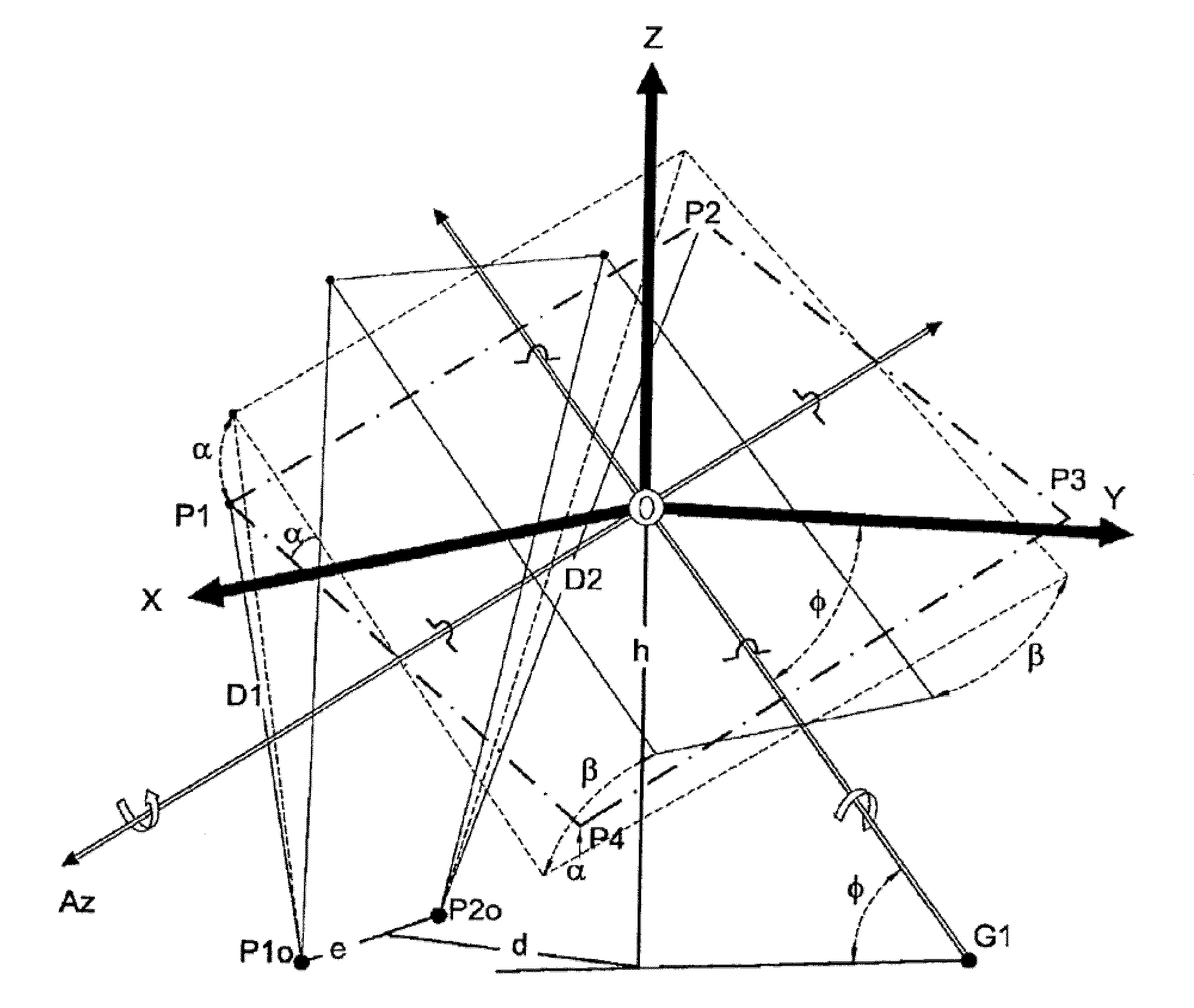
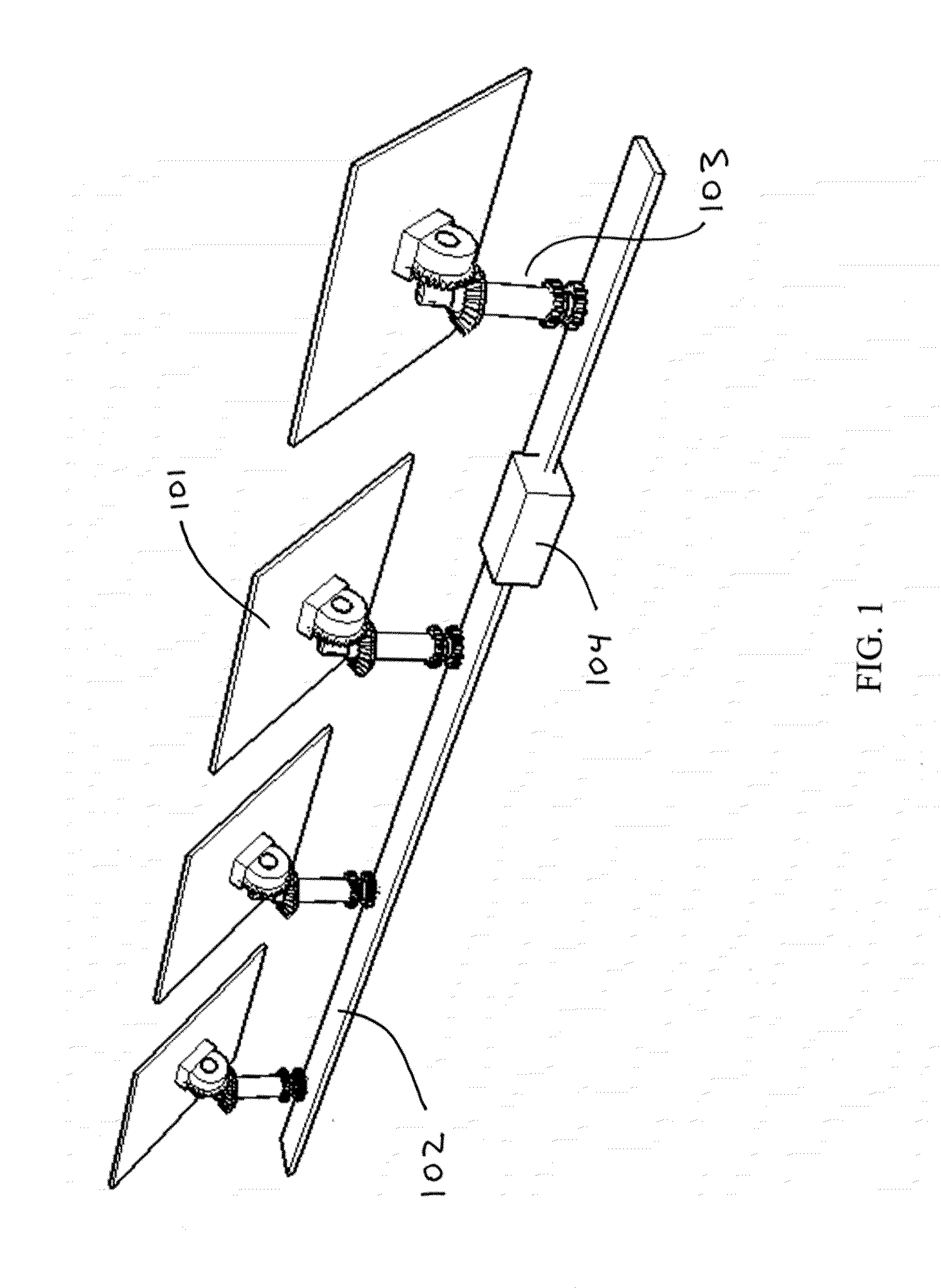
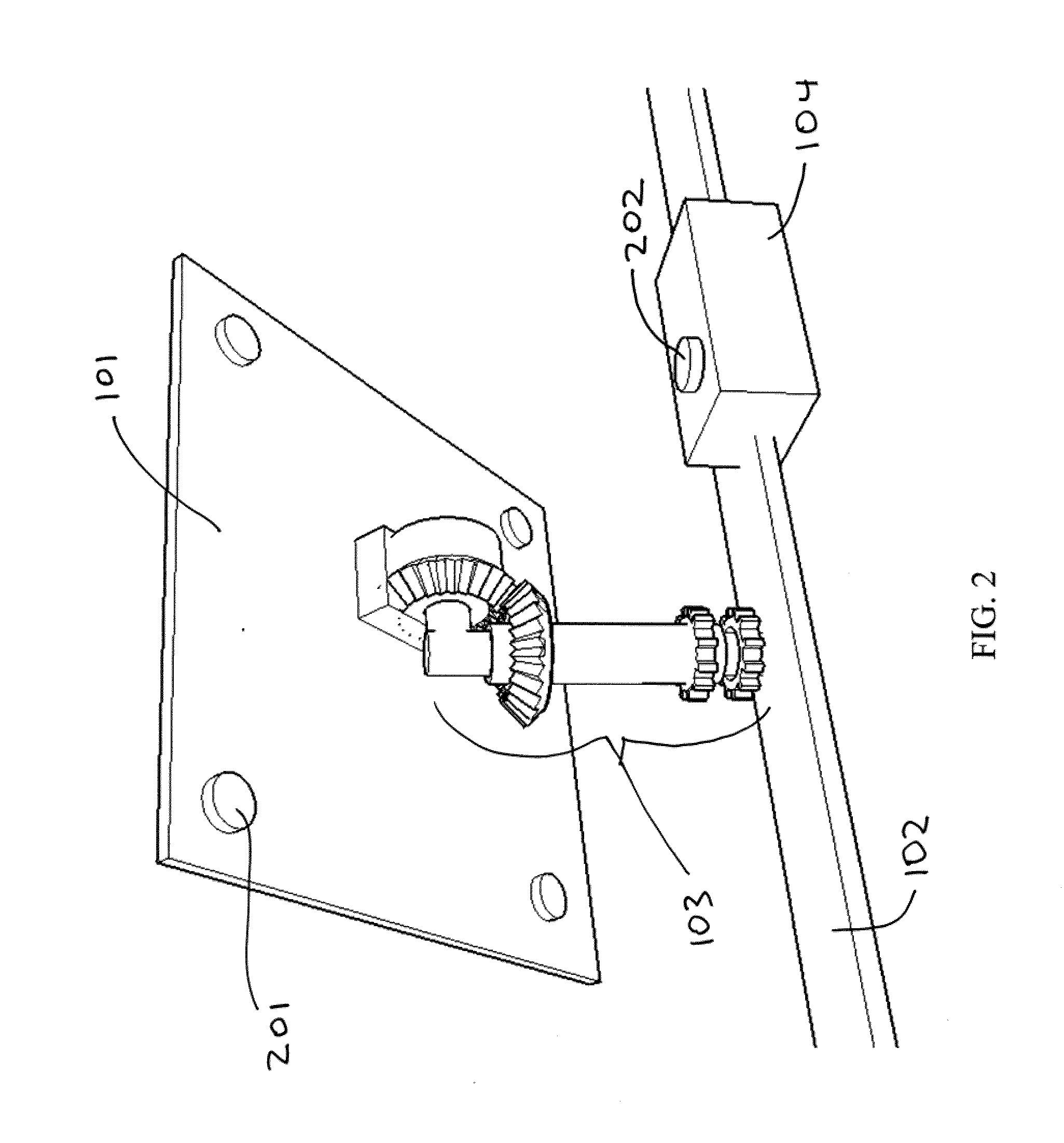
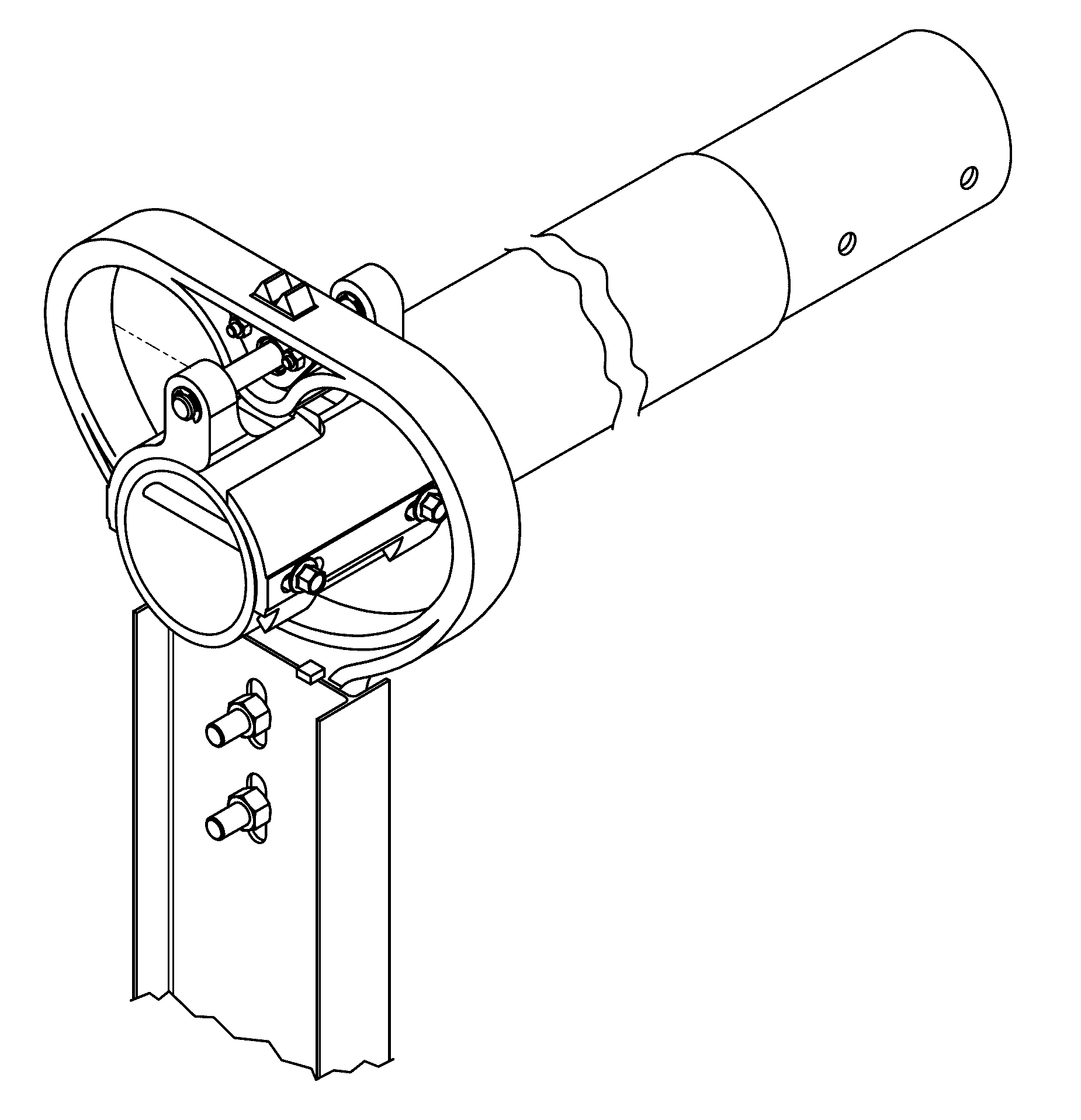
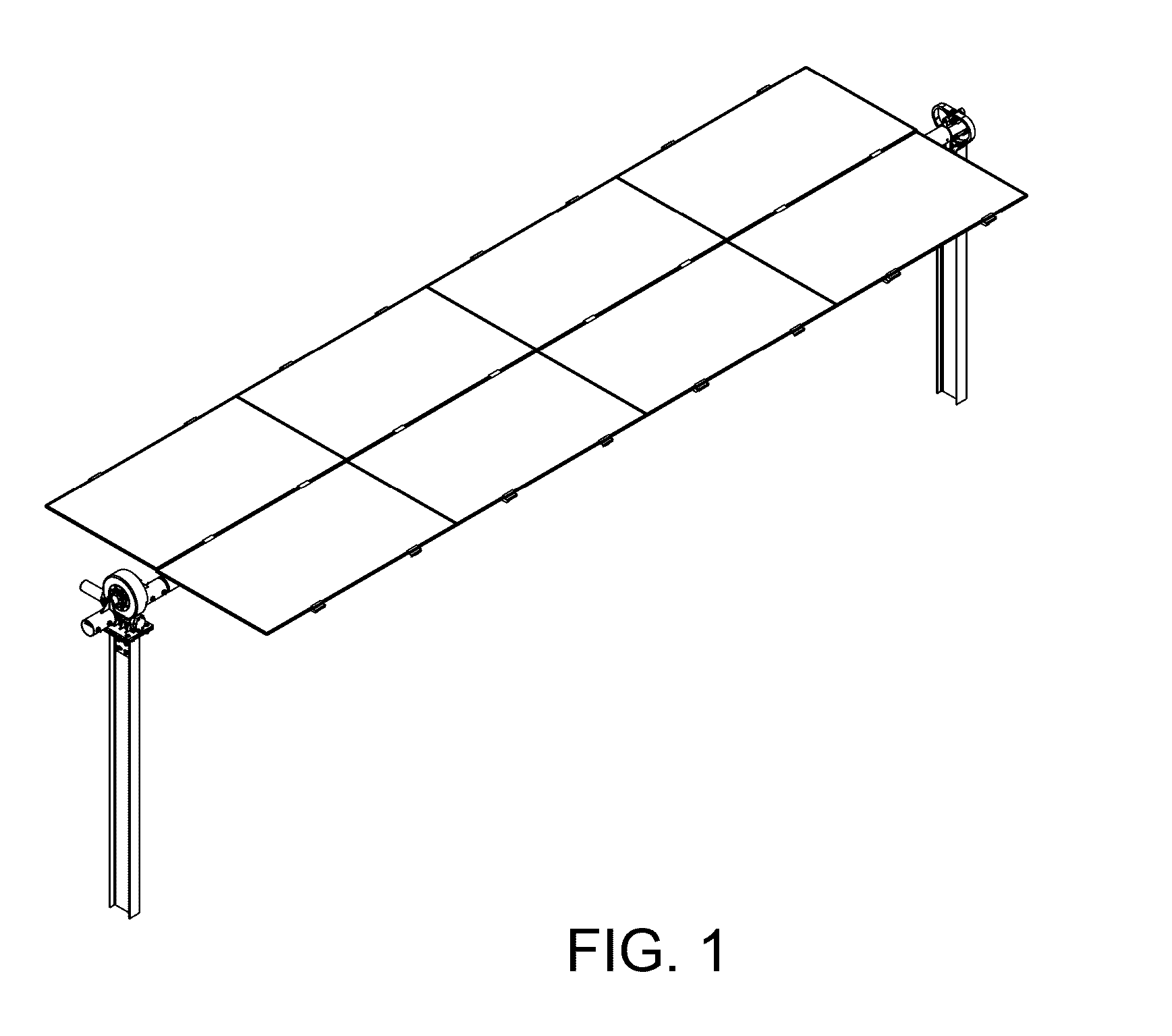
Patents
Literature
486 results about "Solar tracker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
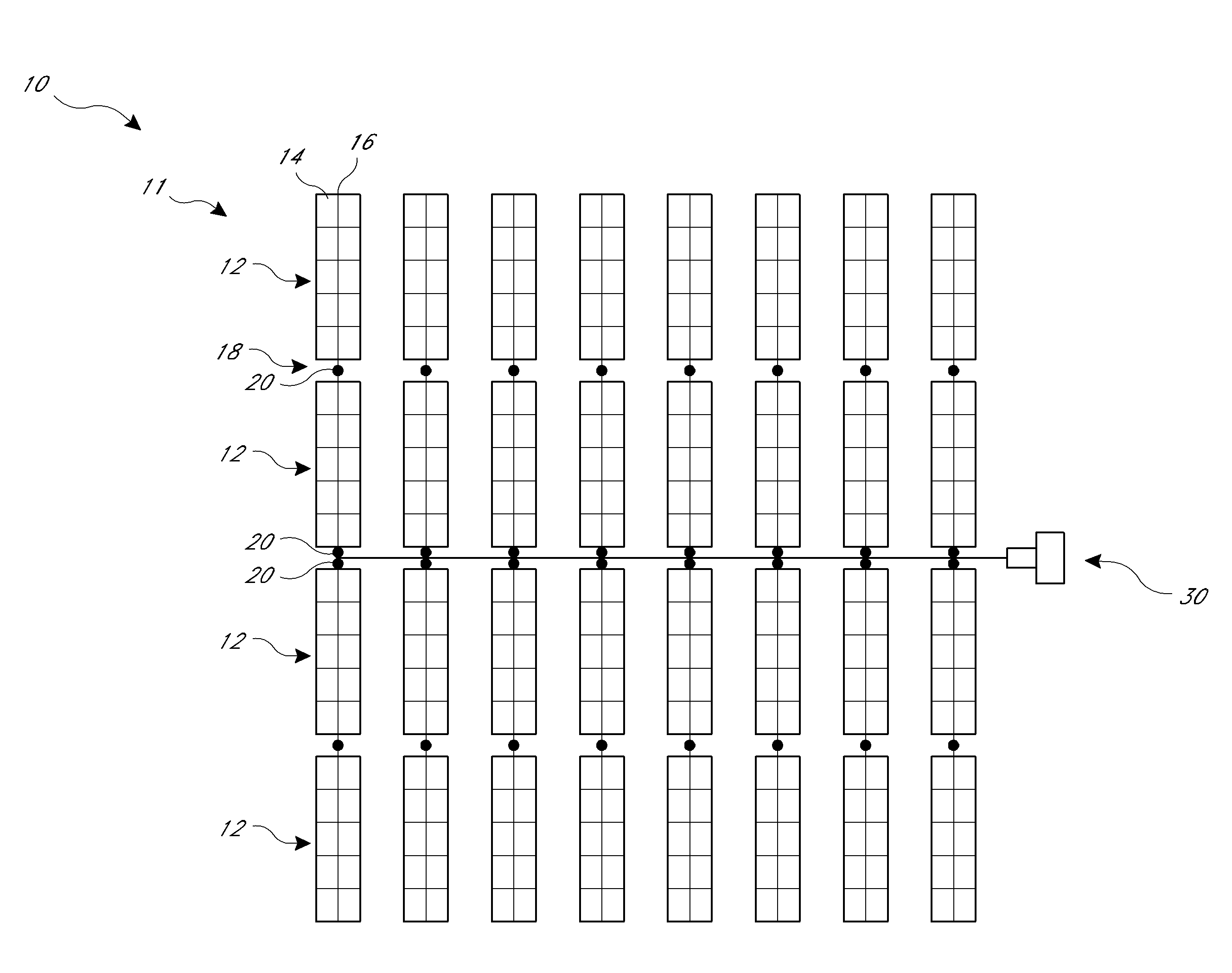
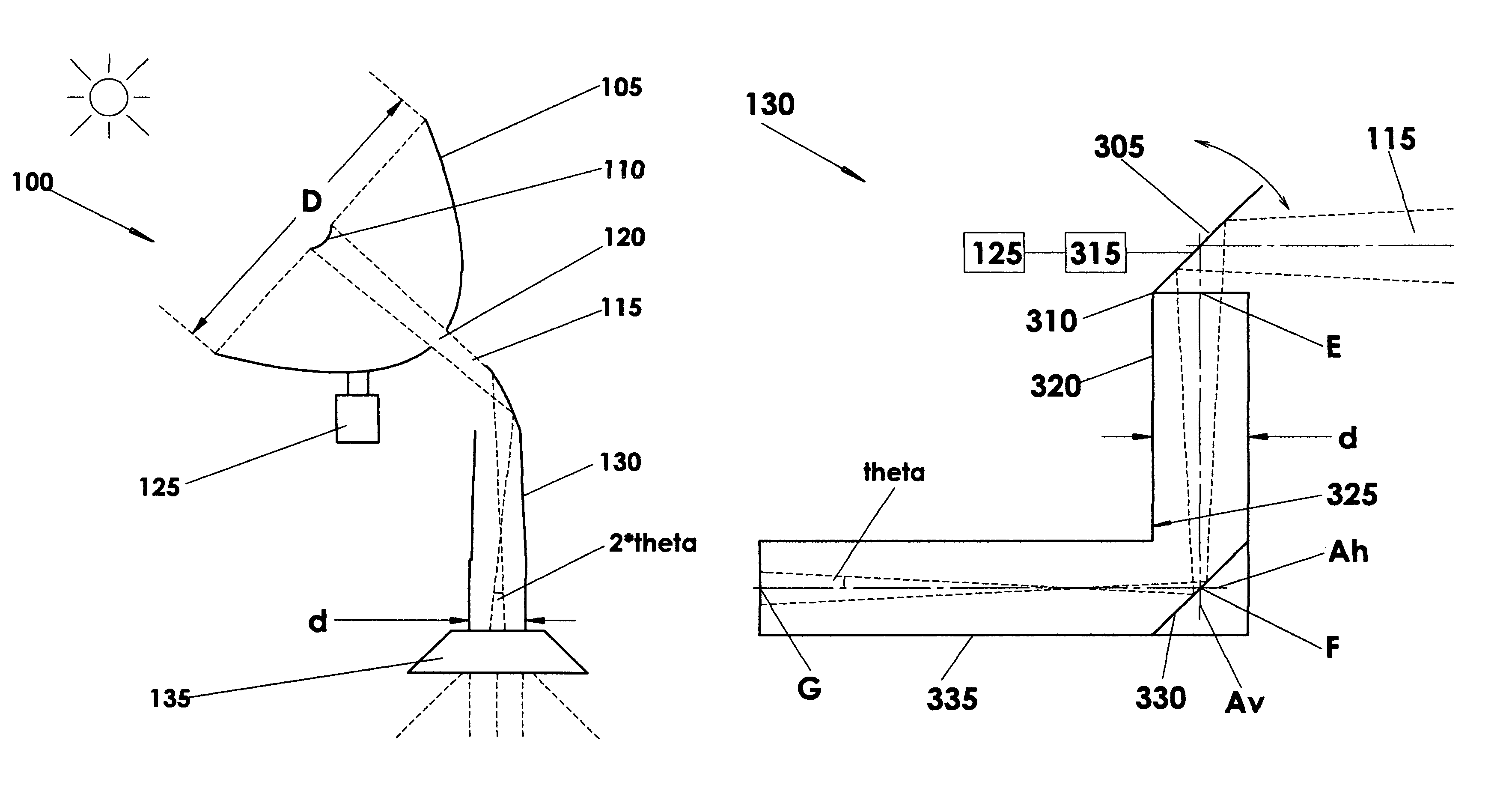
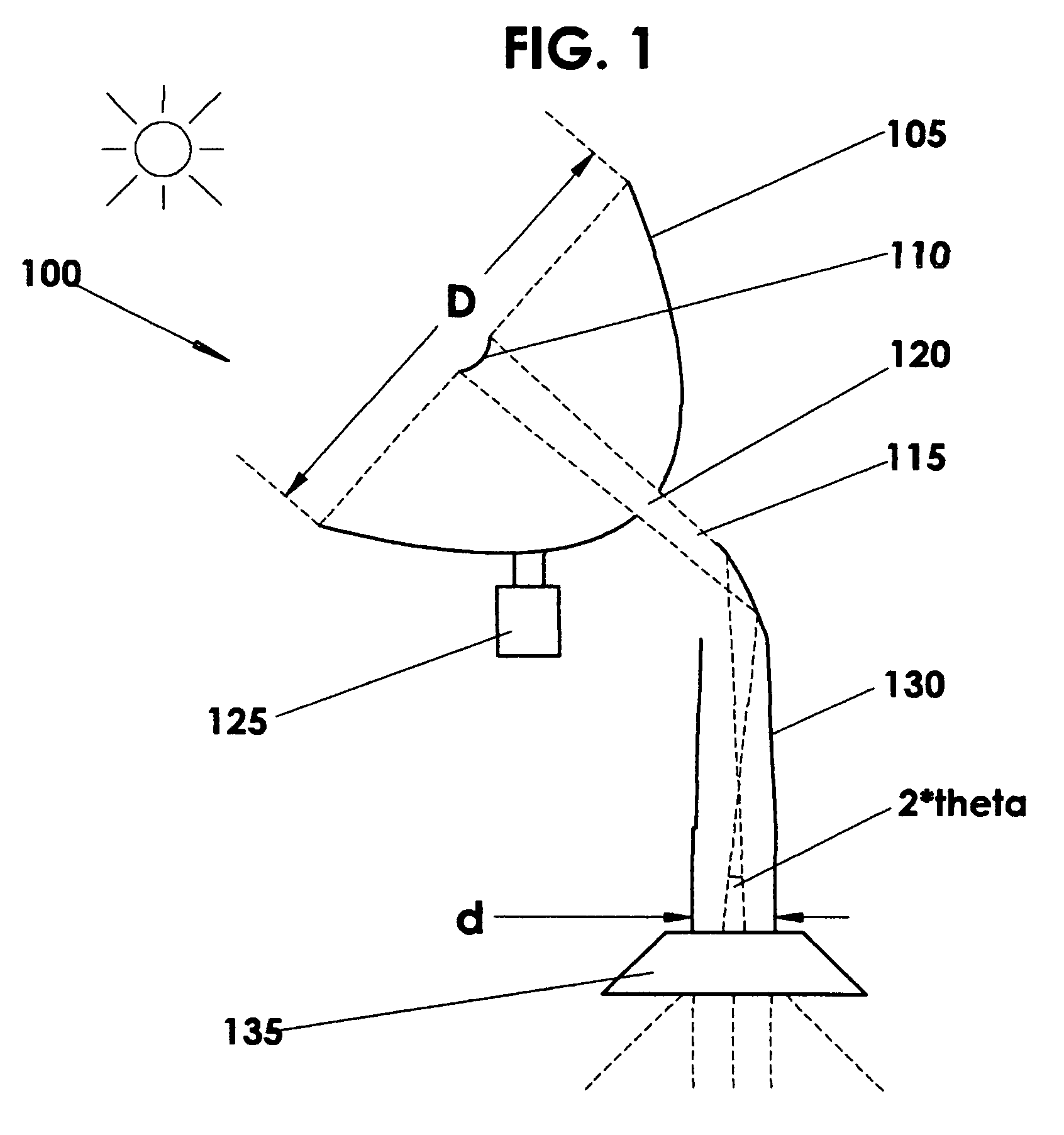
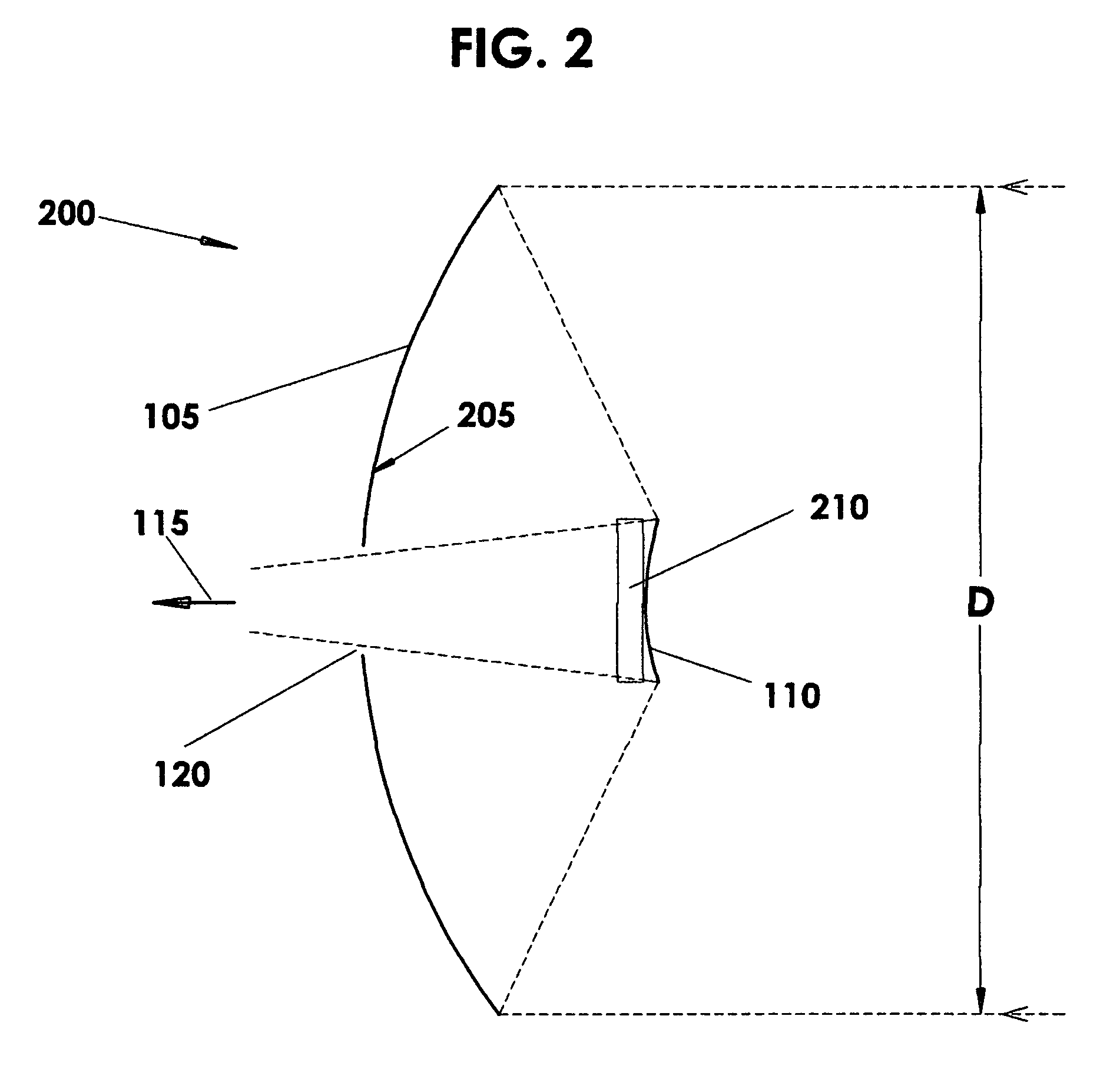
A solar tracker is a device that orients a payload toward the Sun. Payloads are usually solar panels, parabolic troughs, fresnel reflectors, lenses or the mirrors of a heliostat. For flat-panel photovoltaic systems, trackers are used to minimize the angle of incidence between the incoming sunlight and a photovoltaic panel, sometimes known as the cosine error. Reducing this angle increases the amount of energy produced from a fixed amount of installed power generating capacity. In standard photovoltaic applications, it was predicted in 2008-2009 that trackers could be used in at least 85% of commercial installations greater than one megawatt from 2009 to 2012.
