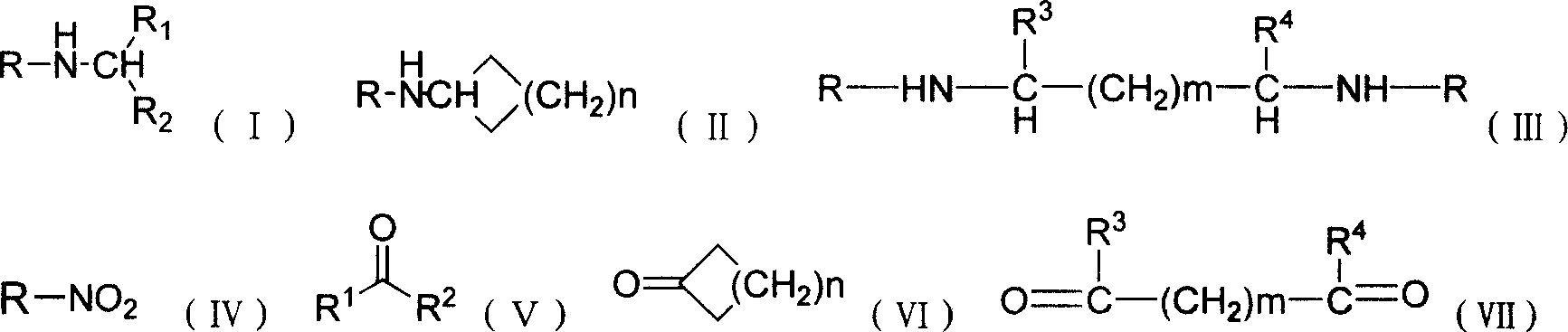
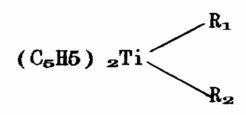Patents
Literature
652 results about "Raney nickel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Raney nickel /ˈreɪniː ˈnɪkəl/, also called spongy nickel, is a fine-grained solid composed mostly of nickel derived from a nickel–aluminium alloy. Several grades are known, but most are gray solids. Some are pyrophoric, most are used as air-stable slurries. Raney nickel is used as a reagent and as a catalyst in organic chemistry. It was developed in 1926 by American engineer Murray Raney for the hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
Synthesis method of D,L-danshensu isopropyl ester
ActiveCN103980120ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getShort reaction stepsPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesOrganic compound preparationHydrogenSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a synthesis method of D,L-danshensu isopropyl ester. The method comprises taking protocatechuic aldehyde as an initial raw material, protecting phenolic hydroxyl by benzyl, carrying out Darzens epoxidation, followed by carrying out catalytic reduction with palladium catalyst / hydrogen or Raney nickel / hydrogen, and thus obtaining the D,L-danshensu isopropyl ester. The purity of the product synthesized by the method can reach 98%, and the yield can reach 55%. Moreover, the synthesis method has the advantages of simple and easily obtained raw materials, short routes and high yield, and is suitable for large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Synthesis method of racemic bornyl beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-hydroxypropionate
ActiveCN104030923ASynthetic Method AdvantagesRaw materials are cheap and easy to getPreparation from carboxylic acid halidesOrganic compound preparationHydrogenSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a synthesis method of racemic bornyl beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-hydroxypropionate. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out Darzens epoxidation on an initial raw material benzyl protected protocatechualdehyde, and carrying out palladium catalyst / hydrogen or Raney nickel / hydrogen catalytic reduction to obtain racemic bornyl beta-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-hydroxypropionate. The purity and the yield of a product synthesized by adopting the method reach 98% and 48.6% respectively. The synthesis method has the advantages of simple and easily available raw material, short route, high yield, and suitableness for large scale industrialized production.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV +1
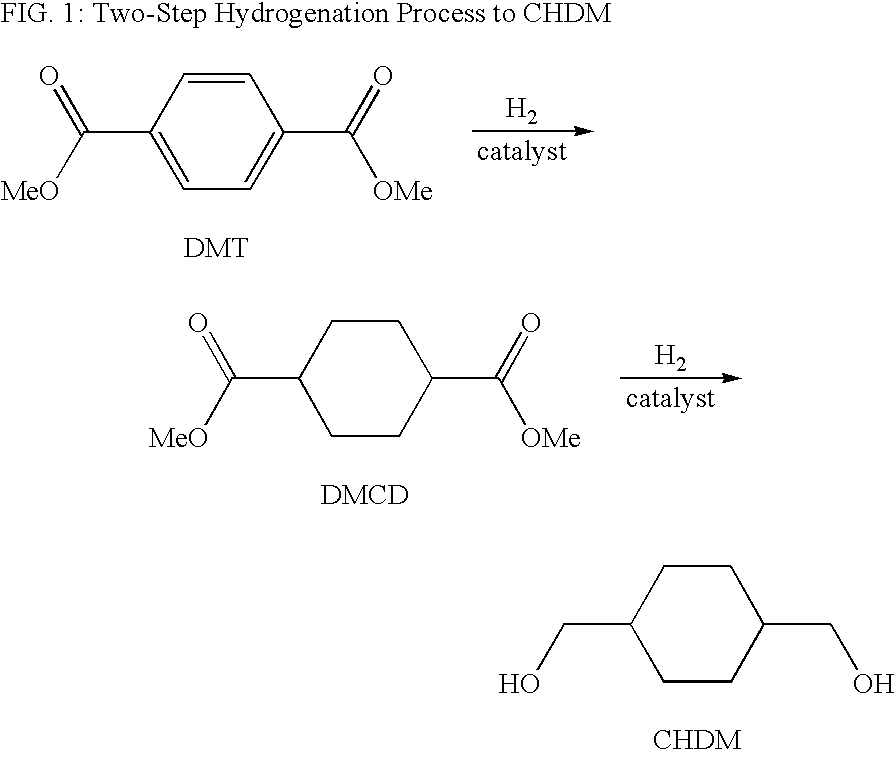
Process for a cyclohexanedimethanol using raney metal catalysts
InactiveUS6919489B1High trans contentOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionRheniumCyclohexanedimethanol
Disclosed is a process for a cyclohexanedimethanol by hydrogenation of a cyclohexane-dicarboxylate ester in the presence of a Raney metal catalyst doped with rhenium. The process is useful for the reparation of 1,4-cyclohexanedimethanol from dialkyl esters of 1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylate or dialkyl terephthalates. When Raney nickel is used as the catalyst, the process produces CHDM having a high trans content.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Gastrodin synthesizing method
InactiveCN102516329AReduce pollutionSuitable for industrial productionSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationKetone solventsPressure reduction
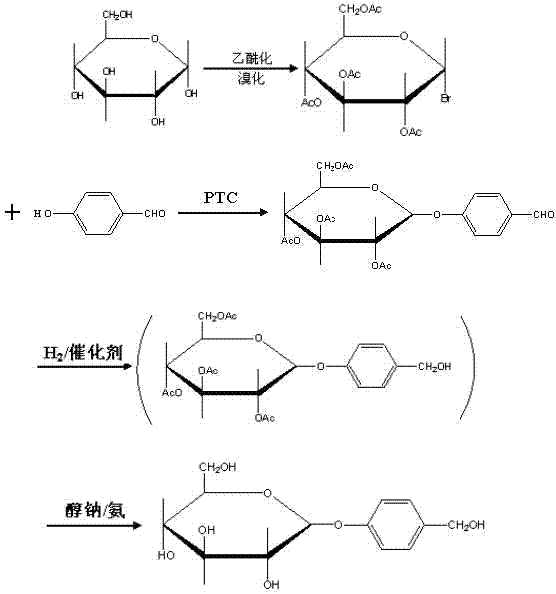
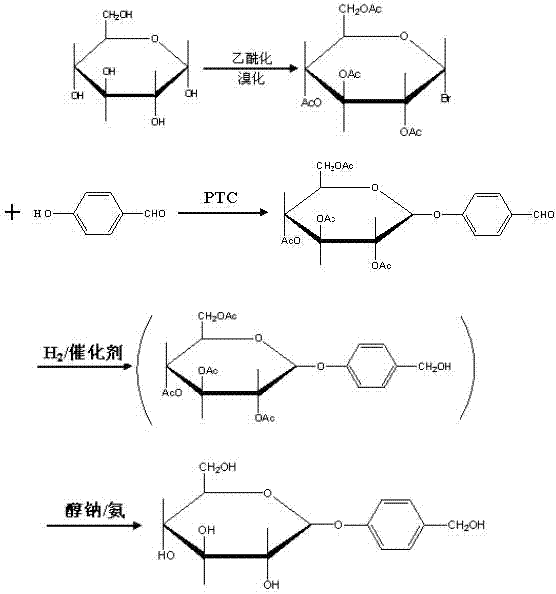
The invention relates to a gastrodin synthesizing method, which can effectively solve the preparation problem of gastrodin to meet the requirements of the gastrodin in pharmaceuticals. The method comprises the steps of adding catalyst perchloric acid, acetylating anhydrous dextrose by using acetic anhydride to produce per-acetyl dextrose, feeding hydrogen bromide to bromizing hemiacetal hydroxyl of the per-acetyl dextrose to produce bromo-tetraacethyl glucose, further and dropwise adding a bromo-tetraacethyl glucose solution into chloroform and tetrabutyl ammonium bromide, carbonate and para hydroxybenzene in water to obtain 4-formyl benzene-2', 3', 4', 6'- tetraacetyl-beta-D-glucopyranose, performing re-crystallization with ethanol, adding raney nickel or palladium and carbon, feeding hydrogen and pressurizing to hydrogenate, performing filtering, adding sodium alcoholate or ammonia in to filtrate to perform protecting group removal until the reaction is finished completely, performing pressure reduction and concentration to obtain crude gastrodin, and re-crystallizing the crude gastrodin by using alcohol or an alcohol and ester solvent or an alcohol and ketone solvent to obtain the gastrodin. The gastrodin synthesizing method is abundant and cheap in raw materials, simple in process, recycled in solvent, small in pollution and high in quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI MODERN HASEN SHANGQIU PHARMA
Method for preparing gamma-valerolactone with high selectivity under mild condition
The invention relates to a method for preparing gamma-valerolactone with high selectivity under the mild condition. The method comprises the following steps of: under the conditions of optimal room temperature and inert gas, with secondary alcohol as a hydrogen source and active Raney nickel as a catalyst, carrying out hydrogen transfer reaction on a levulinic acid ester compound to obtain the gamma-valerolactone. The invention particularly relates to a method of preparing gamma-valerolactone by a lignocellulose derivative with high selectivity under the mild condition, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out alcoholysis reaction on the lignocellulose derivative such as fructose, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural or furfuryl alcohol by a solid acid catalyst in the presence of an alcohol solvent at certain temperature, filtering solid acid, collecting liquid, and obtaining levulinic acid esters through reduced pressure distillation; and with the secondary alcohol as the hydrogen source, catalyzing the obtained esters by Raney Ni as a non-noble metal catalyst at the room temperature to obtain the gamma-valerolactone with high yield.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method and activation method of Raney nickel-aluminum-X catalyst specially for hydrogenation preparation of 1,4-butanediol from 1,4-butynediol
ActiveCN102744083APreparation by hydrogenationCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method and an activation method of a Raney nickel-aluminum-X catalyst specially for hydrogenation preparation of 1,4-butanediol from 1,4-butynediol. The Raney nickel-aluminum-X catalyst is characterized in that a mass ratio of nickel to aluminum is (0.5 to 1): 1; X of which mass is 0.1 to 2% of total mass of nickel and aluminum is adopted; and X represents Mg, B, Sr, Cr, S, Ti, La, Sn, W, Mo or Fe. The preparation method comprises the following steps of putting nickel, aluminum and X into a medium frequency induction smelting furnace according to the mass ratio, carrying out smelting, pouring out melt, cooling, crushing, and grinding to obtain powder which is the Raney nickel-aluminum-X catalyst. The activation method comprises the following steps that an alkali solution and the Raney nickel-aluminum-X catalyst which is powder are uniformly mixed according to a mass ratio of (2: 1) to (10: 1) and then undergo a reaction with stirring, wherein the alkali solution is a sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solution having a concentration of 5 to 25wt%; after the reaction is finished, the reaction products are washed by distilled water and anhydrous ethanol until a pH value of the reaction products is 7; and the reaction products having a pH value of 7 are preserved in ethanol. In the presence of the Raney nickel-aluminum-X catalyst, in hydrogenation preparation of 1,4-butanediol from 1,4-butynediol, a conversion rate is in a range of 98 to 100% and selectivity of 1,4-butanediol is in a range of 90 to 98%.
