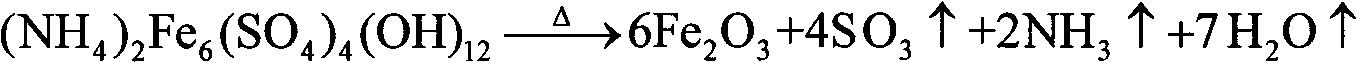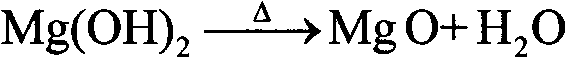Patents
Literature
1143 results about "Sodium sulphide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sodium sulfide is the chemical compound with the formula Na2S, or more commonly its hydrate Na2S·9H2O. Both are colorless water-soluble salts that give strongly alkaline solutions. When exposed to moist air, Na2S and its hydrates emit hydrogen sulfide, which smells like rotten eggs.
Preparation method and applications of ferrous sulfide/biological carbon composite material
ActiveCN106966456ALow biological toxicityEfficient removal abilityWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCarboxymethyl celluloseSulfate
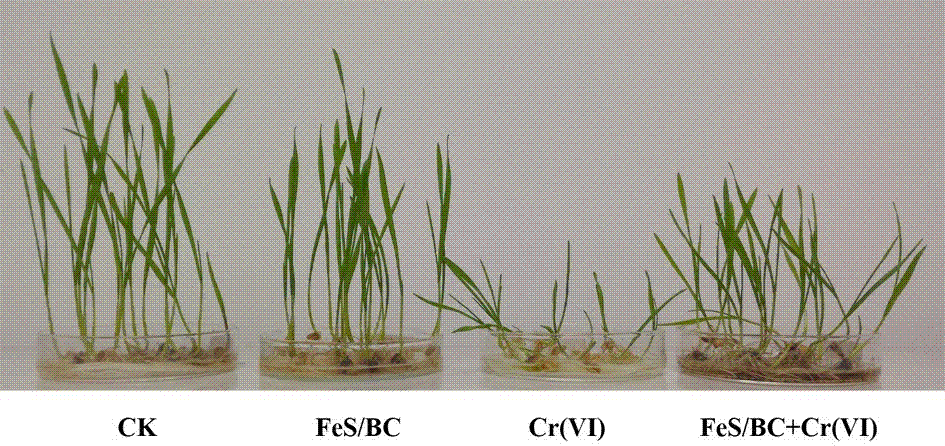
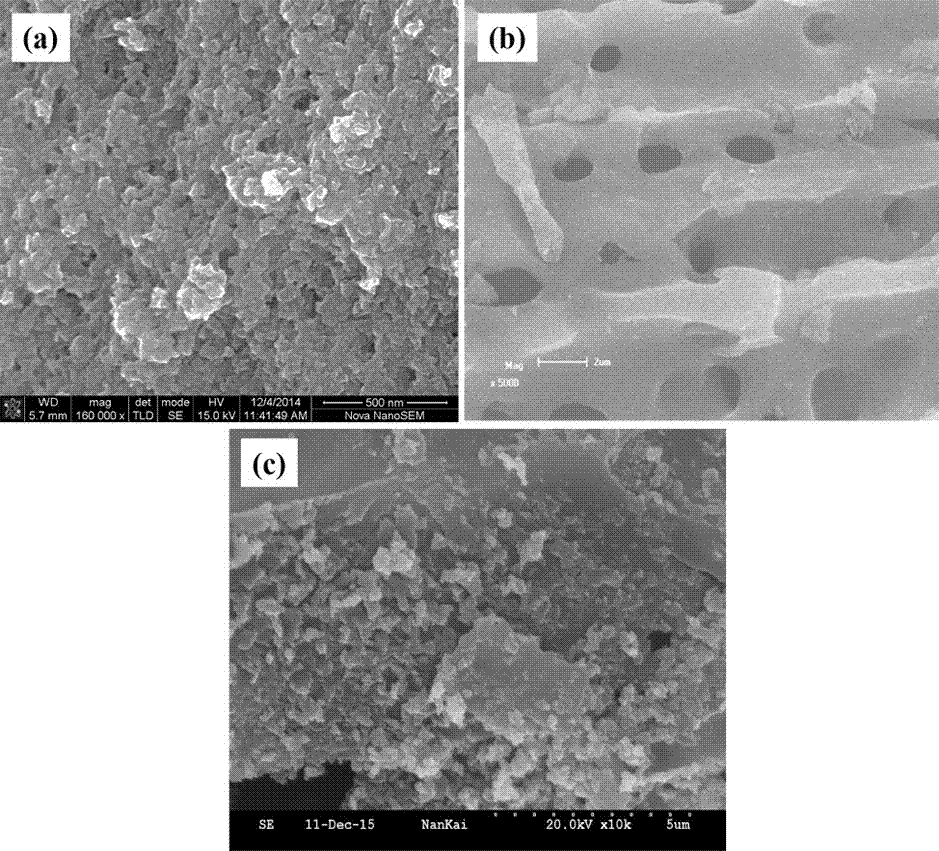
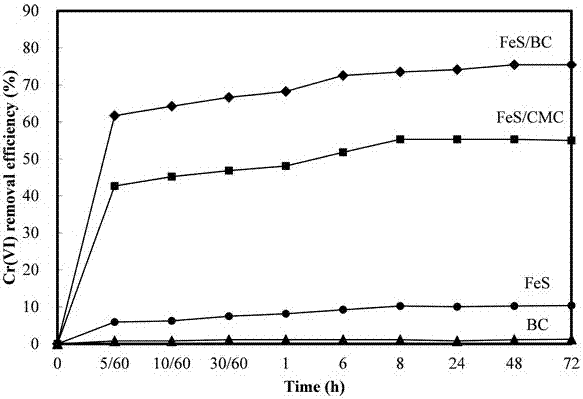
The present invention discloses an efficient ferrous sulfide / biological carbon composite material and a preparation method thereof, and applications of the ferrous sulfide / biological carbon composite material in repair of heavy metal pollution water bodies. According to the present invention, biological carbon is adopted as a carrier, a ferrous sulfate solution and the biological carbon are mixed, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is added as a stabilizer and a dispersant, a sodium sulfide solution is added to the system in a dropwise manner under the nitrogen protection, and vigorous stirring is performed to make the generated ferrous sulfide nanoparticles uniformly grow on the surface of the biological carbon, such that the disadvantage that the ferrous sulfide nanoparticles are easily agglomerated is substantially improved so as to increase the effective contact area between the ferrous sulfide nanoparticles and the pollutant, and the adsorption ability and the oxidation reduction ability of the ferrous sulfide and the biological carbon are integrally combined so as to improve the pollutant removal ability; the preparation method has advantages of simple and rapid process, low production cost, environmental protection and no secondary pollution; and the efficient ferrous sulfide / biological carbon composite material can strongly repair the Cr(VI) polluted water body, can effectively reduce the biological toxicity of the Cr(VI) on wheat seeds, and has wide application prospects in the fields of repair of organic pollution and inorganic pollution in environments.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Compositions for improving the organoleptic qualities of cooked foodstuffs
Compositions for generating a cooked flavor in a foodstuff, comprising specified flavor precursors that react on heating to generate the flavor and maintain a reactive association after inclusion in the foodstuff. The compositions may include combination of a sulphur source, e.g. hydrogen sulphide, methane thiol, a sulfur-containing amino acid, thiamine, cystine, sodium sulphide, ammonium sulphide, ammonium polysulphide, onions, garlic, shallots, eggs, methionine, and mixtures thereof, and at least one reductone, e.g. a furanone, a ketone, a pyrone, an aldehyde, a carbonyl compound, isomaltol, maltol, pyruvaldehyde, hydroxyacetone, 3-deoxyglucosone, 5-hydroxy-5,6-dihydromaltol, 2,3-butanedione, 3-hydroxy-2-butanone, a process flavor, cooked vegetable concentrates, soy sauce, and mixtures thereof.
Owner:KERRY INGREDIENTS UK
Animal fur clean depilation and fur fiber loosing method for preparing leather and application thereof
ActiveCN101235421AEliminate pollution and other issuesFine grainPre-tanning chemical treatmentFiberEnzyme system
The invention provides a method for unhairing leather and loosening leather fiber without sodium sulfide and lime in a leather production process and the application of the method. The method is characterized in that a method for combining unhairing by non-sulfur (sodium sulfide) depilatory under the alkaline condition and enzyme fiber loosening under the under the non-lime (lime) alkaline swelling condition are adopted, the enzyme unhearing and the enzyme fiber loosening take protease, lipase, amylase and glucoamylase as a compound enzyme system. The method achieves the effects for unhairing and loosening the leather fiber through adopting the method for combining compound enzyme water immersion, compound enzyme unhairing, unhairing with sodium sulfide depilatory, expansion regulator-sodium hydroxide expansion and the enzyme unhairing under the alkaline condition and eliminates the pollution which is brought by the sodium sulfide and the lime in animal unhairing or leather fiber loosening procedures in the leather production process. The method of the invention is suitable for unhairing and leather fiber dispersed processing of various animal leather of leather with various usages.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Method for preparing o-phenylenediamine by catalytic hydrogenation of o-nitrophenylamine
InactiveCN102633653ASolve the problem of impuritiesReduce the presence of impuritiesOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationPtru catalystHydrogen pressure
The invention discloses a method for preparing o-phenylenediamine by catalytic hydrogenation of o-nitrophenylamine. The method is characterized in that: in the hydrogenation reaction of o-nitrophenylamine, alcohol is used as a solvent, nickel is used as a catalyst, reduction reaction is performed for 2 to 10 hours under the hydrogen pressure of 1.0 to 6 MPa at the temperature of between 40 and 80 DEG C, and the reaction product is rectified to form the while o-phenylenediamine. The method has the advantages that the alcohol is used as the solvent in the catalytic hydrogenation for producing o-phenylenediamine, the alcohol can be reclaimed and directly used for next reaction, and the waste residue produced by distillation can be used as an organic fuel, so that the problem that a large amount of waste water containing organic substances is produced in reduction of iron powder or sodium sulfide in the conventional process is solved; and thick acid and thick alkali used in the conventional process are avoided in the hydrogenation process, so that corrosion of equipment is greatly reduced, pollution is reduced, and almost zero pollution is realized. In addition, compared with the conventional iron powder or sodium sulfide reduction, the catalytic hydrogenation process has the advantages of low pollution, high yield, high quality, short production period and low energy consumption.
