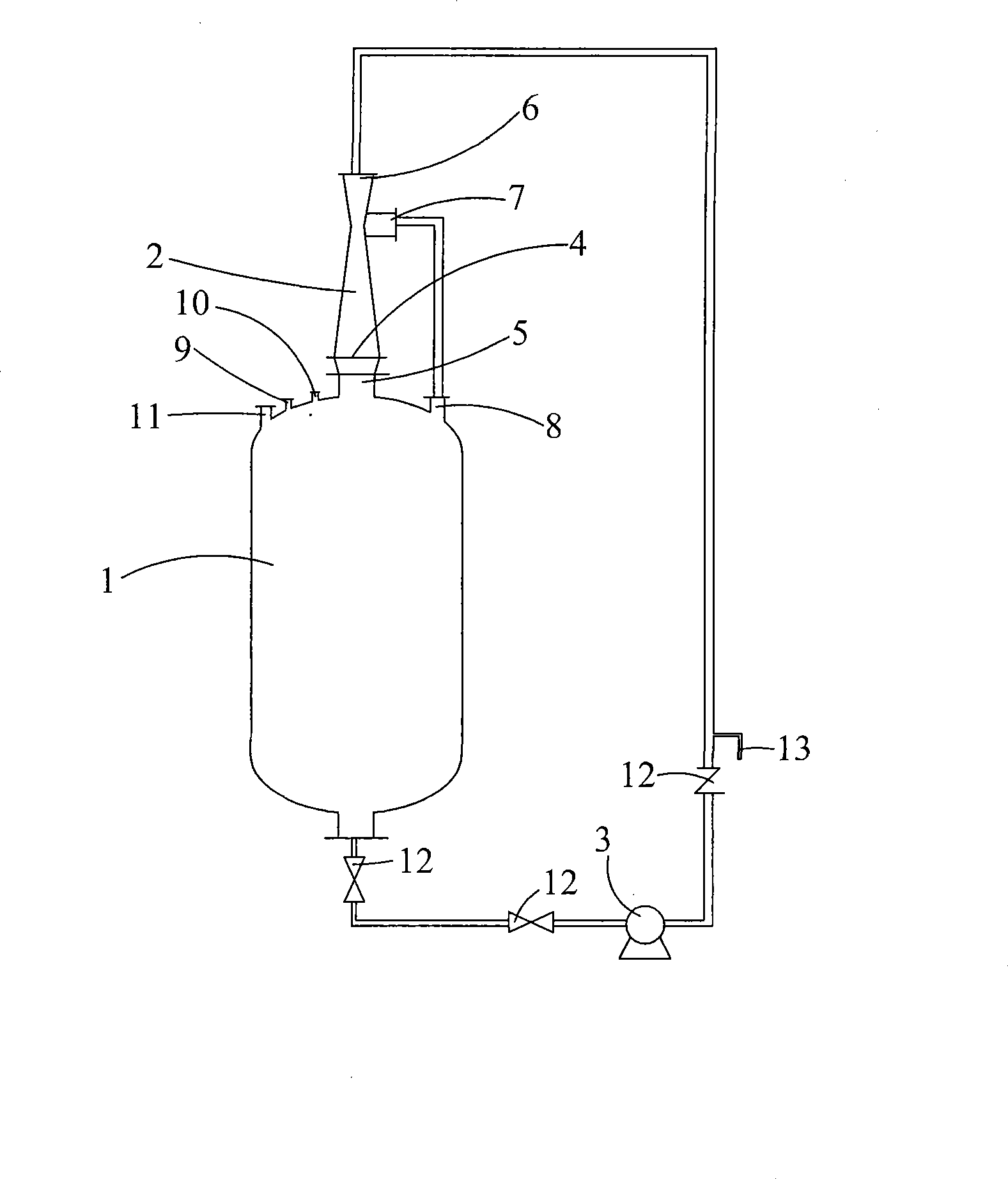
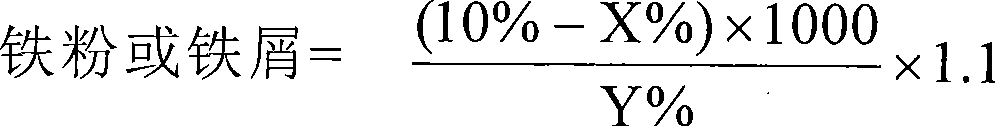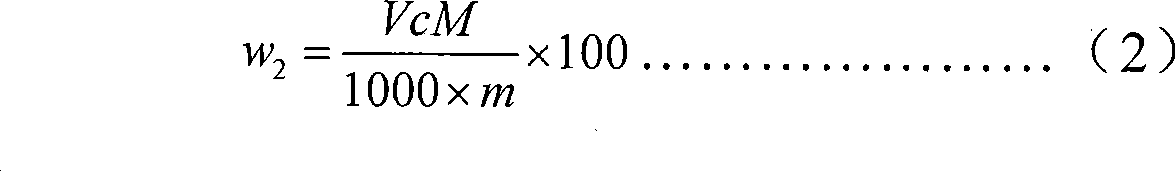Patents
Literature
203 results about "Polyferric chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
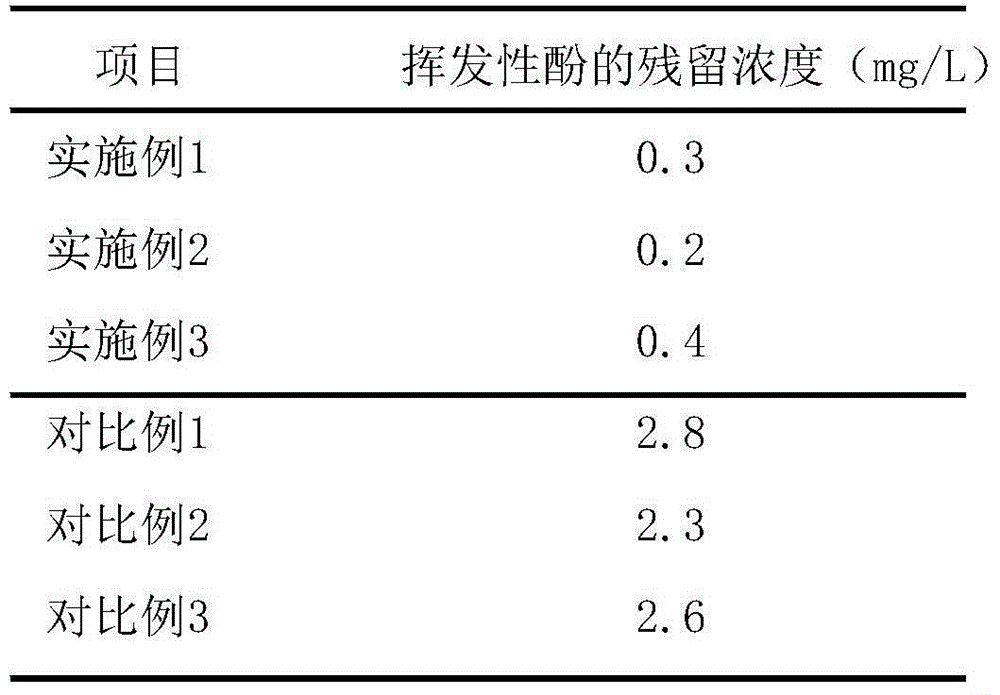
Method for extracting copper from printed circuit board acidic spent etching solution and preparing poly ferric chloride
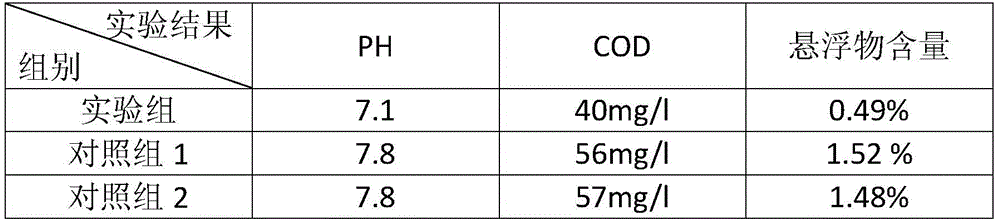
InactiveCN101353795ASolve the rare problem of recyclingPromote resource recyclingPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementAcid etchingElectrolysis
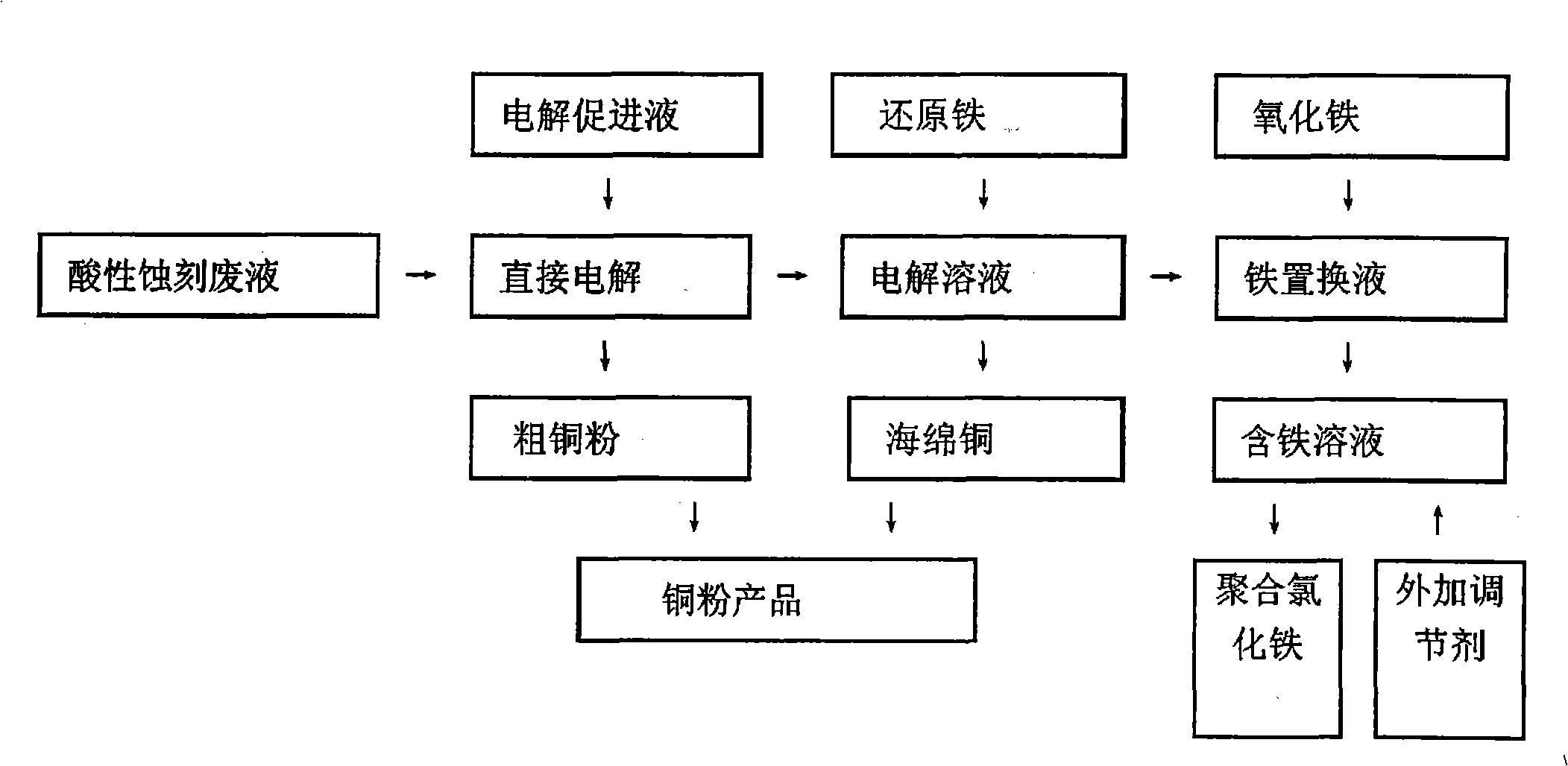
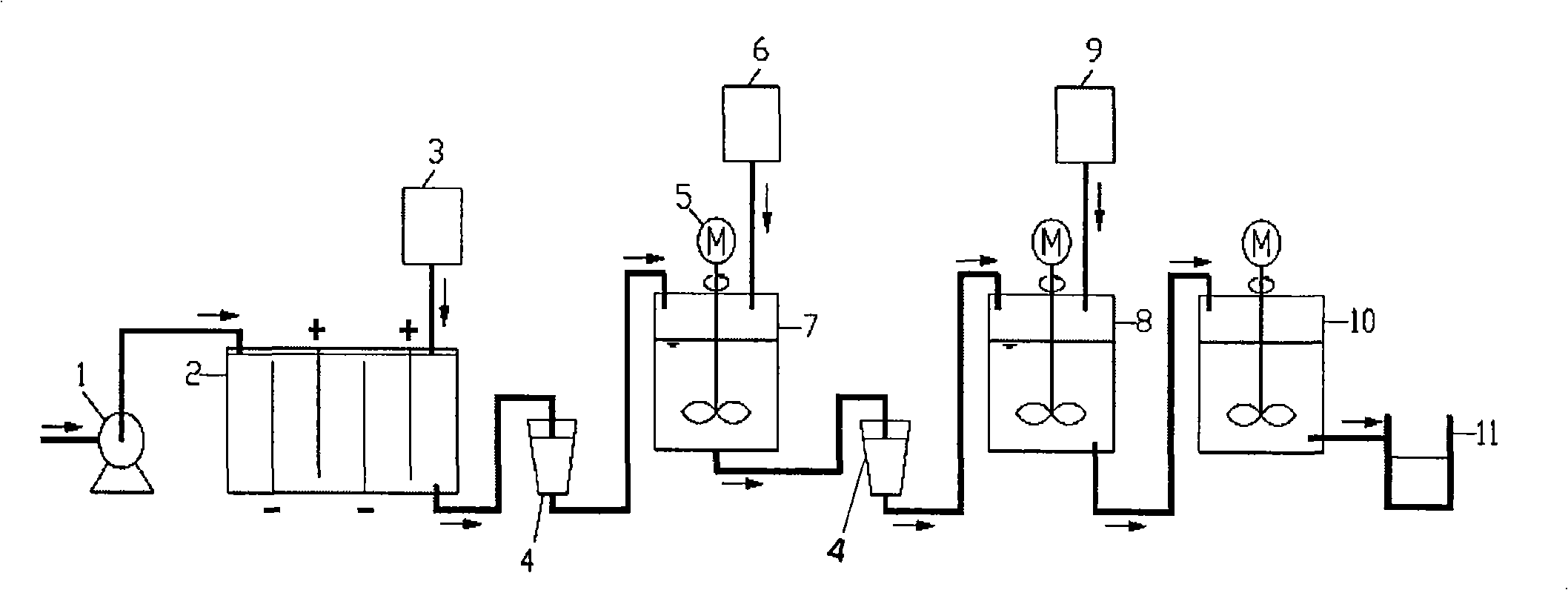
The invention relates to a method for extracting copper of a PCB acid etching waste liquid and preparing polyferric chloride, which comprises the following steps: the PCB acid etching waste liquid is electrolyzed directly and copper powder precipitated by electrolysis is reclaimed; reduced iron is added into a mixed solution after the electrolysis and copper sponge precipitated by replacement reaction is reclaimed; claimed crude copper is purified and prepared into copper powder products; the mixed solution after replacement reaction is added with ferric oxide or a substance containing Fe irons; the mixed solution mingled with the Fe irons is added respectively with a polymeric antioxidant and a stabilizer and simultaneously, the pH value of which is regulated with acid or alkali; and finally, the PFC is prepared. The method of the invention completely realizes reclamation and recycling of wastes and water environment treatment and finally 'zero' emission and has good environmental protection, simple preparation process, high economic benefit and wide application scope.