Owner:HAISO TECH
Bis-Schiff-base-connected symmetrical phenanthroimidazole Fe<3+> fluorescent probe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105694866AHigh selectivityResponsiveOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceOrganic solventFluorescence
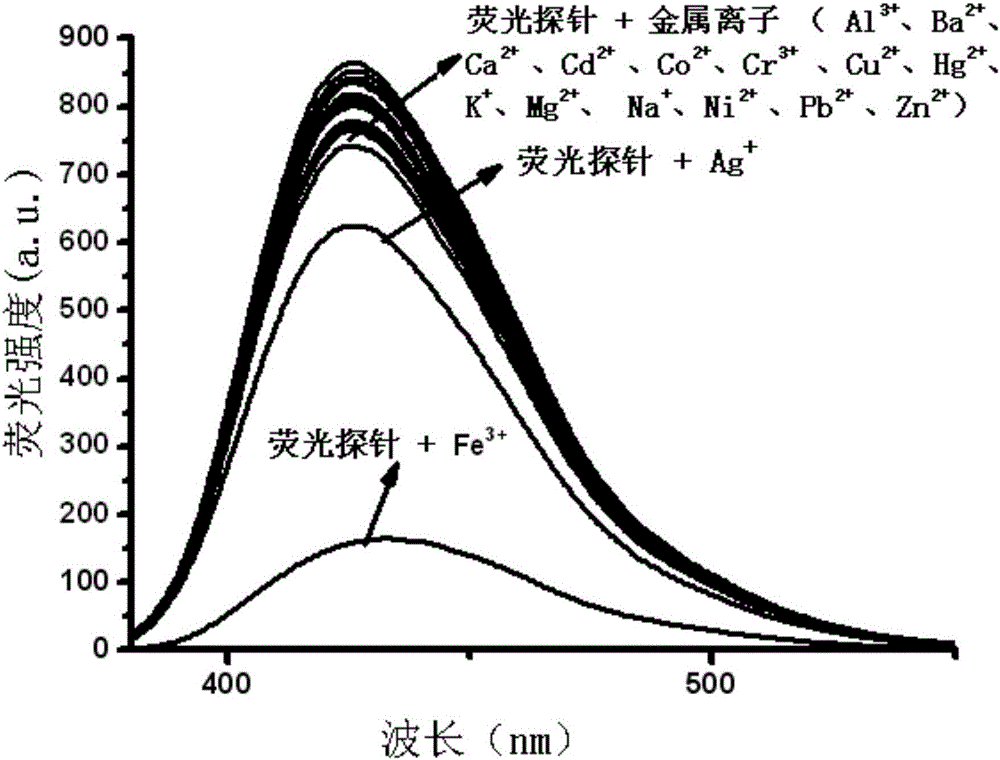
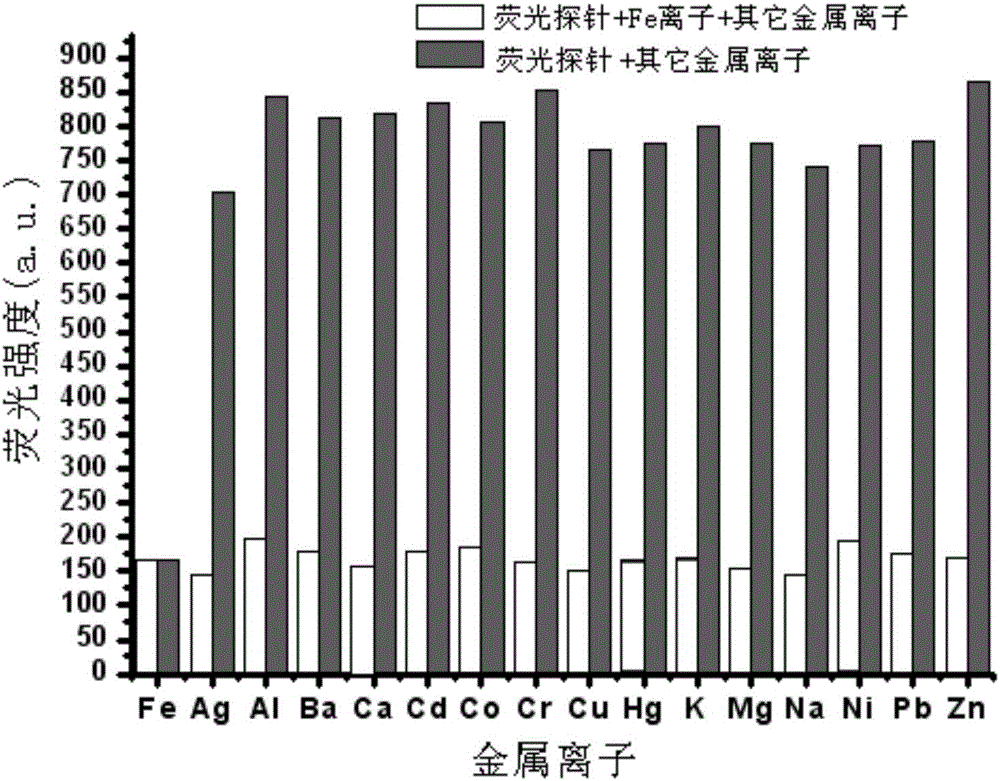
The invention relates to an Fe<3+> fluorescent probe and a preparation method thereof, particularly a bis-Schiff-base-connected symmetrical phenanthroimidazole Fe<3+> fluorescent probe and a preparation method thereof. The invention aims to solve the technical problems that the existing Fe<3+> fluorescent probe needs an organic solvent identification environment and copper ions can interfere with the identification of iron ions. The structural formula of the bis-Schiff-base-connected symmetrical phenanthroimidazole Fe<3+> fluorescent probe is disclosed in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1. synthesizing an intermediate compound I from phenanthrenequinone, o-nitrobenzaldehyde, aniline and ammonium acetate; 2. synthesizing an intermediate compound II from the intermediate compound I, Raney nickel and hydrazine hydrate; and 3. synthesizing the Fe<3+> fluorescent probe from the intermediate compound II and terephthalaldehyde under acidic conditions. The Fe<3+> fluorescent probe can selectively identify Fe<3+> in a water-phase system within the wide pH value range of 1-9; the response time is 2 minutes; and when being used for Fe<3+> inspection, the Fe<3+> fluorescent probe has the advantage of no interference, and is convenient and quick.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Synthesis process of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol
InactiveCN1847206AImprove conversion rateFix security issuesOrganic compound preparationPreparation by hydrogenationCyclohexanonePalladium catalyst
The present invention relates to synthesis process of cyclohexanone and cycloexanol, especially through hydrogenating phenol. Phenol material, C1-C2 fatty alcohol and water in the weight proportion of 1 to 2.5-40 to 10-160 are reacted in one step at 100-300 deg.c temperature and 1-10 MPa pressure and in the action of Renny Ni catalyst or active carbon supported palladium catalyst to synthesize cyclohexanone and cycloexanol. The present invention features no need of outer hydrogen supply for hydrogenating phenol and the use of relatively cheap Renny Ni catalyst, and has the advantages of high safety, simplified technological process, low production cost, high phenol converting rate, high total cyclohexanone and cycloexanol selectivity near 100 %, no side product and easy product separation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for producing raney nickel catalyst
The invention provides a method for preparing a raney nickel catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: in the presence of solid sodium hydroxide and aluminum nickel alloy, leaching the solid mixture by distilled water, then reacting the mixture at a temperature of between 40 and 65 DEG C for 0.5 to 1 hour, removing lye on the upper layer; and in the atmosphere of hydrogen, washing the mixture by the distilled water until the mixture is neutral to obtain the raney nickel catalyst. The obtained raney nickel catalyst has specific surface area of between 80 and 220 square meters per gram, and has quite high activity which is even 3 to 4 times higher than that of the prior catalytic activity; besides, the method saves the time for preparing the catalyst compared with the prior catalyst; and because the catalyst also contains certain amount of aluminum metal, the method creates a condition for the further regeneration of the catalyst, and expands the application range of the catalyst. In particular in the reaction for preparing tetrahydrofuran through the hydrogenation of furan, the furan conversion rate is between 45 and 100 percent, and the selectivity of the tetrahydrofuran is between 70 and 100 percent.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Synthesis method of alpha phenyl ethanol
InactiveCN1911883AImprove conversion rateIncrease profitOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholSynthesis methods
The present invention relates to alpha-phenyl ethyl alcohol synthesizing process, and is especially one in-situ acetophenone hydrogenating process of synthesizing alpha-phenyl ethyl alcohol. Inside the mixed solution of C1-C4 fatty alcohol and water and under the action of Raney nickel catalyst, acetophenone is one-step reacted at 50-300 deg.c and 0.1-10.0 MPa to obtain alpha-phenyl ethyl alcohol. The weight ratio of acetophenone, C1-C4 fatty alcohol and water is 1 to 2.5-60 to 10-160. The present invention has the beneficial effects of no need of outer hydrogen supply, simple technological process, low production cost, use of non-noble metal Raney nickel catalyst, high acetophenone converting rate, high alpha-phenyl ethyl alcohol selectivity up to 90 %, less side products and capacity of separating high purity alpha-phenyl ethyl alcohol.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Production of secondary-amine compound
InactiveCN1939890AThe reaction process is simpleHigh reaction conversion ratePreparation by reductive alkylationNitro compoundSolvent
Production of secondary amine compound is carried out by taking nitro-compound, phenol or aldehyde compound as raw materials, catalytic hydrogenation reacting for 1-20hrs at 0.5-5.0MPa and 30-200 degree under the existence of solvent and catalyst, and separation purifying to obtain the final product. The solvent is fatty alcohol containing 1-4 atoms or its solution or water; the catalyst can be Raney Ni catalyst or nickel-carried catalyst or noble- metal-carried catalyst; the noble-metal-carried catalyst can be palladium-carried or platinum-carried or ruthenium-carried catalyst. It's simple and cheap, has higher conversion percent and better selectivity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
