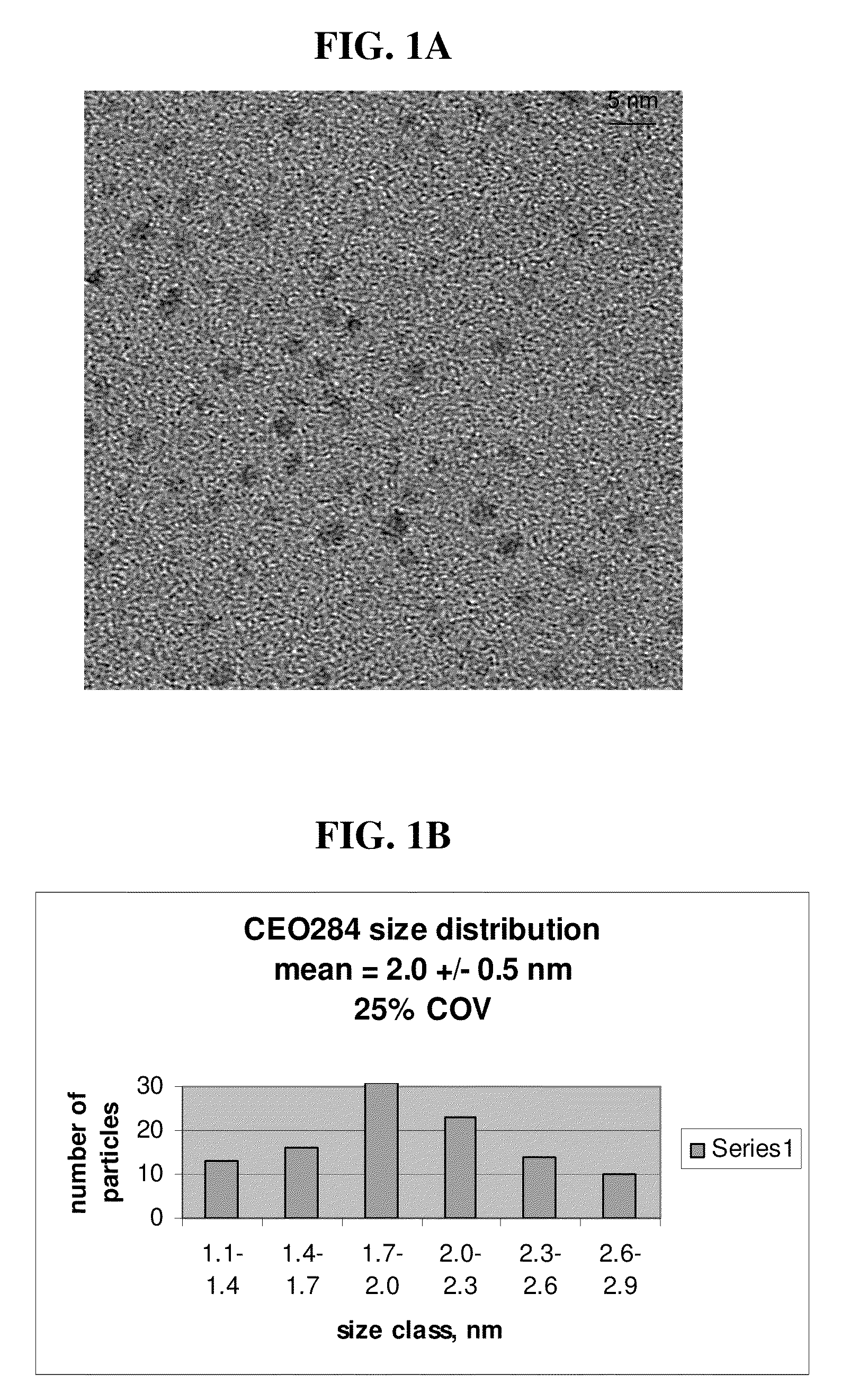
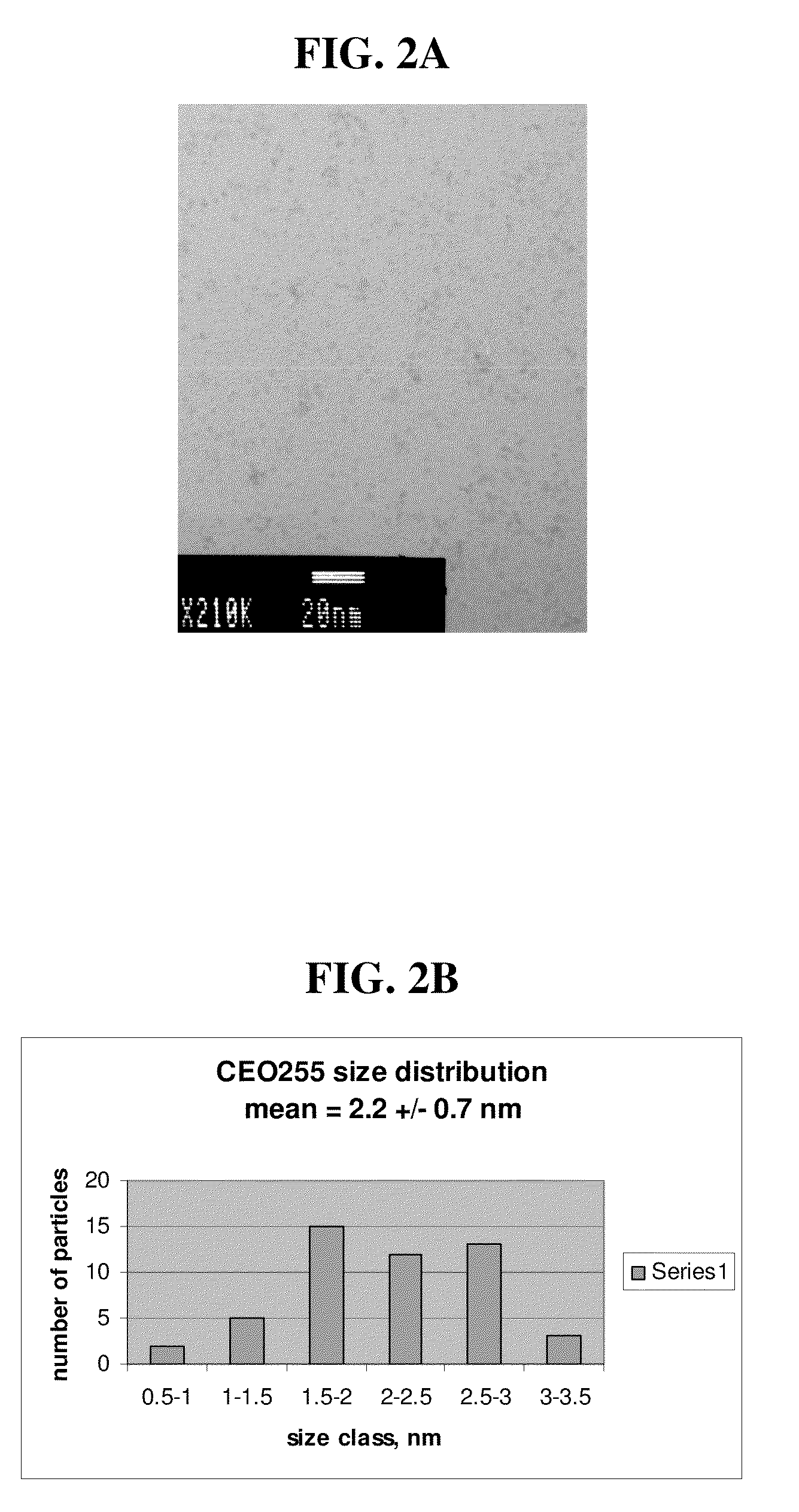
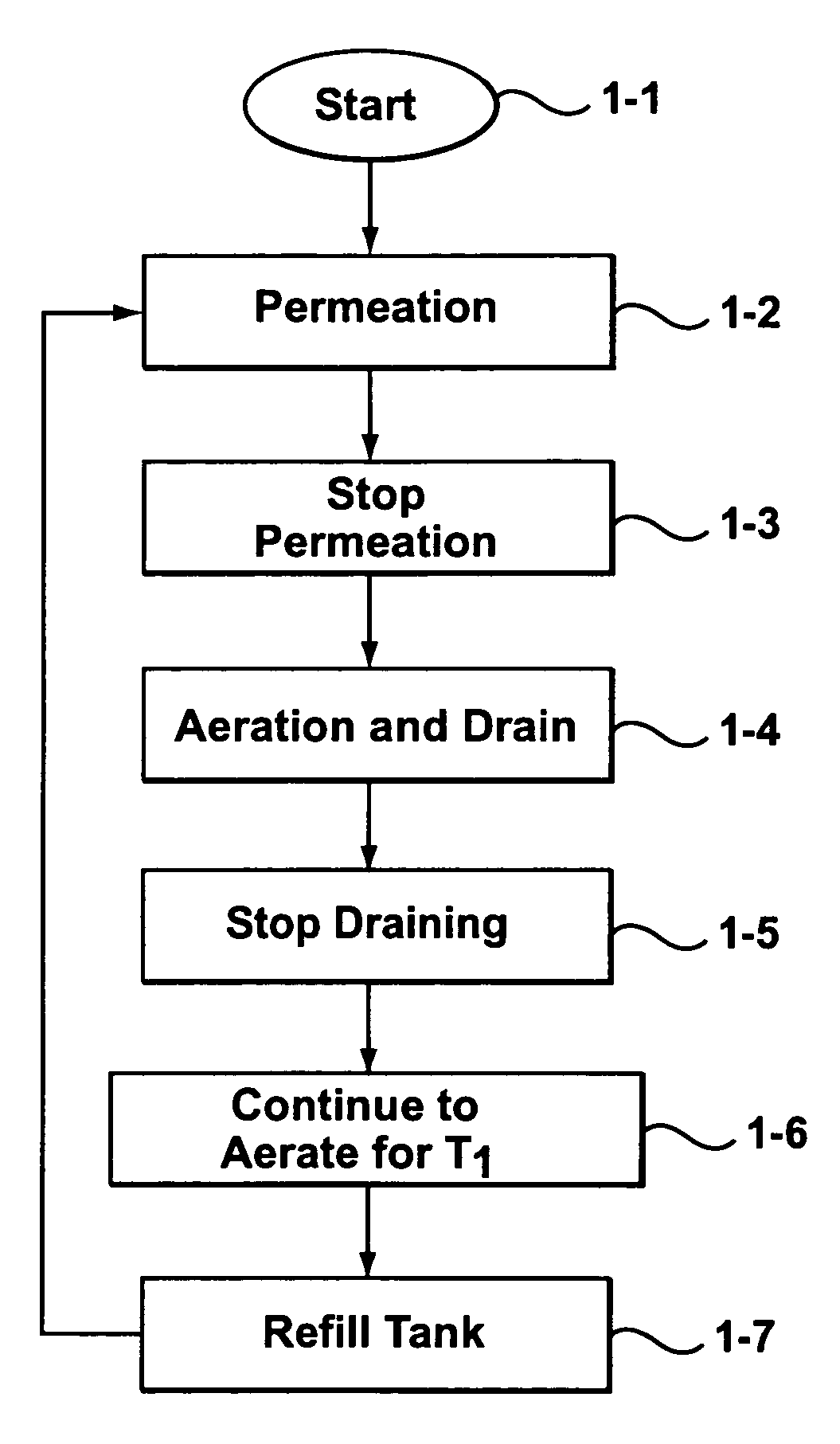
Patents
Literature
2787 results about "Membrane filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MEMBRANE FILTERS. Membrane filters or "membranes" are polymer films with specific pore ratings. Membranes retain particles and microorganisms that exceed their pore ratings by acting as a physical barrier and capturing such particles on the surface of the membrane.
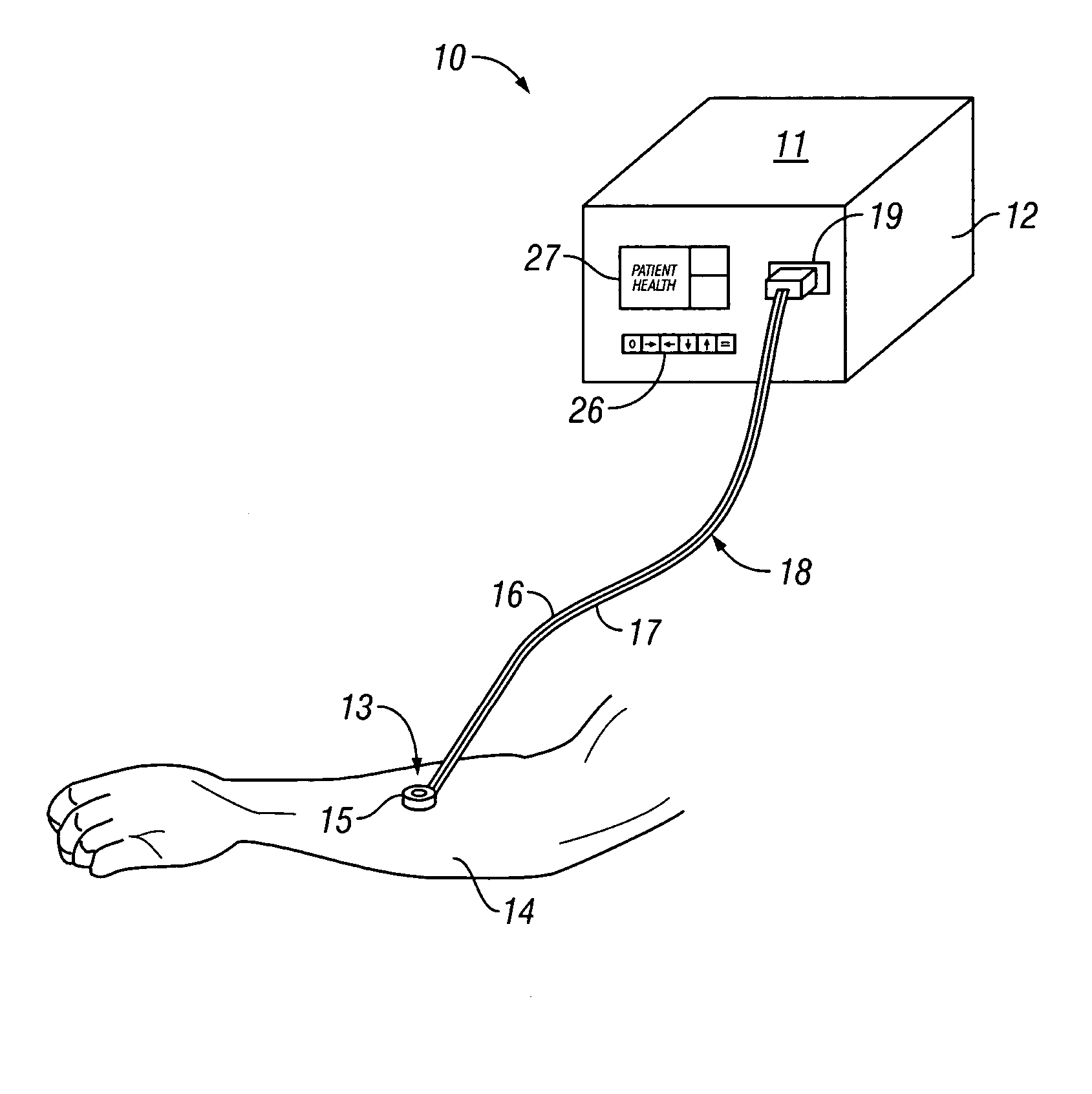
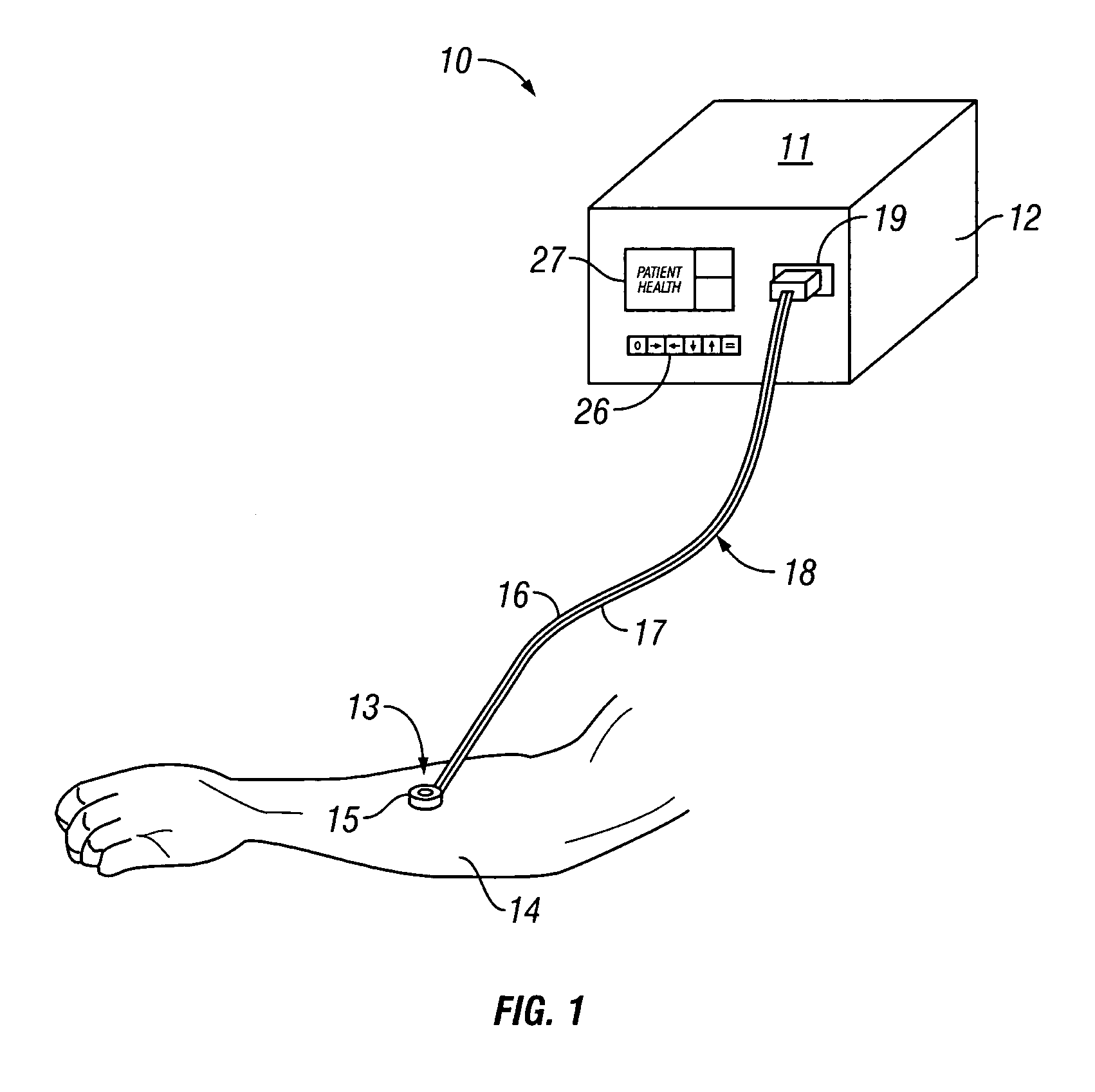
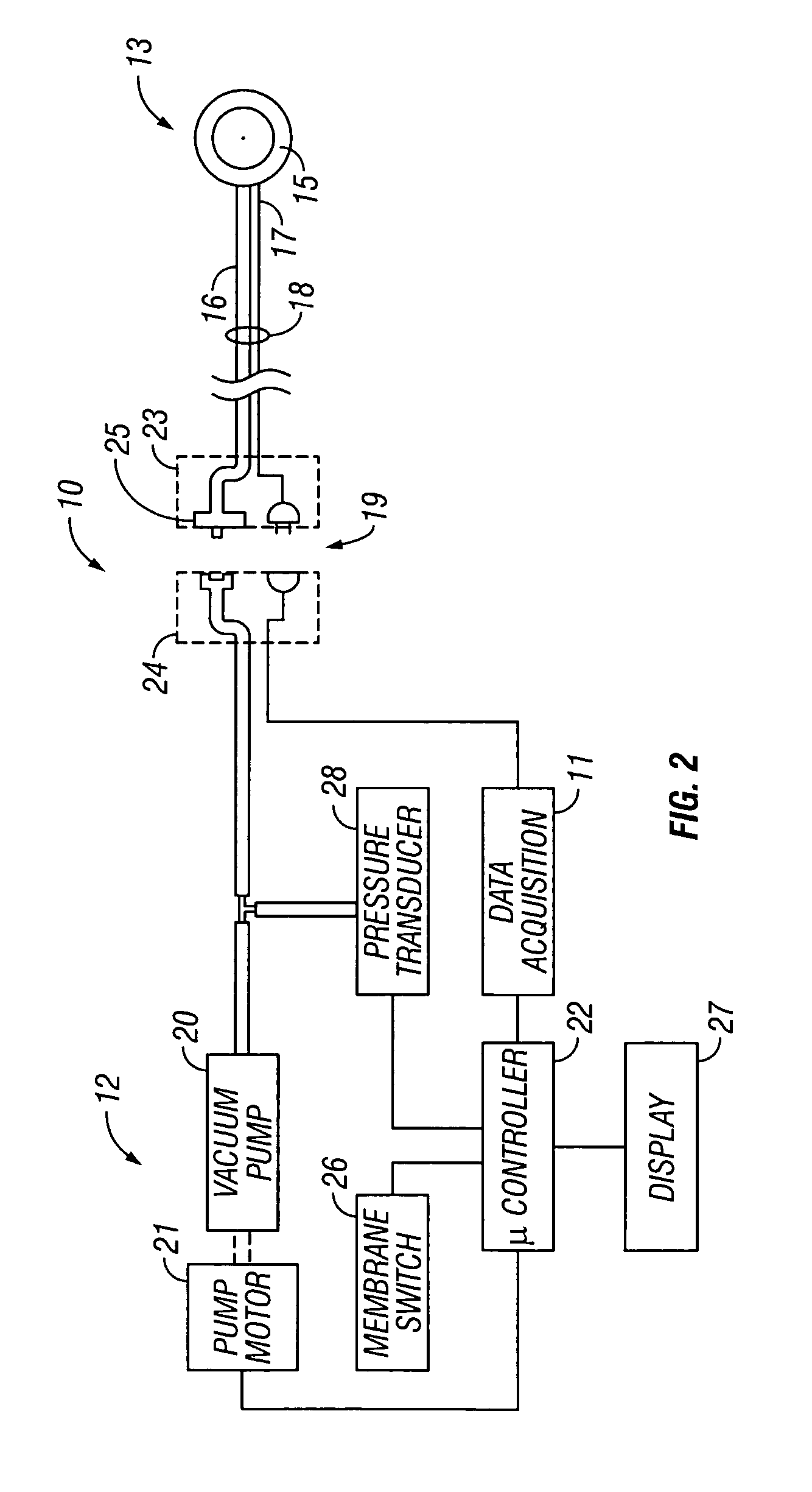
System for combined transcutaneous blood gas monitoring and vacuum assisted wound closure
InactiveUS6856821B2Eliminate opportunitySubstantial riskIntravenous devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerVacuum assisted
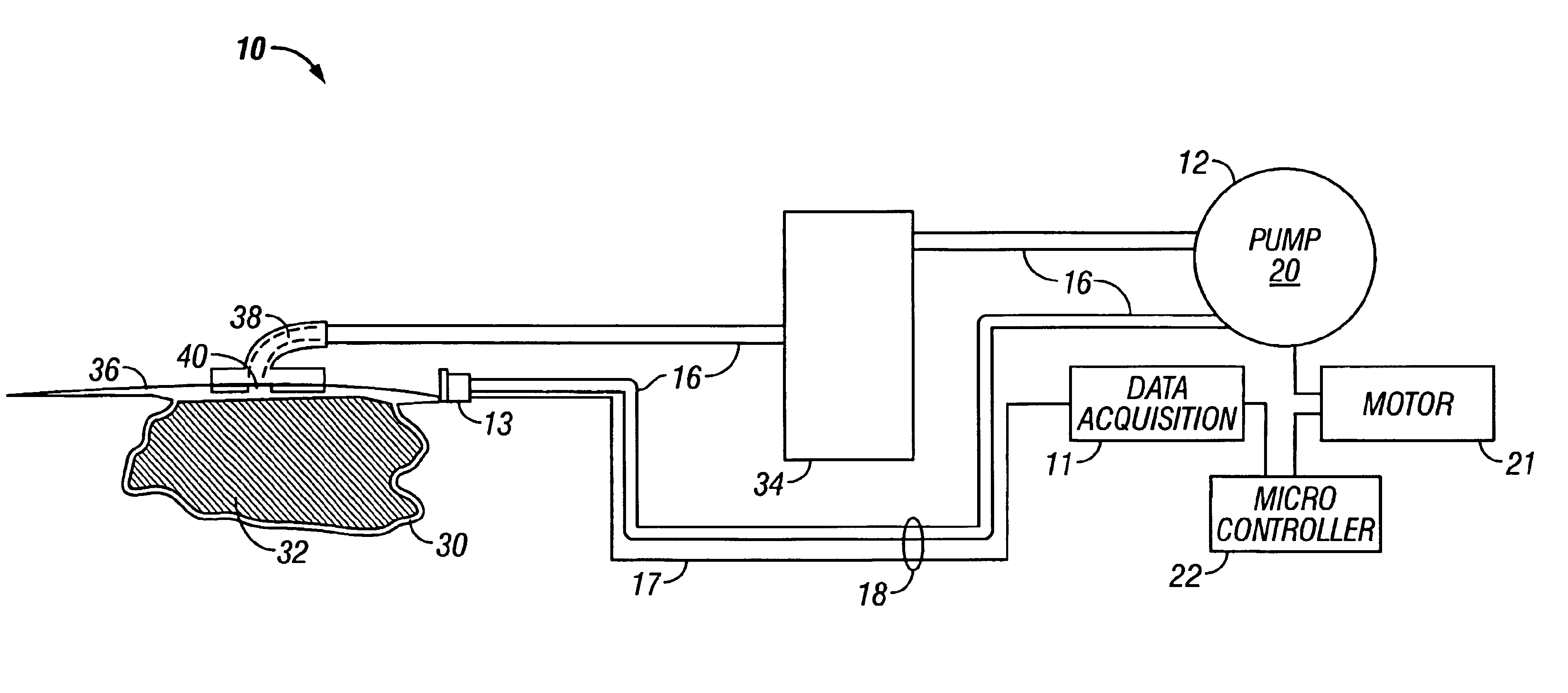
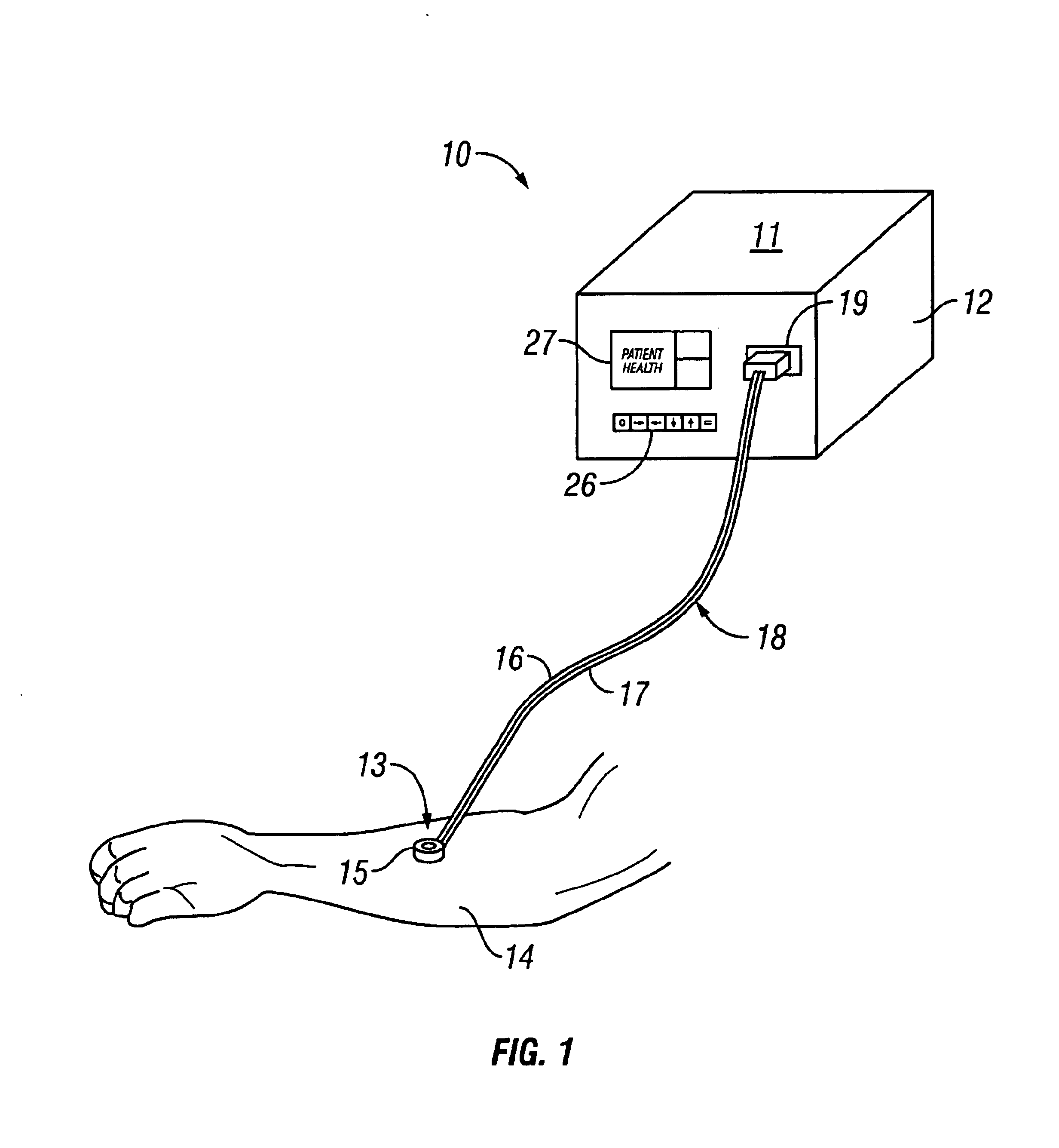
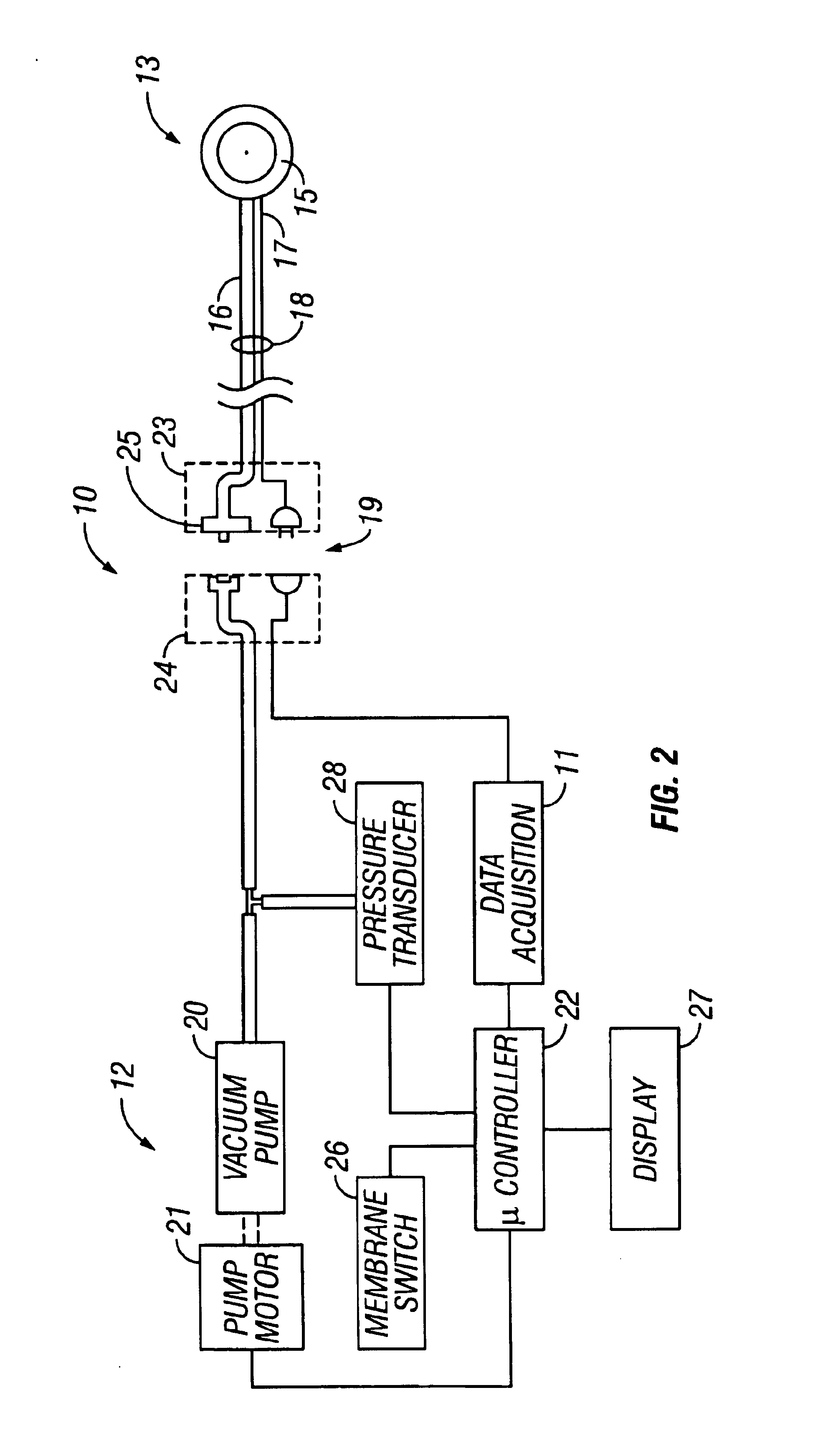
A method and apparatus for the transcutaneous monitoring of blood gases generally comprises a blood gas data acquisition device, a vacuum source and a blood gas transducer unit. The blood gas transducer unit is adapted for application to a patient's skin and administration of a local vacuum at the area of patient application. It further comprises an electrochemical blood gas transducer, well known to those of ordinary skill in the art, which is disposed entirely within the local vacuum at the area of patient application. The vacuum source is placed in fluid communication with the blood gas transducer unit, through a hydrophobic membrane filter for safety purposes, in order to induce a condition of hyperperfusion in the locality of the electrochemical blood gas transducer. Under the control of a microcontroller, or equivalent means, the blood gas acquisition device is then utilized to capture a measure of skin surface oxygen or carbon dioxide pressure. The microcontroller can then utilize this measure to arrive at an estimate of arterial partial pressure of oxygen or carbon dioxide, accordingly. Because vacuum induced perfusion produces the requisite condition of hyperperfusion without local heating and, therefore, without acceleration of the local metabolic function, the present invention results in more accurate than previously available estimates of partial pressure blood gas pressures and does so while eliminating a significant risk for injury to the patient.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Membrane filter apparatus with gas discharge cleaning means
