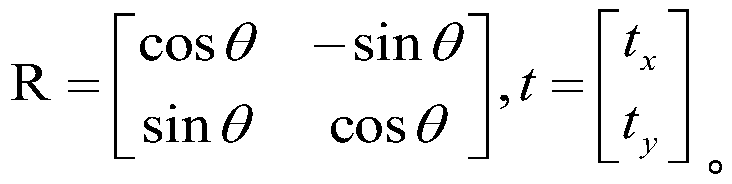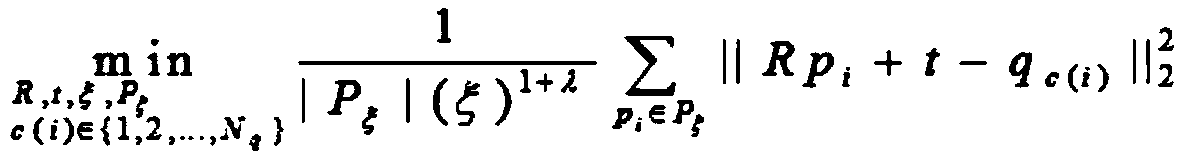Patents
Literature
230 results about "Mobile navigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
One of the common challenges when designing responsive design for mobile is the navigation menu. If the site has many sections or pages, it gets challenging to squeeze all the items into a small mobile resolution. The navigation most likely ends up running into multiple lines or the buttons stacking on top each other.
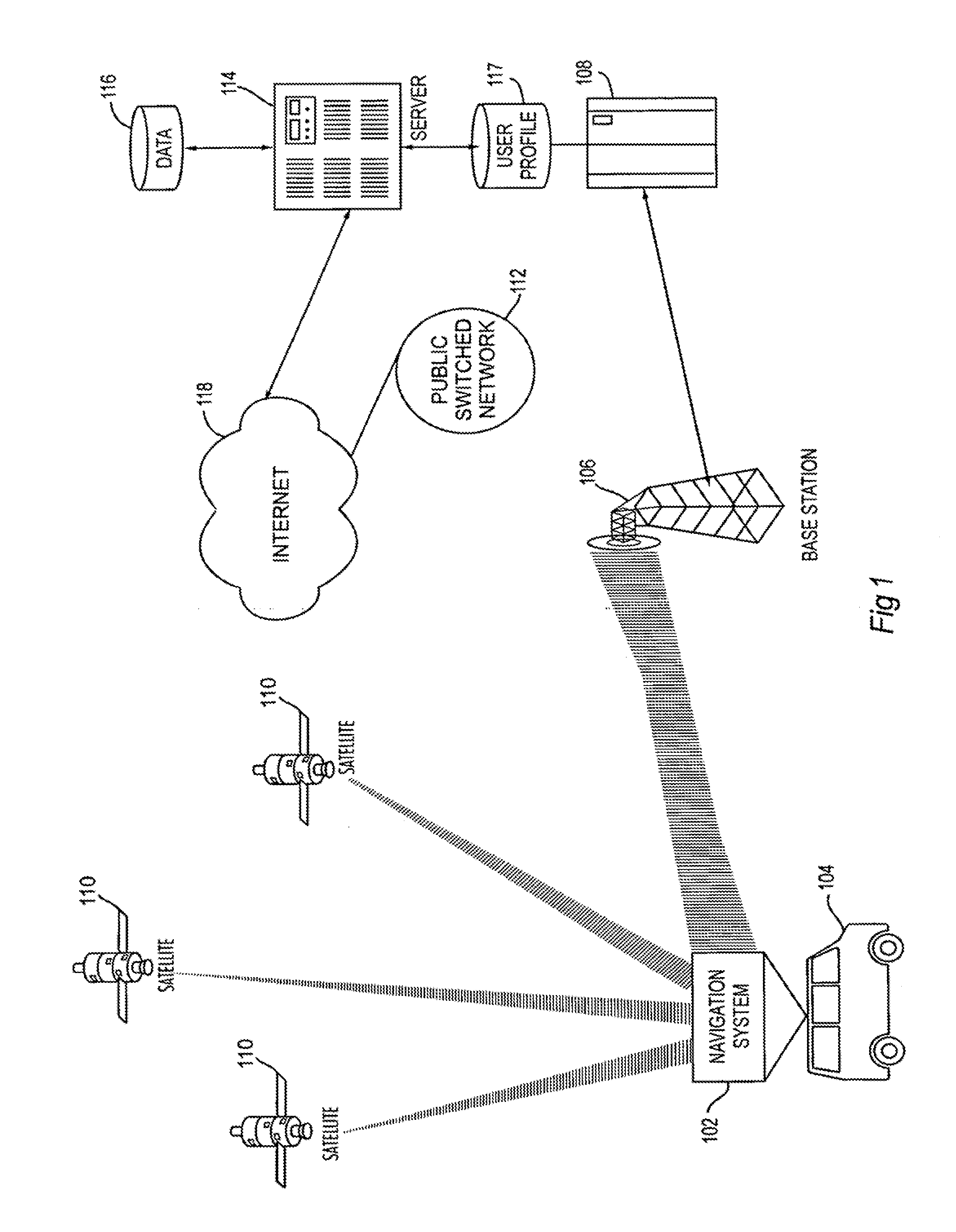
System for personalized mobile navigation information
InactiveUS6349257B1Analogue computers for vehiclesElectric signal transmission systemsPersonalizationMobile navigation
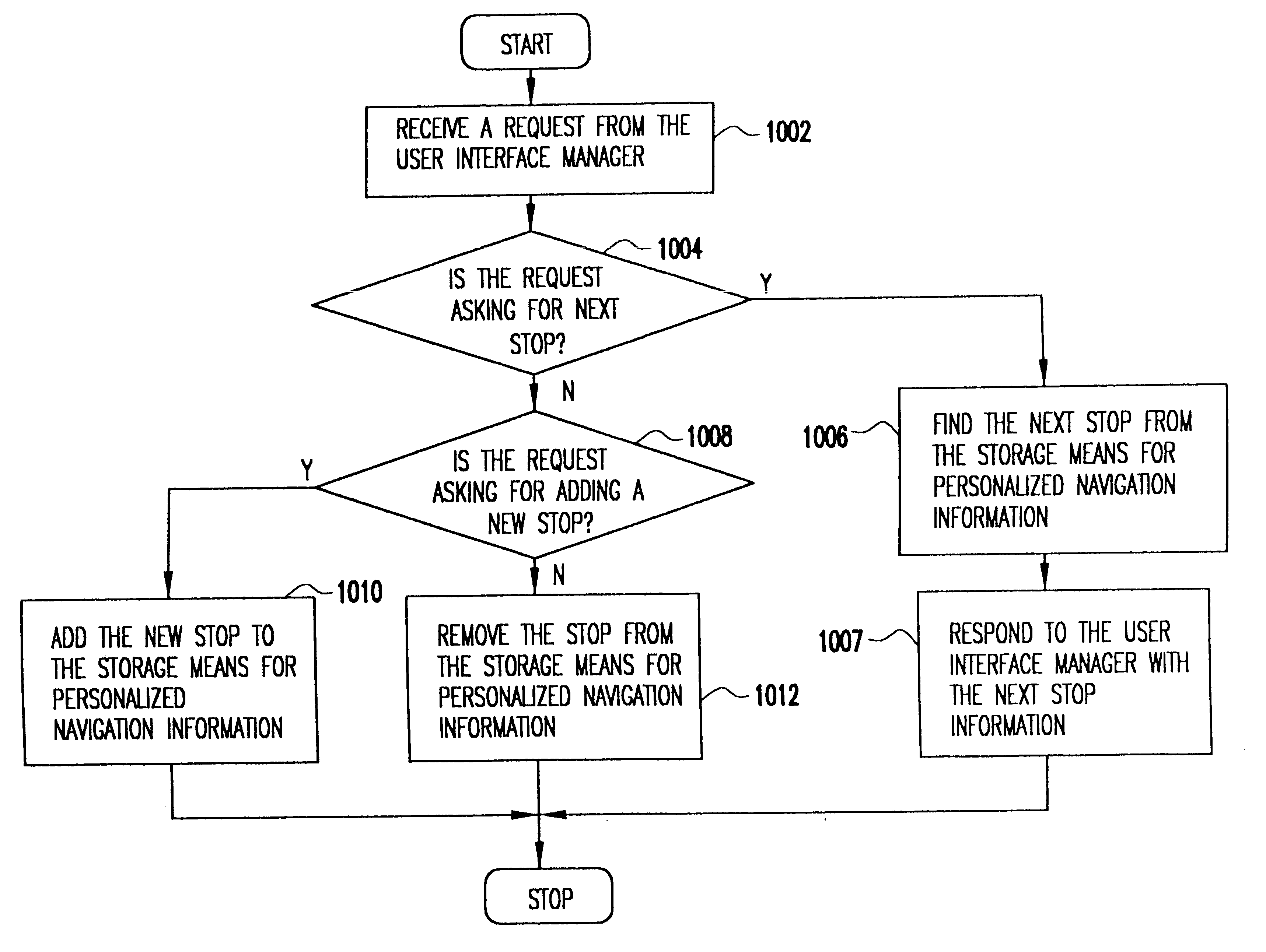
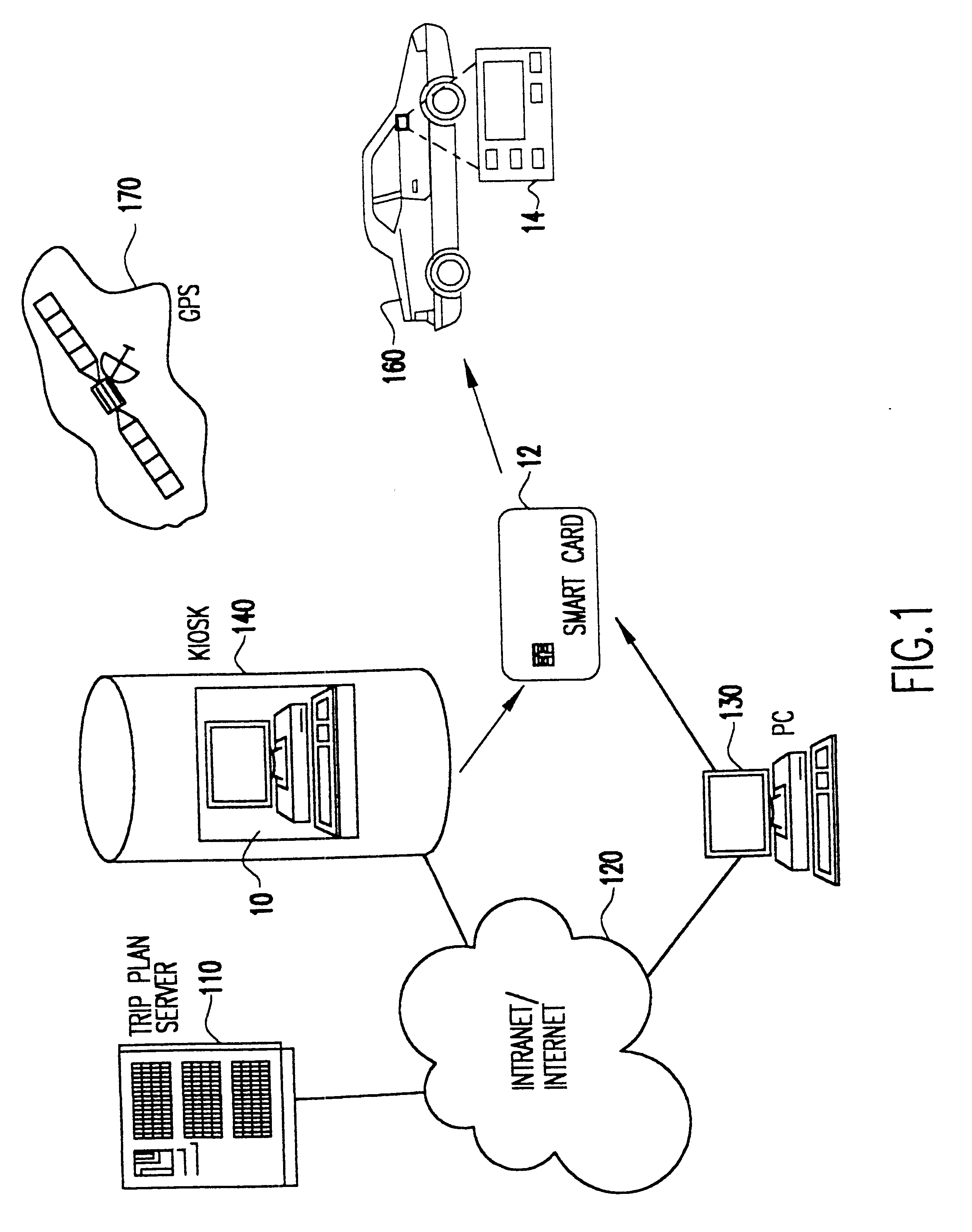
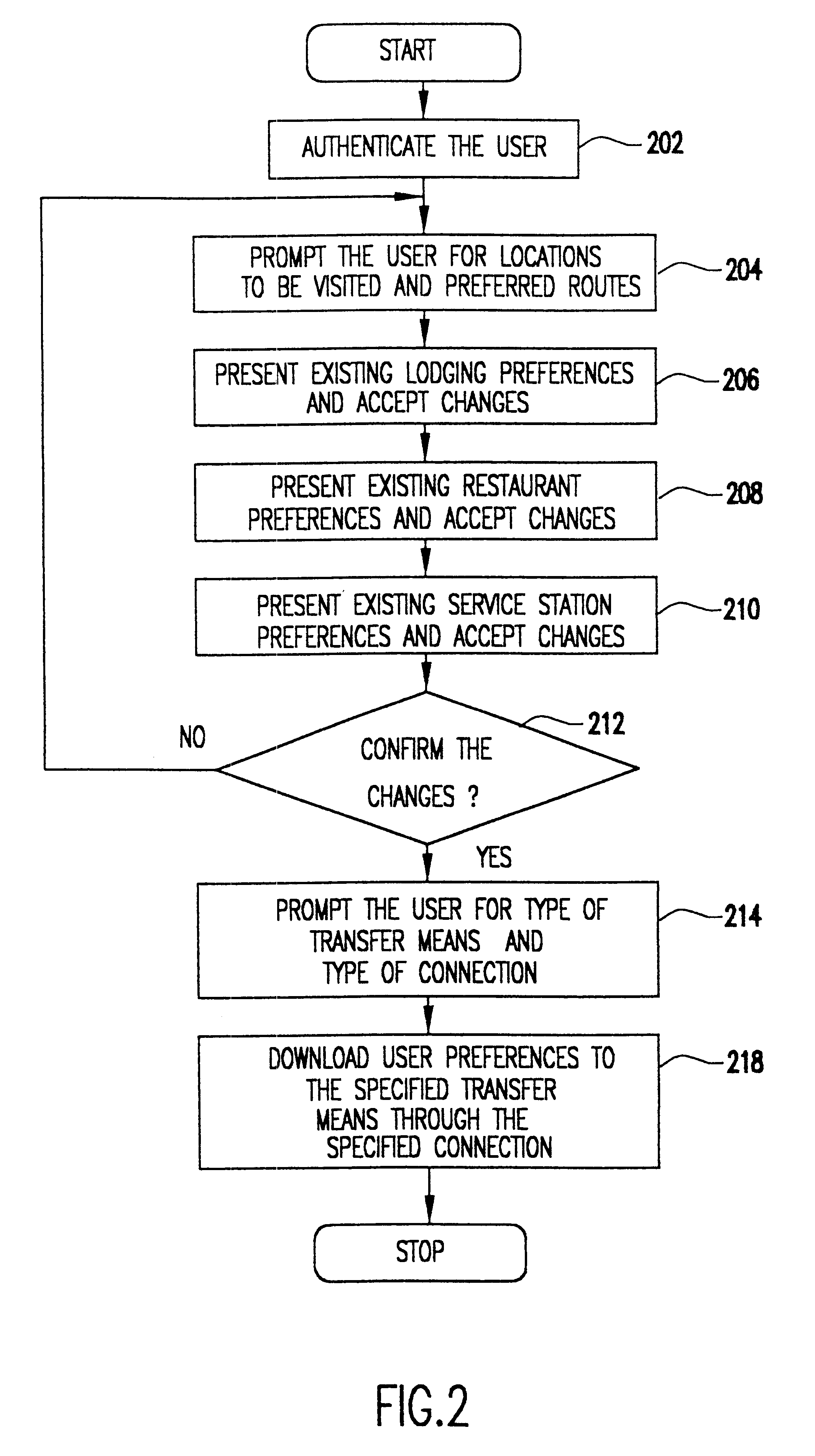
A mobile navigation system implemented as an embedded system in a vehicle is easy to use, does not detract the driver's attention from the road, and limits the number of choices presented to the user of the navigation system according to a predetermined set of preferences or personalized information. Choices are filtered according to a set of driver preferences, according to the vehicle's geographic position, direction of motion, and the driver's intended itinerary. The itinerary, including intermediate stops, is calculated on an external computing system. The information is downloaded from the computing system to a memory device such as, for example, a smart card. The information is then transferred from the smart card to the embedded vehicle navigation system. In one application of the invention, a kiosk located at a car rental agency may be used to create and store personalized navigation information onto a smart card which the customer then inserts into the vehicle navigation system that is installed in the rental car.
Owner:IBM CORP
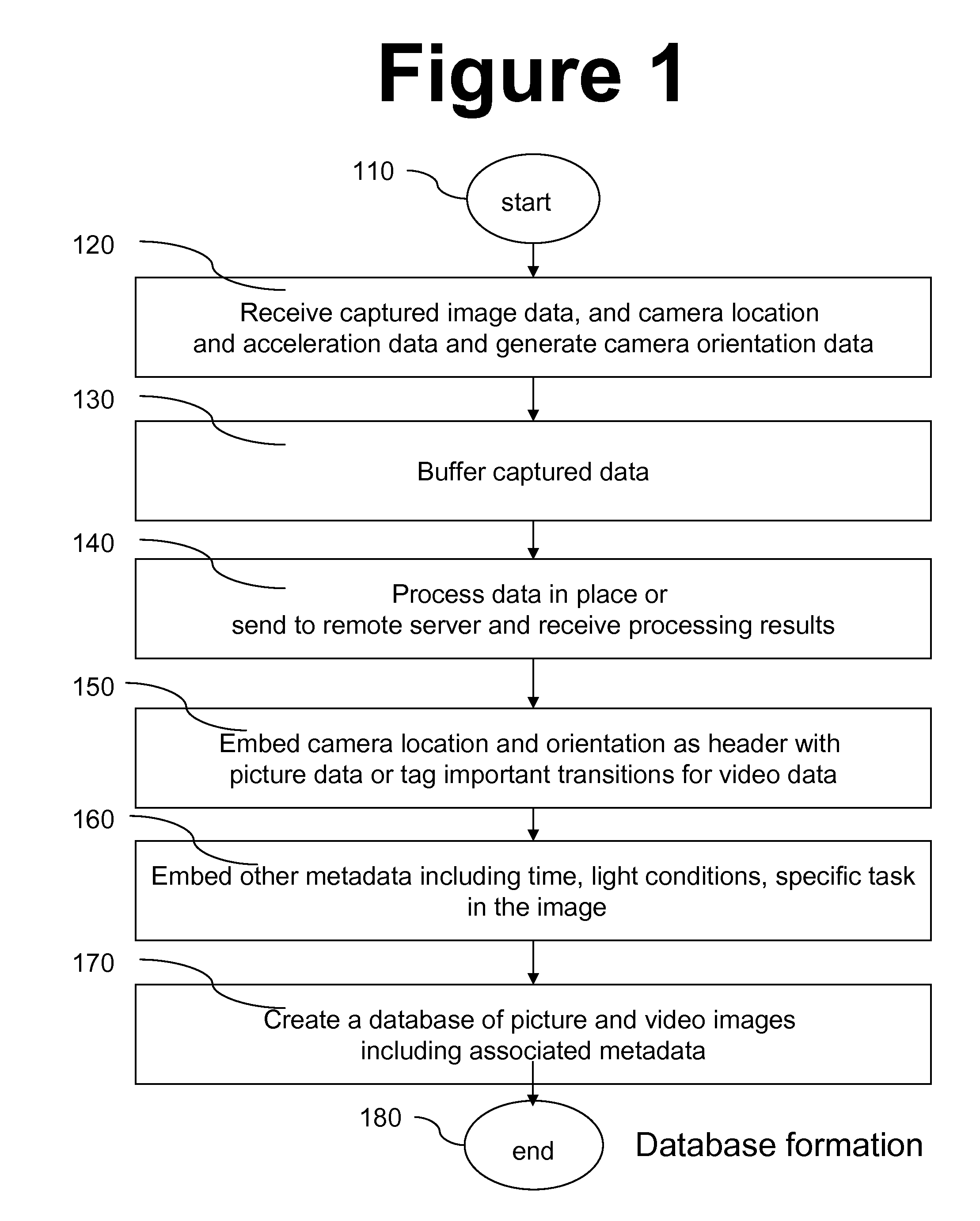
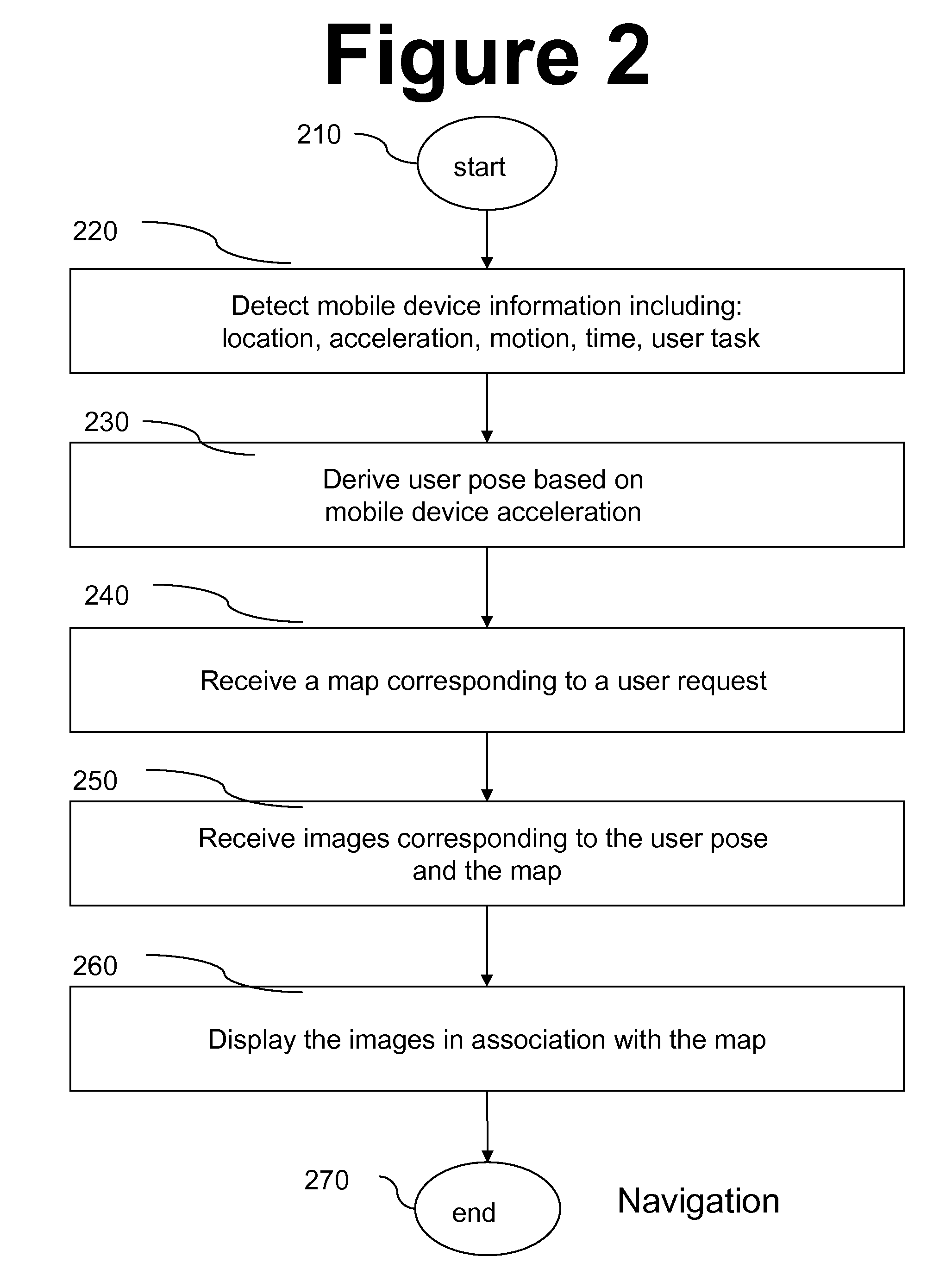
Image matching in support of mobile navigation
ActiveUS20100191459A1Orient themselvesFast and reliableTelevision system detailsInstruments for road network navigationMobile navigationAccelerometer
Method, apparatus and system for improving navigation using mobile devices by adding previously captured media to navigation maps provided by mobile device. Added media include still images and video clips. Media captured at the same location using various camera orientations are available in an image database. Images in database include metadata indicating location, orientation and other parameters associated with each image. User location and pose are matched against metadata indicating location and camera orientation of captured images. User motion may also be matched to metadata indicating camera motion of stored video clips. Other parameters like lighting, seasonal factors, and tasks of walking, biking or driving may also be matched. User pose may be derived from an accelerometer embedded in the mobile device. Some or all of user parameters desired by user may be directly input to mobile device by user instead of being automatically detected by mobile device.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Mobile payment system using barcode capture
The present invention proposes to streamline the process by replacing most of the manual entry and mobile navigation through a mobile client application that will allow the user to [a] capture a barcode using a camera phone or any other camera-equipped communicating device such as a PDA with a camera attachment or a internet connected computer with a web-cam and [b] automatically send—or prepare the transmission of—the relevant information to the vendor directly or through the usage of a centralized platform.
