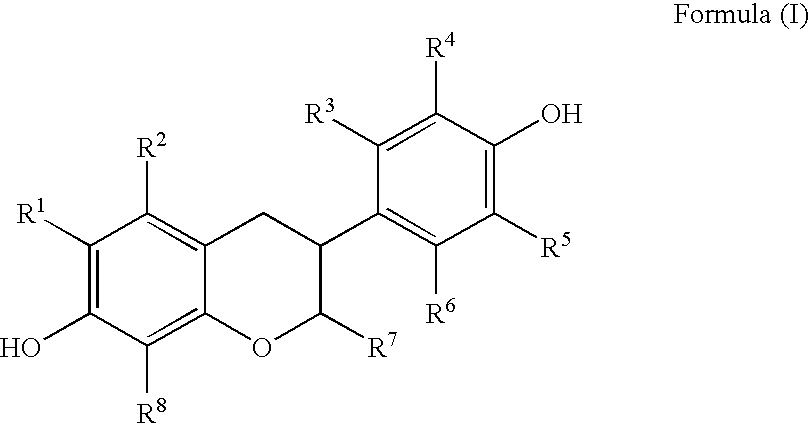
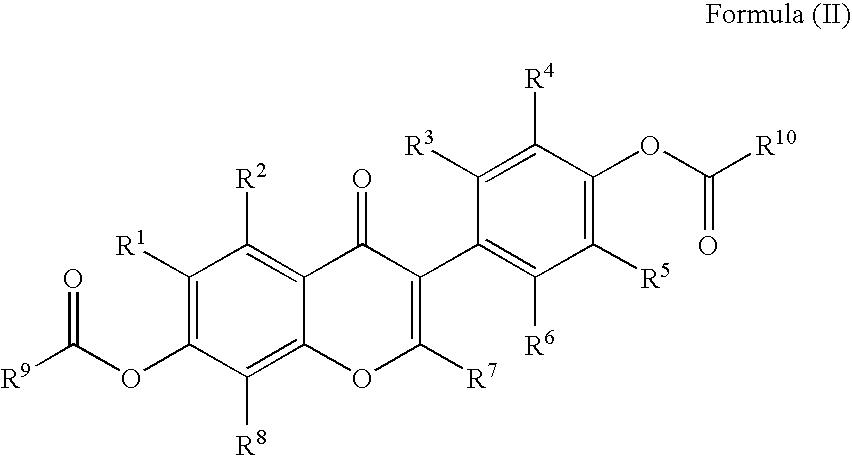
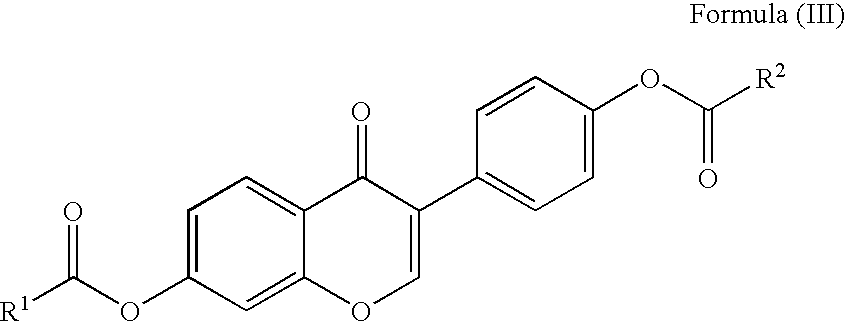
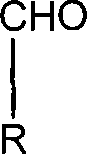Patents
Literature
441 results about "Hydrogen transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
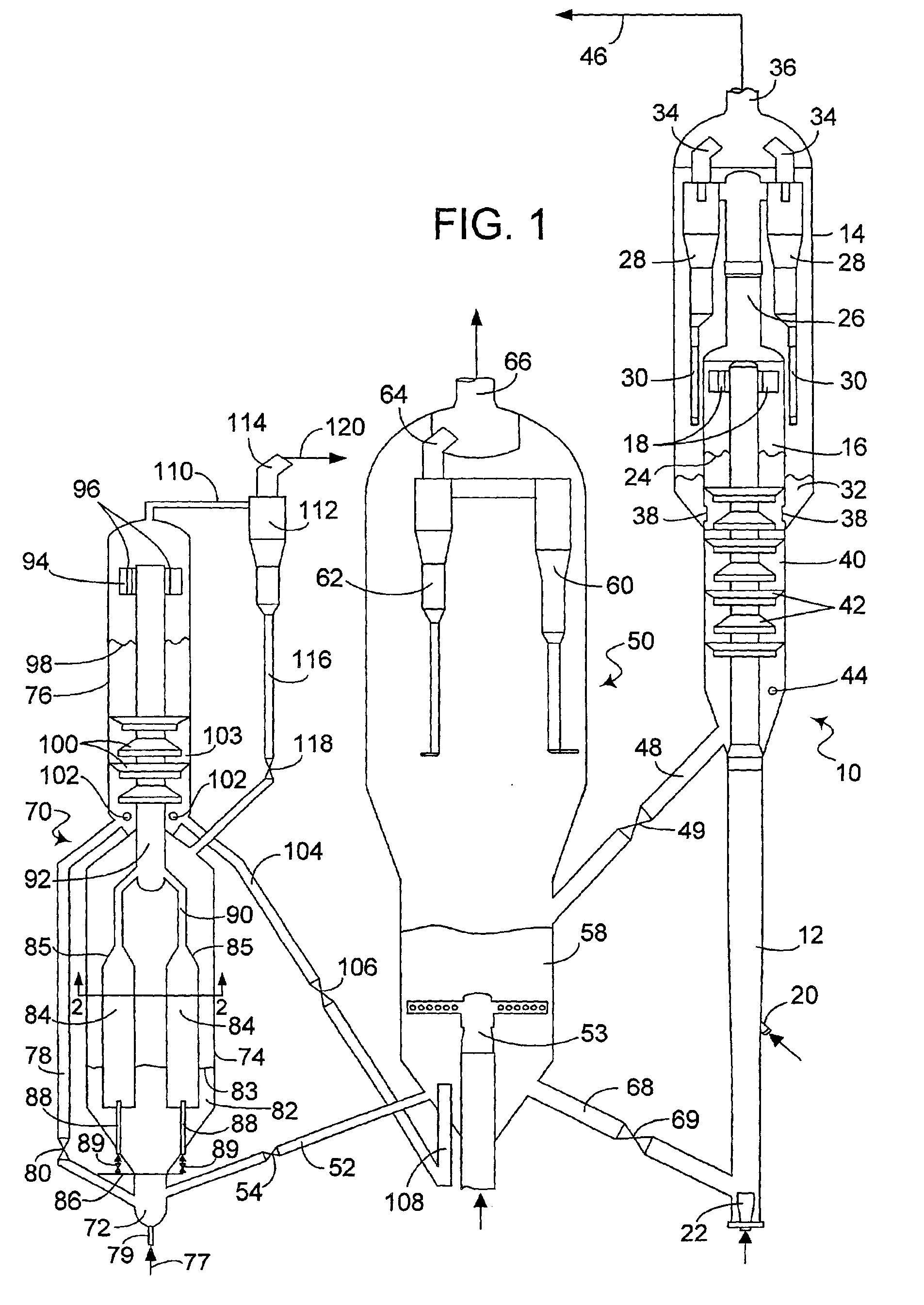
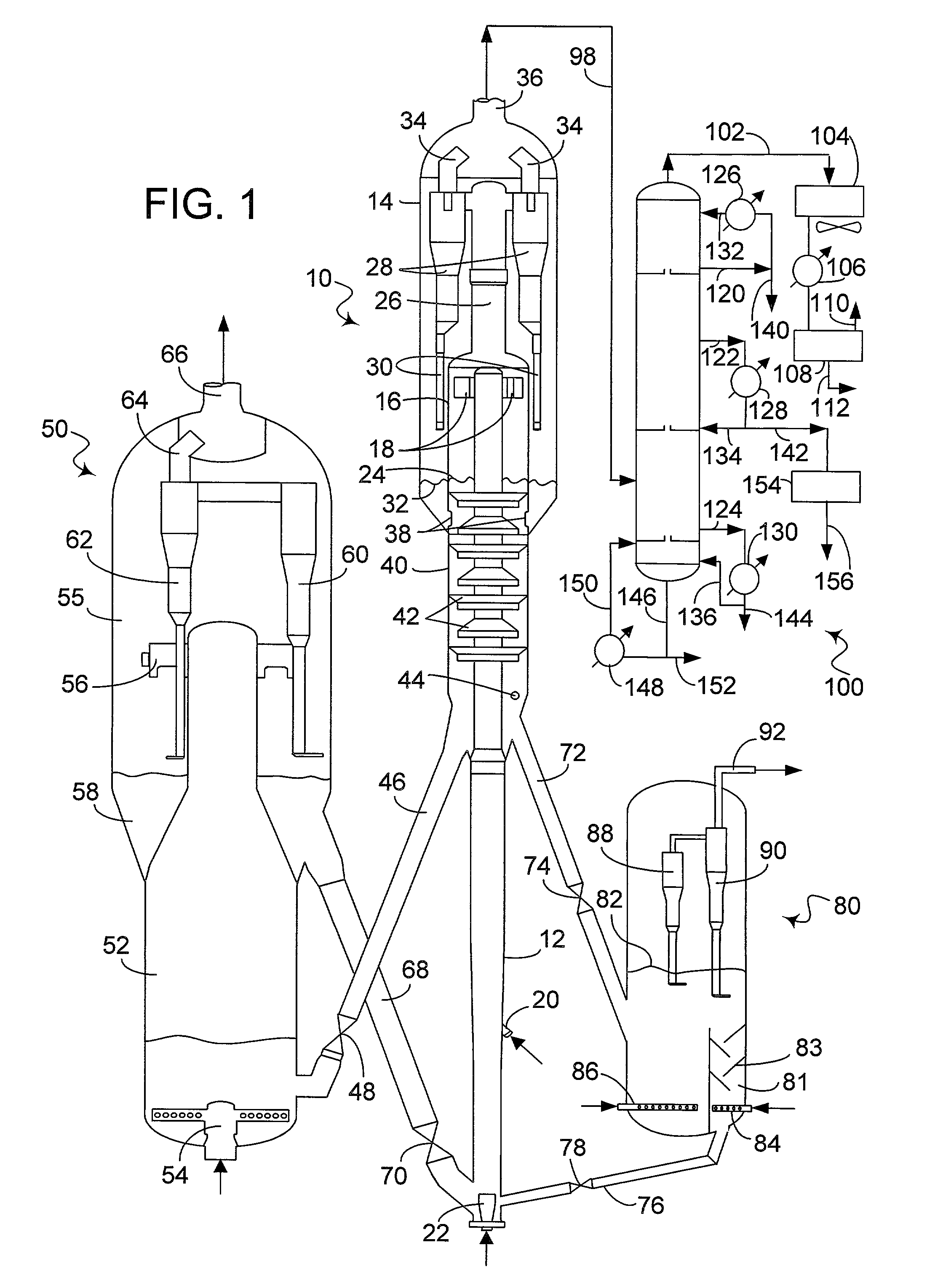
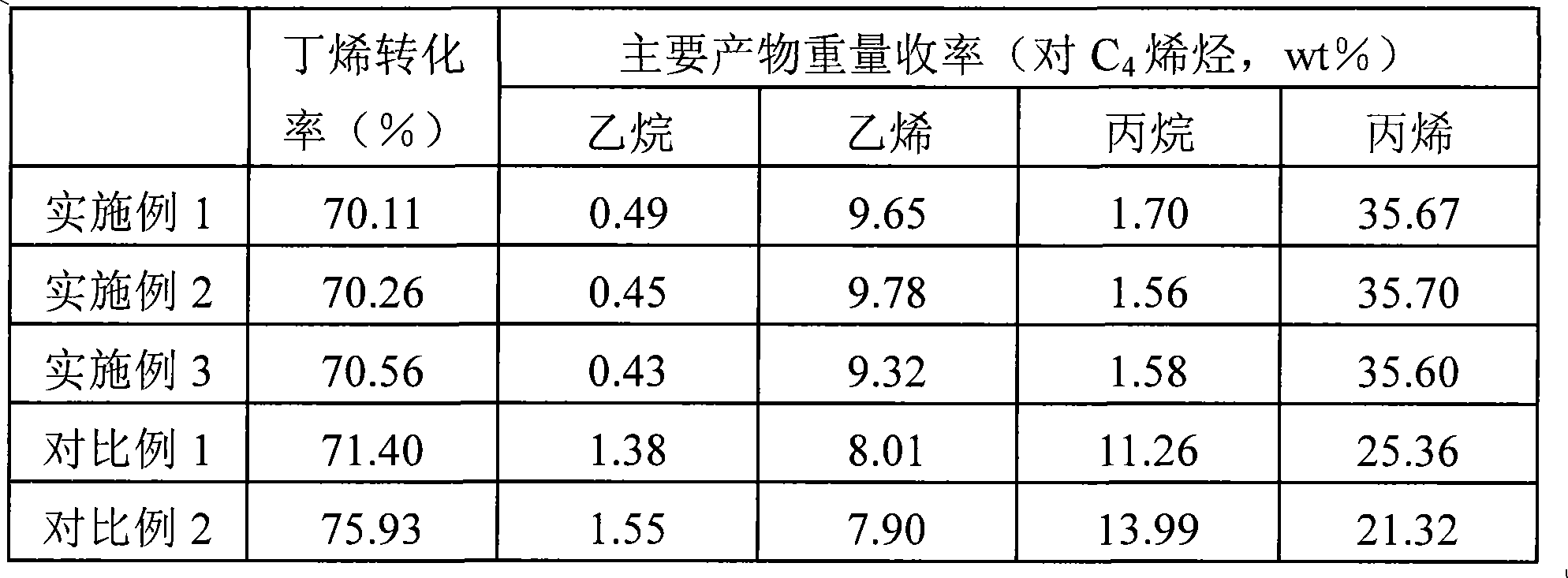
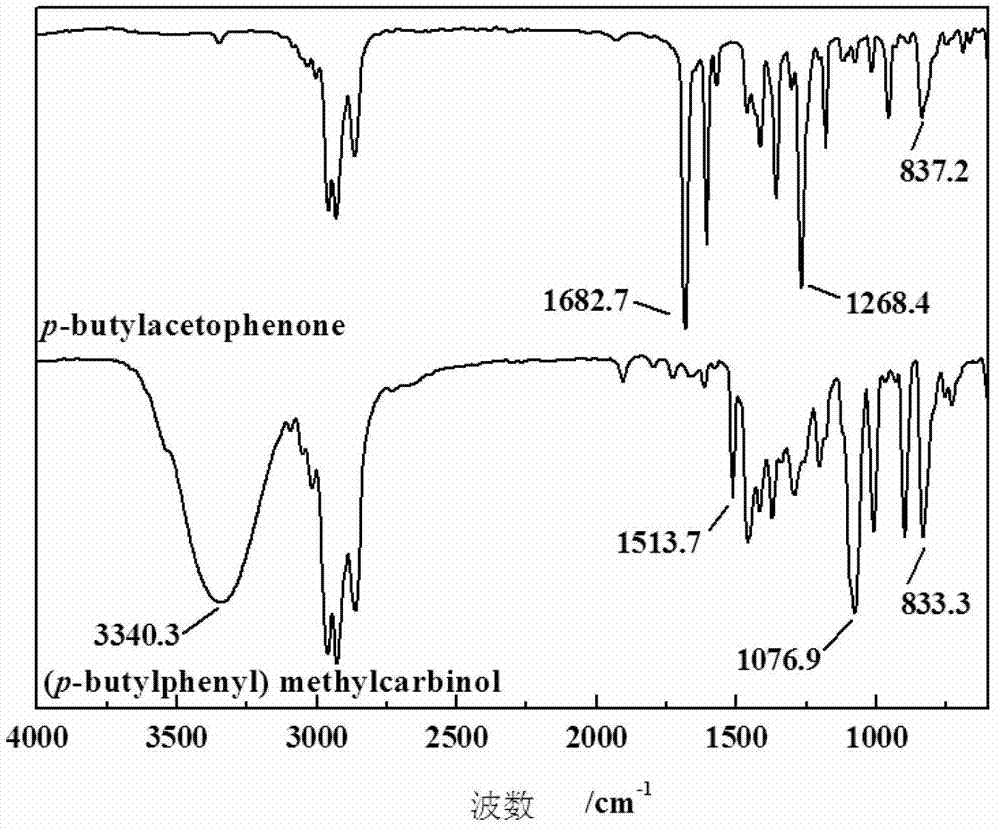
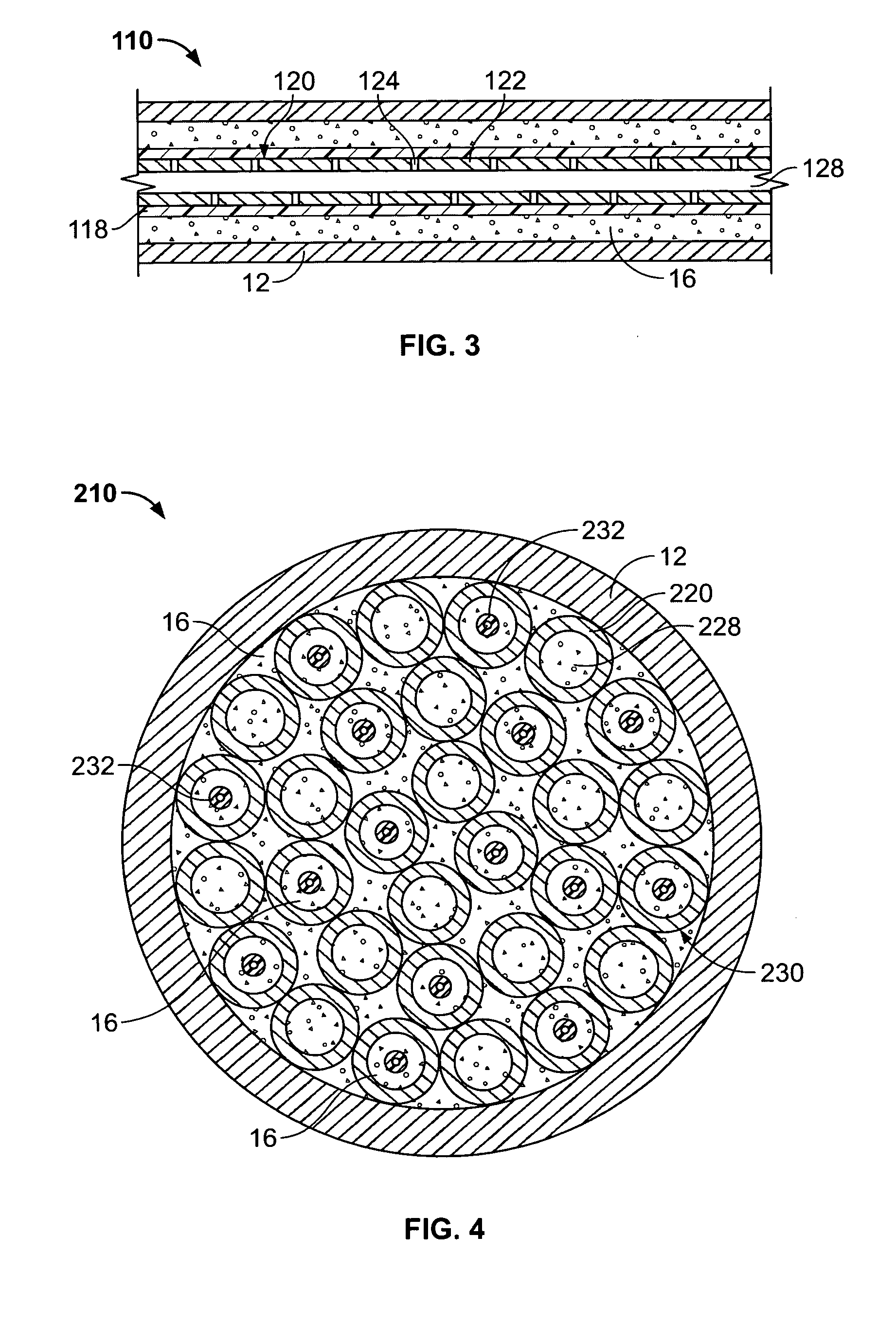
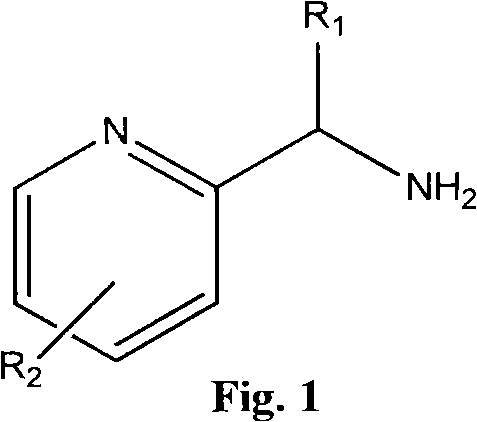
Process and apparatus for upgrading FCC product with additional reactor with thorough mixing
InactiveUS6869521B2Improve responseLess effectivenessTreatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyCatalytic crackingProduct gasHydrocarbon
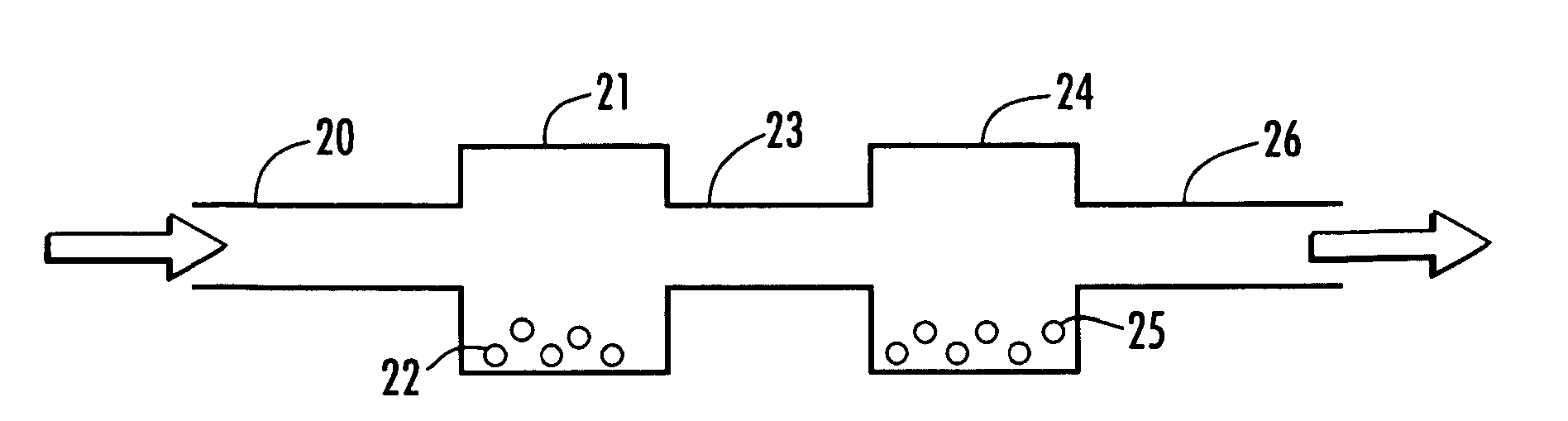
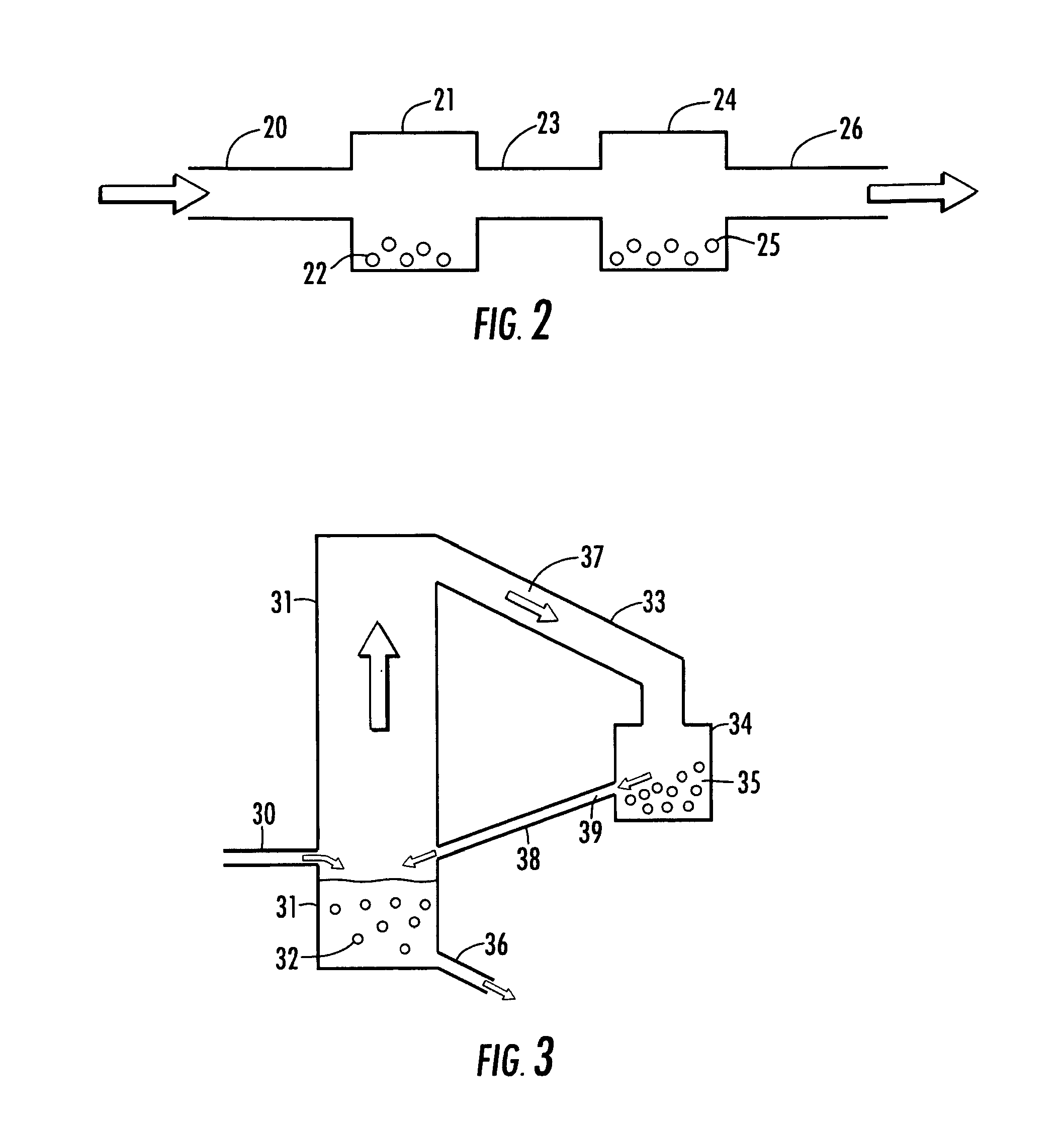
A process and apparatus are disclosed contacting hydrocarbon feed with catalyst in a reactor vessel under conditions more vigorous than bubbling bed conditions and preferably fast fluidized flow conditions. The vigorous conditions assure thorough mixing of catalyst and feed to suppress formation of dry gas and the promotion of hydrogen transfer reactions.
Owner:UOP LLC
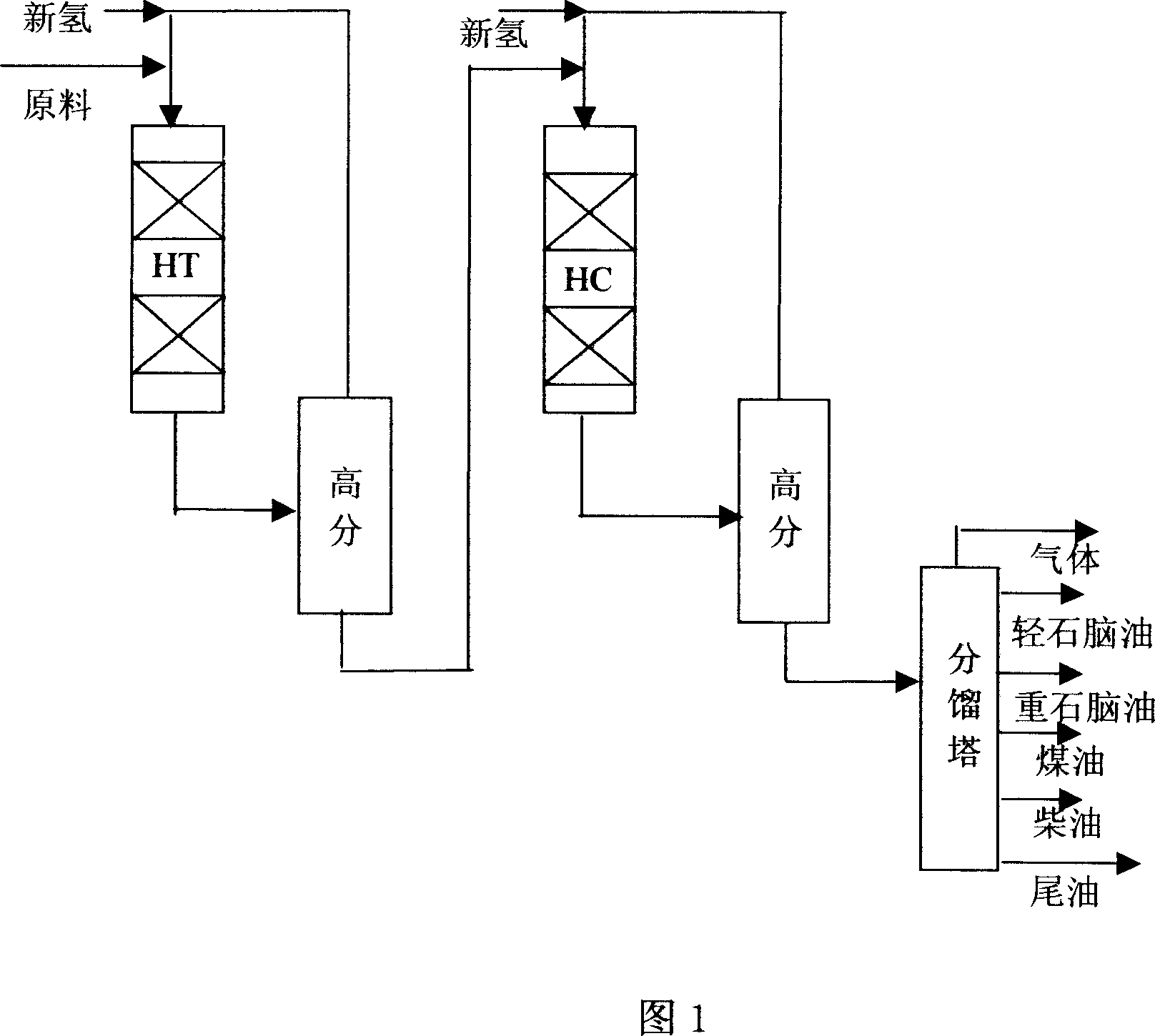
Two-stage hydrocracking method
ActiveCN1955262AEfficient processingLow BMCITreatment with hydrotreatment processesHexadecaneNaphtha
This invention discloses a poor quality catalytic cracking diesel hydrogenation method. This invention includes two stages hydrocracking dealing with catalytic cracking diesel, especially the poor quality catalytic cracking diesel from catalytic hydrogen transfer process. The density of the related poor quality catalytic cracking diesel is 0.90g / ml at 20deg.C, and its aromatic hydrocarbon is over 60wt%, and the value of hexadecane is less than 30. Mixing poor quality catalytic cracking diesel and heavy cracking material and conducting hydrogenation, hydrocracking is conducted after removal of sulphur, nitrogen and other impurities from reaction oil. It is a sufficient utilization of the feature that low hydrogen and high aromatic hydrocarbon content of catalytic cracking diesel to produce Gaofangqian heavy naphtha in order to realize the effective utilization of the poor quality catalytic cracking diesel.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +2