Owner:HUNAN VARY TECH
Passivator for repairing mercury polluted soil, mercury polluted soil repairing method and application
InactiveCN106281332AReduce contentAvoid failureContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSulfur containingPollution
The invention provides a passivator for repairing mercury polluted soil. The passivator is prepared from a sulfur-containing reagent and an iron-containing reagent which are stored separately in a mass ratio of 1:5-5:1, wherein the sulfur-containing reagent is one or more of sulfur, sulfide, hydrosulfide, polysulfide and thiosulfate, and the iron-containing reagent is one or more of zero-valent iron, ferrous sulfate and hydrate thereof, ammonium ferrous sulfate and hydrate thereof, ferric sulfate, ferrous chloride and hydrate thereof, ferric chloride and hydrate thereof, polyferric chloride, poly ferrous sulfate, ferroferric oxide and ferric oxide. The sulfur-containing reagent and the iron-containing reagent in the passivator for repairing mercury polluted soil are stored separately, so that invalidation of effective ingredients of mercury in soil caused by reactions generated by mixing can be avoided. The passivator is wide in raw material source and low in cost. The repairing method is simple and feasible, is not sensitive to the soil type, has a remarkable repairing effect for various forms of mercury, does not have secondary pollution, and can be used for repairing cadmium, lead, zinc, copper or nickel heavy metal polluted soil.
Owner:CHINA CITY ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION ENGINEERING LIMITED COMPANY
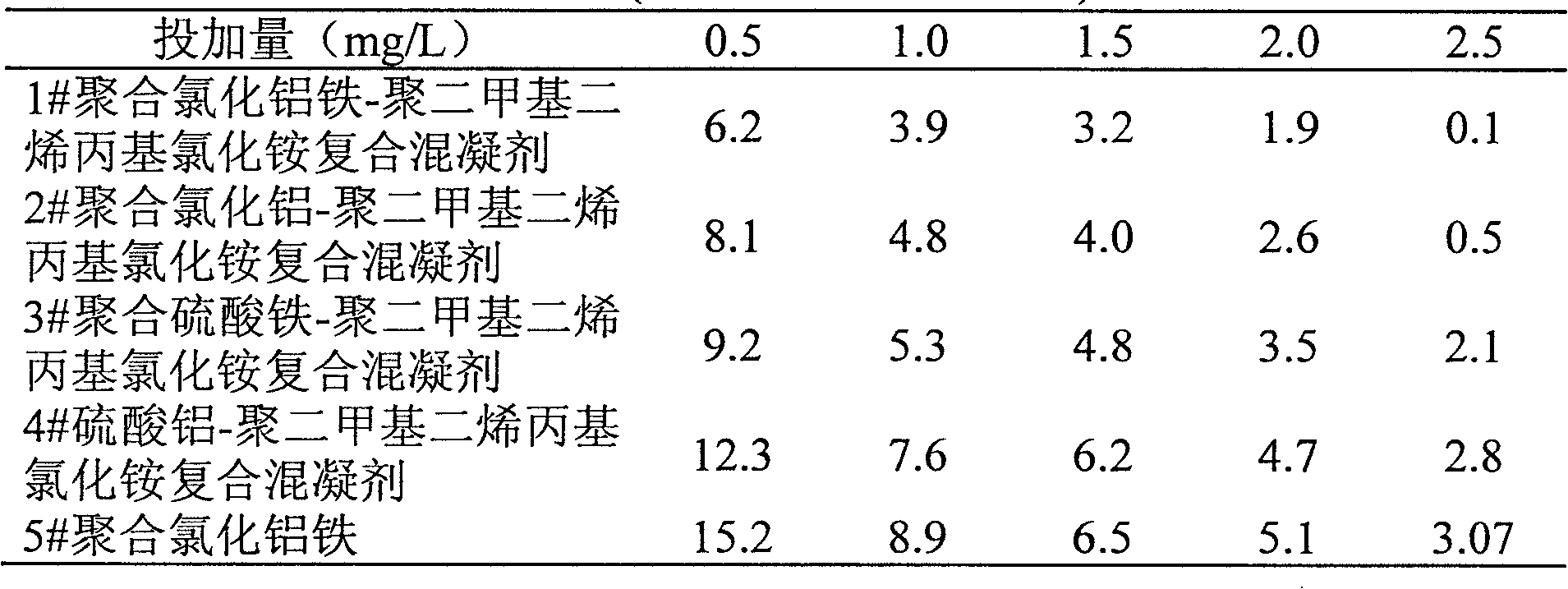
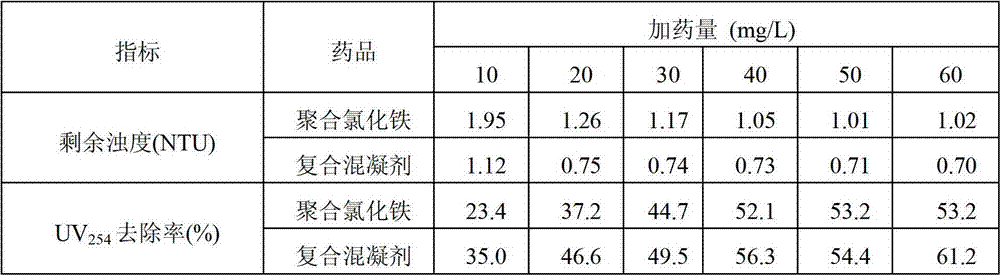
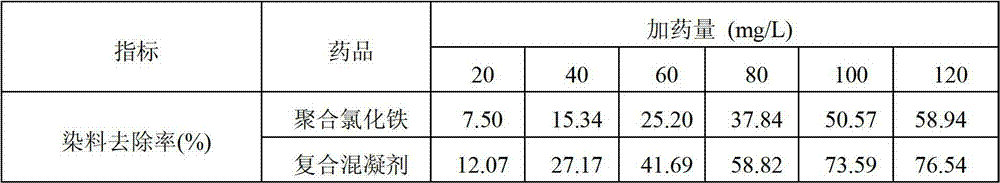
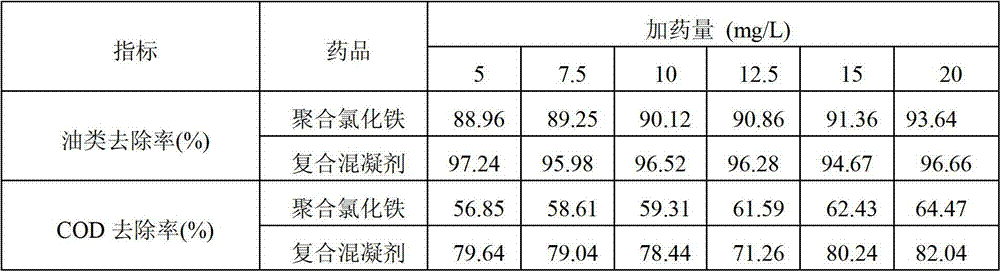
Polymeric aluminum ferric chloride-polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride composite coagulant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101628746AAdvanced technologyEasy to manageSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAluminium chlorohydrateRoom temperature
The invention discloses a polymeric aluminum ferric chloride-polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride composite coagulant and a preparation method and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: heating polyaluminium chloride solution to 40-90 DEG C while stirring the solution, adding polyferric chloride, heating and stirring the solution to perform copolymerization between polyaluminium chloride and polyferric chloride for 0.5-2.0h, obtaining polymeric aluminum ferric chloride solution; adding polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride colloid at room temperature while stirring to obtain a mixed liquor of the two products; stirring at room temperature to ensure that the polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride colloid and polymeric aluminum ferric chloride are completely mutually soluble and obtaining the polymeric aluminum ferric chloride-polydimethyldiallylammonium chloride composite coagulant.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Ferric salt-polyepichlorohydrin-dimethylamine composite flocculant as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103043766AReduce processing costsEasy to dehydrateWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationChemical industryPapermaking
The invention relates to a ferric salt-polyepichlorohydrin-dimethylamine composite flocculant. The composite flocculant is prepared by mixing a ferric chloride solution or a polyferric chloride solution and polyepichlorohydrin-dimethylamine at a normal temperature; the mass concentration of Ferrum in the ferric chloride solution or the polyferric chloride solution is 5-15 g / L; and the mass ratio of the Ferrum in the ferric salt-polyepichlorohydrin-dimethylamine composite flocculant to the polyepichlorohydrin-dimethylamine is (1-10):1. The invention further relates to a preparation method and an application of the ferric salt-polyepichlorohydrin-dimethylamine composite flocculant. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple, convenient, economic and practical, can be widely applied to water supply and waste water treatment in the fields such as dye waste water, surface water, refinery processing wastewater, papermaking, mining and daily-use chemical industry, and has the advantages of simple and fast treatment process as well as good coagulation effect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for preparing flocculant of ferric chloride of polysilicon acid
InactiveCN101003390AImprove stabilityUniform qualityIron halidesWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSilicic acidAcid washing
This invention discloses a method for preparing a stable inorganic polymer flocculant, polyferric silicate chloride, from industrial acid-washing wastewater and iron scale by high-speed shearing, and its application in tap water purification. The method comprises: adding certain amounts of HCl and iron scale according to the contents of free acid and iron in industrial acid-washing wastewater, adding oxidant and stabilizer, oxidizing and polymerizing, adjusting the alkalinity with CaO (or MgO, or mixed slurry of Mg(OH)2 and Ca(OH)2) to obtain stable polyferric chloride, adding poly(silicic acid), and polymerizing under high speed shearing to obtain stable polyferric silicate chloride flocculant. The method has such advantages as simple process, mild reaction conditions and low investment, and is environmentally friendly. The prepared polyferric silicate chloride has better effect on tap water purification than polyferric chloride, ferric chloride and other iron-containing flocculant.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Novel sewage treatment agent
InactiveCN103101999AImprove the coagulation effectLittle drop in pHWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationEnvironmental resistancePolyferric chloride
The invention relates to a chemical reagent and especially relates to a novel sewage treatment agent and belongs to the field of sewage treatment. The novel sewage treatment agent comprises, by weight, 25 to 40 parts of polyferric chloride, 10 to 15 parts of polyacrylamide, 7 to 12 parts of polymine and 28 to 43 parts of bentonite. The polyferric chloride can be dissolved in water easily and has excellent coagulation effects and good product stability. The novel sewage treatment agent has a wide pH application range. A pH value of water treated by the novel sewage treatment agent is reduced slightly. Through utilization of an inorganic-organic component mixture as a coagulant, excellent coagulation effects are obtained. The novel sewage treatment agent has the advantages of fast purification rate, good effect, environmental benefits and no toxicity.