Owner:SCANBUY
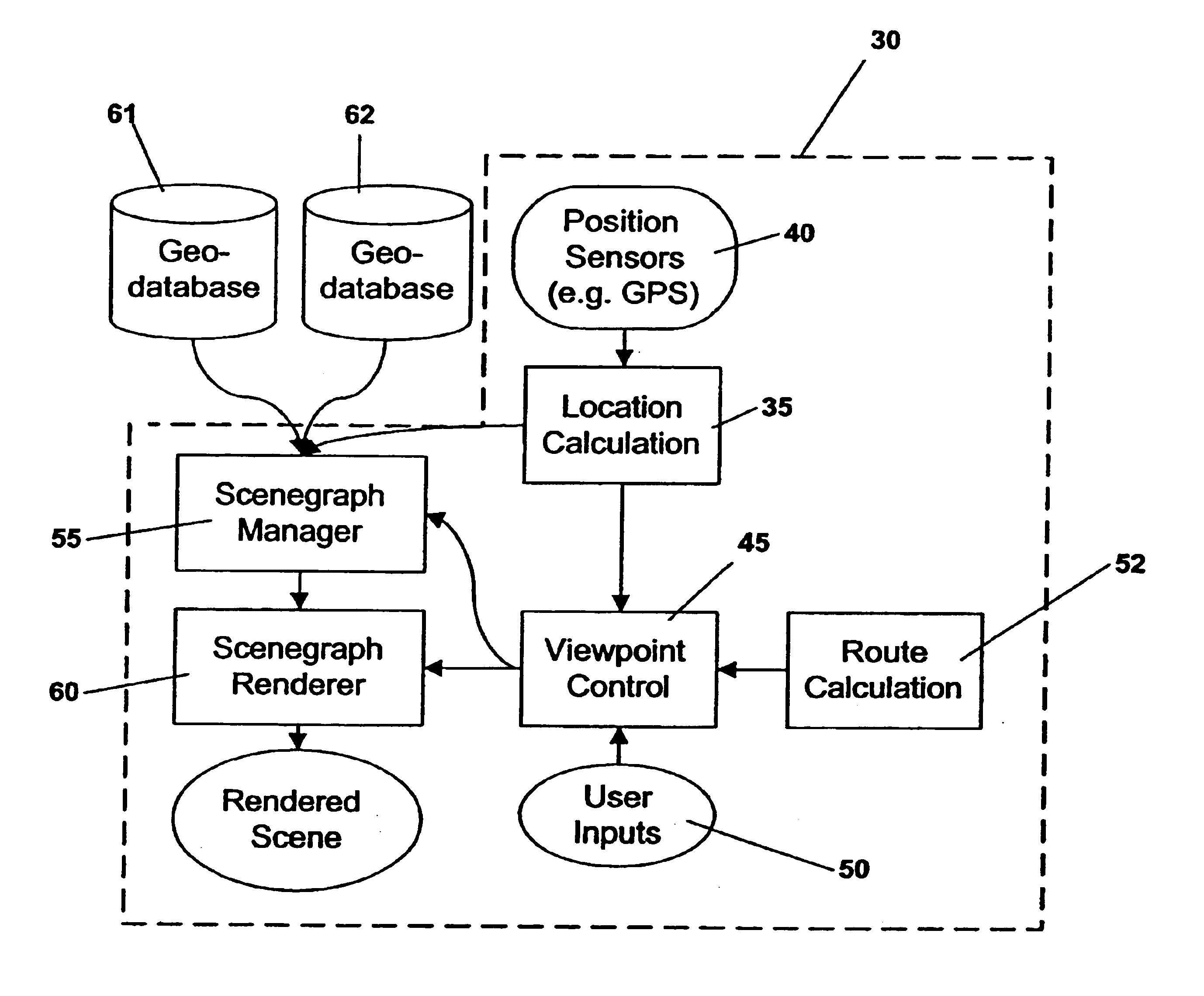
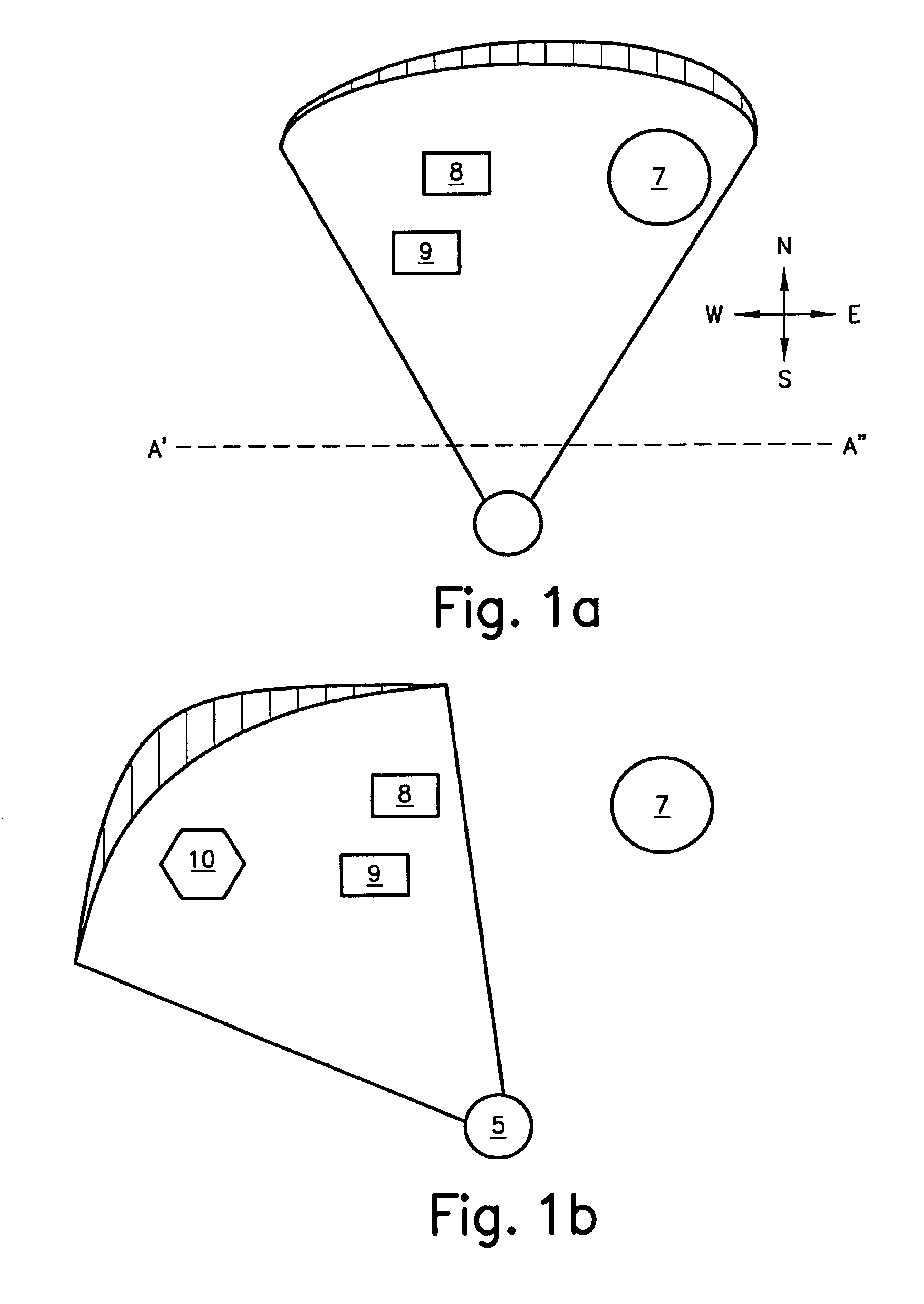
System and method for advanced 3D visualization for mobile navigation units
InactiveUS6885939B2Improve realismReduce unevennessInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile navigationViewpoints
A system providing three-dimensional visual navigation for a mobile unit includes a location calculation unit for calculating an instantaneous position of the mobile unit, a viewpoint control unit for determining a viewing frustum from the instantaneous position, a scenegraph manager in communication with at least one geo-database to obtain geographic object data associated with the viewing frustum and generating a scenegraph organizing the geographic object data, and a scenegraph renderer which graphically renders the scenegraph in real time. To enhance depiction, a method for blending images of different resolutions in the scenegraph reduces abrupt changes as the mobile unit moves relative to the depicted geographic objects. Data structures for storage and run-time access of information regarding the geographic object data permit on-demand loading of the data based on the viewing frustum and allow the navigational system to dynamically load, on-demand, only those objects that are visible to the user.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
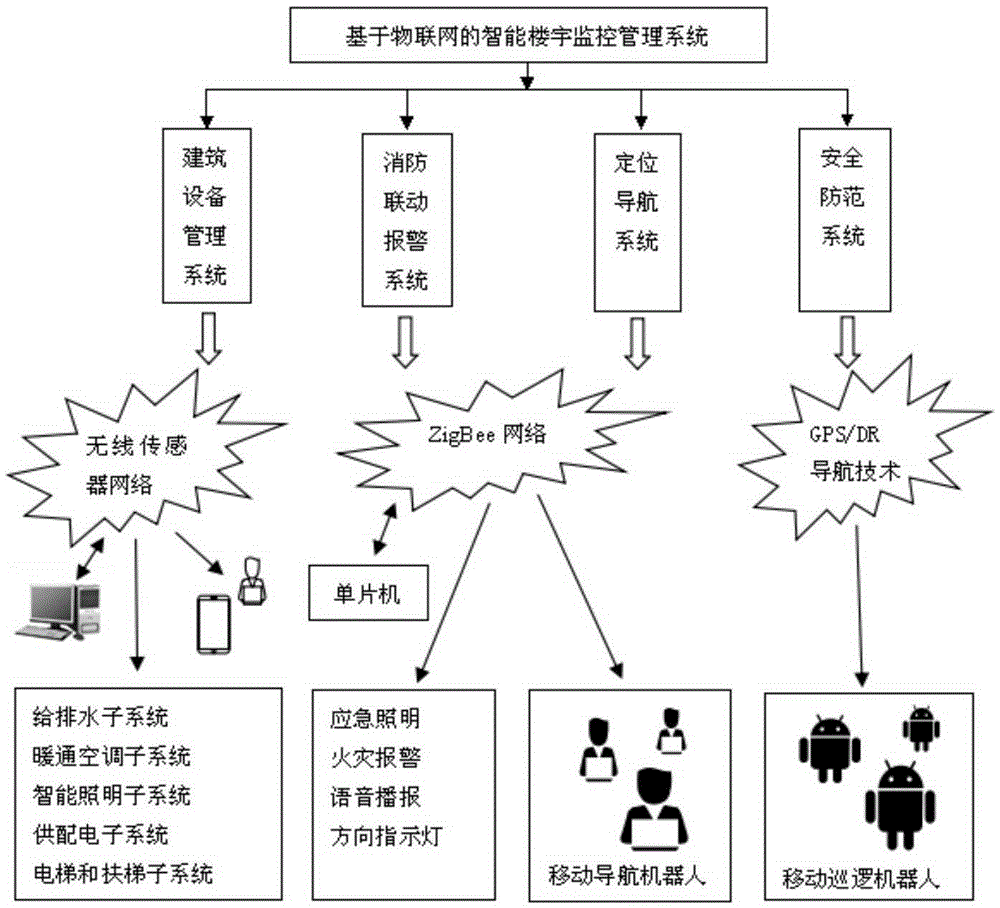
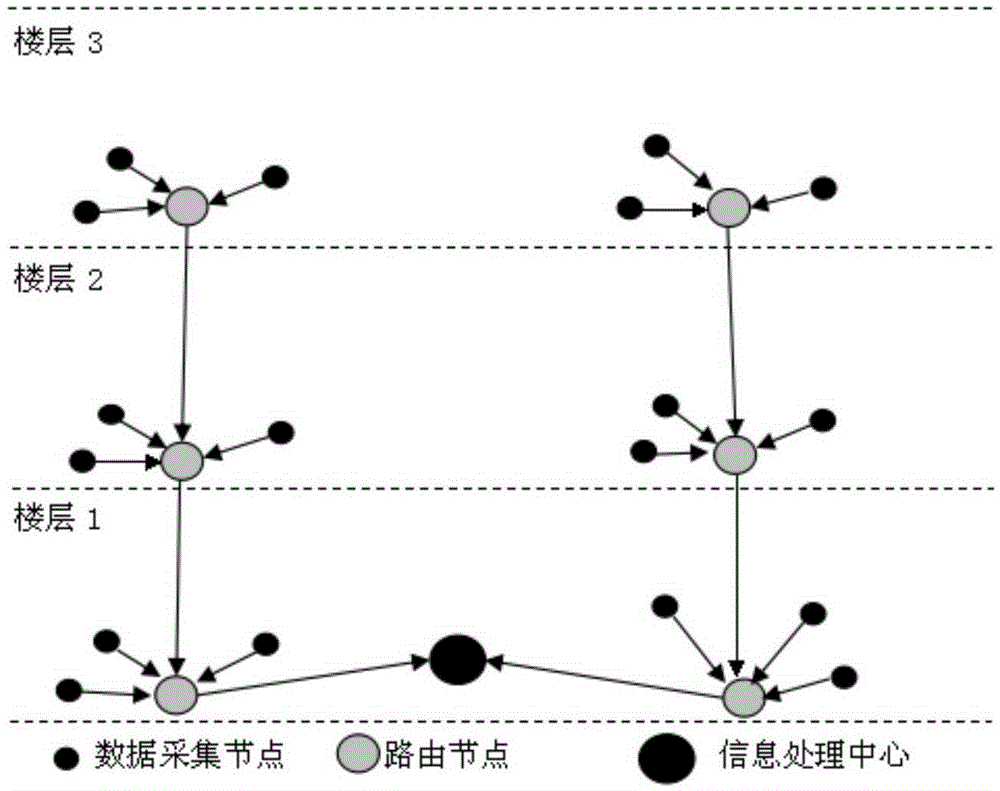
Internet of things-based intelligent building monitoring managing system
InactiveCN105404231AEfficient communicationPrecise positioningProgramme controlComputer controlMobile navigationPatrolBot
The invention discloses an internet of things-based intelligent building monitoring managing system, which mainly realizes remote monitoring and managing on an intelligent building. The system comprises four parts of a building equipment managing system, a firefighting linkage alarm system, a positioning navigation system and a security system; the building equipment managing system realizes concentrated managing on building equipment based on a tree cluster network established by an intelligent sensor module; the firefighting linkage alarm system adopts an optimized A*algorithm to search for an optimal fire escape path; the positioning navigation system is achieved by a mobile navigation robot covering floors of the building, and if a user inputs a destination, the navigation robot directly inserts virtual scene information into a reality scene, and displays a direction mark; the security system is realized by a mobile patrolling robot based on a GPS / DR combined navigation technology, and an intruder is alarmed after being found, the current intelligentized managing requirements of the building are met and the system is suitable for a high-rise building such as a commercial building with a large scale.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Navigation signal receiver trajectory determination
The present invention provides methods and systems that enable a mobile navigation receiver to accurately determine its trajectory with non-current ephemeris in stand-alone mode. In an embodiment, the receiver computes the position for the same location using non-current ephemeris and current ephemeris at different time instances. The receiver then determines a position correction by finding the difference between these two computed positions, and applies this correction to the trajectory generated with non-current ephemeris to obtain a more accurate trajectory. In another embodiment, the receiver computes an initial position of the receiver using non-current ephemeris and finds the difference between the computed initial position and an accurate approximation of the initial position. The receiver then shifts the subsequent receiver trajectory computed using non-current ephemeris by the difference to obtain a more accurate trajectory.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
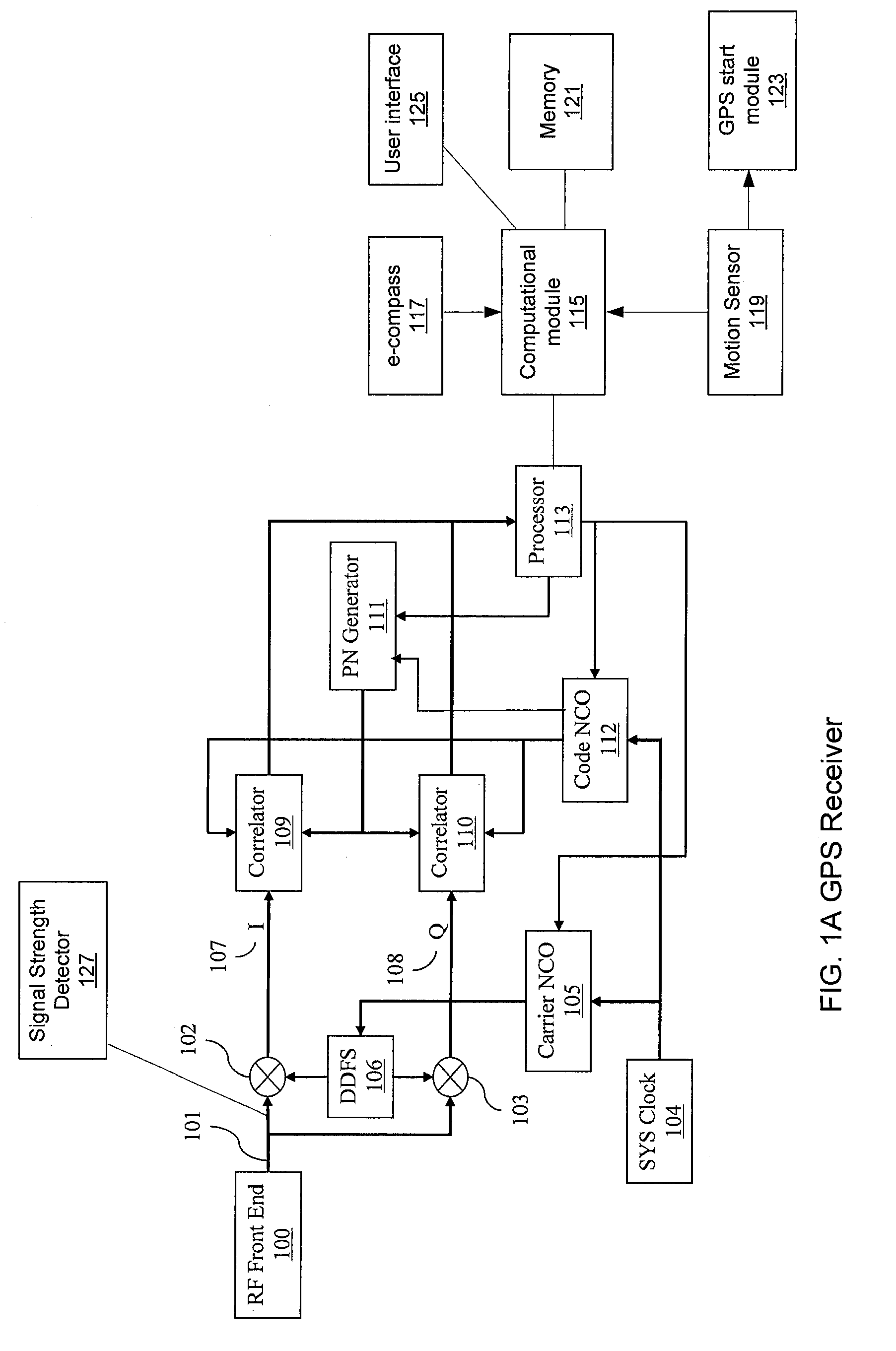
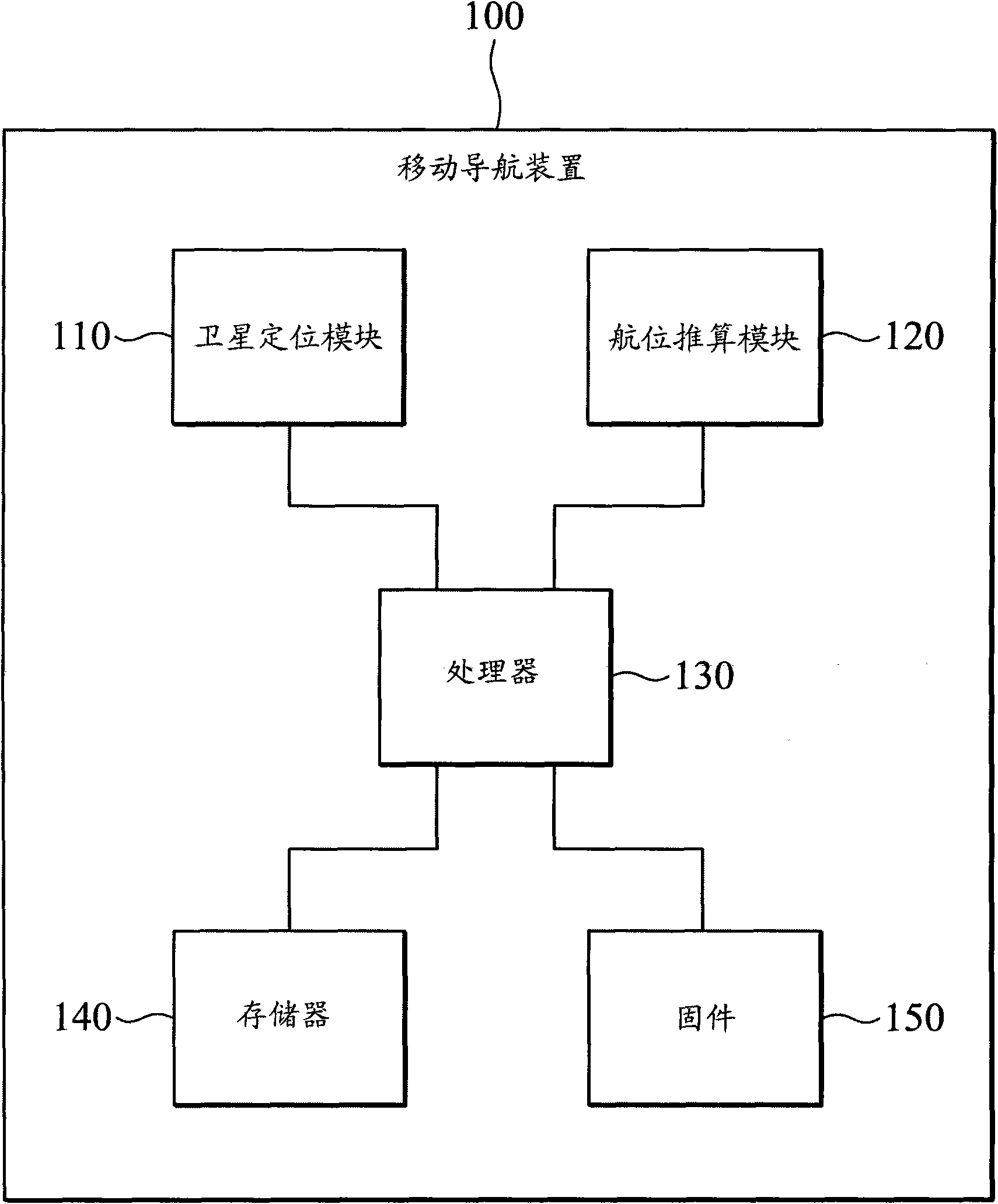
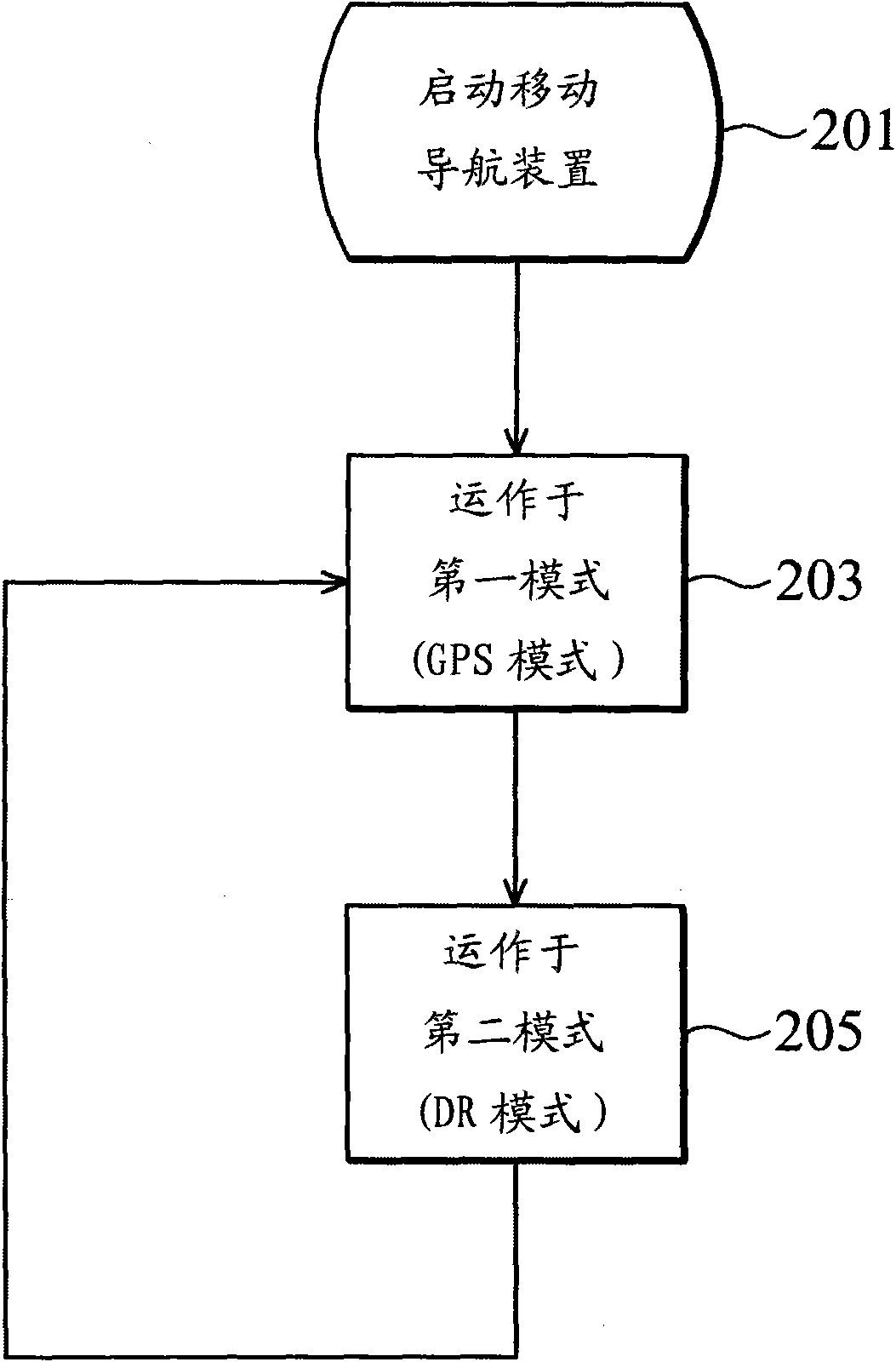
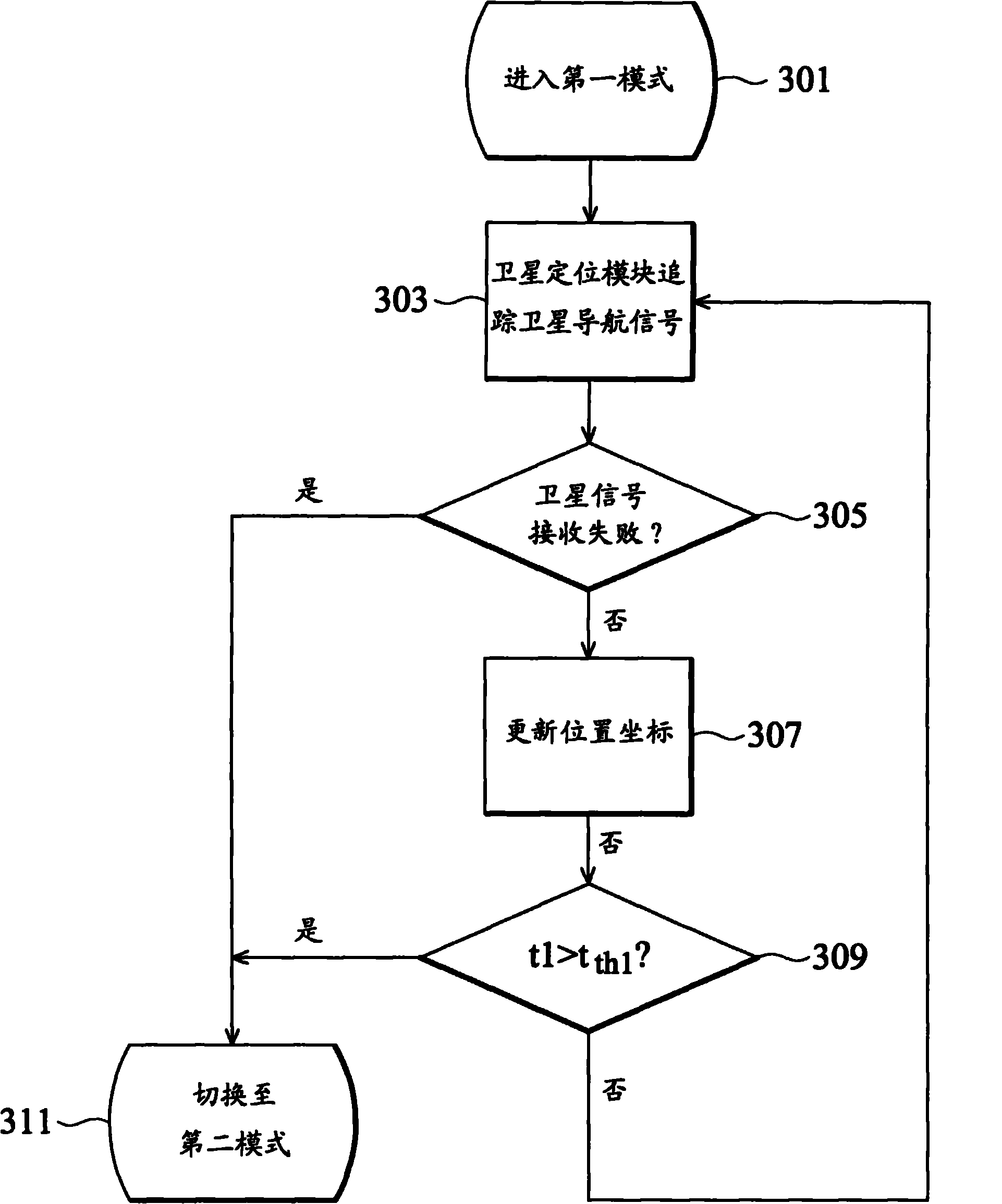
