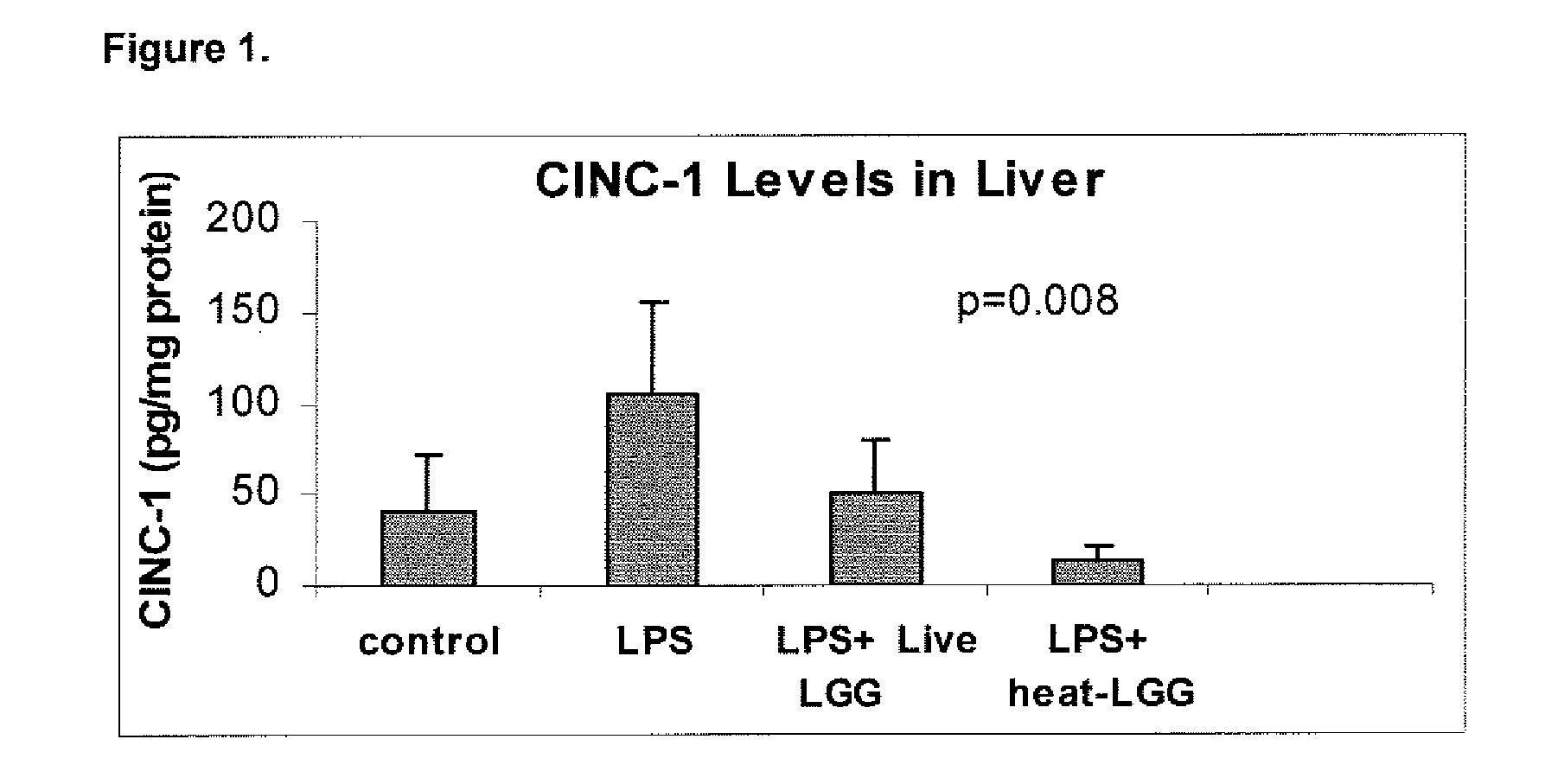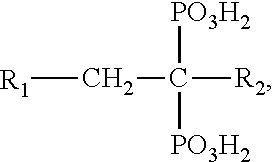Patents
Literature
463results about How to "Avoid seizures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
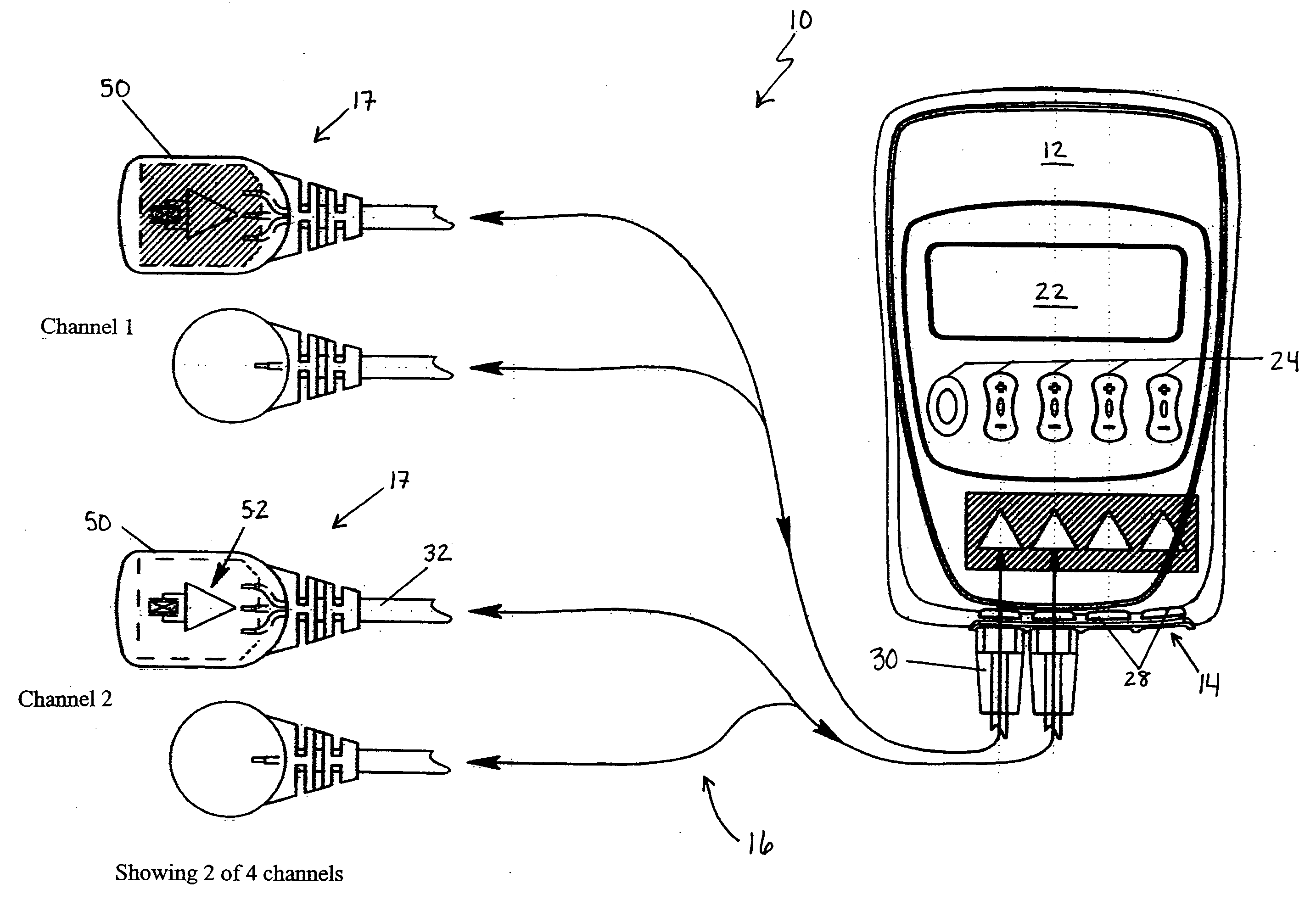
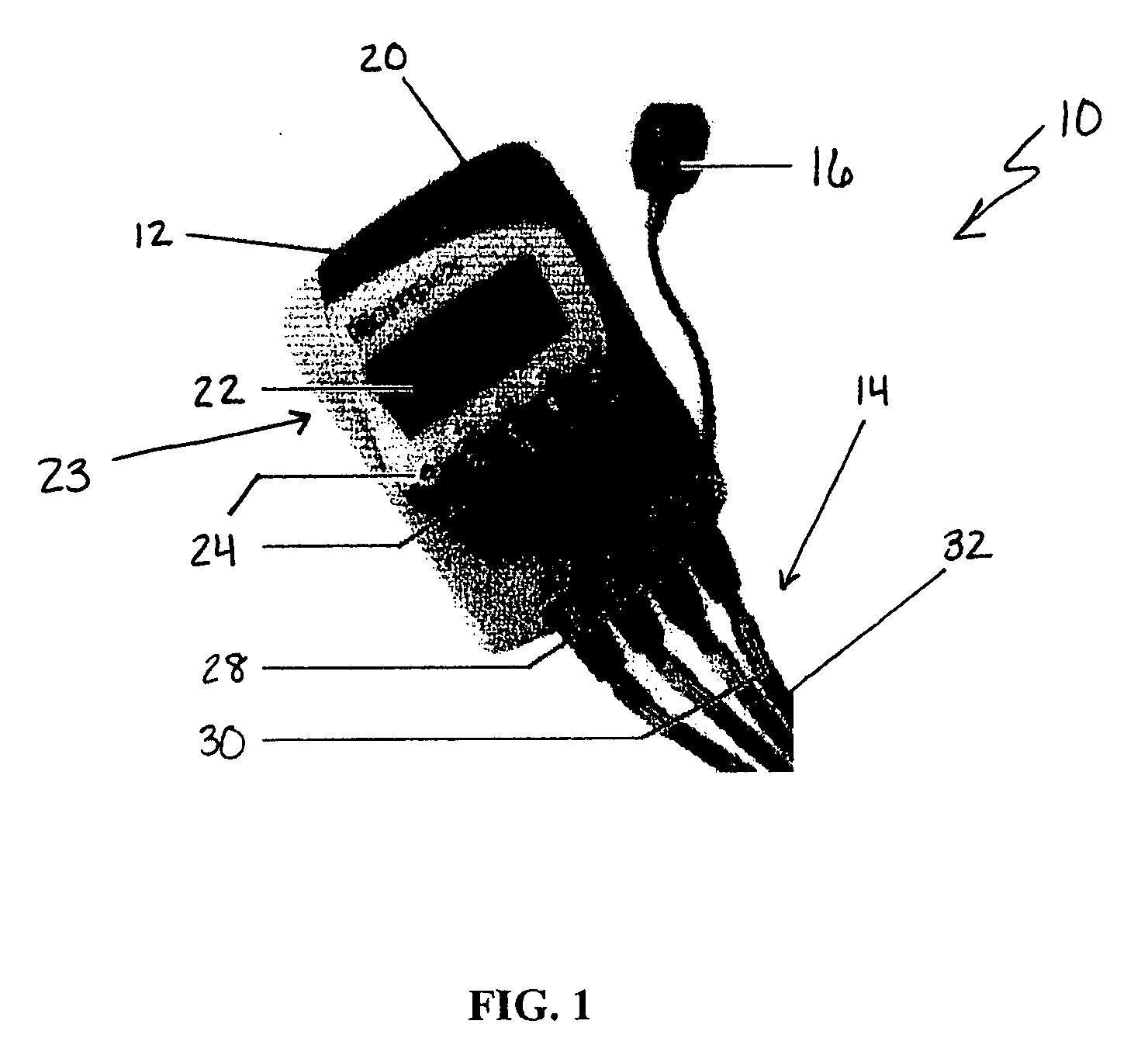
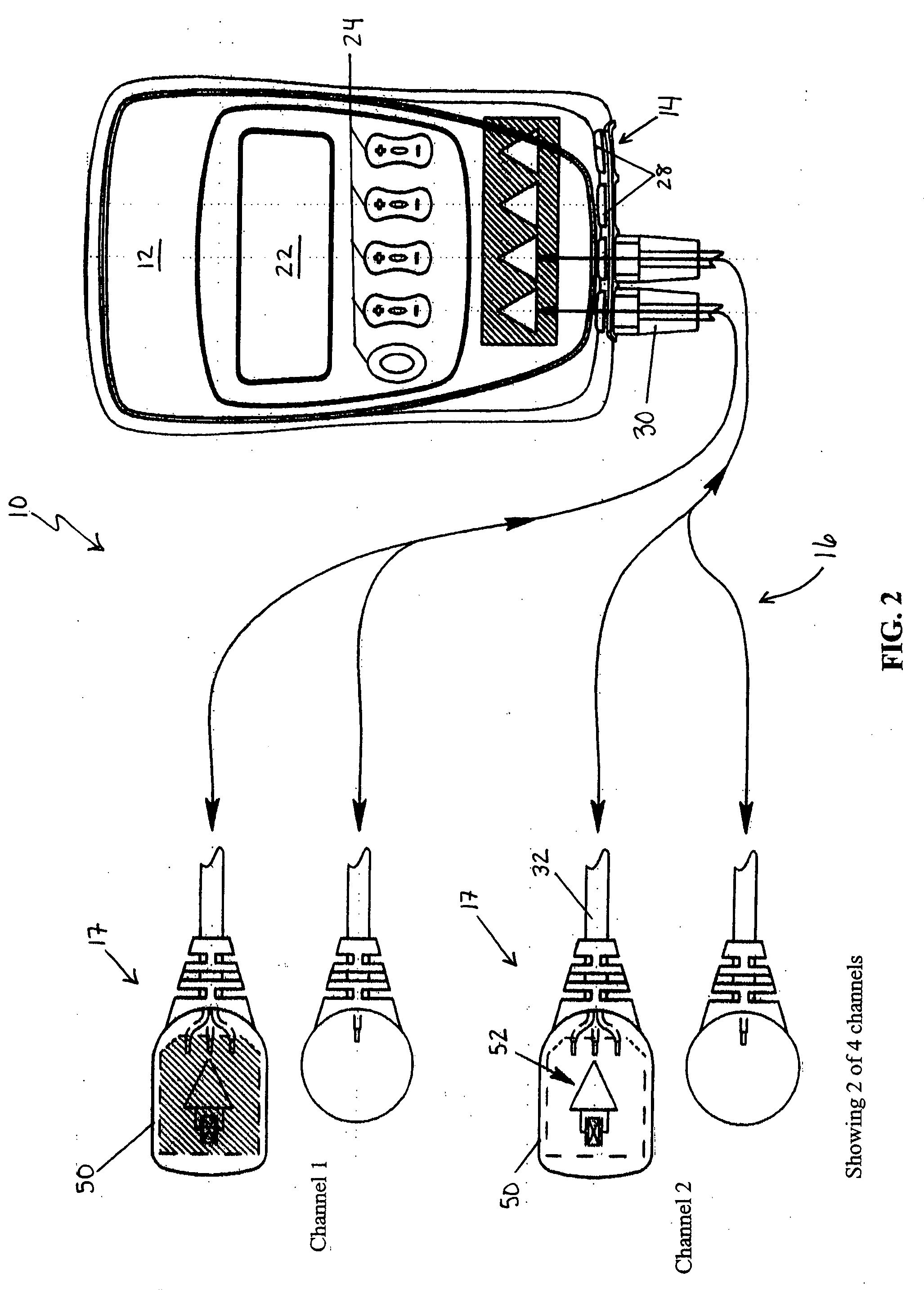
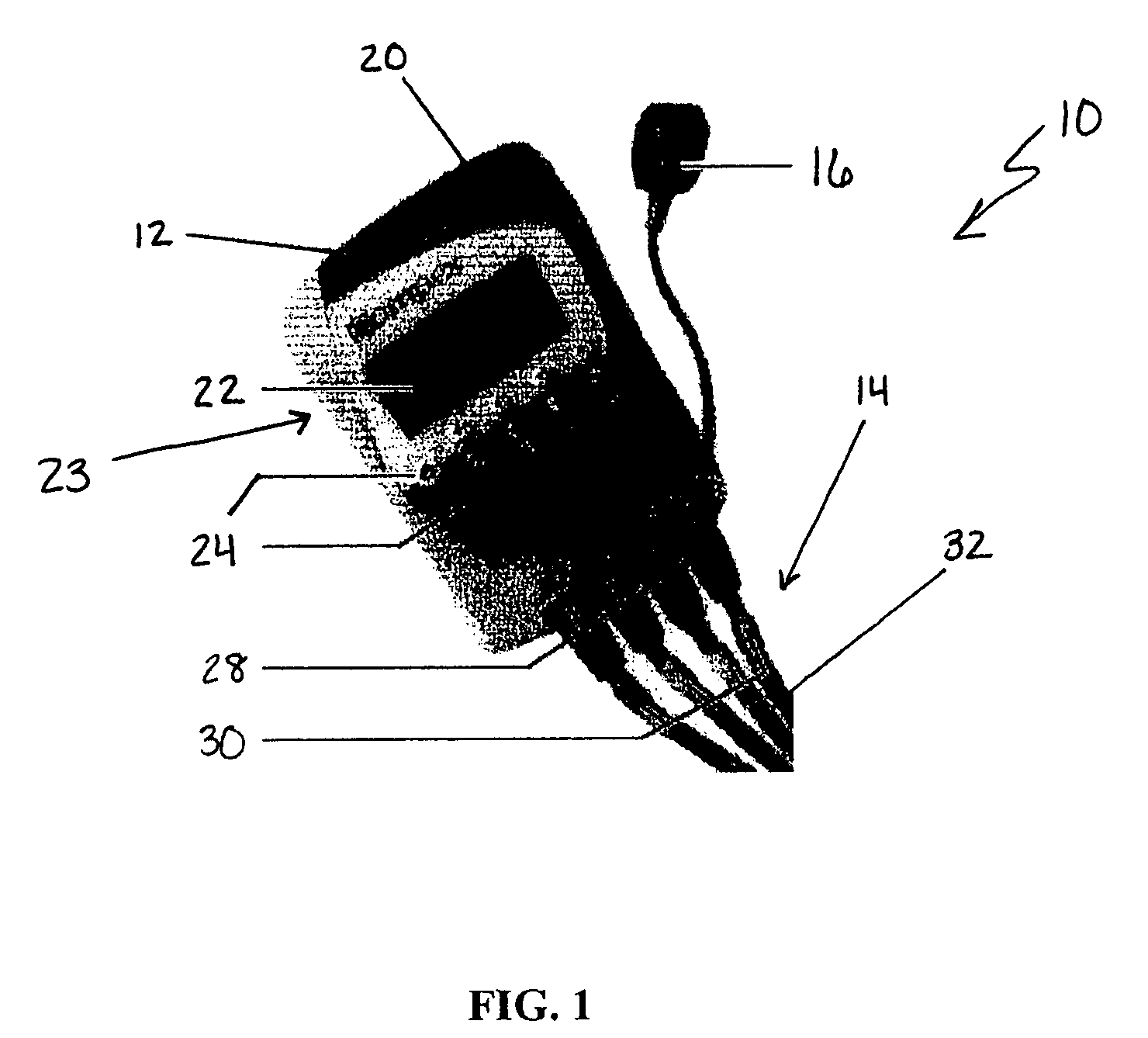
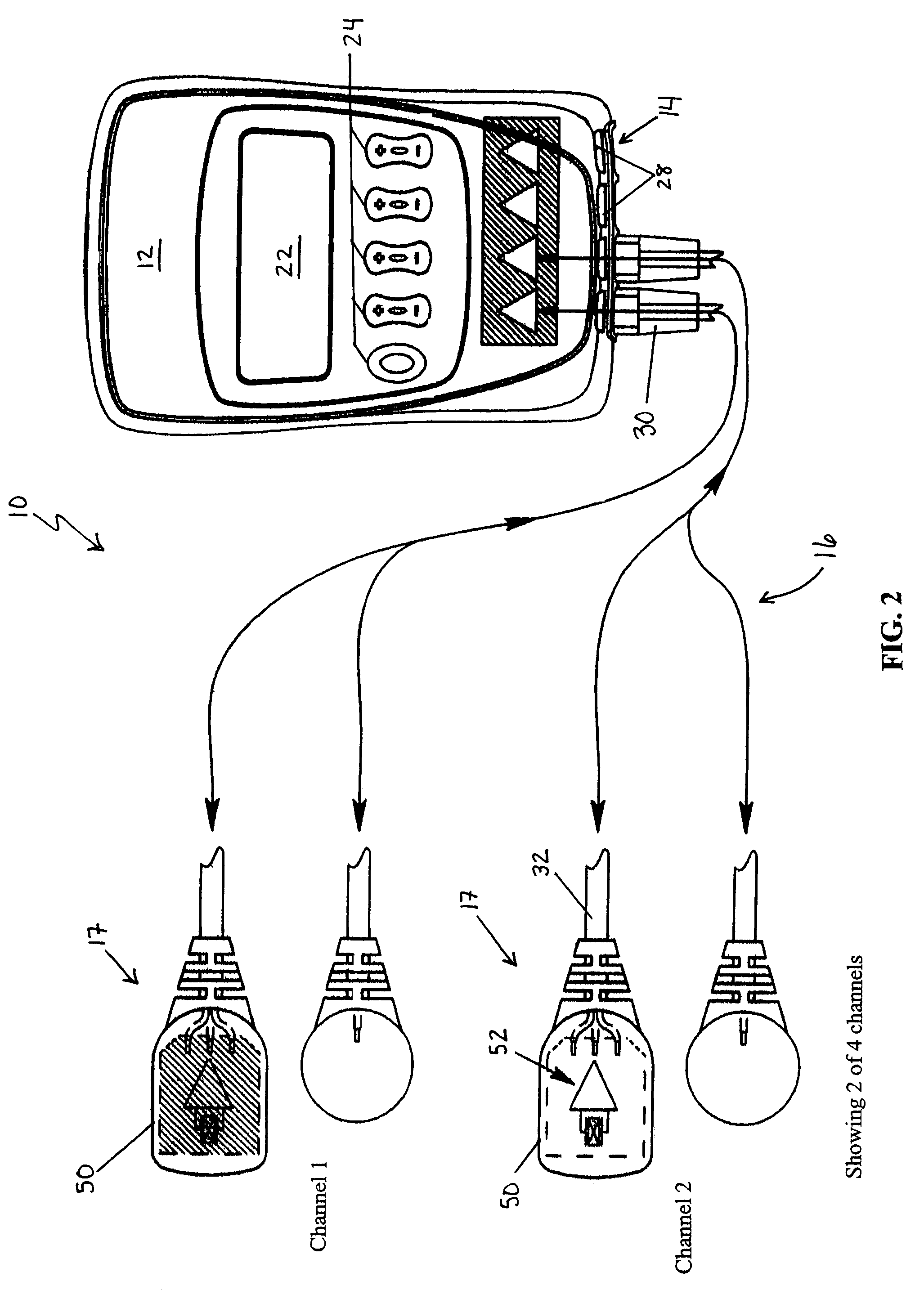
Automated adaptive muscle stimulation method and apparatus
ActiveUS20050283204A1Easy to integrateEnhancing user comfortElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An automated adaptive muscle stimulation system and method are disclosed. The stimulation system includes at least one electrode assembly adapted to deliver a muscle stimulation signal to the tissue of a user, a sensor system adapted to detect a muscle response, and an electrical stimulation device operably coupled to the at least on electrode assembly and the sensor system, the electrical stimulation device including a control system operable to automatically diagnose at least one characteristic of a muscle from the detected muscle response and adjust at least one parameter of the muscle stimulation signal in response thereto to deliver an adjusted muscle stimulation signal. A dual mode muscle stimulation system adapted to accept first and second data sets and provide first and second levels of treatment data is also disclosed.
