Patents
Literature
82 results about "Sulfide ions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sulfide ions are extremely basic. One well-known ionic compound with a sulfide ion is H_2S. The infamous rotten-egg smell often associated with sulfur originates from this compound. Sulfide compounds are fairly soluble. Many compounds such as PbS, CuS, and HgS are insoluble in acidic and basic solutions.
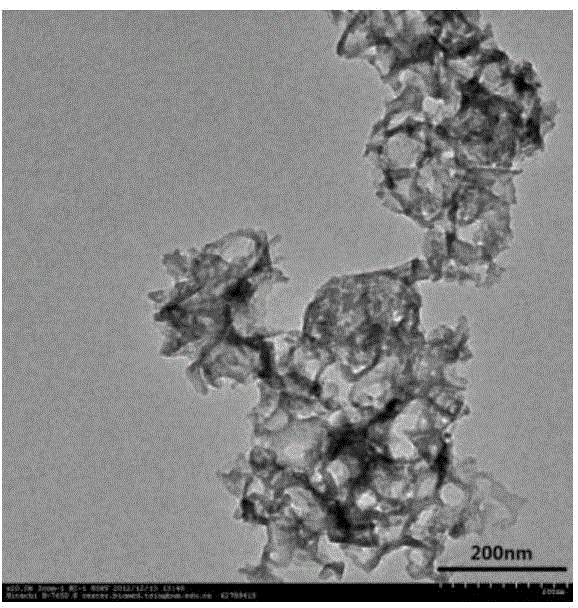
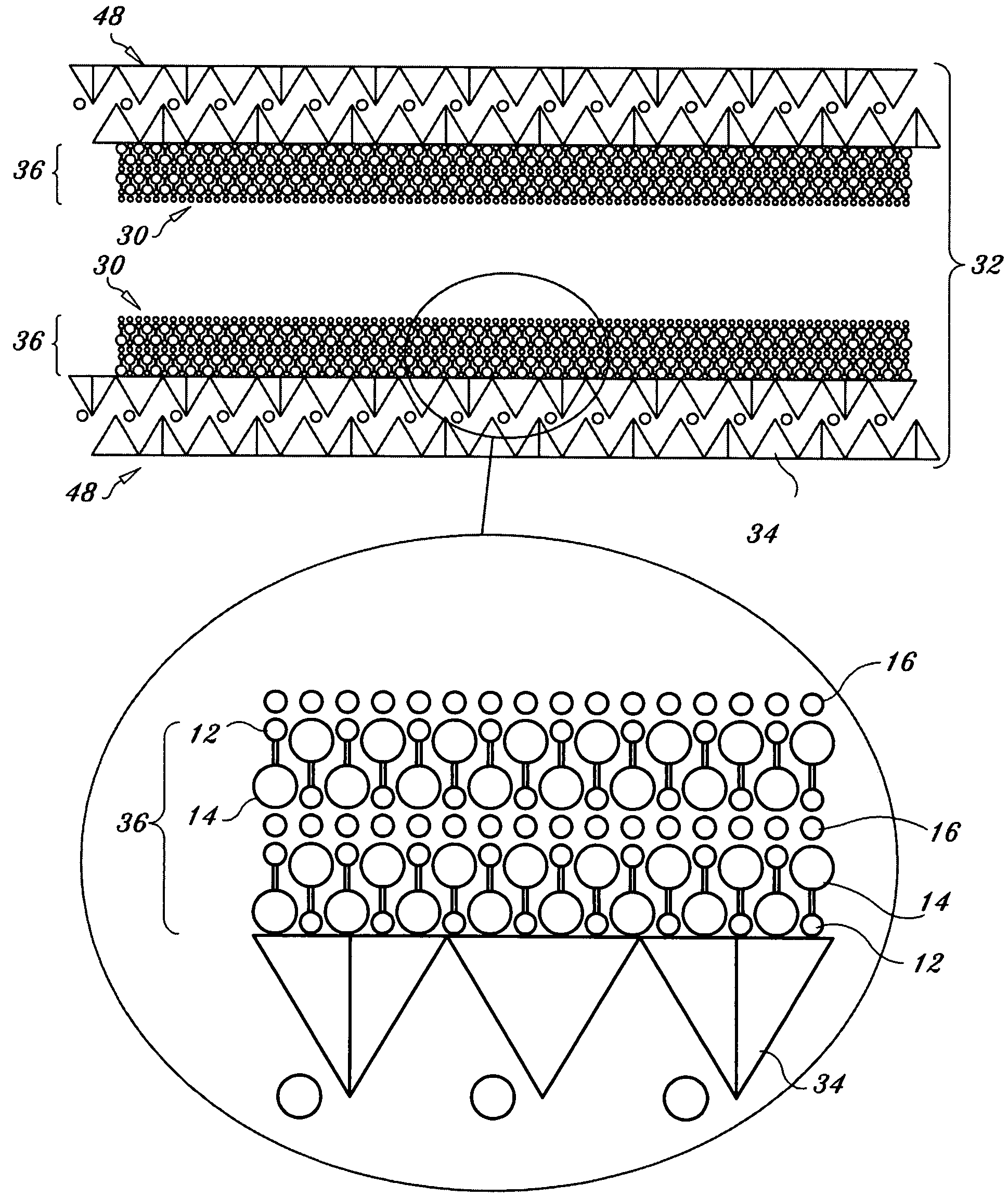
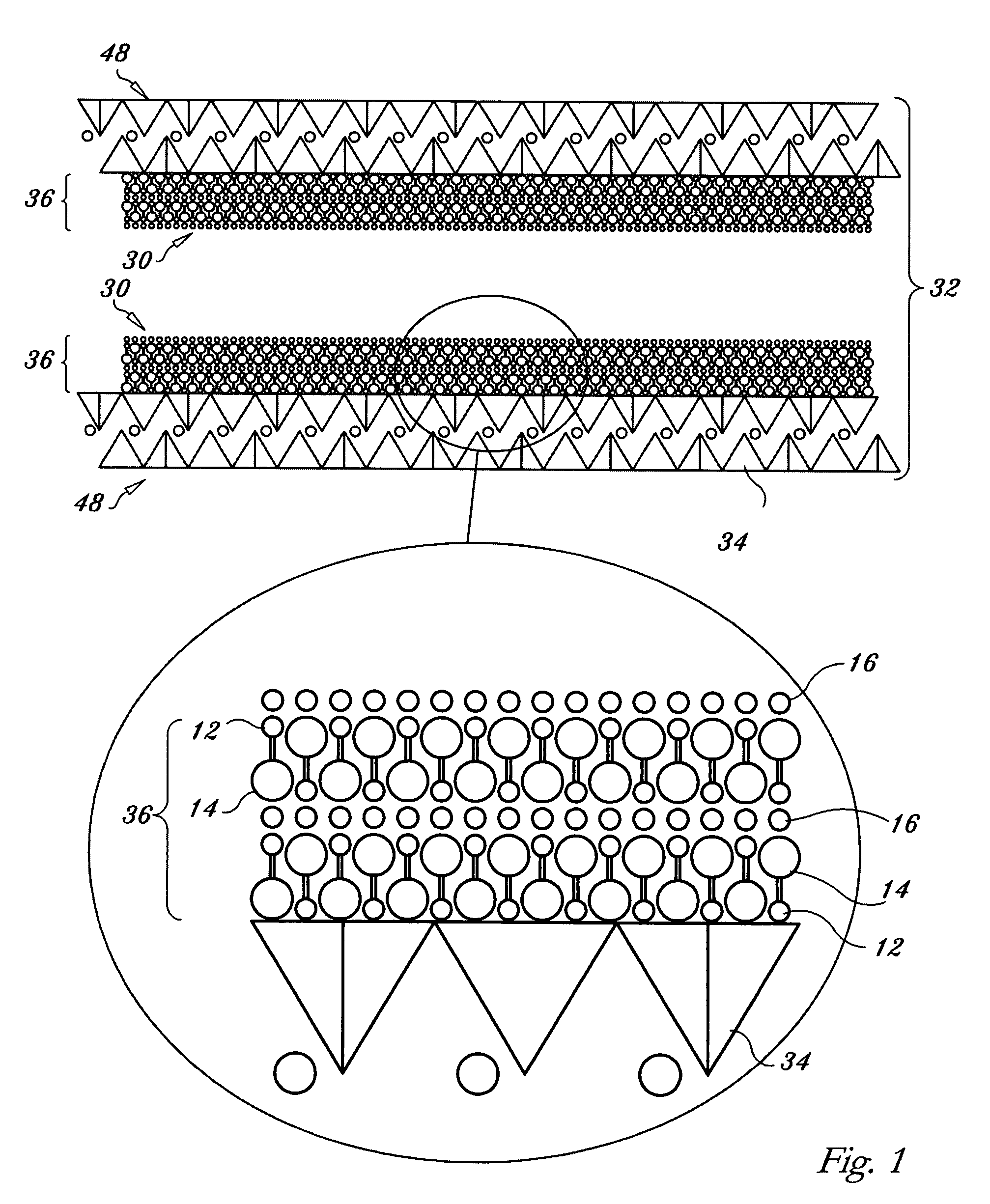
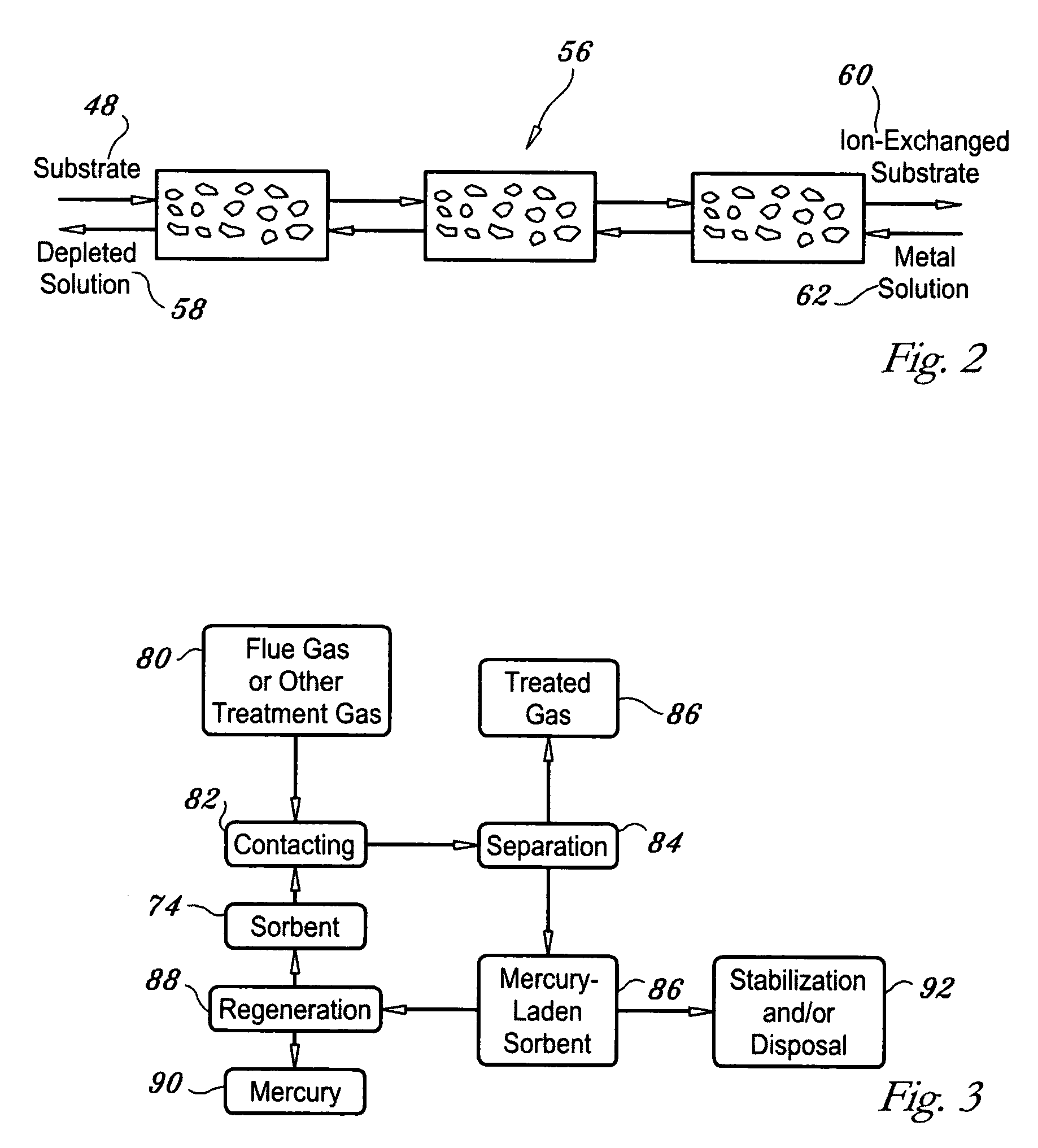
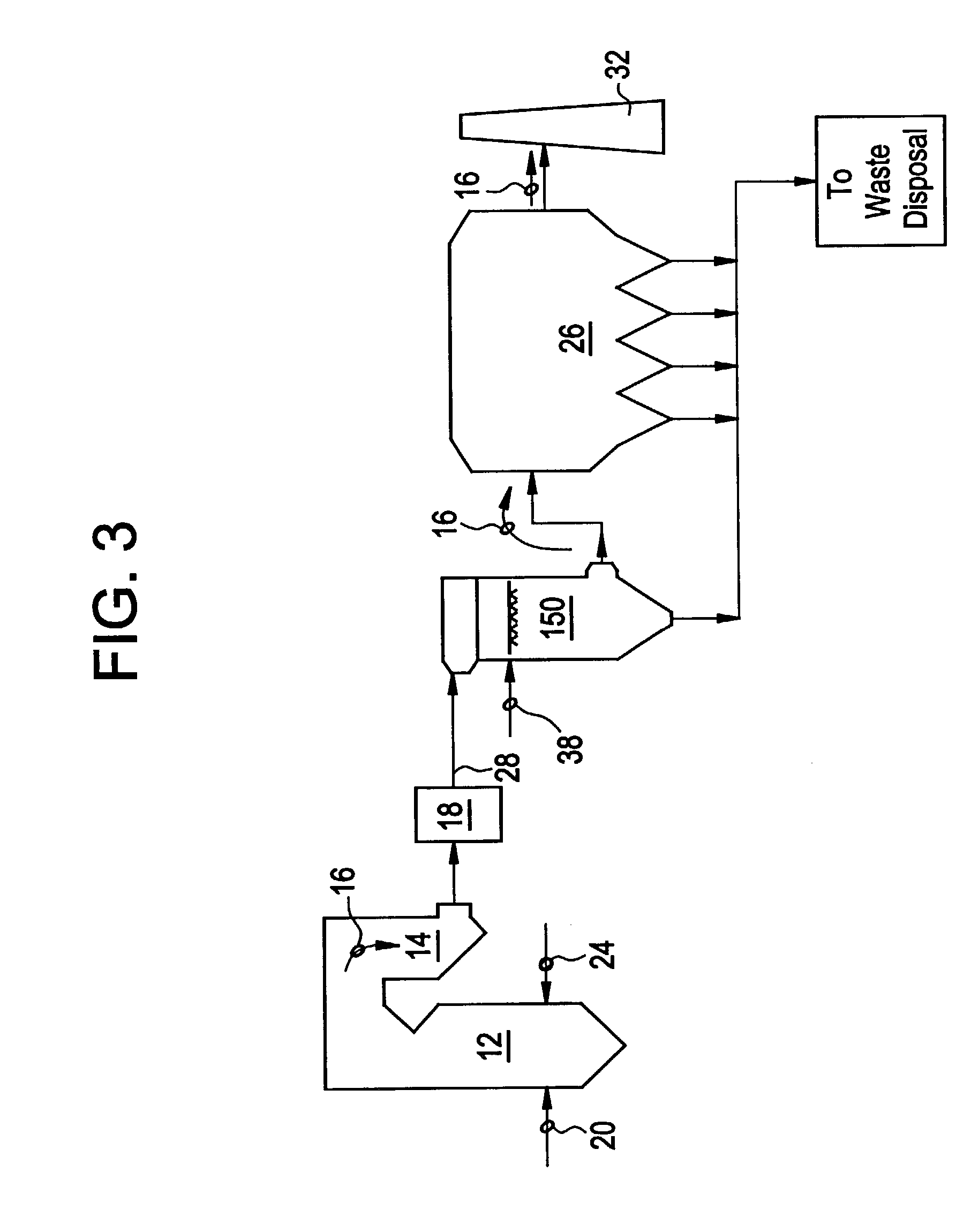
Regenerable high capacity sorbent for removal of mercury from flue gas
InactiveUS7288499B1Low costLower performance requirementsInorganic chemistryGas treatmentSorbentManganese
A regenerable, high-capacity sorbent for removal of mercury from flue gas and processes and systems for making and using the sorbent. A phyllosilicate substrate, for example vermiculite or montmorillinite, acts as an inexpensive support to a thin layer for a polyvalent metal sulfide, ensuring that more of the metal sulfide is engaged in the sorption process. The sorbent is prepared by ion exchange between the silicate substrate material and a solution containing one or more of a group of polyvalent metals including tin (both Sn(II) and Sn(IV)), iron (both Fe(II) and Fe(III)), titanium, manganese, zirconium and molybdenum, dissolved as salts, to produce an exchanged substrate. Controlled reaction of a sulfide ion source with the one or more polyvalent metals that are exchanged on the silicate substrate produces the sorbent. The sorbent is used to absorb elemental mercury or oxidized mercury species such as mercuric chloride from flue gas containing acid gases (e.g., SO2, NO and NO2, and HCl) and other gases over a wide range of temperatures.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL ENERGY SERVICES
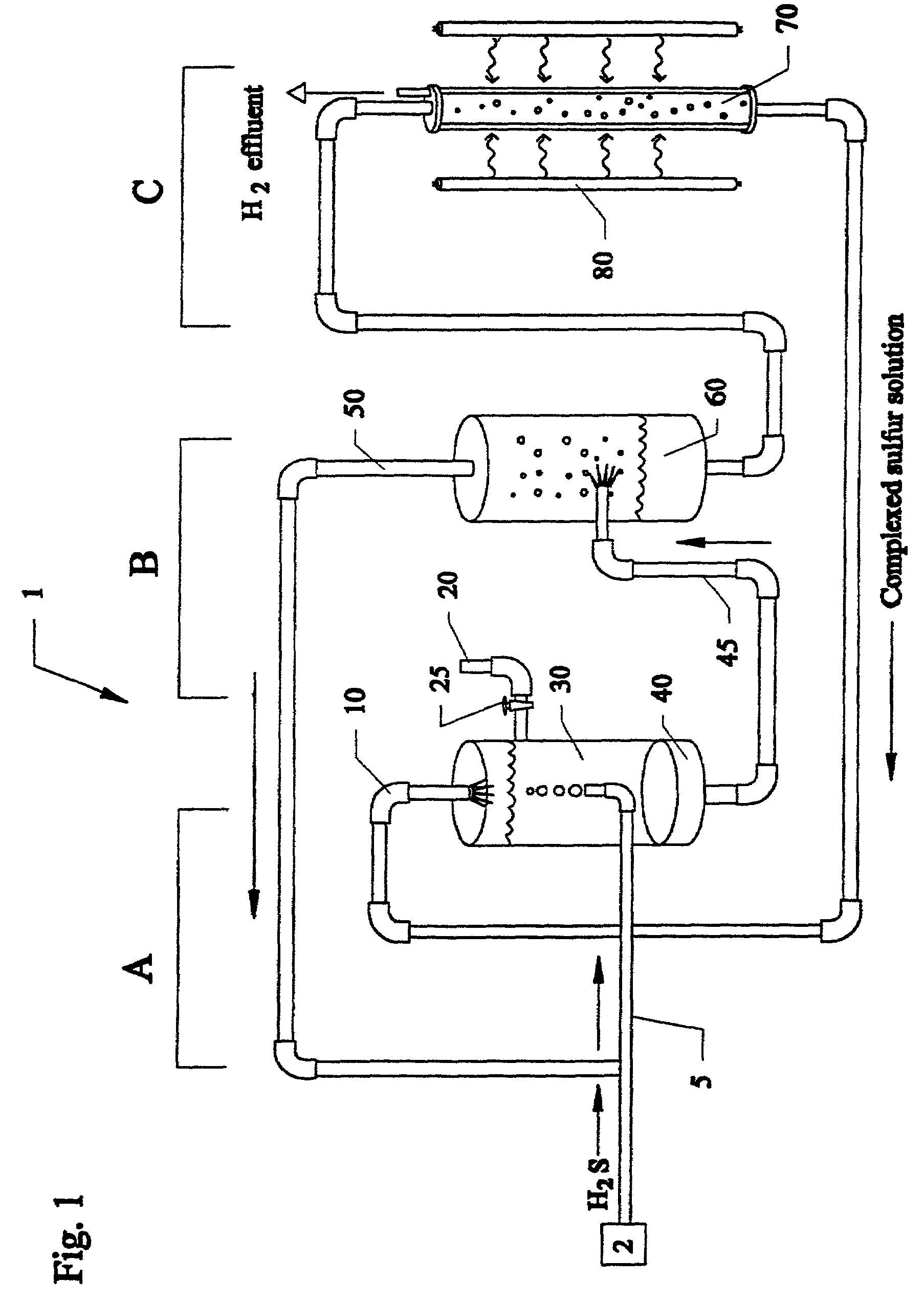
UV photochemical option for closed cycle decomposition of hydrogen sulfide
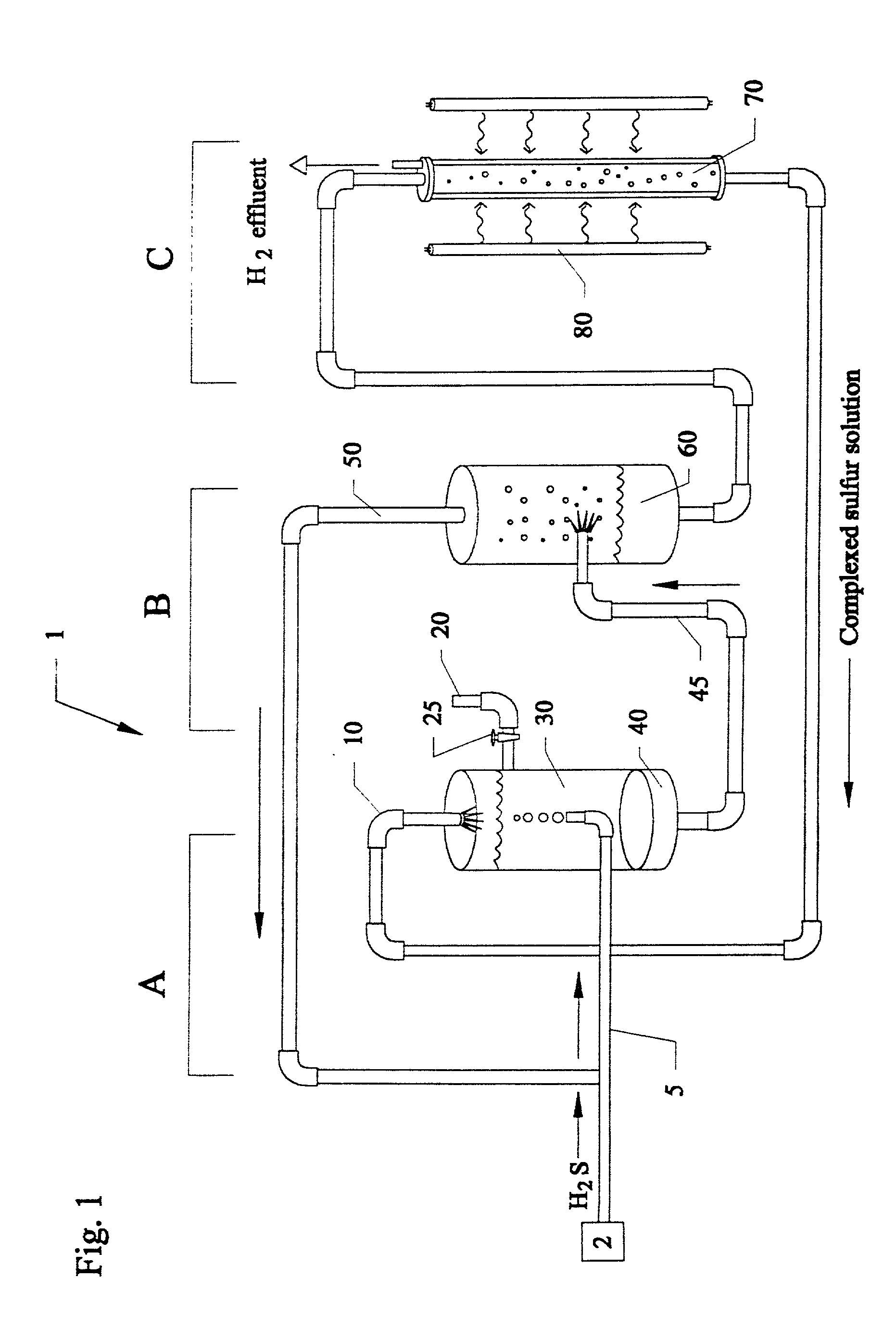
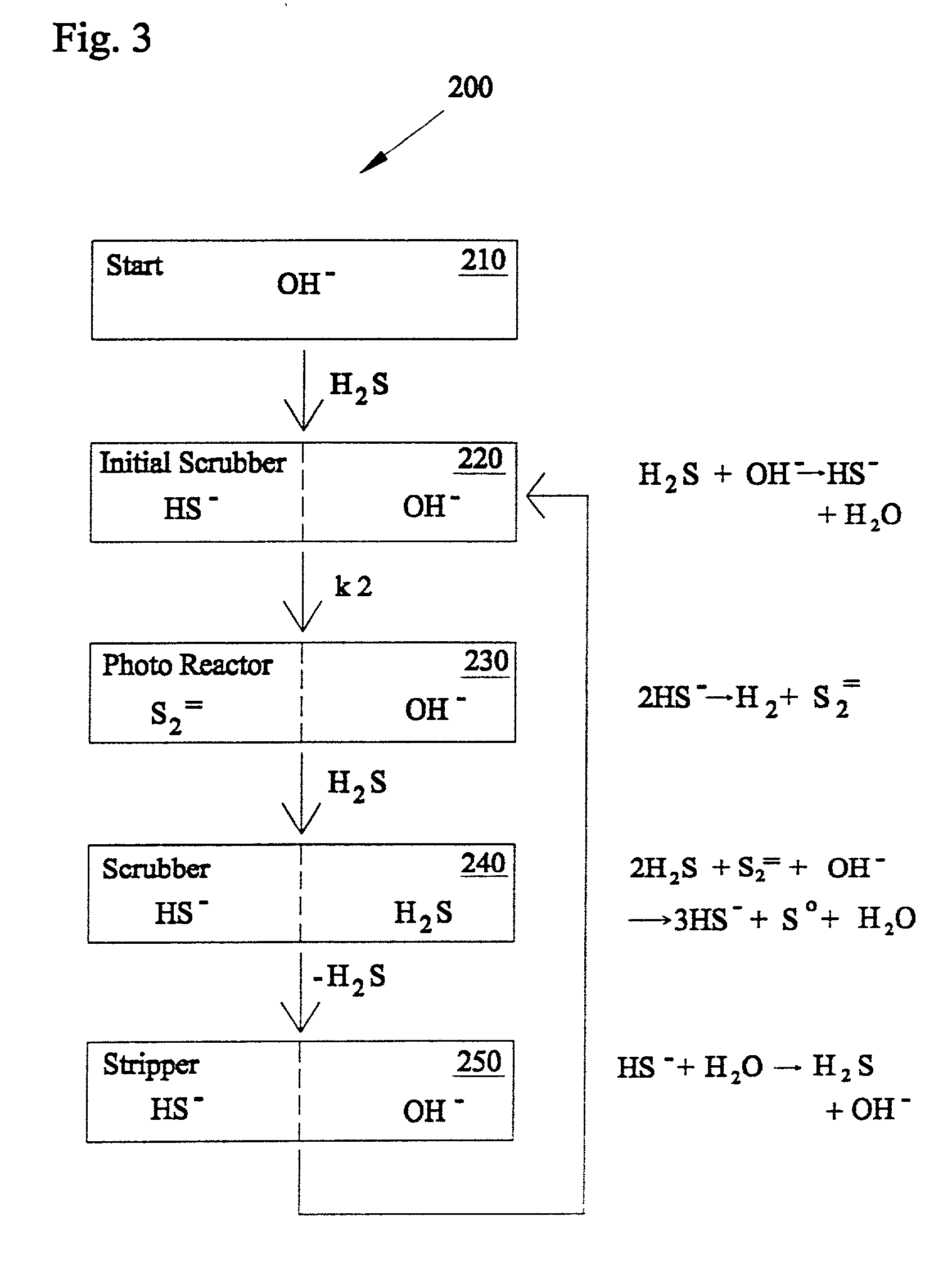
Methods and systems for separating hydrogen and sulfur from hydrogen sulfide(H2S) gas. Hydrogen sulfide(H2S) gas is passed into a scrubber and filtration unit with polysulfide solution. Interaction frees elemental sulfur which is filtered, excess continues to a stripper unit where the excess H2S is removed. The excess H2S returns to the scrubber and filtration unit, while the sulfide solution passes into a photoreactor containing a photocatalyst and a light source. The sulfide solution is oxidatively converted to elemental sulfur and complexed with excess sulfide ion to make polysulfide ion, while water is reduced to hydrogen. Hydrogen is released, while the polysulfide solution is fed back to the scrubber unit where the system operation repeats. In a second embodiment, the photocatalyst is eliminated, and the hydrogen sulfide solution is directly illuminated with ultraviolet radiation with a light source such as a low pressure mercury lamp operating at approximately 254 nm.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC +1
Synthesis of noble metal, sulphide catalysts in a sulfide ion-free aqueous environment
A noble metal sulfide catalyst obtained by reaction of a precursor of at least one noble metal with a thionic species in an aqueous environment essentially free of sulfide ions useful as an electrocatalyst in the depolarized electrolysis of hydrochloric acid.
Owner:ELECTRIC TECHNOLOCY
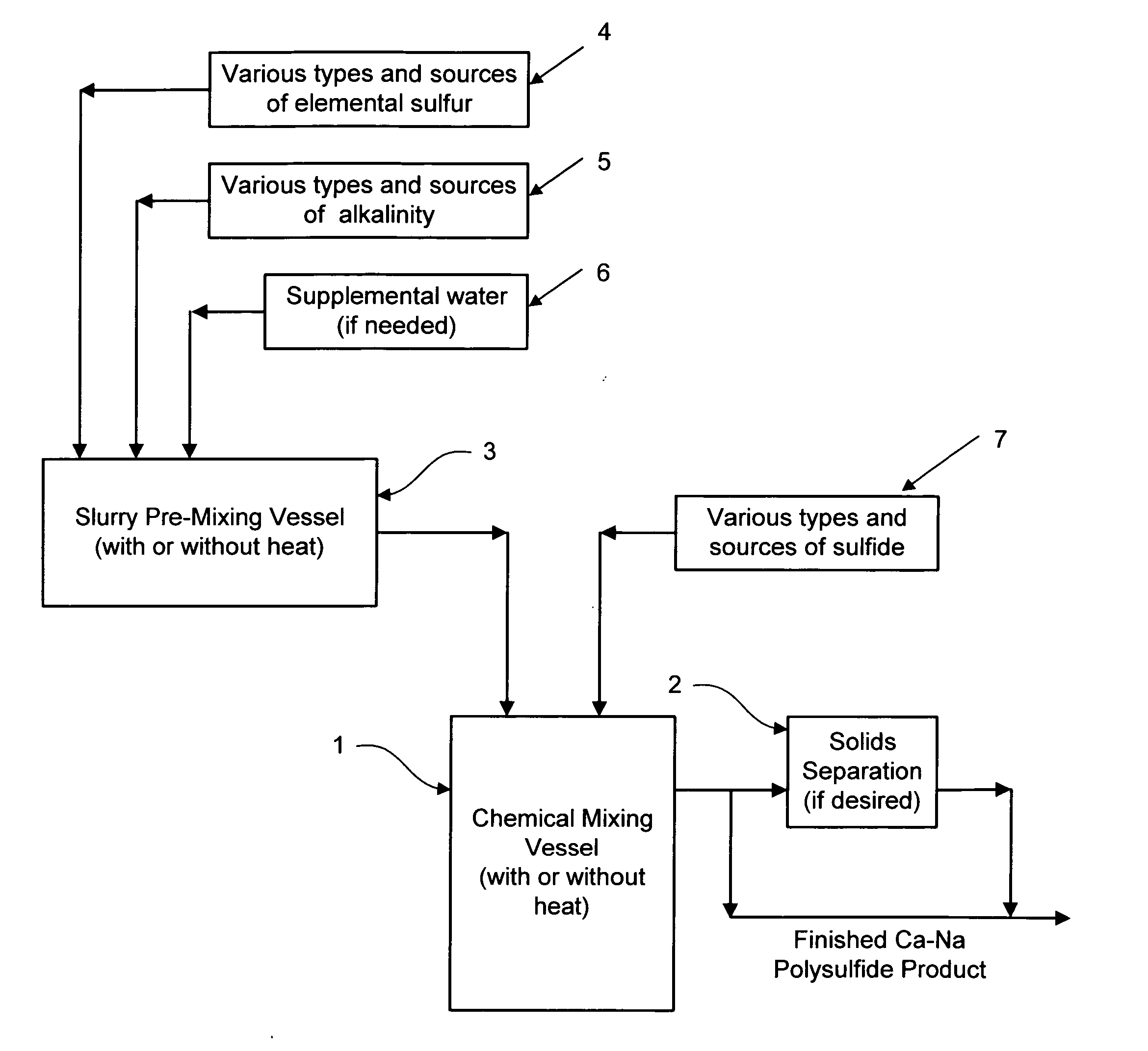
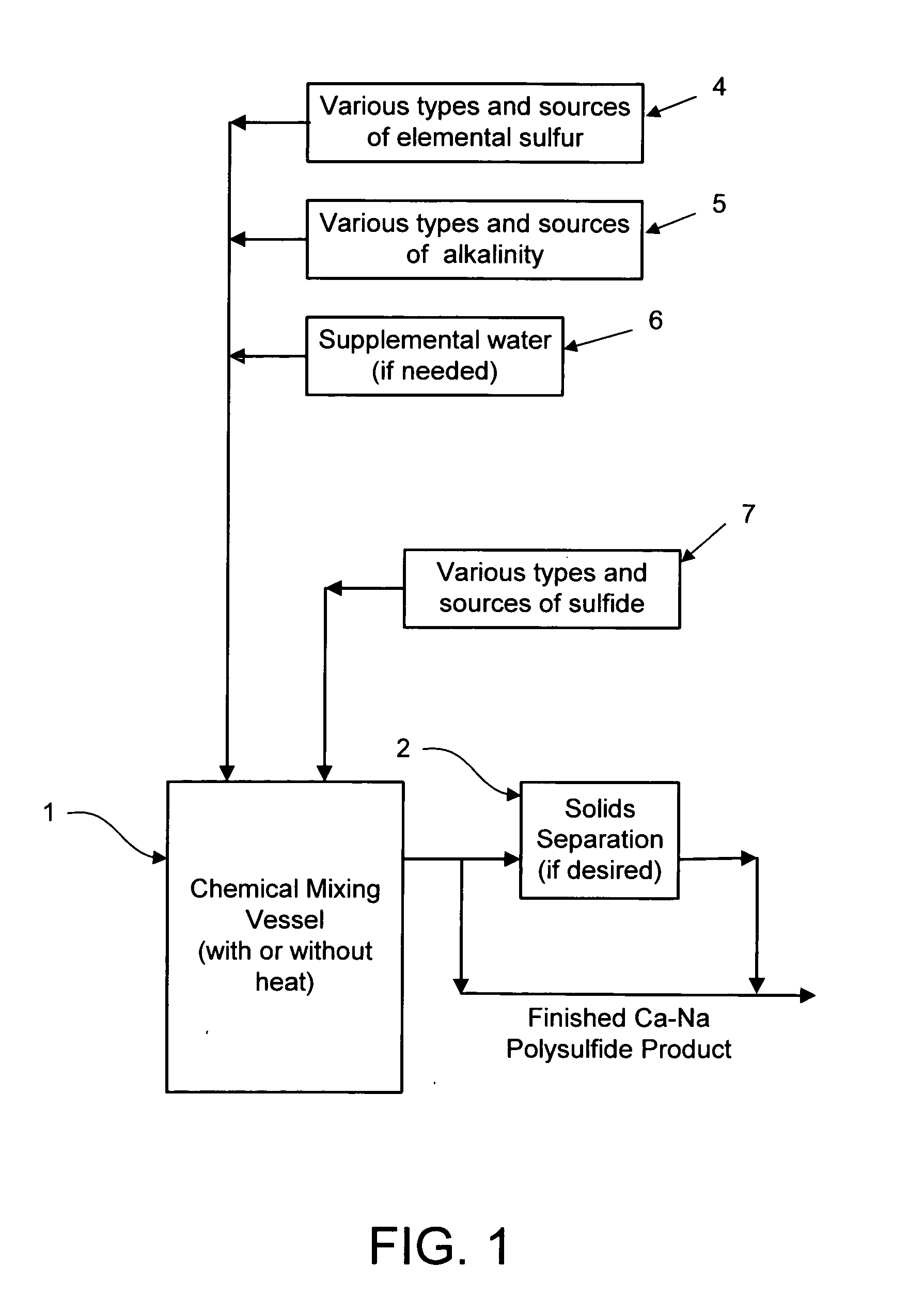
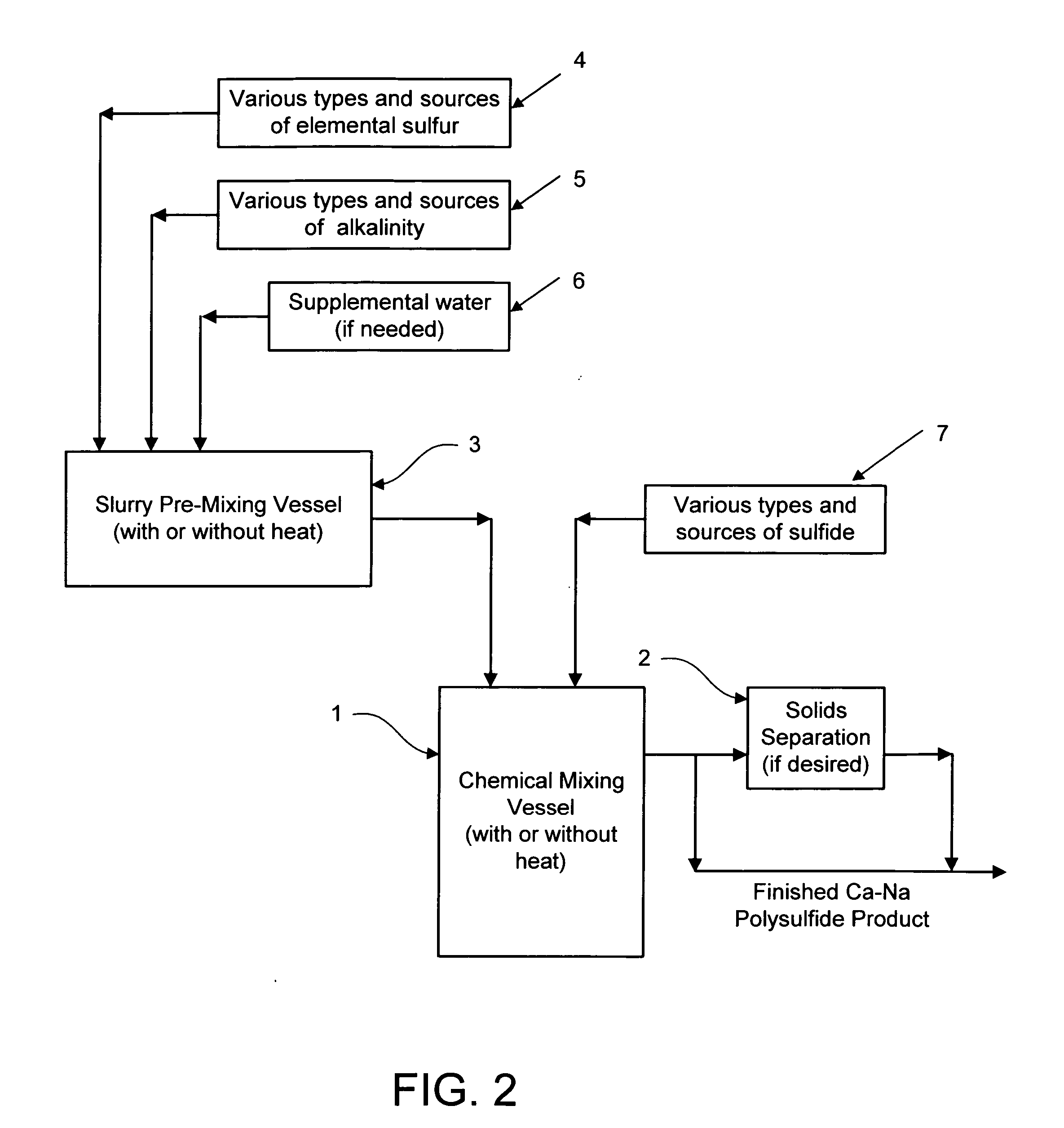
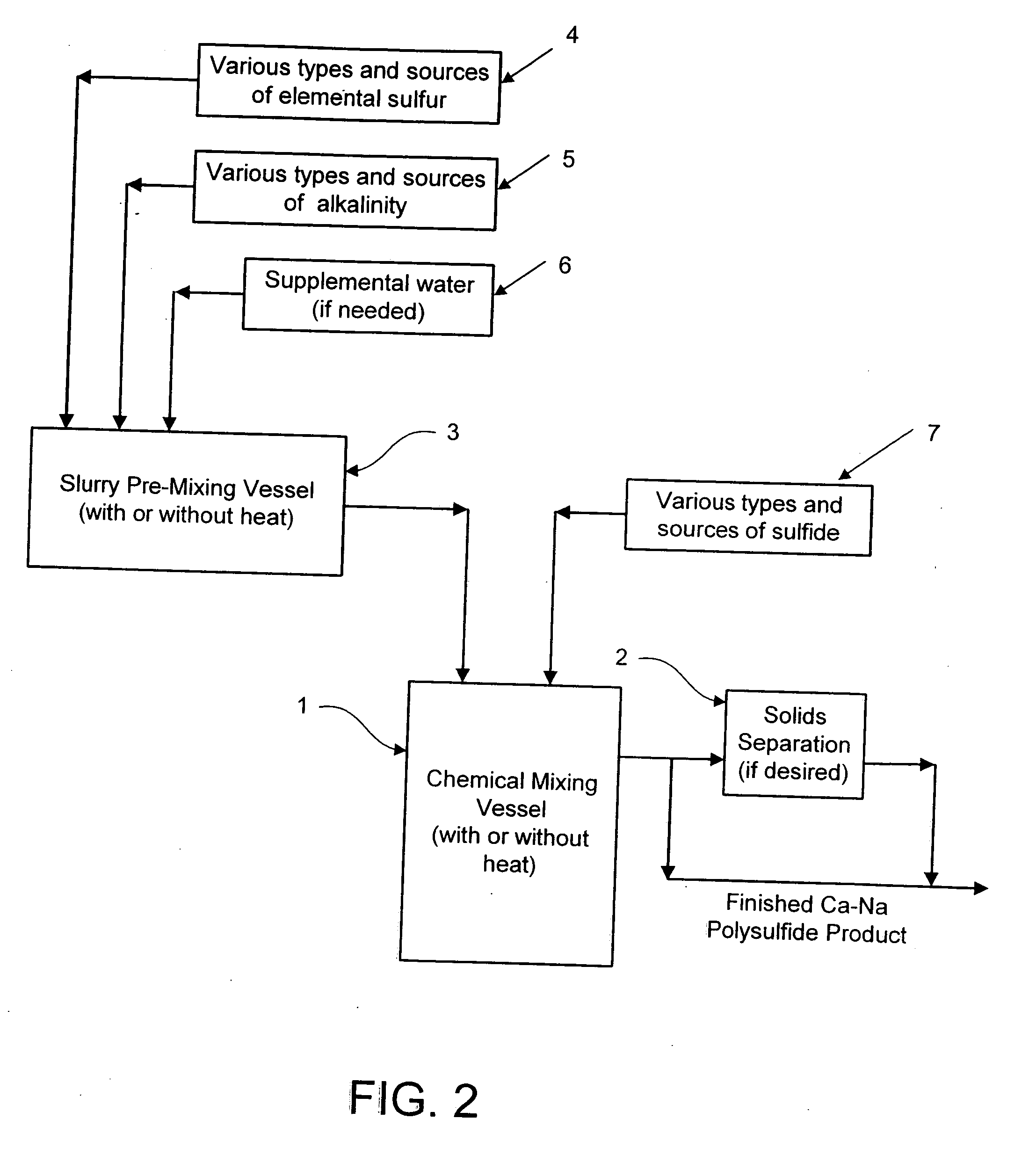
Calcium-sodium polysulfide chemical reagent and production methods
Owner:REDOX TECH GRP
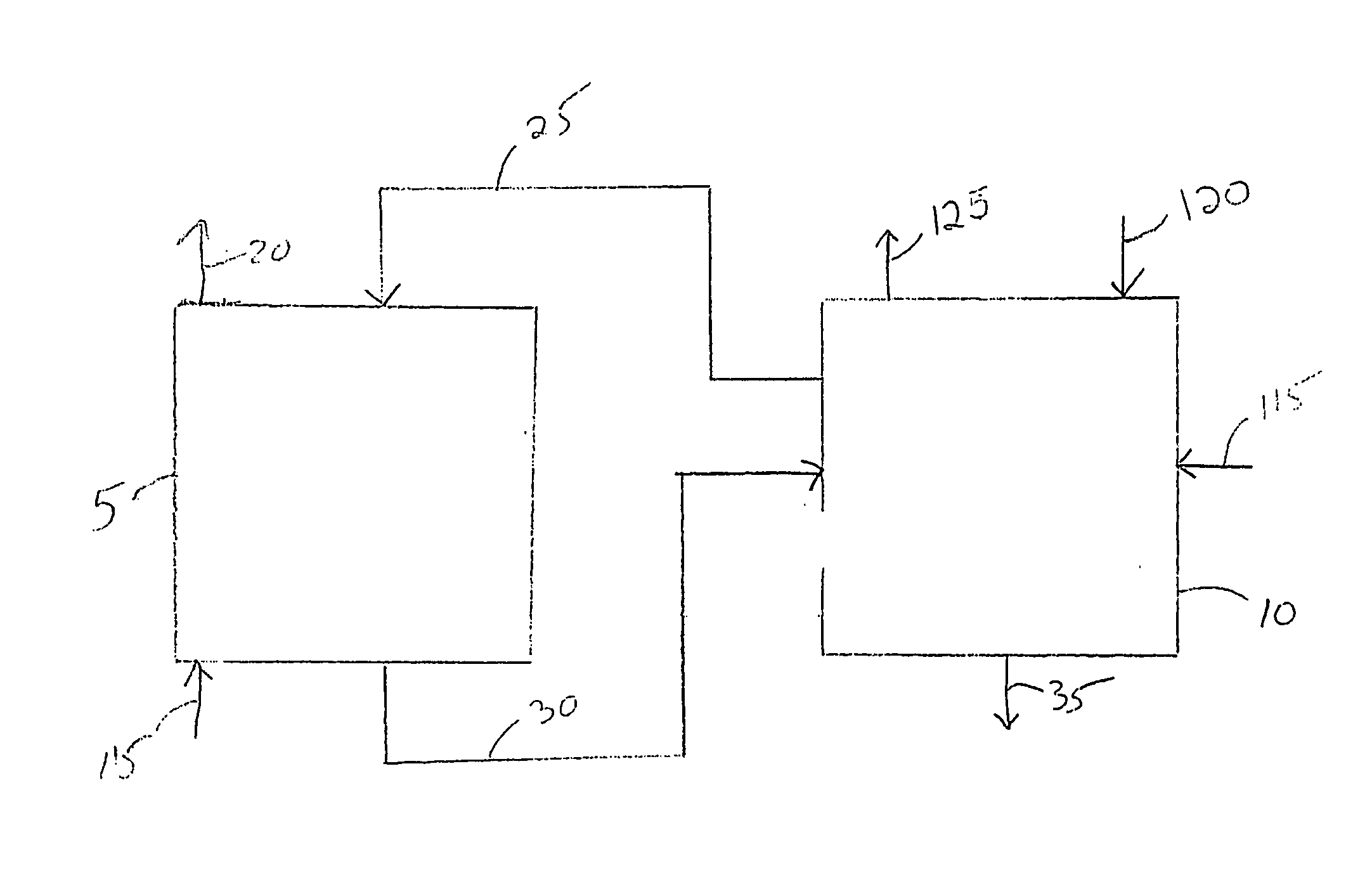
Process for the purification of acidic metal-bearing waste waters to permissable discharge levels with recovery of marketable metal products
InactiveUS20070090057A1Reduce sulfate concentrationQuality improvementWaste water treatment from quariesWater contaminantsBioconversionPrecipitation