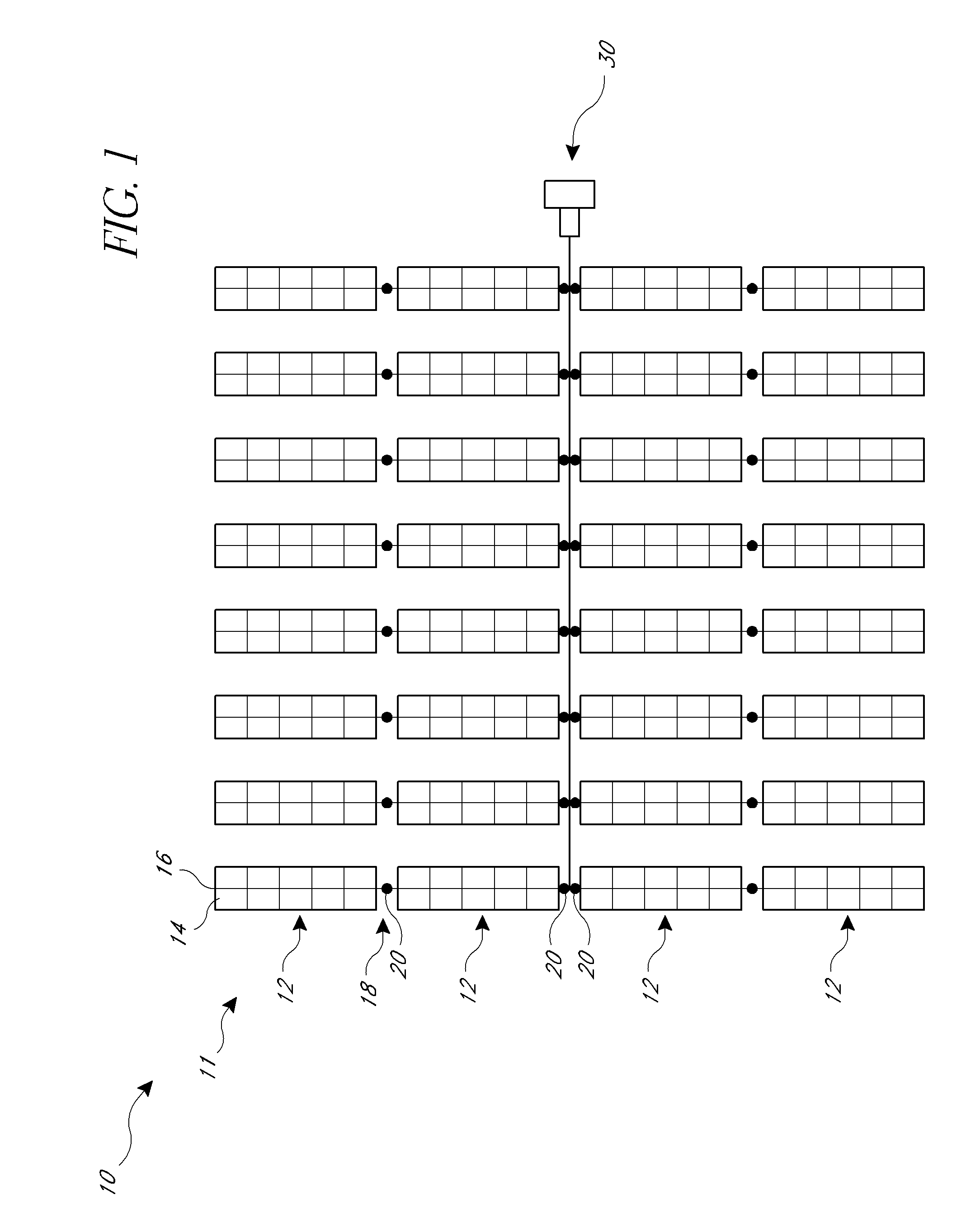
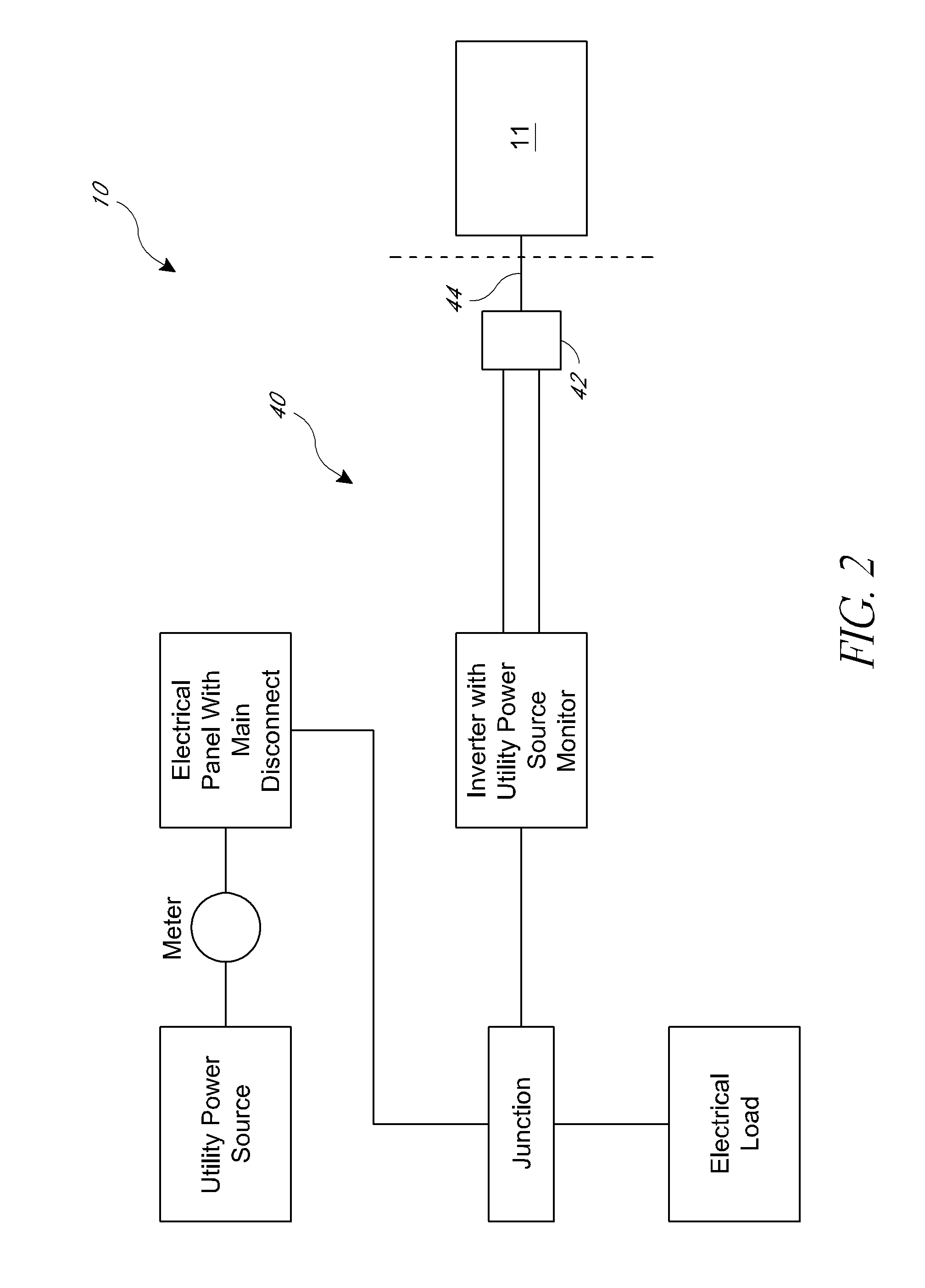
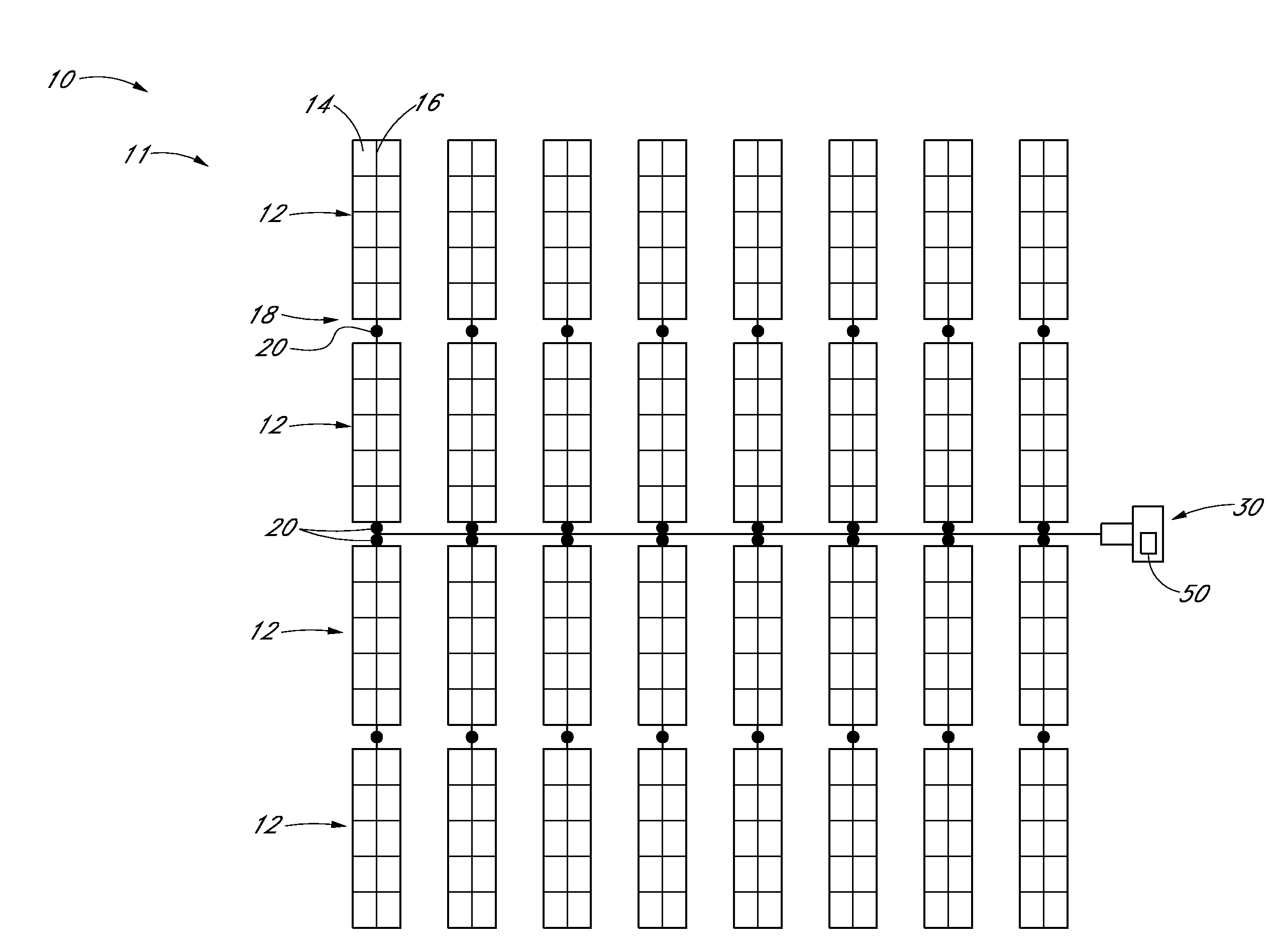
Two-Axes Solar Tracker System and Apparatus for Solar Panel and Likes
InactiveUS20110041834A1Easy to installProlong lifePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyHeliostatEngineering
The present invention relates to a simplified and lower cost two-axes tracker for solar PV (photovoltaic) or CPV (concentrated photovoltaic) solar panel, as well as heliostat solar reflectors and solar Stirling engine. In particular, the disclosure addresses a simplified and gravity centered tracker structure with low cost single or dual linear actuators mounted on the side of ground post which is easier for replacement and maintenance at lower cost.
Owner:LIAO HENRY H
Equipment and Process for Measuring the Precision of Sun Tracking for Photovoltaic Concentrators
InactiveUS20080258051A1Down rateIncrease sampling ratePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityEngineering
Mechanical sun trackers which have optical systems on their surface for concentrating direct solar radiation and its subsequent conversion into electricity through thermal or photovoltaic processes require precision solar tracking, which has to be all the more precise the greater the concentration factor used. Thus the precision required in these systems is generally less than a degree, and frequently of the order of a tenth of a degree. In view of the large dimensions of the surfaces, or apertures, of these trackers, currently in the approximate range of 20-250 m2, the difficulty of aligning these with the sun with such accuracy will be obvious. To achieve this objective a solar tracker must comply with strict rigidity specifications and its transmission must provide high resolution when positioning. In addition to this, equipment which is capable of controlling solar tracking with the specified precision at all times is required.
Owner:SOLFOCUS
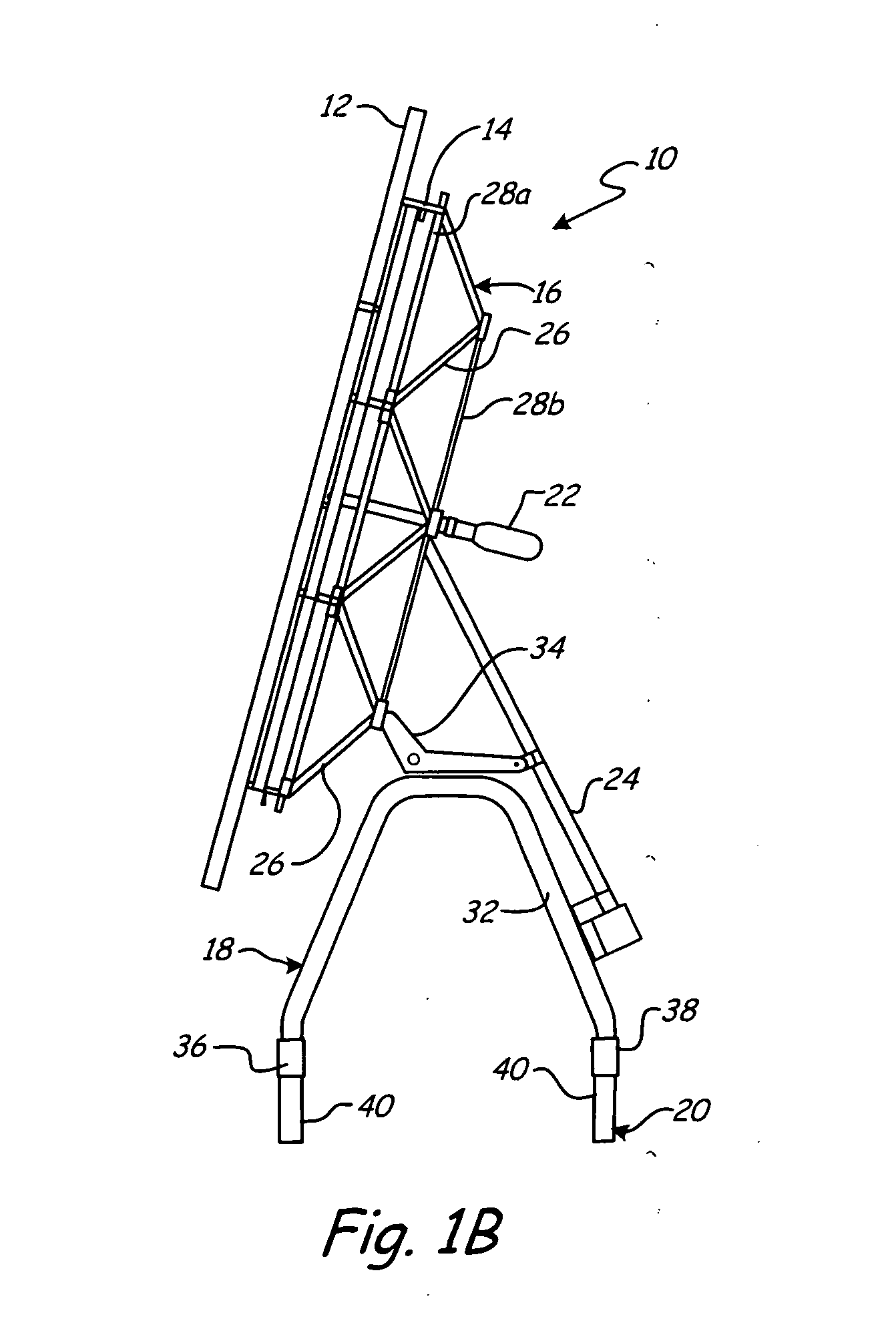
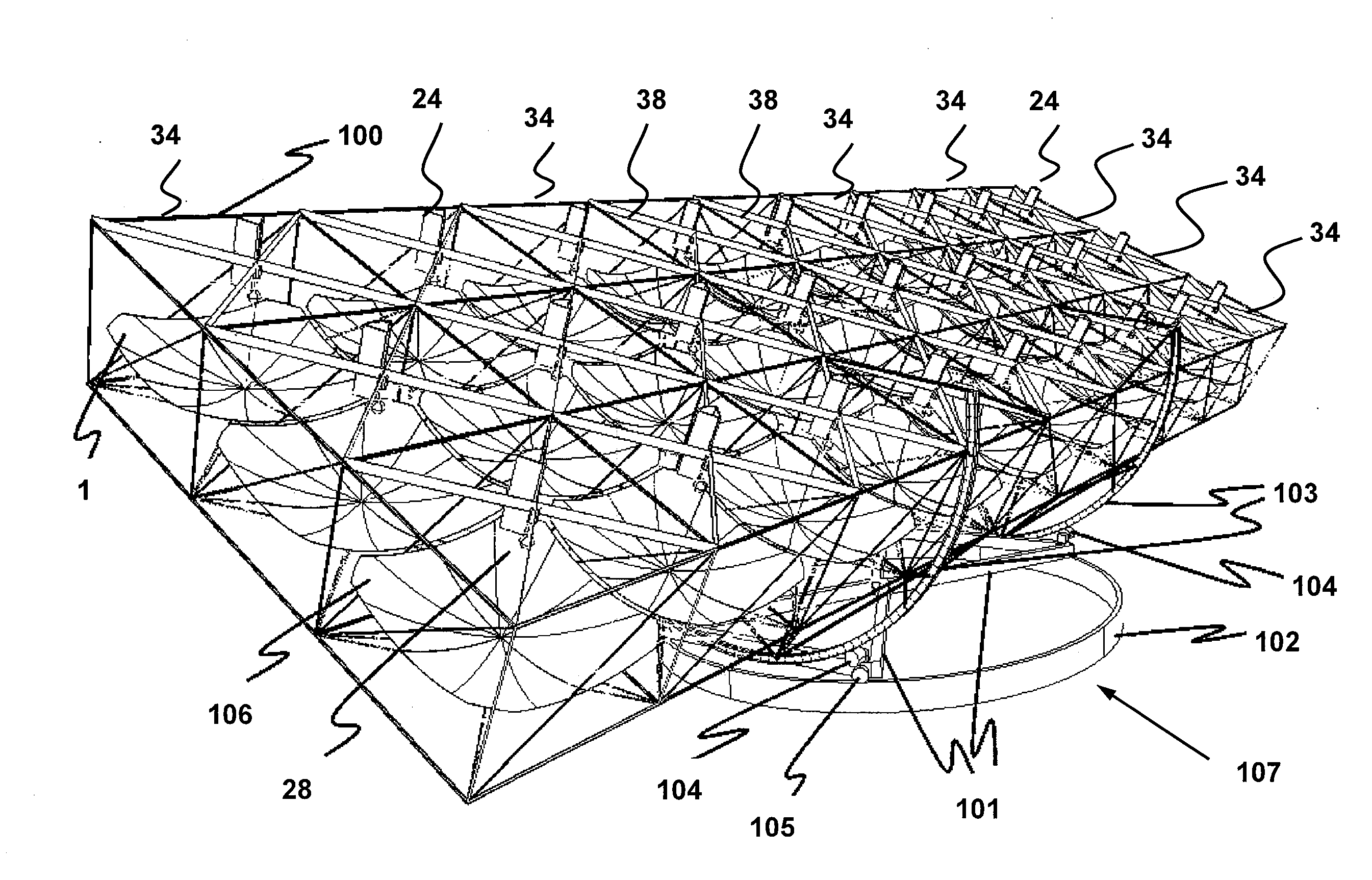
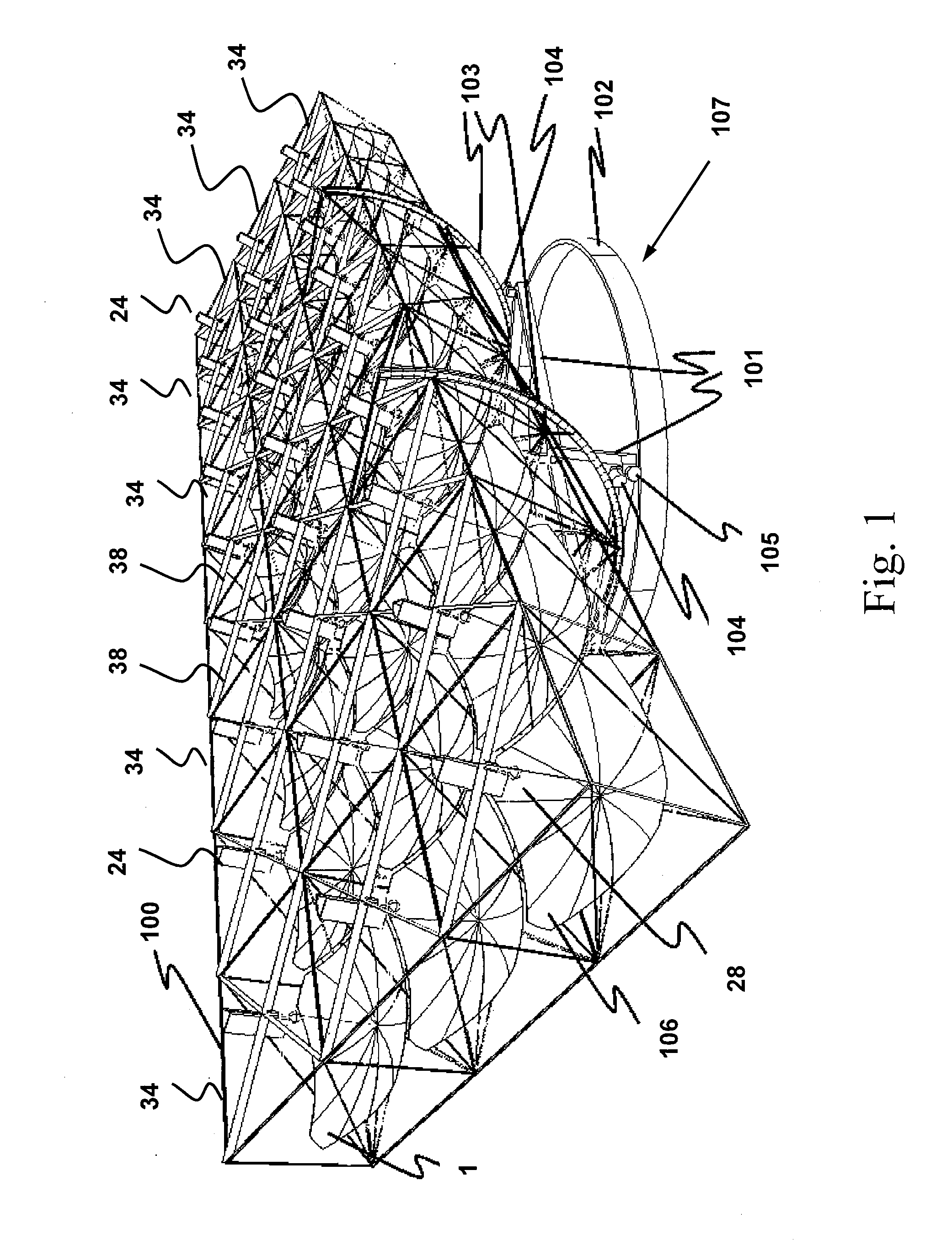
Solar tracker
A two-axis solar tracker is capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions. The solar tracker includes a solar array, a frame, a base, a pivot frame, and a first and second actuator. The solar array is mounted to the frame and captures sunlight. The base is pivotally connected to the frame and defines a pivot axis for elevational movement of the solar array. The pivot frame is also pivotally connected to the frame and defines a pivot axis for azimuthal movement of the solar array. The first actuator controls elevational movement of the solar array and the second actuator controls azimuthal movement of the solar array. The solar tracker is pivotable between a raised position and a stowed position.
