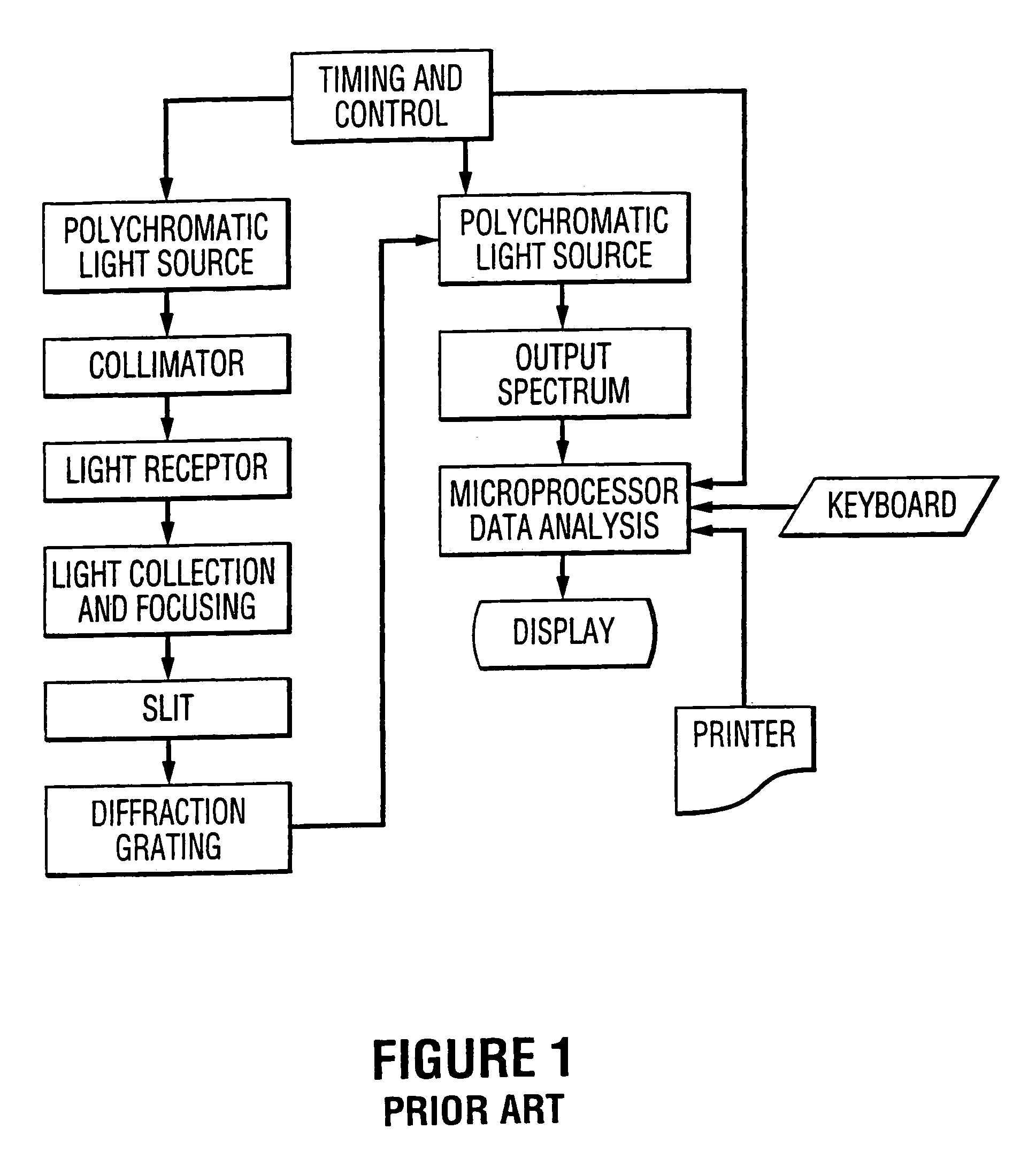
Patents
Literature
138 results about "Blood gas test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A blood gas test or blood gas analysis tests blood to measure blood gas tension values, it also measures blood pH, and the level and base excess of bicarbonate. The source of the blood is reflected in the name of each test; arterial blood gases come from arteries, venous blood gases come from veins and capillary blood gases come from capillaries. The blood gas tension levels of partial pressures can be used as indicators of ventilation, respiration and oxygenation. Analysis of paired arterial and venous specimens can give insights into the aetiology of acidosis in the newborn.
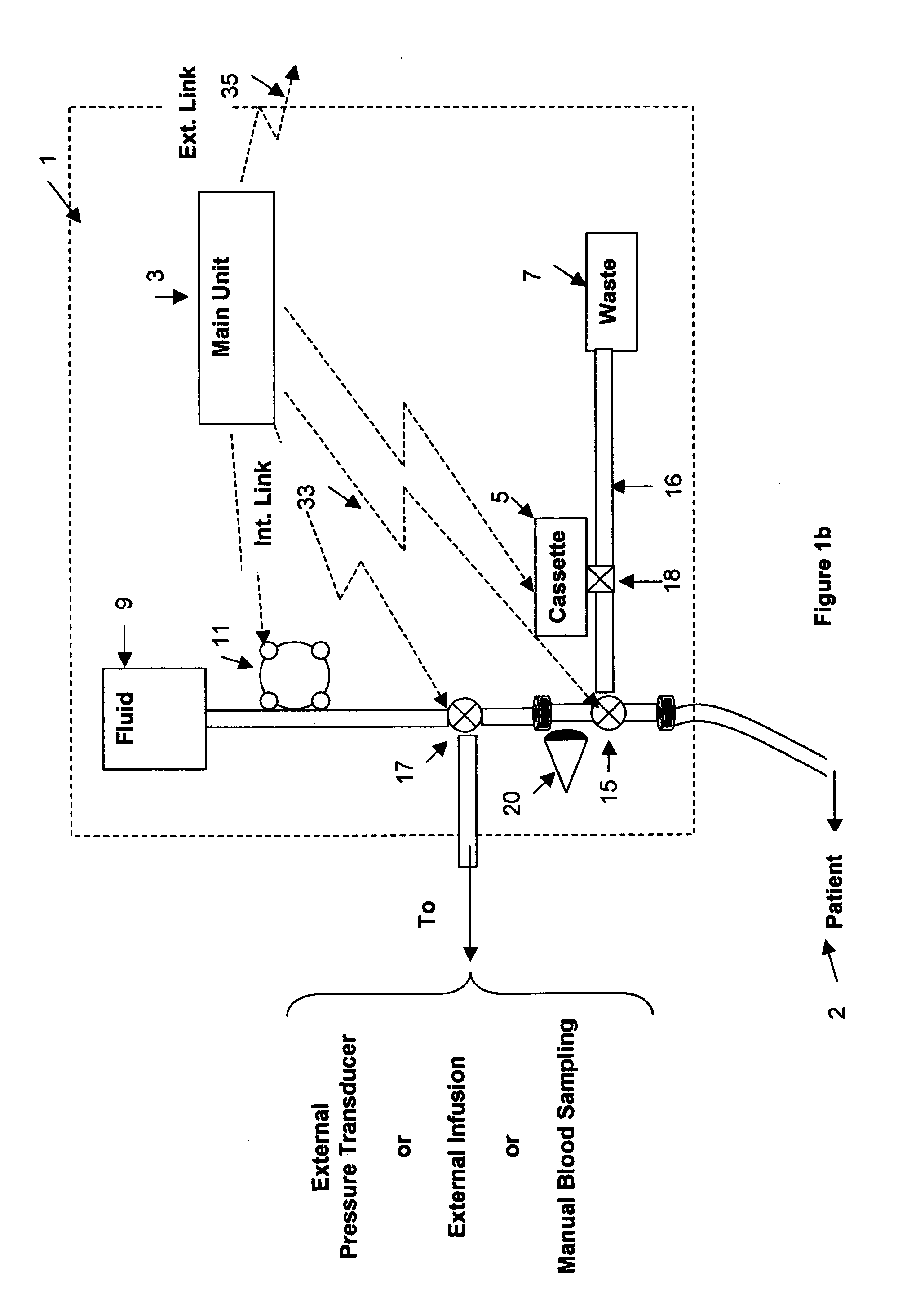
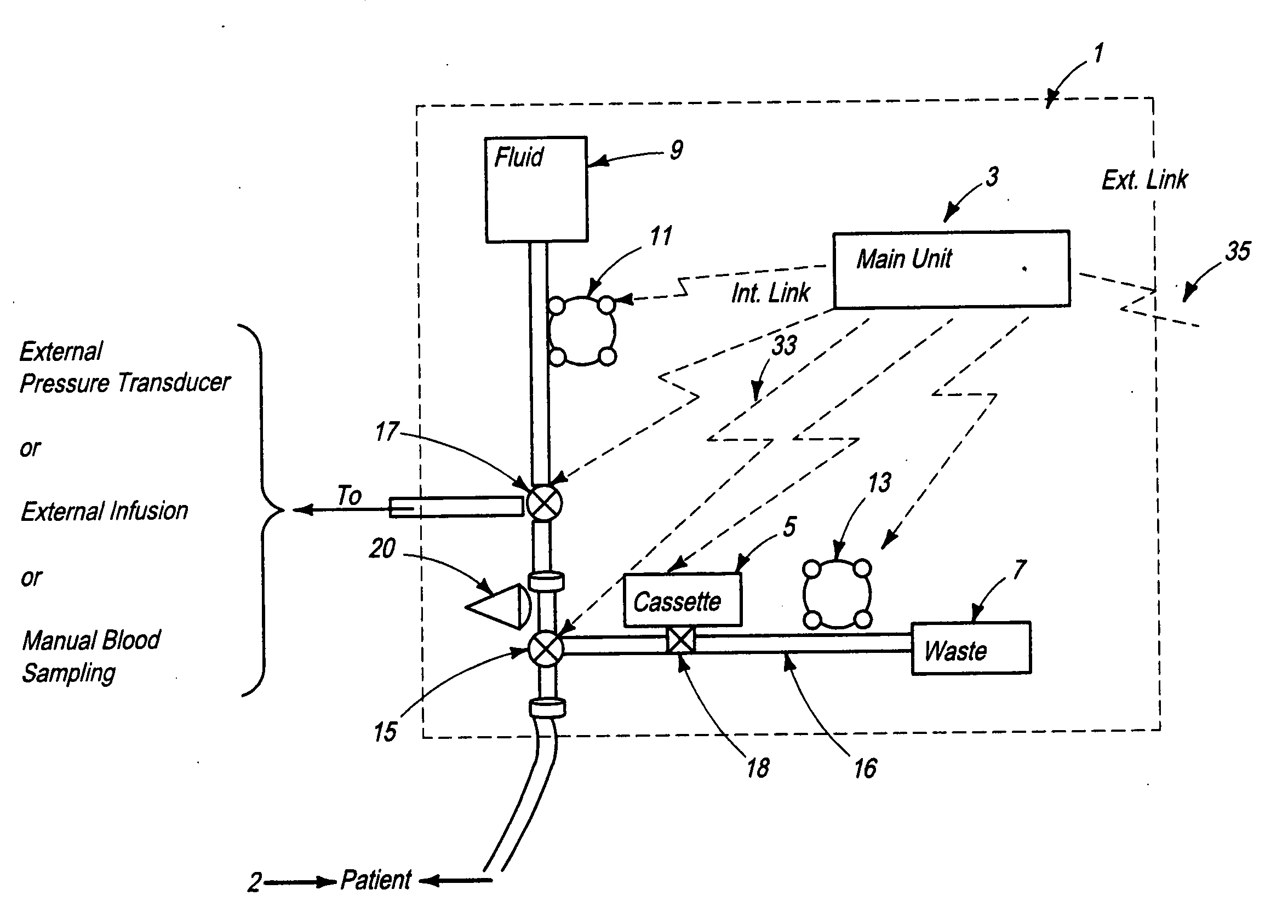
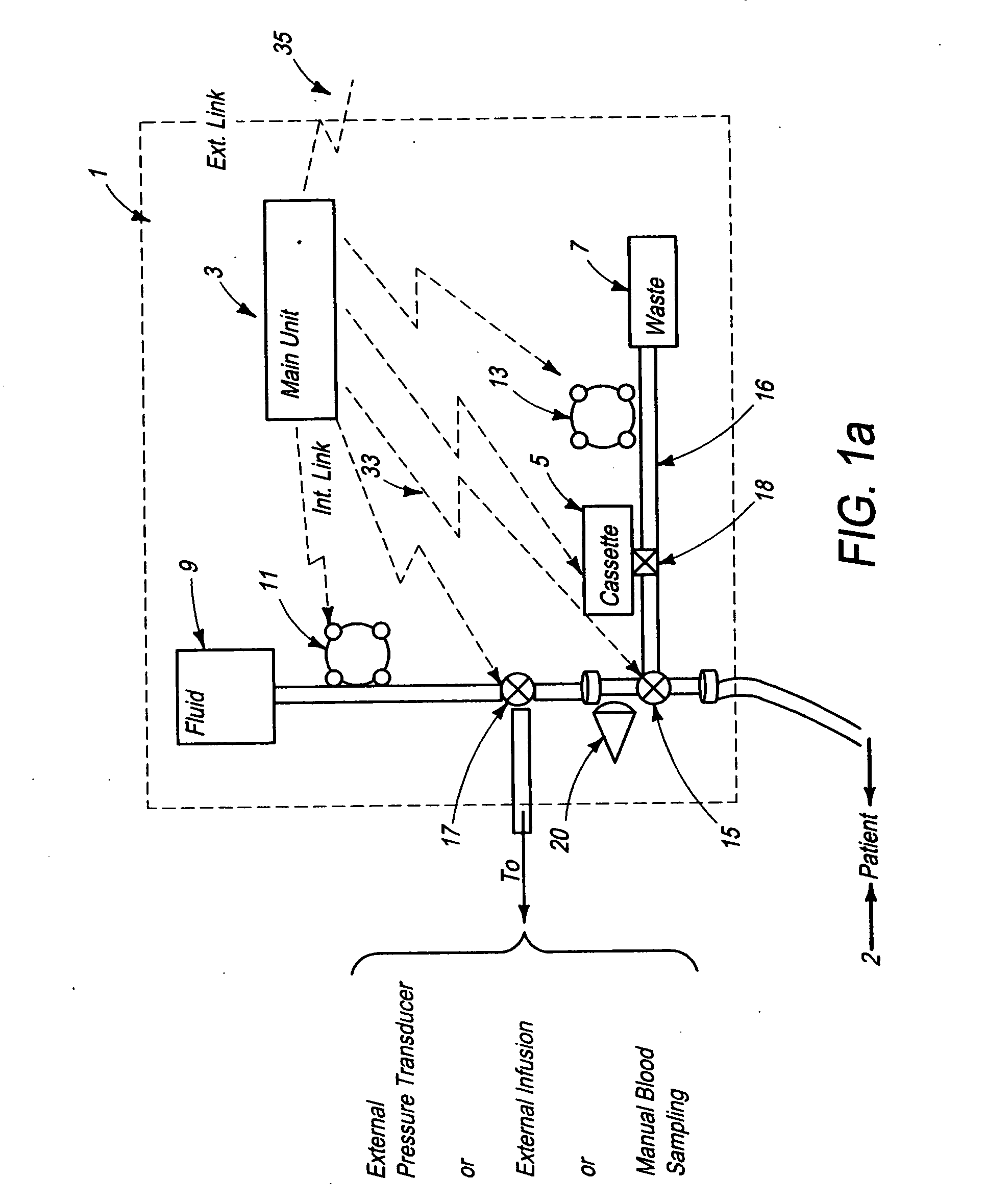
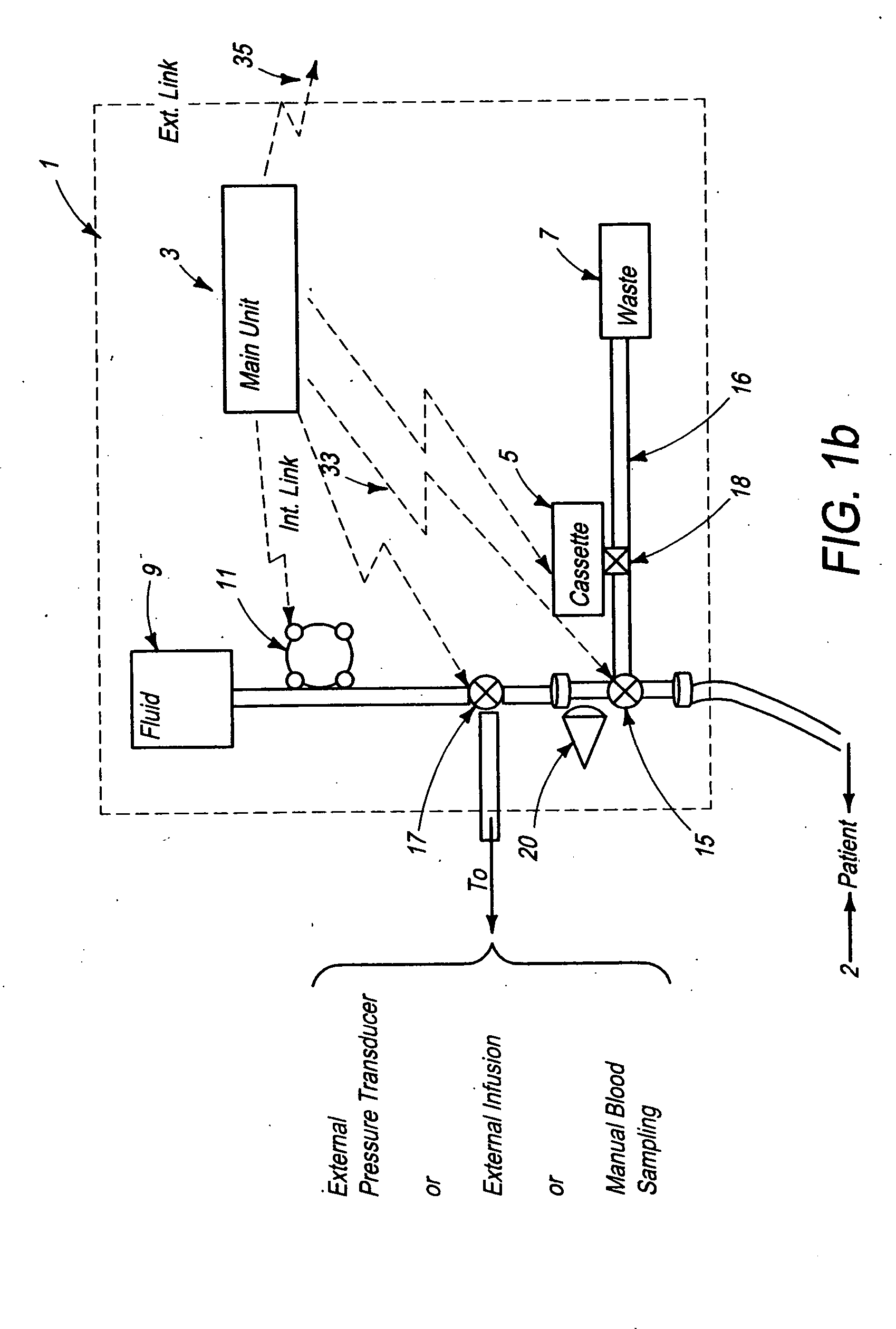
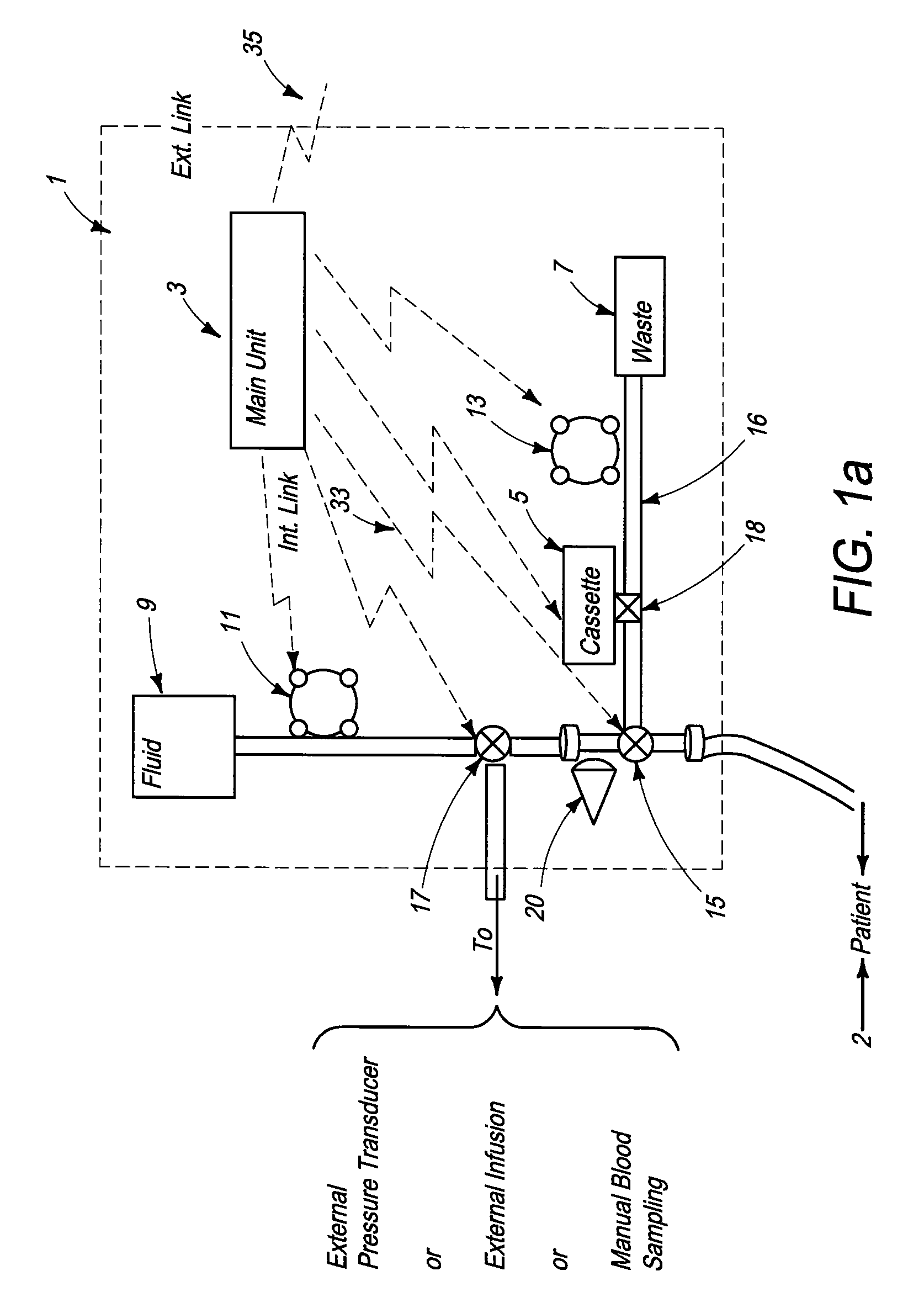
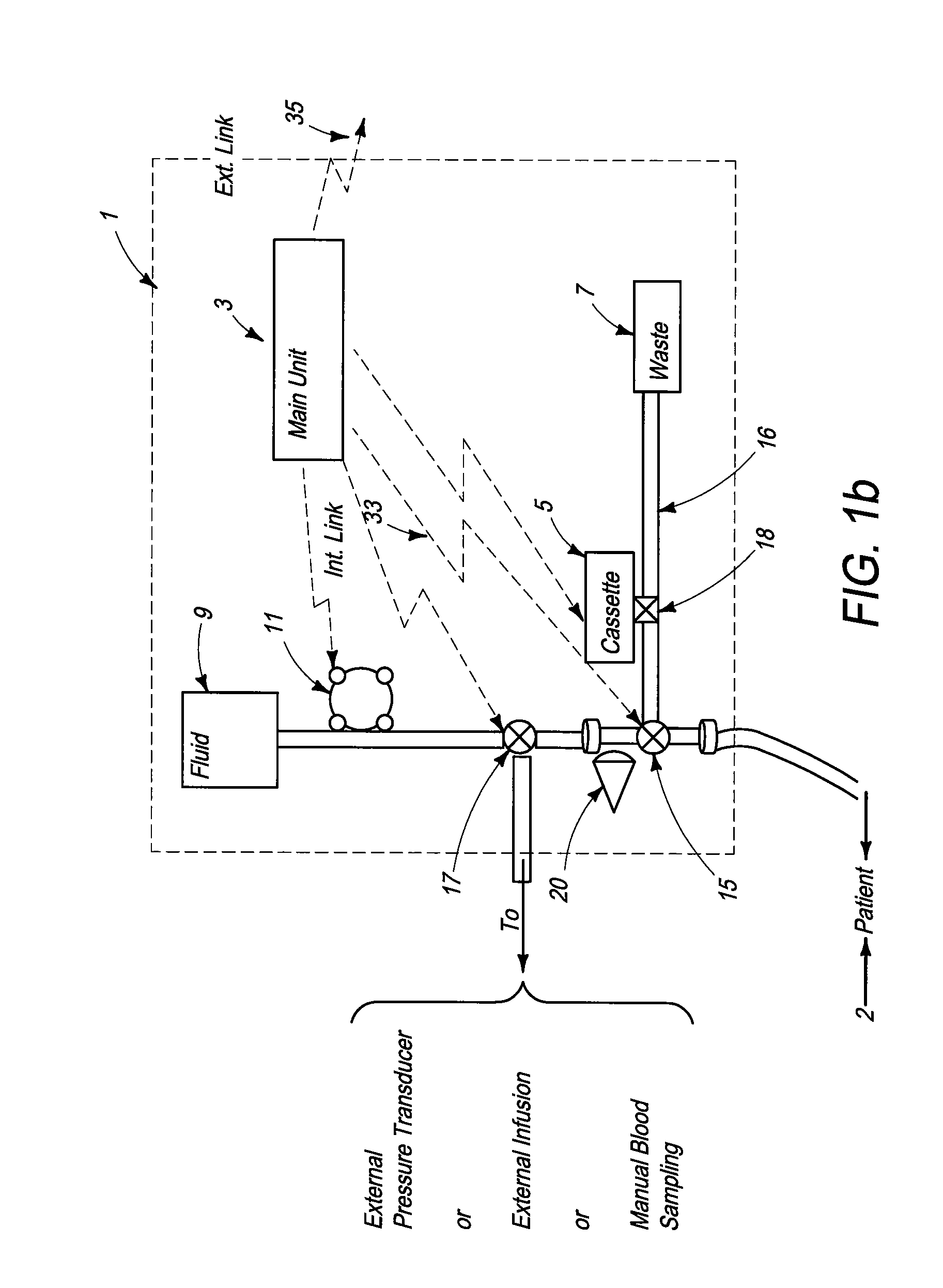
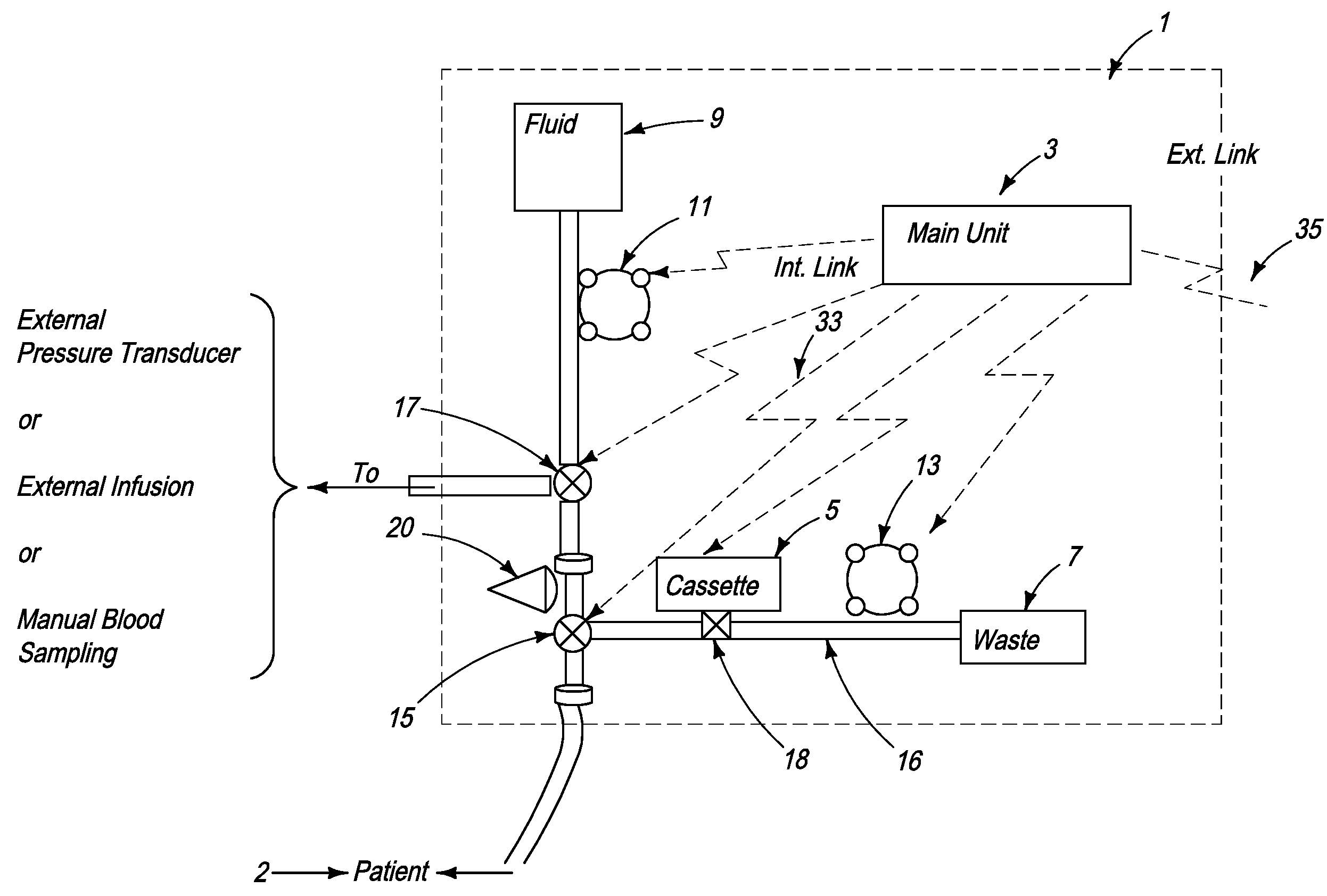
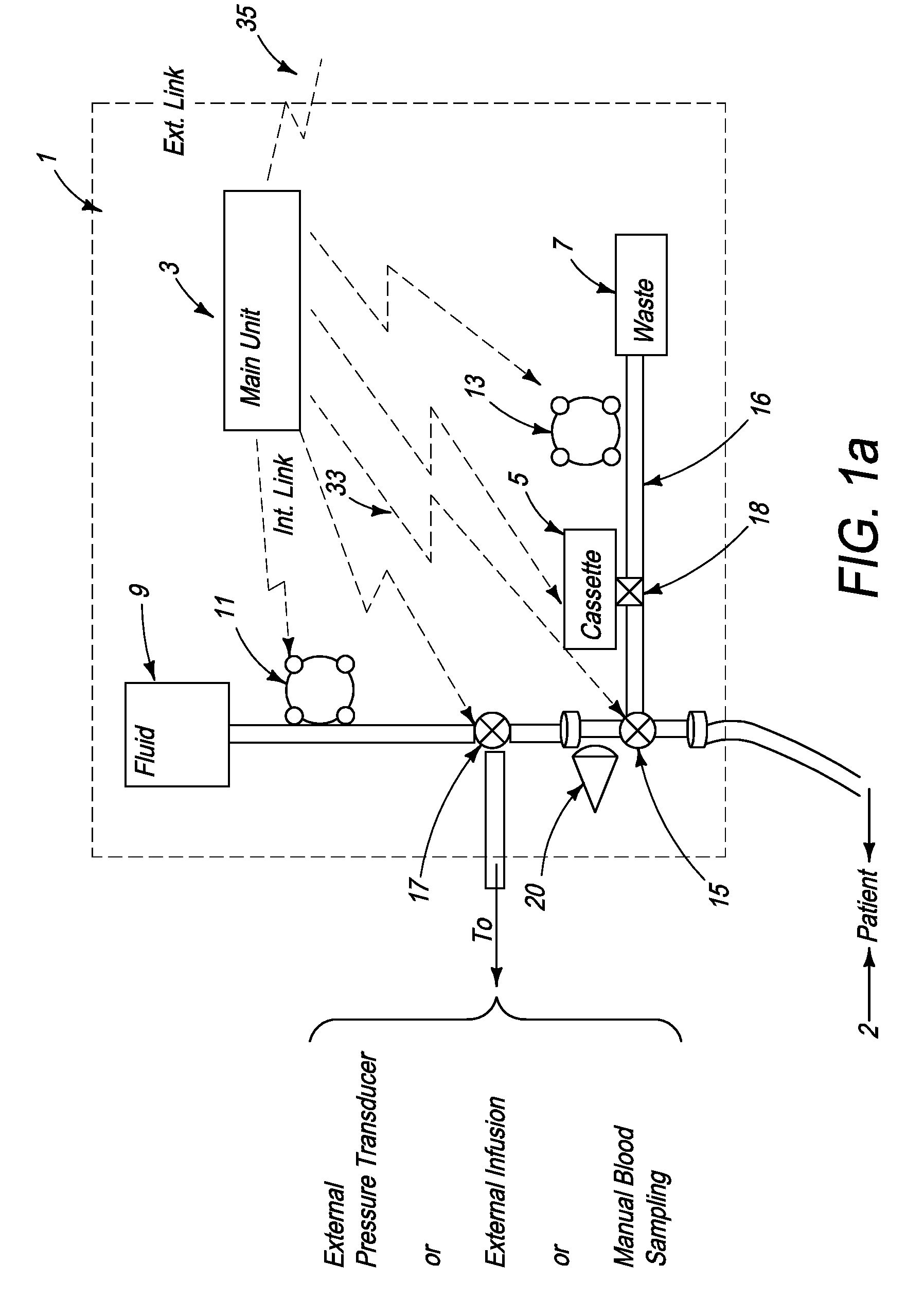
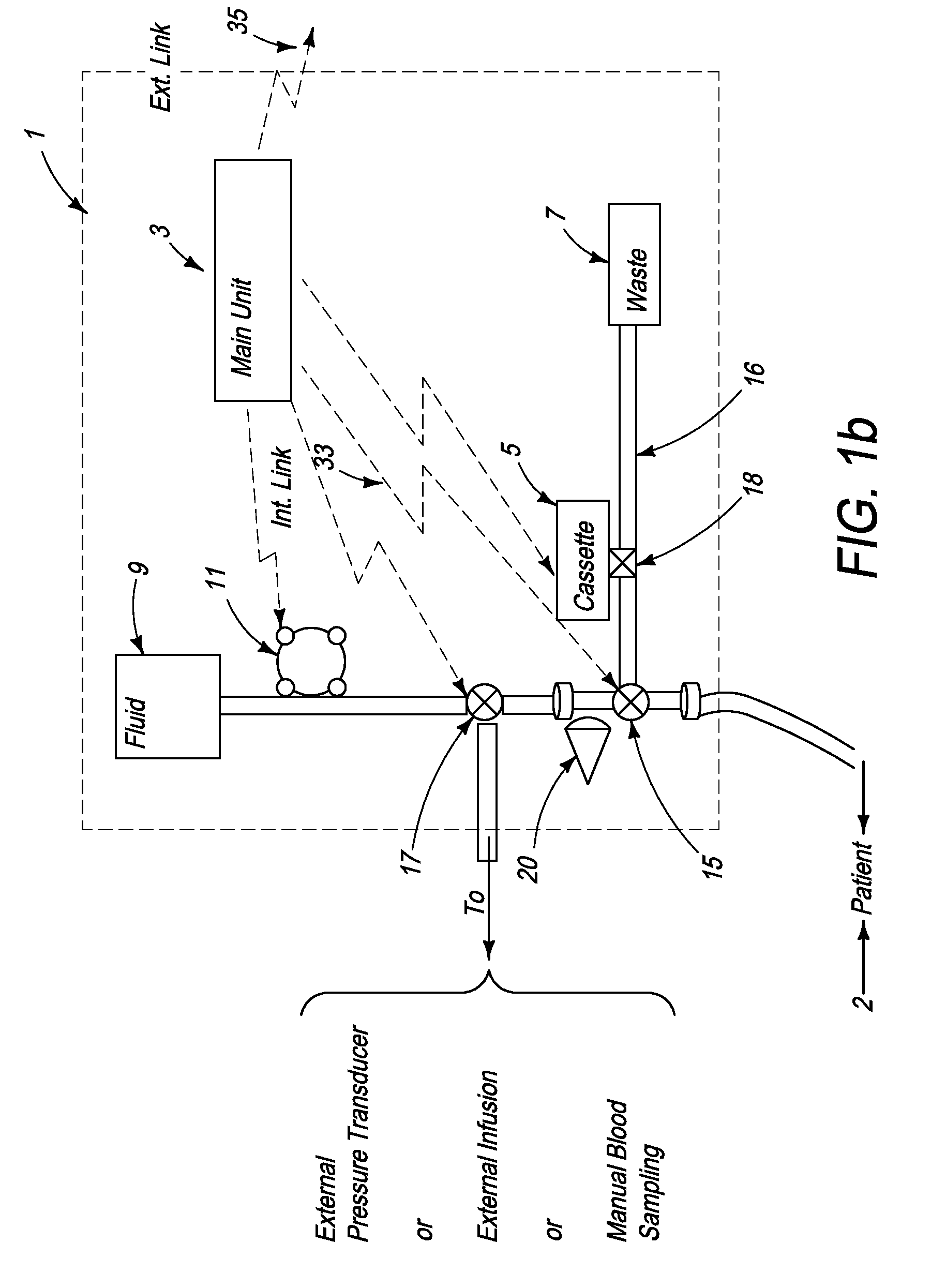
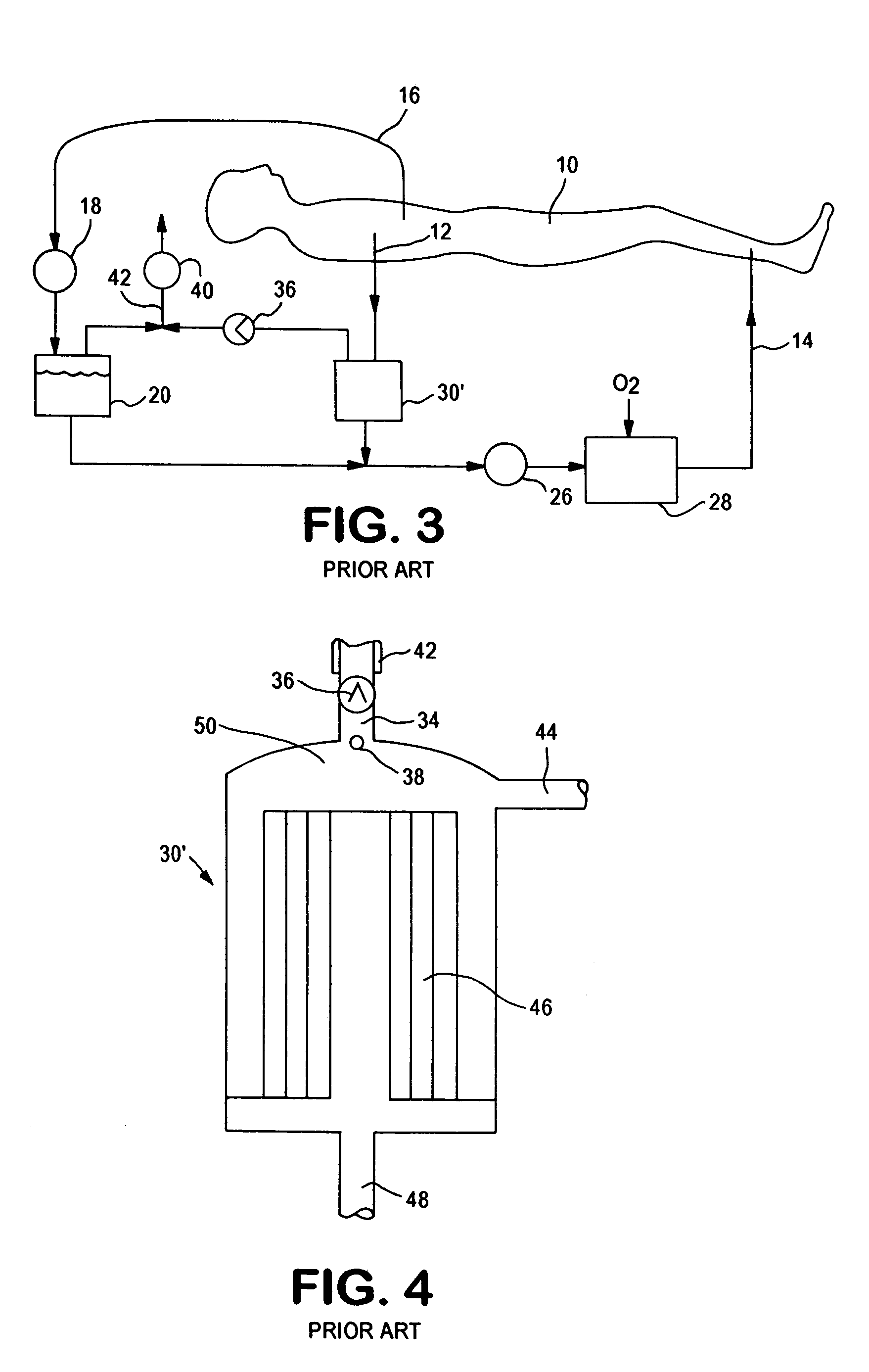
System for combined transcutaneous blood gas monitoring and vacuum assisted wound closure
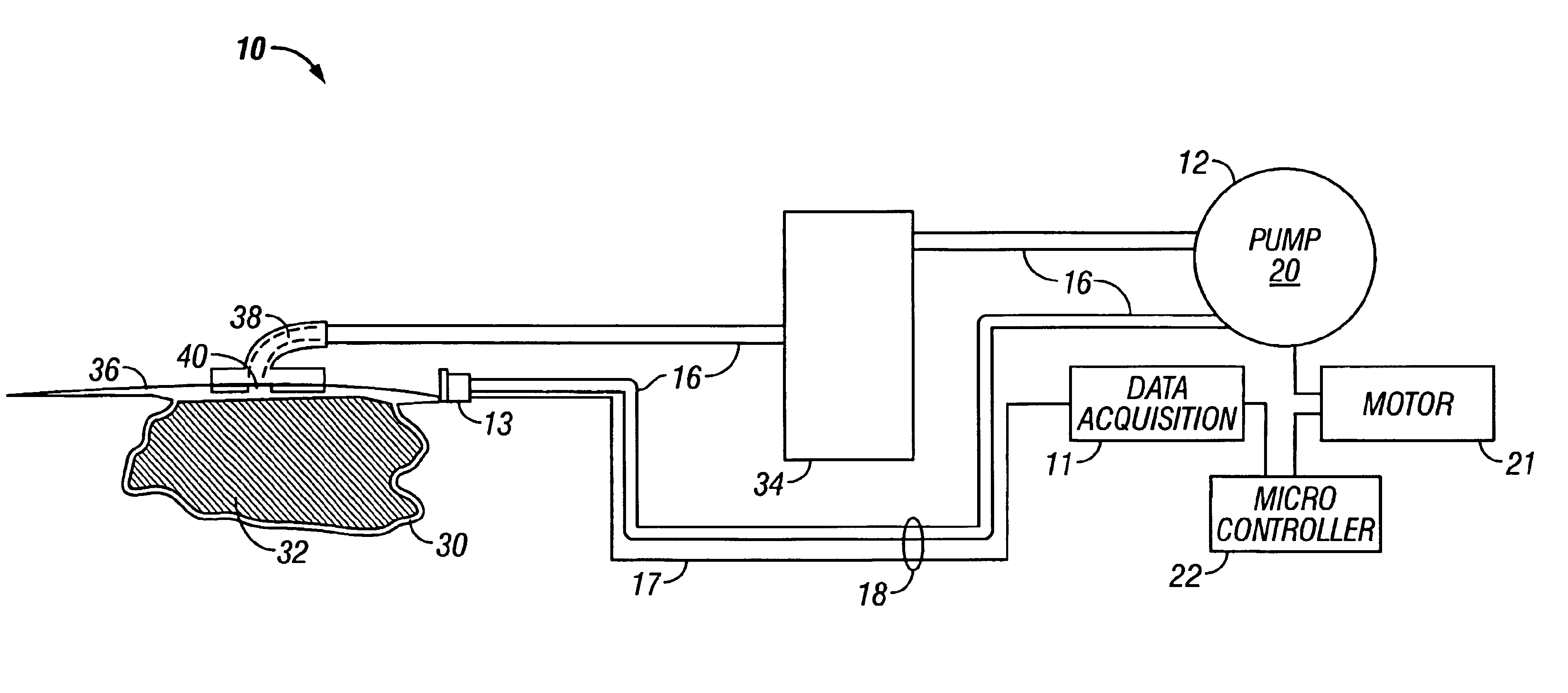
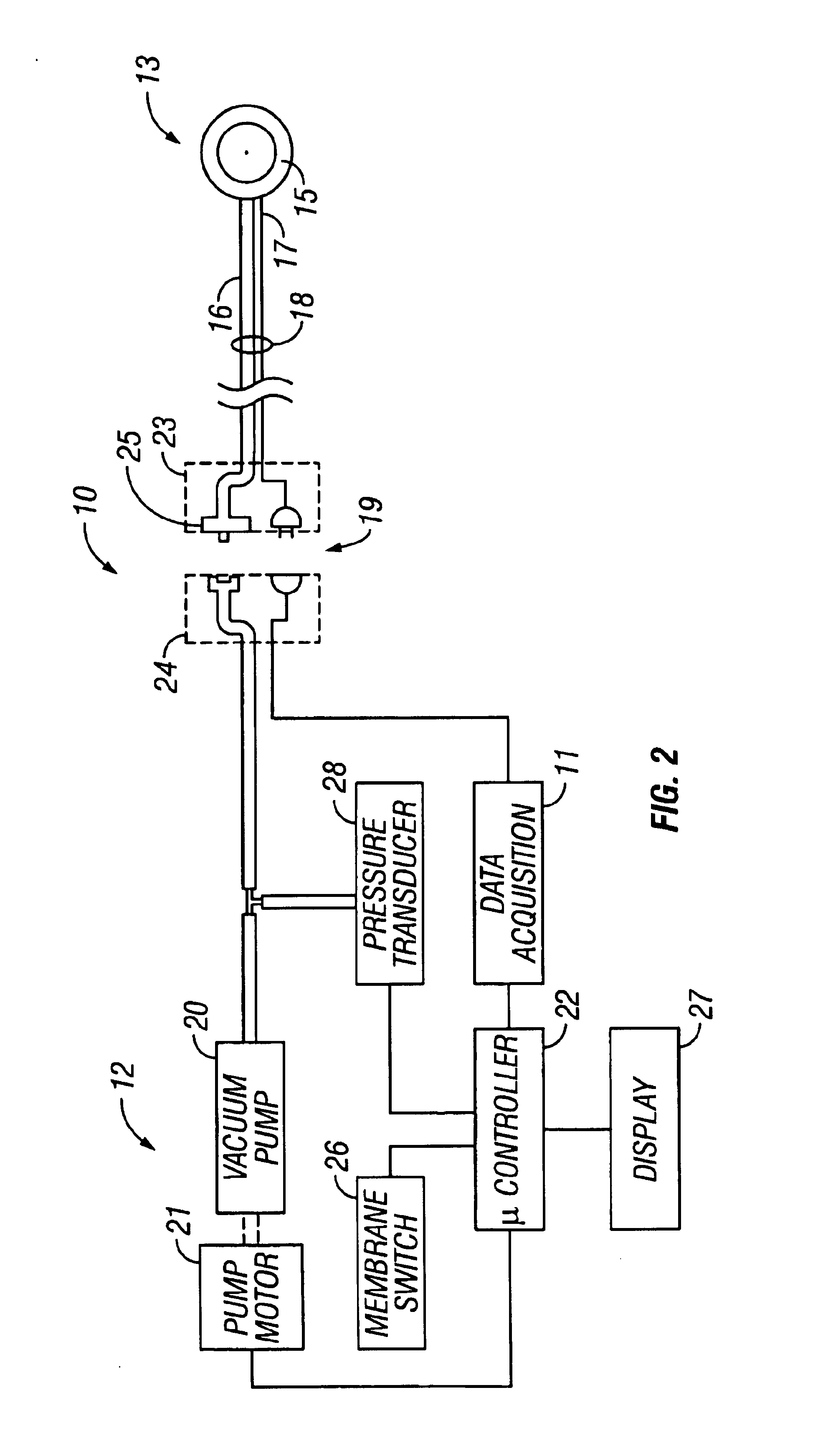
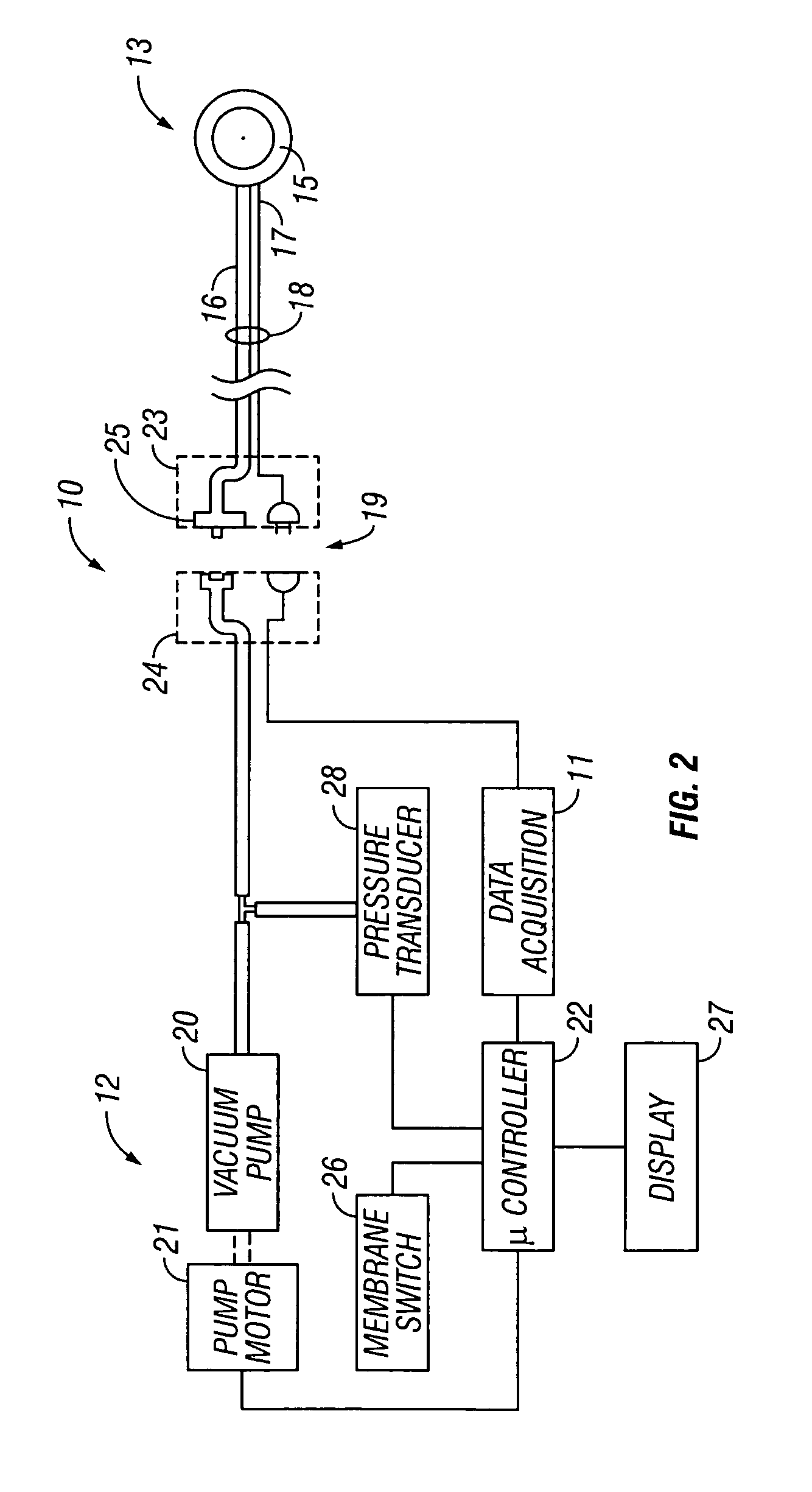
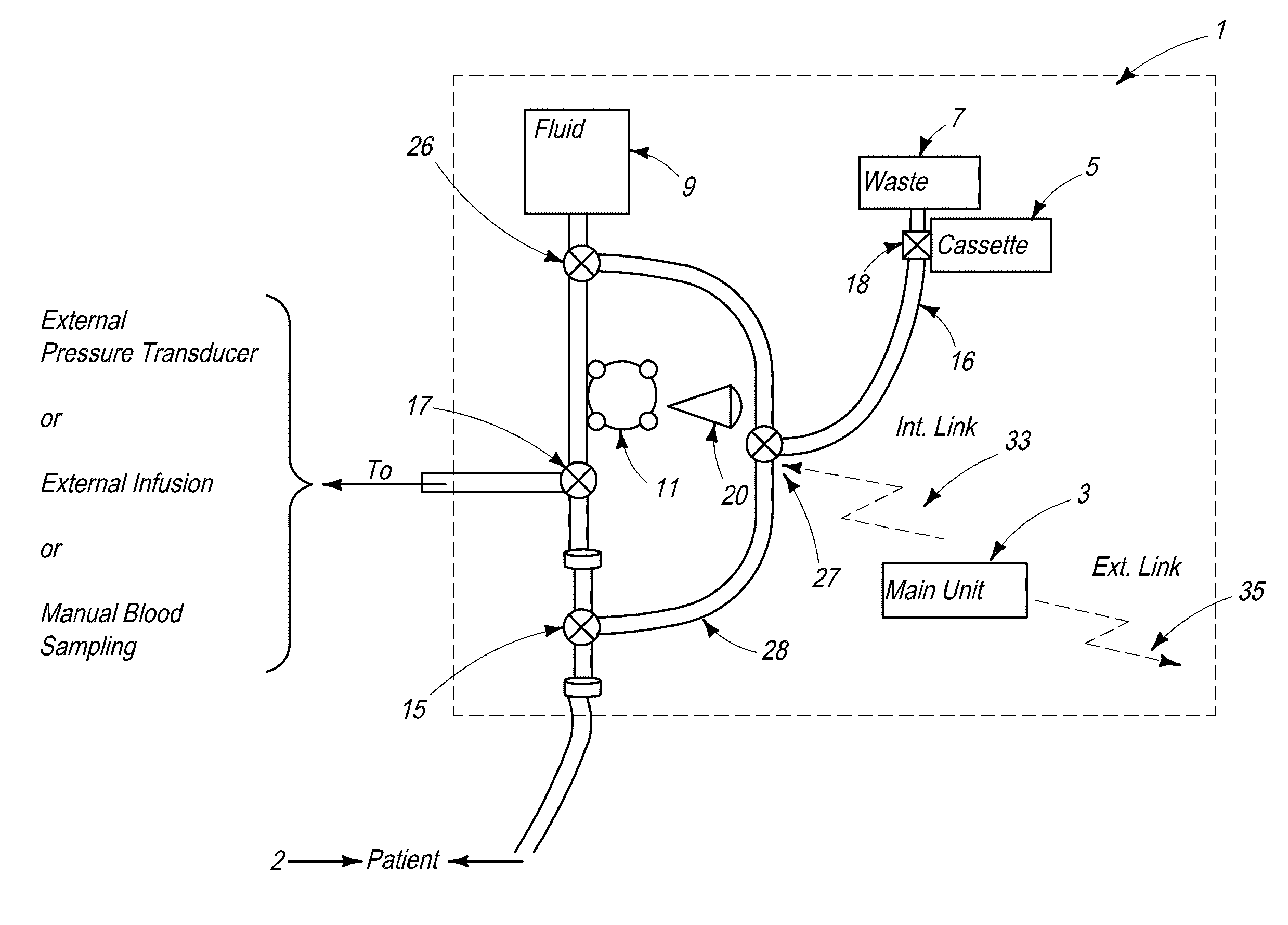
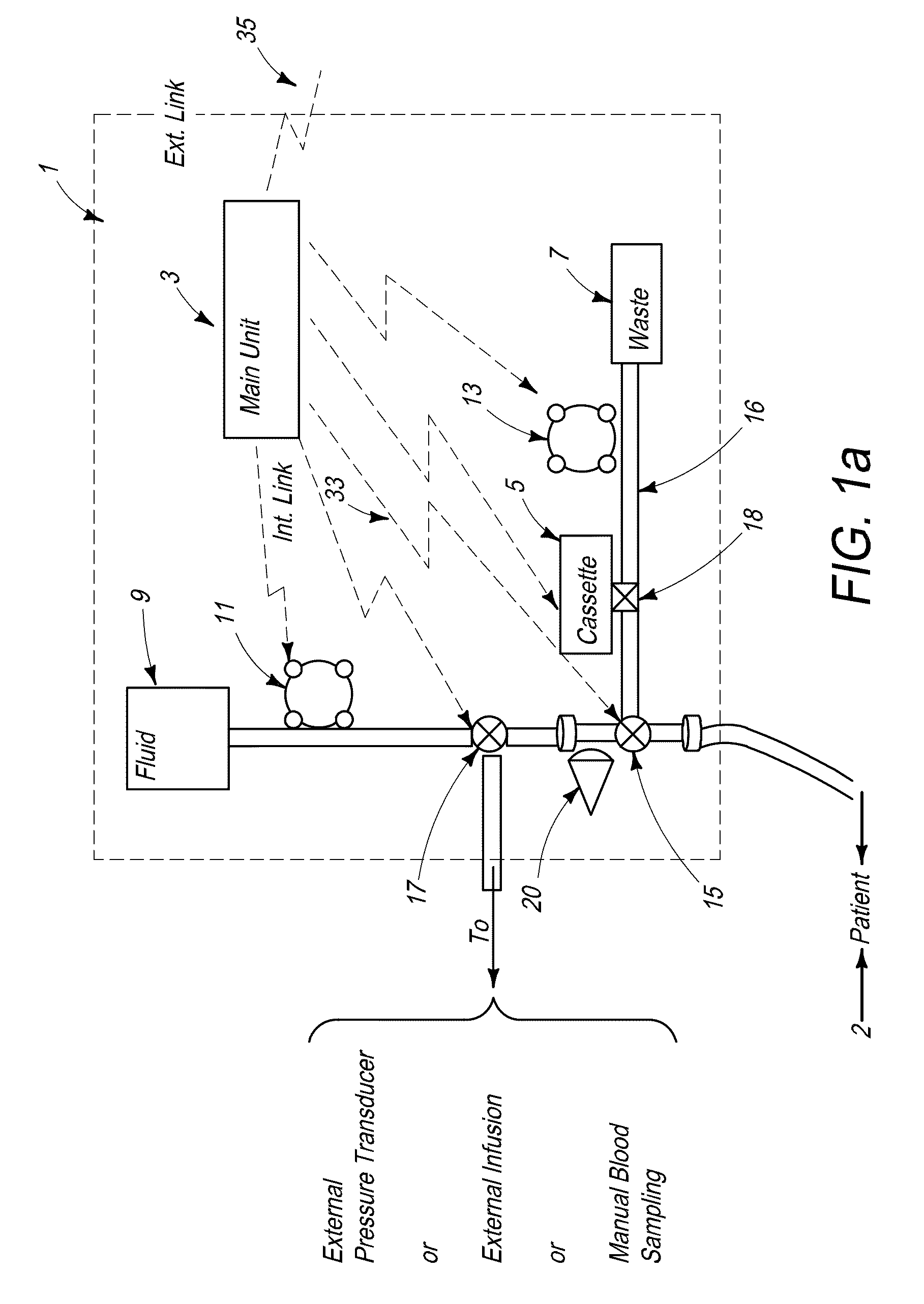
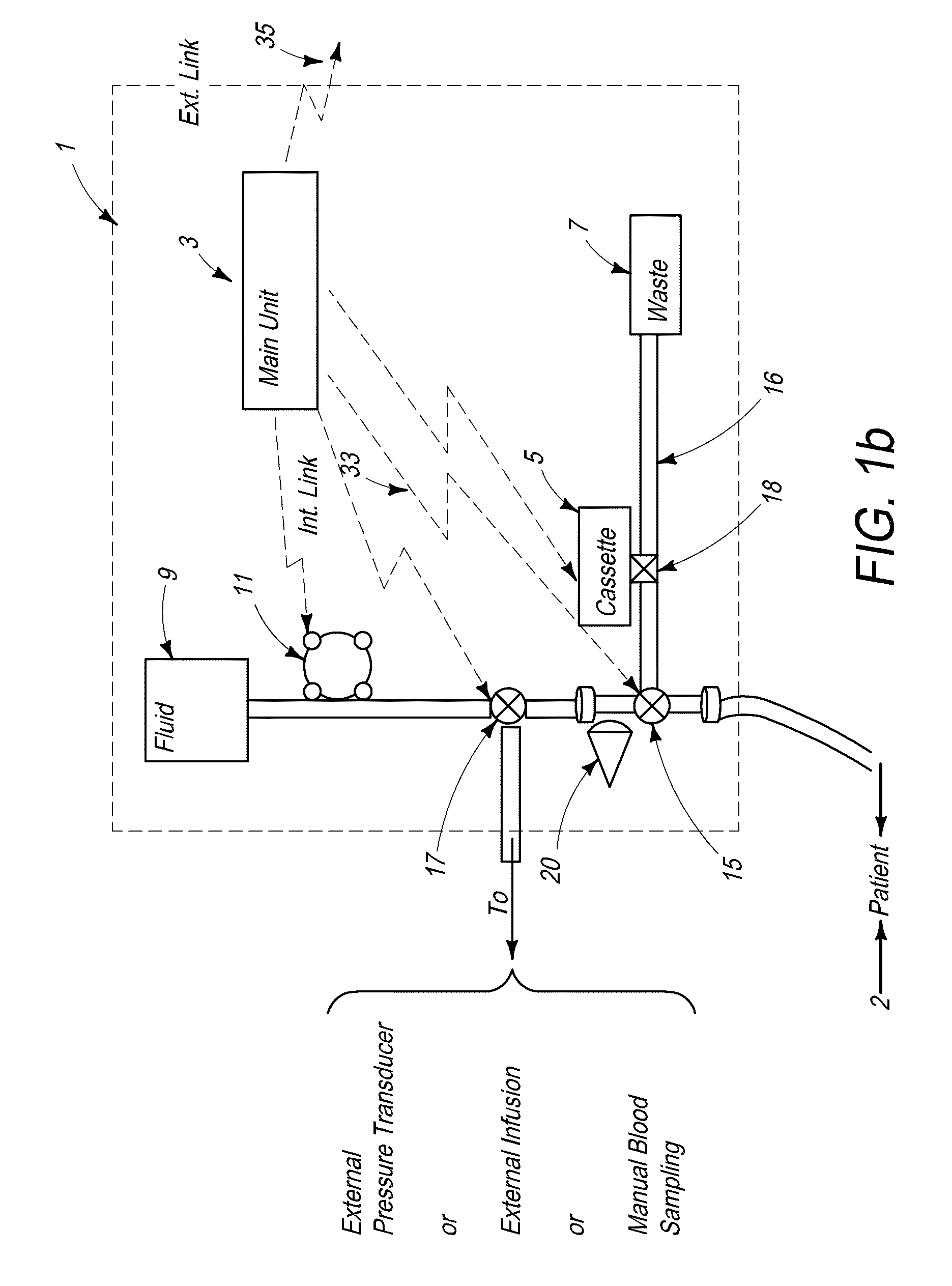
InactiveUS6856821B2Eliminate opportunitySubstantial riskIntravenous devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerVacuum assisted
A method and apparatus for the transcutaneous monitoring of blood gases generally comprises a blood gas data acquisition device, a vacuum source and a blood gas transducer unit. The blood gas transducer unit is adapted for application to a patient's skin and administration of a local vacuum at the area of patient application. It further comprises an electrochemical blood gas transducer, well known to those of ordinary skill in the art, which is disposed entirely within the