Owner:JIANGSU KANGHENG CHEM
Treatment method of heavy metal wastewater
InactiveCN104261526ATo achieve the purpose of purifying wastewaterLarge particle sizeWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsParticulatesFiltration
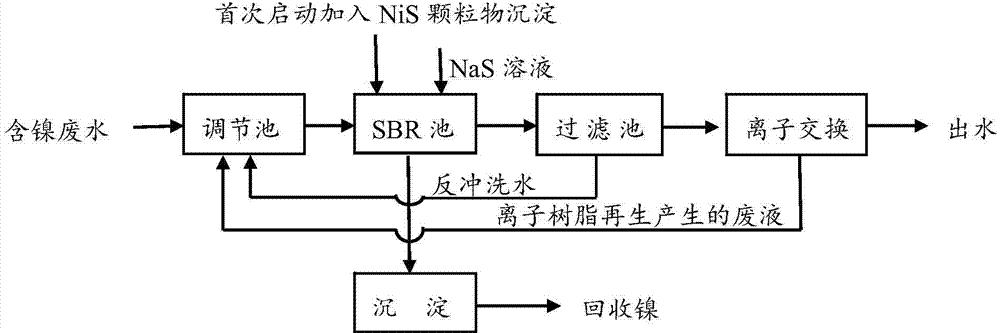
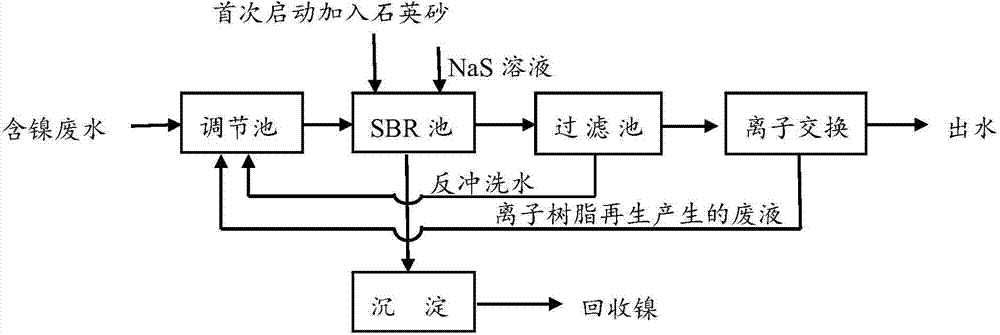
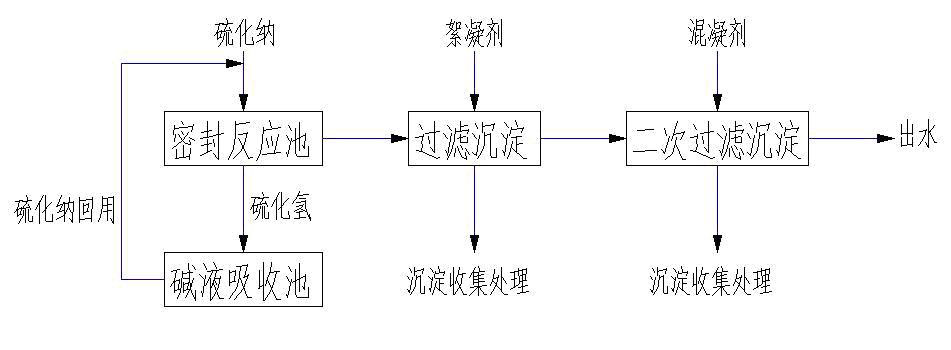
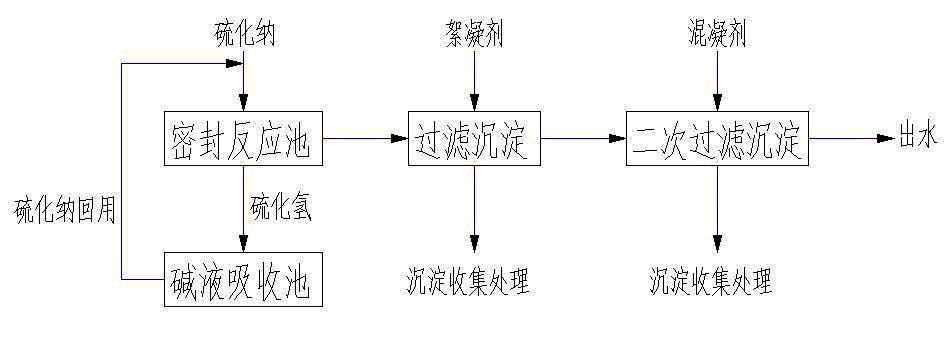
The invention provides a treatment method of heavy metal wastewater, and particularly relates to a method for treating heavy metal wastewater by virtue of a precipitation method. The method comprises the following steps: adding sodium sulfide in a heavy metal wastewater treatment process, reacting sulfur ions with heavy metal ions in the wastewater to generate particulate matters, further adding sulfide precipitates of heavy metal, stirring, standing, and accelerating the sedimentation of micro particulate matters and other substances by using generated particulate matter precipitates; further preferably adding quartz sand, and accelerating the rapid sedimentation of the particulate matters and other substances under the wrapping action of quartz sand; further performing subsequent process treatment including sand filtration and ion exchange on a supernatant liquor obtained after sedimentation to reach the emission standard; and periodically discharging and collecting part of the precipitates, and recycling heavy metals in the precipitates. Because the method provided by the invention is simple in working procedure, low in cost and high in efficiency, the method can be widely applied to the treatment of industrial wastewater particularly the heavy metal wastewater.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Technique method for producing sodium bisulfide
InactiveCN102765700AReduce power consumptionProduction costSulfur compoundsSodium bisulfideSodium hydrosulfide
The invention discloses a technique method for producing sodium bisulfide and belongs to the technical field of the chemical engineering production technology. The technique method for producing sodium bisulfide is low in production cost and can control product quality easily during production. The technique method includes: feeding buffered hydrogen sulfide and process absorption liquid with sodium sulphide as the main ingredient into an absorption tower respectively from the lower portion and the upper portion of the absorption tower, absorbing the hydrogen sulfide and the process absorption liquid on the surface of packing in the absorption tower to generate solution with the sodium bisulfide as the main ingredient, enabling the solution to flow to the bottom of the absorption tower, and discharging the unabsorbed hydrogen sulfide tail gas from the top of the absorption tower; pumping the solution at the bottom of the absorption tower out, returning most of the solution back to the absorption tower for recycling, feeding the small amount of solution to a sodium bisulfide production solution storing tank, and simultaneously adding the process absorption liquid in the absorption tower from the upper portion of the absorption tower during the absorption circulating process; and finally performing evaporation, concentration and dehydration on the solution, cooling the solution for molding, packaging and finishing the production of the sodium bisulfide.
Owner:CHENGDU DEMEI ENG TECH
Method for preparing alkali sulphide by using sulfur dye waste gas
InactiveCN101654226AReduce emission concentrationSolve processing problemsAlkali metal sulfides/polysulfidesSodium bicarbonateReaction temperature
The invention discloses a method for preparing alkali sulphide by using sulfur dye waste gas, which is characterized in that the sulfur dye waste gas containing hydrogen sulfide is used as a raw material and added with alkali to perform reaction at the reaction temperature of between 60 and 85 DEG C, the reaction products are cooled to between 30 and 50 DEG C after the reaction reaches a final point, and the reaction products are filtered to form the alkali sulphide. The alkali added into the sulfur dye waste gas containing the hydrogen sulfide may be one or a mixture of more than two of sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and potassium carbonate, and the ratio of the adding amount of the alkali to the weight of the waste gas is (0.8-1.4): 1. The pressure in the reaction process is -0.12 to -0.06MPa. The alkali sulphide is sodium sulphide and potassium sulfide. The method changes waste into valuable, effectively solves the problem that the sulfurdye waste gas is difficult to treat, reduces the discharge concentration of hydrogen sulfide in the waste gas, achieves the aims of environmental protection, energy conservation and discharge reduction, substance recycle and clean production, has large economic benefit and social benefit, and has the advantages of effectively reducing environment pollution and having less energy consumption.
