Metal-free hydrogenation catalyst and application
A hydrogenation catalyst, metal-free technology, applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalyst, cyanide reaction preparation, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high equipment requirements, flammable air, expensive price, etc., to simplify the production process, catalyze High activity and cost reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
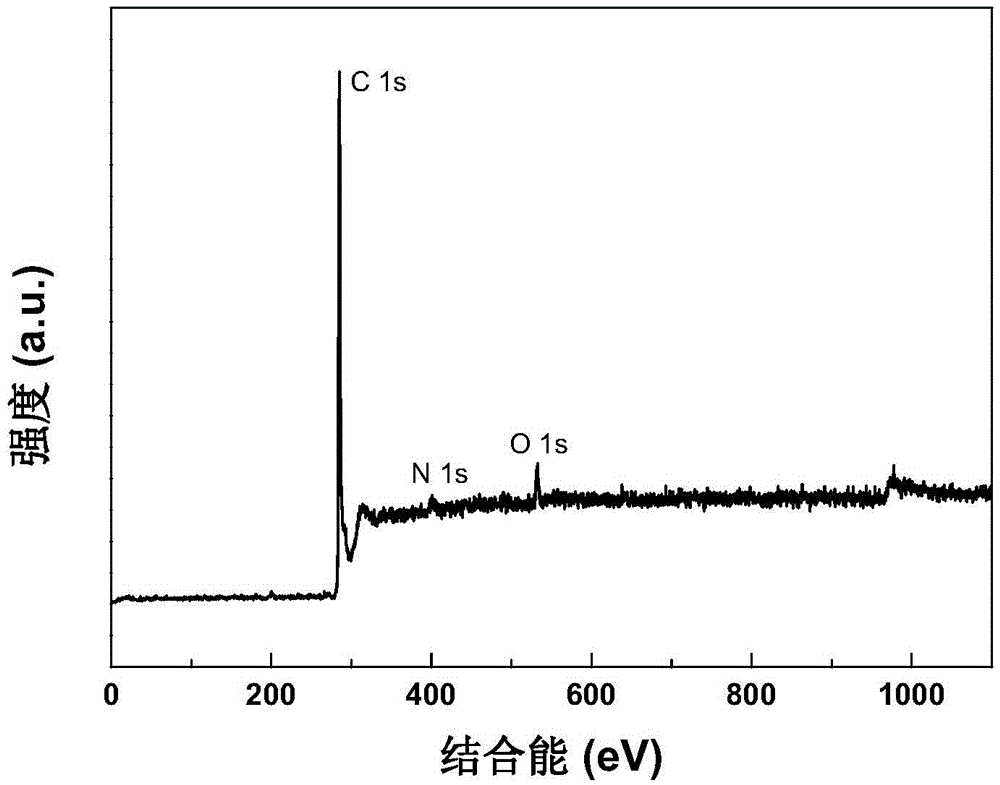
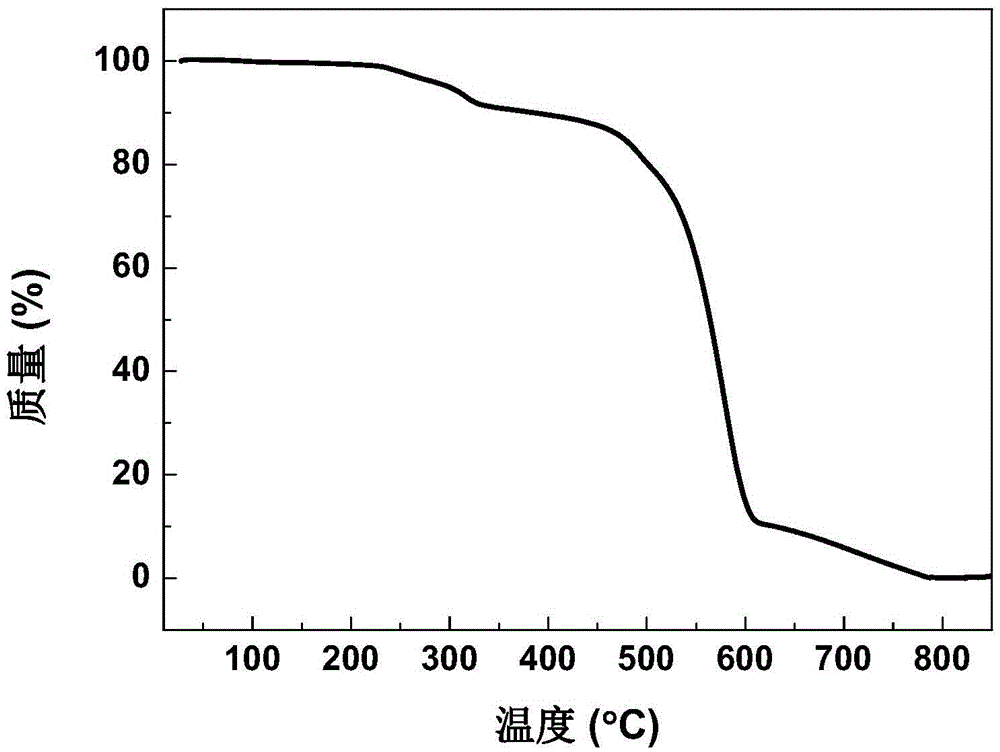
[0027] A metal-free hydrogenation catalyst, prepared by chemical vapor deposition, pyrolyzes iron phthalocyanine (FePc) on a quartz glass sheet at 800-1100°C, and feeds a mixed gas of argon and hydrogen into a quartz reaction tube. The obtained carbon tube is acid-washed to remove the residual iron catalyst to obtain the metal-free hydrogenation catalyst nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, see appendix figure 1 ) and thermogravimetric analysis (TG, see attached figure 2 ) and other means, it can be seen that iron has been completely removed in the resulting catalyst.
