Patents
Literature
97results about How to "Less torque" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
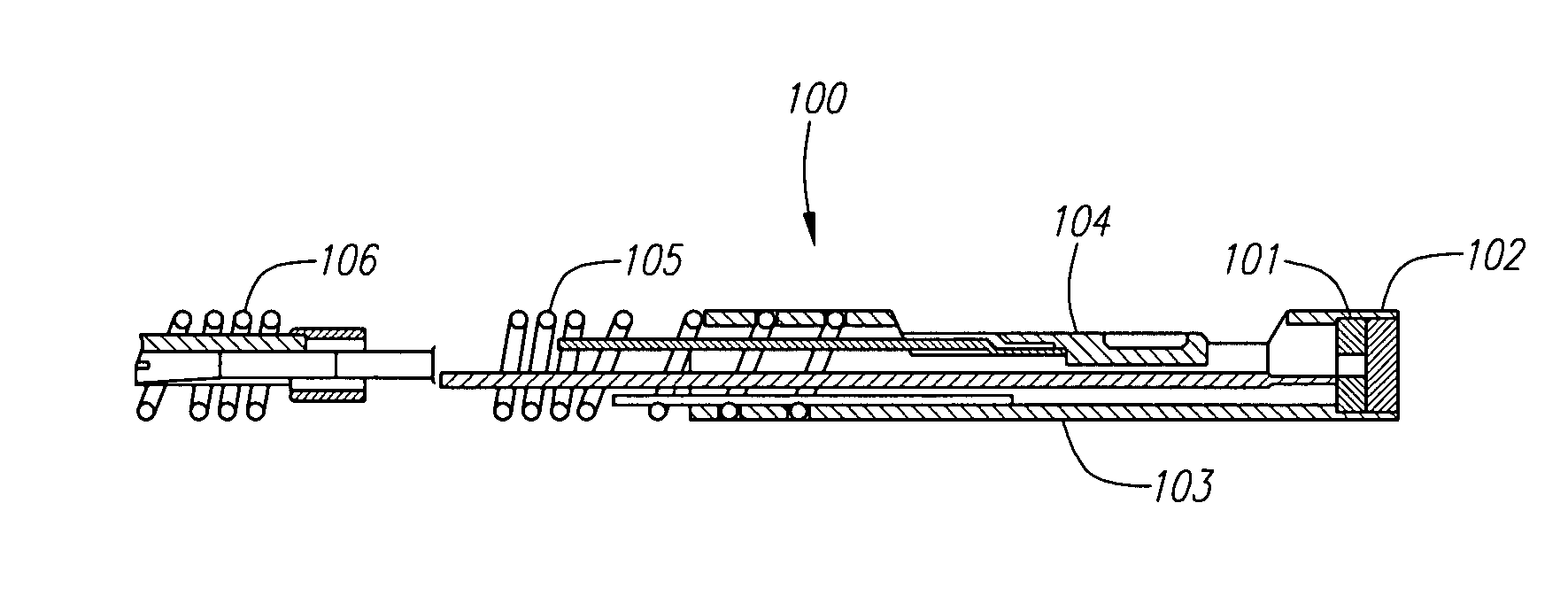
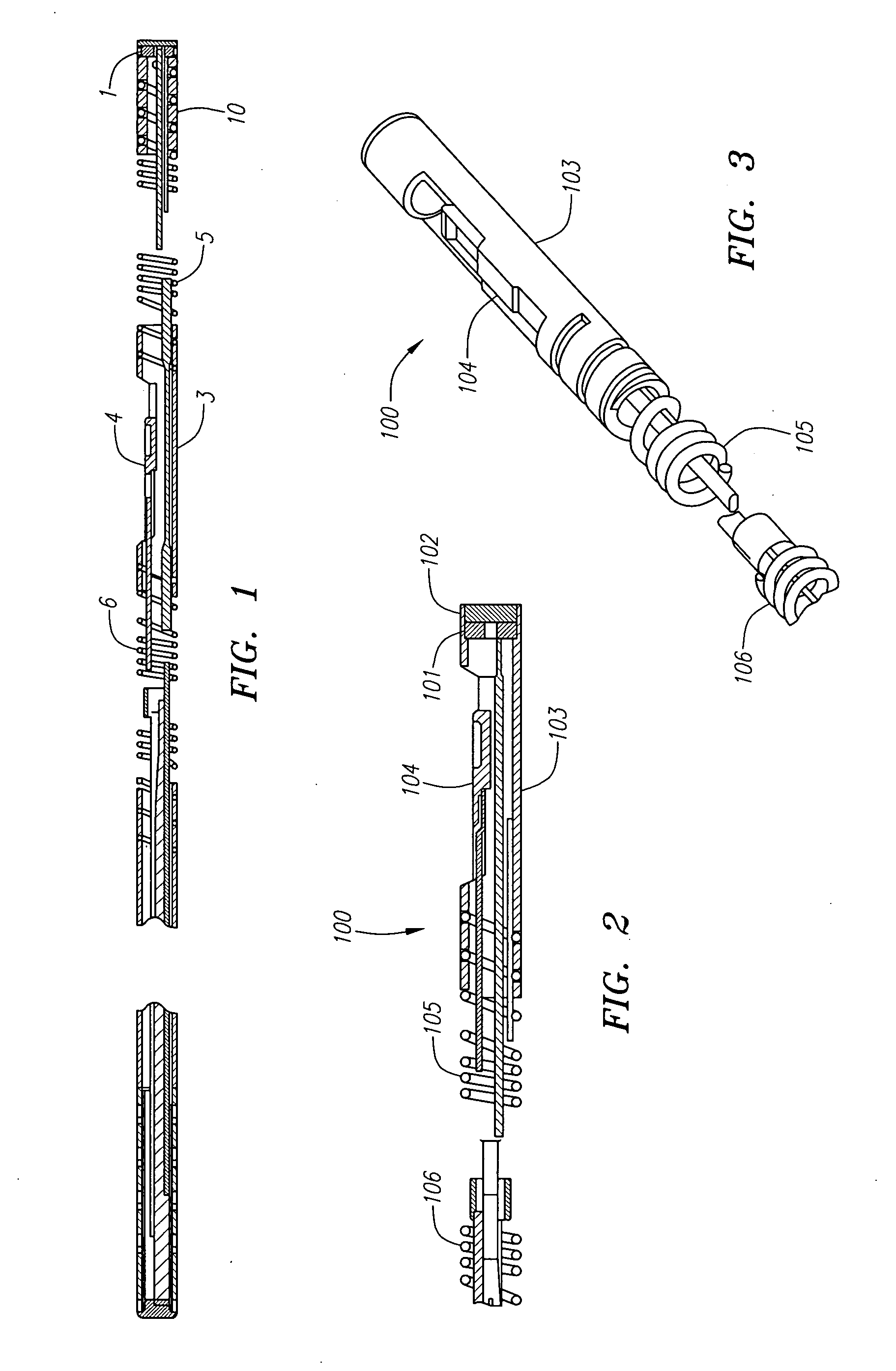
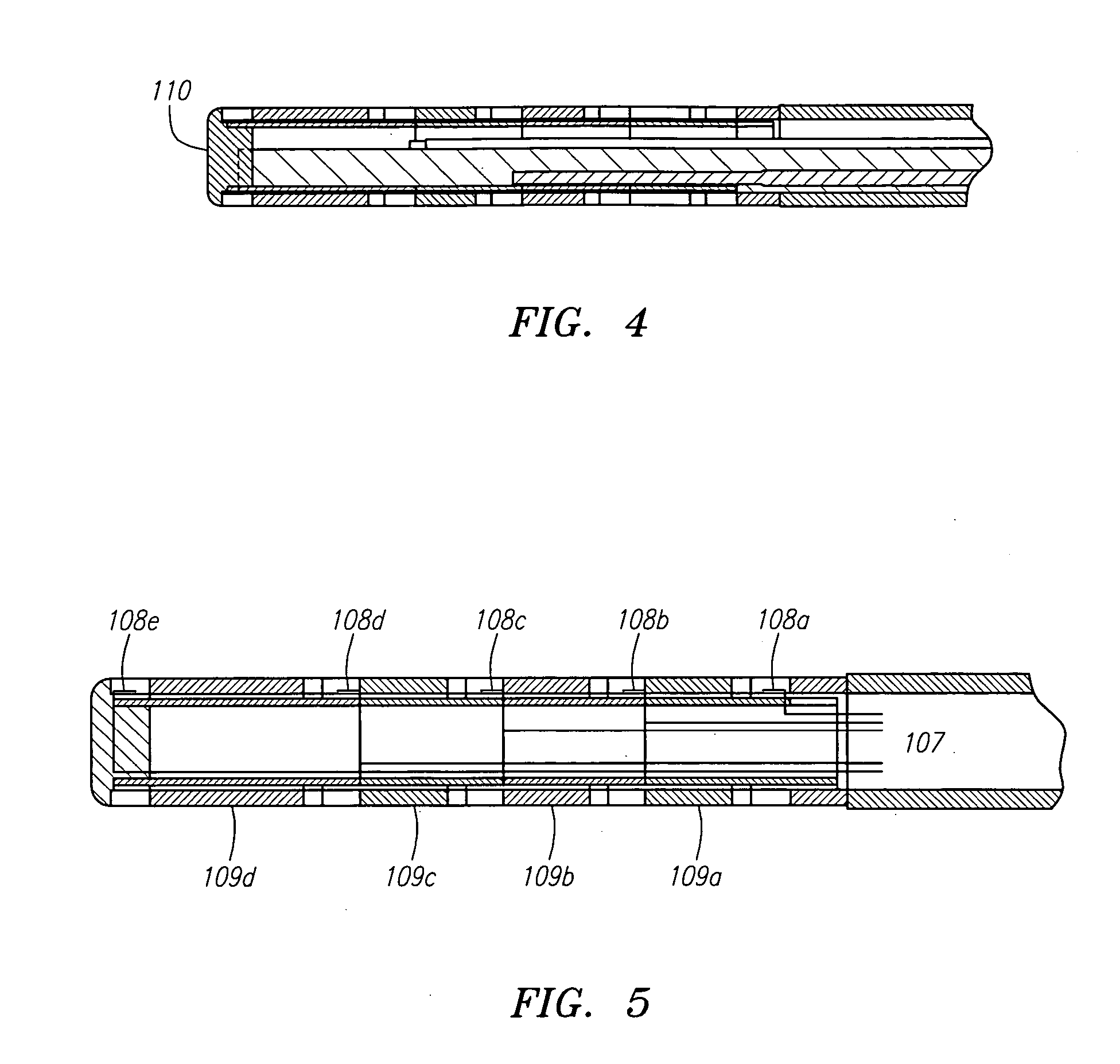
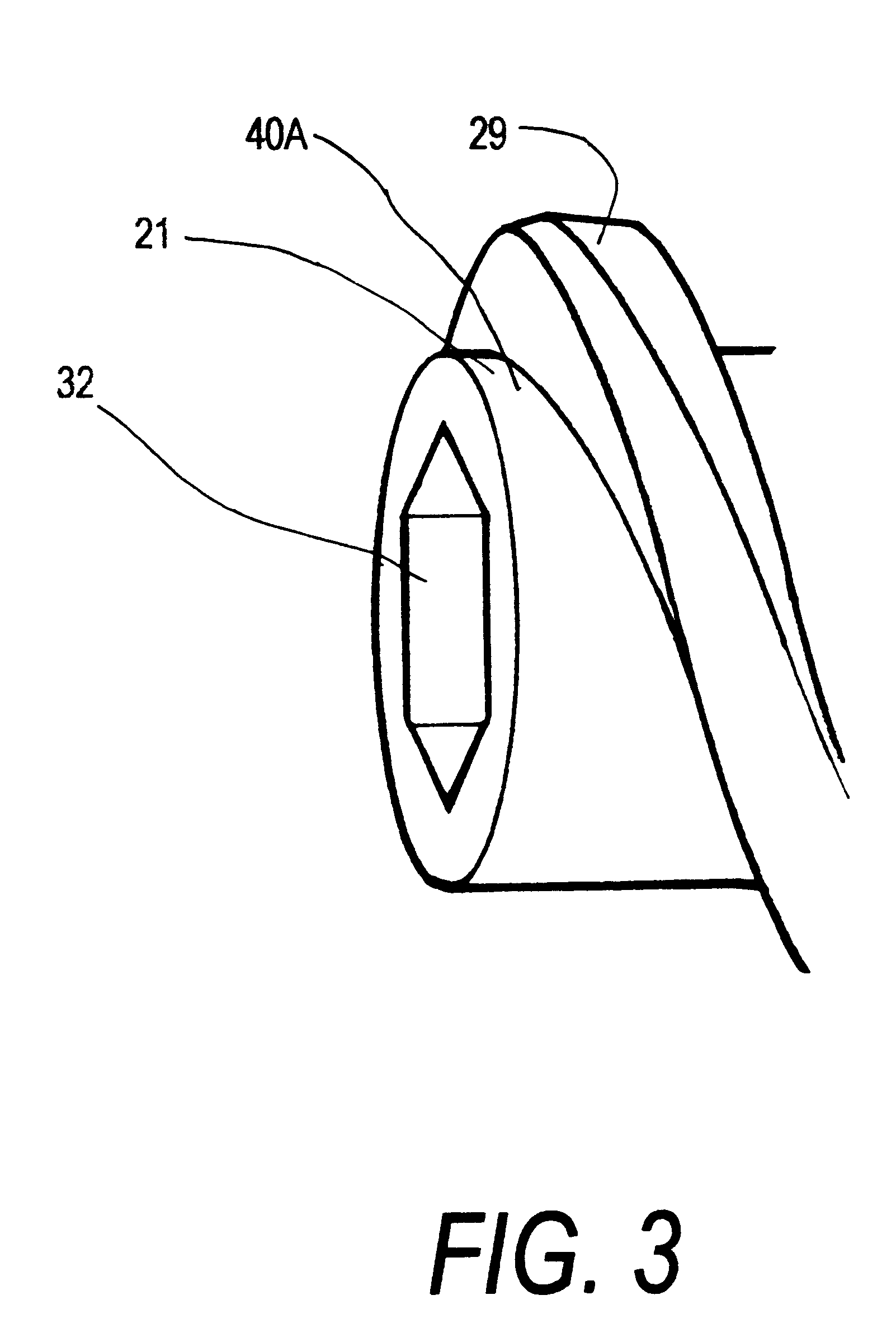
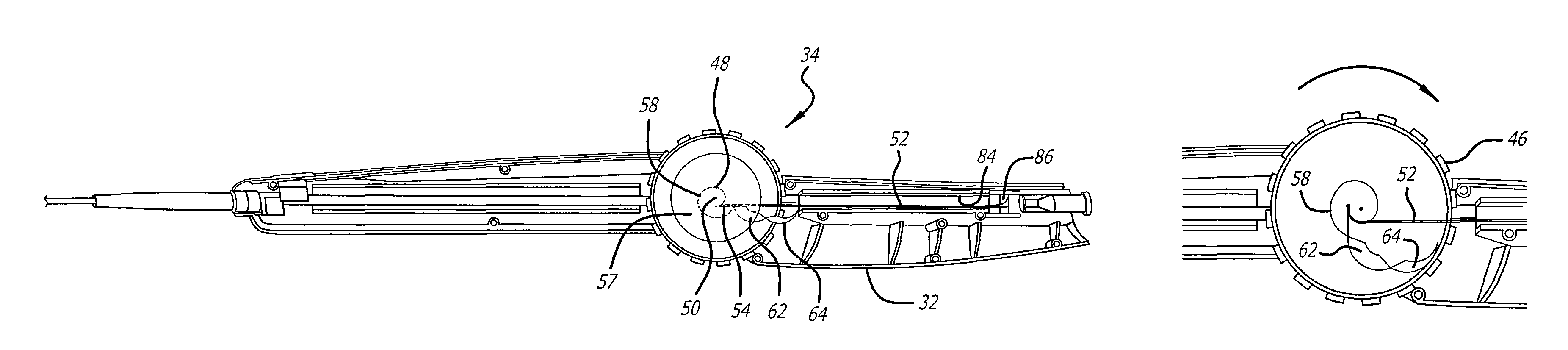
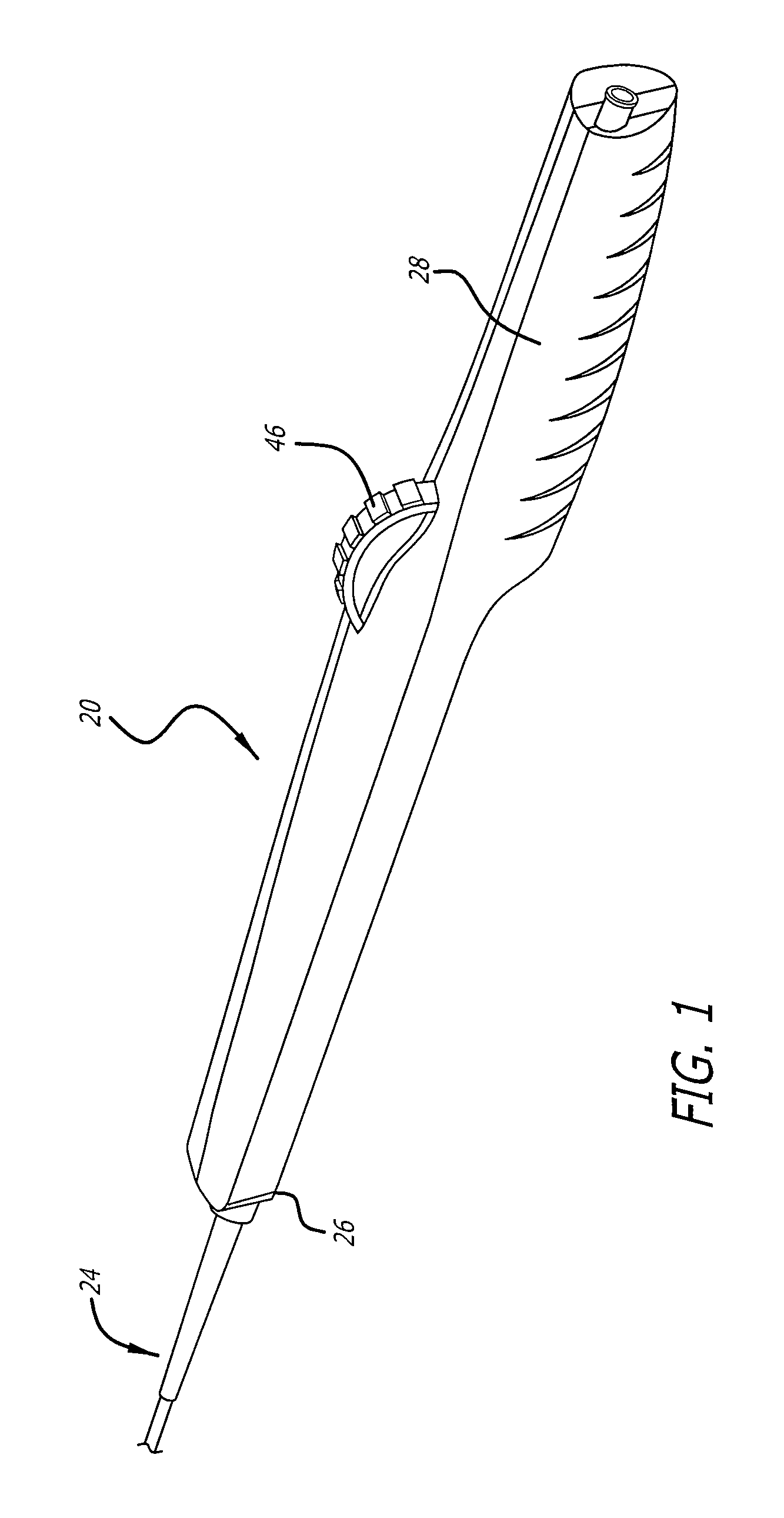
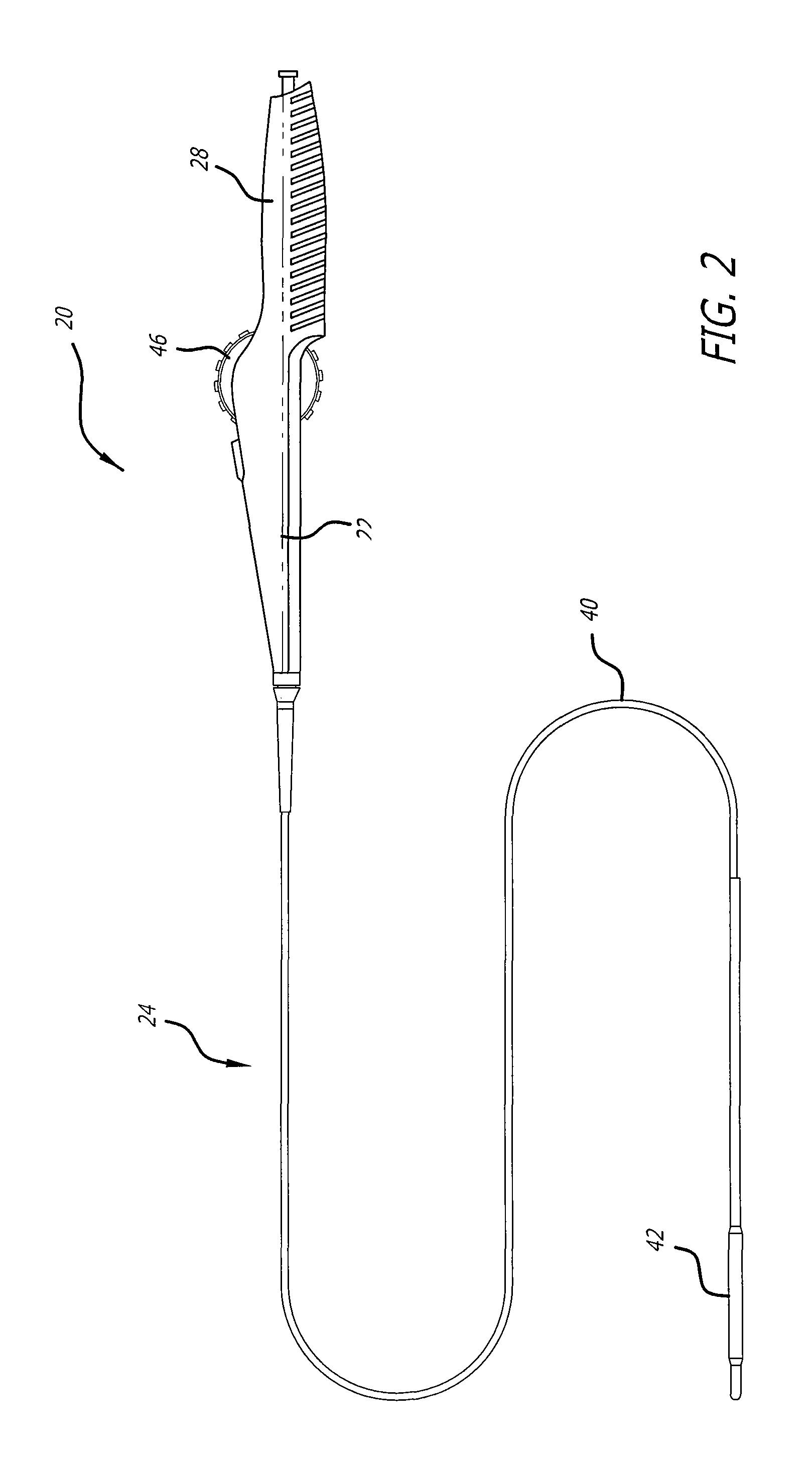
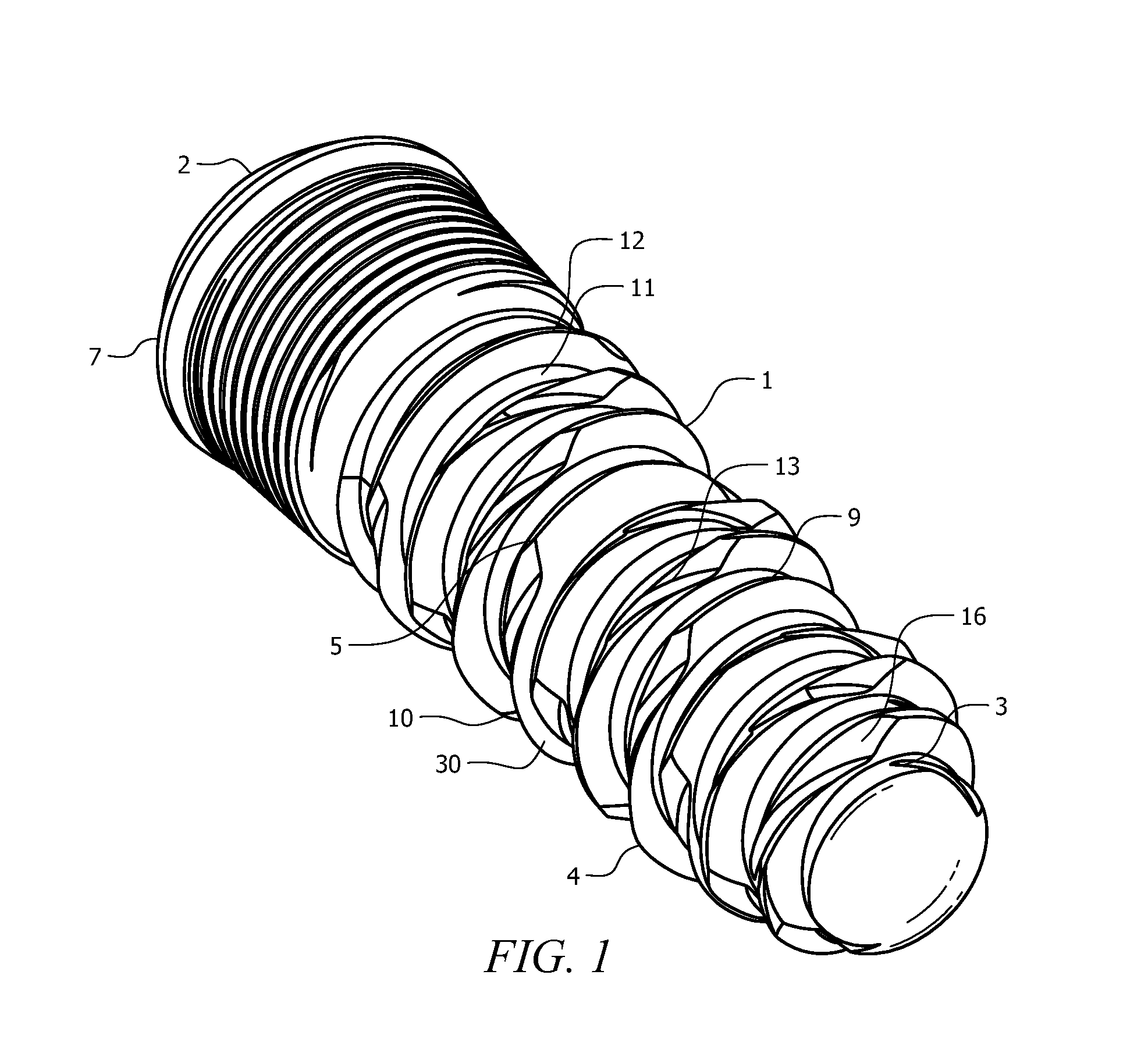
Combination sensor guidewire and methods of use
ActiveUS20060074318A1Improve accuracyImprove consistencyBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterUltrasonic sensorTransducer
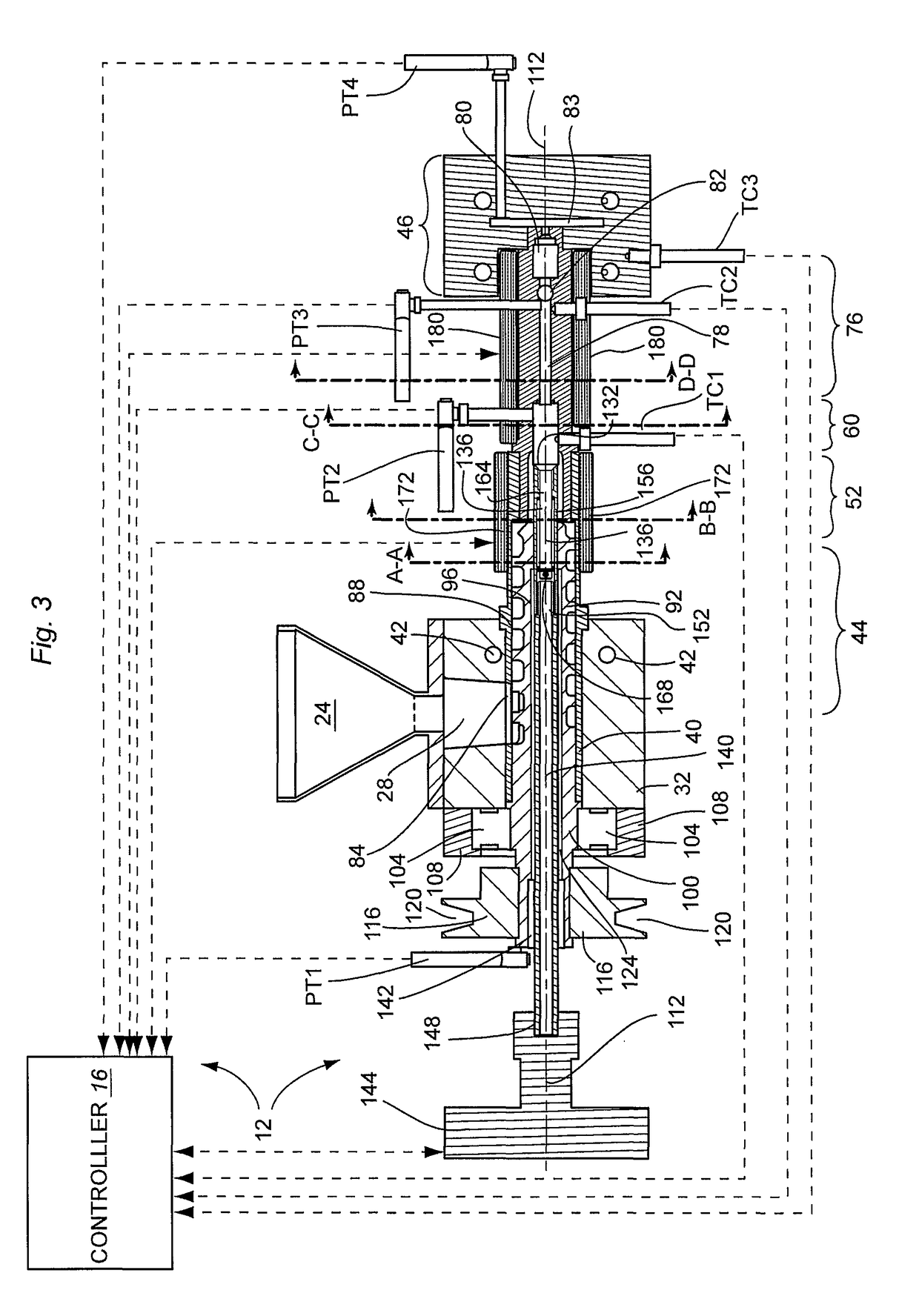
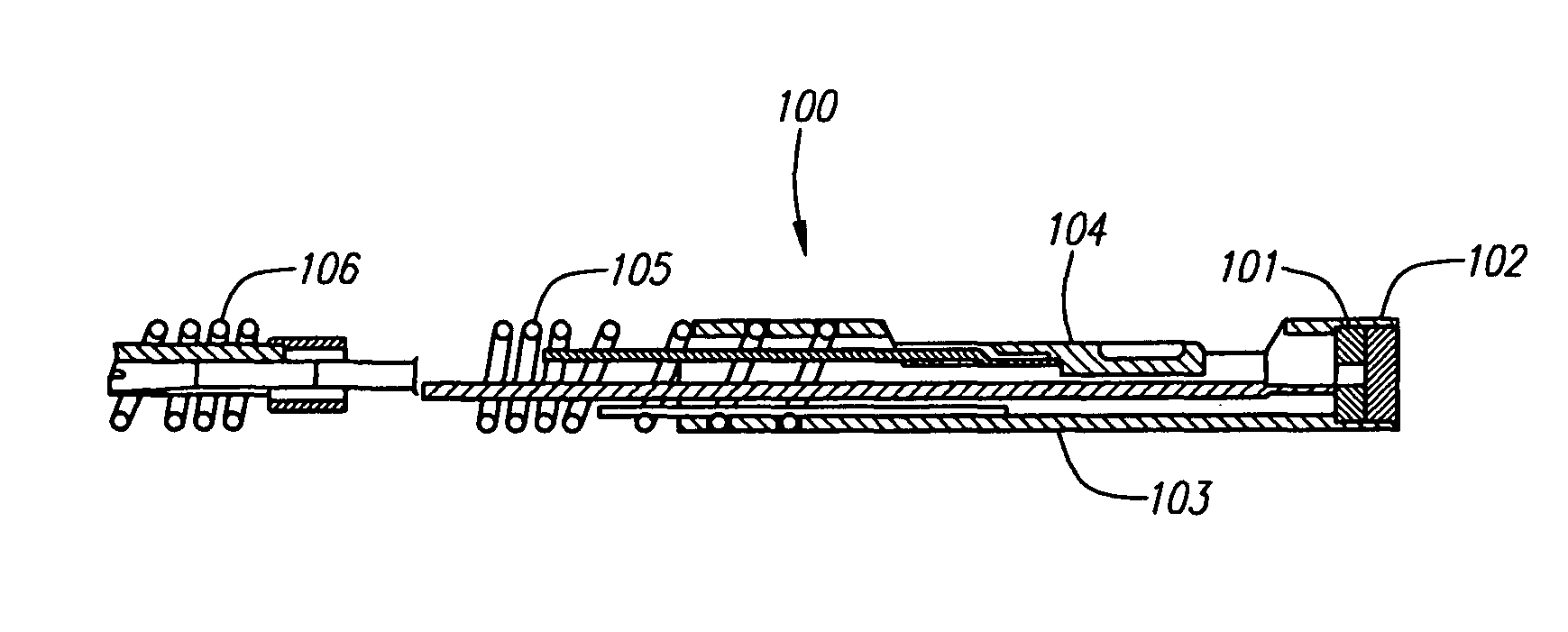
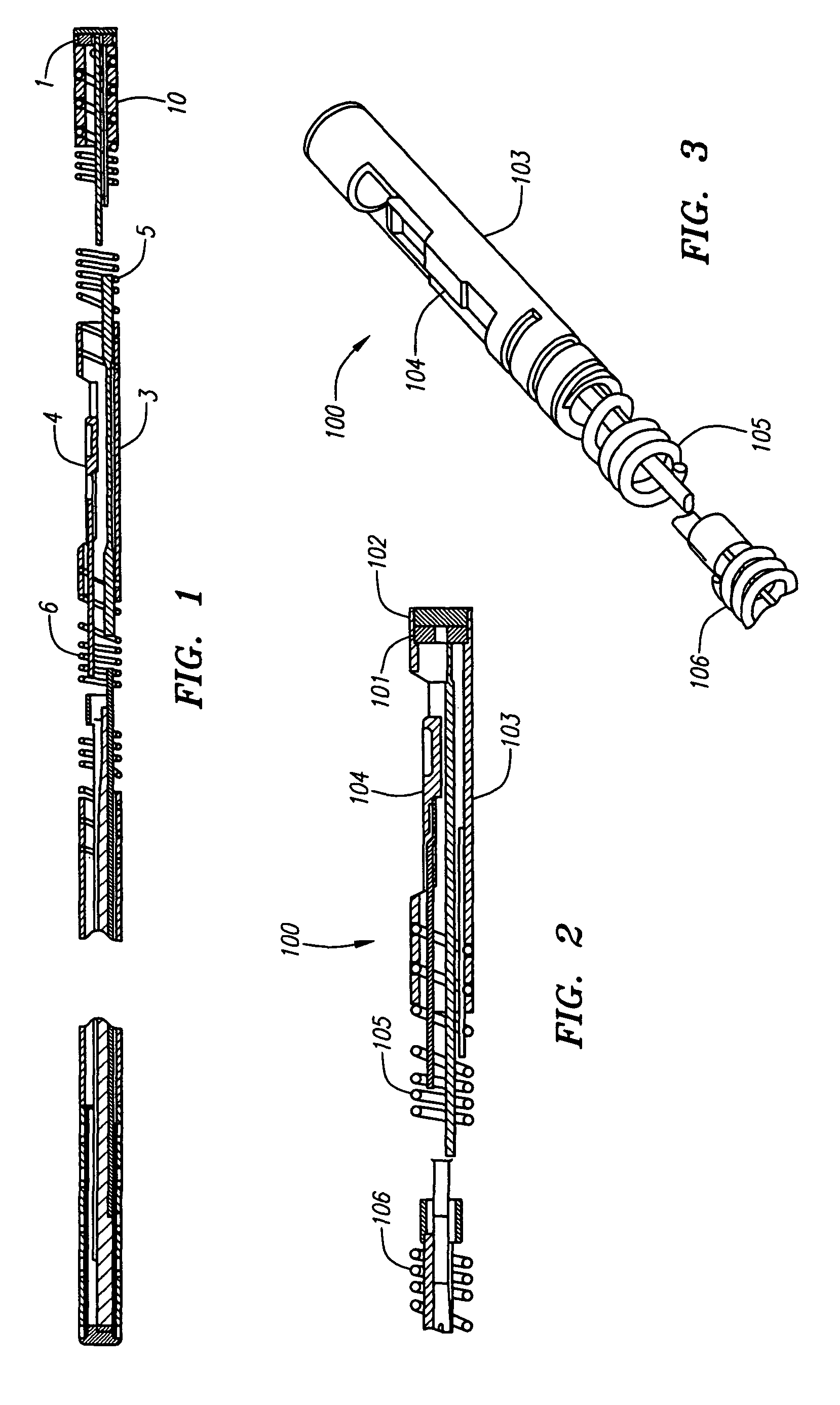
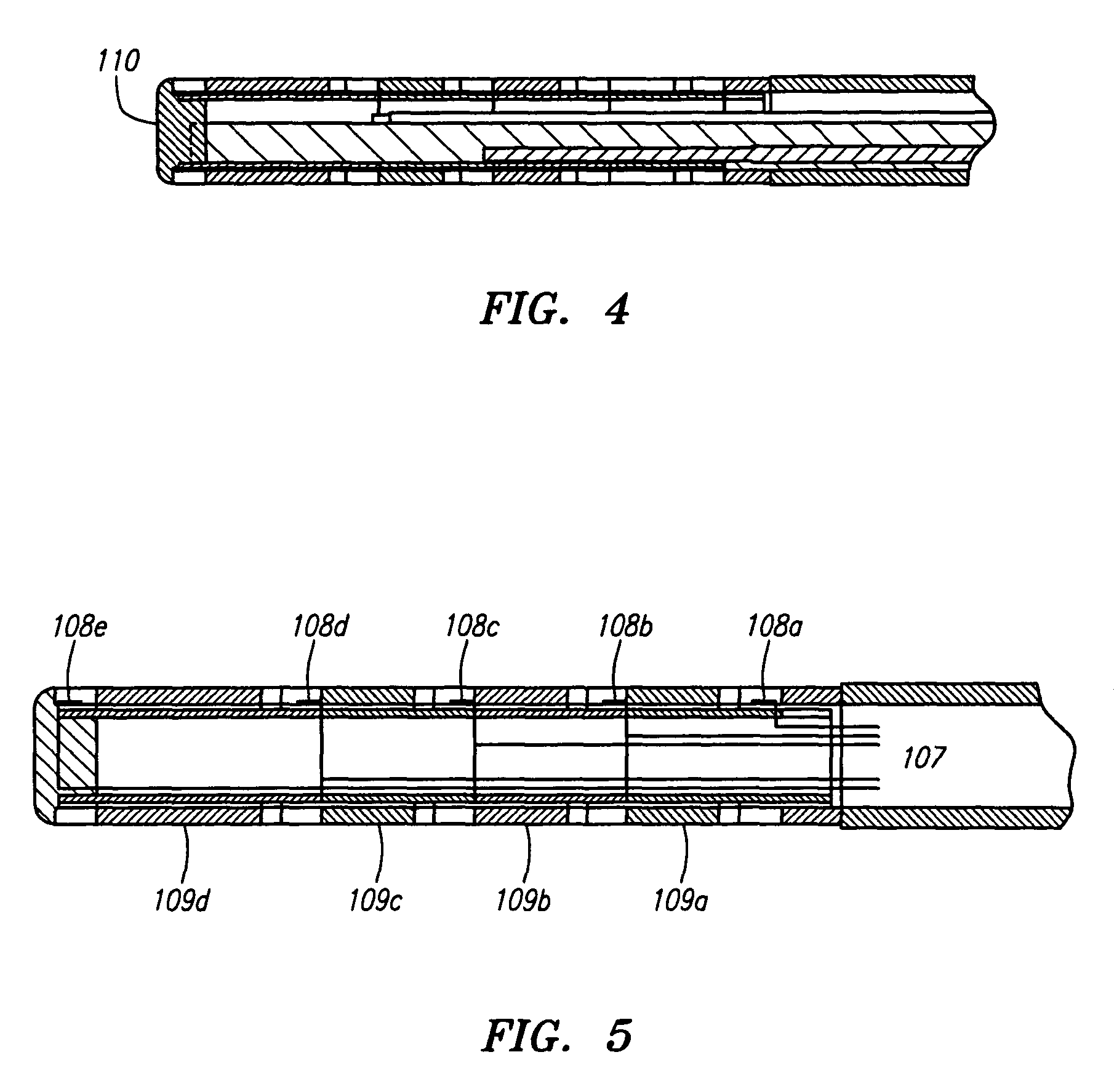
The present invention provides for an improved combination sensor tip that includes an ultrasound transducer and a pressure sensor both disposed at or in close proximity to the distal end of the combination sensor tip. The present invention also provides for an improved connector to couple a guide wire to a physiology monitor that reduces torsional resistance when maneuvering the guide wire.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
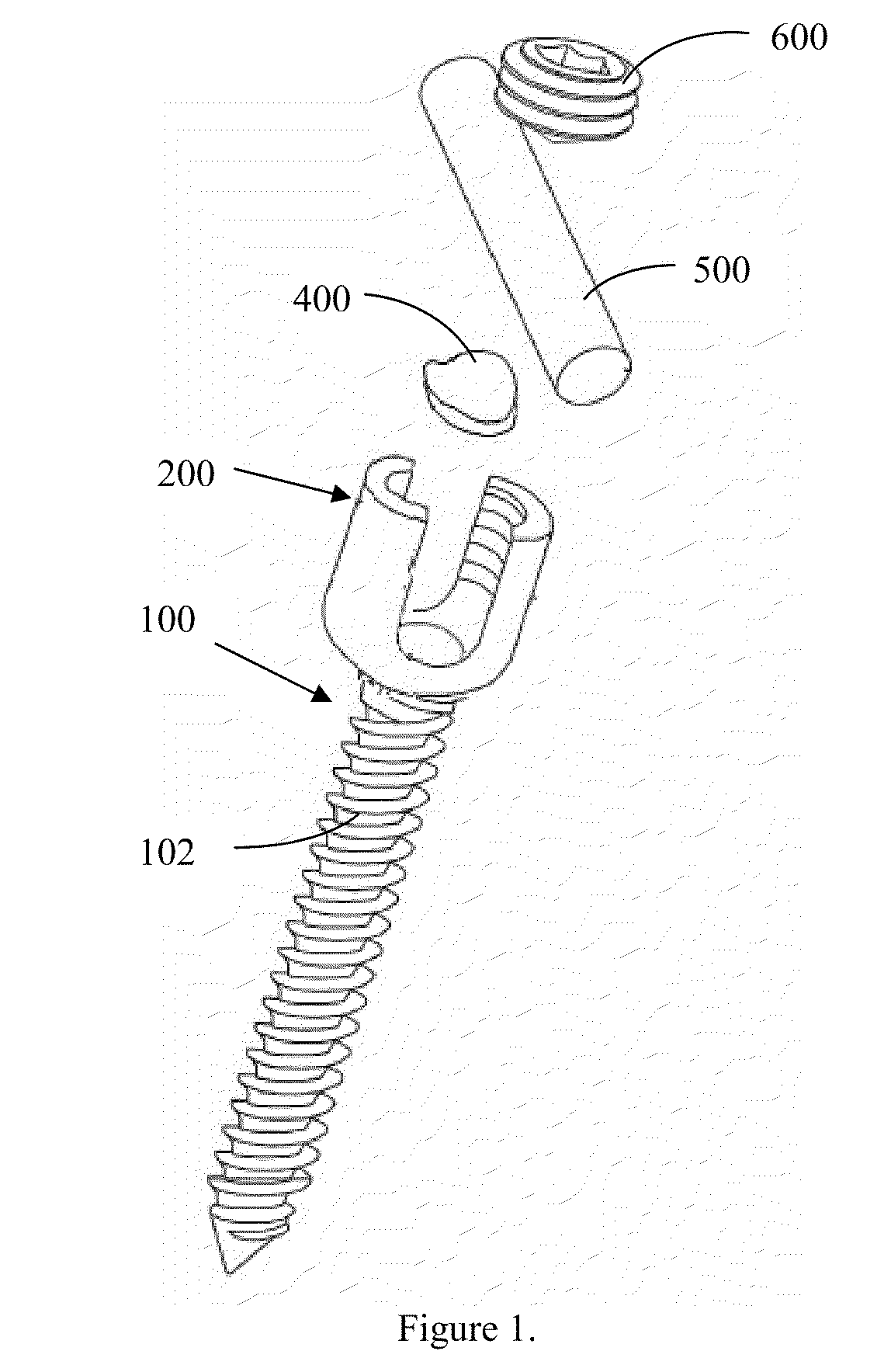
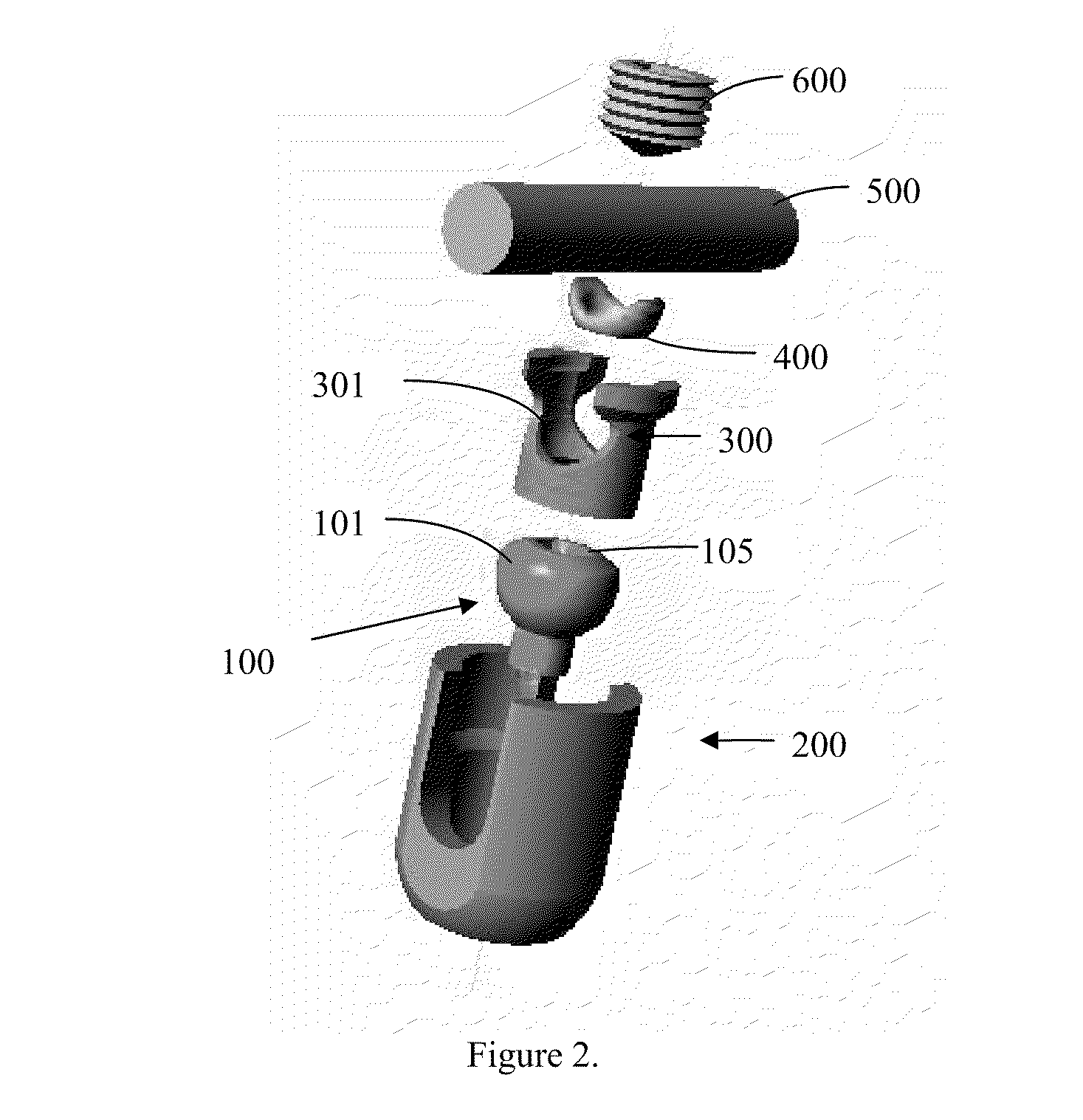
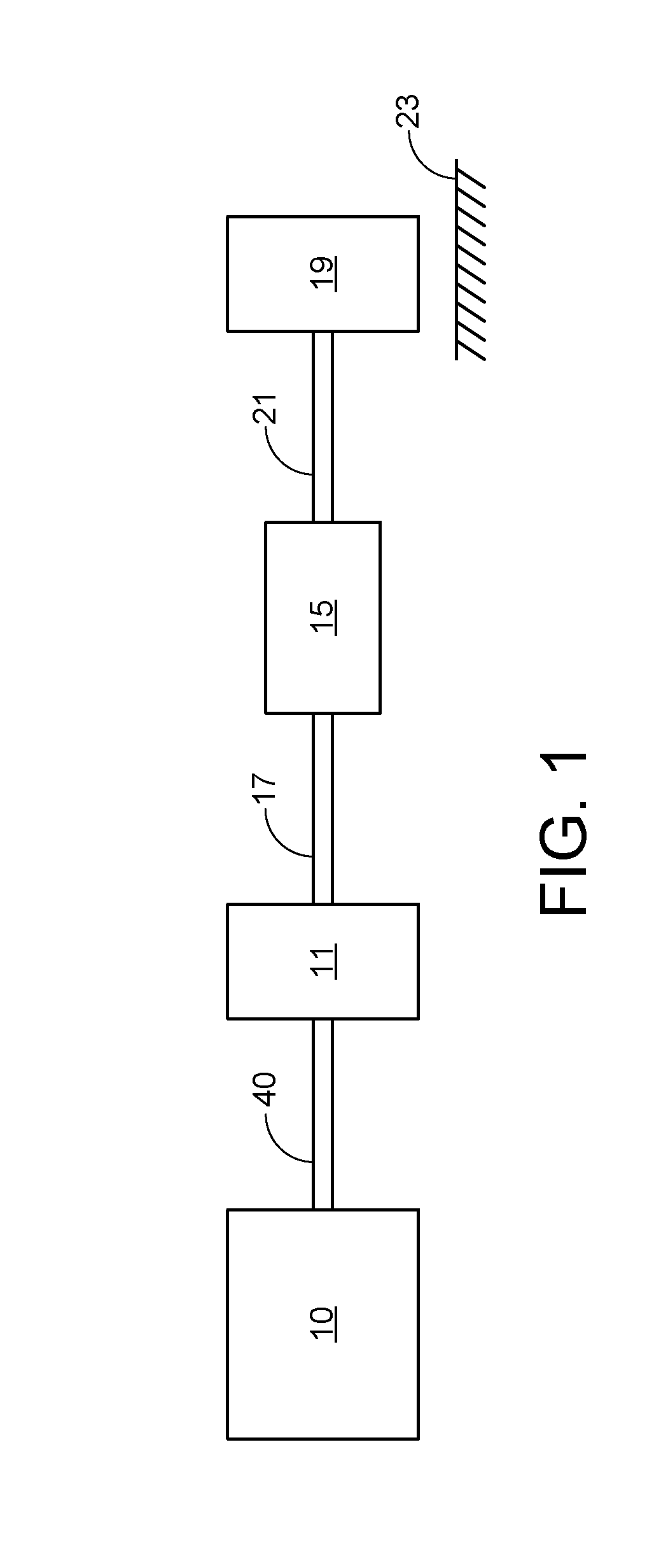
Translational manipulation polyaxial screw head
ActiveUS20100234891A1Minimal disruptionEasy to assembleInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringIliac screw
A novel surgical screw is presented as a polyaxial, multiaxial, or monoaxial screw. The polyaxial screw allows versatile angulation between a bone anchor section and a screw body and allows the surgeon to attach a rod to the invention in a top-loading manner and manipulate the rod to accommodate a patient's body and the surgical goals. The screw uses a rod saddle to seat a rod, and permits the surgeon to sagitally manipulate the rod. After implantation of the screw and insertion of the rod, a locking screw is used to fix the angle and position of the rod and screw body.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