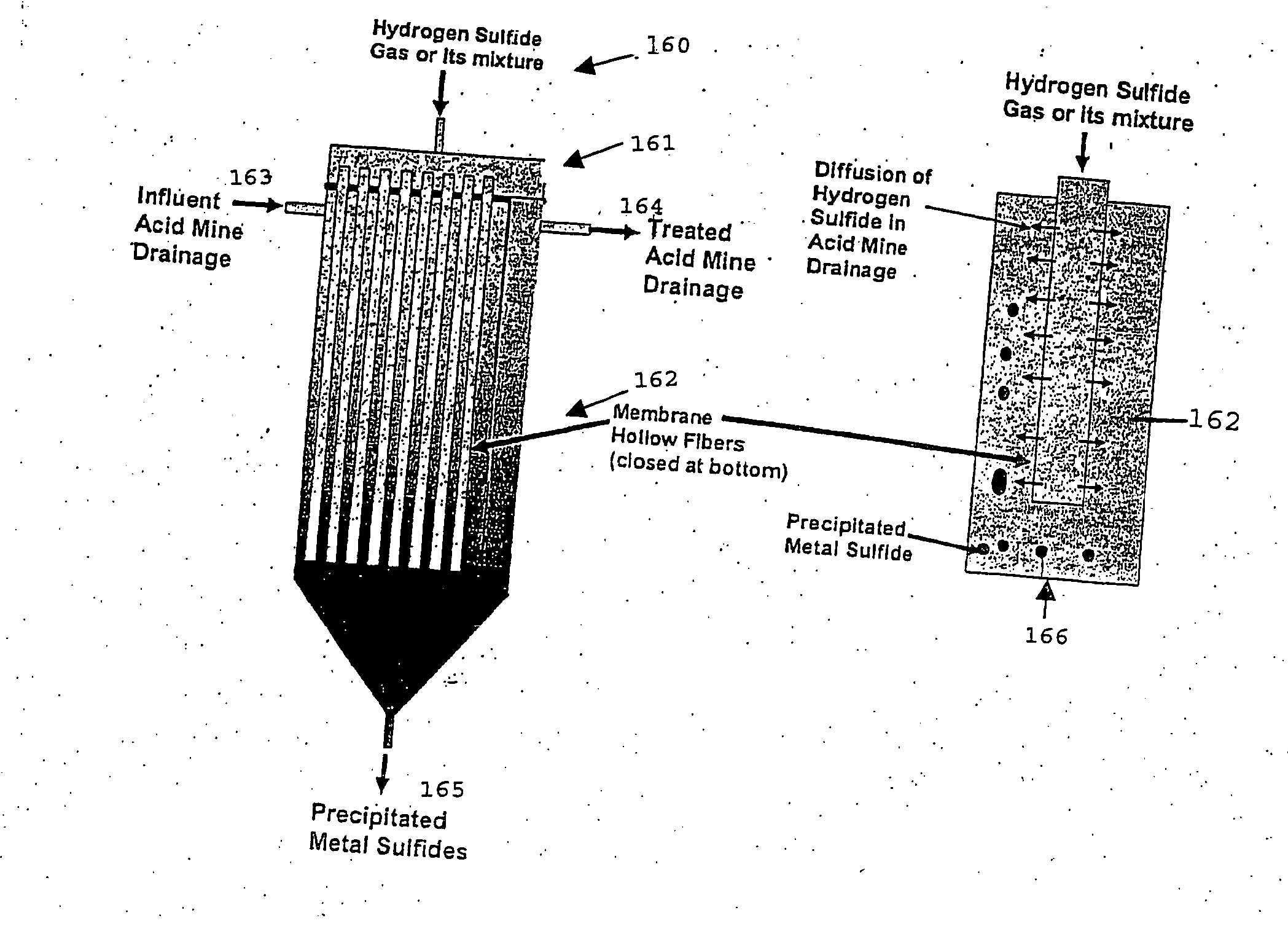
Acidic metal-bearing wastewaters are treated to produce a finished water of sufficient purity to meet discharge standards while recovering metals removed in forms which are commercially valuable. The metals are selectively precipitated, either in a batch or in a continuous system, for removal of individual metal products in a specific sequence of steps from the wastewater. In each step, the pH is adjusted to the specific pH range and sulfide ion is introduced to precipitate the metals, excepting the removal of ferric iron and aluminum which is achieved using hydroxide precipitation. Bioconversion process using unique equipment converts sulfate in the wastewater to the hydrogen sulfide gas required for the precipitation process. This bioconversion process reduces the sulfate in the wastewater so that the water can be directly discharged or used for agricultural applications.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
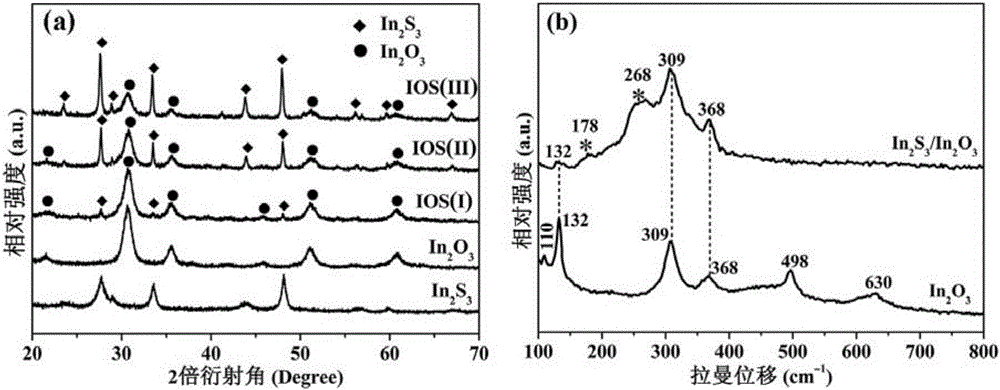
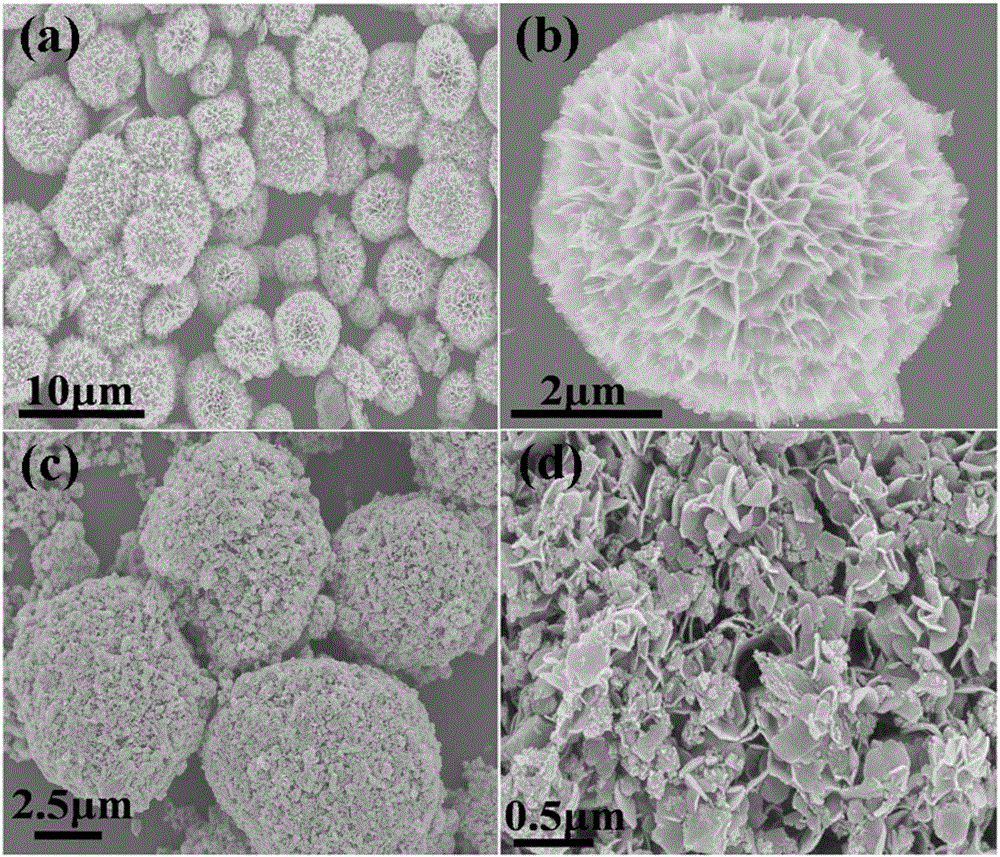
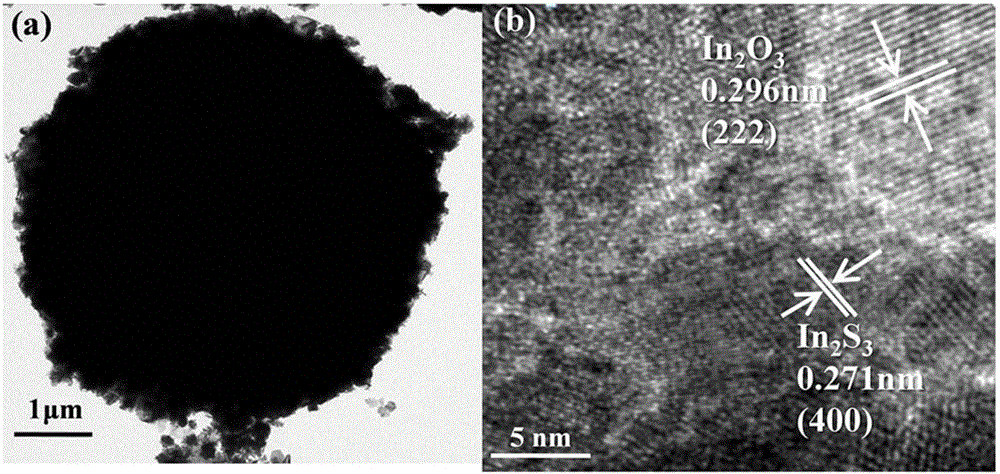
Three-dimensional flower-like In2S3/In2O3 composite microsphere photocatalytic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105664973AIncrease profitInhibitory complexGas treatmentPhysical/chemical process catalystsHeterojunctionLattice oxygen
The invention discloses a three-dimensional flower-like In2S3 / In2O3 composite microsphere photocatalytic material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of pollution control and technology. The preparation method comprises the following steps of taking thioacetamide as a sulfur source, substituting lattice oxygen in the In2O3 with sulfur ions through an ion exchange reaction, performing in situ generation of an In2S3 nanosheet on the surface of flower-like In2O3, and forming a heterojunction structure, wherein the morphology of the three-dimensional flower-like In2O3 is uniform, and the particle size of the three-dimensional flower-like In2O3 is 3.0 to 6.5 microns; coating the surface of / In2O3 microflowers with the In2S3 nanosheet. The used raw materials are low in price and easily-obtained, reaction conditions are easily controlled and the requirement on equipment is low, so the preparation method disclosed by the invention is an environmental-friendly preparation method. By using In2S3 / In2O3 composite microspheres, the utilization rate of the In2O3 to visible light can be improved, and the compounding of photon-generated carriers is inhibited; the In2S3 / In2O3 composite microspheres have good application value and prospect in the field of volatile organic contaminants.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Water Treatment Process
InactiveUS20110233136A1Lower the volumeImprove compactnessSpecific water treatment objectivesMultistage water/sewage treatmentChlorideSulfide ions
Owner:AUXSOL
Use of sulfide-containing liquors for removing mercury from flue gases
InactiveUS7037474B2Inherent safety advantageEfficient removalGas treatmentExhaust apparatusPotassium sulfideIndustrial gas
A method and apparatus for reducing and removing mercury in industrial gases, such as a flue gas, produced by the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, adds sulfide ions to the flue gas as it passes through a scrubber. Ideally, the source of these sulfide ions may include at least one of: sulfidic waste water, kraft caustic liquor, kraft carbonate liquor, potassium sulfide, sodium sulfide, and thioacetamide. The sulfide ion source is introduced into the scrubbing liquor as an aqueous sulfide species. The scrubber may be either a wet or dry scrubber for flue gas desulfurization systems.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
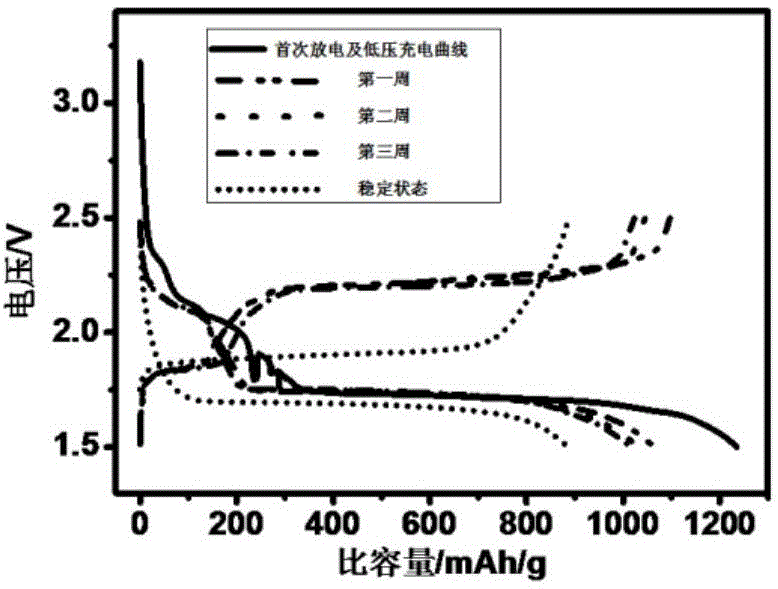
Manufacturing method for long-life lithium sulfur battery positive electrode
InactiveCN105304958ANo pollutionEasy to operateCell electrodesSecondary cells charging/dischargingLithium sulfideSulfide ions