Owner:蔡瑞琳 +2
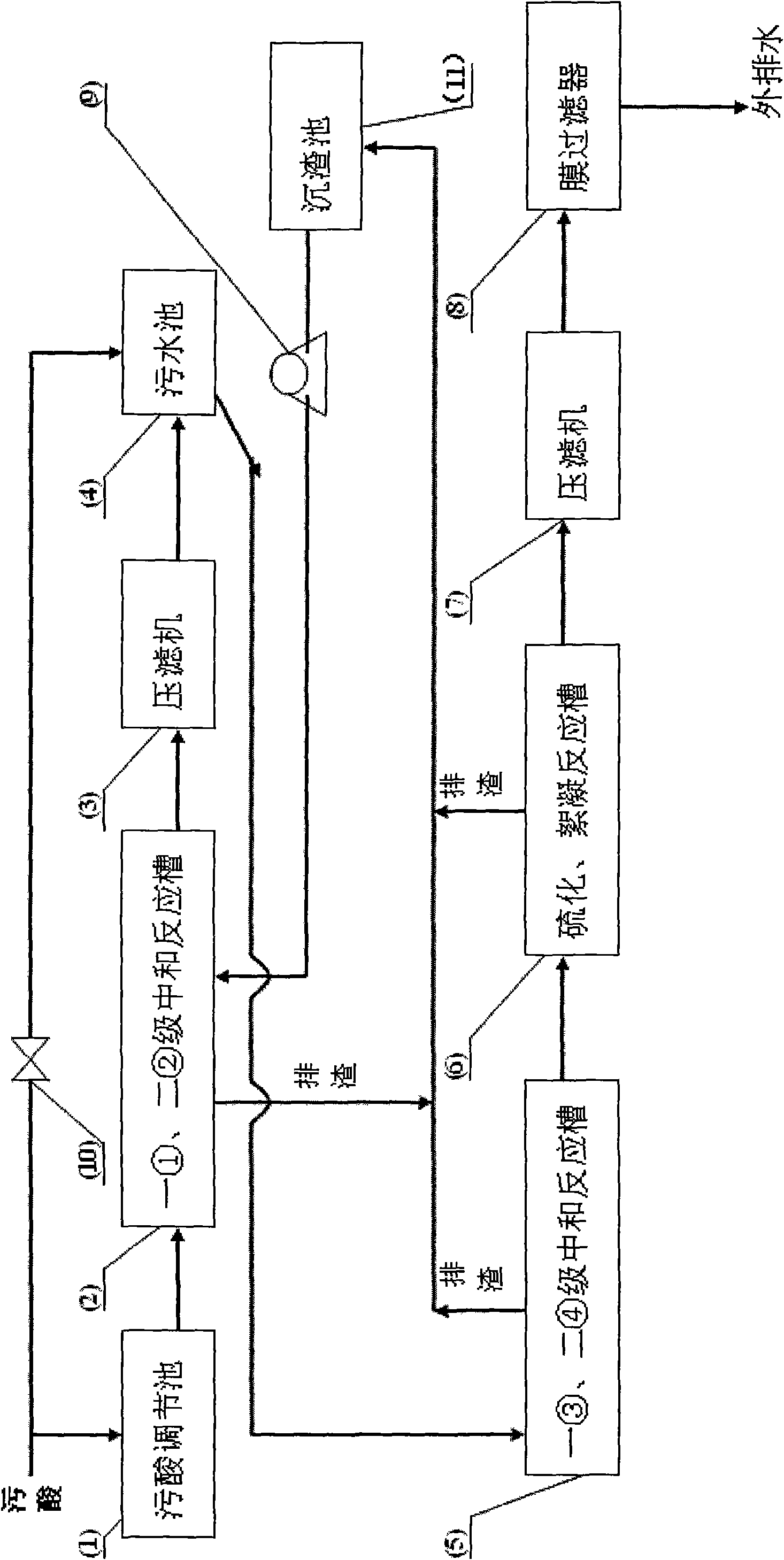
Processing equipment and technique for waste acid and water
InactiveCN101628763AAchieve separationEasy to achieve precise adjustmentWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentFlocculationVulcanization
The invention relates to waste acid and water processing equipment and a technique for processing acidic sewage generated in the process of purification of an acid making system. The technique comprises the following steps: pumping the waste acid into a first-level neutralizing reaction tank in the first stage; adding calcium carbide slag to adjust the pH value between 1 and 6; adding calcium carbide slag to adjust the pH value between 5 and 6, when the liquid overflows into a second-level neutralizing reaction tank in the first stage; carrying out solid-liquid separation; entering a sewage pool; pumping the liquid in the sewage pool into a first-level neutralizing reaction tank in the second stage; adding lime milk to adjust the pH value between 6 and 7; adding lime milk to adjust the pH value between 7 and 8, when the liquid gravitationally flows into a second-level neutralizing reaction tank in the second stage; adding 7% of sodium sulphide and 15% of ferrous sulfate according to weight percentage into a vulcanization and flocculation reaction tank, when the liquid gravitationally flows into the vulcanization and flocculation reaction tank; carrying out solid-liquid separation of fine particles on the liquid by a filter press and a film filter; discharging the liquid, thus the continuous up-to-standard discharging of effluent water is easily realized.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG ZINC IND
Ammonium-amine coupling activation method based on copper mineral sulfurization floatation system
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for carrying out unhairing and liming treatment without dust and akali sulphide during buffalo hide tanning
ActiveCN101445843AEasy to handleSo as not to damagePre-tanning chemical treatmentSodium hydrosulfidePollution
Owner:国家皮革质量监督检验中心(浙江) +1
Process for the production of alcohols from biomass
Alcohols useful as fuel compositions are produced from biomass by pretreating the biomass prior to hydrolysis and fermentation. In the pretreatment, the biomass is contacted with an aqueous solution containing a dilute acid with concentration of up to 10 wt % producing a predigested stream containing an aqueous liquor that contains at least a portion of hemicelluloses and a residual biomass that contains celluloses and lignin; separating at least a portion of the aqueous liquor from the residual biomass providing an aqueous liquor stream and a pre-digested biomass stream; then contacting the pre-digested biomass stream with a cooking liquor containing at least one alkali selected from the group consisting of sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, sodium sulfide, potassium hydroxide, potassium carbonate, ammonium hydroxide, and mixtures thereof and water. A process that allows for higher recovery of carbohydrates and thereby increased yields is provided.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
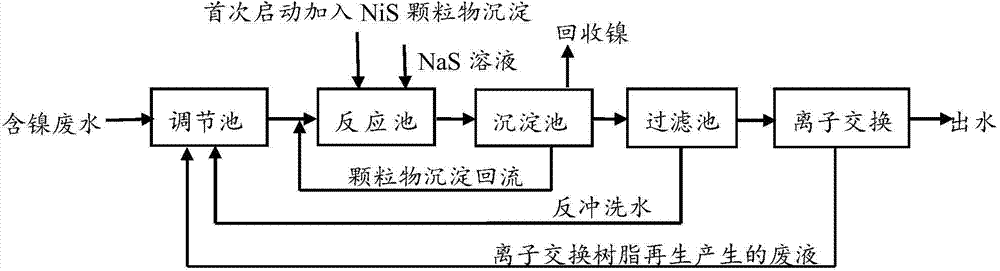
Treatment process for chemical nickel plating waste liquid in circuit board industry
InactiveCN104176852ASolve in-plant processing issuesReduce the risk of excessive emissionsSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningMultistage water/sewage treatmentElectroless nickelSodium hydroxide
The invention provides a treatment process for a chemical nickel plating waste liquid in the circuit board industry. The treatment process comprises the following steps: pumping the chemical nickel plating waste liquid in the circuit board industry into a reaction tank; sequentially adding sulfuric acid for acidifying; adding ferrous sulfate and hydrogen peroxide for Fenton oxidation complexation; adjusting the pH by sodium hydroxide; adding sodium sulfide for a coagu-flocculation reaction; finally, adding PAM until suspended solids are just flocculently separated; after acidification, advanced oxidation complexation, and flocculation, filter-pressing all the waste liquid by a plate-frame; collecting the filtrate and regulating the pH; and sequentially carrying out sand filtering and resin adsorption and discharging after reaching standard level. The treatment process provided by the invention can be used for effectively treating the chemical nickel plating waste liquid in the circuit board industry, so that the treatment cost and the standard-reaching difficulty of the waste liquid in an enterprise are reduced.
Owner:江西红板科技股份有限公司
Vulcanized modification method for Ni-Fe LDH electrode material
InactiveCN106601500AIncrease capacityEasy transferHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceVulcanization
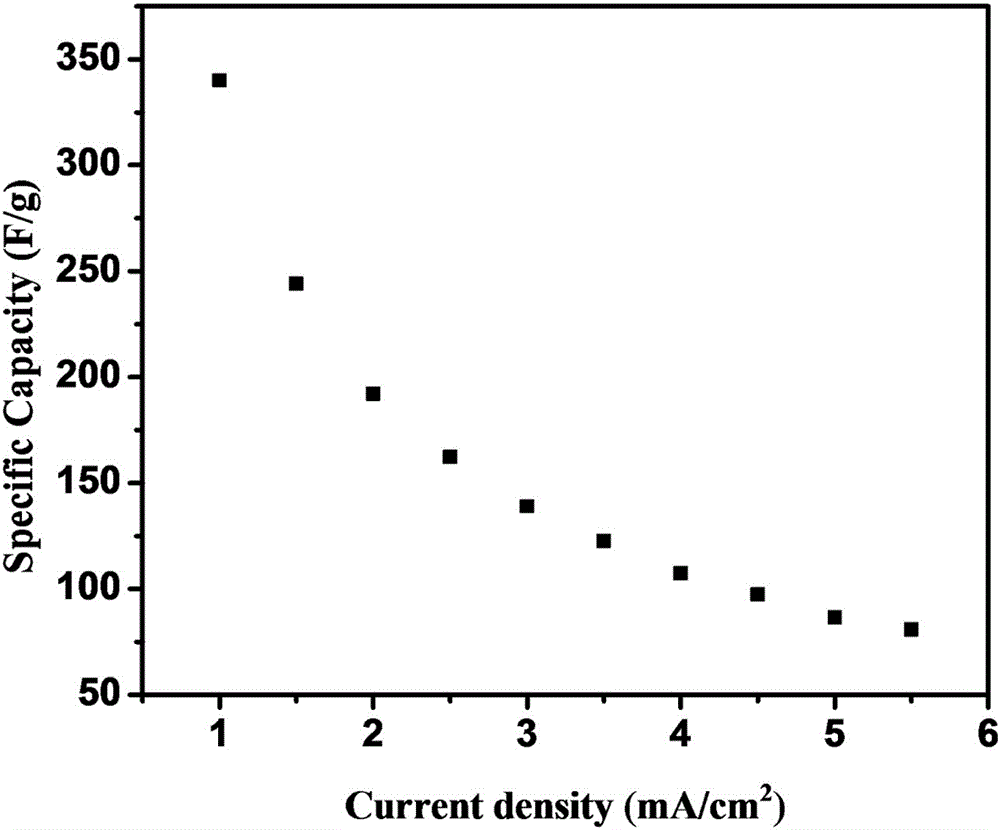
The invention discloses a vulcanized modification method for a Ni-Fe LDH electrode material. Urea is used as a precipitant and ferrous chloride is used as an iron source. Ni-Fe LDH grows on a nickel net substrate; and with a solvothermal method, vulcanization is carried out on the Ni-Fe LDH by using thiourea, sodium sulphide, or thioacetamide as a vulcanizing agent to obtain Ni-Fe LDH-S growing uniformly on the surface of the nickel net based on a cellular structure. Electrochemical performance evaluation is carried out on the Ni-Fe LDH-S in a 1M KOH electrolyte; and a potential window range is stabilized to be -1.1 to 0V. When constant-current charging and discharging are carried out in the potential window, the specific capacitance of the Ni-Fe LDH-S can reach 340 F / g, wherein the specific capacitance of the sample being Ni-Fe LDH without second-step vulcanization is only 45F / g. The result demonstrates that the specific capacity of the Ni-Fe LDH can be improved substantially.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Novel environment-friendly reagent for reducing leaching concentration of various heavy metals
InactiveCN103555340AReduce usage ratioSimplify the restoration construction processWater contaminantsOrganic fertilisersPhosphatePotassium manganate
The invention discloses a novel environment-friendly reagent for reducing leaching concentration of various heavy metals. The formula of the environment-friendly reagent comprises 0-30wt% of sodium polysulfide, 1-25wt% of sodium silicate, 0-15wt% of organic sulfur TMT-15, 0-20wt% of hydrazine hydrate, 1-20wt% of phosphate, 1-10wt% of sodium sulphide, 0-15wt% of ferrous sulfate, 0-5% of potassium permanganate, 0-5wt% of citric acid and 0-5wt% of edetic acid (EDTA). The novel environment-friendly reagent can be applied to ex-situ remediation of the traditional hazardous waste containing the heavy metals, and can also be applied to in-situ remediation of pollution site soil and underground water containing the heavy metals.