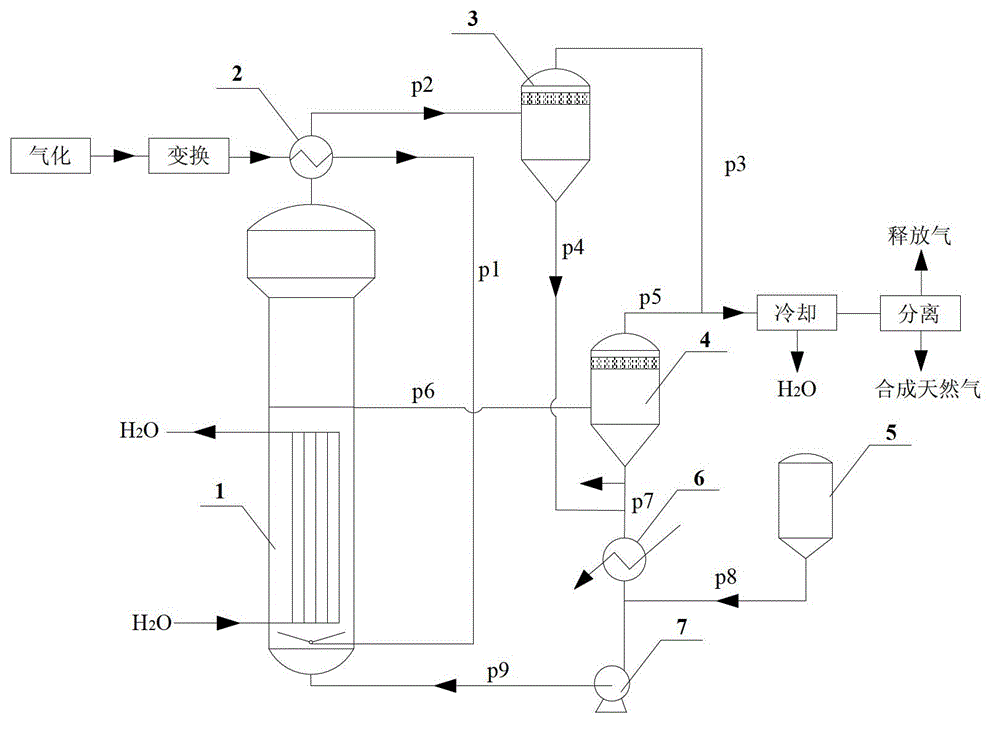
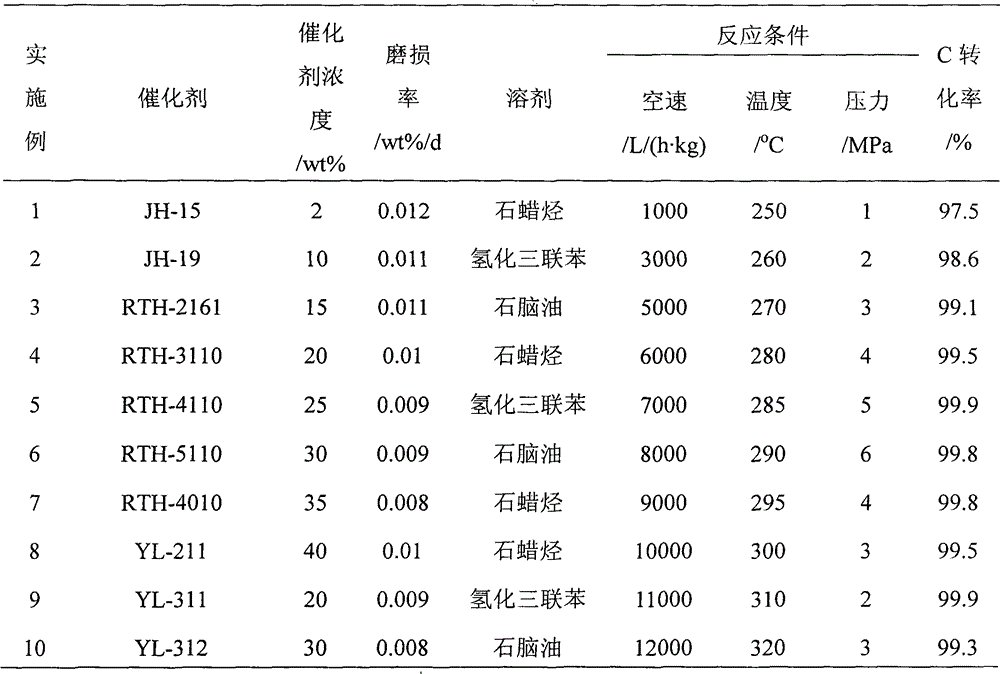
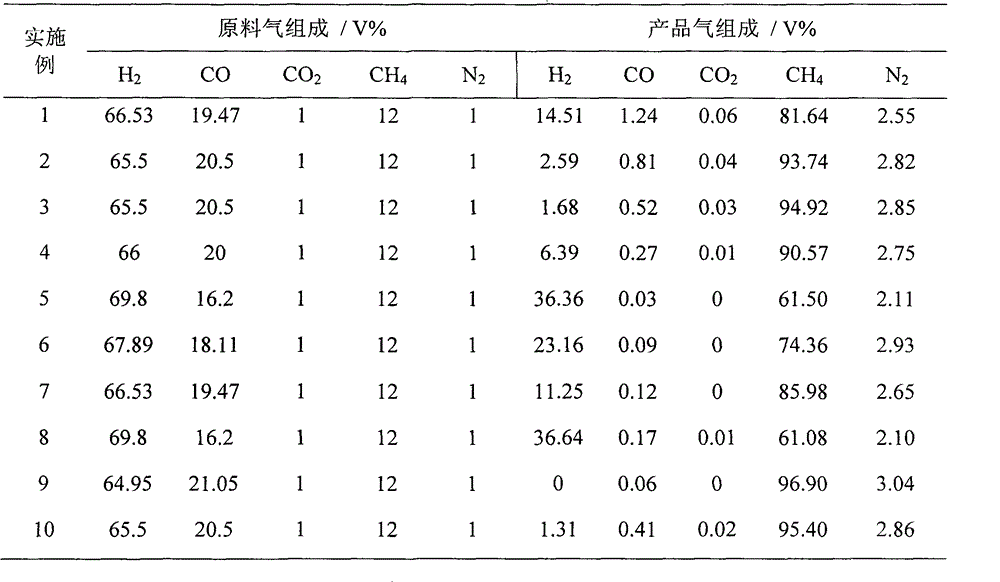
Application of raney nickel as slurry reactor to synthesize methane catalyst
InactiveCN102942971AWith characteristicsHave made significant progressGaseous fuelsLiquid mediumSlurry reactor
The invention provides the application of raney nickel as a slurry reactor to synthesize a methane catalyst, including: adding a raney nickel catalyst dispersed in an inert liquid medium to a reactor for a methanation reaction, feeding product gas and raw material gas to a separator, discharging a liquid phase component I composed of the liquid phase component and the catalyst component in the product gas from the bottom of the separator I, discharging gas phase I from the top of the separator, discharging a part of the inert liquid medium containing the catalyst from the middle of the reactor into a separator II, discharging gas phase II from the top of the separator II, mixing the gas phase II with the gas phase I to get a natural gas product, discharging the inert liquid medium of the catalyst from the bottom of the separator II to mix with the liquid phase component I to get a mixture, and feeding the mixture and the fresh methanation catalyst dispersed in the inert liquid medium together into the reactor for the methanation reaction. The application has the advantages that the raney nickel catalyst does not need reduction, has high mechanical strength and good wear resistance, and can satisfy the requirement of slurry reactor methanation process for low temperature activity.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for synthesizing dihydric alcohol and polyhydric alcohol
InactiveCN101781167ALow reaction temperatureLow reaction pressureOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHydrogen pressureReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing dihydric alcohol and polyhydric alcohol, comprising the following steps of: firstly reacting an aqueous sucrose solution with the pH value of 11-14 and the weight percentage content of 10-50 percent for 0.5-2 hours in the presence of a hydrogenolysis catalyst at the reaction temperature of 130-150 DEG C and the hydrogen pressure of 6-8 MPa, wherein sucrose is used as a raw material; then reacting for 0.5-2 hours at the reaction temperature of 220-250 DEG C and the hydrogen pressure of 10-13 MPa; and cooling, filtering and rectifying a reactionproduct to obtain the dihydric alcohol and the polyhydric alcohol, wherein the hydrogenolysis catalyst is Raney nickel, ruthenium / carbon, nickel / ruthenium or CuO-ZnO, the usage amount of the hydrogenolysis catalyst is 15-30 percent relative to the mass of the sucrose, the dihydric alcohol comprises ethylene glycol, propylene glycol and butanediol, and the polyhydric alcohol comprises propanetriol, sorbierite and mannite. The invention is mainly used for synthesizing the dihydric alcohol and the polyhydric alcohol.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
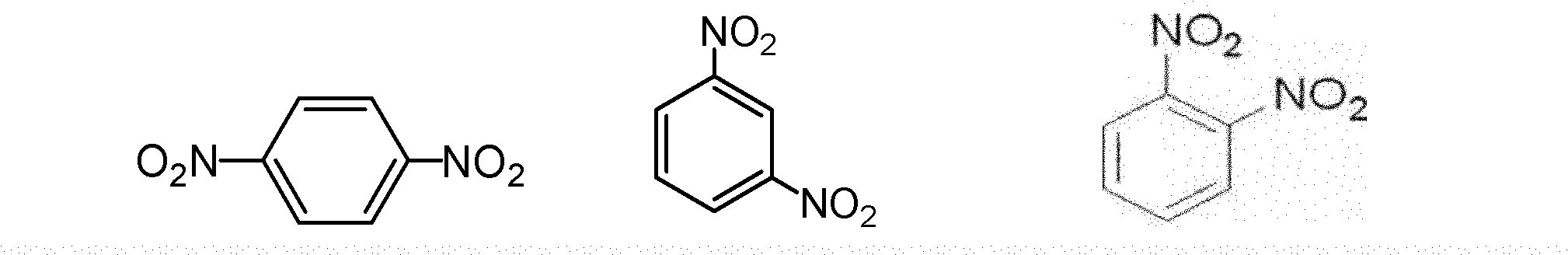
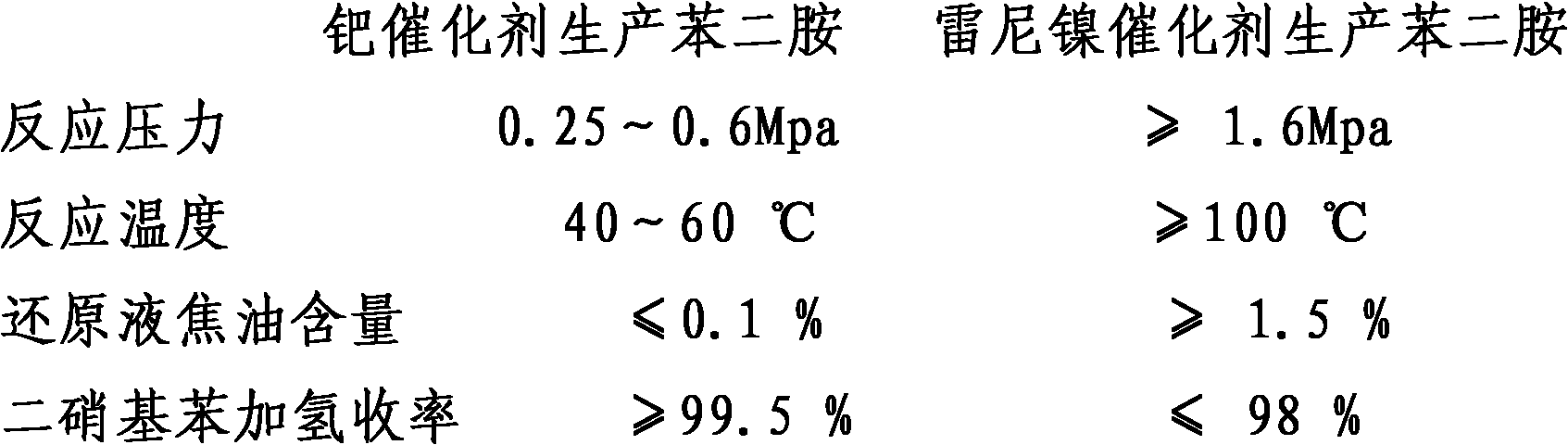
Method for producing phenylene diamine by performing hydrogenation reduction on mixed dinitrobenzene with palladium catalyst
ActiveCN102070464AReduce consumptionImprove product qualityOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationHigh energyPalladium catalyst
The invention belongs to a method for producing phenylene diamine, in particular to the method for producing the phenylene diamine by performing hydrogenation reduction on mixed dinitrobenzene with palladium catalyst. The prior art which produces the phenylene diamine by performing the hydrogenation reduction by adopting a Raney nickel or carrier nickel catalyst has the disadvantages of high energy consumption, low raw material conversion rate, and poor product quality. The method comprises the following steps of: adding 100 weight parts of dinitrobenzene, 100 to 200 weight parts of alcohols solvents and 0.5 to 1 weight part of the palladium catalyst into a reaction kettle, wherein the temperature in the reaction kettle is between 40 and 60 DEG C and the pressure is between 0.25 and 0.60 MPa; performing hydrogenation for 30 to 120 minutes; conveying a reaction product to a filter; dealcoholizing in a dealcoholization tower for recovering to obtain phenylene diamine solution; and obtaining m-phenylenediamine, o-phenylenediamine and p-phenylenediamine products by dewatering, rectifying and separating. The method has the advantages of improving product quality, reducing raw material consumption and reducing production cost.
Owner:上海鸿源鑫创材料科技有限公司 +1
Synthetic method of perfume o-tert-butylcyclohexyl acetate
InactiveCN103193638AExpand sourceLow costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationTert butyl phenolAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a chemical synthetic method, and concretely relates to a synthetic method of a perfume o-tert-butylcyclohexyl acetate. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: reacting a raw material phenol with isobutene under the catalysis of anhydrous aluminum trichloride to obtain o-tert-butyl phenol, carrying out catalytic hydrogenation of o-tert-butyl phenol under the catalysis of Raney nickel to obtain o-tert-butyl cyclohexanol, and carrying out an esterification reaction of o-tert-butyl cyclohexanol and acetic anhydride under the catalysis of anhydrous sodium acetate to obtain o-tert-butylcyclohexyl acetate. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, safe and convenient operation, high reaction yield, fine and strong fragrance of the obtained product, raw material source enlargement and raw material cost saving because of the adoption of industrially cheap phenol and isobutene as initial raw materials, total synthetic reaction yield improvement, suitableness for the industrial adoption, and good economic benefit.
