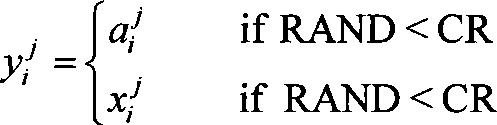Patents
Literature
273 results about "Batch reactor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The batch reactor is the generic term for a type of vessel widely used in the process industries. Its name is something of a misnomer since vessels of this type are used for a variety of process operations such as solids dissolution, product mixing, chemical reactions, batch distillation, crystallization, liquid/liquid extraction and polymerization. In some cases, they are not referred to as reactors but have a name which reflects the role they perform (such as crystallizer, or bioreactor).
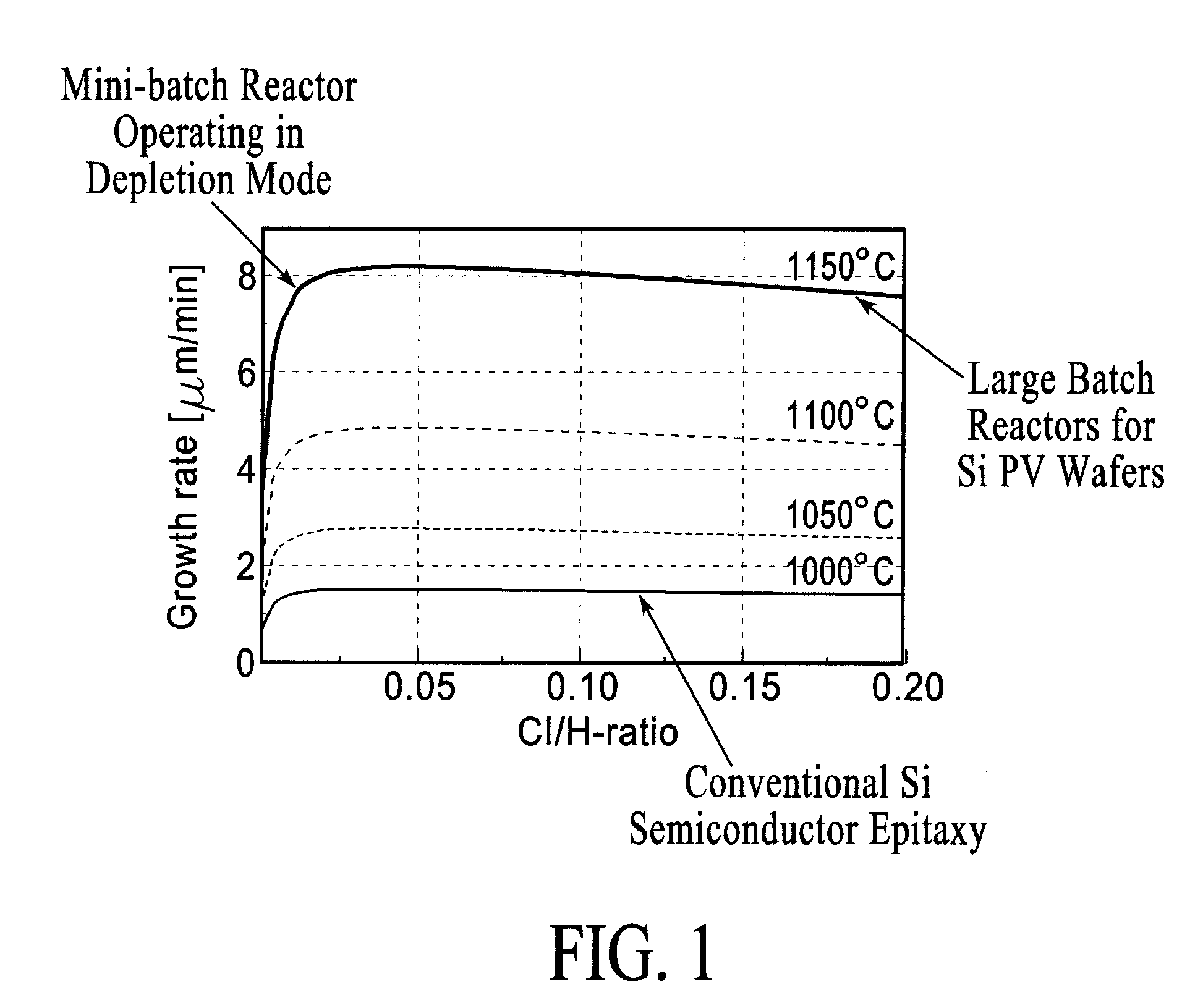
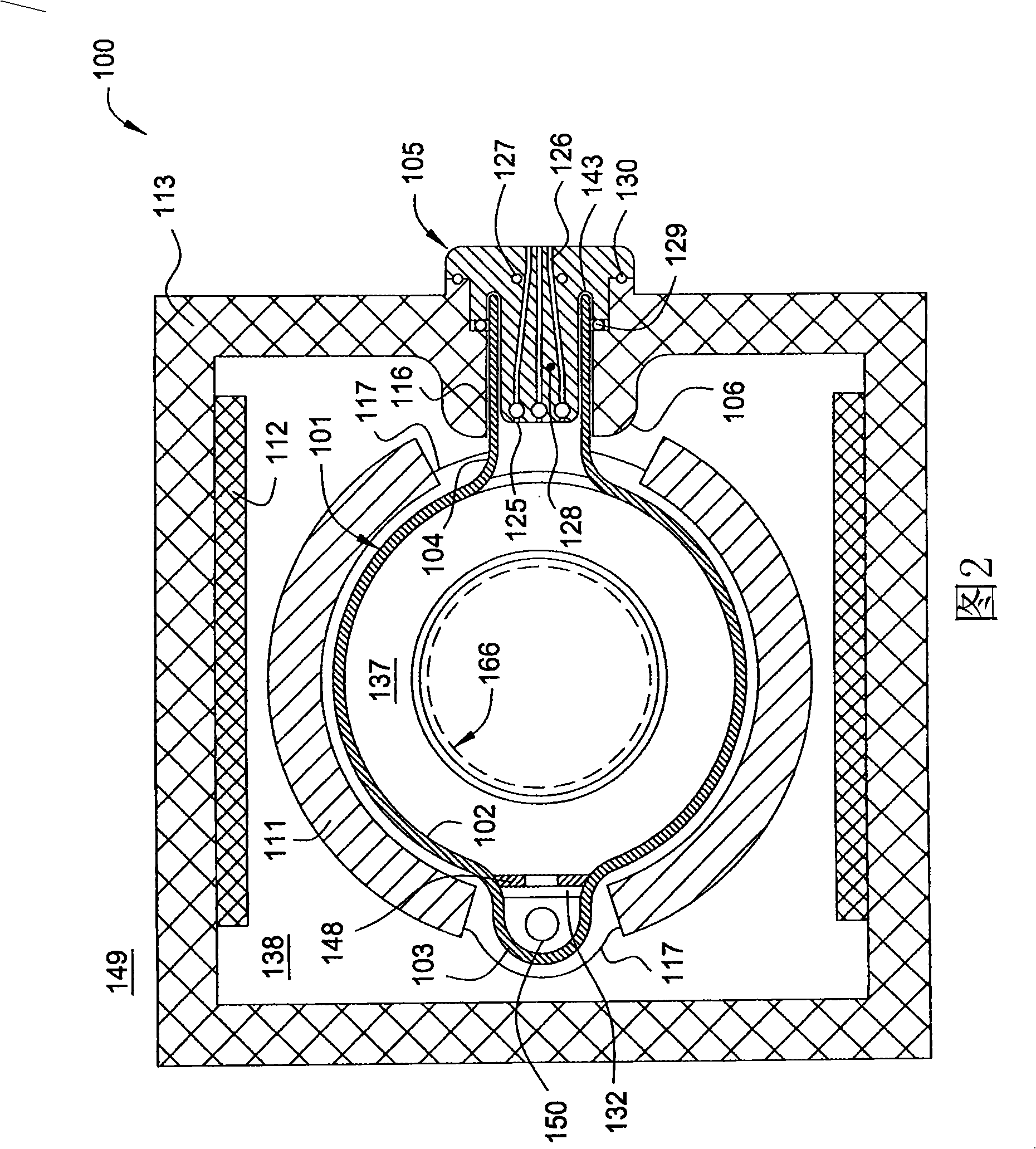
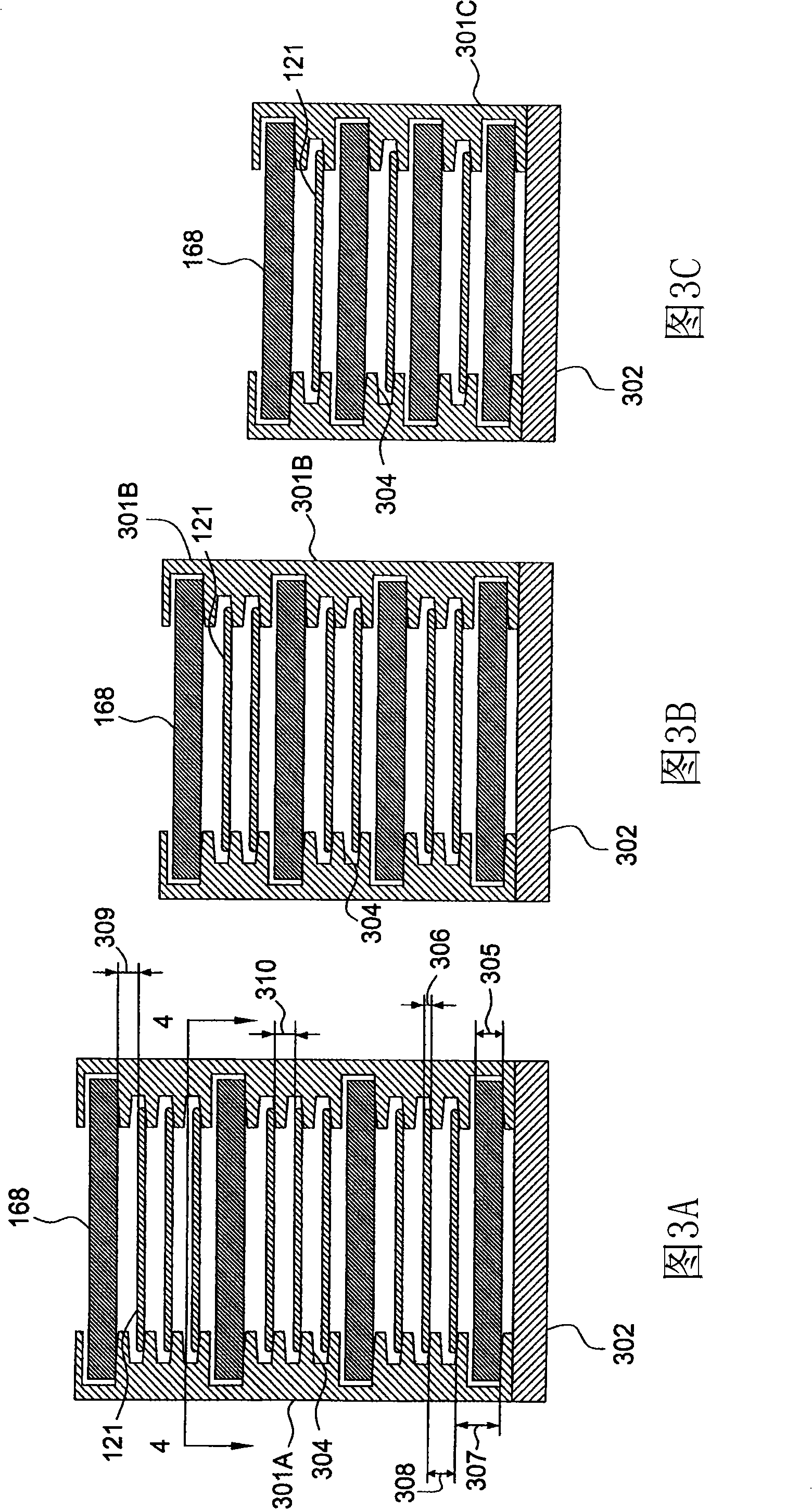
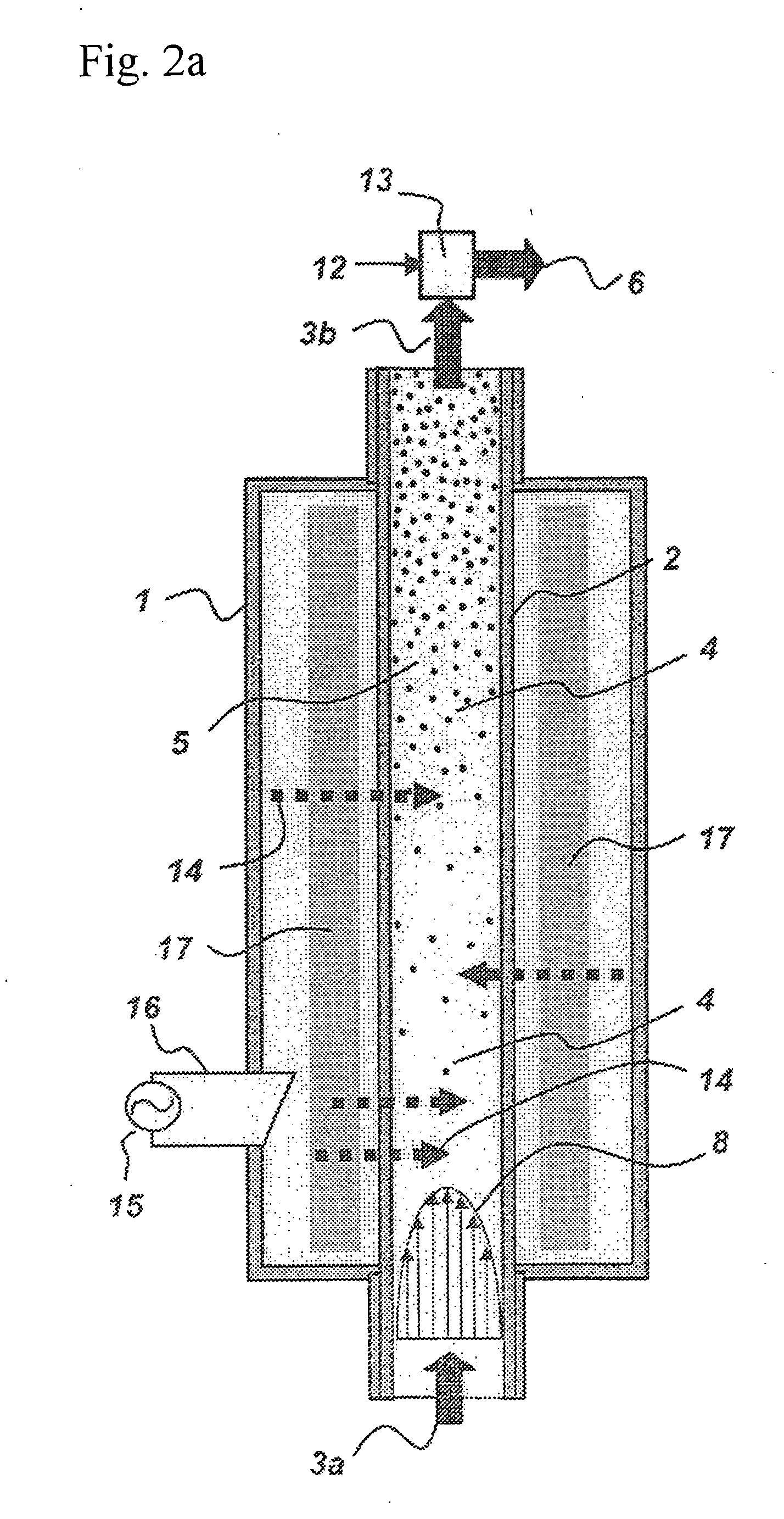
High rate deposition at low pressures in a small batch reactor
InactiveUS20030049372A1Increase ratingsRapid and uniform deposition of materialElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh rateSusceptor
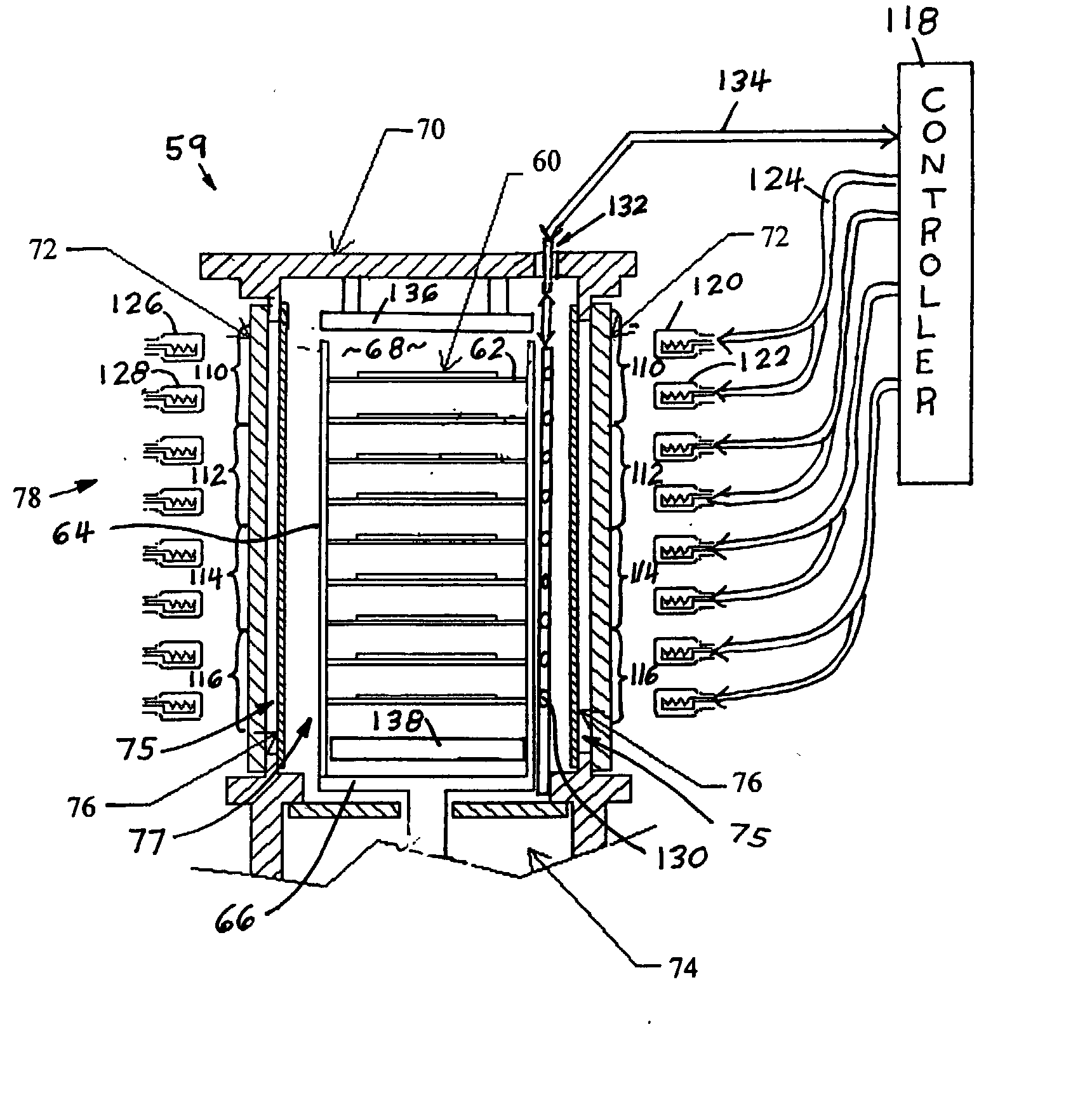
A chemical vapor deposition reactor including a wafer boat with a vertical stack of horizontally oriented susceptors serving as thermal plates and each having pins extending upward for suspending a wafer between a pair of susceptors. Reactant gas injector and exhaust apparatus are positioned to concentrate a forceful supply of reactant gas across each wafer at a speed in excess of 10 cm / sec. The pressure is held in the range of 0.1 to 5,000 mTorr. The forceful gas flow avoids gas depletion effects, thinning the boundary layer and resulting in faster delivery of reactants to substrate surfaces, resulting in surface rate reaction limited operation. A plurality of individually controllable heaters are spaced vertically around the sides of the boat. Temperature sensors monitor the temperature along the boat height and provide input to a controller for adjusting the heater drive to optimize the temperature uniformity.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ozone and teos process for silicon oxide deposition
InactiveUS20090325391A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTetraethyl orthosilicateBatch reactor