Owner:DJO GLOBAL SWITZERLAND SARL
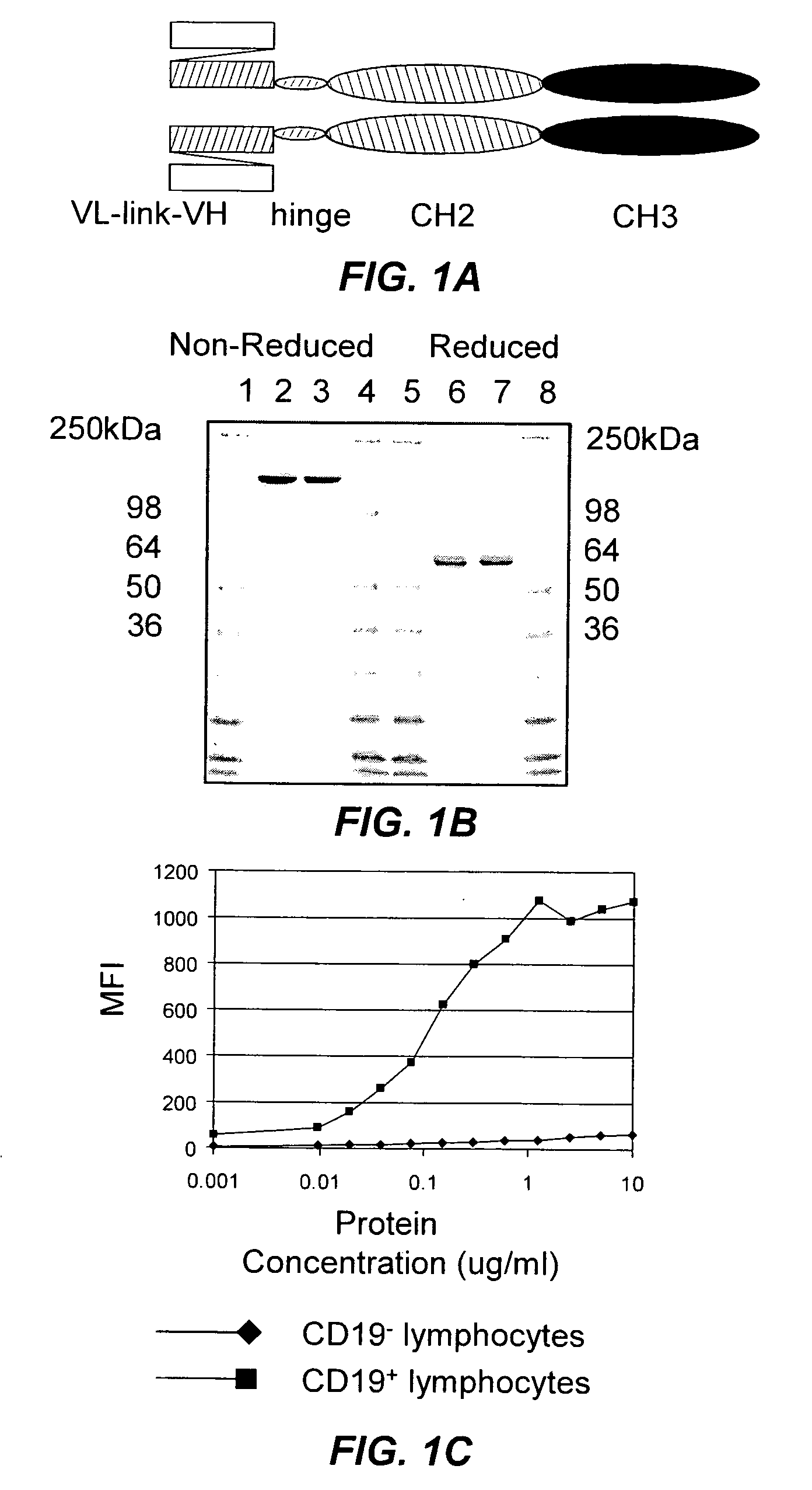
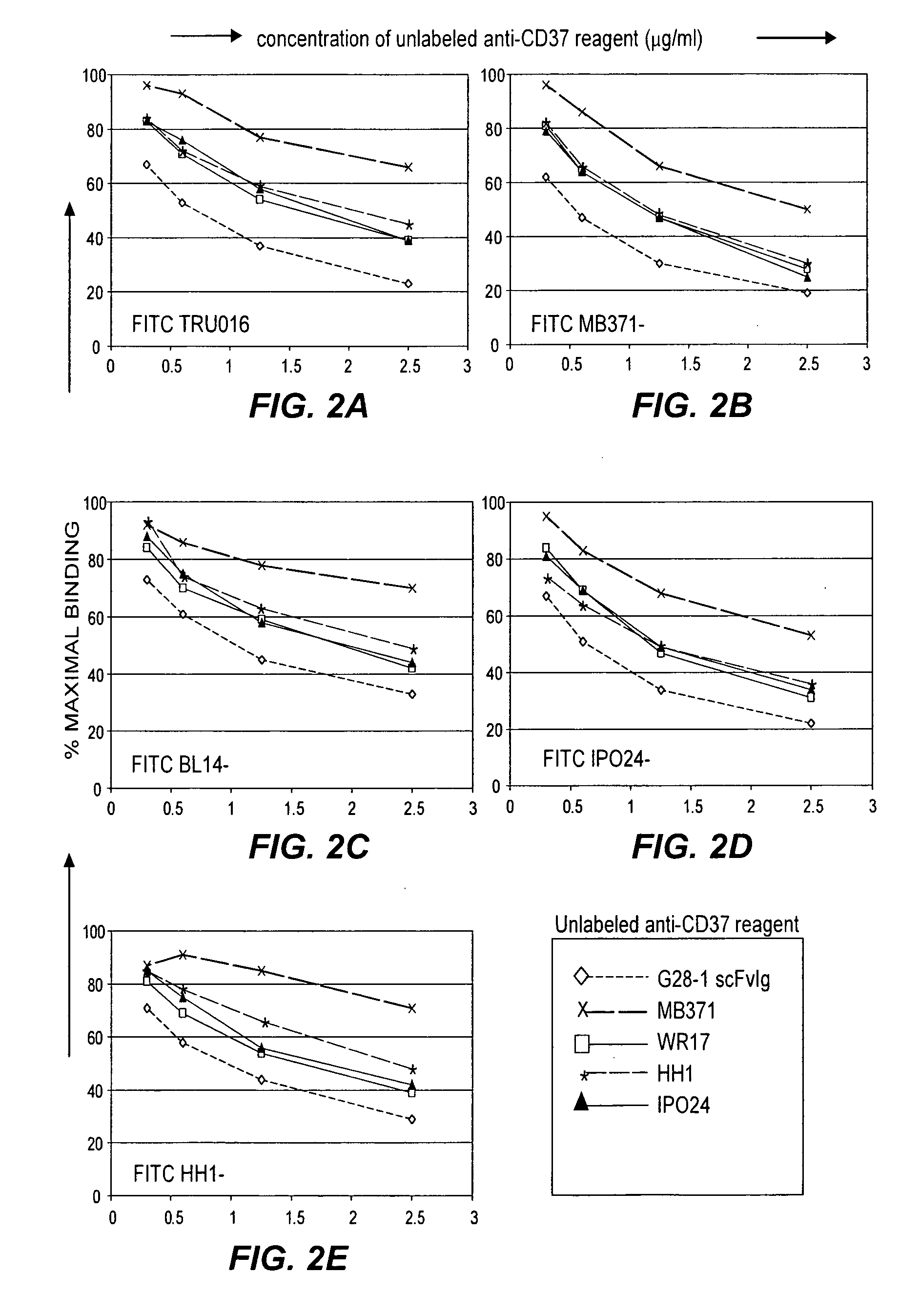
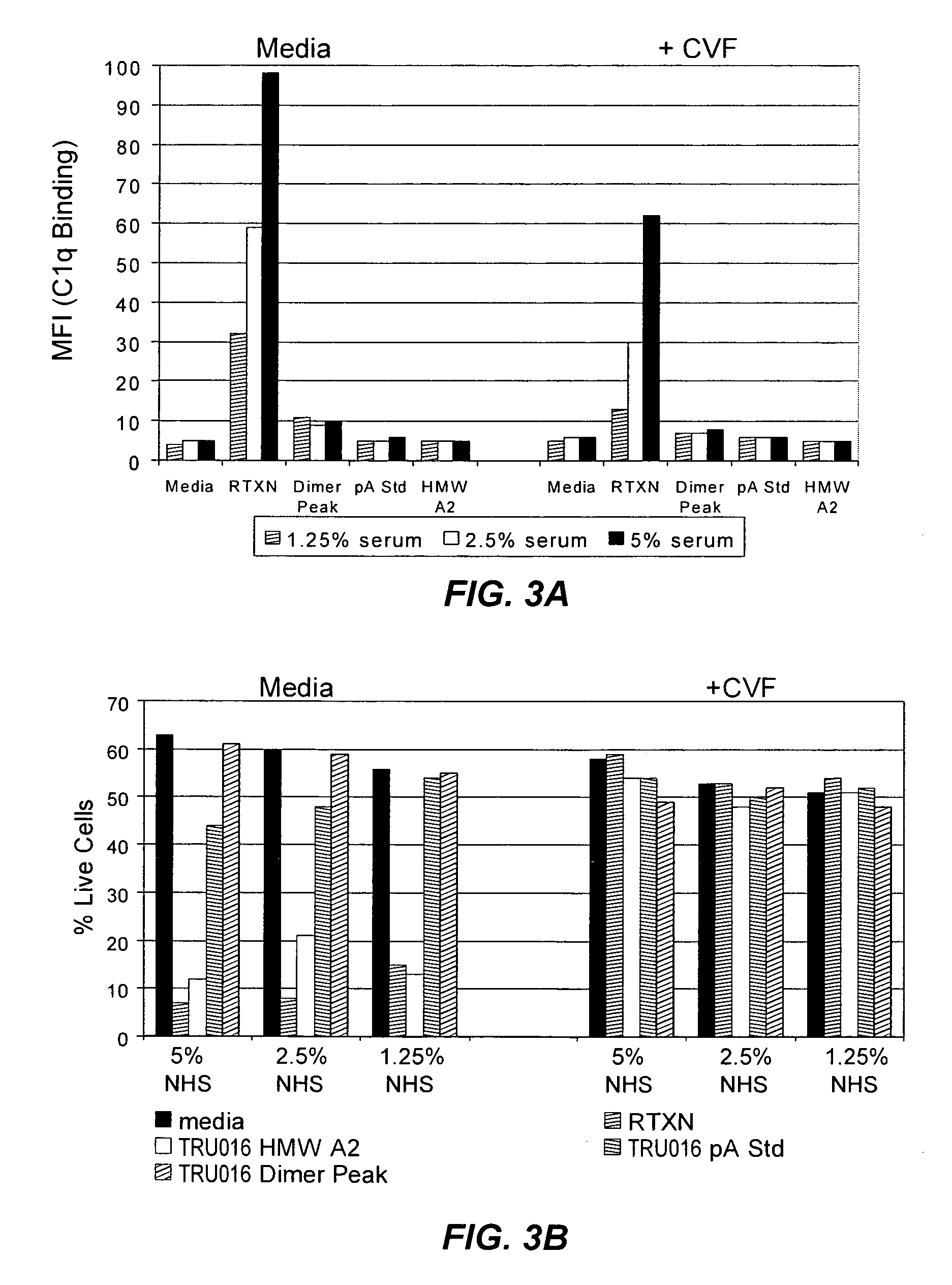
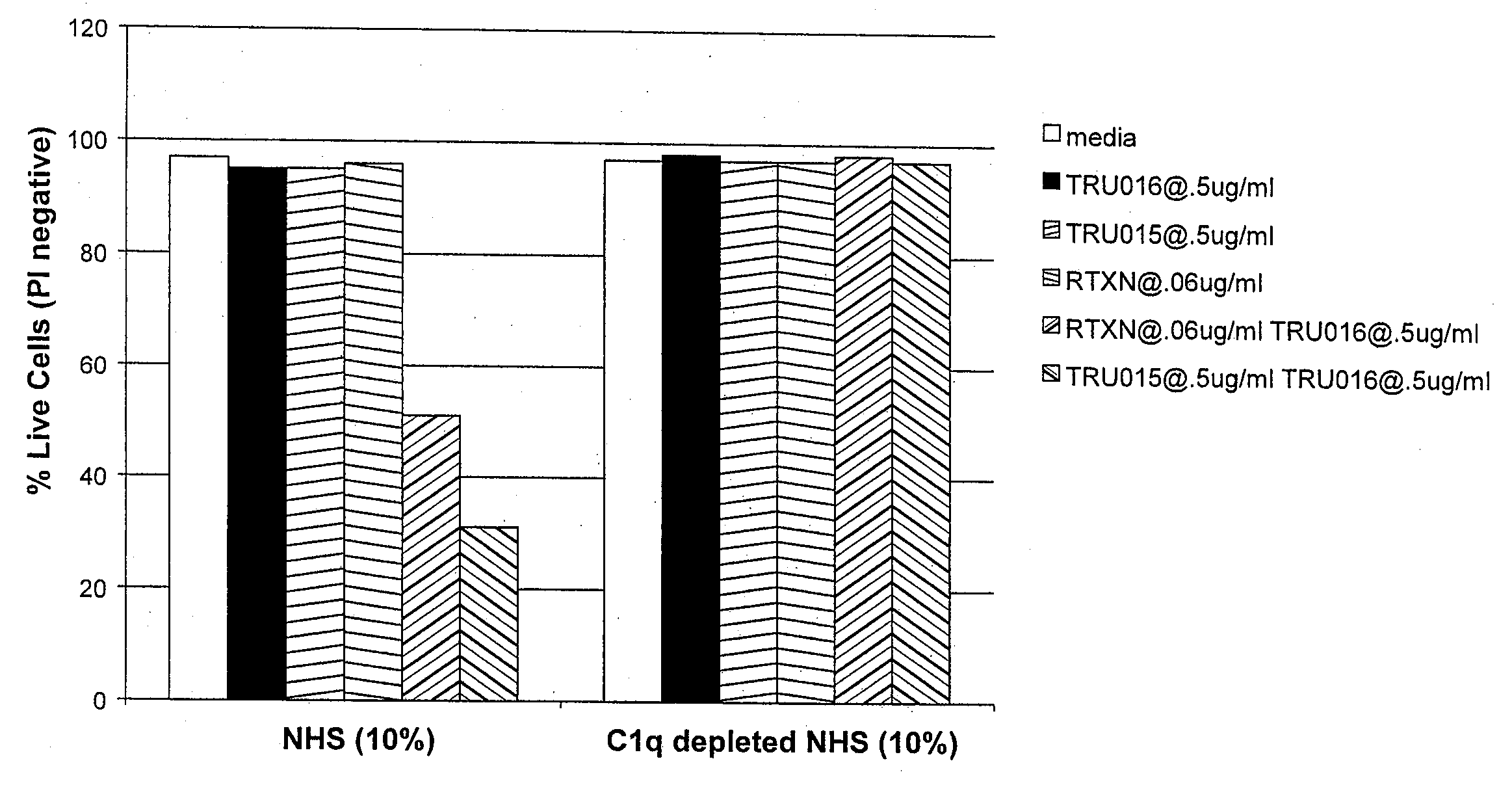
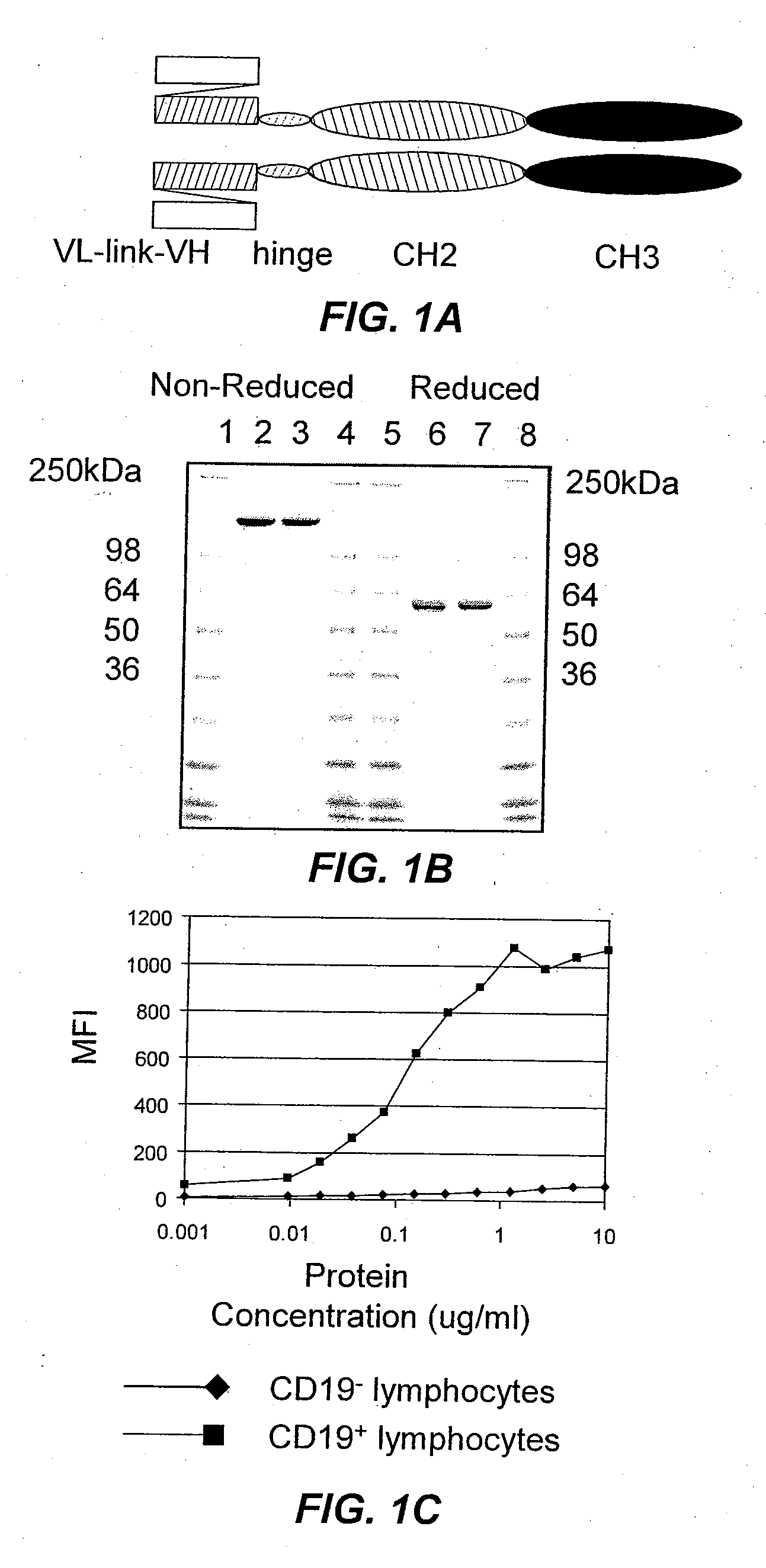
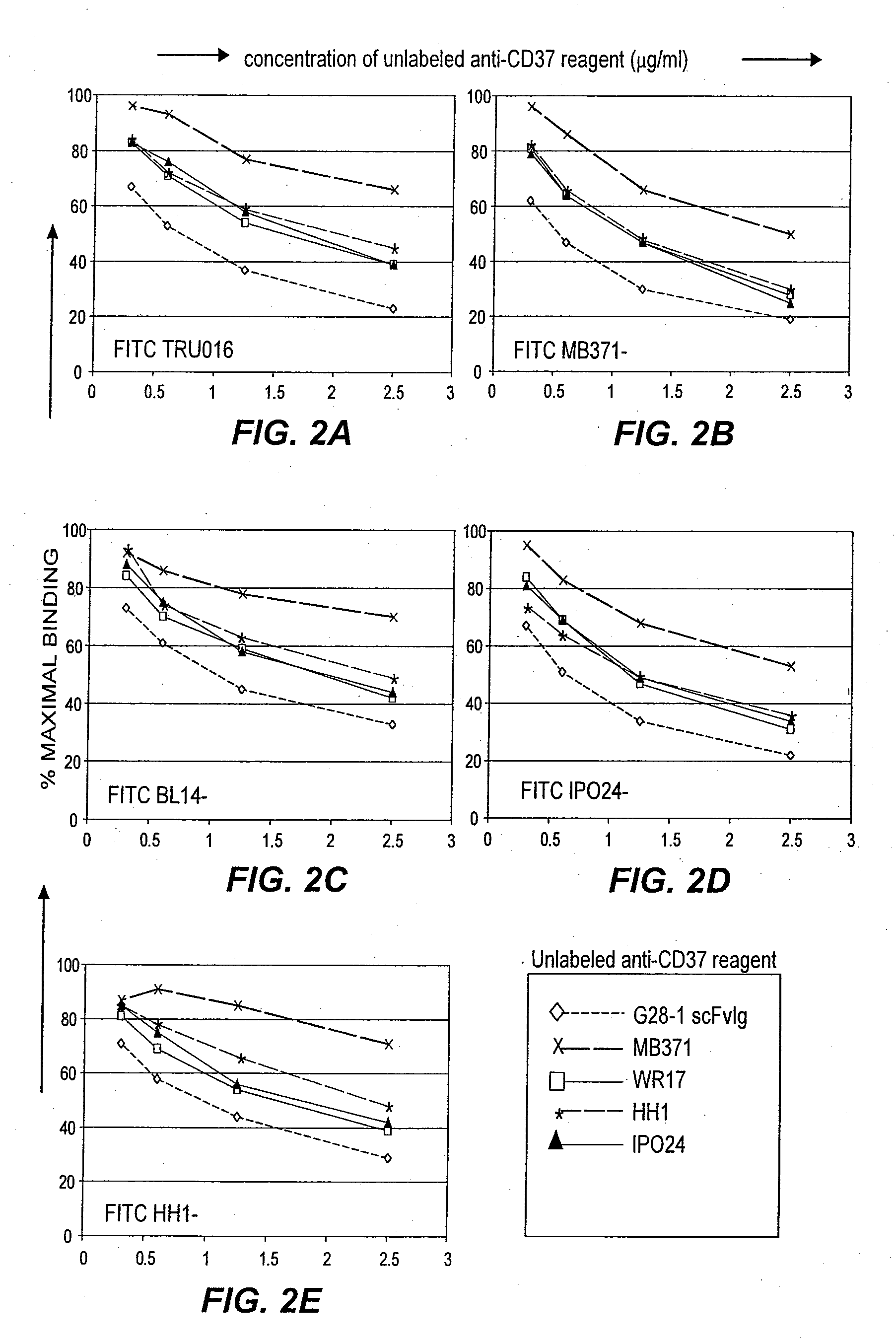
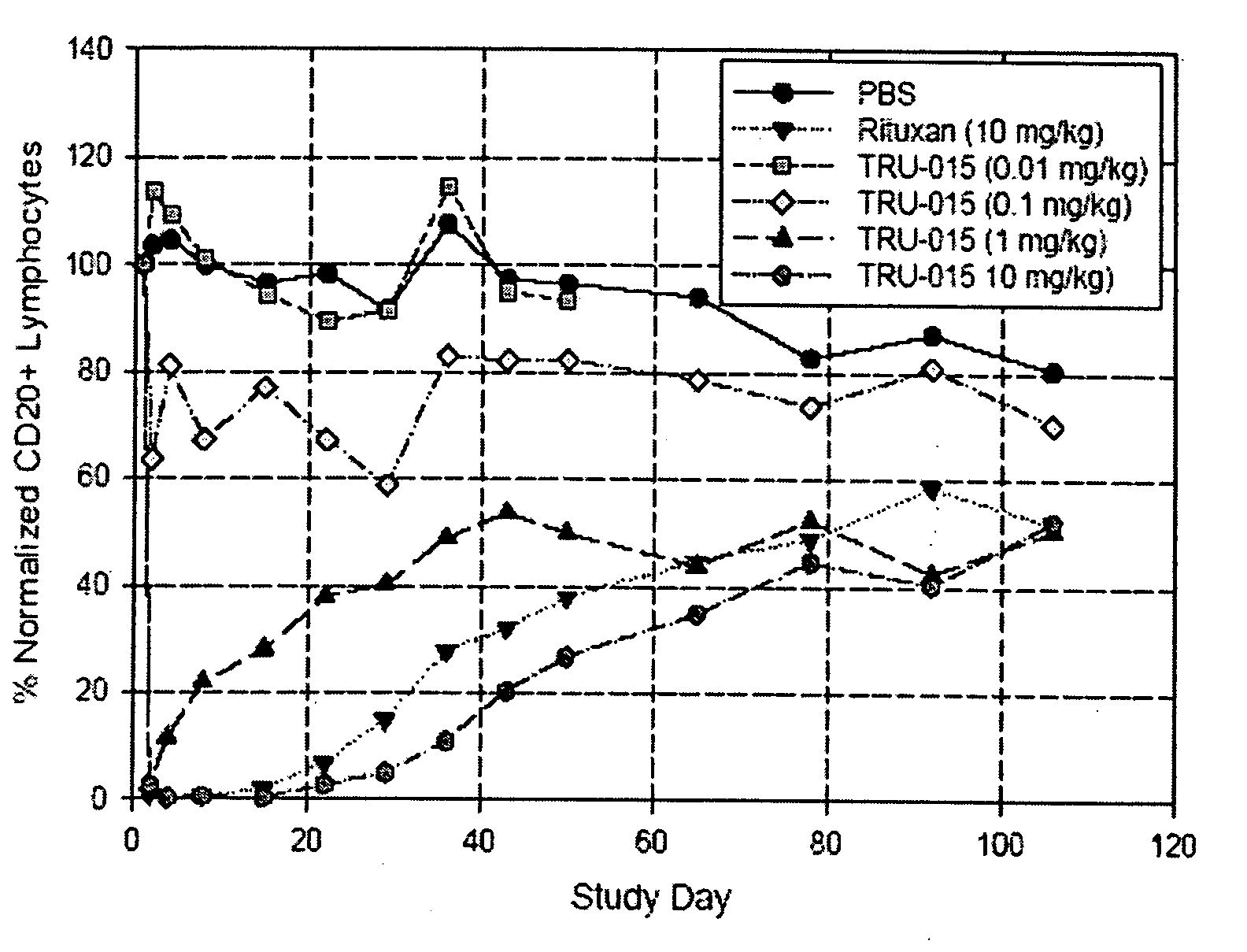
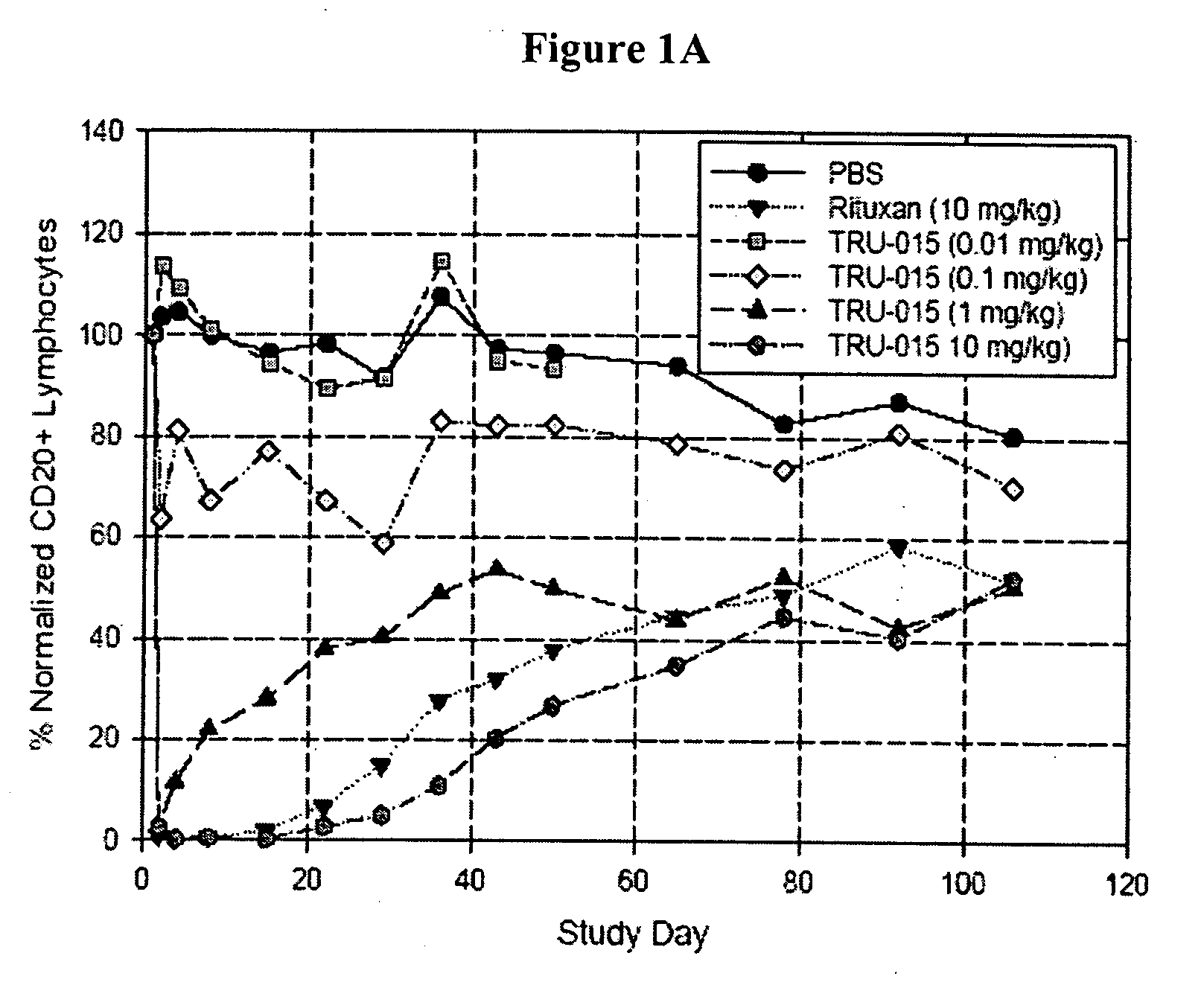
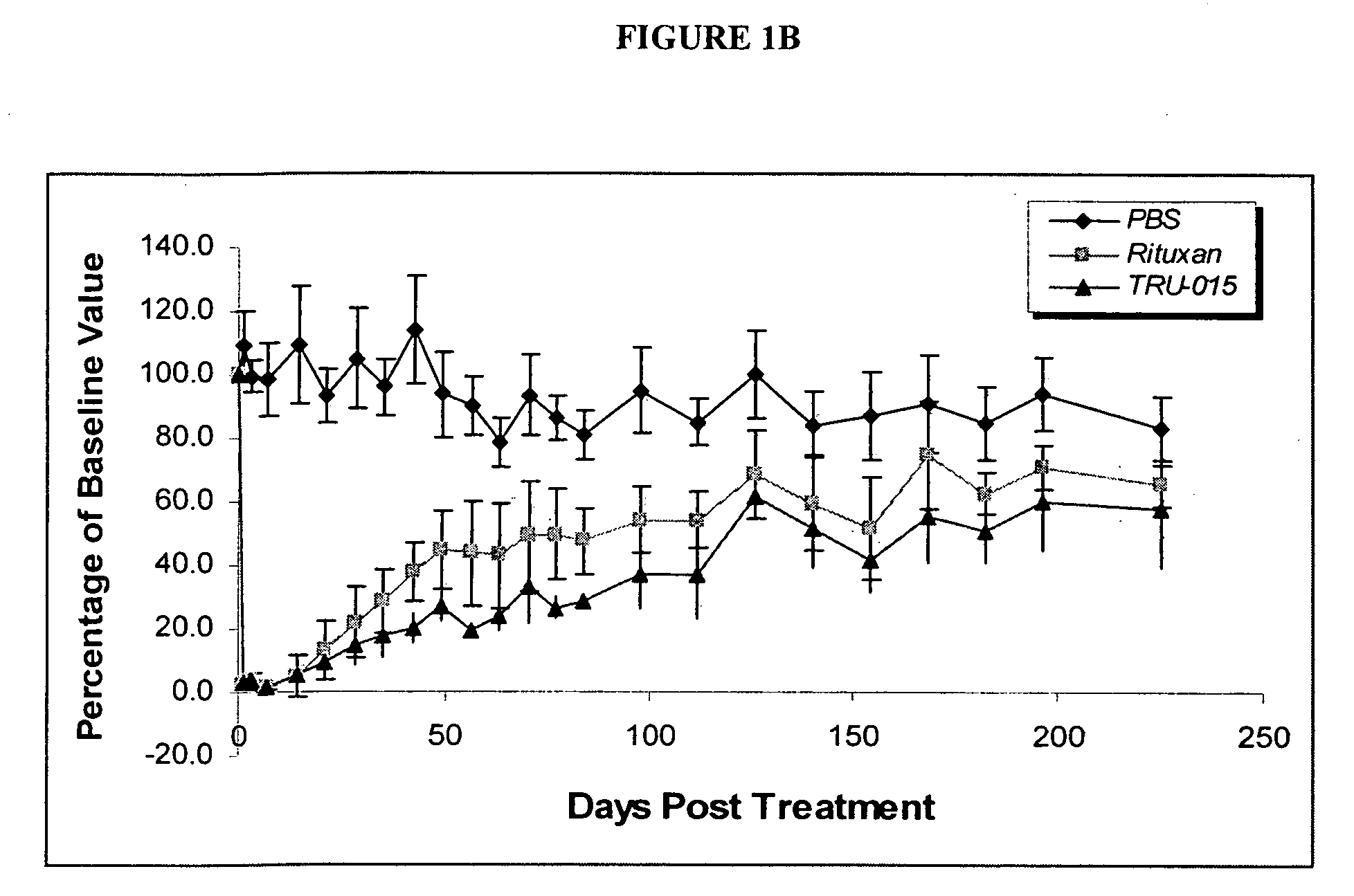
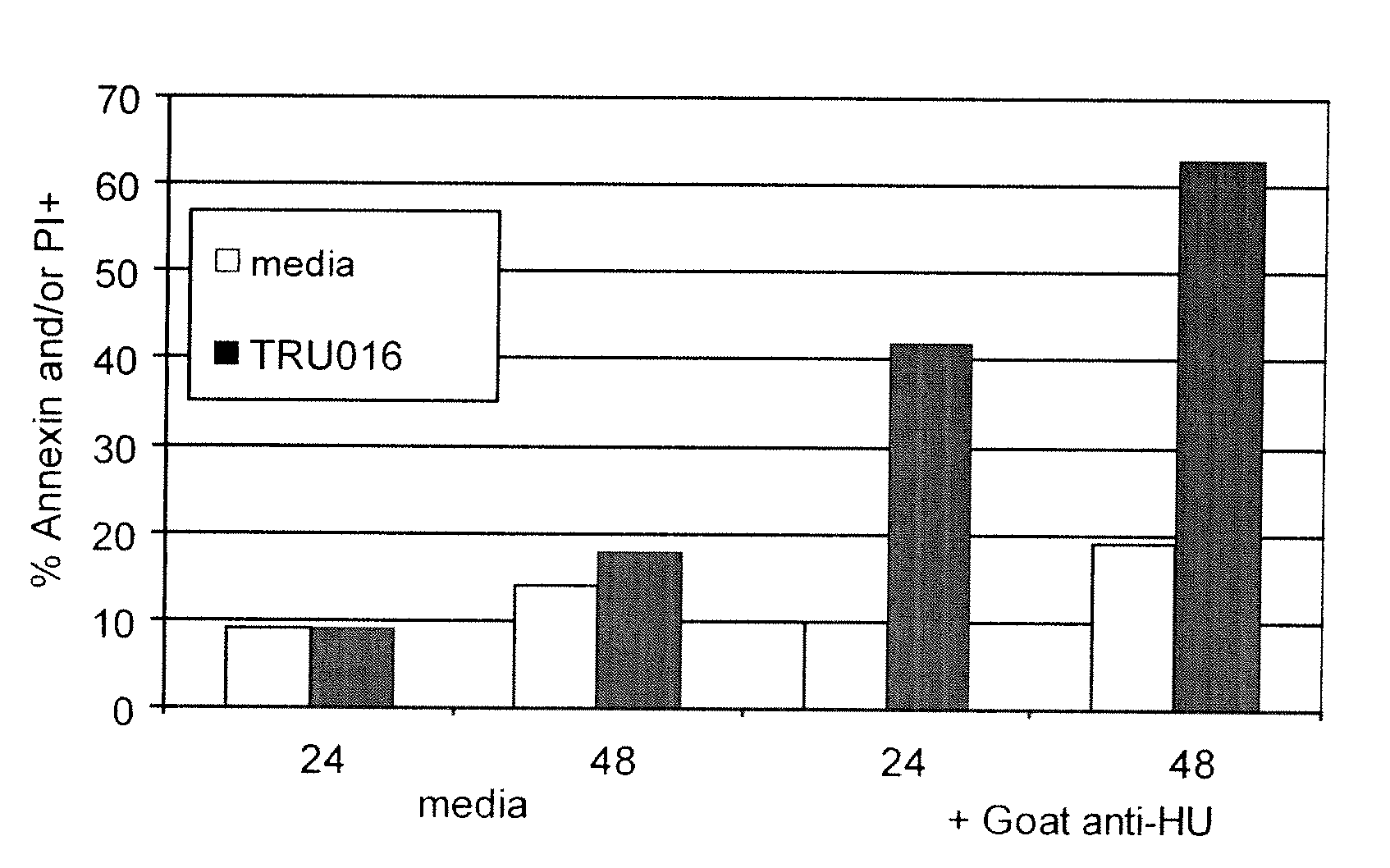
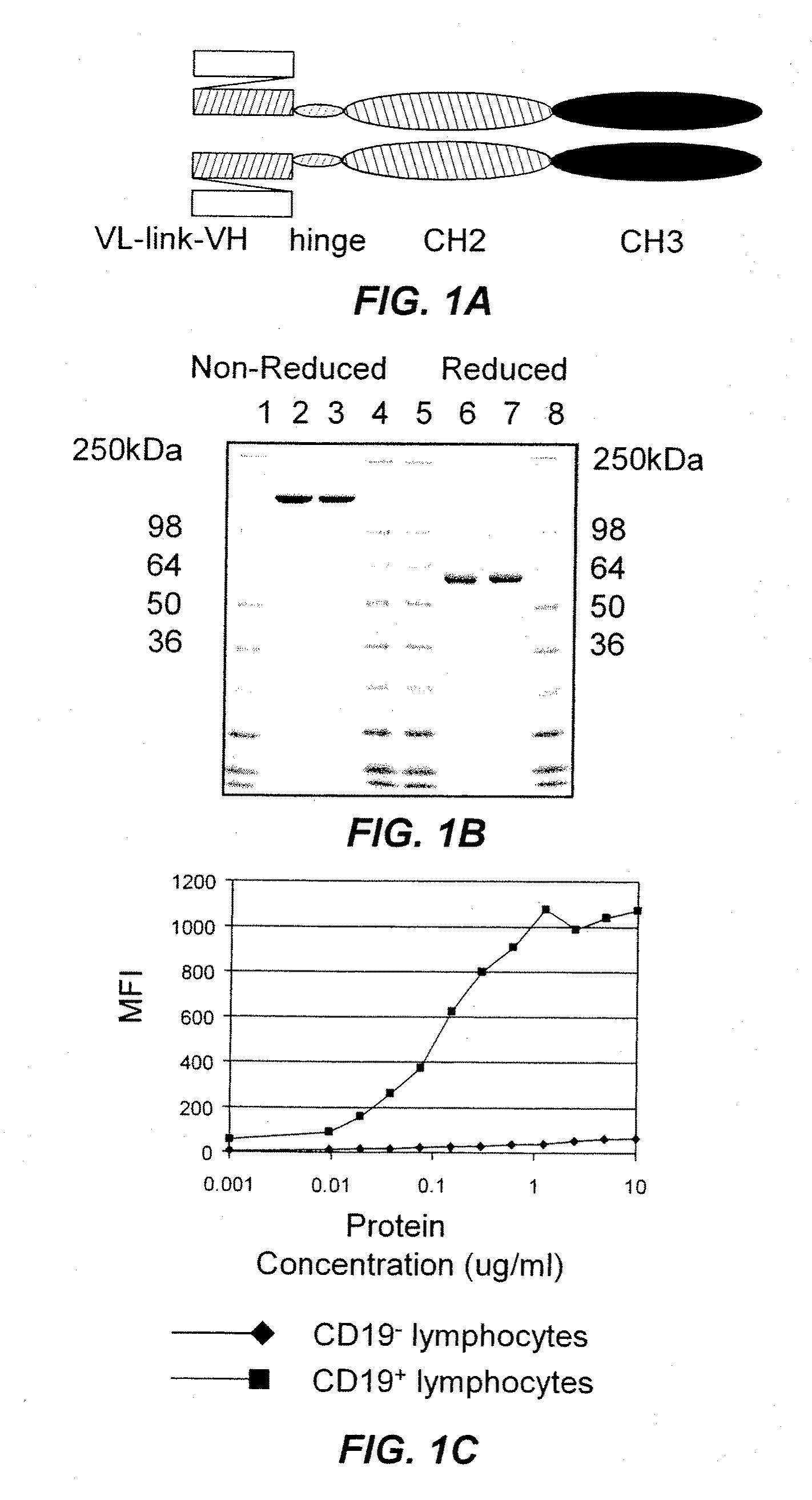
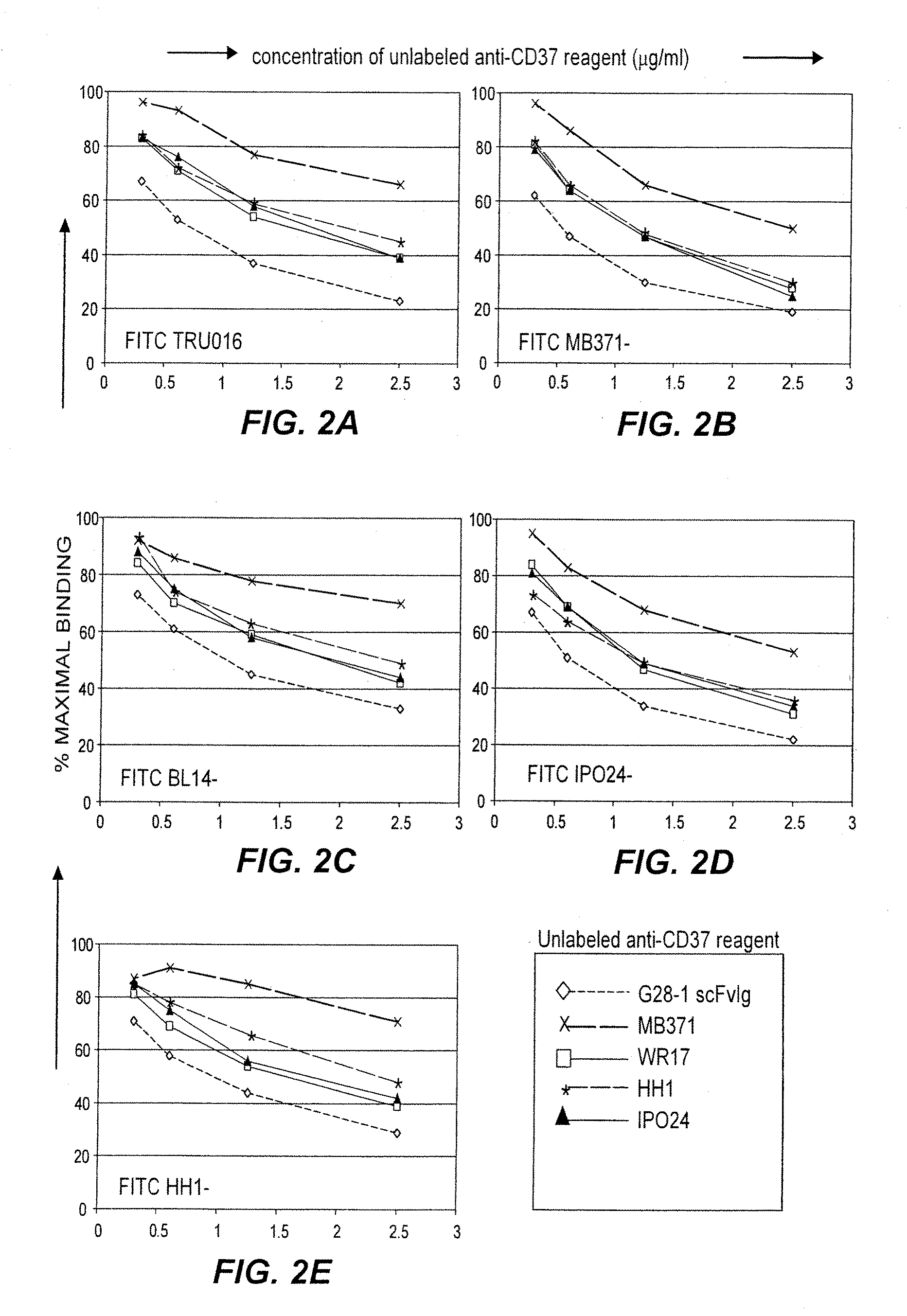
B-cell reduction using CD37-specific and CD20-specific binding molecules
ActiveUS20070059306A1Increase profitPermit absorptionSenses disorderNervous disorderCD20Cell activity
The present invention generally provides methods for B-cell reduction in an individual using CD37-specific binding molecules. In particular, the invention provides methods for B-cell reduction using CD37-specific binding molecules alone, or a combination of CD37-specific binding molecules and CD20-specific binding molecules, in some instances a synergistic combination. The invention further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity. In addition, the invention provides humanized CD37-specific binding molecules.
Owner:APTEVO RES & DEV LLC
Self adaptive cement systems
InactiveUS20070137528A1Avoid seizuresInhibit migrationSolid waste managementDrilling compositionSelf-healingChemical products
