Patents
Literature
393 results about "Solenoid actuator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
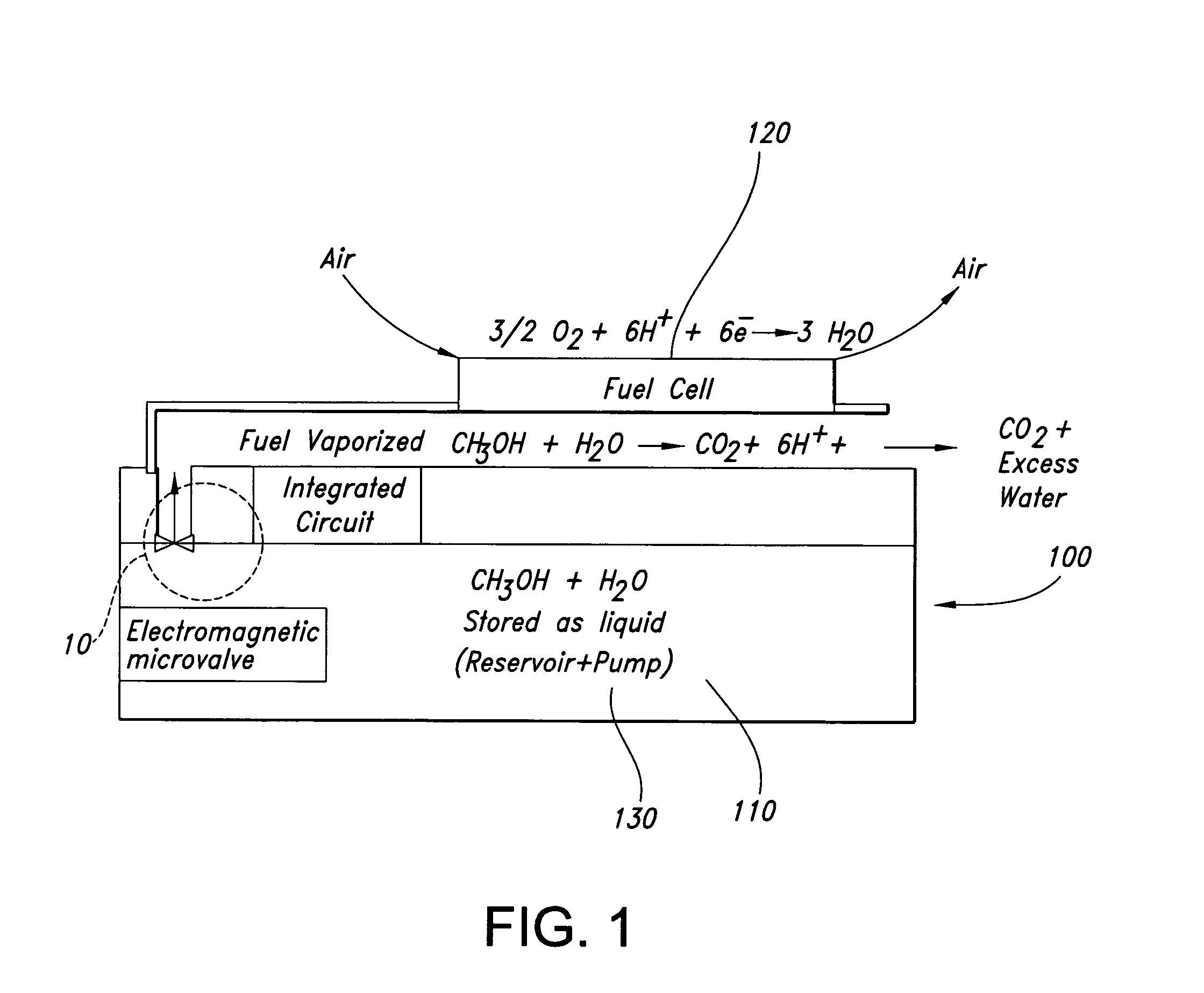
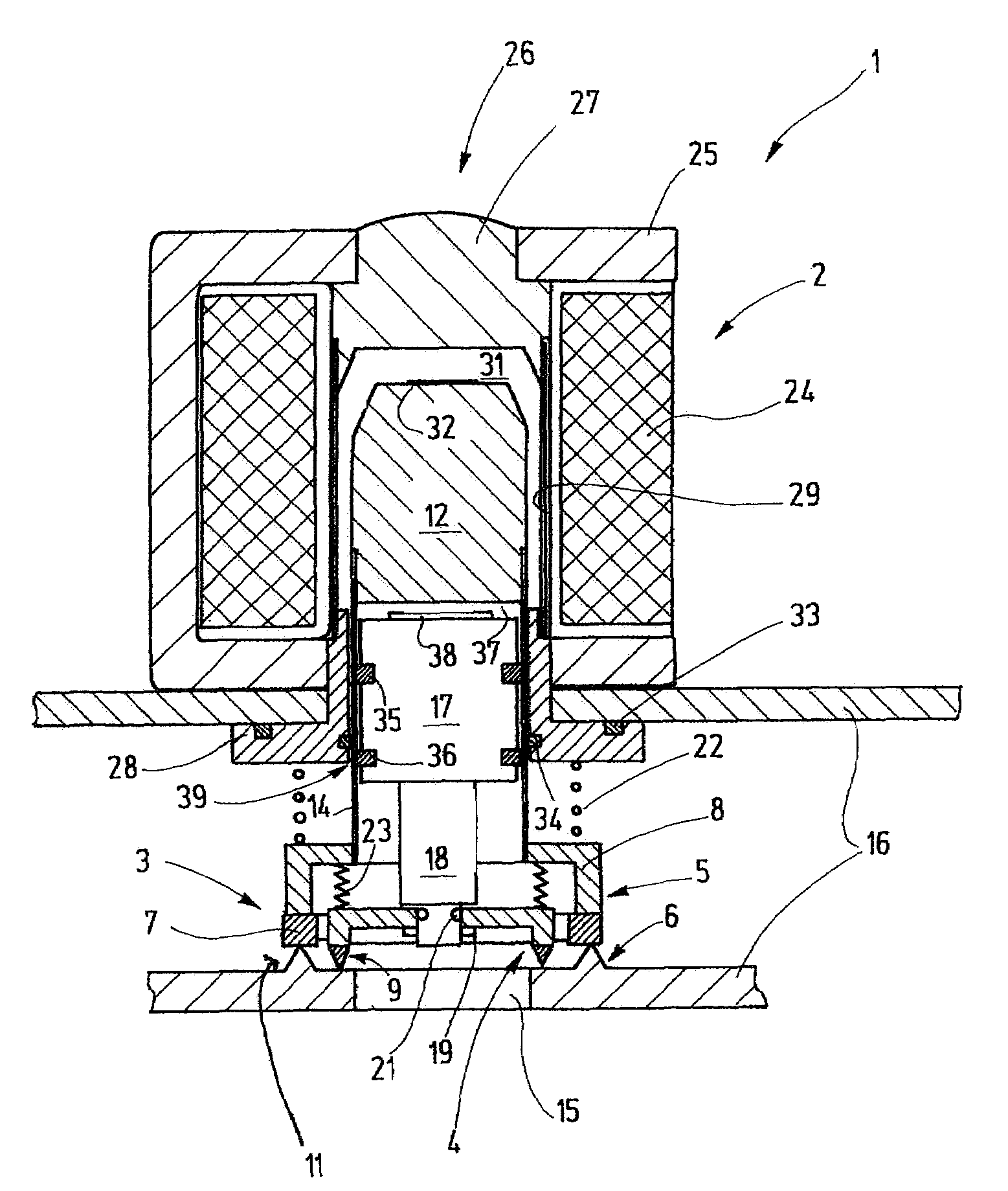
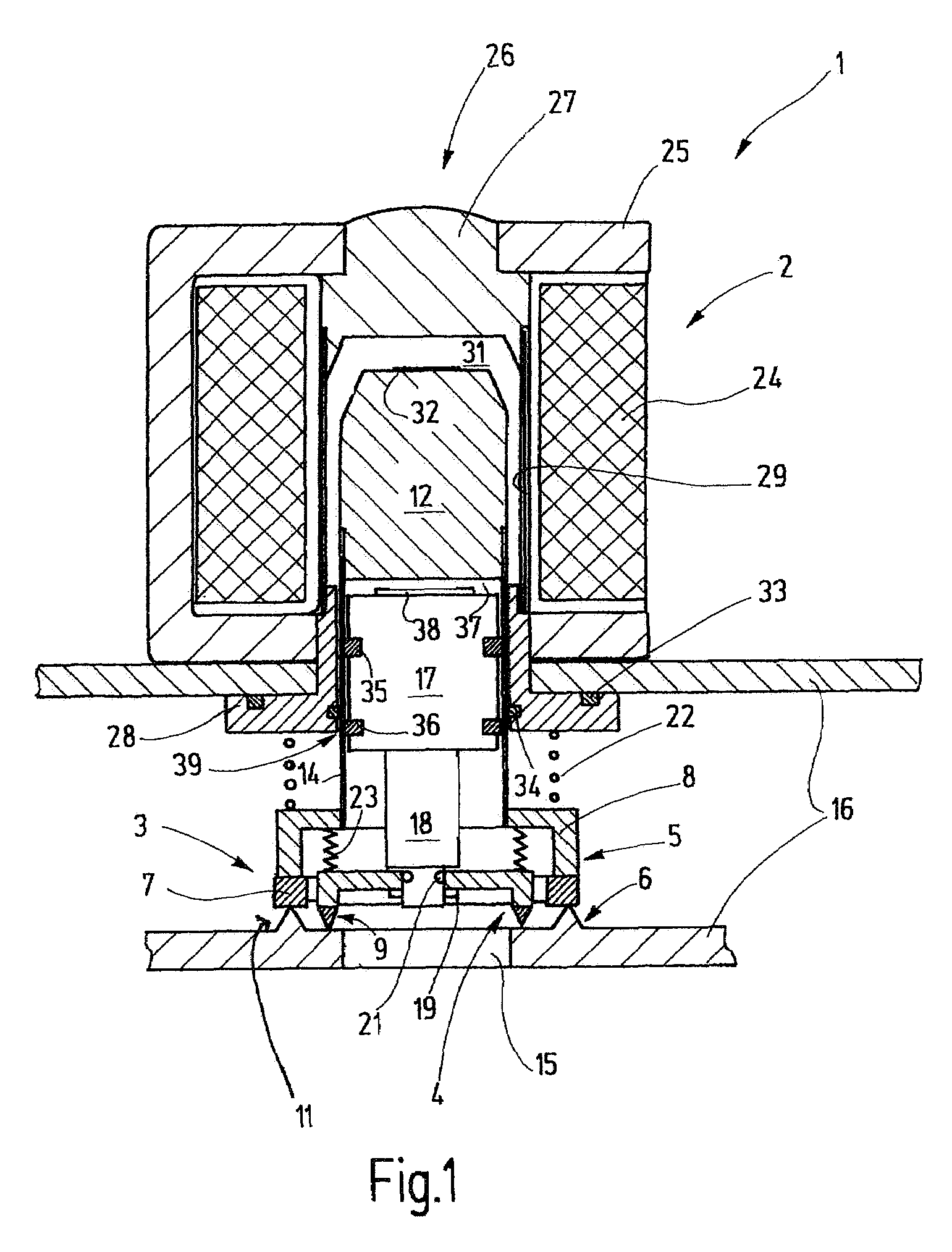
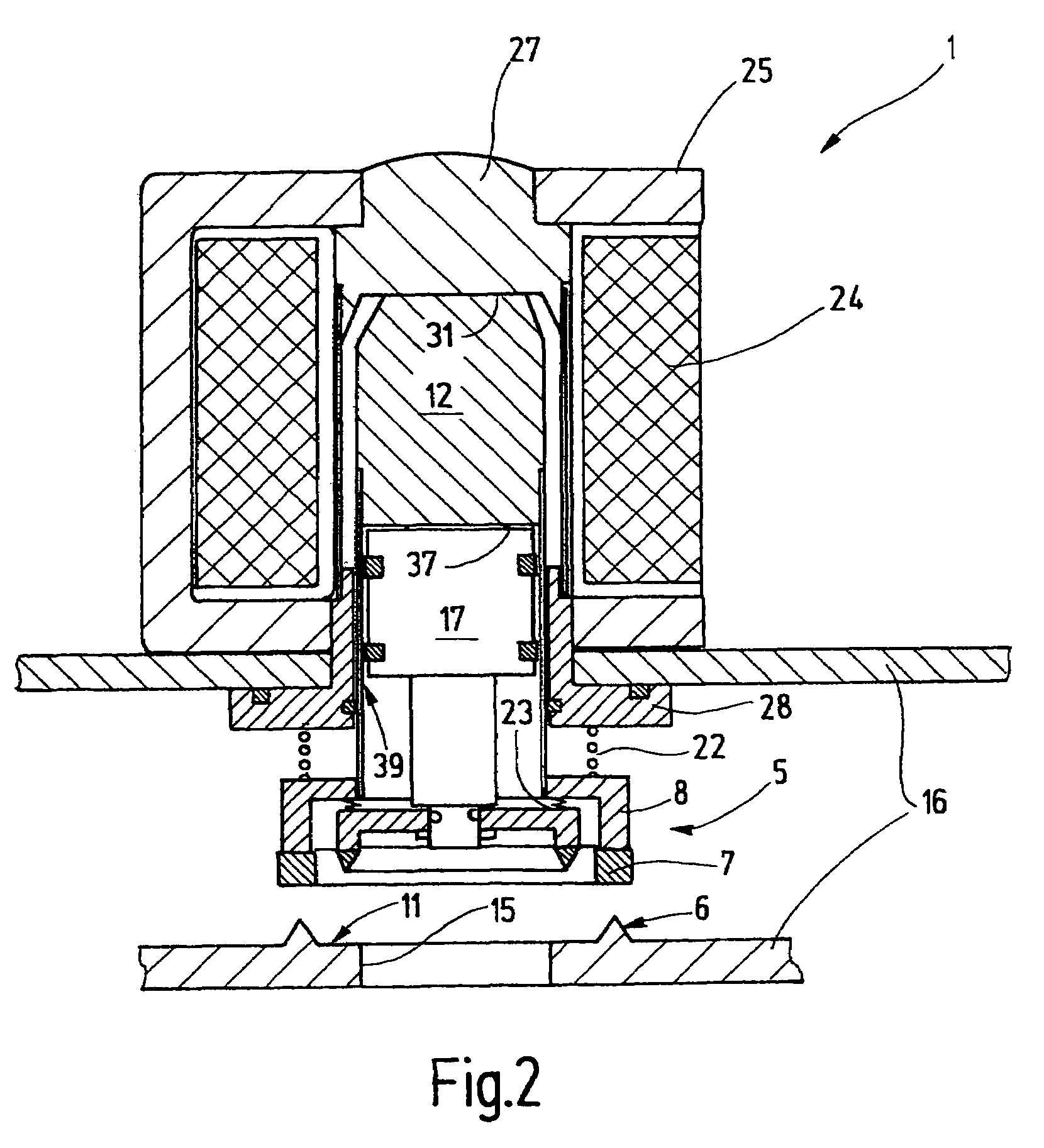
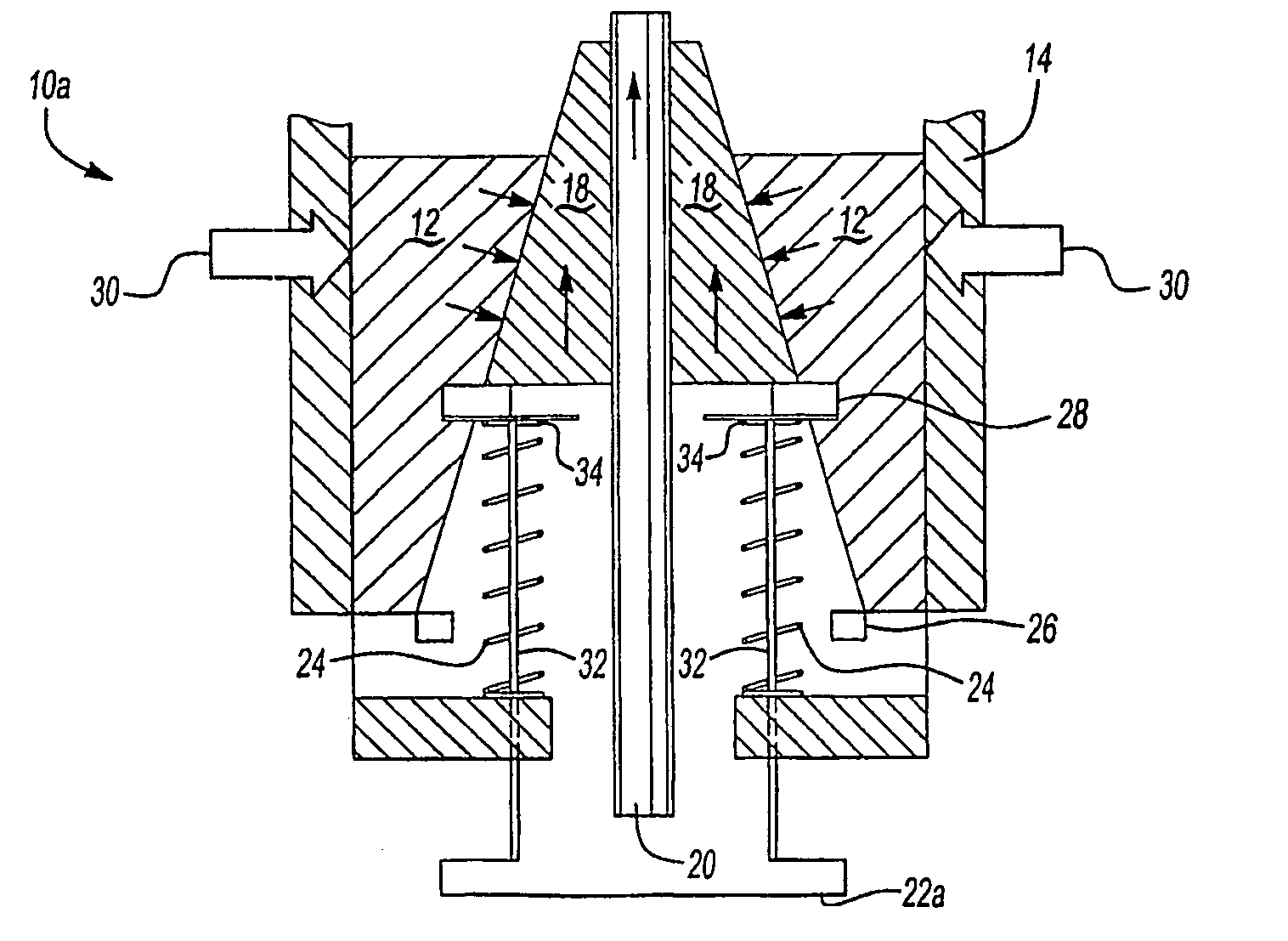
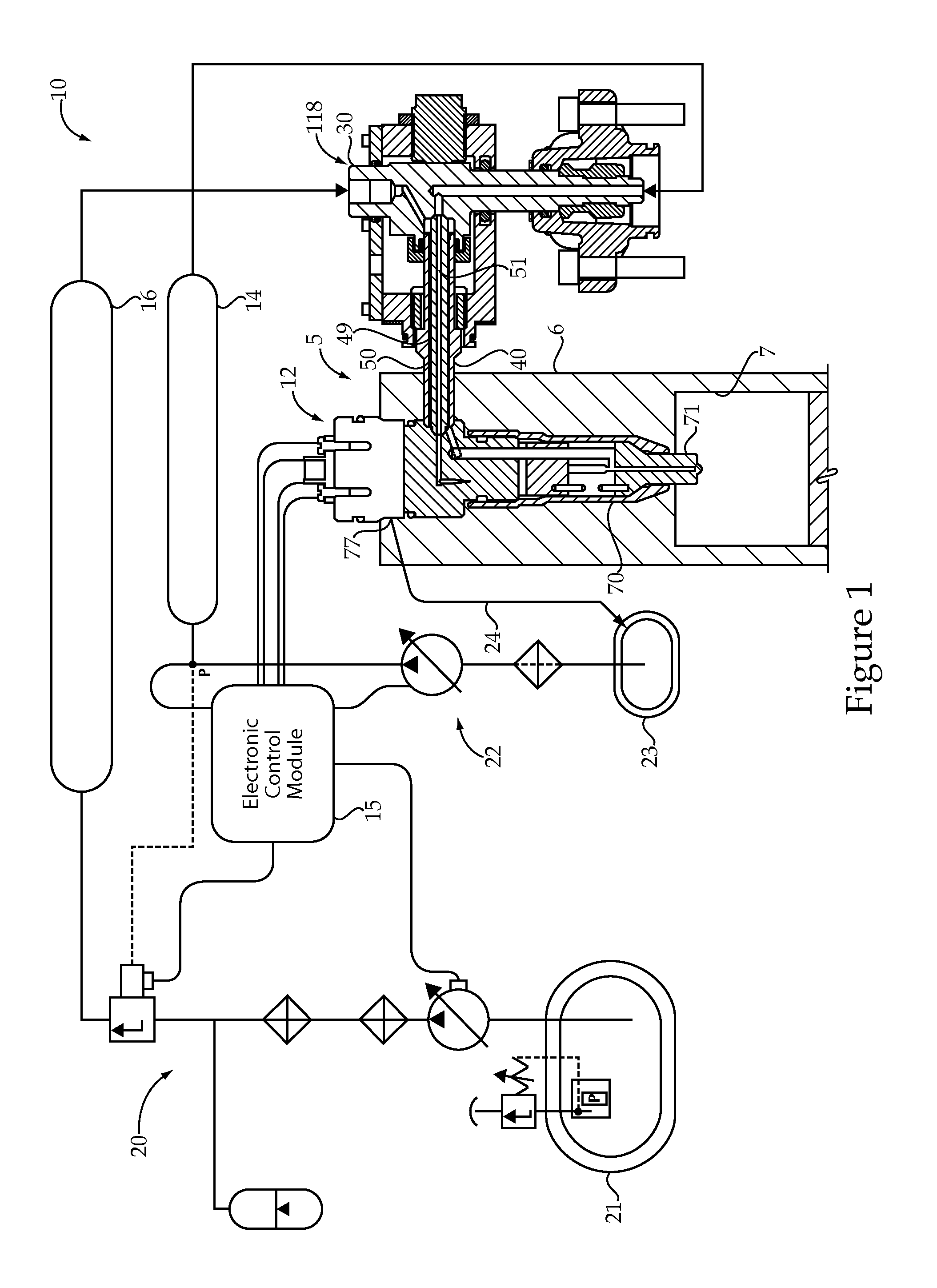
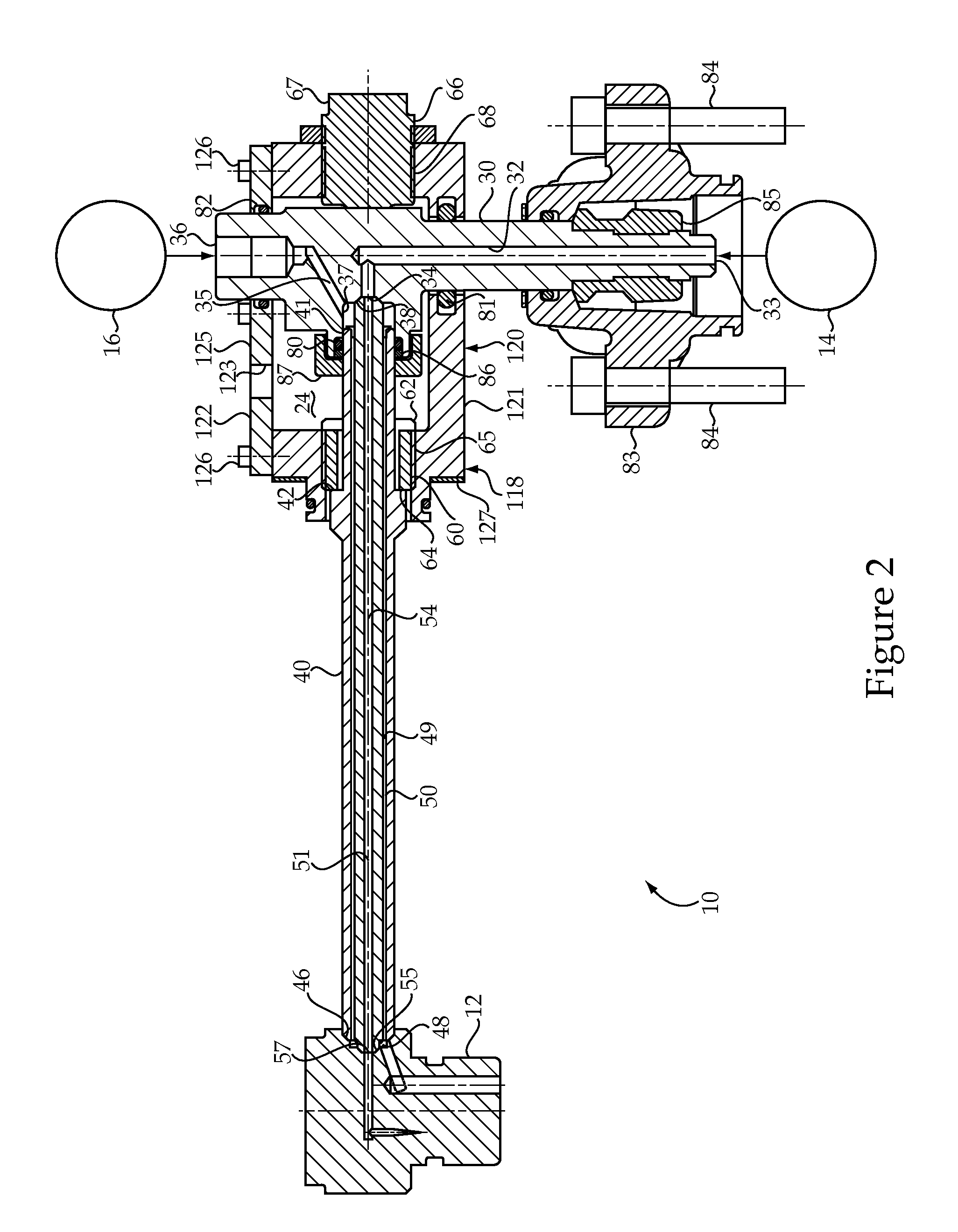
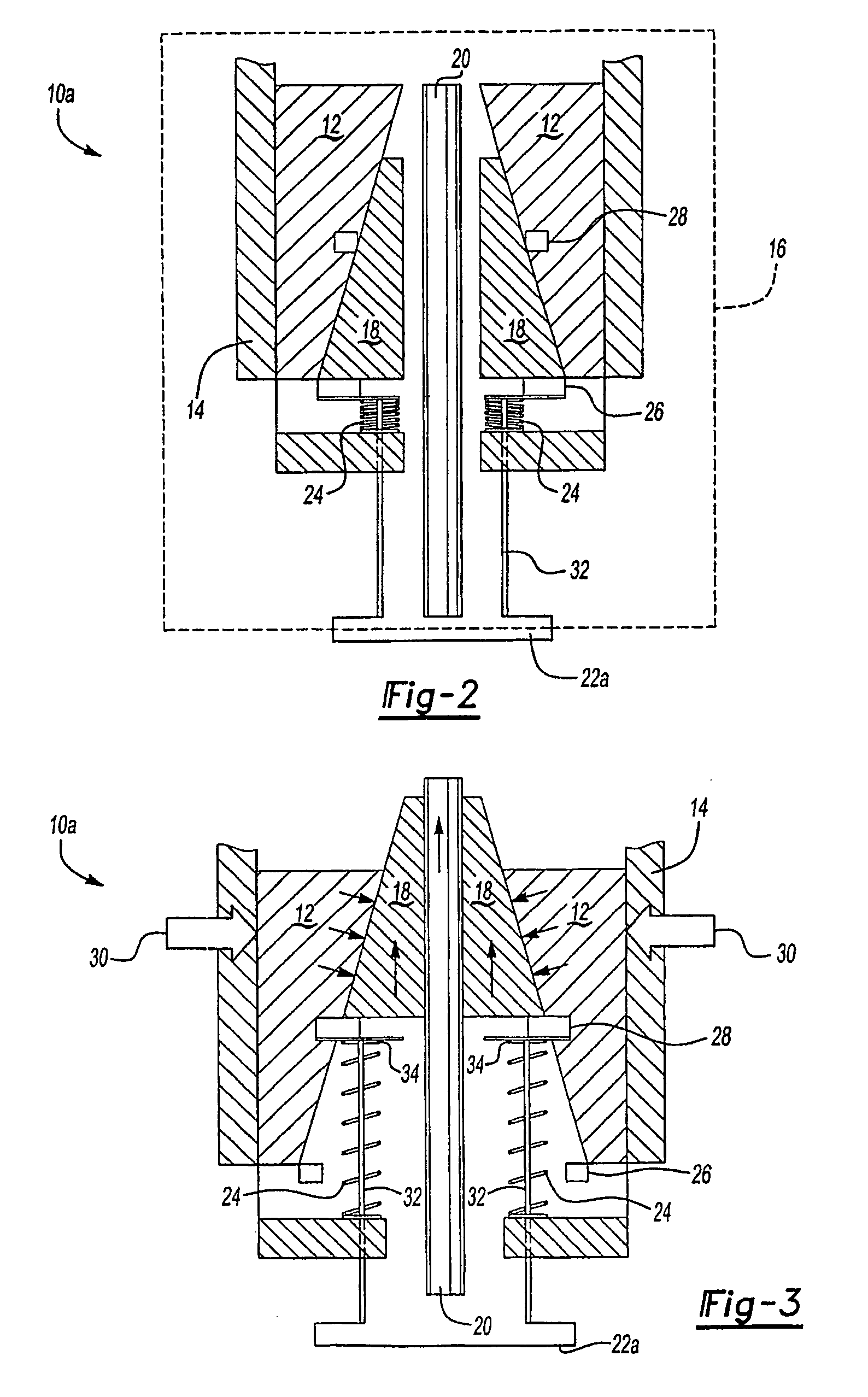
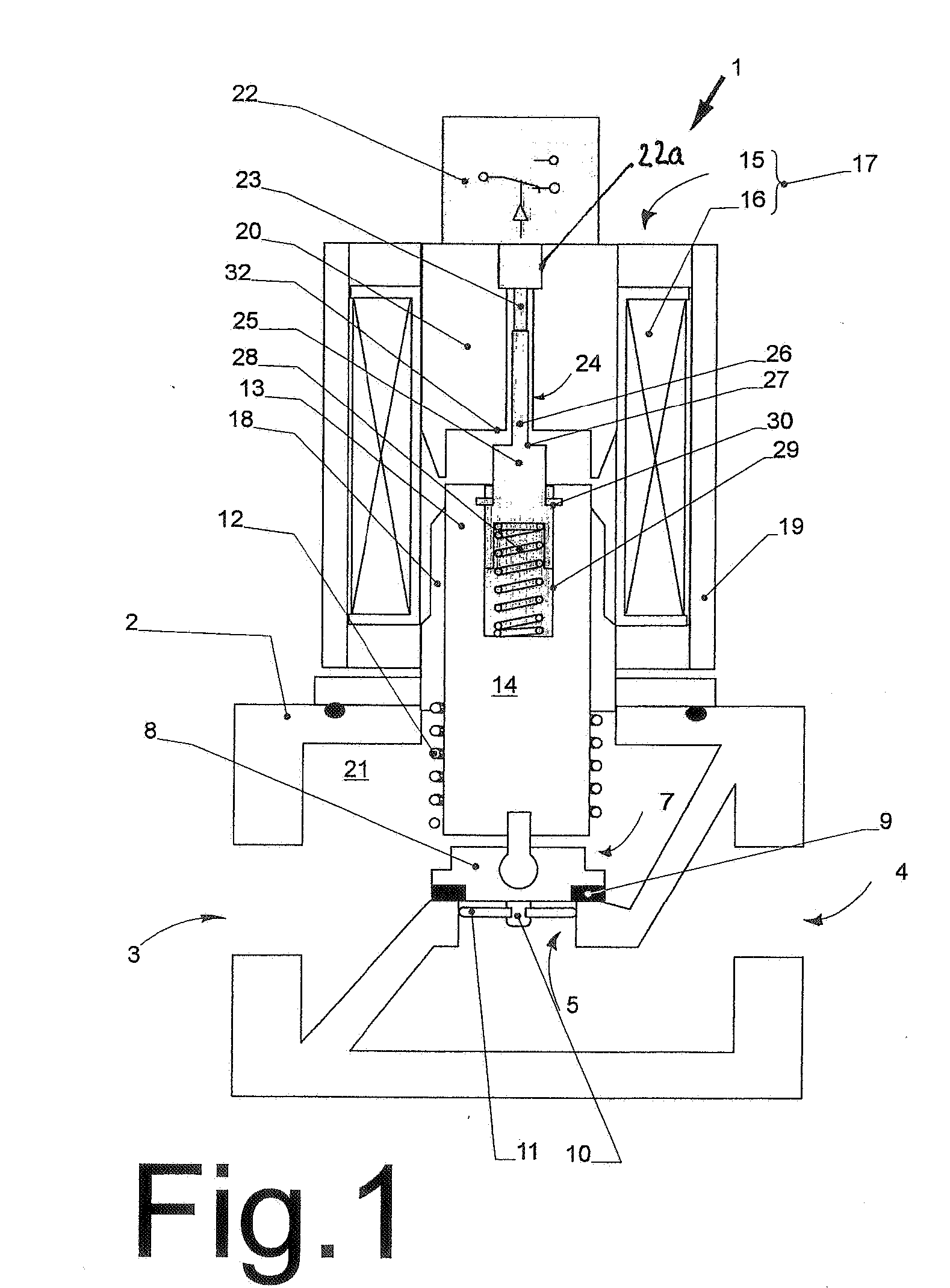
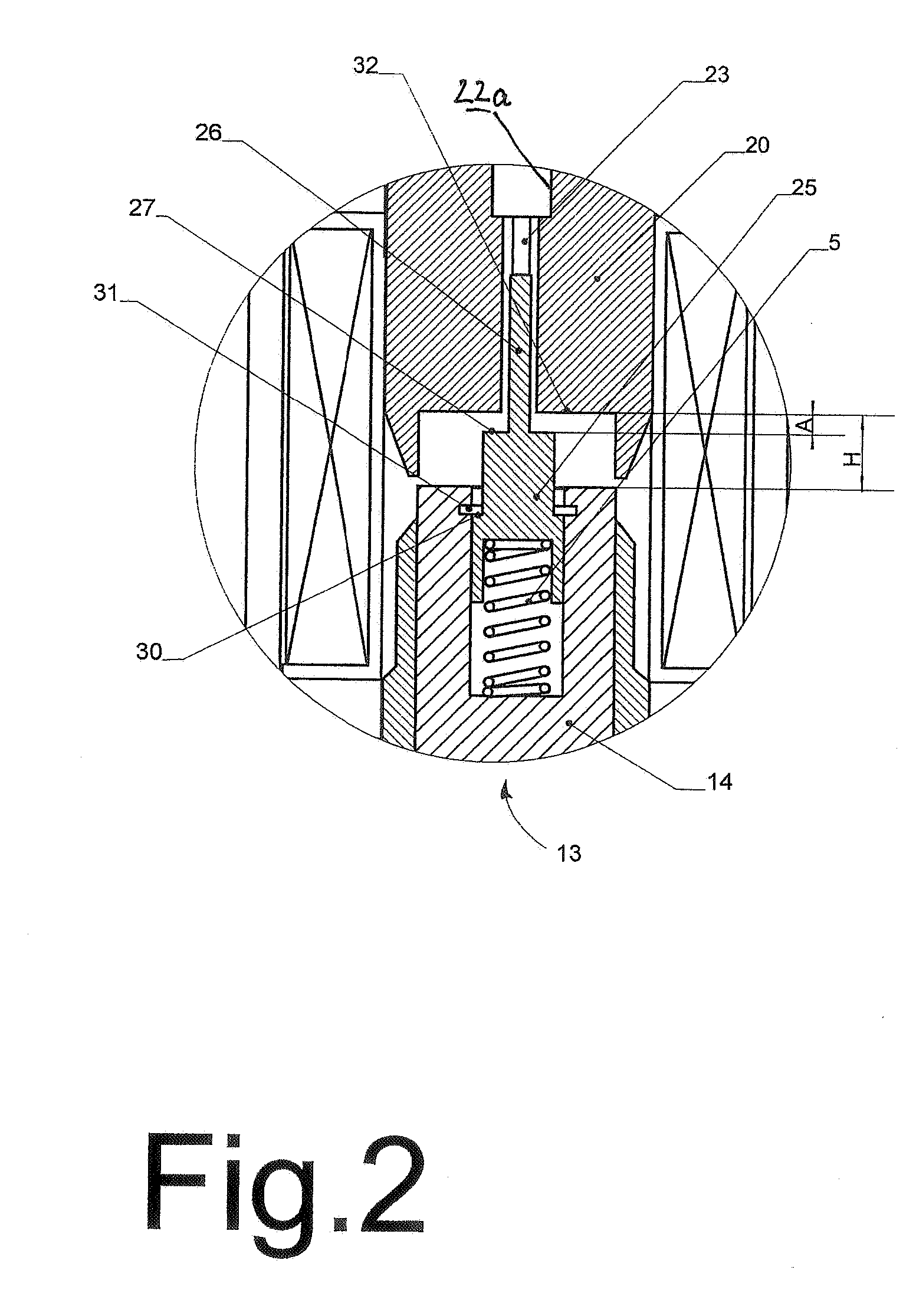
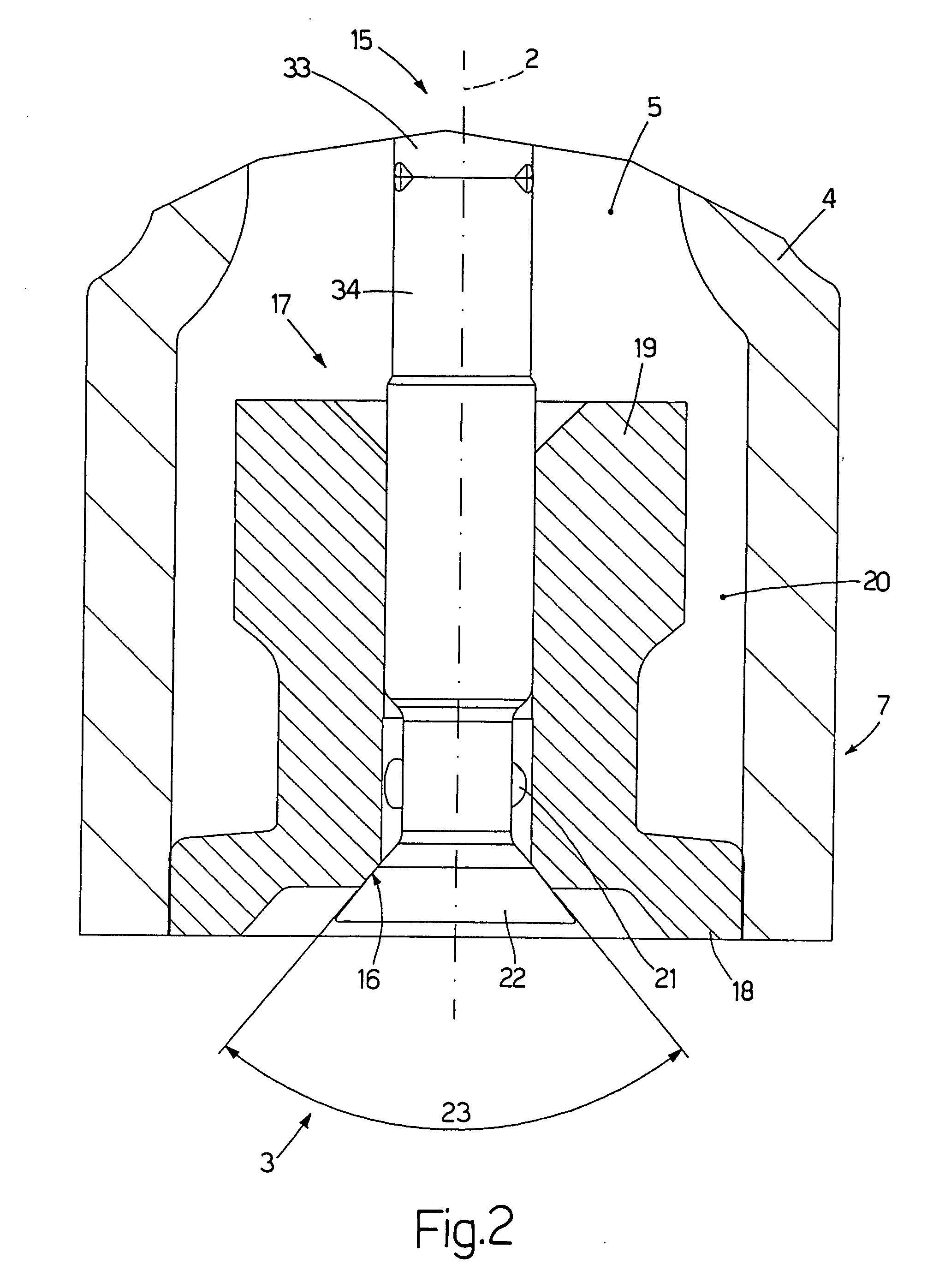
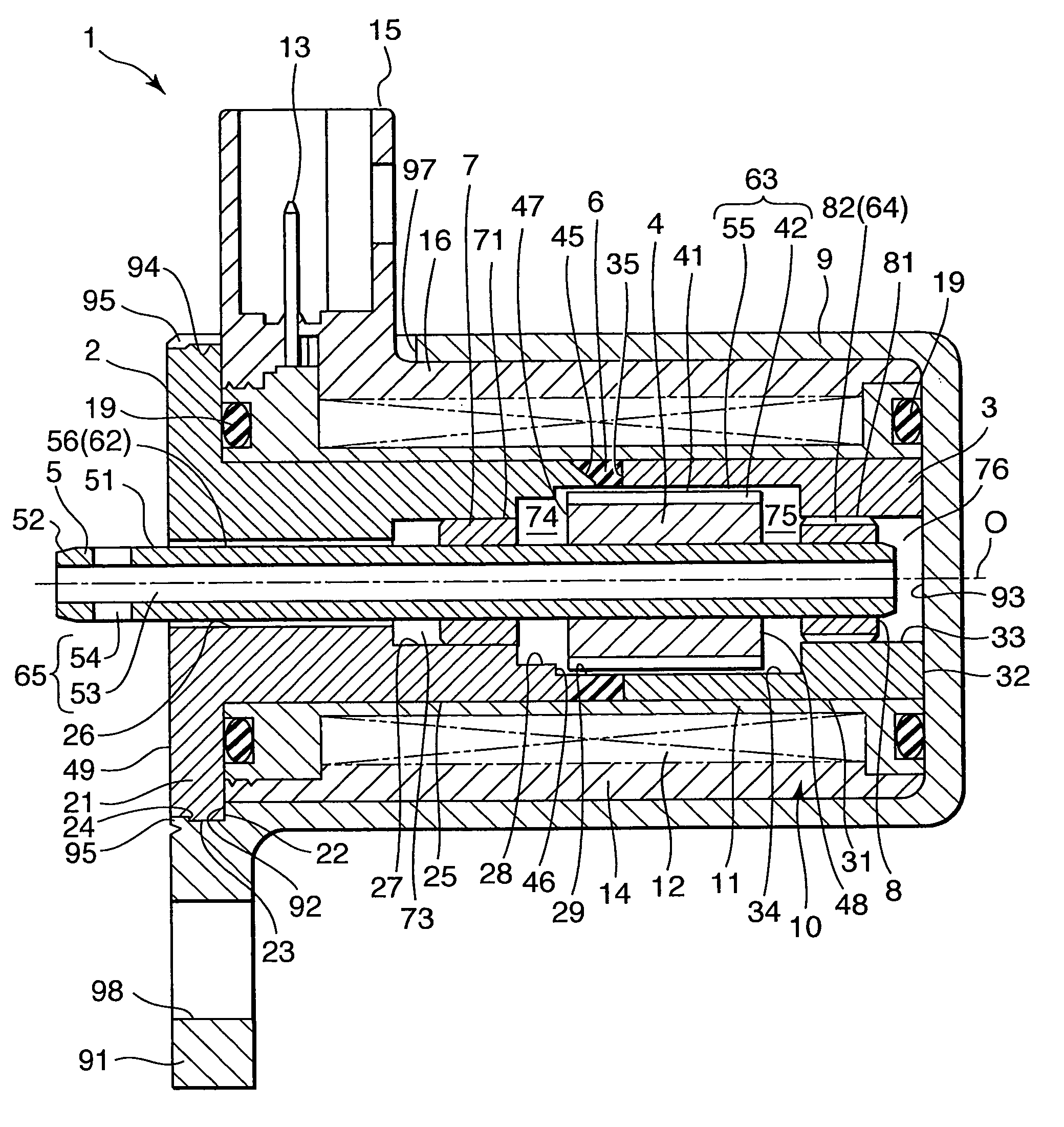
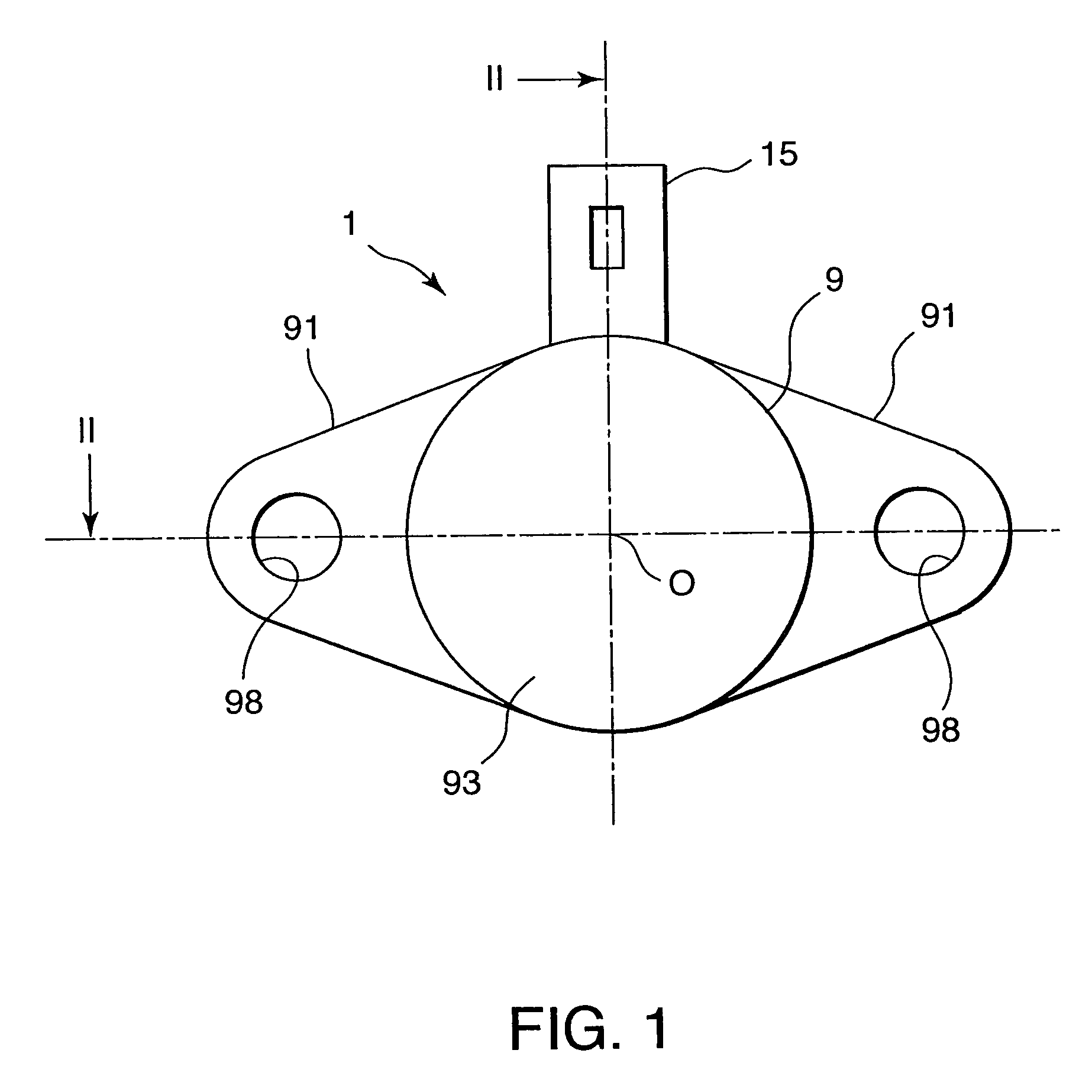
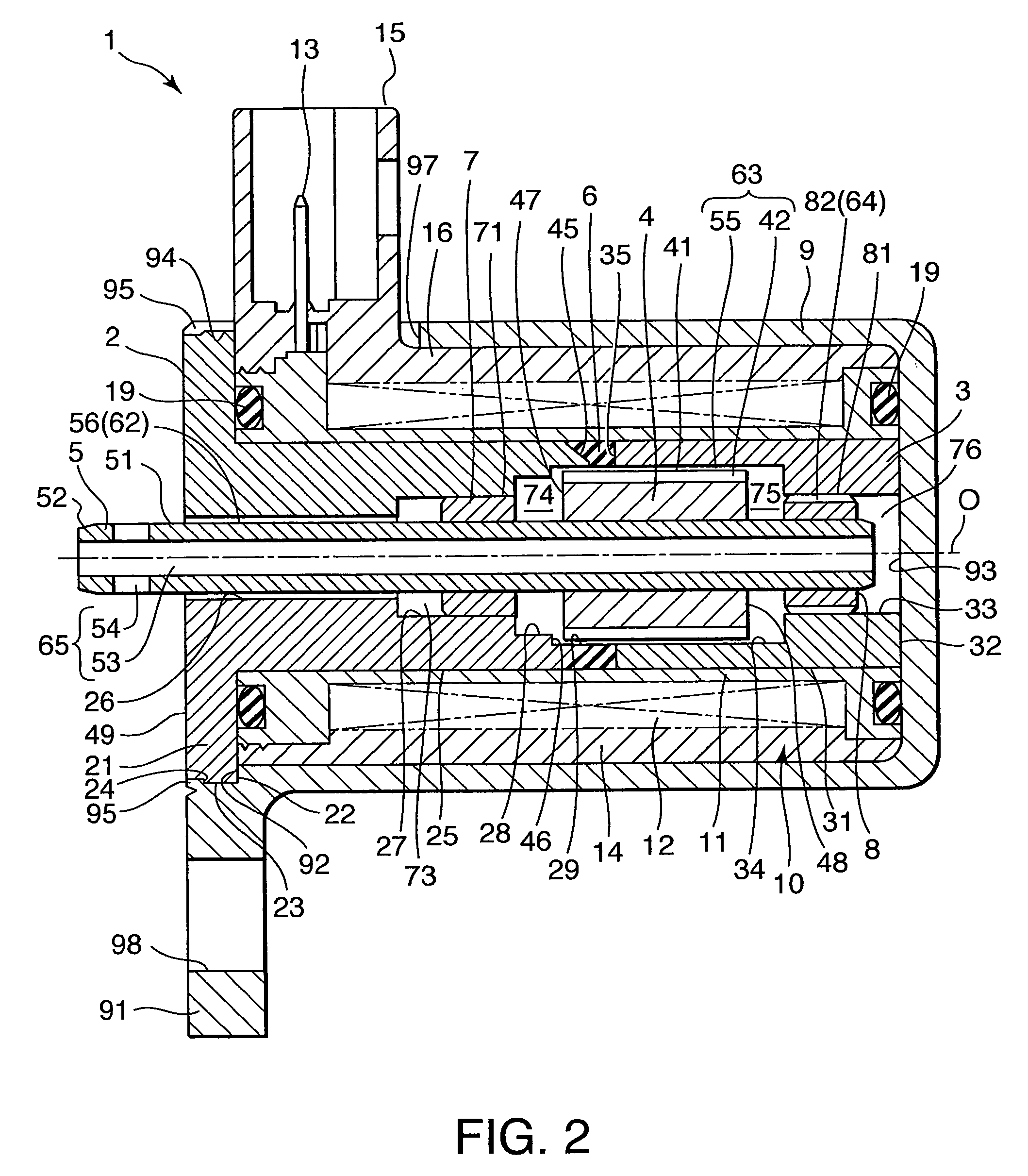
Reagent dispensing valve
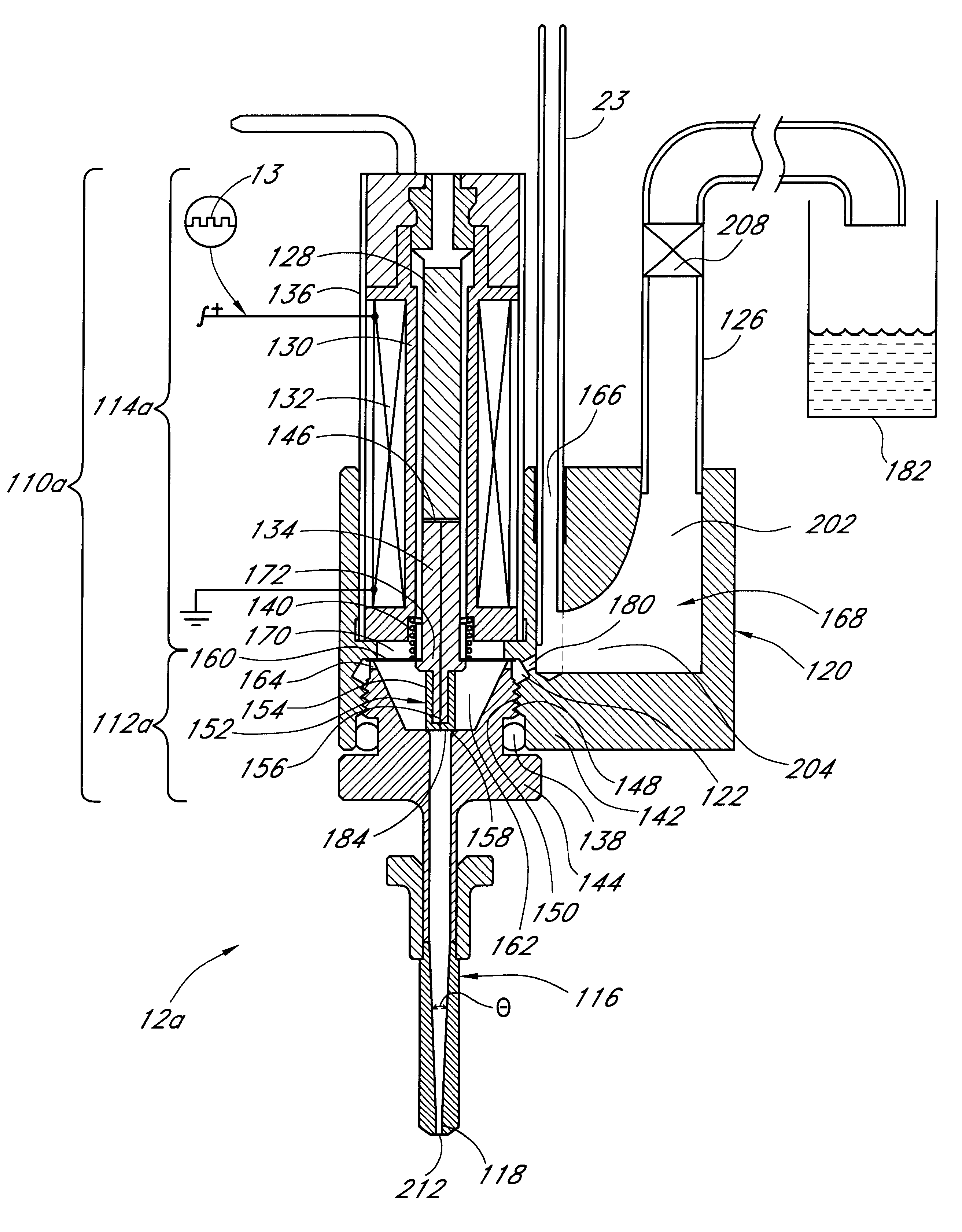
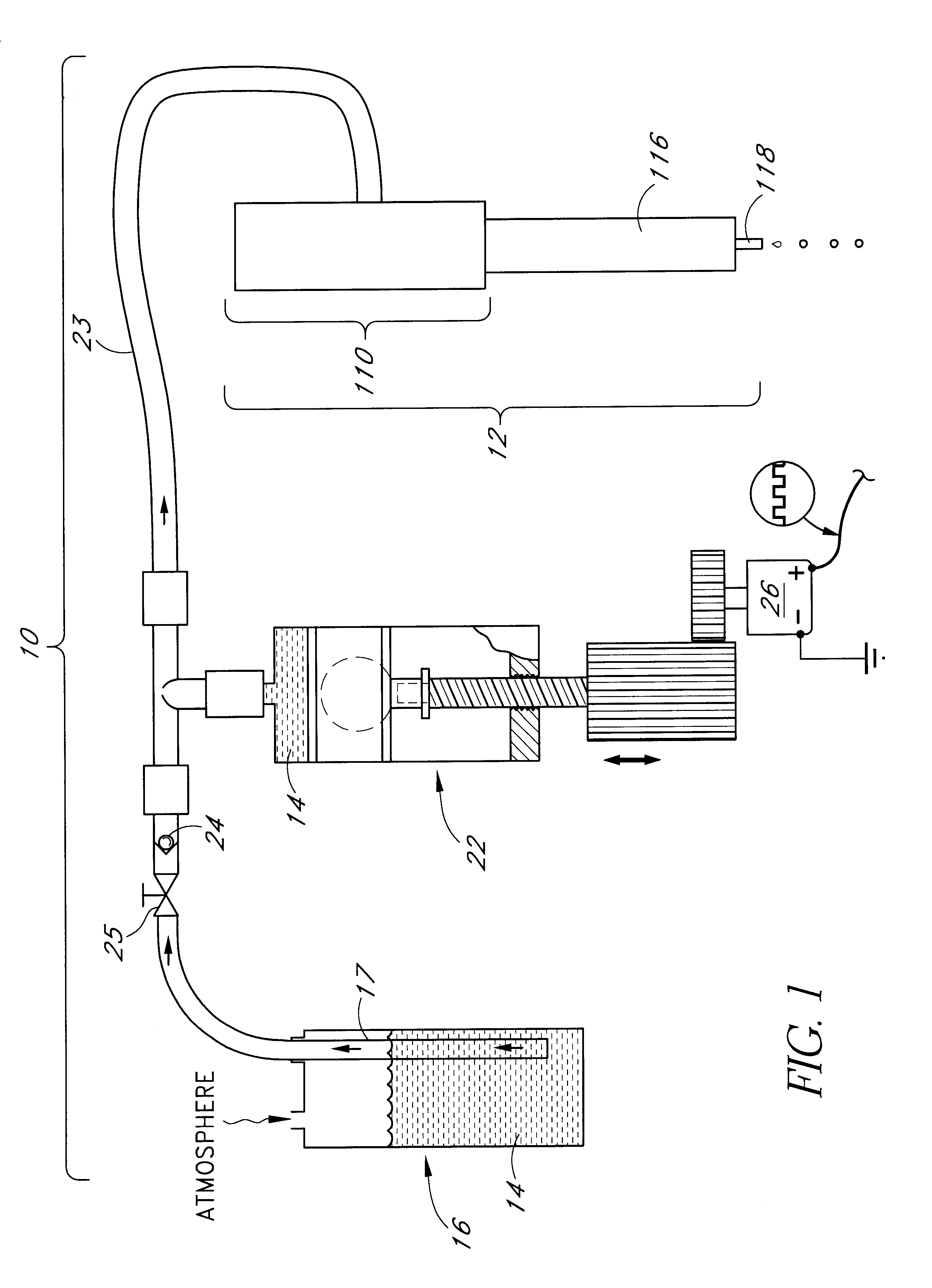
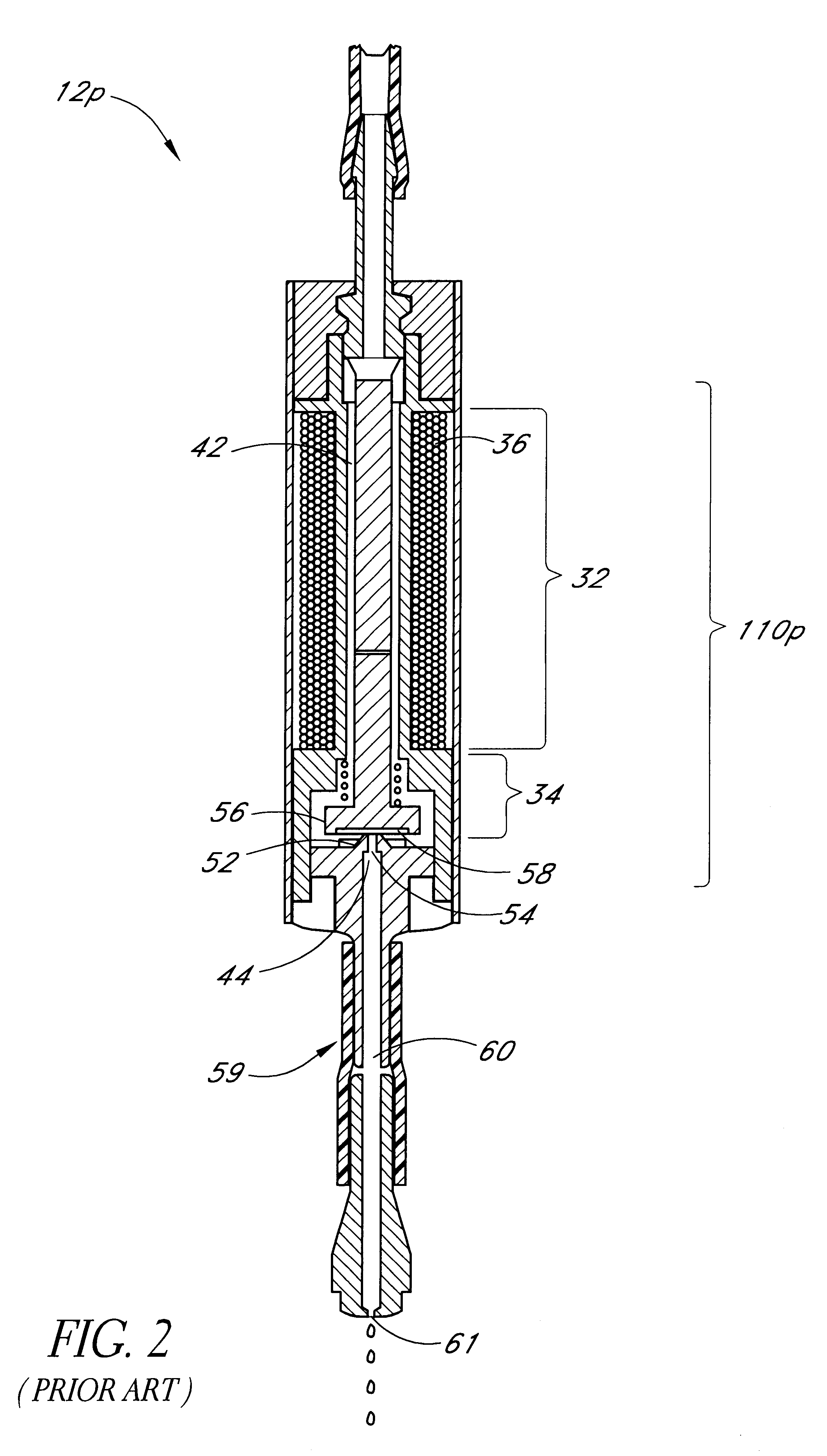
