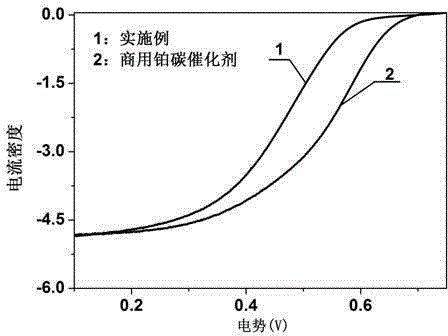
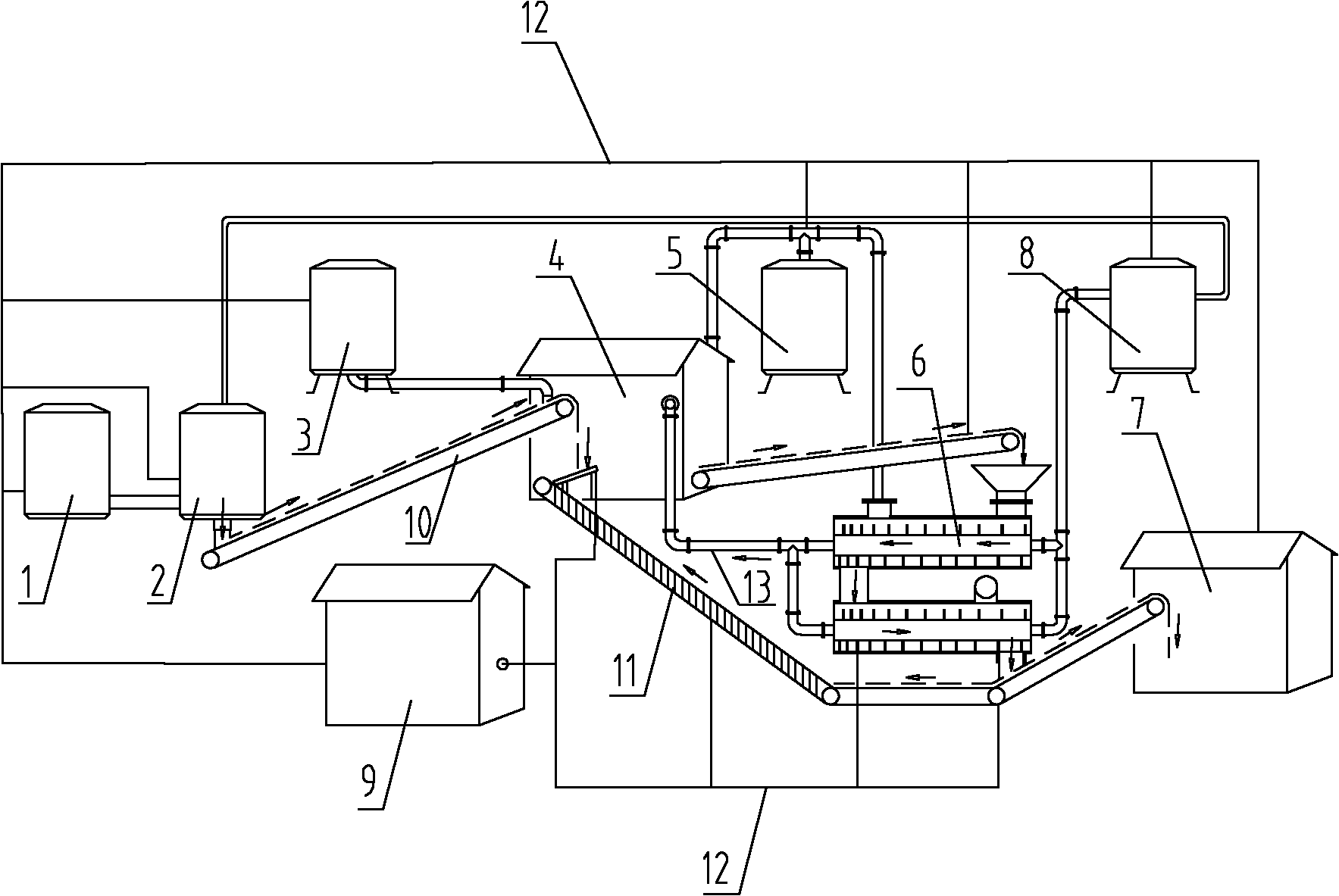
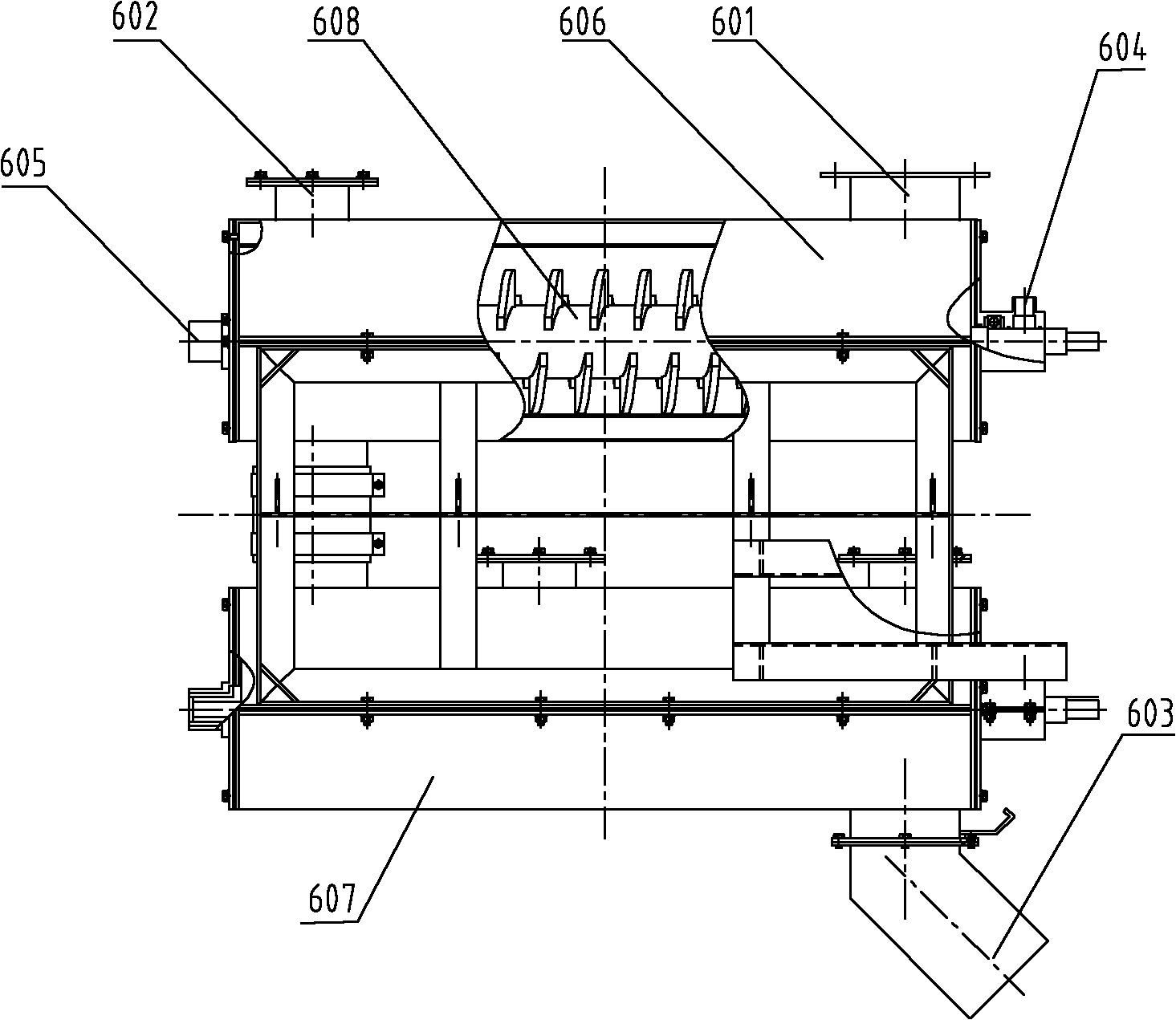
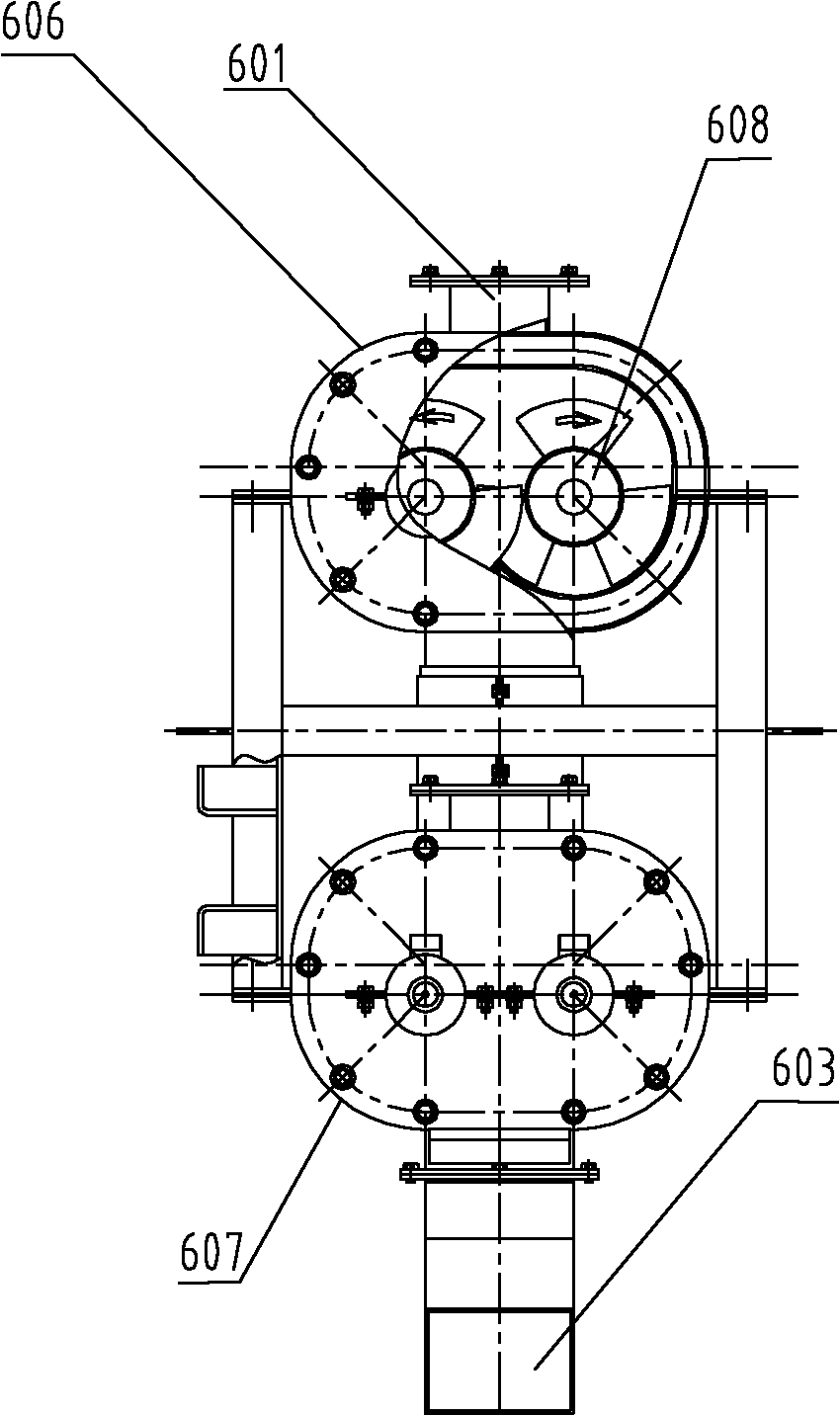
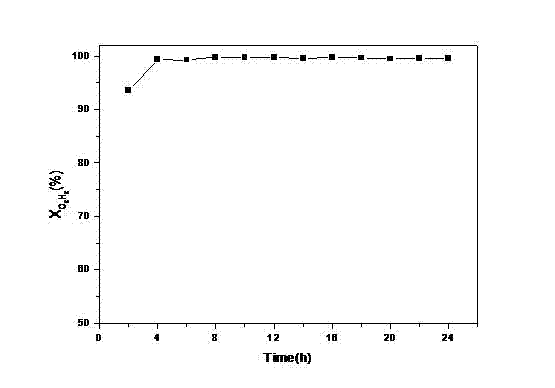
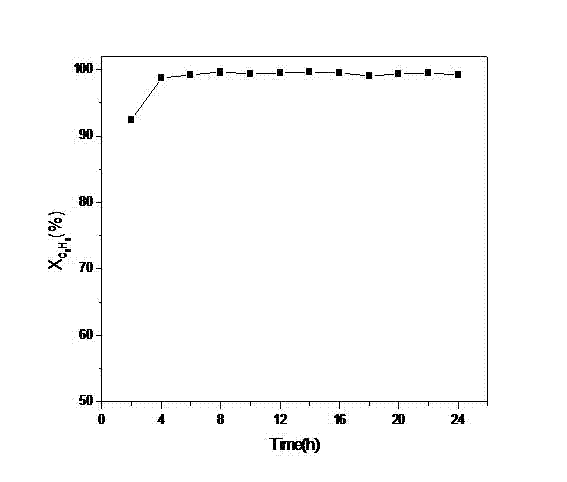
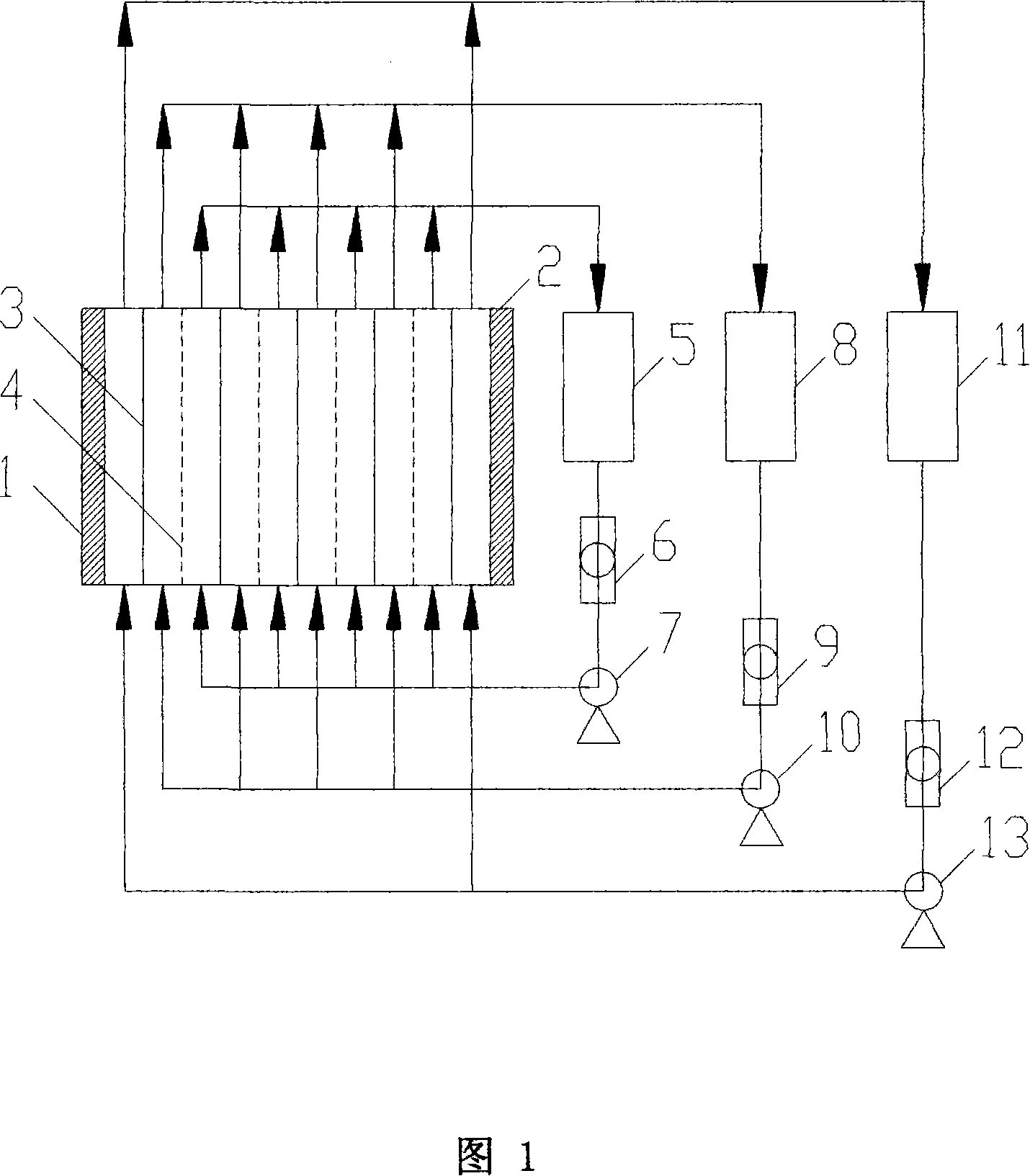
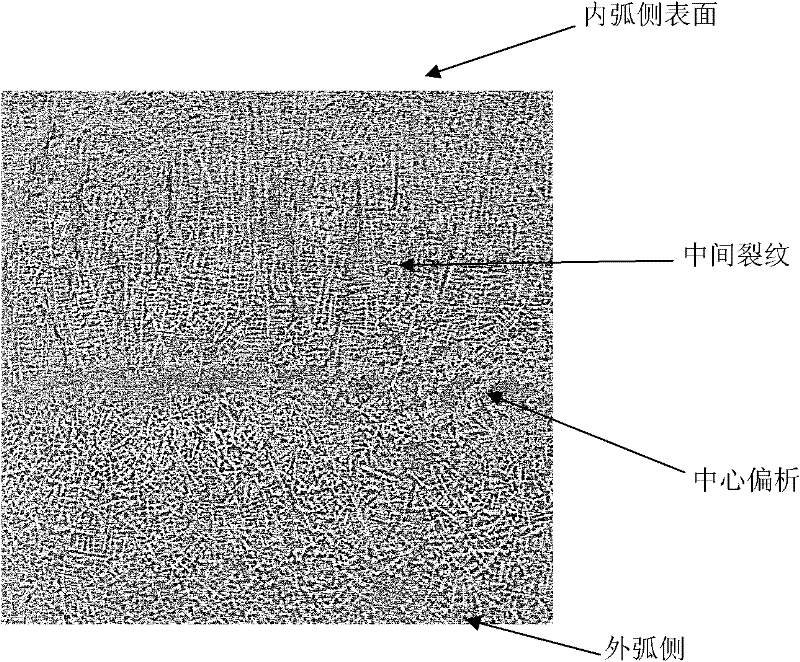
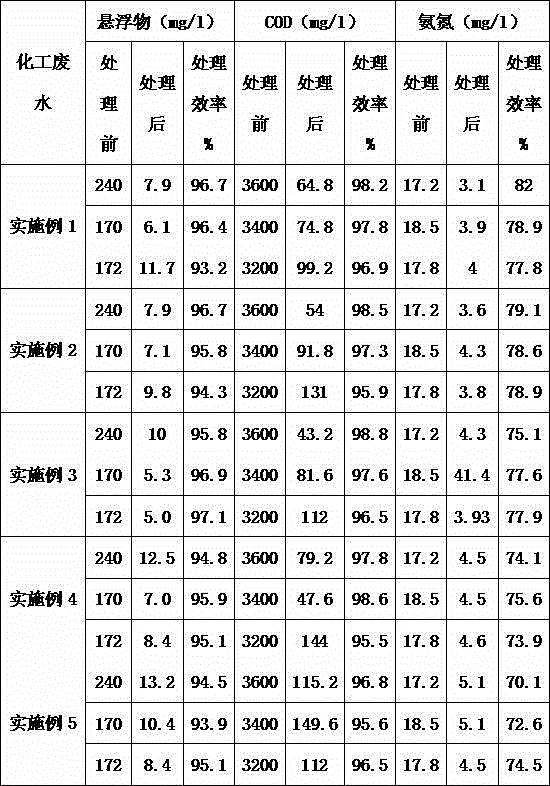
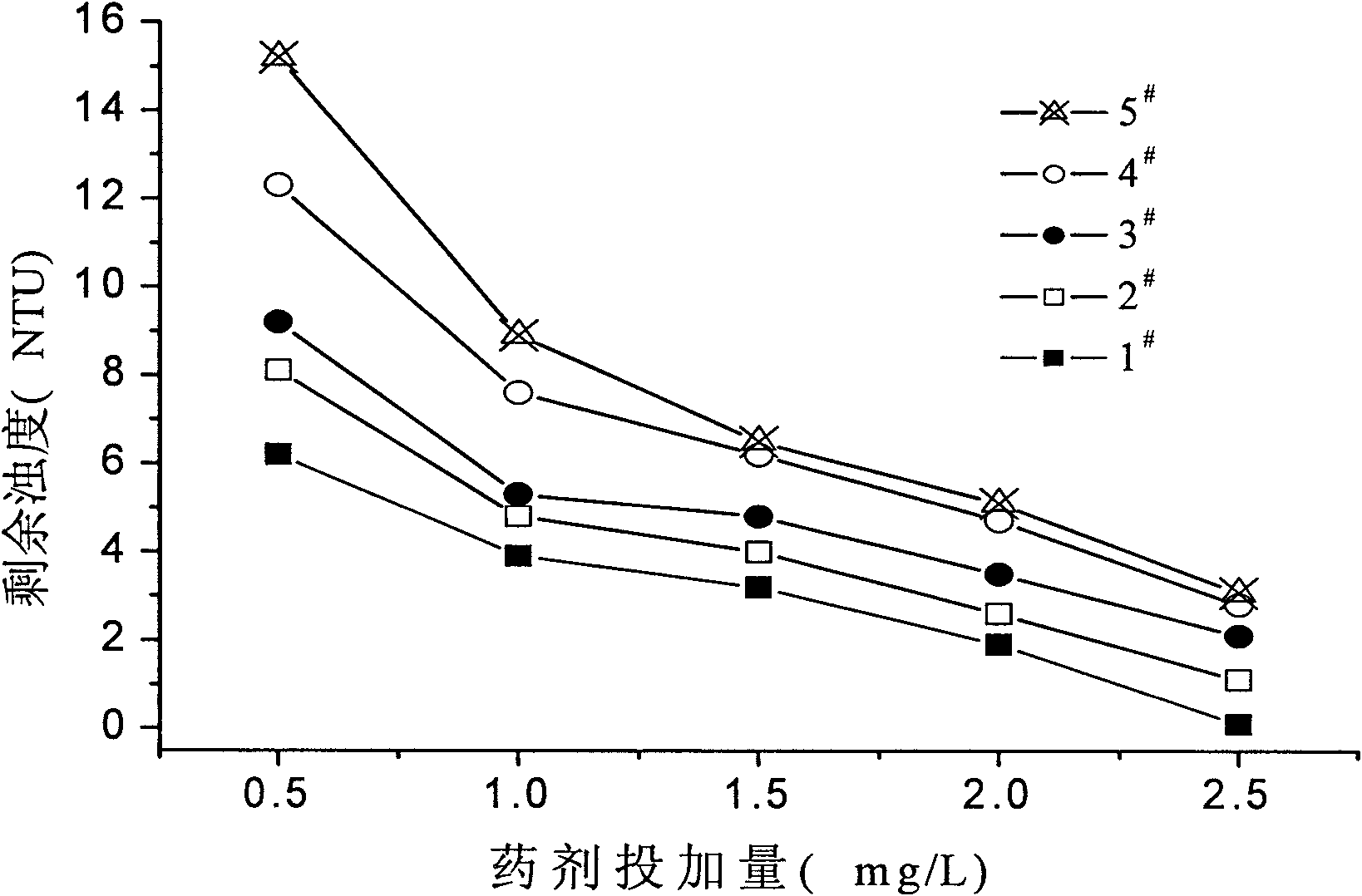
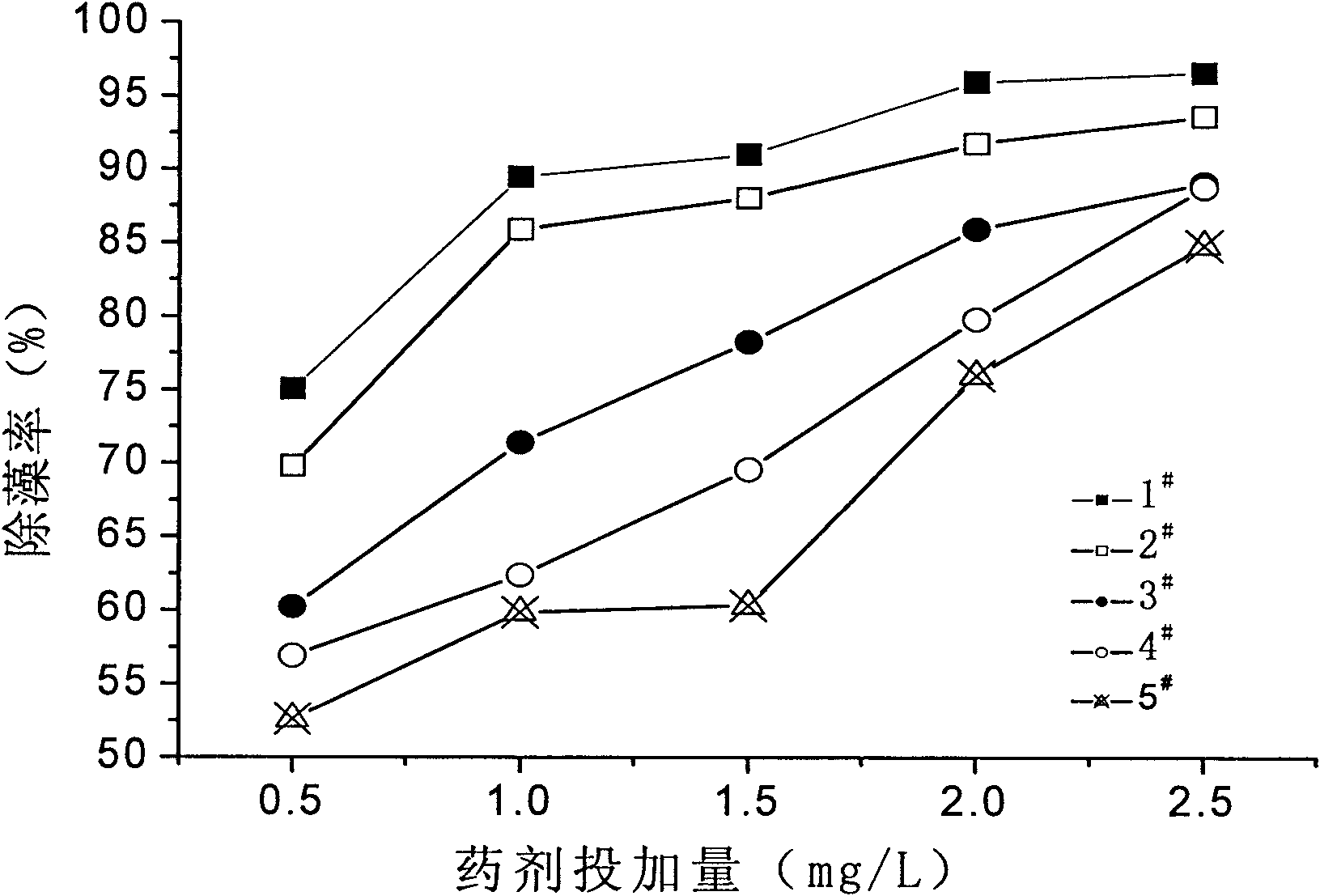
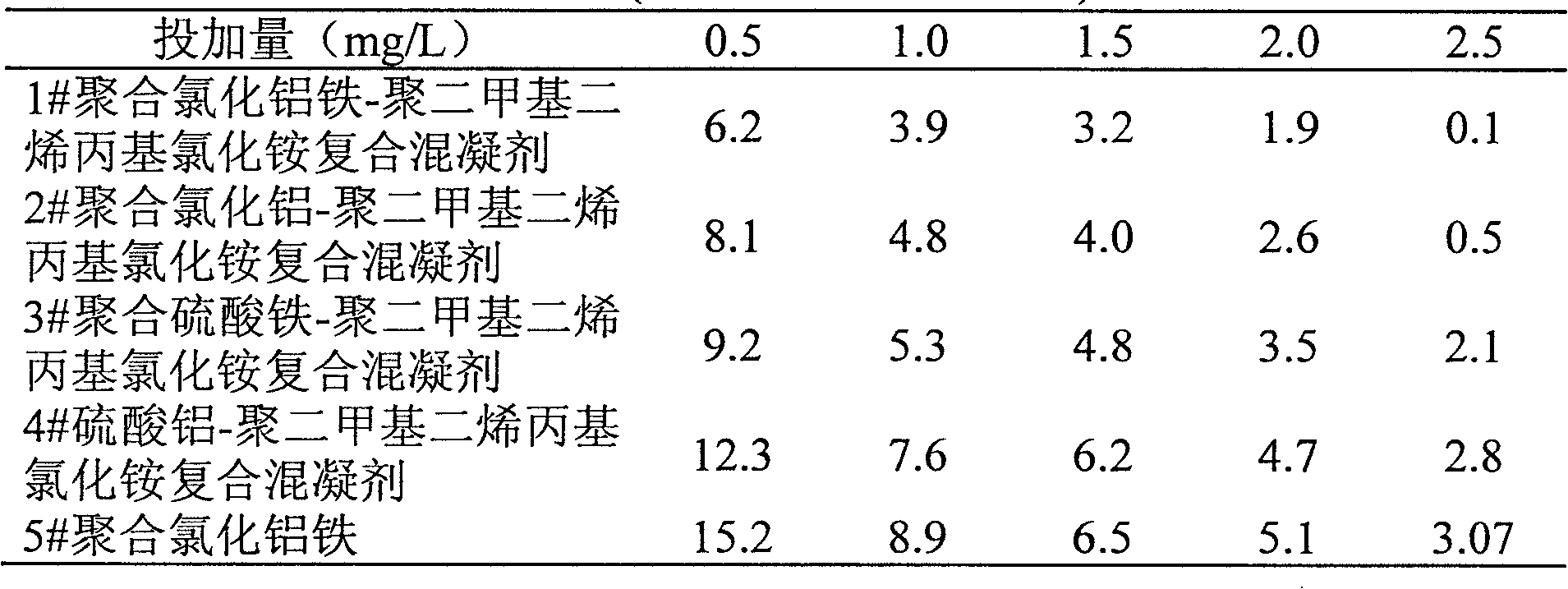
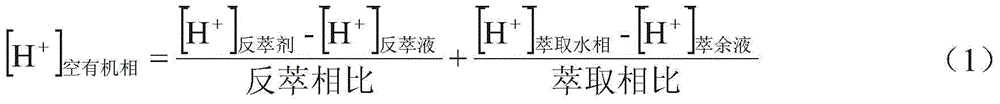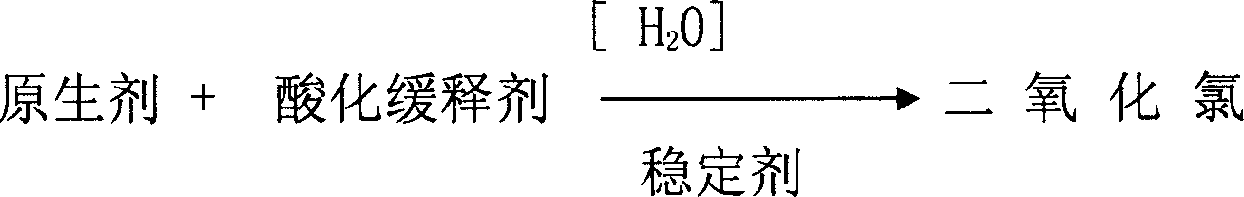Patents
Literature
2419 results about "Iron chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation of 2,2-bi-[4-(4-aminophenoxy)phenyl]propane
InactiveCN1472193AEasy to operateImprove working environmentOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationActivated carbonAlcohol
A process for preparing 2,2-bis-[4-(4-aminophenyloxy)phenyl] propane includes such steps as reflux reacting between 4,4'-dihydroxydiphenyl propane (BPA), 1-chloro-4-nitrobenzene (CNB) and salting agent in the mixture of non-protonic transferring polar solvent and dewatering agent at 110-150 deg.C to obtain 2,2-bis-[4-(4-nitrophenyloxy)phenyl] propane (BNPP), and reducing in alcohol as solvent under action of hexahydrated iron chloride, activated carbon and hydrazine hydrate. Its advantages are simple process, low cost and high quality and output rate of product.