Owner:SHAOXING ENVIRONREM ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
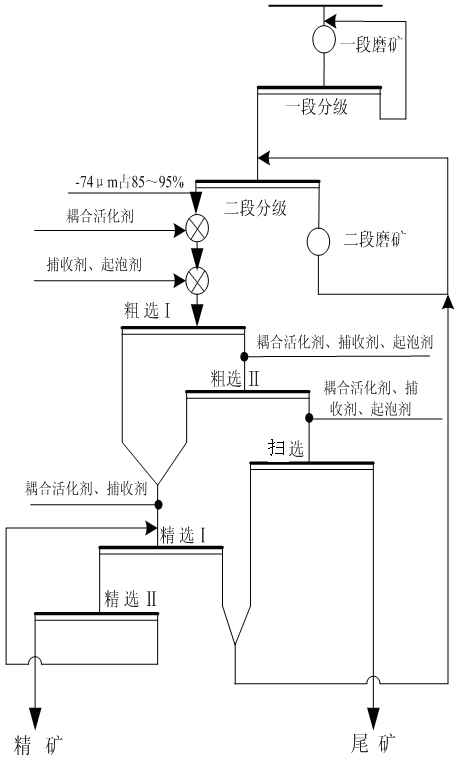
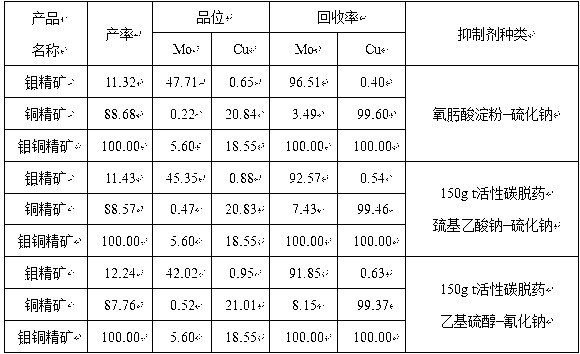
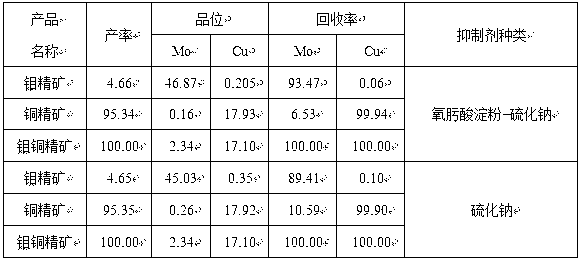
Method for flotation and separation of copper molybdenum sulphide bulk concentrates
The invention discloses a method for flotation and separation of copper molybdenum sulphide bulk concentrates and belongs to the technical field of mineral dressing. The method uses the copper molybdenum sulphide floated bulk concentrates as raw materials, adopts efficient environment-friendly copper ore inhibitor such as hydroxamic acid starch to inhibit copper sulphide ores, performs flotation of molybdenum sulphide ores and performs flotation and separation of copper and molybdenum. Oximido in the hydroxamic acid starch can be combined with active mass points Cu2+ on the surfaces of the copper sulphide ores to produce stable pentabasic chelate rings. Hydroxide radical and other polar radicals in a starch group at the other end of a chelate can be associated with water molecules through hydrogen bonds to enable the copper sulphide ores to be hydrophilic and inhibit the copper sulphide ores. In addition, the enormous hydrophilic water molecules of the hydroxamic acid starch can hide hydrophobic collecting agent molecules absorbed on the surfaces of copper ores, a collecting agent absorbed on the surfaces of the copper ores is not required to be removed, and the flotation and the separation of the copper molybdenum sulphide bulk concentrates do not need mechanical reagent removal or concentrated reagent removal. The hydroxamic acid starch serves as an inhibitor to inhibit the copper ores, sodium sulphide usage can be remarkably decreased, mechanical reagent removal or concentrated reagent removal is not needed, the chemical cost for the separation of the copper and the molybdenum is reduced, copper and molybdenum flotation and separation technological processes are simplified, good separation effect is obtained, and the method is environment-friendly and efficient.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
Method for comprehensively recovering mercury and selenium from metallurgical slag
InactiveCN104498722ALow costNo emissionsProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumMetallurgical slagHydroxylamine
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering mercury and selenium from metallurgical slag and belongs to the field of metallurgy. The method comprises following steps: grinding the metallurgical slag to the range of 130-150 microns, blending the metallurgical slag with quick lime accounting for 10-30% of the metallurgical slag and roasting at a temperature ranging from 750 to 900 DEG C for 6-8 hours; collecting dust from mercury-containing vapor firstly by use of a cloth bag and then by virtue of cyclone, condensing the mercury vapor by use of a two-stage condensation apparatus to recovery the mercury, and returning mercurial soot and a tail gas adsorption filler to the metallurgical slag for reutilization, wherein no pollutant is emitted in the process; next, leaching selenium-containing slag by use of an oxidation solution prepared from hydrochloric acid and sodium chlorate in the ratio of 2:1, analyzing the contents of Hg<2+>, Fe<2+>, Ca<2+> and Mg<2+> in the leachate in the liquid-solid ratio of 2:1, respectively, precipitating the ions by use of sodium sulfide in the ratio of 1:1 to the total content of the ions and then filtering to remove the irons, and reducing for 2 hours by use of hydroxylamine hydrochloride, thereby obtaining the elemental selenium after washing the precipitate. The method for comprehensively recovering mercury and selenium from the metallurgical slag is high in extraction rate and prone to industrial production.
Owner:贵州重力科技环保股份有限公司
Auxiliary-addition-free polyphenylene sulfide resin industrial synthetic process
The invention discloses auxiliary-addition-free polyphenylene sulfide resin industrial synthetic process. The formula of raw materials required in the auxiliary-addition-free polyphenylene sulfide resin industrial synthetic process is as follows: the mole ratio of sodium sulfide to sodium hydroxide to santochlor to N-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone is 0.93-1.15 to 1.00-1.28 to 1.98-2.98 to 1.18 to 1.48. The industrial synthetic process mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, in a sodium hydrosulfide dehydration treatment stage, a pipeline filter is adopted to filtrate a sodium hydrosulfide solution to treat mechanical impurities in the solution, then a sodium hydroxide solution with the concentration 84 mol percent is added in the formula for chemical treatment on the sodium hydrosulfide; secondly, in the condensation polymerization stage, anaerobic deionized water is added to further appropriately adjust the molecular weight and molecular weight distribution coefficient of synthesized polyphenylene sulfide resin; thirdly, deionized water is adopted for repeatedly scrubbing for 3 to 6 times, and finally, the target product of the auxiliary-addition-free polyphenylene sulfide resin industrial synthetic process provided by the invention is obtained. The resin in the obtained product of the auxiliary-addition-free polyphenylene sulfide resin industrial synthetic process is low in polydispersity index and high in oxygen index, and has an excellent electrical insulation property.
Owner:周洪
Method for preparing fatty hydroximic acid collecting agent and application
The invention discloses a method for preparing a fatty hydroximic acid collecting agent, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: stirring alkyl hydroximic acid having more than or equal to 5 to 9 carbon atoms, fatty acid having 5 to 22 carbon atoms and mixed solvent oil having 4 to 30 carbon atoms for reaction at room temperature and then separating an oil phase from a water phase, wherein the oil phase is the fatty hydroximic acid collecting agent. The collecting agent of the invention has good selectivity, high collectivity, proper foaming characteristic and easy dissolution in water. Rare earth metal concentrate is obtained by the following steps of: grinding crude rare earth metal oxide ore; adding sodium hydroxide, water glass, sodium fluorosilicate and sodium sulphide into the grinded ore; adding the fatty hydroximic acid collecting agent of the invention into the mixture; then adding modified starch into the mixture; and finally performing flotation. The collecting agent of the invention is a flotation collecting agent for the rare earth metal oxide which is suitable for industrial production and has simple process and high separation efficiency.