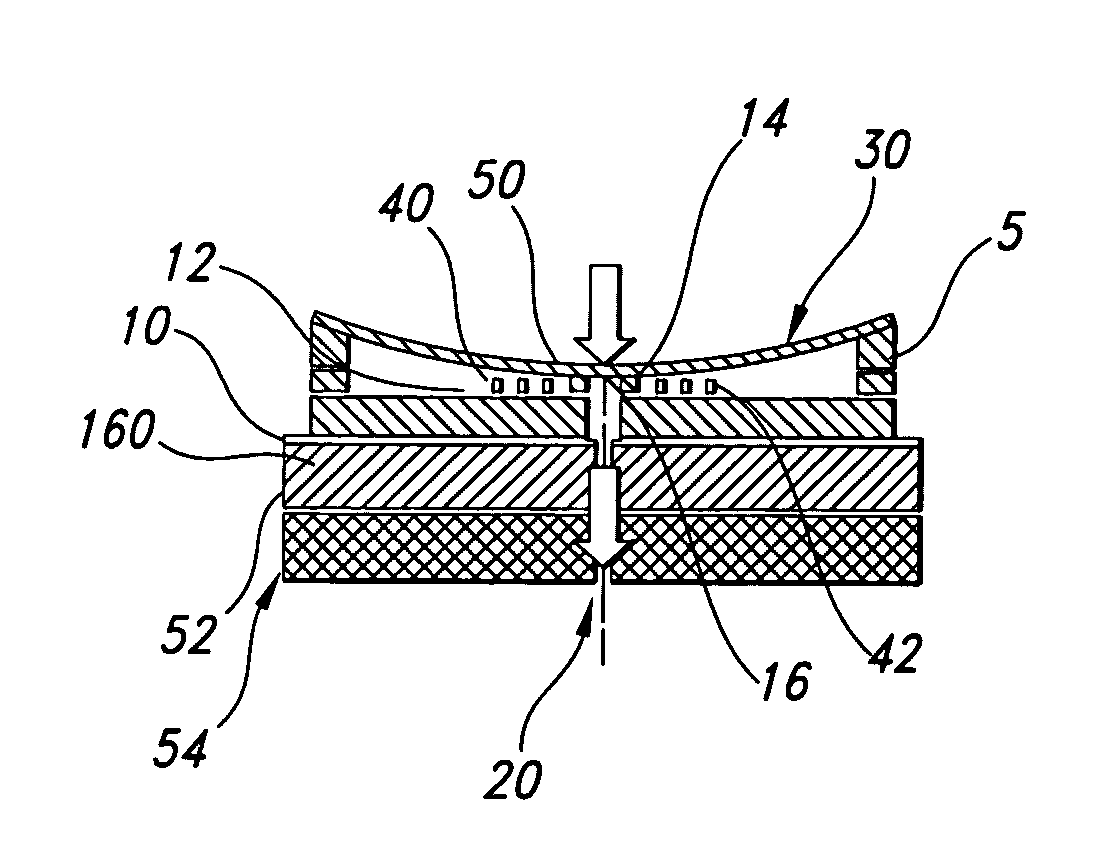
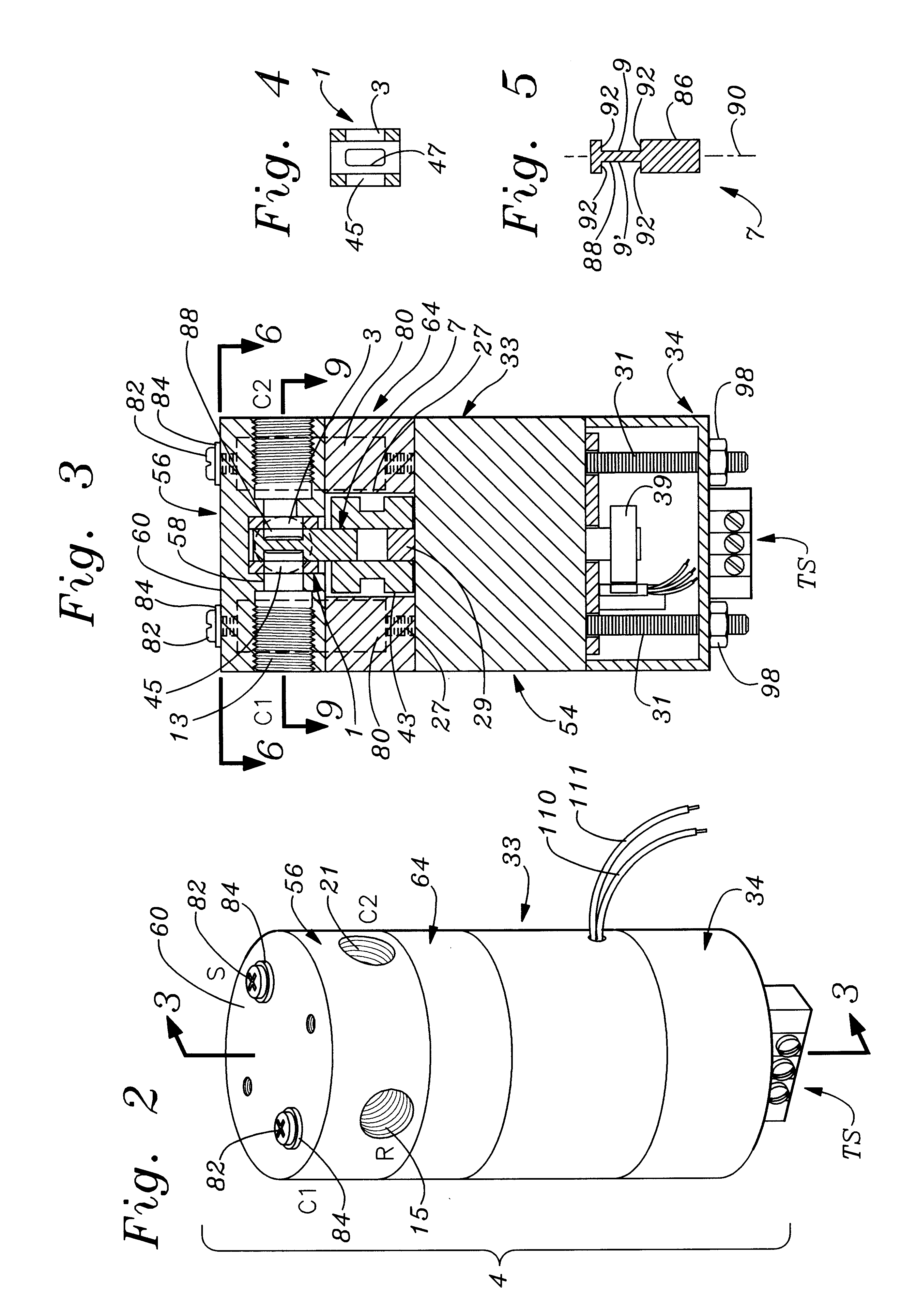
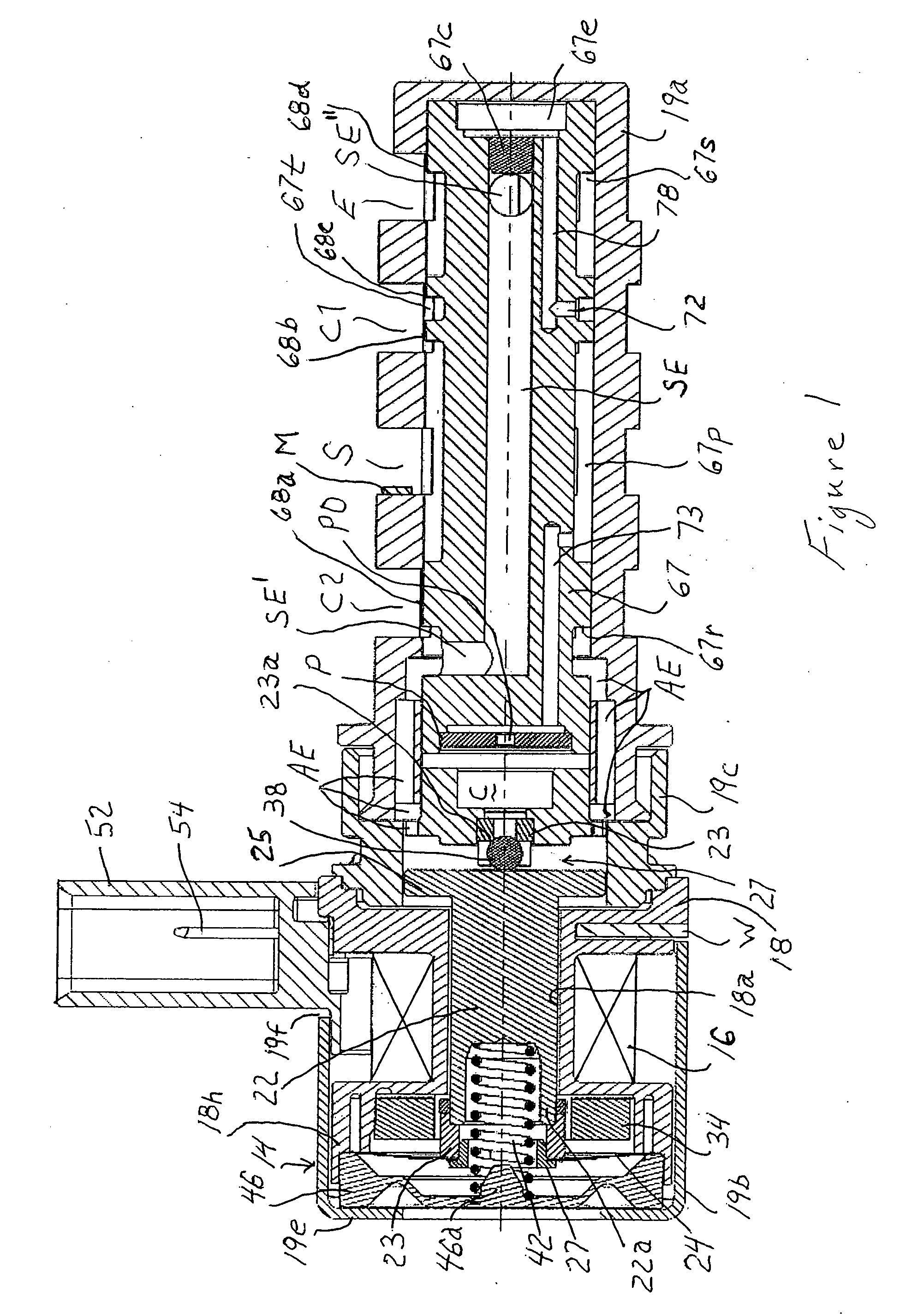
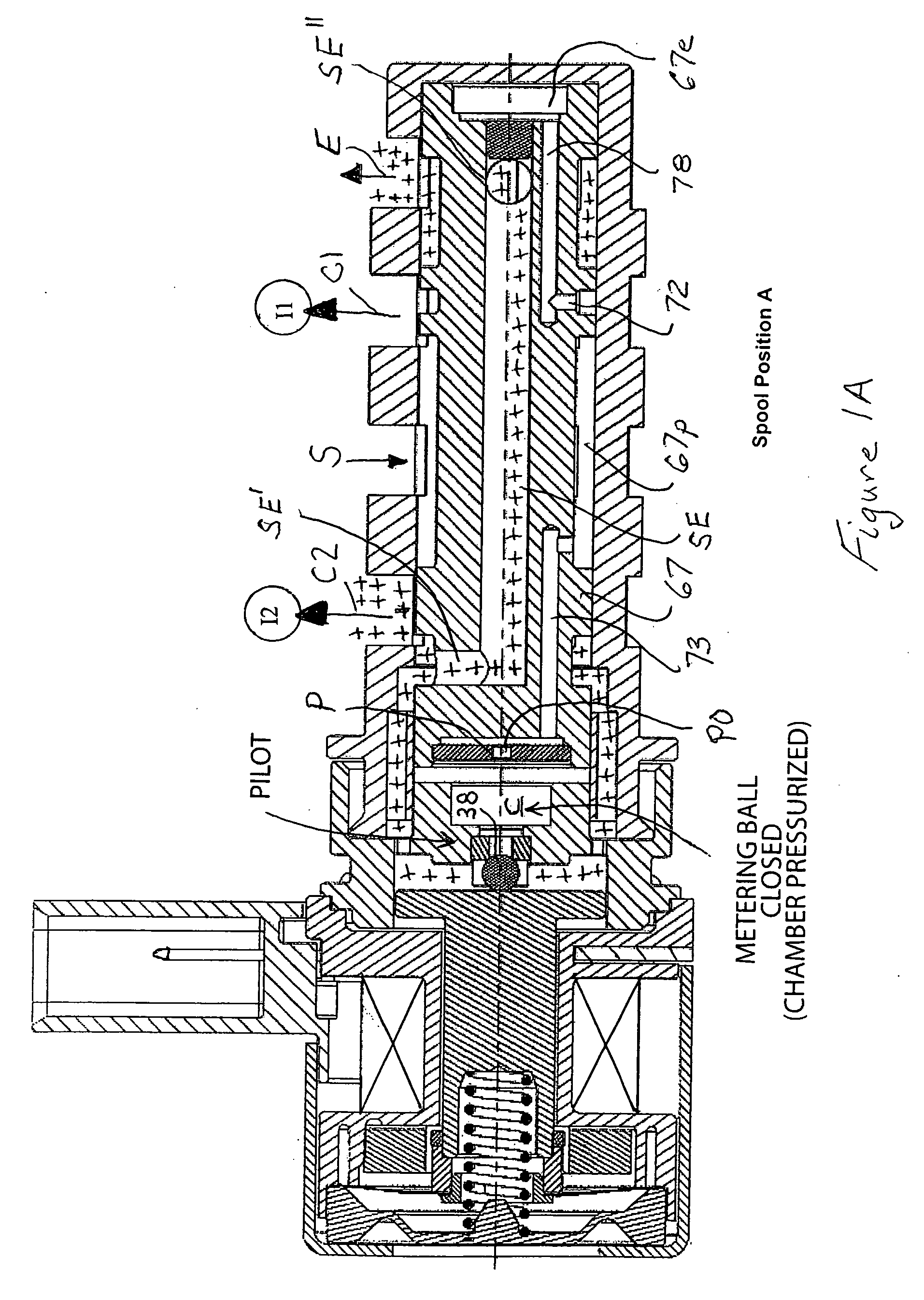
A reagent dispensing valve particularly adapted for dispensing precise microfluidic quantities of fluids. The valve includes a valve portion and a solenoid actuator that are in fluid isolation from one another. The valve portion includes a plunger and seat combination and the actuator is substantially decoupled from the fluid path through the valve. The fluid path through the valve is substantially non-tortuous, thereby minimizing localized fluid pressure drops, and hence undesirable gaseous bubble precipitation within the fluid. The valve is also configured to substantially prevent bubble accumulation. The valve can further include a bubble trap for trapping and removing bubbles.