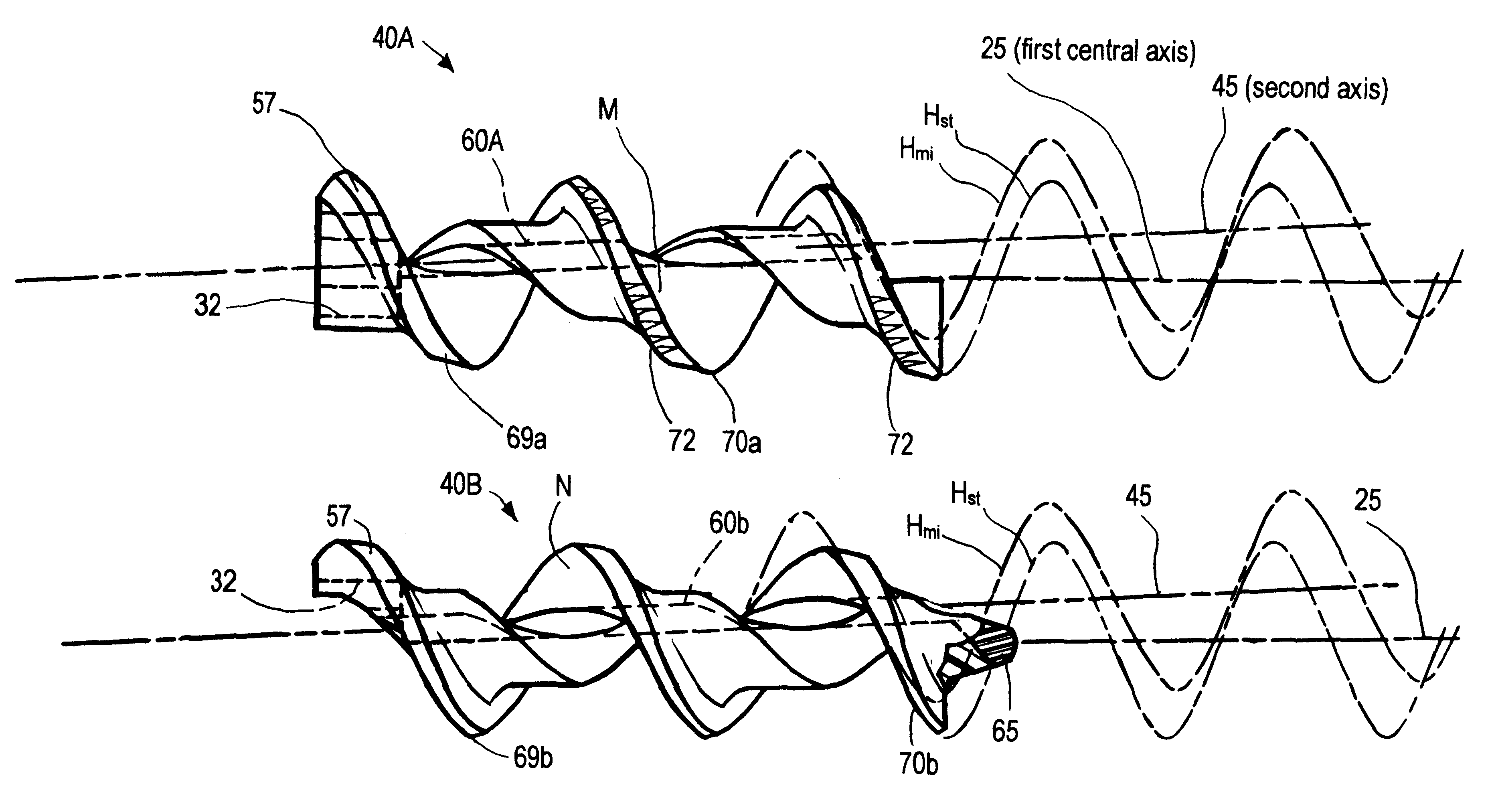
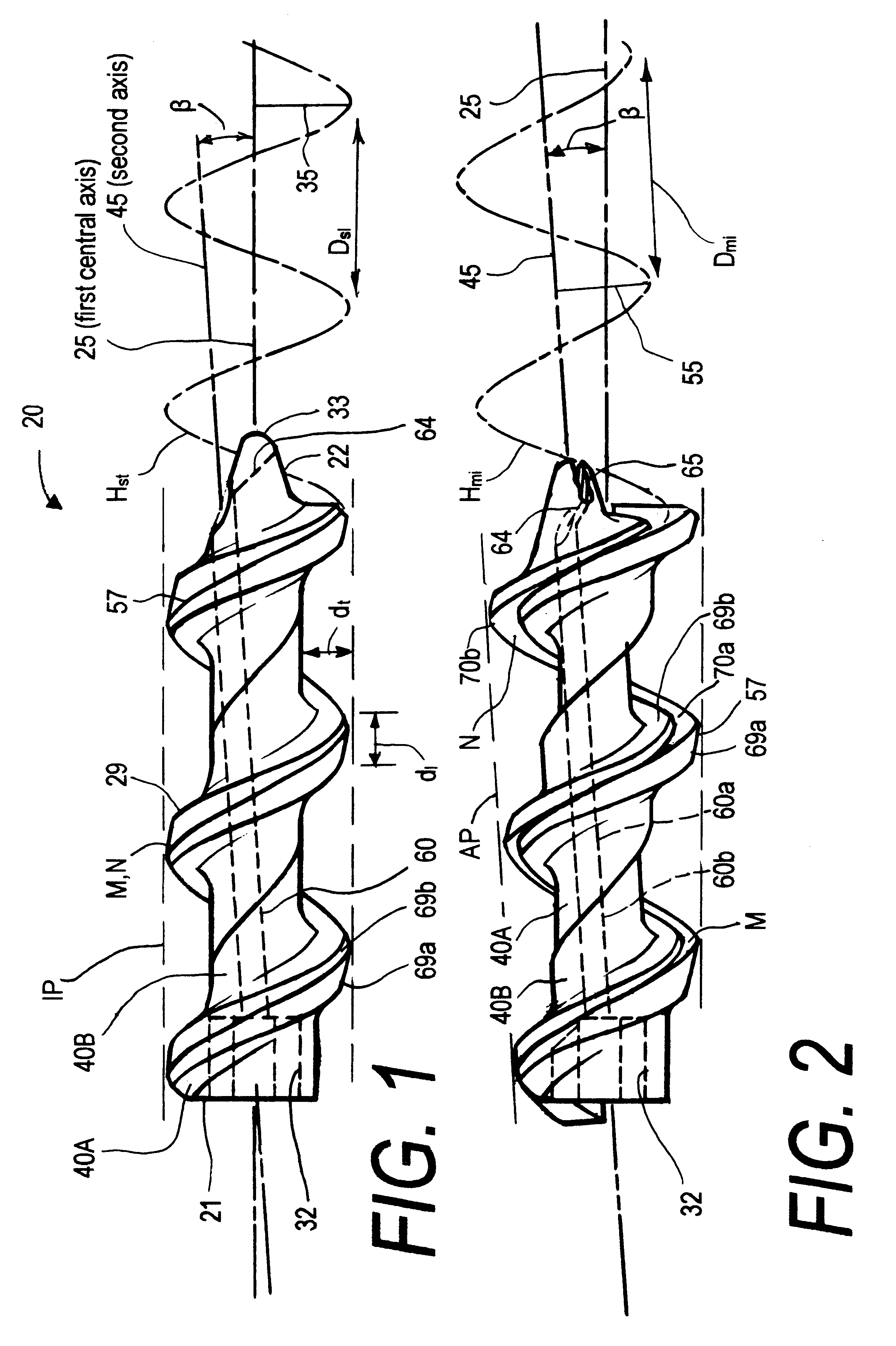
Offset helix surgical fixation screws and methods of use
InactiveUS6503251B1Less torqueReduced driving torqueSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSurgical departmentBiomedical engineering
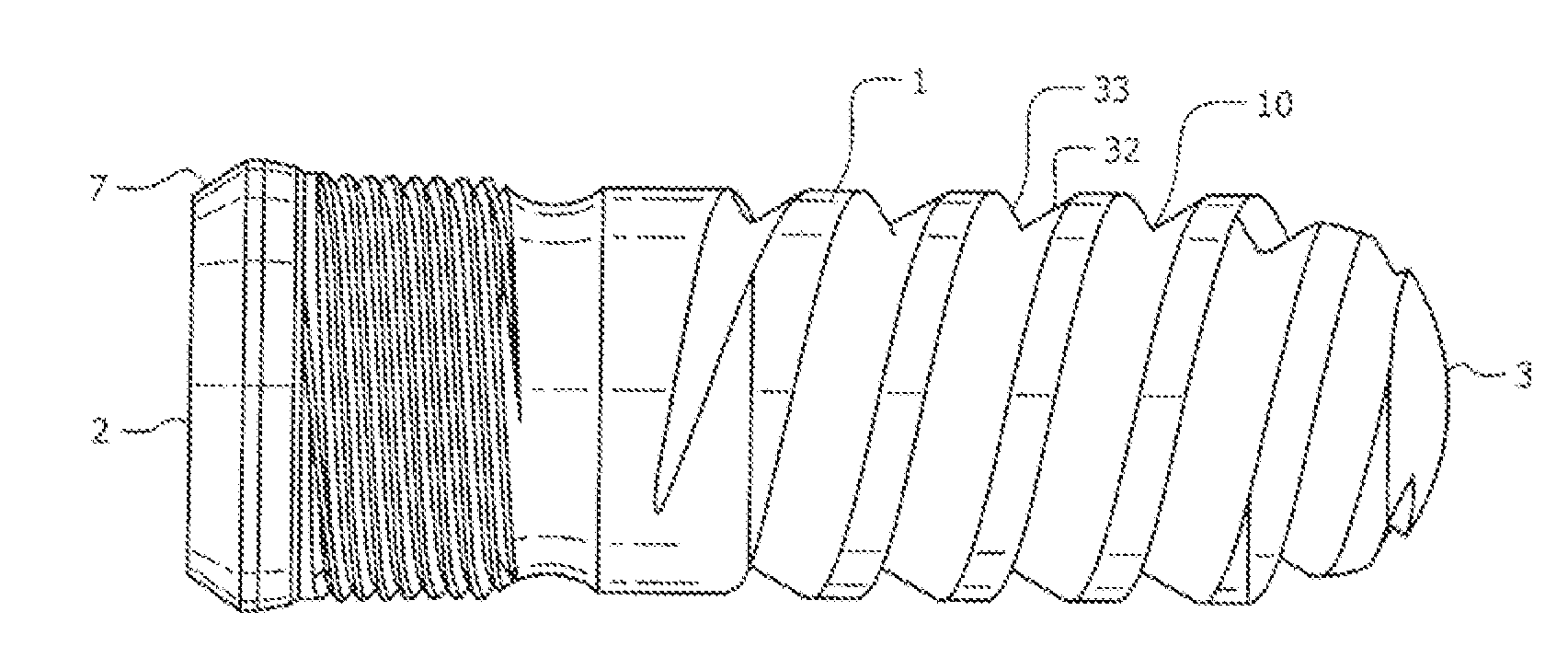
A surgical fixation screw that can be driven with significantly reduced torque thus allowing for theaded fixation bodies to be made substantially of bioabsorbable materials. The novel fixation body, also called an offset helix fixation body, extends along a first (central) axis. The fixation body comprises first and second helically-mating members that mate along a constant-lead helical interface that extends about a second (non-central) axis. The second axis is angularly offset from the first axis of the fixation body from about 1° to 20°. Alternatively, the second axis is parallel to, but laterally offset from, the first axis. Thus, the first and second members of the fixation body can travel helically relative to one another about the helical mating interface between a first insertion configuration and a second anchor configuration. In the insertion configuration, the screw's outer periphery has a first (lesser) transverse sectional dimension to allow reduced torque in helically driving the screw into a space in a bone. After being driven into a space or bore, the first and second members then can be moved helically relative to one another about the helical mating interface to an anchor configuration in which the screws outer periphery is expanded radially outward to provide a second (greater) transverse sectional dimension for securing the fixation body in the space or bore.
