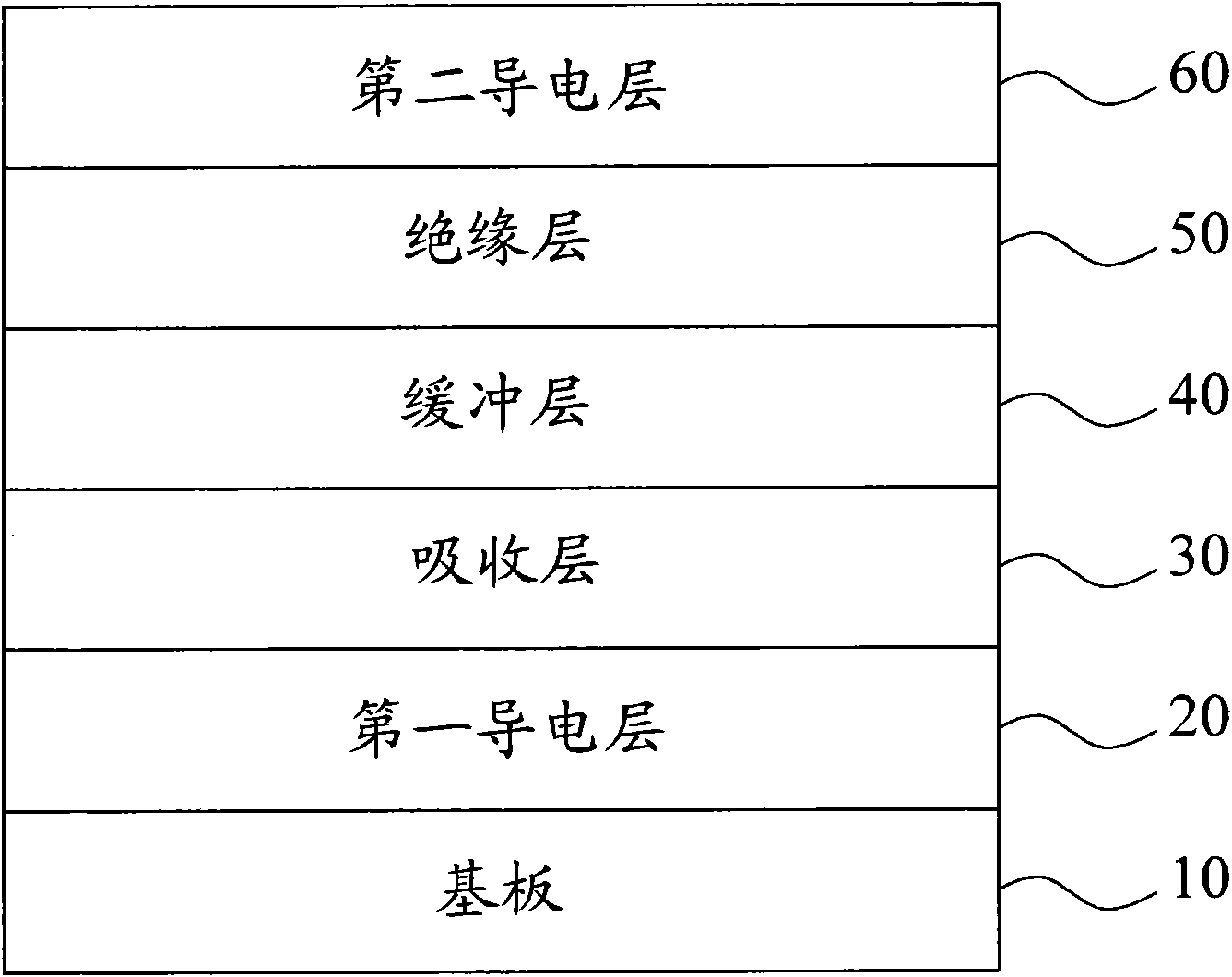
Patents
Literature
65 results about "SULFIDE ION" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
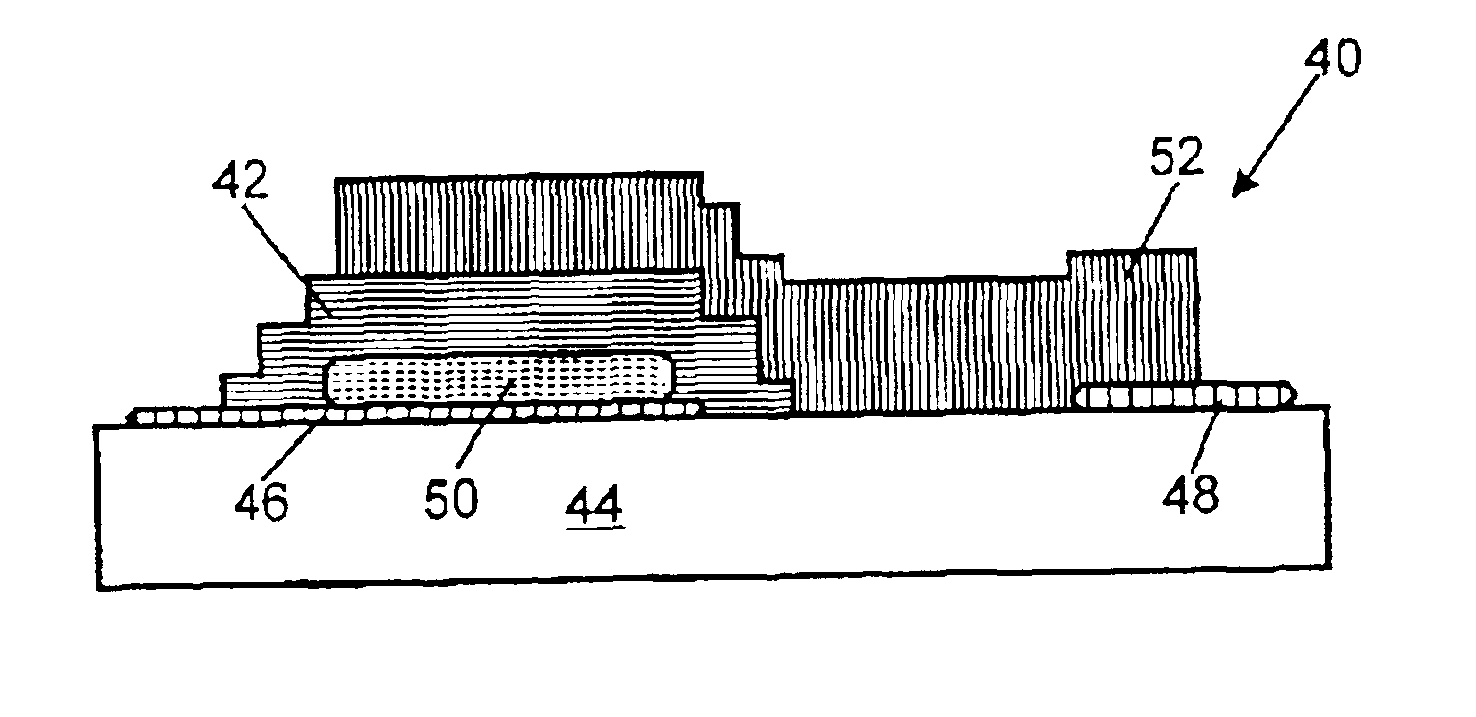
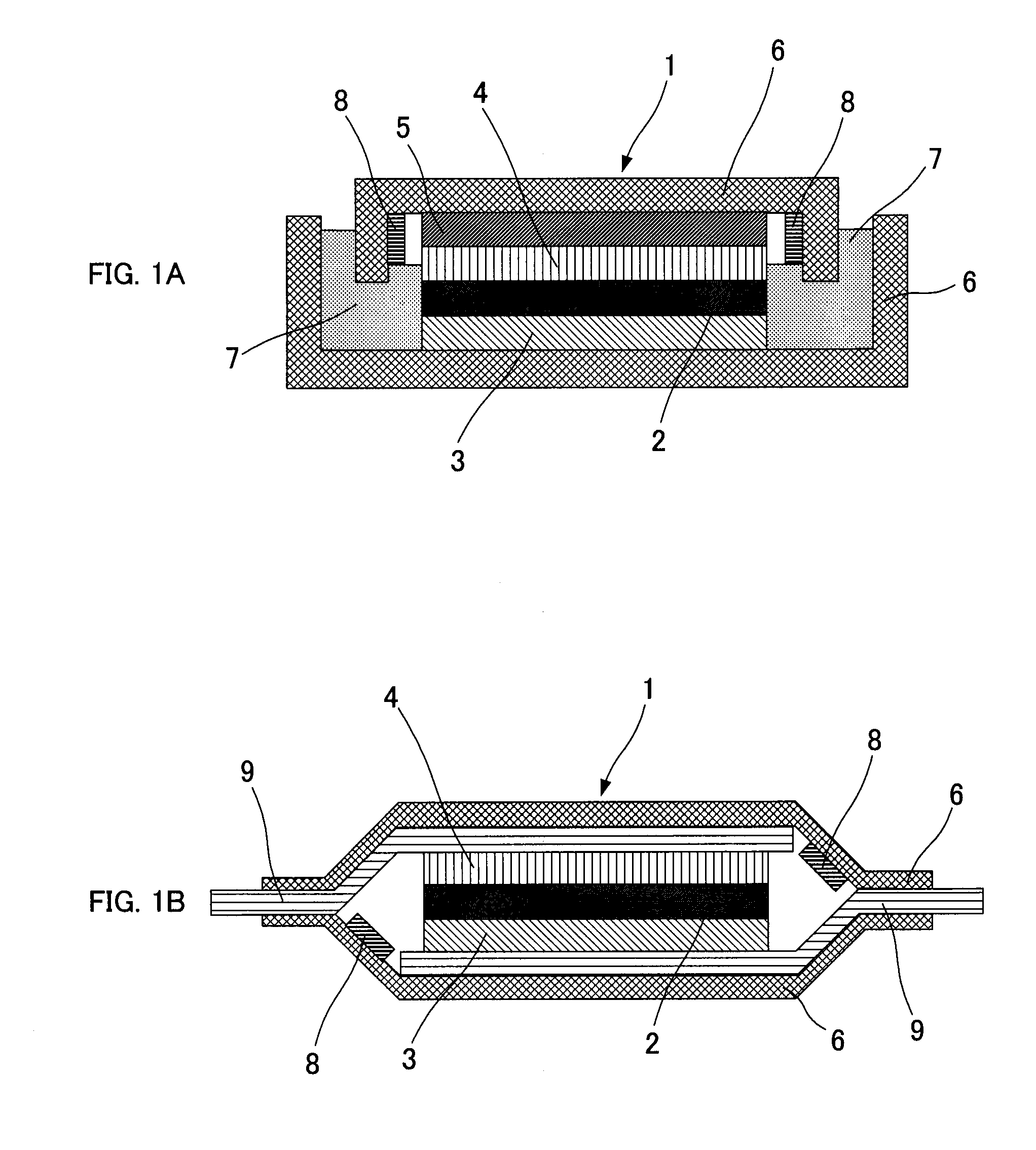
Thin film battery and electrolyte therefor
A solid amorphous electrolyte composition for a thin-film battery. The electrolyte composition includes a lithium phosphorus oxynitride material containing a sulfide ion dopant wherein the atomic ratio of sulfide ion to phosphorus ion (S / P) in the electrolyte ranges greater than 0 up to about 0.2. The composition is represented by the formula: where 2x+3y+2z=5+w, x ranges from about 3.2 to about 3.8, y ranges from about 0.13 to about 0.46, z ranges from greater than zero up to about 0.2, and w ranges from about 2.9 to about 3.3. Thin-film batteries containing the sulfide doped lithium oxynitride electrolyte are capable of delivering more power and energy than thin-film batteries containing electrolytes without sulfide doping.
Owner:OAK RIDGE MICRO ENERGY
All-solid-state lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS20110129723A1Avoid it happening againSolid electrolytesCell electrodesAll solid stateEngineering
A safe and highly-reliable all-solid-state lithium secondary battery using a sulfide-based solid electrolyte material which can restrain generation of hydrogen sulfide gas, in case a large amount of water is entered into a battery case by an accident such as submersion associated with a breakage of the container. An all-solid-state lithium secondary battery using a sulfide-based solid electrolyte material, wherein the battery has a metal salt M-X comprising a metal element “M” and an anionic part “X” in a battery case thereof, and further wherein a metal cation of the metal salt M-X generated by disassociation caused with water can react with a sulfide ion generated by a reaction between the sulfide-based solid electrolyte material and the water.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
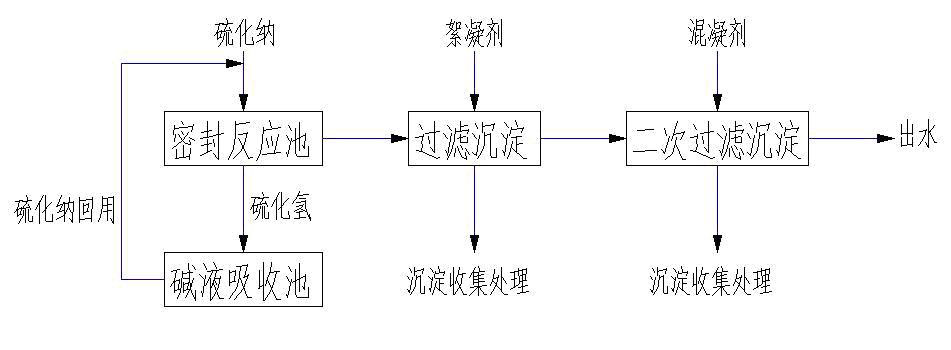
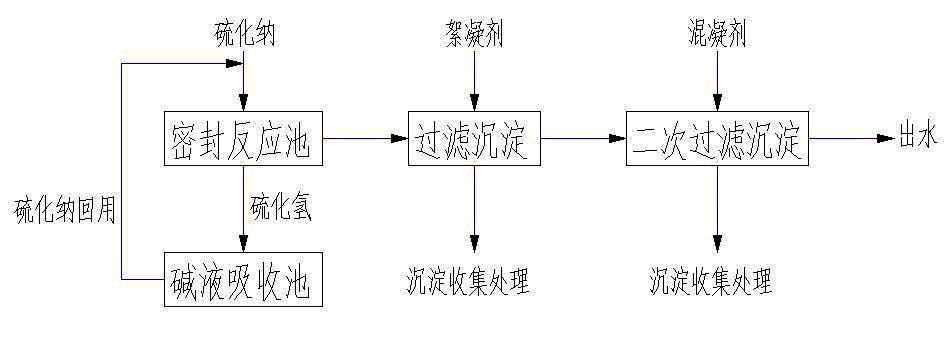
Method for treatment of wastewater containing heavy metal molybdenum
ActiveCN101928083AReduce processing costsReduce contentWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentSulfidationWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to a method for treatment of wastewater containing heavy metal molybdenum. The specific steps are as follows: placing the wastewater which needs to be treated and contains the heavy metal molybdenum into a sealing device; adding sodium sulfide into the device, controlling the pH value of the wastewater after adding the sodium sulfide at 2-3, carrying out reaction for 1-3h at room temperature, and continuously adding the generated sodium sulfide into the molybdenum-containing wastewater for recycling; adding a flocculant into the obtained solution, stirring, carrying out the reaction, standing till precipitate is settled, then discharging supernatant fluid, and passing through a filter device, wherein the precipitate of molybdenum sulfide can be recycled after collection treatment; and adding a mixed coagulant till the pH value of the obtained acid solution is neutral, stirring for removing redundant sulfide ions, standing for 2-5 min till the precipitate is settled, and then discharging the supernatant fluid for ensuring water quality of outlet water. The method for the treatment of the wastewater containing the heavy metal molybdenum has the prominent advantages of good treatment effect, simple treatment equipment, low treatment cost, recycling and utilization of the metal molybdenum and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Electrochemical process for decomposition of hydrogen sulfide and production of sulfur
The present invention includes a process for the removal of hydrogen sulfide from hydrogen sulfide gas containing gaseous streams. In one embodiment, the process comprises feeding a sulfide ion containing solution to an oxidation unit. The method further comprises feeding an oxidizing gas to the oxidation unit and contacting the sulfide ion containing solution with the oxidizing gas under sufficient conditions to form a polysulfide solution comprising polysulfide and hydroxide ions. In addition, the process comprises mixing the polysulfide containing solution with a hydrogen sulfide gas under conditions sufficient for absorption of hydrogen sulfide and precipitation of sulfur from the polysulfide containing solution. In some embodiments, the process comprises separating the precipitated sulfur from liquid.