Owner:BIODOT
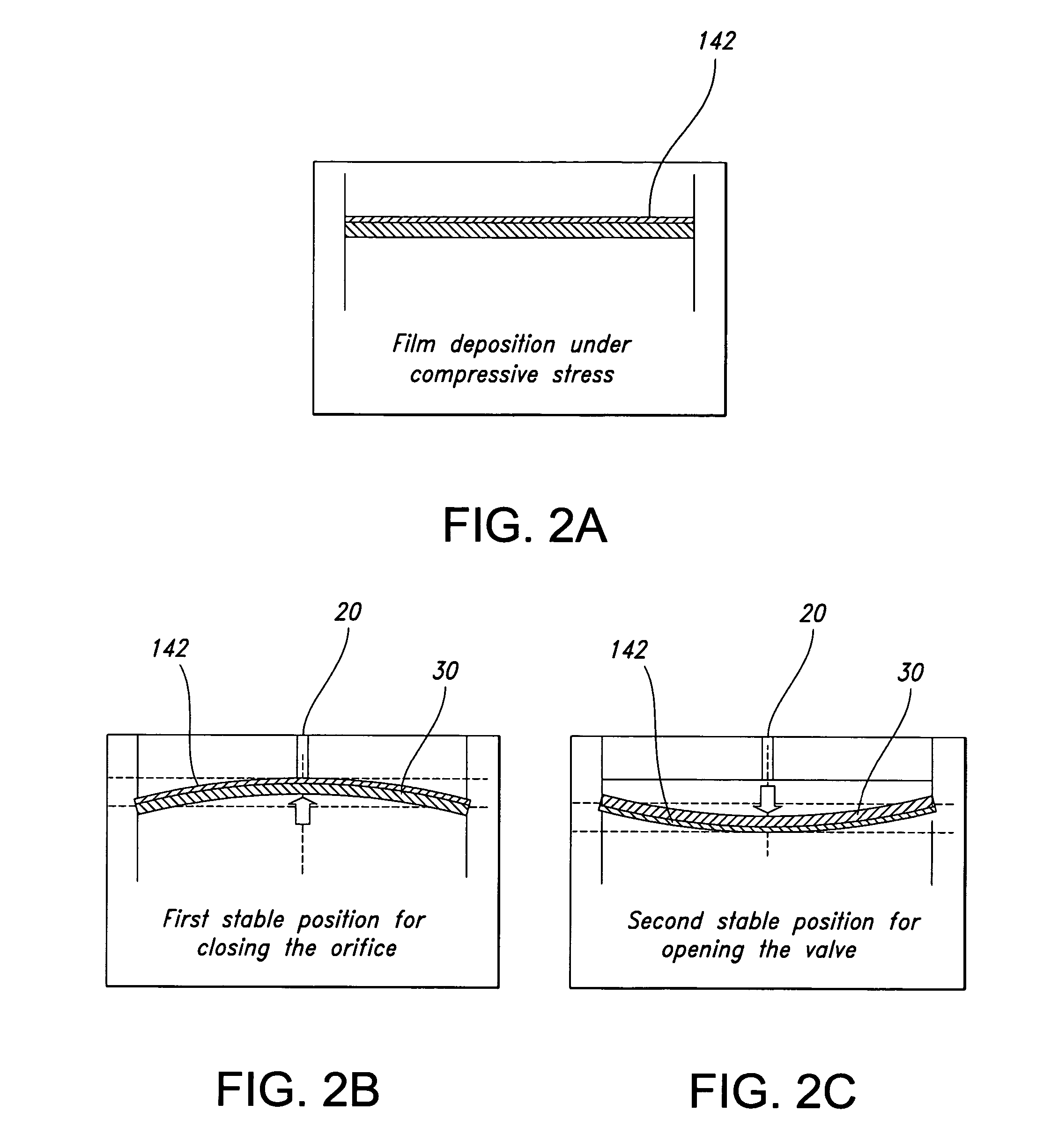
Single substrate electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS20050116798A1Improve dynamic operation of valveLower average currentValve arrangementsAdditive manufacturing apparatusManufacturing technologyEngineering
A microvalve which utilizes a low temperature (<300° C.) fabrication process on a single substrate. The valve uses buckling and an electromagnetic actuator to provide a relatively large closing force and lower power consumption. A buckling technique of the membrane is used to provide two stable positions for the membrane, and to reduce the power consumption and the overall size of the microvalve. The use of a permanent magnet is an alternative to the buckled membrane, or it can be used in combination with the buckled membrane, or two sets of micro-coils can be used in order to open and close the valve, providing the capability for the valve to operate under normally opened or normally closed conditions. Magnetic analysis using ANSYS 5.7 shows that the addition of Orthonol between the coils increases the electromagnetic force by more than 1.5 times. At a flow rate of 1 mL / m, the pressure drop is <100 Pa. The maximum pressure tested was 57 kPa and the time to open or close the valve in air is under 100 ms. This results in an estimated power consumption of 0.1 mW.
Owner:AIR FORCE THE US SEC THE +1
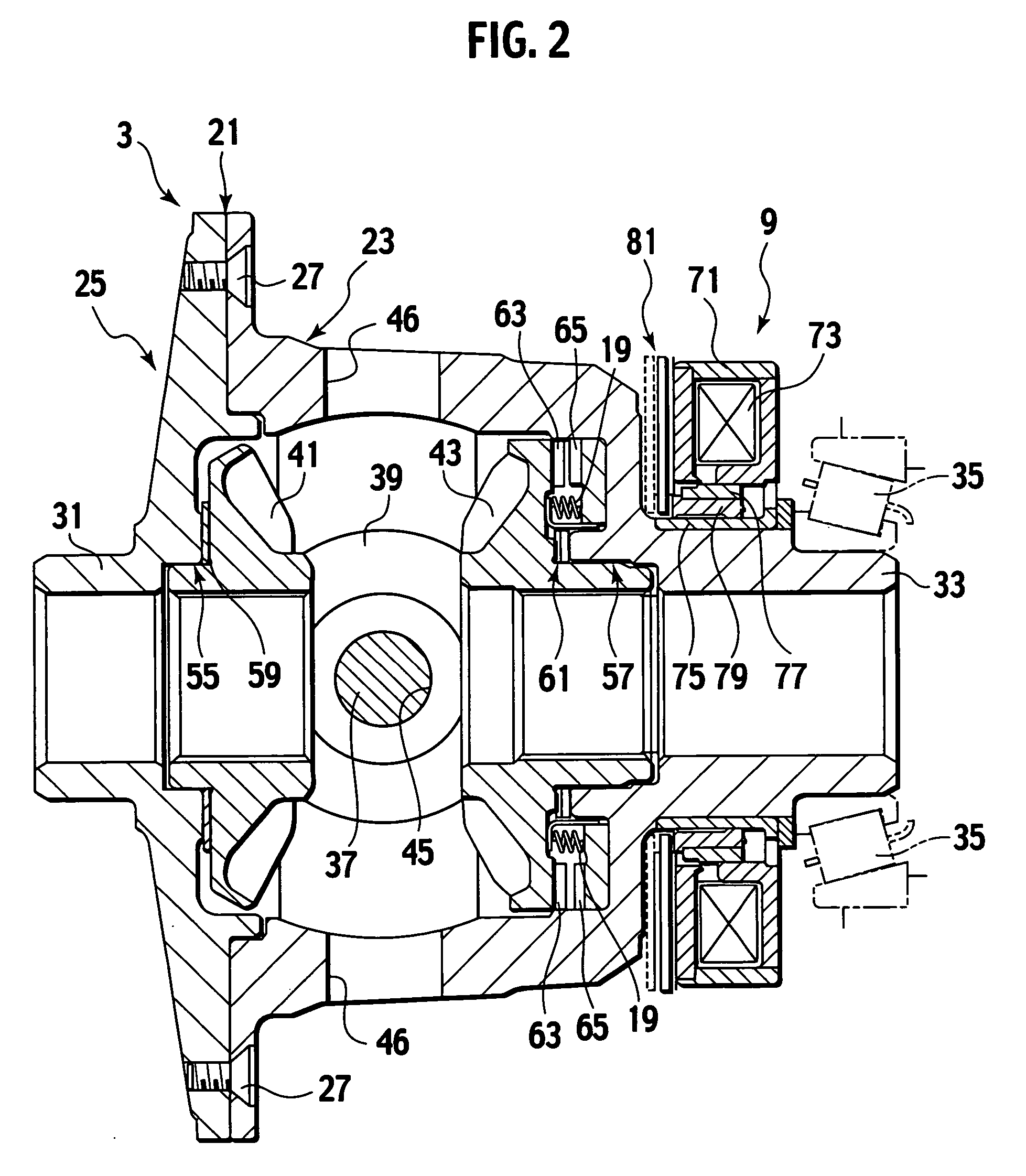
Electromagnetic actuator, and electromagnetic clutch and differential using the same
ActiveUS20050279607A1Inhibit heat generationSuppress power consumptionMechanical actuated clutchesFluid actuated clutchesElectromagnetic clutchEngineering
The electromagnetic actuator includes an electromagnetic coil configured to provide actuation force in accordance with a solenoid current to be supplied, to a clutch and configured to actuate the clutch to control relative rotation between first and second members. The electromagnetic actuator includes a detector configured to detect the clutch actuated to produce a detection signal. The electromagnetic actuator includes a controller configured to respond to the detection signal from the detector to control the solenoid current.
Owner:TOCHIGI FUJI IND CO LTD
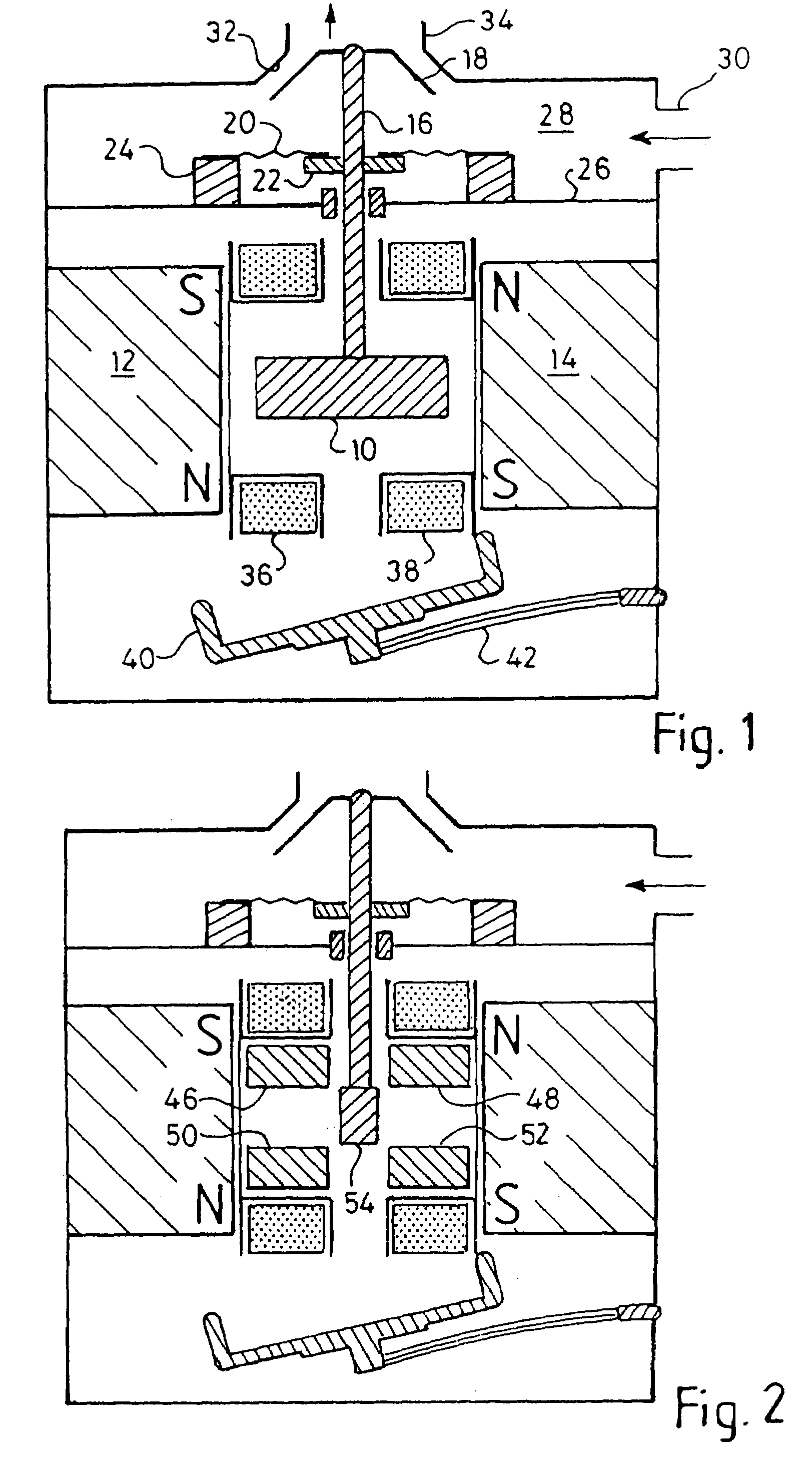
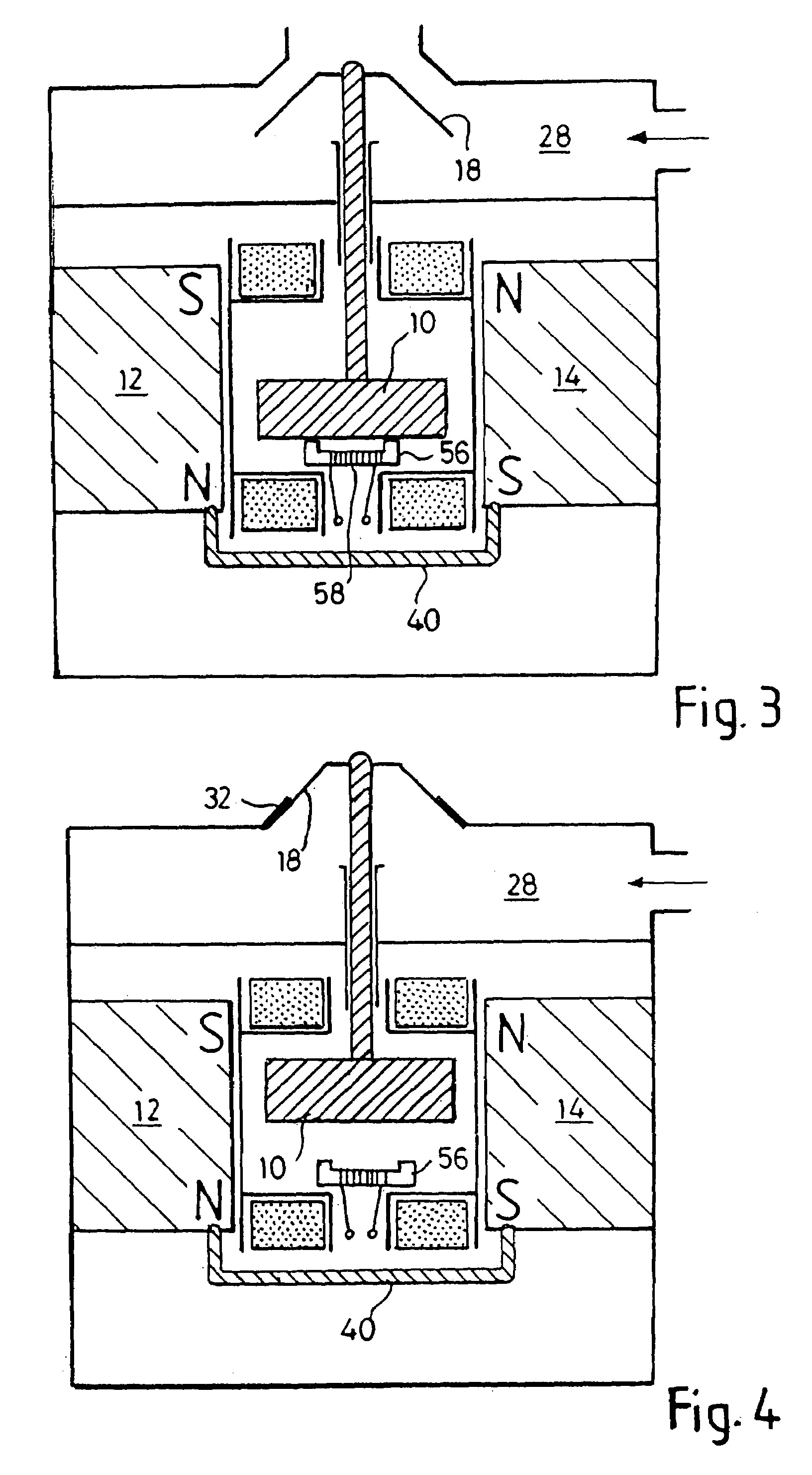
Electromagnetic actuator and integrated actuator and fluid flow control valve
InactiveUS20040025949A1Rapid responseLow driving energyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipeline systemsMagnetic polesEngineering
A magnetic device is formed from a permanent magnet generating magnetic flux, an armature which can occupy two positions between four poles and an electromagnet winding to which current can be supplied to produce a magnetic flux in one direction or the other, the flux from the winding causing the armature to move into one position and continue to remain in that position after the current flow ceases. The device can be incorporated into a fluid valve to act as a drive for opening and closing the valve. It may also serve as the drive for opening and closing electrical contacts. Monostable operation can be achieved by locating a magnetic flux shunt at one end of the armature travel. A holding solenoid may be incorporated. A pivoting armature in a fluid tight chamber comprises a fluid flow controlling device. It can adopt either of two home positions in contact with two magnetic poles and is retained by magnetic flux from a permanent magnet. Fluid can flow into and out of the chamber via a first passage. A second passage extends through one of the poles to an opening in the pole face which is covered by the armature when the latter occupies one home position but is uncovered when the armature occupies its other home position. A third fluid passage extends through and leads to a second opening in another pole, which is covered when the armature occupies its said other home position. Passages in the poles house energy storing springs each of which is compressed as the armature approaches the pole. A push rod can extend through a passage in one of the poles for conveying armature movement externally of the device.
Owner:CAMCOM
Solenoid valve
ActiveUS7347221B2Easy to moveMinimal gap widthFuel supply regulationGaseous fuel feeder/distributionPower flowSolenoid valve
A valve assembly comprises two valves and a single solenoid actuator with only one magnetizing coil that controls both valves. The corresponding magnetic circuit comprises a yoke with only two pole pieces. The valves are arranged concentric to one another. The valve closing element of the outer valve is connected to an armature by means of a sleeve. The cup thus formed receives the armature that is connected to the valve closing element of the inner valve. The pole piece and the armature form a transmission air gap through which the sleeve extends. A coupling air gap is formed between the armatures. The armature and the pole piece form a working air gap. The valves are opened collectively and are able to close independently of one another when the coil is rendered currentless.
Owner:KARL DUNGS
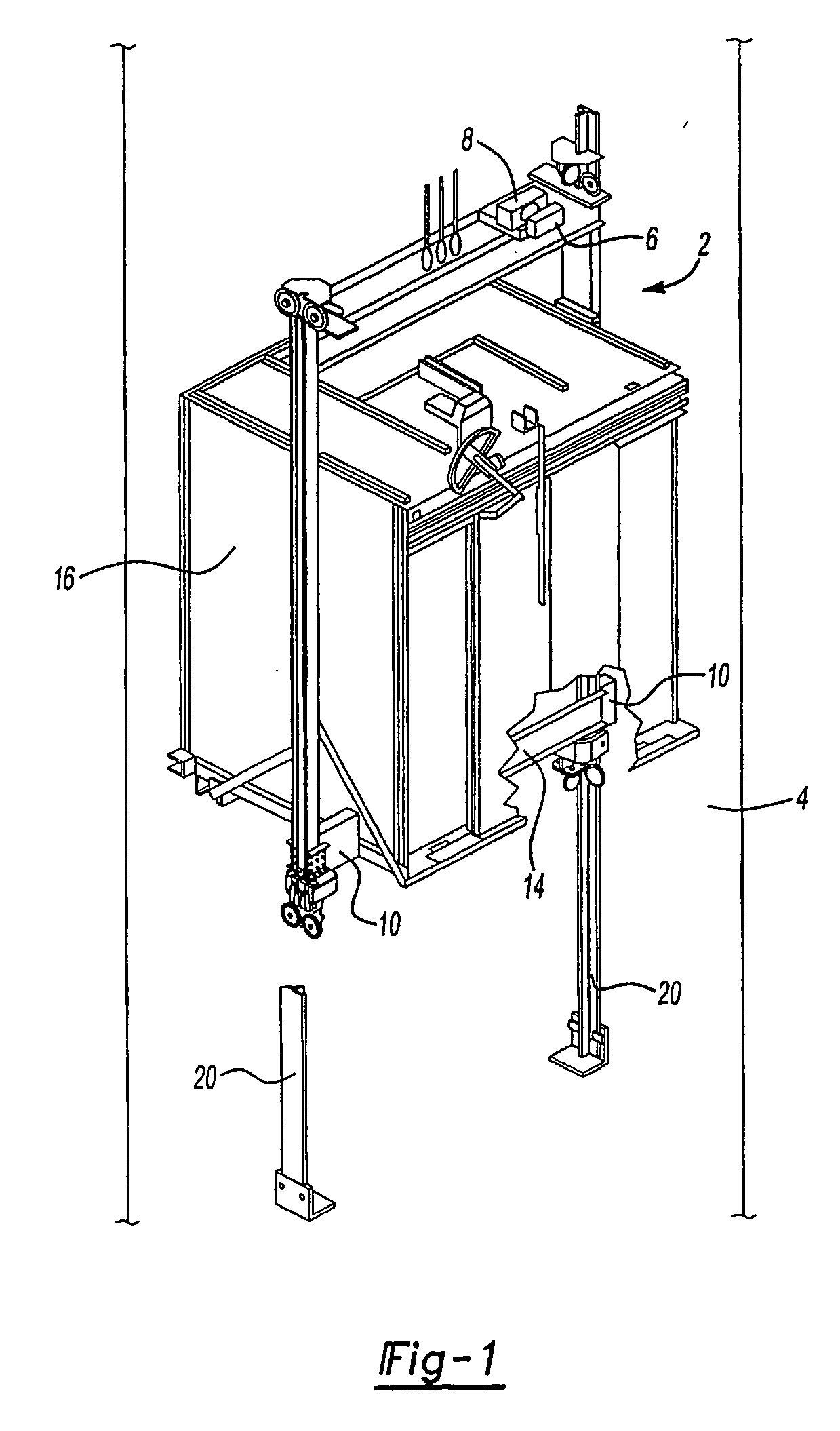
Remotely resettable ropeless emergency stopping device for an elevator
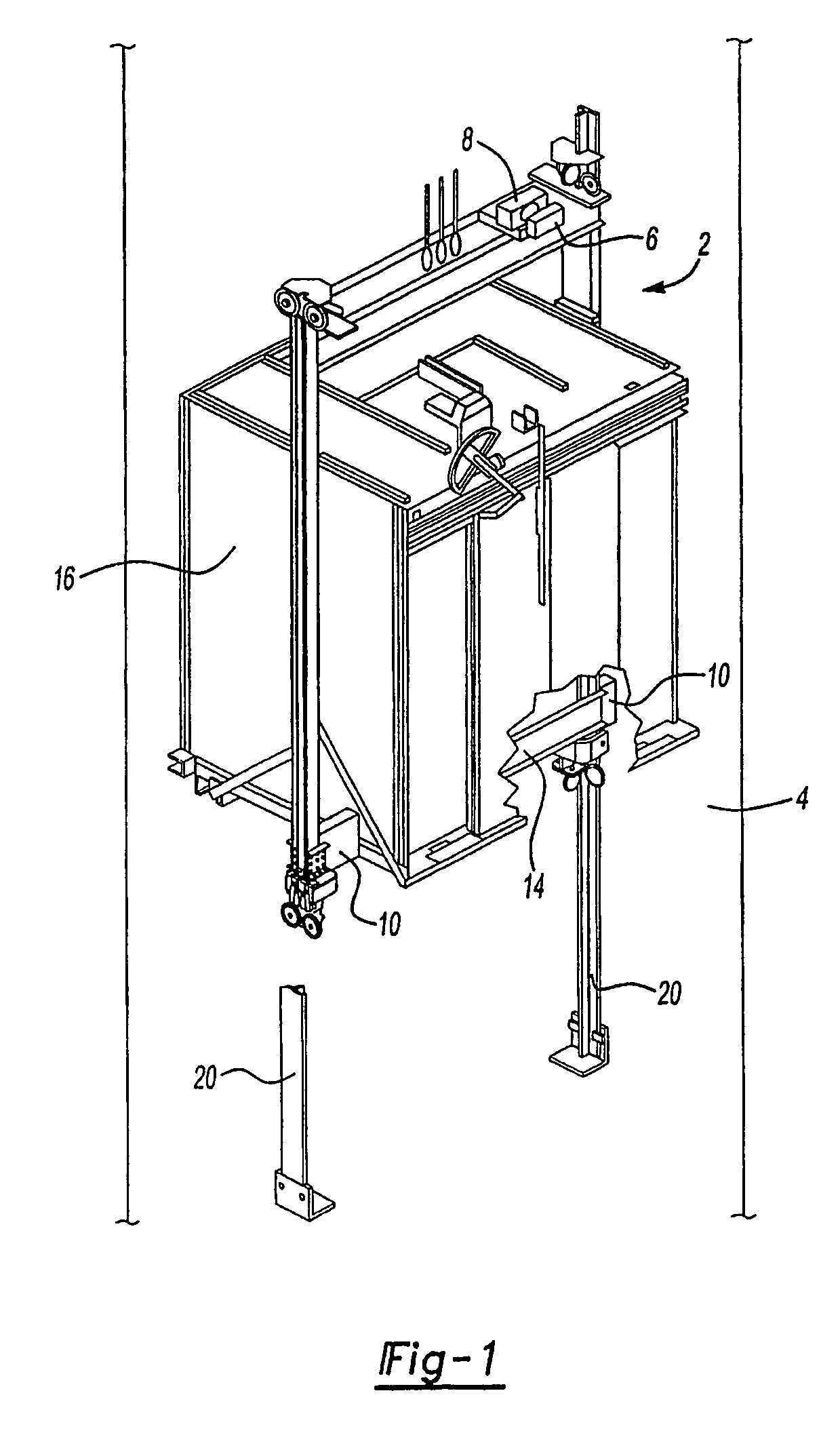
ActiveUS7575099B2Decreases equipment cost and installation timeReduce maintenanceComputer controlElevatorsControl signalStops device
A brake mechanism (10) for an elevator (2) is activated in response to an electronic control signal to prevent movement of an elevator car (16) under predetermined conditions. The brake mechanism is preferably a safety mechanism (10) and does not require a governor sheave, a governor rope, or a tension sheave. The safety mechanism in one disclosed example utilizes a solenoid actuator (22b) and an electric motor (40) and gear box assembly (42) to move safety wedges (18) into engagement with a guide rail (20) to stop the elevator car (16). The safety wedges (18) are held in a non-deployed position during normal elevator operation. If there is a power loss or if elevator car speed exceeds a predetermined threshold, an electronic control signal activates the safety mechanism (10) causing the solenoid to release, which causes the safety wedges (18) move in a direction opposite to that of a safety housing (12) mounted for movement with the elevator car (16). Angled surfaces of the safety housing (12) force the safety wedges (18) into engagement with the guide rail (20). The safety mechanism (10) can be selectively reset from a remote location.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
Solenoid valve
ActiveUS20050166979A1Easy to moveMinimal gap widthFuel supply regulationGaseous fuel feeder/distributionSolenoid valveEngineering
A valve assembly comprises two valves and a single solenoid actuator with only one magnetizing coil that controls both valves. The corresponding magnetic circuit comprises a yoke with only two pole pieces. The valves are arranged concentric to one another. The valve closing element of the outer valve is connected to an armature by means of a sleeve. The cup thus formed receives the armature that is connected to the valve closing element of the inner valve. The pole piece and the armature form a transmission air gap through which the sleeve extends. A coupling air gap is formed between the armatures. The armature and the pole piece form a working air gap. The valves are opened collectively and are able to close independently of one another when the coil is rendered currentless.
