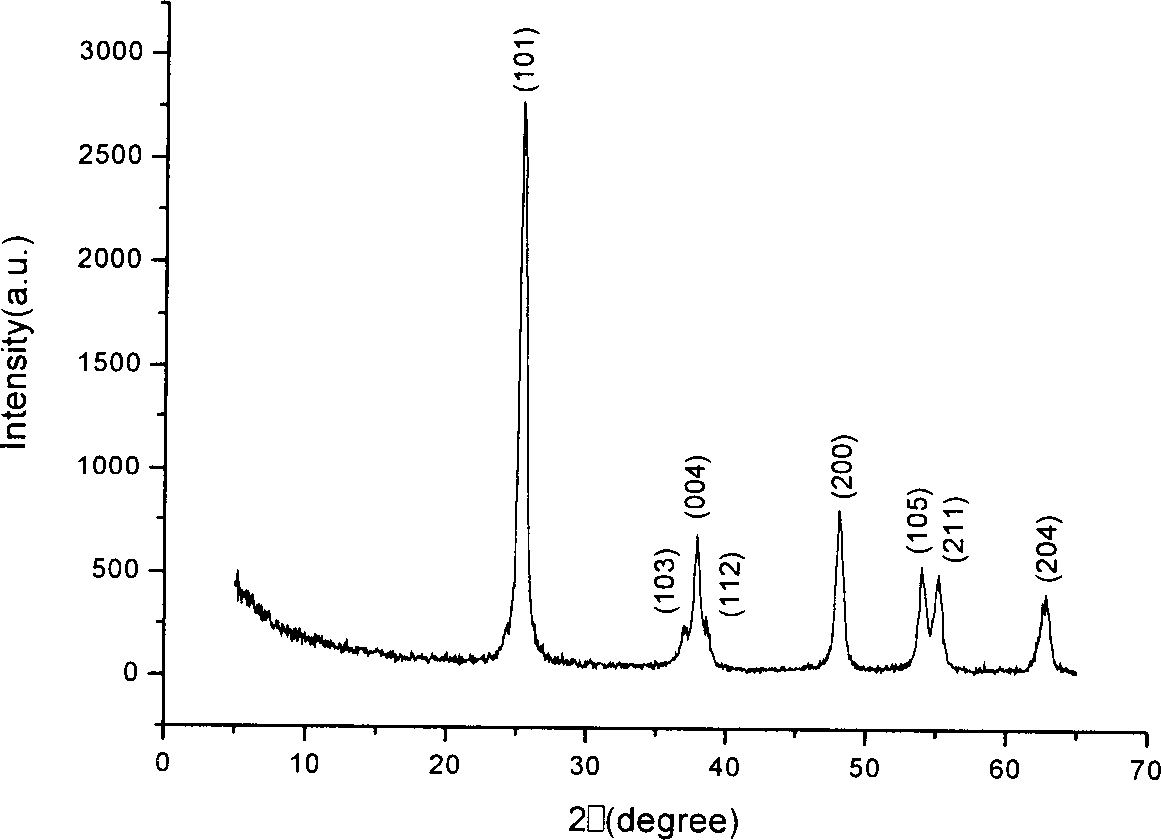
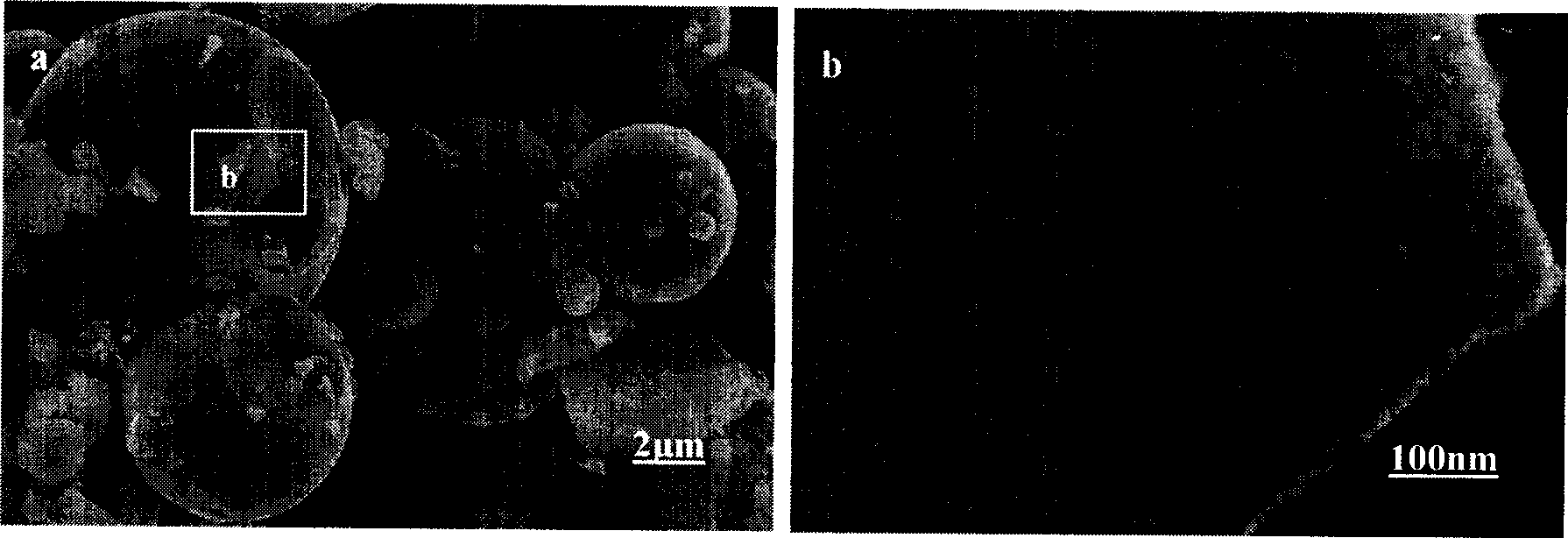
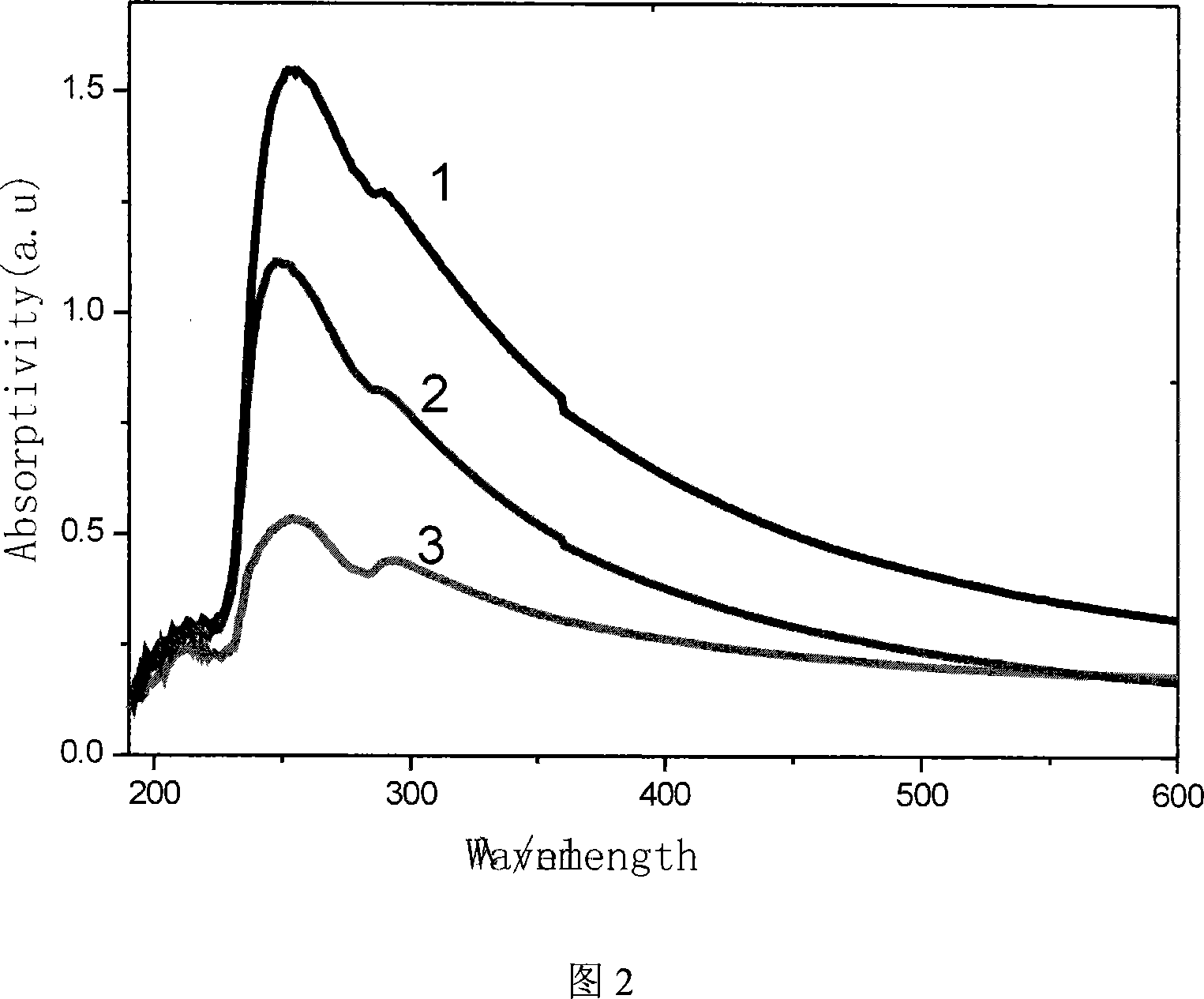
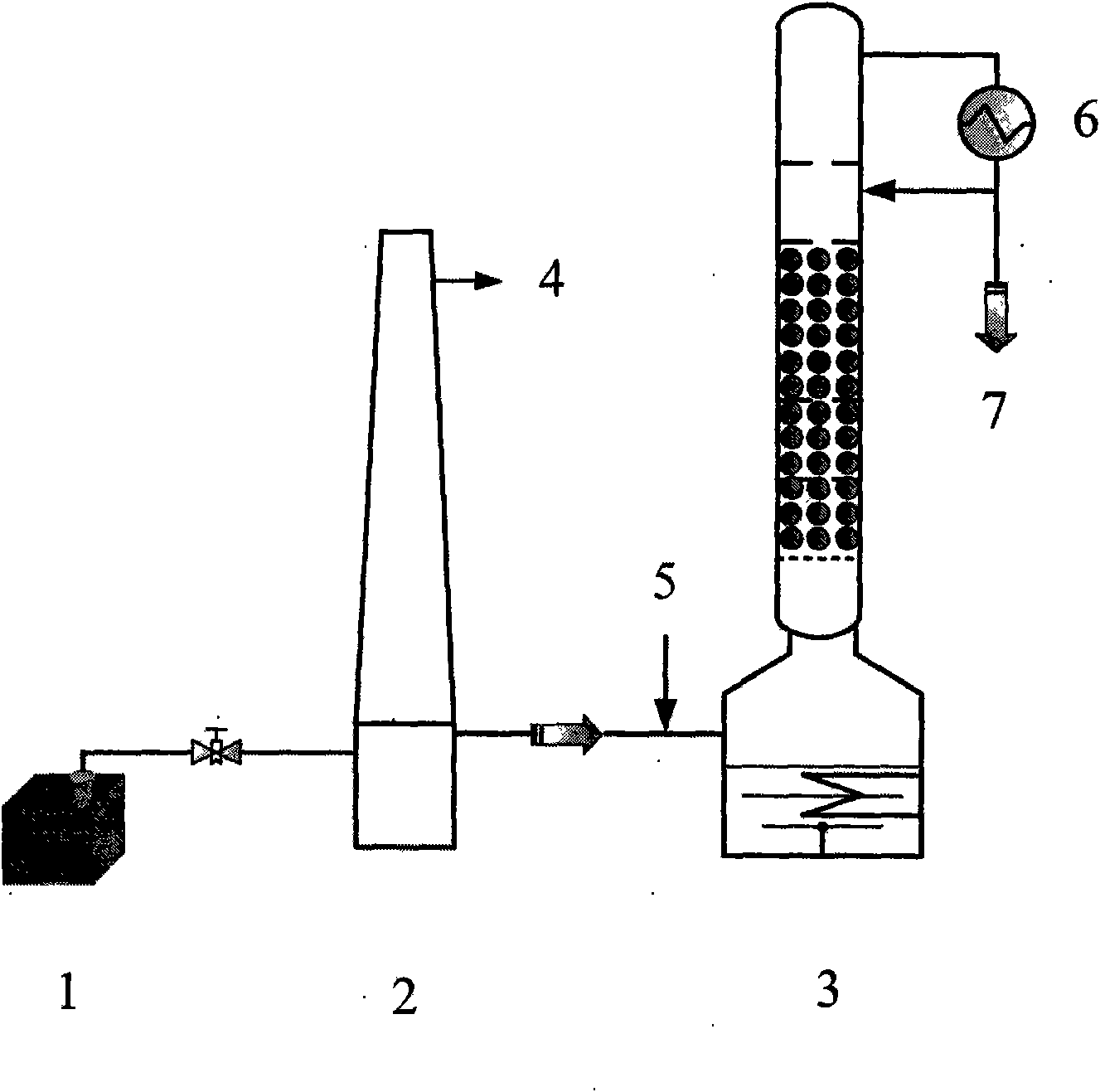
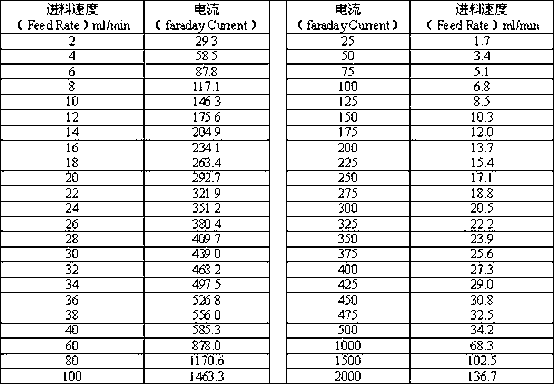
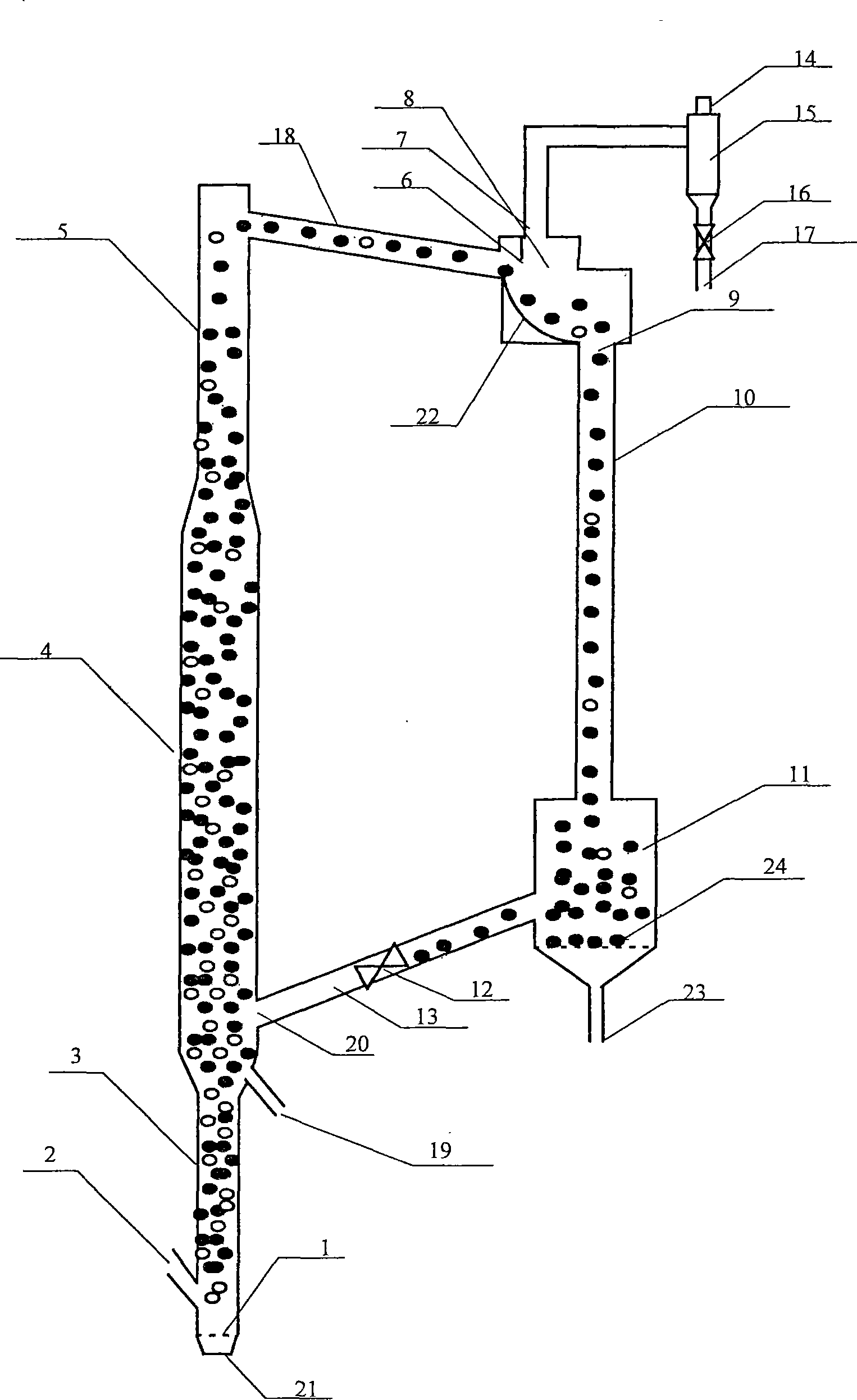
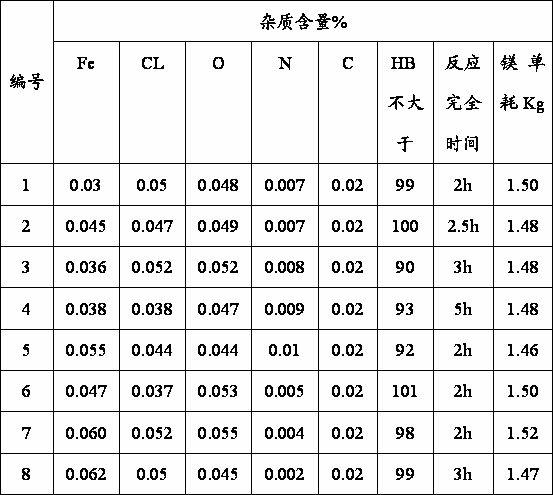
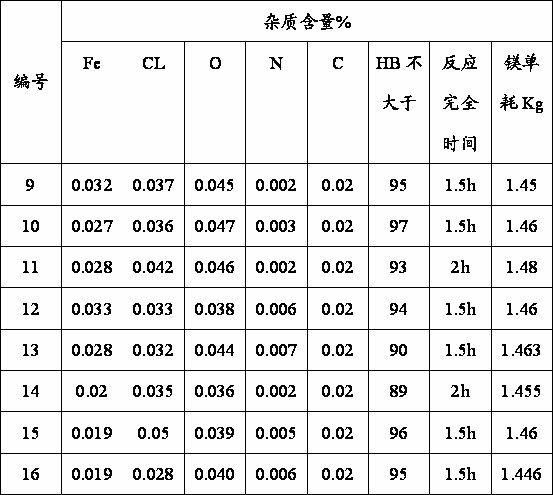
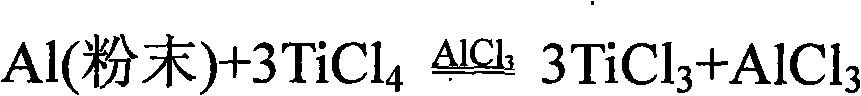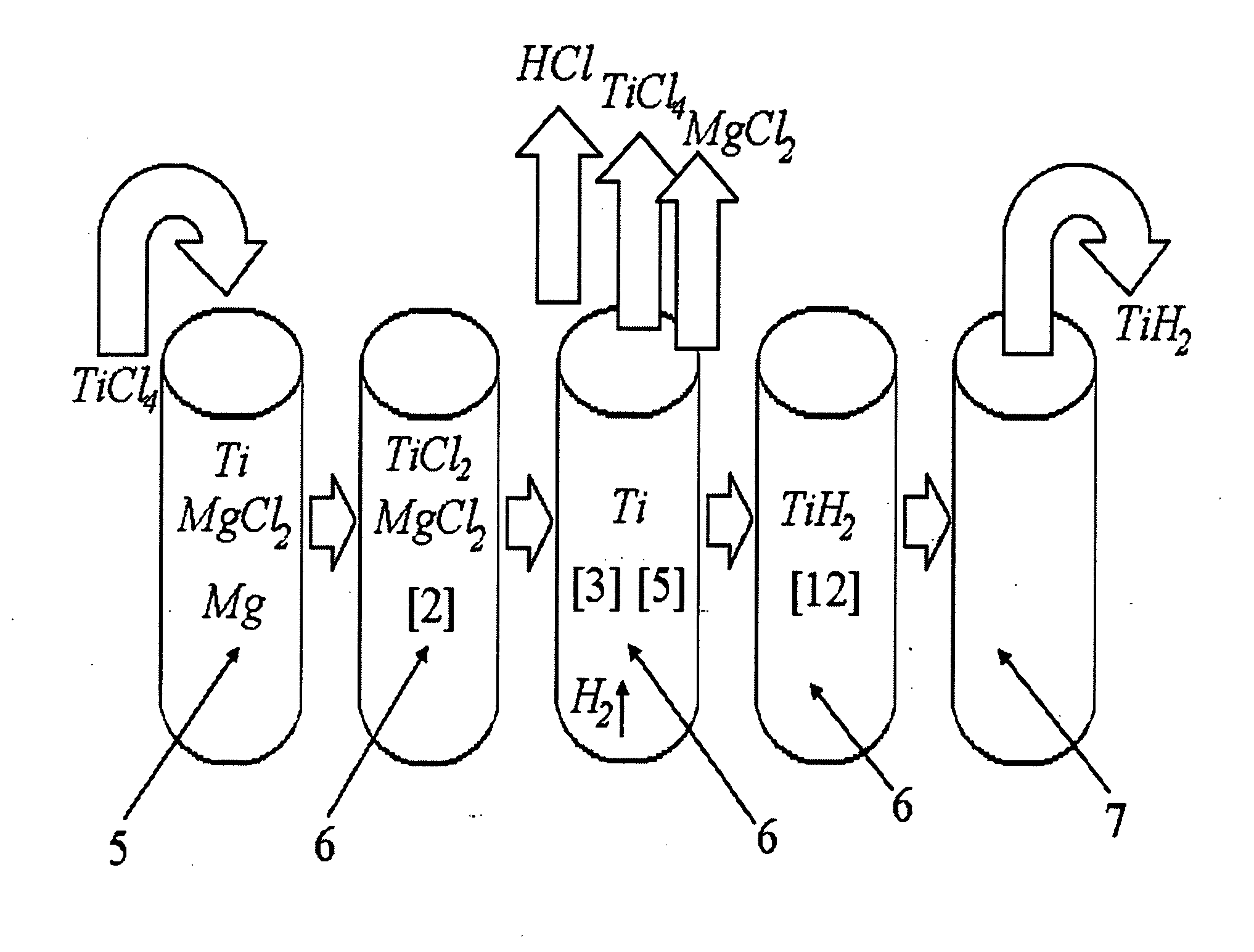Patents
Literature
521 results about "Titanium chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
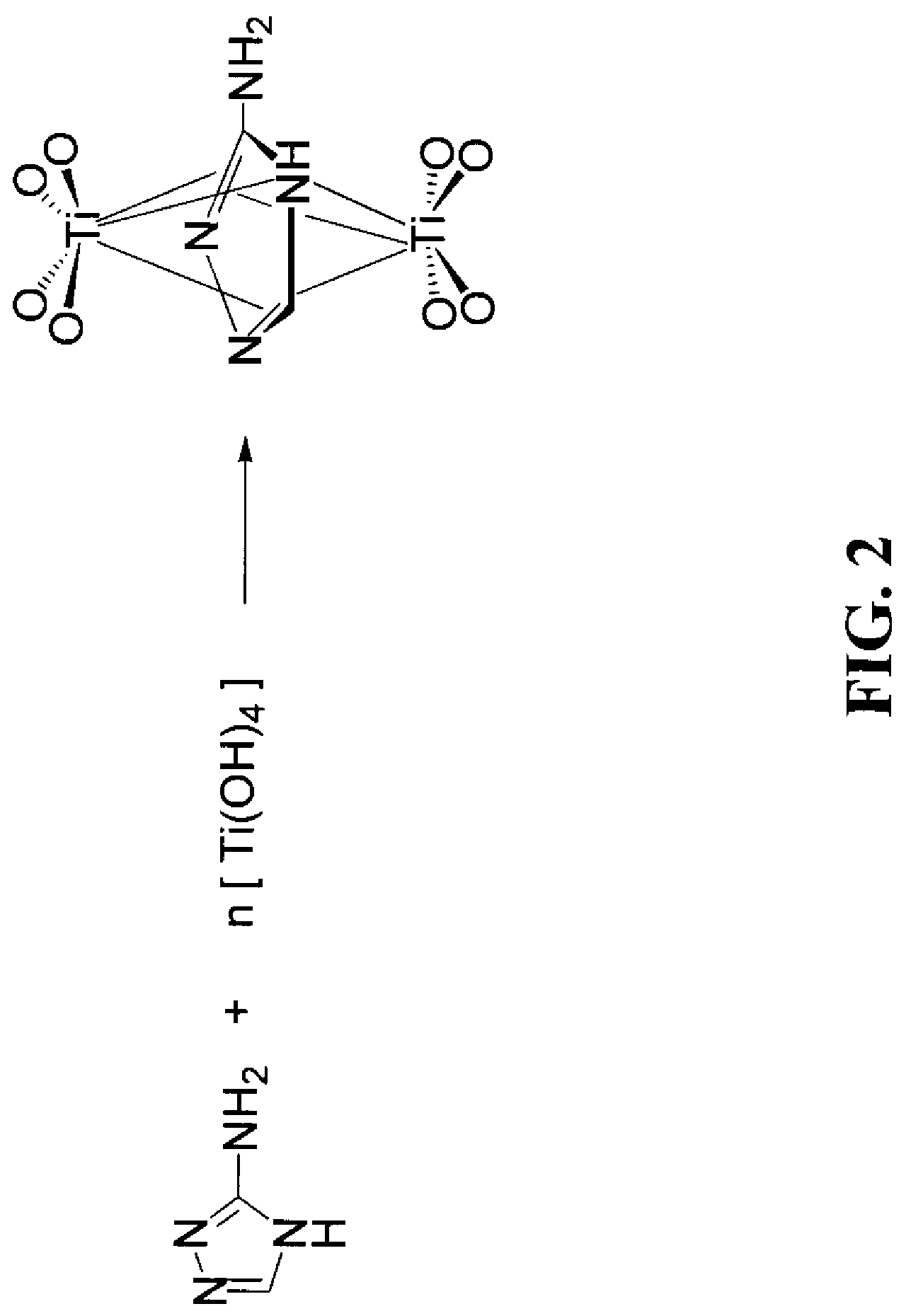
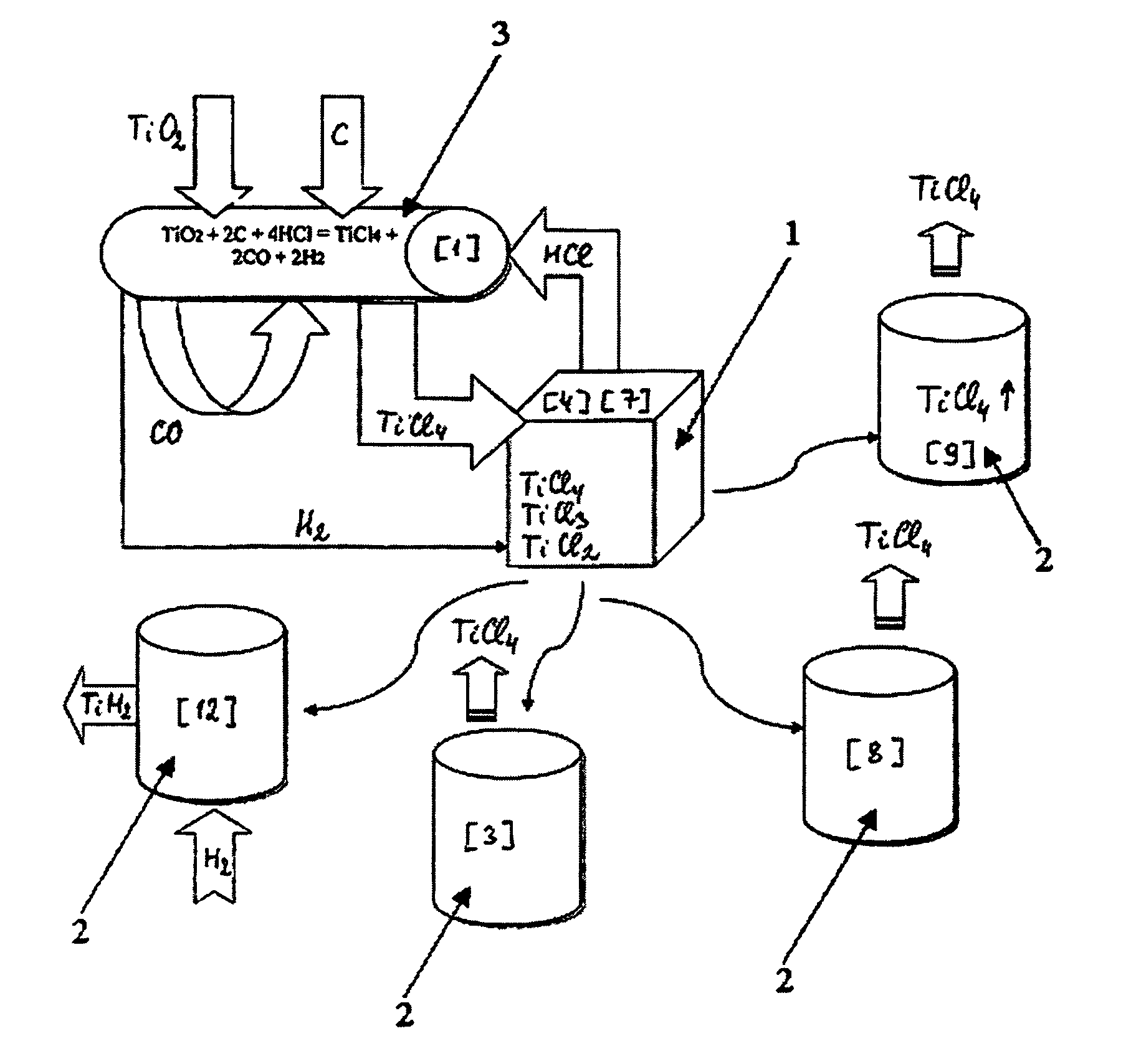
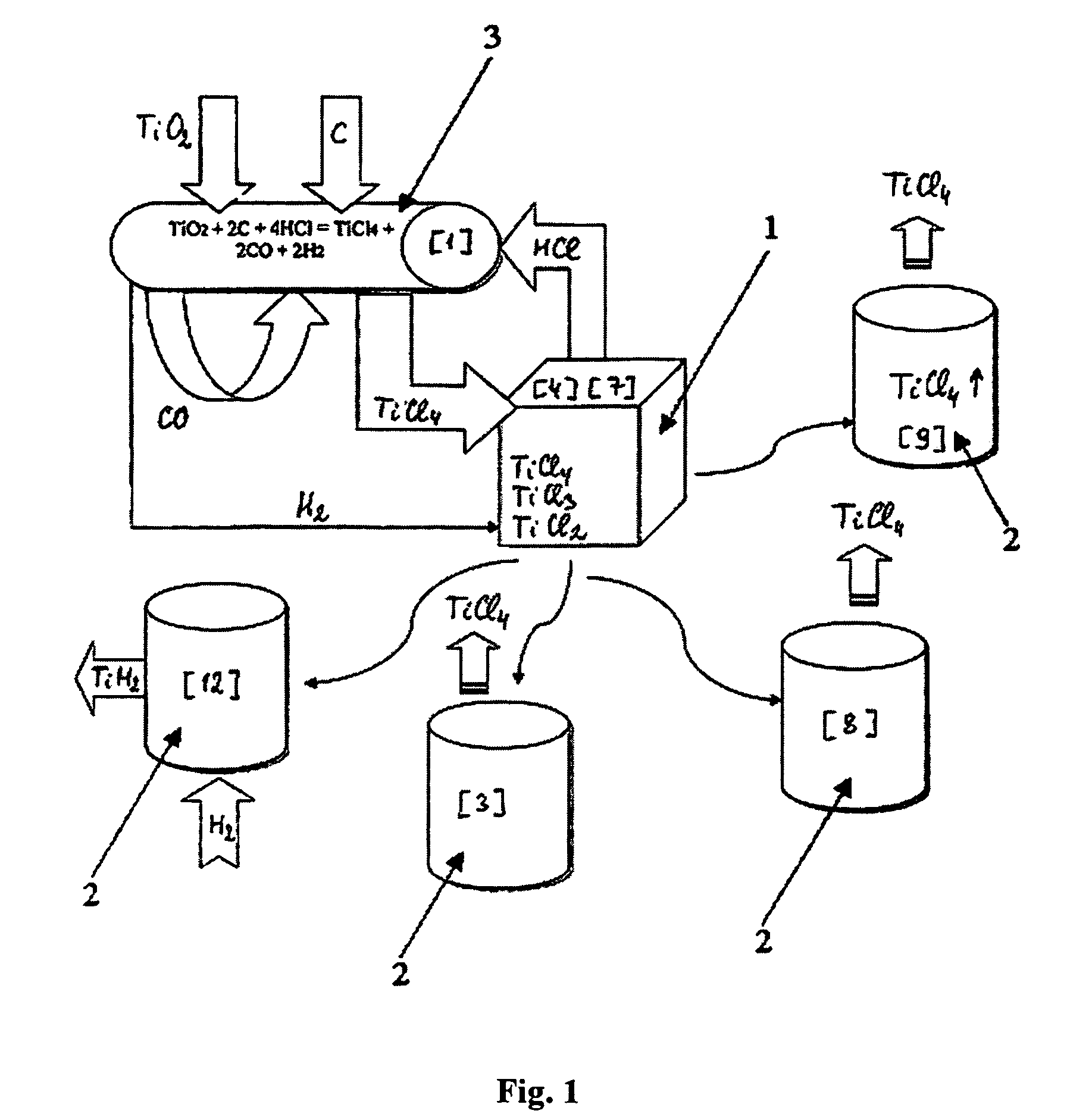
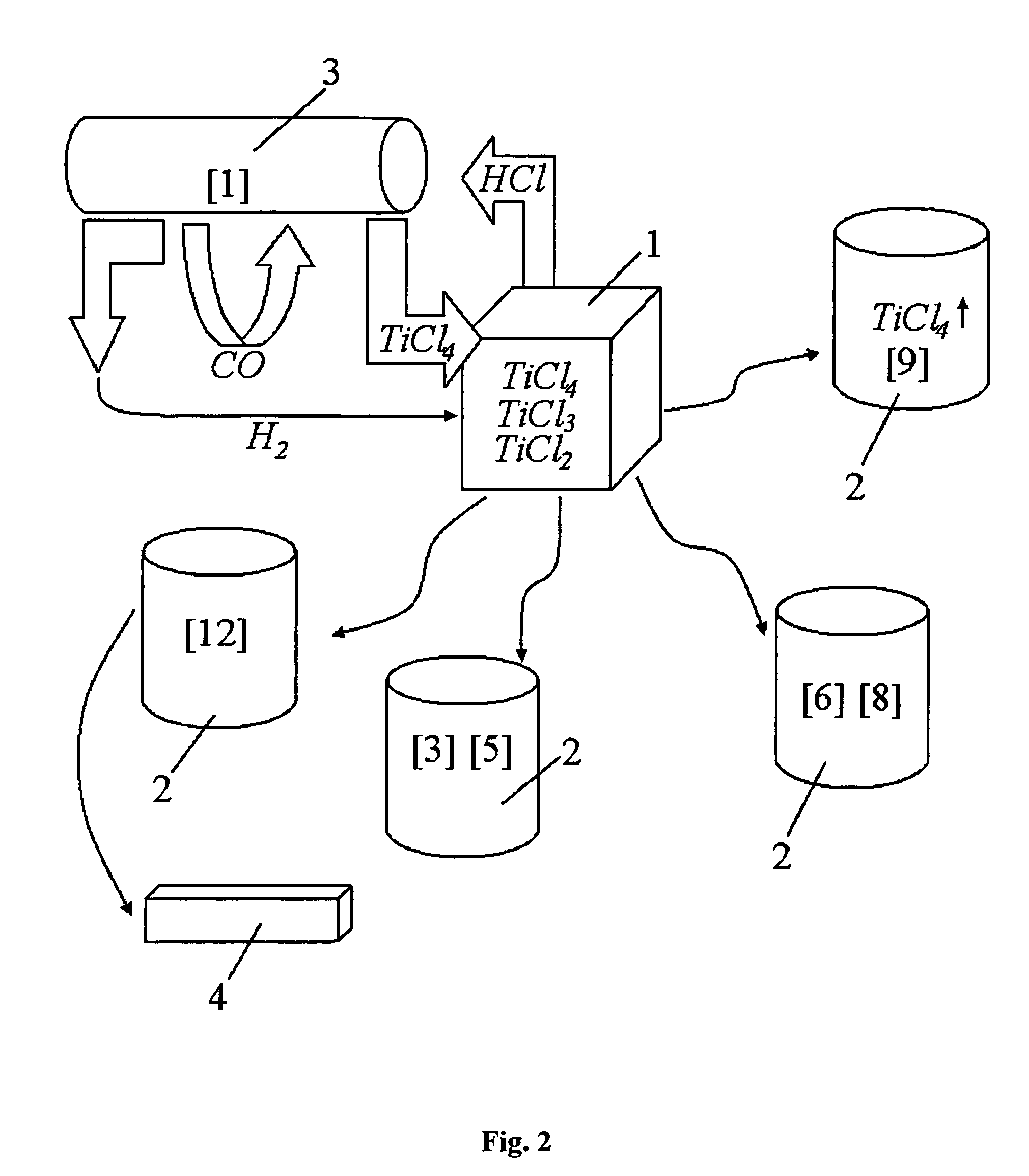
Titanium chloride may refer to: Titanium tetrachloride, TiCl₄ Titanium trichloride, TiCl₃ Titanium dichloride, TiCl₂
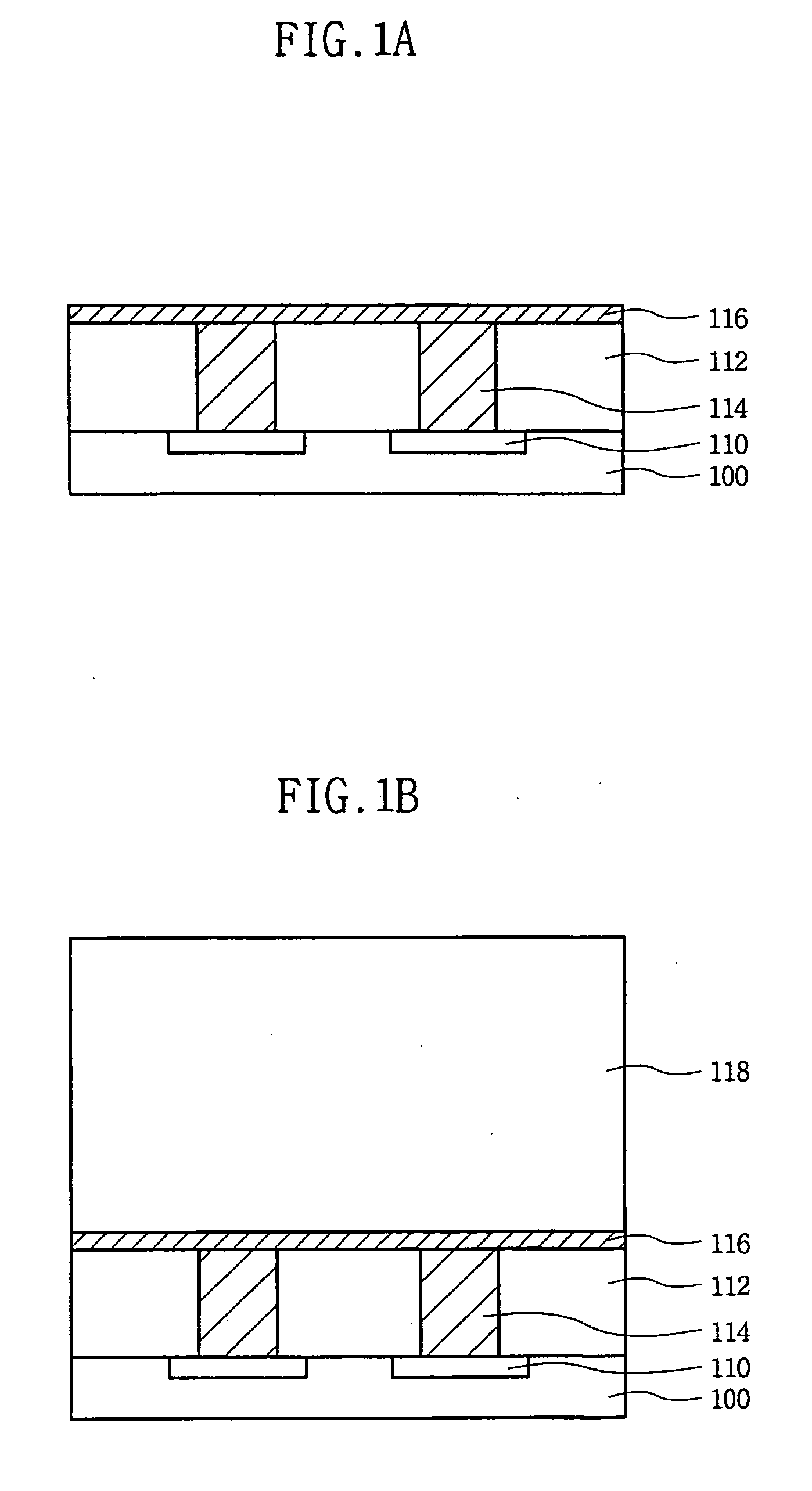
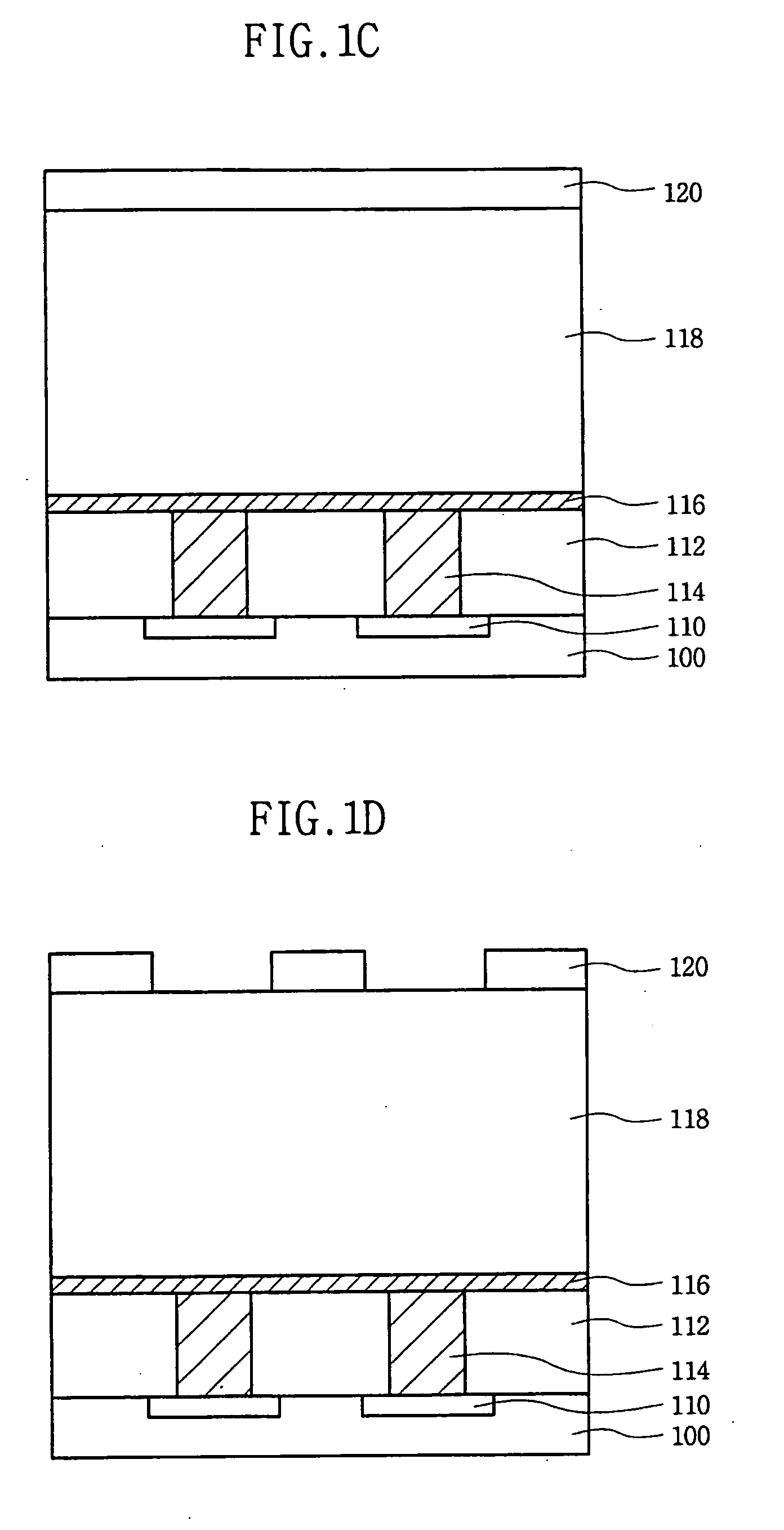
Electrothermal film and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101668359ASimple processEfficient processHeating element materialsResistors adapted for applying terminalsTitanium chlorideMetallurgy
The invention relates to an electrothermal film and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor heating. The electrothermal film is mainly prepared by adopting stannic chloride, titanium tetrachloride, stannic chloride, titanium trichloride, ferric chloride, antimony trichloride, calcium chloride, potassium chloride, cadmium chloride, stannic dioxide, stannictetroxide, hydrofluoric acid, boric acid, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol and inorganic water. By adopting the above formula, the mixture is mixed, stirred and heated to prepare into electrothermal film treating fluid, a semi-finished product of the electrothermal film is obtained by spraying the electrothermal film treating fluid at negative pressure on the electrothermal film carrier, and then silveroxide slurry is coated on the semi-finished product of the electrothermal film for baking to form a finished product of the electrothermal film. The electrothermal film has reasonable proportion andsimple manufacturing process, can be manufactured into various electrothermal film heating devices, has a working temperature capable of being up to 500 DEG C, and has wider application range. The electrothermal film of the invention also has the function of far infrared radiation, can play a role of physical therapy and health care to human body, and can help improve the quality and output of agricultural products.
Owner:GUANGDONG HALLSMART INTELLIGENCE TECH CORP LTD
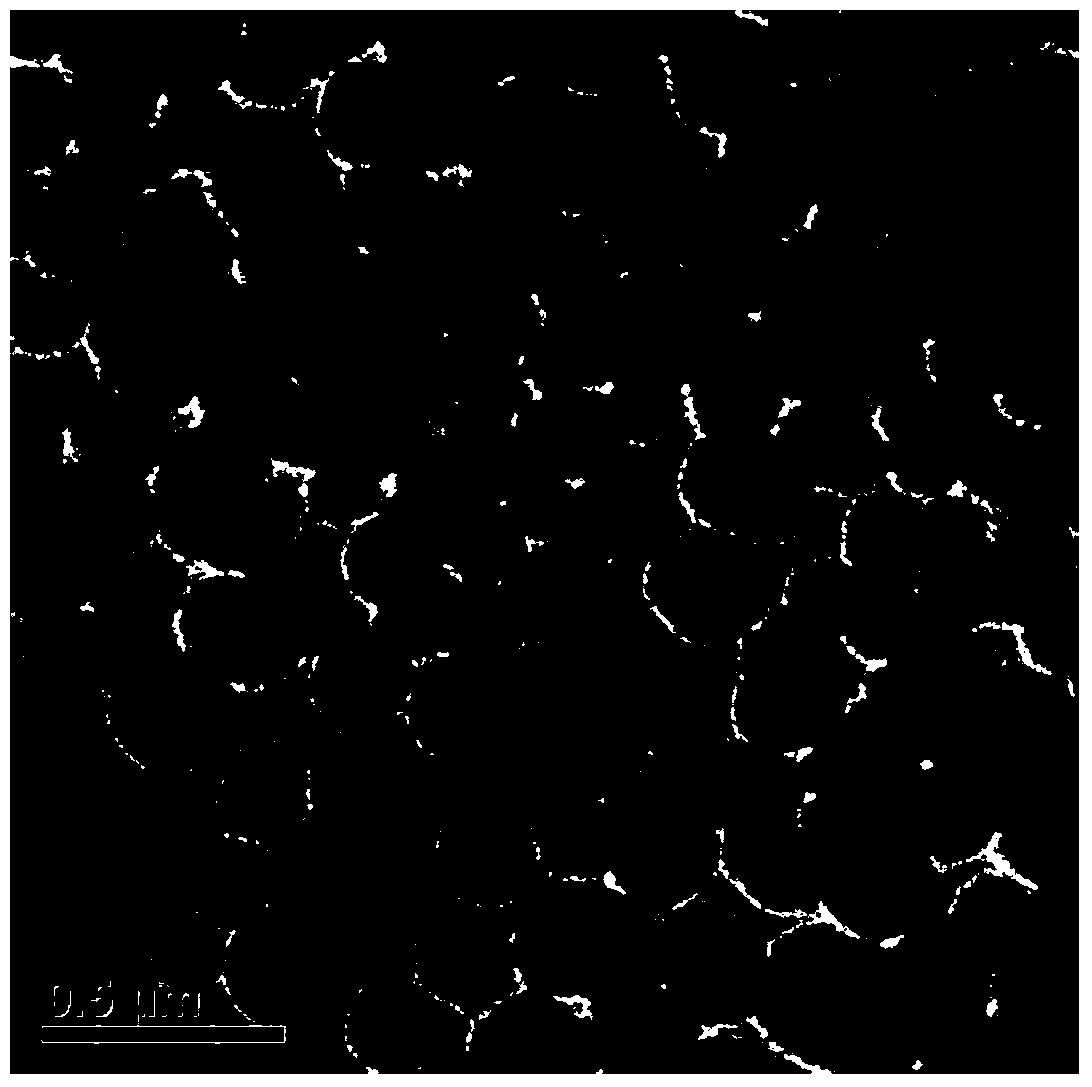
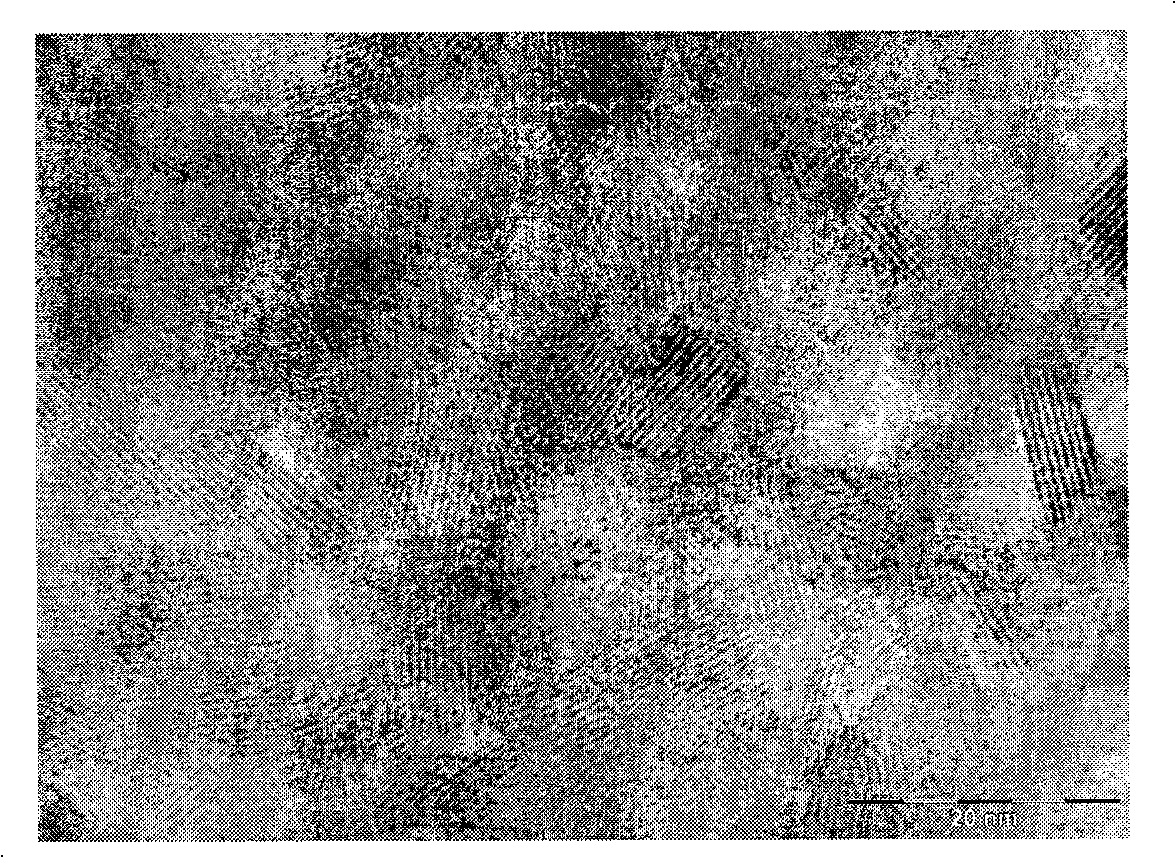
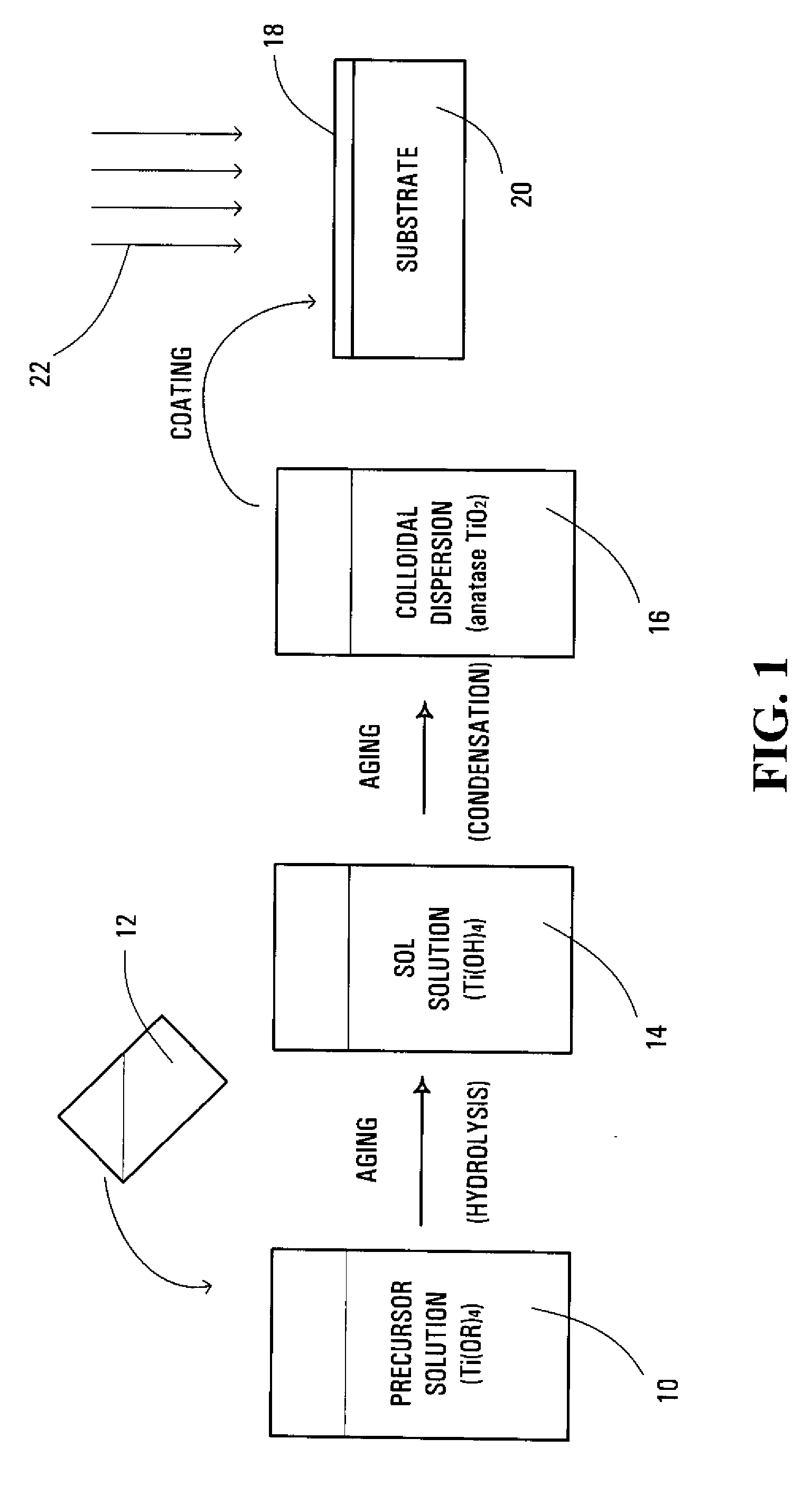
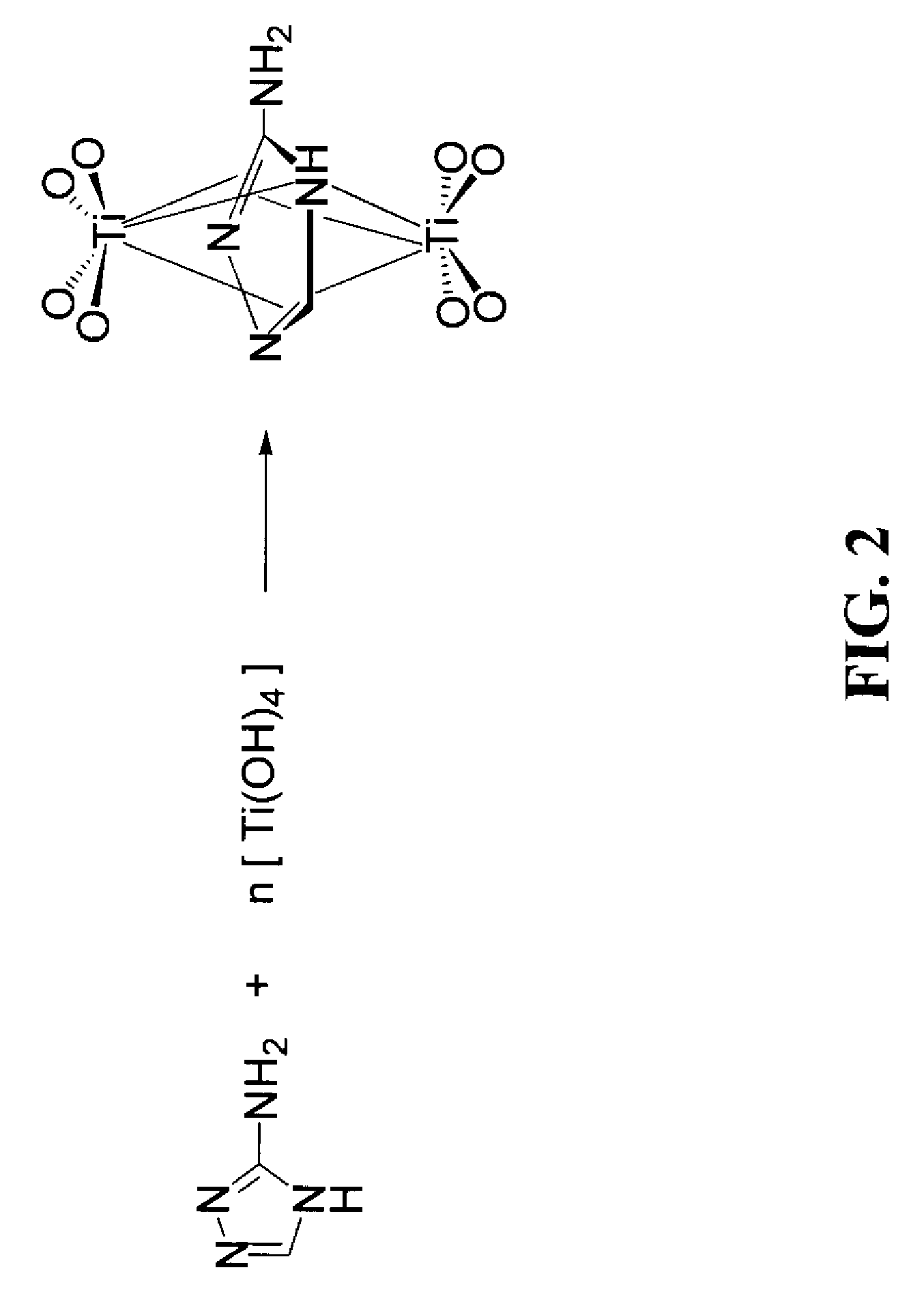
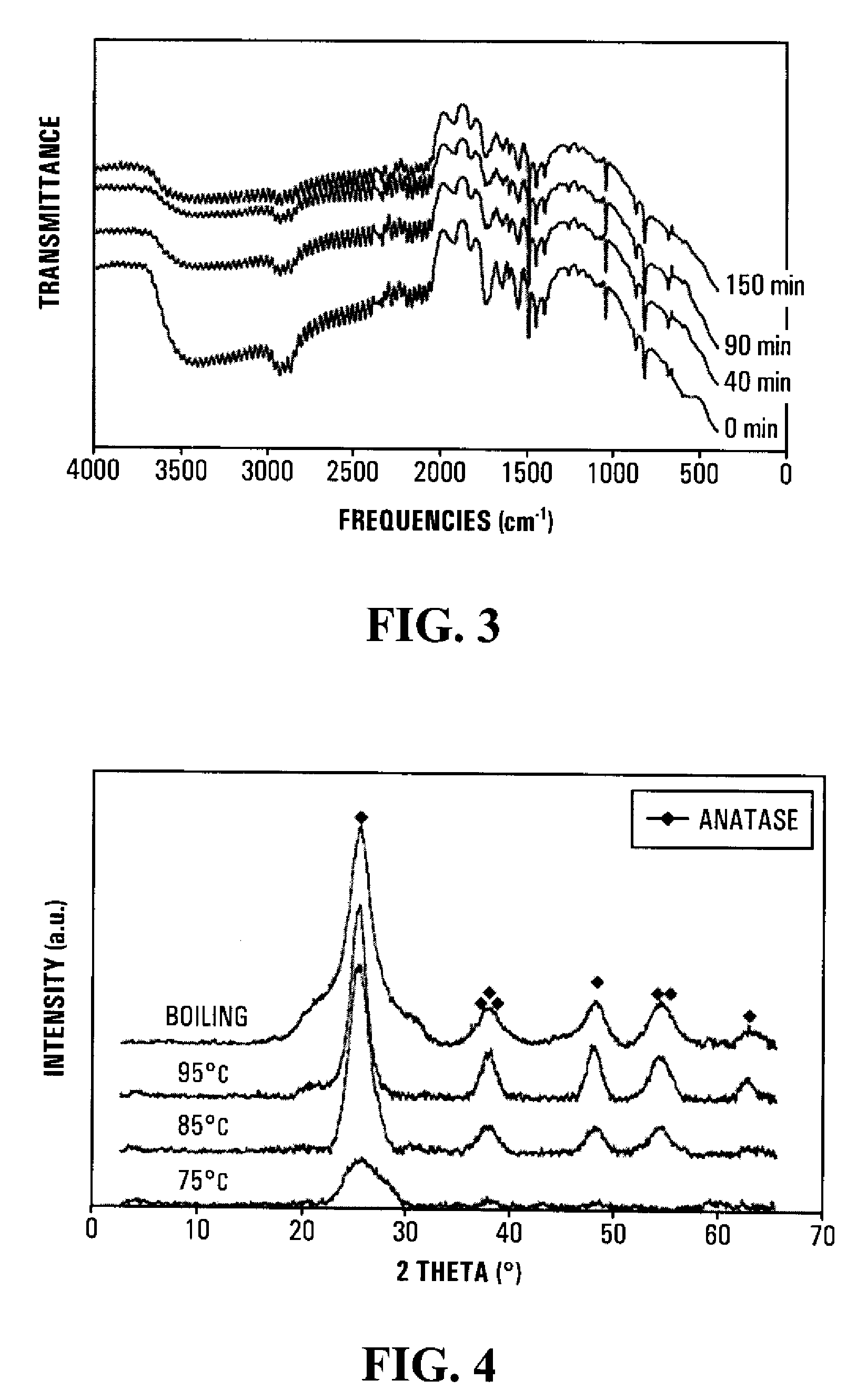
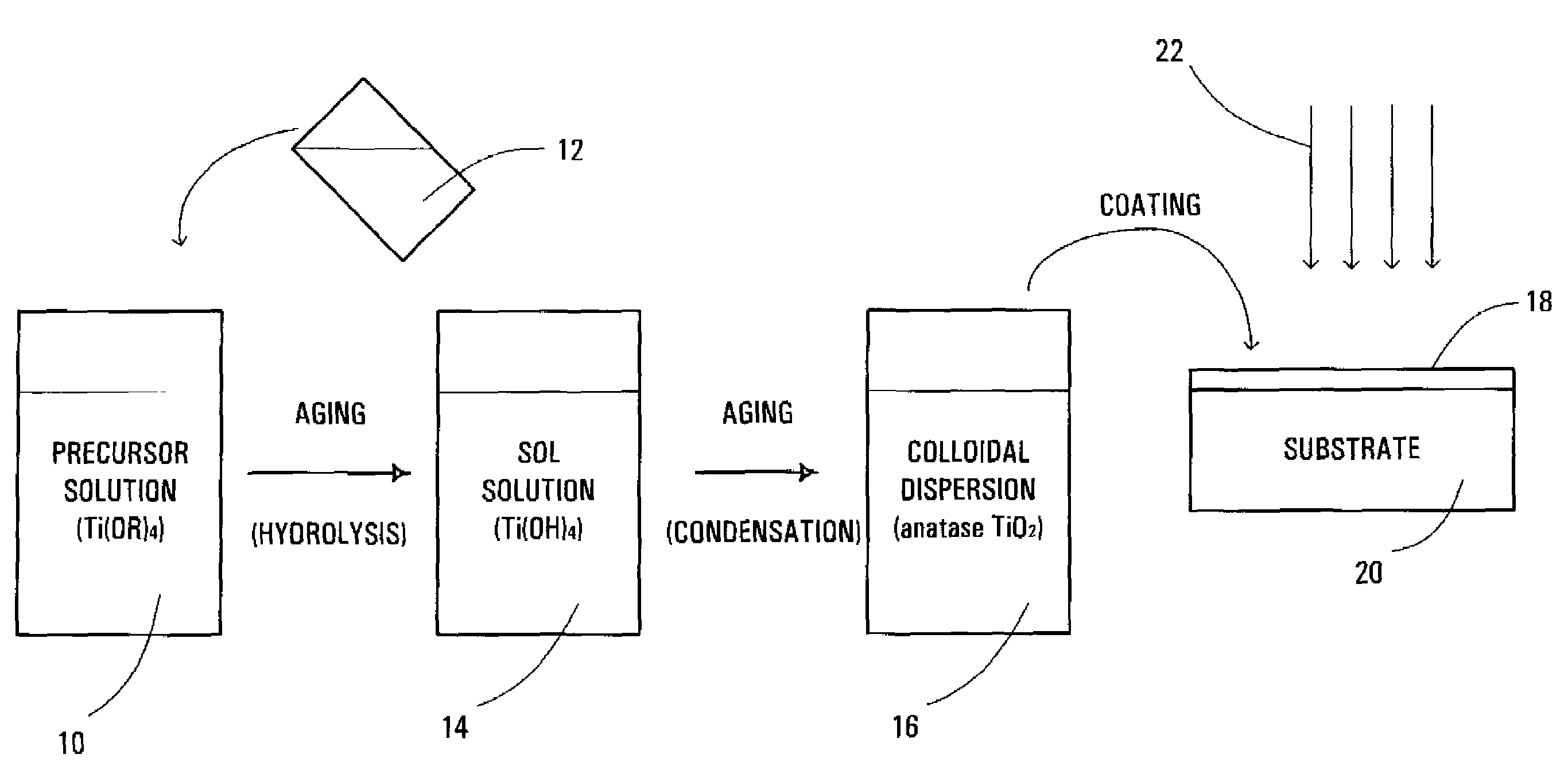
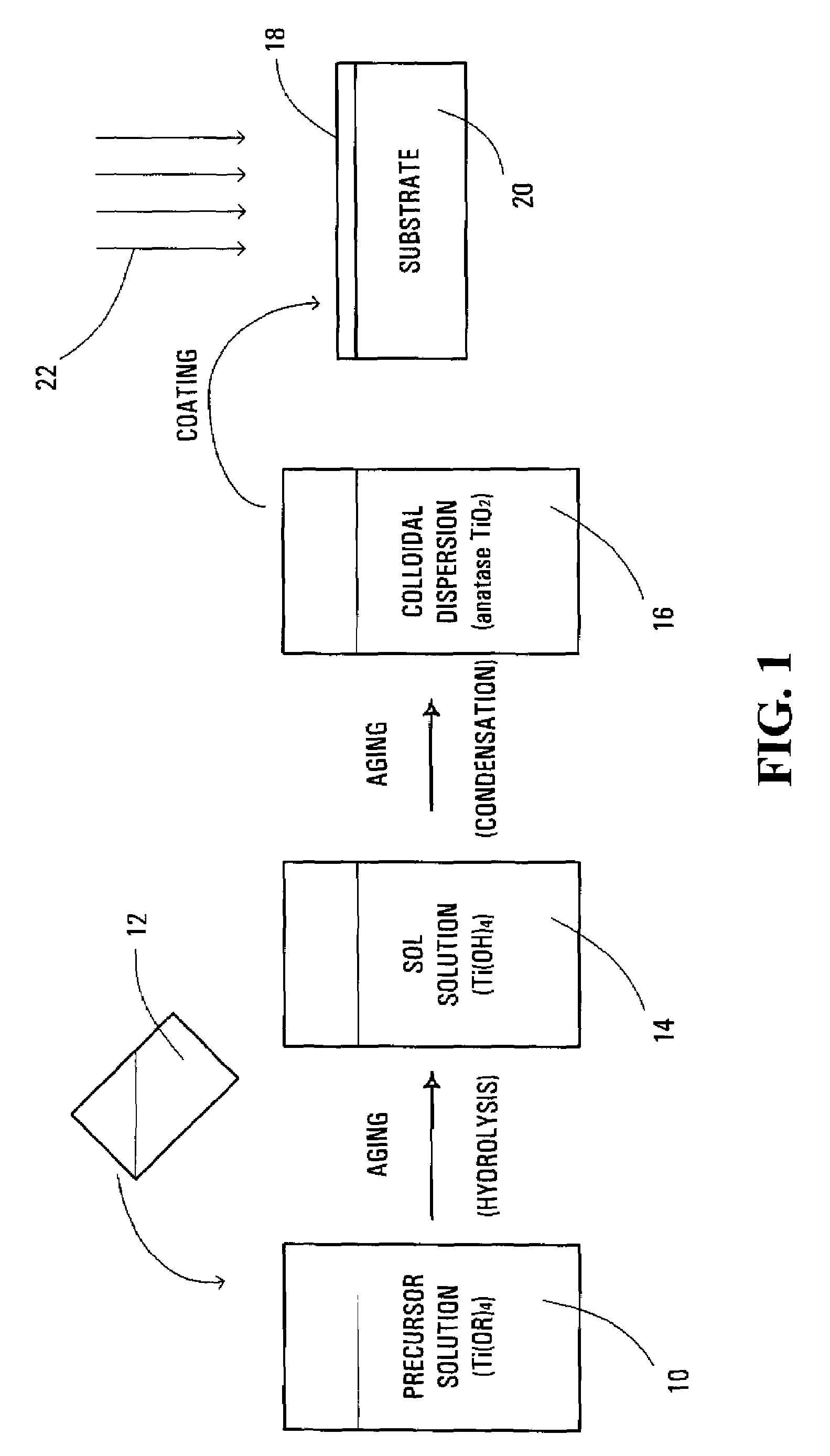
Method and solution for forming anatase titanium dioxide, and titanium dioxide particles, colloidal dispersion and film
InactiveUS20060254461A1Accelerated agingImprove propertiesPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesTitanium chlorideTetrazole