local vacuum at the area of patient application. The vacuum source is placed in fluid communication with the blood gas transducer unit, through a hydrophobic membrane filter for safety purposes, in order to induce a condition of hyperperfusion in the locality of the electrochemical blood gas transducer. Under the control of a microcontroller, or equivalent means, the blood gas acquisition device is then utilized to capture a measure of skin surface oxygen or carbon dioxide pressure. The microcontroller can then utilize this measure to arrive at an estimate of arterial partial pressure of oxygen or carbon dioxide, accordingly. Because vacuum induced perfusion produces the requisite condition of hyperperfusion without local heating and, therefore, without acceleration of the local metabolic function, the present invention results in more accurate than previously available estimates of partial pressure blood gas pressures and does so while eliminating a significant risk for injury to the patient.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
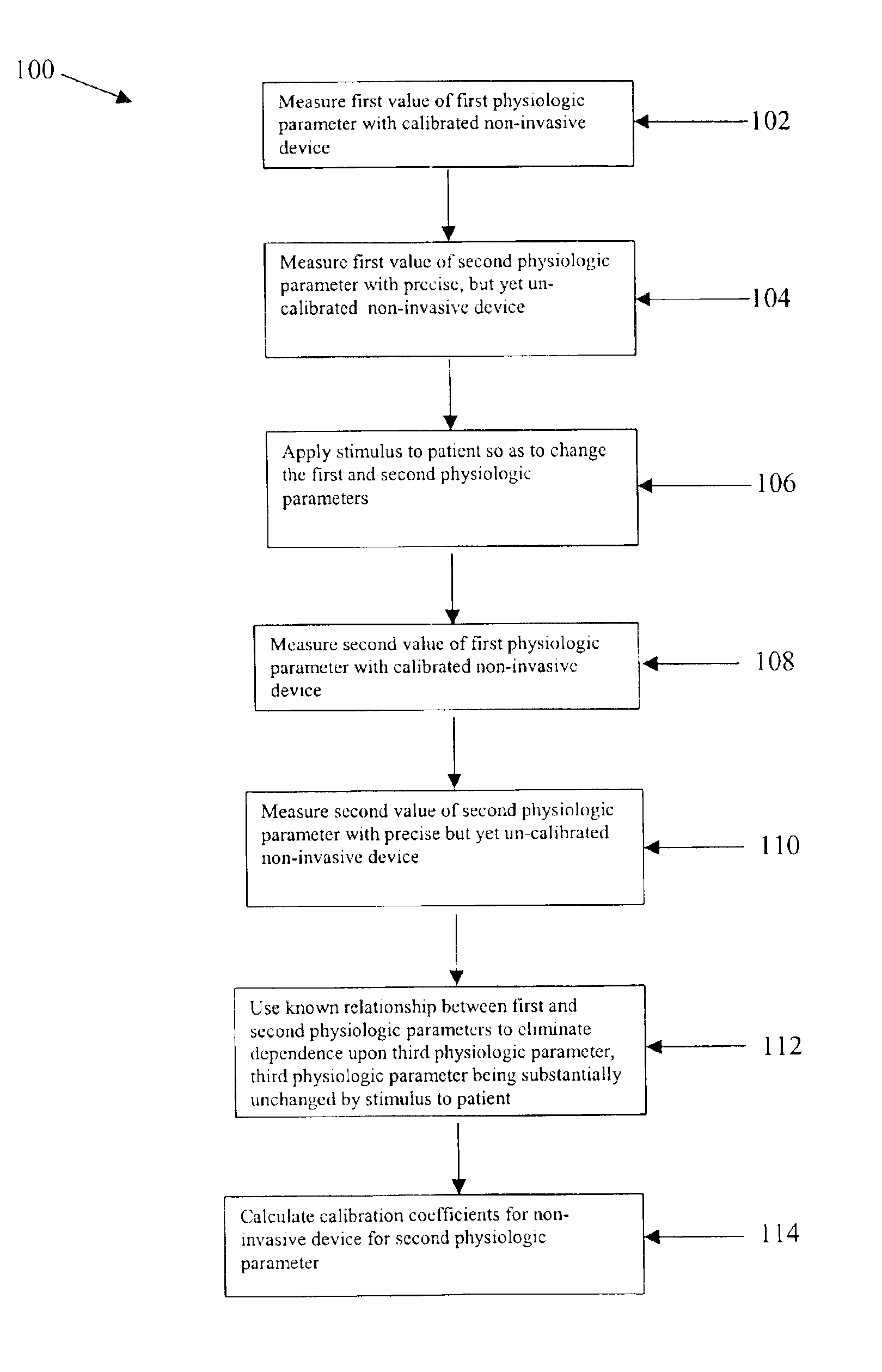
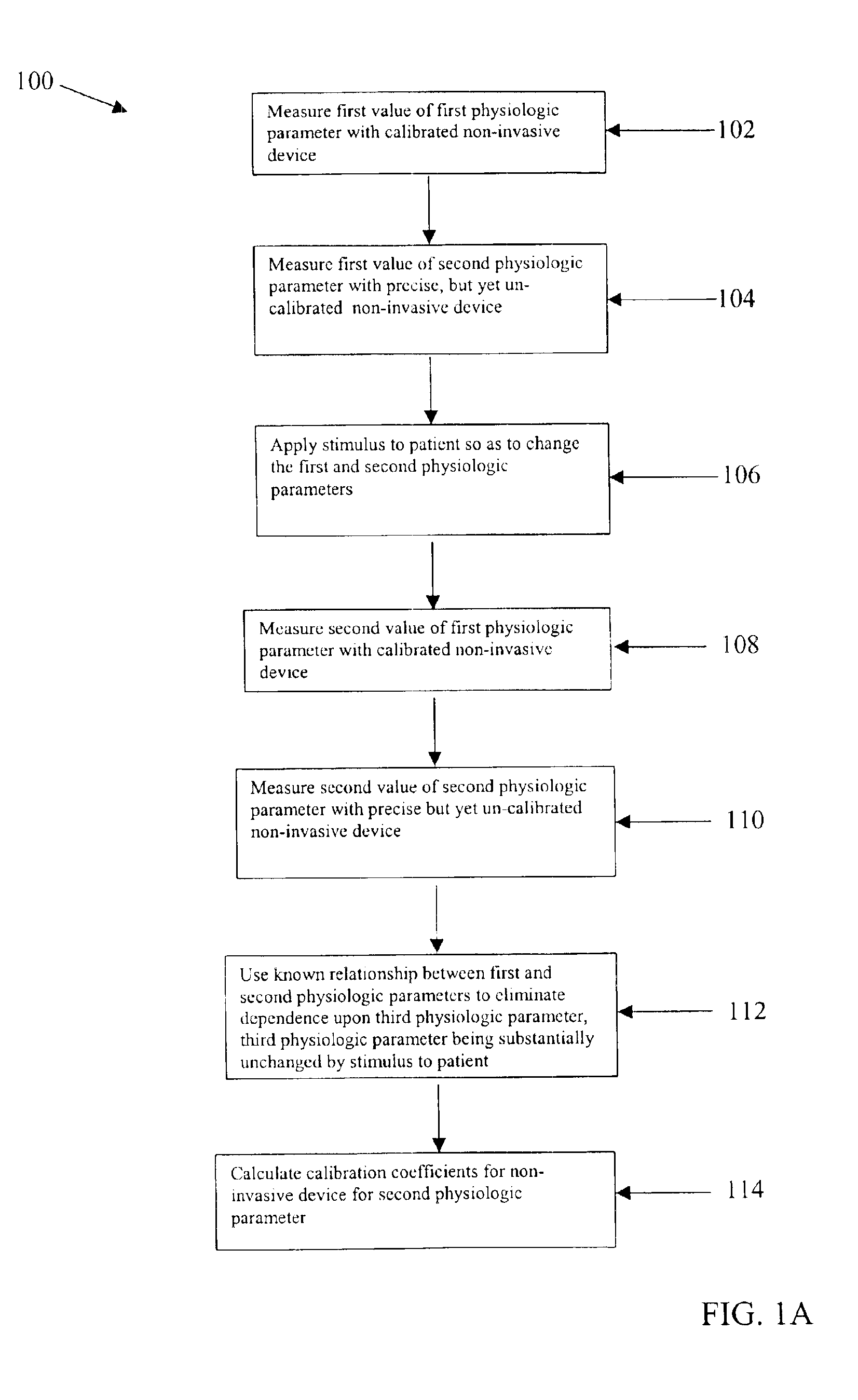
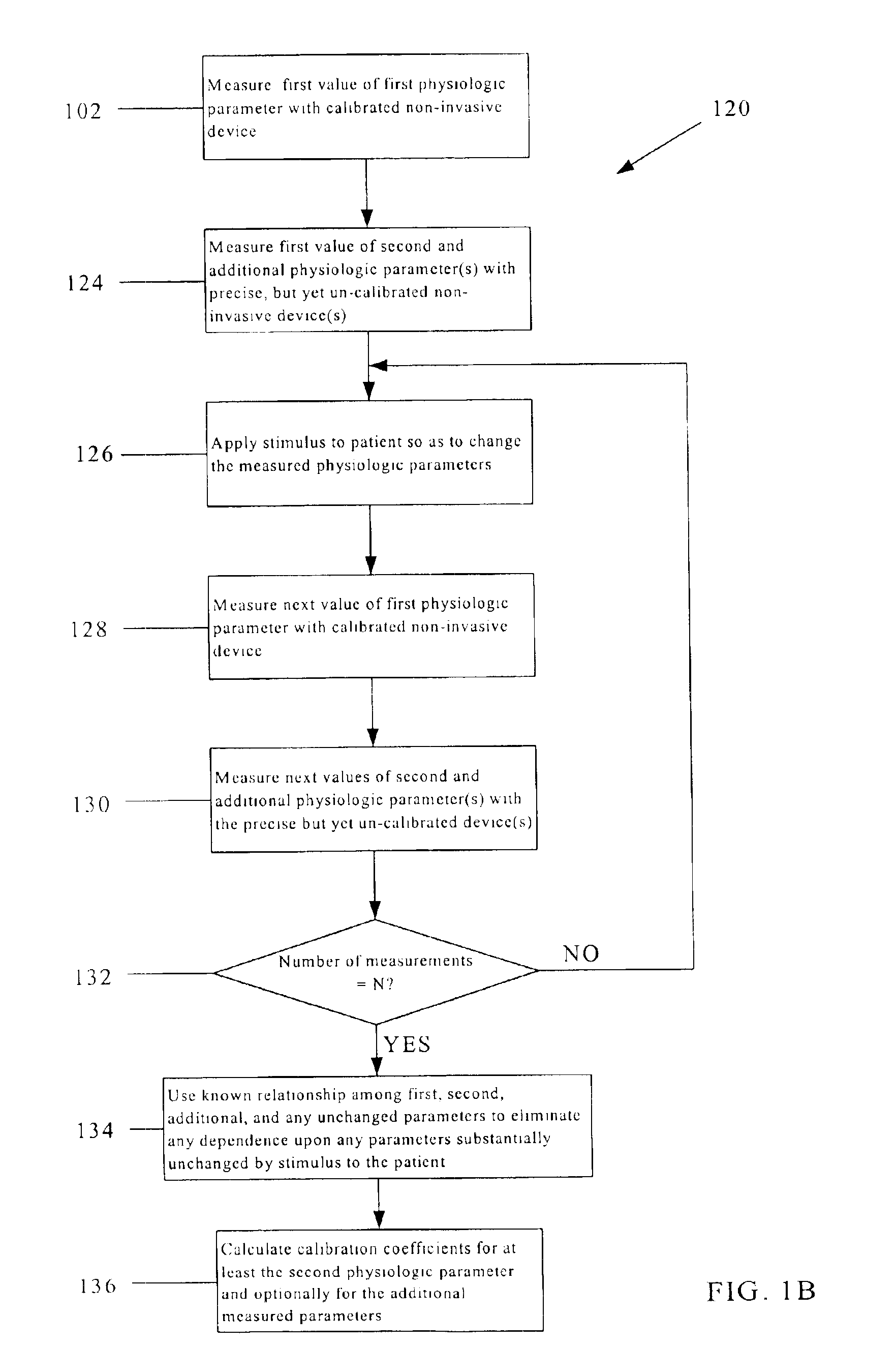
Calibration technique for non-invasive medical devices
There is a need for a non-invasive method of calibrating medical devices at the point of care, where the calibration is performed without the removal of blood or bodily fluids. The invention is directed to an approach for calibrating a first non-invasive sensor in which the tissue being measured is modulated in some way so as to after the value of the parameter being measured by the first optical sensor. A second sensor detects another parameter that also changes with the modulation. The second sensor is absolutely calibrated. Where there is a known relationship between the first and second parameters, a calibration may be derived for the first sensor. Such a technique is applicable to calibrating non-invasive sensors for monitoring a wide variety of physiologic parameters including, inter alia, glucose, blood gases, blood electrolytes and blood pH.
