Patents
Literature
2144results about How to "Act quickly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
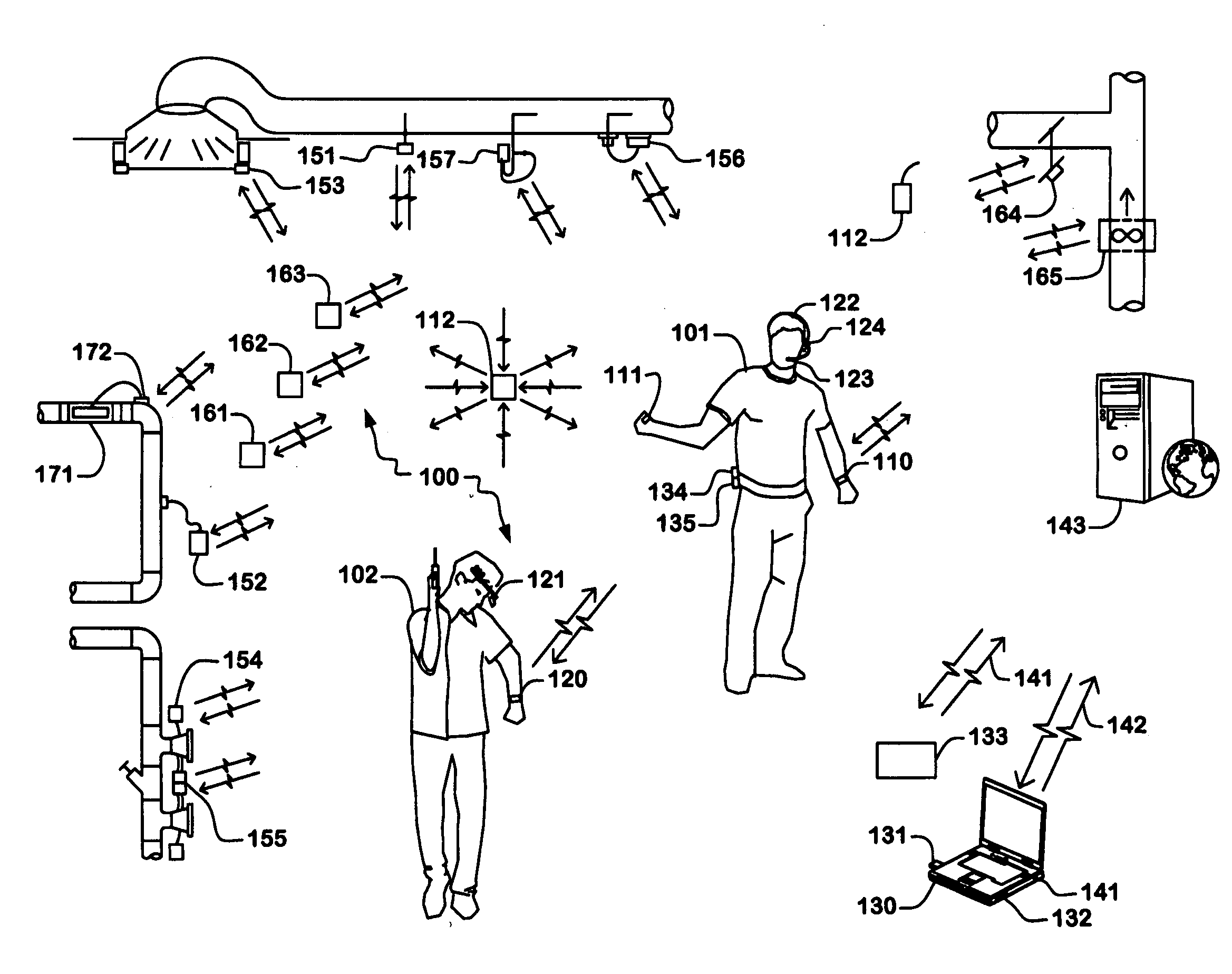
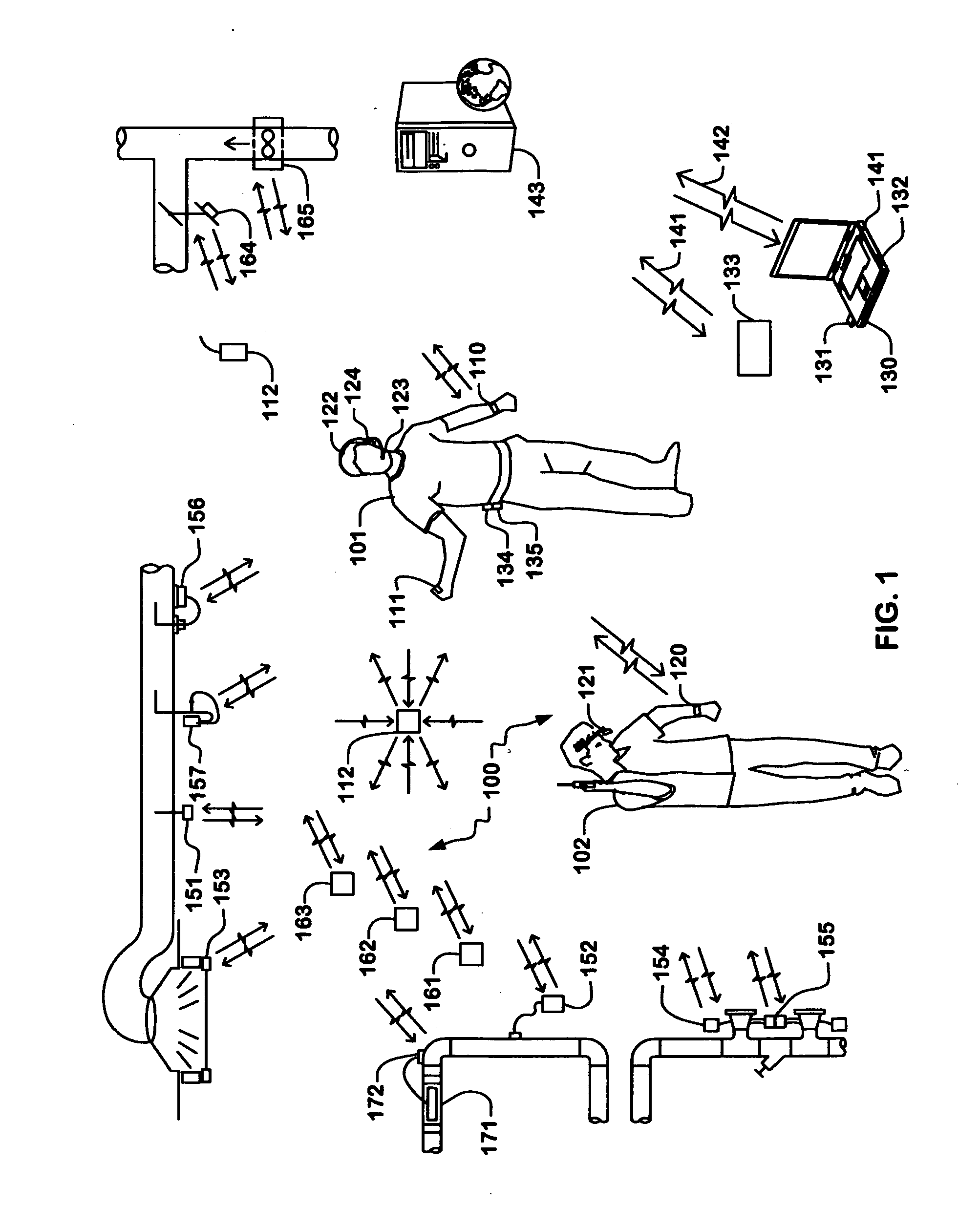
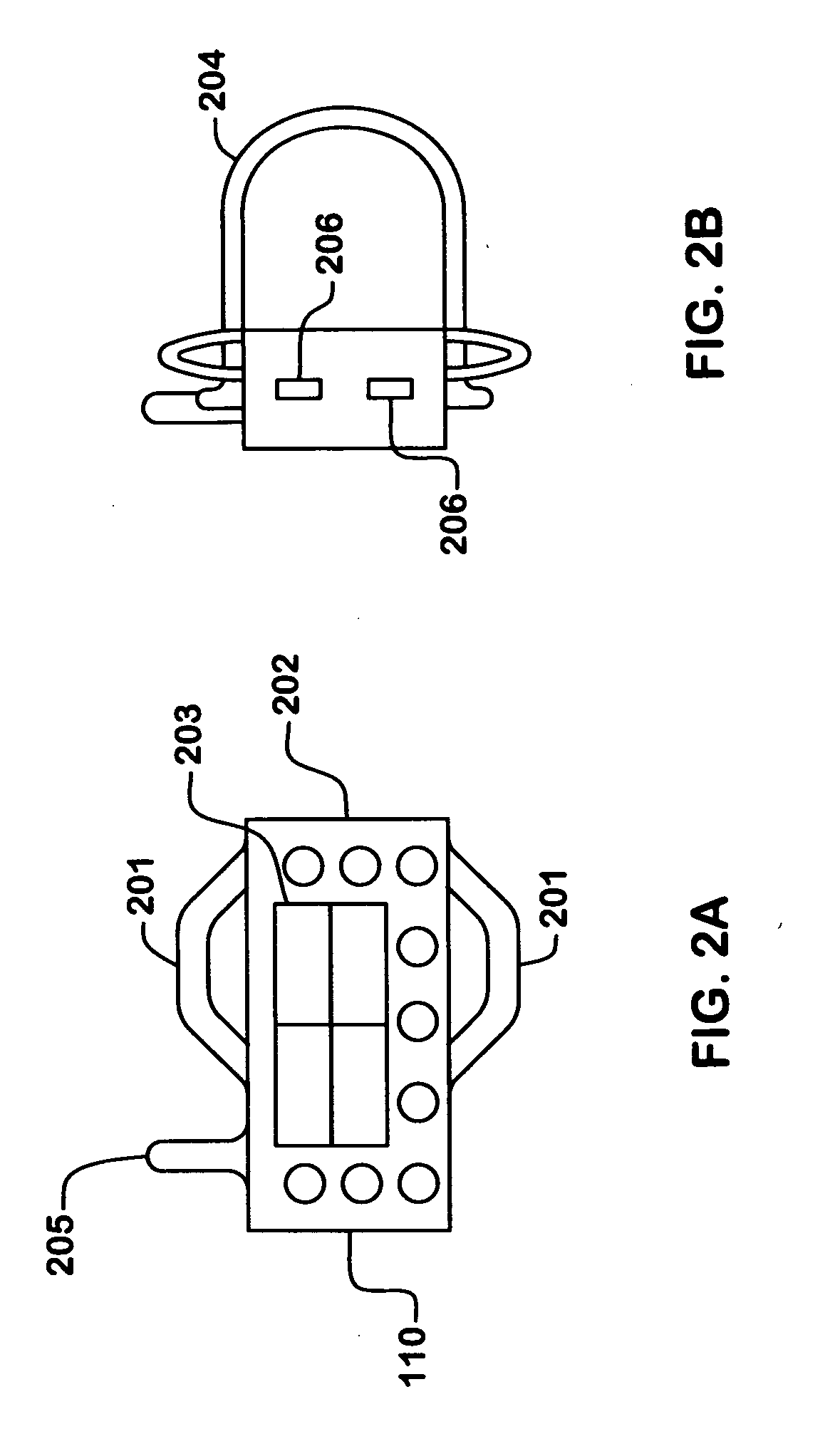
Wireless sensors system and method of using same
ActiveUS20120046792A1Improve understandingAct quicklySpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlEngineeringWater temperature
An apparatus, system, and methods for measuring environmental parameters are disclosed. The apparatus, system, and methods can be used for a variety of applications, including HVAC air balancing and building commissioning. The system includes a variety of wireless sensing modules and wearable modules for control, display, and storage. Parameters measured include air and water temperature, pressure, velocity, and flow. Also included are sensors for light intensity, CO concentrations, and CO2 concentrations.
Owner:EVERGREEN TELEMETRY LLC
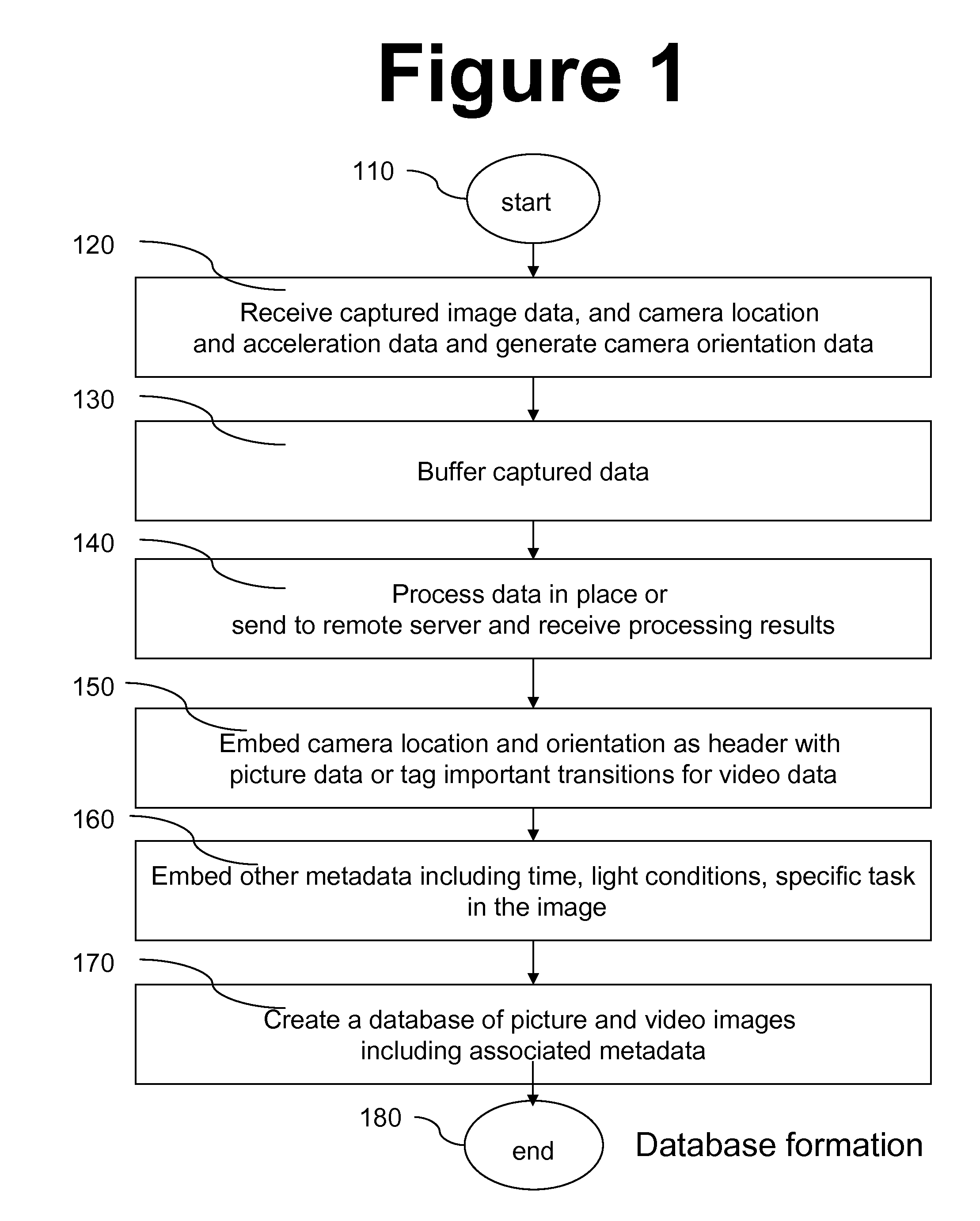
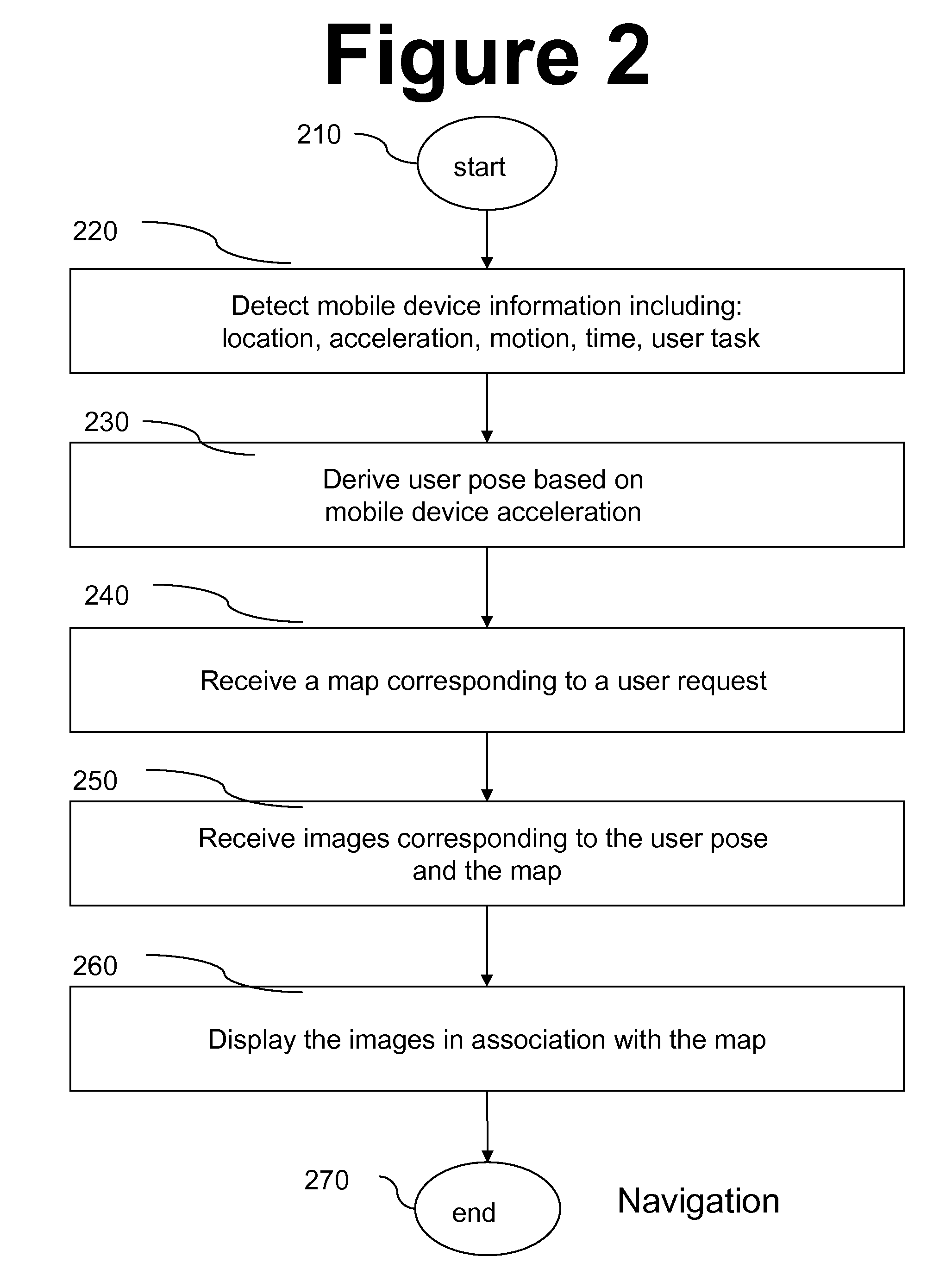
Image matching in support of mobile navigation
ActiveUS20100191459A1Orient themselvesFast and reliableTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationMobile navigationAccelerometer
Method, apparatus and system for improving navigation using mobile devices by adding previously captured media to navigation maps provided by mobile device. Added media include still images and video clips. Media captured at the same location using various camera orientations are available in an image database. Images in database include metadata indicating location, orientation and other parameters associated with each image. User location and pose are matched against metadata indicating location and camera orientation of captured images. User motion may also be matched to metadata indicating camera motion of stored video clips. Other parameters like lighting, seasonal factors, and tasks of walking, biking or driving may also be matched. User pose may be derived from an accelerometer embedded in the mobile device. Some or all of user parameters desired by user may be directly input to mobile device by user instead of being automatically detected by mobile device.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
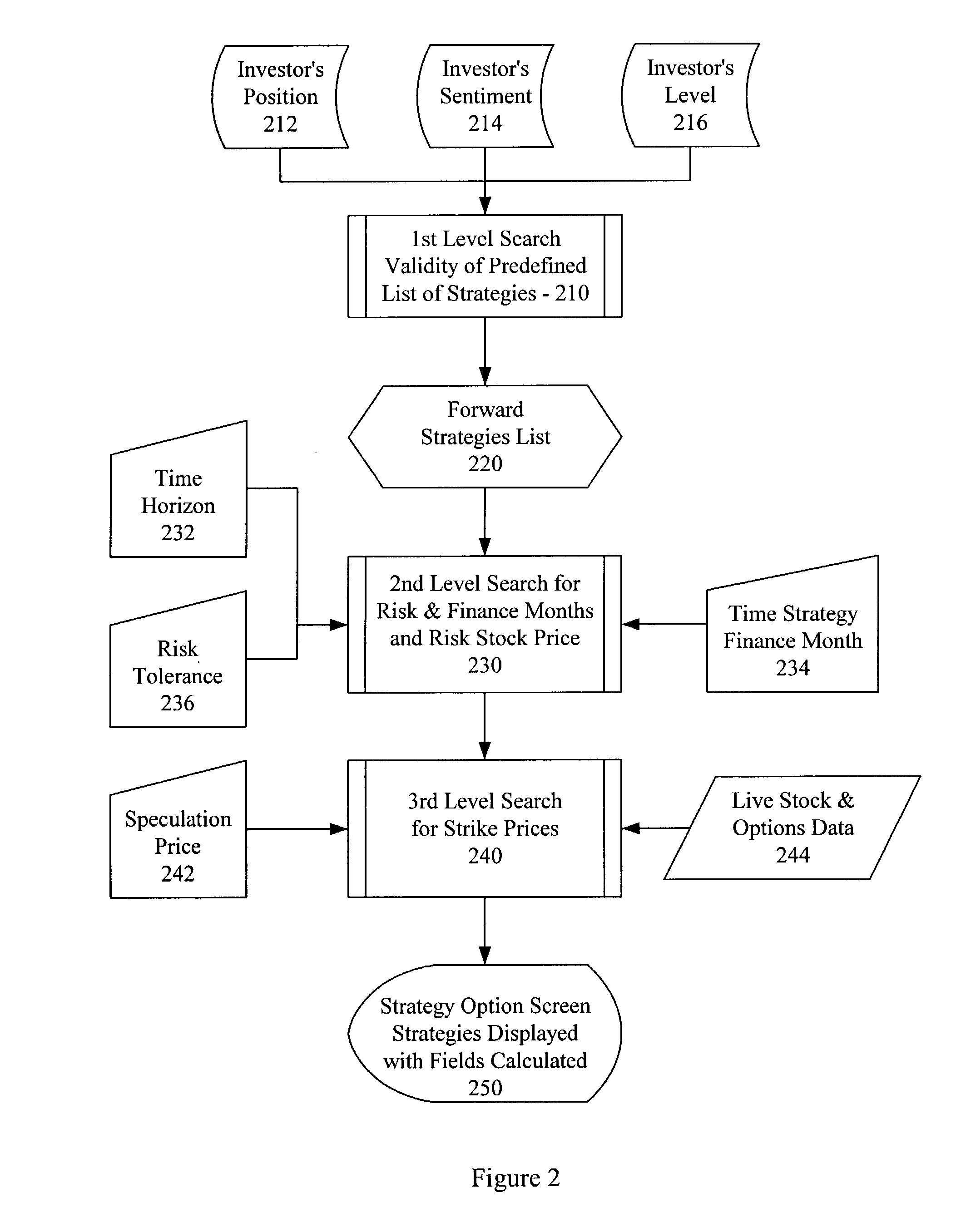
Risk management system for recommending options hedging strategies
InactiveUS20030069821A1Act quicklyReduce lossesFinanceSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringManagement system
A risk management system for use in generating, for any long or short stock position or an entire portfolio, one or more options hedging strategies to protect unrealized profits and to insure the position against directional market risk. The risk management system recommends a preferred options hedging strategy out of many possible strategies based on minimizing losses while maintaining profits, but users of the system can review other possible strategies and make their own selection using predetermined reward, cost, and risk goals. In addition, user's can modify the predetermined goals in a real-time mode and assess alternate options hedging strategies. The risk management system also monitors existing investor profiles and alerts the user when a hedging action is recommended based on pre-established parameters customized for a particular stock position or an entire portfolio. The system accomplishes these features, and others, through an easily learned, fast and efficient user interface.
