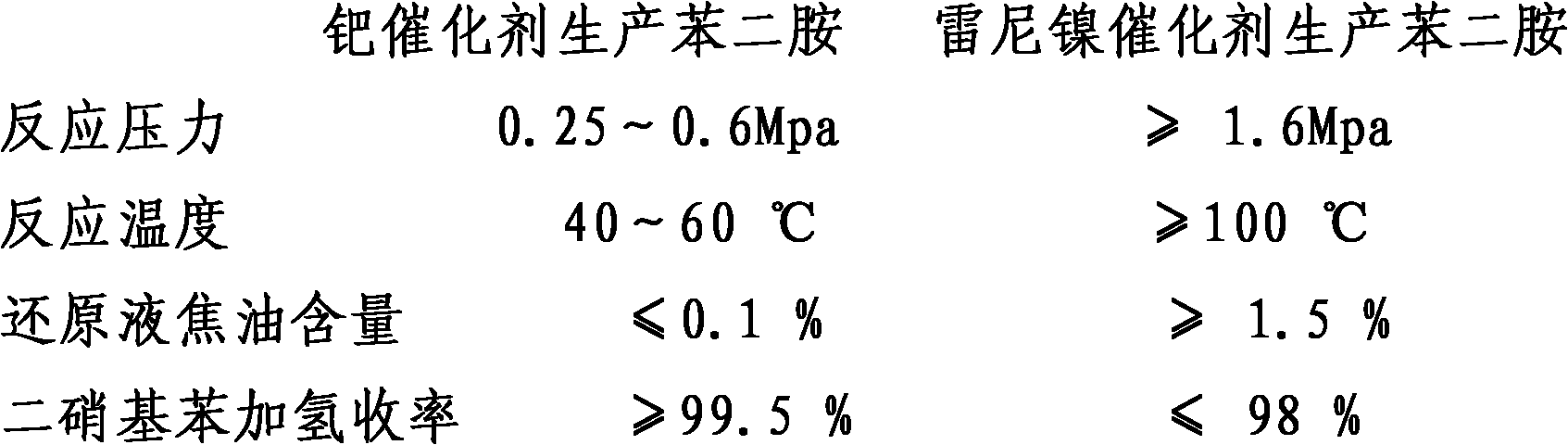
Method for producing phenylene diamine by performing hydrogenation reduction on mixed dinitrobenzene with palladium catalyst
A technology of dinitrobenzene palladium and dinitrobenzene is applied in the field of hydrogenation reduction of mixed dinitrobenzene palladium catalyst to produce phenylenediamine, and can solve the problems of high energy consumption, high reaction temperature, low raw material conversion rate, and the like, Achieve the effect of reducing energy consumption, increasing product output and improving product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] The method step of mixing dinitrophenyl palladium catalyst hydrogenation reduction to produce m-phenylenediamine is as follows:
[0045] Reactor volume 2M 3, add 506 kilograms of mixed dinitrobenzene raw materials in the reactor, wherein 500 kilograms of dinitrobenzene content, the ratio of ortho, meta, right isomer in dinitrobenzene 10:88:2; 1000 kilograms of alcoholic solvents 6 kg of 5% palladium catalyst, closed reactor, nitrogen replacement qualified, steam heating, control the temperature in the reactor 56 ℃, maintain the reaction pressure 0.55Mpa, keep 120 minutes for hydrogenation reaction. After the hydrogenation reaction, HPLC detected that the reduction product contained 320.7 kg of phenylenediamine, and the hydrogenation yield of dinitrobenzene was 99.7%. Pump the reducing solution to the filter to filter the catalyst, then pump the filtered phenylenediamine reducing solution to the dealcoholization tower for dealcoholization; the reducing solution enters t...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The method steps of mixing dinitrophenyl palladium catalyst hydrogenation reduction to produce o-phenylenediamine are as follows:
[0048] Reactor volume 2M 3 , add 505 kilograms of mixed dinitrobenzene raw materials in the reactor, wherein 500 kilograms of dinitrobenzene content, the ratio of ortho, meta, right isomer in dinitrobenzene 12: 85.7: 2.3; 1000 kilograms of alcoholic solvents 5 kg of 5% palladium catalyst, closed reactor, nitrogen replacement qualified, steam heating, control reactor temperature 50 ℃, reaction pressure 0.45Mpa, keep 90 minutes for hydrogenation reaction. After the hydrogenation reaction, HPLC detected that the reduced product contained 320.1 kg of phenylenediamine, and the hydrogenation yield of dinitrobenzene was 99.52%. Pump the reducing solution to the filter to filter the catalyst, then pump the filtered phenylenediamine reducing solution to the dealcoholization tower for dealcoholization; the reducing solution enters the middle part of...
Embodiment 3
[0050] The method step of mixing dinitrobenzene palladium catalyst hydrogenation reduction to produce p-phenylenediamine is as follows:
[0051] Reactor volume 2M 3 , add 506 kilograms of mixed dinitrobenzene raw materials in the reactor, wherein 500 kilograms of dinitrobenzene content, the ratio of ortho, meta, right isomer in dinitrobenzene 11: 86.8: 2.2; 1000 kilograms of alcoholic solvents 5 kg of 5% palladium catalyst, closed reactor, nitrogen replacement qualified, through steam heating, control the temperature in the reactor 60 ℃, pressure 0.5Mpa, keep 100 minutes for hydrogenation reaction. After the hydrogenation reaction, HPLC detected that the reduced product contained 320.2 kg of phenylenediamine, and the hydrogenation yield of dinitrobenzene was 99.55%. Pump the reducing solution to the filter to filter the catalyst, then pump the filtered phenylenediamine reducing solution to the dealcoholization tower for dealcoholization; the reducing solution enters the middl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com