Owner:OPTICAL SENSORS
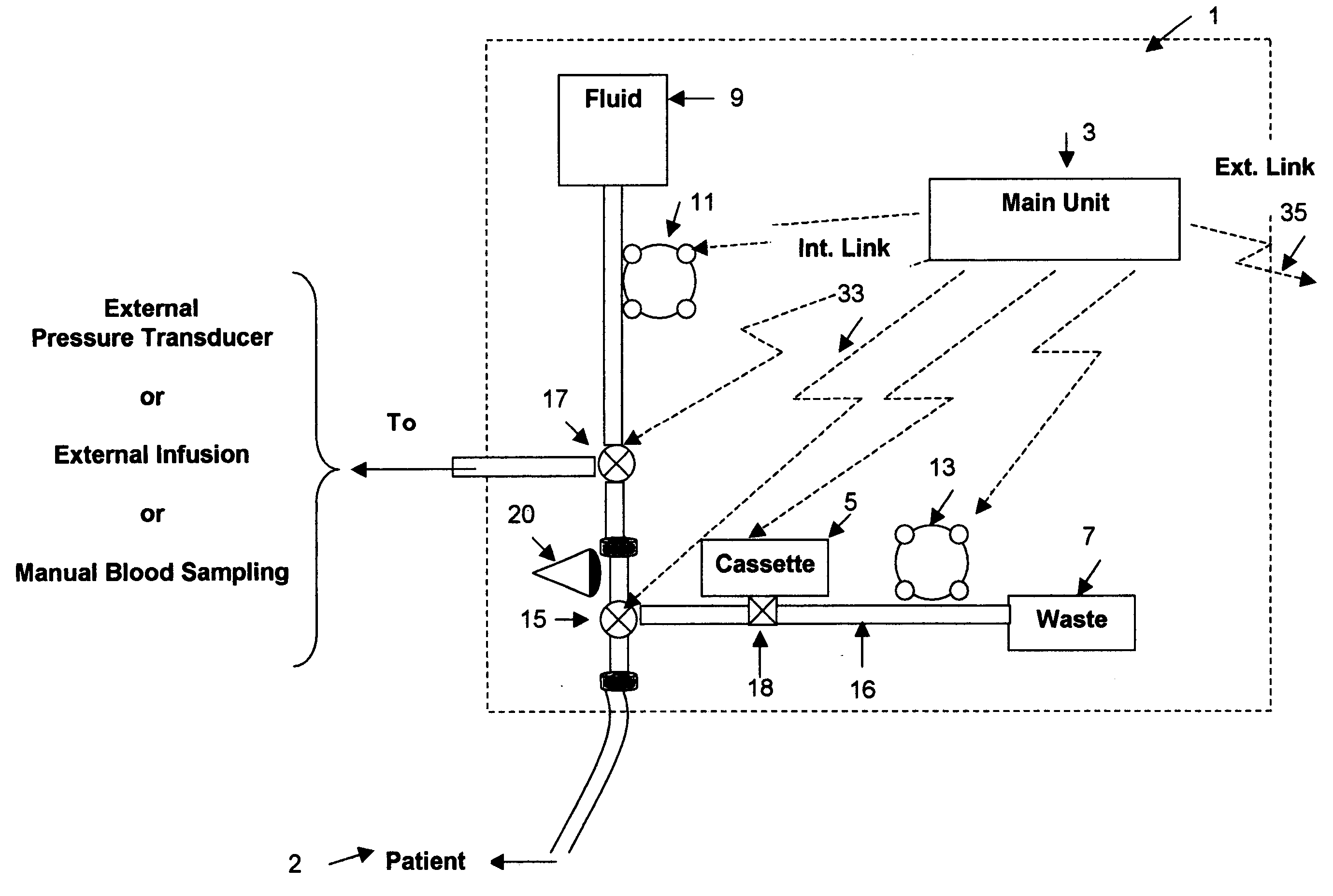
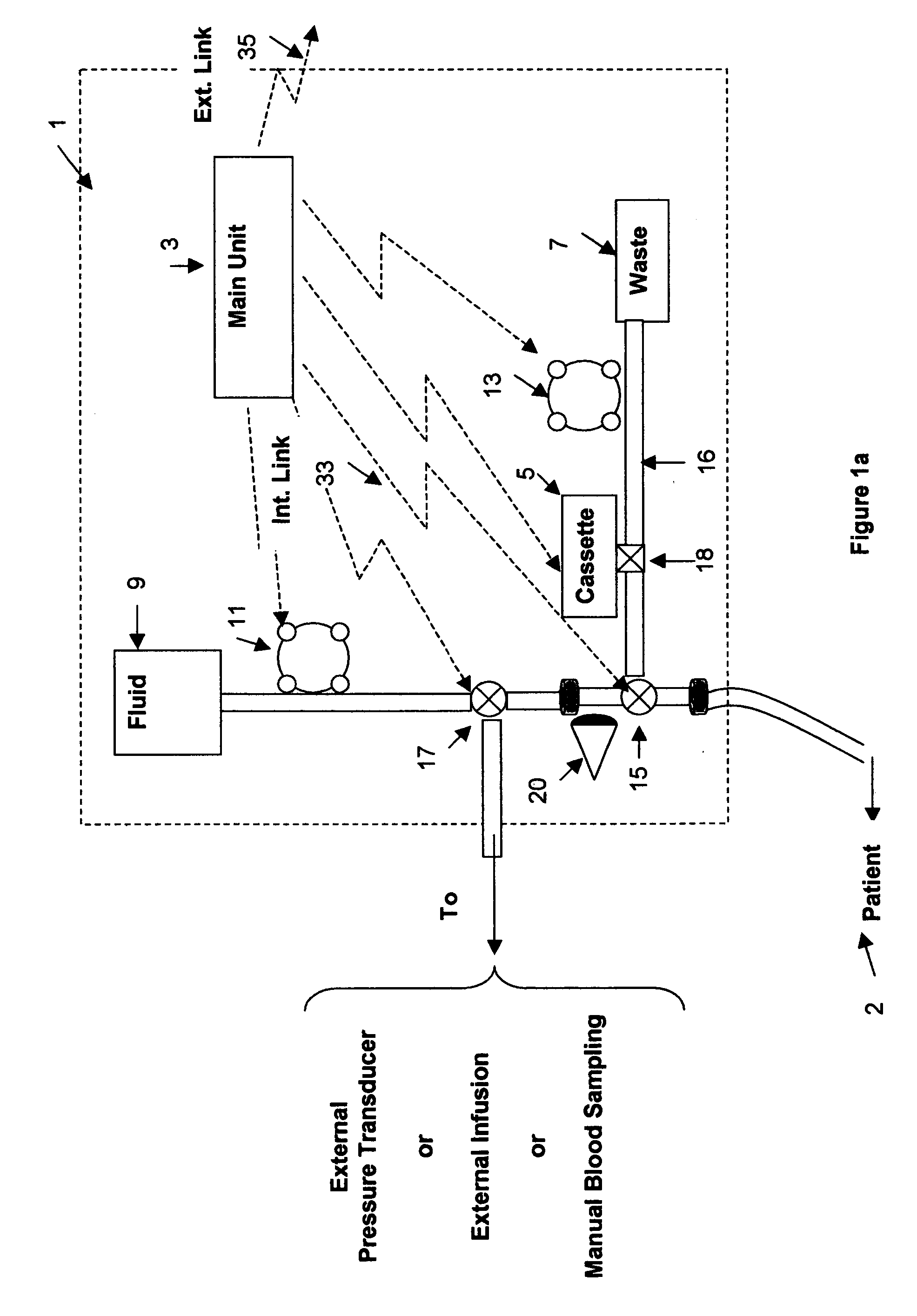
Blood monitoring system
ActiveUS20060079809A1Improve accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBlood chemistryBlood parameters
The present invention is directed towards apparatuses and methods for the automated measurement of blood analytes and blood parameters for bedside monitoring of patient blood chemistry. Particularly, the current invention discloses a programmable system that can automatically draw blood samples at a suitable programmable time frequency (or at predetermined timing), can automatically analyze the drawn blood samples and immediately measure and display blood parameters such as glucose levels, hematocrit levels, hemoglobin blood oxygen saturation, blood gases, lactate or any other blood parameter.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Blood monitoring system
InactiveUS20060229531A1Improve accuracyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical devicesBlood chemistryBlood parameters
The present invention is directed towards apparatuses and methods for the automated measurement of blood analytes and blood parameters for bedside monitoring of patient blood chemistry. Particularly, the current invention discloses a programmable system that can automatically draw blood samples at a suitable programmable time frequency (or at predetermined timing), can automatically analyze the drawn blood samples and immediately measure and display blood parameters such as glucose levels, hematocrit levels, hemoglobin blood oxygen saturation, blood gases, lactate or any other blood parameter.
Owner:GLUCON
System and method for diaphragm stimulation
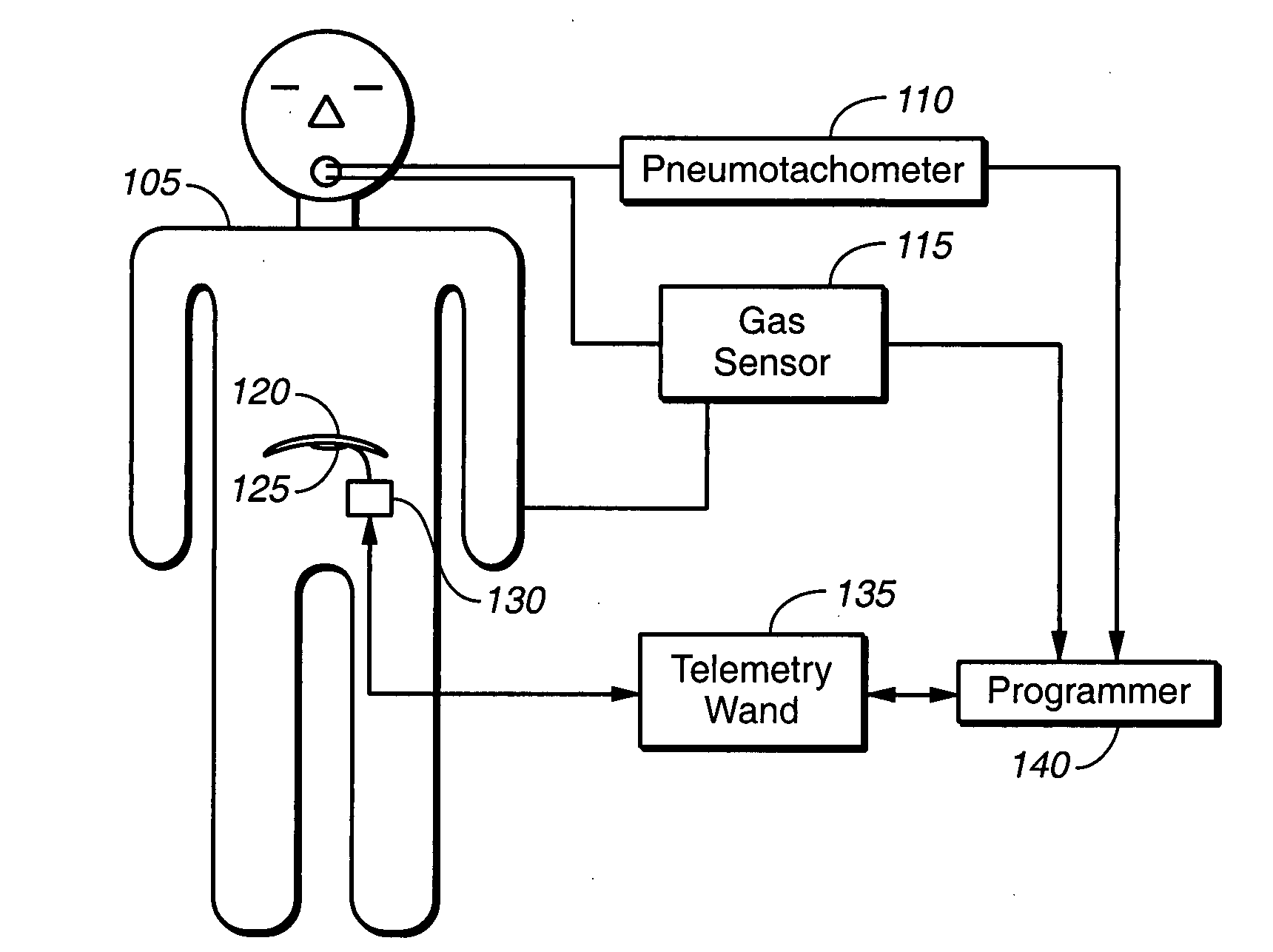
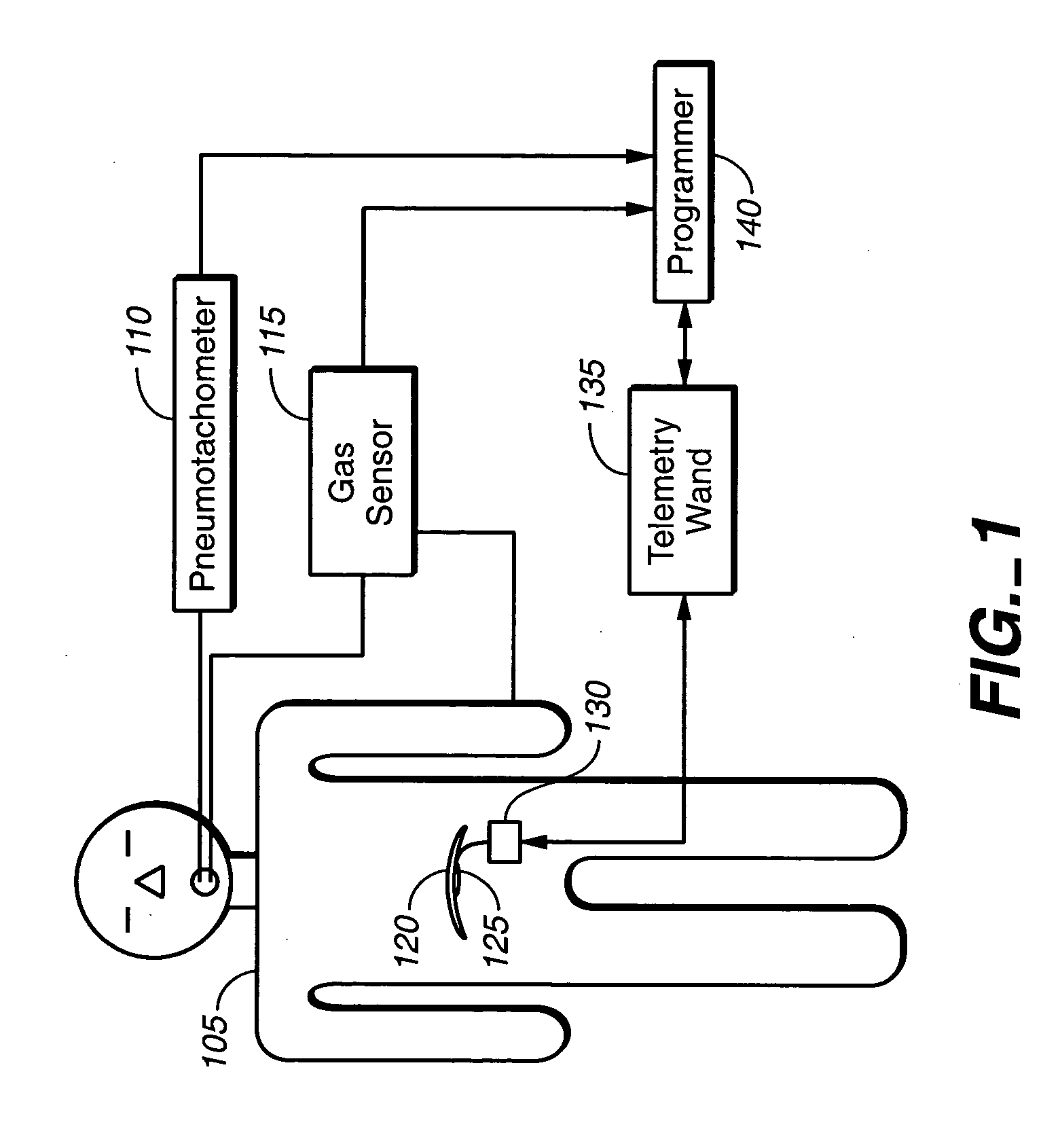
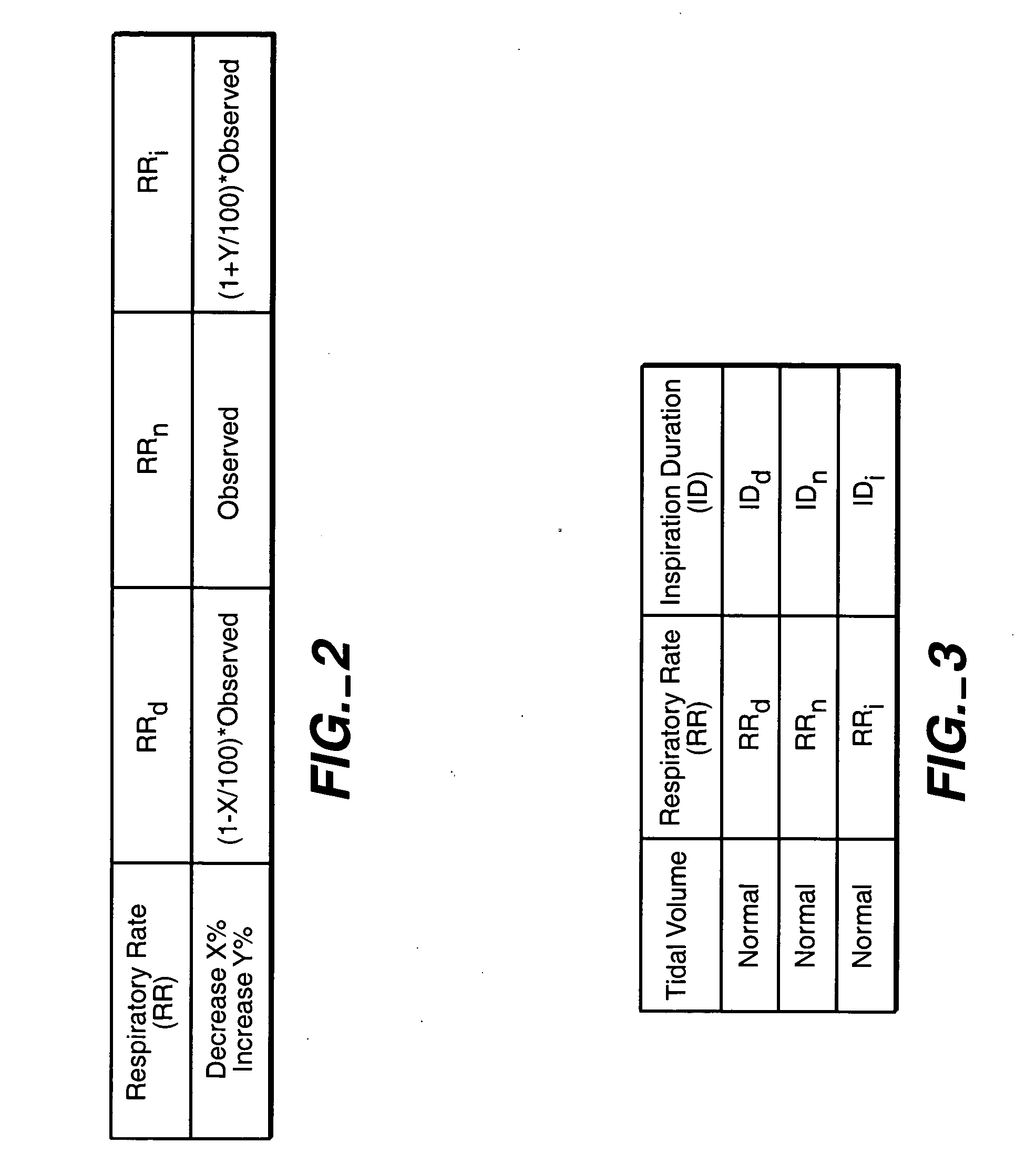
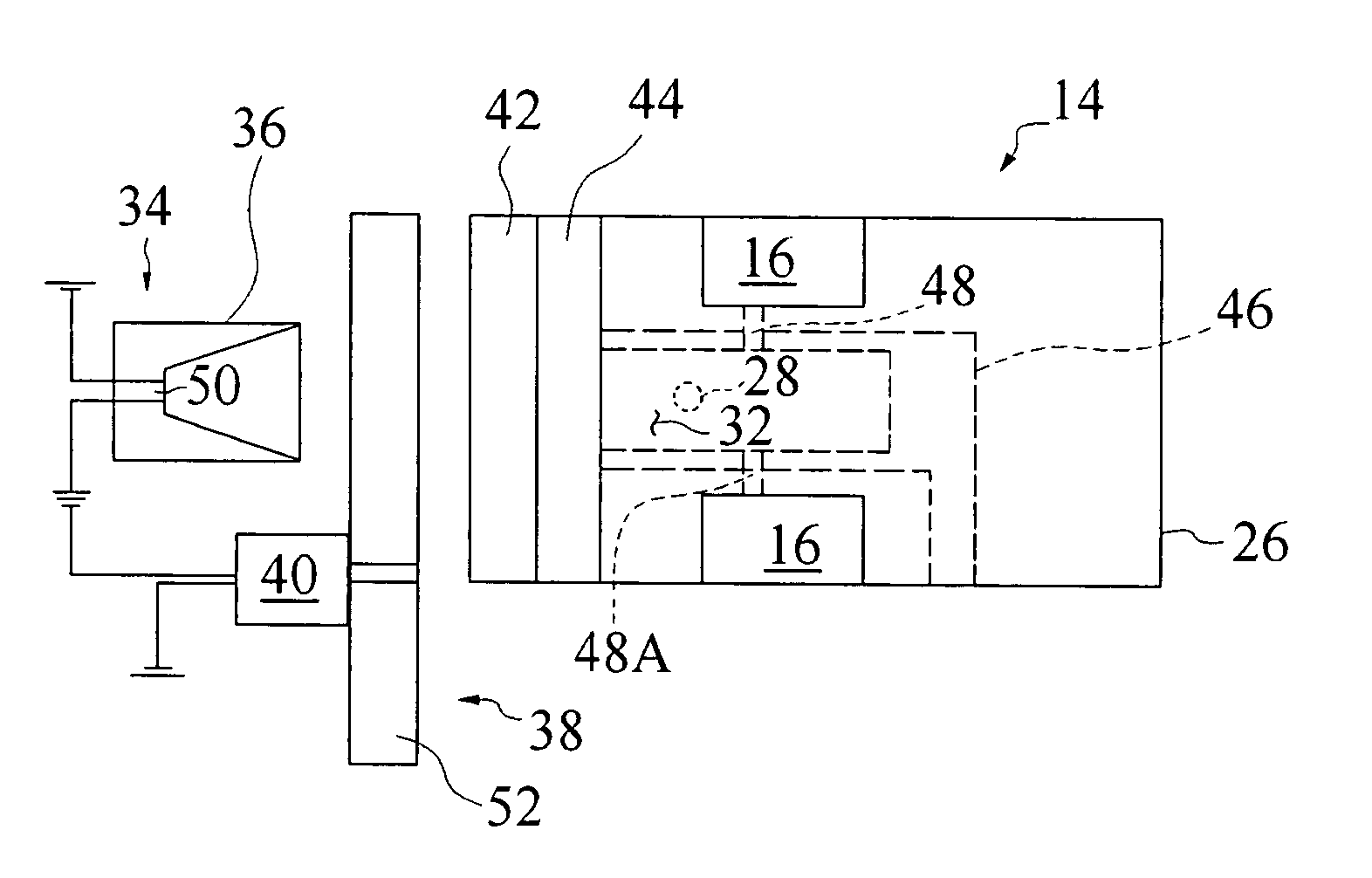
ActiveUS20050085867A1Enhanced negative intrapleural pressureNegative pressureRespiratorsElectrotherapyBlood gas testIntensive care medicine
A stimulation device is provided that stimulates breathing to manipulate blood gas concentrations such as SaO2 or PCO2 and thereby treat underlying causes of breathing disorders and heart failure progression. A programmable device is provided for setting diaphragm stimulation waveforms that adjust minute ventilation about a predetermined baseline value. Normal breathing of the subject is observed to establish a baseline reference minute ventilation, and the device is programmed to produce stimulation waveforms that may provide either a decrease or an increase in the patients minute ventilation. The minute ventilation of the subject may be decreased or increased from the baseline level by decreasing or increasing a parameter that changes minute ventilators.