Methods for depositing silicon oxide in a batch reactor are provided. In some embodiments, a plurality of vertically separated substrates is provided in a reaction chamber. Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) is pulsed into the reaction chamber by direct liquid injection. Ozone is flowed into the reaction chamber simultaneously or alternately with the TEOS. The deposition is performed at about 10 Torr or less to extend the mean free path length of the ozone molecules. According to some embodiments, the deposition allows openings in the substrates to be filled while the occurrence of voids is maintained at a low level.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Batch pyrolysis system
InactiveUS20060163053A1Quality improvementImprove throughputProductsBeehive ovensBatch processingProcess engineering
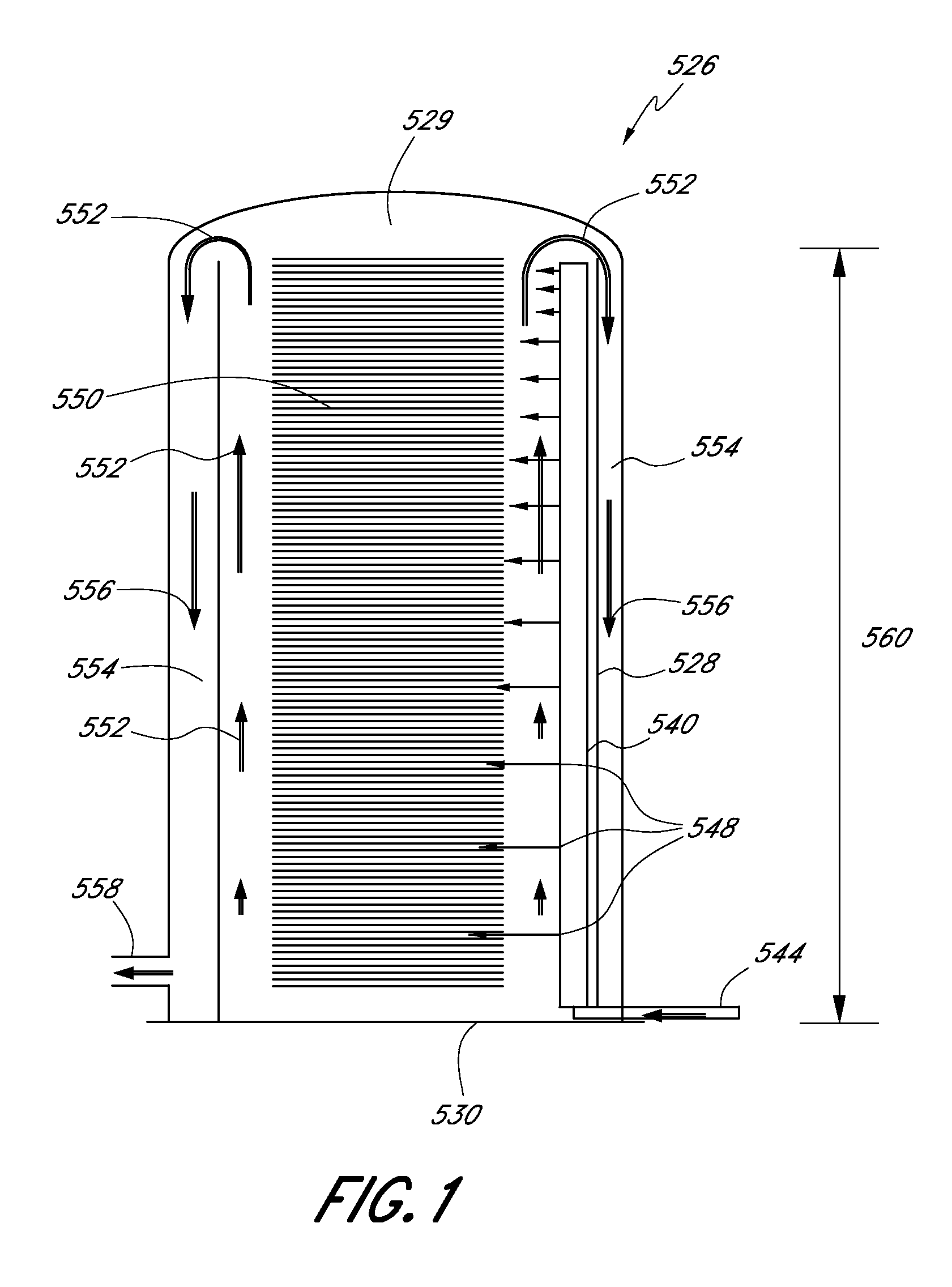
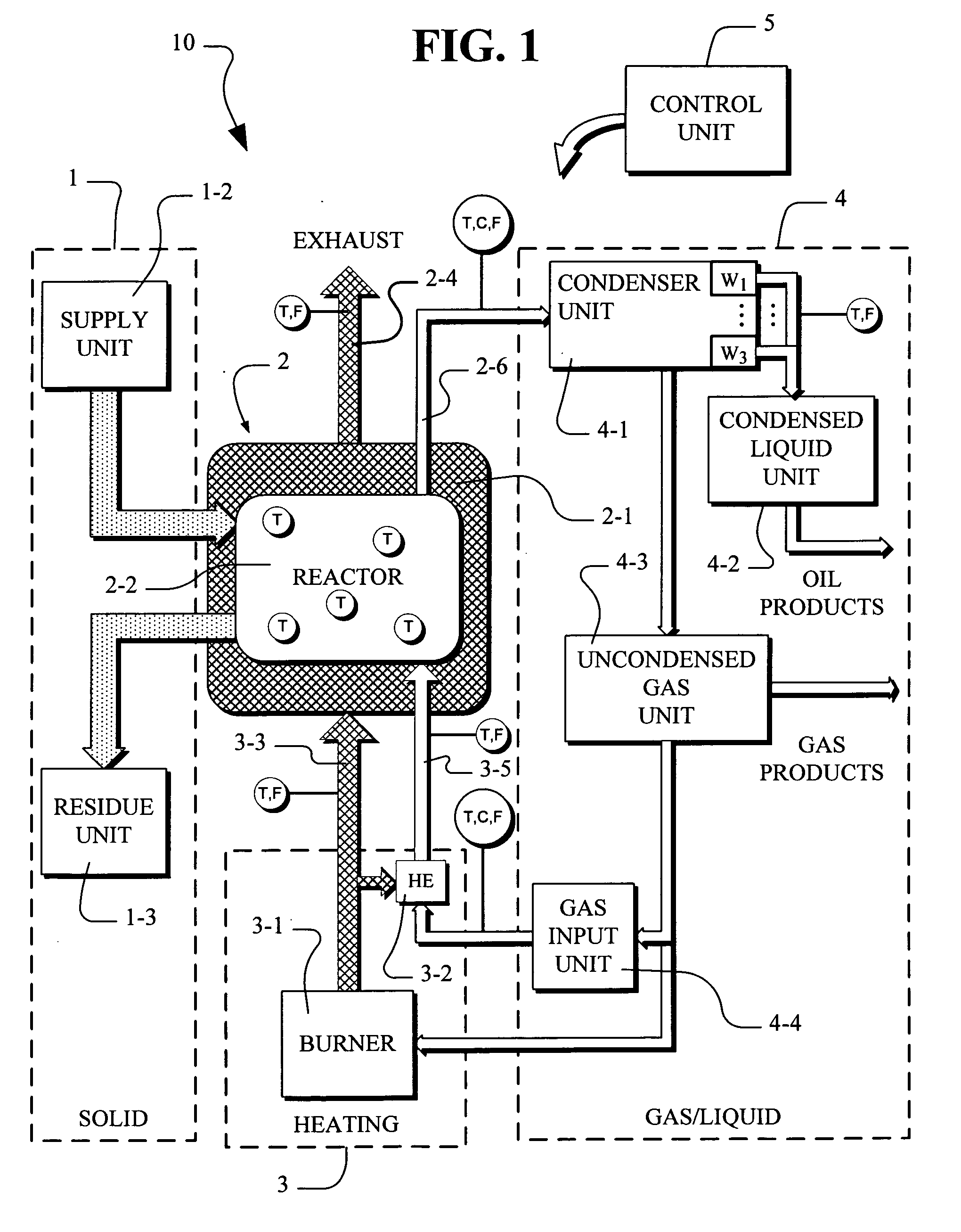
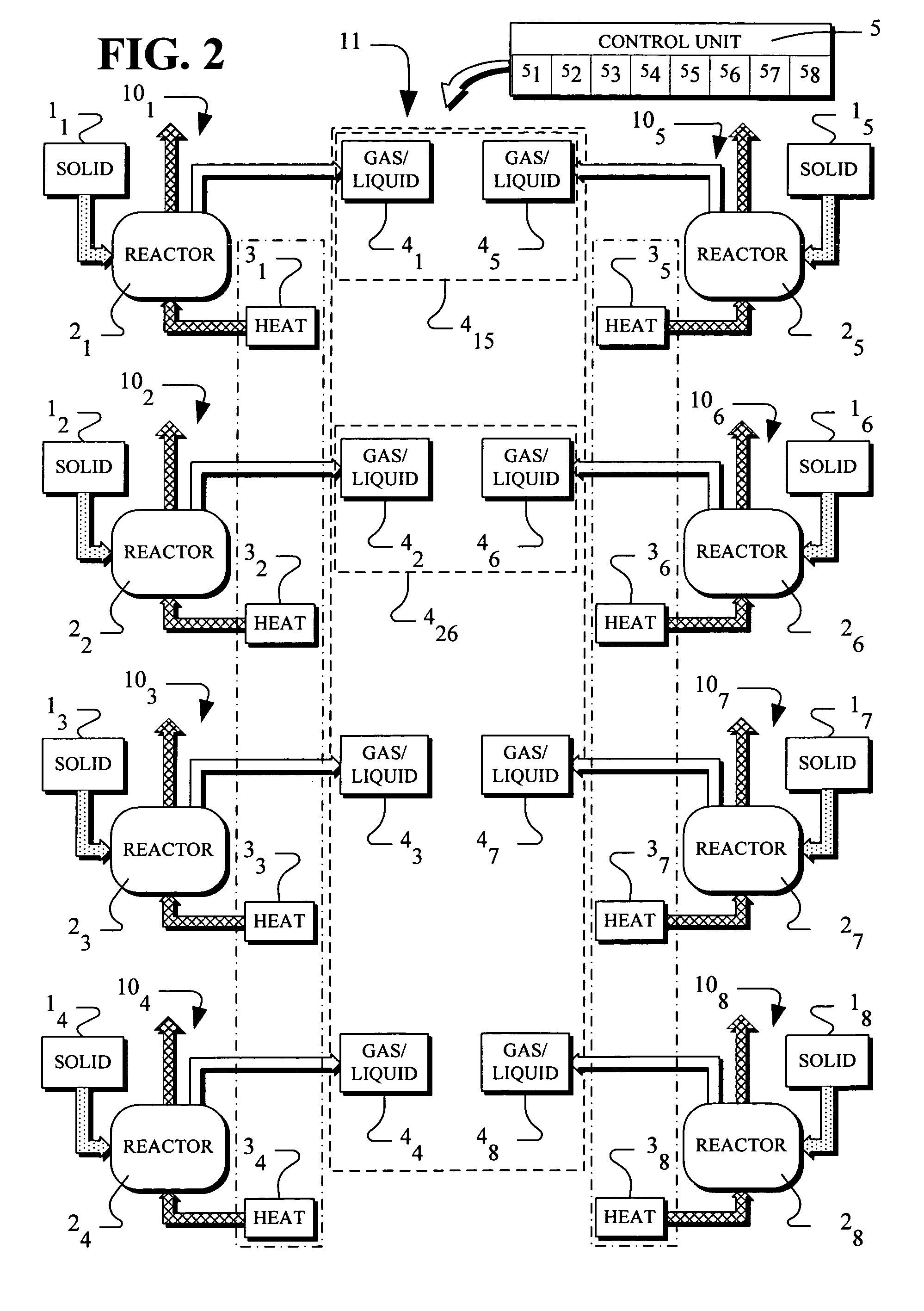
Disclosed is a scaleable pyrolysis system for batch processing of waste vehicle tires and other waste to provide pyrolysis products. The core pyrolysis system includes one or more batch reactors, heating units, solids processing units, gas / liquid processing units and control units. In operation, the temperature gradients internal to the reactor are controlled by preferential channeling of heat to provide pyrolysis products that are of high quality, and hence commercially advantageous, while facilitating high throughput.
Owner:ERSHAG BENGT STURE
Single, multi-walled, functionalized and doped carbon nanotubes and composites thereof
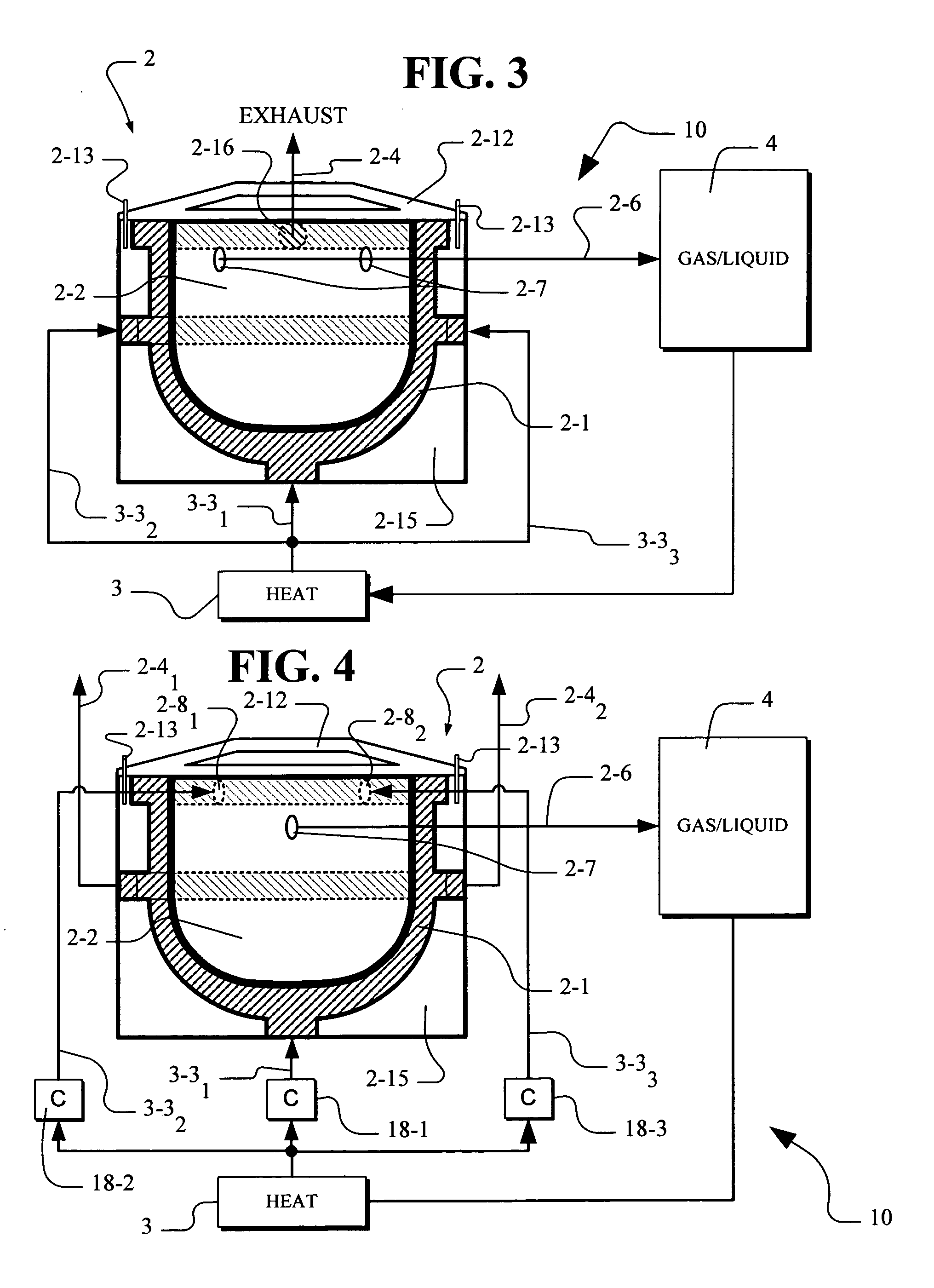
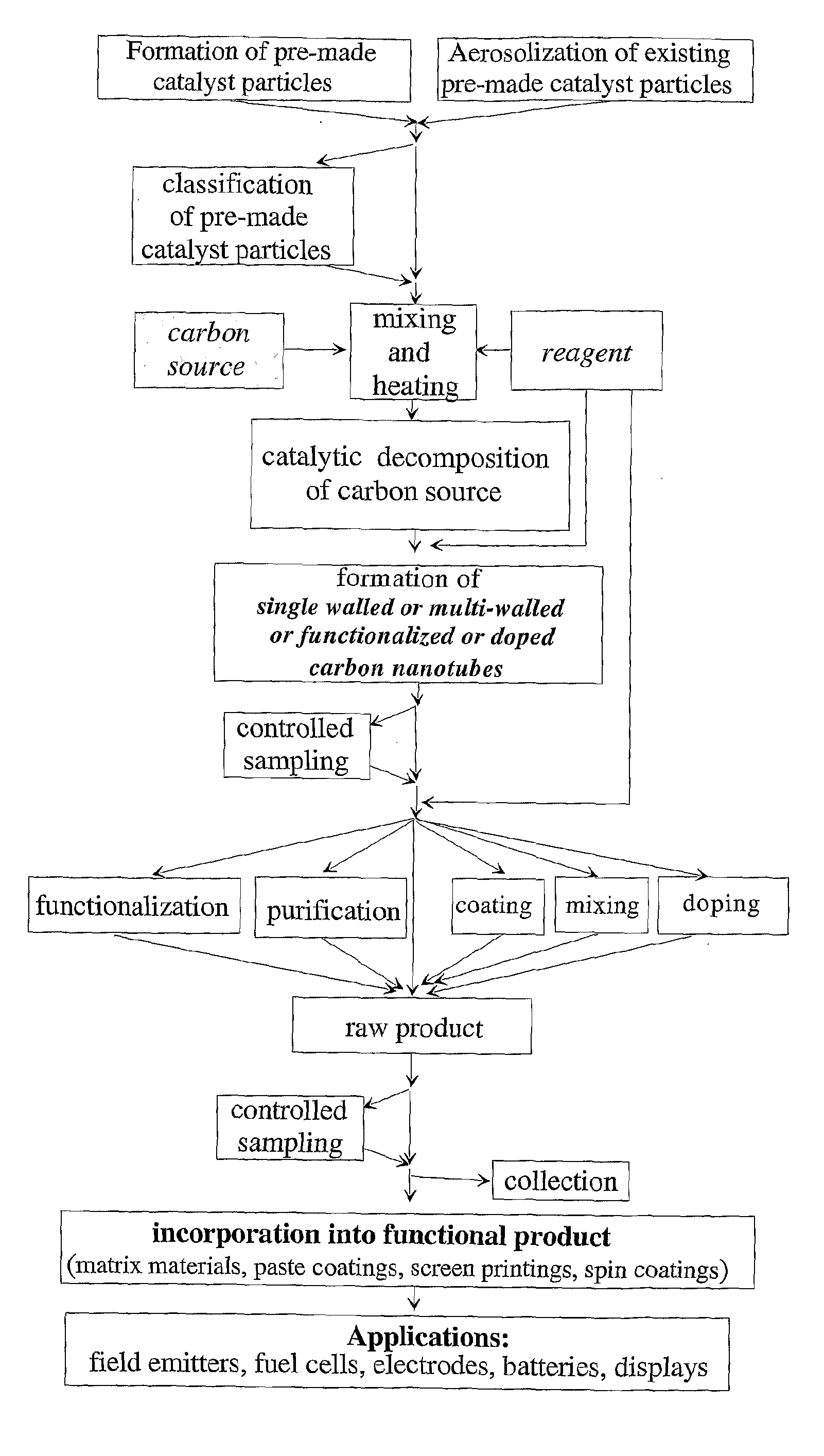
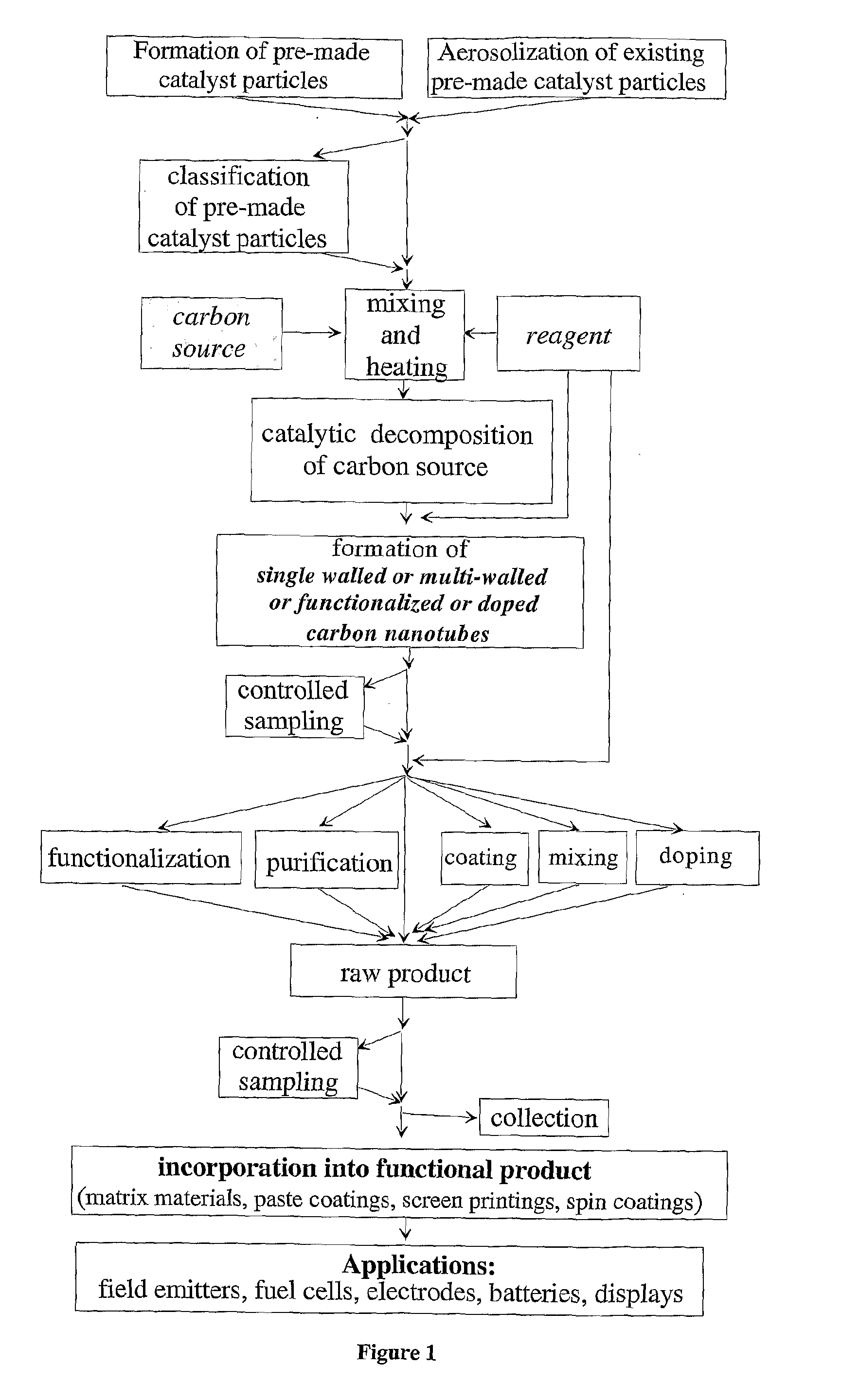
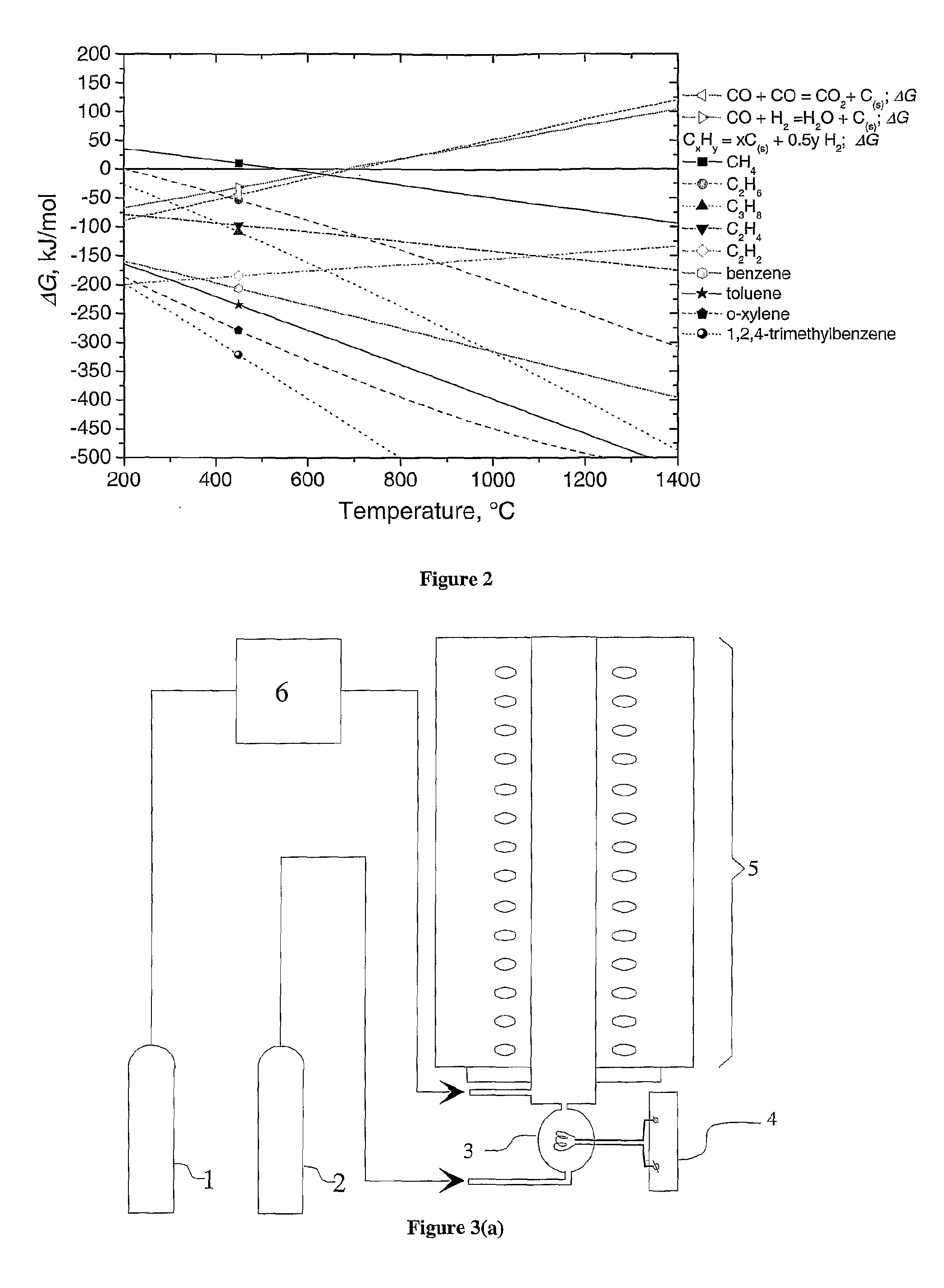
The present invention relates to single walled and multi-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs), functionalized CNTs and carbon nanotube composites with controlled properties, to a method for aerosol synthesis of single walled and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, functionalized CNTs and carbon nanotube composites with controlled properties from pre-made catalyst particles and a carbon source in the presence of reagents and additives, to functional, matrix and composite materials composed thereof and structures and devices fabricated from the same in continuous or batch CNT reactors. The present invention allows all or part of the processes of synthesis of CNTs, their purification, doping, functionalization, coating, mixing and deposition to be combined in one continuous procedure and in which the catalyst synthesis, the CNT synthesis, and their functionalization, doping, coating, mixing and deposition can be separately controlled.