Owner:MARKET COMPASS
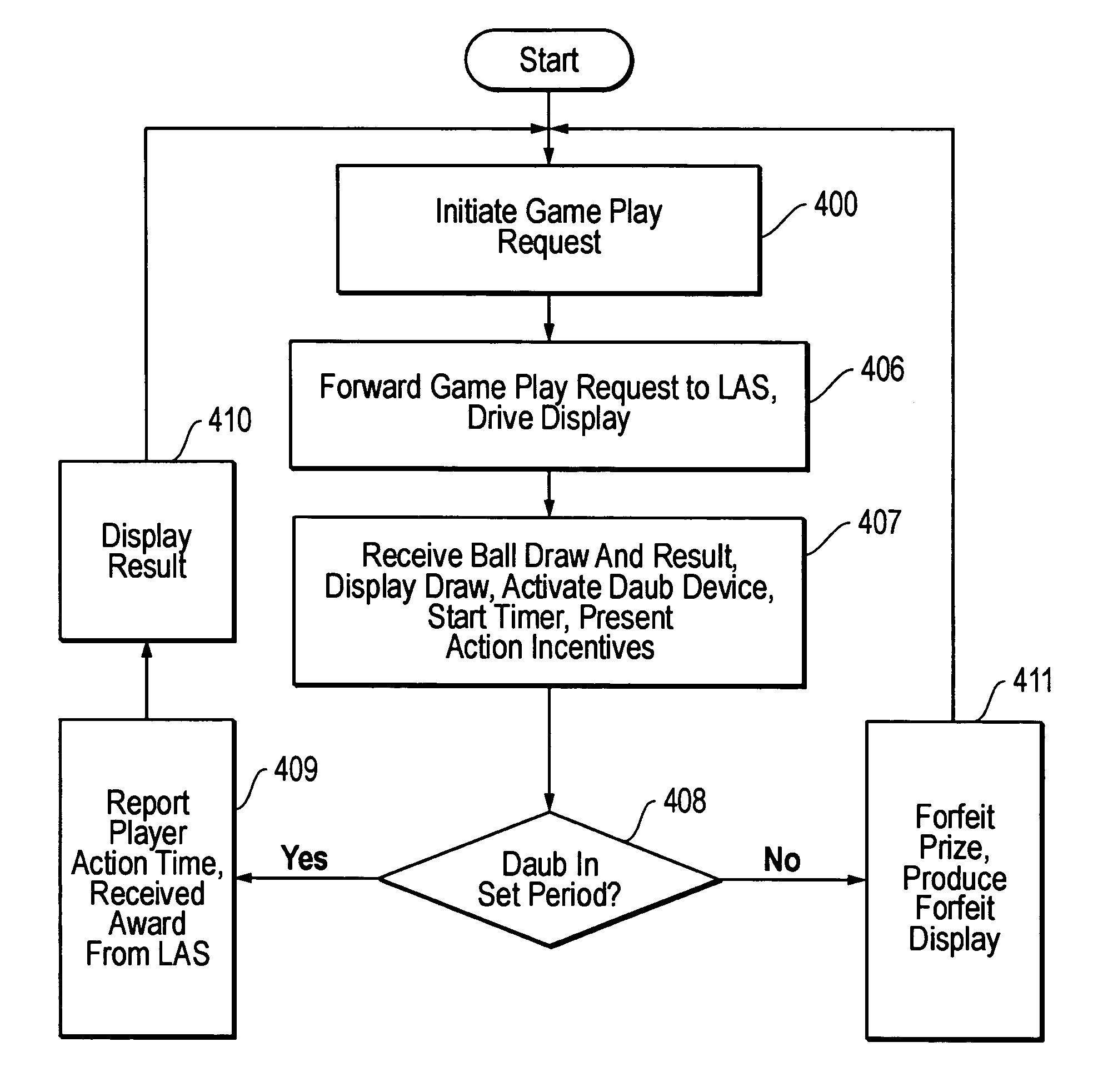
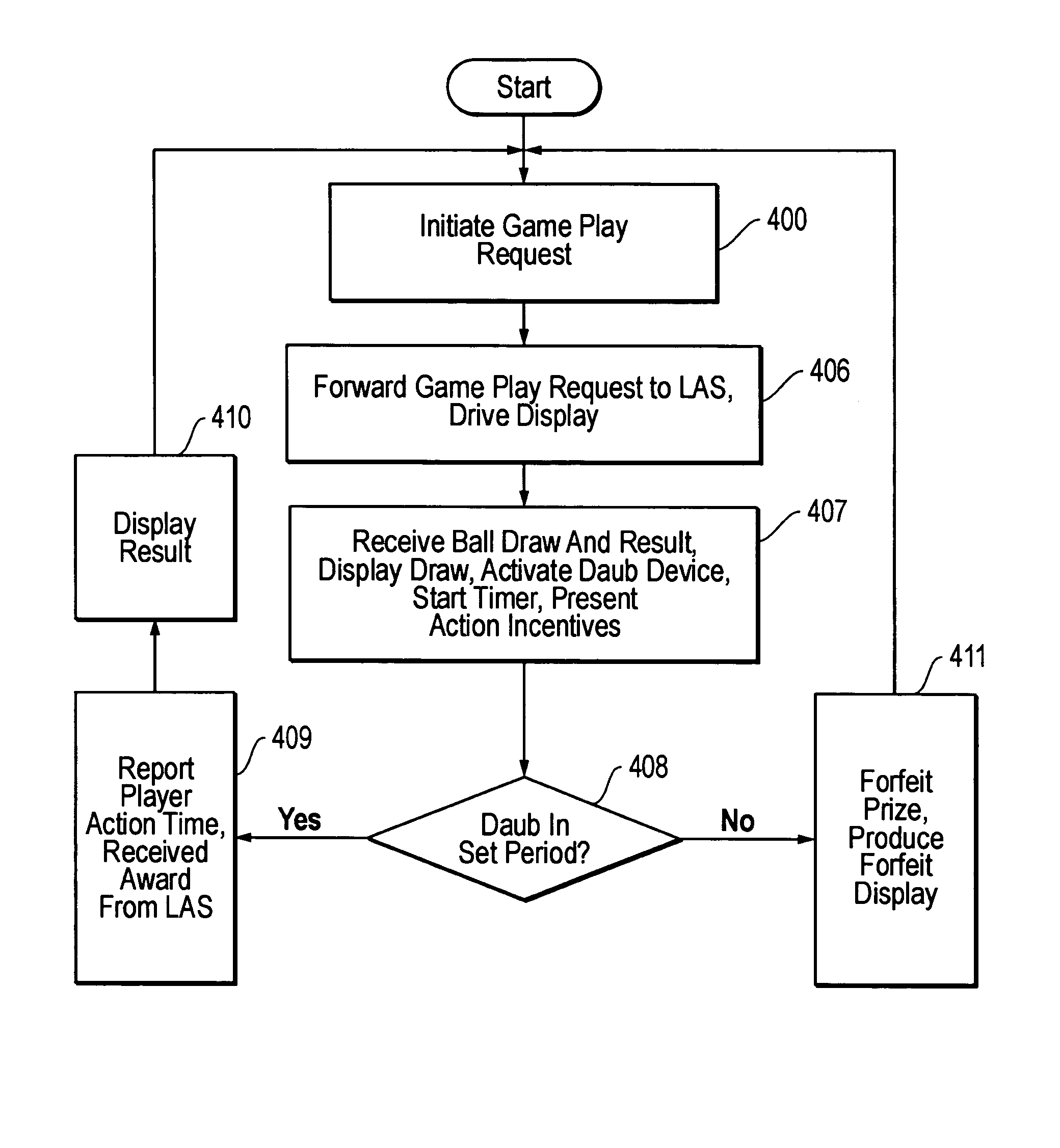
Player action incentive arrangement for gaming systems
ActiveUS20050221881A1Reduce undesirable delayFast playApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesEngineeringGame play
A processing device measures the time it takes for a player to take some action in a game and bases the award or result in the game for the player at least in part on that measured time. A player receives a more desirable result or outcome for a particular game play in response to a shorter player action time and / or receives a less desirable result or outcome for a particular game play in response to a longer player action time. Providing more desirable results for shorter player action times or less desirable results for longer player action times provides players an incentive that influences them to take the appropriate player actions more quickly.
Owner:EVERI GAMES
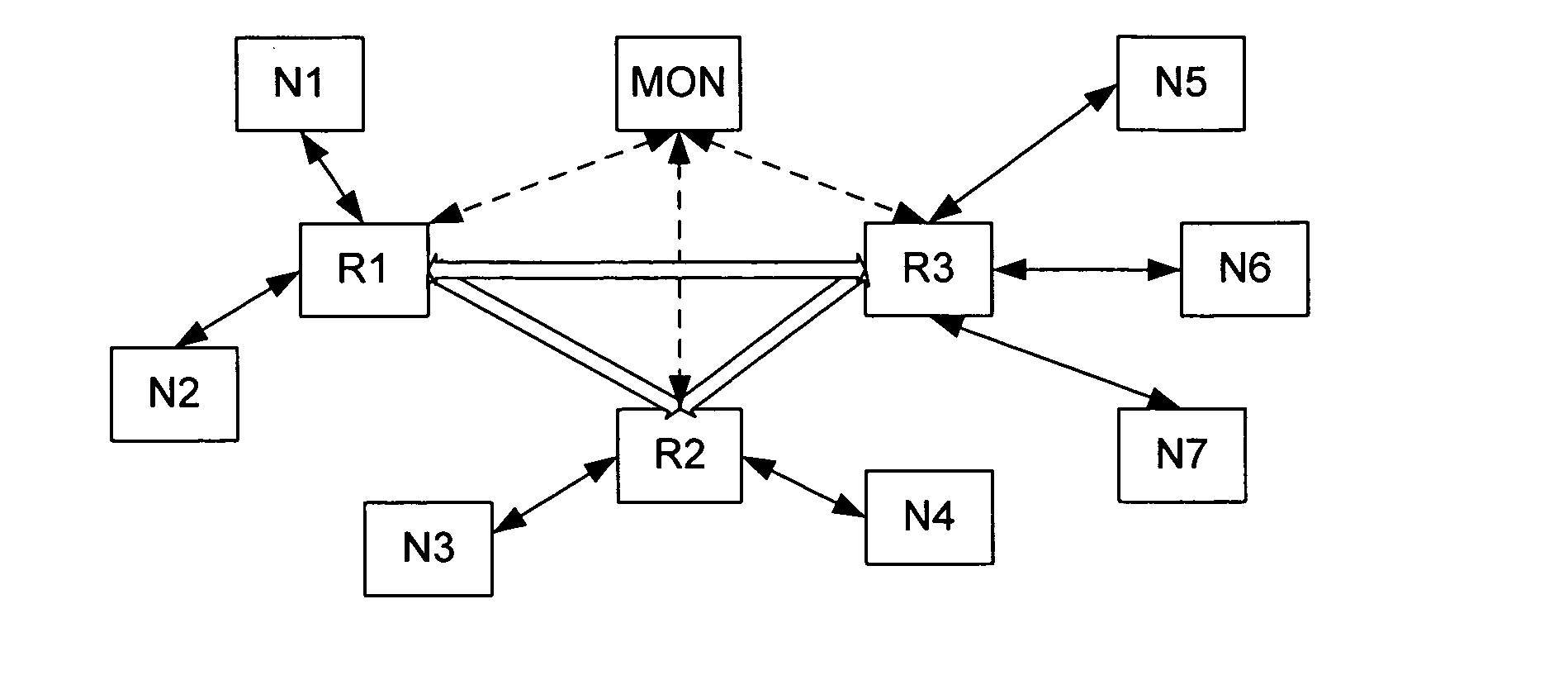
Interactive network monitoring and analysis
InactiveUS20070140131A1Facilitate real-time data-capture controlEasy to analyzeError preventionTransmission systemsGraphicsSummary data
A network monitoring system and method processes captured message data to create a plurality of categories, provides summary data corresponding to each category, and displays the categorized summary data. The categories preferably include an identification of the source node and destination node of each message, and the summary data includes the amount of traffic communicated between each pair of nodes. The display of this summary data includes a graphic display that provides a visual indication of each pair and the volume of traffic between the nodes of the pair.
Owner:OPNET TECH LLC
Methods and systems for risk management