Owner:SHENYANG CHUANGDA TECH TRADE MARKET
Method for preparing polyferric chloride flocculant by using steel wire rope sludge and waste salt
ActiveCN105271436AExcellent purificationReduce turbidityIron halidesWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSludgeSulfide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polyferric chloride flocculant by using steel wire rope sludge and waste salt. According to the method, the steel wire rope pickling sludge is dissolved in waste hydrochloric acid, lead ions in the dissolved solution are removed with a sulfide precipitation method, and the polyferric chloride flocculant is obtained; produced hydrogen sulfide gas meets the national odor pollutant emission standard after being subjected to falling-film absorption, packed tower absorption and activated carbon adsorption treatment, and meanwhile, whole-process sulfur element recycling is realized; cement is added to sludge residues for curing, and heavy metals are cured and stabilized. With the adoption of the method, the recovery rate of iron in the sludge is higher than 90%, the produced polyferric chloride flocculant has excellent performance in purification of domestic sewage, and produced lead sulfide meets the industrial purity requirement and can be used as an industrial raw material. With the adoption of the method, harmless disposal and resource utilization of the steel wire rope pickling sludge and the waste hydrochloric acid are realized simultaneously.
Owner:刘阳生
Process for preparing poly ferric chloride
InactiveCN101462776AReduce concentrationRealize comprehensive utilizationIron halidesChemical recyclingPtru catalystIron chloride
The invention relates to a method for preparing polyferric chloride. The method comprises: placing a pickling solution containing iron or hydrochloric acid pickle into a reaction kettle device and adding iron powder or iron slag into the reaction kettle device at the same time to heat materials with the heat generated in the exothermic reaction of the acid and the iron; and then adding a catalyst in and passing oxygen through the reaction kettle and then starting a circulating pump to circulating the reaction liquid for 3 to 5 hours till the polymerization finishes completely; and transferring the reaction liquid to a precipitation tank for precipitation or separation and enrich of products by filtering. The method for producing polyferric chloride by using the pickling solution and the hydrochloric acid pickle reduces production cost and realizes resource comprehensive use of waste.
Owner:金月祥
Method for producing special-purpose modified mineral materials for black-odor rivers
InactiveCN104857930ALow costEasy to operateOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionAluminium chlorohydrateLanthanum
The invention relates to a method for producing special-purpose modified mineral materials for black-odor rivers, which comprises the following steps: step 1, attapulgite, zeolite and bentonite ores are dried, mixed and coarsely crushed; step 2, calcium nitrate and lanthanum chloride are added to mix and obtain hybrid particles; step 3, water is sprayed to extrude the hybrid particles to be flake clay mixture; step 4, the flake clay mixture is uniformly mixed with polyferric chloride and poly aluminum chloride; and step 5, the special-purpose modified mineral materials for the black-odor rivers are obtained by drying and grinding. The method for producing special-purpose modified mineral materials for black-odor rivers are easy to obtain raw mineral materials, is low in cost, obtains the special-purpose modified mineral materials for the black-odor rivers by optimizing a series of steps such as mixing, crushing, squeezing, drying and grinding and the like particularly by adding the calcium nitrate and the lanthanum chloride during the production process, achieves low cost purification treatment of the black-odor rivers, is simple in operation step and easy to control, and is suitable for large-scale applications in industry.
Owner:江苏玖力纳米材料科技有限公司 +1
Efficient sewage treatment agent
InactiveCN104445556AEasy to handleGood processing effectWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationTreatment effectPolyacrylamide
The invention discloses an efficient sewage treatment agent which contains the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 50-70wt% of a first component and 30-50wt% of a second component, wherein the first component comprises the following materials in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of polyacrylamide, 10-20 parts of polyferric chloride, 15-25 parts of soybean protein, 10-15 parts of ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid, 25-35 parts of sodium humate, 30-50 parts of zeolite particles, 35-45 parts of medical stone particles, 20-35 parts of sepiolite particles and 30-45 parts of activated carbon; and the second component comprises the following materials in parts by mole: 2-5 parts of sodium silicate, 1-4 parts of sodium sulfide and 3-6 parts of hydrogen peroxide. The efficient sewage treatment agent disclosed by the invention is low in cost and good in treatment effect, especially for heavy metals.
Owner:TIANCHANG FEILONG BRAND STEEL GRID
Preparation method of environment-friendly sewage treatment agent
InactiveCN105565403AAdvantages of preparation methodEasy to prepareWater/sewage treatmentActivated sludgePolyacrylamide
The invention provides a preparation method of an environment-friendly sewage treatment agent. The preparation method includes: using ferrous sulfate, diatomite, modified lignin sulfonate, polyferric chloride, activated carbon, sodium carbonate, cottonseed hull, polyacrylamide, activated sludge and water as raw materials; adding ferrous sulfate, diatomite, modified lignin sulfonate, polyferric chloride, activated carbon, sodium carbonate and cottonseed hull into a grinder for grinding, mixing well, adding activated sludge and water while stirring, heating to 35-40 DEG C after reaction for 20-30 min, adding polyacrylamide while stirring, and stirring and mixing well for reaction for 1-5 h. The preparation method is simple and free of secondary pollution, and the treatment agent prepared by the method is high in removal rate of BOD, COD and suspended matter in sewage and wide in application range.
Owner:TIANJIN OUPAN TECH DEV CO LTD
Preparation method of compound coagulant
ActiveCN101759266AHas a decolorizing effectWide range of efficacyWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationAluminium chlorohydratePolyferric chloride
The invention relates to a preparation method of a compound coagulant. The compound coagulant is prepared by commonly mixing polyaluminium chloride, diallydimethylammonium chloride (the viscosity is 8,000-12,000), magnesium sulfate, polyferric chloride and deionized water according to the mass ratio of 30 percent, 2 percent, 5 percent, 1 percent and 62 percent. The invention has the advantages of removing heavy metals and organisms in an organic complex by multiple actions, having the effect of decolorization, wide medicine effect range and simple and convenient operation and replacing a plurality of coagulants for use.