Owner:TANSUO SCI & TECH NANTONG CITY
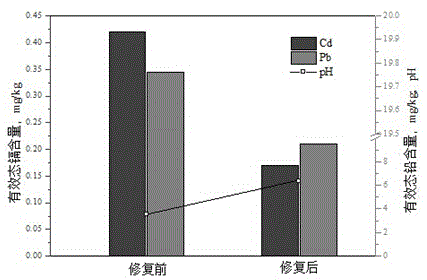
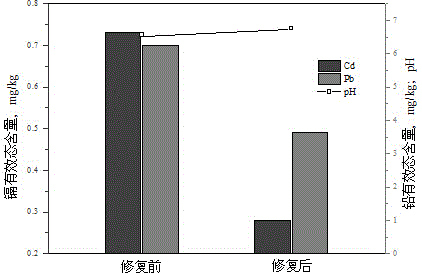
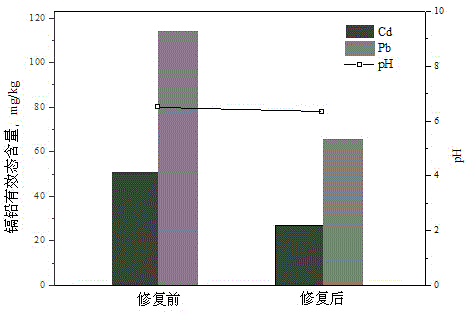
Restoration agent for lowering cadmium/lead effective state content in soil, and use method and application thereof
ActiveCN104650921AReduce the effective contentReduce available lead contentContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSoil scienceSulfate
The invention discloses a restoration agent for lowering cadmium / lead effective state content in soil, which is composed of quicklime, calcium sulfate, wood charcoal, iron chloride and water, wherein the weight ratio of the quicklime, calcium sulfate, wood charcoal and iron chloride is (1-2):(1-2):(1-2):(0.5-1), and the water accounts for 30-45 wt% of the soil. The restoration agent can be used for treating heavily polluted soil; and common chemical passivators can only restore lightly polluted soil, and do not have obvious effect on heavy pollution. The restoration agent can be used for treating both acidic soil and neutral soil. The restoration agent has high remediation efficiency for cadmium polluted soil; the reaction mechanisms relate to chemical precipitation and physical adsorption; and when one action fails due to change of the outside conditions, the other action can perform the guarantee function. The restoration agent has certain control actions on the lead effective state content in the polluted soil.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
Electrothermal film and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101668359ASimple processEfficient processHeating element materialsResistors adapted for applying terminalsTitanium chlorideMetallurgy
The invention relates to an electrothermal film and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor heating. The electrothermal film is mainly prepared by adopting stannic chloride, titanium tetrachloride, stannic chloride, titanium trichloride, ferric chloride, antimony trichloride, calcium chloride, potassium chloride, cadmium chloride, stannic dioxide, stannictetroxide, hydrofluoric acid, boric acid, ethanol, isopropyl alcohol and inorganic water. By adopting the above formula, the mixture is mixed, stirred and heated to prepare into electrothermal film treating fluid, a semi-finished product of the electrothermal film is obtained by spraying the electrothermal film treating fluid at negative pressure on the electrothermal film carrier, and then silveroxide slurry is coated on the semi-finished product of the electrothermal film for baking to form a finished product of the electrothermal film. The electrothermal film has reasonable proportion andsimple manufacturing process, can be manufactured into various electrothermal film heating devices, has a working temperature capable of being up to 500 DEG C, and has wider application range. The electrothermal film of the invention also has the function of far infrared radiation, can play a role of physical therapy and health care to human body, and can help improve the quality and output of agricultural products.
Owner:GUANGDONG HALLSMART INTELLIGENCE TECH CORP LTD
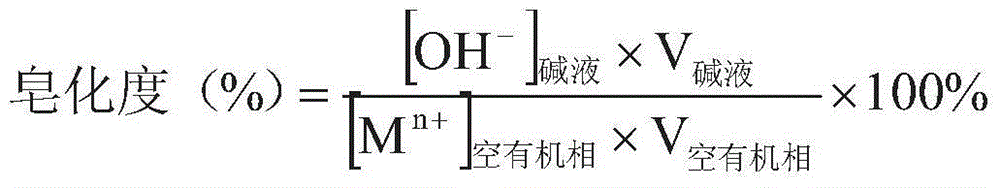
Regeneration method of lithium extraction system
InactiveCN104388677AGuaranteed recyclingSimple regeneration methodProcess efficiency improvementLithiumDiluent
The invention discloses a regeneration method of a lithium extraction system. The lithium extraction system is regenerated by virtue of alkaline saponification and the regeneration method comprises the following steps of mixing empty-loading organic phases subjected to lithium extraction and reverse extraction and alkaline liquor, saponifying and standing for separating phases to obtain a clarified and transparent regenerated and extracted organic phase, wherein the empty-loading organic phases comprise an extractant, a synergistic extractant and a diluent which are involved in the lithium extraction and reverse extraction processes; the synergistic extractant is iron chloride; and the alkaline liquor is any one of sodium hydroxide solution and potassium hydroxide solution. The regeneration method of the lithium extraction system disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity in operation and good saponifying effect; when lithium is extracted by virtue of the saponified, regenerated and recycled extraction organic phase, the extraction efficiency of lithium is high and the extraction effect is good; and by the method, the recycling of the extraction organic phase for extracting lithium is achieved and the process flows of extracting, carrying out reverse extraction, regenerating and extracting for circularly extracting lithium are completed.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
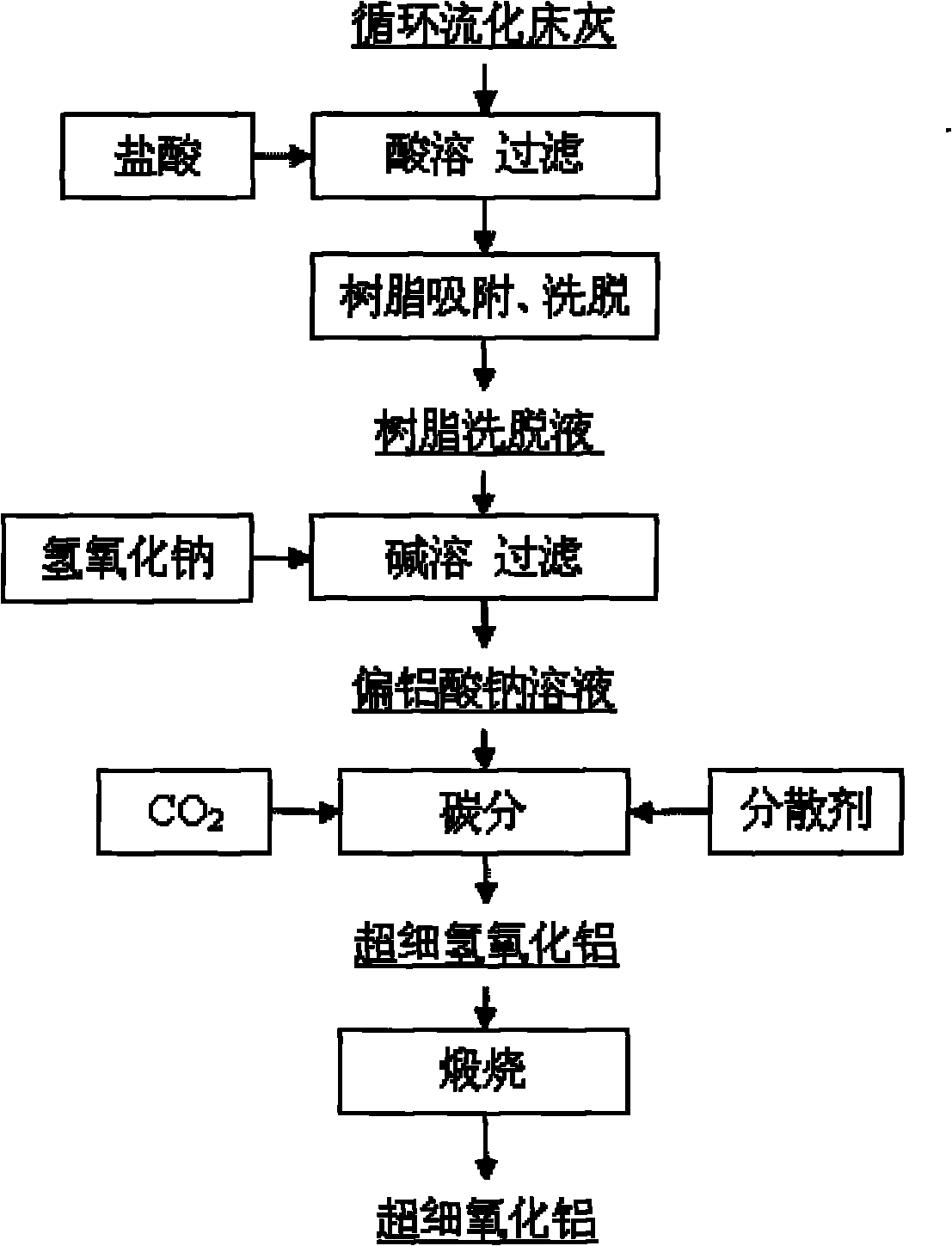
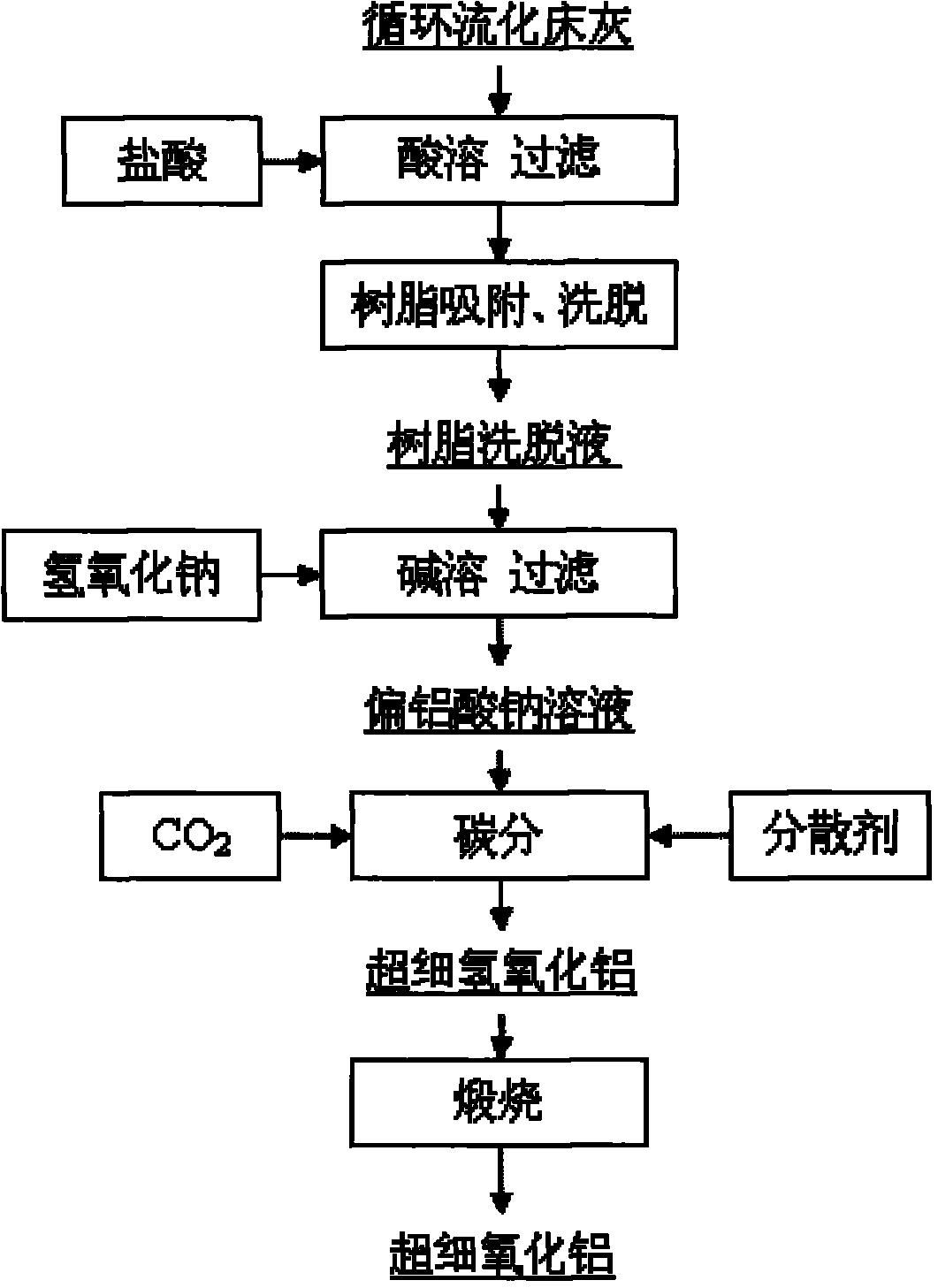
Method for producing superfine aluminium hydroxide and aluminium oxide by using flyash