Owner:PHILLIPS 66 CO
Process for the purification of acidic metal-bearing waste waters to permissible discharge levels with recovery of marketable metal products
InactiveUS7279103B2Quality improvementImprove performanceWaste water treatment from quariesWater contaminantsBioconversionPrecipitation
Acidic metal-bearing wastewaters are treated to produce a finished water of sufficient purity to meet discharge standards while recovering metals removed in forms which are commercially valuable. The metals are selectively precipitated, either in a batch or in a continuous system, for removal of individual metal products in a specific sequence of steps from the wastewater. In each step, the pH is adjusted to the specific pH range and sulfide ion is introduced to precipitate the metals, excepting the removal of ferric iron and aluminum which is achieved using hydroxide precipitation. Bioconversion process using unique equipment converts sulfate in the wastewater to the hydrogen sulfide gas required for the precipitation process. This bioconversion process reduces the sulfate in the wastewater so that the water can be directly discharged or used for agricultural applications.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY US
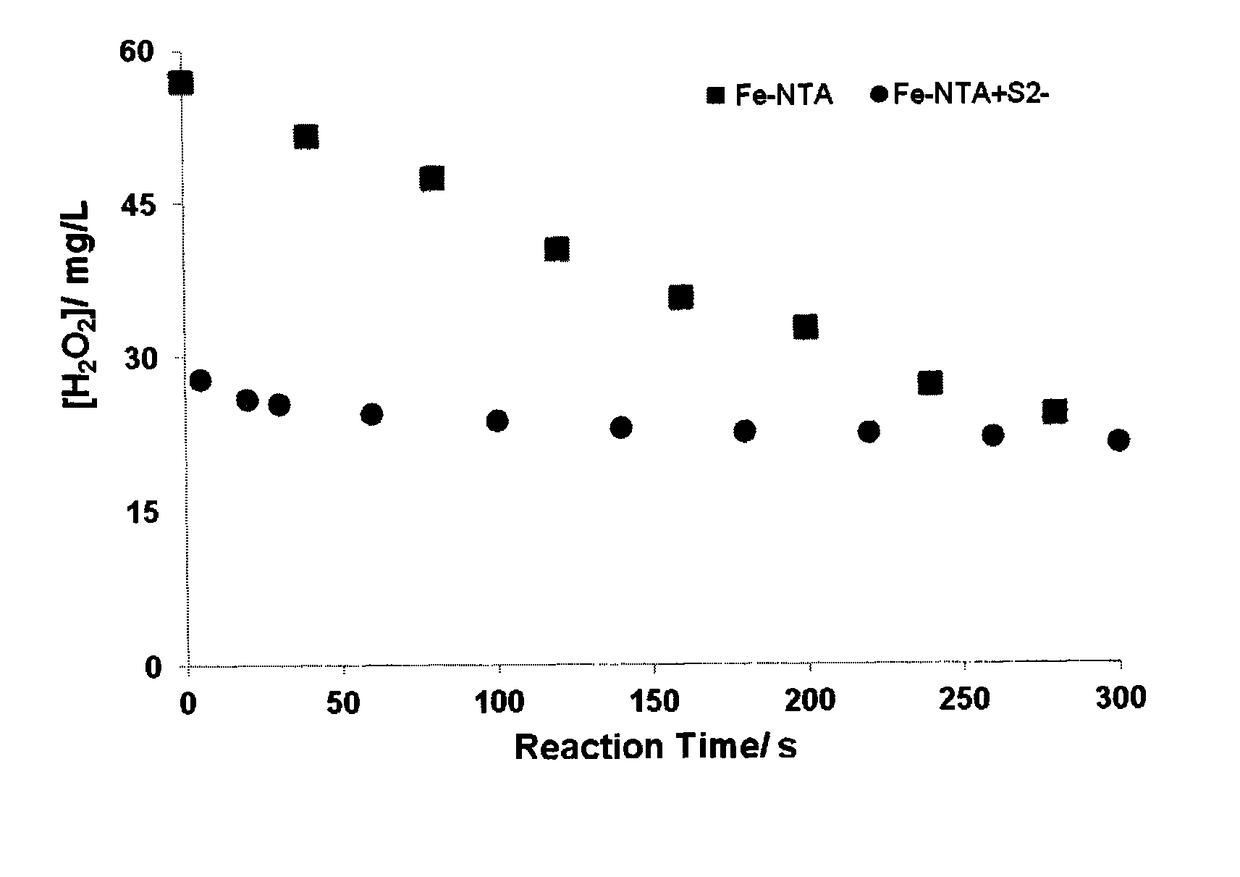
Process for treatment of a fluid comprising an oxidizable containment
ActiveUS20160200605A1Reduce concentrationIncrease ratingsWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsBenzeneWastewater
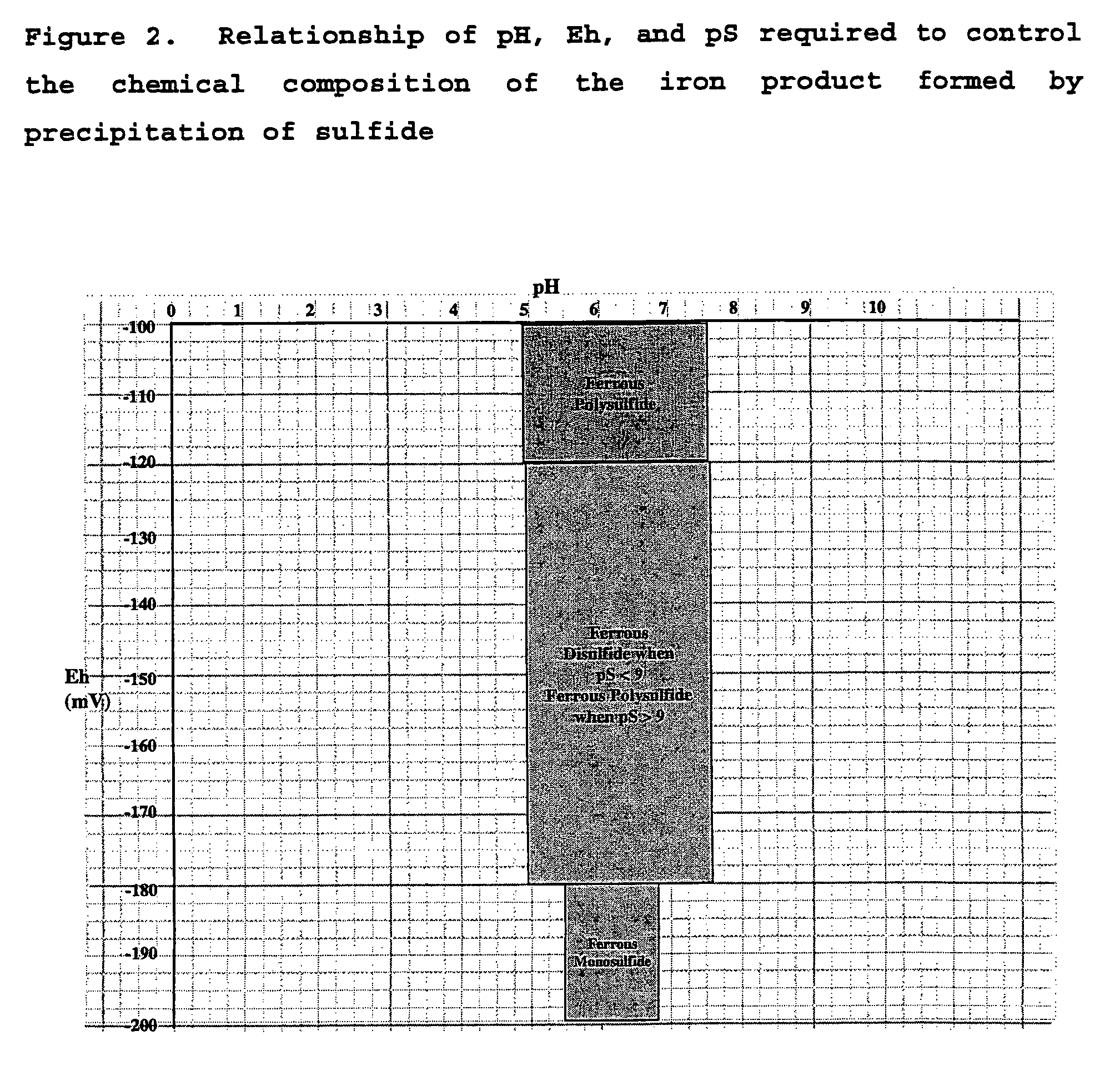
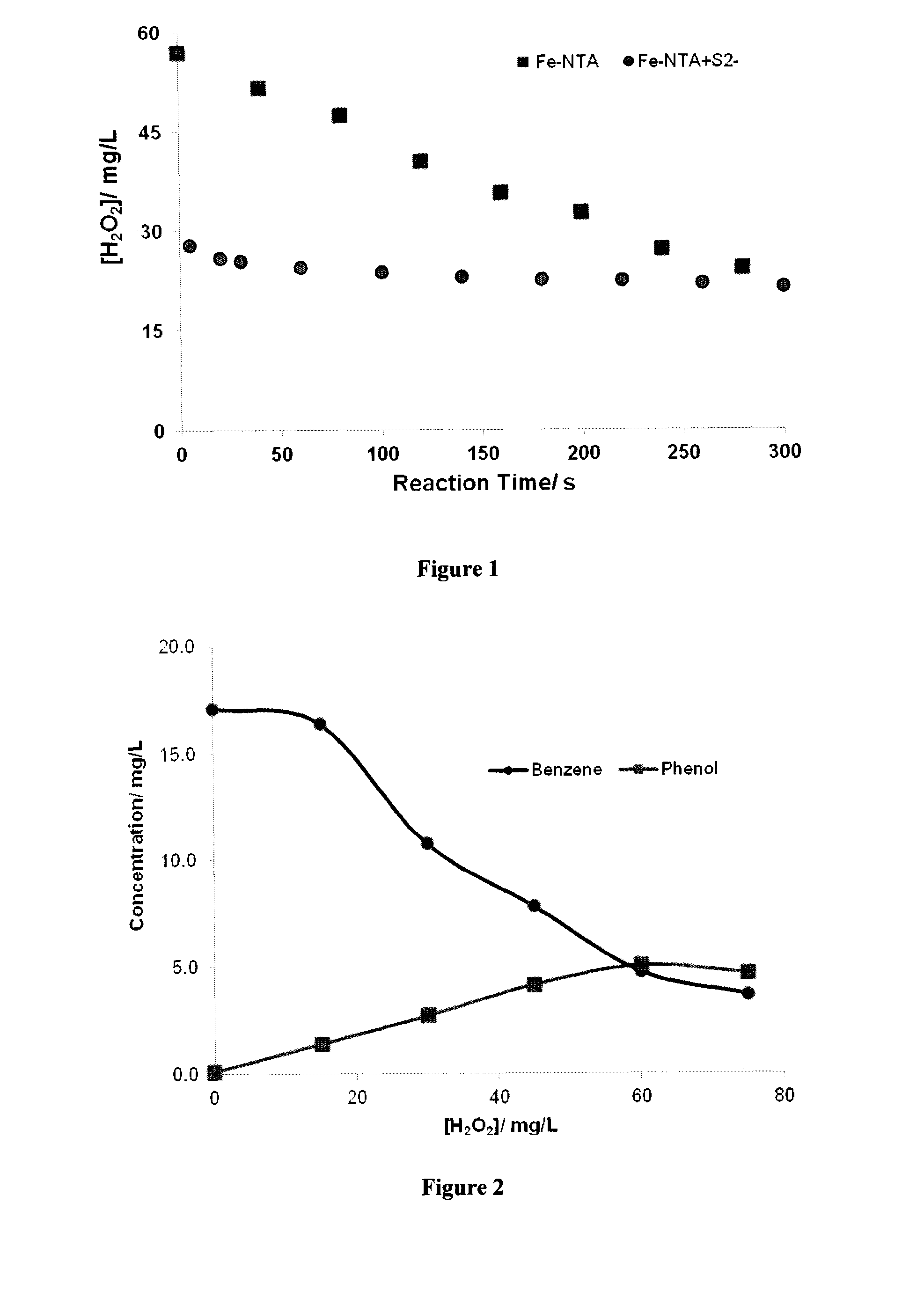
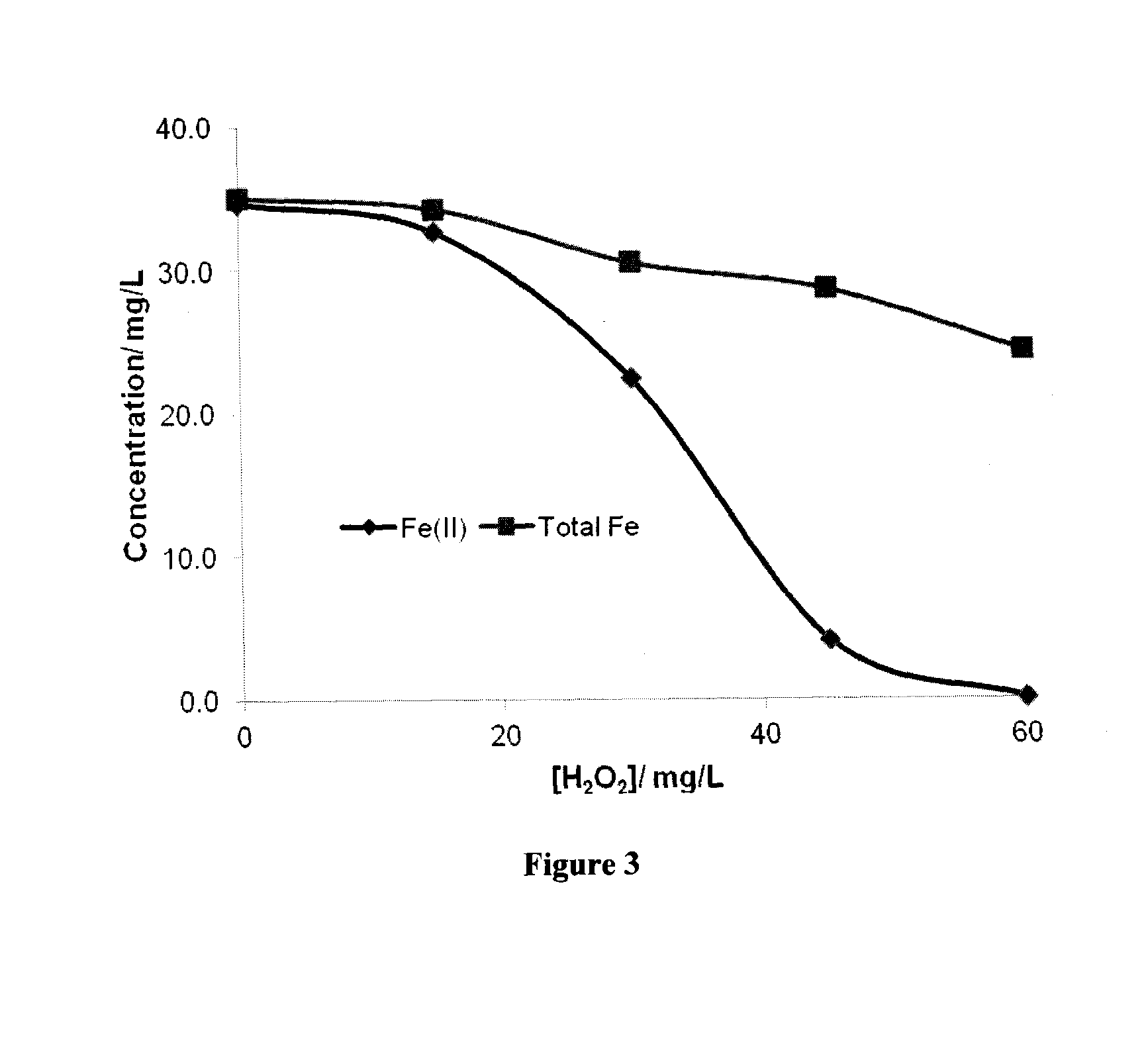
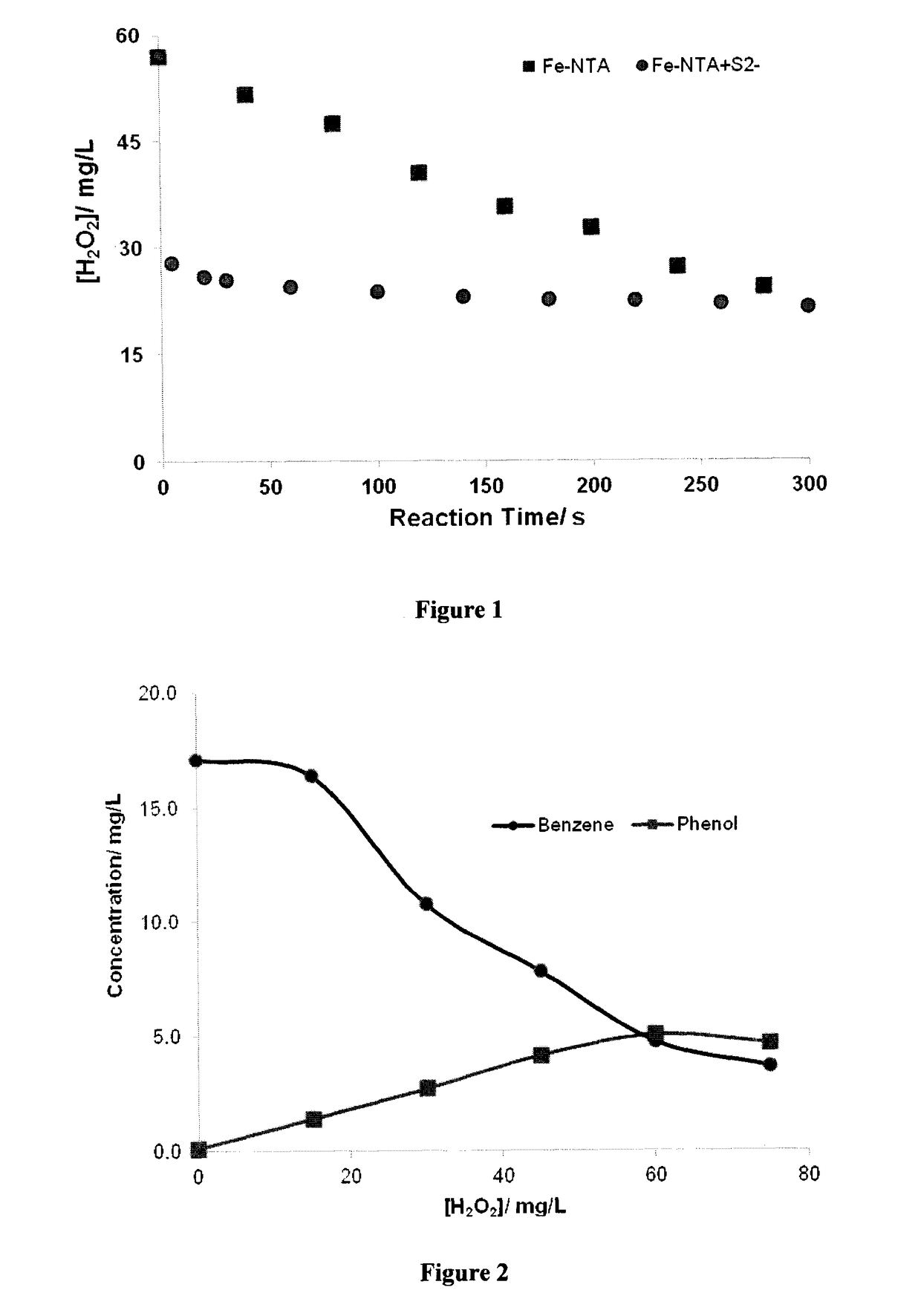
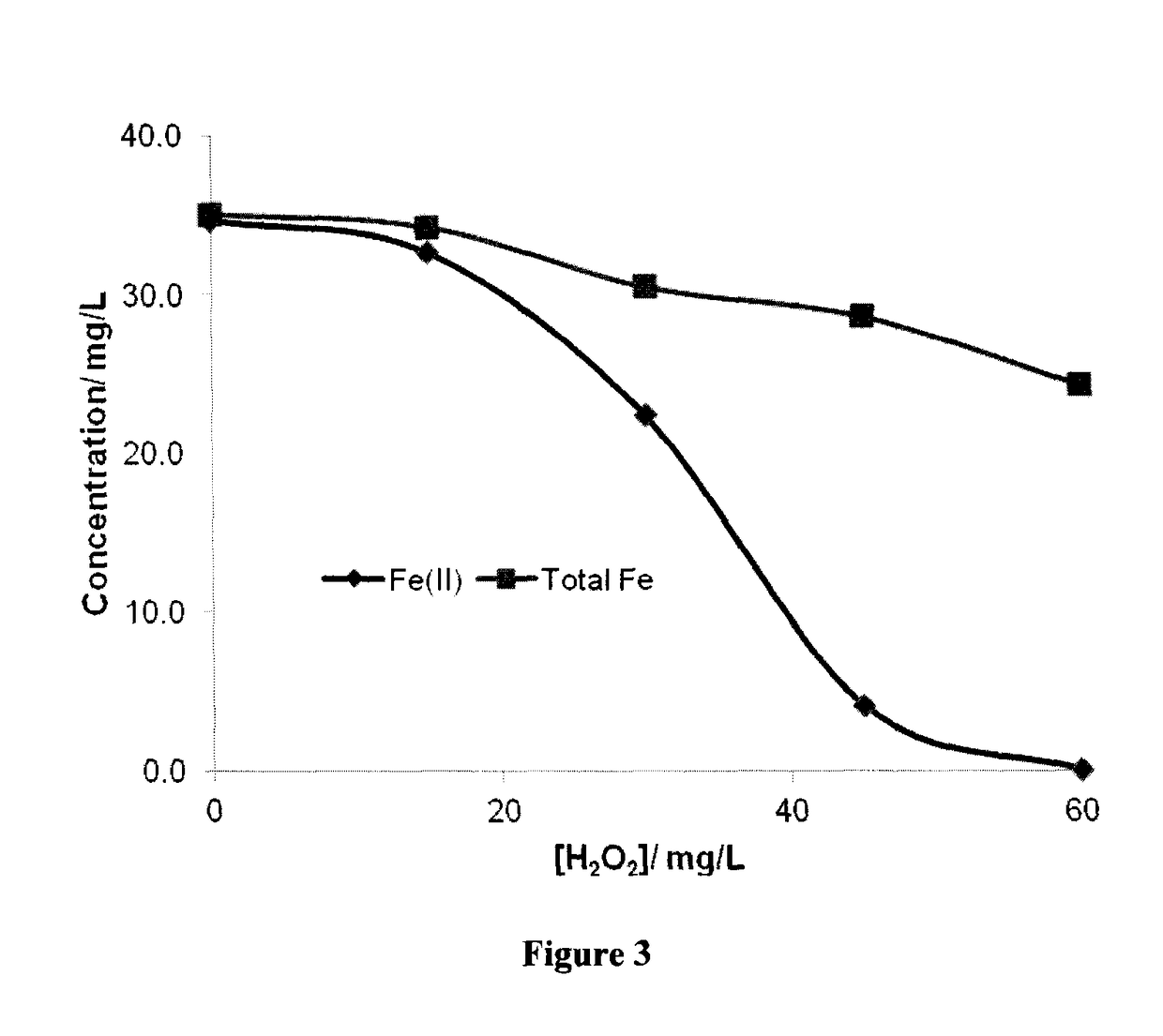
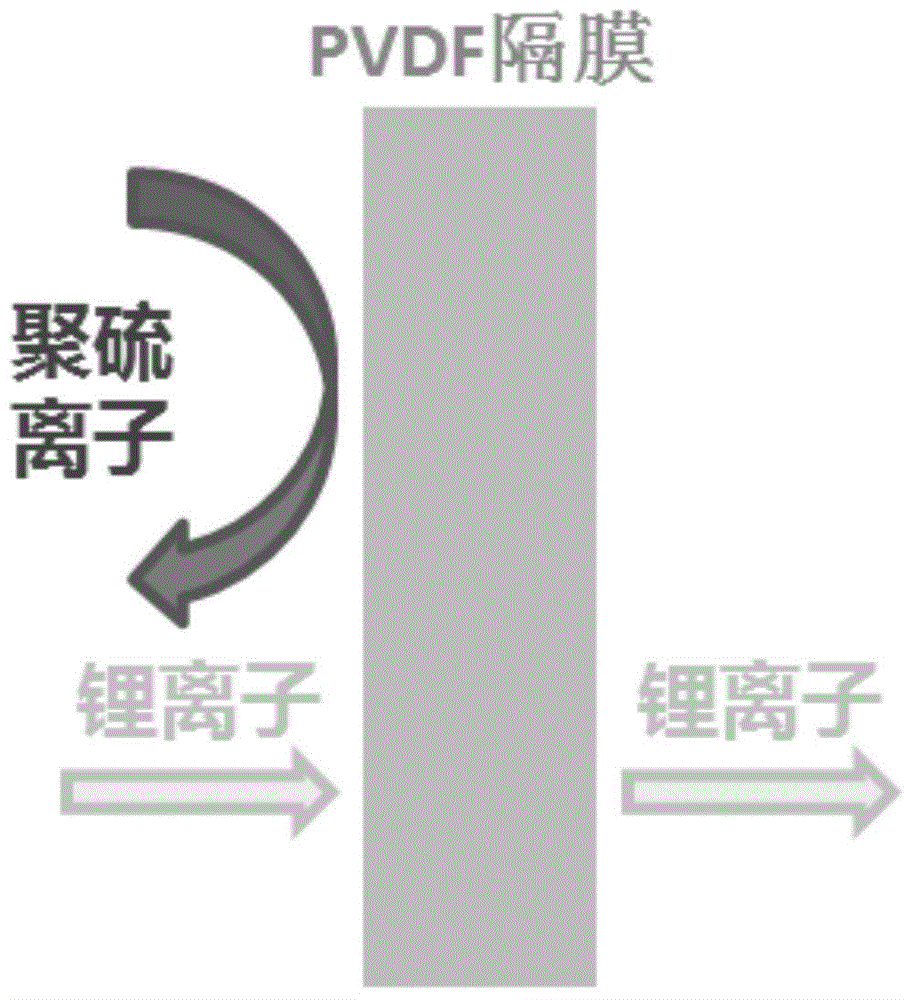
