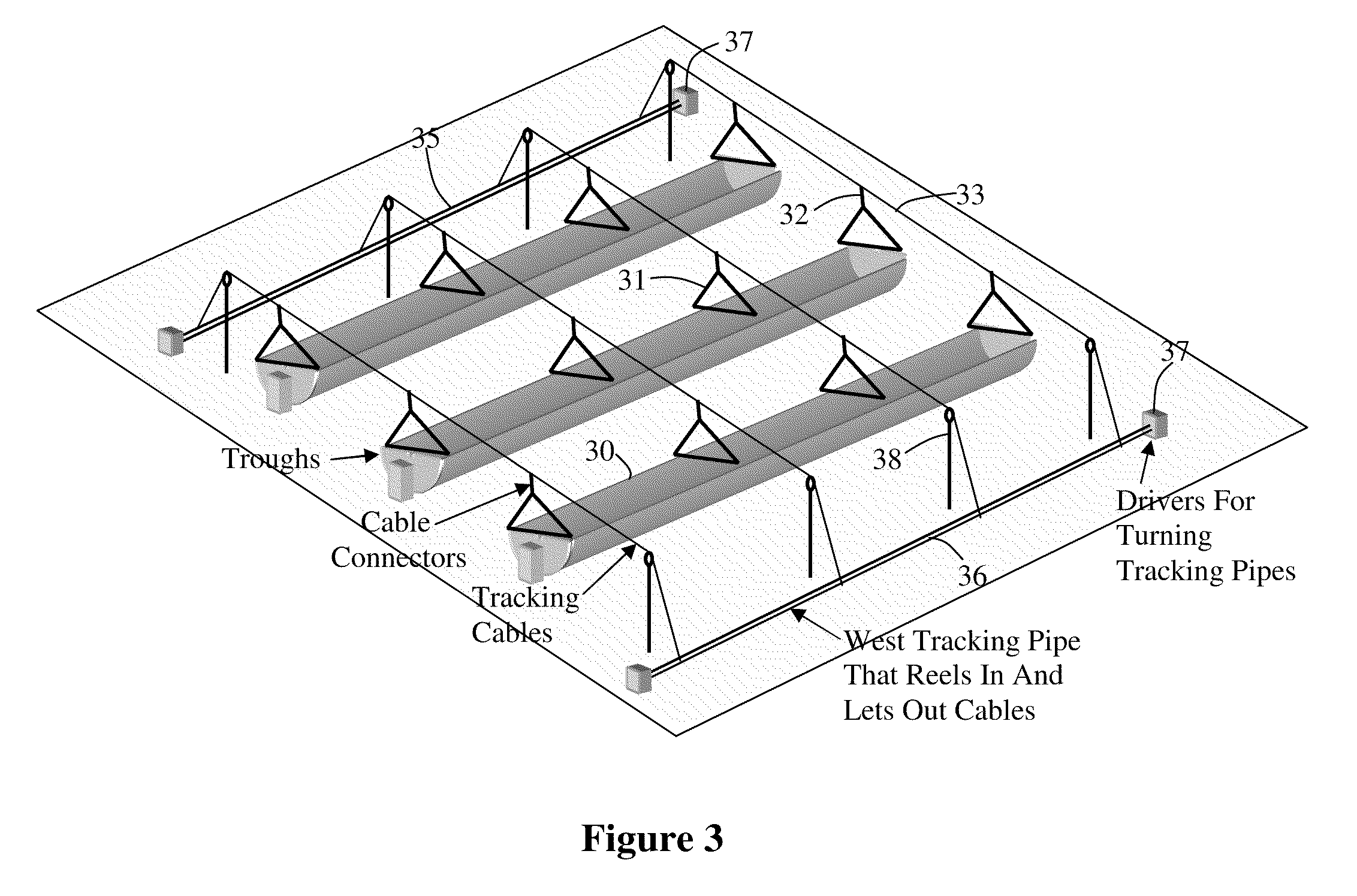
This invention is a trough solar collector that uses the principles of high leverage in order to produce a lightweight, inexpensive thermal solar collector. The parabolic reflectors are held in proper shape by rigid ribs that are spaced apart along the length of the collector. The structure of the trough is held rigid by a unique sun-tracking system that not only guides a long trough row to point it toward the sun, but also maintains the whole length of the row in rigid configuration. Small-diameter cables are wrapped around a rotatable pipe that extends along the row. The cables extend around circular arches attached to the parabolic ribs that provide high leverage for rotating the troughs. Since the arches rotate in unison, the long trough row is maintained in rotational rigidity. Rather than having heavy concrete foundations and heavy structures to support the troughs, lightweight support posts are placed into the ground, and guy wires maintain the position of the posts.
Owner:PRUEITT MELVIN L
Apparatus and A Method for Solar Tracking and Concentration af Incident Solar Radiation for Power Generation
A method and an apparatus are presented for solar tracking and concentration of incident solar radiation for power generation. The apparatus includes a solar tracking system, an optical concentrator system and a radiation collection device. The solar tracking system includes a right ascension track and a declination track for dual axis solar tracking along equatorial coordinates of the sun, wherein the right ascension track and the declination track are driven at their respective rims. The optical concentrator system is moved by the solar tracking system to concentrate the incident solar radiation into a stationary focal point. The radiation collection device couples concentrated incident solar radiation to a power generation means. The radiation collection device is disposed proximate the stationary focal point to collect the incident solar radiation.
