Separation and purification and degradation method for lignin
A lignin and wood powder technology, applied in the field of biomass extraction and utilization, can solve the problems of high energy consumption and increased degradation cost, achieve high conversion rate and selectivity, and reduce pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
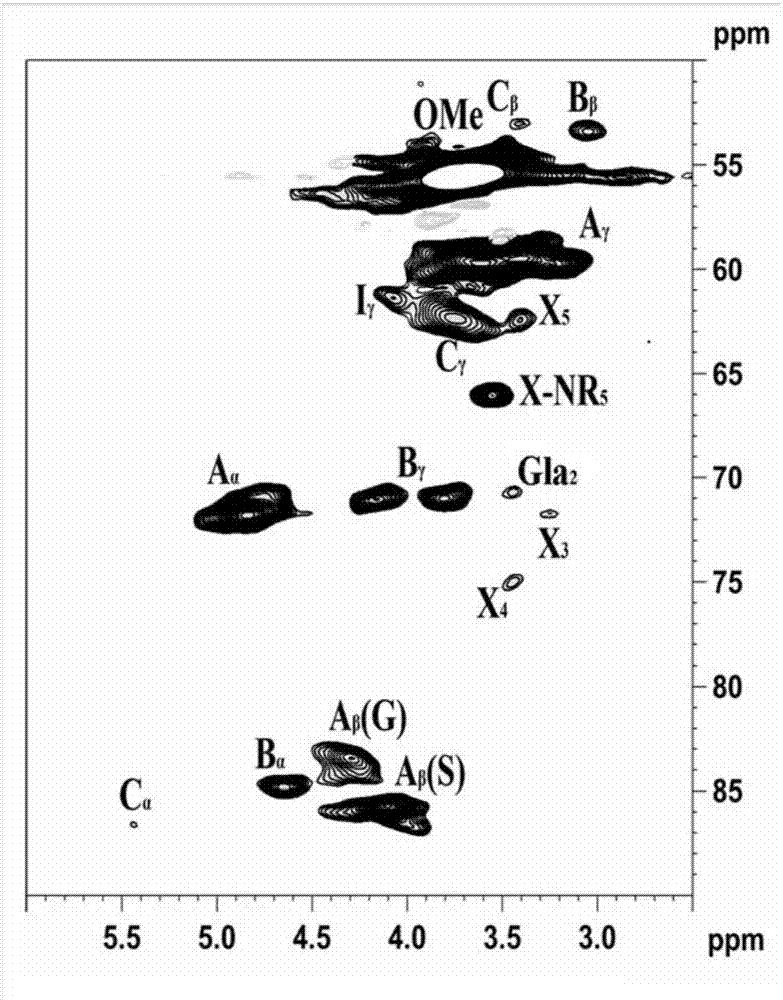
[0041] Preparation of enzymatic residue lignin
[0042] (1) Raw material pretreatment stage: crush the eucalyptus wood raw material to ultra-fine particle size (>200 mesh).
[0043] (2) Enzymatic hydrolysis stage: ball-milled wood powder is added to sodium acetate buffer at a material ratio of 1:25, and the pH is adjusted to 4.8 with acetic acid, then 50 FPU / g of cellulose compound enzyme is added, and enzymatic hydrolysis is carried out at 50°C 48h. After enzymolysis, the mixture was centrifuged, washed with hot acid water (pH=2), and freeze-dried. Subsequently, the freeze-dried residue was ball milled again for 5 hours, and then enzymatically hydrolyzed again. The ball mill residue was added to distilled water according to the material ratio of 1:25, and the pH was adjusted to 4.8 with acetic acid, and then 50 FPU / g of cellulose compound enzyme was added. Enzymolysis was carried out at 50°C for 48 hours. After completion, the mixture was centrifuged, washed with hot acid w...
Embodiment 2
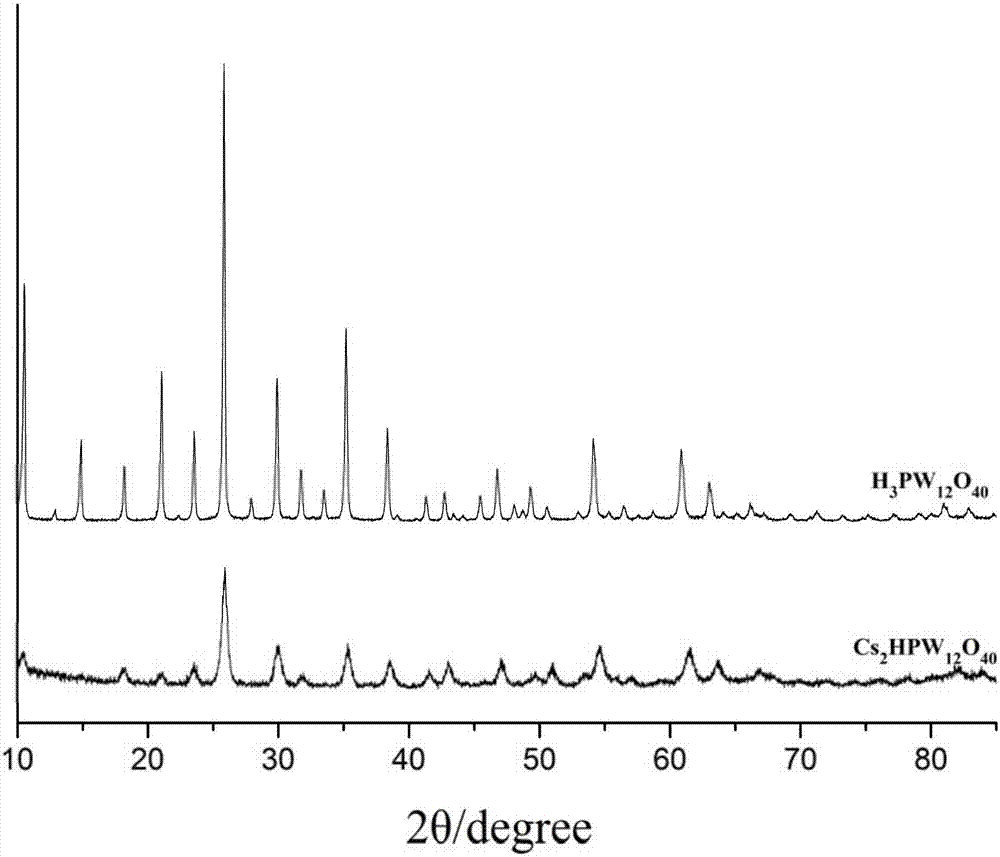
[0054] Compared with Example 1, the enzymatic hydrolysis operation in this example is: adjust the pH to 5.0 with acetic acid, then add 40 FPU / g cellulose complex enzyme, and enzymatically hydrolyze for 54 hours at 47°C. , in the catalytic conversion of the enzymatic residue lignin, change the temperature to 260°C and the pressure to 2MPa; the weight ratio of the heteropolyacid salt to the enzymatic residue lignin is 1:20, the step (5) The weight ratio of Raney nickel to the enzymolysis residue lignin is 1:20.