Owner:SHANGHAI FENGXIN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
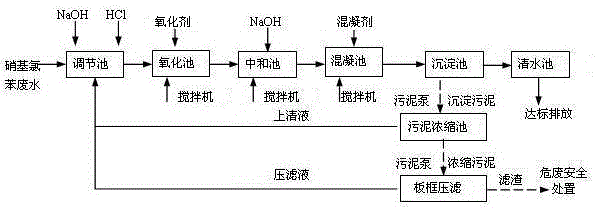
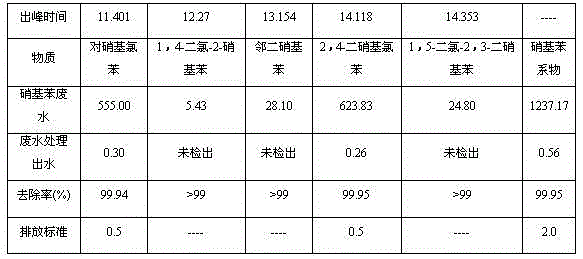
Treatment method and treatment system for nitrochlorobenzene production waste water
InactiveCN103951101AImprove processing efficiencyLow running costMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeFiltration
A treatment method and a treatment system for nitrochlorobenzene production waste water. The method comprises the following steps: pumping nitrochlorobenzene production waste water into an adjustment pool, adjusting the pH value to allow the waste water to be acidic, then allowing the waste water to enter an oxidation pool, adding oxidizing agents of sodium hypochlorite, calcium hypochlorite or hypochloric acid for chemical oxidation treatment, discharging the effluent from the oxidation pool into a neutralization pool, adjusting the pH value to allow the effluent to be neutral, discharging the effluent from the neutralization pool into a coagulation pool, adding coagulants of one or more than one of polyaluminium chloride, polyferric chloride, and polyacrylamide for a coagulation reaction, discharging the effluent from the coagulation pool into a sedimentation pool, allowing a supernatant obtained by sedimentation and separation in the sedimentation pool to overflow into a clean water pool, discharging the clean water that reaches the standard, concentrating and filtering sedimentated sludge at the bottom of the sedimentation pool for safety treatment, and discharging waste liquid generated during the concentration and filtration process into the adjustment pool for re-treatment. According to the invention, the removal rate of nitrochlorobenzene and other nitrobenzene compounds in effluent of the nitrochlorobenzene production waste water treated by the method of the invention is up to 99%, and the method of the invention has the advantages of high treatment efficiency, low operation cost, no secondary pollution, and the like.
Owner:LUOYANG INST OF SCI & TECH
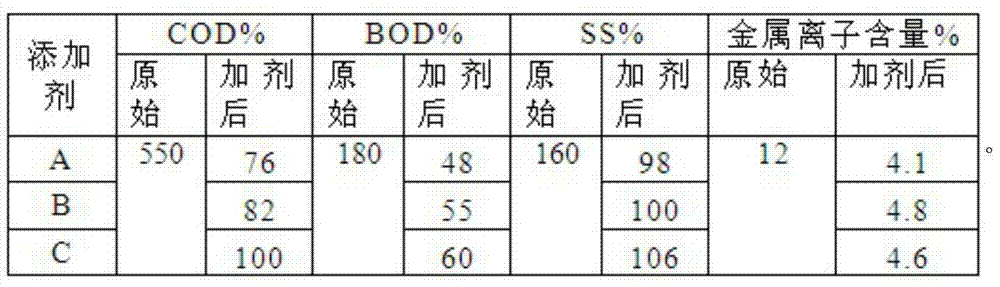
Papermaking sewage treatment agent
ActiveCN103708568AReduce CODReduce BODWater/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from plant processingSodium acetatePapermaking
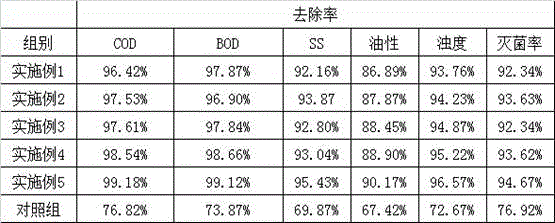
The invention provides a papermaking sewage treatment agent. The papermaking sewage treatment agent comprises dithiocarbamate, ferrous sulfate, citric acid, sodium acetate, polyferric chloride, trimethylcyclopropyl ammonium chloride, chitin and bentonite. The treatment agent allows the physical and chemical indexes of papermaking sewage reach GB18918-2002 standards, and effectively reduces the COD, BOD, SS and the metal ion content in the papermaking sewage.
Owner:珠海横琴森禾生物科技控股有限公司
Production method and process of high-performance polyferric chloride
InactiveCN108033490AImprove stabilitySludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningWater/sewage treatmentOxygenPolyferric chloride
The invention discloses a production method and process of high-performance polyferric chloride. Waste steel scraps, steel hydrochloric acid cleaning waste liquid and hydrochloric acid are used as main raw materials, and oxygen oxidization and mandatory polymerization methods are adopted; a few of or even no oxidants and polymerization additives which possibly contain remaining interference ions are added in an oxidization process and a polymerization process, so as to improve the stability of the product.
Owner:青岛市昌斯达环保科技有限公司
Invert-demulsion coagulating agent, preparation method of invert-demulsion coagulating agent and application of invert-demulsion coagulating agent
ActiveCN105253974AFacilitated DiffusionPromote demulsificationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationHigh concentrationChemical oxygen demand
The invention discloses an invert-demulsion coagulating agent, a preparation method of the invert-demulsion coagulating agent and application of the invert-demulsion coagulating agent. The invert-demulsion coagulating agent is prepared from the following ingredients in percentage by mass: 1 to 50 percent of poly dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride, 0.1 to 50 percent of polyaluminium chloride, 0.1 to 30 percent of polyferric chloride, 0.1 to 30 percent of poly-aluminum ferric silicate sulfate, 1 to 98.2 percent of water and 0.5 to 5 percent of polyether polyol. The sum of the mass percentage of all ingredients is 100 percent. The invert-demulsion coagulating agent has the advantages that the poly dimethyl diallyl ammonium chloride is subjected to modified compounding, so that better demulsification, flocculation and precipitation effects can be achieved on high-pollution wastewater formed by macromolecule organic matters; the demulsification speed is accelerated; the demulsification effect is improved; the invert-demulsion coagulating agent is applicable to the treatment of various kinds of high-concentration COD (chemical oxygen demand) wastewater.
Owner:GUANGZHOU ZHENQING ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Efficient industrial sewage treating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105481034AFast purificationNo corrosionWater/sewage treatmentContaminated waterways/lakes/ponds/rivers treatmentCorrosionAmmonium persulfate
The invention discloses an efficient industrial sewage treating agent and a preparation method thereof. The efficient industrial sewage treating agent is prepared from raw materials in parts by weight as follows: 20-22 parts of corn starch, 18-20 parts of alums, 16-18 parts of potassium peroxodisulfate, 10-12 parts of sodium lignin sulfonate, 12-16 parts of magnesium oxide, 12-18 parts of sodium hypochlorite, 10-18 parts of polyferric chloride, 10-12 parts of calcium hydroxide, 16-20 parts of sodium silicate, 8-12 parts of sodium chloride, 12-18 parts of sepiolite, 16-18 parts of acetic acid, 12-16 parts of titanium dioxide, 18-22 parts of zinc oxide and 16-18 parts of ammonium persulfate. The efficient industrial sewage treating agent is environment-friendly and non-toxic and has no corrosion to equipment and high purification efficiency.