Owner:SHADDUCK JOHN H
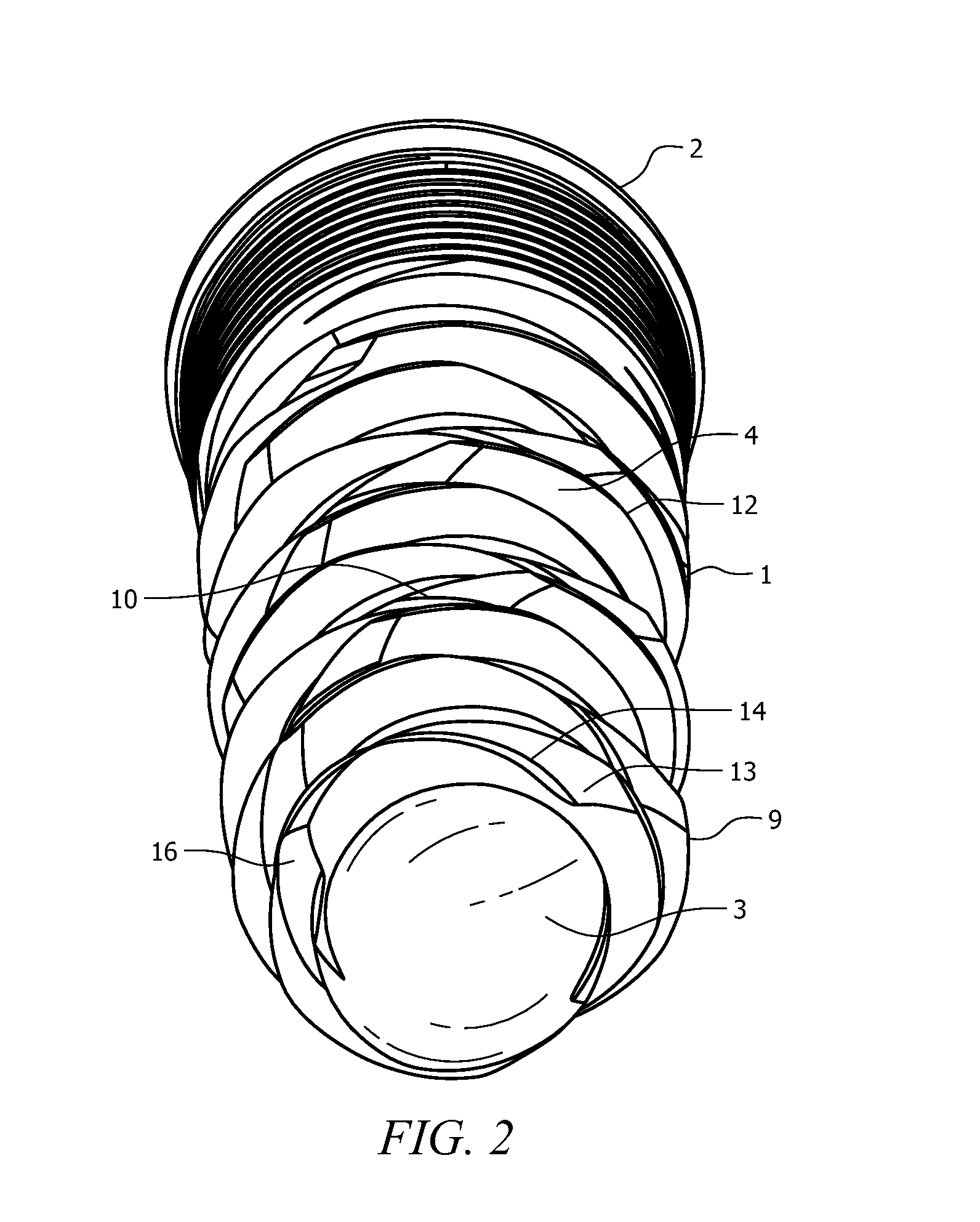
Combination sensor guidewire and methods of use
ActiveUS20060241505A1Good accuracy and consistencyMinimize impactBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterEngineeringGuide wires
The present invention provides for an improved combination sensor tip that includes a pressure sensor and a second sensor other than a pressure sensor, both disposed at or in close proximity to the distal end of the combination sensor tip. The present invention also provides for an improved connector to couple a guide wire to a physiology monitor that reduces torsional resistance when maneuvering the guide wire.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Delivery system with variable delivery rate for deploying a medical device
InactiveUS7976574B2Reduce the amount requiredShorten the timeStentsBlood vesselsStatic frictionEngineering
A delivery system utilizes a handle assembly including an actuating mechanism capable of initially providing sufficient mechanical advantage to overcome static friction when initiating deployment of the medical device. The actuating mechanism includes components which help to increase the speed of deployment as the physician continues to manipulate the actuating mechanism.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
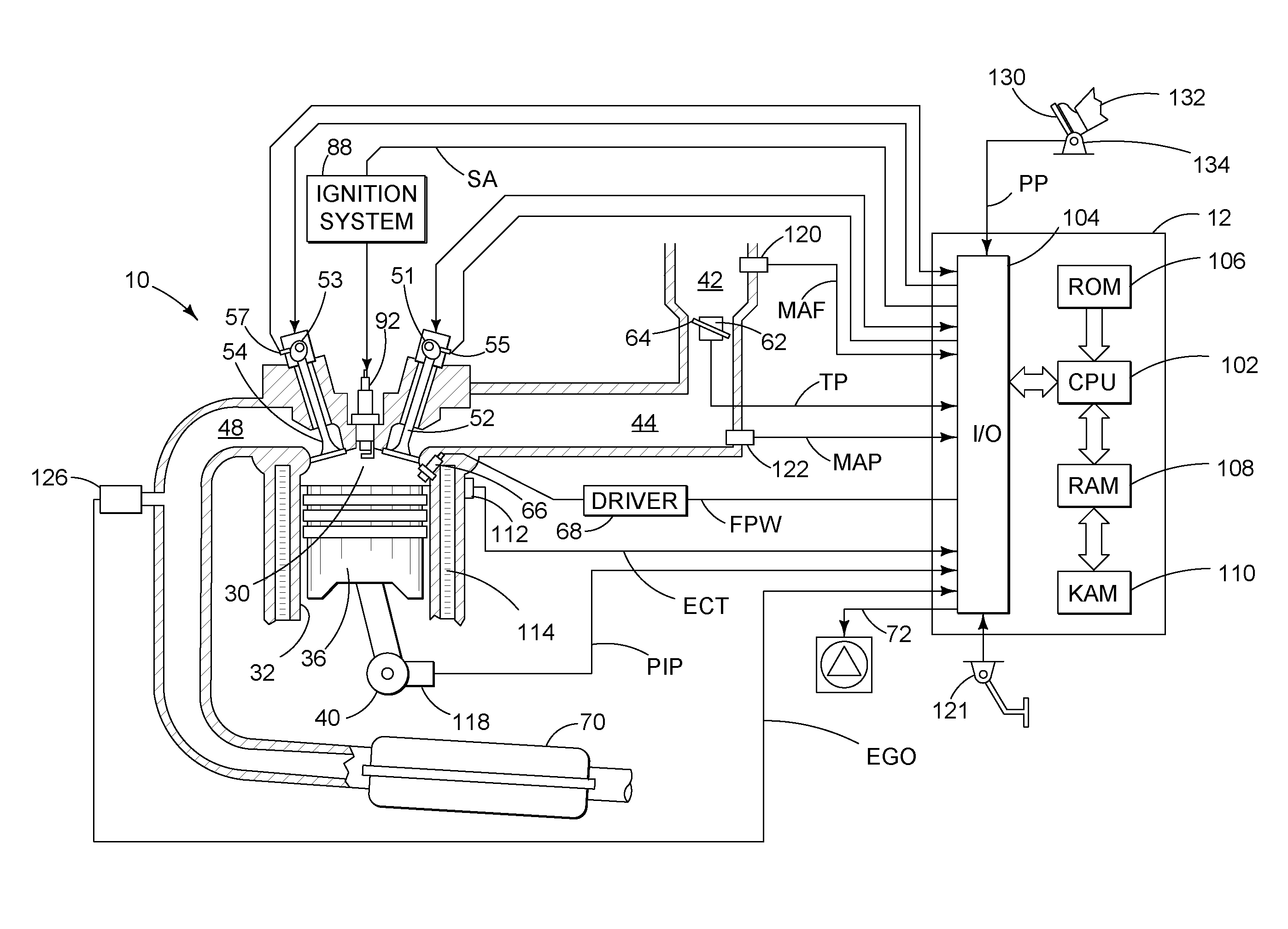
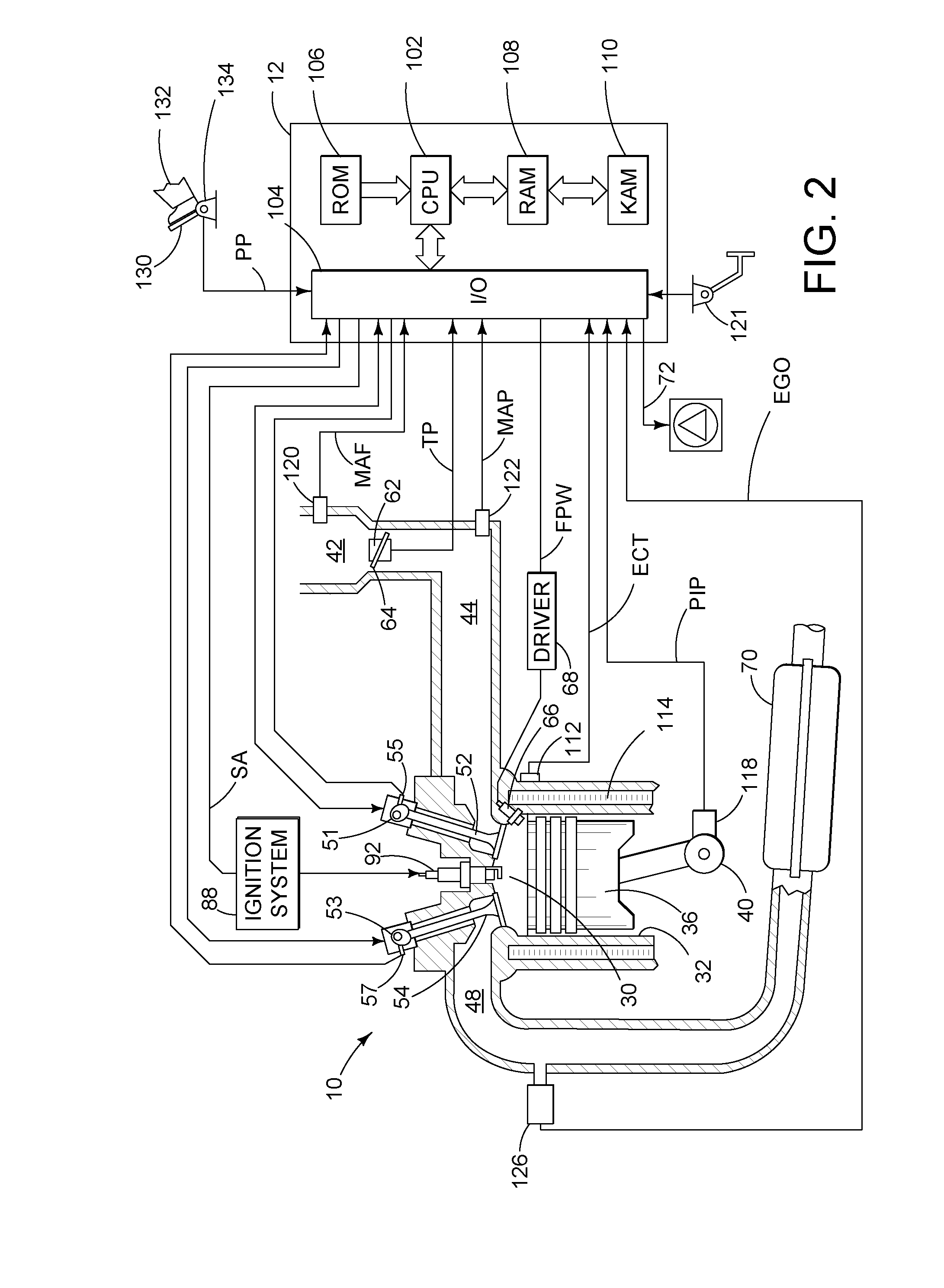
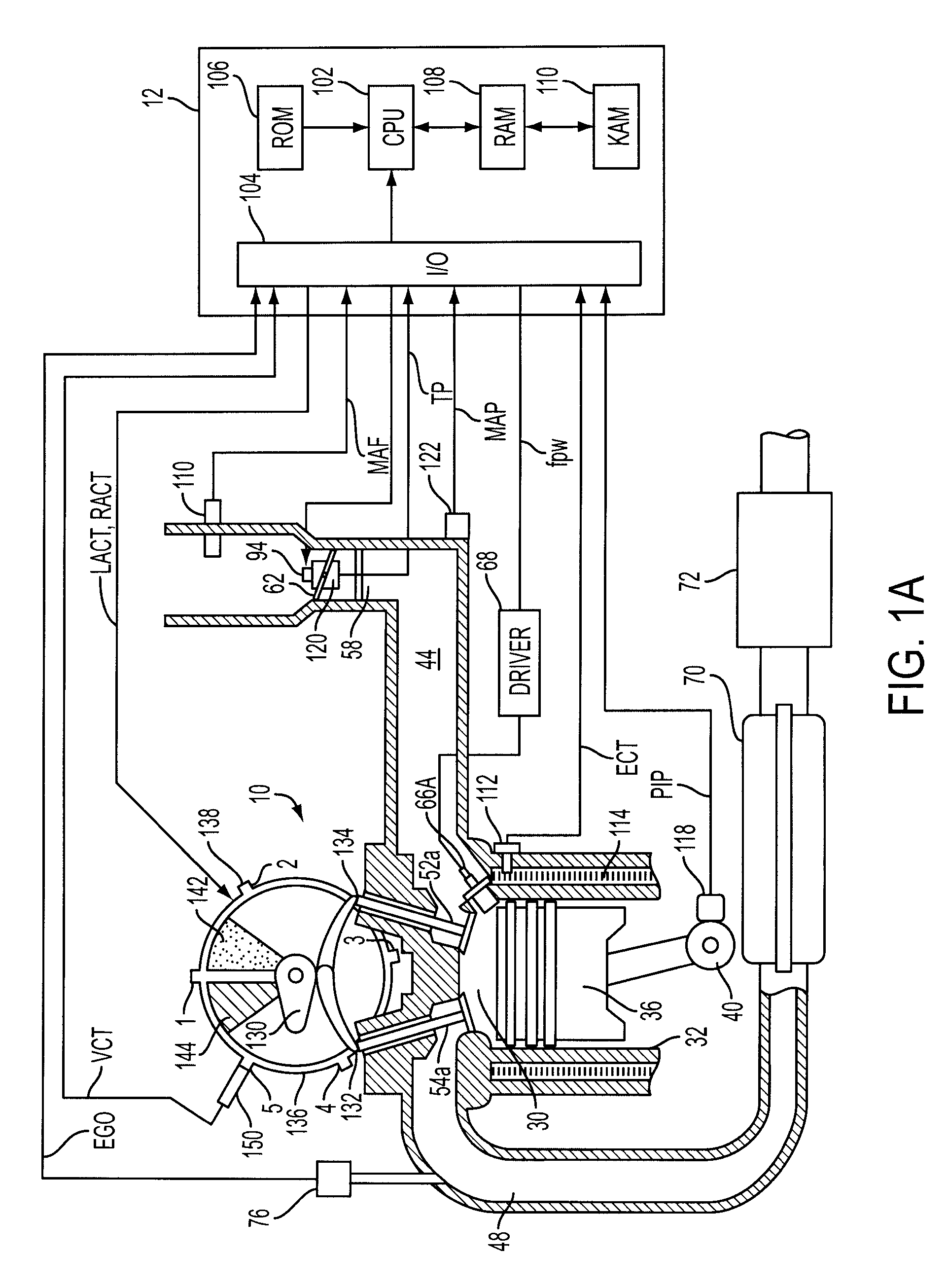
Method for controlling an engine during a restart
ActiveUS20110053735A1Reduce fuel consumptionReduce amountPower operated startersElectrical controlActuatorStarter
Various systems and methods are described for controlling an engine in a vehicle, the engine being coupled to a transmission. One example method comprises, under selected braking conditions, shutting-off the engine and spinning-down the engine to rest while the vehicle is traveling, and in response to a foot-off-brake event, restarting the engine by at least partially engaging the transmission and adjusting engine torque control actuators.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Translational manipulation polyaxial screw head
ActiveUS8277490B2Minimal disruptionEasy to assembleInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringIliac screw
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
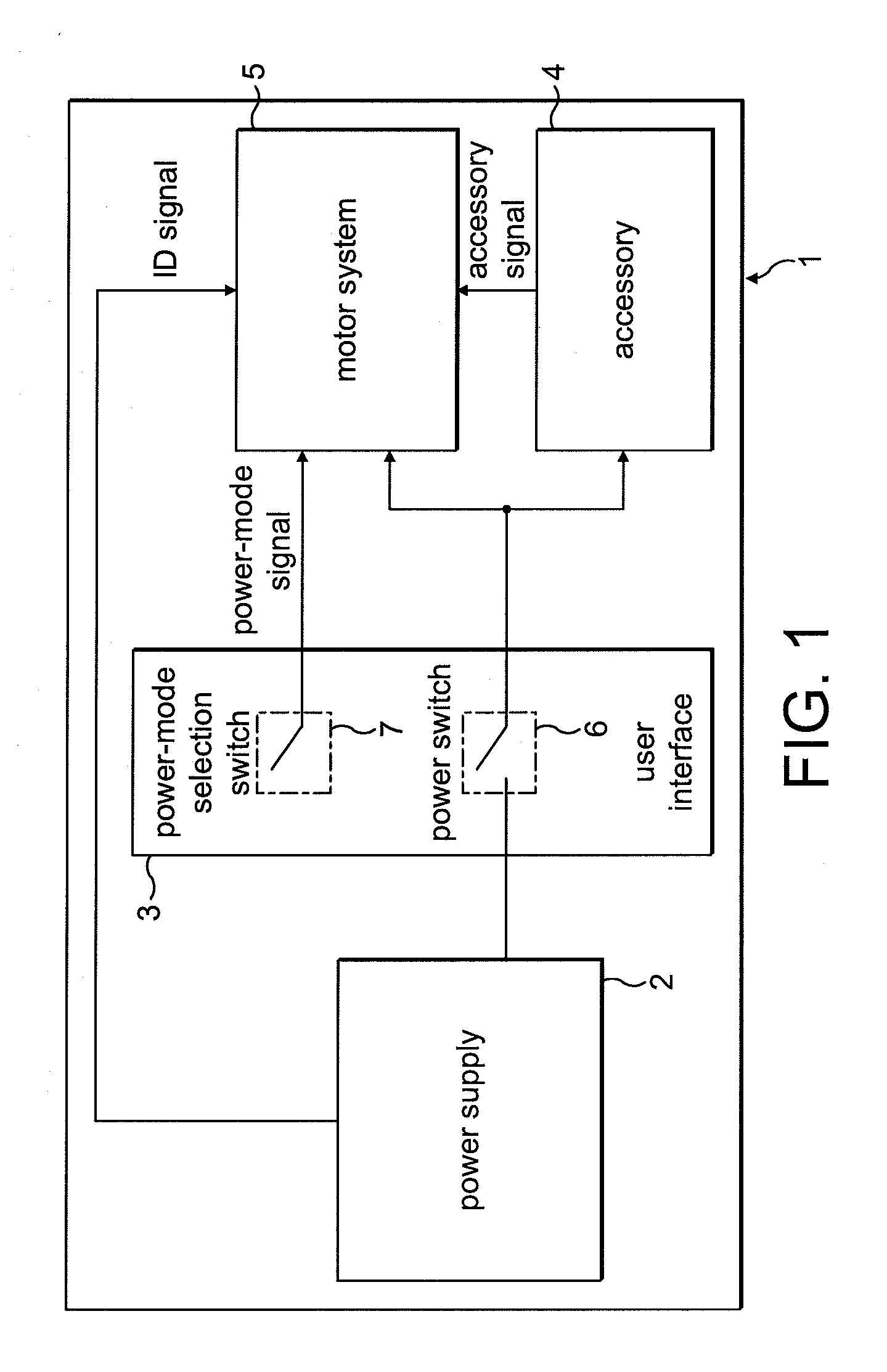
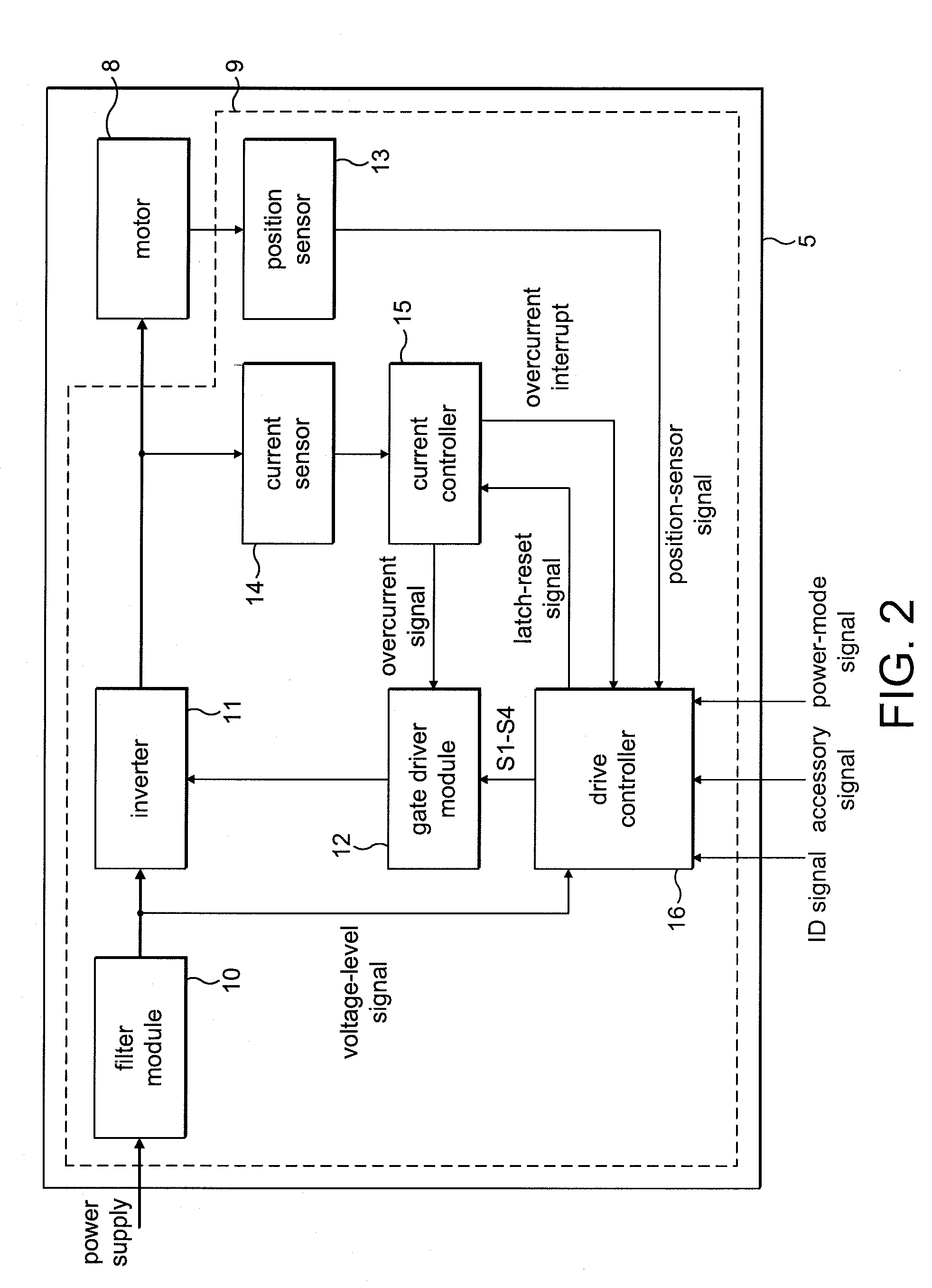
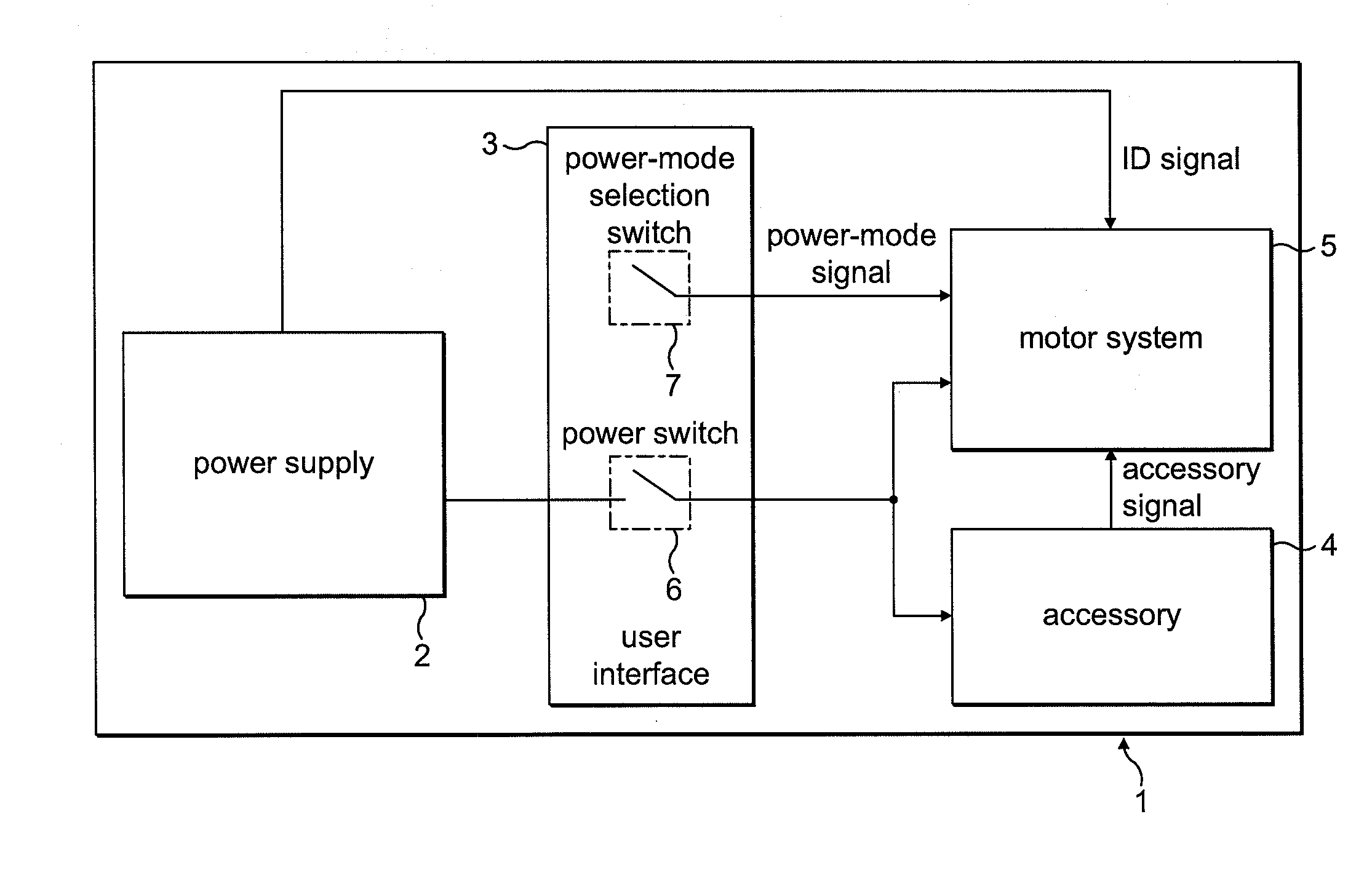
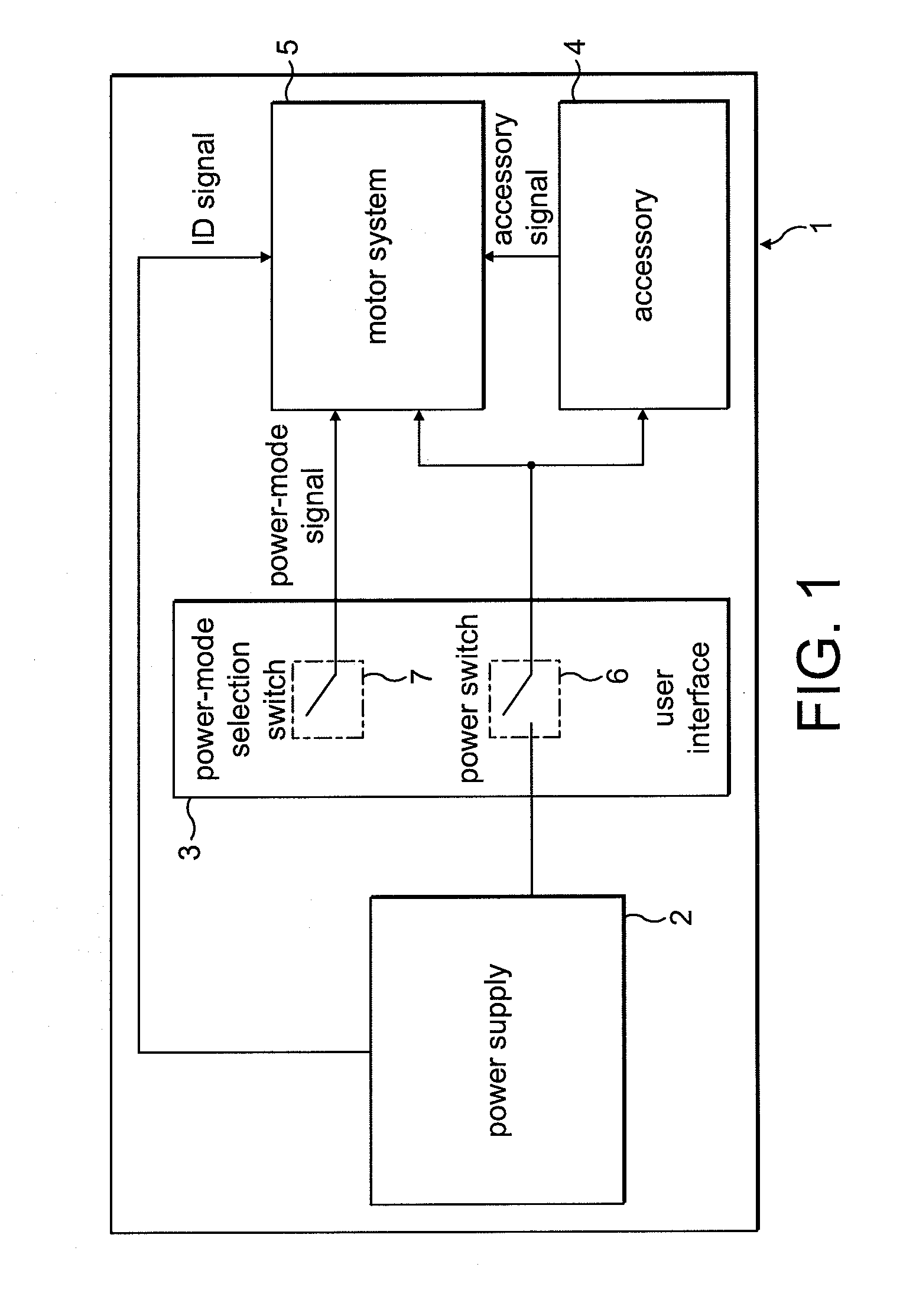
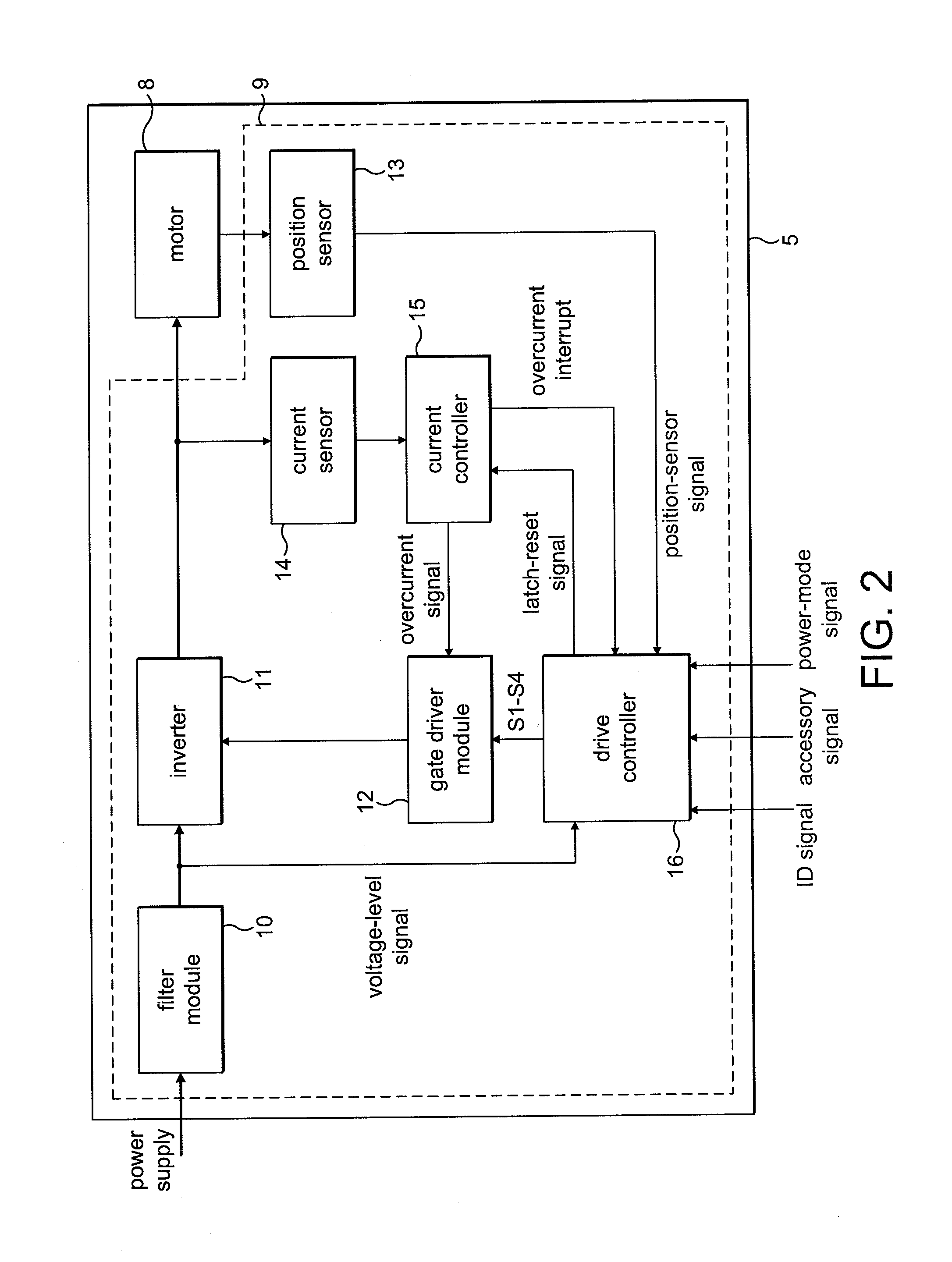
Control of an electric machine
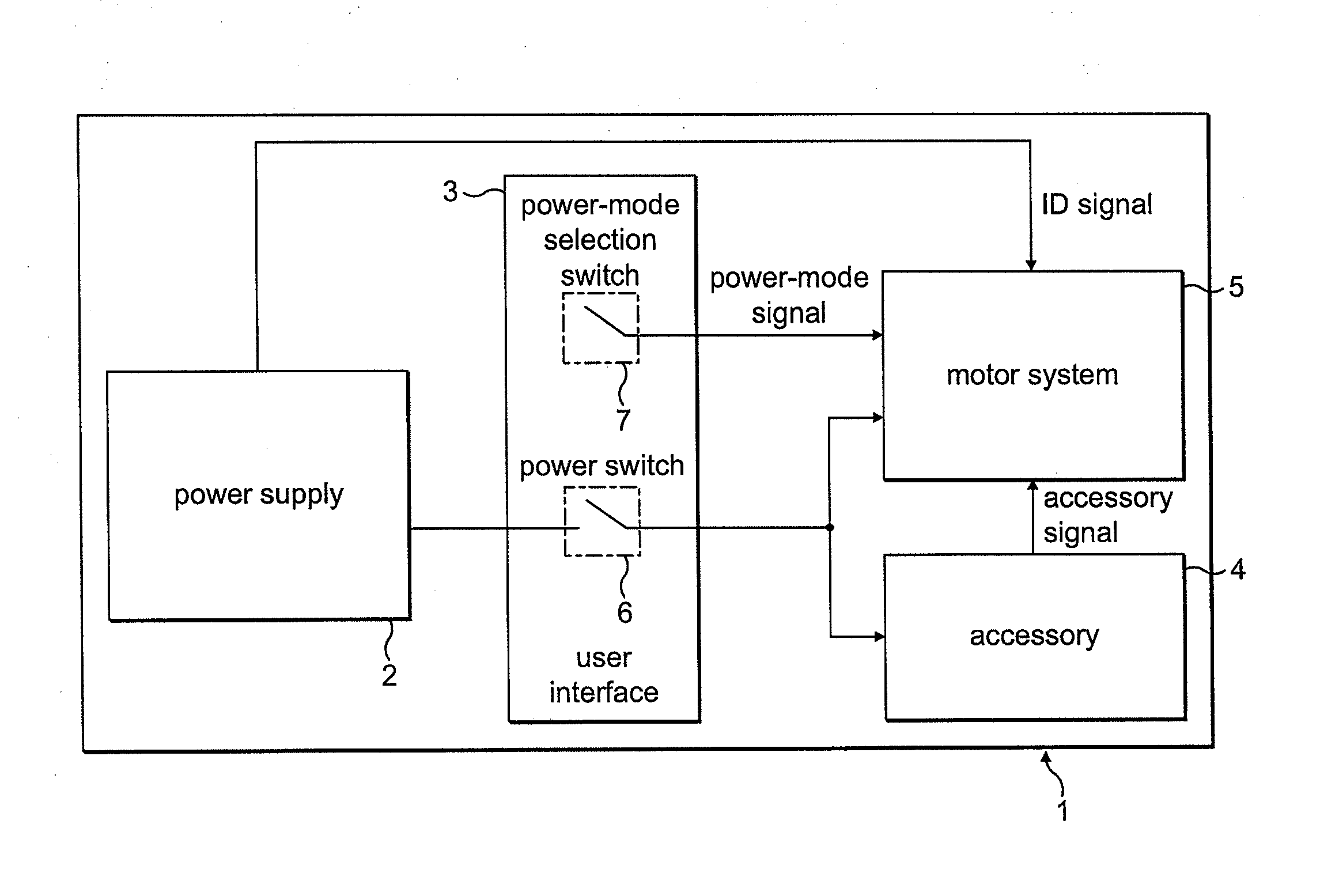
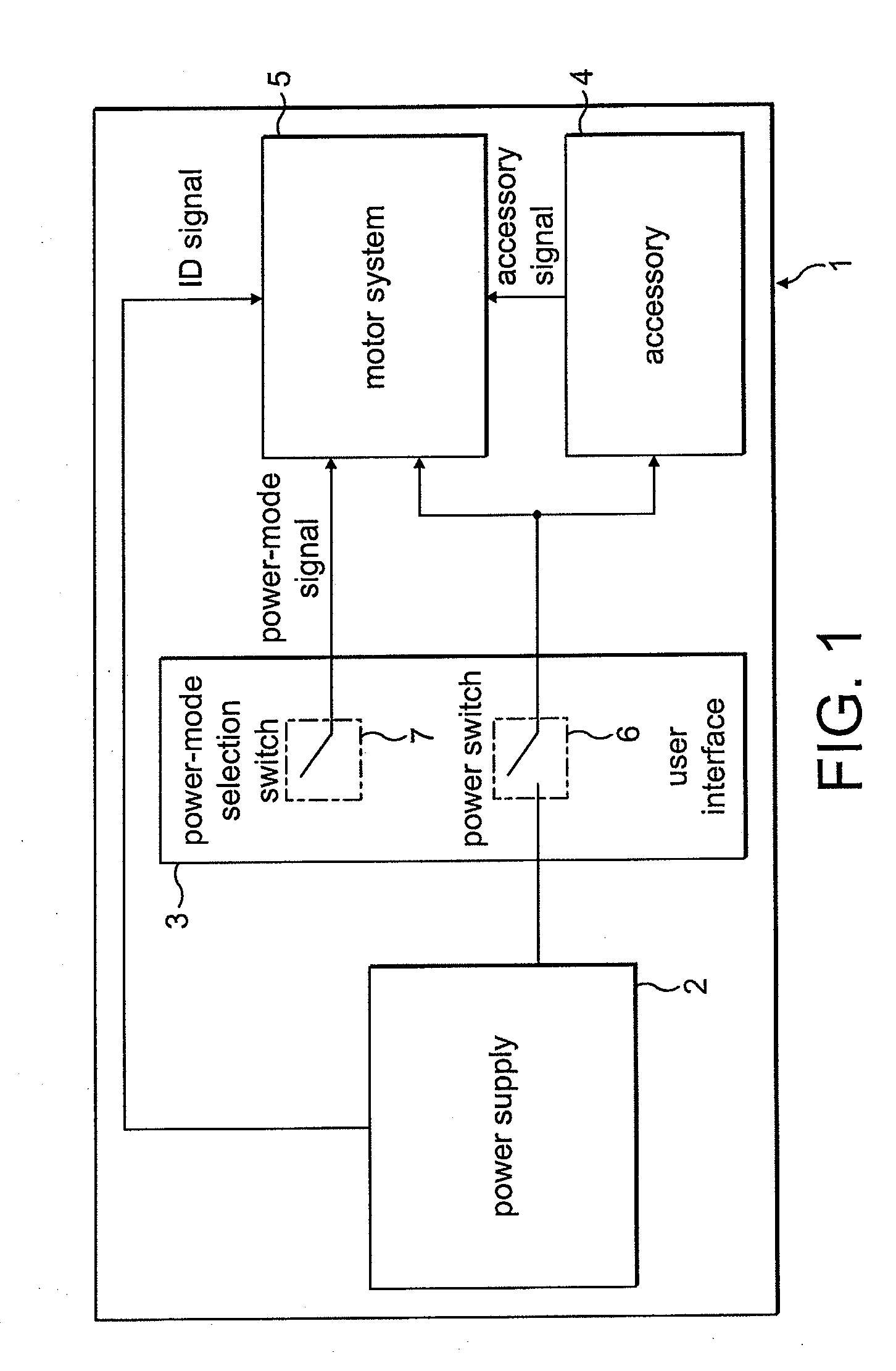
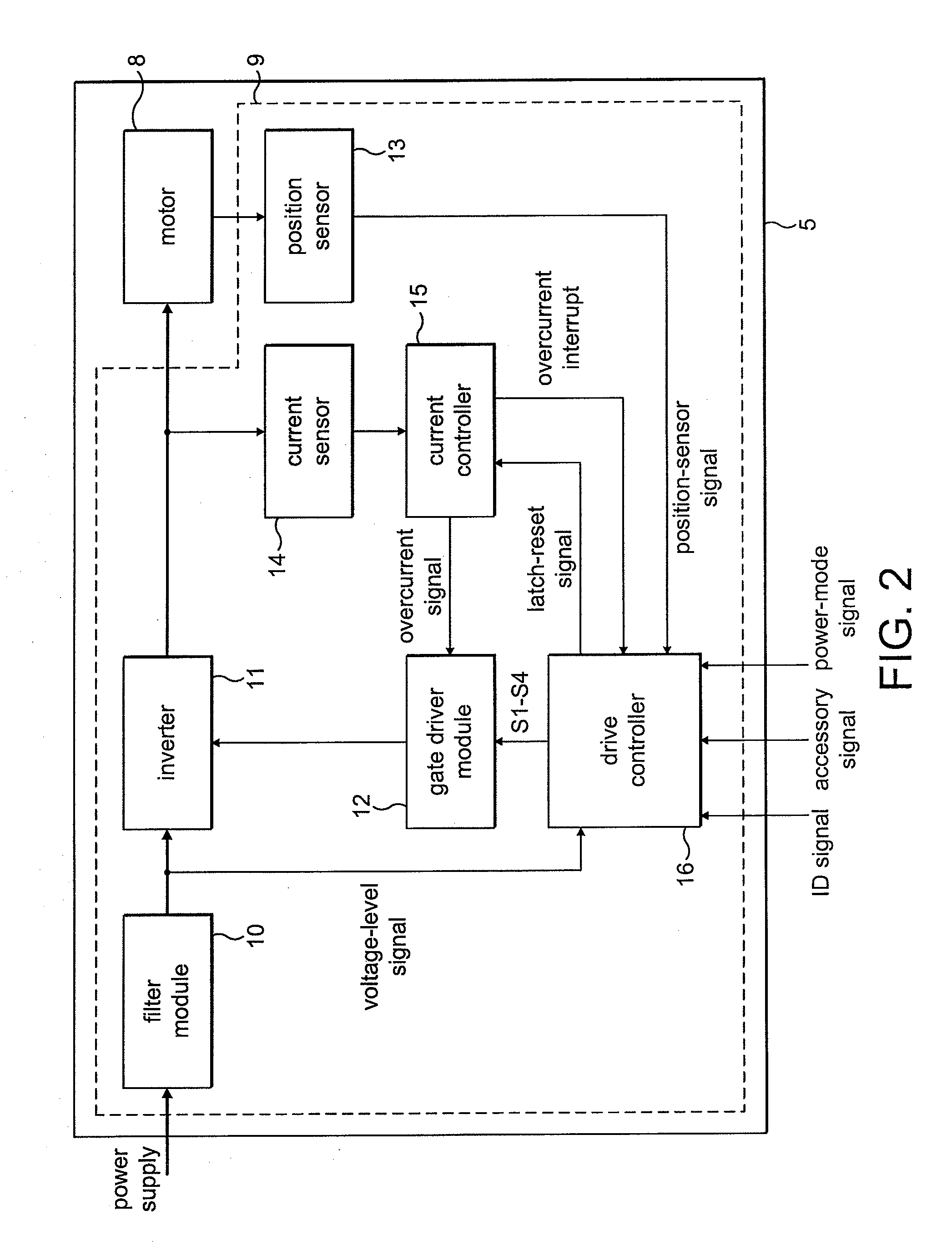
ActiveUS20100253264A1Increase powerLess torqueTorque ripple controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersFreewheelControl system
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited in advance of zero-crossings of back emf in the winding by an advance angle, and the winding is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the advance angle and the freewheel angle in response to changes in the speed of the electric machine. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Low torque and vacuum seed meter
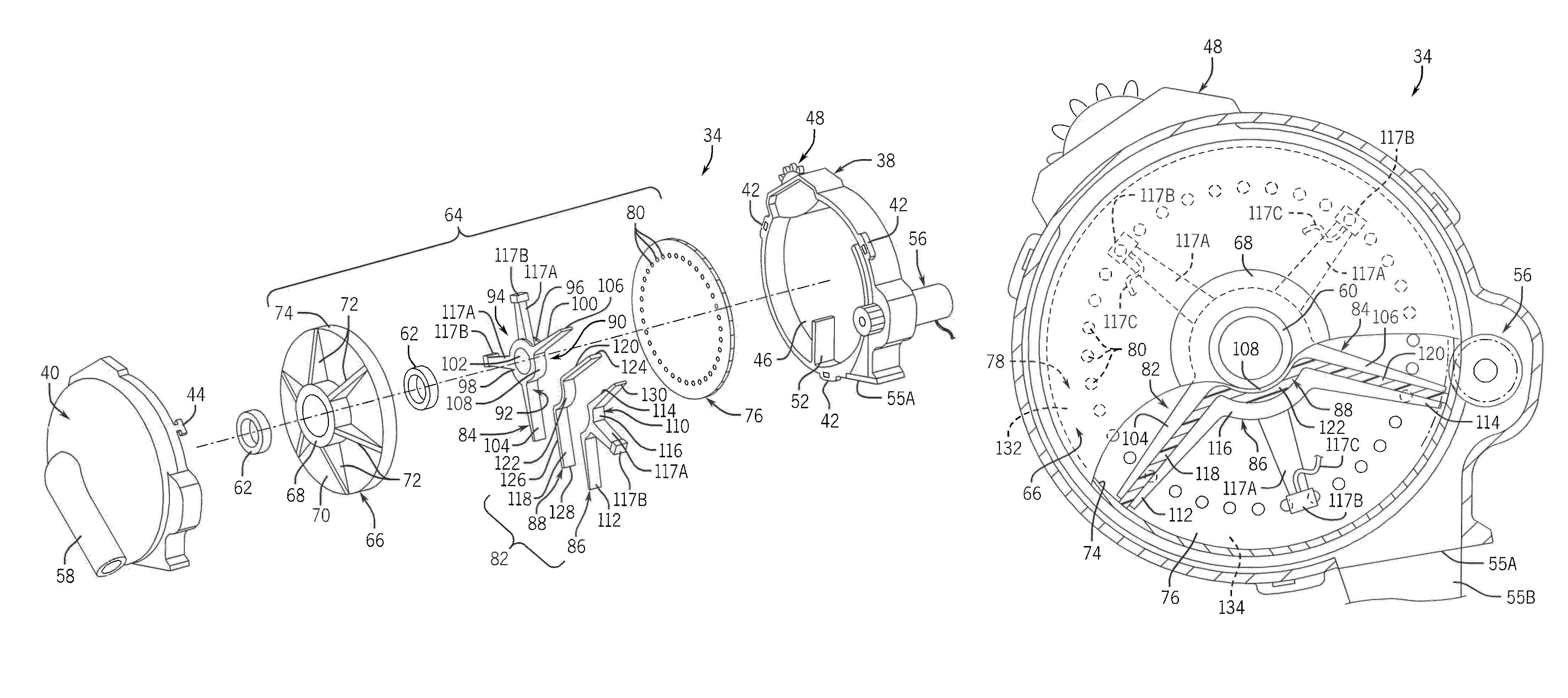
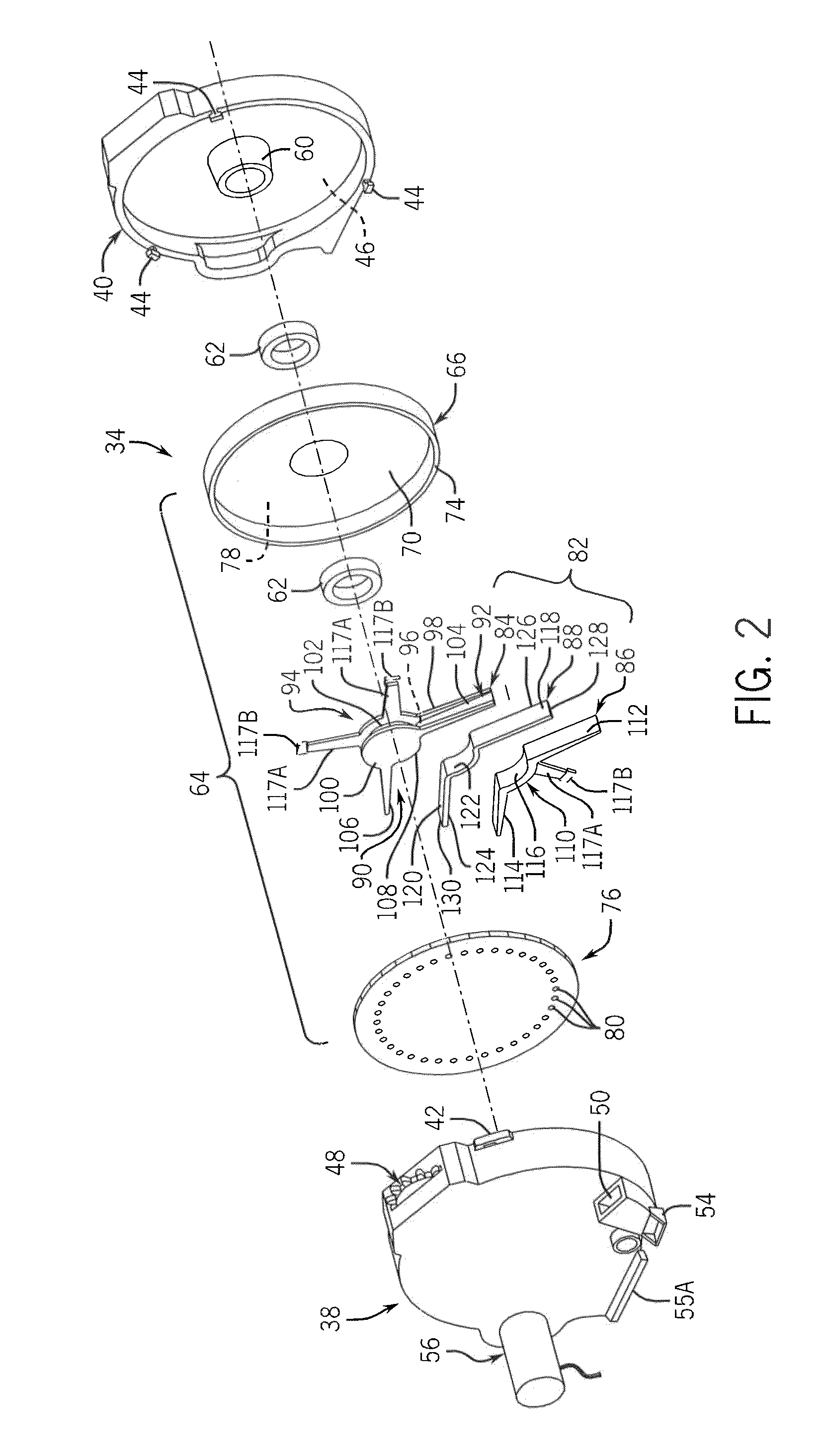
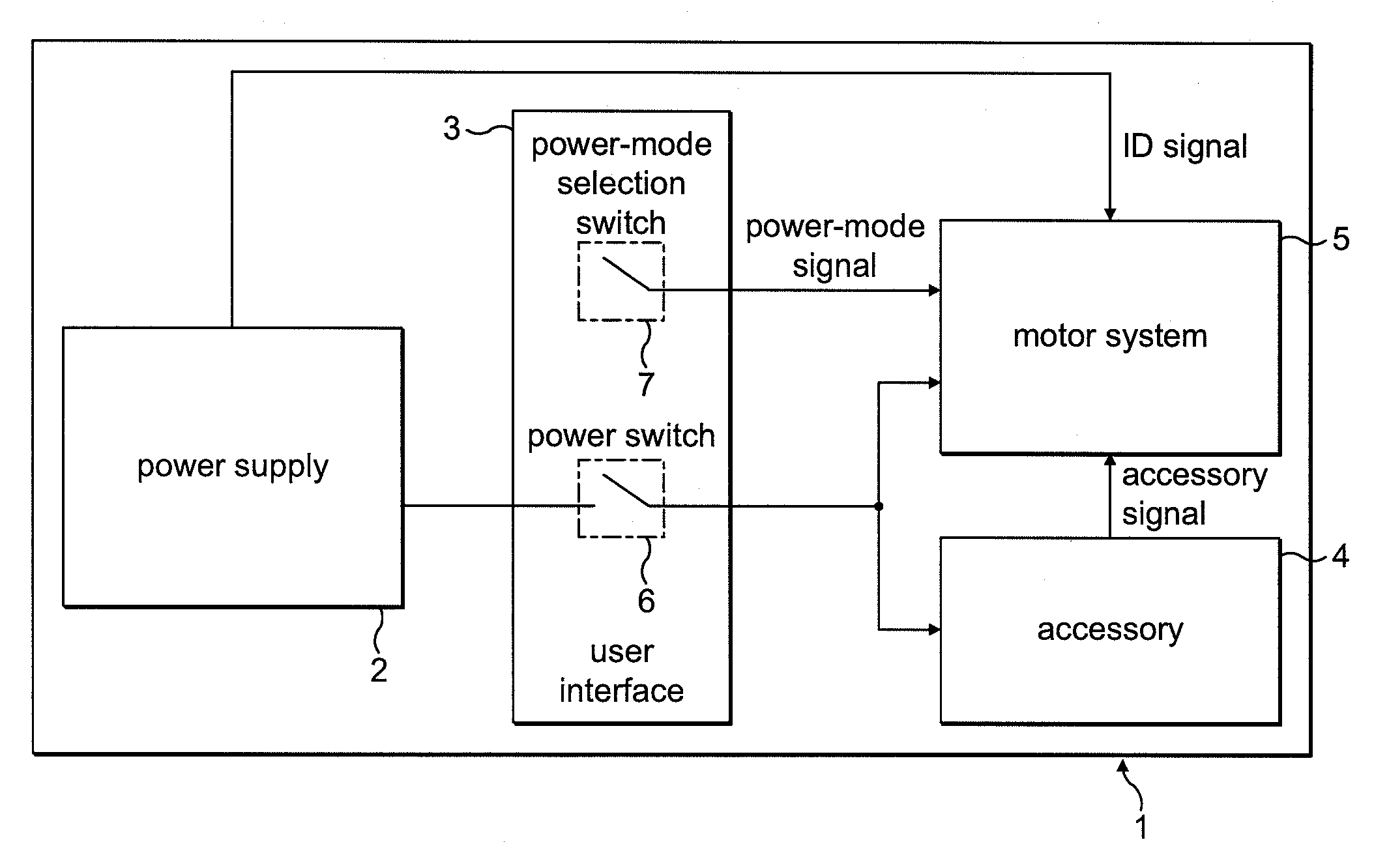
ActiveUS8925471B2Improve uniformityLess input vacuum pressurePotato plantersFurrow making/coveringVacuum pressureEngineering