Method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by carrying out catalytic hydrodeoxygenation on lignin
InactiveCN104744204AWide variety of sourcesRaw materials are renewableHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsEthylene productionIridiumPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a method for preparing aromatic hydrocarbon by carrying out catalytic hydrodeoxygenation on lignin. A catalyst used in the method provided by the invention comprises two active components, namely an acid site being one or combination of more than one of transition metal elements niobium, tantalum, zirconium, molybdenum, tungsten and rhenium and a hydrogenation or hydrogen transfer active site being one or more than one of ruthenium, platinum, palladium, iridium, iron, cobalt, nickel and copper. According to the method provided by the invention, a phenol group, a guaiacol group, a syringa phenolic group compound, natural lignin and industrial lignin are taken as raw materials, water is taken as a solvent, high selectivity catalytic hydrodeoxygenation is carried out at the temperature of 180-350 DEG C and hydrogen pressure of 0.1-5MPa or with methyl alcohol, isopropyl alcohol and formic acid as hydrogen sources, so that C6-C9 aromatic hydrocarbon is obtained, the highest mass yield of aromatic hydrocarbon is 10%, and content of aromatic hydrocarbon in product oil can be up to more than 75%. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that reproducible natural biomass can be used as a raw material, and the raw material is cheap and available; the water is taken as the solvent, so that a reaction process is environment-friendly; and content of aromatic hydrocarbon in the product is high, and reaction conditions are mild.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Aromatic hydrocarbons from depolymerization and deoxygenation of lignin
ActiveUS20130025191A1Speed up the conversion processEconomically beneficialSolid fuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsProcess economicsDepolymerization