Owner:KARL DUNGS
Electronically actuated apparatus using solenoid actuator with integrated sensor
An electromagnetic actuator assembly that includes an annular frame, a coil assembly, an annular armature, a plunger and a sensor. The coil assembly is coupled to the frame and includes an annular core and an annular coil. The annular armature is received in the frame and abutted against the plunger. A sensor target can be coupled to the armature or the plunger and includes a radially outwardly extending sensor target. The sensor is coupled to the frame and configured to sense a position of the sensor target. A method for operating an electromagnetic actuator is also provided.
Owner:AMERICAN AXLE & MFG
Dual Fuel Injector And Engine Using Same
ActiveUS20120285417A1Internal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusLiquid fuelControl theory
A dual fuel injector may be used to injector both gas and liquid fuel into a cylinder of a compression ignition engine. An injector body defines a first set of nozzle outlets, a second set of nozzle outlets, a first fuel inlet and a second fuel inlet. A dual solenoid actuator includes a first armature, a first coil, a second armature and a second coil that share a common centerline. The dual solenoid actuator has a non-injection configuration at which the first armature is at an un-energized position and the second armature is at an un-energized position. The dual solenoid actuator has a first fuel injection configuration at which the first fuel inlet is fluidly connected to the first set of nozzle outlets, the first armature is at an energized position and the second armature is at the un-energized position. The dual solenoid actuator has a second fuel injection configuration at which the second fuel inlet is fluidly connected to the second set of nozzle outlets, the first armature is at the un-energized position and the second armature is at an energized position. The dual solenoid actuator may also include a combined fuel injection configuration.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
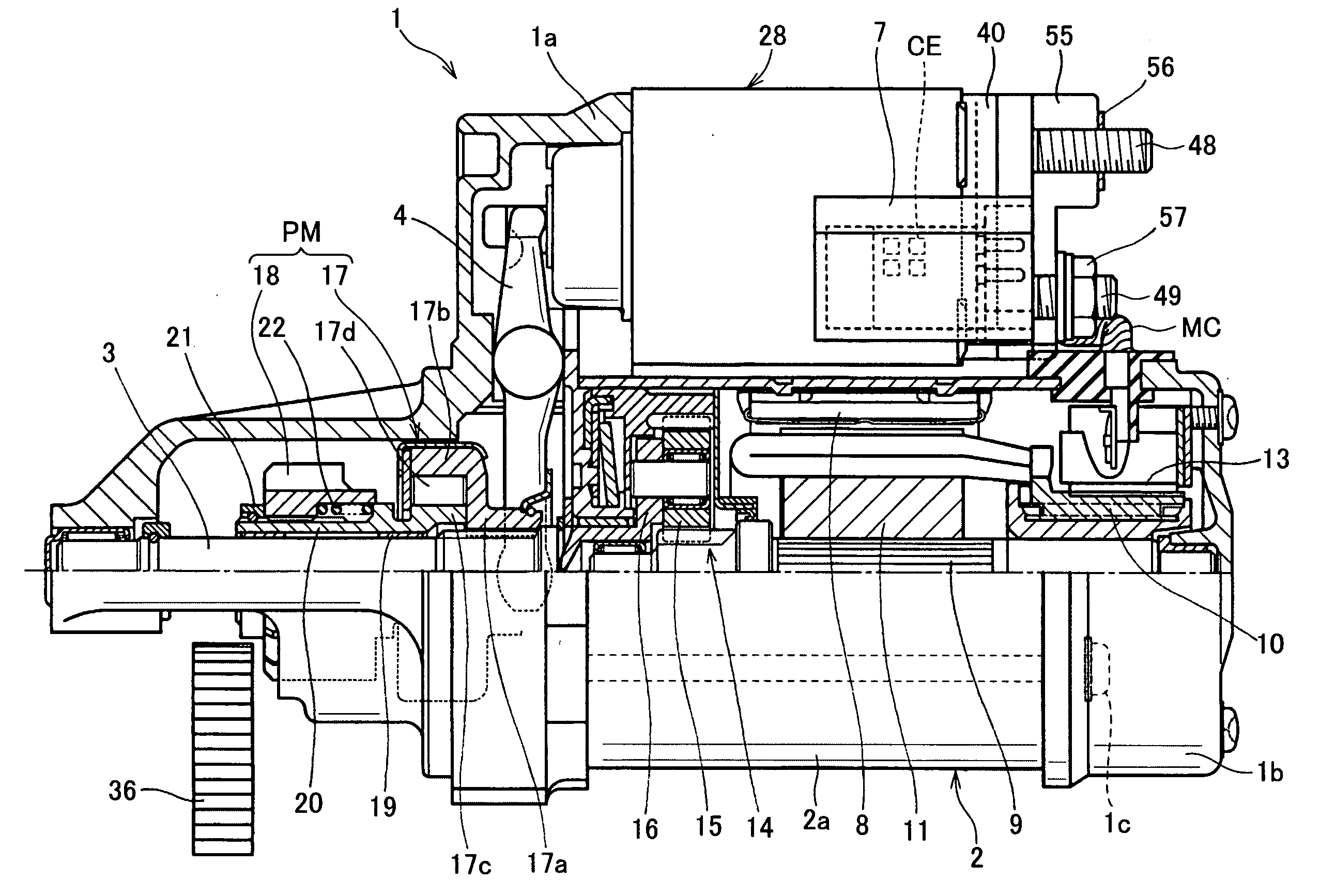
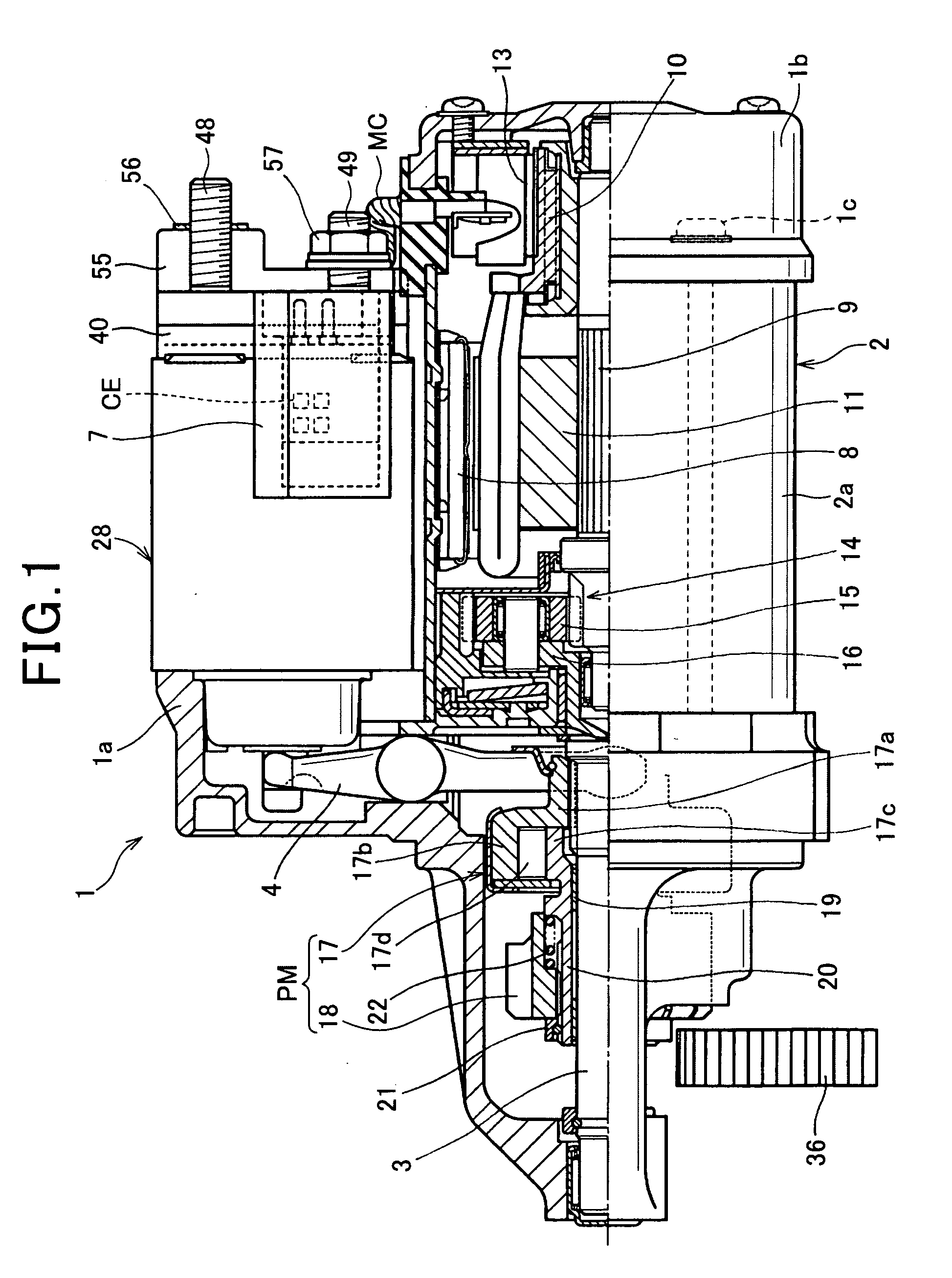
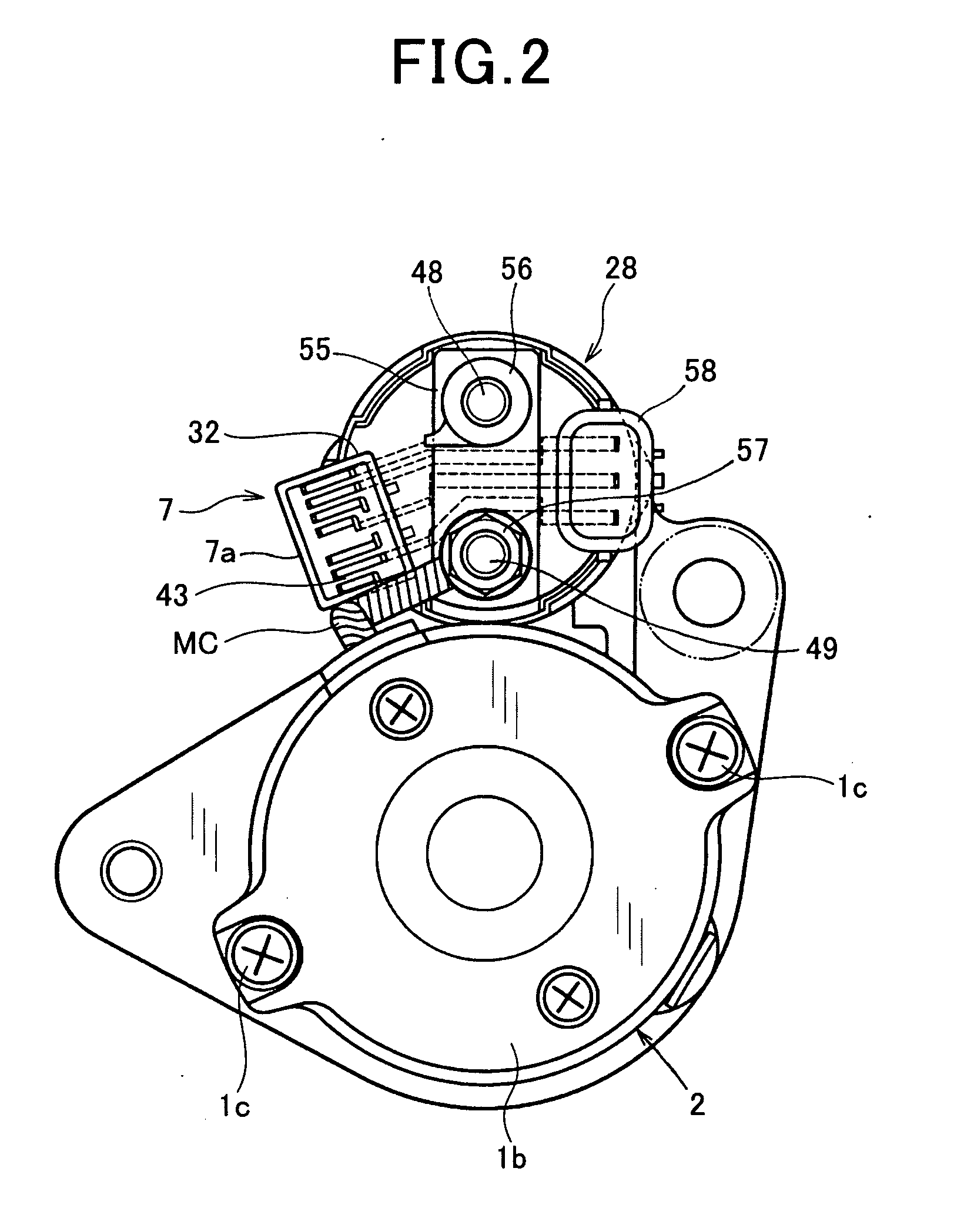
System for starting internal combustion engine
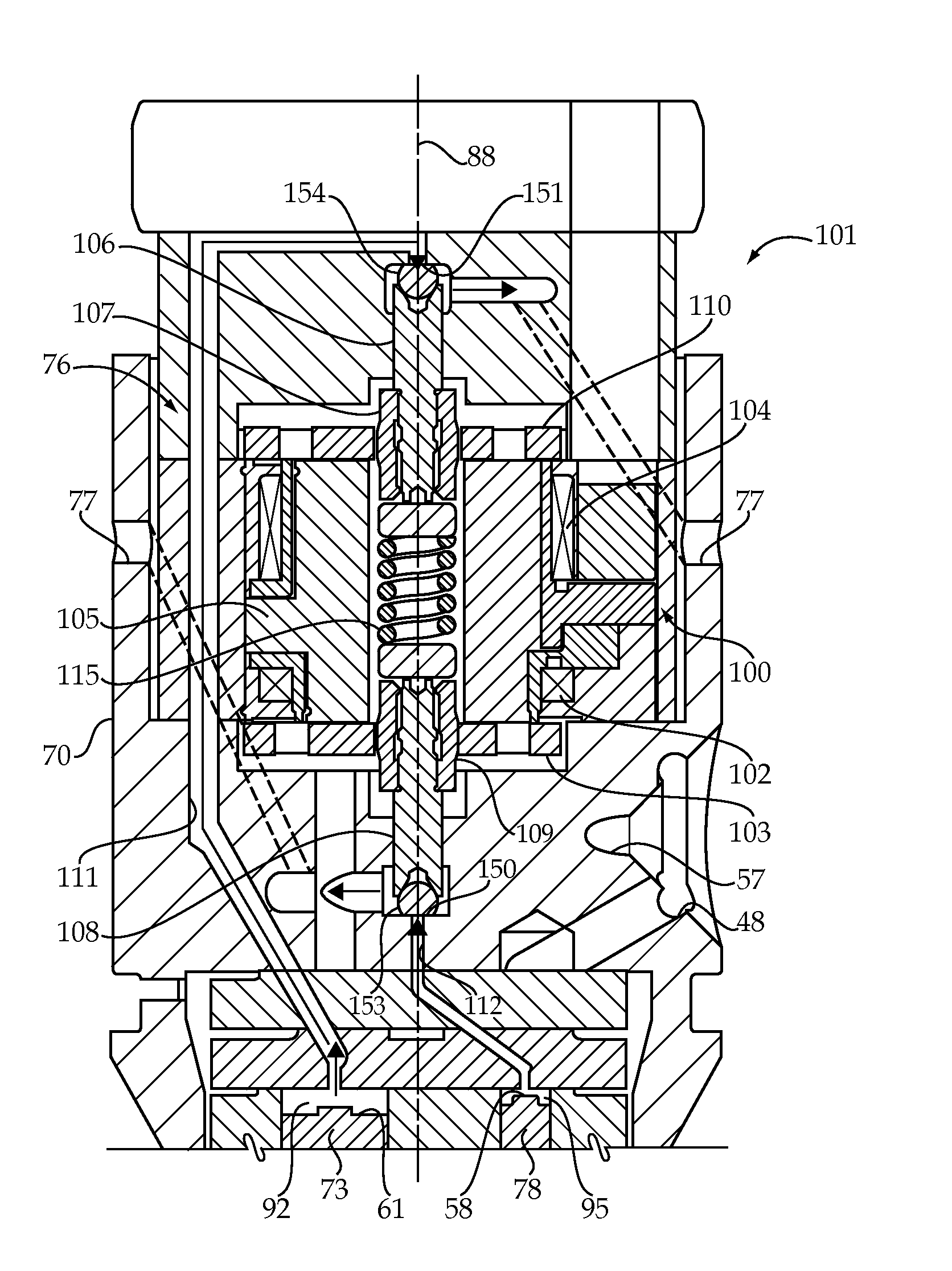
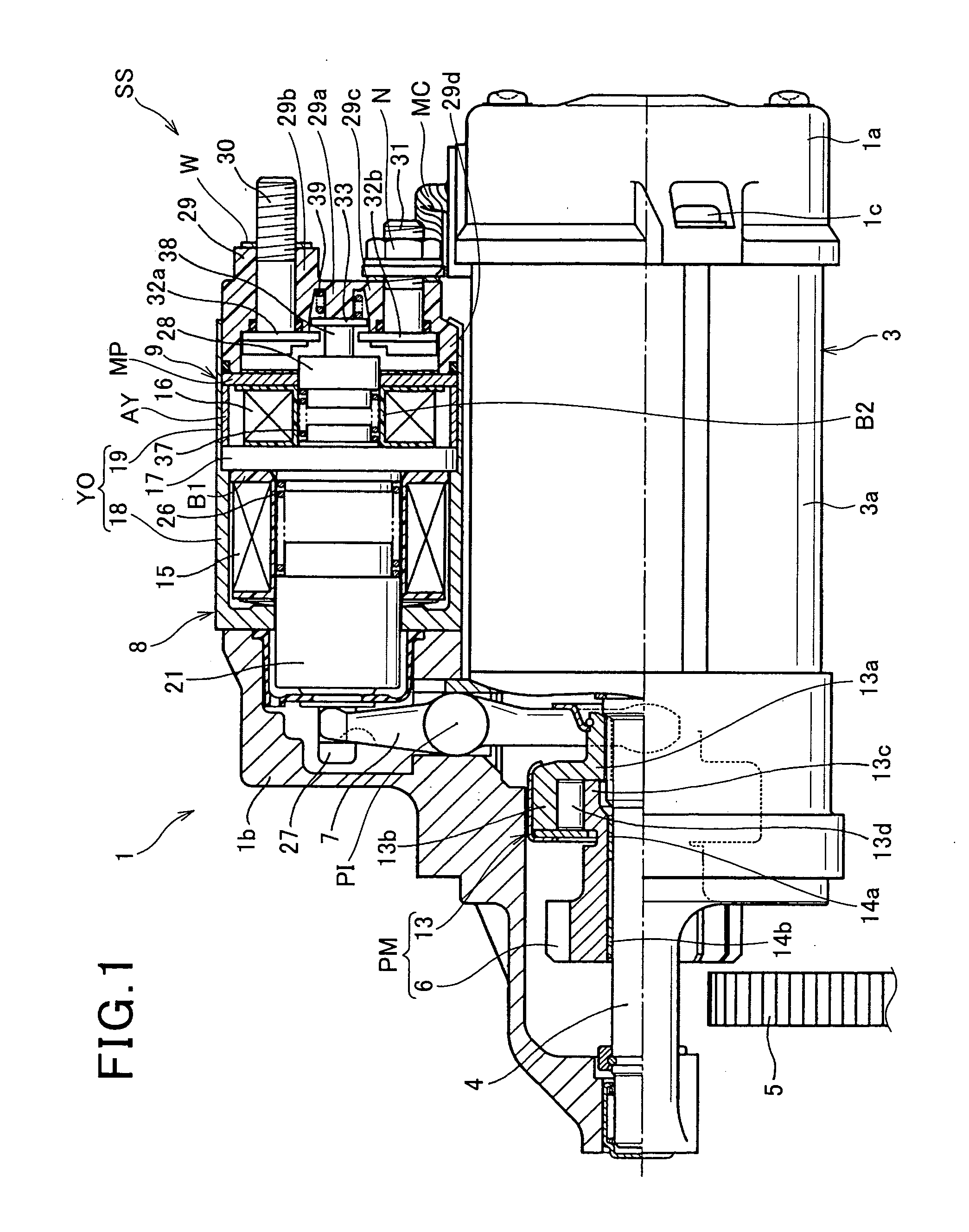
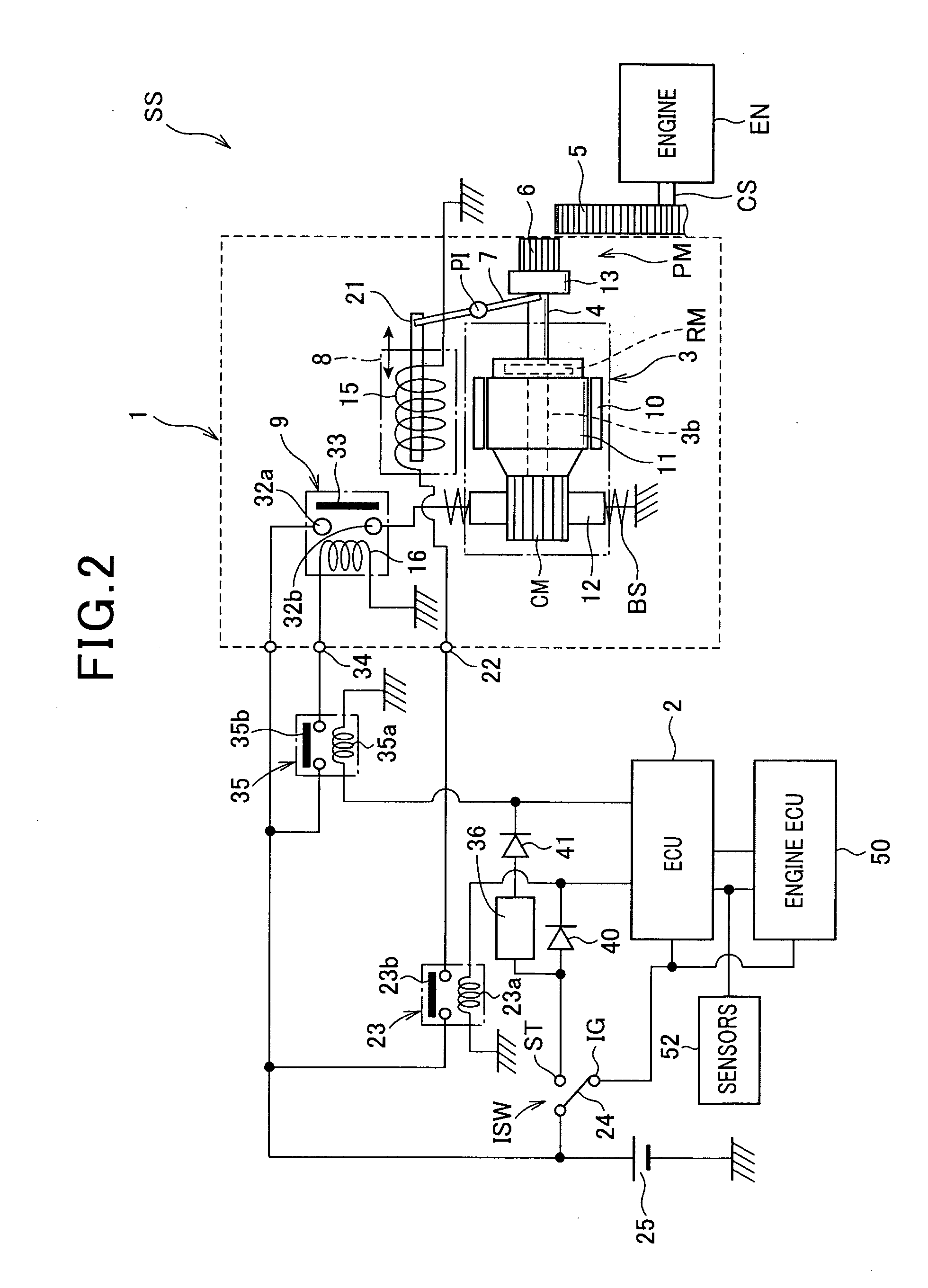
ActiveUS20100282200A1Improving engine-restarting responseQuick restartPower operated startersInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringInternal combustion engine
In an engine starting system, when a first solenoid is energized at a first timing in response to any one of a turning on of a starter switch and an occurrence of an engine restart request, a solenoid actuator shifts a pinion to a ring gear to be engaged with the ring gear. When a second solenoid is energized, a solenoid switch member energizes a motor. A determiner determines a second timing of energization of the second solenoid after the first timing so that a first delay time from the first timing to the second timing when the first timing is responsive to the turning on of the starter switch is different from a second delay time from the first timing to the second timing when the first timing is responsive to the occurrence of the engine restart request.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Rotary servovalve and control system
InactiveUS6269838B1Less torqueIncrease frequency bandwidth of responsivenessOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsFluid controlAngular rotation
An improved rotary servovalve system employs a rotary magnetic solenoid having an armature that includes at least one permanent magnet. The armature is rotatable relative to a stator formed as an electromagnet which is energizable to create alternative electromagnetic fields having opposite polarities from each other. When deenergized, the stator allows the armature to return to a neutral, null position from positions of extreme rotation in opposite angular directions due to the magnetic force of the permanent magnet of the armature. The armature is coupled to carry a movable valve element in angular rotation therewith, so that flow through the servovalve of the system can occur in alternative directions. Also, the valve element is biased toward a position in which all of the valve ports are closed when power is removed from the rotary solenoid. The control circuit employed in the rotary servovalve system expands the bandwidth of response of the solenoid actuator by compensating for frequency variations in the input command signal and in the feedback signal. This compensation is achieved utilizing a combined proportional, integral, and differential amplification circuit. Also, imbalance of fluid forces within the servovalve mechanism can be avoided by utilizing a pair of inlet orifices, a pair of outlet orifices, a pair of first fluid control orifices, and a pair of second fluid control orifices. The orifices within each pair are located on opposite sides of the valve housing from each other.
Owner:WOODWORTH RAYMOND DEXTER
Electromagnetic actuator and integrated actuator and fluid flow control valve
InactiveUS7021603B2Rapid responseLower average energyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipeline systemsMagnetic polesEngineering
A magnetic device is formed from a permanent magnet generating magnetic flux, an armature which can occupy two positions between four poles and an electromagnet winding to which current can be supplied to produce a magnetic flux in one direction or the other, the flux from the winding causing the armature to move into one position and continue to remain in that position after the current flow ceases. The device can be incorporated into a fluid valve to act as a drive for opening and closing the valve. It may also serve as the drive for opening and closing electrical contacts. Monostable operation can be achieved by locating a magnetic flux shunt at one end of the armature travel. A holding solenoid may be incorporated. A pivoting armature in a fluid tight chamber comprises a fluid flow controlling device. It can adopt either of two home positions in contact with two magnetic poles and is retained by magnetic flux from a permanent magnet. Fluid can flow into and out of the chamber via a first passage. A second passage extends through one of the poles to an opening in the pole face which is covered by the armature when the latter occupies one home position but is uncovered when the armature occupies its other home position. A third fluid passage extends through and leads to a second opening in another pole, which is covered when the armature occupies its said other home position. Passages in the poles house energy storing springs each of which is compressed as the armature approaches the pole. A push rod can extend through a passage in one of the poles for conveying armature movement externally of the device.
Owner:CAMCOM
Starter for starting internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20100264670A1Reduce riskLength of wirePower operated startersDC motor speed/torque controlEngineeringBiological activation
In a starter for starting an internal combustion engine with a first output shaft to which a ring gear is coupled, a motor has a second output shaft to which a movable pinion member is coupled and is operative to, when energized, rotate the second output shaft. A solenoid device includes a solenoid actuator linked to the movable pinion member. The solenoid actuator is configured to, when activated, shift the movable pinion member toward the ring gear to be engaged with the ring gear. The solenoid device includes a solenoid switch configure to, when activated, energize the motor. The solenoid actuator and the solenoid switch are integrated with each other to provide the solenoid device. A controller module is configured to individually control an activation of the solenoid actuator and an activation of the solenoid switch. The controller module is mounted on the solenoid device.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Remotely resettable ropeless emergency stopping device for an elevator
ActiveUS20070051563A1Decreases equipment cost and installation timeReduce maintenanceComputer controlElevatorsControl signalSolenoid valve
A brake mechanism (10) for an elevator (2) is activated in response to an electronic control signal to prevent movement of an elevator car (16) under predetermined conditions. The brake mechanism is preferably a safety mechanism (10) and does not require a governor sheave, a governor rope, or a tension sheave. The safety mechanism in one disclosed example utilizes a solenoid actuator (22b) and an electric motor (40) and gear box assembly (42) to move safety wedges (18) into engagement with a guide rail (20) to stop the elevator car (16). The safety wedges (18) are held in a non-deployed position during normal elevator operation. If there is a power loss or if elevator car speed exceeds a predetermined threshold, an electronic control signal activates the safety mechanism (10) causing the solenoid to release, which causes the safety wedges (18) move in a direction opposite to that of a safety housing (12) mounted for movement with the elevator car (16). Angled surfaces of the safety housing (12) force the safety wedges (18) into engagement with the guide rail (20). The safety mechanism (10) can be selectively reset from a remote location.