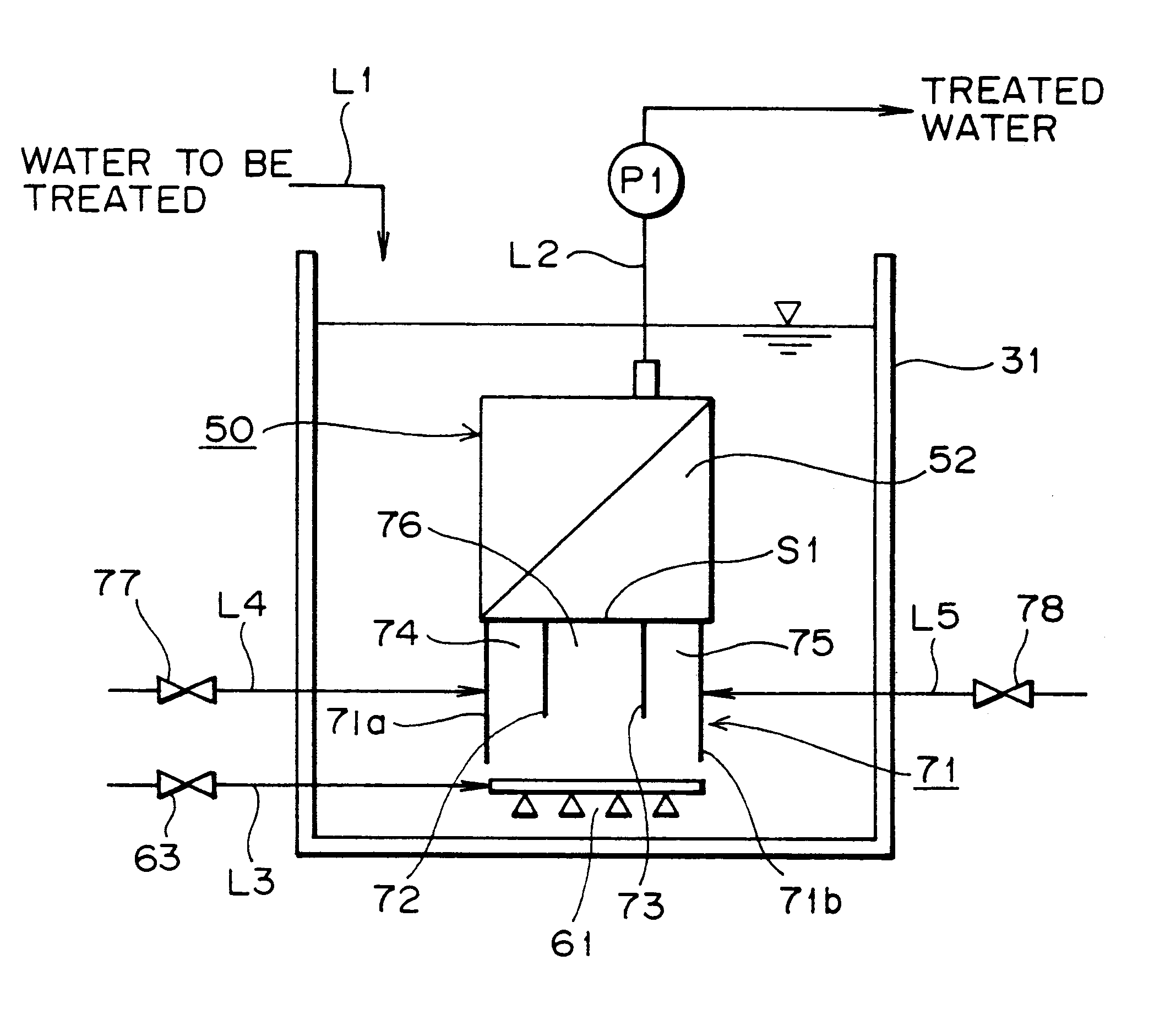
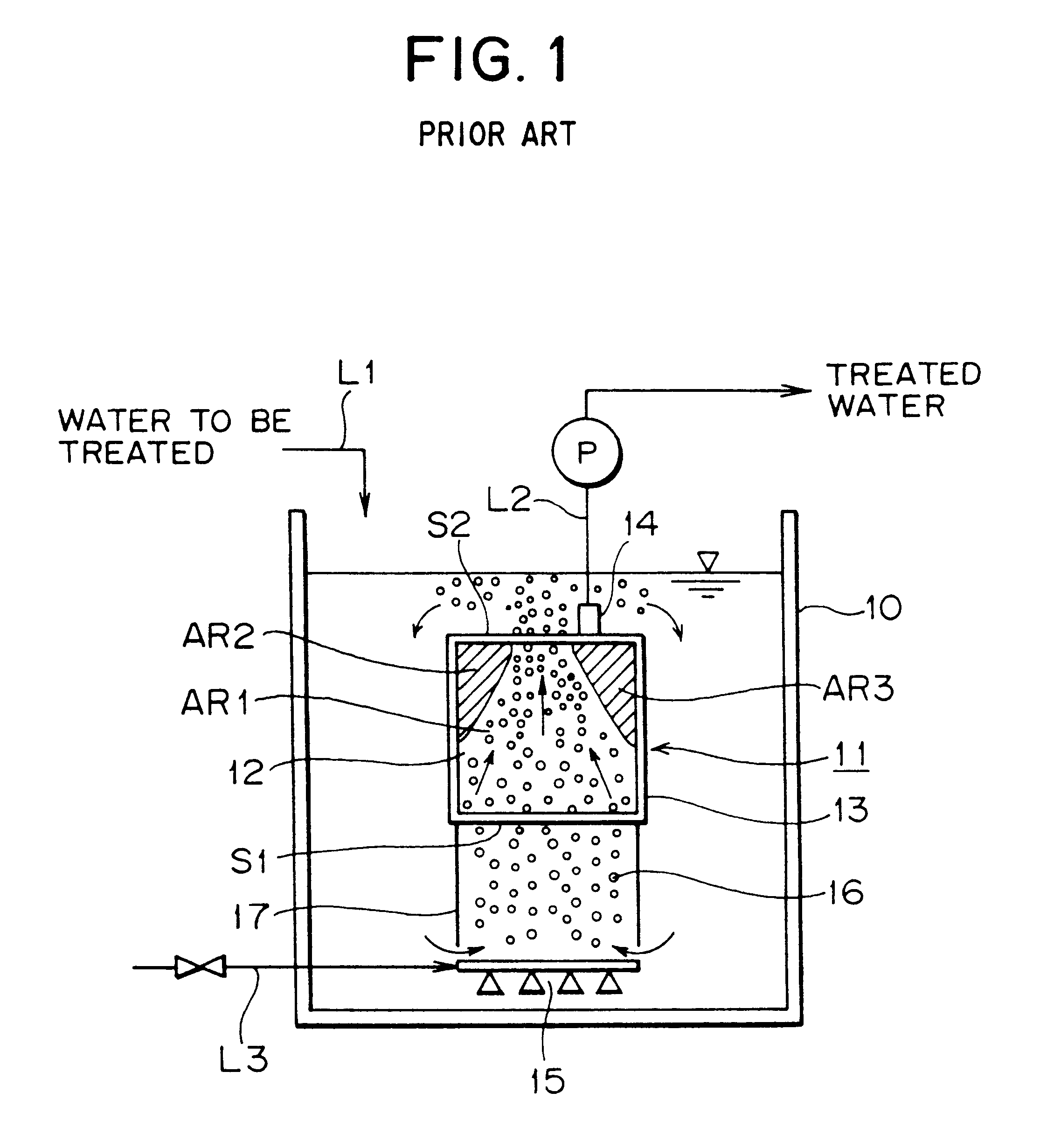
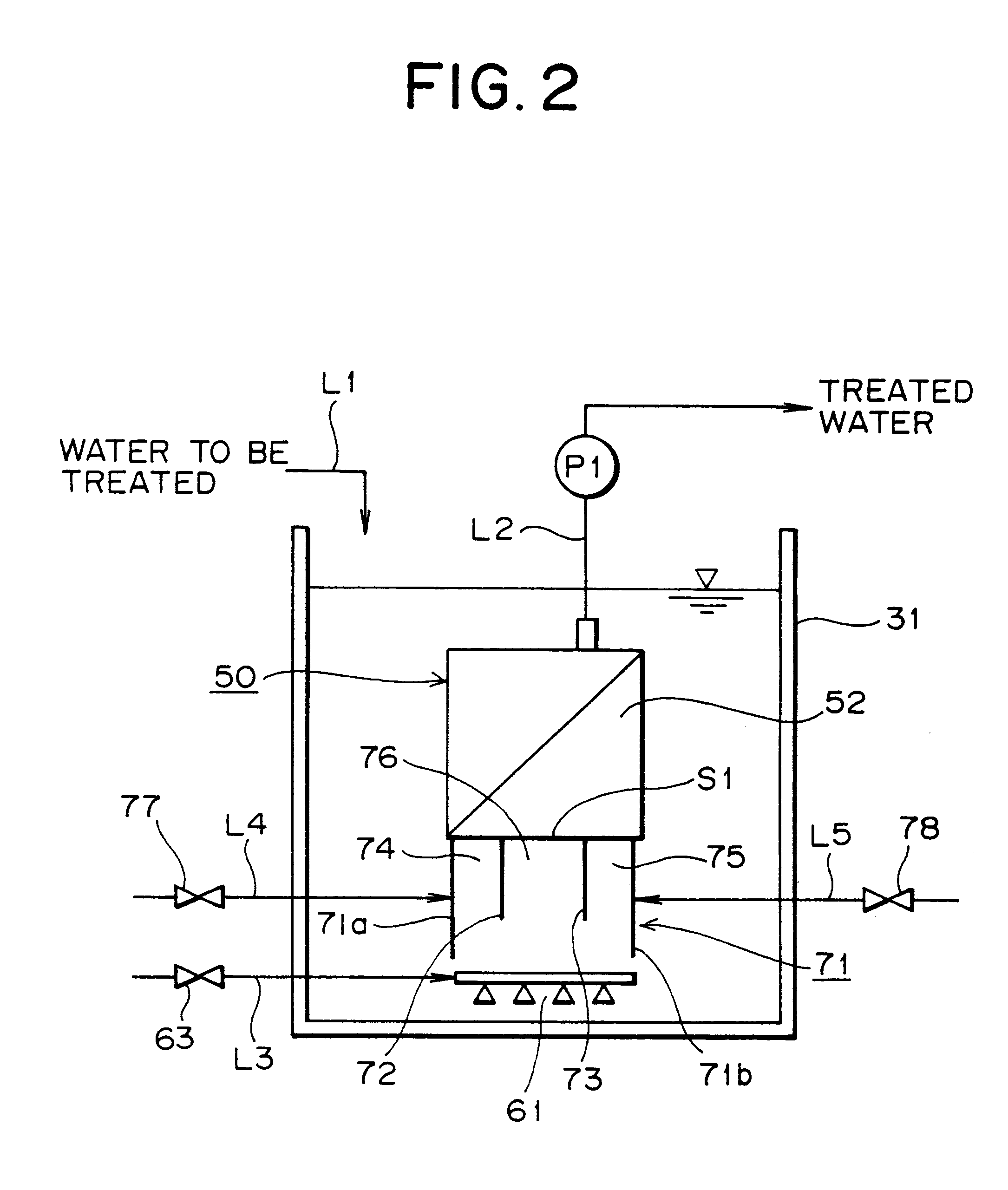
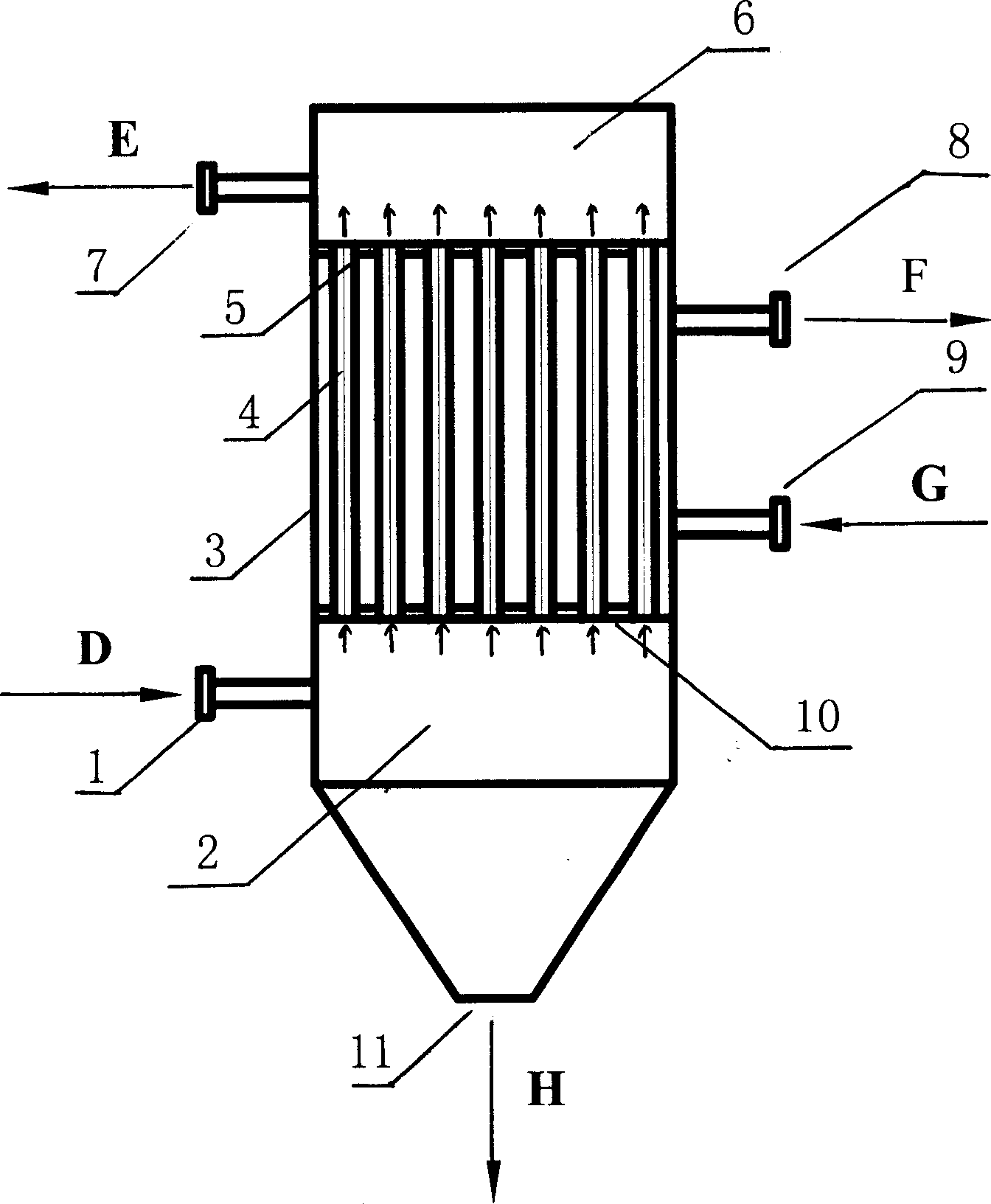
A membrane filter apparatus includes a membrane unit 50 composed of an array of membrane elements 51 disposed within a treatment tank 31. A skirt element 71 is disposed at a bottom portion of the membrane unit and an aerator 61 is disposed under the skirt. A partition is also disposed at the bottom of the membrane unit forming compartments within the skirt element. The gas bubbles discharged from the aerator increase their rising force upon entry into gaps between the membranes. Because of the arrangement of the partition within the skirt element the flow rate of bubbles along the opposite side edge portions of the membrane unit can be increased having the advantage of cleaning the entire surface of each membrane, thereby preventing clogging by sludge, SS, colloid, etc. within the gaps between the membranes. Therefore, filtration can be maintained over a longer period of time and the power required for filtration can be reduced, as well as, the frequency of manual periodic cleaning, chemical cleaning, etc.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
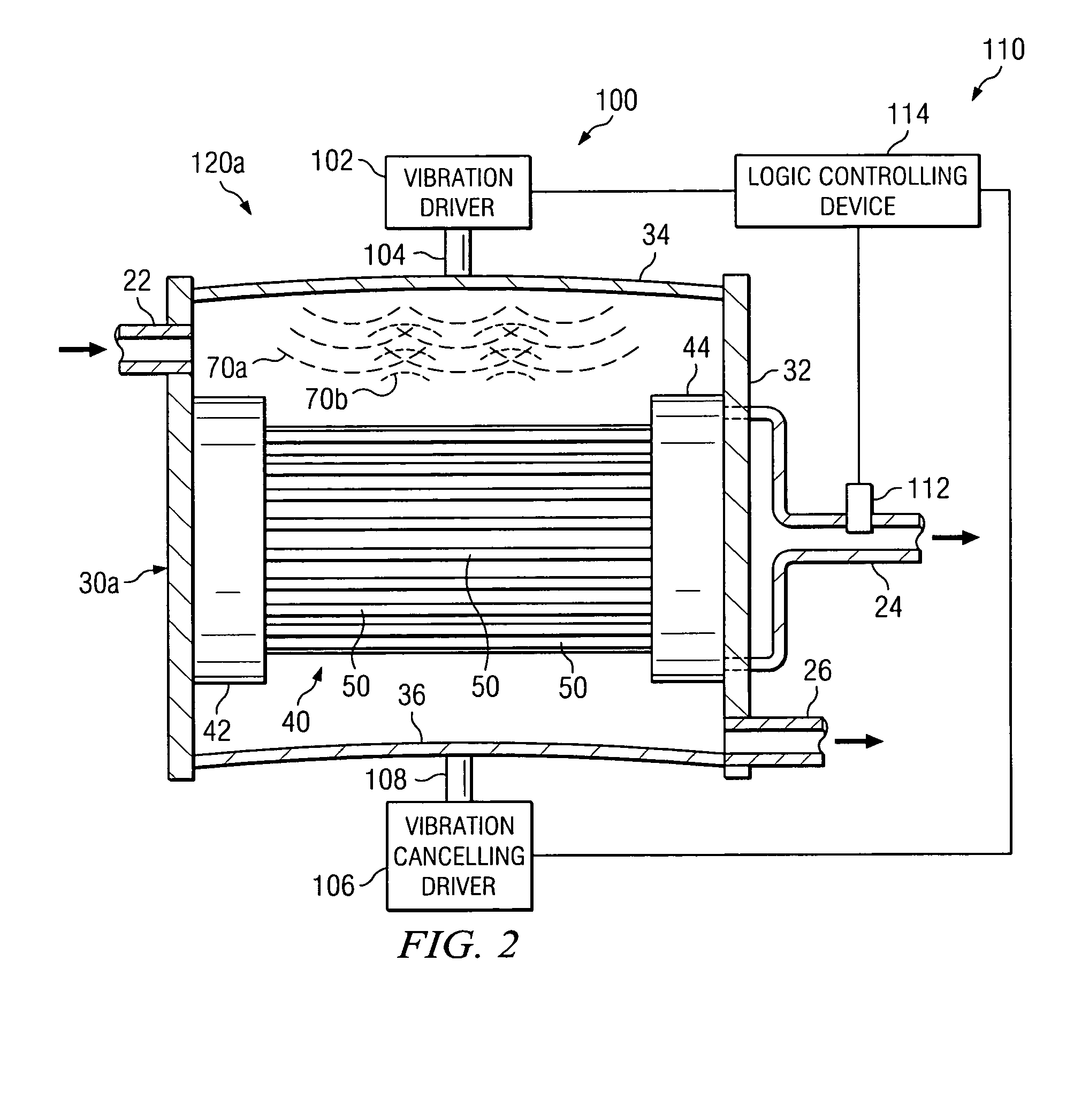
Cleaning hollow core membrane fibers using vibration
InactiveUS20050077227A1Minimize returnMinimize bounce backMembranesSpecific water treatment objectivesParticulatesFiber
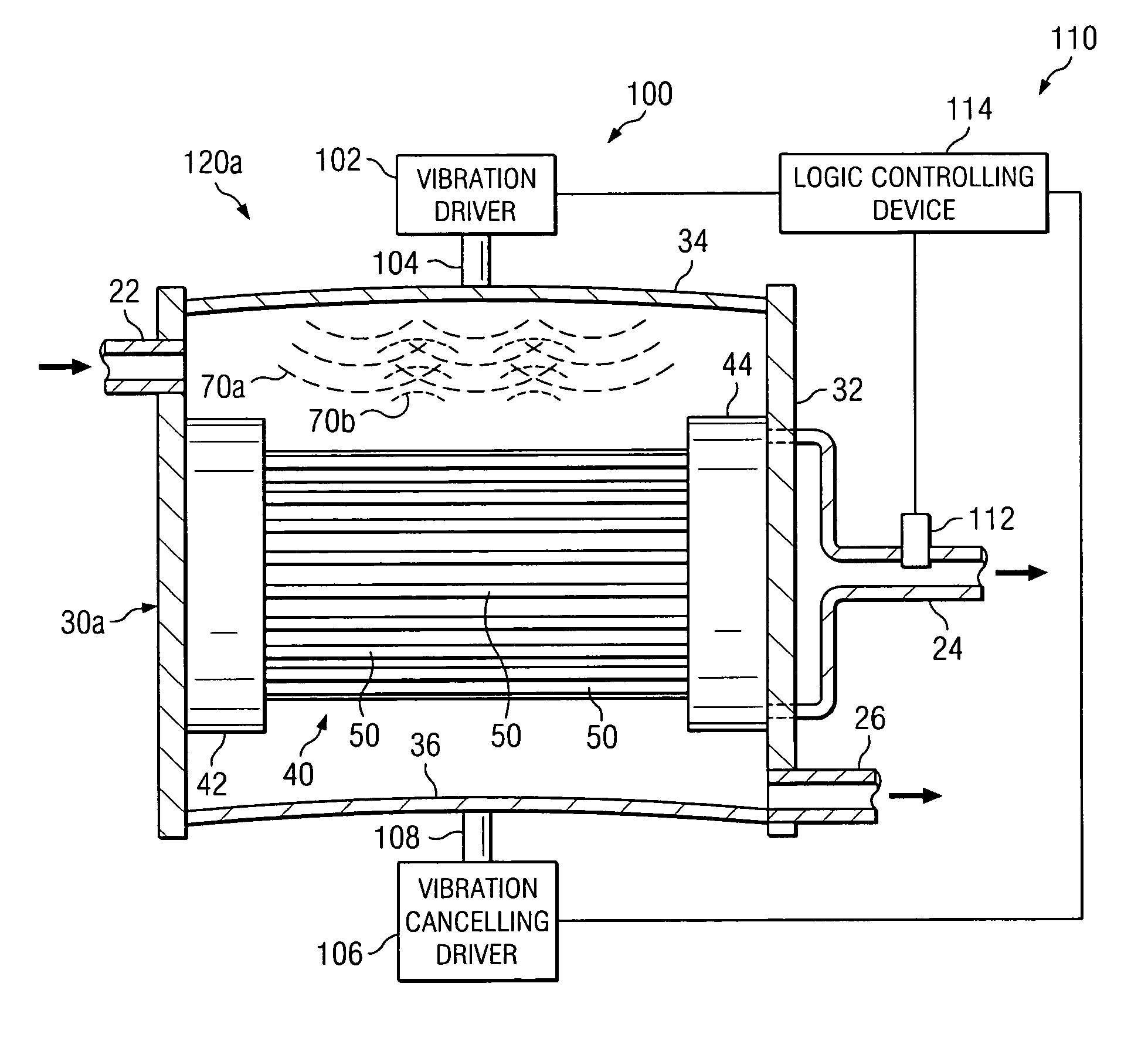
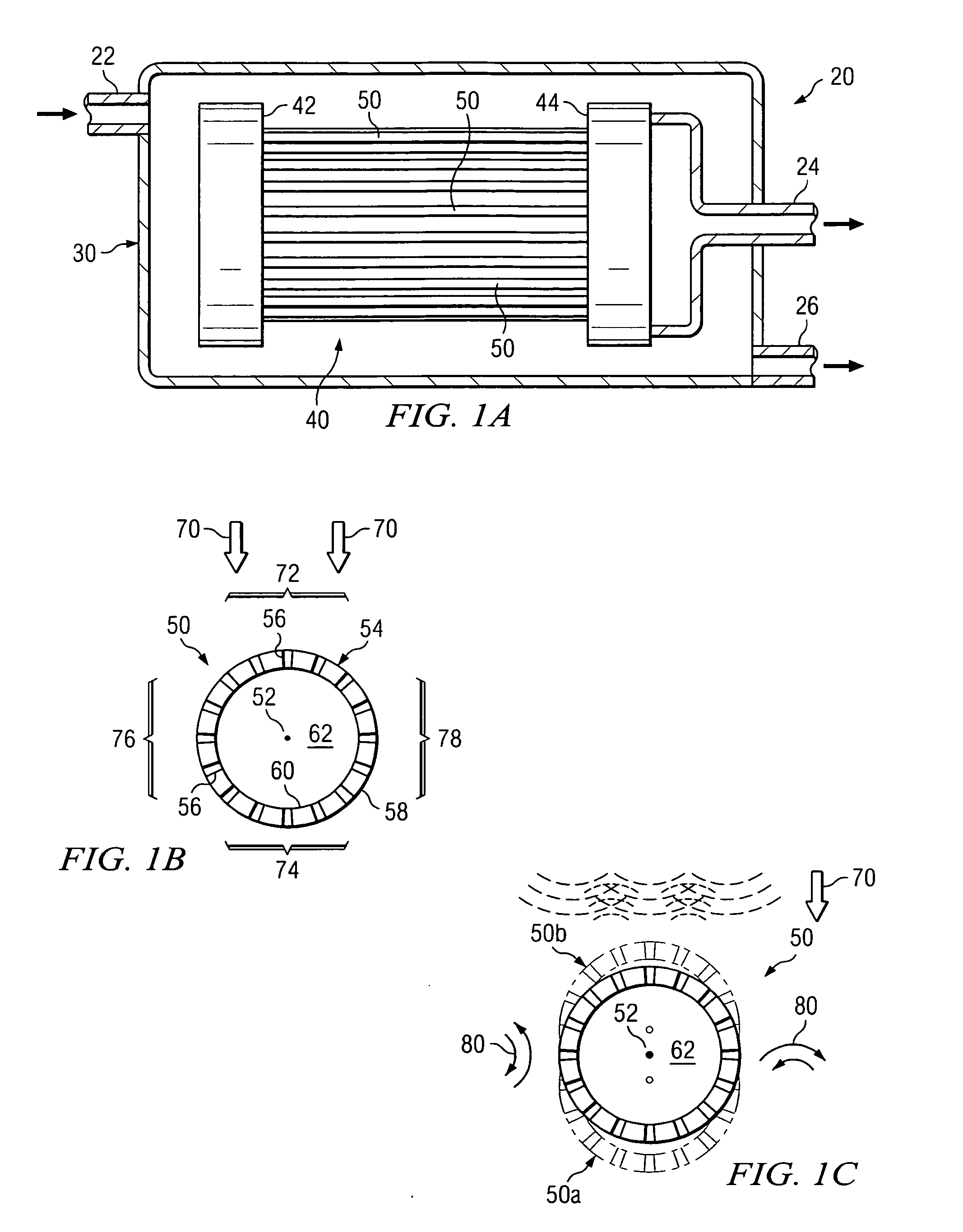
A filtration system is provided with hollow membrane filter elements operable to remove solids, particulate and colloidal matter from a process fluid. Acoustic, vibration and ultrasonic energy may be used to clean exterior portions of the hollow membrane filter elements to allow substantially continuous filtration of process fluids. The filtration system may be satisfactorily used with process fluids having a relatively high concentrations of solids, particulate and colloidal matter.