Owner:RMX
Blood monitoring system
ActiveUS7608042B2Improve accuracyImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteBlood specimen
The present invention is directed towards apparatuses and methods for the automated measurement of blood analytes and blood parameters for bedside monitoring of patient blood chemistry. Particularly, the current invention discloses a programmable system that can automatically draw blood samples at a suitable programmable time frequency (or at predetermined timing), can automatically analyze the drawn blood samples and immediately measure and display blood parameters such as glucose levels, hematocrit levels, hemoglobin blood oxygen saturation, blood gases, lactate or any other blood parameter.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
System for combined transcutaneous blood gas monitoring and negative pressure wound treatment
InactiveUS7524286B2Substantial riskAccurate estimateIntravenous devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerSignificant risk
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Compact device for measuring, tissue analytes
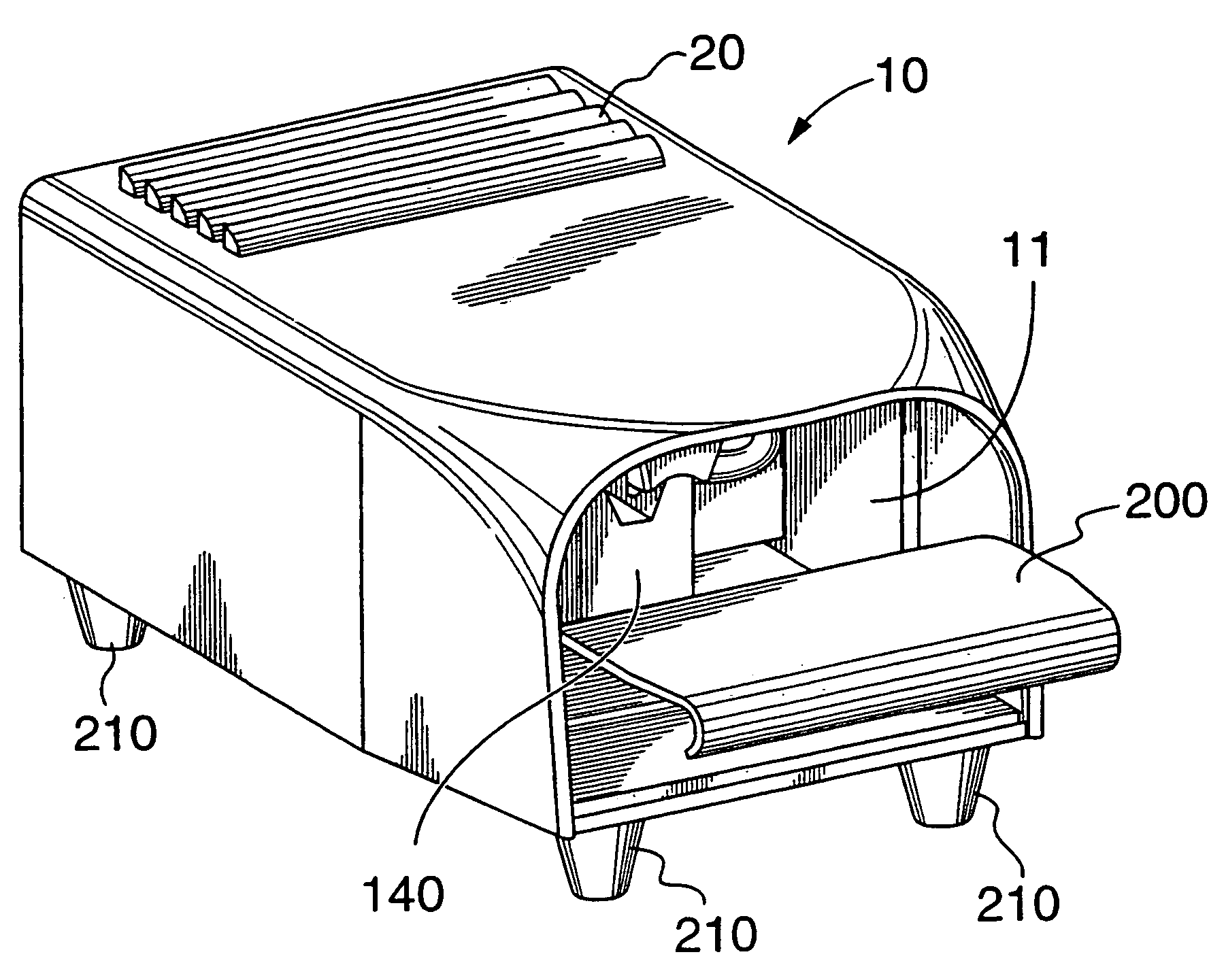
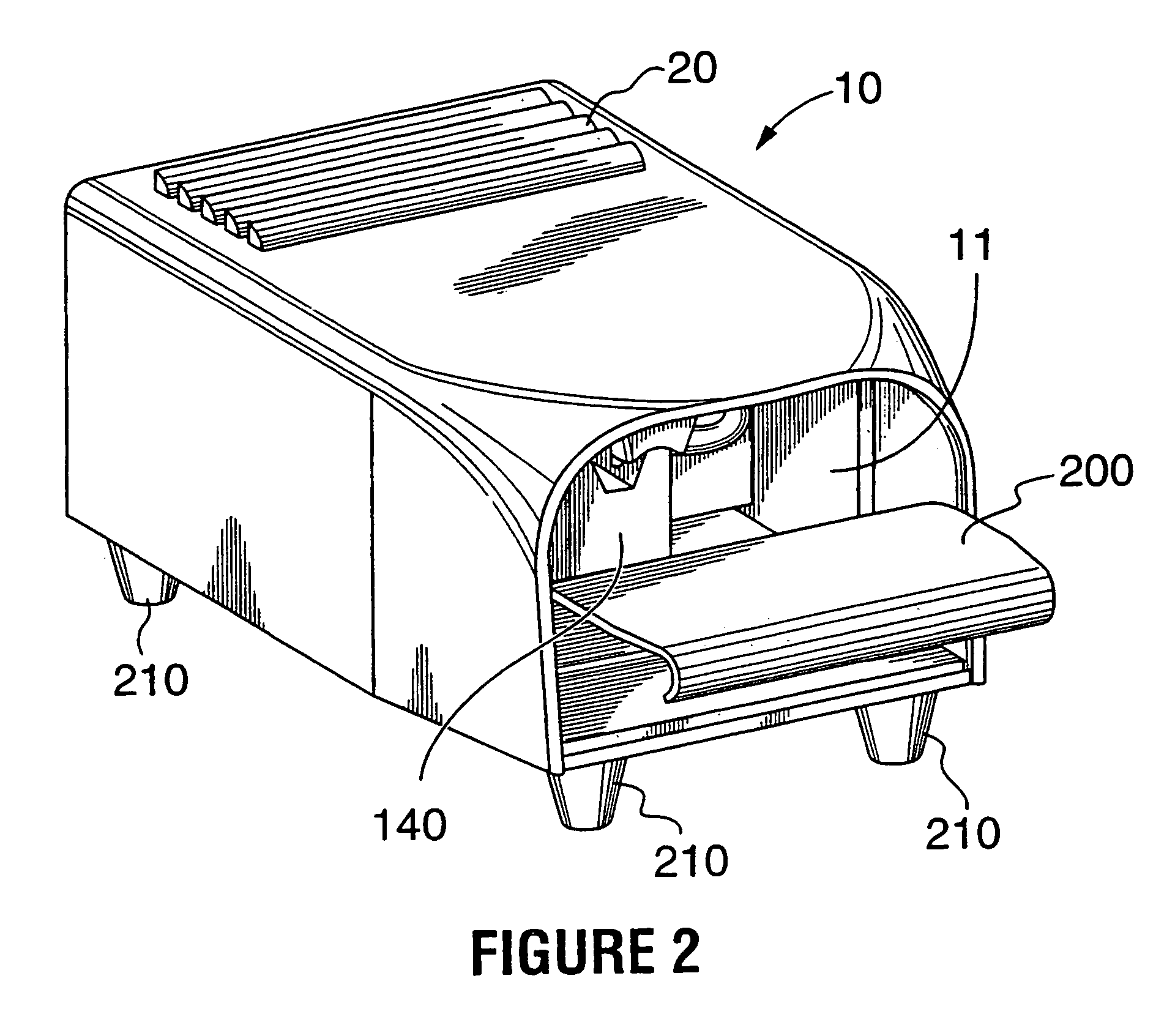
InactiveUS6928311B1Improve stabilityReduced sensitivity to heatSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringCholesterolEngineering
A compact device (20) for non-invasively monitoring concentration levels of blood constituents, including glucose, cholesterol, alcohol, blood gases and various ions. The device includes a finger receptor (140) having a channel for receiving a finger of a user. The channel has a light entrance and a light exit so that light can be passed from a light source (91) through a finger located in the channel in a direction generally normal to the finger. Certain heat generating components, including a stable power supply for the device, are external to the device housing so as to reduce heat generation and thereby increase stability of the device. The device includes a communications interface for interacting with a computer. The device can be used for clinical use or for home use and the memory of the computer can be used to assist with record keeping and with dosage calculations.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Blood monitoring system
The present invention is directed towards apparatuses and methods for the automated measurement of blood analytes and blood parameters for bedside monitoring of patient blood chemistry. Particularly, the current invention discloses a programmable system that can automatically draw blood samples at a suitable programmable time frequency (or at predetermined timing), can automatically analyze the drawn blood samples and immediately measure and display blood parameters such as glucose levels, hematocrit levels, hemoglobin blood oxygen saturation, blood gases, lactate or any other blood parameter.
Owner:GLUCON
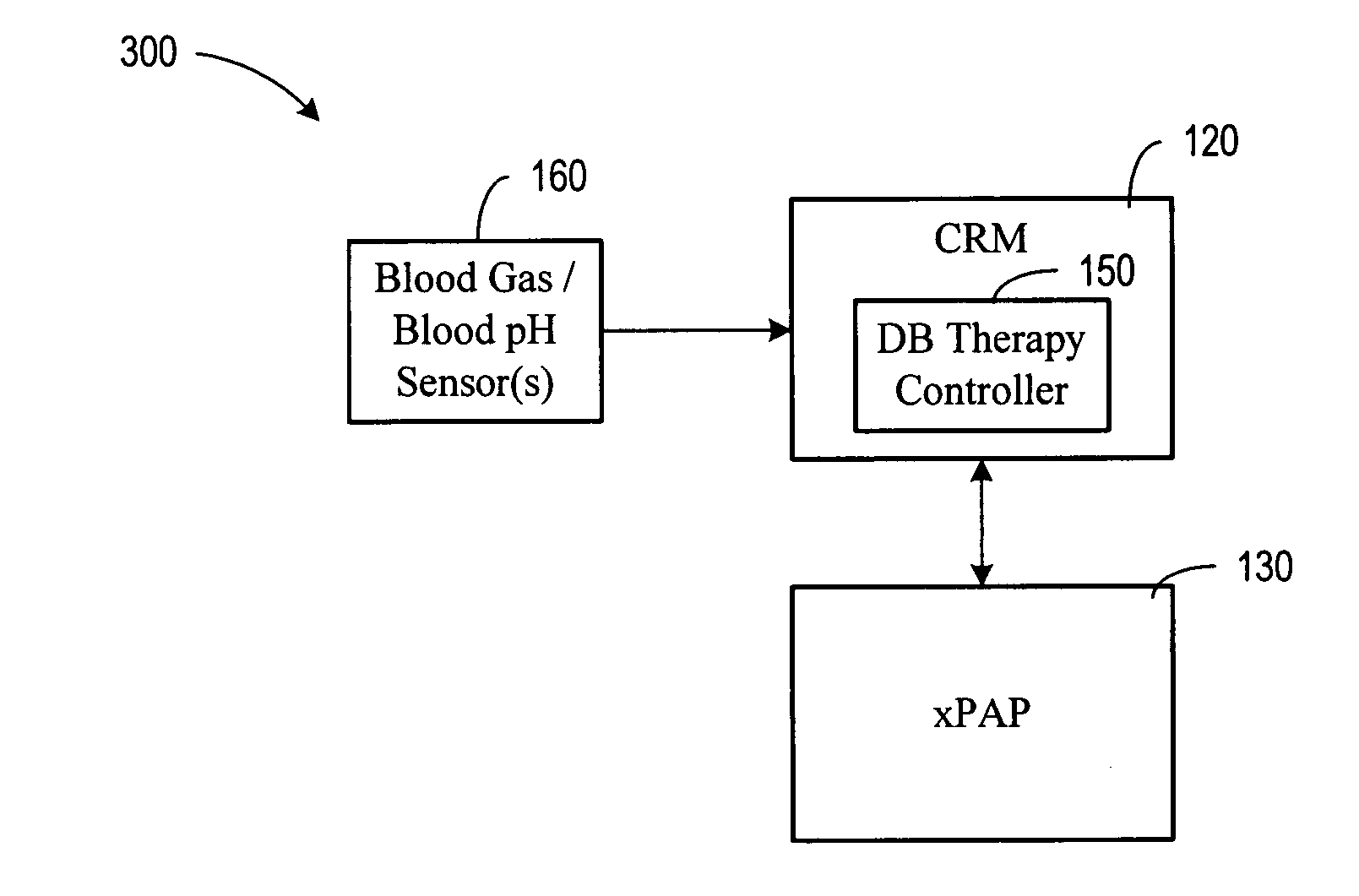
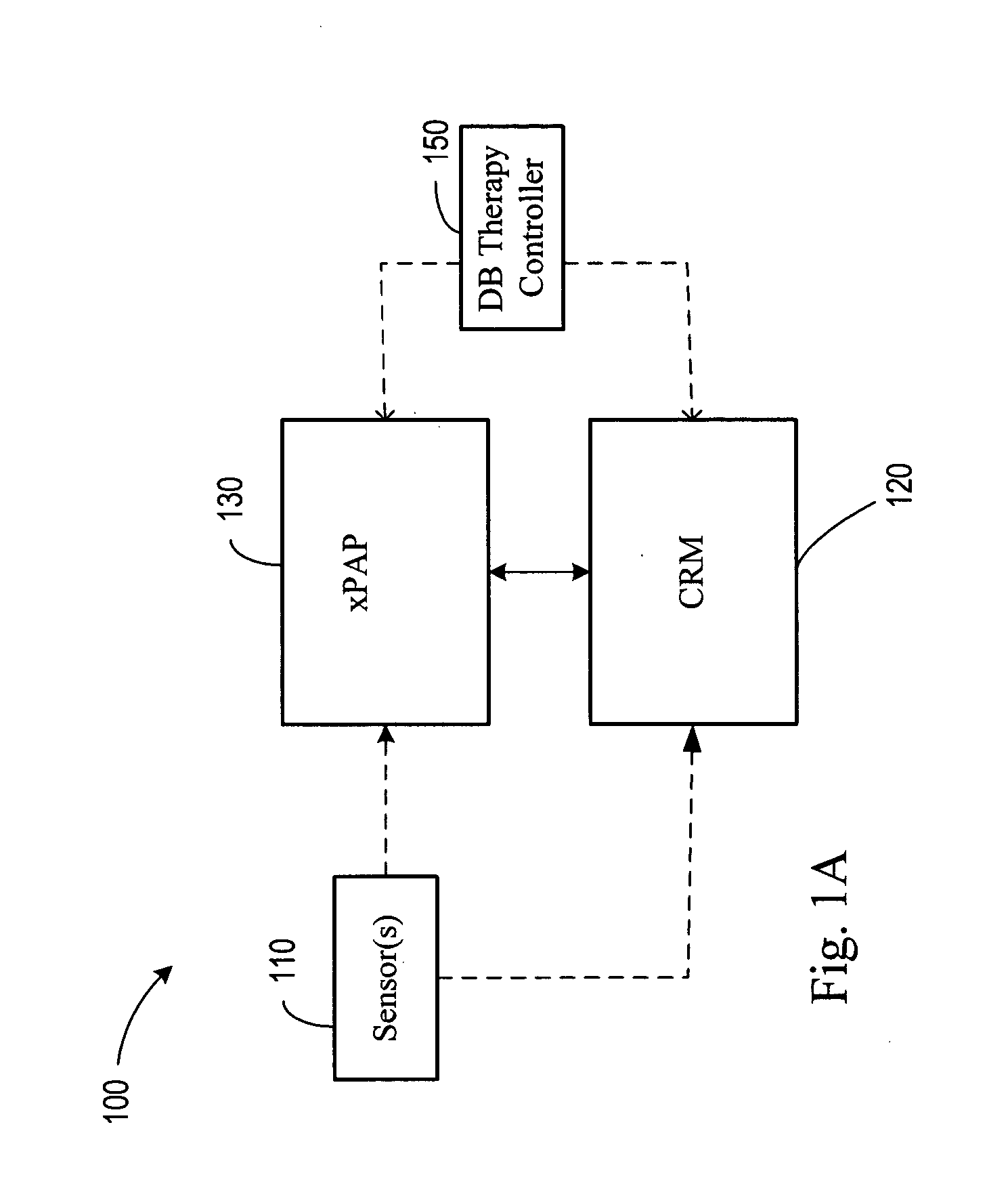
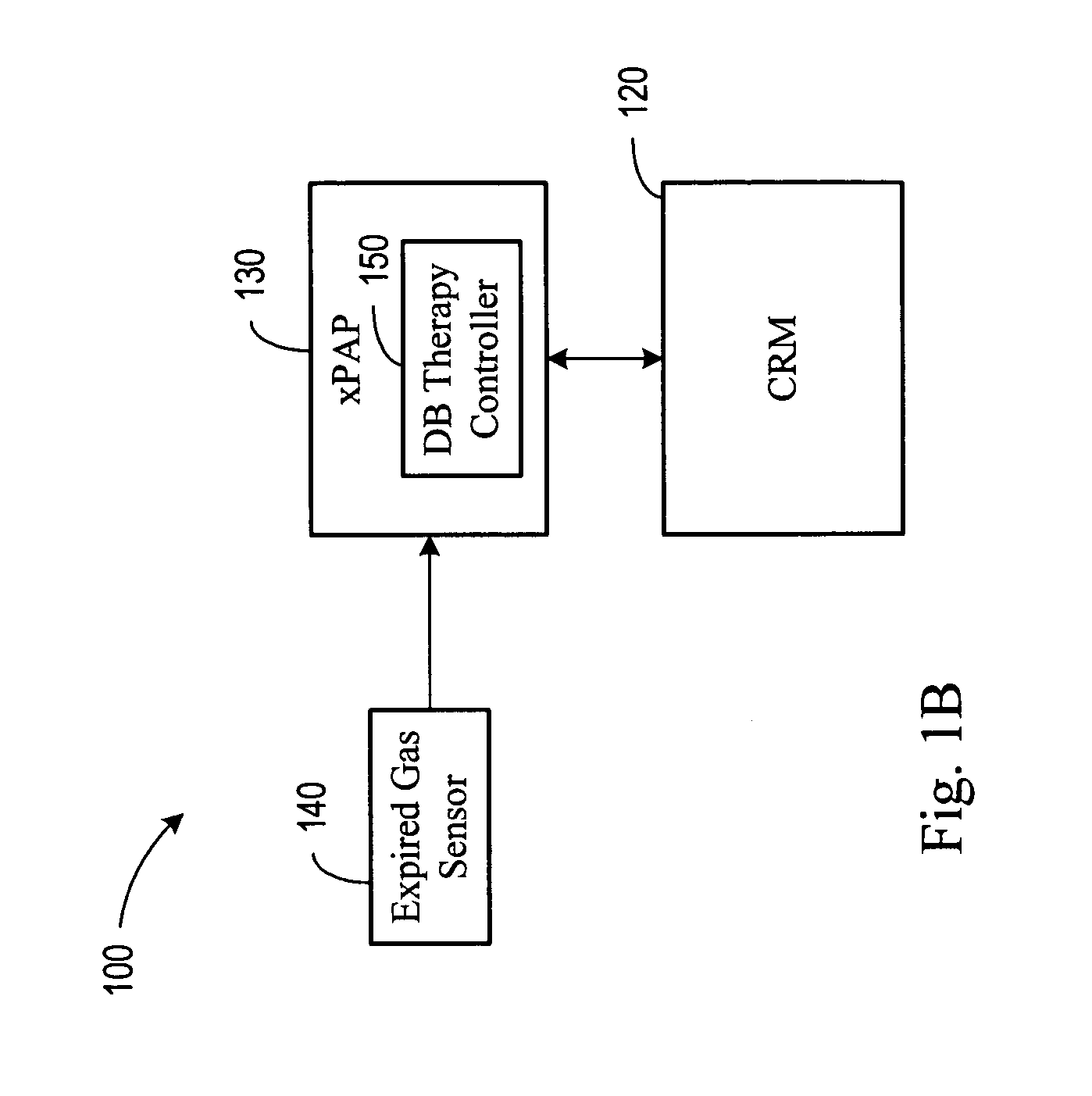
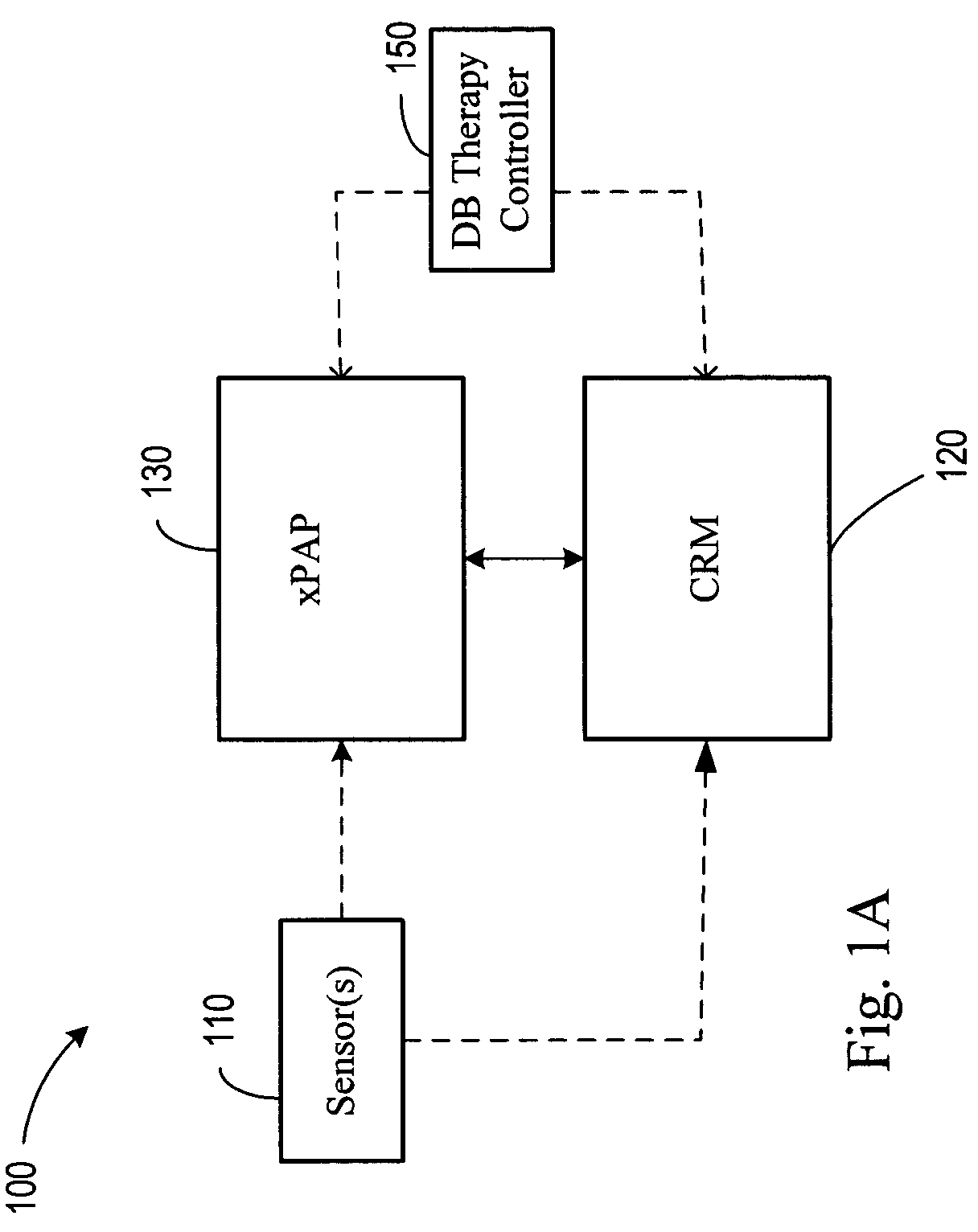
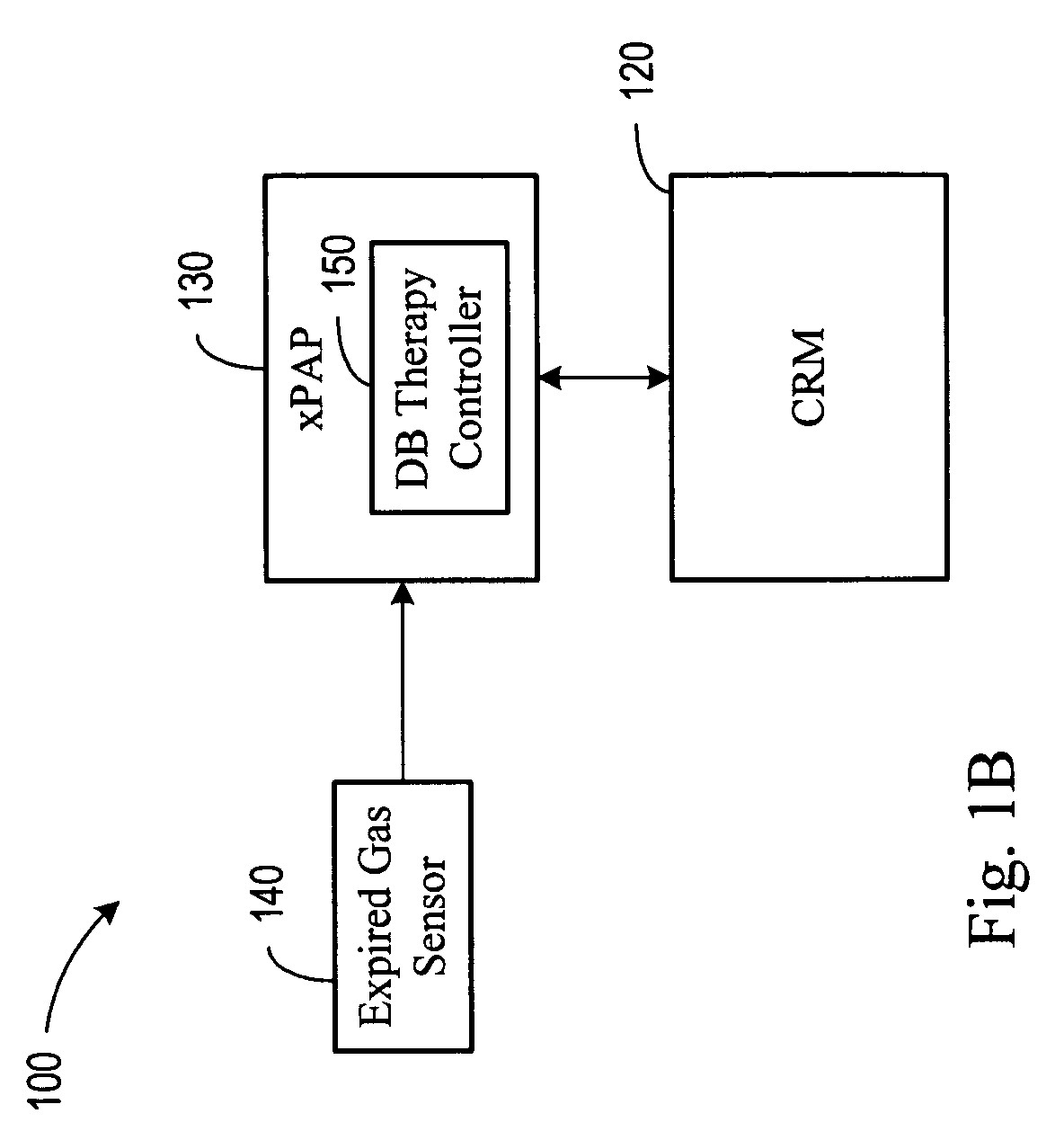
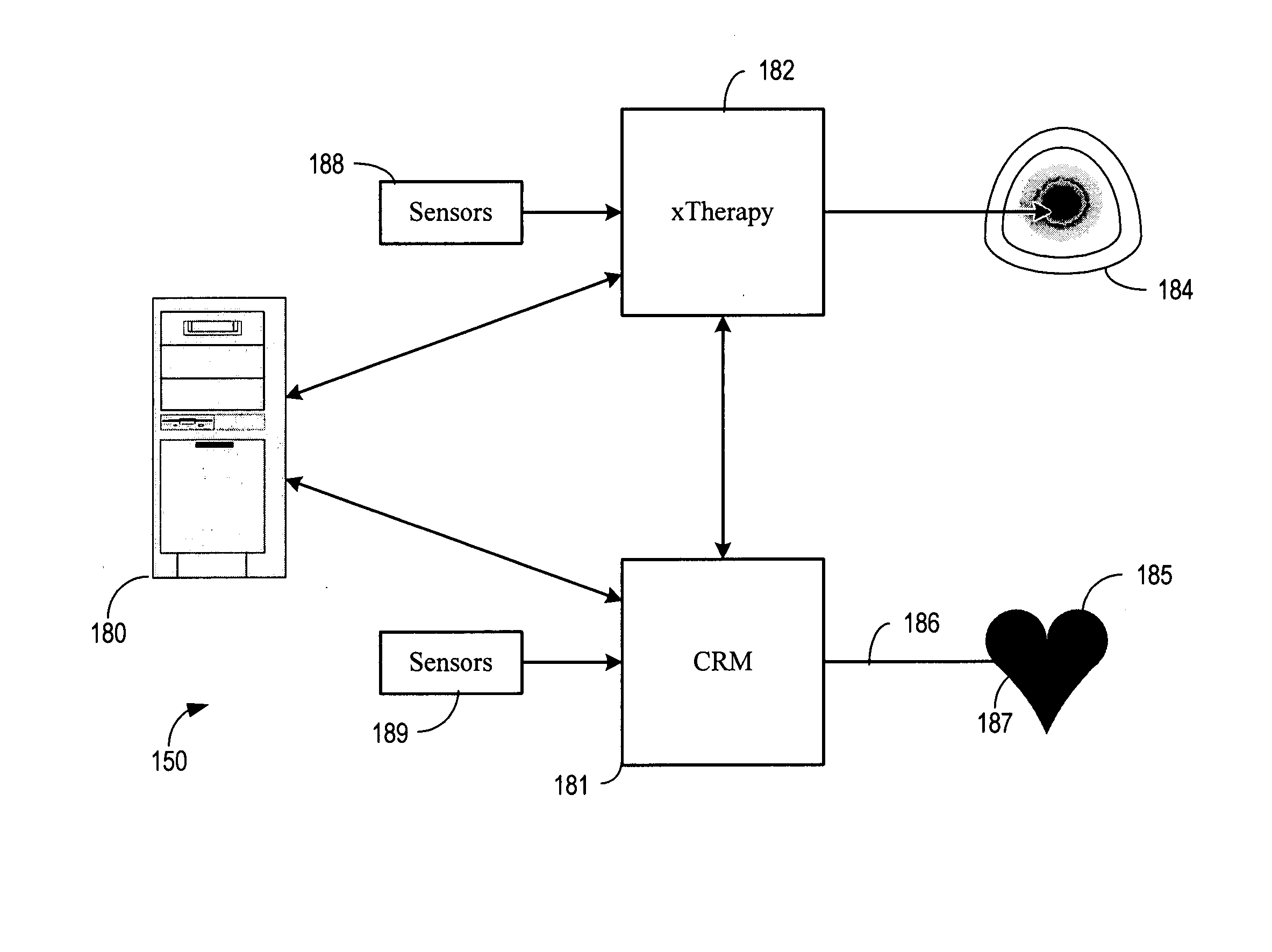
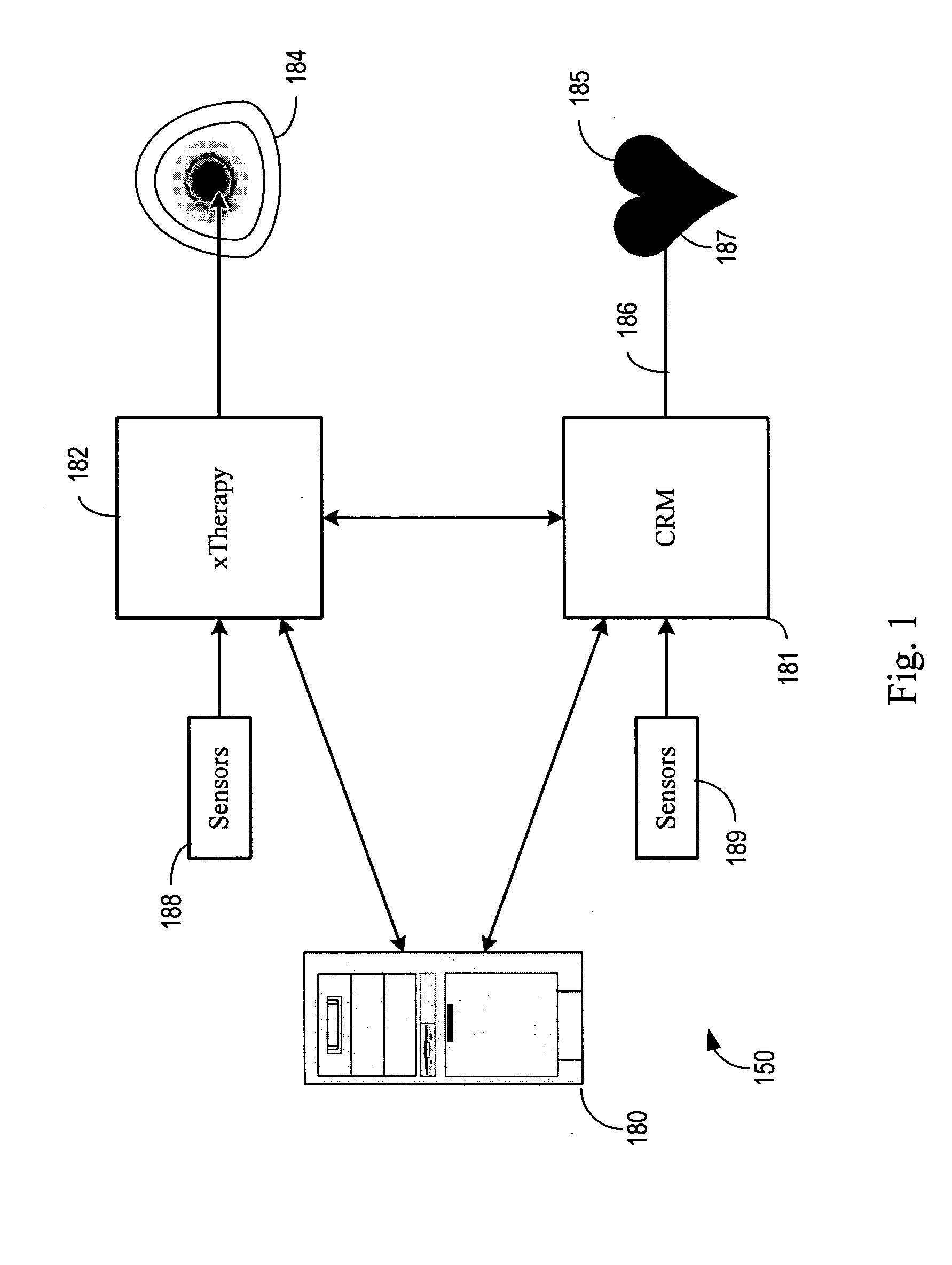
Diagnosis and/or therapy using blood chemistry/expired gas parameter analysis
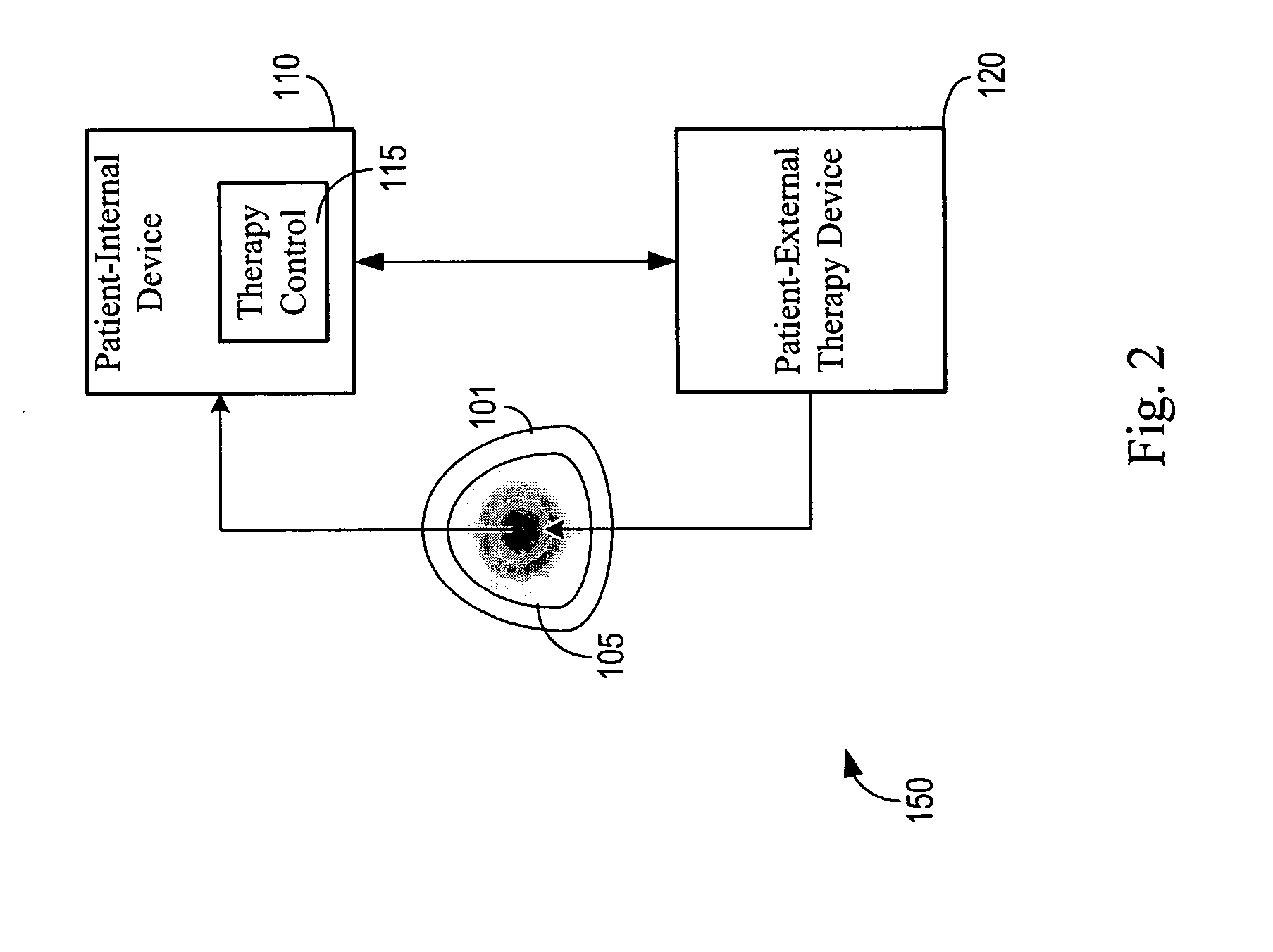
Methods and systems for diagnosing disorders, including, for example, disordered breathing, involve sensing one or more of a blood chemistry parameter and / or an expired gas parameter, such as expired respiratory gas concentration, blood gas concentration, and blood pH. Diagnosis of the disorder may be performed by a medical device, such as a respiratory therapy device or a cardiac therapy device, based on implantably detected blood gas / pH concentration / level or externally detected expired respiratory gas concentration. Cardiac and respiratory therapies for addressing the disorder may be adjusted based on the detected parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and device for measuring blood gas parameters
InactiveUS7491175B2Act quicklyAccurate valueMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMedicineBlood gas test
The invention relates to a method and device for measuring blood gas parameters, preferably pH, pCO2, and pO2, in a blood sample, where the blood sample of a patient is fed into at least one measuring cell of an analyzer. In order to obtain accurate values for the blood gas parameters even in cases where the temperature of the patient deviates from normal temperature, the temperature of the patient or blood sample is measured upon sample withdrawal, and the measured temperature is transmitted to the analyzer or is recorded by the analyzer, and the temperature of the measuring cell of the analyzer is adjusted to the measured temperature by cooling or heating.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Method and apparatus for determining at least one evaluation parameter of a blood sample
ActiveUS20110237913A1Simple processHealth-index calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringBlood gas testBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides a method for determining at least one evaluation parameter of a blood sample, comprising the following steps: providing (S4) at least one blood gas parameter; providing (S5) at least one hemostasis parameter; and determining (S6 . . . 310″) the at least one evaluation parameter as a function of the blood gas parameter and / or the hemostasis parameter.