In one aspect, the invention comprises acquiring background data regarding securities positions and regarding real-time pricing data; performing calculations regarding intermediate measures of performance of the securities; receiving configuration data for a portfolio of securities and one or more data requests, at least one of the data requests comprising a request for a value at risk report regarding the portfolio; and providing a value at risk report based on a Parkinson's volatility estimation. In another aspect, the invention comprises displaying a tree structure display in a first portion of a graphical user interface display; in response to a user selecting an item from the tree structure display, displaying a corresponding listing in a tabular display in a second portion of the graphical user interface display; and in response to the user selecting a listing in the tabular display, displaying a corresponding item in the tree structure display.
Owner:EZE CASTLE SOFTWARE
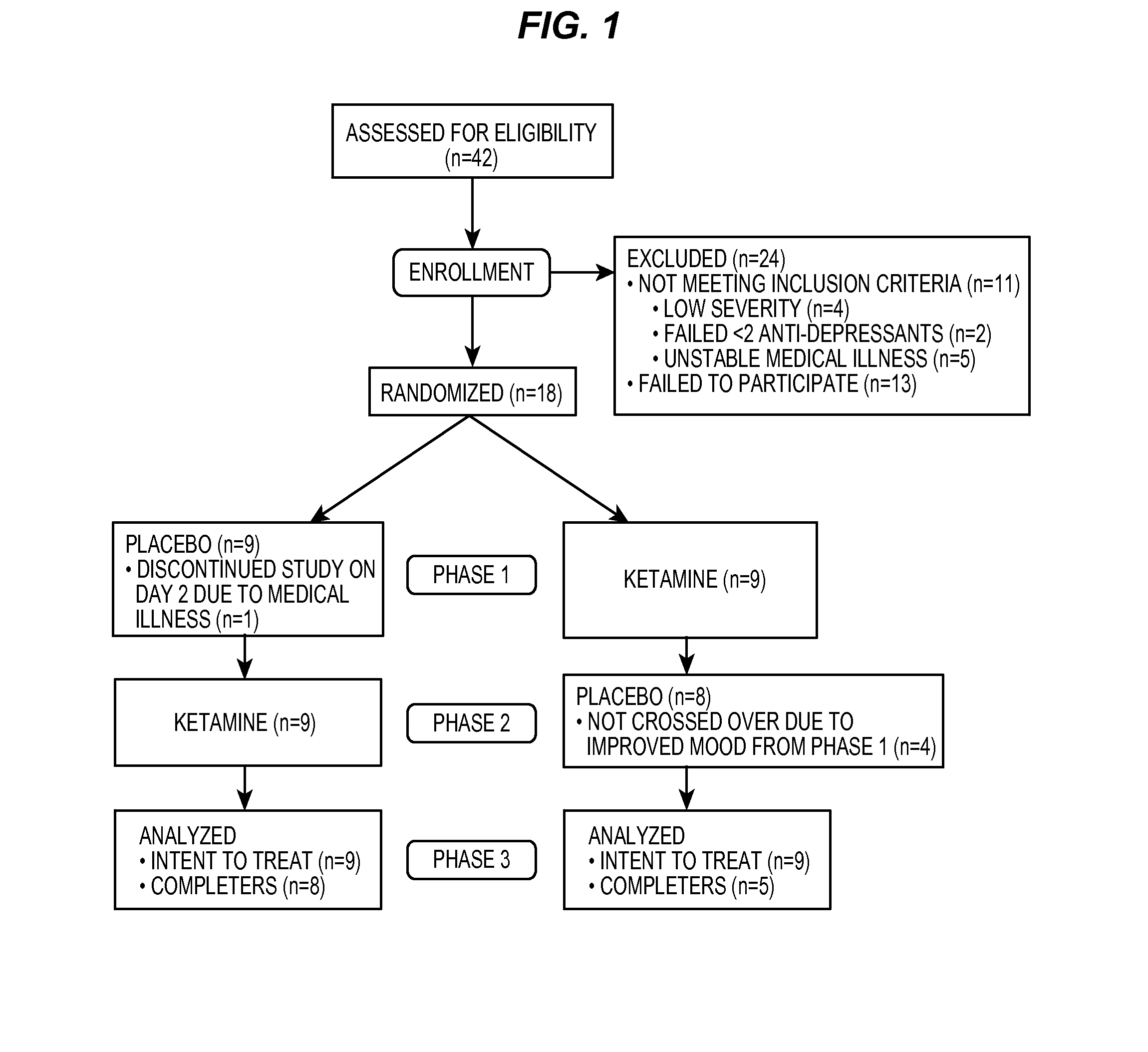
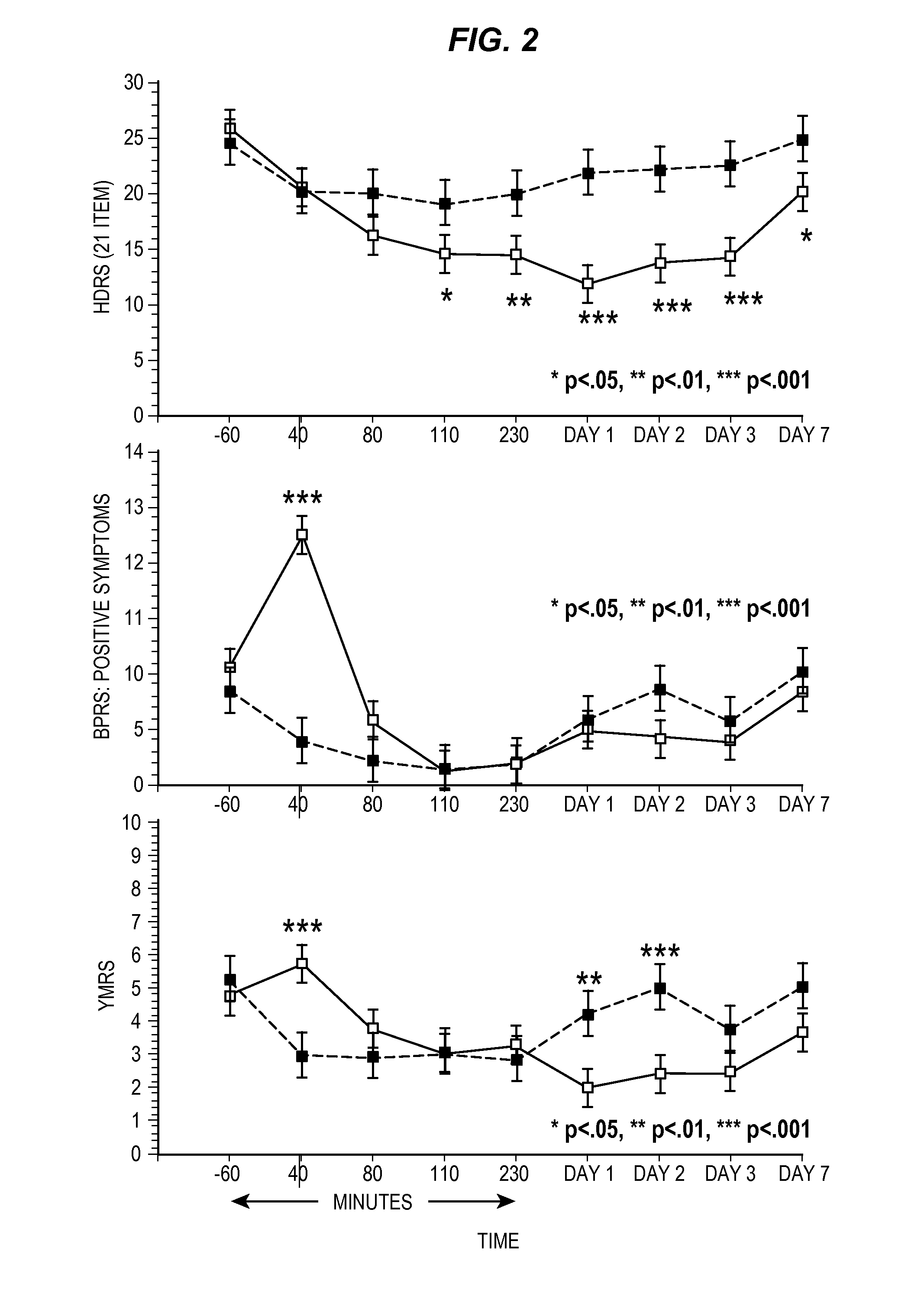
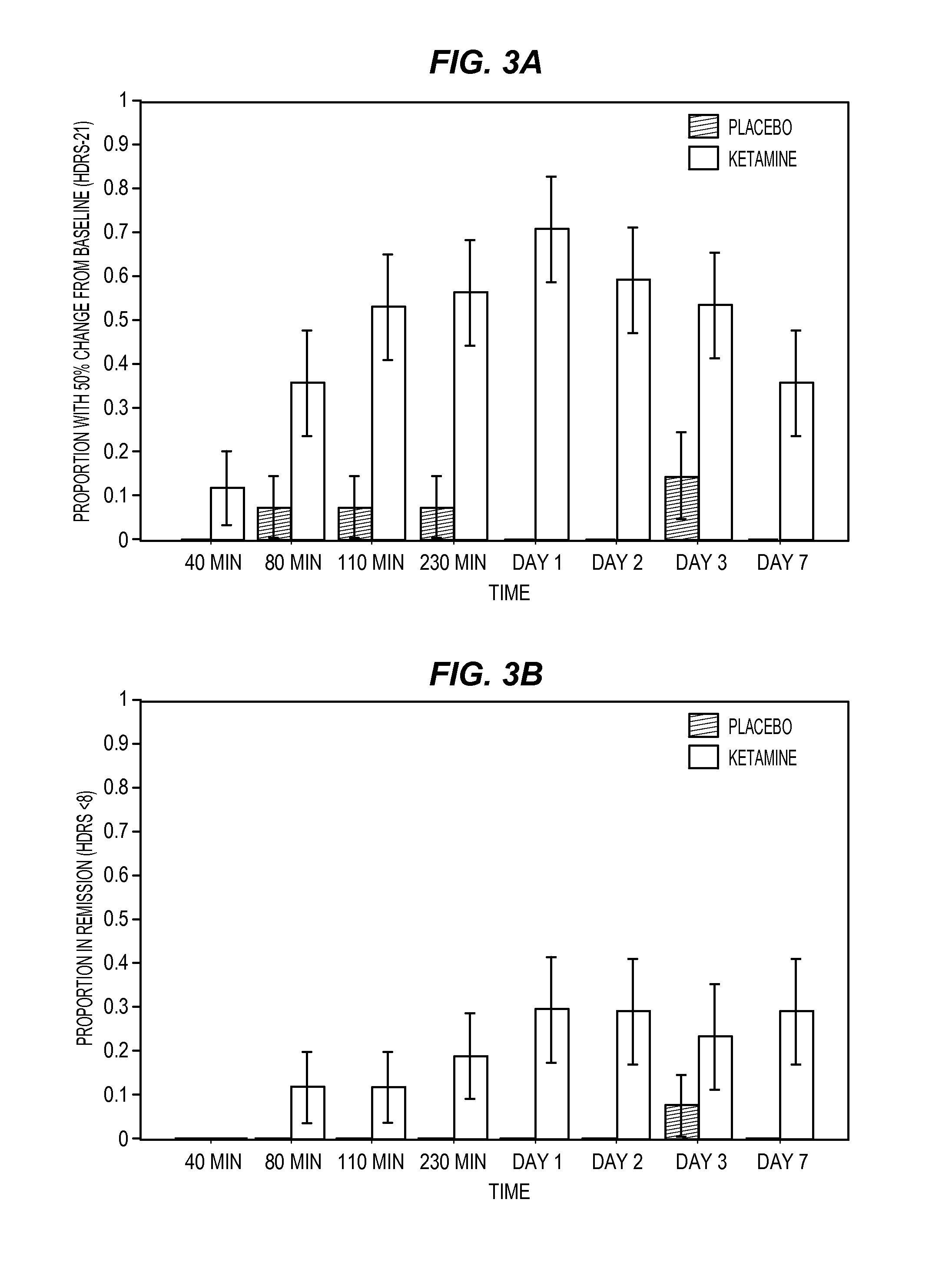
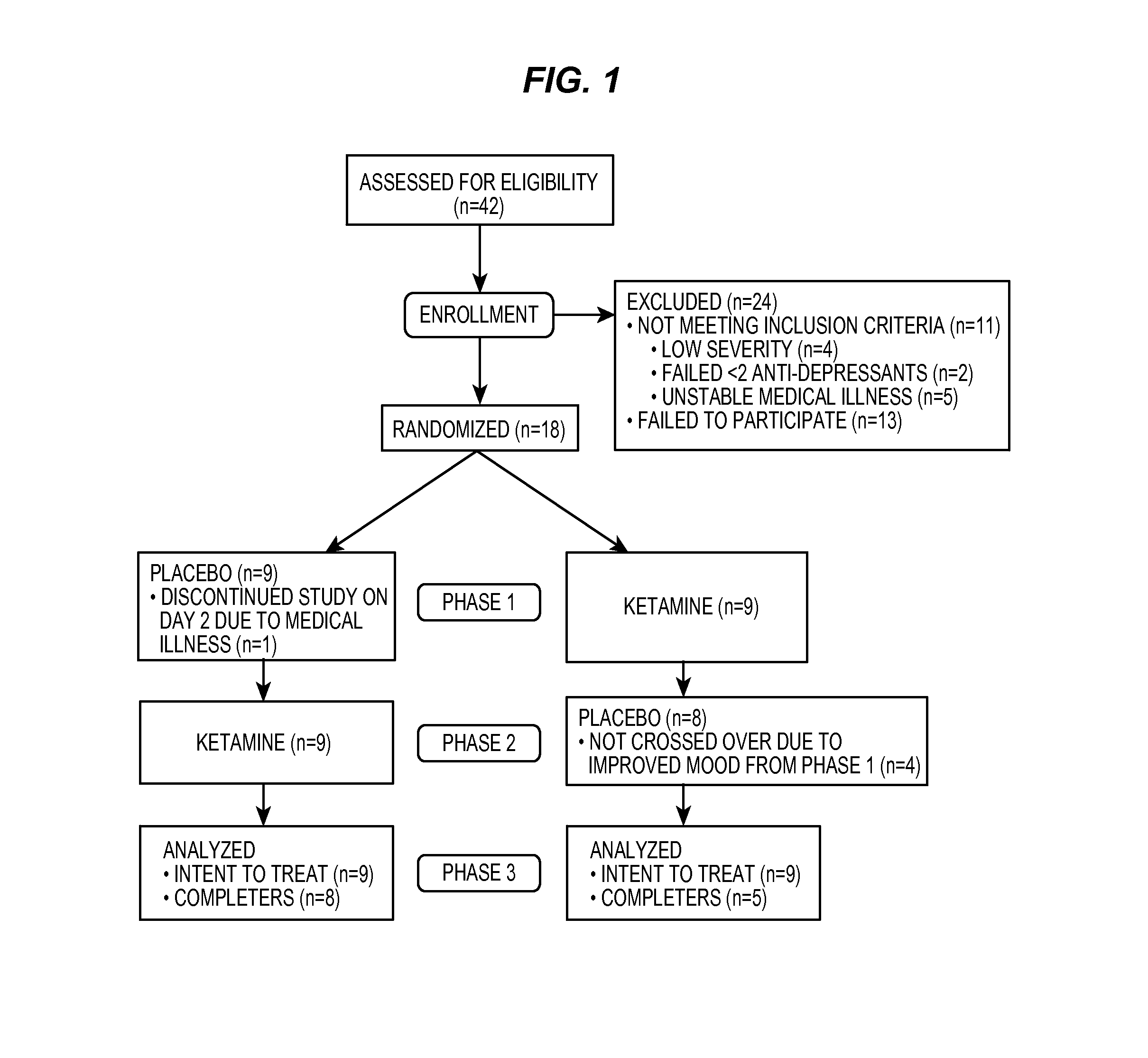
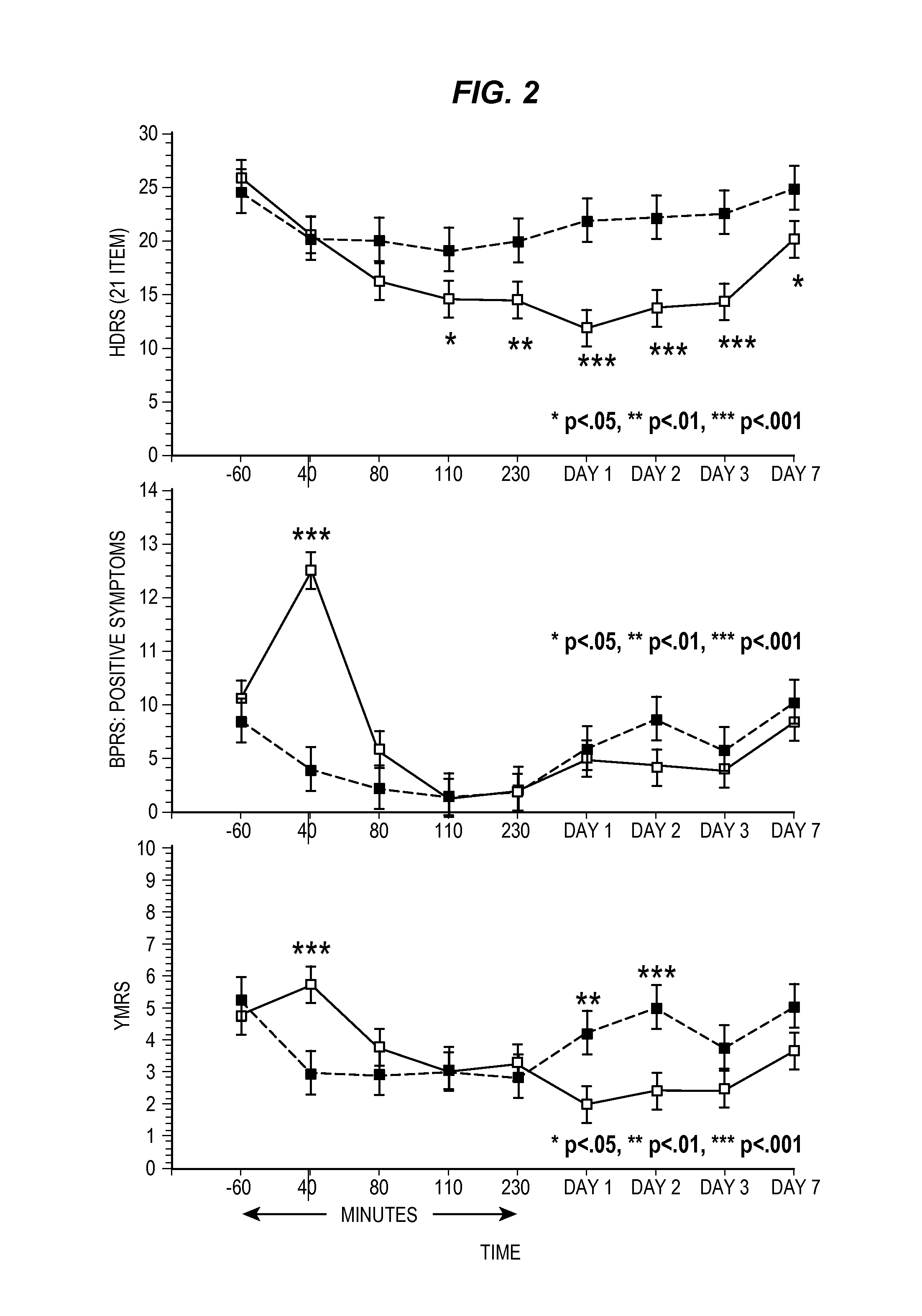
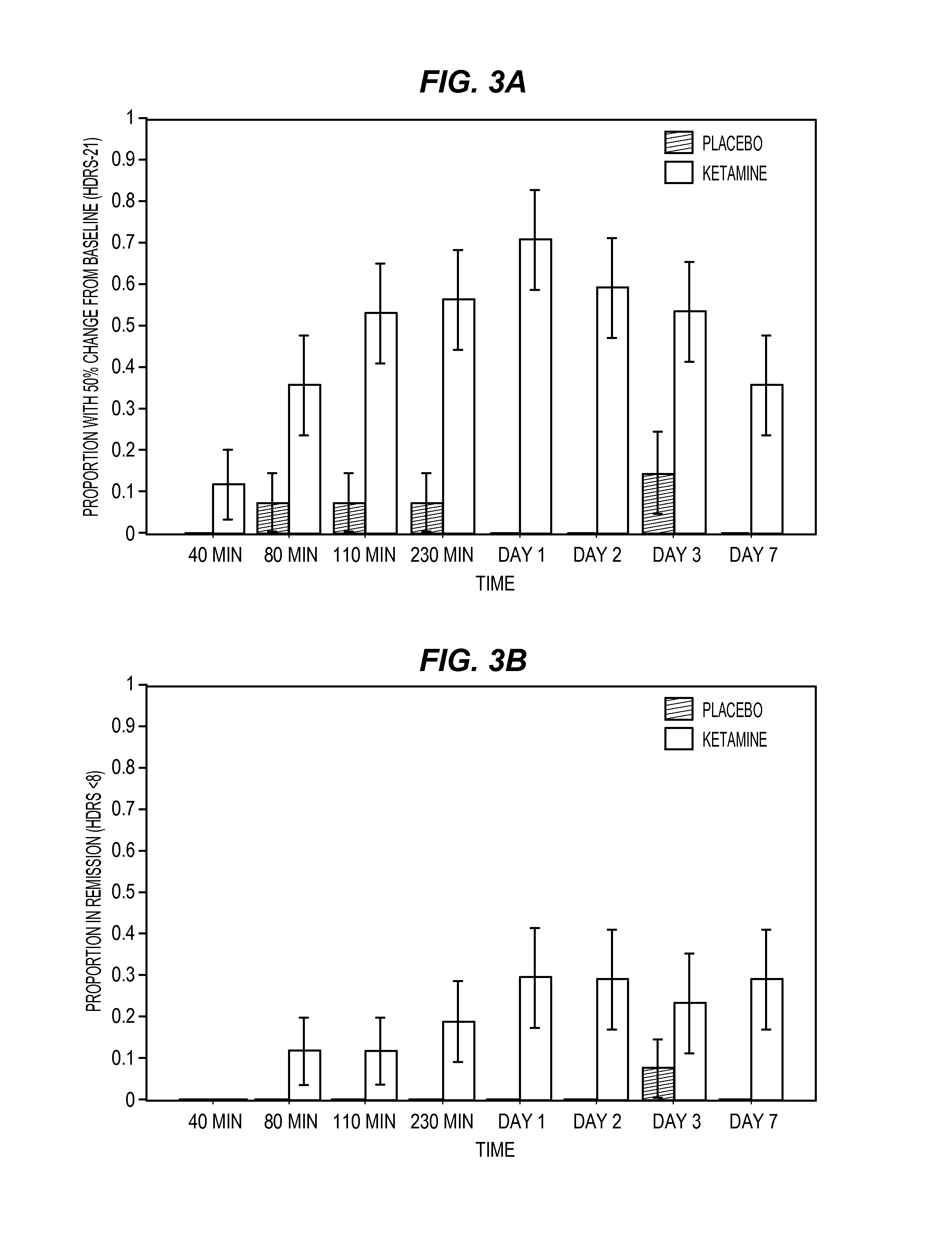
Intranasal Administration of Ketamine to Treat Depression
ActiveUS20070287753A1Readily and inexpensivelyAdverse effectBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChronic depressive disorderDepressive symptoms
Methods and compositions for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression are described. More specifically, the invention demonstrates that intranasal administration of ketamine is effective to ameliorate the symptoms of depression in a patient who has not responded to an adequate trial of one antidepressant in the current episode and has recurrent or chronic depressive symptoms (>2 years).