The invention discloses a new method for on-site synthesis of a lithium ion conductive protection film for preventing poly-sulfide-ions diffusion on a surface of a lithium sulfur battery positive electrode, and an application therefor. The method is carried out by the steps of reducing the initial discharge voltage lower limit of a lithium sulfur battery taking a carbon sulfur composite as the positive electrode material to be lower than the normal working voltage 1.5V to generate the lithium ion conductive protection film; the film is quite high in the lithium ion conductivity and capable of preventing the poly-sulfide-ions from being dissolved in an electrolyte to enable the lithium sulfur battery to realize and maintain higher cycle performance, rate capability, coulombic efficiency and lower self discharge performance, so that the service life of the lithium sulfur battery is prolonged, and the use cost of the lithium sulfur battery is reduced; meanwhile, porous carbon with hierarchical pores used as the supporting material can accommodate the poly-sulfide-ions and lithium sulfide generated in charging and discharging processes of sulphur and the lithium sulfur battery; and the sulphur content in the carbon-sulfur composite material made from the porous carbon with the hierarchical pores is high, so that the comprehensive specific capacity of the carbon-sulfur composite product can be improved so as to further increase the overall energy density of the battery.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Essentially insoluble heavy metal sulfide slurry for wastewater treatment
A product and method for the removal of pollutant heavy metals from aqueous solutions which precludes the end user from storing, handling, feeding and controlling hazardous soluble sulfide materials. The product is a slurry which includes a mixture of a liquid medium and an essentially insoluble salt wherein the salt is the reaction product of heavy metal ions, preferably selected from Mn++ ions, Fe++ ions, and Fe+++ ions, and sulfide ions derived from soluble sulfide sources such as sodium sulfide, hydrogen sulfide, and sodium hydrosulfide. Addition of the subject slurry to a wastewater stream will effect the precipitation of heavy metals with lesser equilibrium sulfide ion concentrations than that of the essentially insoluble salt. Solids collected by this method may be returned to subsequent wastewater streams for additional removal of heavy metals by any excess heavy metal sulfide salt.
Owner:SOUTHERN WATER TREATMENT
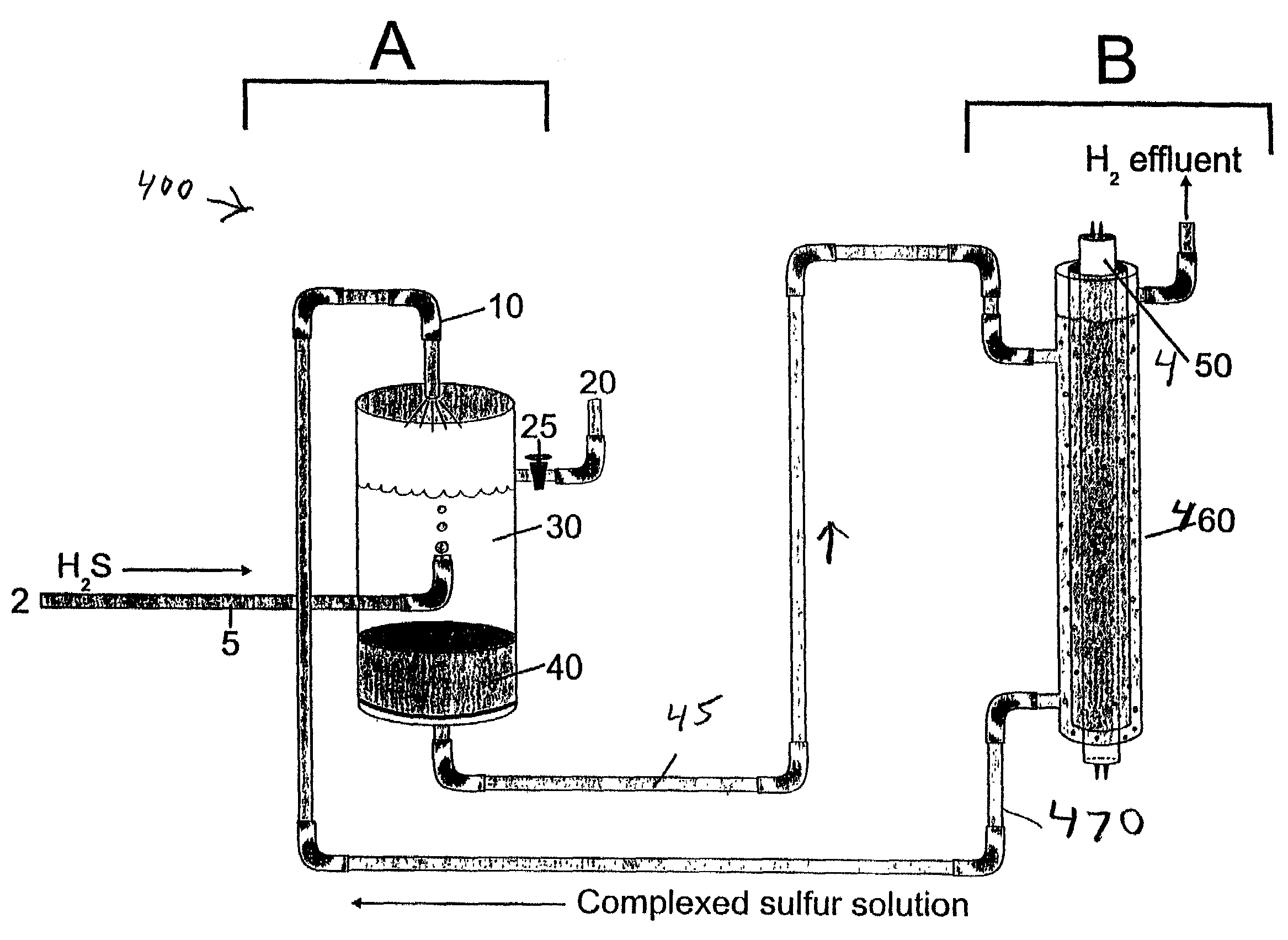
Electrochemical process for decomposition of hydrogen sulfide and production of sulfur
The present invention includes a process for the removal of hydrogen sulfide from hydrogen sulfide gas containing gaseous streams. In one embodiment, the process comprises feeding a sulfide ion containing solution to an oxidation unit. The method further comprises feeding an oxidizing gas to the oxidation unit and contacting the sulfide ion containing solution with the oxidizing gas under sufficient conditions to form a polysulfide solution comprising polysulfide and hydroxide ions. In addition, the process comprises mixing the polysulfide containing solution with a hydrogen sulfide gas under conditions sufficient for absorption of hydrogen sulfide and precipitation of sulfur from the polysulfide containing solution. In some embodiments, the process comprises separating the precipitated sulfur from liquid.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Process for the purification of acidic metal-bearing waste waters to permissible discharge levels with recovery of marketable metal products
InactiveUS7279103B2Quality improvementImprove performanceWaste water treatment from quariesWater contaminantsBioconversionPrecipitation