InactiveCN101870489AHigh purityEliminate high temperature calcination activation stepsProductsReagentsAluminium chlorideDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for producing superfine aluminium hydroxide and aluminium oxide by taking flyash of a recirculating fluidized bed as a raw material. The method comprises the following steps of: a) grinding the flyash, performing wet magnetic separation and deironization, and reacting with hydrochloric acid to obtain hydrochloric acid extract; b) introducing the hydrochloric acid extract into a macroporous cationic resin column for adsorption, after adsorptive saturation of the resin, eluting by using an eluant to obtain eluent containing aluminium chloride and iron chloride; c) removing iron from the eluent by using alkaline solution to obtain solution of sodium metaaluminate; d) adding a dispersing agent into the solution of sodium metaaluminate, and mixing uniformly to obtain dispersion; and e) performing carbon decomposition on the dispersion to obtain the superfine aluminium hydroxide. The superfine aluminium hydroxide is calcined at different temperatures to form gamma-aluminium oxide and alpha-aluminium oxide respectively. Compared with other methods, the method has the advantages of wide sources of raw materials, simple production process and high purity of the products.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +1
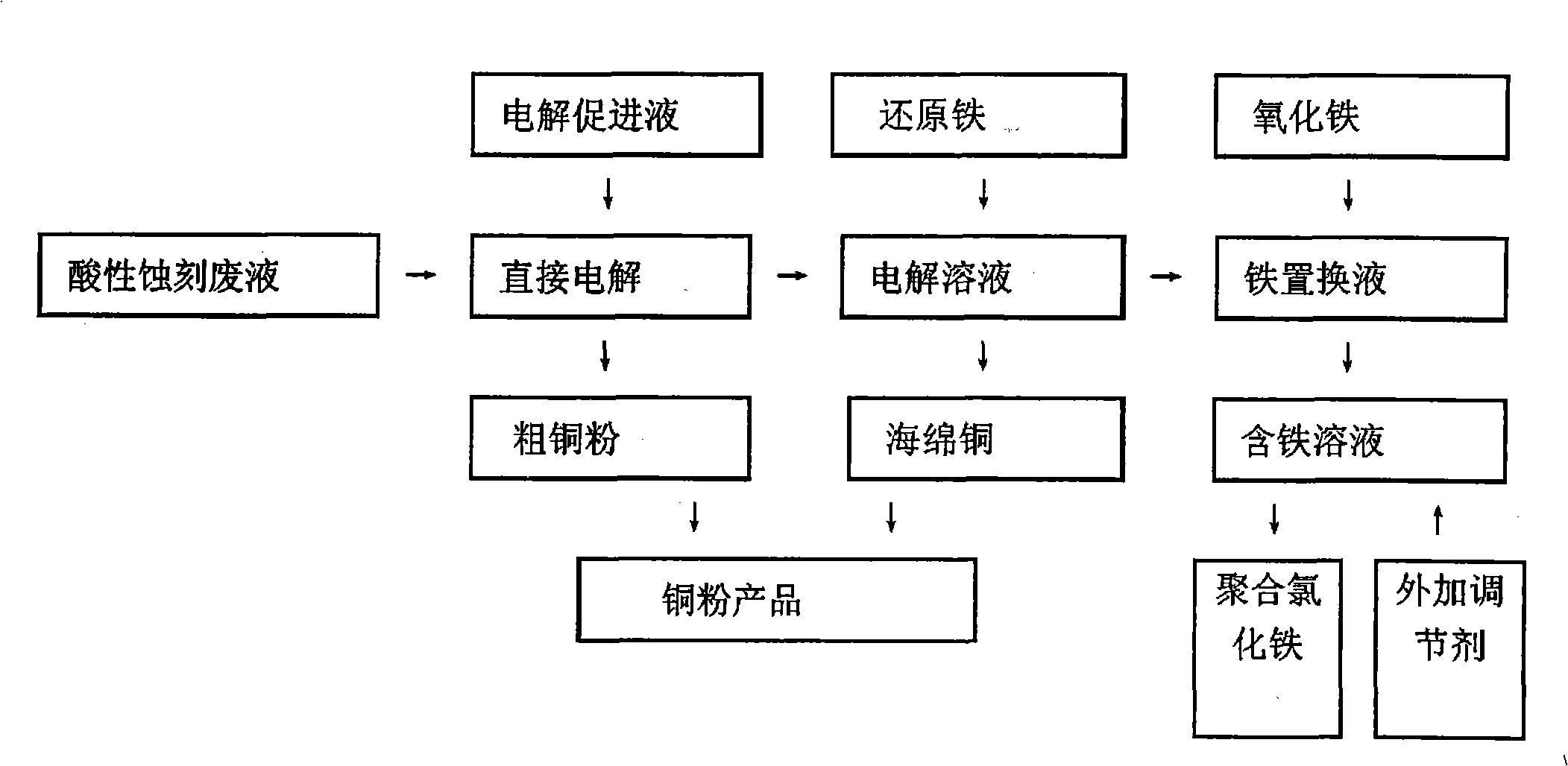
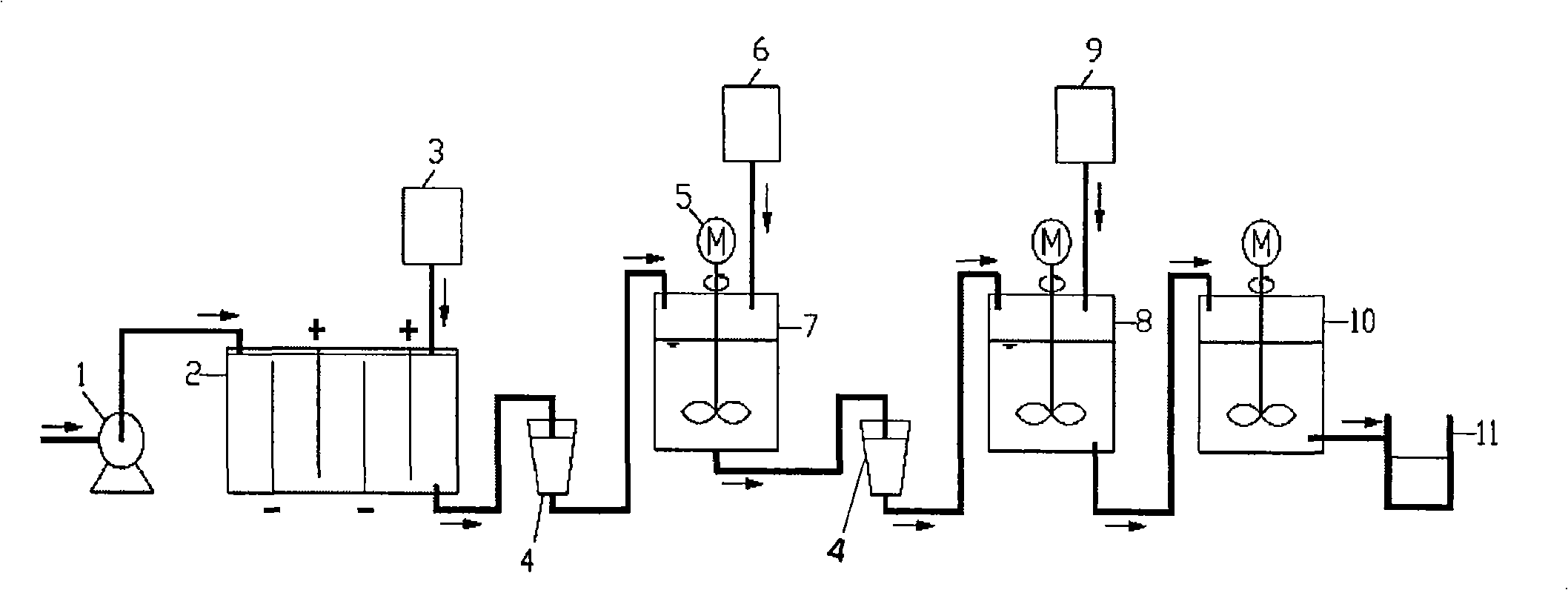
Method for extracting copper from printed circuit board acidic spent etching solution and preparing poly ferric chloride
InactiveCN101353795ASolve the rare problem of recyclingPromote resource recyclingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementAcid etchingElectrolysis
The invention relates to a method for extracting copper of a PCB acid etching waste liquid and preparing polyferric chloride, which comprises the following steps: the PCB acid etching waste liquid is electrolyzed directly and copper powder precipitated by electrolysis is reclaimed; reduced iron is added into a mixed solution after the electrolysis and copper sponge precipitated by replacement reaction is reclaimed; claimed crude copper is purified and prepared into copper powder products; the mixed solution after replacement reaction is added with ferric oxide or a substance containing Fe irons; the mixed solution mingled with the Fe irons is added respectively with a polymeric antioxidant and a stabilizer and simultaneously, the pH value of which is regulated with acid or alkali; and finally, the PFC is prepared. The method of the invention completely realizes reclamation and recycling of wastes and water environment treatment and finally 'zero' emission and has good environmental protection, simple preparation process, high economic benefit and wide application scope.
Owner:HUNAN VARY TECH
Preparation method and application of iron-nitrogen co-doped porous carbon sphere material
InactiveCN104624154ASimple processSave raw materialsPhysical/chemical process catalystsOther chemical processesPtru catalystPorous carbon
The invention discloses a preparation method for an iron-nitrogen co-doped porous carbon sphere material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking 2-aminopyridine as a monomer and taking ammonium persulfate and ferric chloride as oxidants, performing in-situ polymerization reaction in a duct of a porous silicon dioxide template to obtain a precursor; performing high-temperature carbonization treatment on the precursor in a tubular furnace and an inert gas nitrogen-gas environment; and removing the silicon dioxide template by hydrofluoric acid to obtain the iron-nitrogen co-doped porous carbon sphere material which is taken as an electric catalyst to achieve good catalytic effect in oxygen gas reduction reaction. The preparation method has the advantages that the process is simple and easy to perform and the raw materials are cheap. The prepared carbon material contains a three-dimensional communicated pore structure, has a high specific surface area and a large pore volume, can effectively improve the electric catalytic activity through the heteroatom nitrogen-iron doping, has relatively high electric catalytic efficiency while being applied as a low-price electric catalyst, and has an important value and significance in the fields of doped type porous carbon material preparation and proton membrane fuel battery electric catalysis.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Boiler coal combustion-improving desulfurizing and denitrifying agent composition and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a boiler coal combustion-improving desulfurizing and denitrifying agent composition. The composition comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2-7 parts of sodium carbonate, 1-3 parts of alumina, 2-8 parts of aluminium hydroxide, 2-5 parts of ferric trichloride, 2-6 parts of ferric oxide, 3-10 parts of potassium permanganate, 3-10 parts of potassium chlorate, 10-35 parts of activated attapulgite clay, 15-30 parts of urea, 2-4 parts of ammonium formate, 2-4 parts of ammonium chloride, 6-23 parts of ammonium acetate, 3-9 parts of manganese oxide, 9-12 parts of copper chloride, 1-3 parts of copper oxide, 2-4 parts of zinc sulfate, 1-3 parts of zinc nitrate, 7-18 parts of potassium dichromate, 1.0-1.5 parts of titanium dioxide, 0.5-1.0 part of barium molybdate, 0.5-1.5 parts of cobalt sulfate, 0.5-1.5 parts of vanadium pentoxide, 0.3-0.7 part of cerium oxide, 0.1-0.2 part of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate and 0.1-0.2 part of alkyl glyceryl ether. The composition is convenient to use, has stable properties, plays roles of combustion improving, desulfurization and denitrification, has coal saving rate of 8-25% and can remove fixed sulfur by 50-70%.