A sol solution containing poly(titanic acid) and a planar heterocyclic ligand is provided. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles are formed by aging the sol solution at a temperature below about 140° C. The particles have metallocene-like Ti-complexes comprising the heterocyclic ligand and can be substantially in the anatase phase. The heterocyclic ligands can be triazole, tetrazole, or thiadiazole. The sol solution may be prepared by aging a precursor solution. The precursor solution may contain the heterocyclic ligands and a precursor for poly(titanic acid). The precursor may be titanium alkoxide or titanium chloride. The sol solution may also contain at least one of an organic acid, a base, and a surfactant. The aged sol solution may form a colloidal dispersion of the TiO2 particles. A photo-catalytic and transparent film may be formed from the TiO2 particles by depositing a layer of the colloidal dispersion on a support.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
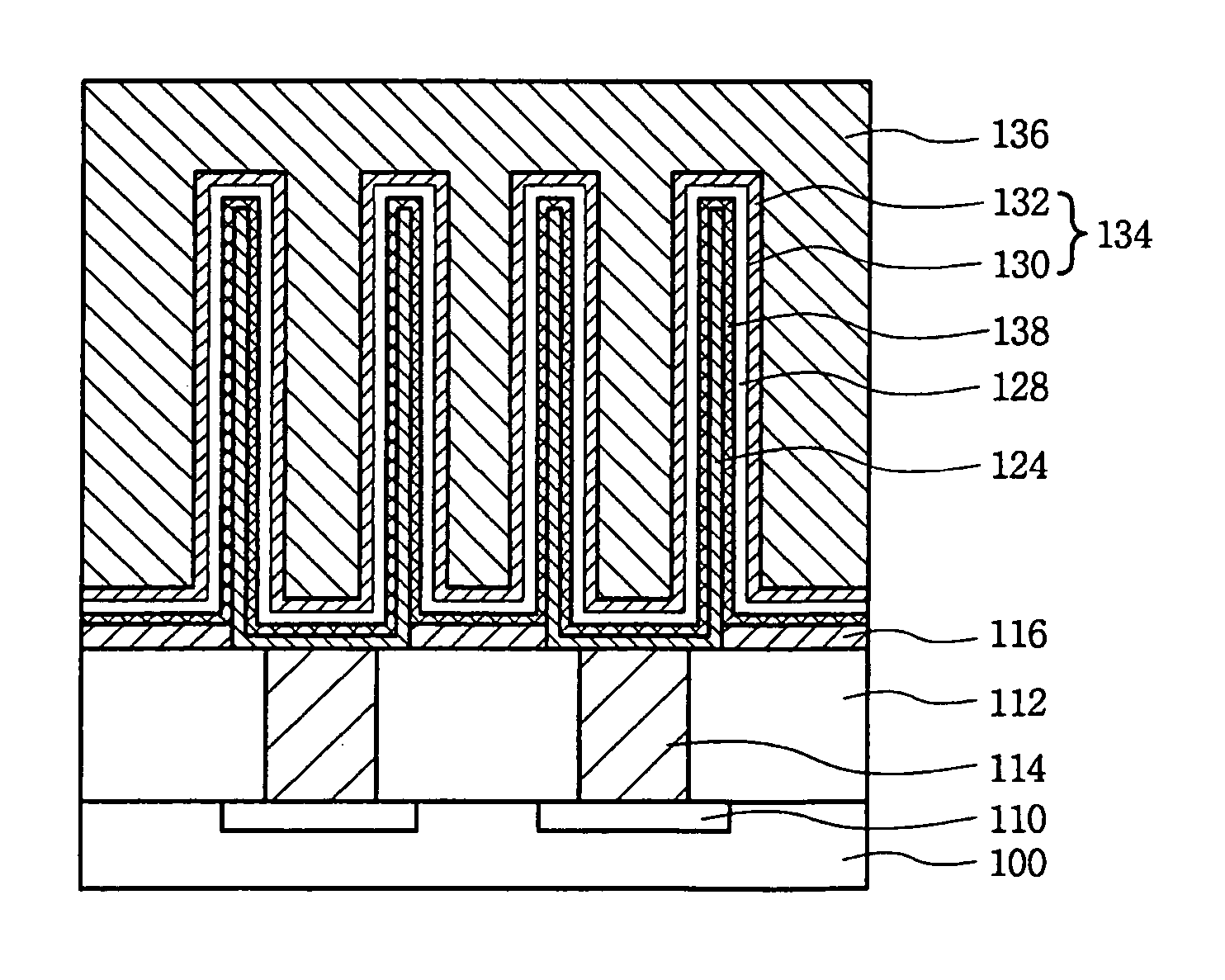
Method of forming titanium nitride layer and method of fabricating capacitor using the same
ActiveUS20060014385A1Suppress generationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTitanium chlorideMetallurgy
A method of fabricating a storage capacitor includes depositing a first titanium nitride layer on a dielectric layer using a chemical vapor deposition technique or an atomic layer deposition technique performed at a first temperature