Patents
Literature
724 results about "Clarifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
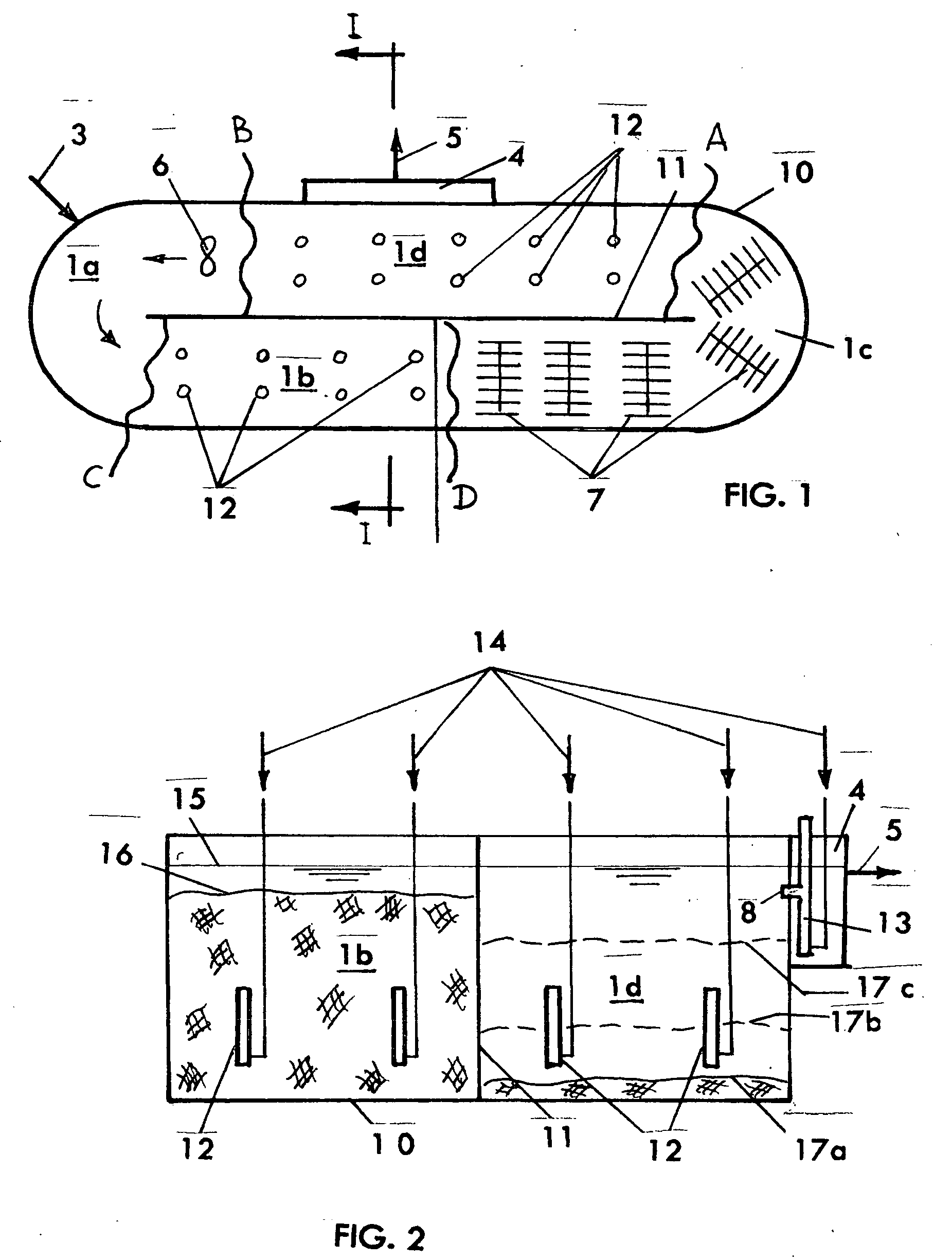
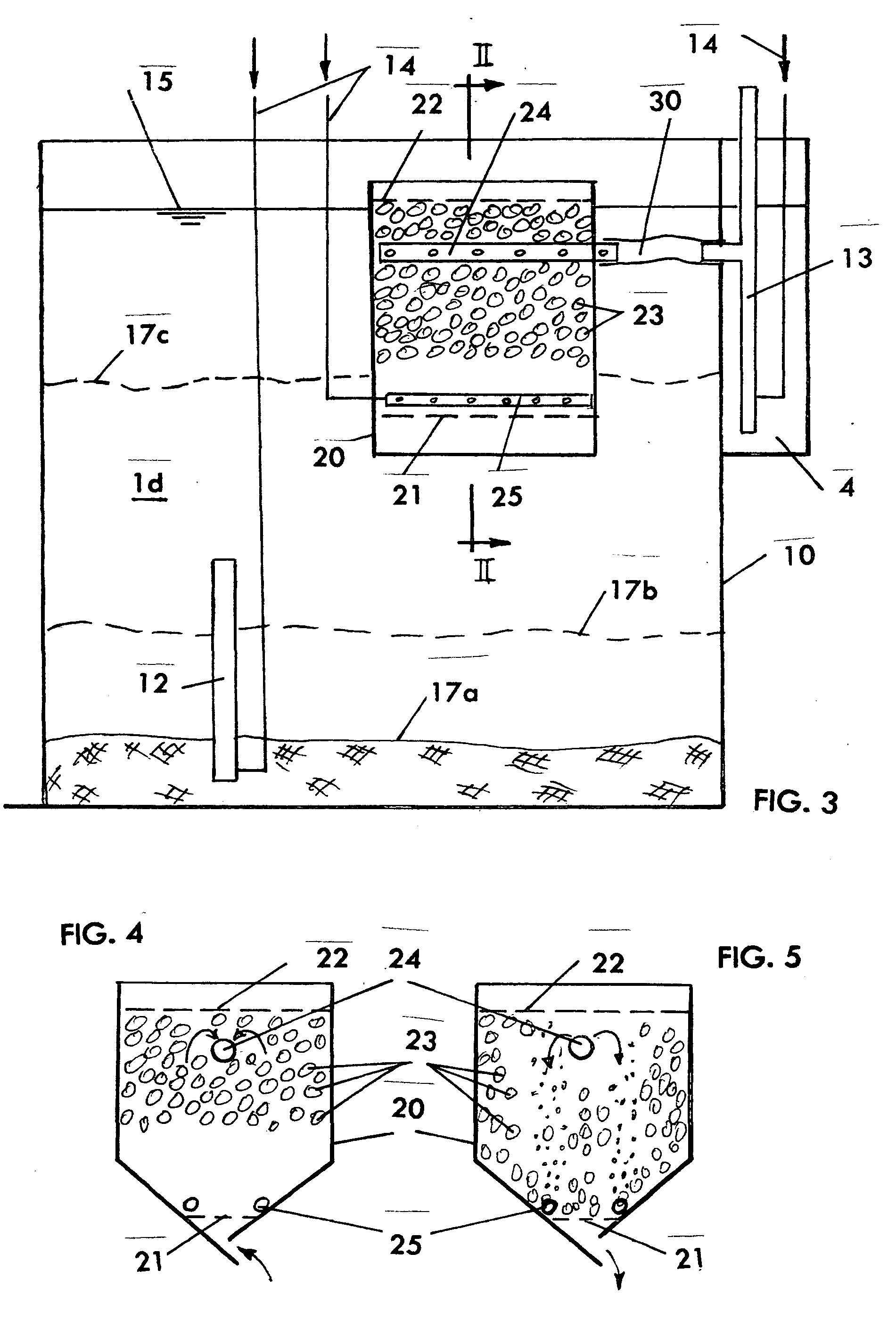
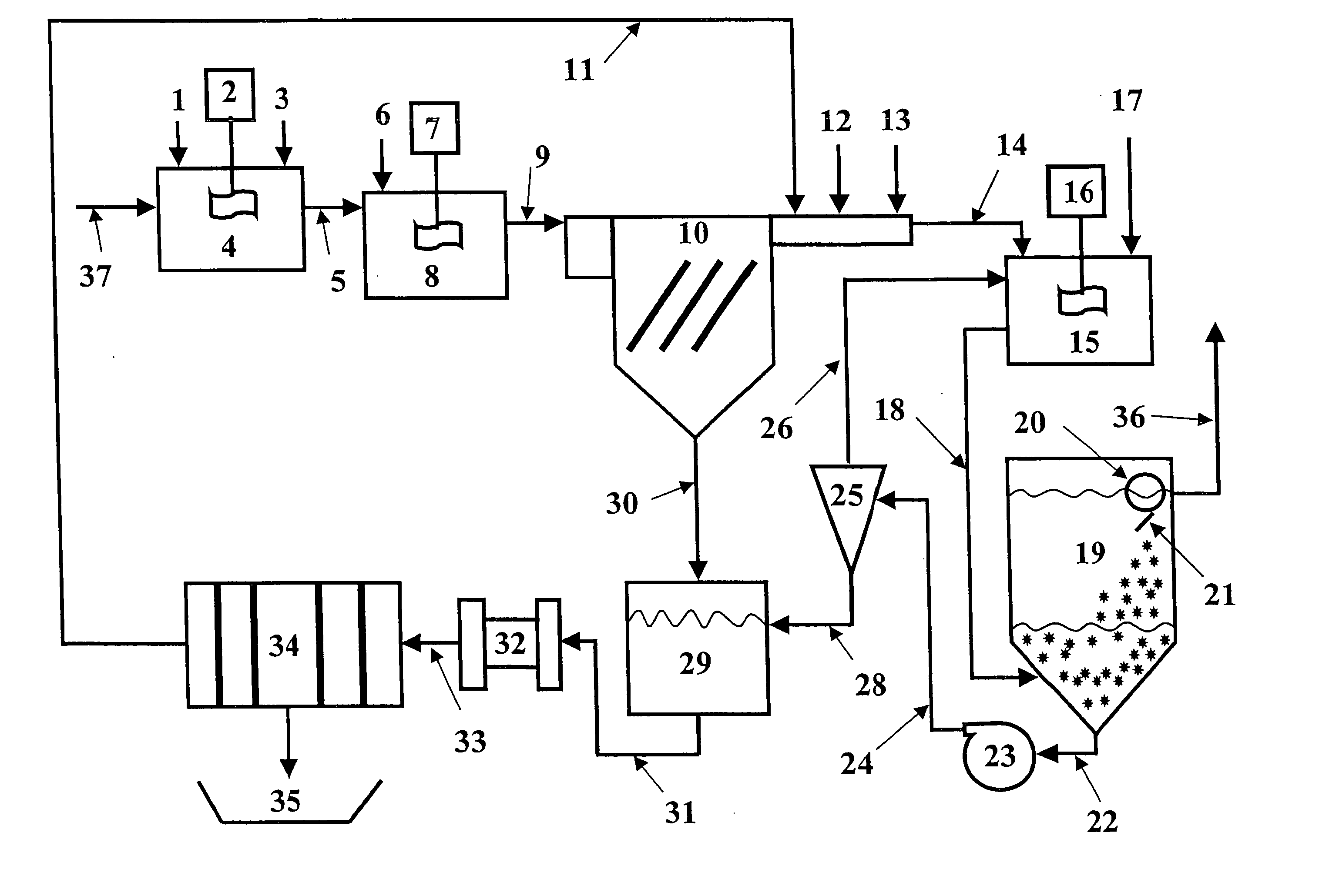
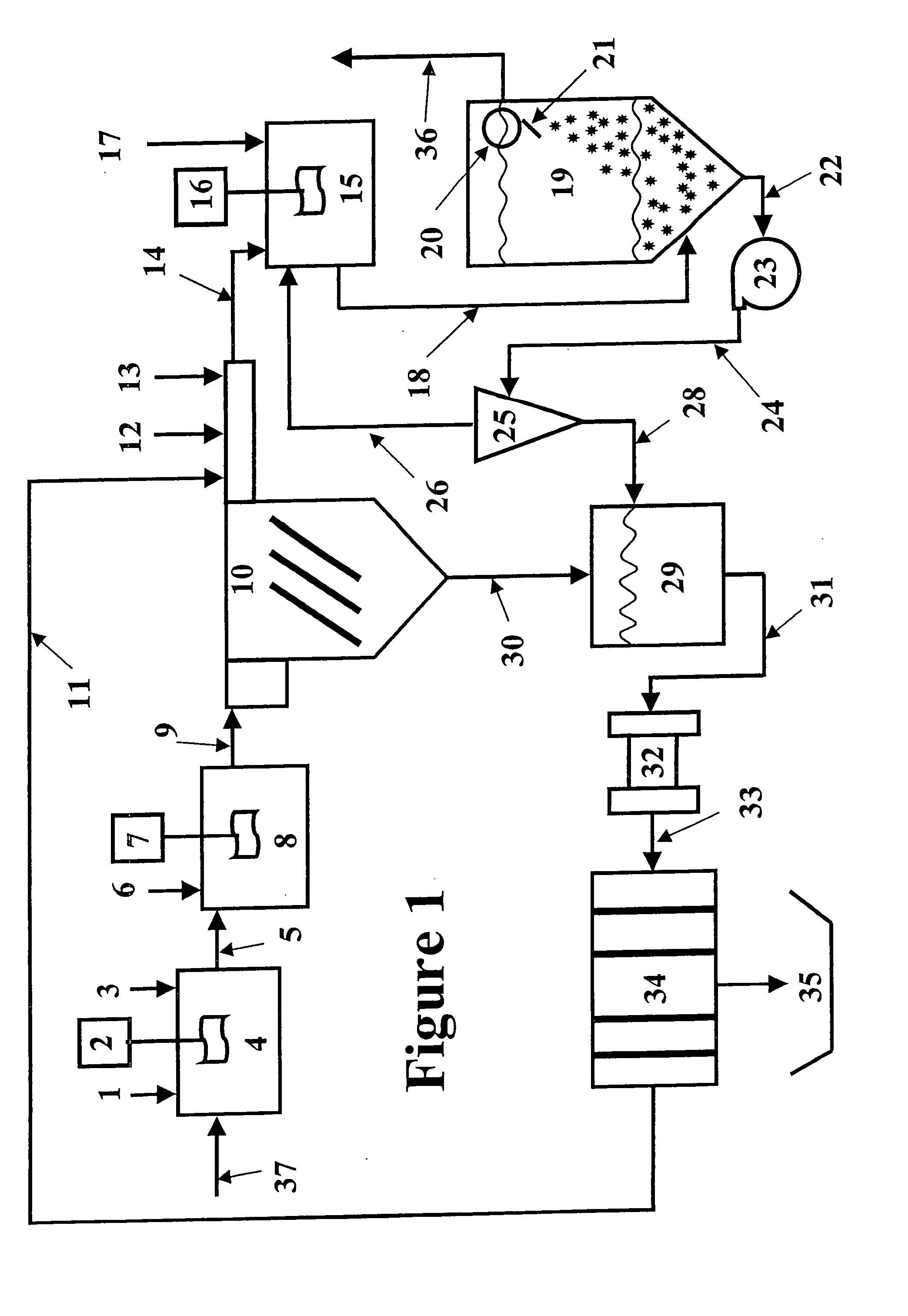
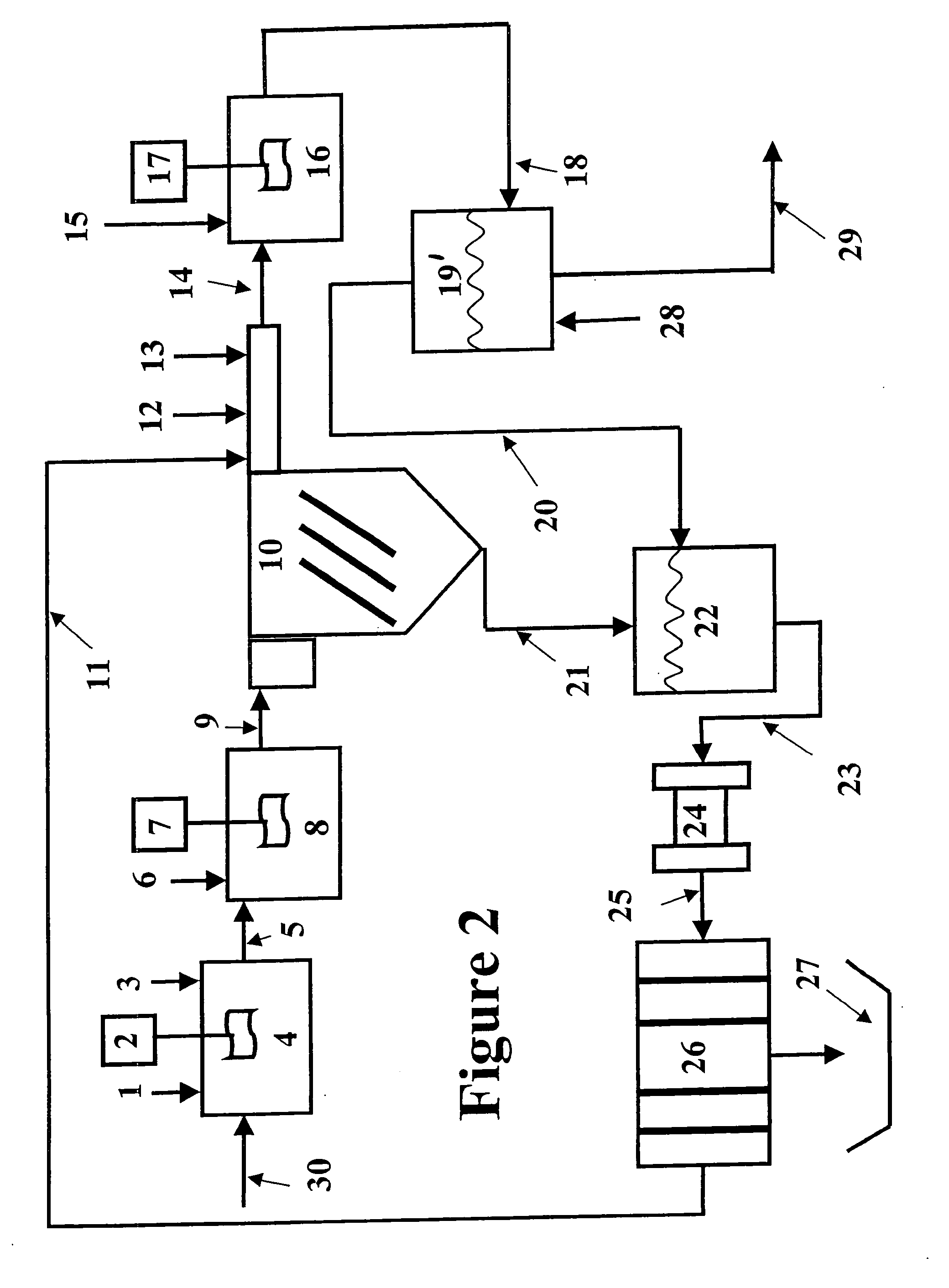
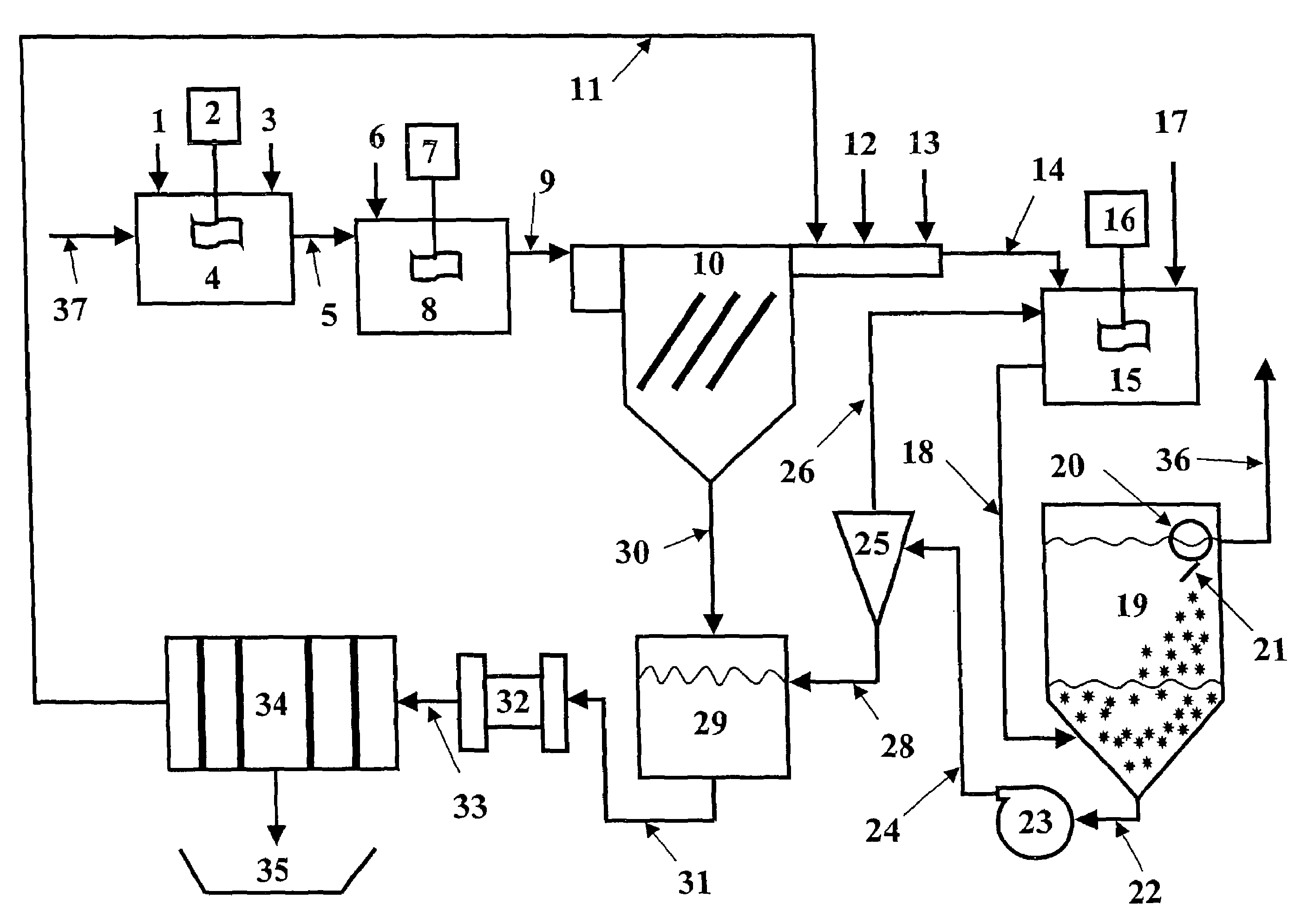
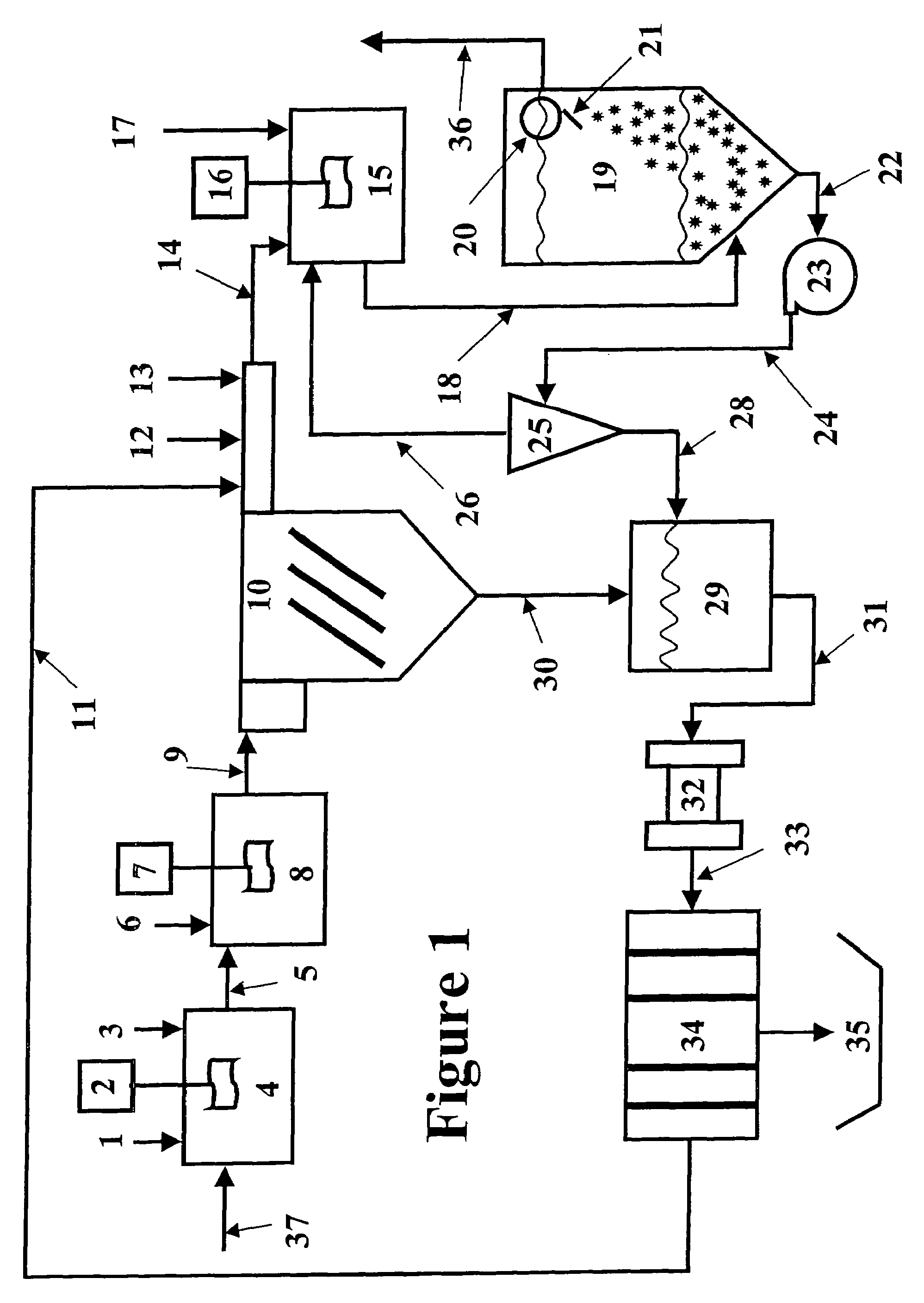
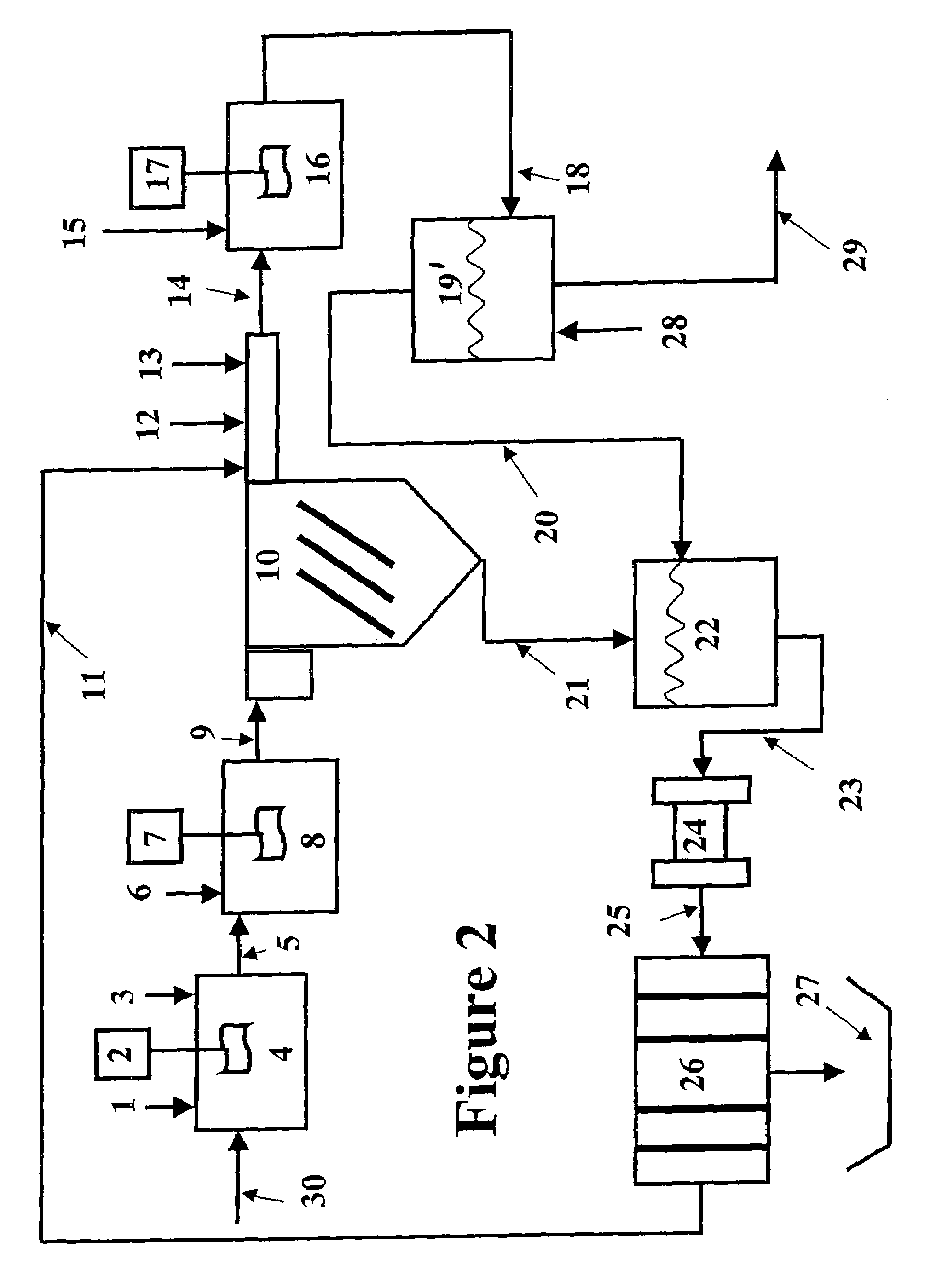
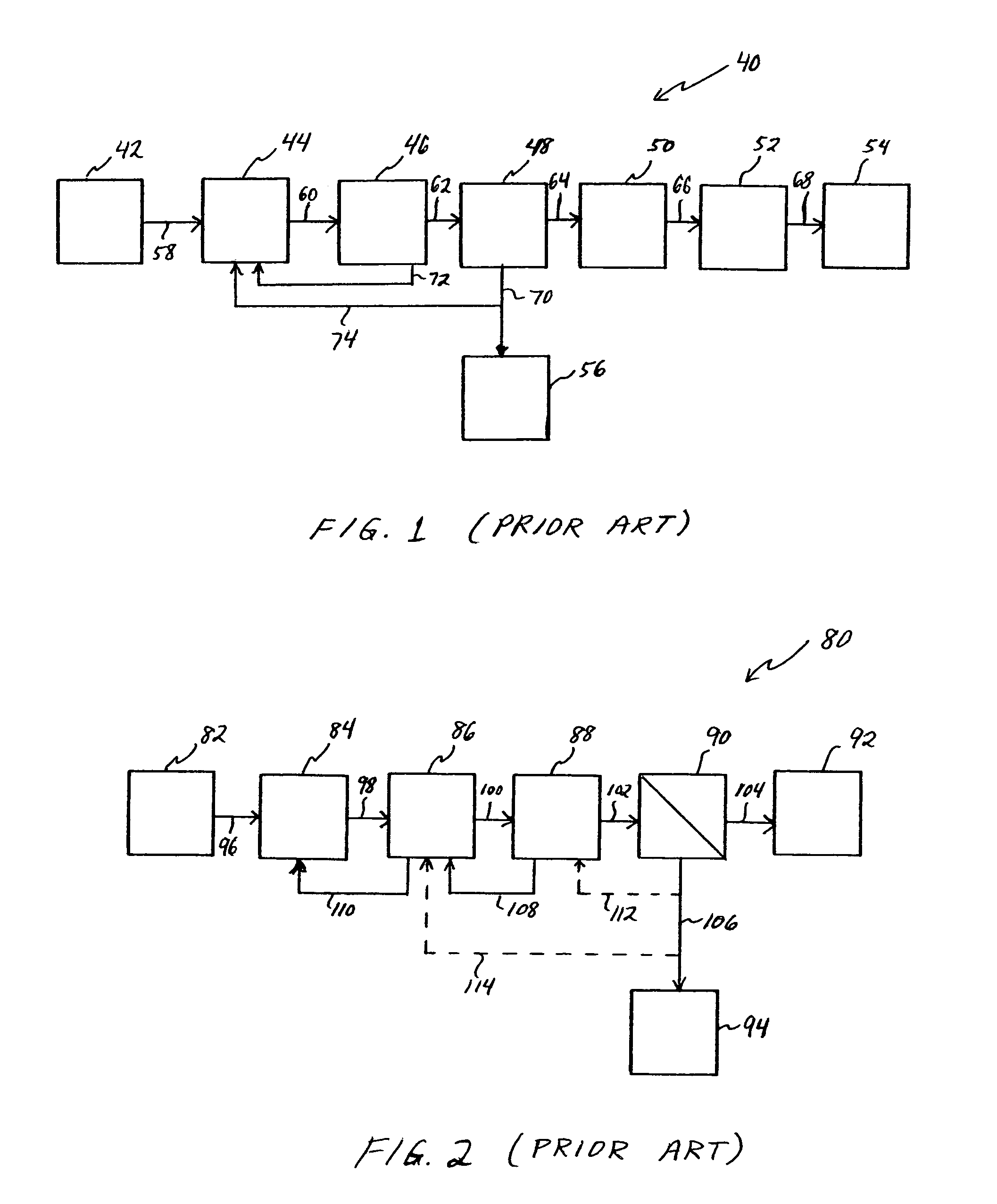
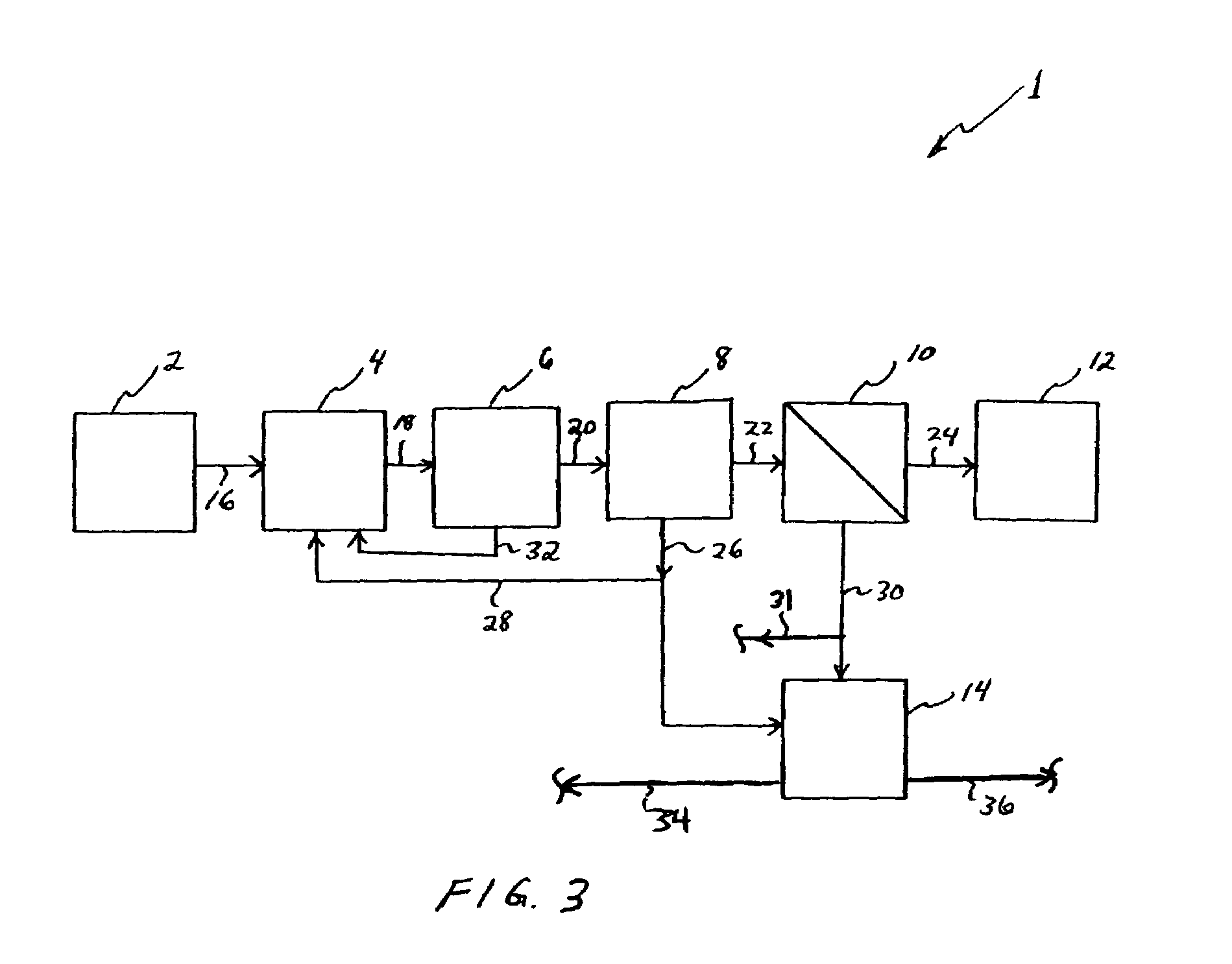
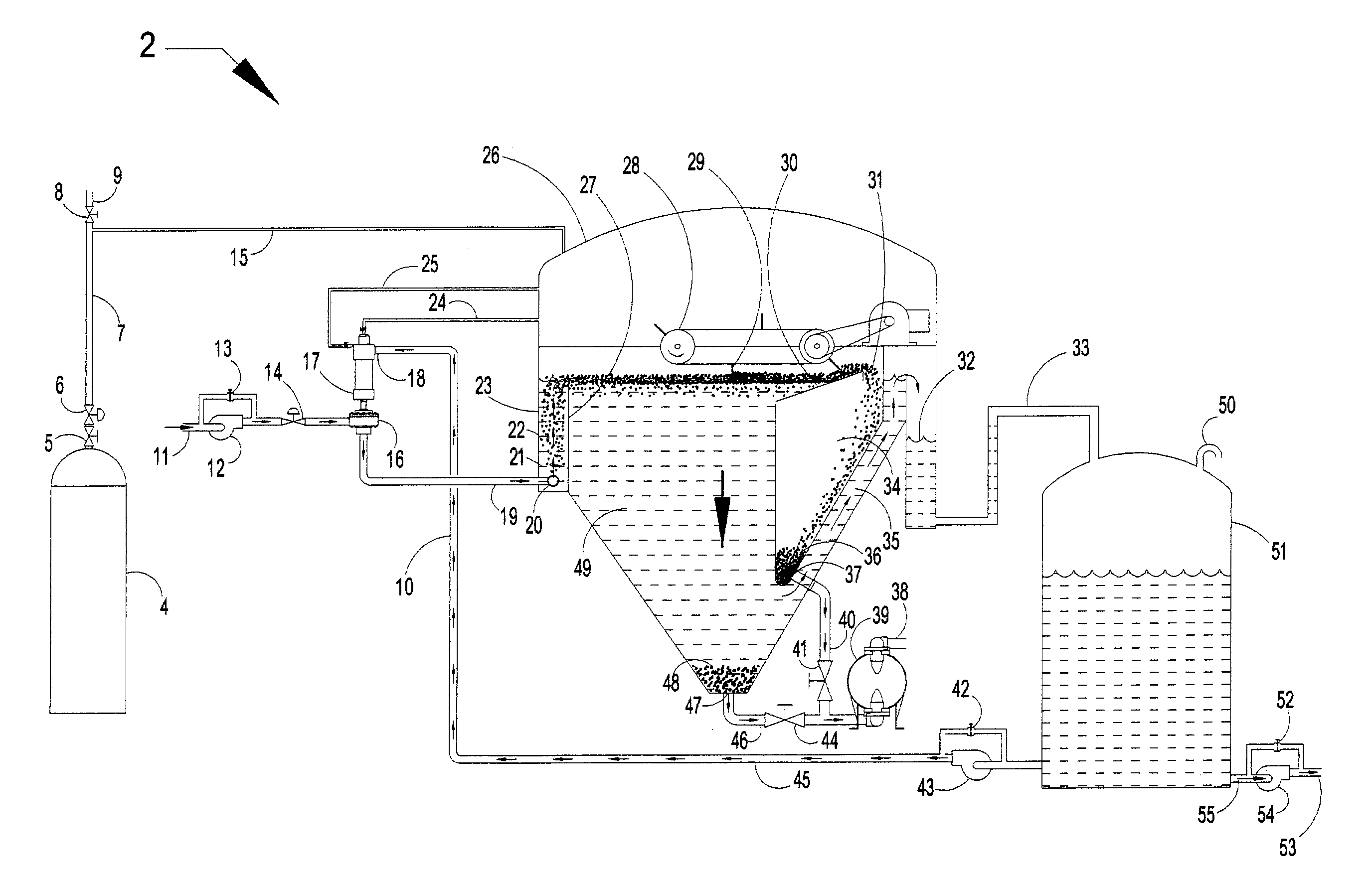
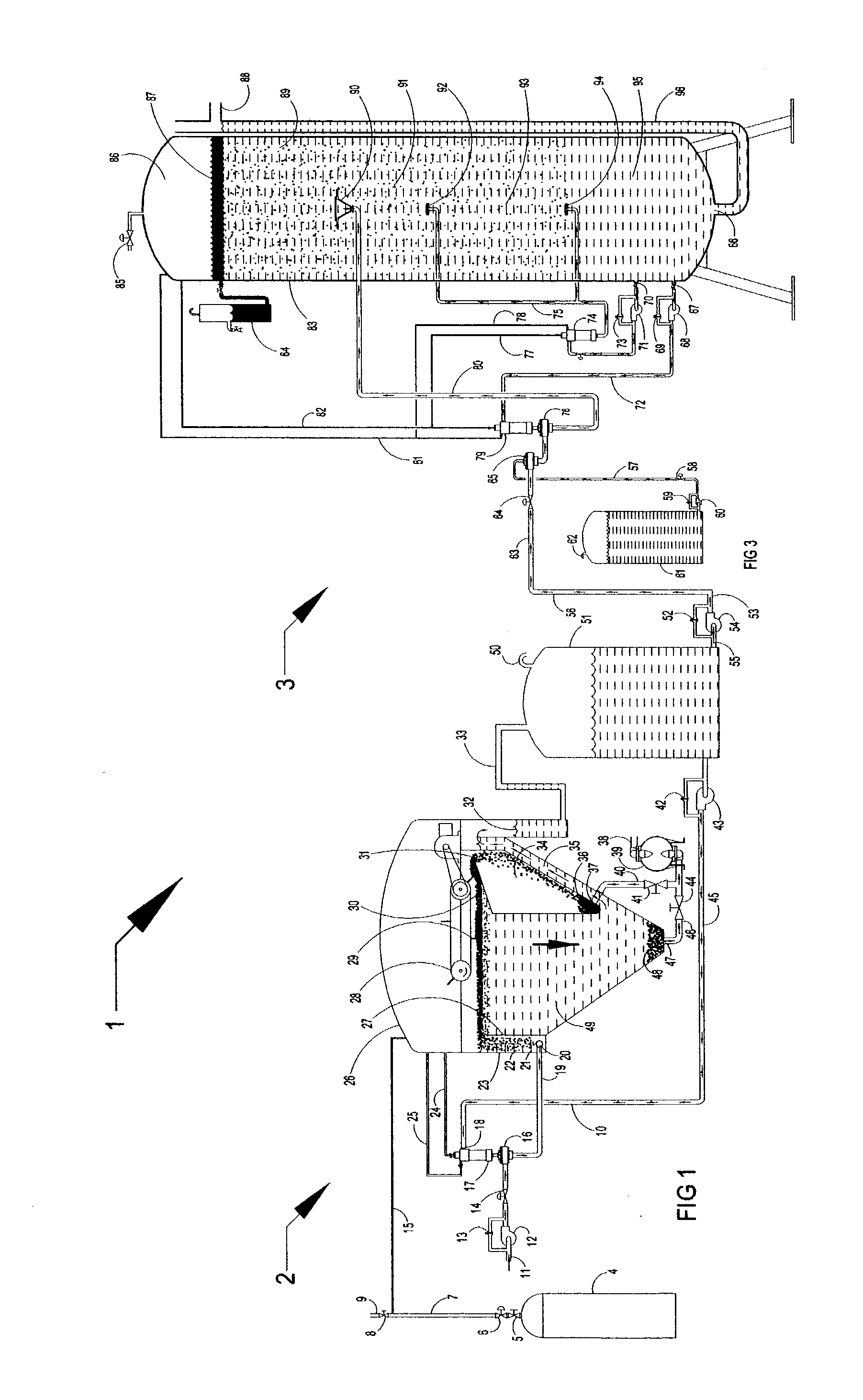