Acidic metal-bearing wastewaters are treated to produce a finished water of sufficient purity to meet discharge standards while recovering metals removed in forms which are commercially valuable. The metals are selectively precipitated, either in a batch or in a continuous system, for removal of individual metal products in a specific sequence of steps from the wastewater. In each step, the pH is adjusted to the specific pH range and sulfide ion is introduced to precipitate the metals, excepting the removal of ferric iron and aluminum which is achieved using hydroxide precipitation. Bioconversion process using unique equipment converts sulfate in the wastewater to the hydrogen sulfide gas required for the precipitation process. This bioconversion process reduces the sulfate in the wastewater so that the water can be directly discharged or used for agricultural applications.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
A Composite Depressant for Inhibiting the Flotation of Copper Sulfide Minerals
The present invention relates to a composite depressant for inhibiting the flotation of copper sulfide minerals. Sodium acetate 20% ~ 80%; The preparation method is: According to the above ratio, under normal temperature and pressure, stir and mix evenly at a speed of 300 ~ 1000rad / min to obtain a compound inhibitor. The present invention overcomes (1) the environmental pollution caused by the application of cyanide; (2) the large amount of sodium sulfide used, the high expense of the medicament, and the poor economic benefit; Activation of sulfide ions on chalcopyrite, pyrite, etc. The compound depressant has improved inhibition effect and inhibition effect, and has the characteristics of wide source of raw materials, easy preparation, low processing cost, stable flotation performance, relatively low price and easy popularization.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF NONFERROUS METALS
Essentially insoluble heavy metal sulfide slurry for wastewater treatment
InactiveUS20050173350A1Water treatment parameter controlCell electrodesLiquid mediumSodium hydrosulfide
A product and method for the removal of pollutant heavy metals from aqueous solutions which precludes the end user from storing, handling, feeding and controlling hazardous soluble sulfide materials. The product is a slurry which includes a mixture of a liquid medium and an essentially insoluble salt wherein the salt is the reaction product of heavy metal ions, preferably selected from Mn++ ions, Fe++ ions, and Fe+++ ions, and sulfide ions derived from soluble sulfide sources such as sodium sulfide, hydrogen sulfide, and sodium hydrosulfide. Addition of the subject slurry to a wastewater stream will effect the precipitation of heavy metals with lesser equilibrium sulfide ion concentrations than that of the essentially insoluble salt. Solids collected by this method may be returned to subsequent wastewater streams for additional removal of heavy metals by any excess heavy metal sulfide salt.
Owner:SOUTHERN WATER TREATMENT
Technology for synthesizing sulfur quantum dots through oil-water interface method
ActiveCN103588178AReduce dispersionSmall particle sizeMaterial nanotechnologySulfur preparation/purificationOil phaseMetallic sulfide
The invention discloses a technology for synthesizing sulfur quantum dots through an oil-water interface method. The technology comprises the following steps: 1, preparing metal sulfide quantum dots; 2, preparing a nitric acid solution; and 3, preparing sulfide quantum dots. In the invention, oleic acid is used as a solvent to prepare oil-soluble metal sulfide quantum dots, an n-hexane solution of a metal sulfide and an aqueous solution of nitric acid are mixed as an oil phase and a water phase respectively, nitric acid oxidizes sulfide ions into elemental sulfur in situ at the phase interface, and the metal sulfide quantum dots are adopted as a template to realize the uniform distribution of the particle sizes of the prepared sulfur quantum dots, so the oil-water interface alleviates the reaction speed and realizes the dispersion and small particle sizes of sulfur nano-particles. The technology allows the sulfur quantum dots to be synthesized by adopting the above technical scheme through the oil-water interface reaction with the n-hexane solution of the metal sulfide as the oil phase and the aqueous solution of nitric acid as the water phase, so the technology has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simple operation, controllable particle size and easy popularization.