Processes are disclosed that achieve a high conversion of lignin to aromatic hydrocarbons, and that may be carried out without the addition of a base. Depolymerization and deoxygenation, the desired lignin convention steps to yield aromatic hydrocarbons, are carried by contacting a mixture of lignin and a solvent (e.g., a lignin slurry) with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. A preferred solvent is a hydrogen transfer solvent such as a single-ring or fused-ring aromatic compound that beneficially facilitates depolymerization and hinders coke formation. These advantages result in favorable overall process economics for obtaining fuel components and / or chemicals from renewable sources.
Owner:UOP LLC
Supported iridium catalysts
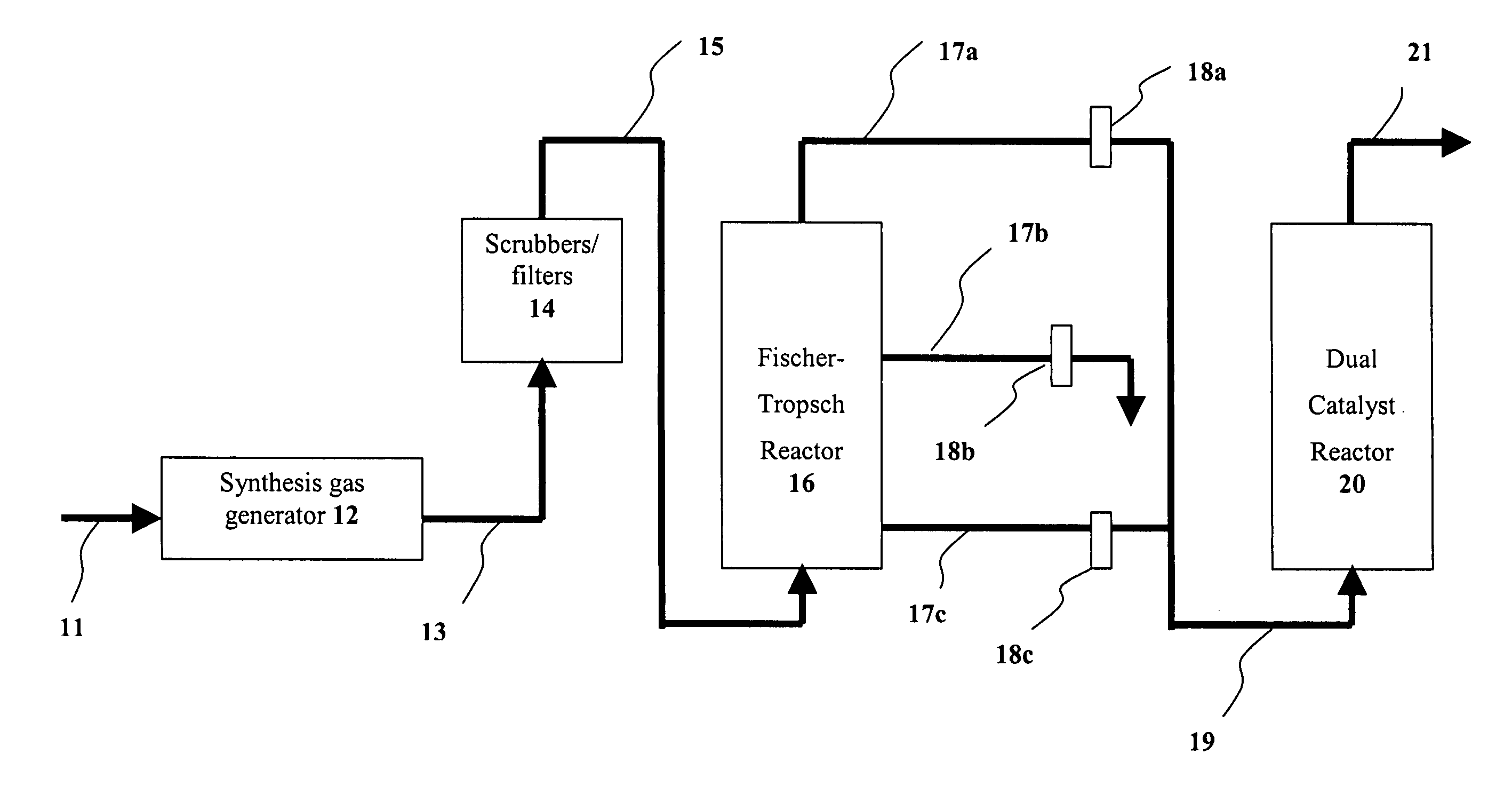
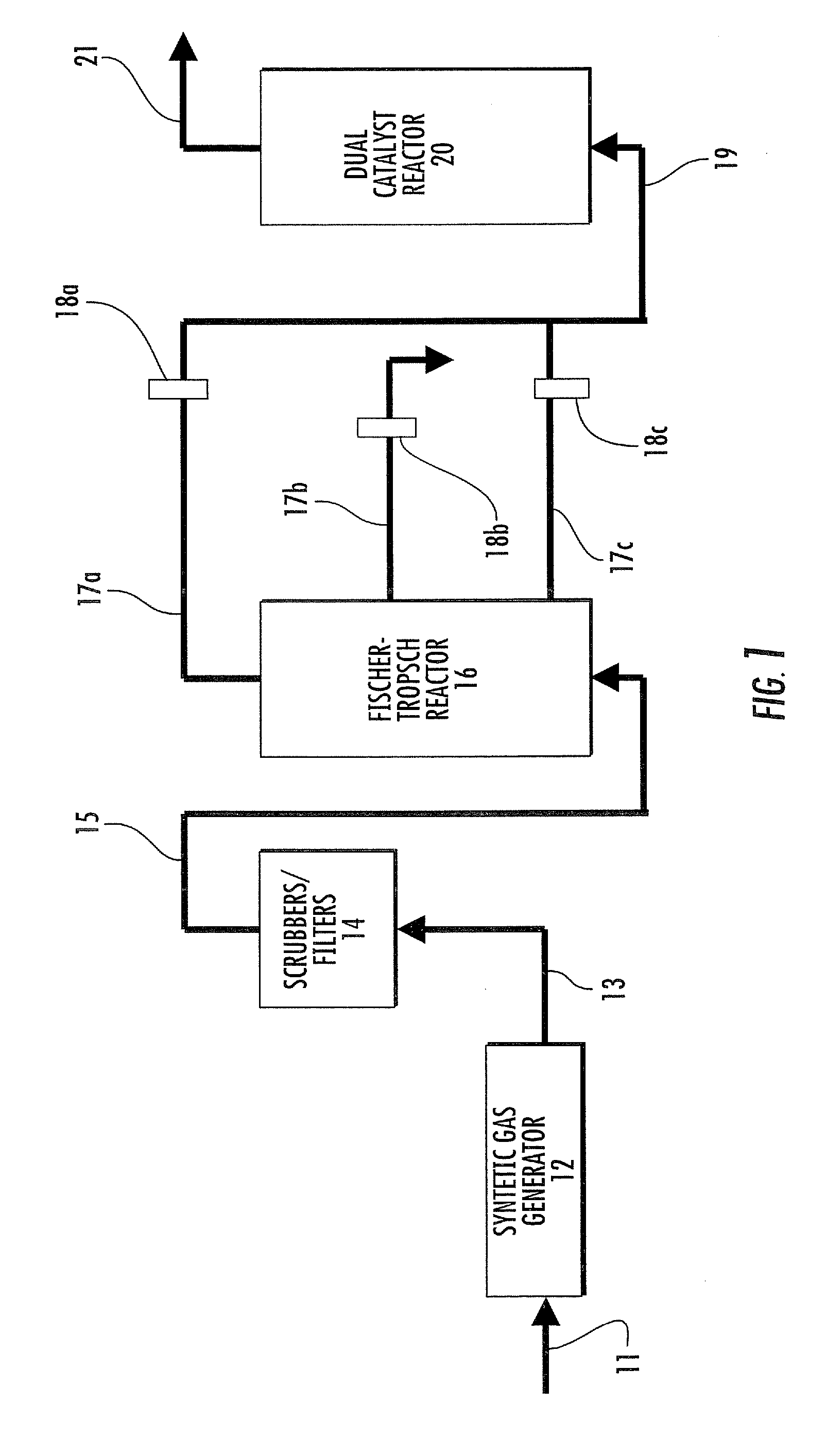
A method of converting at least one first alkane to a mixture of at least one low molecular weight alkane (optionally also including additional lower and / or higher molecular weight alkanes) and at least one high molecular weight alkane, comprises: reacting a first alkane in the presence of dual catalyst system comprising a first catalyst (i.e., a hydrogen transfer catalyst) and a second catalyst (i.e., a metathesis catalyst) to produce a mixture of low and high molecular weight alkanes.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
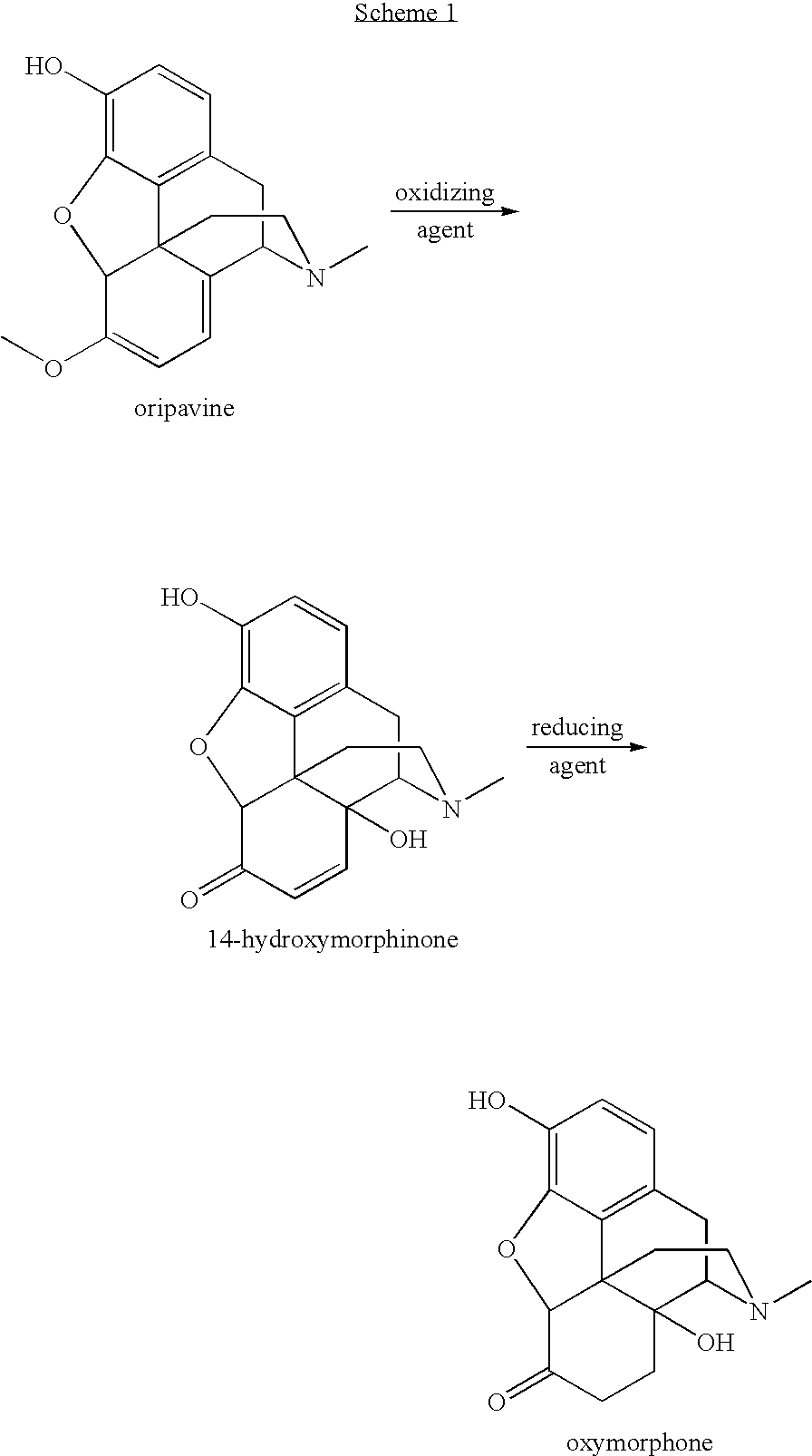
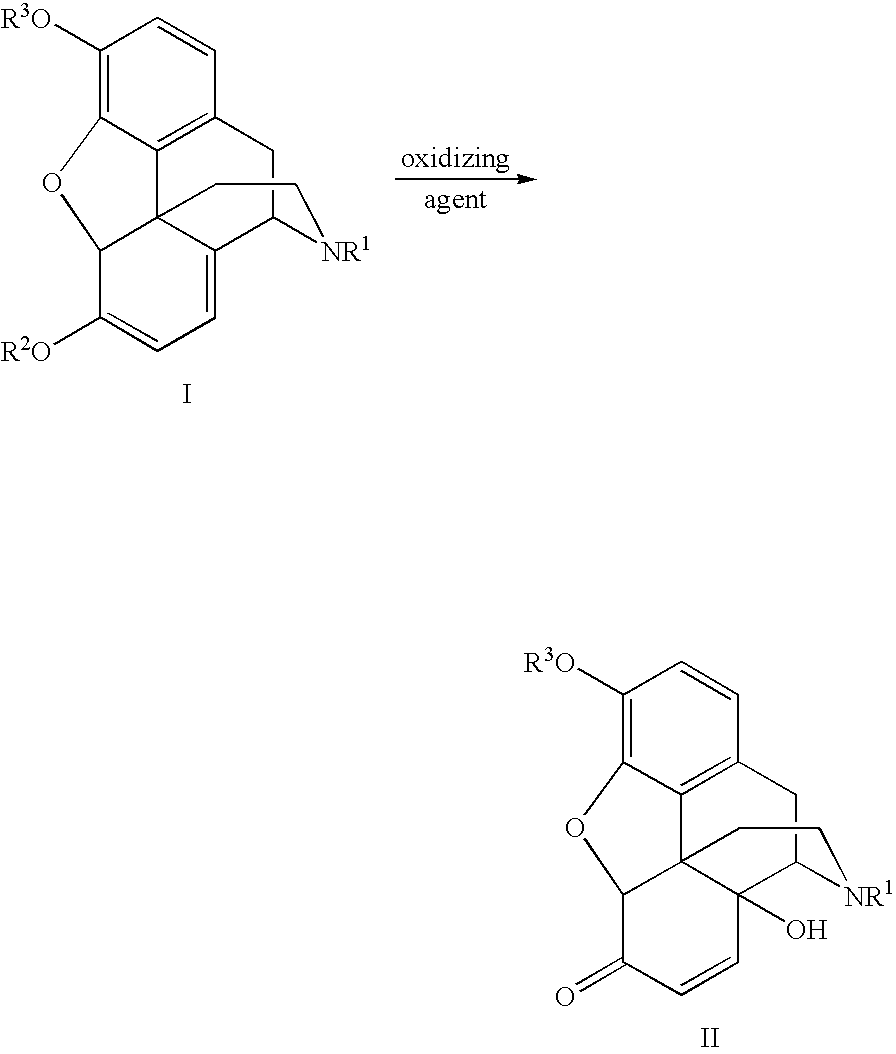
Novel Opiate Reduction Utilizing Catalytic Hydrogen Transfer Reaction
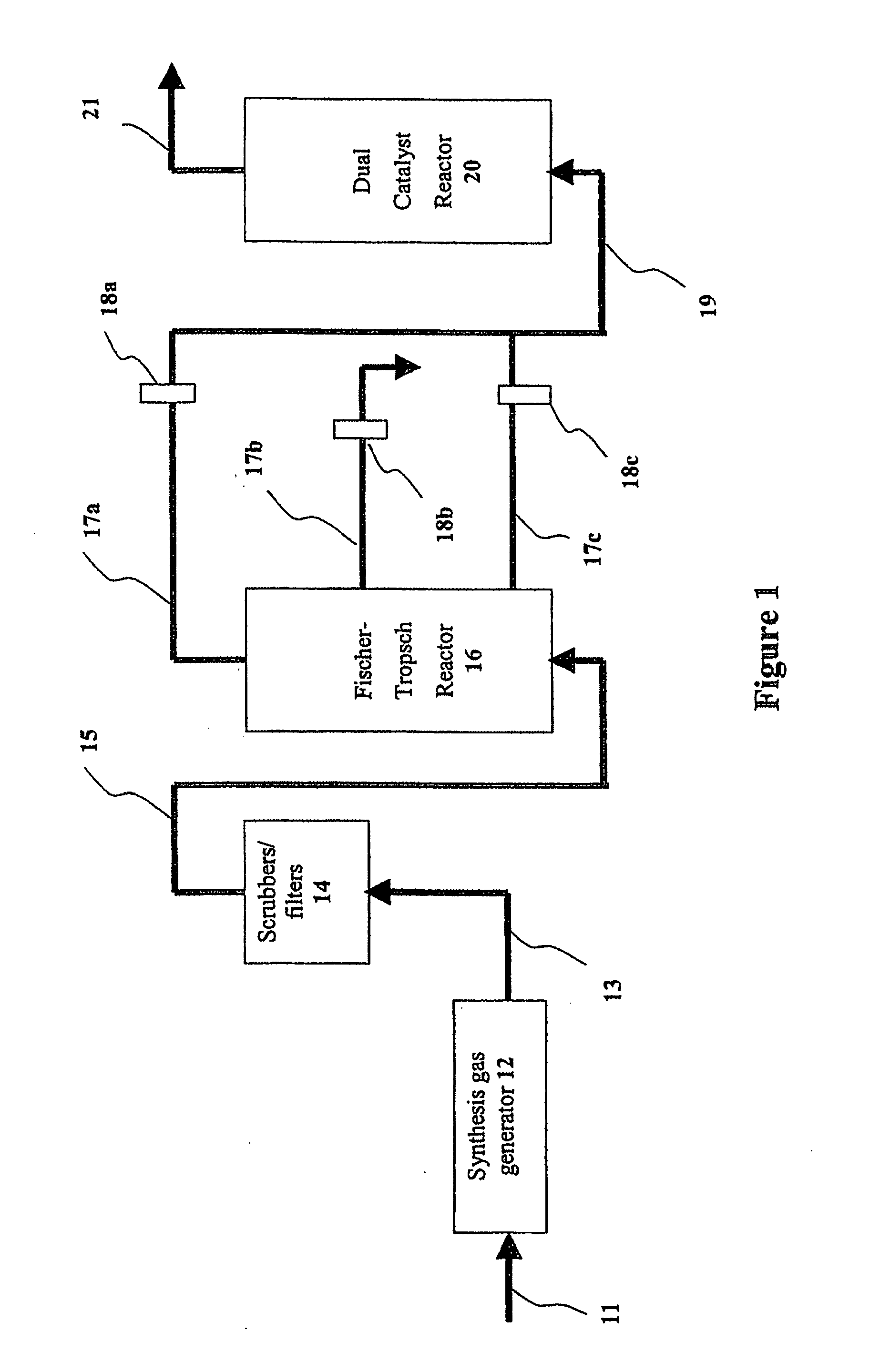
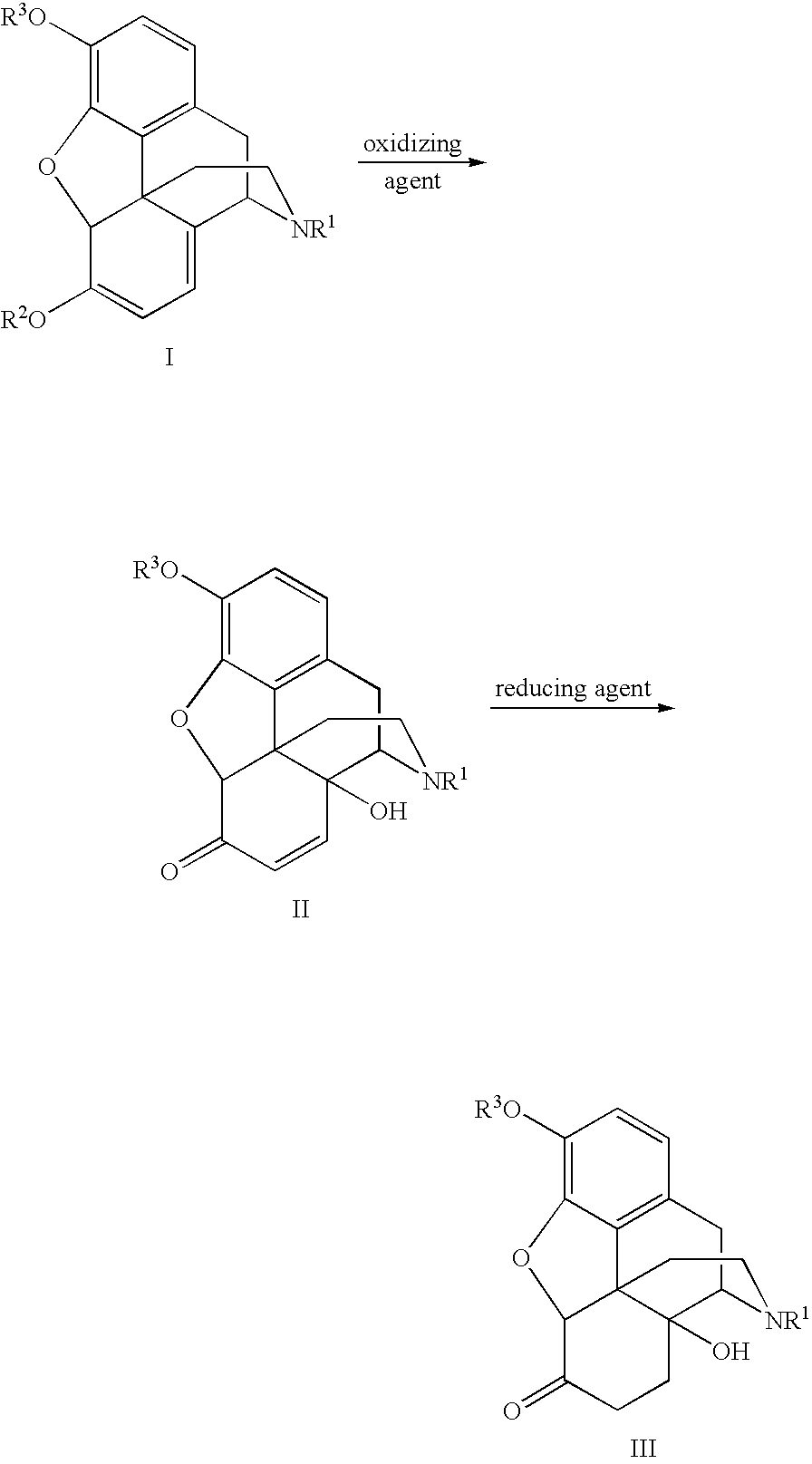
An improved opiate synthesis scheme is provided. An improvement to the oxidation of oripavine and oripavine derivatives comprises the in-situ formation of the peroxacids required to oxidize the oripavine and oripavine derivatives to form an intermediate. An improvement to the reduction of the intermediate to form oxycodone and oxycodone derivatives comprises reduction utilizing a hydrogen transfer reagent. These improvements allow the production of oxycodone and oxycodone derivatives without isolation of the intermediate, providing a one-pot synthesis method.