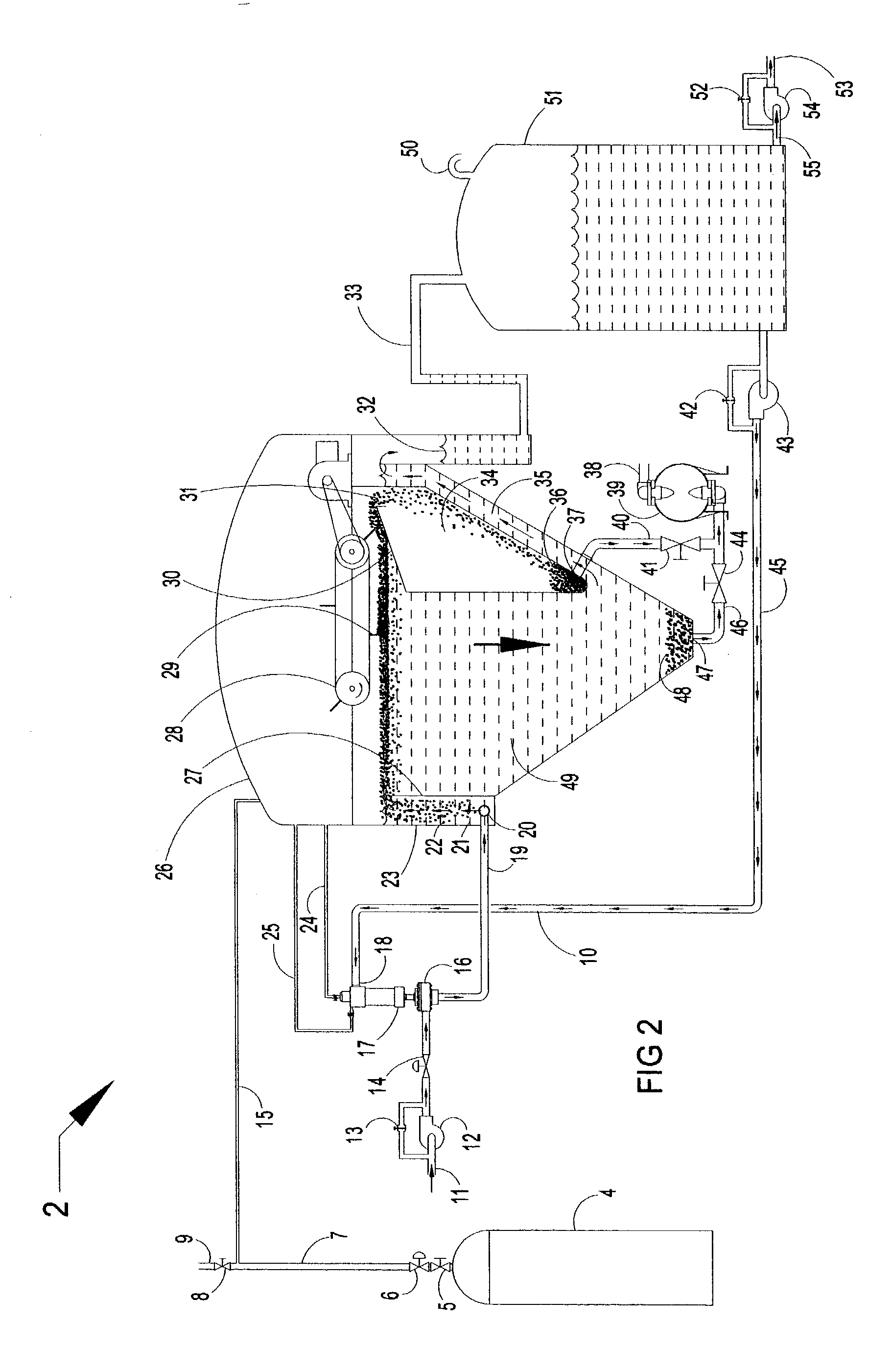
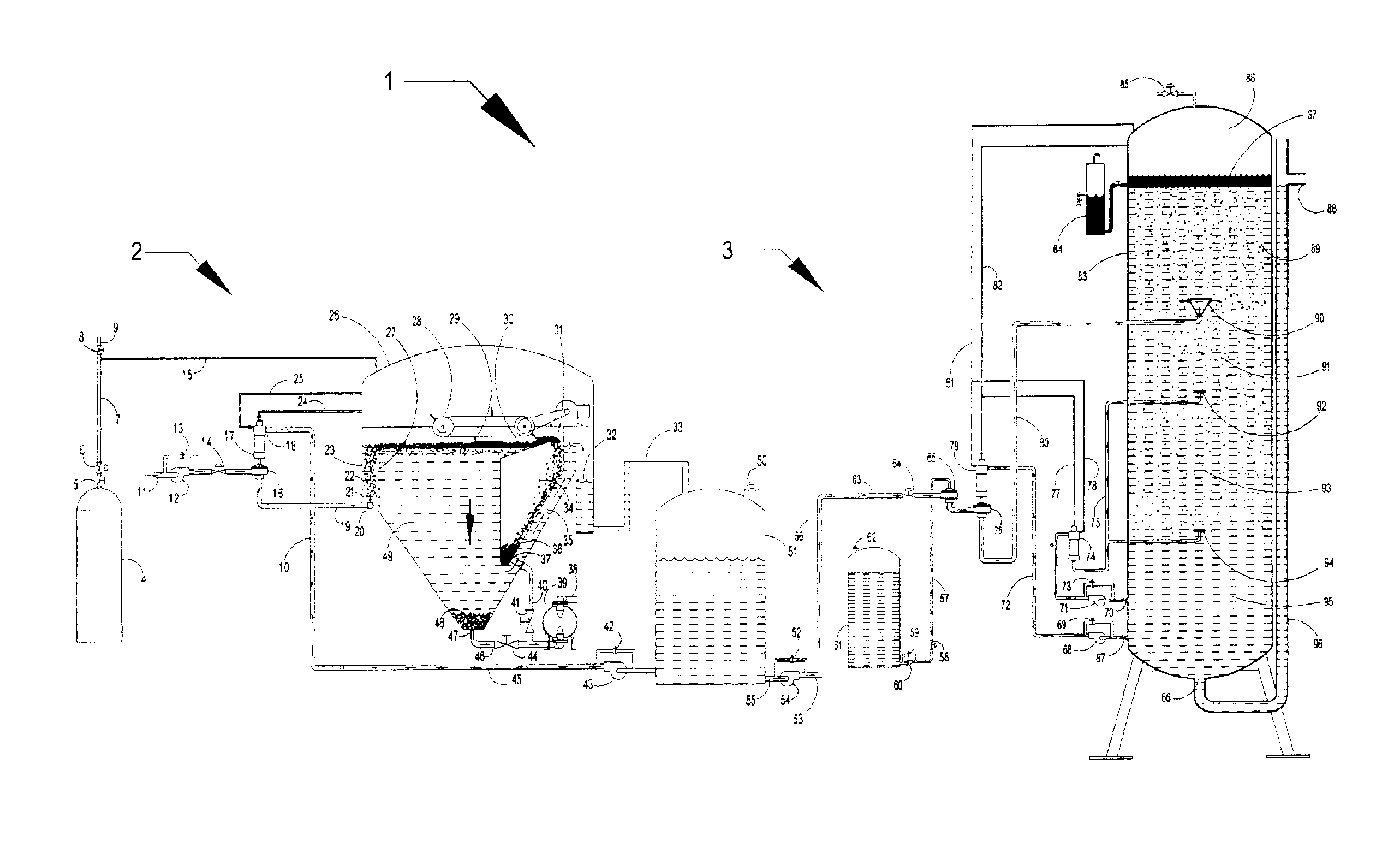
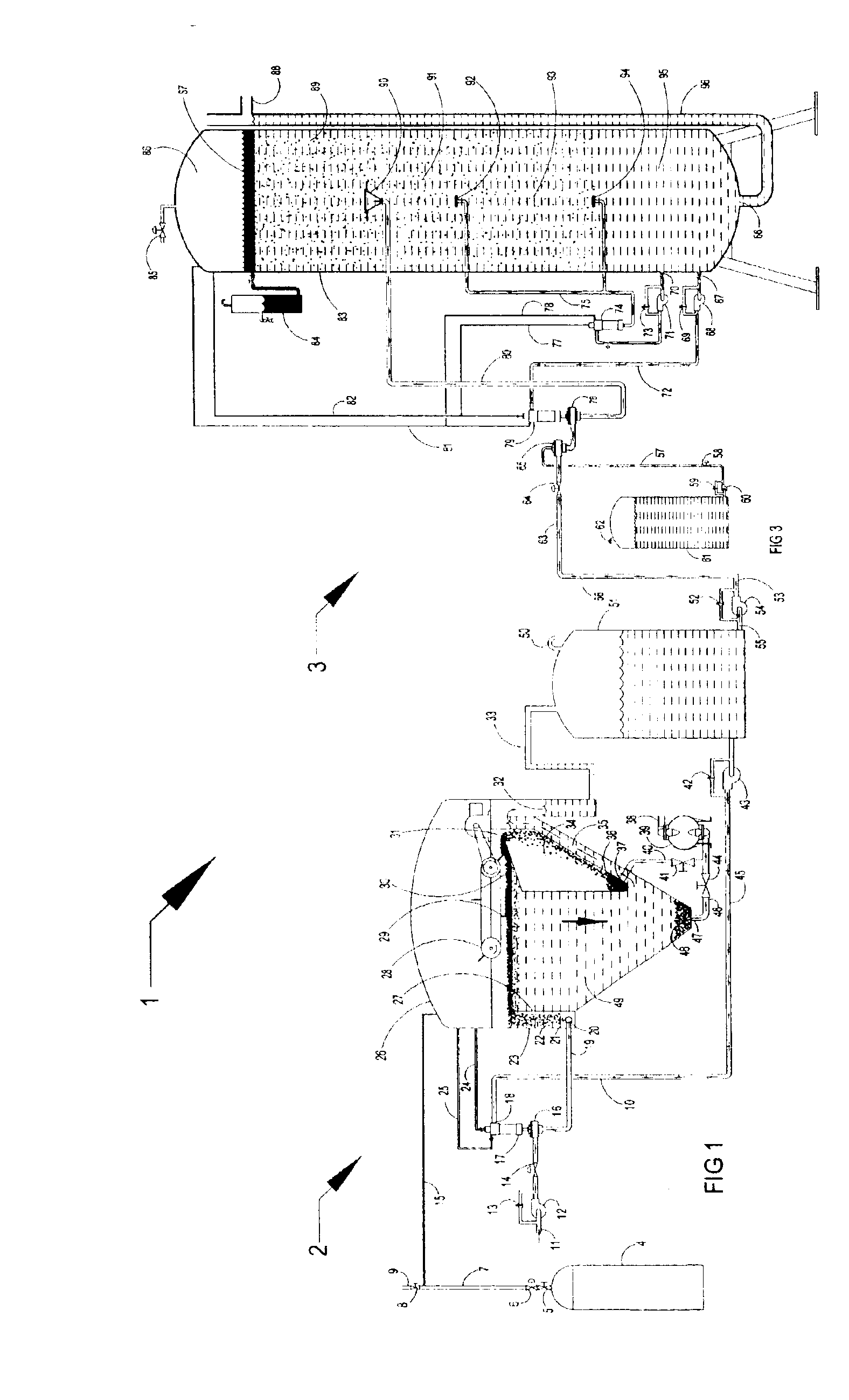
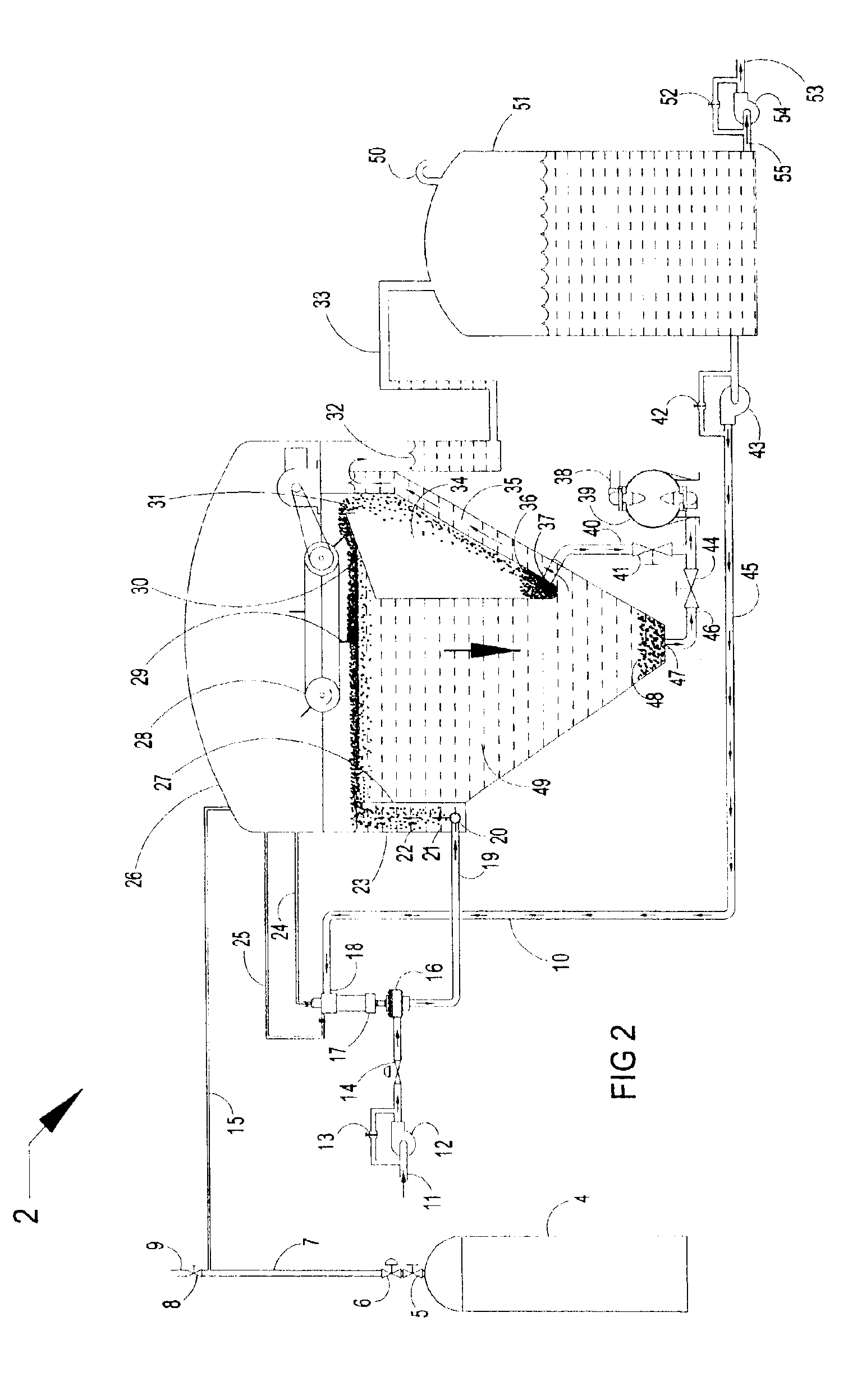
Clarifiers are settling tanks built with mechanical means for continuous removal of solids being deposited by sedimentation. A clarifier is generally used to remove solid particulates or suspended solids from liquid for clarification and (or) thickening. Concentrated impurities, discharged from the bottom of the tank are known as sludge, while the particles that float to the surface of the liquid are called scum.