A self-adaptive cement system includes cement, water and at least one additive that reacts or and expands in contact with oil and gas. Several chemical products have been identified including rubber alkylstyrene, polynorbornene, resins such precrosslinked substituted vinyl acrylate copolymers and diatomaceous earth. These additives have the effect of making the cement self-healing in the event of physical failure or damage such as micro-annuli. The self healing property is produced by the contact with subterranean hydrocarbon fluids, the potential repair mechanism is thus activated if and when needed in case of start of loss of zonal isolation. In another embodiment, the expansion is deliberately induced by pumping a hydrocarbon fluid in the vicinity of the set cement.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
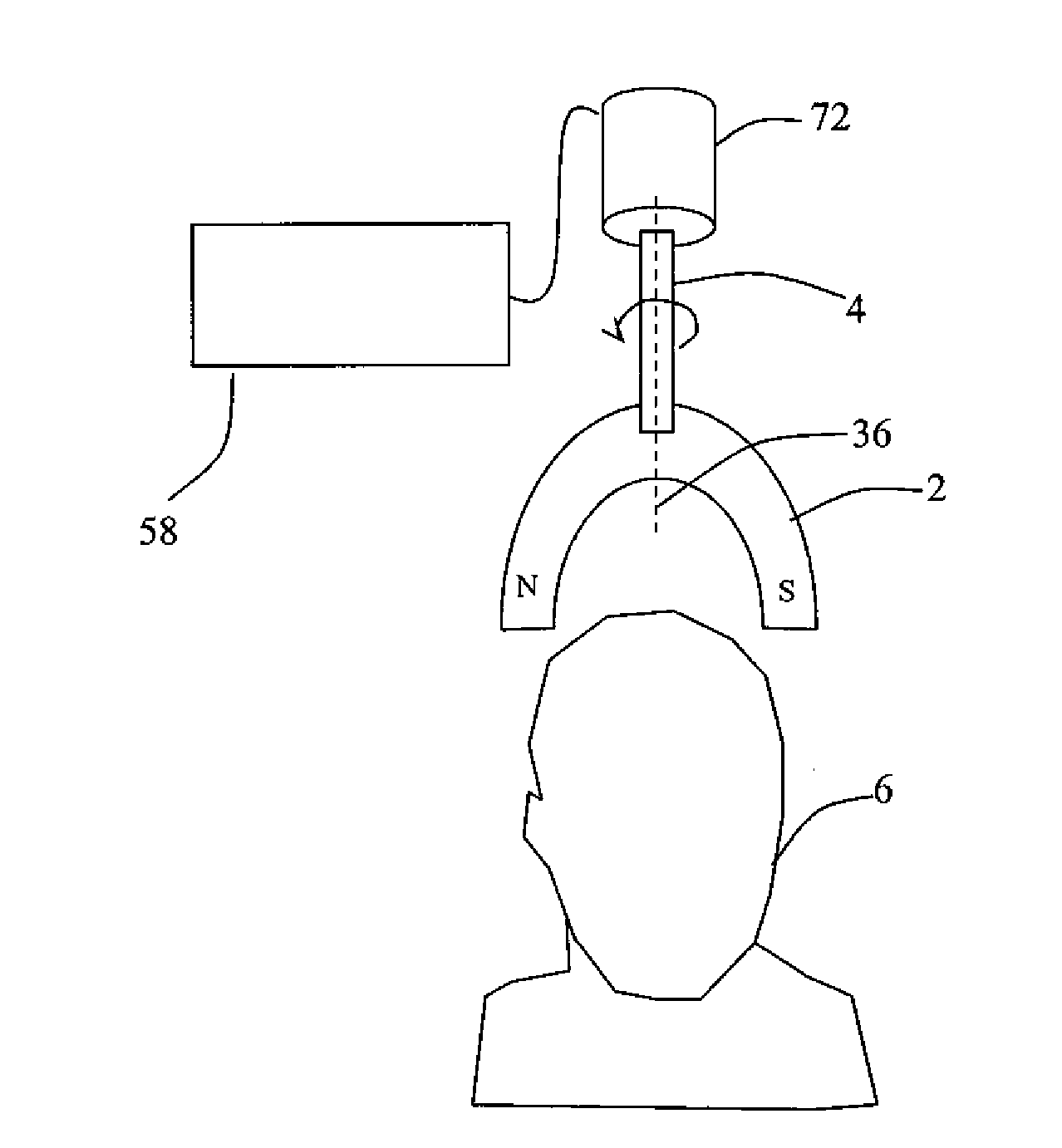
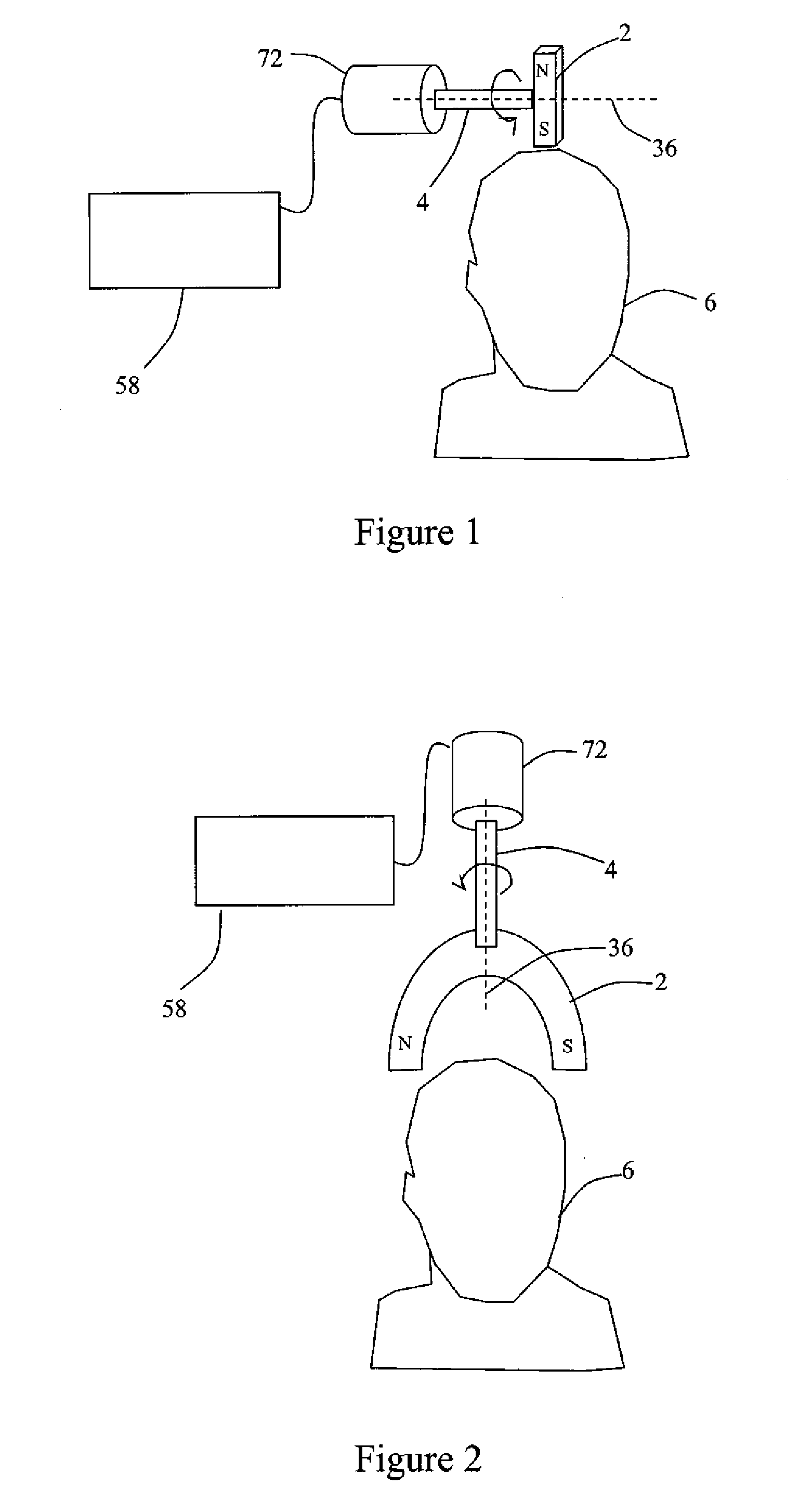
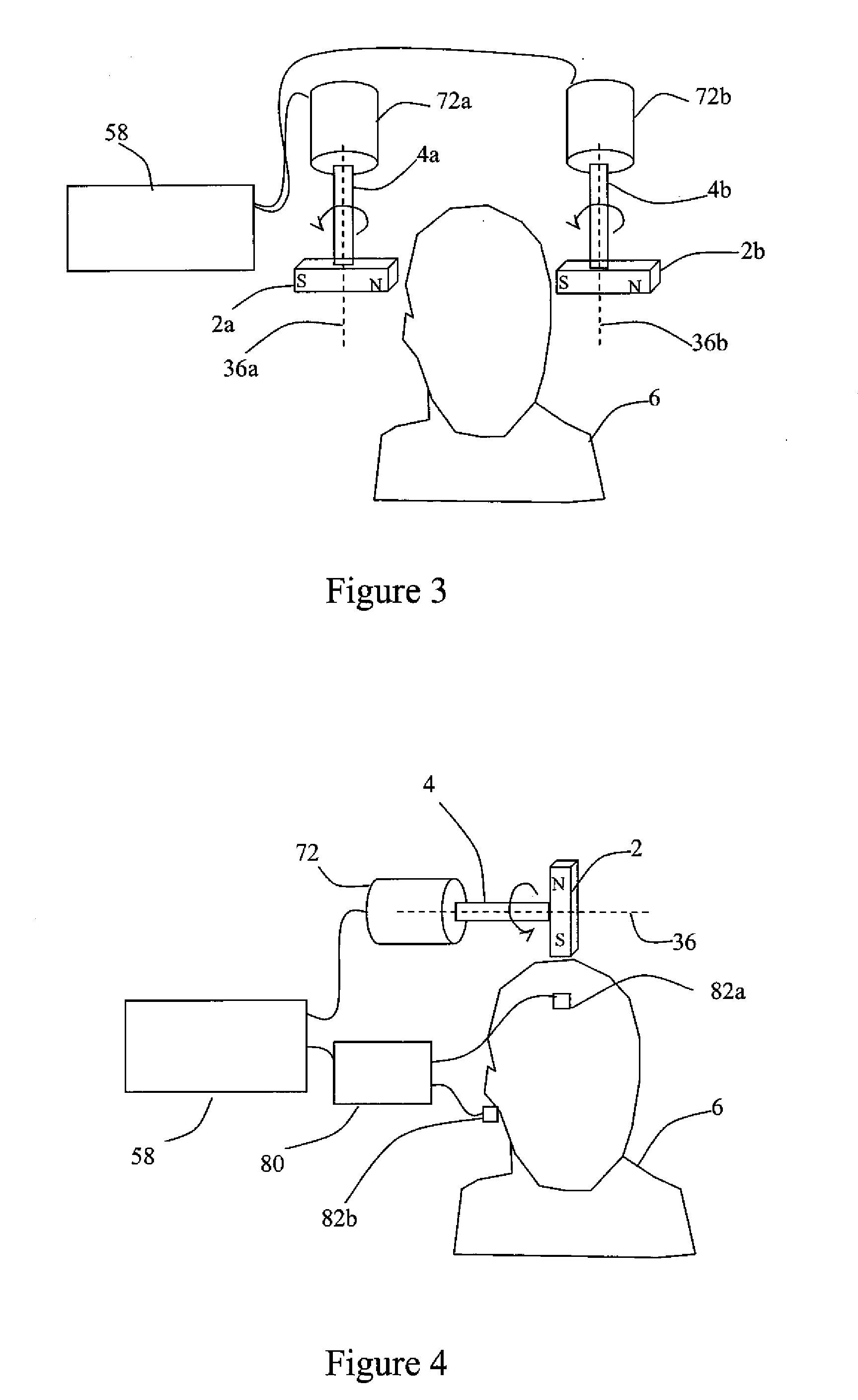
Systems and methods for neuro-eeg synchronization therapy
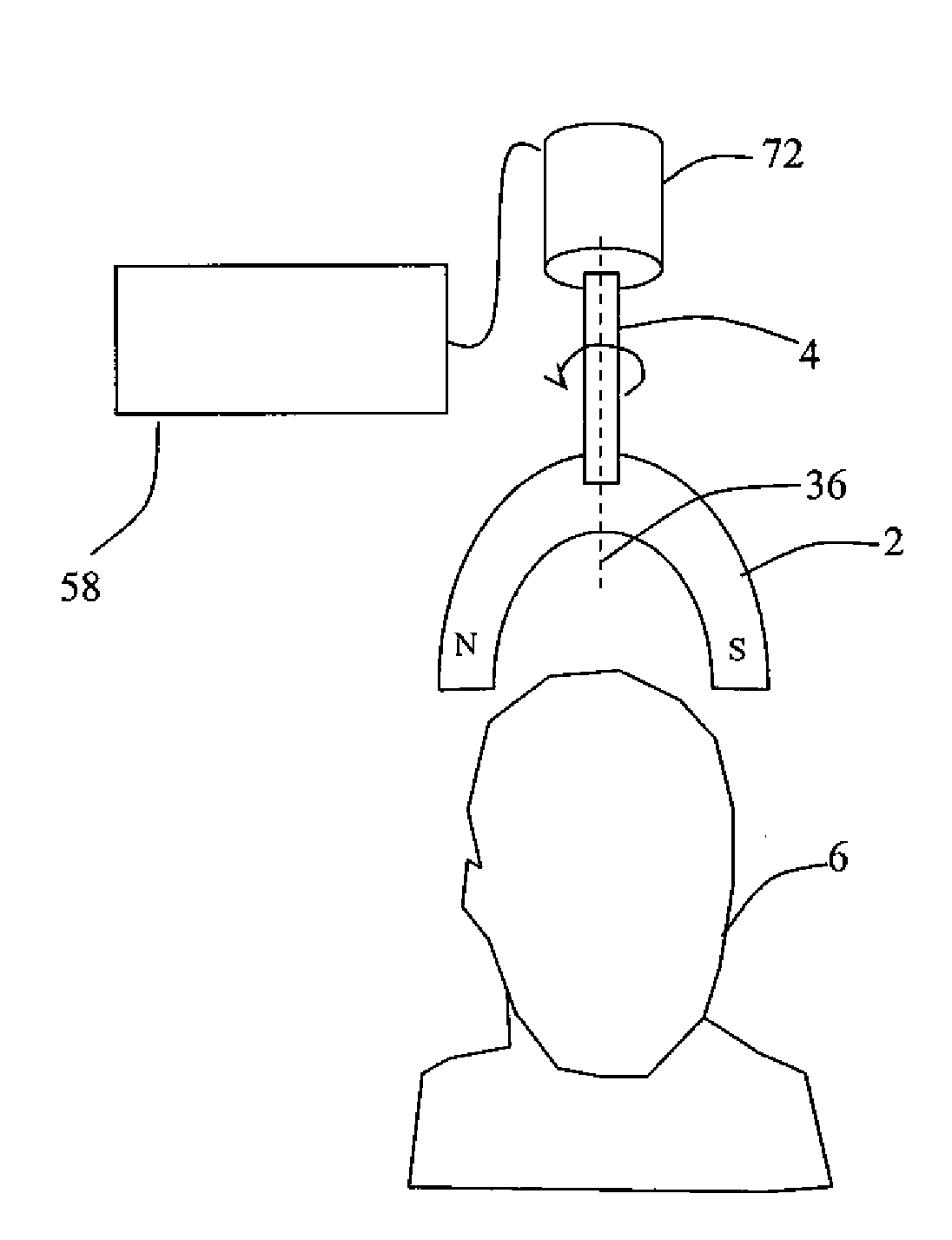
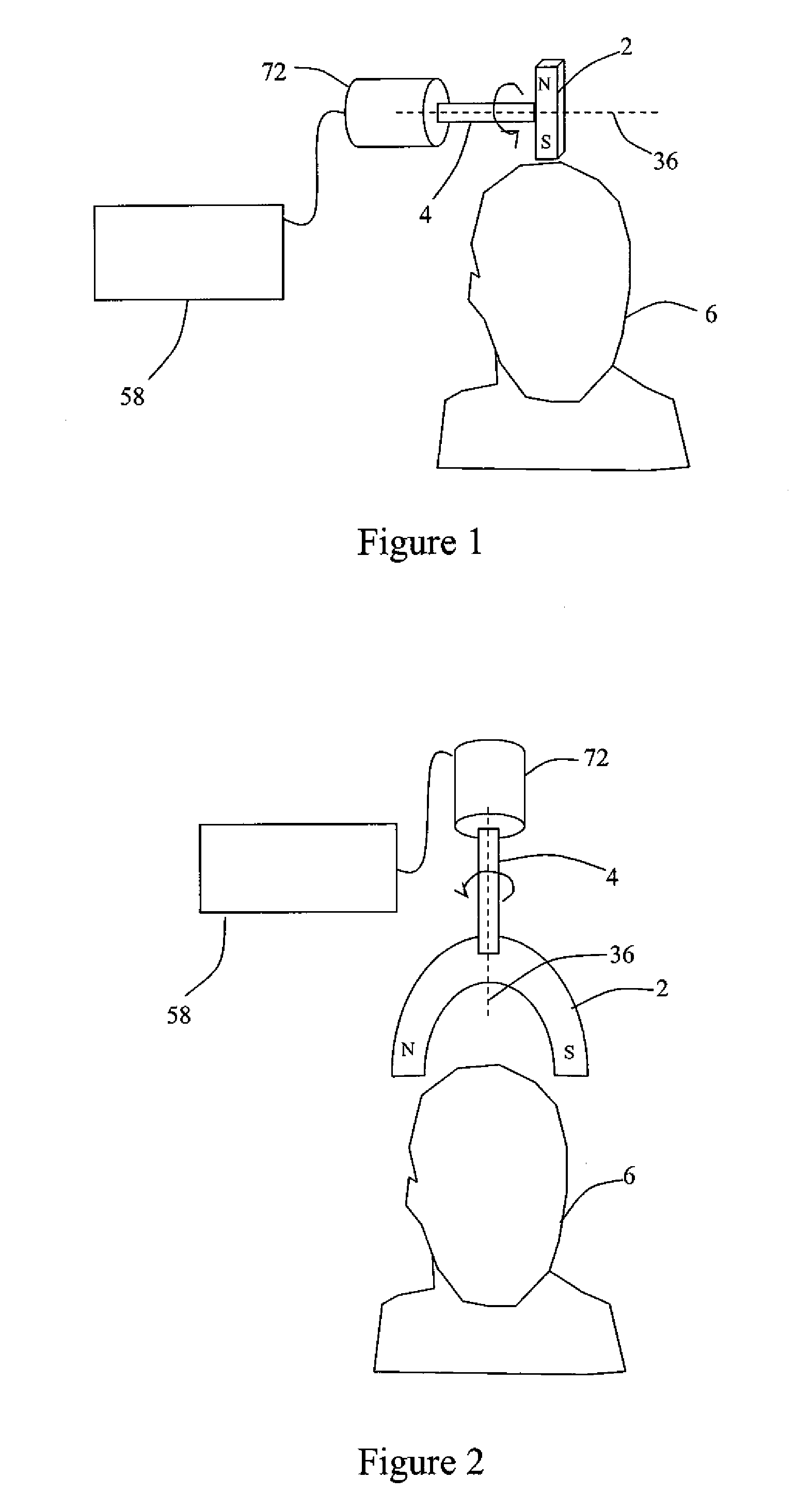
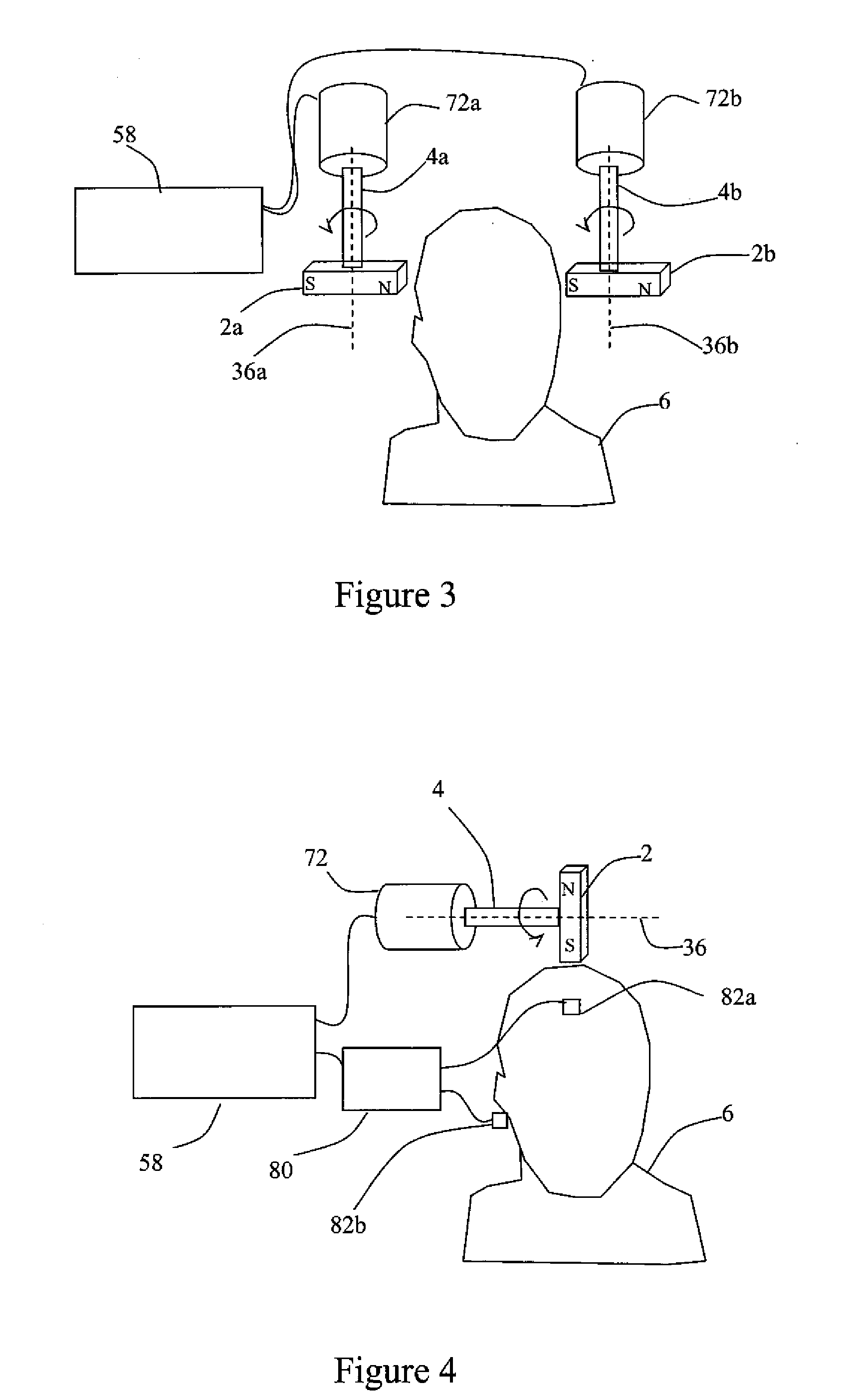
ActiveUS20110112427A1Lower blood pressureIncrease libidoElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyDrugDisease
Described are methods, devices, and systems for a novel, inexpensive, easy to use therapy for a number of disorders. Described are methods and devices to treat disorders that involves no medication. Methods and devices described herein use alternating magnetic fields to gently “tune” the brain and affect mood, focus, and cognition of subjects.