A seed meter is provided for use with a row crop planter or seed planter that includes a seed disk assembly that rotates within a meter housing cavity and that has a seed disk assembly cavity in which a vacuum pressure is applied for pulling seeds into seed pockets of a seed disk of the seed disc assembly. The vacuum pressure is applied to the seed disk assembly by pulling a vacuum airflow through a spindle that supports the seed disk assembly. A wiper seal is arranged in a fixed position within the seed disk assembly cavity and seals against the seed disk assembly as a support plate and seed disk of the seed disk assembly rotate over the wiper seal, so that the wiper seal creates a boundary between a vacuum zone and a non-vacuum zone inside of the seed disc assembly cavity.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253265A1Good control over powerConvenient power controlSynchronous motors startersVacuum cleaner apparatusFreewheelElectric machine
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited in advance of zero-crossings of back emf in the winding by an advance angle, and the winding is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the advance angle and the freewheel angle in response to changes in the voltage used to excite the winding. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
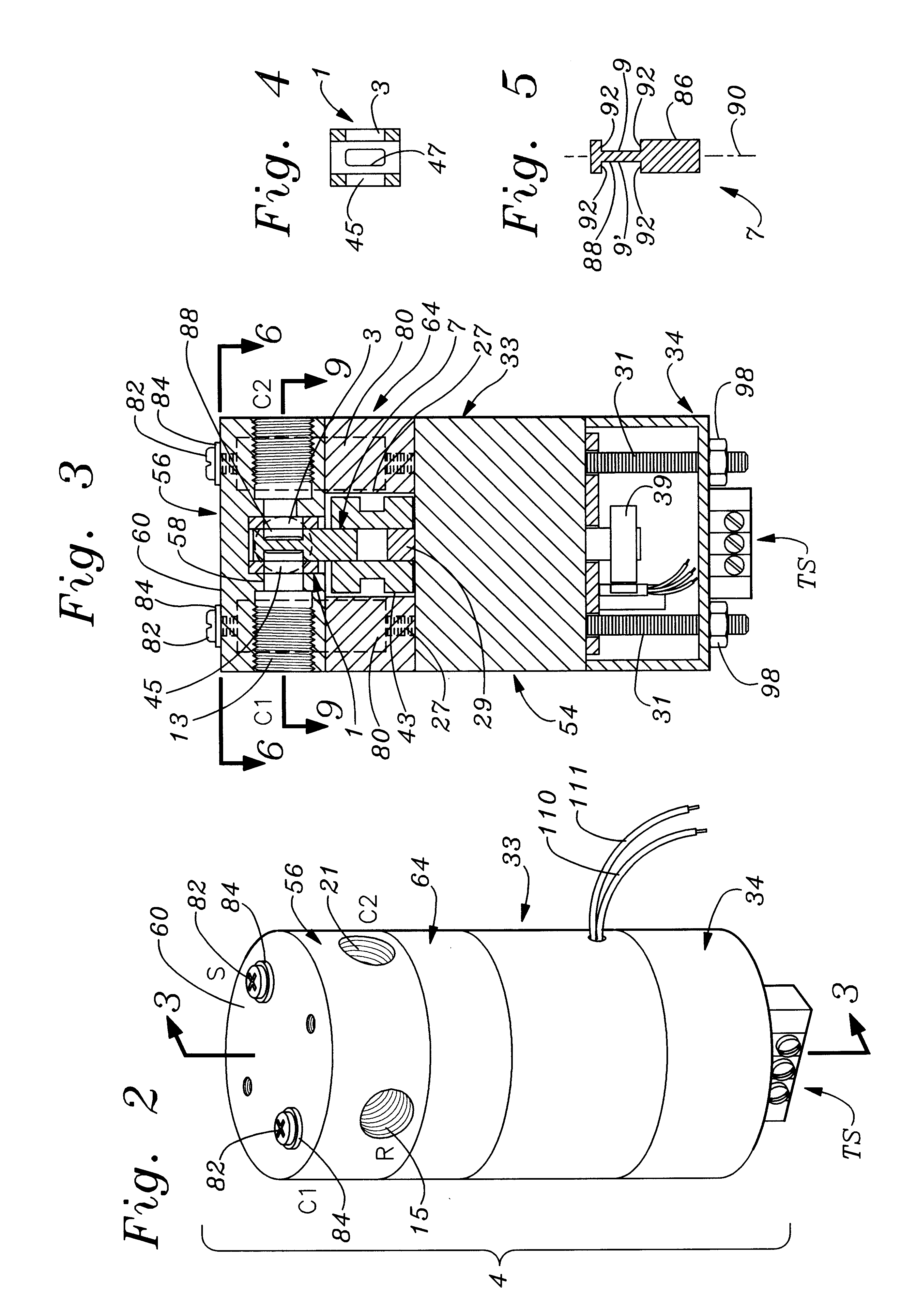
Rotary servovalve and control system
InactiveUS6269838B1Less torqueIncrease frequency bandwidth of responsivenessOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsFluid controlAngular rotation
An improved rotary servovalve system employs a rotary magnetic solenoid having an armature that includes at least one permanent magnet. The armature is rotatable relative to a stator formed as an electromagnet which is energizable to create alternative electromagnetic fields having opposite polarities from each other. When deenergized, the stator allows the armature to return to a neutral, null position from positions of extreme rotation in opposite angular directions due to the magnetic force of the permanent magnet of the armature. The armature is coupled to carry a movable valve element in angular rotation therewith, so that flow through the servovalve of the system can occur in alternative directions. Also, the valve element is biased toward a position in which all of the valve ports are closed when power is removed from the rotary solenoid. The control circuit employed in the rotary servovalve system expands the bandwidth of response of the solenoid actuator by compensating for frequency variations in the input command signal and in the feedback signal. This compensation is achieved utilizing a combined proportional, integral, and differential amplification circuit. Also, imbalance of fluid forces within the servovalve mechanism can be avoided by utilizing a pair of inlet orifices, a pair of outlet orifices, a pair of first fluid control orifices, and a pair of second fluid control orifices. The orifices within each pair are located on opposite sides of the valve housing from each other.
Owner:WOODWORTH RAYMOND DEXTER
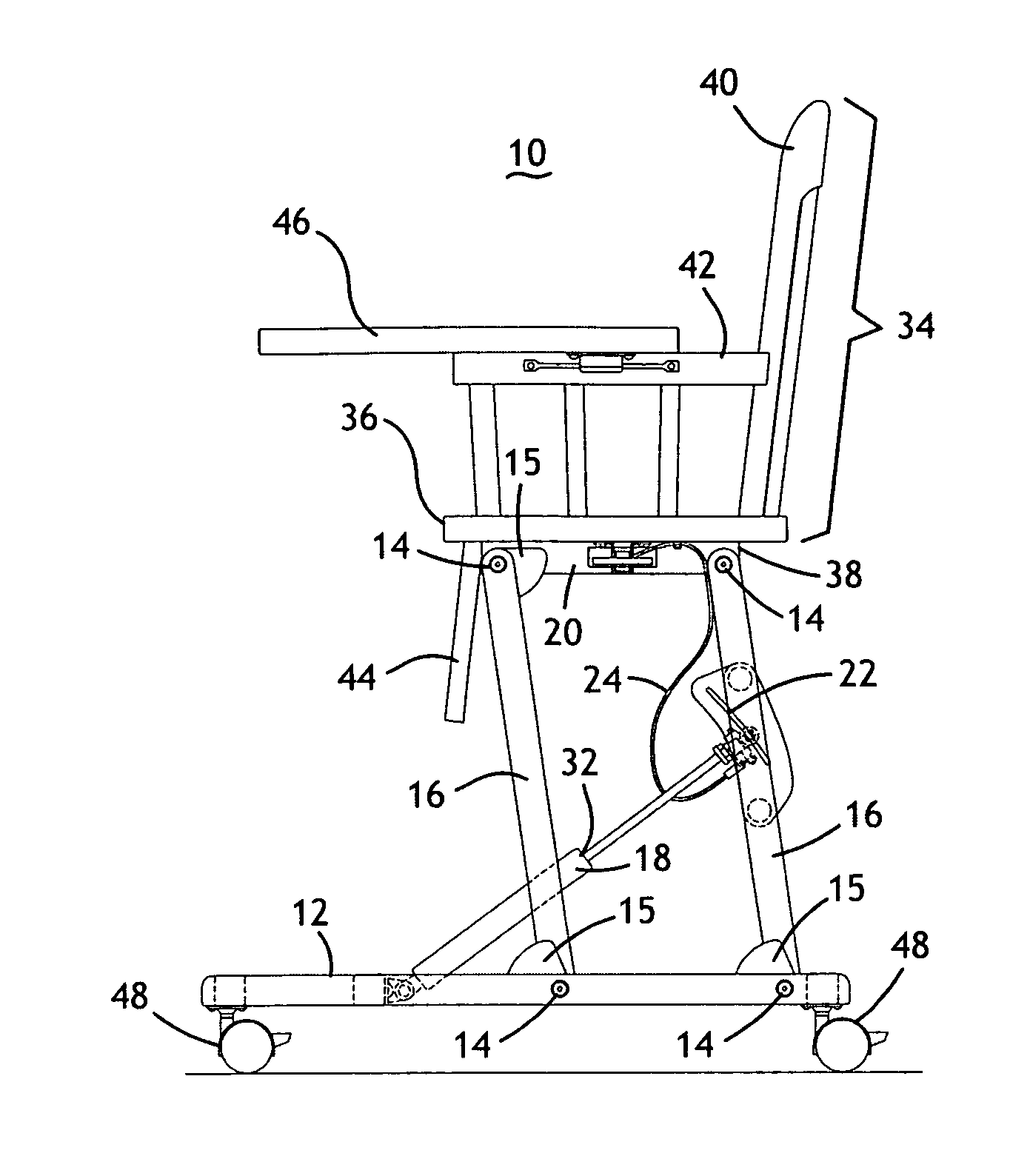
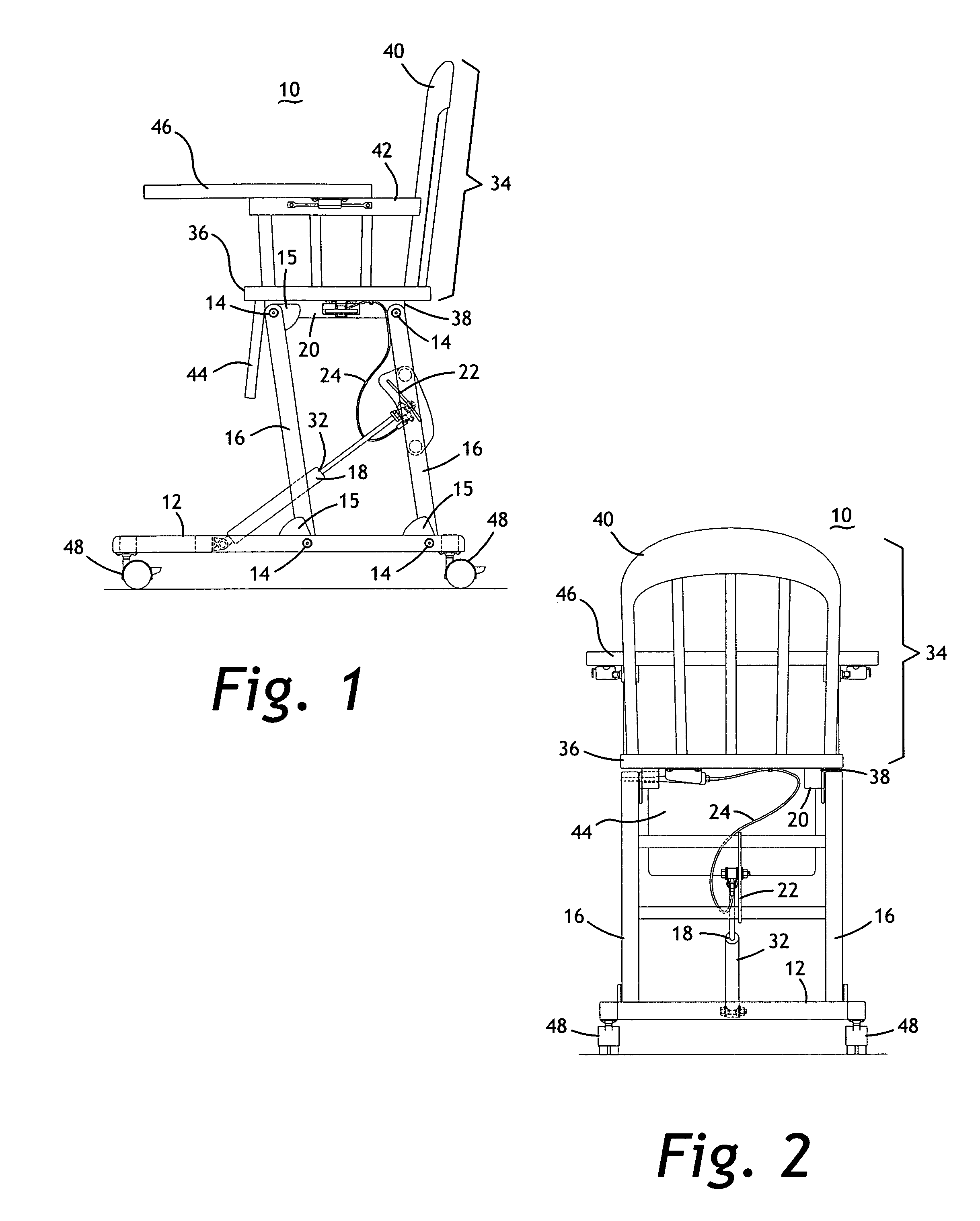
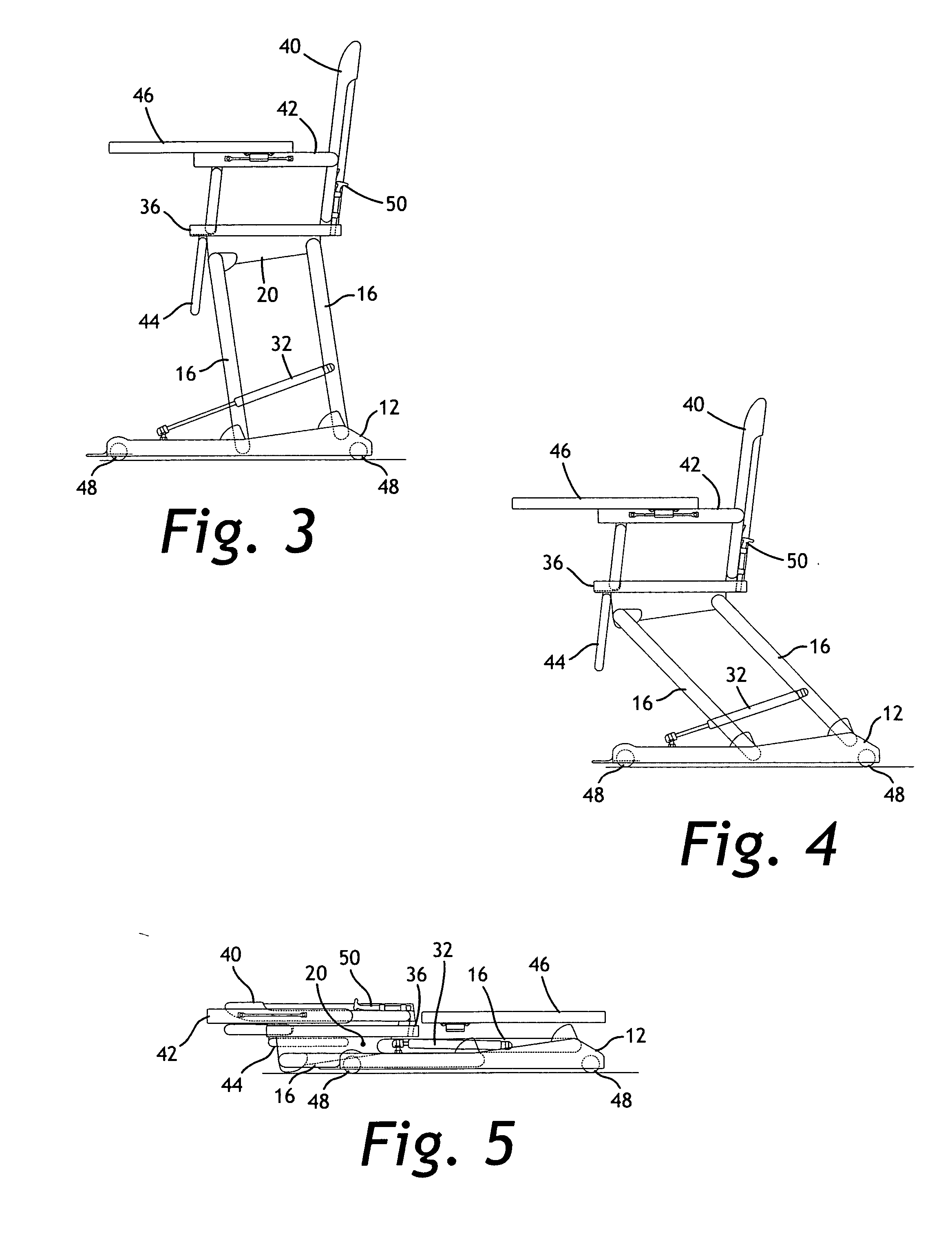
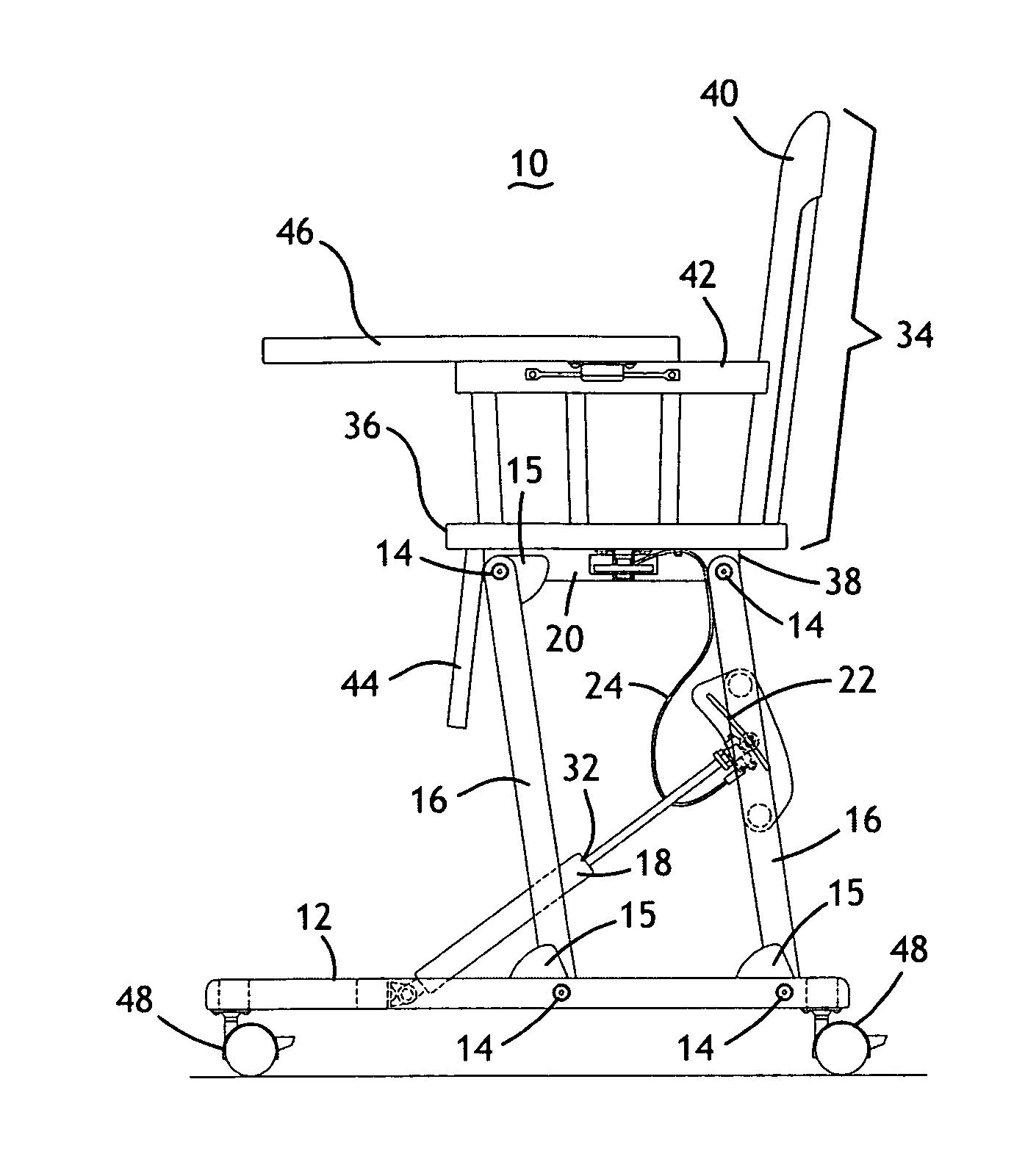
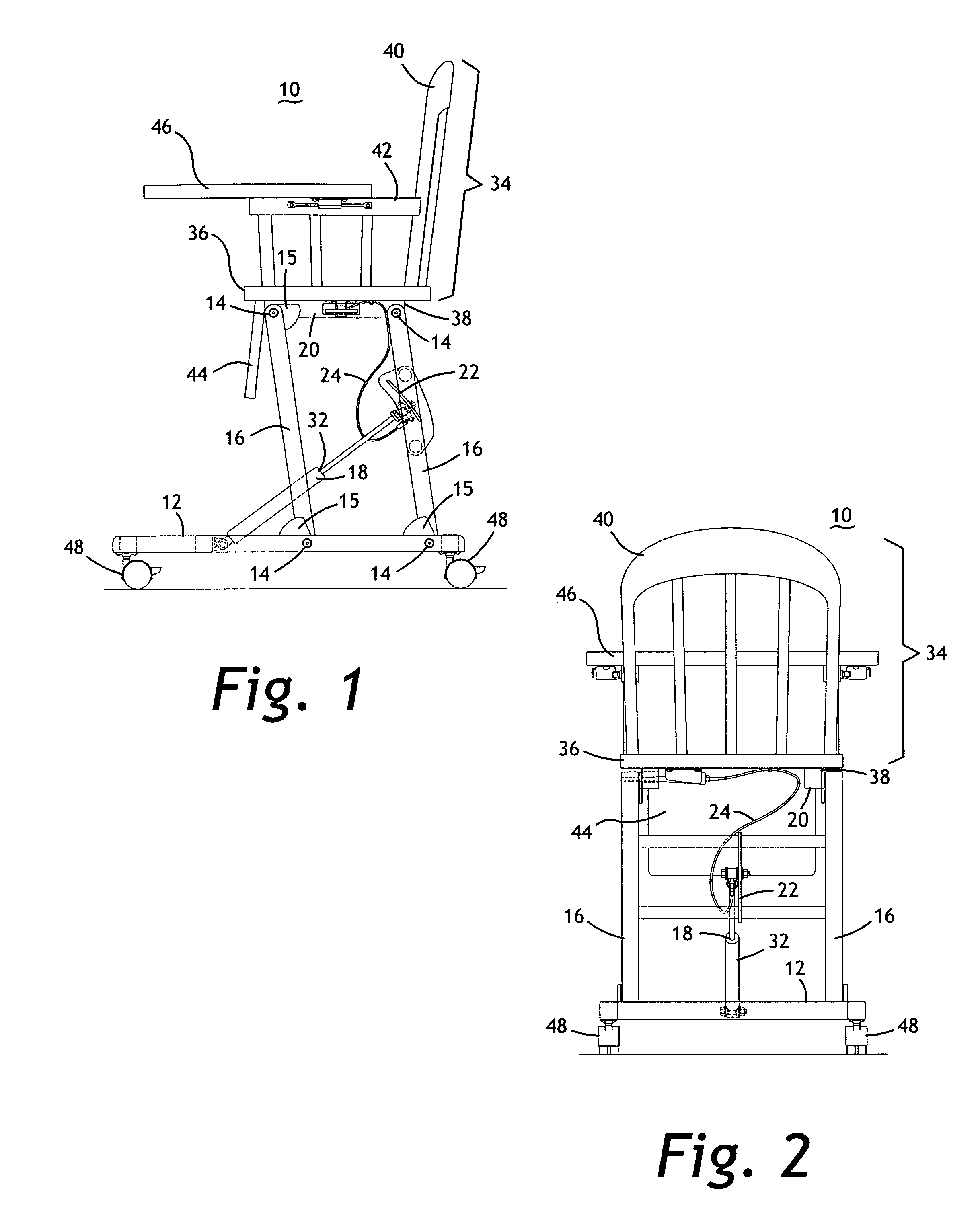
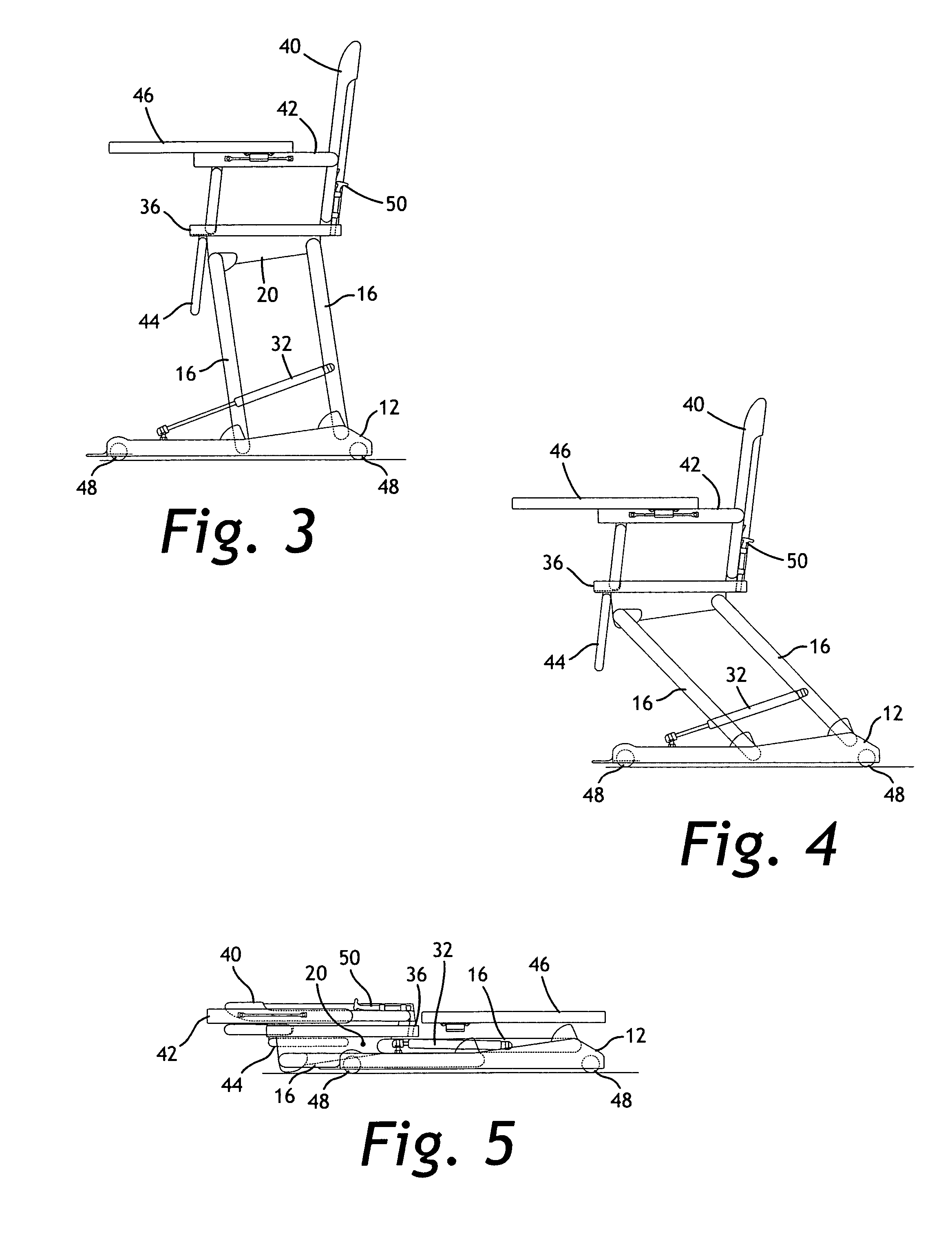
Height-adjustable furnishing system
InactiveUS20070089648A1Easy to adjust heightFacilitates folding of the furnishingOffice tablesFoldable chairGas springEngineering