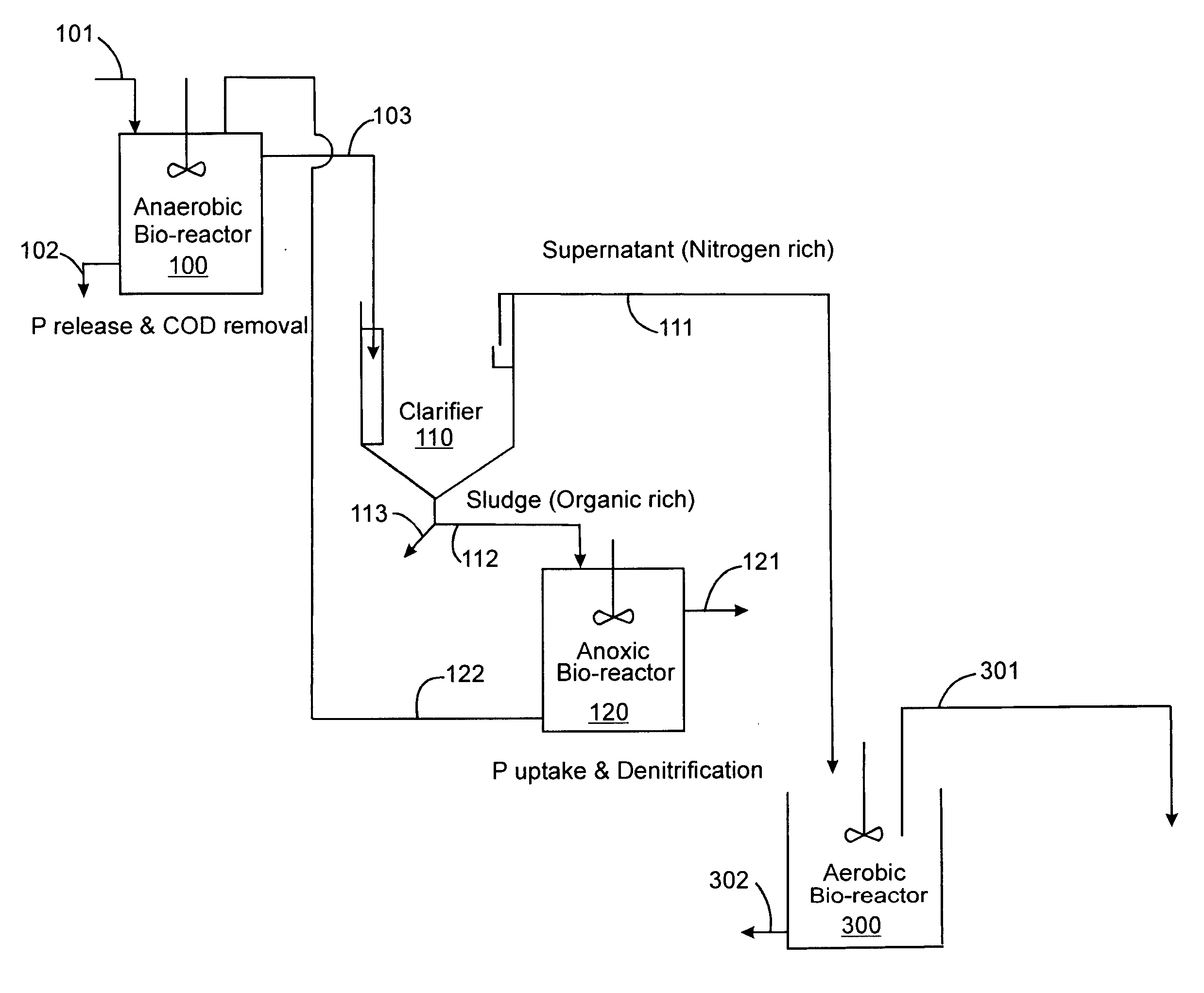
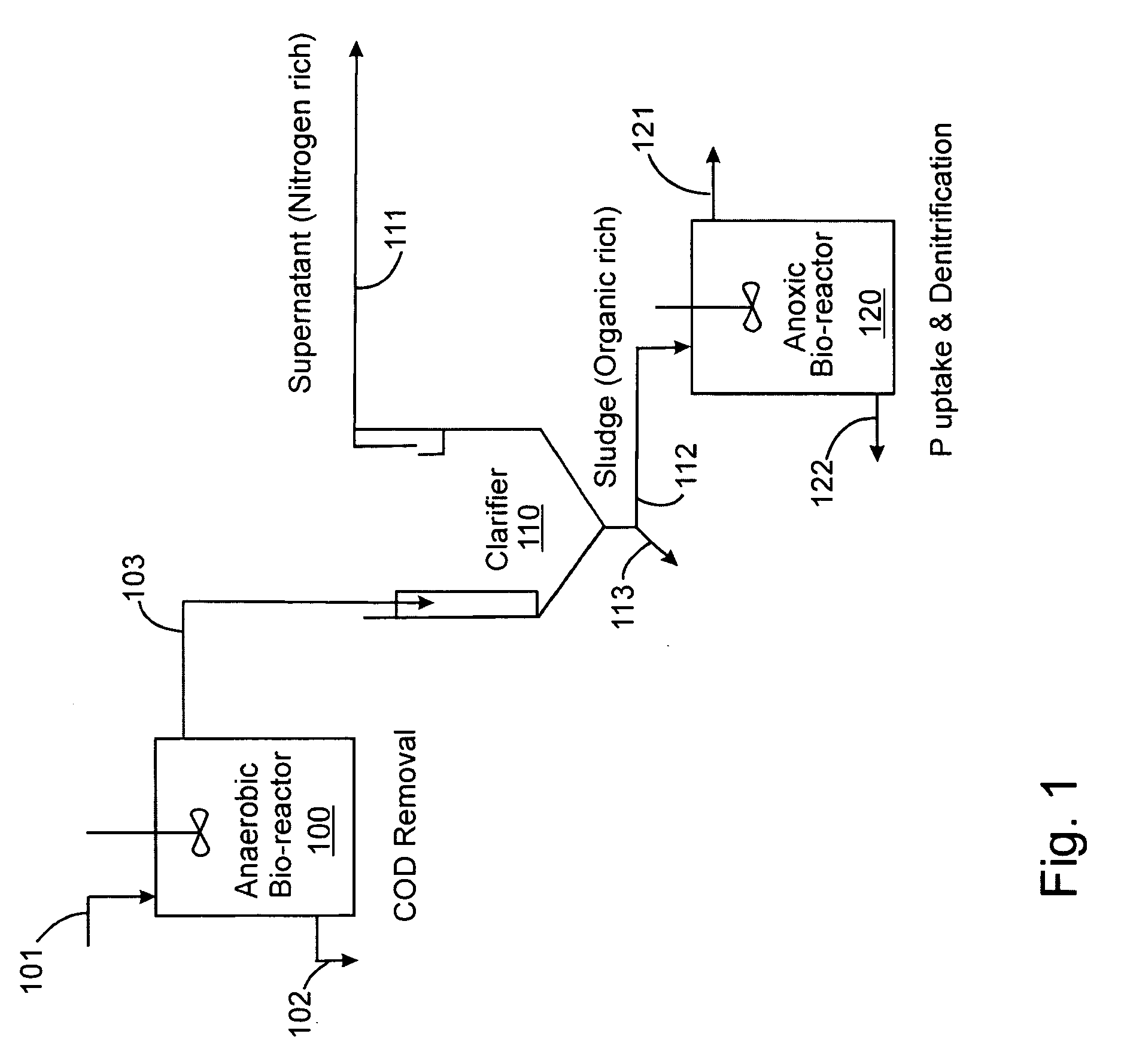
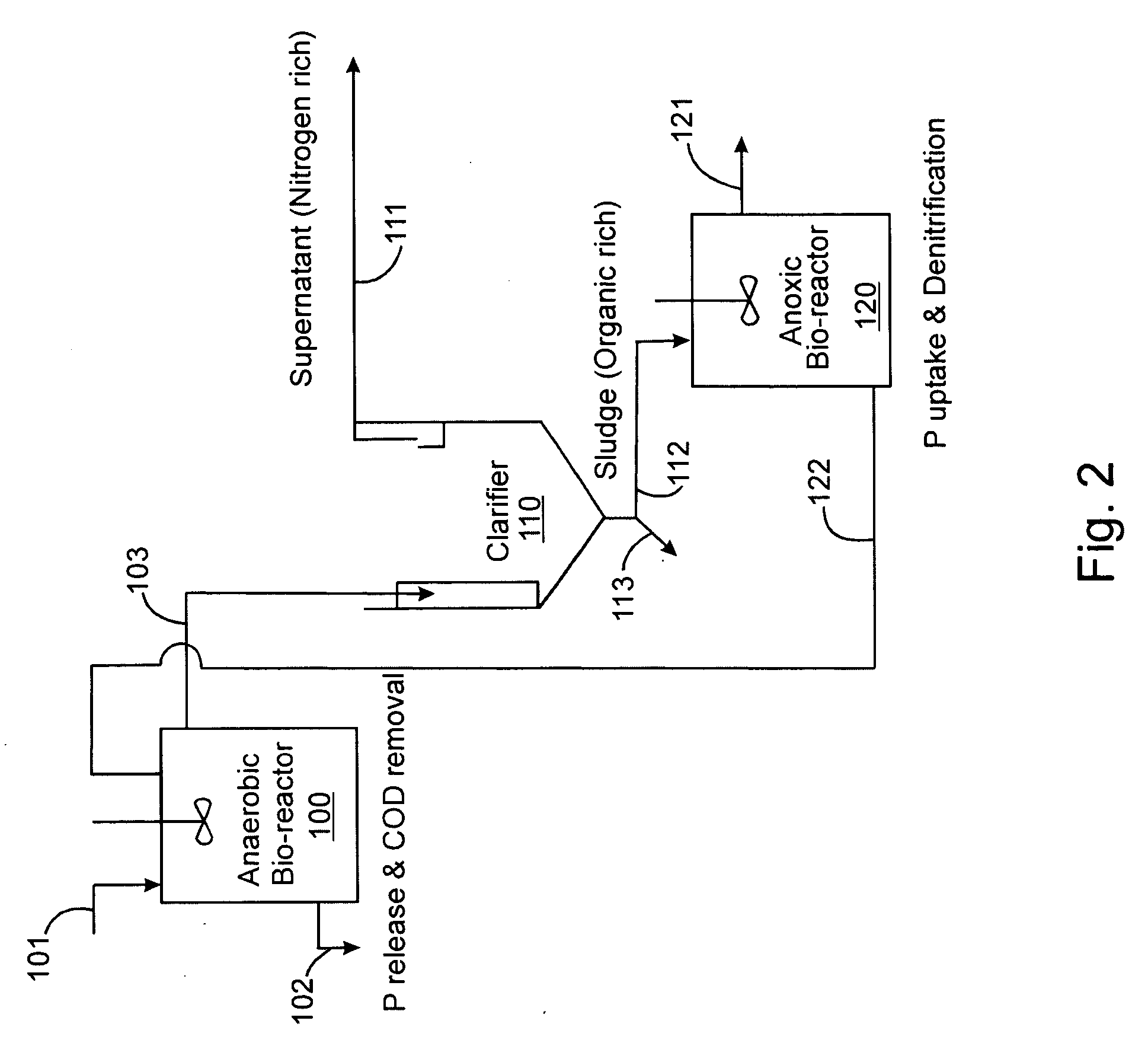
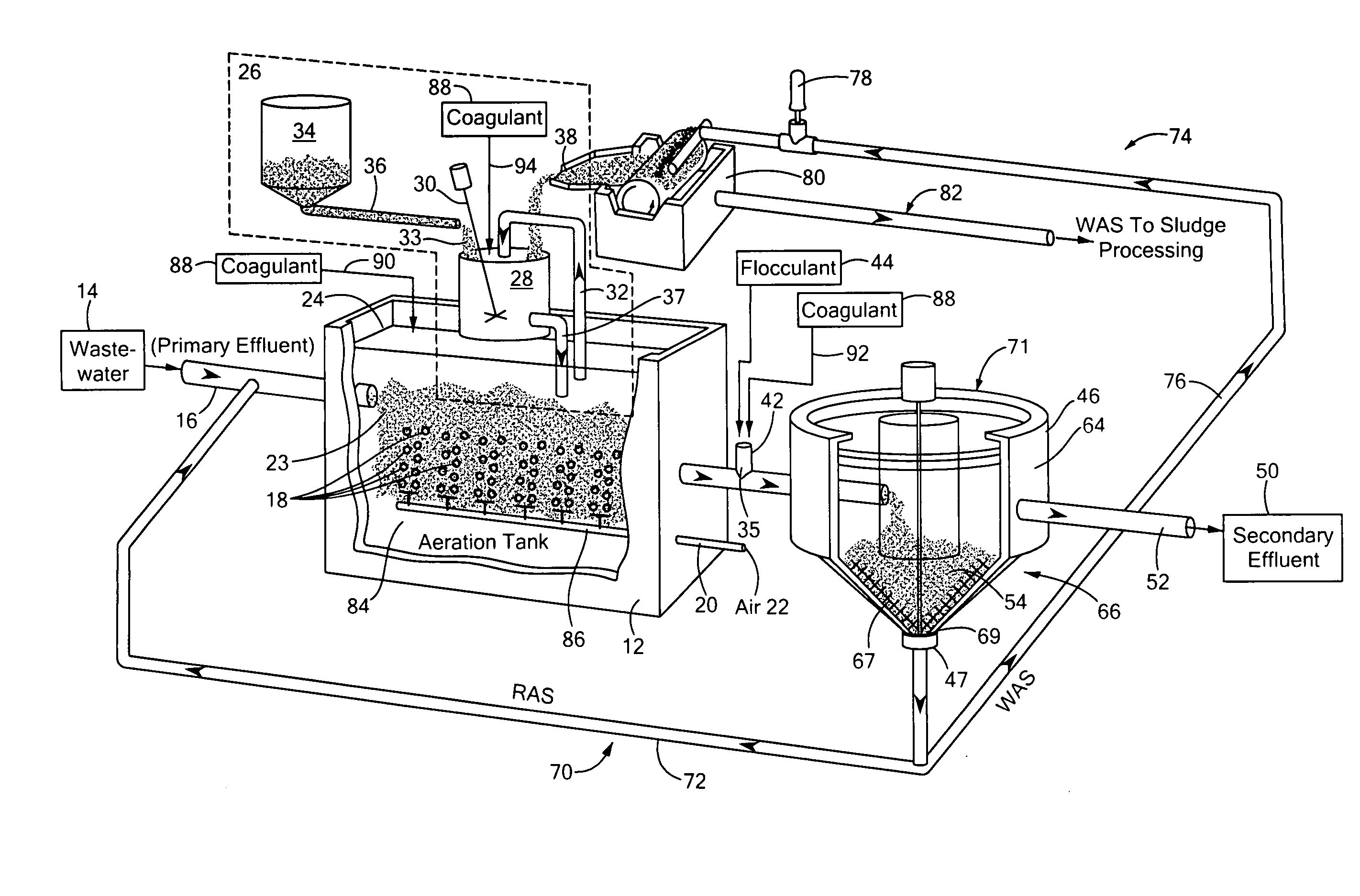
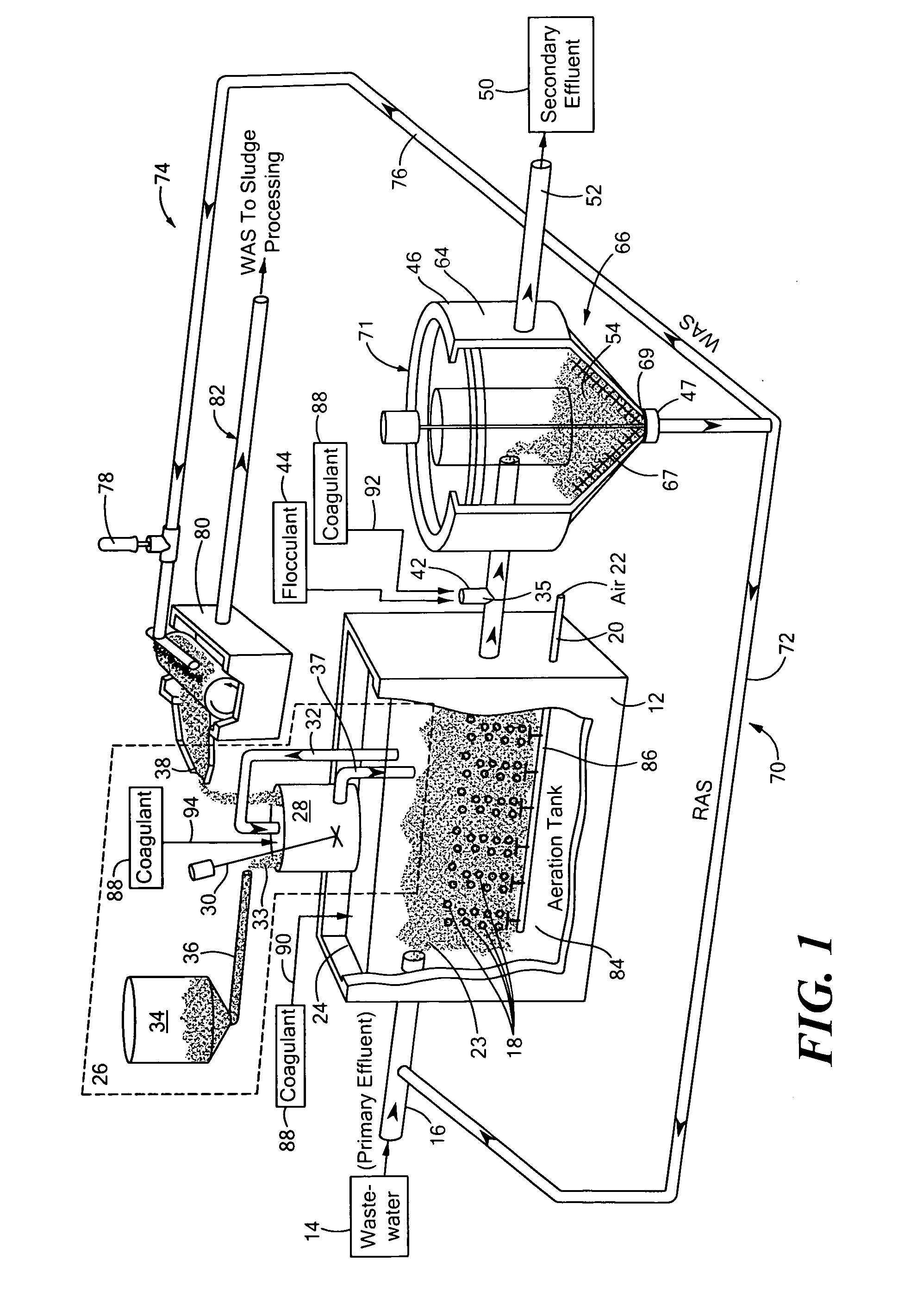
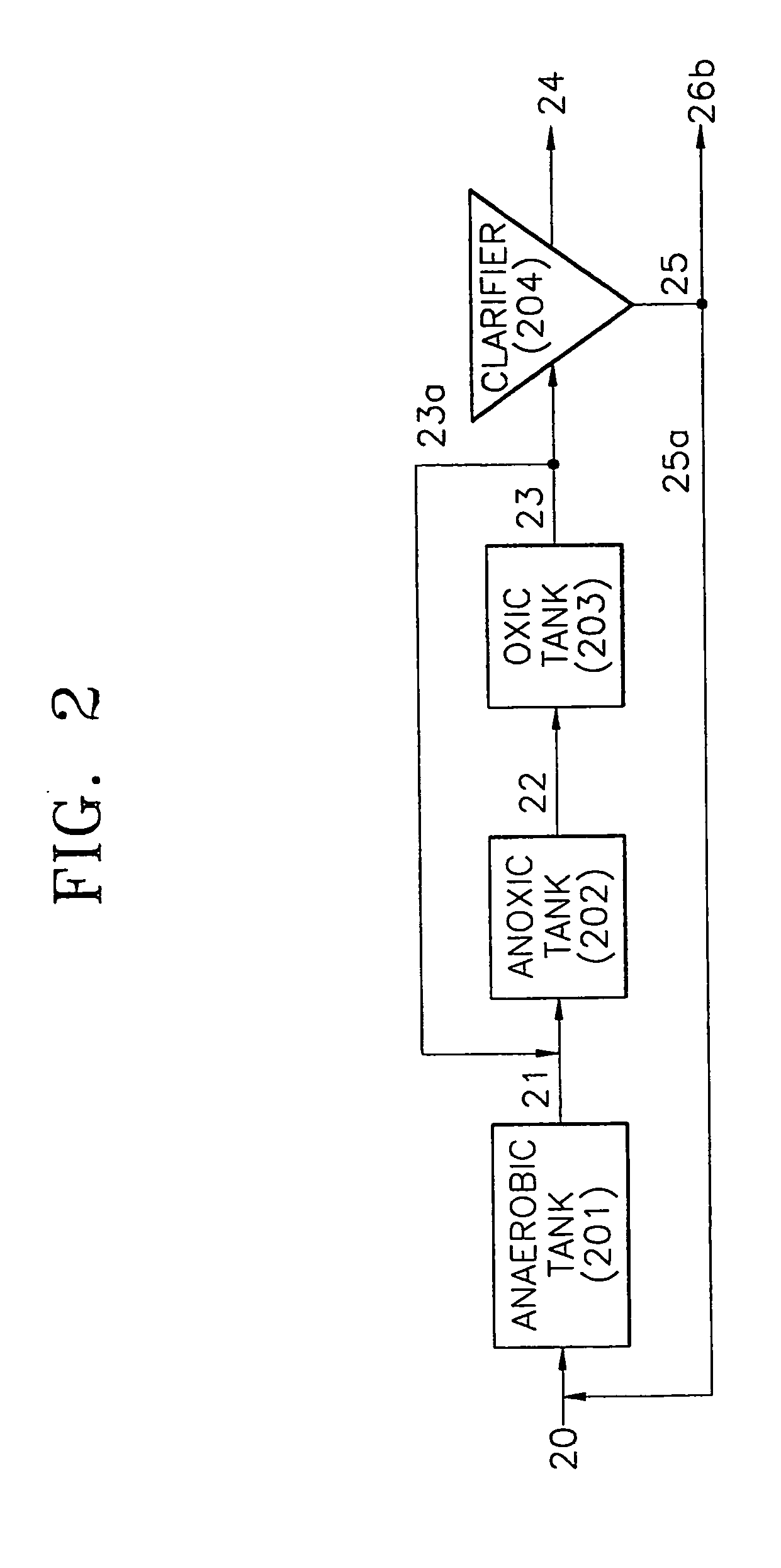
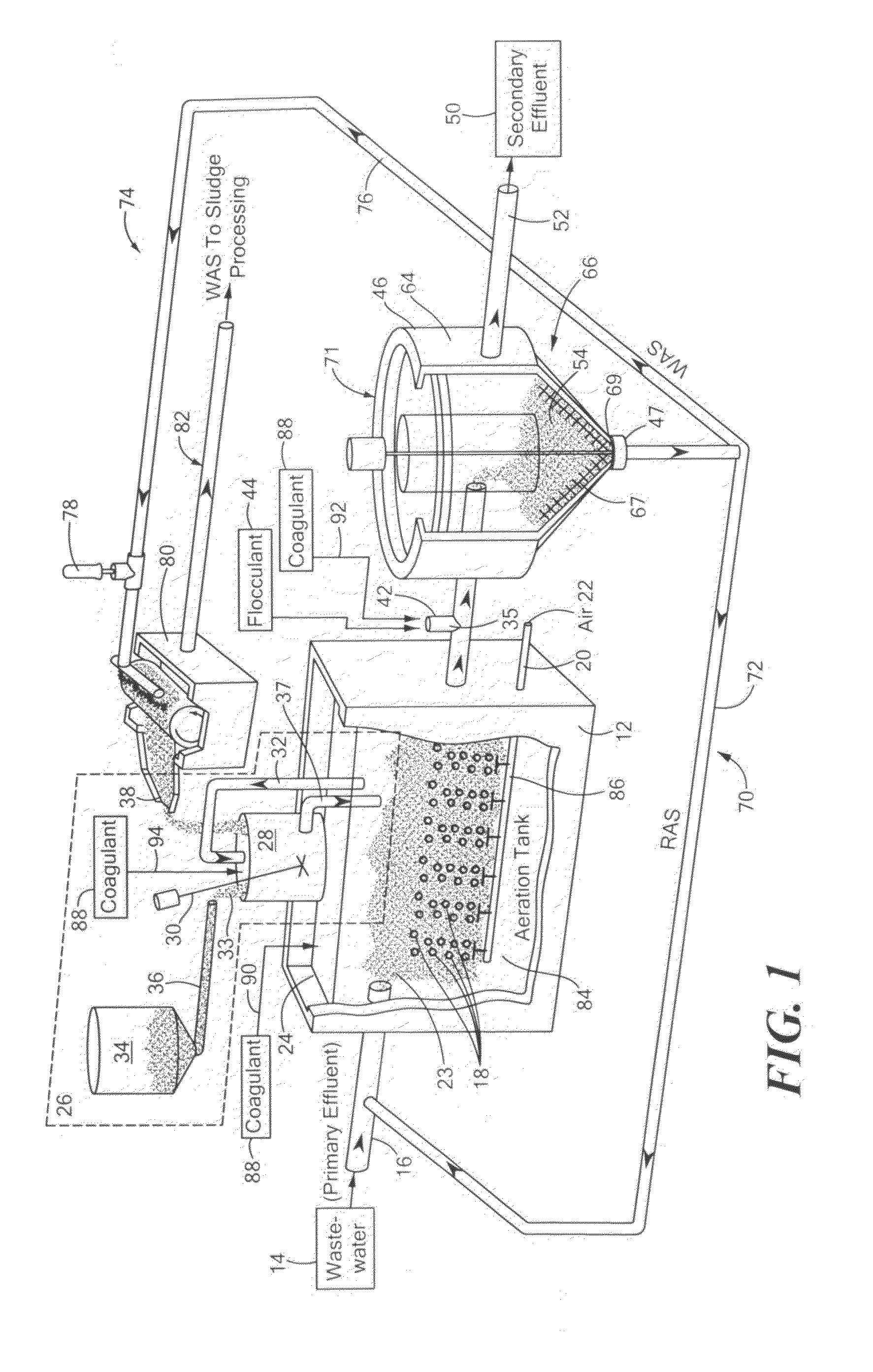
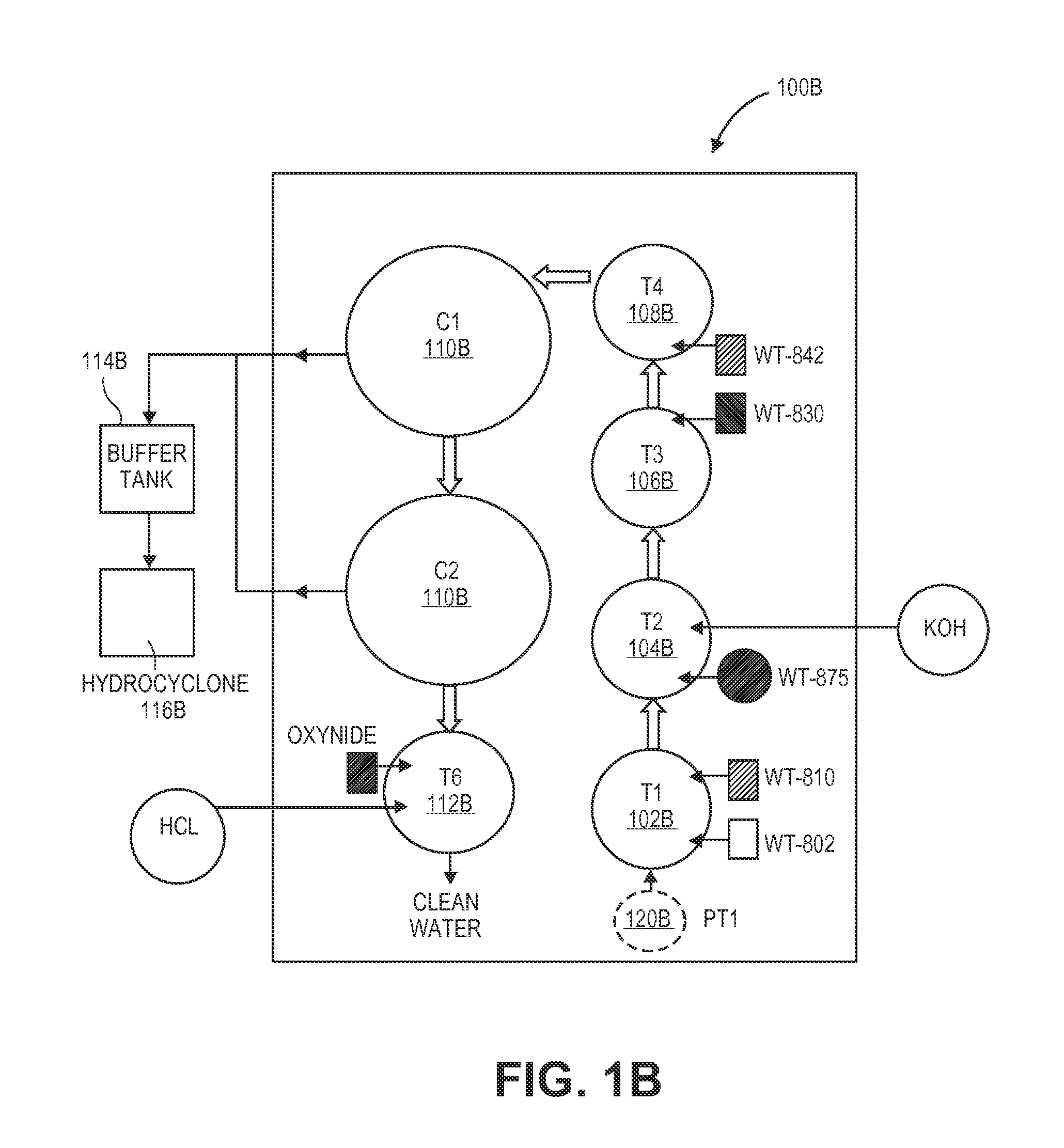
Treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen
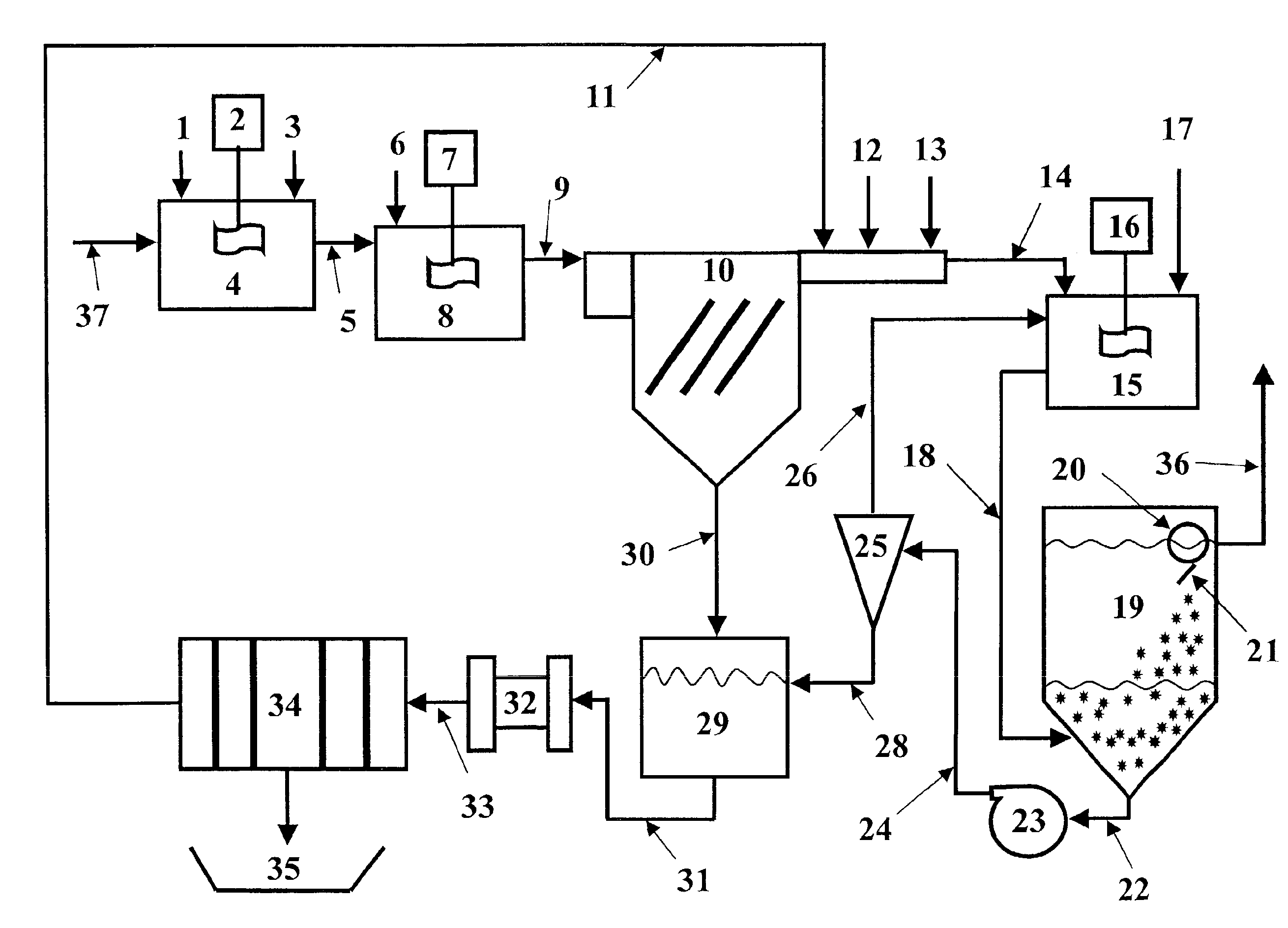
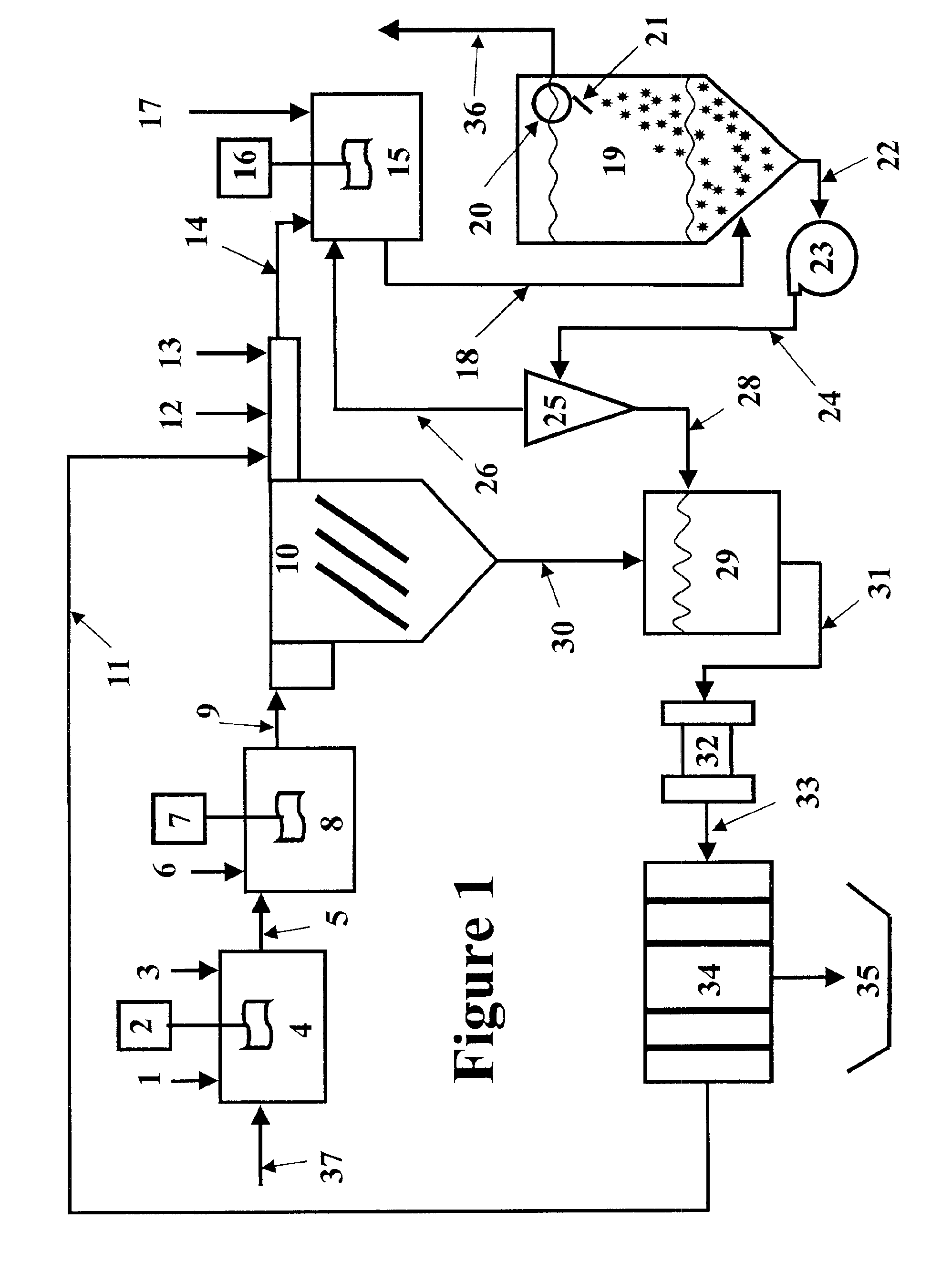
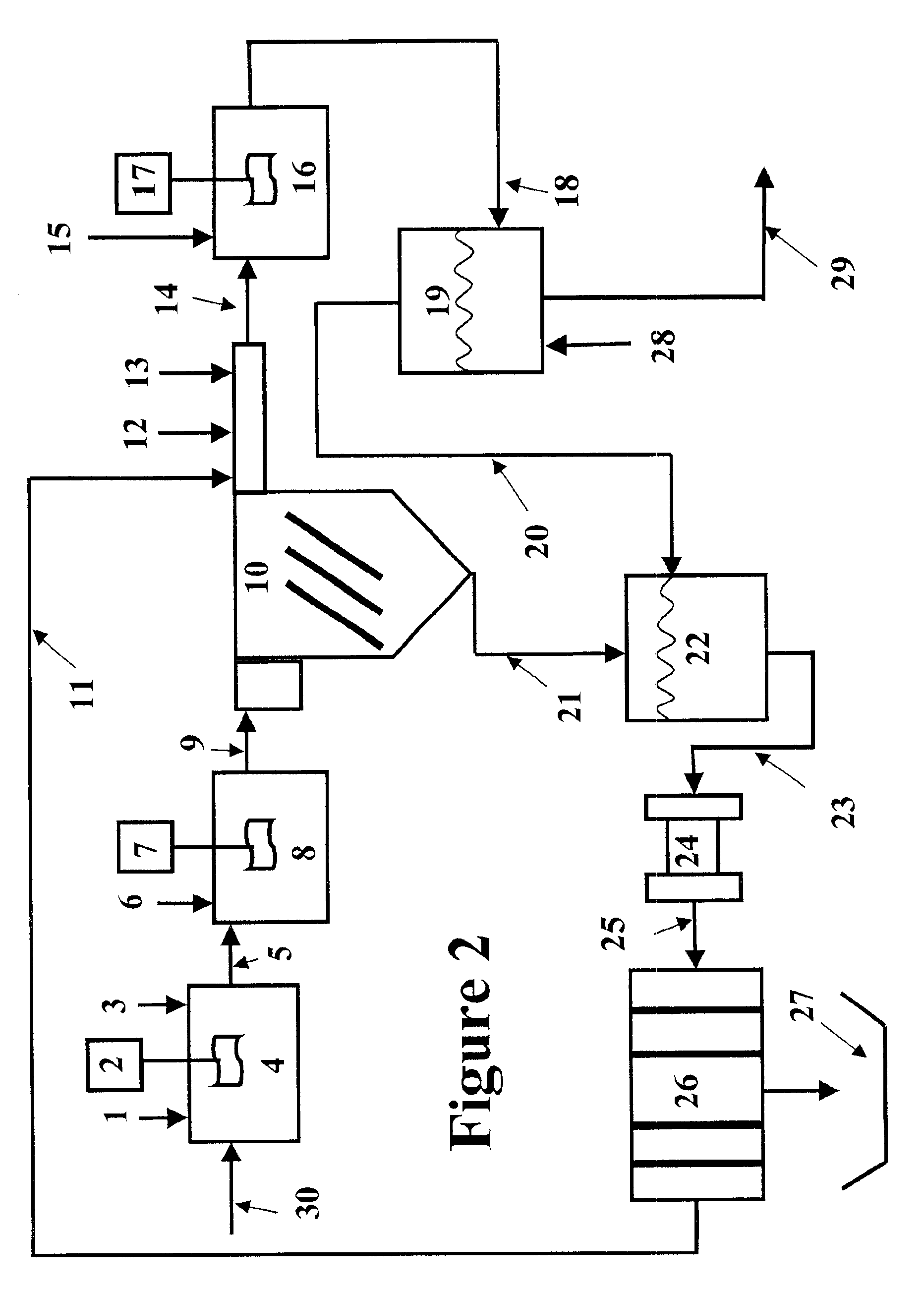
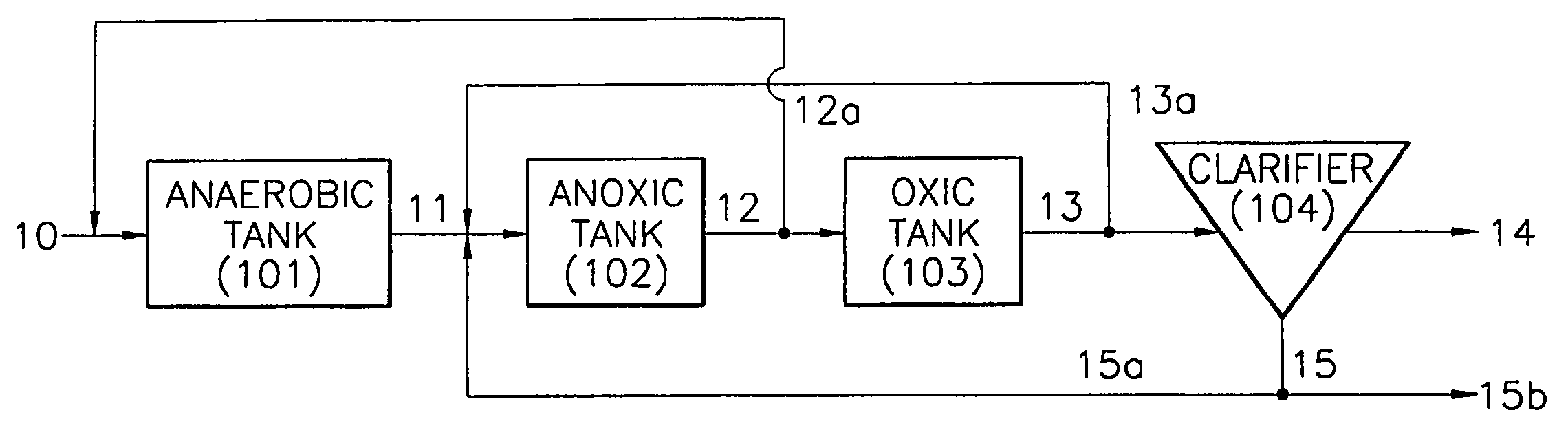
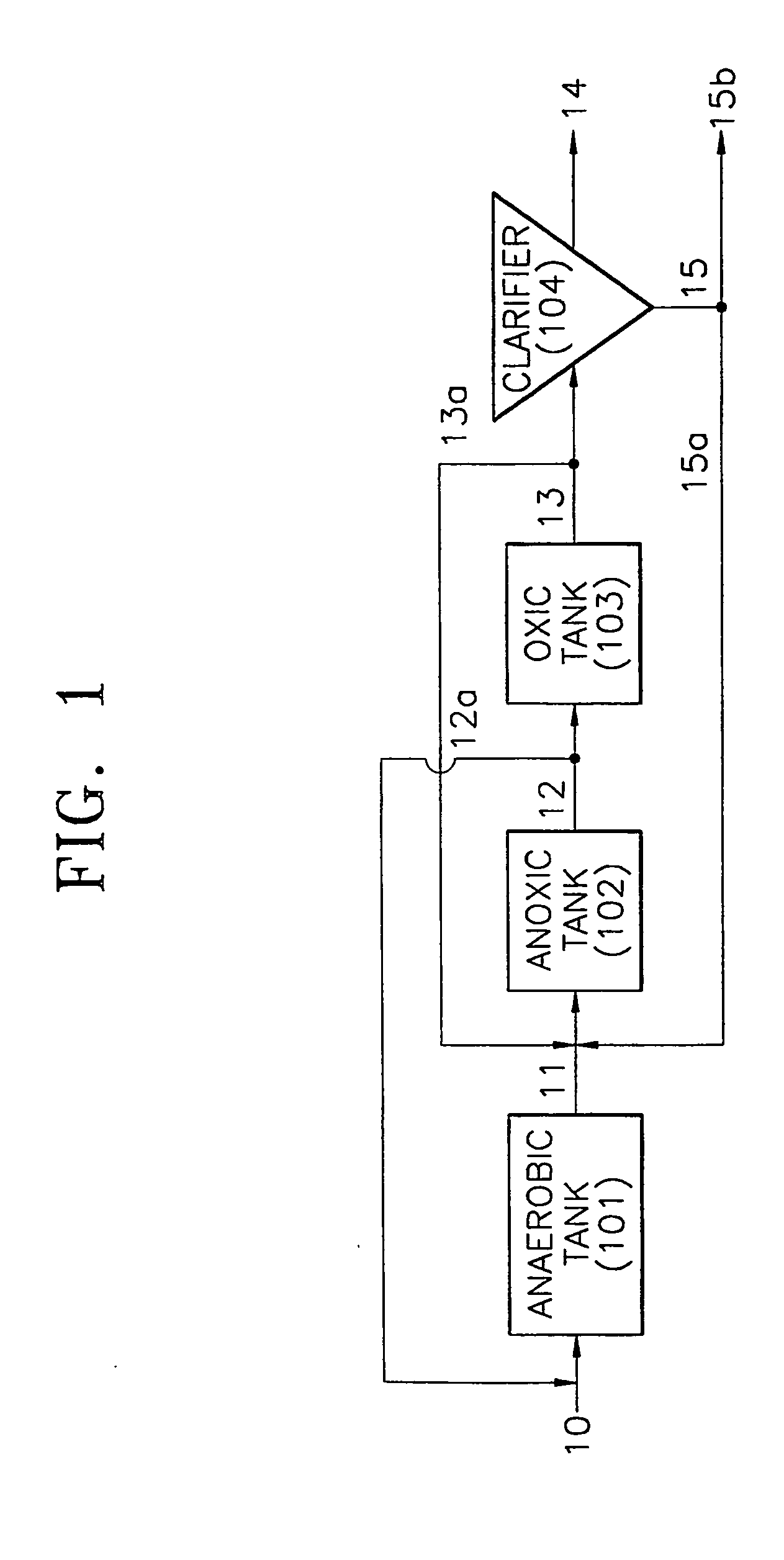
InactiveUS20060249449A1Great extent of P releaseHigh P uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesOxygenClarifier
A method and process for the treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen. The wastewater is first anaerobically treated to produce an anaerobic effluent from which insoluble organic carbon is separated to form a sludge rich in organic carbon that is used as a substrate during anoxic treatment of the wastewater by de-nitrifying phosphorous accumulating organisms (DPAO's) and ordinary de-nitrifying organisms. The separation of insoluble organic carbon is normally conducted using a clarifier located intermediate the anaerobic and anoxic bio-reactors. In one embodiment, the ammonia rich clarifier supernatant is directed to an aerobic reactor for nitrification and the nitrate produced is recycled to the anoxic bio-reactor. The final effluent may be membrane filtered to retain nitrifying biomass within the aerobic bio-reactor. The invention reduces overall hydraulic residence time and sludge volume, which results in a smaller, less expensive wastewater treatment system.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
Dual layer tablet, method of making and use thereof
InactiveUS6863830B1Easy to optimizeComprehensive treatmentOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesPotassium persulfateLithium hypochlorite
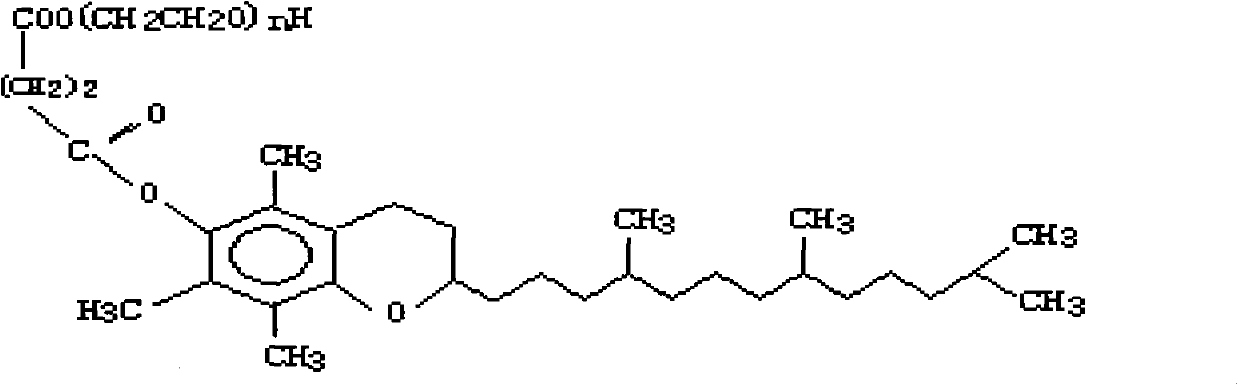
A method for treating a recirculating water system which comprises introducing into said water system a multifunctional, multilayer tablet, wherein the multilayer tablet comprises a fast dissolving layer and a slow dissolving layer, wherein said fast dissolving layer releases a combination of active ingredients including a member selected from the group consisting of lithium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite, trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA), anhydrous sodium dichloroisocyanurate, sodium persulfate, potassium persulfate, potassium monopersulfate, sodium monopersulfate, and mixtures thereof, and at least one of a clarifier, chelating agent, sequesterant, algaestat, water softener, algaecide, corrosion inhibitor, scale inhibitor, flocculent, disintegrant, dispersant, colorant, dissolution control agent, fragrance, or surfactant and, wherein said slow dissolving layer includes a member selected from the group consisting of trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA), calcium hypochlorite, 1,3-dichloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DCDMH), 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DBDMH), 1-bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (BCDMH), 1,3-dichloro-5-ethyl-5-methylhydantoin (DCEMH), 1,3-dibromo-5-ethyl-5-methylhydantoin (DBEMH), 1-bromo-3-chloro-5-methyl-5-ethylhydantoin (BCEMH), and mixtures thereof, and at least one of a clarifier, chelating agent, sequesterant, algaestat, water softener, algaecide, corrosion inhibitor, scale inhibitor, flocculent, disintegrant, dispersant, colorant, dissolution control agent or surfactant.