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
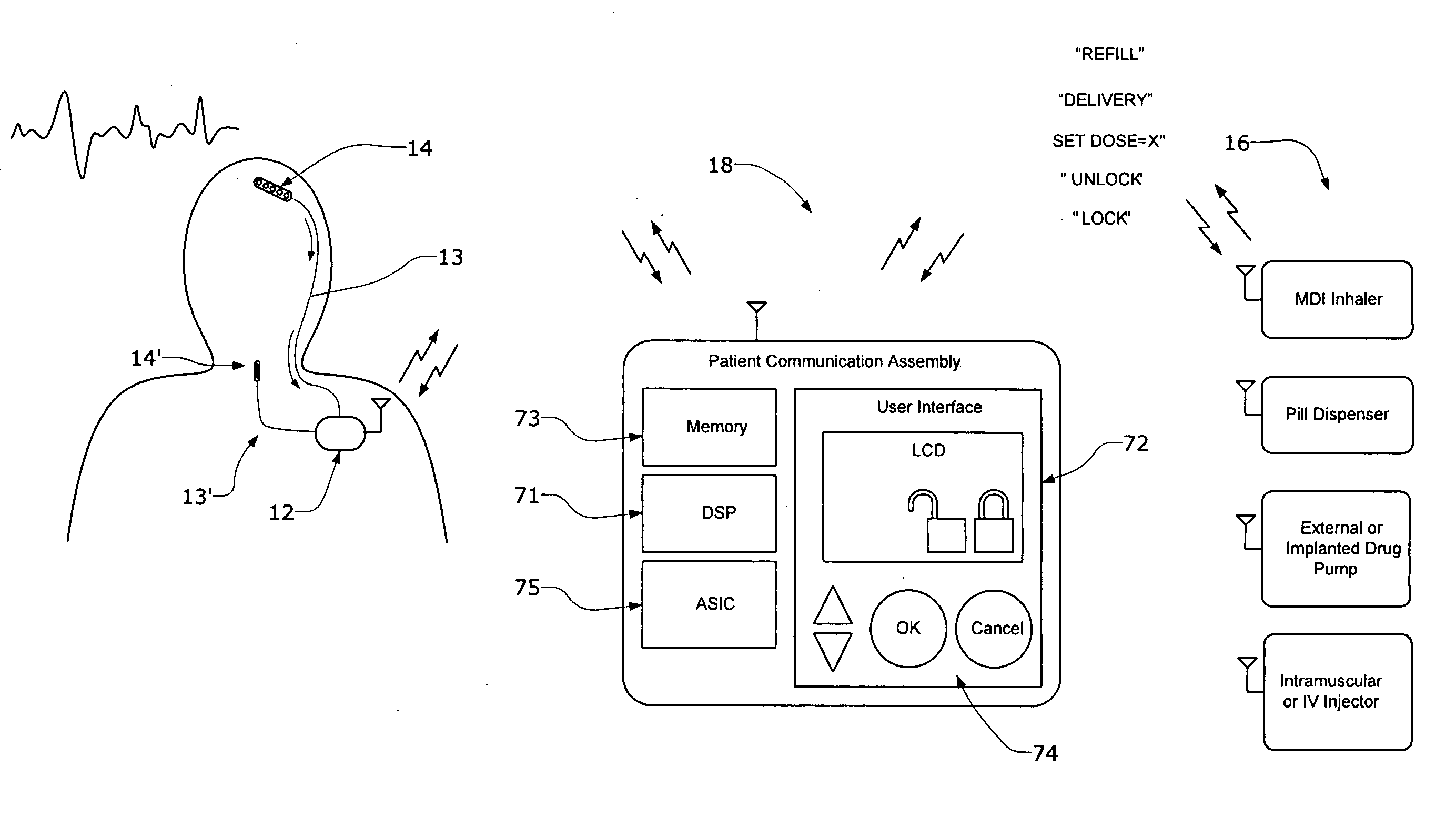
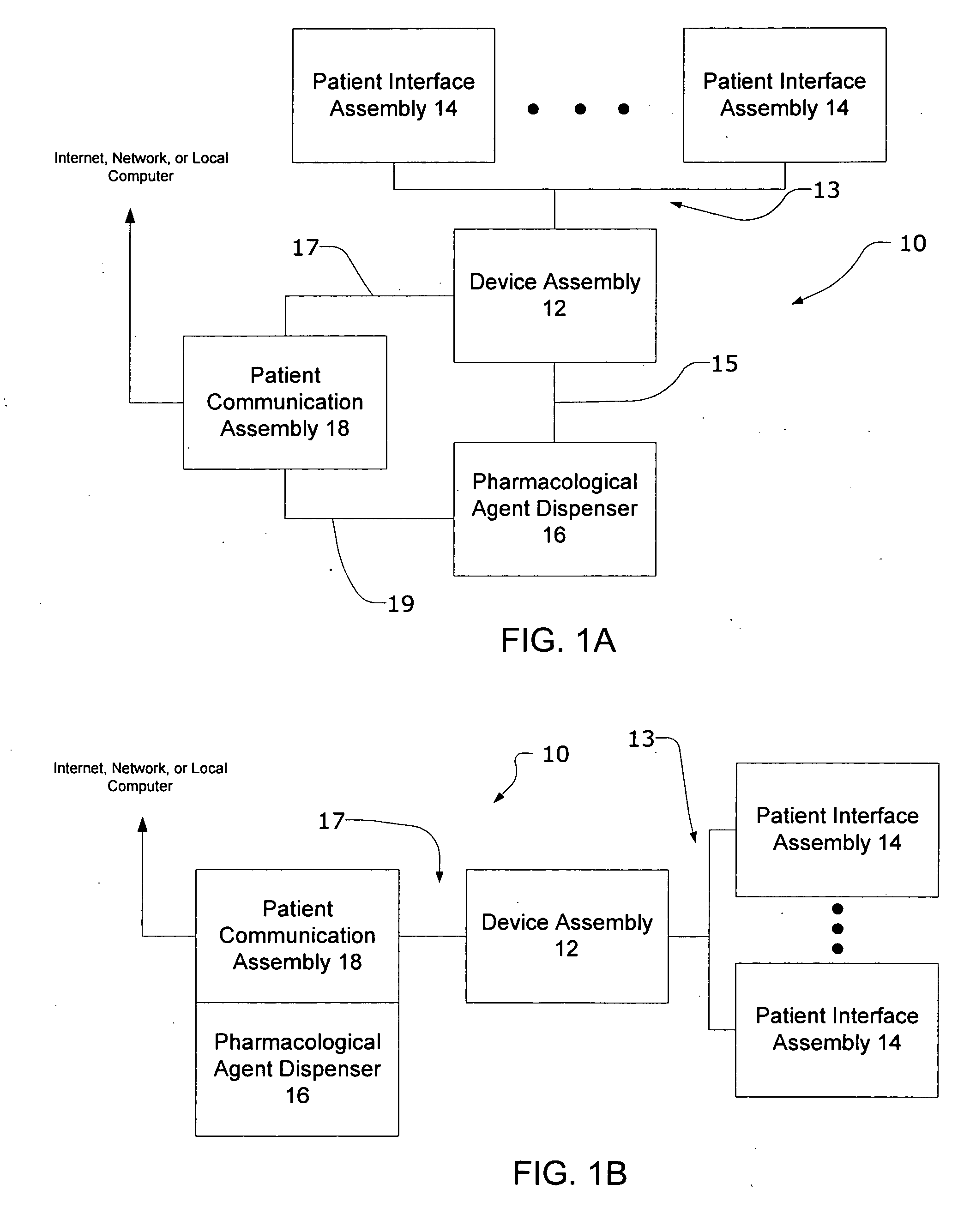
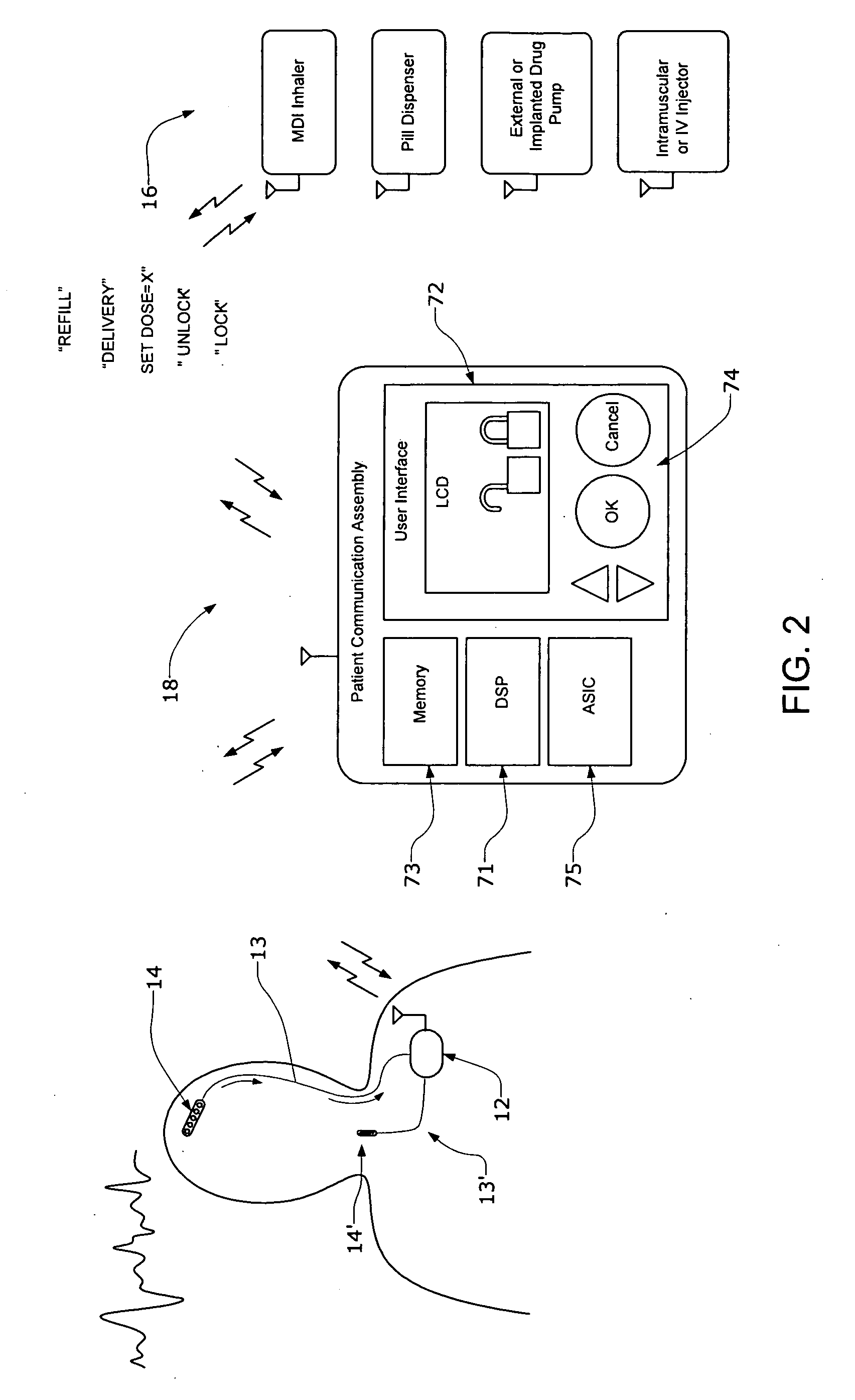
Systems and methods for characterizing a patient's propensity for a neurological event and for communicating with a pharmacological agent dispenser
InactiveUS20070149952A1Selectively limit accessSelectively limit to administrationDrug and medicationsTelemedicinePharmacometricsAntiepileptic drug
The present invention provides systems and methods for managing intake of a pharmacological agent. In one method of the present invention, the systems and methods are for controlling intake of an anti-epileptic drug. In such embodiments, one or more signals from a patient are processed to predict an onset of a seizure. Upon the prediction of the seizure, the patient is allowed to access the pharmacological agent in a pharmacological agent dispenser.
Owner:CYBERONICS INC
Anti-TrkB antibodies
ActiveUS8642035B2Lower blood sugar levelsLose weightMetabolism disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideAntigen binding
The present invention provides improved antibodies or antigen-binding molecules that specifically recognize and agonize the tyrosine receptor kinase B (TrkB) receptor, and methods of their use. Also provided in the invention are polynucleotides and vectors that encode such molecules and host cells that harbor the polynucleotides or vectors.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method for diagnosing risk of type 1 diabetes and for preventing onset of type 1 diabetes
InactiveUS20130108598A1Early diagnosisAvoid seizuresBiocideMetabolism disorderIntestinal microorganismsType 1 diabetes
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Methods and computer program products for determining risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other insulin resistance related disorders
InactiveUS6518069B1Facilitate early detectionAvoid spendingDisease diagnosisAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDiseaseData set
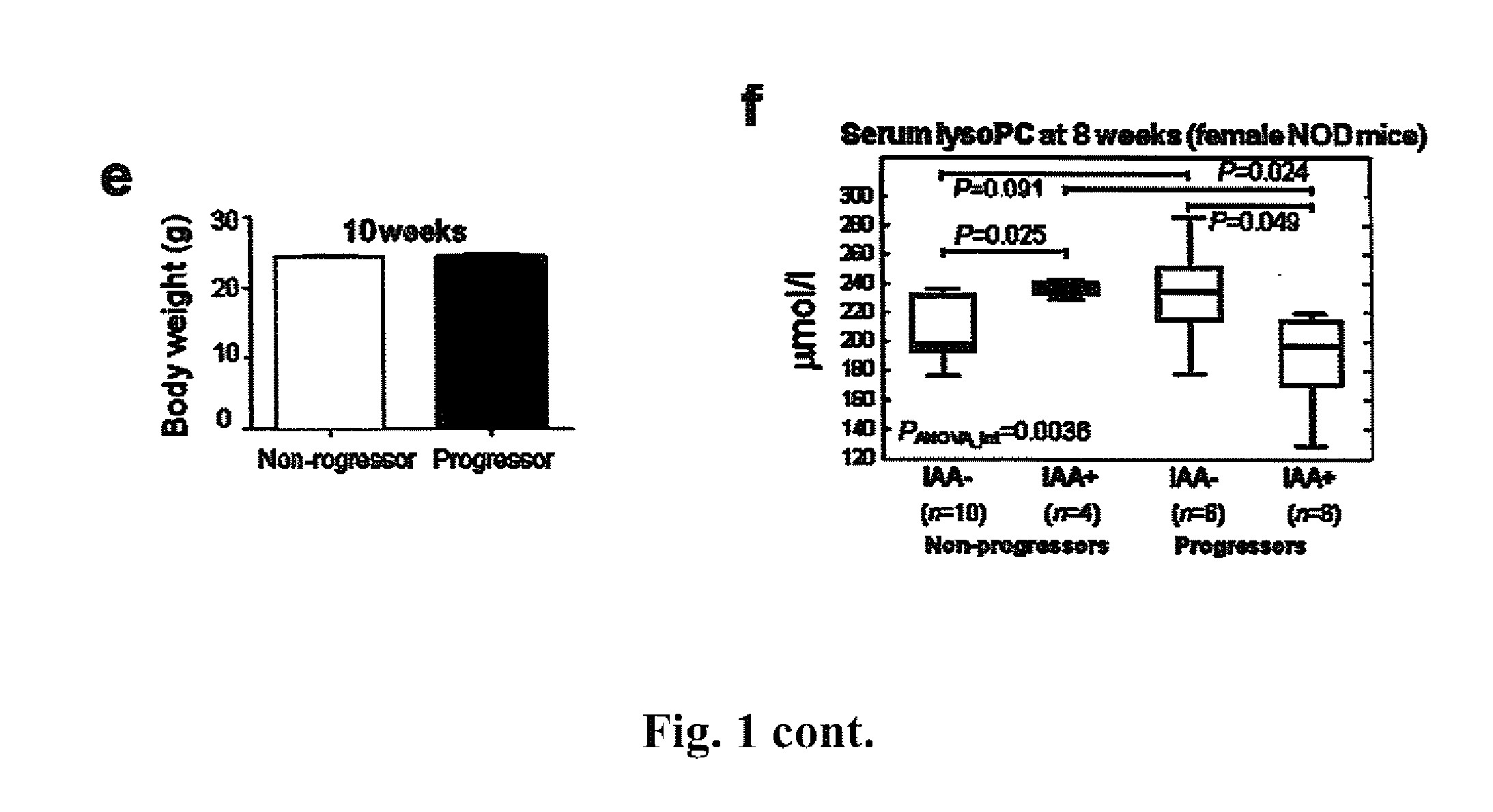
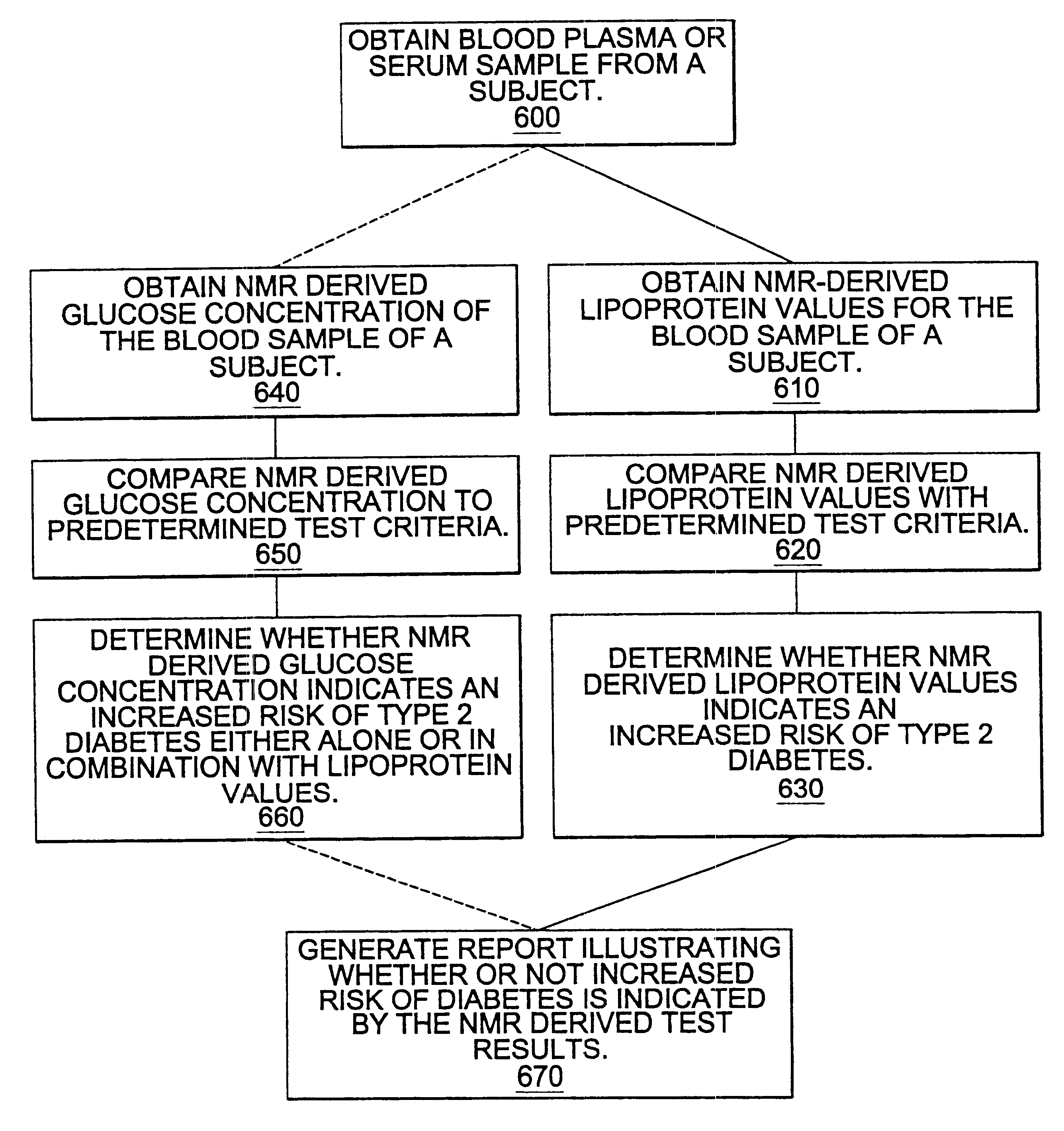
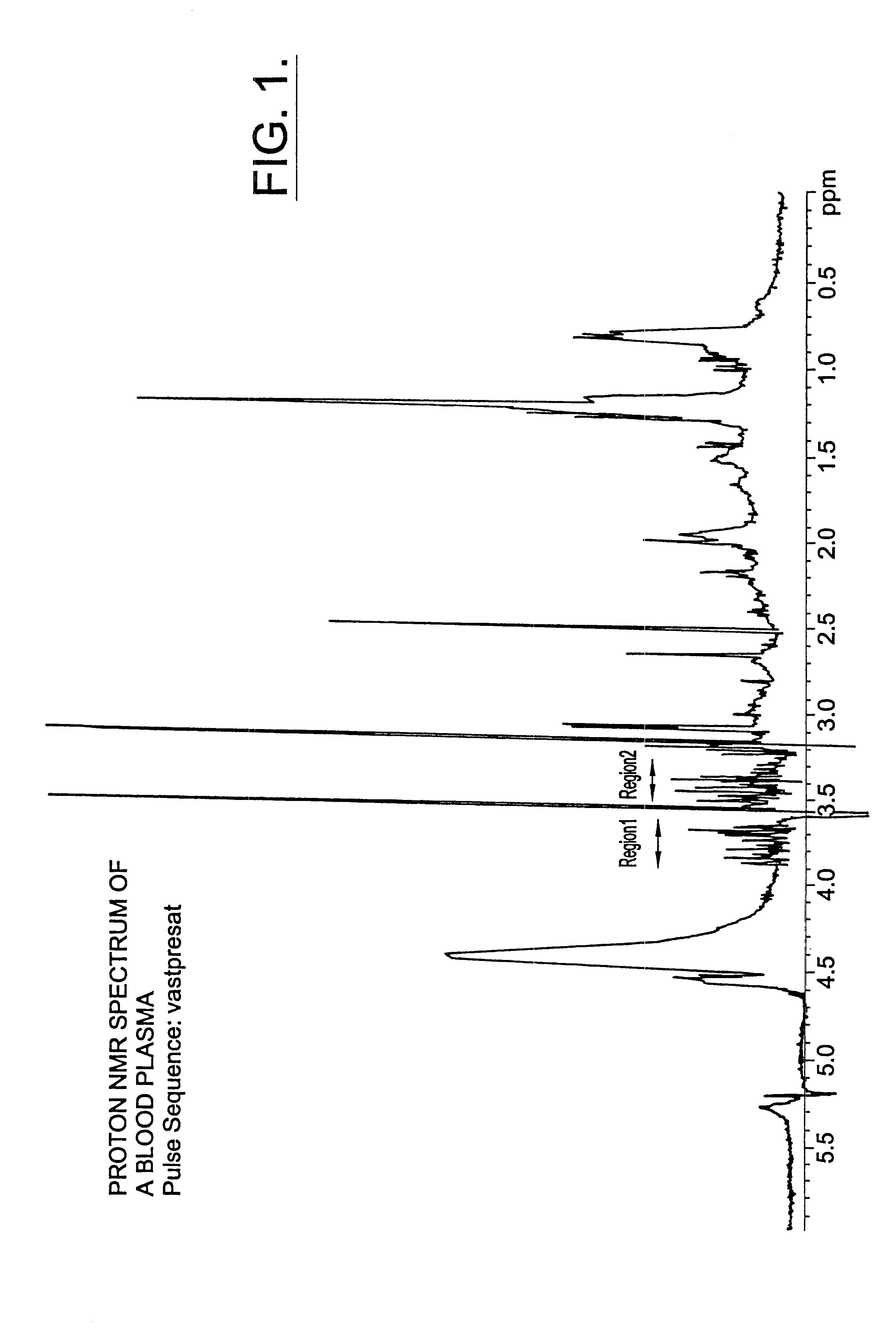
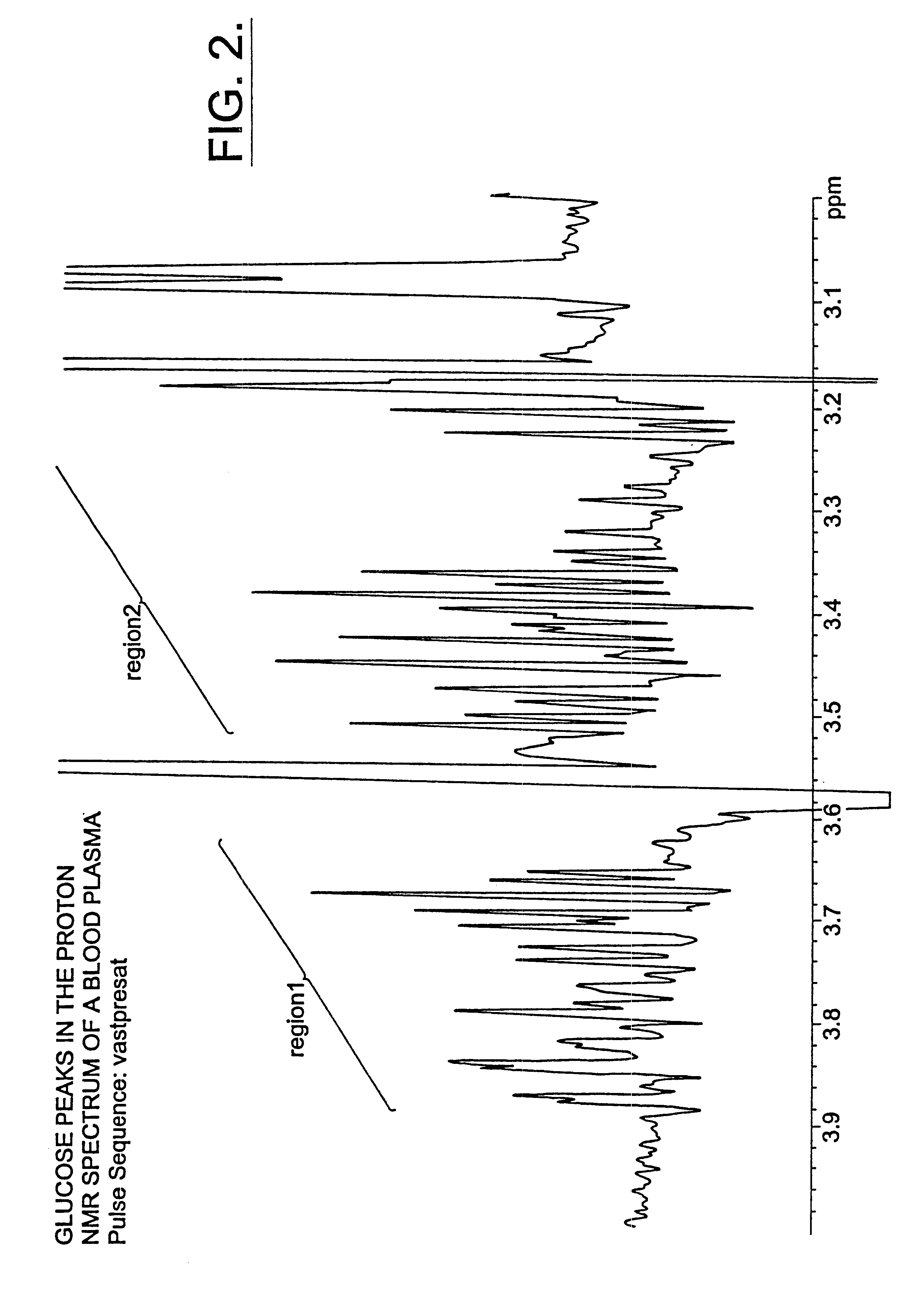
Methods for assessing the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes and other related disorders include obtaining an NMR derived reference spectrum for a known glucose concentration sample and storing this information as a reference standard. A patient blood sample is collected and NMR derived patient spectrums for the blood sample are obtained. The two NMR data sets (the reference and the patient) are compared and a glucose concentration is determined for the patient sample. The glucose concentration can be evaluated with a blood sample undergoing lipoprotein cholesterol evaluation. The NMR based test can be used to concurrently provide a glucose concentration and lipoprotein constituent values based on a single testing event. The disclosure also includes a multi-purpose test, i.e., a test which concurrently provides lipoprotein screening and coronary heart disease risk evaluation along with a diabetes screening and risk assessment for developing Type 2 diabetes. A method for assessing diabetes includes identifying the presence of diabetic dyslipidemia based on the values of predetermined NMR measured lipoprotein constituents.