Owner:南昌洋浦天然香料香精有限公司
Separation and purification and degradation method for lignin
ActiveCN107098803AHigh yieldComplete structureOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical compoundPollution
The invention relates to a separation and purification and degradation method for lignin. The method includes the following steps: 1) primary crushing; 2) primary enzymolysis; 3) secondary crushing; 4) secondary enzymolysis; and 5) degradation of an enzymolysis residue lignin. The invention provides a novel extraction method for preparing lignin having high purity and complete structure, wherein the extracted lignin is subjected to high-effective catalytic degradation through a tandem catalyst (e.g. solid heteropolyacid salt-Raney nickel), thus producing an aromatic platform chemical compound. The invention provides a new approach for refining biomass to obtain lignin, and also reduces pollution due to direct emission of the lignin.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
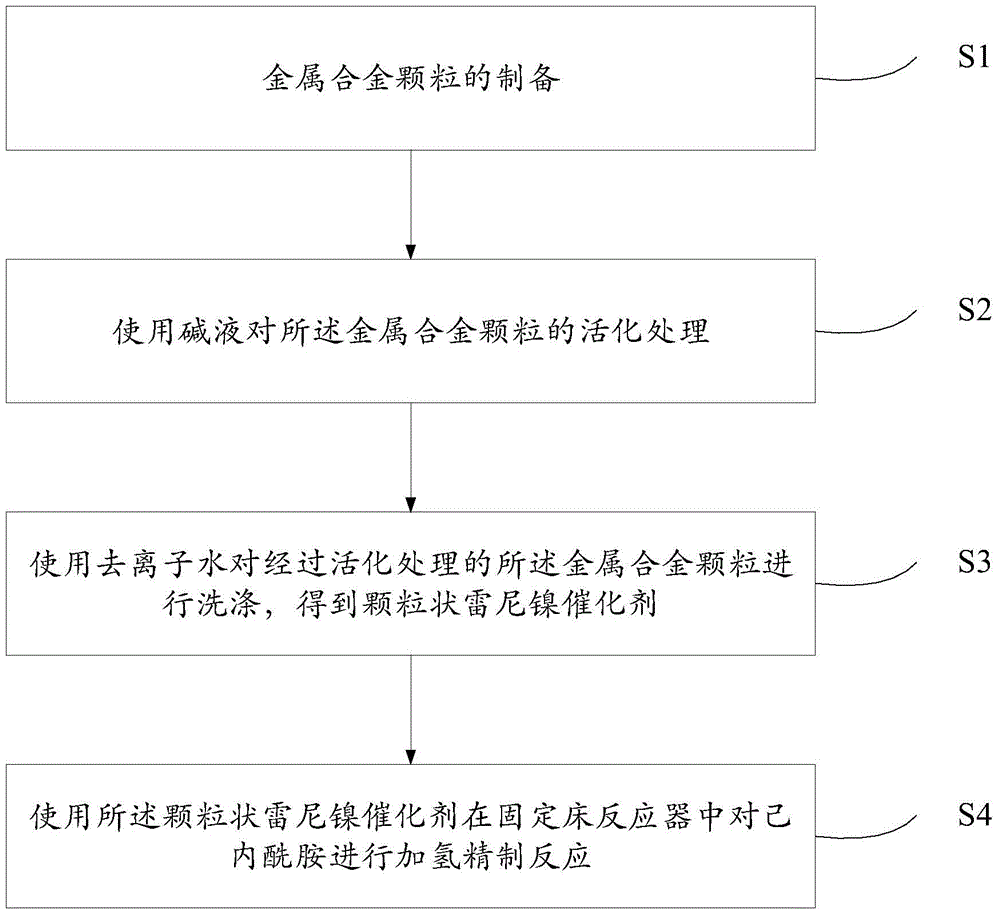
Caprolactam hydrofining catalyst and method
ActiveCN106140195AEasy to prepareHigh activityLactams separation/purificationBulk chemical productionParticulatesMetallurgy
The invention discloses a caprolactam hydrofining catalyst and method. The method comprises the steps of preparing metal alloy particles, activating the metal alloy particles with alkali liquor, washing the activated metal alloy particles with deionized water to obtain a particulate raney nickel catalyst, and conducting hydrofining on caprolactam in a fixed bed reactor by means of the particulate raney nickel catalyst. Operation is easy, hydrofining effect is improved greatly, application prospects are broad, and economic benefits are great.
Owner:SHANGHAI XUNKAI NEW MATERIAL TECH
Method for synthesizing polyether amine
ActiveCN101921392AImprove conversion rateReduce the hydrogenation reaction pressureEpoxyAlkaline earth metal
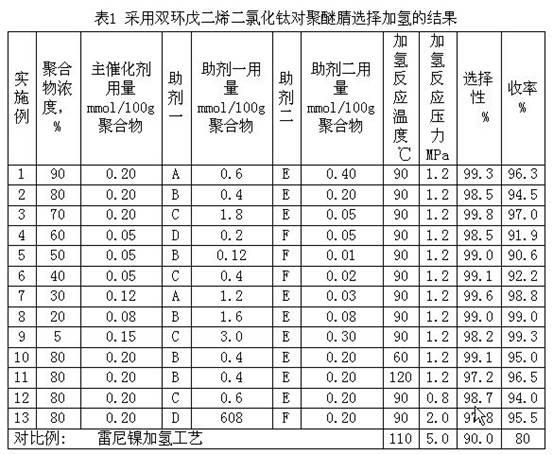
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing polyether amine. The method comprises the following steps of: polymerizing epoxy ethane, epoxy propane or mixture thereof into polyether with different molecular weights; reacting the polyether with acrylonitrile under the catalytic action of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide to prepare polycyanoarylether; and selectively hydrogenating carbon-nitrogen double bond in the polycyanoarylether by using a catalyst complex, wherein the catalyst complex is prepared by compounding a titanocene compound serving as a main catalyst, alkyl aluminum, alkyl lithium or an alkyl compound of another alkaline metal and an alkali earth metal serving as a first cocatalyst and a lewis base such as benzoic ether, siloxane and the like serving as a second cocatalyst; 0.05 to 0.2mmol of titanocene compound, 0.1 to 6mmol of alkyl metal compound and 0.01 to 0.4mmol of lewis base are used in every 100g of polymer; the hydrogenation is performed for 0.5 to 2.0 hours at a certain temperature under the hydrogen pressure; the degree of hydrogenation of a nitrile group in the polymer is over 98 percent; and the degree of hydrogenation of an ether bond is less than 1 percent. The method effectively solves the problem of side reaction of ether bond hydrogenation breakage brought by hydrogenating the conventional polycyanoarylether with raney nickel, and the yield of the polyether amine serving as the target product is over 90 percent.
Owner:YUEYANG KIMOUTAIN SCI TECH
Preparation method of dihydric alcohol
InactiveCN101781166ASimple processReduce stepsOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationCarbon numberHydrogen pressure
The invention discloses a preparation method of dihydric alcohol, comprising the following steps of: reacting dextrose water with the pH value of 12-14 and the weight percentage content of 10-50 percent for 0.5-2 hours in the presence of a hydrogenolysis catalyst at the reaction temperature of 130-150 DEG C and the hydrogen pressure of 6-8 MPa, wherein glucose is used as a raw material; then raising the temperature to 220-250 DEG C, and reacting for 0.5-2 hours at the hydrogen pressure of 10-13 MPa; and cooling, filtering and rectifying a reaction product to obtain the dihydric alcohol, wherein the hydrogenolysis catalyst is Raney nickel, ruthenium / carbon, nickel / ruthenium or CuO-ZnO, the usage amount of the hydrogenolysis catalyst is 15-30 percent relative to the mass of the glucose, andthe dihydric alcohol is a dihydric alcohol which has a carbon number of 2-4. The invention is mainly used for preparing the dihydric alcohol and especially used for preparing the dihydric alcohol which has the carbon number of 2-4.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
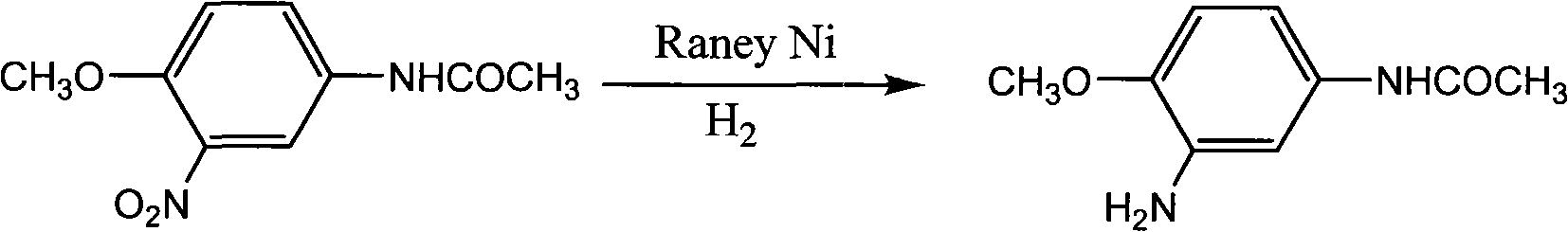
Method for preparing 3-amino-4-methoxyacetanilide by taking Raney nickel as catalyst
InactiveCN101880242AHigh activityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationReaction temperatureOrganic chemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing 3-amino-4-methoxyacetanilide by catalytic hydrogenation of Raney nickel. In the method, Raney nickel is used as a catalyst for efficiently catalyzing 3-nitro-4-methoxyacetanilide to be reduced into the 3-amino-4-methoxyacetanilide. At the reaction temperature of between 80 and 110 DEG C, under the reaction pressure of 0.8 to 2 MPa and in the reaction time of 2 to 6 h, the 3-amino-4-methoxyacetanilide is prepared from the 3-nitro-4-methoxyacetanilide by liquid phase intermittent catalytic hydrogenation; and the material conversion rate is 85.1 to 100 percent, and the selectivity of the product 3-amino-4-methoxyacetanilide is 99.0 to 99.6 percent. The method has the advantages of clean process, low cost, high purity of the prepared product, safe and environment-friendly process and easy industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for preparation of benzene ring phenol compound from alkali lignin
InactiveCN105503540ARaw materials are renewableLow costOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSolventRaney nickel