Owner:兰州熙瑞化工科技有限公司
Sludge dehydrating and drying process method and device
InactiveCN101823825AGood effectLow costSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningEnergy based wastewater treatmentAutomatic controlSlag
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental engineering, in particular to a sludge dehydrating and drying process method and a device. The technical essential points of the invention are that: firstly, adding one or several of fly ash, fine manganese slag, calcined lime, ferric chloride solution and aluminum sulfate solution into sludge and dehydrating and conditioning the sludge; secondly, feeding the sludge into a pre-drying area and simultaneously adding a certain amount of calcined lime, potassium permanganate and finished product of dry sludge and uniformly mixing; feeding the sludge treated in the pre-drying area into a hollow paddle spiral indirect dryer; returning one part of finished product of dry sludge to the pre-drying area and carrying out drier back-mixing with wet sludge; supplying saturated heated steam to a drier by an electric boiler; and introducing steam tail gas from the drier to the pre-drying area for heating the wet sludge. The device is automatically controlled by a control center through a control bus. The process has the advantages of energy saving, environmental protection and high efficiency.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
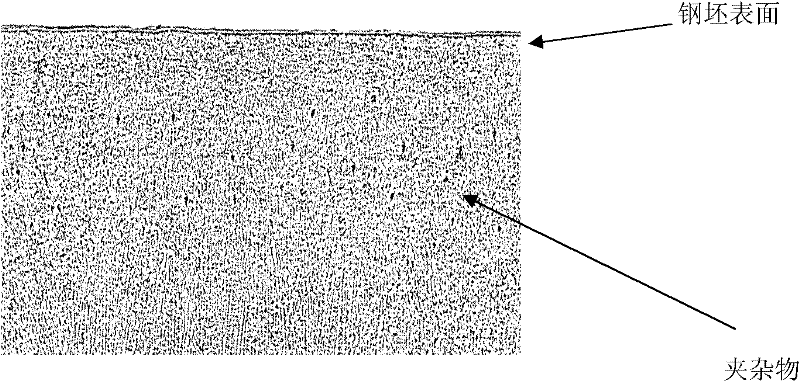
Metallographic etched process for displaying G Cr15 original austenite grain border
InactiveCN101187606AShorten the timeGood reproducibilitySurface/boundary effectPreparing sample for investigationAlcoholMetallography
A metallographic corrosion method for displaying a GCr15 original austenitic grain boundary comprises adding picric acid 5g into distilled water100ml and mixing continuously, then adding sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate 5ml 50% and mixing, finally adding ferric chloride 2g, and using after placing for 24 hours. A sample is grinded roughly, grinded finely, polished, cleared, dried, immersed into caustic erodent for 2-5 minutes according to normal method under a quenching tempering condition until etched surface is changed into silver grey, cleaned up through flowing water, cleaned with alcohol 95%, and dried. If the sample is over-corroded, polishing paste W0.5-1.0 or metallographic polishing egent0.5-1.0 is added on silk polishing cloth, the sample is polished slightly with hands, then cleaned with alcohol 95%, and dried. According to practical condition, grain granularity measurement can adopt methods of picture contrast, grid, intercept, quantitative metallography, and the like, to assess according to relevant standards.
Owner:LUOYANG BEARING SCI & TECH CO LTD
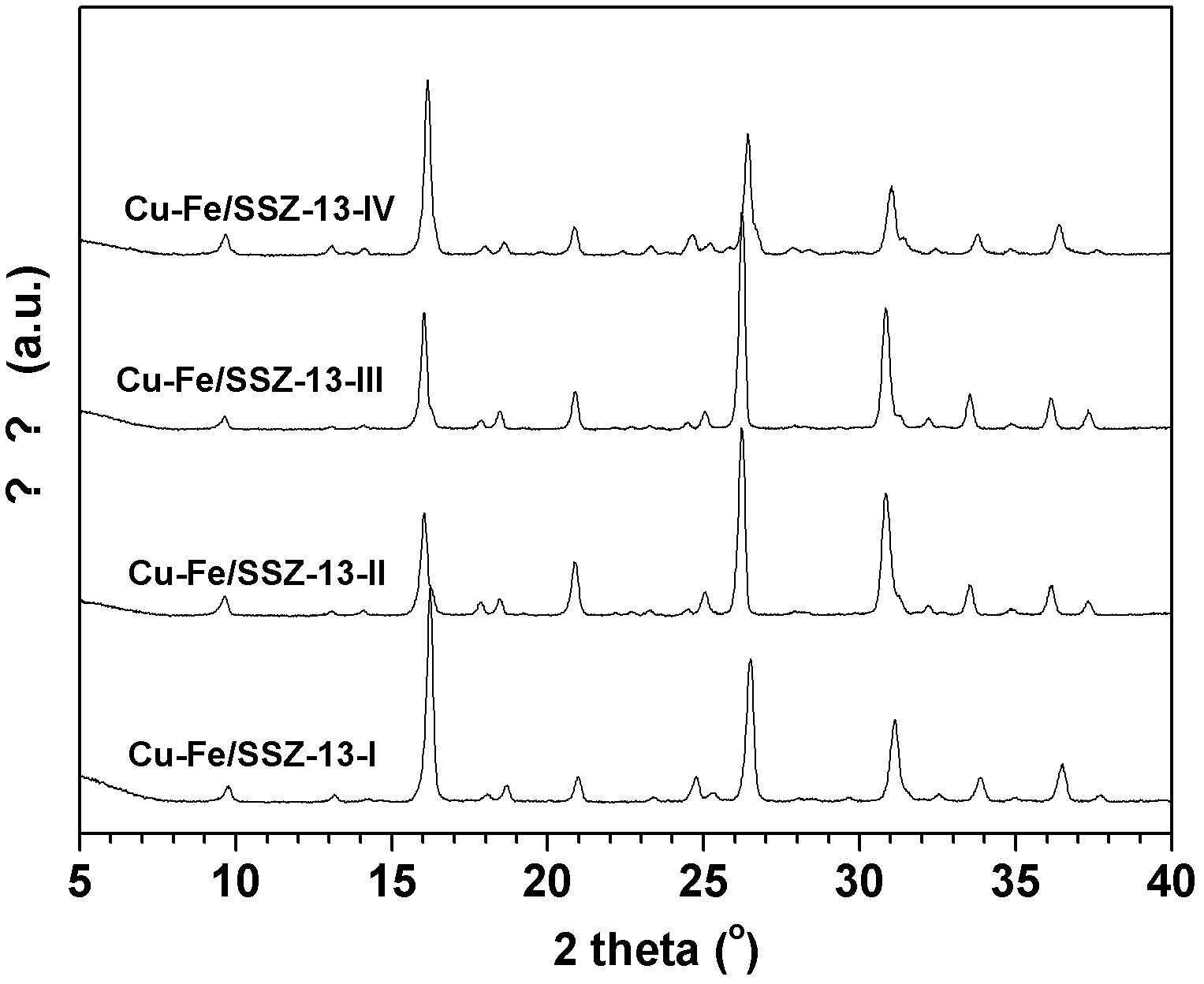
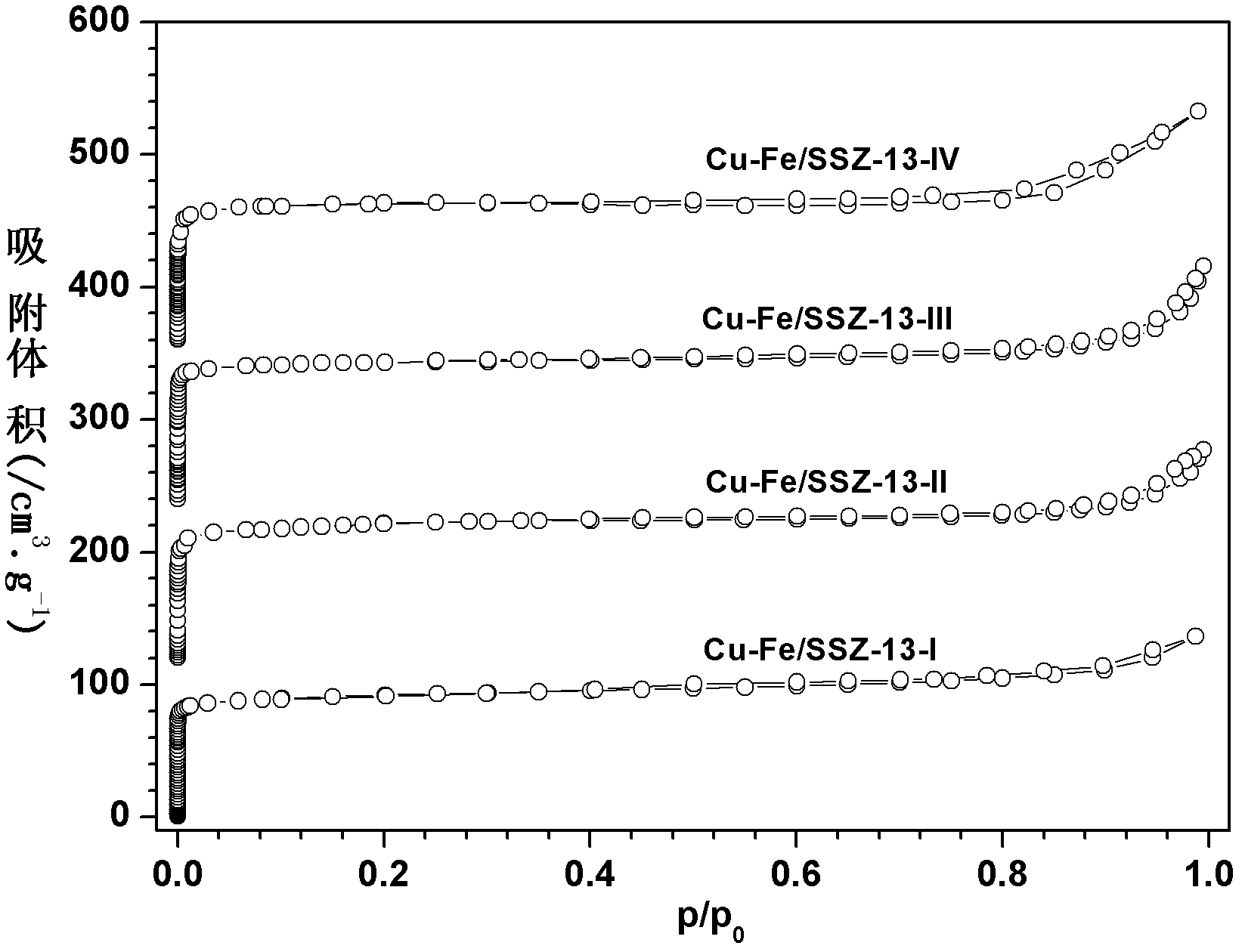
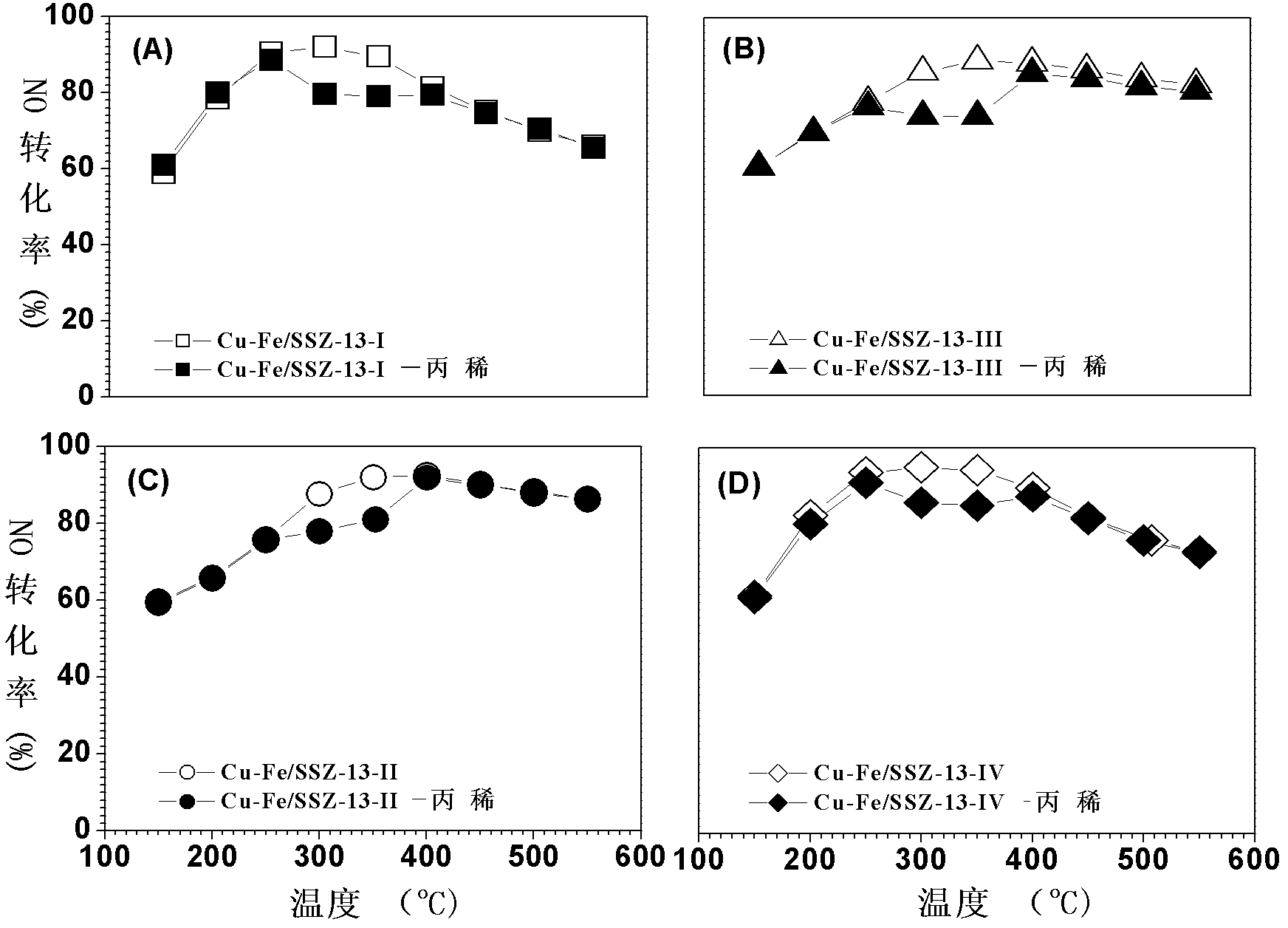
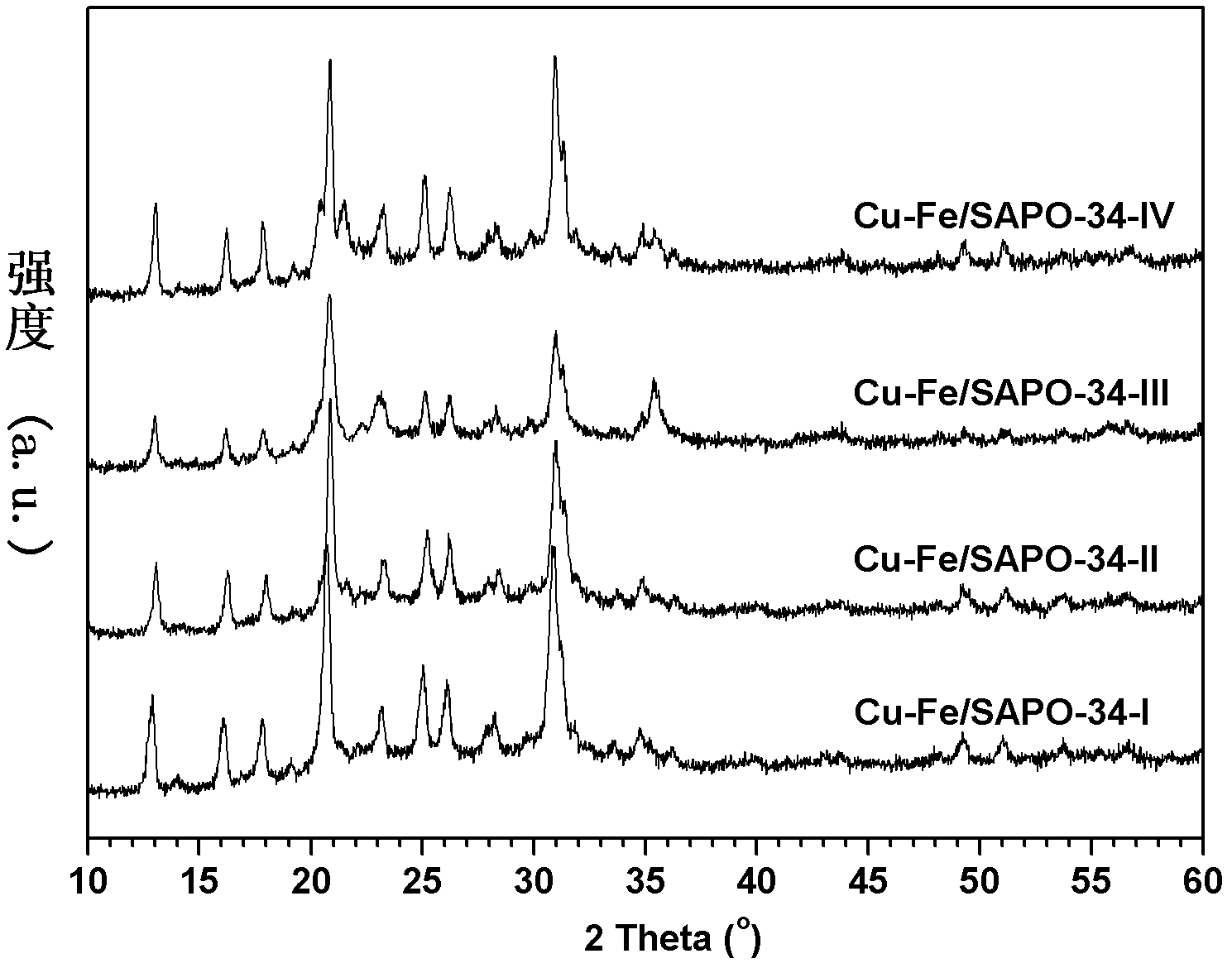
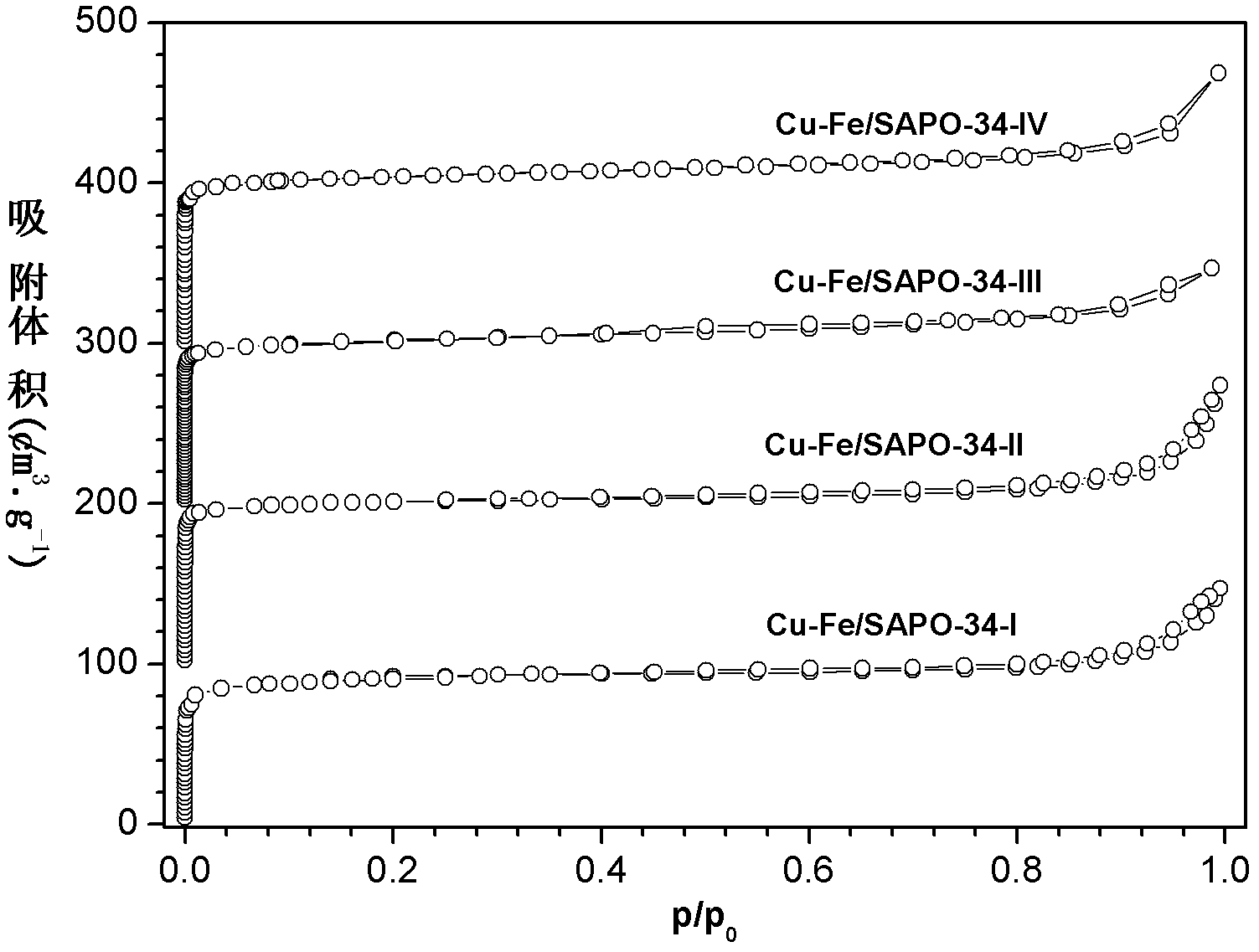
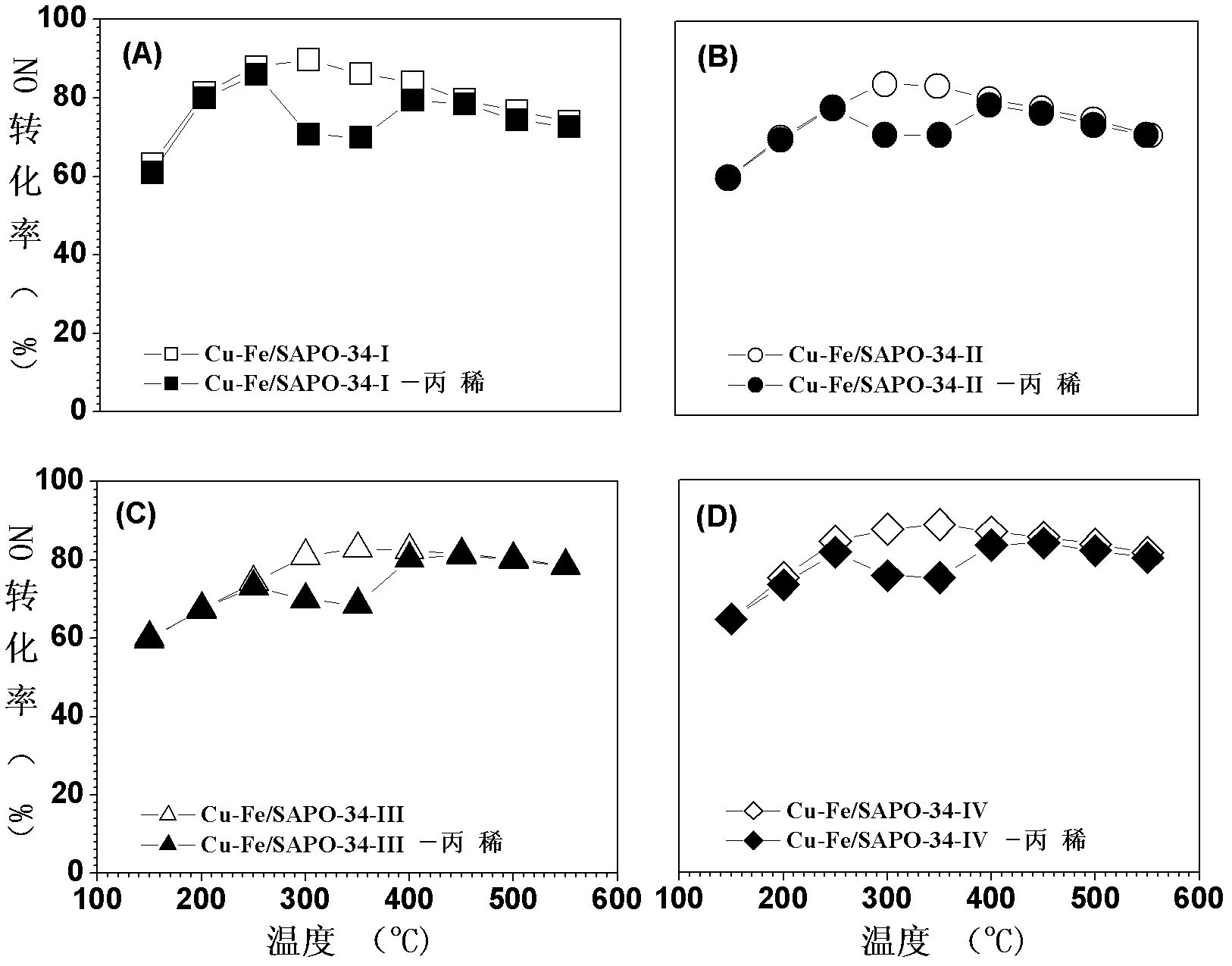
Preparation method of SSZ-13 loaded Cu-Fe catalyst for selectively catalyzing and eliminating NOx by ammonia
InactiveCN102614908AImprove anti-carbon performanceStable activityMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationIonIon exchange
The invention provides a preparation method of a SSZ-13 loaded Cu-Fe catalyst for selectively catalyzing and eliminating NOx by ammonia. The catalyst is used for catalyzing and eliminating nitrogen oxides. A micropore SSZ-13 molecular sieve carrier with high specific surface area (400-550 m2 / g) is prepared by using a soft template method. And then by using a mixed solution of ferric chloride and copper chloride as well as a SSZ-13 molecular sieve ion exchanging method, the SSZ-13 molecular sieve loaded Cu-Fe composite catalyst is prepared. According to the invention, within a wide temperature range (150-550 DEG C), high catalytic eliminating effect and higher stability are obtained for a pollutant with high airspeed (120, 000 mL. (g.h)-1 - 1-360,000 mL.(g.h)-1), high O2 concentration (10vl.%-20v1.%), high H2O content (5wt%-10wt%) and low concentration NO (300-1000 ppm). After a hydrocarbon compound (300-1000 ppm propylene) is added to a reaction system, the catalyst prepared by the preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of high carbon deposition resistance and high hydrothermal stability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Trace elements
The invention discloses a trace element solution, which comprises at least one metal selected from the group comprising selenium, copper, zinc, manganese and chromium and which comprises a concentration of the metal(s) of at least 60 mg / ml. The solution further comprises at least one compound selected from the group comprising iodine, potassium iodide, sodium iodide, iron, iron chloride, zinc oxide, manganese sulphate, sodium selenite, copper carbonate, sodium carbonate, anhydrous disodium EDTA and sodium hydroxide. The trace element solution is prepared by a method consisting essentially of the steps of preparing a MnCO3 mixture in a container; adding an EDTA / NaOH mixture to the container and subsequently adding at least one metal compound; and adding Na2SeO3 to the container to obtain the trace element solution. The method also comprises the step of adding CrCl3.6H2O to the trace element solution.