Owner:MINNAN NORMAL UNIV
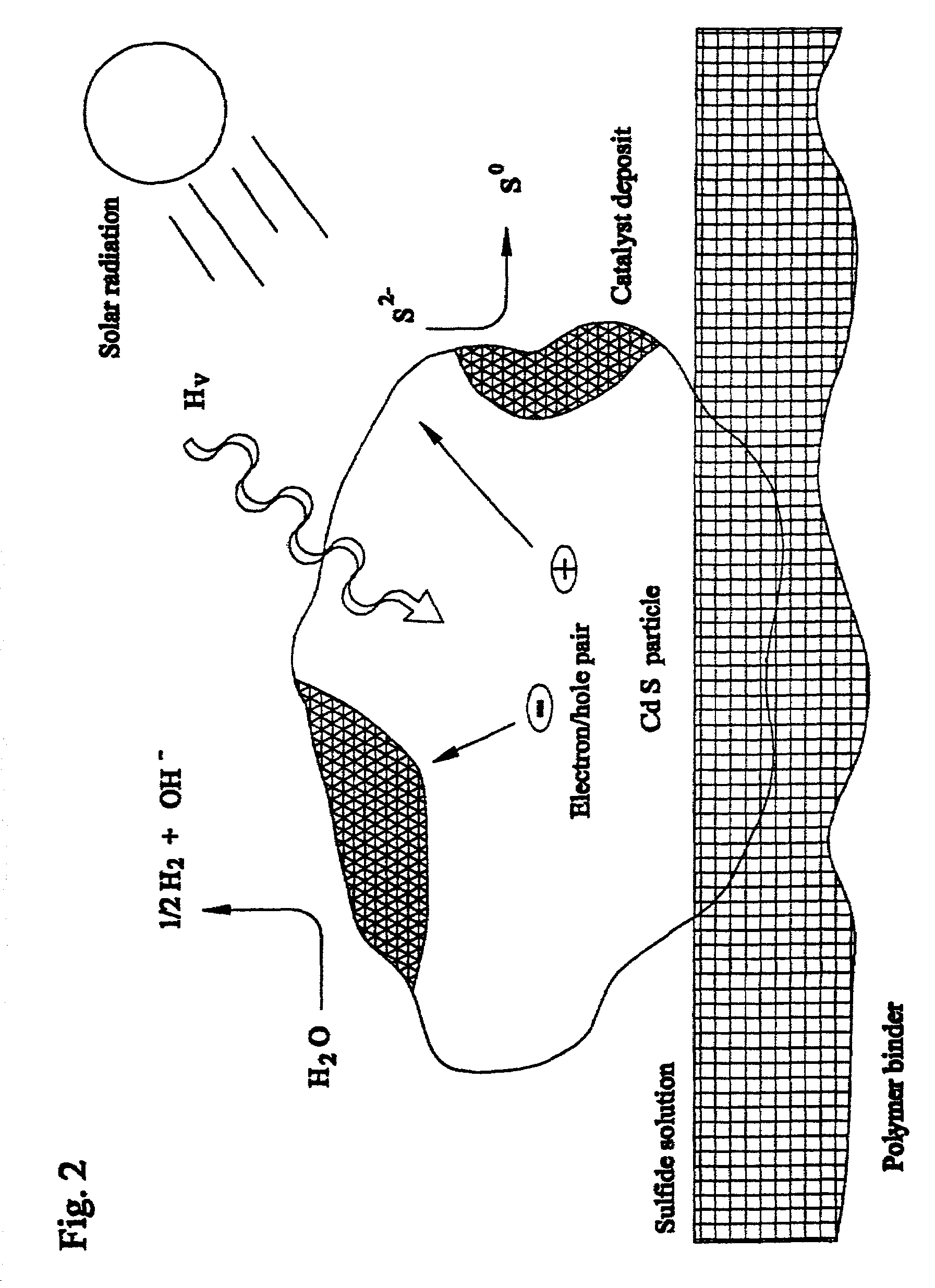
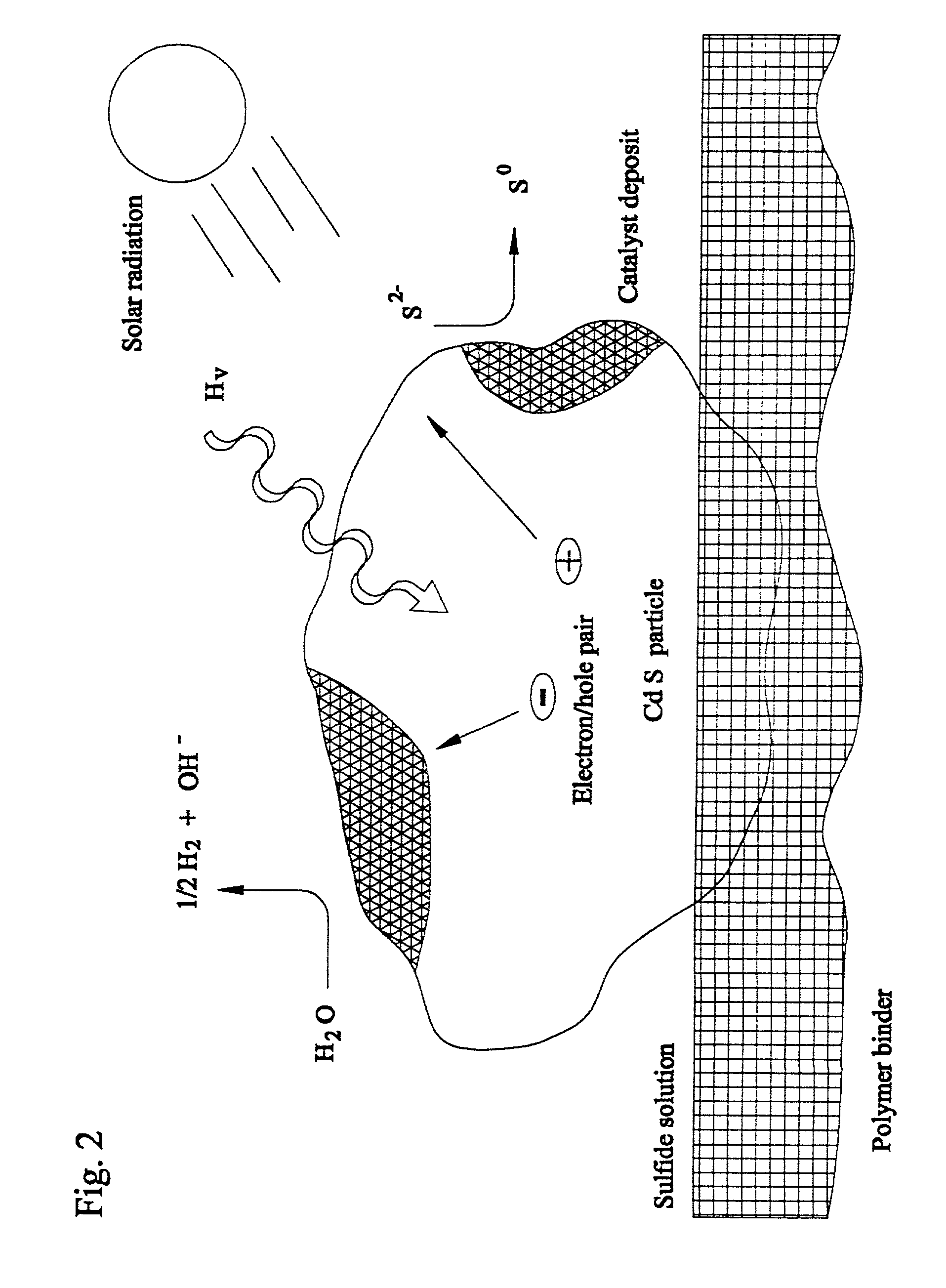
Closed cycle photocatalytic process for decomposition of hydrogen sulfide to its constituent elements
A method and system for separating hydrogen and sulfur from hydrogen sulfide (H.sub.2S) gas being produced from oil and gas waste streams. The hydrogen sulfide (H.sub.2S) gas is first passed into a scrubber and filtration unit where it encounters polysufide solution. Elemental sulfur is freed when the H.sub.2S interacts with the solution, the sulfur is filtered through a porous media such as a ceramic frit, and continues to a stripper unit where the excess H.sub.2S is removed from the sulfide solution. The excess H.sub.2S returns to the scrubber and filtration unit, while the sulfide solution passes into a photoreactor containing a semiconductor photocatalyst such as Cadmium Sulfide (CdS), Platinized Cadmium Sulfide, Pt--CdS, Zinc Sulfide, ZnS, Zinc Ferrate, ZnFe.sub.2O.sub.4, Indium Sulfide, In.sub.2S.sub.3, along with a 450-500 nm light source. The sulfide solution inside the photoreactor consisting mainly of bisulfide ion, is oxidatively converted to elemental sulfur and then complexed with excess sulfide ion to make polysulfide ion, while water is reduced to make hydrogen under the action of the light source. Hydrogen percolates out of the photoreactor, while the polysulfide solution is fed back to the scrubber unit where the system operation starts over again for additional hydrogen sulfide gas.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA
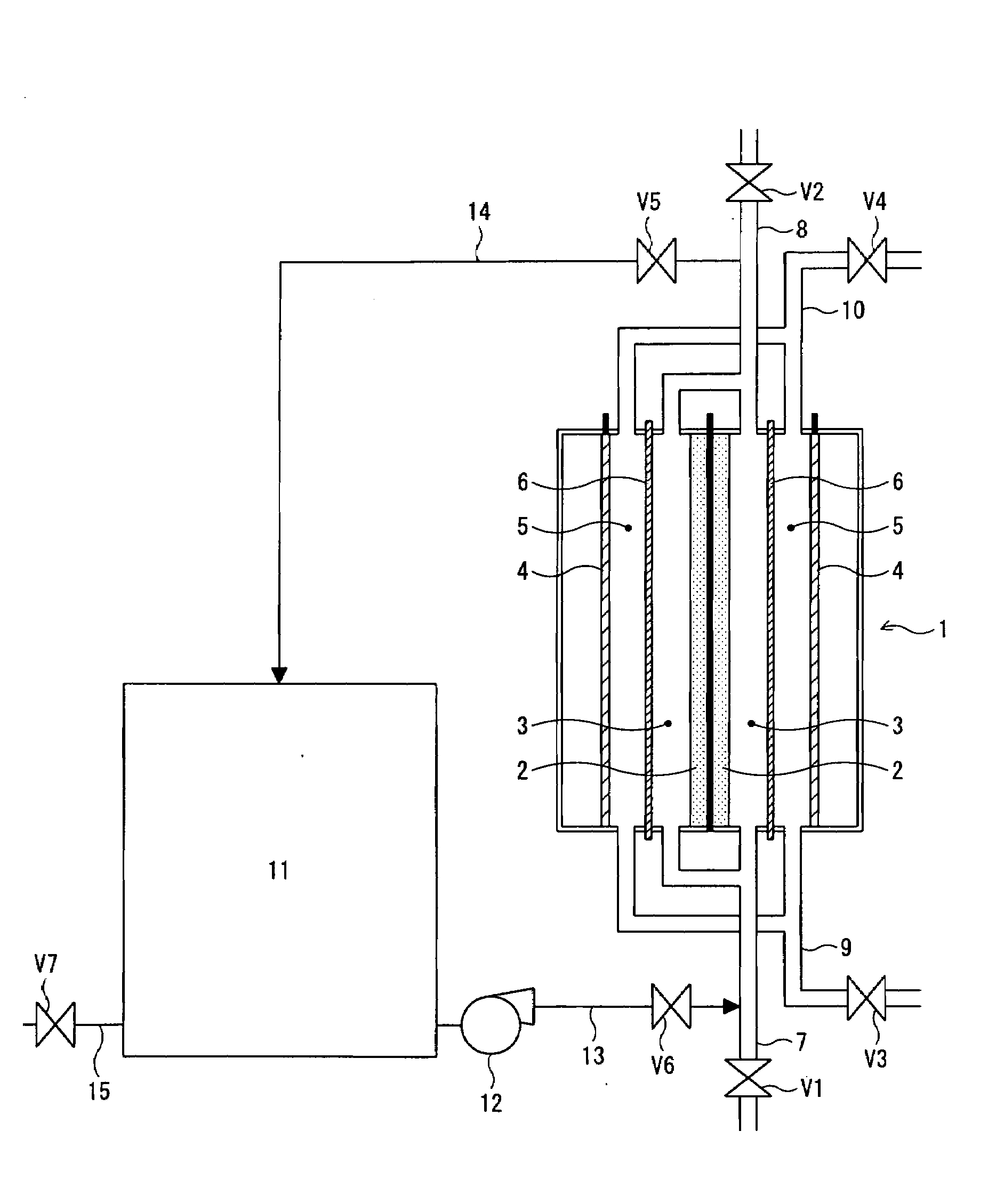
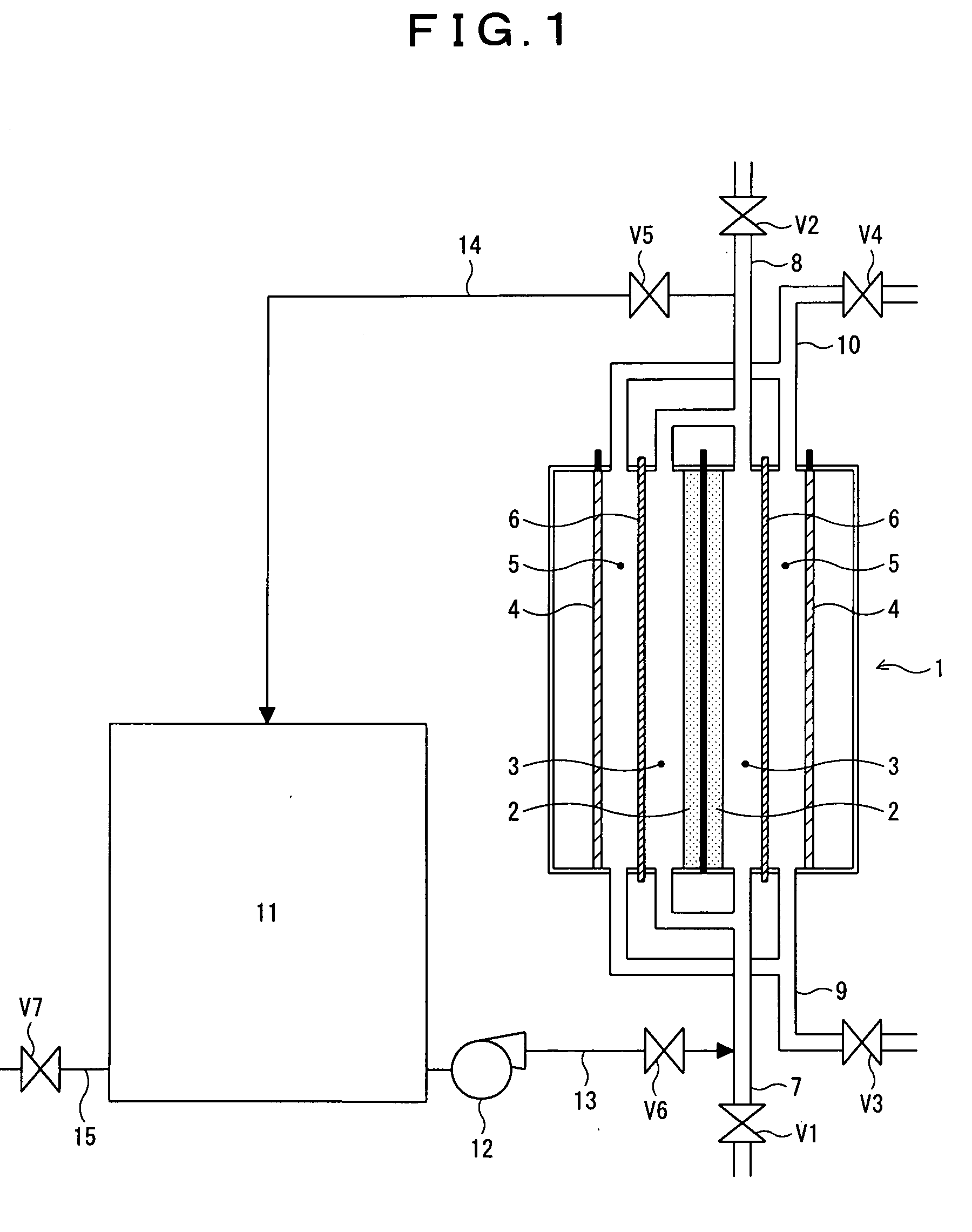
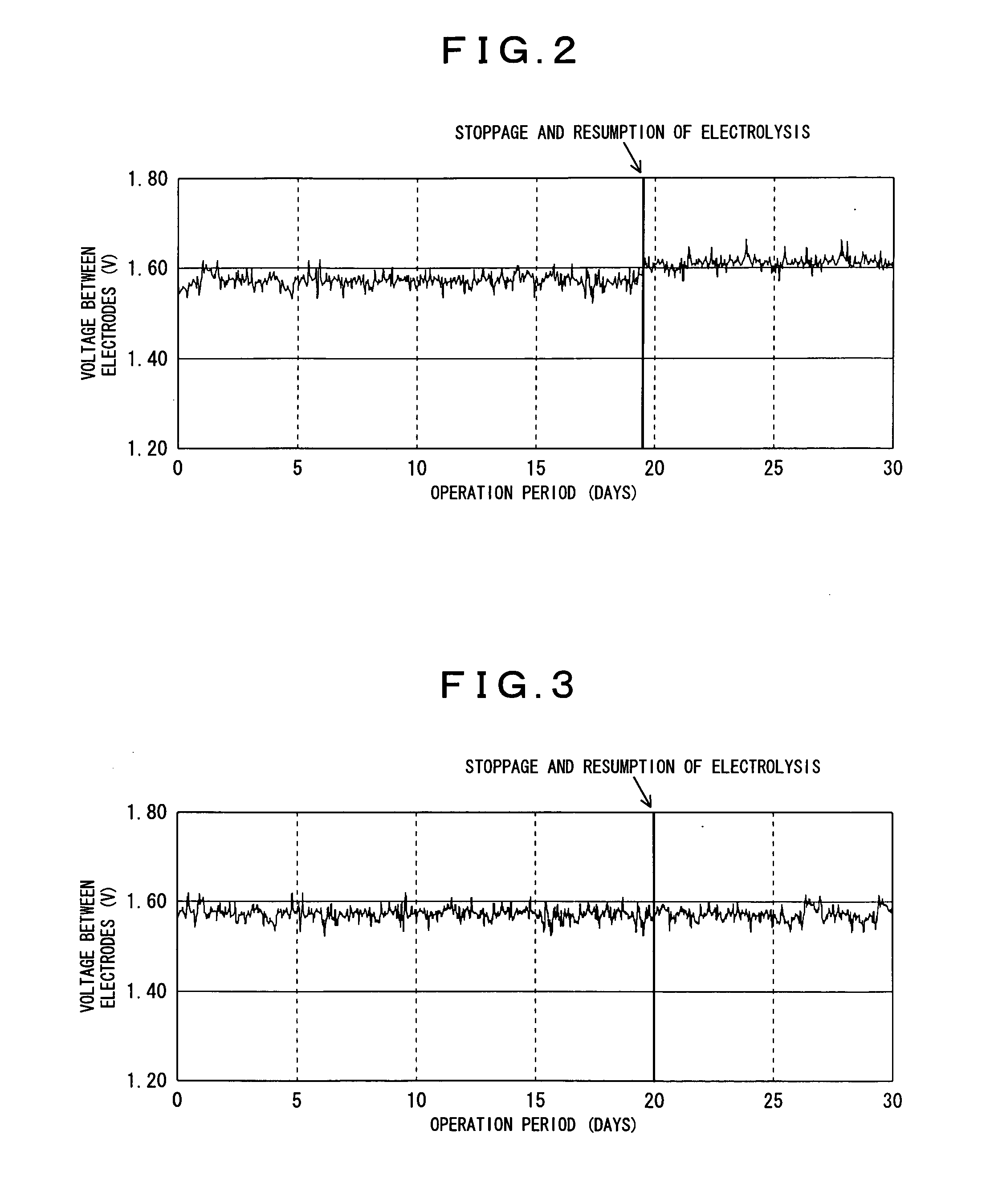
Method for recovering performance of electrolyzer for use in production of polysulfide and method for stopping holding electrolyzer
InactiveUS20090242422A1Maintain performanceImprove efficiencyElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisPolysulfide
In an electrolyzer comprising an anode compartment provided with porous anodes, a cathode compartment, and a membrane providing a partition between the anode compartment and the cathode compartment, wherein a solution containing sulfide ions is introduced into the anode compartment, and an aqueous solution containing caustic soda is introduced into the cathode compartment, thereby producing a polysulfide containing polysulfide sulfur through electrolytic oxidation, wherein the anode compartment of the electrolyzer is cleaned with the use, of an aqueous solution containing at least either one of an inorganic acid, a chelating agent, and a scale-cleaning agent, thereby recovering performance of the electrolyzer. Further, when the contents of the anode compartment are replaced with an alkaline aqueous solution containing not more than 0.1 mass % of sulfide ions and not more than 0.1 mass % of carbonate ions upon stopping the electrolytic oxidation, thereby maintaining the performance of the electrolyzer.
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD +2
Synthesis of noble metal, sulphide catalysts in a sulfide ion-free aqueous environment
A noble metal sulfide catalyst obtained by reaction of a precursor of at least one noble metal with a thionic species in an aqueous environment essentially free of sulfide ions useful as an electrocatalyst in the depolarized electrolysis of hydrochloric acid.