with reactant gases of titanium chloride (TiCl4) gas and ammonia (NH3) gas at a predetermined flow ratio and depositing a second titanium nitride layer on the first titanium nitride layer using a chemical vapor deposition process performed at a second temperature that is greater than the first temperature with reactant gases of titanium chloride (TiCl4) gas and ammonia (NH3) gas.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Coatings on substrates
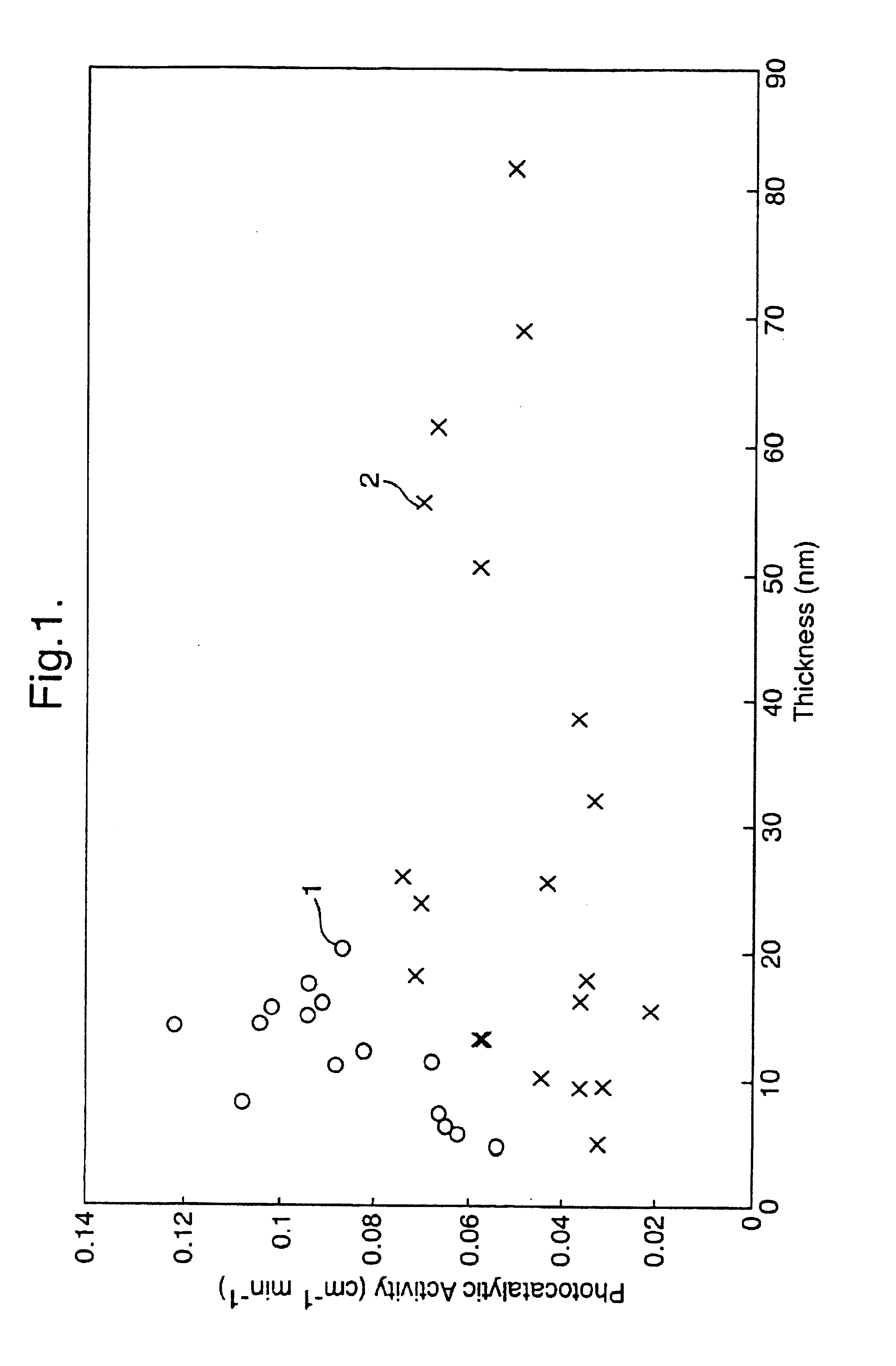
InactiveUS6840061B1Improve photocatalytic activityDeposited in shortPhysical/chemical process catalystsGlass rolling apparatusDeposition temperatureCoated surface
A process for the production of a photocatalytically active self-cleaning coated substrate, especially a glass substrate, which comprises depositing a titanium oxide coating on the surface of the substrate by contacting it with a fluid mixture containing a source of titanium and a source of oxygen, the substrate being at a temperature of at least 600° C. The coated surface has good durability, a high photocatalytic activity and a low visible light reflection. Most preferably the deposition temperature is in the range 645° C. to 7200° C. which provides especially good durability. The fluid mixture preferably contains titanium chloride and an ester, especially ethyl acetate. Also disclosed is a self cleaning coated substrate, especially a glass substrate, having high photocatalytic activity and low visible light reflection and a durable self-cleaning coated glass.