Owner:SPECGX LLC
Method for preparing gamma-valerolactone with high selectivity under mild condition
The invention relates to a method for preparing gamma-valerolactone with high selectivity under the mild condition. The method comprises the following steps of: under the conditions of optimal room temperature and inert gas, with secondary alcohol as a hydrogen source and active Raney nickel as a catalyst, carrying out hydrogen transfer reaction on a levulinic acid ester compound to obtain the gamma-valerolactone. The invention particularly relates to a method of preparing gamma-valerolactone by a lignocellulose derivative with high selectivity under the mild condition, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out alcoholysis reaction on the lignocellulose derivative such as fructose, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural or furfuryl alcohol by a solid acid catalyst in the presence of an alcohol solvent at certain temperature, filtering solid acid, collecting liquid, and obtaining levulinic acid esters through reduced pressure distillation; and with the secondary alcohol as the hydrogen source, catalyzing the obtained esters by Raney Ni as a non-noble metal catalyst at the room temperature to obtain the gamma-valerolactone with high yield.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for preparing propene by catalytic cracking
InactiveCN102302945AInhibition of structuringHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsBulk chemical productionPetrochemicalSide reaction
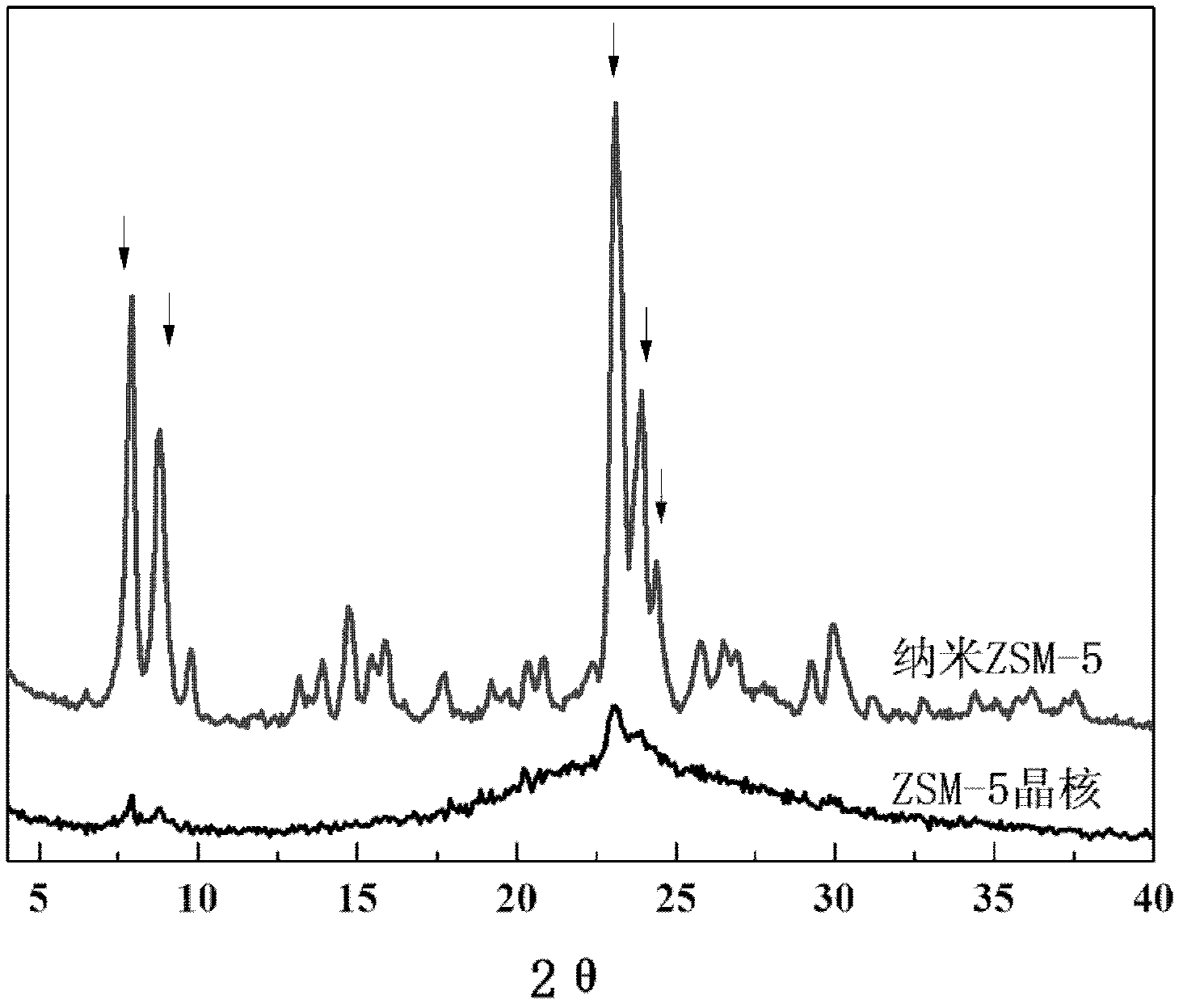
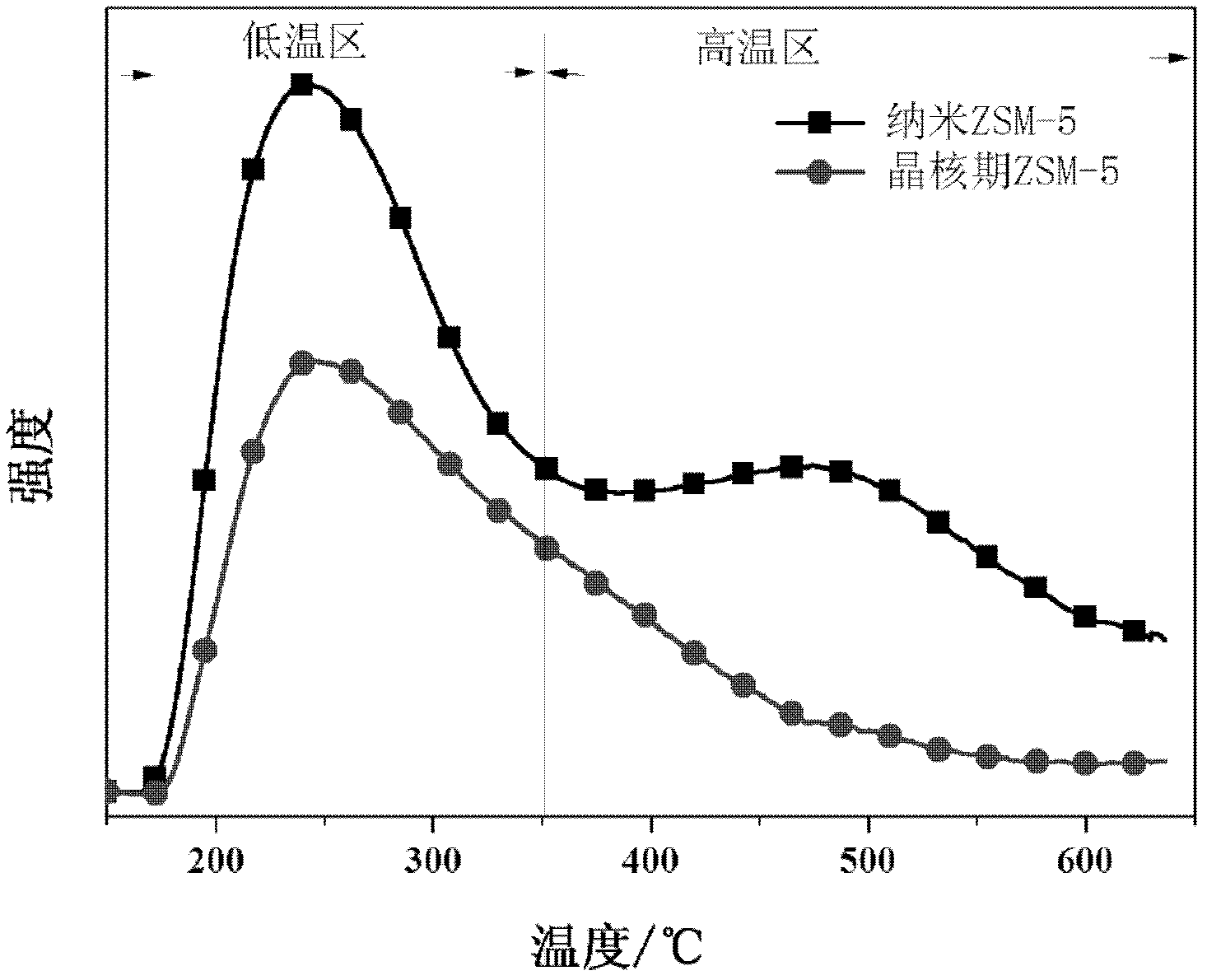
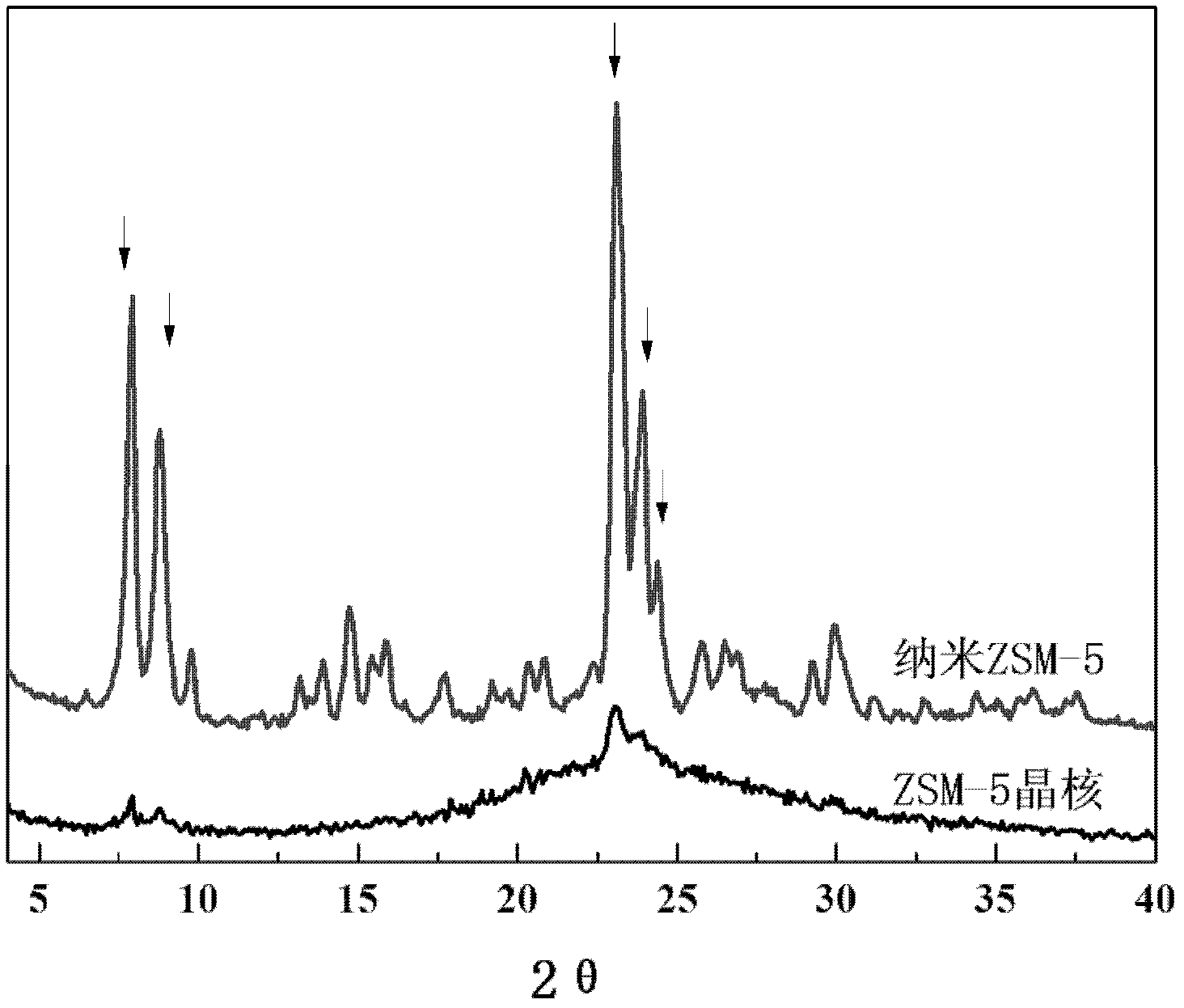
The invention belongs to the field of petrochemical industry, and relates to a method for preparing propene by catalytic cracking, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly synthesizing molecular sieve ZSM-5 crystal nuclei, and preparing a silicon source, seed crystals, templating agent and deionized water into a colloidal liquid; preparing an aluminum source, inorganic acid or alkali and deionized water into a solution; while stirring, adding the solution into the colloidal liquid to prepare a uniform gel; carrying out hydrothermal crystallization on the gel, and stopping crystallization before the crystallization induction period finishes; and preparing the molecular sieve ZSM-5 crystal nuclei into a catalytic cracking catalyst which is used for preparing propylene and isobutylene by cracking olefins. The molecular sieve ZSM-5 crystal nuclei catalyst only has a weak acid center; the crystal grains are very tiny and do not need any modification treatment, and hydrogen transfer aromatization and other side reactions can be obviously inhibited without any negative pressure or diluent gas condition, thereby enhancing the selectivity of the target product, simplifying the catalytic cracking technique and lowering the catalyst cost.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
New type of catalytic materials based on active metal-hydrogen-electronegative element complexes involving hydrogen transfer
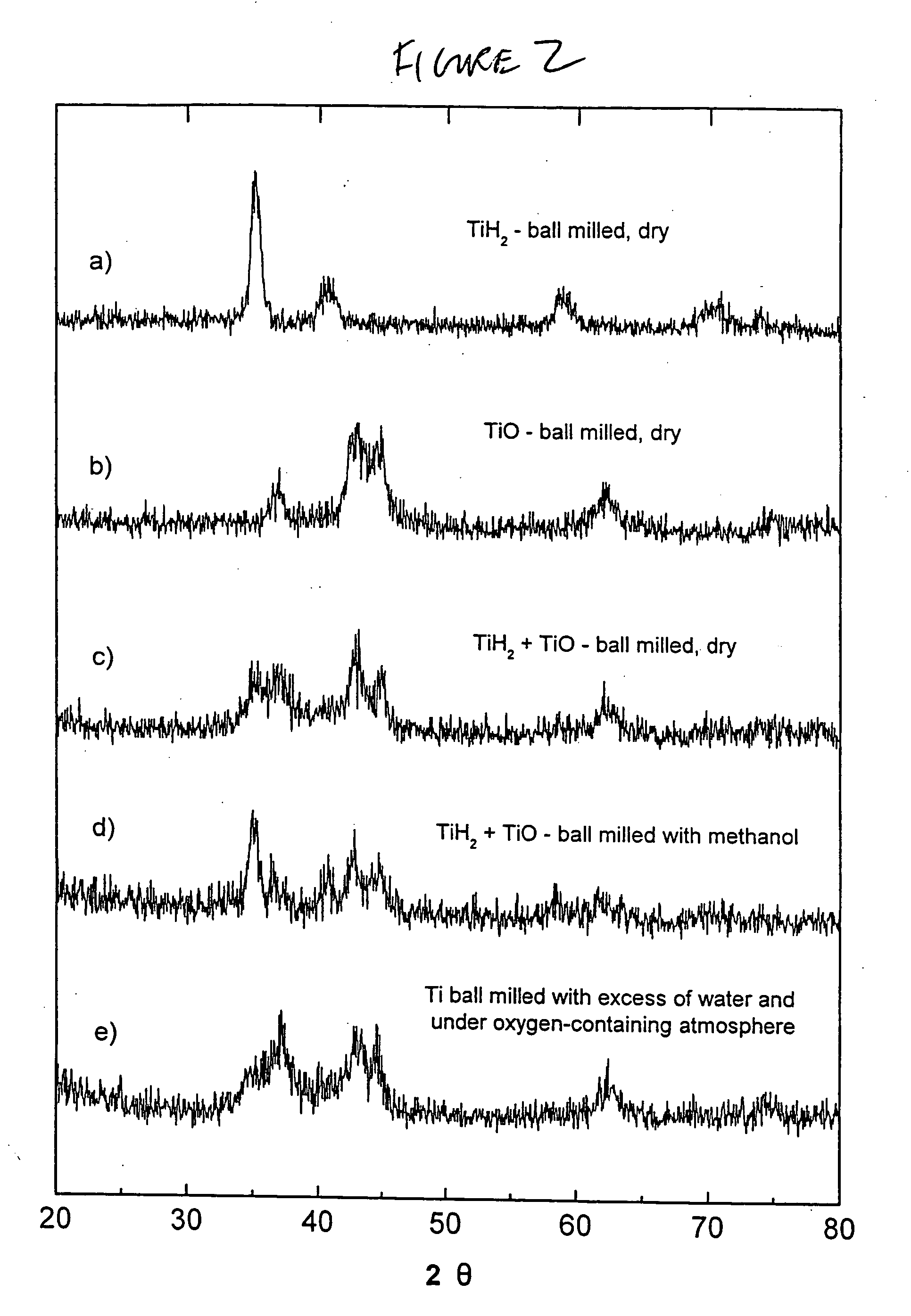
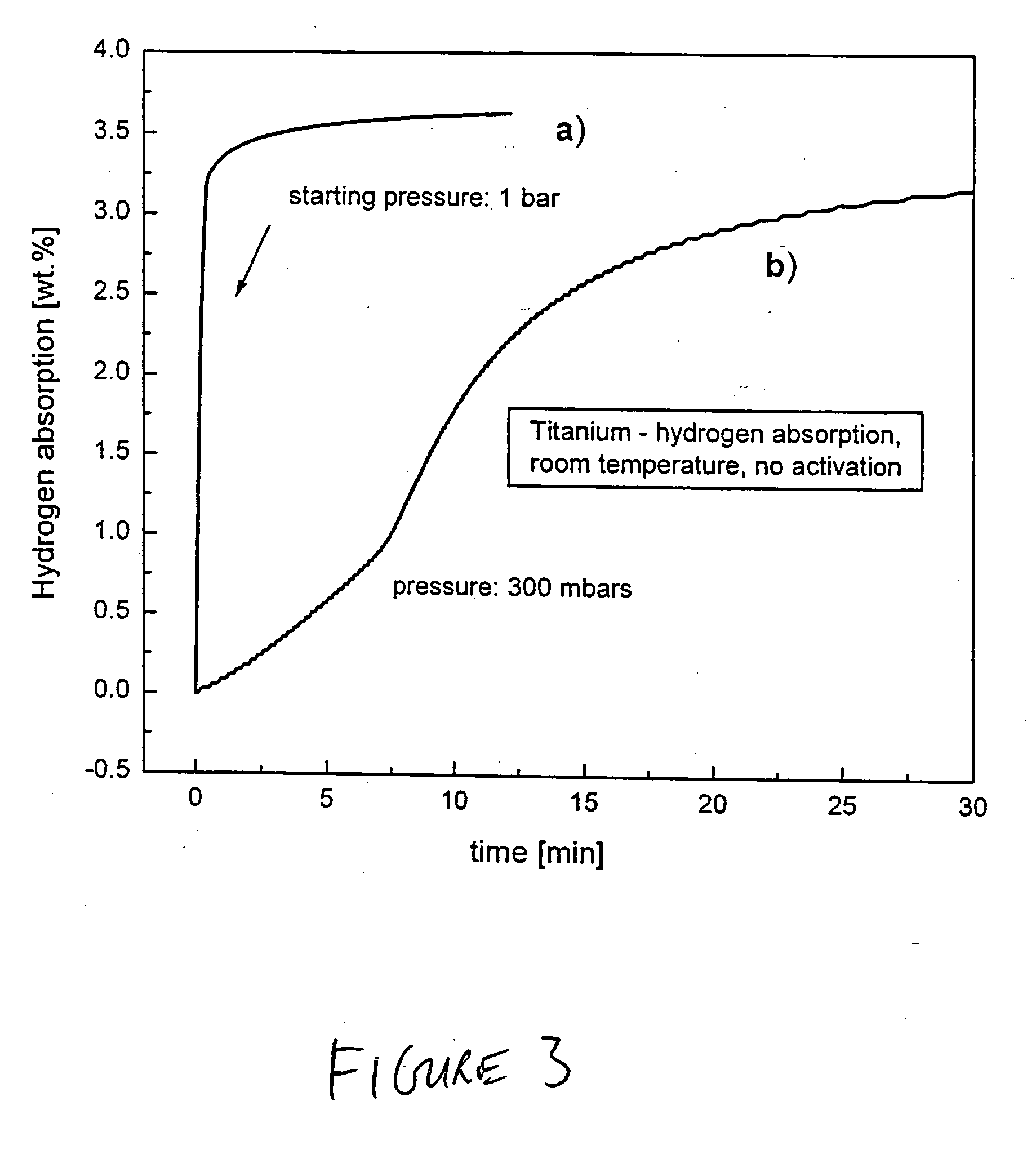
ActiveUS20050002856A1Enhance kinetics of hydrolysisHydrogen productionChemical recyclingAlcoholDesorption
The present invention relates to a hydrogen storage composition prepared in accordance with a method comprising: (a) combining (i) a metalliferous material selected from the group consisting of: (A) metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or an inhomogeneous combination of at least two of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or (B) a hydride of any of: a metal or a metalloid, or alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or an inhomogeneous combination of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, with ii) a liquid consisting essentially of any of: water, at least one alcohol, or a mixture of water and at least one alcohol, to form a first intermediate; and (b) milling the first intermediate for form an hydrogen transfer facilitator; (c) combining the hydrogen transfer facilitator with a second metalliferous material selected from the group consisting of: (A) a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or inhomogeneous combination of at least two of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or (B) a hydride of any of: a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, or an homogeneous or inhomogeneous combination of at least two of a metal or a metalloid, or an alloy thereof, or a compound thereof, such combining effecting sufficient contact between the hydrogen transfer facilitator and the second metalliferous material so that the hydrogen transfer facilitator is configured to effect absorption or desorption of hydrogen by the second metalliferous material.