Owner:LIPOSCI +1
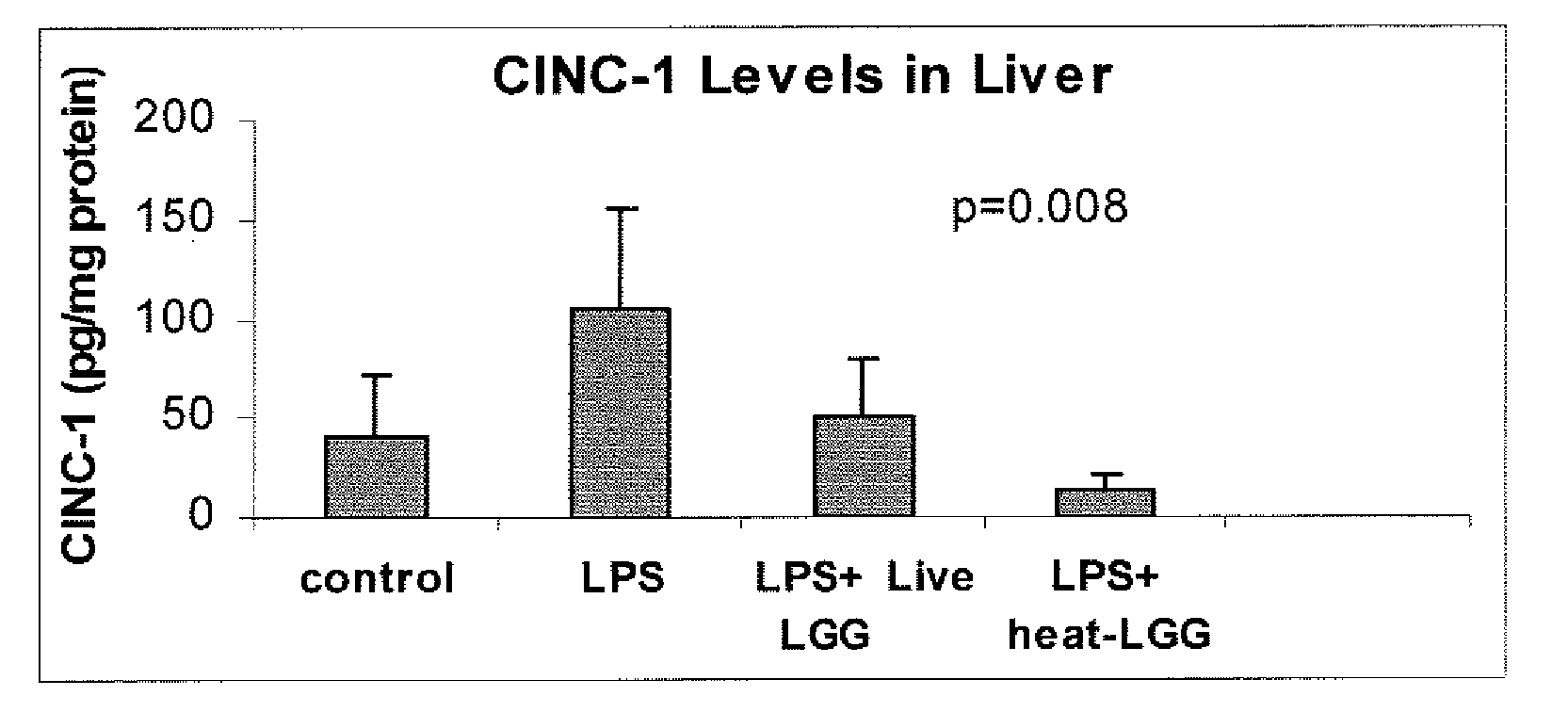
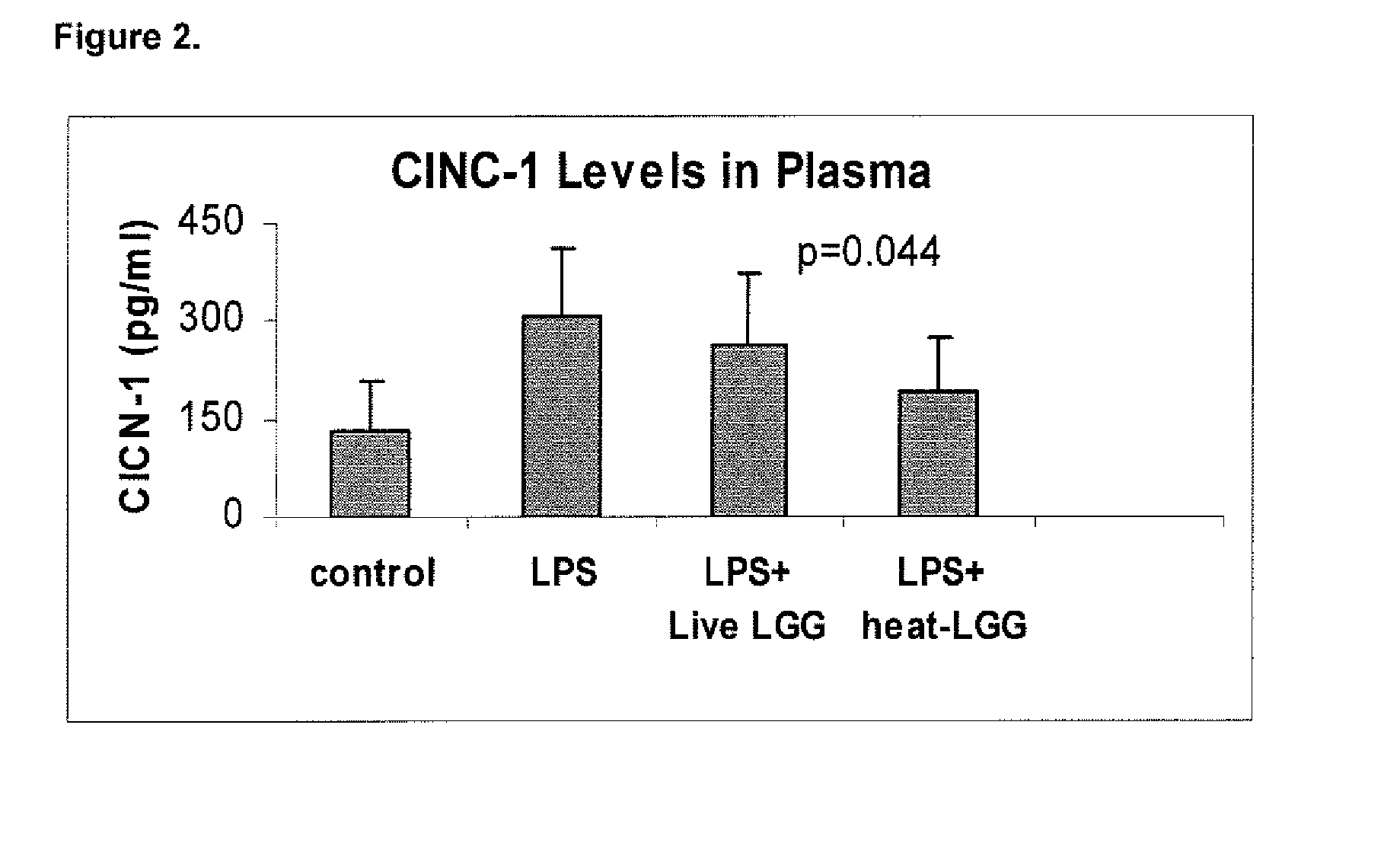
Method for the utilization of and product containing inactivated probiotic
ActiveUS20080206212A1Reduce and prevent systemic and respiratory inflammationReduces prevents releaseBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChemistryProbiotic
Owner:MEAD JOHNSON NUTRITION
B-cell reduction using cd37-specific and cd20-specific binding molecules
The present invention generally provides methods for B-cell reduction in an individual using CD37-specific binding molecules. In particular, the invention provides methods for B-cell reduction using CD37-specific binding molecules alone, or a combination of CD37-specific binding molecules and CD20-specific binding molecules, in some instances a synergistic combination. The invention further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity. In addition, the invention provides humanized CD37-specific binding molecules.
Owner:EMERGENT PRODUCTS DEVELOPMENT SEATTLE LLC
Co-administration of steroids and zoledronic acid to prevent and treat osteoarthritis
ActiveUS8859530B2Reduce productionAvoid seizuresBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsCo administrationCombined Modality Therapy
A combination therapy for treating osteoarthritis is disclosed. The combination therapy includes the co-administration of a steroid and Zoledronic Acid. The coadministration of a steroid decreases the production of cytokines, and, therefore, decreases the pro-inflammatory effects of Zoledronic Acid. The co-administration of Zoledronic Acid with steroids treats osteoarthritis, and helps to prevent the onset of osteoarthritis in patients at risk for osteoarthritis.
Owner:LEVOLTA PHARMA
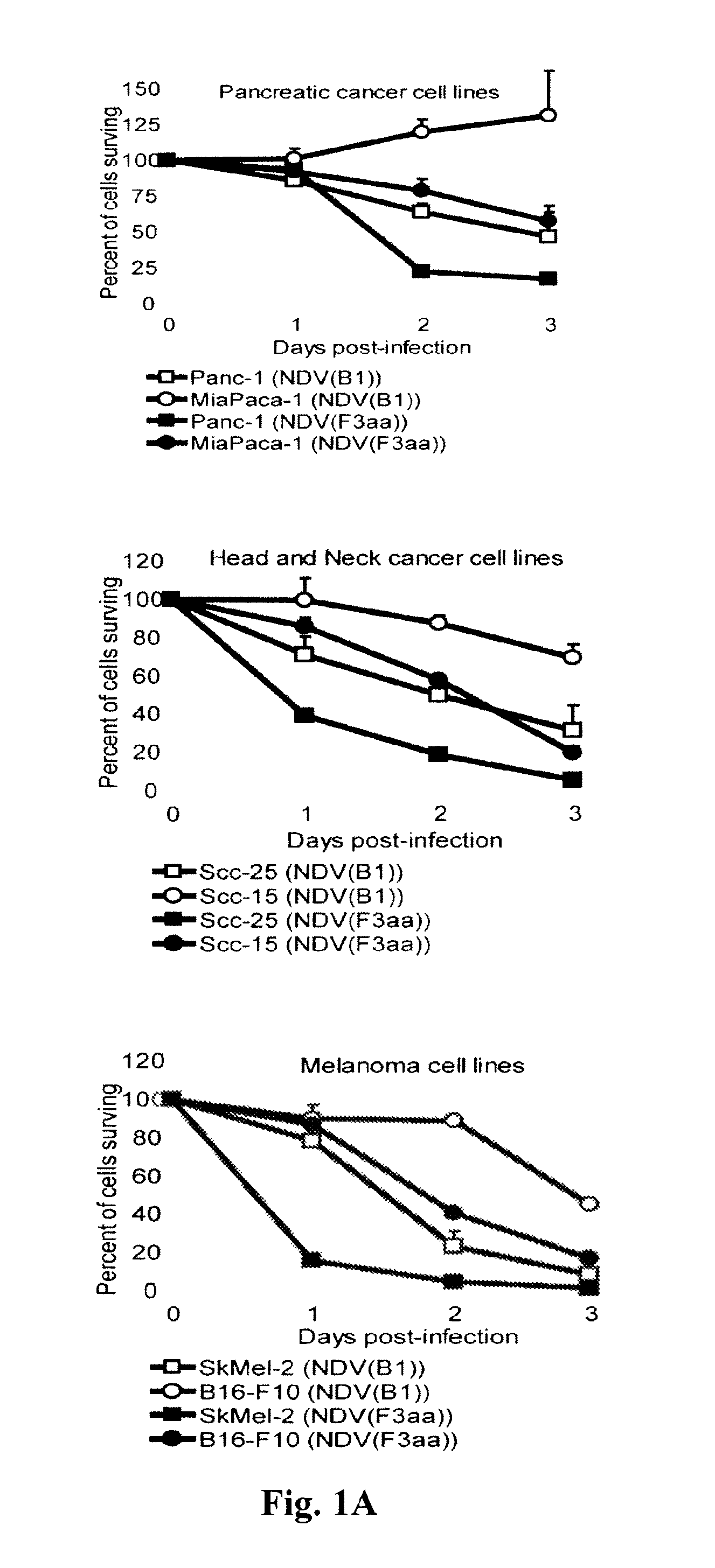
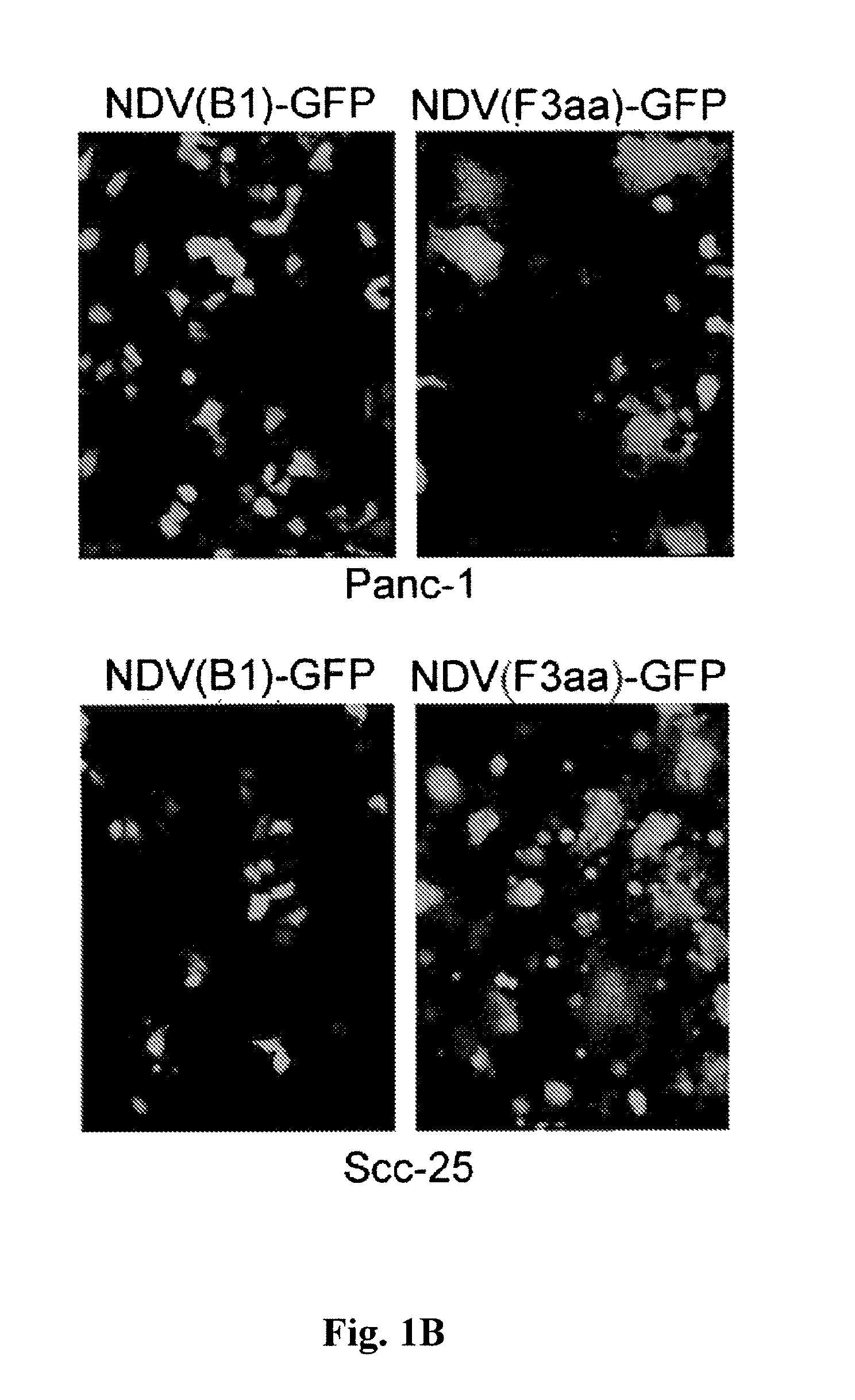
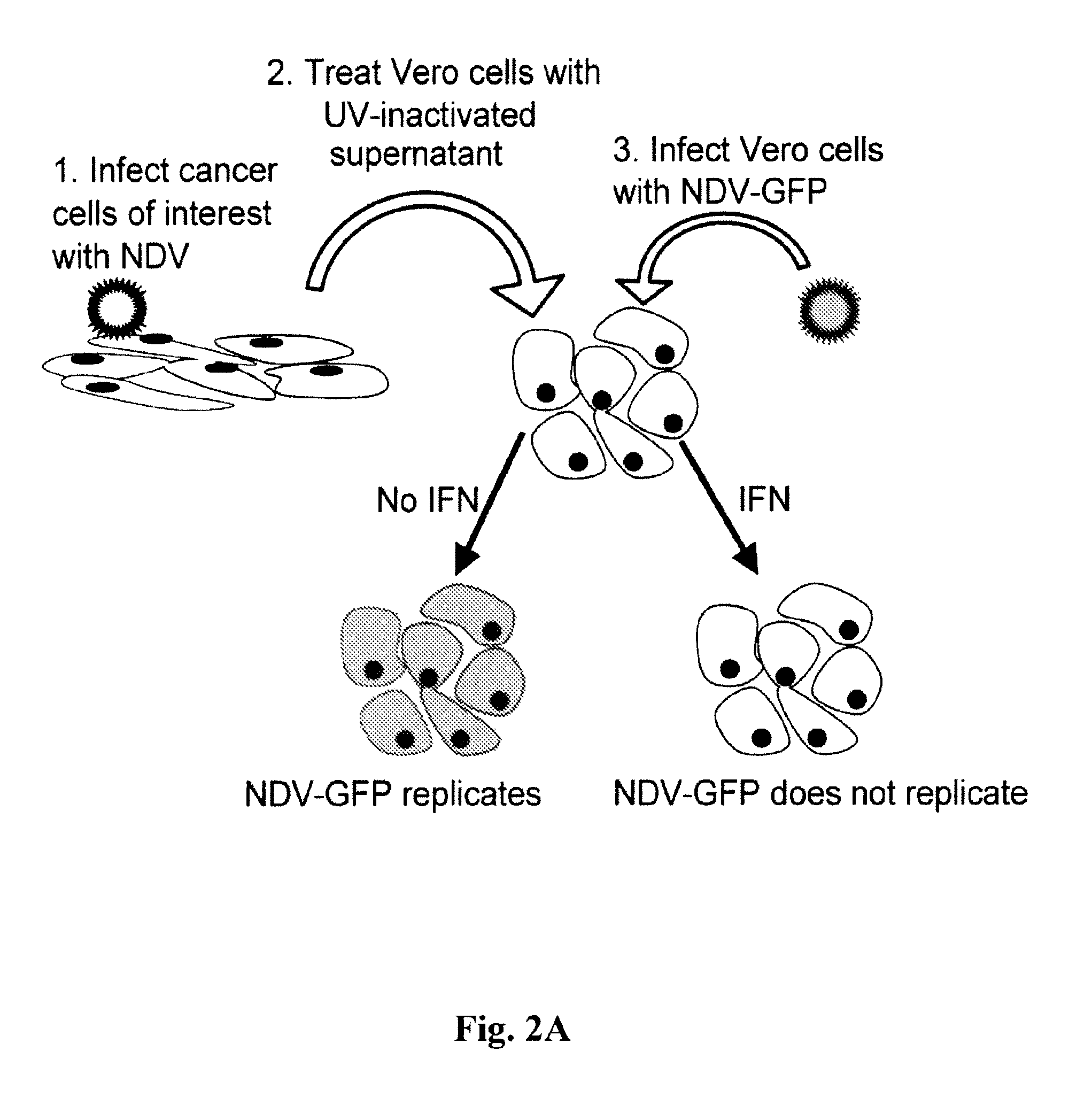
Chimeric Newcastle disease viruses and uses thereof
ActiveUS8591881B2Prevents progression and worseningReduce severitySsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideNewcastle disease virus NDVAntagonist
Described herein are chimeric Newcastle disease viruses engineered to express a heterologous interferon antagonist and compositions comprising such viruses. The chimeric Newcastle disease viruses and compositions are useful in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
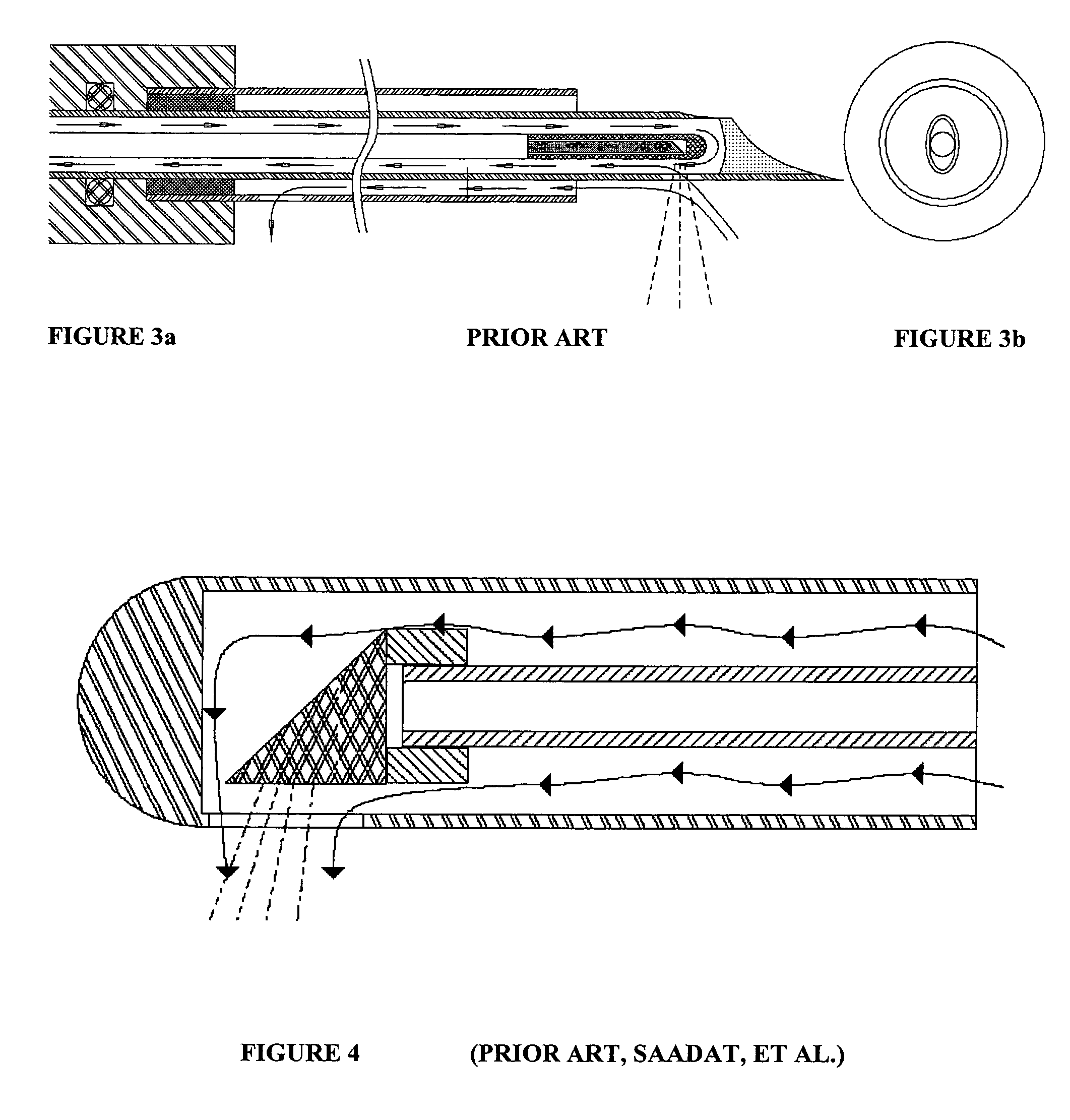
Lateral laser fiber for high average power and peak pulse energy
ActiveUS7909817B2Minimize reflectionAvoid seizuresSurgical instrument detailsFree rotationRefractive index
An improved optical fiber comprising a waveguide with an input for coupling focused laser energy into the waveguide and communicating electromagnetic radiation in a propagation direction to an internally reflective tip of the waveguide, a tissue contacting surface wherein the light path from the reflecting surface to the transmitting surface in substantially homogenous in refractive index and cooled by fluid flow. In minimizing the variations in refractive index within the lateral light path, while providing active cooling directly below the tissue contact surface, the invention prevents internal reflections and beam distortion and greatly improves the efficiency and durability of the laterally directing probe. Free rotation of the tissue contact surface, about the lateral tip, may be provided and tissue vaporization efficiency may be improved by providing a morcellating tool on the tissue contact surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Systems and Methods for Anxiety Treatment Using Neuro-EEG Synchronization Therapy
InactiveUS20090198144A1Symptoms improvedAvoid seizuresElectrotherapyData processing applicationsEeg synchronizationPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Described are methods, devices, and systems for a novel, inexpensive, easy to use therapy for treatment of anxiety. Described are methods and devices to treat anxiety that involves no medication. Methods and devices described herein use alternating magnetic fields to gently “tune” the brain and affect symptoms of anxiety.