Owner:C A CASYSO
Method and display apparatus for non-invasively determining pulmonary characteristics by measuring breath gas and blood gas
InactiveUS20100179392A1Solve the real problemSensorsBlood flow measurementPulmonary vasculatureLung structure
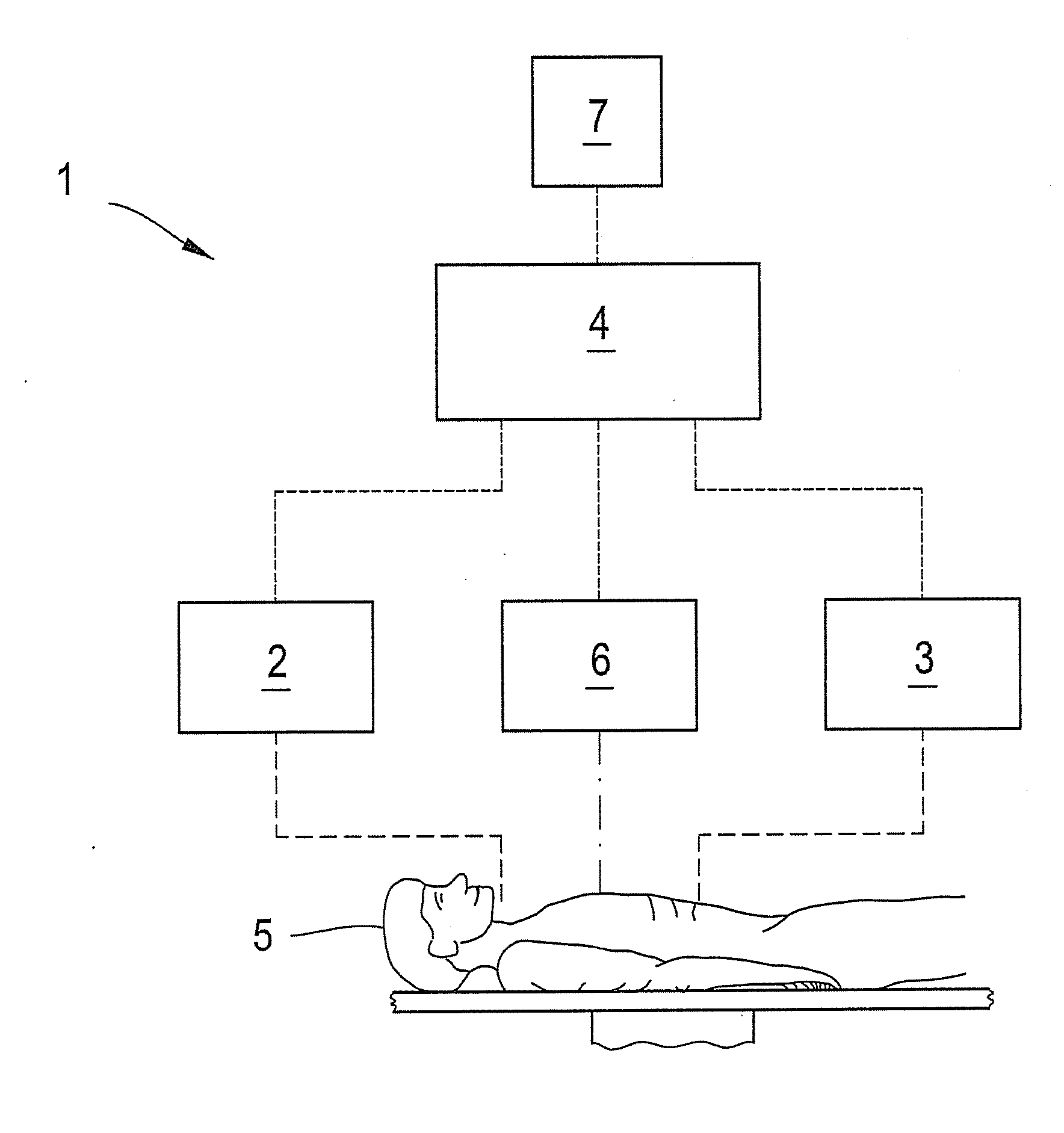
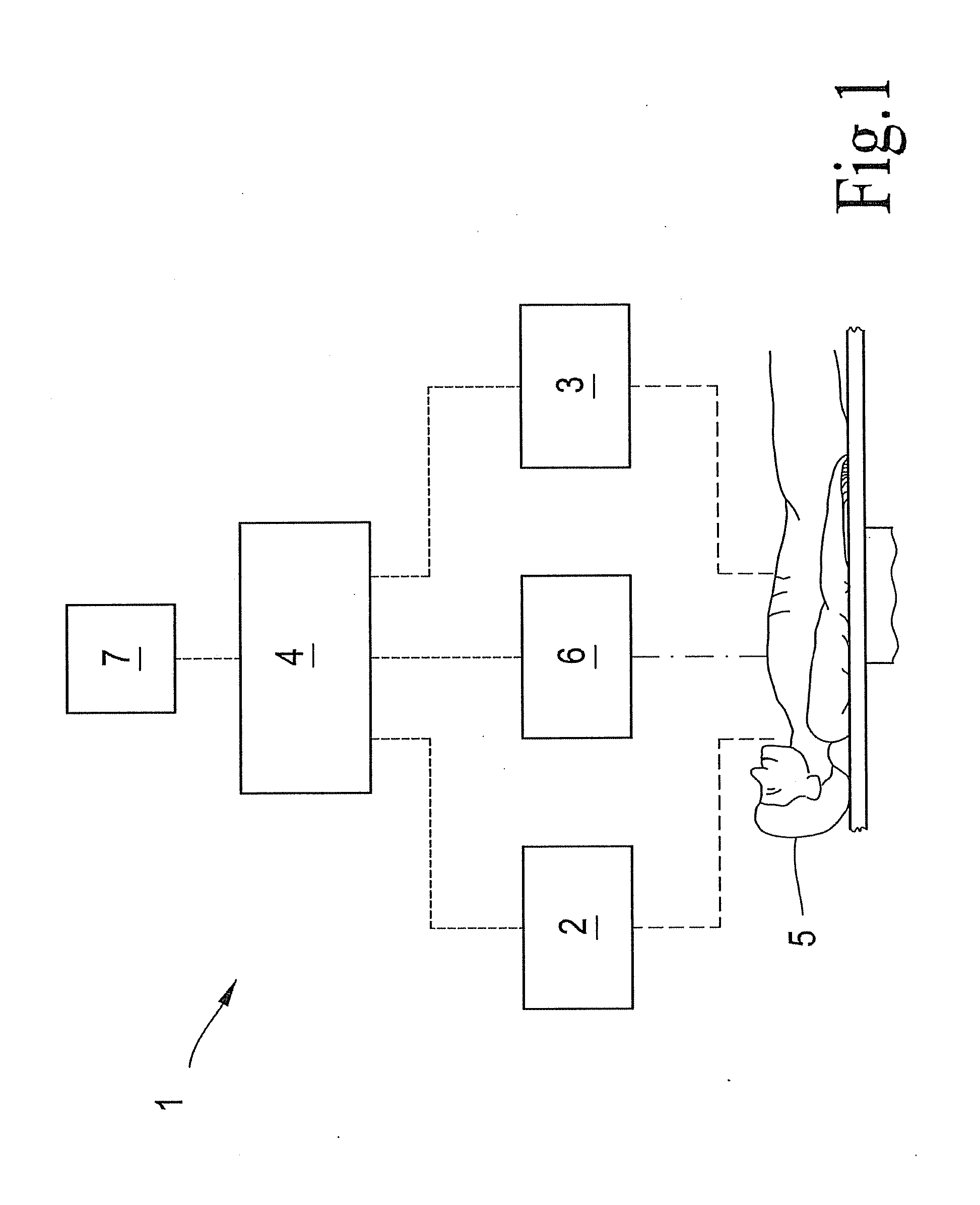
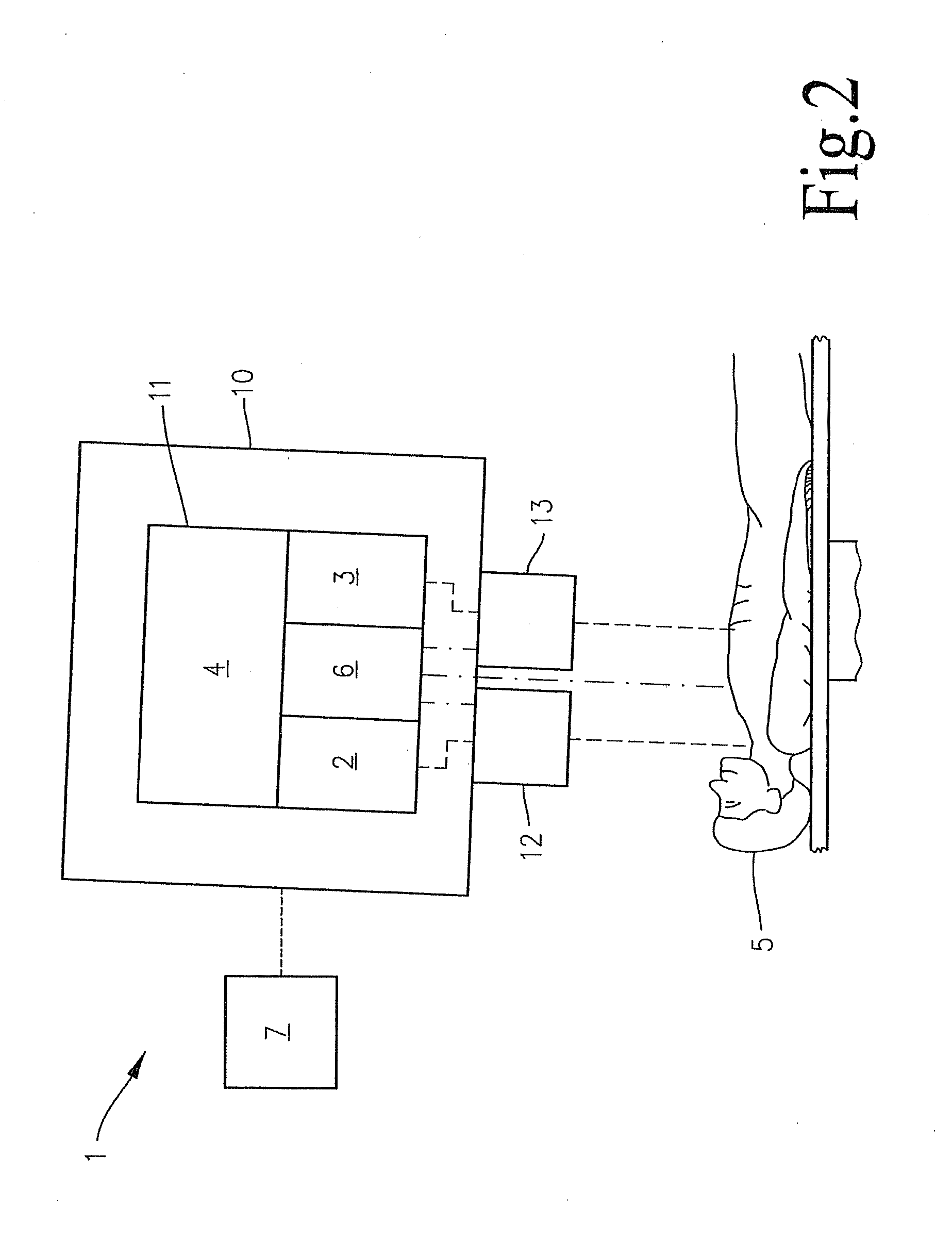
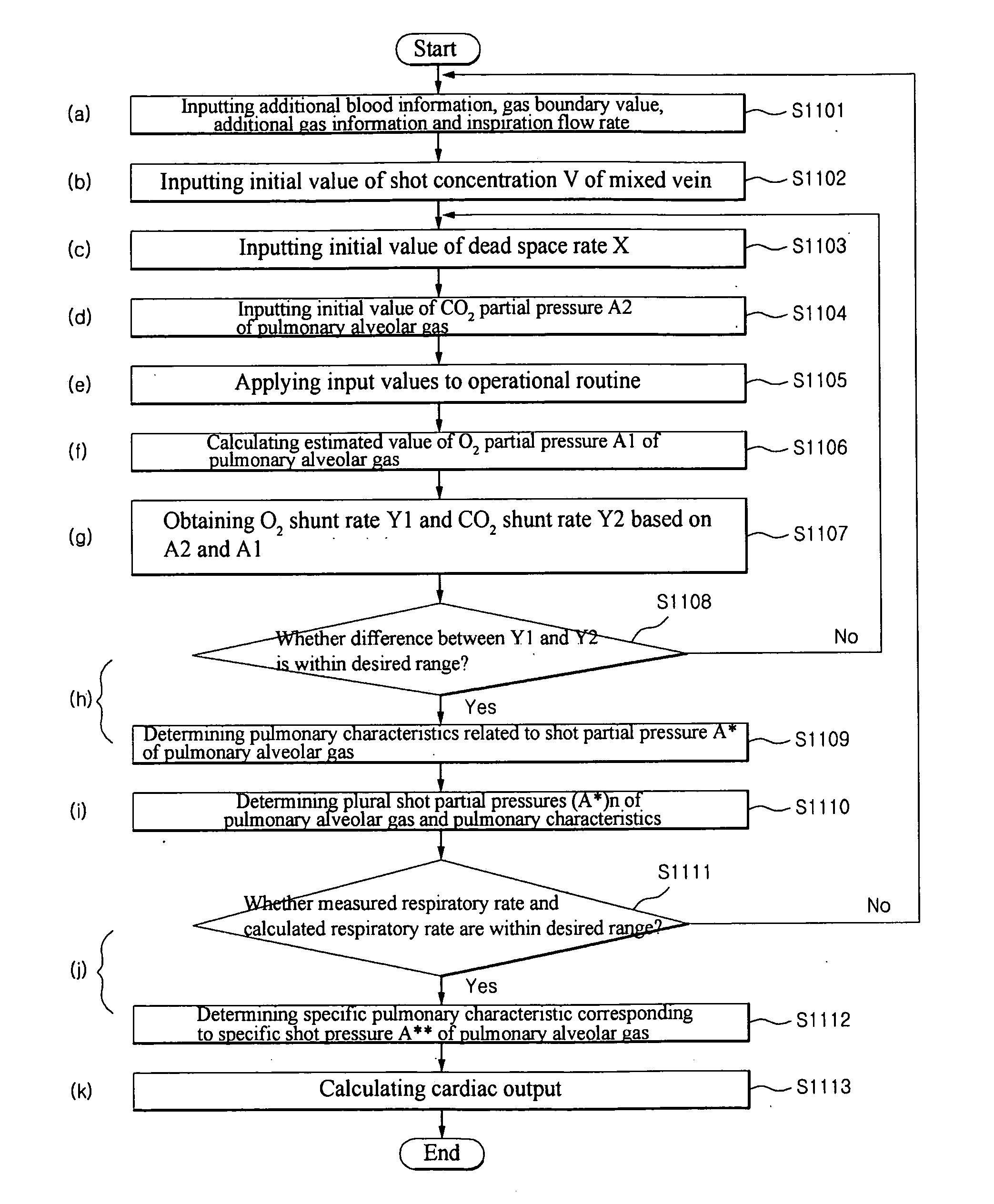
A method for non-invasively determining pulmonary characteristics by measuring breath gas and blood gas and a display apparatus for the same, and for estimating major physiological characteristics, such as respiratory characteristics of lungs-pulmonary circulation system, cardiac functional characteristics, structural characteristics of lungs, etc. by applying primary measurement parameters obtained from ventilation gas and blood during breathing; and a display apparatus useful for the same.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Extracorporeal blood circuit priming system and method
ActiveUS7189352B2Overcome difficultiesSemi-permeable membranesOther blood circulation devicesExtracorporeal circulationAir interface
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a venous blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
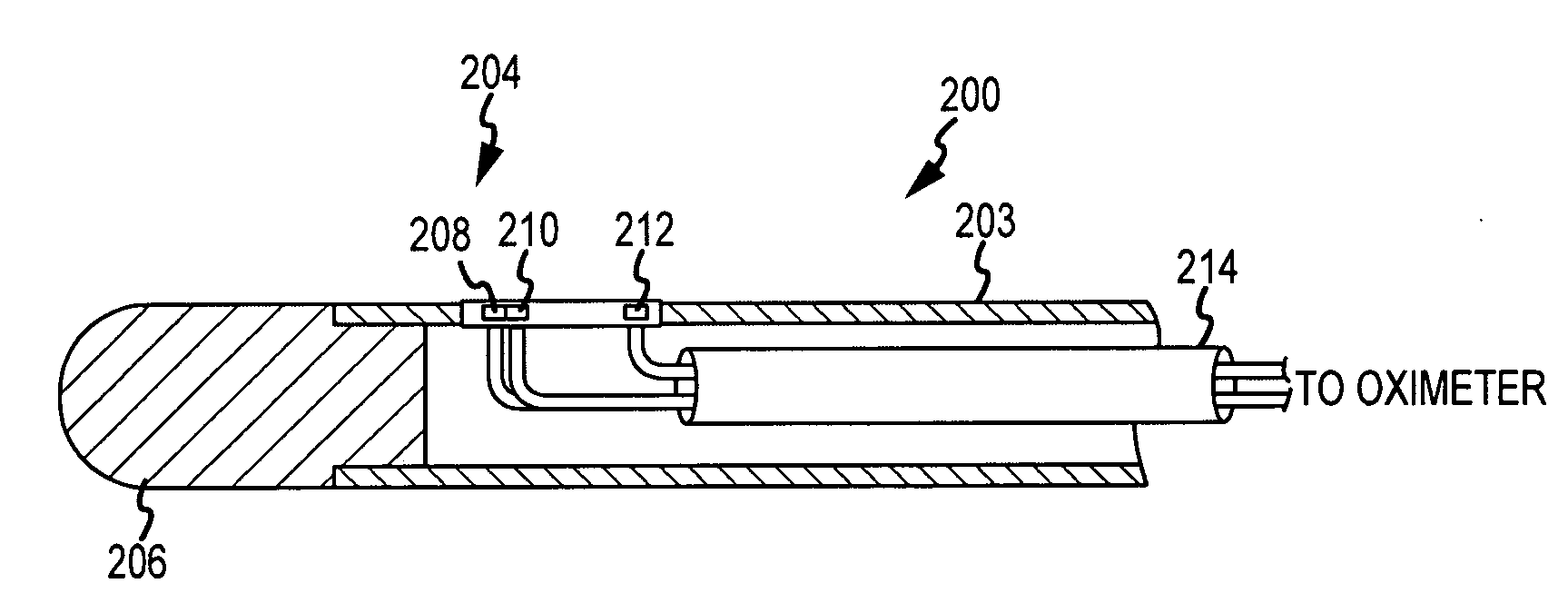
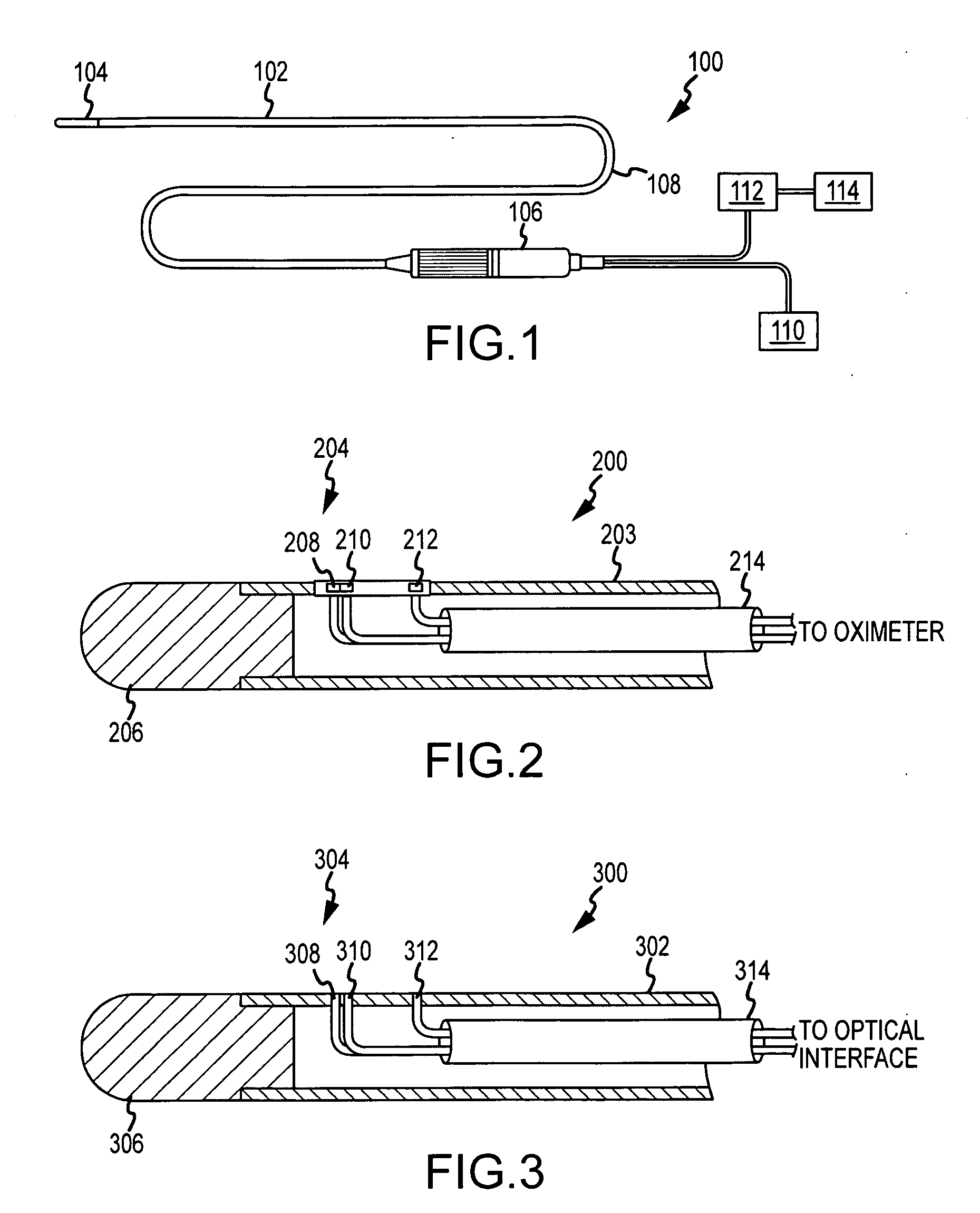
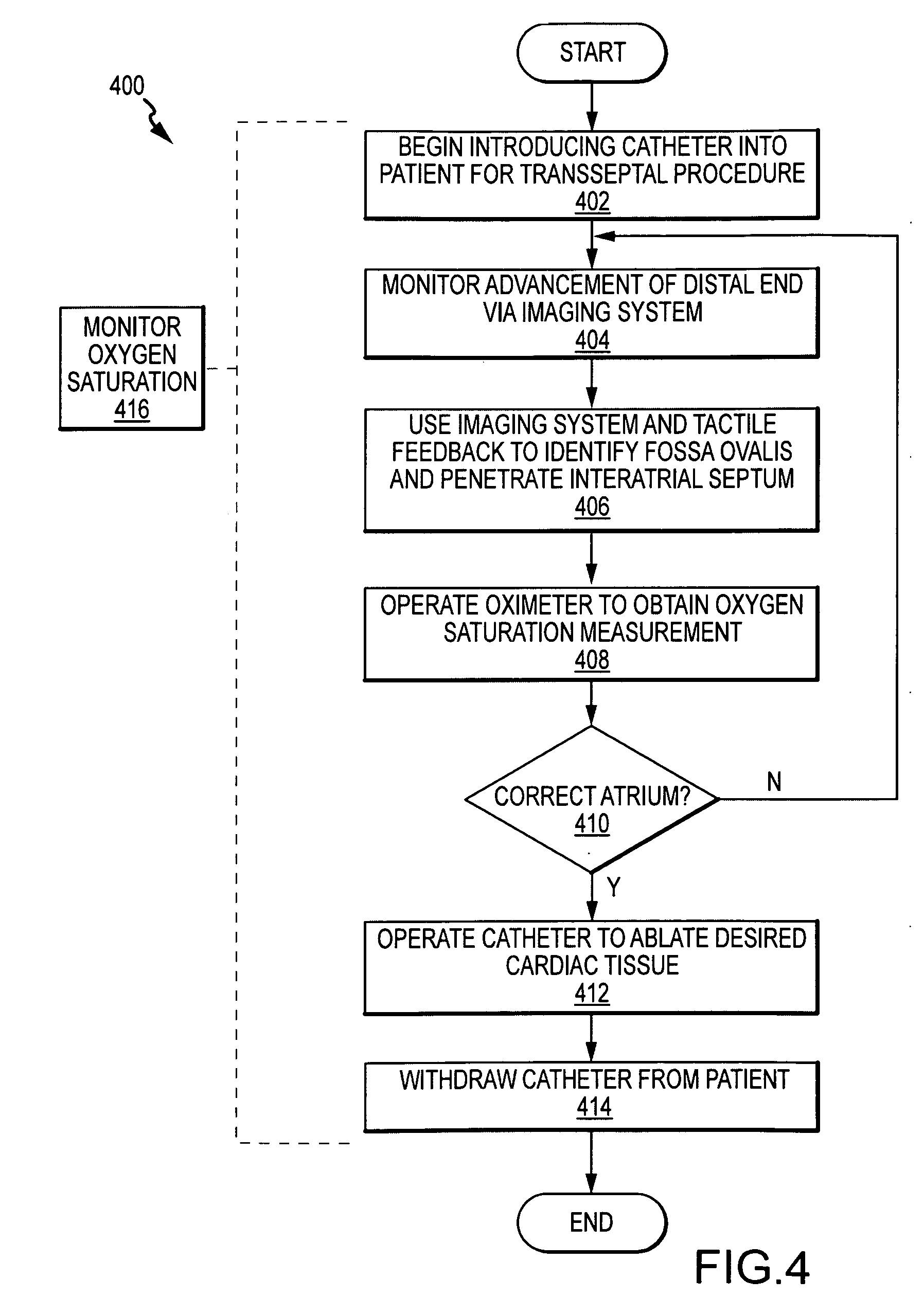
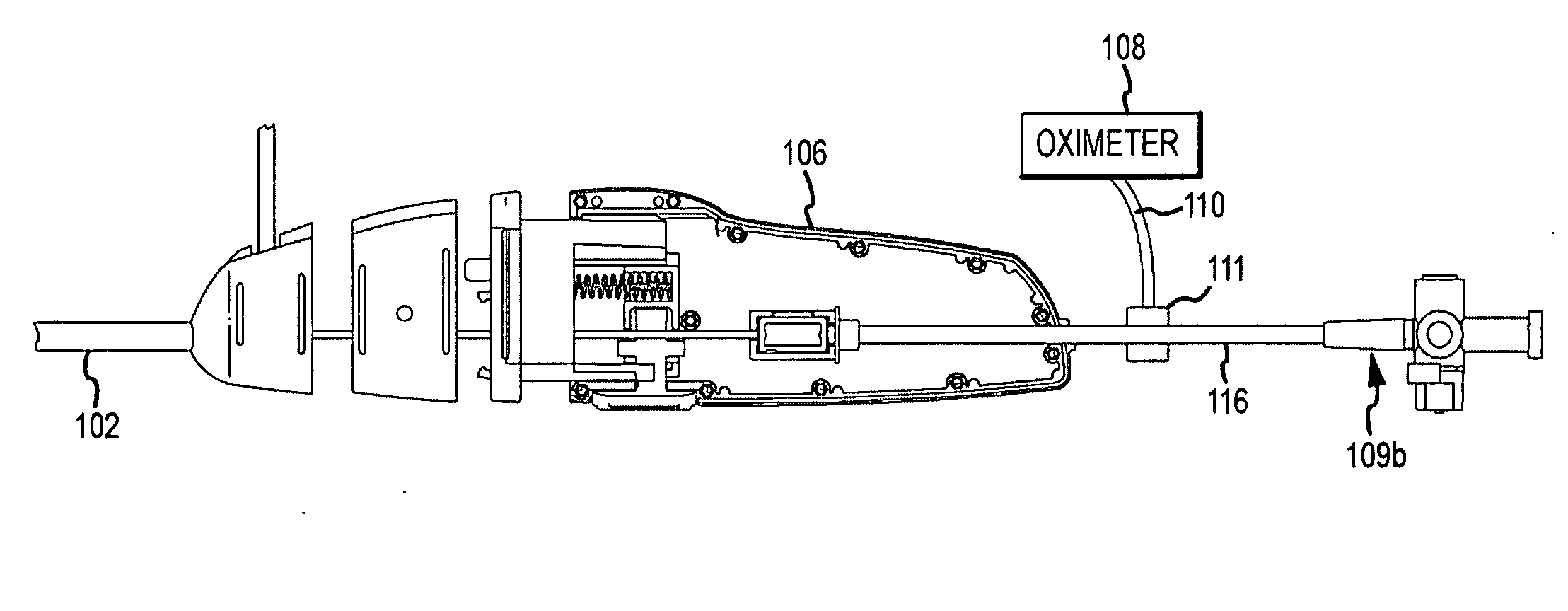
Cardiac ablation catheter with oxygen saturation sensor
Positioning of the distal end of a catheter at a desired location, for example, in the desired atrium of a patient's heart, can be determined or verified through measurement of blood gas values proximate to the distal end. In one embodiment, an oximeter is used to monitor oxygen saturation, for example, to distinguish between de-oxygenated venous blood and well-oxygenated arterial blood. Optical signals may be transmitted to the distal end of the catheter and received therefrom via optical fibers. Specifically, a catheter (300) has a number of optical fiber ends (308, 310 and 312) disposed at a distal end (304) thereof. A first fiber end (310) transmits the red and infrared optical signals. Fiber ends (308 and 312) are used for detecting reflected optical signals. The optical signals are then processed by a detector and an oximeter instrument to provide oxygen saturation readings that can indicate the position of the distal end of the catheter within the patient's heart or successful penetration of the interatrial septum.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Active air removal system operating modes of an extracorporeal blood circuit
ActiveUS7201870B2Overcome difficultiesSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationAir interface
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a venous blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
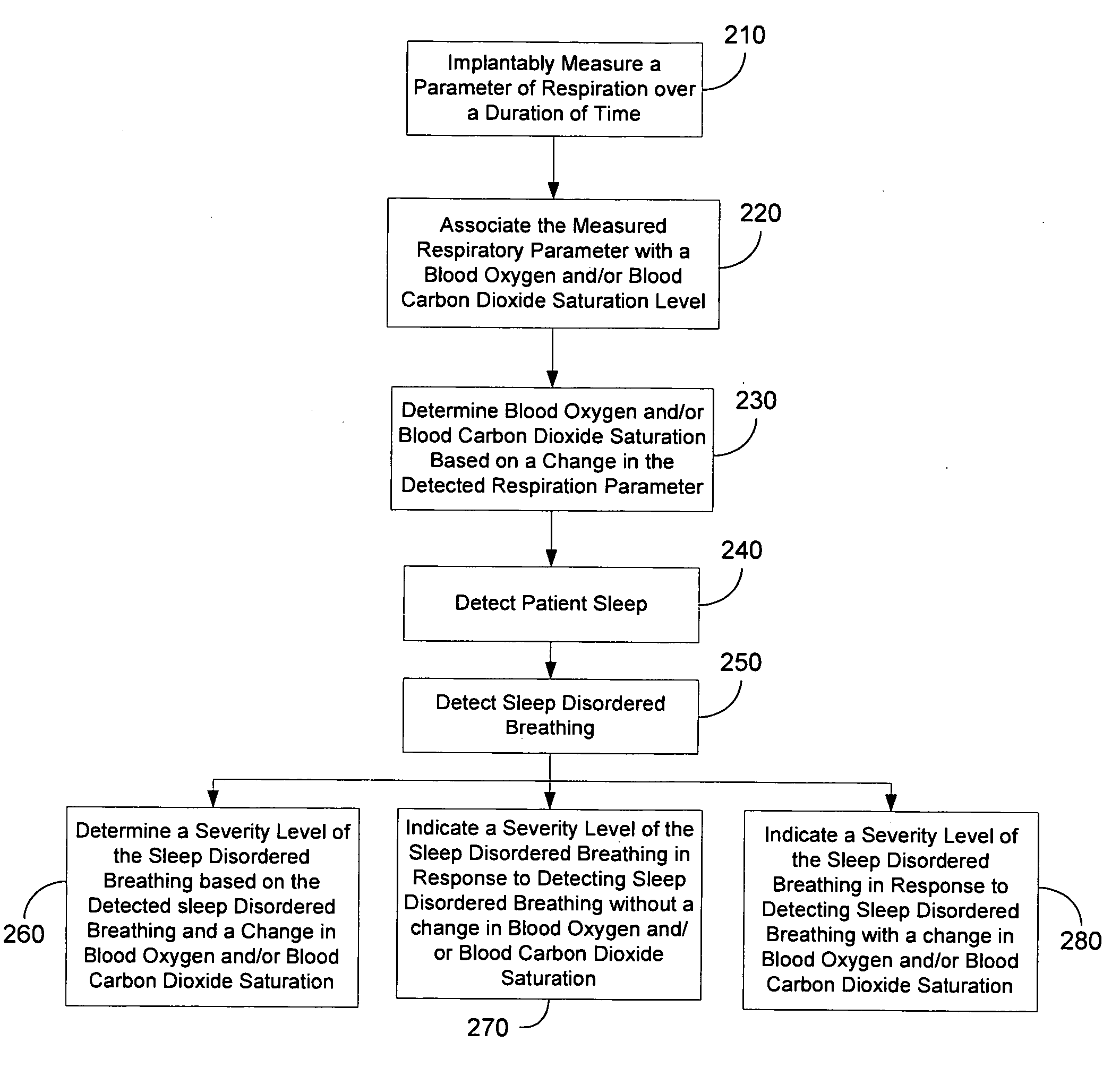
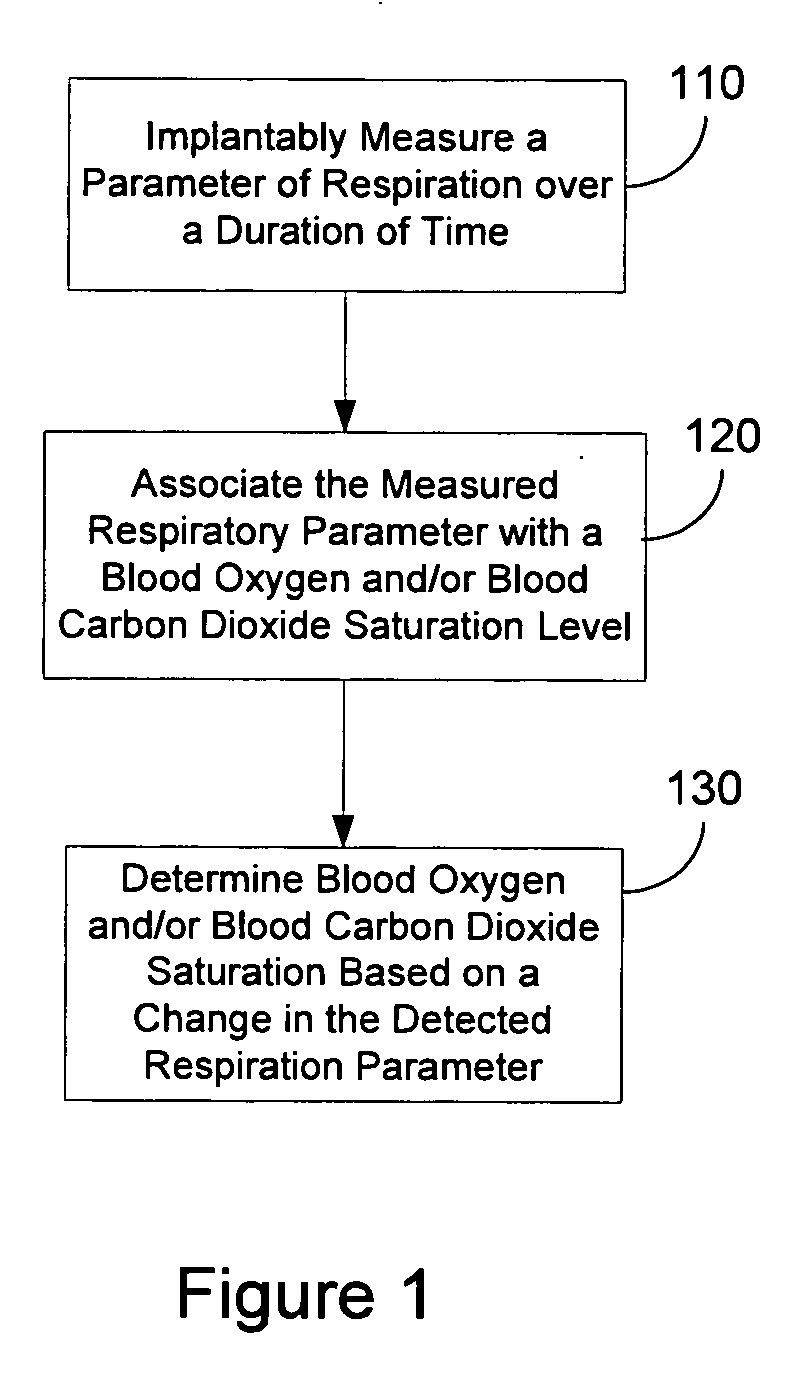
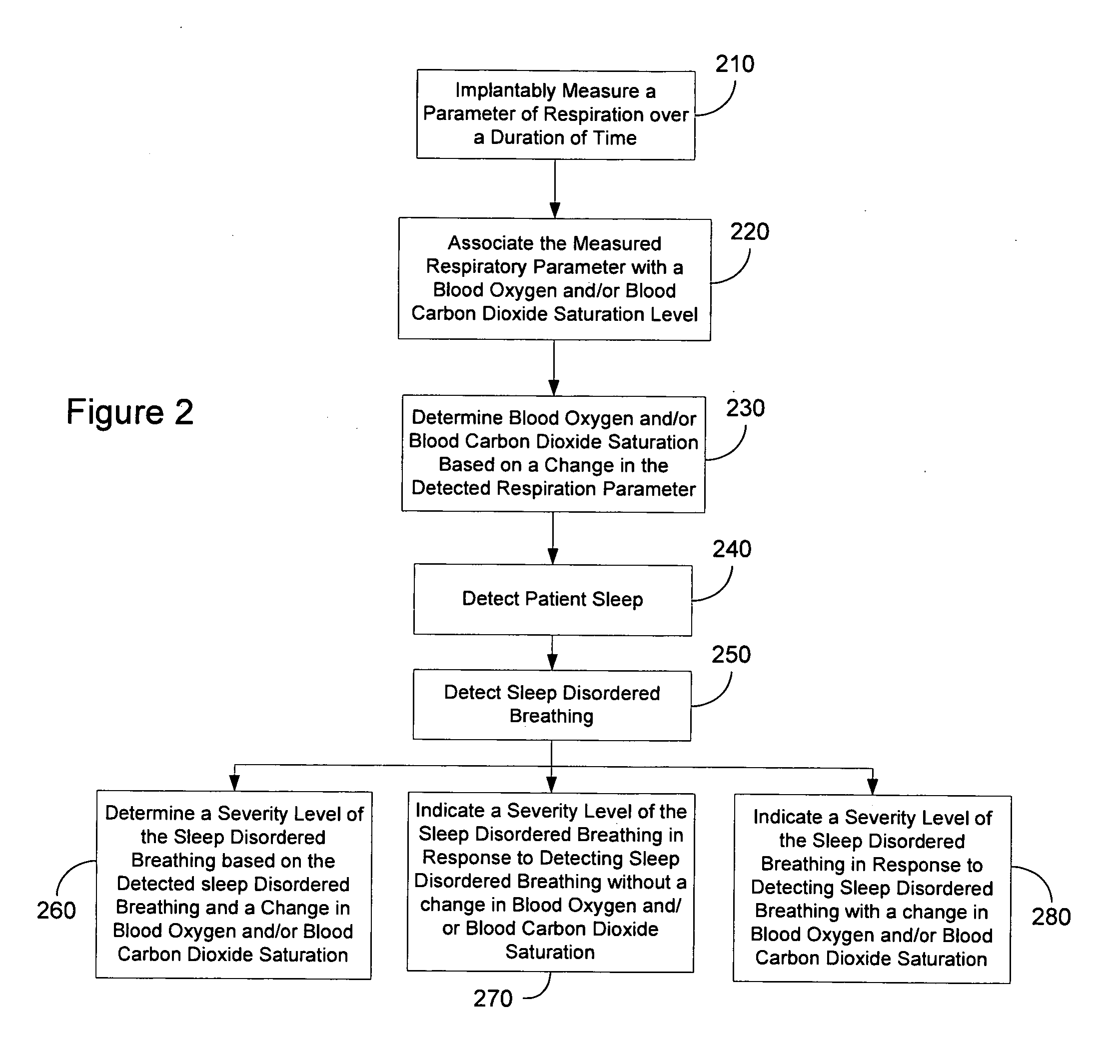
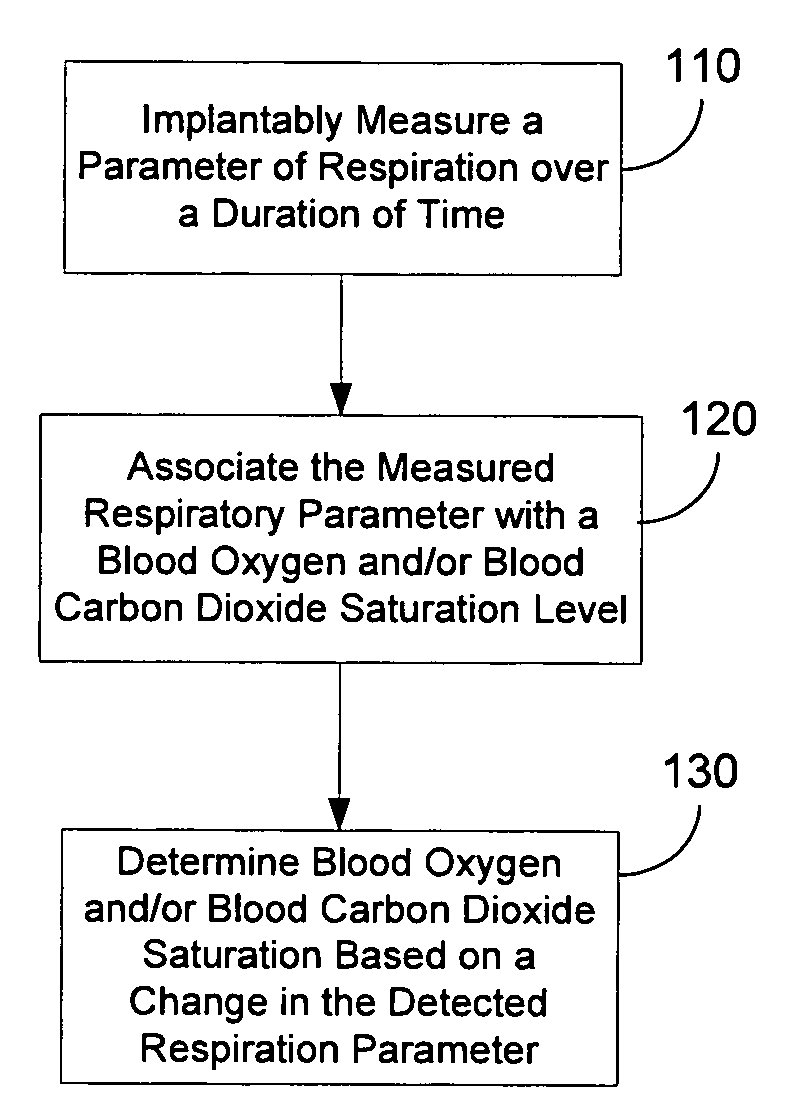
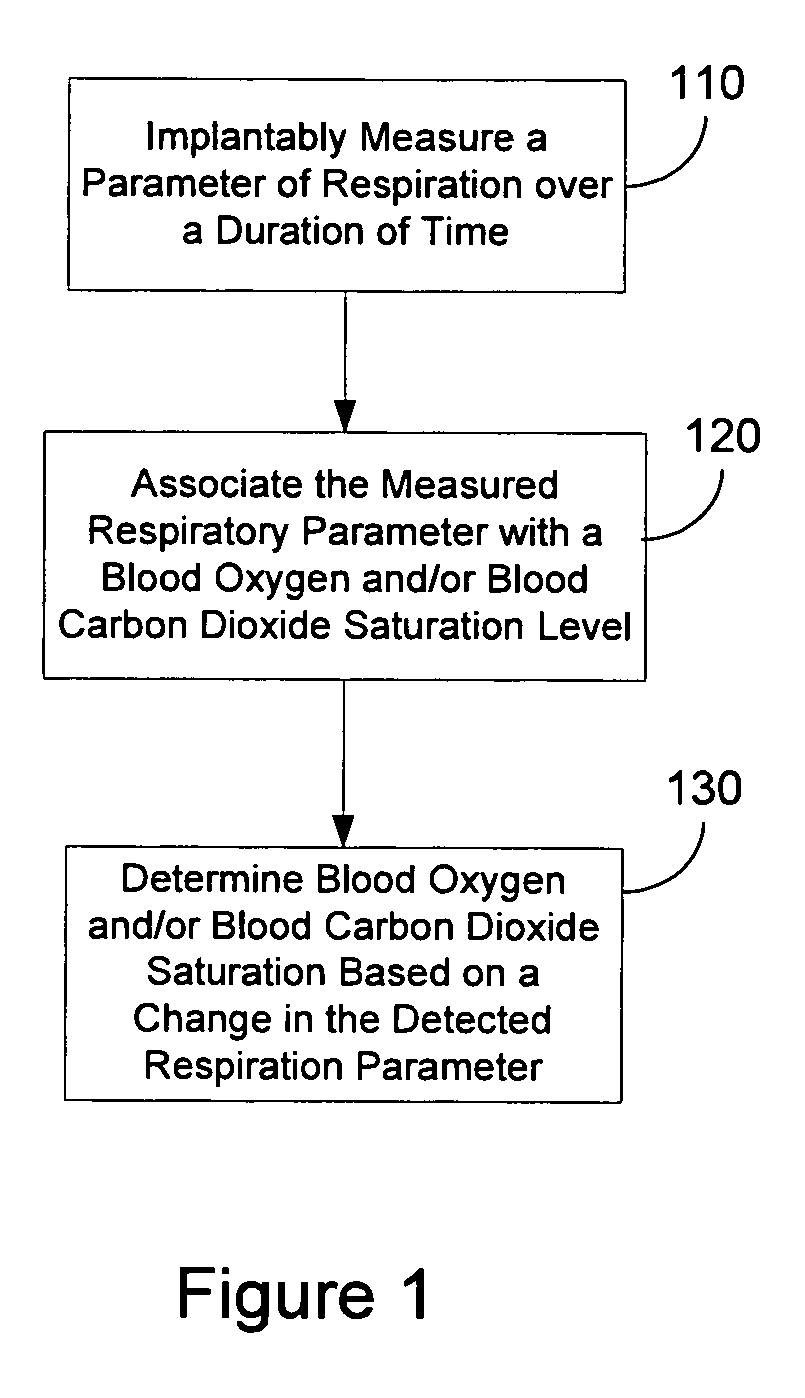
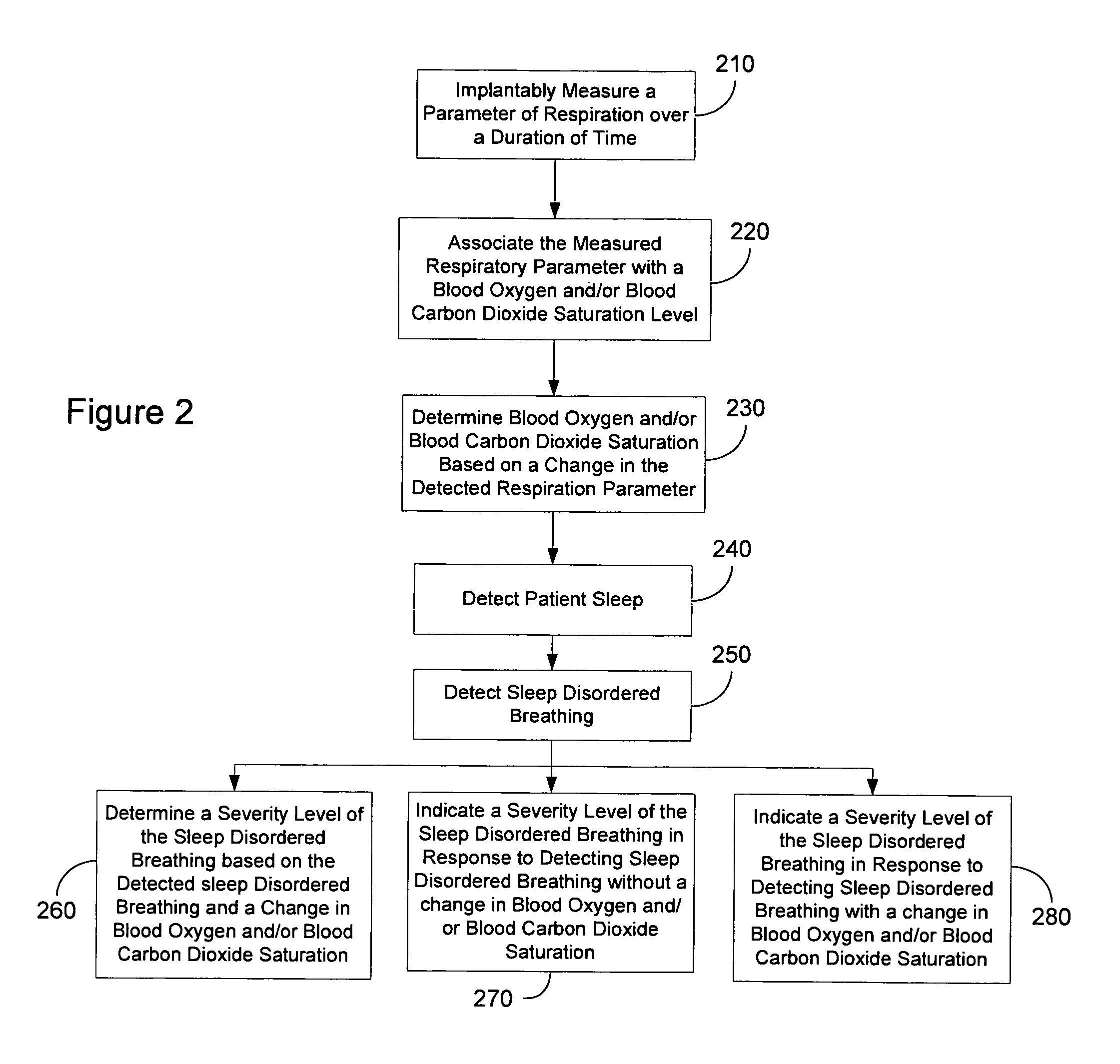
Determining blood gas saturation based on measured parameter of respiration