Owner:BANERJEE RAJARSHI
Solar panel system and methods of passive tracking
ActiveUS20120285509A1Increase volumeMaximize illuminationPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyPassive trackingSolar tracking system
A solar tracking system and methods based on passive tracking of solar illumination impinging on solar panels. The system includes a solar panel having cardinal points of the panel provided with piston assemblies. Actuating of pistons in the piston assemblies orients the solar panel to maximize solar illumination impinging on the solar panel. A conduit facilitates flow of a fluid between a solar illumination sensor and piston assembly based on changes in temperature of a canister and fluid contained within the canister. The heating of the fluid causes the fluid to flow toward and activate the piston assembly to rotate the solar panel about a longitudinal axis or lateral axis, which passively orients the solar panel in a position to maximize solar illumination impinging on a front face of the solar panel.
Owner:SURGANOV ANTHONY
Distributed solar power generation and hot water supplying system
InactiveUS20150357970A1Increase heightWater temperature is difficultPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectrical batterySolar power
Owner:JIANGSU ZHENFA HLDG GRP
Thin film trough solar collector
InactiveUS8056555B2Avoid entanglementInexpensively moldedPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringPlastic film
This invention is a trough solar collector that uses inexpensive aluminized plastic films as the reflecting surface. The films are held in proper shape by stretching them between rigid ribs that are spaced apart along the length of the collector. The structure of the trough is held rigid by a unique sun-tracking system that not only guides a whole of array of troughs on a field to point them toward the sun, but also maintains the whole length of each trough in rigid configuration. It is not necessary to extend rigid metal beams along the trough to maintain the rigidity of the trough. Small-diameter cables are wrapped around rotatable pipes that extend along the east and west sides of the field. The cables extend over the field of the troughs and are attached to connecting points above the troughs in such a way that when the rotatable pipes rotate, the cables move, the troughs move with them, and the cables provide the rigidity of the troughs. The troughs are supported by support posts that are driven into the ground. Since the support posts do not have to supply torque to rotate the troughs, no concrete foundations are necessary.
Owner:PRUEITT FAMILY TRUST S PRUEITT TRUSTEE
Array powered solar tracking system
InactiveUS20170093329A1Requires minimizationMinimizing amount of wiringPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityComputer module
A self-powered solar tracker array system and related method, where a torque tube supporting a plurality of strings of photovoltaic (PV) modules, a DC drive motor with a motor controller circuit, and a drive assembly is capable to rotate the torque tube with torque generated by the drive motor, where the power for operating the drive motor is taken from electricity generated by the PV modules. The system can include a battery to provide a power source for rotating the torque tubes when the PV modules are not generating electricity.
Owner:SOLARCITY
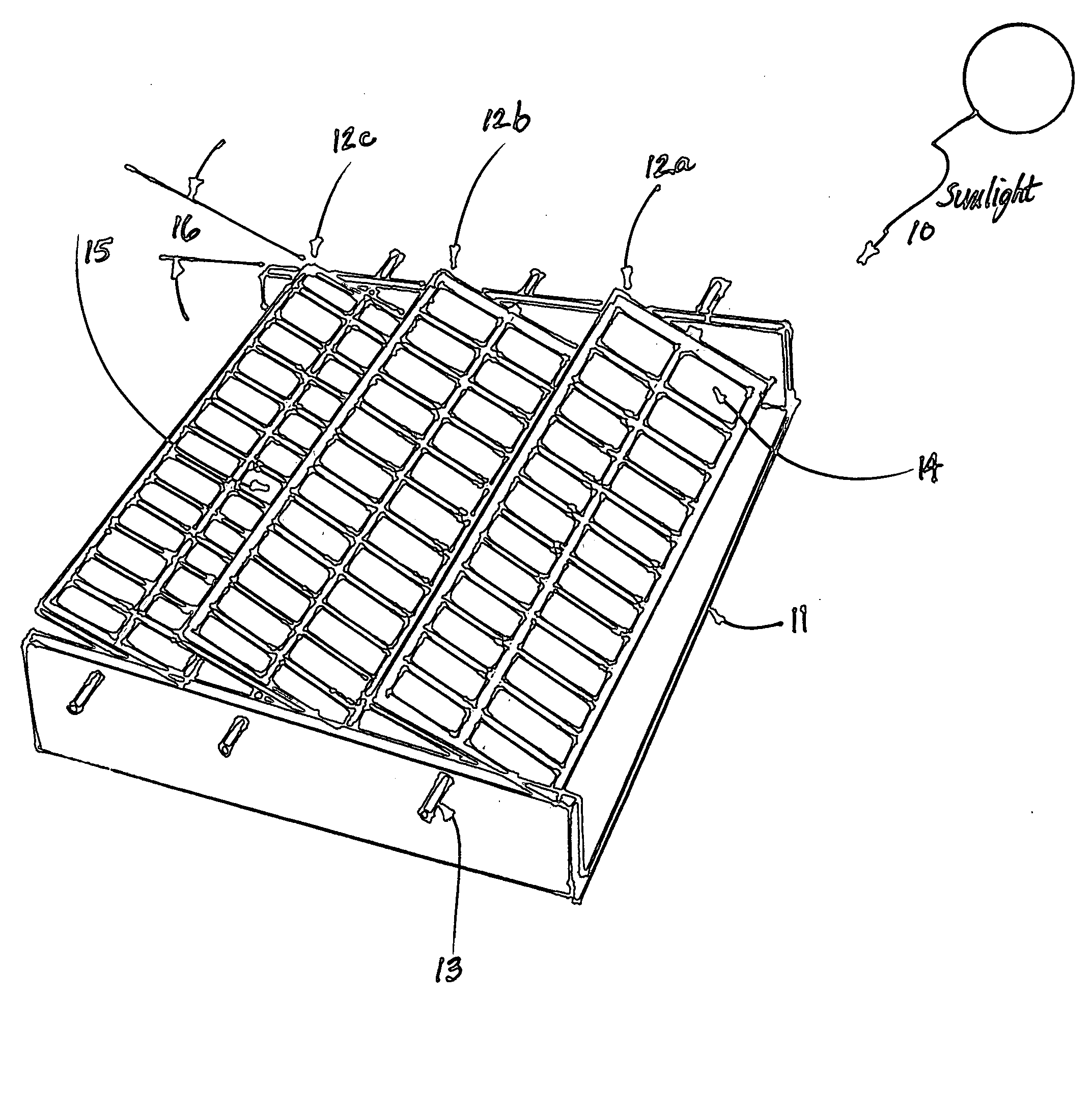
Low profile solar tracking systems & methods
ActiveUS20110061644A1Efficient collectionMinimal shadowingPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyCollection systemEngineering
A solar energy collection system comprises a frame for mounting the system on a suitable substrate and a plurality of solar panels disposed adjacent to one another on the frame. A first set of the solar panels are movable relative to a second set of the solar panels, for tracking movement of the sun during the day. Solar panels of the first set are arranged in alternating fashion with solar panels of the second set. In some embodiments of the invention, the panels in the second set of solar panels are stationary. The second set of solar panels, in some embodiments, are disposed substantially flat, relative to the frame and the substrate on which the frame is mounted. In some embodiments, differing from those in which the second set of solar panels are stationary, the second set of solar panels may be arranged to be movable relative to the first set of solar panels.