Owner:BIO LAB
Batch-continuous process and reactor
InactiveUS20060081533A1Precise positioningTreatment using aerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentRetention timeWastewater
This is a method of batch-continuous operation for treatment and separation of liquid-solid mixtures in a reactor with reactive solids comprising steps of continuously feeding the liquid in the reactor, contacting (possibly, mixing) liquid with the solids in at least a portion of the reactor, periodically separating the liquid from the solids in unmixed, or predominantly unmixed, portion of the reactor, discharging at least a portion of the separated liquid from the reactor, and retaining the separated solids in the unmixed portion of the reactor, and periodically resuspending the solids in the unmixed portion of the reactor and transferring the resuspended soilds into the portion of the reactor for contacting liquid with the solids. The contacting and / or mixing of the liquid with the solids in the mixed portion of the reactor can be continuous or periodic mixing. The unmixed zone differs from the quiescent zone in conventional clarifiers. It is a flow-through zone with a noticeably high velocity of flow as in aeration tanks of biological treatment systems. The retention time in unmixed zones is much shorter than in clarifiers. The method and apparatus can be used to treat water and wastewater, and in various chemical, biochemical, and pharmaceutical processing operations.
Owner:KHUDENKO BORIS M
Methods for removing heavy metals from water using chemical precipitation and field separation methods
InactiveUS20050258103A1Efficient removalEasy to disassembleSedimentation separationDifferential sedimentationParticulatesSulfide
A two-step chemical precipitation process involving hydroxide precipitation and sulfide precipitation combined with “field separation ” technology such as magnetic separation, dissolved air flotation, vortex separation, or expanded plastics flotation, effectively removes chelated and non-chelated heavy metal precipitates and other fine particles from water. In the first-step, the non-chelated heavy metals are precipitated as hydroxides and removed from the water by a conventional liquid / solids separator such as an inclined plate clarifier to remove a large percentage of the dissolved heavy metals. The cleaned water is then treated in a second precipitation step to remove the residual heavy metals to meet discharge limits. In the second precipitation step, any metal precipitant more effective than hydroxide for metal precipitation can be used. The invention improves metal removal, lowers cost because fewer chemicals are used, produces less sludge, and reduces the discharge of toxic metals and metal precipitants to the environment. Magnetic separation is preferred for the separation of particles precipitated in the second stage. Similar methods can be employed for separation of other particulates from water. Particulates can also be removed by causing them to adhere to particles of expanded plastic, forming a floc lighter than water, so that the floc can be removed by flotation.
Owner:CORT CHERYL J
Methods for removing heavy metals from water using chemical precipitation and field separation methods
InactiveUS7255793B2Cost- and chemically-effectiveSedimentation separationWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationParticulatesSulfide
A two-step chemical precipitation process involving hydroxide precipitation and sulfide precipitation combined with “field separation ” technology such as magnetic separation, dissolved air flotation, vortex separation, or expanded plastics flotation, effectively removes chelated and non-chelated heavy metal precipitates and other fine particles from water. In the first-step, the non-chelated heavy metals are precipitated as hydroxides and removed from the water by a conventional liquid / solids separator such as an inclined plate clarifier to remove a large percentage of the dissolved heavy metals. The cleaned water is then treated in a second precipitation step to remove the residual heavy metals to meet discharge limits. In the second precipitation step, any metal precipitant more effective than hydroxide for metal precipitation can be used. The invention improves metal removal, lowers cost because fewer chemicals are used, produces less sludge, and reduces the discharge of toxic metals and metal precipitants to the environment. Magnetic separation is preferred for the separation of particles precipitated in the second stage. Similar methods can be employed for separation of other particulates from water. Particulates can also be removed by causing them to adhere to particles of expanded plastic, forming a floc lighter than water, so that the floc can be removed by flotation.
Owner:CORT CHERYL J
Methods for removing heavy metals from water using chemical precipitation and field separation methods
InactiveUS6896815B2Small sizeChemical cost reductionSolid sorbent liquid separationGold compoundsWater useSludge
A two-step chemical precipitation process involving hydroxide precipitation and sulfide precipitation combined with “field separation” technology such as magnetic separation, dissolved air flotation, vortex separation or expanded plastics flotation, effectively removes chelated and non-chelated heavy metal precipitates and other fine particles from water. In the first-step, the non-chelated heavy metals are precipitated as hydroxides and removed from the water by a conventional liquid / solids separator such as an inclined plate clarifier to remove a large percentage of the dissolved heavy metals. The cleaned water is then treated in a second precipitation step to remove the residual heavy metals to meet discharge limits. In the second precipitation step, any metal precipitant more effective than hydroxide for metal precipitation can be used. The invention improves metal removal, lowers cost because fewer chemicals are used, produces less sludge, and reduces the discharge of toxic metals and metal precipitants to the environment.
Owner:CORT STEVEN L
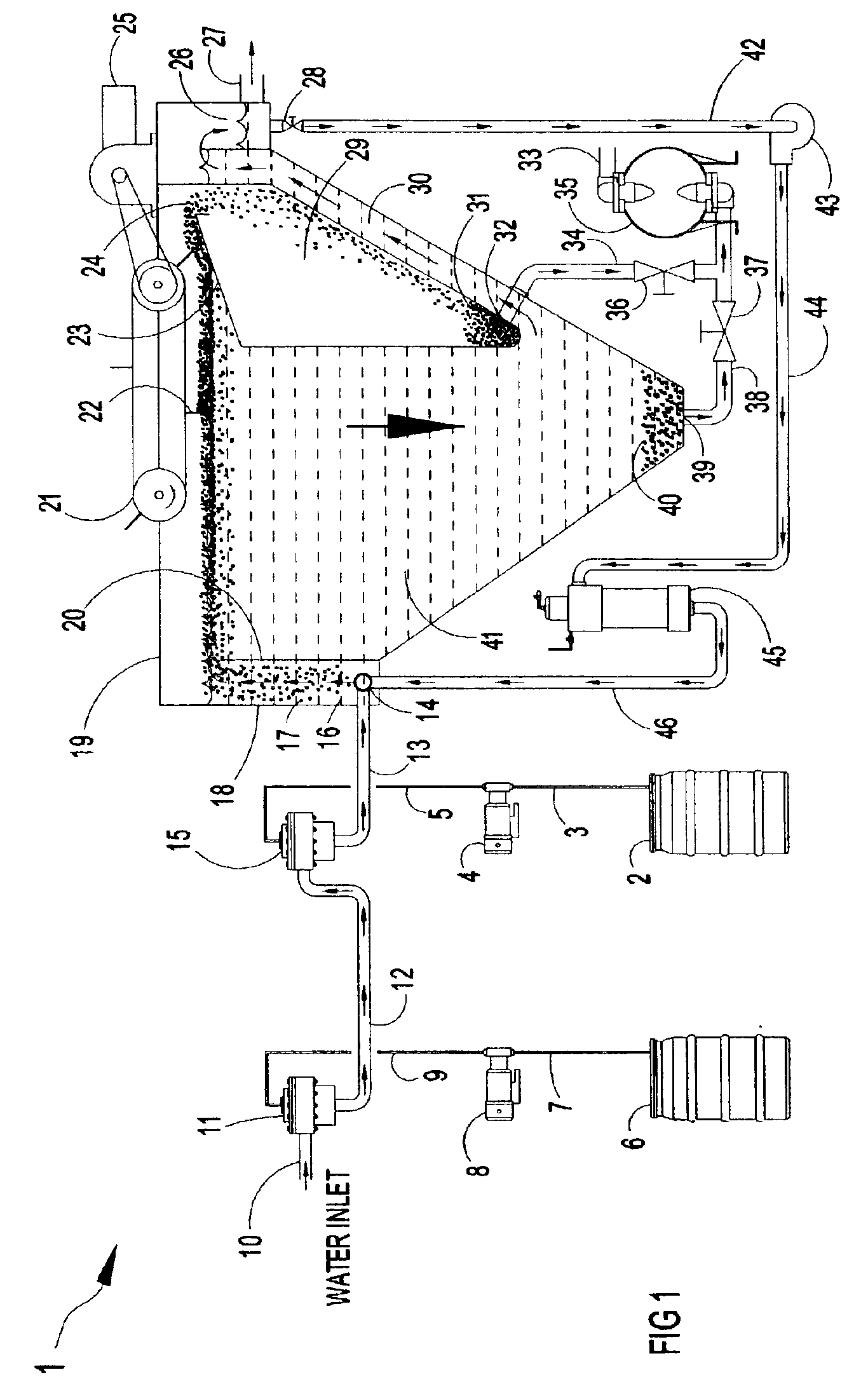
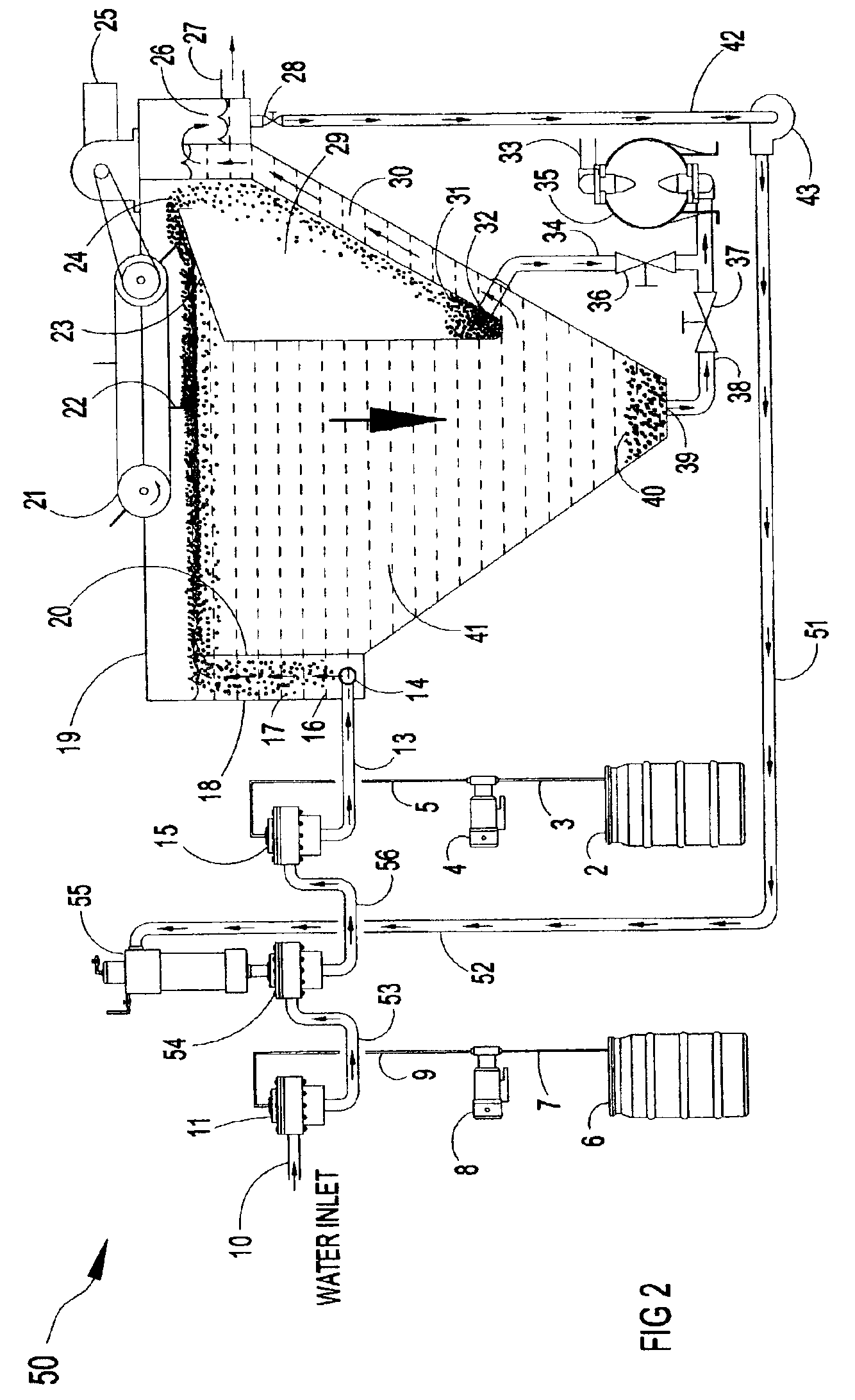
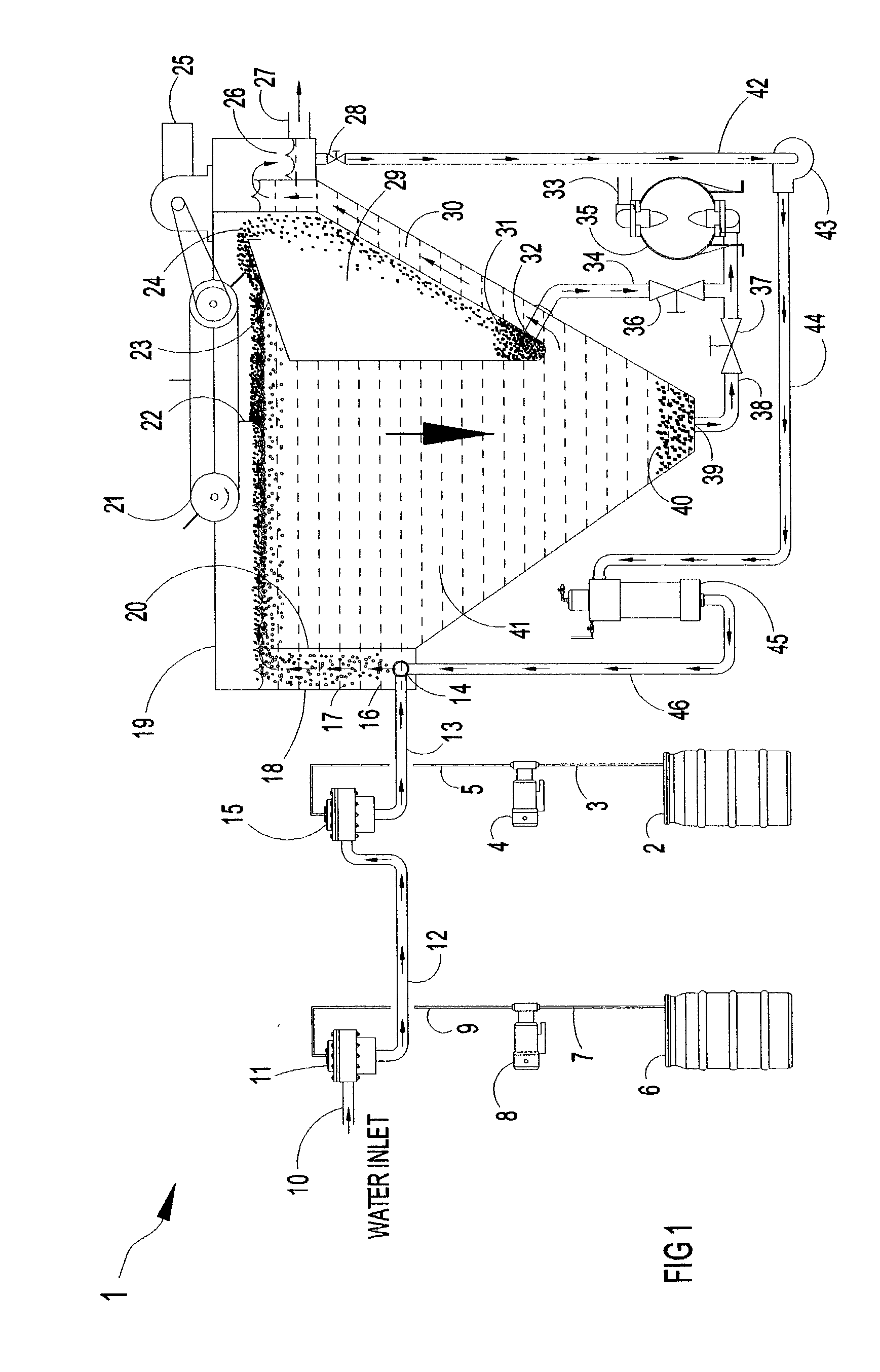
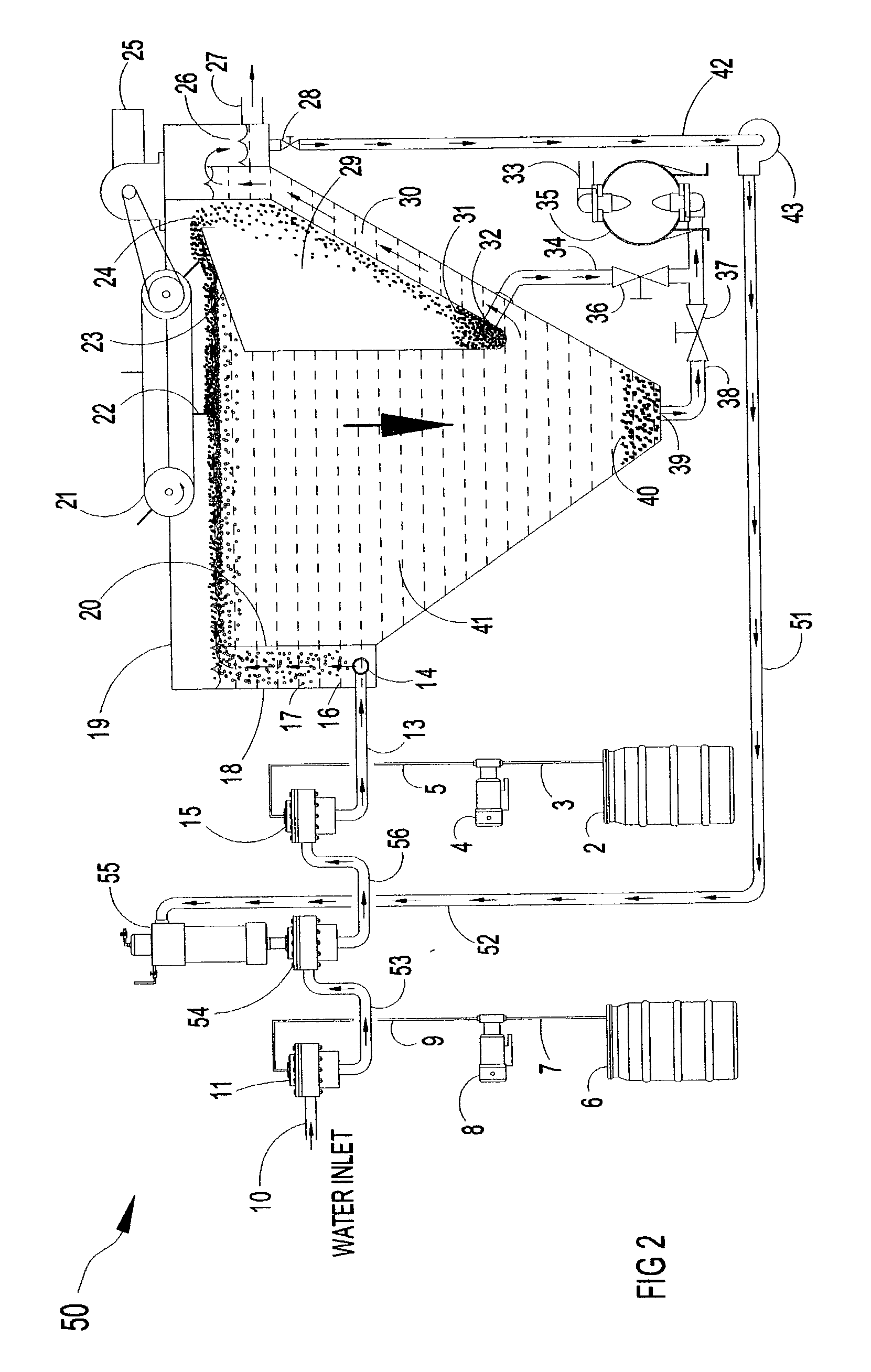
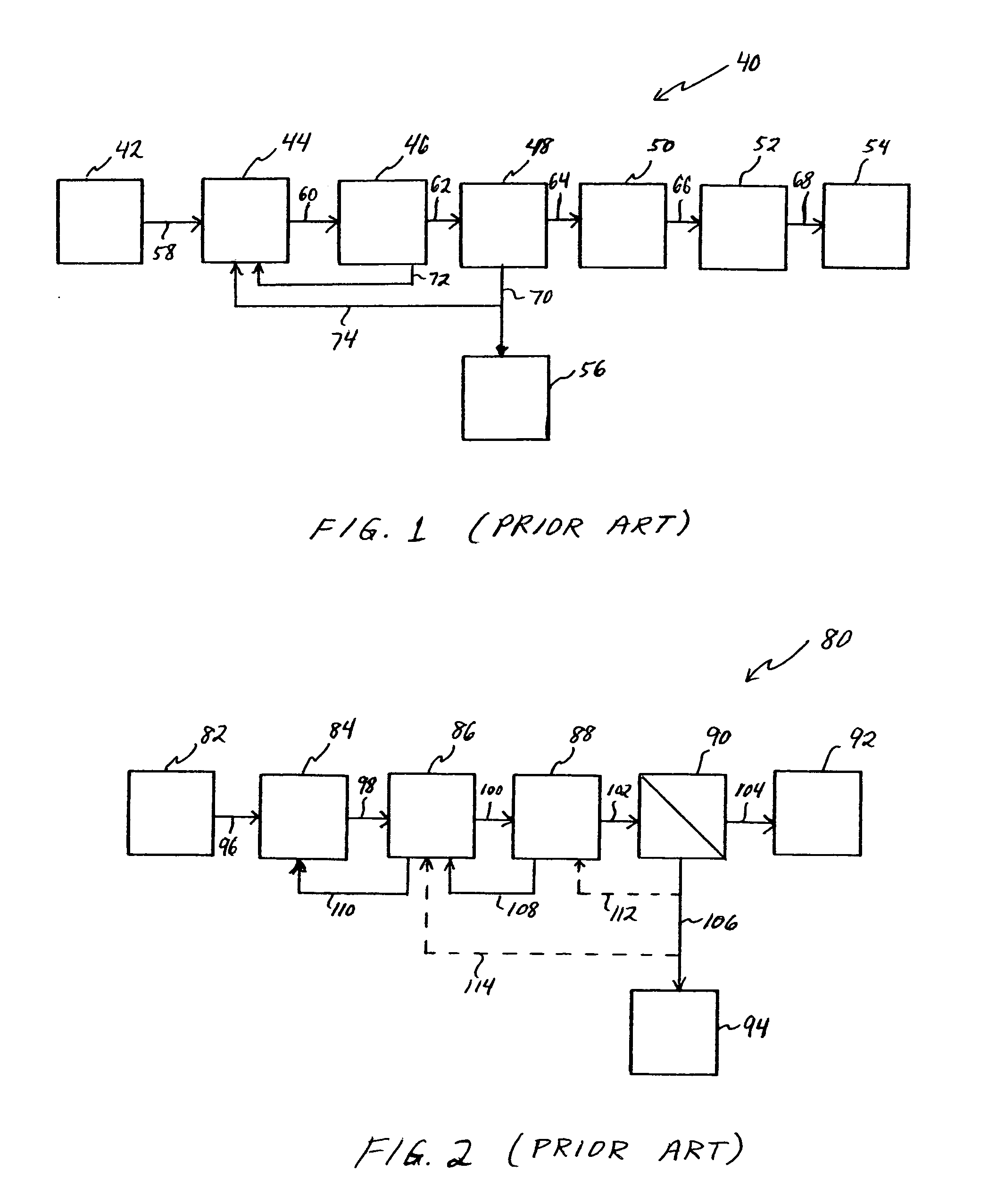
Methods and apparatus for treating wastewater employing a high rate clarifier and a membrane
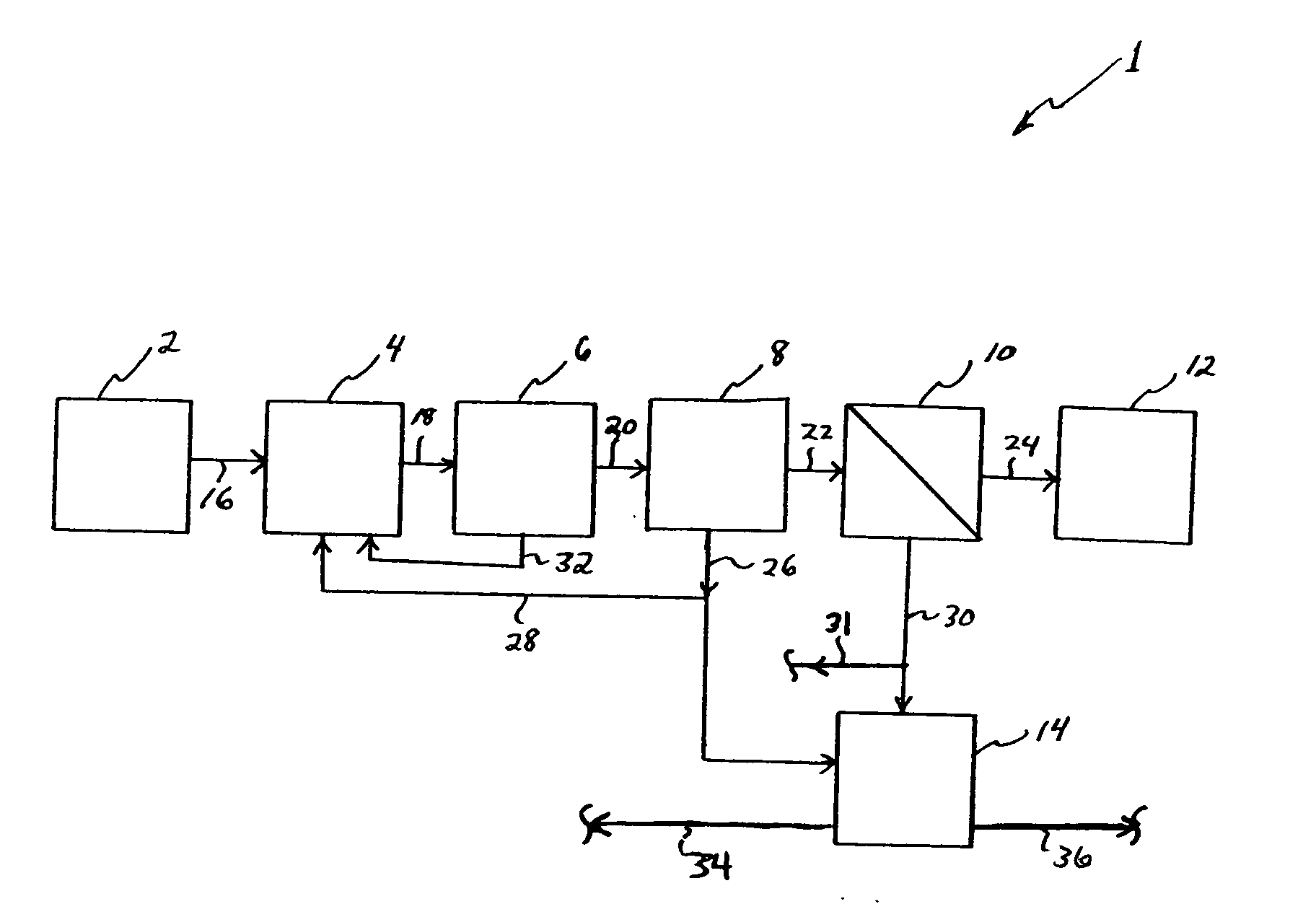
Methods and apparatus for treating wastewater are described, one method embodiment including the steps of flowing a mixed liquor suspended solids to a high rate clarification stage, forming a clarifier effluent, a first waste activated sludge stream, and a return waste activated sludge stream. The high rate clarifier effluent stream then flows to a membrane stage that includes a membrane media, producing a membrane reject (retentate) stream and a treated effluent (permeate) stream. Optionally, the methods include routing a screened raw wastewater to an anaerobic and / or aerated anoxic stage and introducing a gas comprising oxygen to the wastewater during the aerated anoxic stage, and optionally allowing the product of this stage to flow to an aeration stage prior to the high rate clarification stage.