Owner:NEOSYNC
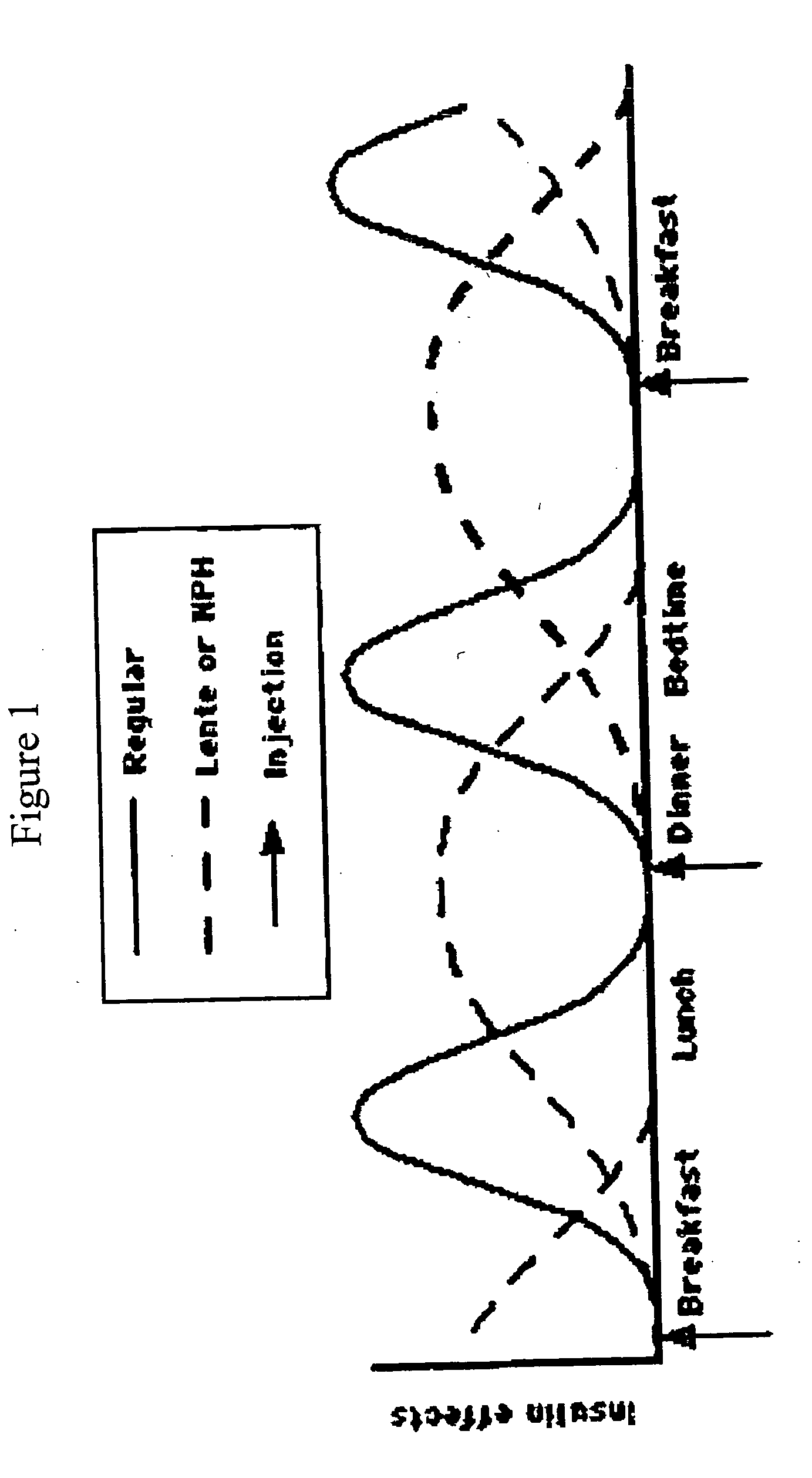
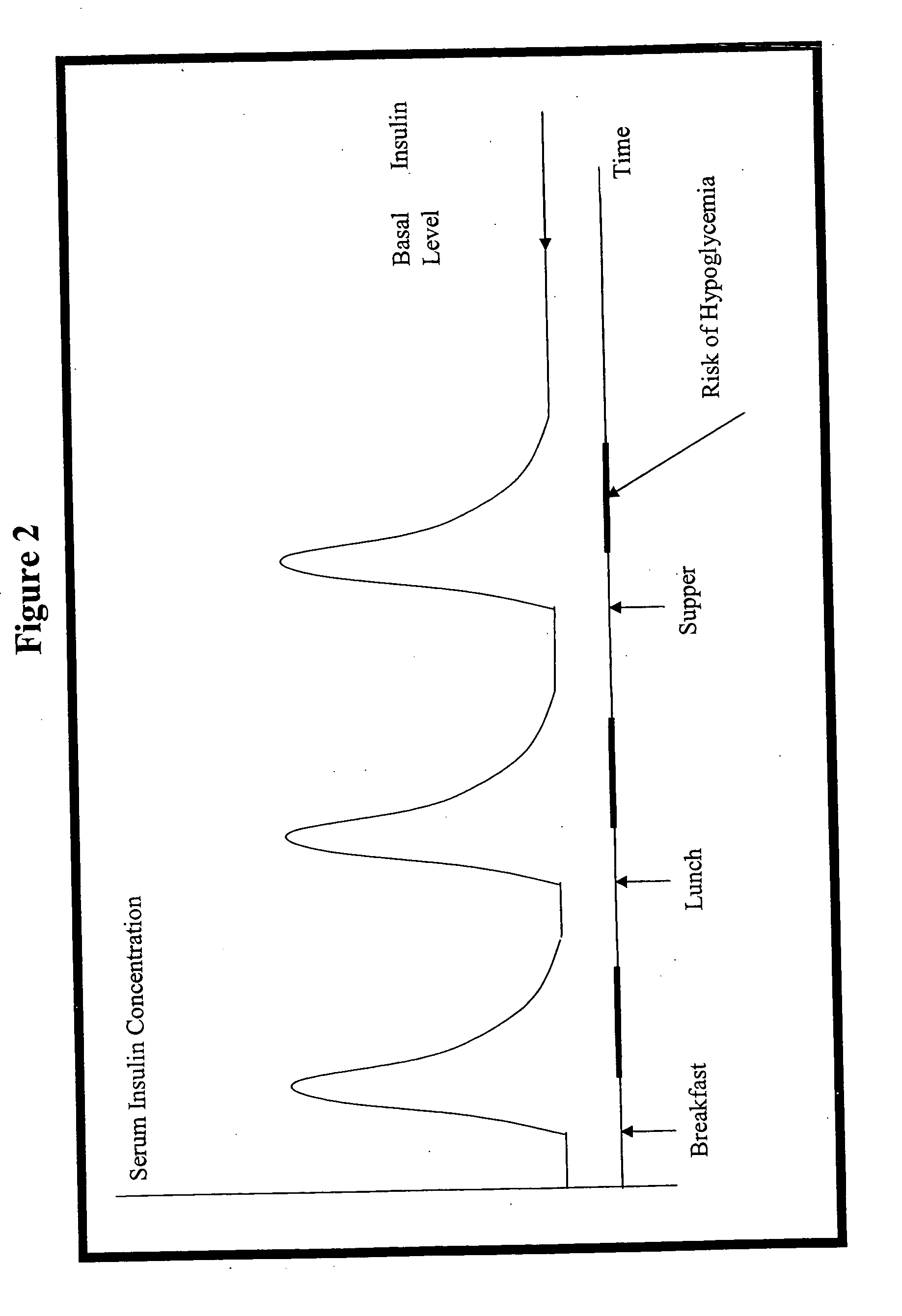
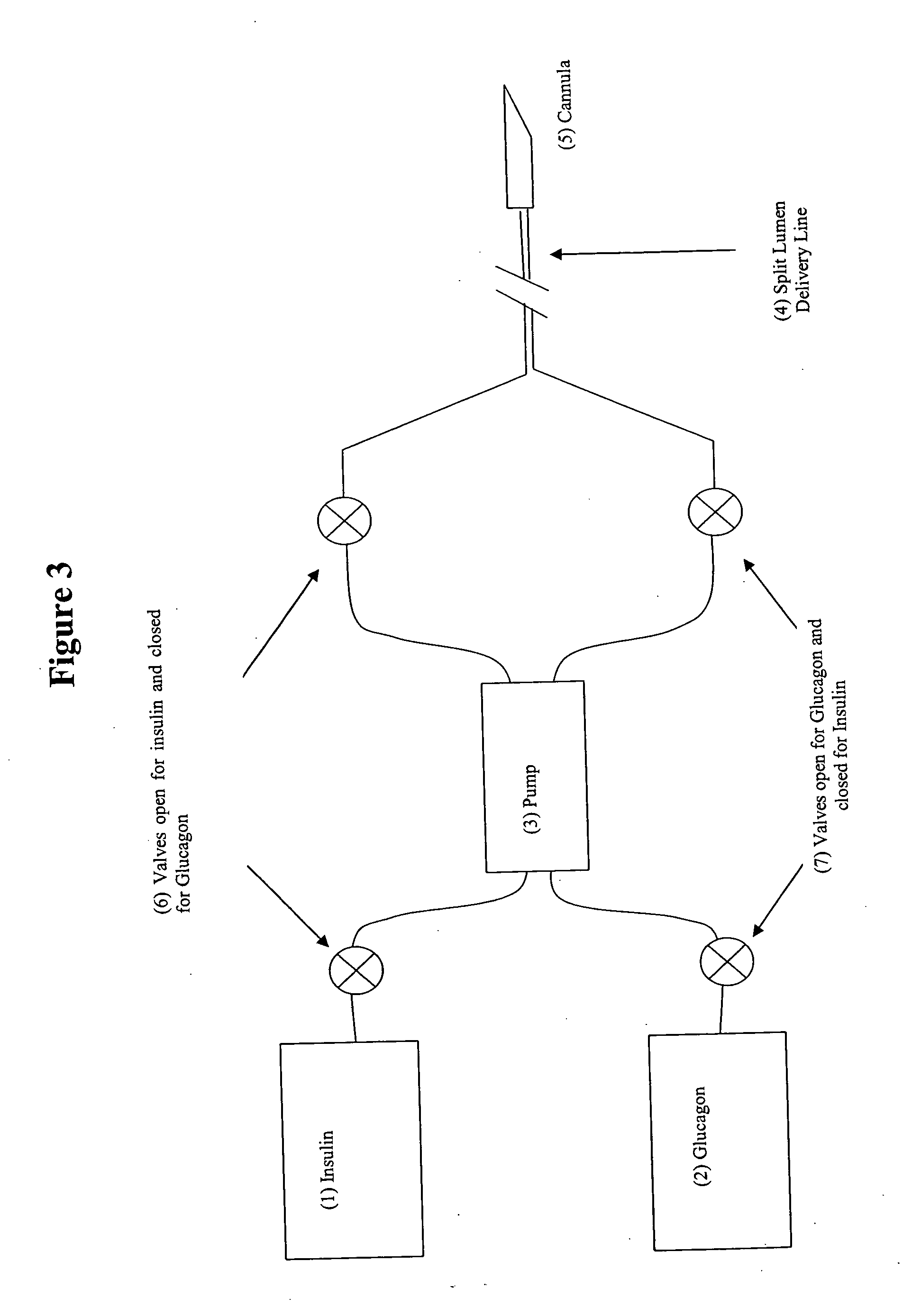
Compositions and methods for the prevention and control of insulin-induced hypoglycemia
InactiveUS20060014670A1Preventing hypoglycemiaPrevents a hypoglycemic eventIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineInsulin induced hypoglycemia
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising both insulin and glucagon can be administered to control and treat diabetes while reducing or eliminating the risk of insulin-induced hypoglycemia.
Owner:ENJECT
Automated adaptive muscle stimulation method and apparatus
ActiveUS7499746B2Easy to integrateEnhancing user comfortElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An automated adaptive muscle stimulation system and method are disclosed. The stimulation system includes at least one electrode assembly adapted to deliver a muscle stimulation signal to the tissue of a user, a sensor system adapted to detect a muscle response, and an electrical stimulation device operably coupled to the at least on electrode assembly and the sensor system, the electrical stimulation device including a control system operable to automatically diagnose at least one characteristic of a muscle from the detected muscle response and adjust at least one parameter of the muscle stimulation signal in response thereto to deliver an adjusted muscle stimulation signal. A dual mode muscle stimulation system adapted to accept first and second data sets and provide first and second levels of treatment data is also disclosed.
Owner:DJO GLOBAL SWITZERLAND SARL
Compositions including krill extracts and conjugated linoleic acid and methods of using same
InactiveUS20060078625A1Reduce disease riskAvoid seizuresBiocideAnthropod material medical ingredientsMedicineKrill
Methods and compositions for the prevention, therapy and / or treatment of several disease states. The methods comprise the administration of a therapeutically effective amount of a composition including krill extract and conjugated linoleic acid. In addition, the present invention provides new and improved therapeutic compositions including krill extracts and conjugated linoleic acid.
Owner:PHARMANUTRIENTS
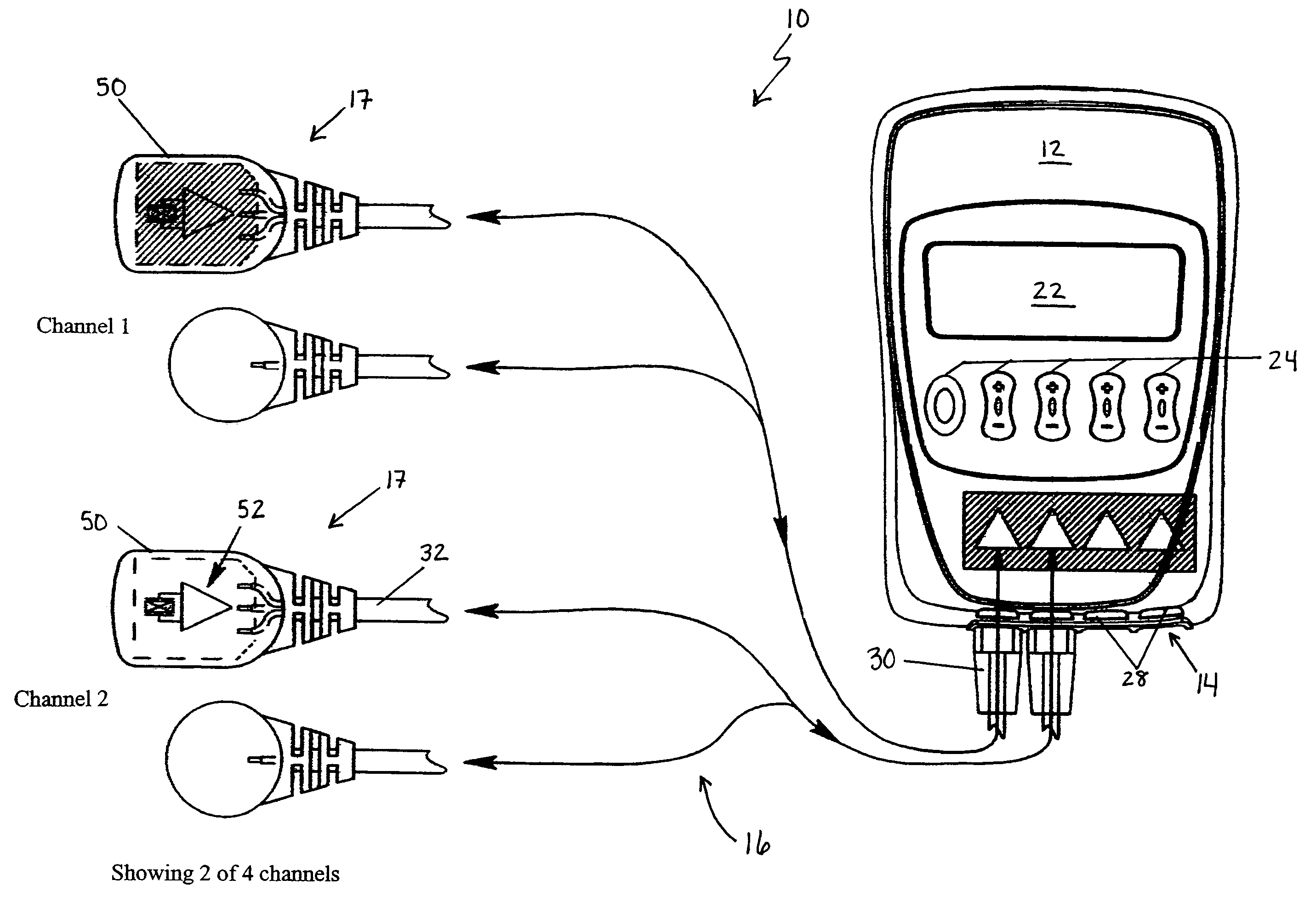
Body-worn sensor for characterizing patients with heart failure
ActiveUS20140187990A1Easy to coverSimple and low-costElectrocardiographySensorsA d converterEngineering
The invention provides a sensor for measuring both impedance and ECG waveforms that is configured to be worn around a patient's neck. The sensor features 1) an ECG system that includes an analog ECG circuit, in electrical contact with at least two ECG electrodes, that generates an analog ECG waveform; and 2) an impedance system that includes an analog impedance circuit, in electrical contact with at least two (and typically four) impedance electrodes, that generates an analog impedance waveform. Also included in the neck-worn system are a digital processing system featuring a microprocessor, and an analog-to-digital converter. During a measurement, the digital processing system receives and processes the analog ECG and impedance waveforms to measure physiological information from the patient. Finally, a cable that drapes around the patient's neck connects the ECG system, impedance system, and digital processing system.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
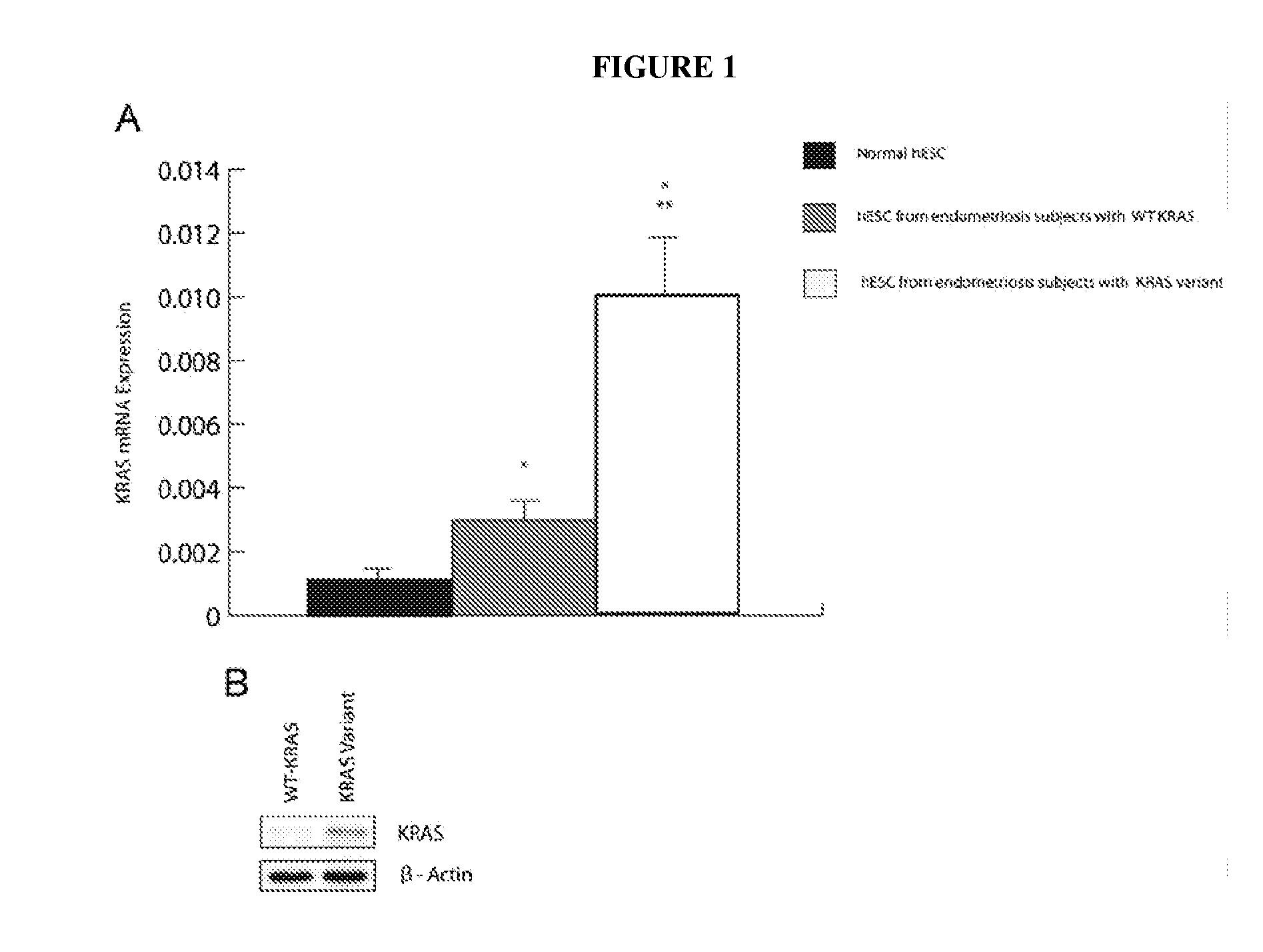
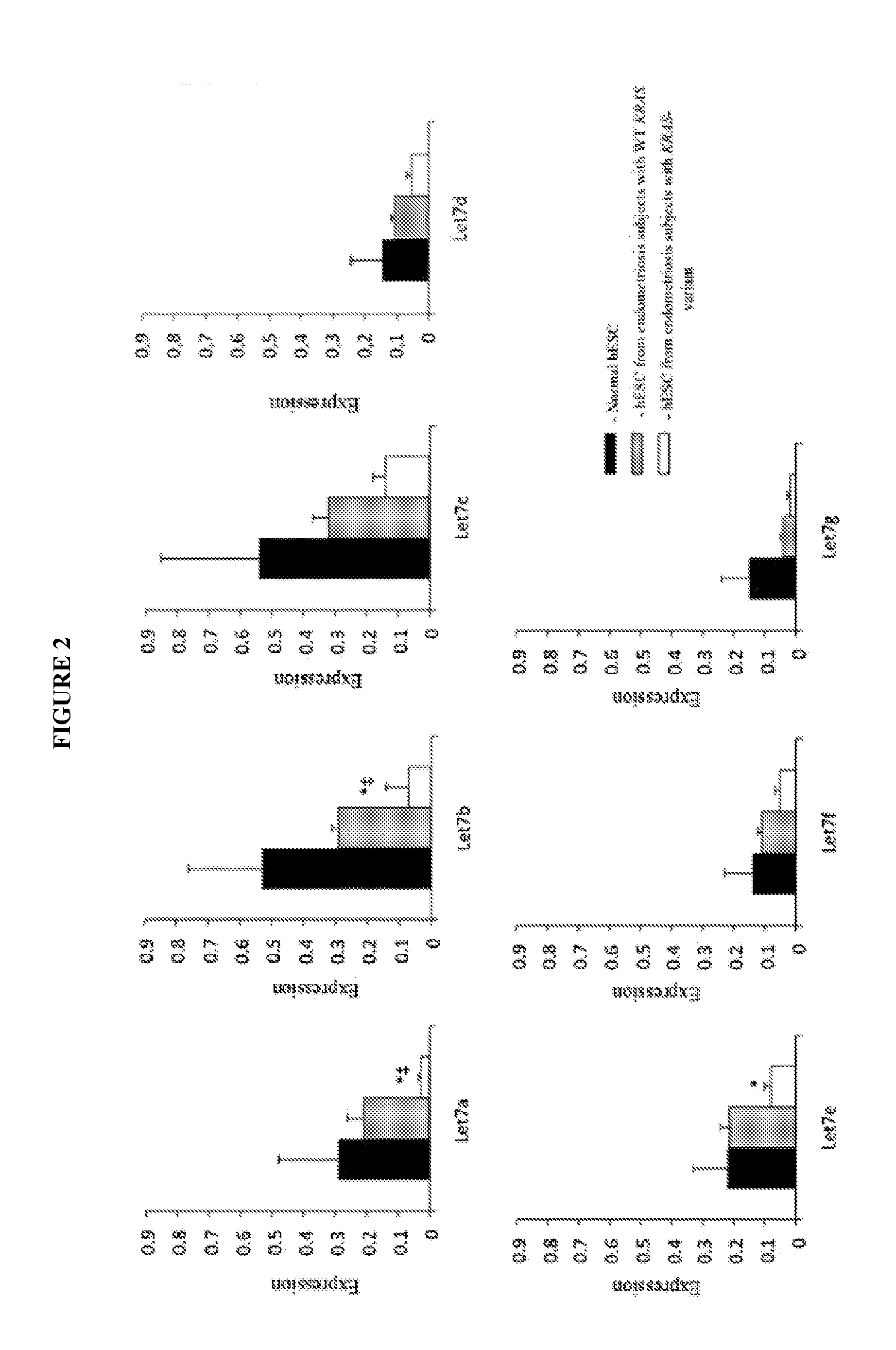
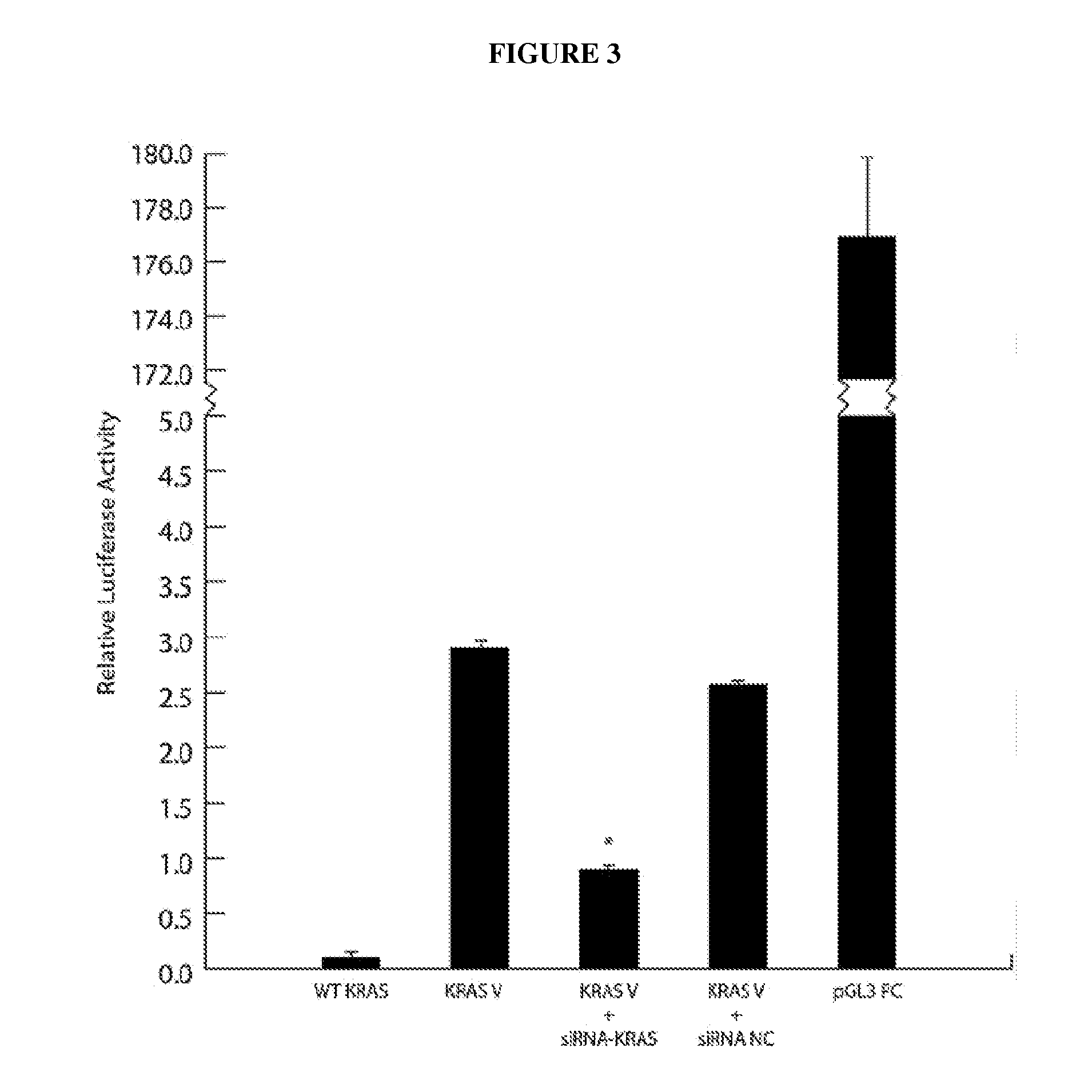
KRAS-Variant And Endometriosis
InactiveUS20140024590A1Prevent onset of endometriosisIncrease riskHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsIncreasing riskEndometriosis
The invention provides methods for predicting an increased risk or probability of developing endometriosis in a patient based upon the patient's KRAS variant status.