Owner:张锐
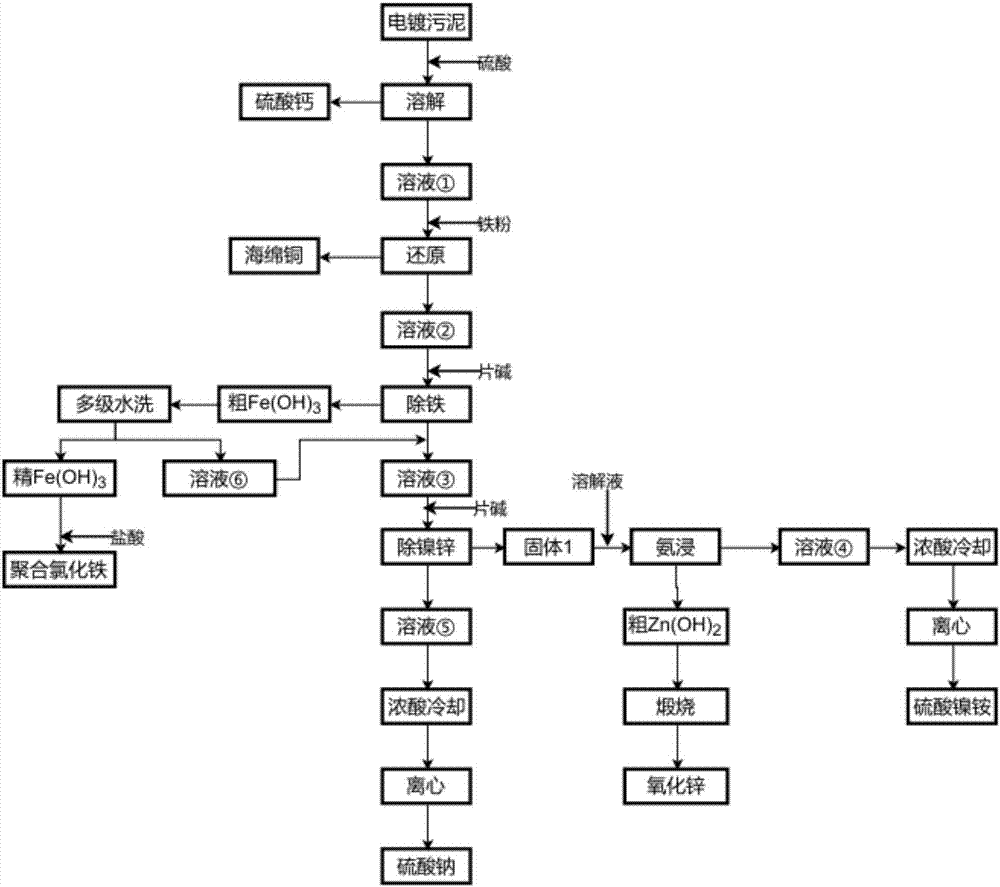
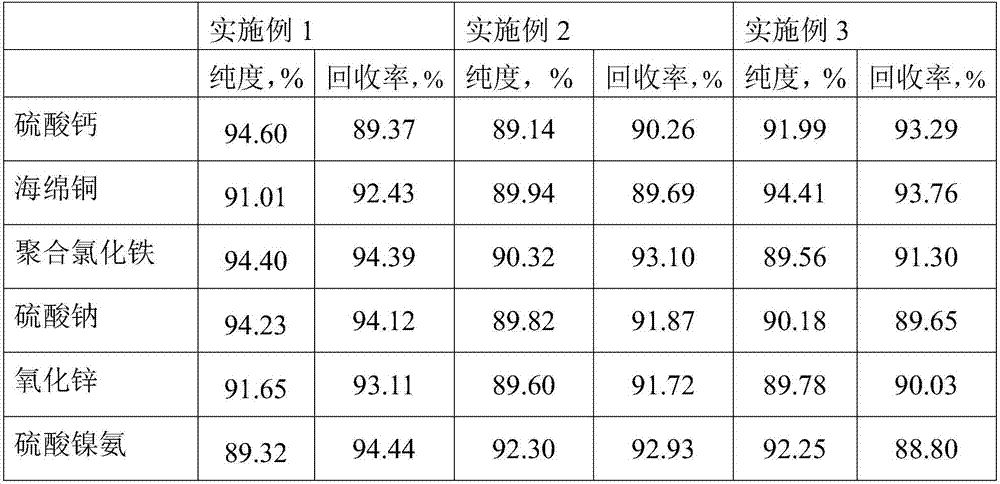
Method for respectively recycling copper, nickel and zinc from electroplating sludge
ActiveCN107287428AOvercome effectivenessOvercoming the disadvantages of high valueProcess efficiency improvementZinc hydroxideSludge
An applicator provides a method for respectively recycling copper, nickel and zinc from electroplating sludge. The method comprises the following steps: adding sulfuric acid into the electroplating sludge to be dissolved to obtain a solution, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain calcium sulfate; carrying out reductive treatment on the obtained solution (1) after dissolution to obtain sponge copper; adding hydrochloric acid into refined iron hydroxide obtained by carrying out multi-stage washing, heating and copolymerizing to obtain polyferric chloride; enabling the solution (6) produced by carrying out multi-stage washing to renewedly return to the solution (3) for recycling; calcining coarse zinc hydroxide subjected to ammonia leaching to obtain zinc oxide; carrying out concentration and cooling treatment on the solution (4) obtained by carrying out ammonia leaching to prepare nickel ammonium sulfate; and carrying out concentration and cooling treatment on the solution (5) obtained by carrying out nickel and zinc removal to prepare sodium sulfate. The invention provides an electroplating sludge treatment process with simple operation, high applicability, no pollution, high value of valuable metals, and environmental protection.
Owner:盛隆资源再生(无锡)有限公司
Environment-friendly water treatment flocculation material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106219706AEfficient removalConvenient sourceBiocideDead animal preservationHigh concentrationChemical adsorption
The invention discloses an environment-friendly water treatment flocculation material and a preparation method thereof. The environment-friendly water treatment flocculation material comprises a Chinese herbal medicinal active antibacterial component and a chemical adsorption component; the Chinese herbal medicinal active antibacterial component is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 6 to 12 parts of radix angelicae, 4 to 10 parts of mint, 2 to 8 parts of lonicerae japonicae flos, 4 to 10 parts of folium artemisiae argyi, 6 to 12 parts of broom cypress fruit, 8 to 14 parts of pomegranate peel and 10 to 16 parts of castor oil; the chemical adsorption component is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20 to 32 parts of polyacrylamide, 16 to 28 parts of activated carbon, 10 to 22 parts of lignin, 4 to 10 parts of aluminium oxide, 6 to 12 parts of polyferric chloride, and 4 to 10 parts of polyferric sulphate. The environment-friendly water treatment flocculation material can effectively remove high-concentration organic pollutants and suspended solids in a wastewater treatment system; the chemical adding amount is small; the decolouration performance is excellent; the decolouration rate is high; the floc settling velocity is high; the floc size is small; the environment-friendly water treatment flocculation material is safe and environment-friendly, is low in wastewater treatment energy consumption, low in treatment cost, and is helpful to improve the current situation of wastewater treatment in China.
Owner:肇庆市高新区创客科技有限公司
Industrial wastewater flocculating agent
InactiveCN104310558AReduce COD valueLower BOD valueWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationWater/sewage treatment by sorptionIndustrial waste waterAdsorption effect
The invention discloses an industrial wastewater flocculating agent, and belongs to the field of environmental protection. The industrial wastewater flocculating agent comprises 5-10 parts of polyferric chloride, 4-6 parts of aluminum sulfate, 1-4 parts of polyoxyethylene, 1-4 parts of barium carbonate and 5-8 parts of a chitosan derivative. The industrial wastewater flocculating agent has a good adsorption effect, can effectively remove suspending substances in industrial wastewater, and reduces the COD value and the BOD value in the industrial wastewater in order to make the industrial wastewater reach national industrial water discharge standards.
Owner:QINGDAO BAIZHONG CHEM TECH
Sewage treatment agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105948275AImprove adsorption capacityEfficient decompositionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processParticulatesMicrobial agent
The invention provides a sewage treatment agent and a preparation method of the sewage treatment agent. The sewage treatment agent comprises the following components: 20 to 30 parts of modified diatomite, 20 to 40 parts of medical stone, 20 to 30 parts of slag, 20 to 30 parts of sodium lignosulfonate, 10 to 15 parts of chitosan, 10 to 20 parts of seabed mineral mud, 5 to 10 parts of polymeric silicate aluminum sulfate, 10 to 20 parts of polyferric chloride, 10 to 20 parts of phosphonate, 10 to 20 parts of ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonic acid, 10 to 20 parts of microbial agents and 100 to 160 parts of deionized water. The treatment agent disclosed by the invention can effectively adsorb particles in sewage, and further remove pathogenic bacteria and heavy metals in the sewage.
