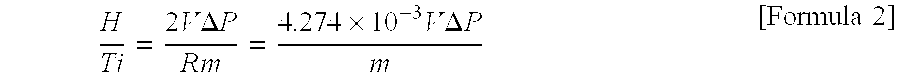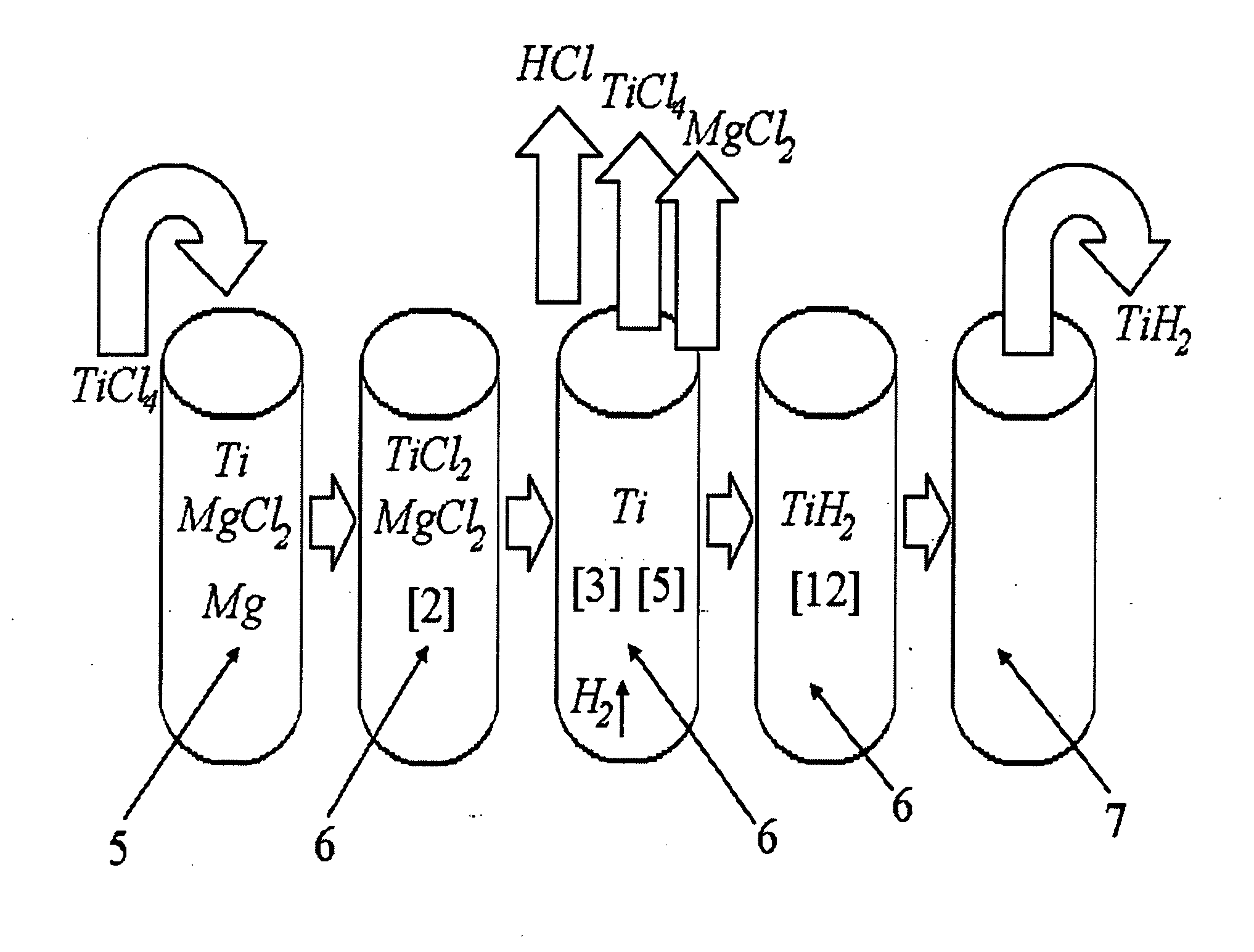Patents
Literature
121results about "Transition element hydrides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
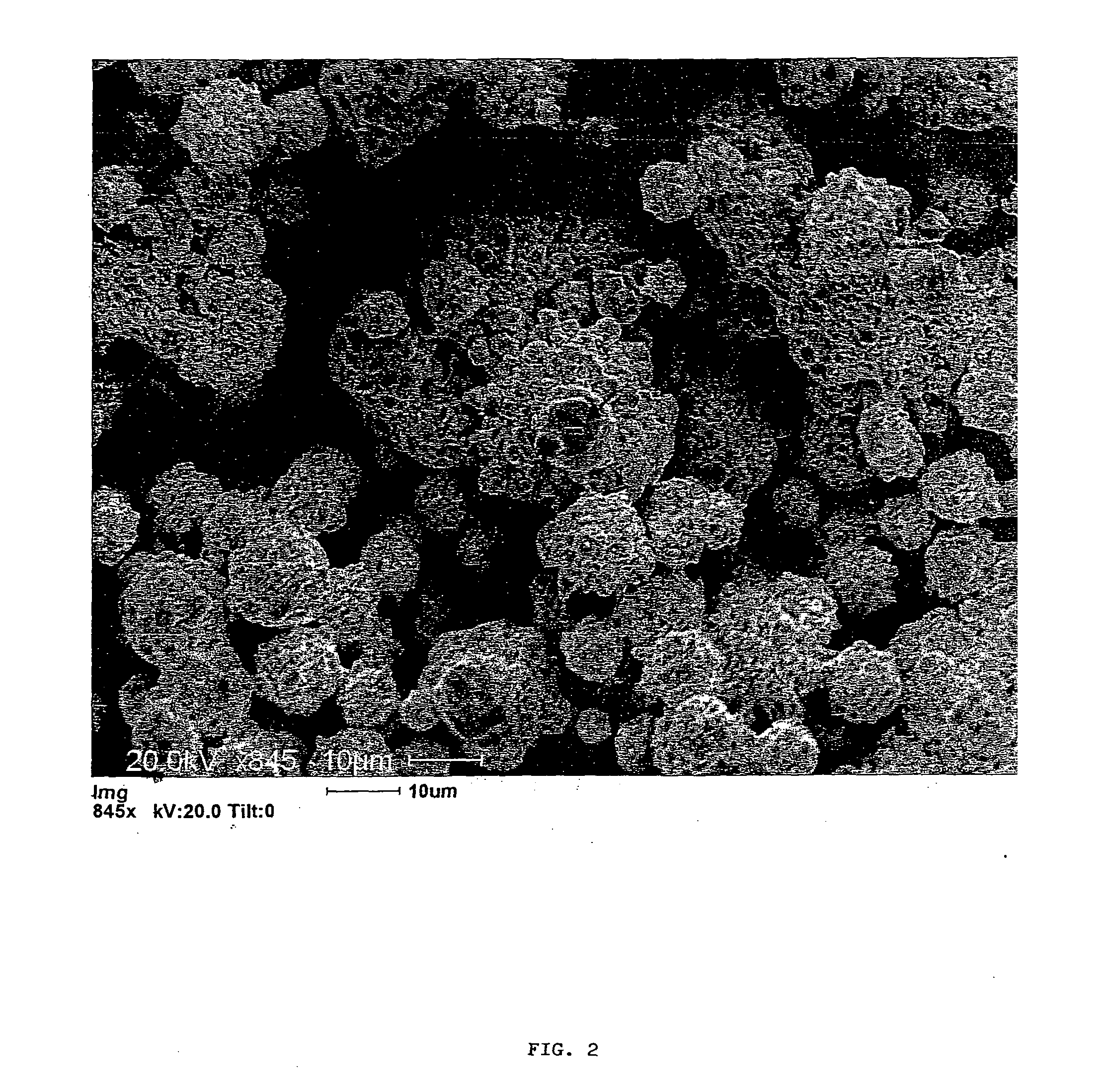
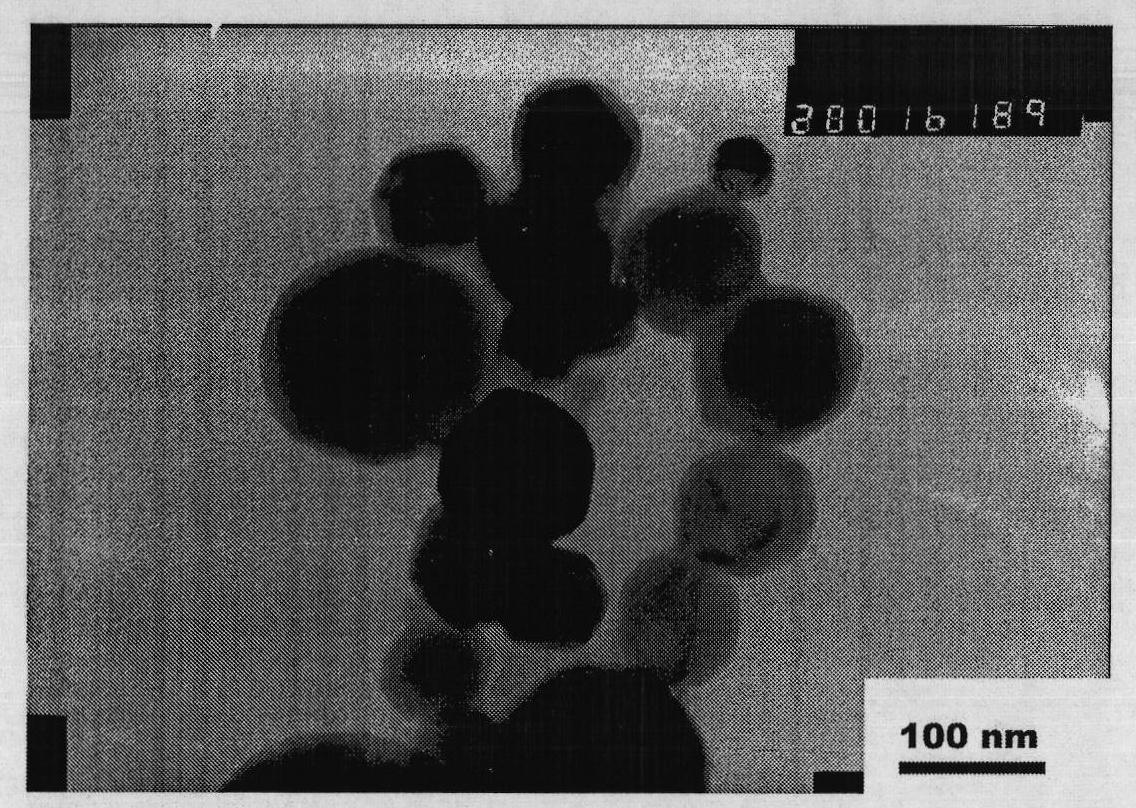
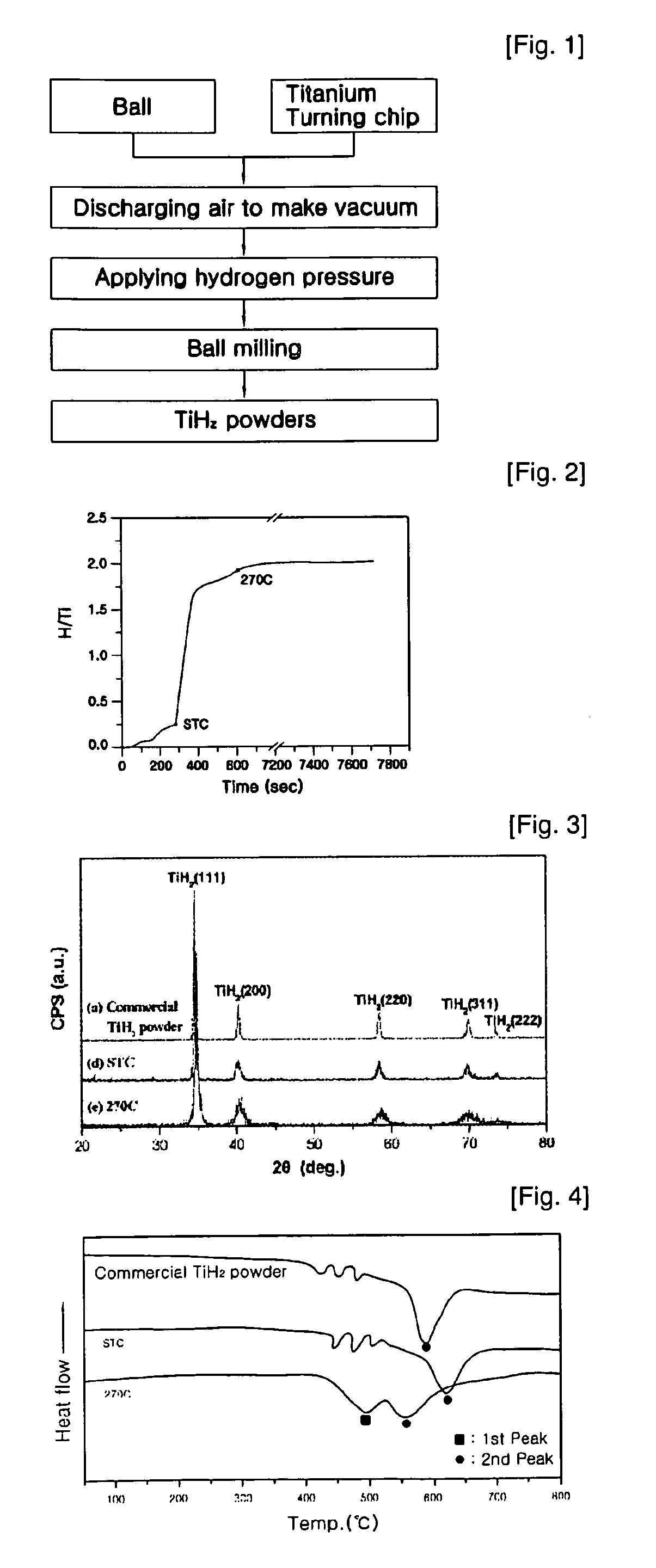
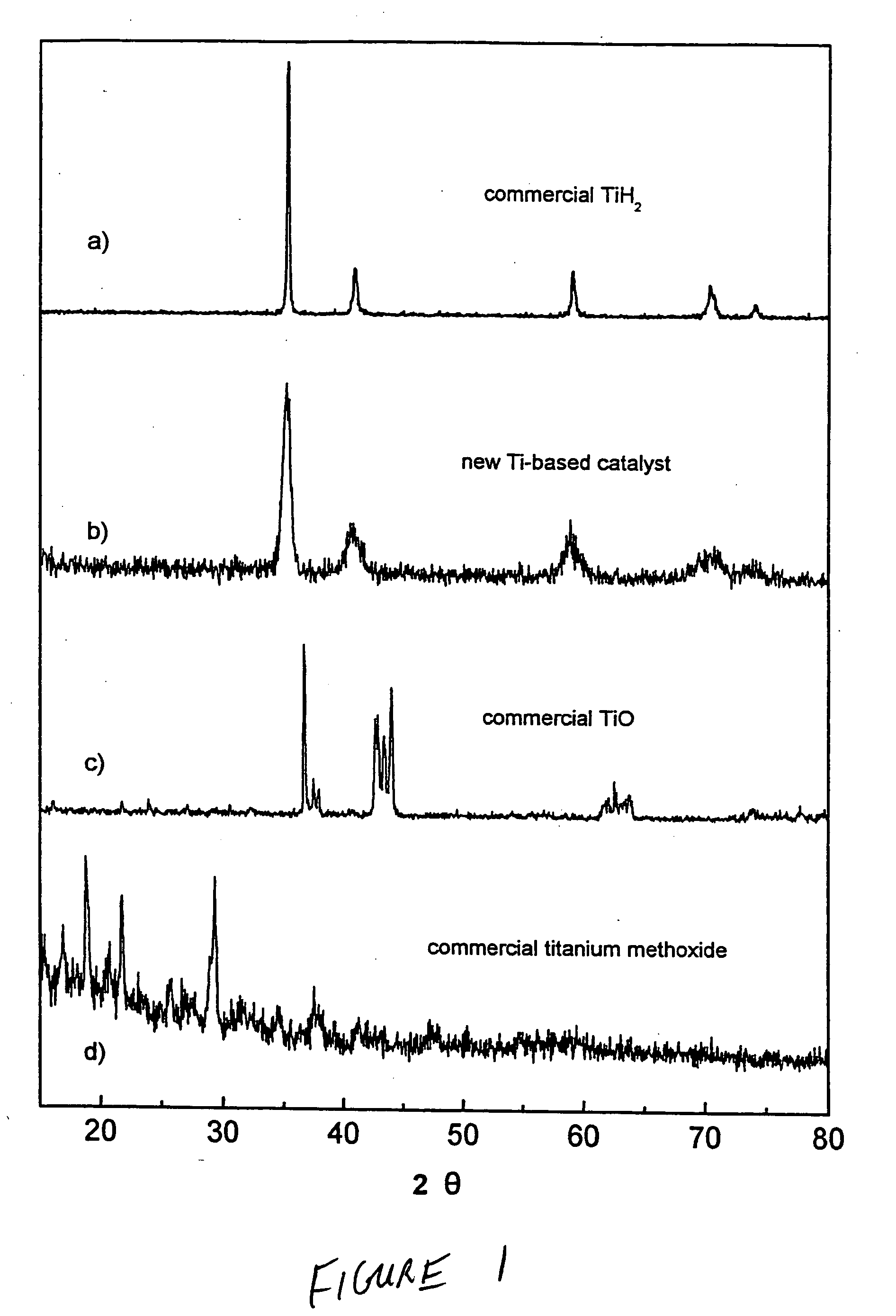
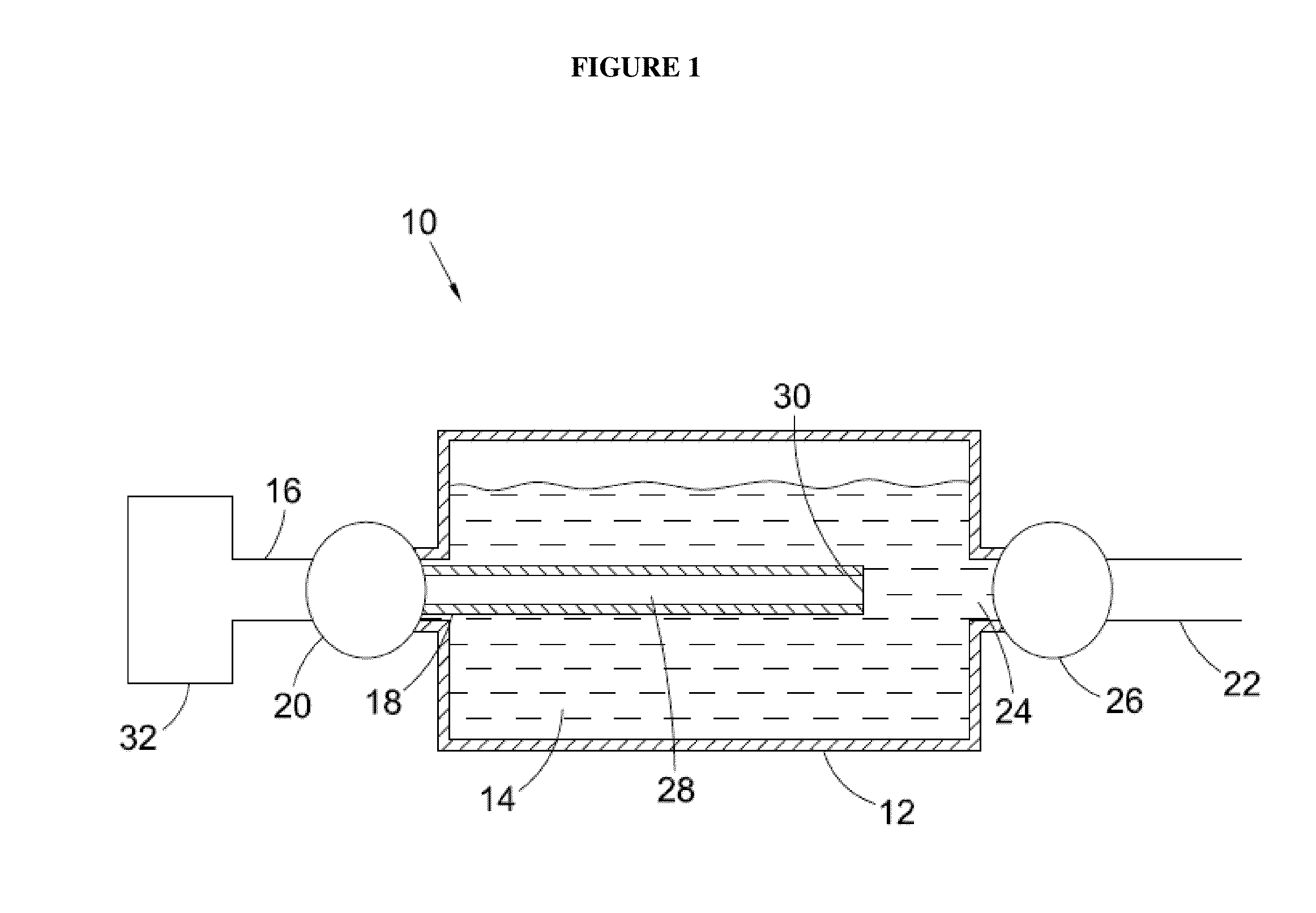
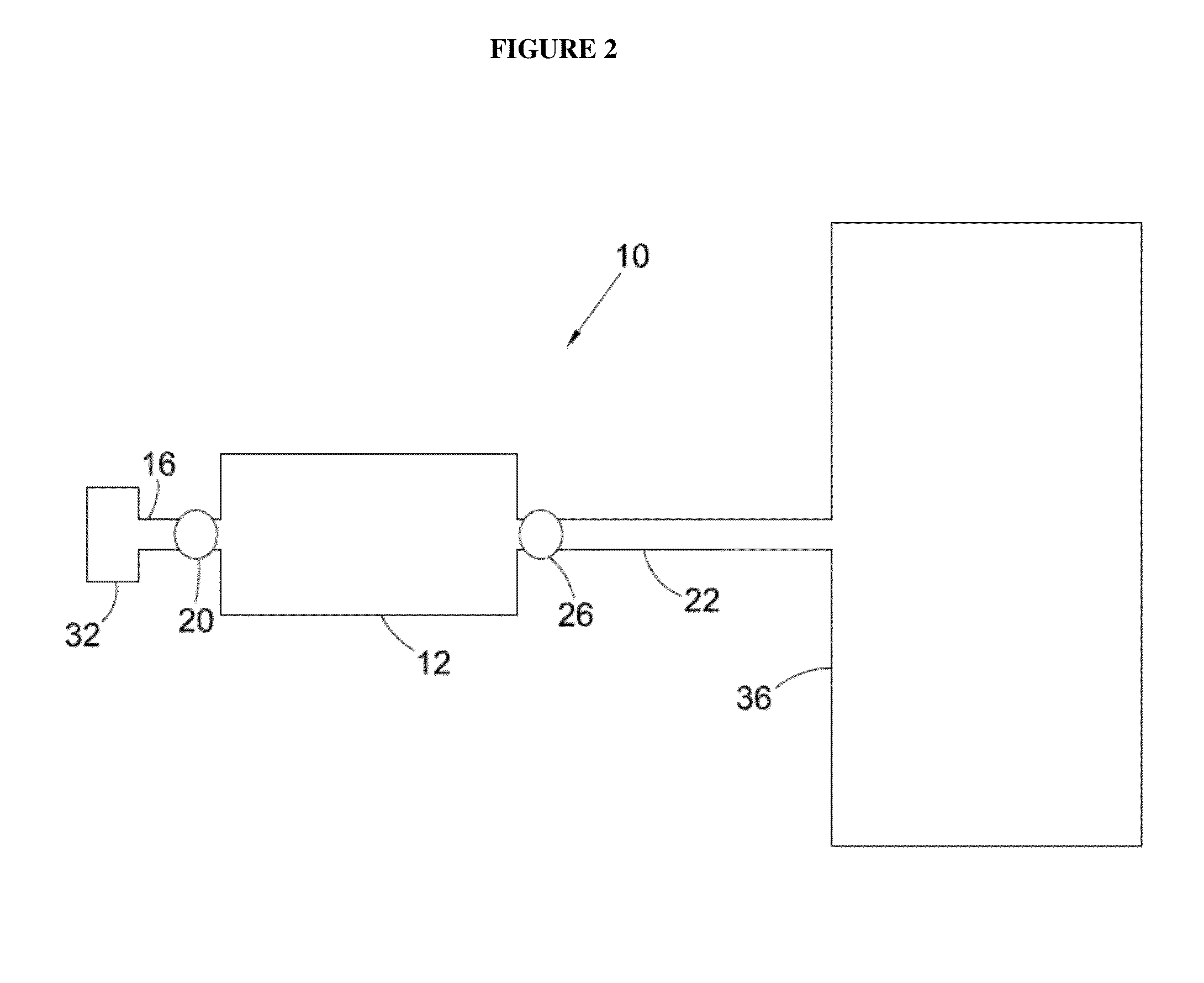
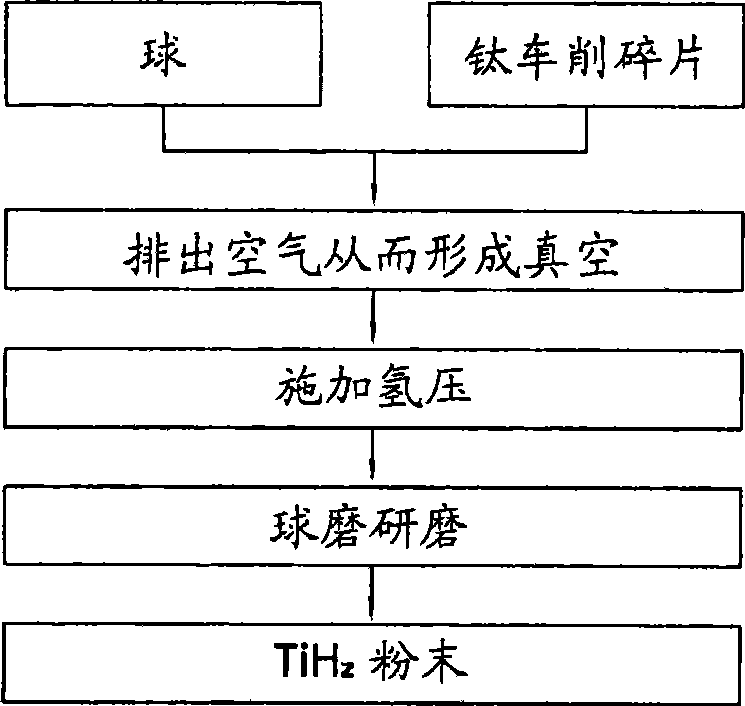
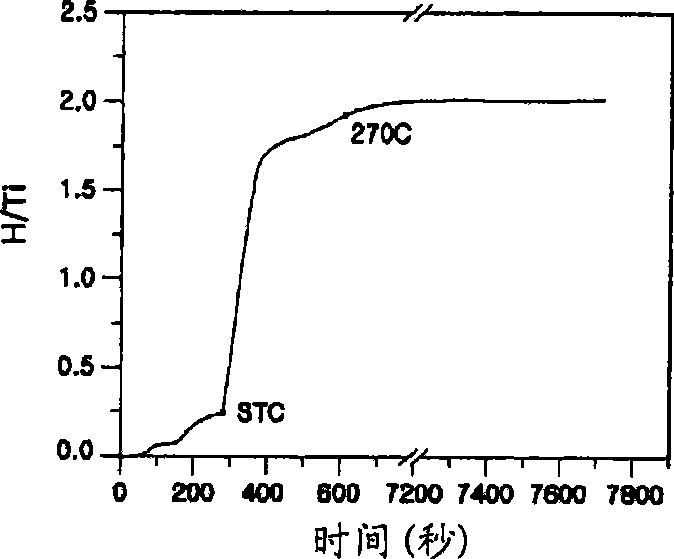
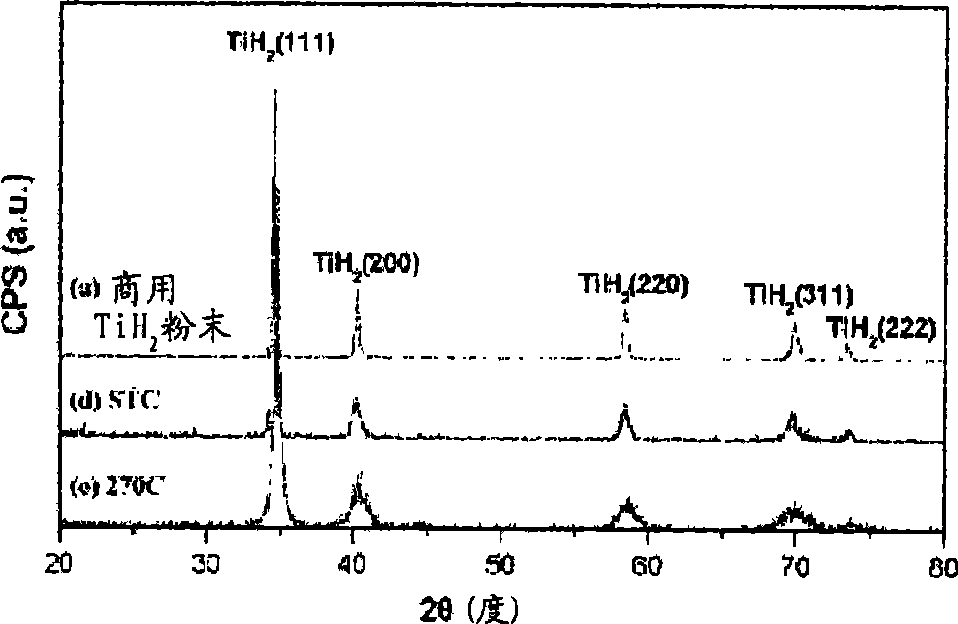
Manufacturing method for titanium hydride powders
InactiveUS20100061925A1Reduce energy costsReduce equipment costsTitanium compoundsTransition element hydridesProduction rateMaterials science
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method of manufacturing titanium hydride powder that is capable of manufacturing titanium hydride by using titanium scrap generated during machining as a raw material. Further, according to the method of manufacturing titanium hydride powder, since the titanium scrap is hydrogenated and changed into powder at the same time for a short time, it is possible to reduce the number of processes and manufacturing cost and to improve productivity. In order to achieve the object, according to an embodiment of the present invention, a method of manufacturing titanium hydride powder includes charging titanium scrap into a reaction container, removing air in the reaction container and supplying hydrogen gas to the reaction container, and performing ball milling.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
Method and apparatus for carrying out nickel and hydrogen exothermal reaction
InactiveUS20110005506A1Produce energyEasy to controlHydrogenExothermal chemical reaction heat productionHydrogenHydrogen atom
A method and apparatus for carrying out highly efficient exothermal reaction between nickel and hydrogen atoms in a tube, preferably, though not necessary, a metal tube filled by a nickel powder and heated to a high temperature, preferably, though not necessary, from 150 to 5000 C are herein disclosed. In the inventive apparatus, hydrogen is injected into the metal tube containing a highly pressurized nickel powder having a pressure, preferably though not necessarily, from 2 to 20 bars.