Owner:OTIS ELEVATOR CO
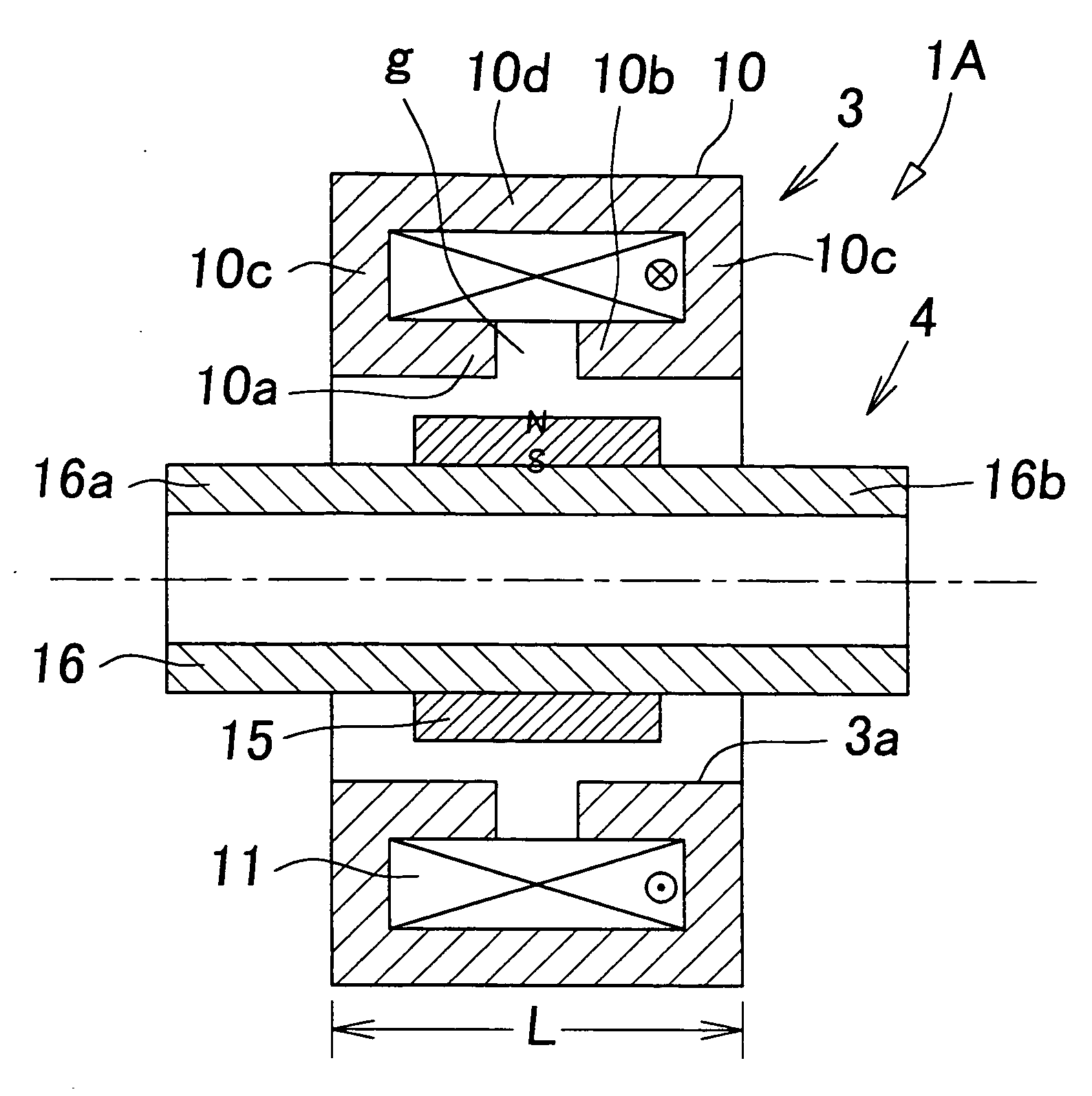
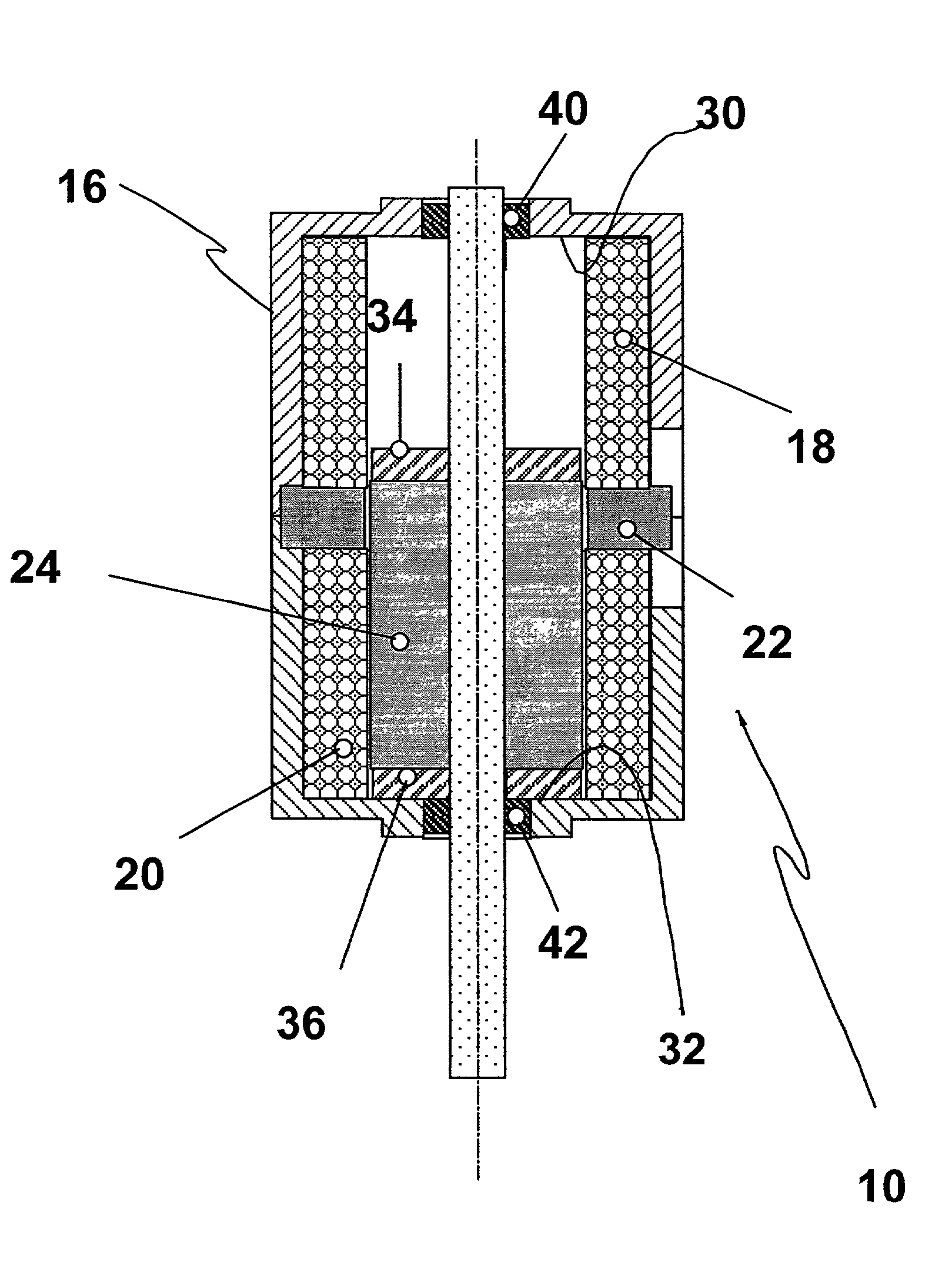
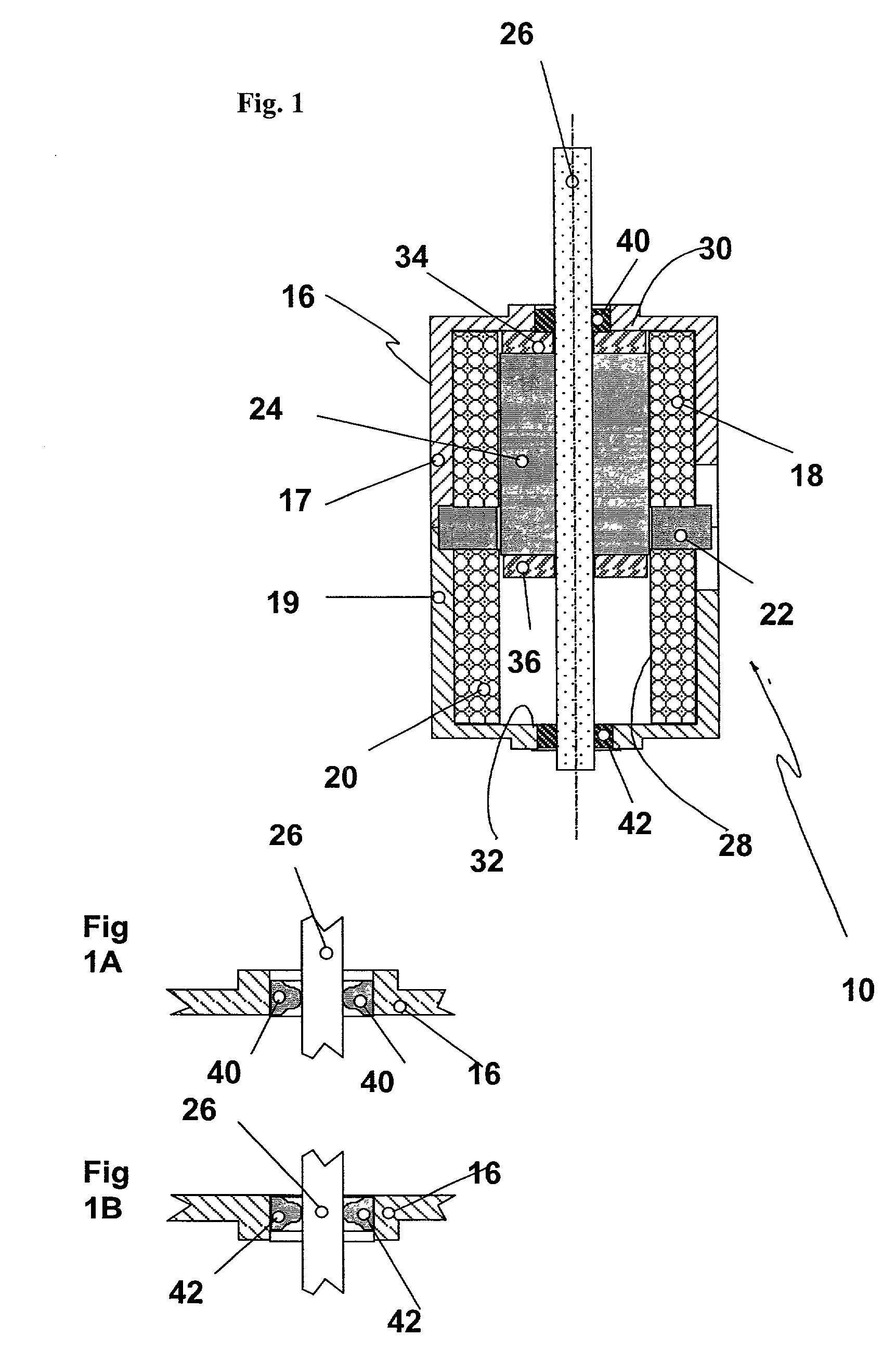
Electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS20050104456A1Large thrustPropulsion systemsElectromagnets with armaturesSolenoid actuatorElectromagnetic actuator
An electromagnetic actuator comprises: a fixed core of a magnetic material provided with one pair of pole teeth, which are cylindrical and face each other; exciting coils wound on the fixed core; and a moving object which is movably disposed in the direction of the axis line coaxially with the pole teeth, wherein the moving object includes: cylindrical permanent magnet, in which the N pole and the S pole have been magnetized in the radial direction; and a cylindrical movable core of magnetic material which is coaxially connected to the permanent magnet and is displaced together with the permanent magnet.
Owner:SMC CORP
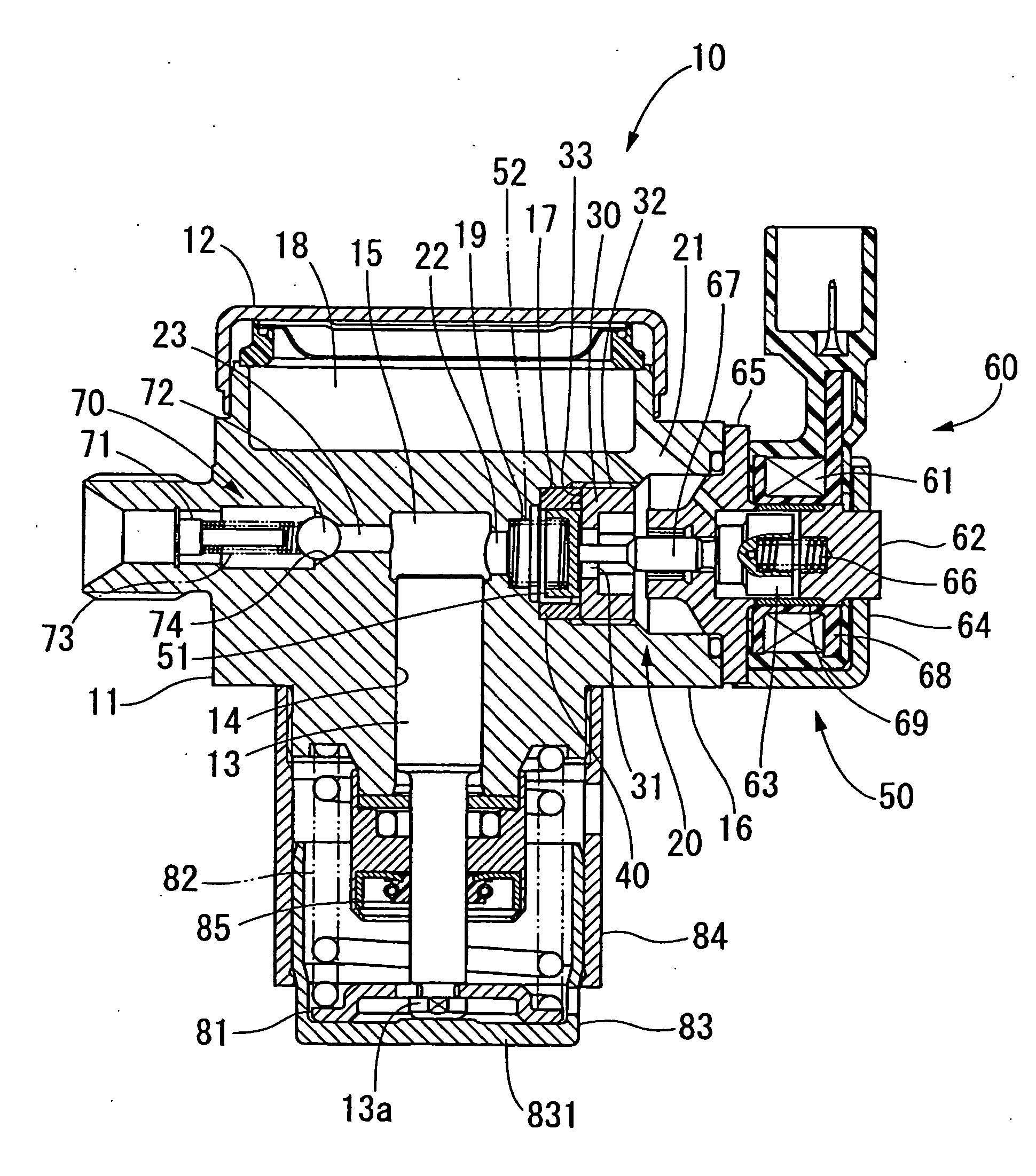
Electrohydraulic valve having a solenoid actuator plunger with an armature and a bearing
ActiveUS20090256091A1Drag minimizationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMultiple way valvesEngineeringElectromagnetic field
A solenoid operated valve has a valve body with a plurality of ports and a spool slideable within the valve body to interconnect the ports in different combinations. An actuator drives the spool into several operating positions. The actuator has a solenoid assembly with an armature that moves within a bore in response to an electromagnetic field. A push member projects from the armature and has a bearing secured thereto. The bearing has a cage that retains a plurality of rollable elements in slots separated by walls that are resilient enabling the rollable elements to be forced into the slots during assembly and thereafter be captured in the cage when the walls return to their original positions. A latch on the cage engages the push member to affix the bearing in place.
Owner:HUSCO AUTOMOTIVE HLDG
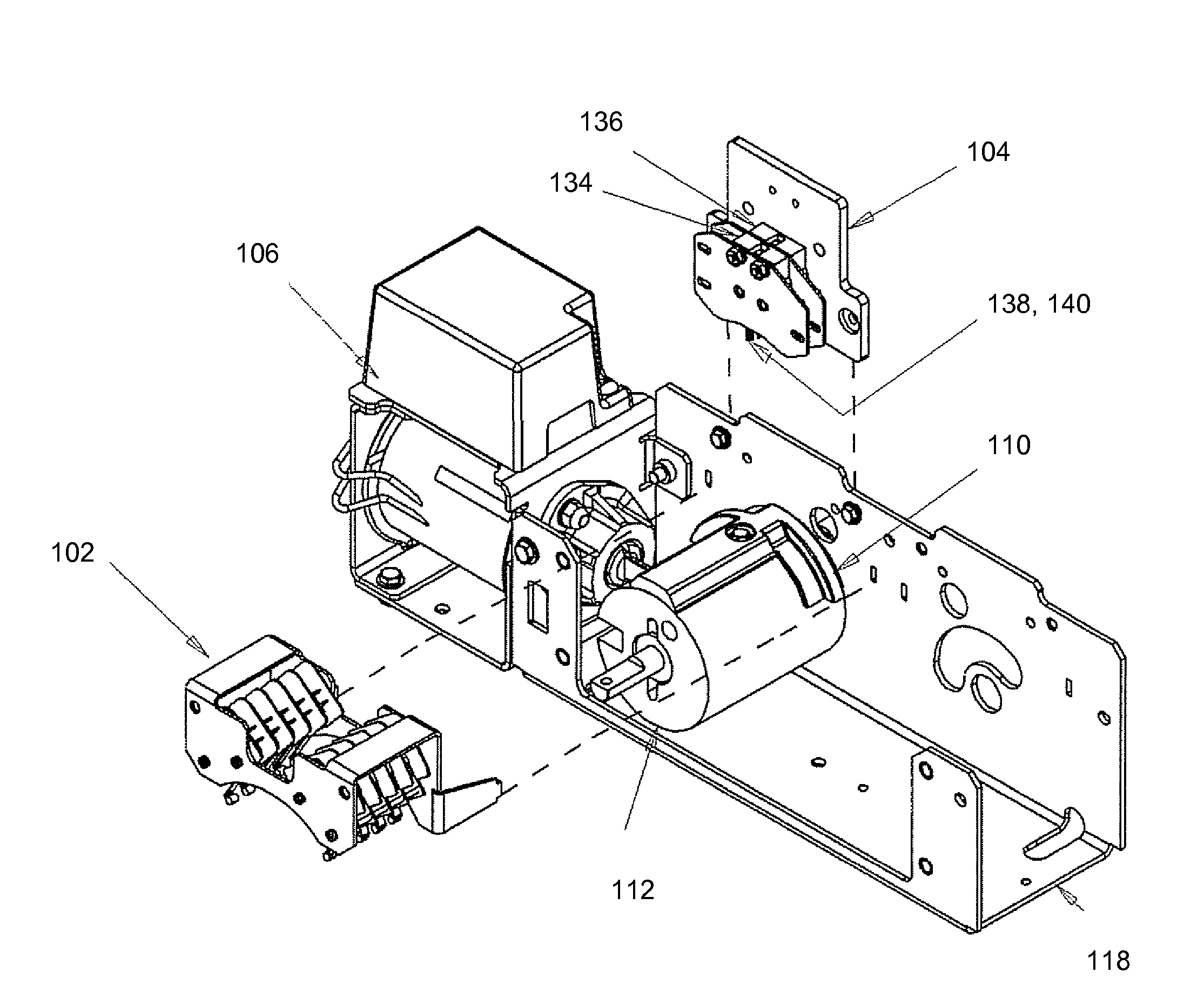
Method and apparatus for control contacts of an automatic transfer switch
ActiveUS7898372B2Good time controlEasy to assembleBatteries circuit arrangementsSwitch power arrangementsTransfer switchEngineering
An automatic transfer switch includes a solenoid control contacts assembly, an auxiliary contacts assembly, a dual purpose cam attached to a cylindrical shaped weight, and a solenoid actuator. When energized, the solenoid actuator rotates the cylindrical weight and the dual purpose cam actuates both the solenoid control contacts assembly and the auxiliary contacts assembly.
Owner:ASCO POWER TECH LP
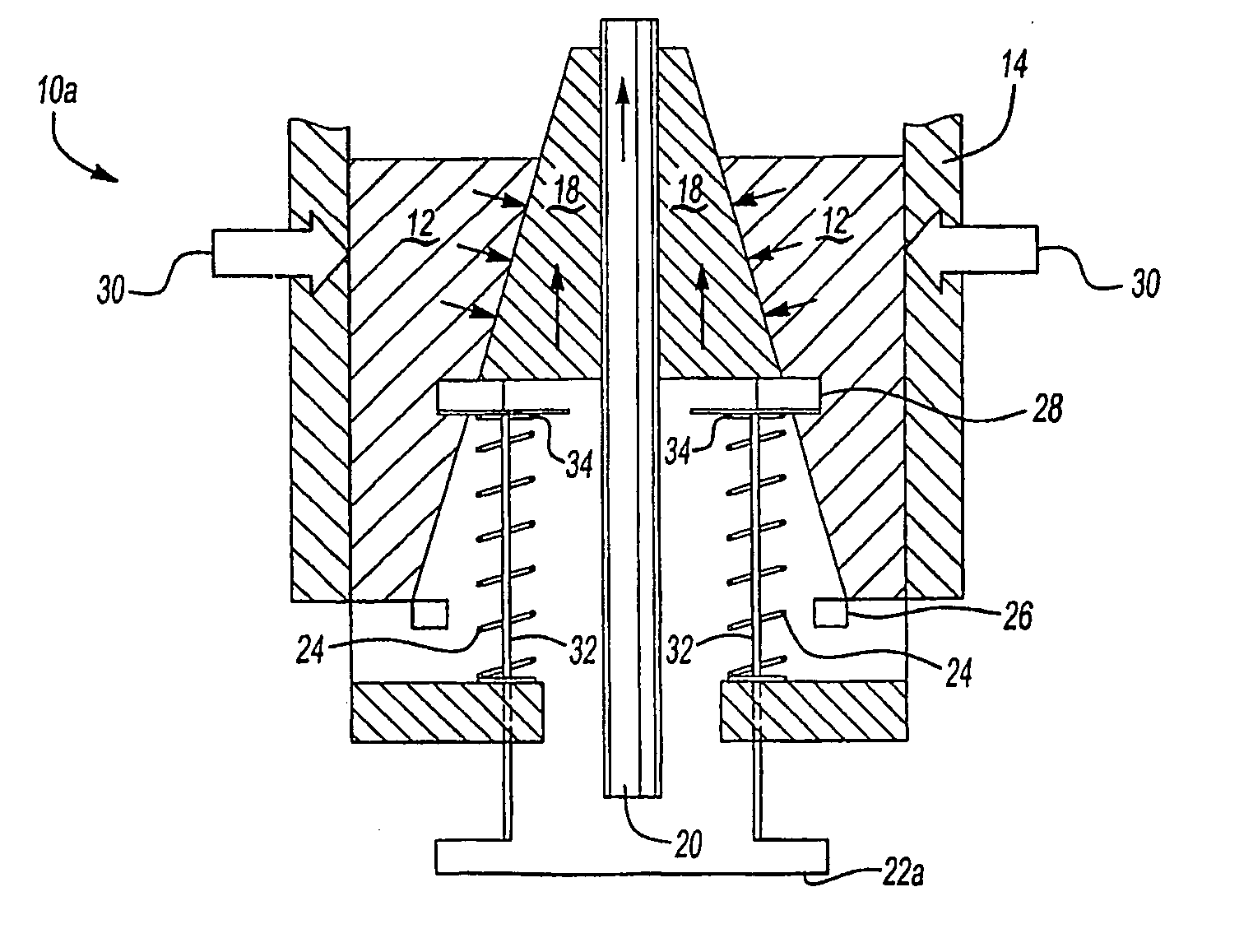
Valve with end position switching
InactiveUS20060272712A1Avoid destructionImprove sealingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipeline systemsEngineeringTappet
For detecting closing or opening of a valve activated preferably by a solenoid actuator, a switch activated by a tappet spring mounted on an armature of the actuator is provided. A stop and an associated surface limit the stroke of the tappet with reference to the switch. Preferably, a valve closing element opens the gas flow only when the armature has already executed a part of its opening stroke. The trigger point of the switch is set in this first part of the opening stroke of the armature, in which the valve closing element has not yet opened. The stroke limiting of the tappet for activating the switch is also preferably set in this region of the opening stroke of the armature. However, the stop limits the stroke of the tappet independent of the opening stroke size of the armature, so that the same switch can be used for different valves with different nominal diameters and opening strokes.
Owner:KARL DUNGS
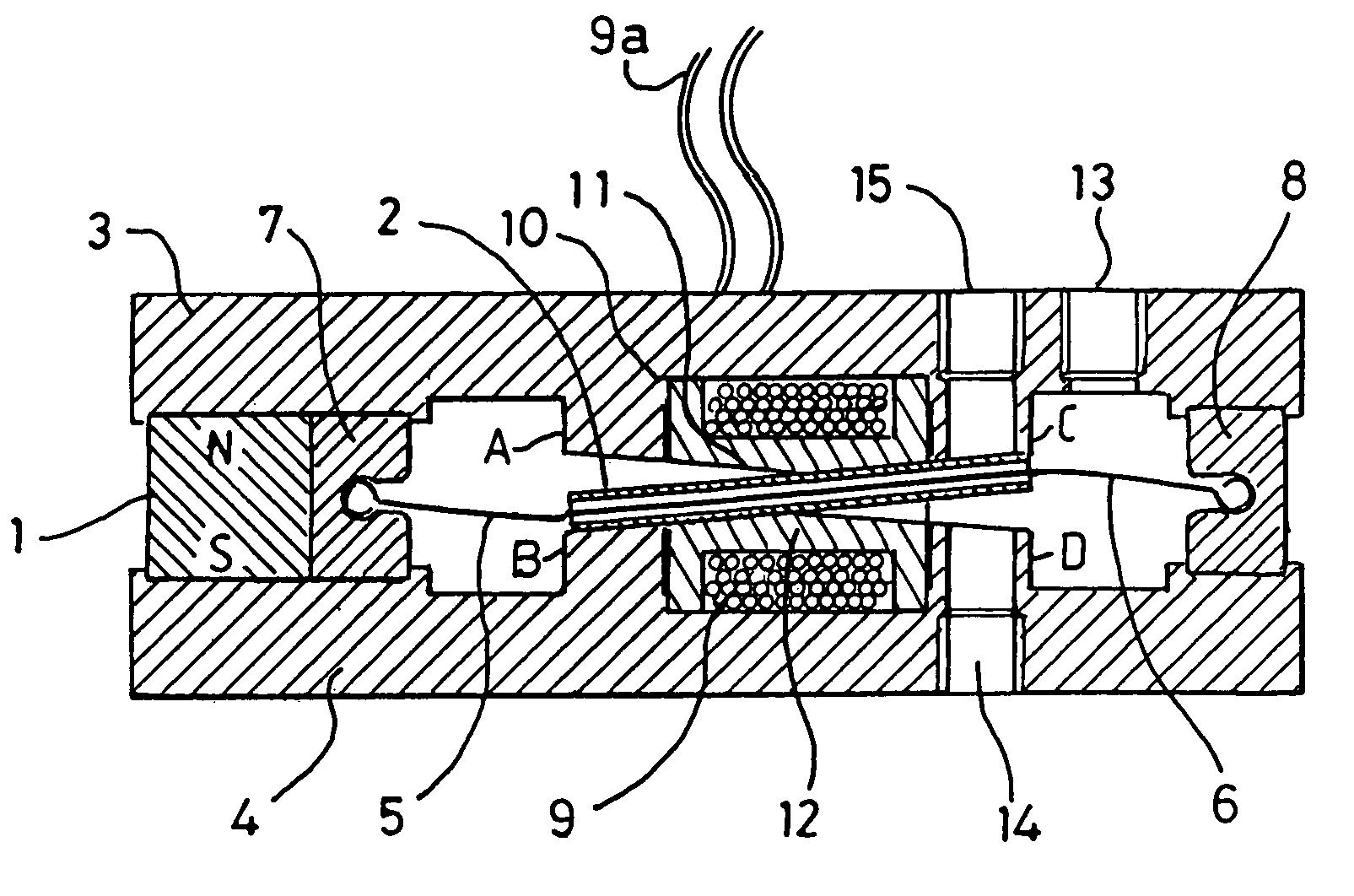
Electromagnetic actuator
An electromagnetic micro actuator, e.g. for use in fiber optics, is operated by a ferromagnetic piston mounted within two electromagnetic coils inside a housing. The piston is held in place and magnetized by a plurality of permanent magnets. The coils are wired for opposite polarity and energizing the coils will tend to push the piston away from one coil and draw it towards another. A ceramic shaft attached to the piston protrudes from both ends of the micro actuator housing and moves with said piston. Energizing the coils thus moves the piston in one or the opposite direction depending on the current direction. Tapered jewel bearings guide the shaft with minimal friction.
