Process for producing starch sugar
A production process and technology for starch sugar, applied in the field of starch sugar production technology, can solve the problems of unfriendly environment, poor production environment, increase the color of saccharification liquid and difficulty in refining, etc., and achieve improved purity, low operating cost, and removal of macromolecules. material effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
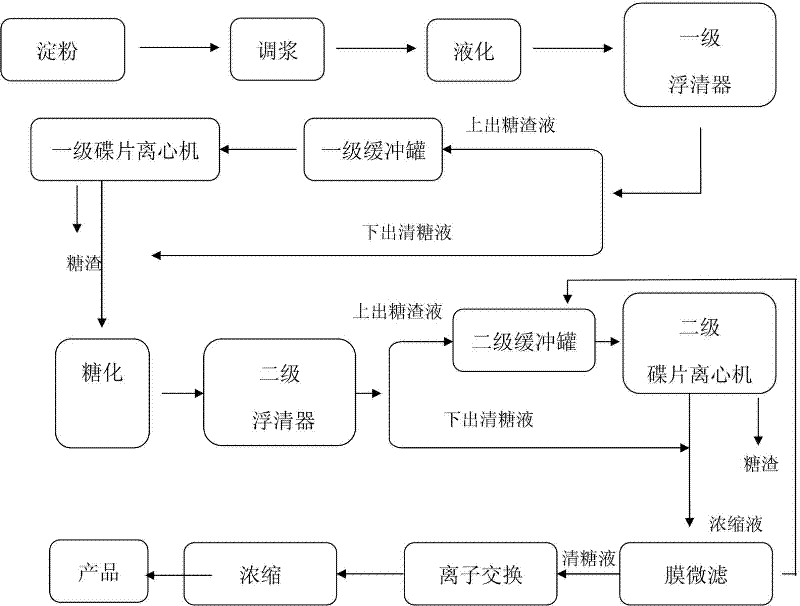
[0040] (1) Starch mixing: 100 parts by mass of cornstarch and water are added to make starch milk with 18-19 degrees Baume, and the pH value is adjusted to 5.4 with 5% dilute hydrochloric acid solution or 5% sodium carbonate solution ~5.6, add Liquozyme Supra high temperature resistant α-amylase equivalent to 0.030% of the edible starch mass;
[0041] (2) Liquefaction: At 105°C~110°C, the material is continuously sprayed for 5 minutes for the first time, and after flash evaporation, it is kept at 95~100°C for 90 minutes; then at 130°C~135°C, the material is subjected to the second spraying Continuous spray treatment for 3 minutes, flash depressurization and temperature reduction, liquefied liquid at 98 ° C for 20 minutes;
[0042] (3) Primary extraction of sugar slag: the liquefied liquid directly enters the first-stage floater without cooling down, and the liquefied liquid passes through the floater for 20 minutes. The clear liquid from the bottom of the device flows out of ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] (1) Starch mixing: 100 parts by mass of cornstarch, add water to make starch milk with 16-17 degrees Baume, adjust the pH value to 5.4 with 5% dilute hydrochloric acid solution or 5% sodium carbonate solution ~5.6, add Liquozyme Supra high temperature resistant α-amylase equivalent to 0.030% of the edible starch mass;
[0050] (2) Liquefaction: At 105°C~110°C, the material is continuously sprayed for 5 minutes for the first time, and after flash evaporation, it is kept at 95~100°C for 60 minutes; then at 125°C~130°C, the material is subjected to the second spraying Continuous spraying treatment for 3 minutes, after flash depressurization and cooling, add 0.005% edible starch quality Liquozyme Supra high-temperature-resistant α-amylase, and keep the liquefied solution at 98°C for 20 minutes;
[0051] (3) Primary extraction of sugar slag: the liquefied liquid directly enters the primary floater without cooling down. The time for the liquefied liquid to pass through the fl...
Embodiment 3
[0058] (1) Starch mixing: 100 parts by mass of cornstarch, add water to make starch milk with 16-17 degrees Baume, adjust the pH value to 5.4 with 5% dilute hydrochloric acid solution or 5% sodium carbonate solution ~5.6, add Liquozyme Supra high temperature resistant α-amylase equivalent to 0.030% of the edible starch mass;
[0059] (2) Liquefaction: At 105°C~110°C, the material is continuously sprayed for 5 minutes for the first time, and after flash evaporation, it is kept at 95~100°C for 60 minutes; then at 125°C~130°C, the material is subjected to the second spraying Continuous spraying treatment of 3min, flash depressurization and temperature reduction, liquefied liquid is kept at 98°C for 20min;
[0060] (3) Primary extraction of sugar slag: the liquefied liquid is cooled to 65-75°C and enters the primary floater. The time for the liquefied liquid to pass through the floater is 30 minutes. Adjust the outflow valve of the lower clear liquid of the floater to control the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solid content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com