There is described a process for treatment of a fluid comprising an oxidizable contaminant. The process comprises the step of contacting the wastewater with a combination of: (i) a sulfide, (ii) a complex of Fe(III) and a chelating agent, and (iii) an oxidant. It has been discovered that of treatment of a fluid containing an oxidizable contaminant employing iron(III)-chelates as the Fenton catalyst may be significantly improved by including a sulfide in the reaction scheme. As described herein, by employing sulfide ion, the present inventors have been able to: (i) increase the rate of iron recycling from minutes or hours to a few seconds, and (ii) destroy benzene in an oil and gas refinery (OGR) wastewater in less than one minute. It is believed that these findings in OGR wastewater can be extended to other fluids containing other oxidizable contaminants.
Owner:TROJAN TECH
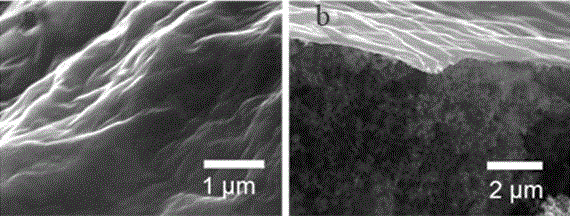
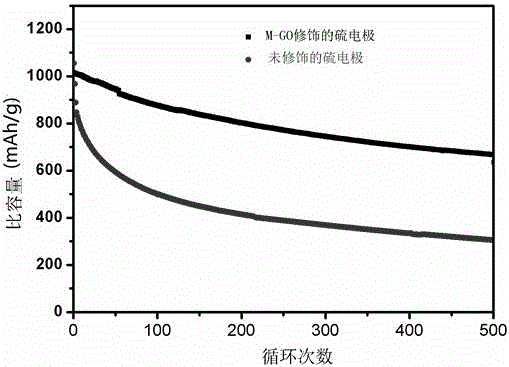
Lithium sulfur battery based on modification of graphene oxide thin film
InactiveCN105047982AImprove cycle stabilityImprove energy efficiencyCell electrodesLi-accumulatorsMetallic lithiumElectrolytic agent
The invention discloses a lithium sulfur battery. The lithium sulfur battery comprises a sulfur electrode, a metallic lithium electrode and a diaphragm and an electrolyte which are arranged between the sulfur electrode and the metallic lithium electrode. The lithium sulfur battery is characterized in that the sulfur electrode is modified by a graphene oxide thin film, and the sulfur electrode is prepared according to the following steps of: grinding and mixing a carbon sulfur compound, a conductive agent and an adhesive according to proportions, dissolving the obtained materials in N-methyl pyrrolidone to prepare paste, applying the paste onto a current collector, and drying the current collector to prepare the sulfur electrode for modification; preparing graphene oxide, and dissolving the graphene oxide in ethanol, wherein the concentration is 0.5-5 mg / mL; and uniformly adding the ethanol solution of the graphene