Owner:ZALUSKA ALICJA +1
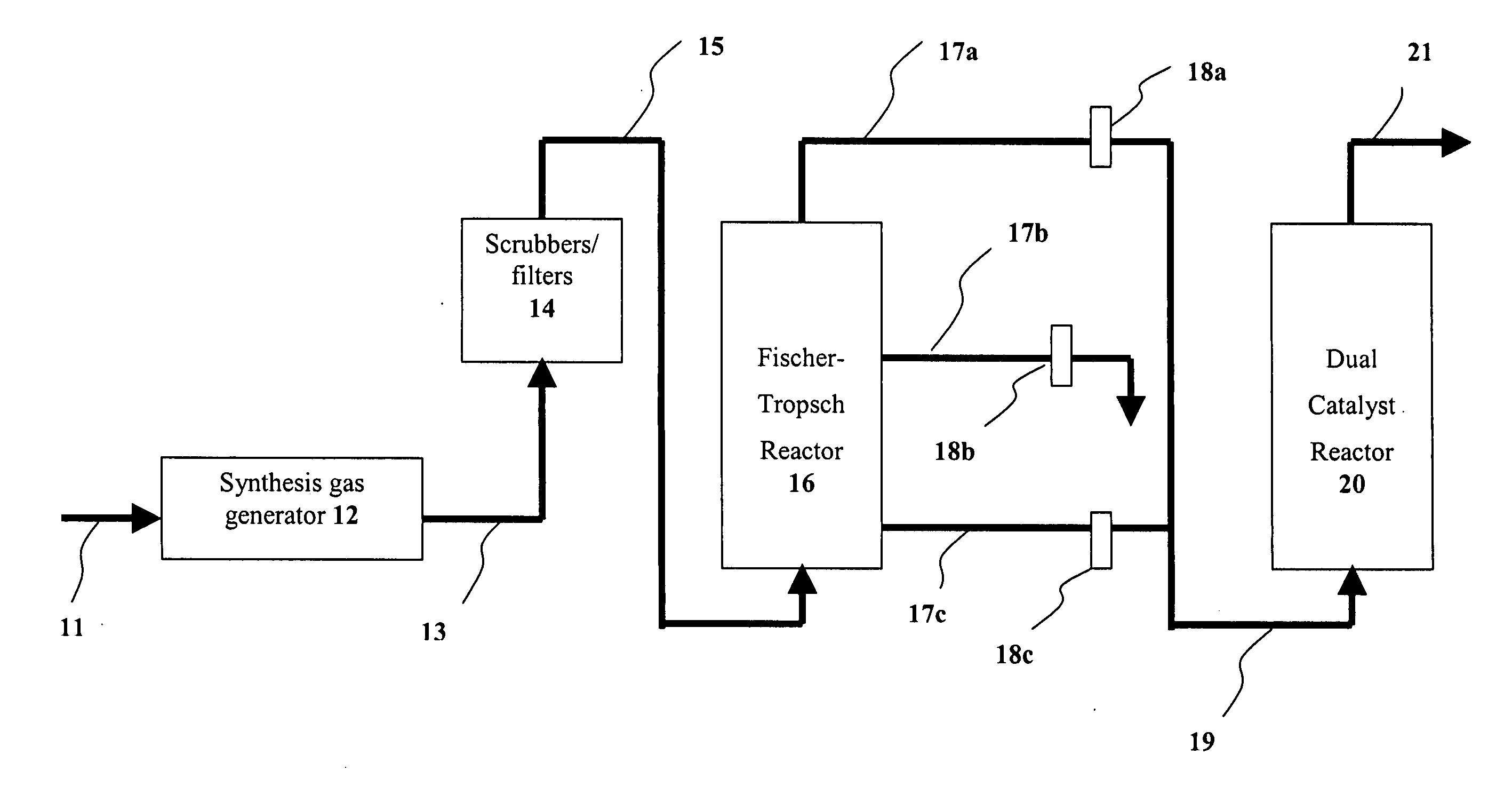
Dual catalyst system for alkane metathesis
InactiveUS7902417B2Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsAlkanePtru catalyst
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
Catalytic conversion method for increasing propylene yield
ActiveCN102952577ADoes not affect distributionNo need to replaceTreatment with plural serial stages onlyCatalytic transformationIsomerization
The invention provides a catalytic conversion method for increasing propylene yield. The method is characterized in that high-quality catalytic cracking raw oil is contacted with a thermal regenerated catalyst having lower mean activity and activities distributed relatively uniformly in a first reaction zone of a reactor to carry out cracking reaction, the generated oil gas and a carbon-containing catalyst carry out selective hydrogen transfer reaction and isomerisation reaction in a certain reaction environment in a second reaction zone, the reaction products and a spent catalyst are separated, the reaction products are further separated into liquefied gas, light gasoline fractions, heavy gasoline fractions, diesel and other products by a fractionating system, the separated spent catalyst is recycled after being stripped and regenerated, and the C4 fraction and / or the light gasoline fractions are injected into the reactor for further reaction. By the method, the propylene yield can be increased and product distribution can be simultaneously improved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for synthesizing light aromatic hydrocarbon and liquefied petroleum gas from low carbon number oxygen-containing compound mixed raw material
ActiveCN102992931AEasy to prepareReduce dependenceGaseous fuelsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsCarbon numberOxygen
A method for synthesizing light aromatic hydrocarbon and liquefied petroleum gas from low carbon number oxygen-containing compound mixed raw material. The method comprises steps of: preheating and vaporizing low carbon number oxygen-containing compound mixed raw material, and sending the material into a reactor; under the effect of catalyst, conversing the reaction material into liquid aromatic hydrocarbons rich in benzene, toluene and xylene, through a dehydration reaction, polymerization and an aromatization reaction; conversing the liquid aromatic hydrocarbons into a liquefied petroleum component rich in propane, butane and isobutane through hydrogen transfer and a cracking reaction; conversing the liquid aromatic hydrocarbons into a liquefied petroleum component rich in propane, butane and isobutane through hydrogen transfer and a cracking reaction; The invention provides a novel method, which employs low carbon number oxygen-containing compound from biomass and renewable resource as a raw material to produce aromatic compounds (benzene, toluene and xylene) under the effect of the catalyst, and aims to reduce dependence of aromatic hydrocarbon production on fossil fuels.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
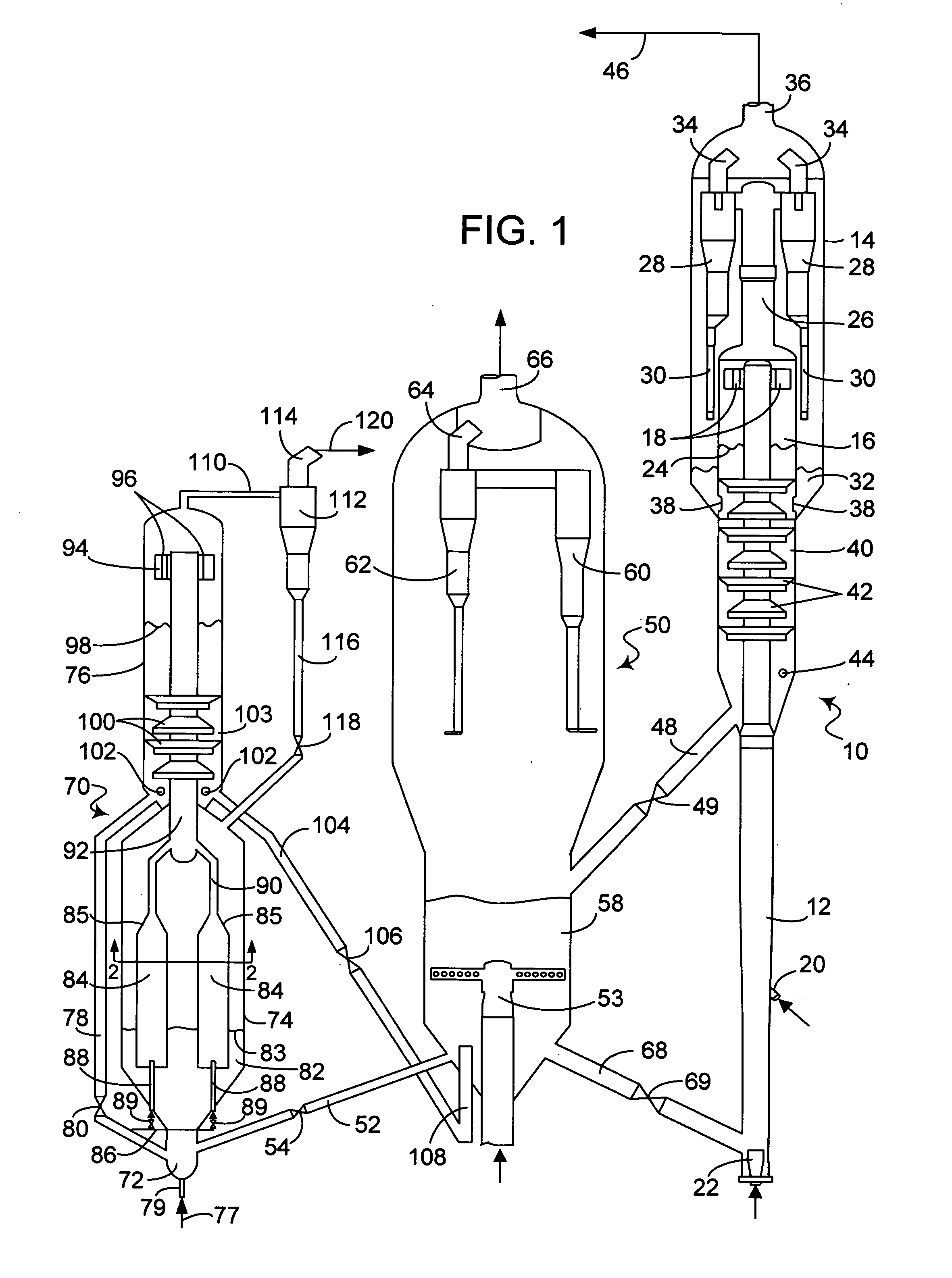
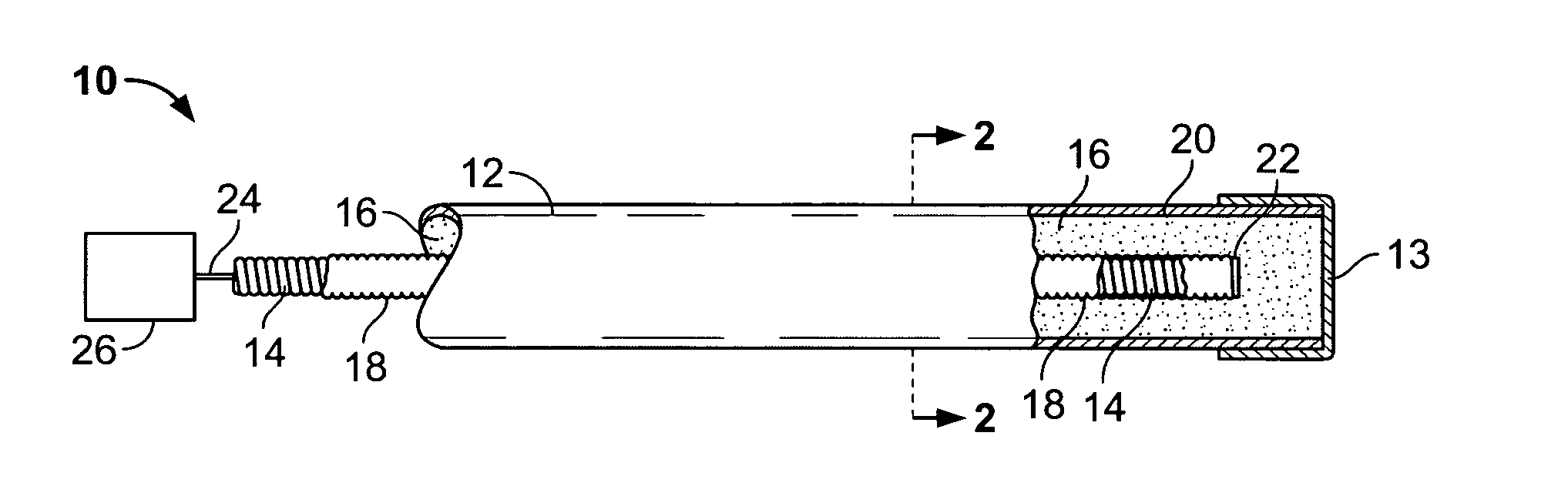
Process for upgrading fcc product with additional reactor
InactiveUS20040140246A1Catalytic naphtha reformingTreatment with plural serial stages onlySulfurNitrogen
A process is disclosed for taking a cut from an FCC reactor product and reacting it in a separate reactor to upgrade the product quality Cracking or reformulating reactions in the separate reactor give reductions in olefins and reformulating hydrogen-transfer reactions convert undesirable olefins to isoparaffins and aromatics without reducing octane value Catalyst particles from the FCC reactor may be cycled to the separate reactor This process has also been found to substantially diminish concentrations of nitrogen and sulfur compounds fed to the separate reactor.
Owner:UOP LLC
Catalyst and method for improving selectivity of preparation of aromatic hydrocarbon products from methanol
InactiveCN105949019AInhibition of recombinationHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieve catalystAlkaneDehydrogenation
The invention relates to a catalyst and a method for improving the selectivity of preparation of aromatic hydrocarbon products from methanol in order to mainly solve the problem of low aromatic hydrocarbon yield caused by generation of a large amount of low carbon alkanes due to a hydrogen transfer reaction in the aromatization process. ZSM-5 molecular sieve is modified with different concentrations of Zn, Ag, Ni, Mo, Cu, Pt, Ga and other dehydrogenation metals, the modified ZSM-5 molecular sieve is processed to contain high valence oxide of V, Ce, Fe, La, Co, Au or Cr, the obtained ZSM-5 molecular sieve catalyzes efficient aromatization of methanol in weak oxidation gas and other inert diluted gas mixed reaction atmosphere, the partial pressure ratio of methanol is 0.1-10, the reaction temperature is 350-550DEG C, and the operating pressure is 0.1-4.0MPa. A catalyst is used to accelerate dehydrogenation aromatization of intermediate olefin substances, and the high valence metal oxide in the catalyst accelerates activation, and cooperates with weak oxidation gas to realize in situ elimination of hydrogen, so the alkane content in the product reaches the aromatic hydrocarbon selectivity improving purpose, and the aromatic hydrocarbon selectivity is higher than 72wt%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
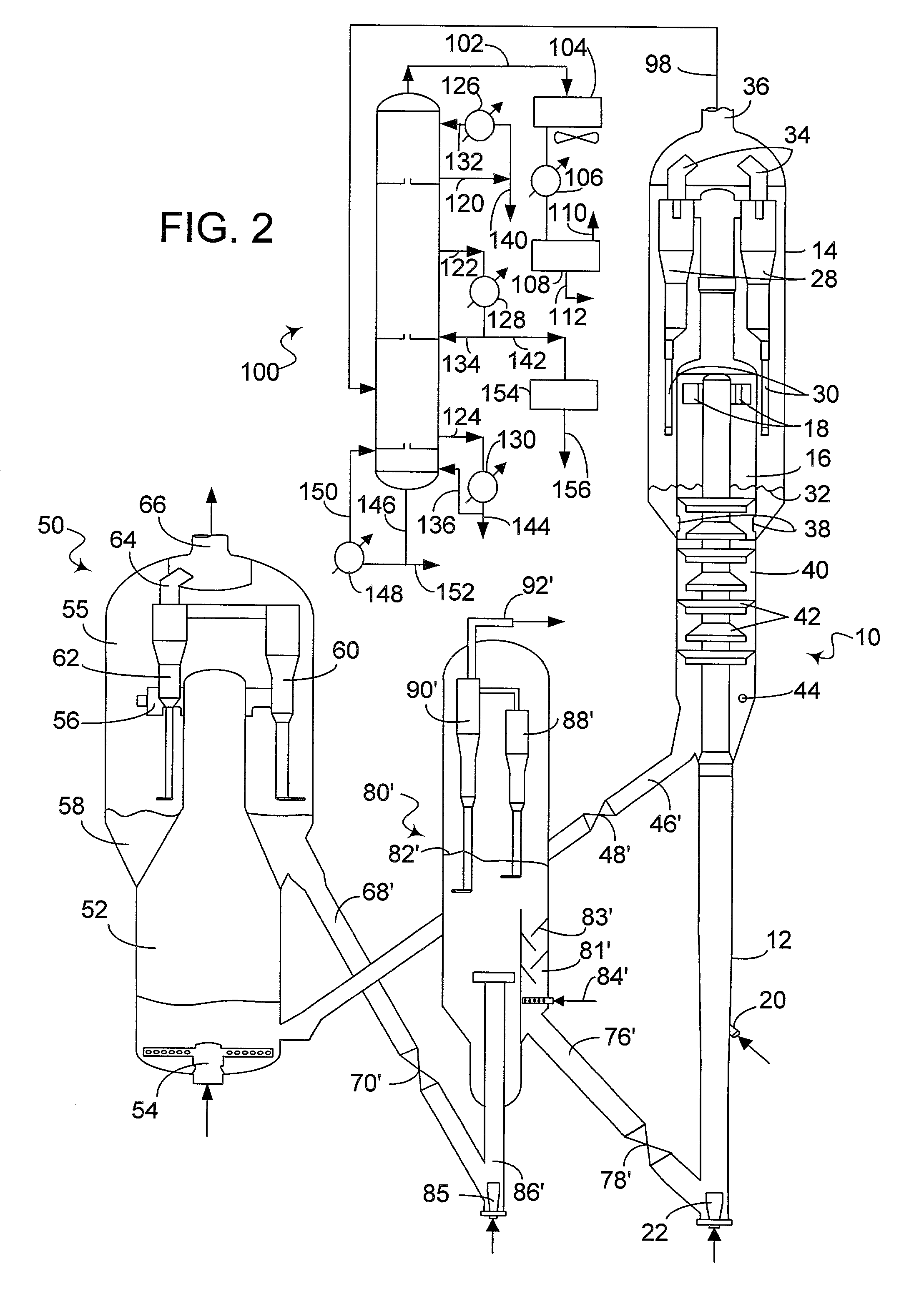
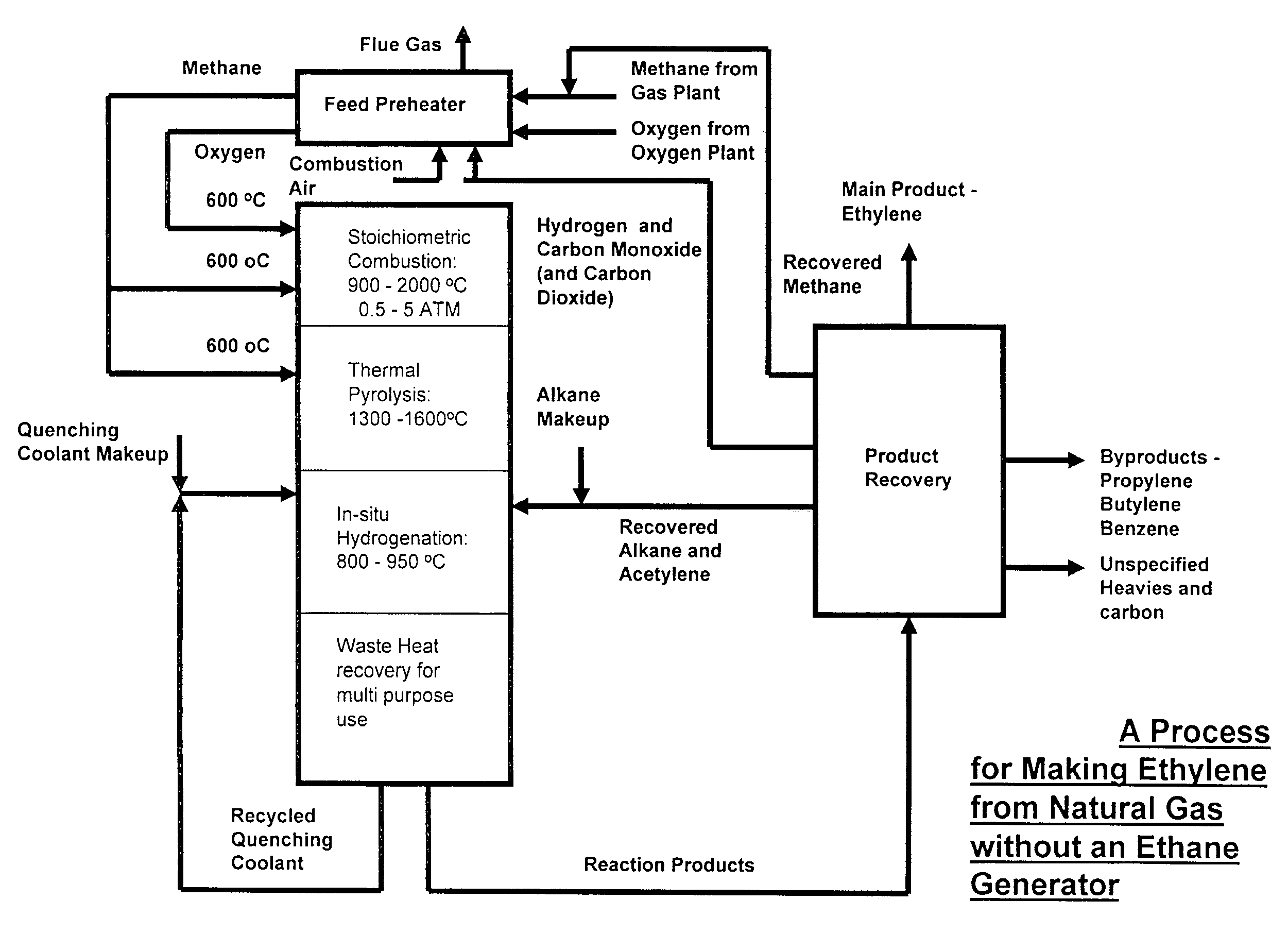
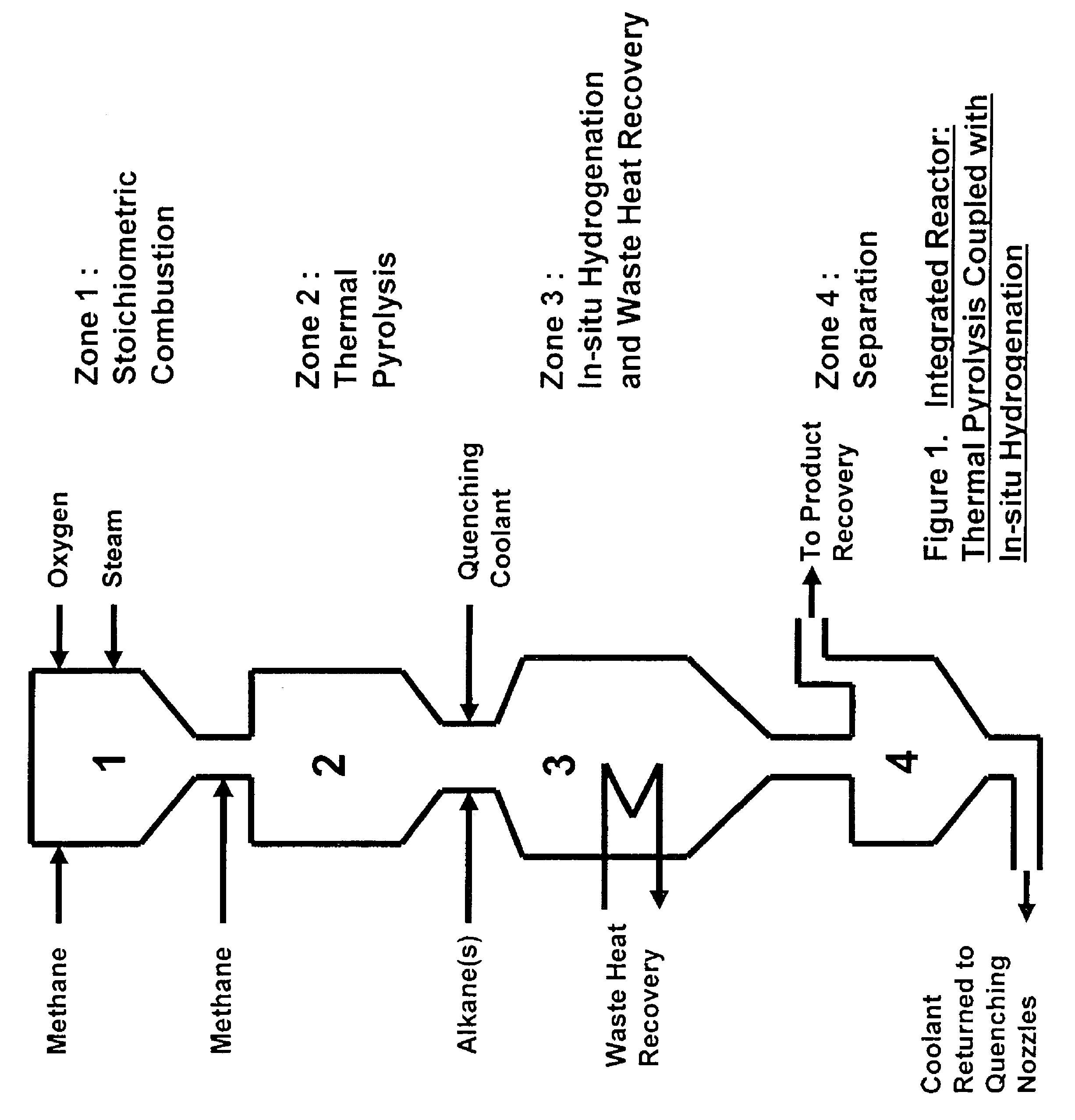
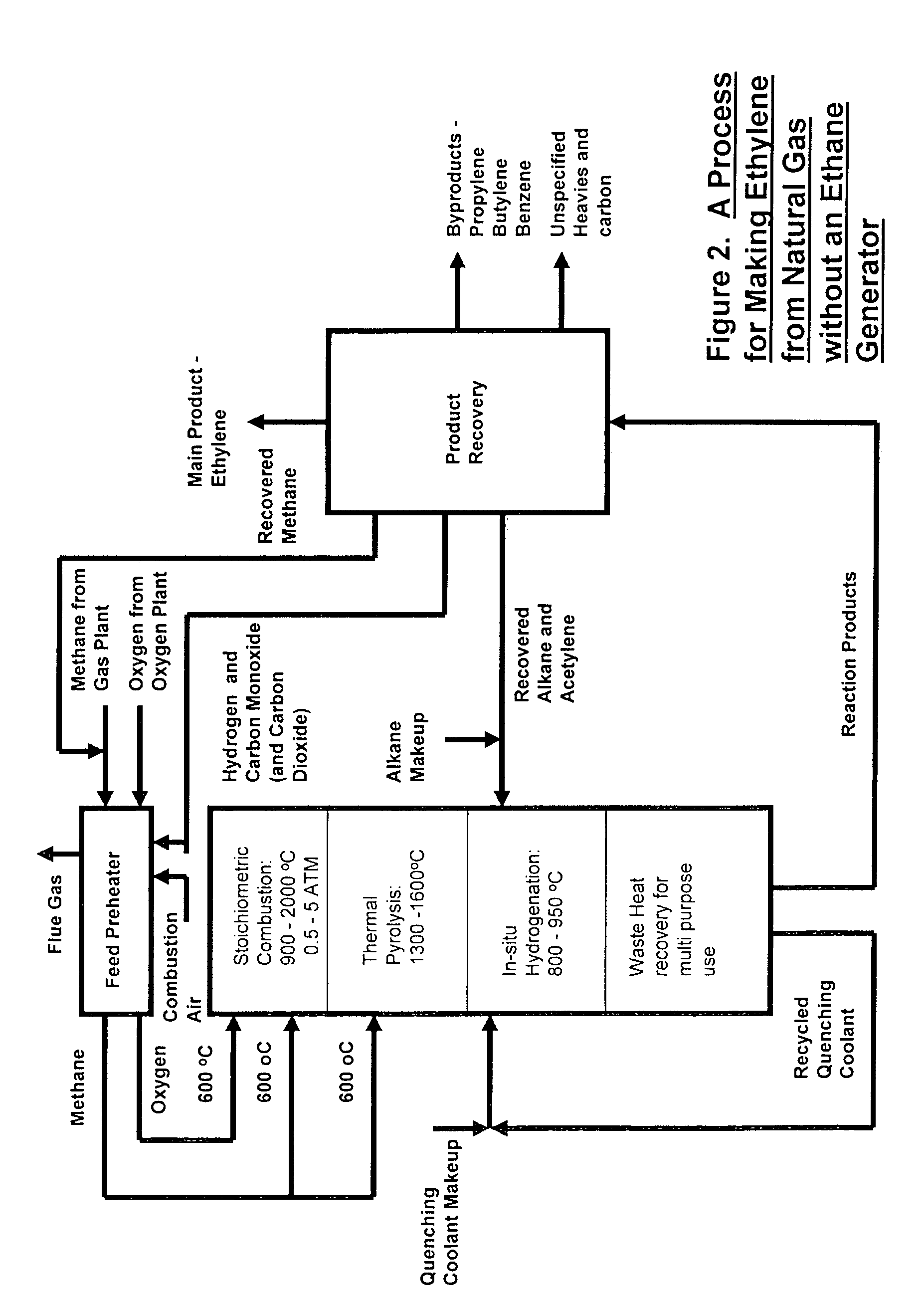
Process for the production of ethylene from natural gas with heat integration
InactiveUS8080697B2Improved economic and energy and environmental aspectHighly effective in conversionHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationHydrocarbon by hydrogenationProcess engineeringAcetylene
The present invention relates to a process for the production of ethylene, comprising the following steps of: (a) thermally converting a feed charge containing methane into acetylene as an intermediate, (b) in-situ hydrogenation of the acetylene produced in step (a) into ethylene by a non-catalytic hydrogen transfer mechanism, characterized by (c) recovering heat from hot effluents obtained in step (b) which may be utilized for different purposes.