A height-adjustable furnishing system includes a base component, a plurality of legs, a height adjustment mechanism, and a platform component. The base has a planar bottom surface and a top surface with a plurality of attachment points for pivotally attaching two, three or four legs. The height-adjustment mechanism is adjustably attached between the base component and at least one of the plurality of legs, or between a forward leg and a rear leg. A platform component is pivotally attached to the plurality of legs to form a parallelogram linkage when viewed from the side. The height-adjustment mechanism may include a gas spring, a cam clamp, a travel block, a release lever, a cable release, a release trigger and may also be hand- or foot-operated. The entire system folds to a generally planar configuration for storage. The legs are erect when they are approximately 10 degrees from vertical.
Owner:HARRISON JOSEPH HUNTER +1
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100251512A1Less torqueSmoother currentSynchronous motors startersSingle motor speed/torque controlZero crossingConductor Coil
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes exciting a winding of the electric machine in synchrony with zero-crossings of back emf when operating over a first speed range. The method then includes exciting the winding in advance of the zero-crossings by a fixed period of time when operating over a second speed range, and exciting the winding in advance of the zero-crossings by a period of time that varies with speed when operating over a third speed range. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
High-speed electric system
ActiveUS20100251509A1Improve efficiencyConstant output powerSynchronous motors startersMultiple motor speed/torque controlElectric machineControl system
An electric system that includes a single-phase permanent-magnet electric machine and a control system for driving the electric machine under load at speeds in excess of 60 krpm. Additionally, a product that includes the electric system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Injection molding method and apparatus
InactiveUS7906048B2Enhanced performance characteristicReduce pressure applyAuxillary shaping apparatusFood shapingSource materialInjection molding process
A thermoplastic injection molding system and method of use is described for molding parts from heated plastics and other organic resins. The machine uses heat sources located along the barrel to heat the source material while an auger screw transports the source material in the barrel. This transport step does not shear the source material, nor does it use friction to produce the heat necessary to melt the source material. The material becomes substantially liquid or melted during the heating process, and the melted material is forced, by the auger screw, into a chamber whereupon a plunger, situated concentrically with the auger screw, injects the material from the chamber into a mold. Sensors located along the barrel and in the chamber ensure consistency between mold cycles. The controller dynamically adjusts the injection molding process to achieve more consistent and reliable molded parts.
Owner:KOALESCE
Combination sensor guidewire and methods of use
ActiveUS8231537B2Good accuracy and consistencyMinimize impactBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterEngineeringGuide wires
The present invention provides for an improved combination sensor tip that includes a pressure sensor and a second sensor other than a pressure sensor, both disposed at or in close proximity to the distal end of the combination sensor tip. The present invention also provides for an improved connector to couple a guide wire to a physiology monitor that reduces torsional resistance when maneuvering the guide wire.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Control of an electric machine