Owner:LEONARDO +1
Process for preparing titanium and titanium alloy from titanium hydride powder
The invention discloses a process for preparing a metallurgical powder product from titanium hydride powder preparedmade by hydrogenating sponge titanium instead of titanium powder. The process comprises the following steps of: firstly, hydrogenating sponge titanium, crushing and, rating and mixing brittle titanium hydride, and mixing the titanium hydride with an alloy element; and then, carryingout near-net shape pressing to finish dehydrogenation in a vacuum sintering process. In the process of directly forming the titanium hydride powder, because of the secondary crushing of the brittle titanium hydride powder, the pressed green density is higher than that obtainedan occasion when titanium or titanium alloy powder is used, and the titanium is prevented from being oxidized. In the sintering process, the density of a sintering blank can rapidly rise (to be higher than 99 percent) because of the decomposition of the titanium hydride. The method has the characteristics short process flows, high yield and product density, low cost and oxygen content and good performance.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
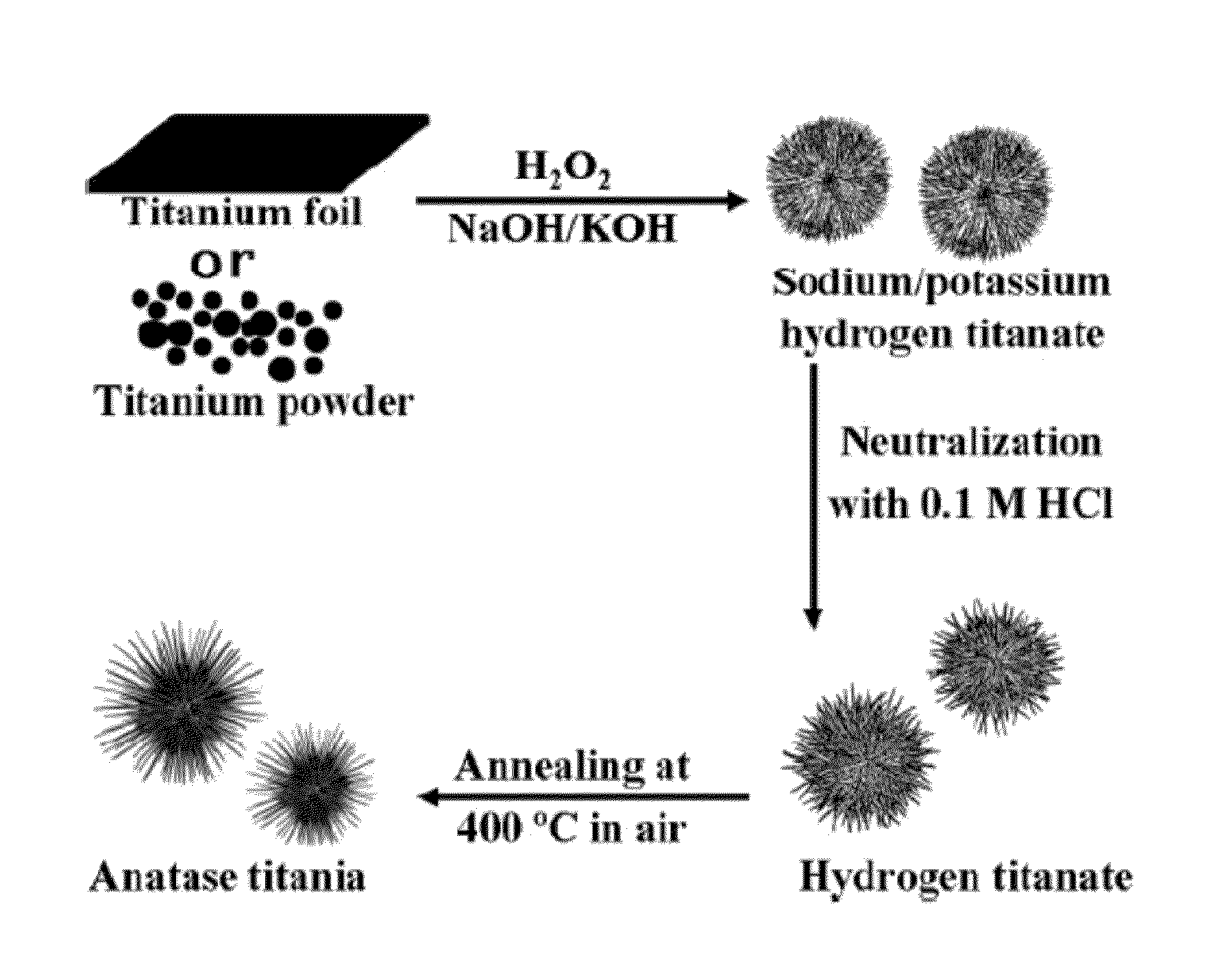
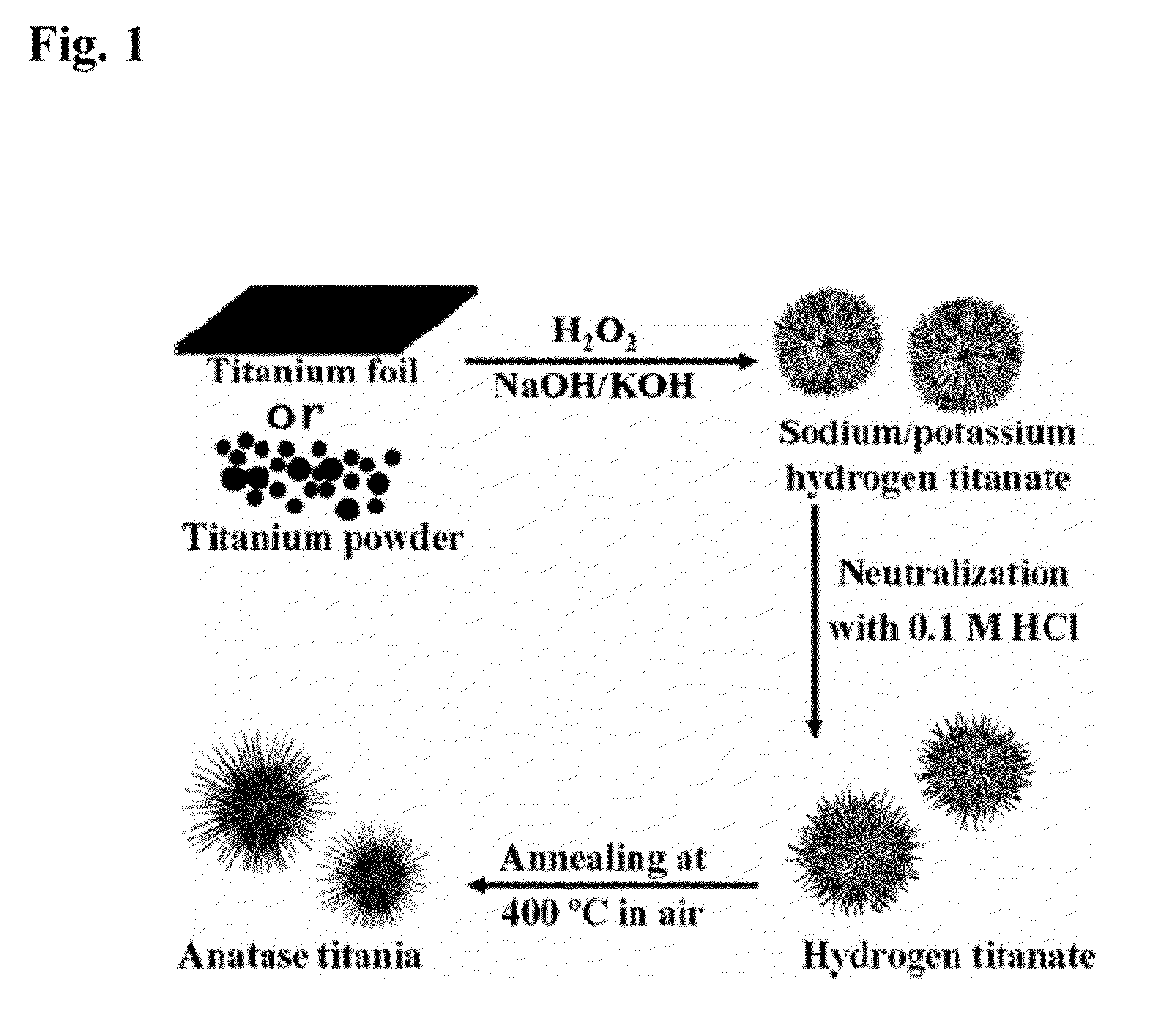
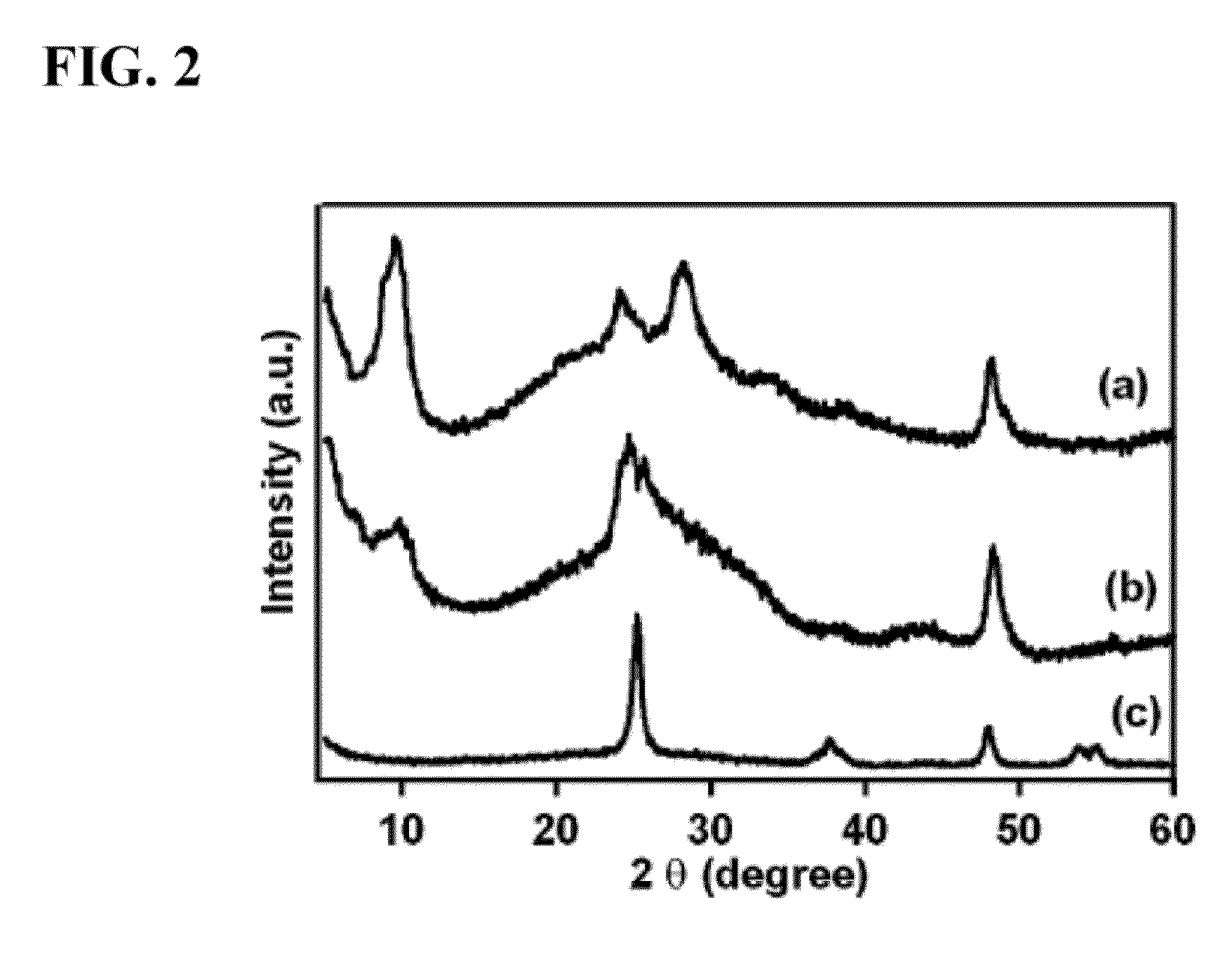
Titanate and titania nanostructures and nanostructure assemblies, and methods of making same
ActiveUS20130102458A1Improve scalabilityImprove photocatalytic performanceMaterial nanotechnologyHydrogenMicrometer scaleTitanium
The invention relates to nanomaterials and assemblies including, a micrometer-scale spherical aggregate comprising: a plurality of one-dimensional nanostructures comprising titanium and oxygen, wherein the one-dimensional nanostructures radiate from a hollow central core thereby forming a spherical aggregate.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
New type of catalytic materials based on active metal-hydrogen-electronegative element complexes involving hydrogen transfer
ActiveUS20050002856A1Enhance kinetics of hydrolysisHydrogen productionChemical recyclingAlcoholDesorption
The present invention relates to a hydrogen storage composition prepared in accordance with a method comprising: (a) combining (i) a metalliferous material selected from the group consisting of: (A) metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or an inhomogeneous combination of at least two of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or (B) a hydride of any of: a metal or a metalloid, or alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or an inhomogeneous combination of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, with ii) a liquid consisting essentially of any of: water, at least one alcohol, or a mixture of water and at least one alcohol, to form a first intermediate; and (b) milling the first intermediate for form an hydrogen transfer facilitator; (c) combining the hydrogen transfer facilitator with a second metalliferous material selected from the group consisting of: (A) a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or inhomogeneous combination of at least two of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or (B) a hydride of any of: a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or inhomogeneous combination of at least two of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, such combining effecting sufficient contact between the hydrogen transfer facilitator and the second metalliferous material so that the hydrogen transfer facilitator is configured to effect absorption or desorption of hydrogen by the second metalliferous material.
Owner:ZALUSKA ALICJA +1
Imide/amide hydrogen storage materials and methods
InactiveUS6967012B2Alkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesNitrogen compoundsImideAmide hydrogen