Owner:WARBURTON TECH
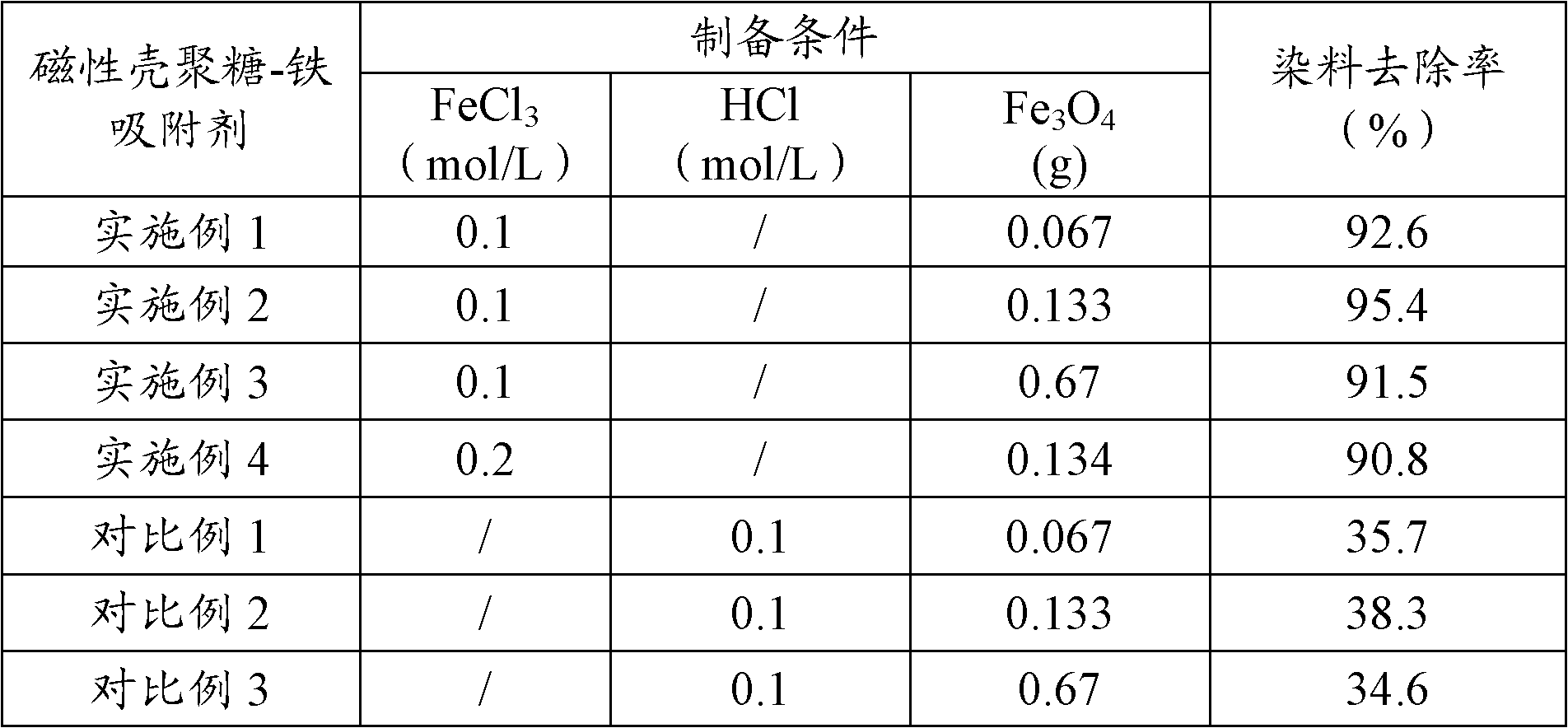
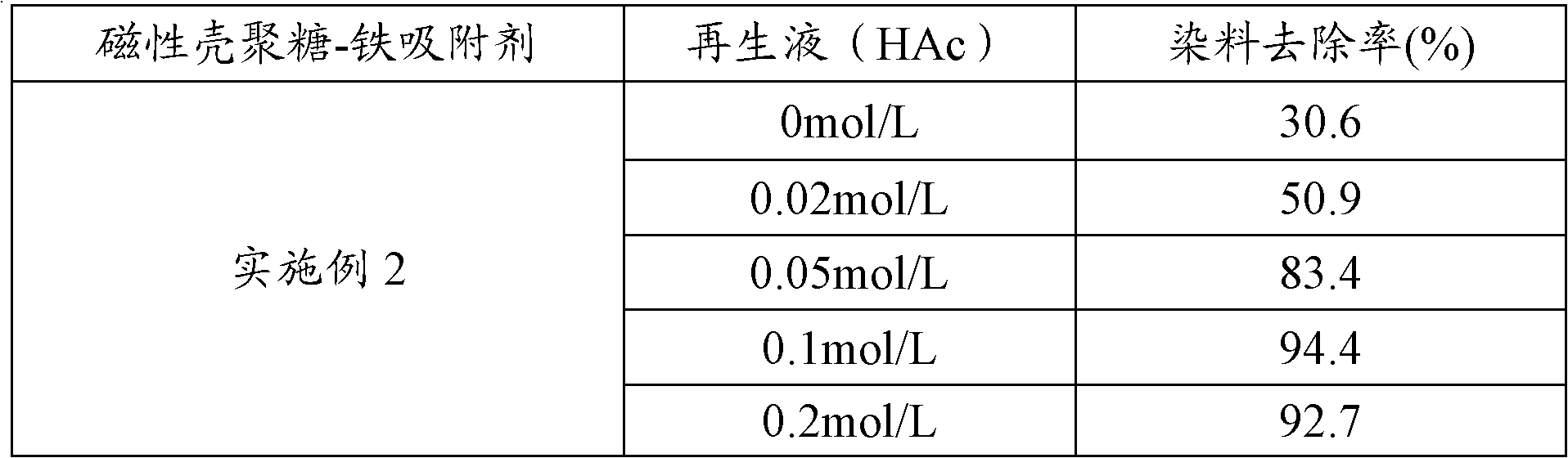
Method for removing sulfonic-group-containing dye in alkaline waste water by using magnetic chitosan adsorbent
InactiveCN102107980AQuick removalEasy to separateOther chemical processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentCross-linkSorbent
The invention discloses a method for removing sulfonic-group-containing dye in alkaline waste water by using a magnetic chitosan adsorbent, which comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving chitosan in an iron chloride water solution, stirring, adding ethanol to precipitate a solid, filtering out the solid, washing, mixing the solid with nano magnetic ferroferric oxide, carrying out cross-linking reaction with a glutaric dialdehyde water solution, and carrying out after-treatment to obtain a magnetic chitosan adsorbent; (2) adding the obtained magnetic chitosan adsorbent into an alkaline waste water solution containing the sulfonic-group-containing dye, stirring, carrying out magnetic separation, and drying to obtain the dye-adsorbed magnetic chitosan adsorbent; and (3) adding the dye-adsorbed magnetic chitosan adsorbent into a water solution containing a desorbing agent, stirring, and filtering to obtain a dye recovered solution and the recovered magnetic chitosan adsorbent. The method disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, has the advantages of environment friendliness and low cost, and has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Modified prussian blue material, sodium ion battery positive electrode plate and preparation method
InactiveCN106960956ALow crystal water contentReduce defectsCell electrodesSecondary cellsWater contentPyrrole
The invention discloses a modified prussian blue material, a sodium ion battery positive electrode plate and a preparation method. The preparation method for the modified prussian blue material at least comprises the steps of performing a reaction on methyl orange, ferric chloride and pyrrole based on a certain proportion to obtain a solution, then performing a reaction on the obtained solution with a mixed solution of sodium ferrocyanide and inorganic acid, and next, performing processing of centrifuging, washing, drying and the like to obtain the modified prussian blue material. Compared with the conventional synthesis method, the prepared modified prussian blue material is lower in crystal water content, less in defects, high in tubular polypyrrole conductivity and relatively high in environment stability, so that an electrolyte can permeate rapidly, and rapid diffusion of Na+ can be promoted to form a three-dimensional conductive network with prussian blue nanoparticles; therefore, the material conductivity is improved, and the material is novel and unique; in addition, the cycling performance and the rate capability of the material are greatly improved; and the modified prussian blue material is more suitable for application of an energy storage material, such as the positive electrode material of the sodium ion battery.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINOPOLY JIAHUA BATTERY TECH
Ammonia-selective preparation method of SAPO-34 supported Cu-Fe catalyst for catalytically removing NOx
InactiveCN102614910AHigh activityImprove anti-carbon performanceNitrous oxide captureMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveCopper chloride
The invention relates to an ammonia-selective preparation method of an SAPO-34 supported Cu-Fe catalyst for catalytically removing NOx. The catalyst is used for catalytically removing oxynitrides. A soft template method is used for preparing the SAPO-34 micropore molecular sieve carrier with high specific area (400-550m<2> / g); and an iron chloride-copper chloride mixed solution and an SAPO-34 molecular sieve ion-exchange method are utilized to prepare the SAPO-34 molecular sieve supported Cu-Fe composite catalyst. In a wide temperature range (150-550), the invention has high catalytic removal effect and high stability for pollutants with high air speed (120000-360000mL.(g.h)<-1>), high O2 concentration (10-10 vl.%), high H2O content (5-10 wt%) and low NO concentration (300-1000ppm). After adding hydrocarbons (300-1000ppm of propylene) into the reaction system, the catalyst provided by the invention has high anti-carbon performance and high hydrothermal stability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
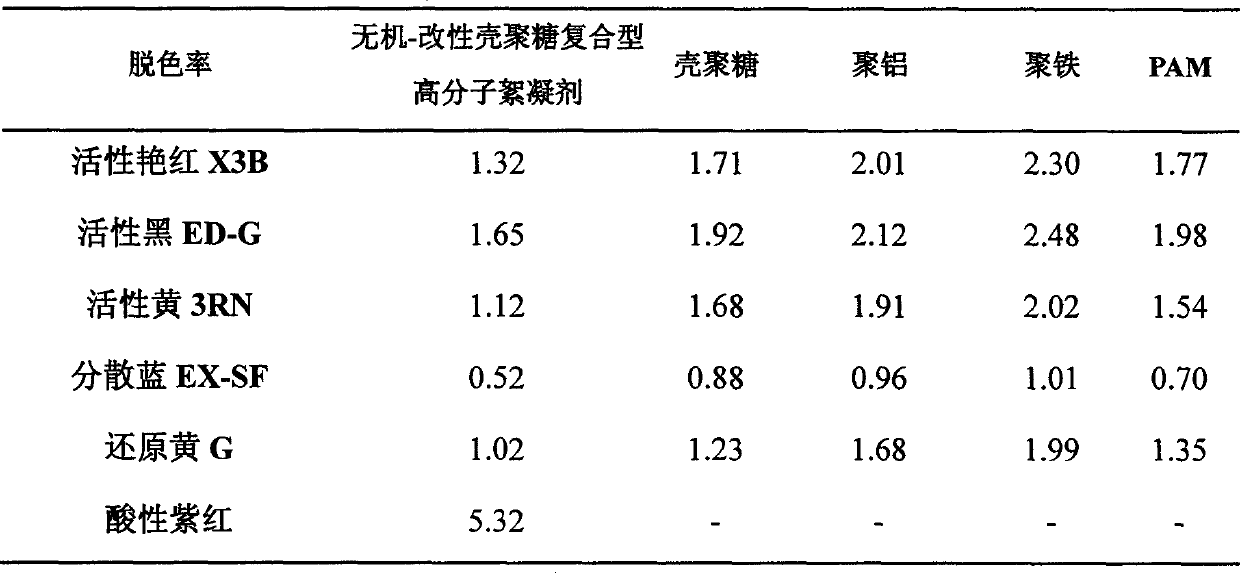
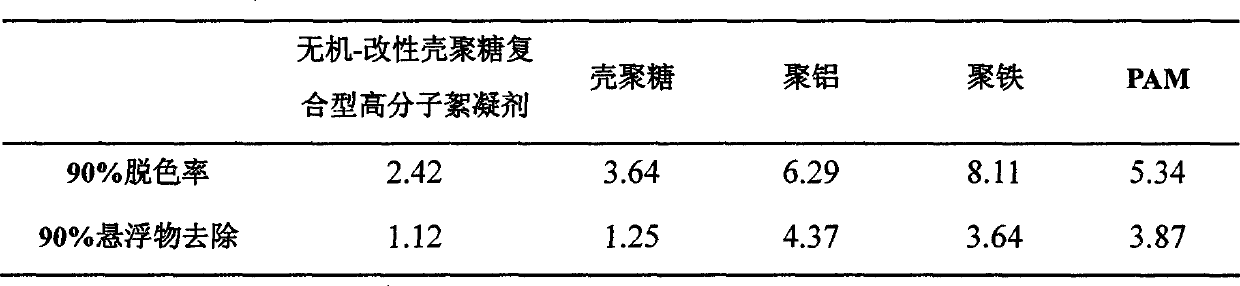
Inorganic-modified chitosan composite type polymeric flocculant
InactiveCN103121742ASimple structureRich sourcesWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAluminium chlorideMeth-
The invention relates to an inorganic-modified chitosan composite type polymeric flocculant. The inorganic-modified chitosan composite type polymeric flocculant is characterized in that a method for preparing the composite type polymeric flocculant comprises the following steps of: taking polyacrylamide-modified chitosan as a raw material and methacryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride, maleic acid and ceric ammonium nitrate as initiators, synthesizing a modified chitosan copolymer under a faintly acidic condition and blending the modified chitosan copolymer with polymerized ferric chloride and polymerized aluminium chloride to obtain the inorganic-modified chitosan composite type polymeric flocculant. According to the steps, the mass ratio of modified starch to the chitosan is (1-2): 1, the reaction temperature is 50-60 DEG C, the reaction time is 2-3 hours, and the use amount of the initiators accounts for 0.02 part of the total mass of the system. The inorganic-modified chitosan composite type polymeric flocculant prepared by using the method has the characteristics of high efficiency, low cost and low secondary pollution to environment; and aiming at different sludges, compared with a conventional flocculant, the inorganic-modified chitosan composite type polymeric flocculant disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the wastewater decoloring rate and the wastewater deturbidity rate can reach more than 99 percent under the condition of low use amount.