Owner:CANATU OY
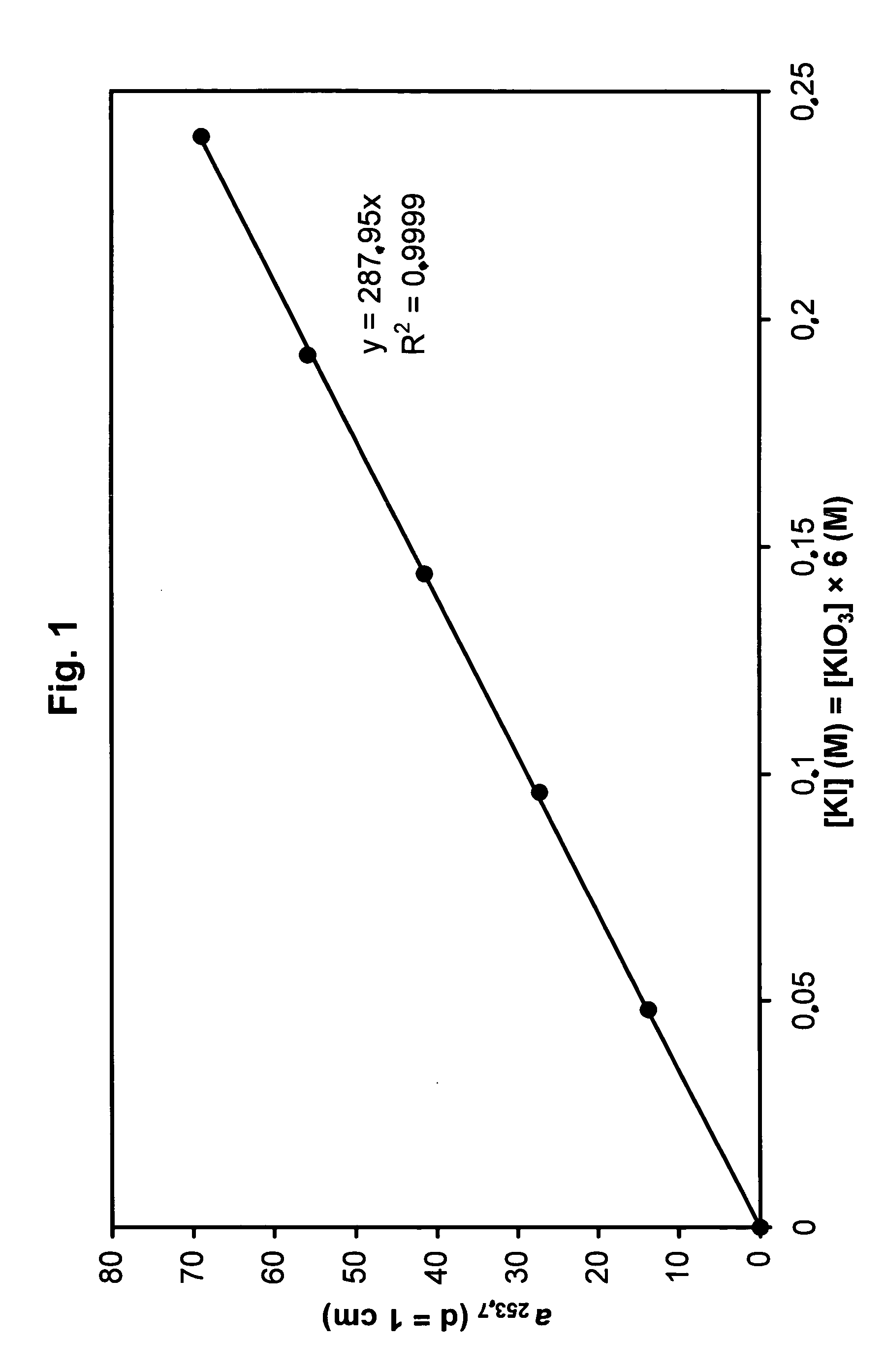
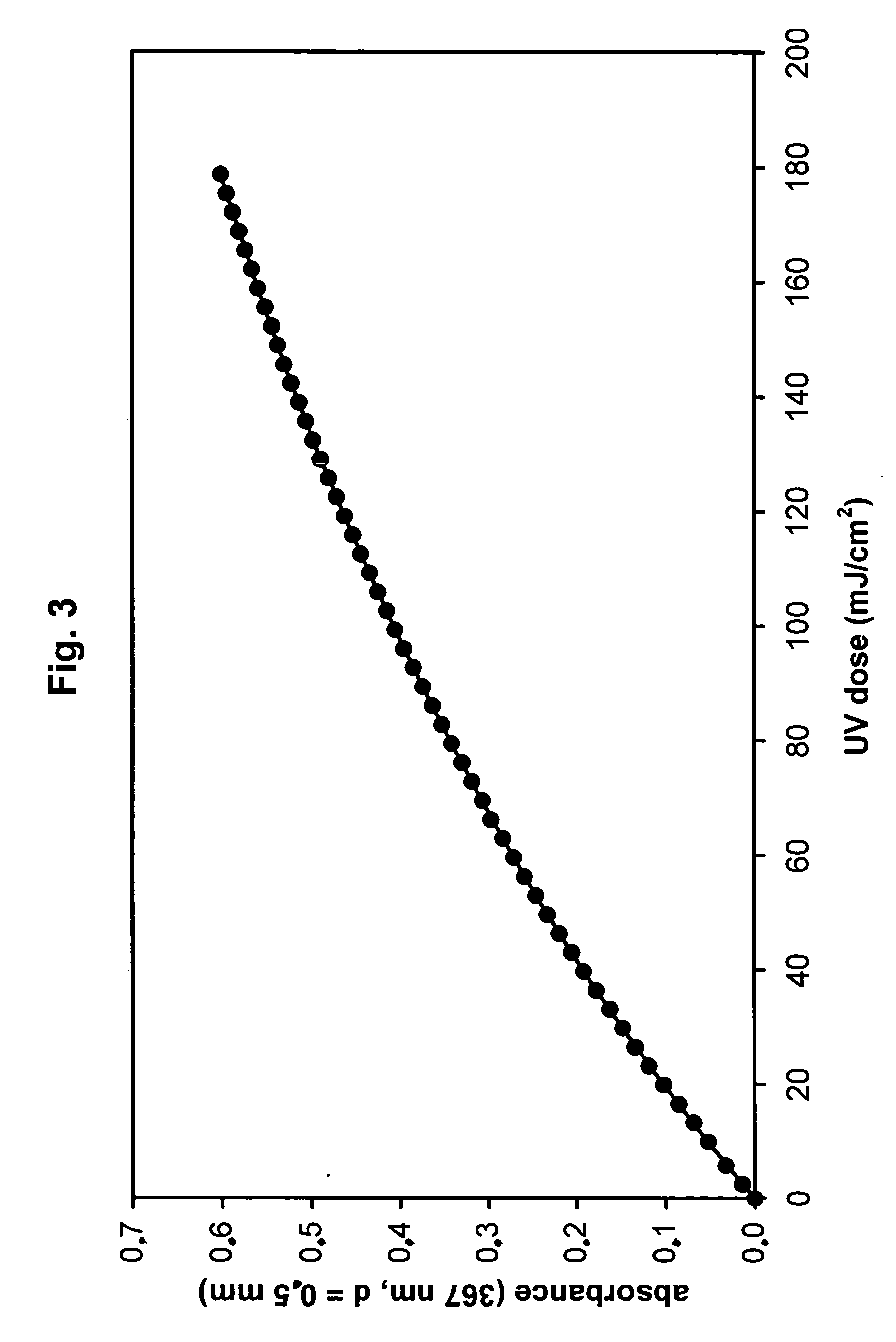
Methods for the inactivation of microorganisms in biological fluids, flow through reactors and methods of controlling the light sum dose to effectively inactivate microorganisms in batch reactors
The present invention relates to a method for determining an effective dose of monochromatic or polychromatic light from one or more light sources to inactivate microorganisms present in a biological fluid, preferably a non-transparent fluid. Moreover, there is provided a method for the inactivation of microorganism in a biological fluid in a flow-through-reactor. Moreover, the invention advantageously provides a flow-through-reactor with one or more thermostated light sources. The invention further provides a method of controlling the light sum dose of monochromatic or polychromatic light emitted from one or more light sources to effectively inactivate microorganisms present in a biological fluid in a batch reactor.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Method for preparing positive electrode active material precursor and positive electrode material for lithium secondary battery having concentration-gradient layer using batch reactor, and positive electrode active material precursor and positive electrode material for lithium secondary battery prepared by the method
ActiveUS20130202966A1Increase capacityHigh densityNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodesLi-accumulatorsLithiumConcentration gradient
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a positive electrode active material precursor and a positive electrode material for a lithium secondary battery having a concentration-gradient layer using a batch reactor, and to a positive electrode active material precursor and a positive electrode material for a lithium secondary battery prepared by the method. The method for preparing a positive electrode active material precursor and a positive electrode active material for a lithium secondary battery having a concentration-gradient layer using a batch reactor involves supplying a predetermined amount of a chelating agent into the batch reactor, and simultaneously supplying transition metals while continuously adjusting the concentration of the transition metals such that the concentration-gradient layer can be formed from a core to a shell of the positive electrode active material in a more economically advantageous and stable manner, and at the same time a positive electrode active material having an elongated lifespan and improved thermal stability can be provided.
Owner:ECOPRO MATERIALS CO LTD (50)
Method for preparing naphthalene sulphonic acid by sulfonating sulfur trioxide in microreactor
InactiveCN101607925ALarge specific surface areaImprove heat transfer performanceChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesSulfonic acid preparationReaction temperatureNitromethane
The invention relates to a method for preparing naphthalene sulphonic acid by sulfonating sulfur trioxide in a microreactor, belonging to methods for preparing dye intermediates in the field of fine chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: taking alkyl halide and nitromethane as an organic solvent, naphthalene and derivative thereof as the raw material and organic solution of liquid sulfur trioxide as a sulfonating agent, preparing a solution according to the mol ratio of the organic solvent, the raw material and the sulfonating agent of 19-74:1:1-3 in the microreactor of with channel with the diameter of 10-50 microns, and sulfonating the reaction solution to prepare the naphthalene sulphonic acid by controlling the sulfonation reaction temperature to be between 17DEG C below zero and90 DEG C. The method adopts a continuous flow reactor, solves the problem of impossible transient mixing in the conventional reactor, prevents secondary reaction caused by local excess, and is especially suitable for strong exothermic reaction, fast reaction and flammable and explosive reaction. Compared with the preparation technology in the traditional batch reactor, the invention has the advantages of no generation of waste water and waste acid, clean and environment-friendly technology, consumption of sulphonic acid close to the theoretical quantity, fast reaction speed, low sulfonation temperature, high product yield, good repeatability, high labor productivity and low equipment cost.
Owner:SPECIAL CHEM CO LTD DALIAN FIRSTAR
Titanium silicon nitride deposition
ActiveUS20100151681A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseTitanium
Titanium silicon nitride (TiSiN) films are formed in a cyclic chemical vapor deposition process. In some embodiments, the TiSiN films are formed in a batch reactor using TiCl4, NH3 and SiH4 as precursors. Substrates are provided in a deposition chamber of the batch reactor. In each deposition cycle, a TiN layer is formed on the substrates by flowing TiCl4 into the deposition chamber simultaneously with NH3. The deposition chamber is subsequently flushed with NH3. to prepare the TiN layer for silicon incorporation. SiH4 is subsequently flowed into the deposition chamber. Silicon from the SiH4 is incorporated into the TiN layers to form TiSiN. Exposing the TiN layers to NH3 before the silicon precursor has been found to facilitate efficient silicon incorporation into the TiN layers to form TiSiN.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Energy-efficient biological treatment with membrane filtration
ActiveUS20060081534A1Easy to operateLiquid separation auxillary apparatusTreatment using aerobic processesSequencing batch reactorUltrafiltration
A membrane filtration system comprising one or more submerged ultrafiltration or microfiltration membrane assemblies at ambient pressure, each membrane assembly positioned 100-240 mm from a nearest wall, baffle, or adjacent membrane assembly and no more than 1 meter above a floor and at least 150 mm below the liquid level. Mixed liquor is discharged underneath each membrane assembly to create a vertical flow velocity in a range of 1-8 mm / second along an entire length of the membrane assembly. In a sequenced batch reactor system, a coarse bubble air diffuser for scouring each membrane assembly is supplied with air only during the backwash cycle of the filtration system and not during the filtration cycle. In a membrane bioreactor system, the biological treatment section is physically separated from the filtration section and fine bubble air diffusion is used in the biological treatment section.
Owner:ITT MFG ENTERPRISES LLC
Methods for the inactivation of microorganisms in biological fluids, flow through reactors and methods of controlling the light sum dose to effectively inactivate microorganisms in batch reactors