Owner:YALE UNIV +2
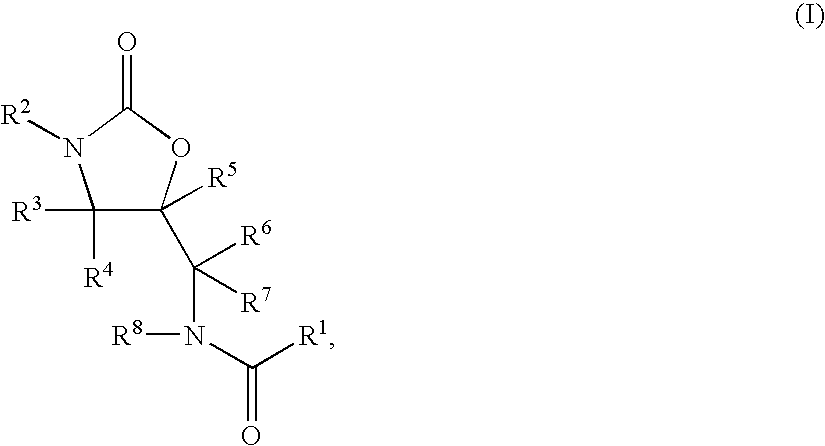
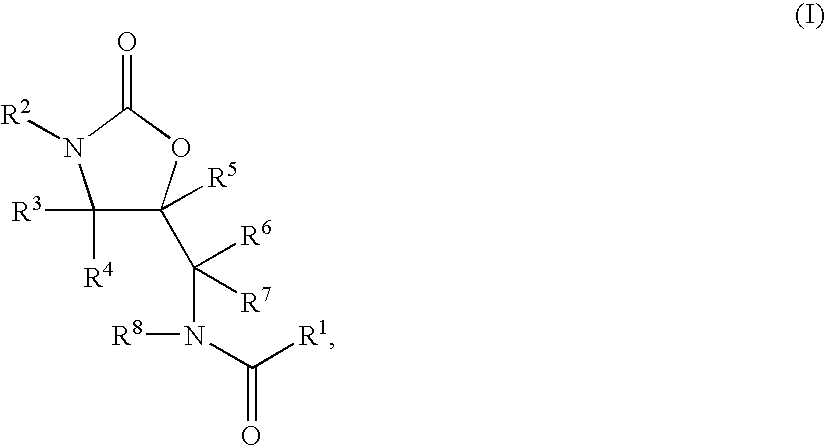
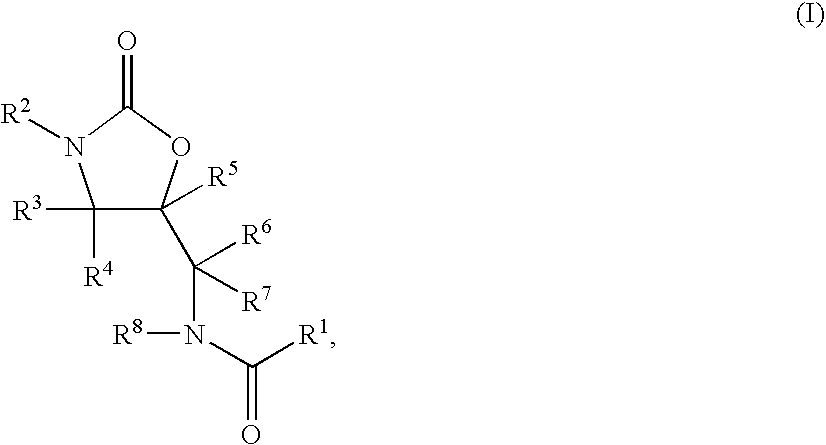
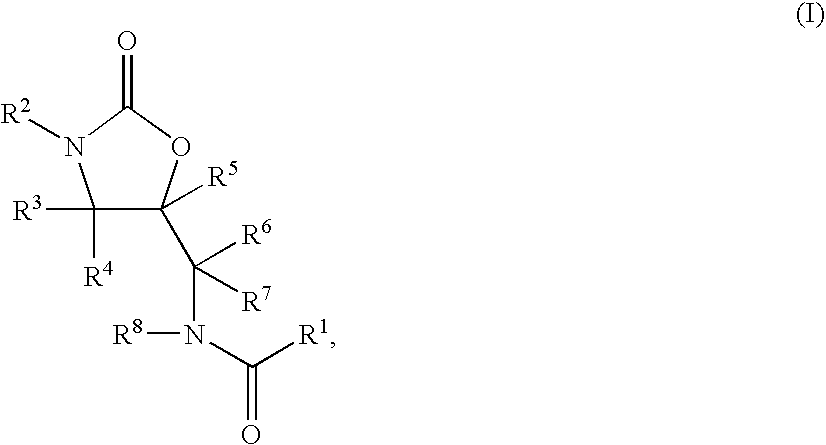
Substituted Oxazolidinones and Their Use in the Field of Blood Coagulation
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
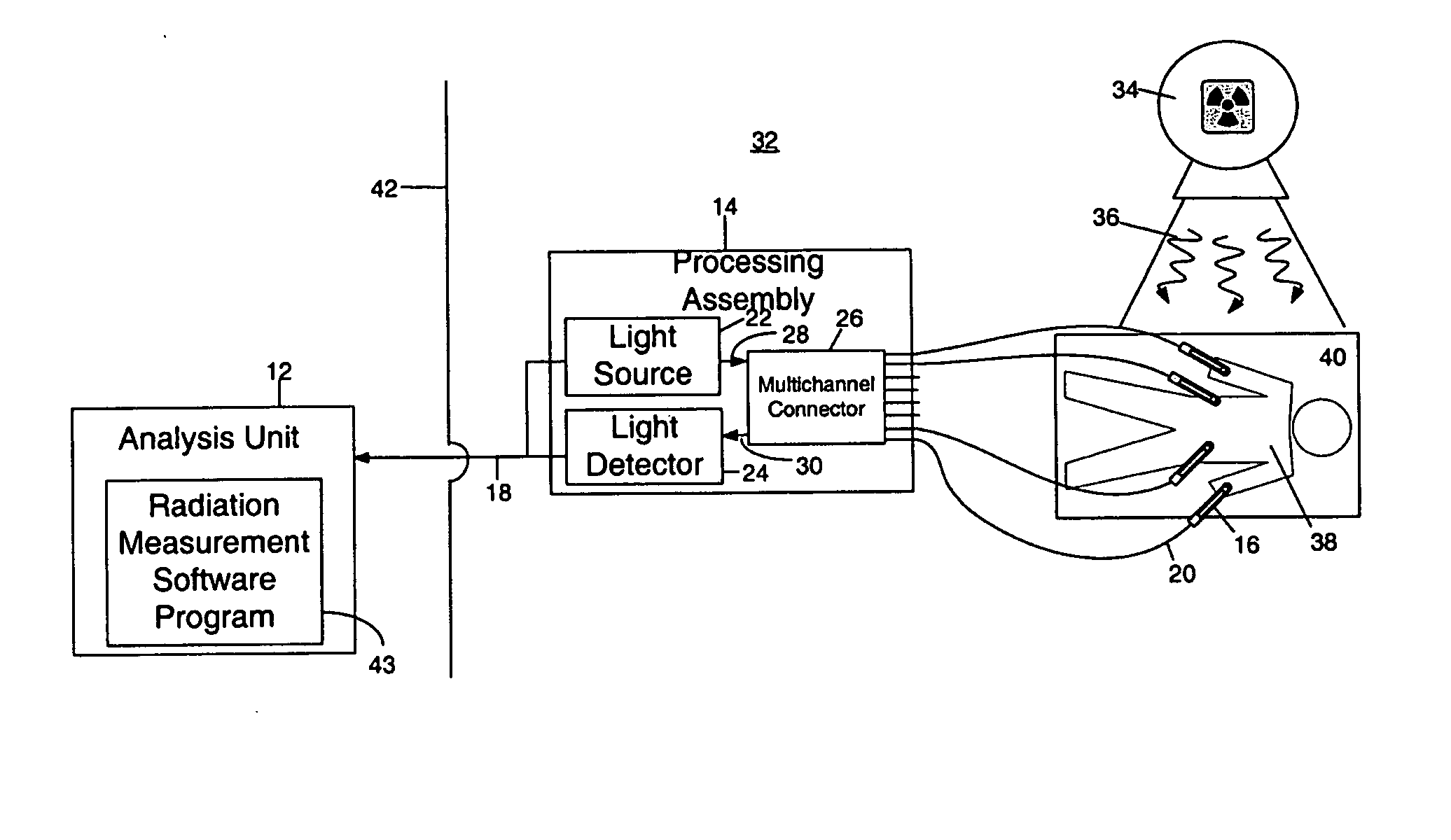
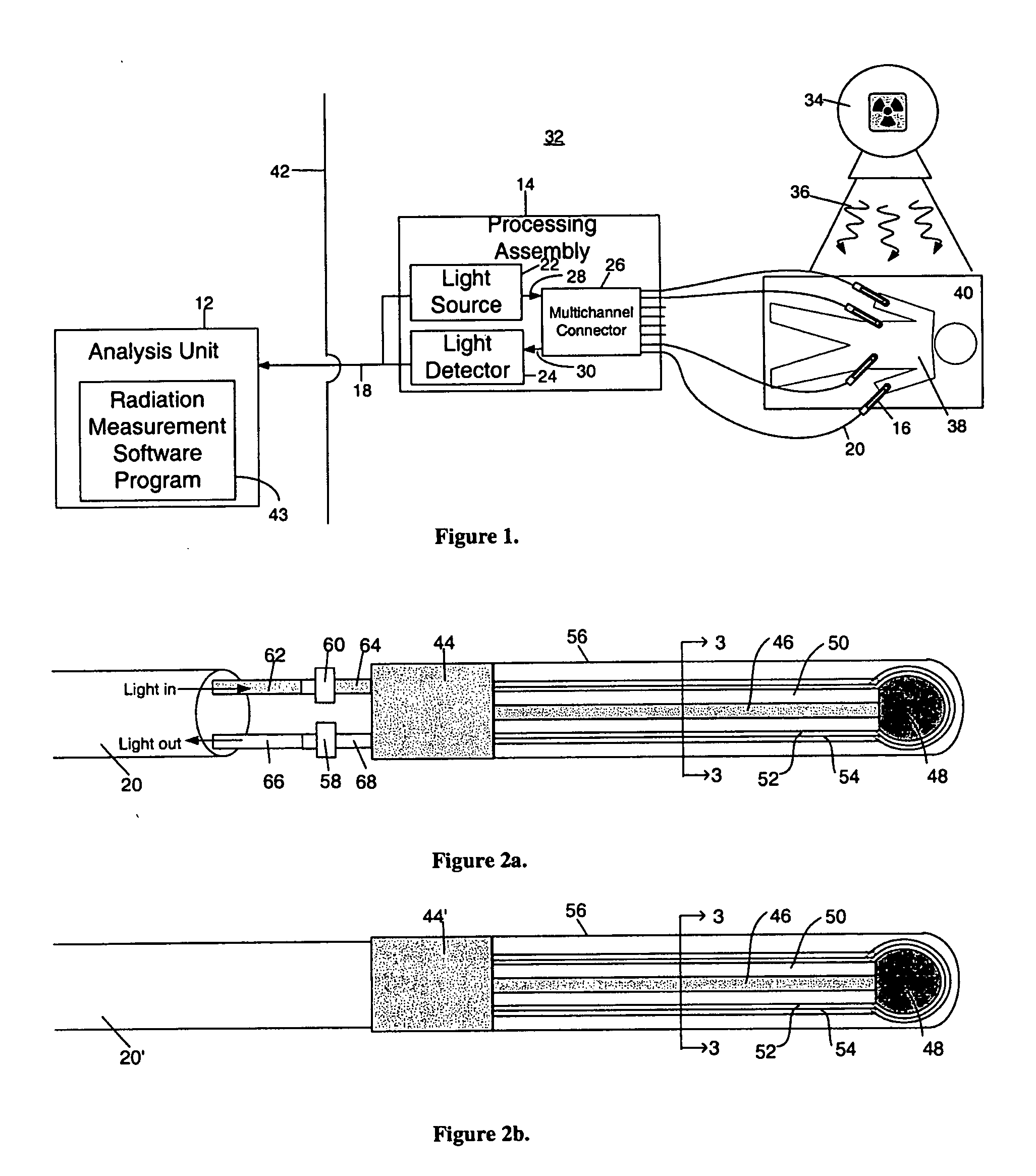
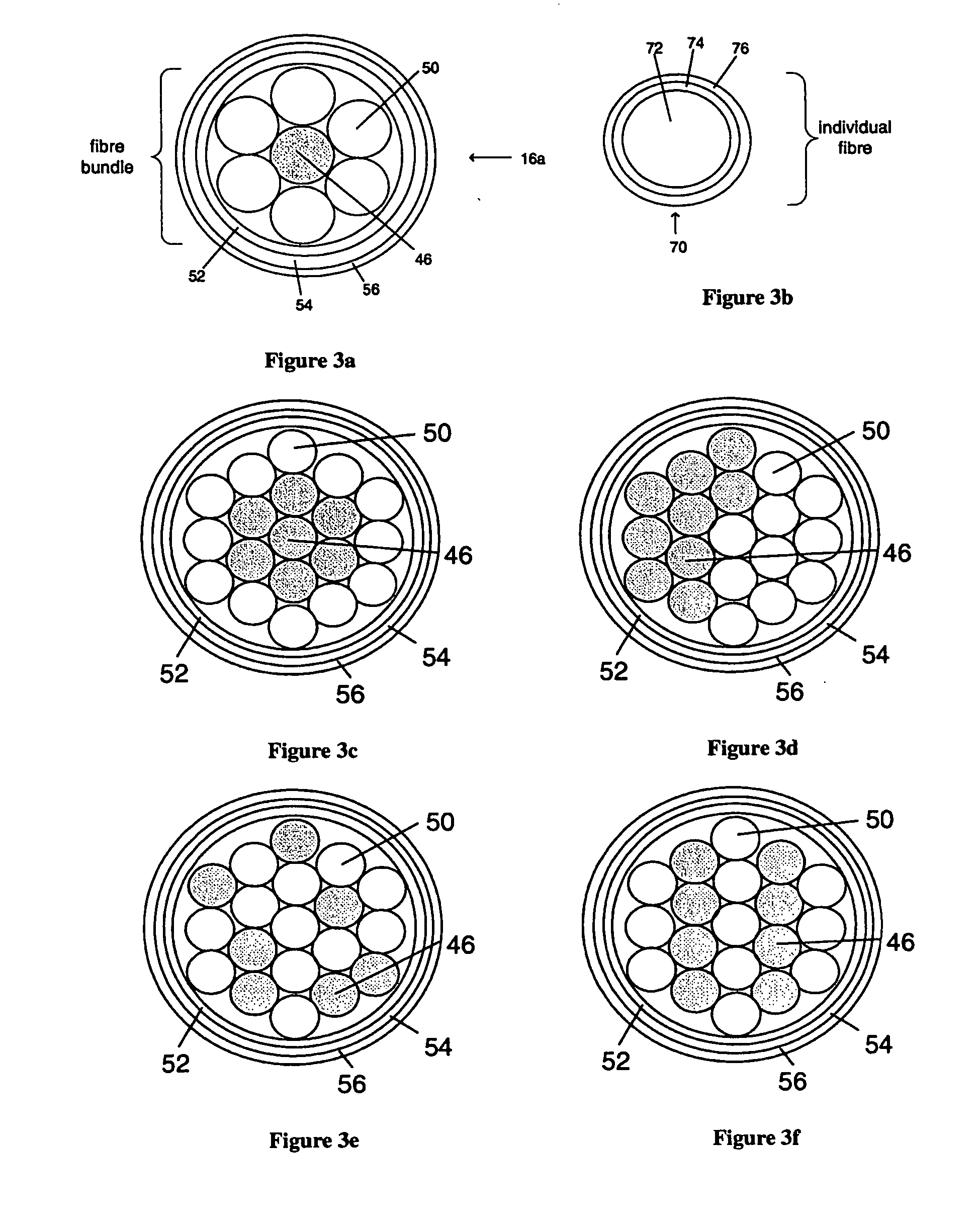
Apparatus and method for determining radiation dose
ActiveUS20060017009A1Minimal disturbanceAct quicklyElectroluminescent light sourcesPhotometryOptical propertyDosimeter
A radiation dosimeter system and method for estimating a deposited radiation dose to an object involves locating at least one radiation dosimeter at the object. The radiation dosimeter includes a radiation sensitive medium having an optical property that changes due to the deposited radiation dose. An optical interrogation signal is provided to the radiation dosimeter via an enclosed optical path for interacting with the radiation sensitive medium. During irradiation, the optical interrogation signal is transformed into an optical information signal that encodes an ionizing radiation induced change in the optical property of the radiation sensitive medium. The radiation dosimeter system then processes the optical information signal for estimating the deposited radiation dose.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Amylin formulations
InactiveUS20080248999A1Reduce in quantityAct quicklyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGLP-1 MimeticsBefore Breakfast
A combined insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the insulin is decreased so that the amylin and / or GLP-1 remains soluble when mixed together with the insulin. In the preferred embodiment, a bolus insulin is administered by injection before breakfast, providing adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, without producing hypoglycemia after the meal. This can be combined with an adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of the insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic combination. A GLP-1 mimetic may be combined with either rapid acting or basal insulin formulations. As a result, a patient using the combination formulation therapy may only need to inject half as many times per day.
Owner:BIODEL INC
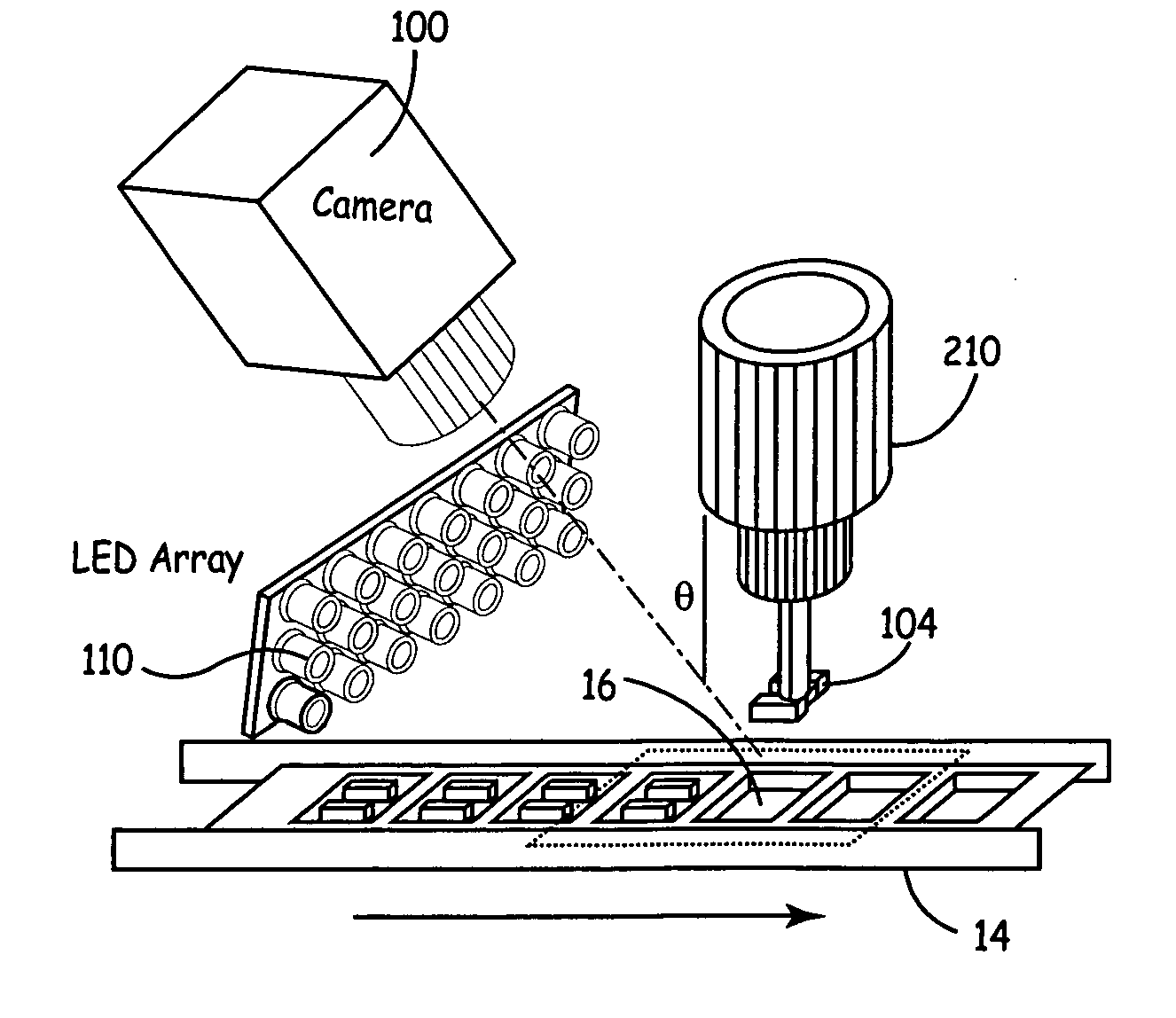
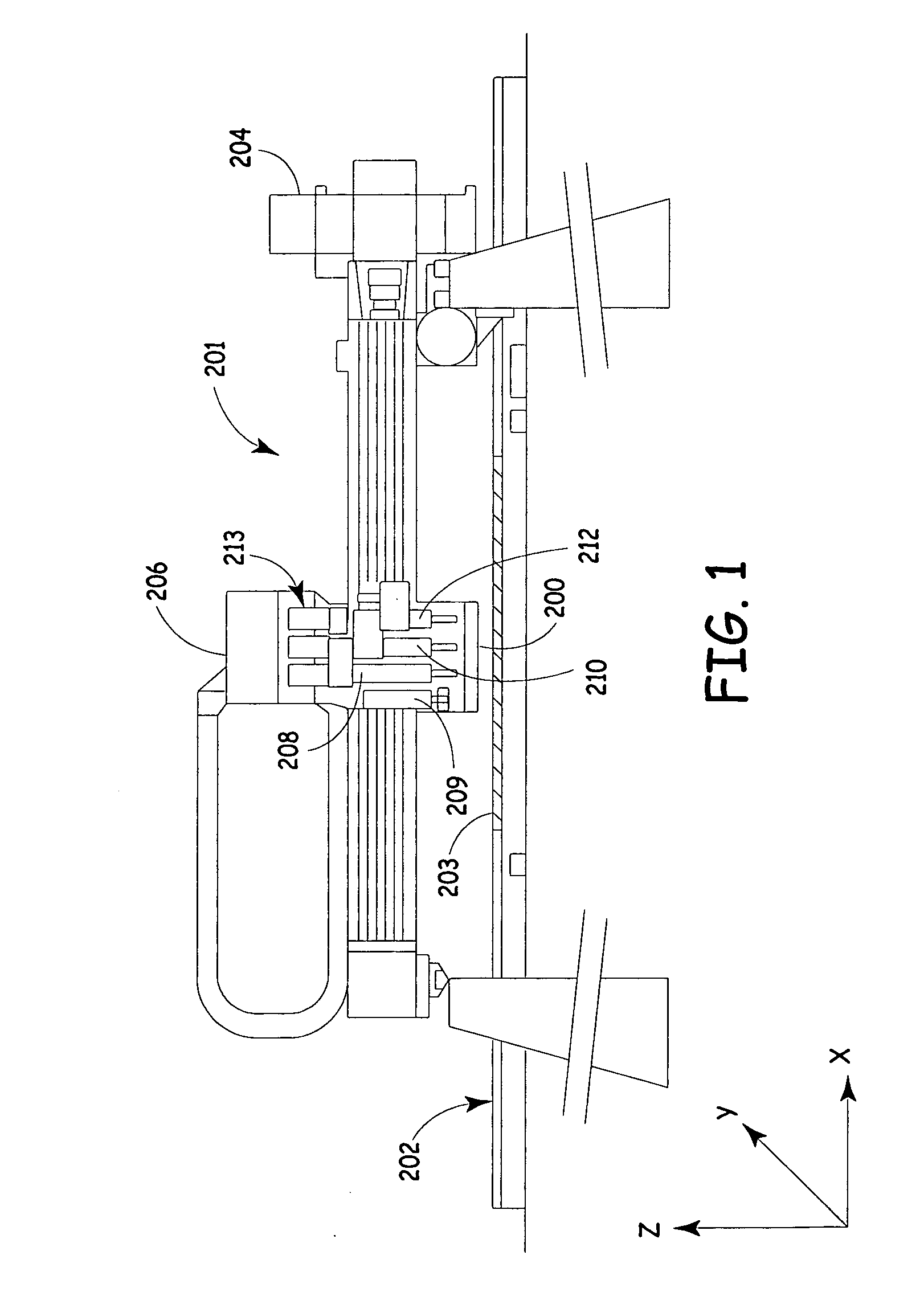
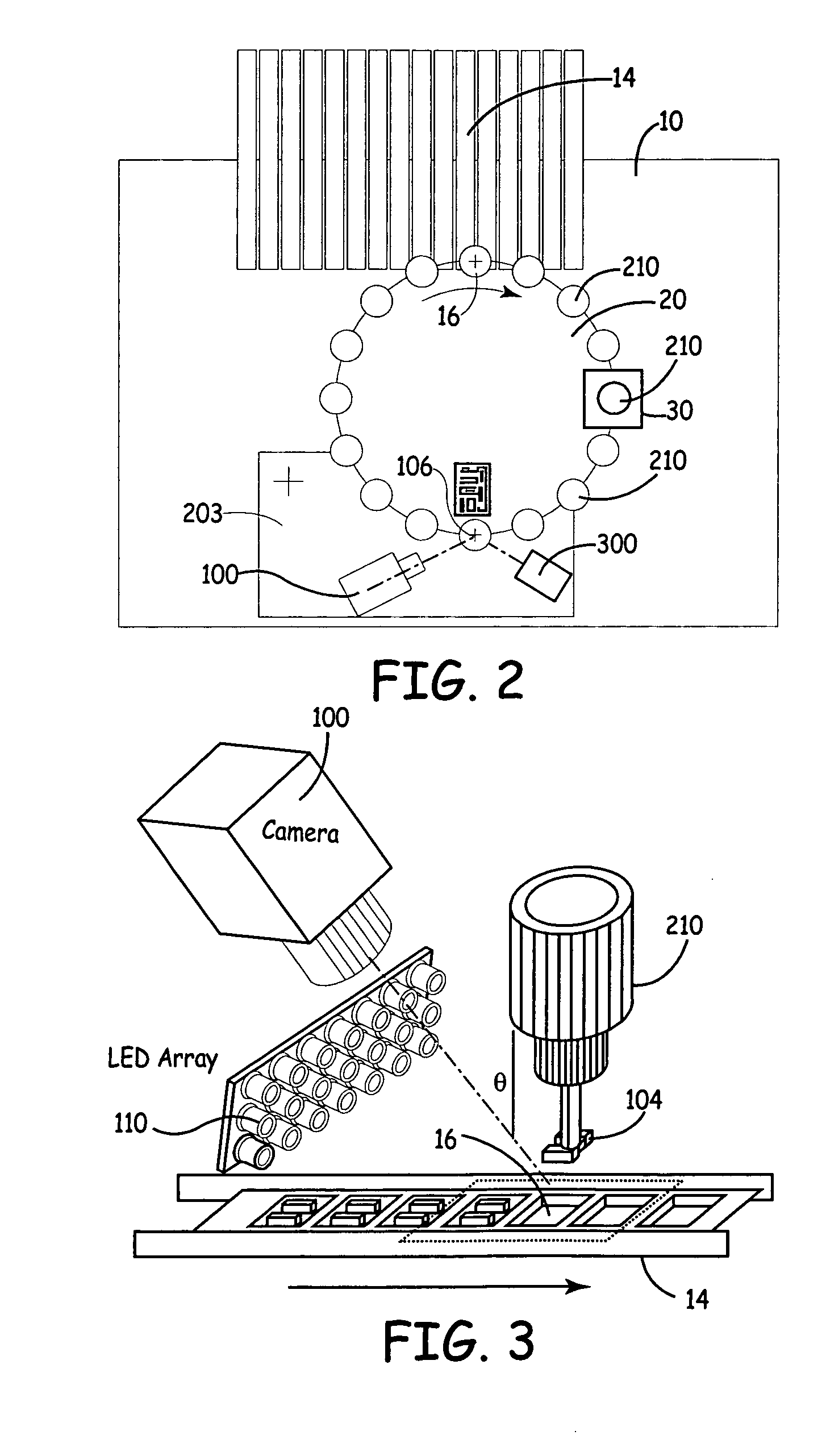
Pick and place machine with improved component pick up inspection
Embodiments of the present invention improve upon component level inspection performed by pick and place machines. Such improvements include inspecting the pick operation in pick and place machines by collecting images of the pick event inside the machine and identifying errors as they happen. By detecting and displaying this information as it generated on the machine, the operator or machine can take prompt and effective corrective actions.