Owner:PILKINGTON PLC +1
Deposition of TiN films in a batch reactor
ActiveUS20060060137A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingTitanium chlorideTitanium nitride
Titanium nitride (TiN) films are formed in a batch reactor using titanium chloride (TiCl4) and ammonia (NH3) as precursors. The TiCl4 is flowed into the reactor in temporally separated pulses. The NH3 can also be flowed into the reactor in temporally spaced pulses which alternate with the TiCl4 pulses, or the NH3 can be flowed continuously into the reactor while the TiCl4 is introduced in pulses. The resulting TiN films exhibit low resistivity and good uniformity.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Prepn. process of mesic hole hollow ball-shape titania powder
This invention relates to a method to prepare mezoporous empty-centered titanium dioxide powders, which comprises following steps: titanium chloride is made into hydrosol with pure water, diluted and introduced into a spray dryer for spray drying. The subsequent product is empty-centered ball-shaped powder made up of nanosized titanium dioxide particles and the preceding titanium chloride is titanium tetrachloride or titanium trichloride. The titanium dioxide particles prepared in this invention all have mezoporous empty-centered ball-shaped structure and the empty-centered wall is made up of nanosized titanium dioxide particles and mezopores, on the surface of which titanium atoms possess a fraction of as high as 70%. As only titanium tetrachloride is adopted as precursor and no other reagent is necessary, the product is highly pure and has excellent photocatalytic properties. This method has the advantages of high yield, low cost, easily controlled technique and convenience for magnification experiment. Besides, there are not severe requirements for facilities and this method is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method of preparing sericite ultraviolet radiation screening agent
InactiveCN101058679AGood coating effectGood dispersionOther chemical processesInorganic pigment treatmentChlorideVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses a making method of ultraviolet masking agent of sericite mica, which comprises the following steps: 1) preparing fined sericite mica; 2) activating the sericite mica powder; 3) adding water in the sericite mica to form the suspension with density at 2. 5-5%; adjusting the pH value to 2. 0-2. 5 through alcaine as system C; 4) allocating titanic chloride solution with density at 10-15%; adding zinc chloride in the titanic chloride solution; making the molar rate of Zn and Ti at 1: 2; obtaining the solution D; 5) dripping the solution D into the system D; controlling the pH value to 7. 0; 6) filtering the sediment; washing; drying at 95 deg. c; 7) grinding the drier; placing the drier in the electric furnace at 600 deg. c for 2-3h; 8) grinding the sintered material; beating to 10-15um; obtaining the product.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Method of refining titanium tetrachloride by using aluminium powder and vash oil mixture
InactiveCN101549885AEfficient removalImprove refining efficiencyTitanium halidesTitanium chloridePhysical chemistry
Method of refining titanium tetrachloride by using aluminium powder and vash oil mixture. The method is refining of coarse titanium tetrachloride containing high content of vanadium impurities. Mixing aluminium powder, vash oil and a few AlCl[3] in certain percentage and adding into bottom of fractionating tower containing coarse titanium tetrachloride. Heating the bottom of fractionating tower at a temperature of 139 DEG and regulating reflux ratio of the tower, this moment the aluminium powder and mineral oil deoxidizing the VOCl[3] into lower valency indissoluble precipitate VOCl[2] and being removed, and the TiCl[4] and some low boiling point chemical compounds volatilizing into a reflux unit, extracting cuts of 136-137 DEG boiling point, then condensing to get fine titanium tetrachloride. The vanadium-removed fine titanium tetrachloride contains vanadium content of V%<=0.0007%. The vanadium removing process and the fractionating process are all proceeded in the fractionating tower that saves device. The invention reduces a large amount of residue and sewage discharge, and consumes less materials relative to technics of using aluminium powder and mineral oil to remove vanadium alone, the invention provides high refining efficiency, simple operation and continuous, and has economic and environmental benefit of energy-saving and emission-reduction.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for preparing titanium sponge through magnesium and chlorine recycling
ActiveCN102181670ALess investmentReduce manufacturing costProcess efficiency improvementTitanium chlorideCopper wire
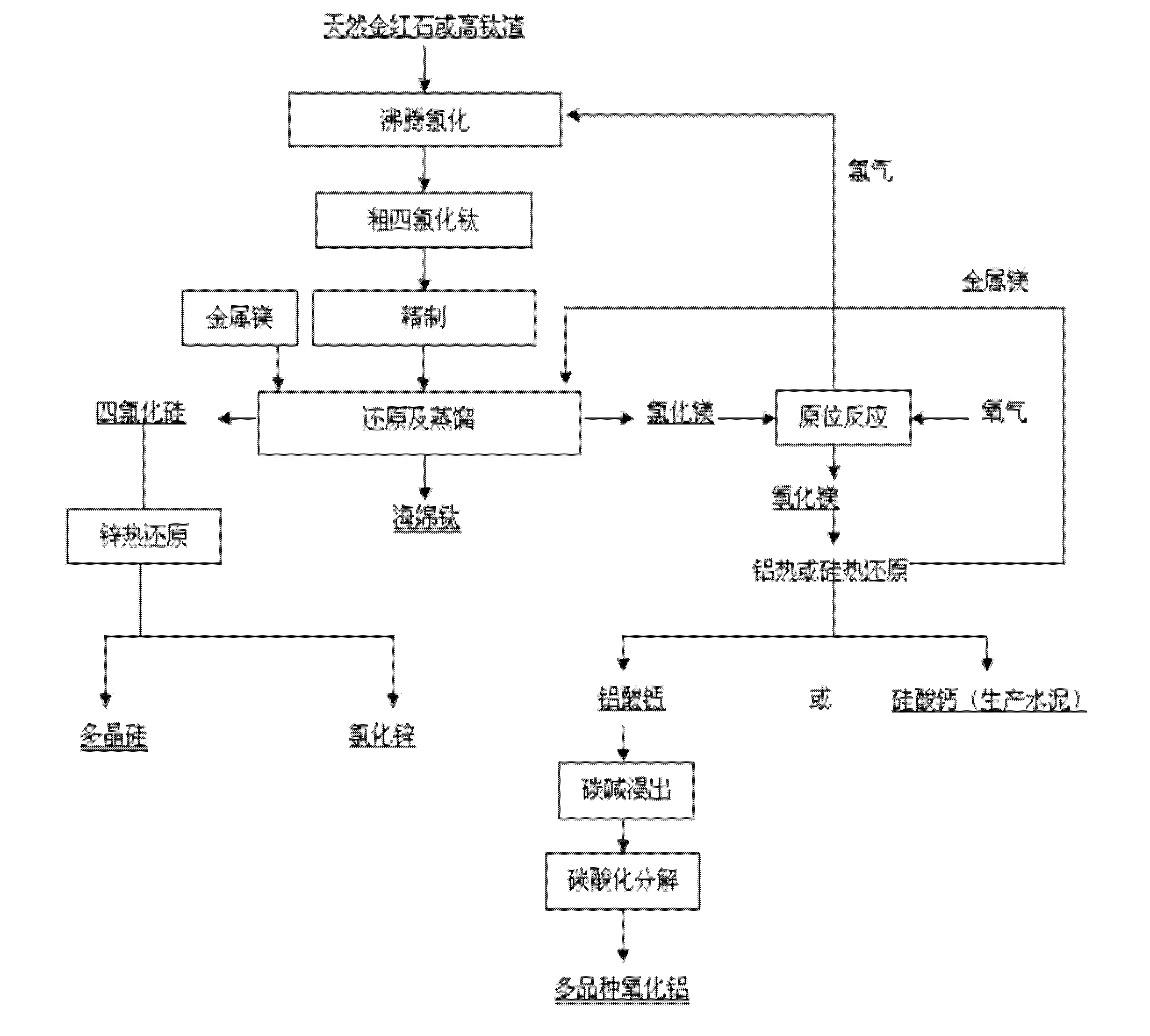
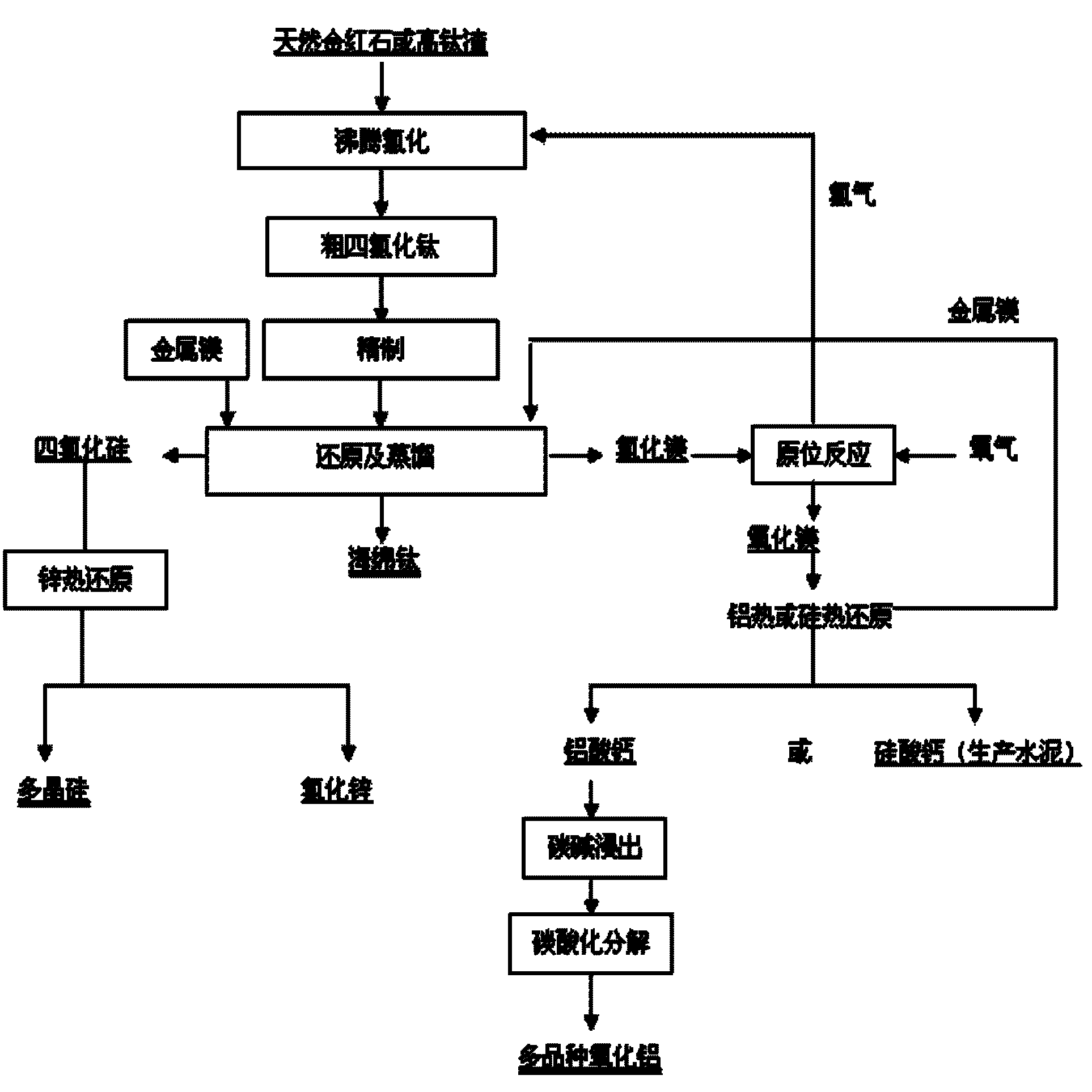
The invention relates to the technical field of preparation of nonferrous metal, in particular to a method for preparing titanium sponge through magnesium and chlorine recycling. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing natural rutile or titanium-rich slag, finely grinding to -0.25mm and chlorinating to obtain rough titanium tetrachloride; removing iron from the rough titanium tetrachloride by using a distillation tower with bottom temperature of between 140 DEG C and 145 DEG C and top temperature of 137 DEG C; removing silicon through a rectification tower with bottom temperature of 140 DEG C and top temperature of between 57 DEG C and 70 DEG C; removing vanadium by using copper wires to obtain a titanium tetrachloride product with purity of more than 99 percent; proportioning refined titanium tetrachloride and metal magnesium according to a mass ratio of magnesium to titanium as (1.3:1)-(1.8:1) and reacting at the temperature of between 700 DEG C and 1,000 DEG C to obtain mixture of the titanium sponge, the magnesium chloride and the silicon tetrachloride; and distilling the mixture of the titanium sponge, the magnesium chloride and the silicon tetrachloride for 30-35 hours under the conditions of temperature of between 880 DEG C and 1,000 DEG C and final vacuum degree of less than 0.1Pa to separate the titanium sponge and the magnesium chloride.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method of Manufacturing Pure Titanium Hydride Powder and Alloyed Titanium Hydride Powders By Combined Hydrogen-Magnesium Reduction of Metal Halides
ActiveUS20130315773A1Reduce oxideFacilitated DiffusionMultiple metal hydridesTransition element hydridesTitanium chloridePowder mixture
The invention relates to energy-saving manufacturing of purified hydrogenated titanium powders or alloying titanium hydride powders, by metallo-thermic reduction of titanium chlorides, including their hydrogenation, vacuum separation of titanium hydride sponge block from magnesium and magnesium chlorides, followed by crushing, grinding, and sintering of said block without need for hydrometallurgical treatment of the produced powders.Methods disclosed contain embodiments of processes for manufacturing high-purity powders and their use in manufacturing near-net shape titanium and titanium-alloy articles by sintering titanium hydride and alloyed titanium hydride powders produced from combined hydrogen-magnesium reduction of titanium chlorides, halides and hydrides of other metals. Additional titanium hydride powder introduced with titanium tetrachloride beneficially affects the kinetics of magnesium-thermic reduction due to formation of the additionally-emitted atomic hydrogen, which helps to reduce presence of oxides and so cleans inter-particle interfaces of the product and enhances diffusion between all of components of the powder mixture.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS PRODS
Method for preparing precious metal titanium dioxide core-shell structure
ActiveCN103933972AGood monodispersityGood catalytic hydrogen production effectHydrogen productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCore shellNanometre
The invention discloses a method for preparing a precious metal titanium dioxide core-shell structure. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a precious metal nano particle colloidal solution; (2) adjusting the pH value of a titanium trichloride solution by adding alkaline matter; (3) adding the solution prepared in the step (1) to the solution obtained in the step (2) and reacting; (4) carrying out solid-liquid separation so as to obtain a nano material with the precious metal titanium dioxide core-shell structure. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and feasible, and is good in repeatability, the prepared core-shell structure is good in monodispersity, and the thickness of a titanium dioxide shell layer can be controlled by adjusting the pH of the reaction system. Therefore, the core-shell structure can be applied to the field of hydrogen production of photocatalytic decomposition of water.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Method and device for producing titanium by fused salt electrolysis process
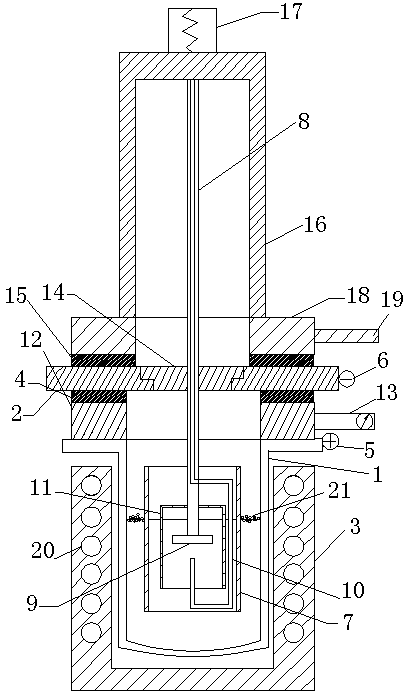
The invention provides a method and device for producing titanium by a fused salt electrolysis process, relating to a device adopting titanium tetrachloride as a raw material to directly produce high purity titanium by the fused salt electrolysis process. The method is characterized by adopting titanium tetrachloride as the raw material, introducing titanium tetrachloride into mixed fused salt of sodium chloride and potassium chloride, adopting magnesium as an anode and titanium as a cathode to electrolyze titanium tetrachloride to generate magnesium chloride and titanium, directly depositing the generated titanium on the titanium cathode and separating the generated titanium to obtain a titanium product. The method and device for producing titanium by a fused salt electrolysis process have the beneficial effects that the method and the device can be used for directly producing the high purity titanium from titanium tetrachloride without using titanium sponge as a raw material, can save the cost and can be used for producing titanium with higher purity; the produced high purity titanium is shaped like a cylinder or a square column; and a titanium ingot in the shape can be directly used as a raw material of an electron beam smelting furnace or a consumable electrode vacuum furnace in the next process, thus saving the processes of briquetting and welding and further saving the cost.