The present invention relates to a method for determining an effective dose of monochromatic or polychromatic light from one or more light sources to inactivate microorganisms present in a biological fluid, preferably a non-transparent fluid. Moreover, there is provided a method for the inactivation of microorganism in a biological fluid in a flow-through-reactor. Moreover, the invention advantageously provides a flow-through-reactor with one or more thermostated light sources. The invention further provides a method of controlling the light sum dose of monochromatic or polychromatic light emitted from one or more light sources to effectively inactivate microorganisms present in a biological fluid in a batch reactor.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Systems and methods for anaerobic digestion of biomaterials
ActiveUS20120125840A1Biological treatment regulationWaste water treatment from animal husbandryEngineeringBiological materials
Systems and methods for performing anaerobic digestion of biomaterials using a clarifier, a batch reactor, and / or a digester are disclosed. The clarifier performs pretreatment processing of biomaterial to improve anaerobic digestion. The batch reactor and / or the digester are coupled to the clarifier and are configured to digest the processed biomaterial. A control system for an anaerobic digestion process includes a flow control system, a temperature control system, and a totalization system. The flow control system controls the flow of biomaterial and the delivery of chemical agents to the biomaterial based on conductivity, temperature, pressure, and / or composition of the biomaterial. The temperature control system includes a heat source and heat exchangers that control the temperature of the biomaterial. The totalization system senses the volume of biomaterial in at least one stage of an anaerobic digestion process and a controller controls the flow control system based upon the sensed volume of biomaterial.
Owner:EPCOT CRENSHAW CORP
Deposition of TiN films in a batch reactor
ActiveUS20060060137A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTitanium chlorideTitanium nitride
Titanium nitride (TiN) films are formed in a batch reactor using titanium chloride (TiCl4) and ammonia (NH3) as precursors. The TiCl4 is flowed into the reactor in temporally separated pulses. The NH3 can also be flowed into the reactor in temporally spaced pulses which alternate with the TiCl4 pulses, or the NH3 can be flowed continuously into the reactor while the TiCl4 is introduced in pulses. The resulting TiN films exhibit low resistivity and good uniformity.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
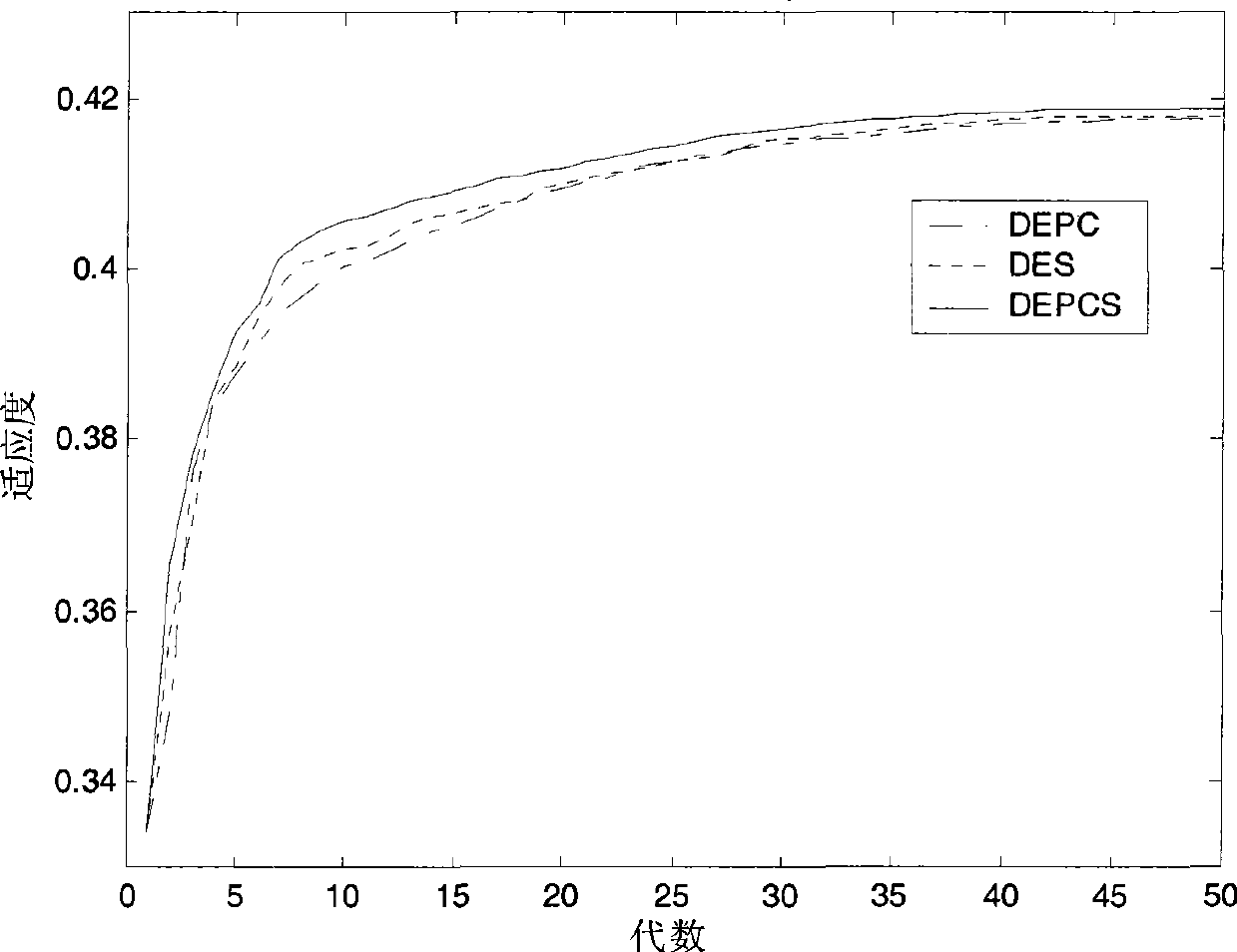
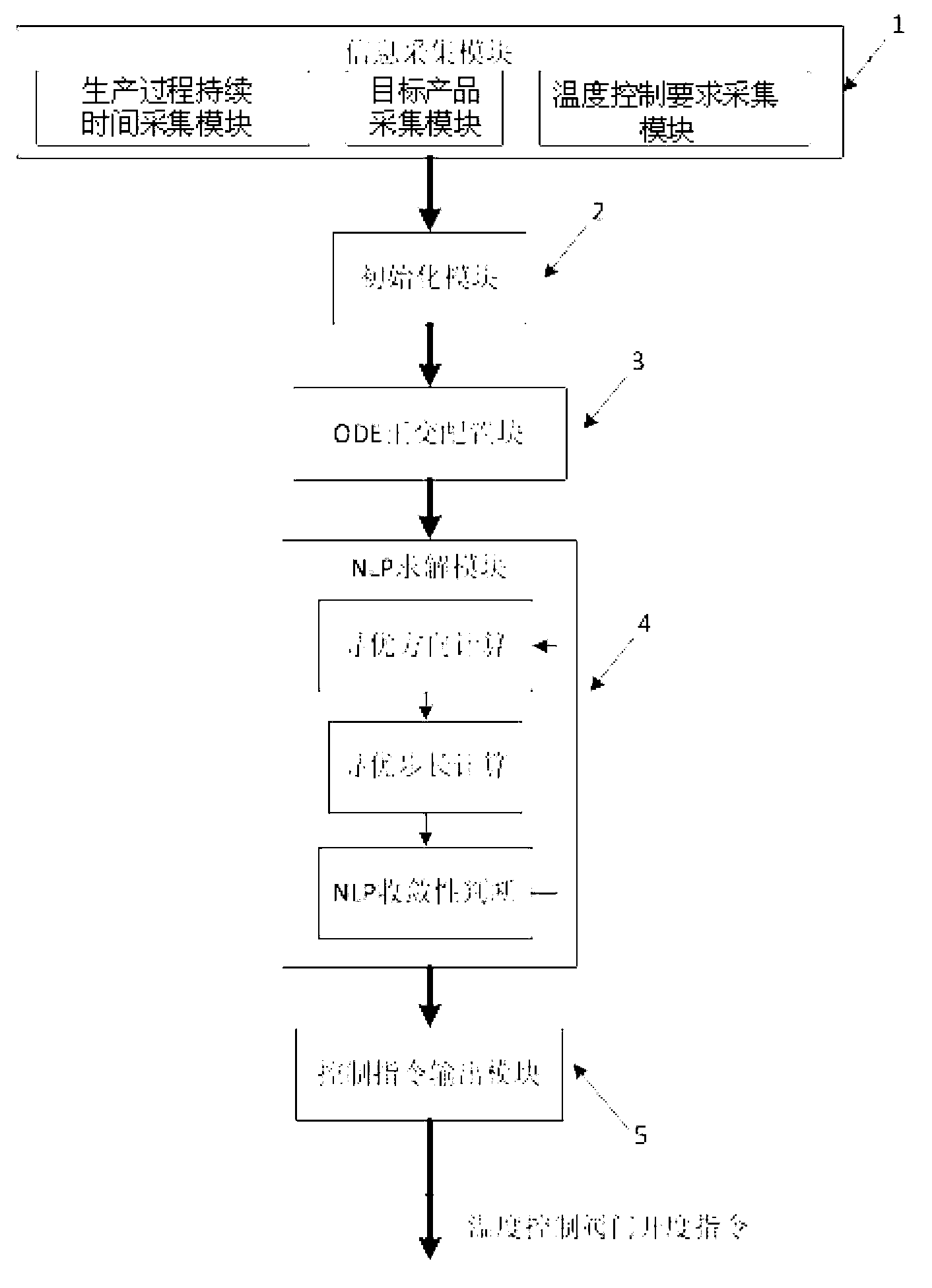
Batch reactor optimal control method based on single population and pre-crossed differential evolution algorithm
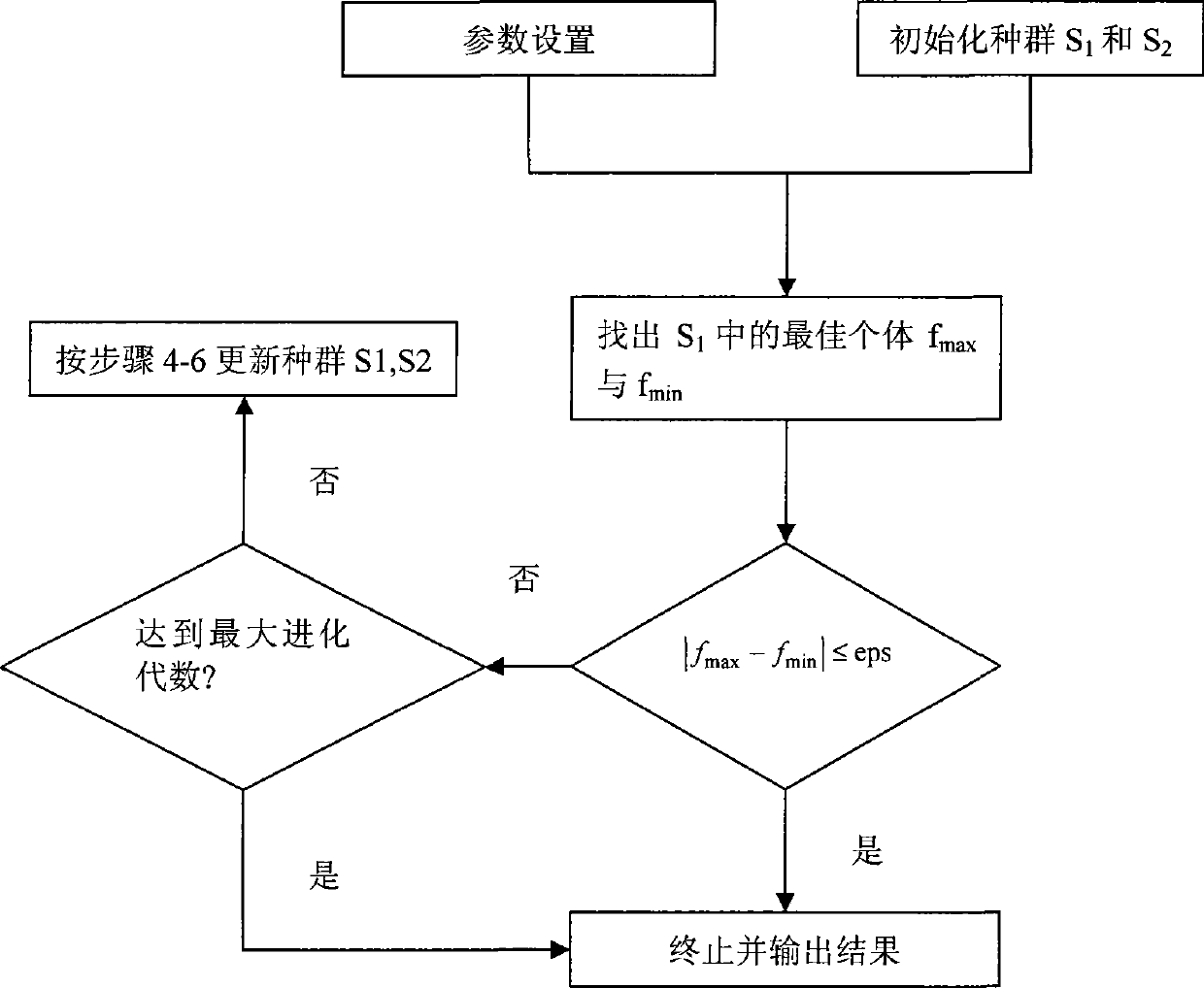
An optimal control method for a batch reactor of a differential evolution algorithm based on a single population and pre-crossover comprises the following steps: 1), an evolutional generation g is caused to be equal to 1, and an individual number i is caused to be equal to 1, and a parameter is initialized; 2), the population is initialized; 3) the highest fitness and the lowest individual fitness in S1 are respectively fmax and fmin; if |fmax minus fmin| is smaller than or equal to an eps, then the algorithm is stopped, and a final result is output; if not, g is caused to be equal to g plus 1, and i is caused to be equal to 1; whether an evolutional generation is maximized or not is judged; and if yes, the algorithm is stopped and a change curve of the yield of a target product is output, and if not, the algorithm is continued; 4) a pre-crossover operation is conducted; 5) i is caused to be equal to i plus 1; if i is equal to a pop, step 3) is returned, and if not, step 4) is returned; and 6), three individuals are selected from S1 at random to conduct an mutation crossover operation, and an acquired experimental individual is yi; if f(yi) is smaller than f(xi), yi is used for replacing xi; and if f(yi) is larger than f(xi) and f(yi) is smaller than f (xi'), yi is used to replace xi', and step 5) is returned. The optimal control method has the advantages of simple operation, high convergence rate and high searching ability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
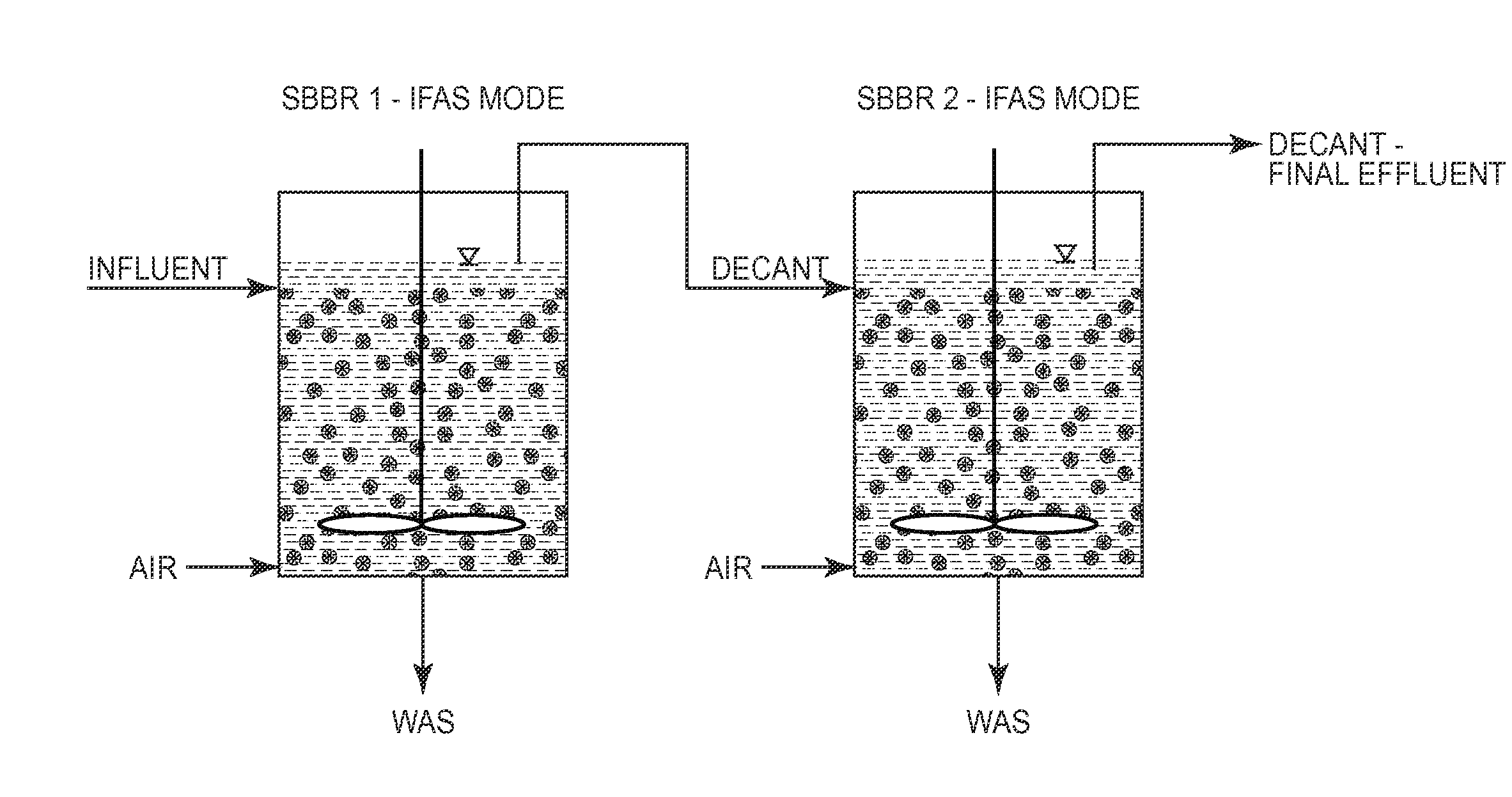
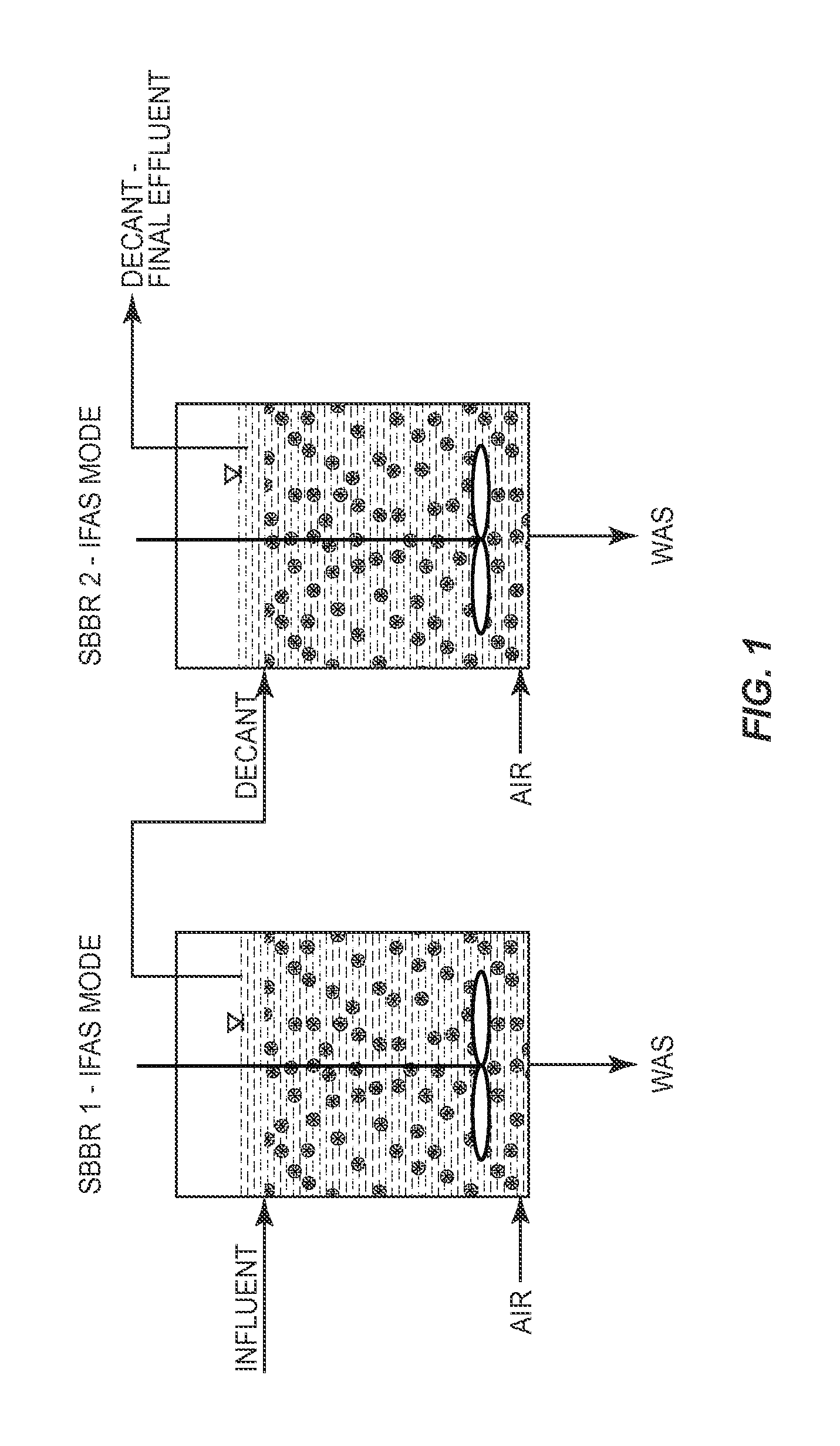
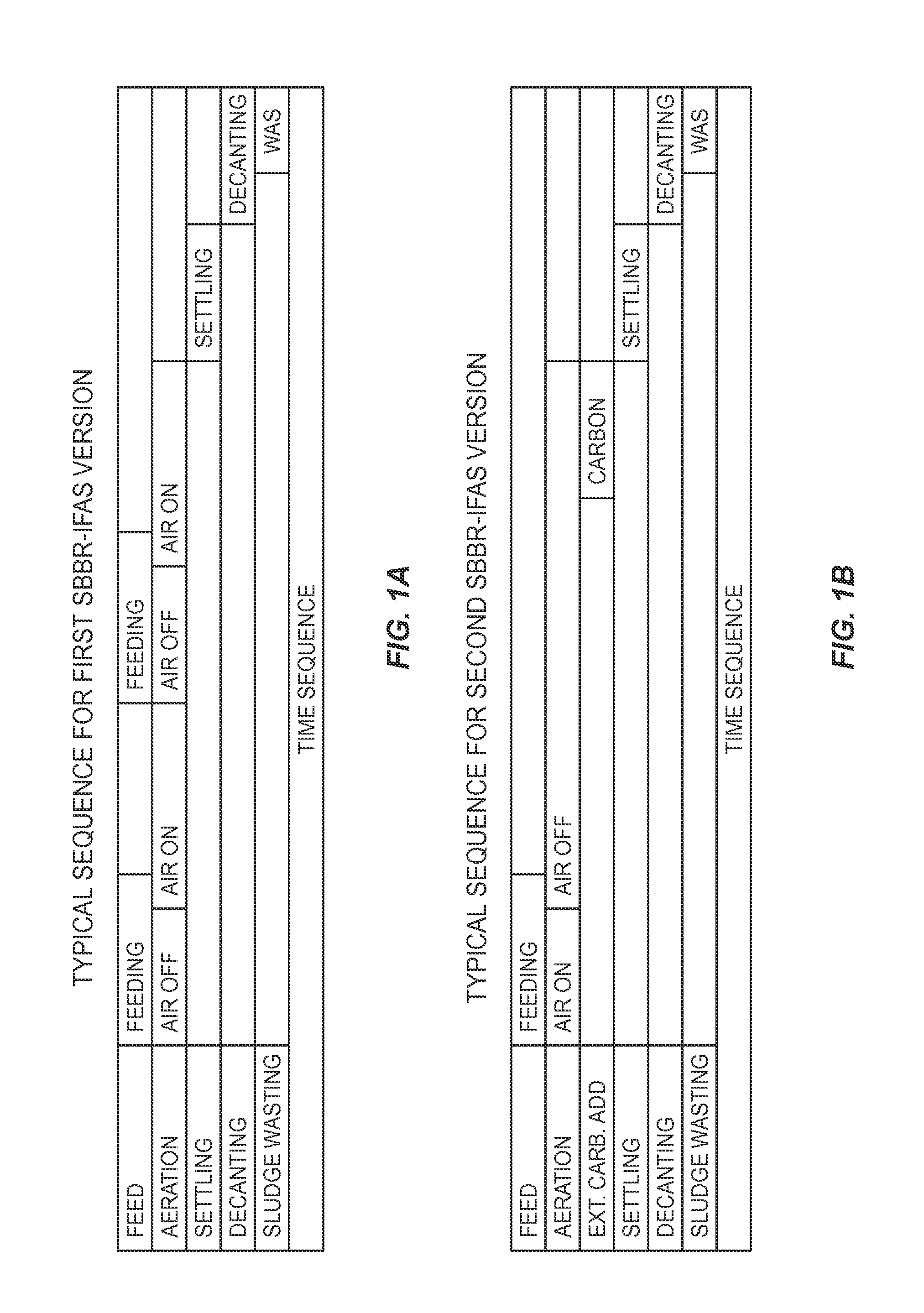
Process for Treating Municiple Wastewater Employing Two Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactors
InactiveUS20140238931A1Reduce concentrationPromote growthTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSustainable biological treatmentSequencing batch reactorSewage
A method is provided for removing BOD and ammonium from wastewater in a mainstream process that includes deammonification. Wastewater including BOD and ammonium is directed to a first sequence batch reactor (SBBR). The wastewater is treated in the first SBBR and in the process nitrite is accumulated such that the wastewater includes a nitrite-to-ammonium stoichiometric ratio that enables anammox bacteria to effectively remove ammonium and nitrite from the wastewater. Thereafter the wastewater is directed the wastewater from the first SBBR to a second SBBR. The second SBBR is operated under anoxic conditions and employs anammox bacteria to remove ammonium and nitrite from the wastewater. In certain embodiments, a pre-denitrification step or process is employed in the first SBBR to remove BOD. In addition, in certain embodiments, the second SBBR includes an oxic phase for converting some ammonium to nitrite and, in some cases, an external carbon source is added to the wastewater under anoxic conditions to reduce the concentration of the nitrate in the wastewater.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
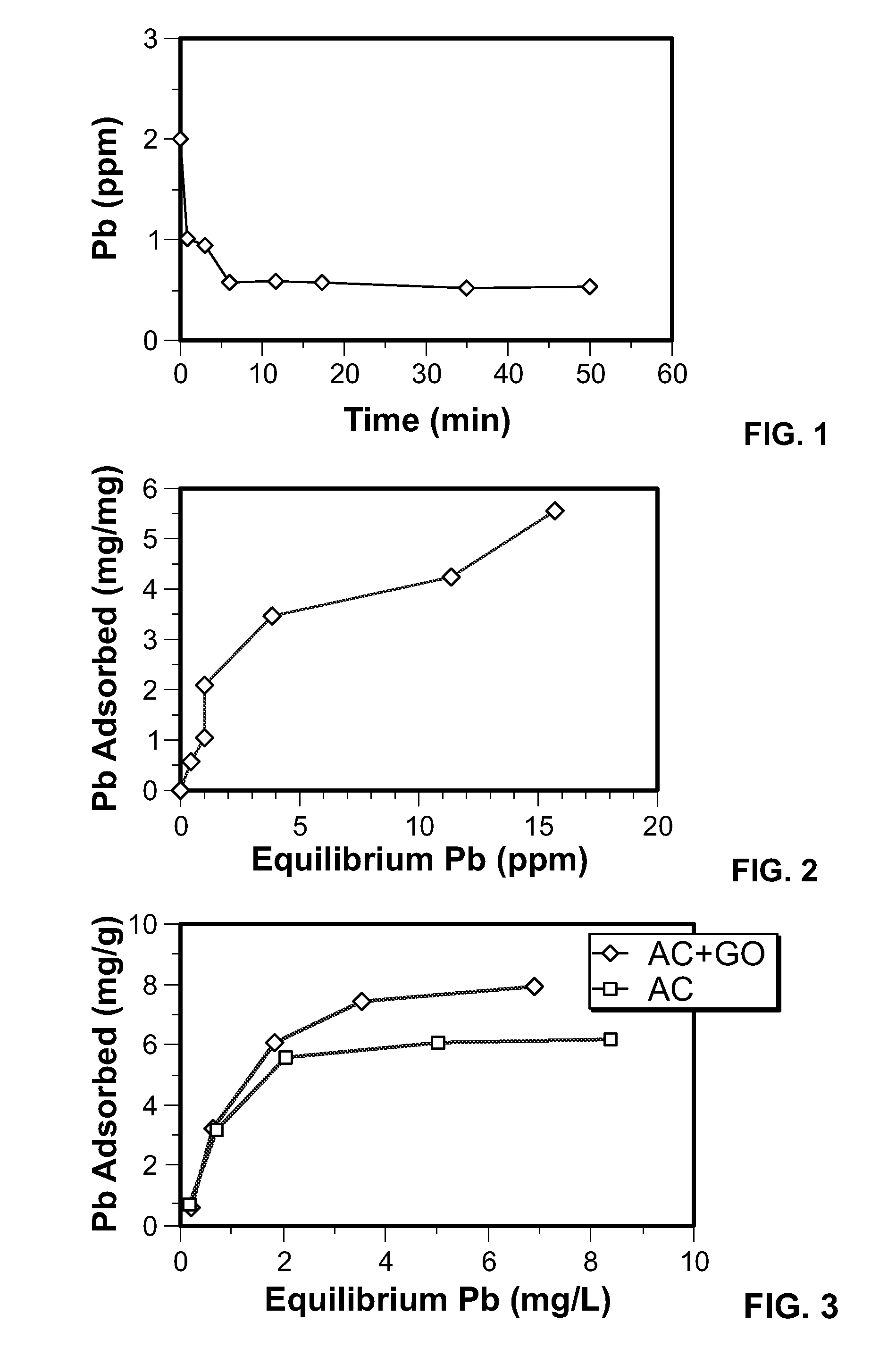
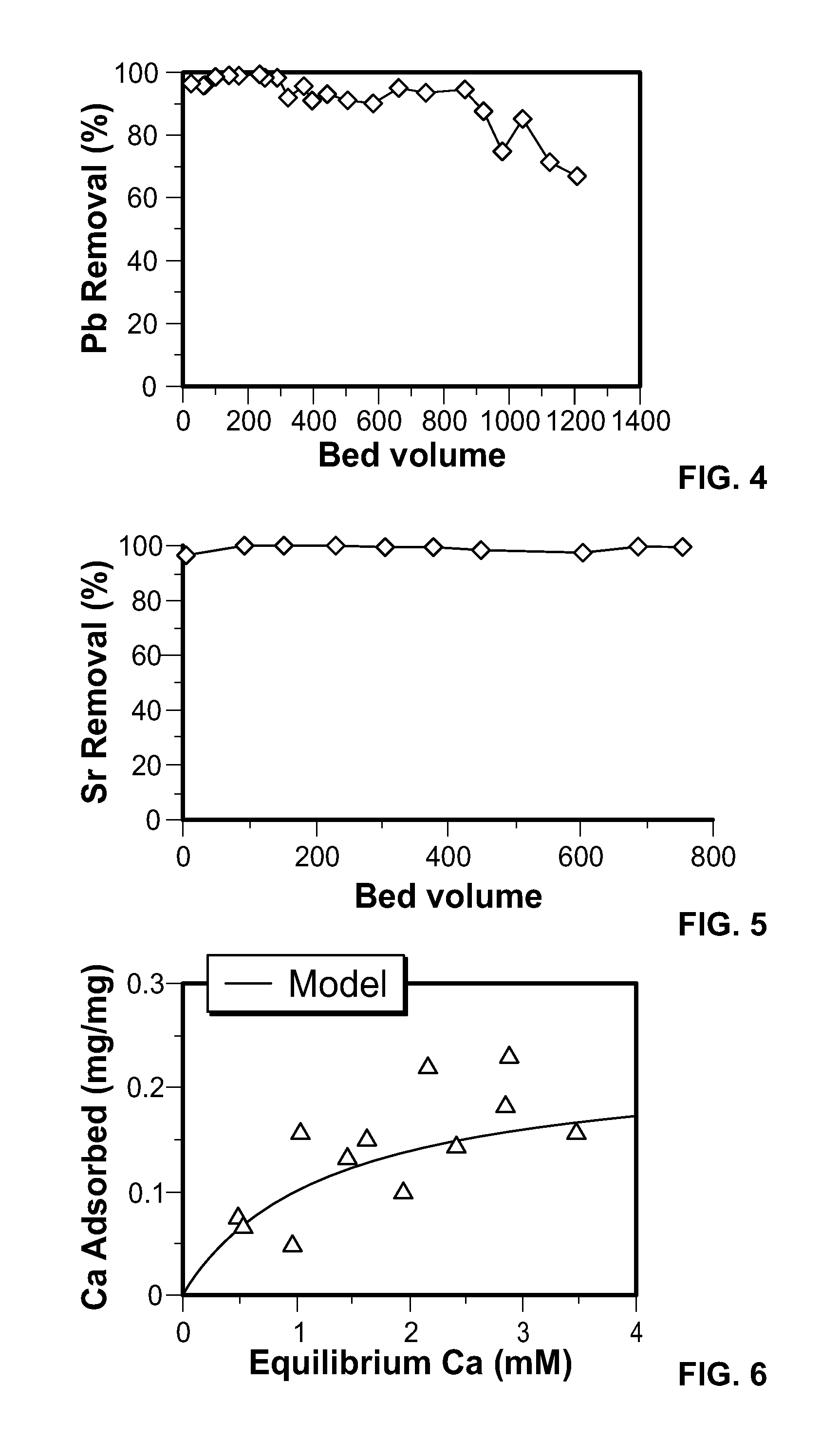
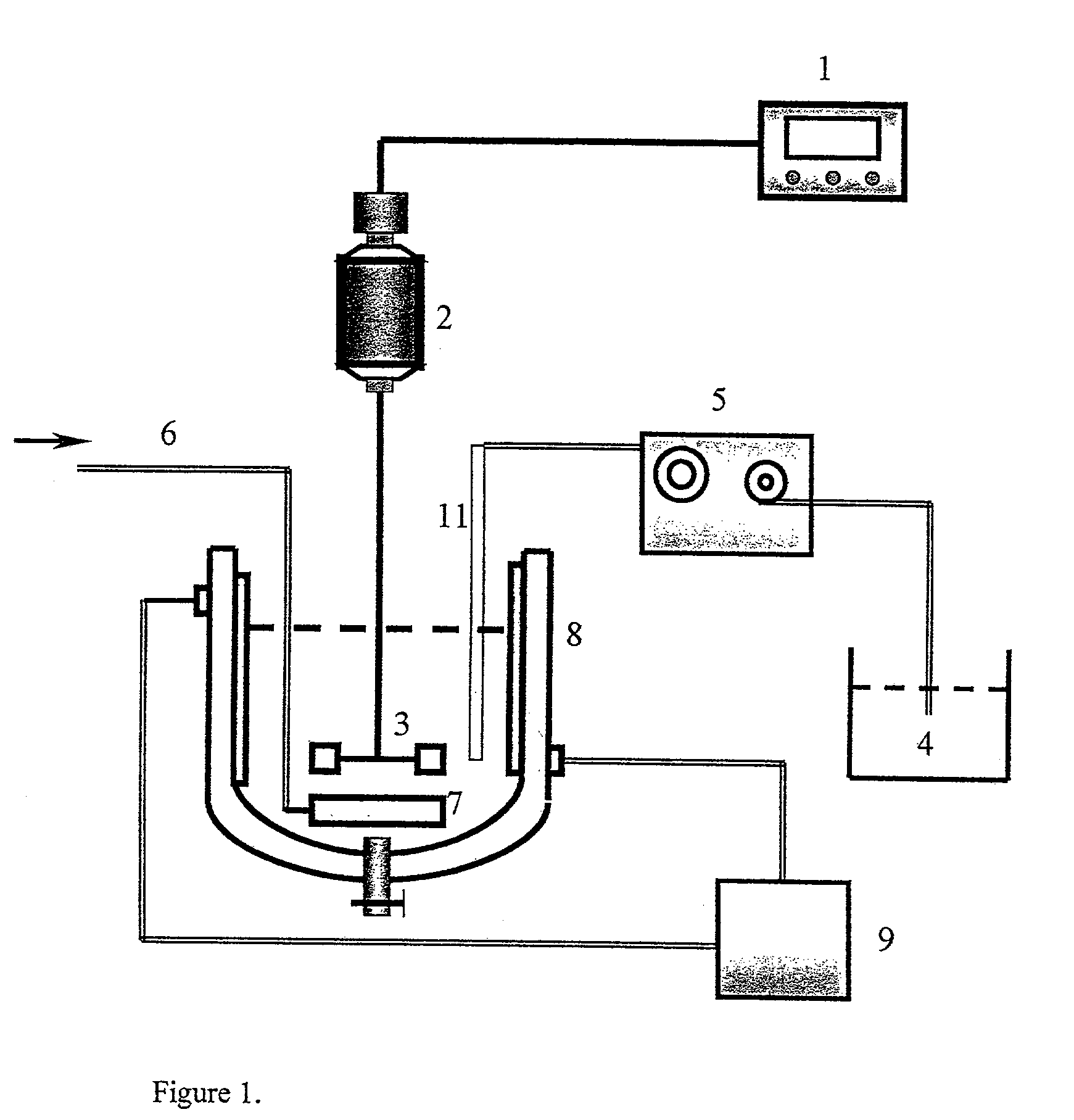
Graphene oxide-modified materials for water treatment
InactiveUS20150129502A1Low costLarge specific surface areaLiquid surface applicatorsOther chemical processesParticulatesSorbent
A graphene oxide adsorbent for removing dissolved substances from water or other liquids comprises a substrate having a coating layer of graphene oxide. The dissolved substances may be dissolved heavy metals, radioactive compounds, or other organic and inorganic substances. The substrates may be particulate substrates. The substrates may be adsorbents. The graphene oxide adsorbents can be beneficially used in filters and batch reactors, among other devices, for water treatment and for environmental remediation. In some embodiments, graphene oxide alone may be used as the graphene oxide adsorbent,
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparation of nanometer cerium-based oxide particles
InactiveUS7025943B2Small particle sizeUniform shapeMaterial nanotechnologyCerium oxides/hydroxidesRoom temperatureCerium