Owner:PHASE
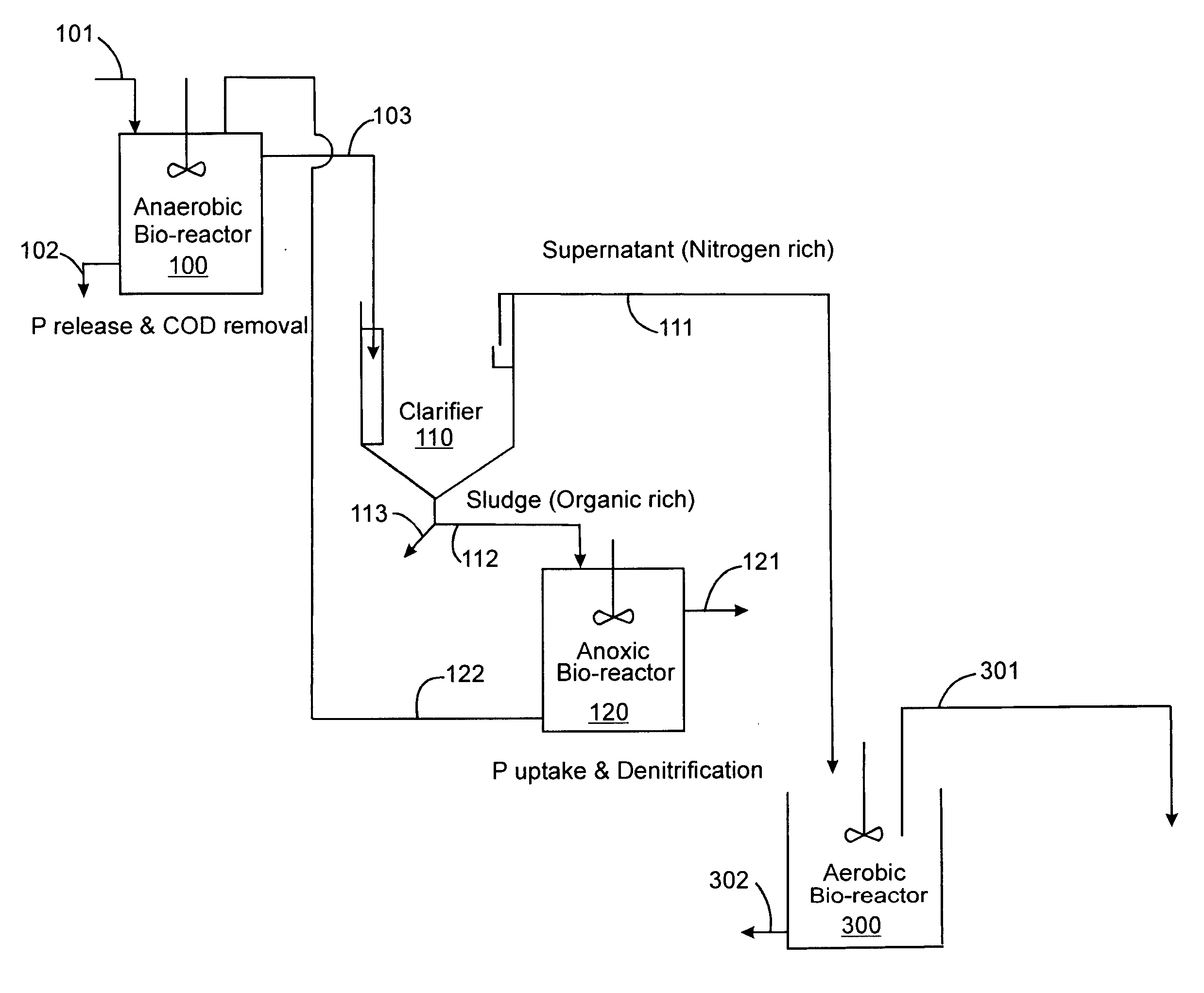
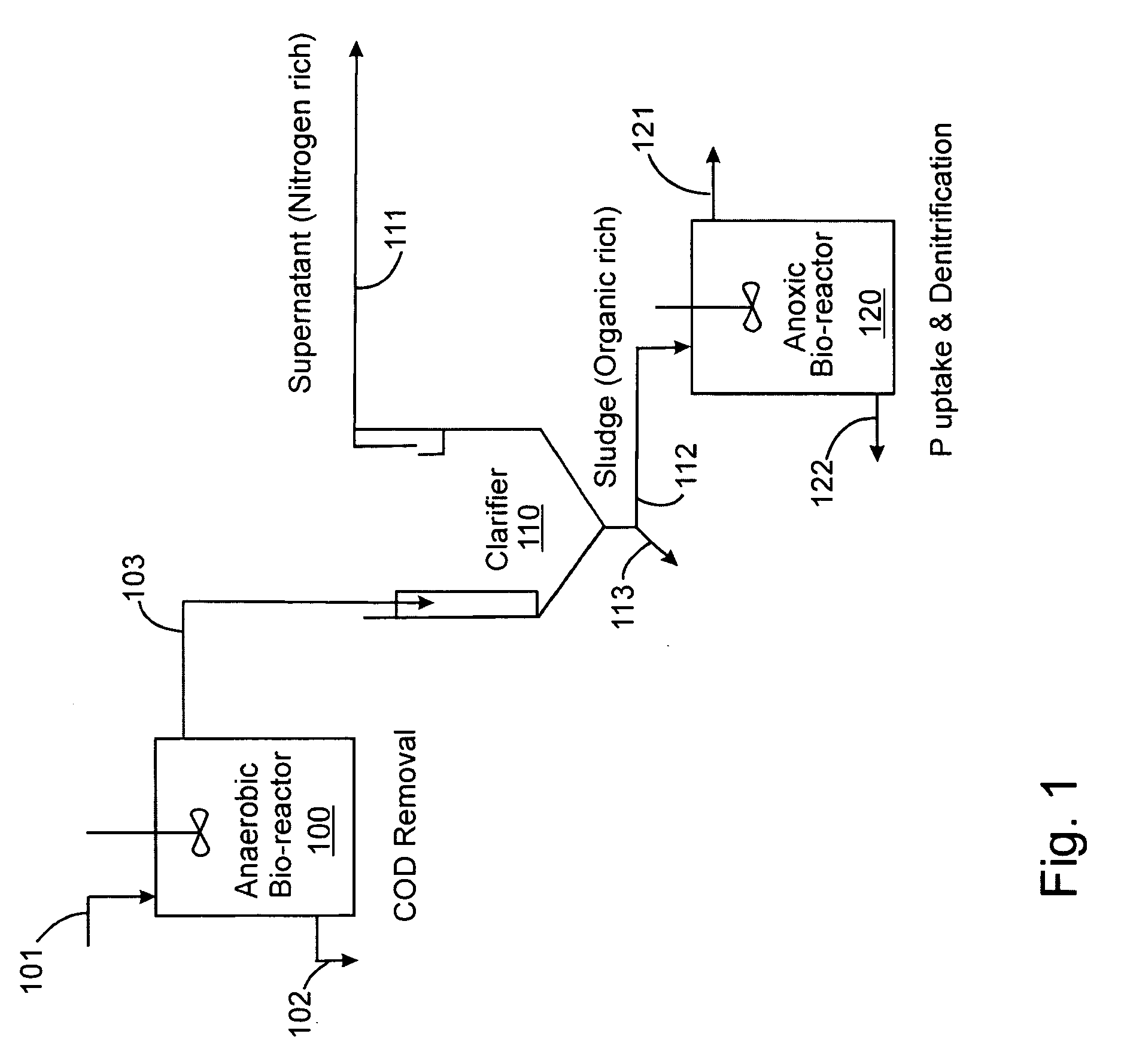
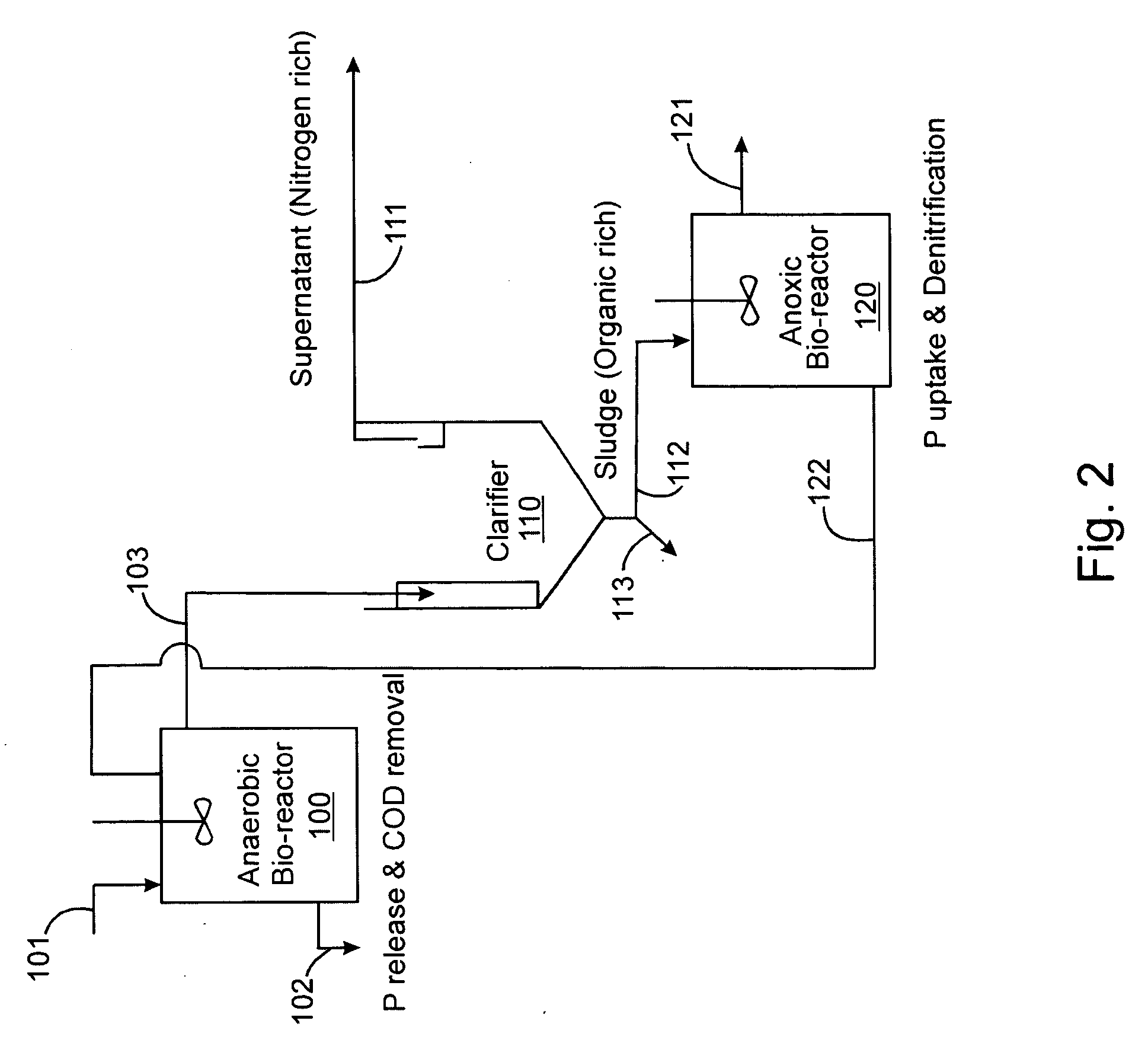
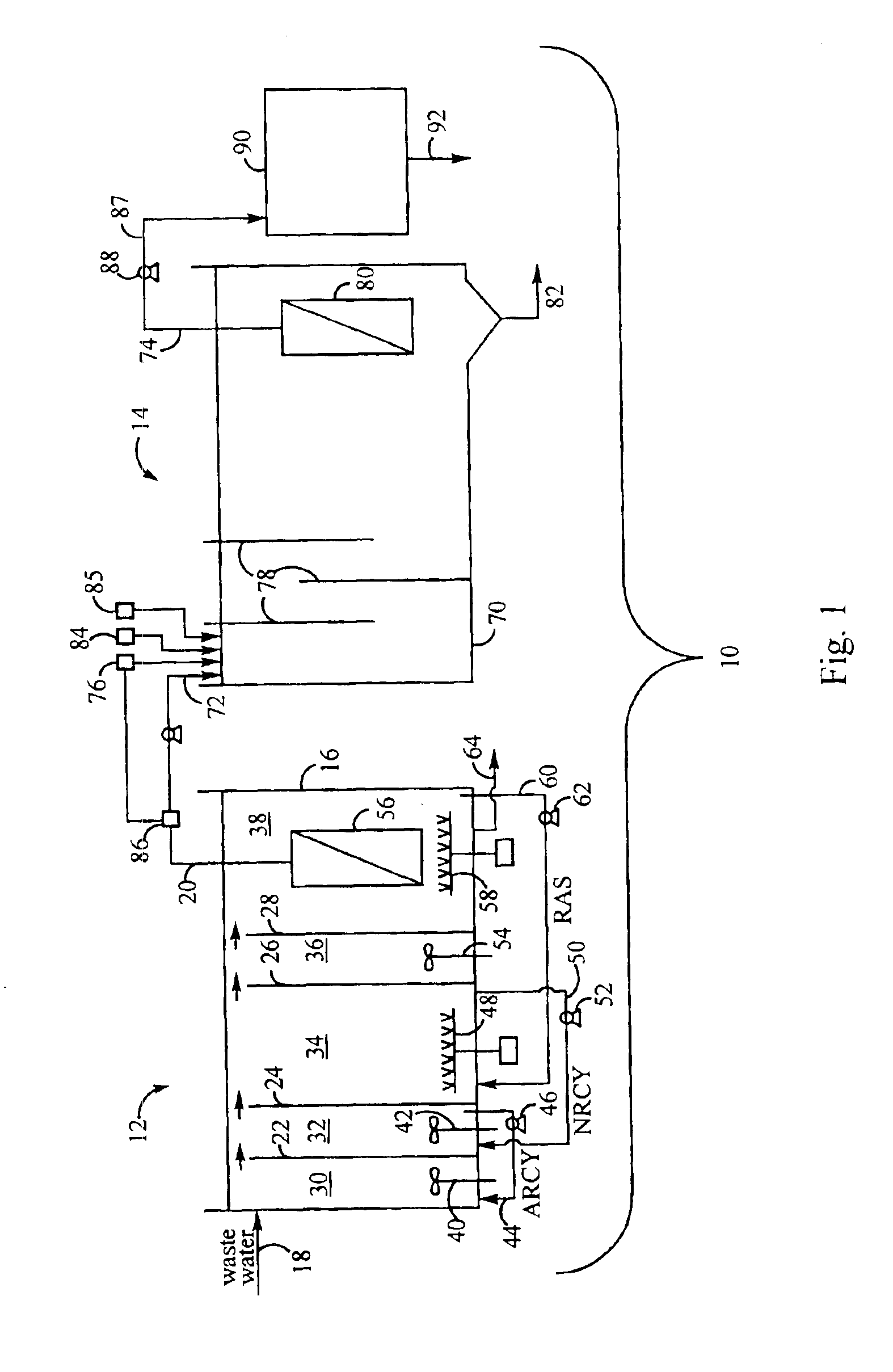
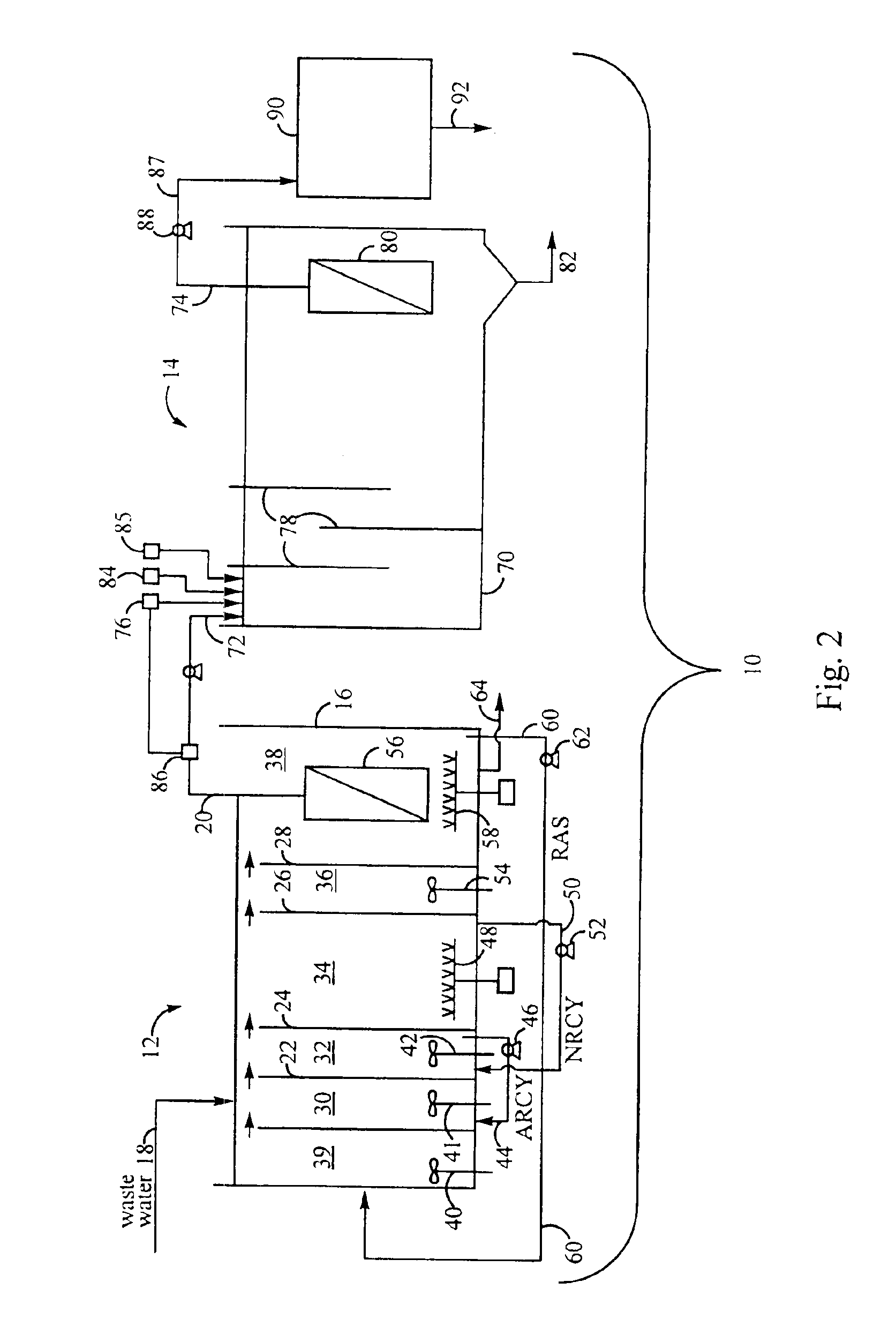
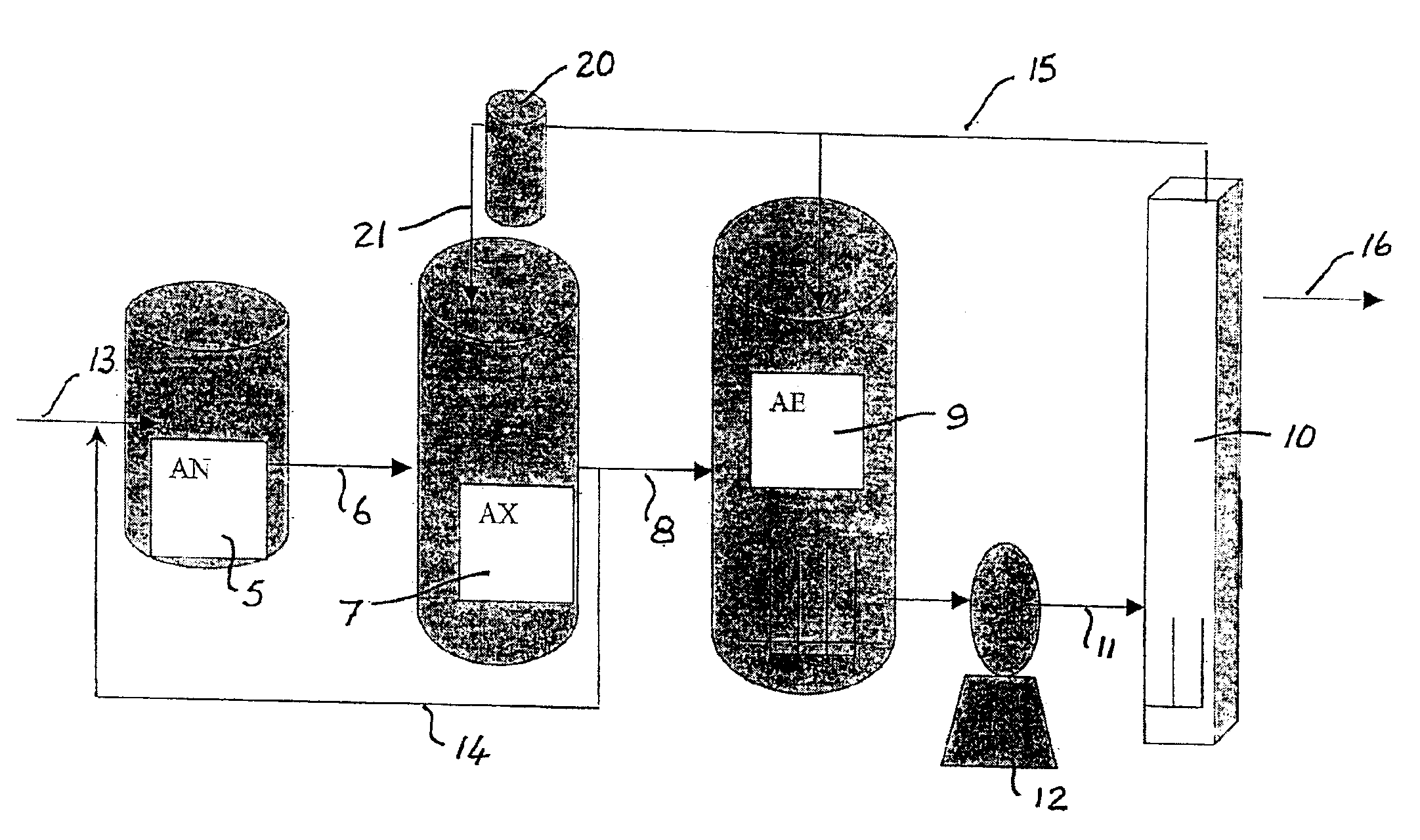
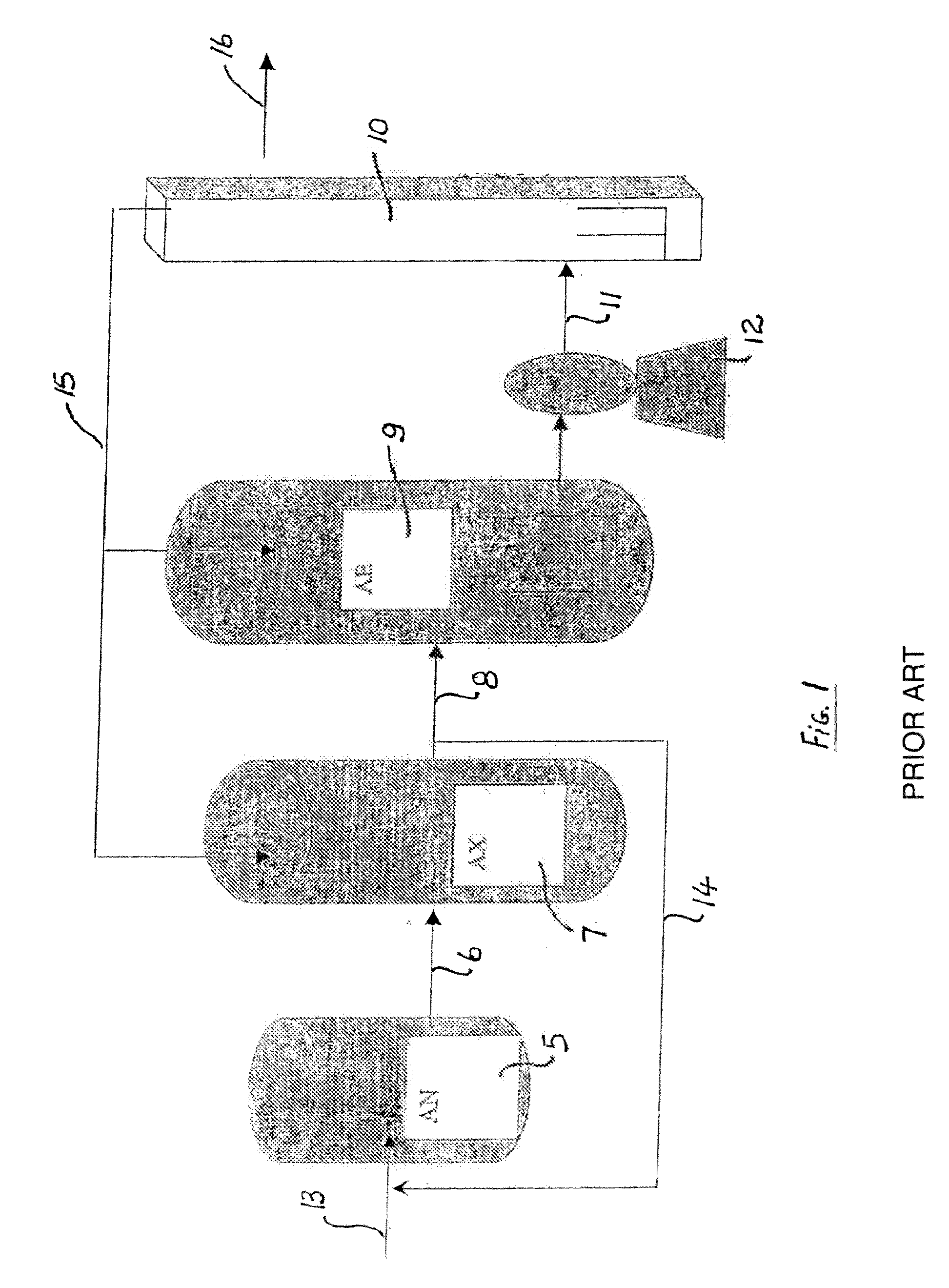
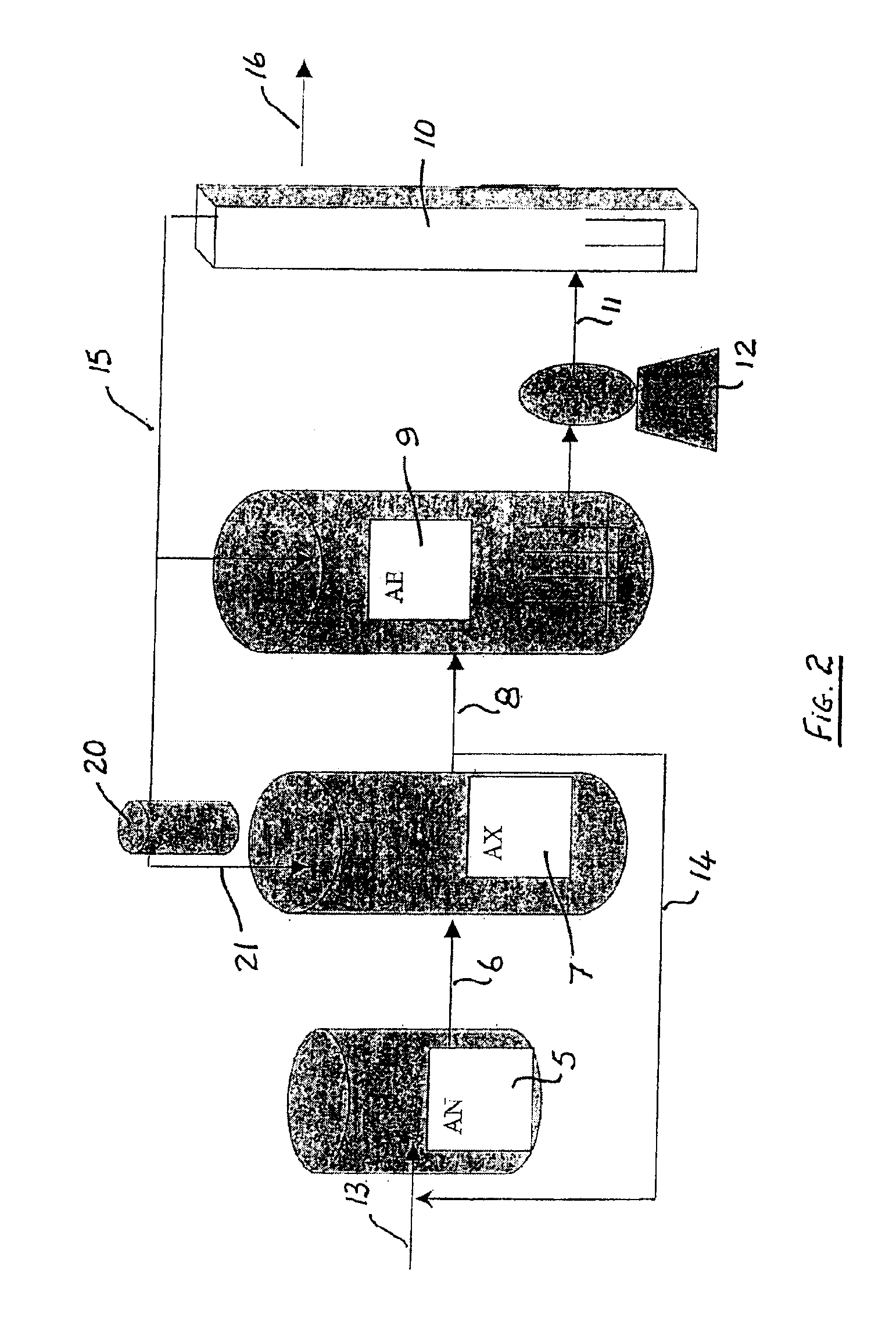
Treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen
InactiveUS20060249449A1Great extent of P releaseHigh P uptakeTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesOxygenClarifier
A method and process for the treatment of wastewater containing phosphorous and nitrogen. The wastewater is first anaerobically treated to produce an anaerobic effluent from which insoluble organic carbon is separated to form a sludge rich in organic carbon that is used as a substrate during anoxic treatment of the wastewater by de-nitrifying phosphorous accumulating organisms (DPAO's) and ordinary de-nitrifying organisms. The separation of insoluble organic carbon is normally conducted using a clarifier located intermediate the anaerobic and anoxic bio-reactors. In one embodiment, the ammonia rich clarifier supernatant is directed to an aerobic reactor for nitrification and the nitrate produced is recycled to the anoxic bio-reactor. The final effluent may be membrane filtered to retain nitrifying biomass within the aerobic bio-reactor. The invention reduces overall hydraulic residence time and sludge volume, which results in a smaller, less expensive wastewater treatment system.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
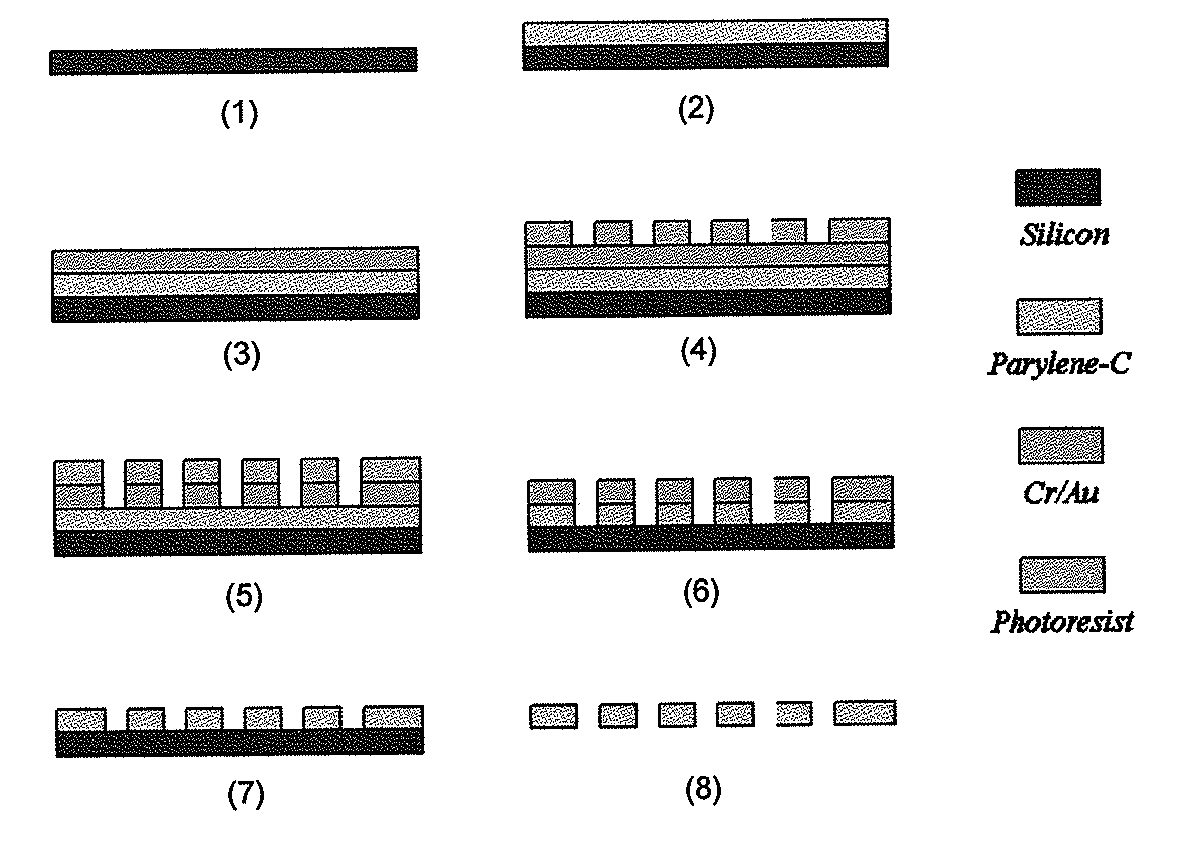
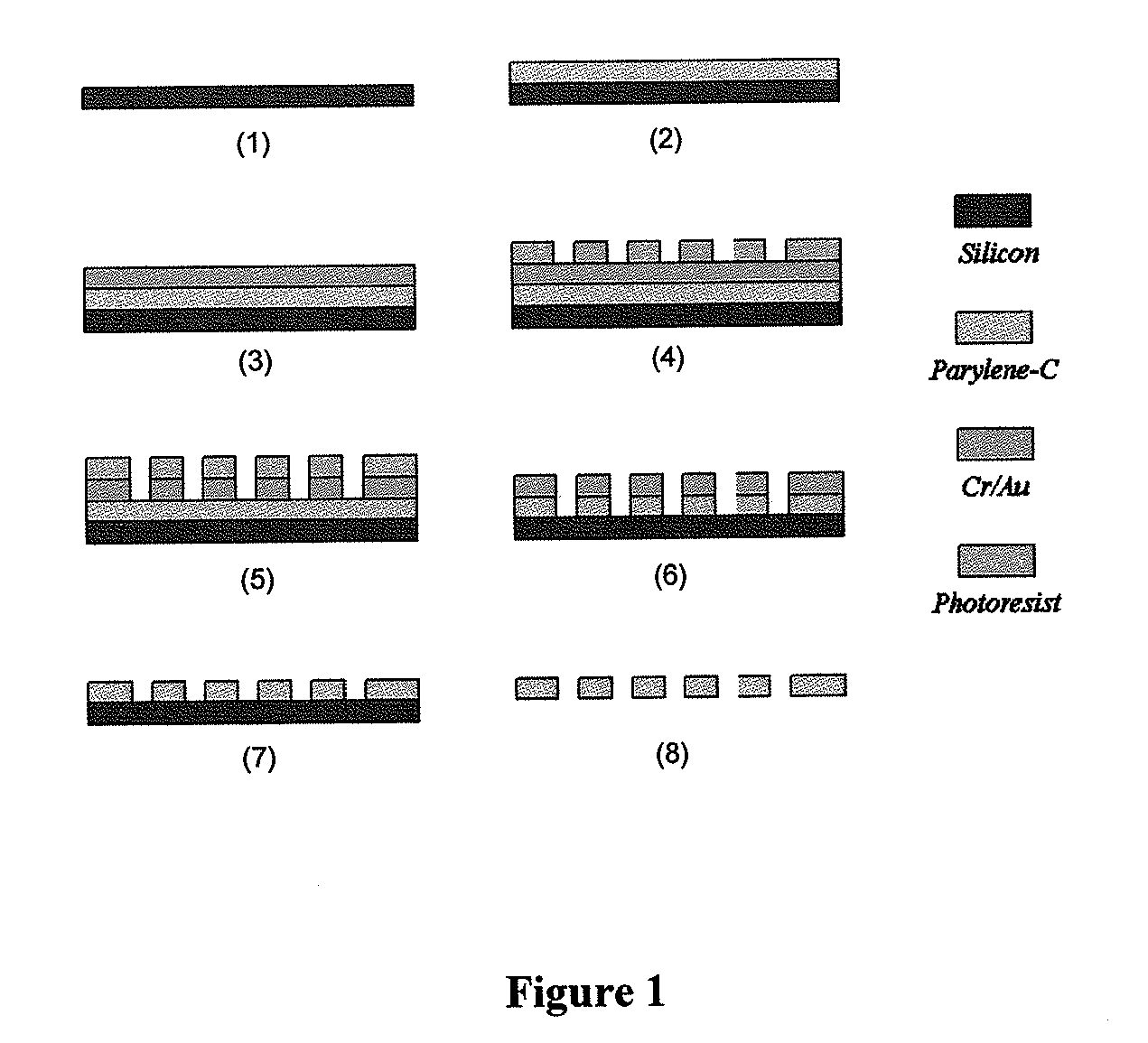
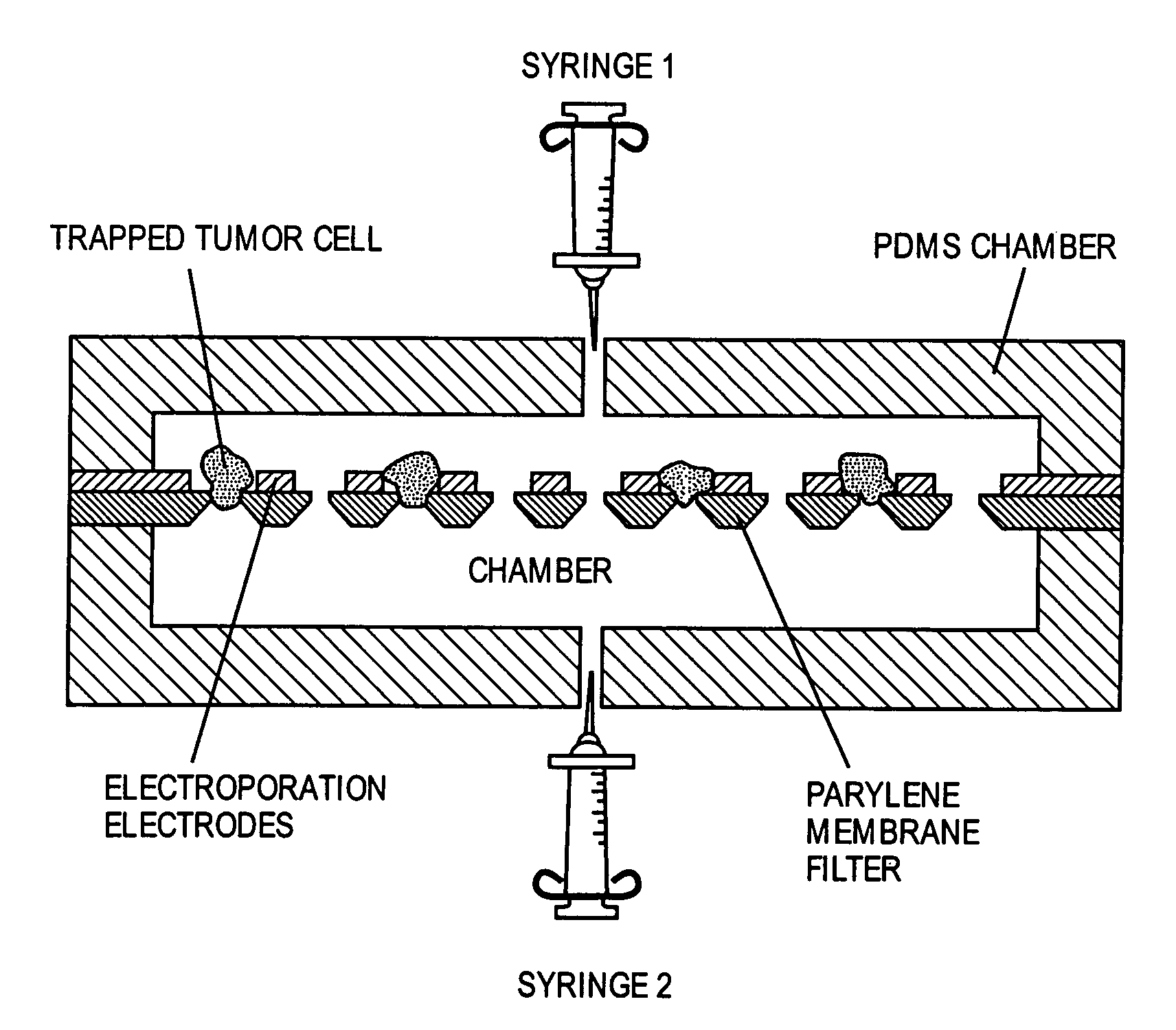