Owner:CYBEROPTICS
Therapeutic formulation for reduced drug side effects
ActiveUS20110262496A1Eliminate side effectsReduce releaseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSide effectDrug side effect
The present invention provides drug therapy formulations for reducing the side effects associated with a therapeutic. In some embodiments, the present invention provides a reduction in sleep- and diet-related side effects associated with a therapeutic.
Owner:KEMPHARM INC
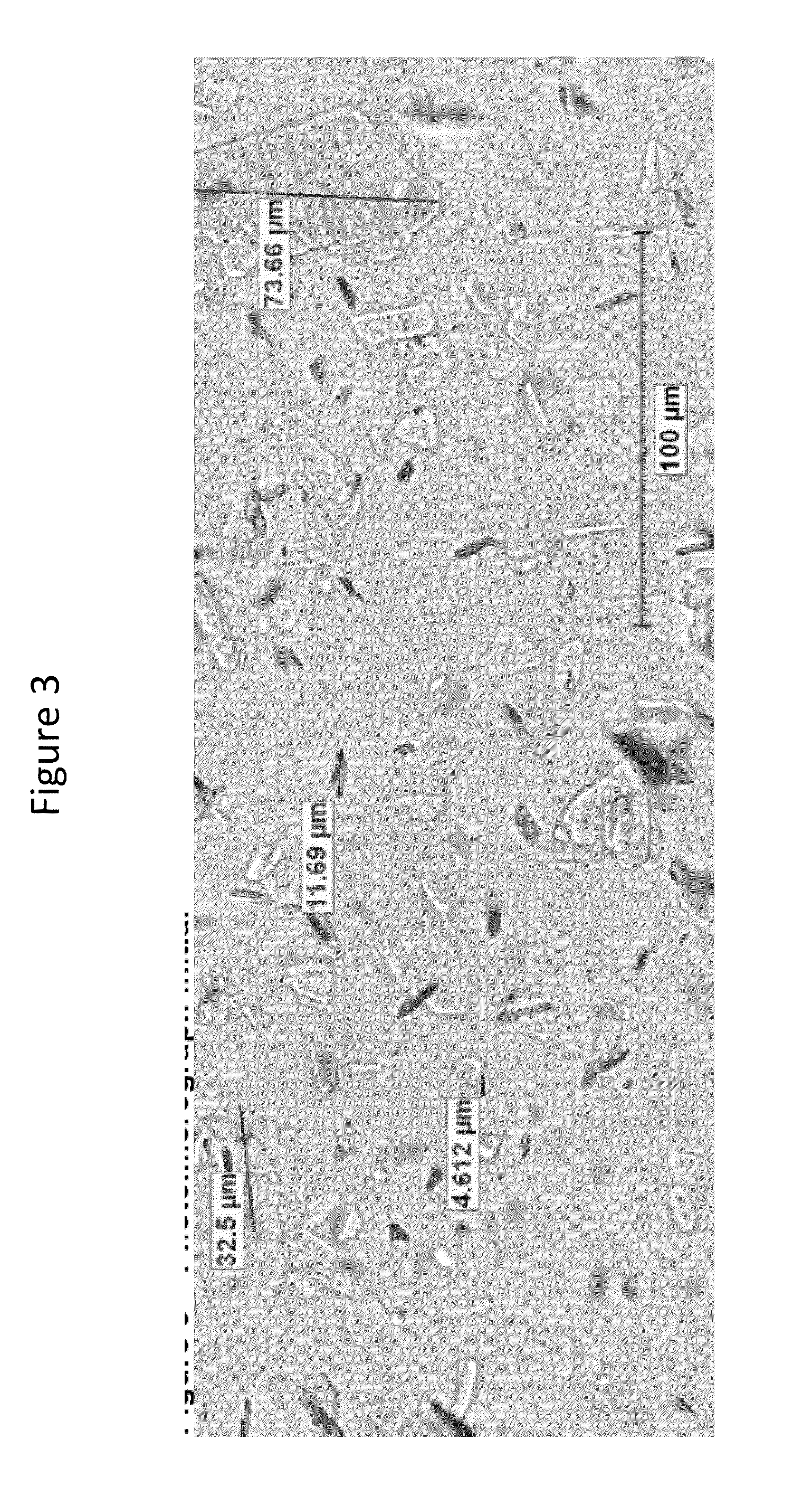
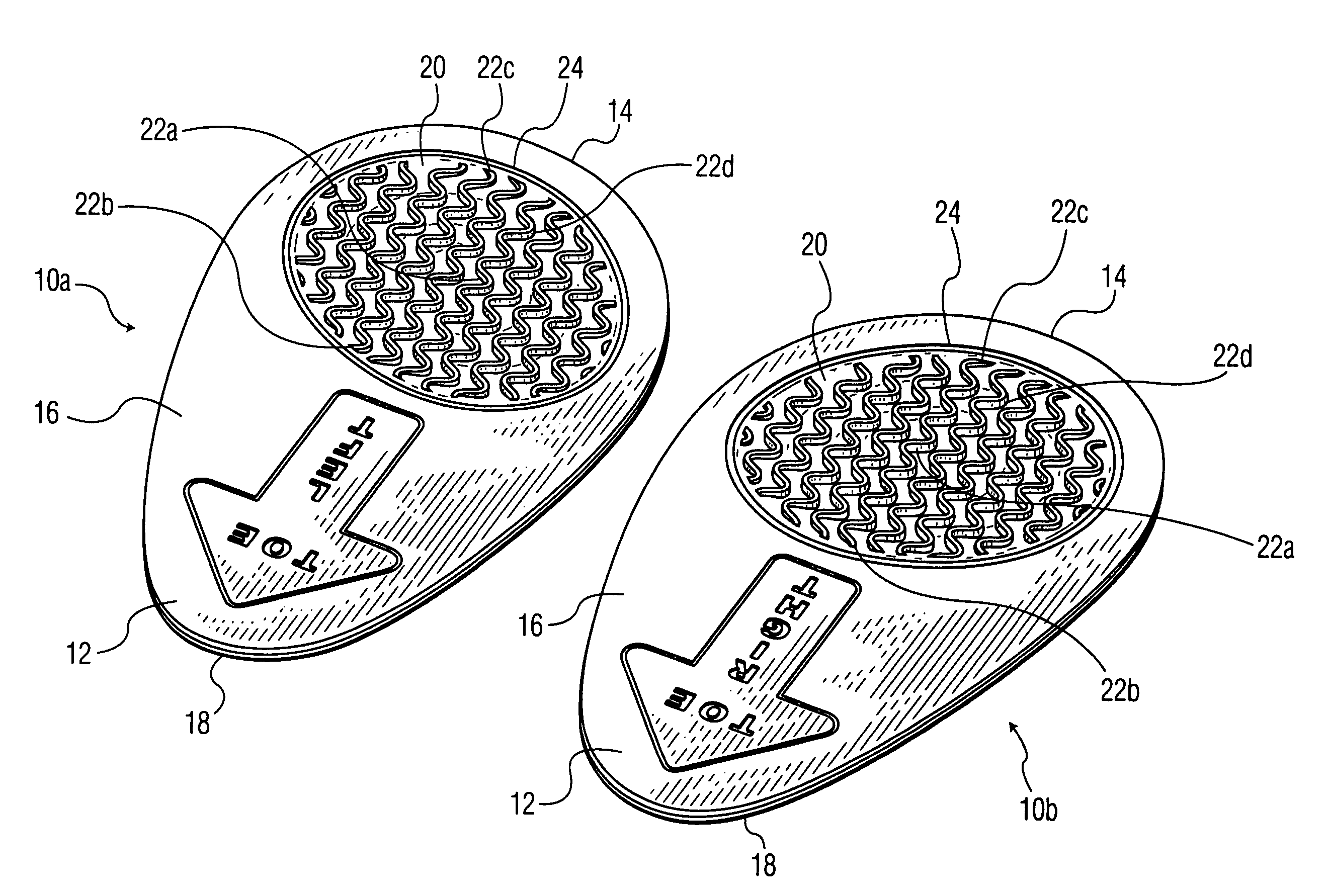
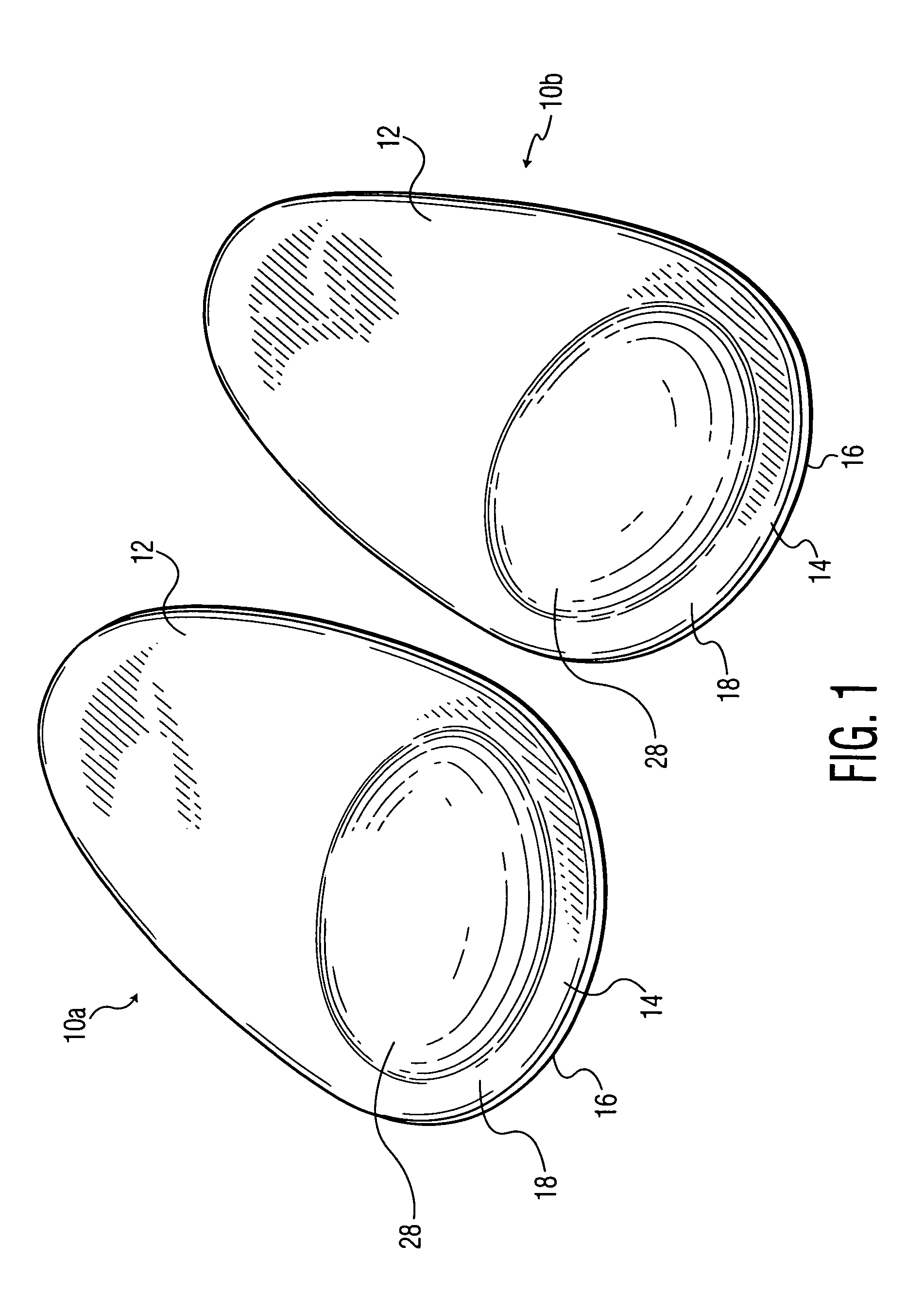
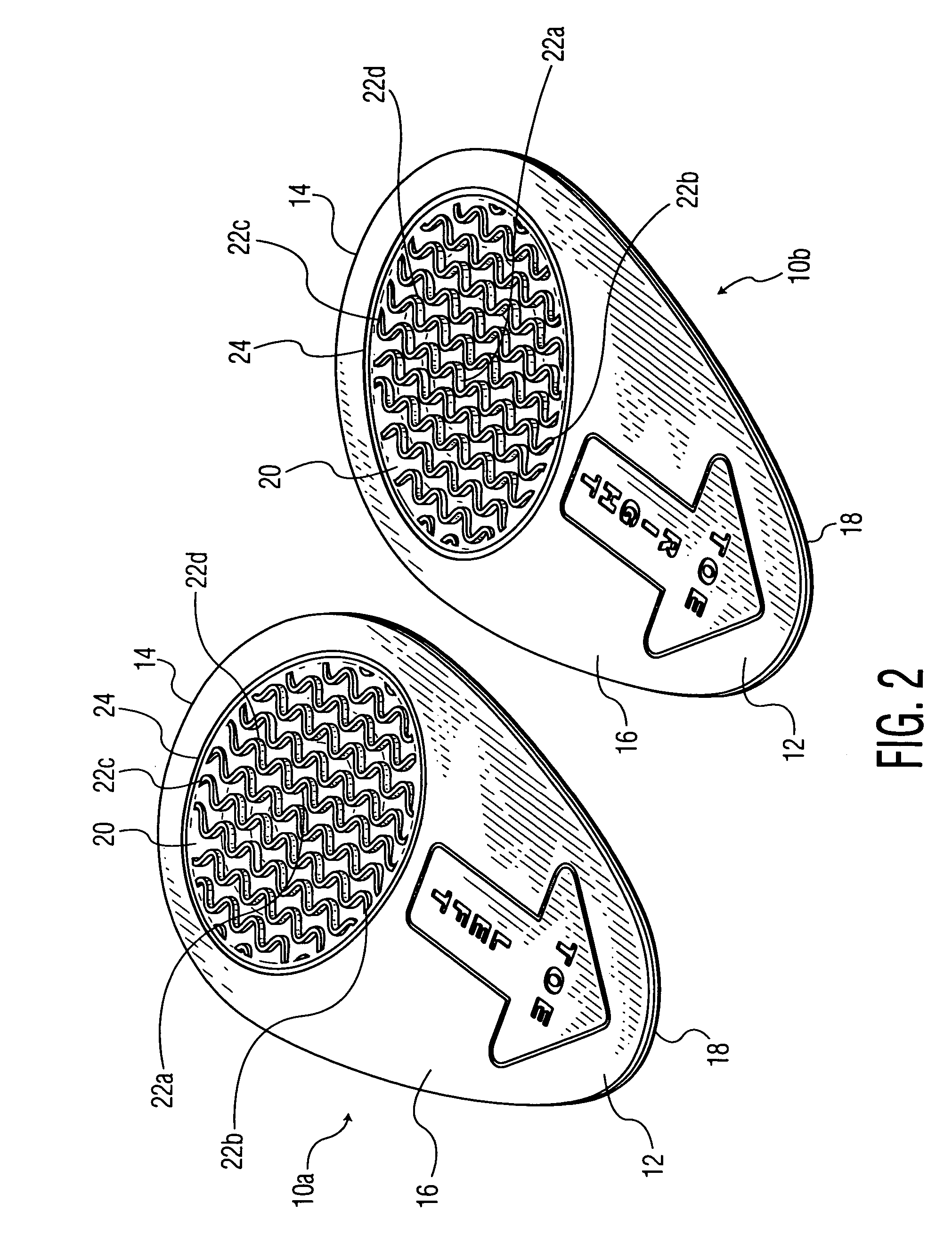
Ball of foot shoe inserts
Owner:MSD CONSUMER CARE INC
Player action incentive arrangement for gaming systems
ActiveUS7314411B2Fast playUndesirable delayApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesEngineeringGame play
A processing device measures the time it takes for a player to take some action in a game and bases the award or result in the game for the player at least in part on that measured time. A player receives a more desirable result or outcome for a particular game play in response to a shorter player action time and / or receives a less desirable result or outcome for a particular game play in response to a longer player action time. Providing more desirable results for shorter player action times or less desirable results for longer player action times provides players an incentive that influences them to take the appropriate player actions more quickly.
Owner:EVERI GAMES
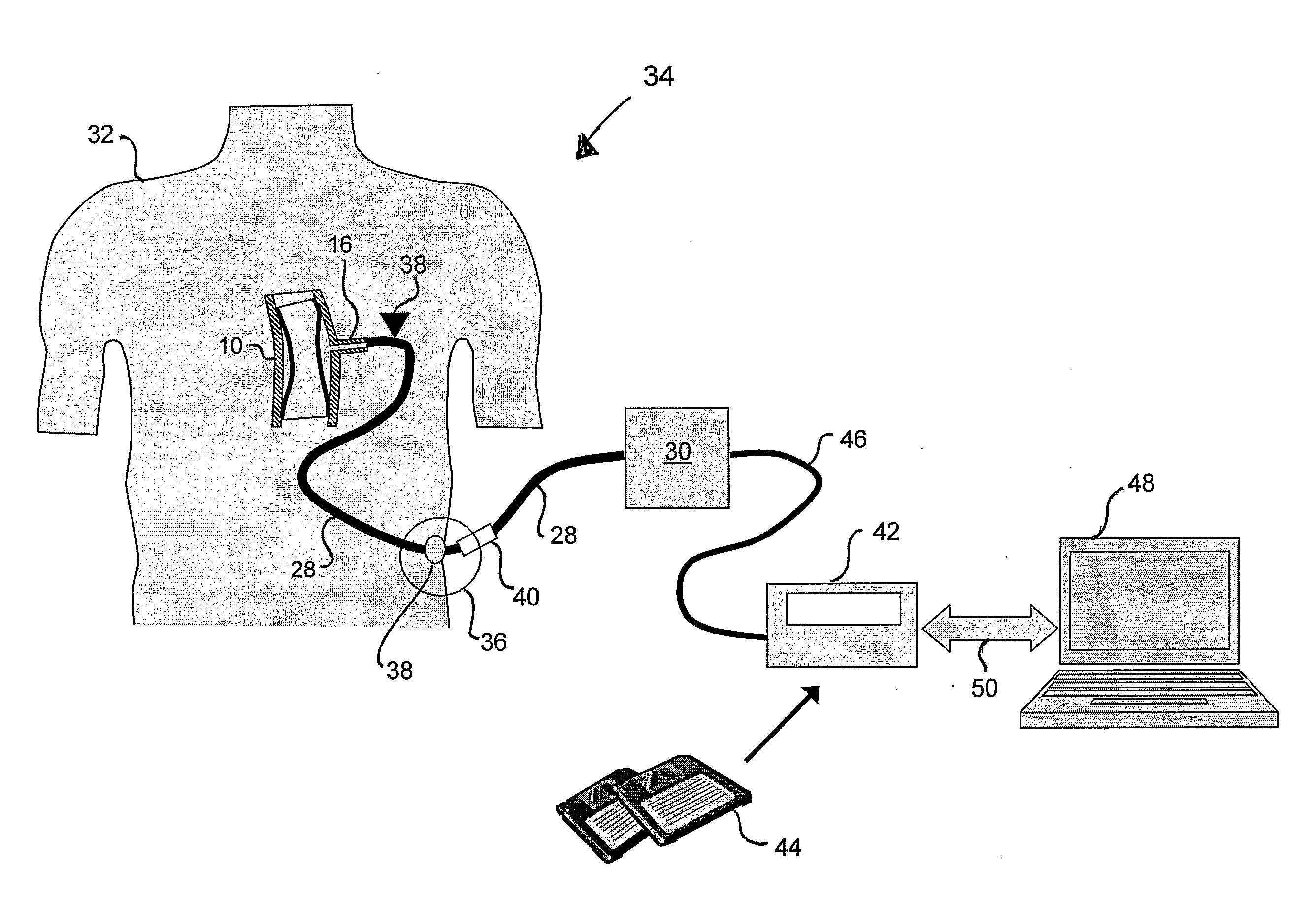
Pulsatile blood pump
InactiveUS20100204539A1Reduce workloadIncrease perfusionControl devicesBlood pumpsMembrane configurationPump blood
There is provided a pulsatile blood pump (10) for implantation into a patient. The pulsatile blood pump comprises a substantially tubular body (12) a flexible membrane (14) and a port (16). The substantially tubular body is for replacing a resected portion of a blood vessel of the patient. The substantially tubular body has first and second ends with a blood passageway extending therebetween for the passage of blood. The flexible membrane is attached to the tubular body so as to form a fluid chamber between the flexible membrane and an inner surface of the tubular body. The flexible membrane thereby separates the fluid chamber from the blood passageway. The tubular body comprises the port. The port is arranged to allow fluid to flow into and out of the fluid chamber such that the volume of the fluid chamber increases and the volume of the blood passageway decreases when fluid flows into the fluid chamber via the port, and such that the volume of the fluid chamber decreases and the volume of the blood passageway increases when fluid flows out of the fluid chamber via the port. The blood pump is thereby enabled to pump blood along the blood passageway.