The invention comprises novel undoped and doped nanometer-scale CeO2 particles as well as a novel semi-batch reactor method for directly synthesizing the novel particles at room temperature. The powders exhibited a surface area of approximately 170 m2 / g with a particle size of about 3–5 nm, and are formed of single crystal particles that are of uniform size and shape. The particles' surface area could be decreased down to 5 m2 / g, which corresponds to a particle size of 100 nm, by thermal annealing at temperatures up to 1000° C. Control over the particle size, size distribution and state of agglomeration could be achieved through variation of the mixing conditions such as the feeding method, stirrer rate, amount of O2 gas that is bubbled through the reactor, the temperature the reaction is carried out at, as well as heating the final product at temperatures ranging from 150° to 1000° C.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) and SBBR (Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactor) municipal sewage high-efficiency biological treatment method and device based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation
ActiveCN103601341AEasy to trainAvoid sludge ageMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorMembrane reactor
The invention provides a SBR (Sequencing Batch Reactor) and SBBR (Sequencing Biofilm Batch Reactor) municipal sewage high-efficiency biological treatment method and device based on anaerobic ammonia oxidation, and belongs to the technical field of sewage biological treatment. The device is provided with an SBR and an SBBR and is characterized in that sewage enters the SBR firstly, so that the biological phosphorus removal is realized through anaerobic-aerobiotic alternate operation, and meanwhile, organic matters in water are removed through heterotrophic bacteria; by controlling the short sludge age and no occurrence of nitrification, the surplus sludge quantity is large, and the phosphorous and organic matter removal effect is good; and yielding water of the SBR enters the SBBR, so that the partial nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation autotrophic nitrogen removal is realized through low-oxygen aeration operation. The process operation method comprises the following steps: (1) sludge inoculation and initialization phase; and (2) operational phase. The method and the device are suitable for the treatment of municipal sewage with low carbon nitrogen ratio, are energy-saving and have good nitrogen and phosphorous removal effects and high removal rate of pollutants; and the system control is flexible.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for culturing microbial flora for purifying waste water
InactiveCN101914441AReduce CODReduce ammonia nitrogen contentBacteriaBiological water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeOperation mode
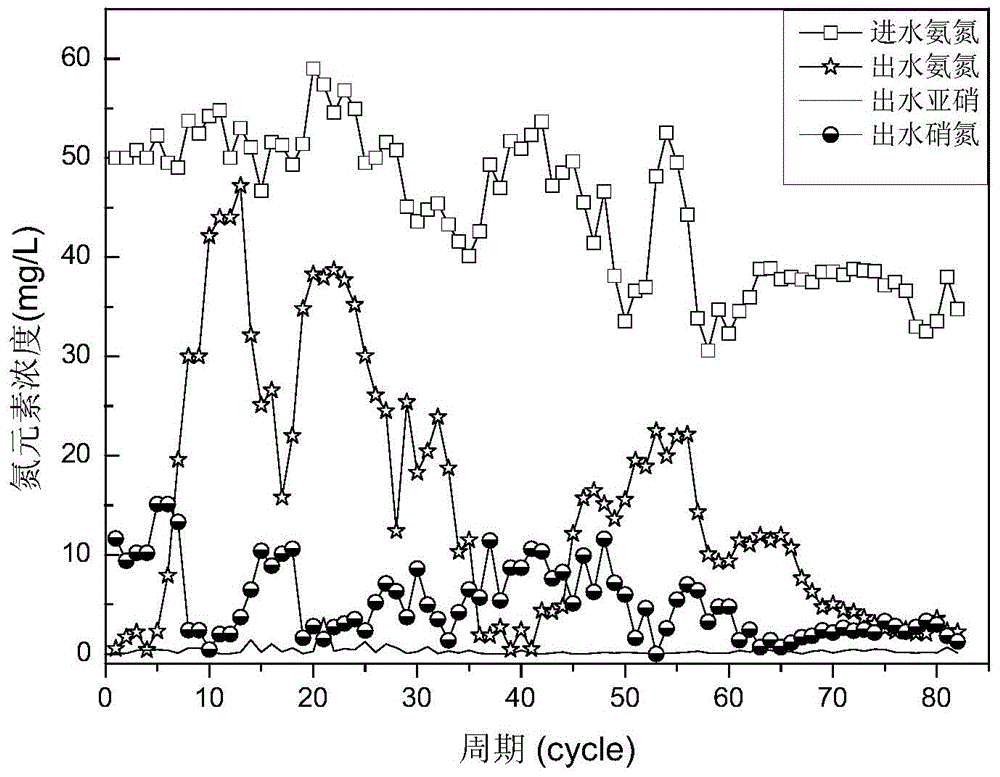
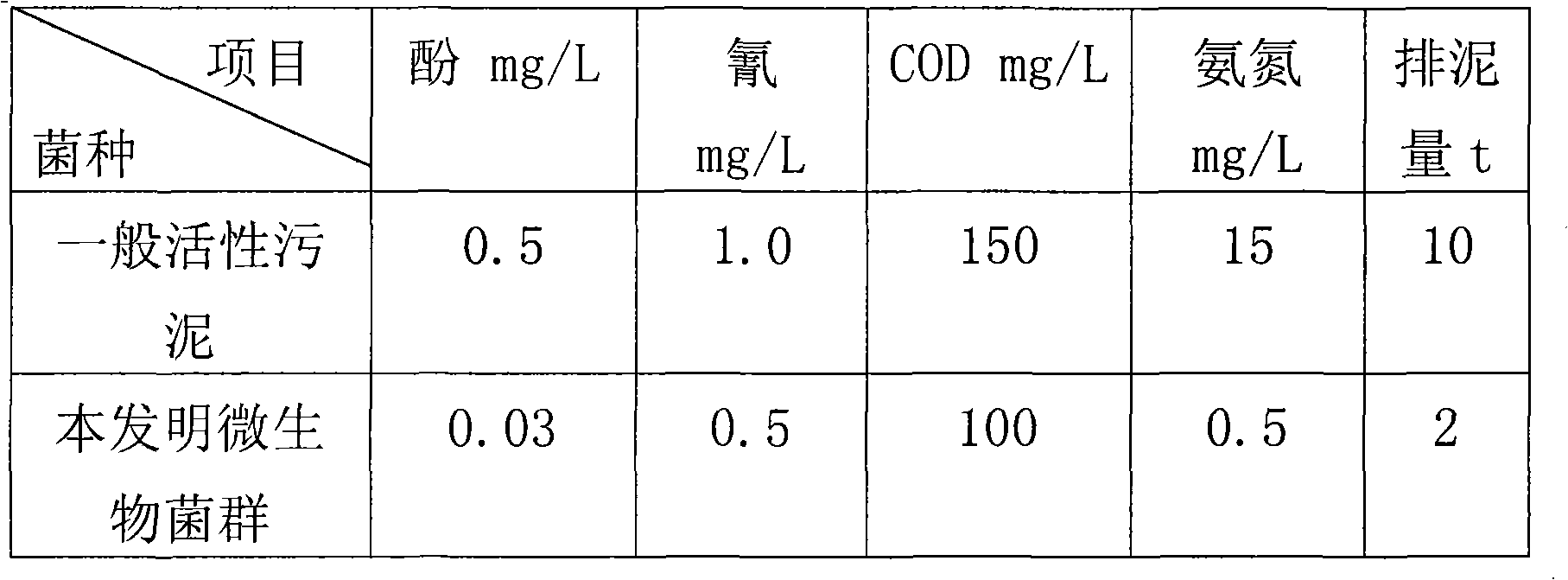
The invention discloses a method for culturing a microbial flora for purifying waste water, which comprises the following steps: A, filtering, settling and concentrating active sludge, adding coking wastewater at the temperature of below 33 DEG C, adding nutrients, proteins and microbial growth hormone at the same time, aerating for 3 to 5 days under a constant-temperature condition, settling, discharging supernatant, adding glucose solution and domesticating according to the operation mode of a batch reactor activated sludge process; B, at the end of domestication, screening cocci, bacilli and spirilla, placing into containers for low-temperature storage respectively, injecting 10 percent glucose solution into the containers for repair, and taking the bacterial strains out 24 hours later for mixing; and C, performing aerobic and anaerobic culture of the mixed bacterial strains, and adding a stabilizer and strain protective agent. For common active sludge, the method can reduce the phenol, cyanogens, COD and ammonia nitrogen content of coking wastewater more effectively and reduce sludge discharge obviously.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL (GROUP) CORP
Orthogonal collocation optimization based batch reactor control system
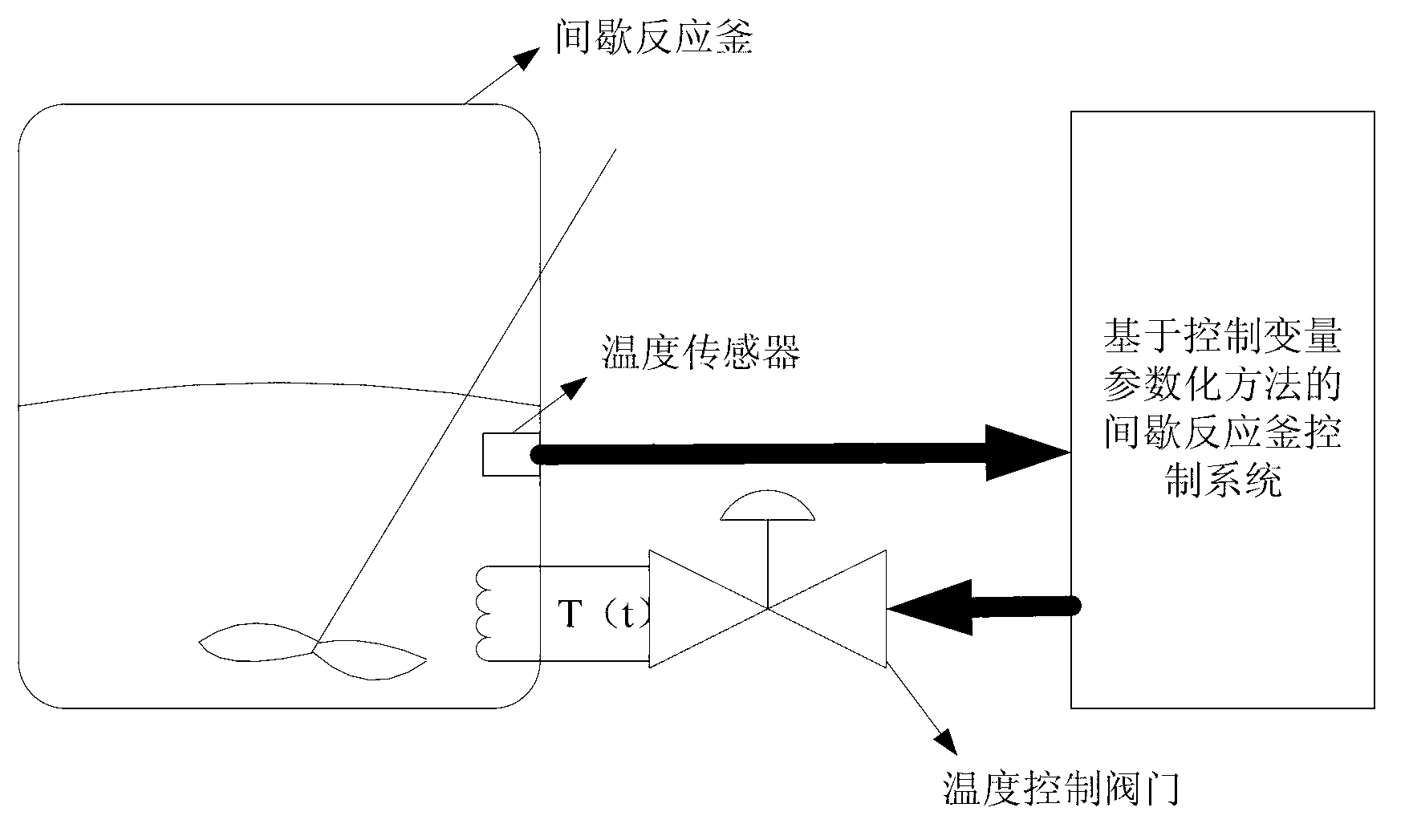
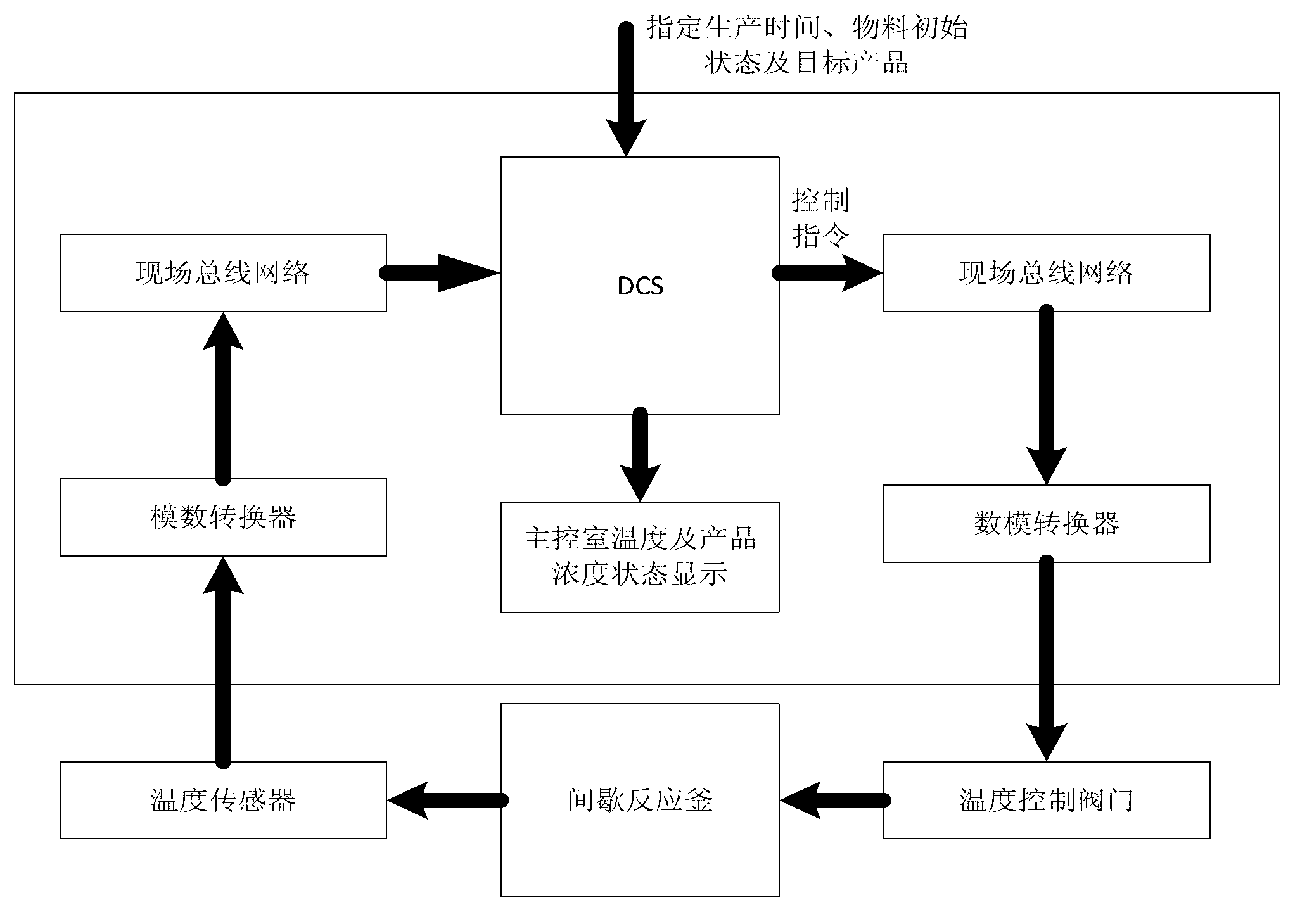
InactiveCN103309234AConcentration maximizationRealize tapping potential and increasing efficiencyChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsAdaptive controlTemperature controlDigital analog converter
The invention discloses an orthogonal collocation optimization based batch reactor control system. The orthogonal collocation optimization based batch reactor control system comprises a batch reactor body, a temperature sensor at the end of the batch reactor body, an analog to digital converter, field bus networks, a DCS (distributed control system), a main control room temperature and product concentration state displayer, an analog to digital converter at the end of a temperature control valve and the temperature control valve. After an engineer in a control room specifies duration of a production process, initial concentration states of materials in the batch reactor body and a target product needing concentration increasing, the DCS executes an internal orthogonal collocation optimization method to compute a temperature control strategy enabling the concentration of the target product to be maximum, the temperature control strategy is converted into an opening instruction of the temperature control valve, and the opening instruction is sent to the analog to digital converter at the end of the temperature control valve through the field bus networks so as to enable the temperature control valve to act correspondingly according to a received control instruction. By the system, the concentration of the target product can be maximized, and potential tapping and efficiency improvement are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
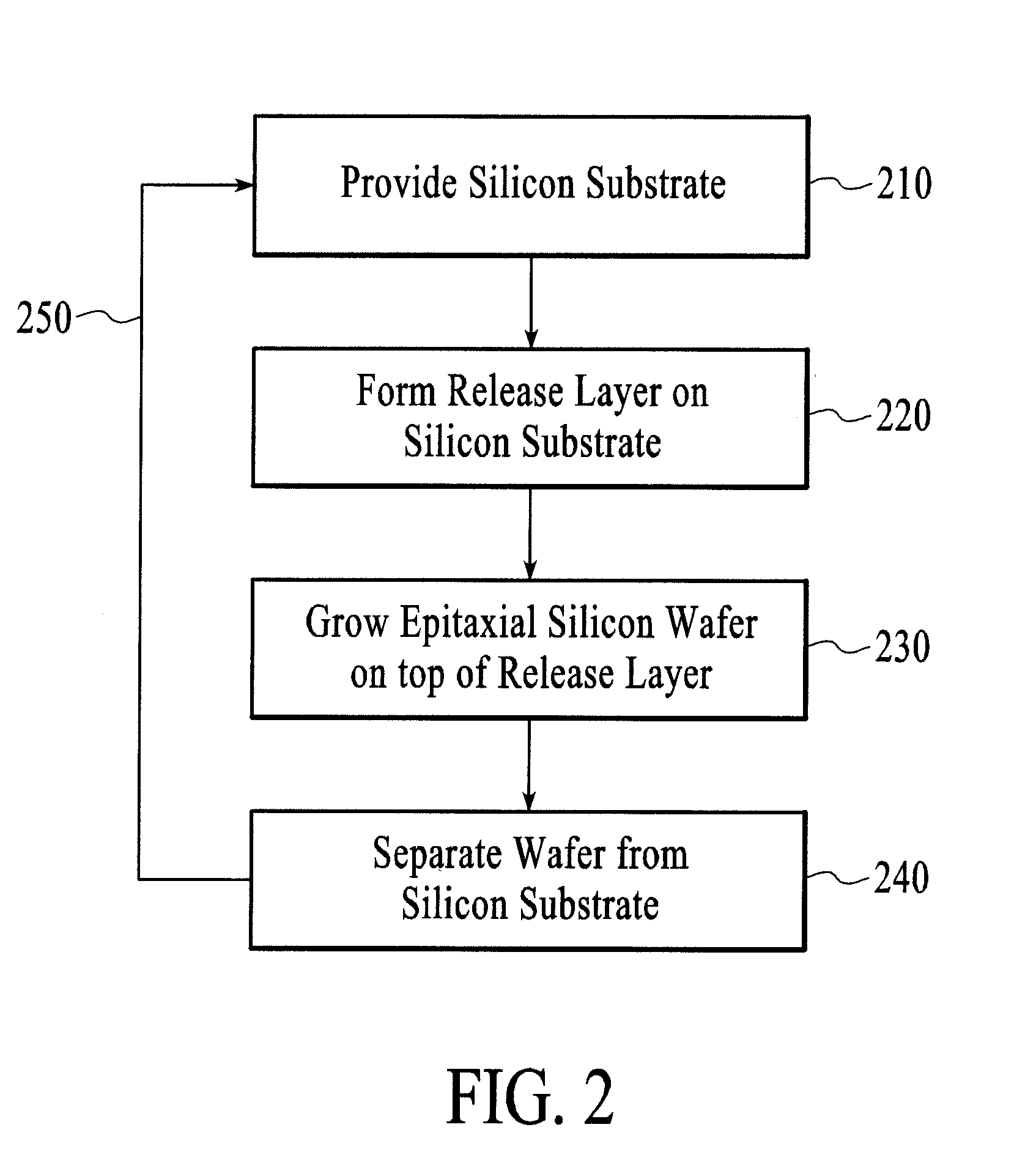
Silicon wafers by epitaxial deposition
InactiveUS20130032084A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTemperature controlEmissivity
A system for depositing thin single crystal silicon wafers by epitaxial deposition in a silicon precursor depletion mode with cross-flow deposition may include: a substrate carrier with low total heat capacity, high emissivity and small volume; a lamp module with rapid heat-up, efficient heat production, and spatial control over heating; and a manifold designed for cross-flow processing. Furthermore, the substrate carrier may include heat reflectors to control heat loss from the edges of the carrier and / or heat chokes to thermally isolate the carrier from the manifolds, allowing independent temperature control of the manifolds. The carrier and substrates may be configured for deposition on both sides of the substrates—the substrates having release layers on both sides and the carriers being configured to have equal process gas flow over both surfaces of the substrate. High volume may be addressed by a deposition system comprising multiple mini-batch reactors.