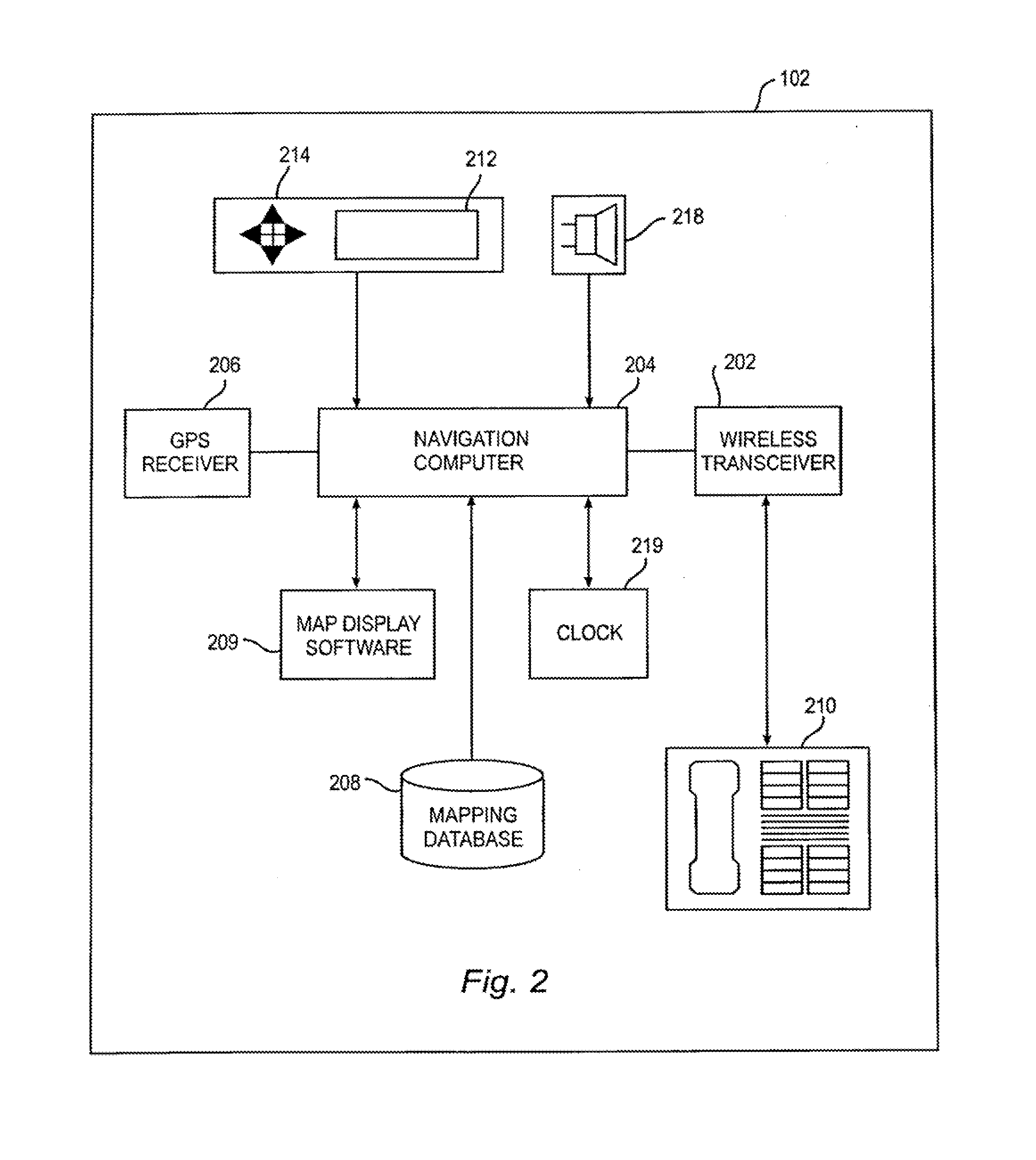
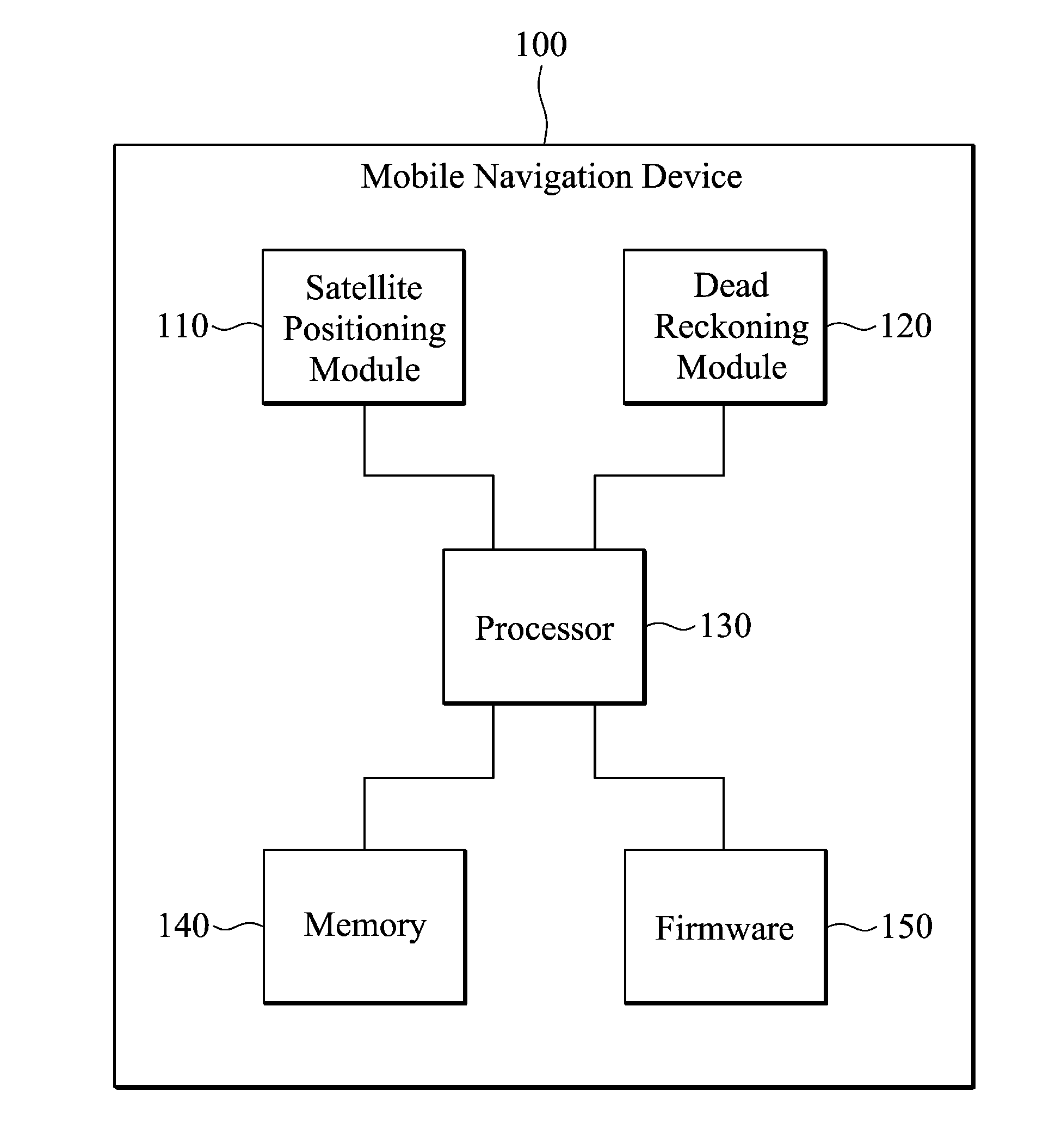
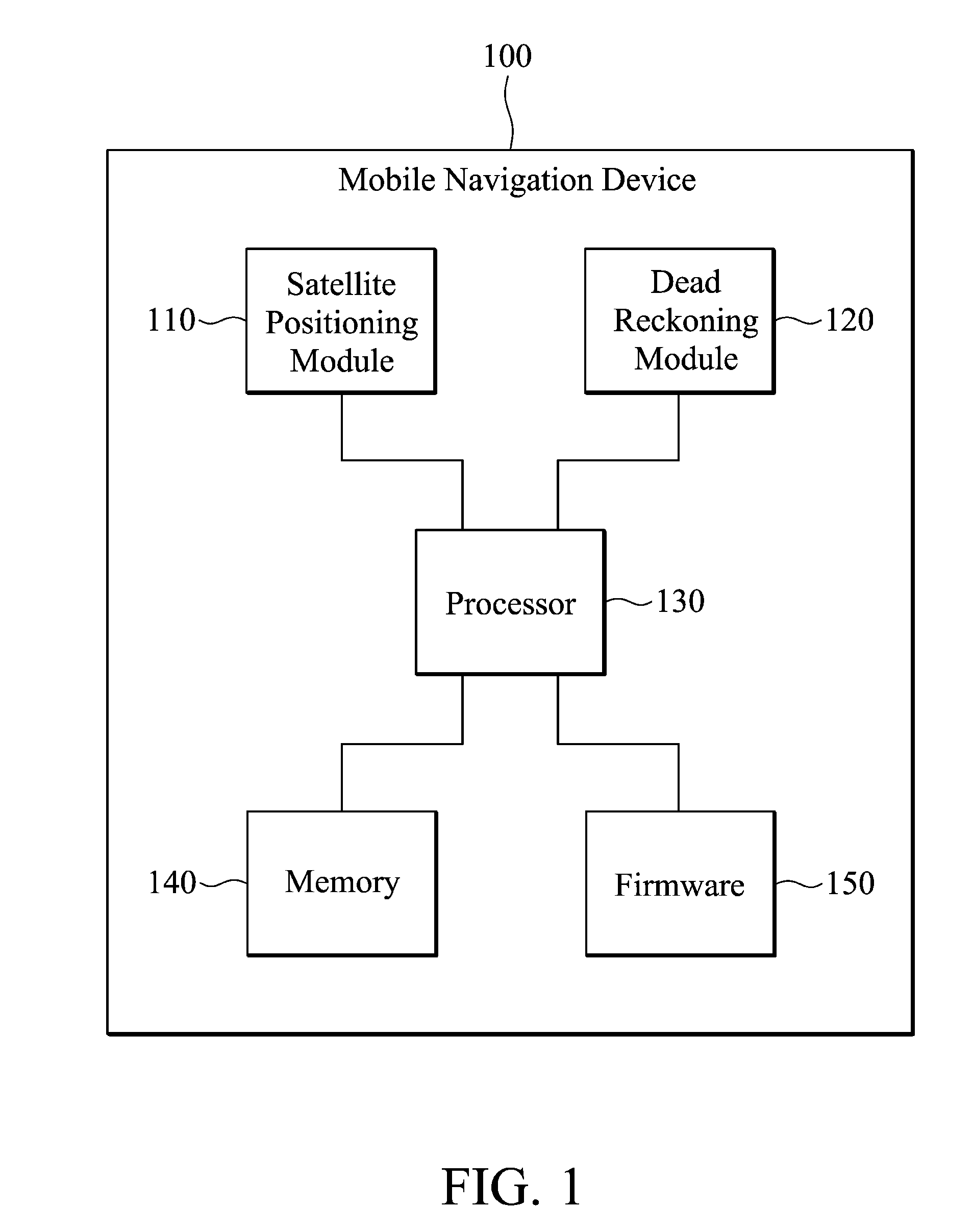
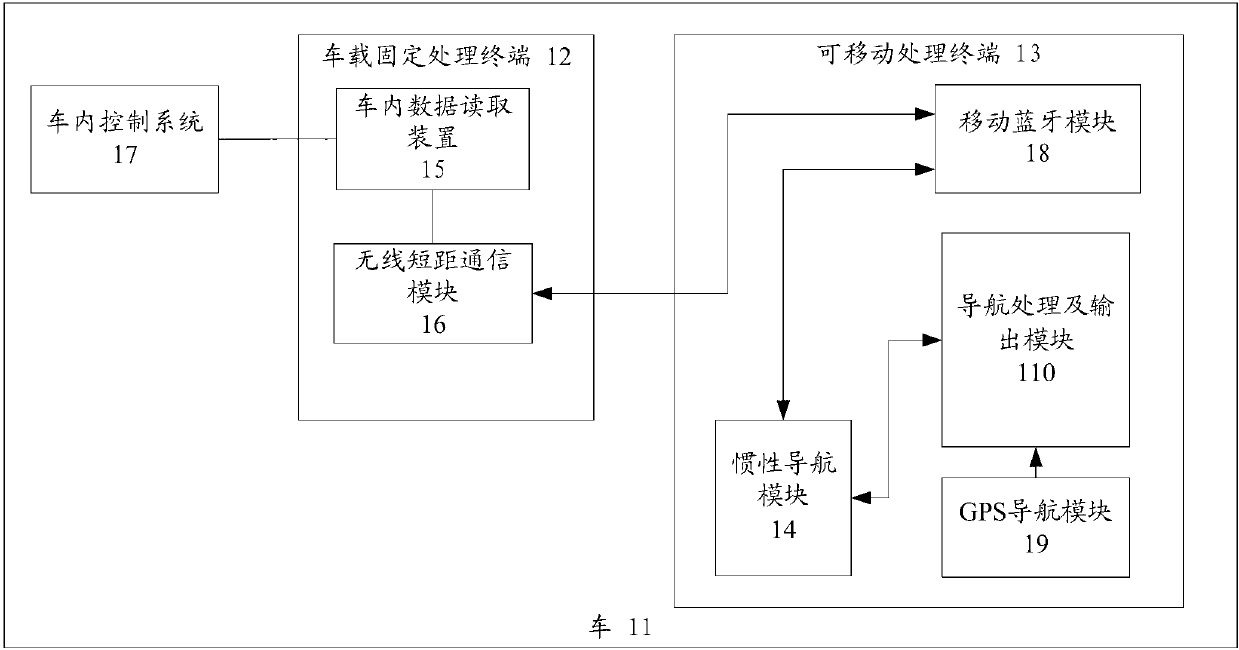
Mobile navigation device
The invention relates to a mobile navigation device, which alternately operates in first and second modes. In the first mode, a satellite positioning module is started up, a dead reckoning module is closed, and a processor calculates a position coordinate according to a satellite navigation signal. In the second mode, the satellite positioning module is closed, the dead reckoning module is started up, and the processor updates the position coordinate according to movement and rotation.
Owner:HTC CORP
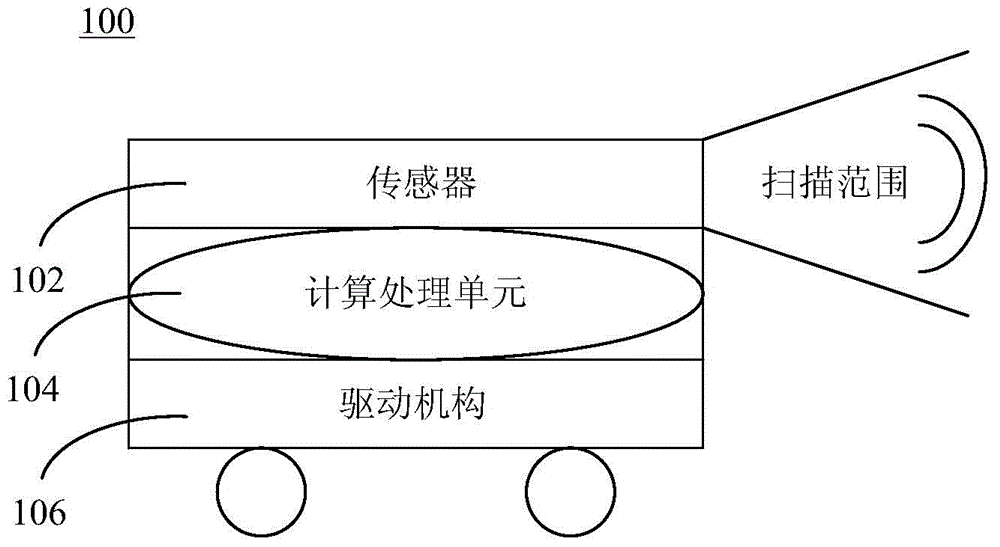
Mobile navigation method and system
ActiveCN104536445AImprove real-time performanceImprove work efficiencyInstruments for road network navigationPosition/course control in two dimensionsMobile navigationNavigation system
A mobile navigation method and system comprise a sensor, a computer processing unit and a driving mechanism. The sensor is used for collecting environmental data. The computer processing unit is used for calculating the collected data from the sensor to build a 3D map, and a path planning from a start point to a destination point is provided according to the 3D map. The driving mechanism is used for driving a mobile navigation system to move according to the path provided by the computer processing unit. The mobile navigation method and system further provide a map building method and a path planning method by using the mobile navigation system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
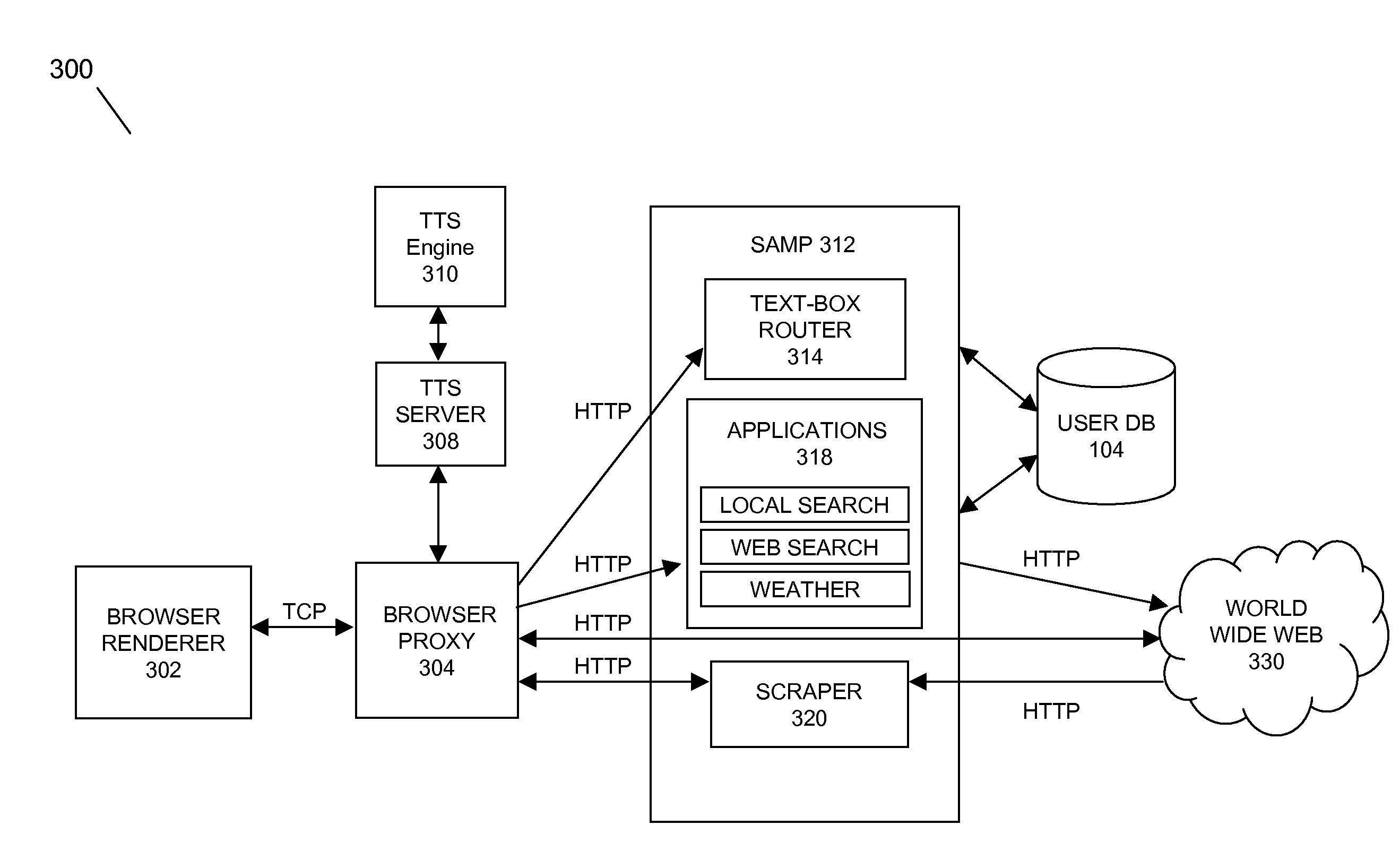
Mobile navigation environment speech processing facility
In embodiments of the present invention improved capabilities are described for a mobile environment speech processing facility. The present invention may provide for the entering of text into a navigation software application resident on a mobile communication facility, where speech may be recorded using the mobile communications facility's resident capture facility. Transmission of the recording may be provided through a wireless communication facility to a speech recognition facility. Results may be generated utilizing the speech recognition facility that may be independent of structured grammar, and may be based at least in part on the information relating to the recording. The results may then be transmitted to the mobile communications facility, where they may be loaded into the navigation software application. In embodiments, the user may be allowed to alter the results that are received from the speech recognition facility. In addition, the speech recognition facility may be adapted based on usage.
Owner:VLINGO CORP +1
Mobile navigation system
InactiveUS20120253659A1Level of detail necessary for the client-installed mapping database is minimalReduce failureInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlDatabase interfaceMobile navigation
Owner:INFOGATION CORP
Method for updating digital maps using altitude information
ActiveUS20120004845A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGuidance systemMobile navigation
This invention relates to a method for updating digital maps and for matching global navigation devices to a digital map. Such navigation devices rely upon GPS signals (20, 24) from satellites (22, 26). One well-documented cause of position error in navigation devices arises from the phenomenon of GPS multi-path. It has been observed that GPS multi-path errors in the latitude / longitude direction are highly correlated with errors in altitude. By comparing altitude value of GPS probe data with reference specifications for altitude, unreliable probe data (outliers) can be easily identified and culled. Such techniques can be used as well by a mobile navigation device to confirm a match to a particular road segment and if not revert to other positioning techniques such as inertial guidance systems and the like. If the local altitude is not reliably known, an estimation can be derived directly from the collected probe data.