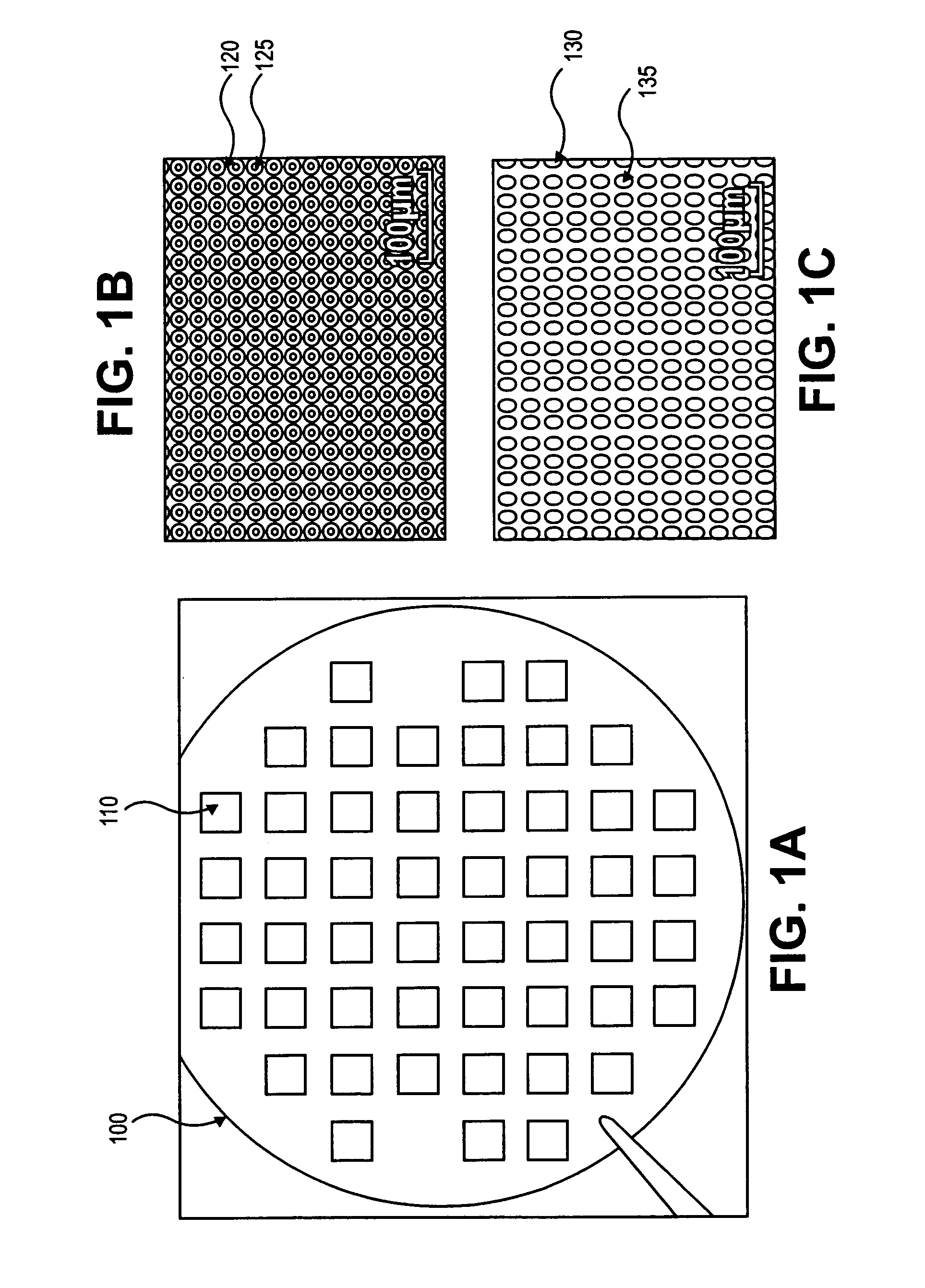
Uses of parylene membrane filters
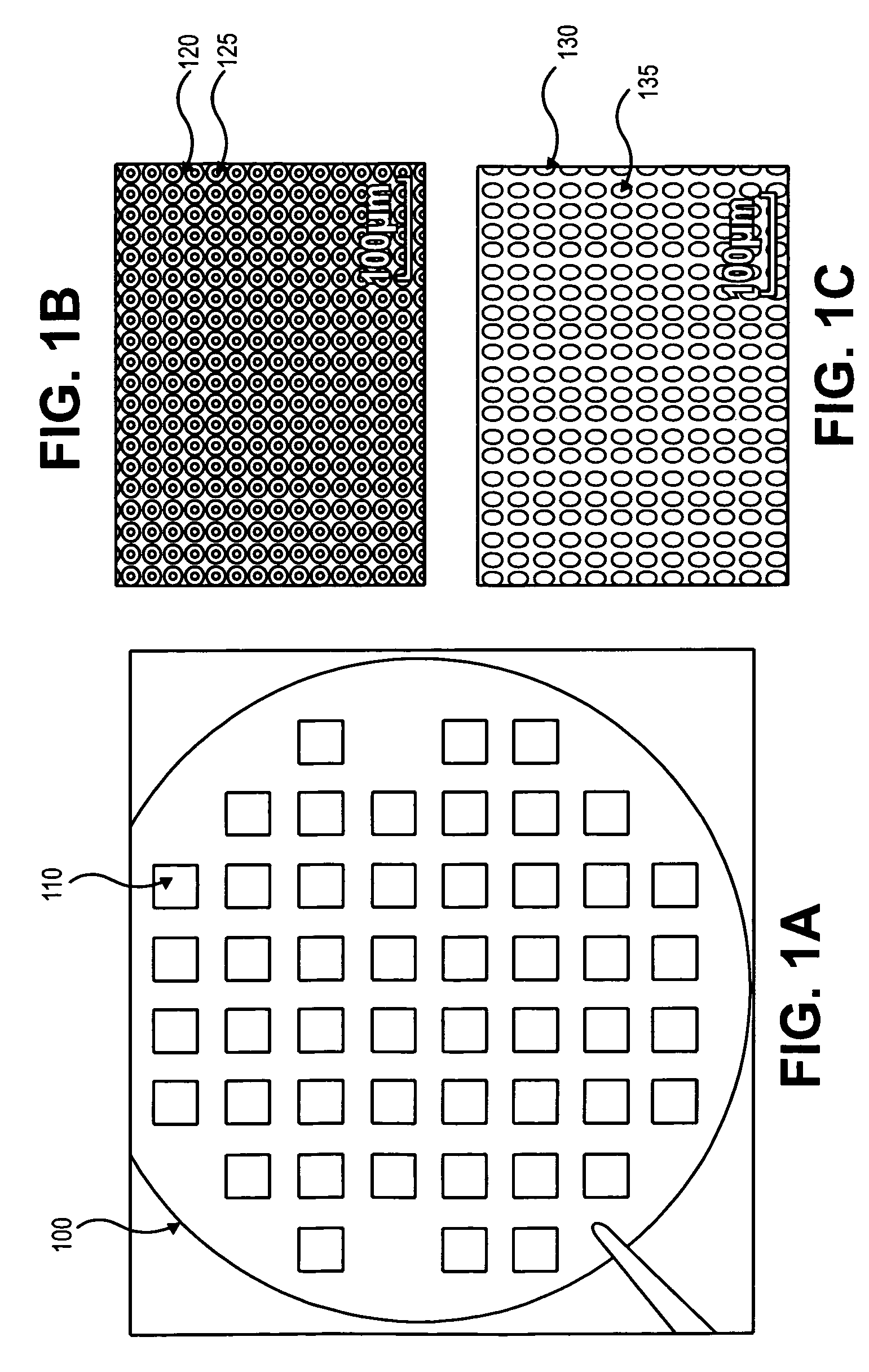
ActiveUS20070025883A1Improve efficiencyEffective meanUltrafiltrationLaboratory glasswaresParyleneFigure of merit
The invention provides parylene membrane filters, filter devices and methods of making them and using them in the mechanical separation of cells and particles by size. The provision of parylene membrane filters with high figures of merit and finely controlled hole sizes allows the separation of cells and particles in a variety of biological and other fluids according to sizes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Method and apparatus for treating wastewater using membrane filters
InactiveUS6863818B2Good removal effectEfficient workTreatment using aerobic processesBiological treatment regulationActivated sludgeBioreactor
An apparatus using activated sludge for the removal of biological nutrients from a wastewater includes a bioreactor for containing a mixture of wastewater under treatment and activated sludge. The bioreactor is divided into a plurality of serially connected treatment zones and includes a wastewater inlet, a downstream aerobic zone and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone. A method for removal of nutrients from a wastewater includes providing a wastewater to an inlet of a serial, multi-zone, activated sludge bioreactor containing an activated sludge. The bioreactor has a downstream aerobic zone from which water is removed and an upstream aerobic zone between the wastewater inlet and the downstream aerobic zone, the upstream and downstream aerobic zones being separated by an anoxic zone.