Owner:广东省资源综合利用研究所
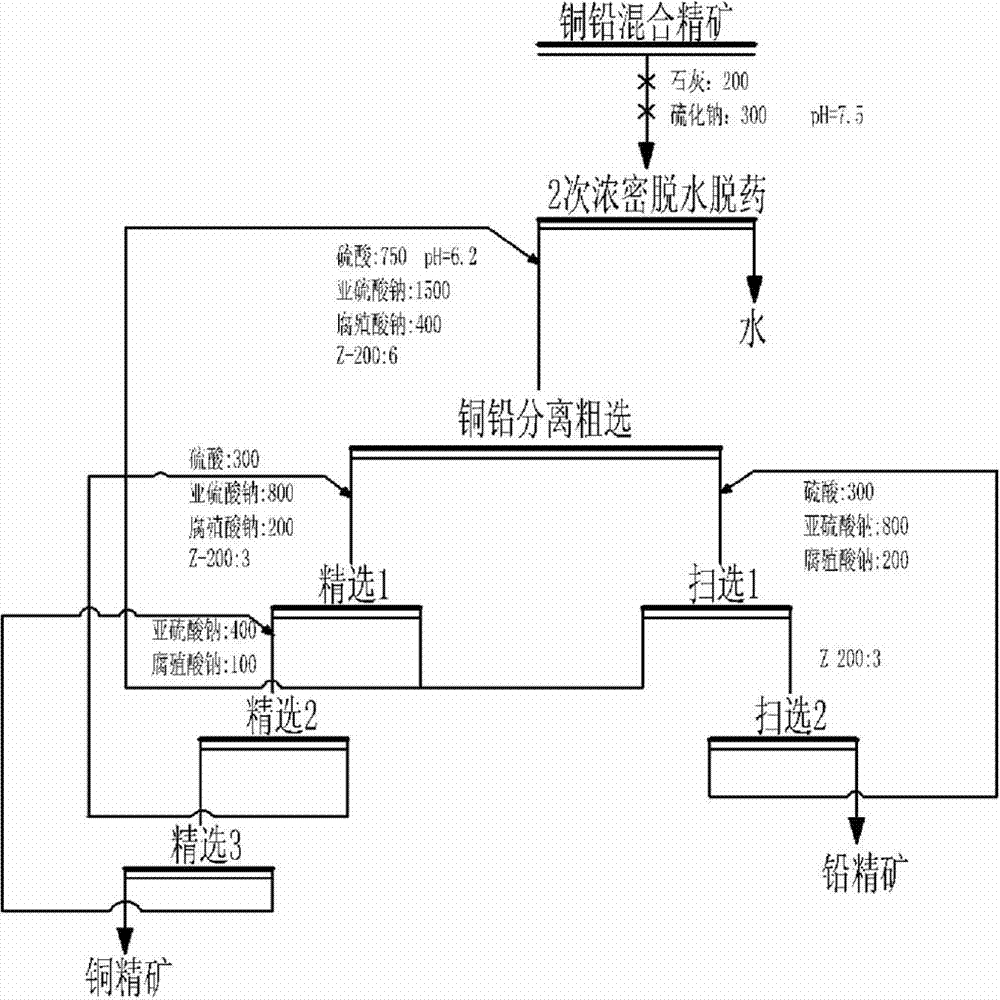
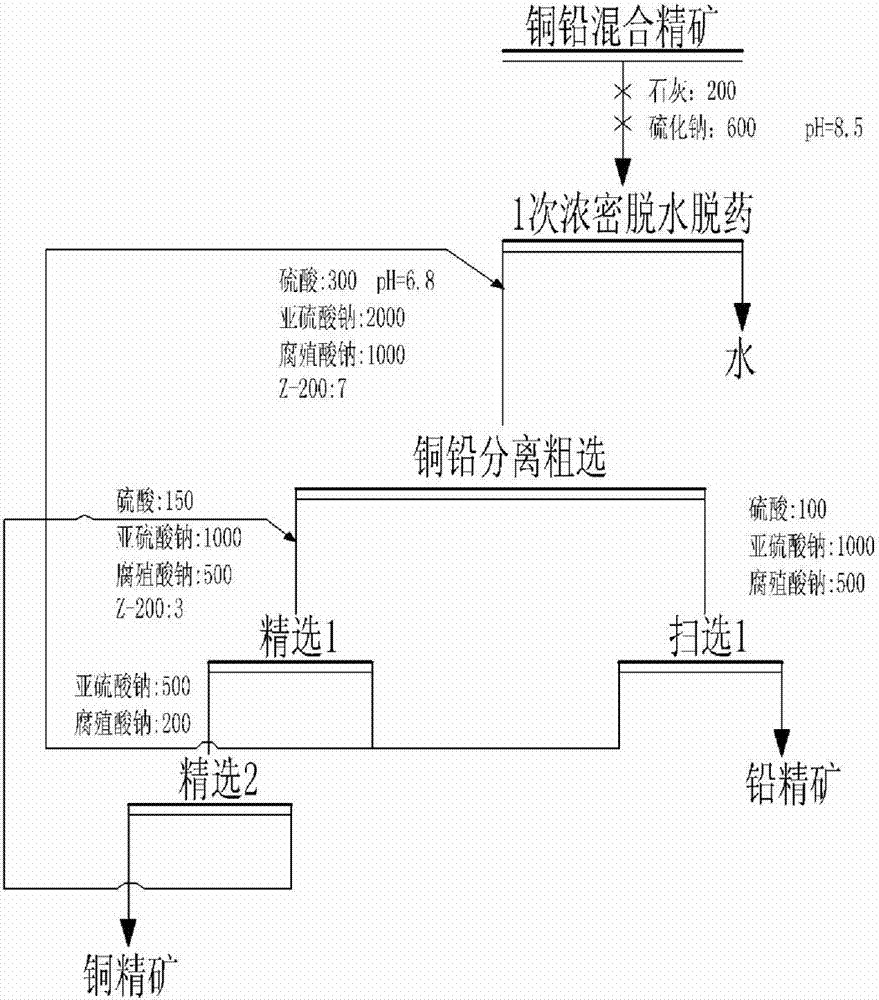
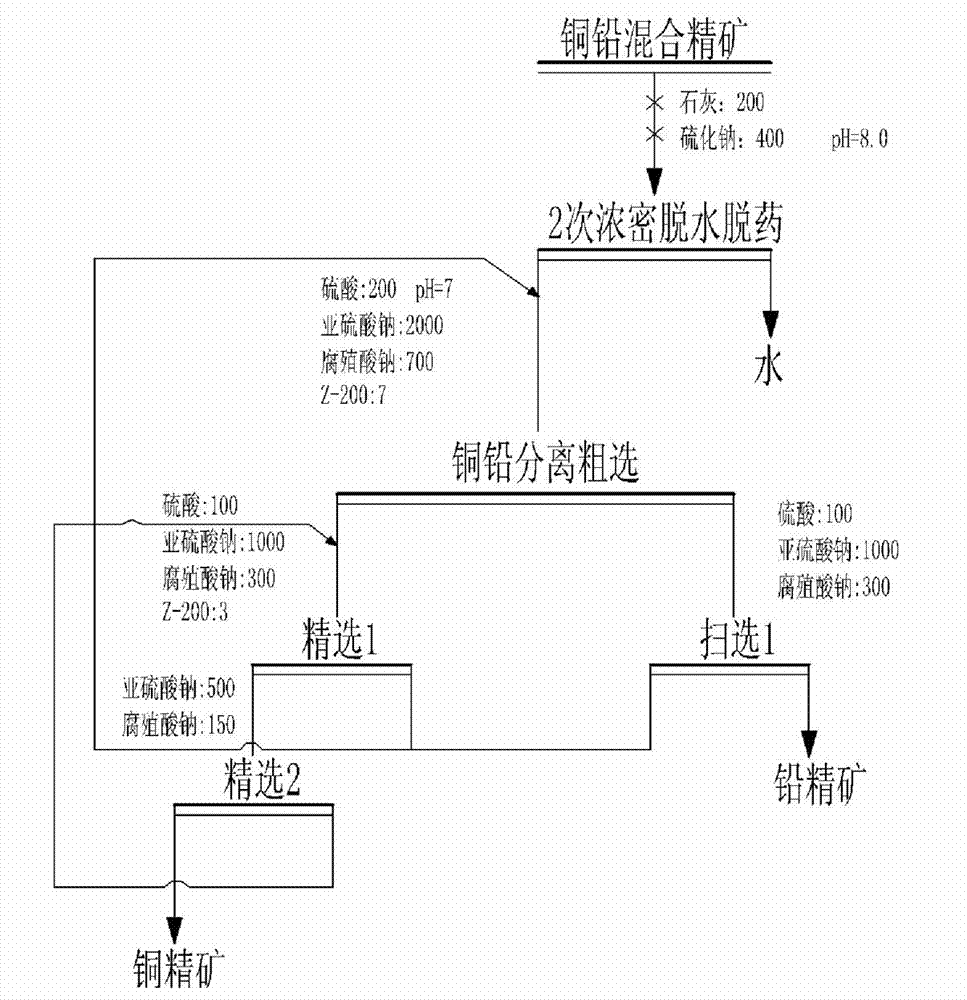
Flotation separation process for mixed copper and lead concentrate
The invention discloses a flotation separation process for mixed copper and lead concentrate. The flotation separation process comprises the following steps of adding lime and sodium sulphide to the mixed copper and lead concentrate after being separated from raw ore, and then, stirring for 2-4min until the lime and the sodium sulphide are stirred evenly; dehydrating and removing agents through a thickener, and then, adding a combined inhibitor and a collecting agent; performing rough concentration to obtain copper coarse ore and lead coarse ore; refining the copper coarse ore to obtain copper concentrate; scavenging the lead coarse ore to obtain lead concentrate, wherein the combined inhibitor is the combination of sulfuric acid, sodium sulfite and sodium humate. According to the flotation separation process disclosed by the invention, the grade and the recovery rate of the copper concentrate and the lead concentrate can be obviously increased, the copper and lead content is reduced, and the copper and lead separation effect is obvious; meanwhile, the mixed copper and lead concentrate has the characteristics of being stable in flow, high in adaptability, non-toxic and environmental friendly, can be used for replacing toxic agents, such as potassium dichromate, and is capable of overcoming the disadvantages that certain non-toxic agents are instable in flow, not obvious in effect, low in adaptability, and the like.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
Reagent formula used for zinc leaching residue floatation process and application method of reagent formula
The invention relates to a reagent formula used for a zinc leaching residue floatation process and an application method of the reagent formula. The reagent is a floatation reagent which is added into floatation processes such as sulfurizing, rough floatation, scavenging and concentration. The reagent formula is characterized in that 1) one or two of sodium sulphide and sodium hydrosulfide are added into a sulfurizing process as a sulfurizing reagent; 2) in the rough floatation process, N,N-sodium diethyldithiocarbamate, butyl ammonium black powder and 25# black powder are added as lead mineral collecting agents, Y89 and (or) pentyl xanthate are added as silver mineral collecting agent(s); 3) in a scavenging process, one or two of sodium sulphide and sodium hydrosulfide are added as the sulfutizing agent(s), N,N-sodium diethyldithiocarbamate, butyl ammonium black powder and 25# black powder are added as the lead mineral collecting agents, and the Y89 and (or) pentyl xanthate are added as the silver mineral collecting agent(s); and 4) carboxymethylcellulose is added as a gangue inhibiting agent in a concentration process. After applying the reagent formula disclosed by the invention, by adopting one-time rougher floatation, one-time scavenging and one-time concentration, lead yield can reach up to more than 95% and lead tail run can reach 0.1-0.2%.