Owner:TOMTOM POLSKA
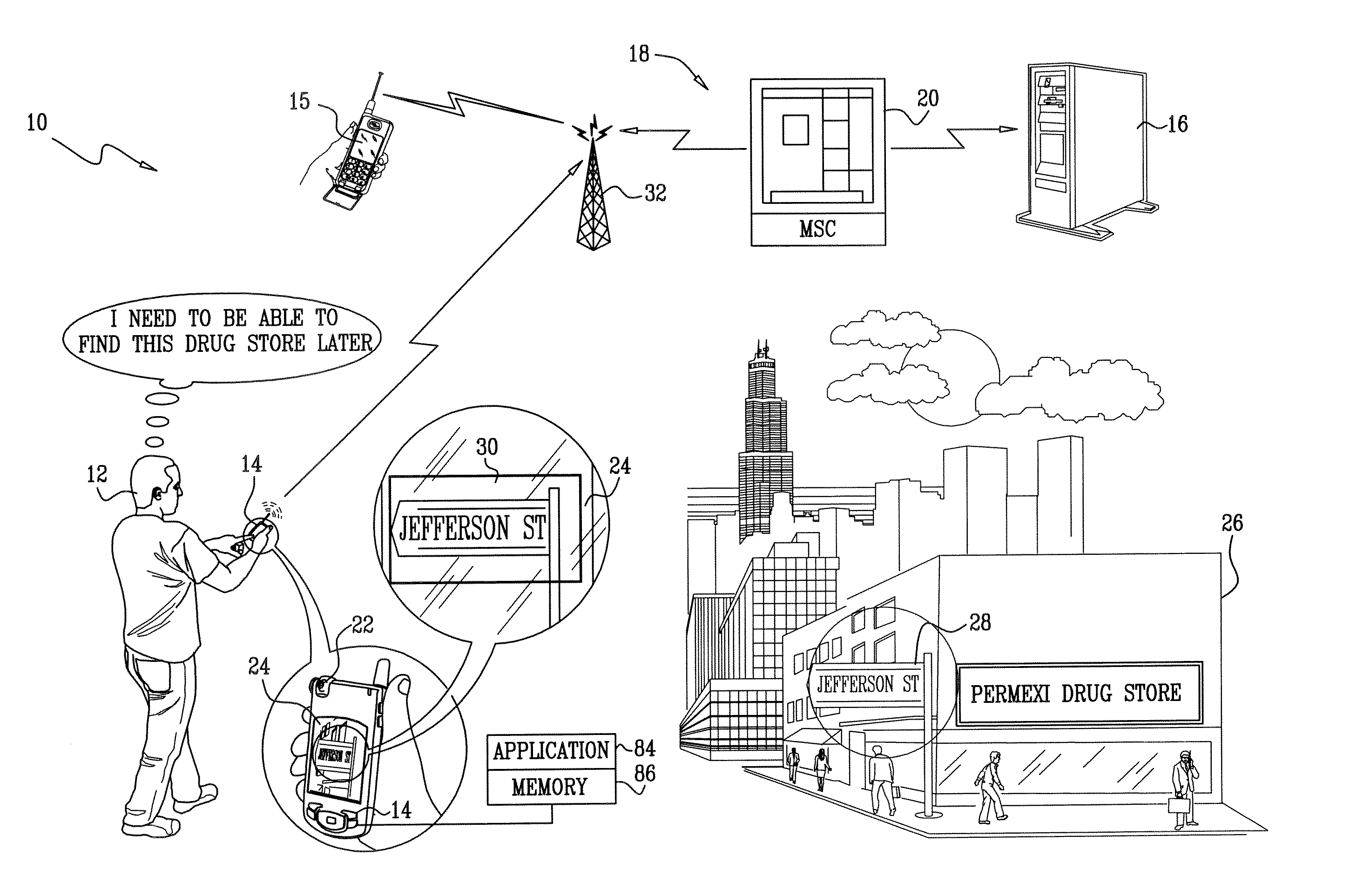
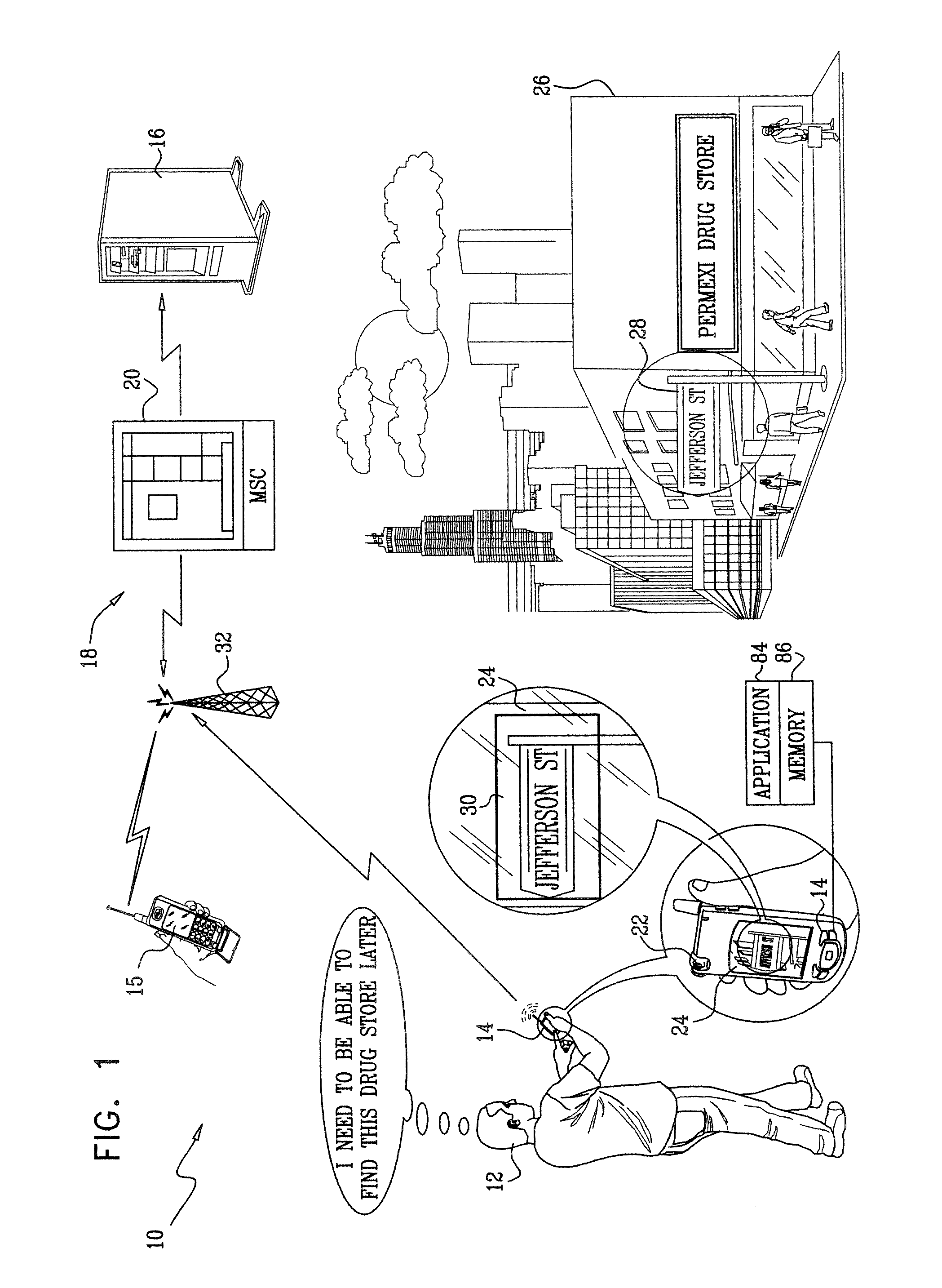
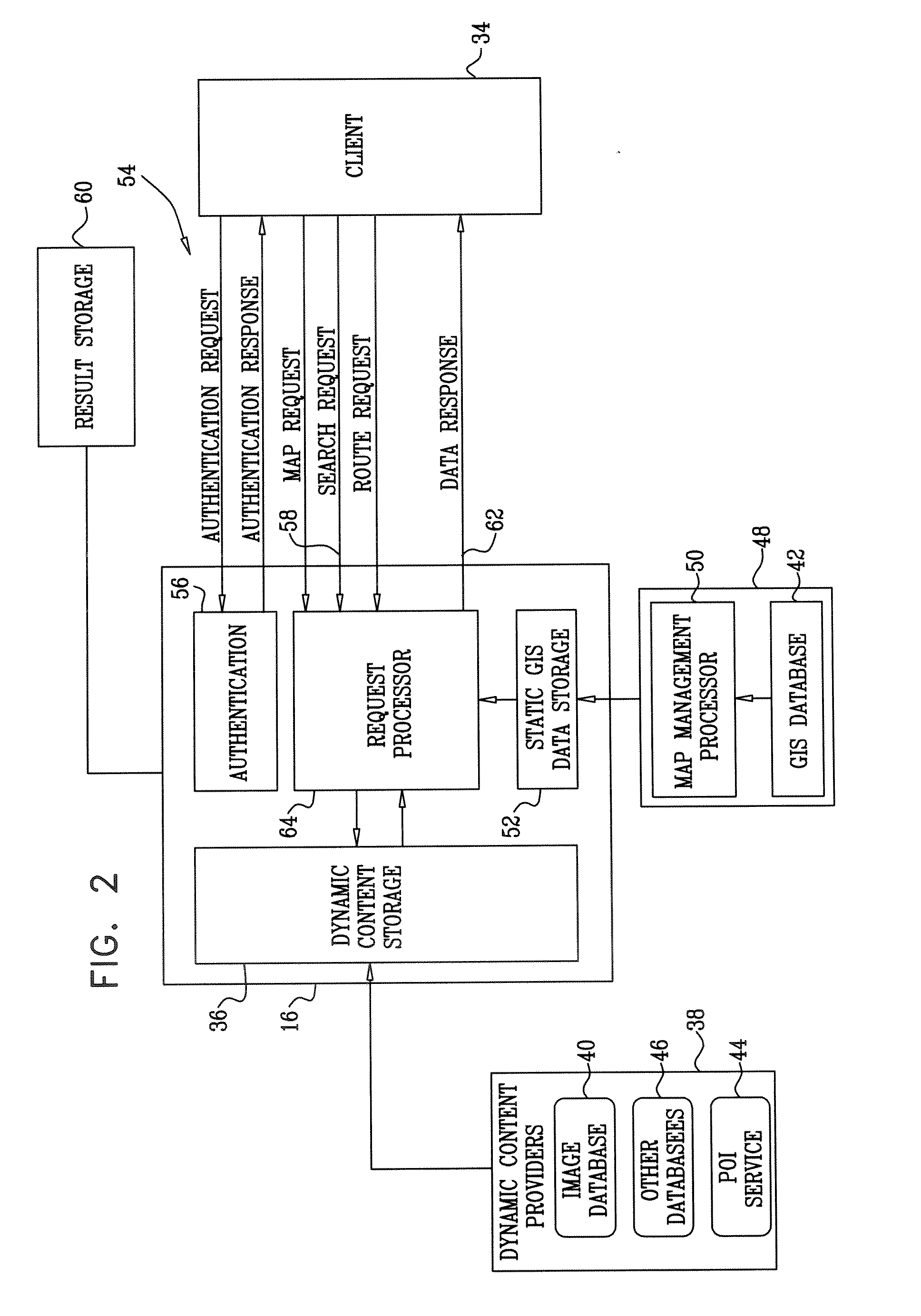
Visual inputs for navigation
InactiveUS20080039120A1Improve performanceOvercome technical difficultiesNavigational calculation instrumentsWireless communicationMobile navigationNavigation system
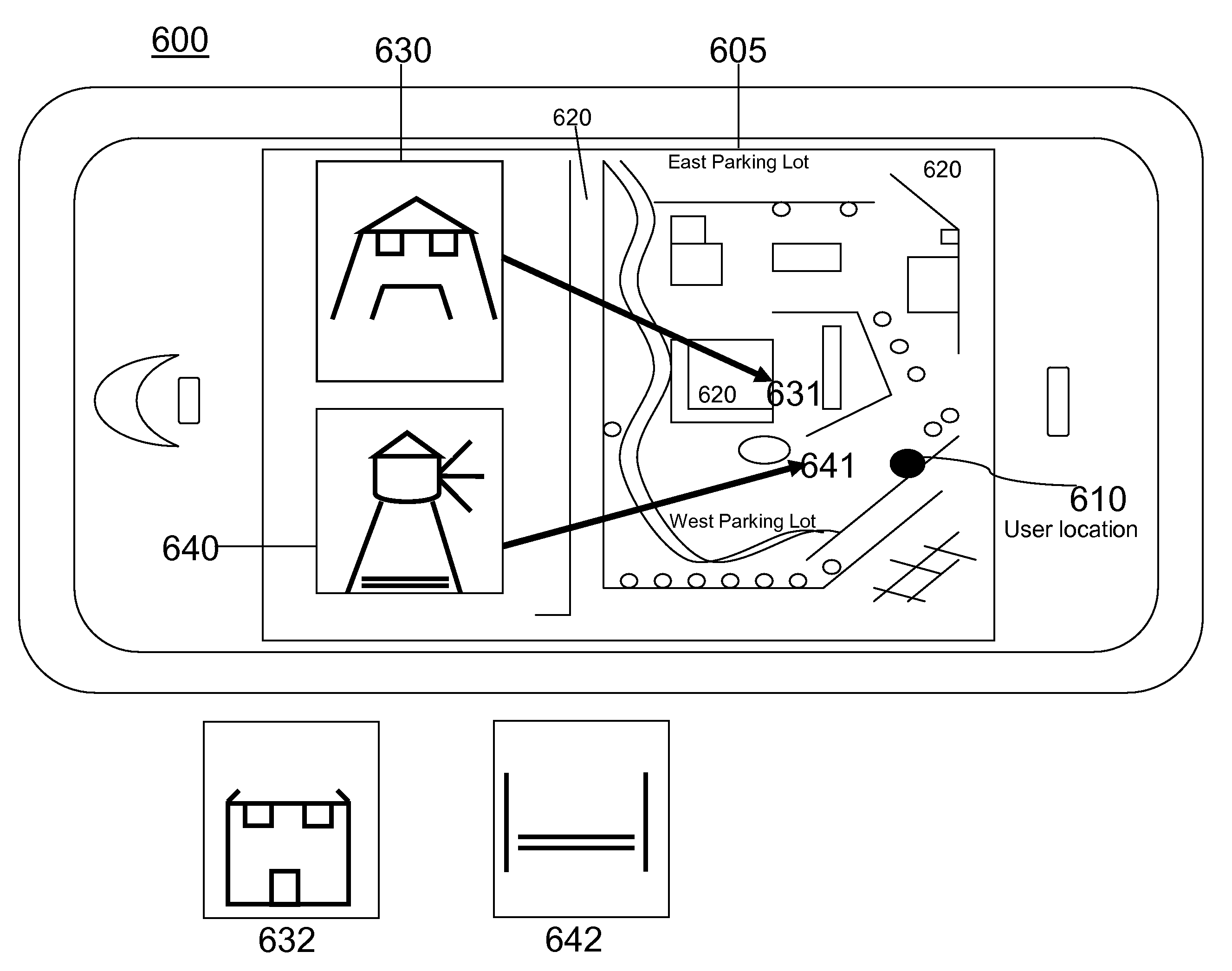
An interface is provided to a mobile navigation system in which an optical image of a point-of-interest acquired by cellular telephone devices is an input to the system. Textual and optionally other location information is extracted from the image, and used by the navigation system to identify coordinates and vectors relating to the point-of-interest. The results are stored and may be subsequently recalled to provide mapping and routing information to the cellular telephone device, whose position relative to the point-of-interest may have changed. Optical images may be uploaded from telephone device to the navigation system automatically or interactively, and can be processed remotely, generally without further user interaction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for updating embedded mobile electronic map data base in real time
InactiveCN101556165AAvoid refreshImplement incremental updatesInstruments for road network navigationMobile navigationLongitude
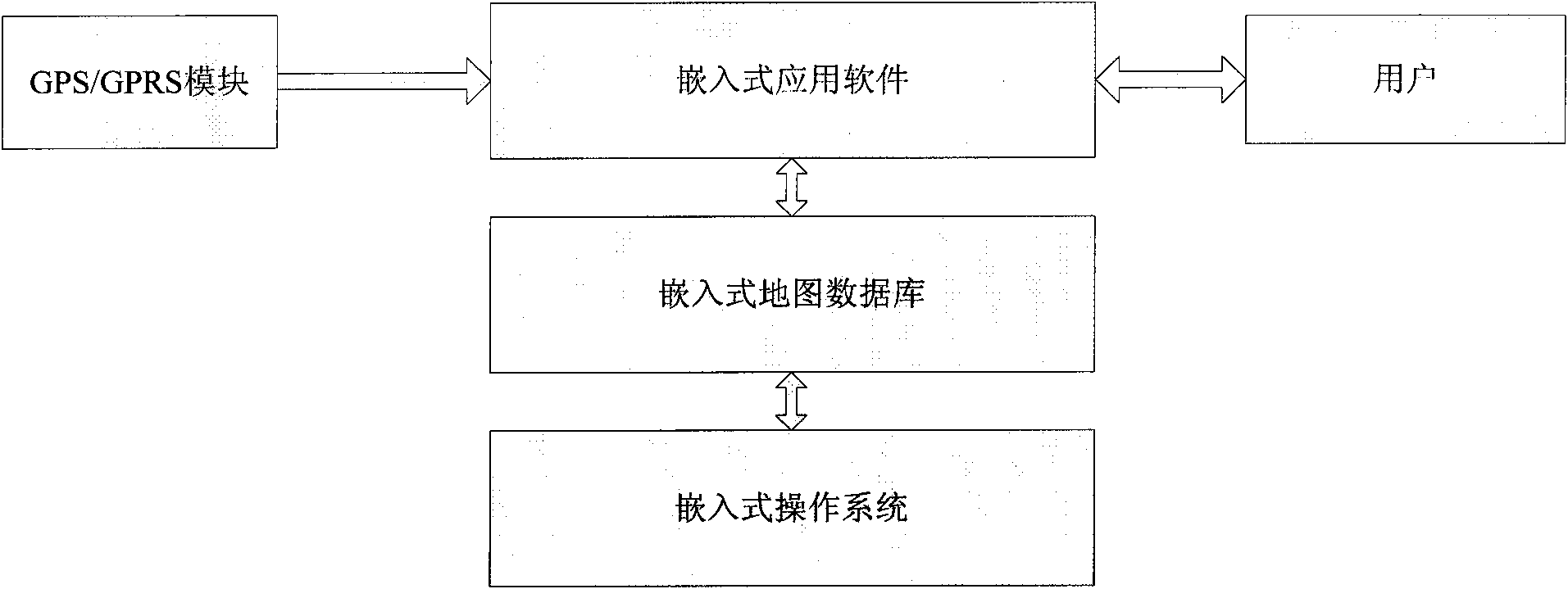
The invention relates to a method for updating an embedded mobile electronic map data base in real time, wherein map elements in the electronic map data base is firstly coded, and the IDs of the map elements are determined; the data of the relationship among the map elements is stored into the corresponding memory area of a map information storing device according to the IDs of the map elements; one item or a plurality of items of data of the relationship among the map elements can be extracted from the memory area of the map data, and the IDs of the map elements and the update state thereof are be obtained; data is acquired from a GPS / GPRS module and then is converted into geographic data compatible with the map data base, and whether the current travelling route belongs to certain map element is judged according to the coordinate figures of longitude and latitude; whether the map elements requires addition or modification is hinted according to the judged result; or by setting the travelling time threshold value, the map elements are automatically added when being more than the threshold value; finally, the updated data and the update state are stored into the map information memory area, thus electronic map data of a mobile navigation device can be stored and updated.
Owner:NOAH SOLUTION SUZHOU
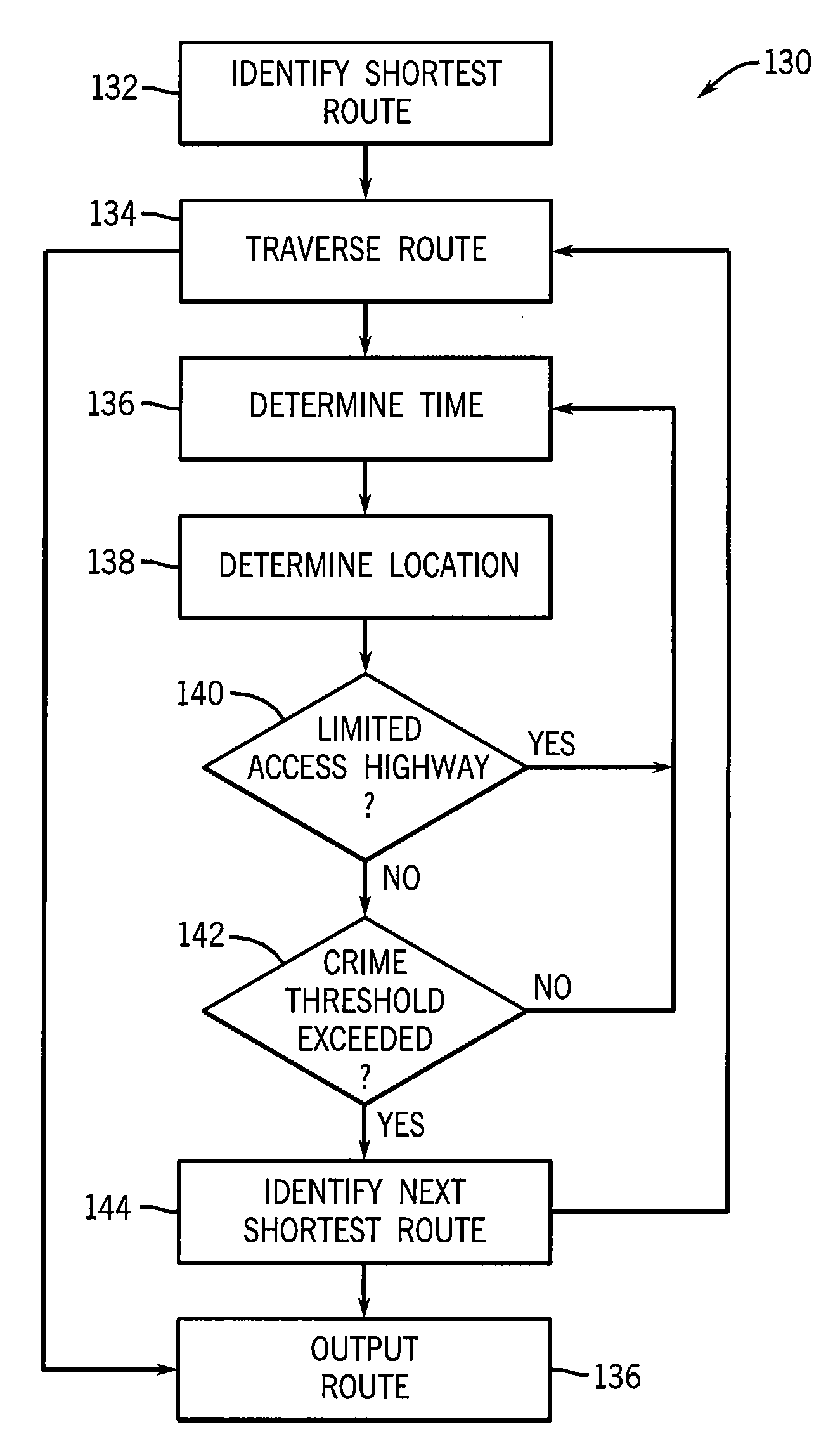
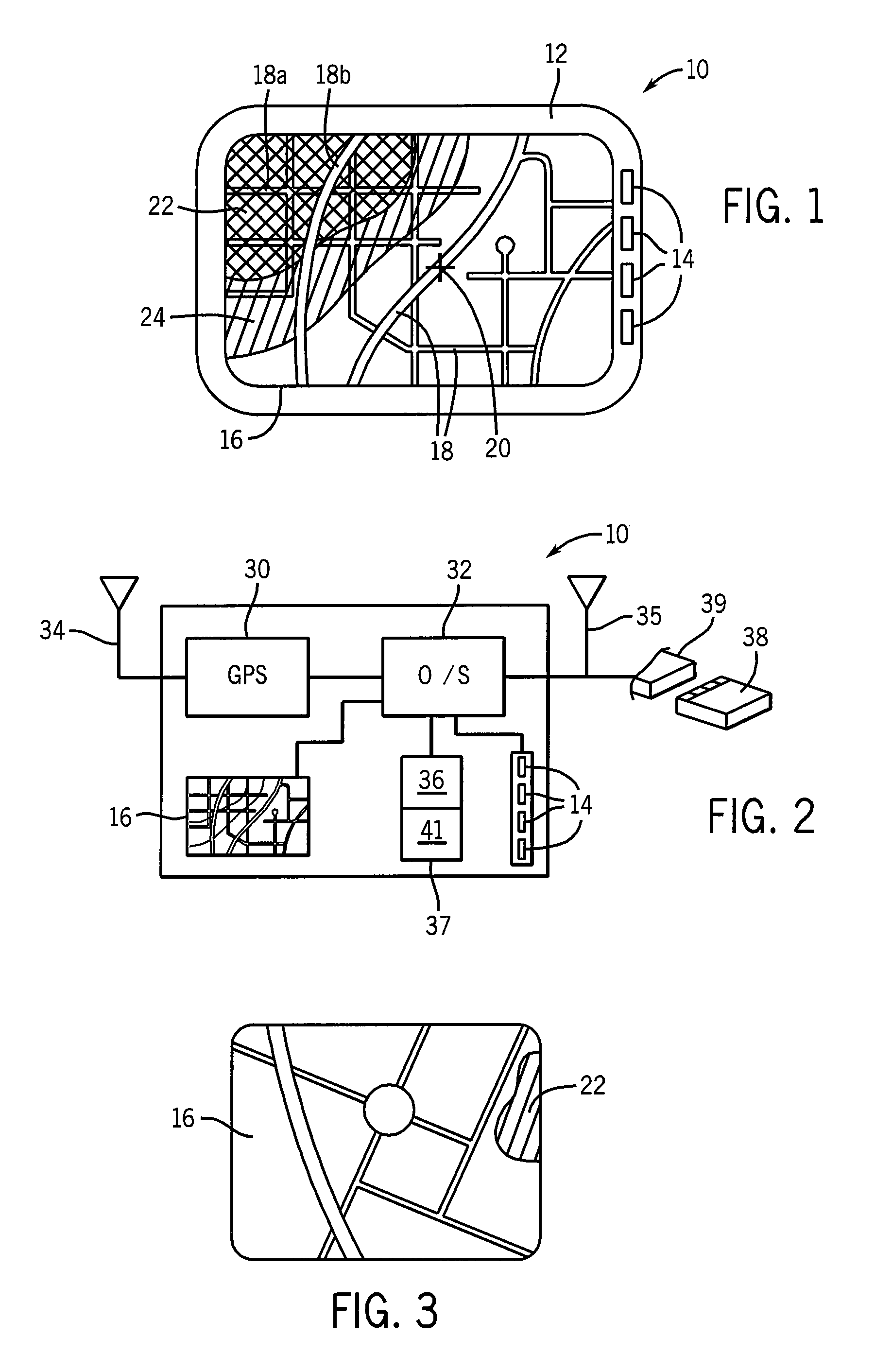
Mobile Navigation System with Graphic Crime-Risk Display
ActiveUS20100100319A1High crimeInformed decisionInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsGraphicsStatistical correlation
A navigation system for mobile use includes street map data used for creating a dynamic map display tracking movement of the vehicle and includes crime data used to provide an overlay on the dynamic display indicating a risk of crime to the vehicle's occupants from the surrounding area. Crime data may be harvested from police websites and / or generated using statistical correlation techniques from other proxy information. Presented crime data indicate crime risk, type of crime, crime date or time of occurrence, and linkage to environmental conditions such as type of weather, temperature, and moonlight.
Owner:RIO SISA IDEA FARM
Mobile payment system using barcode capture
The present invention proposes to streamline the process by replacing most of the manual entry and mobile navigation through a mobile client application that will allow the user to [a] capture a barcode using a camera phone or any other camera-equipped communicating device such as a PDA with a camera attachment or a internet connected computer with a web-cam and [b] automatically send—or prepare the transmission of—the relevant information to the vendor directly or through the usage of a centralized platform.