Owner:PIZZARELLO GUY A +1
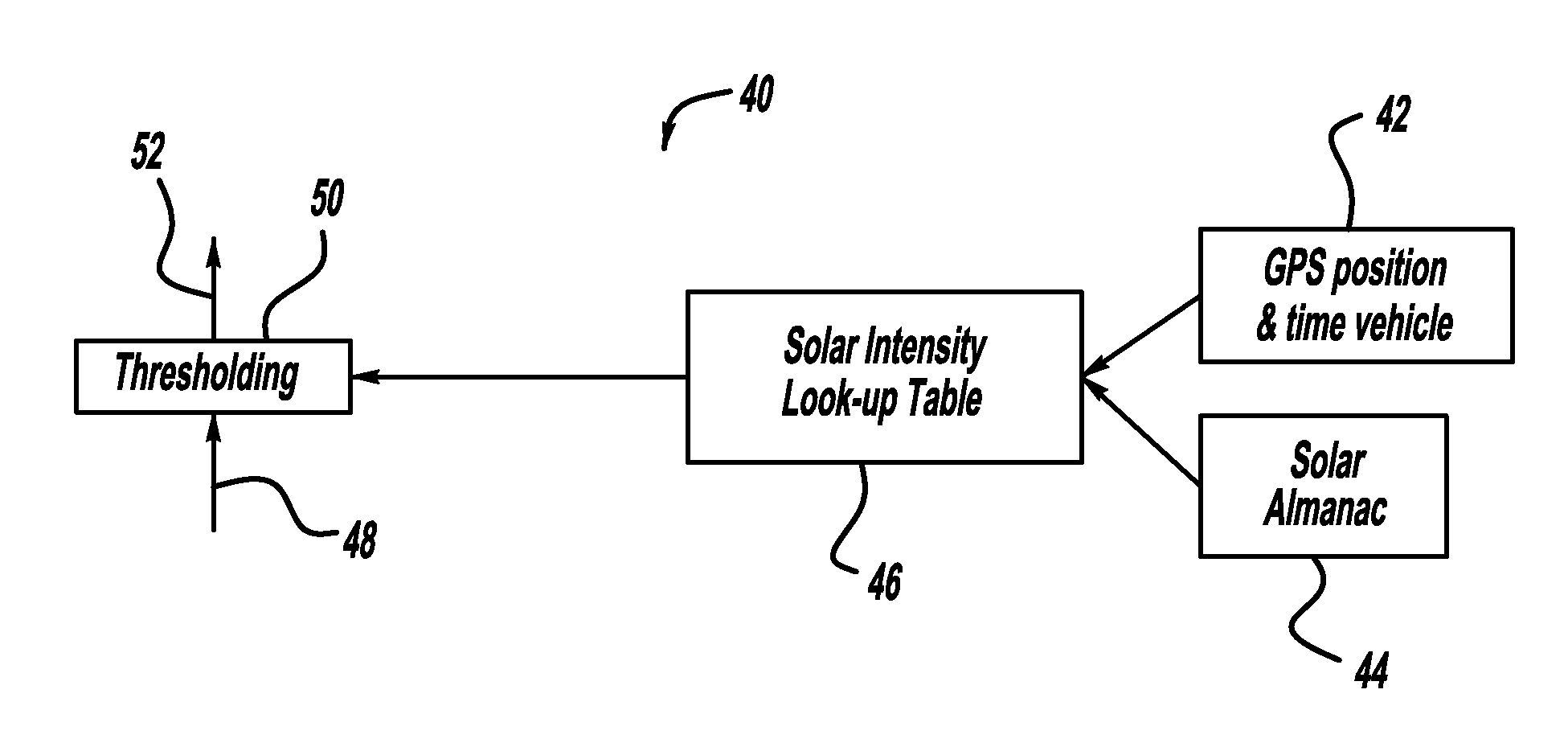
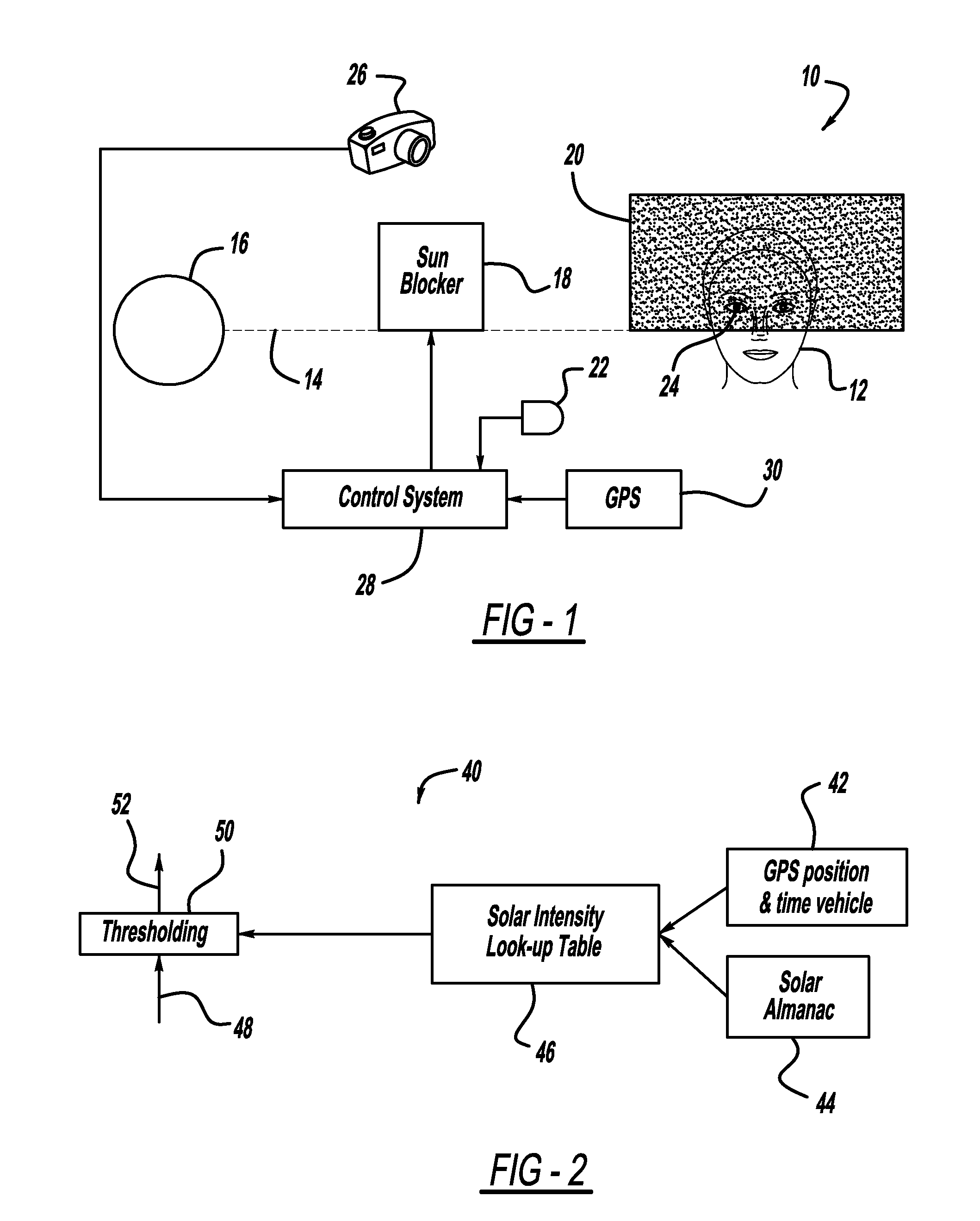
Automatic camera calibration using GPS and solar tracking
InactiveUS20110096165A1Automatically calibratingTelevision system detailsVehicle fittingsSolar tracking systemEnvironmental geology
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for solar energy utilization
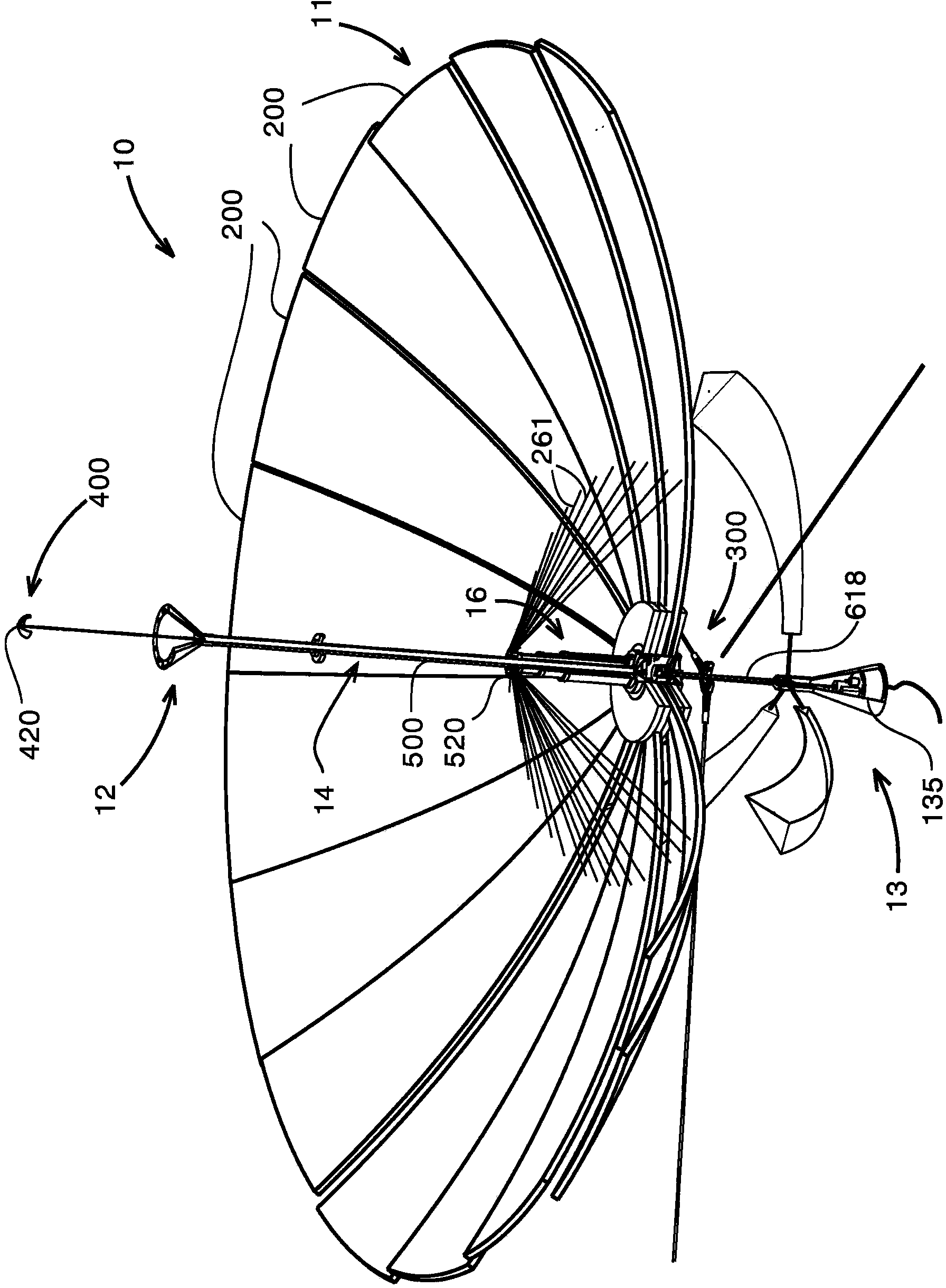
InactiveCN104114957AReduce usageEasy to replacePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringPosition of the Sun
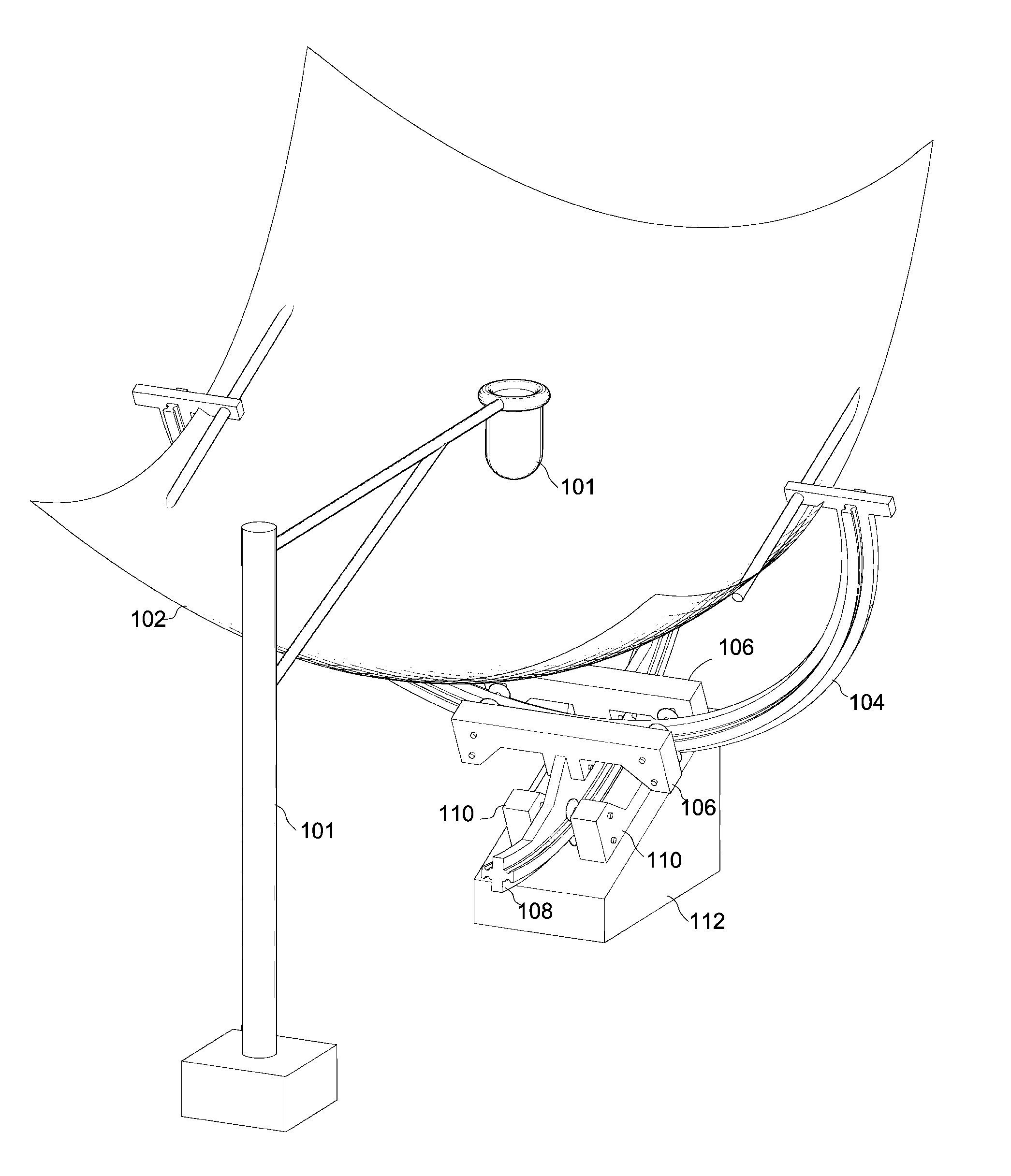
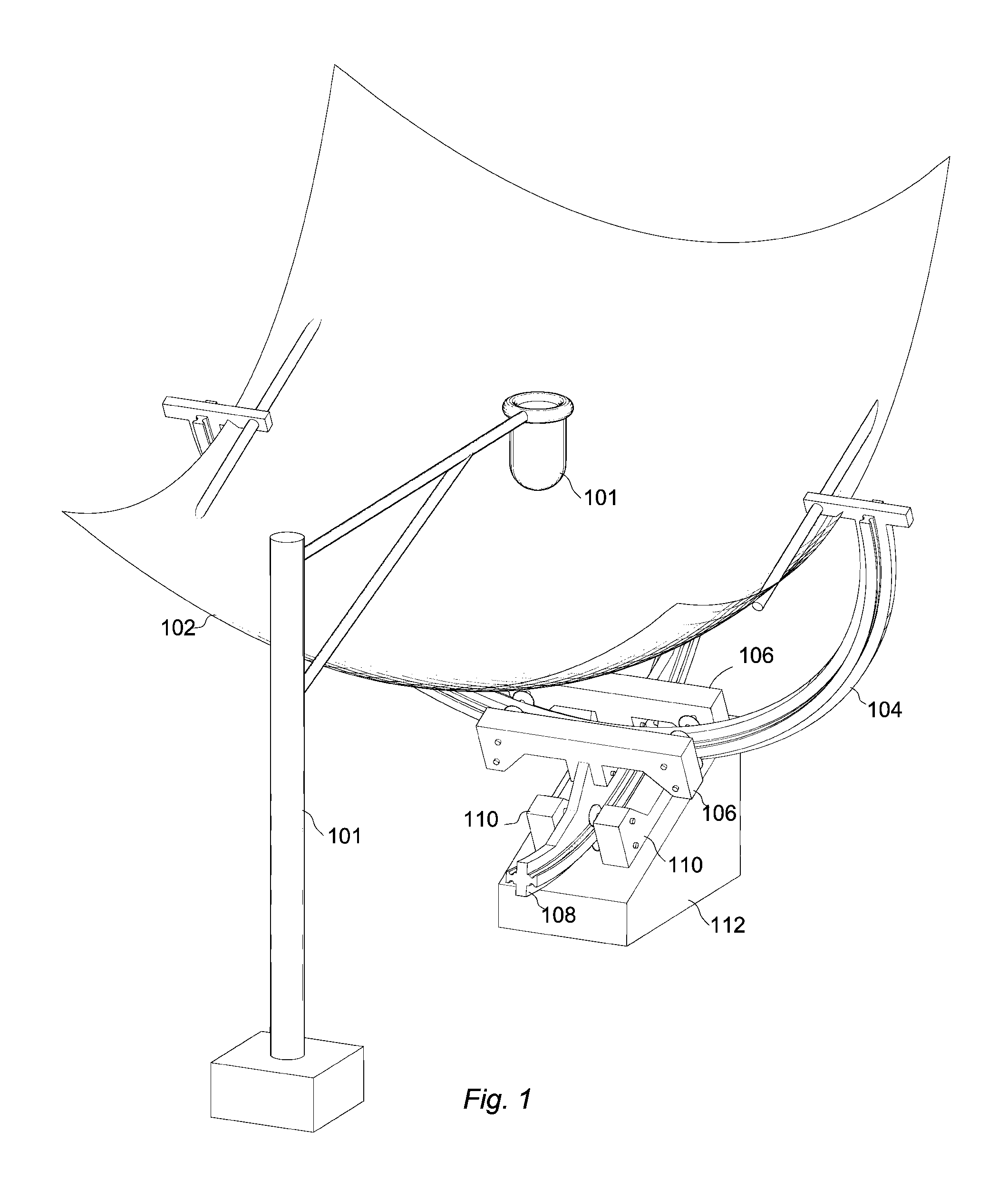
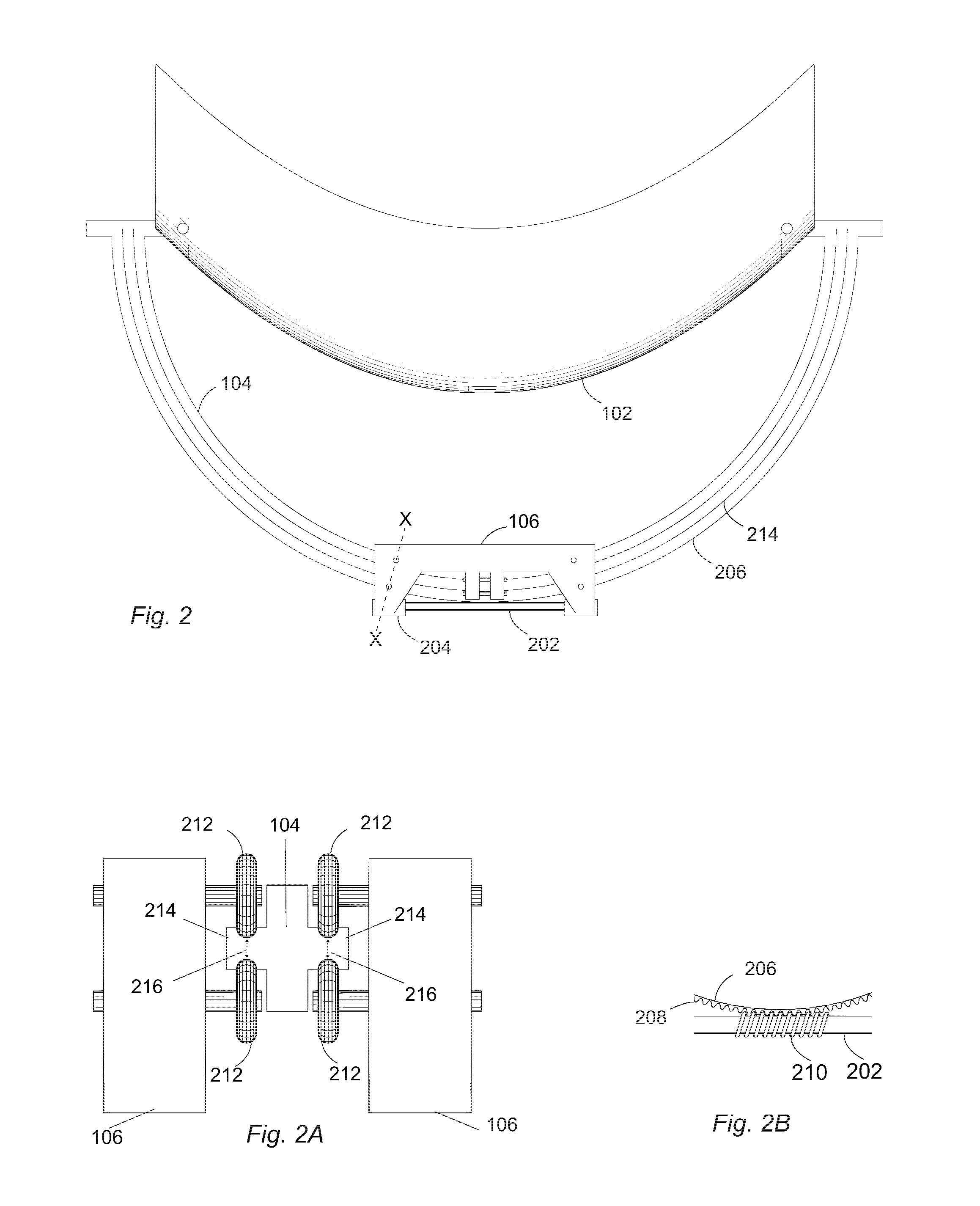
A system for solar energy utilization is described. The system comprises a solar receiver, a solar energy concentrator mounted on a pole extending from the solar receiver along the main axis of the system, and a