Owner:ALFA LAVAL ASHBROOK SIMON HARTELY INC
Dual layer tablet, method of making and use thereof
InactiveUS20050040116A1Easy to optimizeComprehensive treatmentOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesPotassium persulfateLithium hypochlorite
A method for treating a recirculating water system which comprises introducing into said water system a multifunctional, multilayer tablet, wherein the multilayer tablet comprises a fast dissolving layer and a slow dissolving layer, wherein said fast dissolving layer releases a combination of active ingredients including a member selected from the group consisting of lithium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite, trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA), anhydrous sodium dichloroisocyanurate, sodium persulfate, potassium persulfate, potassium monopersulfate, sodium monopersulfate, and mixtures thereof, and at least one of a clarifier, chelating agent, sequesterant, algaestat, water softener, algaecide, corrosion inhibitor, scale inhibitor, flocculent, disintegrant, dispersant, colorant, dissolution control agent, fragrance, or surfactant and, wherein said slow dissolving layer includes a member selected from the group consisting of trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA), calcium hypochlorite, 1,3-dichloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DCDMH), 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DBDMH), 1-bromo-3-chloro-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (BCDMH), 1,3-dichloro-5-ethyl-5-methylhydantoin (DCEMH), 1,3-dibromo-5-ethyl-5-methylhydantoin (DBEMH), 1-bromo-3-chloro-5-methyl-5-ethylhydantoin (BCEMH), and mixtures thereof, and at least one of a clarifier, chelating agent, sequesterant, algaestat, water softener, algaecide, corrosion inhibitor, scale inhibitor, flocculent, disintegrant, dispersant, colorant, dissolution control agent or surfactant.
Owner:BIO LAB
Methods and apparatus for oil demulsification and separation of oil and suspended solids from produced water
InactiveUS20040031742A1Liquid separation auxillary apparatusMixing methodsDissolved gas flotationWater treatment system
Methods and apparatus for demulsifying oil in water by dilution and impact, and for separation of the oil and suspended solids by dissolved gas floatation, are described. A produced water treating system is also described. The produced water treating system may include a dissolved gas floatation clarifier system, an oil demulsification system, and a separation system. A demulsification subsystem is also described. The apparatus may include a liquid-liquid fluid mixer and a gas generator.
Owner:HYDROTREAT
Methods and apparatus for oil demulsification and separation of oil and suspended solids from produced water
InactiveUS6875351B2Liquid separation auxillary apparatusUsing liquid separation agentDissolved gas flotationWater treatment system
Methods and apparatus for demulsifying oil in water by dilution and impact, and for separation of the oil and suspended solids by dissolved gas floatation, are described. A produced water treating system is also described. The produced water treating system may include a dissolved gas floatation clarifier system, an oil demulsification system, and a separation system. A demulsification subsystem is also described. The apparatus may include a liquid-liquid fluid mixer and a gas generator.
Owner:HYDROTREAT
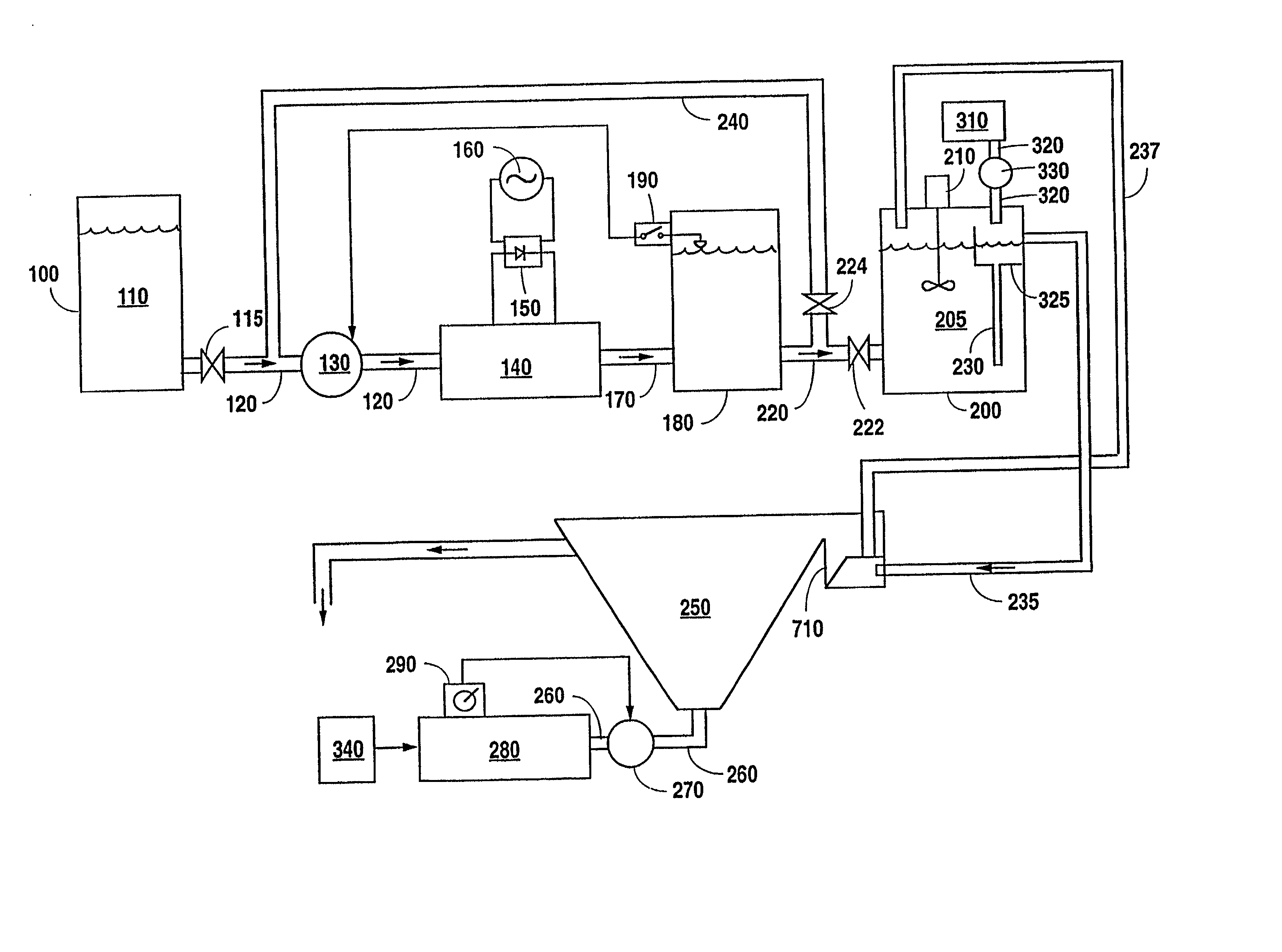
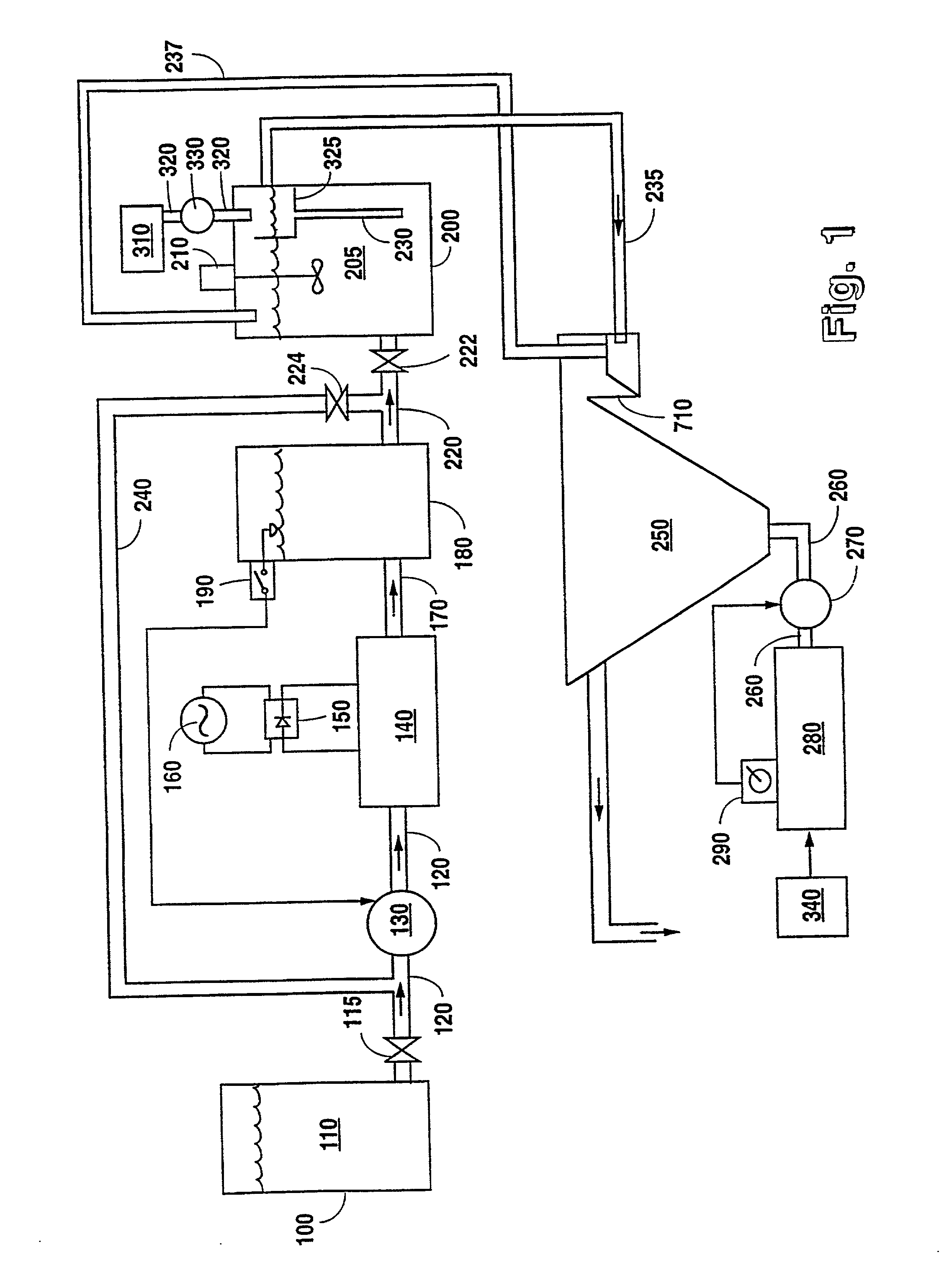
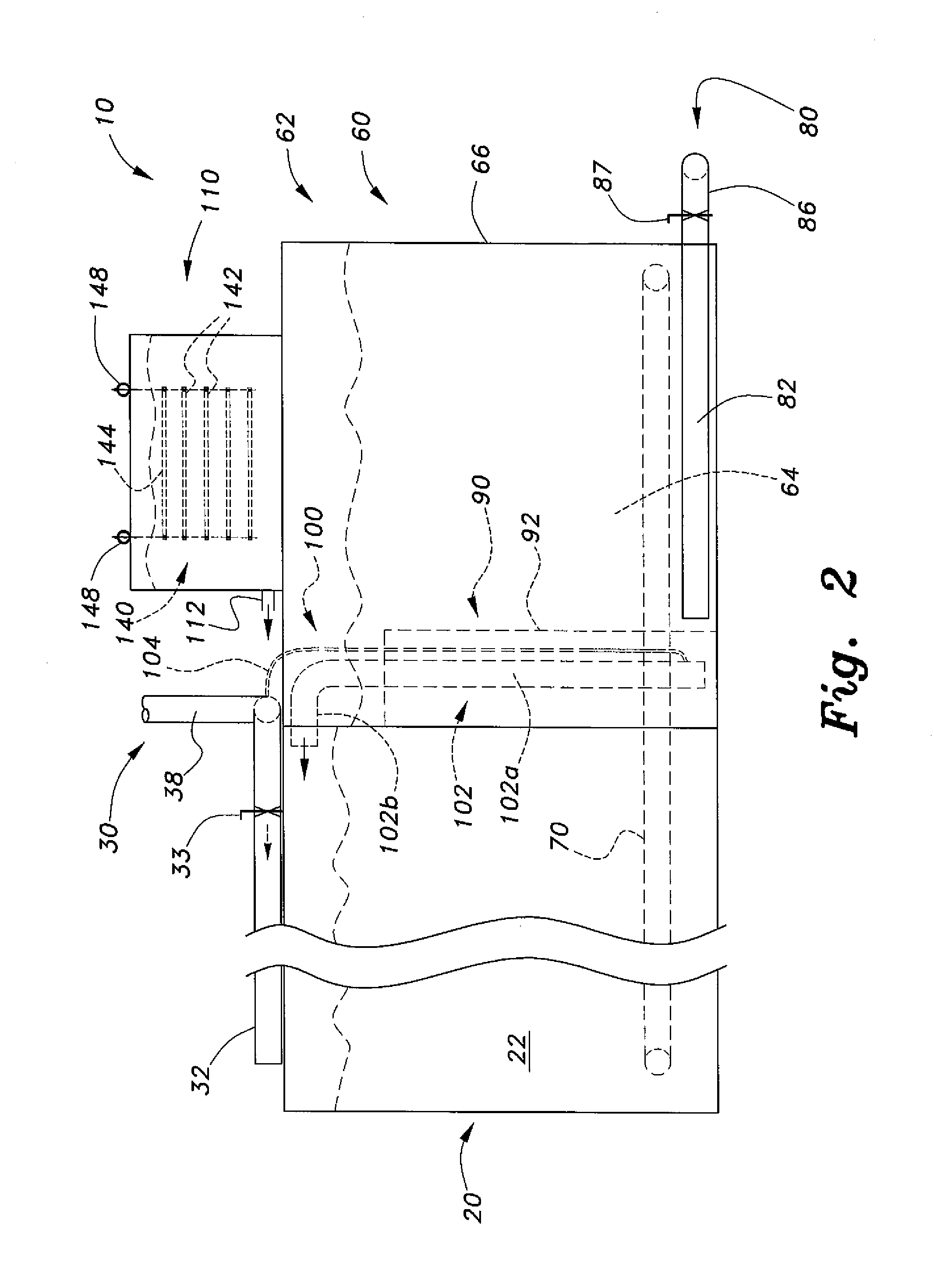
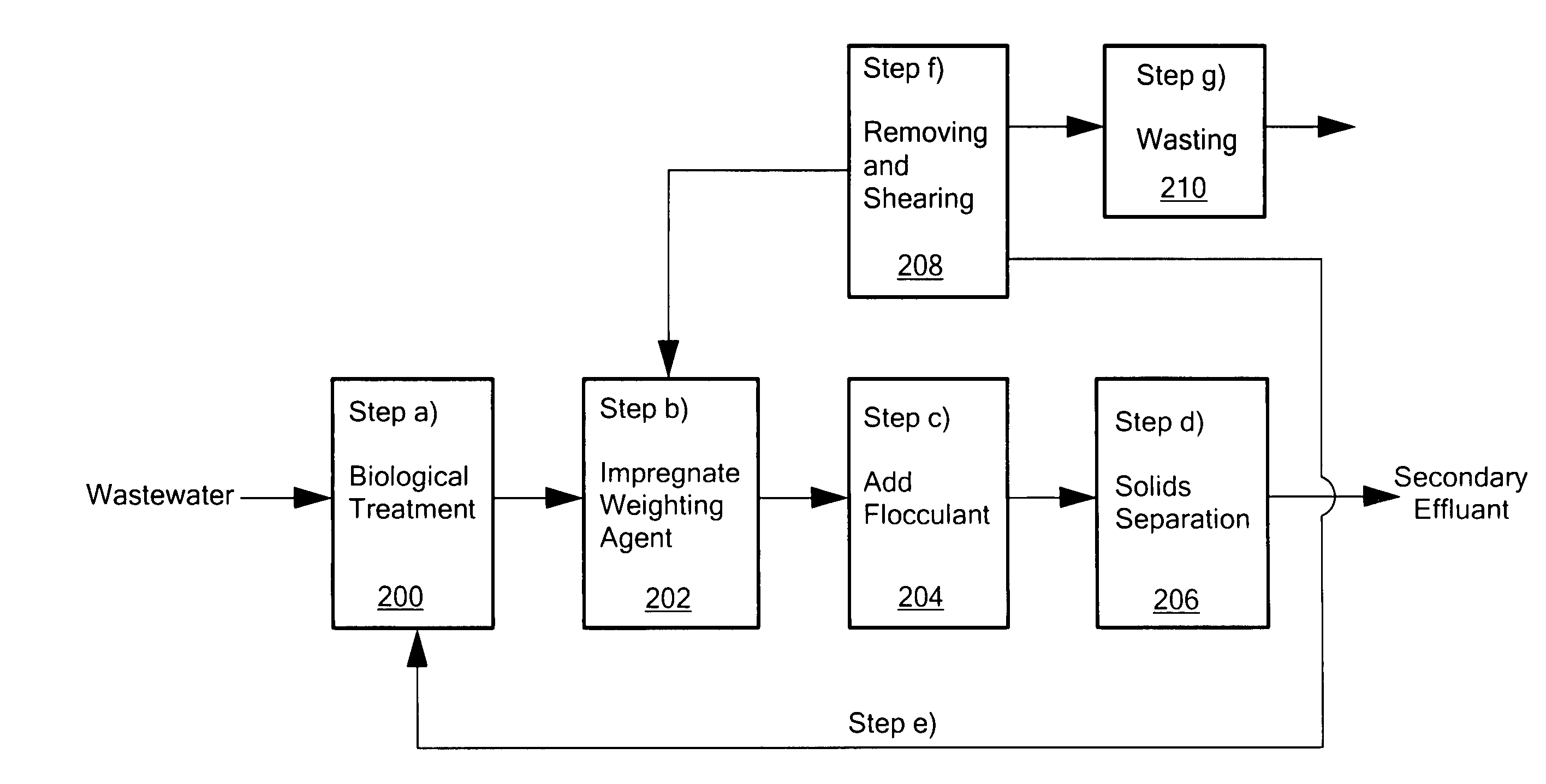
System and method for enhancing an activated sludge process
ActiveUS20080203015A1Enhance settlingGood thickeningTreatment using aerobic processesOther chemical processesMixed liquor suspended solidsInjection port
A system for enhancing an activated sludge process that includes at least one aeration tank subsystem for receiving a flow a wastewater and for introducing dissolved oxygen to a population of microorganisms to promote growth of biological flocs in a mixed liquor defined by a concentration of mixed liquor suspended solids. A weighting agent impregnation subsystem includes an impregnation tank for mixing the mixed liquor, virgin weighting agent, and recycled weighting agent to impregnate the weighting agent into biological flocs suspended in the mixed liquor to form weighted biological flocs. A flocculant injection port located downstream from at least one aeration tank for introducing a flocculant to the mixed liquor for enhancing settling and thickening of the weighted biological flocs and for providing agglomeration of non-impregnated biological flocs and / or partially impregnated biological flocs with weighted biological flocs. At least one clarifier separates and collects the weighted biological flocs from the mixed liquor to provide a secondary effluent and a settled sludge. A return activated sludge subsystem recycles the majority of the settled sludge to the at least one aeration tank. A weighting agent recovery subsystem removes and shears the remaining settled sludge and recovers the weighting agent therefrom and reintroduces the weighting agent to the at least one aeration tank. A wasting subsystem wastes the remaining sludge of the weight agent recovery subsystem to control the population of the microorganisms in the mixed liquor.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
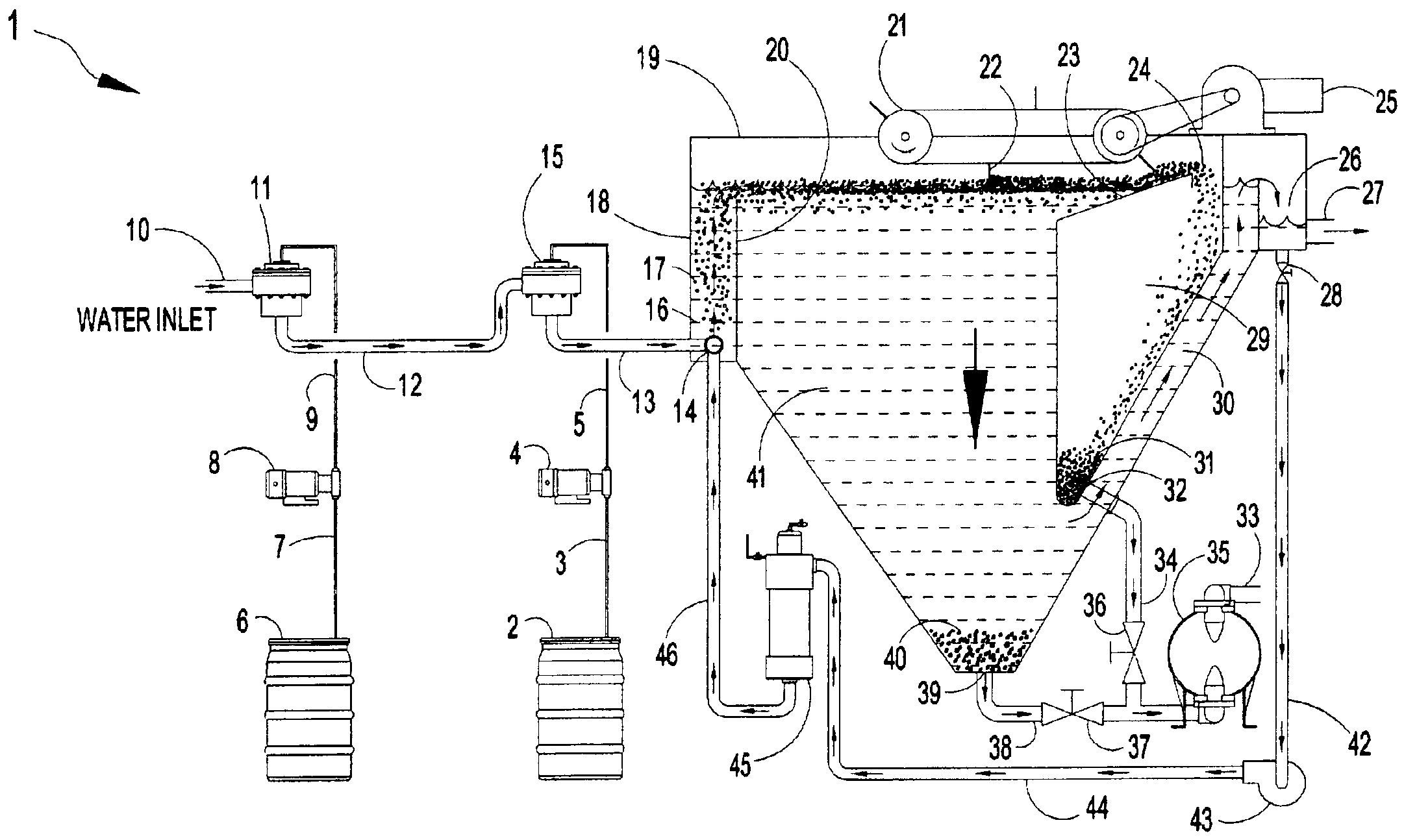
Apparatus for the separation of solids from liquids by dissolved gas floatation
InactiveUS6960294B2Liquid separation auxillary apparatusLiquid degasificationPhysical chemistryProduct gas
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for separation of solids from liquids and separation of liquids from liquids (such as oil from water) by dissolved gas floatation. A dissolved gas floatation clarifier is described as is a liquid-gas mixer, a liquid-liquid mixer, and solid-liquid chemical feeders. The methods and apparatus of the present invention are particularly suitable for supplying dissolved air and mixing of chemicals for use in separation of solids in dissolved air floatation clarifiers.
Owner:HYDROTREAT
Process and apparatus for electrocoagulative treatment of industrial waste water
InactiveUS20020040855A1Efficient removalEasy to manufactureElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentElectrocoagulationIndustrial waste water
An electrocoagulation system for removing contaminants from waste effluents comprising an electrocoagulation reactor having charged and uncharged plates and allowing serial flow of water therethrough. The reactor is connected to a voltage source to charge some of the plates positive and some negative, with uncharged plates between the positive and negative plates. The system allows waste water to enter the reactor for coagulation therein, the waste water leaving the reactor to enter a defoam tank for agitation which allows trapped bubbles to rise to the surface of the tank as foam. From the defoam tank, waste water goes through a sludge thickener, to allow sludge to settle at the bottom thereof and waste water is drawn off from the sludge thickener to flow to a clarifier. The pump removes sludge forming at the bottom of clarifier to take it back to the sludge thickener. The sludge is drawn out the bottom of the sludge thickener for transport to a press where most of the water is removed therefrom. Water is drawn off the top of the clarifier for transport to a conventional sewer system, or for reuse.