Owner:SIX NINE TECH
Method for preparing titanic chloride by half cycle fluidization
InactiveCN101475210AReduce agglomerationSolve the conundrum problemFluidised-bed furnacesTitanium halidesNitrogenLower grade
The invention discloses a method for preparing titanium tetrachloride through semi-circulating fluidization, which relates to a method for preparing the titanium tetrachloride. The method takes low-grade high titanium slag and coke as solid raw materials, takes chloride and nitrogen as gas raw materials, and utilizes a semi-circulating fluidized bed to obtain a finished product through a chlorination reaction, cooling and gas-solid separation. The method avoids the agglomeration and adhesion of the particles by circulating coke particles with smaller viscosity and suspending high titanium slag particles with larger viscosity in a fluidized bed reactor, can fully utilize low-grade high titanium slag resource, and has the characteristics of high production efficiency, good product quality, simple and convenient operation, suitability for industrial mass production and the like. The method can be widely applied to the preparation of the titanium tetrachloride by utilizing titanium ore, and is particularly suitable to utilize the low-grade high titanium slag to prepare the titanium tetrachloride.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method of manufacturing pure titanium hydride powder and alloyed titanium hydride powders by combined hydrogen-magnesium reduction of metal halides
ActiveUS9067264B2Cost-effectiveAvoid pollutionMultiple metal hydridesTransition element hydridesTitanium chloridePowder mixture
The invention relates to energy-saving manufacturing of purified hydrogenated titanium powders or alloying titanium hydride powders, by metallo-thermic reduction of titanium chlorides, including their hydrogenation, vacuum separation of titanium hydride sponge block from magnesium and magnesium chlorides, followed by crushing, grinding, and sintering of said block without need for any hydro-metallurgical treatment of the produced powders. Methods disclosed contain embodiments of processes for manufacturing high purity high-purity powders and their use in manufacturing near-net shape titanium and titanium-alloy articles by sintering titanium hydride and alloyed titanium hydride powders produced from combined hydrogen-magnesium reduction of titanium chlorides, halides and hydrides of other metals. Additional titanium hydride powder introduced with titanium tetrachloride beneficially affects the kinetics of magnesium-thermic reduction due to formation of additionally-emitted atomic hydrogen, which helps to reduce presence of oxides, and so cleans inter-particle interfaces of the product and enhances diffusion between all components of the powder mixture.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS PRODS
Method for preparing titanium sponge
The invention discloses a method for preparing a titanium sponge, comprising the following steps of: placing metallic magnesium in a reactor; adding magnesium chloride blocks to the metallic magnesium according to the weight ratio (4:1) of metallic magnesium to magnesium chloride; using a Roots pump for vacuum pumping for 30 minutes, and inputting argon; achieving the following temperature variation after being put into a furnace: respectively carrying out constant temperature degasification at 150 DEG C for two hours, at 200 DEG C for two hours, and at 300 DEG C for two hours; raising the temperature to 800 to 880 DEG C, and adding titanium tetrachloride liquid for reduction reaction; adding titanium tetrachloride for ten times; and adding the magnesium chloride by ten times. The invention reduces the impurity content of the product, changes the surface color thereof, increases the rate of finished products and improves the product quality.
Owner:朝阳金达钛业股份有限公司
Metallic ion doped nano TiO2 transparent photo-catalytic emulsion and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101062476AAchieve purificationAchieve degradationPhysical/chemical process catalystsSpectral responseAmmonium metavanadate
The metal ion mixed with TiO2 transparent optical catalyst lotion features in 0. 5-10% TiO2, mixed with V, Tin, Zn, Fe, OP emulsifier 1-10% with the rest being water, comprising a making of titanic chloride water solution, hydrolysis to generate TiO2+, VO3+, Sn4+, Zn2+, Fe3+ or Ce3+ compound oxidation deposit, low temperature complexing, hydrolysis to get the metal mixed nanometer TiO2 transparent catalyst lotion. It uses cheap titanium tetrachloride and ammonium vanadate, white copperas, Fe2cl3,tin tetrachloride as the inorganic material, using low temperature complex hydrolysis to allow higher ability to mix, expanding spectral response zone. Its maximum advantage is the direct use of sun light or fluorescent lamp, realizing complete degradation of organic pollutants, improving the speed and efficiency of photochemical catalysis and degradation for environmental purification.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and Methods for the Production of Metal Compounds
ActiveUS20090165597A1Improve thermal conductivityInexpensive materialsBlast furnace detailsManufacturing convertersAluminium chlorideTitanium chloride
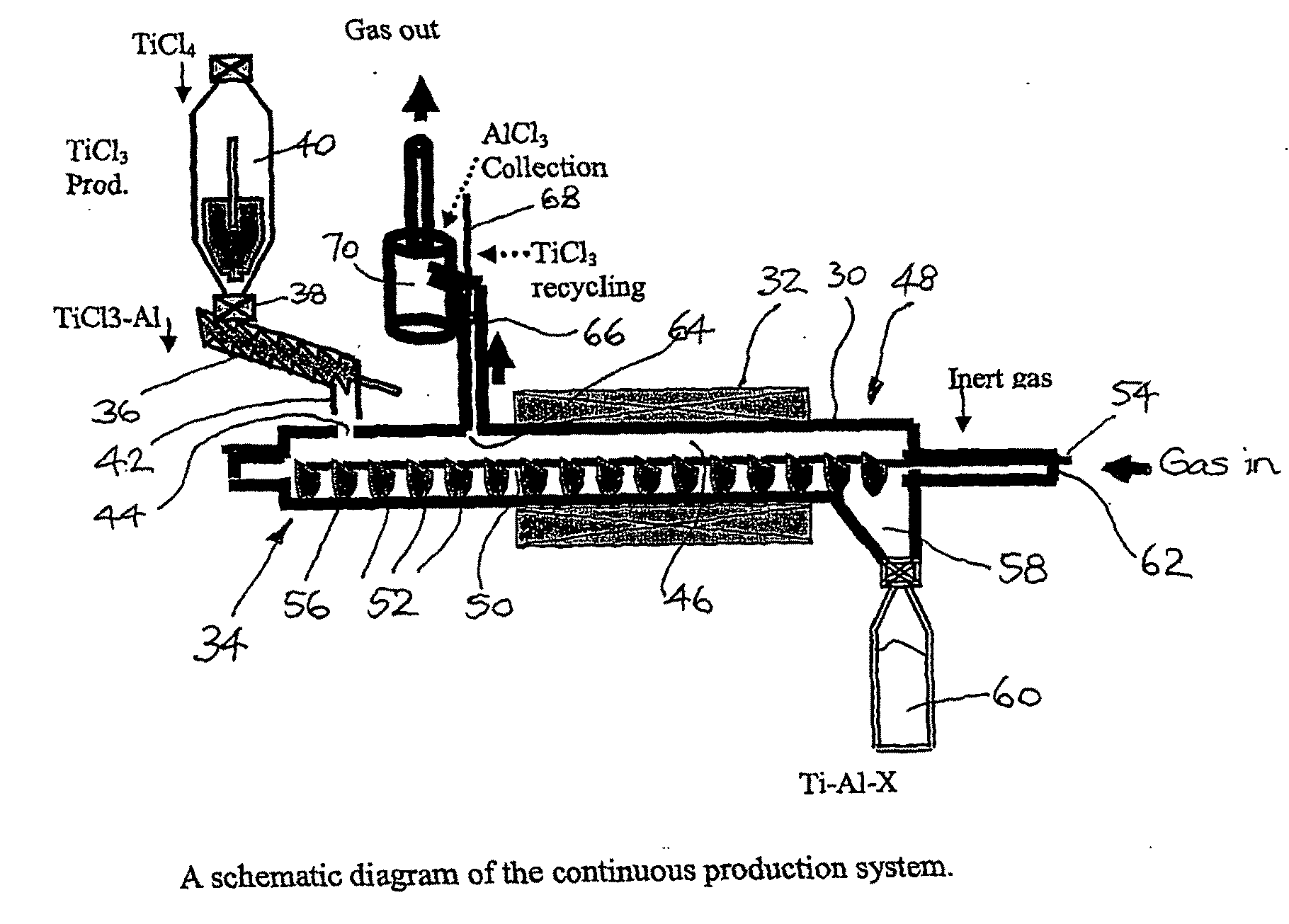
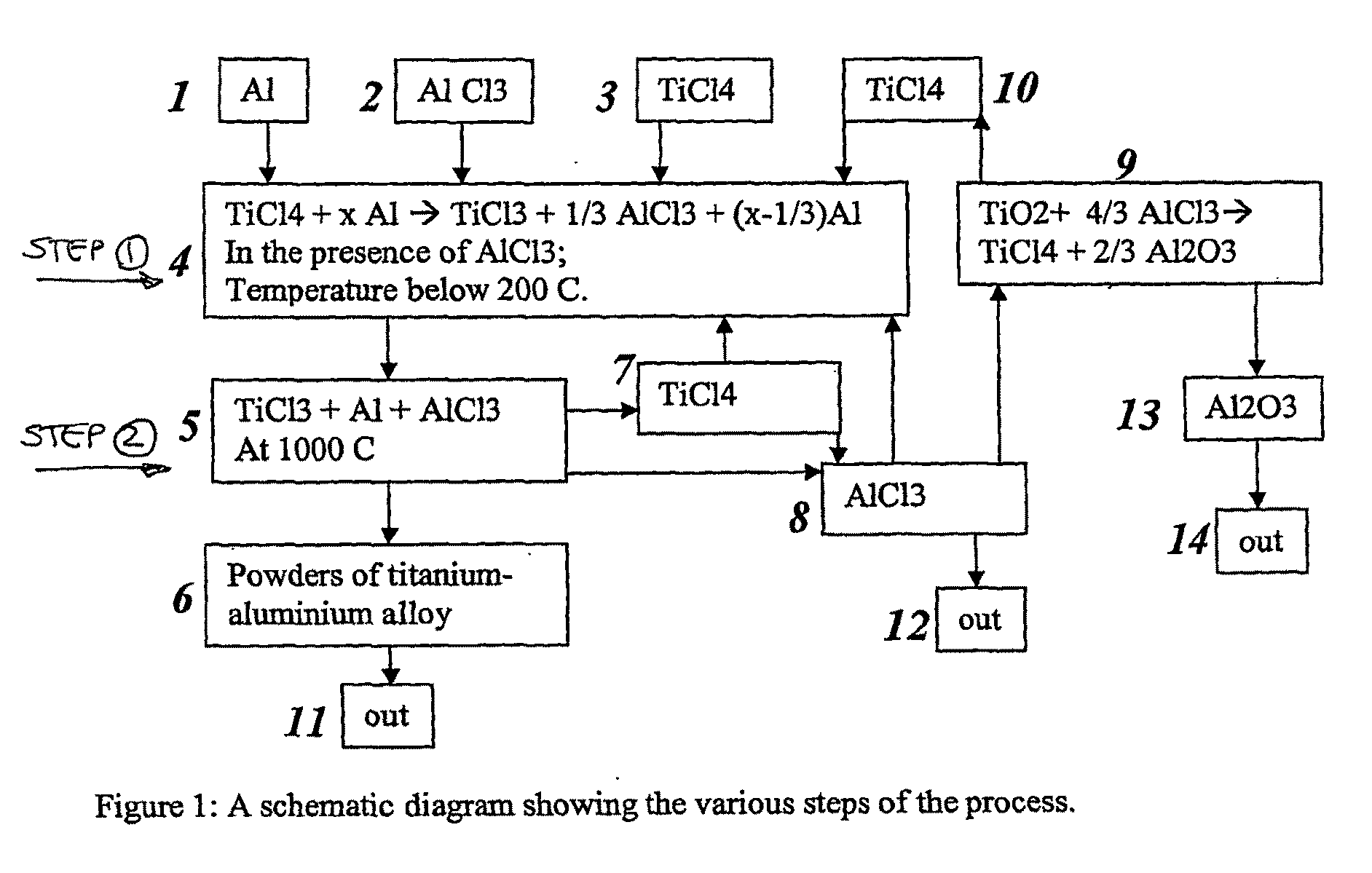
The present invention relates to a stepwise method for the production of titanium-aluminium compounds and some titanium alloys and titanium-aluminium inter-metallic compounds and alloys. In a first step an amount of aluminium is mixed with an amount of aluminium chloride (AlCl3) and then an amount of titanium chloride (TiCl4) is added to the mixture. The mixture is heated to a temperature of less than 220° C. to form a product of TiCl3, aluminium and AlCl3. In a second step, more aluminium can be added if required, and the mixture heated again to a temperature above 900° C. to form titanium-aluminium compounds. This method results in the production of powdered forms of titanium-aluminium compounds with controllable composition. Suitable reactor apparatus is also described.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Preparation method of titanium dioxide photocatalyst of plant graded structure
InactiveCN101491756AFull preservation of hierarchical structure featuresGood photolysis efficiencyCatalyst activation/preparationDistilled waterTitanium tetrachloride
The invention relates to a method for preparing a titanium dioxide photocatalyst with a plant hierarchical structure in the technical field of photocatalysis. The method comprises the following steps: selecting a plant with a hierarchical structure as a template, and pre-treating the surface of the plant; preparing titanium tetrachloride solution or titanium alcoholic solution as a precursor solution; putting the treated plant into the prepared precursor solution to carry out ultrasonic treatment; and after the ultrasonic treatment is finished, taking out the plant, cleaning the plant by distilled water, drying the cleaned plant, and roasting the plant to remove the biological template to obtain a titanium dioxide material keeping the plant hierarchical structure. The titanium dioxide with the plant hierarchical structure prepared by the method has larger specific surface area and three-dimensional communicated pore canal structure, has higher photocatalysis property, and has wide application prospect on environmental governance such as organic pollutant degradation, and the like, self-cleaning, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for preparing vanadium oxide by using sodium salt roasting lixivium of titanium tetrachloride refined tailings
ActiveCN104017993AHigh puritySolve pollutionVanadium oxidesProcess efficiency improvementTitanium chlorideSlag
The invention discloses a method for preparing vanadium oxide by using sodium salt roasting lixivium of titanium tetrachloride refined tailings. The method comprises the following steps: adding an aluminum remover and an adsorbent in heated sodium salt roasting lixivium of titanium tetrachloride refined tailings to remove impurities, and then filtering to obtain purified liquor; adding a soluble ammonium salt into the purified liquor and carrying out molybdenum precipitation, then, filtering to obtain ammonium metavanadate precipitates, washing, drying and roasting the ammonium metavanadate precipitates to obtain vanadium pentoxide. According to the method disclosed by the invention, sodium salt roasting lixivium of titanium tetrachloride refined tailings is directly adopted, molybdenum precipitation is directly carried out after further removing aluminum, and the purity of the prepared titanium tetrachloride is greater than 99.9wt%, the content of impurities such as silicon, chromium, iron, calcium and aluminum, is less than 0.005wt%, the yield of vanadium is over 90wt%, so that not only can a long-term pollution problem of waste slag on environment be solved, but also a vanadium resource is recycled and high-purity vanadium oxide is prepared, so that the method has very good social and economic benefits.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Norbornene, maleic anhydride and vinyl acetate ternary polymerization catalyst and ternary polymerization method
InactiveCN103626919AHigh catalytic efficiencyEasy to wash and separateReaction temperatureCarvacryl acetate
The invention relates to a catalyst for ternary polymerization of norbornene, maleic anhydride and vinyl acetate and a ternary polymerization method. The catalyst is characterized by being prepared by a method comprising the following steps: dissolving tri(cyclopentadienyl) neodymium, titanium tetrachloride and a ligand compound in a solvent in a dry single-opening glass bottle in an inert gas atmosphere, and sealing the opening of the bottle by using a latex tube, so as to obtain a titanium complex catalyst. Compared with the prior art, the invention provides a novel titanium complex catalyst and a ternary polymerization method using the same, the preparation method is simple, the titanium complex catalyst can generate catalytic activity in a nitrogen protection system at 40-90 DEG C to catalyze ternary polymerization of norbornene, maleic anhydride and vinyl acetate, and after being soaked in methanol, a polymerization product can be easily washed and separated; the catalyst has the characteristics of high yield, low reaction temperature, low price, availability, high catalytic efficiency and the like.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Continuous and semi-continuous process of manufacturing titanium hydride using titanium chlorides of different valency
InactiveUS20110171116A1Reduce manufacturing costCost-effective and highly-productive manufactureTransition element hydridesTitanium chlorideOxygen
The invention relates to the manufacture of titanium hydride powder using continuous or semi-continuous process, and using titanium slag or synthetic rutile as raw materials, while hydrogen, titanium tetrachloride, titanium trichloride, titanium dichloride, and hydrogen chloride are participate as intermediate reaction products. The continuous comprises: (a) reduction of TiCl4 to low titanium chlorides followed by cooling a mixture, (b) separating of residual TiCl4 from solid low chlorides by heating the mixture in argon or vacuum up to 150° C. followed by removing the titanium tetrachloride from the mixture, (c) dissociation of TiCl3 to TiCl2 at 450° C. in vacuum followed by removal of gaseous titanium tetrachloride from the reaction zone, condensation to the liquid, and returning back into the reaction retort, (d) dissociation of TiCl2 in vacuum at 750-850° C. to manufacture fine powder of metallic titanium and titanium tetrachloride, whereby hydrogen heated up to 1000° C. is used to accelerate this reaction, and (e) saturation of the fine titanium powder by hydrogen at 400-640° C. to manufacture final product of titanium hydride powder which is free of oxygen or nitrogen. The semi-continuous process includes the Kroll's process as the very first step.
Owner:ADMA PRODS
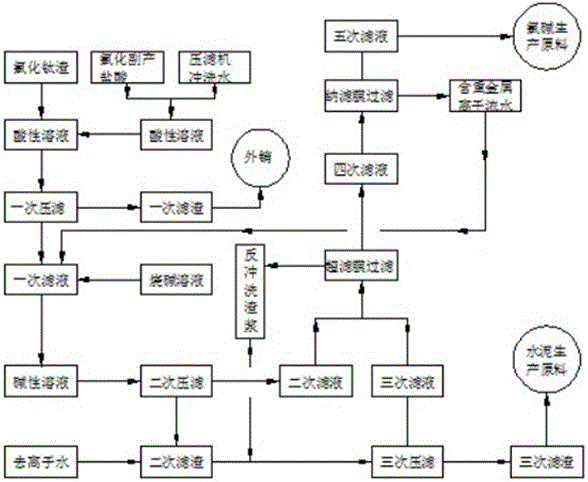
Method for comprehensively utilizing titanium chloride residues and filter liquid thereof in chlorination-process technologies for titanium dioxide powder
ActiveCN106044799AEliminate the step of evaporative crystallizationReduce pollutionCement productionAlkali metal chloridesTitanium chlorideSodium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for treating byproducts in chlorination-process technologies for titanium dioxide powder, and particularly discloses a method for comprehensively utilizing titanium chloride residues and filter liquid thereof in chlorination-process technologies for titanium dioxide powder. The method includes dissolving the titanium chloride residues in diluted hydrochloric acid to obtain acidic solution and neutralizing the acidic solution by the aid of sodium hydroxide solution; carrying out pH (potential of hydrogen) regulation, deionized water treatment and multi-step filter processes to obtain the filter liquid with sodium chloride which is a main component; feeding the obtained filter liquid to brine working procedures of chlorine-alkali systems and carrying out re-saturation treatment on the filter liquid to obtain raw materials for chlorine-alkali production. The method has the advantages that metal reducing agents do not need to be added into the acidic solution with the titanium chloride residues; steps for carrying out evaporative crystallization on the filter liquid can be omitted; the ultimately obtained filter liquid can be used as the production raw materials for chlorine-alkali technologies, and accordingly the chlorination-process technologies for the titanium dioxide powder can be organically combined with the chlorine-alkali production technologies.