solar tracking system. The solar receiver is configured for receiving solar energy from the sun and concentrating the received solar energy at a predetermined spot area. The solar receiver includes a plurality of flexible mirrors independent of each other and radially arranged around a main axis of the system. The flexible mirrors are configured to be either deployed for operation or collapsed, for example for transportation or in the cases of possible damage of the system. The solar energy concentrator is located at the predetermined spot area in which the solar energy reflected from said plurality of flexible mirrors is concentrated, and configured for converting the concentrated reflected energy into electric energy. The solar tracking system is configured for sensing position of the sun and tilting the system for directing the solar receiver towards the sun to receive and reflect maximum sunlight onto the predetermined spot area.
Owner:OR HAMA ENERGY
Device for tracking location of sun
InactiveUS20110108112A1Easily and reliably drivingSimple structurePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringSolar battery
A solar tracking system, including: a horizontal support; a panel frame connected to the horizontal support such that the panel frame can be tilted forwards and backwards, with a solar battery installed on the panel frame; a support unit connected both to the horizontal support and to the panel frame such that the support unit in cooperation with the horizontal support and the panel frame forms a triangular arrangement, wherein the support unit is slidably connected to either the horizontal support or the panel frame such that the support unit can slide relative to either the horizontal support or to the panel frame, thus tilting the panel frame forwards and backwards according to variations in a slidable position thereof; and a drive unit for sliding the support unit relative to the horizontal support or the panel frame. The solar tracking system realizes a simple, stable support structure and allows the solar battery panel to track the position of the sun with a low amount of power.
Owner:MIRAE ENERGY TECH +1
Automatic solar tracking device
ActiveCN102778896AImprove calculation accuracyRealize closed-loop controlControl using feedbackPosition angleControl system
The invention relates to an automatic solar tracking system which tracks the sun accurately in real time and is used for efficiently collecting and using solar energy. The automatic solar tracking device comprises a solar energy photovoltaic array, an adjusting device connected with the solar energy photovoltaic array and used for adjusting the position of the solar energy photovoltaic array, a stand column for supporting the adjusting device and a control system. The adjusting device is composed of a pitch angle adjusting assembly and a position angle adjusting assembly, wherein the pitch angle adjusting assembly is connected with the position angle adjusting assembly through a vertical shaft, the position angle adjusting assembly is arranged on the stand column, and the control system is used for performing closed loop control on the adjusting device. The accuracy in solar tracking of the automatic solar tracking device is smaller than 0.1, the energy consumption only occupies for 0.5% of the electric energy production of the driving photovoltaic array, and the automatic solar tracking system has the advantages of being long in service life, intact in protection function and the like.