ActiveUS20100253263A1Convenient power controlDecreasing freewheel angleMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersFreewheelFree rotation
A method of controlling an electric machine that includes sequentially exciting and freewheeling a winding of the electric machine. The winding is excited by an excitation voltage and is freewheeled over a freewheel angle. The method then includes varying the freewheel angle in response to changes in the excitation voltage. Additionally, a control system for an electric machine, and a product incorporating the control system and electric machine.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Self-Clearing Self-Cutting Implant
ActiveUS20110195380A1Reduce frettingReduce torqueDental implantsThread cutting machinesBone implantBiomedical engineering
Owner:INTRA LOCK INT
Motor mechanism
ActiveUS20110215597A1Prevent excessive outputLess torqueGearingNon-mechanical controlsElectric machineControl theory
In one use, a motor mechanism for an electronic lock is disclosed. In one embodiment, the motor mechanism includes a split nut that travels along a threaded screw drive. When the split nut is physically limited from further travel along the screw drive, the split nut decouples and recouples with the screw drive to reduce drag on the motor and thereby reduce motor burnout. As a result, smaller, more cost effective and efficient electric motors may be utilized together with simplified electronics.
Owner:ASSA ABLOY AB
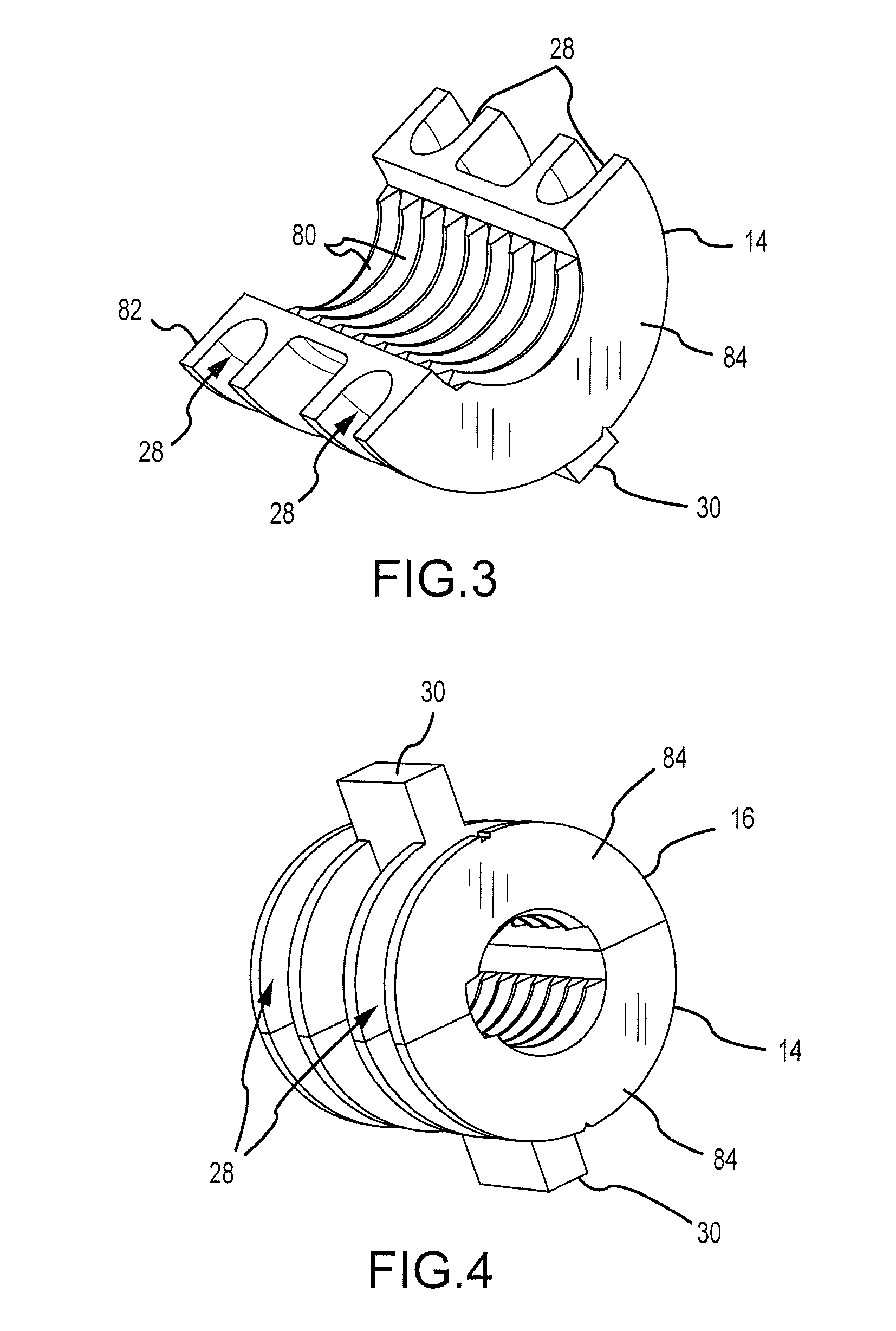
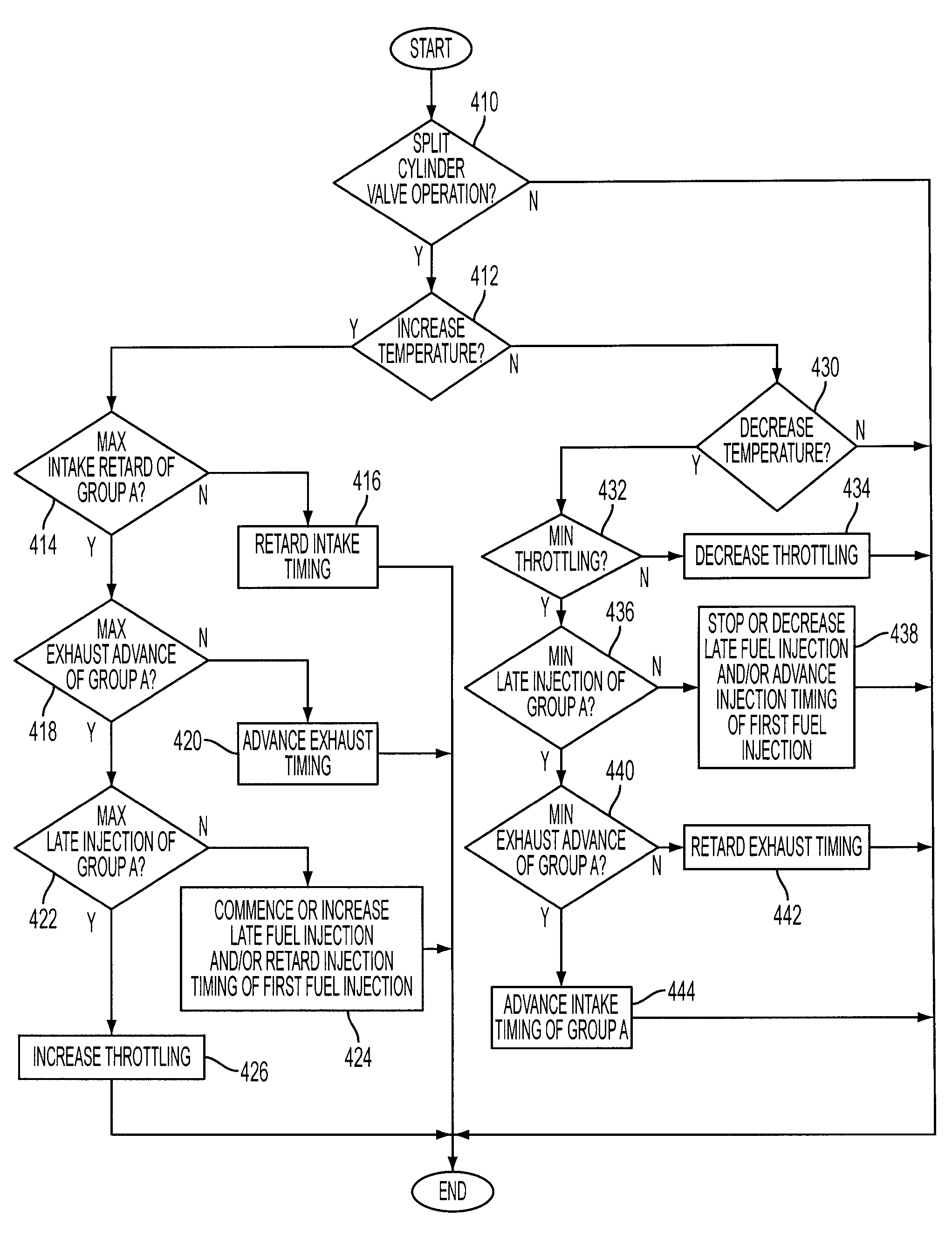
Diesel engine with differential cylinder group operation
InactiveUS7246595B1Less torqueIncreasing throttlingValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustionExhaust valve
A method for controlling operation of a diesel engine having a plurality of cylinders, the engine including a first group of cylinders and a second group of cylinders, the method comprising of operating the first group of cylinders with a first intake and exhaust valve timing, the first group of cylinders inducting air and performing diesel compression ignition combustion of injected fuel; and operating the second group of cylinders with a second intake and exhaust valve timing, the second group of cylinders inducting air and performing diesel compression ignition combustion of injected fuel, wherein said second intake valve timing is retarded compared to said first intake valve timing or said second exhaust valve timing is advanced compared to said first exhaust valve timing.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Constant-power electric system
ActiveUS20100251510A1Easy to controlKeep for a long timeSynchronous motors startersSingle motor speed/torque controlConstant powerControl system
An electric system that includes a single-phase permanent-magnet electric machine and a control system for driving the electric machine. The control system sequentially excites and freewheels a winding of the electric machine so as maintain substantially constant power over an operating speed range spanning at least 10 krpm and / or an excitation voltage range extending between a minimum voltage and a maximum voltage, the minimum voltage being less than 80% of the maximum voltage. Additionally, a product comprising the electric system.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
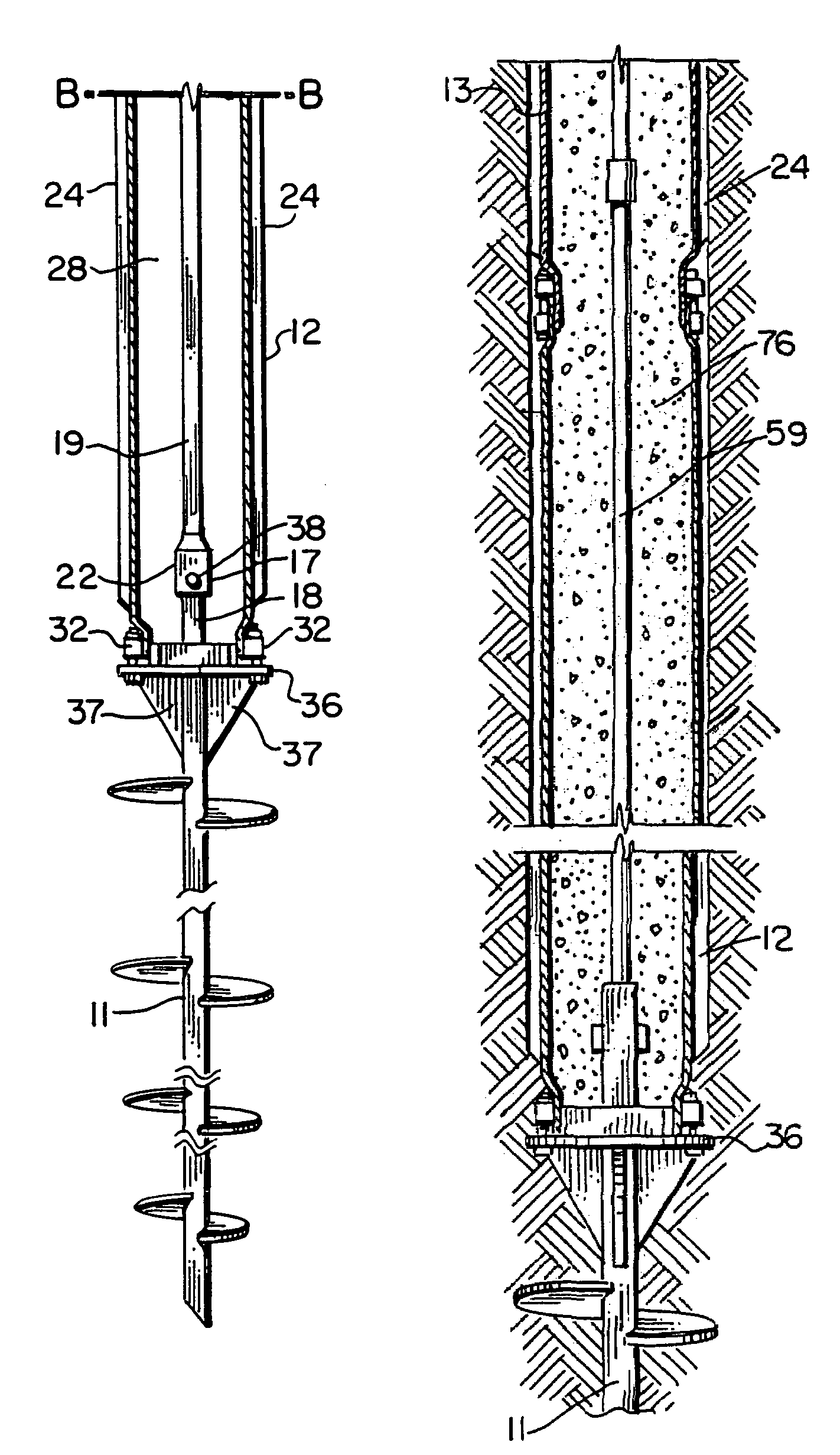
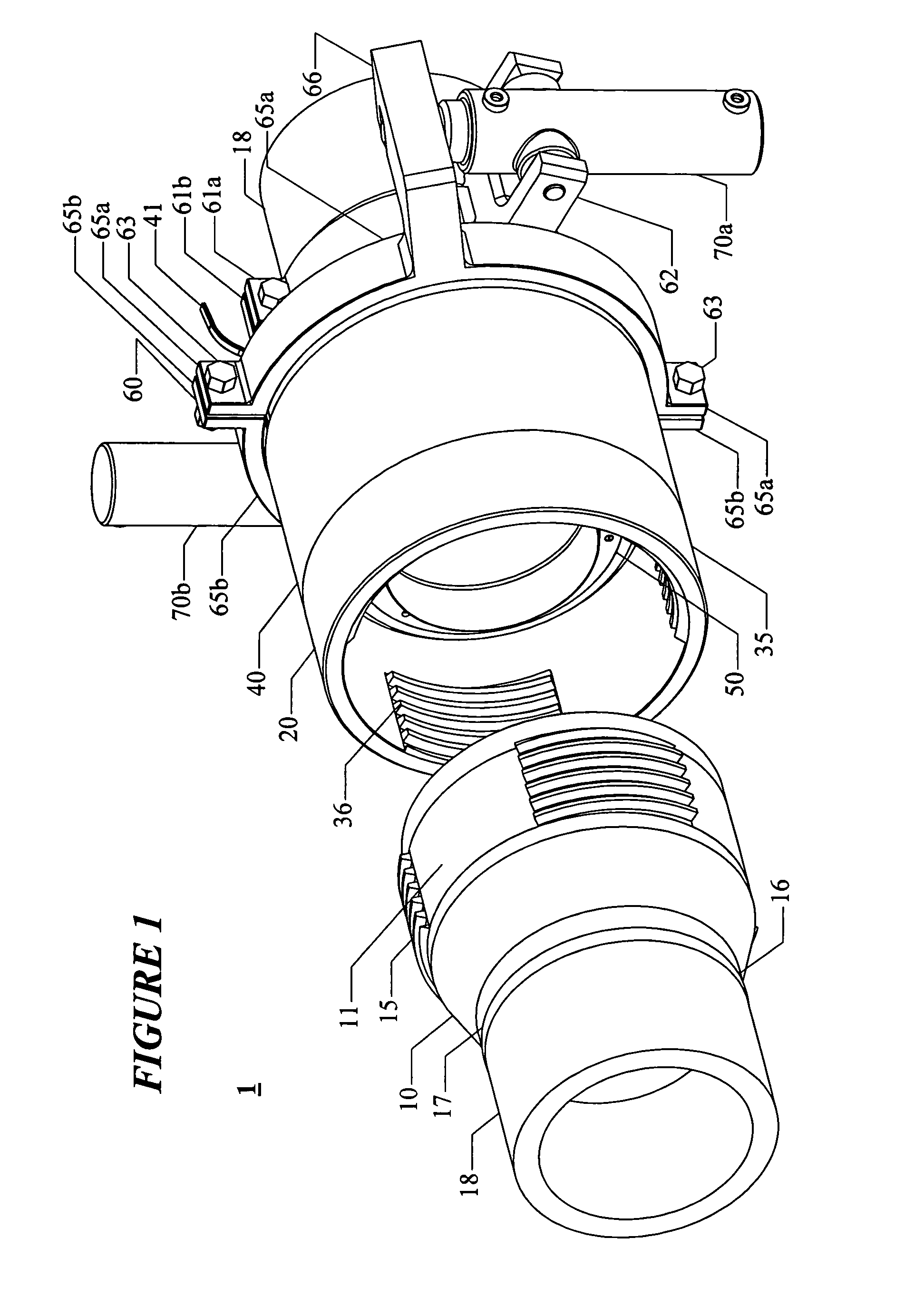
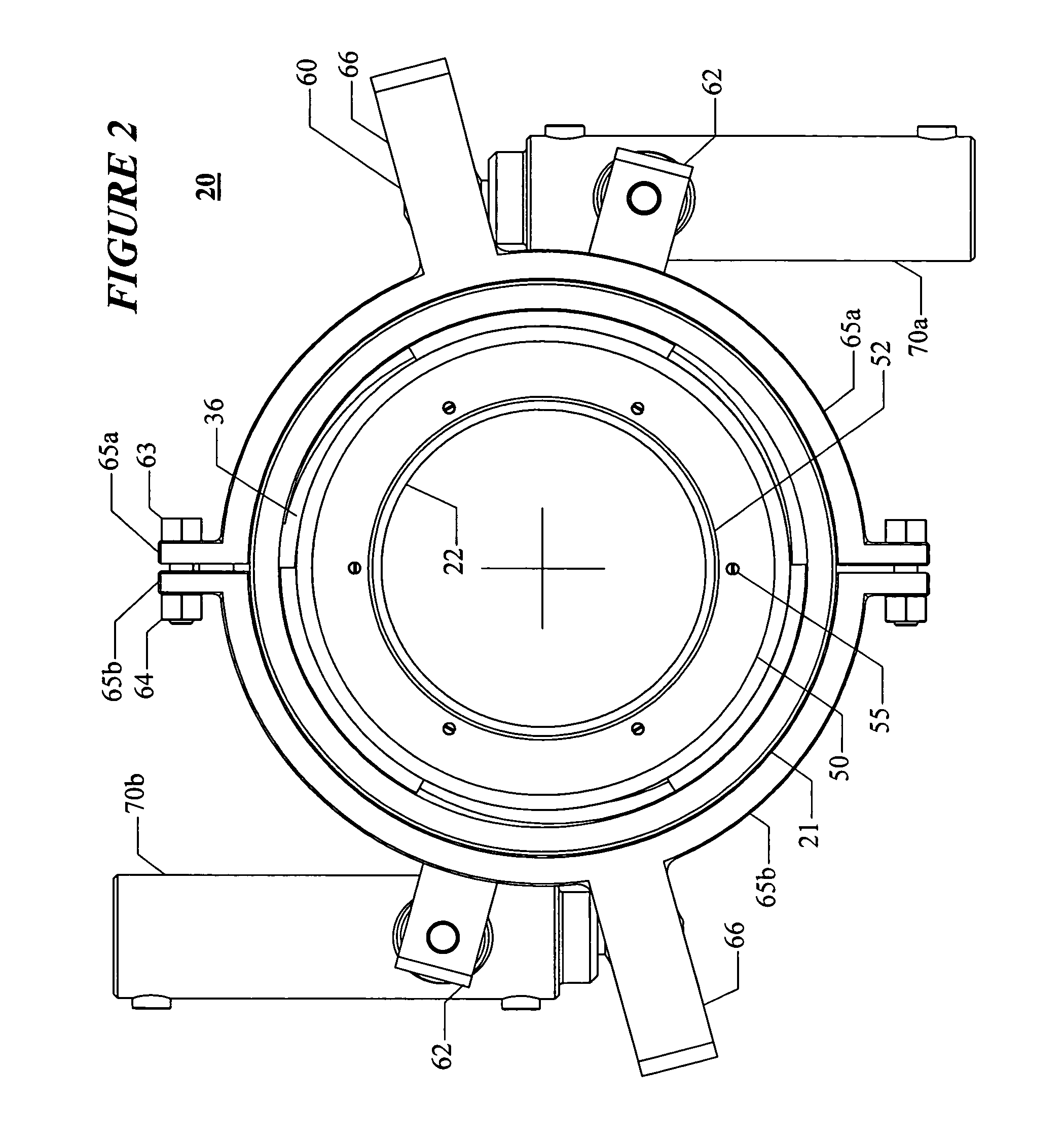
Piling apparatus having rotary drive
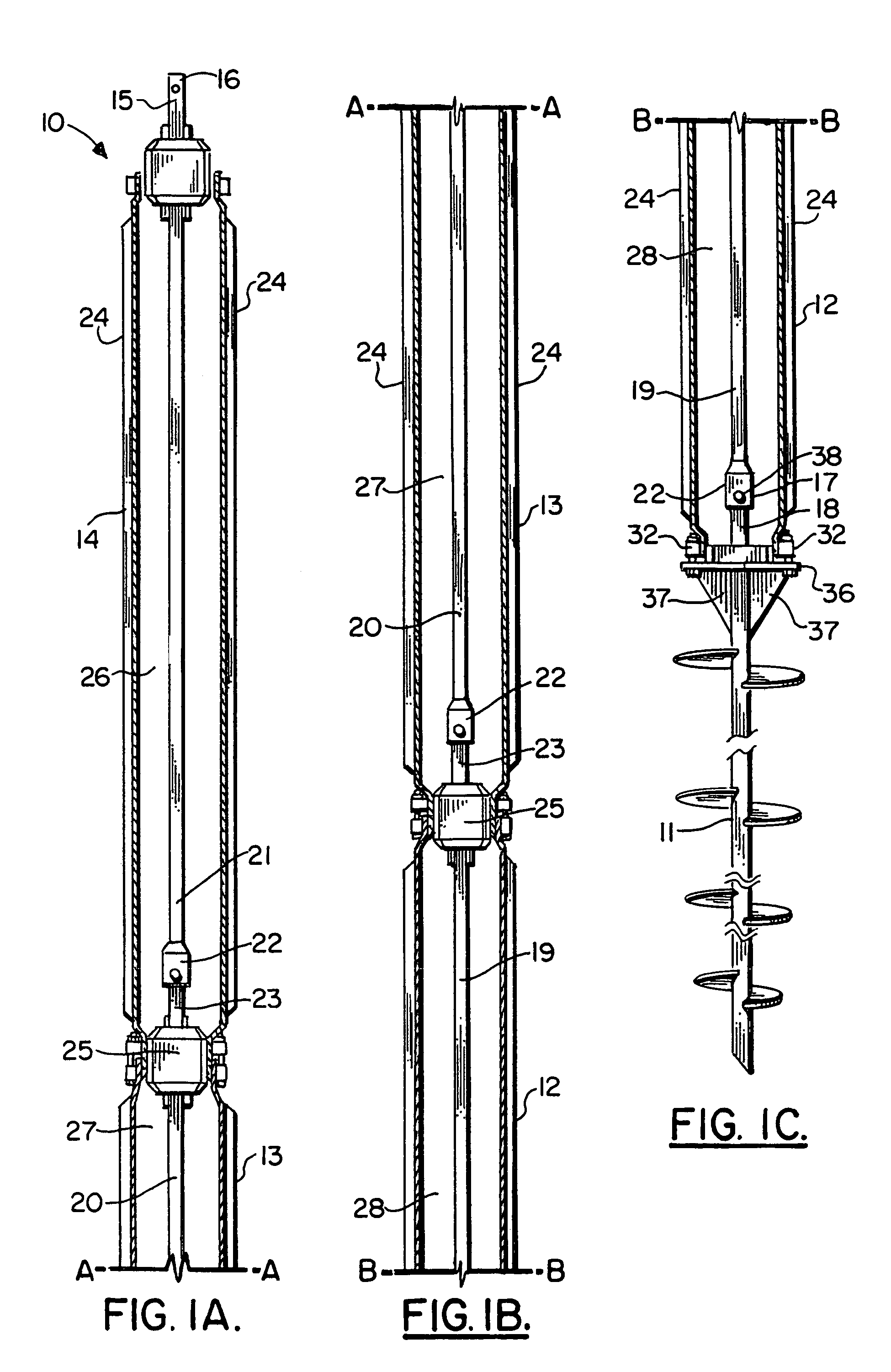