The invention relates to a method for preparation of a benzene ring phenol compound from alkali lignin. At a reaction temperature of 150DEG C-300DEG C, under a hydrogen pressure of 0.1MPa-13Mpa, under the action of a metal catalyst, in a solvent containing choline ionic liquid, alkali lignin is taken as the reaction raw material, hydrogenation degradation of alkali lignin is carried out to prepare the benzene ring phenol compound. Specifically, the solvent containing choline ionic liquid can be one of a solvent only containing choline ionic liquid, a mixed solvent composed of choline ionic liquid and an inorganic solvent, or a mixed solvent composed of choline ionic liquid and an organic solvent; and the metal catalyst is raney nickel and / or loaded metal catalyst. The method provided by the invention has the significant advantages of cheap and easily available raw materials, simple catalyst preparation process, easy recovery, easy separation of product and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metal-free hydrogenation catalyst and application
InactiveCN106807426APromote sustainable developmentLow pricePhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationHydrogenation processHeteroatom
The invention discloses a metal-free hydrogenation catalyst. The metal-free hydrogenation catalyst comprises a carbon-based material containing heteroatoms; the metal-free hydrogenation catalyst does not contain a metal component. The invention further discloses application of the metal-free hydrogenation catalyst. Especially, the application of the metal-free hydrogenation catalyst to catalytic hydrogenation reaction, provided by the invention, can be used for preparing an aromatic amine compound through a catalytic hydrogenation method. The metal-free hydrogenation catalyst provided by the invention is low in price, high in catalytic activity and good in stability, is environment-friendly and can replace a noble metal catalyst and a Raney nickel catalyst in an existing hydrogenation process; a production process is effectively simplified and the cost is reduced; the metal-free hydrogenation catalyst has important practicability and economical efficiency.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
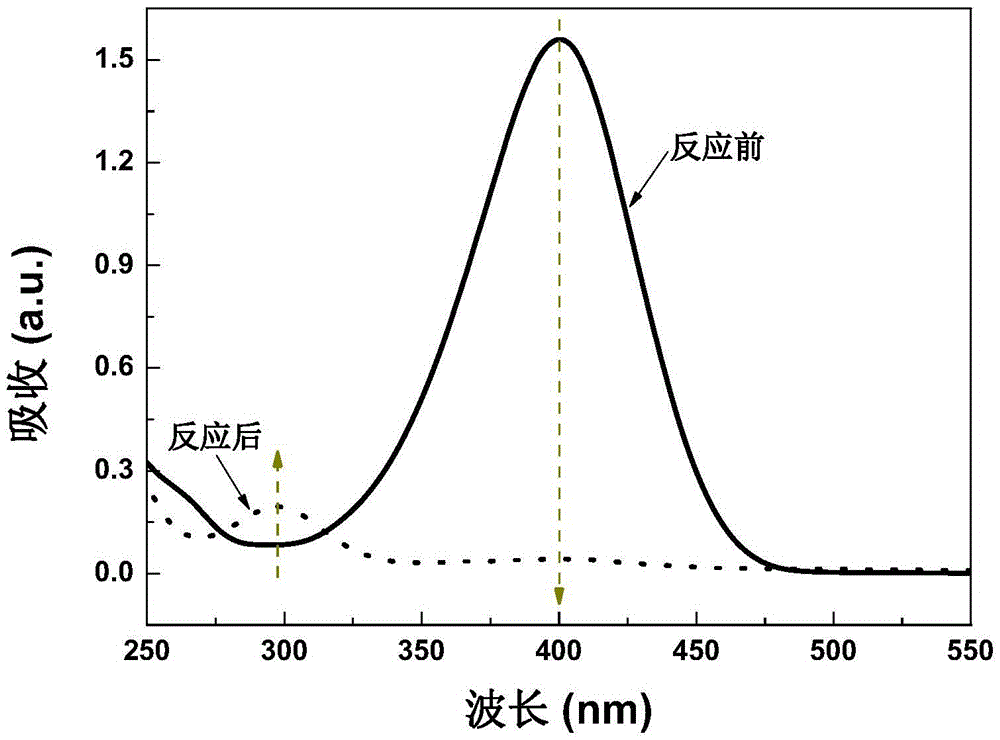
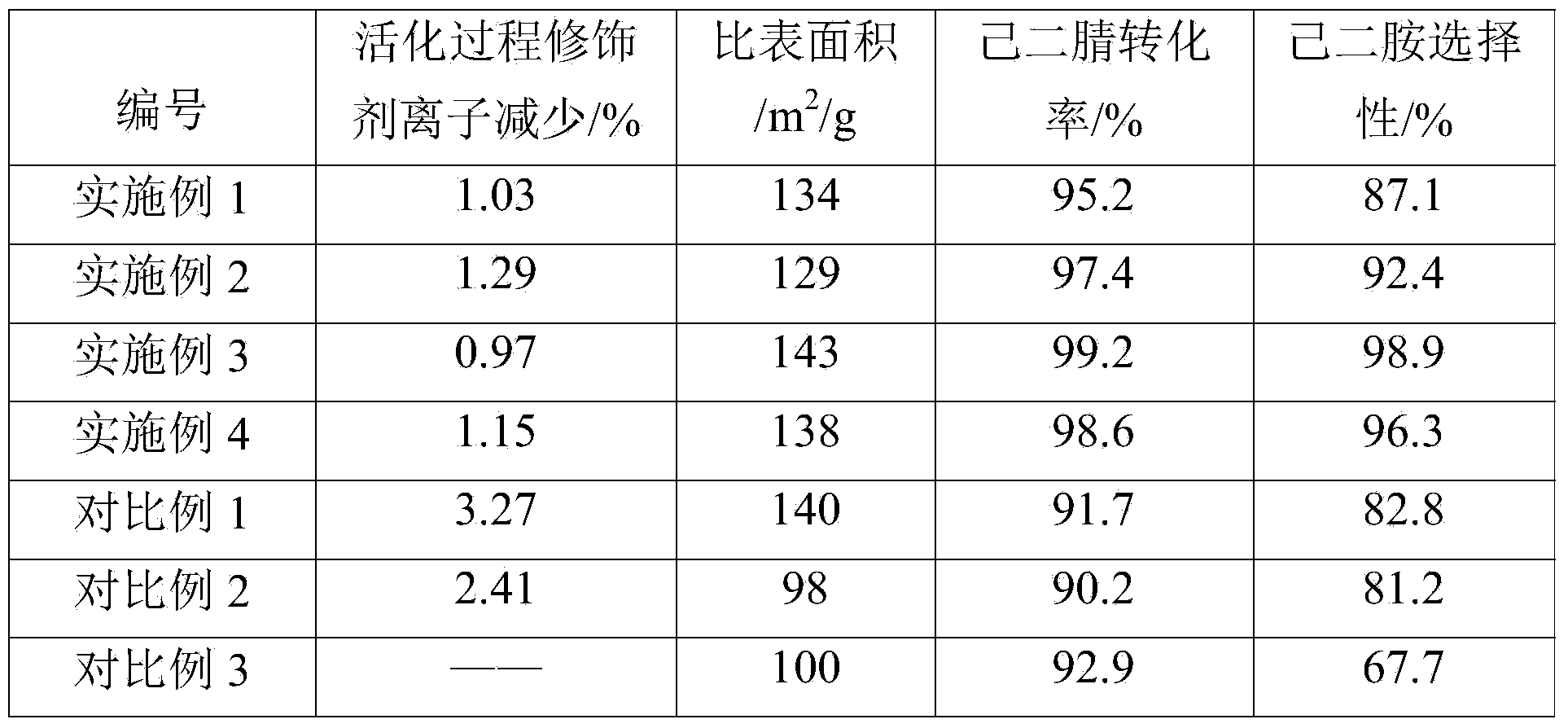
Method for activating adiponitrile hydrogenation catalyst
ActiveCN103977819AReduce churnActive ingredient retentionOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationHexamethylenediamineManganese
The invention discloses a method for activating an adiponitrile hydrogenation catalyst. The method is characterized in that the catalyst is a modified raney nickel catalyst and is activated by the method comprising the following steps: preparing a mixing solution from iron, chromium, molybdenum, bismuth, manganese or tungsten soluble salts and NaOH respectively; slowly adding the modified raney nickel catalyst and ammonium salt; heating with microwave and reacting, and then washing; the modified raney nickel catalyst is prepared by the method comprises the following steps: grinding nickel-aluminum alloy into powder; adding to a mixing solution to dissolve part of aluminum, wherein the mixing solution is prepared through NaOH, ammonium salt and ammonium hydroxide in certain ratio; washing with deionized water and absolute ethyl alcohol; adding the powder to the mixing solution consisting of ferric nitrate and a modifier under a microwave condition and reacting to obtain a solid; drying and roasting the solid; and then charging hydrogen and reducing to obtain the modified raney nickel catalyst. With the adoption of the method for activating the adiponitrile hydrogenation catalyst, the prepared catalyst is relatively large in specific surface area, loss of the modifier is small, and high conversion rate of adiponitrile and high selectivity of hexamethylenediamine are achieved in the adiponitrile catalytic hydrogenation process.
Owner:CHINA TIANCHEN ENG +1
Preparation method for fixed bed Raney nickel catalyst
The invention discloses a preparation method for a fixed bed Raney nickel catalyst, which comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment: soaking ketone solvents by using foaming nickel, then taking out and washing the foam nickel by using water; (2) immersing and plating aluminum; immersing the foam nickel obtained from the step (1) into aluminum salt solution, then adding reducing solution into the mixed solution and standing the mixed solution for 1 to 12 hours; (3) baking: washing and drying a sample obtained from the step (2), and baking the sample at a temperature of between 600 and 1,000 DEG C in inert atmosphere for 5 to 600 minutes; and (4) leaching: leaching the sample obtained from the step (3) in sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solution for 1 to 48 hours, and obtaining the fixed bed Raney nickel catalyst. The preparation method has the advantages that the preparation process is simple; and the catalyst prepared by the method has higher catalytic activity, stronger mechanical strength and longer service life. The invention belongs to the technical filed of catalyst preparation.
Owner:HANERGY TECH
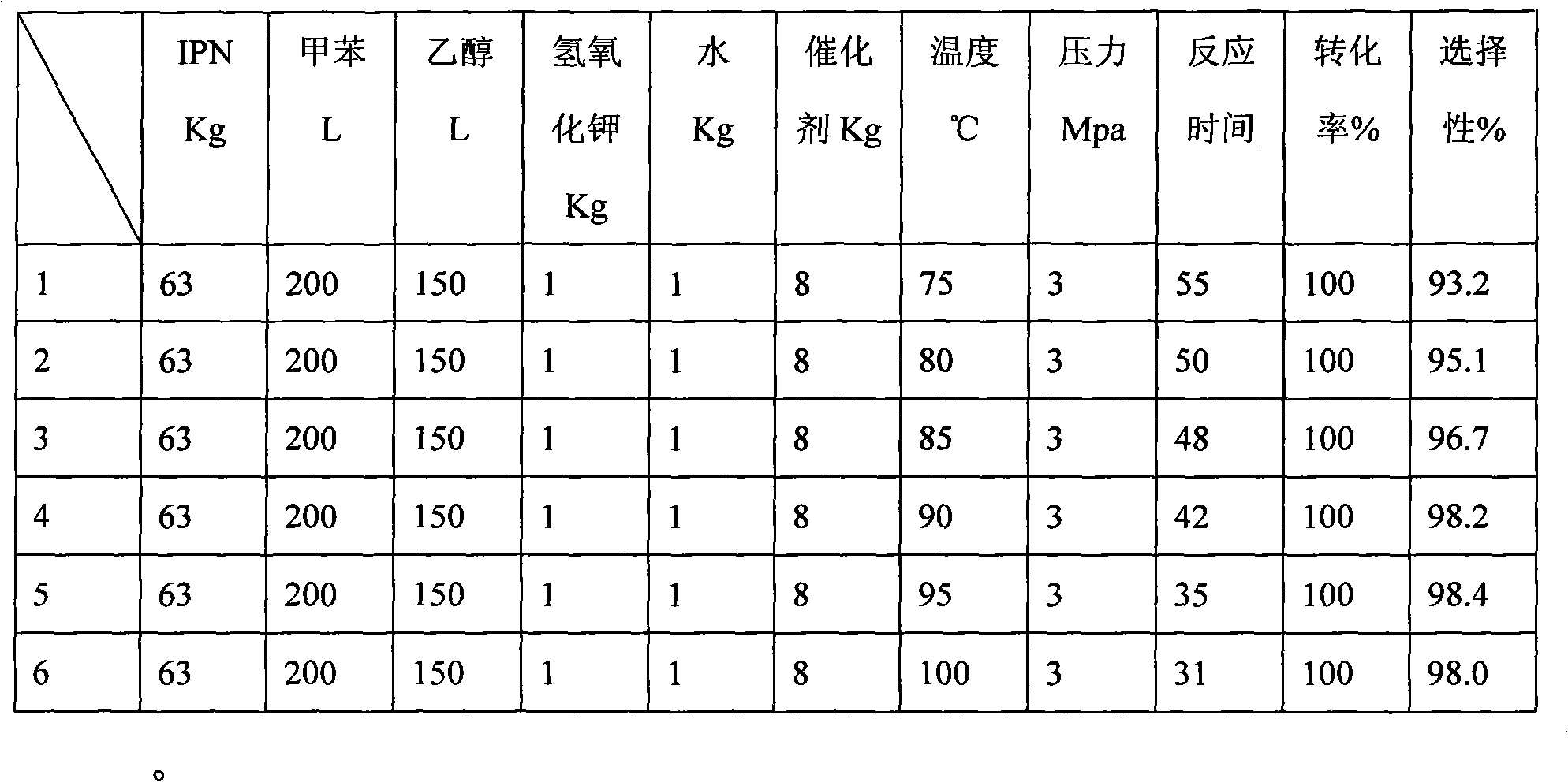
Preparation method of meta-xylylene diamine
ActiveCN101955433AIncrease contactSmall diameterOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationXylyleneAlcohol
The invention discloses a preparation method of meta-xylylene diamine. In an autoclave, Raney Nickel is used as a catalyst, the mixture of arene and alcohol is used as a solvent, and a hydrogenation reaction of m-phthalonitrile is performed for 20 to 90 minutes at the temperature of 40 to 120 DEG C and under a pressure of 2 to 10 MPa to generate the meta-xylylene diamine, wherein the hydrogenation reaction is performed by using a hydrogen intake distributor in the autoclave; the heat exchanger of the autoclave employs an external circulating heat exchanger and the reaction liquid in need of exchanging heat is pumped into the external circulating heat exchanger by a high pressure pump to exchange heat. The reaction of the preparation method of meta-xylylene diamine is stable and performed quickly under a low pressure with high yield.