Owner:SAUDI BASIC IND CORP SA
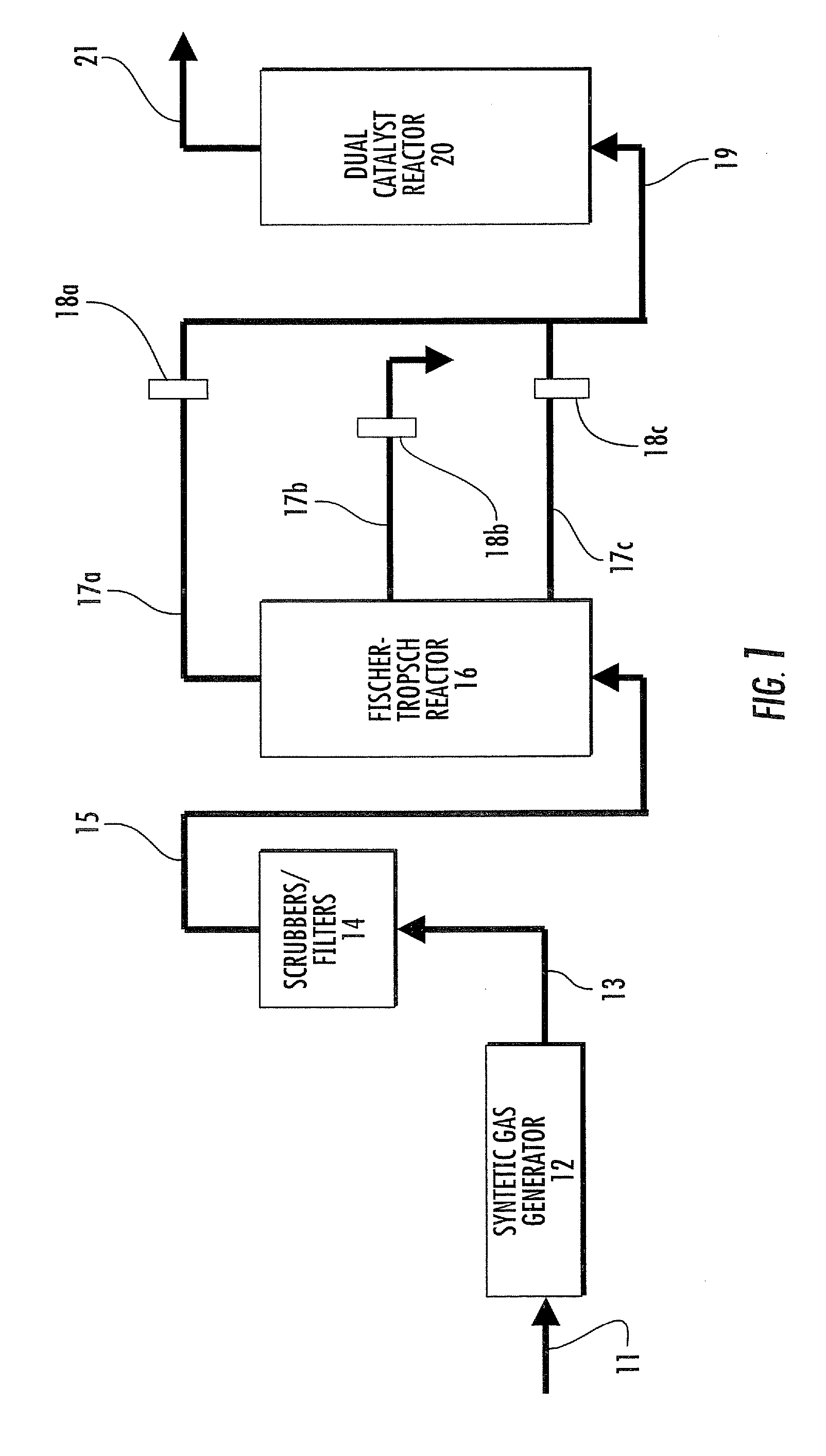
Dual catalyst system for alkane metathesis
InactiveUS20070060781A1Organic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalystsAlkaneOrganic chemistry
A method of converting at least one first alkane to a mixture of at least one low molecular weight alkane (optionally also including additional lower and / or higher molecular weight alkanes) and at least one high molecular weight alkane, comprising: reacting a first alkane in the presence of dual catalyst system comprising a first catalyst (i.e., a hydrogen transfer catalyst and preferably an iridium pincer complex catalyst) and a second catalyst (i.e., a metathesis catalyst) to produce a mixture of low and high molecular weight alkanes.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV +1
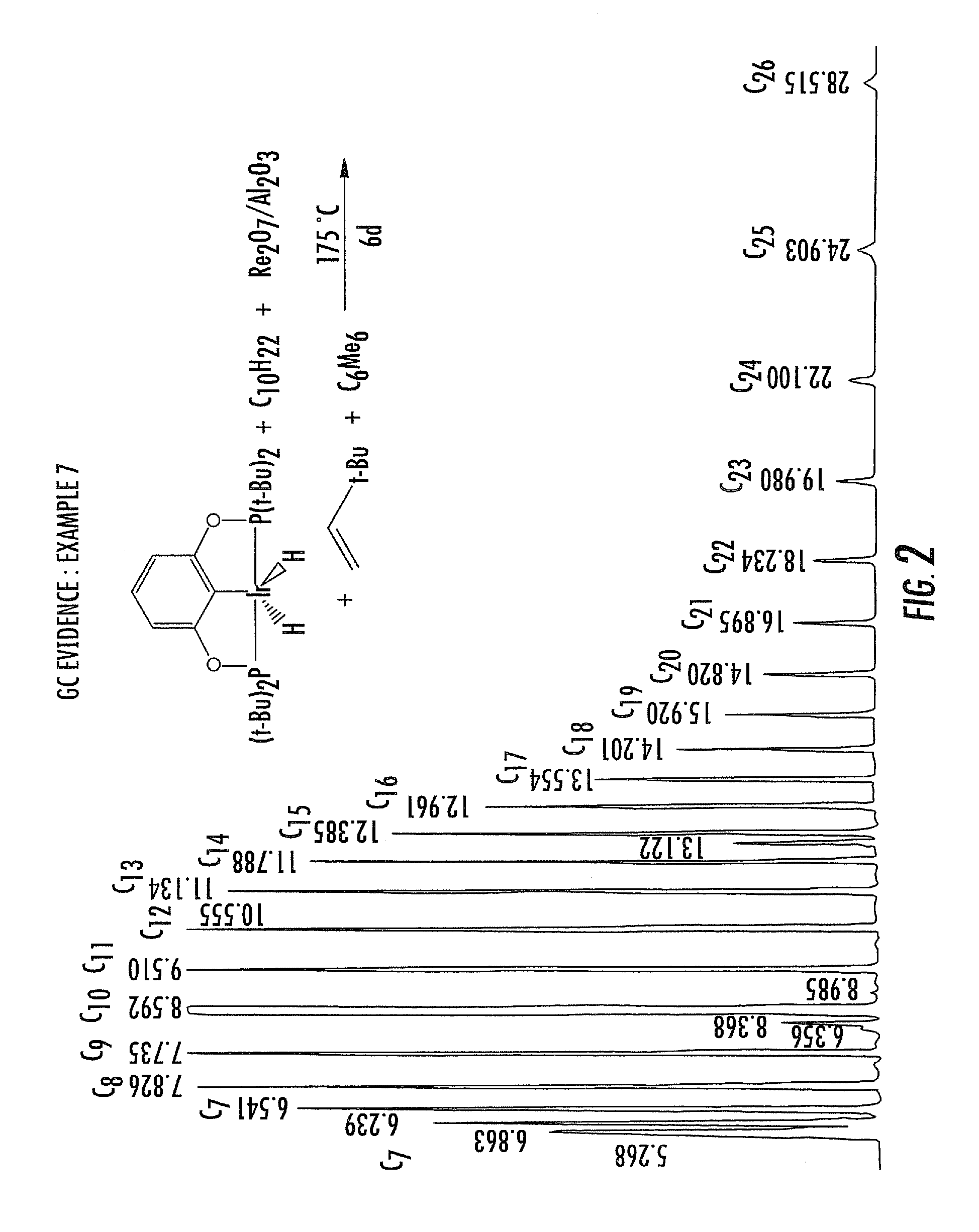
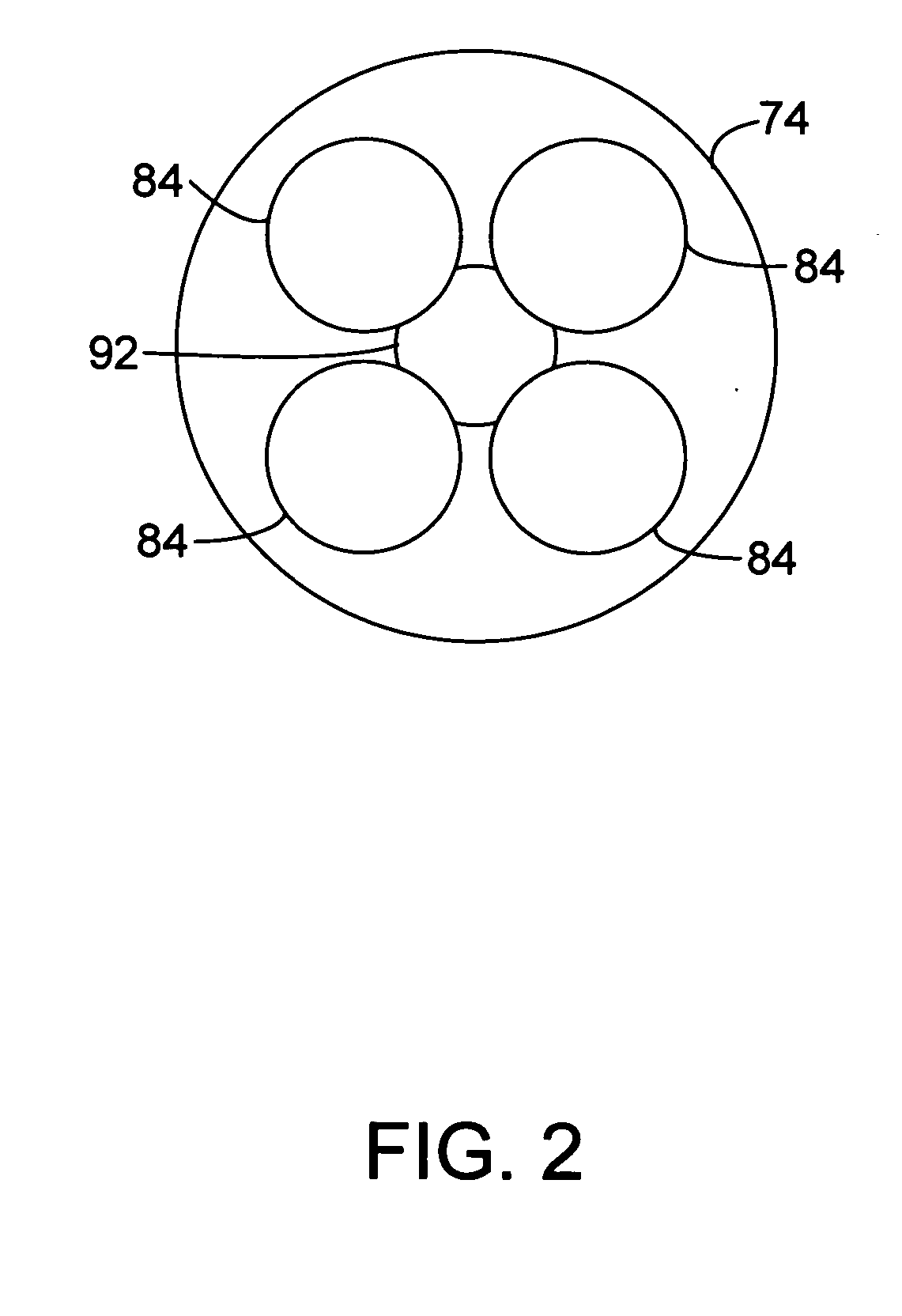
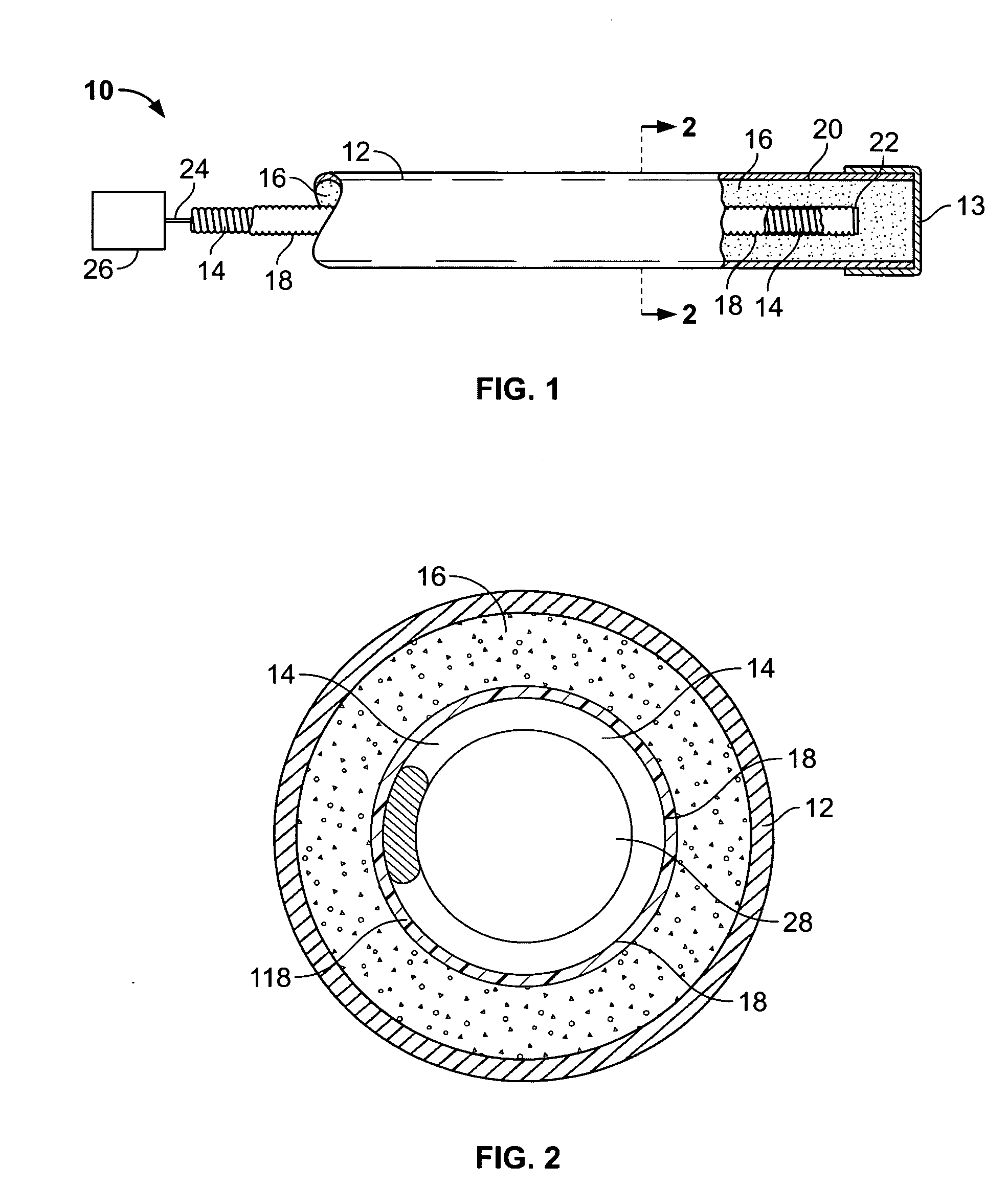
Process and apparatus for upgrading FCC product with additional reactor with thorough mixing
InactiveUS20050118076A1Improve responseLess effectivenessCatalytic crackingFluidised-bed furnacesHydrocarbonChemistry
A process and apparatus are disclosed contacting hydrocarbon feed with catalyst in a reactor vessel under conditions more vigorous than bubbling bed conditions and preferably fast fluidized flow conditions. The vigorous conditions assure thorough mixing of catalyst and feed to suppress formation of dry gas and the promotion of hydrogen transfer reactions.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for preparing aromatic amine, alcohol and alkane by heterogeneous catalytic hydrogen transfer
InactiveCN101182274AWide variety of sourcesHigh activityOrganic reductionOrganic compound preparationChemical industryNitro compound
The invention belongs to the chemical industry technical field and concretely provides a method of preparing for aromatic amine, alcohol or alkane by multi-phase catalytic hydrogenation transfer. The invention considers aromatic nitryl compound, aldehyde ketone and alkene compound as a substrate, hydrogenous polyatomic molecule as a hydrogen donor and loading type nano-gold as catalyst for reflux and stirring for the multi-phase catalytic hydrogenation transfer reaction under 80 DEG C to 200 DEG C and 0.4 to 0.6MPa to prepare for the aromatic amine, alcohol or alkane. The reaction condition of the method of the invention is gentle; the environment is friendly; the applied catalyst has high reaction activity and good selectivity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Preparation of Flavonoid Compounds
Disclosed is an improved method for preparing the isoflavonoid compound (+ / −)-equol, the method comprising reducing an organic diester of the isoflavone daidzein under hydrogen-transfer conditions using palladium hydroxide catalyst.