Owner:NOTTINGHAM UNIV HOSPITALS NHS TRUST
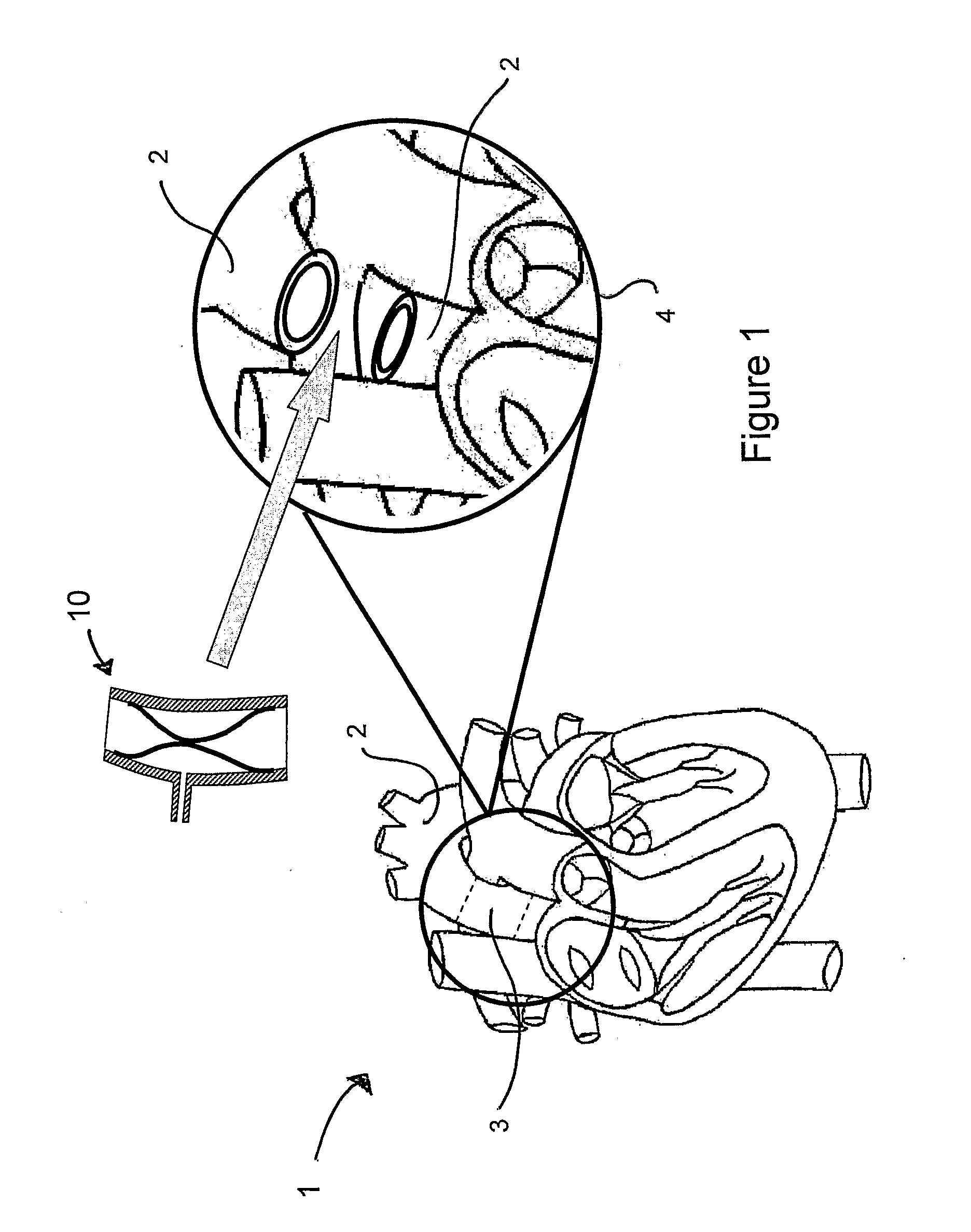
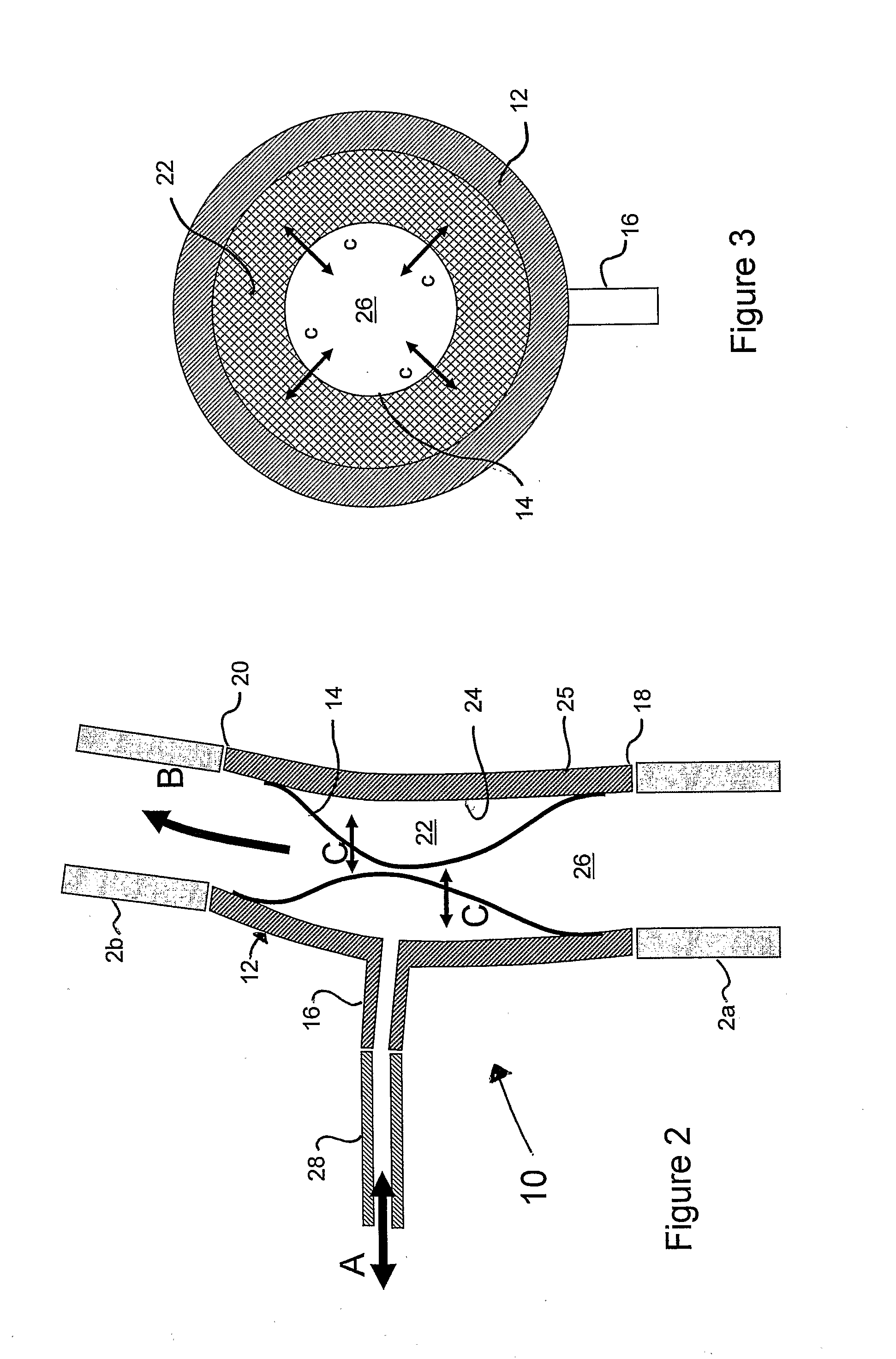
Rapid Acting and Long Acting Insulin Combination Formulations
InactiveUS20080039365A1Promote absorptionAct quicklyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBefore BreakfastIntensive insulinotherapy
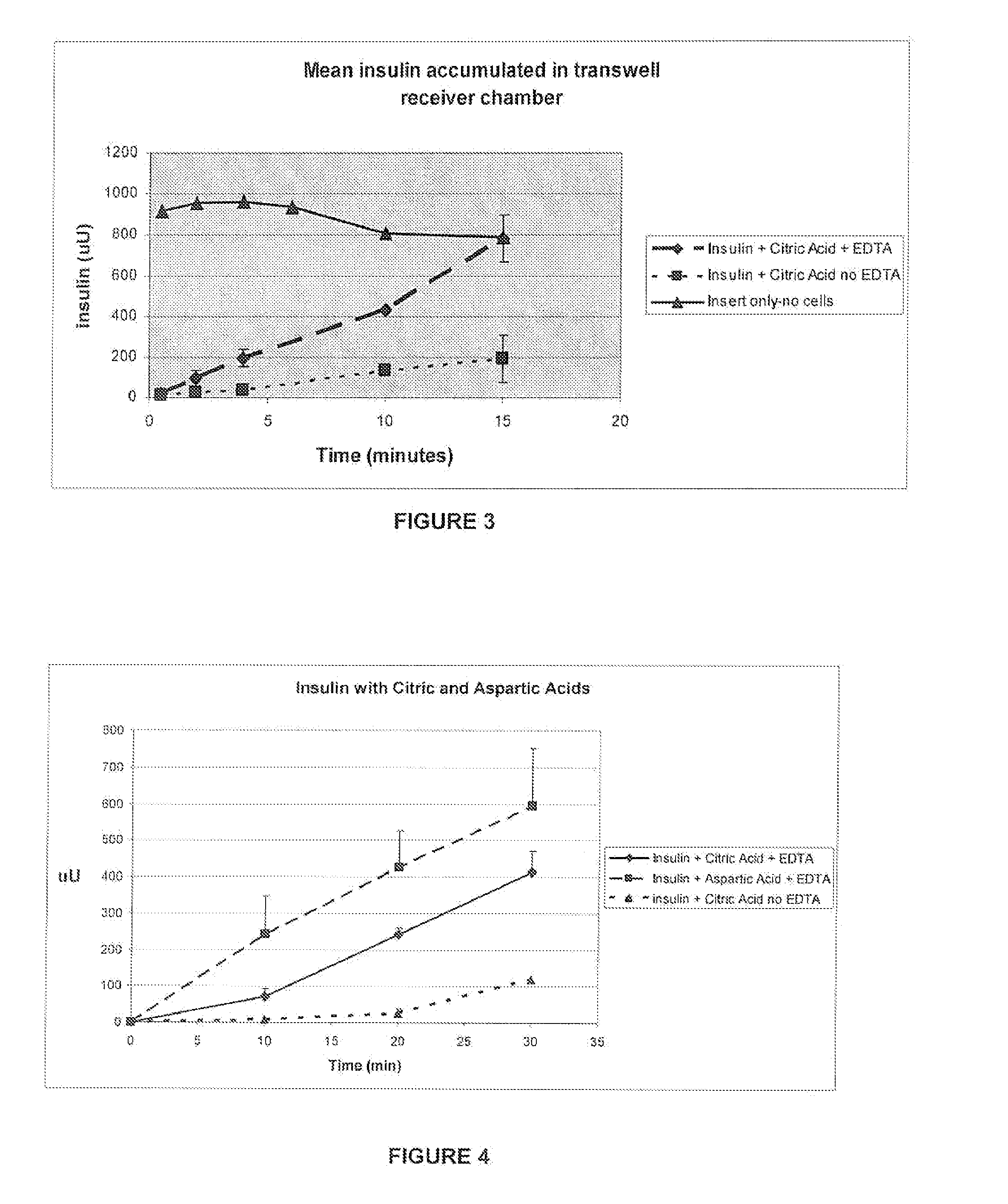
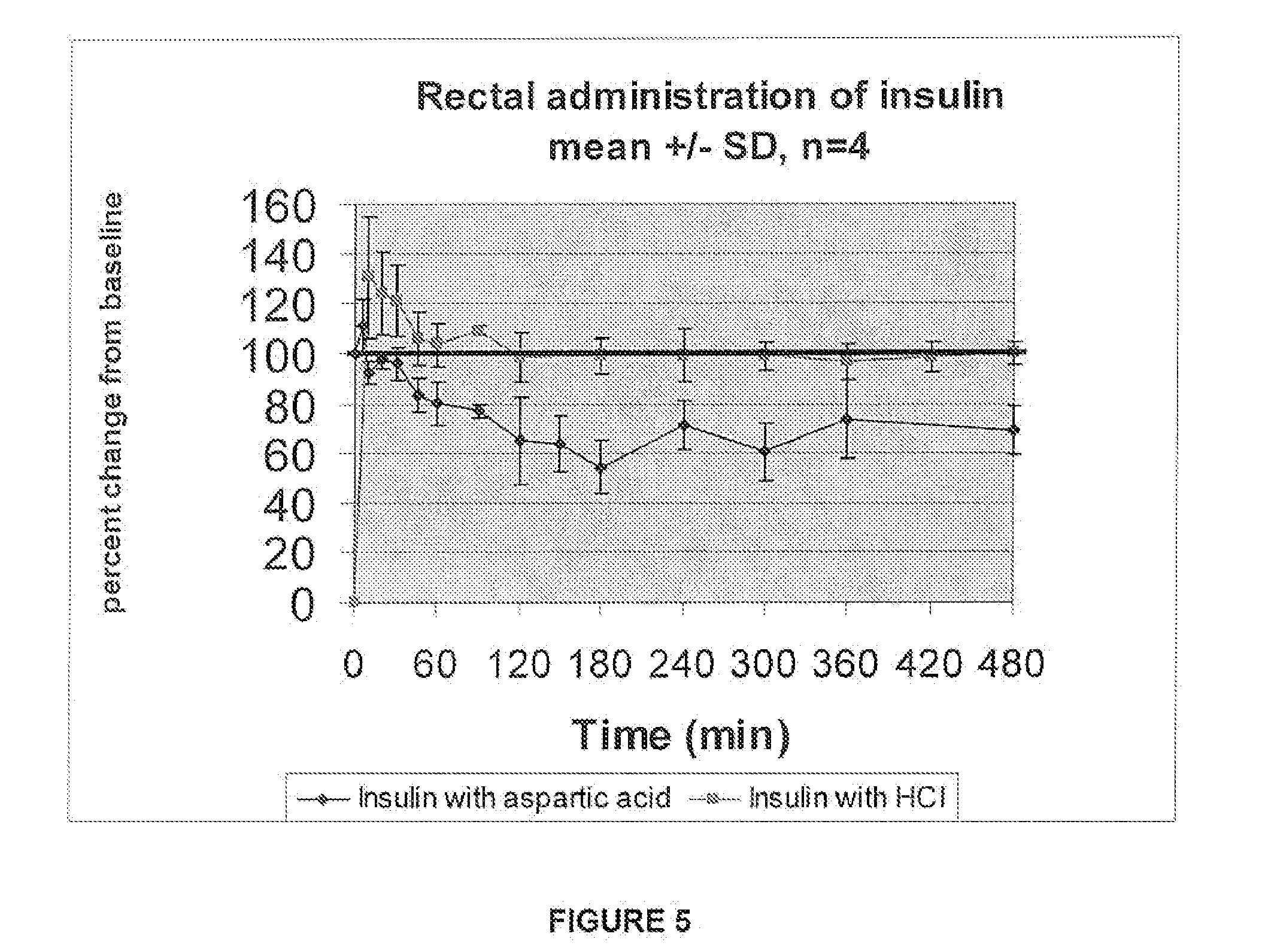
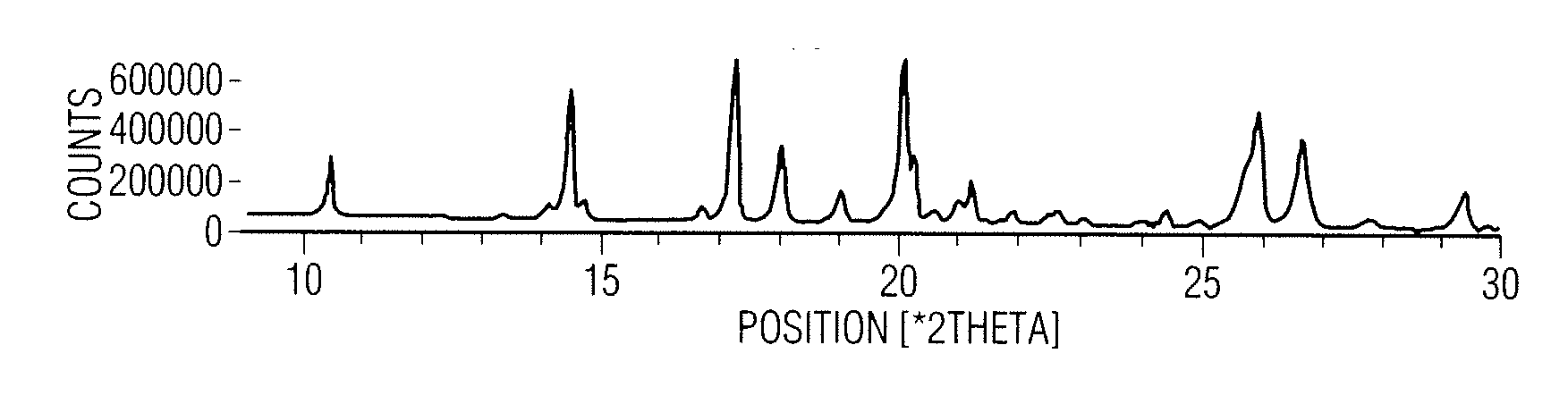
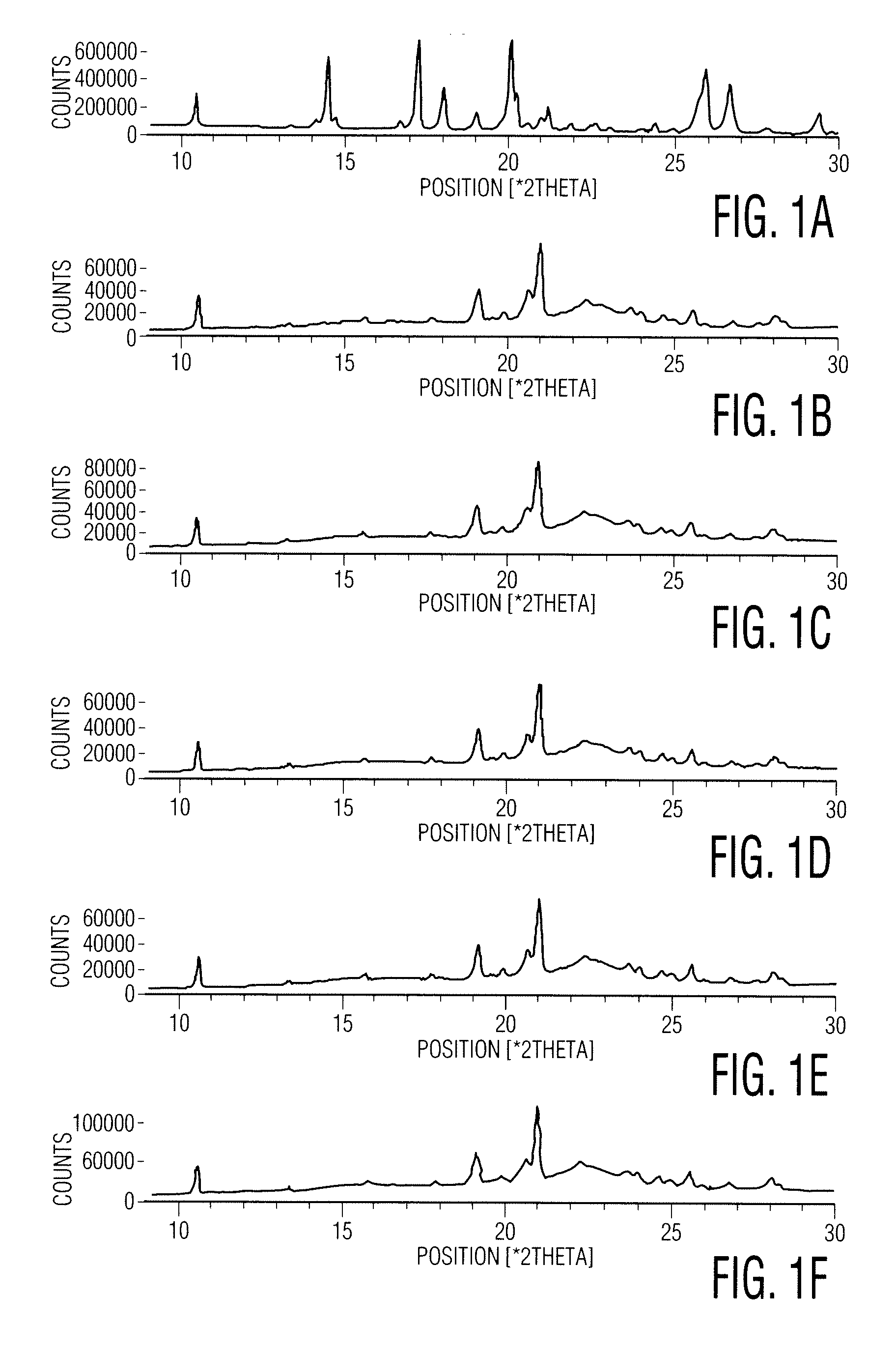
A combined rapid acting-long acting insulin formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the rapid acting insulin is decreased so that the long acting glargine remains soluble when they are mixed together. In the preferred embodiment, this injectable basal bolus insulin is administered before breakfast, provides adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, does not produce hypoglycemia after the meal and provides adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of a fast acting, or a rapid acting or a very rapid acting insulin. As a result, a patient using intensive insulin therapy should only inject three, rather than four, times a day. Experiments have been performed to demonstrate the importance of the addition of specific acids to hexameric insulin to enhance speed and amount of absorption and preserve bioactivity following dissociation into the monomeric form by addition of a chelator such as EDTA. As shown by the examples, the preferred acids are aspartic, glutamic and citric acid. These are added in addition to a chelator, preferably ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). The results show that the citric acid formulation was more effective at dropping the blood glucose rapidly than the identical rapid acting formulation prepared with HCl in swine. Charge masking by the polyacid appears to be responsible for rapid insulin absorption. EDTA was not effective when used with adipic acid, oxalic acid or HCl at hastening the absorption of insulin. These results confirm the results seen in clinical subjects and patients with diabetes treated with the rapid acting insulin in combination with citric acid and EDTA.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Non-benzodiazepine hypnotic compositions
InactiveUS20070098788A1Quick releaseAct quicklyPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsImmediate releaseEnantiomer
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising non-benzodiazepine hypnotic drugs or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, enantiomers or mixtures and processes for preparing the same. The invention also includes immediate release and extended release pharmaceutical compositions comprising non-benzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, useful for sleep induction and sleep maintenance.