Owner:CH2M HILL
System for combined transcutaneous blood gas monitoring and negative pressure wound treatment
InactiveUS7524286B2Substantial riskAccurate estimateIntravenous devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerSignificant risk
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
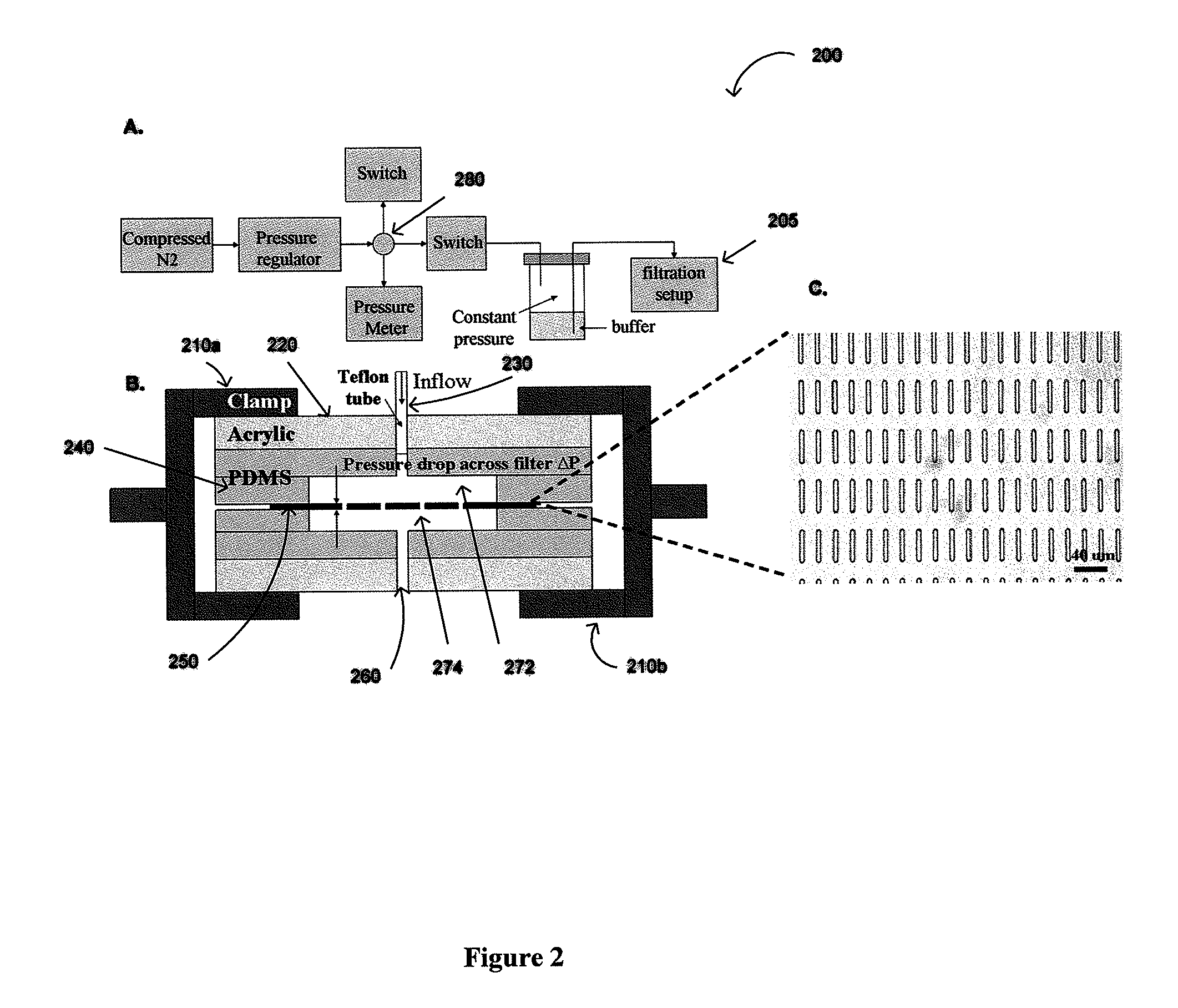
Method for cancer detection, diagnosis and prognosis
ActiveUS20110053152A1Rapidly and efficiently captureImprove capture efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTelomeraseParylene
The present invention provides a method for diagnosing cancer, predicting a disease outcome or response to therapy in a patient sample. The method involves isolating a circulating tumor cell (CTC), for example, a viable CTC, from a sample using a parylene microfilter device comprising a membrane filter having or consisting of a parylene substrate, which has an array of holes with a predetermined shape and size; and detecting and quantifying telomerase activity in blood circulating tumor cells. The invention further provides methods of using cells live-captured in various applications.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
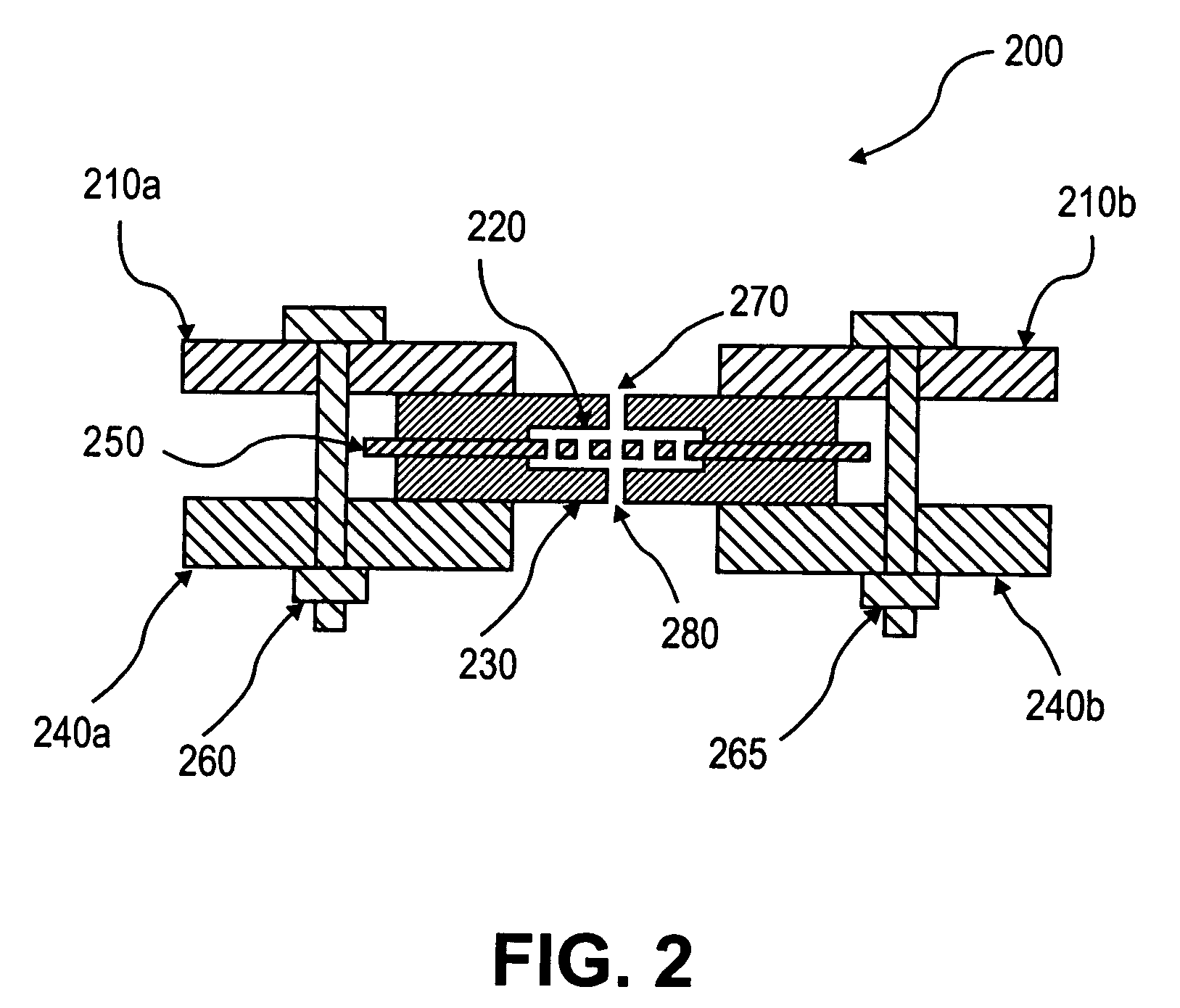
Membrane filter for capturing circulating tumor cells
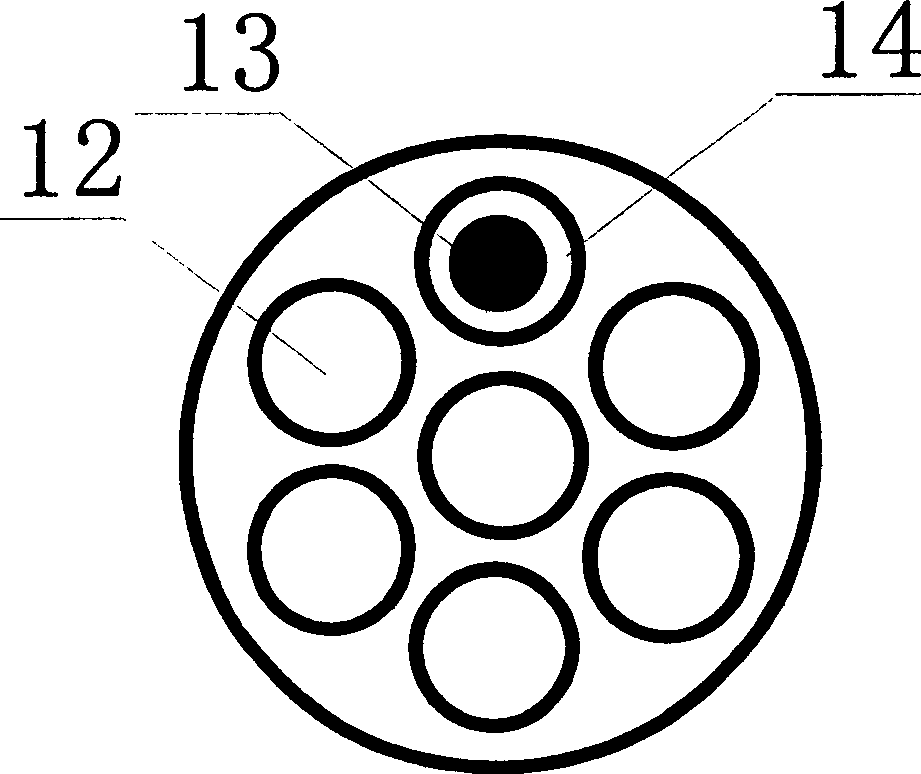
ActiveUS20060254972A1Highly efficient in capturingEffective membraneBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParyleneGeometric design
The present invention provides a parylene-based membrane filter device for capturing of circulating tumor cells (CTC). The membrane filter has an array of holes having a predetermined geometric design with precisely controlled size, shape and density. In one aspect, the device has a stack of substantially parallel membrane filters with uniformly-spaced and / or monodispersed holes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Process for Solvent Shifting a Nanoparticle Dispersion
ActiveUS20100152077A1Less polar phaseEfficient and economical processSolvent extractionTransportation and packagingSolventNanometre
A process for replacing the continuous phase of a nanoparticle dispersion with a less polar phase, includes filtering the dispersion through a semi-permeable membrane filter to remove the continuous phase, and introducing a less polar phase.
Owner:CERION
Membrane filter cleansing process
InactiveUS20060065596A1Reduce accumulationLower the liquid levelMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFiberHollow fibre membrane
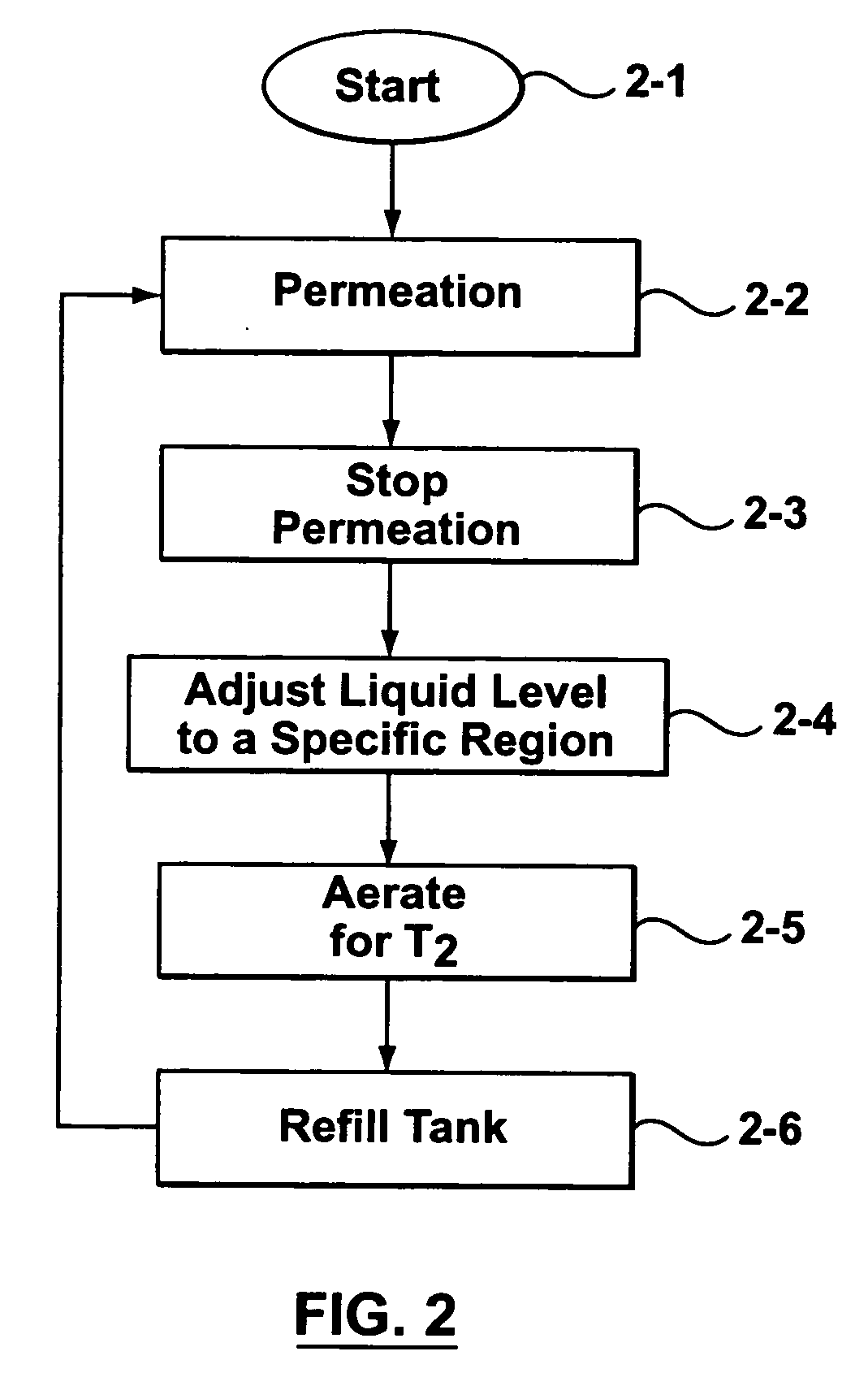
Immersed hollow-fiber membrane filtration systems sometimes encounter process problems as a result of solids accumulation in and around the hollow fibers. The solids can accumulate to the point where they begin to dewater and form a mud like substance known as sludge. In some embodiments of the invention there is provided a process for substantially preventing the accumulation of sludge build-up on membrane fibers and / or cleansing membrane fibers that have been fouled by a substantial sludge build-up. Many of these embodiments involve aerating a membrane tank in which the membrane fibers are immersed after the water level has been reduced to near the level of solids accumulation. In some embodiments of the invention, the energy released by bursting bubbles at the liquid-air interface is employed to prevent fouling of membrane fibers and / or cleanse fouled membrane fibers.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNERSHIP
Cooling device for electrical subassemblies
InactiveUS6885554B1Easy constructionEasy to cleanCombination devicesIsotope separationAccess networkFiltration
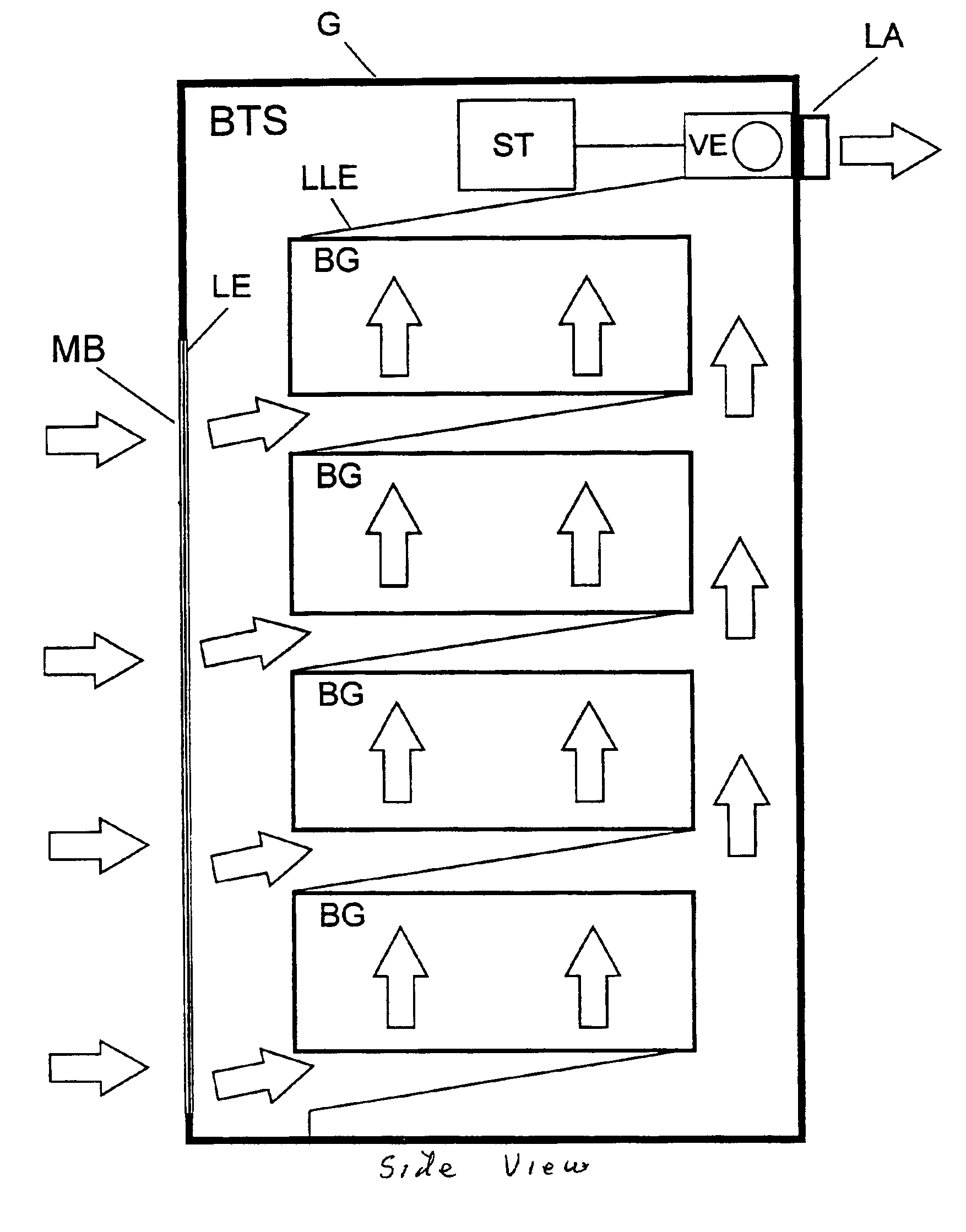
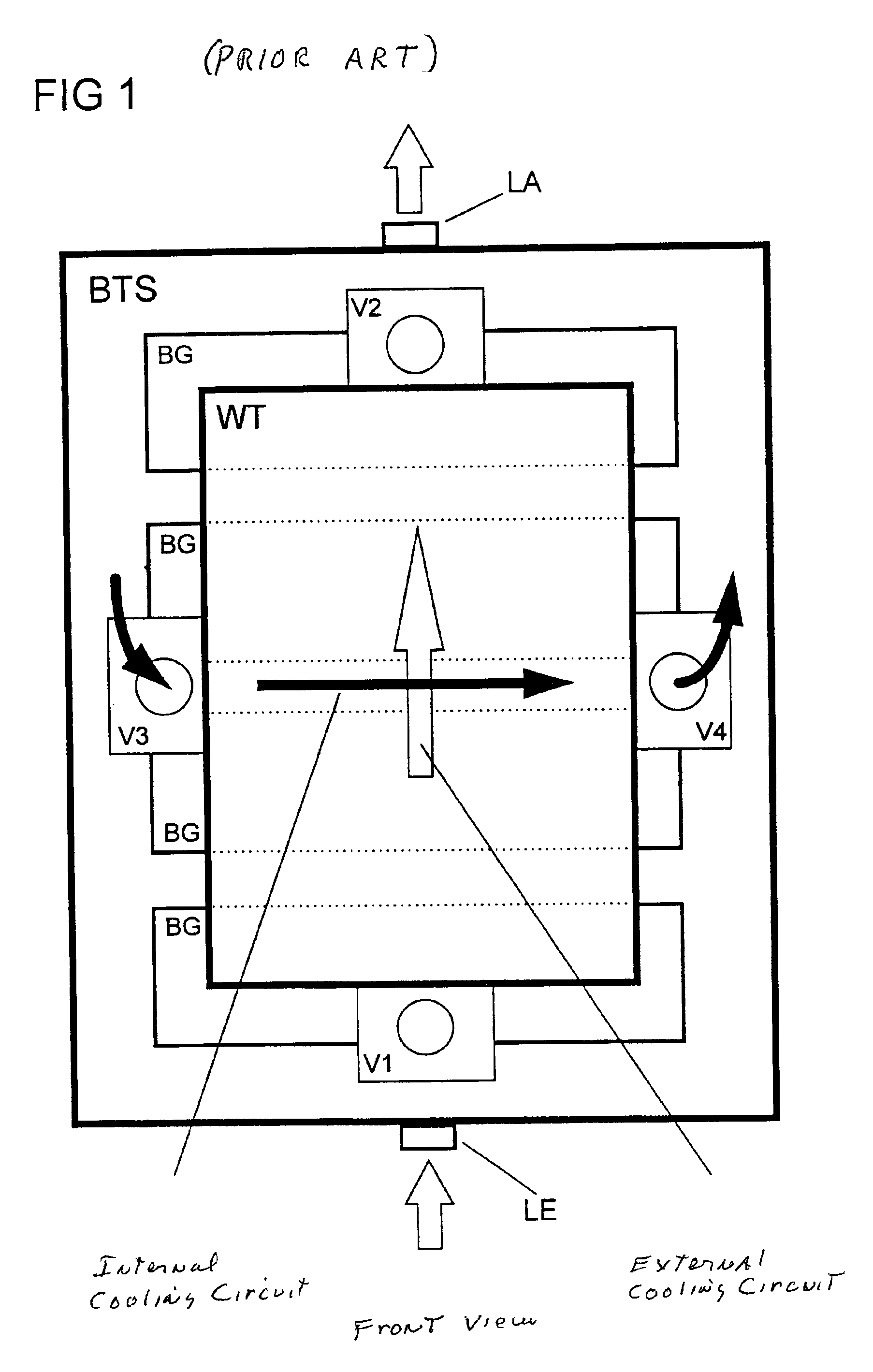
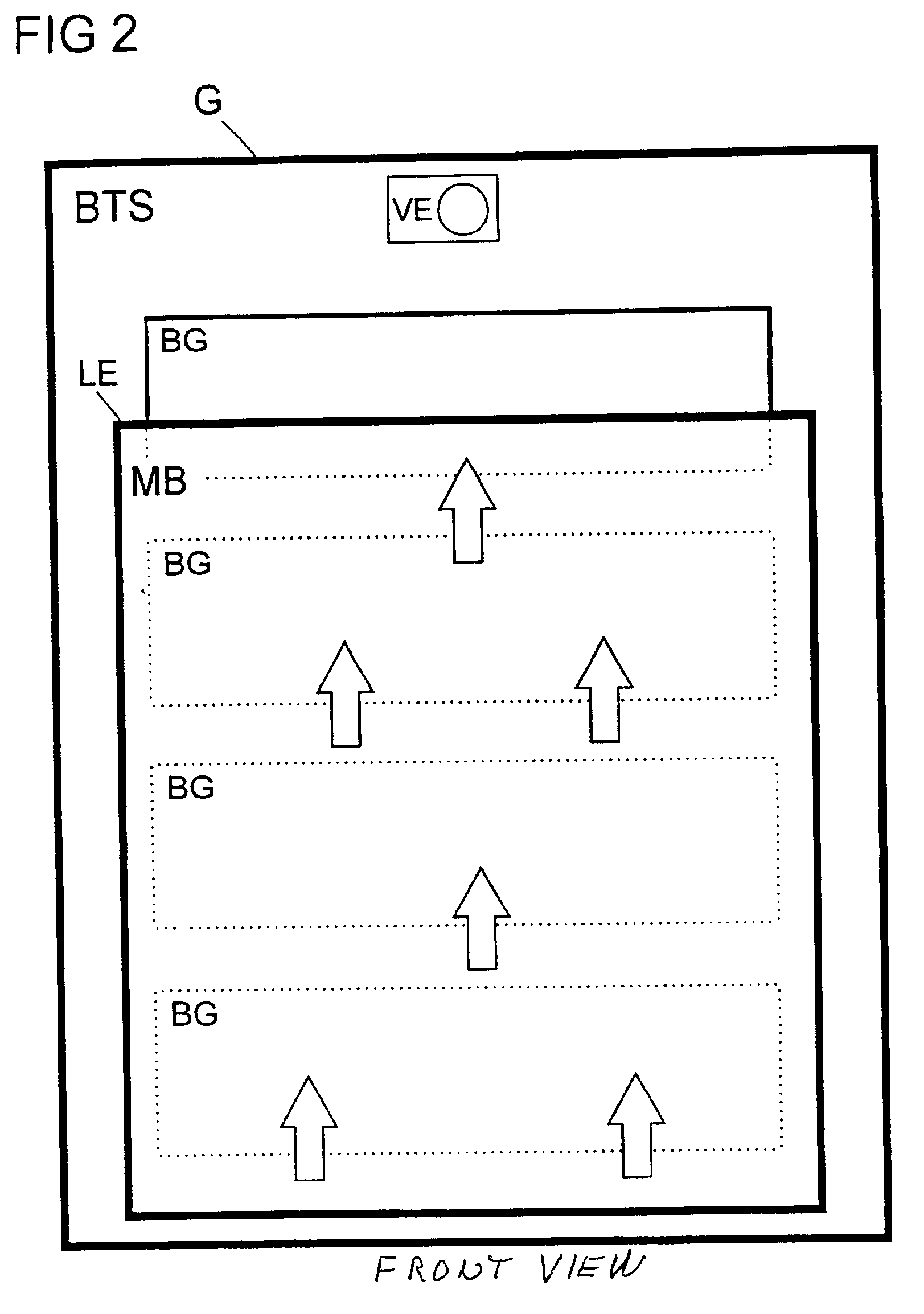
The invention relates to an arrangement for cooling electrical subassemblies arranged in a housing, in particular for use in base stations of a mobile radio system or access network system. The arrangement has at least one water-repellent membrane filter, in each case arranged in an air inlet of the housing, for the surface filtration of dirt particles from cooling air flowing in for cooling electrical subassemblies, as well as at least one cooling device to build up an airflow and to lead the filtered cooling air, heated because of flowing through the subassemblies, out of the housing through at least one air outlet.