Owner:UNITED RENTALS NORTH AMERICA INC
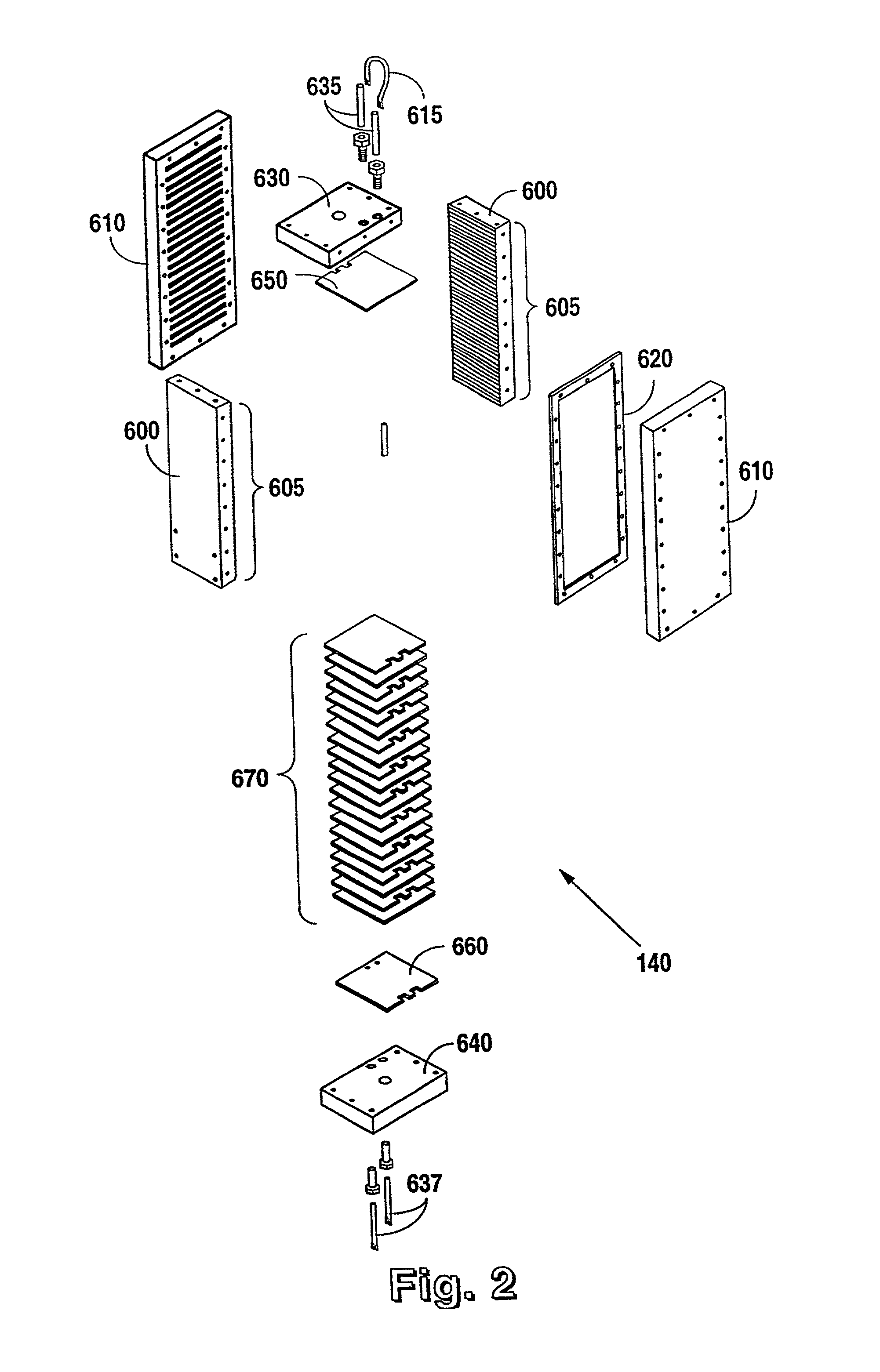
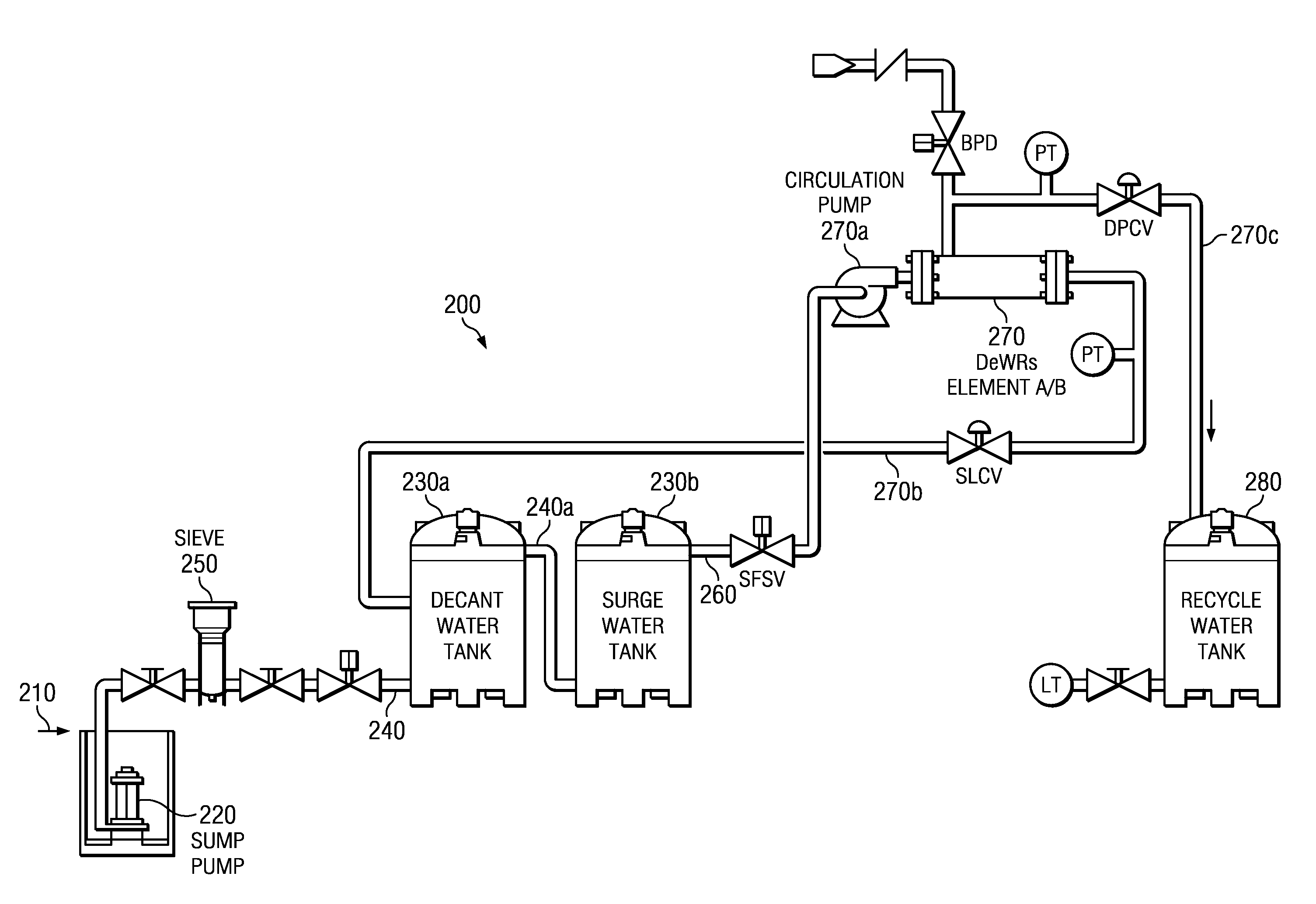
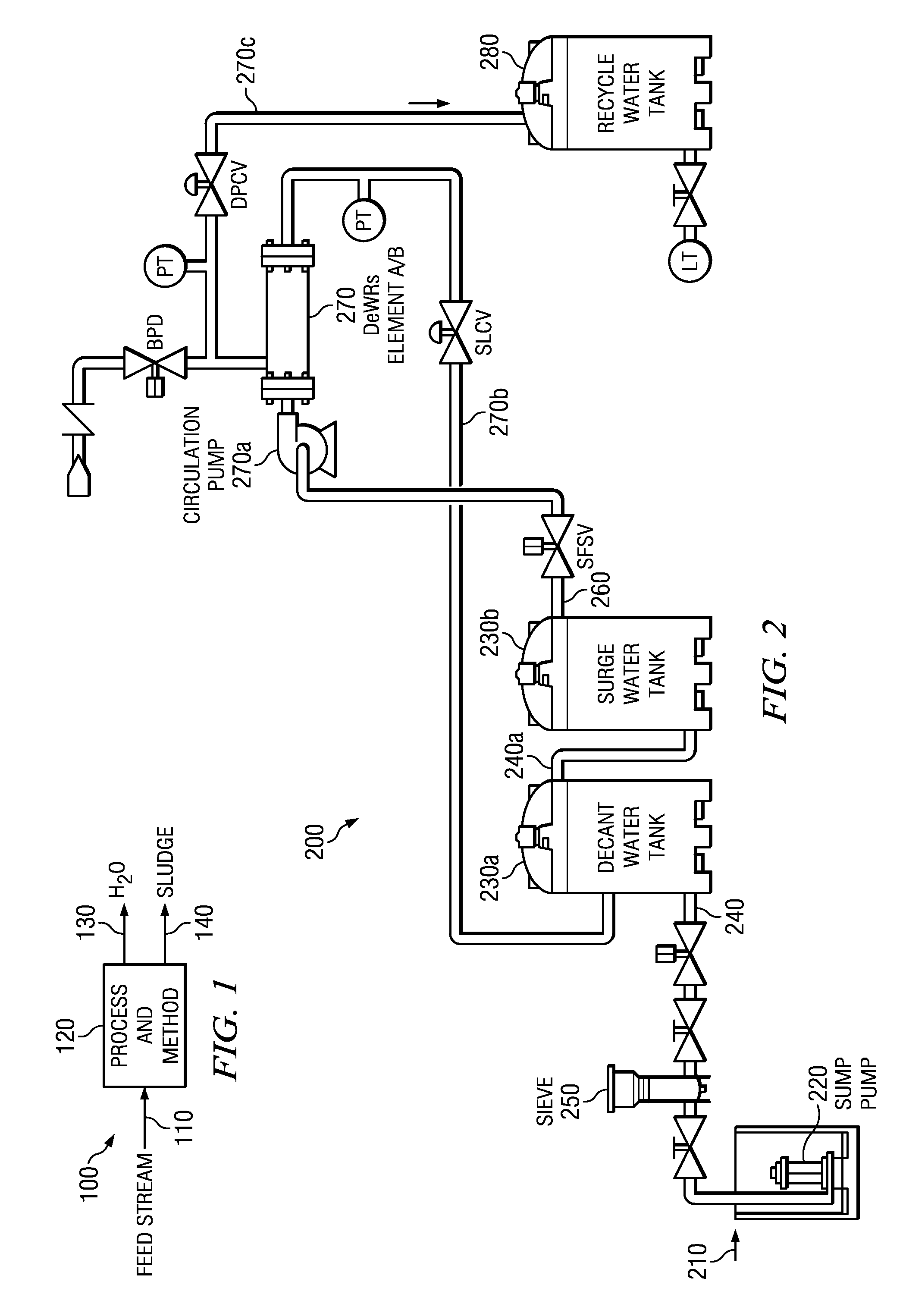
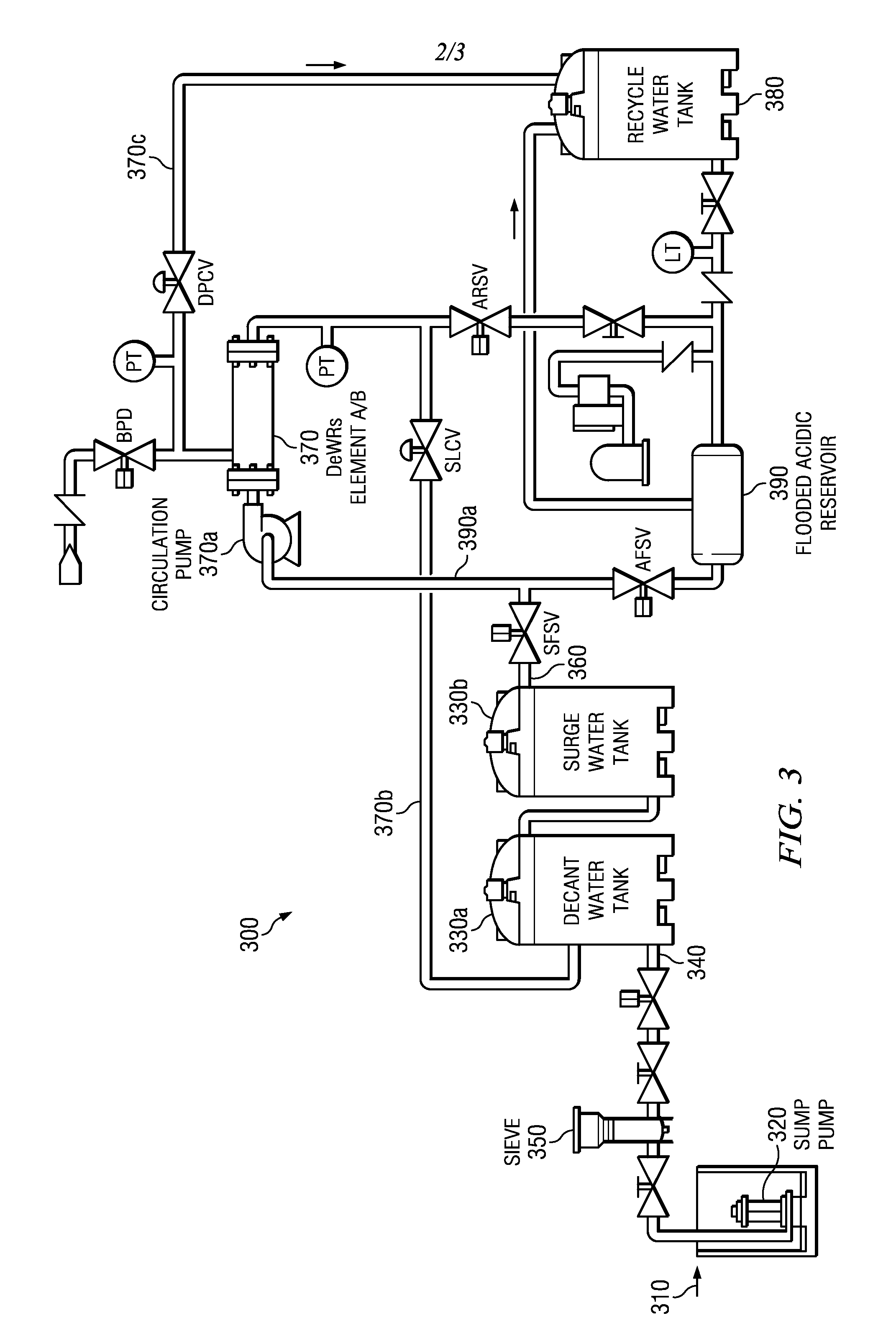
Integrated particulate filtration and dewatering system
The disclosed principles for providing a chemical-free filtering of particulate down below sub-micron levels, while concentrating the particulate into a sludge. The disclosed principles integrate cross-flow filtration (i.e., micro-filtration or ultra-filtration) with a settling tank (or “weir”) to provide sequential filtration and dewatering of an aqueous media. The disclosed technique operates chemical-free and is continuous. Applications for systems and processes in accordance with the disclosed technique are wide, and include aggregate fines removal, sediment removal, replacement for clarifiers, etc.
Owner:PURIFICS ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Device for turbulence reduction
ActiveUS9023216B2Reducing momentum and velocityReduce or even eliminate large-scale turbulent eddiesJuice extractionFluid dynamicsMomentumMechanical engineering
Apparatus is disclosed for substantially reducing the momentum, velocity, or both of a first liquid that is flowing into a second liquid. The device allows one to substantially reduce or even eliminate large-scale turbulent eddies that could otherwise be produced by liquid flowing into or within a vessel, for example in a clarifier. Suitably-sized and positioned plates and baffles induce changes of flow direction in a limited volume. By the time the fluid leaves this volume, the fluid velocity is low, and turbulence is nearly or entirely eliminated. Several of the devices may be placed at different inputs within a single clarifier, and thus increase efficiency further.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Wastewater treatment apparatus and method for removing nitrogen and phosphorus
InactiveUS20050087480A1Reduce maintenanceReduce repairTreatment using aerobic processesIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic matterOxygen
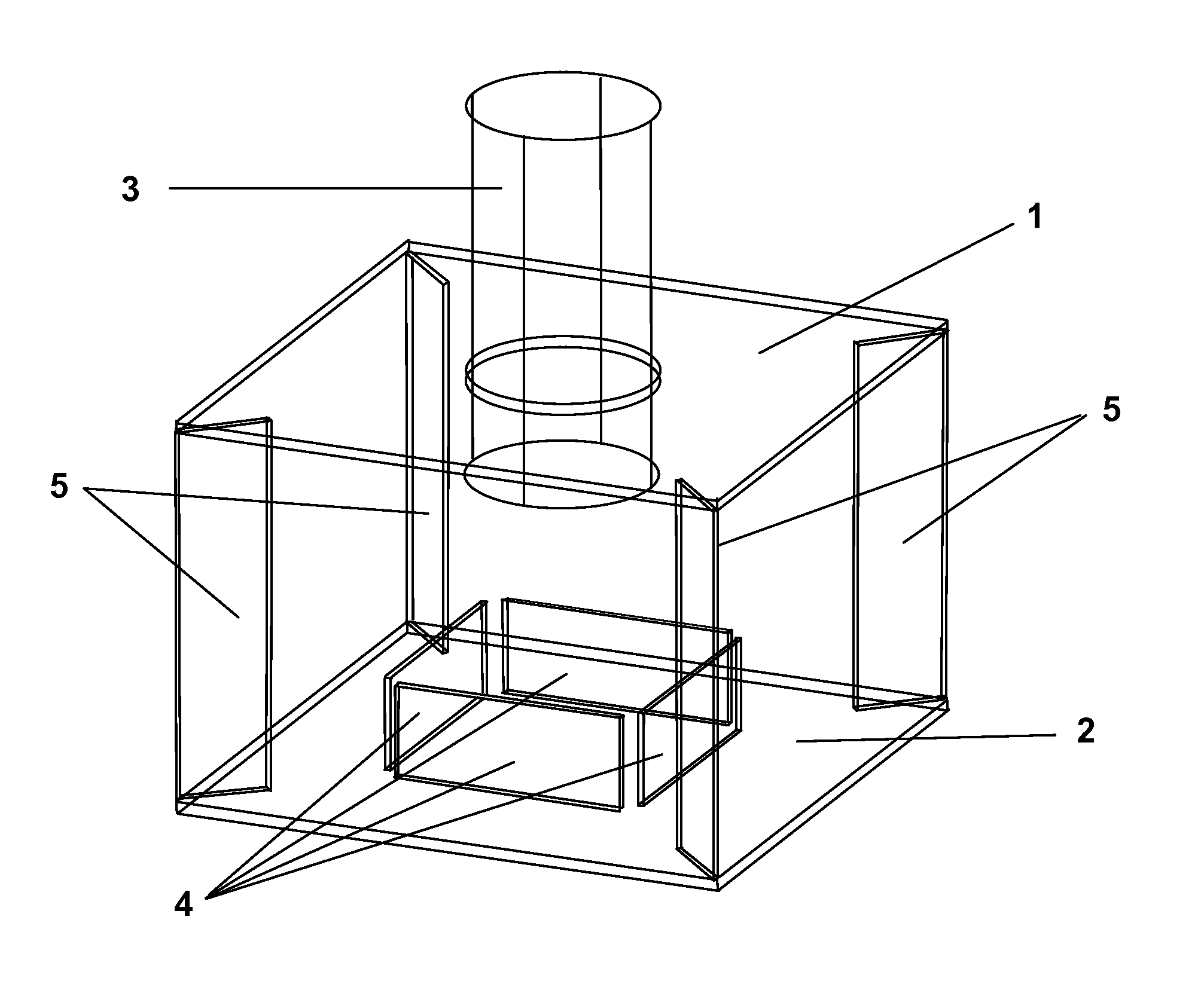
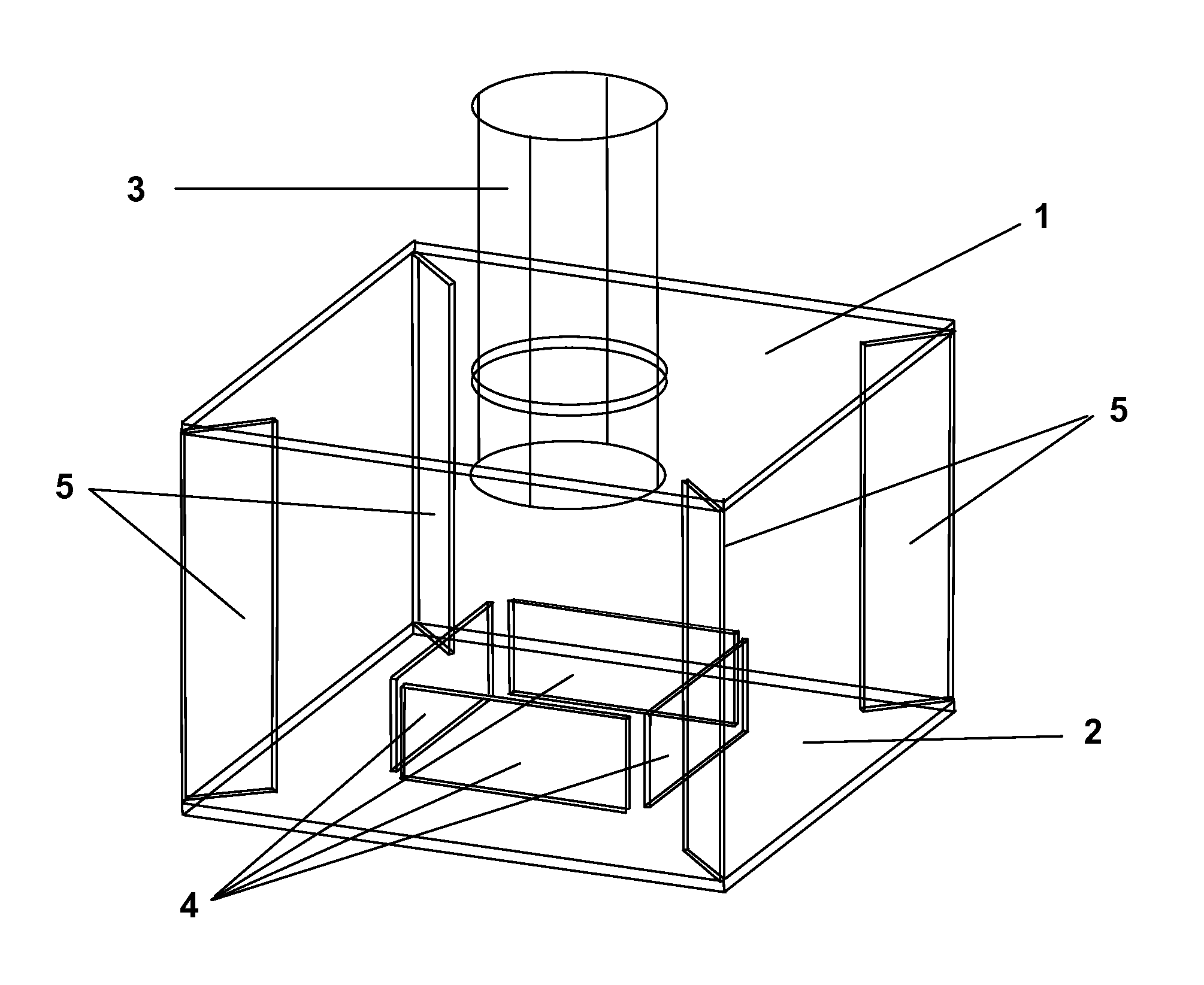
Provided is a wastewater treatment apparatus for removing nitrogen and phosphorus having an anaerobic tank, an anoxic tank, an aerobic tank and a clarifier, wherein the aerobic tank includes has a baffle installed at one side thereof to form a dissolved oxygen reducing zone for reducing the concentration of dissolved oxygen contained in internally recycled wastewater returned from a dissolved oxygen reducing zone while increasing the concentration of dissolved oxygen contained in treated effluent supplied from a part other than the dissolved oxygen reducing zone of the aerobic tank to a clarifier in a subsequent stage. Since organic matter present in wastewater is effectively used, the efficiency of removing nitrogen and phosphorus can be increased and the amounts of oxygen required throughout the treatment process and organic matter required for denitrification can be reduced. Also, synthesis of cells of microorganisms is suppressed. Therefore, the repair and maintenance costs can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ENGINEERING CO LTD
Production method of sulfurless superior saccharose
InactiveCN101323885AHigh purityPurity is higher than mixed puritySugar crystallisationSugar juice purificationRetention timeFiltration
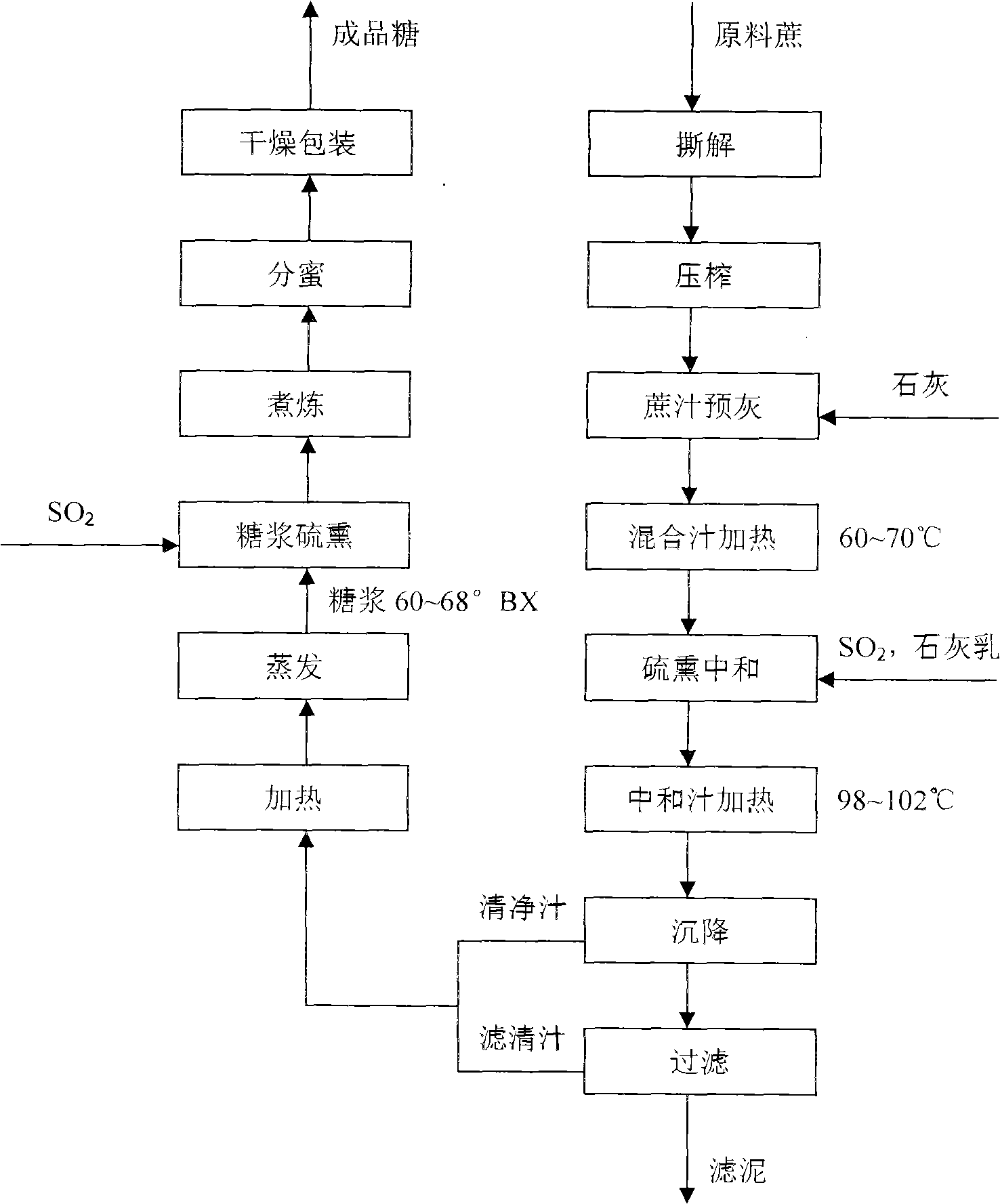
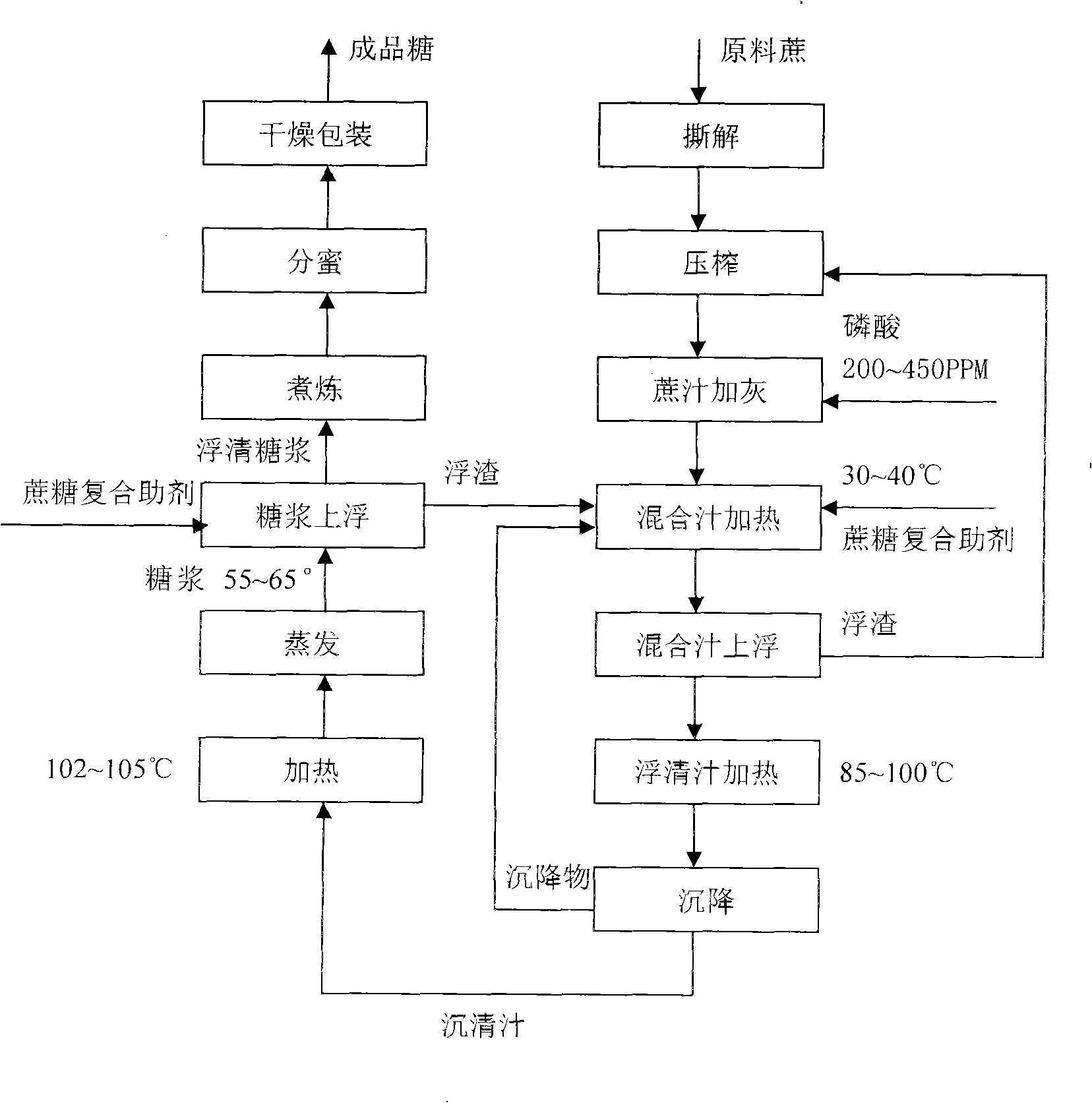
The invention relates to a production method of high-quality sugar, specifically to an improvement of a technology of sugar refinement and purification. High-quality white granulated sugar products are obtained after sugar canes are torn, pressed, cane juice is defecated, mixed juice is heated, a cane sugar complex auxiliary agent is added, the mixed juice is stirred up, floating juice is heated, sedimentated and vaporized, phosphoric acid and the cane sugar complex auxiliary agent are added, syrup is stirred up, the process of honey separation is carried out, the mixture is boiled, refined, crystallized, dried and packed. As the method of the invention adopts a low-temperature technology and a floating treatment method of adding the phosphoric acid, lime and the cane sugar auxiliary agent to lead the floating juice to reach or exceed the effect of the floating juice by original traditional technology, and utilizes a syrup floating principle and a scruff repressing method to substitute the sediment, filtration and stoving technology in the prior art, and cancels such technologies and equipment thereof as filtration, neutralization and sulfur dioxide gas system, retention time in cane juice production process is shortened, sulfur is used as a clarifier during the whole technical process, and sugar without sulfur is produced, thus improving product quality as well as reducing cost.
Owner:高晓军 +1
Methods and apparatus for separation of solids from liquids by dissolved gas floatation
InactiveUS20030173288A1Liquid separation auxillary apparatusSemi-permeable membranesPhysical chemistryLiquid gas
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for separation of solids from liquids and separation of liquids from liquids (such as oil from water) by dissolved gas floatation. A dissolved gas floatation clarifier is described as is a liquid-gas mixer, a liquid-liquid mixer, and solid-liquid chemical feeders. The methods and apparatus of the present invention are particularly suitable for supplying dissolved air and mixing of chemicals for use in separation of solids in dissolved air floatation clarifiers.
Owner:HYDROTREAT
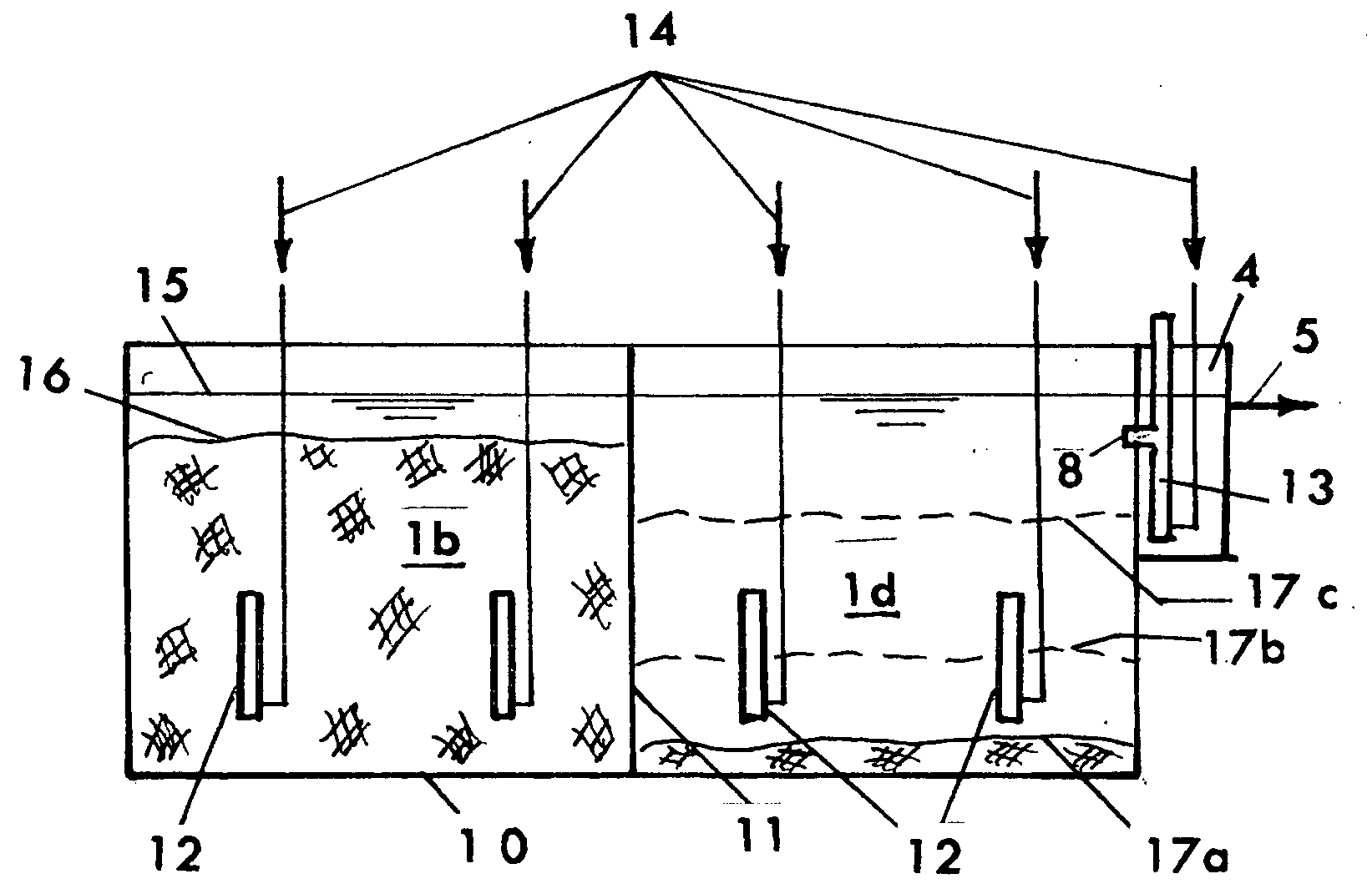
Shrimp culturing system
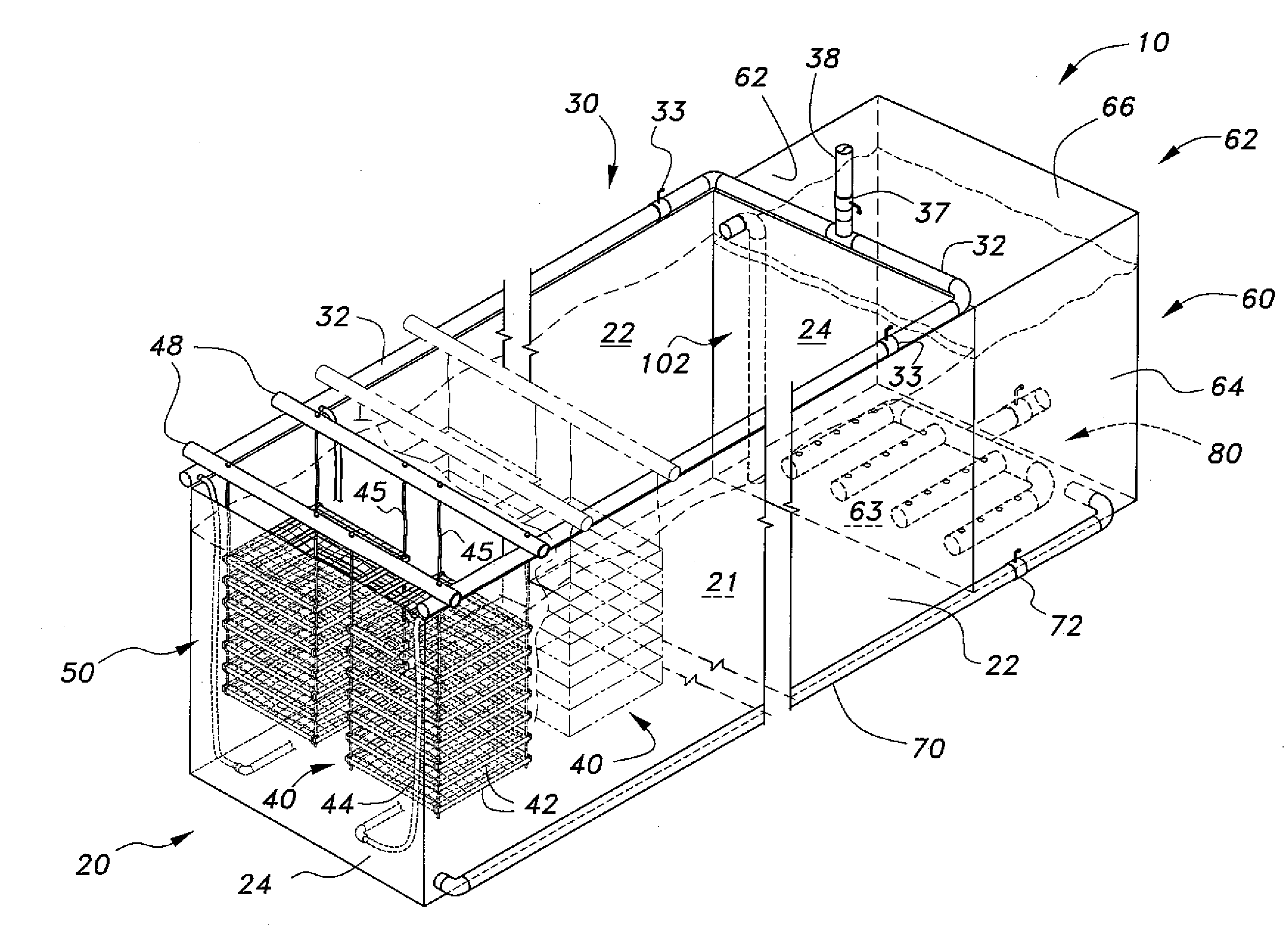
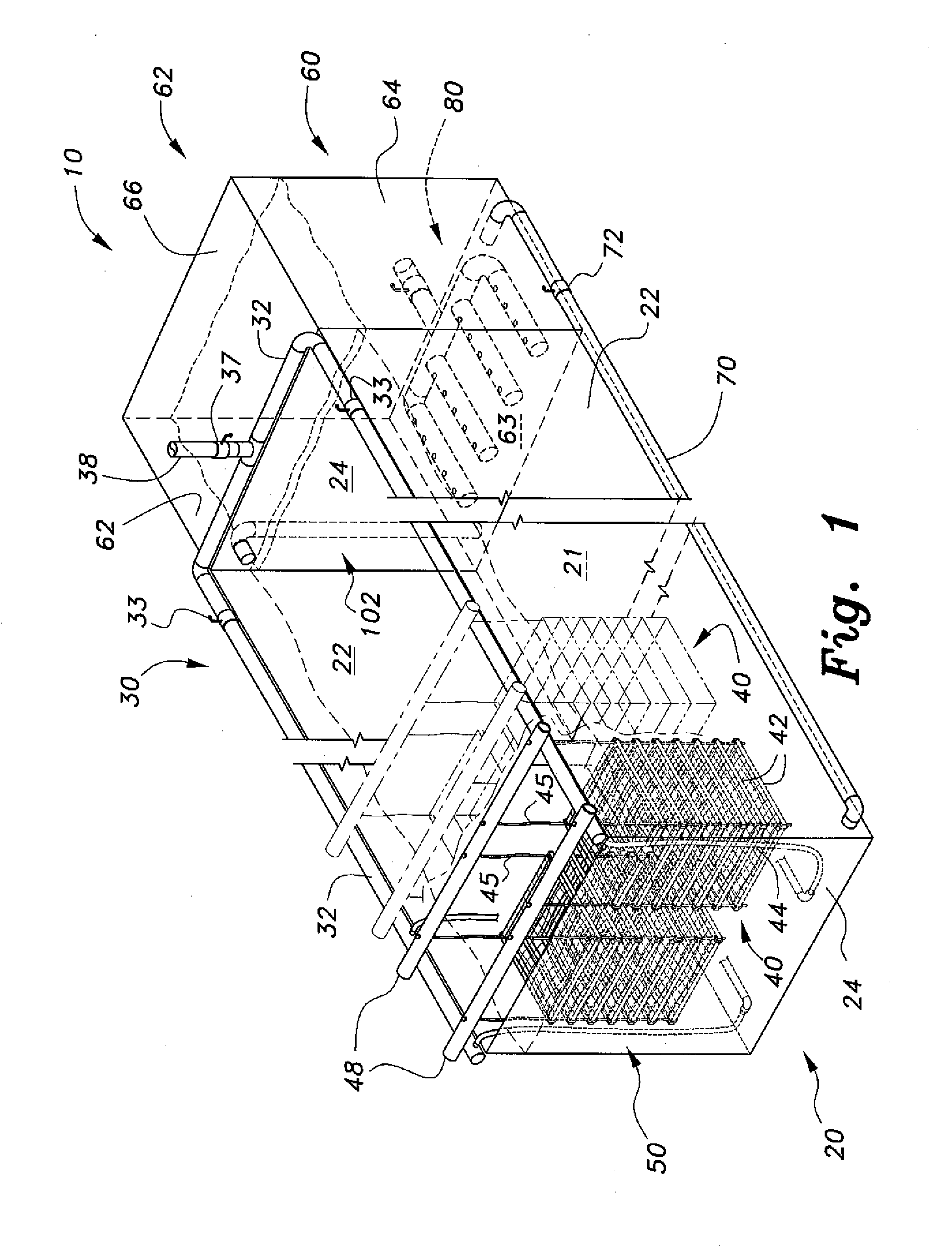
The shrimp culturing system includes a culturing tank and a clarifier tank. A plurality of shrimp cubes are suspended in the culture tank by set pairs of support bars. Each shrimp cube includes a plurality of stacked frames set at predetermined intervals. Each frame supports a mesh therein providing living space for the shrimp, and each stack is interconnected by ropes, which connect to the support bars to be suspended thereby. The shrimp cubes provide maximal space for culturing shrimp. The waste water from the culture tank cycles into the clarifier tank, which nurtures a biofloc to consume the waste and assimilate nitrogen, thereby producing their own waste that can be consumed by the shrimp. Excess solid waste drains via a solids removal manifold, and clarified water is airlifted back into the culture tank. A post-larval tank can be stacked onto the clarifier tank to introduce new batches of shrimp.