Owner:SOLARRESERVE TECH
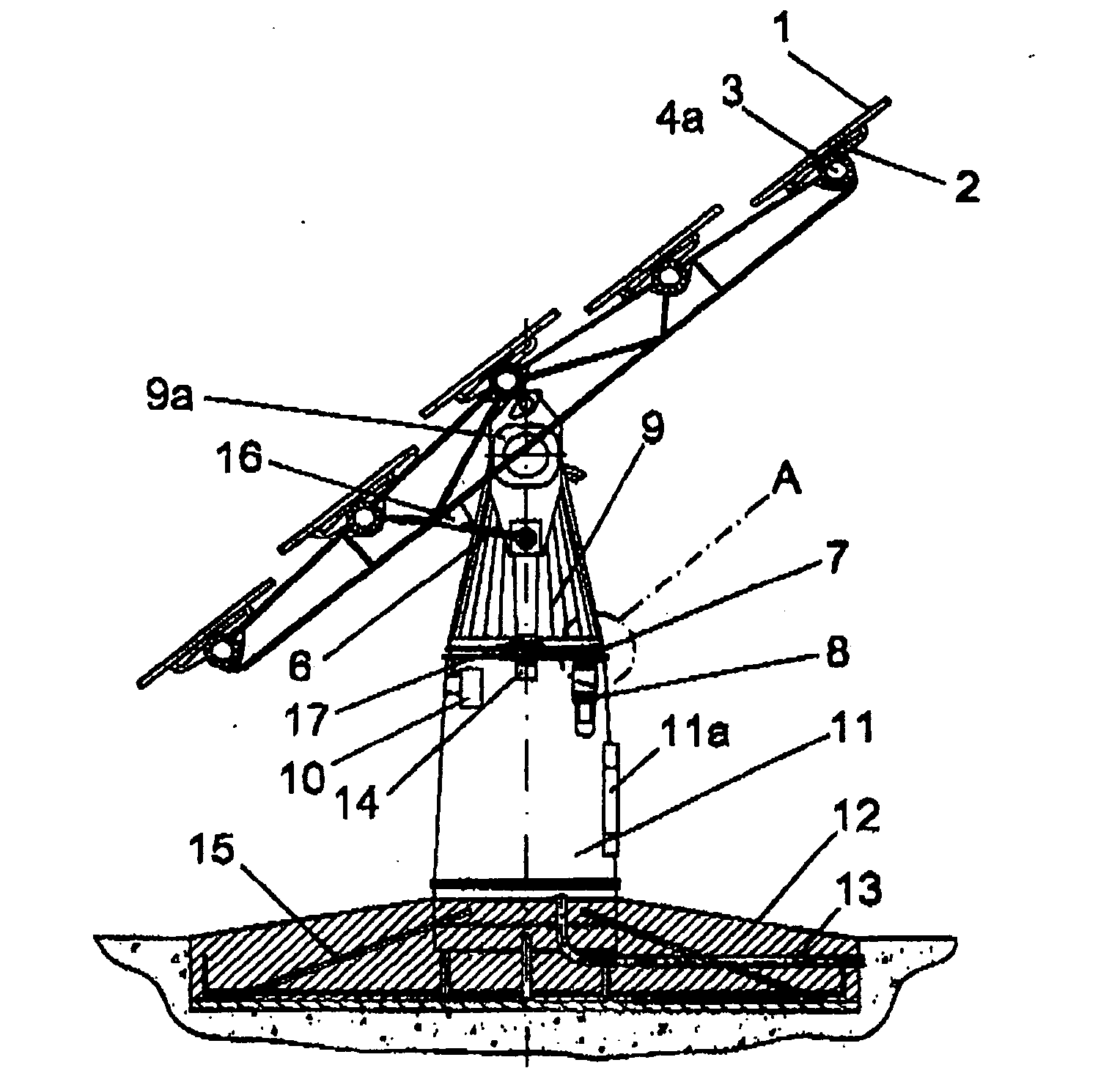
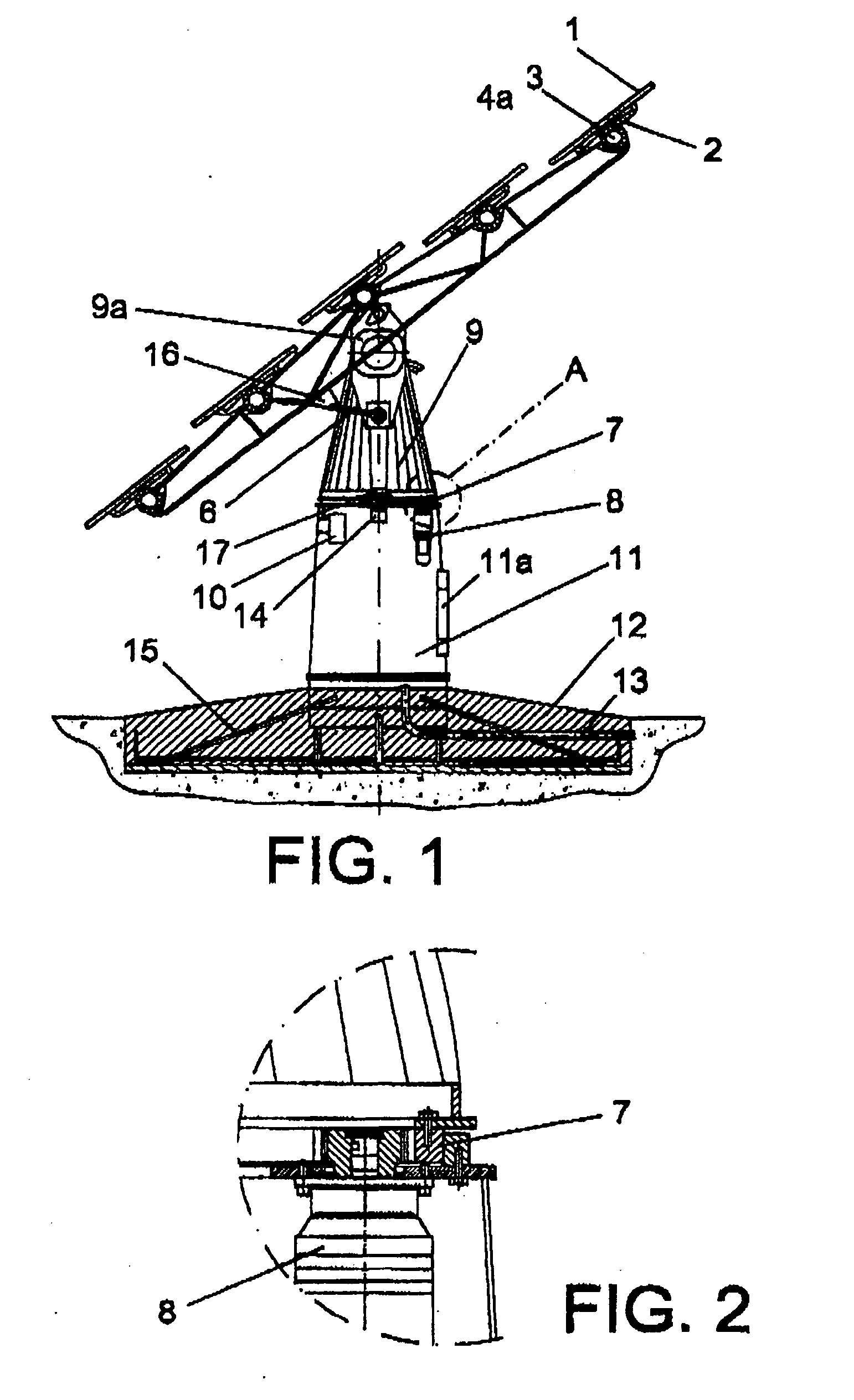
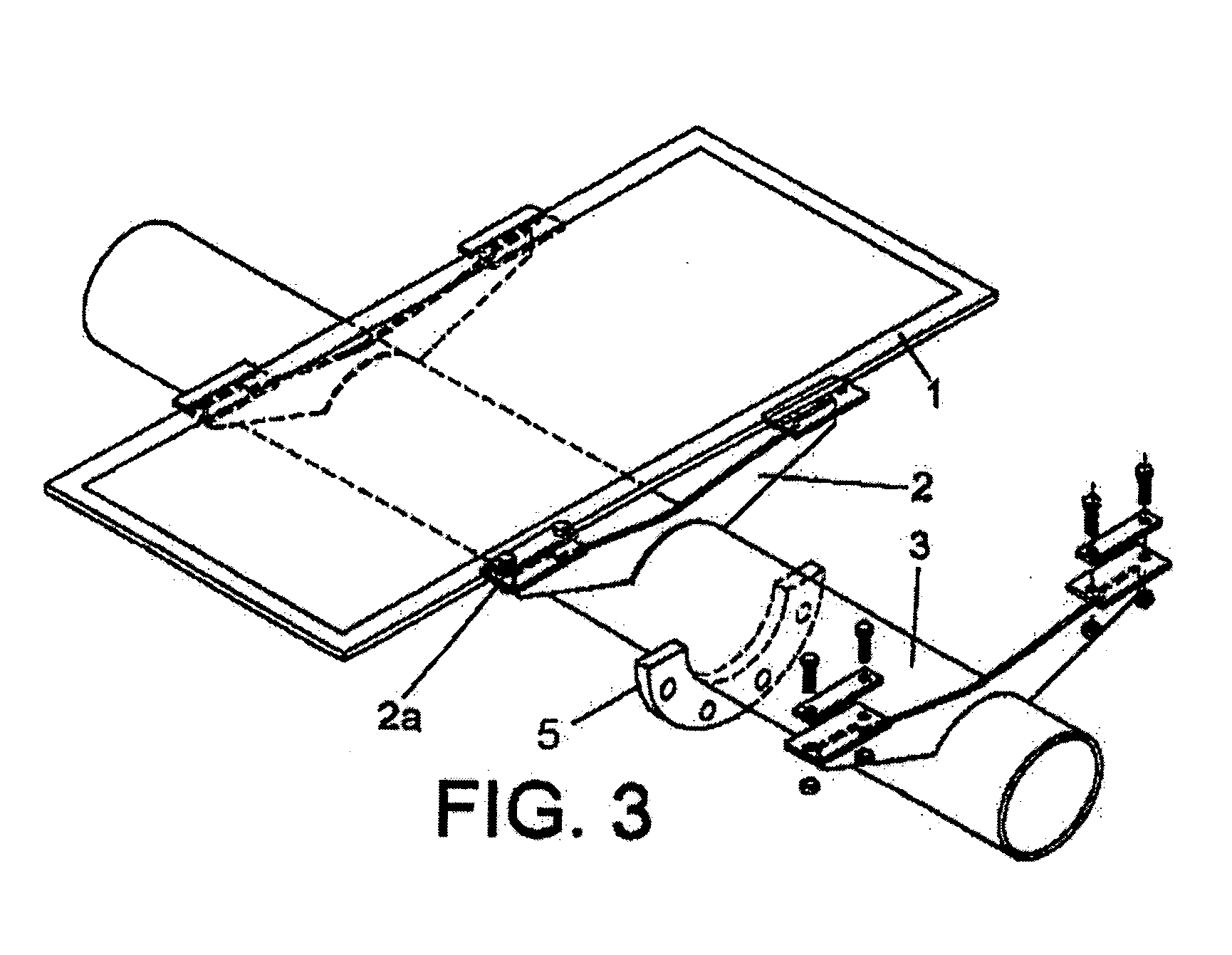
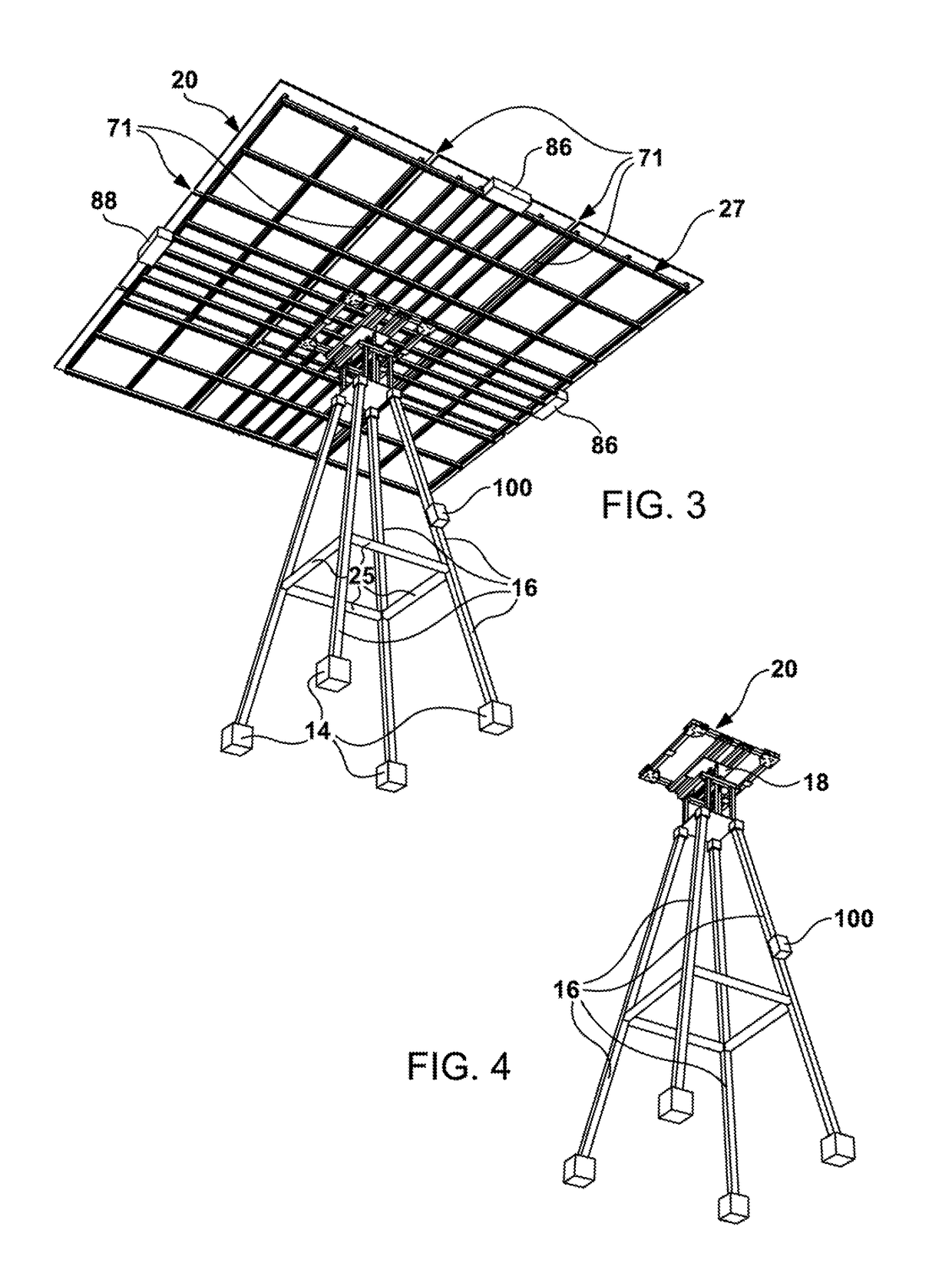
Solar tracker
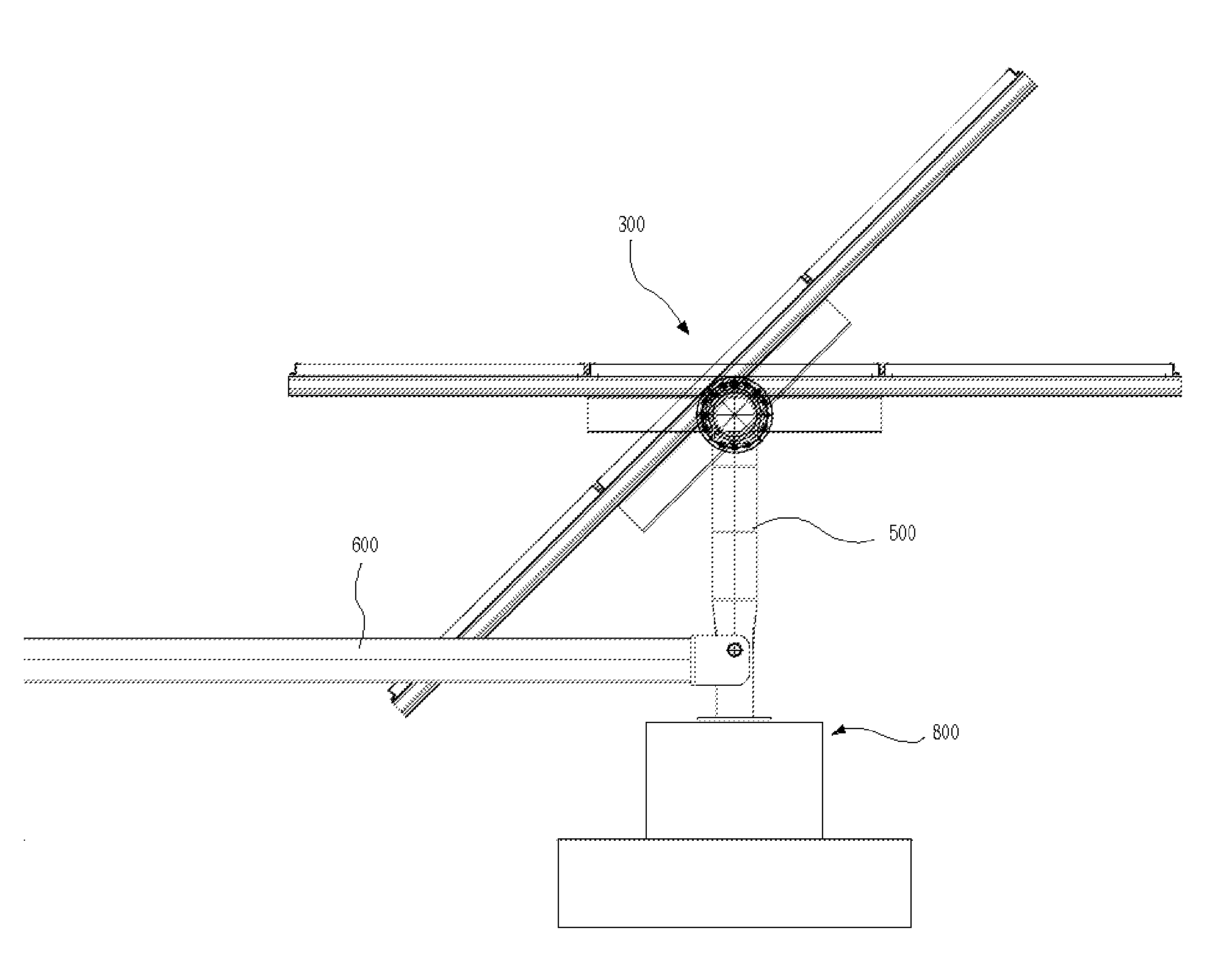
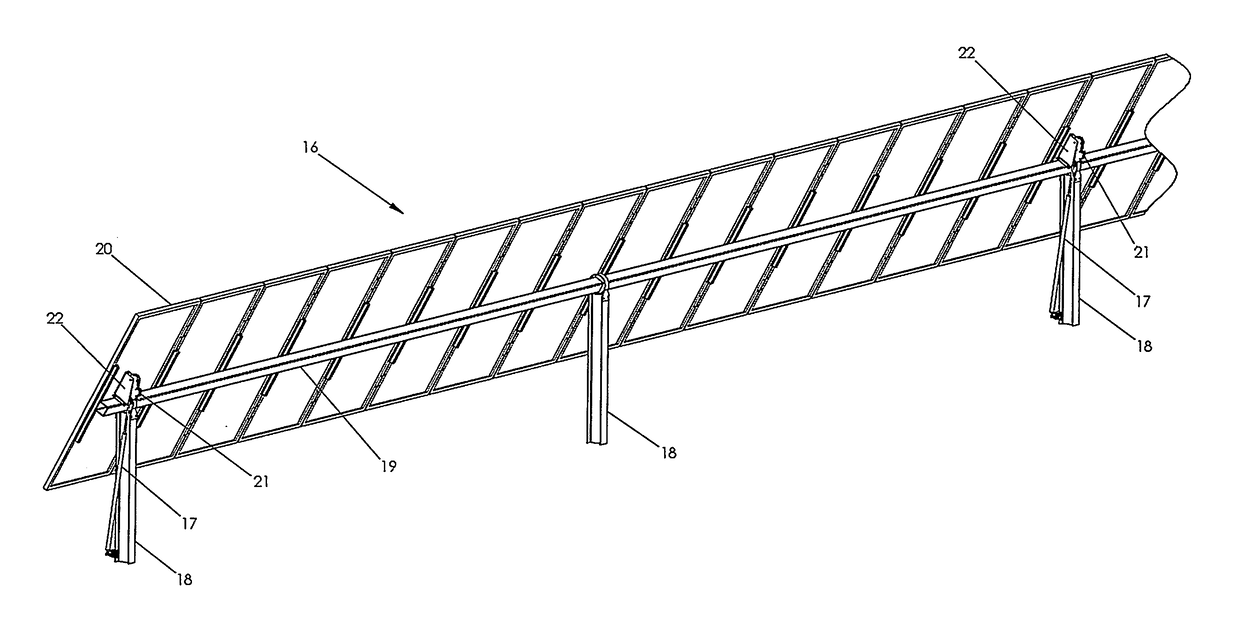
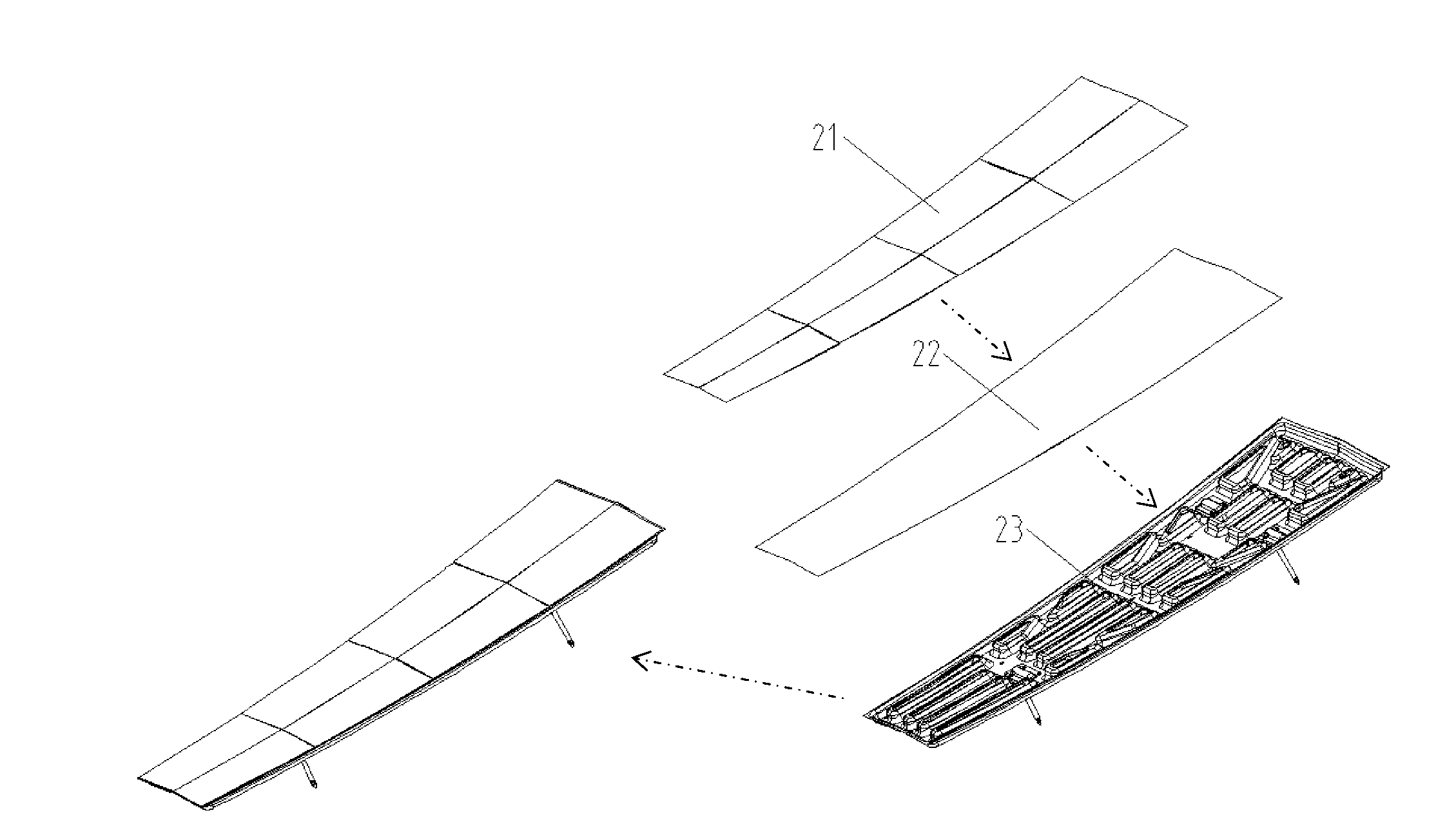
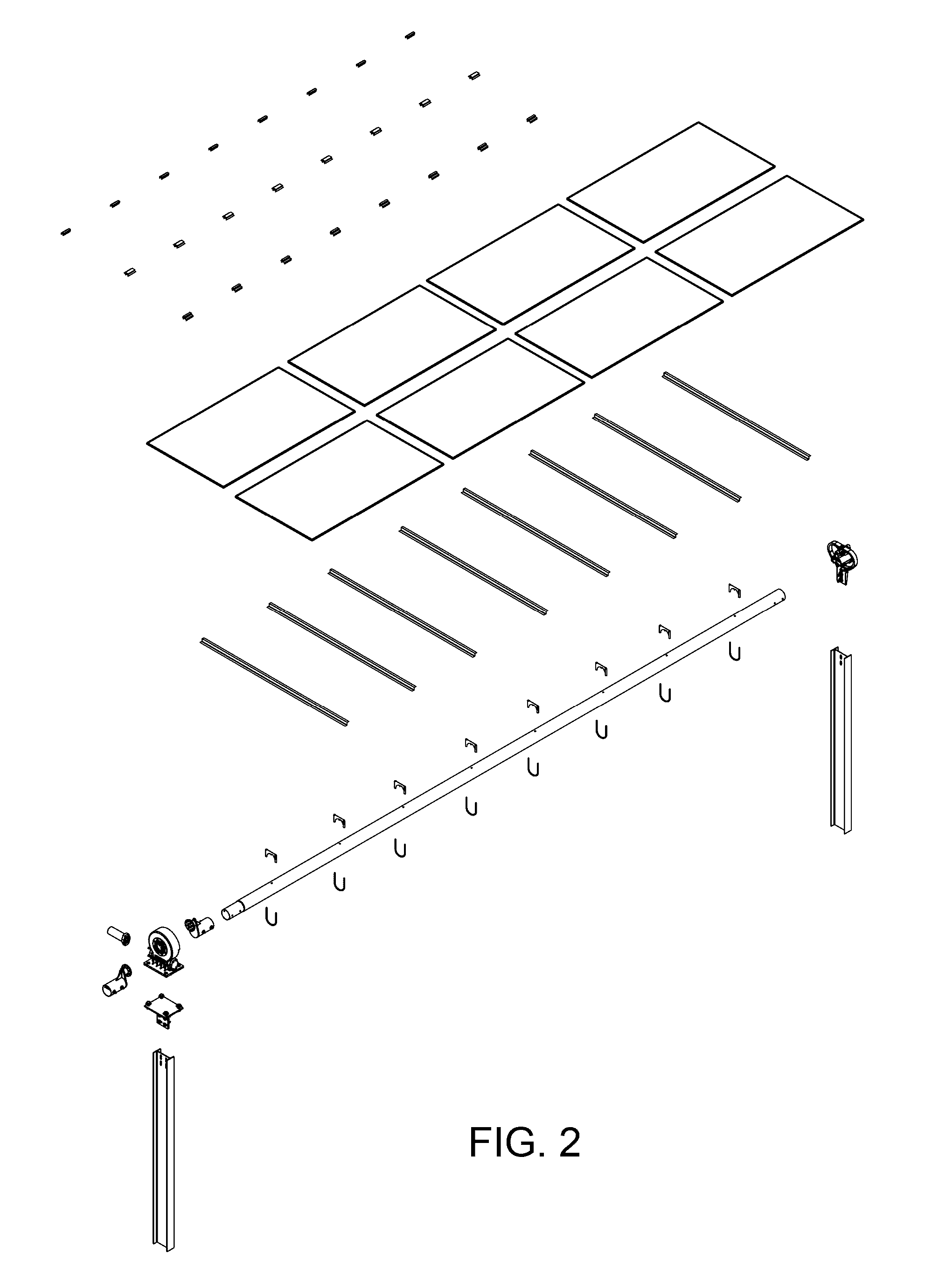
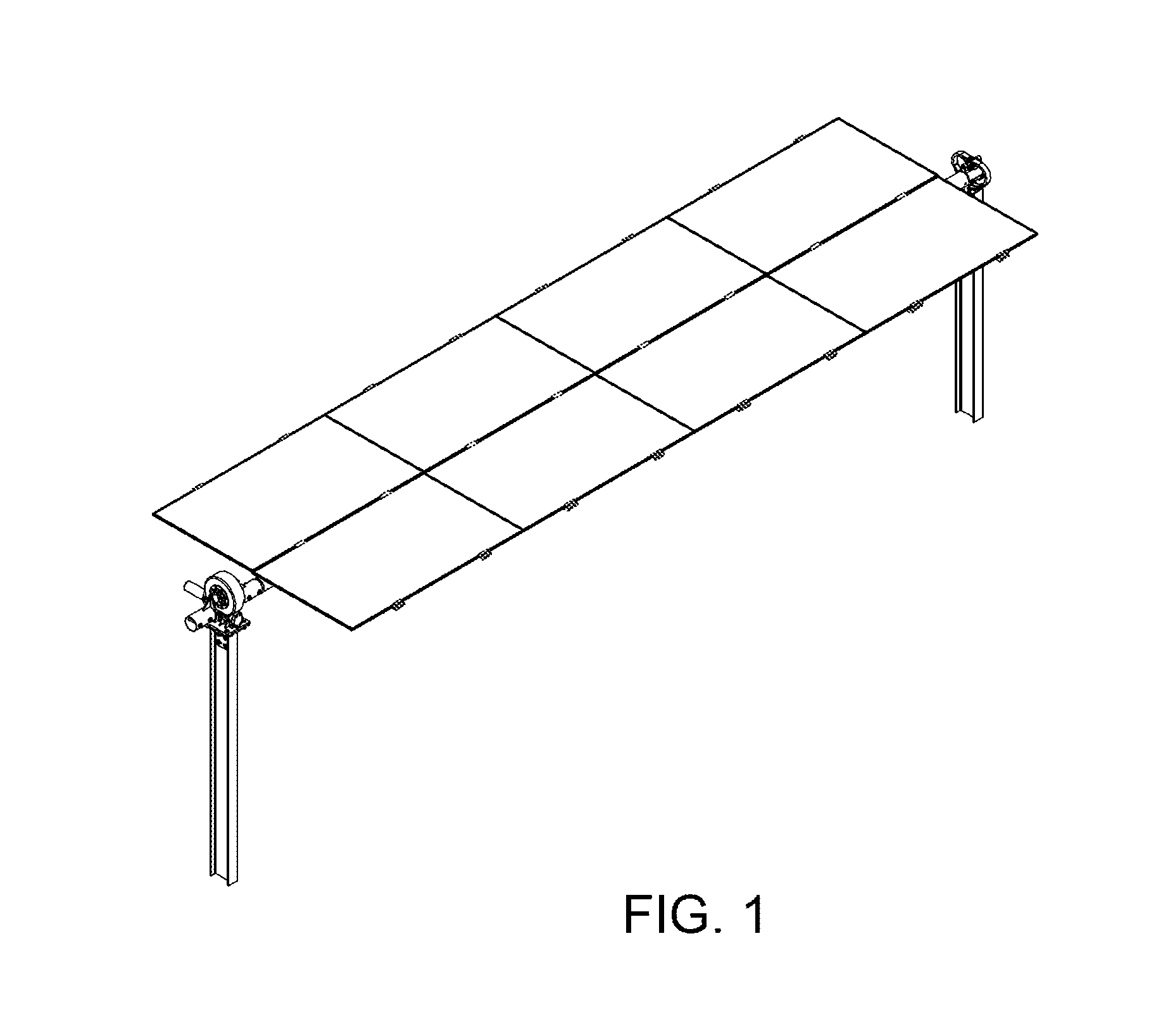
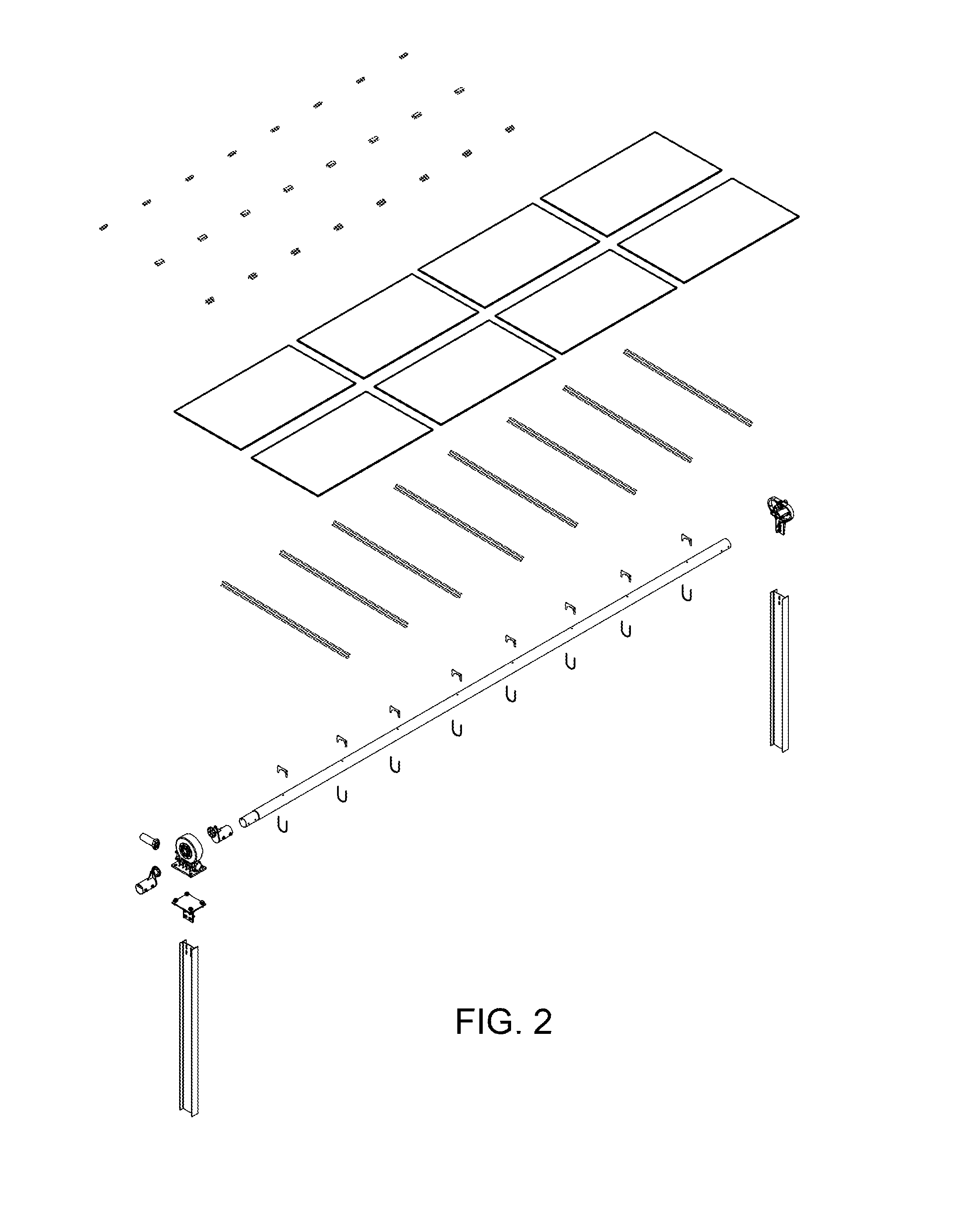
The invention relates to a solar tracker characterized by having photovoltaic panels arranged in spaced rows at different levels and two slopes, favouring their ventilation and the expansion of the frame; the panels being fixed by means of yokes and clips to a support (3) anchored to the H-shaped frame (4) resting on swivelling supports of a tower having little height supporting the entire structure, its tilt being variable by means of a tension device, the side longitudinal beams (4a) being extendible to house more rows of panels (1) since the remaining structural components, tower, bearings, column and base have been oversized for that purpose.