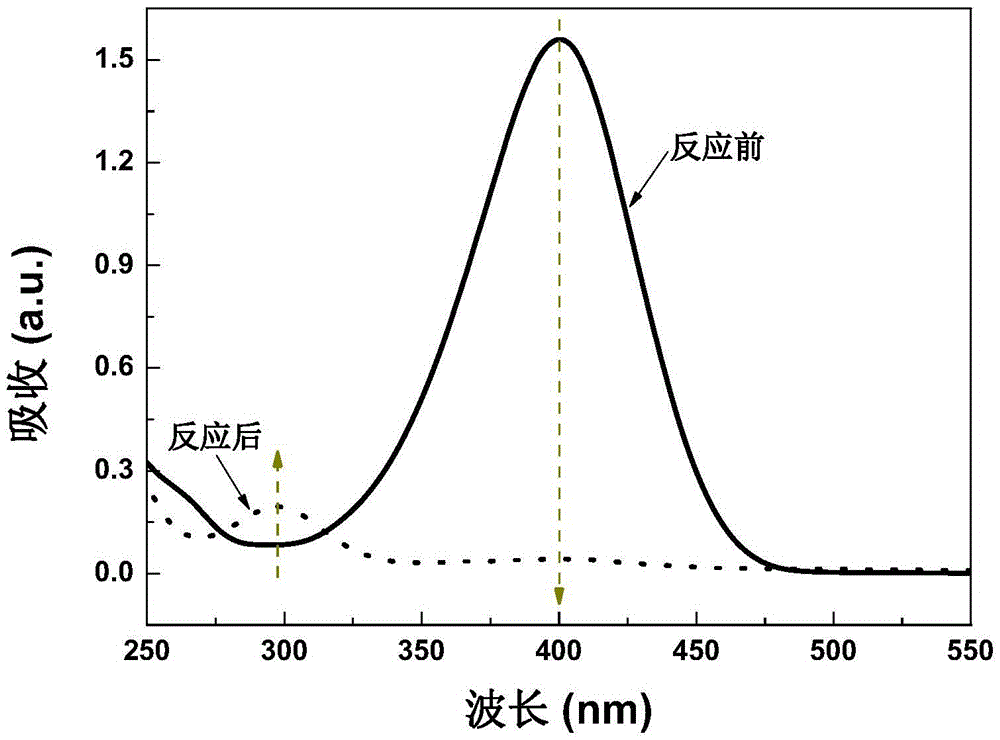
[0028] The nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes obtained above are used for liquid-phase hydrogenation reduction to prepare p-aminophenol, using p-nitrophenol solution as a raw material, reacting at room temperature, and using excess sodium borohydride solution as a hydrogen source and reducing agent. First, sodium borohydride solution is added to the nitrophenol solution. It can...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The catalyst used is the same as in Example 1, except that high-pressure hydrogenation catalysis is used.
[0031] The reaction process is carried out in a stainless steel high-pressure reactor with a magnetically driven stirring device. First, add an appropriate amount of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes and a certain concentration of p-nitrophenol solution in the kettle, stir quickly, and replace it with hydrogen for 4-5 minutes after sealing. After heating to the predetermined reaction temperature, hydrogen gas was introduced to raise the predetermined pressure, and then the reaction was started by timing. The reaction pressure is 1.6MPa, the reaction temperature is 100°C, and the temperature and pressure are kept constant during the reaction process. After the reaction, the pressure is released and cooled. The reaction effect is close to that of Example 1. The reaction rate can be controlled by factors such as catalyst dosage, reaction temperature, reaction pressure,...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Repeat Example 1 with the difference that the reducing agent used is potassium borohydride. Its catalytic effect is close to that of Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com