Owner:CAC NANTONG CHEM
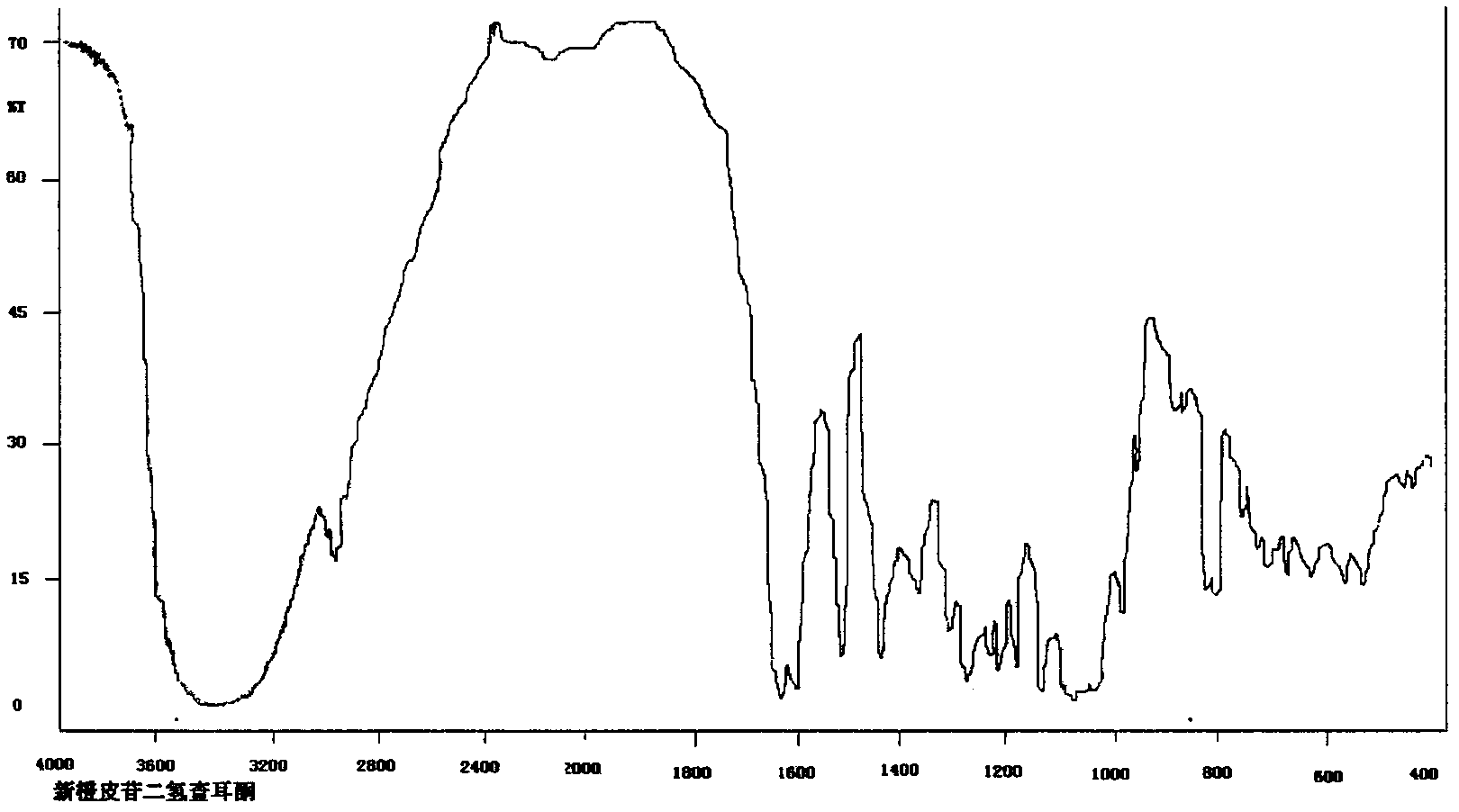
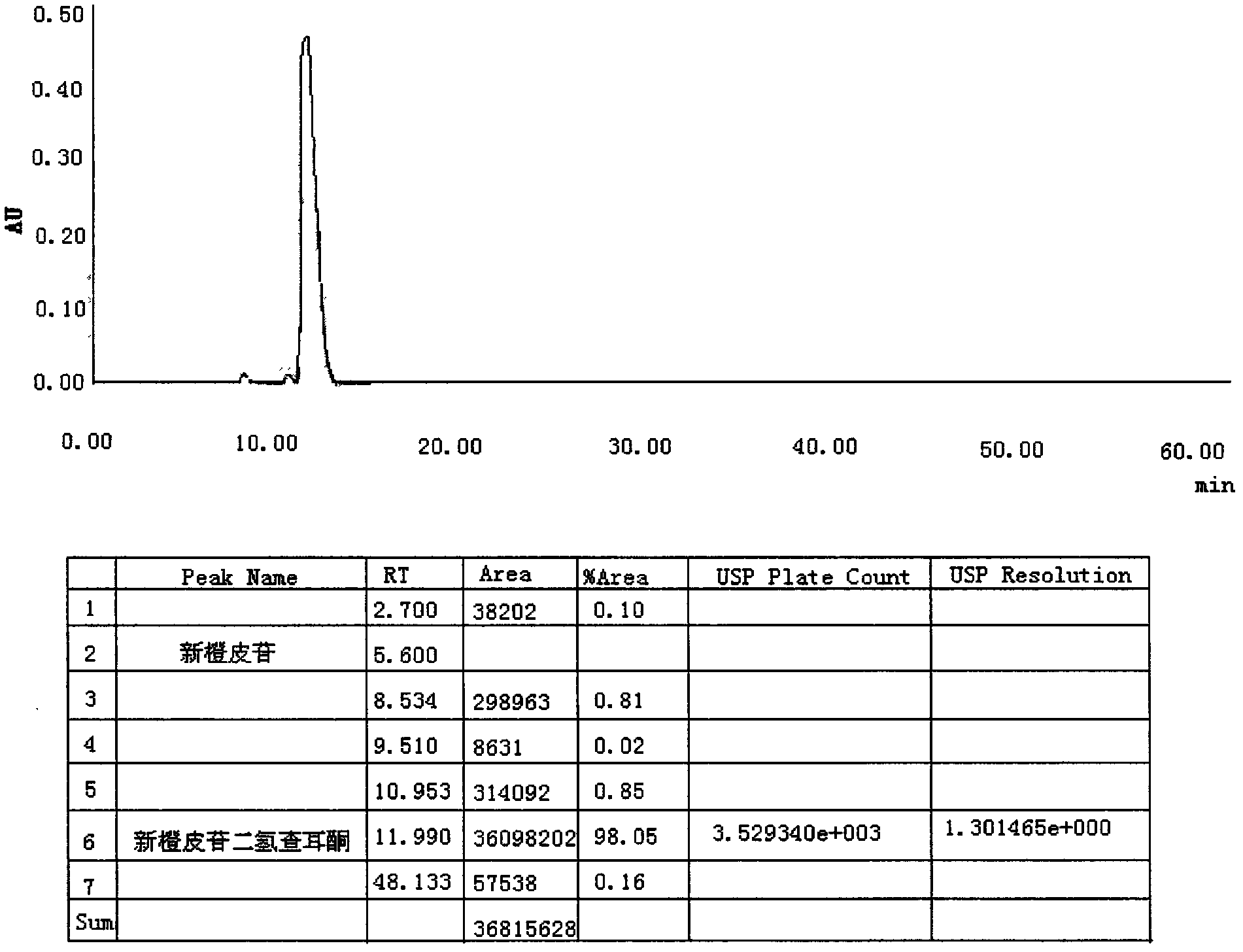
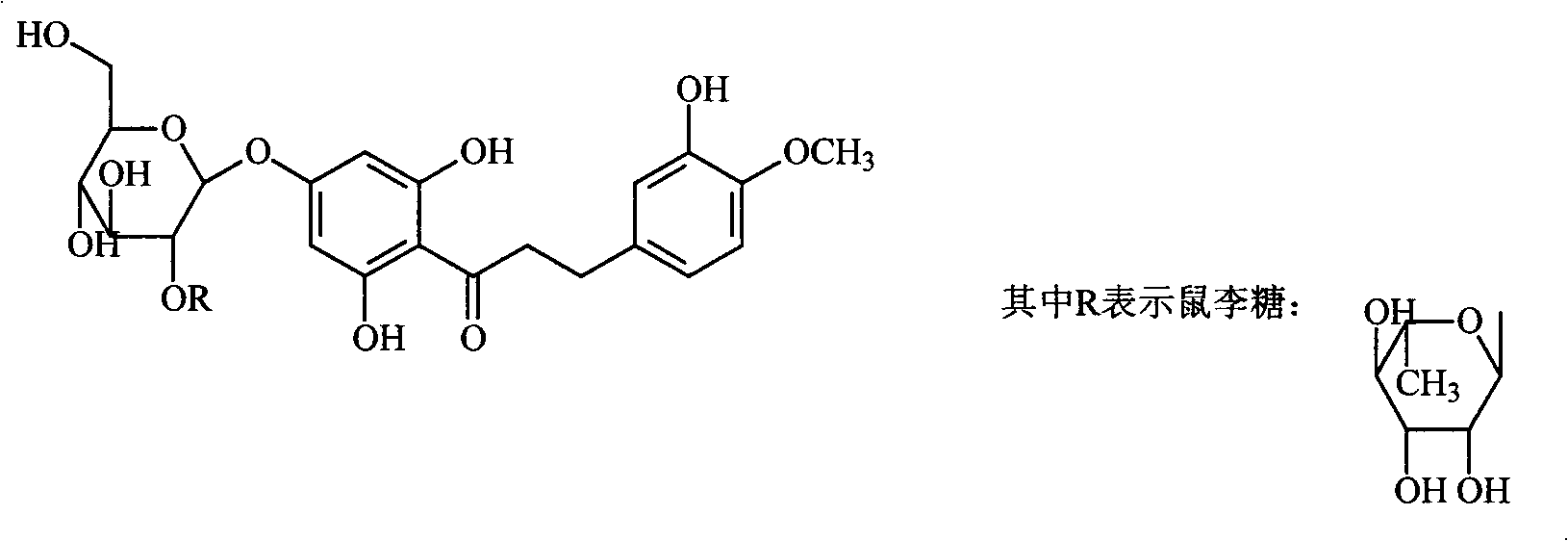
Preparation method of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone
InactiveCN102351921AHigh yieldQuality improvementSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationHydrogen pressureHydrogenation reaction
The invention discloses a preparation method of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, comprising the following steps of: (1) dissolving potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide in water with stirring so as to prepare 3-6% of an alkaline solution; (2) adding neohesperidin into the alkaline solution with stirring for dissolution, wherein the ratio of neohesperidin to the alkaline solution is 1: 5-8; (3) adding raneys nickel which accounts for 5-8 wt% the weight of neohesperidin after stirring and dissolving, carrying out a hydrogenation reaction at the hydrogen pressure of 0.01-0.1 MPa, stirring, and reacting for 4-6 hours to obtain a reaction solution; (4) adjusting the pH of the reaction solution to pH 7-7.5 by the use of hydrochloric acid, staying for 24-28 hours, and filtering out crystal solids to obtain the neohesperidin dihydrochalcone crude product. The preparation method disclosed in the invention requires no large pressure to carry out the hydrogenation reaction, is less dangerous, and is convenient for industrial production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HANFANG PHARMA
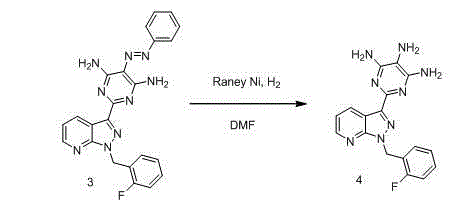
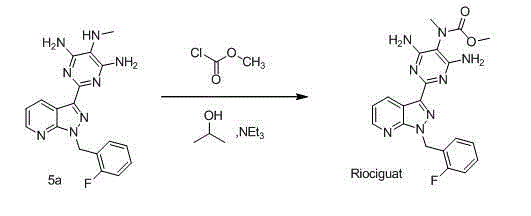
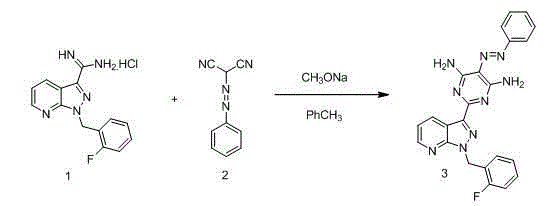
Method for synthesizing riociguat
ActiveCN104530044AImprove responseThorough responseOrganic chemistrySolventFormamidine hydrochloride
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing riociguat. The method includes the following steps: 1, a compound 1-(2-fluorobenzyl)-1H-[3,4-b] pyridine derivative-3-formamidine hydrochloride (1) and a compound benzeneazomalononitrile (2) are reacted in methylbenzene under the condition that sodium methylate exists to obtain a compound (3); 2, the compound (3) is dissolved into DMF, then raney nickel is added to serve as catalysts, and hydrogenation reduction is carried out to obtain a compound (4); 3, a formyl group is firstly synthesized into the compound (4), then reduction is carried out through boron hydride to obtain a single-methyl compound (5a); 4, isopropyl alcohol is used as solvents to be reacted with methylclhlorofonmate to obtain the product riociguat. The synthesizing method has the advantages of being easy and convenient to operate, gentle in condition, high in total yield and high in product purity, and is suitable for large-scale synthesizing of the high-purity riociguat.