Owner:DR REDDYS LAB LTD +1
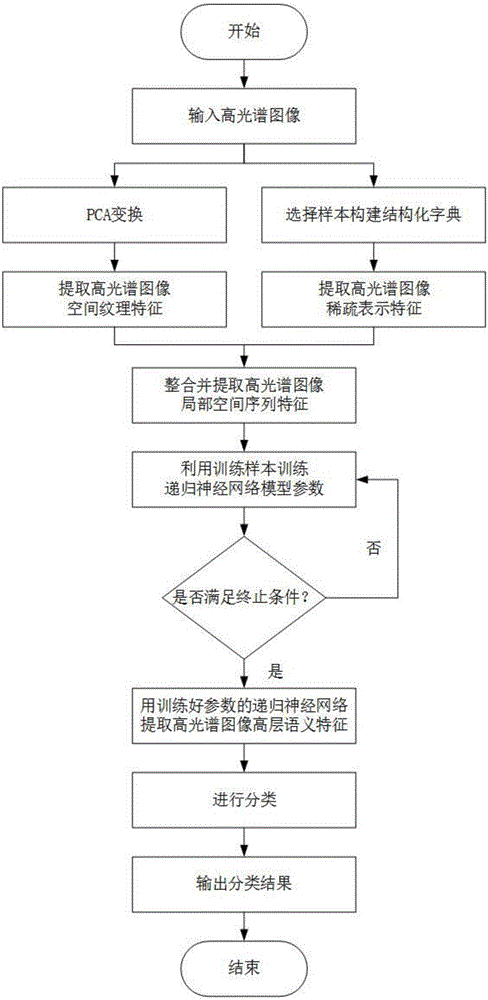
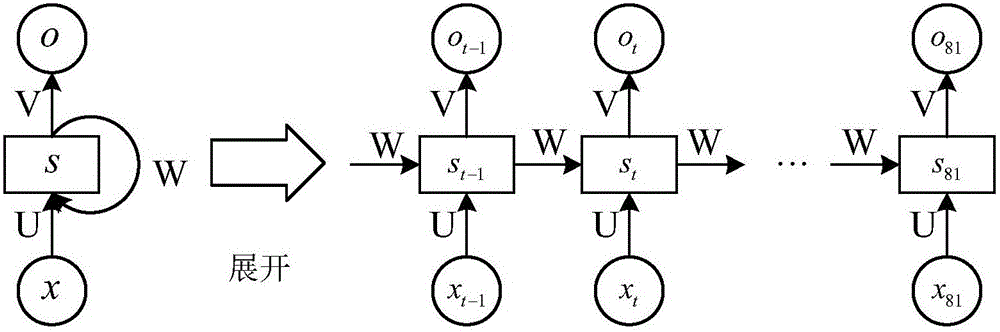
Hyper-spectral image classification method based on recurrent neural network
ActiveCN106815601AImprove purityImprove discrimination abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDisaster monitoringClassification methods
The invention discloses a hyper-spectral image classification method based on recurrent neural network with the object to solving the problems that in prior art, the input characteristic determination ability is weak and that the extraction of local spatial characteristics is not complete. The method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting the spatial texture characteristics and the sparse representation characteristics of a hyper-spectral image and piling and combining them as the low-level characteristics; 2) extracting from the low-level characteristics the sample local spatial sequence characteristics; 3) according to the local spatial sequence characteristics, creating a recurrent neural network model; and utilizing the training sample local spatial sequence characteristics to train the recurrent neural network model parameters; and 4) inputting the testing sample local spatial sequence characteristics into the well-trained recurrent neural network model; obtaining the highly abstract high-level semantic characteristics and obtaining the classification information of the testing sample. According to the deep learning method of the invention, the correct efficiency for hyper-spectral image classification is increased and the method can be used for vegetation investigation, disaster monitoring, map making and intelligence obtaining.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Solar energy powered electric vehicle
InactiveUS6021862AEasy to switchIncrease supplyPropulsion by humans/animalsVehicle transmissionElectrical batteryCold weather
A tricycle is driven by an electric motor supplied by batteries recharged by solar panels. Electric braking is used. The batteries and a battery charger are enclosed in a thermally insulated compartment and the batteries are kept warm in cold weather by the heat produced by the battery charger and by electric braking. The solar panels are mounted on the roof of the passenger cabin and / or on the insulated compartment and are oriented towards the sun by a stepper motor.
Owner:SHARAN ANAND M
Filter closure system with bayonet closure
InactiveUS20090242470A1Simple methodAvoid misuseDispersed particle filtrationSedimentation separationBiomedical engineering
A filter closure system has a connecting end at an end face of a cylindrical filter housing and a connecting head matching the connecting end. The connecting end is insertable axially into the connecting head and connected positive-lockingly to the connecting head by an insertion-rotation movement. Connecting end and connecting head have a bayonet connection with receiving slots or receiving projections and matching insertion projections. The matching insertion projections engage the receiving slots or projections when the bayonet connection is closed. The receiving slots or projections and the insertion projections each are arranged substantially in a perpendicular plane relative to the insertion direction. The receiving slots or projections are elongate and circumferentially do not extend completely around but are segmented. The receiving slots or projections are sequentially arranged in the insertion direction and are substantially parallel to one another. The insertion projections are also sequentially arranged in the insertion direction.
Owner:MANN HUMMEL GMBH
Antimicrobial cidality formulations with residual efficacy, uses thereof, and the preparation thereof
InactiveUS20090074881A1Easy to manufactureEasy to prepareBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsMicroorganismDistilled water
The present invention is a quick-kill formulation that is able to kill organisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, mold, spore-forming bacteria and combinations thereof. In addition, the formulation contains a residual kill component that is effective for at least one day. The unique formulation is effective without being corrosive. This is an advantage that allows it to be used in a wide range of applications, one application being in the medical field for sterilizing instruments. Another improvement of this formulation over the prior art is that it is stabilized such that, unlike prior art formulations, tap water, as opposed to distilled water, may be used in its manufacture.
Owner:YCLEAN ENTERPRISES LLC
Intranasal administration of ketamine to treat depression
ActiveUS8785500B2Minor adverse side effectAct quicklyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsEnteral administrationKetamine
Methods and compositions for the treatment of treatment-resistant depression are described. More specifically, the invention demonstrates that intranasal administration of ketamine is effective to ameliorate the symptoms of depression in a patient who has not responded to an adequate trial of one antidepressant in the current episode and has recurrent or chronic depressive symptoms (>2 years).
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +3
Traditional Chinese medicine solid type mixed culture fermentation tech. and its application
The invention discloses a Chinese drugs multi-bacterium species mixture solid fermenting method and its application. It is made up from crushing the Chinese drugs, filtering, adjusting water content and pH value, adding bean pulp, bran, and inorganic salt, sterilization, cooling and adding bacterium species fermenting liquid to take ferment, and drying. The invention could be used to make drugs and feed additive that has antibiotic, antivirus and growth improvement functions. The invention has the features of simple process method, and improving the growth benefit bacterium.
Owner:NANJING SBEED BIOTECH +1
Method for preparing active calcium carbonate
InactiveCN101967309AImprove hydrophobicityReduce reunionPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsPigment treatment with non-polymer organic compoundsAdhesiveFatty acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing active calcium carbonate, which comprises the following steps of: adding 1 to 10 weight parts of one or a mixture of more of fatty acid and fatty acid salt and 0.05 to 5 weight parts of coupling agent into suspension containing 100 weight parts of calcium carbonate, and modifying at the temperature of between 60 and 90 DEG C for 0.5 to 5 hours to prepare the active calcium carbonate. The method has a simple preparation process and is stable in performance; and the surface of the prepared active calcium carbonate has the good hydrophobicity, is easy to disperse in rubber and resin, improves the combination property of polymers, and can be used in fields of the rubber, adhesives and the like.
Owner:山东海泽纳米材料有限公司
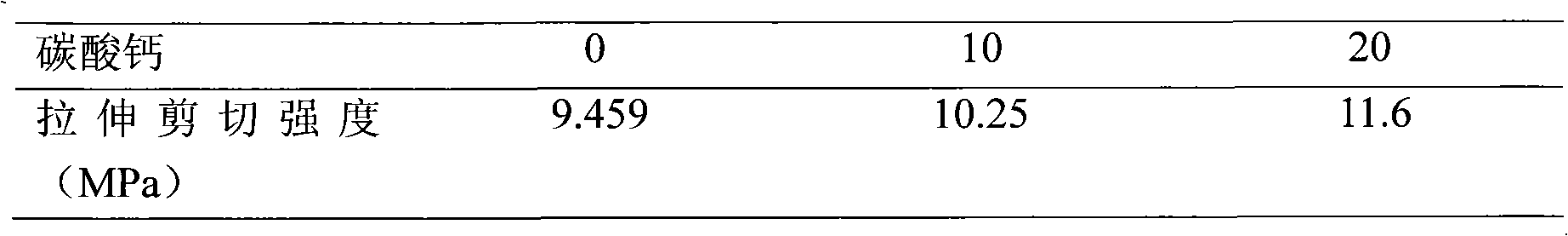
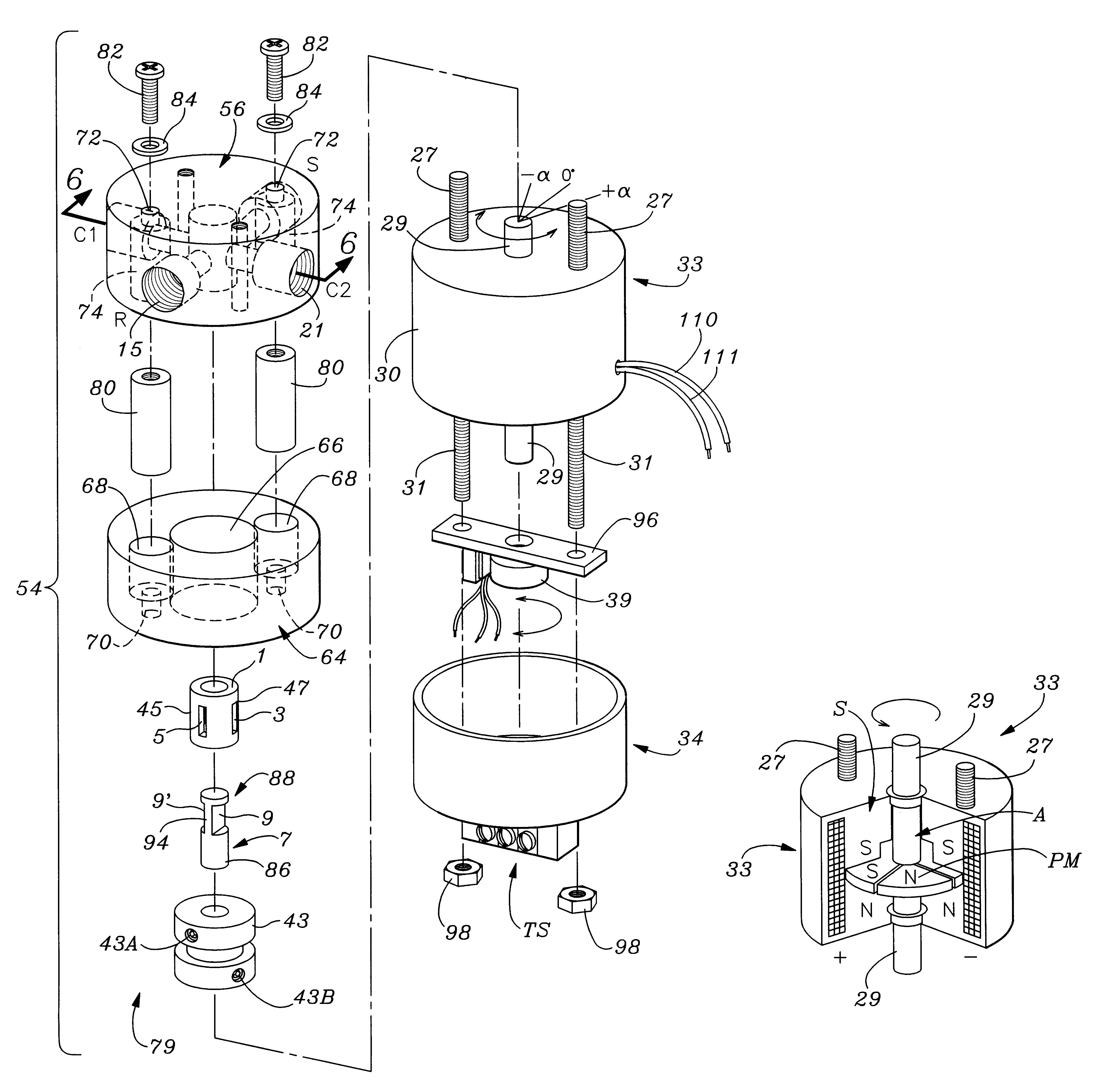
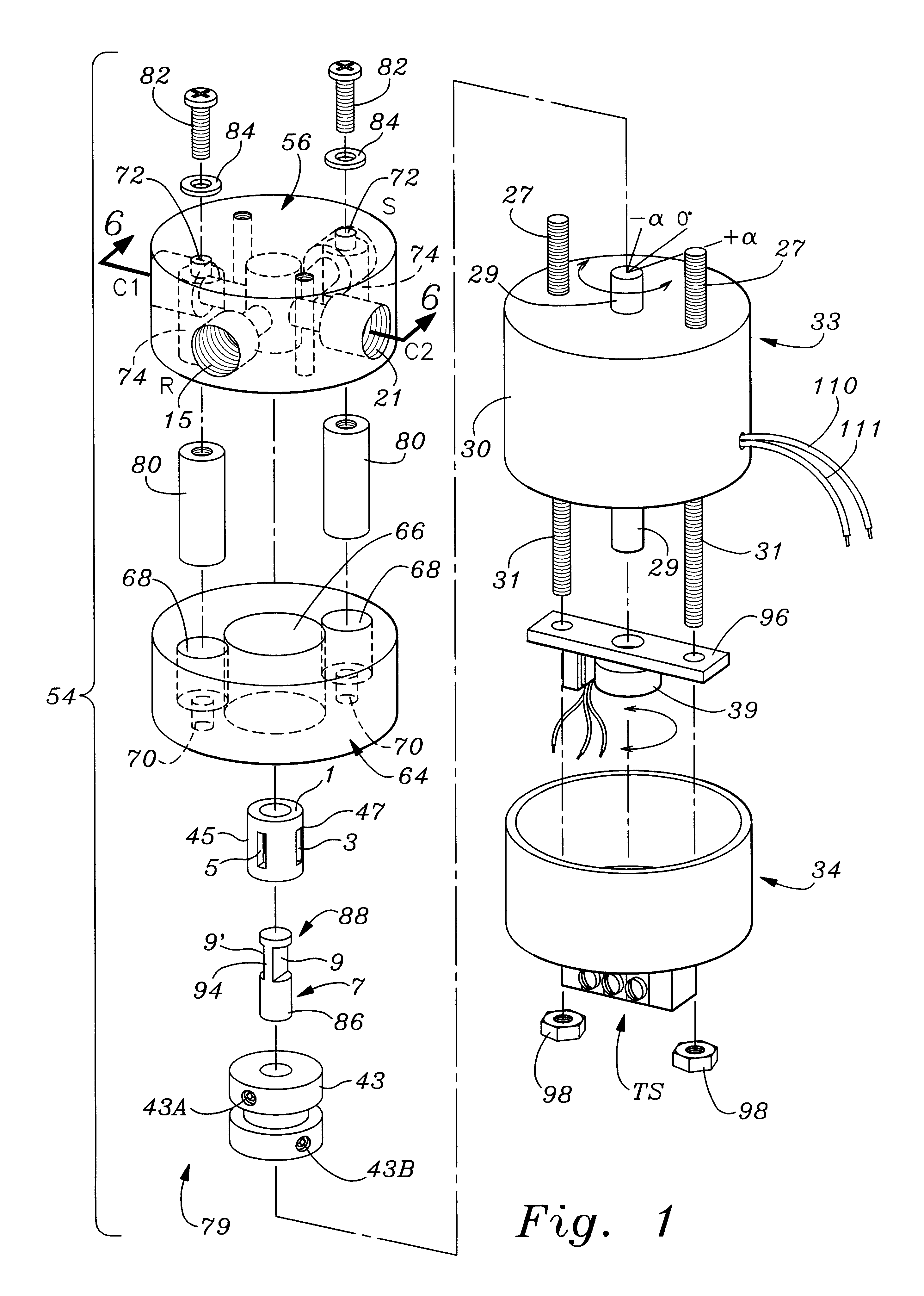
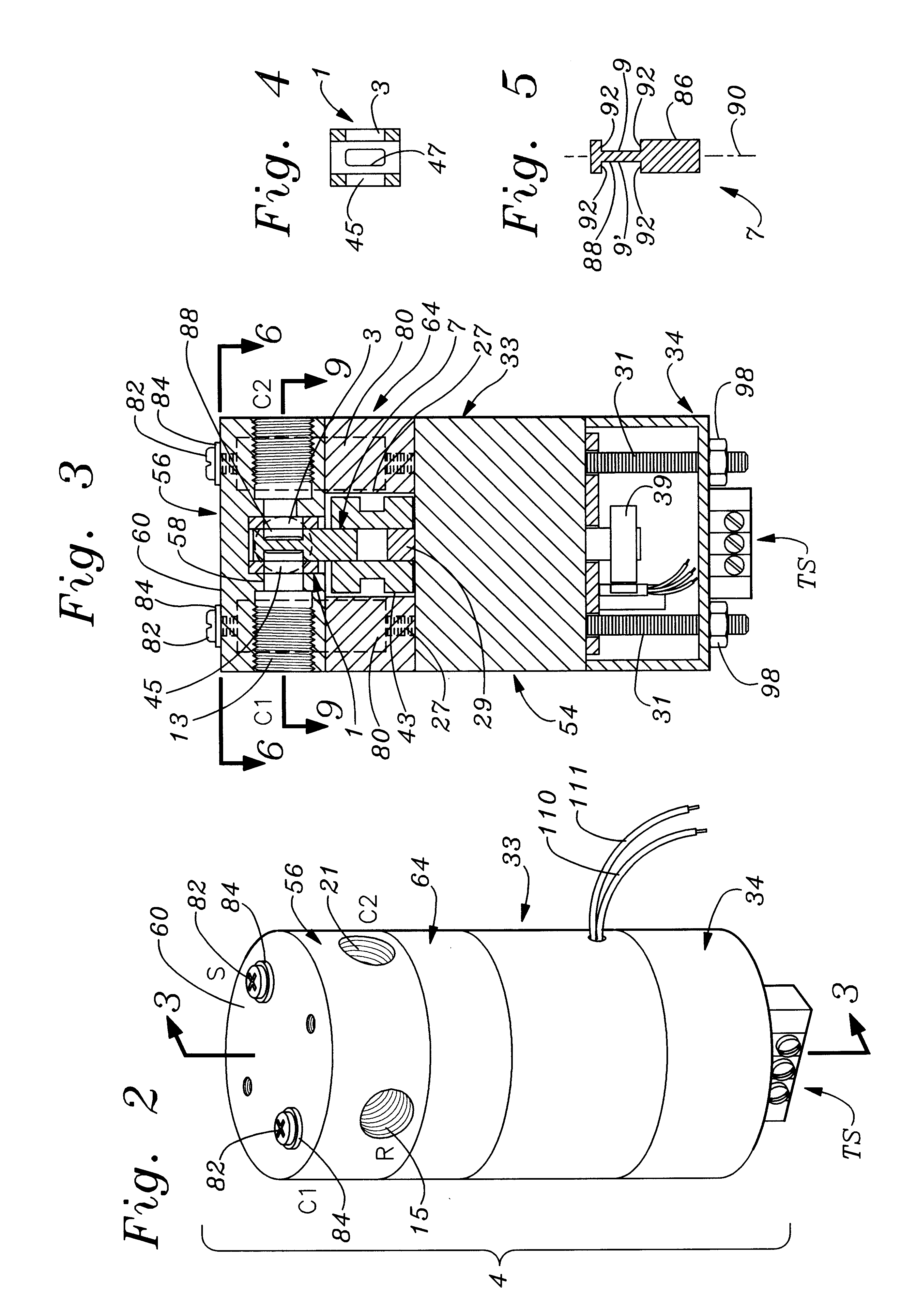
Rotary servovalve and control system
InactiveUS6269838B1Less torqueIncrease frequency bandwidth of responsivenessOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsFluid controlAngular rotation
An improved rotary servovalve system employs a rotary magnetic solenoid having an armature that includes at least one permanent magnet. The armature is rotatable relative to a stator formed as an electromagnet which is energizable to create alternative electromagnetic fields having opposite polarities from each other. When deenergized, the stator allows the armature to return to a neutral, null position from positions of extreme rotation in opposite angular directions due to the magnetic force of the permanent magnet of the armature. The armature is coupled to carry a movable valve element in angular rotation therewith, so that flow through the servovalve of the system can occur in alternative directions. Also, the valve element is biased toward a position in which all of the valve ports are closed when power is removed from the rotary solenoid. The control circuit employed in the rotary servovalve system expands the bandwidth of response of the solenoid actuator by compensating for frequency variations in the input command signal and in the feedback signal. This compensation is achieved utilizing a combined proportional, integral, and differential amplification circuit. Also, imbalance of fluid forces within the servovalve mechanism can be avoided by utilizing a pair of inlet orifices, a pair of outlet orifices, a pair of first fluid control orifices, and a pair of second fluid control orifices. The orifices within each pair are located on opposite sides of the valve housing from each other.
Owner:WOODWORTH RAYMOND DEXTER
Amylin Formulations
InactiveUS20090192075A1Reduce in quantityAct quicklyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderGLP-1 MimeticsBefore Breakfast
A combined insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic formulation has been developed wherein the pH of the insulin is decreased so that the amylin and / or GLP-1 remains soluble when mixed together with the insulin. In the preferred embodiment, a bolus insulin is administered by injection before breakfast, providing adequate bolus insulin levels to cover the meal, without producing hypoglycemia after the meal. This can be combined with an adequate basal insulin for 24 hours. Lunch and dinner can be covered by two bolus injections of the insulin and amylin and / or GLP-1 mimetic combination. A GLP-1 mimetic may be combined with either rapid acting or basal insulin formulations. As a result, a patient using the combination formulation therapy may only need to inject half as many times per day.