Owner:WUHAN SLOAN ELECTRIC
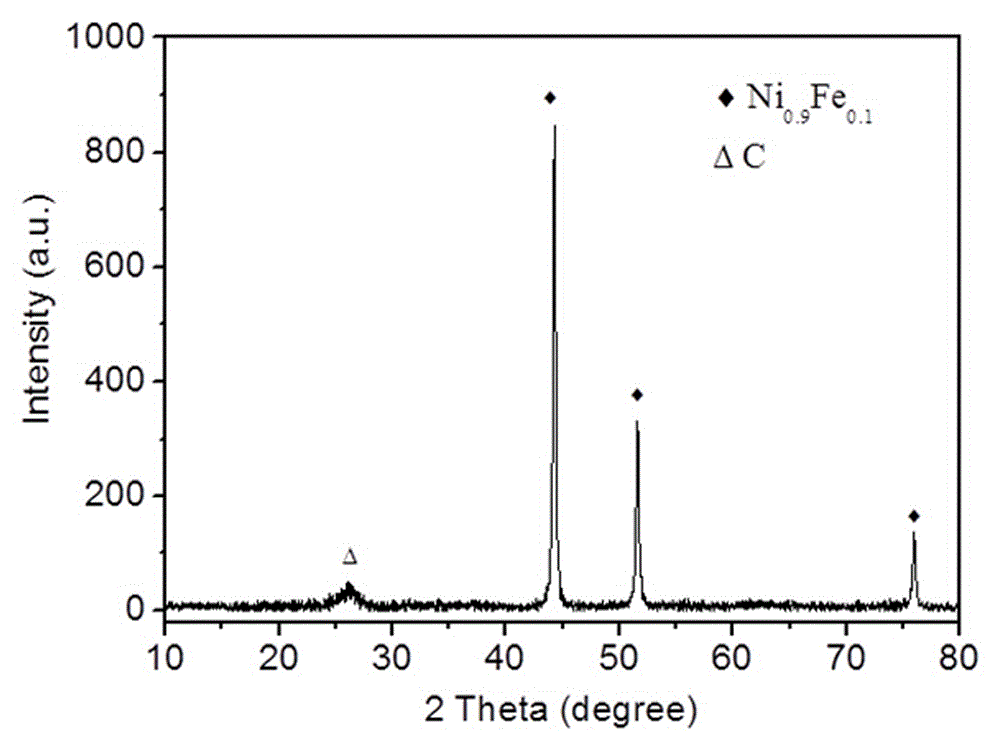
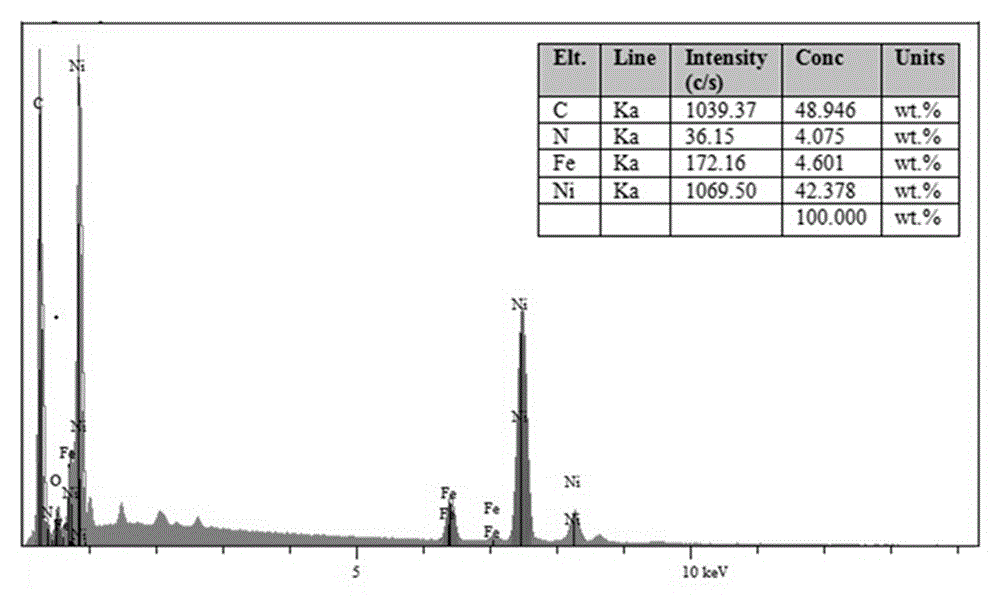
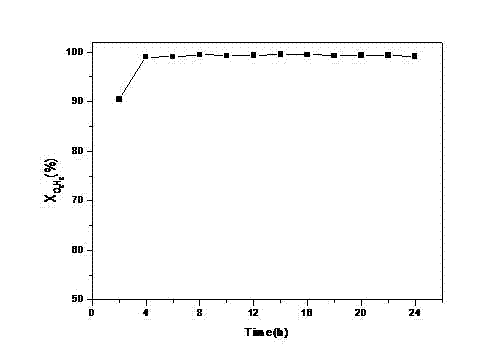
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube nickel-iron coated oxygen evolution catalytic material for water electrolysis and application
ActiveCN105107540ALarge specific surface areaImprove performanceElectrolysis componentsPhysical/chemical process catalystsThioureaEthylic acid
The invention relates to preparation and application of a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube nickel-iron coated oxygen evolution catalytic material for water electrolysis. A general formula of the composite electrode material is Ni0.9Fe0.1@CNx, wherein CN is nitrogen-doped carbon, and x is greater than or equal to 0.01 and less than or equal to 0.1. The specific preparation method of the catalytic material comprises the steps of uniformly mixing nickel acetate and ferric chloride with citric acid and thiourea according to certain molar percentages, and then carrying out calcinations for 1-10h under an N2 gas flow rate of 10-100 mL / min at 600-900 DEG C to prepare the catalytic material. The preparation method provided by the invention effectively achieves one-step preparation of the Ni0.9Fe0.1@CNx oxygen evolution catalytic material with set ratios of Ni, Fe, C and N by an in-situ solid-phase method, and the product is nanotube-shaped, porous and large in specific surface area, and has excellent performance when being used as an oxygen evolution electrode material for water electrolysis. The method provided by the invention is convenient to operate, the process is simple and easy to control, raw materials are low in price and easy to obtain, and the catalytic material is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Low-mercury catalyst used for synthesizing vinyl chloride
InactiveCN102962082APlay a fixedActivePhysical/chemical process catalystsPreparation by halogen halide additionPtru catalystCopper chloride
The invention discloses a low-mercury catalyst used for synthesizing vinyl chloride. The low-mercury catalyst takes mercuric chloride as a main active component, one or more of precious metals such as Au, Pd, Pt, Ru, Rh, Os and Ir salts or complexes thereof as active regulators, and one or more of potassium chloride, ferric chloride, zinc chloride and copper chloride as cocatalysts. By adding trace amount of precious metal salt into the mercuric chloride, the low-mercury catalyst forms a stable composite metal compound, plays a role in fixing and activating mercuric chloride, and still maintains very high catalytic activity and stability when the load capacity of the mercuric chloride is reduced to 0.1-2%.
Owner:DALIAN RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
Production of polymerized ferric-aluminum chloride composite coagulating agent
InactiveCN101074128AReduce manufacturing costLow costWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationPhosphateChlorate salt
Production of inorganic polymer coagulating agent is carried out by controlling Fe2+ concentration between 75-90g / L in hydrochloric acid pickling effluent, taking it as ferric source, taking calcium aluminate powder as aluminum source with Al2O3 content 47-56 wt%, putting two kinds of raw material into reactor in proportion of calcium aluminate powder: hydrochloric acid pickling effluent=0.05-0.10, reacting while agitating at 50-80 degree for 1-3 hrs, adding into minor chlorate oxidant and phosphate stabilizer, heating, reacting while agitating, and cooling to room temperature to obtain final product. It's simple and can be used for domestic sewage and industrial effluent treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method of eliminating sodium chloride in iron-dextran complex compound water solution and device thereof
ActiveCN101108194AEliminate burningEliminate explosion hazardsOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSolventAqueous solution
The invention relates to a method and device for eliminating sodium chloride in the aqueous solution for the complex of ferrodextran, which is characterized in that: the ferrodextran is prepared with dextran and ferric trichloride. The sodium chloride in the ferrodextran is eliminated with an electrodialysis film, that is, eliminating the sodium chloride of the solvent by electrodialysis process in the ferrodextran complex solvent with iron content is more than or equal to 40mg / ml, sodium chloride content is more than or equal to 5.0 per cent wt and viscosity of 3.0mpa is multiplied by s (20 DEG C.) under the temperature of 10 to 90 DEG C. Compared with the technique of eliminating sodium chloride with alcohol precipitation, the invention prevents the safety hazard from flammable and combustible alcohol and reduces the production cost.
Owner:GUANGXI RES INST OF CHEM IND CO LTD
Method for recycling iron and zinc containing waste hydrochloric acid solution
ActiveCN105696010ATake advantage ofSolve the problem of no separation and recyclingProcess efficiency improvementZinc hydroxideChloride
The invention discloses a method for recycling an iron and zinc containing waste hydrochloric acid solution. The method specifically comprises the following steps that 1, acid consuming and reducing are carried out, acidity is made to meet the requirement, and ferric iron in waste acid is reduced into ferrous iron; 2, zinc and iron are extracted and separated, and a ferrous chloride solution is obtained; 3, an organic phase transfers zinc into a strip liquor through reverse extraction, and the organic phase is extracted for reuse; and 4, the strip liquor is subjected to subsection kalizing treatment, zinc hydroxide is obtained, and the strip liquor is reused. According to the method, iron and zinc are separated through different extracting capacities of N235 to the ferrous iron and zinc, and therefore pure ferrous chloride liquid and zinc hydroxide solids are obtained. Ferrous chloride can be oxidized into ferric trichloride, and ferrous chloride and ferric trichloride both can be used as a water treatment agent; and zinc hydroxide can be used as a raw material for preparing zinc oxide or zinc chloride.
Owner:3R ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Dendritic crystal corrosion macroscopic examination reagent for solidification structures and defects of continuous cast blank and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102174699ASolve the problem that the dendritic solidification structure of the continuous casting slab cannot be clearly displayedDisplay without reductionPreparing sample for investigationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationAlcoholCopper chloride
The invention discloses a dendritic crystal corrosion macroscopic examination reagent for solidification structures and defects of a continuous cast blank and a preparation method thereof. The reagent comprises the following components by mass percent: 0.28-1.09% of copper chloride, 0.17-0.27% of magnesium chloride, 0.56-1.60% of ferric chloride, 1.28-1.30% of hydrochloric acid with the mass concentration of 36-38%, 54.70-55.80% of absolute ethyl alcohol and the balance of water. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding the water into a container, and then adding the copper chloride, magnesium chloride, ferric chloride and hydrochloric acid; and adding the absolute ethyl alcohol after all the added raw materials are fully dissolved, and evenly stirring. Compared with the prior art, the invention solves the problem that other corrosive reagents can not clearly display the dendritic crystal solidification structures of a continuous cast blank; and the reagent has the characteristic of original-size display without expansion or reduction for interior defects of a continuous cast blank when used for dendritic crystal corrosion macroscopic examination on the solidification structures and defects of the continuous cast blank.
Owner:苏州东大汉森冶金实业有限公司
Method for recycling tin from waste tin-stripping solution based on tin-stripping solution of hydrochloric acid-tin salt system
ActiveCN103741142AAvoid the Cons of PollutionStrong oxidation abilityPhotography auxillary processesSolution treatmentTetrachloride
The invention discloses a method for efficiently recycling tin from a waste tin-stripping solution based on a tin-stripping solution of a hydrochloric acid-tin salt system. According to the tin-stripping solution, the components and the contents are as follows: 110-230g / L of tin tetrachloride, 70-220g / L of hydrochloric acid, 10-30g / L of iron chloride, 0.5-2.5g / L of a stabilizing agent, 5-30g / L of an accelerant and 2-5g / L of a brightener. The waste tin-stripping solution obtained by tin stripping is subjected to diaphragm electrodeposition treatment by using a cathode room and an anode room of an anion diaphragm electrolytic cell to recycle tin, the tin tetrachloride and ferric trichloride. According to the method for treating the waste tin-stripping solution, not only can the tin be effectively recycled from the waste tin-stripping solution, but also the tin tetrachloride and ferric trichloride can be regenerated and returned to prepare the waste tin-stripping solution to use; the problems of resource wastes, serious environment pollution and the like of a traditional waste tin-stripping solution treatment method are completely avoided.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
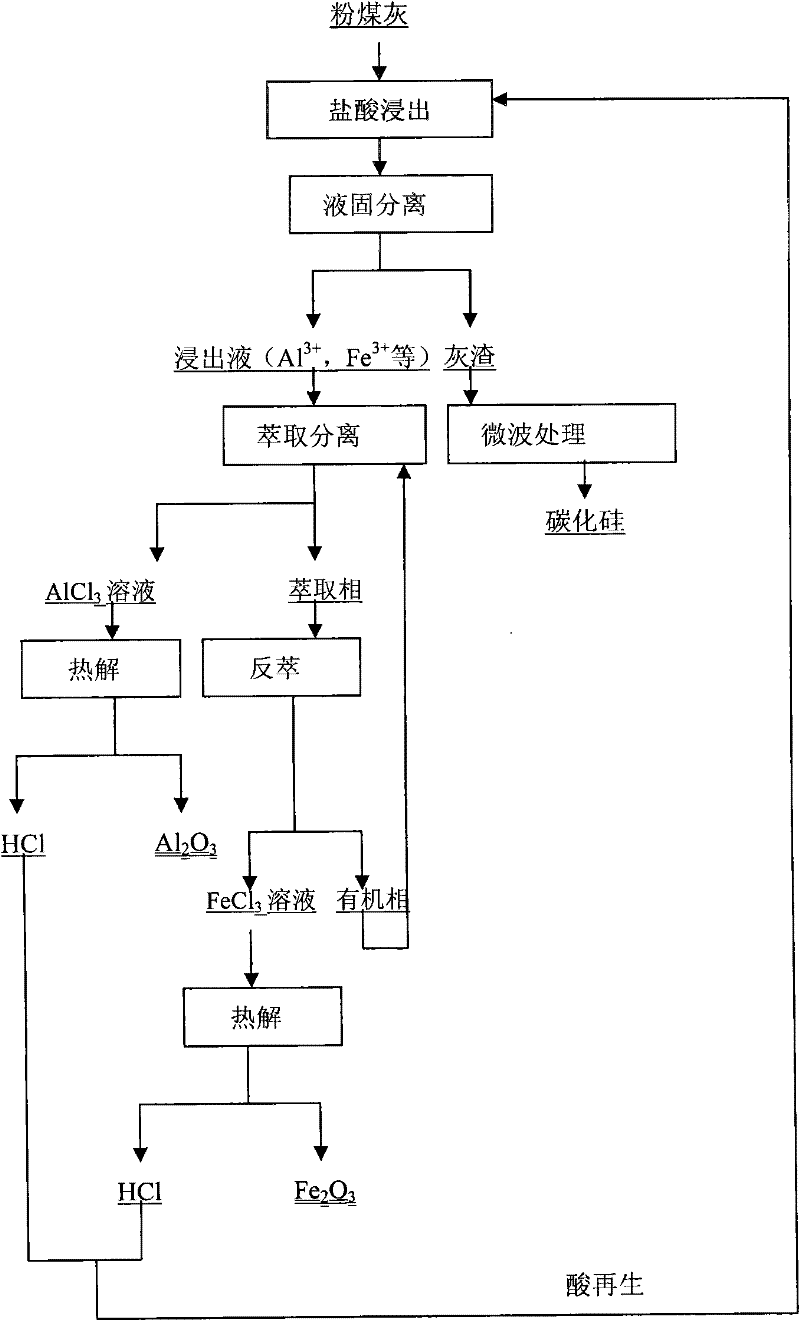
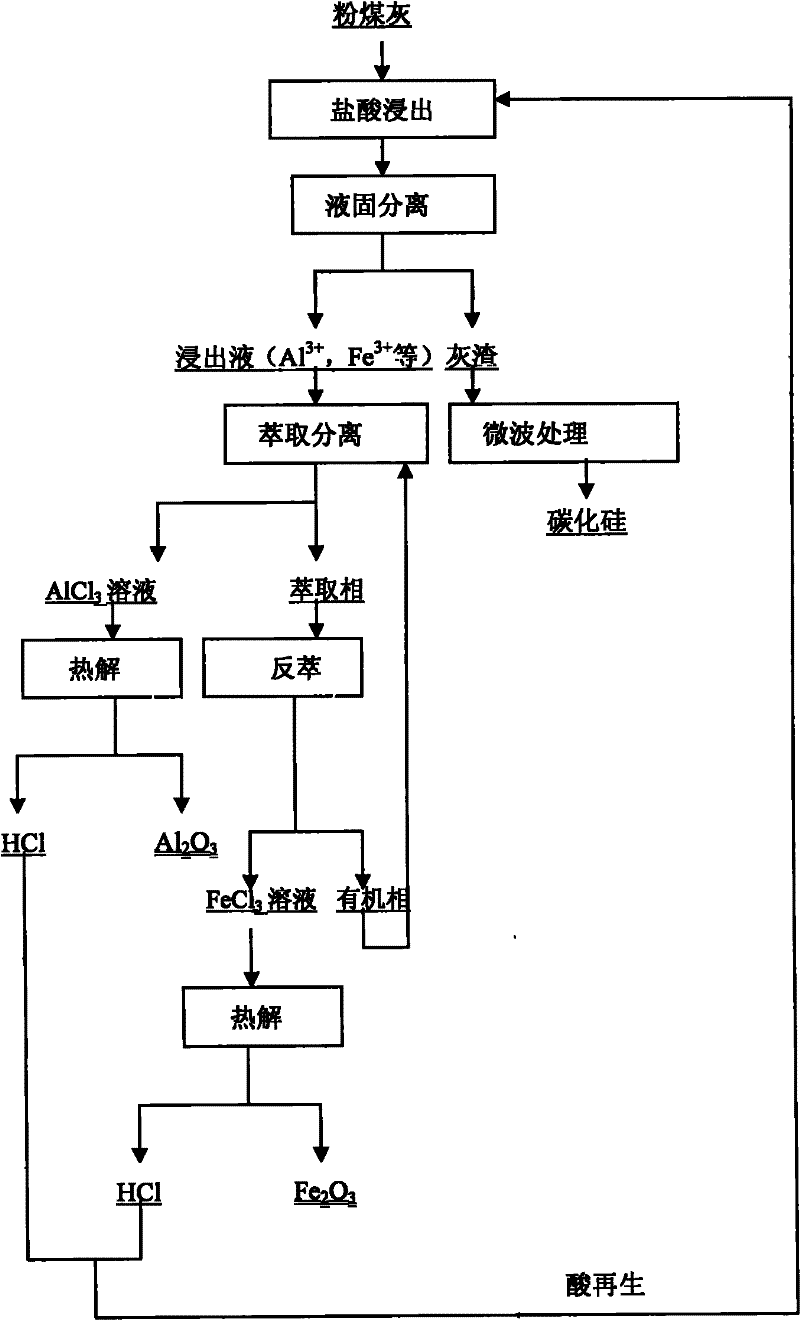
Ecological synthetic utilization method of fly ash
ActiveCN102241410ARealize comprehensive utilizationShort processChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideSolid waste disposalSilicon oxideMaterials science
The invention relates to an ecological synthetic utilization method of fly ash, and the method has the following steps: (1) selecting fly ash which contains aluminum oxide, iron oxide and silicon oxide as a raw material, wherein the mass content of aluminum oxide, iron oxide and silicon oxide are respectively 20-45%, 10-40% and 30-50%, performing a fine grinding and then leaching; (2) filtering and separating to obtain a leaching solution and leaching residue; adding tributyl phosphate and a diluent in the leaching solution to extract, wherein aluminum enters in raffinate phase to form an aluminum chloride solution as well as iron enters in raffinate phase; (3) performing a liquid atomizing pyrolysis to aluminum chloride to obtain aluminum oxide; (4) using water as a re-extraction preparation in raffinate phase for carrying out a re-extraction, wherein iron enters in the re-extraction preparation to form an iron chloride solution; performing a liquid atomizing pyrolysis to iron chloride to obtain iron red. According to the invention, the valuable elements of aluminum, iron, silicon and the like in fly ash are synthetically utilized, the process flow is short and the operation is simple, so that the ecological synthetic utilization method realizes the synthetic utilization of all the valuable elements of aluminum, iron, silicon and the like in fly ash.