Owner:SHERIFF RICHARD L
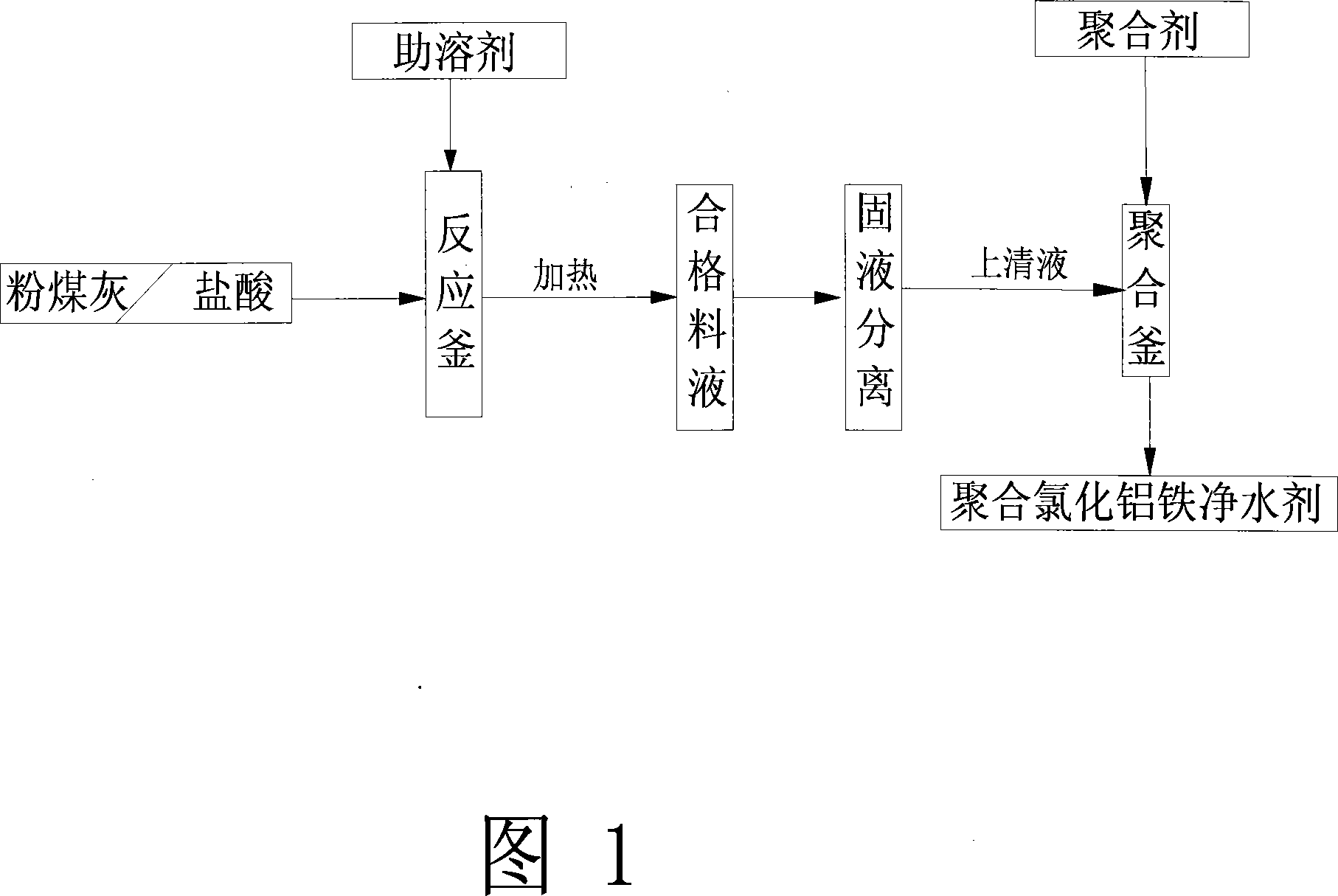
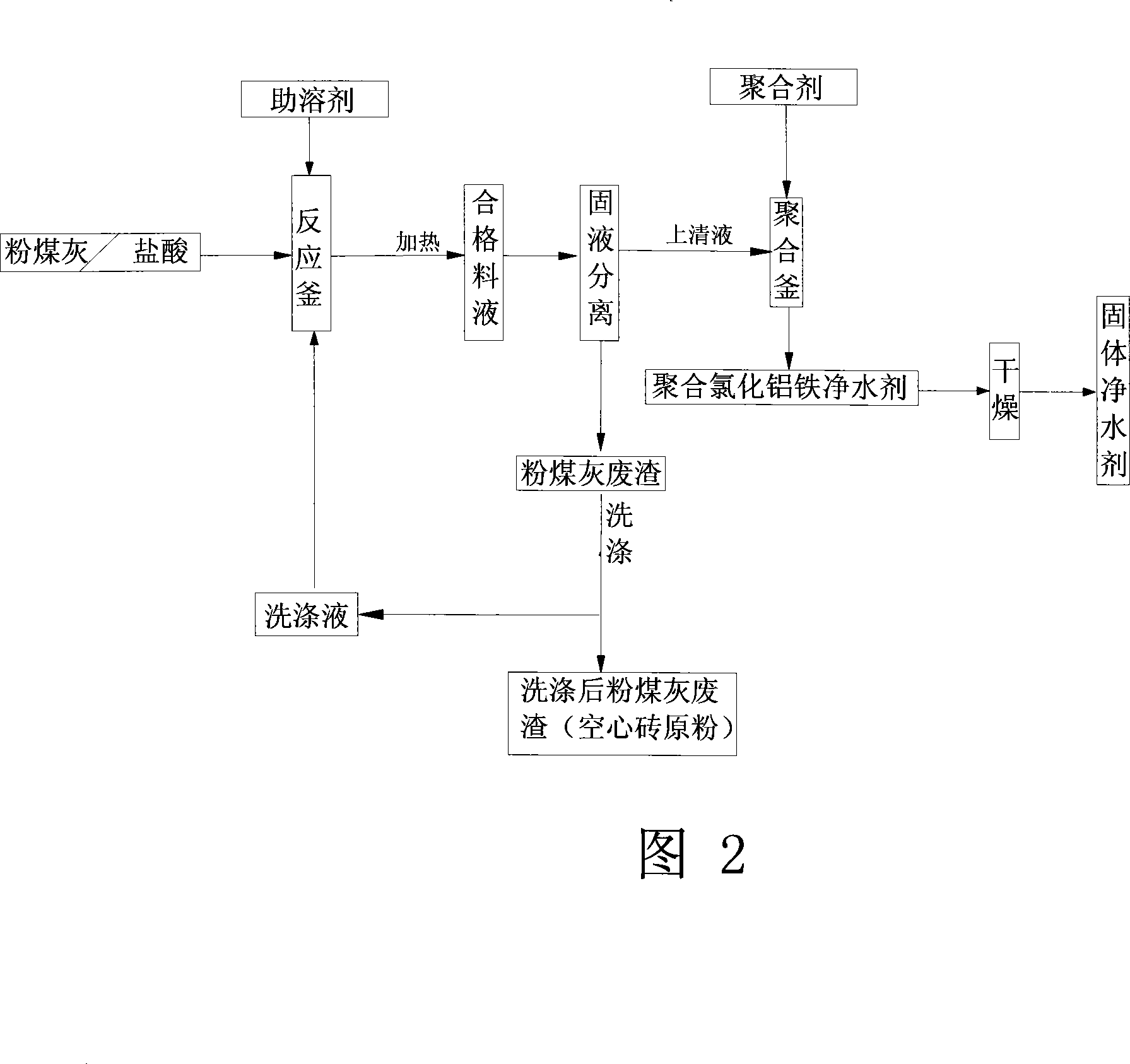
Method for industrial production of polymeric aluminum ferric chloride water purification agent with coal ash
InactiveCN101172684AReduce use costHigh dissolution rateWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationDissolutionCoal
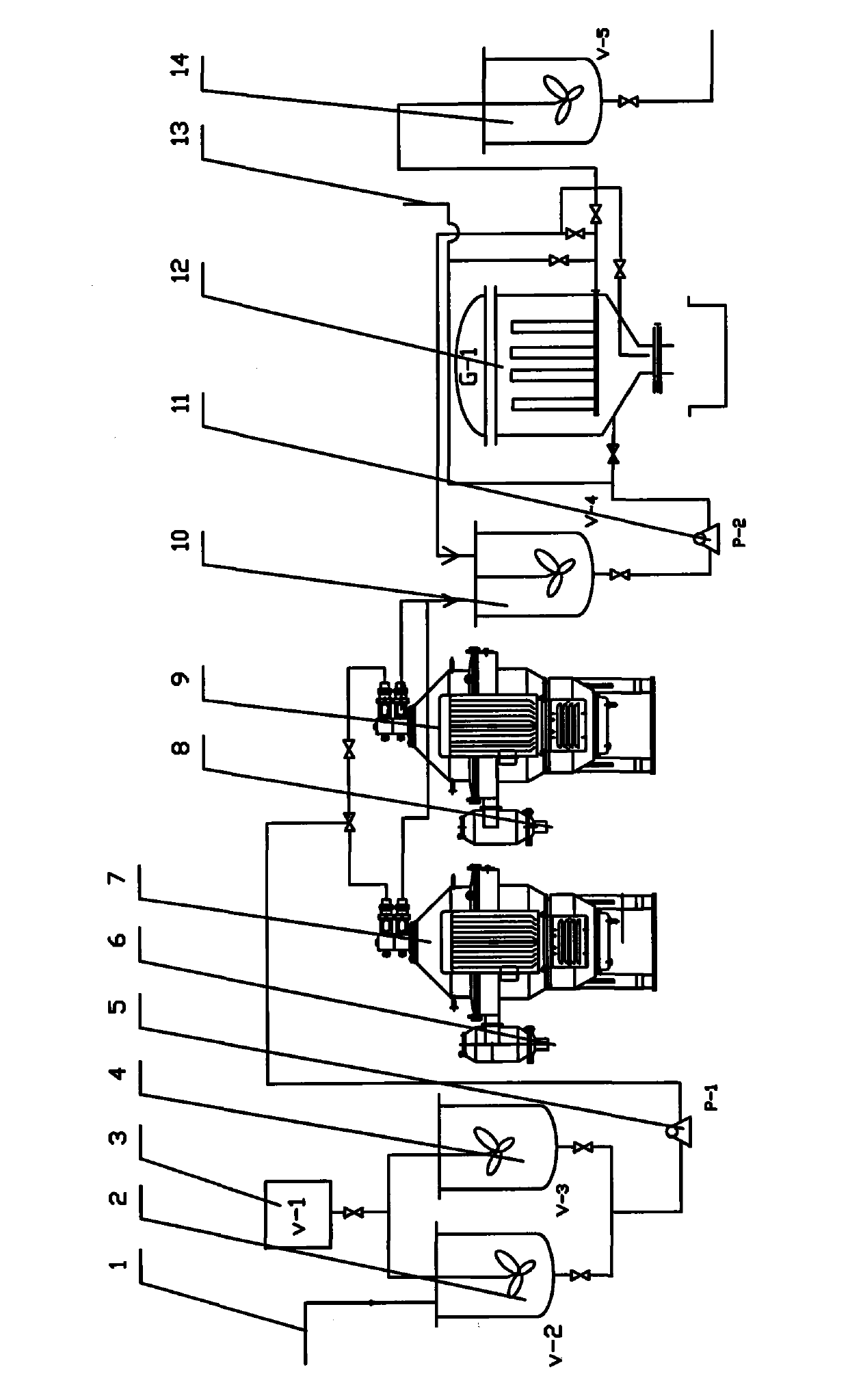
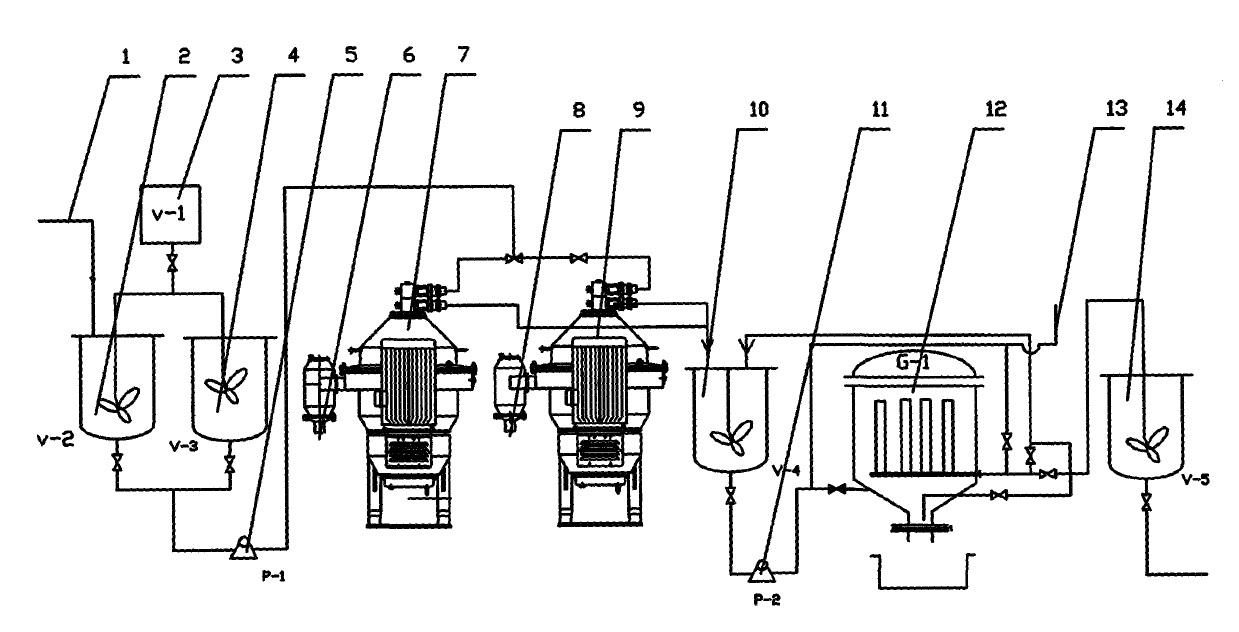
The invention discloses a method for industrially producing polyaluminum ferric chloride water purifying agent by utilizing fly ash. , put the obtained qualified feed liquid into the clarifier for solid-liquid separation, the separated supernatant liquid is injected into the polymerization kettle, add the polymerization agent, fully stir, and obtain the polyaluminum ferric chloride liquid water purifier through the polymerization reaction. The production process flow is short, the operation is simple, the production cost is low, the economic performance is good, the use cost of the raw material is reduced, the reaction time is shortened, and the reaction energy consumption is reduced. The aluminum dissolution rate in fly ash is high, the raw material cost is low, and industrial production is realized. Adding a cosolvent in the reaction process promotes the cleavage of the silicon-aluminum bond, increases the dissolution rate of aluminum, shortens the reaction time, reduces the consumption of hydrochloric acid, reduces the production cost, and improves the economic benefit of the product. The industrialization of using fly ash to produce polyaluminum ferric chloride has been realized.
Owner:王贵明 +1
System and method for enhancing an activated sludge process
ActiveUS7695623B2Increase settlement rateSpeed up the processTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsMixed liquor suspended solidsInjection port
A system for enhancing an activated sludge process that includes at least one aeration tank subsystem for receiving a flow a wastewater and for introducing dissolved oxygen to a population of microorganisms to promote growth of biological flocs in a mixed liquor defined by a concentration of mixed liquor suspended solids. A weighting agent impregnation subsystem includes an impregnation tank for mixing the mixed liquor, virgin weighting agent, and recycled weighting agent to impregnate the weighting agent into biological flocs suspended in the mixed liquor to form weighted biological flocs. A flocculant injection port located downstream from at least one aeration tank for introducing a flocculant to the mixed liquor for enhancing settling and thickening of the weighted biological flocs and for providing agglomeration of non-impregnated biological flocs and / or partially impregnated biological flocs with weighted biological flocs. At least one clarifier separates and collects the weighted biological flocs from the mixed liquor to provide a secondary effluent and a settled sludge. A return activated sludge subsystem recycles the majority of the settled sludge to the at least one aeration tank. A weighting agent recovery subsystem removes and shears the remaining settled sludge and recovers the weighting agent therefrom and reintroduces the weighting agent to the at least one aeration tank. A wasting subsystem wastes the remaining sludge of the weight agent recovery subsystem to control the population of the microorganisms in the mixed liquor.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
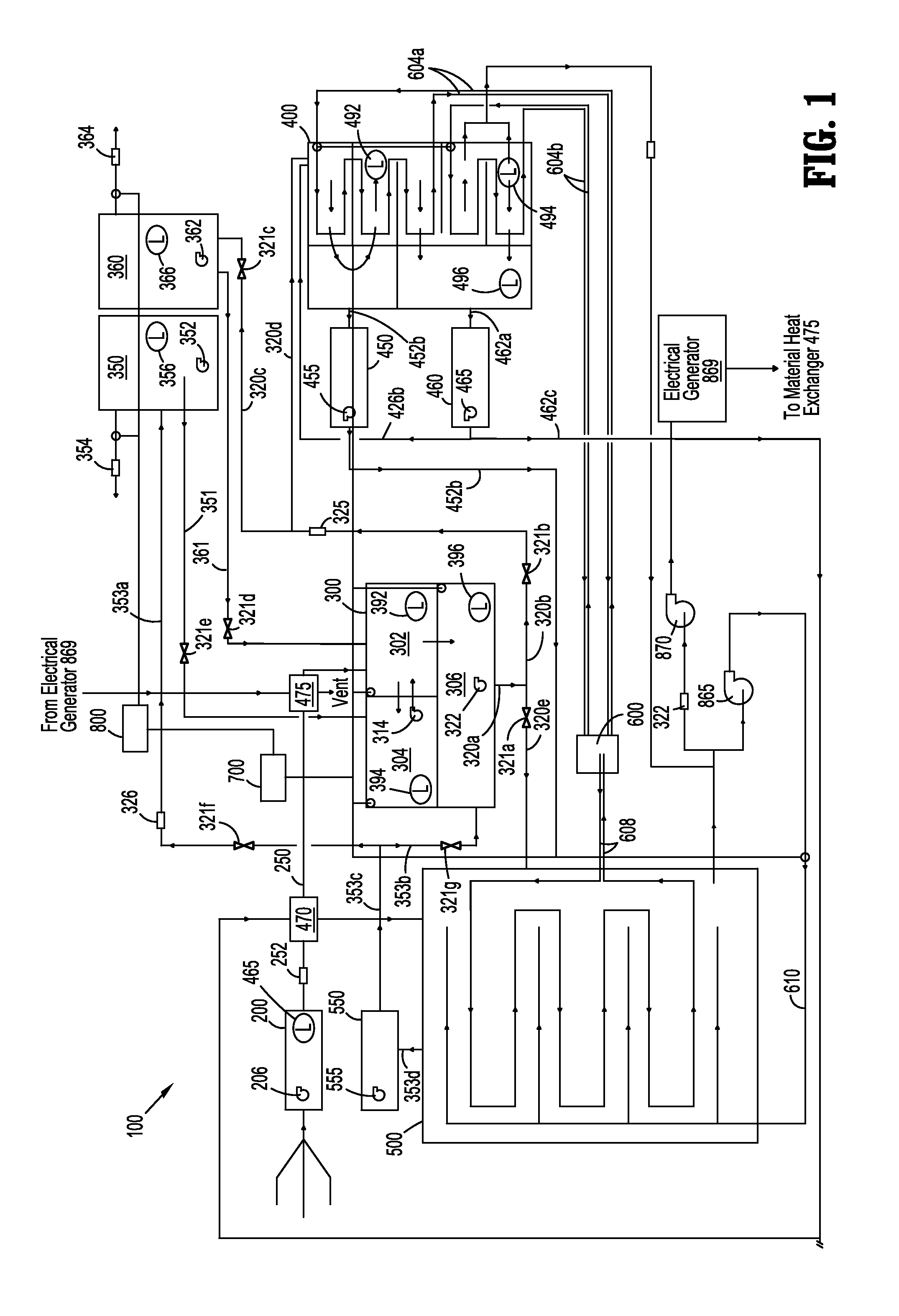
Oil field water recycling system and method
InactiveUS20120168364A1Reduce water hardnessReduce chain lengthWaste water treatment from quariesOther chemical processesFlocculationChemical treatment
A system is used for treating contaminated water, that may include some amount of polyacrylamides, emulsified hydrocarbons, and sequestered divalent cations. The system includes at least one pre-treatment tank for initial processing of the contaminated water. Thereafter, the water may be fed to at least one chemical treatment tank fluidically connected to the pre-treatment tank. This treatment tank includes a chemical injection system connected to an interior thereof for introducing a variety break operations, coagulant addition operations, and / or flocculent addition operations. At least one clarifier is fluidically connected to the at least one chemical treatment tank, and includes a mechanical contaminant removal system. A filter skid is fluidically connected to the at least one clarifier, and includes a plurality of filter cartridges.
Owner:EVANS THOMAS S
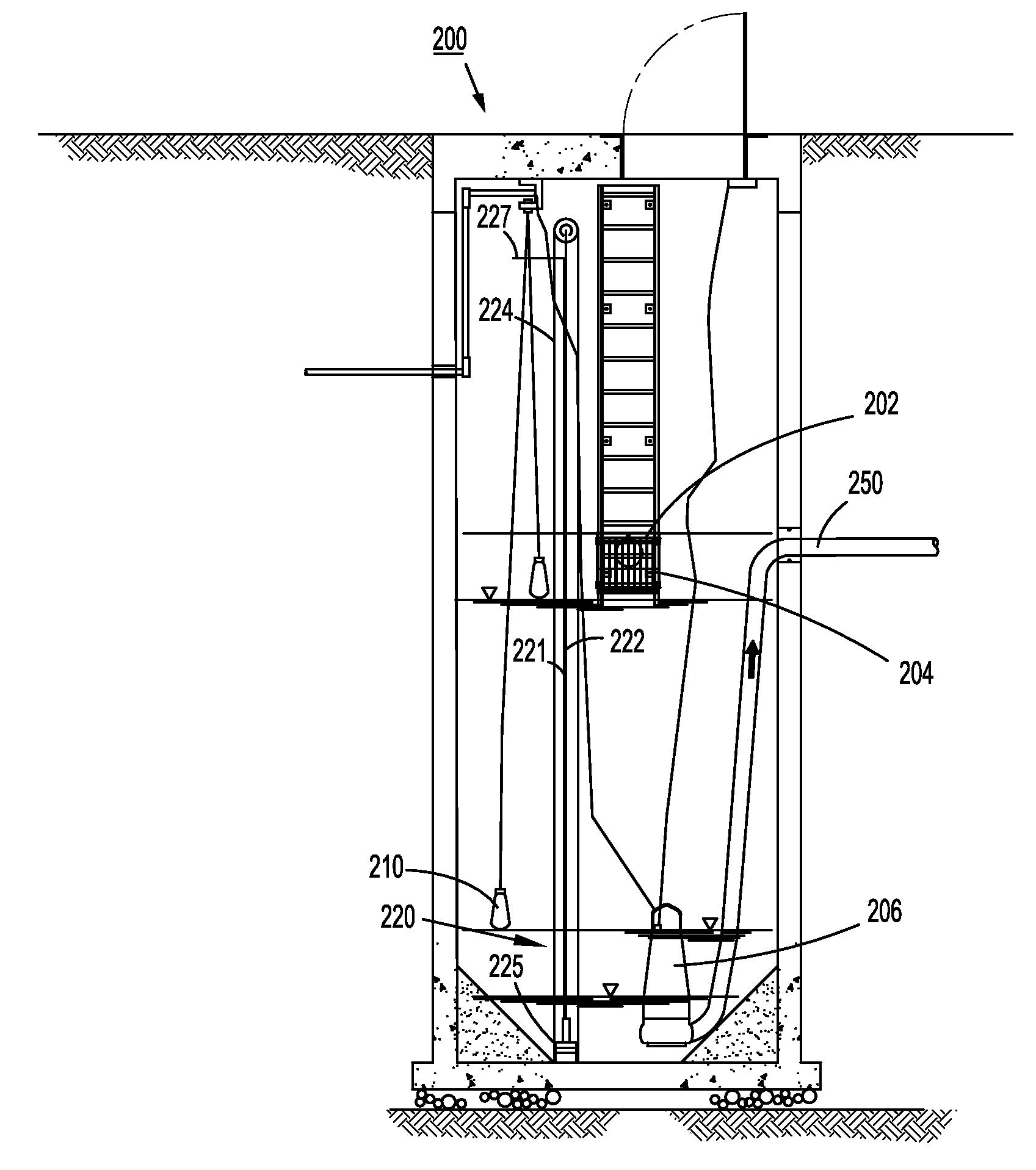
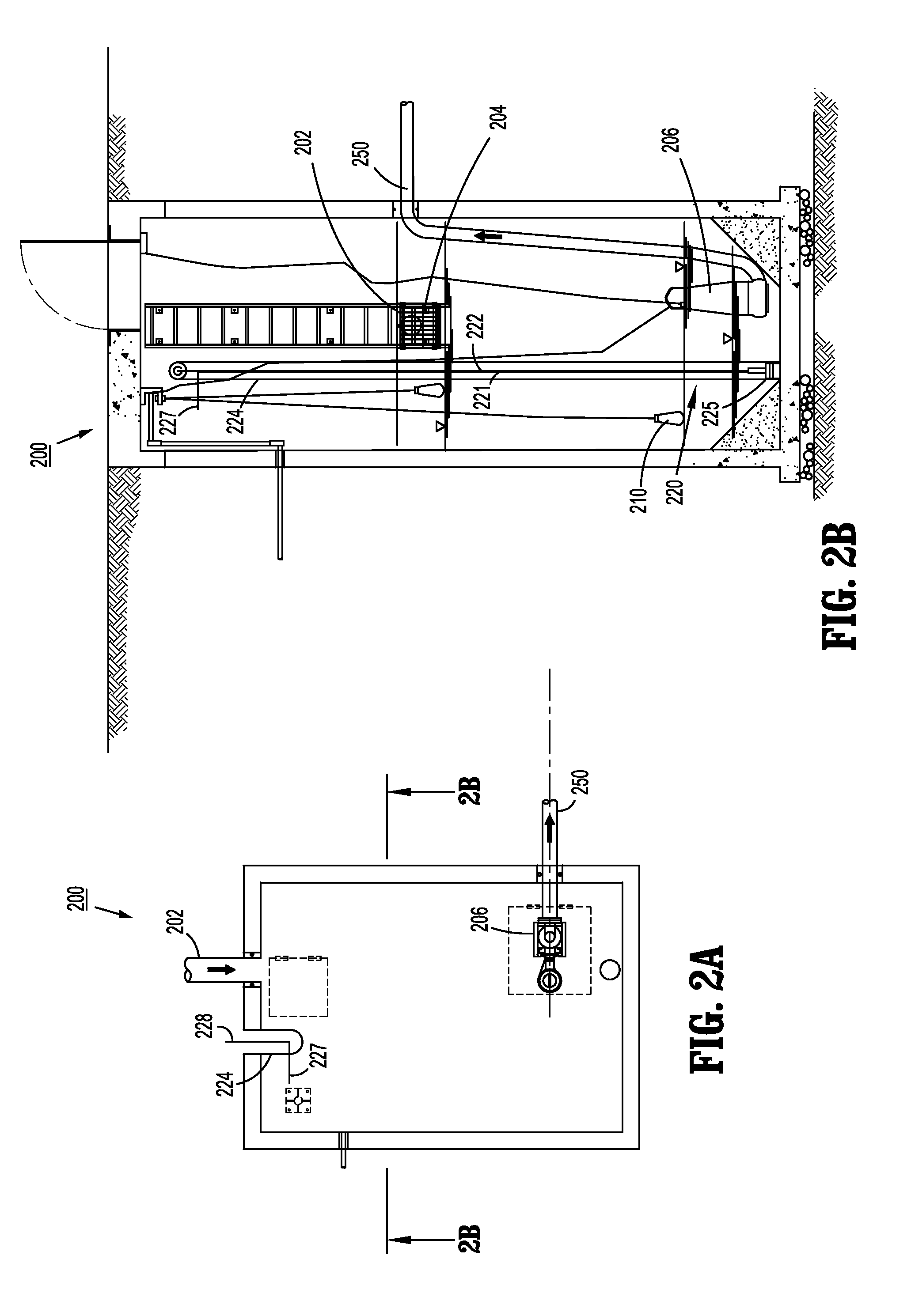
Systems and methods for anaerobic digestion of biomaterials
ActiveUS20120125840A1Biological treatment regulationWaste water treatment from animal husbandryEngineeringBiological materials
Systems and methods for performing anaerobic digestion of biomaterials using a clarifier, a batch reactor, and / or a digester are disclosed. The clarifier performs pretreatment processing of biomaterial to improve anaerobic digestion. The batch reactor and / or the digester are coupled to the clarifier and are configured to digest the processed biomaterial. A control system for an anaerobic digestion process includes a flow control system, a temperature control system, and a totalization system. The flow control system controls the flow of biomaterial and the delivery of chemical agents to the biomaterial based on conductivity, temperature, pressure, and / or composition of the biomaterial. The temperature control system includes a heat source and heat exchangers that control the temperature of the biomaterial. The totalization system senses the volume of biomaterial in at least one stage of an anaerobic digestion process and a controller controls the flow control system based upon the sensed volume of biomaterial.