Owner:YIBIN TIANYUAN GRP CO LTD +1
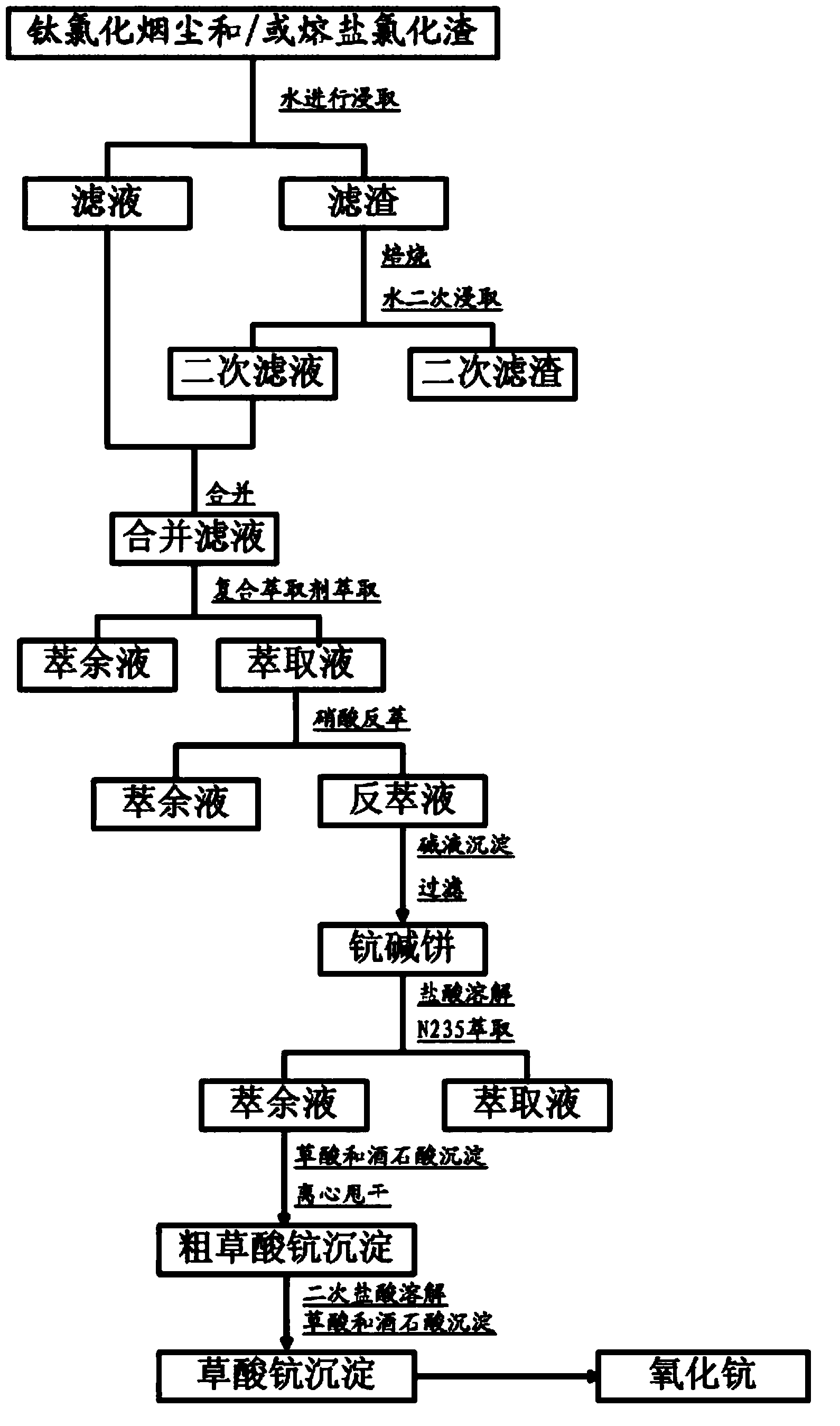
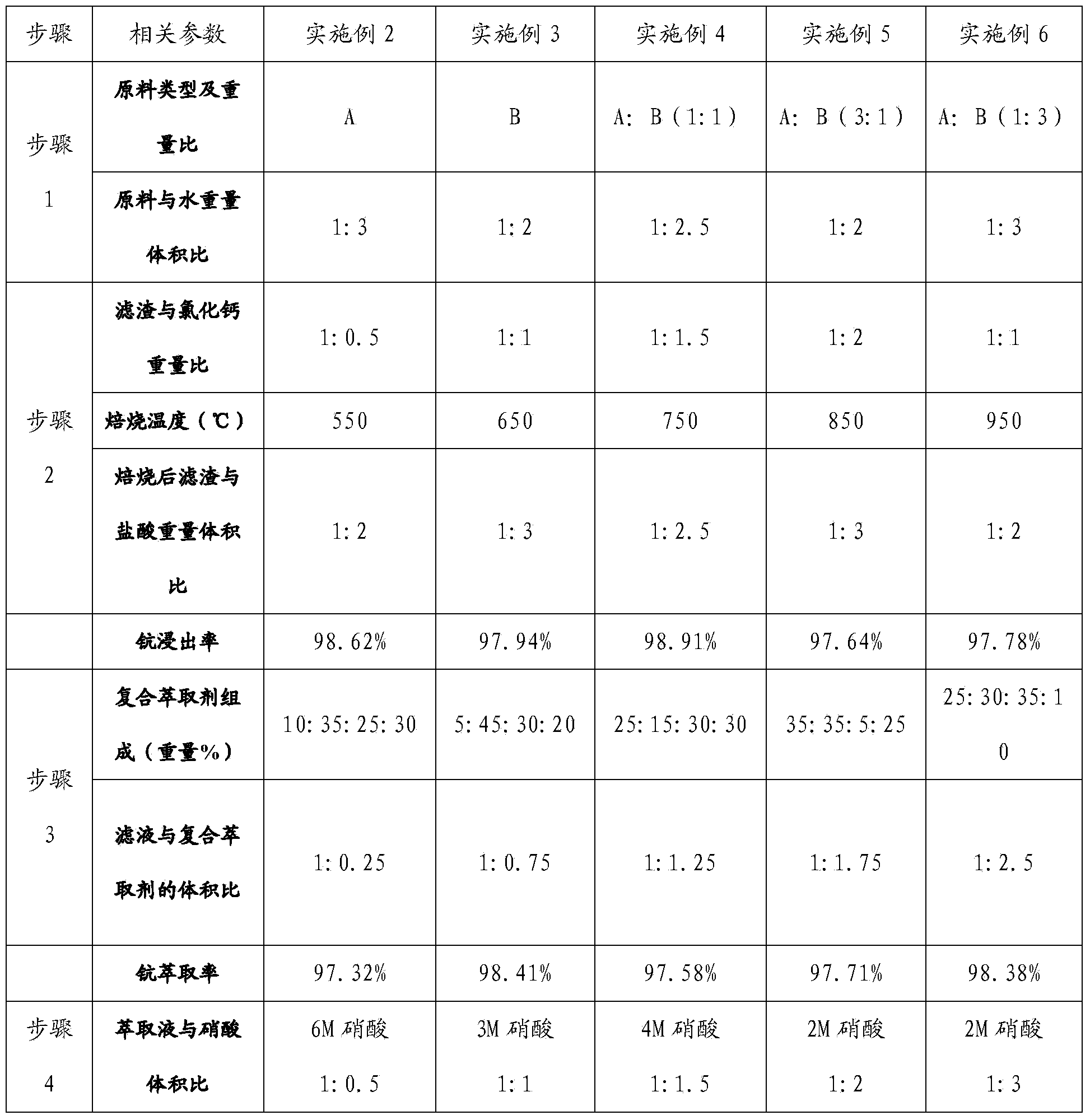
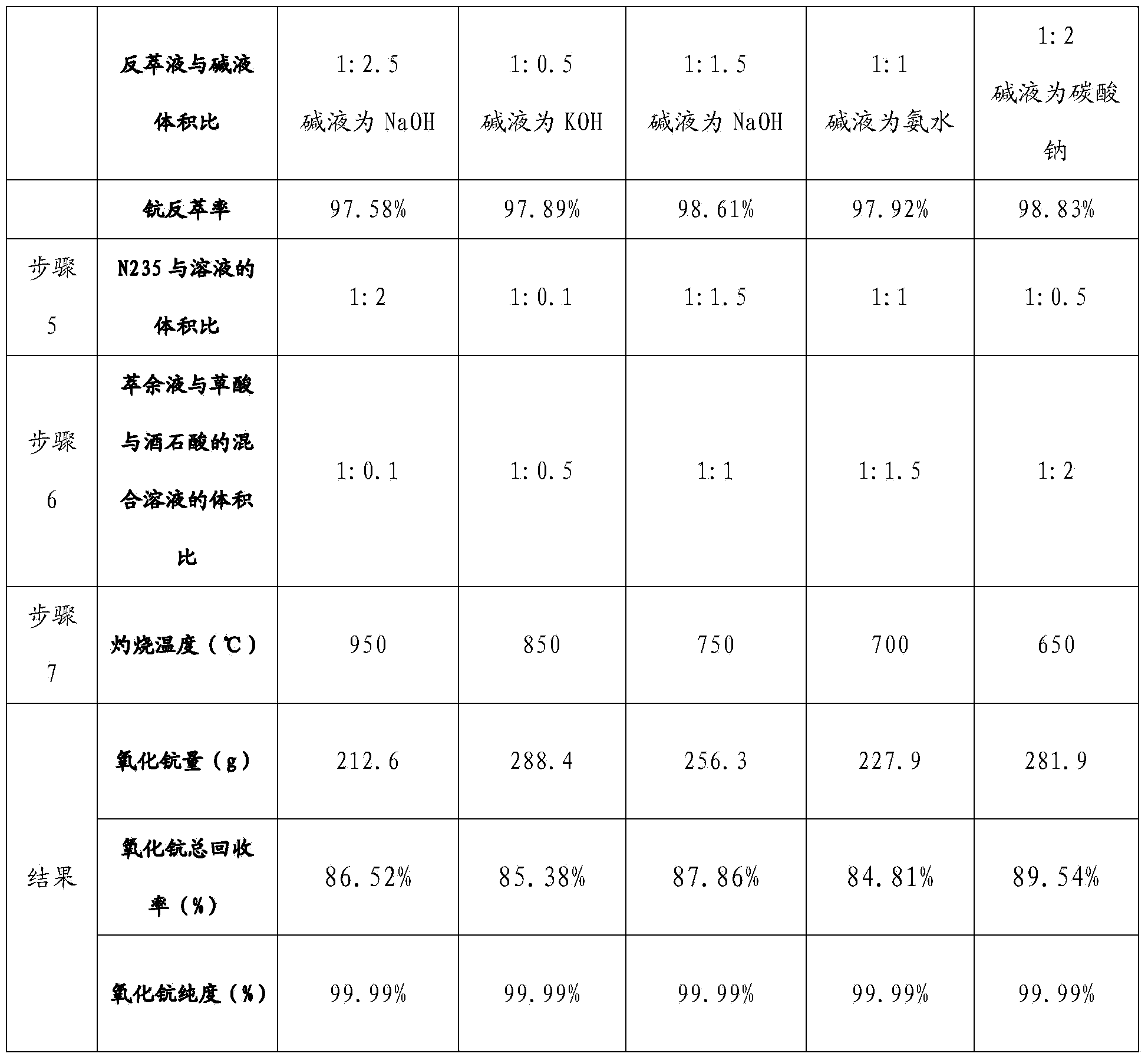
Method for extraction of scandium in titanium chloride smoke dusts and fused salt chloride residues by using compound extraction agent
InactiveCN103436700AHigh extraction rateHigh selectivityLiquid solutions solvent extractionProcess efficiency improvementTitanium chlorideKerosene
The invention relates to a method for the extraction of scandium in titanium chloride smoke dusts and fused salt chloride residues by using a compound extraction agent, and belongs to the technical field of rare-earth metals. The weight percent of particular components of the compound extraction agent is that: 5%-35% of P350, 15%-45% of TBP, 5%-35% of secondary-octyl alcohol, and 5%-35% of kerosene oil. According to the invention, a high purity scandium oxide is obtained through twice leaching, extraction, nitric acid reverse extraction, oxalic acid sedimentation, and scorching. The extraction method adopts once direct water leaching, and twice hydrochloric acid leaching after roasting to improve the leaching rate; the leaching rate of scandium surpasses 96%, meanwhile the using of acid is reduced, the industrialized production is facilitated, and the total recovery of scandium is high and surpasses 85%.
Owner:连云港市丽港稀土实业有限公司
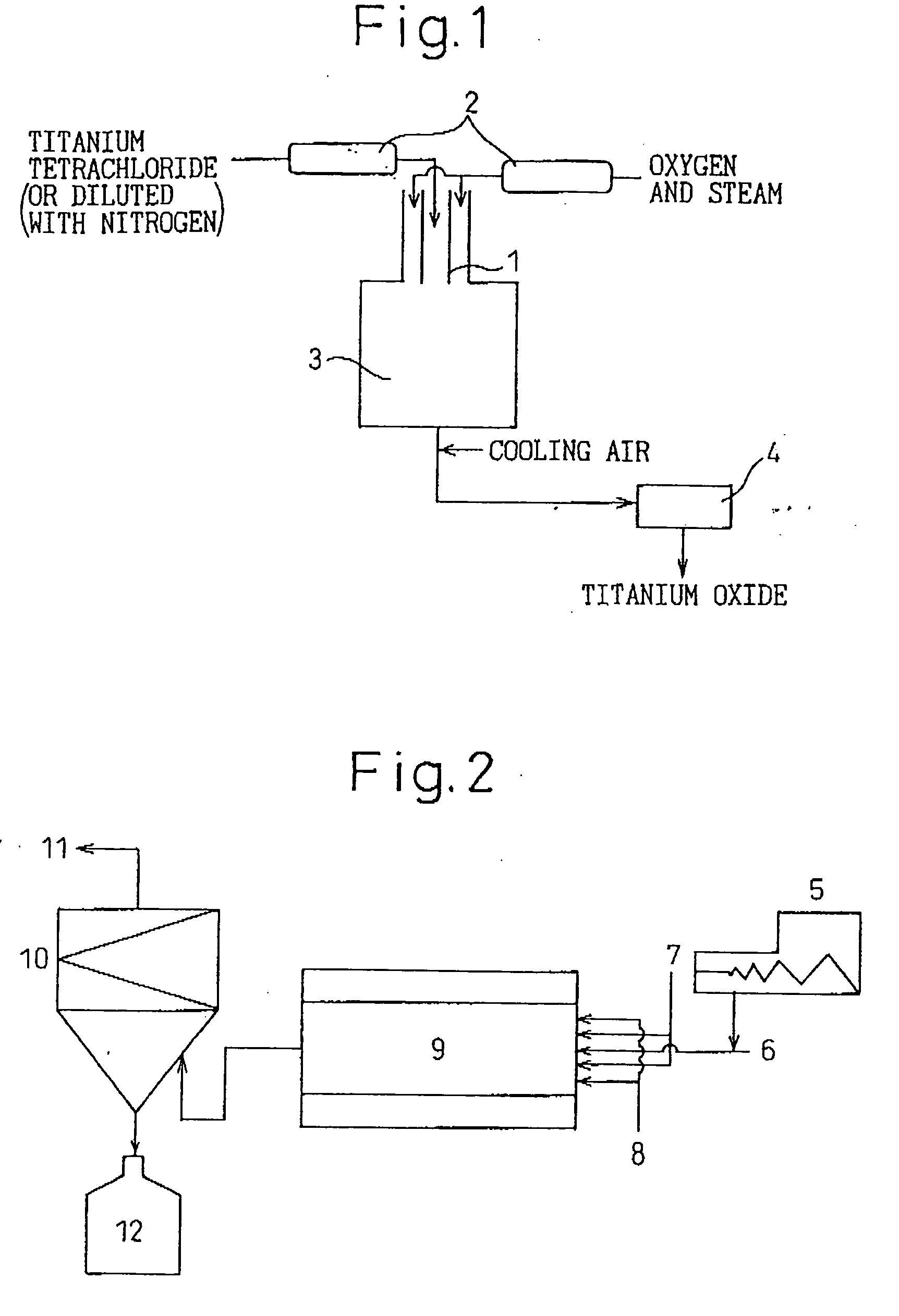
High purity titanium oxide and production process thereof
InactiveUS20060074173A1Good dispersionEasy to supervisePigmenting treatmentCosmetic preparationsGas phaseCombustible gas
A titanium dioxide characterized by having an average particle size of 5 to 200 μm as measured through laser particle size analysis; having a purity of at least 99.5 mass % as reduced to TiO2; and having an Fe content of 20 mass ppm or less, an Ni content of 20 mass ppm or less, a Cr content of 20 mass ppm or less, an Al content of 20 mass ppm or less, a Zr content of 20 mass ppm or less, an Si content of 40 mass ppm or less, a Cl content of 0.05 mass % or less, and an S content of 50 mass ppm or less. The titanium dioxide is produced by a process comprising bringing titanium dioxide serving as a raw material into a high-temperature flame formed by use of a combustible gas and a combustion-supporting gas, to thereby yield spherical titanium dioxide, characterized in that said raw material titanium dioxide has been produced through a vapor-phase process in which titanium tetrachloride is oxidized with an oxidative gas at high temperature.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
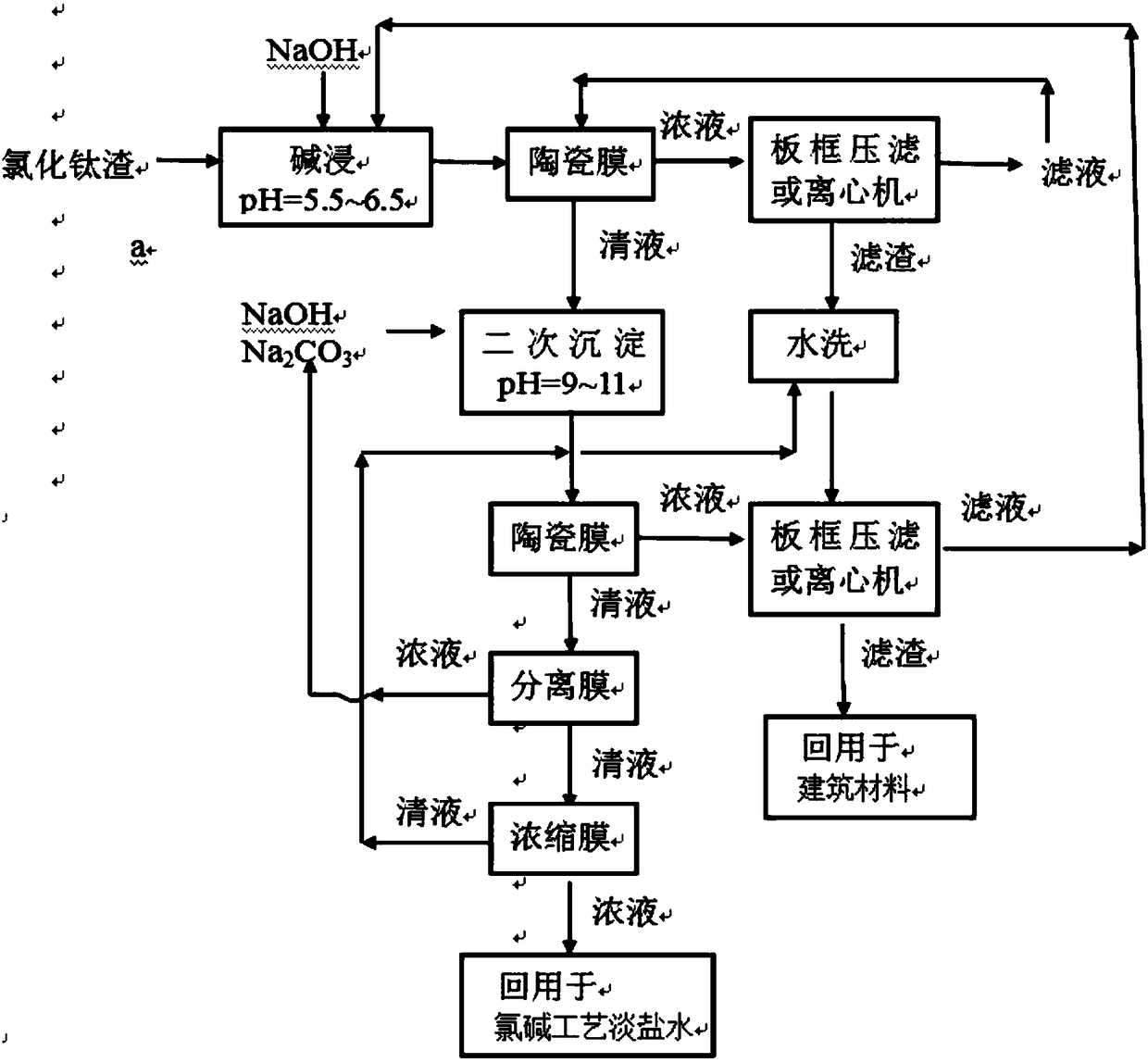
Resource utilization method of titanium chloride slag and device thereof
PendingCN108372185AAdvancedObvious economySolid waste disposalProcess efficiency improvementTitanium chlorideSeparation technology
The invention relates to a resource utilization method of titanium chloride slag and a device thereof and belongs to the chemical field of titanium dioxide. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out alkaline leaching to form slag slurry; S2, carrying out solid-liquid separation on the slag slurry; S3, washing the separated solid in the step 2 again; S5, second settlement: adjusting the pH to 9-10 of the filtrate after solid-liquid separation in the step 2 with sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide jointly, and carrying out settlement to remove heavy metal ions therein to formsecondary slag slurry; and S6, filtering the secondary slag slurry with a ceramic film, wherein solid-liquid separation is carried out on concentrated liquor and washing slag slurry through a plate-and-frame filter press or a centrifugal machine; and the clean liquor is deeply treated by a membrane separation technology to prepare salt dissolving light salt brine for a chlor-alkali process. The method converts environment-harmful titanium chloride slag into harmless building raw material and light salt brine for the chlor-alkali process, and turns wastes into wealth, so that the method has obvious economical and environmental benefits.