Owner:XINGMIN TECH ZHUZHOU
Method for recycling lithium salt and solvent in preparation of polyphenylene sulfide
The invention discloses a method for recycling lithium salt and a solvent in preparation of polyphenylene sulfide. The method comprises the following operation processes: 1', washing a polyphenylene sulfide product by use of an N-methyl pyrrolidone solution of which the percentage by weight of water is not larger than 50% at the temperature of 150 to 250 DEG C in an inert gas environment, and combining the washing solution with a reaction medium solution; 2', transforming sodium sulfide into sodium chloride under the condition that the pH value of the combined solution is regulated to 6.5-7.0 in the inert gas environment; 3', adding water into the solution transformed in the step 2 so that the low-molecular polyphenylene sulfide is precipitated and then separated; and 4', respectively separating and recycling the sodium chloride, the N-methyl pyrrolidone and the lithium chloride from the separated solution under the inert gas environment. According to the method, the solvents need not to be evaporated out completely, so the energy consumption is reduced greatly; the method can be performed in various intermittent or continuous ways and convenient and easy to implement, degradation caused because the solvent is at high temperature for a long time is avoided, so the recycle rate of the solvent is high, and the recycling quality is good; a separated and recycled polyphenylene sulfide oligomer is utilizable, the purity of the recycled lithium chloride is not lower than 98%, and the quality of the recycled sodium chloride is excellent.
Owner:SHANDONG MINGHUA NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
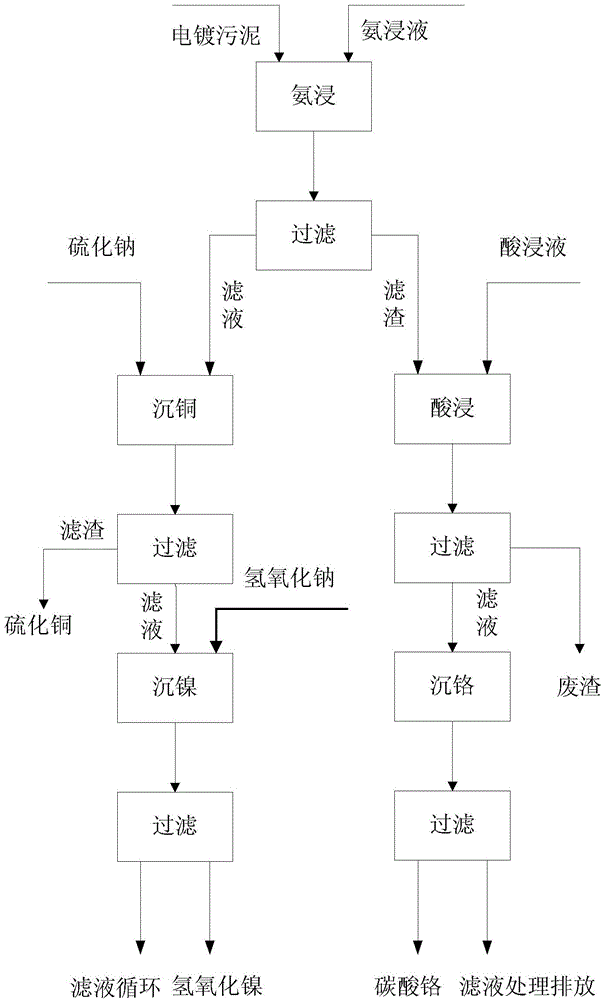
Method for comprehensive recovery of valuable metals in electroplating sludge
The invention discloses a method for comprehensive recovery of valuable metals in electroplating sludge. According to the method, an ammonia leaching-acid leaching combined technology is adopted for recovery of copper, nickel and chromium in the electroplating sludge. The method comprises the following steps: first, leaching copper and nickel in the electroplating sludge with an ammonia leaching solution, recovering cooper with sodium sulfide through precipitation, and recovering nickel with sodium hydroxide through precipitation; then, leaching chromium in the electroplating sludge with sulfuric acid, and recovering chromium with sodium carbonate through precipitation, wherein waste residues remaining after the treatment reach the general solid waste standard. The method has the benefits that the valuable metals in the electroplating sludge can be efficiently recovered, the cost is low, and secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:HENGYANG NORMAL UNIV
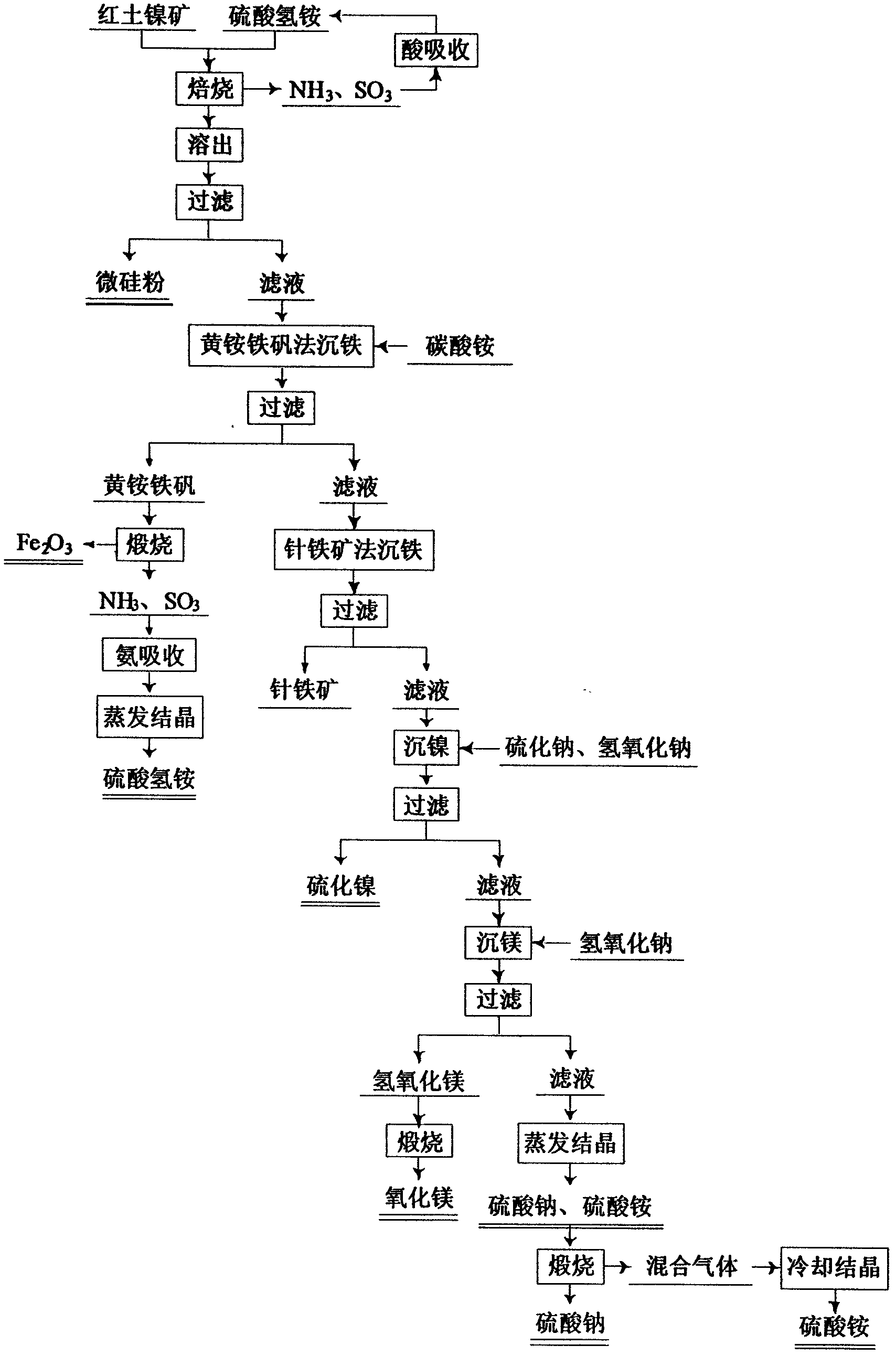
Method for comprehensive utilization of laterite nickel ore
A method for comprehensive utilization of laterite nickel ore comprises the following steps: (1) pulverizing laterite nickel ore, grinding, mixing with ammonium bisulfate, and roasting; (2) dissolving and filtering the roasted clinker to obtain a filtrate, depositing iron by an ihleite method, and depositing iron by a goethite method; (3) performing nickel deposition of the filtrate obtained after iron deposition by sodium sulfide, preparing a nickel sulfide product; (4) performing magnesium deposition of the filtrate obtained after nickel deposition by sodium hydroxide to obtain magnesium hydroxide; (5) washing, drying and calcining magnesium hydroxide to prepare a magnesium oxide product; (6) using the roasted clinker dissolved slag as a microsilica fume product directly, wherein the main component of the slag is silica; (7) calcining ammonium jarosite to obtain an iron oxide product.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Cascade recovery method for arsenic-containing antimony-containing gold ore difficult to process
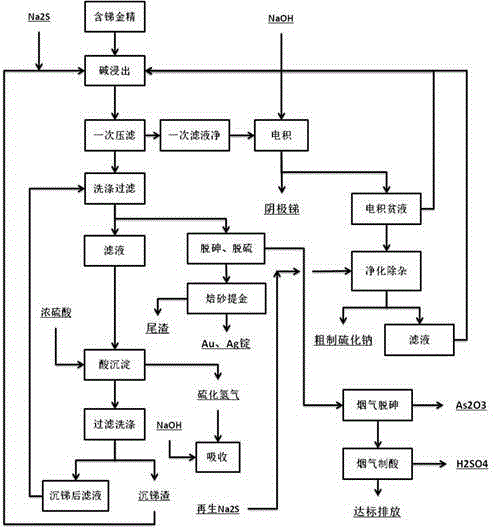
ActiveCN105063354AAddressing the Impact of Recycling RatesHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodMaterials science