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Production of substantially spherical metal powers
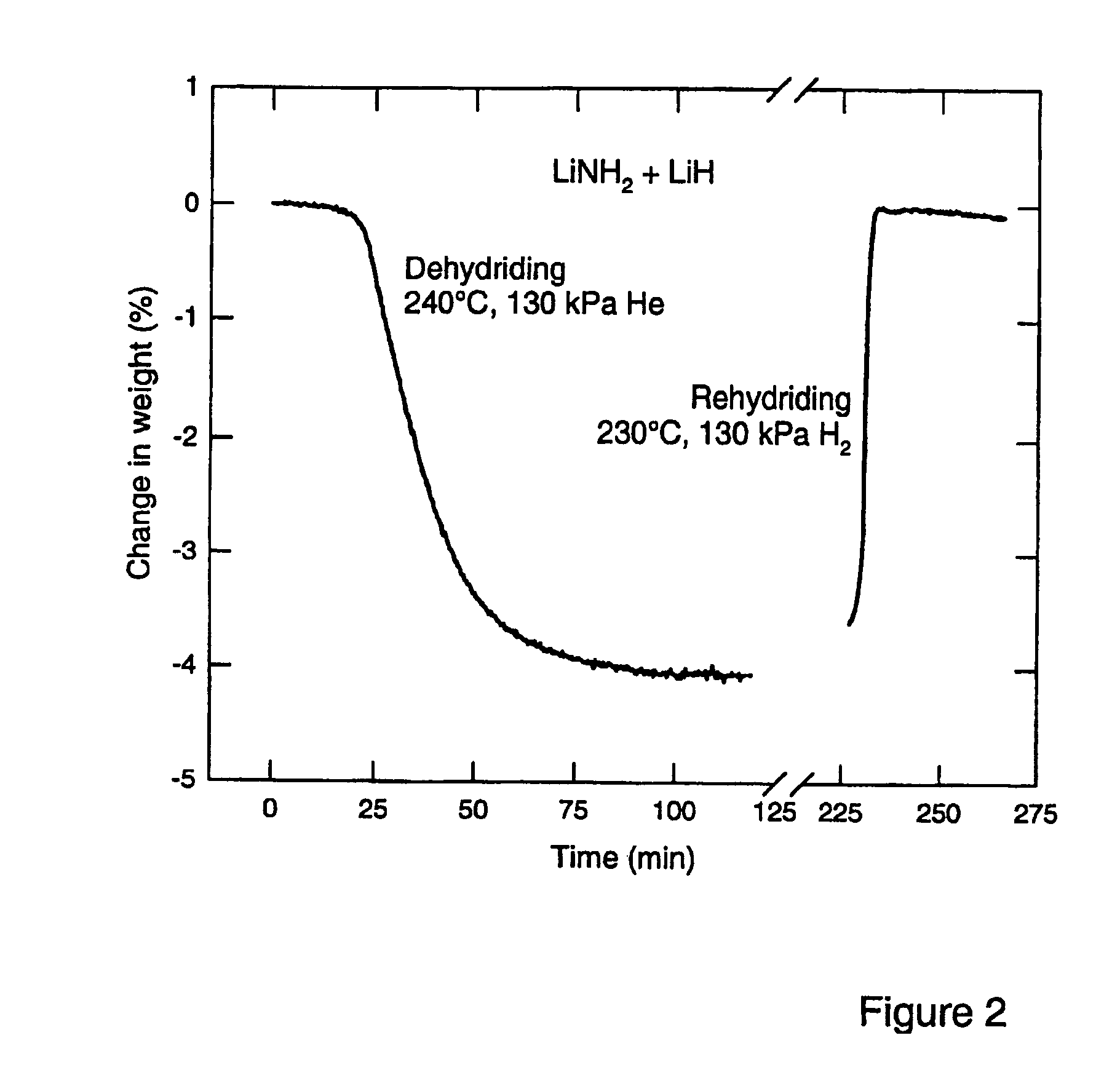
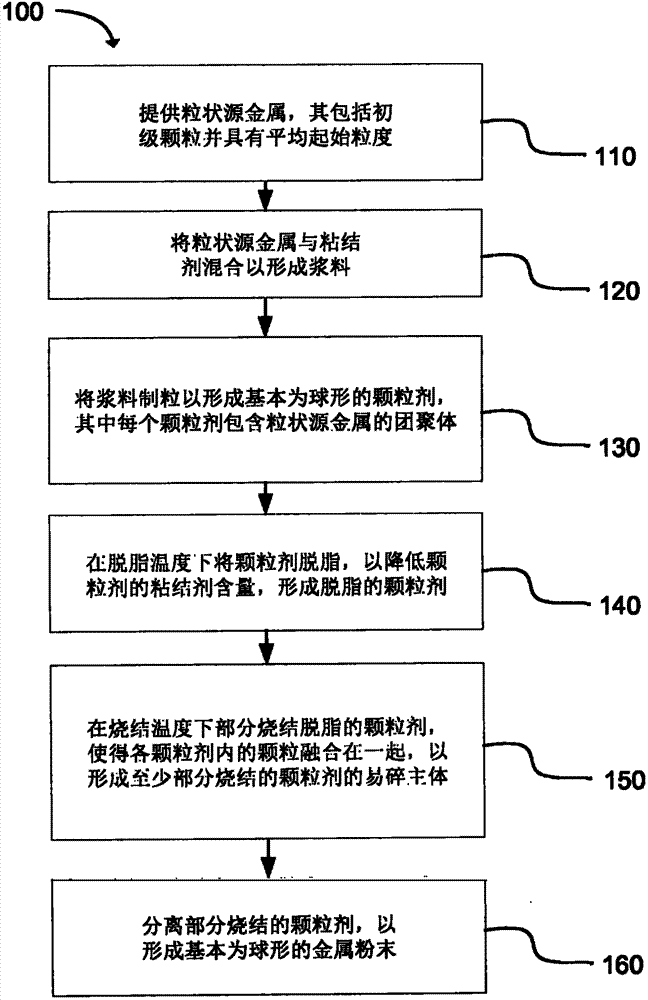
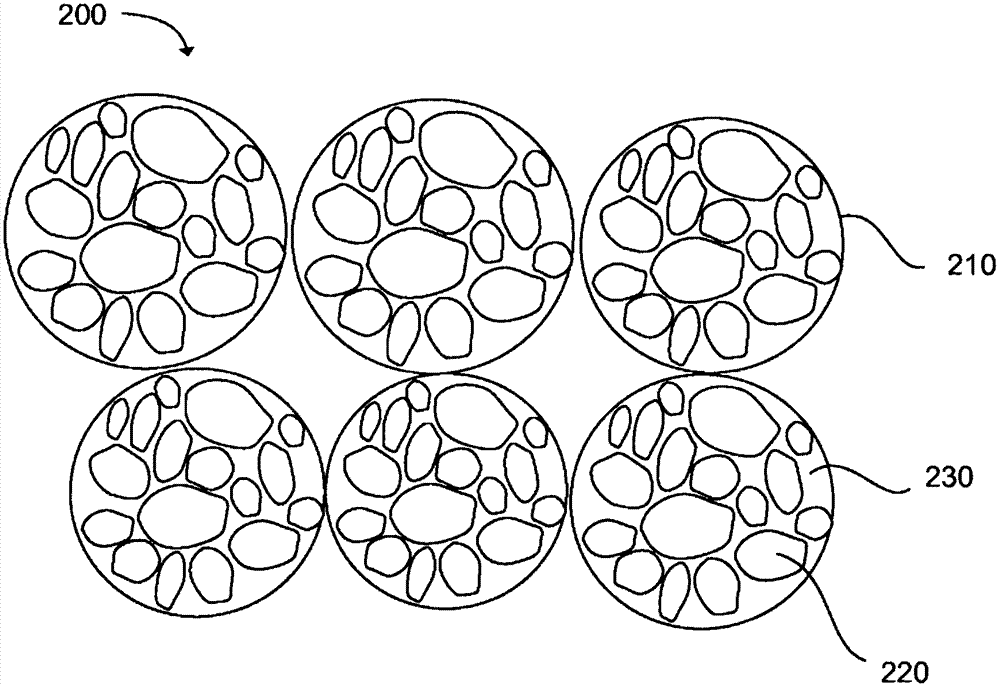
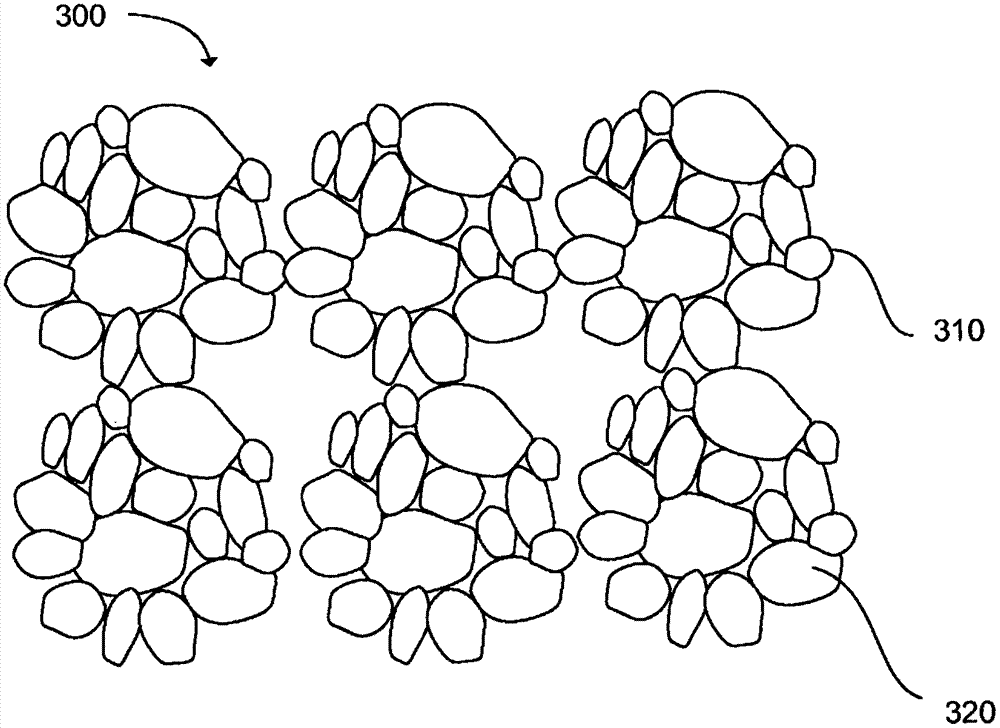
A method (100) for producing a substantially spherical metal powder is described. A particulate source metal includes a primary particulate and has an average starting particle size (110). The particulate source metal is optionally ball milled and mixed with a binder in a solvent to form a slurry (120). The slurry is granulated to form substantially spherical granules (130), wherein each granule comprises an agglomeration of particulate source metal in the binder. The granules are debinded (140) at a debinding temperature to remove the binder from the granules forming debinded granules. The debinded granules are at least partially sintered (150) at a sintering temperature such that particles within each granule fuse together to form partially or fully sintered solid granules. The granules can then be optionally recovered to form a substantially spherical metal powder (160).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Method of Manufacturing Pure Titanium Hydride Powder and Alloyed Titanium Hydride Powders By Combined Hydrogen-Magnesium Reduction of Metal Halides
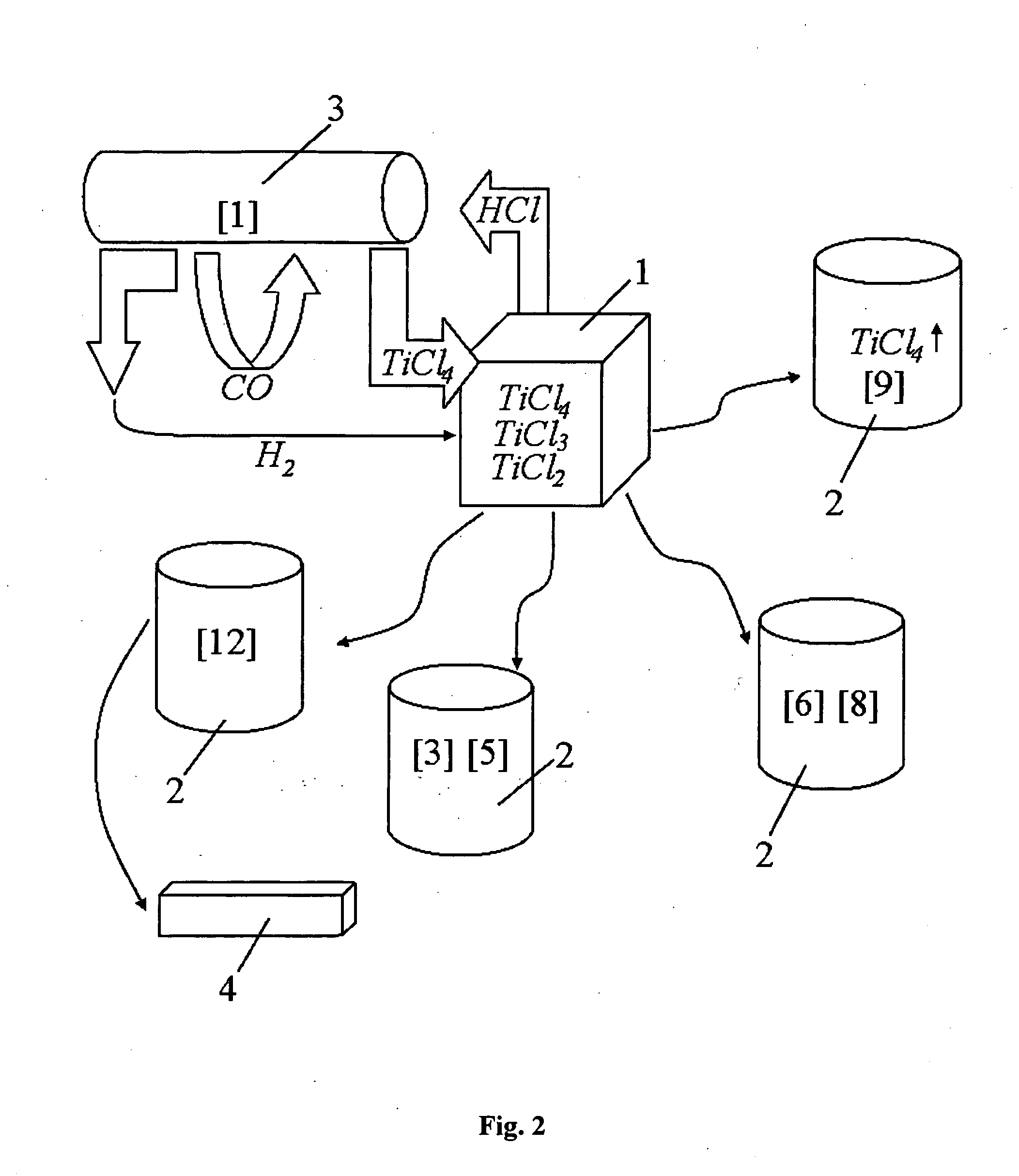
ActiveUS20130315773A1Reduce oxideFacilitated DiffusionMultiple metal hydridesTransition element hydridesTitanium chloridePowder mixture
The invention relates to energy-saving manufacturing of purified hydrogenated titanium powders or alloying titanium hydride powders, by metallo-thermic reduction of titanium chlorides, including their hydrogenation, vacuum separation of titanium hydride sponge block from magnesium and magnesium chlorides, followed by crushing, grinding, and sintering of said block without need for hydrometallurgical treatment of the produced powders.Methods disclosed contain embodiments of processes for manufacturing high-purity powders and their use in manufacturing near-net shape titanium and titanium-alloy articles by sintering titanium hydride and alloyed titanium hydride powders produced from combined hydrogen-magnesium reduction of titanium chlorides, halides and hydrides of other metals. Additional titanium hydride powder introduced with titanium tetrachloride beneficially affects the kinetics of magnesium-thermic reduction due to formation of the additionally-emitted atomic hydrogen, which helps to reduce presence of oxides and so cleans inter-particle interfaces of the product and enhances diffusion between all of components of the powder mixture.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS PRODS
Method of manufacturing pure titanium hydride powder and alloyed titanium hydride powders by combined hydrogen-magnesium reduction of metal halides
ActiveUS9067264B2Cost-effectiveAvoid pollutionMultiple metal hydridesTransition element hydridesTitanium chloridePowder mixture
The invention relates to energy-saving manufacturing of purified hydrogenated titanium powders or alloying titanium hydride powders, by metallo-thermic reduction of titanium chlorides, including their hydrogenation, vacuum separation of titanium hydride sponge block from magnesium and magnesium chlorides, followed by crushing, grinding, and sintering of said block without need for any hydro-metallurgical treatment of the produced powders. Methods disclosed contain embodiments of processes for manufacturing high purity high-purity powders and their use in manufacturing near-net shape titanium and titanium-alloy articles by sintering titanium hydride and alloyed titanium hydride powders produced from combined hydrogen-magnesium reduction of titanium chlorides, halides and hydrides of other metals. Additional titanium hydride powder introduced with titanium tetrachloride beneficially affects the kinetics of magnesium-thermic reduction due to formation of additionally-emitted atomic hydrogen, which helps to reduce presence of oxides, and so cleans inter-particle interfaces of the product and enhances diffusion between all components of the powder mixture.