Owner:EPCOT CRENSHAW CORP
Process for producing starch sugar
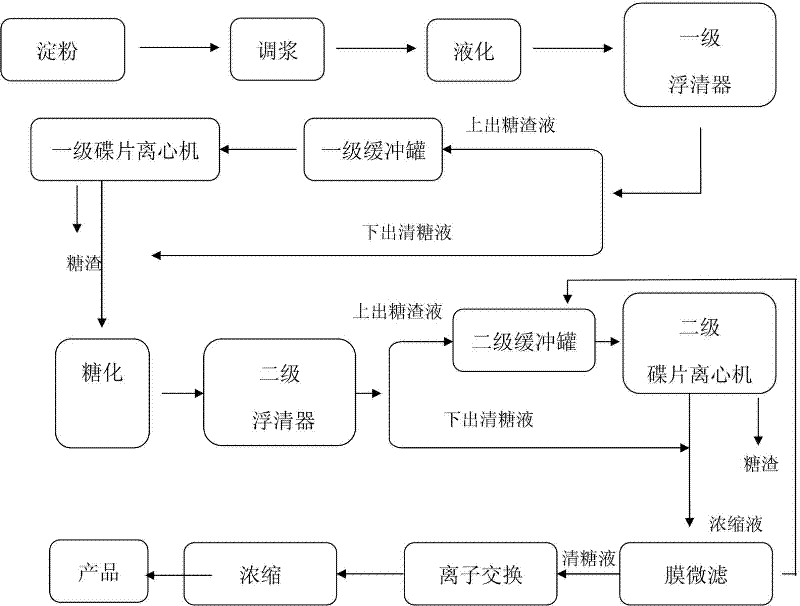
ActiveCN102337316AQuality improvementImprove function and effectAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsActivated carbonChaptalization
The invention discloses a process for producing starch sugar. The process comprises the following steps of: pulp-conditioning edible starch; liquefying; passing liquefied starch through a primary floating clarifier, guiding an upper floating sugar dreg liquid into a primary buffer tank, and then entering a primary disc-type centrifuge to be centrifugated and separated so as to extract sugar dregs; combining a clear sugar liquid flowing out of the primary disc-type centrifuge and a clear sugar liquid flowing out of the primary floating clarifier and flowing into a saccharifying tank to be saccharified into a saccharified liquid; passing the saccharified liquid through a secondary floating clarifier, guiding an upper floating sugar dreg liquid into a secondary buffer tank, and then enteringa secondary disc-type centrifuge to be separated so as to extract sugar dregs; combining a clear sugar liquid flowing out of the secondary disc-type centrifuge and a clear sugar liquid flowing out ofthe secondary floating scum clearing device and filtering by passing through a membrane micro-filtration system; and flowing a micro-filtered concentrated liquid containing dregs back to the secondary buffer tank, entering a micro-filtered clear sugar liquid into an ion exchange system to be decolorized and desalted, and then finally concentrating into a product. According to the process for producing the starch sugar disclosed by the invention, filter aids and activated carbon are not required in the clarification and the filtration processes, and high-purity sugar liquid can be obtained through the efficient operation of solid-liquid separation equipment; and meanwhile, sugar dregs without the filter aids and the activated carbon are extracted and can be used as a feedstuff raw materialfor animals, thereby changing waste into valuable, and no discharge of filtered solid wastes during the whole process exists.
Owner:双桥(厦门)有限公司
High recovery sulfate removal process
InactiveUS20110163032A1Improve processingWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment parameter controlSulfateWaste stream
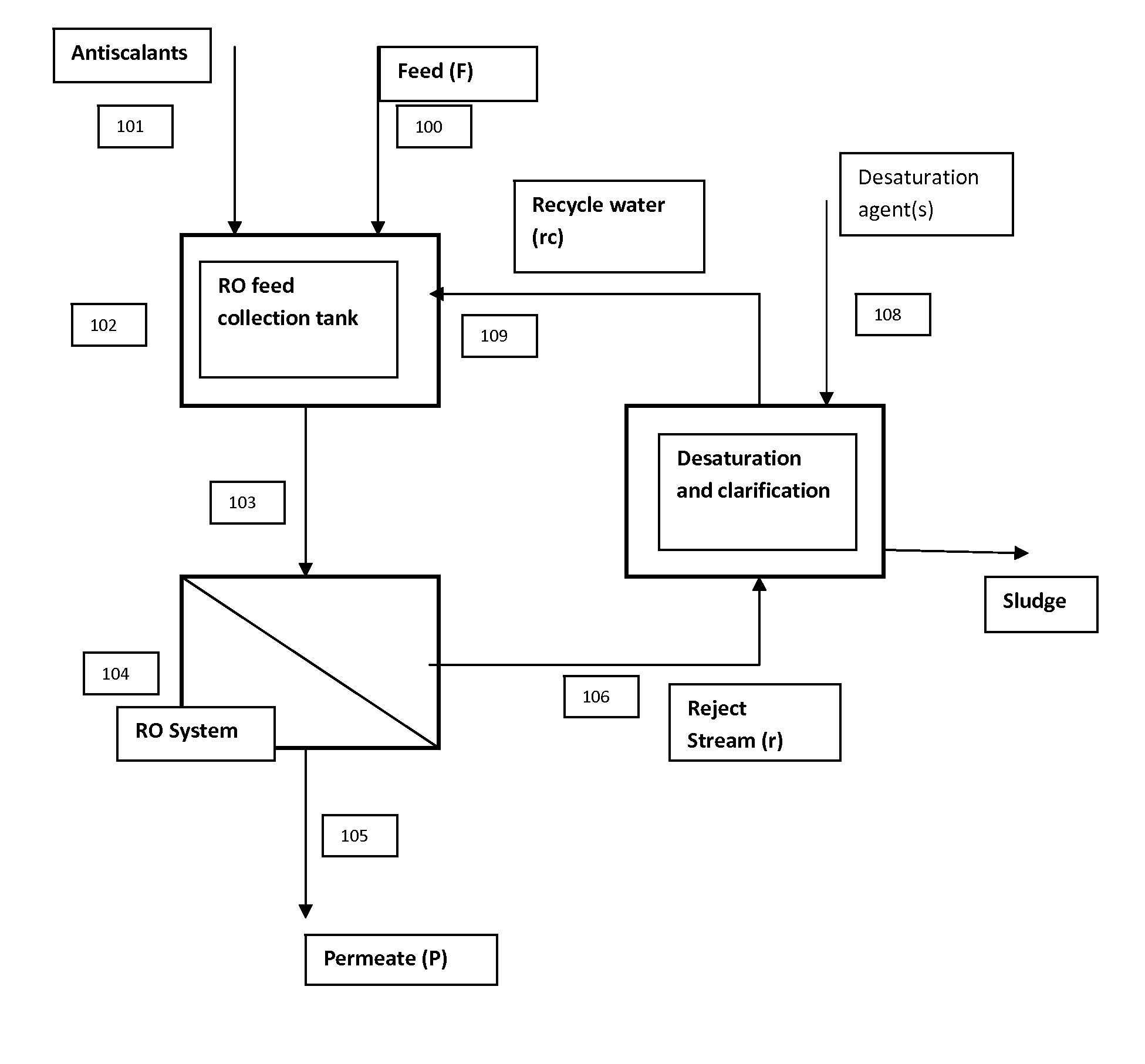
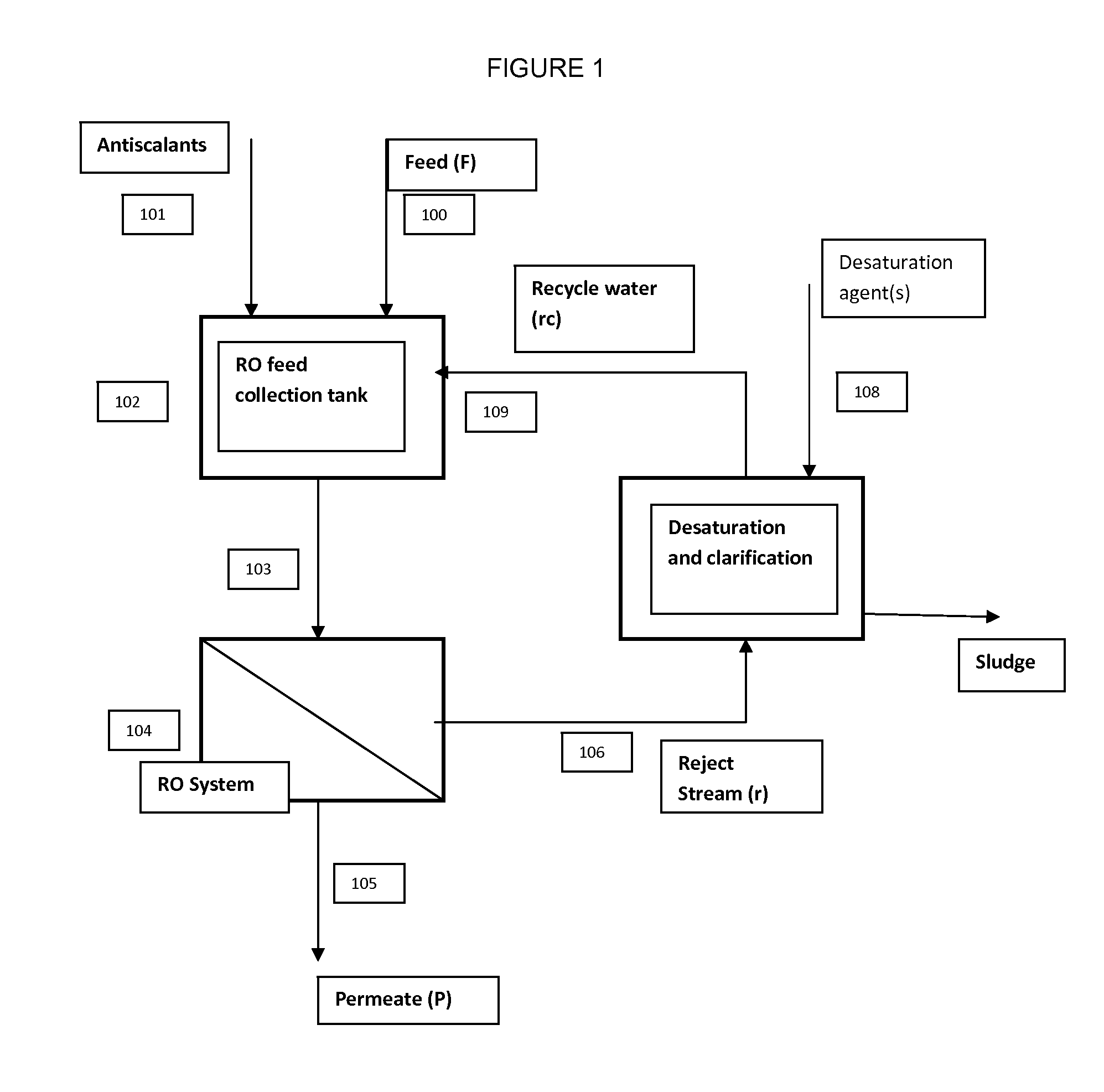
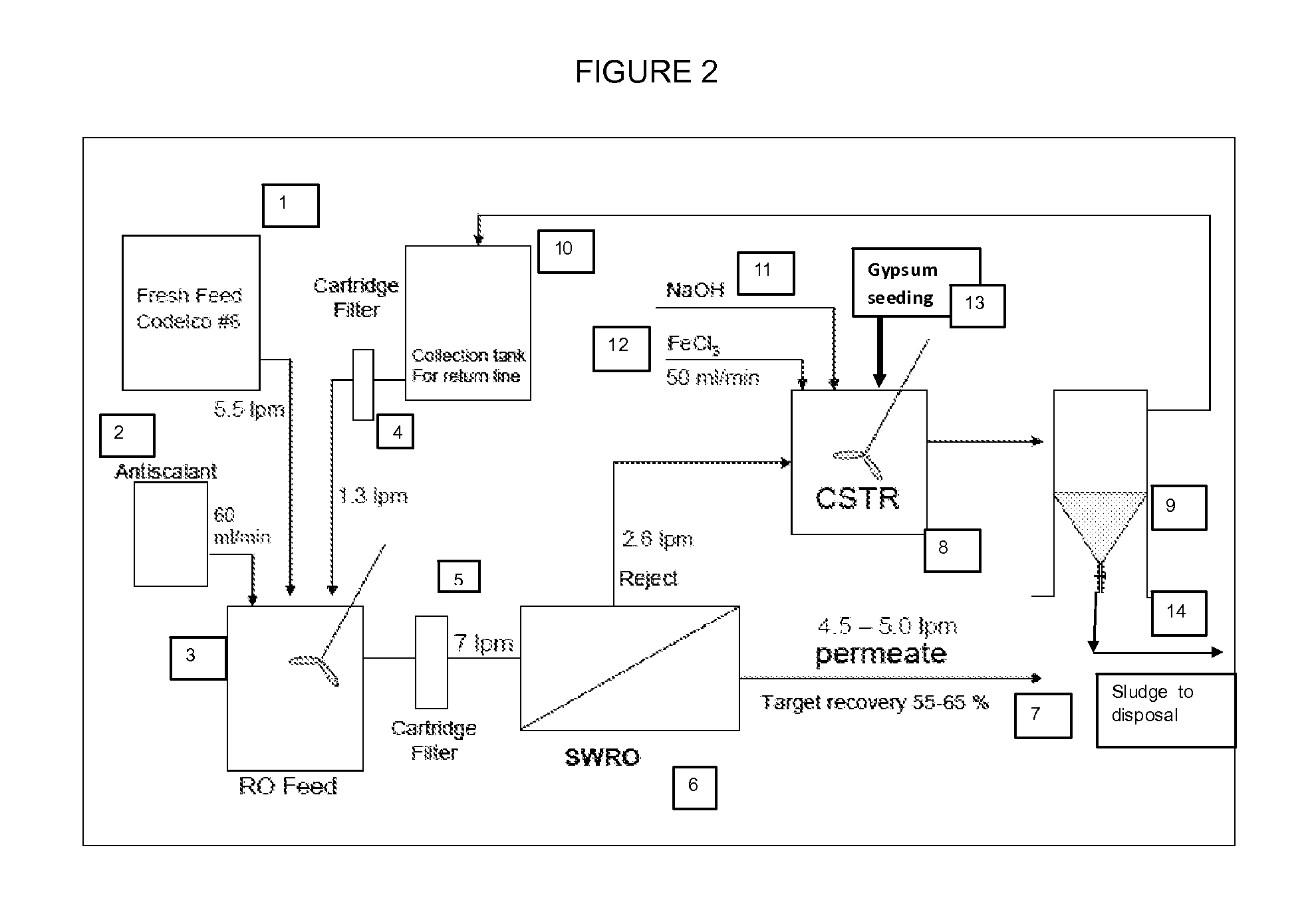
A high recovery sulfate removal process comprises treating a feed water stream conditioned with antiscalant from a source with a reverse osmosis membrane system to produce a purified water permeate stream and a reject stream containing the retained or rejected ions and organic matter. The reject stream is further treated to remove dissolved and suspended species. The reject stream flows to a desaturation / clarification process. A preferred process includes a constant stirred tank reactor (CSTR) where co-precipitation agent is added followed by a clarifier. Water recycled from the clarifier overflow is blended with feed water stream. The removed solids are collected as sludge or a slurry and disposed of in a manner consistent with applicable regulations.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH PTE LTD
Desulfurization waste water zero discharge processing system and processing method
InactiveCN106365371AQuality assuranceSave on medicine costsWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsSludgeClarifier
The invention discloses a desulfurization waste water zero discharge processing system and a processing method. The desulfurization waste water zero discharge processing system comprises a regulation sedimentation basin, triple connecting tanks, a defecator and a nanofilter which are connected in sequence, wherein the concentrated water outlet end of the nanofilter is connected with a mistorizer which sprays the concentrated water into a chimney flue; the triple connecting tanks include a neutralization tank, a reaction tank and a flocculation tank which are connected in sequence, wherein the neutralization tank is communicated with the water outlet of the regulation sedimentation basin, and is used for adjusting the pH value of desulfurization waste water, so that bicarbonate ions in the desulfurization waste water are removed; the reaction tank provides a reaction chamber for removing calcium ions in the desulfurization waste water; the flocculation tank is connected with the defecator. The desulfurization waste water zero discharge processing system and the processing method have the advantages of saving the cost of the agent for removing magnesium ions in the desulfurization waste water, reducing the quantity of sludge, lowering the operating cost, using no lime milk and improving the site working conditions. The sodium chloride salt in the waste water is purified and then crystallized, thus the recycle of the sodium chloride salt in the desulfurization waste water is achieved, the solid waste disposal cost is reduced, and certain economic benefits are produced.
Owner:SHANDONG SHANDA WIT ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING CO LTD
Enhanced High Water Recovery Membrane Process
InactiveUS20110094965A1Speed up the processSolution to short lifeLiquid separation auxillary apparatusScale removal and water softeningIon exchangeInorganic compound
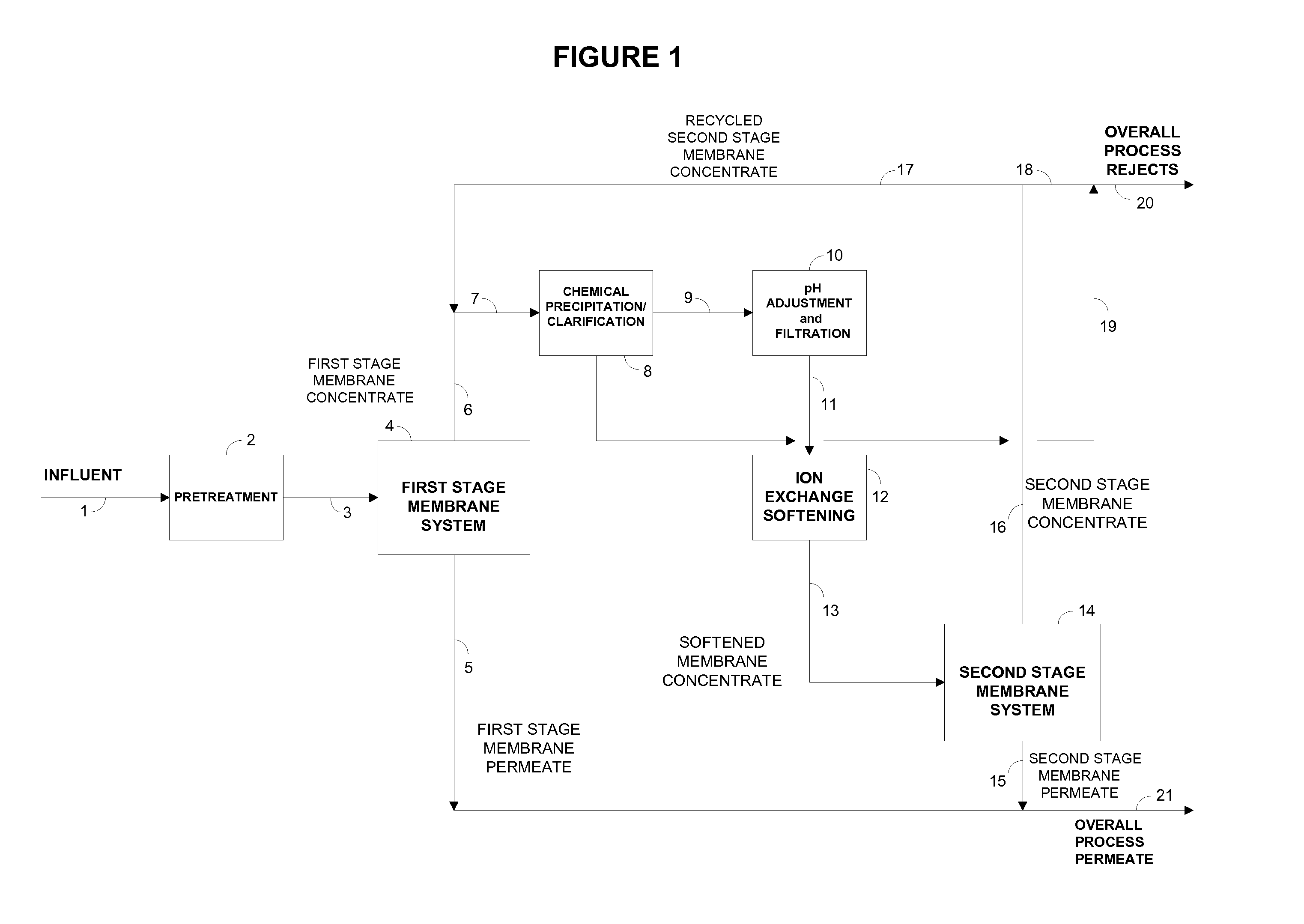
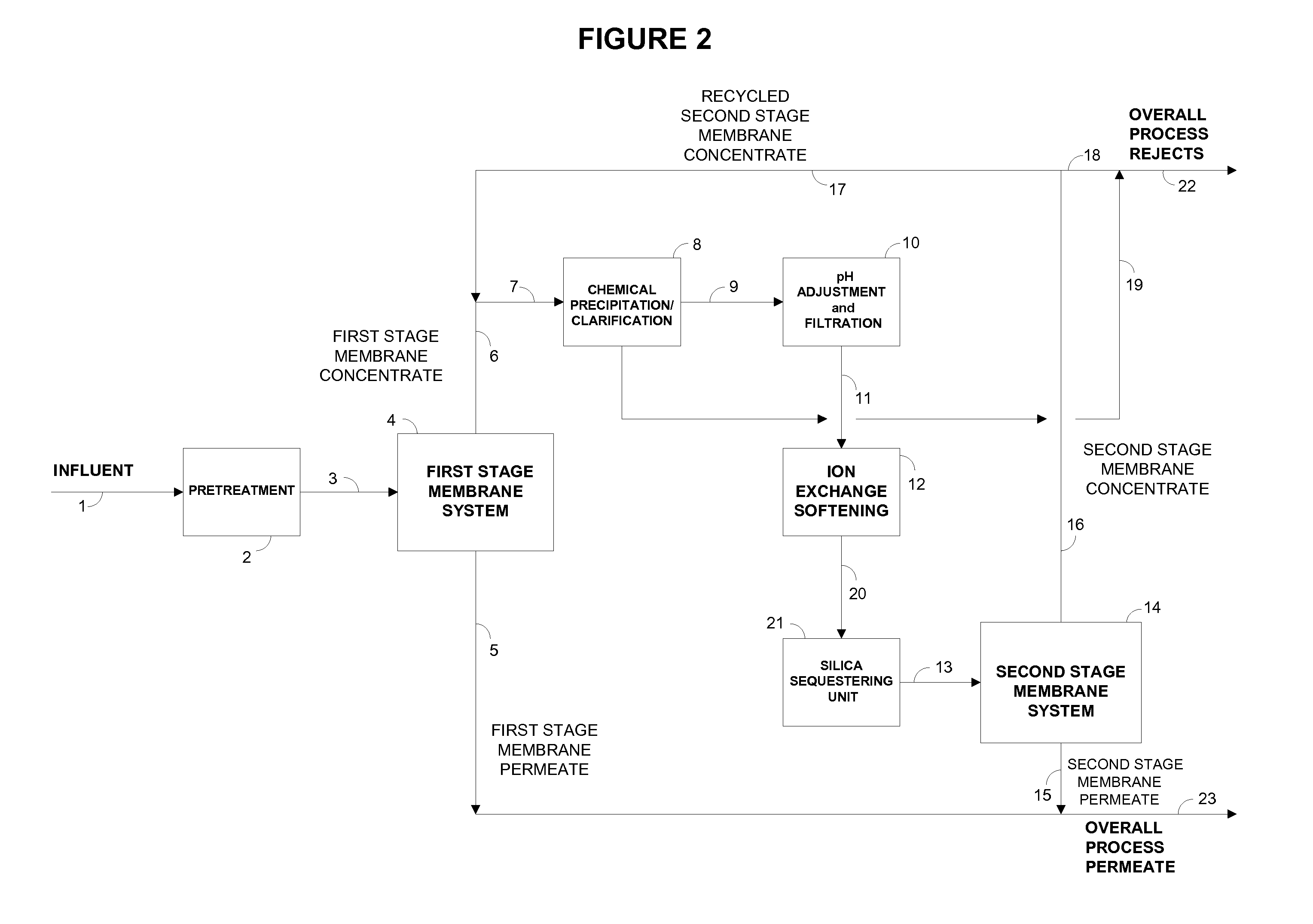
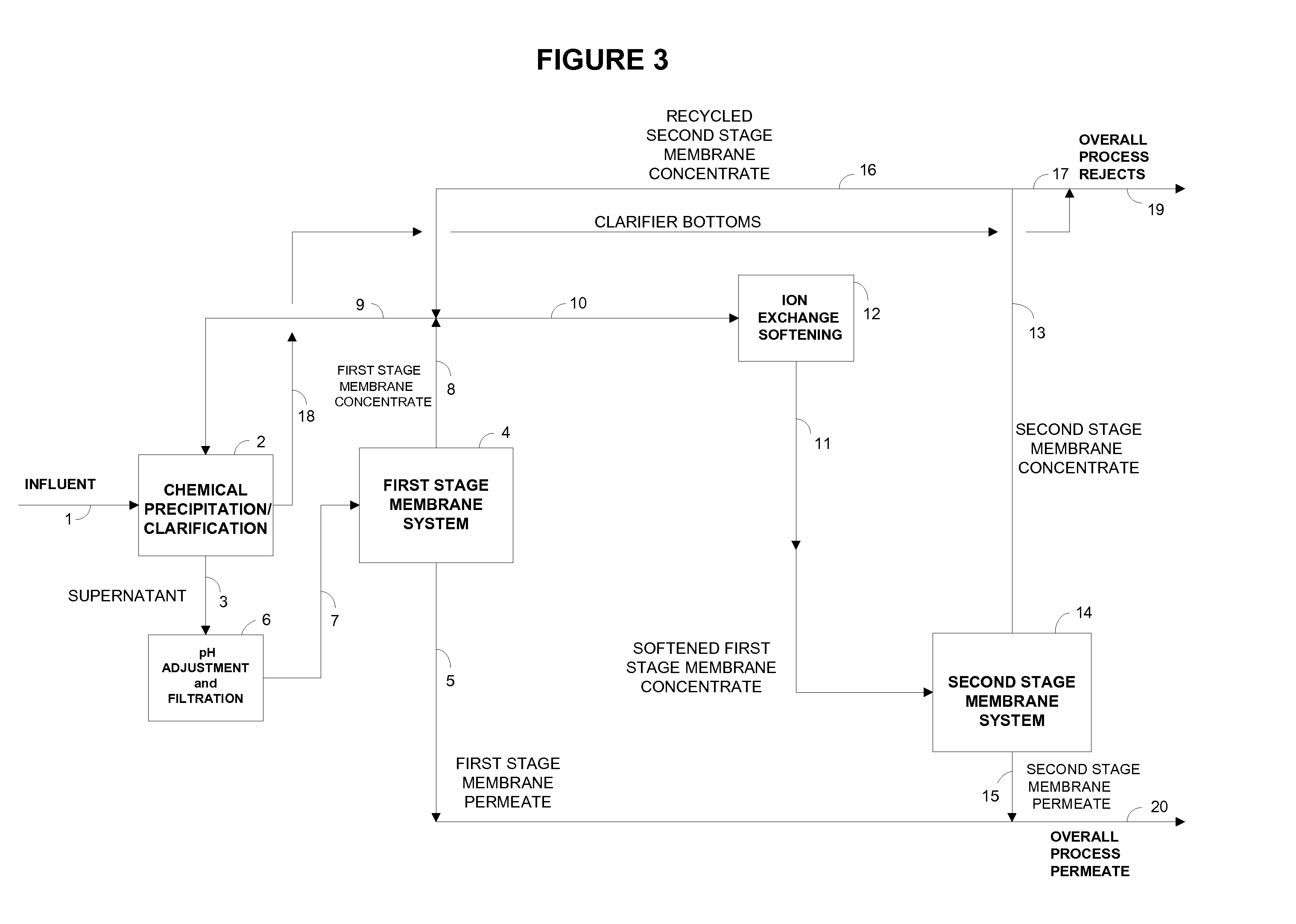
Disclosed is an economical process for the purification of water containing soluble and sparingly soluble inorganic compounds using single-stage or two-stage membrane processes that integrate membrane water purification with chemical precipitation softening and residual hardness and silica removal from the membrane concentrates using ion exchange resins and silica sequestering media, respectively. The purified water recovery is not adversely affected by design and / or operational deficiencies in the chemical precipitation softening system that may result in higher residual hardness and silica in the supernatant from the clarifier.
Owner:AL SAMADI RIAD A
New comprehensive impurity removing process and system for reconstituted tobacco raw material extract
The invention discloses a new comprehensive impurity removing process and a comprehensive impurity removing system for reconstituted tobacco raw material extract, and belongs to the technical field of production of reconstituted tobacco. The new comprehensive impurity removing process comprises the following steps of: flocculating stem and tail extract by using an absorption clarifier special forimpurity removal of the reconstituted tobacco raw material extract; performing solid-liquid separation on settled stem and tail extract by using a disk type separator; adding a mixed filter aid; and filtering by using a plate type sealed filter and feeding filtrate into a refining liquid tank. The process and the system have the advantages of effectively improving residue removing rate and mechanical settling efficiency. The separation process is easy to control, high repeatability is guaranteed, and the process and the system are suitable for industrial production conditions. A product has nice aroma, and miscellaneous gases and aftertaste are improved.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND +1
Methods and apparatus for treating wastewater employing a high rate clarifier and a membrane
InactiveUS20060169636A1Reduce and overcomeMembranesTreatment using aerobic processesMembrane methodMixed liquor suspended solids
Methods and apparatus for treating wastewater are described, one method embodiment including the steps of flowing a mixed liquor suspended solids to a high rate clarification stage, forming a clarifier effluent, a first waste activated sludge stream, and a return waste activated sludge stream. The high rate clarifier effluent stream then flows to a membrane stage that includes a membrane media, producing a membrane reject (retentate) stream and a treated effluent (permeate) stream. Optionally, the methods include routing a screened raw wastewater to an anaerobic and / or aerated anoxic stage and introducing a gas comprising oxygen to the wastewater during the aerated anoxic stage, and optionally allowing the product of this stage to flow to an aeration stage prior to the high rate clarification stage.
Owner:ALFA LAVAL ASHBROOK SIMON HARTELY INC
Pharmaceutical wastewater treatment process
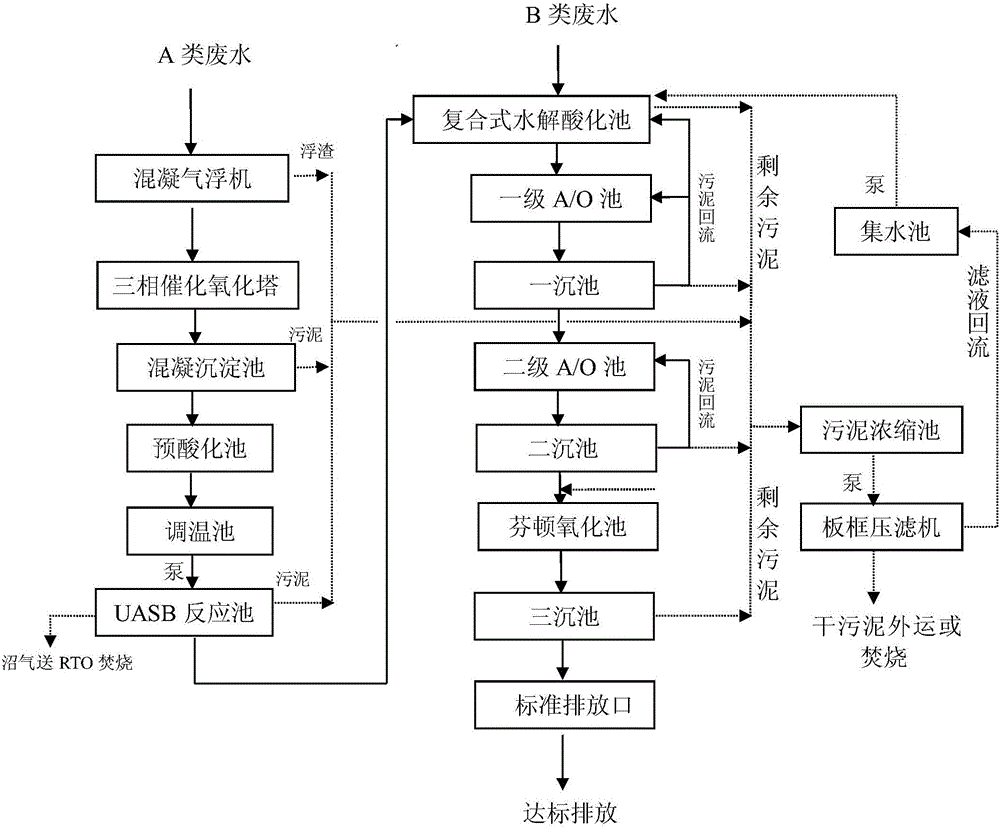
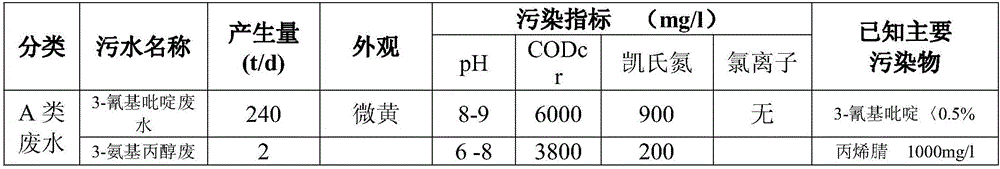
ActiveCN106007221AHigh activityHigh removal rateSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater treatment parameter controlCatalytic oxidationHydrolysis
The invention relates to the technical field of wastewater treatment, and discloses a pharmaceutical wastewater treatment process which comprises steps: preforming wastewater pre-treatment and comprehensive treatment, pumping wastewater into a coagulation gas floatation clarifier, adding polyaluminum chloride and polyacrylamide in a water input pipeline through a coagulation medicine adding system, then enabling mixed wastewater to enter a three-phase catalytic oxidation tower, a coagulative precipitation tank, a pre-acidification pool, a thermoregulation pool, a UASB reaction pool and a combined type hydrolysis acidification pool sequentially, subjecting the mixed wastewater to hydrolysis acidification, enabling the wastewater to enter a primary A / O pool, a primary precipitation pool, a secondary A / O pool, a secondary precipitation pool, a Fenton oxidation pool and a tertiary precipitation pool sequentially, and discharging standard outlet water from a standard discharging opening. The process has the advantages of stable running effect, high ammonium-nitrogen removal rate, and low running cost, thereby being suitable for treatment of wastewater, which is refractory to degrade, in the pharmaceutical industry.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUANYAO ENVIRONMENTAL CONSTR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com