Owner:SVAGOS TECHNICK INC
Reactor for preparing isophorone nitrile and method for continuously preparing isophorone nitrile by adopting reactor
ActiveCN103301799AImprove heat transfer efficiencyImprove mass transfer efficiencyChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsPreparation by hydrogen cyanide additionMicron scaleIsophorone
The invention provides a reactor for preparing isophorone nitrile and a method for continuously preparing the isophorone nitrile by adopting the reactor. A plurality of millimeter to micron-sized narrow regular reaction channels which are arranged in parallel are arranged in the reactor, and inner members are arranged in the reaction channels, so that the reactor has good heat and mass transfer effects, and the dwell time can be accurately controlled, thereby obtaining a high reaction conversion rate and a high product yield. Compared with a traditional batch reactor or a common continuous tubular reactor, the method has obvious advantages on many aspects of improvement in the reaction effect in preparation of the isophorone nitrile, safety in production, energy conservation, consumption reduction and the like.
Owner:WANHUA CHEM GRP CO LTD +1
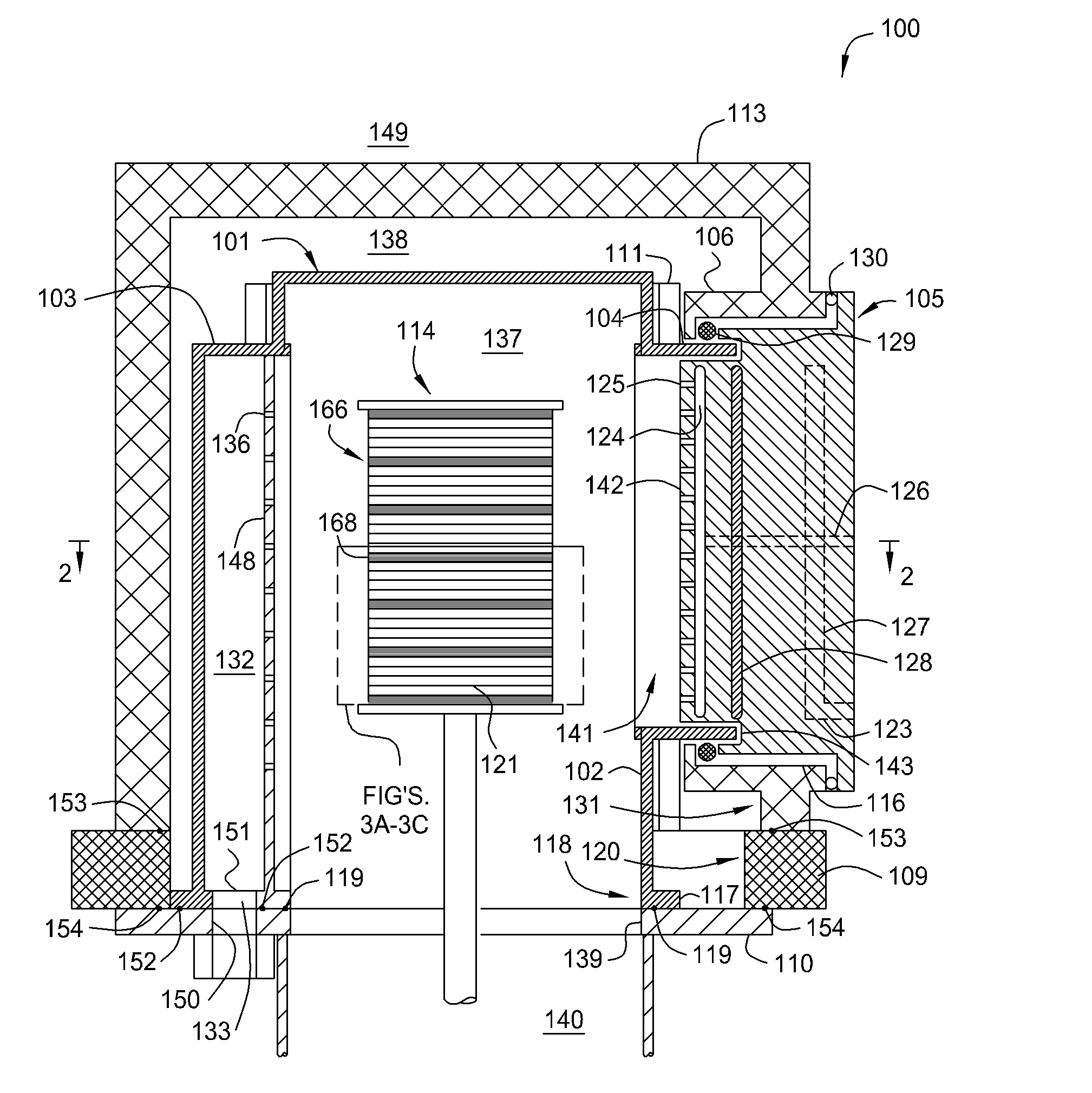
Thermal batch reactor with removable susceptors
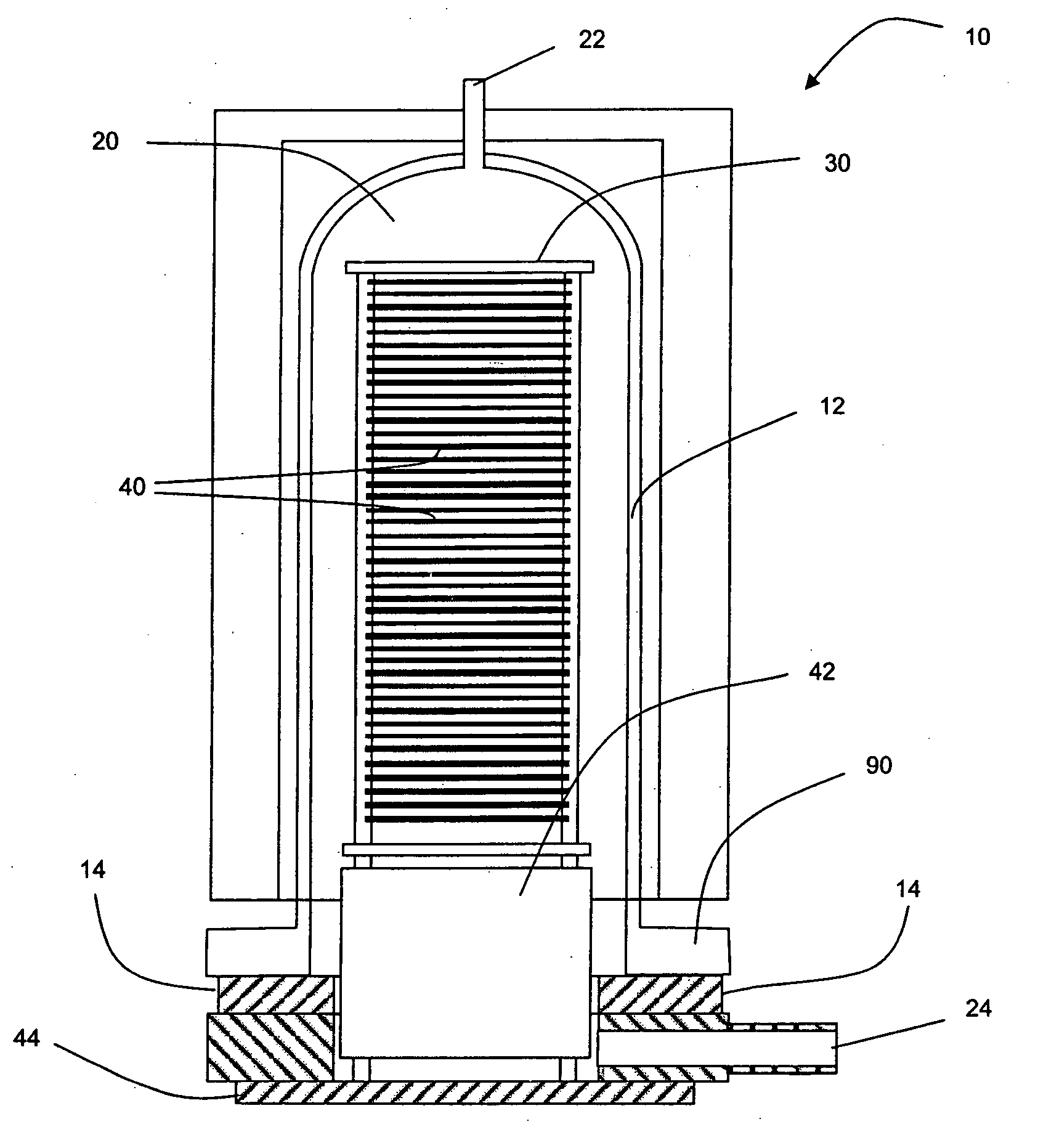
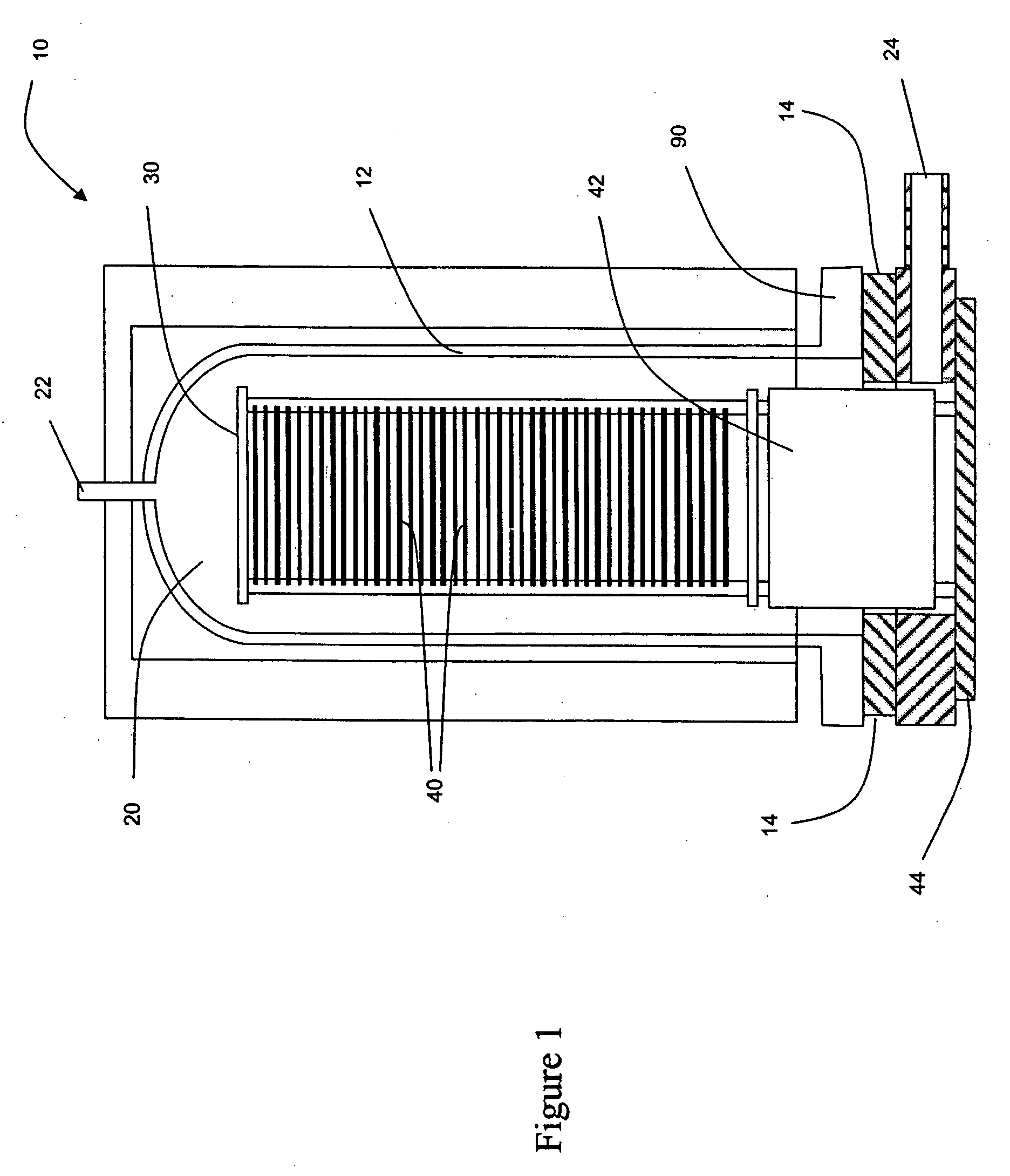
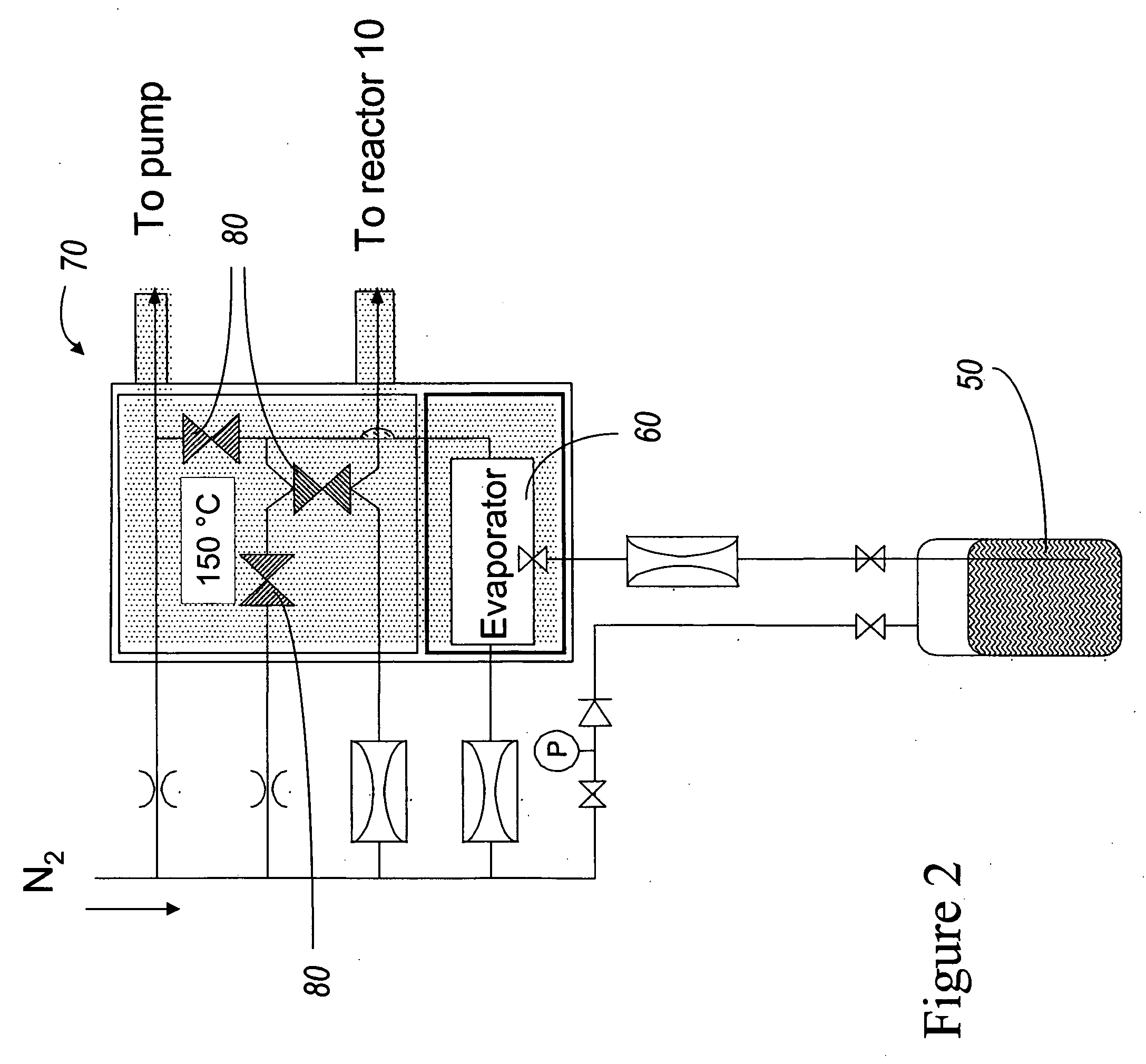
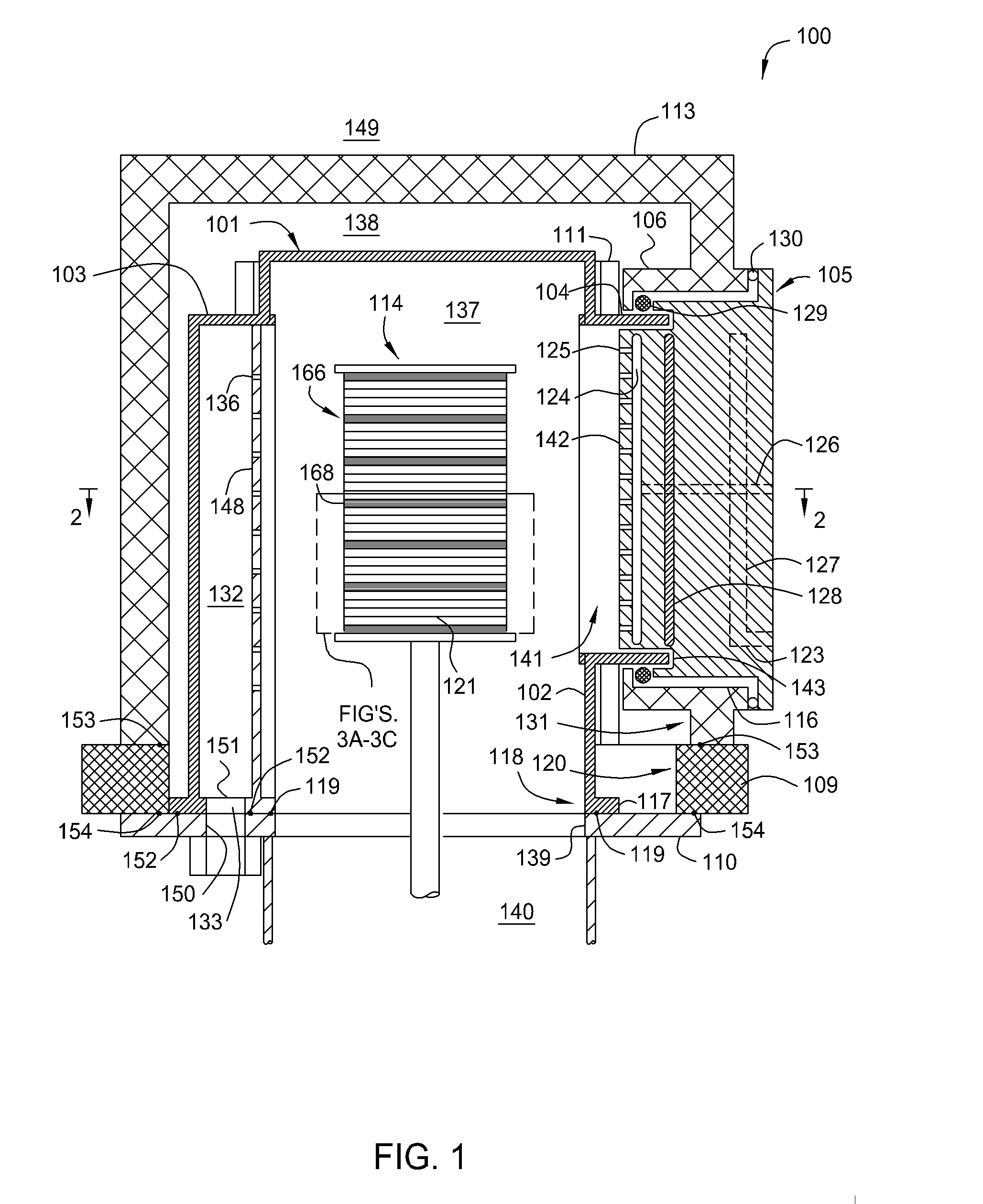
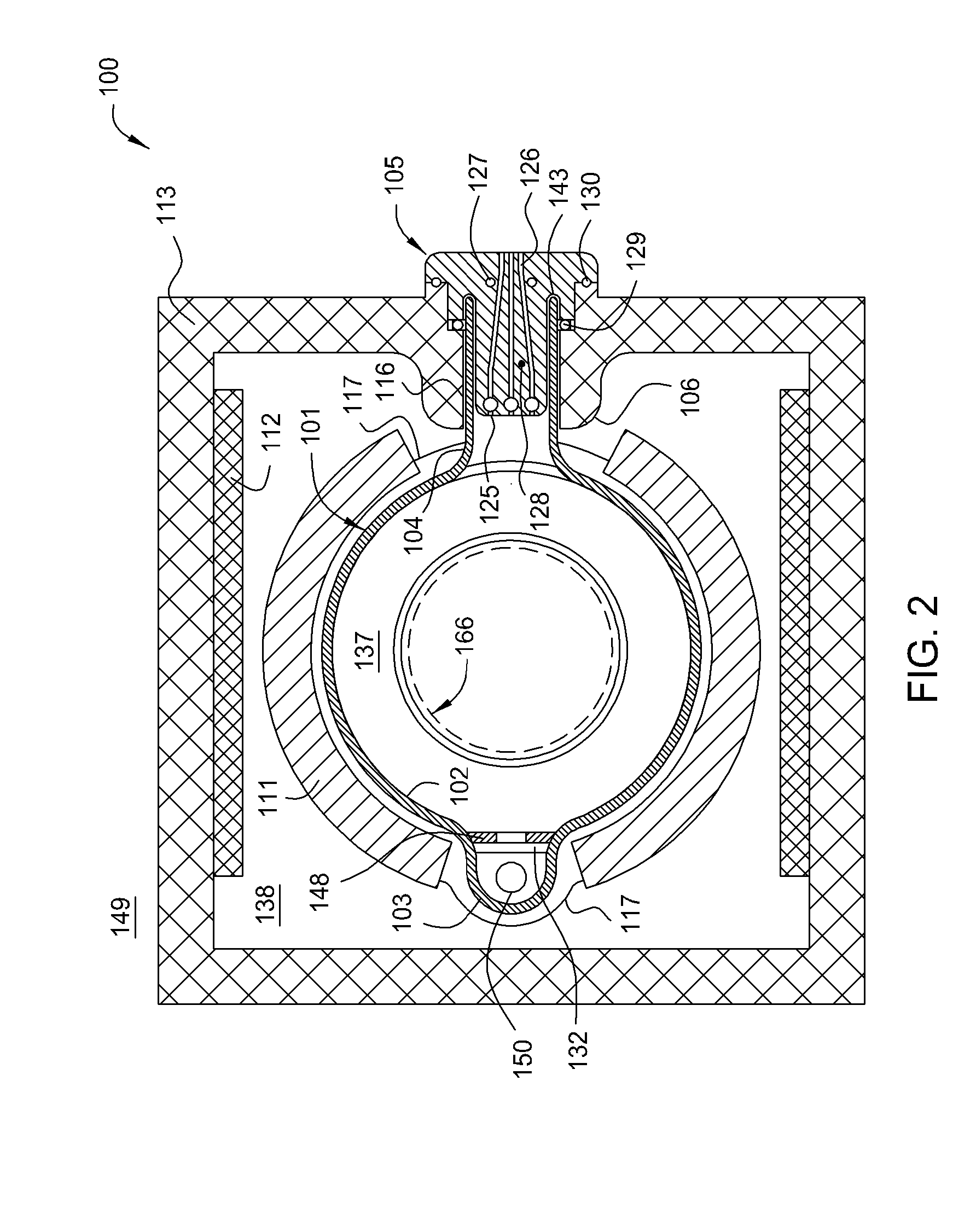
InactiveCN101338414ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSusceptorBatch processing
An apparatus and method for uniform heating and gas flow in a batch processing chamber are provided. The apparatus includes a quartz chamber body, removable heater blocks which surround the quartz chamber body, an inject assembly coupled to one side of the quartz chamber body, and a substrate boat having removable susceptors. In one embodiment, the boat may be configured with a plurality of susceptors to control substrate heating during batch processing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
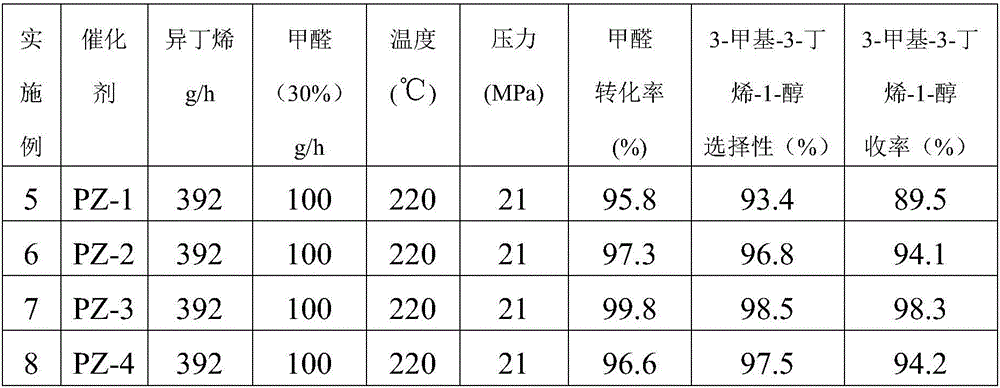
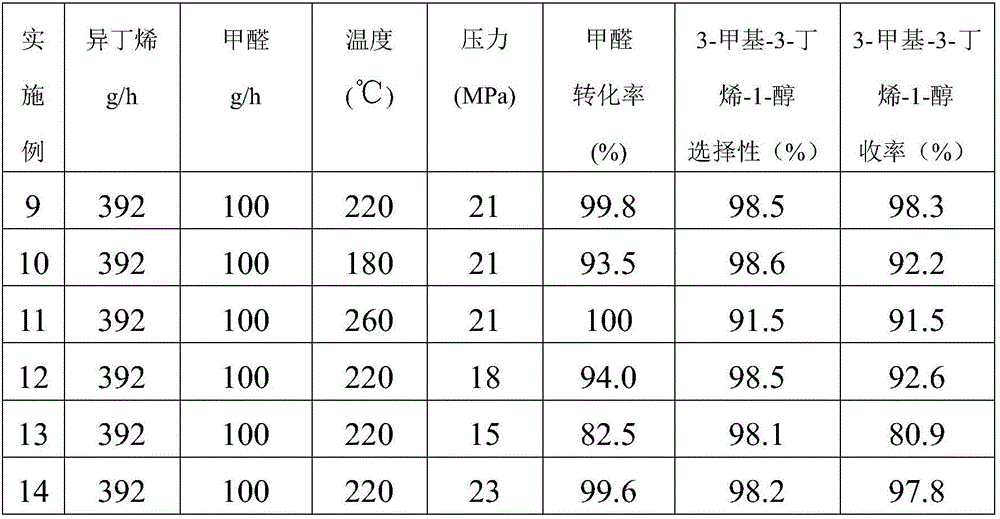
Modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve, preparation method, and synthetic method for catalytically preparing 3-methyl-3-butene-1-alcohol
ActiveCN106582788AEasy to separateImprove securityMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationFixed bedSolvent