Owner:ELECTRIC TECHNOLOCY
Electrochemical process for decomposition of hydrogen sulfide and production of sulfur
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Testing Method and Kit for Detecting Lead, Mercury, and Chromate in Paint , Varnish, and Other surface Coatings
InactiveUS20110283785A1Accurately and precisely determineAvoid interferenceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsWeather/light/corrosion resistanceDark colorSulfide ions
Owner:ASKIN DANIEL P +1
Method for preparing monodispersion bismuth sulfide nano granule by template method
InactiveCN101391813ANo pollution in the processGood biocompatibilityBismuth compoundsNanoparticleTM compound
The invention relates to a method for preparing bismuth sulphide nanometer grains, in particular to a method for preparing mono-dispersion bismuth sulphide nanometer grains through a template method, which is characterized in that: the method for preparing bismuth sulphide nanometer grains comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing precursor solution containing bismuth: dissolving the compound containing bismuth into a dispersion medium to form the bismuth compound solution, and then putting the solution into dispersion stabilizer, and stirring for 0.5 to 3 hours, to acquire the bismuth precursor solution; 2) according to a molar ratio of sulfide ions in the sulfur compound solution to the bismuth ions in the bismuth precursor solution between 3: 2 and 1: 2, selecting the sulfur compound solution as well as the bismuth precursor solution; adjusting the pH value of the bismuth precursor solution between 1.0 and 5.0 by a pH regulator, and adding the sulfur compound solution while stirring at a high speed at the normal temperature; controlling the reaction time between 1 and 48 hours; and carrying out centrifugal separation for the acquired suspension liquid and getting rid of the supernatant, to prepare the mono-dispersion bismuth sulphide nanometer grains. The method for preparing mono-dispersion bismuth sulphide nanometer grains has the advantages of low cost, no pollution to the environment, high yield, narrow distribution of nanometer grain diameters and simple and convenient operation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Copper electroplating solution and copper electroplating apparatus
ActiveUS20140197038A1Increasing overall electroplating processImprove processing efficiencyCellsSemiconductor devicesNitrogenAqueous electrolyte
An electroplating solution includes an aqueous electrolyte solution including water soluble copper salts, sulfide ions and chloride ions, an accelerator including an organic material having sulfur (S), the accelerator accelerating copper (Cu) reduction, a suppressor including a polyether compound, the suppressor selectively suppressing the copper reduction, and a leveler including a water soluble polymer having nitrogen that is dissolved into positive ions in the aqueous electrolyte solution.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Determination method for total sulfur in water quality
ActiveCN104807949AColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical analysis using precipitationSulfate radicalsDecomposition
The invention discloses a determination method for total sulfur in water quality. The method includes the following four steps: while sulfurous gas which can leak out is fixed by calcium oxide, potassium permanganate oxidation, nitric acid oxidation, hydrochloric acid regulation and barium chromate spectrophotometry are used for determining sulfate radical, which is converted into sulfur content. During total sulfur determination in water sample, calcium oxide and potassium permanganate are first added to oxidate sulfide ions under alkaline condition, sulfur in other valence states is then oxidated or decomposed into the sulfate radical under the joint oxidation of potassium permanganate and nitric acid, hydrochloric acid solution is then added to regulate the water sample and remove the color of the potassium permanganate, finally, the sulfate radical content in water quality is determined by barium chromate spectrophotometry, and total sulfur content is worked out. According to the characteristics of the sulfur in different valence states in water quality, by fixation, oxidation and decomposition, the method finally converts the sulfur in all valence states into the sulfate radical, and utilizes barium chromate spectrophotometry to determine the sulfate radical, and thereby the total sulfur in water quality is determined. Determination is simple, the result is accurate, and the method can be applied in fields such as environment protection and monitoring, food monitoring and sulfur balance analysis.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST
METHOD OF PREPARATION OF ZnS AND CdS NANOPARTICLES FOR DECHLORINATION OF POLYCHLOROBIPHENYLS IN OILS
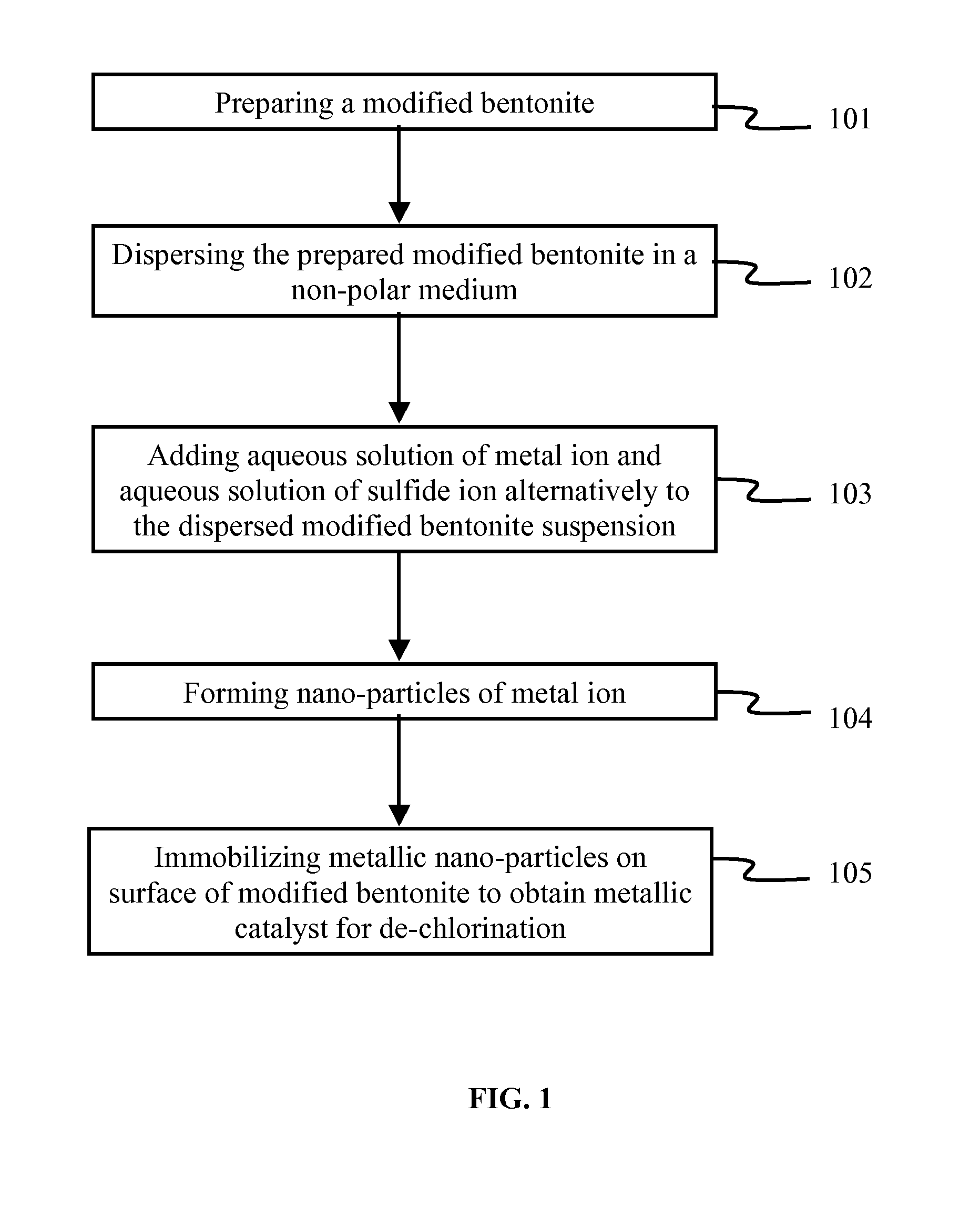
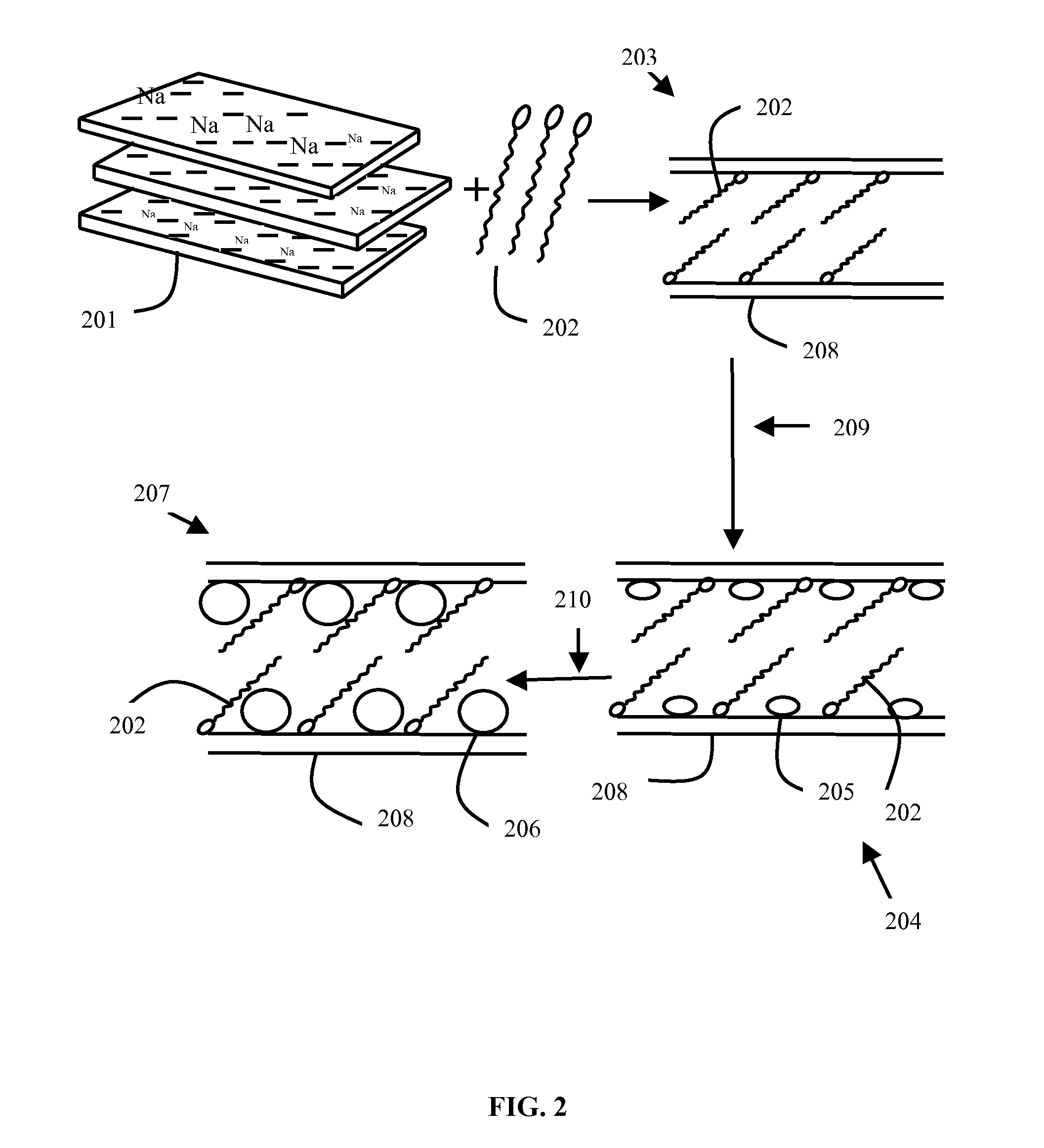
InactiveUS20110160512A1Material nanotechnologyCatalyst activation/preparationPolychlorinated biphenylMetallic sulfide
The various embodiments herein provide a method of preparation of a nano-material for dechlorination of polychlorobiphenyls (PCB) from oil. The method involves preparing a modified bentonite prepared by treating with hexadecyl pyridinium bromide surfactant and dispersing the modified bentonite in cyclohexane. Aqueous solutions of metal ion such as Cadmium Nitrate or Zinc Nitrate and sulfide ions such as sodium sulfide are added alternately to obtain metal sulphide nano-particles. zinc nitrate is more preferable. The method of dechlorination of polychlorobiphenyls from oil involves irradiating a mixture of oil, nano-material and a solvent such as toluene under UV light for 2-6 h. A nano-material including a modified bentonite with a mono-layer of surfactant and metal sulphide nano-particles such as ZnS and CdS for remediation of oil containing PCB, is also provided.
Owner:GHIACI MEHRAN +1
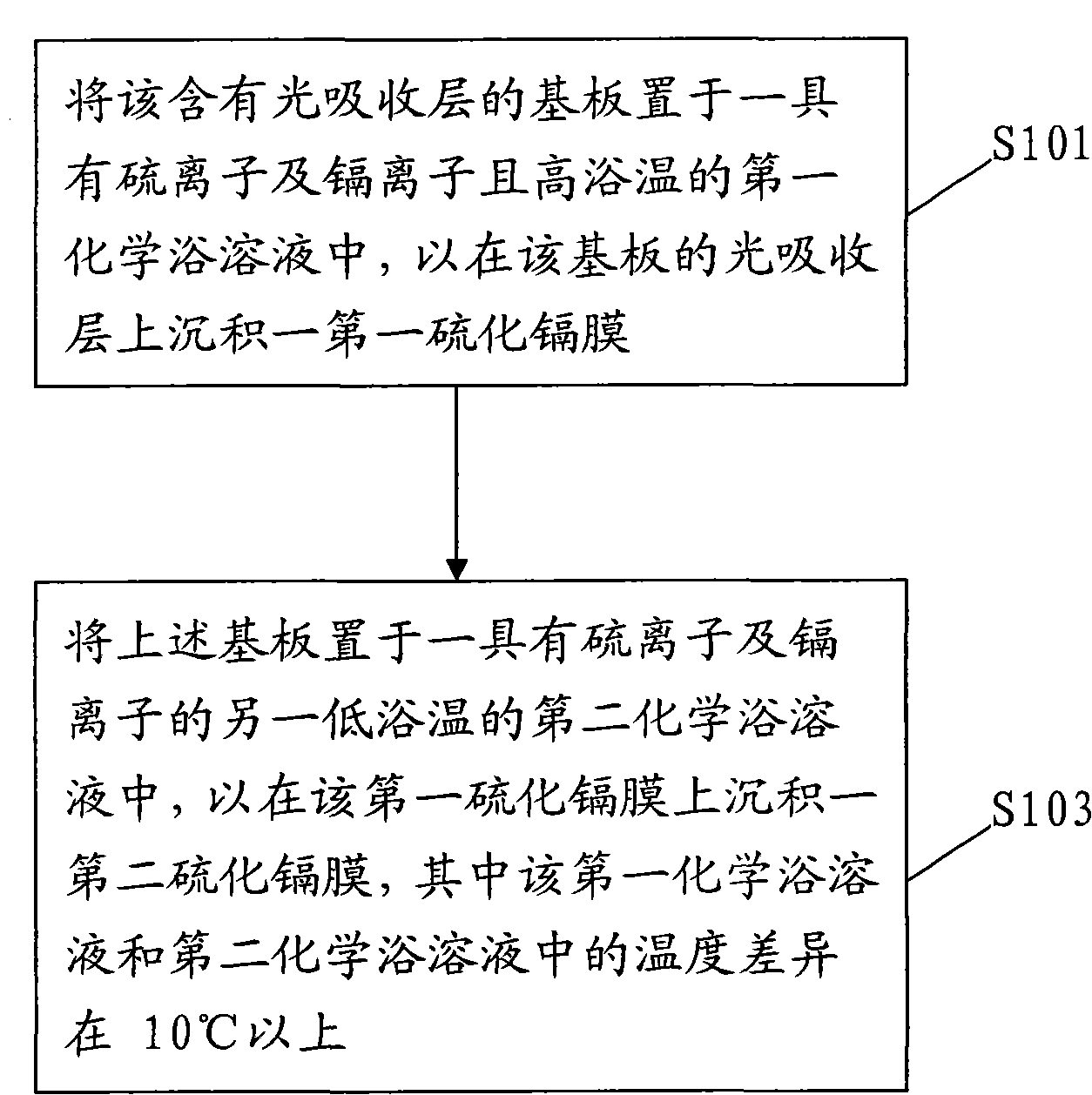
Deposition method of multi-section camium sulfide thin film
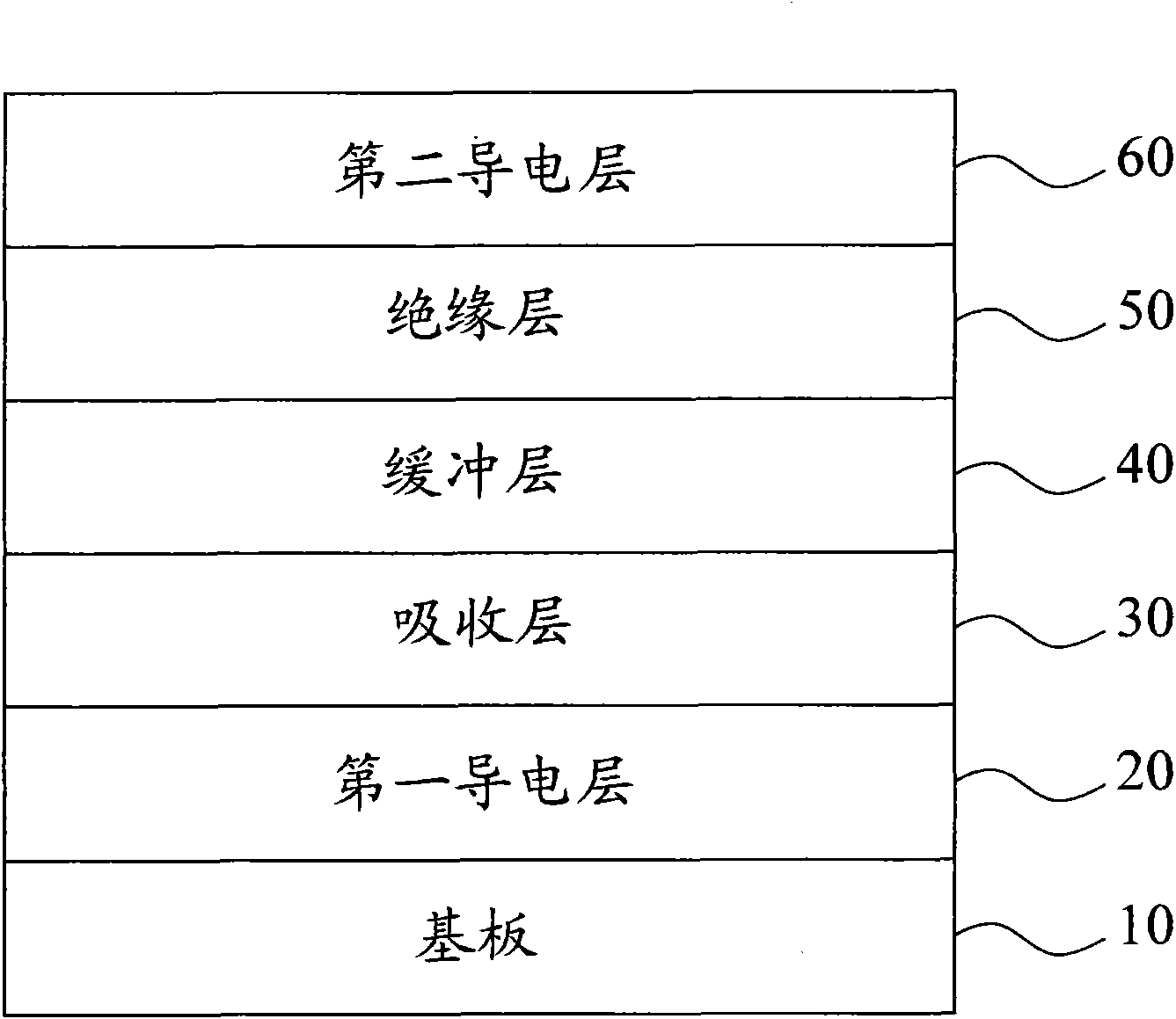
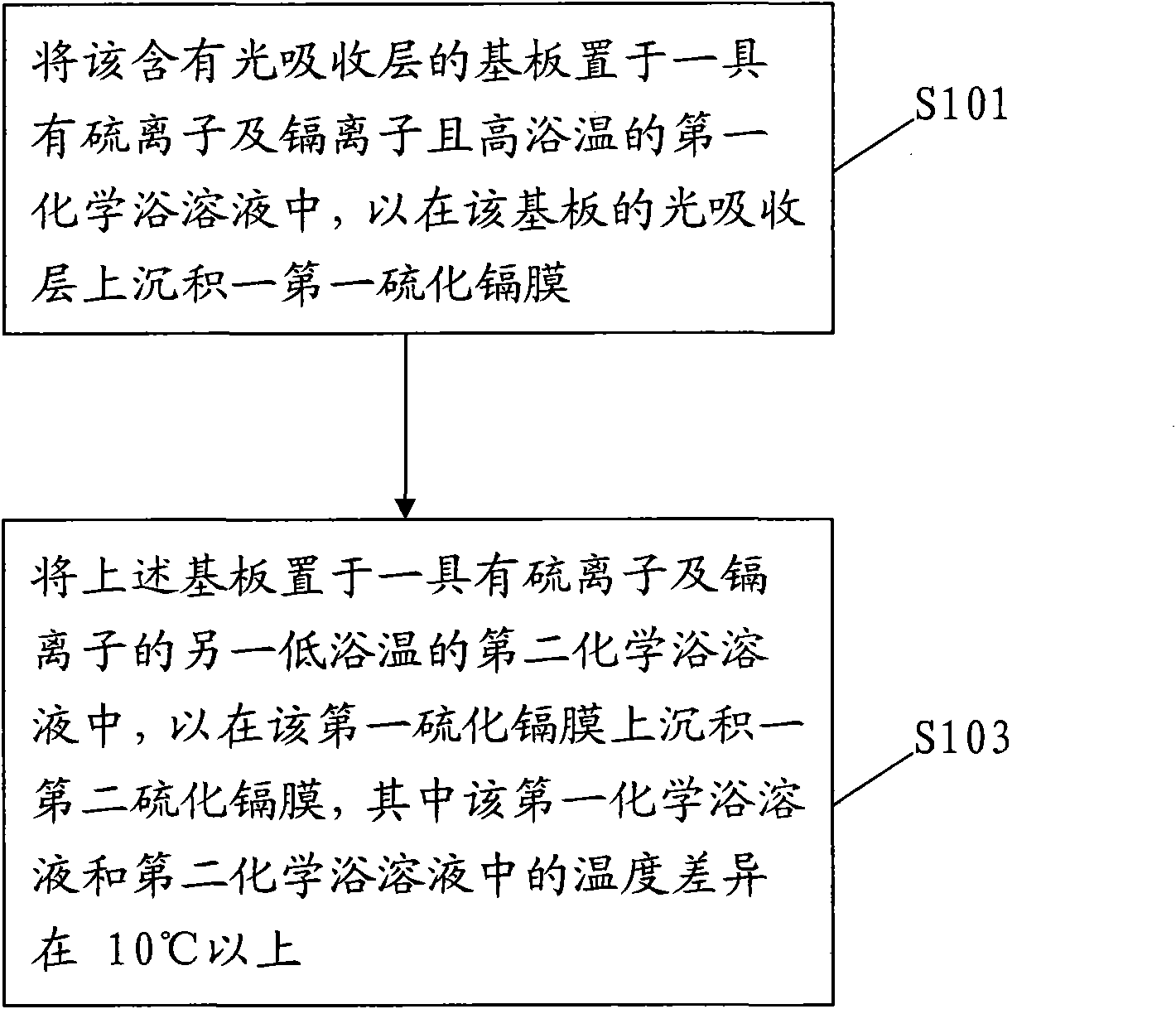
InactiveCN101820028AImprove uneven coverageSignificant progressFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesPhysical chemistryCompound (substance)
The invention relates to a deposition method of a multi-section camium sulfide thin film, comprising the following steps of: 1, placing a substrate containing a light-absorbing layer in first chemical bath solution with sulfide ions, cadmium ions and high bath temperature for depositing a first camium sulfide film on the light-absorbing layer of the substrate; and 2. placing the substrate into second chemical bath solution with sulfide ions, cadmium ions and low temperature for depositing a second camium sulfide film on the first camium sulfide film, wherein the temperature difference between the first chemical bath solution and the second chemical bath solution is above 10DEG C.