Owner:ADVANCED MATERIALS PRODS
Novel Metal Hydrides And Their Use In Hydrogen Storage Applications
ActiveUS20130181162A1Reducing pressure of hydrogenReduce pressureReversible hydrogen uptakeOther chemical processesChemistryHydride
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
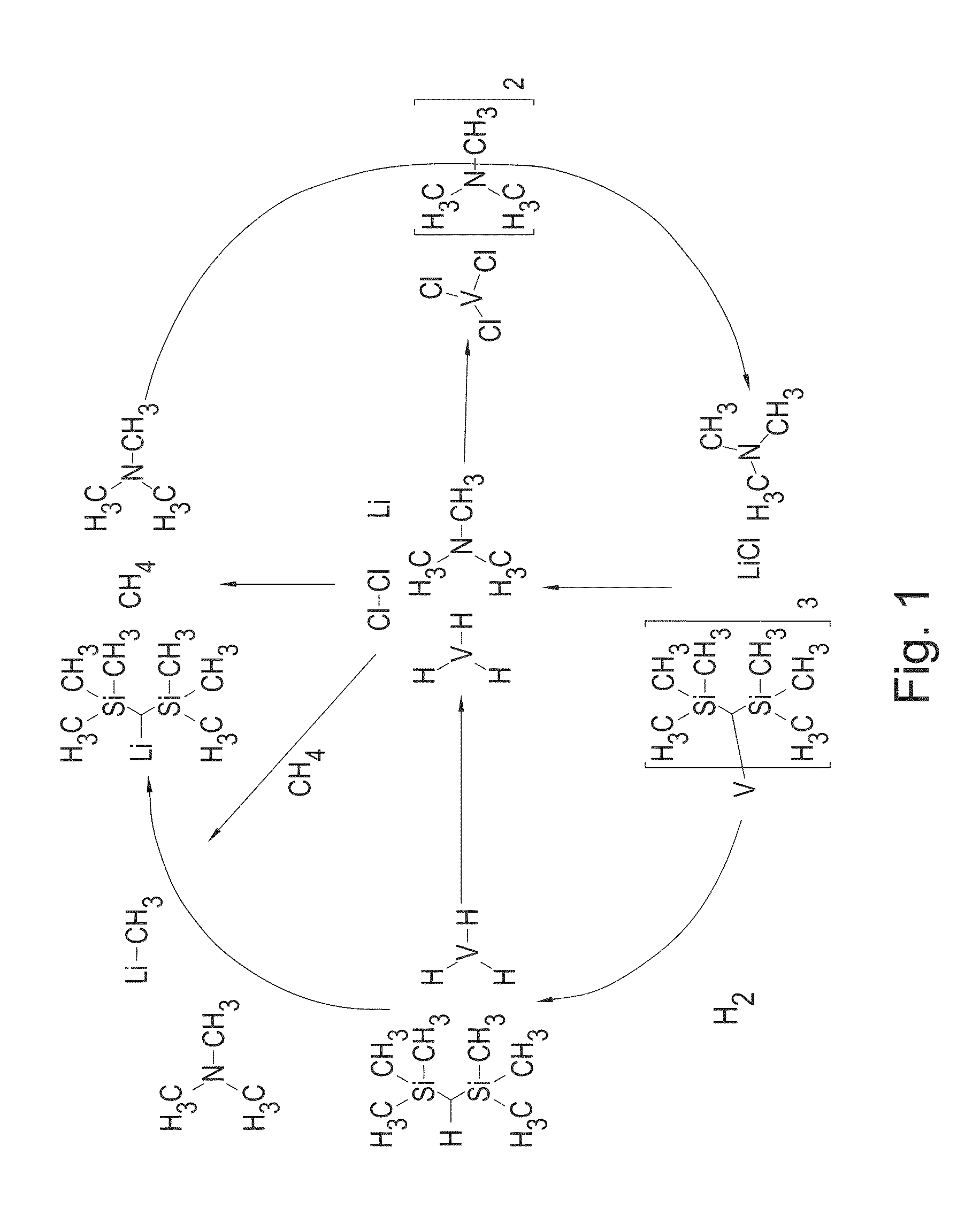
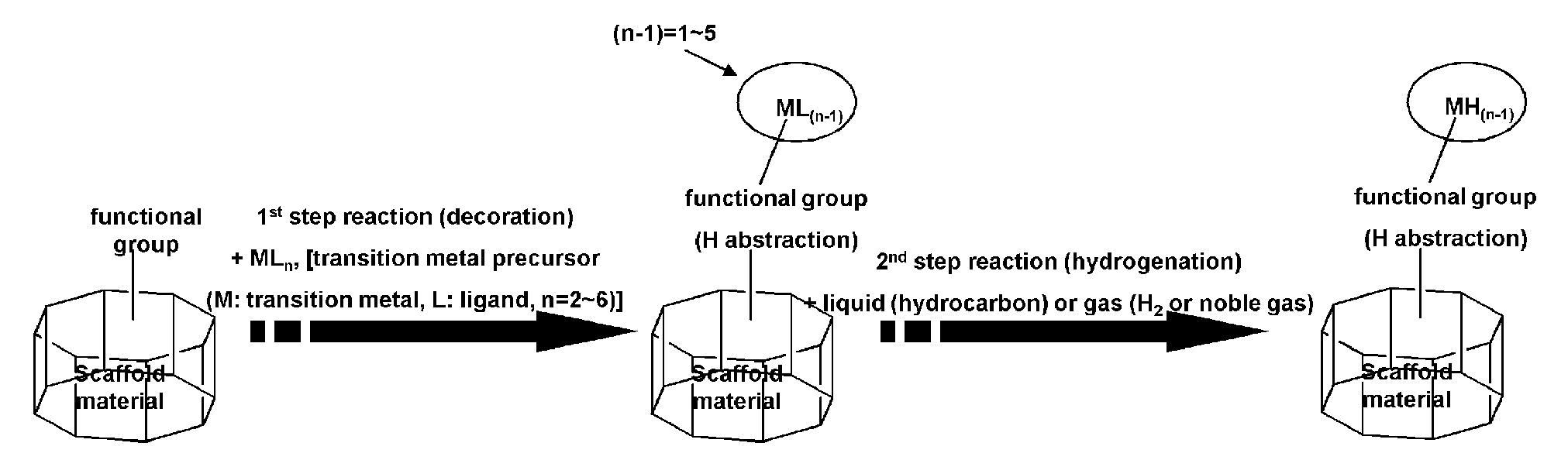
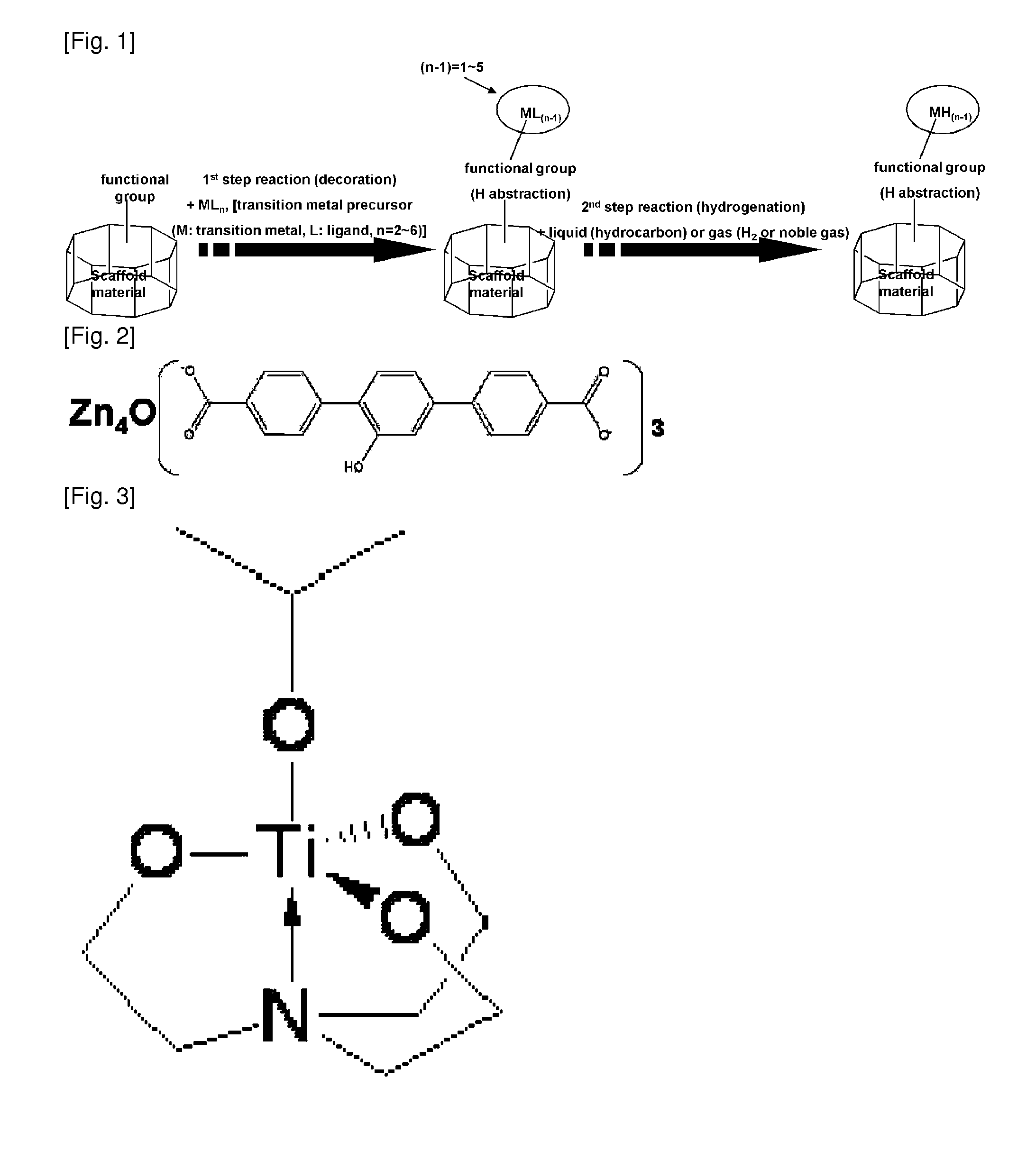
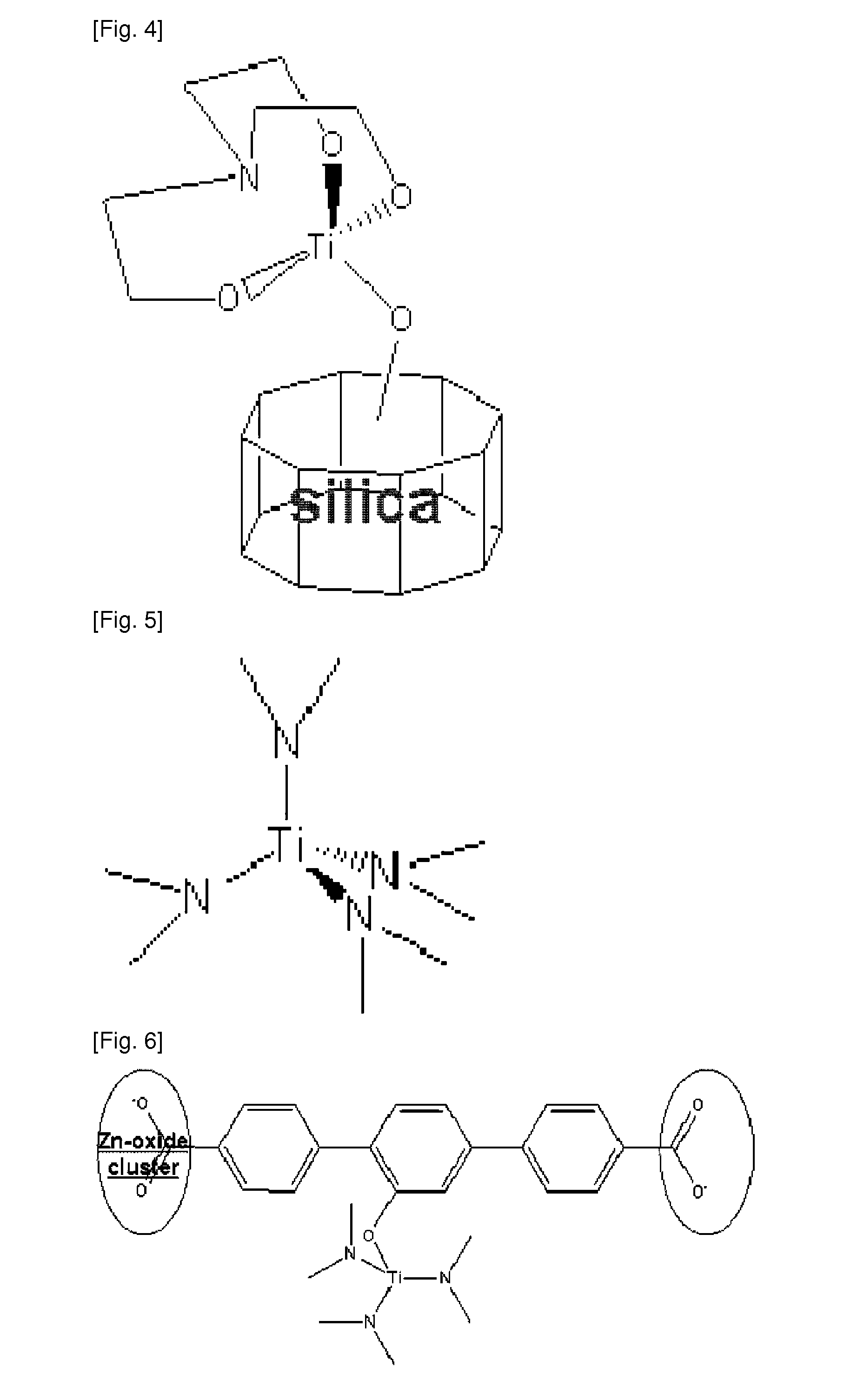
Scaffold Materials-Transition Metal Hydride Complexes, Intermediates Therefor and Method for Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20110201834A1Avoid disintegrationLow pour pointSilicon organic compoundsMaterial nanotechnologyAdsorption desorptionPolymerization catalysts
The present invention relates to substances which can be applied to the technical fields of gas storages, polymerization catalysts and optical isomers, their intermediates, and processes for preparing the same, which is characterized in that 1) possible disintegration of structure of the scaffold material (SM) is impeded, and 2) they are prepared by a simple manufacturing system as compared to the substances conventionally suggested in the application field. Specifically, it relates to scaffold material-transition metal hydride complexes comprised of scaffold material (SM) and transition metal hydride (M1H(n-1)) which is chemically bonded to the functional groups formed on the scaffold material, SM-transition metal halide complex and SM-transition metal ligand complex as the precursors, and a process for preparing the same. The SM-transition metal hydride complex according to the present invention is a substance for hydrogen storage which adsorbs hydrogen via Kubas adsorption. The complex according to the invention can store high capacity of hydrogen with safety and reversibility, while disintegration of its structure does not occur even with repeated adsorption-desorption of hydrogen.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
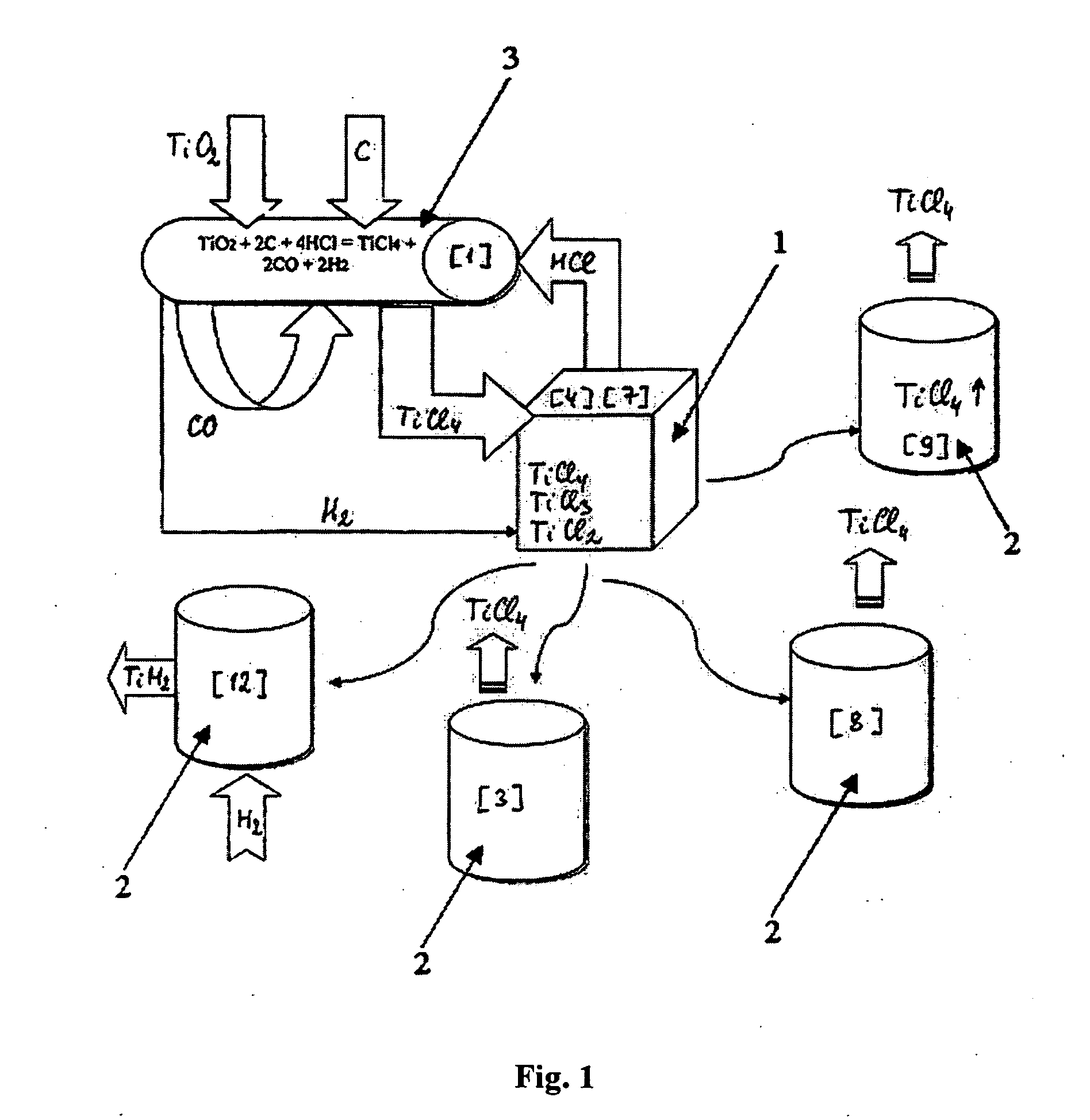
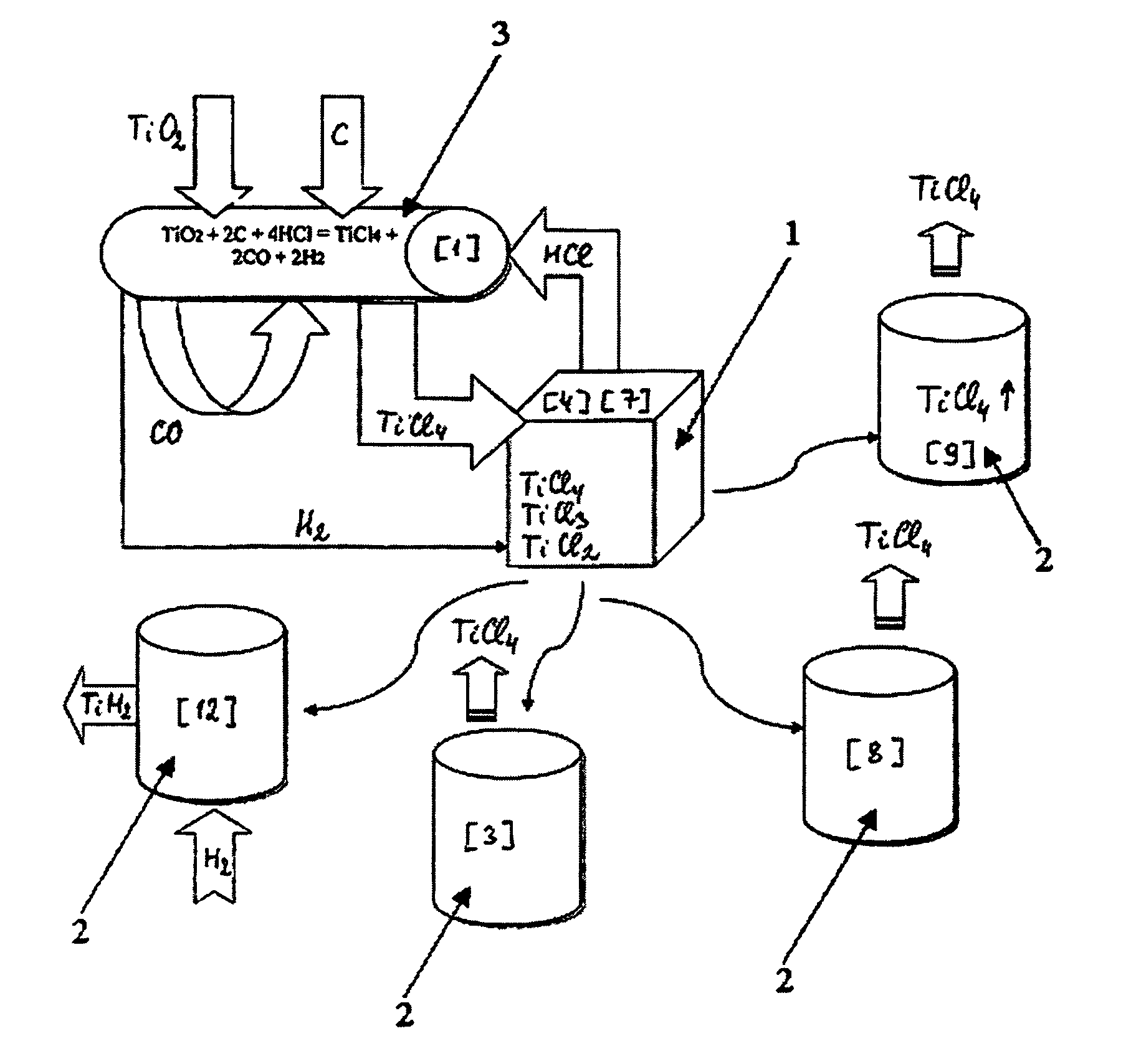
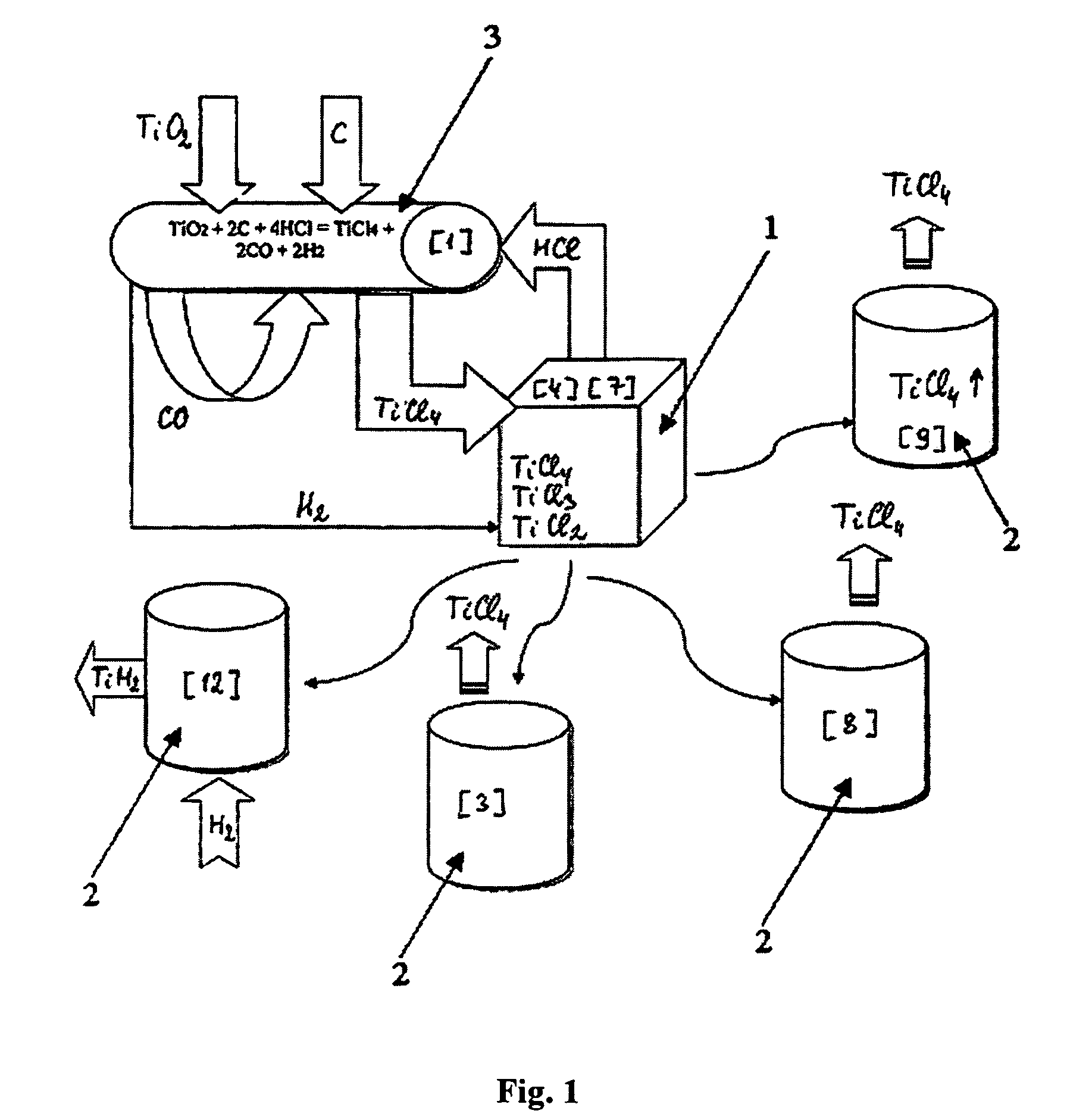
Continuous and semi-continuous process of manufacturing titanium hydride using titanium chlorides of different valency
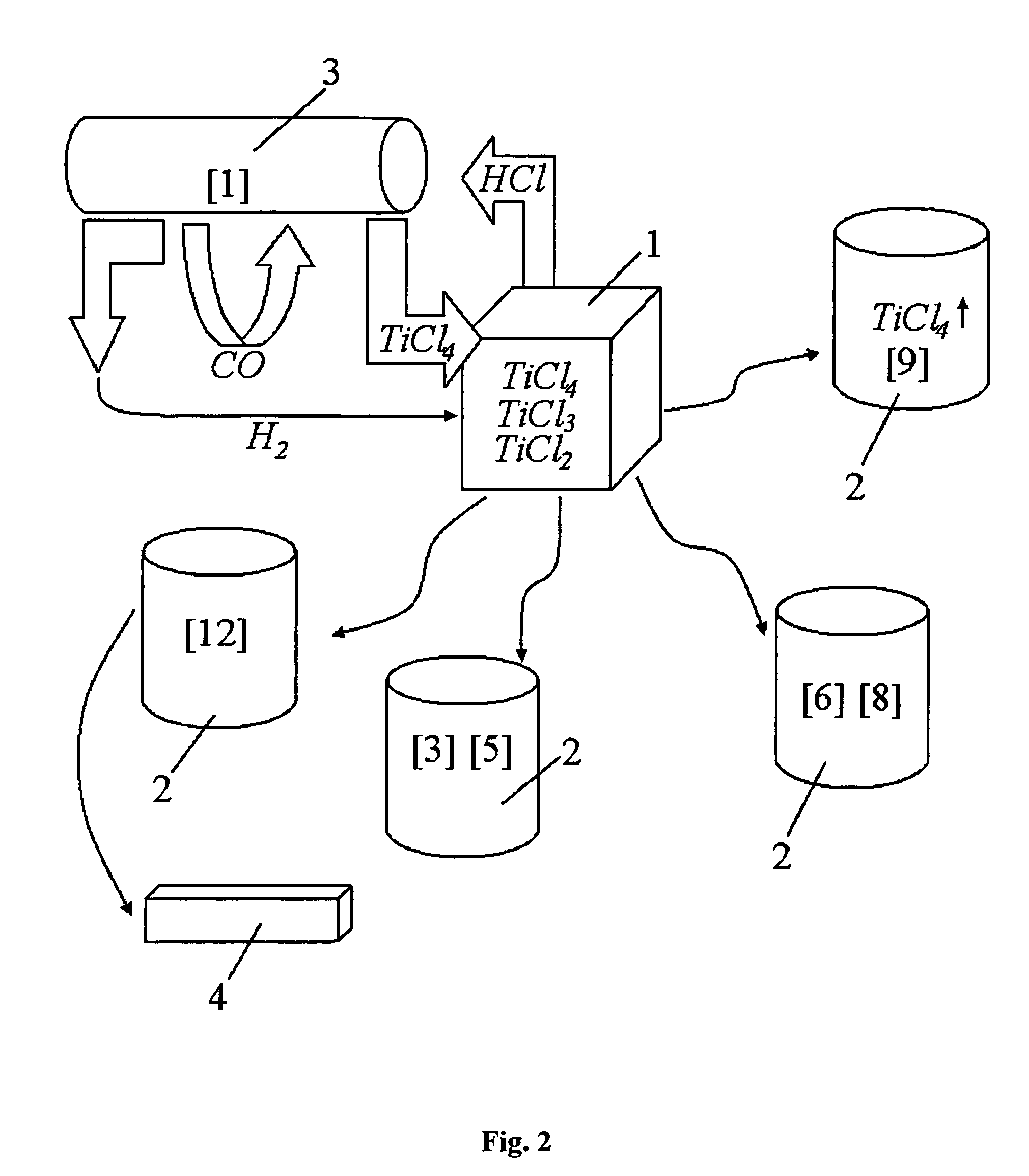
InactiveUS20110171116A1Reduce manufacturing costCost-effective and highly-productive manufactureTransition element hydridesTitanium chlorideOxygen
The invention relates to the manufacture of titanium hydride powder using continuous or semi-continuous process, and using titanium slag or synthetic rutile as raw materials, while hydrogen, titanium tetrachloride, titanium trichloride, titanium dichloride, and hydrogen chloride are participate as intermediate reaction products. The continuous comprises: (a) reduction of TiCl4 to low titanium chlorides followed by cooling a mixture, (b) separating of residual TiCl4 from solid low chlorides by heating the mixture in argon or vacuum up to 150° C. followed by removing the titanium tetrachloride from the mixture, (c) dissociation of TiCl3 to TiCl2 at 450° C. in vacuum followed by removal of gaseous titanium tetrachloride from the reaction zone, condensation to the liquid, and returning back into the reaction retort, (d) dissociation of TiCl2 in vacuum at 750-850° C. to manufacture fine powder of metallic titanium and titanium tetrachloride, whereby hydrogen heated up to 1000° C. is used to accelerate this reaction, and (e) saturation of the fine titanium powder by hydrogen at 400-640° C. to manufacture final product of titanium hydride powder which is free of oxygen or nitrogen. The semi-continuous process includes the Kroll's process as the very first step.