Owner:DONGDA NONFERROUS SOLID WASTE TECH RES INST LIAOLING CO LTD
Industrial wastewater treating agent
InactiveCN104591362AGood effectImprove water qualityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSodium bicarbonateIron sulfate
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment and particularly relates to an industrial wastewater treating agent. The industrial wastewater treating agent comprises the following components in parts by mass: 0.8-3 parts of polyacrylamide, 25-35 parts of aluminium polychlorid, 25-55 parts of alums, 3-8 parts of iron trichloride, 0.8-3.4 parts of polymeric ferric sulfate, 1.2-2.5 parts of a coagulant aid, 2-10 parts of plant fiber, 10-30 parts of coal ash, 0.8-2.5 parts of sodium silicate, 2.5-5 parts of sodium sulfite, 0.5-3.5 parts of sodium hypochlorite, 5-10 parts of hydrogen peroxide, 8-15 parts of a sodium carbonate-sodium bicarbonate buffer system and 10-20 parts of sodium-based bentonite. The treating agent has the beneficial effects of wide treated pollutant range, good effect, wide production raw material source, environmental friendliness, no toxicity, good discharged water quality, short process flow, and high process operating safety. The treating agent disclosed by the invention can treat various kinds of wastewater such as chemical wastewater produced in oil fields, mining, steel, electroplating wastewater, dyes, pesticides, wine-making and chemical engineering, and sanitary sewage, papermaking wastewater, river and lake water, rubbish seeping water, leather-making wastewater, and the like; and the treating agent is good in treatment effect.
Owner:湖北源绿高科技节能环保有限公司
Polymeric aluminum ferric chloride-polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride composite coagulant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101628746AAdvanced technologyEasy to manageSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAluminium chlorohydrateRoom temperature
The invention discloses a polymeric aluminum ferric chloride-polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride composite coagulant and a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: heating polyaluminium chloride solution to 40-90 DEG C while stirring the solution, adding polyferric chloride, heating and stirring the solution to perform copolymerization between polyaluminium chloride and polyferric chloride for 0.5-2.0h, obtaining polymeric aluminum ferric chloride solution; adding polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride colloid at room temperature while stirring to obtain a mixed liquor of the two products; stirring at room temperature to ensure that the polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride colloid and polymeric aluminum ferric chloride are completely mutually soluble and obtaining the polymeric aluminum ferric chloride-polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride composite coagulant.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
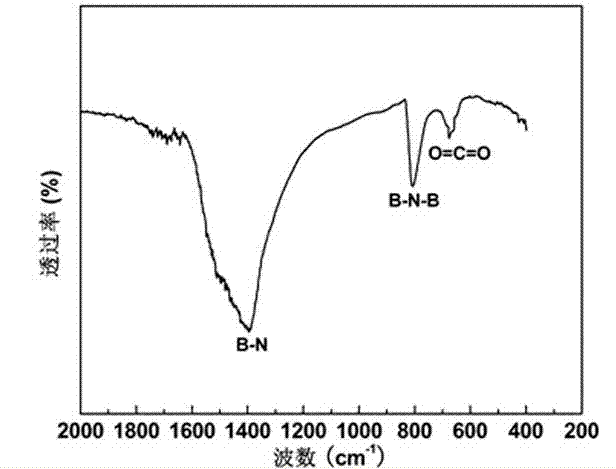
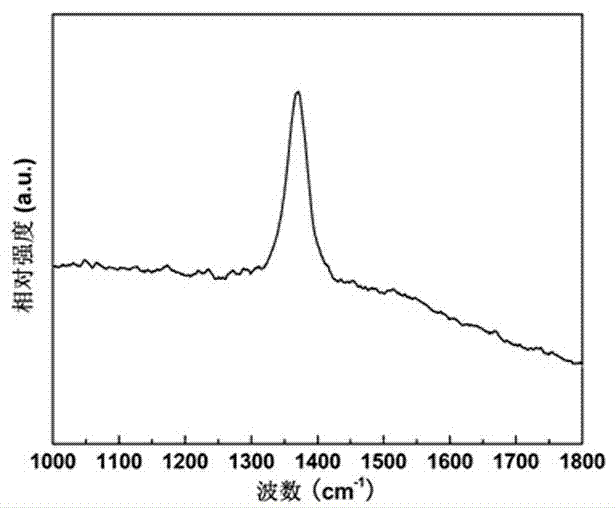
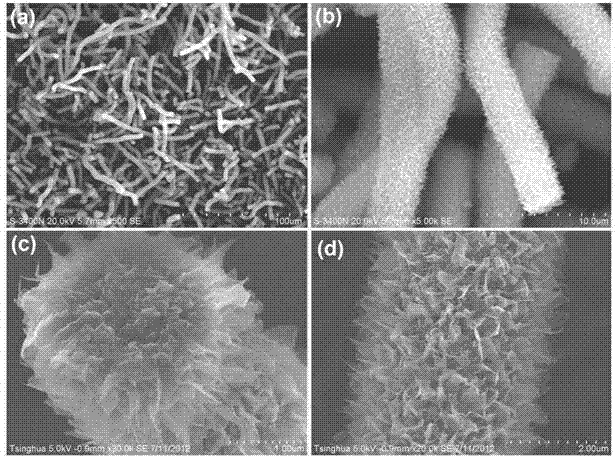
Method for preparing hexagonal boron nitride nano composite structure
InactiveCN103043633AIncrease the degree of mixingIncrease productionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsChemical industryMicro nano
As an important III-V main group compound, hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) has multiple excellent physical and chemical properties, such as high-temperature resistance, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, self-lubrication and high thermal conductivity, and can be widely used in the fields of chemical industry, machinery, electronics, aerospaces, and the like. In recent years, a research on BN is relatively focused on BN nanotubes; by contrast, the research on BN nanowires is little, and a report on relevant BN micro-nano composite structures is rarer. The novel BN micro-nano composite structure is synthesized by taking amorphous boron powder, ferric chloride hexahydrate, absolute ethyl alcohol, high-purity nitrogen and liquid ammonia as raw materials. The synthetic method is simple in technology; the raw materials are nontoxic, environment-friendly and low in cost; the product purity is high; the yield is high; no purification is required; and scale production is facilitated. In addition, the novel BN micro-nano composite structure has a very high specific surface area, and has very wide development and application prospects in the fields of catalyst carrier materials, novel energy storage materials, ceramic compound materials and polymer composites.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Preparation method of stainless steel-resin composite and stainless steel-resin composite prepared by same
InactiveCN103895161ASize has little effectEasy injection moldingMetal layered productsPolymer scienceSS - Stainless steel
The invention relates to a preparation method of a stainless steel-resin composite and a stainless steel-resin composite prepared by the same. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1. putting a pretreated stainless steel substrate in a corrosive solution to perform electrochemical corrosion, wherein the corrosive solution is a 2-25 wt% hydrochloric acid and / or 5-35 wt% iron trichloride solution; and S2. carrying out injection molding on a resin composition to the surface of the stainless steel substrate obtained in the step S1, and forming to obtain the stainless steel-resin composite. The stainless steel-resin composite has the advantages of high binding force between stainless steel and resin, simple technique, low requirements for resin, wide application range and no pollution, and can easily implement large-scale production.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Carbon and electrospun nanostructures
The present invention is directed to the production of nanostructures, e.g., single wall carbon nanotubes (“SWNT”) and / or multi-wall carbon nanotubes (“MWNT”), from solutions containing a polymer, such as polyacrylonitrile (PAN). In particular, the invention is directed to the production of nanostructures, for example, SWNT and / or MWNT, from mixtures, e.g., solutions, containing polyacrylonitrile, polyaniline emeraldine base (PANi) or a salt thereof, an iron salt, e.g., iron chloride, and a solvent. In one embodiment, a mixture containing polyacrylonitrile, polyaniline emeraldine base or a salt thereof, an iron salt, e.g., iron chloride, and a solvent is formed and the mixture is electrospun to form nanofibers. In another embodiment, the electrospun nanofibers are then oxidized, e.g., heated in air, and subsequently pyrolyzed to form carbon nanostructures.
Owner:PHYSICAL SCI
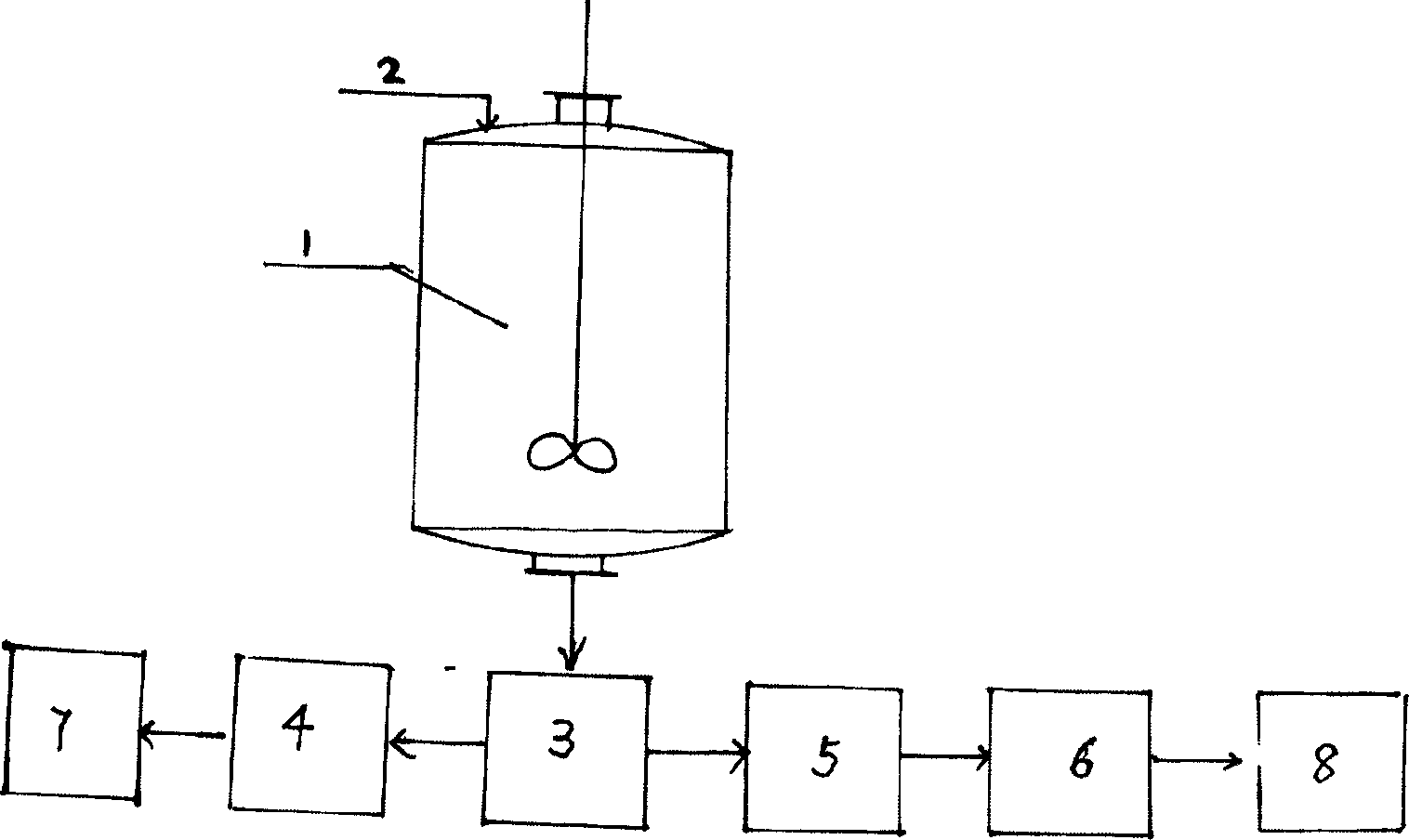
Controlled release formulation of solid chlorine dioxide
InactiveCN1759679AEasy to useConvenient storage and transportationBiocideDisinfectantsSodium bicarbonateAluminium sulfate
A slowlly-releasing solid ClO2 for deodoring, sterilizing, disinfecting and antistaling purposes is prepared from sodium chlorite, quaternary ammonium salt, quaternary ammonium base, calcium chloride, iron chloride, aluminium sulfate, talc powder, calcium carbonate, and sodium dicarbonate through proportional mixing.
Owner:山东营养源食品科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com