Owner:昆山正富机械工业有限公司
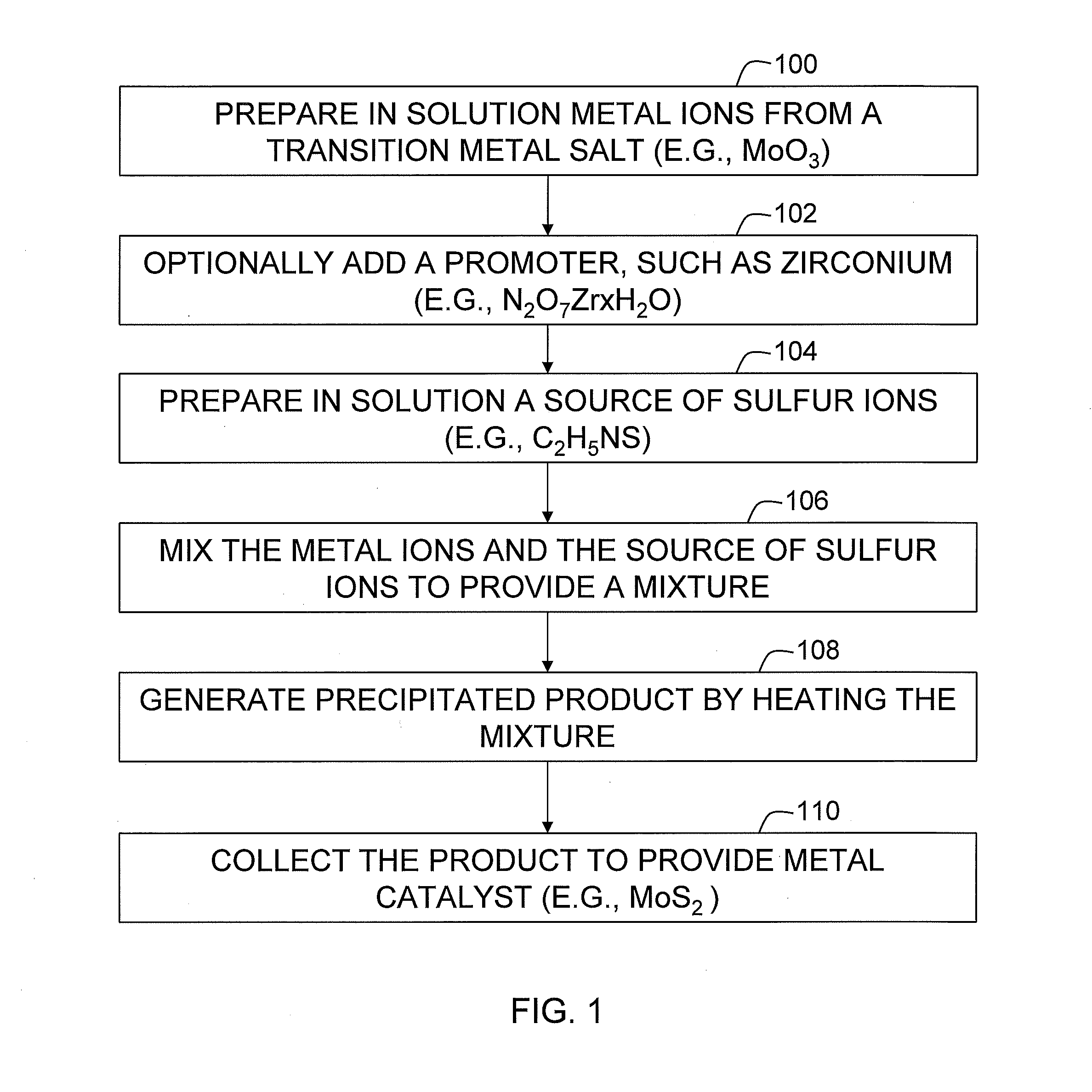
Metal sulfide catalysts and methods of making same
Methods and apparatus relate to catalysts and preparation of the catalysts, which are defined by sulfides of a transition metal, such as one of molybdenum, tungsten, and vanadium. Precursors for the catalysts include a metal ion source compound, such as molybdenum trioxide, and a sulfide ion source compound, such as thioacetamide. Once the precursors are dissolved if solid and combined in a mixture, homogenous precipitation from the mixture forms the catalysts. Exemplary uses of the catalysts include packing for a methanation reactor that converts carbon monoxide and hydrogen into methane.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
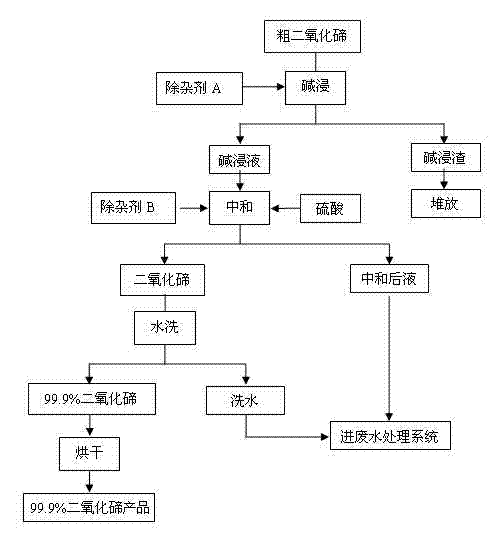
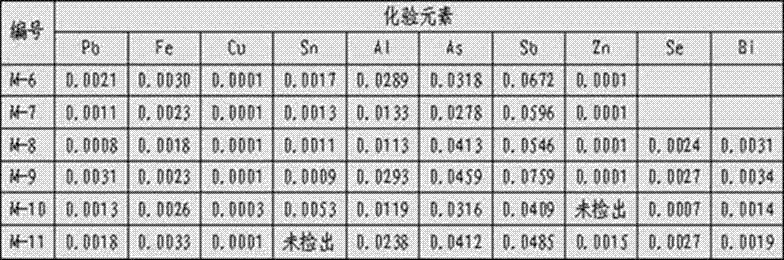
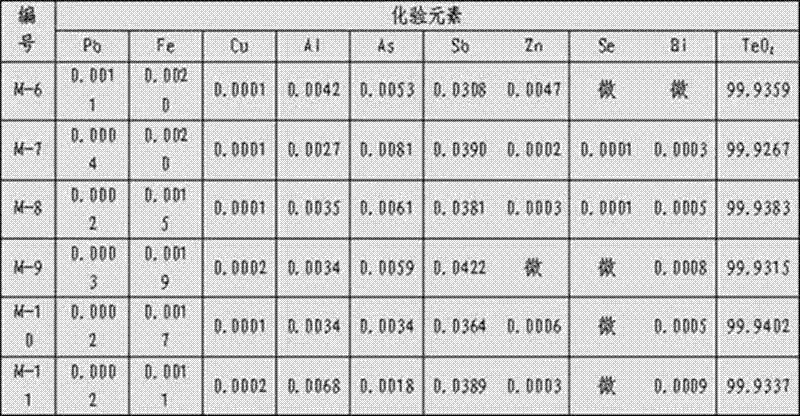
Tellurium dioxide purification method
ActiveCN102897725AHigh purityThe process is simple and clearBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsEthylene diaminePurification methods
The invention relates to a tellurium dioxide purification method which comprises the following steps: 1, performing alkaline leaching; 2, neutralizing, 3, washing with water; and 4, drying, wherein an impurity removal agent A is added in the alkaline leaching process, and an impurity removal agent B is added in the neutralizing process of an alkaline leaching filtrate; the impurity removal agent A added in the alkaline leaching process is ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and the impurity removal agent B added in the neutralizing process is EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) complexing agent; and a small amount of sodium sulfide is added in the alkaline leaching process to remove lead in the solution to ensure that no free sulfide ions exist in the solution. A precipitating impurity removal method, a complexing impurity removal method and a washing impurity removal method are organically combined, so that the content of impurity elements (such as selenium, lead, bismuth, copper, arsenium, stibium, tin, iron and the like) in the tellurium dioxide product can be directly and effectively lowered, the main components of the tellurium dioxide product are increased, the content of the main components of the tellurium dioxide product obtained after the processing steps is higher than 99.9%, and the whiteness is favorable.
Owner:SHUI KOU SHAN NONFERROUS METALS LTD
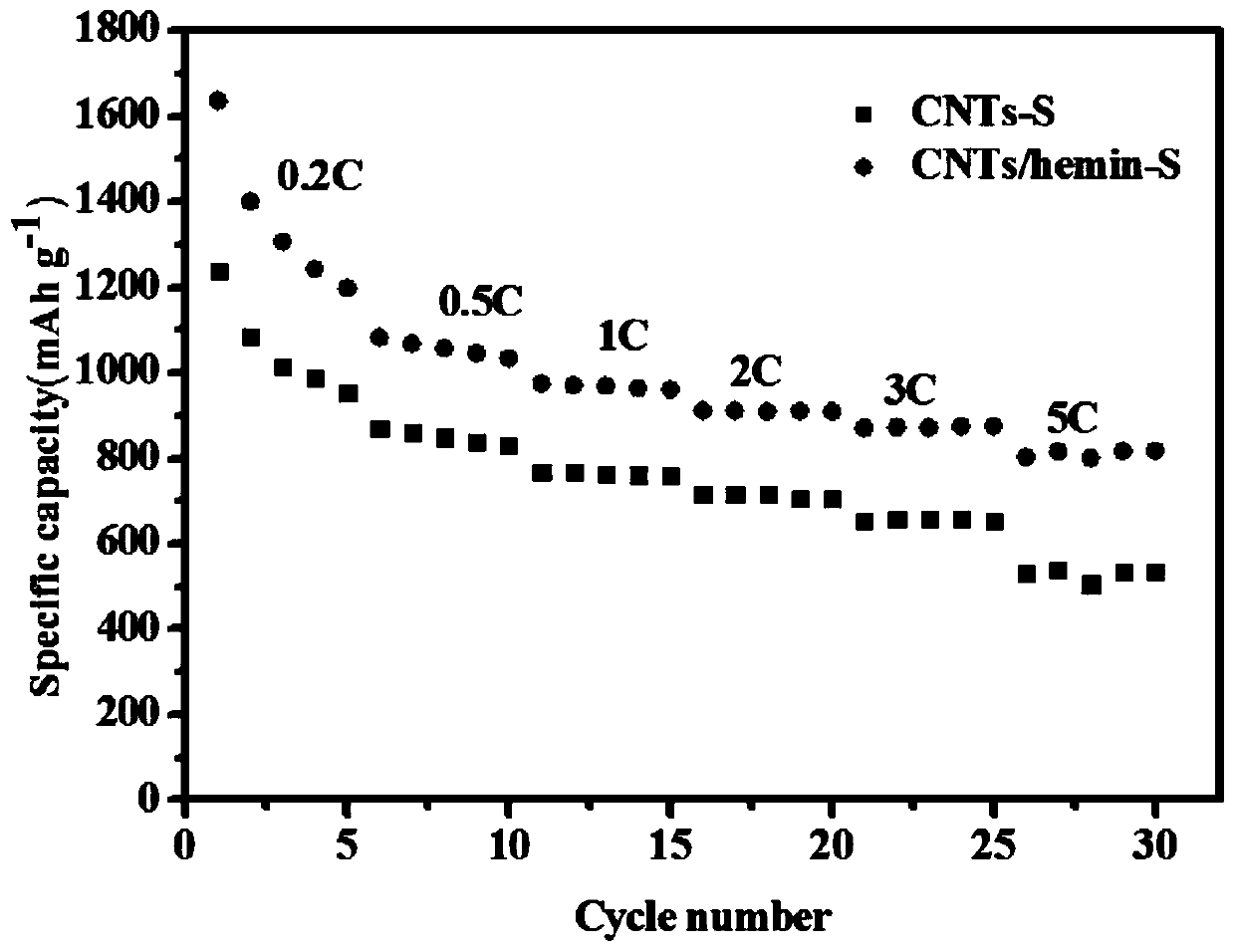
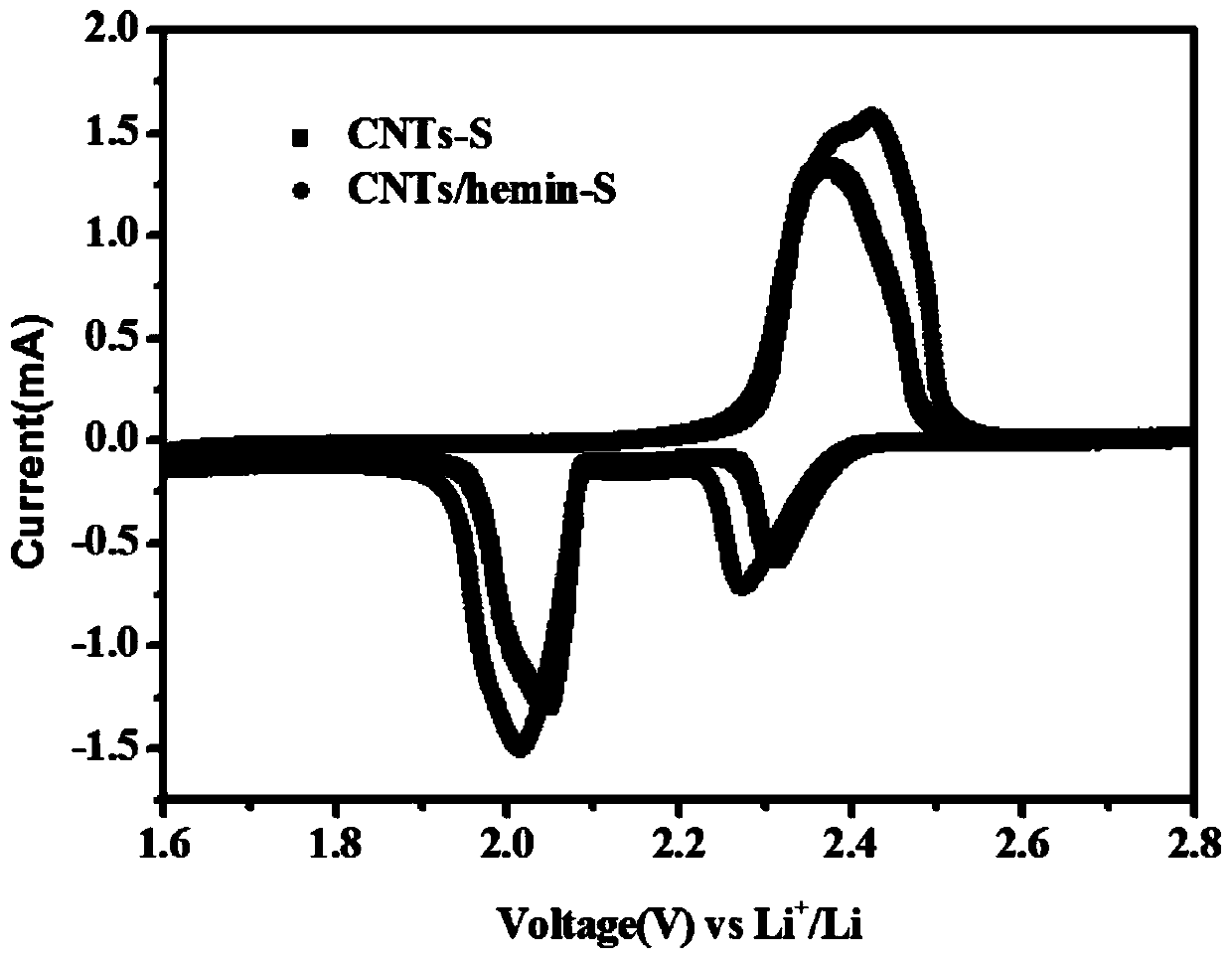
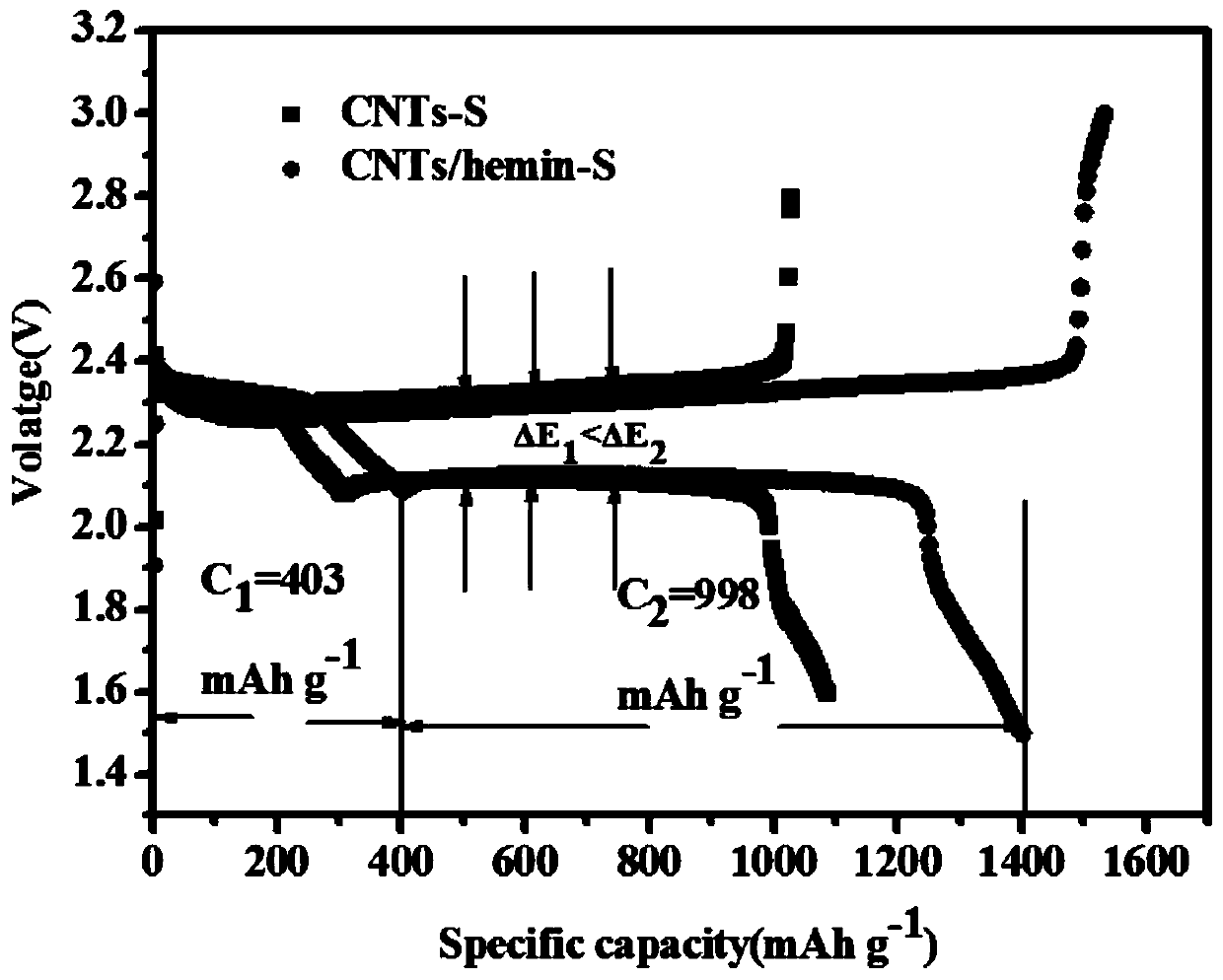
Preparation method of iron-containing porphyrin/carbon nano tube composite cathode material and application of composite cathode material in lithium-sulfur battery cathode
ActiveCN109755504ALow costLower internal resistanceCell electrodesFinal product manufactureCarbon nanotubePorphyrin
The invention provides a preparation method of an iron-containing porphyrin / carbon nano tube composite cathode material and application of the composite cathode material in a lithium-sulfur battery cathode. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking right amount of a carbon material by adopting a carbon tube, mixing and grinding with a sulfur elementary substance, adding CS2, fully stirring, and then drying, so that an iron-containing porphyrin / carbon nano tube composite cathode material is obtained; mixing the iron-containing porphyrin / carbon nano tube composite cathode material with carbon nano tubes and polyvinylidene fluoride, then adding N-methyl pyrrolidone and 1-10% iron-containing porphyrin, stirring, and ultrasonically and uniformly dispersing, so that slurry isobtained; and uniformly coating the obtained slurry on a current collector aluminum foil, and then drying, so that the iron-containing porphyrin / carbon nano tube composite cathode material is obtained. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple to operate, mild in conditions and easy for large-scale production; the problem that multiple sulfide ions are dissolved in liquid state electrolyte in charging and discharging processes of a lithium-sulfur battery can be solved, shuttle effect is effectively inhibited, and coulomb efficiency and cycling stability of the lithium-sulfur battery are improved.