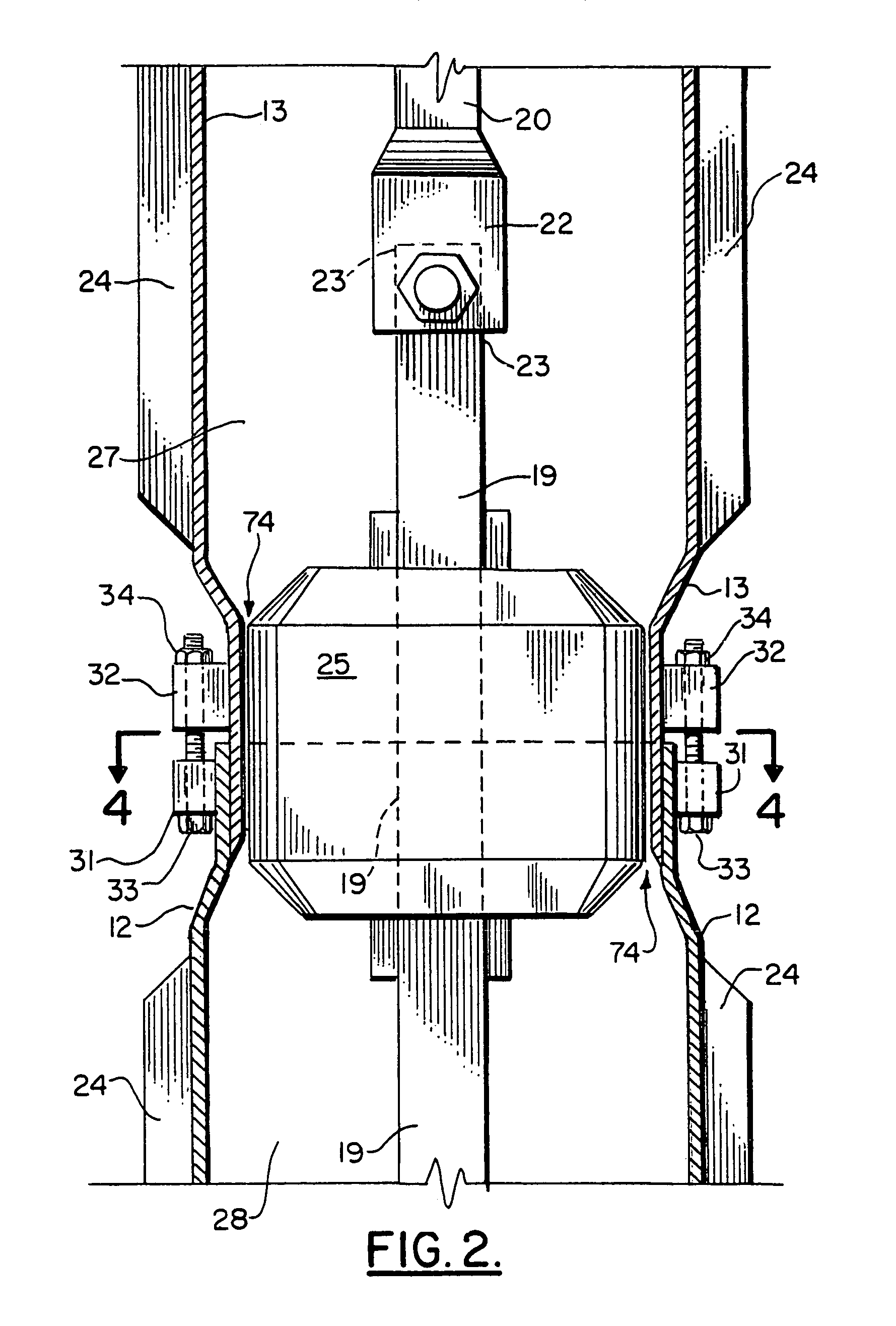
An in-situ pile apparatus 10 includes a helical anchor to which a plurality of elongated generally cylindrically shaped sections can be added. Each of the sections has a specially shaped end portion for connecting to another section. An internal drive is positioned in sections inside the bore of each of the connectable pile sections. The internal drive includes enlarged sections that fit at the joint between pile sections. In one embodiment, the internal drive can be removed to leave a rod behind that defines reinforcement for an added material such as concrete. The rod also allows for a tension rod connection from the anchor tip to an upper portion attachment point.
Owner:WHITSETT MICHAEL
Dental Implant and Method for Rapid Integration
The invention relates to methods of stabilizing bone implants, comprising inserting a self tapping implant having at least two helical grooves running in opposite directions around the implant wherein the implant generates a minimum of bone debris during insertion and implant is integrated within 3-6 weeks.
Owner:INTRA LOCK INT
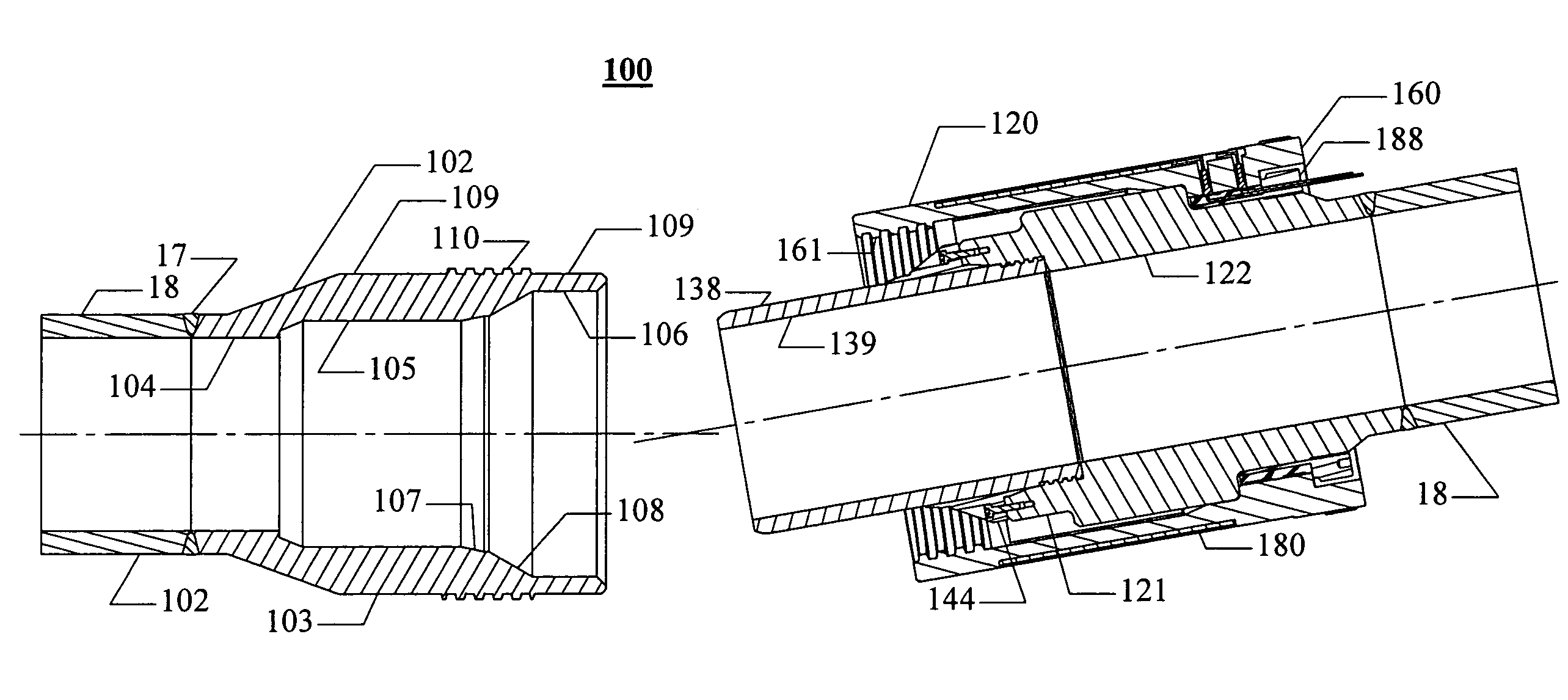
Pressure-containing tubular connections for remote operation
InactiveUS7431351B2Rapid and reliable and accurateReduce the amount requiredSleeve/socket jointsFluid pressure sealed jointsElectricityControl manner
Owner:RUSSELL LARRY R
Height-adjustable furnishing system
InactiveUS7703726B2Easy to adjust heightFacilitates folding of the furnishingOffice tablesFoldable chairGas springEngineering
Owner:HARRISON JOSEPH HUNTER +1
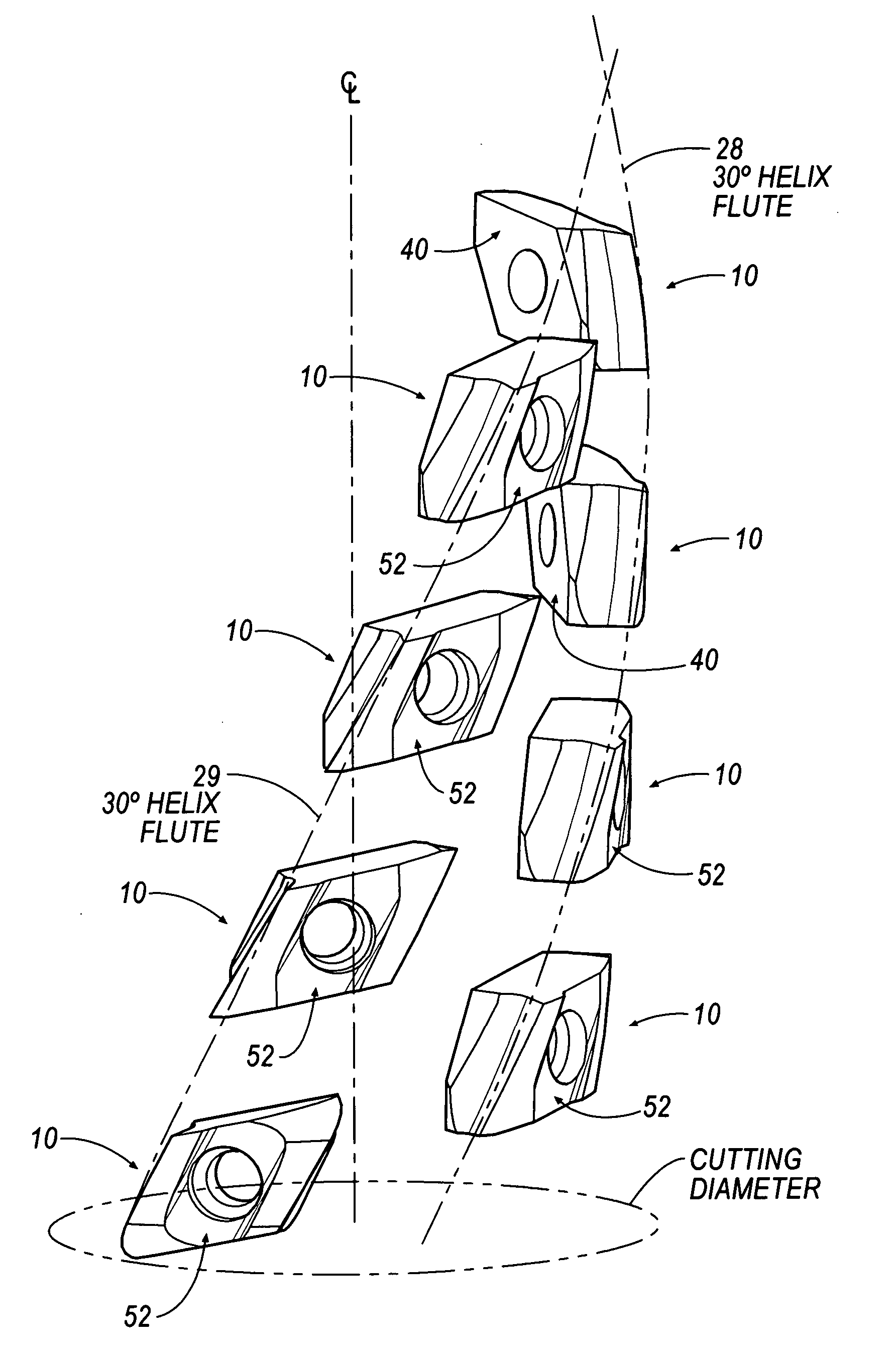
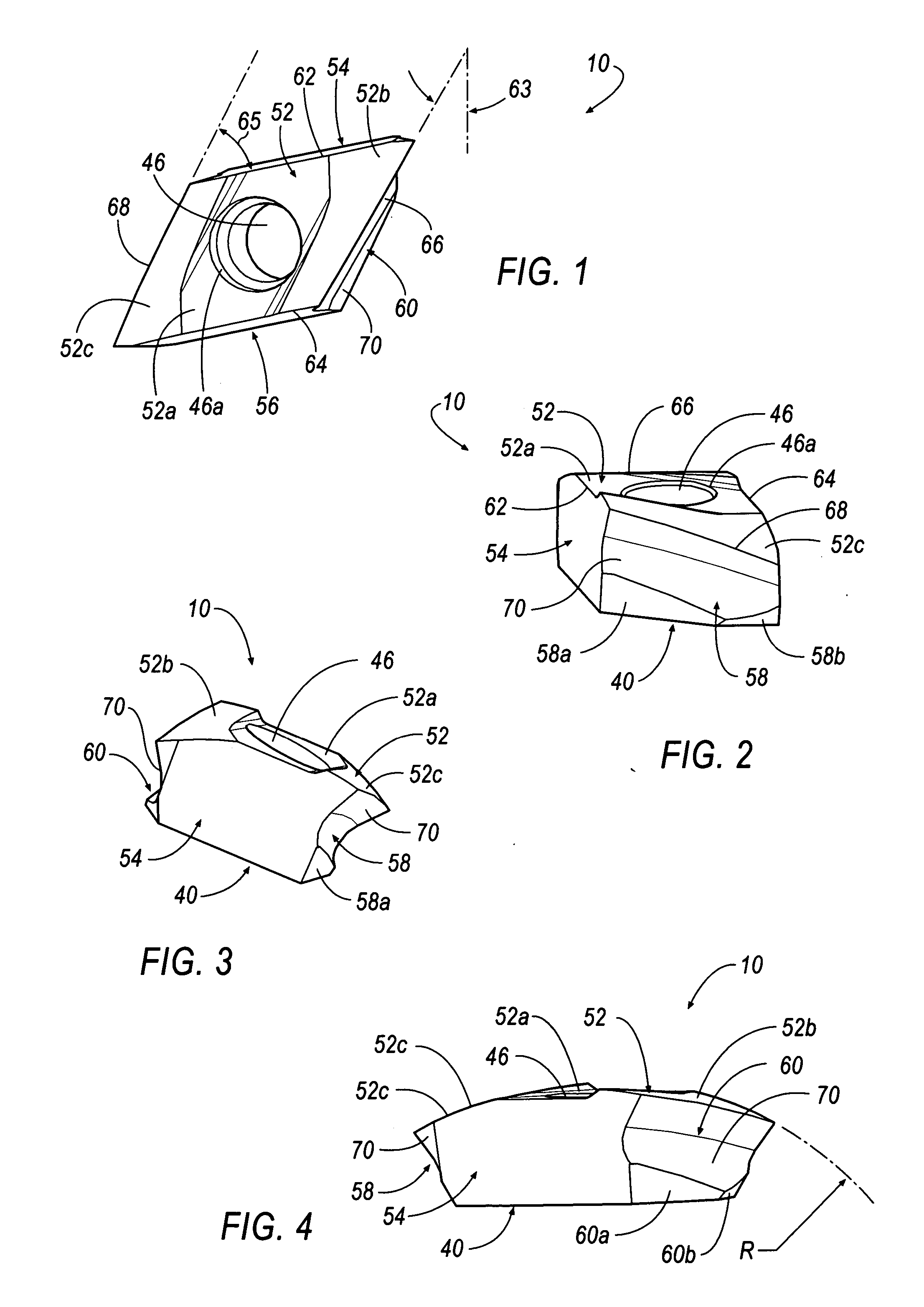
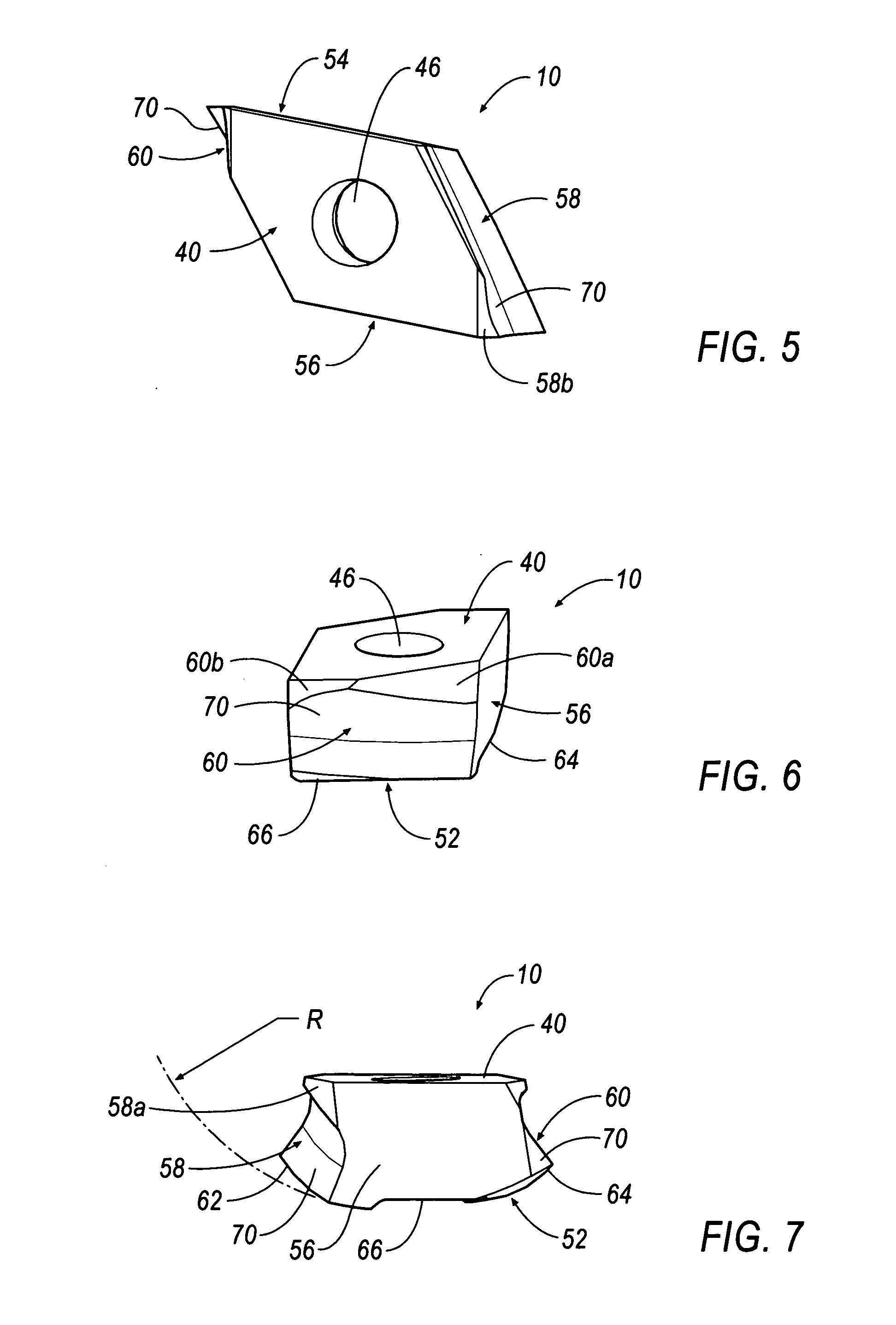
Helical cutting insert with progressive cutting edge
InactiveUS20060280567A1Less powerLess torqueMilling cuttersShaping cuttersEngineeringMechanical engineering
An indexable, helical cutting insert includes at least one axial clearance slash extending from a bottom surface to one of said side walls forming a wiper on an edge of the axial clearance slash. In another embodiment, the cutting insert includes at least one inside cutting edge that extends outwardly a distance from the side wall. In another embodiment, the helical cutting insert includes at least one progressive cutting edge. In another embodiment, the cutting insert includes at least one helical cutting edge that is curved inwardly to enable the cutting insert to perform machining operations on cutters having different diameters.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Tamper evidence device for roll-on pilfer proof closures
Methods and apparatus of sealing bottles with Roll-on Pilfer Proof (ROPP) closures and providing tamper evidence are provided. More specifically, the present invention relates to novel ROPP closures that may be used to seal a bottle shaped container which can subsequently receive a tamper evidence device. The bottle can have a neck portion formed without a skirt portion. Optionally, the bottle can include an annular ring. The ROPP closure generally includes a body portion. In one embodiment, the body portion has a curl. A tamper evidence device can be applied to a bottle sealed with a ROPP closure by a capping apparatus. The tamper evidence device may be visually altered when the ROPP closure is rotated in an opening direction. In one embodiment, the ROPP closure cannot be rotated while the tamper evidence device is associated with the bottle. In another embodiment, the tamper evidence device includes at least one protrusion which extends inwardly at least partially into the bottle annular ring.