Owner:ROMEO MANUEL LAHUERTA
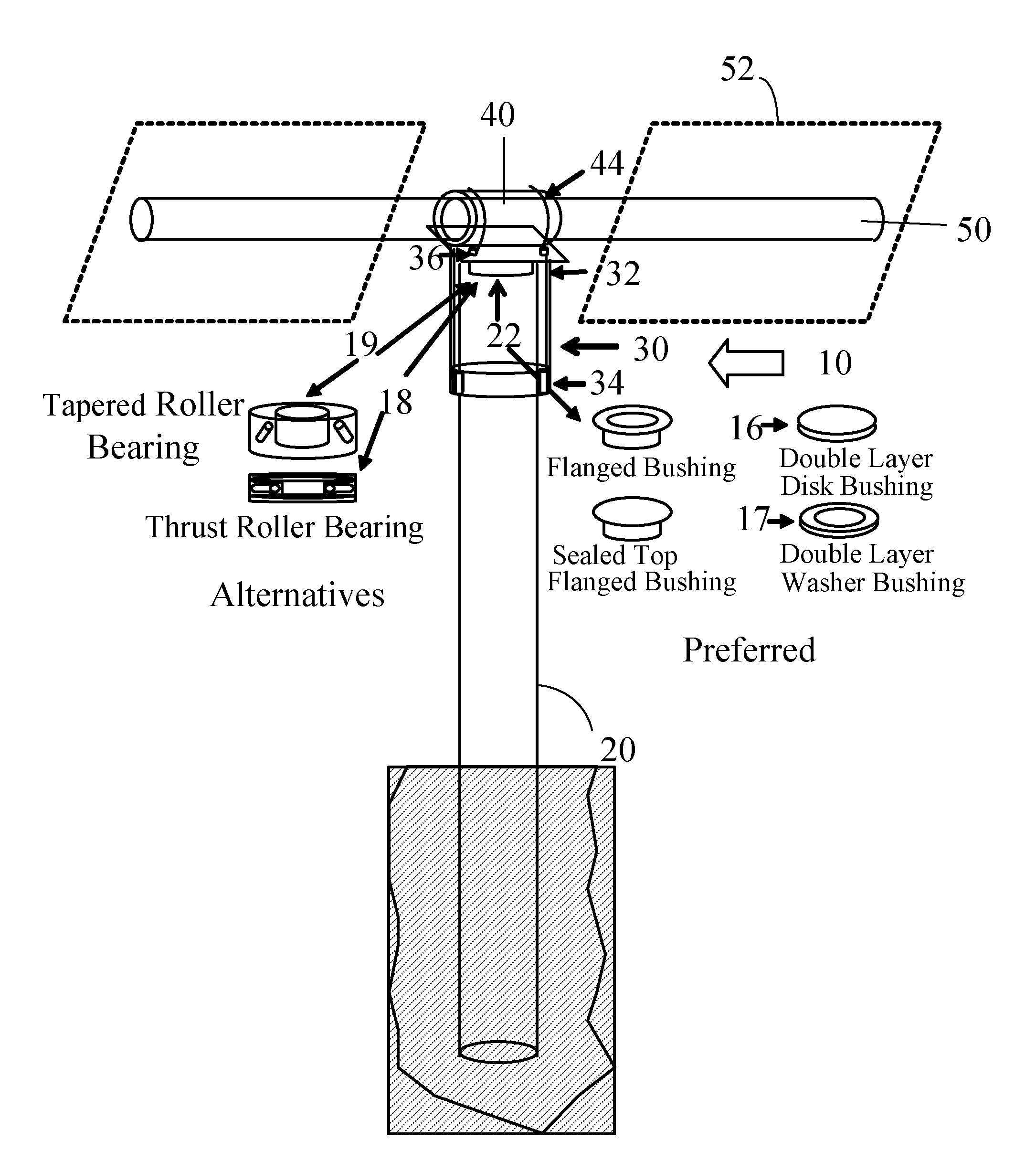
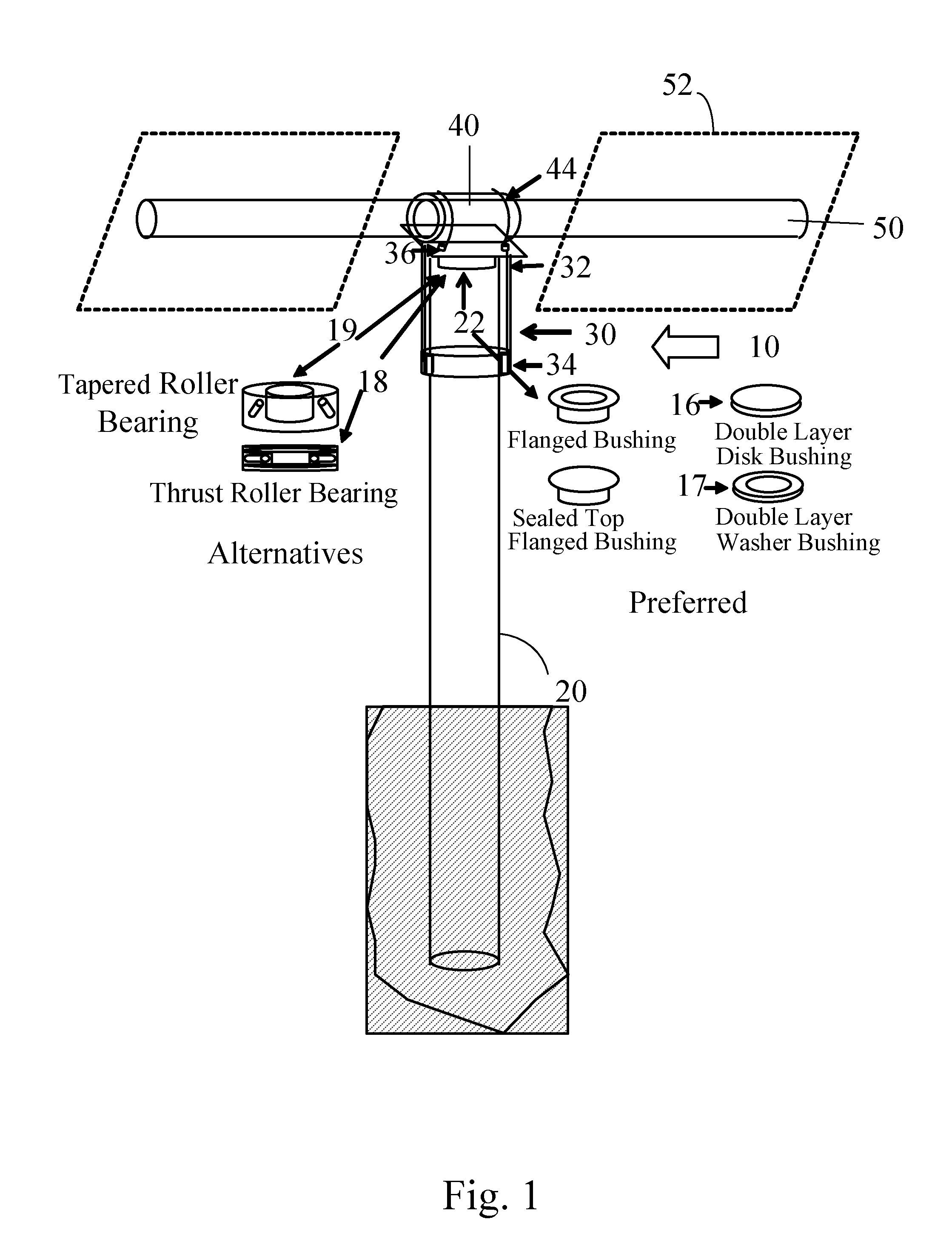
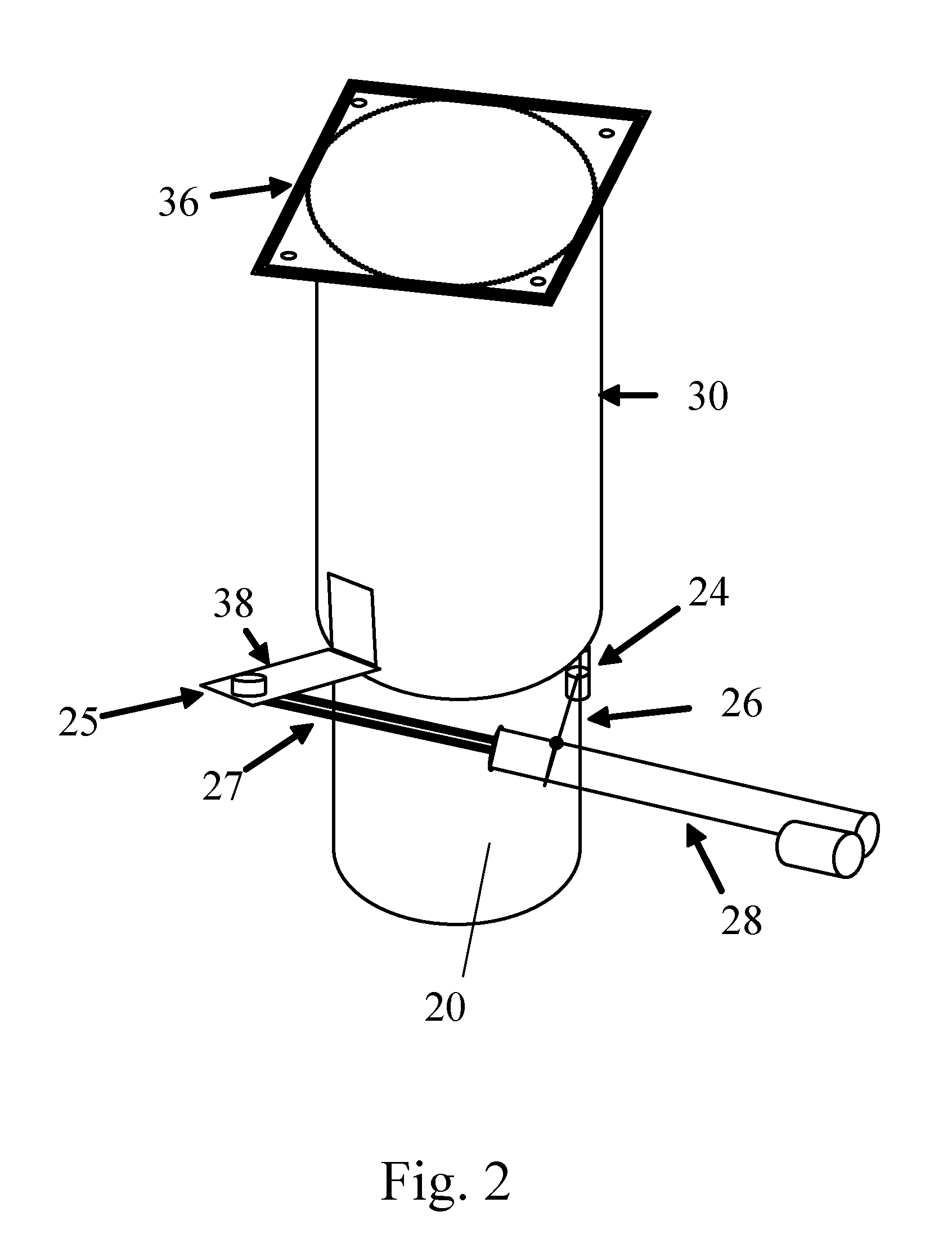
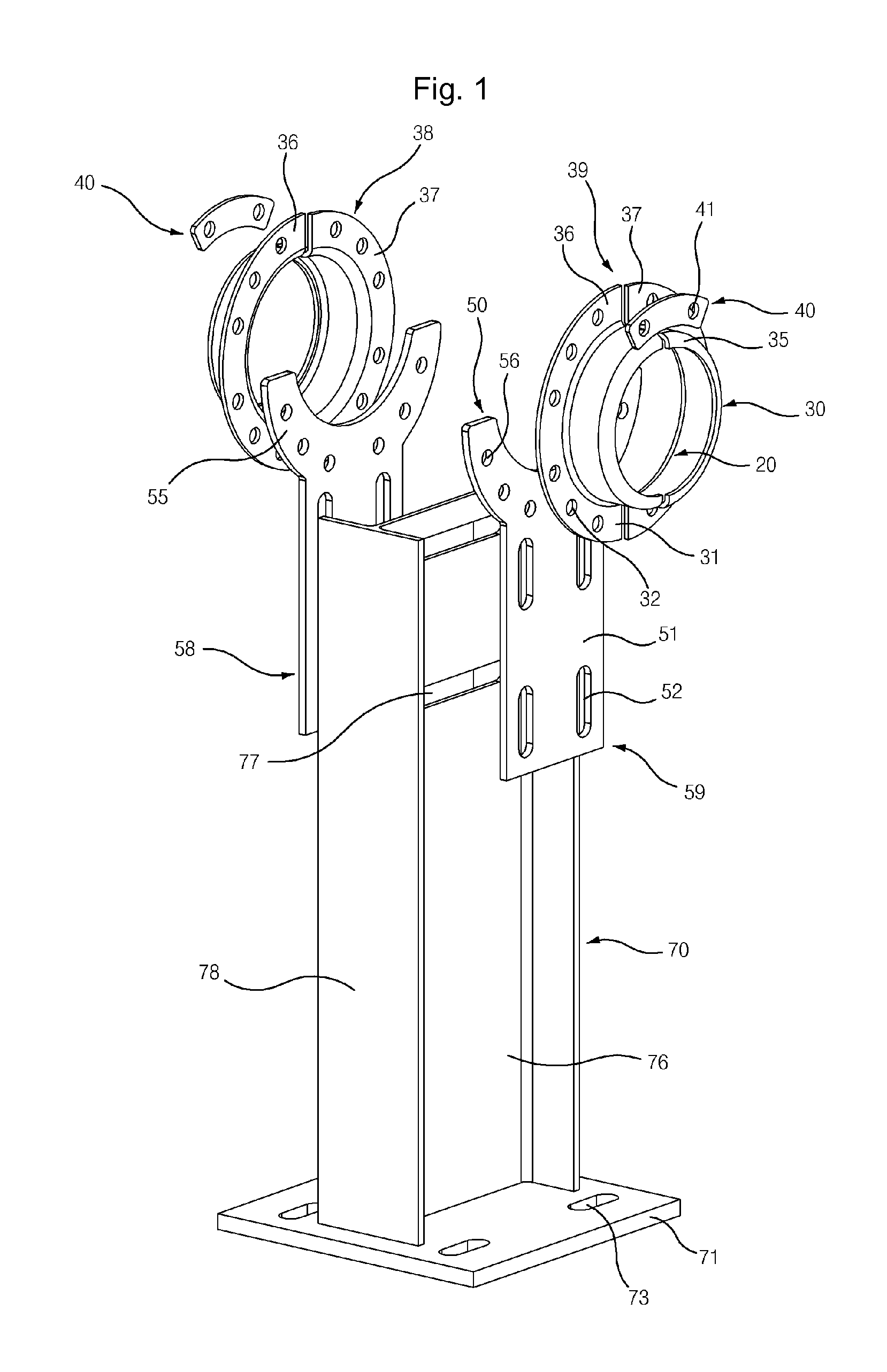
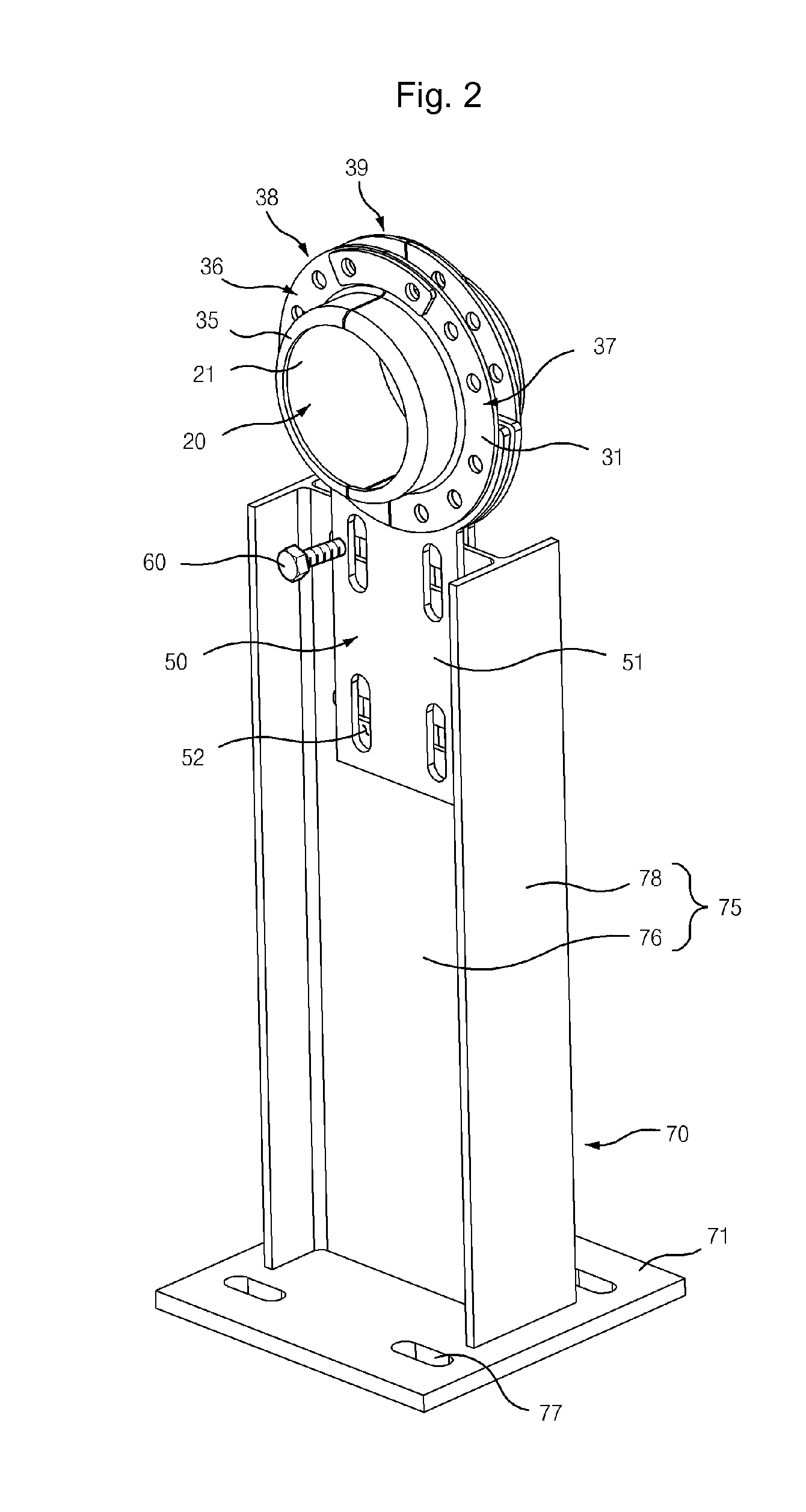
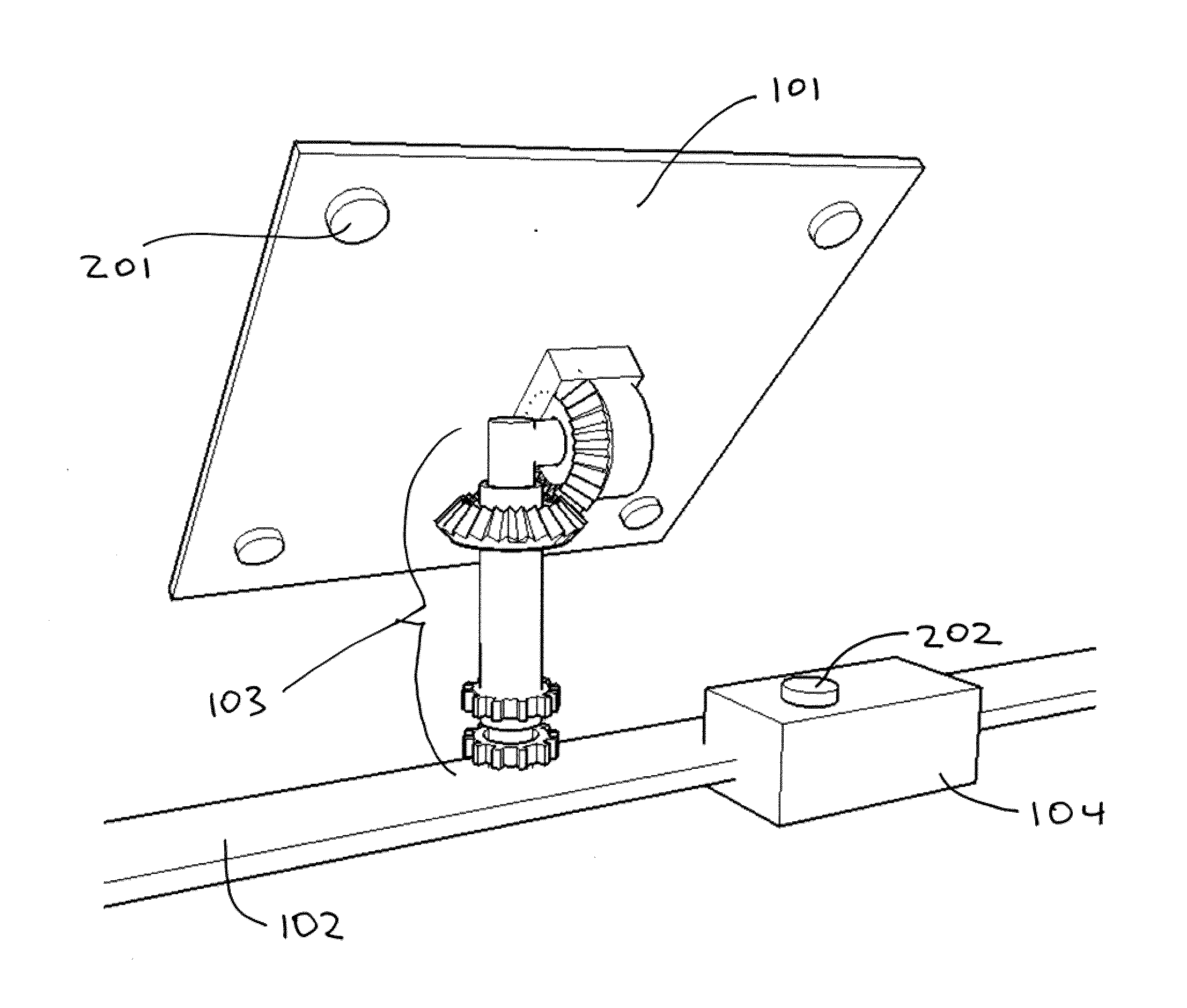
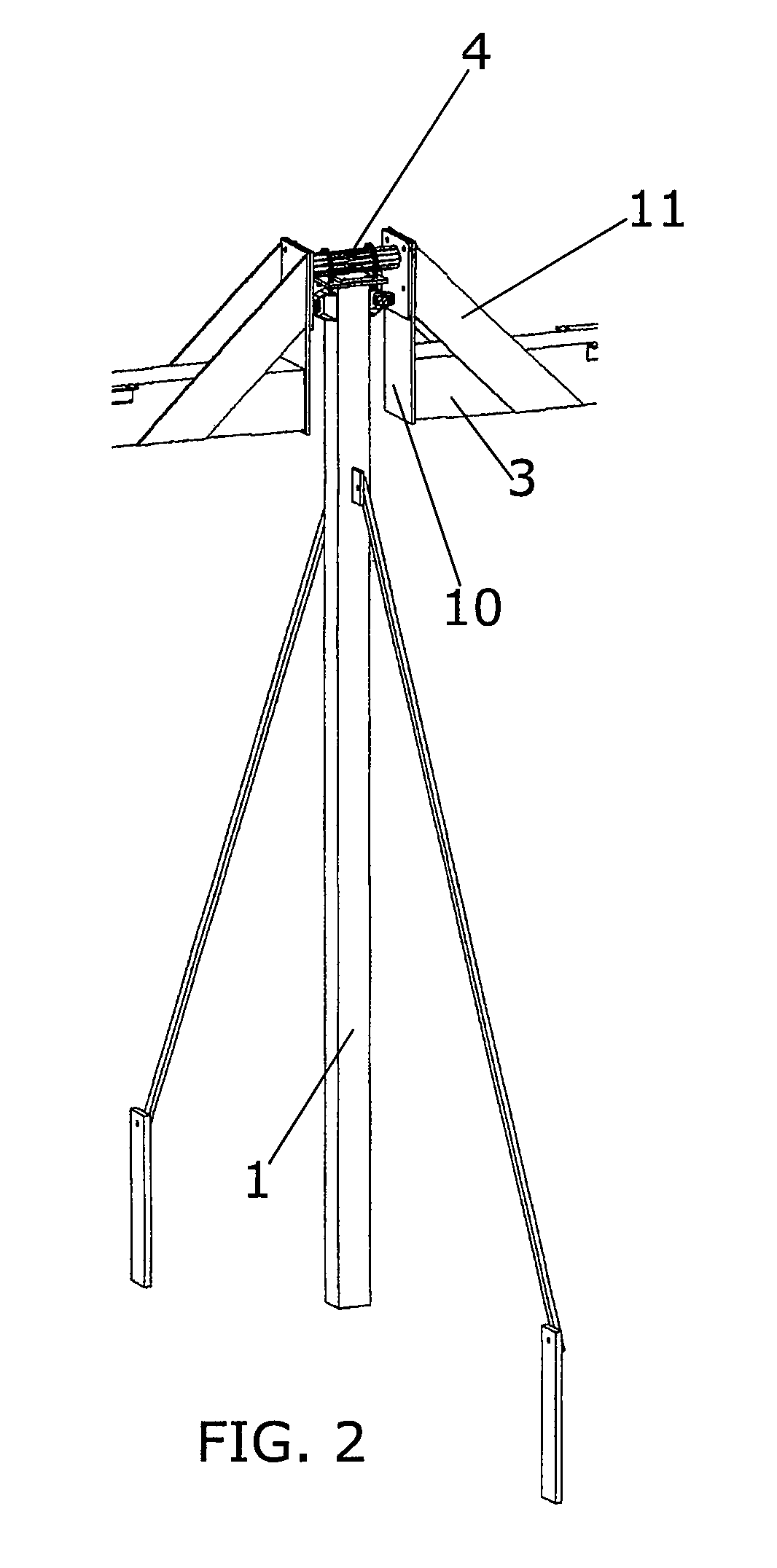
Torque tube supporter and solar tracker using the same
InactiveUS20110253195A1Improve long-term durabilityMinimize overloadPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyControl theorySolar tracker
A torque tube supporter and a solar tracker using the same are provided. The torque tube supporter includes a cylindrical bearing supporting a cylindrical torque tube, a bearing cover having a cylindrical middle portion for supporting the bearing, a flange radially protruding from the circumference of the bearing cover, a half journal section having an arcuate upper portion to which the flange is fixed, and a post supporting the half journal section.
Owner:UST SOLAR INC
Solar tracker drive
InactiveUS20120216852A1Low costPerformed quickly and accuratelyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyCollection systemFeedback control
A solar energy collection system can include a drive configured to adjust a tilt position of a solar collector assembly so as to tract the sun. The drive can include hardware for providing feedback control of the orientation of the solar collector assembly. A method for calibrating the drive can include moving the drive to a reference position and saving an output value from a sensor configured to detect the orientation of the drive. The reference value output from the sensor can then be used in determining the target output value from the sensor required to achieve a desired orientation.