Owner:ADMA PRODS
Preparation method of rare earth hydride nanoparticle
The invention relates to a preparation method of rare earth hydride nanoparticles, which belongs to the technical field of nano material preparation. The rare earth hydride is an important functional material, and can be widely applied in hydrogen storage batteries, optical devices, hydrogen sensors, pressure actuators and other fields. However, the rare earth hydride can not be prepared easily. In the preparation method of the rare earth hydride nanoparticles with related raw materials, one of such rare elements as lanthanum, praseodymium, neodymium, terbium and dysprosium is adopted as an anode, metal tungsten is adopted as a cathode, the preparation is carried out under the hydrogen and argon mixed atmosphere (wherein the ratio of the hydrogen is 20-80 percent by volume) with the total pressure being 1 atmosphere, the arc current of 100-200A, the arc voltage of10-40V and the arcing time of 0.5-2 hour(s) are selected. The particle sizes of the rare earth hydride nanoparticles provided by the invention are uniform and are less than 100nm. The adjustment of the average particle size of the produced rare earth hydride nanoparticles can be realized through adjusting process parameters for the same rare element.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
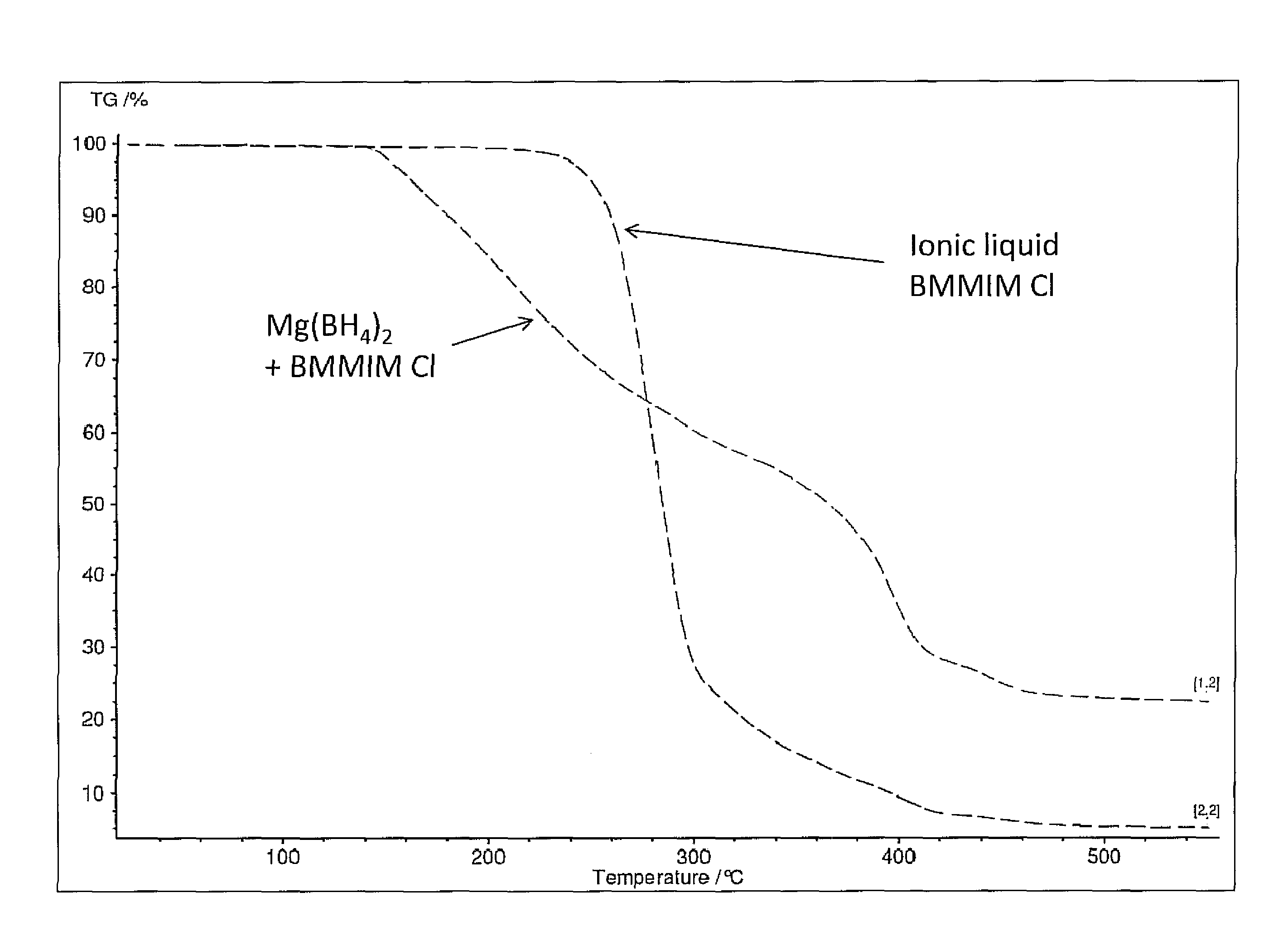
Hydrogen release from complex metal hydrides by solvation in ionic liquids
InactiveUS8771635B2Organic chemistryAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesComplex metal hydrideSolvation
A hydrogen release material includes a complex metal hydride and an ionic liquid wherein the hydrogen release material has a lower hydrogen release temperature in comparison to the complex metal hydride alone. Also disclosed is a process of releasing hydrogen from a storage material including the steps of: providing a complex metal hydride; combining the metal hydride with an ionic liquid in a desired amount forming a mixture; and heating the mixture to a temperature releasing hydrogen wherein the temperature is lower in comparison to the complex metal hydride alone.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
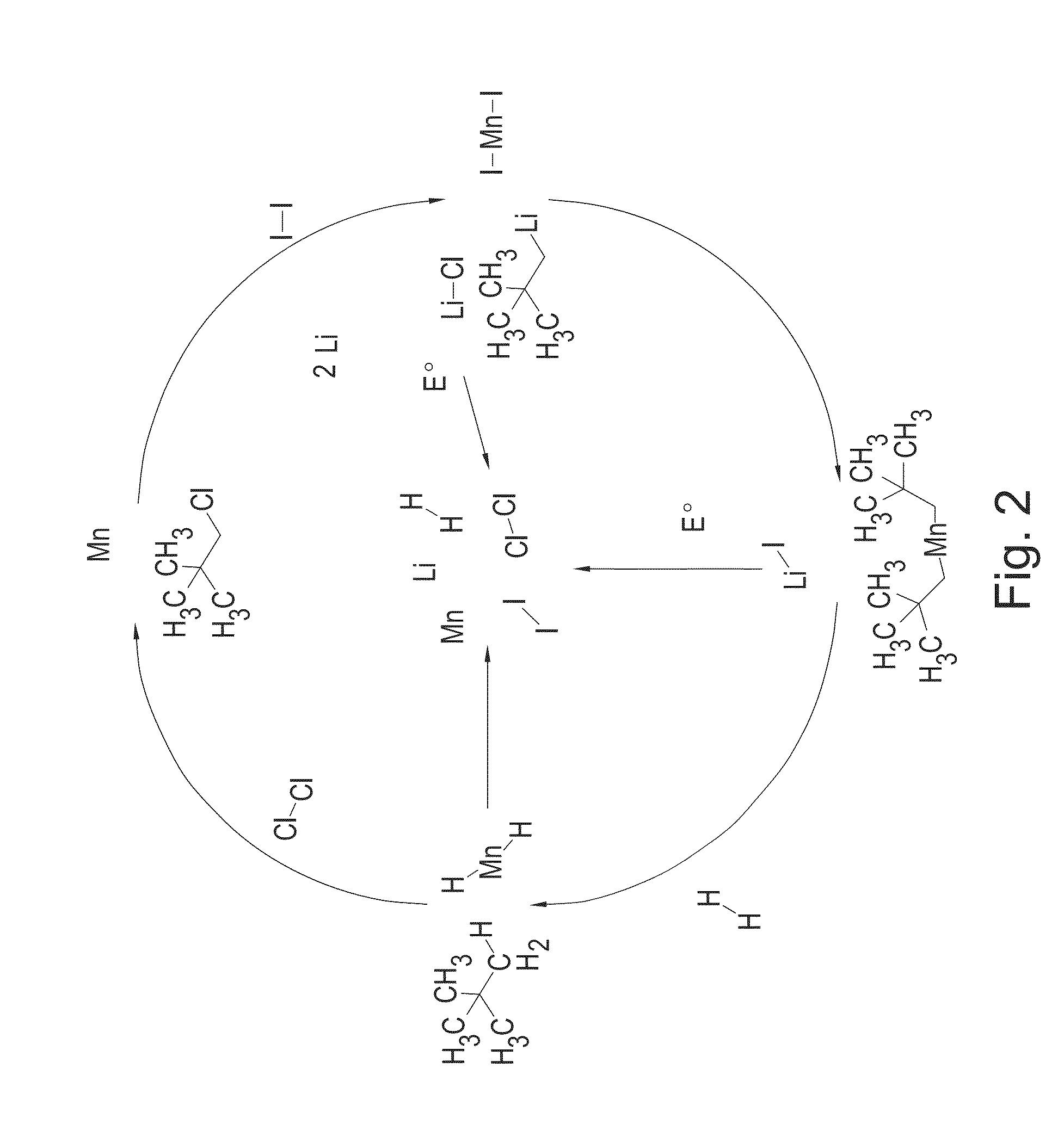
Synthesis and hydrogen storage properties of novel mangenese hydrides
ActiveUS20140370406A1High yieldHigh purityReversible hydrogen uptakeOther chemical processesManganeseHydride
This disclosure relates to novel manganese hydrides, processes for their preparation, and their use in hydrogen storage applications. The disclosure also relates to processes for preparing manganese dialkyl compounds having high purity, and their use in the preparation of manganese hydrides having enhance hydrogen storage capacity.