Owner:SIEMENS AG +1
Chemical Clean For Membrane Filter
ActiveUS20080203017A1Facilitate wetting out and dissolvingLower the volumeSpecific water treatment objectivesUltrafiltrationConcentration gradientCleansing Agents
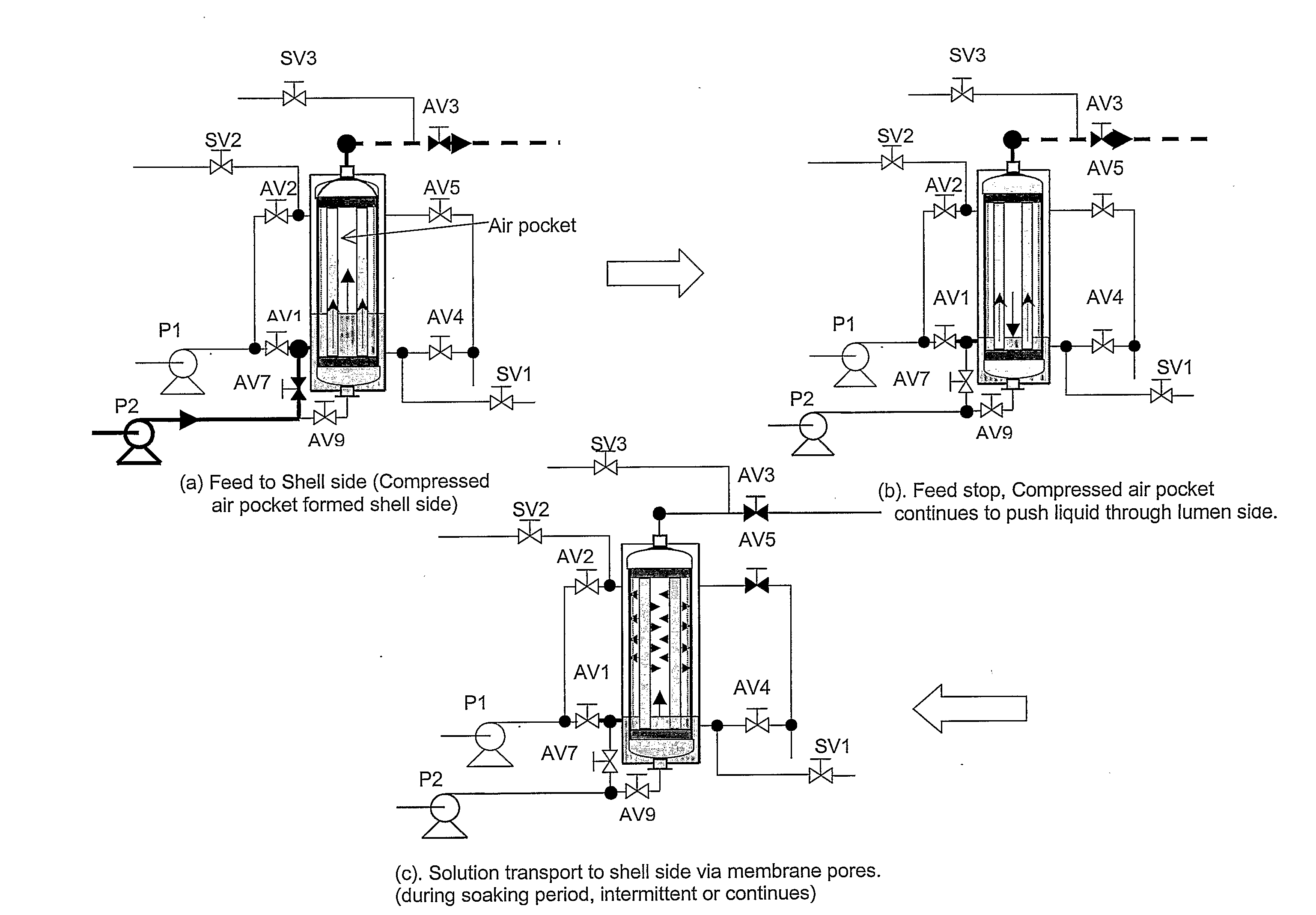
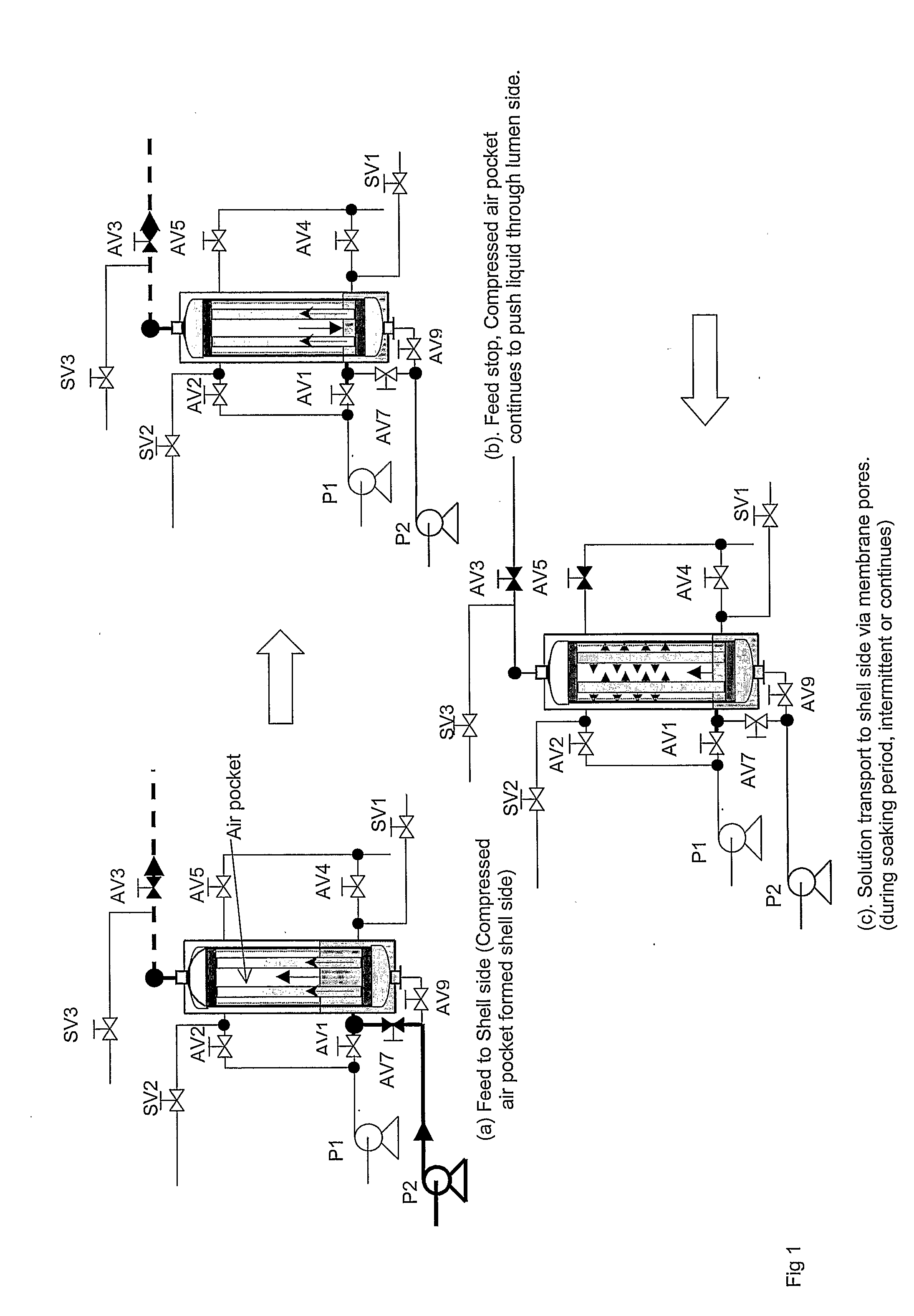
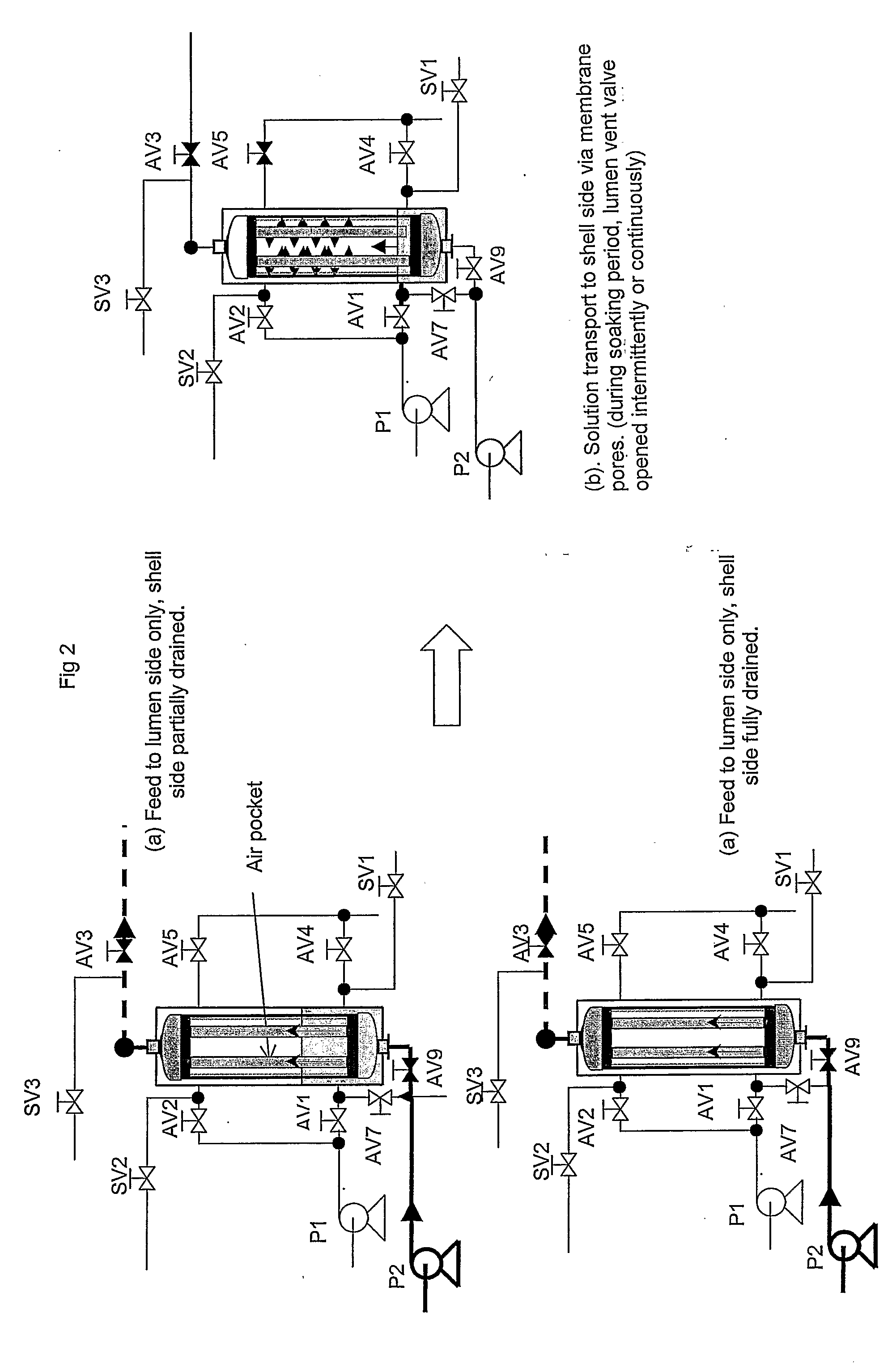
A method of cleaning a porous polymeric membrane having a feed side and a permeate side including the steps of introducing a fluid containing a cleaning agent to the permeate side of a membrane allowing the cleaning agent to contact the permeate side of the membrane for a predetermined time, and contact the pores of the membrane, or introducing a fluid containing a cleaning agent to the feed side of a membrane; applying a transmembrane pressure to force the fluid containing the cleaning agent from the feed side to the permeate side of the membrane; allowing the cleaning agent to contact the permeate side of the membrane for a predetermined time, and contact the pores of the membrane. Preferably a concentration gradient between the feed side fluid and the lumen side fluid containing the cleaning agent causes cleaning agent to diffuse into the feed side fluid. Pressure may be applied to the fluid containing a cleaning agent to dislodge, where present, dissolved and undissolved solid from the membrane pores. The pressure may be applied in a pulsed fashion, and can be by way of compressed air at a pressure not more than the membrane's bubble point. The methods of the present invention may be preceded by, or followed with a backwash.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Disposable, rapid extraction apparatus and methods
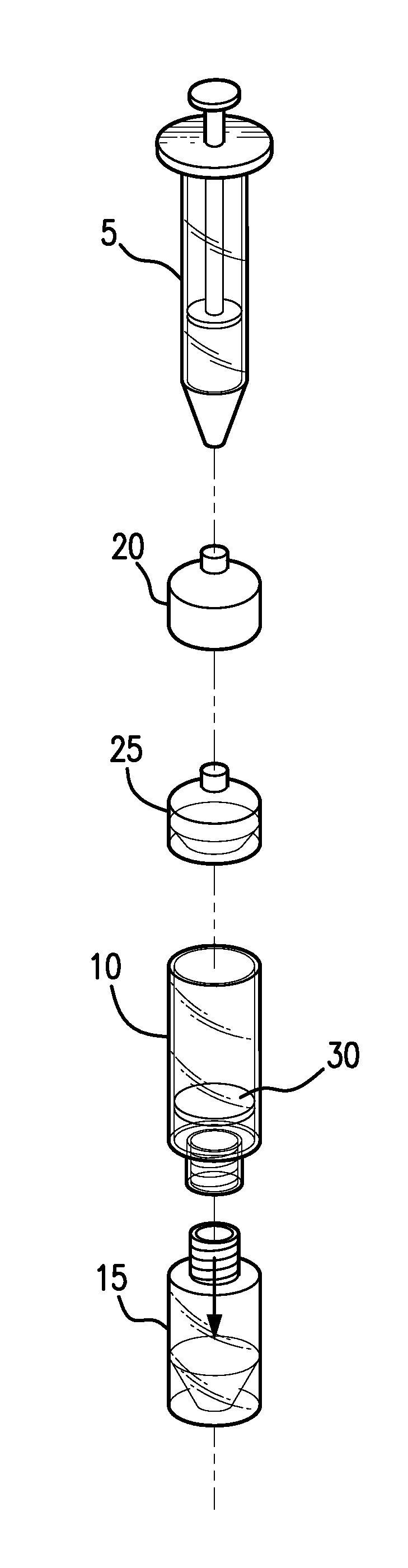
An extraction apparatus and methods adapted to extract and preferably also isolate structures of interest from a test sample. The extraction apparatus contains a volume-dispensing mechanism that facilitates control over the injection of a sample suspected of containing a structure of interest into a filtration vessel that contains a membrane filter that associates with the structure of interest, preferably by adsorbing or binding thereto, and a collection container associated therewith. Methods of extracting, isolating, testing, and instructions regarding such methods are also included.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
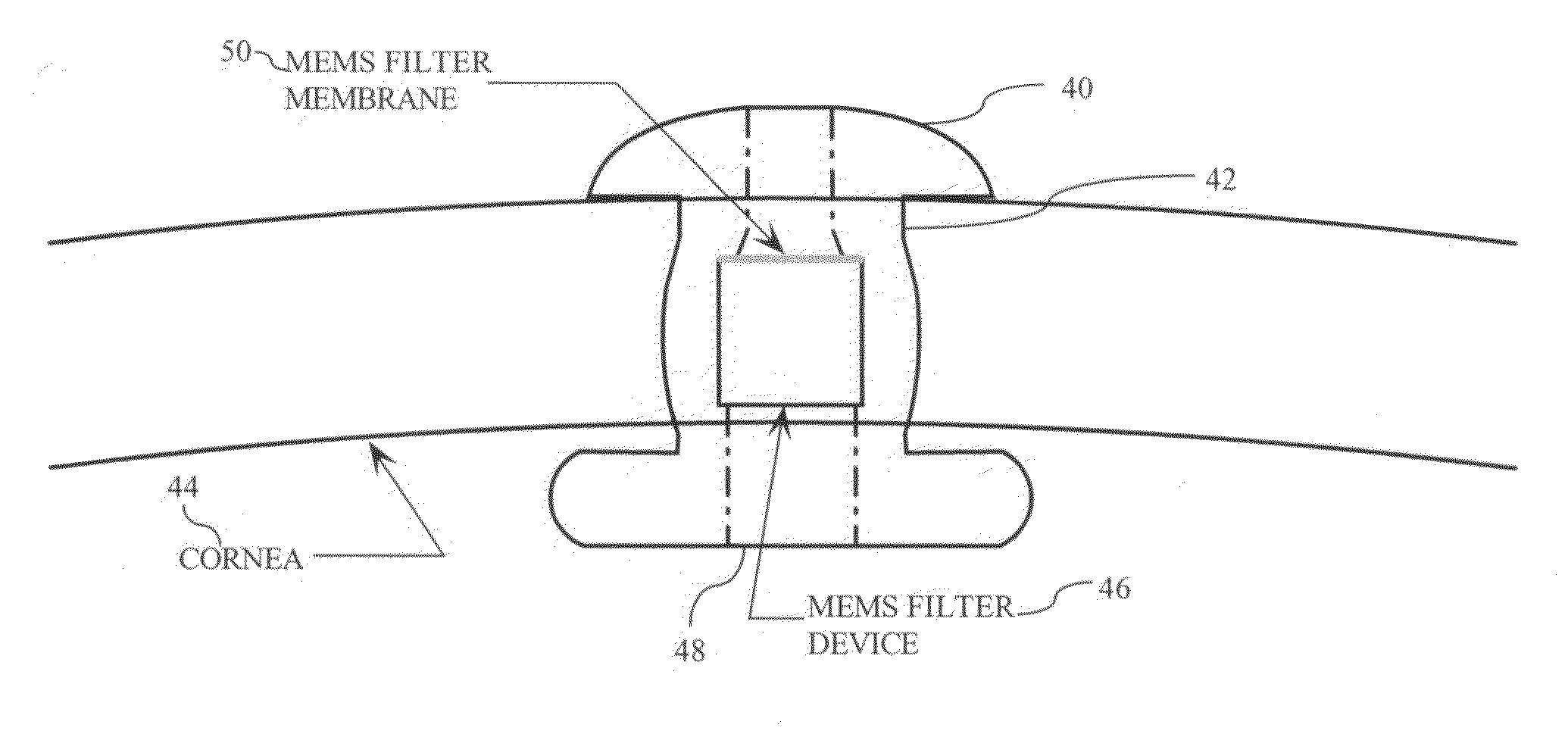
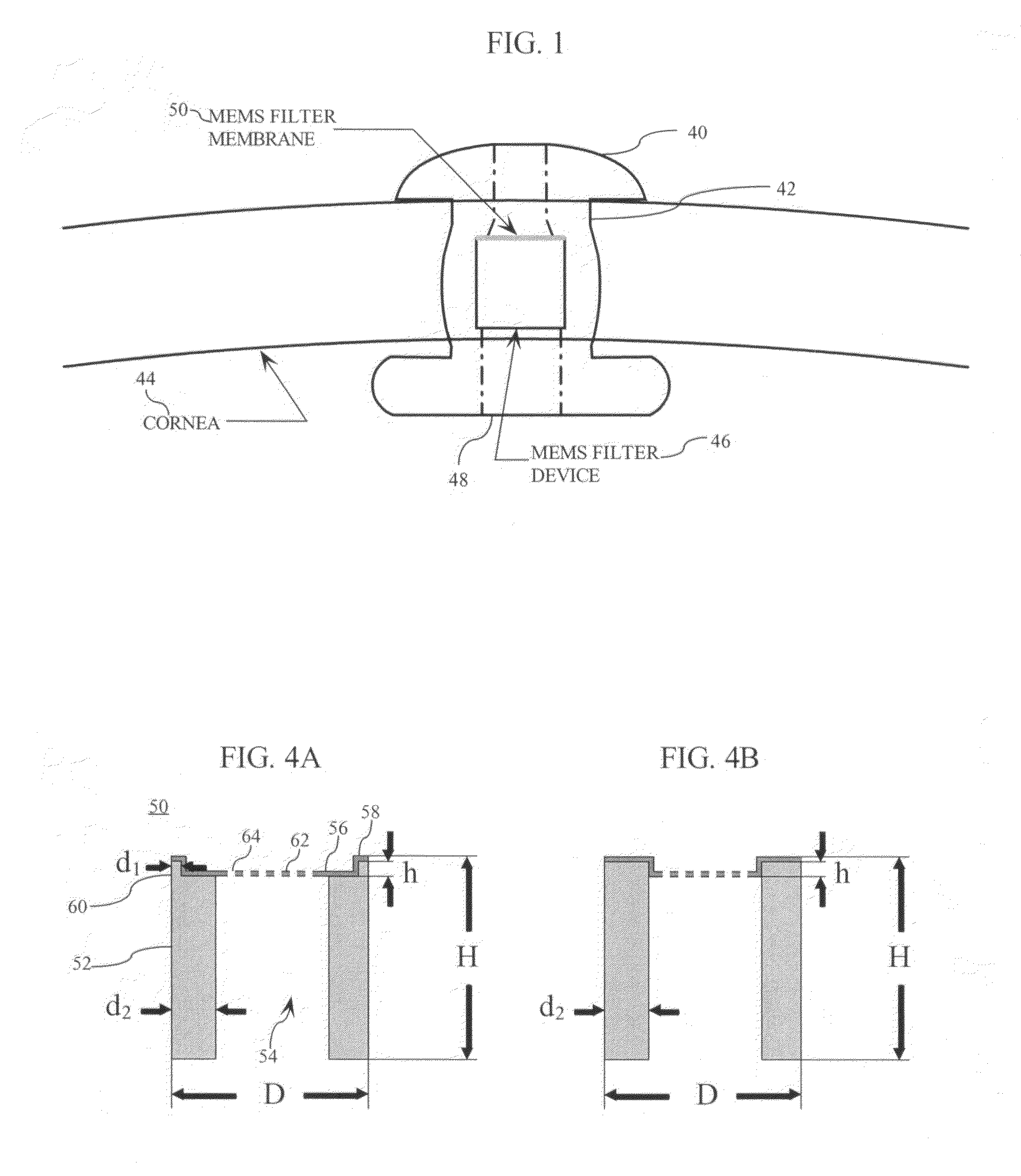
Micromachined membrane filter device for a glaucoma implant and method for making the same
InactiveUS20080277332A1LimitingProvide controlMembranesSemi-permeable membranesGlaucomaConformal coating
A MEMS-fabricated filter device for an ophthalmic shunt and a method for making the same. The filter device may include: a membrane with a plurality of pores, substantially uniformly sized to achieve a therapeutic flow rate while substantially preventing bacterial passage therethrough; a pair of substrates, each bonded to an opposing side of the membrane, and each having an axial inlet opening at a distal end thereof, and a cross-shaped support disposed in one of the substrates, the cross-shaped support supporting the membrane. The filter device may also include: a substrate having a passage therethrough; a membrane, axially recessed from opposing ends of the substrate and having a plurality of pores, substantially uniformly sized to achieve a therapeutic flow rate while substantially preventing bacterial passage therethrough; and a conformal coating covering the membrane. The method may include depositing a membrane layer on a substrate, patterning pores in the membrane layer to define an initial size of the pores, backside etching the substrate to the membrane layer, and conformally coating the membrane layer.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
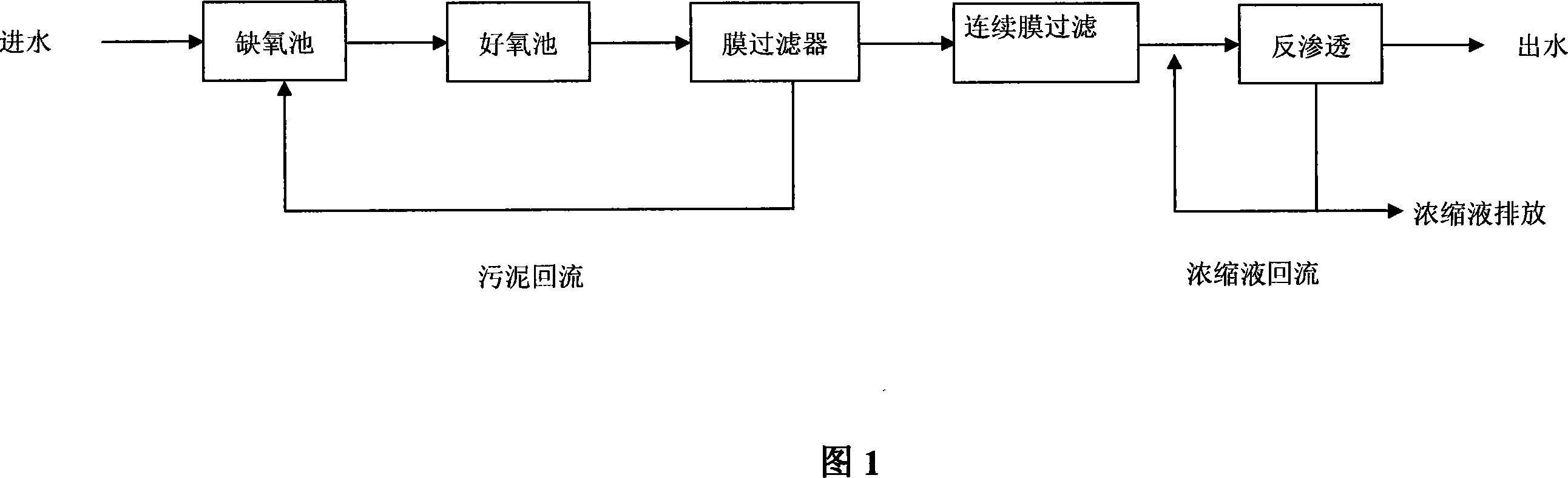
Technological process of treating papermaking effluent for reuse based on membrane integrating technique
ActiveCN101088941AAchieve recyclingEfficient deep processingWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesReverse osmosisPapermaking
The technological process of treating papermaking effluent for reuse based on membrane integrating technique has membrane bioreactor, continuous membrane filter and reverse osmosis unit integrated for high efficiency treatment of papermaking effluent. The papermaking effluent treating process includes drum filtering and flocculating deposition to eliminate most suspended matter and colloid matter, anaerobic and aerobic biochemical treatment, filtering in membrane separating element, continuous membrane filtering, and treating with reverse osmosis membrane to reach the papermaking water standard. The present invention is especially suitable for treating hard-to-treat papermaking effluent.