oxide onto the surface of the modified sulfur electrode dropwise, and drying the surface of the modified sulfur electrode. By the graphene oxide thin film prepared according to the invention, polysulfide ions can be effectively bound and are greatly prevented from diffusing to the outside of the sulfur electrode, meanwhile, lithium ion transmission cannot be blocked, thus, oxidation shuttle effect in the lithium sulfur battery is suppressed, and the problem that the capacity is reduced dramatically due to the loss of active substance sulfur is solved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
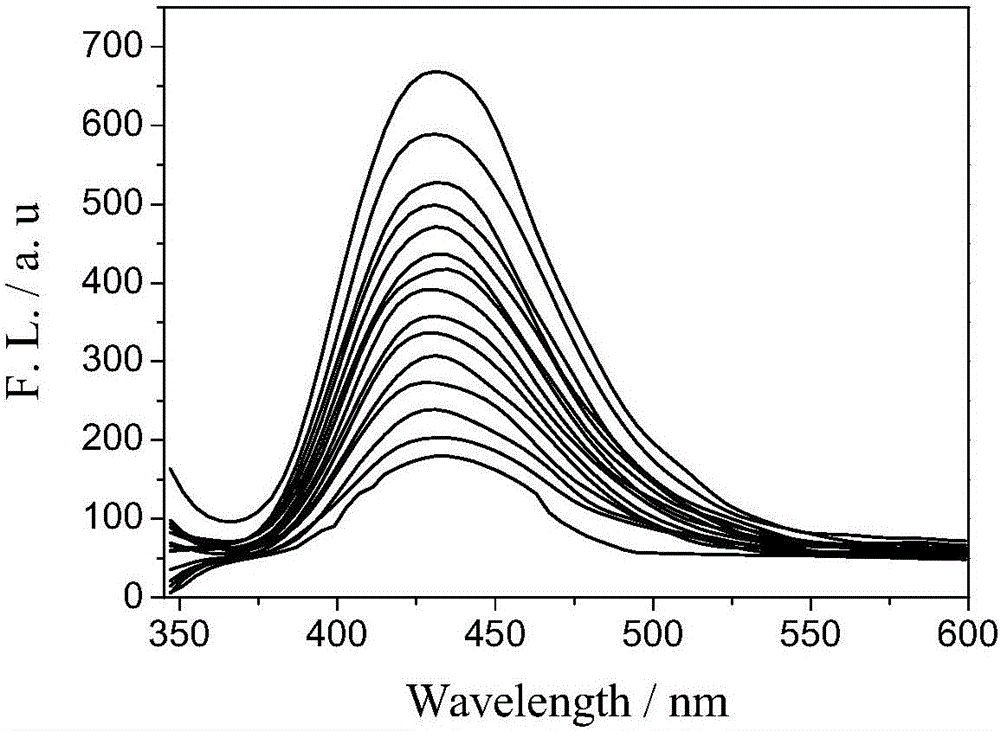
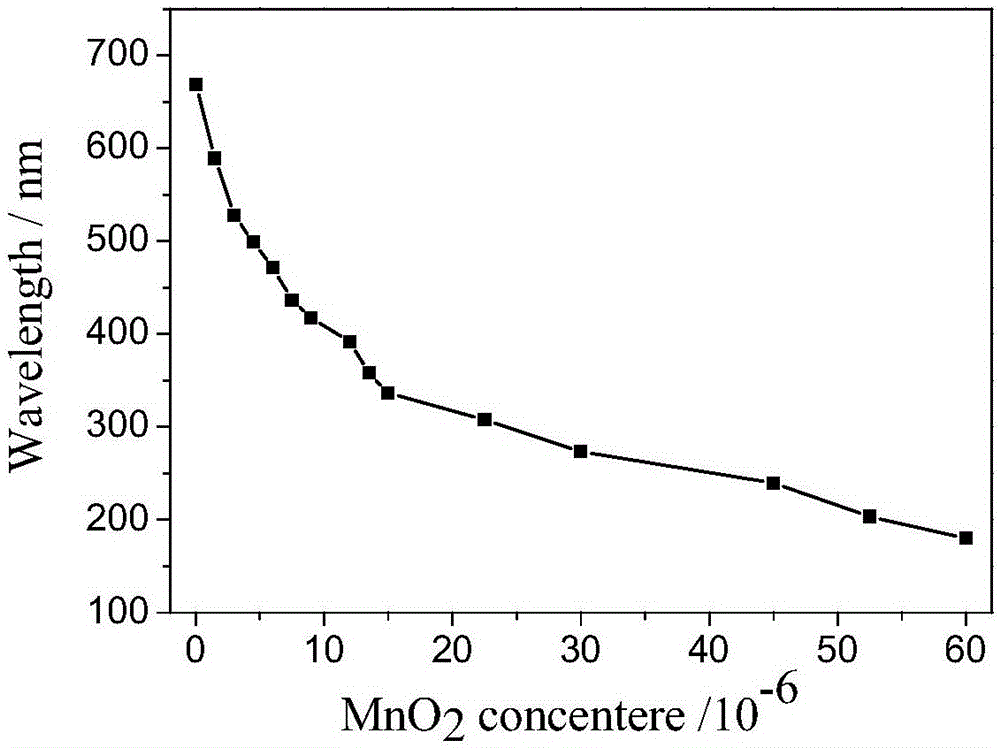
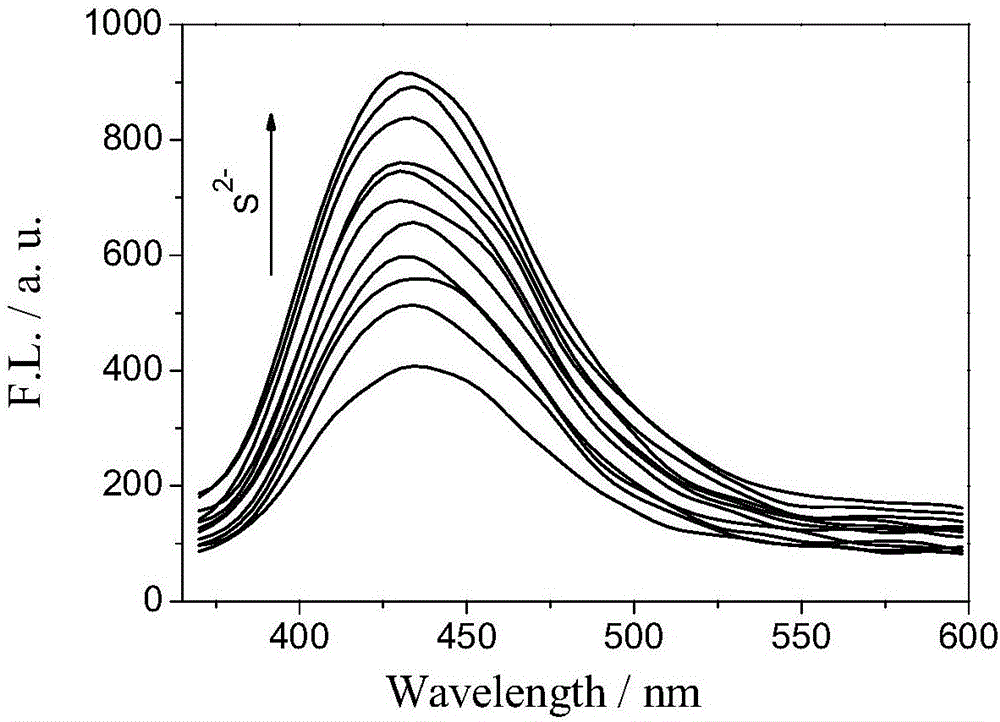
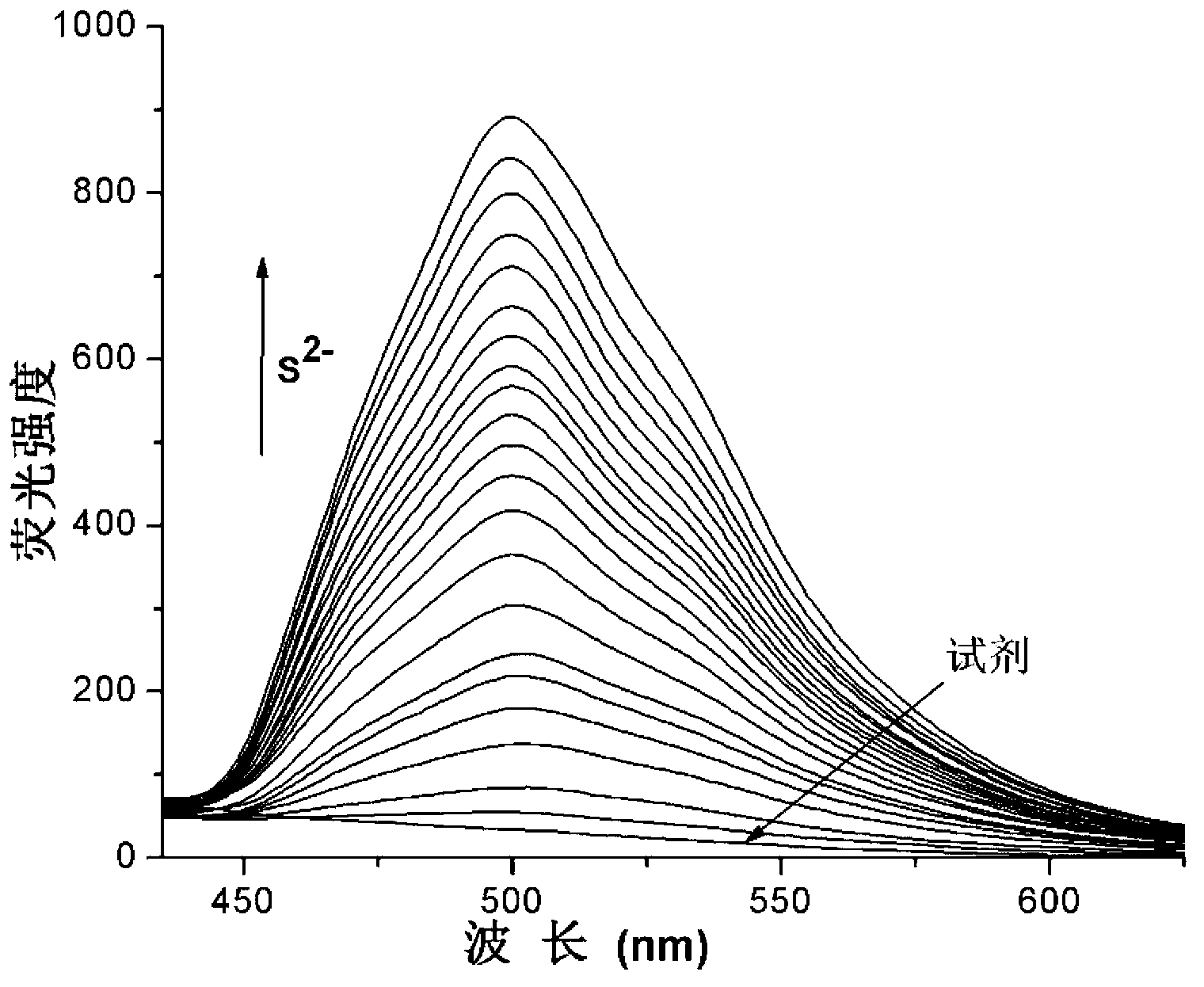
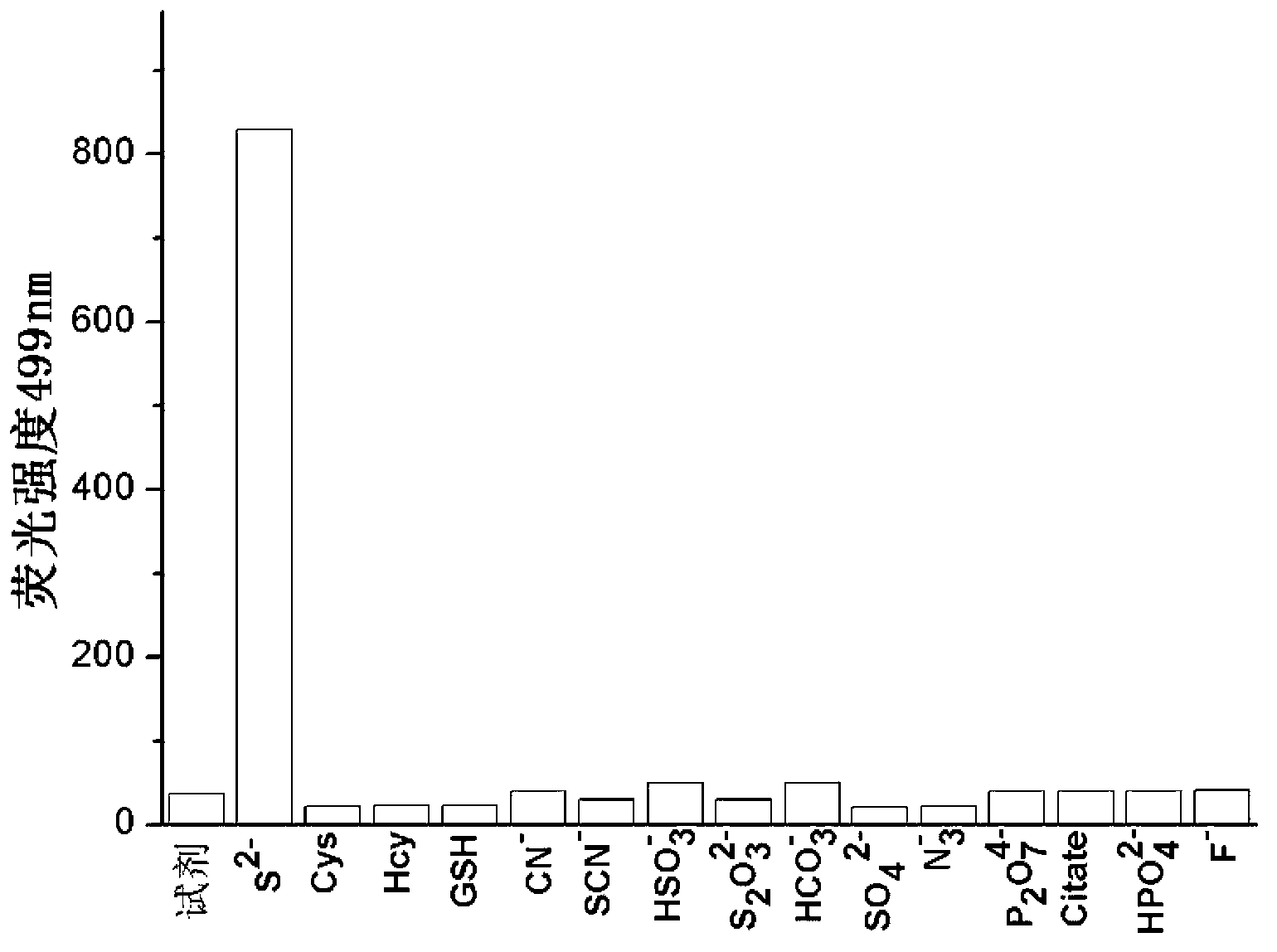
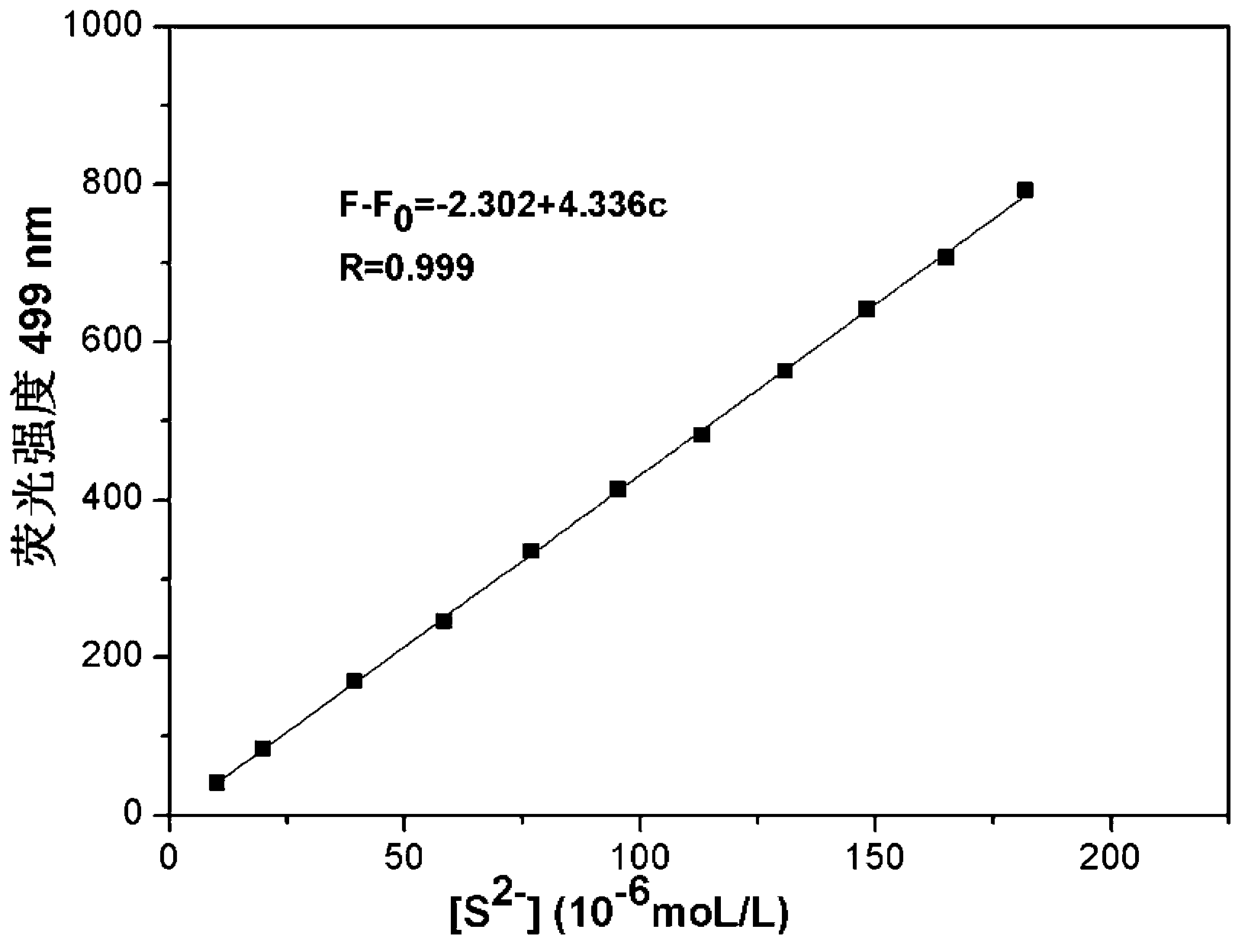
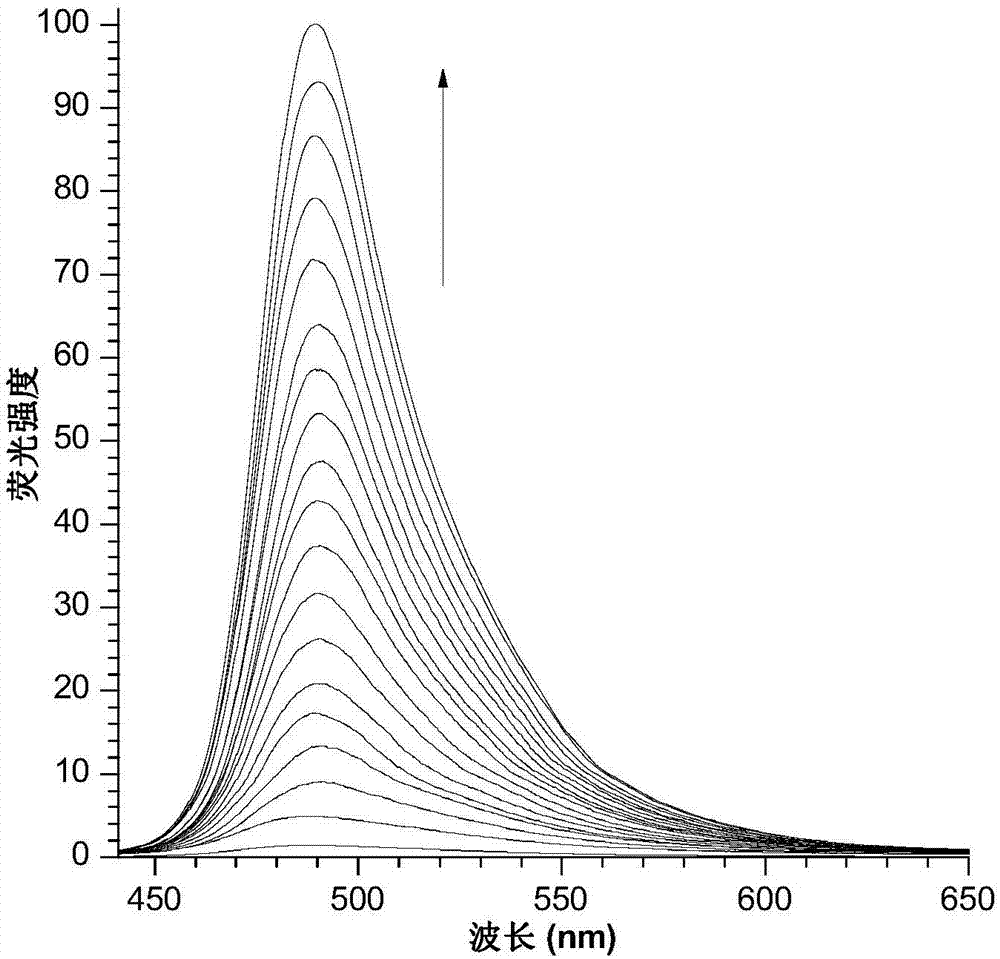
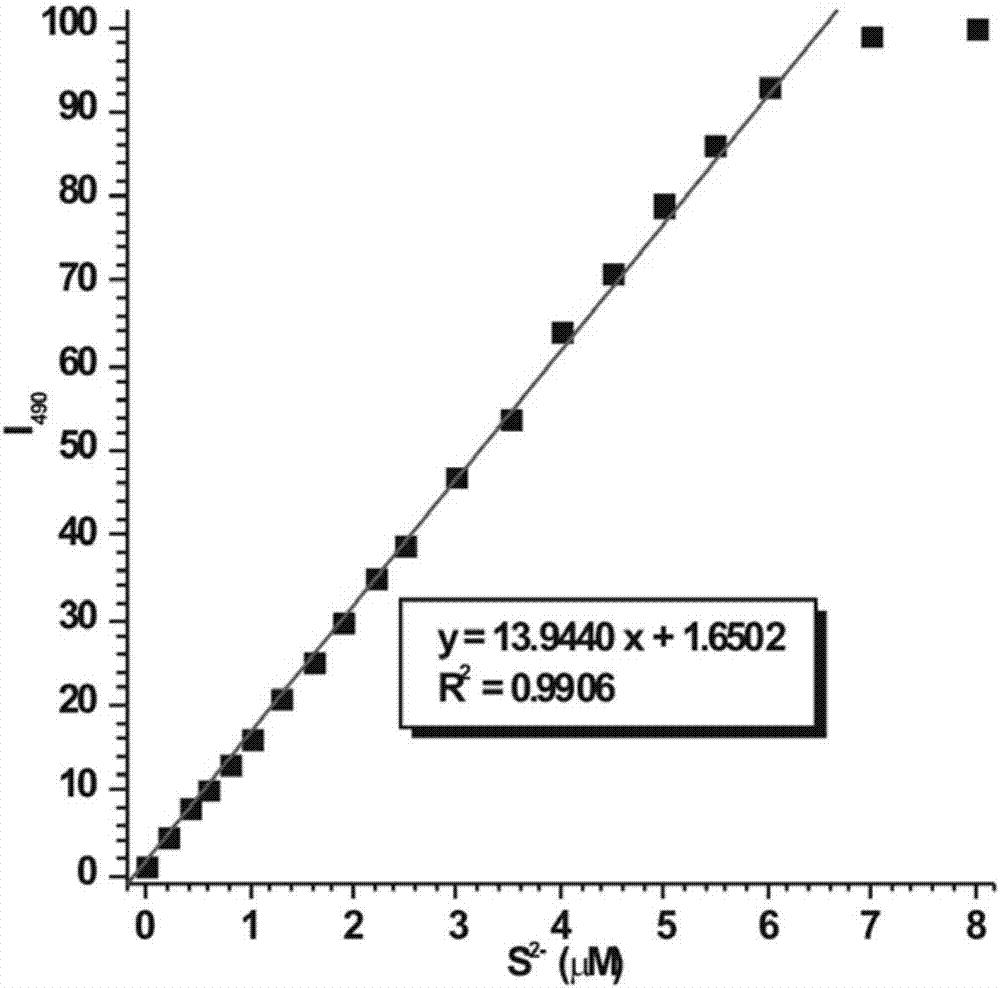
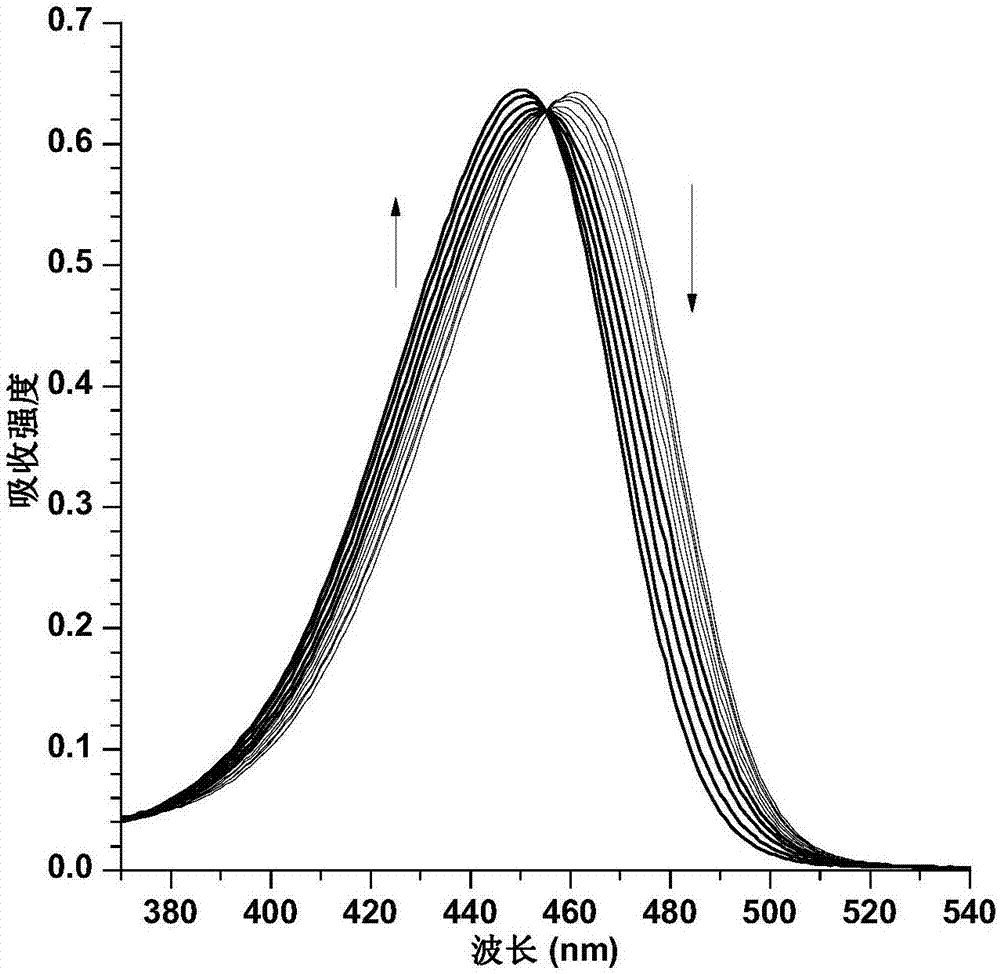
Fast sulfide ion test method
ActiveCN106442448ALarge specific surface areaRich structural diversityFluorescence/phosphorescenceSulfonateLinear relationship
The invention provides a fast sulfide ion test method. The method uses a property of ANS that the fluorescence of 4-Amino-1-Naphthalene sulfonate (ANS) can be effectively quenched by MnO2 nano-material to prepare the ANS / MnO2 composite system. When tiny portion of S<2-> is added in the system, because the oxidation-reduction reaction occurs between the S<2-> and MnO2 to generate divalent manganese ions in the solution, thus enhancing the fluorescence intensity of the ANS, and the increase of the fluorescence intensity is in a linear relationship with the S<2-> ions concentration, thus achieving the test of S<2-> ion. Compared with prior art the method has the advantages of being simple in operation and being able to test the S<2-> ion in a fast and real time mode.