Owner:JIANGSU JIUWU HITECH +1
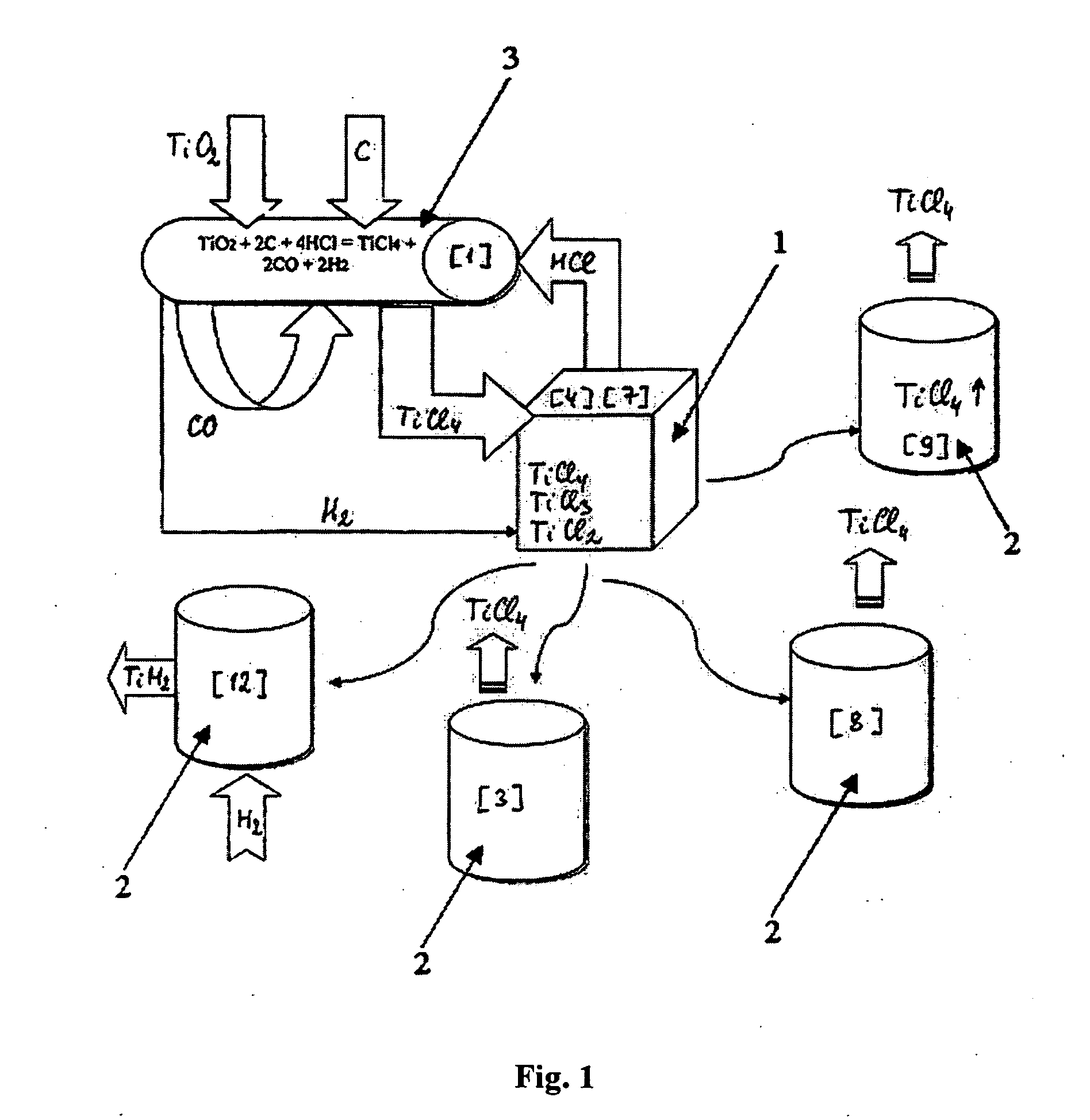
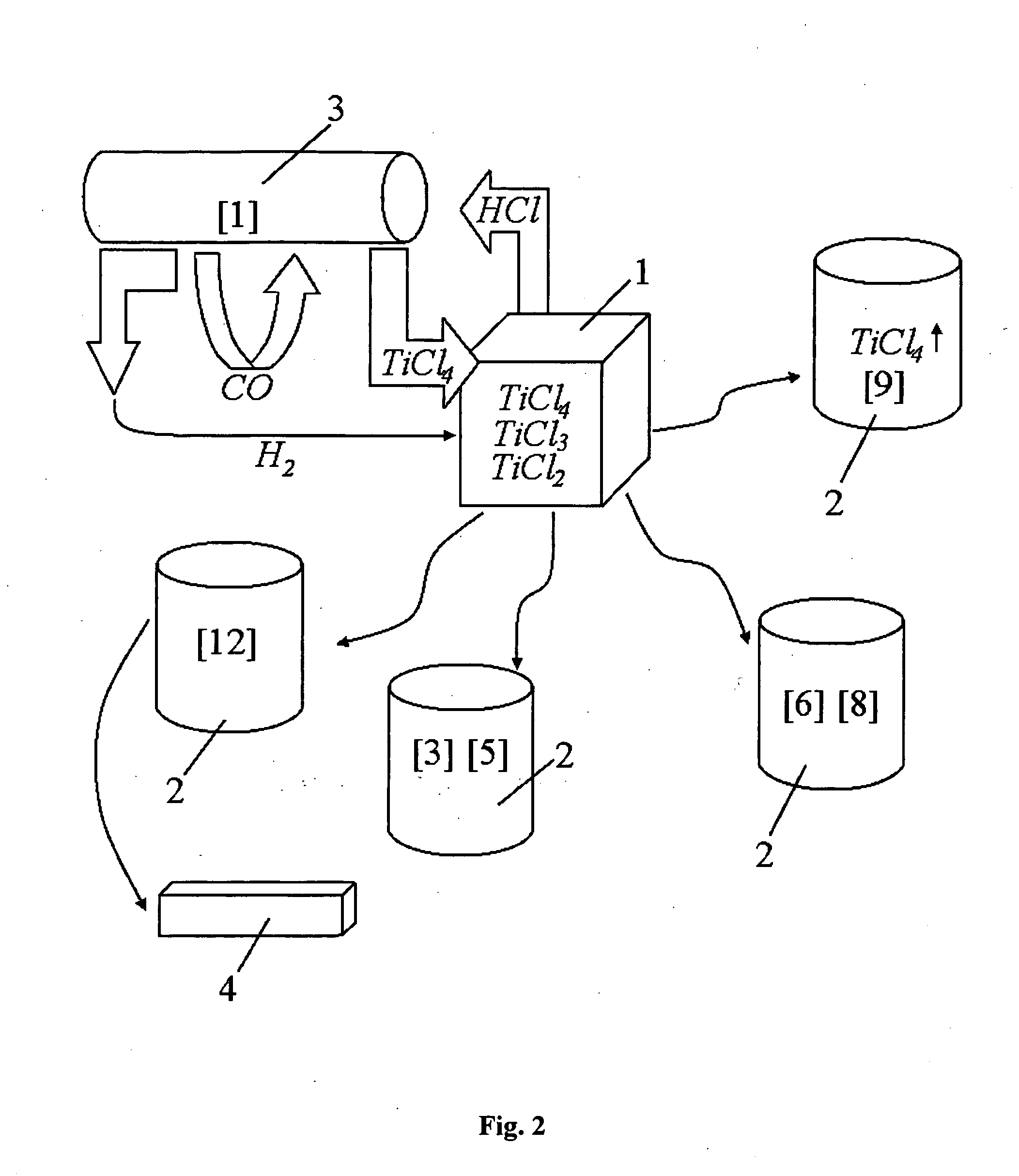
Process for manufacturing lower chlorides of titanium
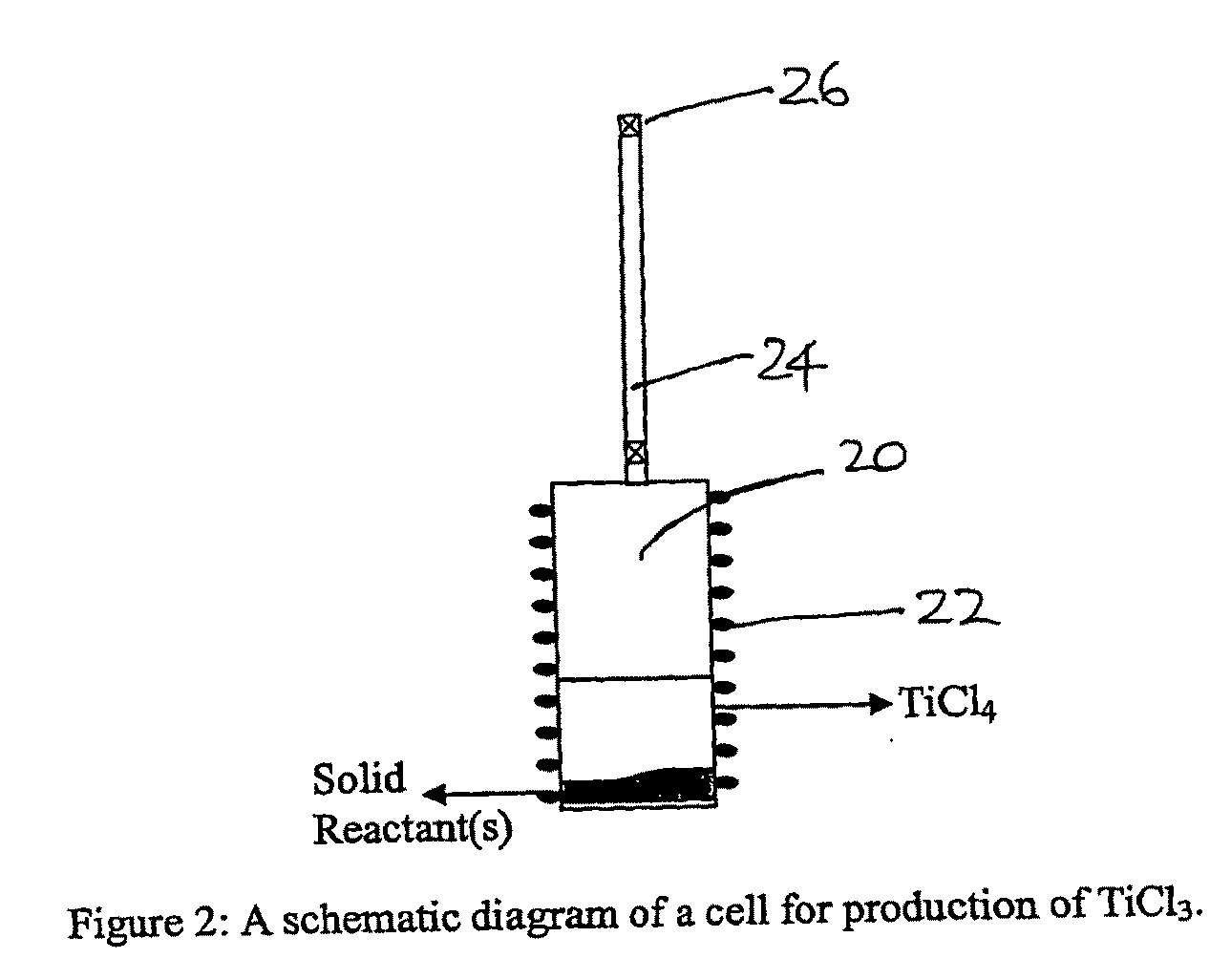
A process for preparation of lower chlorides of titanium is provided, in which titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) is reduced using a reducing agent in at least one molten alkali metal salt at a temperature of about 300 to about 1400 DEG C to obtain a reduced mass containing lower chlorides of titanium. A process for preparation of titanium metal from the lower chlorides of titanium is also provided.
Owner:凯基·霍尔穆斯吉·格哈达
Method and solution for forming anatase titanium dioxide, and titanium dioxide particles, colloidal dispersion and film
InactiveUS7534293B2Improved propertyAccelerated agingOther chemical processesWater-repelling agents additionOrganic acidTitanium chloride
A sol solution containing poly(titanic acid) and a planar heterocyclic ligand is provided. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles are formed by aging the sol solution at a temperature below about 140° C. The particles have multi-coordinated Ti-complexes comprising the heterocyclic ligand and can be substantially in the anatase phase. The heterocyclic ligands can be triazole, tetrazole, or thiadiazole. The sol solution may be prepared by aging a precursor solution. The precursor solution may contain the heterocyclic ligands and a precursor for poly(titanic acid). The precursor may be titanium alkoxide or titanium chloride. The sol solution may also contain at least one of an organic acid, a base, and a surfactant. The aged sol solution may form a colloidal dispersion of the TiO2 particles. A photo-catalytic and transparent film may be formed from the TiO2 particles by depositing a layer of the colloidal dispersion on a support.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Manufacture of cost-effective titanium powder from magnesium reduced sponge
InactiveUS6638336B1Save energyReduce in quantityTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusTitanium chlorideHydrogen pressure
The cost-effective titanium powder is manufactured by (a) magnesium-thermic reduction of titanium chlorides characterized by the formation of a hollow block of the reaction mass having an open cavity in the center of the block, (b) thermal-vacuum separation of the hollow block from excessive Mg and MgCl2 at 850-950° C. and residual pressure of 10<-2>-10<-3 >mm Hg, (c) cooling of obtained titanium hollow block in a H2-contained atmosphere at an excessive hydrogen pressure, (d) crushing the hydrogenated titanium block, (e) grinding the crushed titanium pieces into the powder combined with a hydro-metallurgical treatment of obtained titanium powder in a diluted aqueous solution of at least one chloride selected from magnesium chloride, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, or titanium chloride, and (f) drying and, optionally dehydrating the titanium powder ground to a predetermined particle size. The formation of the hollow block of the reaction mass with the open cavity in the center of the block is carried out by accelerating the reaction mass on the inside surface of the reactor. The hydro-metallurgical treatment of titanium powder is carried out in the solutions having the total content of chlorides of 0.5-10 wt. %, at the powder-to-solution weight ratio from 1:1 to 1:4. The cooling of the titanium hollow block in the hydrogen-contained atmosphere is carried out to the temperature of 550-450° C. at the excessive hydrogen pressure of 0.2 bar or higher. The productivity of the innovative process is higher, the energy consumption is lessened more than double, the duration of the processing cycle is decreased by 3. The shorter time of high-temperature stages results in significant improvement of titanium powder quality because it prevents the oxidation and nitrogenation of the metal. The powder dispersion is increased caused by porous and poorly sintered structure of the reaction mass. Cooling the block in the presence of hydrogen also increases the powder quality and the yield of fine powder fractions during the hydro-metallurgical treatment.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS PROD INC OF OHIO USA
Continuous and semi-continuous process of manufacturing titanium hydride using titanium chlorides of different valency
InactiveUS8388727B2Cost-effective and highly-productive manufactureImprove machining productivityTransition element hydridesTitanium chlorideTitanium(II) chloride
Owner:ADMA PRODS
Preparation of crude titanic chloride
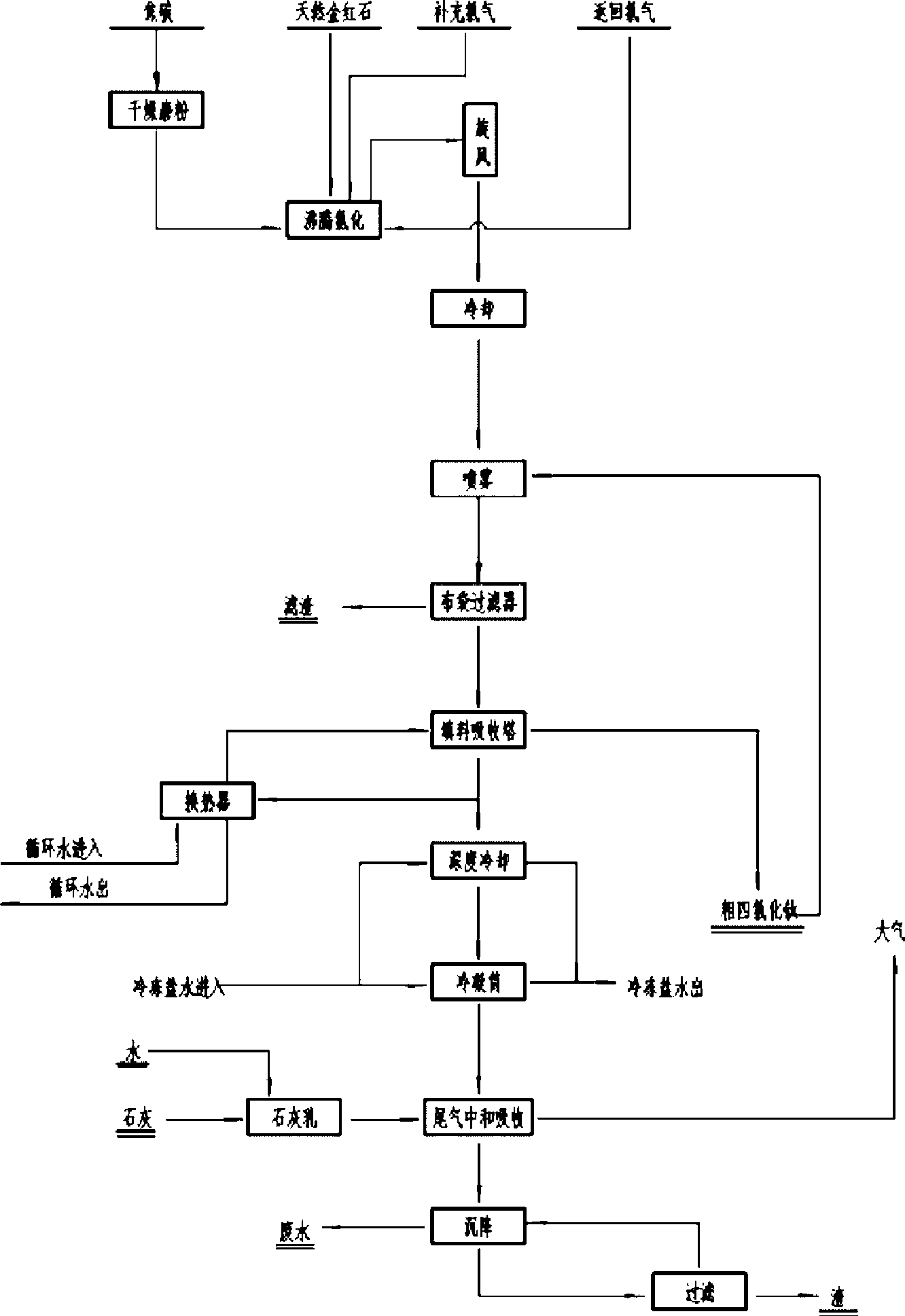
InactiveCN101462767ABroaden sources of raw materialsHighly Valuable ElementsTitanium halidesLeucoxeneFiltration
The invention provides a method for preparing coarse titanium tetrachloride. The method uses natural leucoxene as a raw material and metallurgical coke as a reducing agent to obtain the coarse titanium tetrachloride through the addition of chlorine for boiling chloridization, the cooling of a cyclone exhaust fan, atomization, the filtration of a cloth envelop collector and the absorption of a packed absorption tower. The invention has the advantages of expanding the sources used for producing the coarse titanium tetrachloride by using the natural leucoxene as a raw material, and removing slag and collecting titanium tetrachloride in a mixed furnace gas discharged from the top of a chlorination furnace. In the prior art, furnace slag produced during the production of titanium tetrachloride by using high titanium slag as a raw material is discharged from the bottom of the furnace, and the operation environment is severe and requires a gas mask for operation.
Owner:GUIYANG AL-MG DESIGN & RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com