Owner:LUOYANG NORMAL UNIV
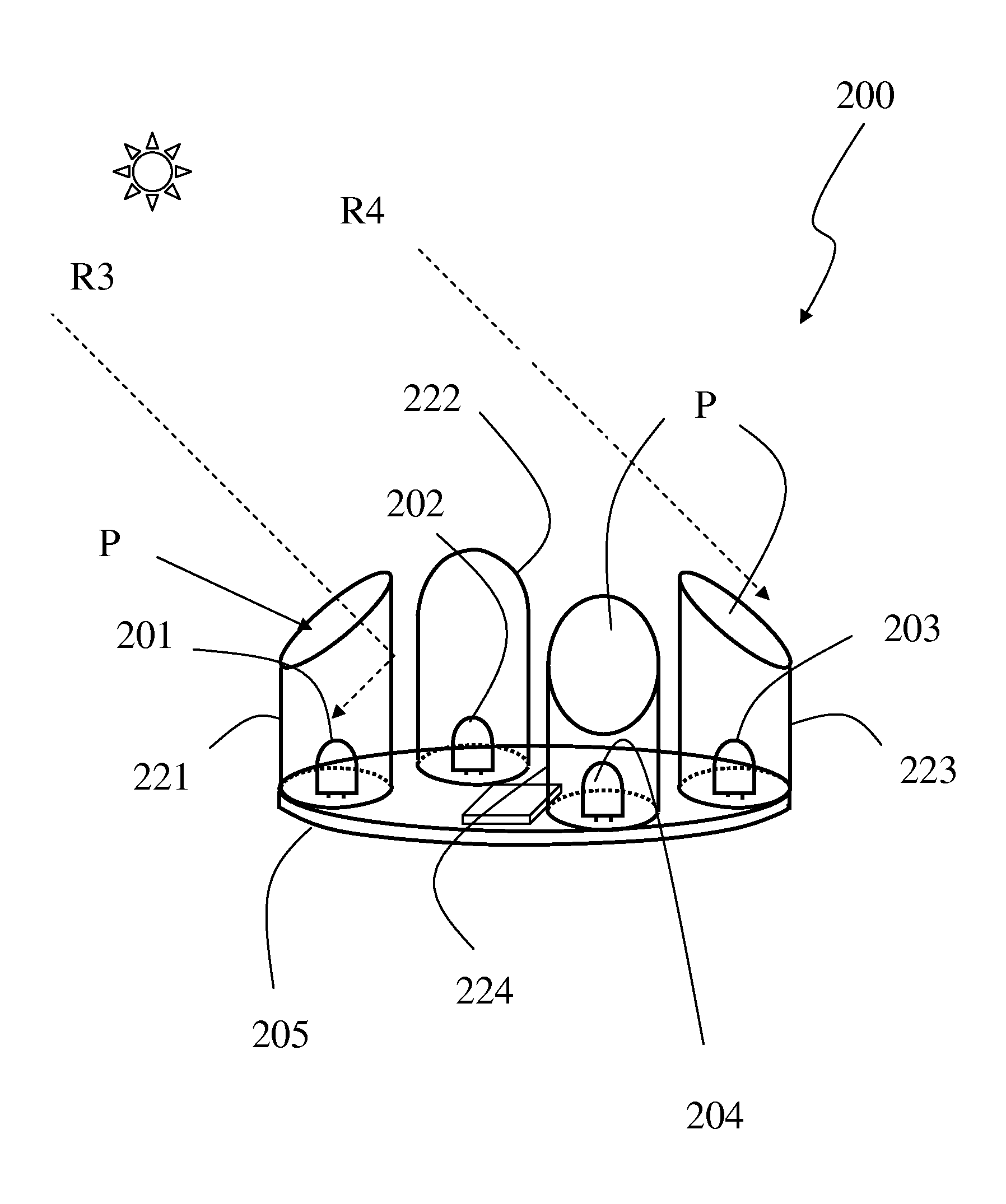
Solar tracking system using cross-divider shade board and sensor solar panels
InactiveUS20140014157A1The effect is accurateReduce the amount of solutionPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyControl systemEngineering
A solar tracking assembly that incorporates a cross-divider shade board, four sensor solar panels, and a control system to automatically track sunlight. The design of this solar tracking system is very simple and economical, and it can achieve high efficiency in the power generation. The design is simple and economical because the tracking mechanism is by utilizing the same solar panels for sensing sunlight as well as for power generation. Together with a cross-divider shade board, signal wires, and a control system, the four sensor solar panels and additional standard solar panels can be assembled to facilitate automatic sun tracking. No additional electronic devices for sensing are needed other than using the standard solar panels.
Owner:LEE TSUNG CHIEH +1
Concentrated Solar Heating
InactiveUS20110017273A1Easy to manufactureReduce lossesSolar heating energySolar heat devicesWorking fluidAbsorbed energy
A system for concentrating solar energy comprising a collector consisting of a number of reflective panels, a receiver which absorbs reflected energy, a working fluid which absorbs the energy, a highly transmissive cover and internal colorings or coatings to collect indirect radiation, and a solar tracking system to maintain reflector orientation. Optional photo-voltaic panels could also be used for providing electrical energy and are kept at near ambient temperatures. Under normal conditions, solar energy is concentrated by reflectors on the receiver, which transfers the energy to a working fluid which is then used for either hot water heating, desiccant drying for a solar air conditioner, or as a power source. Additional energy is collected from indirect sources using the greenhouse effect.
Owner:THE LAW OFFICE OF MICHAEL E KONDOUDIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com