Owner:广西弘远环境监测有限公司
Method for detecting sulfide ions
The invention provides a fluorescence detection method for sulfide ions, which is a method for quantitatively detecting the sulfide ions based on perylene-3, 4, 9, 10-tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps of: adding sulfide ions into HEPES (4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid) containing the perylene-3, 4, 9, 10-tetracarboxylic acid dianhydride with the pH of 7.0 (without fluorescence emission), producing strong fluorescence emission and realizing the detection of the sulfide ions. According to the detection method, high sensitivity and selectivity are showed against the sulfide ions, and the method has the advantages of low price of a detection reagent, simplicity and convenience in detection process, sensitivity, quickness and accurate detection result.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Complex for rapidly detecting sulfide ions, and quantitative analysis method and applications thereof
ActiveCN106957321AQuick responseSignificant fluorescence enhancement responseOrganic chemistryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological cellImaging analysis
The invention discloses a complex for rapidly detecting sulfide ions. The complex is a coumarin derivative and copper ion complex, and is applied as a sulfide ion fluorescent sensor. When being used for detecting sulfide ions in an aqueous solution as the fluorescent sensor, the complex shows obvious fluorescence enhancement response, the response speed is fast, and the real-time detection on the sulfide ions can be realized; the detection sensitivity is high, the detection limit is low up to 90nM; the concentration of sulfide ions in a to-be-detected sample can be accurately quantitatively analyzed by utilizing a standard curve; the complex has superhigh selectivity on the sulfide ions, and has almost no interference to other common negative ions; the complex has good biocompatibility and can be successfully applied for fluorescence imaging analysis of the sulfide ions in biocells; and both the fluorescence spectrum and ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum are responded, and the double-channel detection on the sulfide ions can be realized.
Owner:襄阳市大学科技园发展有限公司
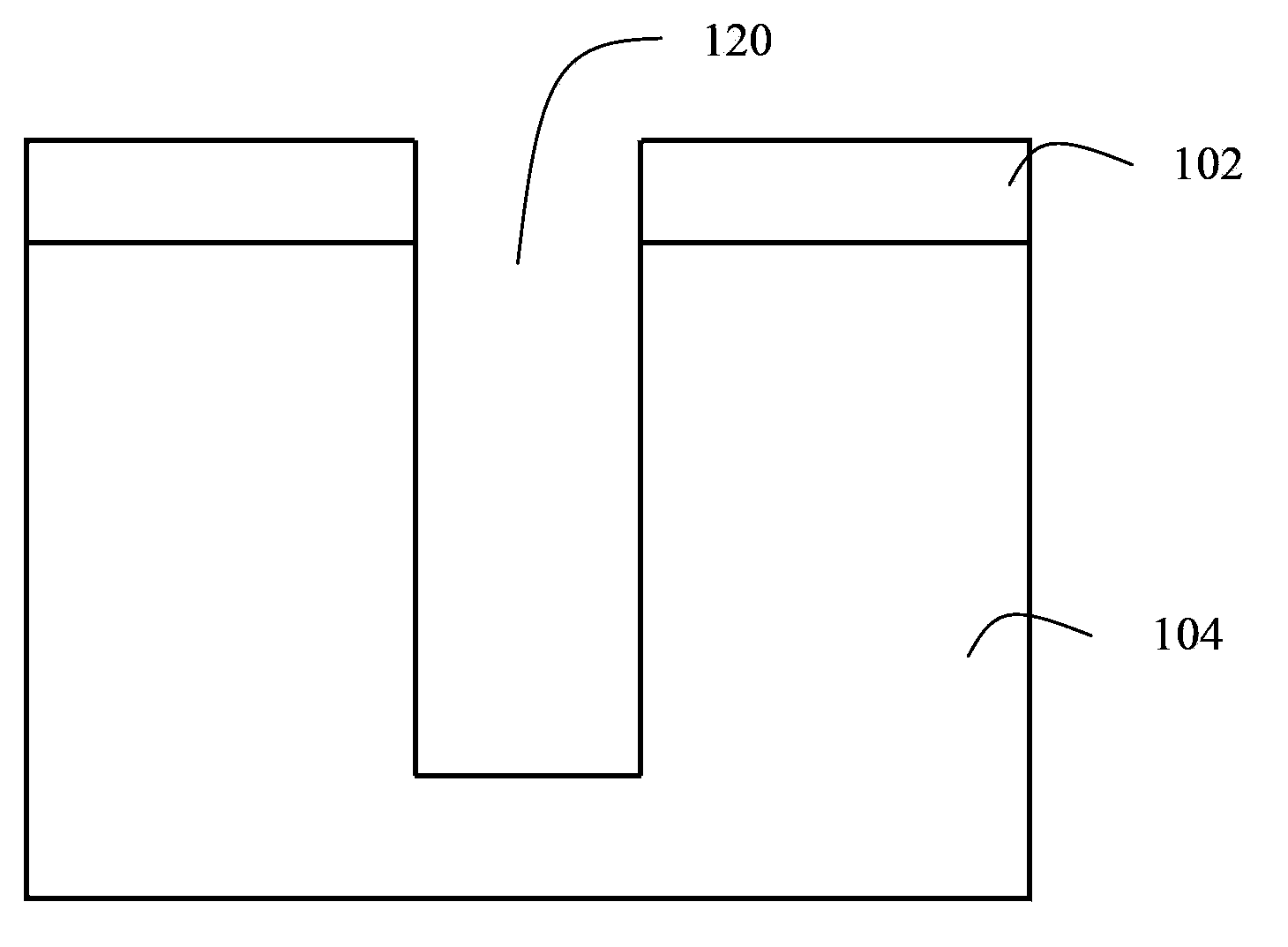
Method for improving the shape of side wall of through hole
InactiveCN103779201ASlow etch rateSlow lateral etch rateSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbon ionHydrogen
The invention provides a method for improving the shape of the side wall of a through hole. The method comprises the following steps: a silicon substrate is placed in a plasma etching chamber; reaction gases are bubbled into the plasma etching chamber, wherein the reaction gases include a fluorine-containing gas and one or two of COS and H2S; and carbon ions, oxygen ions, hydrogen ions and sulfide ions which are generated by COS or H2S are reacted with side wall silicon to produce a carbon-silicon compound, a silicon-oxide compound, a silicon-sulfur compound and a silicon-hydrogen compound, and the compounds are attached to the side wall and the bottom of a silicon through hole to form a passivation layer. An F plasma vertically bombards the passivation layer or Si at the bottom under high power, Si at the bottom of the hole can be quickly etched, and the F plasma etches the passivation layer at a low speed as the F plasma does not apply vertical kinetic energy force to the side wall of the hole. Therefore, in the whole etching process, the rate of lateral etching is low, and the aeolotropism is good.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO FAB EQUIP INC CHINA
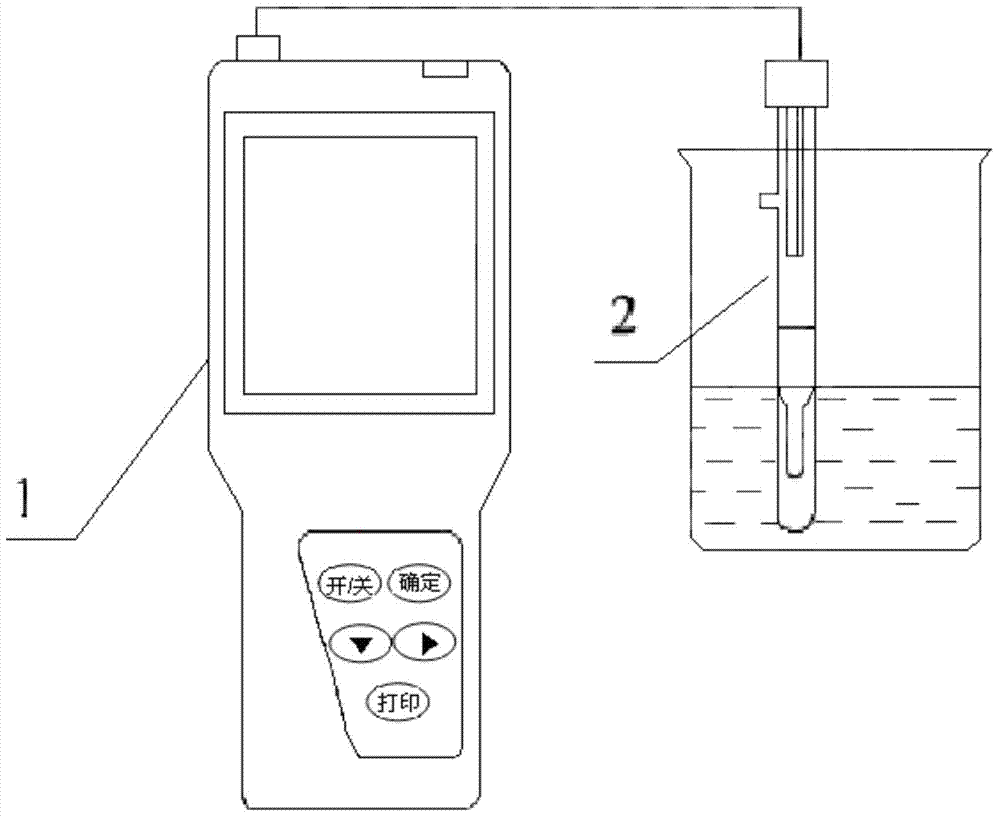
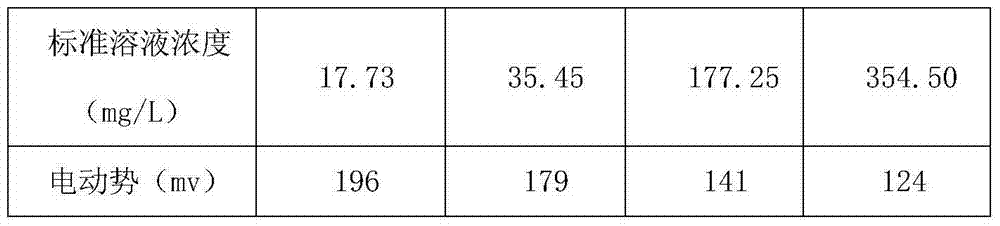
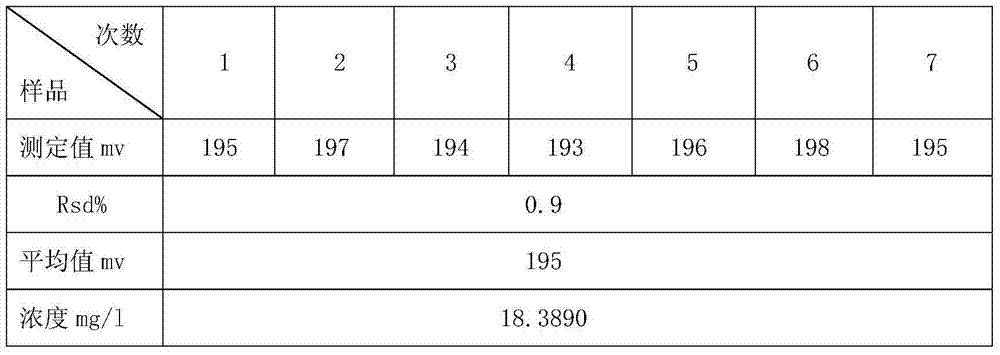
Sample treatment method for testing chloride ions in cement through ion selective electrode method
InactiveCN103592162AEliminate distractionsExtended service lifePreparing sample for investigationIon contentAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a sample treatment method for testing chloride ions in cement through an ion selective electrode method. The method adopts a CISA solution for being directly mixed with an acid-soluble sample, and can be used for eliminating interferences of hydroxide ions, ammonia water, thiosulphate ions, bromide ions, sulfide ions, iodide ions, cyanide ions and the like, improving the test repeatability and accuracy, protecting a membrane of a chloride ion selective electrode to the maximum extent and prolonging the service life of the electrode. Therefore, the method for testing the chloride ion content through the ion selective electrode method by adding the CISA solution is suitable for testing cement materials with complex base body ingredients and also is suitable for testing the content of chloride ions in other building materials.