Owner:安徽联创生物医药股份有限公司
Preparation method of fixed-bed Raney nickel catalyst
ActiveCN101537360AUniform catalytic activity distributionHigh catalytic activityRaney catalystsOrganic solventFixed bed
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fixed-bed Raney nickel catalyst, comprising the following specific steps: nickel foam is cleaned by diluted acid solution after being put in an organic solvent to be soaked for 10-120 min, and then is dried after being washed by water; the plating is carried out at a temperature of 80 DEG C to 200 DEG C, with the current density of 1-10A / dm<3> for 10-60 min, and then the aluminized nickel foam is obtained by taking an aluminum sheet as an anode, the nickel foam as a cathode and fuse salt as electrolyte; and the obtained aluminized nickel foam is calcined under the protection of inert gas at a temperature of 600 DEG C to 1100 DEG C for 0.5-3h, and then is leached in a sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide solution to obtain the Raney nickel catalyst. The fixed-bed Raney nickel catalyst has the advantages of high strength, good catalytic activity, uniform catalytic activity and good repeatability and belongs to the field of catalyst preparation.
Owner:HANERGY TECH
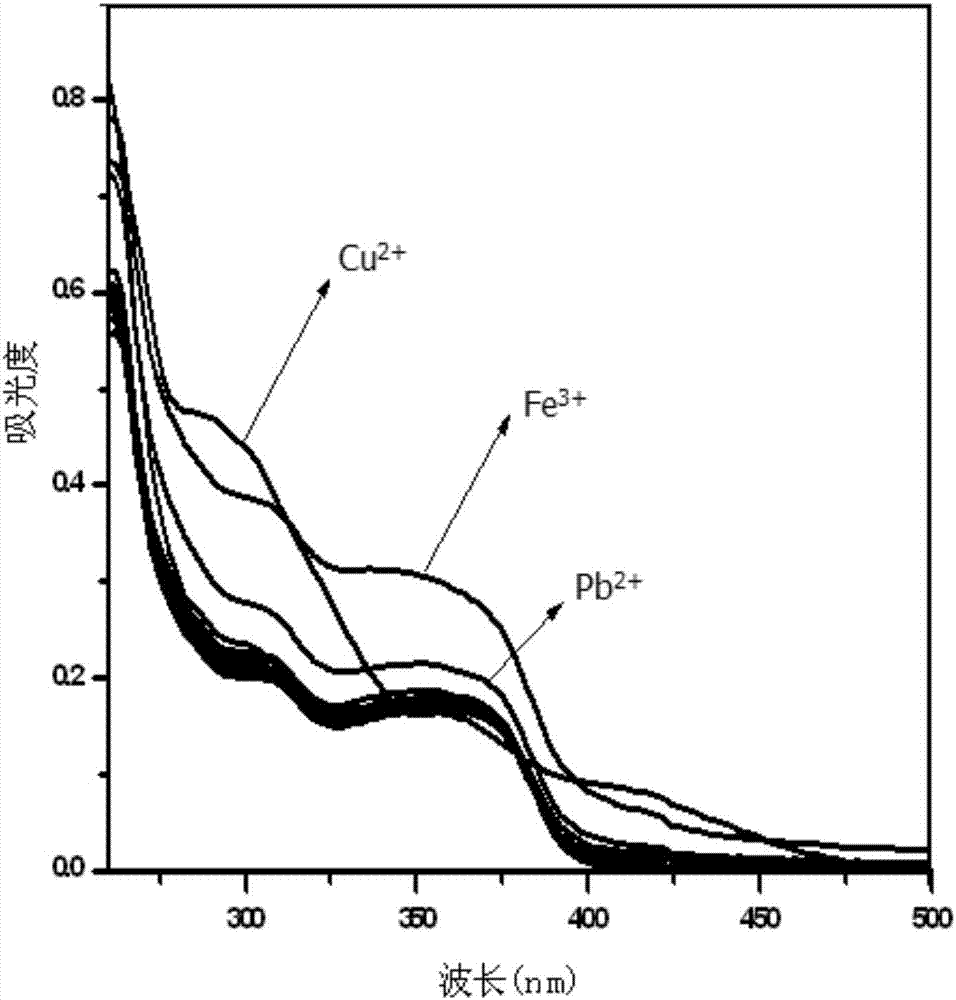
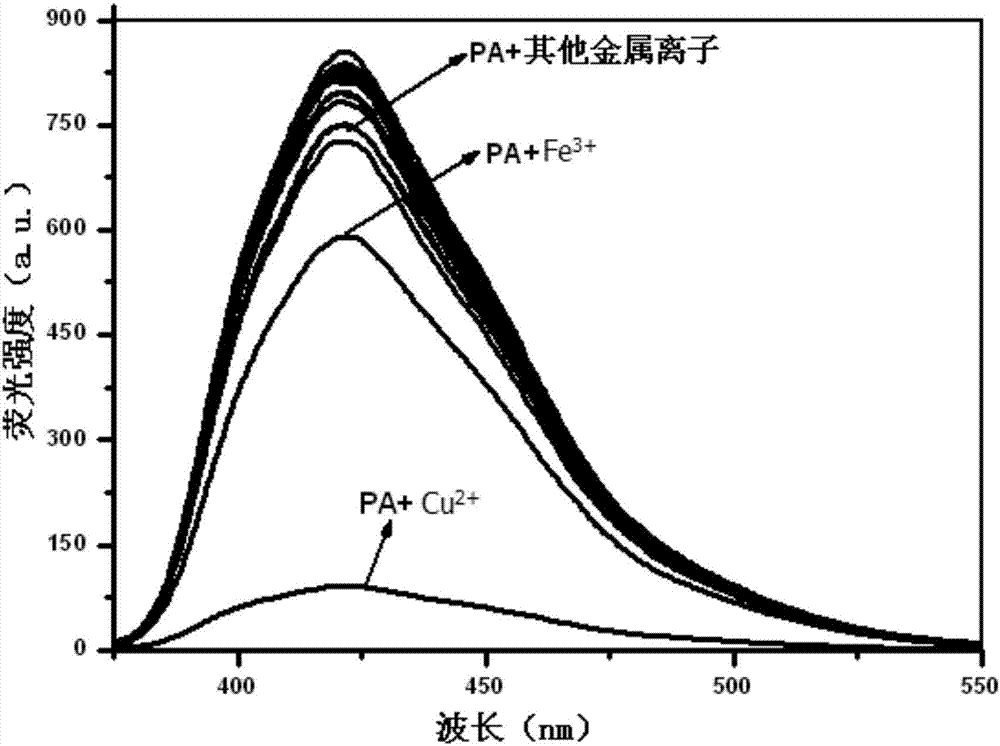
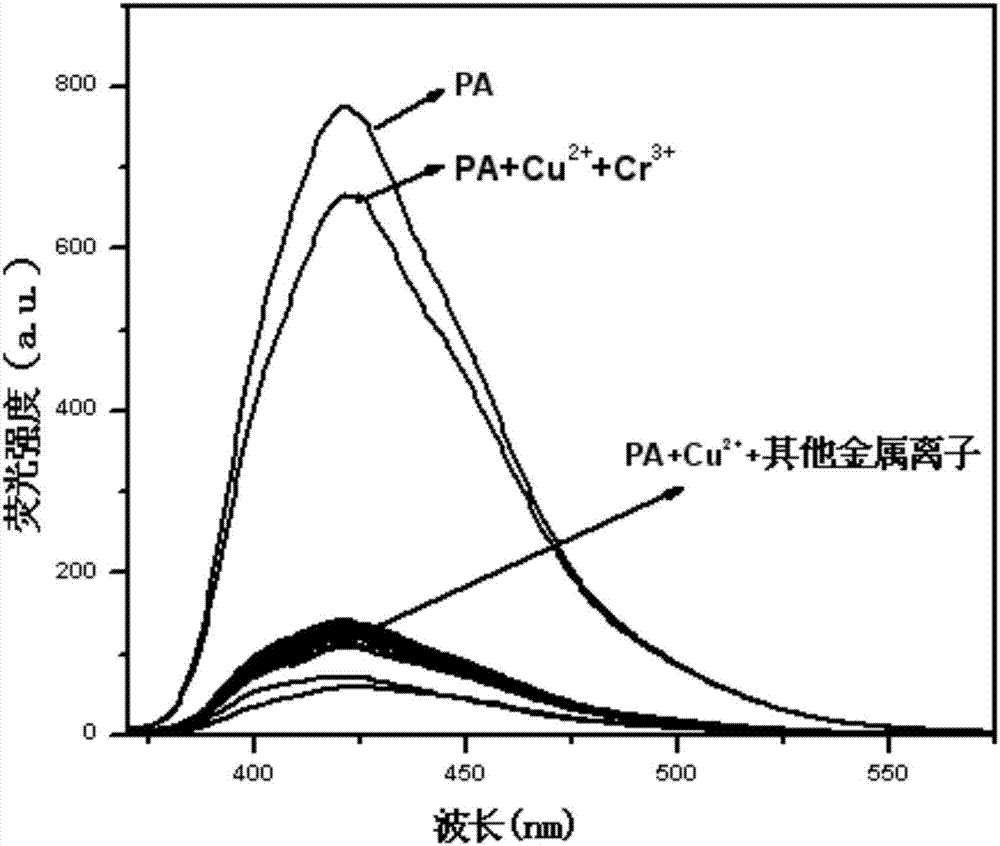
Phenanthrene imidazole reversible fluorescence probe for Cu<2+> detection, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106883183AHigh selectivityIncreased sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceSalicylaldehydeStructural formula
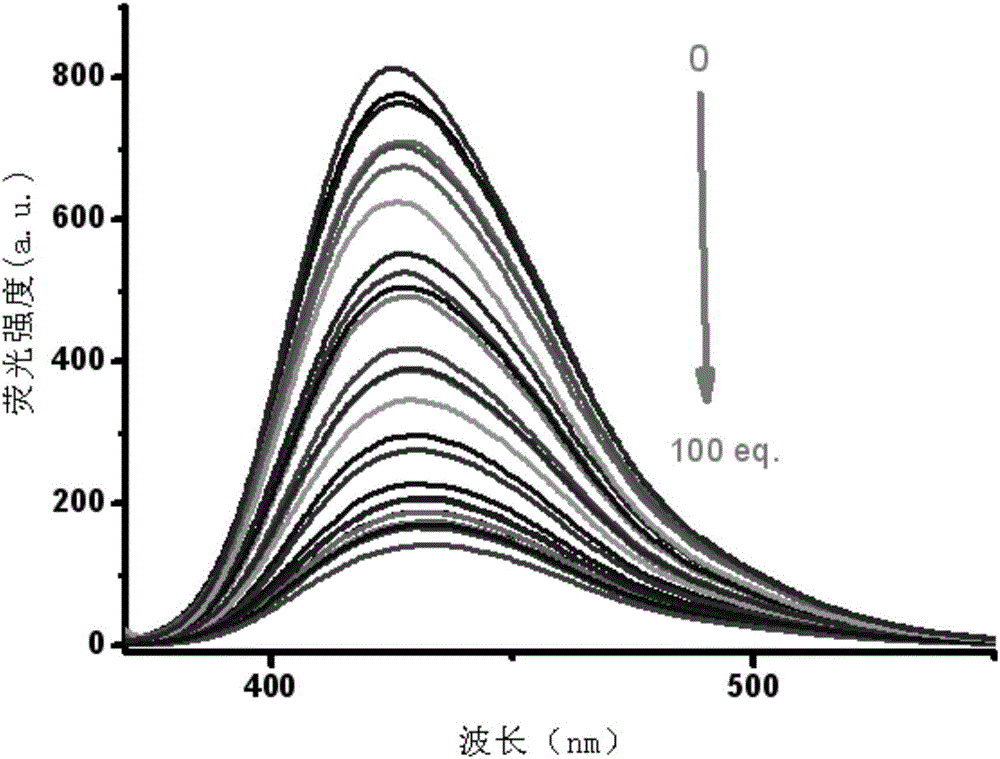
The invention relates to a phenanthrene imidazole reversible fluorescence probe for Cu<2+> detection, and a preparation method and application thereof, relates to the fluorescence probe for the Cu<2+> detection, and the preparation method and the application thereof, and aims to solve the technical problems of an existing fluorescence molecular probe is poor in Cu<2+> detection reversibility and easy to be interfered by other metal ions. The reversible fluorescence probe provided by the invention has a structural formula as shown in the figure. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) using phenanthrenequinone, o-nitrobenzaldehyde and ammonium acetate for synthesizing an intermediate compound I; (2) using the intermediate compound I, raney nickel, ethanol and hydrazine hydrate for synthesizing an intermediate compound II; (3) reacting the the intermediate compound II and salicylaldehyde, and obtaining the phenanthrene imidazole reversible fluorescence probe for the Cu<2+> detection. During detection, after the reversible fluorescence probe is acted with Cu<2+>, the fluorescence intensity is quenched; after Cr<3+> is added, the fluorescence intensity is recovered and can be used for detecting pollution of the Cu<2+> and the Cr<3+> in water.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Manufacture of phenyl ethylamine compounds, in particular venlafaxine
InactiveUS7026513B2Reduce the cyanocarbinol most effectivelyPreparation by oxidation reactionsOrganic compound preparationPhenyl groupEthylamine
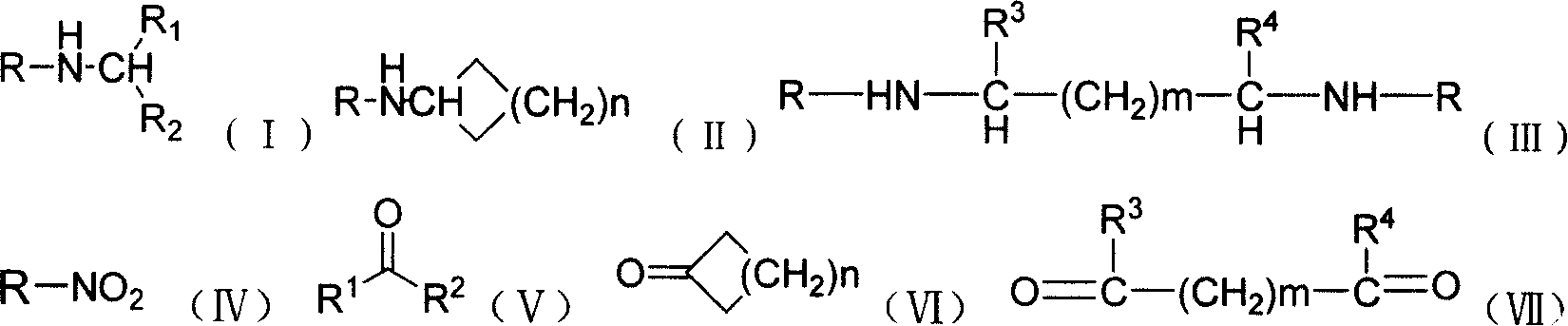
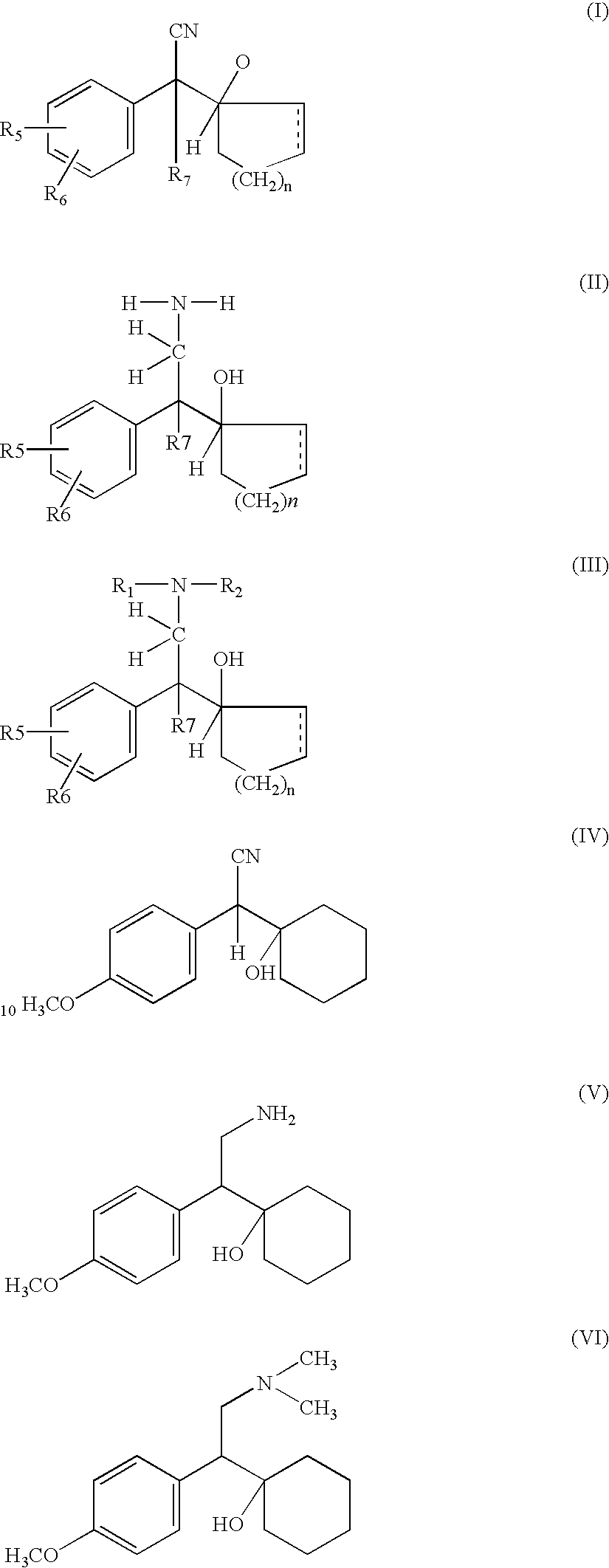
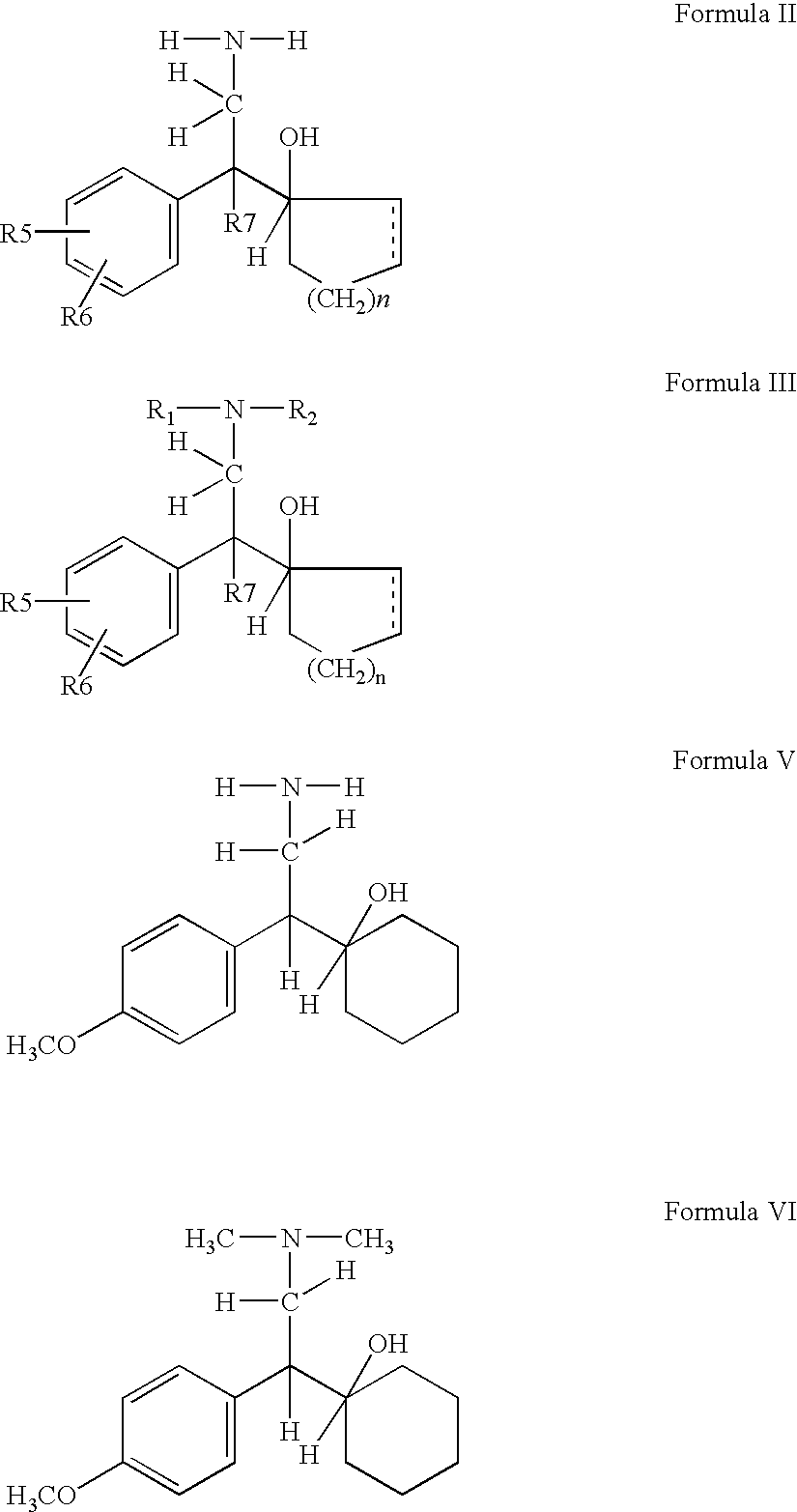
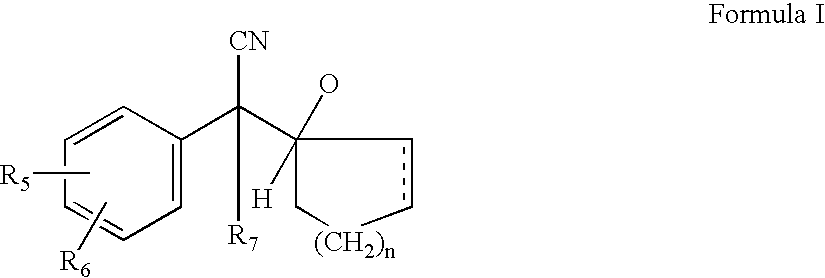
A process for the preparation of hydroxy(cycloalkane / cyclokene) phenylethyl amine of the general formula (III) comprising alkylation of its precursor amine of general formula (II) which is in turn produced by an effective reduction process from its precursor cyanide having the general formula (I) using Raney Nickel (CORMIII) as catalyst where, either of R5 and R6 independently could be in meta or para position and R5, R6 are independently hydrogen, hydroxyl, alkyl, alkanoyloxy, cyano, nitro, alkylmercapto, amino, alkylamino, allkanamido, halo, trifluoromethyl, or taken together methylenedioxy, n is 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, R7 is hydrogen of alkyl of 1–7 carbon atom, R1 IH or alkyl of 1–3 carbon atom and R2 is alkyl 1–3 carbon atom, the dotted line represents optional unsaturation. Compounds of formulae IV, V and VI are respectively derivatives of compounds I, II and III respectively.
Owner:NICHOLAS PIRAMAL INDIA LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com