Owner:安徽森诺膜技术有限公司 +1
Biological phosphorus removal
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
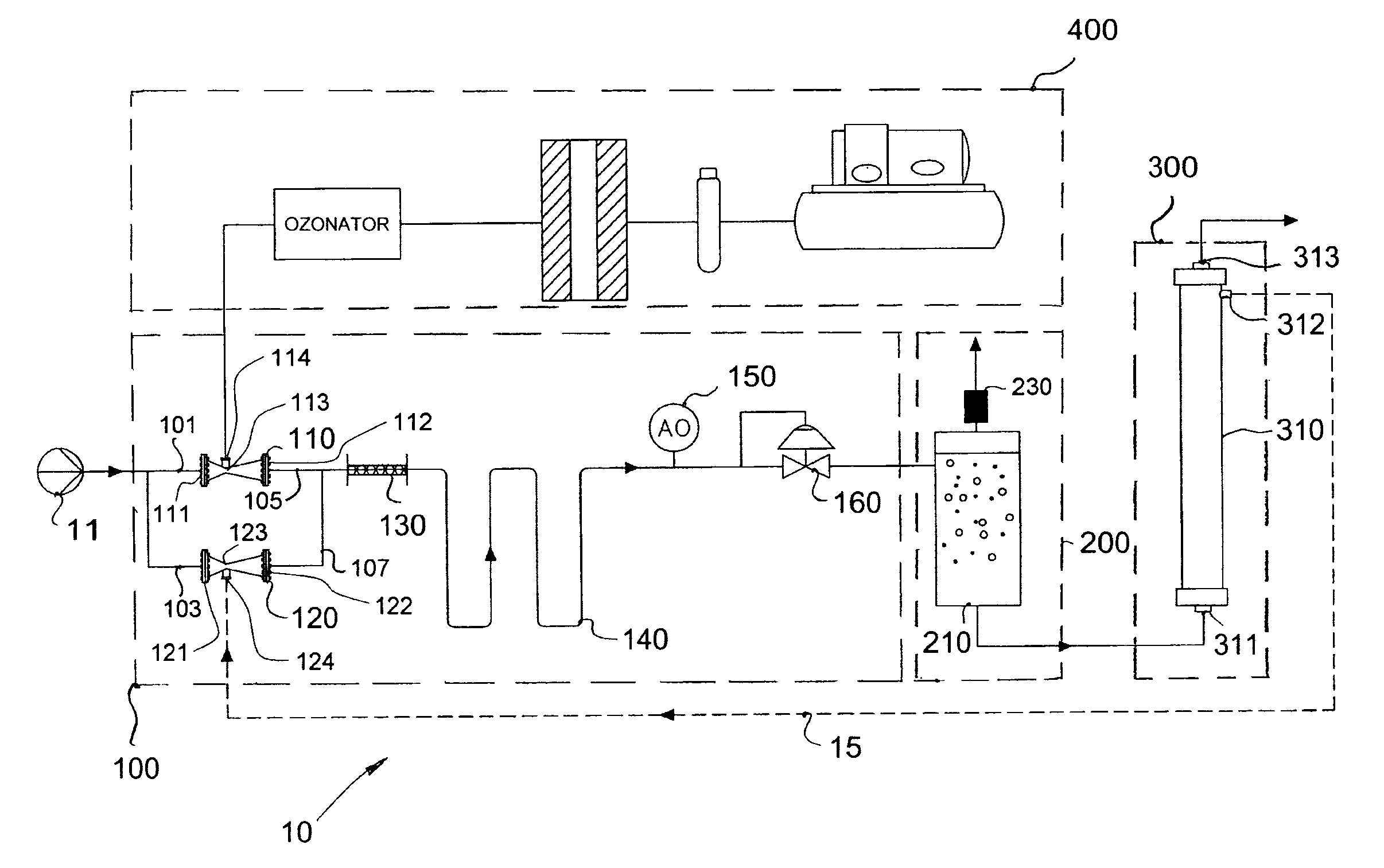
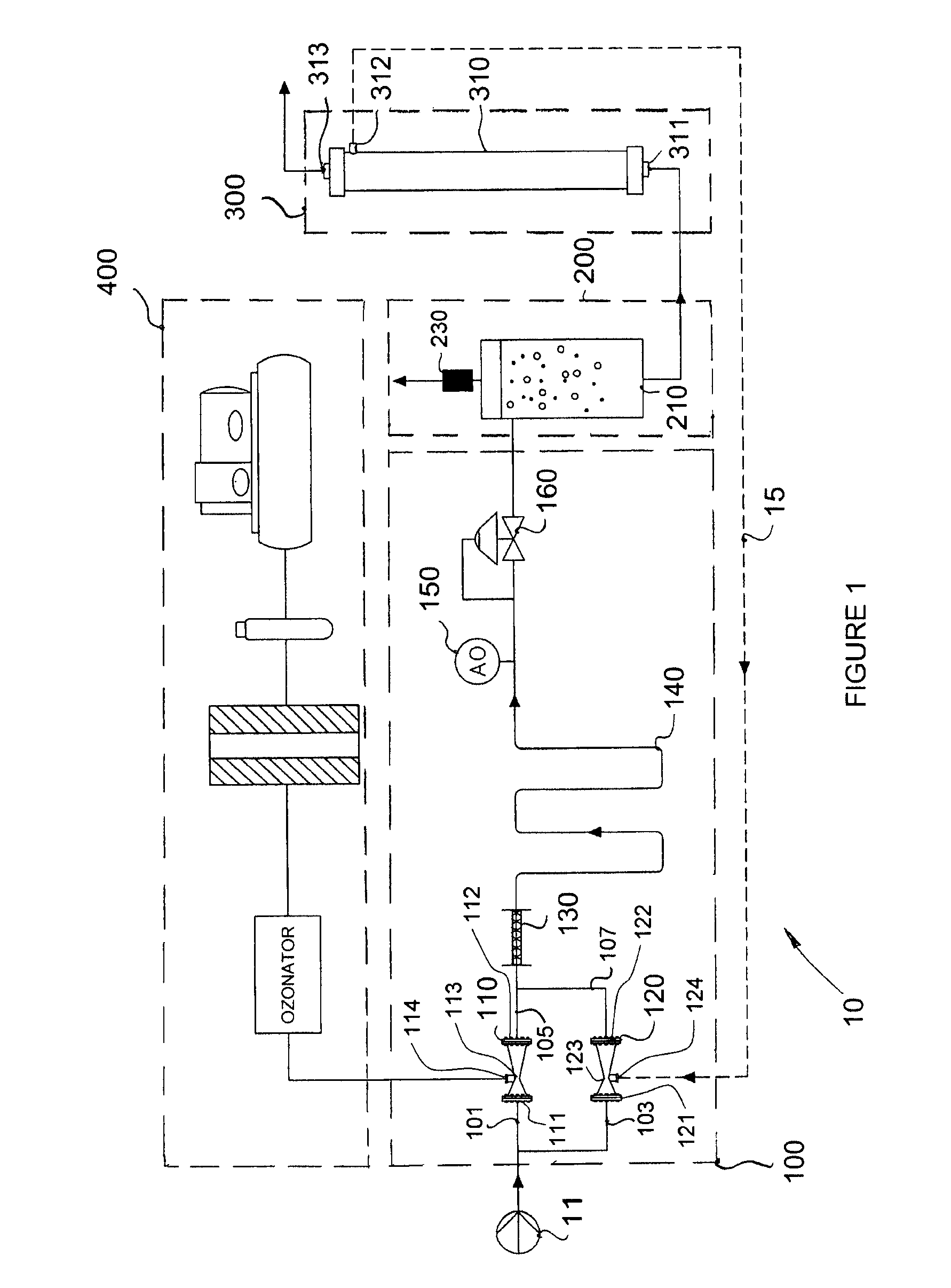
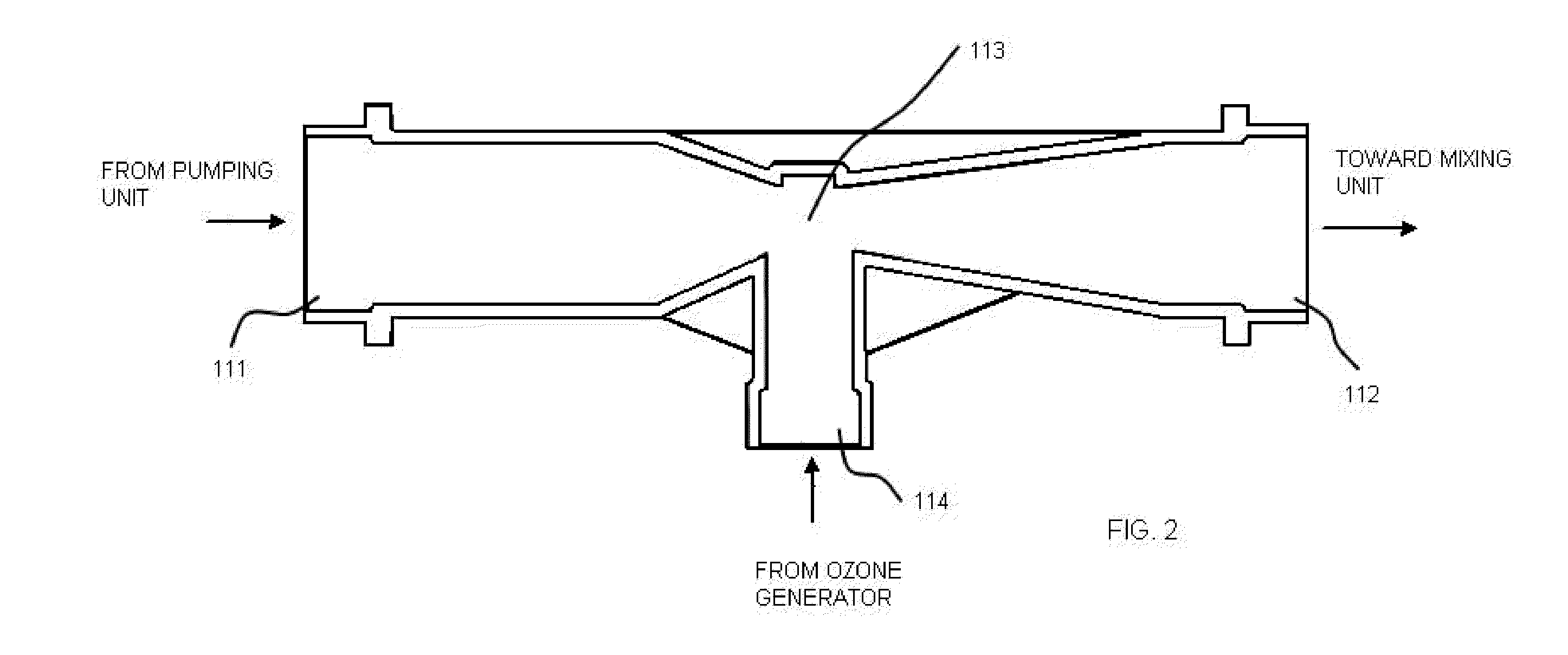
Water Treatment Apparatus and Method
ActiveUS20100219137A1Beneficial usEffective dissolutionMembranesSemi-permeable membranesMicrobubblesThree stage
An apparatus and a method for an ozone-based treatment of polluted water are disclosed. The apparatus and the method generally comprise three stages. The first stage is an ozone treatment stage wherein the polluted water is treated with ozone gas. The second stage is a gas-liquid separation stage wherein excess non-dissolved gases, from the ozone treatment stage, are removed from the water whereby the water exiting the gas-liquid separation stage is substantially saturated with dissolved gases and substantially free of non-dissolved gases. The last stage is a membrane filtration stage wherein the gas-saturated water generally undergoes micro-filtration or ultra-filtration. Microbubbles formed during this final stage generally prevent the accumulation of particles and pollutants on the surface of the membranes and / or inside the openings or pores thereof; thereby acting as a self-cleaning mechanism for the membrane filter.
Owner:8452059 CANADA
Membrane filter for capturing circulating tumor cells
ActiveUS7846393B2Highly efficient in capturingEffective membraneBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParyleneGeometric design
The present invention provides a parylene-based membrane filter device for capturing of circulating tumor cells (CTC). The membrane filter has an array of holes having a predetermined geometric design with precisely controlled size, shape and density. In one aspect, the device has a stack of substantially parallel membrane filters with uniformly-spaced and / or monodispersed holes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
Green tea beverage, and its prepn. method
InactiveCN1718030AIncrease nutritional contentImprove retentionTea extractionNutritive valuesGreen tea
A green tea beverage is prepared from the fresh organic green tea leaves through breaking, squeezing to obtain tea juice, filtering, fine filtering by membrane, mixing it with water in ratio of 1:(15-25),membrane filtering for removing bacteria, and aseptic canning. Its advantages are unique fragrance and high nutritive value.
Owner:YUNNAN LANCANGJIANG BEER ENTERPRISE GRP CO LTD
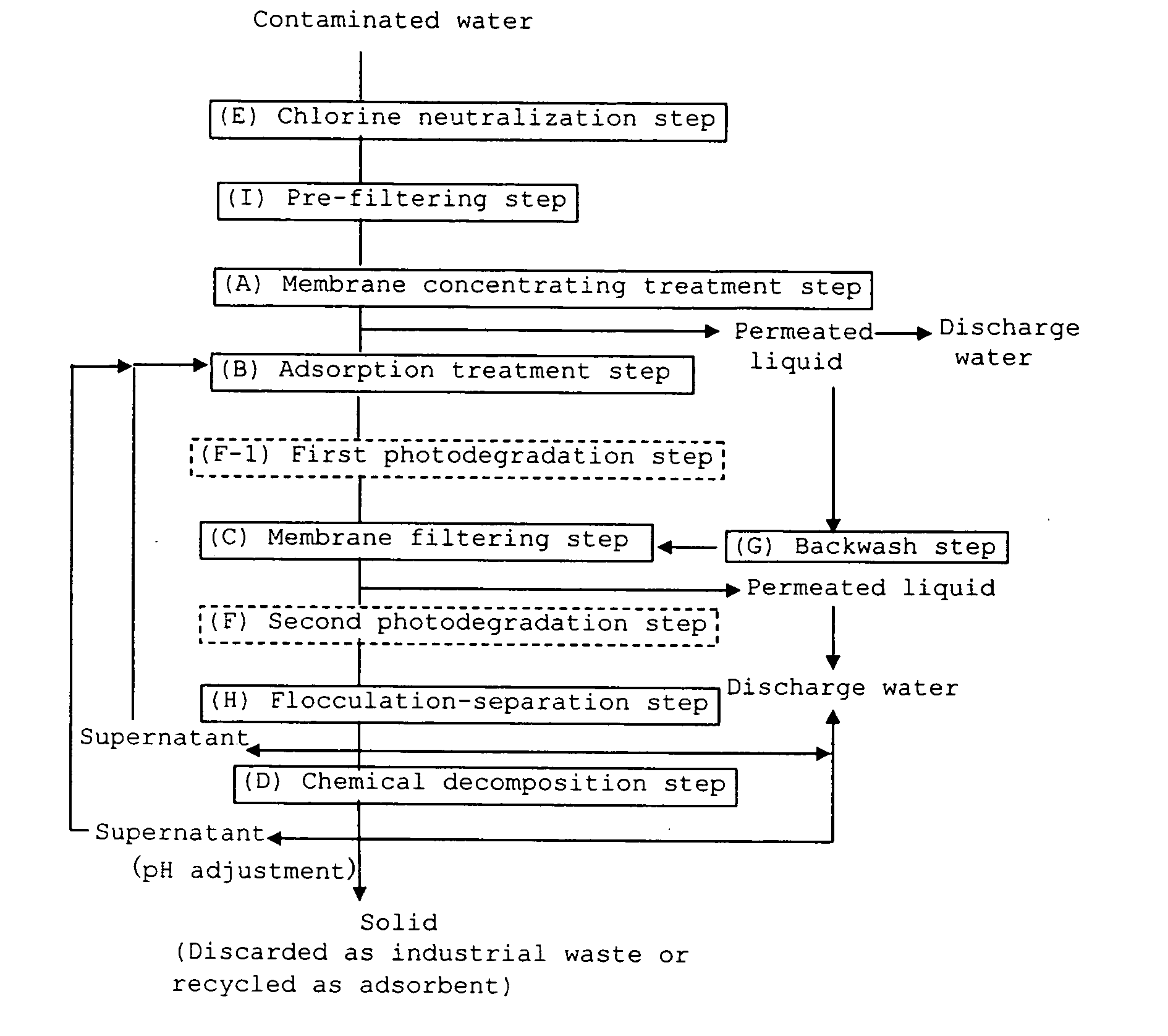
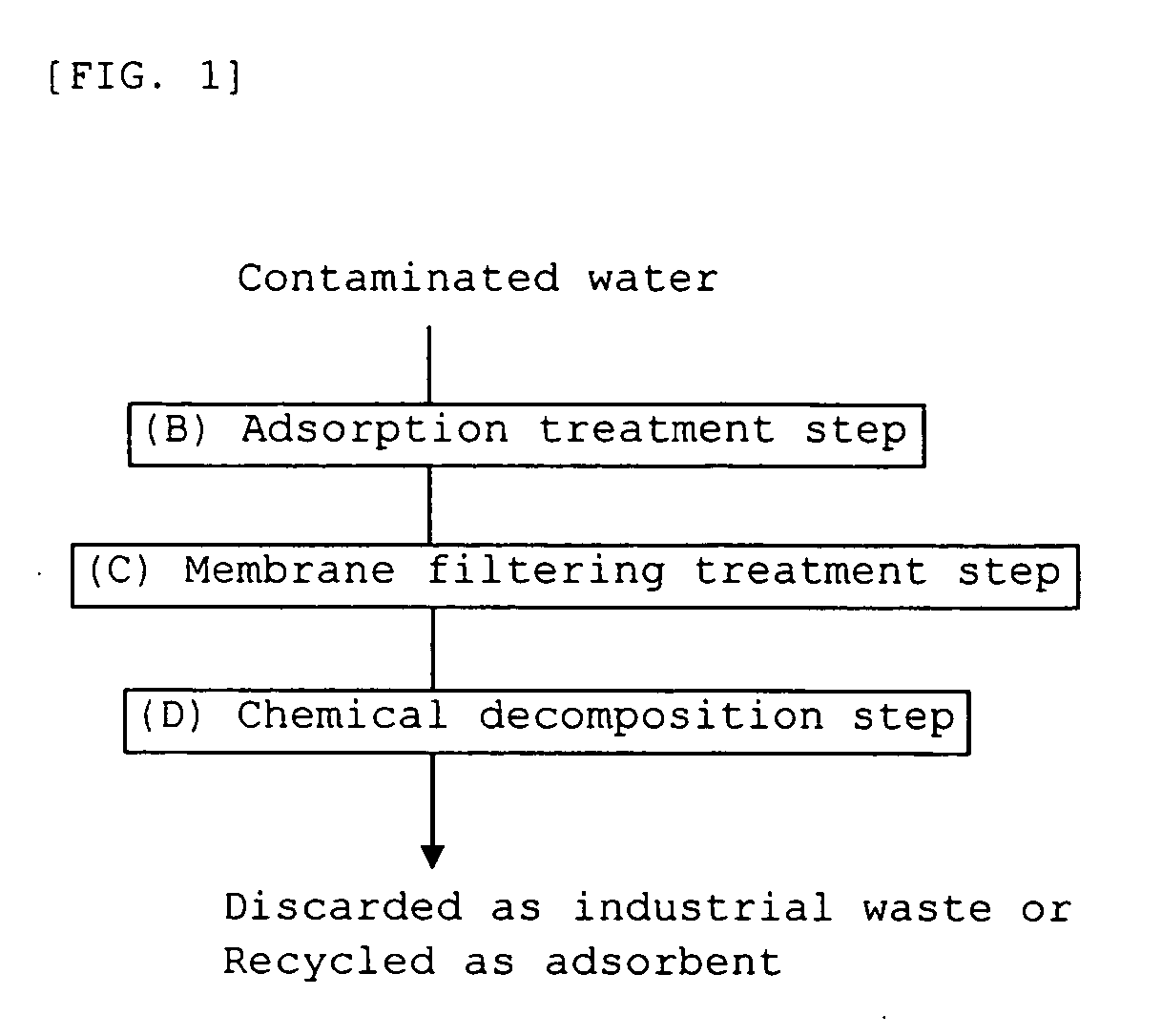
Method for treating raw water containing hardly decomposable substance
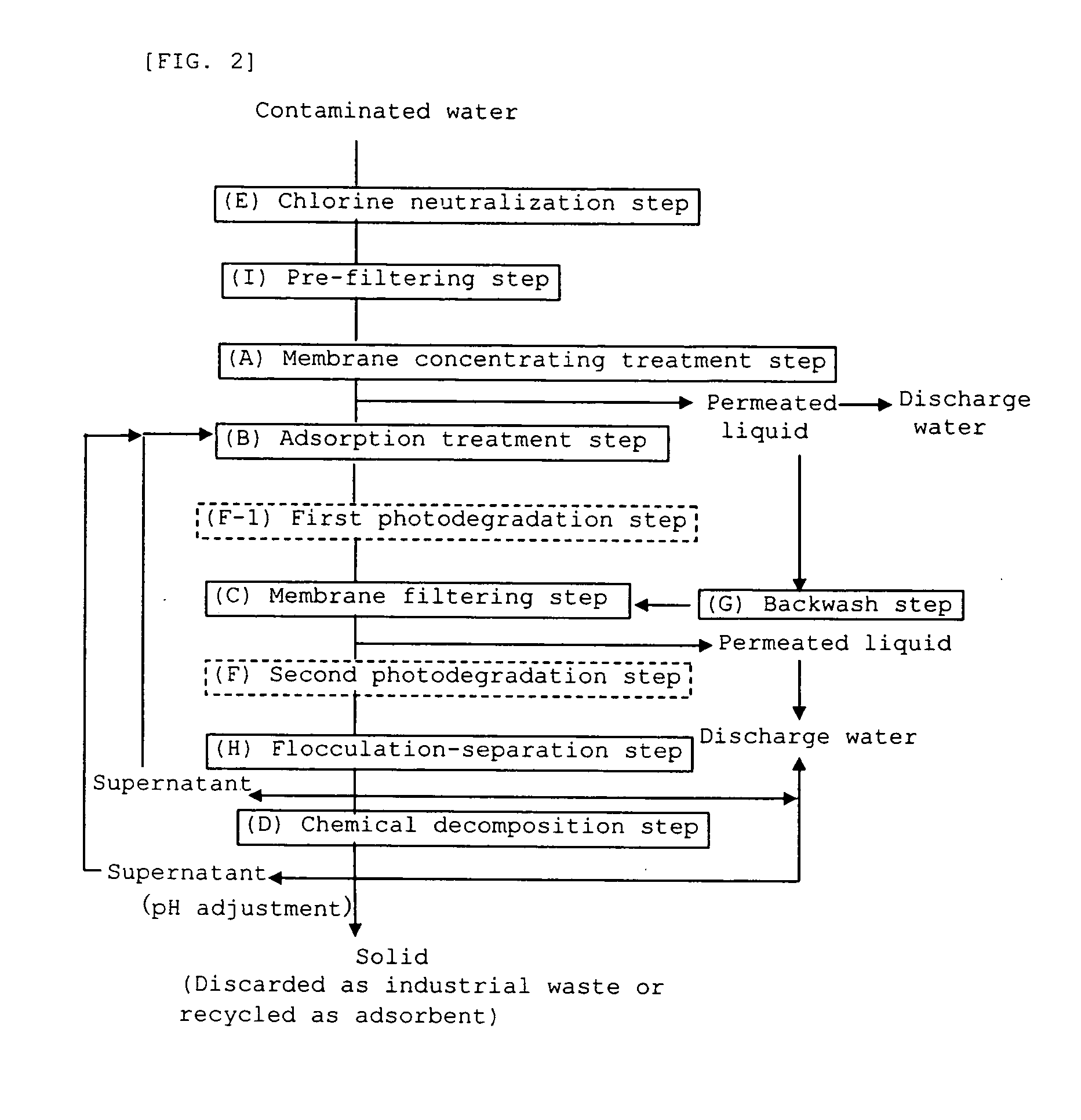
InactiveUS20070119779A1Efficient decompositionReduce concentrationUltrafiltrationSolid sorbent liquid separationDesorptionSorbent
Provided a method for treating hardly-decomposable-substance-containing water, in which hardly decomposable substances such as dioxins, contained in contaminated water (treatment raw water) are concentrated and rendered harmless by providing the steps of (B) adding an adsorbent to water containing a hardly decomposable substance (treatment raw water) to cause the hardly decomposable substance to be adsorbed on the adsorbent (adsorption treatment step), (C) separating a permeated liquid through a filter membrane to concentrate the adsorbent adsorbing the hardly decomposable substance (membrane filtering treatment step), and (D) chemically decomposing the hardly decomposable substance adsorbed on the concentrated adsorbent with a peroxide without any operation of desorption from the adsorbent (chemical decomposition step), and the method can be applied to water containing a reducing substance such as bisulfate that neutralize free chlorine and can render the hardly decomposable substances harmless efficiently at a low cost without being limited by properties of the hardly decomposable substances contained.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Uses of Parylene Membrane Filters
ActiveUS20110111412A1Improve efficiencyEffective meanMembranesMicrobiological testing/measurementParyleneFigure of merit
The invention provides parylene membrane filters, filter devices and methods of making them and using them in the mechanical separation of cells and particles by size. The provision of parylene membrane filters with high figures of merit and finely controlled hole sizes allows the separation of cells and particles in a variety of biological and other fluids according to sizes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
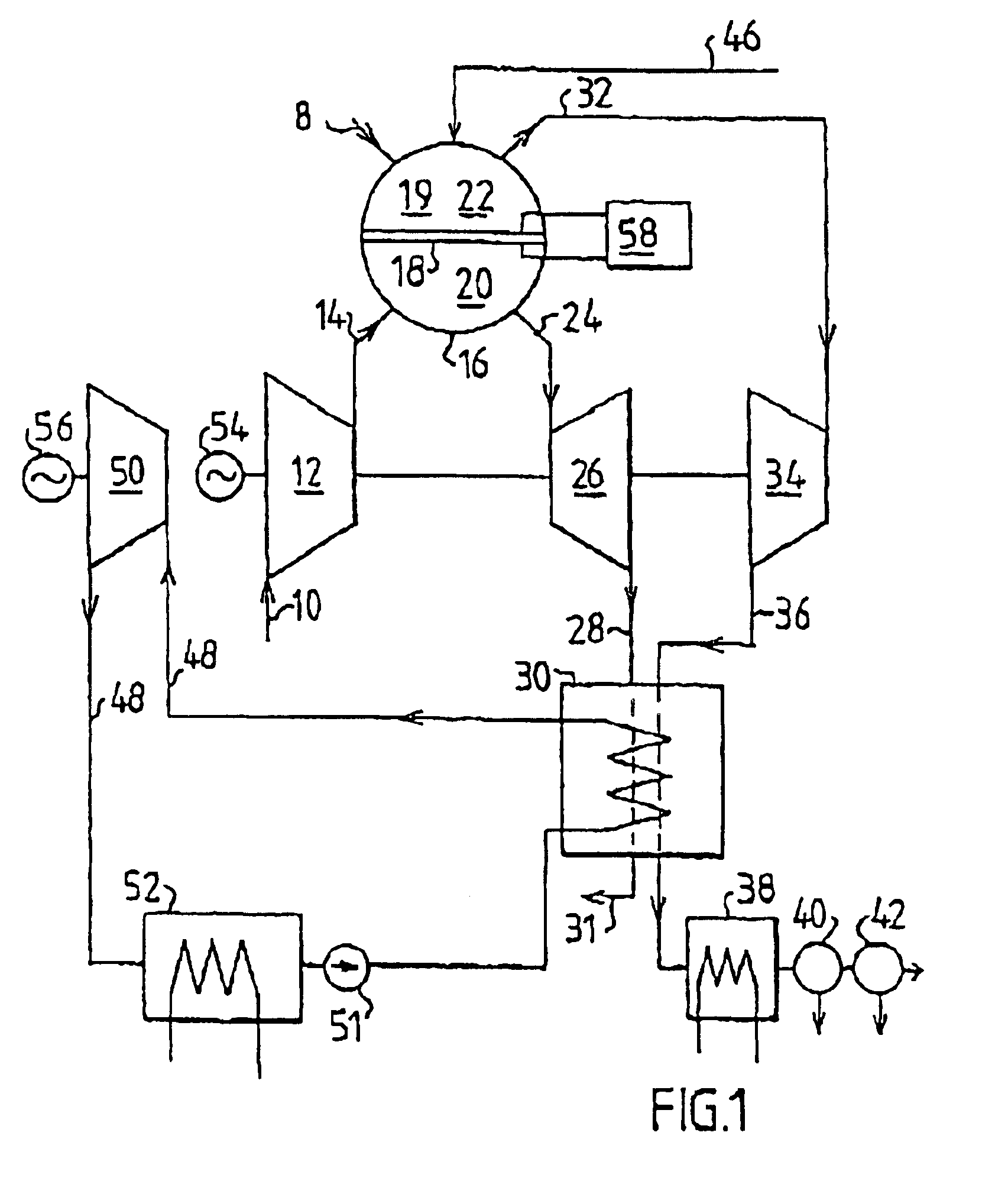
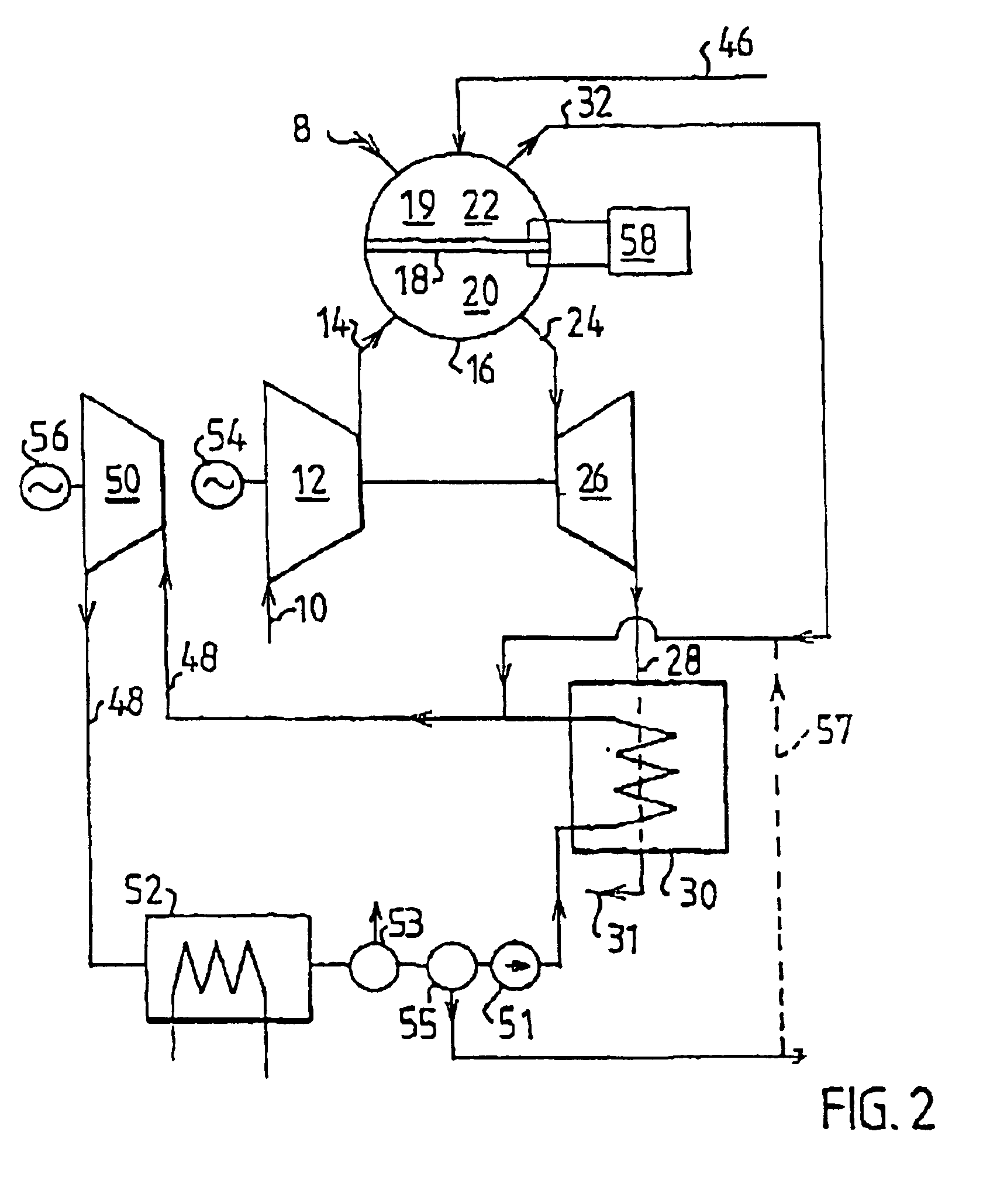
Method of operating a combustion plant and a combustion plant
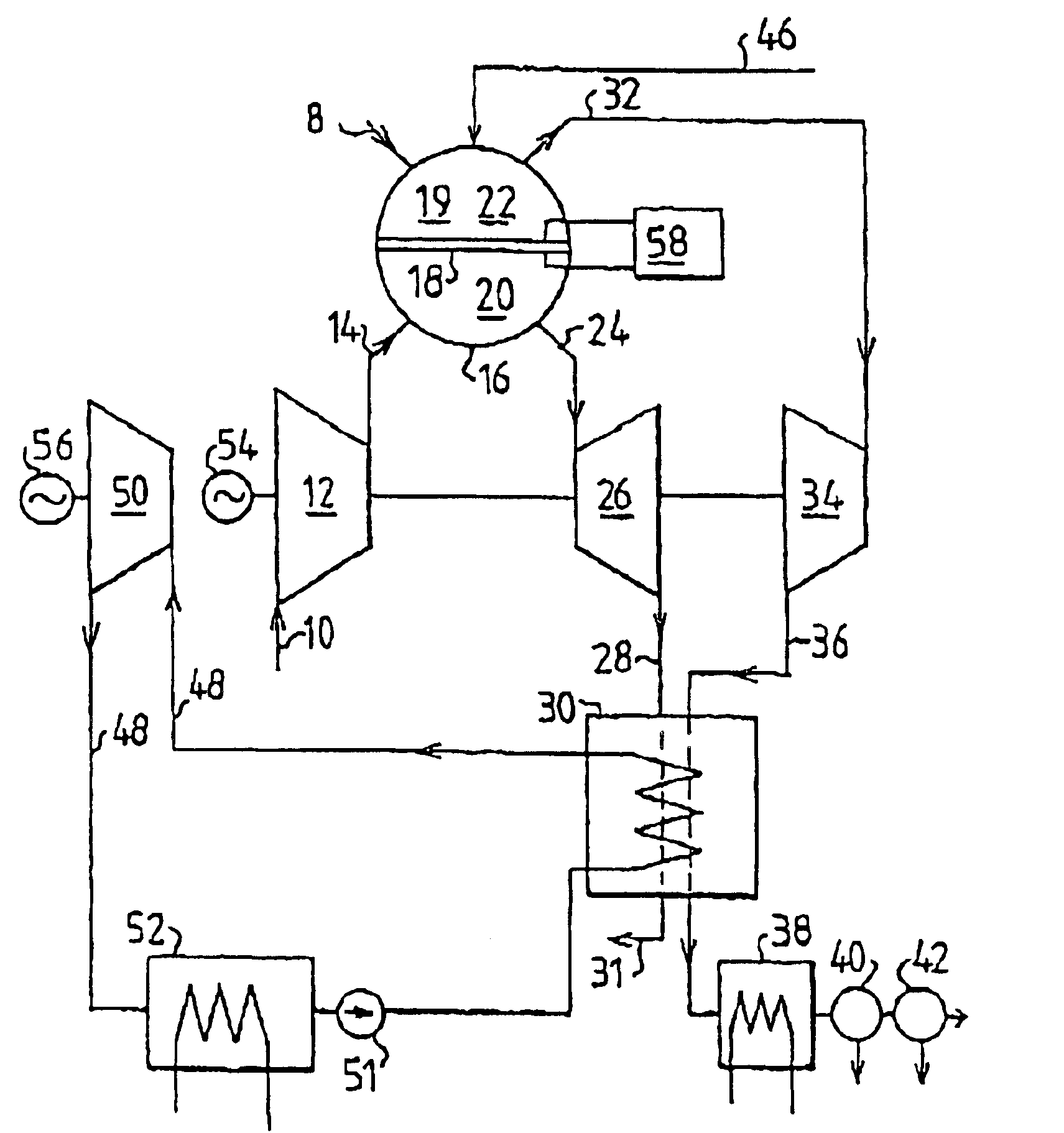
InactiveUS6877319B2Improve efficiencyAvoid emissionsDispersed particle separationGas turbine plantsProduct gasProcess engineering
The invention concerns a method of operating a combustion plant comprising at least a first gas turbine (26), a second turbine (34, 50) and a membrane reactor device (16) which comprises a membrane filter device (18) for separating oxygen from a gas mixture and a combustion space (19). A gas mixture containing oxygen is supplied to the membrane reactor device (16). At least some oxygen is separated from the gas mixture with the help of the membrane filter device (18). The separated oxygen is used at the combustion in the combustion space (19). The oxygen-depleted gas that is obtained after the separation of oxygen and which has not gone through a combustion process is used to run the first gas turbine (26). Combustion gases run the second turbine (34, 50). The invention also concerns a combustion plant for carrying out the method.
Owner:NORSK HYDRO ASA +1
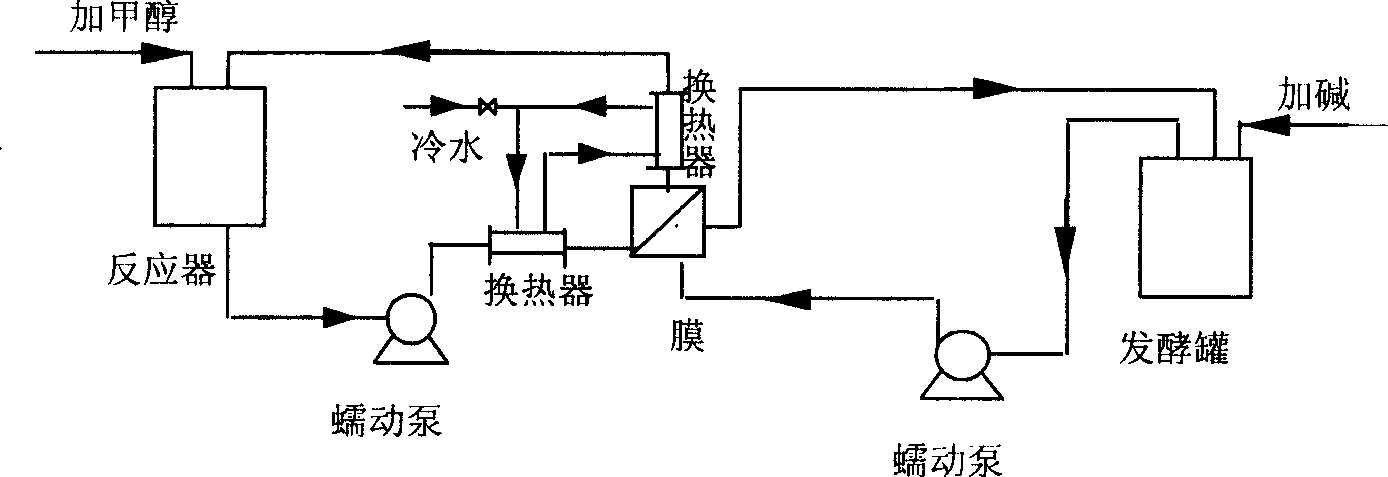
Process for coupling producing bioloigical diesel oil and 1,3-propylene glycol
InactiveCN1648207AReduce or even eliminate poison inactivationSave on separation costsOrganic chemistryLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBiodieselMicrobial transformation
The present invention belongs to the field of bioengineering technology, and especially a kind of couple producing biological diesel oil and 1, 3-propylene glycol. The present invention features that the course of lipase catalyzed reaction between methanol or ethanol and fat to produce biological diesel oil and the course of biologically converting glycerin into 1, 3-propylene glycol are coupled via membrane filtering for simultaneous proceeding. The present invention has the effects of eliminating the suppression of short-chain alcohol and glycerin on lipase, prolonging the service life of immobilized enzyme, omitting the glycerin separating and extracting step, lowering the production cost, saving time, raising production efficiency and providing economic and feasible process for producing biological diesel oil and 1, 3-propylene glycol.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Sewage treating device and process