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Magnesium base hydride composite system for hydrolysis hydrogen production and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101811667ASimple processEase of industrial mass productionAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesHydrogen productionCombustionGraphite
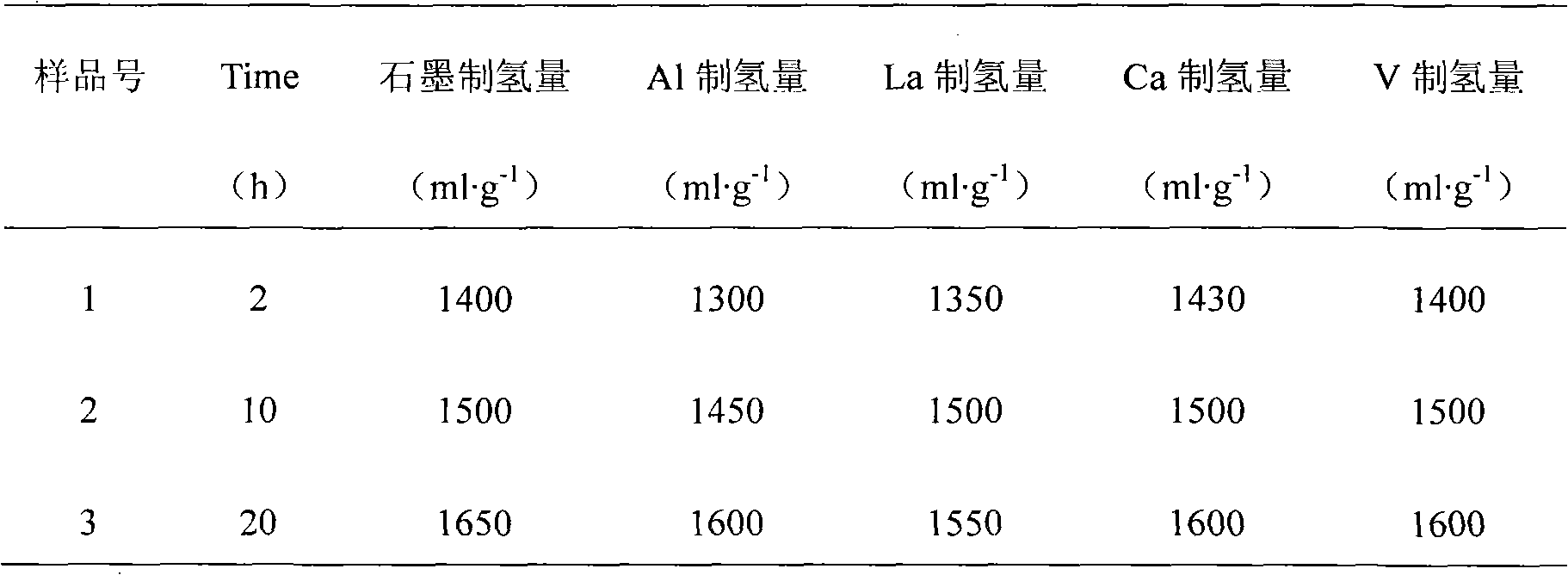
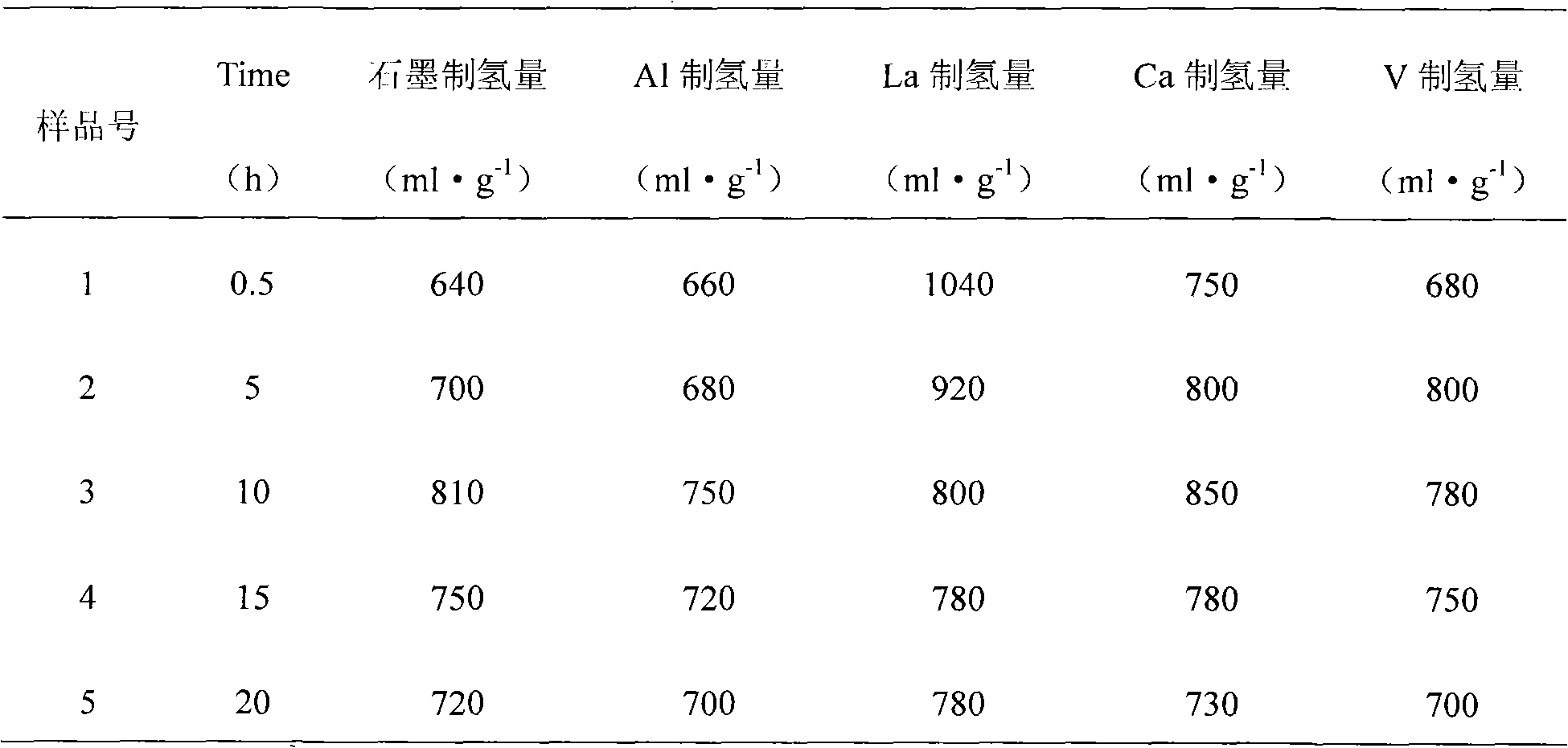
The invention discloses a magnesium base hydride composite system for hydrolysis hydrogen production and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite system is prepared by a method comprising the following steps of: taking magnesium powder and nickel powder in a mole ratio of 30:1-49:1; performing hydrogenation combustion synthesis under the action of a catalyst and an organic dispersant which account for 3 to 10 percent of the total weight of the mixture of the magnesium powder and the nickel powder; and performing strong mechanical ball milling. The magnesium hydride in the prepared magnesium base hydride composite system for the hydrolysis hydrogen production accounts for 95 to 98 percent of the weight of hydride, and the magnesium nickel hydride accounts for 2 to 5 percent; the catalyst is one of graphite, B, Al, La, Ca, V, Ce and Nb; the magnesium hydride is MgH2; and the magnesium nickel hydride is a mixture of Mg2NiH4 and Mg2NiH0.3 in any ratio. The theoretical hydrogen production amount of the composite system is up to 1,600 ml / g, and a preparation process of the magnesium base hydride composite system is time-saving, energy-saving and simple and is easy for industrial production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
More advanced preparation method of organic-transition metal hydride complexes containing aryl group or alkyl group as hydrogen storage materials
InactiveUS20100036145A1Strong reducing powerHigh yieldGroup 1/11 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsArylAlkaline earth metal
The present invention relates to a more advanced preparation method of organic-transition metal hydride as a hydrogen storage material, precisely a more advanced preparation method of organic-transition metal hydride containing aryl or alkyl group that facilitates safe and reverse storage of massive amount of hydrogen.The present invention relates to a preparation method of an organic-transition metal hydride comprising the steps of preparing a complex reducing agent composition by reacting alkali metal, alkali earth metal or a mixture thereof and (C10˜C20) aromatic compound in aprotic polar solvent; and preparing organic-transition metal hydride by reacting the prepared complex reducing agent composition and organic-transition metal halide.The method of the present invention has advantages of minimizing the numbers and the amounts of byproducts by using a complex reducing agent and producing organic-transition metal hydride safely without denaturation under more moderate reaction conditions.
Owner:HANWHA CHEMICAL CORPORATION
Continuous and semi-continuous process of manufacturing titanium hydride using titanium chlorides of different valency
InactiveUS8388727B2Cost-effective and highly-productive manufactureImprove machining productivityTransition element hydridesTitanium chlorideTitanium(II) chloride
Owner:ADMA PRODS
Fine metal hydride particles, their production process, dispersion containing fine metal hydride particles and metallic material
ActiveUS20060070493A1Good storage stabilityLower resistanceNanotechOther chemical processesPalladium hydrideMetallic materials
It is to provide fine particles of copper, nickel or palladium hydride having an average particle diameter of at most 50 nm, which are hardly oxidized in the atmosphere and are excellent in storage stability and are thereby very suitable for formation of metallic materials, and their production process. Further, it is to provide a dispersion containing fine particles of copper, nickel or palladium hydride, which is excellent in storage stability, and a metallic material obtained by applying the dispersion, followed by baking. The fine particles of copper, nickel or palladium hydride and the dispersion thereof, to be obtained by the present invention, are applicable to various applications, and they can be used for e.g. formation and repair of printed wiring, etc. employing a dispersion, interlayer wiring in semiconductor packages, and joining of printed wiring boards and electronic components.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Titanium hydride compound foam powder and quantitative combination process thereof
InactiveCN101648699AReduce processing costsReduce lossTransition element hydridesPorosityDecomposition
The invention relates to a titanium hydride compound foam powder and a quantitative combination process thereof. The hydrogen content of titanium hydride in the foam powder is 2-3.5% of undercapacity.The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing titanium powder in a high-vacuum indirect boat-pushing type tube furnace, heating to a defined temperature, filling undercapacity hydrogen quantitatively to ensure that titanium is directly reacted with hydrogen to form saturated and unsaturated titanium hydride compounds with different hydrogen contents. The foam powder with unsaturated titanium hydride compounds can well solve the problems that the decomposition degassing rate is too fast, the volatilizing loss is too large, the production process is extremely unstable, the yieldis low and the like in the production of aluminum foam with small bubble size and high porosity.
Owner:刘学晖
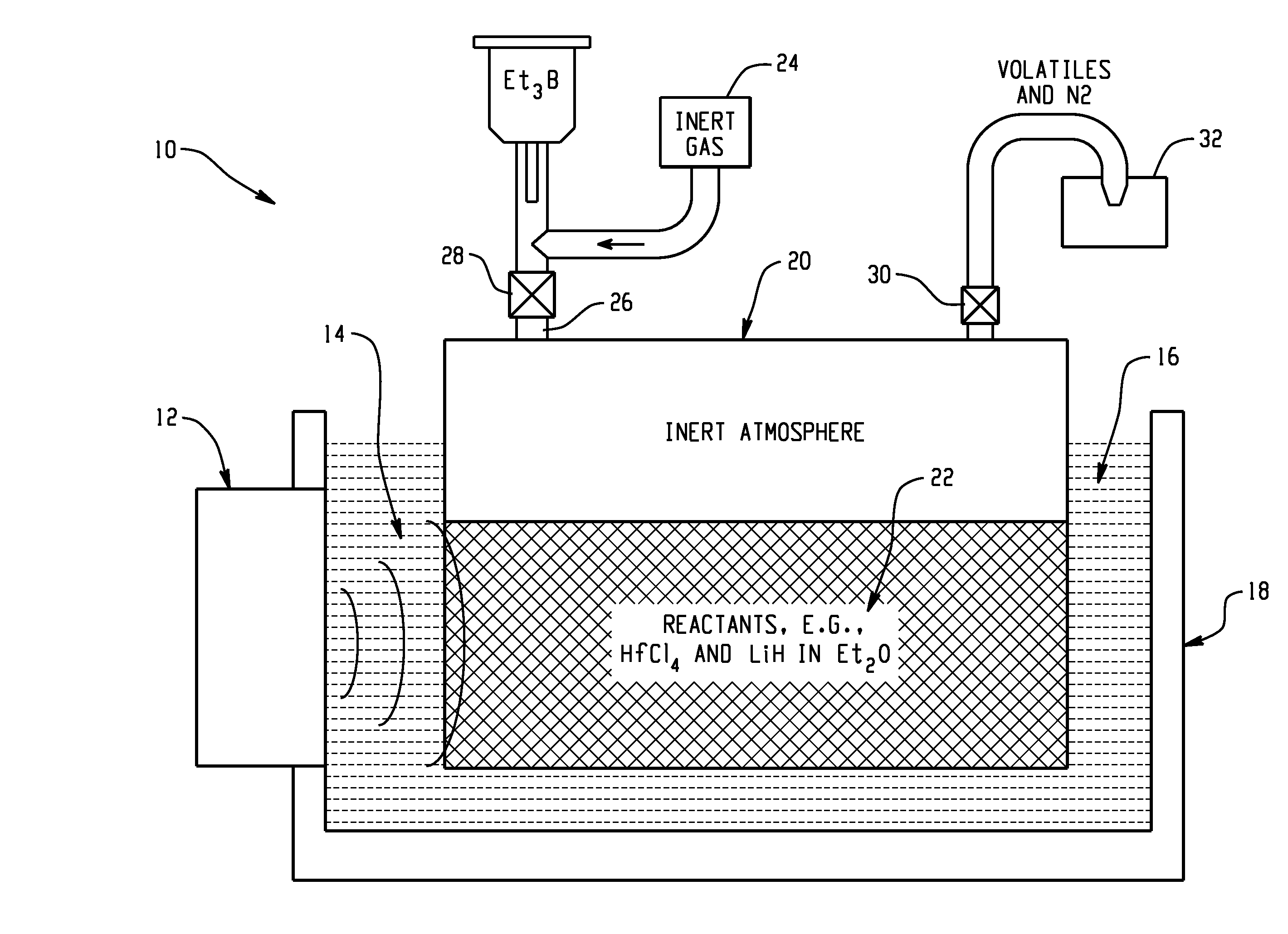
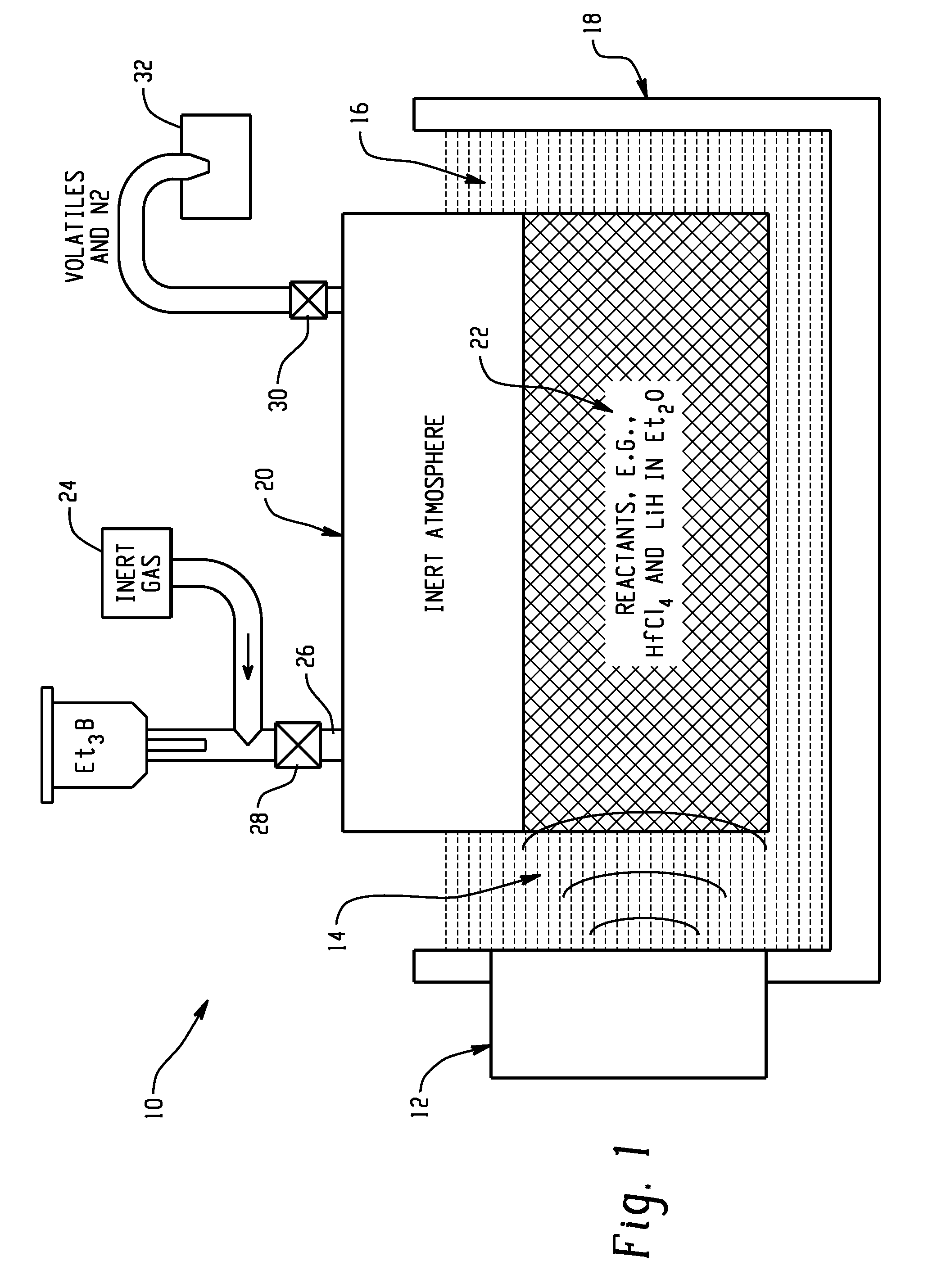
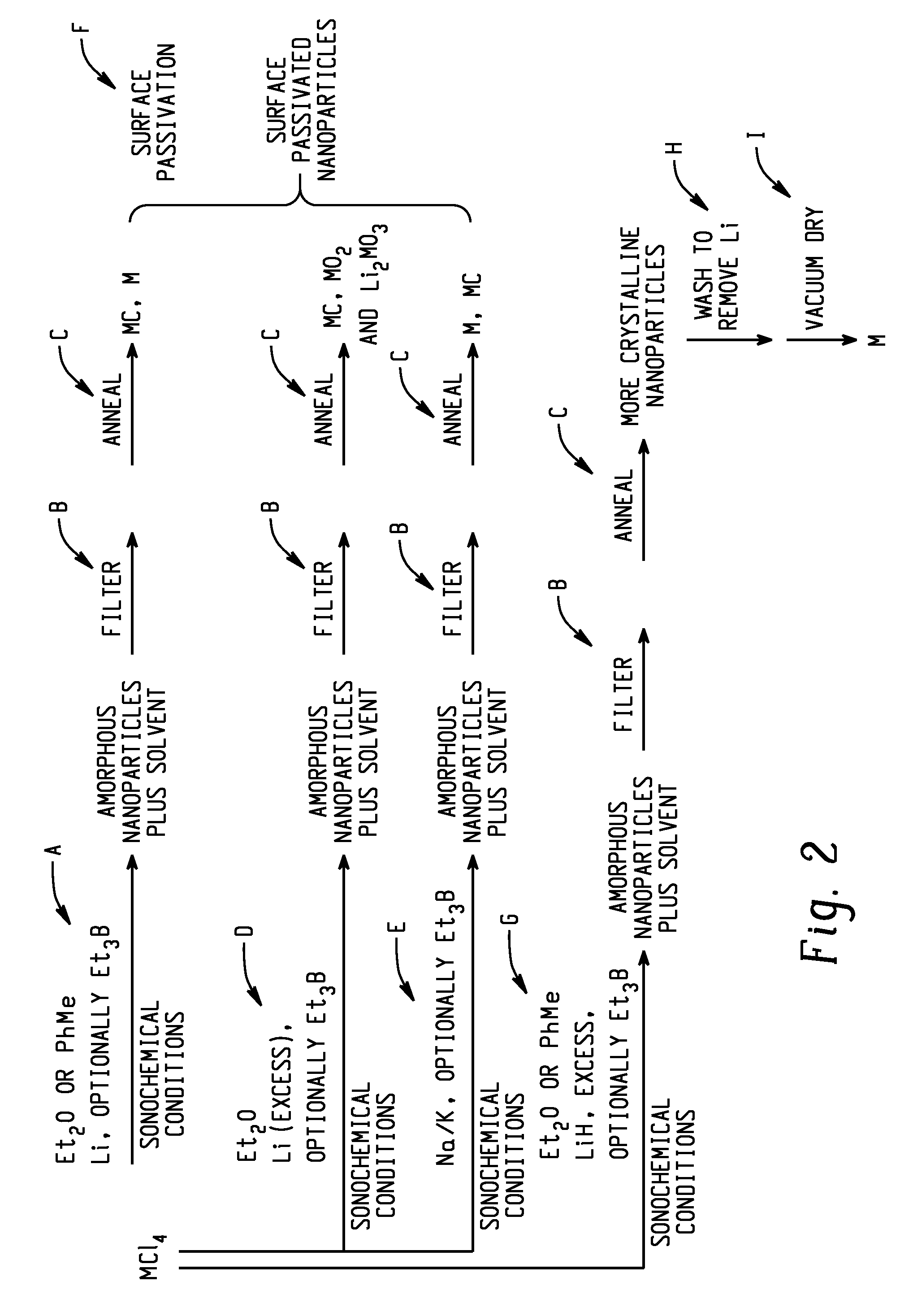
Sonochemically mediated preparation of nanopowders of reactive metals
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method of producing a chemical hydride
InactiveUS7294323B2Easy to produceAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesMonoborane/diborane hydridesChemical hydridesHydrocarbon
A method of producing a chemical hydride is described and which includes selecting a composition having chemical bonds and which is capable of forming a chemical hydride; providing a source of a hydrocarbon; and reacting the composition with the source of the hydrocarbon to generate a chemical hydride.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
New type of catalytic materials based on active metal-hydrogen-electronegative element complexes for hydrogen transfer
InactiveUS20060099127A1HydrogenAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesDehydrogenationAlloy
The present invention relates to a composition of matter prepared in accordance with a method comprising the steps of: (a) combining a substance selected from the group consisting of: metal or metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or inhomogeneous combination of at least two of the metal or metalloid, the alloy thereof, or the compound thereof, with a source of hydrogen, to form a first intermediate, (b) milling the first intermediate to effect reaction between the substance and the hydrogen to form a second intermediate, (c) combining the second intermediate with a source of an electronegative element, to form a third intermediate, and (d) milling the third intermediate to effect reaction between the second intermediate and the electronegative element. The composition of matter could be used as a hydrogen transfer facilitator or catalyst to enhance the kinetics of hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions.