Owner:SUNPOWER CORPORATION
Solar Tracker System for Large Utility Scale Solar Capacity
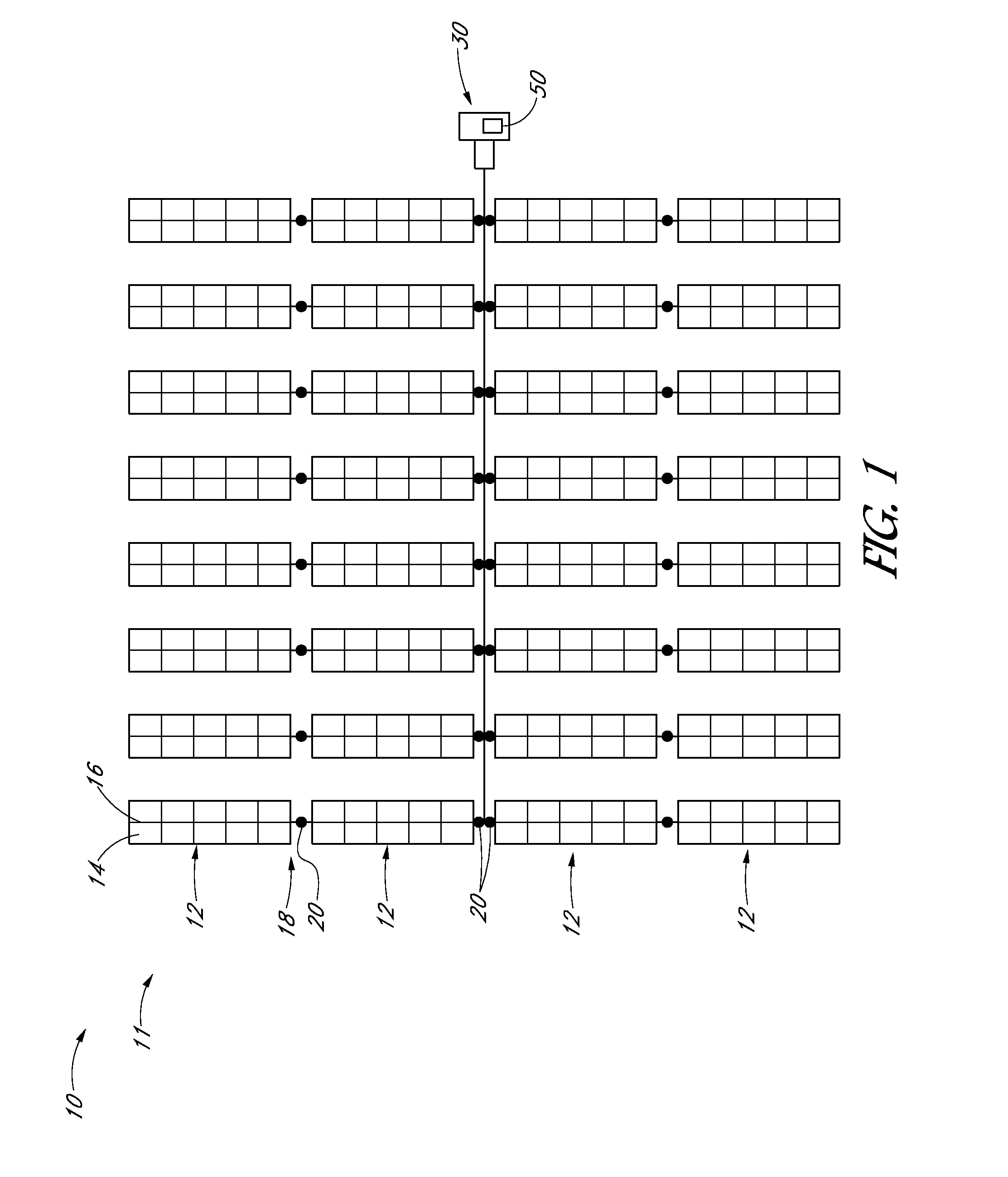
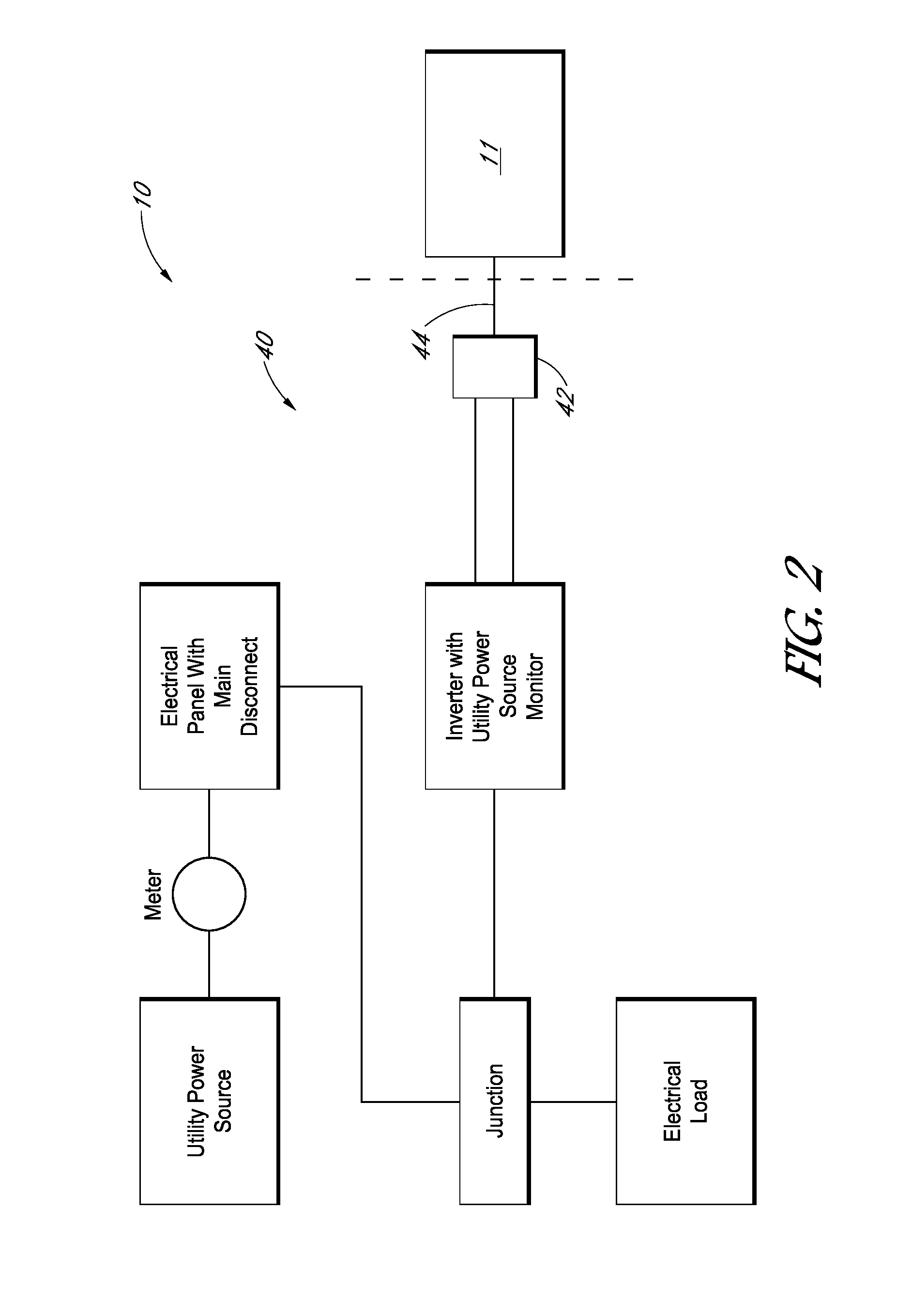
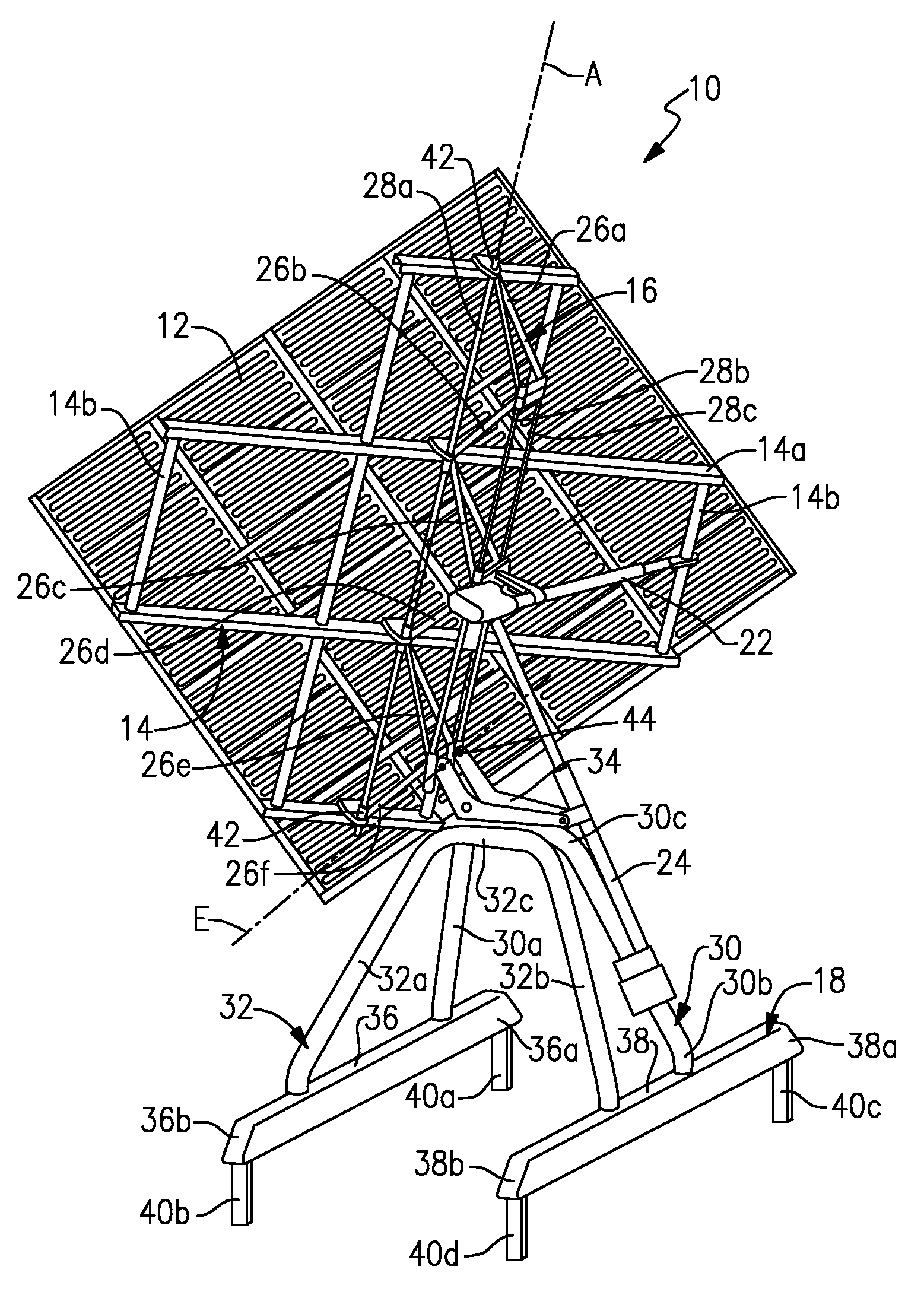
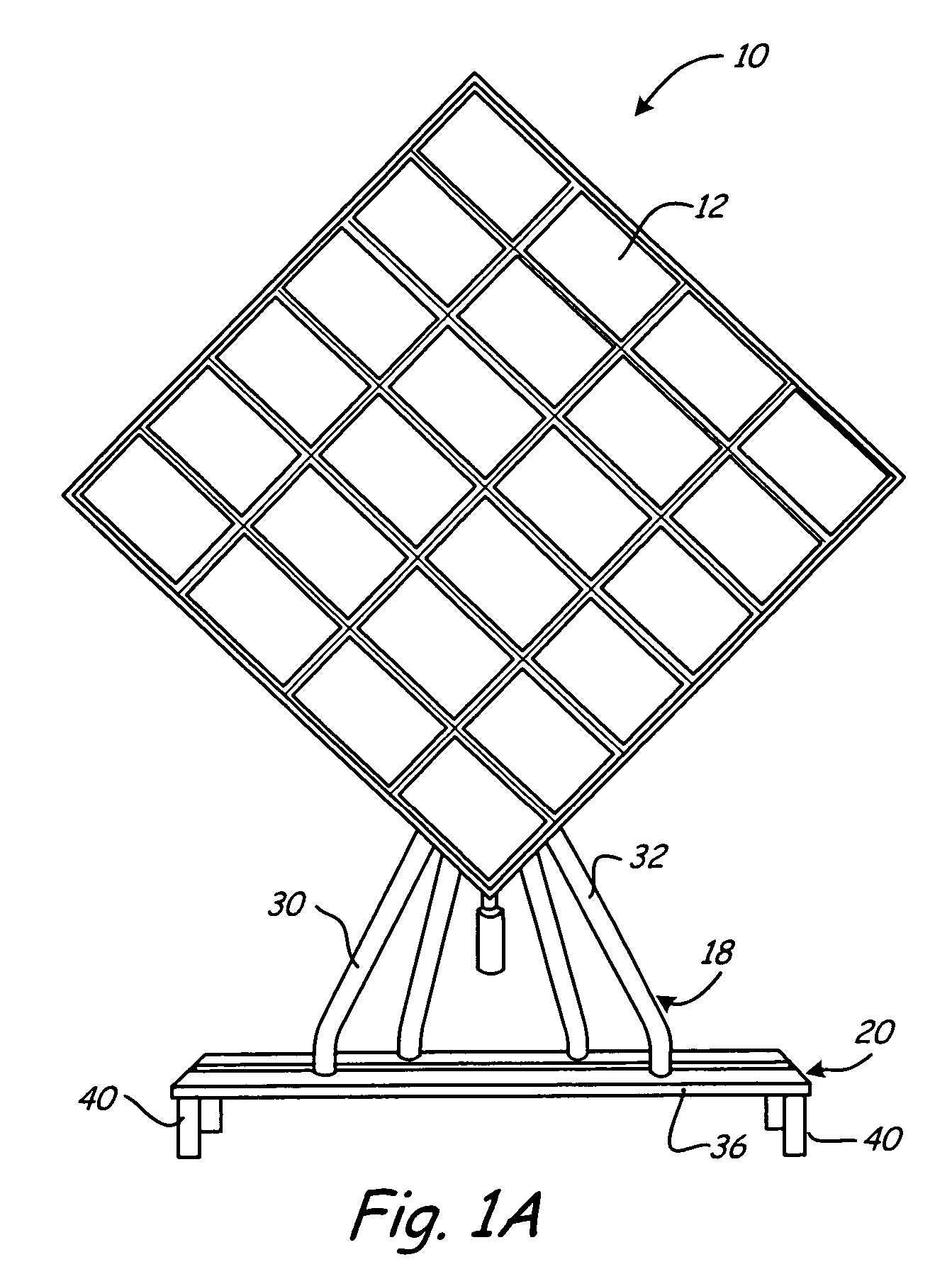
The present invention solar tracker system is directed to a solar tracker that includes a main platform capable of supporting a plurality of solar panels, a sub-platform, one or more support poles supporting the sub-platform and a linking mechanism that connects the sub-frame to the apex of the one or more supporting poles, wherein the linking mechanism rotates in a first axis, a second linking mechanism rotates in a second axis. The mail planar platform hosting the solar panels is encompassed with edge disrupters and spacing channels for adverse wind condition management. The system includes a solar tracker system includes a radiation sensor for determining the best tracking position for maximizing capture of solar energy. The large scale solar tracker system also includes at least two linear hydraulic actuators, each linear hydraulic actuator containing a distal end and proximal end, a rotational joint that connects the distal end of the linear actuators to the sub-platform and the proximal end to the support beam. The second embodiment of the present invention is a plurality of solar tracker apparatus specifically arranged into a large utility scale field system.
Owner:LOKEY ROGER F
Solar tracker having louver frames
InactiveUS20090032089A1Lower vertical heightLow costPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyLouverSolar tracker
A solar tracker does not need to stand high. The solar tracker has a strong structure and a stable center of gravity for tracking sunlight. Thus, the solar tracker does not need a foundation to be connected for standing upon. And the solar tracker is fit to be used on a bare ground or roof with a low cost.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Solar concentrator apparatus with large, multiple, co-axial dish reflectors
ActiveUS20090277440A1Reduce supporting costsMaximizes stiffnessSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersElectricityEngineering
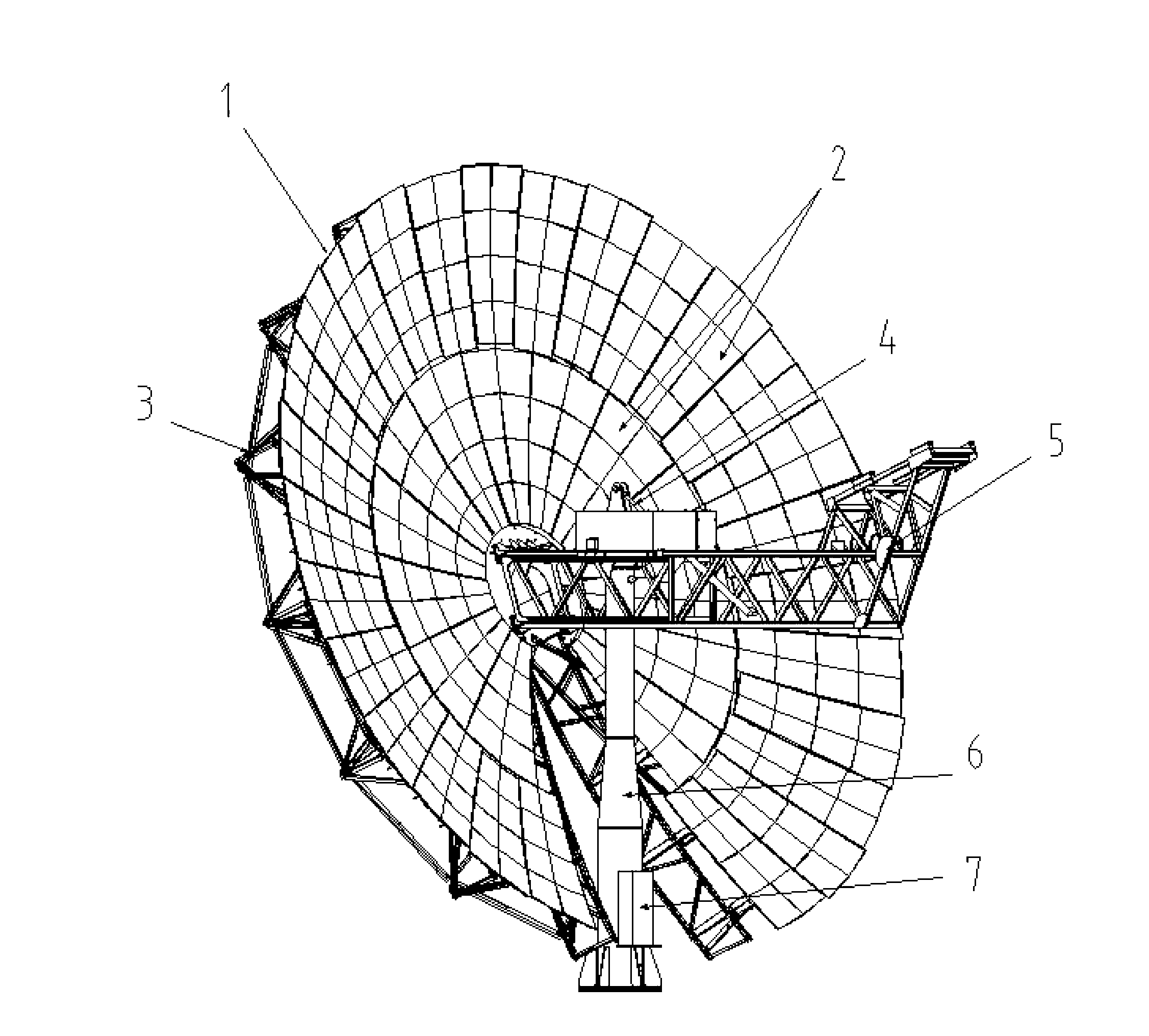
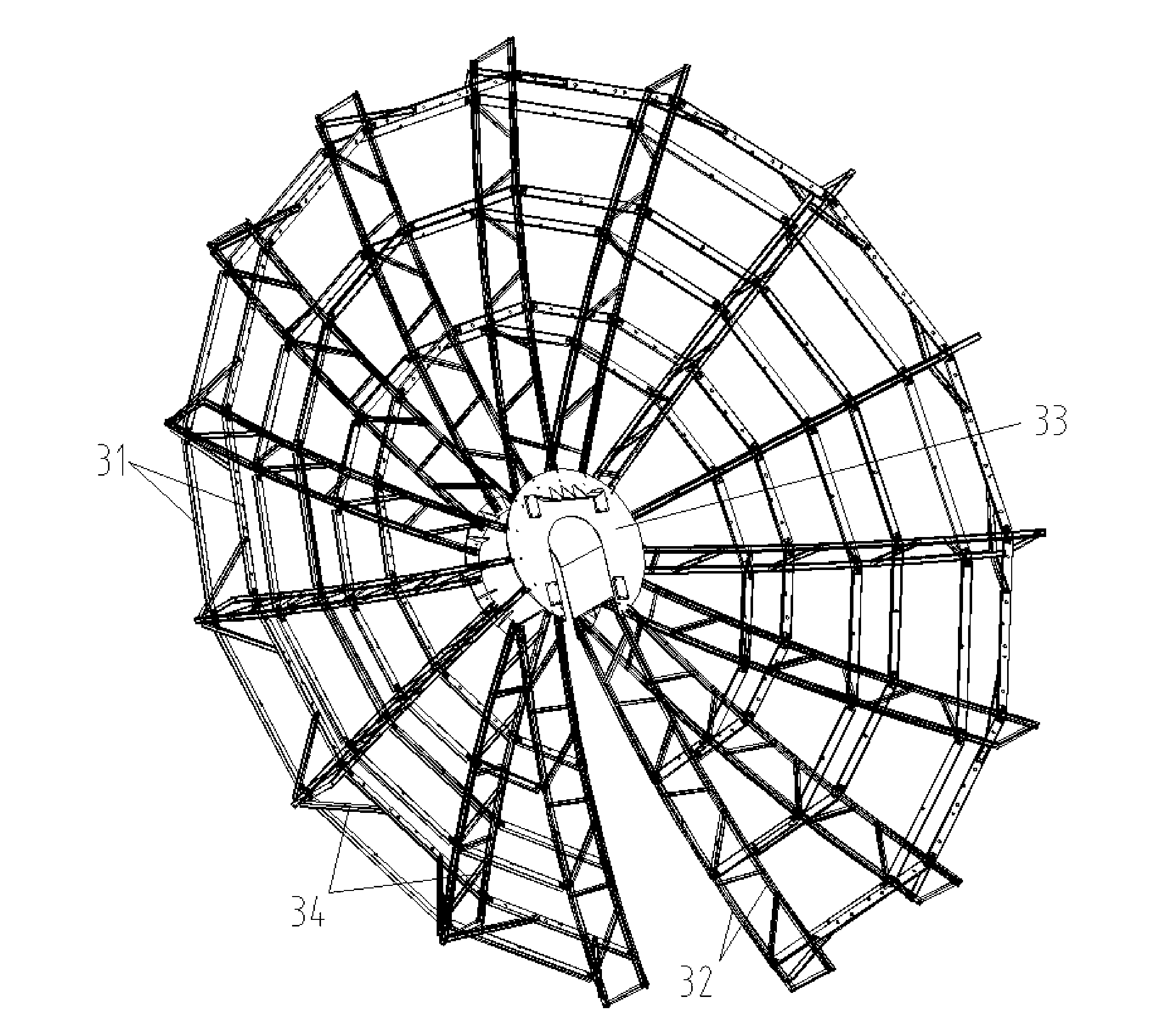
A two-axis solar tracker apparatus is disclosed having multiple dish-shaped monolithic reflectors for concentrating sunlight. The dish-shaped monolithic reflectors are co-axially aligned in an array supported by a moveable frame. The moveable frame forms the elevation structure of a two-axis tracker that has control means for following the movement of the sun across the sky. Each dish-shaped monolithic reflector produces a region of concentrated sunlight suitable for generation of solar energy. A generator is positioned at the focus of each reflector. A preferred generator uses photovoltaic cells to generate electricity at a high output power due to the high solar power input that is directed to the generator by the dish-shaped monolithic reflector.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Solar tracker drive
ActiveUS20150377518A1Increase productionReduce power outputSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersAngular deviationEngineering
A sun-tracking solar drive can include hardware and / or be operated in accordance with a method in which angular deviations are compensated for operation including during forward tracking and backtracking. For example, the effects of thermal expansion and mechanical slop associated with certain components can be calculated and used for calculation of target angles that can provide for increased power output and improved shading avoidance.
Owner:SUNPOWER CORPORATION
Solar tracker