Systems and methods provide for determining blood gas saturation based on one or more measured respiration parameters. A parameter of respiration is measured implantably over a duration of time. The measured respiratory parameter is associated with a blood gas saturation level. Blood gas saturation is determined based on the measured respiration parameter. At least one of associating the measured respiratory parameter and determining blood gas saturation is preferably preformed implantably.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
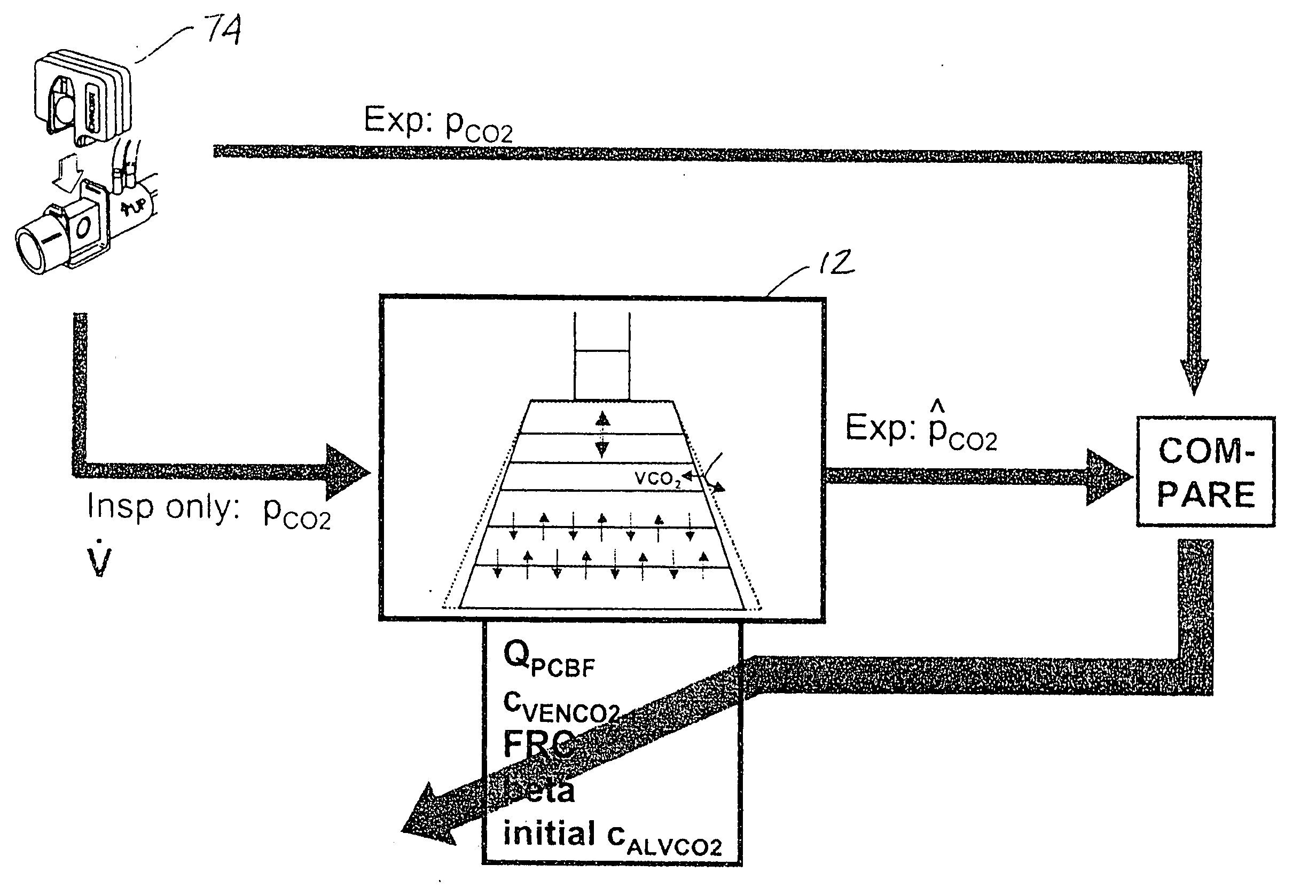
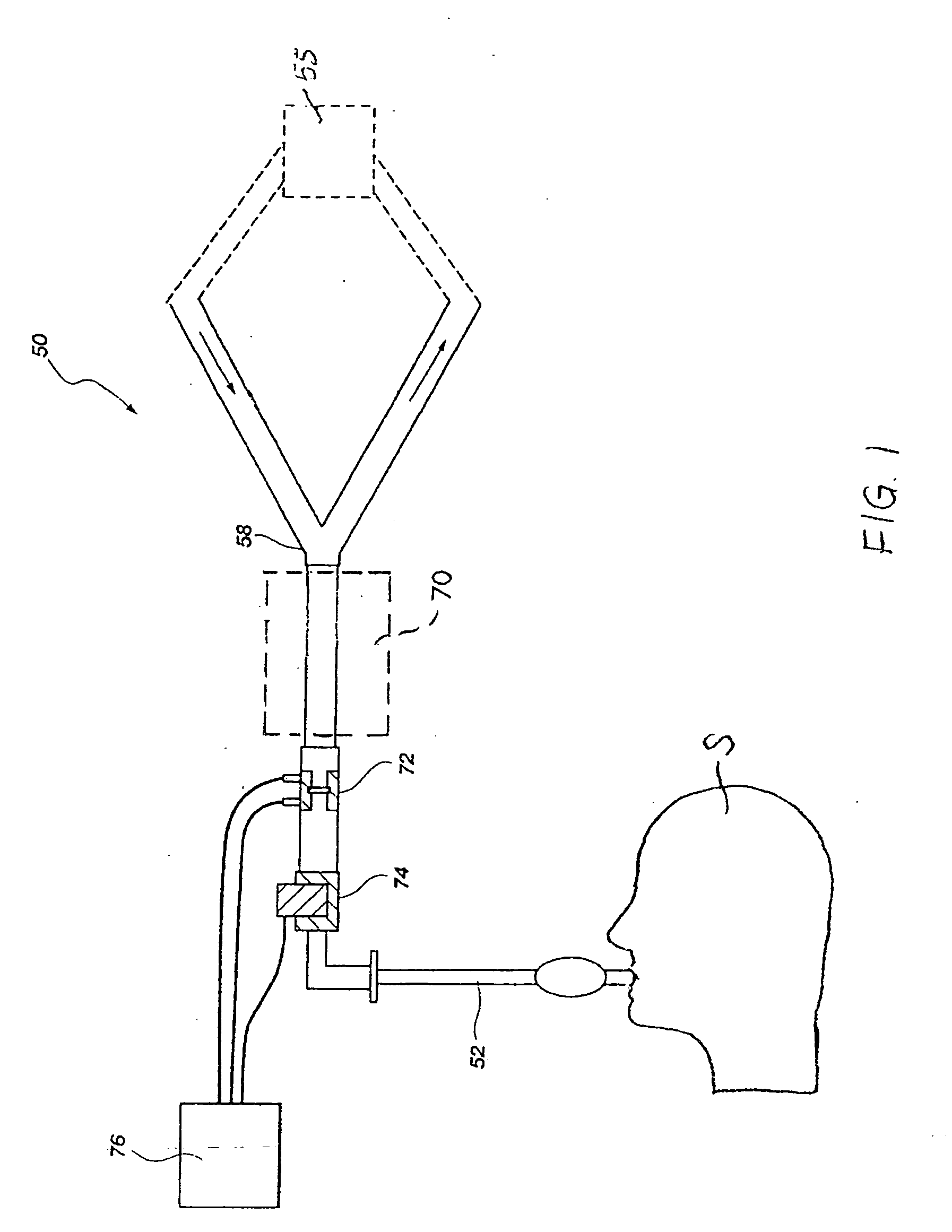
Lung model-based cardiopulmonary performance determination
InactiveUS20060004297A1Accurately resemble measured parameterRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsBlood flowBlood gas test
Methods for noninvasively evaluating indicators of cardio-pulmonary performance of a subject, such as cardiac output, pulmonary capillary blood flow, and blood carbon dioxide content, include obtaining data of an expiratory carbon dioxide signal and comparing data generated by an algorithmic lung model to the data of the expiratory carbon dioxide signal of a subject. The variables that are input into the algorithmic lung model are adjusted until the data generated thereby reflects that of the measured expiratory carbon dioxide signal with a desired degree of accuracy. Once the algorithmic lung model replicates the data of the measured expiratory carbon dioxide signal with the desired degree of accuracy, one or more of the input values may be used to determine one or more of the cardiac output, pulmonary capillary blood flow, or a blood gas content of the subject from which the expiratory carbon dioxide signal was obtained.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
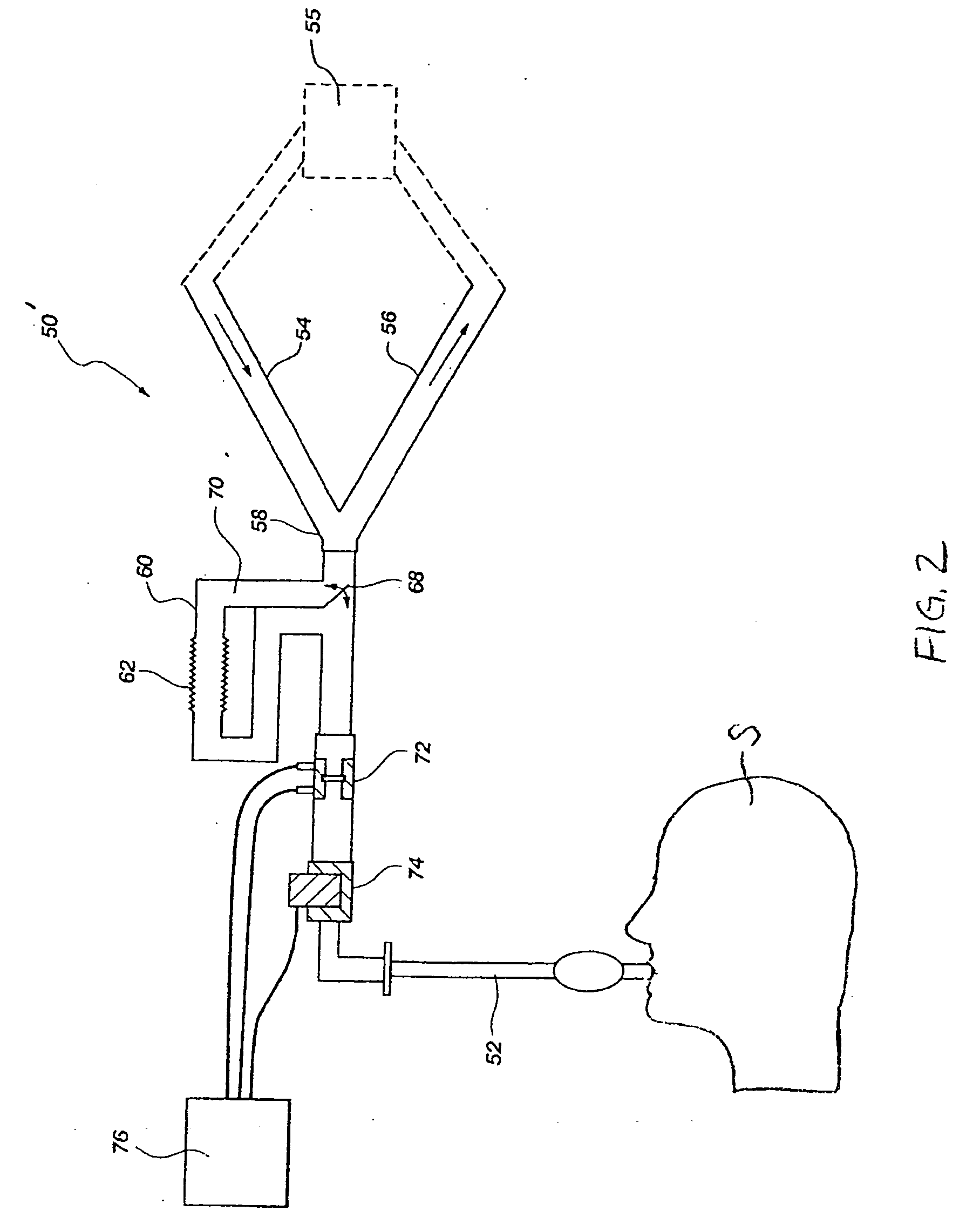
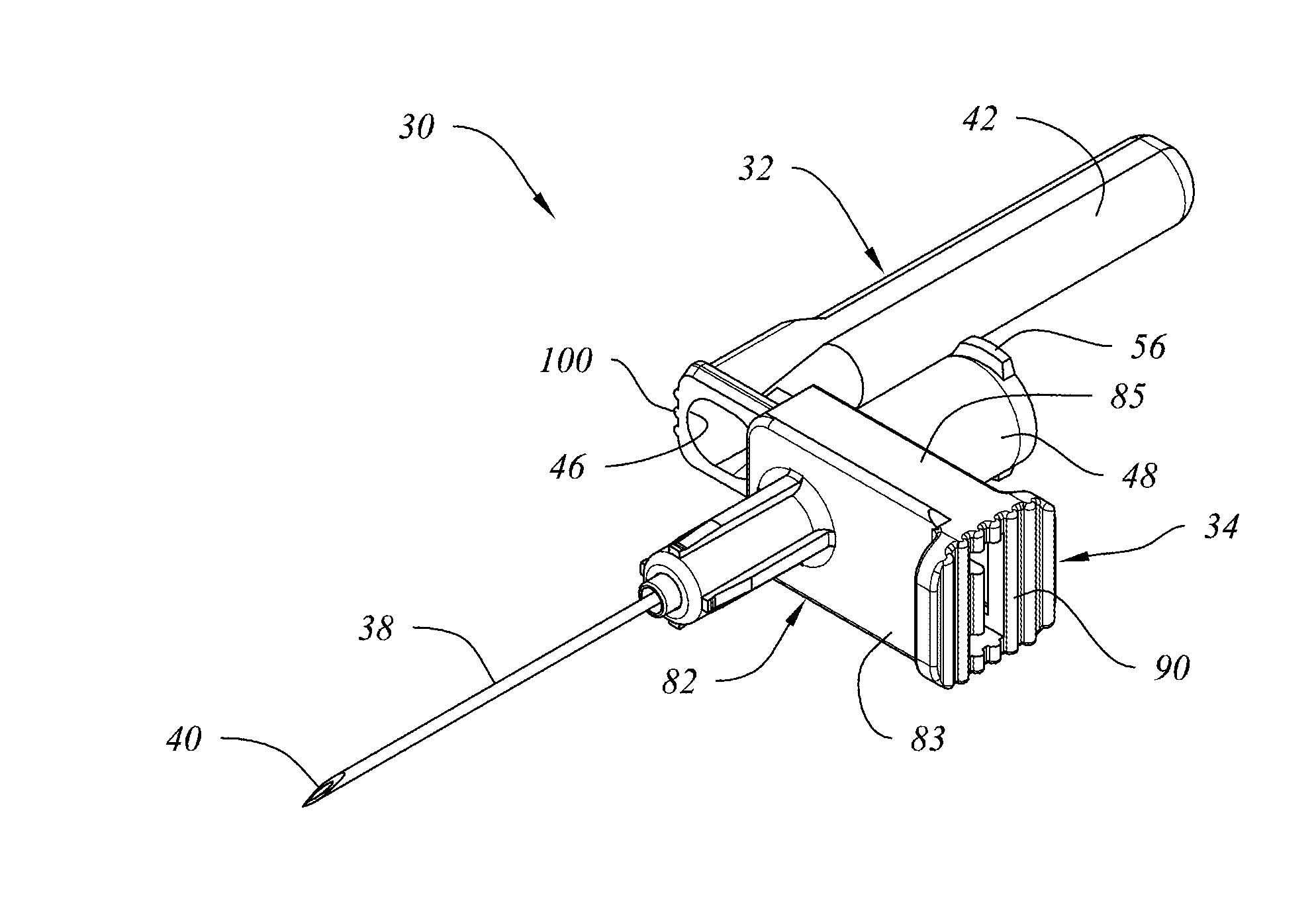
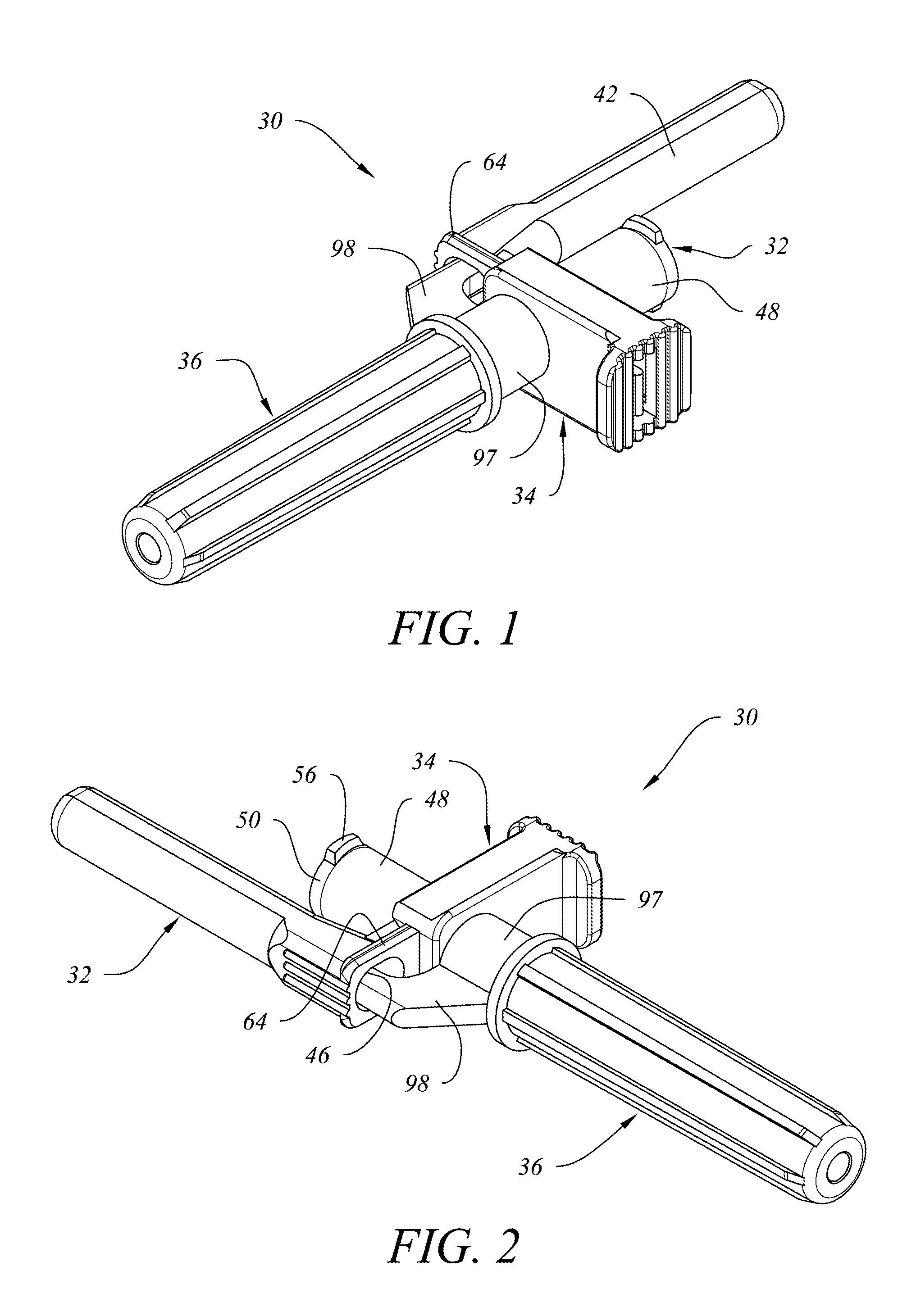
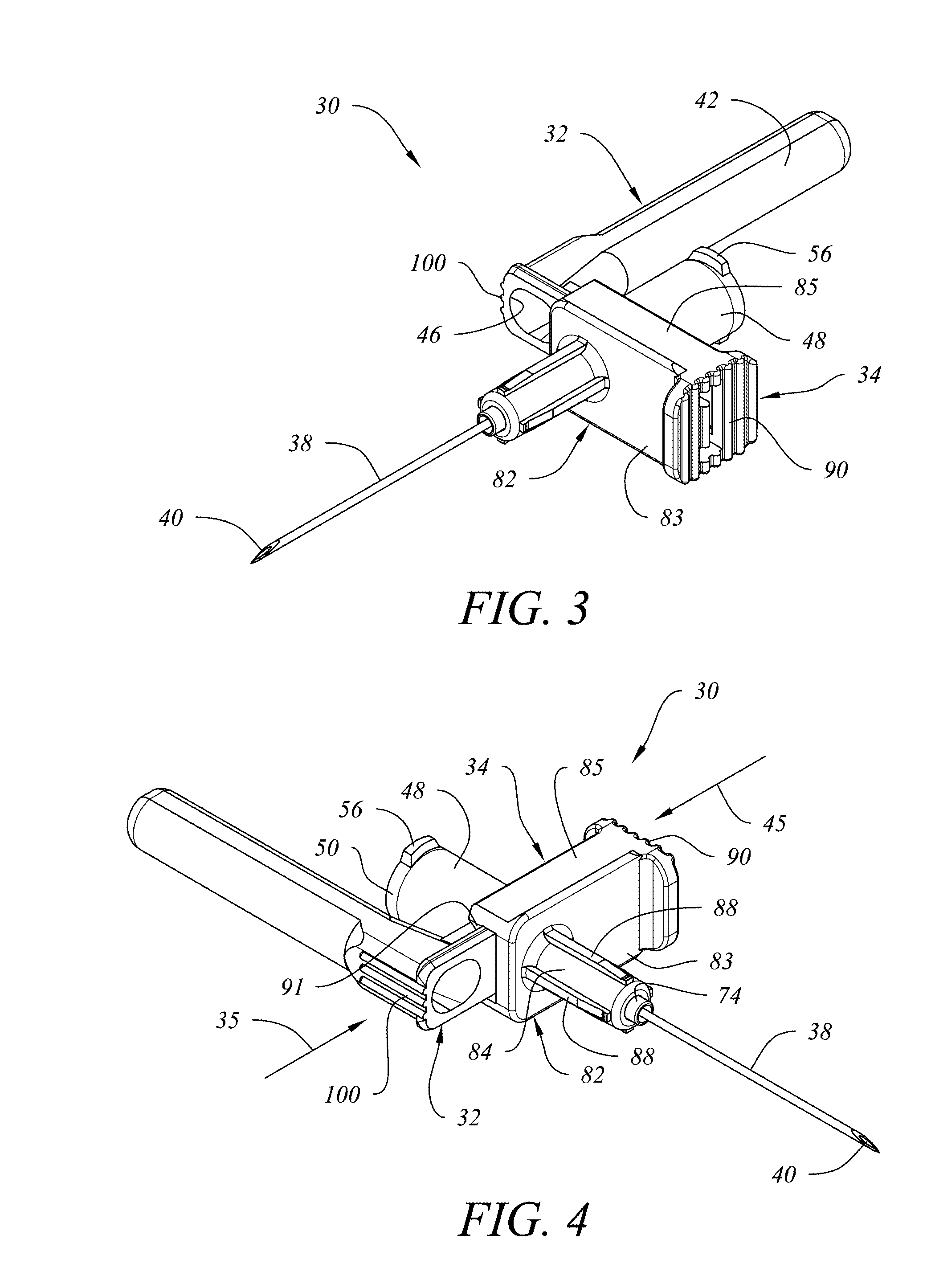
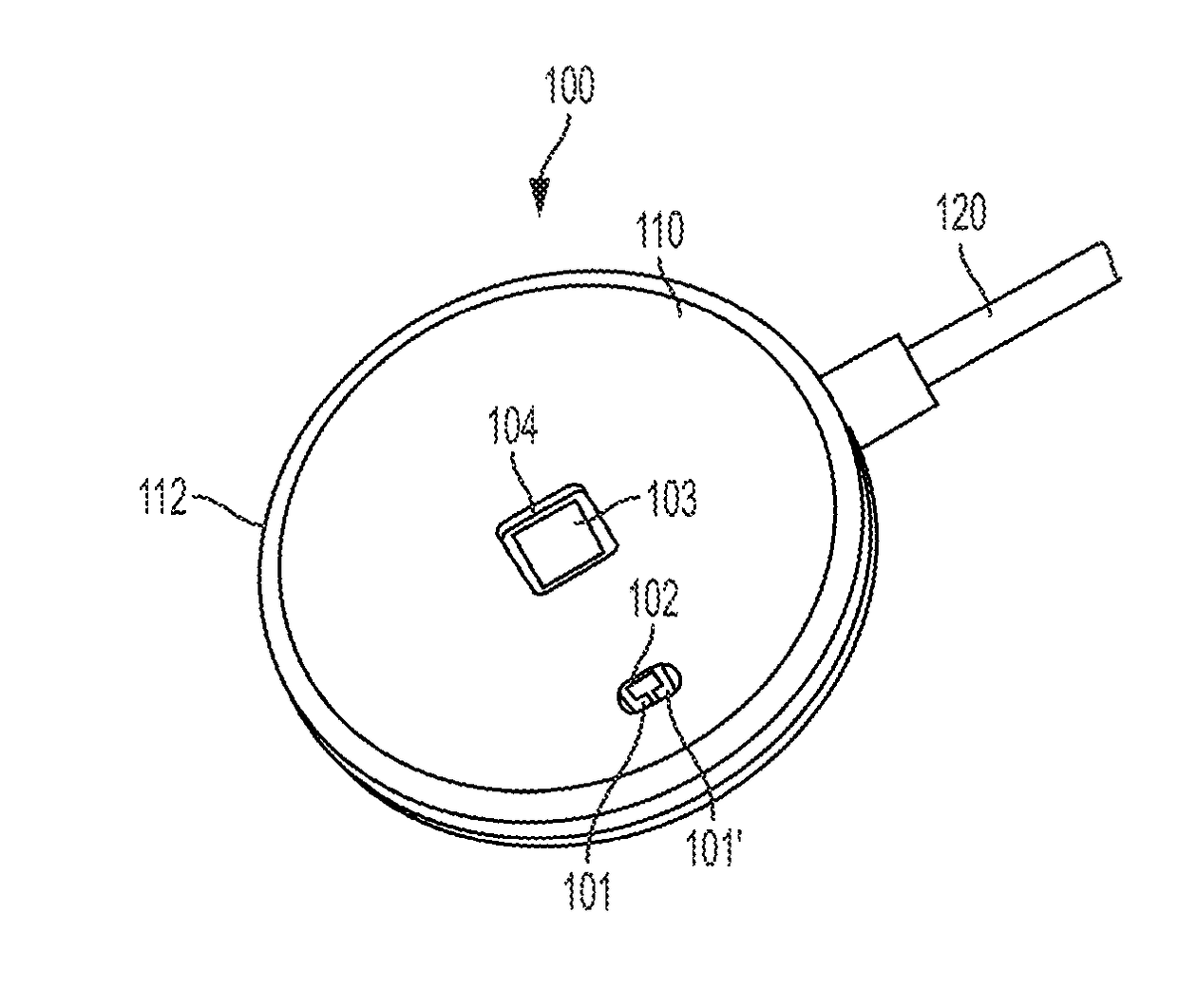
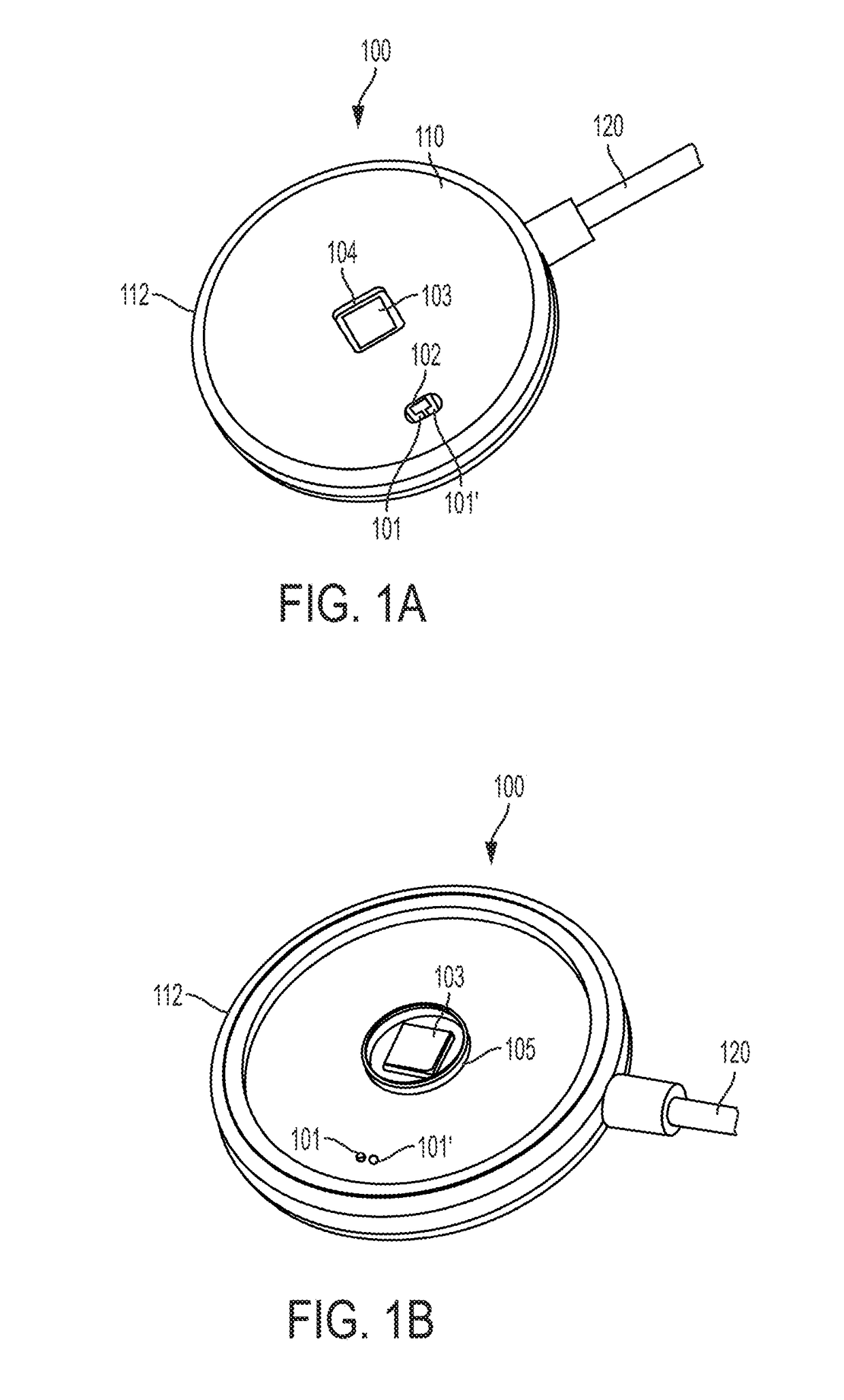
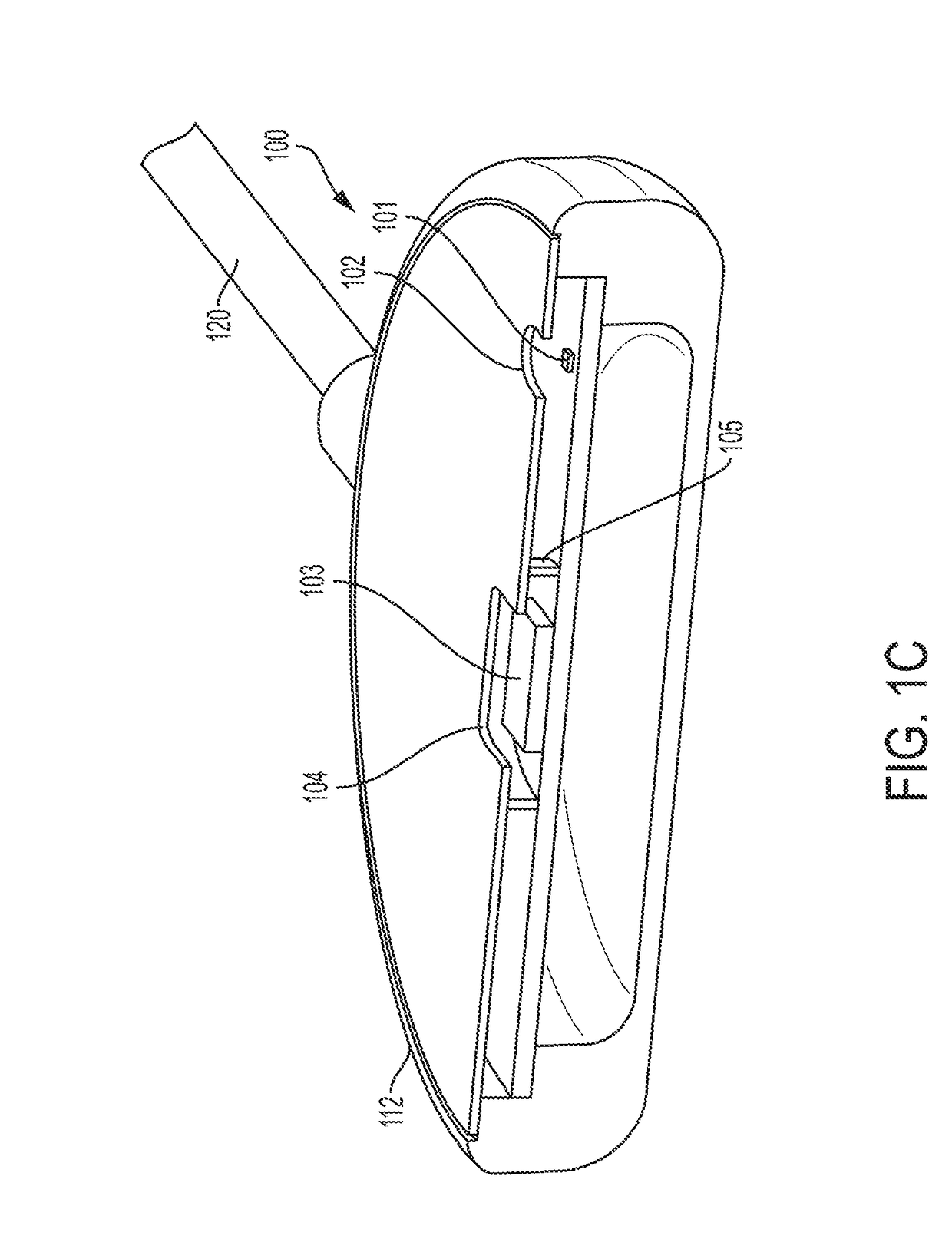
Retractable Needle for Blood Gas Sampling
ActiveUS20150073303A1Easily and inexpensively moldedEasy to operateMedical devicesCatheterBlood gas testEngineering
A medical device having a frontal attachment and a connector housing having at least a body part of an associated medical apparatus, the frontal attachment slidably engaging the connector housing and having a forwardly projecting, rearwardly biased needle and a needle retraction assembly, and the connector housing having a needle retraction cavity laterally offset from the needle in a first position, the needle retraction cavity being selectively movable relative to the frontal attachment following use to reposition the needle retraction cavity into alignment with the needle to permit retraction. The subject device is desirably specially modified for use in blood gas sampling by the addition of a filter plug.
Owner:RETRACTABLE TECH INC
Optical physiologic sensors and methods
ActiveUS20170112422A1High strengthIntensity continuous body motionDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsPhysical exhaustionBlood gas analysis