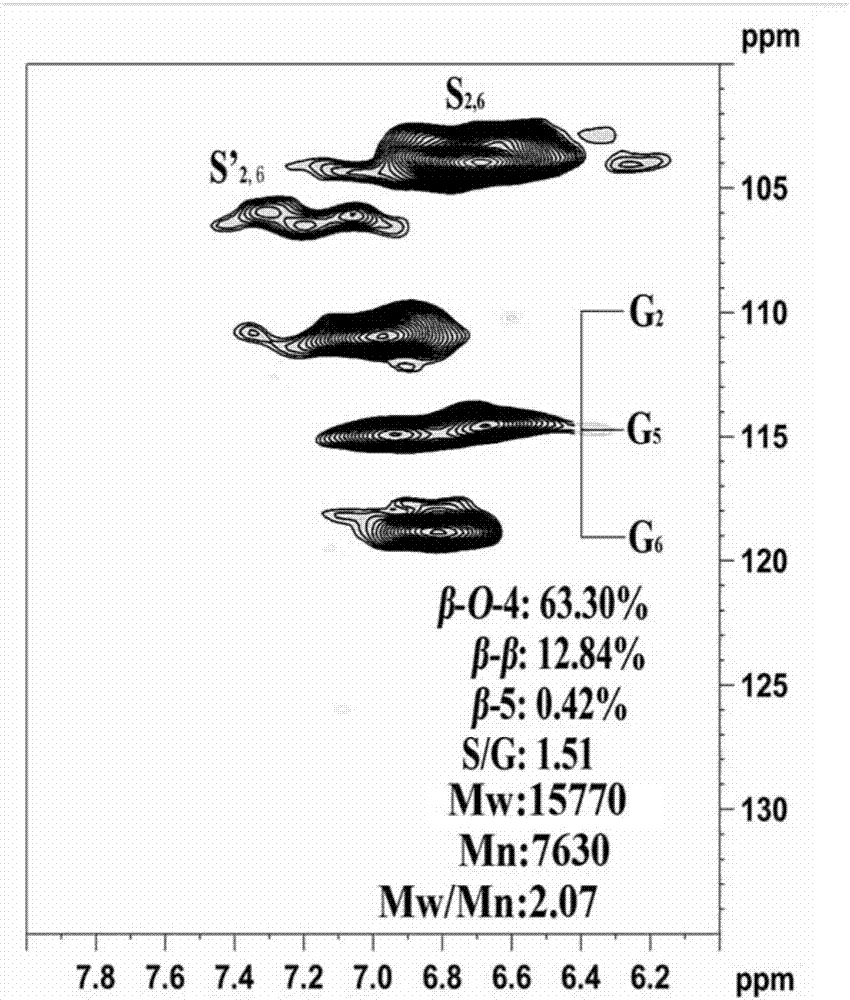
[0055] Structural characterization of lignin degradation products from enzymatic hydrolysis residues:
[0056] Under this condition, the lignin conversion rate was 92.93%, among which the organic phase lignin degradation product yield was 63.9%, the aqueous phase lignin degradation product yield was 18.18%, and the coke yield was 10.85%. Compared with 250°C, at 260°C, the yields of aqueous lignin depolymerization products and organic phase lignin degradation products a...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Compared with Example 1, the enzymatic hydrolysis operation in this example is as follows: adjust the pH to 4.8 with acetic acid, then add 30 FPU / g cellulose compound enzyme, and enzymatically hydrolyze for 72 hours at 45°C. , in the catalytic conversion of the enzymatic residue lignin, change the temperature to 270°C and the pressure to 3MPa; the weight ratio of the heteropolyacid salt to the enzymatic residue lignin is 1:10, the step (5) The weight ratio of Raney nickel to the enzymolysis residue lignin is 1:10.
[0059] Structural characterization of lignin degradation products from enzymatic hydrolysis residues:
[0060] Under this condition, the conversion rate of lignin was 100.69%, the yield of lignin degradation products in organic phase was 77.54%, the yield of lignin degradation products in aqueous phase was 15.16%, and the yield of coke was 7.99%. We found that under this condition, the yield of lignin degradation products in the organic phase increases, whi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com