The invention provides a cascade recovery method for arsenic-containing antimony-containing gold ore difficult to process, and relates to a method for separating and extracting antimony, arsenic and gold of the gold ore difficult to process. The method is characterized in that the recovery process includes the steps that (1) sodium sulphide is added under the alkaline condition, and antimony leaching is carried out; (2) electrodeposition is conducted on leaching liquid to obtain cathode antimony liquid; (3) leaching residues are washed, and concentrated sulfuric acid is added into the washed liquid for antimony deposition; (4) the leaching residues are roasted for arsenic removal and desulfuration, so that pozzuolite enters smoke, the smoke is chilled and crystallized to recover arsenic trioxide, and acid making with smoke is achieved after arsenic recovery; and (5) gold and silver in the roasted residues are separated after antimony, arsenic and sulphur are extracted. The method is special for the arsenic-containing antimony-containing gold ore difficult to process, the influences of arsenic and antimony on the recovery rate of noble metal are effectively eliminated, the problem that arsenic and antimony are difficult to separate is solved through selective leaching, valuable elements such as antimony, arsenic and sulphur are comprehensively recycled, and the recovery rate of gold and silver is also increased. According to the technology, raw material adaptability is high, the technology process is short, and energy consumption is low.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Electrocatalyst for catalyzing water decomposition to produce hydrogen, and preparation method and application thereof
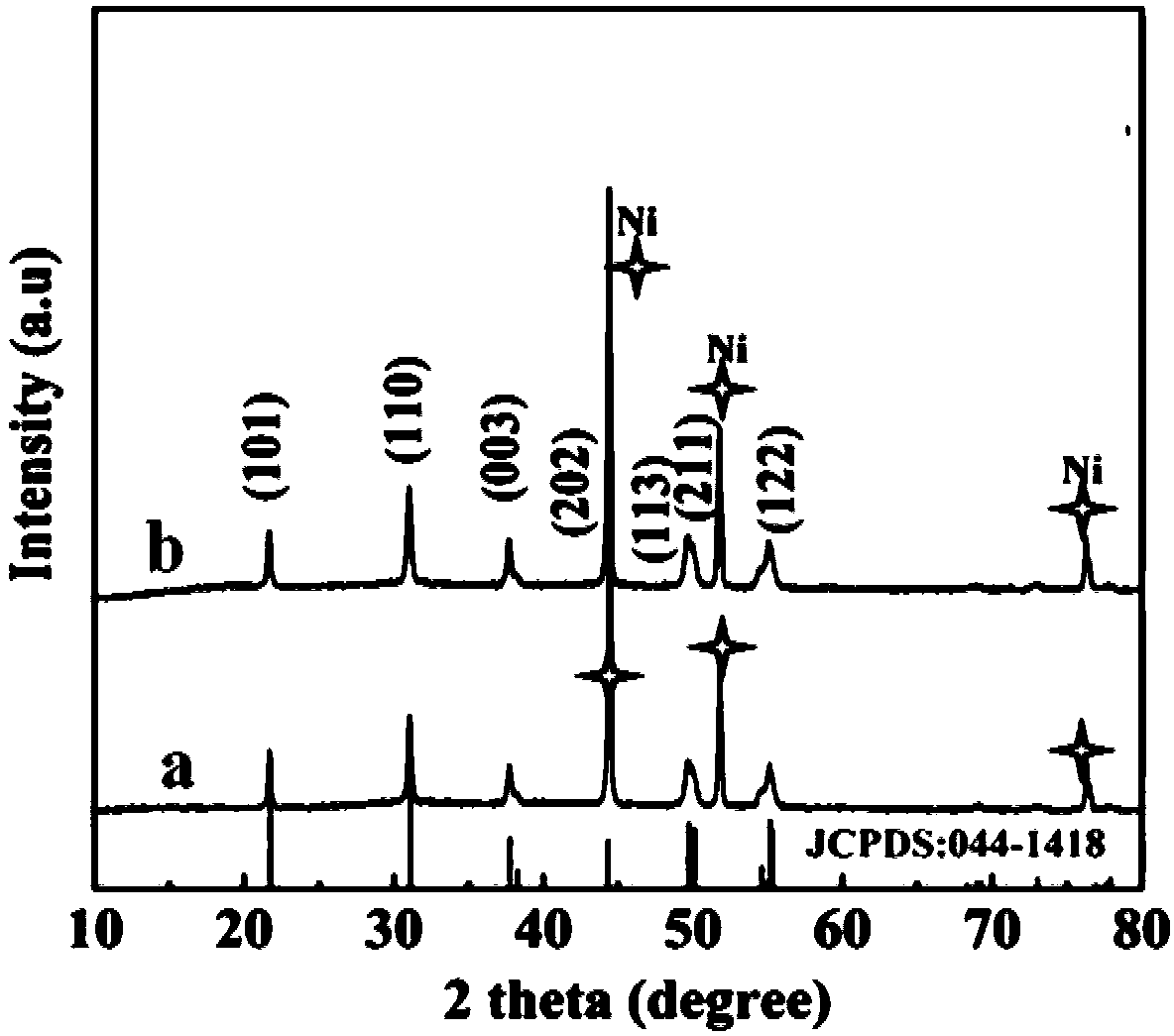
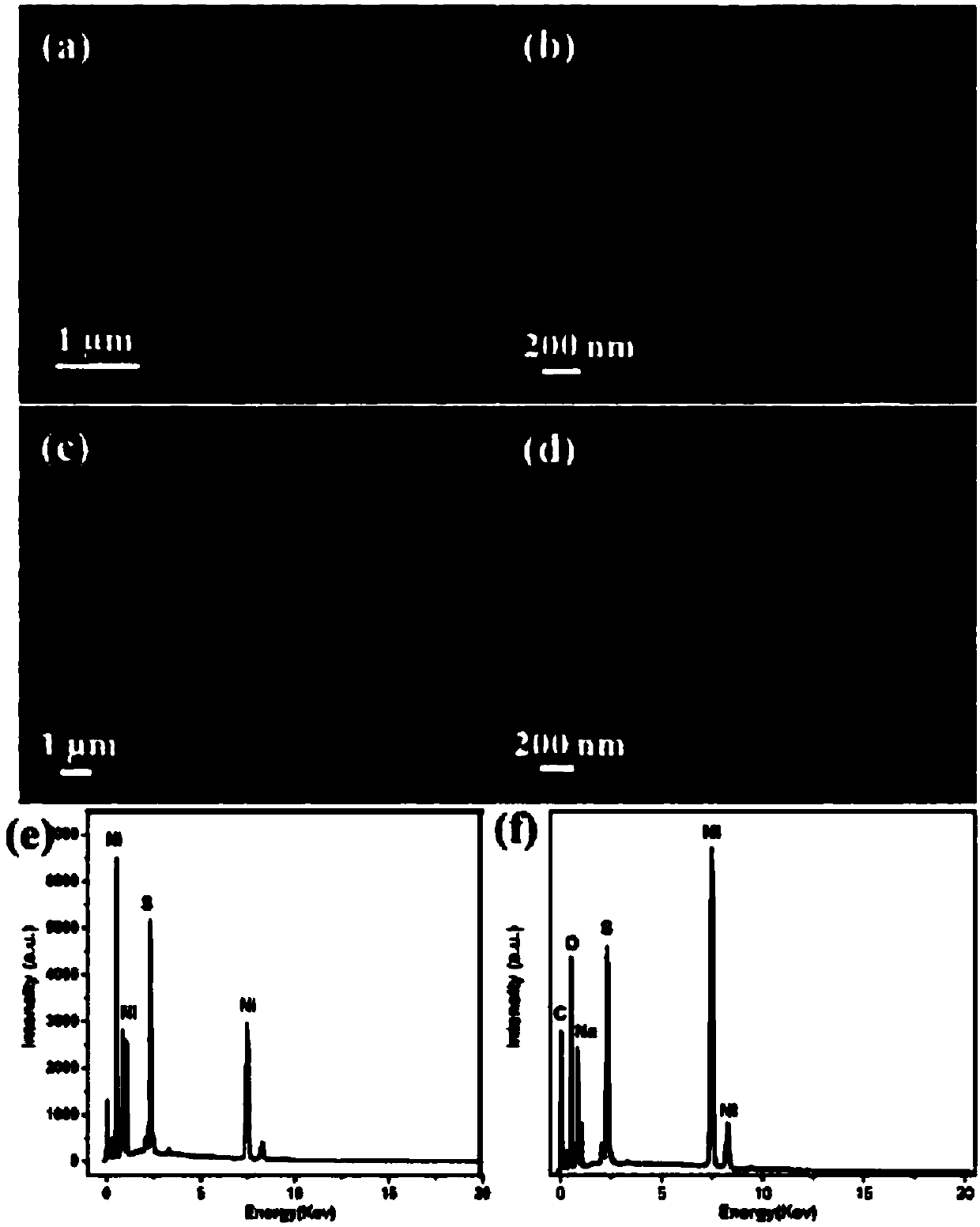
InactiveCN108097270ASimple preparation processHigh activityCatalyst activation/preparationElectrodesDecompositionSodium sulphide
The invention relates to the technical field of electrocatalytic water decomposition hydrogen production, in particular to an electrocatalyst Ni3S2@NiOOH@NF for catalyzing water decomposition to produce hydrogen, and a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst adopts nickel foam (NF) as a substrate and a nickel source, adopts a sodium sulphide water solution as a sulfurizing reagent, and is obtained through a hydrothermal method and an electrodeposition method. The Ni3S2@NiOOH composite catalyst is of a multi-channel core-shell structure, so that a material and an electrolyte are fully contacted favorably. The Ni3S2@NiOOH adopts the nickel foam as the nickel source to grow, and is firmly combined with the substrate, so that rapid transmission of charge is facilitated. The catalyst prepared by the method provided by the invention shows favorable electrocatalytic activity in alkaline electrolyte and under lower overpotential; in addition, after the catalyst is tested for 4to 5 hours under different current densities, the stability is not remarkably reduced, so that the catalyst can be effectively applied to the field of electrocatalytic water decomposition hydrogen production.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Method for treatment of wastewater containing heavy metal molybdenum
ActiveCN101928083AReduce processing costsReduce contentWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentSulfidationWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to a method for treatment of wastewater containing heavy metal molybdenum. The specific steps are as follows: placing the wastewater which needs to be treated and contains the heavy metal molybdenum into a sealing device; adding sodium sulfide into the device, controlling the pH value of the wastewater after adding the sodium sulfide at 2-3, carrying out reaction for 1-3h at room temperature, and continuously adding the generated sodium sulfide into the molybdenum-containing wastewater for recycling; adding a flocculant into the obtained solution, stirring, carrying out the reaction, standing till precipitate is settled, then discharging supernatant fluid, and passing through a filter device, wherein the precipitate of molybdenum sulfide can be recycled after collection treatment; and adding a mixed coagulant till the pH value of the obtained acid solution is neutral, stirring for removing redundant sulfide ions, standing for 2-5 min till the precipitate is settled, and then discharging the supernatant fluid for ensuring water quality of outlet water. The method for the treatment of the wastewater containing the heavy metal molybdenum has the prominent advantages of good treatment effect, simple treatment equipment, low treatment cost, recycling and utilization of the metal molybdenum and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Repair method of chromium-contaminated soil
ActiveCN104070060AHigh removal rateImprove sedimentation efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationSodium sulphideWater treatment