Owner:ANHUI WAYEE SCI & TECH CO LTD
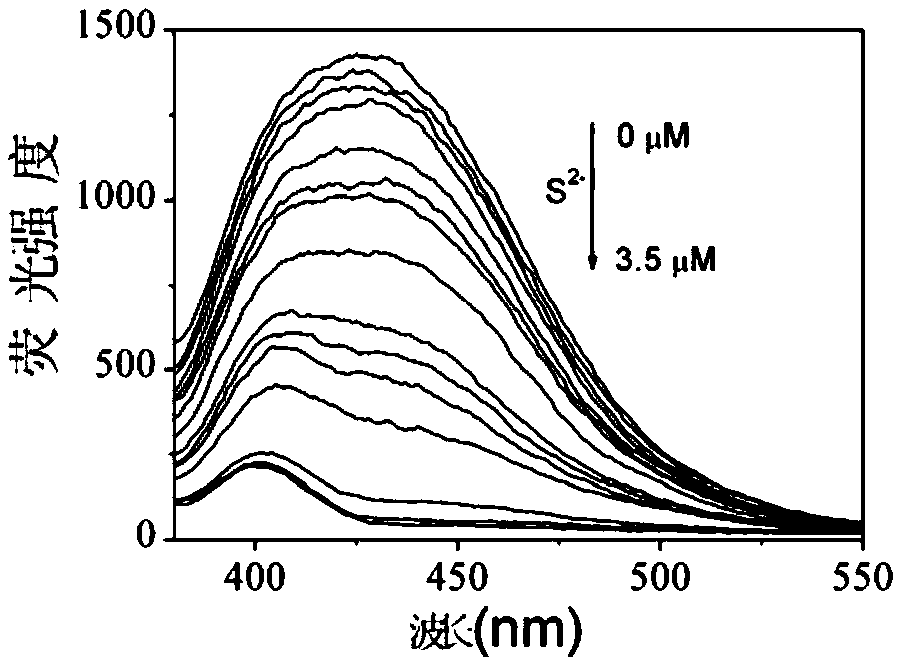
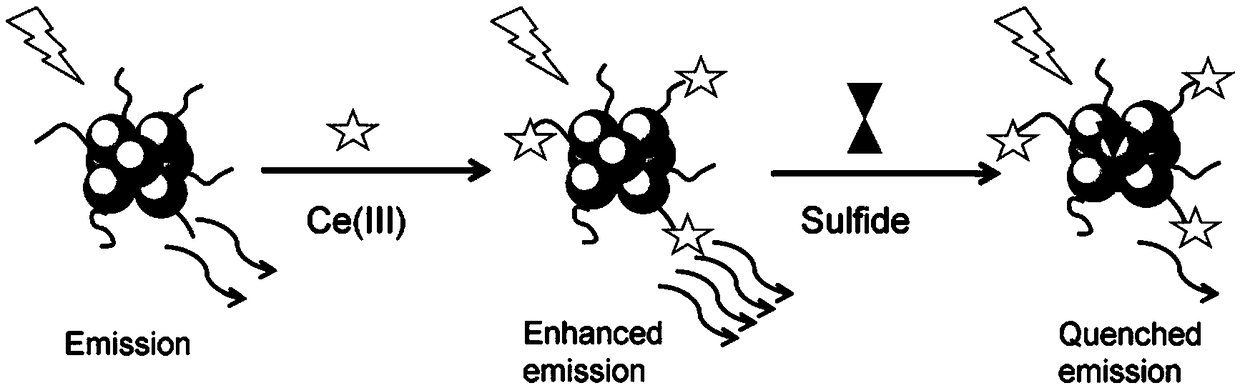
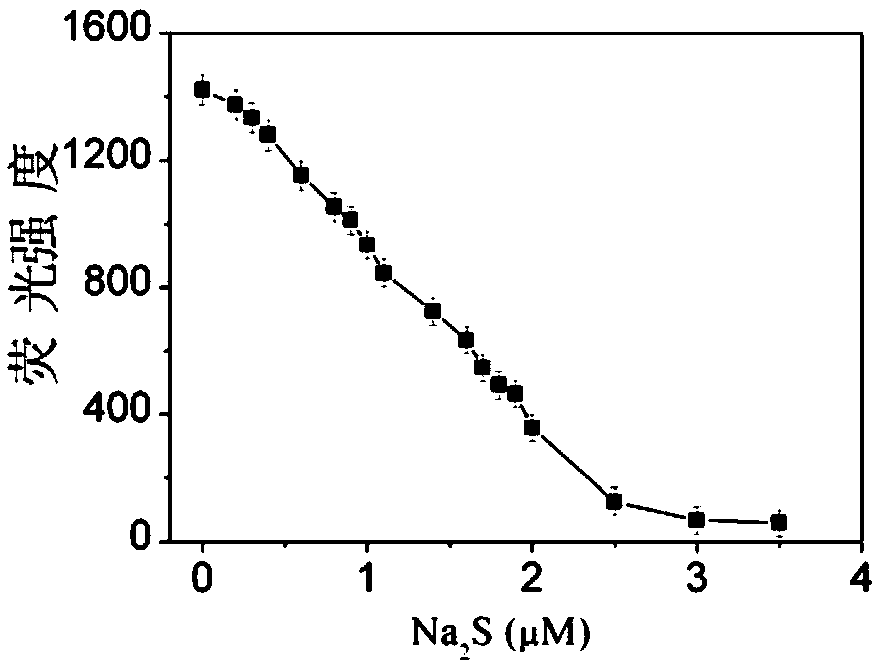
Sulfide ion detection method based on Ce(III)/AgNCs composite nano cluster material
InactiveCN109211856ARapid Trace DetectionHigh fluorescence intensityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLinear relationshipUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a sulfide ion detection method based on a Ce(III) / AgNCs composite nano cluster material. Ce(III) ions can effectively enhance fluorescence emission of AgNCs, so as to form a Ce(III) / AgNCs composite system. When a trace of S<2-> is added to the system, S<2-> reacts with Ag atoms in the Ce(III) / AgNCs composite system, consequently, an original structure of the Ce(III) / AgNCs composite system is damaged, then the fluorescence strength of the Ce(III) / AgNCs composite system is eliminated, the eliminated fluorescence strength and concentration of S<2-> ions are in a linear relationship, so that the S<2-> ion detection method is created. The method is easy to operate, and can detect a trace of S<2-> rapidly in real time.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Sulfide ion detection kit based on bovine serum albumin-nano platinum/bismuth
InactiveCN105717097AEasy to manufactureReduce processing requirementsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceColor/spectral properties measurementsPeroxidaseBovine serum albumin
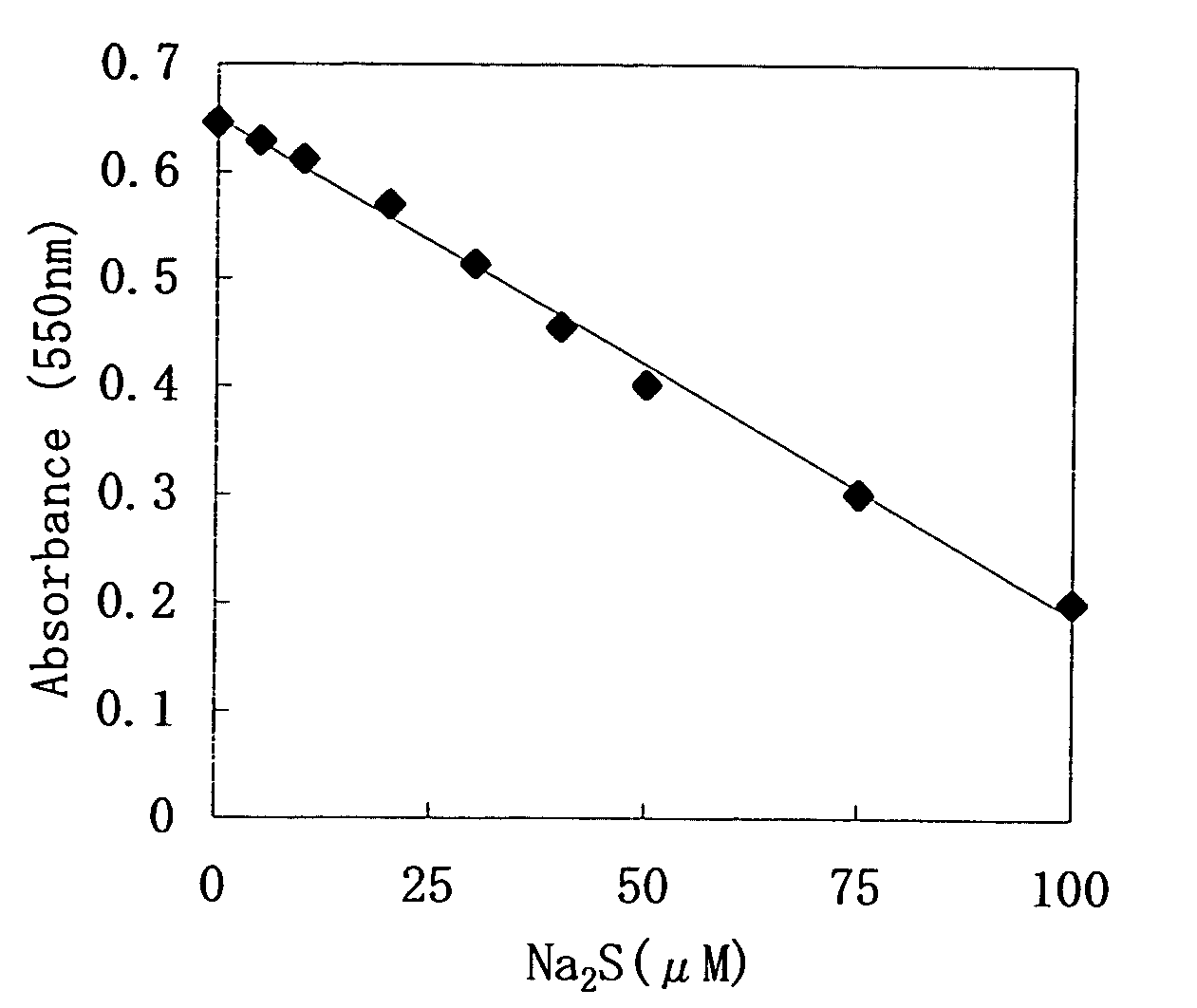
The invention discloses a sulfide ion detection kit based on bovine serum albumin-nano platinum / bismuth. Bovine serum albumin-nano platinum / bismuth reacts with sulfide ions and then simulates the change of peroxidase activity, 3,3',5,5'-tetramethyl benzidine hydrochloride is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide to develop a color under the