Physiologic sensors and methods of application are described. These sensors function by detecting recently discovered variations in the spectral optical density at two or more wavelengths of light diffused through the skin. These variations in spectral optical density have been found to consistently and uniquely relate to changes in the availability of oxygen in the skin tissue, relative to the skin tissue's current need for oxygen, which we have termed Physiology Index (PI). Current use of blood gas analysis and pulse oximetry provides physiologic insight only to blood oxygen content and cannot detect the status of energy conversion metabolism at the tissue level. By contrast, the PI signal uniquely portrays when the skin tissue is receiving ‘less than enough oxygen,’‘just the right amount of oxygen,’ or ‘more than enough oxygen’ to enable aerobic energy conversion metabolism. The PI sensor detects one pattern of photonic response to insufficient skin tissue oxygen, or tissue hypoxia, (producing negative PI values) and a directly opposite photonic response to excess tissue oxygen, or tissue hyperoxia, (producing positive PI values), with a neutral zone in between (centered at PI zero). Additionally, unique patterns of PI signal response have been observed relative to the level of physical exertion, typically with a secondary positive-going response trend in the PI values that appears to correspond with increasing fatigue. The PI sensor illuminates the skin with alternating pulses of selected wavelengths of red and infrared LED light, then detects the respective amount of light that has diffused through the skin to an aperture located a lateral distance from the light source aperture. Additional structural features include means of internally excluding light from directly traveling from the light emitters to the photodetector within the sensor. This physiology sensor and methods of use offer continuous, previously unavailable information relating to tissue-level energy conversion metabolism. Several alternative embodiments are described, including those that would be useful in medical care, athletics, and personal health maintenance applications.
Owner:REVEAL BIOSENSORS INC
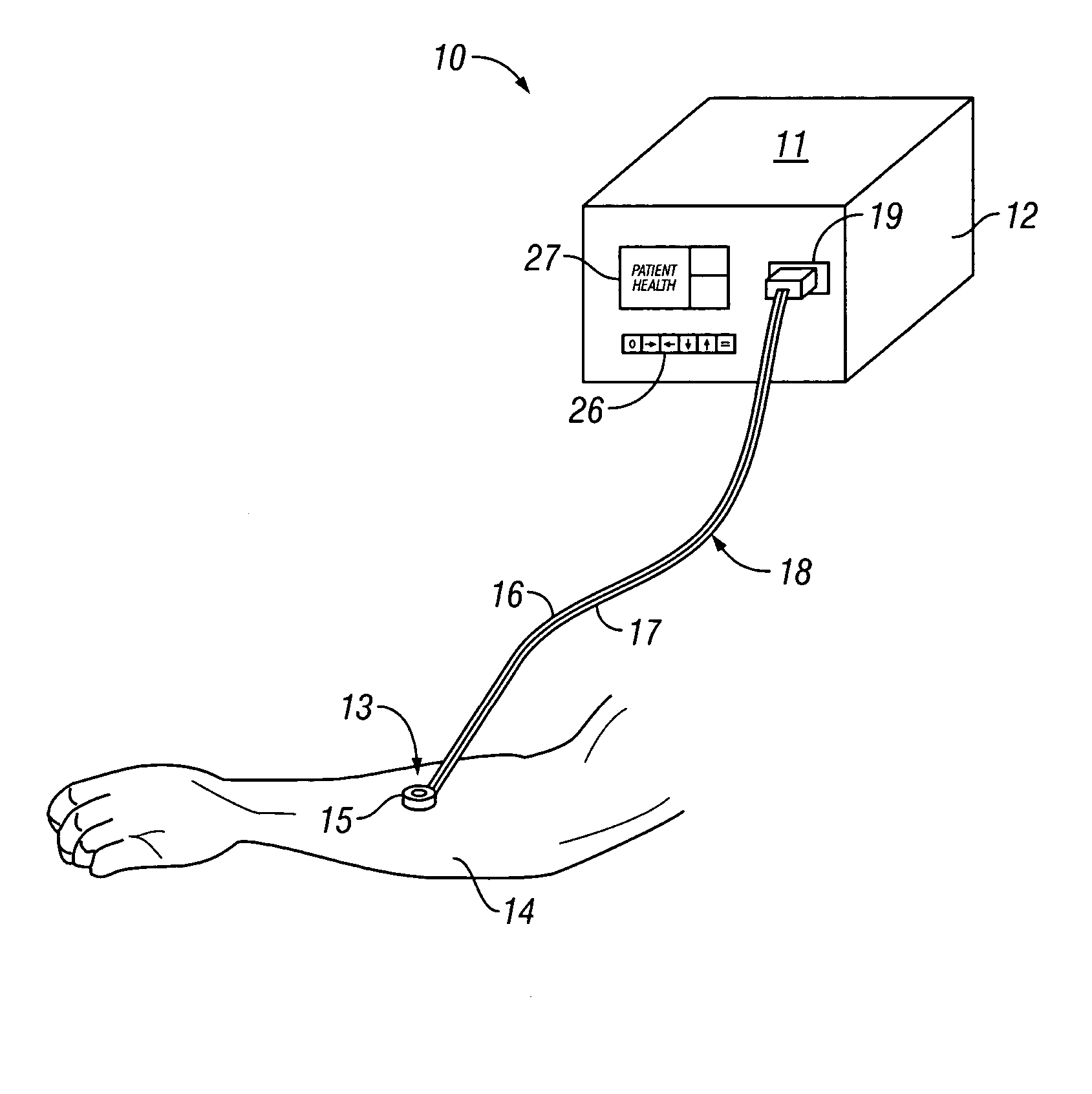
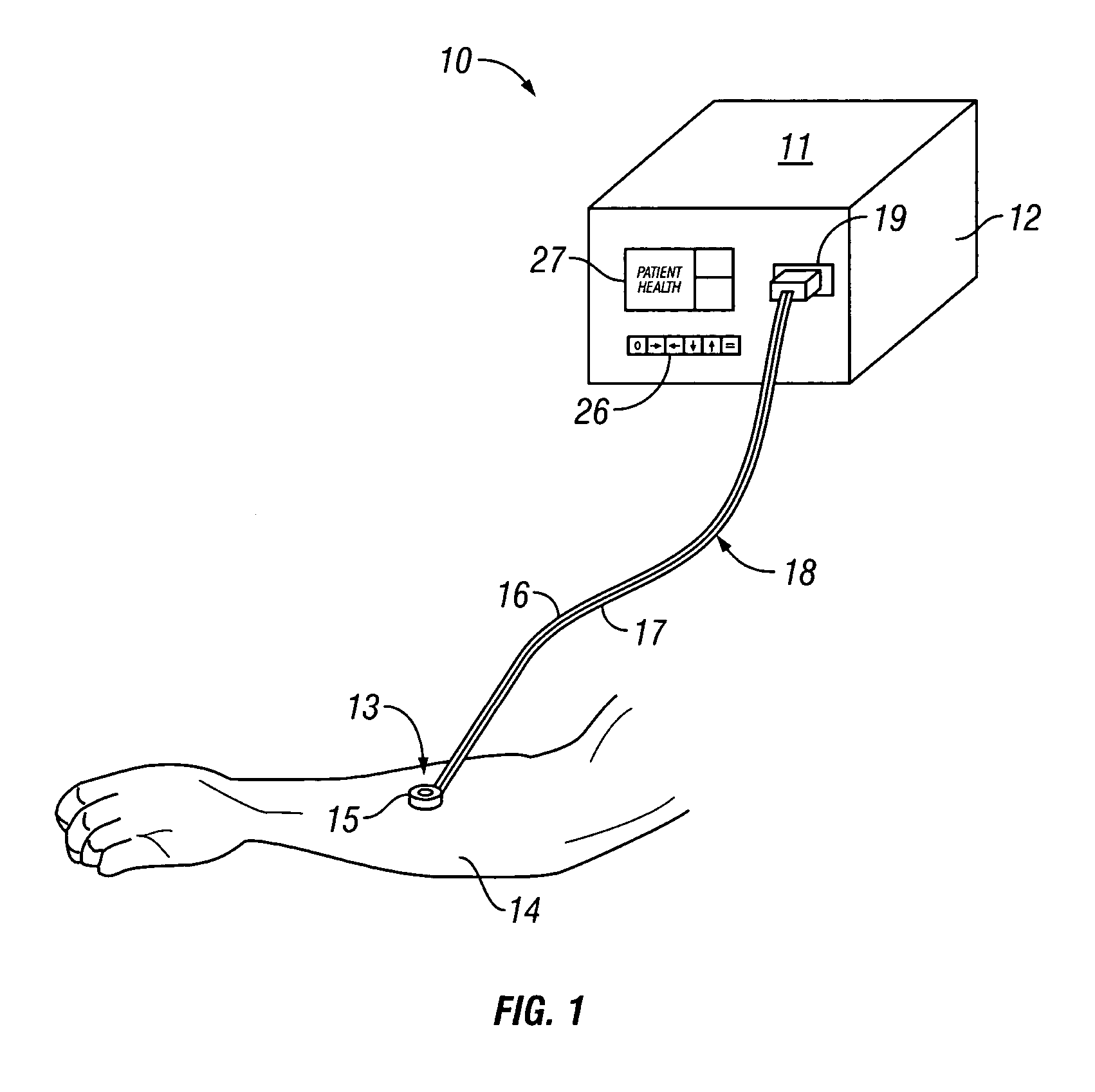
Catheter systems with blood measurement device and methods
InactiveUS20090156916A1Improve accuracyReduces oxygen saturationCatheterSensorsMeasurement deviceBlood gas test
Catheter systems with blood measurement device and methods are disclosed. An exemplary catheter system for use in positioning a distal end of a catheter body at a desired location in a patient's body may include a needle provided at the distal end of the catheter body to withdraw blood from the patient's body. The needle is fluidically connected to a proximal end of the catheter body. The catheter system may also include a measurement device provided at the proximal end of the catheter body. The measurement device is configured to receive blood withdrawn by the needle for measuring a blood gas value of the blood for use in positioning the distal end of the catheter body at the desired location in the patient's body.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
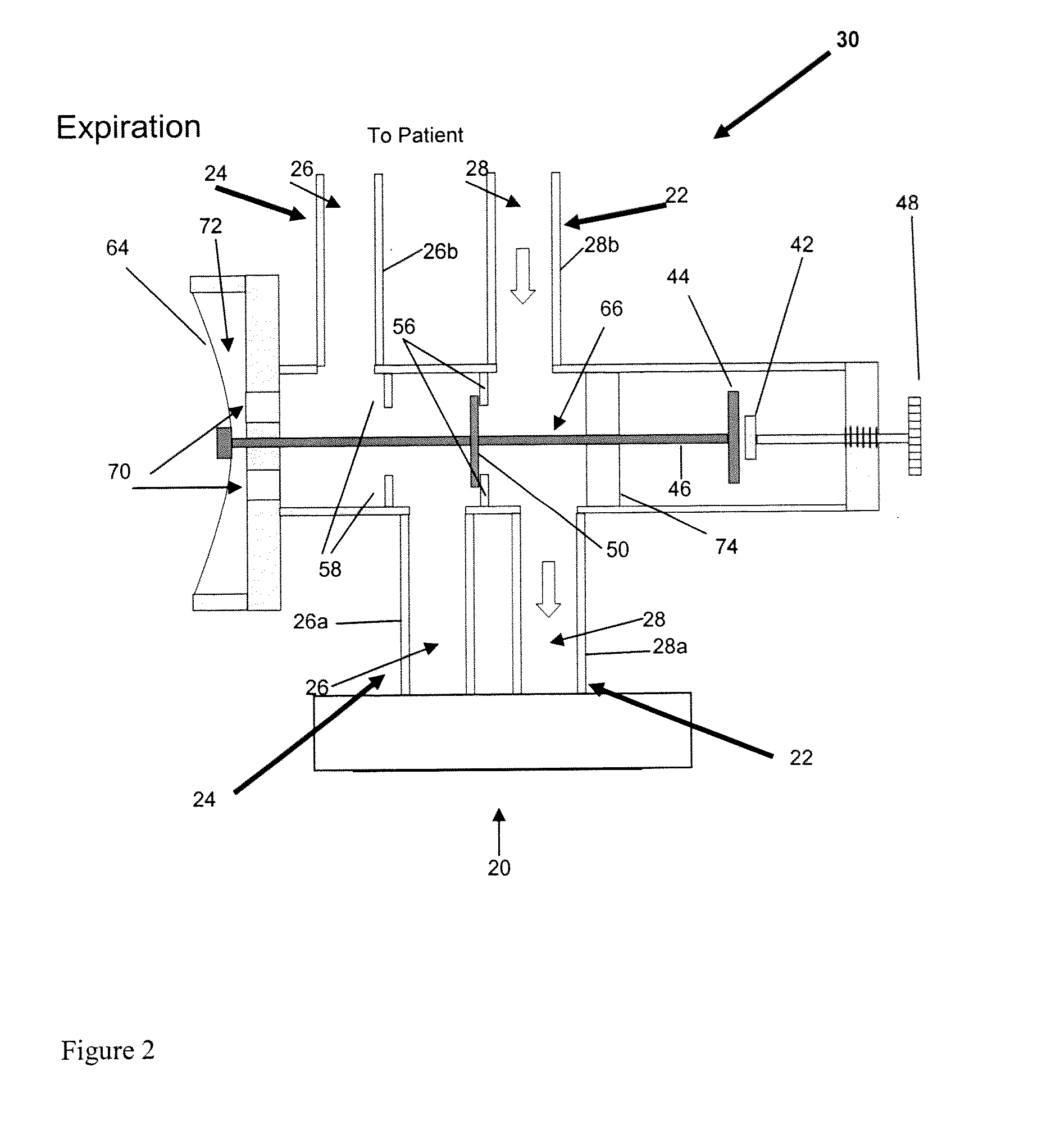
Non-invasive arterial blood gas determination
A breathing circuit for use in conjunction with a ventilator serving a mechanically-ventilated patient includes an expiratory gas airflow pathway; an inspiratory gas airflow pathway; and a gas mixing mechanism operable to mix inspiratory gas and expiratory gas in an amount sufficient to equilibrate the patient's PETCO2 and arterial PCO2 such that the patient's PETCO2 is a clinically reliable approximation of the patient's PaCO2.