The invention discloses a modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve, a preparation method thereof, and a synthetic method for catalytically preparing 3-methyl-3-butene-1-alcohol. The synthetic method for catalytically preparing the 3-methyl-3-butene-1-alcohol comprises the following steps of adopting formaldehyde and isobutylene as starting materials, adopting the modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve as a catalyst, and carrying out Prins condensation reaction in a fixed bed reactor so as to prepare the 3-methyl-3-butene-1-alcohol, wherein the yield can be up to more than 98 percent. The ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyst is modified by adopting high temperature steam treatment and transition metal. According to the process method provided by the invention, the product yield is high, meanwhile, a solvent is not introduced additionally, and a solid catalyst and a fixed bed continuous process technology are adopted, so that a reaction liquid and the catalyst are separated easily, and the operation and the energy consumption of separation are relieved. Compared with batch reactor type reaction, the process method provided by the invention has the characteristics of safety, simplicity in operation, large production capacity and the like.
Owner:CHINA CATALYST HLDG CO LTD
Sequential batch reactor wastewater treatment process
InactiveUS20070175823A1Enhance biological nutrient removalHigh precisionWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesSequencing batch reactorEngineering
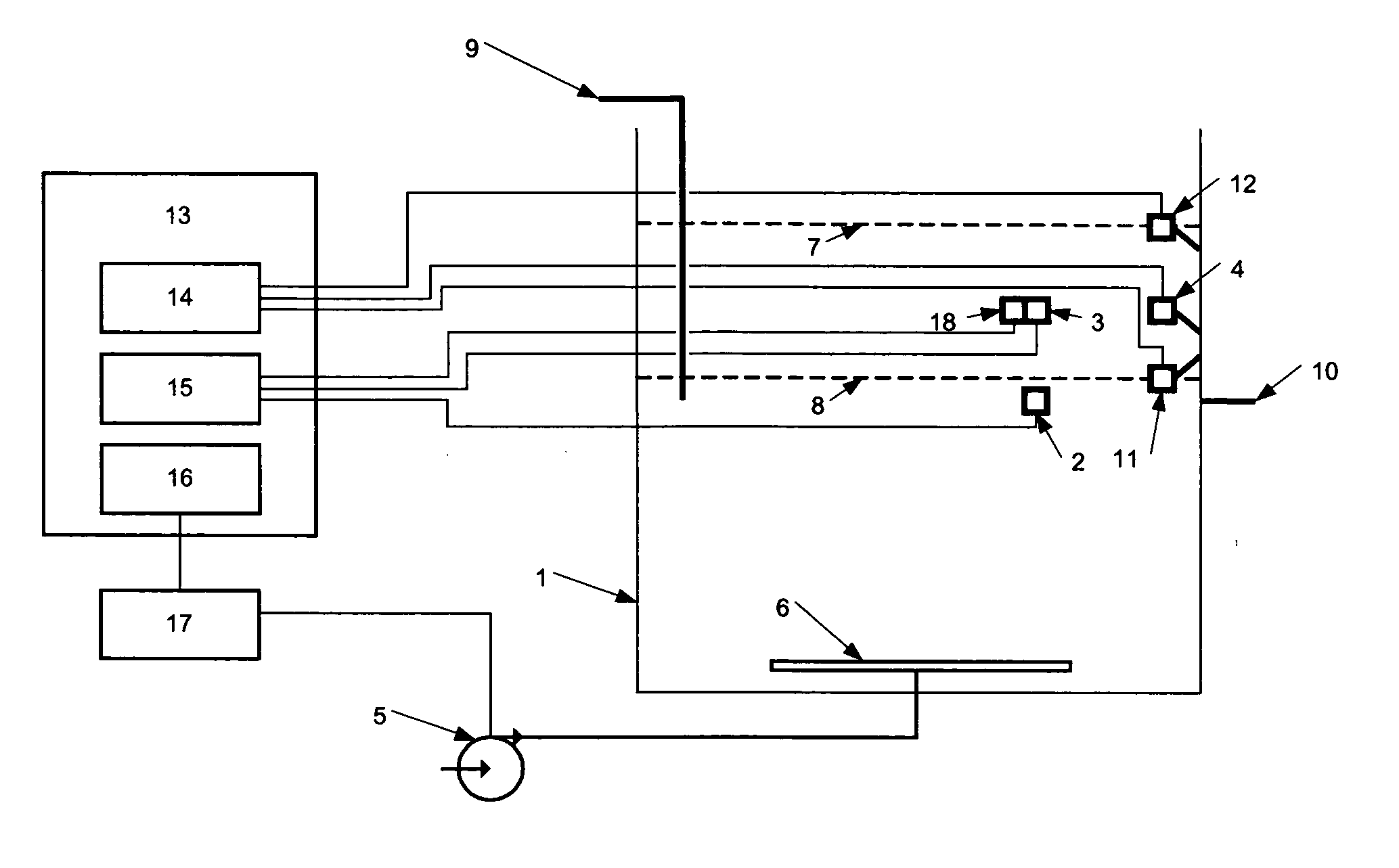
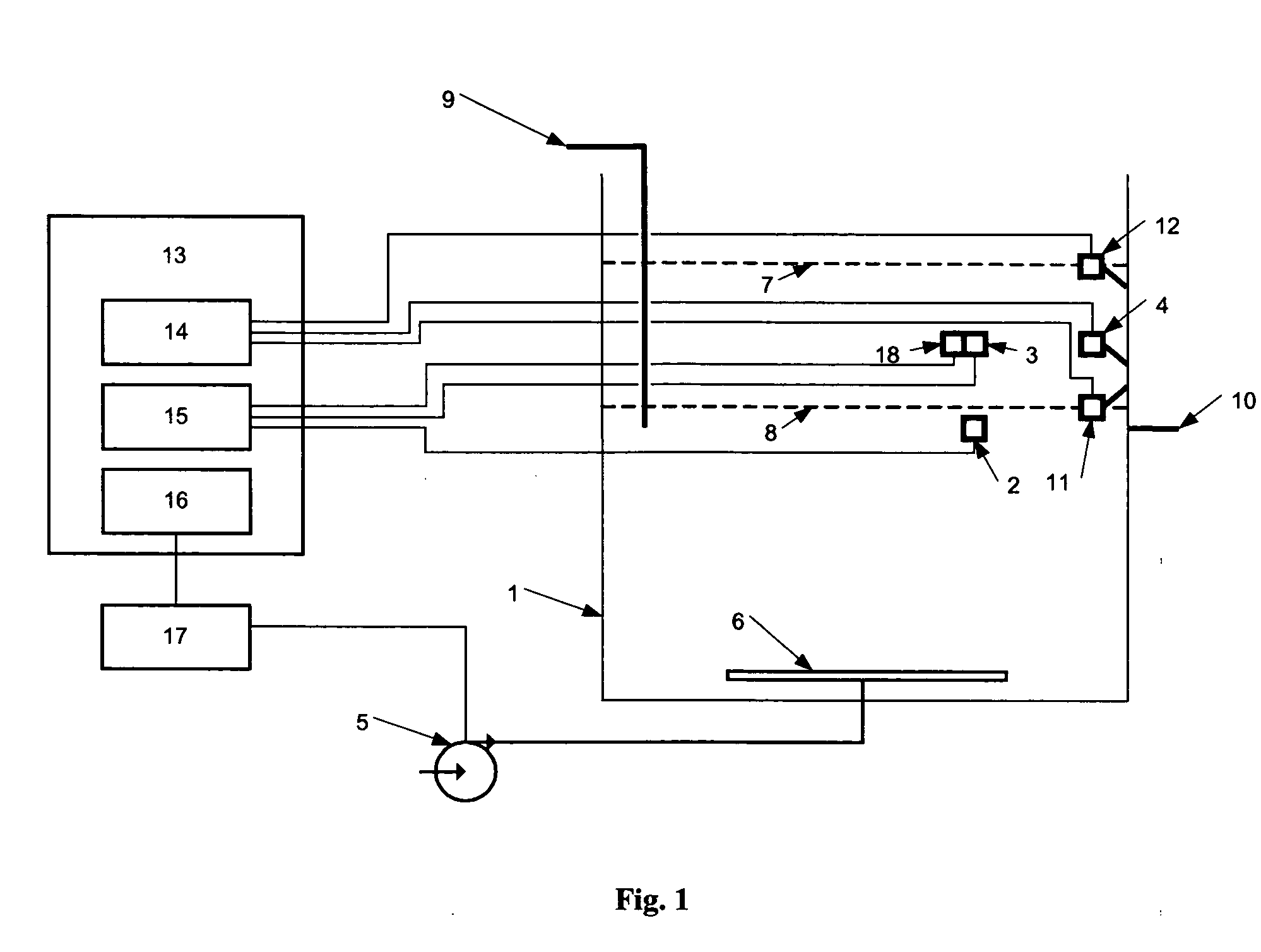
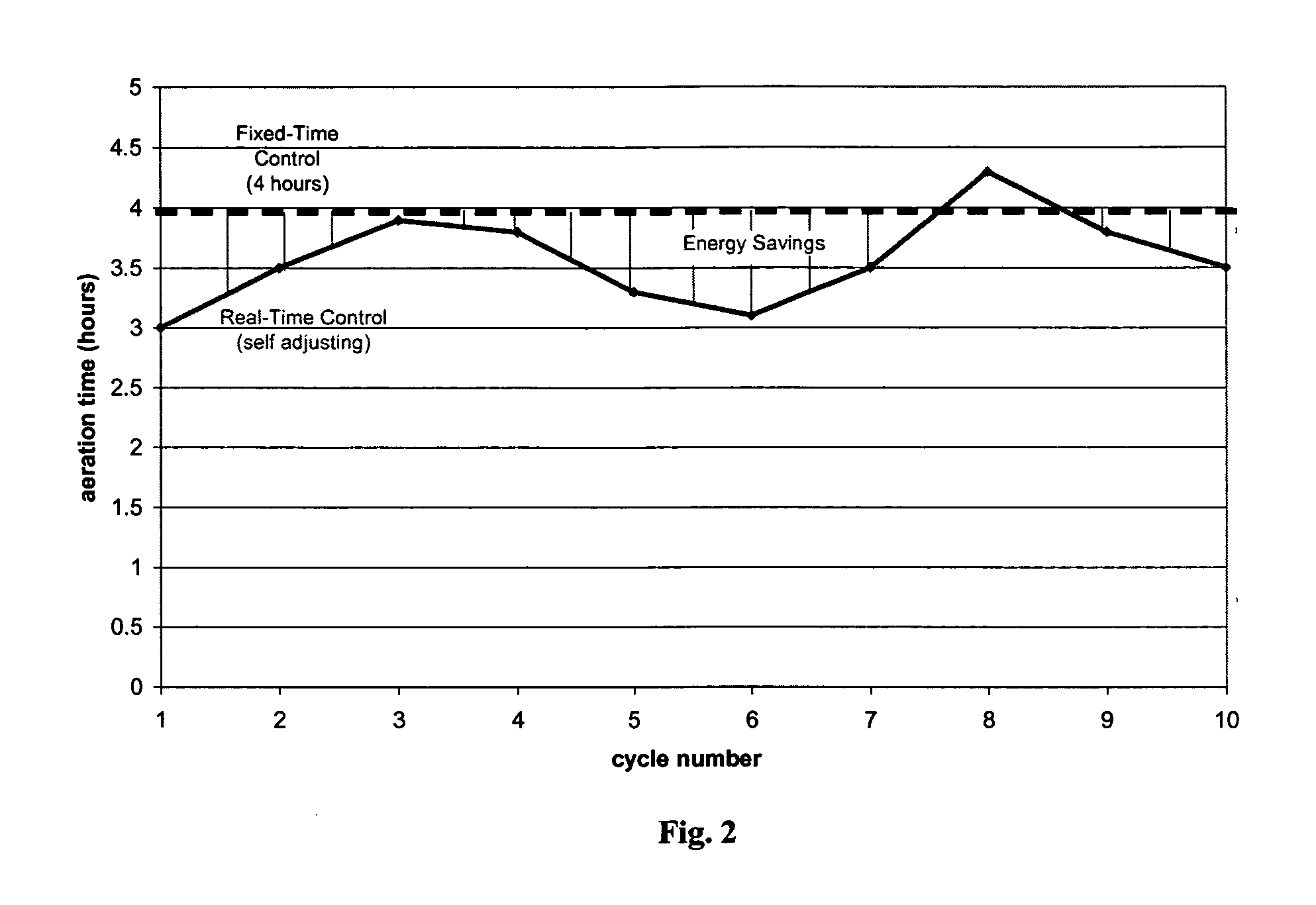
A system for controlling the aerobic phase of a wastewater treatment cycle in a sequencing batch reactor, comprising a tank, an air blower, at least one sensor for measuring the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the tank, and means to control the length of time that the air blower introduces air into the wastewater and to maintain at a constant level the volume of air introduced per time by the air blower. The length of time that the air blower introduces air is determined by the change in the slope of the curve representing the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the wastewater. The volume of air to be introduced per time by the air blower is determined based on the average concentration of dissolved oxygen from the previous wastewater treatment cycle.