Owner:SCANBUY
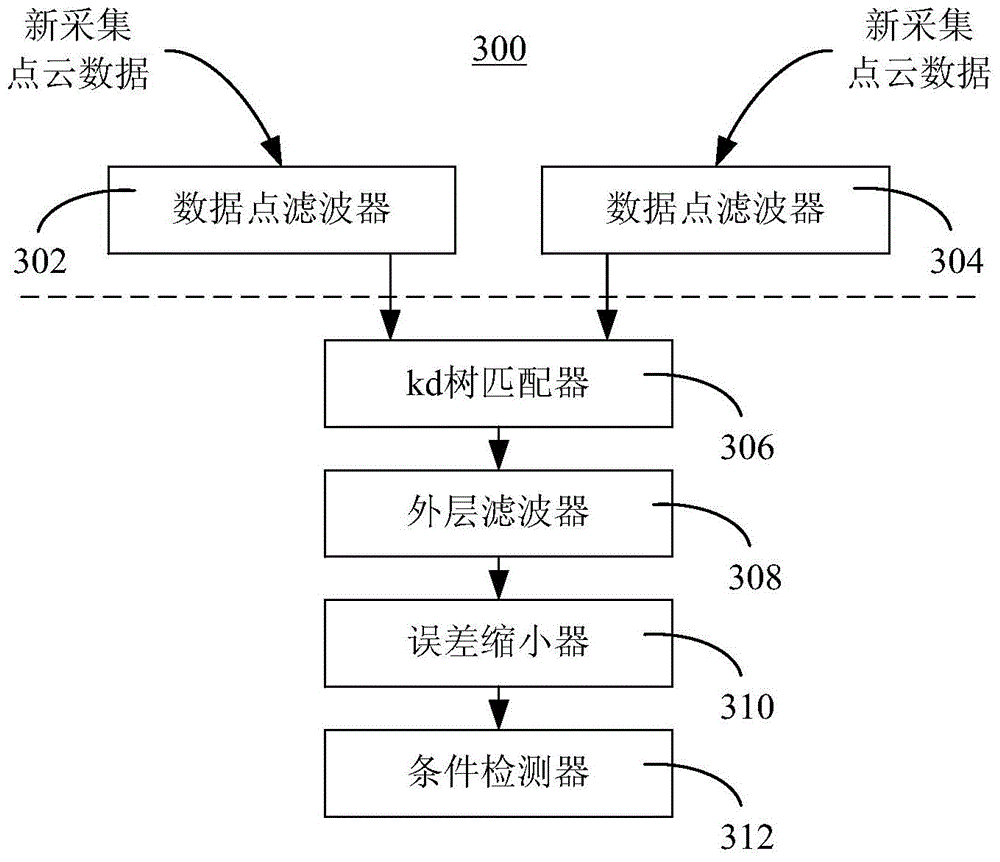
Fusion method of indoor SLAM map based on visual perception and laser detection
InactiveCN109857123AImprove accuracyRich relevant informationPosition/course control in two dimensionsMobile navigationPoint cloud
The invention discloses a fusion method of an indoor SLAM map based on visual perception and laser detection. The method comprises the steps of the laser detection, constructing a three-dimensional point cloud map, filtering and projection processing and map fusion; through the steps, on the one hand, a two-dimensional laser detection map containing ground height information is obtained, on the other hand, a three-dimensional visual perception point cloud map is obtained, and then after the three-dimensional visual perception point cloud map is filtered and projected, a two-dimensional visualperception map containing obstacle information is obtained; and finally, the two-dimensional laser detection map and the two-dimensional visual perception map are fused to obtain a two-dimensional fusion map. According to the fusion method of the indoor SLAM map based on the visual perception and the laser detection, the influential obstacle information in the process of robot navigation can be fused into two-dimensional map information to generate a two-dimensional map with high accuracy and rich information, and the practicability in an indoor environment for robot mobile navigation and pathplanning is high.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Gyro sensor module and angular velocity detection method
InactiveUS7814793B2Improve detection accuracyAcceleration measurement using interia forcesTesting/calibration apparatusMobile navigationGyroscope
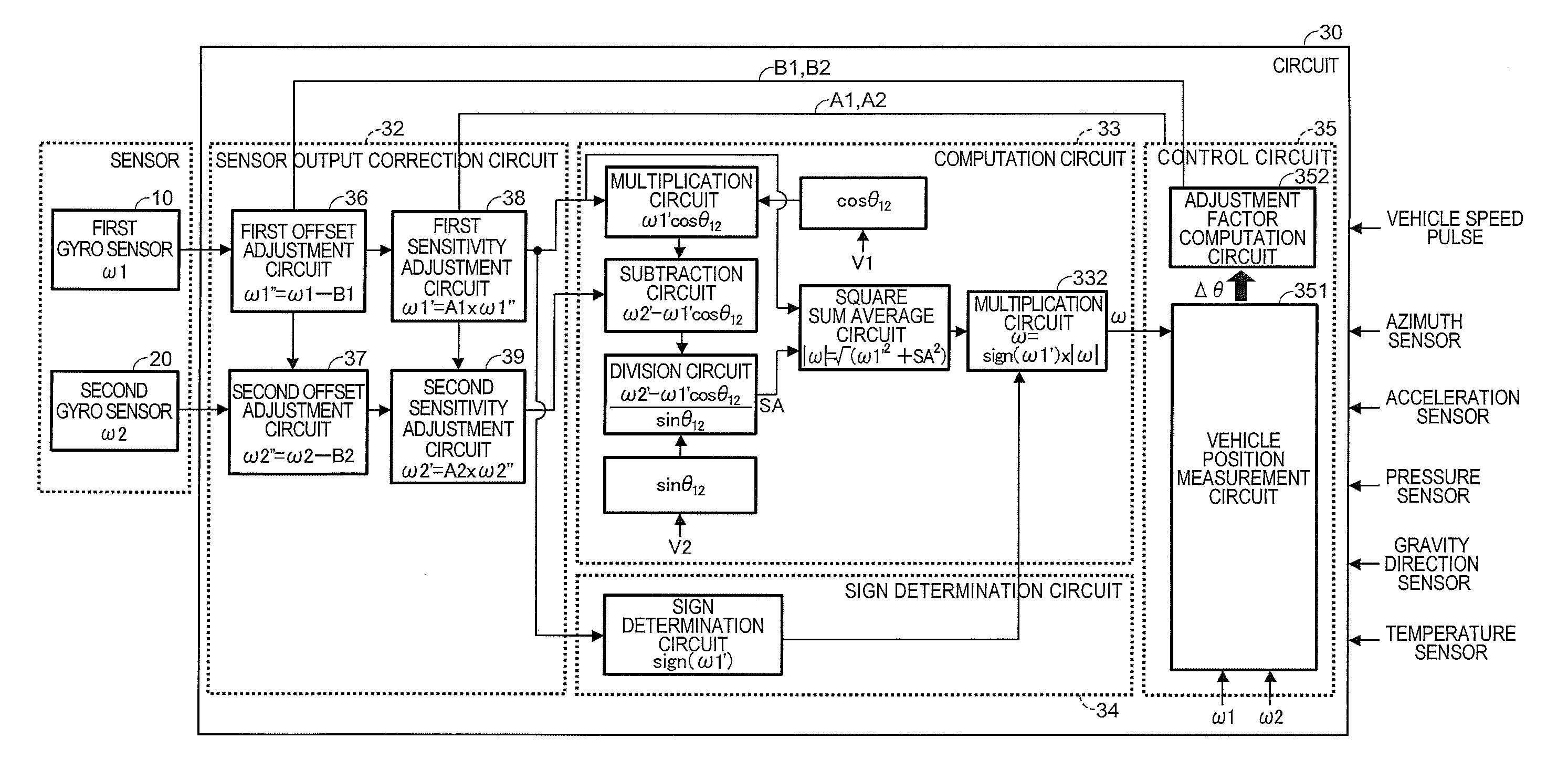
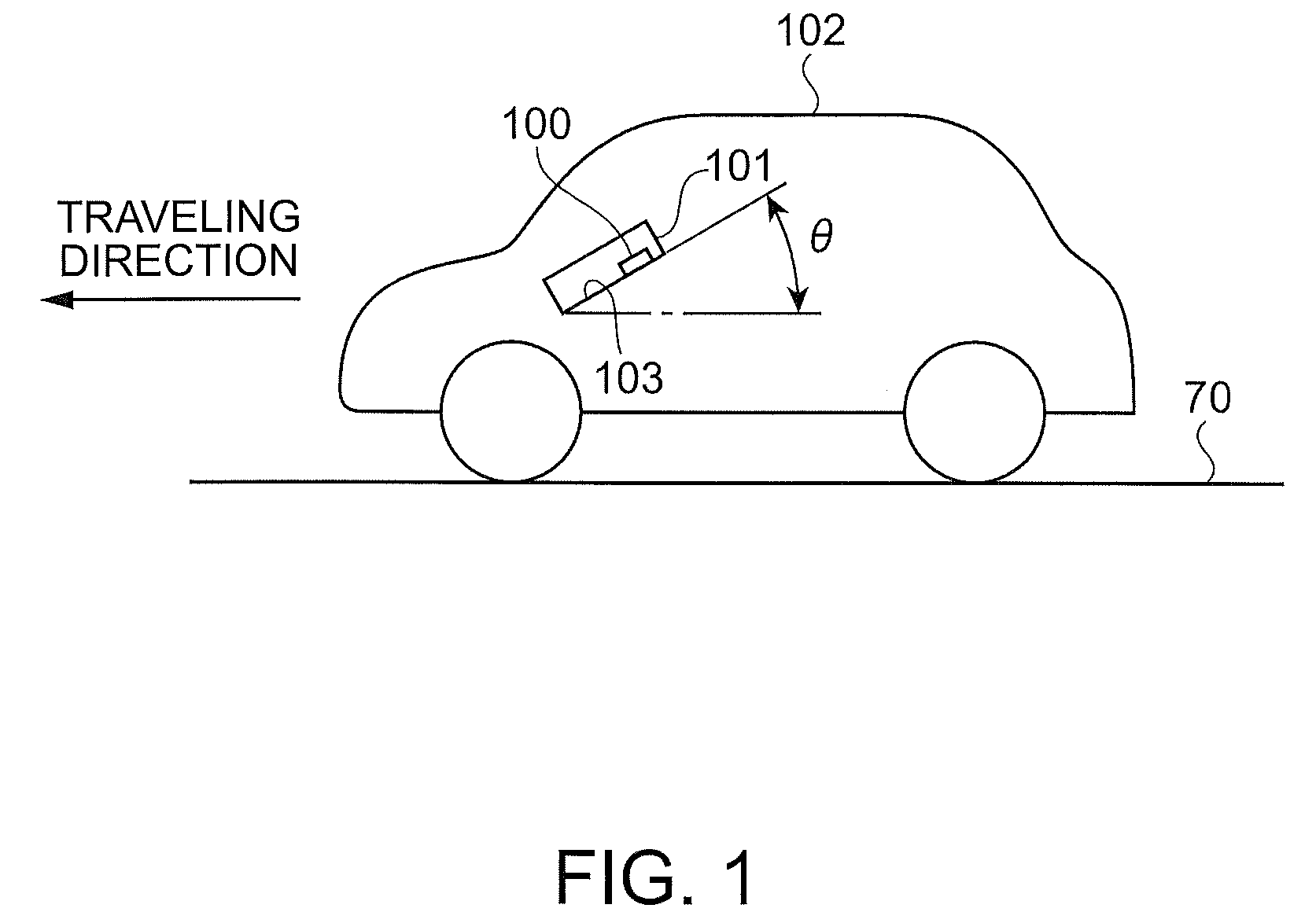
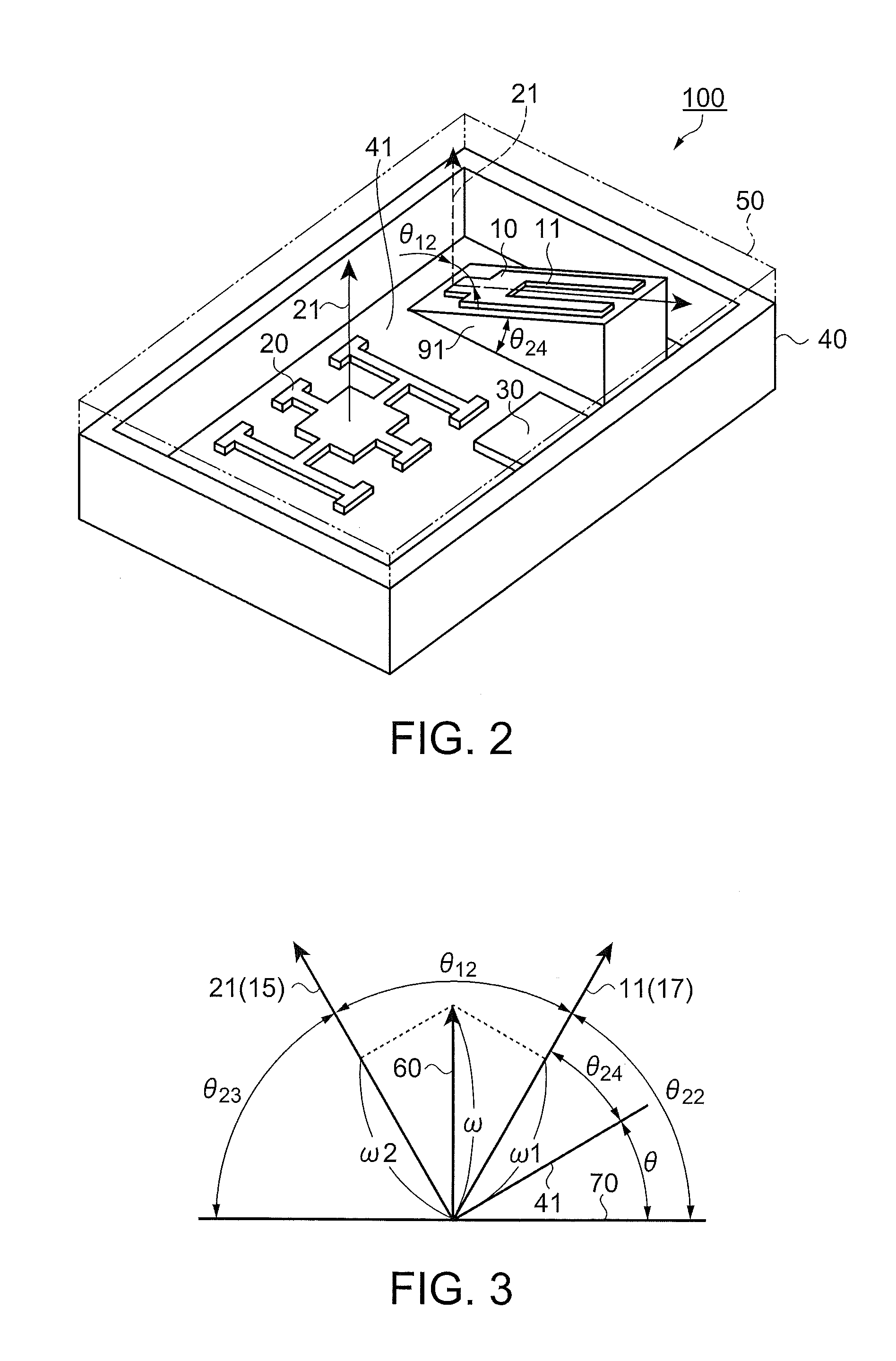
A mobile navigation system gyro module comprises: first and second gyro sensors outputting angular velocities ω1, ω2 around first and second axes intersecting at an acute angle θ12; a sign determination circuit determining a sign of ω1; a correction circuit correcting the first and second gyro sensor outputs; and a computation circuit computing ω′=√(ω1′2+SA2) and SA=(ω2′−ω1′ cos θ12) / sin θ12 using angular velocities ω1′, ω2′ from the correction circuit, and outputting angular velocity ω by multiplying ω′ by the sign of ω1, wherein the correction circuit includes: first and second offset adjustment circuits outputting ω1″ and ω2″ by respectively subtracting from ω1 and ω2, corrections B1 and B2 corresponding to the first and second gyro sensor outputs when the mobile unit stops; and the angular velocity ω is around an axis coplanar with and between the first and second axes.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
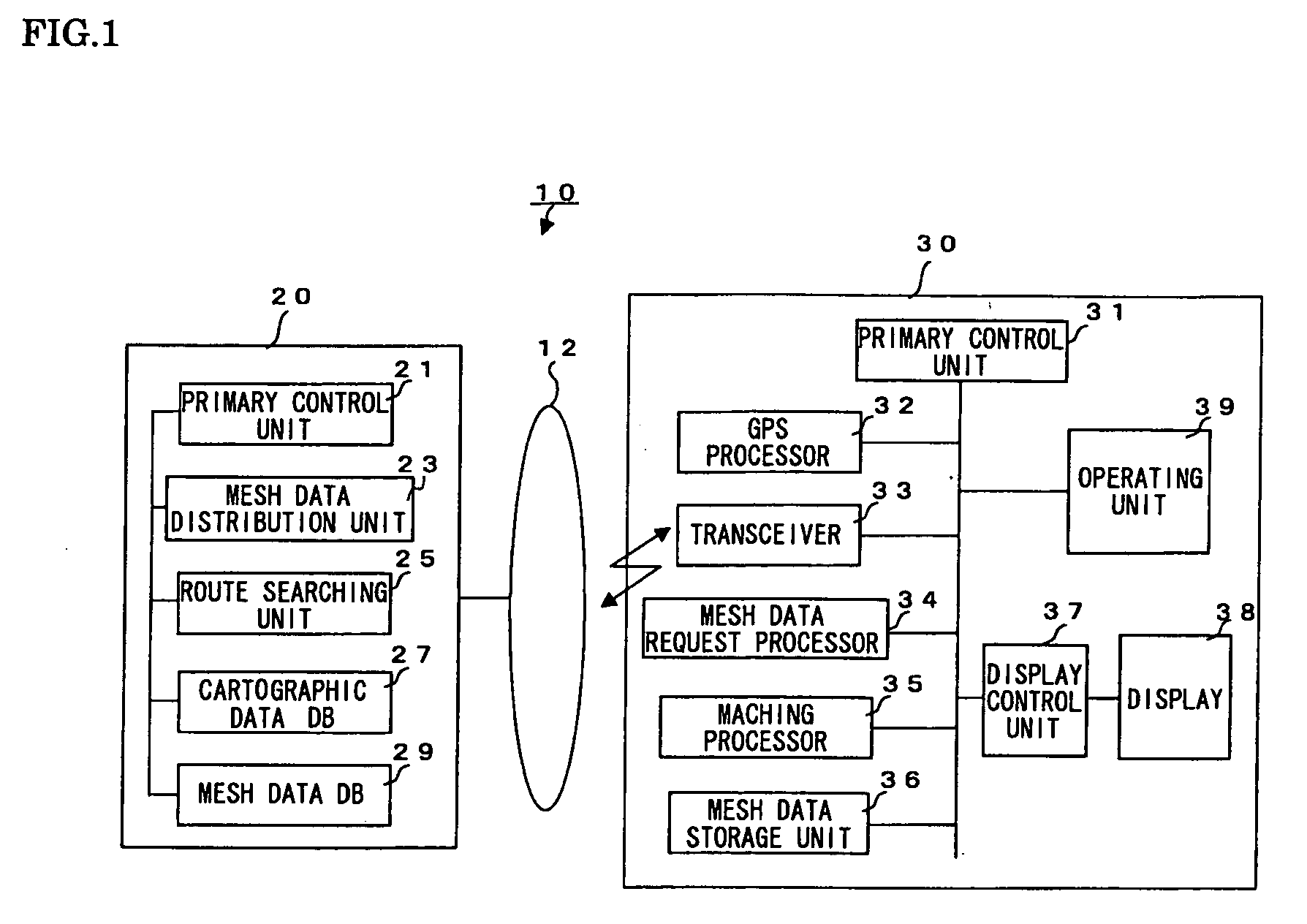
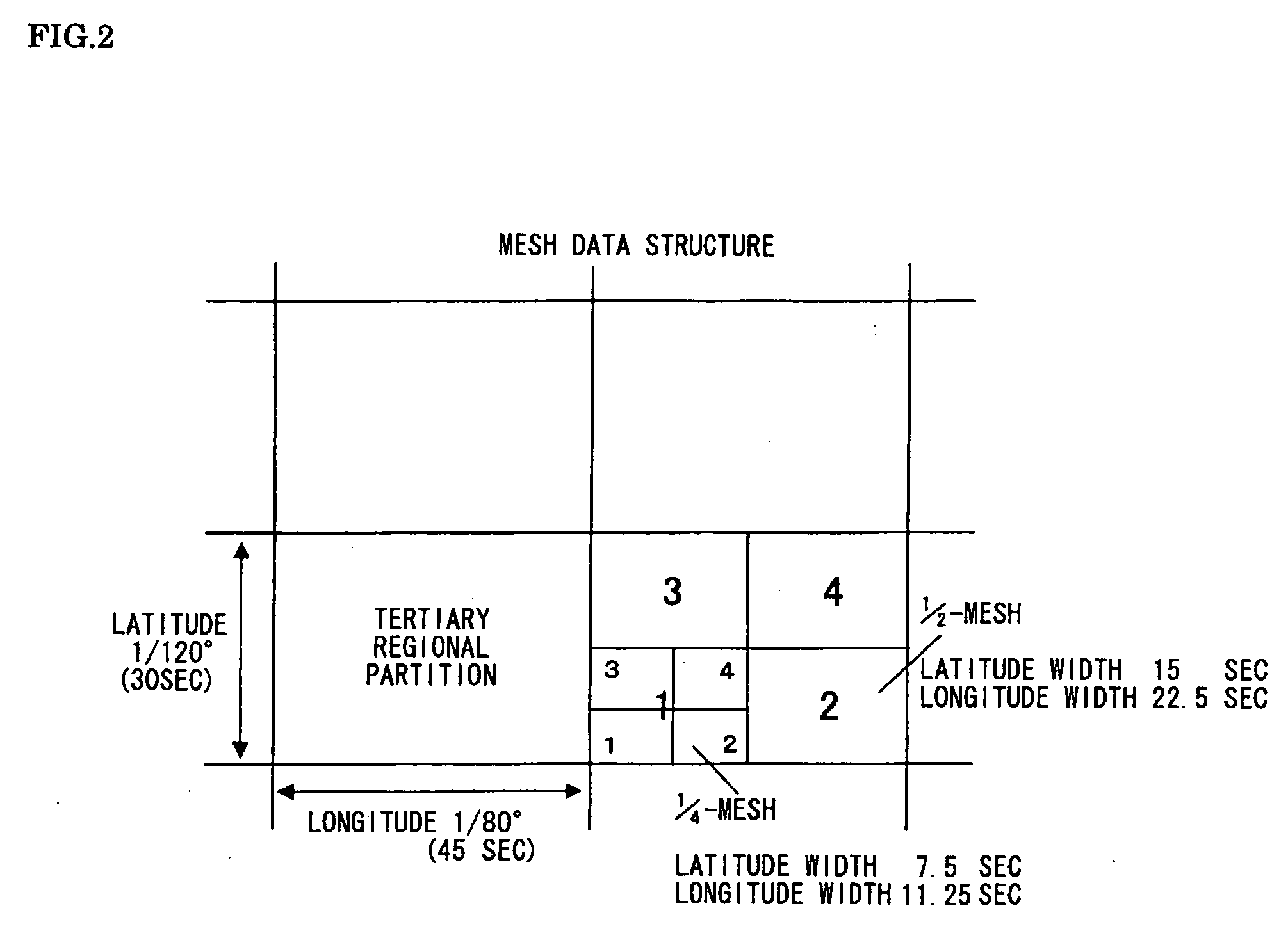
Communicative Navigation System, Information Distribution Server, and Mobile Navigation Terminal
InactiveUS20080201070A1Reduction in network transmission loadFacilitating visual recognitionInstruments for road network navigationControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorMobile navigationRoute search
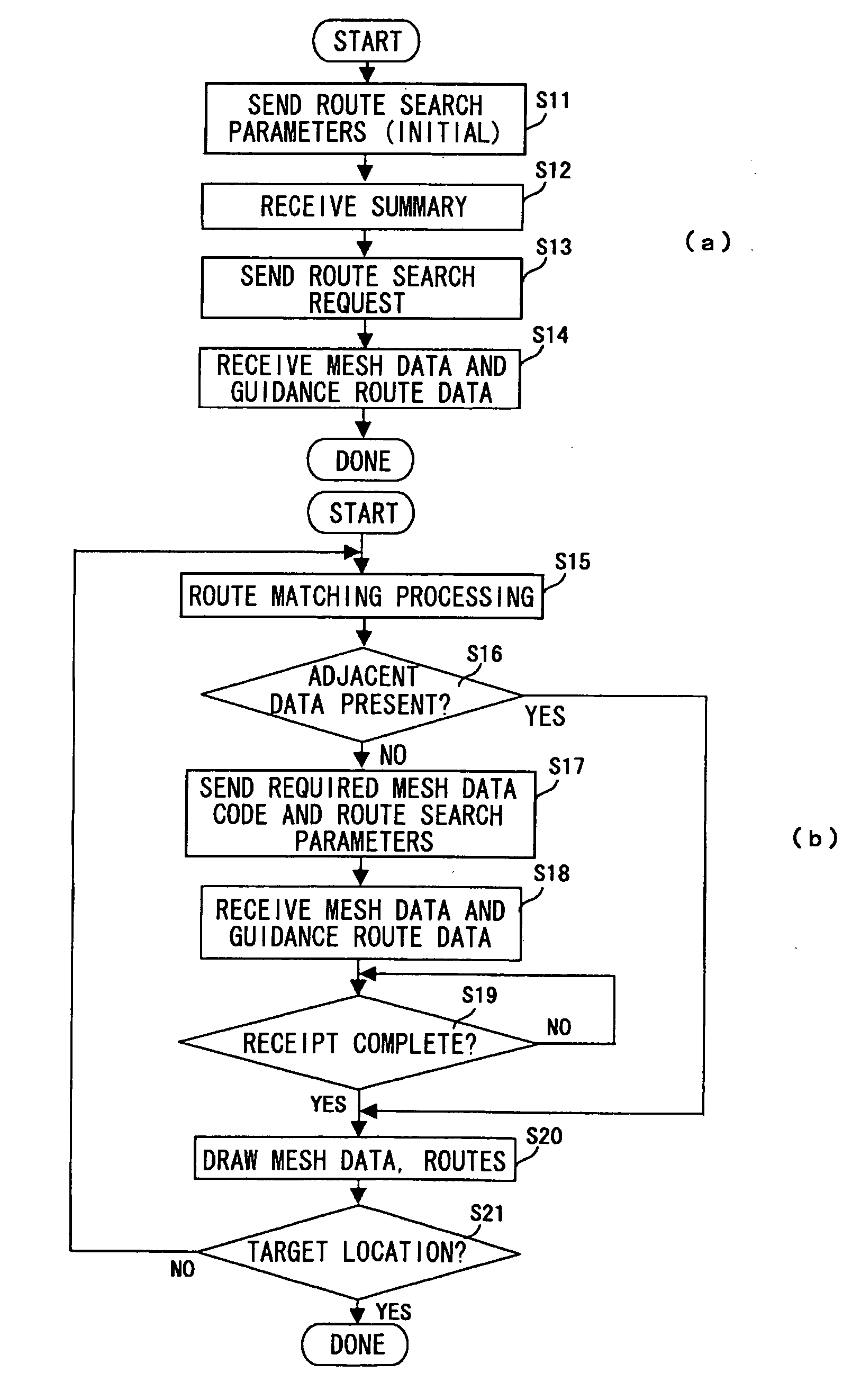
There are provided a mobile navigation terminal and an information distribution server that includes a geographical database for route searching and a mesh database storing therein meshes into which images produced from aerial photographs have been divided. The mobile navigation terminal includes GPS means; matching means for matching a measured location with a route to determine a current location; and a mesh data requesting part for calculating mesh data for which to request the information distribution server anew in connection with the current location. The mobile navigation terminal transmits a route search request and / or a mesh data distribution request to the information distribution server. The information distribution server, which includes a route searching part and a mesh dada distributing part, uses the geographical database to search for a route. If there exists a guide route in the mesh data as requested for, then the information distribution server adds the guide route data to the mesh data and distributes them to the mobile navigation terminal. The mobile navigation terminal displays the guide route on the distributed mesh data.
Owner:NAVITIME JAPAN CO LTD
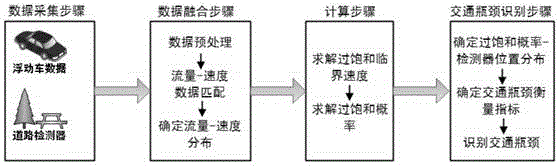
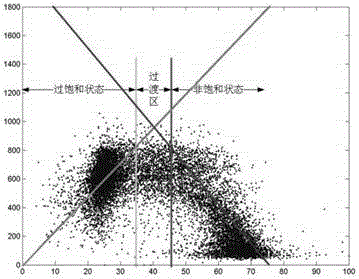
System and method for identifying urban expressway traffic bottlenecks
ActiveCN105825669ARealize data fusion and utilizationImplement data miningDetection of traffic movementMobile navigationSimulation
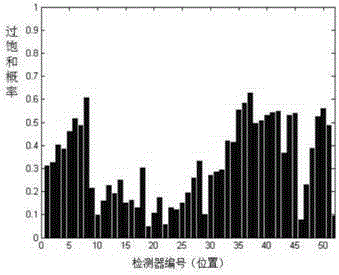
The invention provides a method for identifying urban expressway traffic bottlenecks. The method comprises a step of collecting the mobile navigation data of a road vehicle and road fixed detector data, a step of carrying out pretreatment on the collected data, matching the data of different sources, and determining the flow-speed distribution of each detector section, a step of determining a supersaturation critical speed and a supersaturation probability according to the flow-speed distribution, a step of determining supersaturation probability and detector position distribution, and identifying traffic bottlenecks; and classifying the identified urban expressway traffic bottlenecks, and giving corresponding control measures for different types of traffic bottlenecks.
Owner:北京数行健科技有限公司
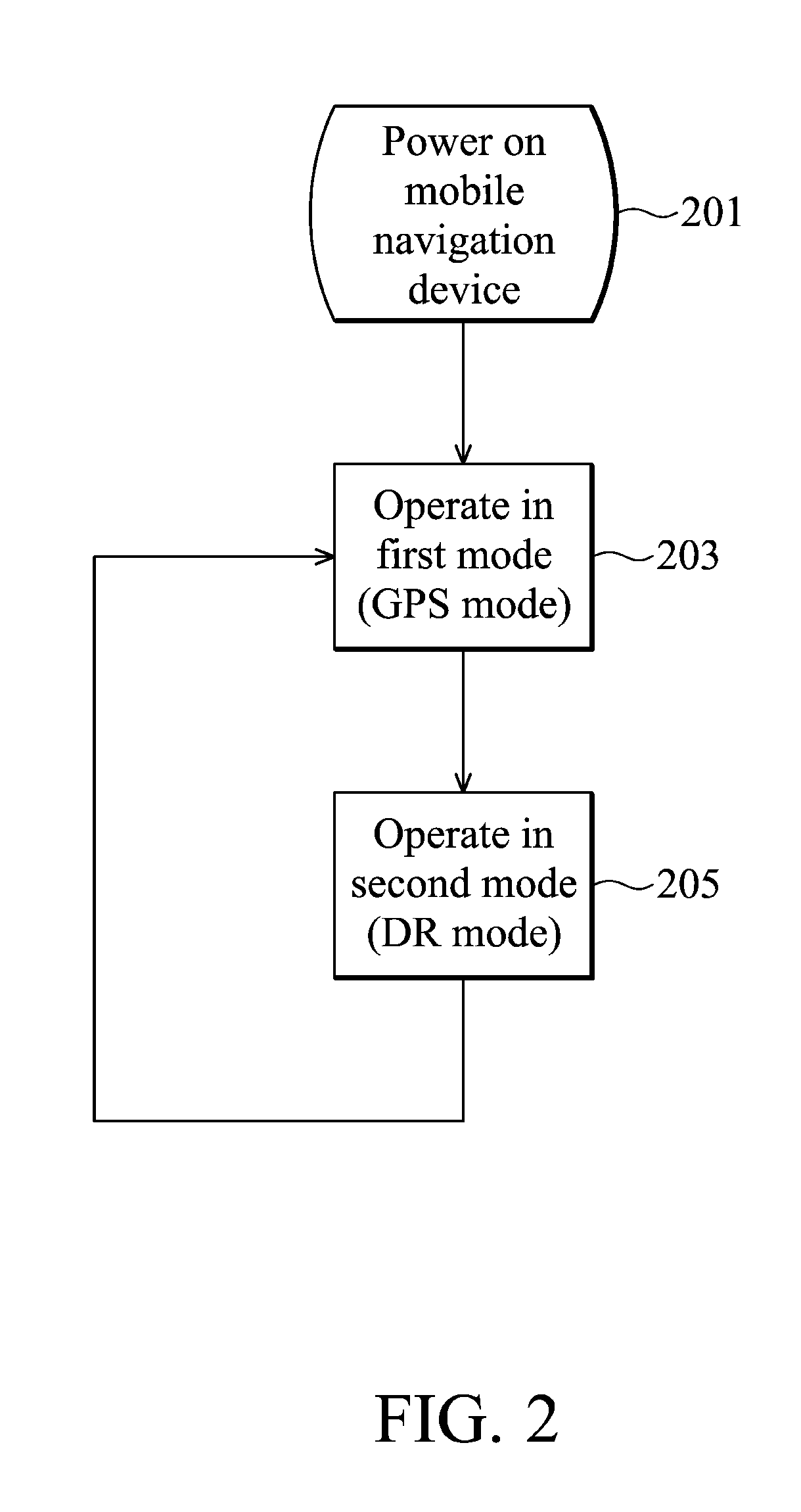
Mobile navigation device
ActiveUS20110208430A1Instruments for road network navigationPosition fixationMobile navigationSatellite positioning
A mobile navigation device operating in a first mode and a second mode is provided. In the first mode, a satellite positioning module is activated while a dead reckoning module is disabled. A processor calculates the coordinates of the mobile navigation device based on the satellite navigation signals received by the satellite positioning module. In the second mode, the satellite positioning module is disabled while the dead reckoning module is activated, and the processor updates the coordinates based on displacements and rotations detected by the dead reckoning module.