The invention discloses a repair method of chromium-contaminated soil, which belongs to the technical field of environment engineering. The method comprises the following steps: reducing hexavalent chromium in the chromium-contaminated soil, removing trivalent chromium and performing sewage treatment. Ferrous sulfate is added into the chromium-contaminated soil, and the reaction environment is adjusted, so that the efficiency for reducing the hexavalent chromium in the chromium-contaminated soil into the trivalent chromium is improved, and conditions are provided for removing chromium; chromium in the soil is extracted by adopting disodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate, the removal rate of the chromium in the soil is increased by adopting microwave heating, and the reaction time is shortened; sodium sulphide is added into chromium sewage, and the reaction environment is adjusted, so that the settling efficiency of heavy metals in the sewage is improved; and additionally, the sewage is converted into disodium ethylenediamine tetraacetate solution, so that resource recovery and utilization are realized. According to the method, the hexavalent chromium is converted into the trivalent chromium to be treated, so that the environmental risk in the repair process is reduced; the chromium-contaminated soil is converted into chromium sewage for treatment, so that the treatment efficiency is improved, and the treatment effect is guaranteed; and the method has the characteristics of no secondary pollution, high efficiency, rapidity, high resource utilization rate and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGYI ECOLOGICAL SOIL INST +1
Method for ash-free and no-sulfurizing alkaline liming treatment for making pigskin leather
InactiveCN1900321AImprove leather yieldGood power savingPre-tanning chemical treatmentChemistrySodium sulphide
The no-ash and no-sodium sulfide liming process for making pigskin leather features its greatly reduced pollution, and no use of pollutant sodium sulfide, sodium hydrosulfide and lime makes it easy to treat exhausted waste water. Compared with conventional technological process, the present invention has the advantages of no deposit, reduced waste water exhaust, short production period, saving in material and lowered comprehensive cost.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Municipal solid waste incineration fly ash resource utilization method
ActiveCN103128005ARealize resource utilizationMeet harmless requirementsFlotationBrickResource utilization
The invention provides a municipal solid waste incineration fly ash resource utilization method and relates to municipal solid waste treatment. The method includes a first step of mixing fly ash and water in a floatation tank, adding in sodium sulphide and stirring the mixture so as to enable salt in the fly ash to be dissolved into the water, and enabling heavy metal such as plumbum (Pb) and zinc (Zn) in an oxidation state in the fly ash to achieve vulcanizing to generate plumbum sulfide (PbS) and zinc sulfide (ZnS), a second step of adding collecting agents into the floatation tank again and stirring so as to enable the collecting agents to fully contact with the fly ash and enable the collecting agents to be adsorbed on the surfaces of vulcanized heavy metal, a third step of adding foaming agents and terpenic oil in the floatation tank, carrying out flotation separation and centrifugal dewatering, adding cement, sand, water, exciting agents, namely sodium delicate, and alum into the obtained fly ash and stirring, filling stirred samples into a trial mould, compacting the stirred samples, placing and maintaining the stirred samples and then demoulding to obtain cement blocks, and a fourth step of carrying out centrifugal dewatering on floating objects in the floatation tank, sending the floating objects into a household garbage incineration plant, and carrying out high-temperature processing on dioxin, wherein the dioxin can be completely resolved under an environment with the temperature larger than 850 DEG C and smoke stay time more than 2 hours (s), and smoke reaches the standard and is exhausted.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
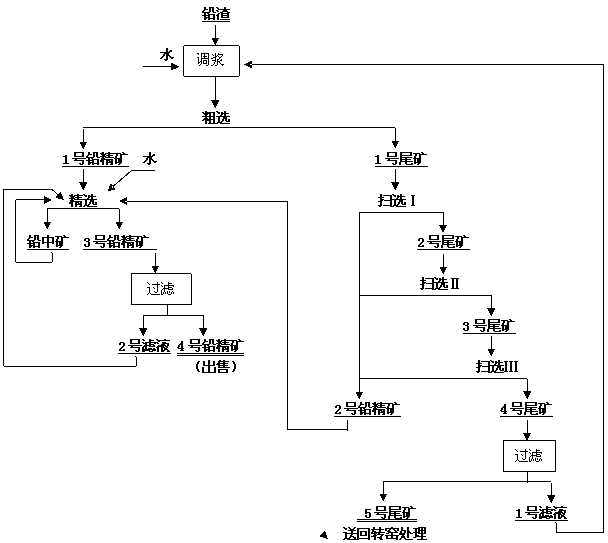
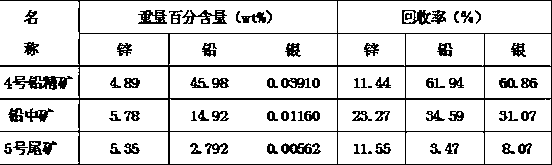
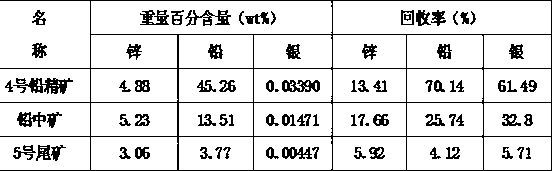
Method for comprehensively recovering lead and silver from lead slag
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively recovering lead and silver from lead slag. The lead slag produced in an electric zinc factory serves as the raw material and mainly contains 10-18wt% of lead, 7-10wt% of zinc and 0.01-0.02wt% of silver. The flotation process of one roughing, three times of scavenging and one cleaning is adopted, lead in the lead slag is selected in flotation mode, silver enters lead concentrate, tailings enter a rotary kiln for volatilizing, and further the remained valuable metals in the lead slag are recovered. During flotation, sodium carbonate serves as regulators, sodium sulfide serves as vulcanizers, zinc sulfate serves as inhibitors, and butyl amine aerofloat, butyl xanthate and diethyldithiocarbamate serve as collecting agents. Lead recovery rate can reach 95-97%, and silver recovery rate can reach 90-95%.
Owner:YUNNAN LUOPING ZINC & ELECTRICITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com