Owner:YASOO HEALTH
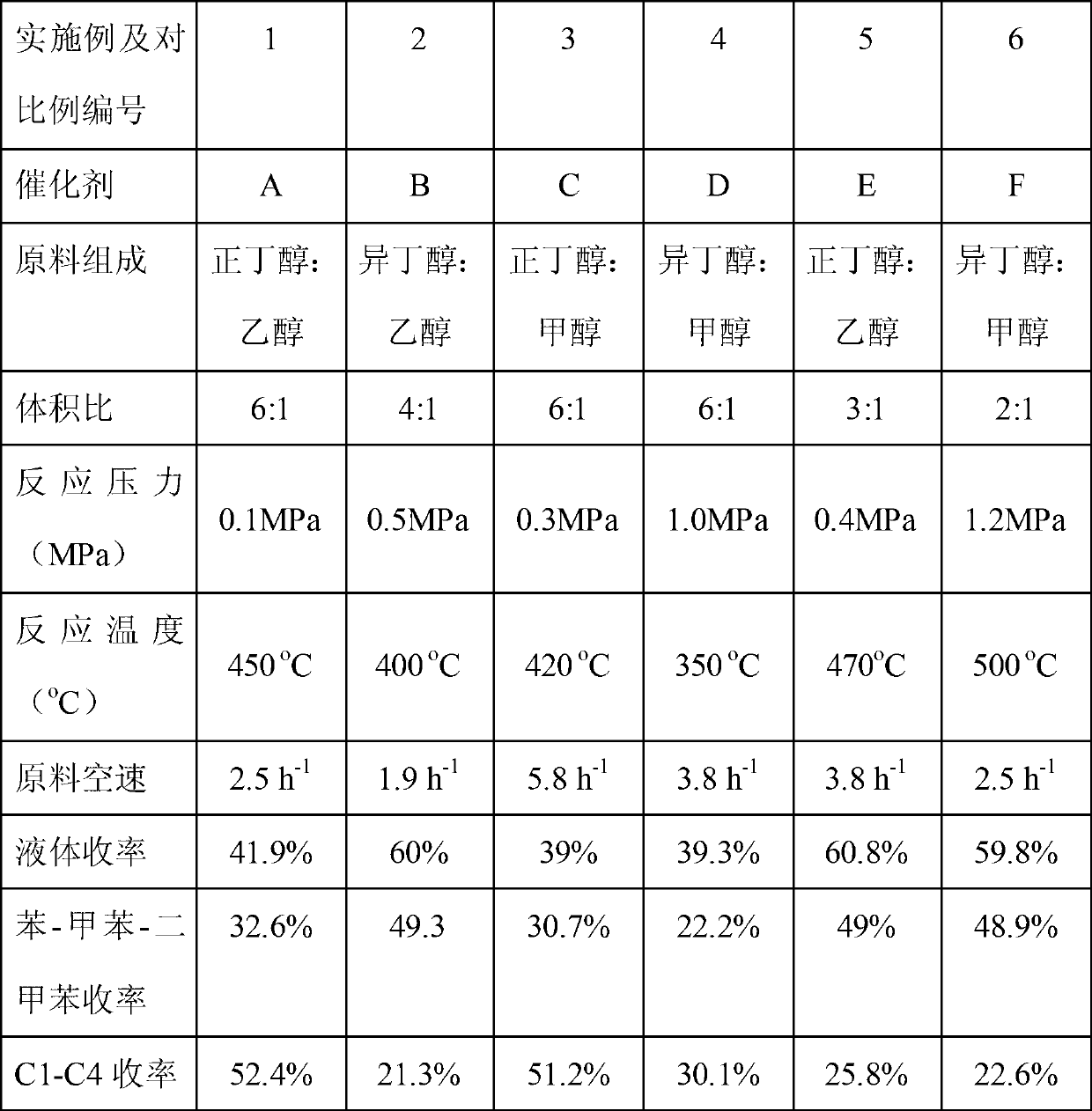
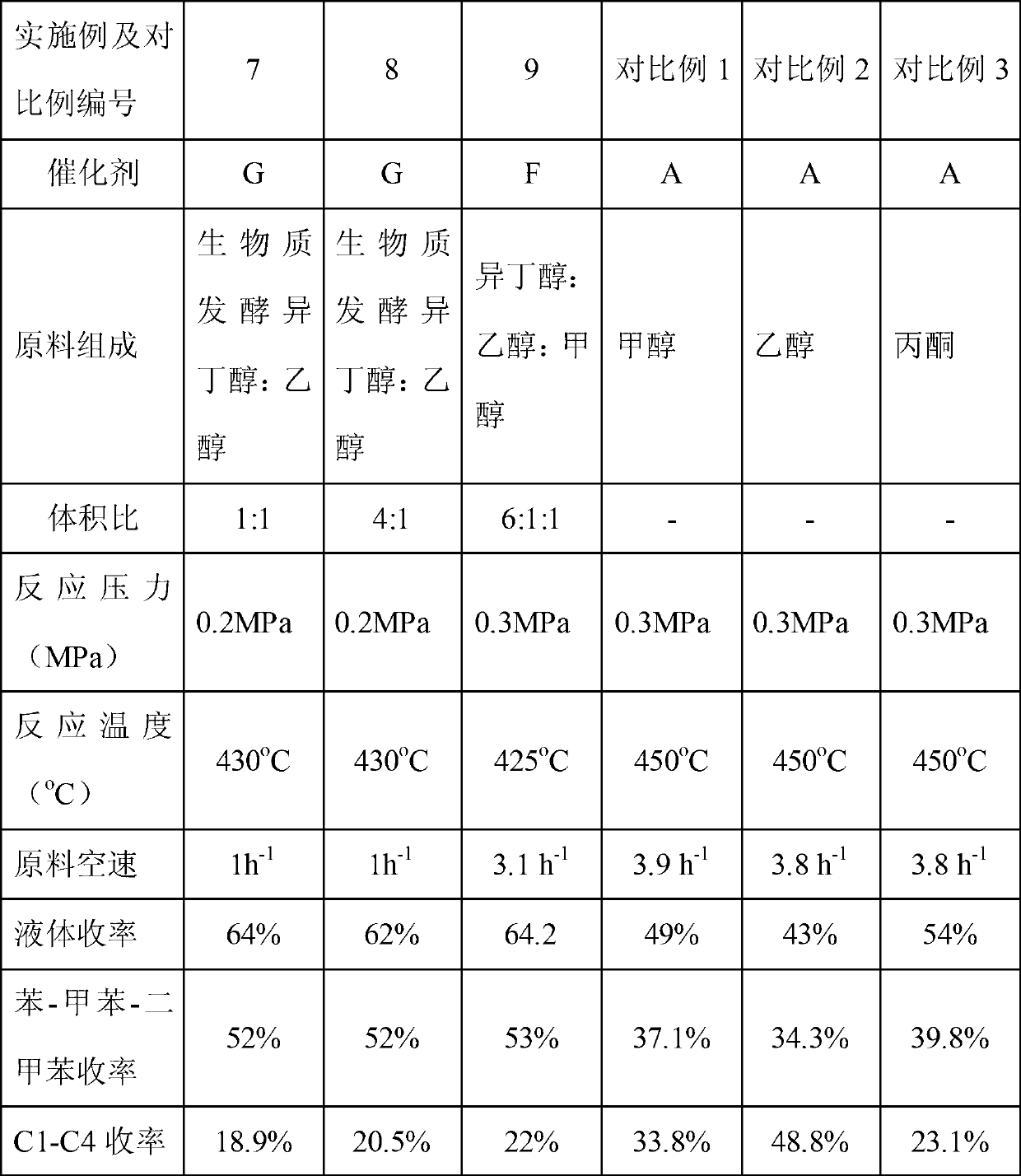
Method for synthesizing liquefied petroleum gas and BTX aromatics by butyl alcohol
InactiveCN103131456AReduce dependenceMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsNitrogen gasPolymerization
The invention provides a method for synthesizing liquefied petroleum gas and BTX aromatics by butyl alcohol. The method for synthesizing the liquefied petroleum gas and the BTX aromatics by the butyl alcohol comprises the steps that butyl alcohol raw materials or mixed reaction raw materials of butyl alcohol raw materials and nitrogen are put into a reaction area; the reaction raw materials are converted into a liquid-phase aromatic hydrocarbon compound rich in benzene, methylbenzene and dimethylbenzene under the action of catalytic agents and through dehydration reaction and polymerization and aromatization reaction; the liquid-phase aromatic hydrocarbon compound is converted into a liquefied petroleum gas component rich in dimethylmethane, hydride butyl and iso-butane through hydrogen transfer and cleavage reaction; and the liquid-phase aromatic hydrocarbon compound and the liquefied petroleum gas component are recovered through gas-liquid separation. According to the method for synthesizing the liquefied petroleum gas and the BTX aromatics by the butyl alcohol, non-fossil resources are adopted as raw materials, the aromatic hydrocarbon compound (the benzene, the methylbenzene and the dimethylbenzene) is produced under the condition that the catalytic agents exist, and dependence on disposable consumption of fossil raw materials (hydrocarbon, naphtha, and diesel oil) is reduced for the production of the aromatic hydrocarbon compound.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
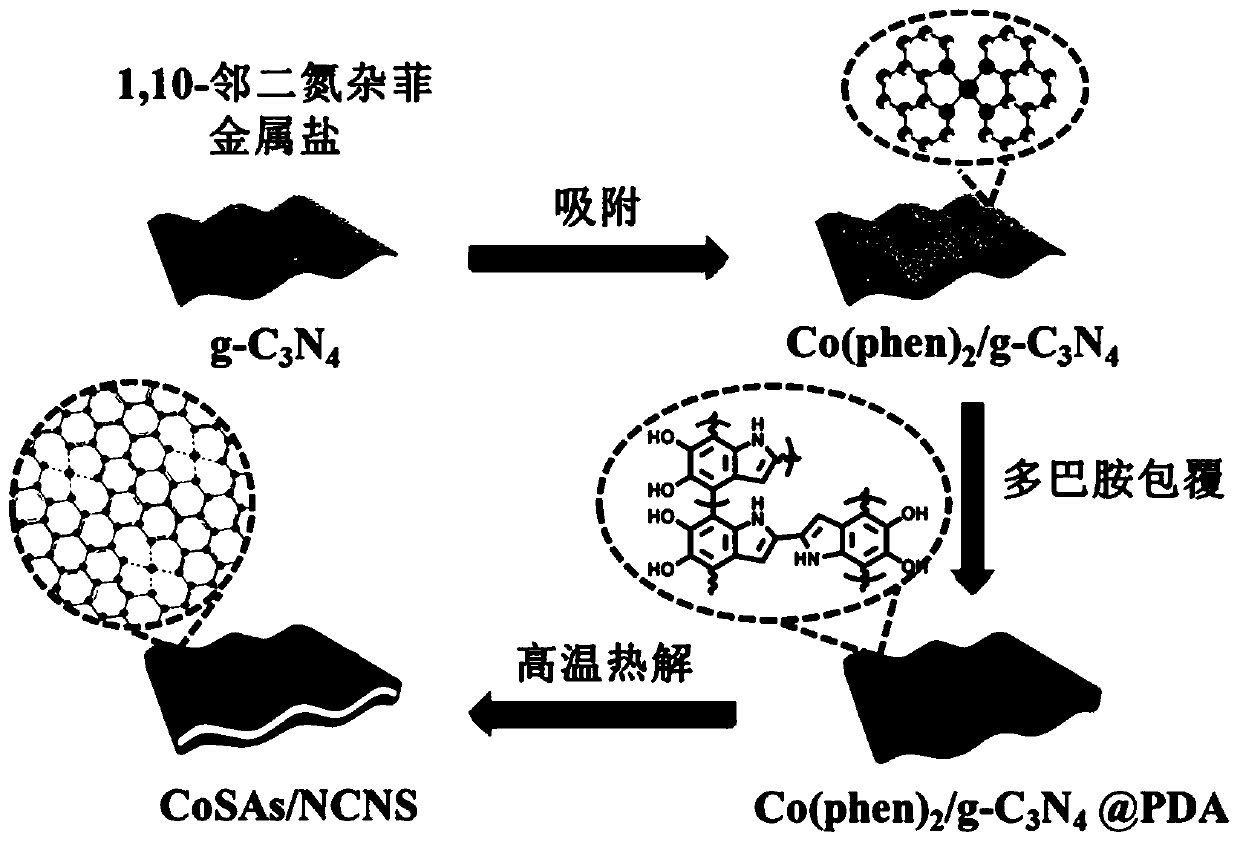
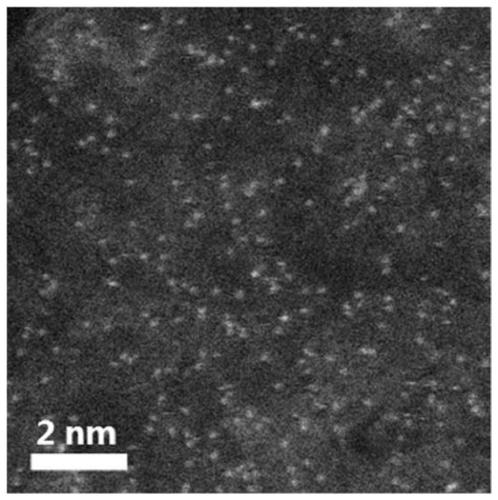
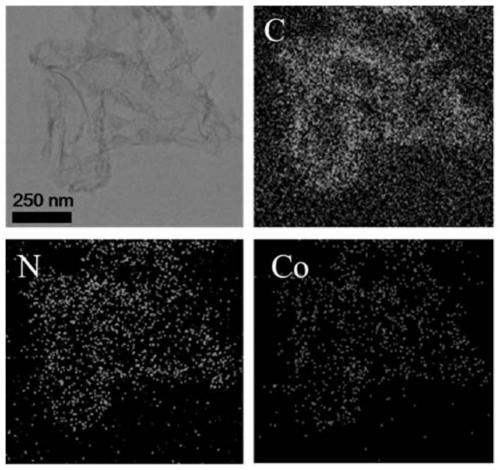
Nitrogen-doped ultra-thin carbon nanosheet loaded monoatomic catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109939717AResolve low activityHigh activityOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationCobaltNitrogen doped
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped ultra-thin carbon nanosheet loaded monoatomic catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The monoatomic catalyst uses the nitrogen-doped ultrathin carbon nanosheet as a carrier, the metal loading is adjustable, the preparation method is simple and feasible and the reproducibility is good, and the preparation method is suitable for various metals (such as Co, Fe, Ni, Cu, Mn and the like). According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of: (1) adsorbing a complex formed by a metal salt and a ligand on g-C3N4;(2) spreading a layer of dopamine polymer outside the obtained complex; (3) carrying out high-temperature treatment on the coated material in an inert atmosphere to obtain the metal monoatomic catalystloaded on the nitrogen-doped ultrathin carbon nanosheet. The cobalt monatomic catalyst shows excellent activity and selectivity in nitrobenzene hydrogen transfer reaction, and the TOF value of the catalyst under similar reaction conditions is 20 times of the best result reported by the literature, so that the cobalt monatomic catalyst has great application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
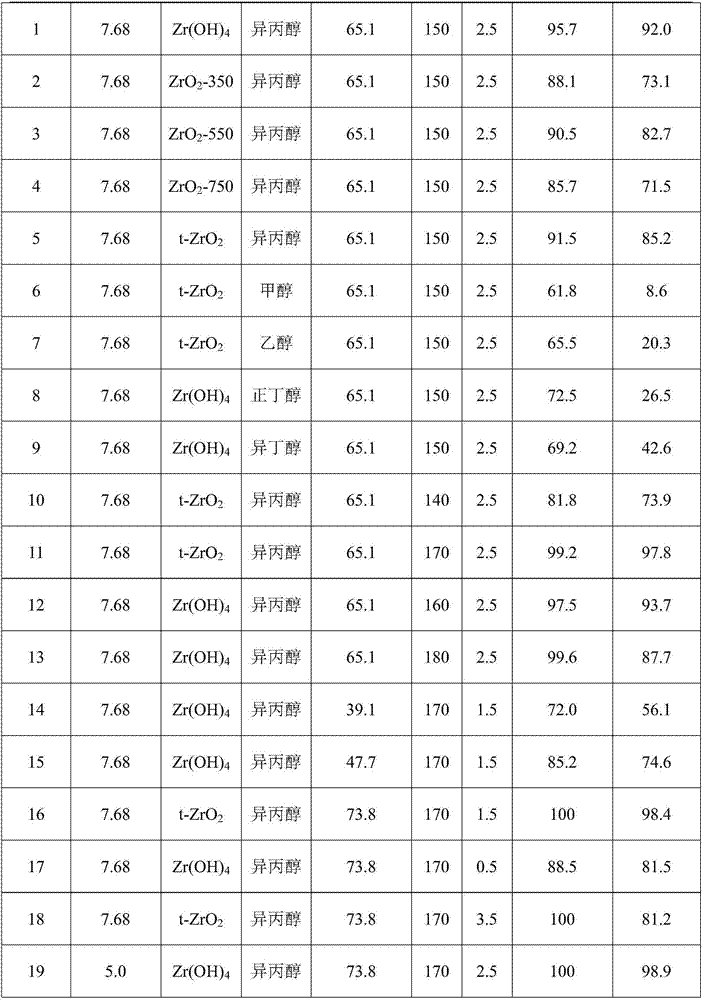
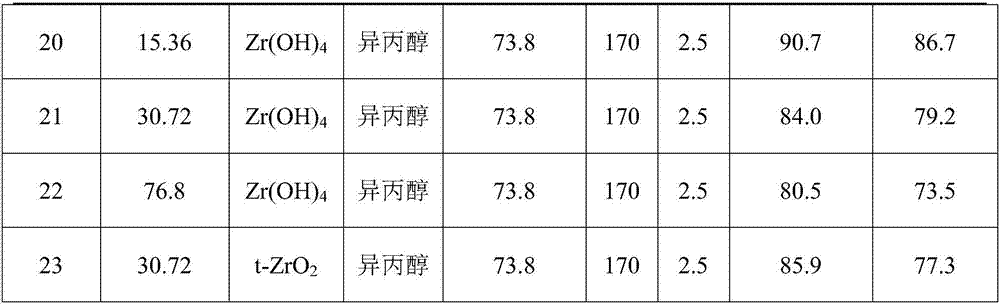
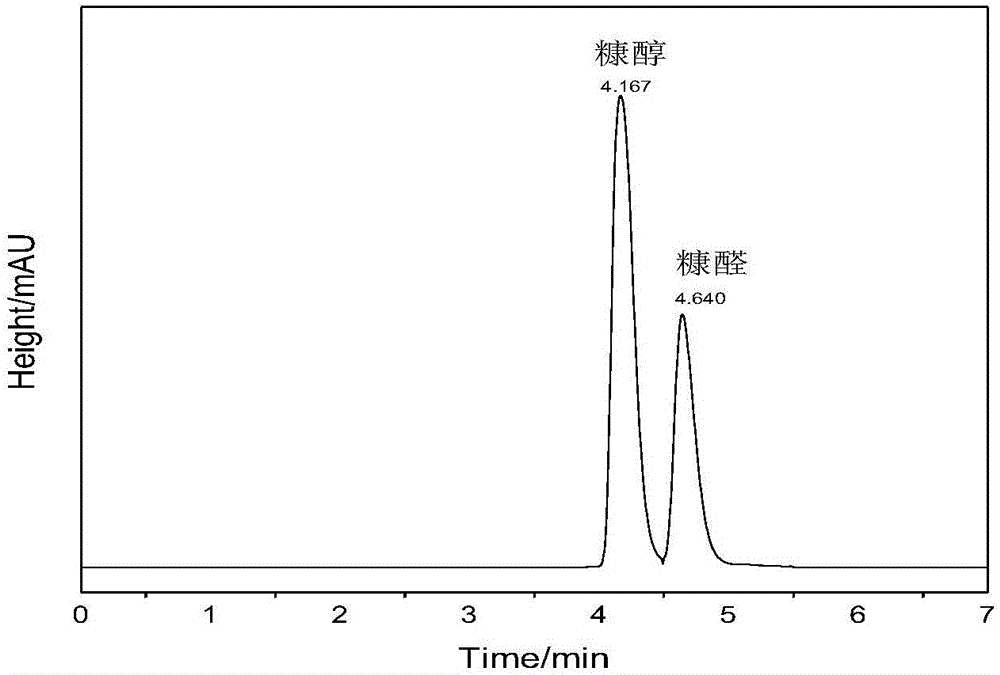
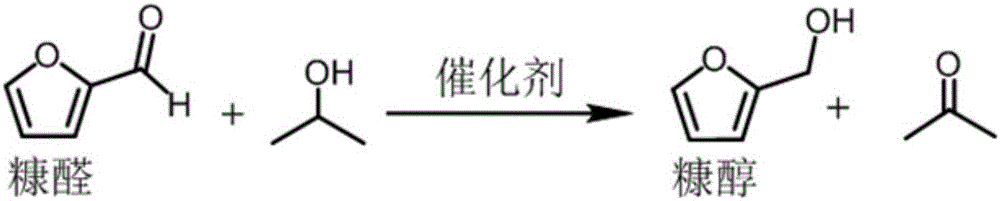
Method for preparing furfuryl alcohol by utilizing hydrogen transfer reaction to catalyze furfuraldehyde
The invention discloses a method for preparing furfuryl alcohol by utilizing hydrogen transfer reaction to catalyze furfuraldehyde. The method comprises the following steps: by taking low alcohol as a solvent and a hydrogen source, and taking a zirconium compound as a catalyst, preparing furfuryl alcohol by catalyzing the furfuraldehyde transfer and hydrogenation reaction under the condition of ordinary pressure nitrogen atmosphere in low alcohol, wherein the reaction temperature is at 140-180 DEG C and the reaction time is 0.5-3.5h. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process, mild reaction condition, low energy consumption of production, low production difficulty, high operation safety, environment protection, safety, low cost, percent conversion of furfuraldehyde as high as 100%, furfuraldehyde yield as high as 98% or above and benefit in popularization.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing furfuryl alcohol by utilizing hydrogen transfer reaction to catalyze furfural
InactiveCN106543115ASimple processEasy to operateOrganic chemistryPhysical/chemical process catalystsReaction temperatureGamma-Valerolactone
The invention provides a method for preparing furfuryl alcohol by utilizing a hydrogen transfer reaction to catalyze furfural. The method comprises the following steps that under the catalysis of a heterogeneous catalyst, namely magnetic hydroxyapatite, the furfural and alcoholic compounds with hydrogen donors are subjected to the hydrogen transfer reaction, wherein the ratio of the magnetic hydroxyapatite to the alcoholic compounds to the furfural is 20-120 g to 8-20 L to 1 mol. A reaction container is filled with nitrogen (N2) of which pressure is 1-20 bar at room temperature, the reaction temperature is 100 DEG C-200 DEG C, and a reduced product, namely the furfuryl alcohol, is obtained after 1-12 h. The method for preparing the furfuryl alcohol by utilizing the hydrogen transfer reaction to catalyze the furfural is simple in process, convenient to operate and safe and environmentally friendly. The catalyst is a non-precious metal catalyst and cheap and easy to obtain, has magnetism and is easy to separate, and can be reused repeatedly. The activity does not decrease. The industrial cost of preparing the furfuryl alcohol can be lowered to a large extent, ethyl levulinate can be catalyzed to react and gamma-valerolactone is generated, and other compounds containing C=O bonds can be also reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Catalyst for preparation of propylene and ethylene from mixed C4 alkenes and application thereof
ActiveCN101664692AReduced responseMolecular sieve catalystsBulk chemical productionAlkali metal oxideReaction temperature
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparation of propylene and ethylene by transforming mixed C4 alkenes and application thereof. The modified components including lanthanide metal oxides, alkalimetal oxides and phosphorus oxides are introduced into the catalyst so that the catalyst has high propylene yield and low hydrogen transfer degree. The catalyst catalyzes the reactions of preparing the propylene and the ethylene by transforming the mixed C4 alkenes under the following reaction conditions that: the reaction temperature is between 460 and 600 DEG C, the pressure is between -0.05 and 0.3 MPa, the weight ratio of feed water to feed C4 is 0 to 1, and the weight space velocity is 1-20 h<-1>. By using the catalyst in the process of catalyzing the reaction of preparing the propyleneand the ethylene by transforming the mixed C4 alkenes, compared with an unmodified molecular sieve, the catalyst can obviously improve the yield of the propylene and the ethylene. Simultaneously, theyield of byproducts C1-C3 alkanes is obviously reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
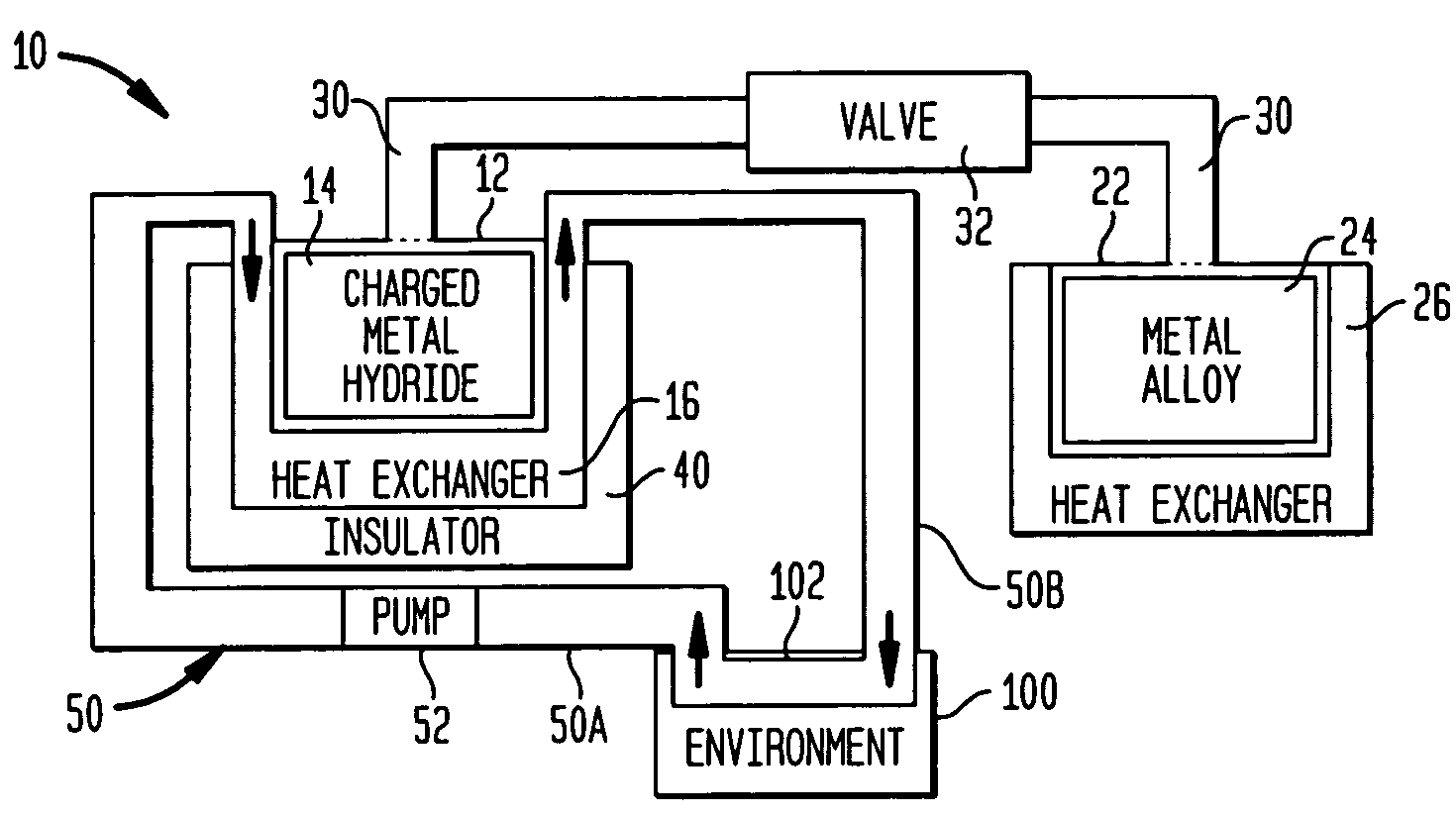