Owner:ZALUSKA ALICJA +1
Preparation technology of crack-free titanium hydride electrode source sheet
InactiveCN104944375AExtend your lifeImprove discharge stabilityTransition element hydridesCooling curveCrack free
The invention discloses a preparation technology of a crack-free titanium hydride electrode source sheet. The technology includes: (a) using metal titanium as the raw material to manufacture an electrode source sheet workpiece, and conducting pretreatment on the surface; (b) subjecting the pretreated electrode source sheet workpiece obtained in step (a) to high temperature annealing under vacuum; (c) carrying out hydrogen absorption reaction on the annealed electrode source sheet workpiece; and (d) setting a cooling curve to make the hydrogen absorption reaction undergo for certain time, and cooling the workpiece subjected to hydrogen absorption to room temperature, thus obtaining the finished product electrode source sheet. The electrode source sheet produced by the invention has a surface smooth hydrogenated layer free of macrocrack, under the circumstance of strong magnetic pulse discharge, all parts of the hydrogenated layer receive the same external shock, and spray cracking does not happen and form, thus greatly enhancing the discharge stability of the product, and also significantly prolonging the electrode source sheet life.
Owner:INST OF FLUID PHYSICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
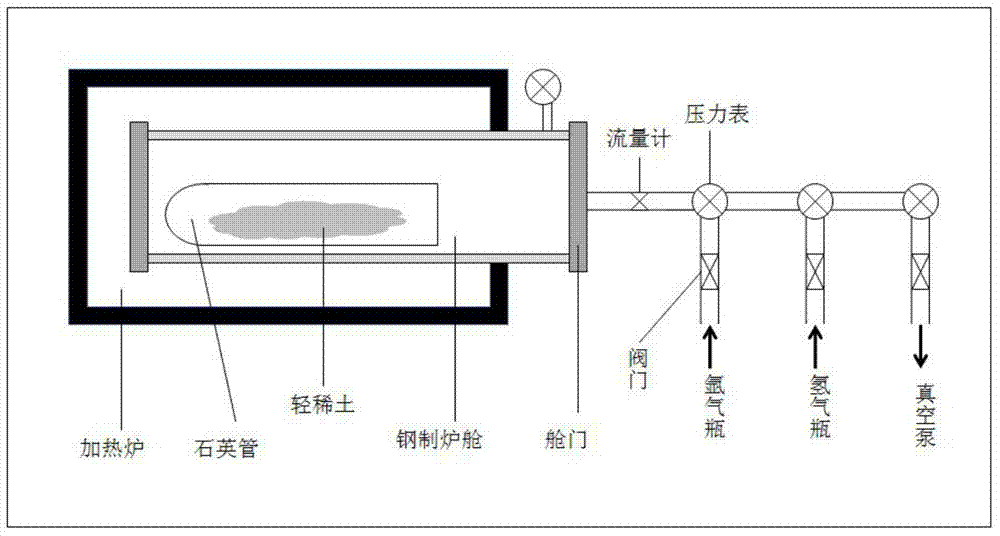
Method for preparing light rare earth hydride by high-temperature direct method
ActiveCN104291270ANo harmImprove manufacturing levelTransition element hydridesHydrogen pressureEvaporation
The invention belongs to the field of material science and technology and specifically relates to a method for preparing a light rare earth hydride by a high-temperature direct method. The method comprises the following main implementation steps: placing light rare earth with purity being greater than 99% and particle size being 2-15mm into a quartz glass test tube under the inert gas protection, removing air in a boiler room by the use of inert gas, closing an air evaporation valve, rapidly heating the boiler room at the heating rate of 2-20 DEG C / min until heating to 300-1000 DEG C, controlling inflow of hydrogen to 200-10,000 ml / min, and keeping the temperature and continuously reacting until a hydrogen pressure gauge and pressure in a heating reaction furnace are completely balanced, so as to obtain the required light rare earth hydride and corresponding light rare earth hydride powder. Purity of the light rare earth hydride prepared by the above method is 97-99.99%, and conversion rate of the light rare earth hydride powder is 97-99.99%. Thus, the hydride preparation purity problem in an industrial preparation technology is solved. The method is safe, reliable and is pollution-free, and is of great significance for industrialized and large-scale production of the light rare earth hydride.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Synthesis and hydrogen storage properties of novel metal hydrides
ActiveUS20150362129A1Improve hydrogen storage performanceMinimize impactSilicon organic compoundsReversible hydrogen uptakeHydrogen storage systemHydride
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Manufacturing method for titanium hydride powders
ActiveCN101511735AImprove productivityTitanium compoundsTransition element hydridesProduction rateRaw material
It is an object of the present invention to provide a method of manufacturing titanium hydride powder that is capable of manufacturing titanium hydride by using titanium scrap generated during machining as a raw material. Further, according to the method of manufacturing titanium hydride powder, since the titanium scrap is hydrogenated and changed into powder at the same time for a short time, it is possible to reduce the number of processes and manufacturing cost and to improve productivity. In order to achieve the object, according to an embodiment of the present invention, a method of manufacturing titanium hydride powder includes charging titanium scrap into a reaction container, removing air in the reaction container and supplying hydrogen gas to the reaction container, and performing ball milling.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
Metal hydrides and their use in hydrogen storage applications
ActiveUS9376316B2Reduce pressureReversible hydrogen uptakeCell electrodesPhysical chemistryMetallic hydrogen
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
Method for reducing magnesium-based hydride hydrogen-release temperature by utilizing solid-solution doping of transition metal
ActiveCN104386649ALow priceEasy to makeAlkali/alkaline-earth/beryllium/magnesium hydridesHydrogen productionMaterials preparationSolid solution
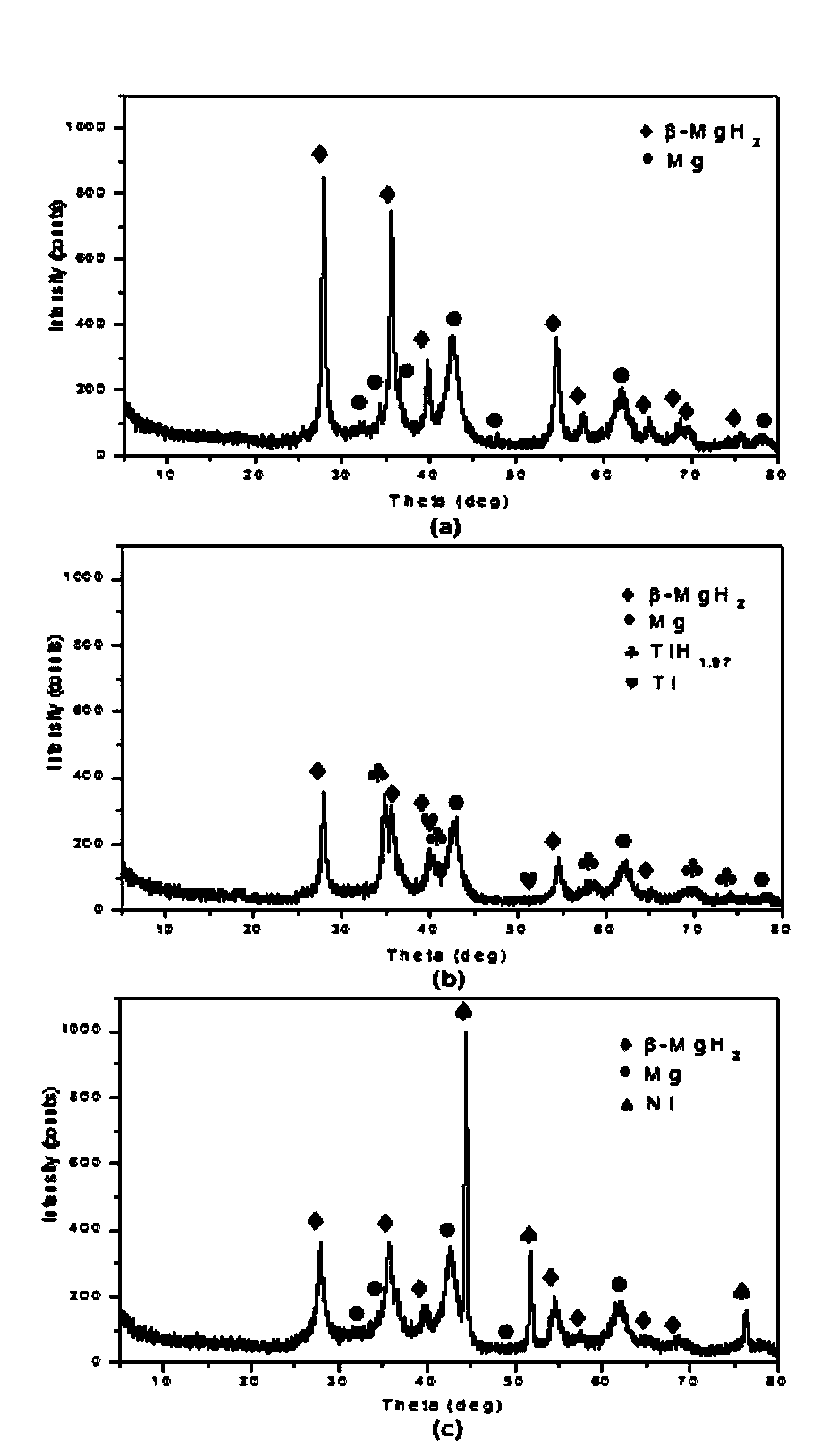
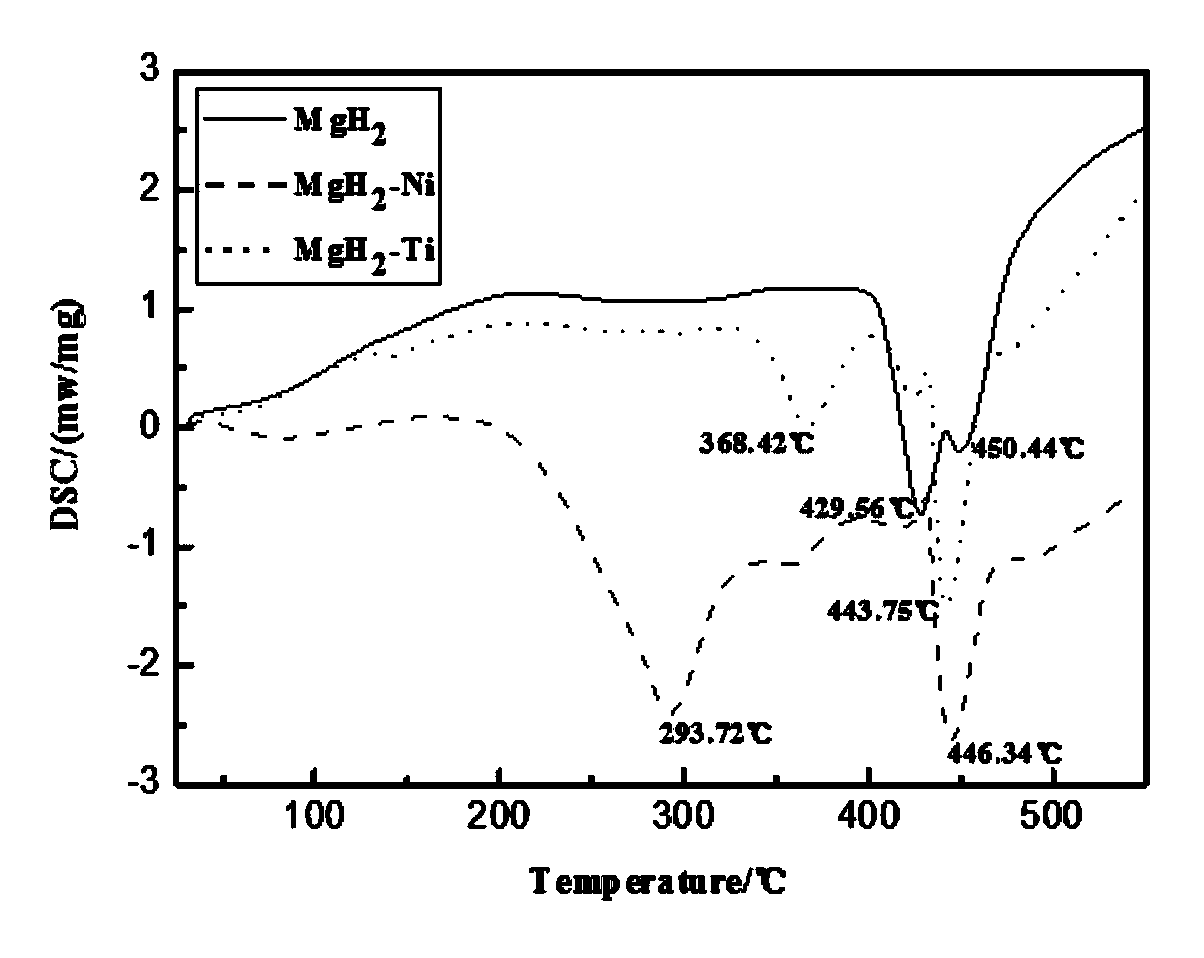
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydrogen storage, and especially relates to a method for reducing magnesium-based hydride hydrogen-release temperature by utilizing solid-solution doping of a transition metal. According to the method, a mechanical ball milling process is utilized for together ball milling of MgH2 and a less amount of a transition metal Ti or Ni, and a MgH2-Ti and MgH2-Ni hydrogen-storage composite system is finally obtained. The composite system prepared by using the method is granular, the granule dimension is in the level of several hundred nanometer, partial Ti or Ni atoms are dissolved in a MgH2 matrix in the form of a solid solution during ball milling, and thus the crystal lattice of the MgH2 matrix is deformed and the thermodynamic stability is reduced. Compared with a pure MgH2 system under same ball milling conditions, the initial hydrogen-release temperature of the ball-milling composite system is substantially reduced, the solid-solution doping of Ti and Ni causes the initial hydrogen-release temperature of the MgH2 matrix to respectively reduced by 61.14 DEG C and 135.84 DEG C, and the hydrogen-release performance of the magnesium-based hydride is effectively improved. The employed raw materials are easily obtained, and the material preparation method is maturely developed, also is convenient to operate and controllable in process, and is an effective method for reducing the hydrogen-release temperature of the magnesium-base hydride.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Niobium powder, niobium granulated powder, niobium sintered body, capacitor and production method thereof
InactiveUS20060260437A1Small leakage current valueImprove reliabilityElectrolytic capacitorsTransportation and packagingCapacitanceVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention provides a method of efficiently producing niobium powder, niobium alloy powder, niobium hydride powder or niobium hydride alloy powder for a capacitor, which enables production of capacitor having a high capacitance per unit mass and good leakage current characteristics with narrow variation, and also provides a production method for sintered body and a capacitor using the niobium powder, niobium alloy powder, niobium hydride powder or niobium hydride alloy powder. According to the present invention, by grinding niobium hydride powder or niobium hydride alloy powder with a grinding aid having a density of 2 to 3.6 g / cm3 and a fracture toughness value of 1.5 MPa·m1 / 2 or more, such as beads made of silicon nitride or a compound containing silicon nitride, a niobium powder with high capacitance can be efficiently produced.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com