Owner:HTC CORP
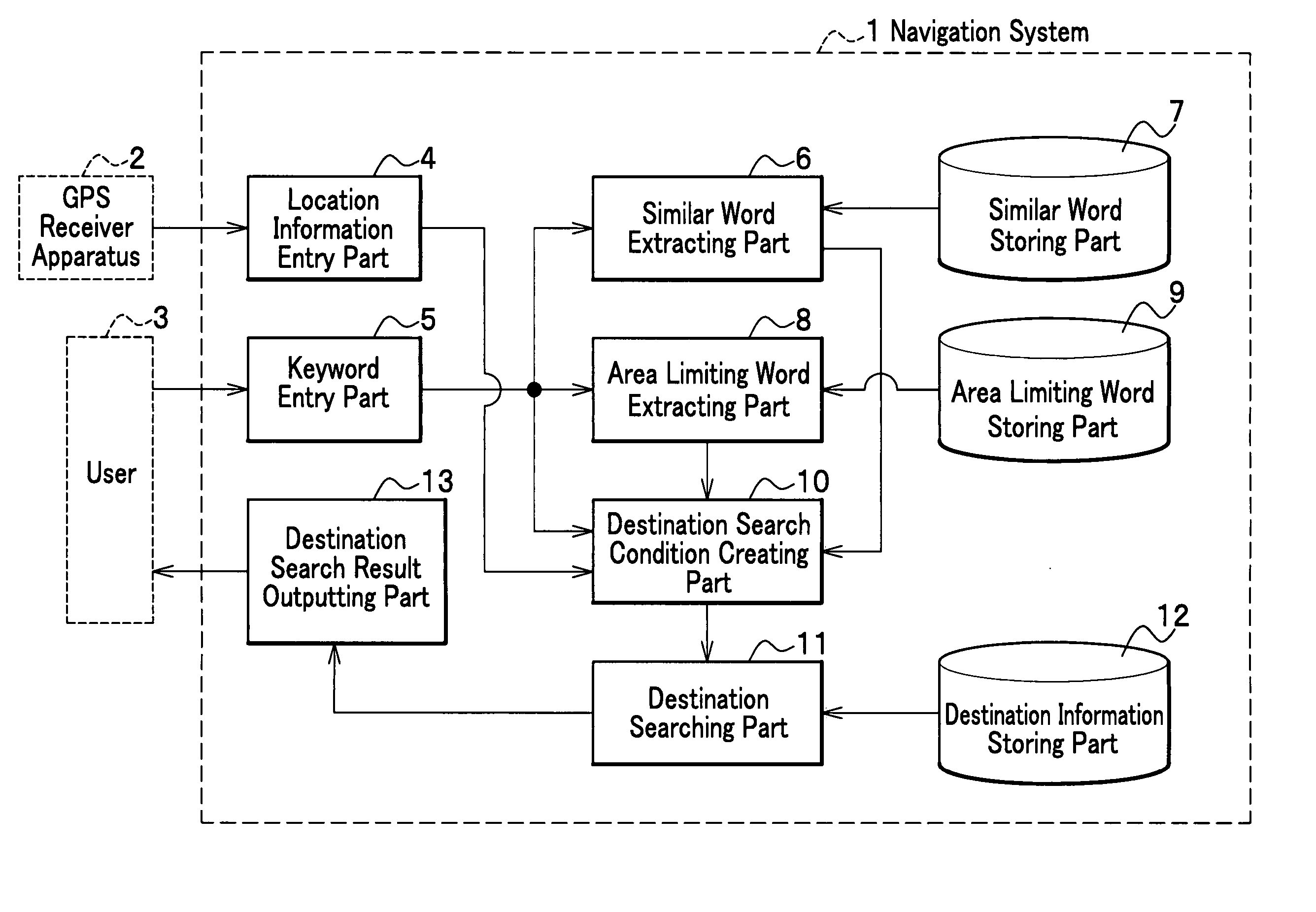
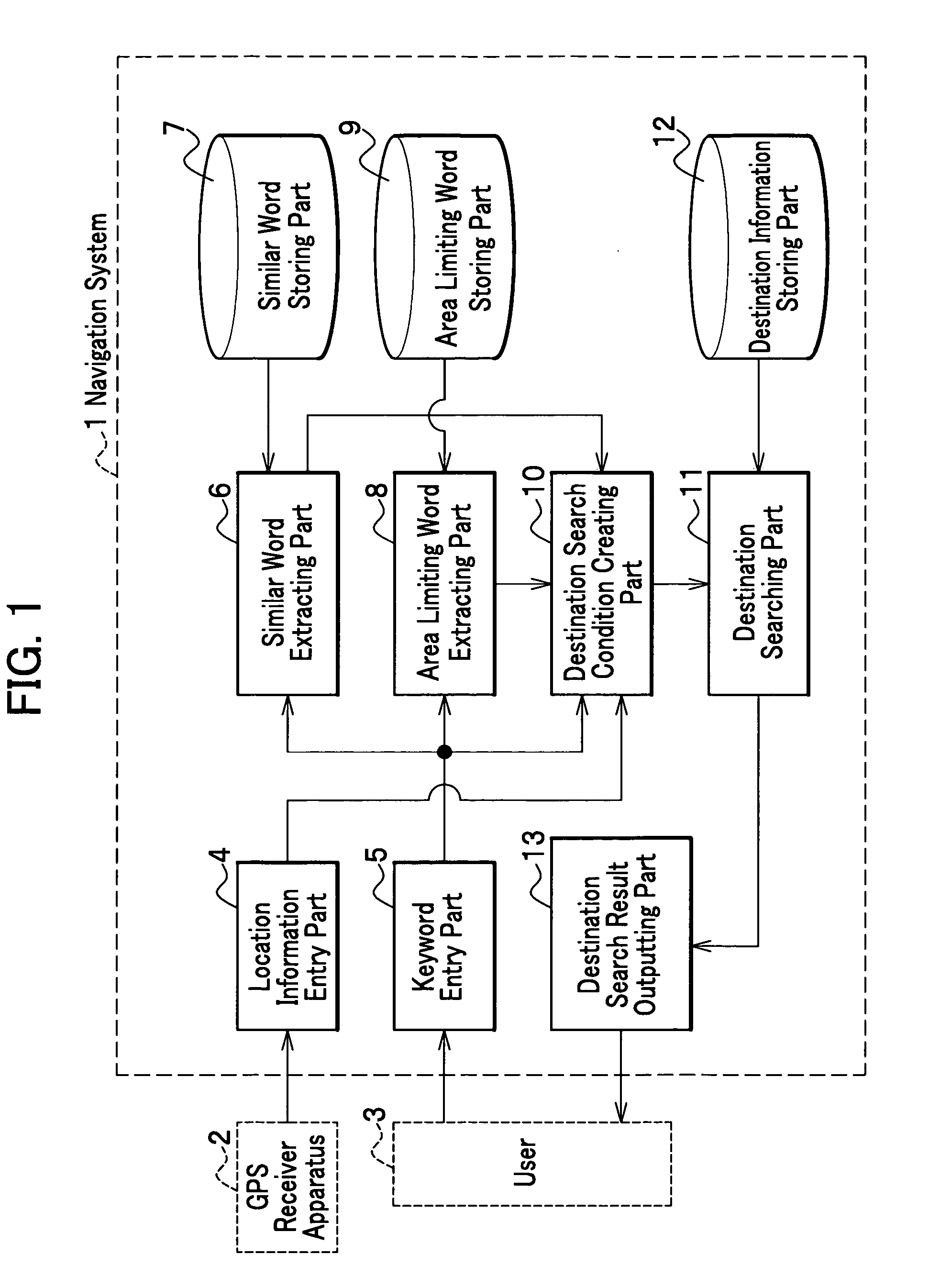
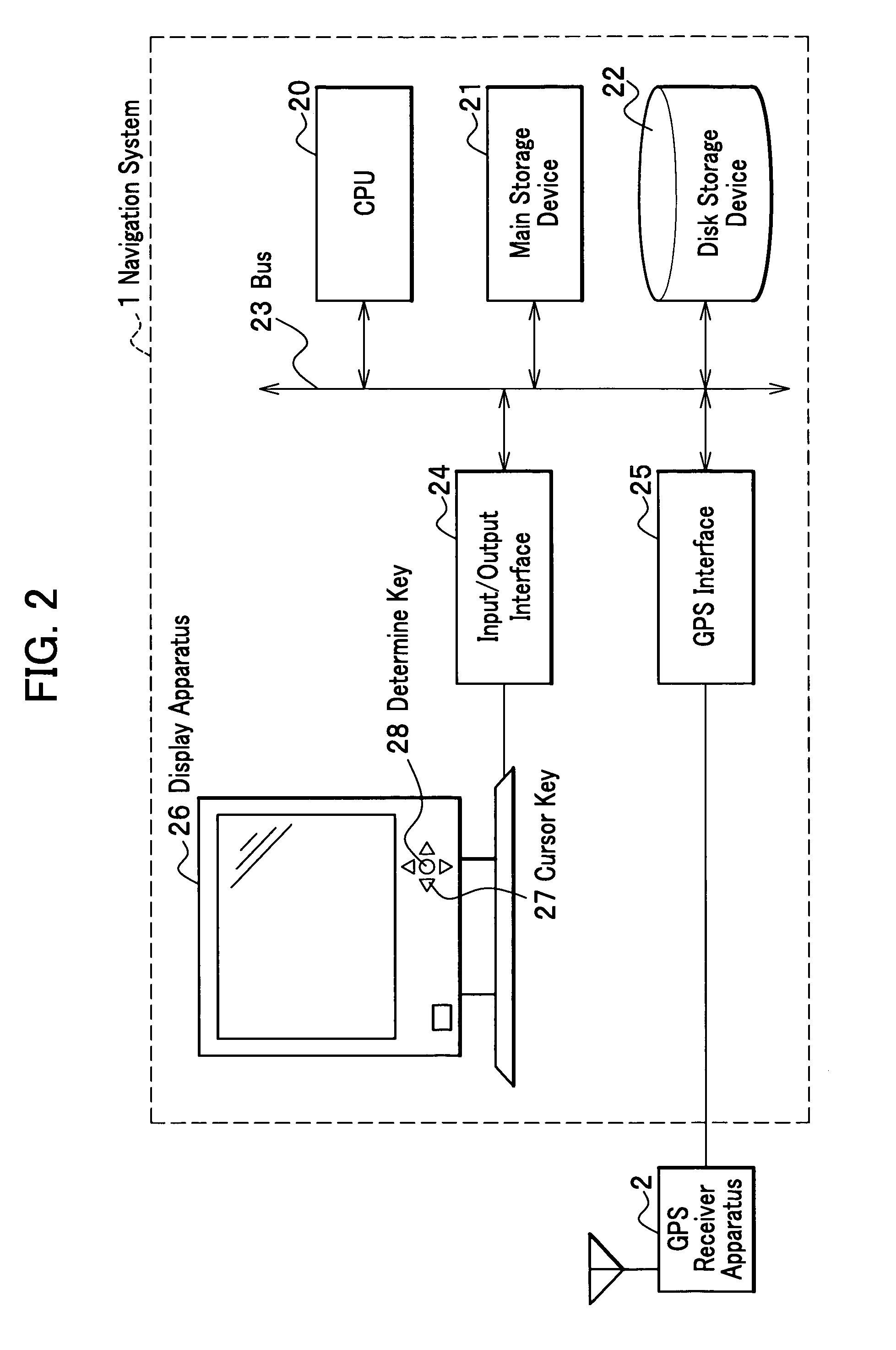
Mobile body navigation system and destination search method for navigation system
InactiveUS20050210021A1Relieve stressInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsMobile navigationNavigation system
An area limiting word storing part which stores area limiting words whose meanings limit an area is disposed in a navigation system, and as the area limiting word storing part is referred to, area limiting words are extracted from among keywords, based on the area limiting words, a condition to narrow down a smaller search area is created. A similar word storing part which stores similar words is further disposed, and as the similar word storing part is referred to, similar words to a keyword are extracted and a search condition to expand the range of a search based on the keyword is created. These search conditions together are destination search conditions, in accordance with which a destination information storing part is searched.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Vehicle navigation method and system and vehicle mobile navigation
ActiveCN103344980AImprove usabilityImprove accuracySatellite radio beaconingMobile navigationGps navigation
The invention discloses a vehicle navigation method. The method comprises the steps of judging GPS positioning status information in current GPS navigation data to determine whether the current GPS navigation data are usable navigation data or not, achieving navigation according to the current GPS navigation data, or, obtaining inertial navigation data according to history GPS navigation records and vehicle running data and achieving navigation according to the inertial navigation data. Therefore, the problem that due to the influence of covering landforms in the GPS vehicle navigation process, vehicle navigation cannot be achieved is solved. The usability and accuracy of vehicle navigation under various landforms and position environments are improved, the service environment of a vehicle navigation system is expanded, and accordingly the reliability and safety of vehicle navigation when vehicle navigation is in use are improved.
Owner:鲍晓东
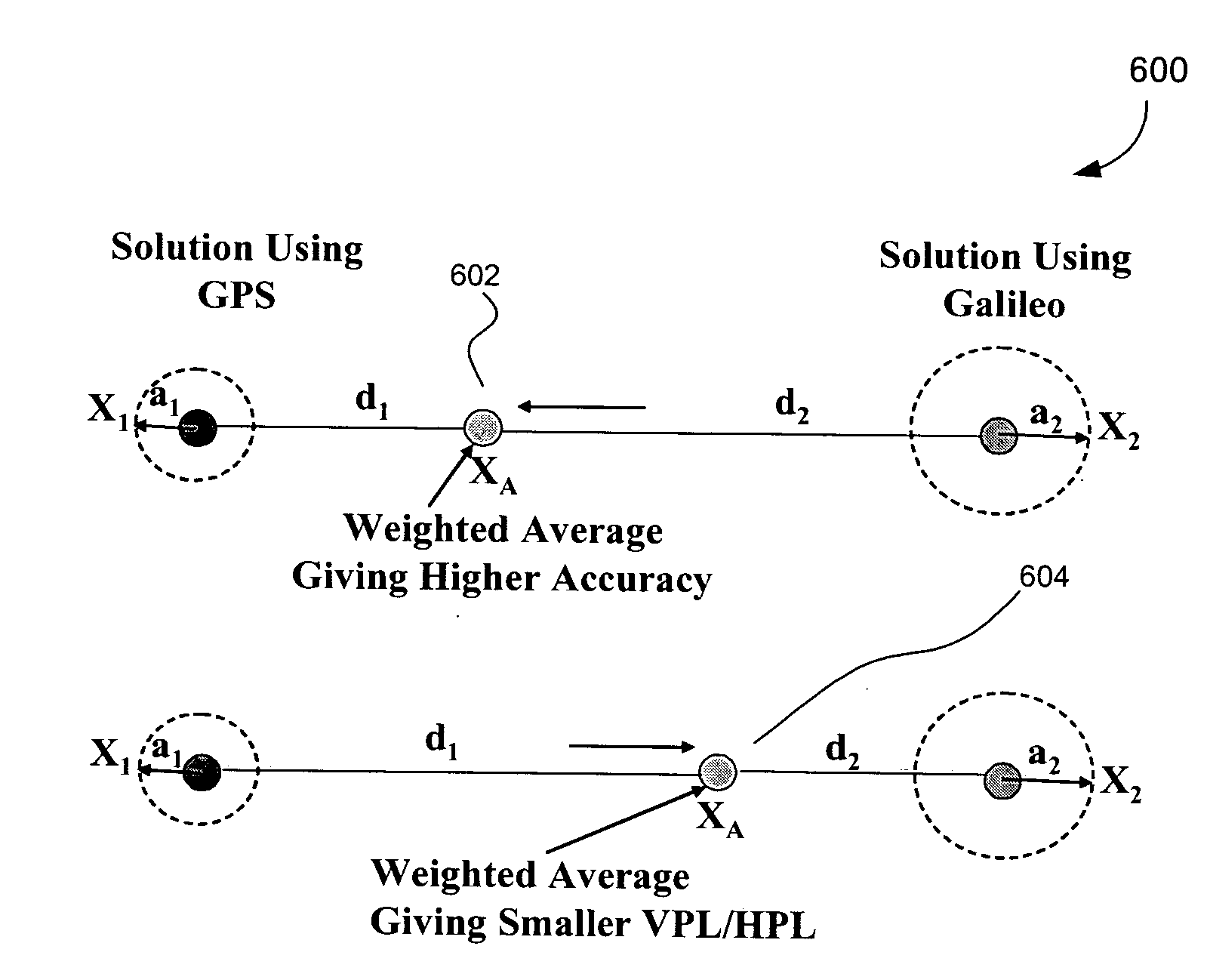
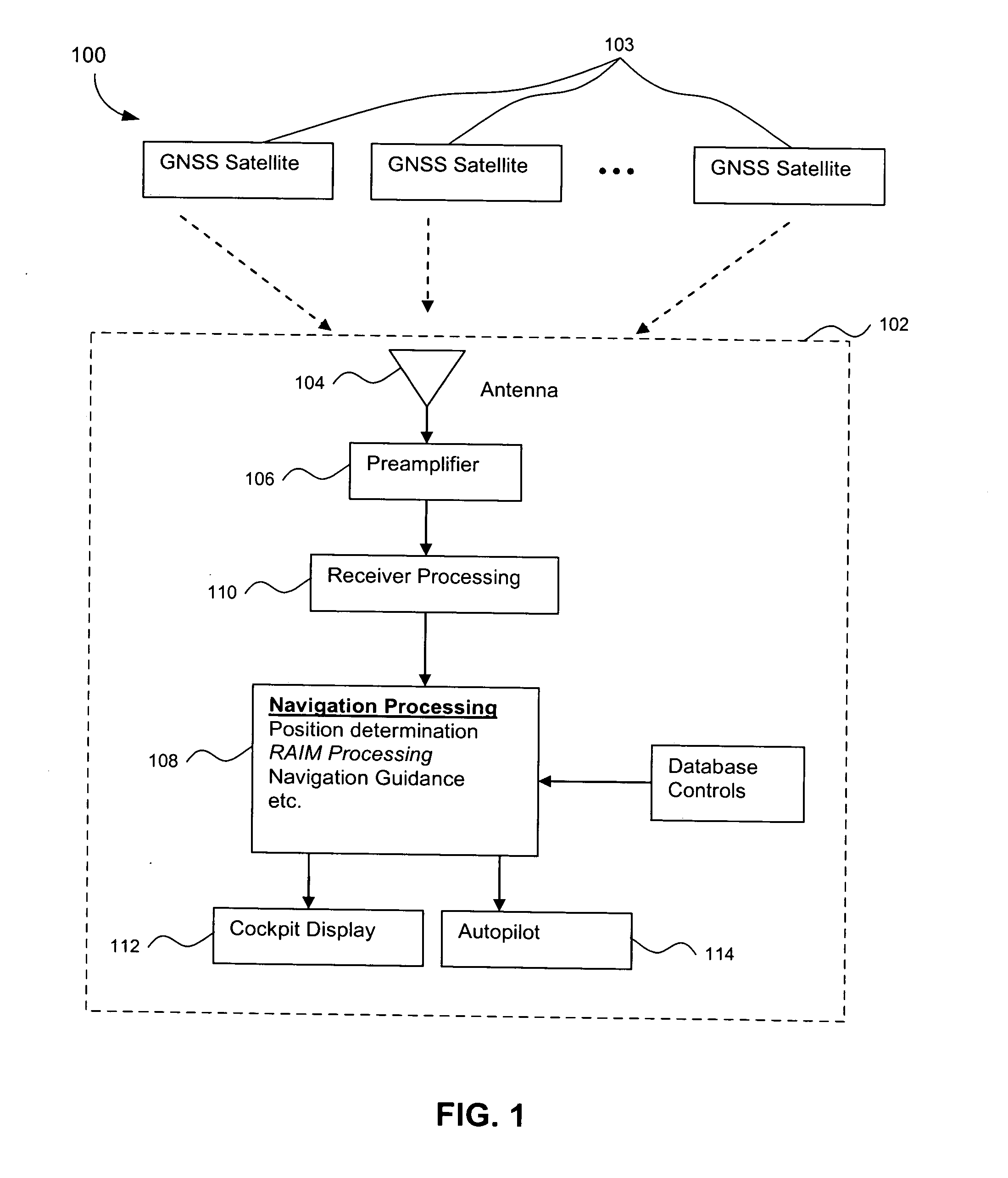
Methods and systems for mobile navigational applications using global navigation satellite systems
ActiveUS20080062041A1Improve usabilityPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingMobile navigationHigh availability
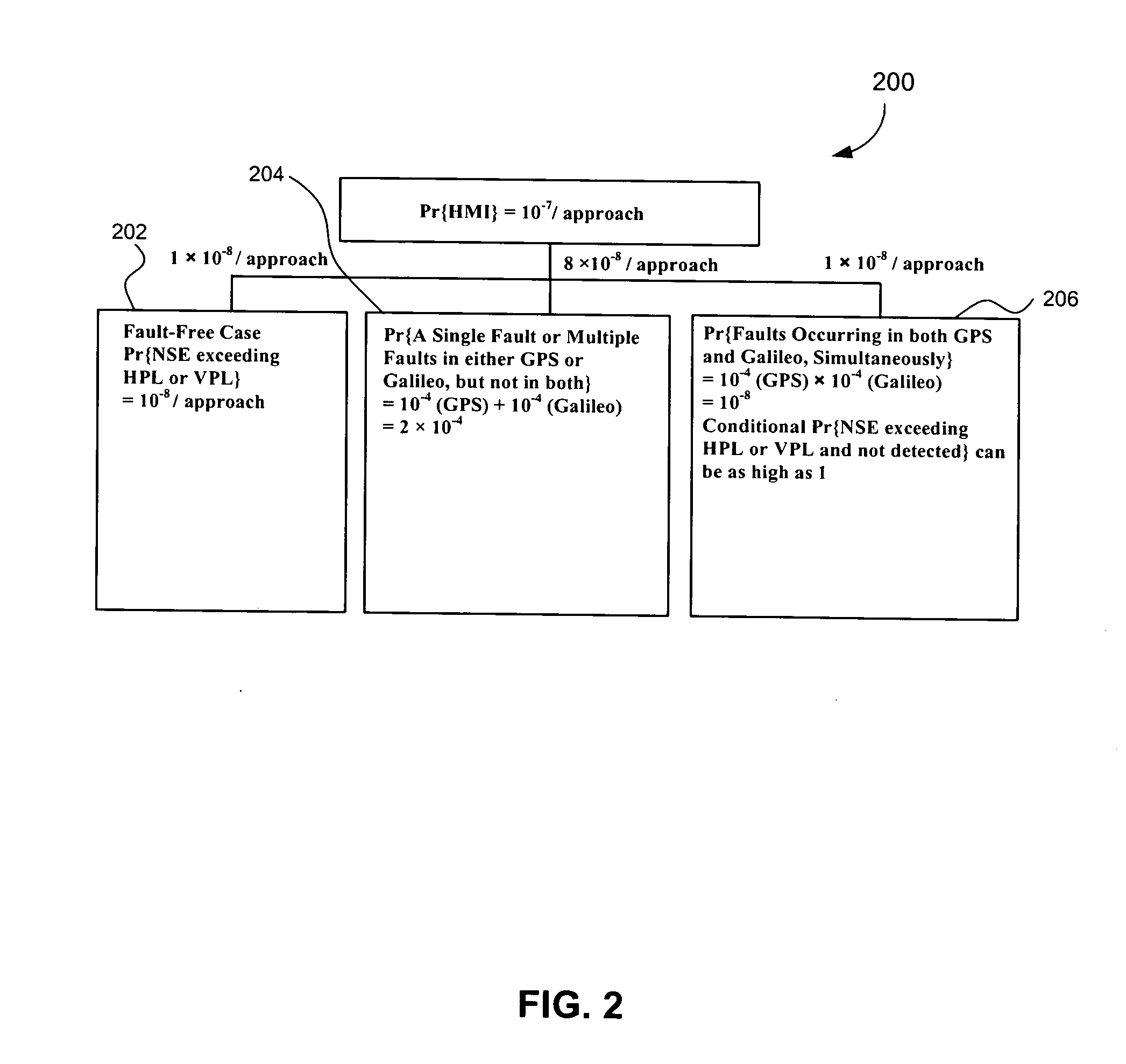
The present invention relates to providing navigation guidance for mobile users, using Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs) for applications where the user position needs to be determined in real time while meeting the navigation requirements, especially integrity requirement, for the given application. The present invention assists in providing guidance with a high availability of integrity function by trading accuracy for integrity for two different types of navigation applications. A first type of application requires a capability of detecting an occurrence of multiple satellite signal faults; the first embodiment of the invention provides this capability with a high availability of integrity, using two or more independent GNSSs. A second type of application requires a capability of detecting an occurrence of a single satellite signal fault; the second embodiment of the invention provides this capability with a high availability of integrity, using any one or a combination of GNSSs. The detecting and deriving of both methods are (i) in position domain and (ii) determinative of mobile user safety.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
Ionospheric delay correction method for leo satellite augmented navigation systems
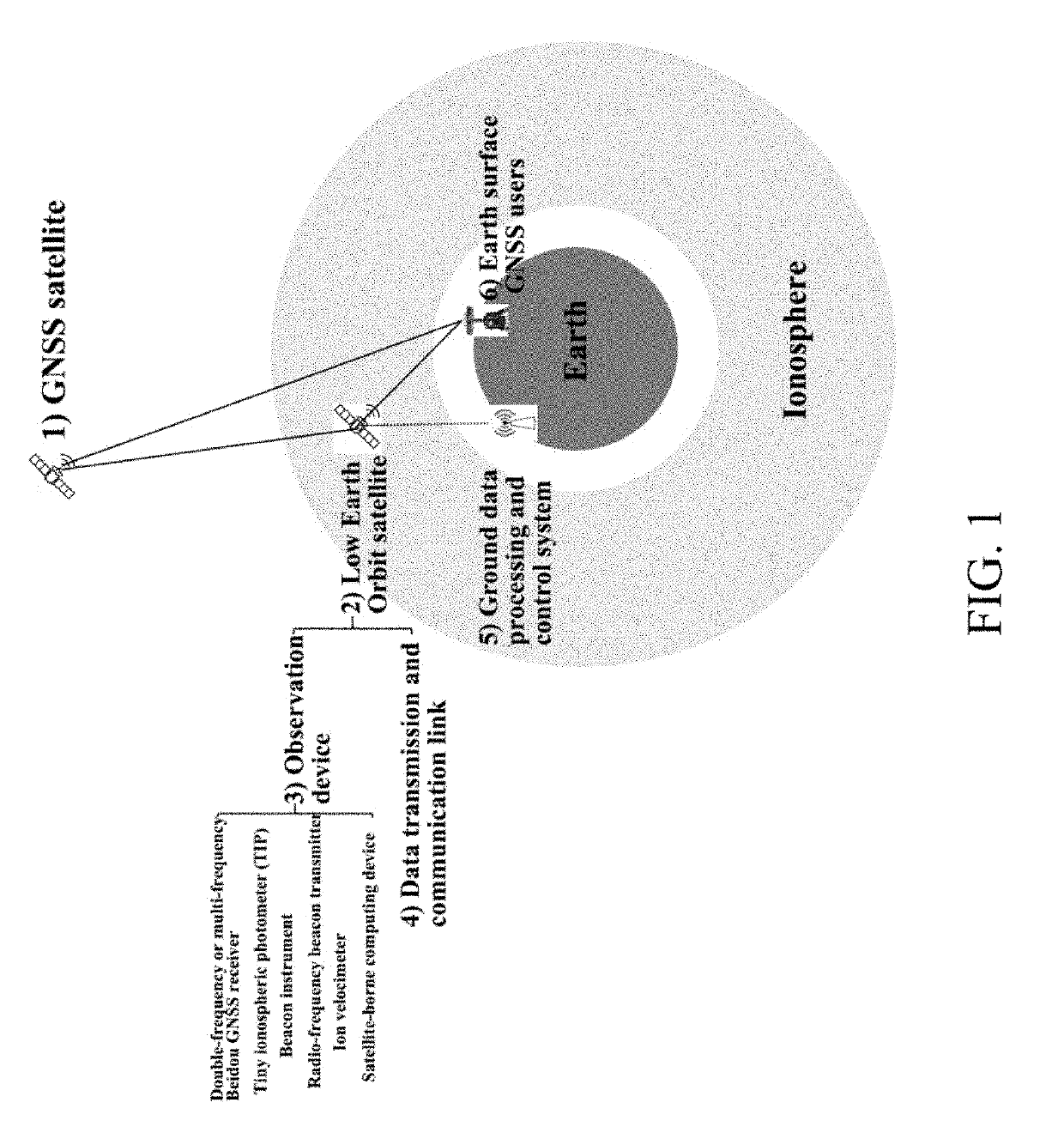
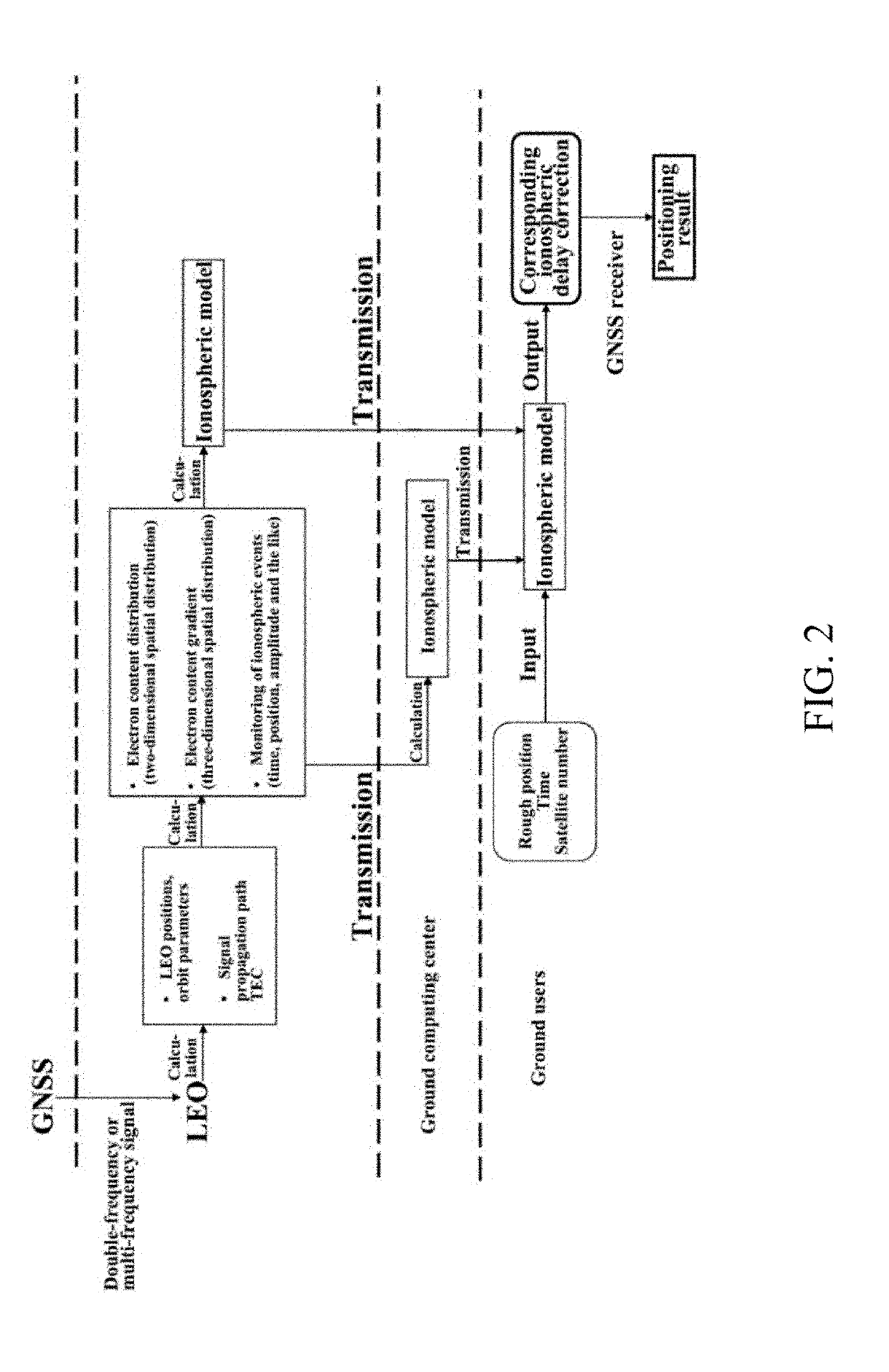
ActiveUS20190271782A1Improve accuracy reliability comprehensivenessReduce system costSatellite radio beaconingMobile navigationIonosphere
The invention discloses an ionospheric delay correction method for LEO satellite augmented navigation systems for GNSS. According to the method, GNSS satellite navigation signals received by LEO GNSS receiver loads are used for providing ionospheric information for navigation augmentation for earth surface users. In the method, as a set of mobile navigation augmentation reference stations, LEO satellites continuously observe the global ionosphere to generate ionospheric delay correction information, and the ionospheric delay correction information is sent to the earth surface users to obtain augmented navigation performance. By adoption of the method, ionospheric delay correction data covering the whole world instead of covering certain areas and particularly ionospheric delay correction data covering the vast marine areas are obtained; ionospheric gradient data are provided; and compared with traditional approaches, ionospheric delay correction accuracy is higher than that of traditional approaches; ionospheric activities and events are monitored in orbit to provide complete ionospheric delay correction information.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Atmospheric environment intelligent management system based on integration of space and air and earth