Owner:R AUDEMARS
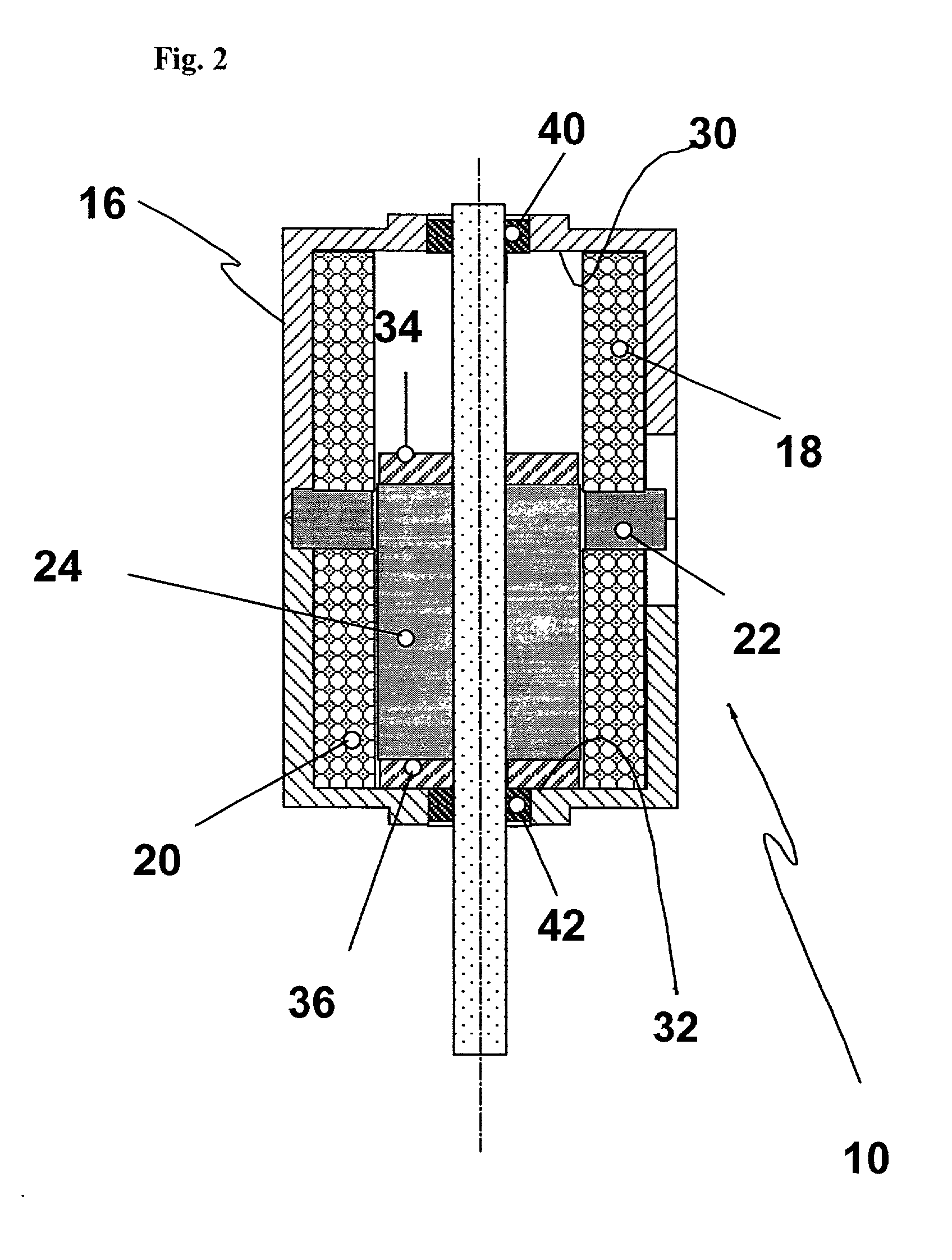
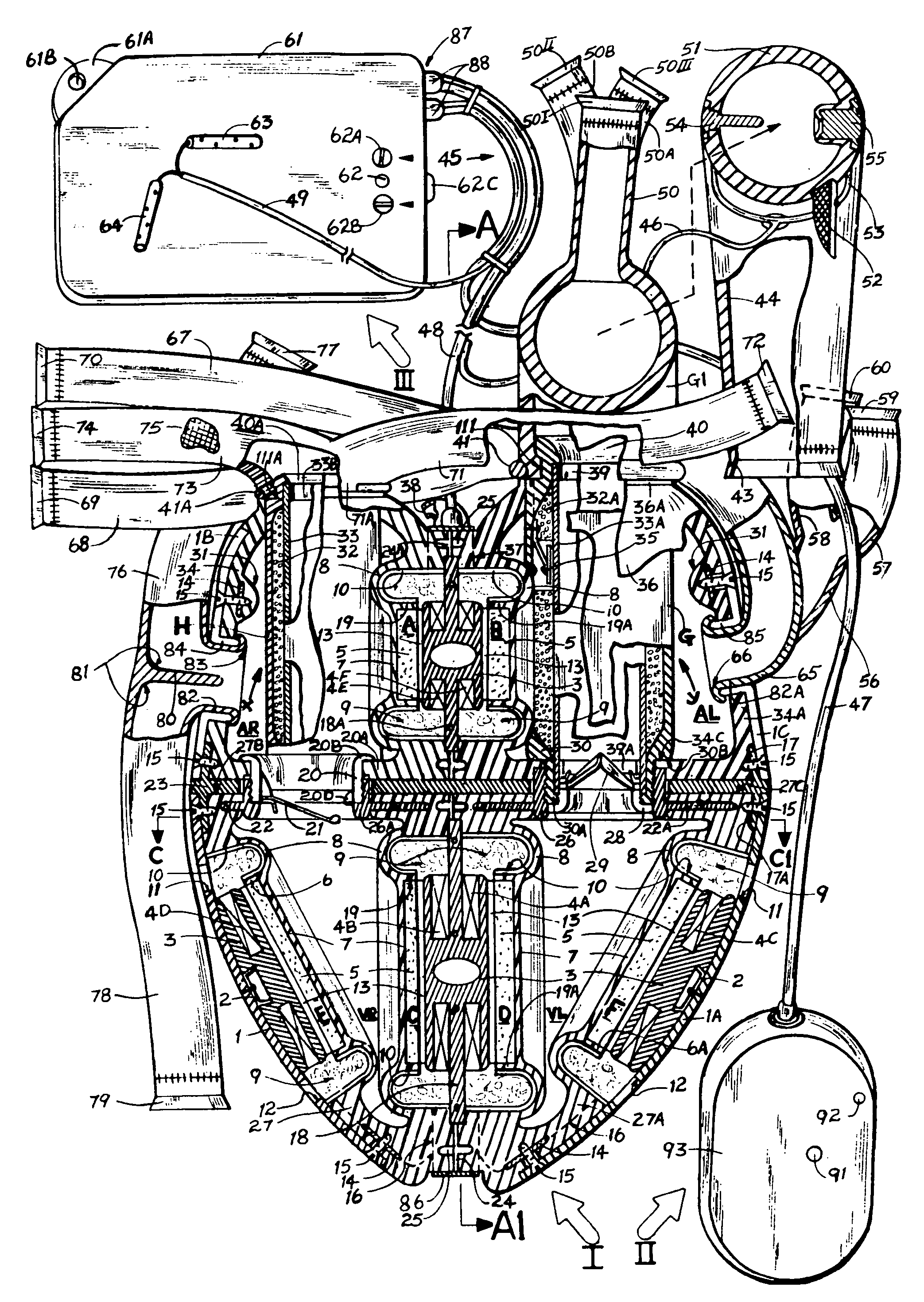
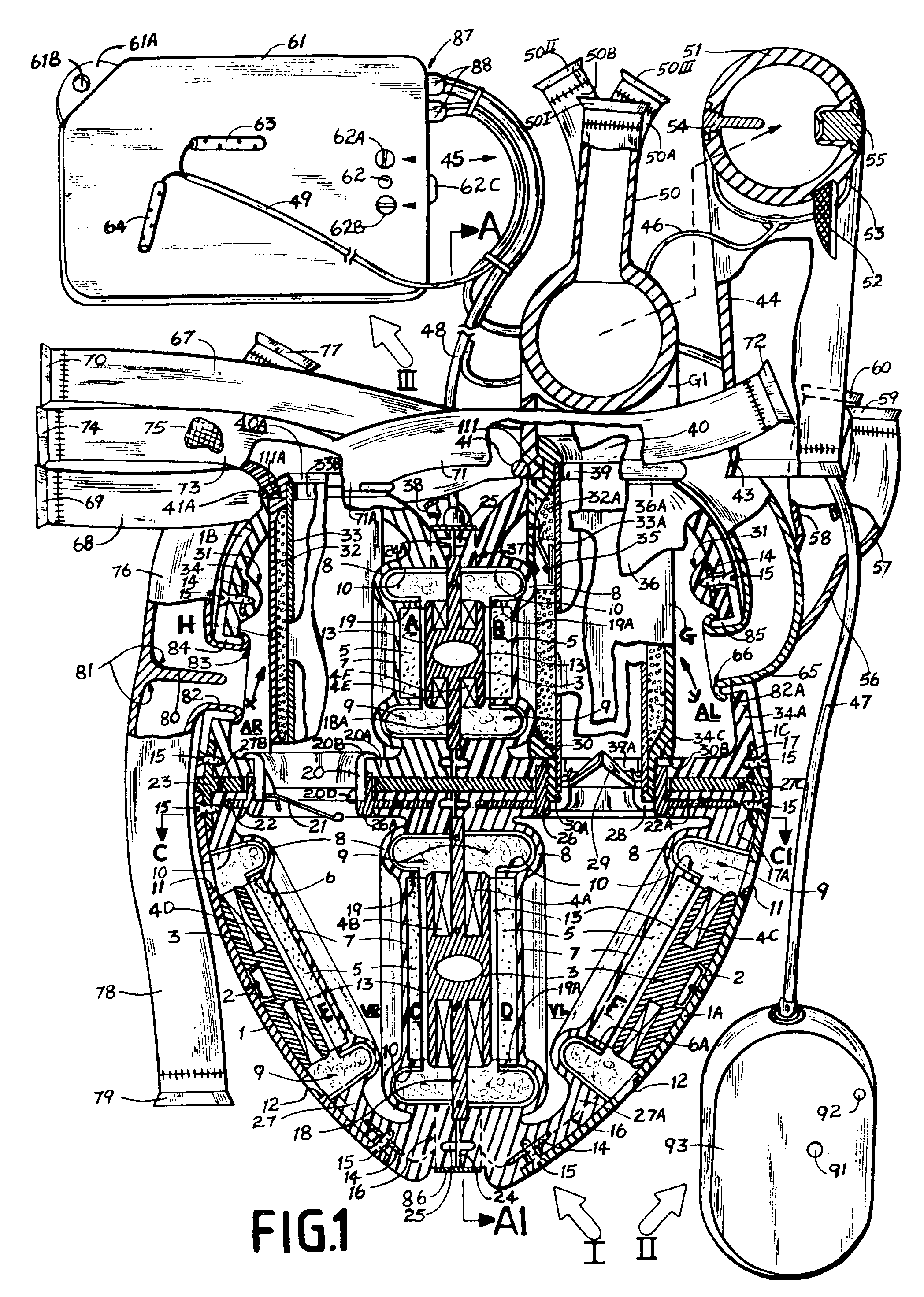
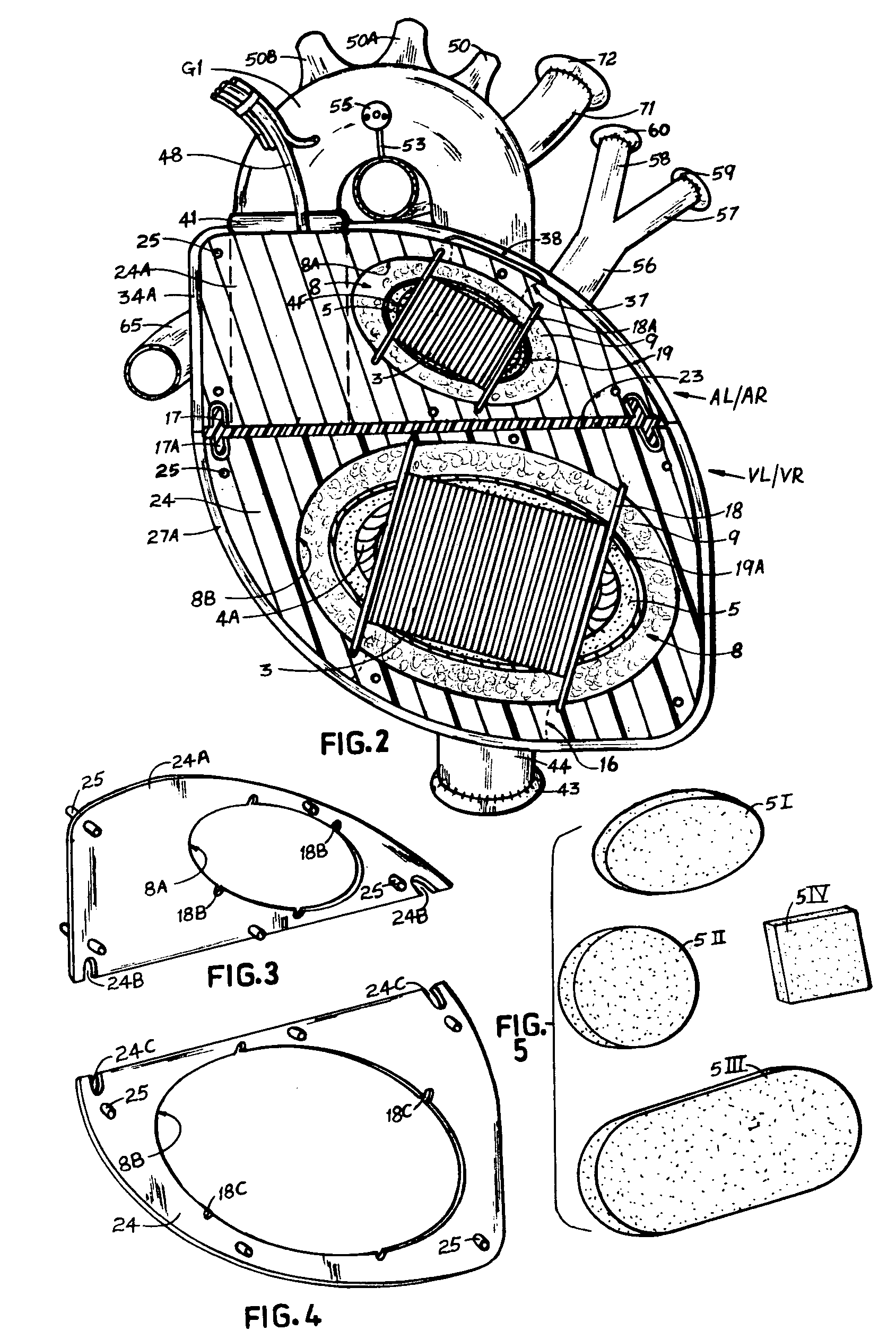
Wholly implantable non-natural heart for humans
InactiveUS20090287305A1Efficient solutionSuitable for miniaturizationControl devicesBlood pumpsHigh energyBreast bone
A wholly implantable non-natural heart for humans is a double pump configuration provided with two auricles and two ventricles. Both the said auricles and ventricles are driven by solenoid actuators interacting with high energy magnets; the auricles and ventricles which are hollow chambers are provided with one-way valves in the usual manner, for the purpose of effectively and rhythmically moving blood to and from the said chambers; power generation for driving said solenoid actuators, as well as an electronic control unit is accomplished by a power generating module which could be a simple battery, a miniature spring-driven generator, a mems generator or a redundant self-sustaining generator or a combination of all of the above; the self-sustaining generator has been proposed and designed to power this present artificial heart and will be presented in a separate patent application in the near future as a follow up to this present one; the aforementioned electronic control unit is preferably configured to amplify the signals from the power generating unit as well as utilizing input / output signals from temperature and pressure sensors embedded in the heart to vary contractile force and frequency of beats, based on bodily requirements, thereby mimicking some functions of the natural heart; the electronic unit is also preferably provided with a translator chip that converts signals from the cardiac / vargus trunks (sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves) via electrodes into clear electric currents for varying actuator outputs; the heart would be implanted in the normal position in the chest, atop the diaphragm, while the electronic control unit and the power generation module would preferably be implanted behind the breastbone and lower abdomen respectively; all components of the present invention are amenable to current mass production techniques and miniaturization for the purpose of fitting into individuals of various sizes; as is clearly shown in FIG. 1, this present invention is an integral three-tiered configuration constituted of pumping unit I, the power generating unit II and the controller III. Also, as aforementioned, additional signals from the embedded temperature and pressure sensors, as well as nerve connecting electrodes are used to manipulate instantaneous outputs. The said electrodes are in the form of cuffs and are to be implanted on the vargus nerves (sympathetic and parasympathetic); Texas Instruments (TI) manufactures reliable operational and instrumentation amplifiers which can detect condition, and amplify nerve signals. The VCO in the controller uses the signals to manipulate instantaneous outputs of the actuating solenoids.
Owner:AMALAHA LEONARD D
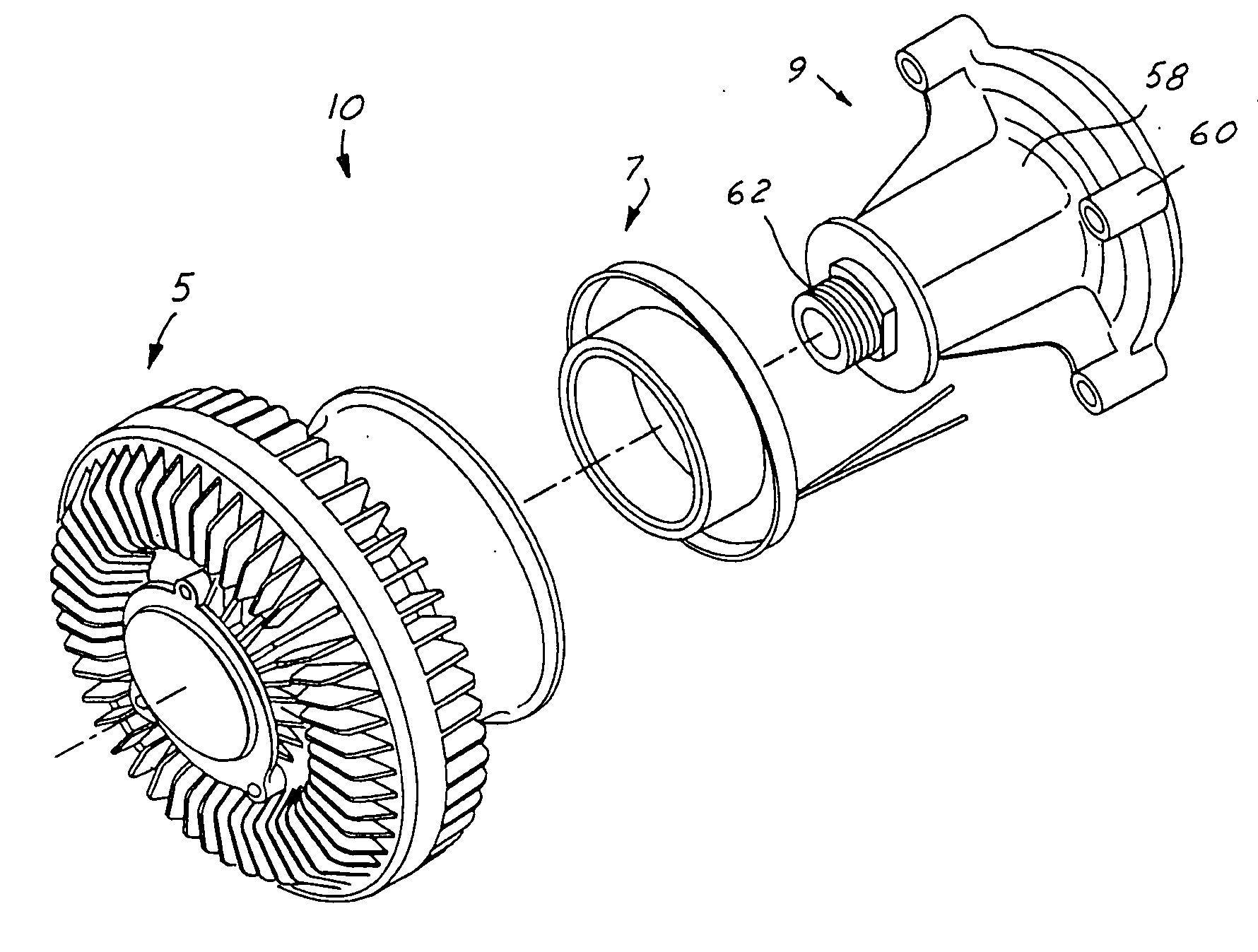
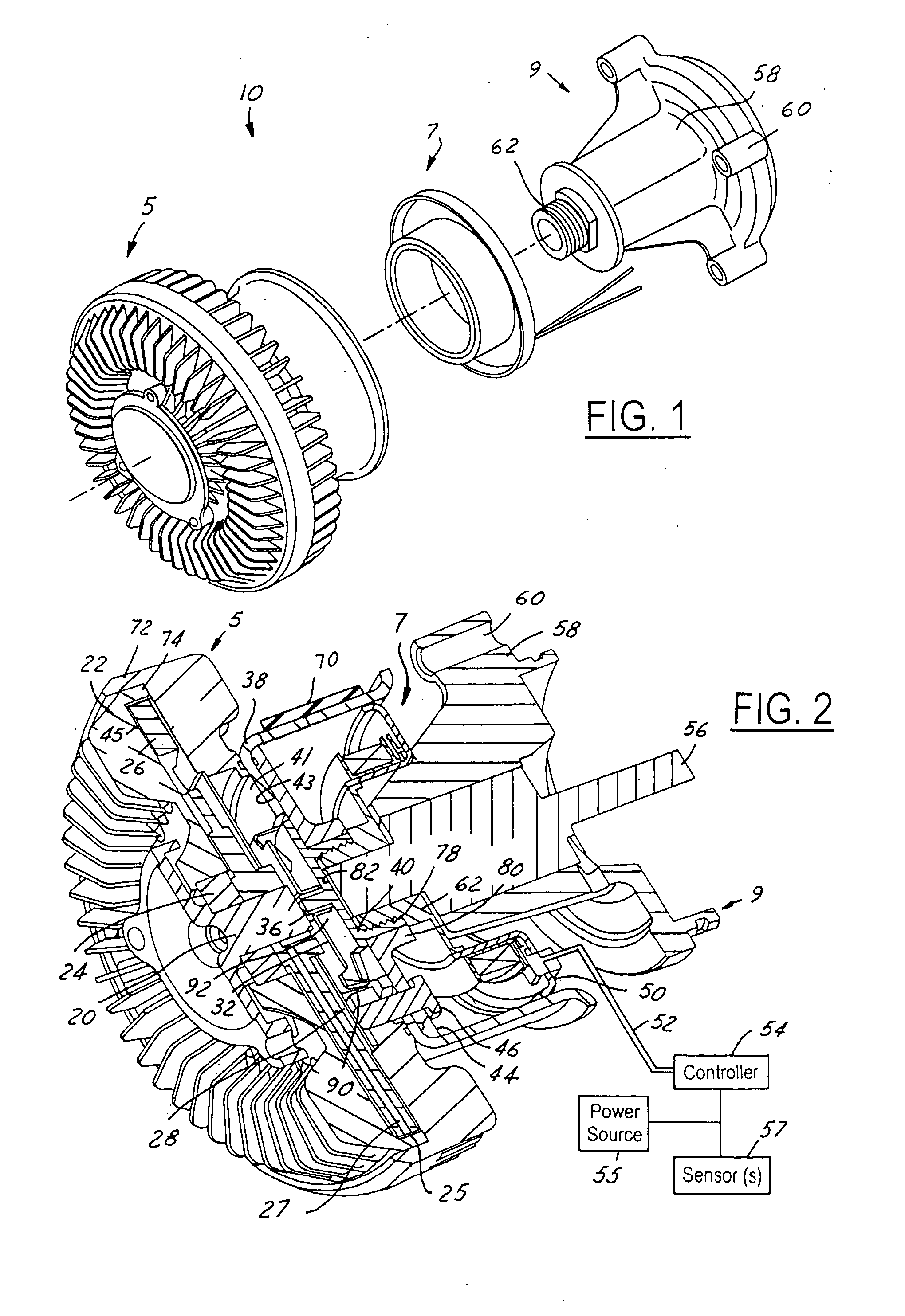
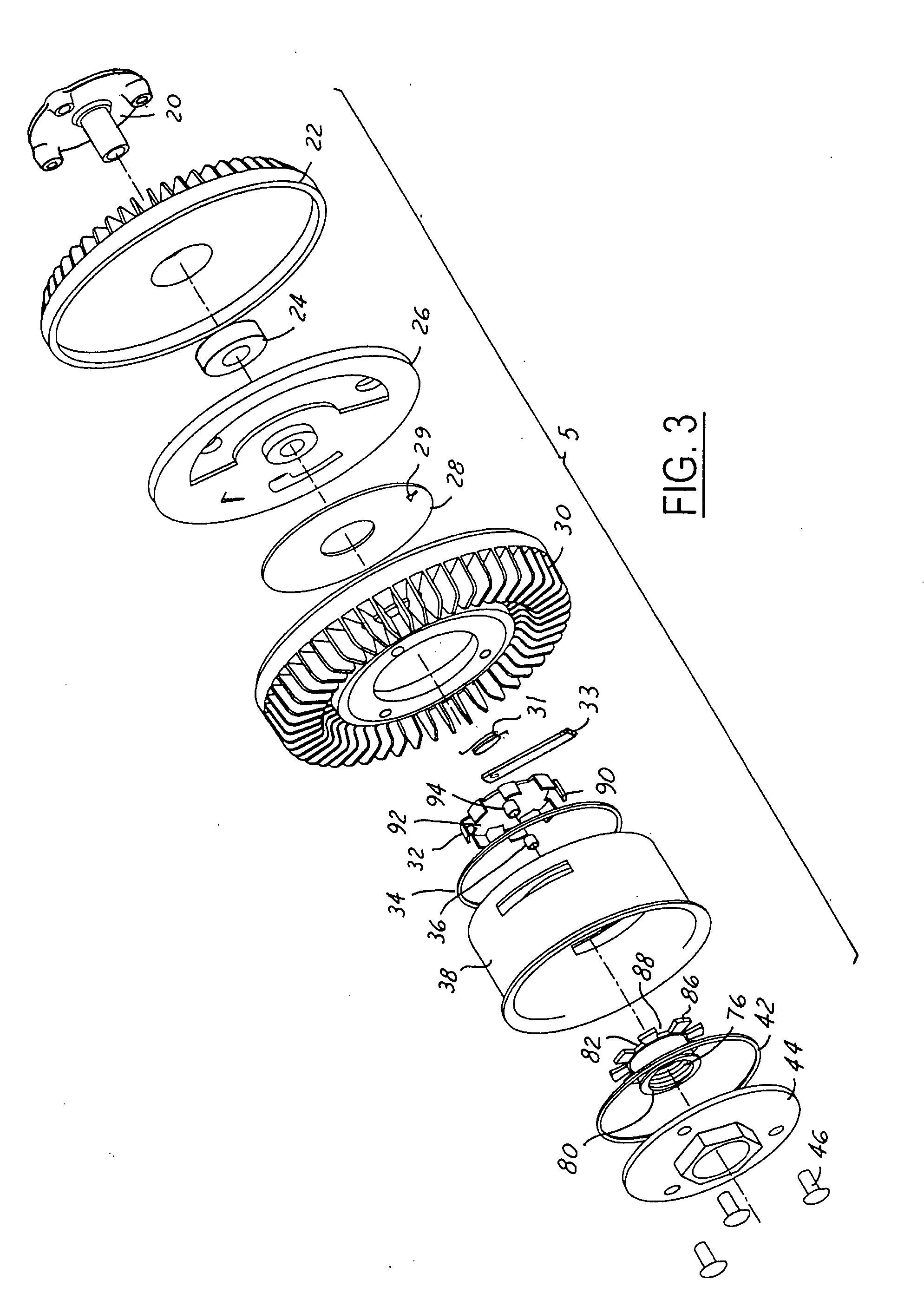
Electronically controlled fluid coupling device
InactiveUS20060042902A1Minimizes problemFast response timeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid couplingsFluid couplingControl theory
An electronically-controlled fluid coupling device having a front mounted fan and electrical actuation without a tethered harness. The fluid coupling device combines an inverted viscous clutch, drive pulley and a split electromagnetic actuator package. In this arrangement, the electrical portion of the split electromagnetic actuator is not physically attached to the fan drive, but is instead mounted to a stationary member. The remaining actuator components are integral to the fan drive and are composed of only mechanical parts. The inverted clutch arrangement having remote electronic control allows three output modes: engaged, partially engaged, or disengaged.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
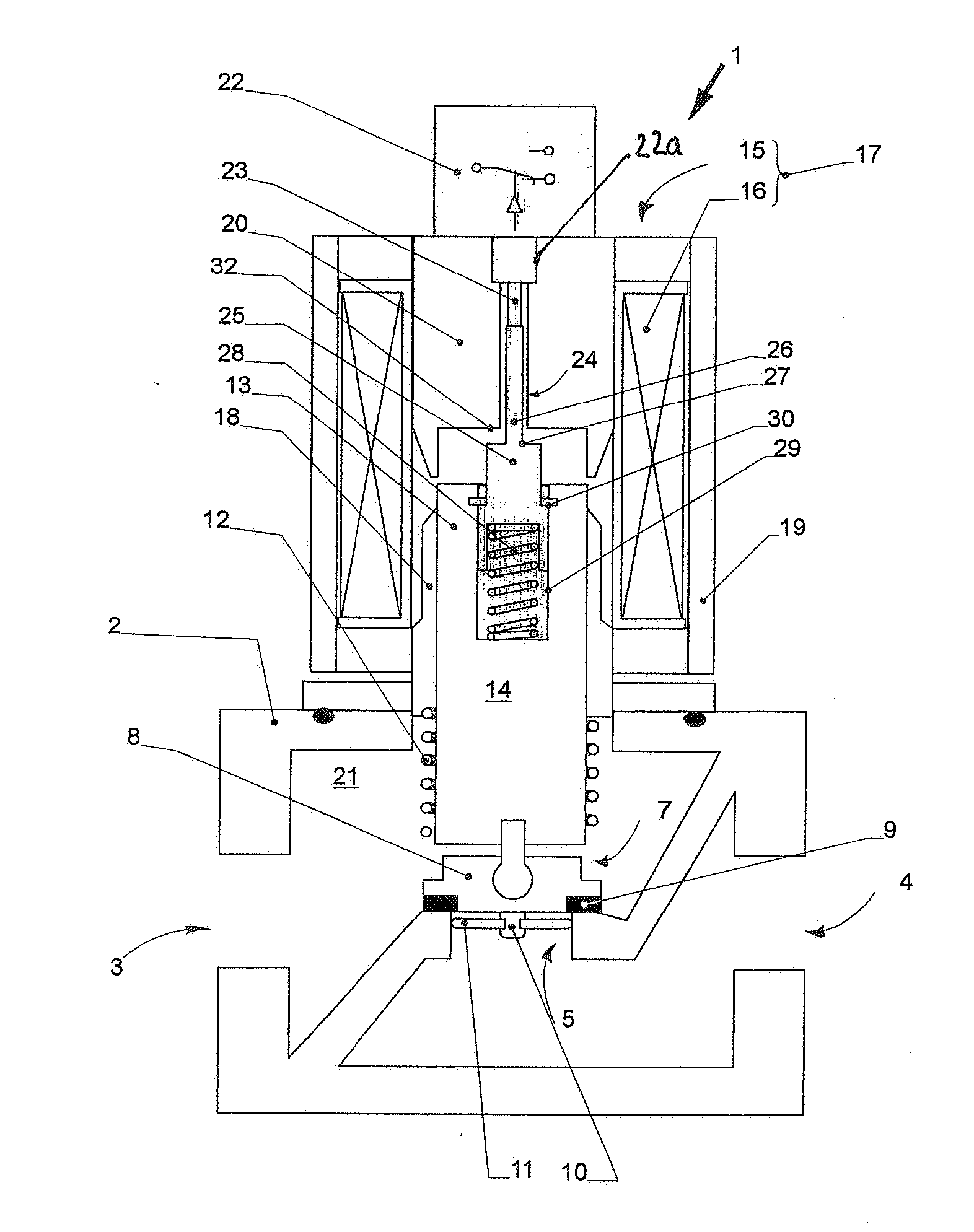
Solenoid operated fluid control valve
ActiveUS20080258090A1Improve liquidityIncrease control pressureOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsSpool valveFluid control
Solenoid operated fluid control valve for a cam phasing mechanism of an internal combustion engine includes first and second control ports, a 2-stage hydraulically pilot-actuated, pressure balanced spool having an integral control feedback passage and a linear force solenoid actuator operably coupled to a pilot valve of a pilot stage. The spool valve includes an exhaust path common to pilot and spool exhaust passages.