ActiveCN101274810AWell mixedReduce operating energy consumptionMembranesWater treatment parameter controlActivated sludgeSewage
The invention discloses a sewage treatment device which comprises a biological reaction pool and membrane separation equipment. The membrane separation equipment is arranged outside the biological reaction pool, the interior of which is provided with mixing equipment. The interior of the membrane separation equipment or the interior of the container that holds the membrane separation equipment isprovided with aeration equipment, and the membrane separation equipment or the container that holds the membrane separation equipment is communicated with the biological reaction pool through a pipeline. The interior of the membrane separation equipment is provided with the mixing equipment in the invention, and leads the concentrated solution which reflows through the membrane separation equipment or the container that holds the membrane separation equipment to be fully mixed with the mixing solution in the biological reaction pool, thereby avoiding the wasting phenomenon of energy consumption caused by high strength aeration in a membrane filter pool, which is common in existing negative pressure external membrane bioreactors; therefore, the gas-water ratio of the membrane bioreactor isgenerally reduced to 12:1 and even less than 10:1, which is basically close to other sewage biological treatment techniques of a traditional active sludge method, etc., thus leading the energy consumption in operation of a sewage treatment system to be maintained at a relatively low level.
Owner:BEIJING ECOJOY WATER TECH
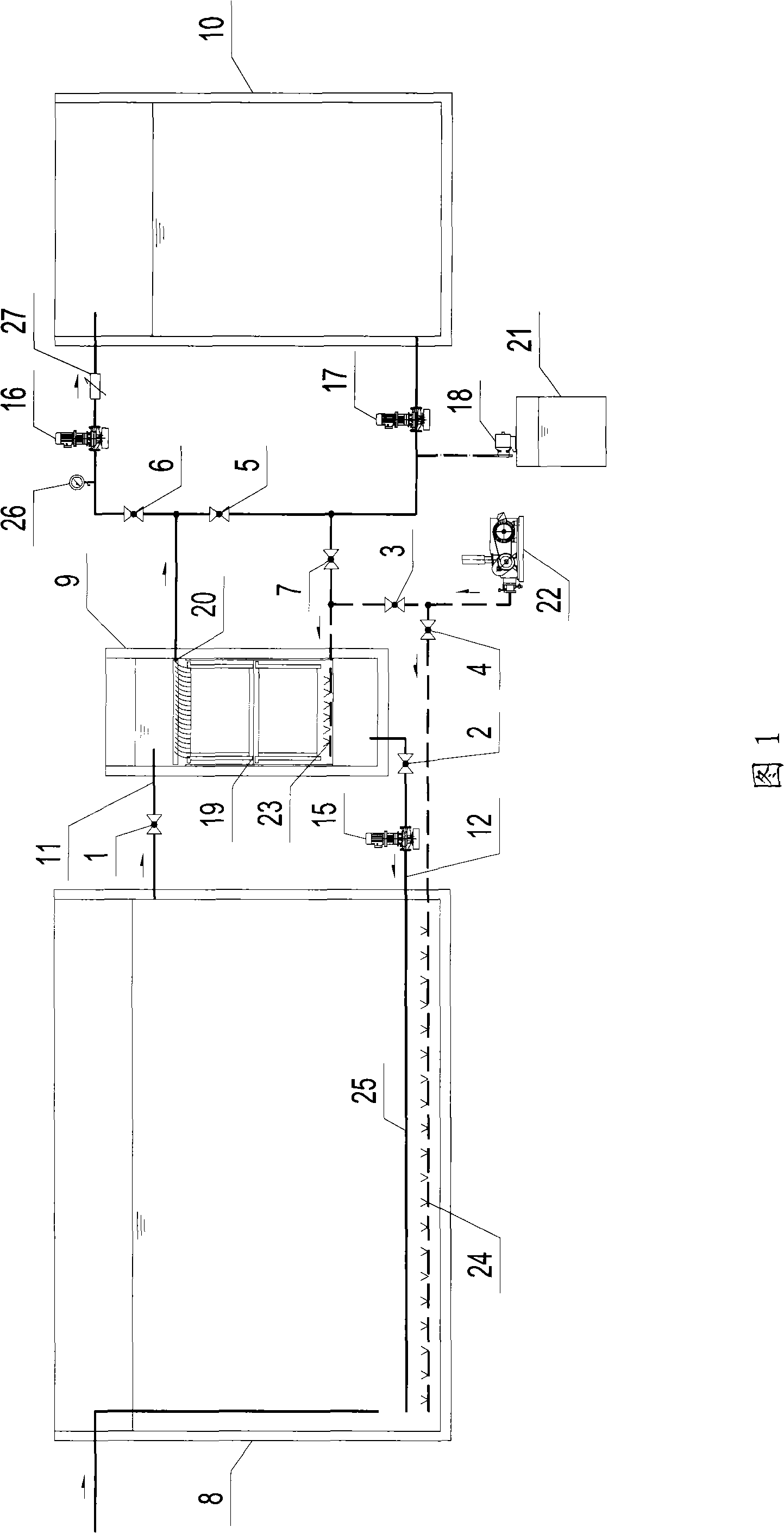
Mobile Water Purification System
InactiveUS20140021115A1Increase productionHigh energy consumptionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationGeneral water supply conservationReverse osmosisCross-flow filtration
The present invention relates to a mobile water purification system employing crossflow filtration, such as reverse osmosis filtration. One embodiment of the invention discloses a mobile water purification system comprising a housing, a pump unit and a piping system for providing fluid communication between a water inlet, a pre-filtration unit, a crossflow filtration unit, a disinfection unit and an outlet for supply of purified water, wherein the pre-filtration unit comprises sediment / cartridge filtrations means and dechlorination means, the cross-flow filtration unit comprises a plurality of parallel and / or sequentially arranged membrane filters, and the piping system is reconfigurable such that the crossflow filtration unit can be bypassed. The present water purification system is adapted to be deployed in remote areas substantially anywhere in the world.
Owner:PURE H2O
Preparation of paris polyphylla saponin
InactiveCN1490320AGood repeatabilityQuality improvementSugar derivativesGlycosidesActivated carbonAlcohol
A process for preparing the common saponin of Chinese paris rhizome includes such steps as extracting, separating and purifying, and features that the extracting in alcohol, membrane filtering, resin adsorbing, resin decoloring, decoloring with activated carbon and defatting with acetone are combined. Its advantages are high extracting rate and low cost.
Owner:云南白药集团天然药物研究院
Uses of parylene membrane filters
ActiveUS7846743B2Improve efficiencyEffective meanUltrafiltrationLaboratory glasswaresParyleneFigure of merit
The invention provides parylene membrane filters, filter devices and methods of making them and using them in the mechanical separation of cells and particles by size. The provision of parylene membrane filters with high figures of merit and finely controlled hole sizes allows the separation of cells and particles in a variety of biological and other fluids according to sizes.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
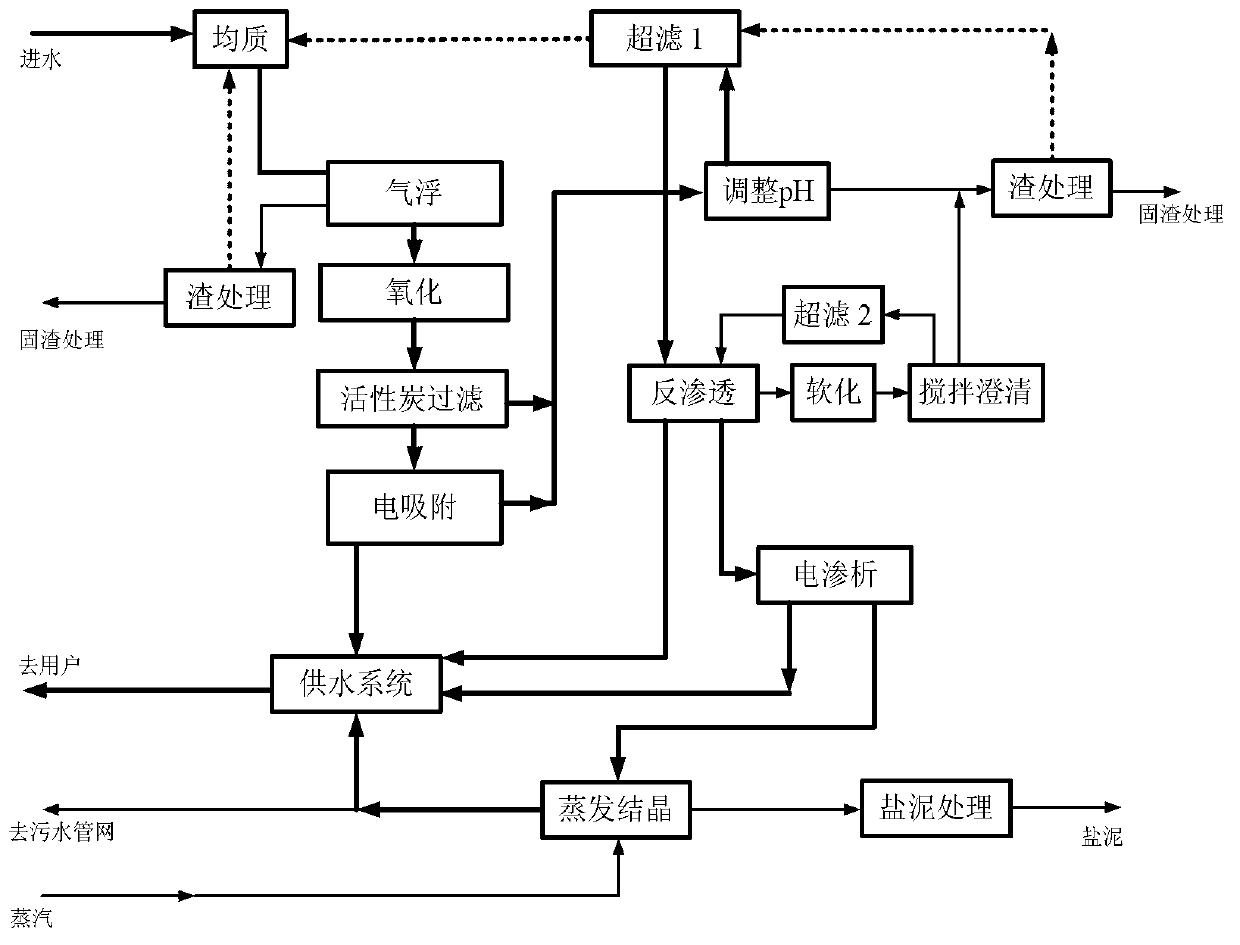
Near zero emission process of salt-containing waste water
ActiveCN103342432AHigh recovery rateReduce processing costsDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisChemical oxygen demandUltrafiltration
The invention relates to a near zero emission process of salt-containing waste water. The process specifically comprises the following steps of: 1) pretreatment, namely, removing part of COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand), suspended solids, hardness and the like from raw water; 2) electric absorption, namely, removing inorganic salt in pretreated partial water, wherein concentrated water generated in the process and part of oxidized waste water which is not subjected to electric adsorption treatment enter into a membrane filtering system together; 3) treatment in a membrane treatment system, wherein the membrane treatment system mainly comprises ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis and electroosmosis processes; and 4) evaporative crystallization and salty mud treatment process, namely, evaporating and crystallizing concentrated salty water generated by electroosmosis, wherein fresh water generated in the process enters into a water supply system while solids generated in the process enter into the salty mud treatment system. The comprehensive water recovery rate of the near zero emission process can reach 99.5%, so that resource and harmful treatment of the salt-containing waste water is realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH +1
Method of refining salt by membrane filtration
ActiveCN1868878AReduce processing loadImprove permeabilitySemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisIon exchangeCross-flow filtration
A membrane filter process for refining saline includes such steps as dissolving salt to obtain saturated solution, adding sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate and barium chloride, reaction to generate magnesium hydroxide, calcium carbonate and barium sulfate, adding coagulating precipitant and oxidant for pre-treating, adsorbing and depositing to remove magnesium hydroxide colloid and part of particles, cross-flow filtering by inorganic membrane, and ion exchange.
Owner:JIANGSU JIUWU HITECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com