Owner:YALE UNIV
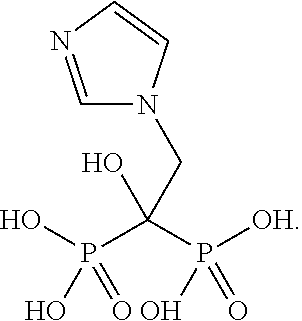
Chromium compositions and methods for using the same for inhibiting drug-induced insulin resistance
InactiveUS20050214384A1Avoid seizuresAvoid developmentBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsDietary ChromiumInsulin resistance
A method for inhibiting drug-induced insulin resistance is provided which includes administering a dietary chromium complex to an individual receiving a contemporaneous dose of a drug that induces insulin resistance, wherein the amount of chromium complex administered is an amount effective to inhibit the development of insulin resistance. Advantageously, the amount of chromium complex administered per day is between about 300 and 1,000 micrograms per day. Compositions including a drug which induces insulin resistance in combination with a chromium complex are similarly described.
Owner:N21 ACQUISITION HLDG
Methods and compositions for treating polycystic ovary syndrome
InactiveUS7105489B2Reduce insulin resistanceIncrease insulin sensitivityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxy compound active ingredientsPhysiologyGlucagon-like peptide-1
The present invention relates to methods of treating polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) comprising administering glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) to subjects suffering therefrom.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
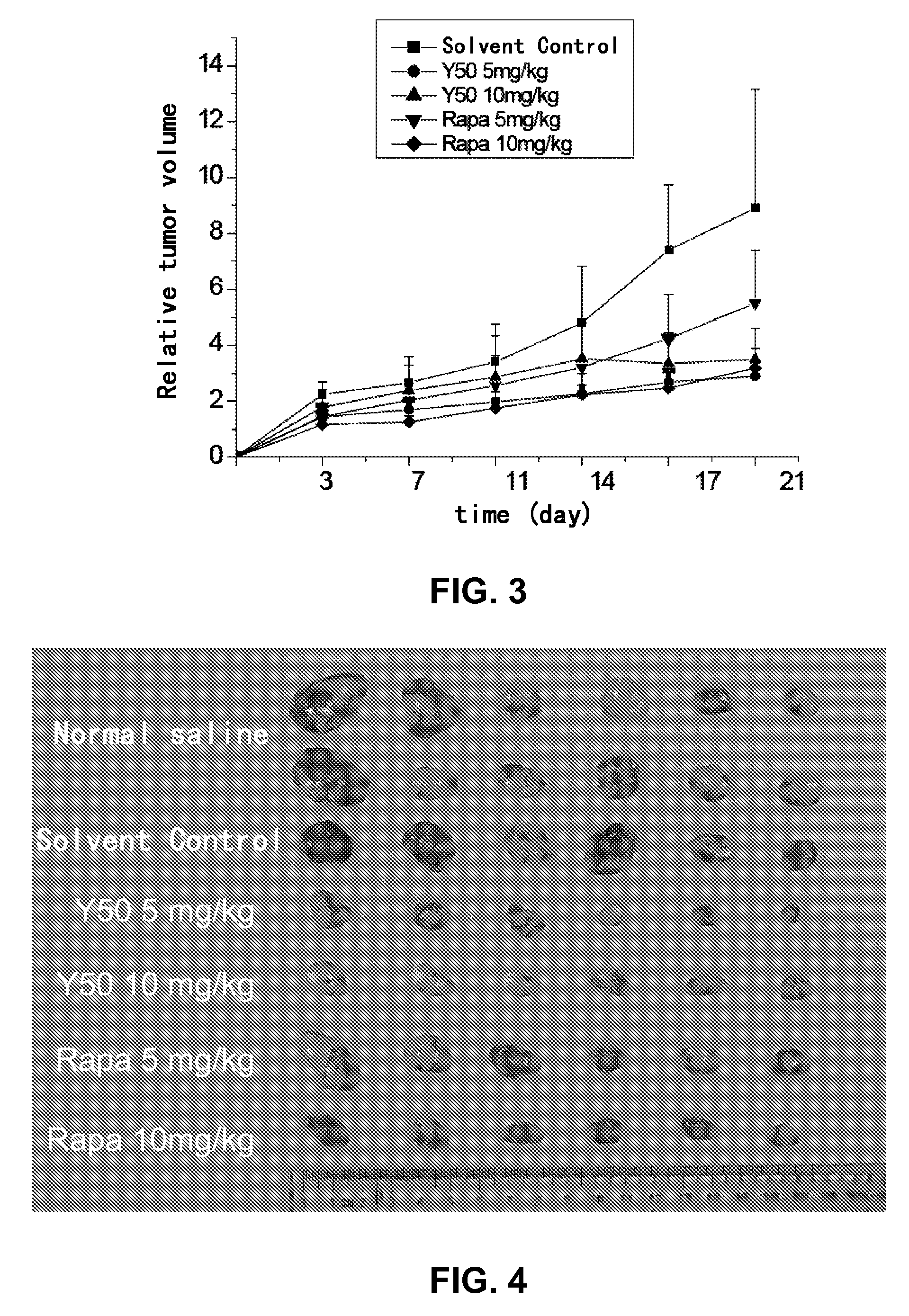
Rapamycin carbonic ester analogues, pharmaceutical compositions, preparations and uses thereof
InactiveUS8455510B2Superior anti-tumor and anti-cancer activitiesImproved pharmacokinetic propertiesBiocideOrganic chemistrySolubilityWater soluble
Rapalogs of formula I, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, pharmaceutical compositions, and preparation methods and uses thereof. The rapalogs have the structure of formula I and can be used as an anti-tumor medicament. Comparing with rapamycin, the rapalogs of the present invention exhibit enhanced water solubility, and improved pharmacological and pharmacokinetic properties by introducing a hydrophilic and polar group such as a hydroxyl.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
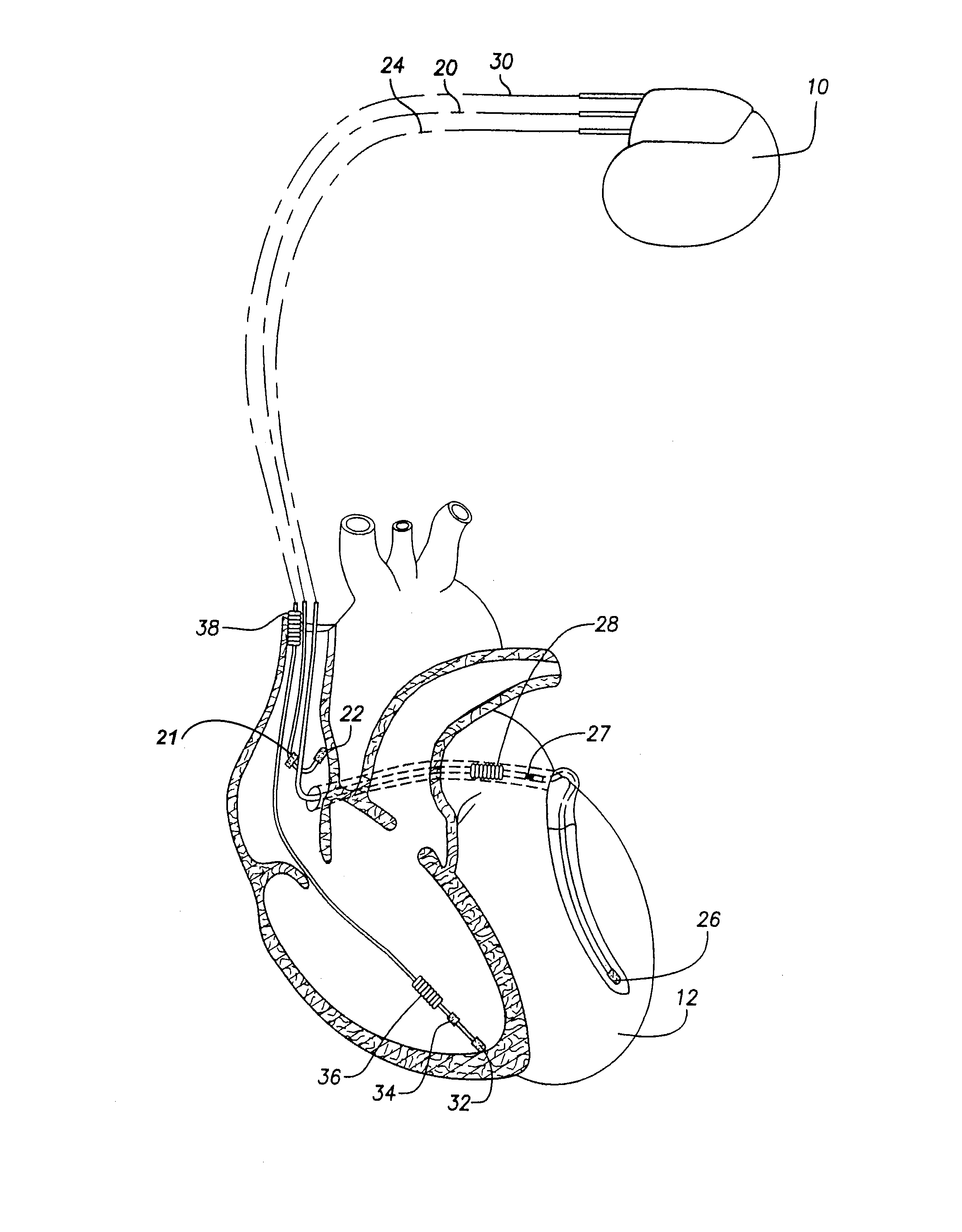
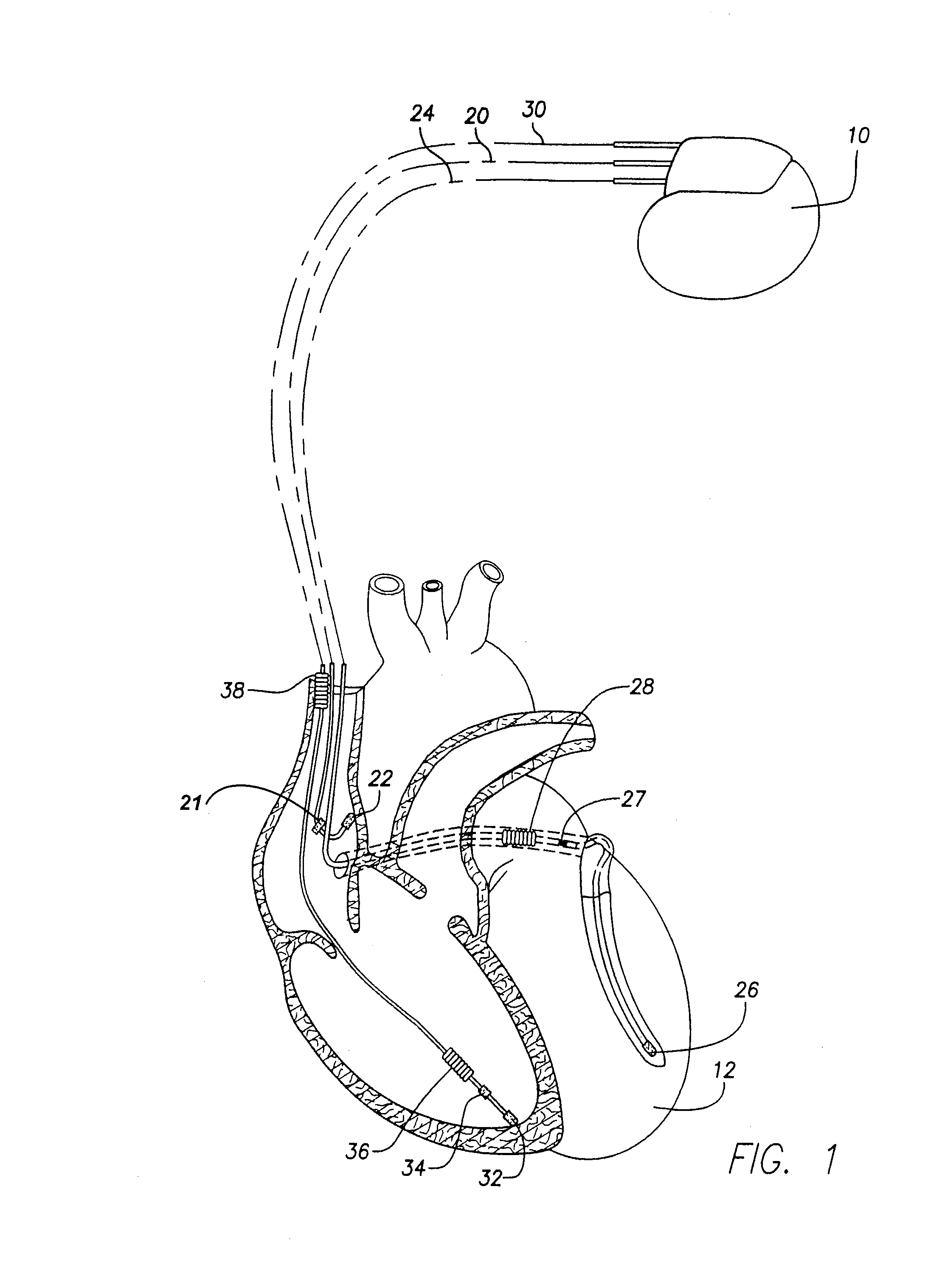
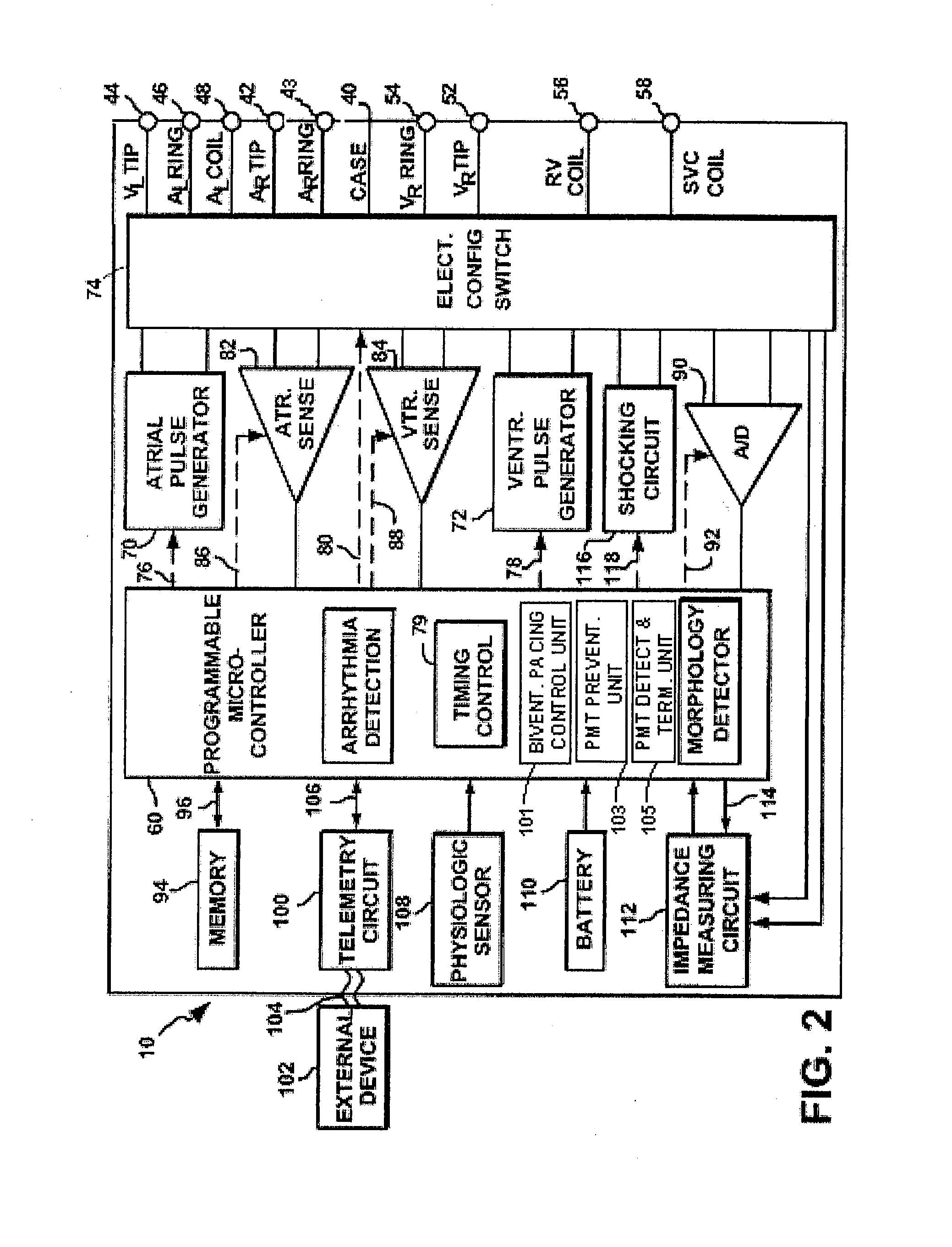
Systems and methods for preventing, detecting, and terminating pacemaker mediated tachycardia in biventricular implantable cardiac stimulation systems
Various techniques are described for preventing pacemaker mediated tachycardia (PMT) within biventricular pacing systems and for detecting and terminating PMT should it nevertheless arise. In a first prevention technique, refractory periods applied to the atrial channel are synchronized to begin with a second of a pair of ventricular pacing pulses to more effectively prevent T-wave oversensing on the atrial channel. In a second prevention technique, the sensitivity of the atrial channel is reduced during T-waves also to prevent T-wave oversensing. In a third prevention technique, template matching is performed on the ventricular channels to prevent T-wave oversensing. In a fourth prevention technique, T-wave detection windows are applied to both the ventricular and atrial channels subsequent to any paced or sensed events. In a first detection technique, PMT is detected based upon a degree of variation within V-pulse to P-wave pacing intervals. In a second detection technique, PMT is detected based upon a degree variation within ventricular pacing intervals. In either case, if the degree of variation is too low, indicative of PMT, ventricular refractory periods are expanded to terminate the PMT.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
B-Cell Reduction Using CD37-Specific and CD20-Specific Binding Molecules
The present invention generally provides methods for B-cell reduction in an individual using CD37-specific binding molecules. In particular, the invention provides methods for B-cell reduction using CD37-specific binding molecules alone, or a combination of CD37-specific binding molecules and CD20-specific binding molecules, in some instances a synergistic combination. The invention further provides materials and methods for treatment of diseases involving aberrant B-cell activity. In addition, the invention provides humanized CD37-specific binding molecules.