Owner:FLEXTRONICS AUTOMOTIVE USA
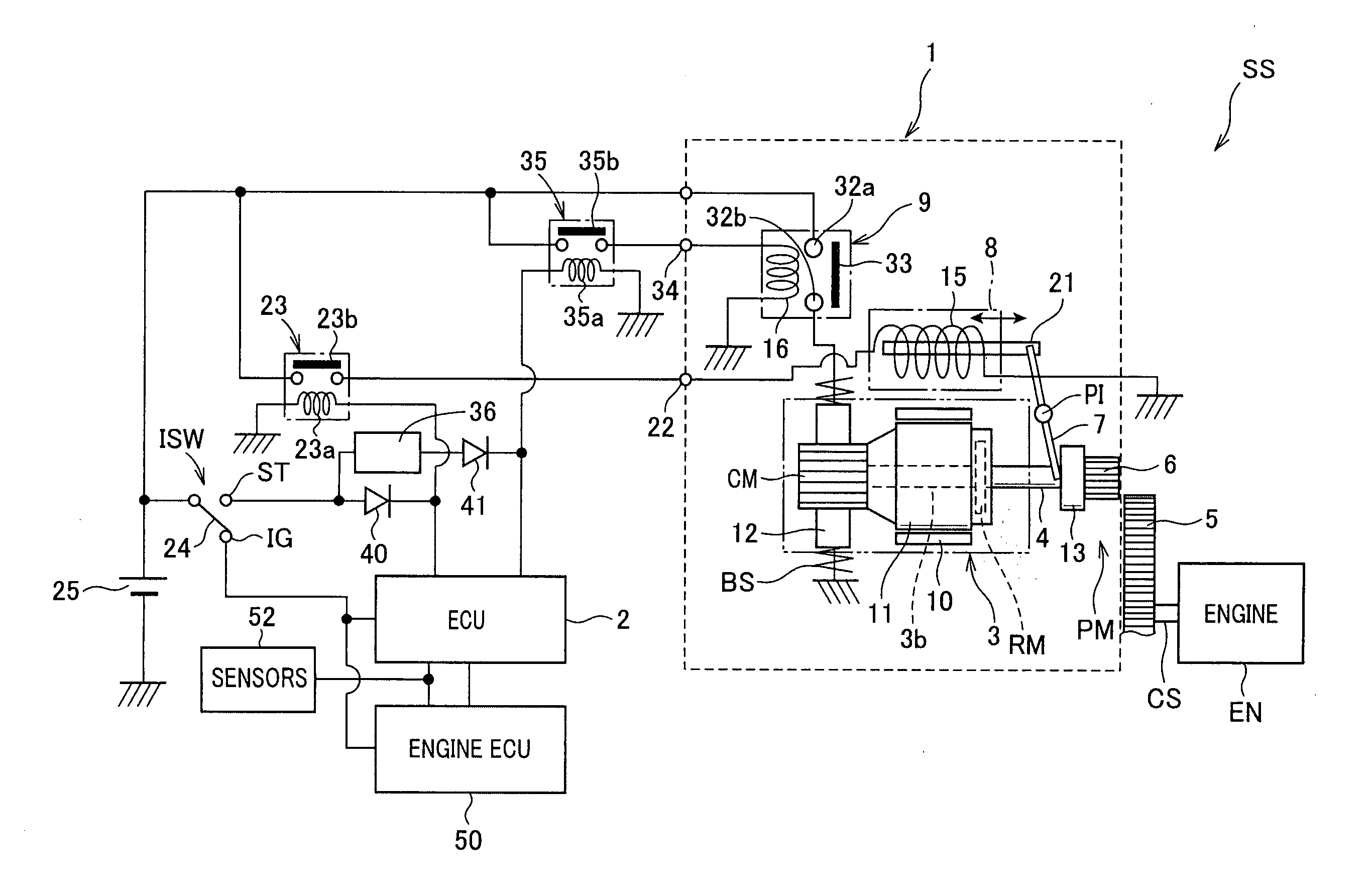
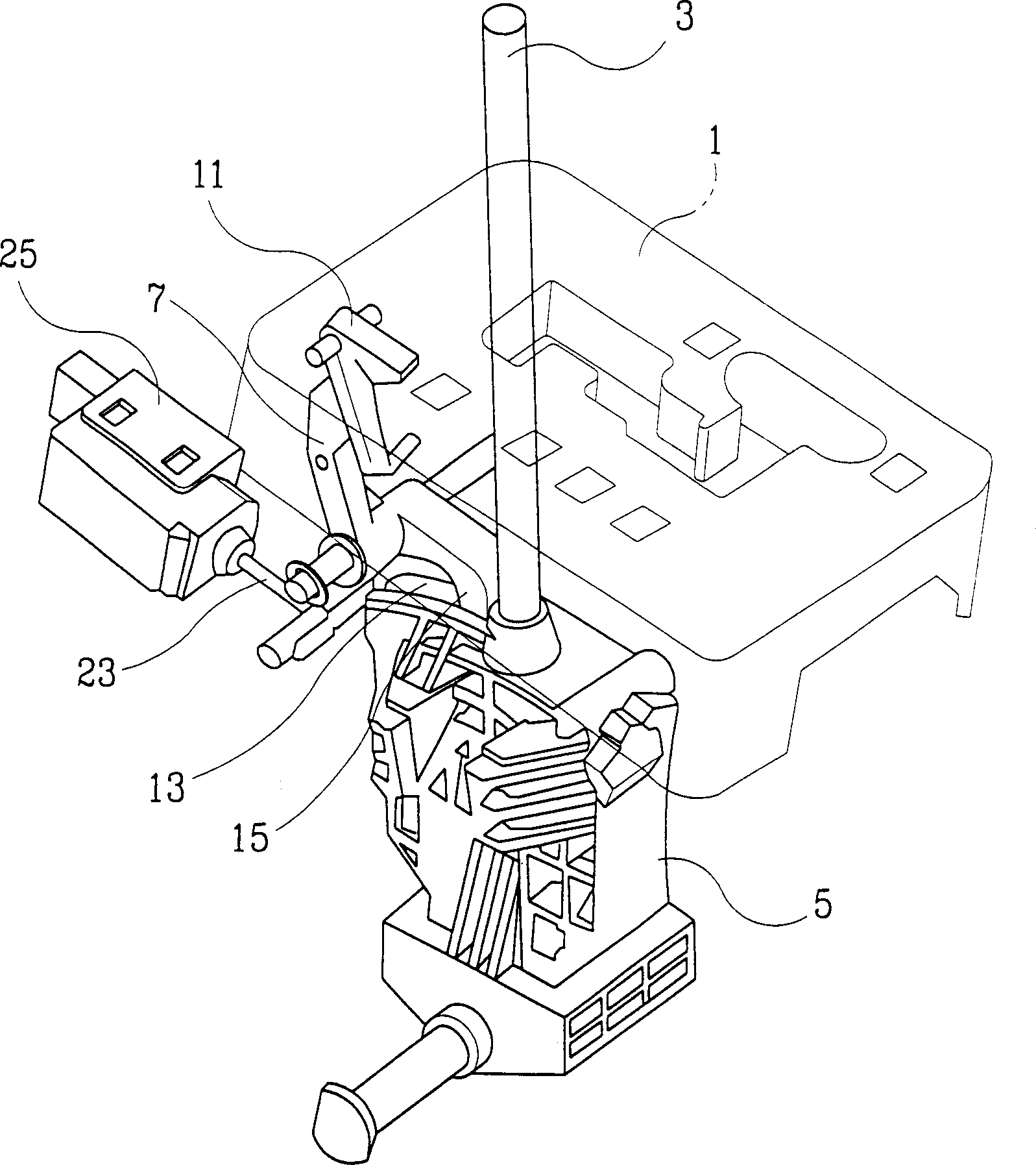
Geashift locking device of automatic speed variator gear lever
InactiveCN1492168ASmooth and safe releaseEliminate the install operationGearing controlControl devicesElectricityAutomatic transmission
A shift lock device for a shift lever of an automatic transmission, wherein the manipulation or non-manipulation of a brake pedal by a driver is received in the form of an electrical signal to prompt a solenoid actuator to rotate a single rotating cam and to perform a P range shift lock function and a shift lock function from the N range to the R range in a simple structure, such that the conventional cumbersome mounting operation of a shift cable can be eliminated and a simple manipulation of a brake pedal enables a smooth and secured release of the shift lock, thereby improving the convenience of a vehicle.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
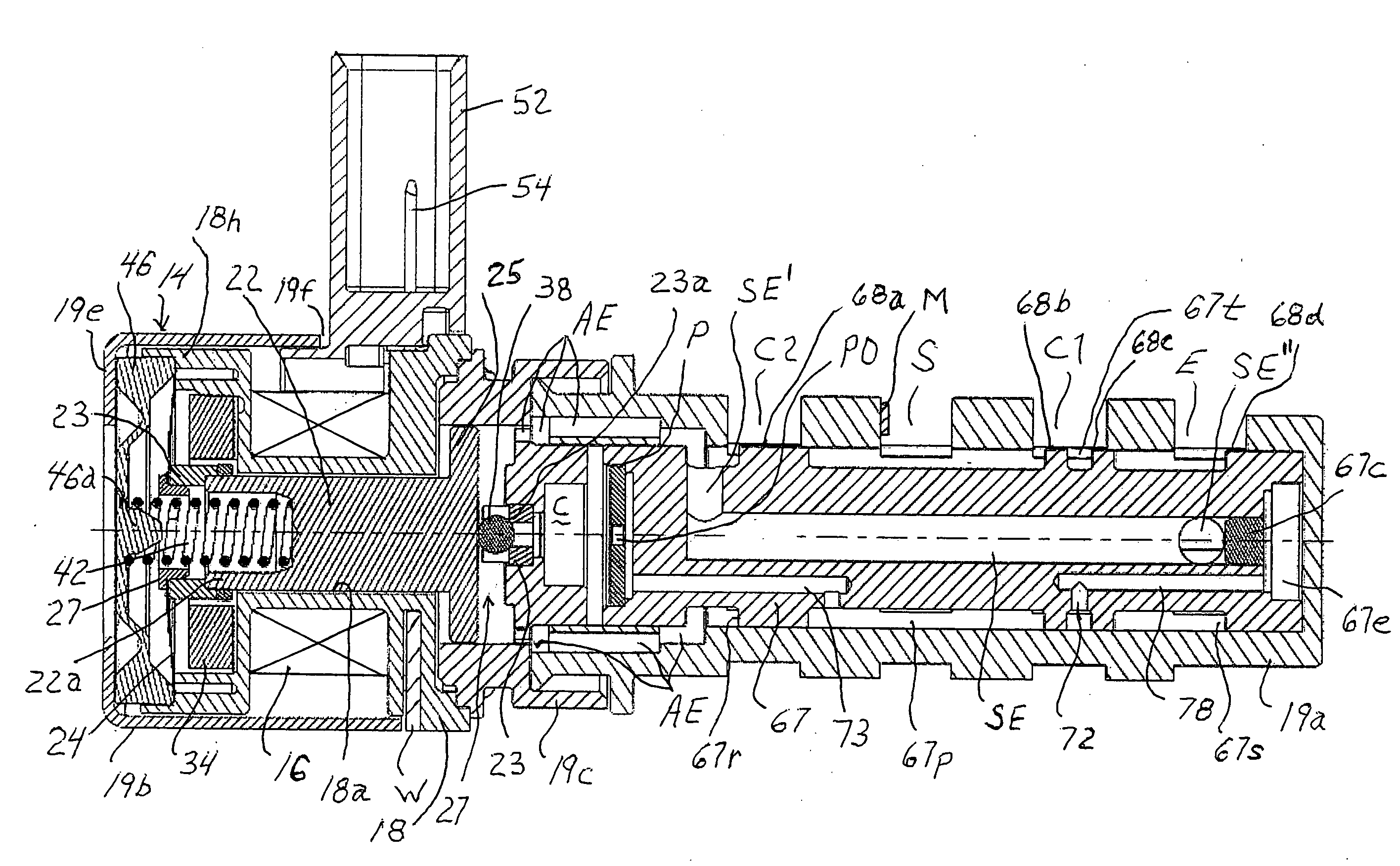
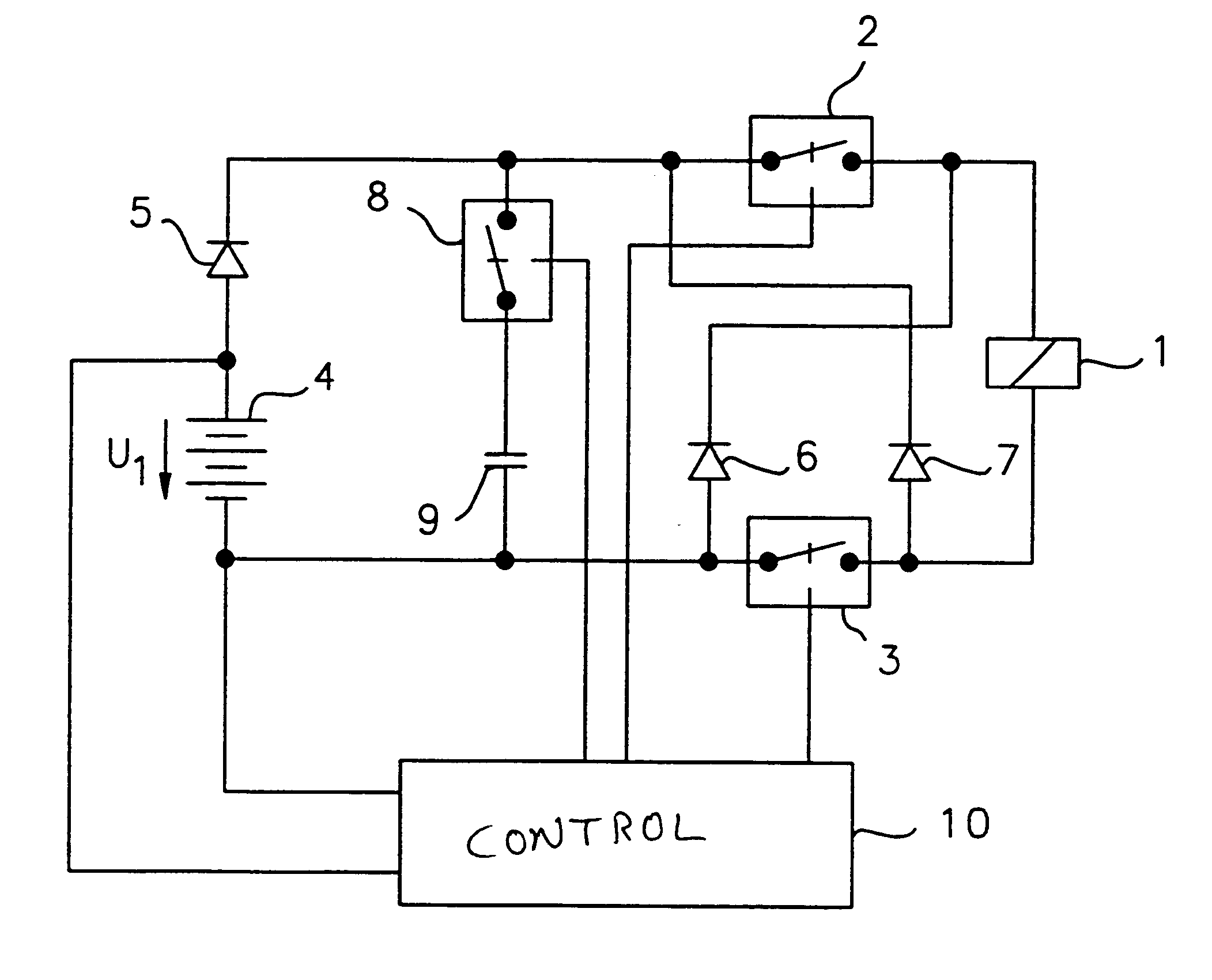
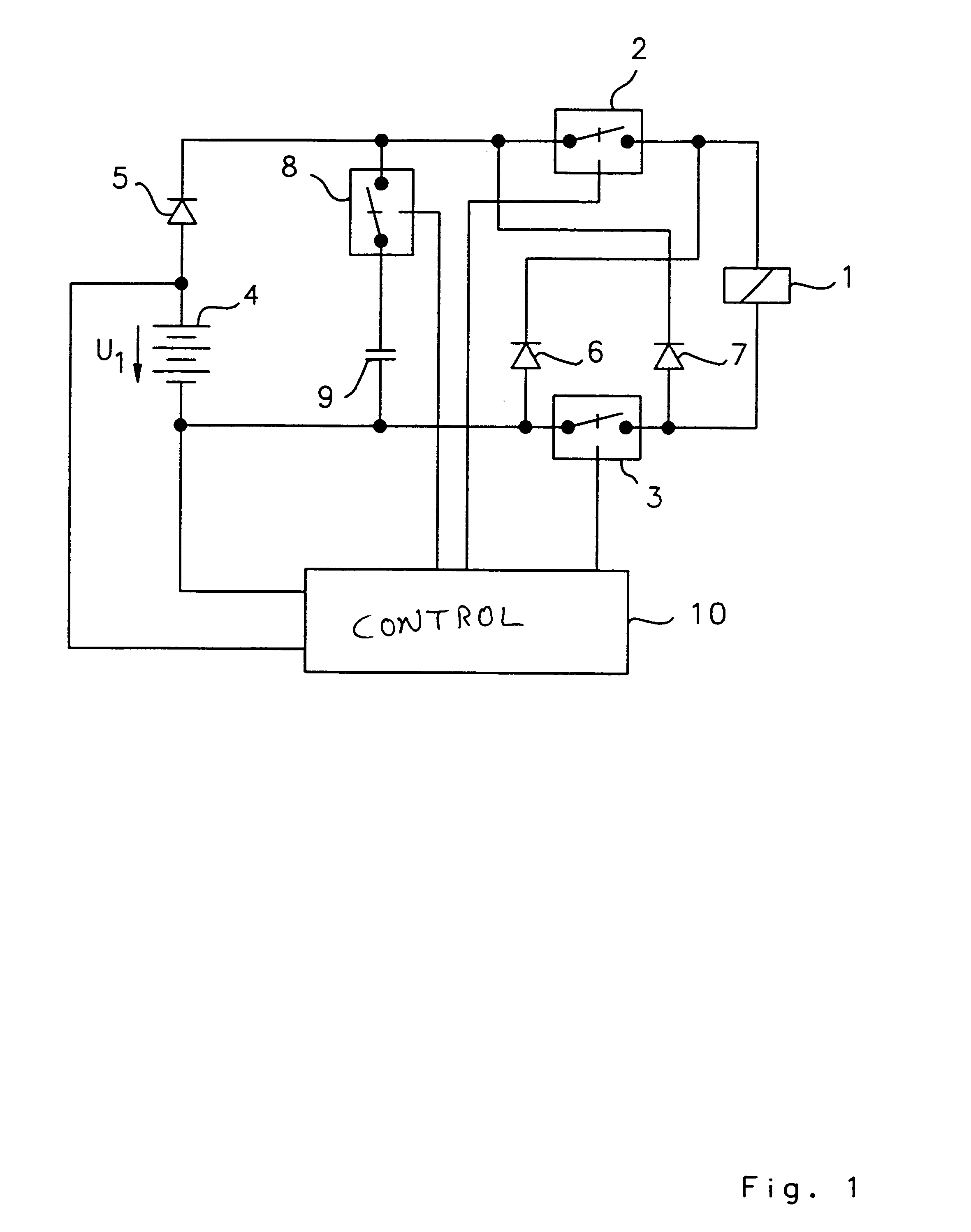
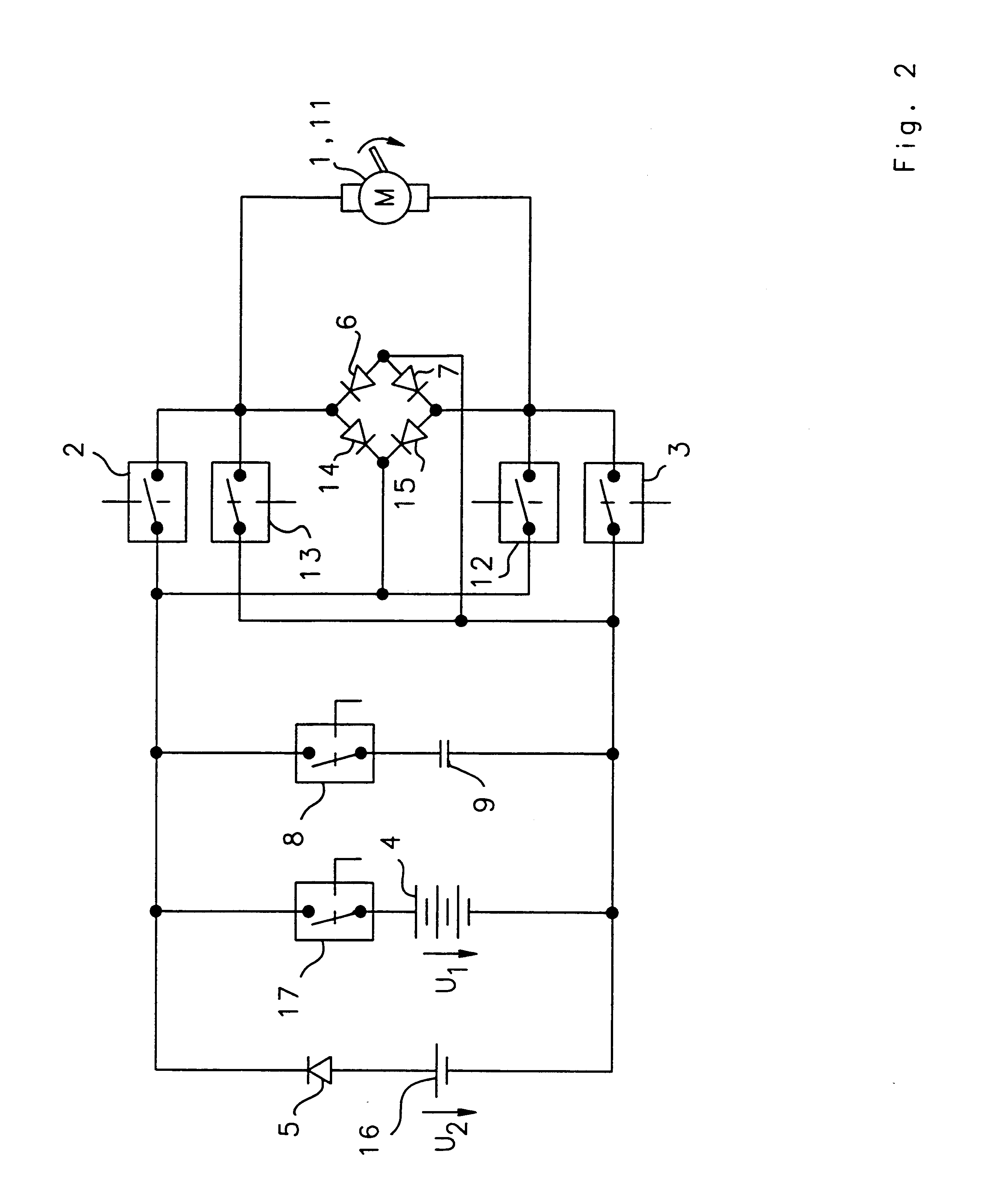
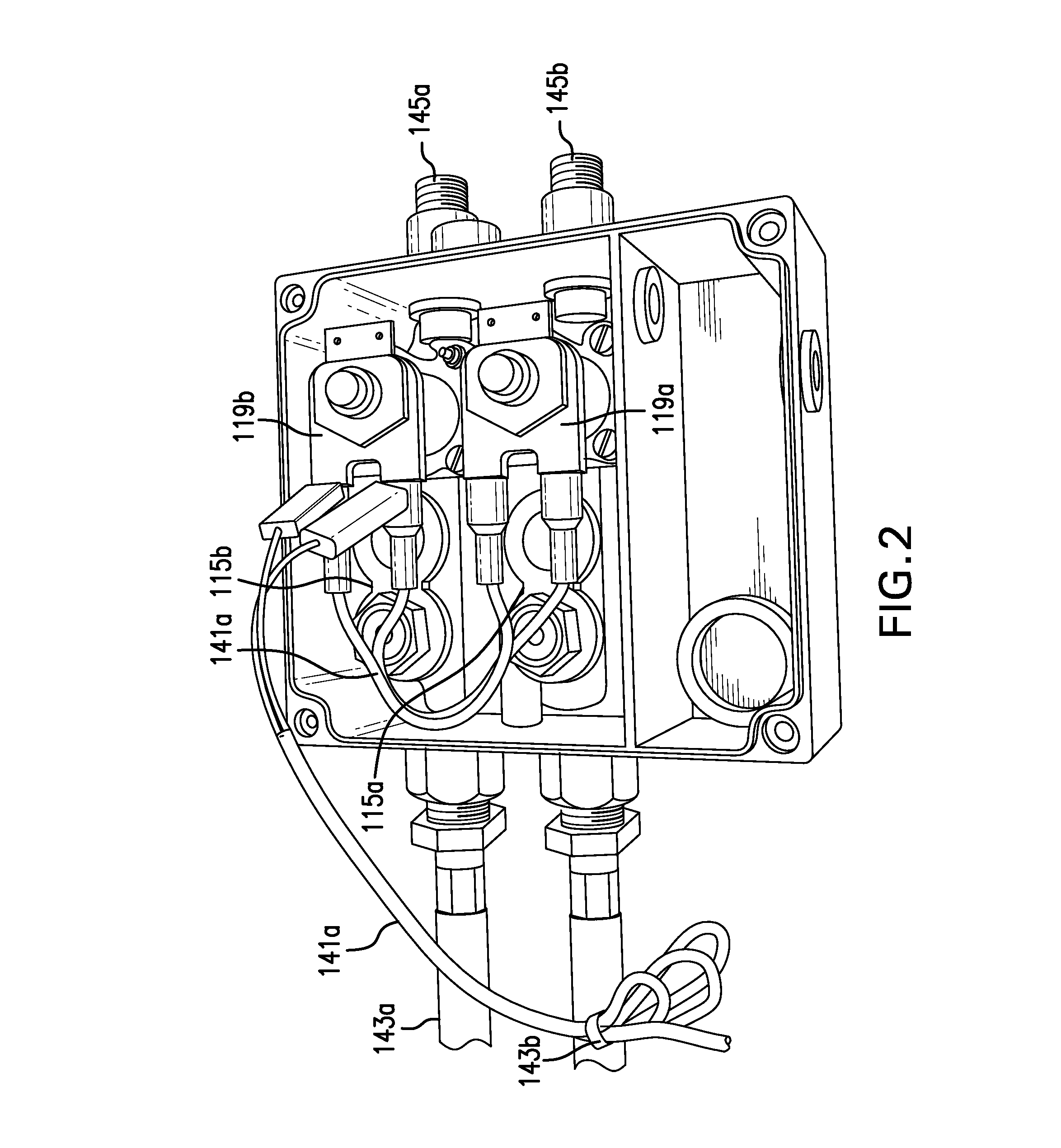
Circuit arrangement for operating a solenoid actuator
InactiveUS6646851B1Increase speedIncrease inductanceCircuit-breaking switches for excess currentsBatteries circuit arrangementsConductor CoilSolenoid actuator
A circuit arrangement for operating a solenoid actuator, for example, an electric motor provided in the form of a switched reluctance motor, permits operation of the motor in the event of malfunction or failure of part of an energy supply. The circuit arrangement advantageously includes an auxiliary battery serving as a redundance in addition to a main battery. The auxiliary battery is smaller and has a lower nominal voltage than the main battery. In order to permit continued operation of the electric motor in the event of failure, with a nominal operating voltage which is adapted to the nominal voltage of the main battery, a capacitor which can be switched on and off is connected in series to the batteries. An energy quantity can be accumulated in the capacitor by switching the current switching through an exciter winding of the electric motor in the manner of a switching regulator, whereby the nominal voltage of the capacitor finally exceeds the voltage in the auxiliary battery. When a sufficient quantity of energy has been accumulated, the electric motor can be actuated for a short time by means of the energy accumulated in the capacitor. Electrically actuated braking systems in commercial vehicles represent a significant and preferred area of application for the invention.
Owner:WABCO GMBH
Damping force control type shock absorber
ActiveUS20110073424A1Simple structureAppropriate damping forceSpringsShock absorbersSpring forceHydraulic fluid
The flow of hydraulic fluid induced by sliding movement of a piston in a cylinder is controlled by a pilot-type main valve and a pilot valve, which is a pressure control valve, thereby generating damping force. By thrust from a solenoid actuator, the valve-opening pressure of the pilot valve is controlled, and the pressure in a pilot chamber is also controlled to control the valve-opening pressure of the main valve. When there is a failure, a valve body of the pilot valve is retracted to abut against a fail-safe disk by spring force of a valve spring. Thus, damping force is generated by the fail-safe disk at the downstream side of the pilot valve, and the valve-opening pressure of the main valve is also controlled by the fail-safe disk to obtain an appropriate damping force.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
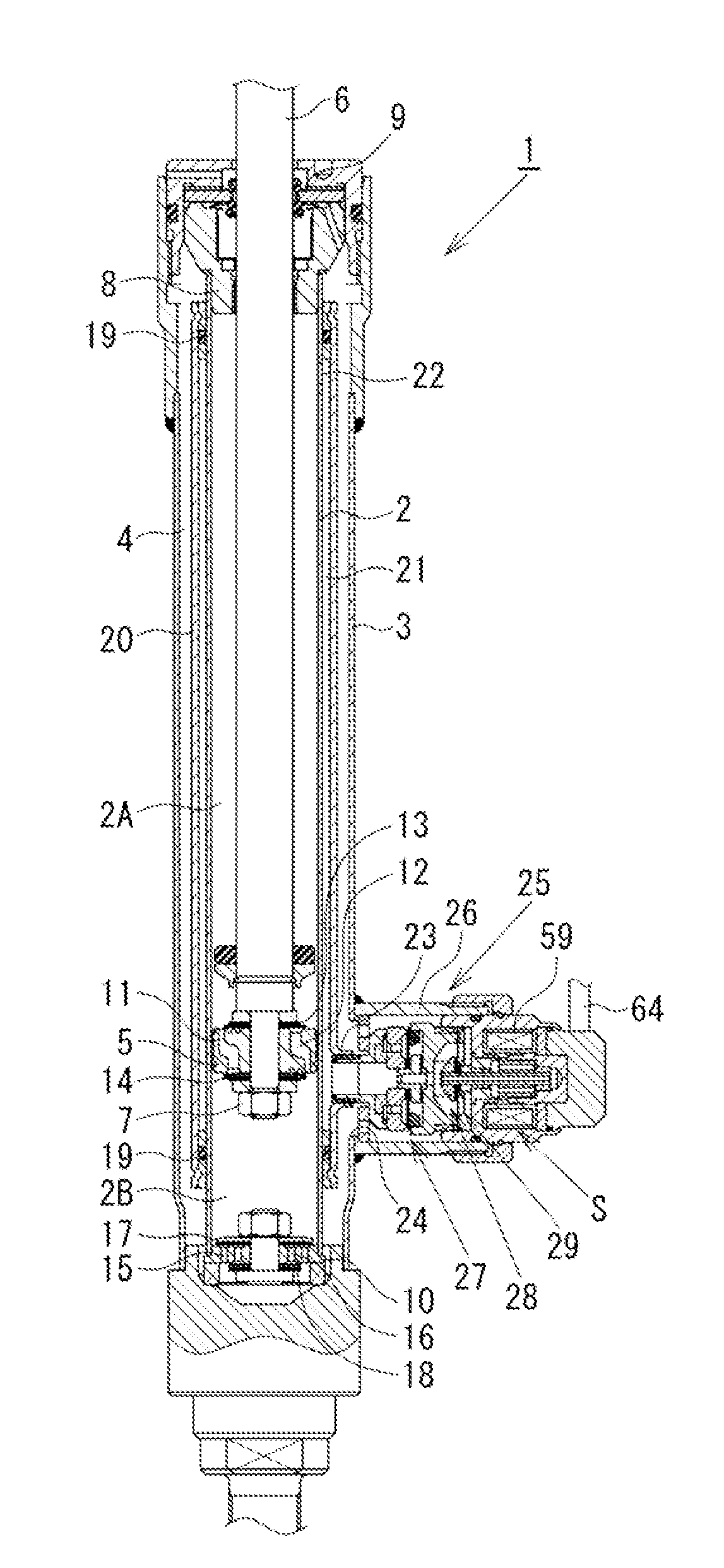
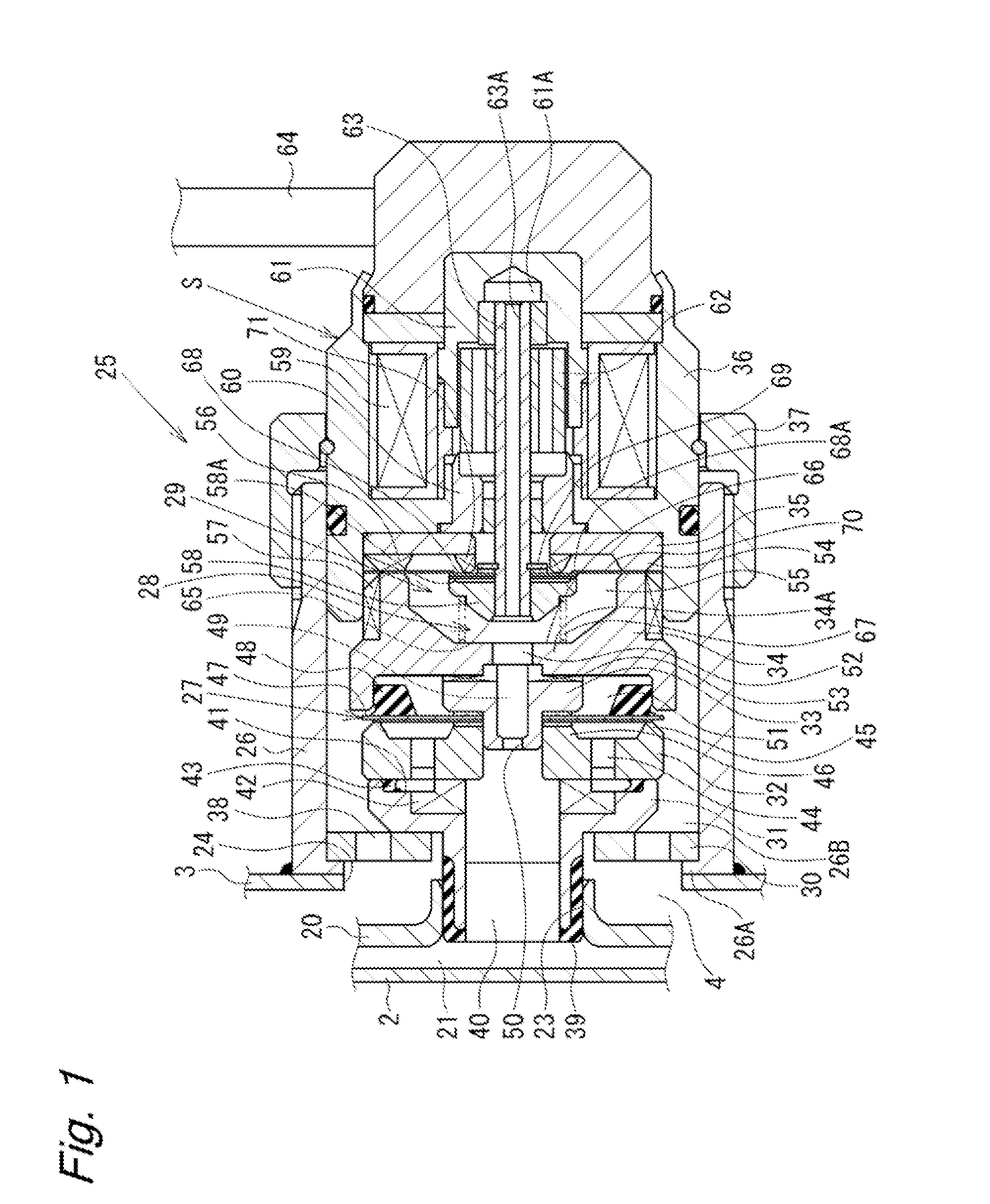
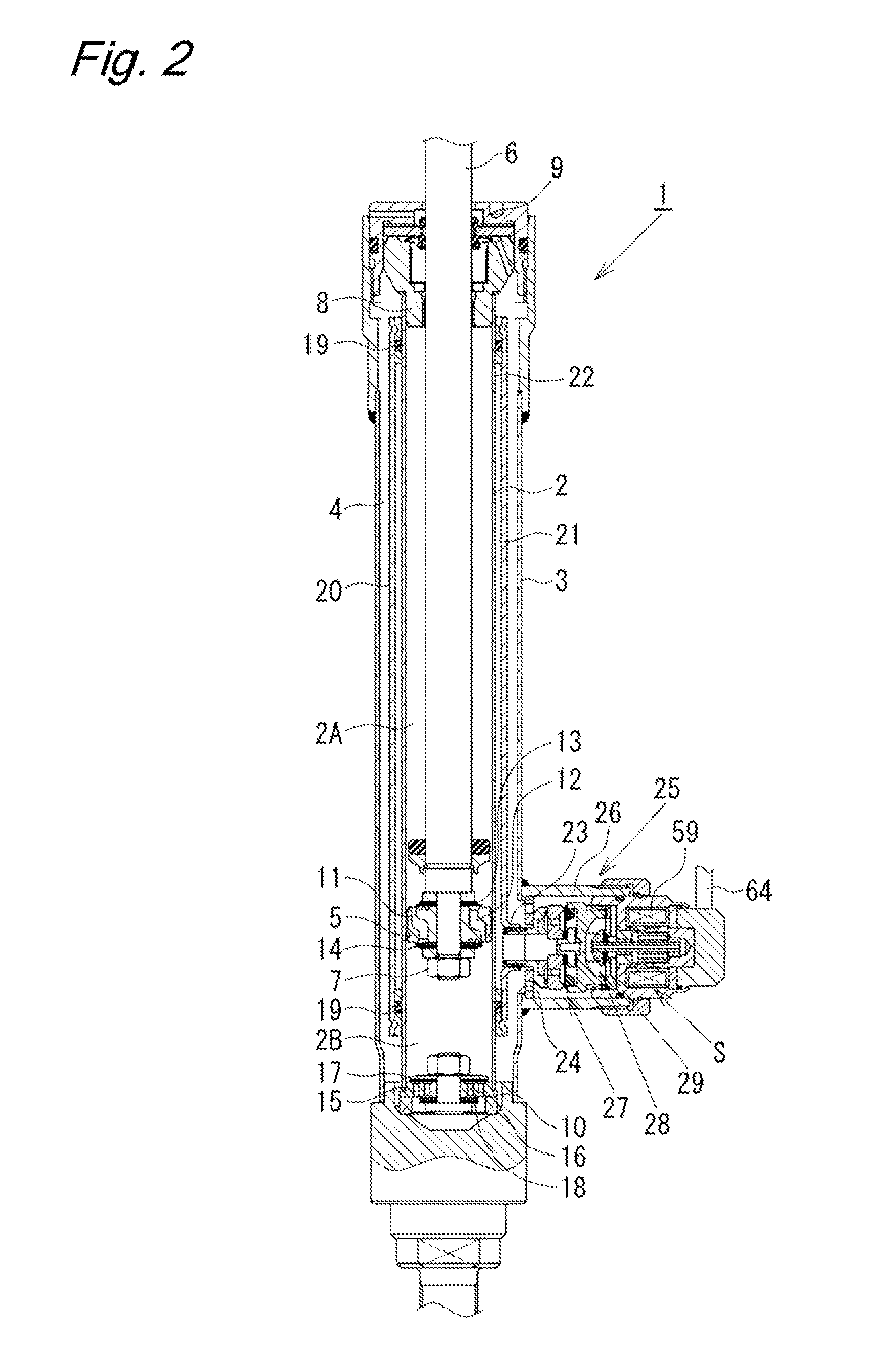
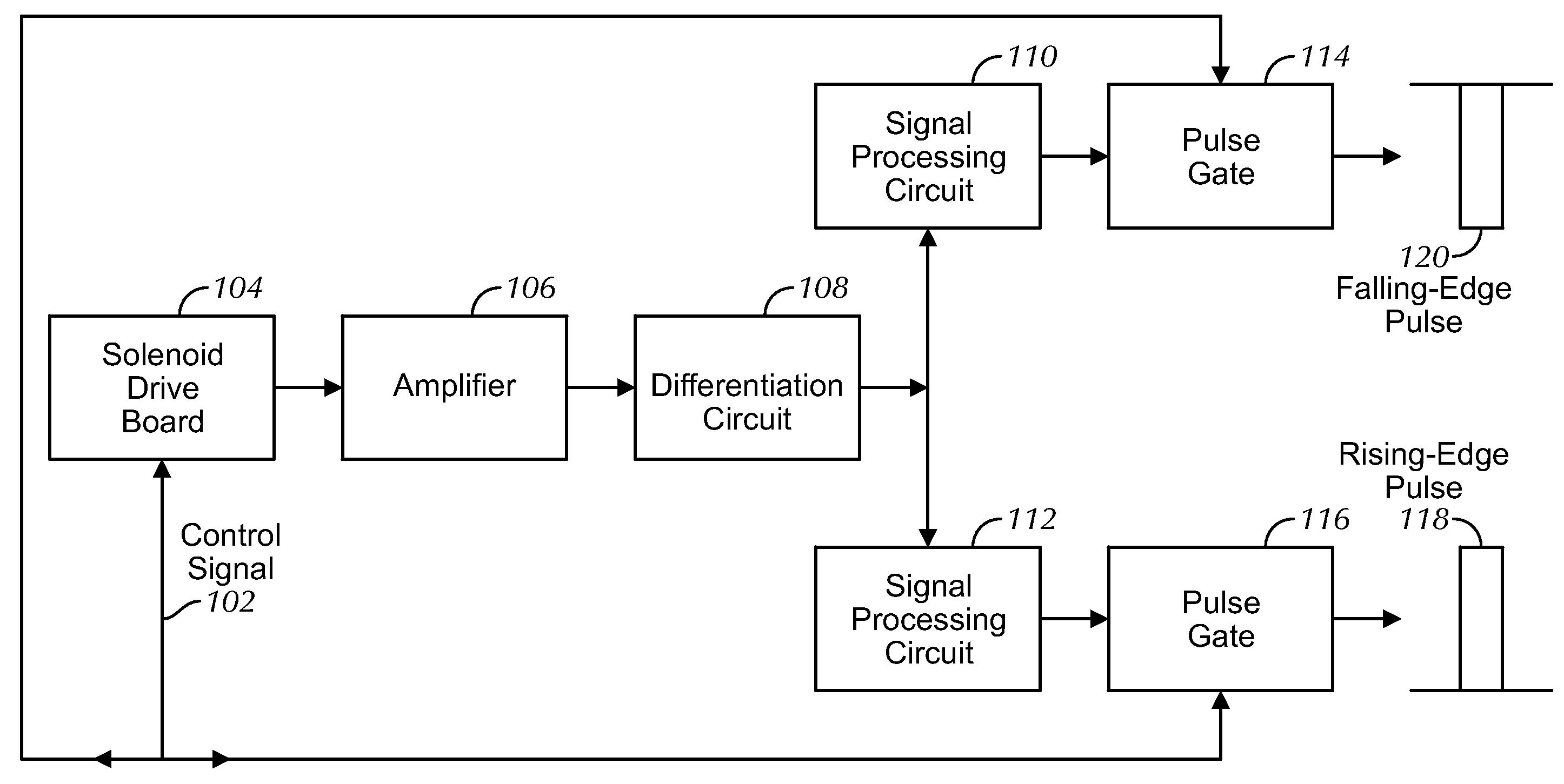
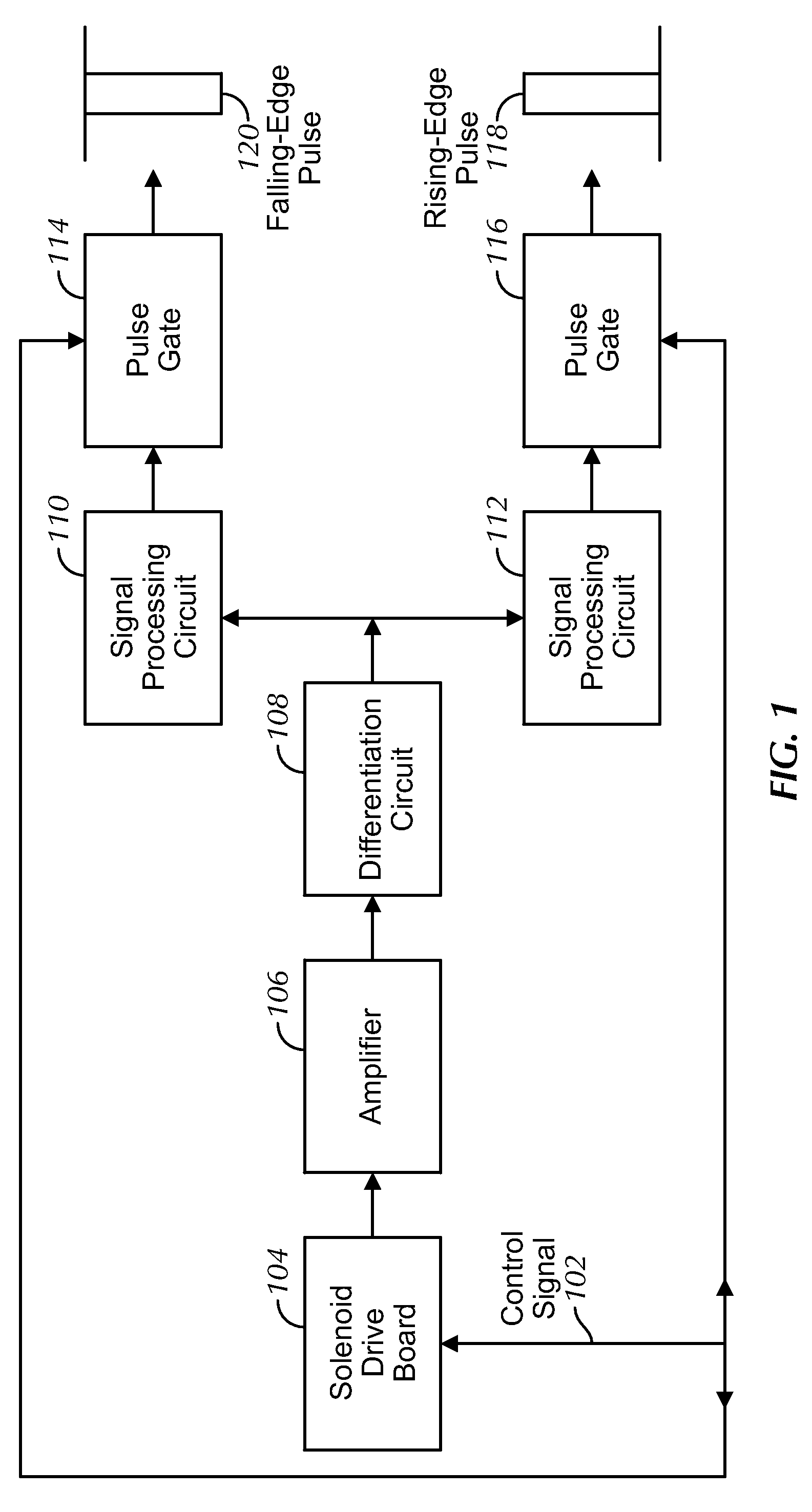
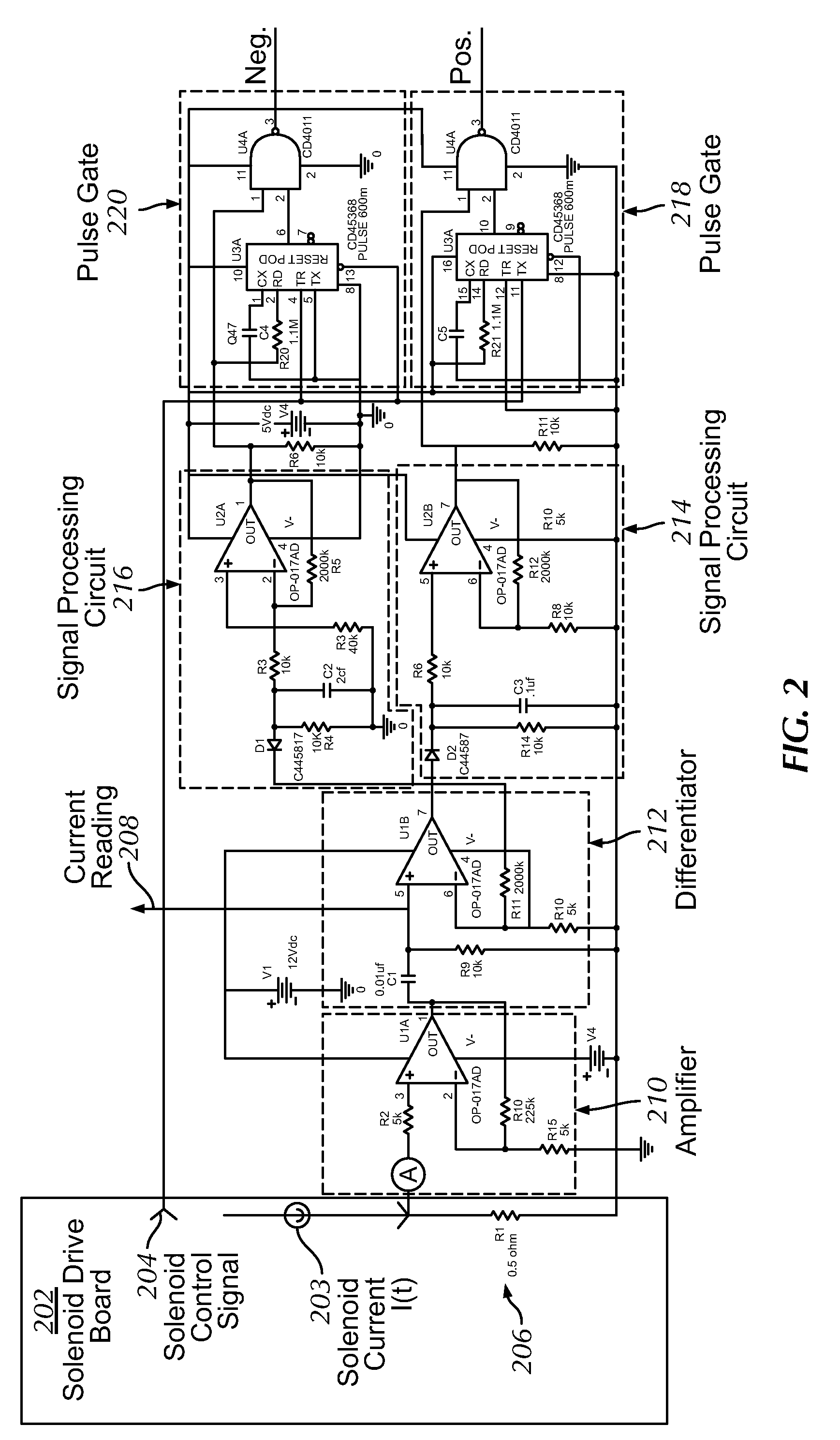
Movement detection circuit of solenoid shear seal valve on subsea pressure control system and method of detecting movement of solenoid actuator
A solenoid current monitoring circuit of a solenoid actuator includes a solenoid drive board configured to receive a control signal, a sensing resistor configured to detect a current signal of a solenoid coil of the actuator resulting from the control signal, and a differentiator configured to differentiate the current signal. The solenoid current monitoring circuit detects the movement of the solenoid actuator based on a change in the differentiated current signal caused by a change in inductance of the solenoid coil.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Fuel injector with electromagnetic actuator
InactiveUS20060255185A1Simple and economic to produceSpray nozzlesFuel injection apparatusEngineeringSolenoid actuator
A fuel injector equipped with an injection valve comprising a mobile plunger ending with a sealing head; a support body having a tubular shape and comprising a feed channel; and a sealing body, in which is defined a valve seat of the injection valve; the sealing head is of a frustoconical shape, is arranged externally relative to the guide element, is thrust by a spring against said guide element in a direction contrary to the direction of feed of the fuel; the valve seat has a frustoconical shape which is a negative reproduction of the frustoconical shape of the sealing head in order to impart an internally hollow conical shape to the injected fuel.