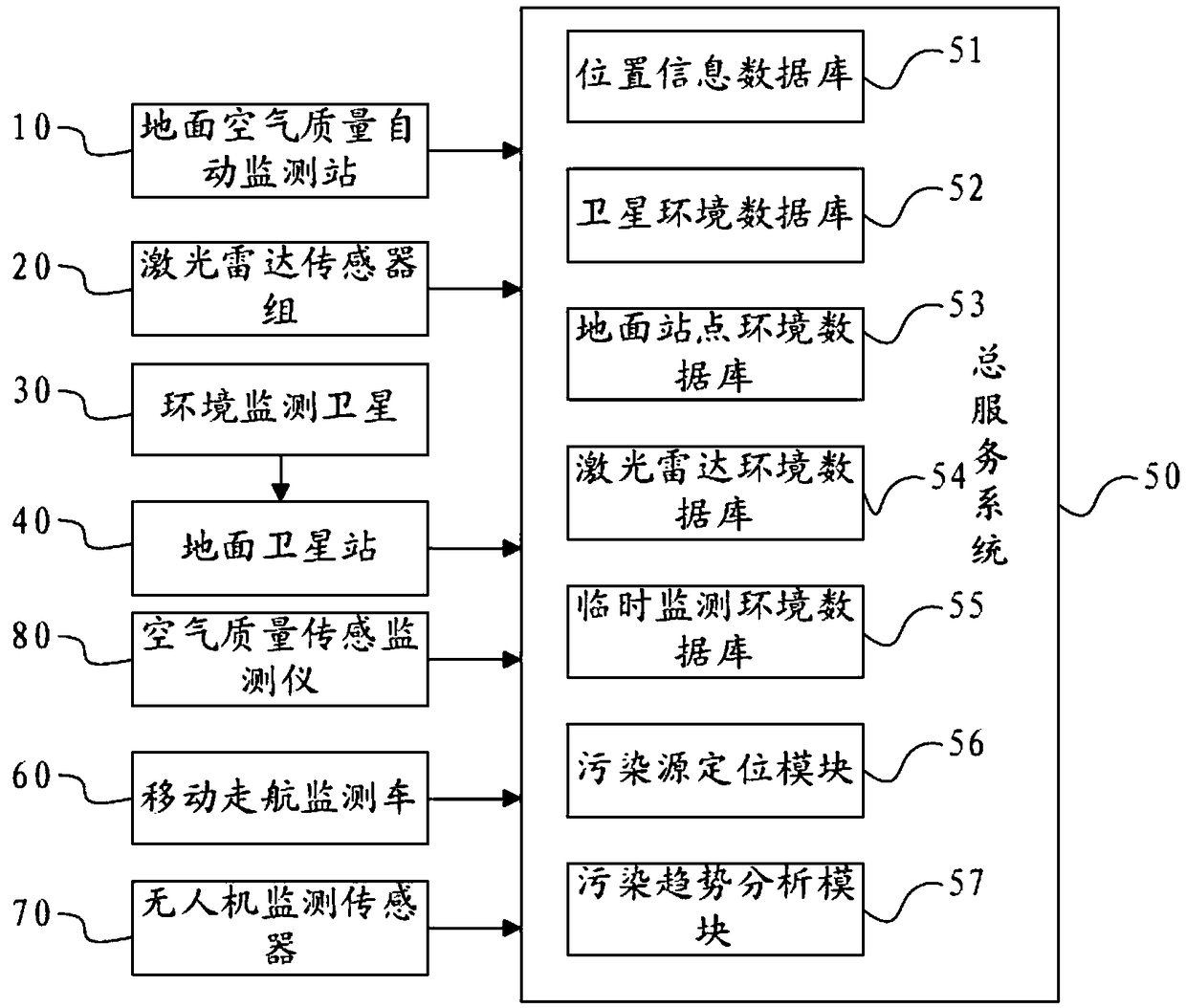
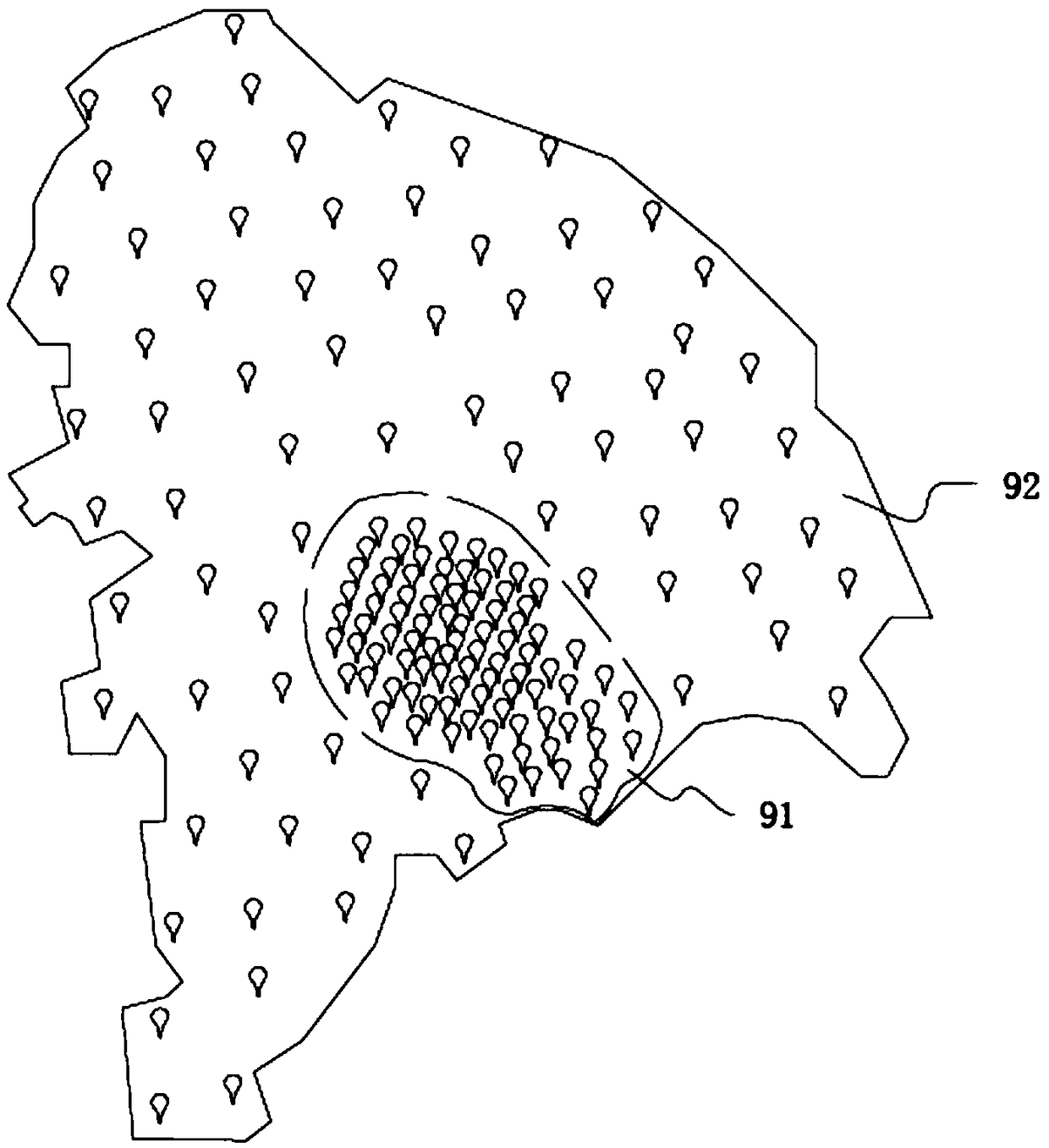
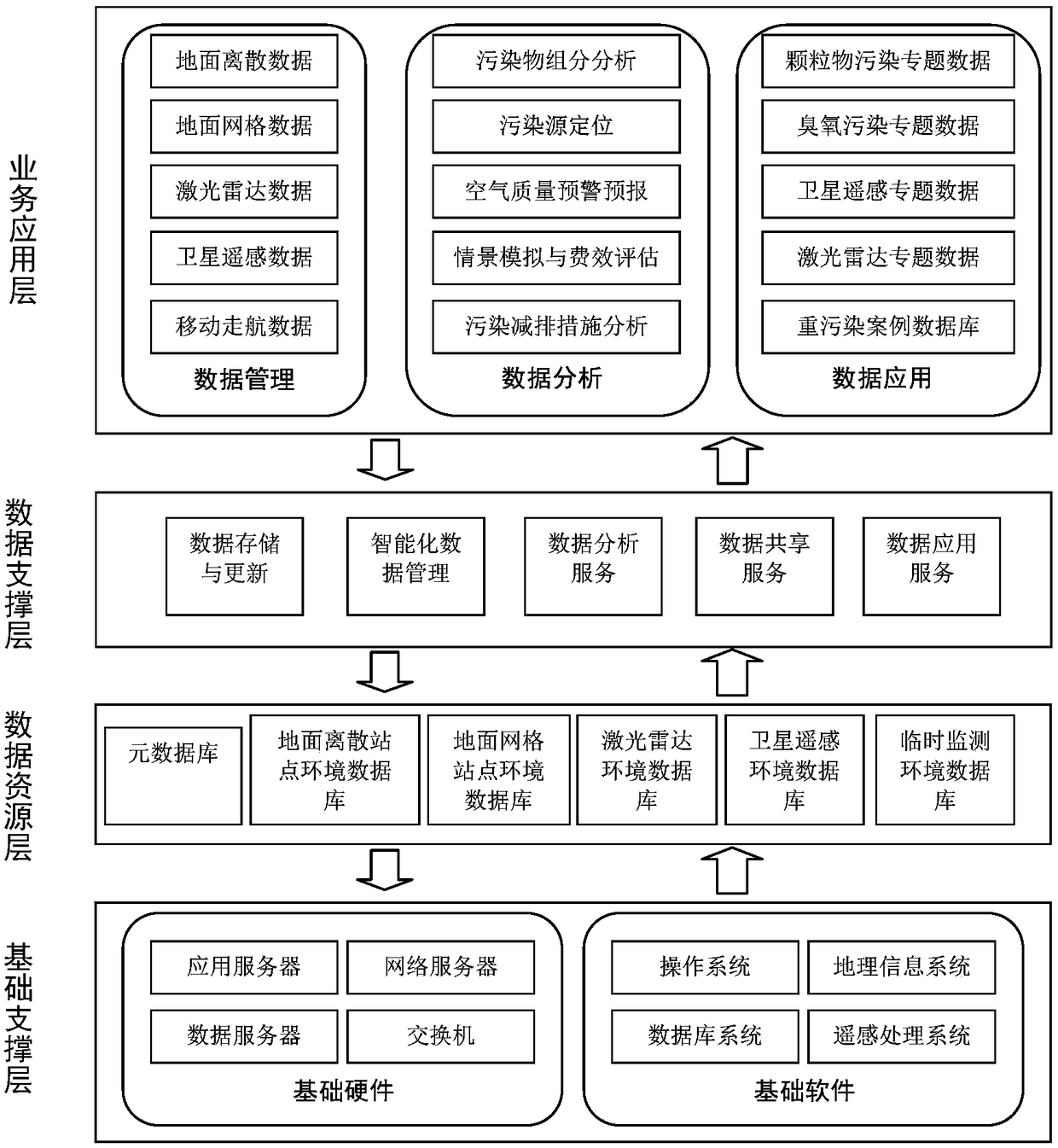
PendingCN108805368AAchieve integrationAchieving processing powerMeasurement devicesForecastingMobile navigationSparse grid
The invention discloses an atmospheric environment intelligent management system based on integration of space and air and earth. The atmospheric environment intelligent management system comprises multiple discrete ground air quality automatic monitoring stations, multiple environment monitoring satellites and ground satellite stations, laser radar sensor groups which are networked and arranged according to the pollution transmission characteristics, air quality sensing monitors which are distributed in the key pollution area according to the dense grid and distributed in the sub-key pollution area according to the sparse grid, mobile navigation monitoring vehicles which are organized according to the heavy pollution event and unmanned aerial vehicle monitoring sensors. The monitoring data of the ground air quality automatic monitoring stations, the ground satellite stations, the laser radar sensor groups, the air quality sensing monitors, the mobile navigation monitoring vehicles andthe unmanned aerial vehicle monitoring sensors are summarized to form an overall service system of the pollution layout. The mode of combination of the present ground monitoring network and network monitoring is used so that the disadvantage of the conventional ground monitoring network random distribution can be further improved and the data support can be provided for accurate haze treatment.
Owner:天津珞雍空间信息研究院有限公司
Method for automatically switching software interface display styles according to horizontal and vertical screens
ActiveCN103472997ASimple and user-friendly operationFunction increaseSubstation equipmentInput/output processes for data processingMobile navigationGraphical user interface
The invention relates to a method for automatically switching software interface display styles according to horizontal and vertical screens. The hardware characteristics are combined, and the improvement and expansion are carried out on the basis of a navigation software, so that the navigation software can automatically modify the styles according to the horizontal and vertical screens; signals are digitally coded by an ADC module built in an SOC, and the state determination of horizontal and vertical screens of equipment is carried out; a management module switches a vehicle-mounted style and a mobile phone style of navigation according to the determined state results of the horizontal and vertical screens; the management module adopts a threshold decision-time delay processing mode, and realizes the switching of the interface styles by setting a GUI (Graphical User Interface) loading layout theme data; in navigation application, when the styles are switched, the management module is provided with a navigation service layer, so that the corresponding style can be switched. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that through the placement of the horizontal and vertical screens, the styles of the navigation software is automatically switched, and the functions of a mobile phone software is expanded, so that the mobile phone navigation software simultaneously has the functions which are fully consistent with the vehicle-mounted navigation, and thus the mobile phone navigation software is more simple and humane to operate.
Owner:SHENYANG MXNAVI CO LTD
Navigation system and control unit for navigation system
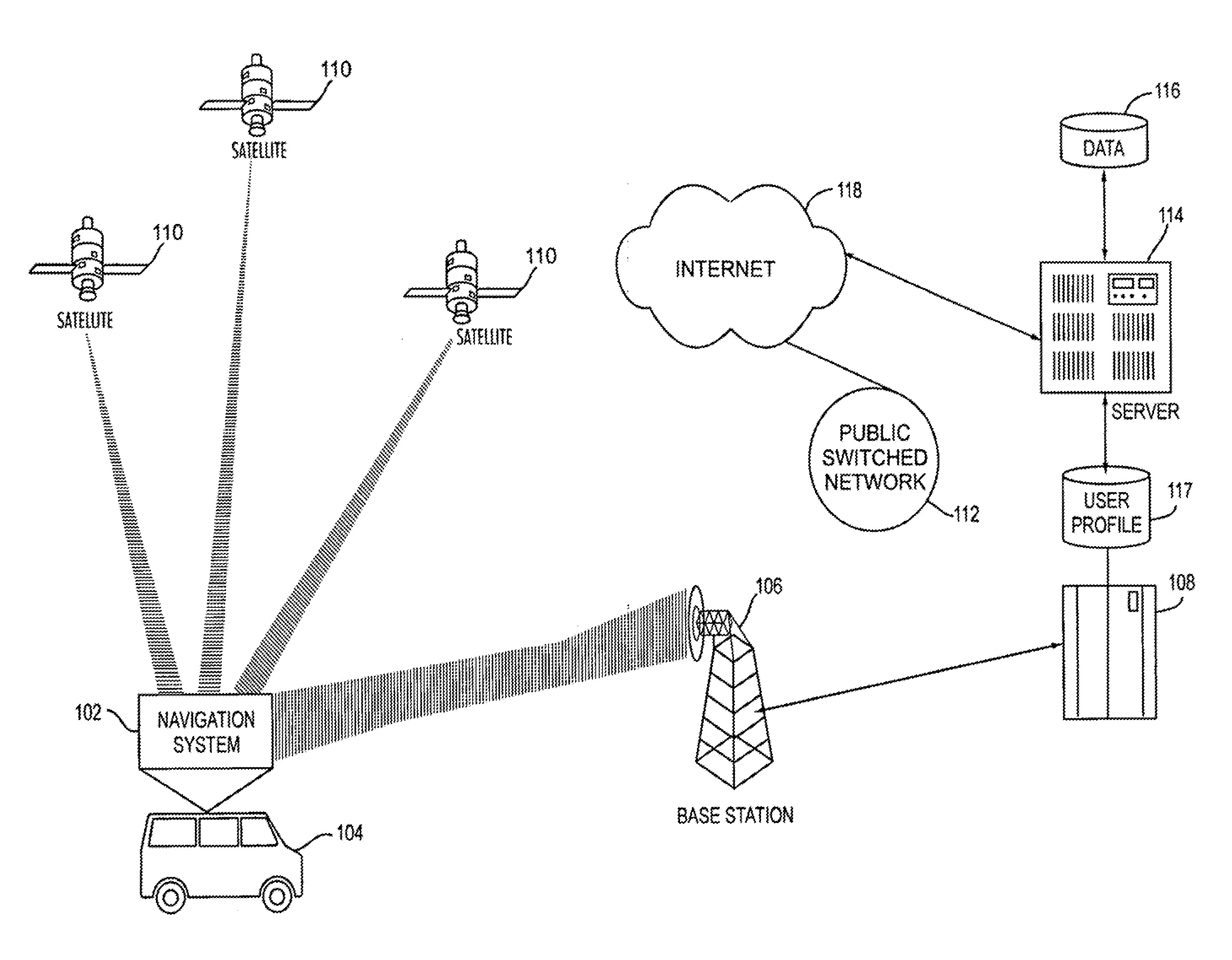
ActiveUS9250090B2Technical and/or financial involvement for the central control unit is accordingly lowerImprove performanceInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationMobile navigationTelecommunications link
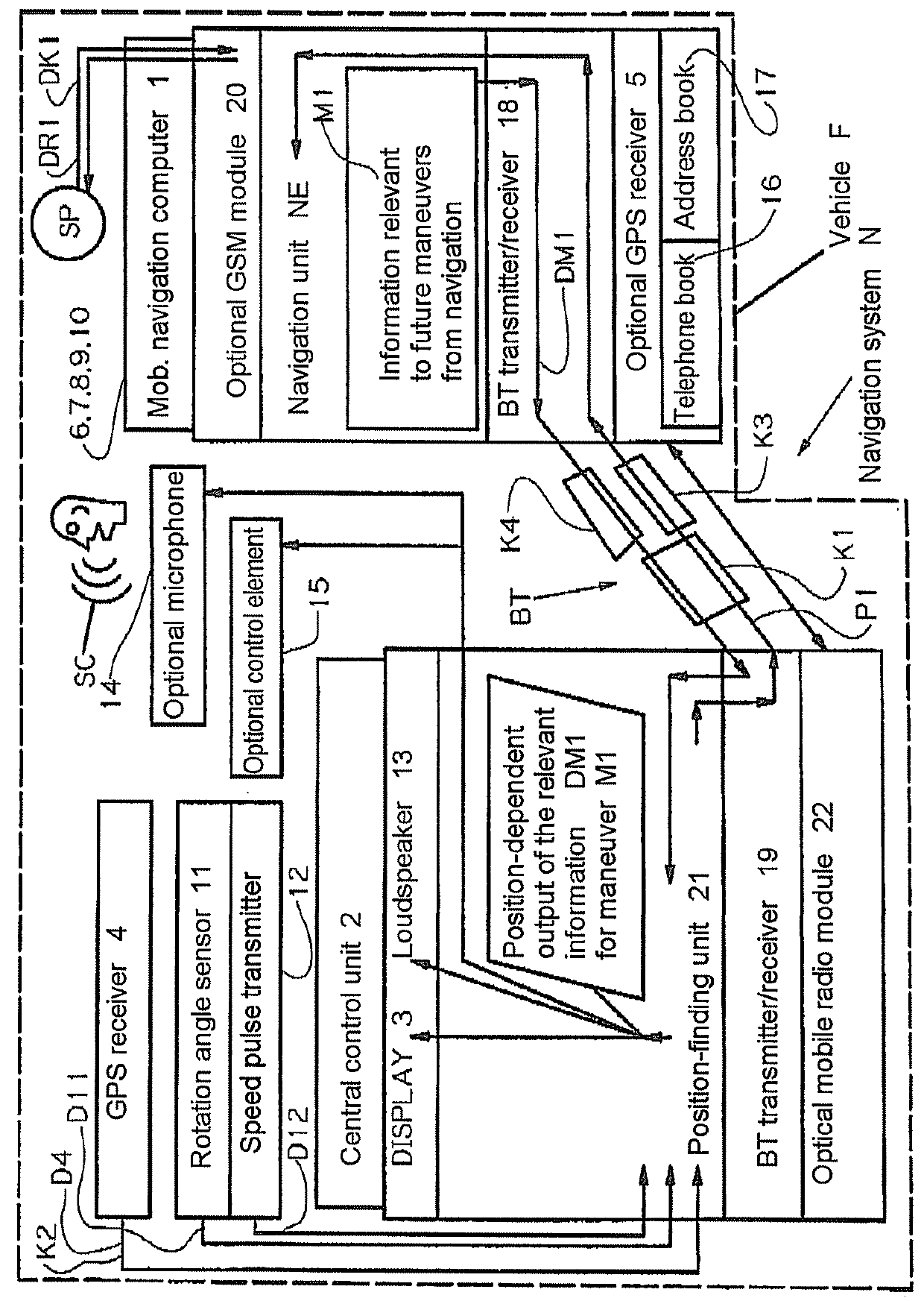
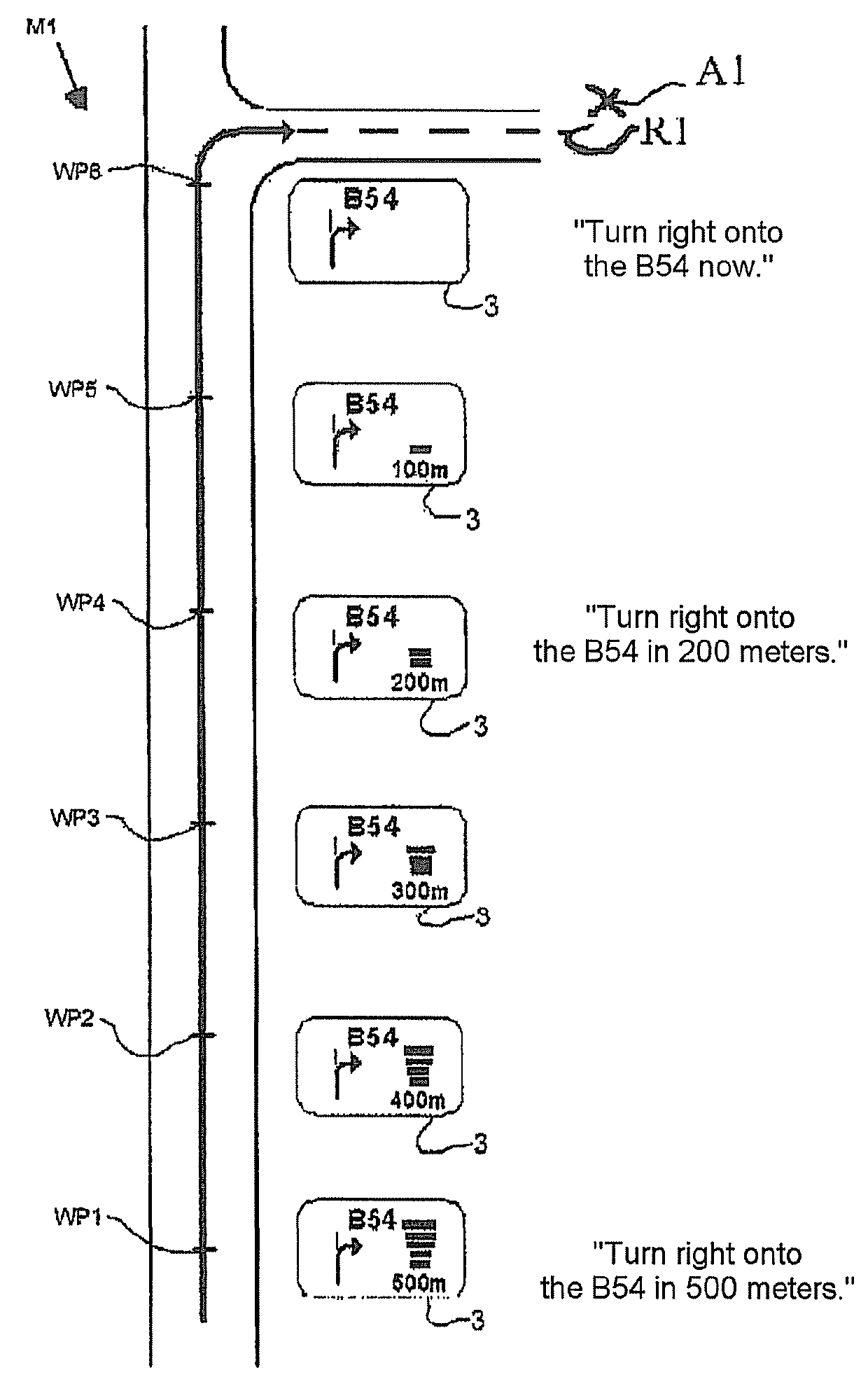
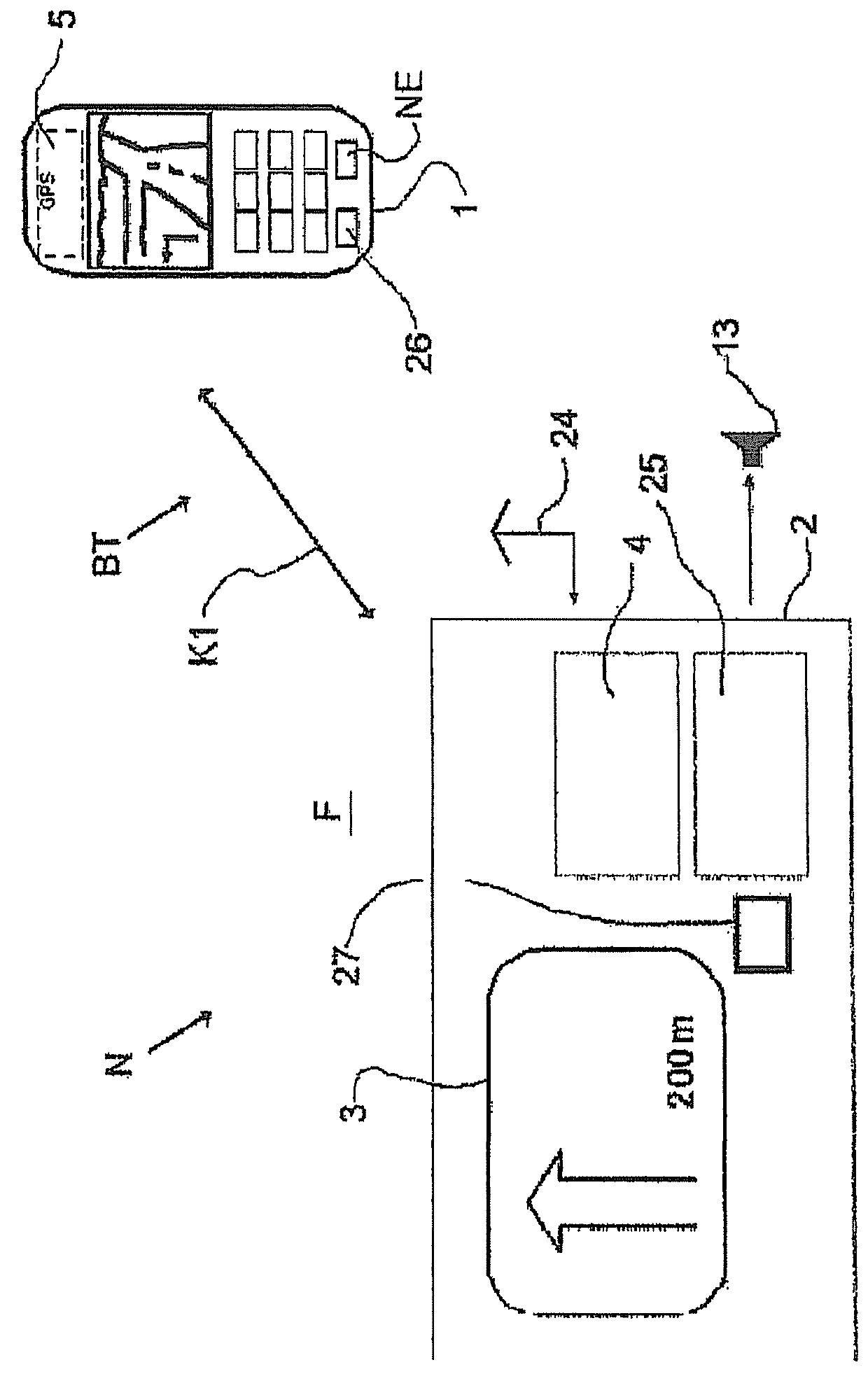
A navigation system for a vehicle including a mobile navigation computer, a vehicle-based central control unit, a GPS receiver, a communication link between the mobile navigation computer and the central control unit, wherein position data for the vehicle is processed in a navigation unit in the mobile navigation computer to form information relevant to the navigation. The navigation information is transmitted from the navigation computer to the control unit for a respective maneuver which is to be performed, and this information is output in at least one of visual and audible forms via the central control unit. The position data for the vehicle is determined by the position-finding unit of the central control unit, and is transmitted to the mobile navigation computer, wherein the vehicle is navigated on the basis of data calculated in the navigation unit of the mobile navigation computer.