A two-axis solar tracker is capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions. The solar tracker includes a solar array, a frame, a base, a pivot frame, and a first and second actuator. The solar array is mounted to the frame and captures sunlight. The base is pivotally connected to the frame and defines a pivot axis for elevational movement of the solar array. The pivot frame is also pivotally connected to the frame and defines a pivot axis for azimuthal movement of the solar array. The first actuator controls elevational movement of the solar array and the second actuator controls azimuthal movement of the solar array. The solar tracker is pivotable between a raised position and a stowed position.
Owner:SOLARRESERVE TECH
Dual axis solar tracker apparatus and method
InactiveUS8895836B2Strength optimizationPrecise positioningPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyMicrocontrollerSky
The dual axis solar tracker apparatus and method uses an azimuth actuator to adjust the azimuth of an attached solar panel and an elevation actuator to adjust the elevation of a panel seat holding the solar panel to track the azimuth and elevation of the sun as it moves through the sky. The panel seat rotatably supports the solar panel with two pins, and a support structure supports the panel seat with an elevation tracking pivot. The actuators are controlled with an actuator controller circuit that is controlled by a microcontroller. The microcontroller uses information about latitude, longitude, time of day and date to control the actuators and track the motion of sun without the need for sensors.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
Dual axis solar tracker apparatus and method
InactiveUS20130098425A1Optimizes its designed strengthPrecise positioningPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyMicrocontrollerActuator
The dual axis solar tracker apparatus and method uses an azimuth actuator to adjust the azimuth of an attached solar panel and an elevation actuator to adjust the elevation of a panel seat holding the solar panel to track the azimuth and elevation of the sun as it moves through the sky. The panel seat rotatably supports the solar panel with two pins, and a support structure supports the panel seat with an elevation tracking pivot. The actuators are controlled with an actuator controller circuit that is controlled by a microcontroller. The microcontroller uses information about latitude, longitude, time of day and date to control the actuators and track the motion of sun without the need for sensors.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
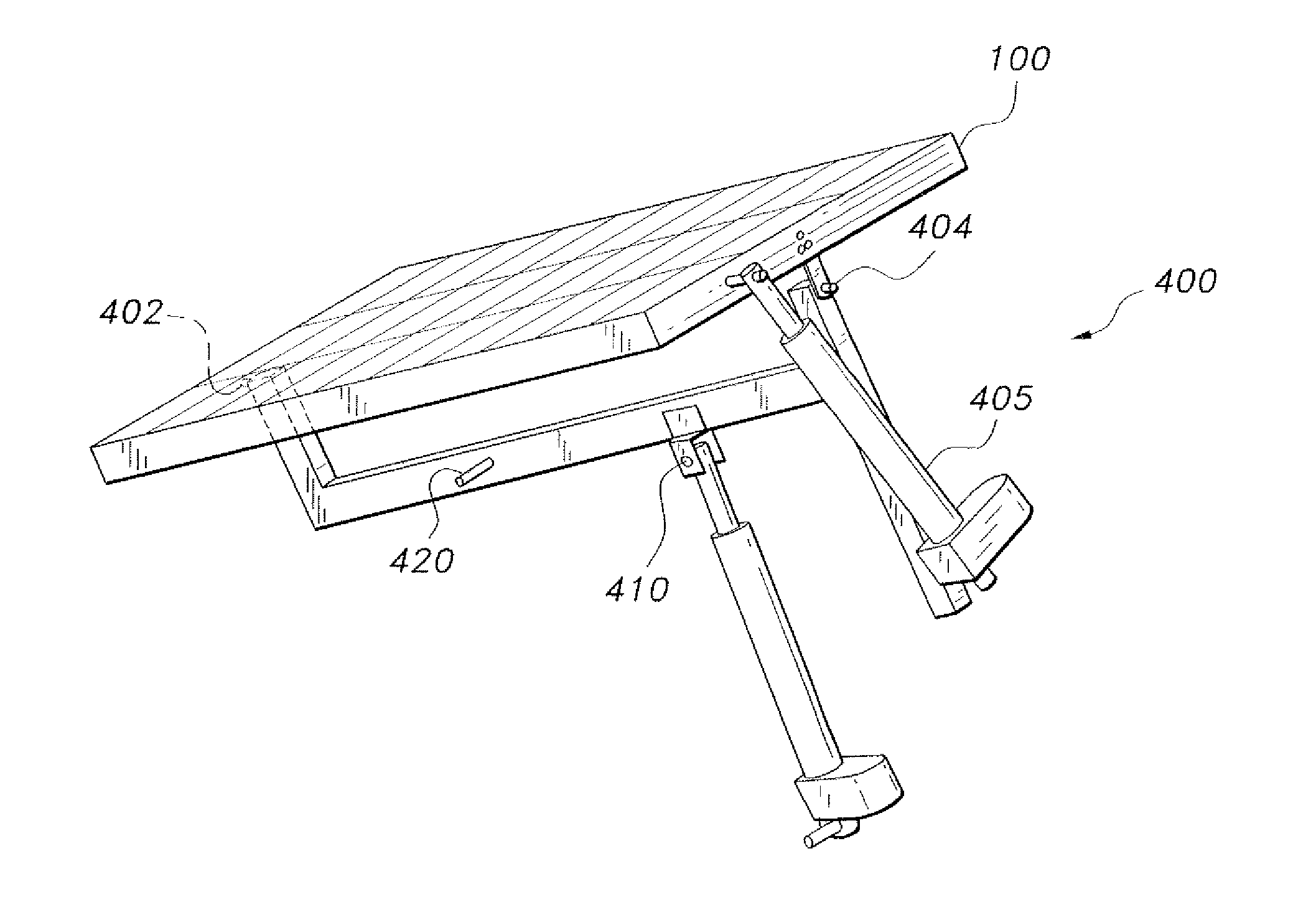
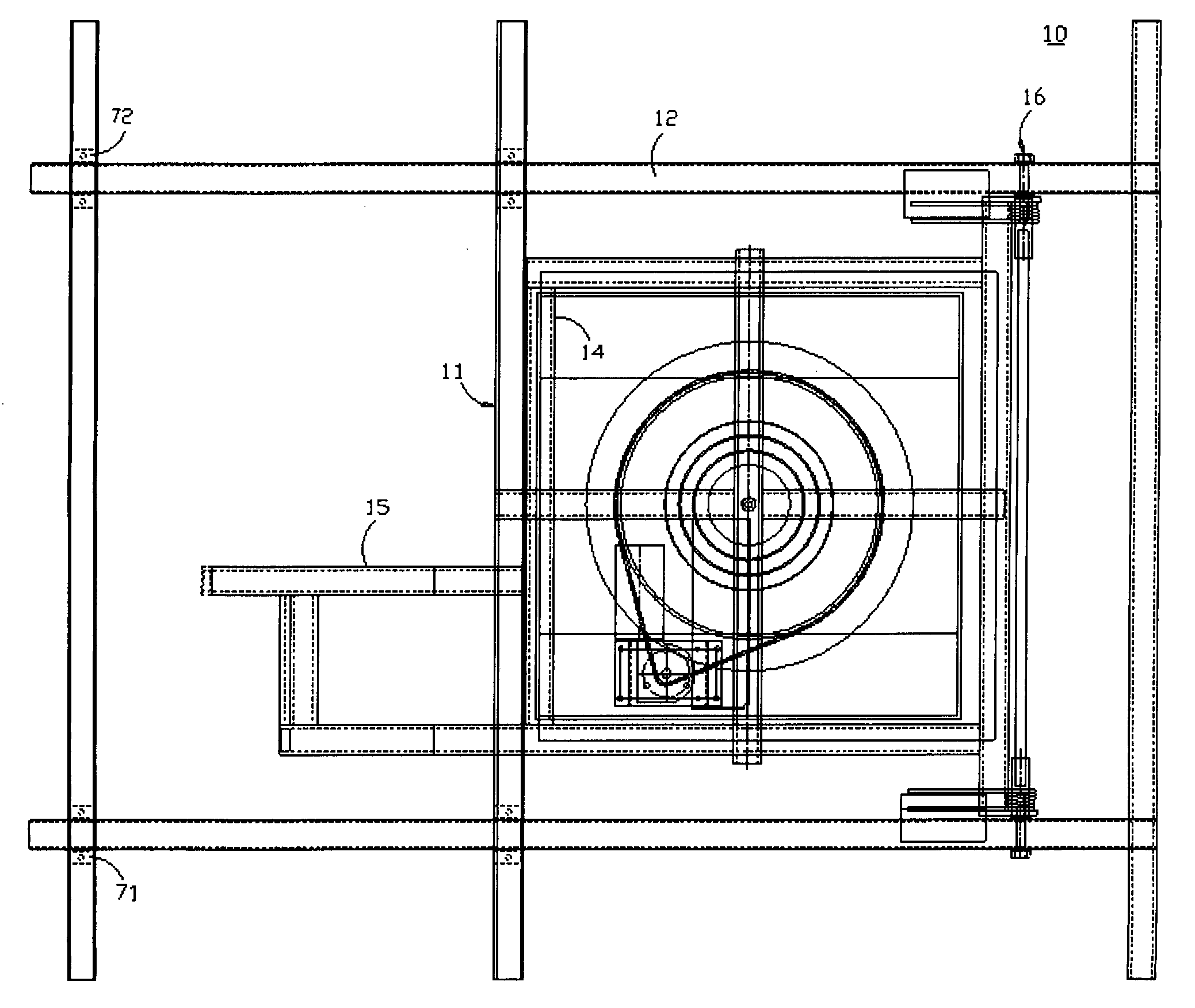
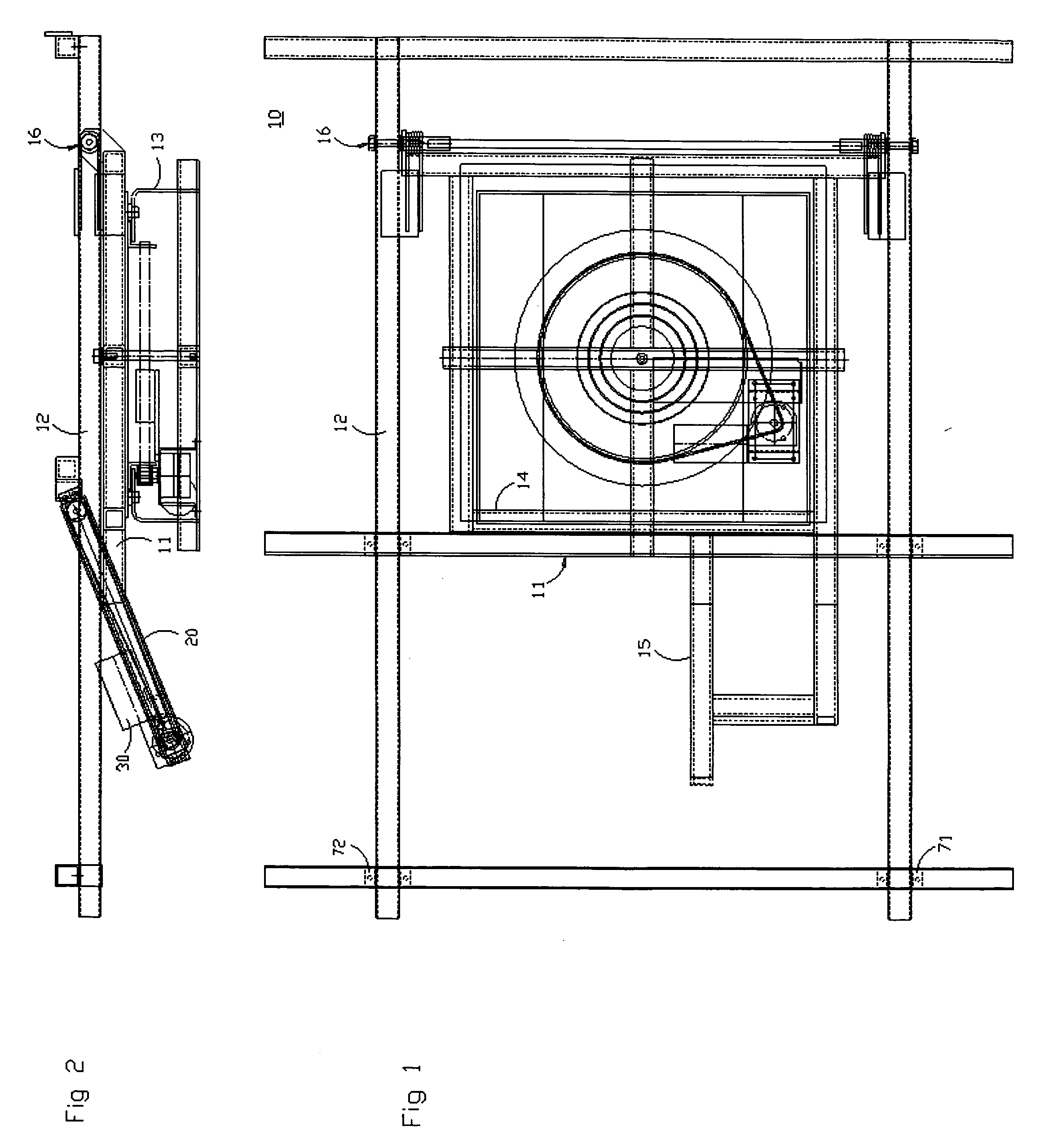
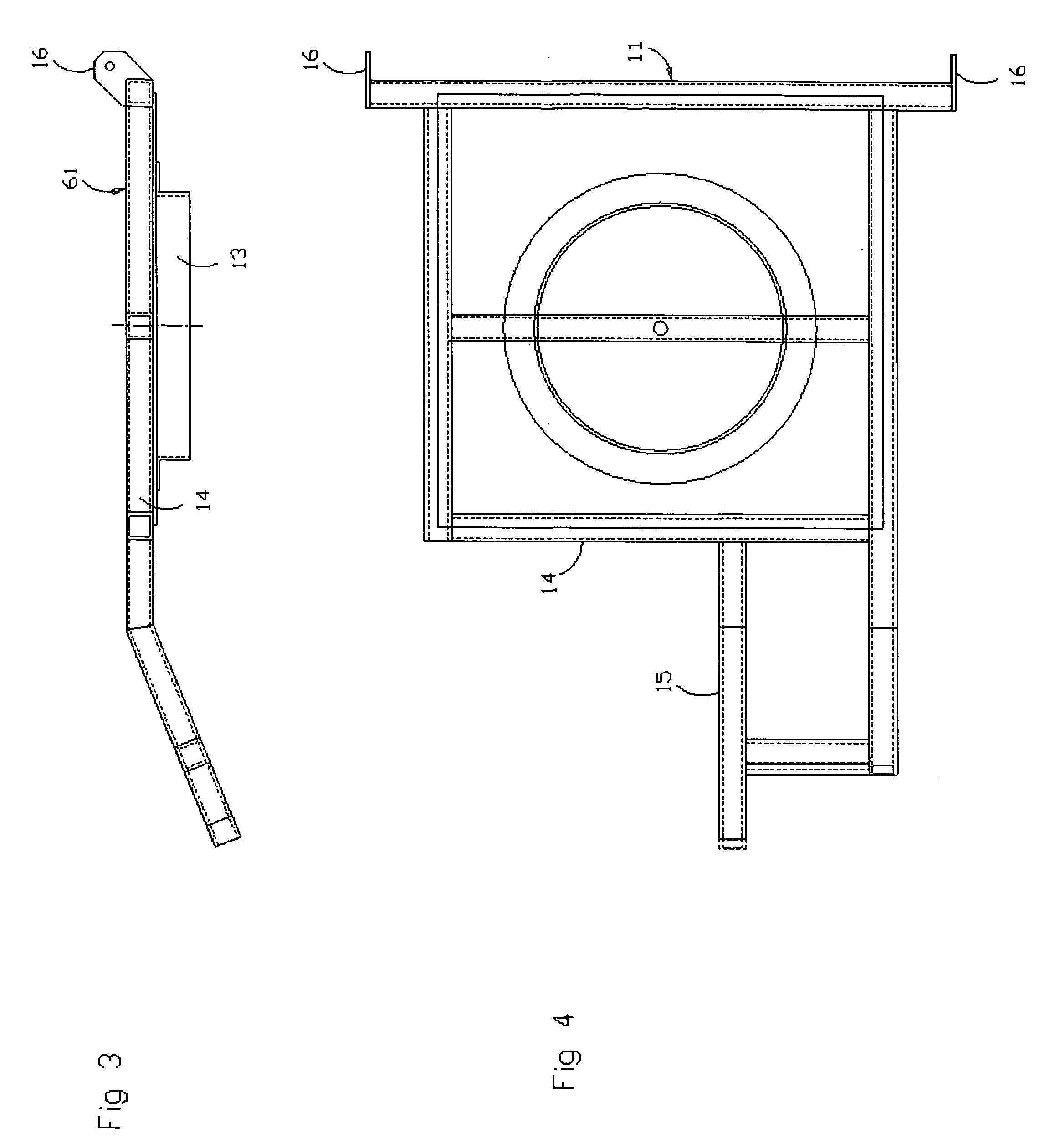
Bidirectional solar tracker
InactiveUS20100095955A1Avoiding unnecessary stressDissipate kinetic energySolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersActuatorSupport point
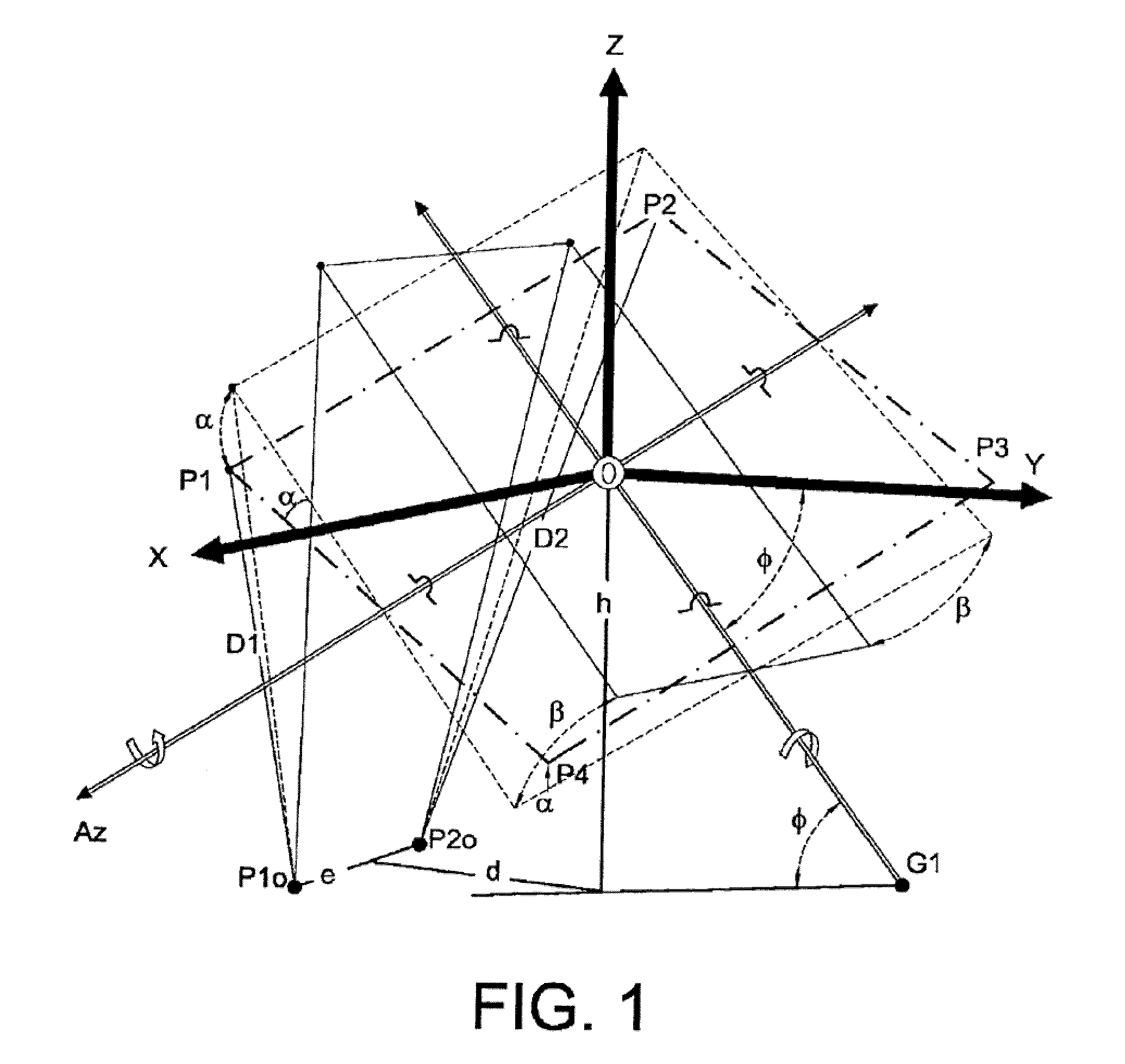
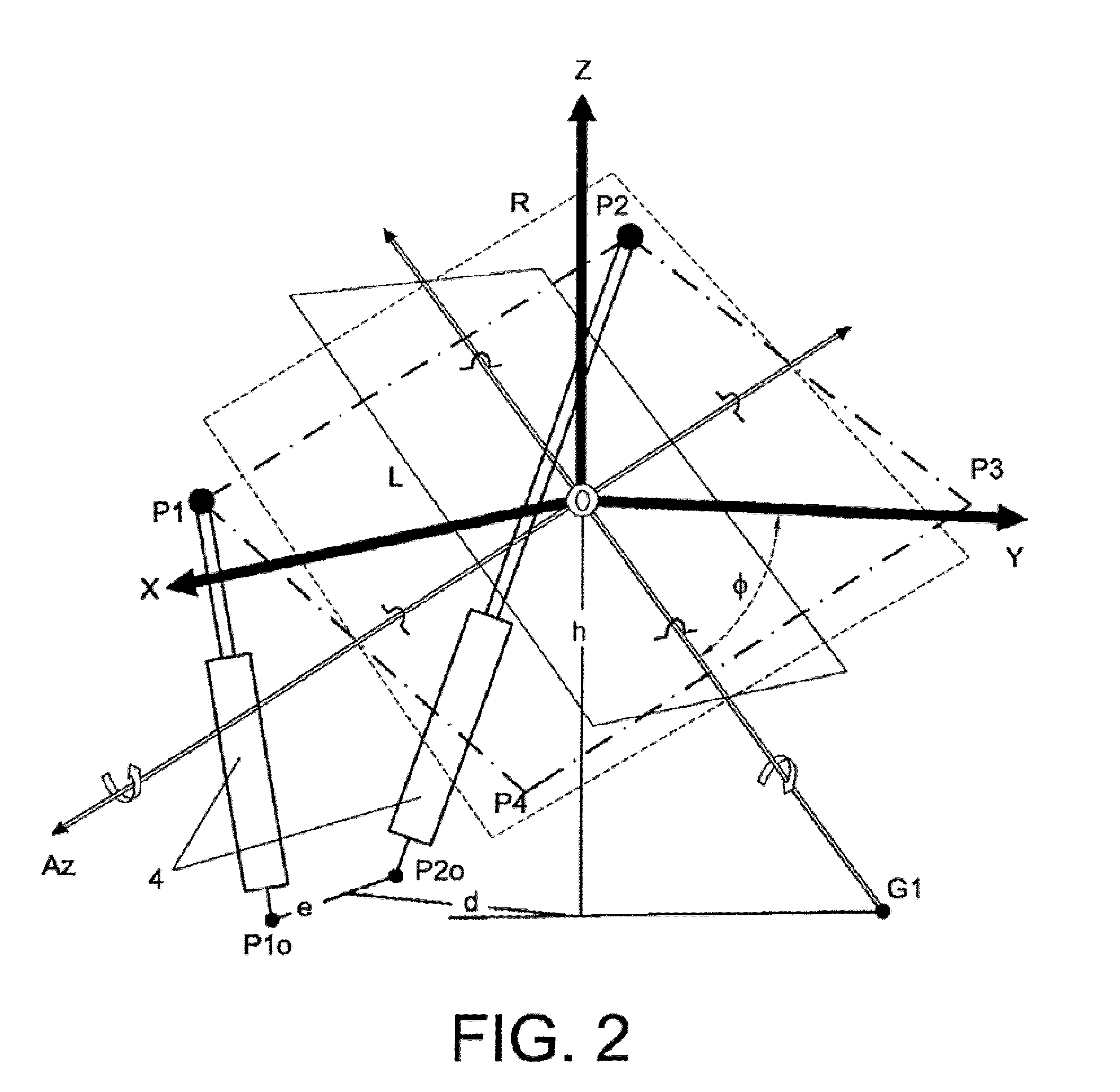
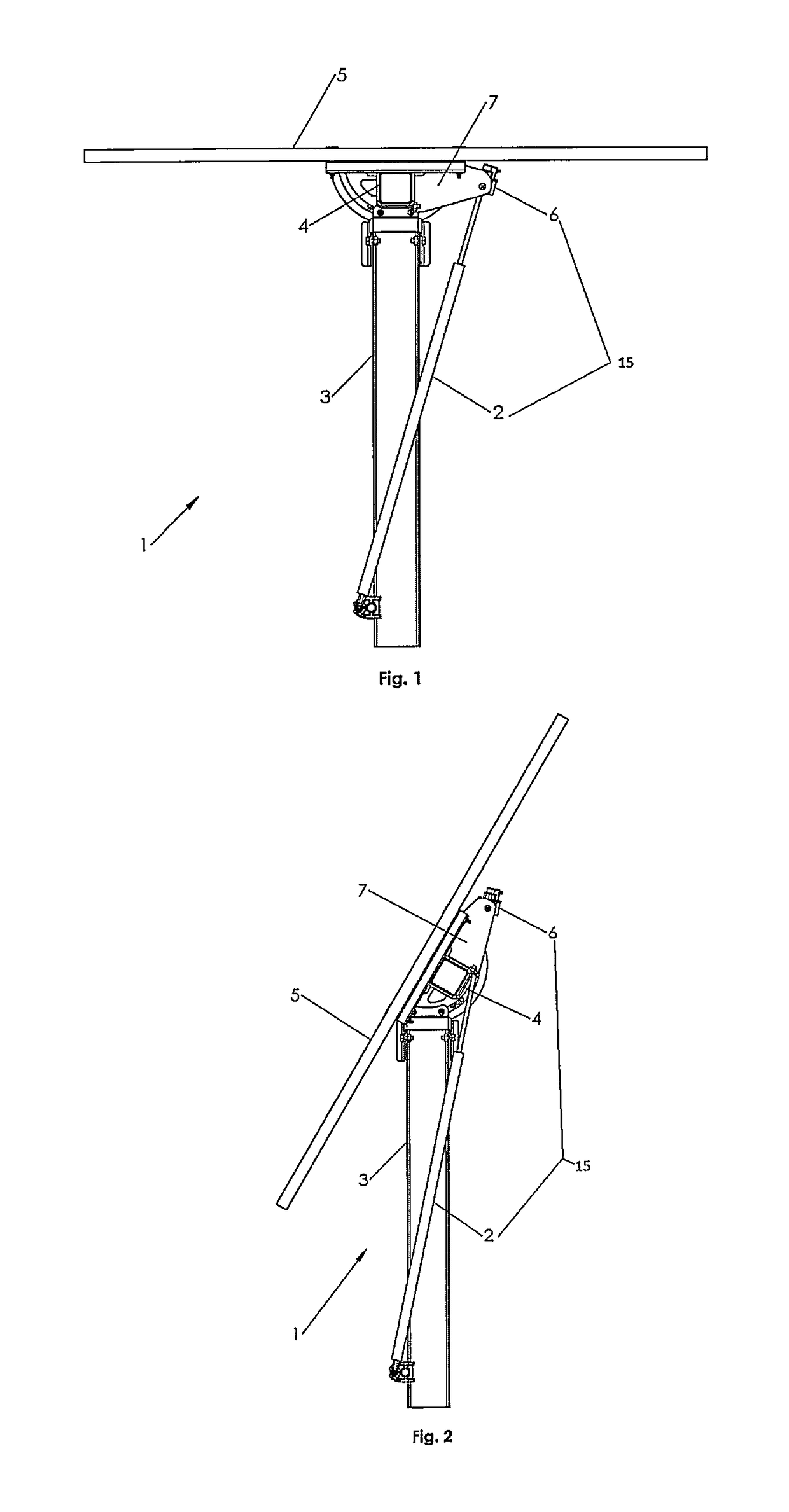
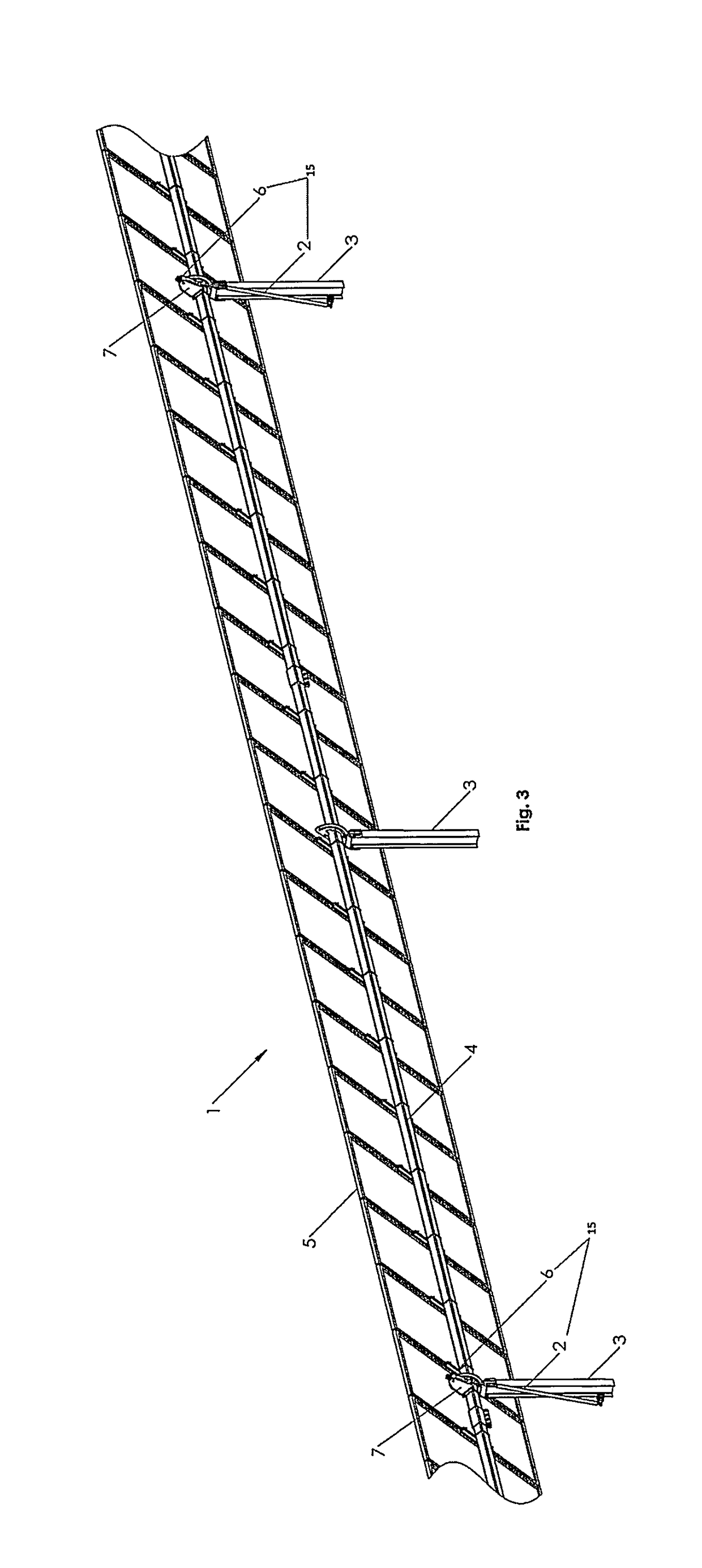
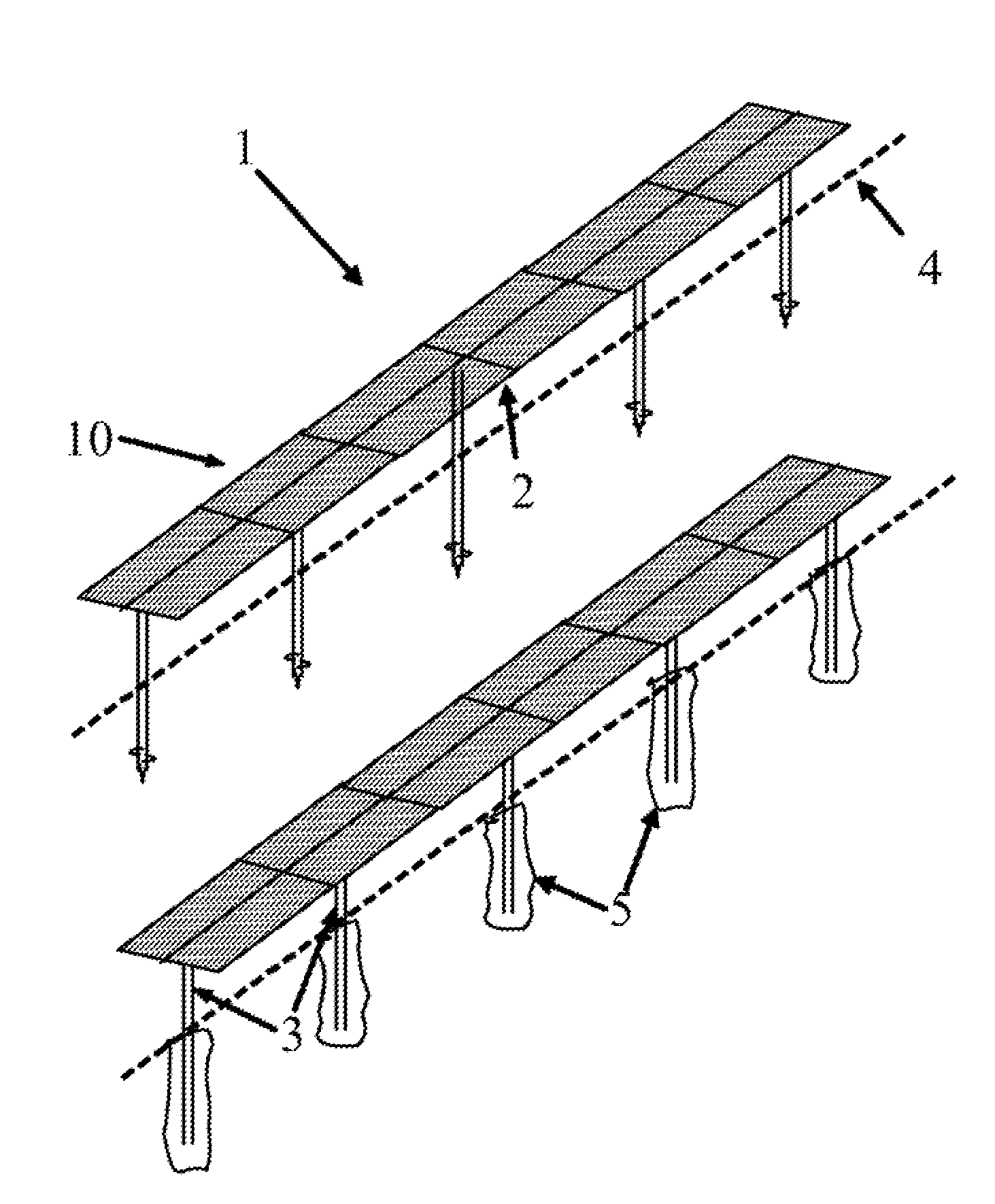
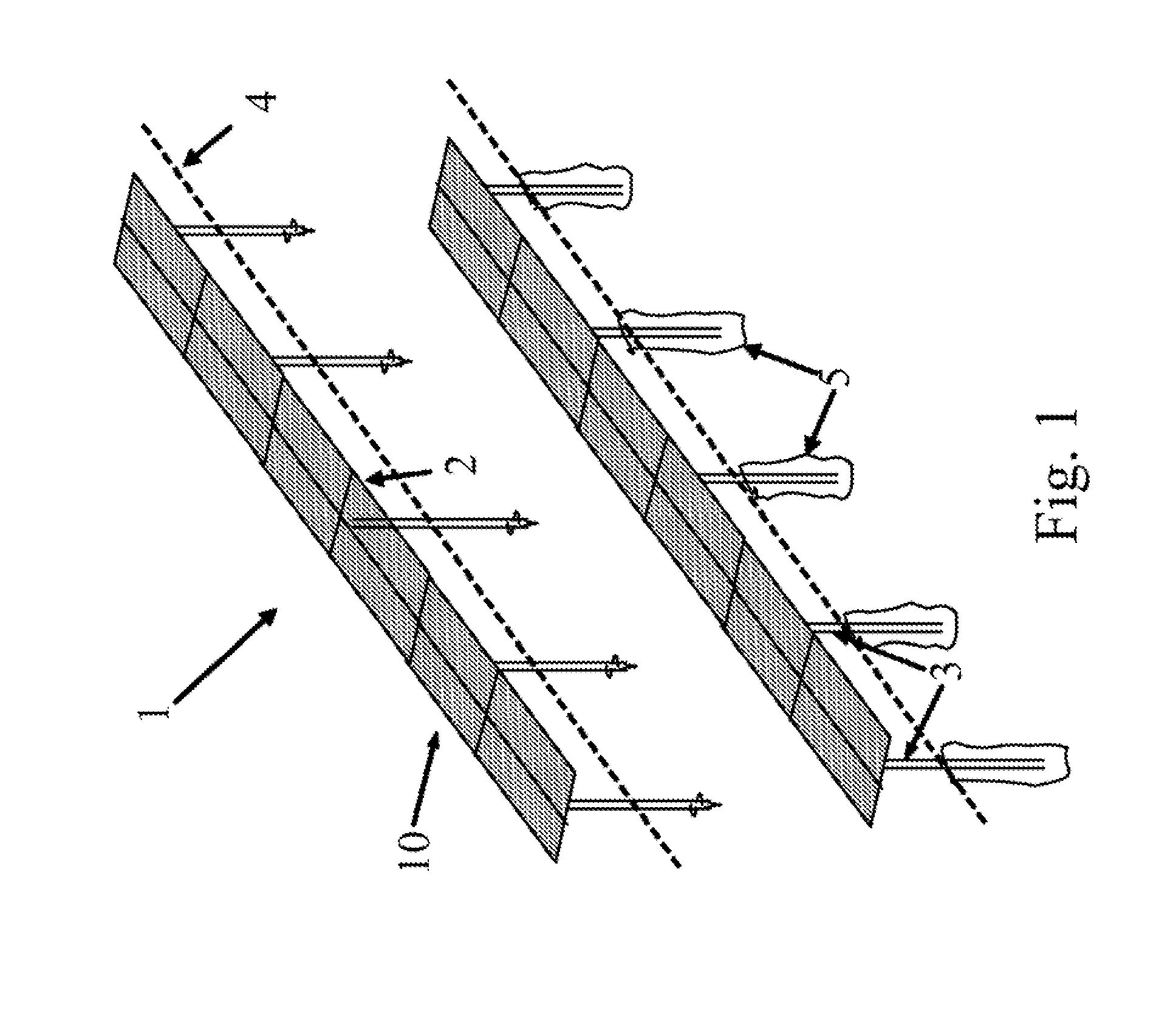
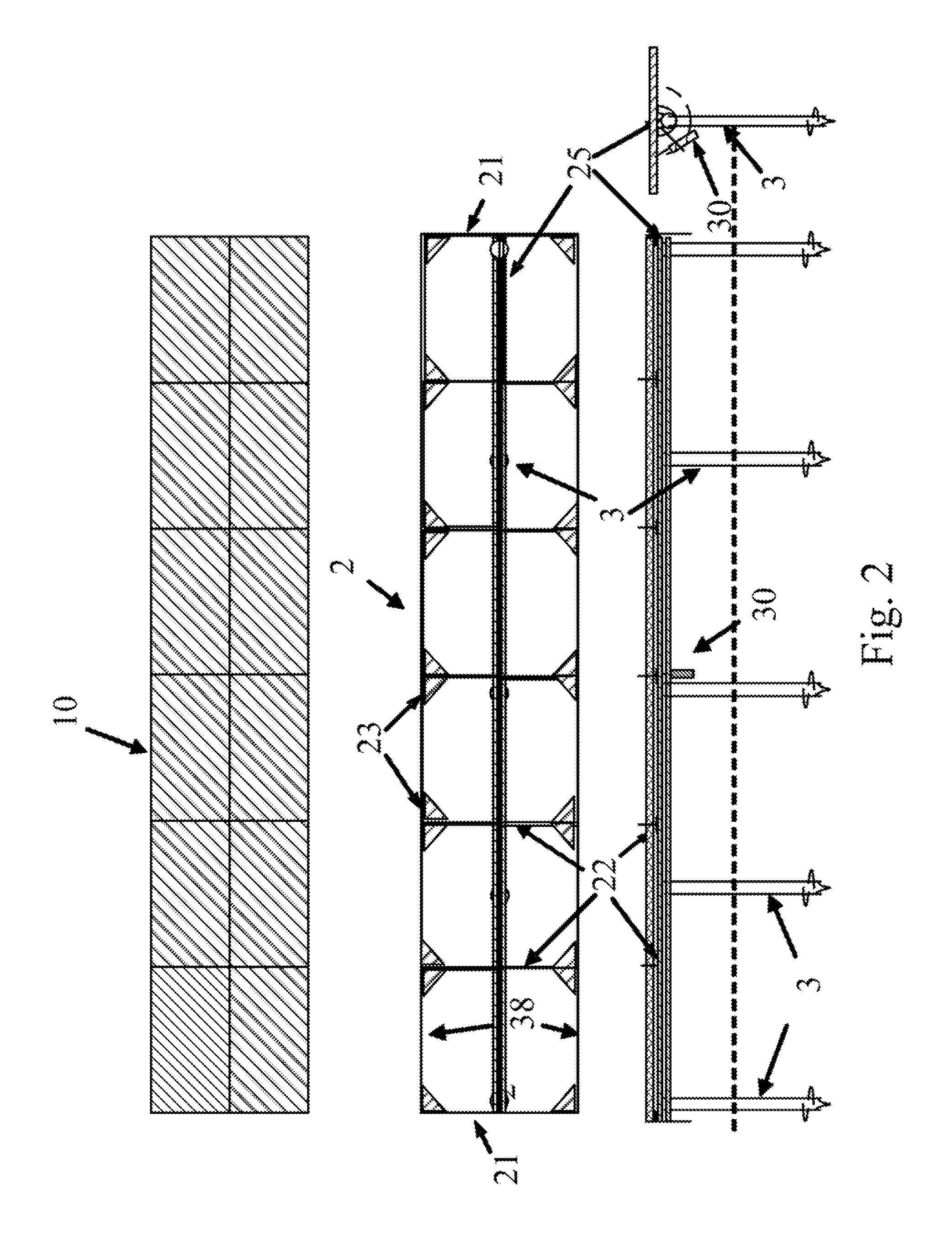
The tracker is formed by a structure (3) bearing a platform (1) carrying the solar panels (2) that varies both the azimuth and elevation orientation thereof in order to track the sun. This movement is achieved by means of two actuators (4) connected respectively to fixed points (P1o, P2o) on the ground and other vertices (P1, P2) of the platform (1), thereby causing the platform to rotate around a central support point “O” of the same. The distances (D1, D2) between the points which join the actuators (4) have a one-to-one relation with the rotation angles (β, α) of the platform (1) around both perpendicular axes: an oblique fixed axis (O-Cl) and another axis (0-Az) that angularly varies the inclination thereof with respect to the first.