Owner:VISION ENVIROTECH INT
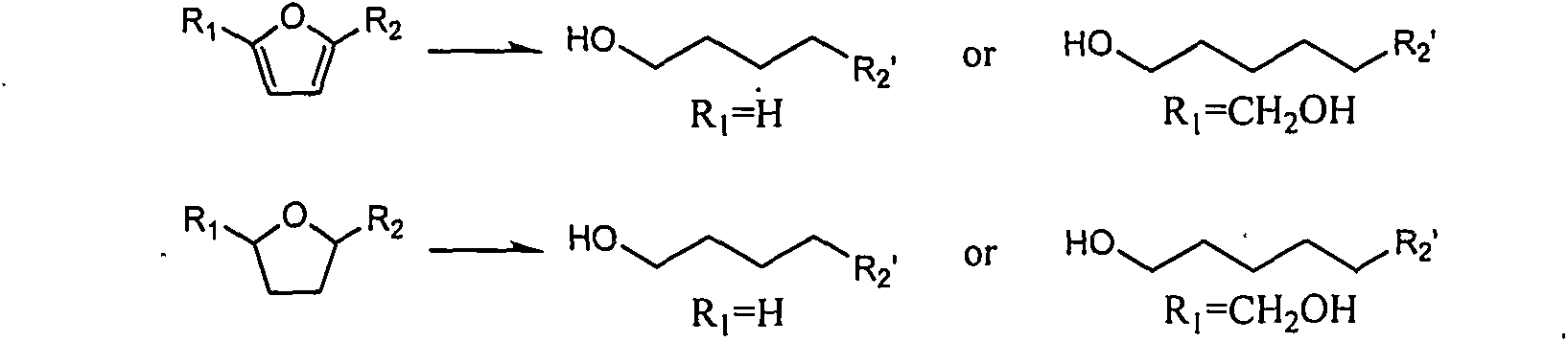
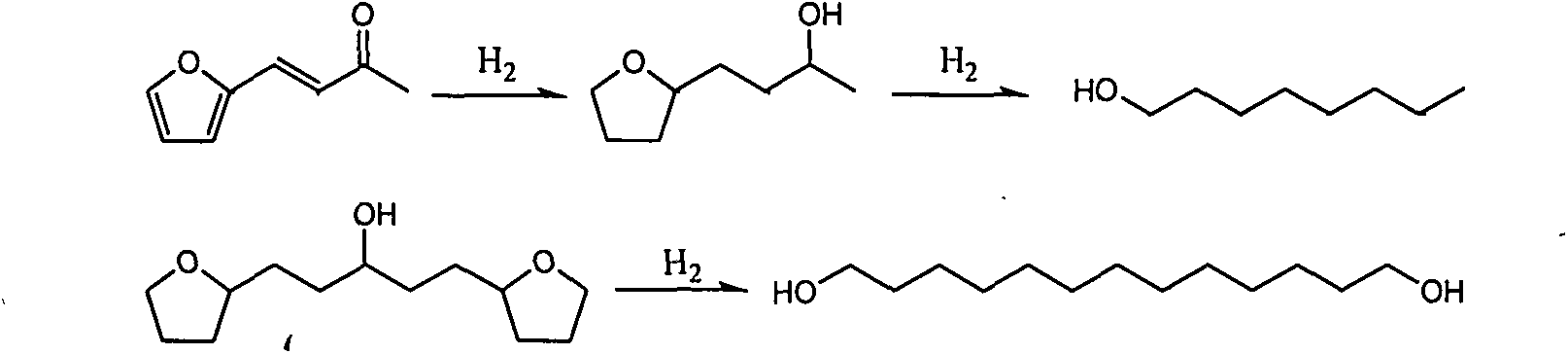
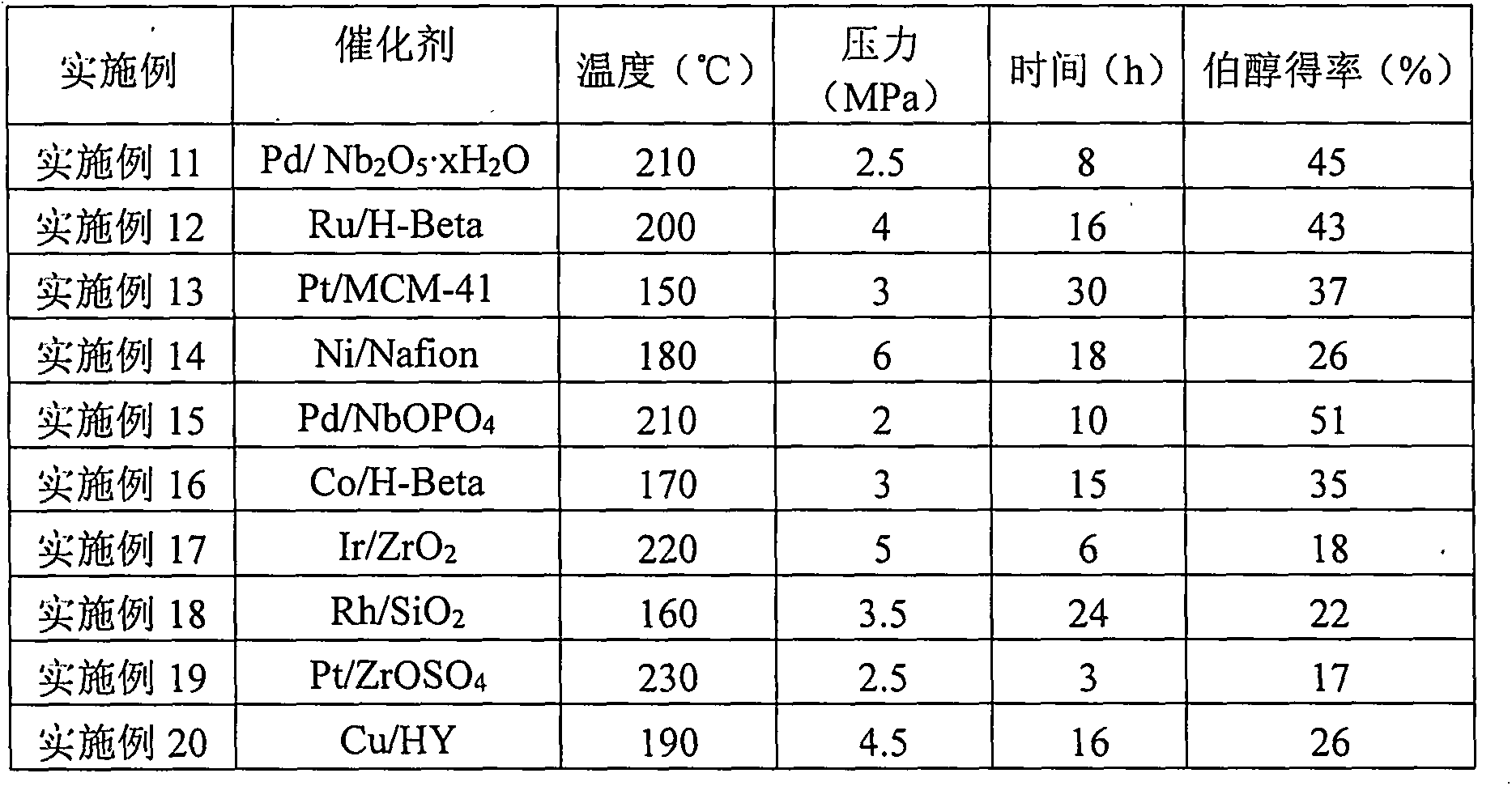
Environment-friendly novel method for preparing primary alcohol from furan or tetrahydrofuran derivatives
The invention provides a novel method for preparing middle / long-chain primary alcohol from furan or tetrahydrofuran derivatives. Specifically, a double-function catalyst is adopted, and such catalyst comprises two activity centers, namely, a hydrogenation activity center and an acid center; water is taken as a solvent in the reaction, the reaction is carried out in a batch reactor, and by utilizing the characteristic that the middle / long-chain primary alcohol is not dissolved in water, the generated primary alcohol is naturally separated from water and the catalyst, and alkane is prevented from being generated because of hydrogen over-addition or hydrogenolysis. Due to the characteristic that the primary alcohol and the water are not dissolved with each other, the primary alcohol can be conveniently separated, the separation cost is greatly lowered, and good industrial prospect is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thermal Batch Reactor with Removable Susceptors
An apparatus and method for uniform heating and gas flow in a batch processing chamber are provided. The apparatus includes a quartz chamber body, removable heater blocks which surround the quartz chamber body, an inject assembly coupled to one side of the quartz chamber body, and a substrate boat having removable susceptors. In one embodiment, the boat may be configured with a plurality of susceptors to control substrate heating during batch processing.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for continuous preparation of nanometer-sized hydrous zirconia sol using microwave
The present invention relates to a method for continuous preparation of a hydrous zirconia sol dispersed by nanometer-sized spherical hydrous zirconia particles having an average diameter(dp) of 1˜250 nm, which method comprises supplying the aqueous solution of a zirconium salt at a concentration of 0.001-0.2 mole / l to a reactor consisting of one or more than two reaction tubes, and then irradiating microwave to the stream of the said aqueous solution in the reactor so that the said solution may be heated in a flow state. Contrary to the method employing a conventional batch-type reactor or semi-continuous stirred-type reactor, the method for continuous preparation of a hydrous zirconia sol according to the present invention can allow various operational parameters to be controlled in a certain range and thus contributes to remarkably improve the quality of a hydrous zirconia sol to be prepared or of the zirconia powder obtainable as a final product.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
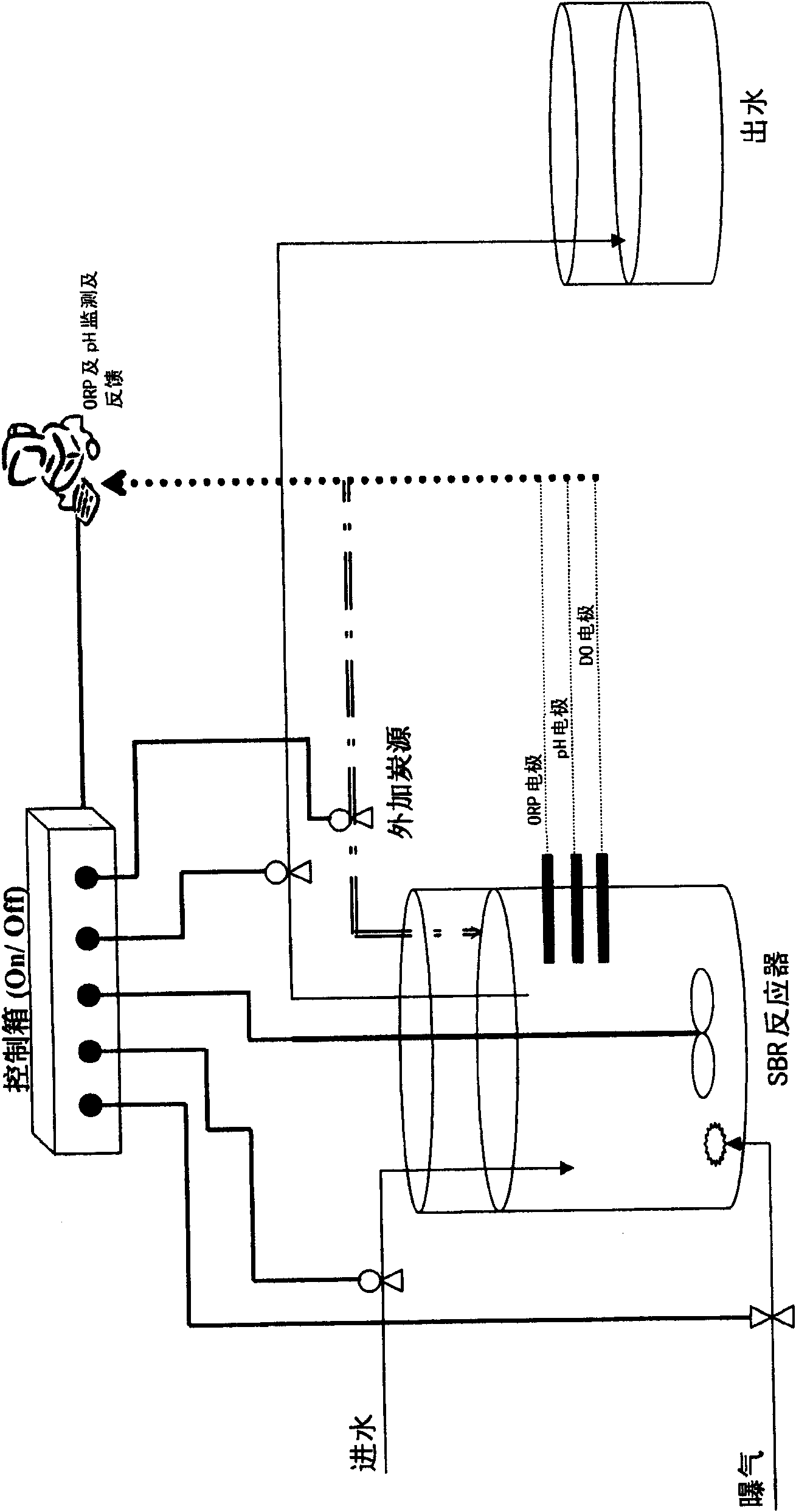
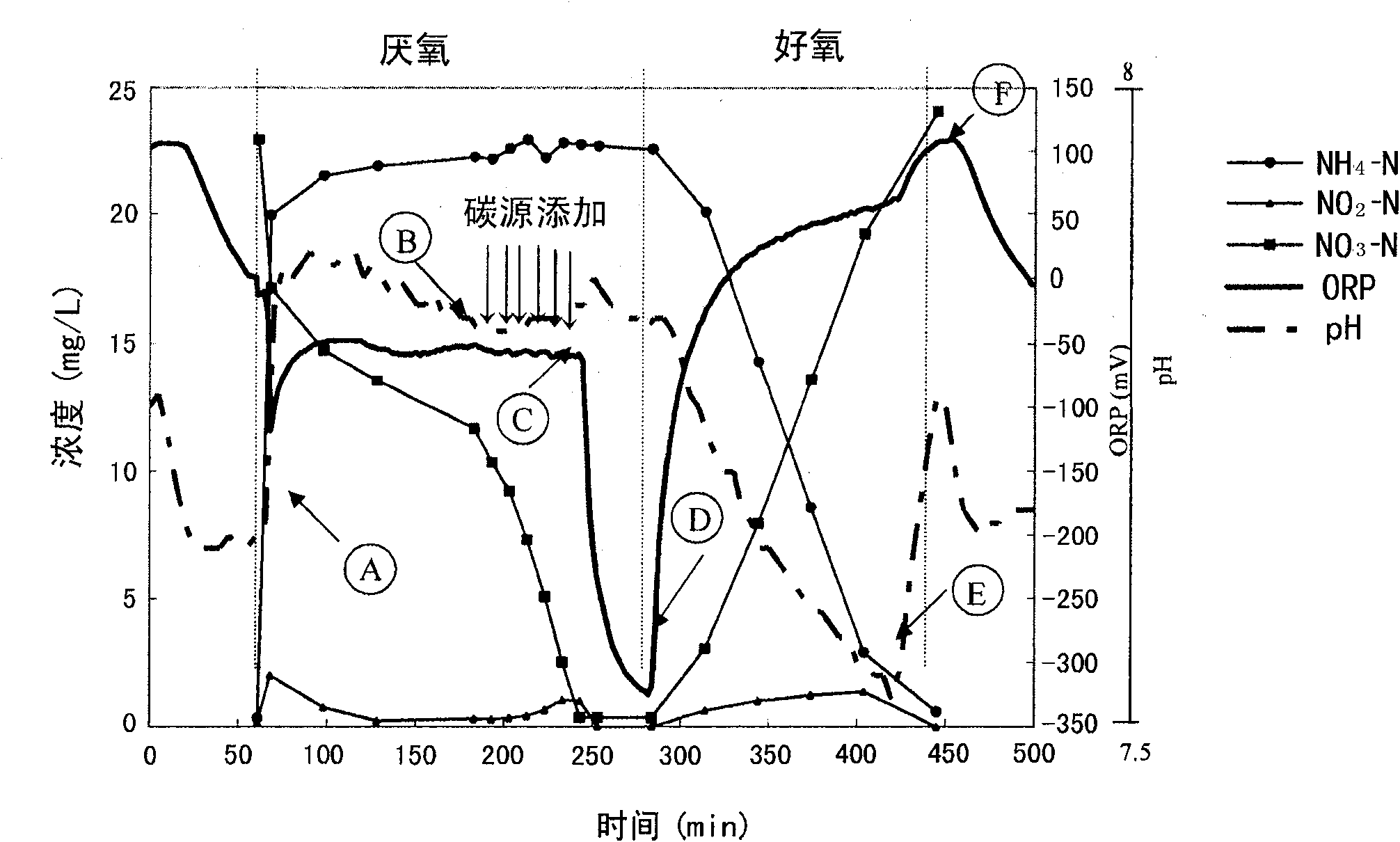
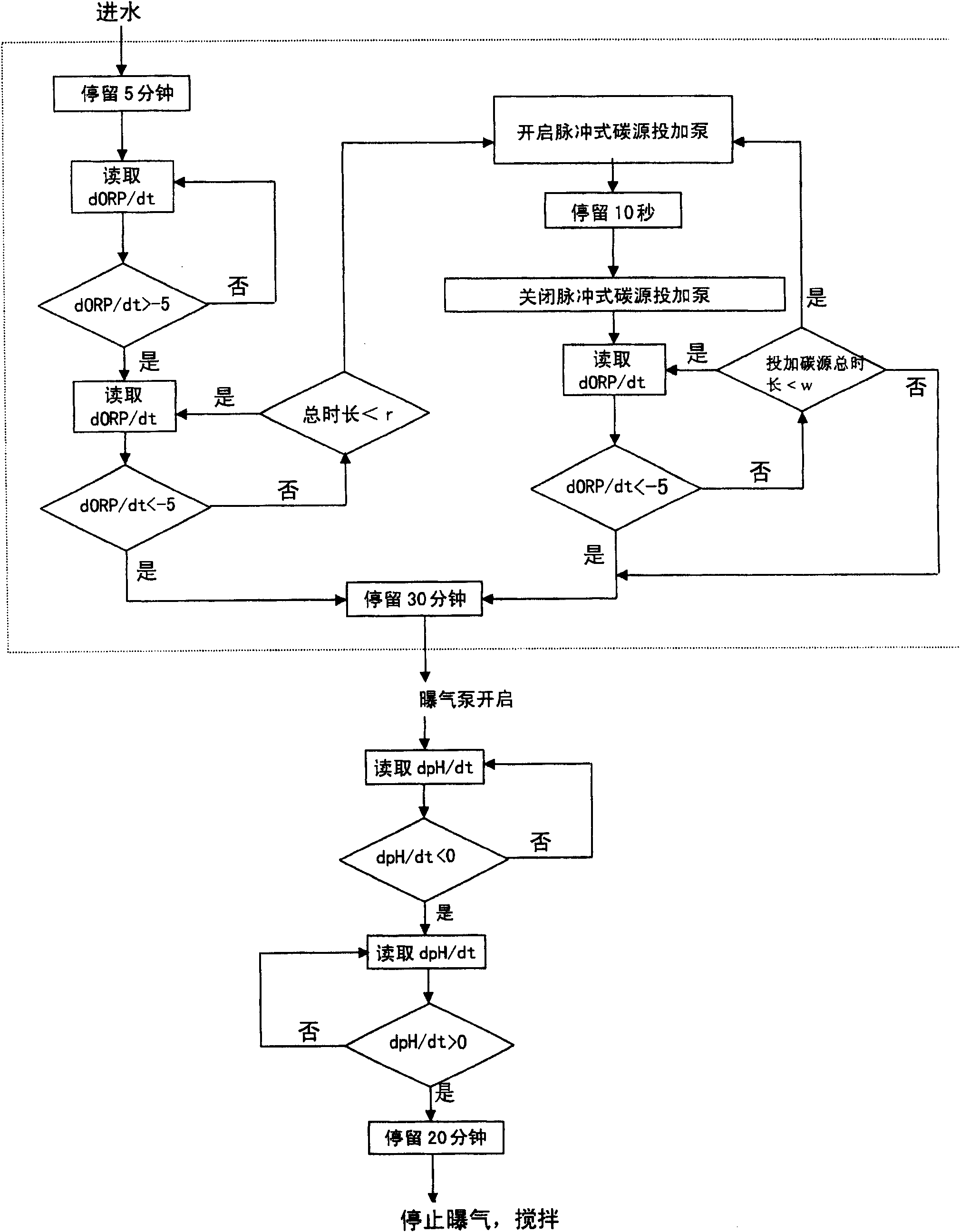
Method for adding a denitriding sequencing batch reactor activated sludge reaction carbon source
InactiveCN101618909AStabilizationConsumption optimizationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorActivated sludge
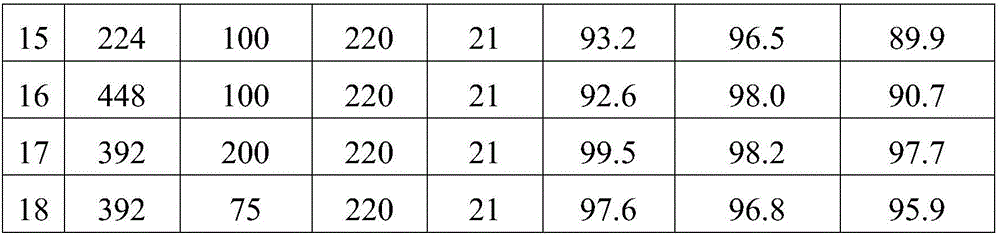
The invention relates to an optimal carbon source supplement real time control system used in a sequencing batch reactor activated sludge process for denitriding nitrogen-containing wastewater with a low C / N ratio. In the conventional sequencing anaerobic-aerobic batch reactor activated sludge process, the automatic control system uses an oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), a pH value and a DO curve slope variation value as control parameters and particularly adopts technology for automatically controlling optimal denitrification external carbon source addition at an anaerobic (aerobic) stage. The aeration time is controlled in the aerobic stage of the reaction and the addition amount of external nutrients is automatically controlled in the anaerobic stage of the reaction to optimize the system. The system can automatically adjust the hydraulic retention time in reaction processes according to the treatment conditions of the system such as inflowing water quality, a nitrification degree and a denitrification degree so as to ensure stable quality (ammonia nitrogen removal rate of over 99 percent) of treated water and optimal energy consumption.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
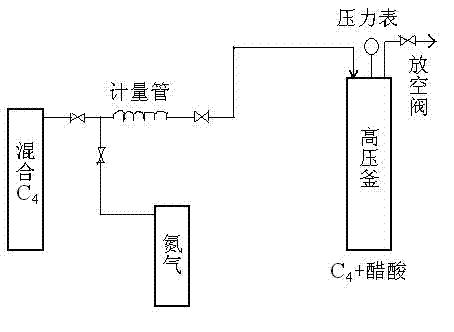
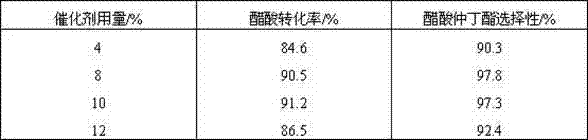
Method for producing sec-butyl acetate by synthesizing acetic acid and mixed C4
InactiveCN102344364AHigh activityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPtru catalystReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for producing sec-butyl acetate by synthesizing acetic acid and mixed C4, which belongs to the chemical field. The invention aims to provide the method for producing the sec-butyl acetate by synthesizing the acetic acid and the mixed C4, which is used for fully and reasonably utilizing byproduct mixed C4 resources of petrochemical enterprises, broadening the way to comprehensively utilize C4 hydrocarbon, and producing fine chemical products with high added value. According to the invention, a kettle type batch reactor is adopted, strong-acid cation exchange resin is adopted as solid catalyst, the acetic acid and the mixed C4 are used as the raw materials to synthesize the sec-butyl acetate, the reaction pressure is 2.0-6.0MPa, the reaction temperature is 80-160 DEG C, the reaction time is 5-15h, the molar ratio of olefine acid is 0.2-1.5, and the catalyst amount is 4-12 percent of the acetic acid. According to the synthetic process of the sec-butyl acetate, the acetic acid and butane (refinery byproduct mixed C4 contains 1-butane and 2-butane) are adopted as the raw materials to be directly synthesized through addition reaction under the action of acid catalysts, an olefin resource is directly utilized, and ethanol is unnecessary to be an intermediate, so that the production cost of the sec-butyl acetate is reduced, the obvious economic advantage is achieved, the refinery mixed C4 resource is effectively utilized, and the method is an effective way to improve chemical utilization of C4 hydrocarbon.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Production method of polyamide
In a repeated batch production of polyamide, a dicarboxylic acid component and a diamine component fed to a batch reactor are melt-polymerized in the absence of solvent. After adding the diamine component to the molten dicarboxylic acid component, the melt polymerization is further continued at a temperature equal to or higher than the melting point of polyamide being produced for at least 10 min while maintaining the pressure of the vapor phase in the batch reactor at higher than 0.1 MPaG by introducing water vapor. The polyamide thus produced is hardly affected by gels even when the melt polymerization is conducted in the presence of polyamide remaining after the previous batch production. Molded articles thereof contain little fisheyes.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com