Owner:HEFEI TIANXIANG ENVIROMENT PROJECT
Papermaking wastewater treatment agent and application method thereof
InactiveCN104709987ALow costEasy to handleMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationSodium acetateSodium bicarbonate
The invention discloses a papermaking wastewater treatment agent and an application method thereof. A wastewater treatment agent is prepared from calcium oxide, sodium carbonate, aluminum polychloride, polyferric chloride, magnesium sulfate, seaweed soil, corn starch, activated carbon, sodium acetate, sodium chlorite and sodium bicarbonate. The application method comprises the following steps: in wastewater, adding the calcium oxide and the sodium carbonate, and then adding the aluminum polychloride, the polyferric chloride, the magnesium sulfate and the seaweed soil; removing precipitate and impurities, then adding the activated carbon and the sodium acetate, and finally adding the sodium chlorite and the sodium bicarbonate for sterilization and disinfection. The papermaking wastewater treatment agent has dual functions of flocculent precipitate purification and sterilization and disinfection for wastewater, therefore can remove sediment and impurities in the wastewater, can also remove harmful substances, and carries out sterilization and disinfection. The wastewater treatment agent has the advantages of being wide in raw material source, low in cost, good in treatment effect and high in efficiency, cannot produce secondary pollution, saves energy, protects environment, and is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:高彬
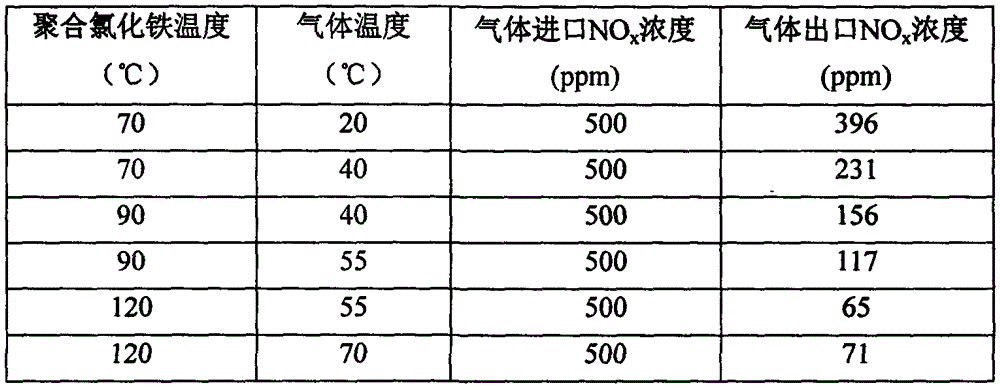
Method for removing nitrogen oxide in airflow
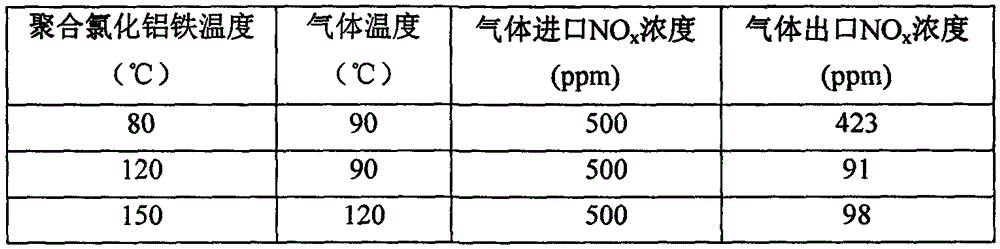
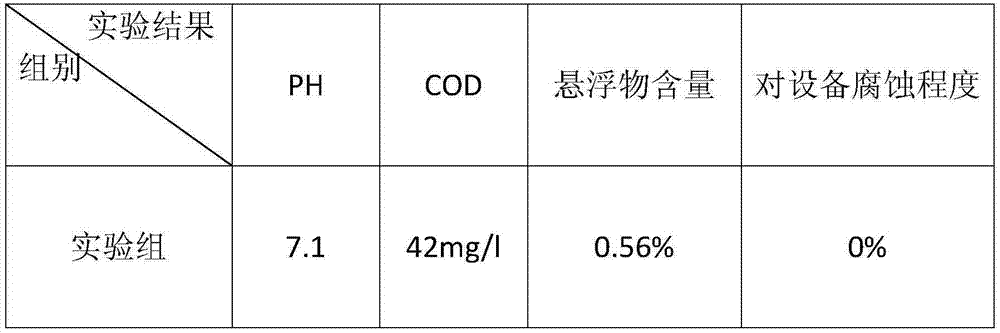
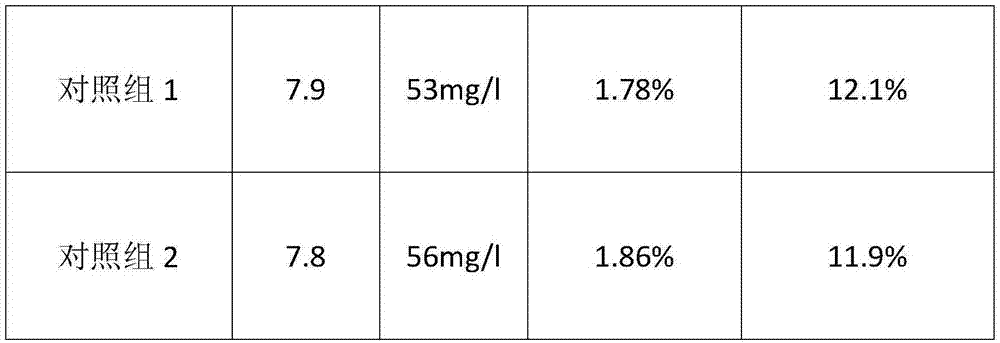
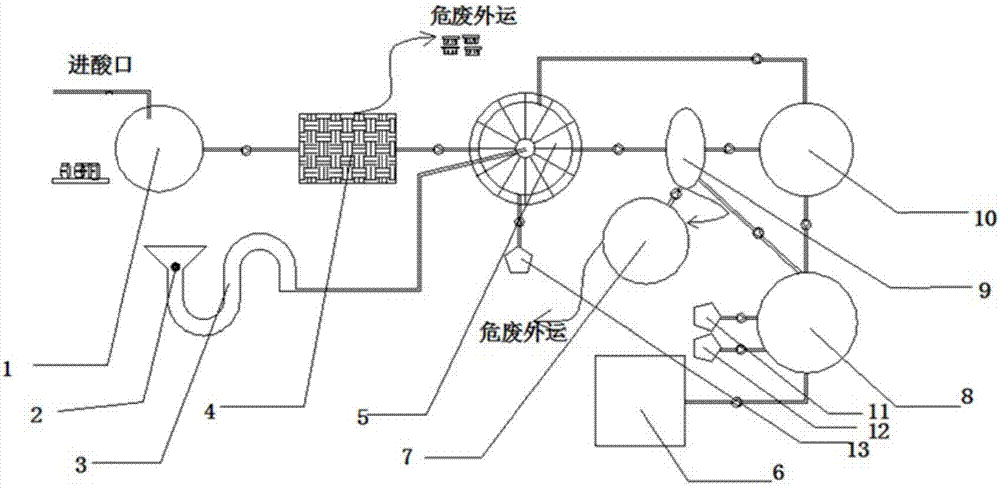
InactiveCN105536500ATo achieve the purpose of purificationLow costGas treatmentDispersed particle separationChemical reactionSolid particle
The invention provides a method for removing nitrogen oxide in airflow and belongs to the technical fields of atmosphere pollution control and environment protection. The treatment process in the method includes the steps that treated gas is introduced into a gas-solid reaction tower, meanwhile polyferric chloride or polyaluminum chloride solid particles are introduced into the gas-solid reaction tower, at a certain temperature, nitrogen oxide in gas and polyferric chloride or polyaluminum chloride have a gas and solid chemical reaction in the gas-solid reaction tower so that the nitrogen oxide can be absorbed and removed, and the aim of purifying the gas is achieved. The invention further provides a special device which has the advantages that investment cost and operation cost are low, use is safe, by-products can be recycled, operation is easy, treatment efficiency is high, and the treatment amount is large.
Owner:黄立维
Sewage treatment agent and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105439220AFast purificationImprove purification effectWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatmentPotassium persulfateSodium Bentonite
The invention discloses a sewage treatment agent and a preparing method thereof. The sewage treatment agent is prepared from, by weight, 30-36 parts of kaolin, 28-32 parts of bentonite, 26-28 parts of seaweed meal, 22-24 parts of activated carbon, 20-24 parts of aluminum ash, 20-22 parts of poly-silicon aluminum sulfate, 18-24 parts of citric acid, 18-22 parts of polyferric chloride, 14-18 parts of zinc acetate, 18-20 parts of sodium carbonate, 16-18 parts of potassium persulfate, 14-18 parts of sodium hydroxide, 20-22 parts of chitosan, 22-24 parts of barium sulfide and 18-22 parts of dimethyl diallyl. The sewage treatment agent is environmentally friendly, free of toxicity, high in purification speed and good in purification effect.