Owner:TRUBION PHARM INC
Lateral laser fiber for high average power and peak pulse energy
ActiveUS20060282068A1Minimize reflectionAvoid seizuresSurgical instrument detailsFree rotationActive cooling
An improved optical fiber comprising a waveguide with an input for coupling focused laser energy into the waveguide and communicating electromagnetic radiation in a propagation direction to an internally reflective tip of the waveguide, a tissue contacting surface wherein the light path from the reflecting surface to the transmitting surface in substantially homogenous in refractive index and cooled by fluid flow. In minimizing the variations in refractive index within the lateral light path, while providing active cooling directly below the tissue contact surface, the invention prevents internal reflections and beam distortion and greatly improves the efficiency and durability of the laterally directing probe. Free rotation of the tissue contact surface, about the lateral tip, may be provided and tissue vaporization efficiency may be improved by providing a morcellating tool on the tissue contact surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Sealed crimp connection methods
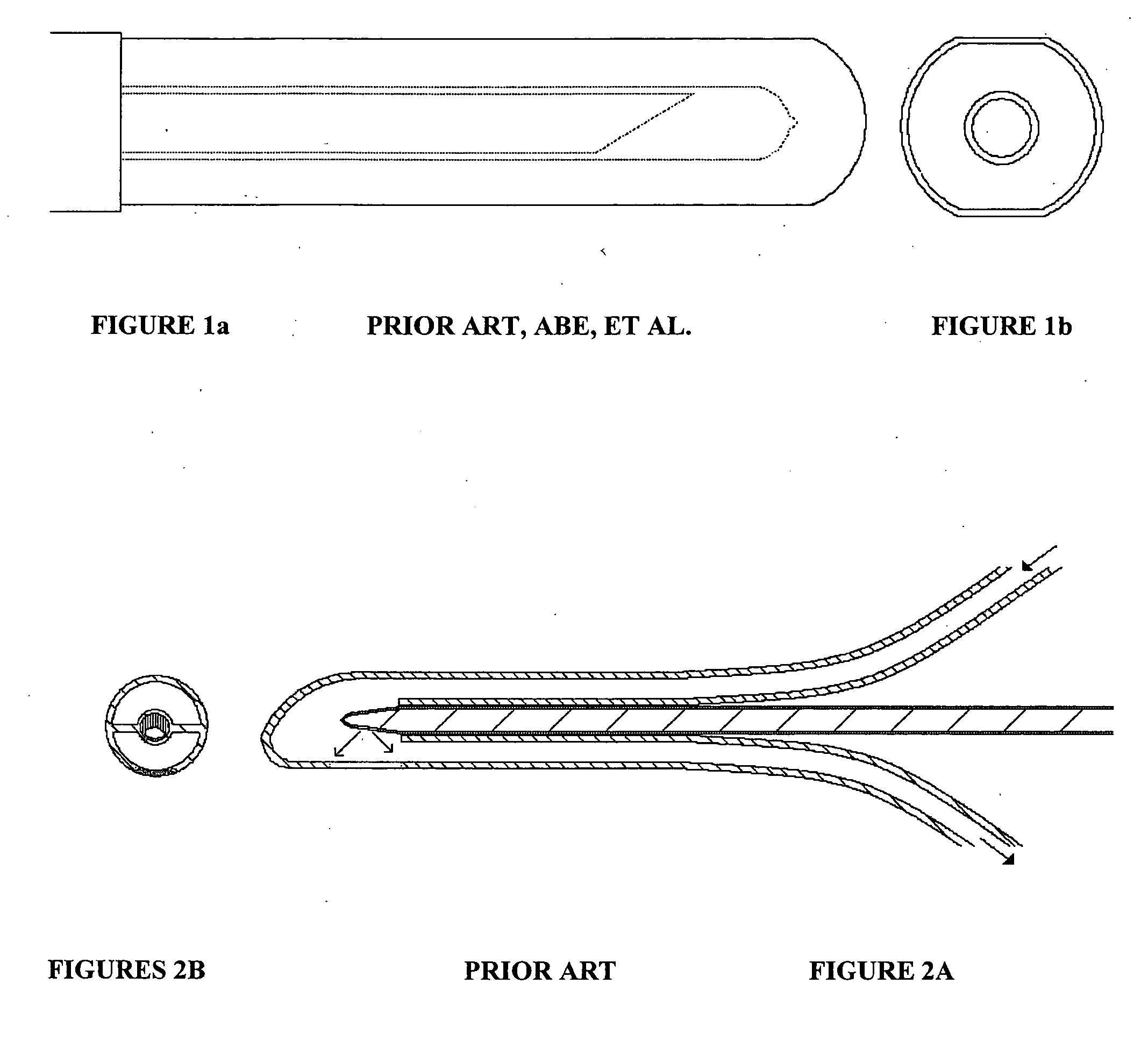
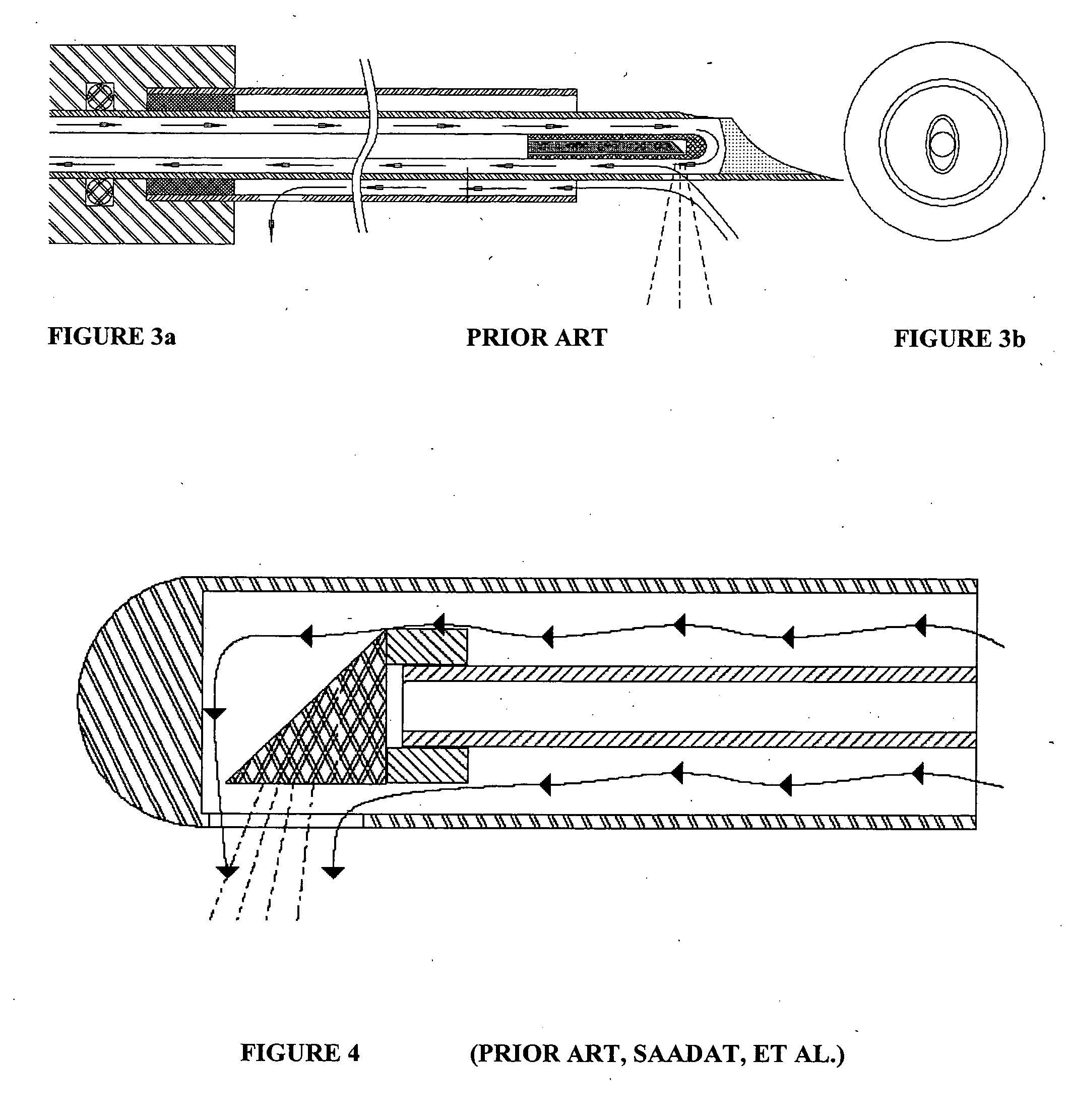
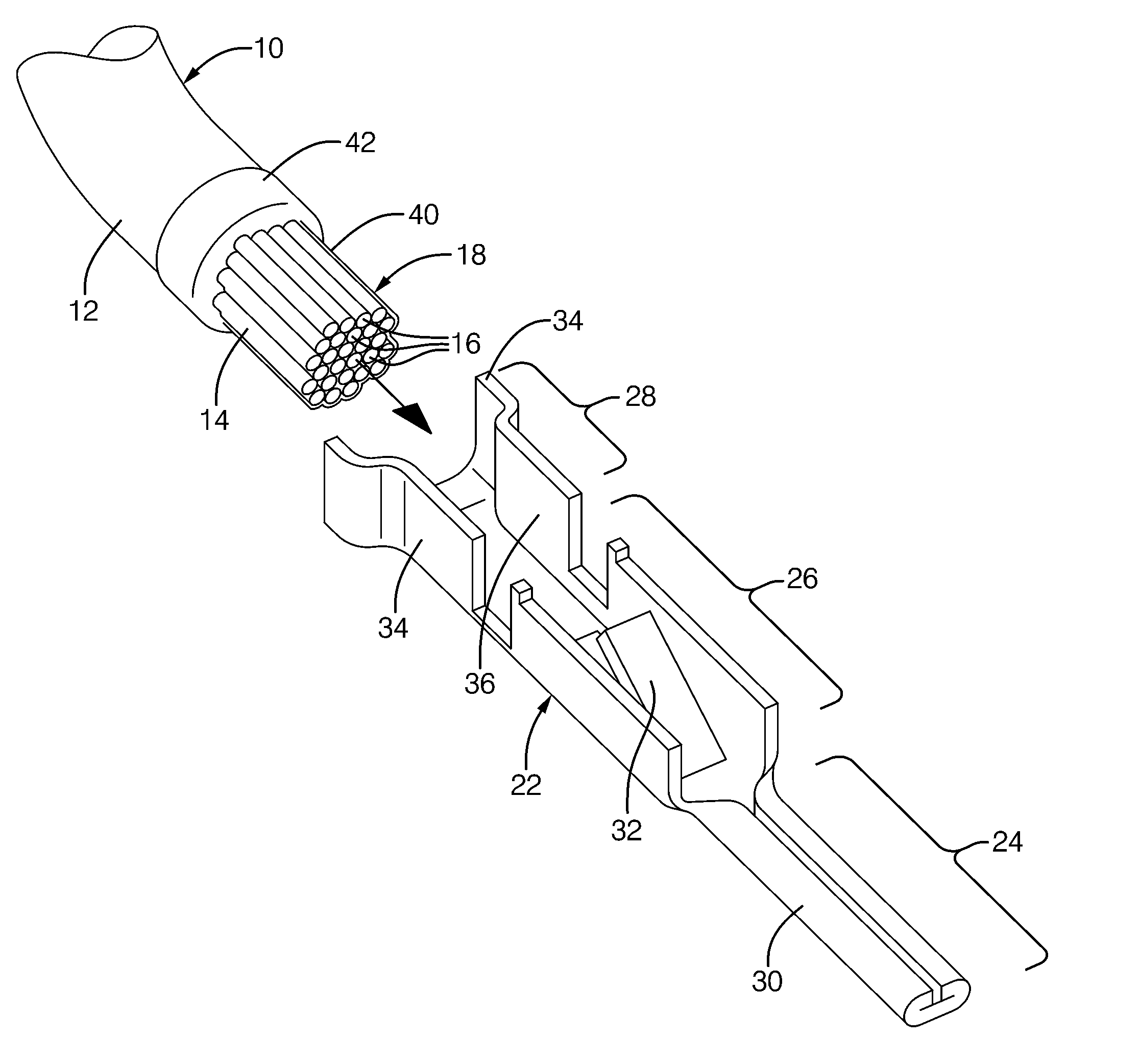
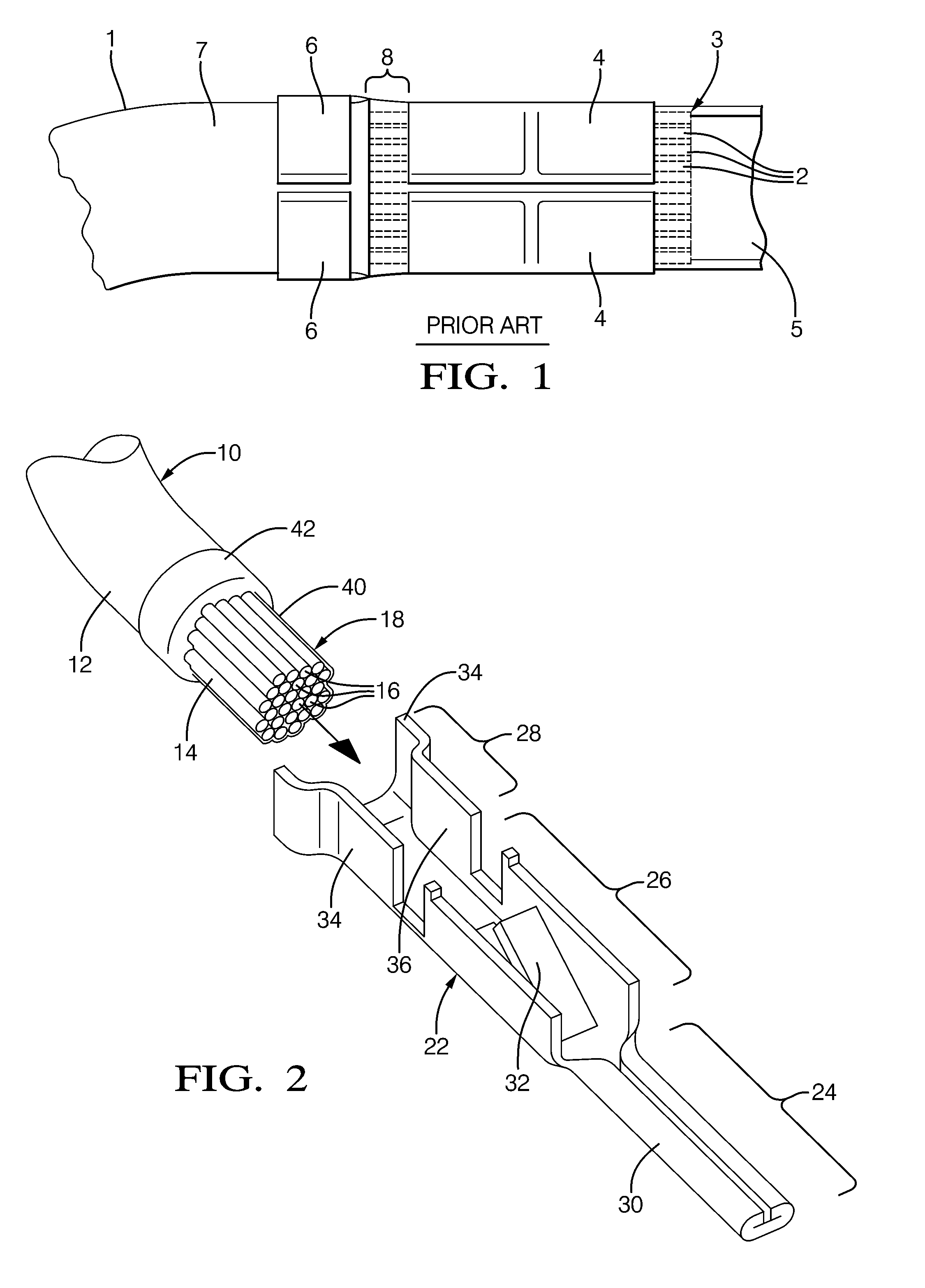
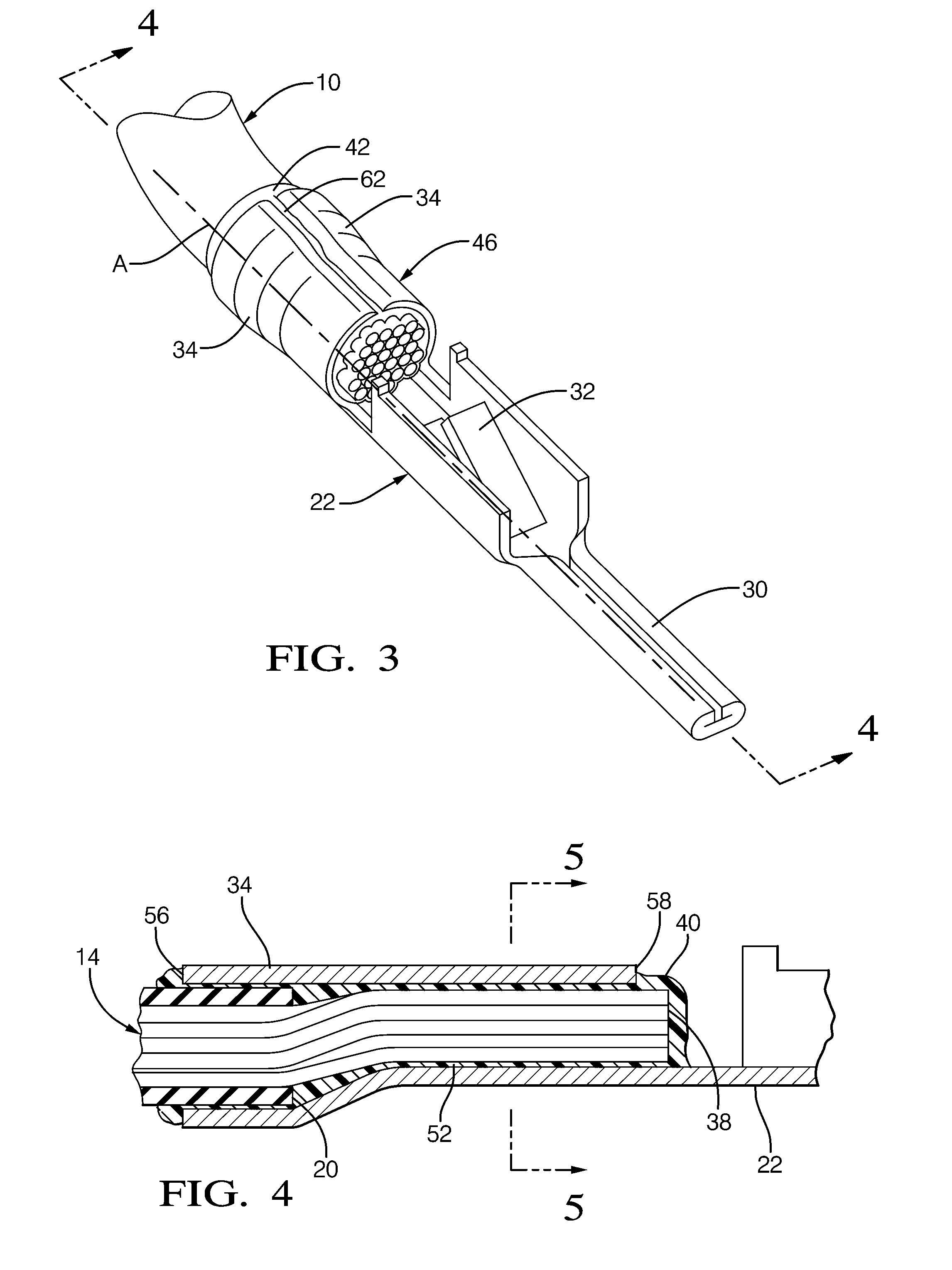
ActiveUS20110083324A1Improve protectionAvoid seizuresCoupling device detailsElectrically conductive adhesive connectionsEngineeringAssembly line
Methods of making a sealed crimp connection attaching a terminal to a wire conductor are provided. A layer of fluid conformal coating is applied to overlie a terminal and underlie at least a lead of the wire conductor upon at least the lead being received into the terminal. The terminal, the fluid layer, and at least the lead of the wire conductor are crimped to form the crimp connection. Fluid conformal coating is displaced where an abutting surface of the terminal makes contact with at least the lead of the wire conductor. The fluid conformal coating is cured to a non-fluid state. The fluid conformal coating may be formed of an acrylated urethane material that may provide an increased pull force and a low crimp resistance in the crimp connection. The crimp connection may be constructed using a manufacturing process on an automated assembly line.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Systems and Methods for Depression Treatment Using Neuro-EEG Synchronization Therapy
ActiveUS20090204015A1Symptoms improvedAvoid seizuresElectrotherapyData processing applicationsEeg synchronizationTreatment use
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
Food products for diabetics
Disclosed is a novel food product characterized by a low glucose or glucose free content, a balanced functional fat content, and a proactive agent aimed for the diabetic and diabetic-prone populations. The food product of the invention is a functional food which may be used clinically to lower the lipid level in people suffering from an imbalanced lipid profile and which may progress towards diabetes complications and coronary vascular disorders. In particular embodiments the proactive agent can be any of a naturally occurring lipid, a synthetic or mimetic lipid which is not digestible by humans and interferes with body weight gain / loss, plant extracts and substances derived therefrom, antioxidants, animal-derived substances, minerals and pharmaceuticals, and any mixture thereof.
Owner:ENZYMOTEC
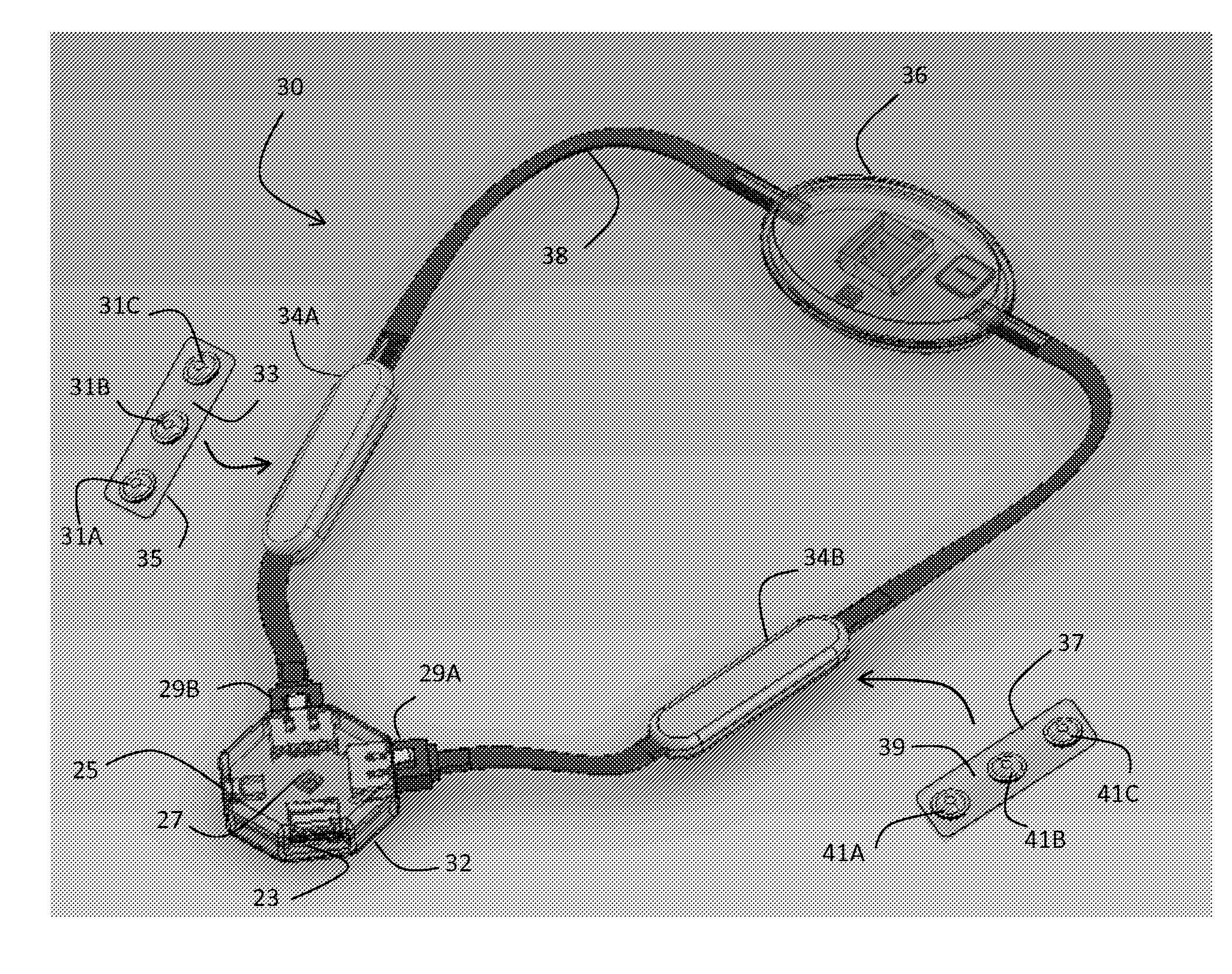
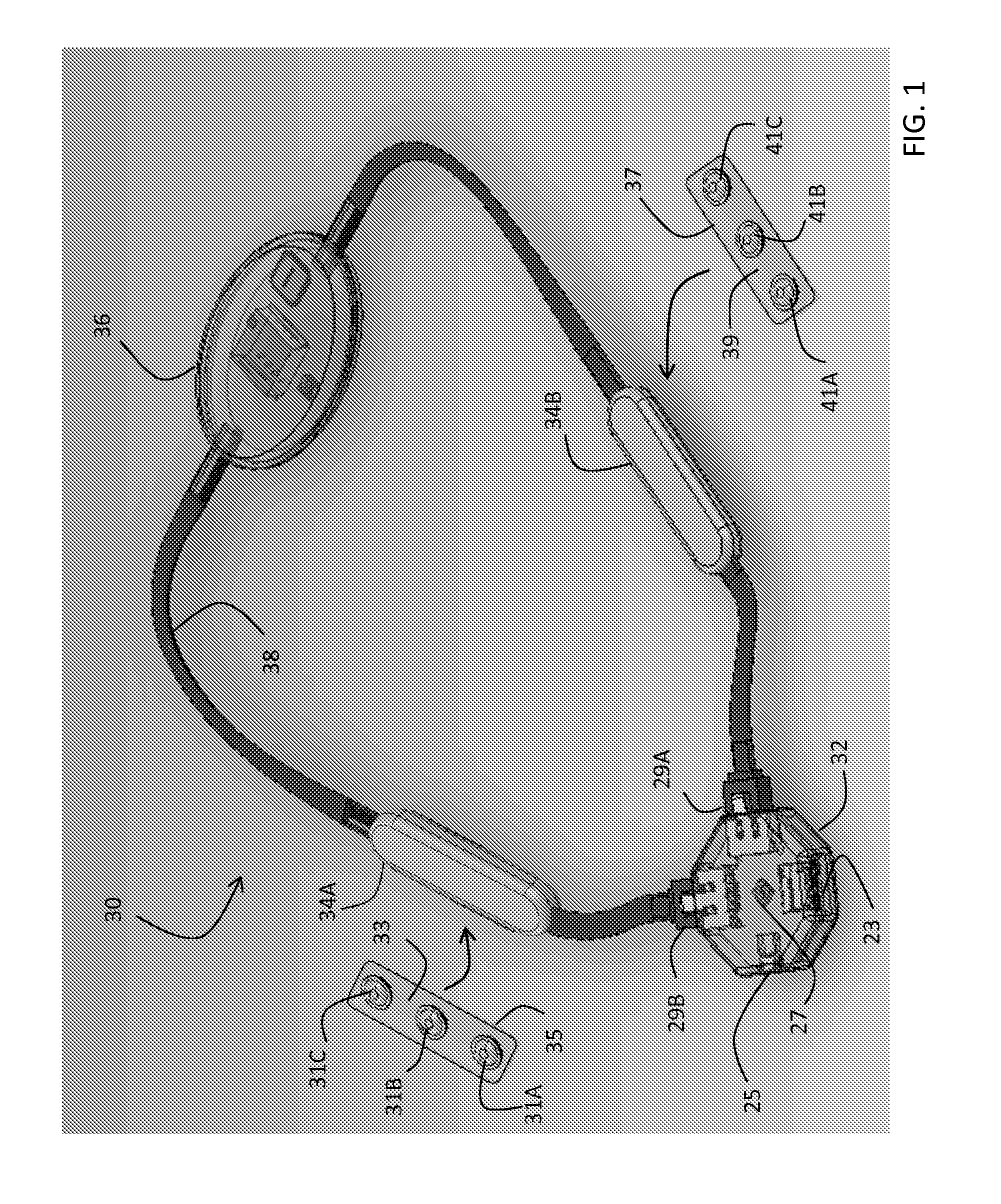
Closed-loop vagus nerve stimulation
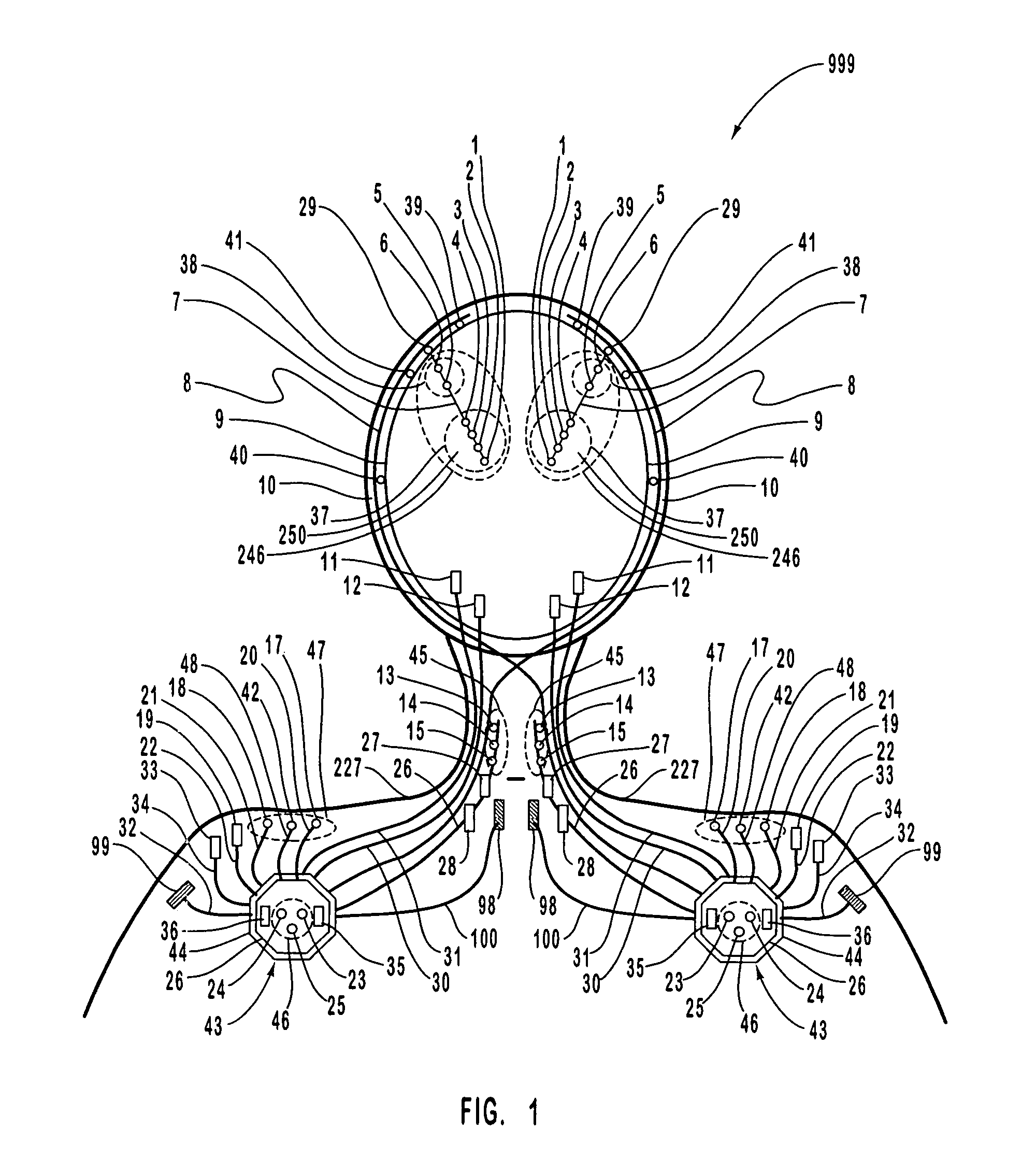
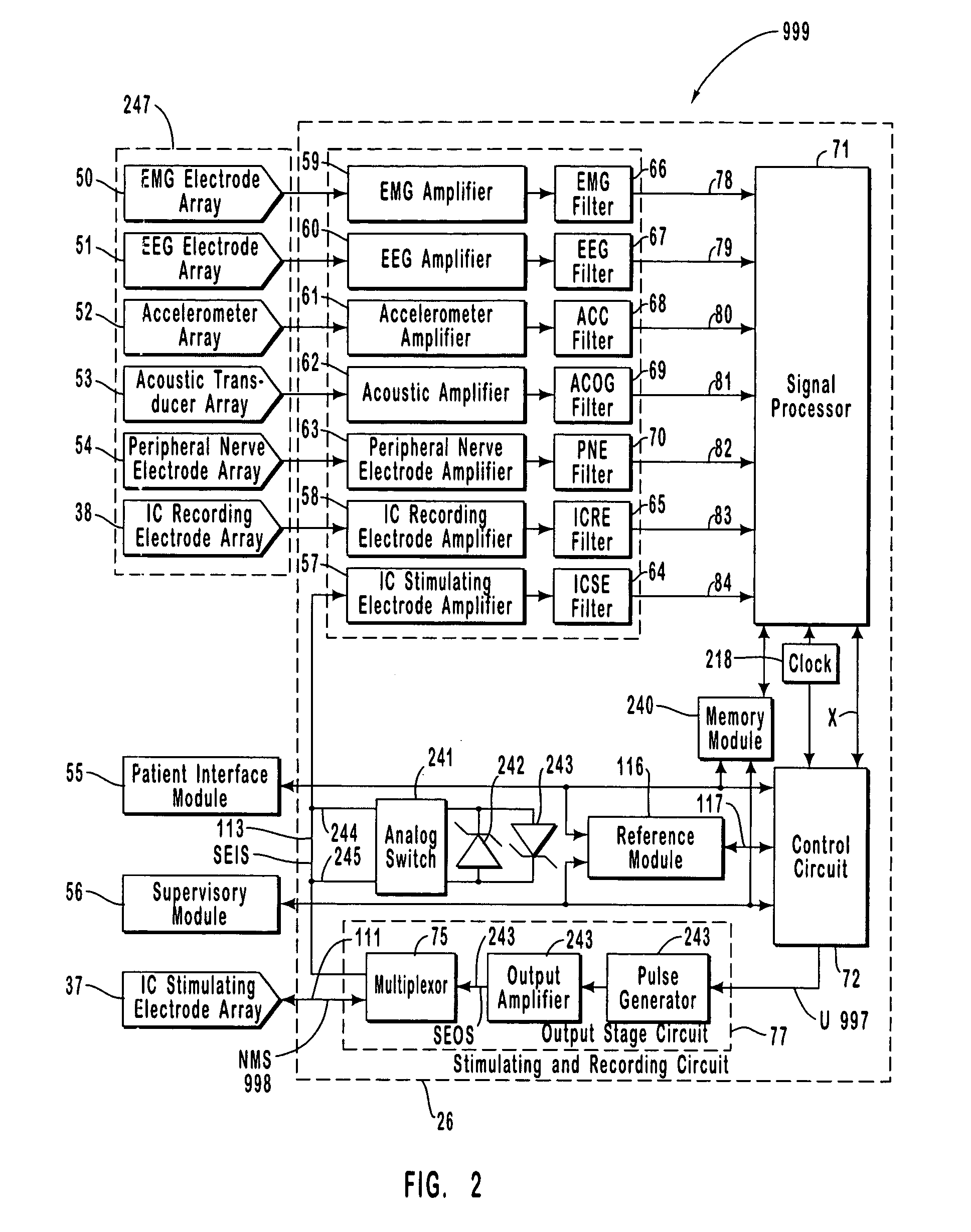
InactiveUS9042988B2Avoid seizuresShorten the construction periodHead electrodesImplantable neurostimulatorsDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides a closed-loop system for treating neurological disorders, such as epilepsy. In one embodiment the system comprises an input assembly that is adapted to receive one or more signals from a patient that are indicative of a patient's neurological state. The input assembly processes the one or more signals to generate one or more control input signals. An output assembly receives the one or more control input signals from the input assembly and generate a neuromodulation signal that is a function of the patient's neurological state. An electrode array is configured to deliver the neuromodulation signal to a patient's peripheral nerve, such as the vagus nerve.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com