Reconfigurable hydrogen transfer heating/cooling system
A reconfigurable system is provided for effecting temperature changes. A first thermally-conductive container stores a metal hydride while a second thermally-conductive container stores a metal alloy that is capable of absorbing hydrogen atoms at a pressure that is less than the storage pressure of the metal hydride. A valved conduit links the metal hydride and the metal alloy. A thermal insulator is disposed about one of the containers depending on whether the system is to be used for cooling or heating. A circulating fluid is placed in thermal communication with the insulated container and with an environment requiring temperature changes. When the conduit's valve is opened, hydrogen atoms desorbed from the metal hydride are transported through the conduit and are absorbed by the metal alloy. Desorption of the hydrogen generates a cooling effect while absorption of the hydrogen generates heat.
Owner:NAVY SEC OF UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE
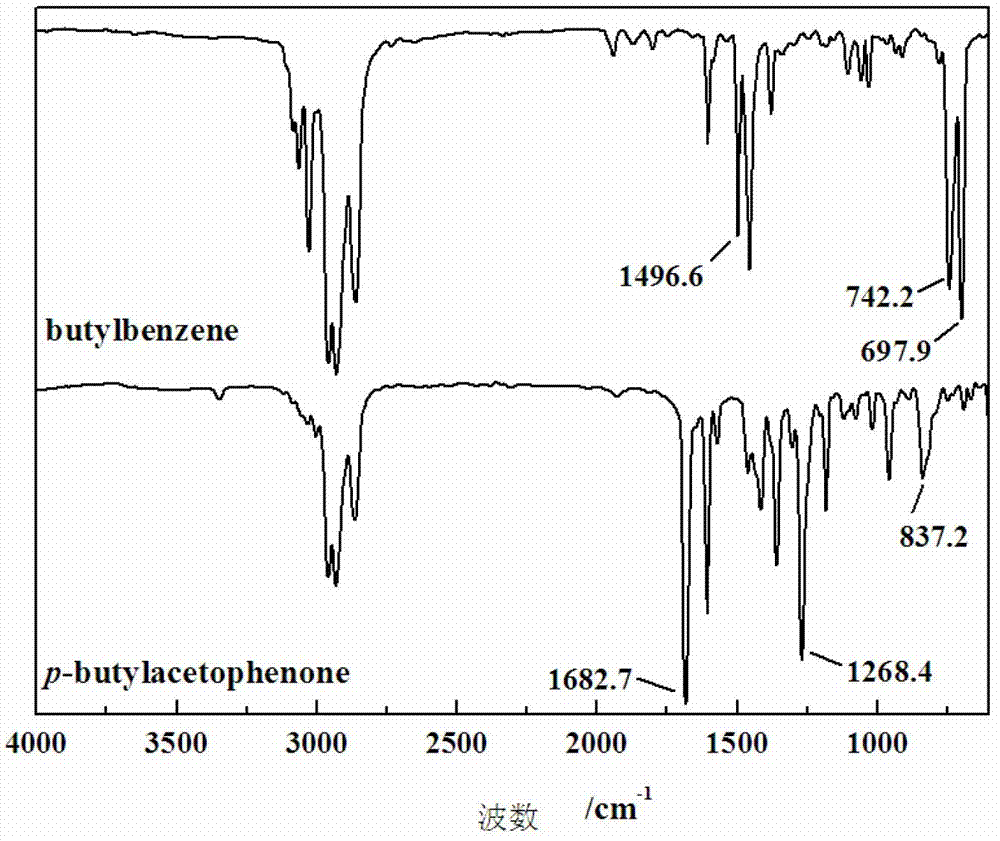
Hydrophobic monomer for synthesizing temperature sensitive polymer oil-displacing agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103396284ARaw materials are easy to getLow costHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsDrilling compositionPolymer scienceChemical reaction
The invention discloses a hydrophobic monomer for synthesizing a temperature sensitive polymer oil-displacing agent and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of the design of oilfield chemical agents. In order to solve the problems of bad temperature resistance, salt resistance and anti-shear ability of a part of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide serving as an oil-displacing agent and solve the problems of complex synthesis method, dissolution difficulty and high cost of modified temperature-resistant and salt-resistant polymer oil-displacing agents, the invention provides a method for synthesizing a temperature sensitive polymer oil-displacing agent with a thermo-thickening function by copolymerizing poly N-alkyl acrylamide, acrylamide and a temperature-resistant, salt-resistant and hydrophobic monomer. According to the design, n-butylbenzene is used as a raw material, and the hydrophobic monomer p-n-butylbenzene ethylene is synthesized through three chemical reactions of Friedel-Crafts acylation, negative hydrogen transfer reduction and dehydration of alcohol to alkene. The reaction conditions are mild, the purification method is simple, the product is pure, and the requirements of temperature resistance and salt resistance of the hydrophobic monomer for forming the temperature sensitive polymer oil-displacing agent can be met.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Flexible and semi-permeable means of hydrogen delivery in storage and recovery systems
InactiveUS20060065552A1Equally distributedProvide protectionReactant parameters controlDrying solid materials without heatMechanical engineeringMaterial Perforation
A container for use in hydrogen transfer includes structural tubular members and perforations for fluid communication with a central passage covered with a film that is selectively permeable to hydrogen, but not to other gases. The tubular member walls comprise a sturdy material to fix the hydride powder, preventing it from shifting within the container. The hydrogen flow, when being absorbed or desorbed by the metal hydride, will pass through the film both as it is absorbed in the hydride material and also after it is desorbed to pass into the central passage. Simultaneously, the tubular member material, acting as a flexible cover or support for the film, retains contaminant gases within the conduit passage, but permits hydrogen to flow therethrough. Alternatively, a flexible conduit may be interspersed within selected ones of the longitudinal structural members, and hydride material may be packed within the springs, which provide for expansion protection.
Owner:MPD TECH
Nitrogen heterocycle ligand transition metal complex, and preparation and catalytic application thereof
ActiveCN102417523AThe synthesis method is simpleRuthenium organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationDiphosphinesKetone
The invention relates to a novel nitrogen heterocycle ligand / phosphine ligand transition metal complex, and preparation and application thereof in asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation and hydrogen transfer. The complex has the following structural formula: [MLnL' XY], wherein the transition metal M is Ru, Rh, Ir, Pd, Pt, Co, Ni or Os. The complex also contains a nitrogen heterocycle ligand, two monophosphine ligands or one diphosphine ligand, and the like. The transition metal compound, dinitrogen or mononitrogen ligand and diphosphine or monophosphine ligand react at 0-120 DEG C in an organic solvent for 0.5-20 hours to obtain the complex. The complex is used for asymmetric catalytic transfer hydrogenation or asymmetric hydrogenation reaction, and especially for asymmetric catalytic hydrogenation reaction of ketones, esters, hypnones and derivatives thereof, diphenyl ketones and derivatives thereof, beta-N,N-dimethylamino-alpha hypnones and derivatives thereof and other ketone compounds of which the alpha site is a large steric hindrance alkyl group.
Owner:ENANTIOTECH CORP
Styrene monomer polymerization inhibition using substituted dihydroxyarenes and nitroxides
InactiveUS6284936B2Inhibition of polymerizationEffectively inhibit the polymerization of styreneOther chemical processesDistillation purification/separationNitrogen oxideOrganic chemistry
It has been discovered that the polymerization of vinyl aromatic compounds, such as styrene, may be inhibited by the addition of a composition that contains an alkyl-dihydroxyarene, a hydrogen transfer agent, and a stable nitroxide. In another, preferred embodiment of the invention, these three components are blended in an organic amine.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
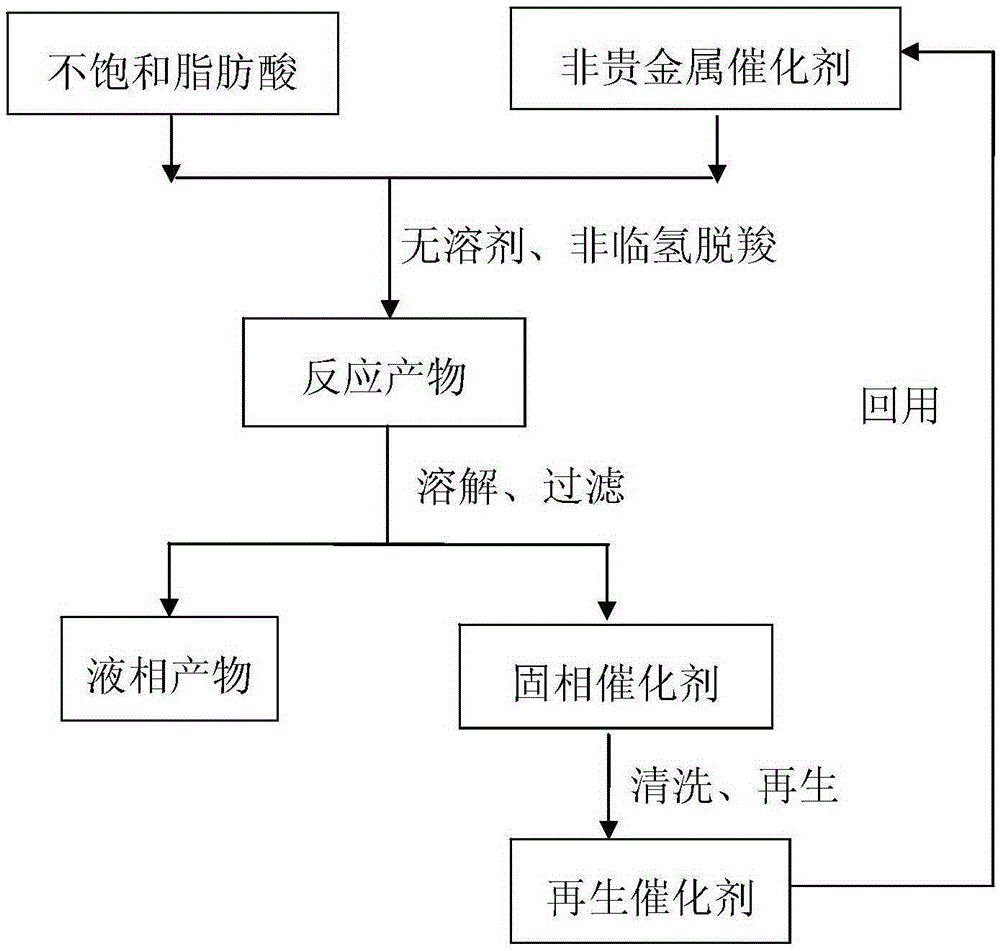
Method for preparation of long-chain alkane from unsaturated fatty acid at zero hydrogen consumption
ActiveCN105237319AEasy to separateIncrease the rate of the decarboxylation reactionMolecular sieve catalystsHydrocarbonsAlkaneLiquid product
The invention discloses a method for preparation of long-chain alkane from unsaturated fatty acid at zero hydrogen consumption. The method includes: 1) adding unsaturated fatty acid and a non-noble metal catalyst in a mass ratio of 4:1-20:1 into a high temperature and high pressure reaction kettle; 2) conducting heating to 300-390DEG C to carrying out reaction for 1-8h; 3) cooling the reaction product, dissolving the product in an organic solvent, and performing filtering to obtain a liquid product and a solid catalyst; and 4) subjecting the catalyst to cleaning and regeneration for reuse. The catalyst is a double-active non-noble metal loaded catalyst, is prepared by co-precipitation method or impregnation method, and is regenerated by reduction calcination in hydrogen. According to the invention, solvent is unnecessary in the reaction process, the energy consumption is low, and the emission is little. The non-noble metal catalyst can effectively catalyze in-situ hydrogen transfer and non-hydrogen decarboxylation reaction, the catalyst is low in cost and is easy to recover, and the process is simple and green, and has zero hydrogen consumption.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com