Owner:BALL CORP
On-demand hydraulic pump for a transmission and method of operation
A fixed displacement binary pump is provided for a powertrain on a vehicle. A hydraulic system is operatively connected with first and second discharge ports of the pump and is operable to alternately permit fluid flow through both discharge ports (i.e., full displacement or volumetric output of the pump) or permit flow through only the first discharge port (i.e., partial displacement or volumetric output of the pump). The pump may be packaged in a front support of the transmission. An auxiliary pump may be provided that is operable to supplement the output of the binary pump or to be used when the binary pump is off. A method of operating the binary pump and auxiliary pump is provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
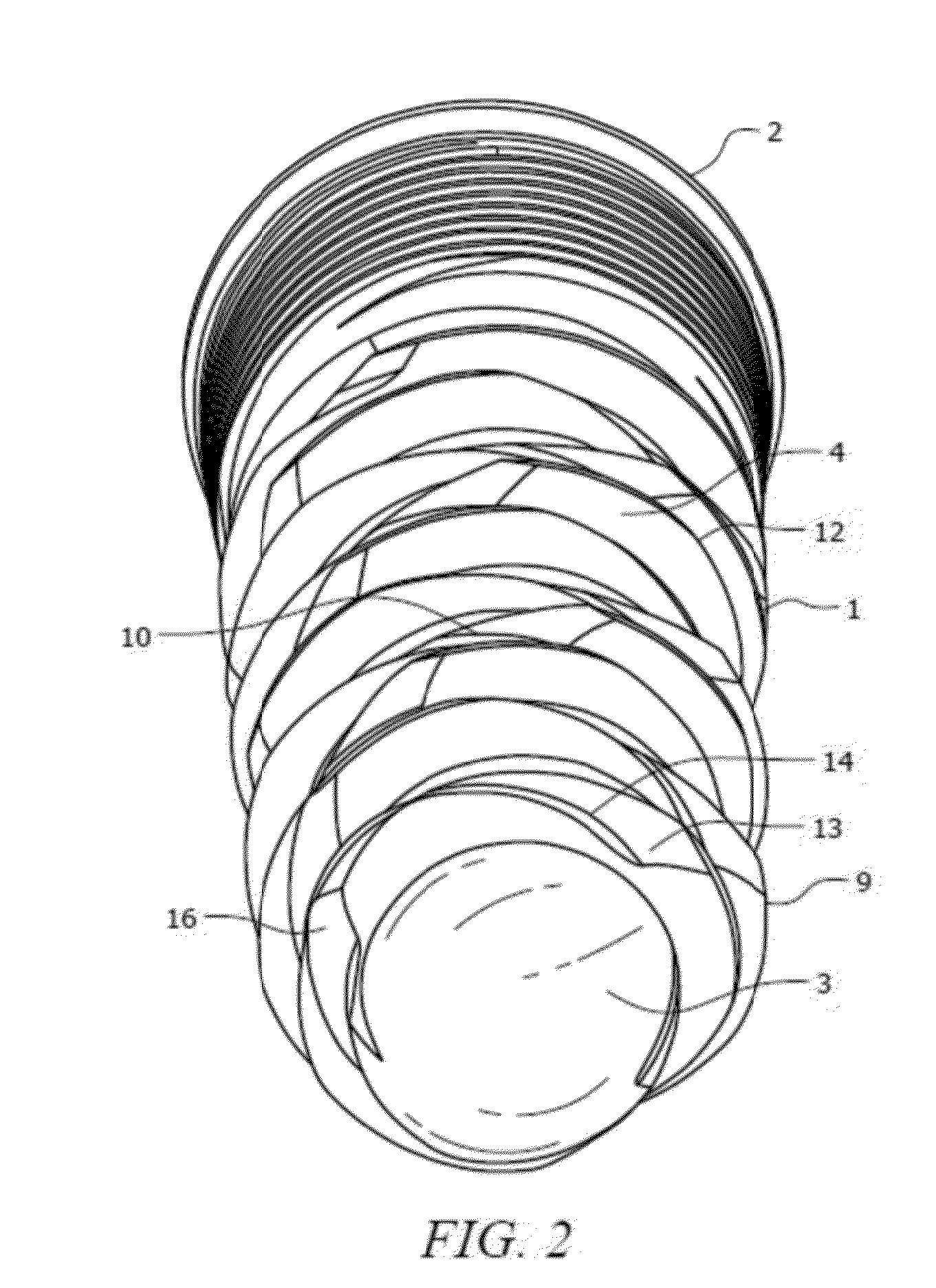
Metal container
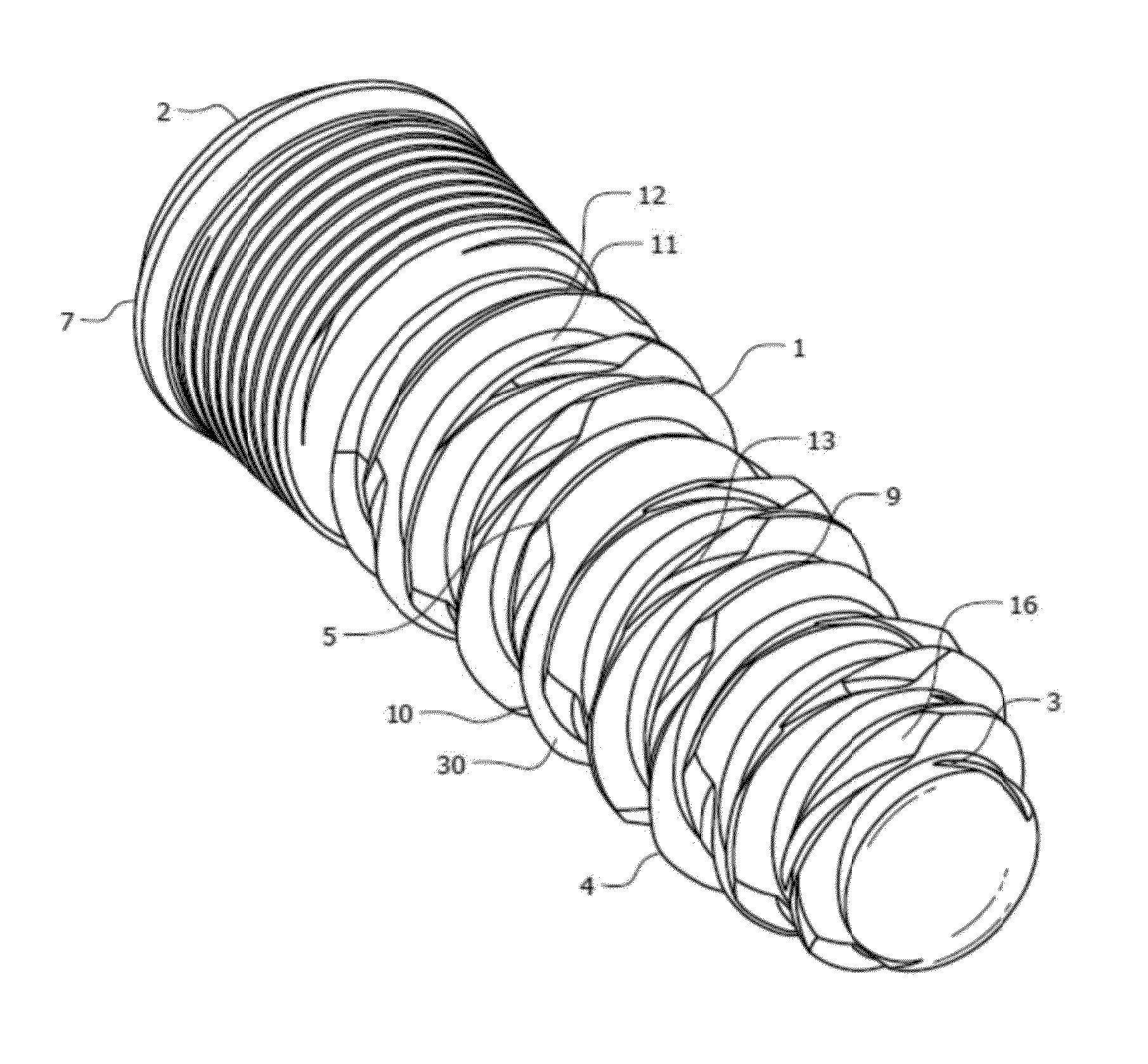
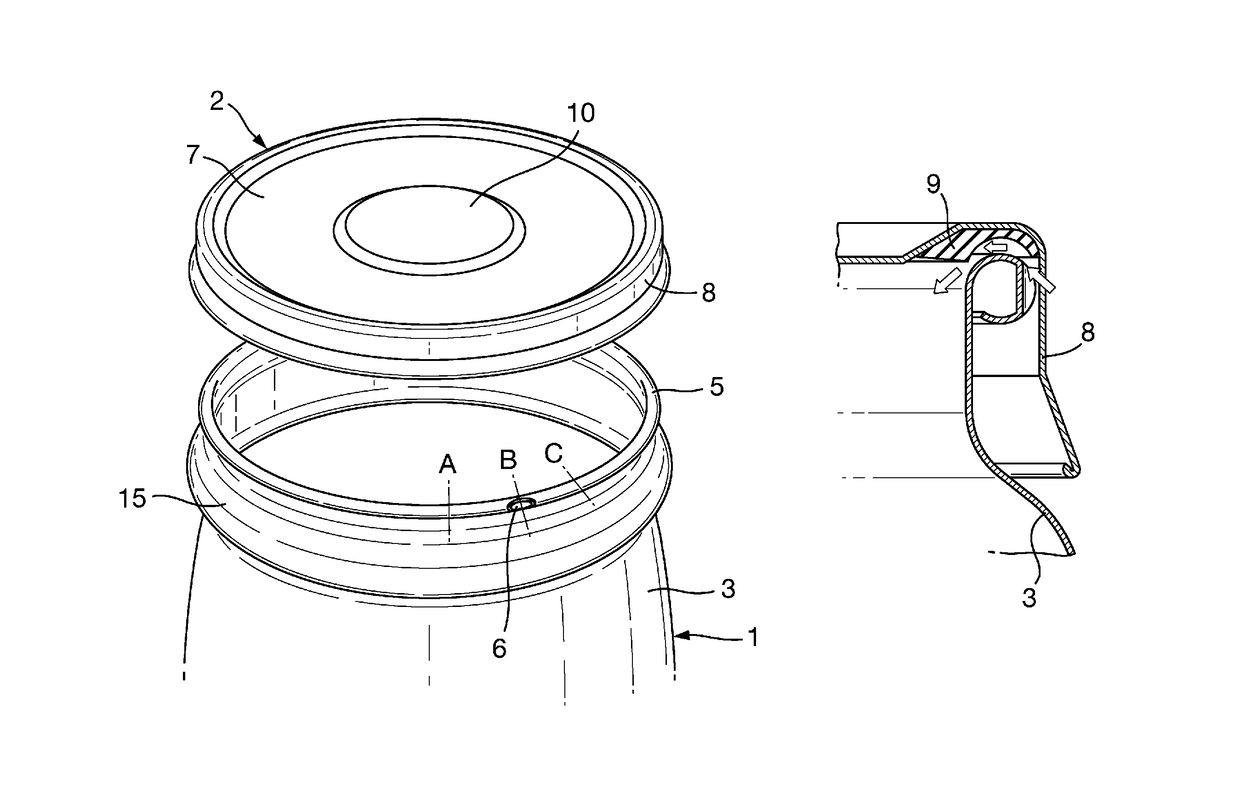
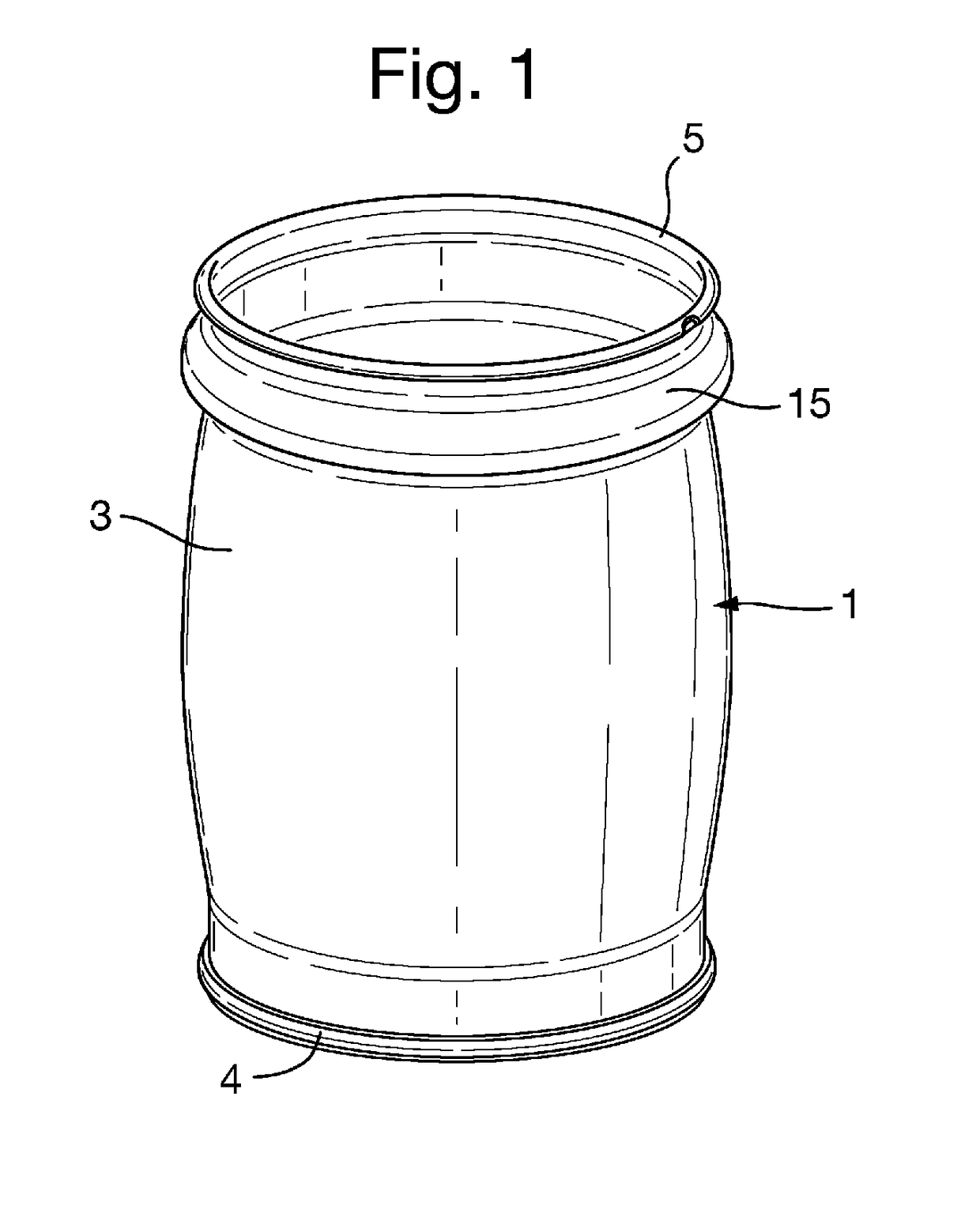
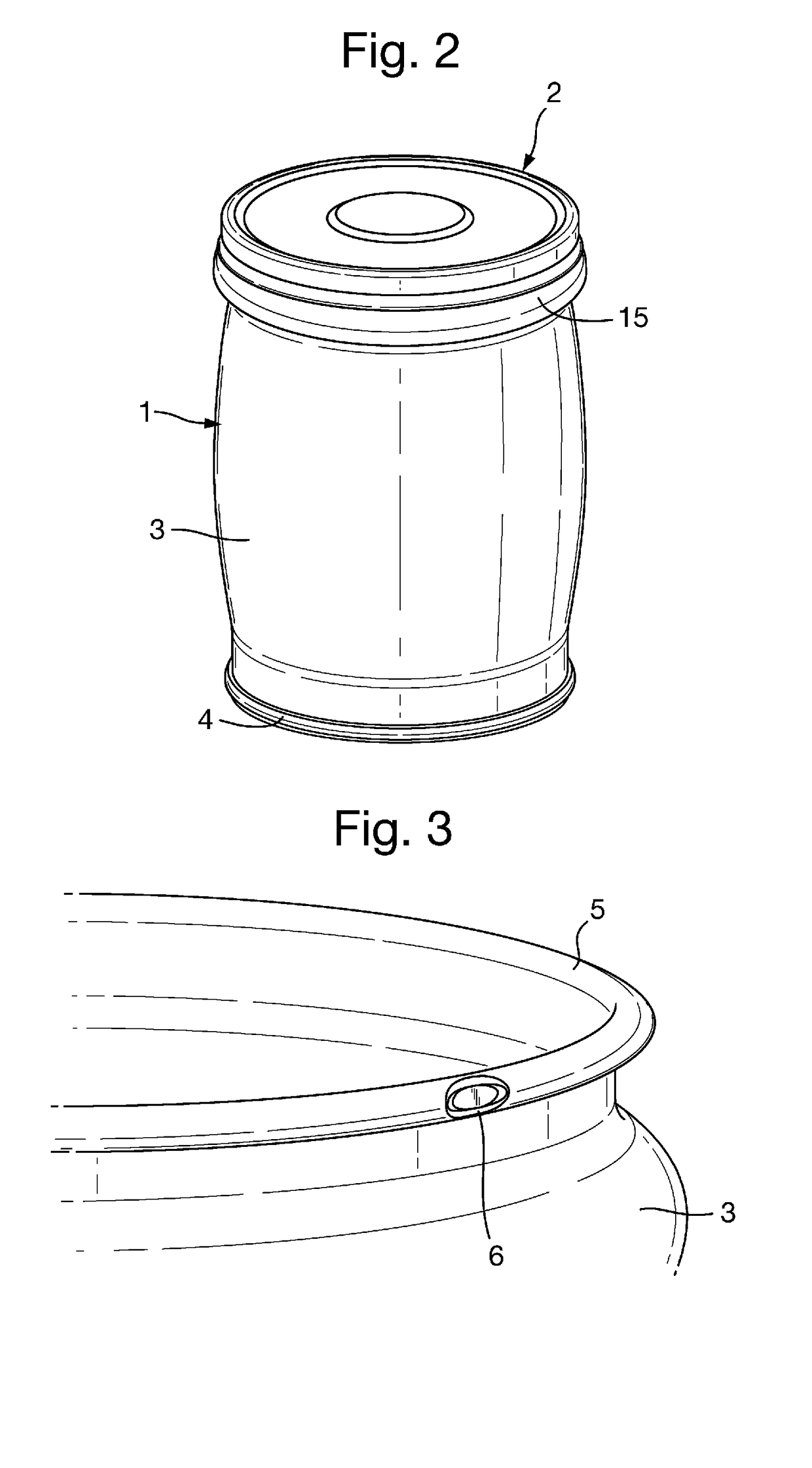
A metal container body 1 comprises a base and a generally cylindrical side wall 3. The top edge of the cylindrical side wall is rolled over to form a hollow annular bead 5 surrounding the upper open end of the container body and a notch 6 is formed at a circumferential point in the annular bead. The container body is for use with a releasable closure 2 formed with an end wall 7 and a depending skirt 8 and having an annular layer of sealing material 9 provided on the inside of the end wall adjacent the skirt. When the closure is pressed onto the container body, the annular bead engages the annular layer of sealing material and some of that material extends into the notch 6. The closure is held on the container only by the partial vacuum formed therein during processing of a food product in the container. After processing, the user opens the container by rotating the closure. Sealing material in the notch forces the closure to lift off from the container to break the seal and release the closure.
Owner:CROWN PACKAGING TECH
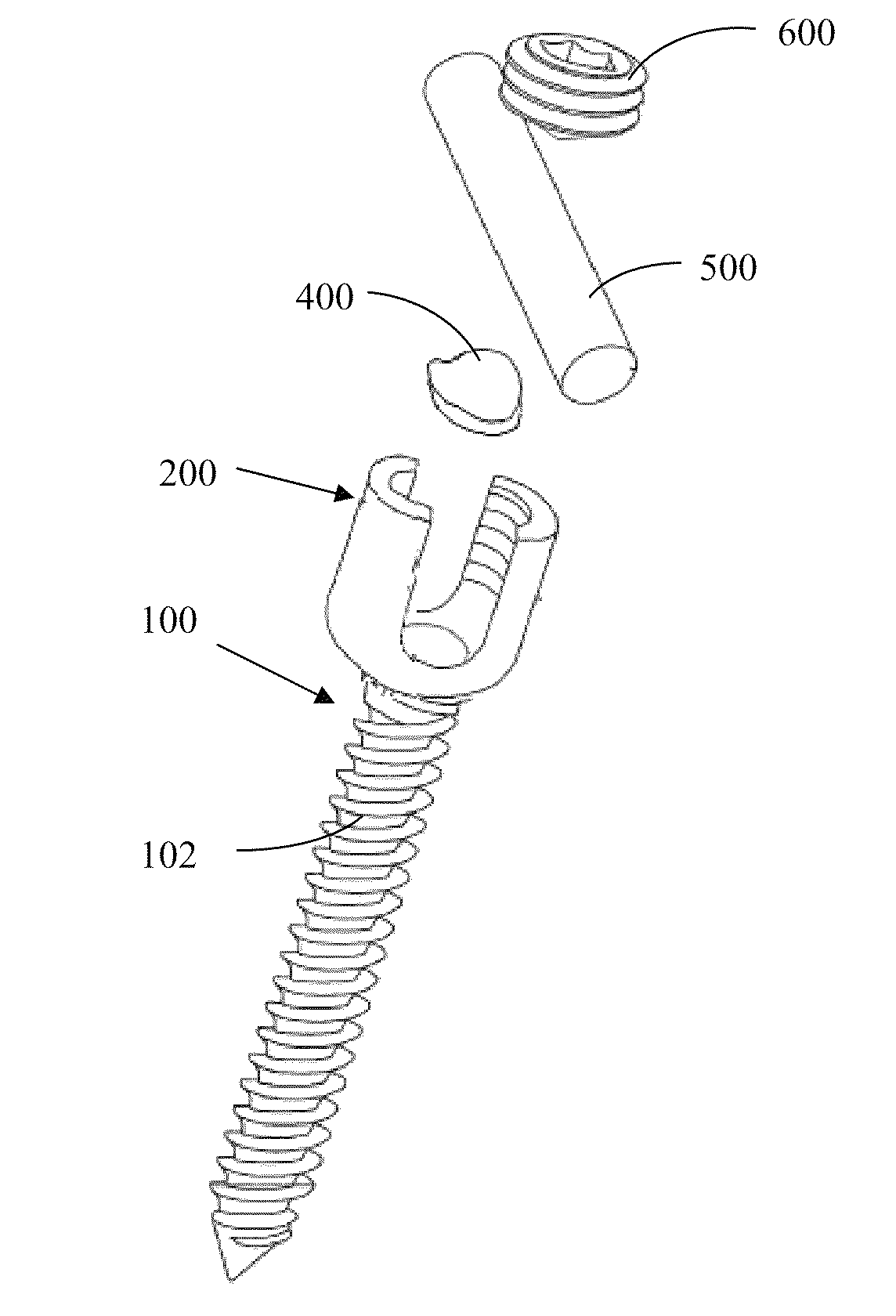
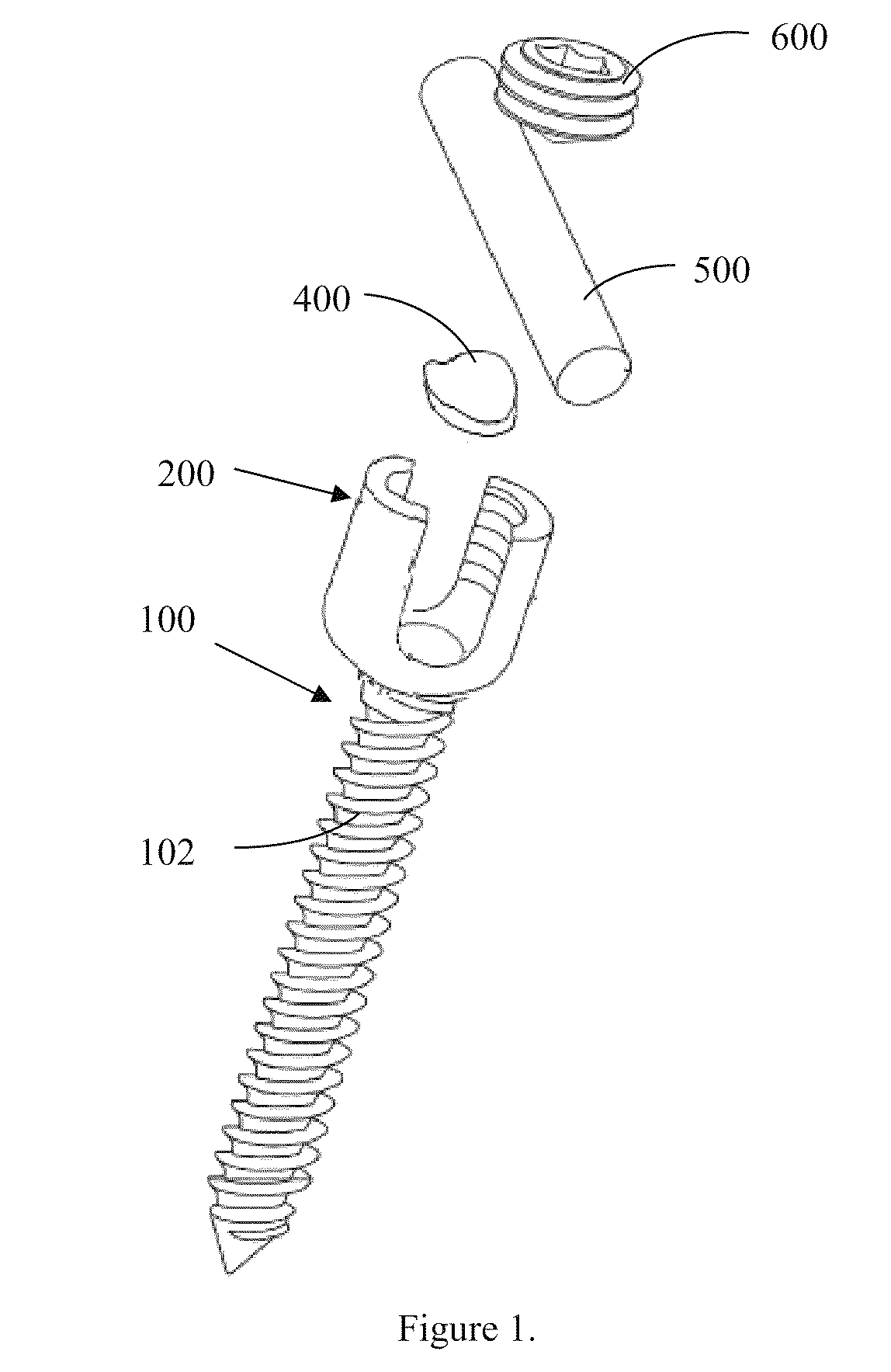
Bone stabilization device
ActiveUS20170196609A1Less torqueFinger jointsInternal osteosythesisBiomedical engineeringStable fracture
A device and method for stabilizing a broken bone while it heals is disclosed. The device preferably has a (a) first (or proximal) section with a driving head, threads and a first diameter, and (b) second (or distal) section that is threaded and has a second diameter. The first section is preferably greater in diameter than the second section so that greater torque can be applied to tighten the device. The device may include one or more self-tapping structures to lessen the torque required to screw it into a bone.
Owner:EXSOMED CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com