catalysis action of bovine serum albumin-nano platinum / bismuth, and therefore changes of the solution color and ultraviolet absorption spectrum features are shown up. The linear range of absorbancy measurement is 0.08-4 micromol / L, and the detection limit is 50 nanomol / L. After a water sample is simply pretreated, the content of sulfide ions in the water sample can be measured well by adopting the method and the kit.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
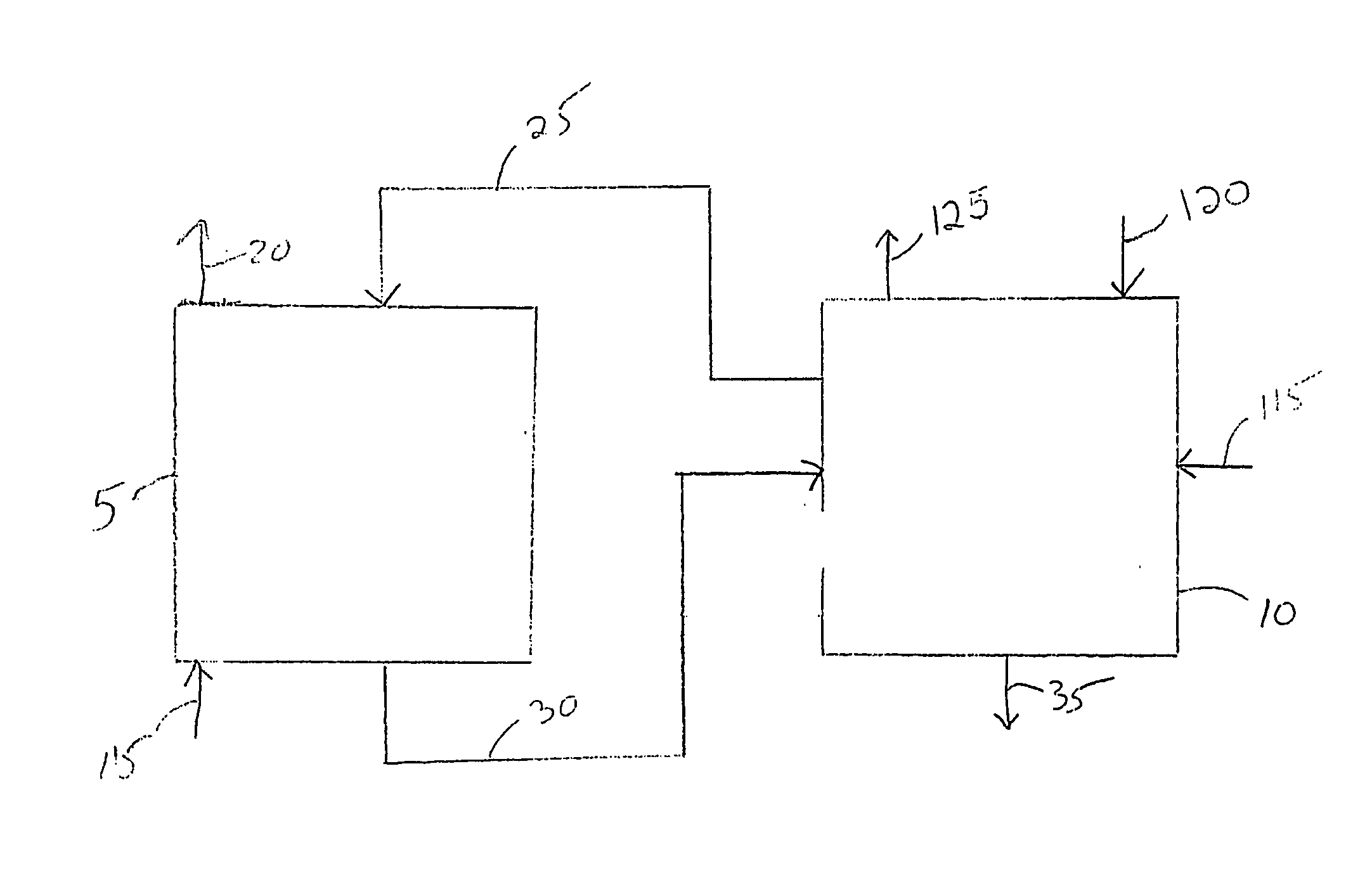
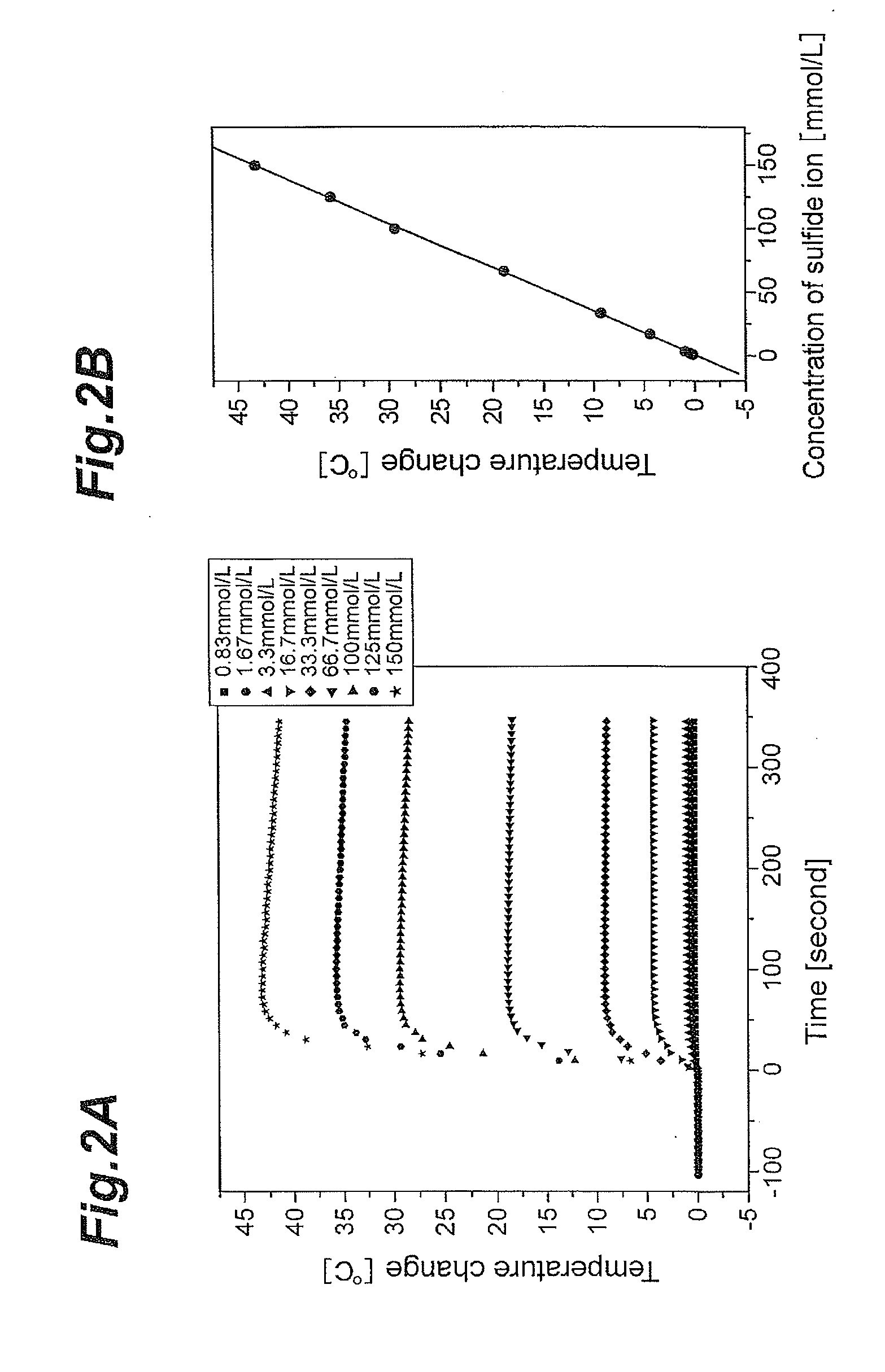
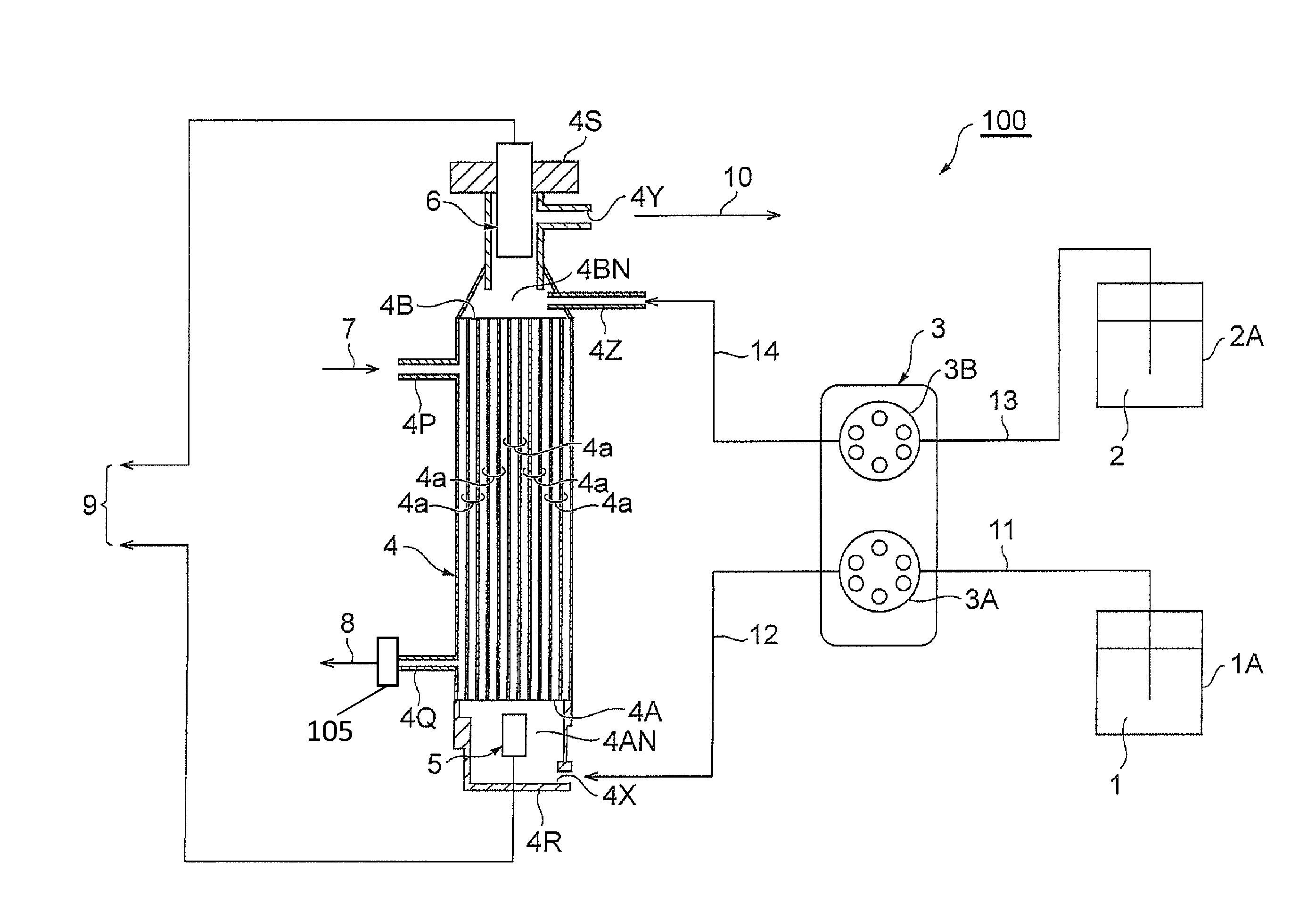
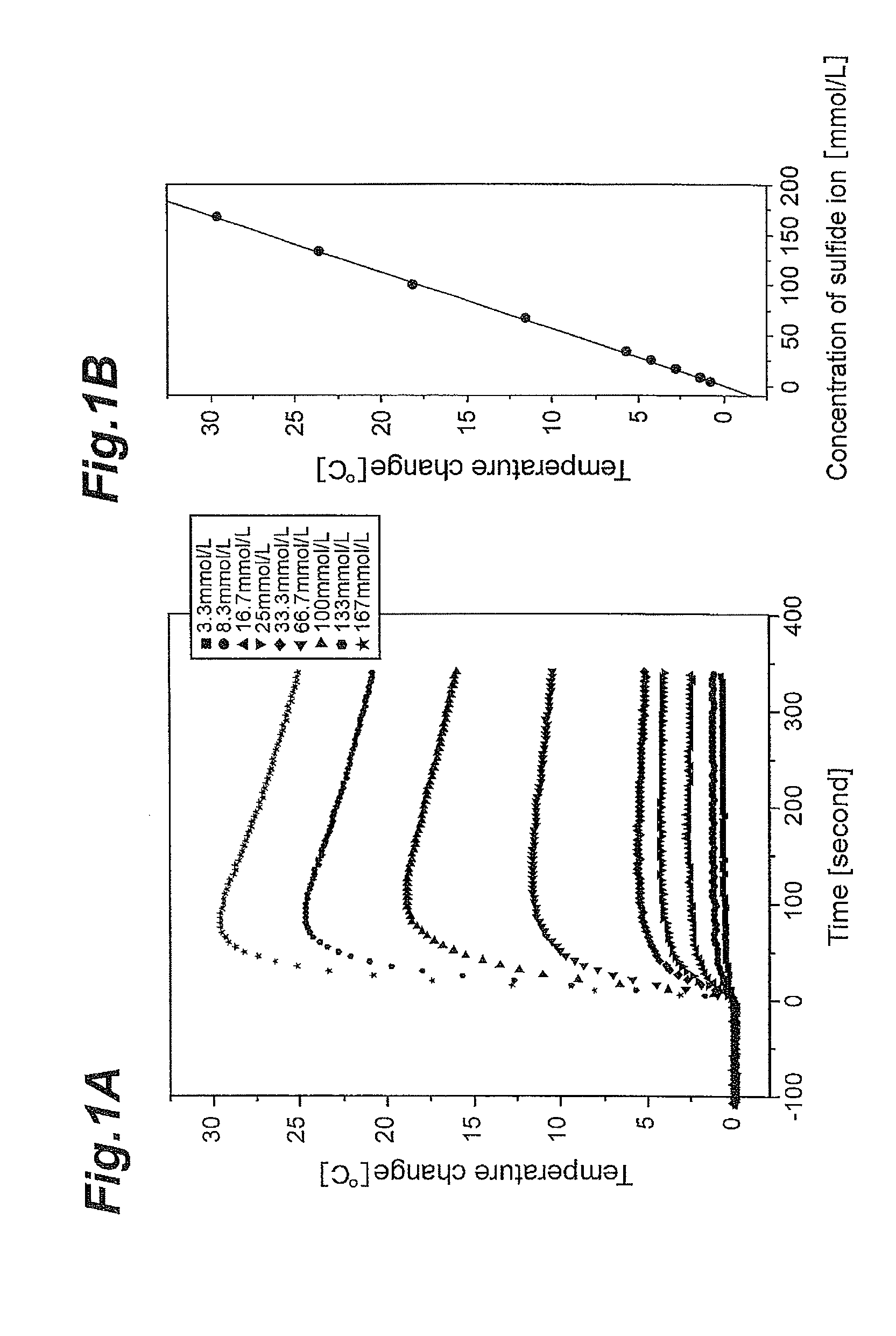
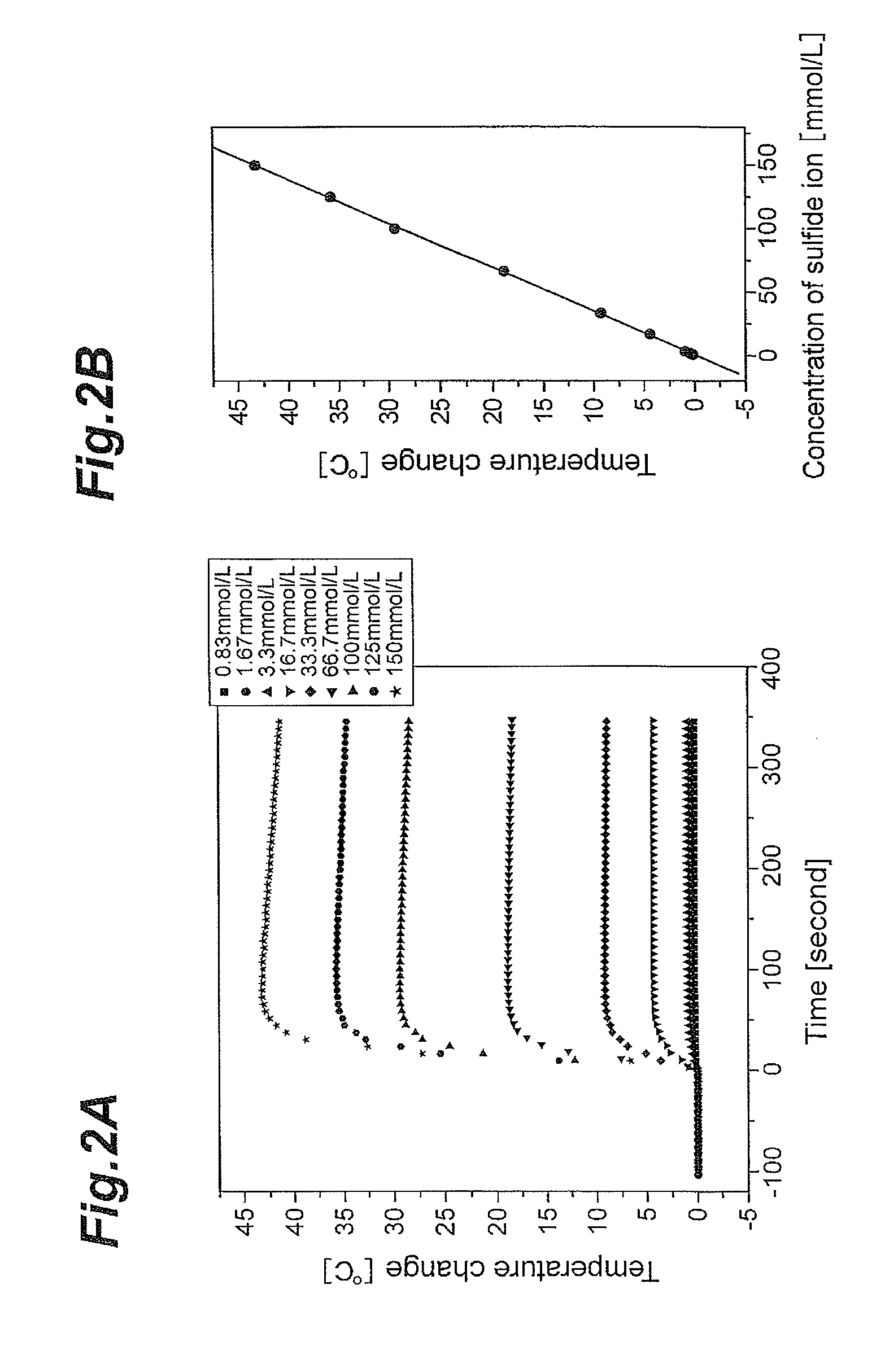
Concentration measuring apparatus for hydrogen sulfide in gas flow, and method for determining sulfide ion
ActiveUS20110217787A1High selectivityEasy to adjustComponent separationBiological testingHollow fibre membraneGaseous hydrogen
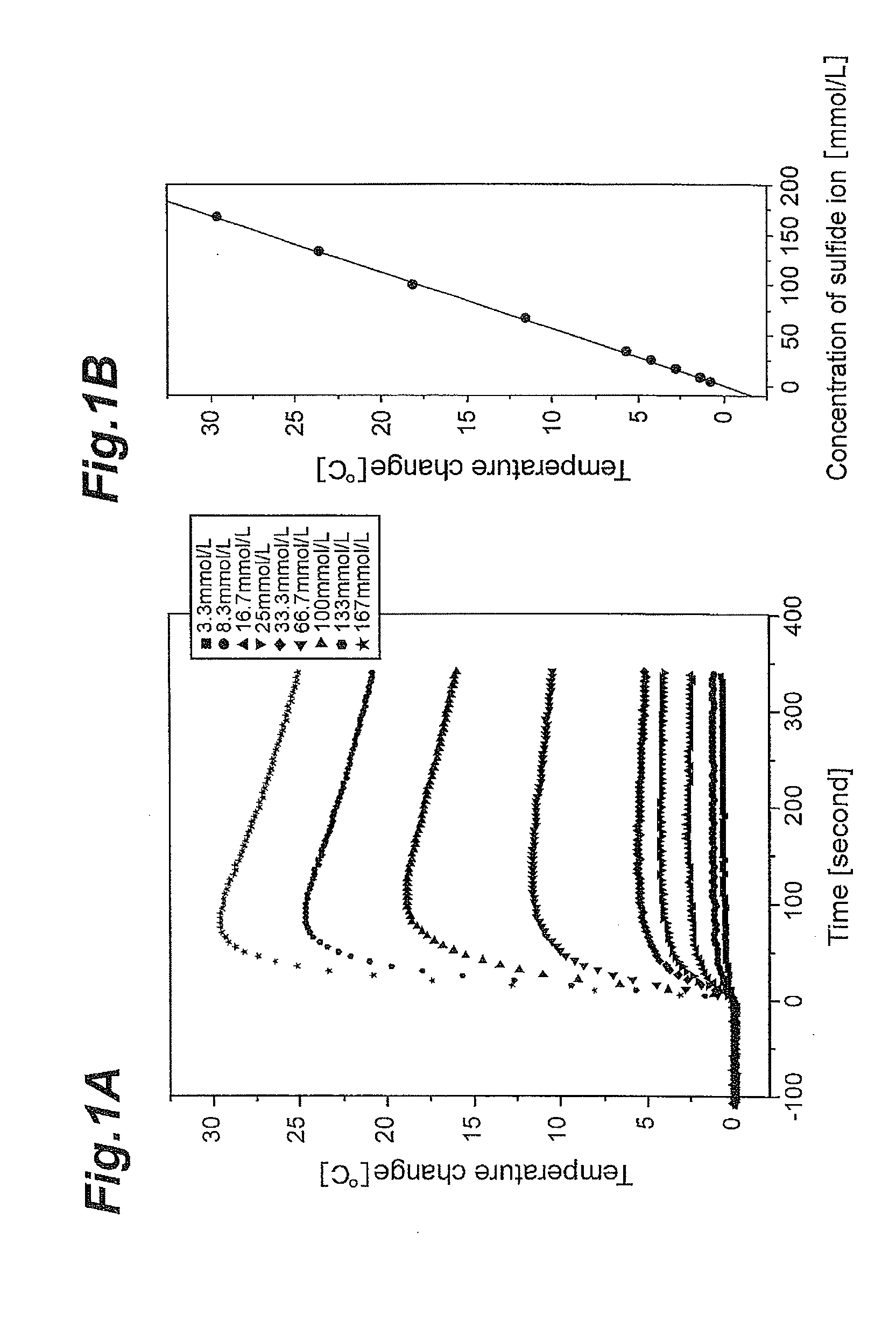
A concentration measuring apparatus for hydrogen sulfide includes an absorbing liquid that can absorb gaseous hydrogen sulfide as sulfide ion; a hollow fiber membrane contactor that contacts a gas flow with a flow of the absorbing liquid through a membrane, so that the absorbing liquid absorbs gaseous hydrogen sulfide in the gas flow as sulfide ion; a pump for a first channel that feeds the absorbing liquid to the hollow fiber membrane contactor; an oxidizer that exothermically reacts with sulfide ion; a pump for a second channel that feeds the oxidizer to the absorbing liquid; a first thermometer that measures a temperature of the absorbing liquid before the sulfide ion that the absorbing liquid has absorbed exothermically reacts with the oxidizer; and a second thermometer that measures the temperature of the absorbing liquid after the sulfide ion that the absorbing liquid has absorbed exothermically reacts with the oxidizer.