Owner:WENZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting sulfide in sewage
ActiveCN103226126AImprove antioxidant capacityEliminate oxidationMaterial electrochemical variablesVoltmeterTurbidity
The invention provides a method for detecting sulfide in sewage. The method for detecting the sulfide in the sewage comprises the following steps that stabilizer and buffered solution are sequentially added in a water sample to be detected, pH of the water sample is adjusted to be 10.2-11.8, under magnetic stirring, a sulfide-ion-selective electrode and a reference electrode are adopted, standard zinc ion solution with 0.01mol / L concentration is used for titrating sulfide ions, a voltmeter is used for measuring electric potential change, positions before and after an equivalent point where abrupt changes occur in the electric potential are reaction endpoints, a second-order differential method is used for calculating the use level of the standard solution, and therefore sulfide ion content is calculated. According to the method for detecting the sulfide in the sewage, a sulfide-ion-selective electrode potentiometric titration mode is used for measuring the sulfide in the sewage, complex pretreatment for the water sample is unnecessary, and the measurement is not affected by ingredients, color and turbidity of the water sample, and the method for detecting the sulfide in the sewage is easy and convenient to operate, fast to analyze, accurate in results, good in effects of the adopted stabilizer, the buffered solution and titrating solution, and free of environmental damage.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
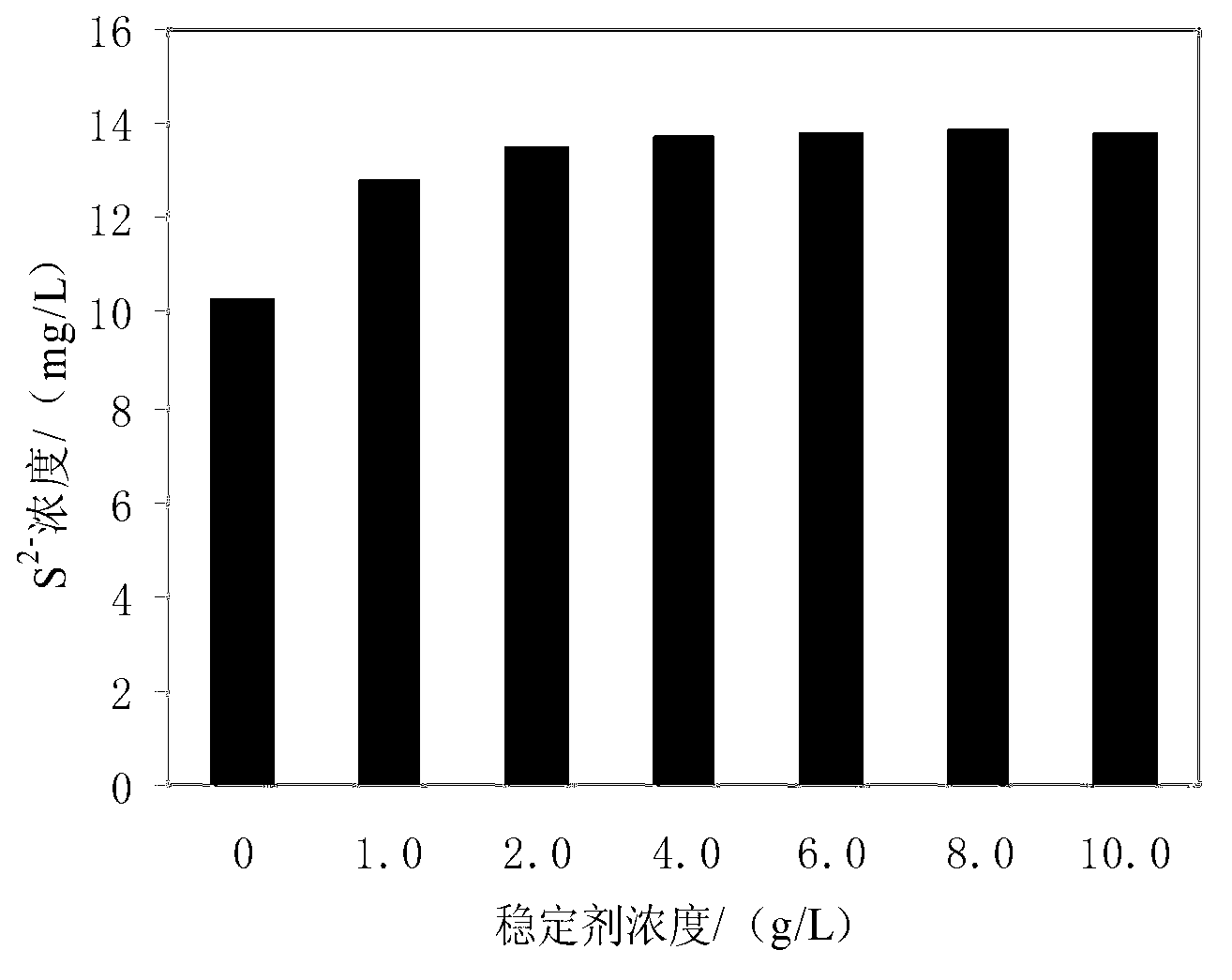
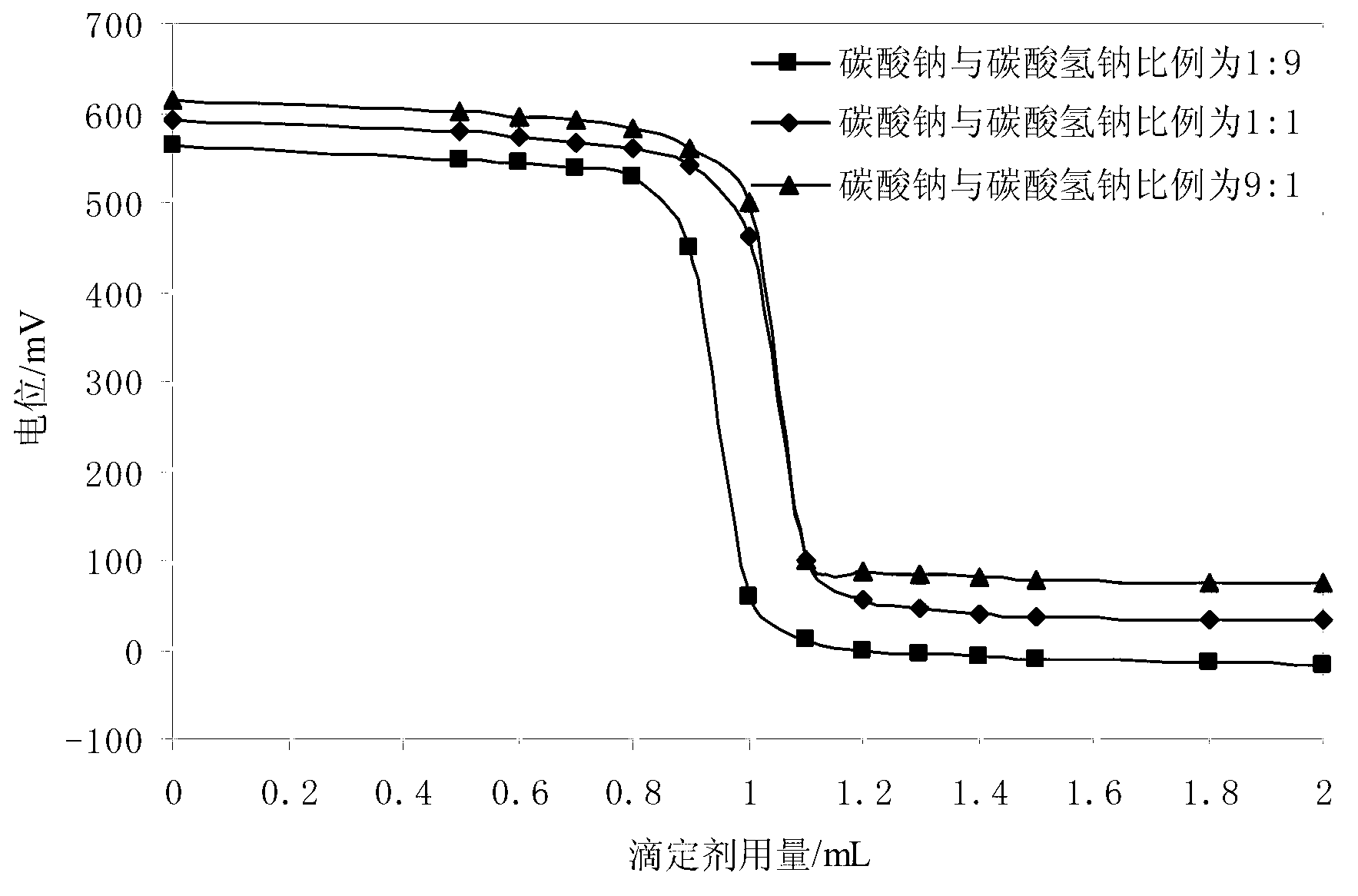
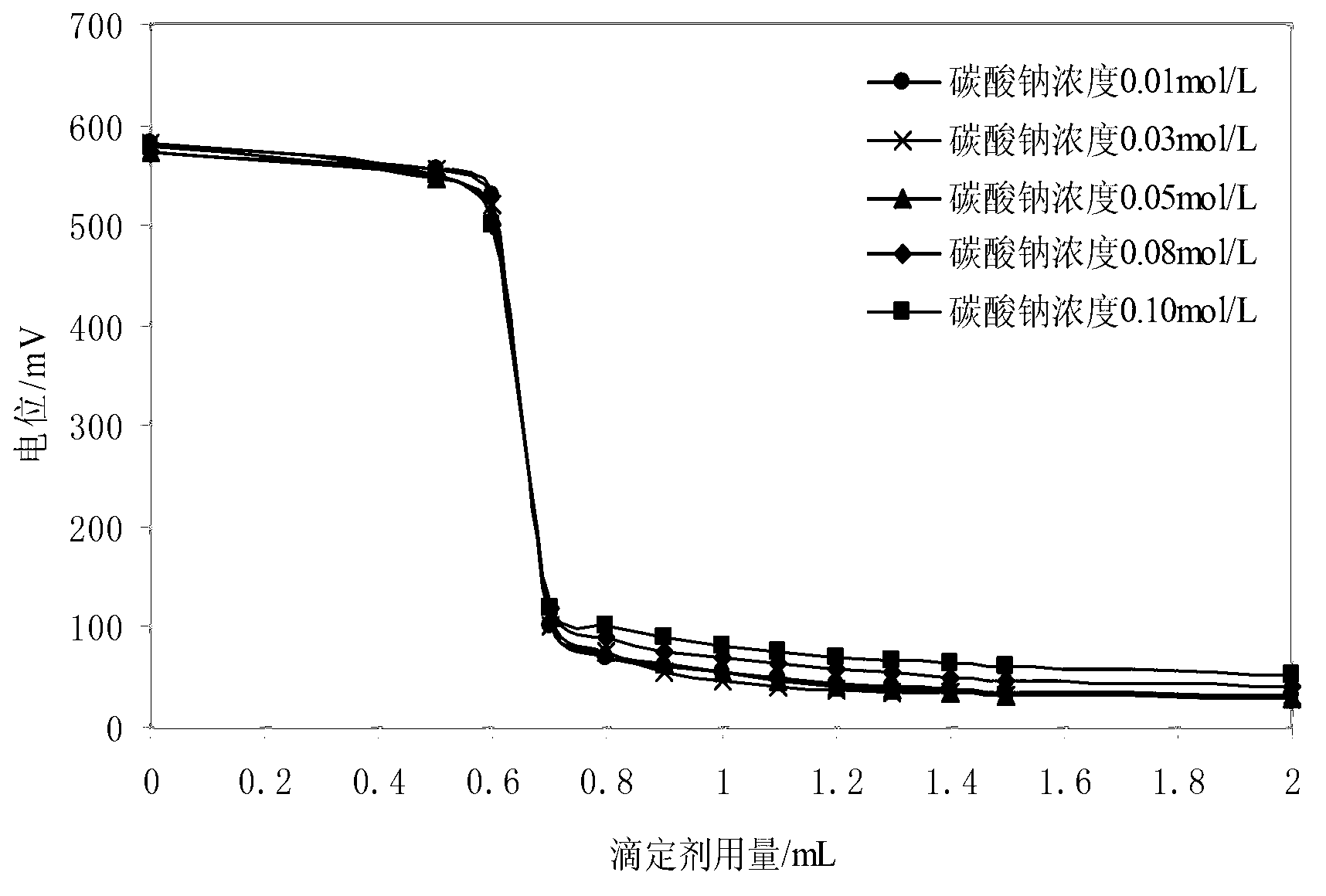
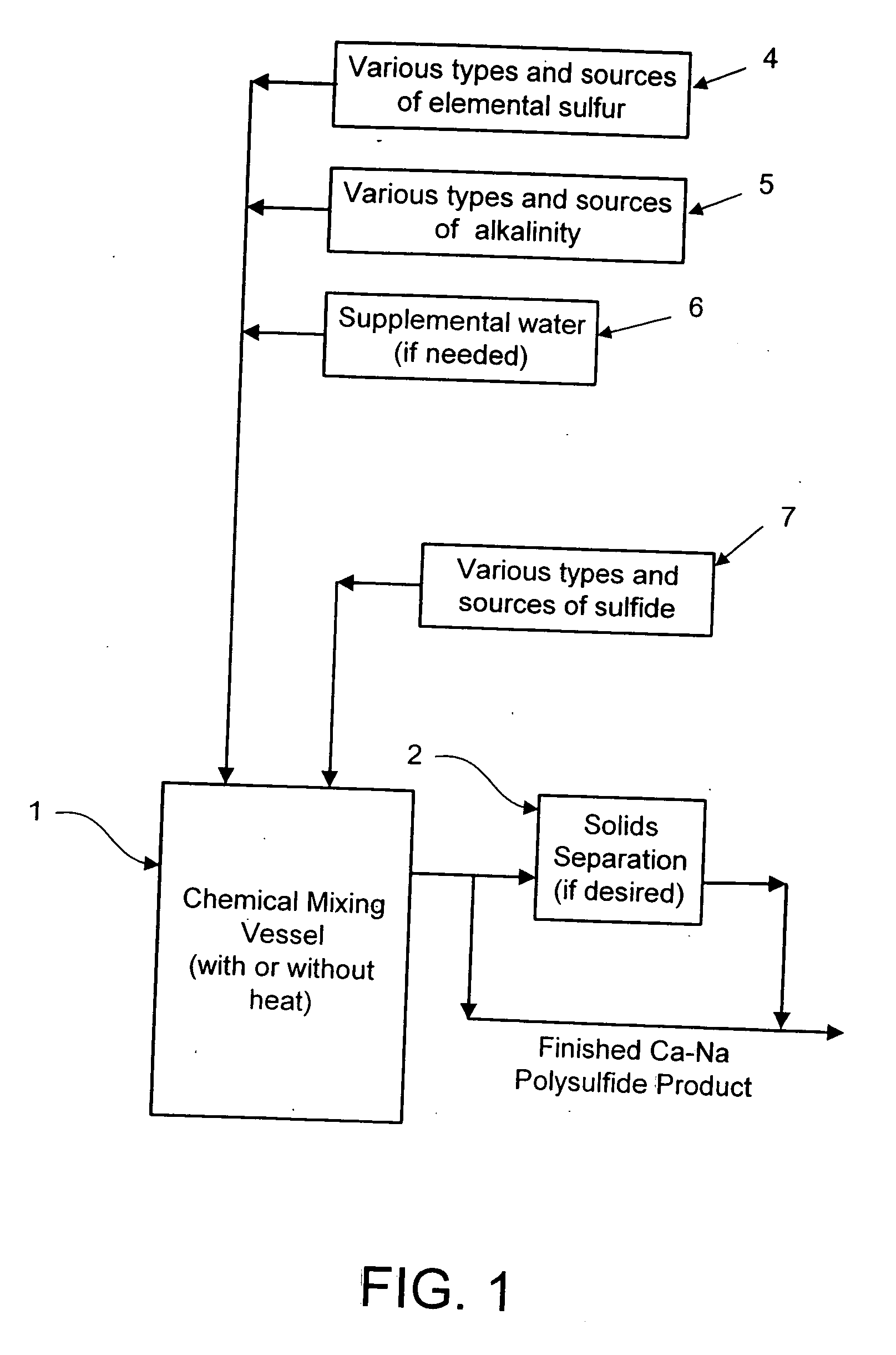
Calcium-sodium ploysulfide chemical reagent and production methods
InactiveUS20090202424A1Stabilize the oxyanion of chrome against excessive leachingFinal product manufactureDispersed particle separationWaste materialSodium polysulfide
A calcium-sodium polysulfide chemical reagent and methods for producing the reagent. The reagent is a blend of calcium polysulfide and sodium polysulfide that can be prepared using various types, sources and ratios of lime, elemental sulfur and sulfide ion using either virgin or waste materials. The reagent is amenable to inexpensive and high rate production methods at ambient or warmer temperatures. The reagent can be used to precipitate metals from wastewater, stabilize hexavalent chrome in hazardous waste residues, remove mercury from coal fired power plants, and as an electrolyte in large-scale bromide / polysulfide electrical storage batteries
Owner:REDOX TECH GRP LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com