Owner:PEIKER ACUSTIC GMBH & CO KG
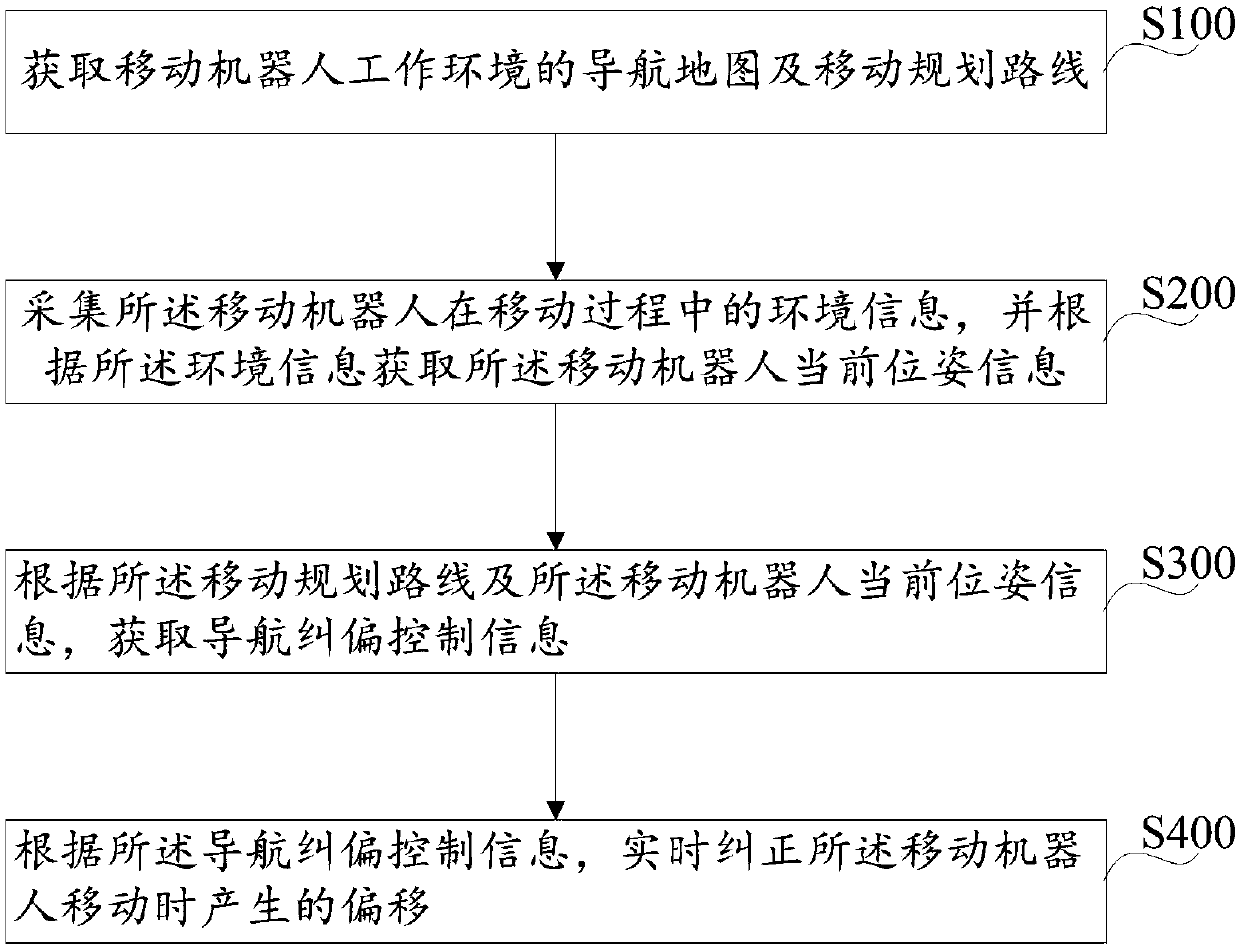
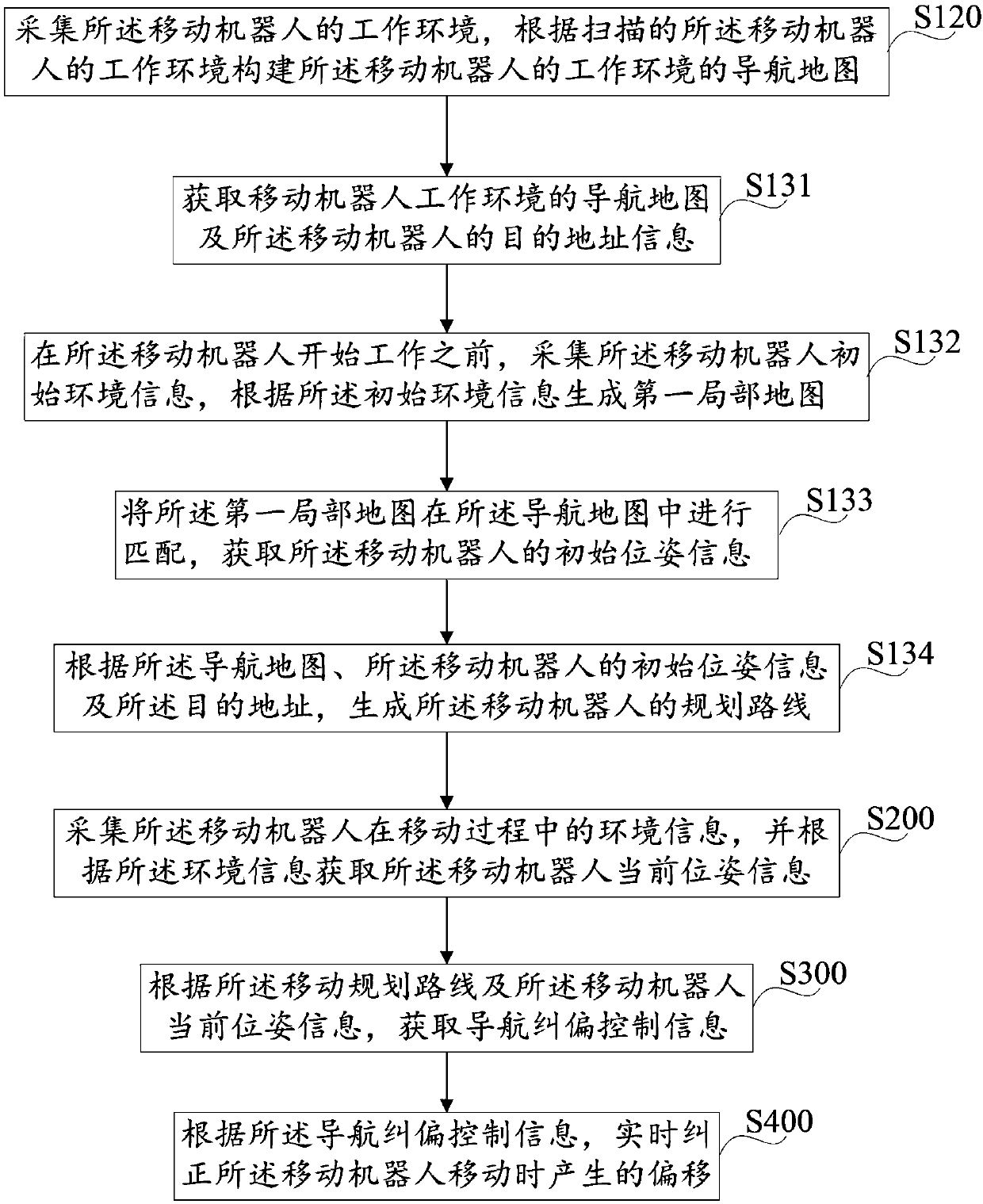
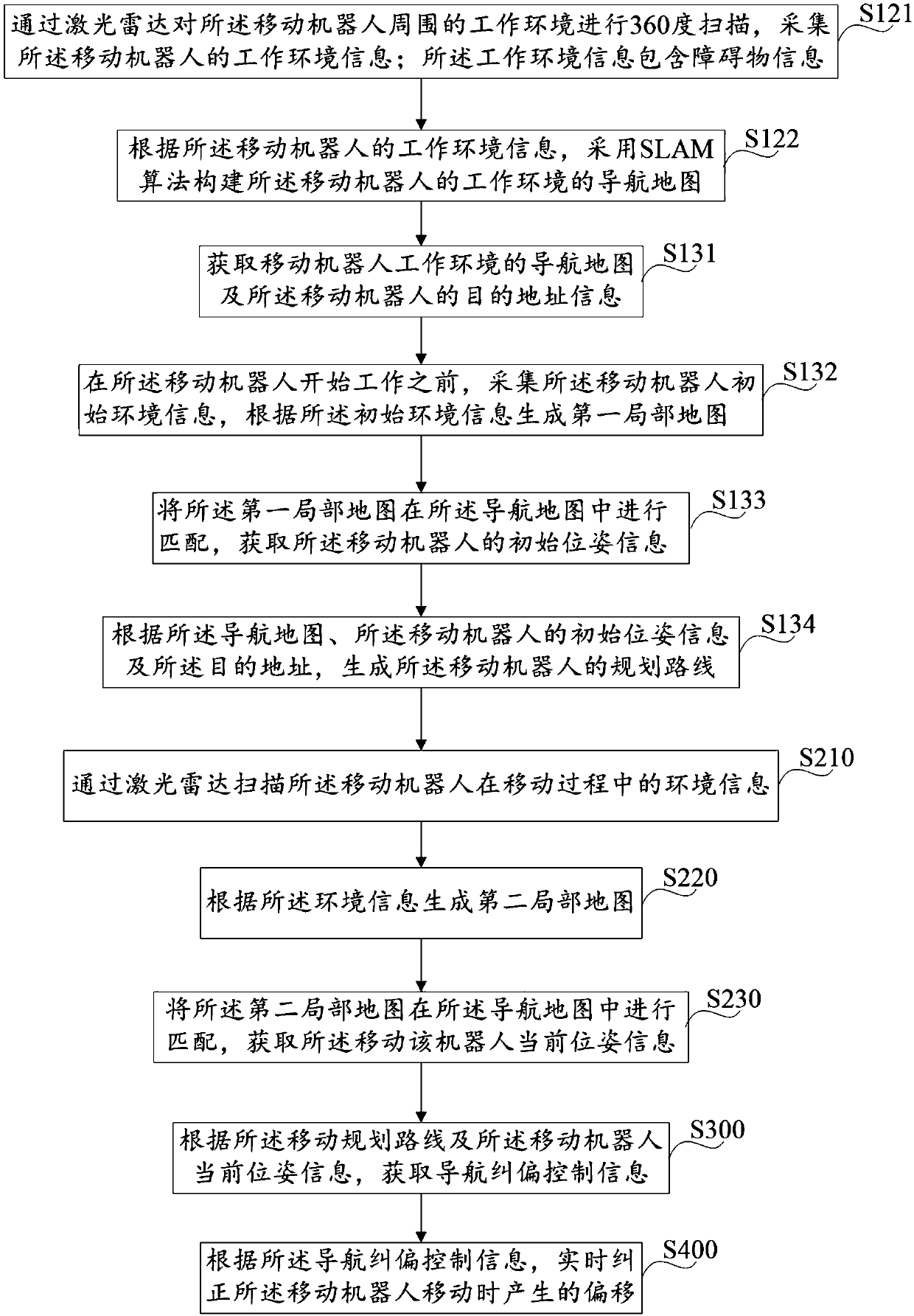
Mobile robot navigation offset correction method and device
InactiveCN107918391AStable controlImprove navigation accuracyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesDevice typeMobile navigation
The invention discloses a mobile robot navigation offset correction method comprising the following steps: obtaining a navigation map and mobile programmed routes of the mobile robot work environment;gathering environment information of the mobile robot in a moving process, and obtaining the current pose information of the mobile robot according to the environment information; obtaining navigation offset correction control information according to the mobile programmed route and the current pose information of the mobile robot; correcting the offset of the moving robot in real time accordingto the navigation offset correction control information. In addition, the invention also discloses a mobile robot navigation offset correction device. The method and device can correct the offsets ofthe mobile robot in the moving process, thus enabling the mobile robot to precisely arrive at the destination. The navigation offset correction method and device are simple and practical, low in realization cost, and high in precision.
Owner:台州市吉吉知识产权运营有限公司
Mobile navigation device
InactiveUS7082323B2Simple structureImprove yieldManual control with multiple controlled membersElectric switchesMobile navigationCantilever
A mobile navigation device including a roller, a support, a plurality of terminals, and a body. The roller including an insulated bushing and a conductive ring. By matching the plurality of protrusions on an inner end surface of the insulated bushing with a plurality of slots on one end of the conductive ring, the conductive ring is plugged inside of the insulated bushing. The support including two braces, wherein each of the braces has a cantilever that is plugged into the conductive ring to sustain the conductive ring and the insulated bushing. The plurality of terminals are plugged into the conductive ring by prestress on the inner surface of the conductive ring, and each terminal extends out of the conductive ring to connect with a default circuit contact. The body includes a plurality of fixture parts and a plurality of raised spots. The whole structure is movable forward, backward, rightward, leftward, and downward.
Owner:SPEED TECH
Indoor mobile robot human-machine integration navigation device and method
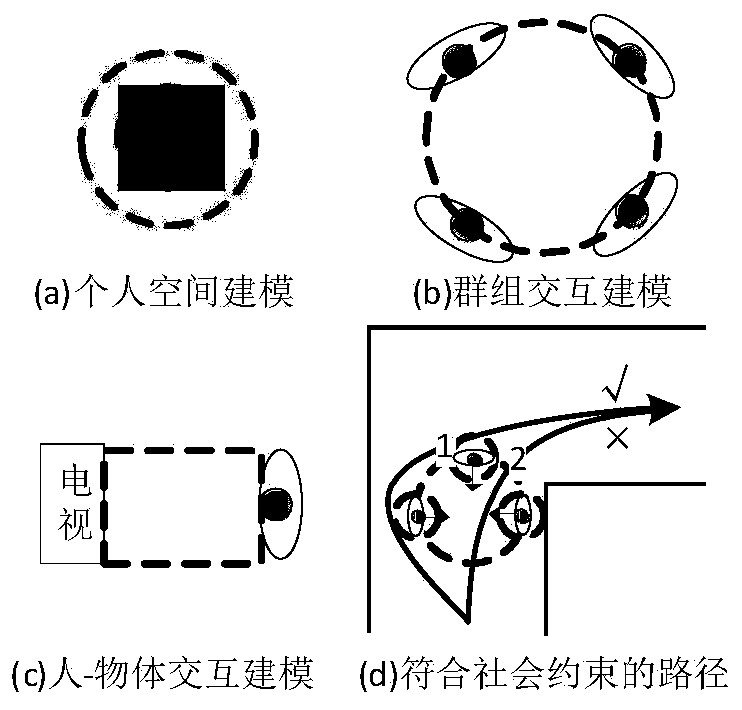
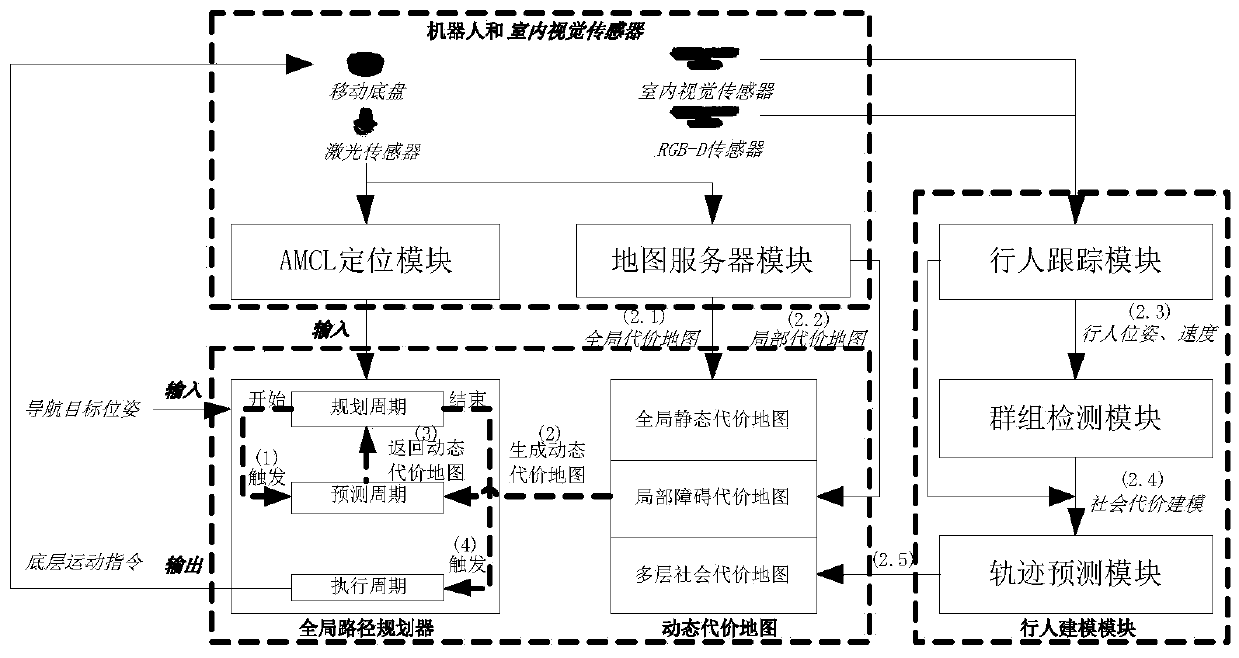
ActiveCN110285813AGood conditionGood planning resultsNavigational calculation instrumentsDynamic planningMobile navigation
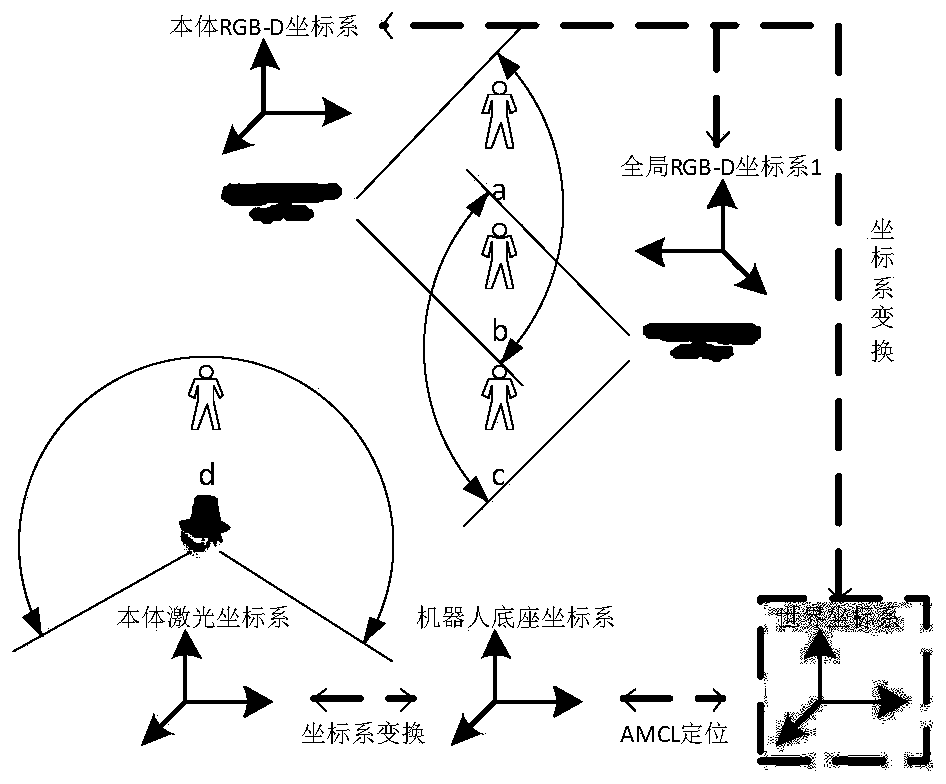
The invention discloses an indoor mobile robot human-machine integration navigation device and method. The device comprises a pedestrian modeling module, a dynamic cost map, a global path planner, a robot and an indoor vision sensor. The pedestrian modeling module is used for converting the pedestrian perception information into a cost map required by the global path planner search map. The dynamic cost map provides the global path planner with the information of social constraints in the future. The global path planner is the core of the whole system and is responsible for receiving the navigation target pose and the AMCL positioning information, using the "planning-prediction-execution" time series period to carry out dynamic planning and building the search map based on the dynamic cost map to calculate the optimal planning result of the current planning period in each planning period. The robot and the indoor vision sensor are responsible for global environmental perception. In addition, the robot moving chassis receives the underlying motion commands for mobile navigation. The device and the method can be effectively and flexibly applied to the actual indoor environment.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com