Owner:HISPANOTRACKER
One-axis solar tracker system and apparatus with wind lock devices
InactiveUS8671930B2Shorten the timeLeast machinery and labor costSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersLow latitudeHot band
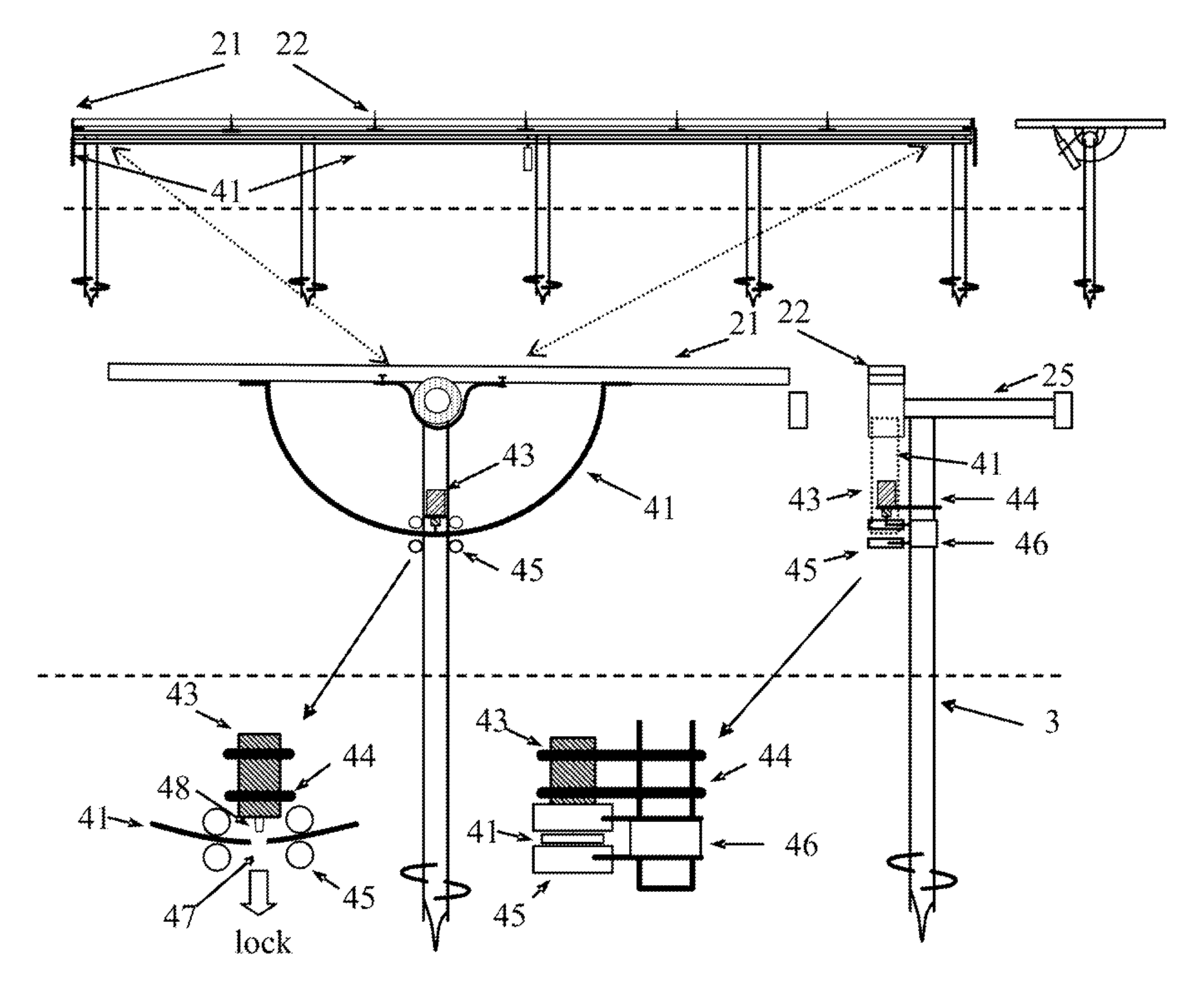
The present invention proposes a one-axis solar tracker system and apparatus which is simple to install, lower cost and with the provision of an electric-magnetic locking device to resist from medium to strongest wind condition like hurricane or typhoon. Solar farms is more and more popular to use one-axis tracker due to lower cost, higher wind resistance and easier for large scale solar farm installation, especially at lower latitude tropic zones. This disclosure proposes a one-axis tracker with multiple posts support using a single or dual linear actuators driving mechanism for rotation. It is also equipped with a wind lock device to lock the solar tracker in horizontal neutral position during strong wind condition such as hurricane or typhoon. The stepwise wind lock device can further be applied to locking the solar tracker following each step of linear actuator activation enabling the disclosed solar tracker to operate in windy conditions.
Owner:THE LIAOS FAMILY
Horizontal balanced solar tracker
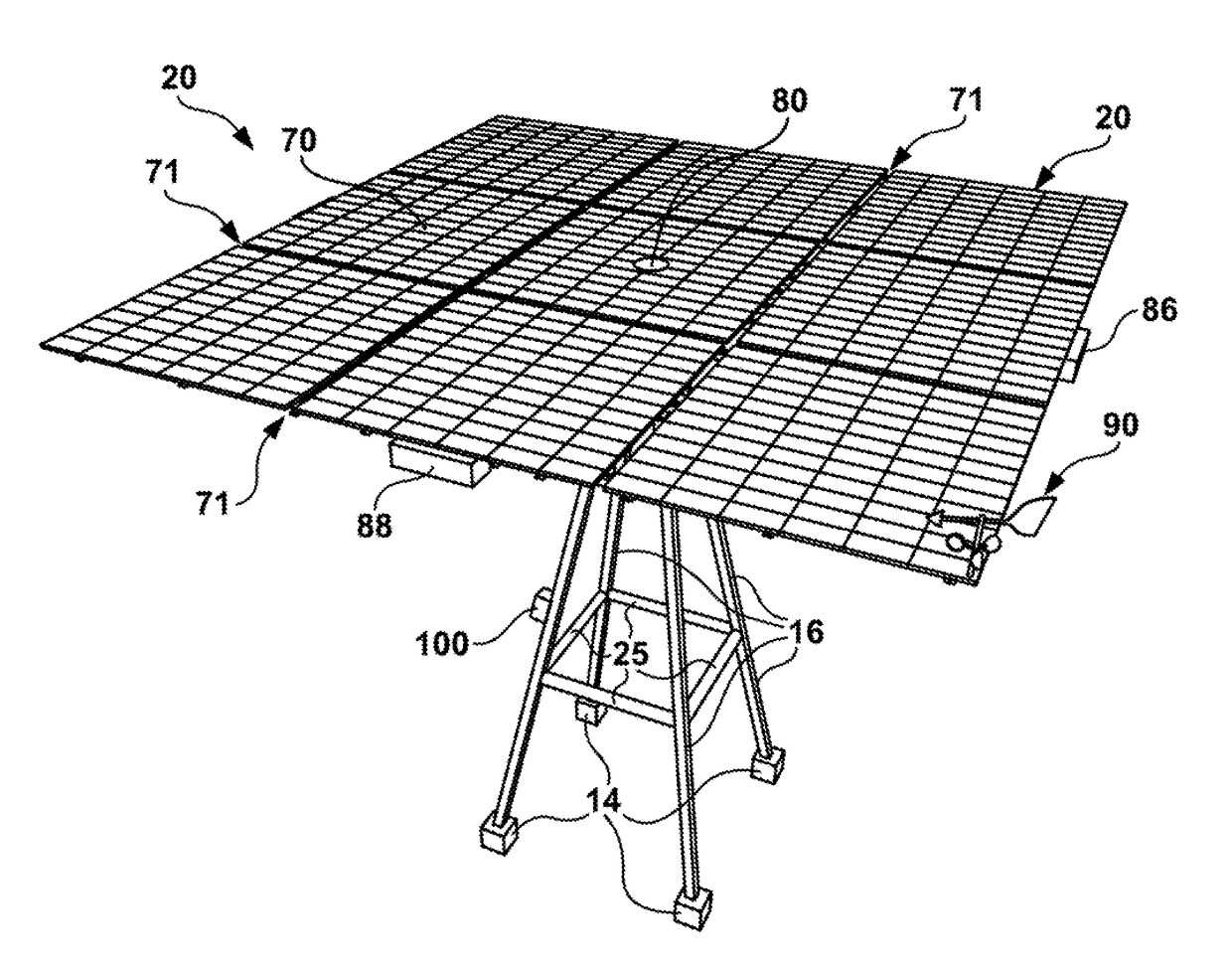
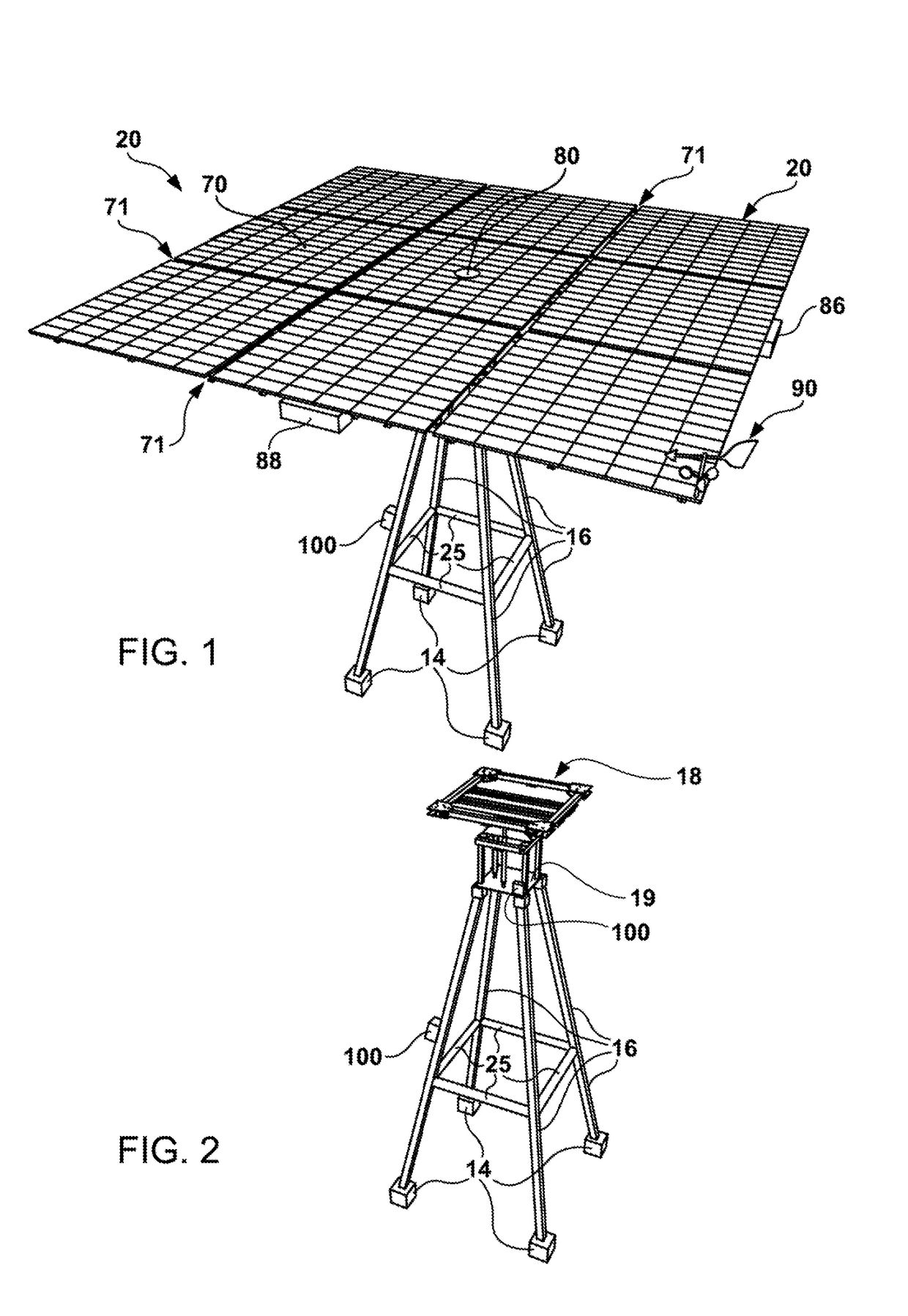
In an example, the present invention provides a solar tracker apparatus. In an example, the apparatus comprises a center of mass with an adjustable hanger assembly configured with a clam shell clamp assembly on the adjustable hanger assembly and a cylindrical torque tube comprising a plurality of torque tubes configured together in a continuous length from a first end to a second end such that the center of mass is aligned with a center of rotation of the cylindrical torque tubes to reduce a load of a drive motor operably coupled to the cylindrical torque tube. Further details of the present example, among others, can be found throughout the present specification and more particularly below.
Owner:NEXTRACKER LLC
Dynamic stabilizer for solar trackers
ActiveUS20180013380A1Raise the natural frequencyIncrease stiffnessPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyControl systemSnubber
A non-drive dynamic stabilizer includes a damper and an actuator. The dynamic stabilizer provides multiple states of support to a solar tracker structure. These states may include 1) flexible movement and / or damping during normal operation (i.e. tracking) and / or 2) rigid or locked, whereby the dynamic stabilizer acts as a restraint. The dynamic stabilizer is actuated by a control system according to the real-time demands on the structure. Sensors to provide input to the control system may include wind speed sensors, wind direction sensors, snow sensors, vibration sensors and / or displacement sensors.
Owner:COROSOLAR LLC
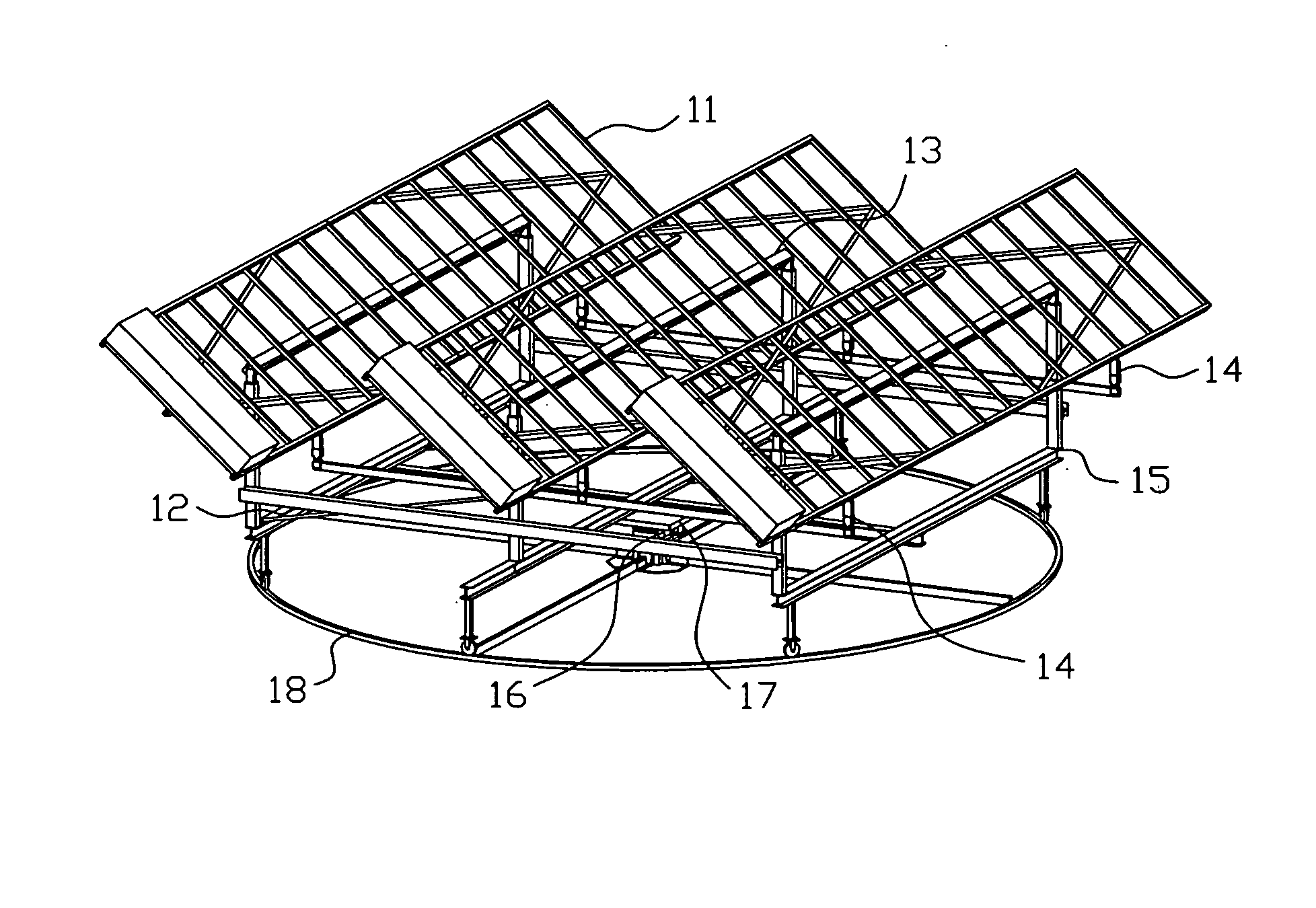
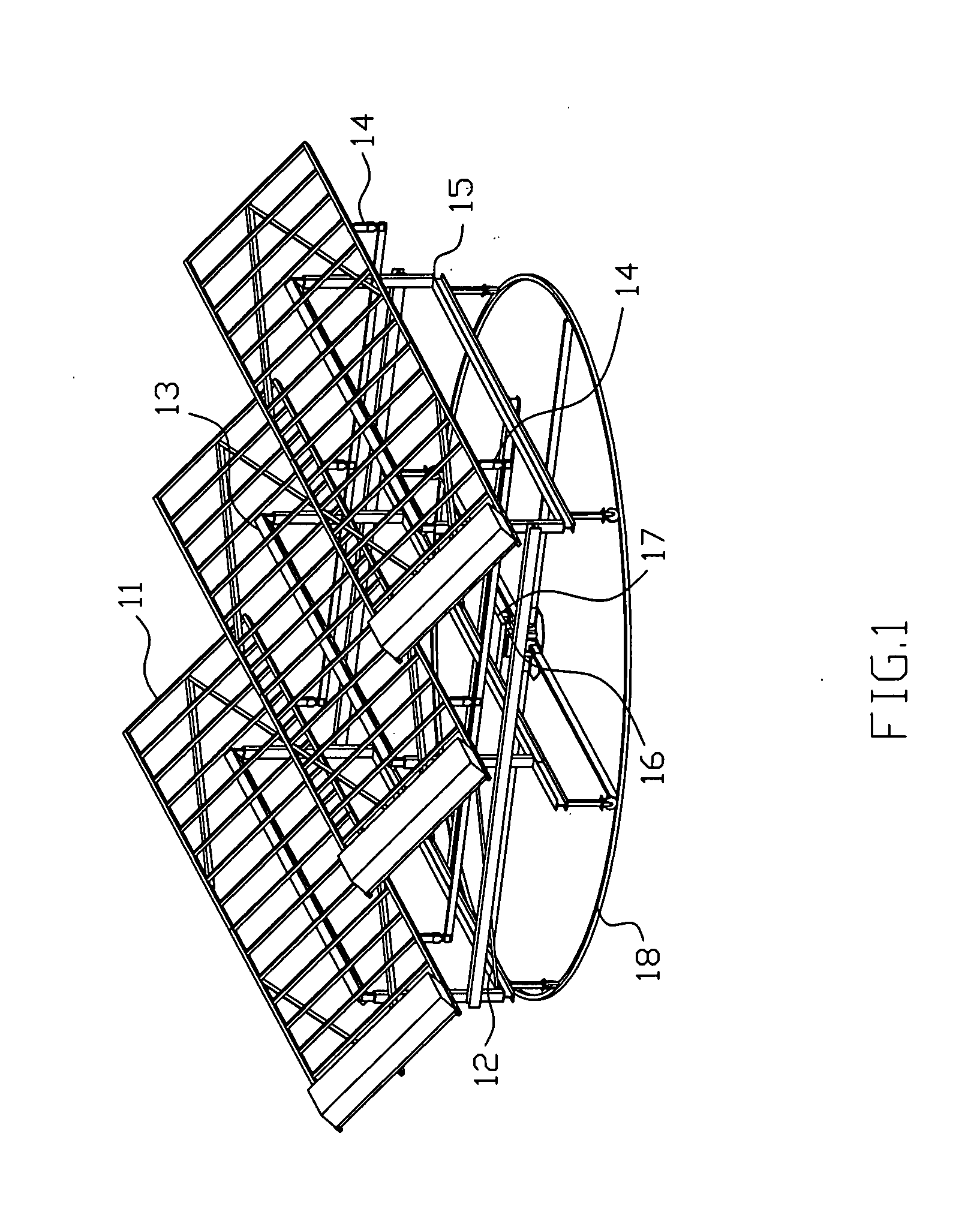
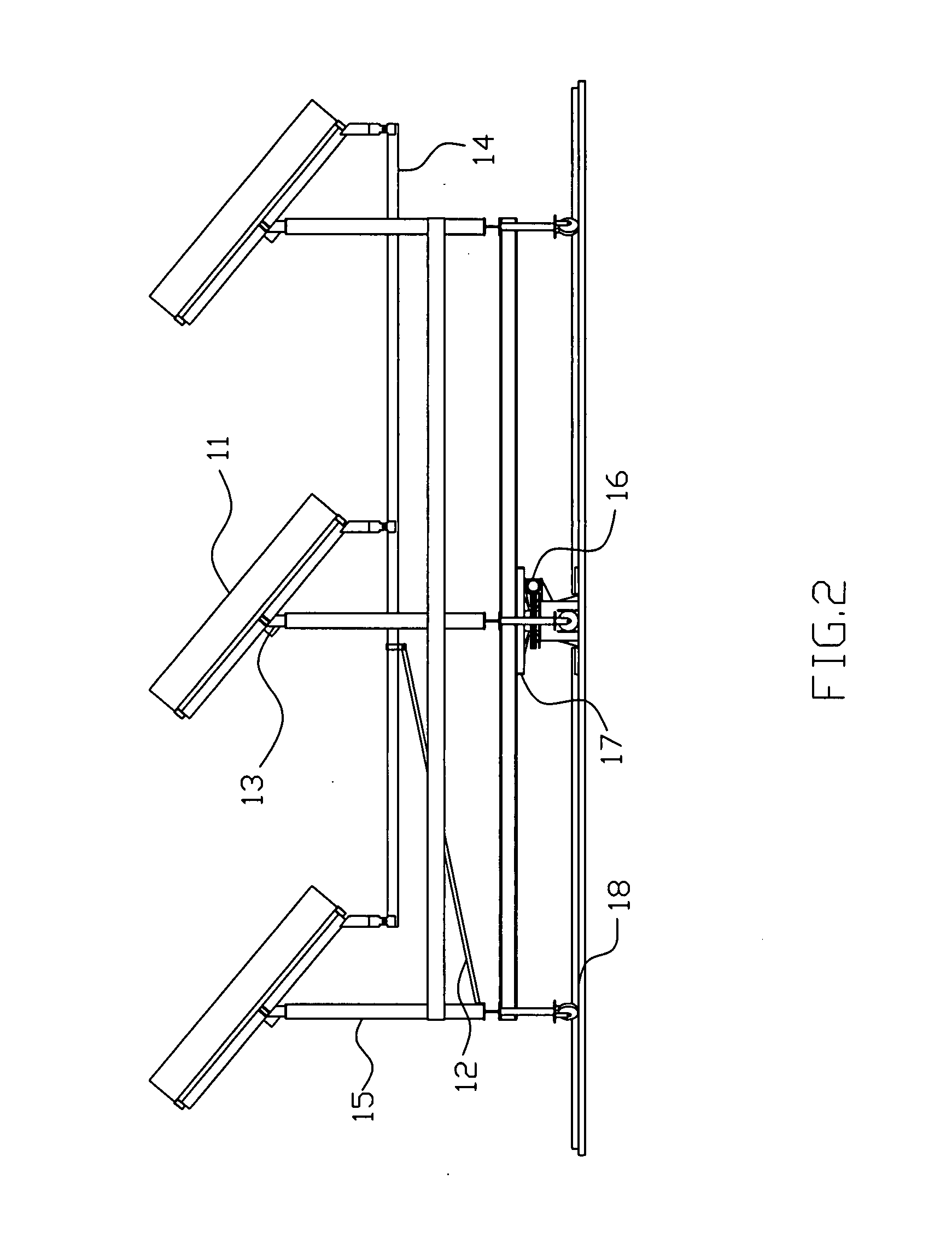
Horizontal solar disk-type light condensation system and solar power generation system adopting same
InactiveCN102705187AReduce the impactReduce wasteFrom solar energyMachines/enginesControl systemElectrical control
The invention discloses a horizontal solar disk-type light condensation system and a solar power generation system adopting the horizontal solar disk-type light condensation system. The horizontal solar disk-type light condensation system comprises a light condensation reflecting lens system, a back support, a Stirling engine support, a double-shaft solar tracker, a support upright column and an electrical control system, wherein the light condensation reflecting lens system is segmented to sectors and multiple sector-shaped light condensation reflecting lens groups are spliced to form a rotating paraboloid structure; the back support is used for supporting and installing the light condensation reflecting lens system; the Stirling engine support is fixedly connected with the back support; the double-shaft solar tracker is arranged at the top of the support upright column and connected with the back support; the support upright column is fixed on foundation; and the electrical control system is electrically connected with the double-shaft solar tracker and controls the running of the horizontal solar disk-type light condensation system.
Owner:DALIAN GREAT OCEAN NEW ENERGY DEV
Bearing assembly for solar trackers
A solar tracker bearing assembly has a rotating element sandwiched between two mounting brackets and held together by fasteners. The rotating element includes an arc-shaped slot such that the rotating element can pivot against the fixed mounting brackets. Bearings may be positioned within the arc-shaped slot. The rotating element can be configured to accept toque tubes of various cross-sections.
Owner:COROSOLAR LLC
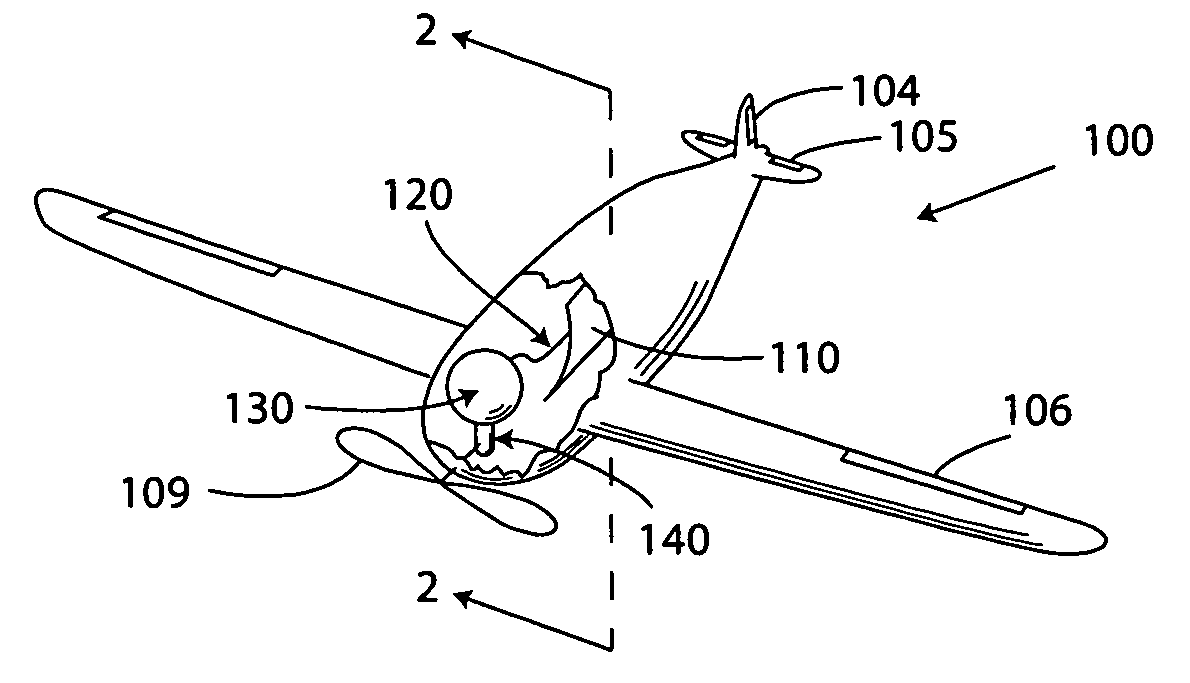
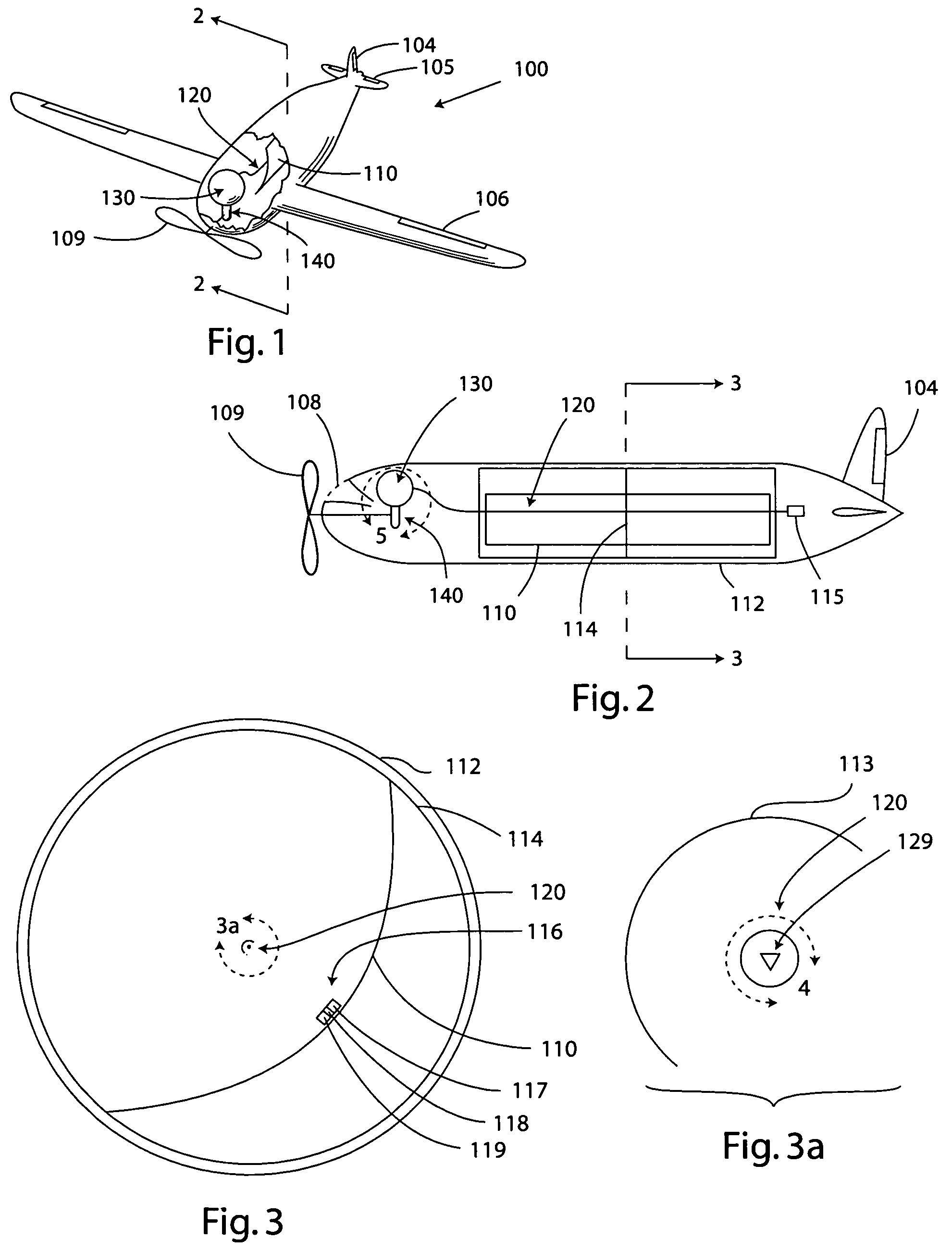
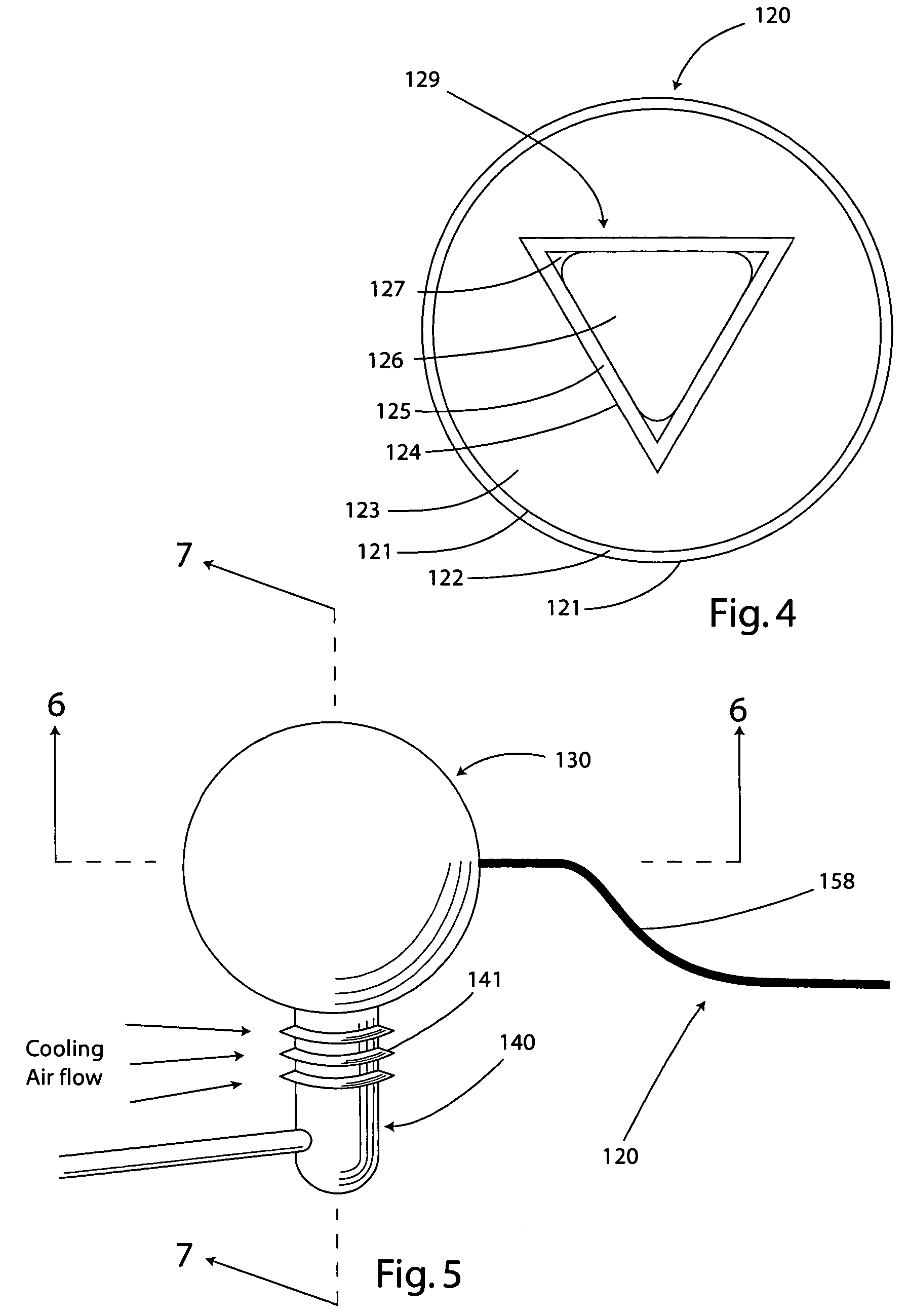
Solar thermal aircraft
A solar thermal powered aircraft powered by heat energy from the sun. A heat engine, such as a Stirling engine, is carried by the aircraft body for producing power for a propulsion mechanism, such as a propeller. The heat engine has a thermal battery in thermal contact with it so that heat is supplied from the thermal battery. A solar concentrator, such as reflective parabolic trough, is movably connected to an optically transparent section of the aircraft body for receiving and concentrating solar energy from within the aircraft. Concentrated solar energy is collected by a heat collection and transport conduit, and heat transported to the thermal battery. A solar tracker includes a heliostat for determining optimal alignment with the sun, and a drive motor actuating the solar concentrator into optimal alignment with the sun based on a determination by the heliostat.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Low numerical aperture (low-NA) solar lighting system
InactiveUS8184372B1Reduce in quantityConvenient lightingSolar heating energyMirrorsNumerical apertureTransmission system
A low numerical aperture (low-NA) light concentration and transmission system collects, concentrates and transmits light for interior illumination. A solar tracker aligns a primary light concentrator to collect light and direct the light to a secondary light concentrator and a filter for removing ultraviolet and infrared radiation. On exiting the secondary light concentrator, the optical axis of the concentrated light is aligned to optimize the numerical aperture of the concentrated light with a numerical aperture (NA) optimizer having a light guide to direct the concentrated light to an interior luminaire. The method of the low numerical aperture transmission of light has the advantages of fewer reflections in the light guide, low loss, low cost, and easy installation and operation.