Owner:潍坊农丰宝环境科技有限公司
Sewage treatment agent
InactiveCN105858916AMaterial effect is remarkableCooperate scientifically and reasonablyWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentParticulatesMedicine
The invention belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment and particularly relates to a sewage treatment agent which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 15-25 parts of polyferric chloride, 10-30 parts of starch acetate, 3-11 parts of tannin, 12-28 parts of rice straw, 5-20 parts of fly ash and 5-13 parts of lipase. With scientific and reasonable cooperation of the raw materials and under the synergistic effect of the components, the sewage treatment agent provided by the invention has a good flocculation effect, and realizes a remarkable effect of eliminating COD, soluble inorganic matters, organic pollutants, heavy metals and other harmful particulate matters in sewage; and the water quality completely reaches the discharge standard.
Owner:杨添凯
Domestic sewage treatment agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107758823AGood flocculation effectFast hydrolysisWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPorous carbonTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a domestic sewage treatment agent and a preparation method of the domestic sewage treatment agent. The domestic sewage treatment agent comprises the following raw materials inparts by weight: 12-15 parts of polyferric chloride, 20-30 parts of meerschaum, 5-10 parts of modified silkworm excrement based porous carbon material, 10-15 parts of sodium hydroxide, 12-15 parts ofpolyacrylamide, 10-15 parts of sodium carbonate and 1-5 parts of bio-based porous composite material. According to the treatment agent, two novel biological carbon materials are added, so that the adsorption purification capacity of the sewage treatment agent is improved; the treatment agent can effectively treat domestic sewage of residents under matching of the other raw materials, and is good in treatment effect, lower in cost and stable in performance; and treated pollution reaches a national sewage discharge standard.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHONGHAILONG NEW ENERGY
Rapid purifying agent for urban black and odorous water body
InactiveCN107162135AWith slow-release oxygenation functionSettling fastWater/sewage treatment by substance additionWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationCalcium silicateAluminum silicate
The invention belongs to the technical field of water environment treatment and relates to a sewage purifying agent. An urban sewage rapid purifying agent is composed of 0.1-25 parts of boron-iron-aluminum polysilicate, 2-10 parts of calcium peroxide, 1-10 parts of magnesium peroxide, 1-15 parts of aluminum ferric polysilicate, 1-10 parts of polyacrylamide, 1-10 parts of ployferric sulfate, 1-15 parts of calcium nitrate, 1-3 parts of sodium silicate and 1-2 parts of polyferric chloride. The agent provided by the invention has the advantages that pH after hydration can be controlled to be 7.5-9.5, and tight composite mineralized sediments which are provided with sustained release oxygen and are mainly calcium silicate, magnesium silicate, aluminum silicate, calcium aluminosilicate and aluminosilicic acid can be gradually formed. Therefore, suspending particular matters and various kinds of harmful impurities in sewage can be rapidly settled, sustained release and oxygenation functions on mud at the water bottom can be realized, bottom mud with a tight structure also can be formed after settlement, and the sewage purifying agent can be applied to treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater, urban polluted landscape water and urban inland river black and odorous water.
Owner:GUANGDONG RUIJIE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG CO LTD
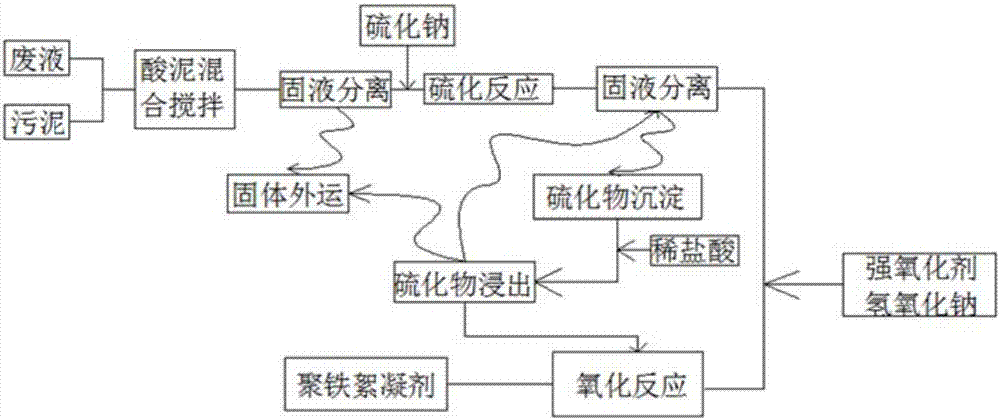
System and method for treating waste pickling liquor and sludge in wire rope factories
PendingCN107235575AEnsure safetyGuarantee industrial cycle productionWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSludge treatmentSludgeSodium sulphide
The invention discloses a system and a method for treating waste pickling liquor and sludge in wire rope factories, which belong to the field of environmental governance. The system for treating waste pickling liquor and sludge in wire rope factories disclosed by the invention comprises an acid-sludge mixing unit, a hydrogen sulfide warning unit, a hydrogen sulfide absorption unit, a vacuum filtration unit, a lead-zinc waste liquor sodium sulfide treatment unit, a polyferric chloride flocculant storage unit, a polyferric chloride flocculant preparation unit, an industrial centrifuge, and a vulcanization reaction treatment effect safety unit. The method for treating waste pickling liquor and sludge in wire rope factories disclosed by the invention includes acid-sludge mixing, solid-liquid separation, vulcanization reaction, and oxidation reaction. The invention can realize the co-disposal of pickling liquor and sludge of wire ropes, can effectively remove zinc and lead elements, and can prepare industrial polyferric chloride flocculant product with high added value.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
High-efficiency treating agent for municipal sewage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106396041AEasy to handleHigh decontamination efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationPhosphateThiourea
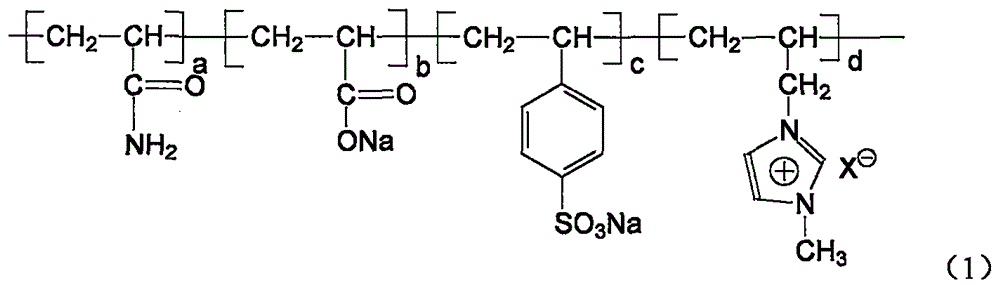
The invention provides a composite sewage treating agent, comprising modified nanometer meerschaum powder, polyferric silicate sulfate, aminotrimethylene phosphate, polyferric chloride, sodium lignosulfonate, modified chitosan, resorcinol-thiourea-formaldehyde polycondensate, modified coconut shell-based active carbon and a copolymer as shown in a formula (I) which is defined in the specification. Through synergism of the above components of the sewage treating agent, the sewage treating agent has excellent comprehensive sewage treating capacity.
Owner:TIANJIN YUANZHUO AUTOMATION EQUIP MFG CO LTD
Method for preparing polyferric chloride by using wastewater produced in pickling of steel with hydrochloric acid
InactiveCN109250762AIncrease concentrationSimple processIron halidesWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationPhosphateReaction temperature
The invention relates to a method for preparing polyferric chloride by using wastewater produced in pickling of steel with hydrochloric acid. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating hydrochloric acid pickling wastewater, and quantitatively feeding the filtered hydrochloric acid pickling wastewater into a reaction kettle; adding a phosphate buffer in batches, wherein 0.03 to 0.04 tonof the phosphate buffer is added for per ton of the concentrated hydrochloric acid pickling wastewater; carrying out sufficient stirring to completely dissolve the phosphate buffer; and adding an oxidizing agent under the conditions of stirring and constant-temperature heating for an oxidative polymerization reaction, wherein the concentration of the oxidizing agent is 120-150 mg / L, 0.7 to 1.1 kg / h of the oxidizing agent is added for per ton of the concentrated hydrochloric acid pickling wastewater, the rotating speed of an agitator in a reaction vessel is 200 to 400 rpm, a reaction temperature is 40 to 60 DEG C, and after sufficient reaction for 14 to 26 h, the polyferric chloride is obtained. The method has the following advantages: process flow is simple; only one reaction kettle is needed in a core production procedure; and the oxidative polymerization reaction is implemented in the reaction kettle.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com