Owner:FAB ITAL MAGNETI MARELLI SPA
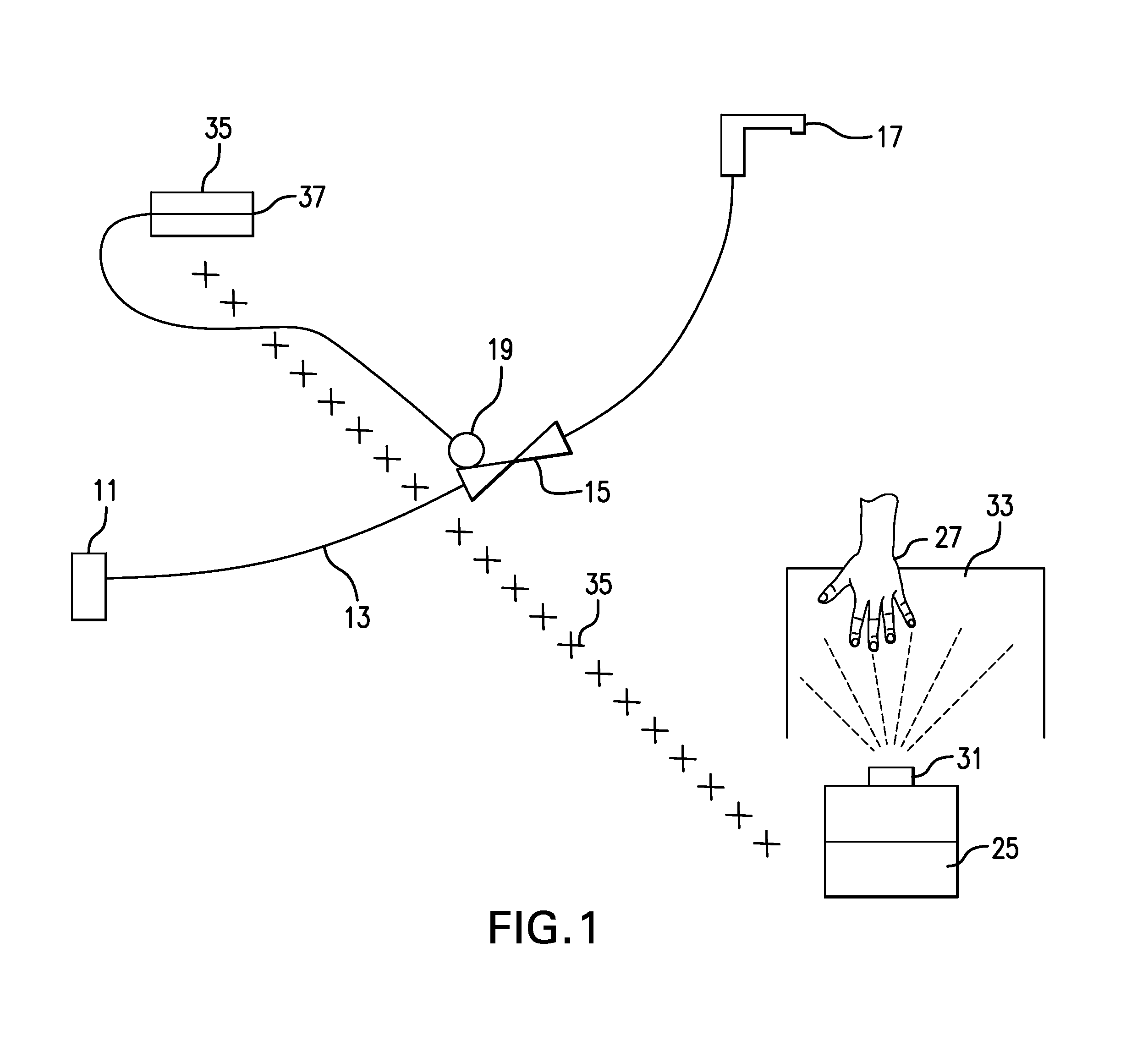
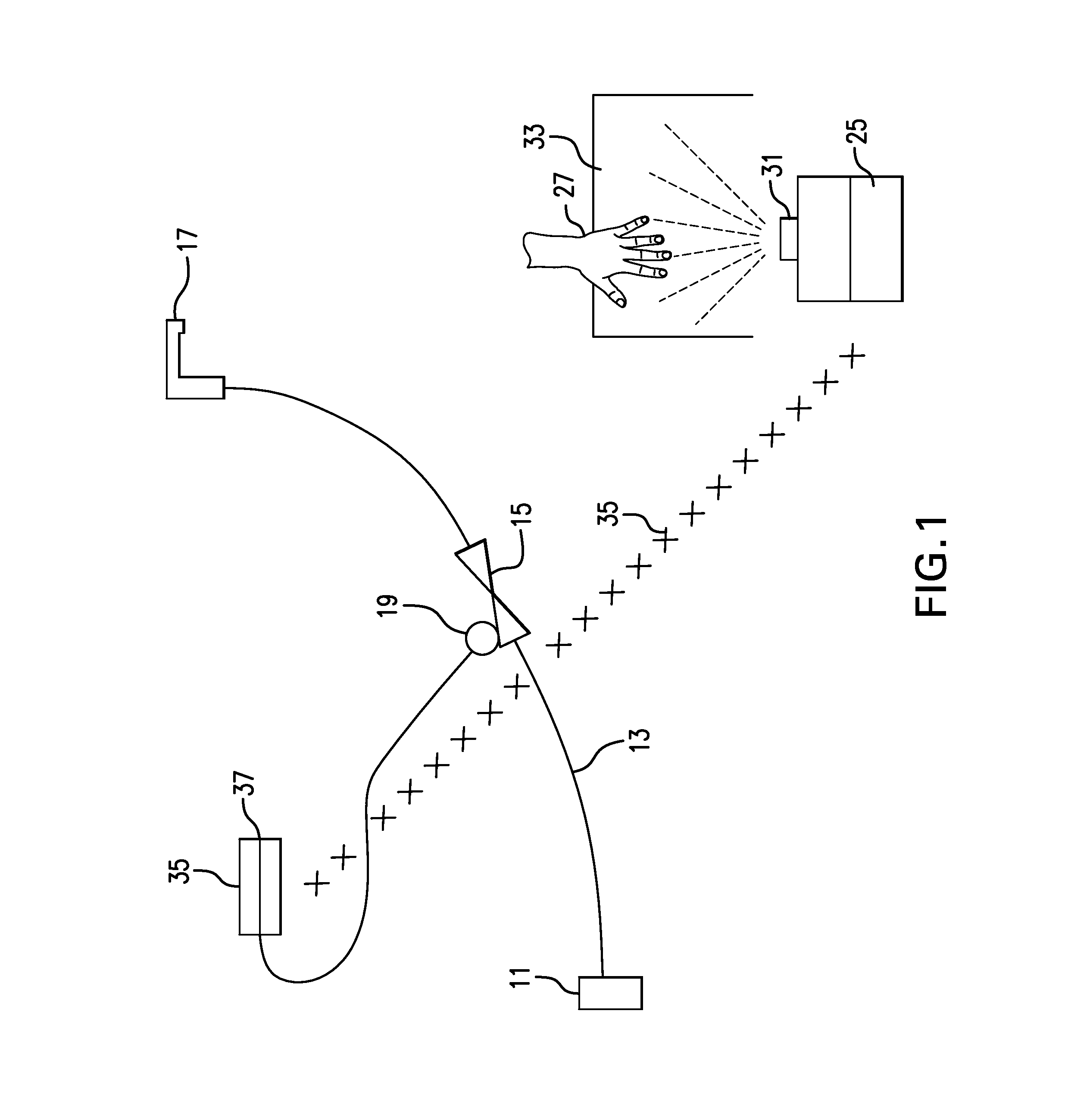
Touchless, Remotely Activatable Assembly for Fluid Flow Regulation, Related Systems and Methods
ActiveUS20140345726A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesDomestic plumbingElectricityWater source
The invention includes an assembly for remotely controlling fluid flow between a fluid source, such as a water source, and an outlet that includes at least one electrically operable valve, such as an electromagnetically-actuatable valve, to be interposed between the fluid source and the outlet, the valve being actuatable between an open position, in which the source and the outlet are fluidly connected, and a closed position in which the source and the outlet are not fluidly connected; at least one actuator, such as a solenoid actuator, operably connected to the at least one valve for actuating the valve between the open and closed positions; a controller comprising a receiver for receiving a wireless signal, wherein the controller is operably connected to the actuator and capable of actuating the actuator upon receipt of a wireless signal by the receiver; and an activator device comprising (i) a user-activatable sensor for detecting a stimulus when the stimulus enters a detection zone and (ii) a transmitter that transmits the wireless signal upon activation of the sensor by a user to the receiver. In an embodiment, it may be desirable that the electrically operable valves are also mechanically actuatable or that one or more (additional) manually activatable valves in included in the assembly.
Owner:AS AMERICA
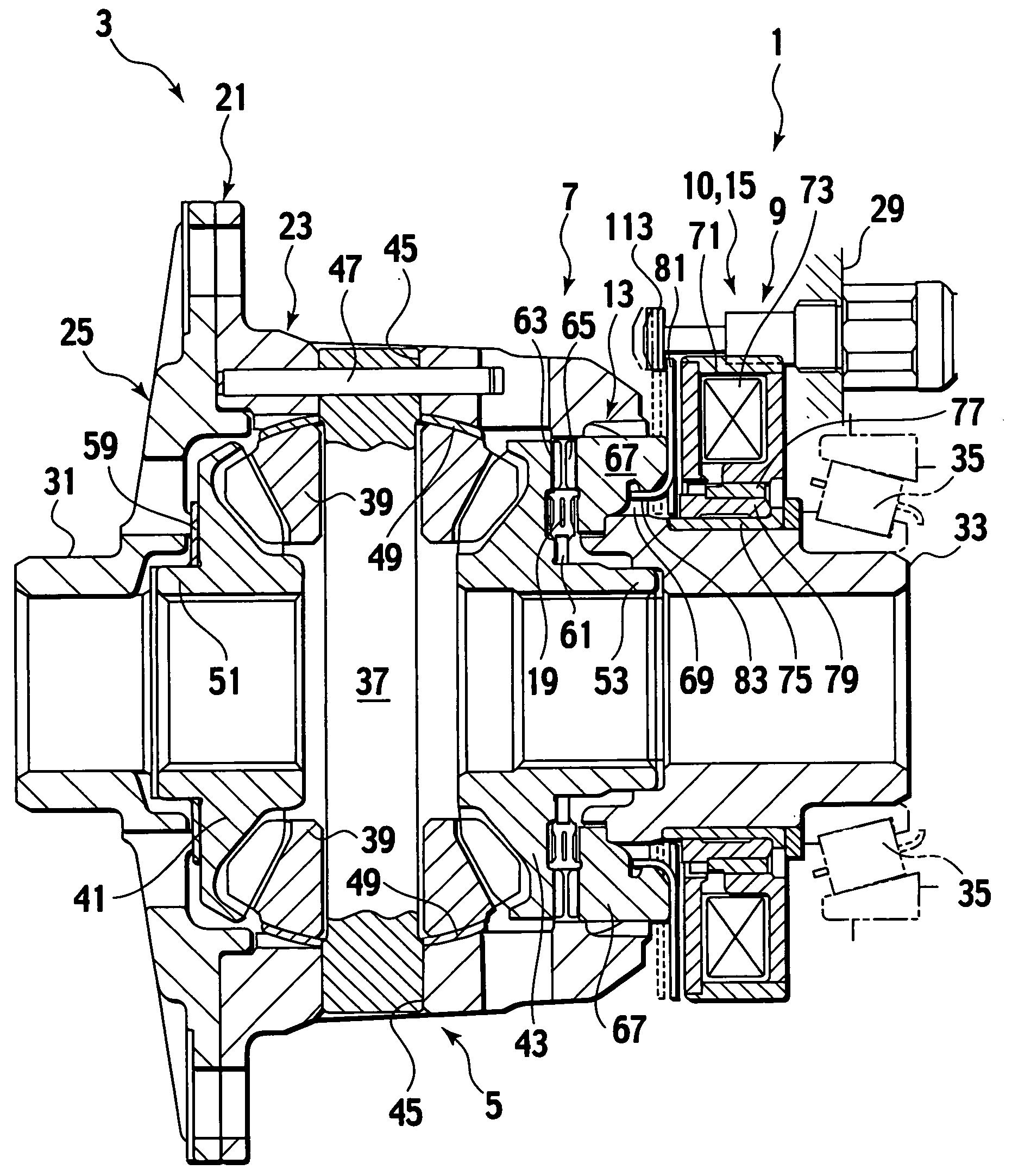
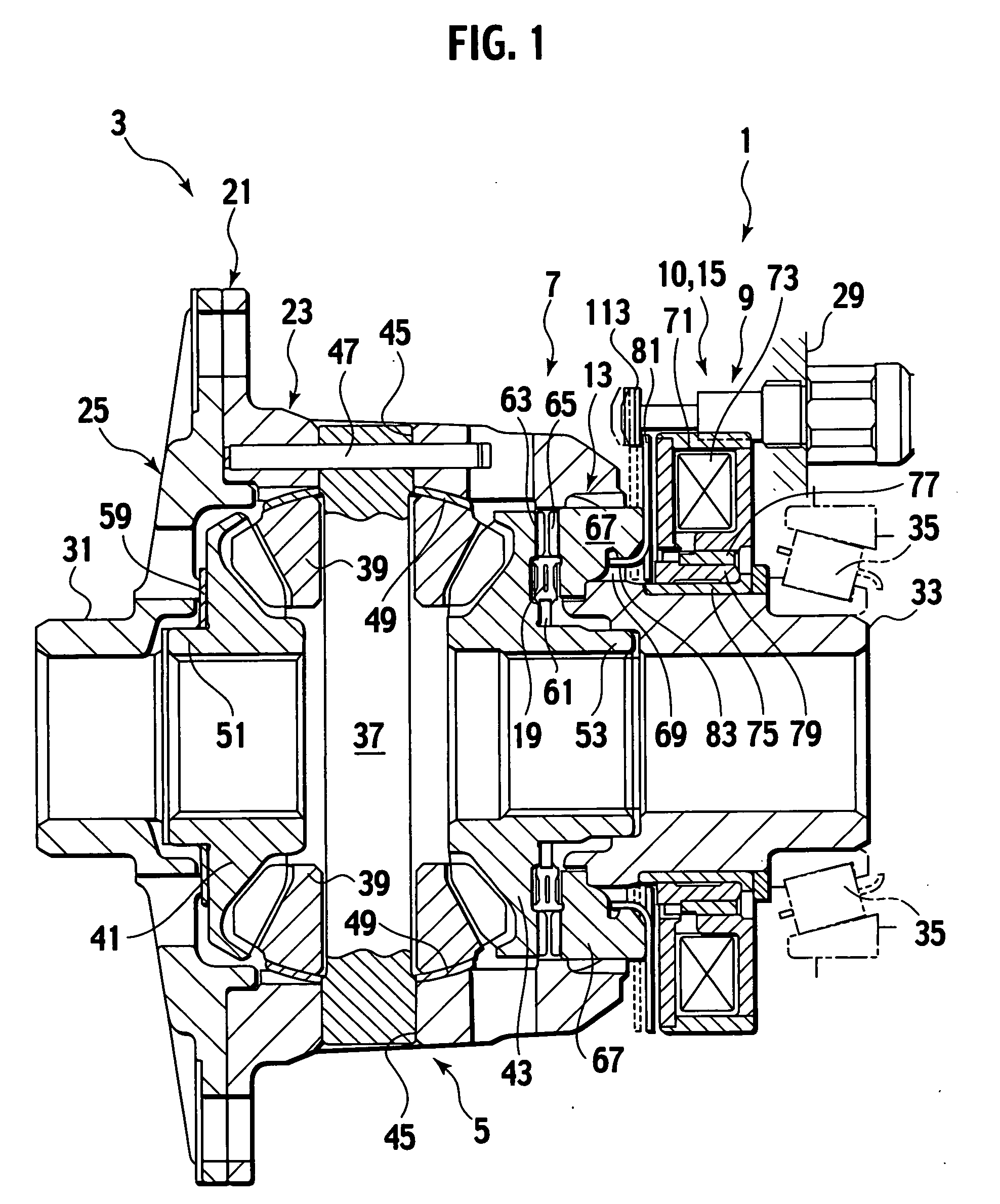
Solenoid actuator
InactiveUS7973627B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic materialsHydraulic equipmentEngineering
Owner:KYB CORP
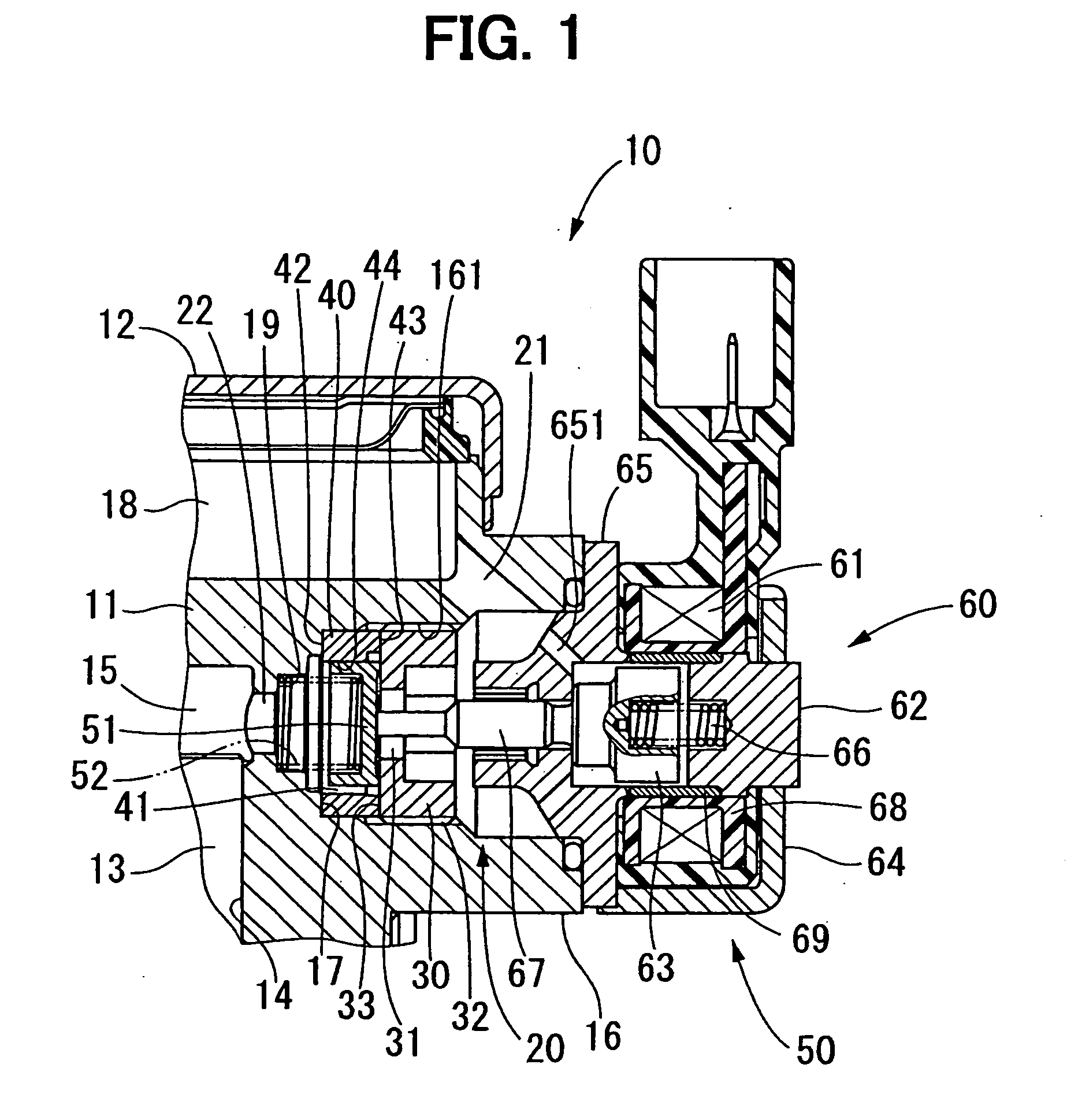
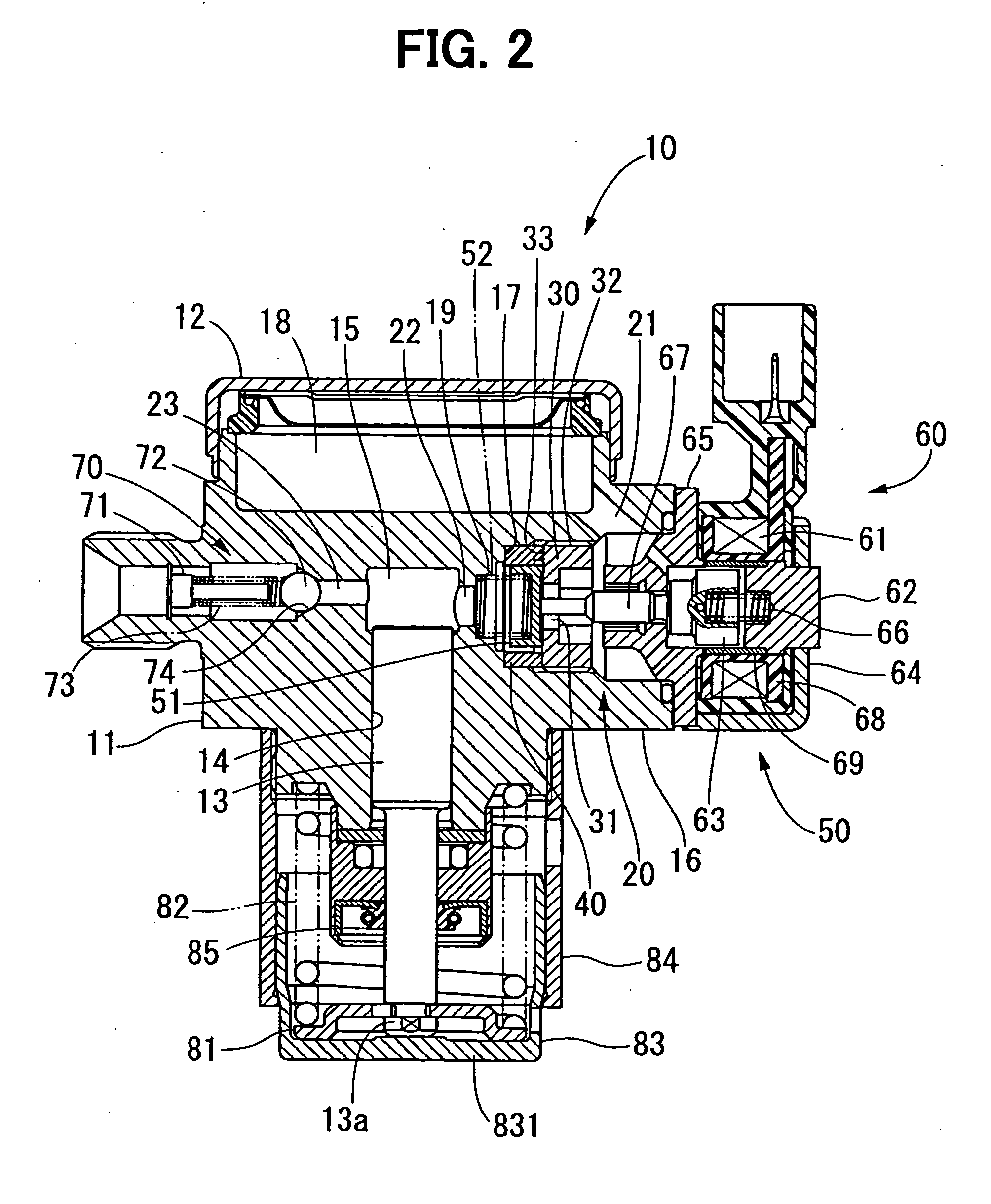
High pressure pump having solenoid actuator
ActiveUS20060239846A1Reduce hydraulic pressurePositive displacement pump componentsFuel injecting pumpsEngineeringHigh pressure
A pump includes a housing that has a compression chamber for pressurizing fluid and a fluid passage for guiding fluid into the compression chamber. A valve is located midway through the fluid passage for communicating and blocking the fluid passage. A solenoid actuator is located on a substantially opposite side of the compression chamber with respect to the valve for operating the valve. A regulating member is located between the valve and the solenoid actuator for regulating pressure of fluid in the compression chamber from being applied to the solenoid actuator.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com