Owner:GU BINGWU
Heliostat repositioning system and method
ActiveUS20110240007A1Low costEliminate needPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyHeliostatComputer module
A system and method for providing real time control of a heliostat array or CPV / PV module that reduces actuation cost, the disclosure reduces the fixed cost of calibrating and repositioning an individual surface. This simultaneously removes the core engineering assumption that drives the development of large trackers, and enables a system and method to cost effectively track a small surface. In addition to lower initial capital cost, a small heliostat or solar tracker can be pre-assembled, mass-produced, and shipped more easily. Smaller mechanisms can also be installed with simple hand tools and do not require installers to rent expensive cranes or installation equipment.
Owner:SOLARCITY
Balanced solar tracker clamp
In an example, the present invention provides a solar tracker apparatus. In an example, the apparatus comprises a center of mass with an adjustable hanger assembly configured with a clam shell clamp assembly on the adjustable hanger assembly and a cylindrical torque tube comprising a plurality of torque tubes configured together in a continuous length from a first end to a second end such that the center of mass is aligned with a center of rotation of the cylindrical torque tubes to reduce a load of a drive motor operably coupled to the cylindrical torque tube. Further details of the present example, among others, can be found throughout the present specification and more particularly below.
Owner:NEXTRACKER LLC
One-Axis Solar Tracker System and Apparatus with Wind Lock Devices
InactiveUS20110186040A1Reduce the time required for installationLeast labor costSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersLow latitudeHot band
The present invention proposes a one-axis solar tracker system and apparatus which is simple to install, lower cost and with the provision of an electric-magnetic locking device to resist from medium to strongest wind condition like hurricane or typhoon. Solar farms is more and more popular to use one-axis tracker due to lower cost, higher wind resistance and easier for large scale solar farm installation, especially at lower latitude tropic zones. This disclosure proposes a one-axis tracker with multiple posts support using a single or dual linear actuators driving mechanism for rotation. It is also equipped with a wind lock device to lock the solar tracker in horizontal neutral position during strong wind condition such as hurricane or typhoon. The stepwise wind lock device can further be applied to locking the solar tracker following each step of linear actuator activation enabling the disclosed solar tracker to operate in windy conditions.
Owner:THE LIAOS FAMILY
Off-set swivel drive assembly for solar tracker
Owner:NEXTRACKER LLC
Off-set swivel drive assembly for solar tracker
In an example, the present invention provides a solar tracker apparatus configured with an off-set drive assembly. In an example, the apparatus has an inner race structure, which has a cylindrical region coupled to a main body region, the main body comprising an off-set open region. The cylindrical region is an annular sleeve structure coupled to the main body region, which occupies the spatial region within the cylindrical region. In an example, the apparatus has an outer race structure coupled to enclose the inner race structure, configured to couple the inner race structure to allow the inner race structure to move in a rotational manner about a spatial arc region; and configured to allow the inner race structure to pivot about a region normal to a direction of the spatial arc region. In an example, the solar tracker has a clamp assembly that is configured to pivot a torque tube.
Owner:NEXTRACKER LLC
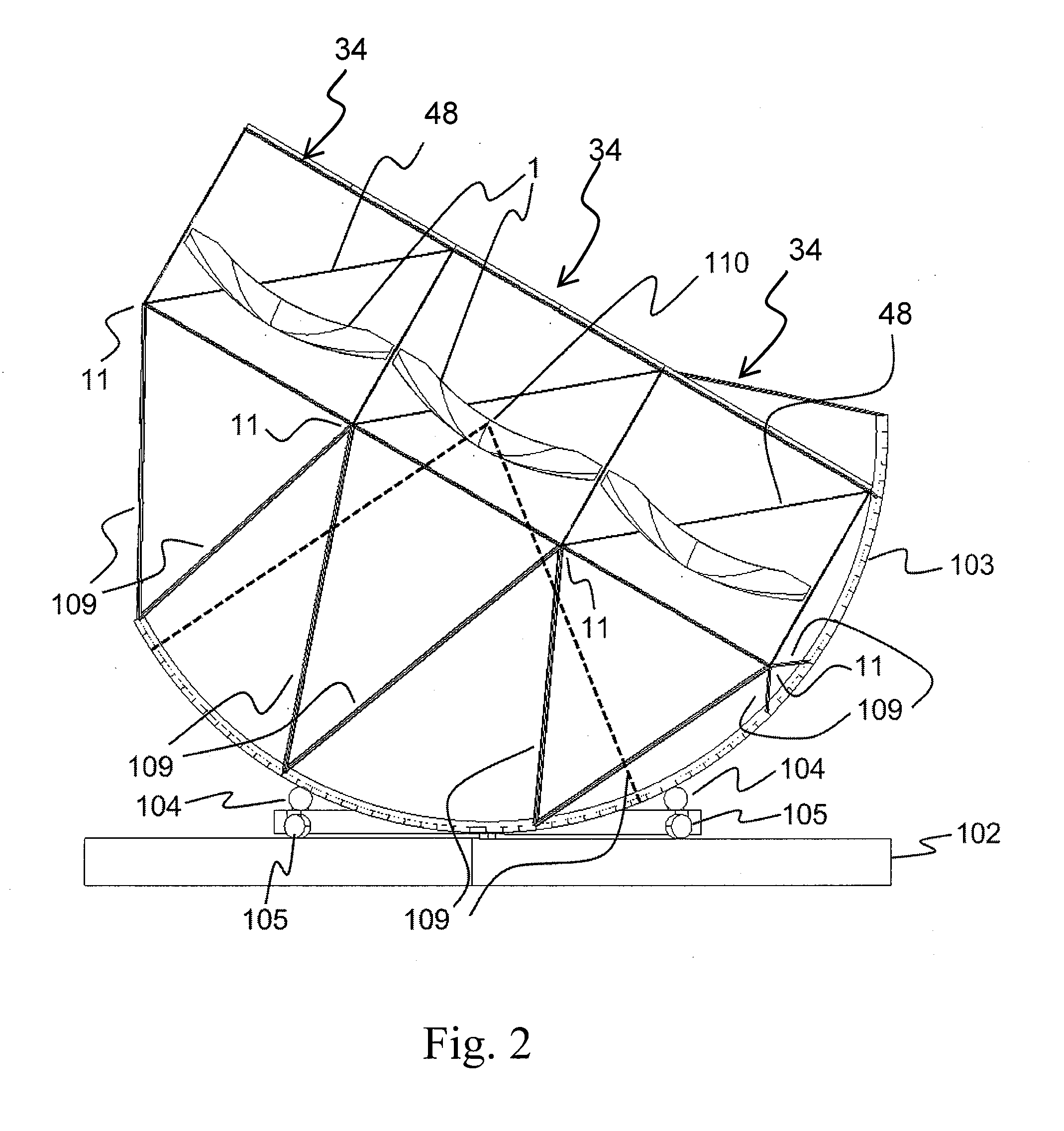
Dual axle solar tracker
InactiveUS8203110B2Reduce sensitivityConsiderable structural advantageSolar heating energyPhotometry using reference valueMedial axisGravity center
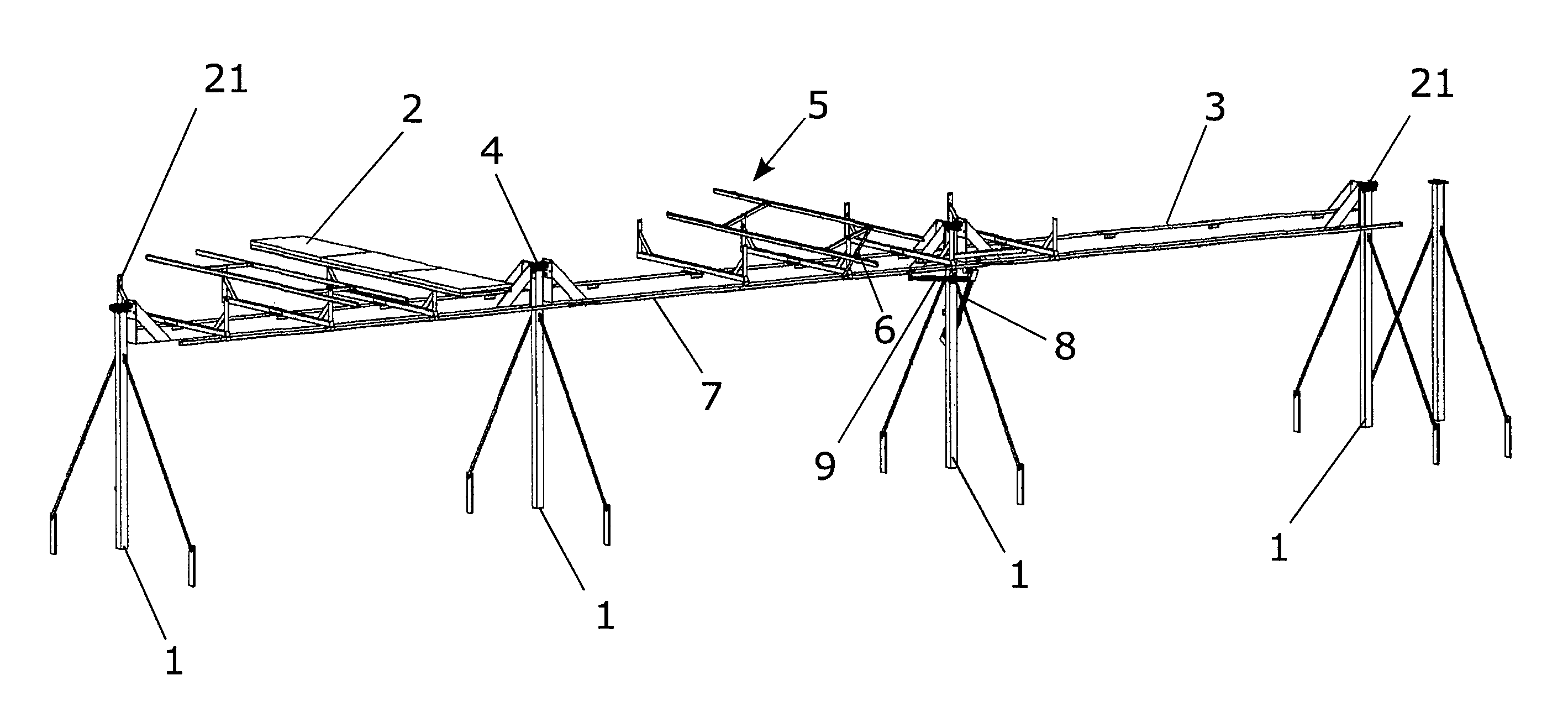
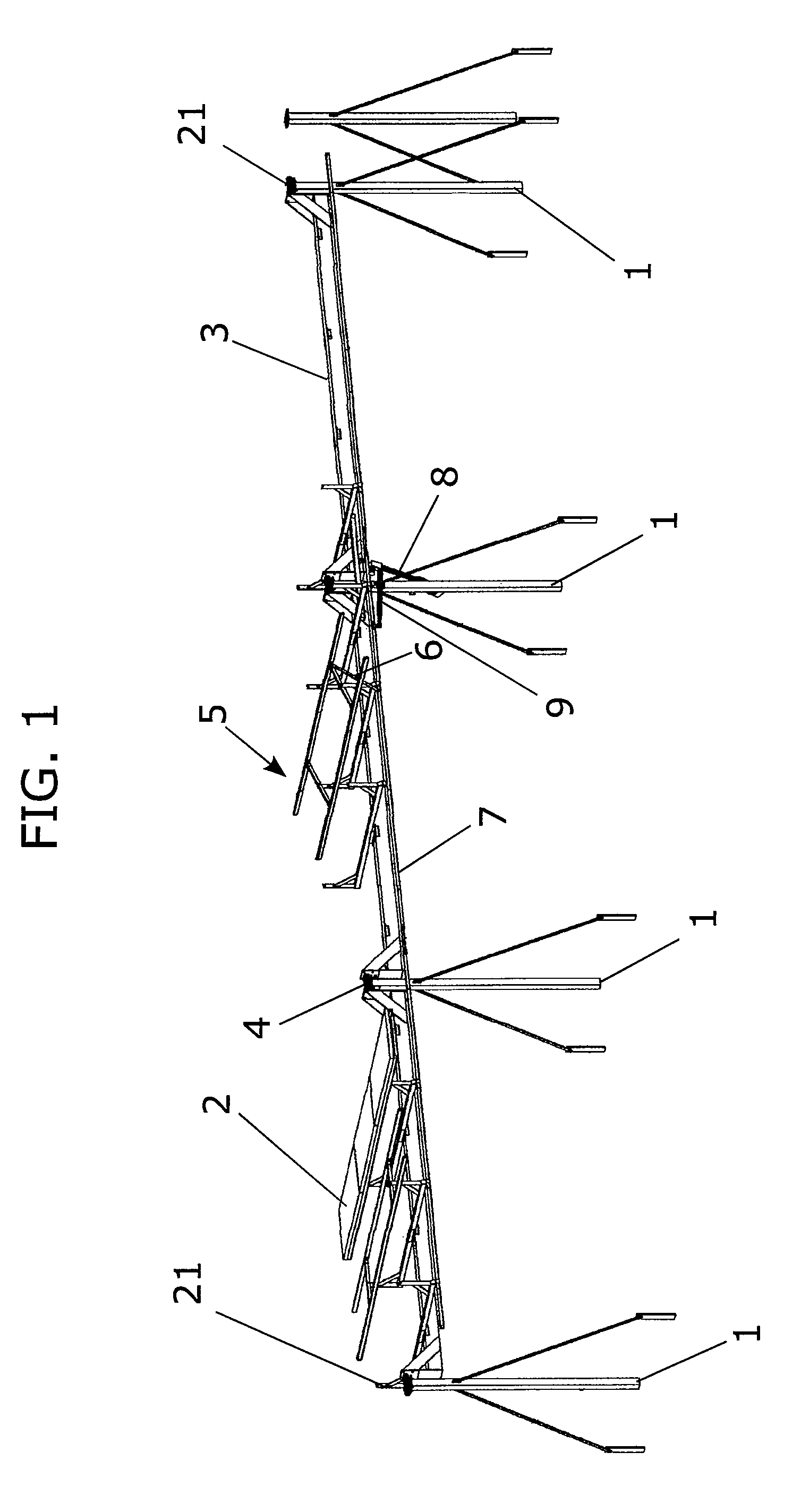
Solar tracker with a principal substructure comprising a series of posts between which sections of beams are arranged, joined by intermediate axles and which can turn in respect of a longitudinal axle; it is also provided with secondary substructures comprising a frame for attachment of the solar panels which rotate in respect of an axle transversal to the longitudinal and with connection parts between the frames and the beams, and in respect of which they are articulated, with the frames being activated by connecting rods joined to a common slide. The centre of gravity of the structure overall is arranged such that it is very close to the longitudinal axle, which facilitates its actuation, reduces wind sensitivity and facilitates erection in addition to being provided with a certain degree of longitudinal tolerance, which enables better use to be made of land, as it is possible to achieve greater power per square meter.
Owner:ENERGIA ERCAM
Sun tracker for solar panels
The elevation of a solar panel to follow the course of the sun is achieved in a manner to require relatively little power. The elevation mechanism utilizes a system of wires and pulleys which cooperate with springs which are compressed when the panel is in the collapsed position. The springs operate to overcome inertia when panel elevation first commences. The wire and pulley system operates to extend in opposite directions a pair of arms, one connected to the panel base member, the other connected to the top of the panel pivoting member.
Owner:AARON JACK
Rotary luffing sun tracker
InactiveCN101923355AImprove performanceStrong wind resistancePhotovoltaic supportsControl using feedbackEngineeringSolar tracker
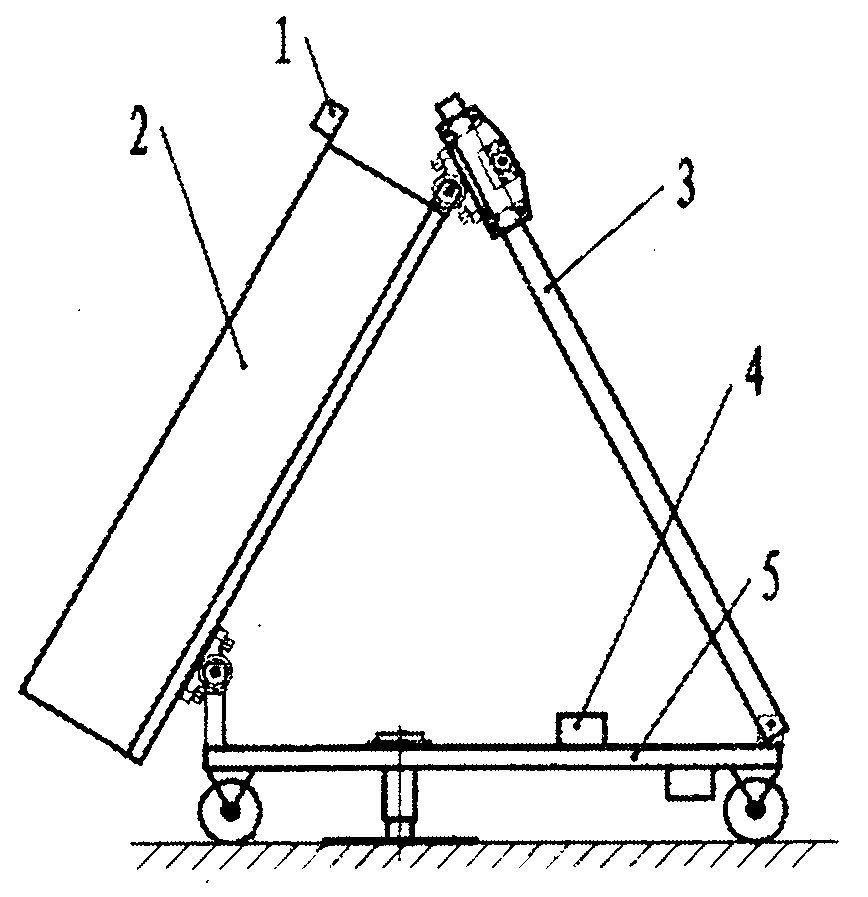
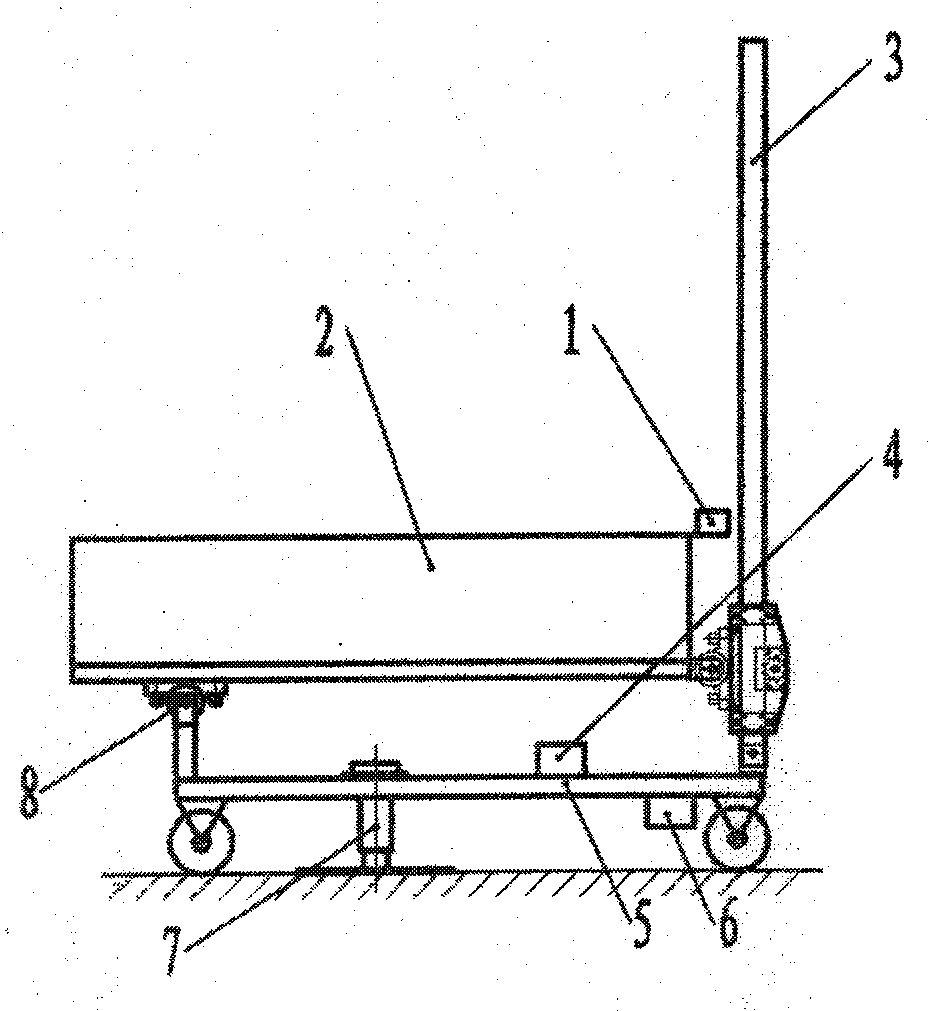
The invention discloses a rotary luffing sun tracker, which belongs to the field of solar energy application and is used for real-time dynamic tracing of the sun orientation of a solar energy concentrating and collecting system and a solar energy photovoltaic power generating system. The rotary luffing sun tracker is characterized by consisting of a two-coordinate high-precision sun tracing sensor 1, a rigid bearing platform 2, a set of or a pair of electrical push rods 3, a set of two-circuit electrical equipment driving systems 4 and a set of electric horizontally-rotating platforms 5, wherein the two-coordinate high-precision sun tracing sensor 1 is arranged on a light facing face of the rigid bearing platform 2; the lower ends of the set of or pair of electrical push rods 3 are hinged on the platform faces of the electric horizontally-rotating platforms 5 while the upper ends are hinged with the rigid bearing platform 2; one or one group of supporting feet is fixedly connected to the platform faces of the electric horizontally-rotating platforms 5; a group of coaxial hinging supporting holes are formed on the supporting feet; and the lower abdomen of the rigid bearing platform2 is hinged with the hinging supporting holes. The rigid bearing platform 2 can be pushed to perform luffing up and down around a hinged shaft of the electric horizontally rotating platforms 5 on the platform faces of the electric horizontally rotating platforms 5 at an angle of within 90 degrees through the up and down movement of moveable sleeves of the electrical push rods 3; and then the electric horizontally rotating platforms 5 carry the rigid bearing platform 2 to trace the sun motion in all directions through the rotation of the electric horizontally-rotating platforms 5 in the horizontal direction so that the light receiving face of the rotary luffing sun tracker always faces the sun.
Owner:陈鼎凌
Infrared multi-constituent monitoring method and monitoring system for monitoring emission flux of gas in pollution source
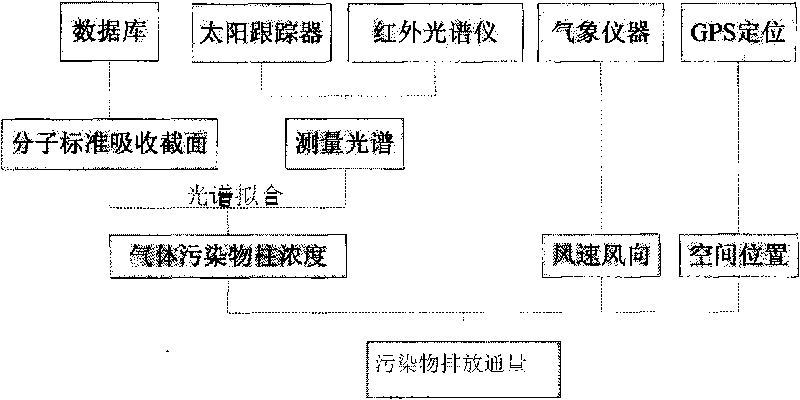
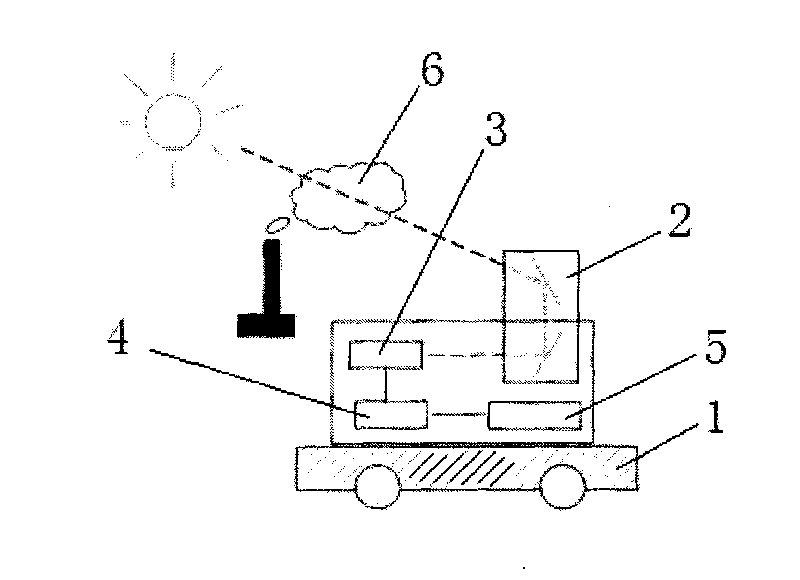
ActiveCN101694461AAccurate monitoringEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredMeasurement point
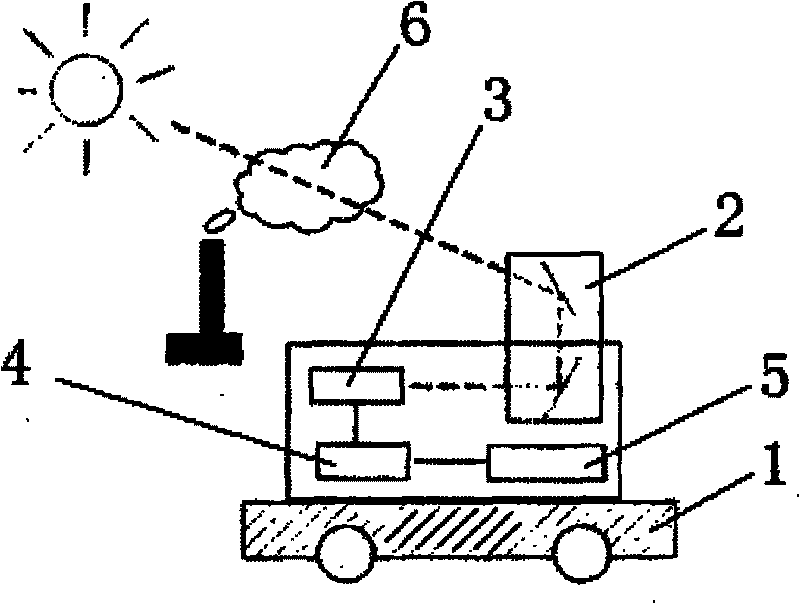
The invention discloses an infrared multi-constituent monitoring method and a monitoring system for monitoring emission flux of gas in pollution sources, which is characterized in that the monitoring system comprises a movable platform which is provided with a solar tracker, an infrared spectrometer, a computer and a GPS localizer; The monitoring method comprises the following steps: taking the sun as a light source, which penetrates the polluted gas and is absorbed selectively by the gas molecule; guilding the sunlight into the infrared spectrometer by the solar tracker and measuring the solar spectrum; analyzing and calculating the column concentration of the pollutant molecule by a software; moving the movable platform and measuring the column concentrates of different positions; measuring the distances of different points by the GPS localizer; furthermore, and obtaining the emission flux of the pollution gas in the whole measurement area by the calculation of the software by combining the wind speed information of all measuring points,. In the invention, the emission flux of the gas in the pollution source can be monitored quickly and exactly, the whole set of system is simple for operation, the cost is relatively cheap, the monitoring process is completely controlled automatically by the software, with convenient use.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com