Owner:BIODEL INC
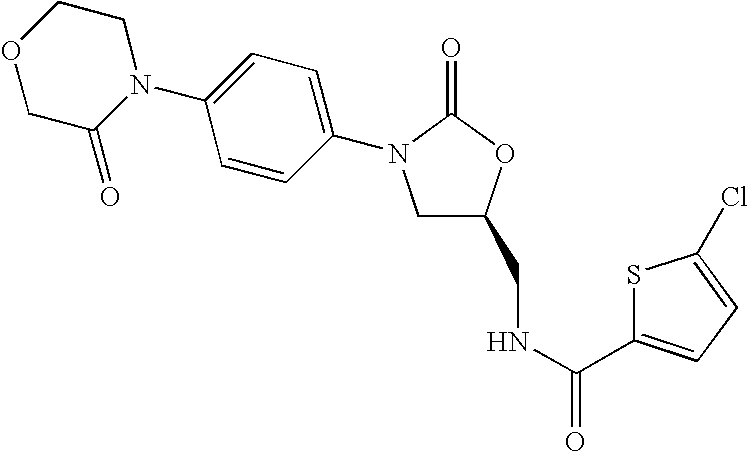
Substituted oxazolidinones and their use in the field of blood coagulation
InactiveUS20080090815A1Reduce bleeding riskEasy to adjustBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseOxazolidine E
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Topical compositions with long lasting effect
InactiveUS20080014252A1Lasting effectAvoid seizuresAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAdrenergic DrugsActive agent
Topical pharmaceutical formulations and compositions for transdermal delivery of a variety of active agents are described. The formulations and compositions are formulated to provide a long lasting effect of the agent being delivered. The formulations and compositions of the present invention contain a transdermal vehicle and an adrenergic drug. The formulations and compositions may also contain guaifenesin.
Owner:DELPRETE KEITH
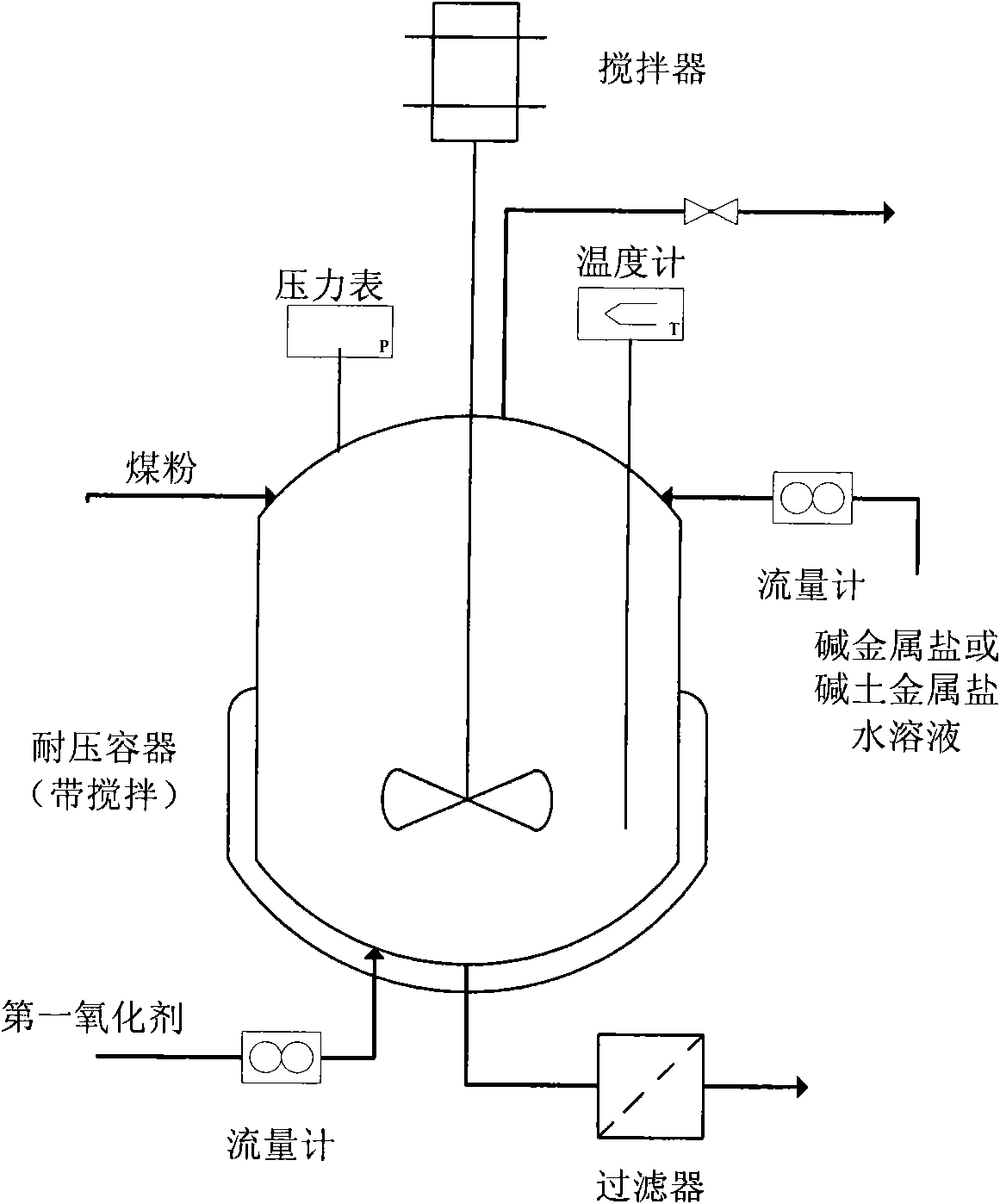
Method for preparing methane by catalyzing and gasifying coal
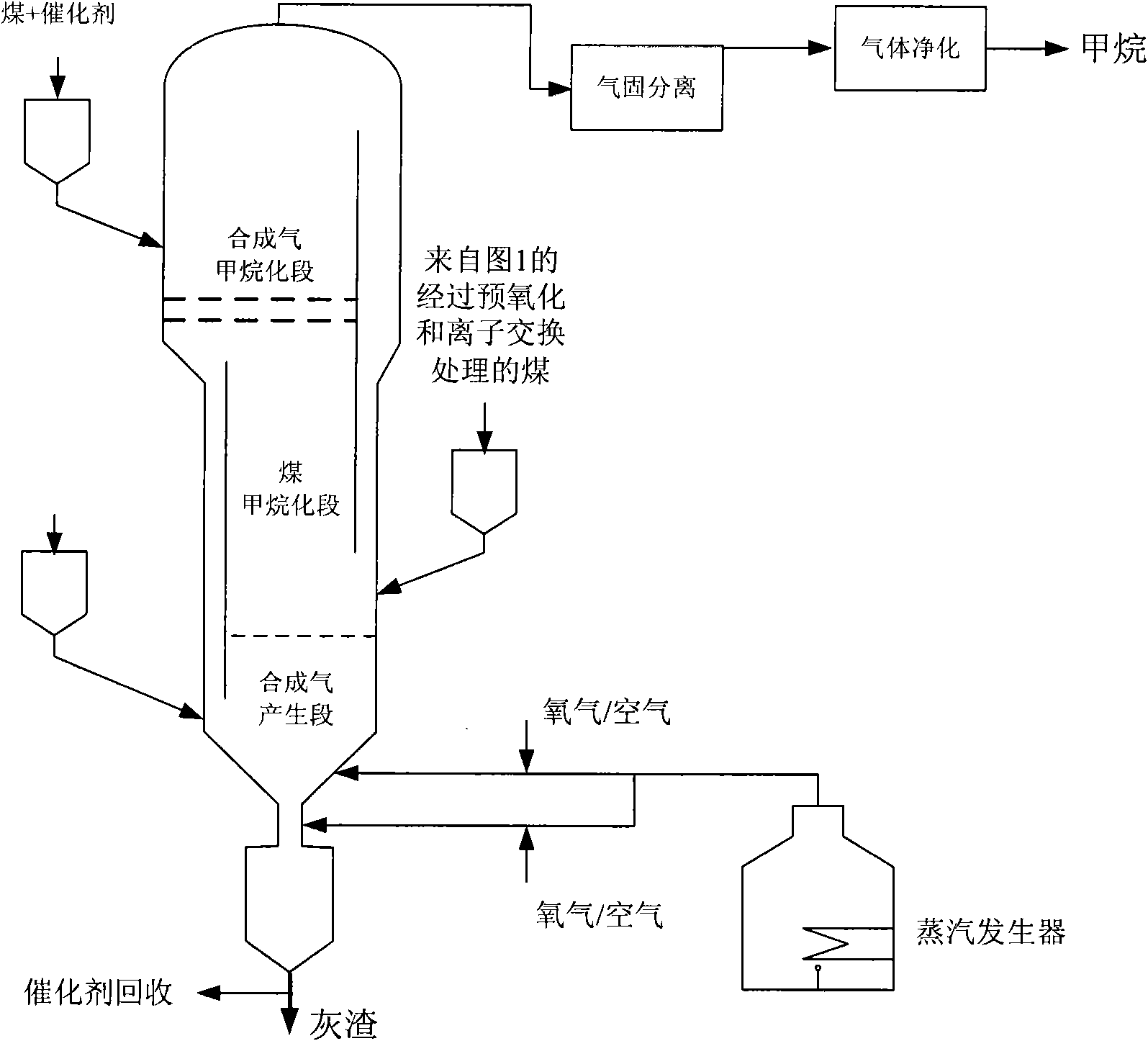
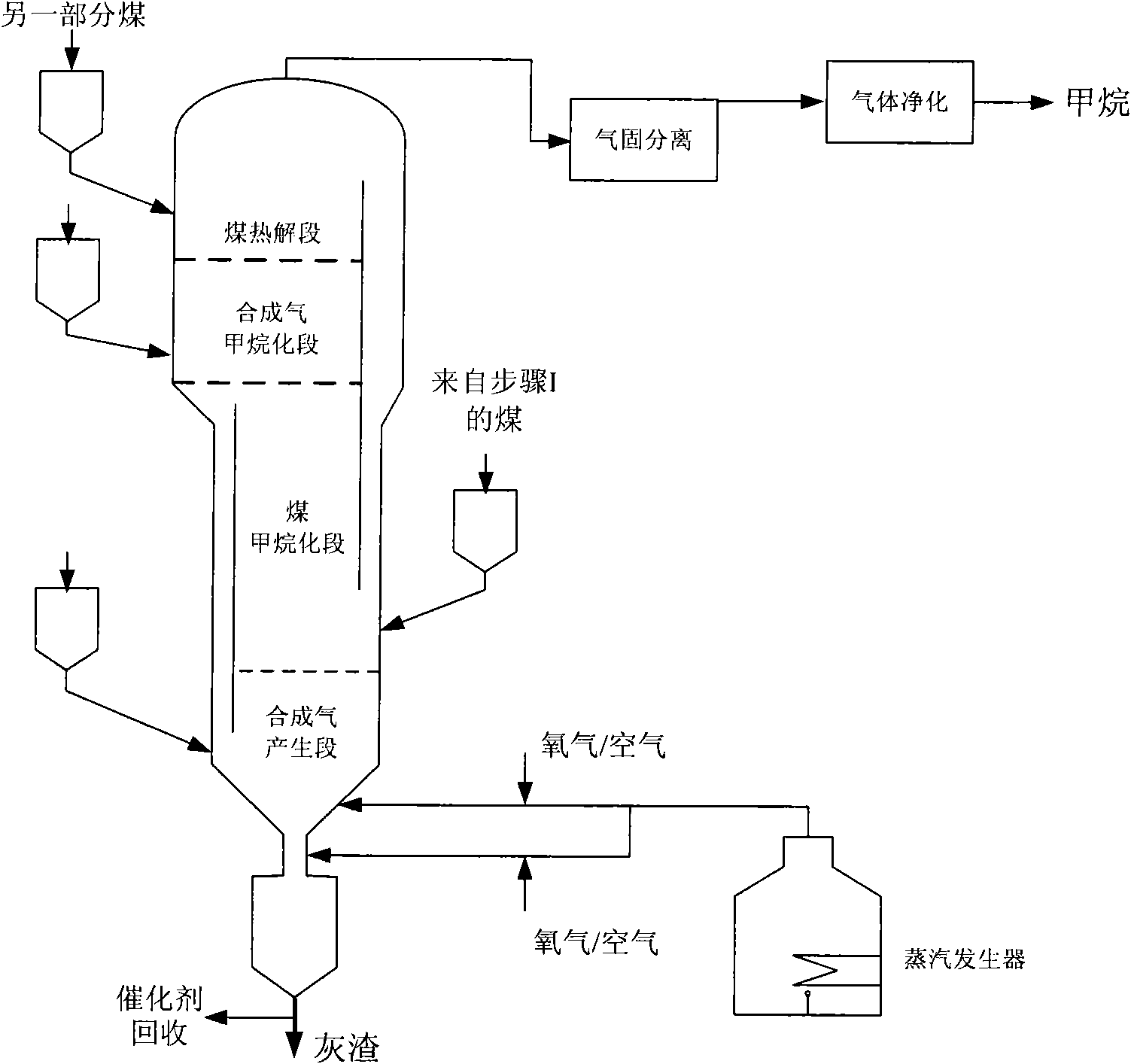
ActiveCN102465047AIncrease the amount of chemical bindingDoes not affect movement characteristicsHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesGaseous fuelsMethanationIon exchange
The invention relates to a method for preparing methane by catalyzing and gasifying coal. The method sequentially comprises the following two steps: 1, successively or simultaneously carrying out preoxidation and ion exchange treatment on coal in a slurry containing coal and water; and 2, gasifying the product obtained in step 1 by sending it to a gasification furnace which sequentially comprises a gas generation segment, a coal methanation segment, a synthetic gas methanation segment and an optional coal pyrolysis segment from bottom to top to obtain a gas product containing methane.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
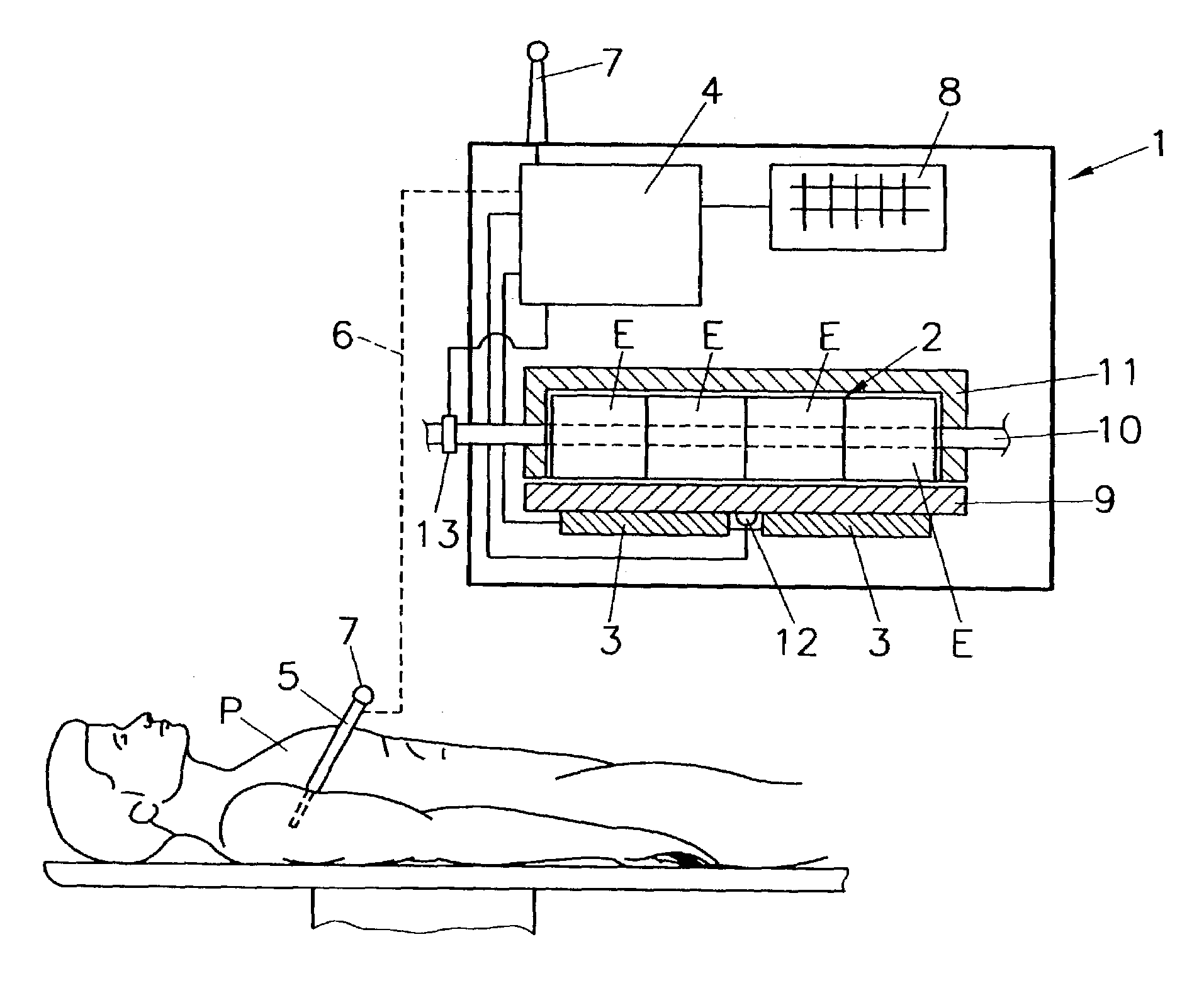
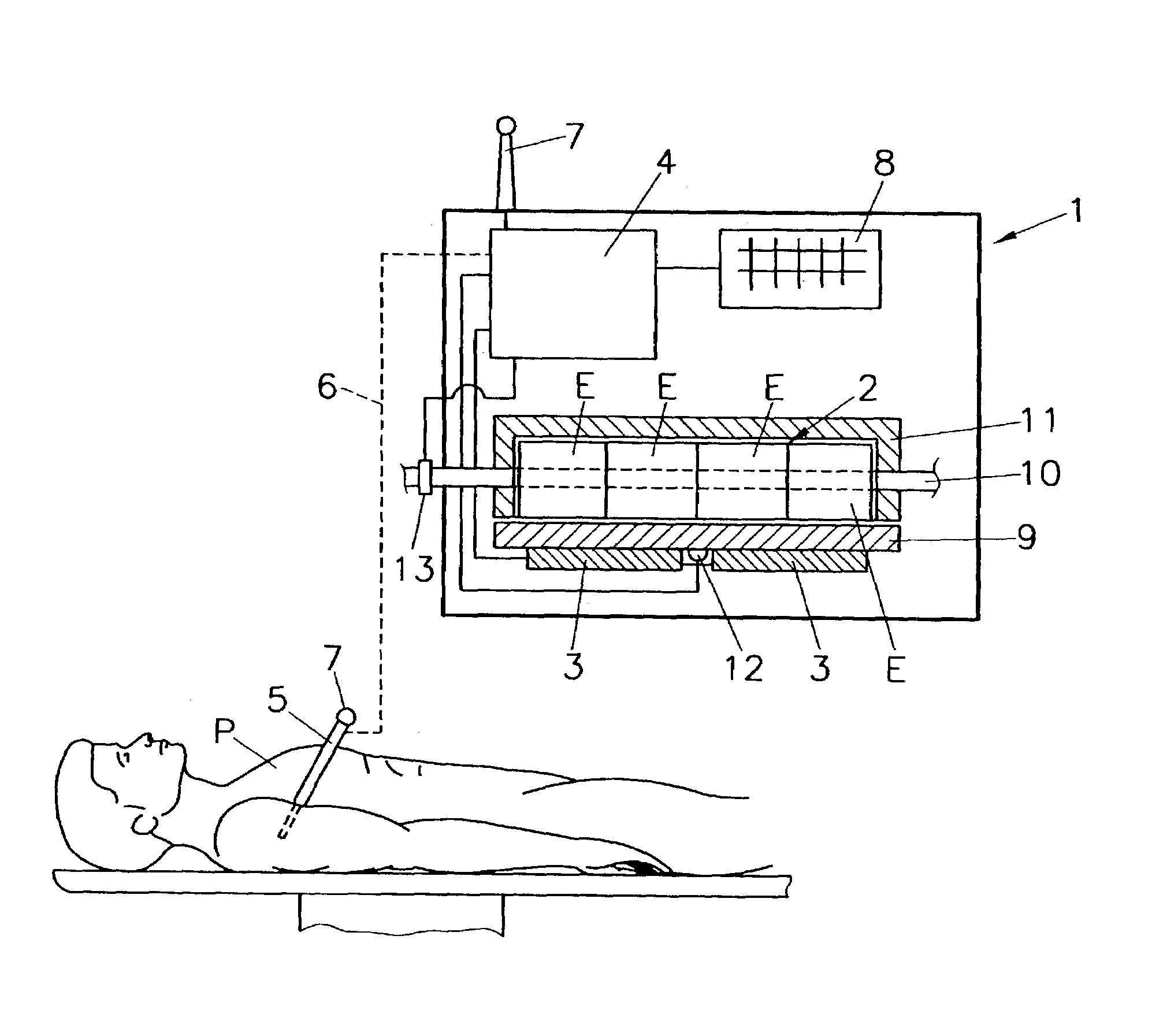
Method and device for measuring blood gas parameters
InactiveUS7491175B2Act quicklyAccurate valueMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMedicineBlood gas test
The invention relates to a method and device for measuring blood gas parameters, preferably pH, pCO2, and pO2, in a blood sample, where the blood sample of a patient is fed into at least one measuring cell of an analyzer. In order to obtain accurate values for the blood gas parameters even in cases where the temperature of the patient deviates from normal temperature, the temperature of the patient or blood sample is measured upon sample withdrawal, and the measured temperature is transmitted to the analyzer or is recorded by the analyzer, and the temperature of the measuring cell of the analyzer is adjusted to the measured temperature by cooling or heating.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com