Owner:THORNHILL SCI INC
Determining blood gas saturation based on measured parameter of respiration
Systems and methods provide for determining blood gas saturation based on one or more measured respiration parameters. A parameter of respiration is measured implantably over a duration of time. The measured respiratory parameter is associated with a blood gas saturation level. Blood gas saturation is determined based on the measured respiration parameter. At least one of associating the measured respiratory parameter and determining blood gas saturation is preferably preformed implantably.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Blood monitoring system
InactiveUS20100020309A1Improve accuracyMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMedical devicesBlood chemistryBlood parameters
Owner:INTELLECTUAL INSPIRATION
Diagnosis and/or therapy using blood chemistry/expired gas parameter analysis
Methods and systems for diagnosing disorders, including, for example, disordered breathing, involve sensing one or more of a blood chemistry parameter and / or an expired gas parameter, such as expired respiratory gas concentration, blood gas concentration, and blood pH. Diagnosis of the disorder may be performed by a medical device, such as a respiratory therapy device or a cardiac therapy device, based on implantably detected blood gas / pH concentration / level or externally detected expired respiratory gas concentration. Cardiac and respiratory therapies for addressing the disorder may be adjusted based on the detected parameters.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
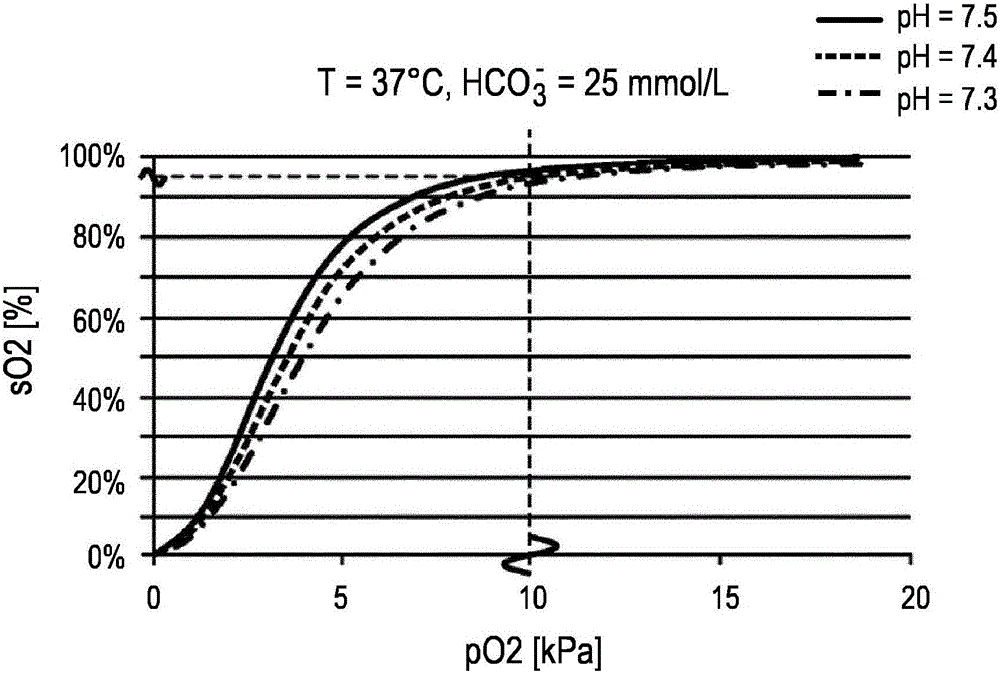
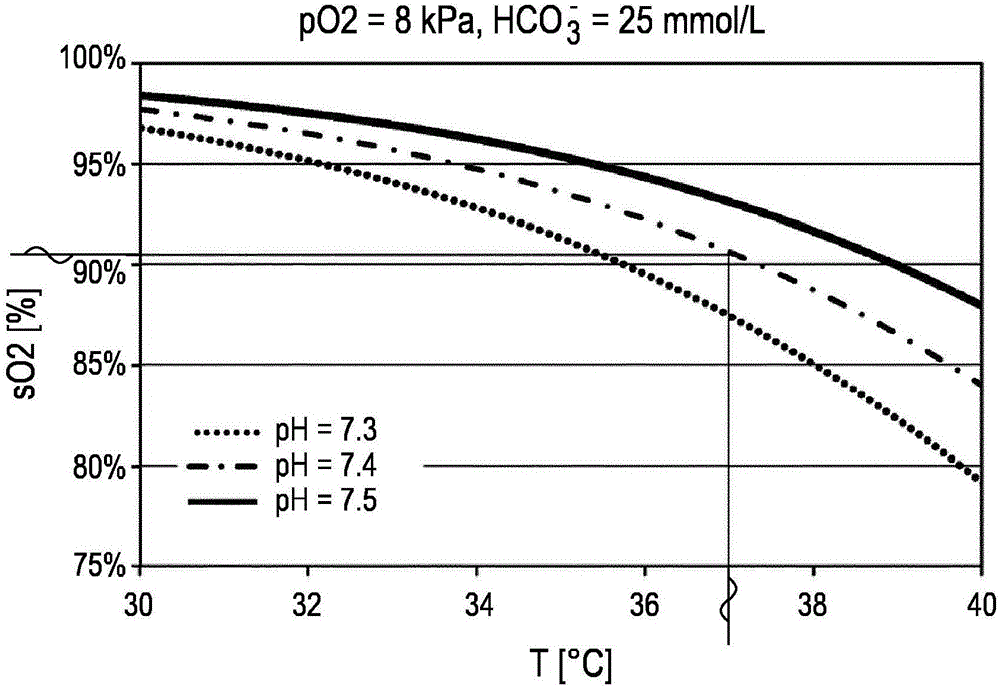
Device and method for determining a partial carbon dioxide pressure in a subject of interest
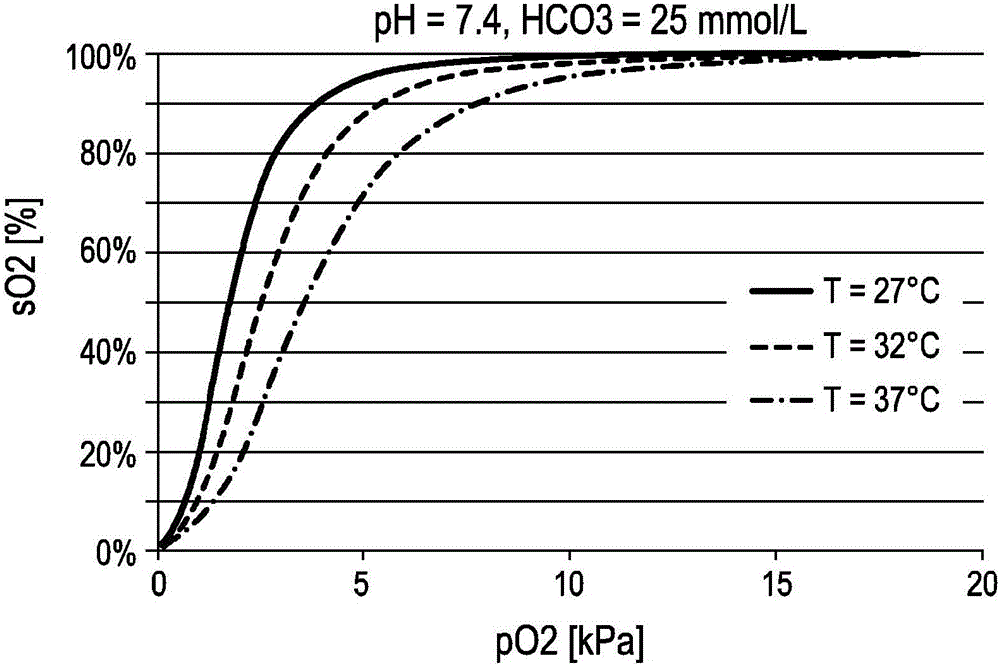
The present invention relates to a device (30) and a related method for determining a blood gas partial pressure in blood in a circulatory system of a subject (12) of interest. Also a system for ventilating a patient is disclosed. Temperature-related measurement values indicative of given blood temperature levels are detected. Oxygen saturation measurements of the blood of said subject (12) under consideration of said temperature-related measurement values are derived. A blood gas partial pressure of a monitored subject (12) from said derived oxygen saturation measurements is determined under consideration of present blood temperature levels of said subject (12). Preferably, pH- representative values attributable to present blood pH-values of the subject (12) are determined. More preferably, the pH-representative values are derived from an oxygen dissociation curve under consideration of changes in said derived oxygen saturation measurements of the blood attributable to detected temperature-related measurement values of the subject's blood.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Blood monitoring system
InactiveUS20050056080A1Reduce postoperative complicationsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOther blood circulation devicesMedicineMonitoring system
A method and apparatus for measuring blood gas concentrations and partial pressures, in real time, using a pneumatic detector to indicate partial pressure variations in the blood gas.
Owner:ENSION
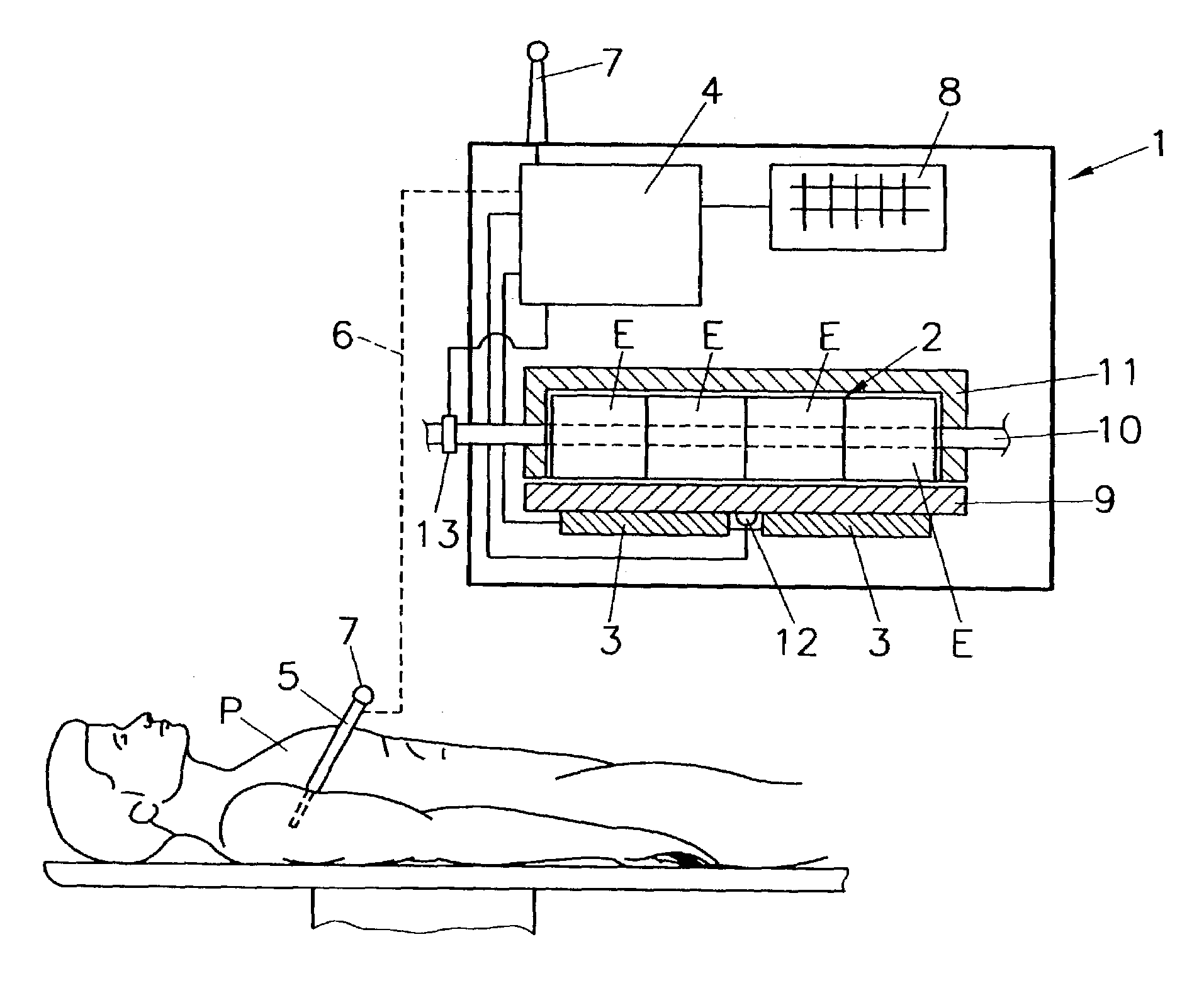
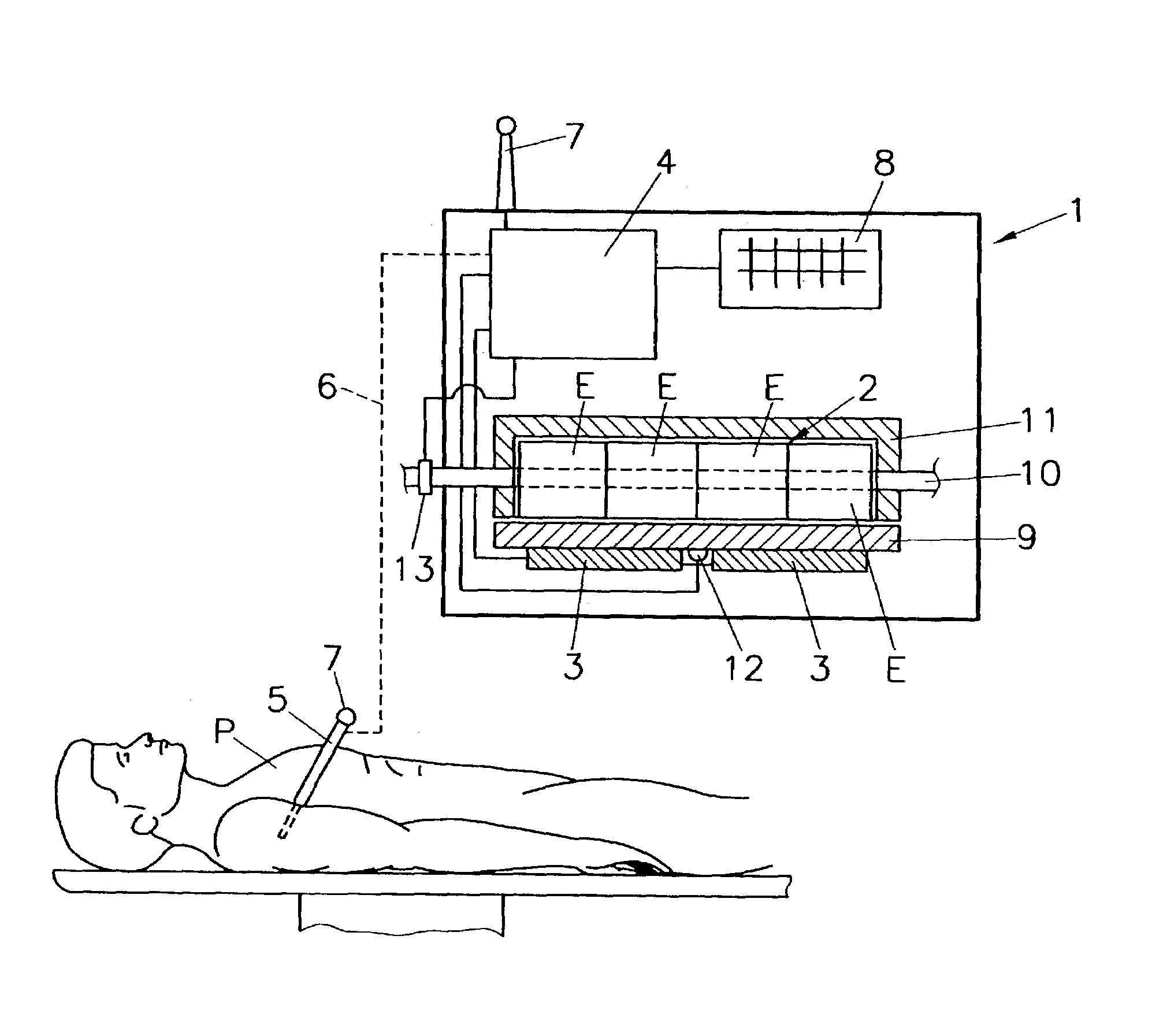
Blood-gas reaction monitoring and control device
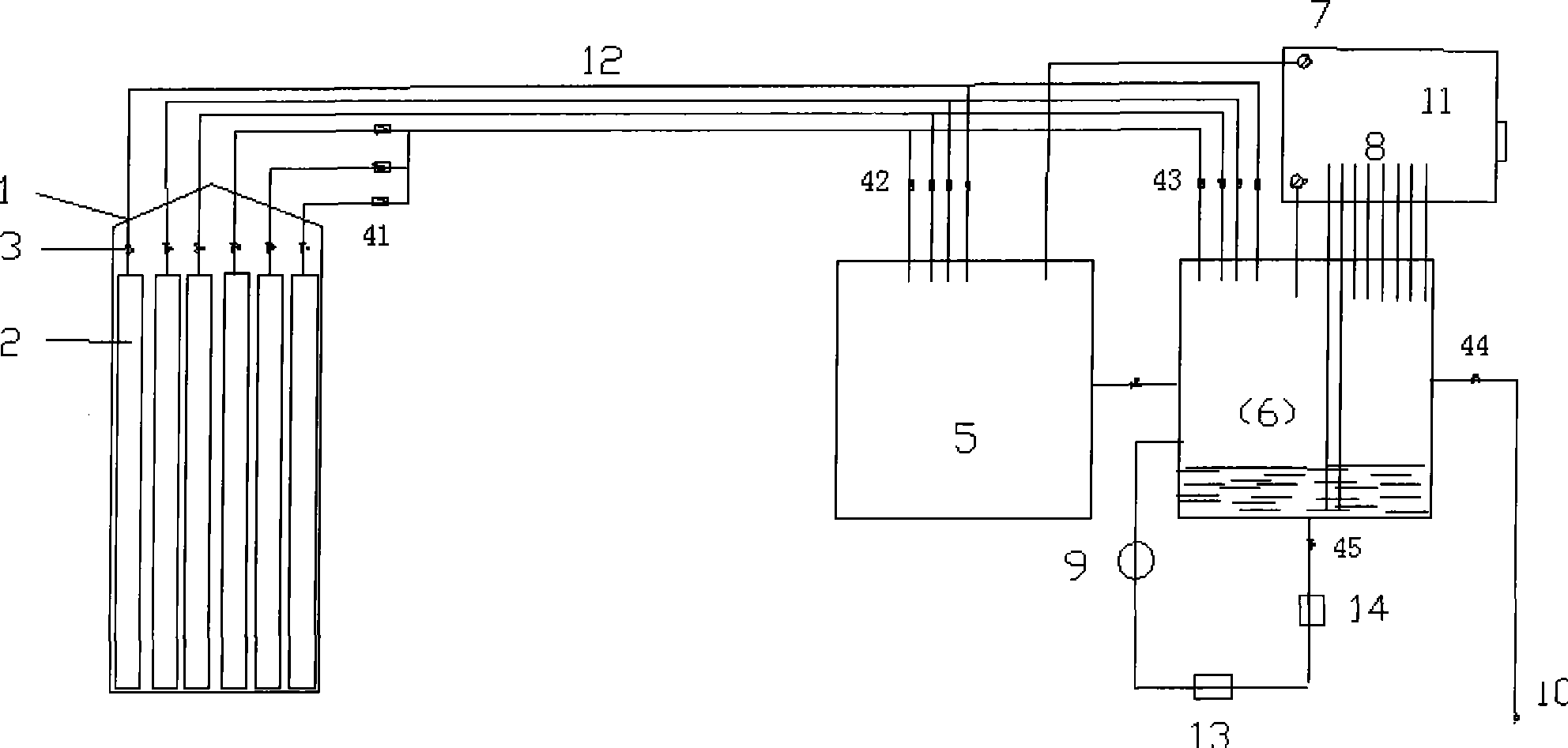
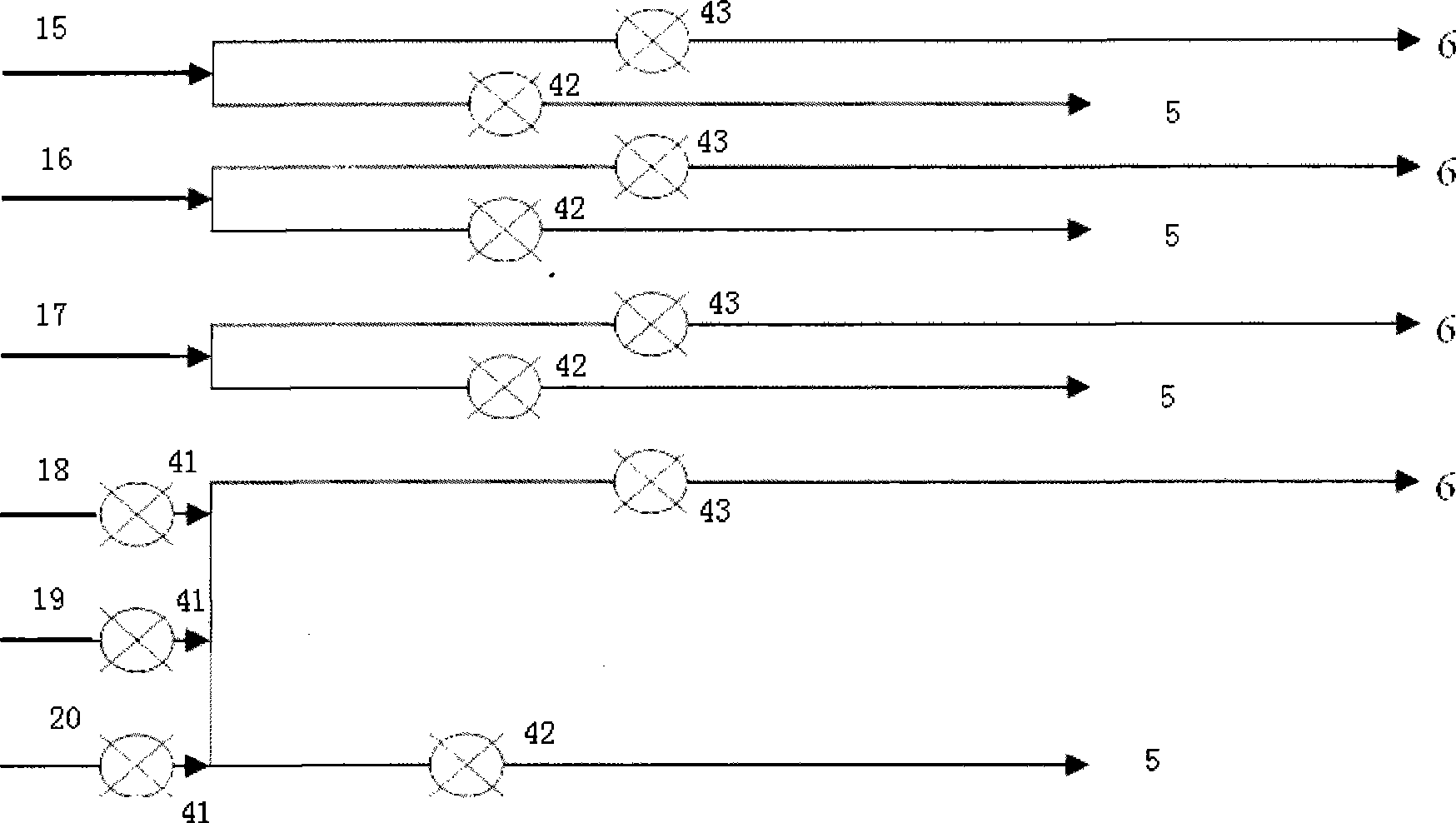
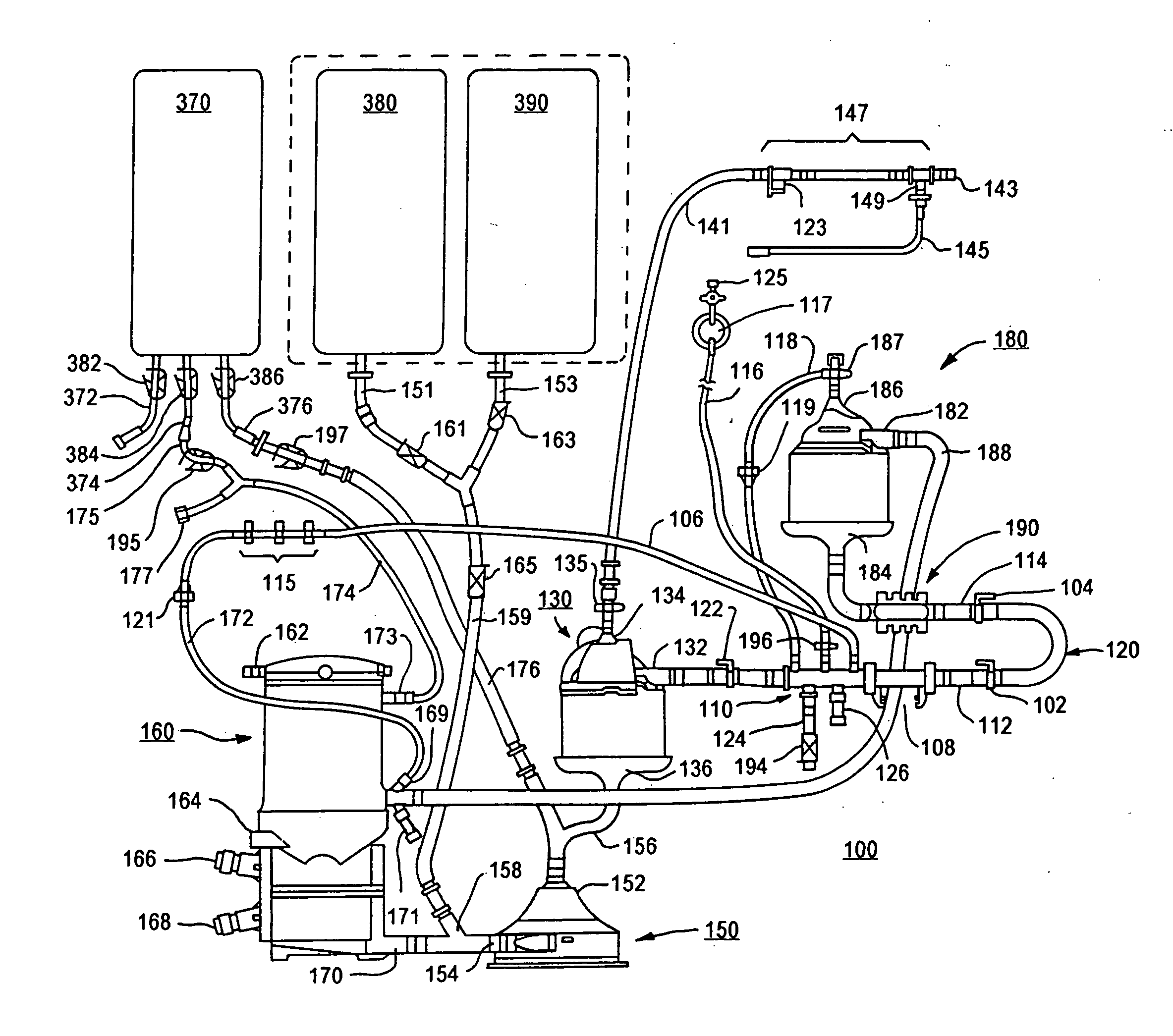
The invention relates to a blood-gas reaction monitor and control device which belongs to the technical field of fluid detection and comprises a gas supply system, a gas mixing tank, a gas-liquid reaction tank and a data acquisition and control device, wherein the gas supply system comprises a steel bottle cabinet and a steel bottle arranged in the steel bottle cabinet; through respective pipeline, the steel bottle and electromagnetic valves arranged on the pipelines are respectively connected with the gas mixing tank and the gas-liquid reaction tank which are communicated; the gas mixing tank is mutually communicated with the gas-liquid reaction tank; the gas mixing tank is internally provided with a pressure sensor, and the gas-liquid reaction tank is internally provided with a liquid-level detector, a pressure sensor, a pH electrode and a dissolved oxygen sensor; a plurality of gas concentration sensors are fixed on the lateral wall above the gas-liquid reaction tank; and the data acquisition and control device is used for controlling the electromagnetic valves connected to the pipelines and acquiring the measured data from the pressure sensor, the pH electrode, the dissolved oxygen sensor and the gas concentration sensors. The invention is suitable for the detection of aqueous solution and non aqueous solution, can detect gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide, nitrogen dioxide, and the like, is also suitable for the carrier gas performance analysis of natural blood including human and animals, and also has all functions of a blood gas analyzer.
Owner:INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
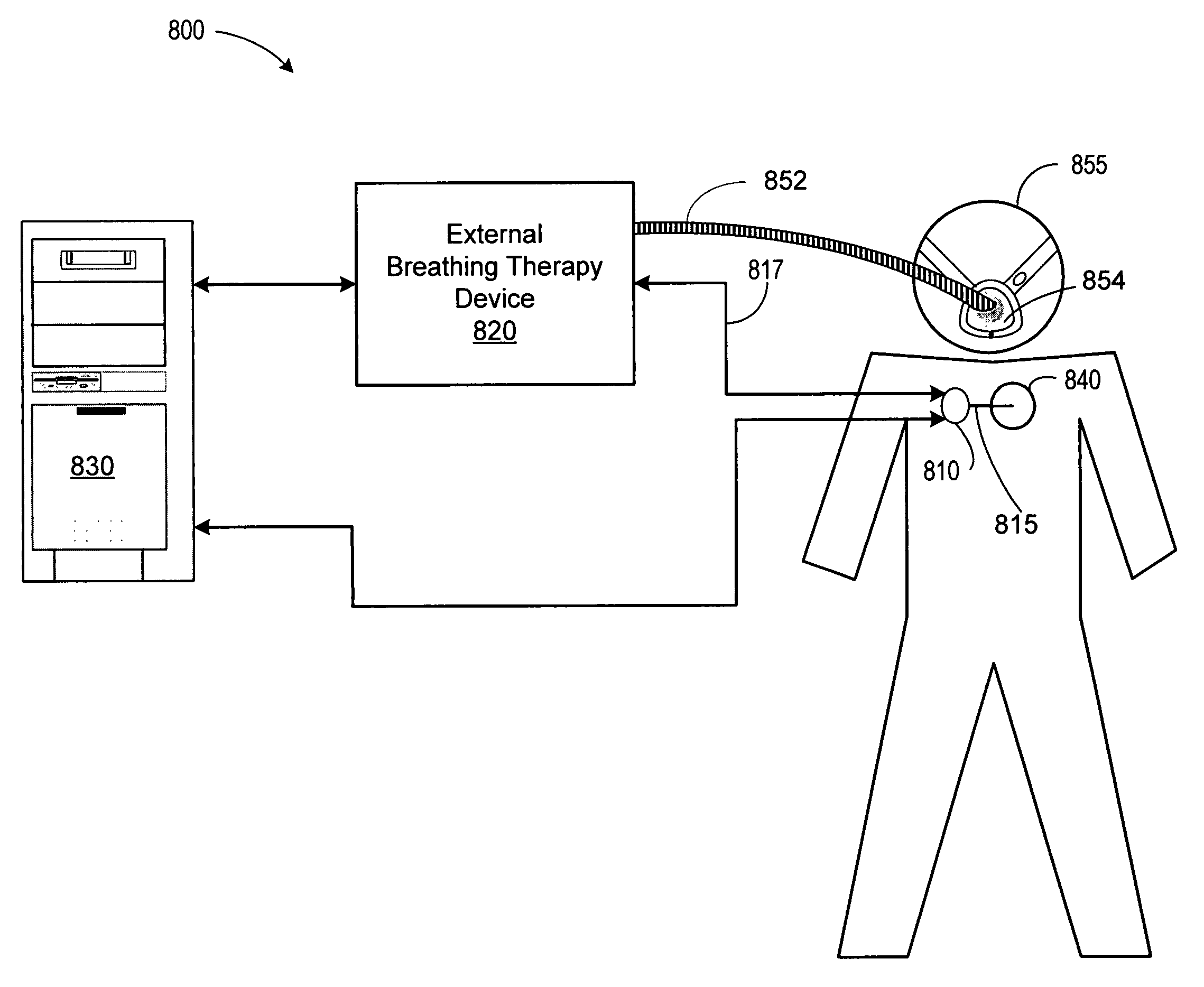
Methods and systems for control of gas therapy
InactiveUS20050061323A1Mitigate carbon dioxide instabilitySuppress the disordered breathingRespiratorsElectrocardiographyBlood gas testPositive airway pressure device
A gas therapy system involves sensing the blood gas concentration of the patient and adapting a gas therapy based on the sensed gas concentration. Disordered breathing may be detected bases on blood gas concentration, and gas or cardiac electrical therapy may be adapted to treat the detected disordered breathing. One or more of sensing the blood gas concentration, detecting disordered breathing, or adapting the therapy may be performed at least in part implantably. The gas therapy is delivered to the patient through an external respiratory device, such as a positive airway pressure device.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Active air removal from an extracorporeal blood circuit
A disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit employed during cardiopulmonary bypass surgery performs gas exchange, heat transfer, and microemboli filtering functions in a way as to conserve volume, to reduce setup and change out times, to eliminate a venous blood reservoir, and to substantially reduce blood-air interface. Blood from the patient or prime solution is routed through an air removal device that is equipped with air sensors for detection of air. An active air removal controller removes detected air from blood in the air removal device. A disposable circuit support module is used to mount the components of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit in close proximity and in a desirable spatial relationship to optimize priming and use of the disposable, integrated extracorporeal blood circuit. A reusable circuit holder supports the disposable circuit support module in relation to a prime solution source, the active air removal controller and other components.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com