Owner:JAPAN COOPERATION CENT +1
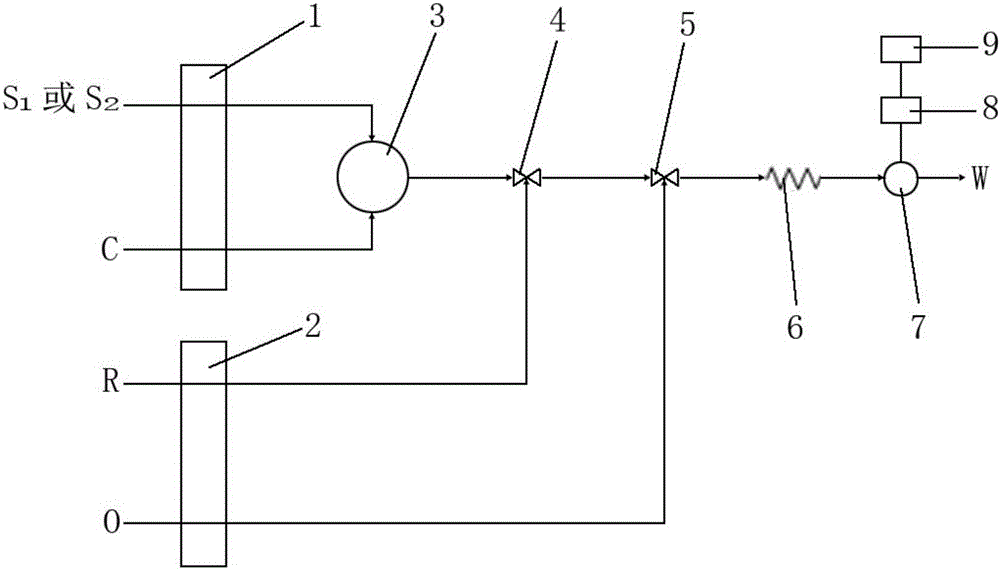
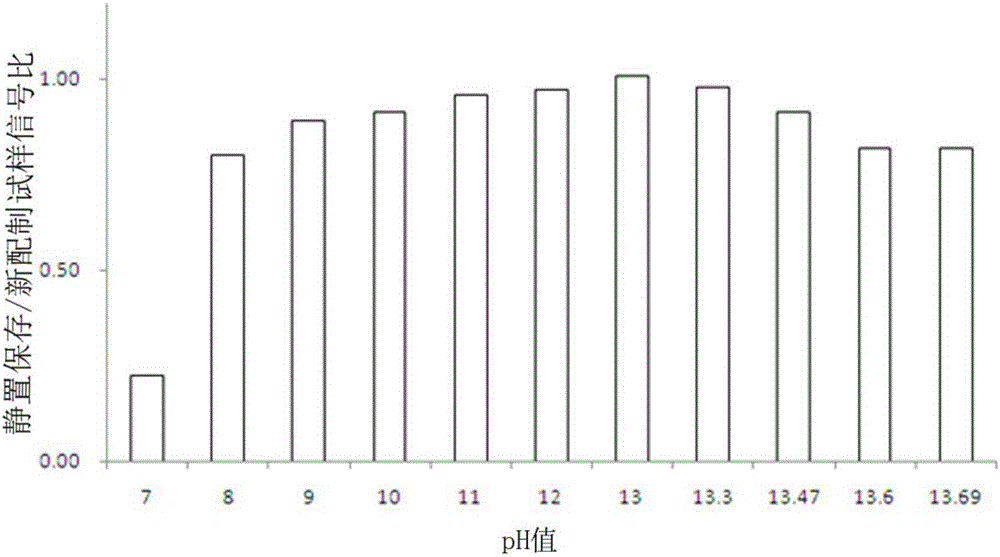
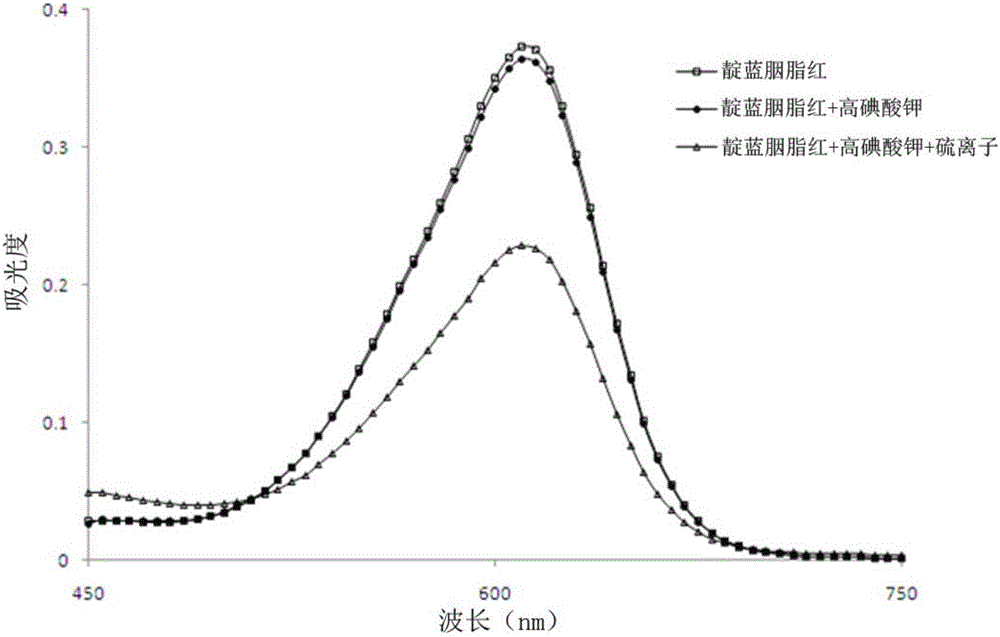
Preservation method and automatic analysis method of trace divalent sulfide ions in water sample
InactiveCN105738640ARapid determinationDetermination no longer interferesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPreparing sample for investigationOptical flowHandling system
The invention discloses a preservation method of trace divalent sulfide ions in a water sample. The preservation method comprises the following operating steps: collecting a water sample containing divalent sulfide ions, immediately adding sodium hydroxide into the water sample until the concentration of hydroxy radicals in the water sample reaches 0.1-0.2 mol / L, and leaving to stand for no more than 24 h' s preservation at the room temperature. The invention further discloses an automatic analysis method of trace divalent sulfide ions in the water sample; the automatic analysis method uses analytical instruments comprising a first low pressure pump, a second low pressure pump, an injection valve, a first mixer, a second mixer, a reactor, an optical flow-through cell, an optical detector and a computer processing system and further comprises the following steps: (1) determining a base line; (2) determining a spectrogram of divalent sulfide ions in a test sample; (3) drawing a standard work curve; (4) calculating the concentration of divalent sulfide ions to be measured in the test sample according to the peak height value of the spectrogram of the divalent sulfide ions and the regression equation of the working curve. According to the preservation method and the automatic analysis method of trace divalent sulfide ions in the water sample, provided by the invention, preservation operations of divalent sulfide ions in the water sample are simplified, and low-cost automatic analysis of divalent sulfide ions is also realized.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
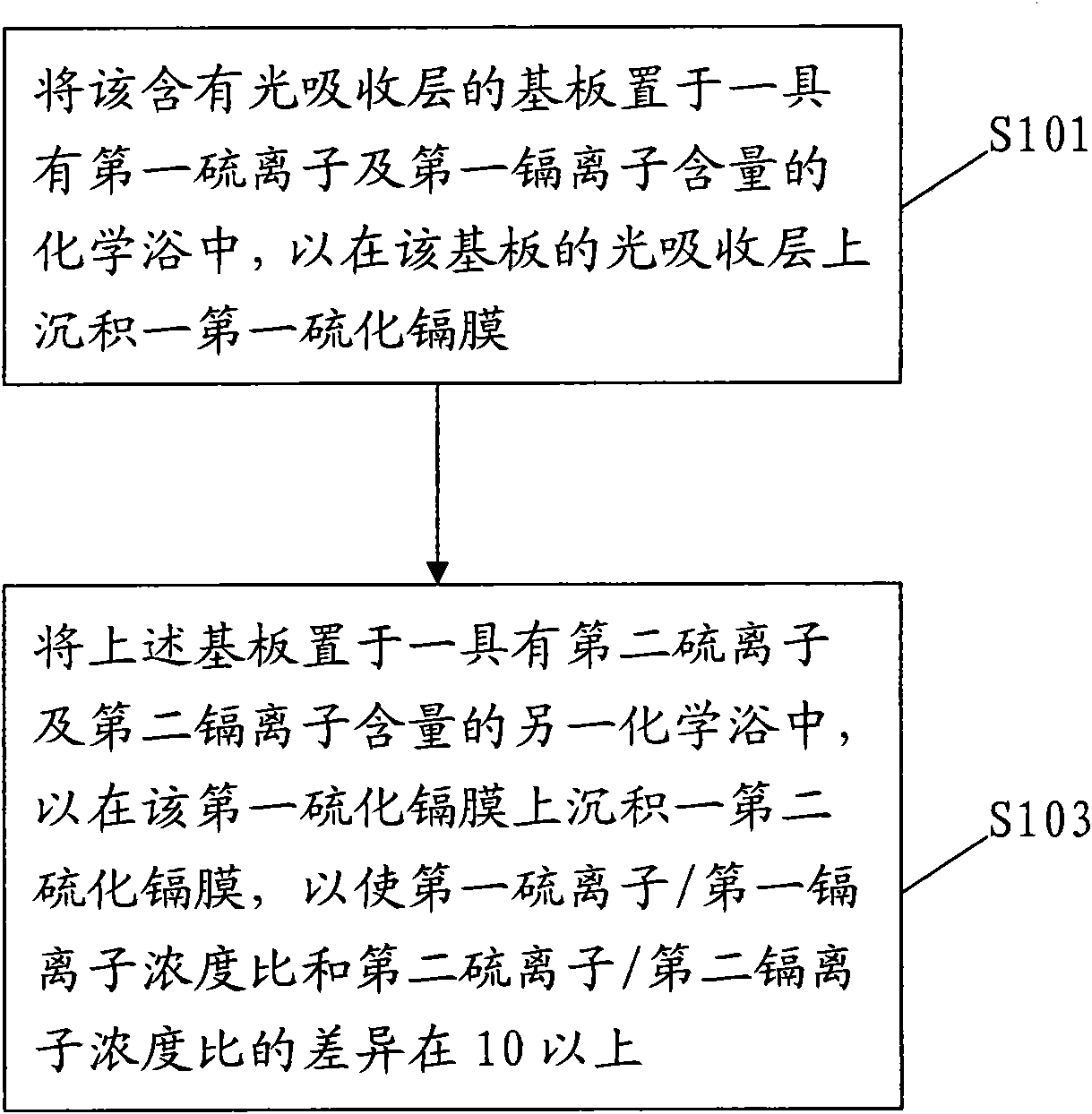
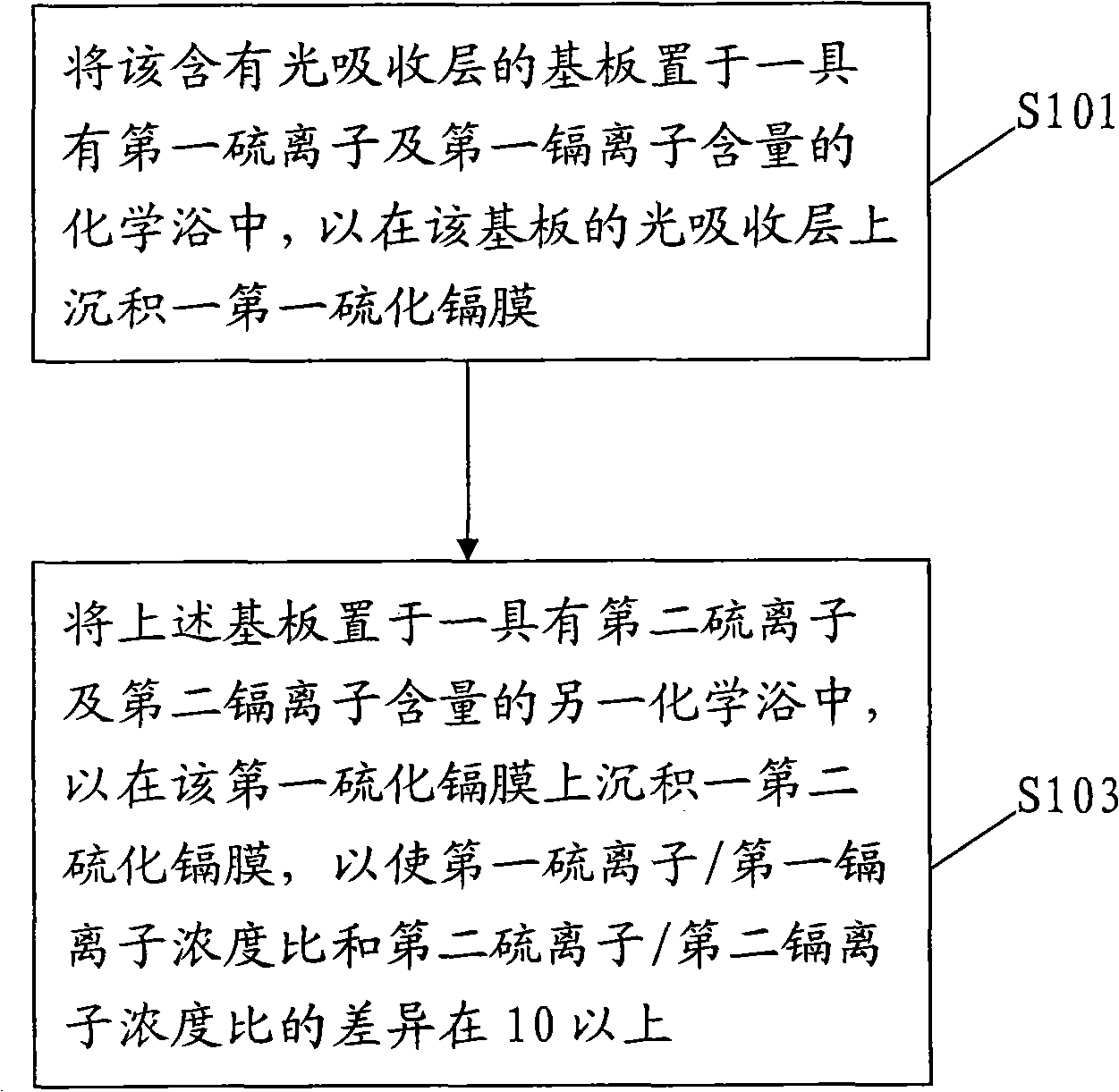
Deposition method of multi-section camium sulfide thin film
InactiveCN101820027ASignificant progressFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesConcentration ratioCadmium sulphide
The invention relates to a deposition method of a multi-section camium sulfide thin film, at least comprising the following steps of: placing a substrate containing a high-absorbing layer in a chemical bath with the contents of first sulfide ions and first cadmium ions for depositing a first camium sulfide layer on the light-absorbing layer of the substrate; and placing the substrate in another chemical bath with the contents of second sulfide ions and second cadmium ions for depositing a second camium sulfide layer on the first camium sulfide film so that the concentration ratio different between concentration ratio of the first sulfide ions to the first cadmium ions and the concentration ratio of the second sulfide ions to the second cadmium ions is above 10.
Owner:昆山正富机械工业有限公司
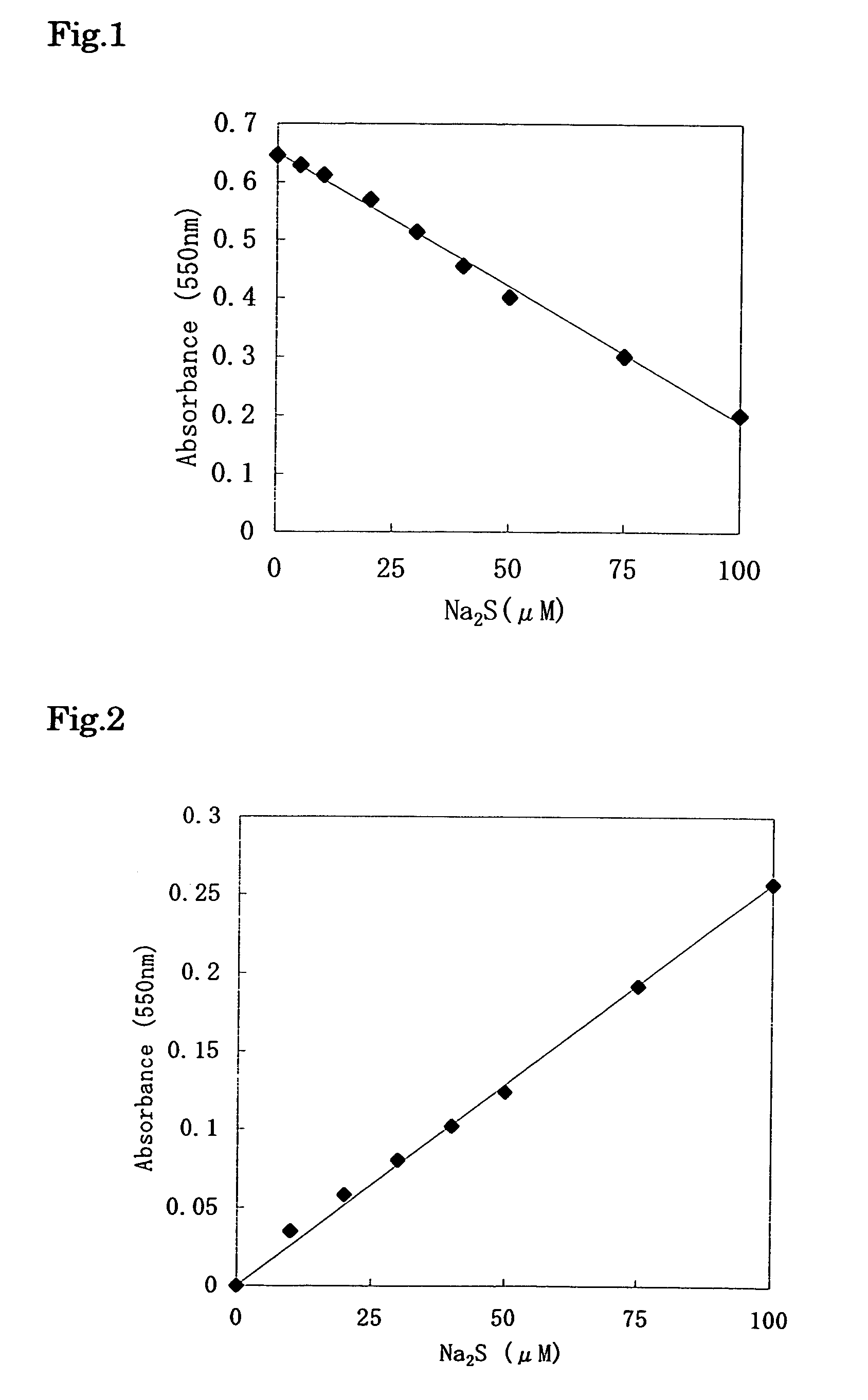
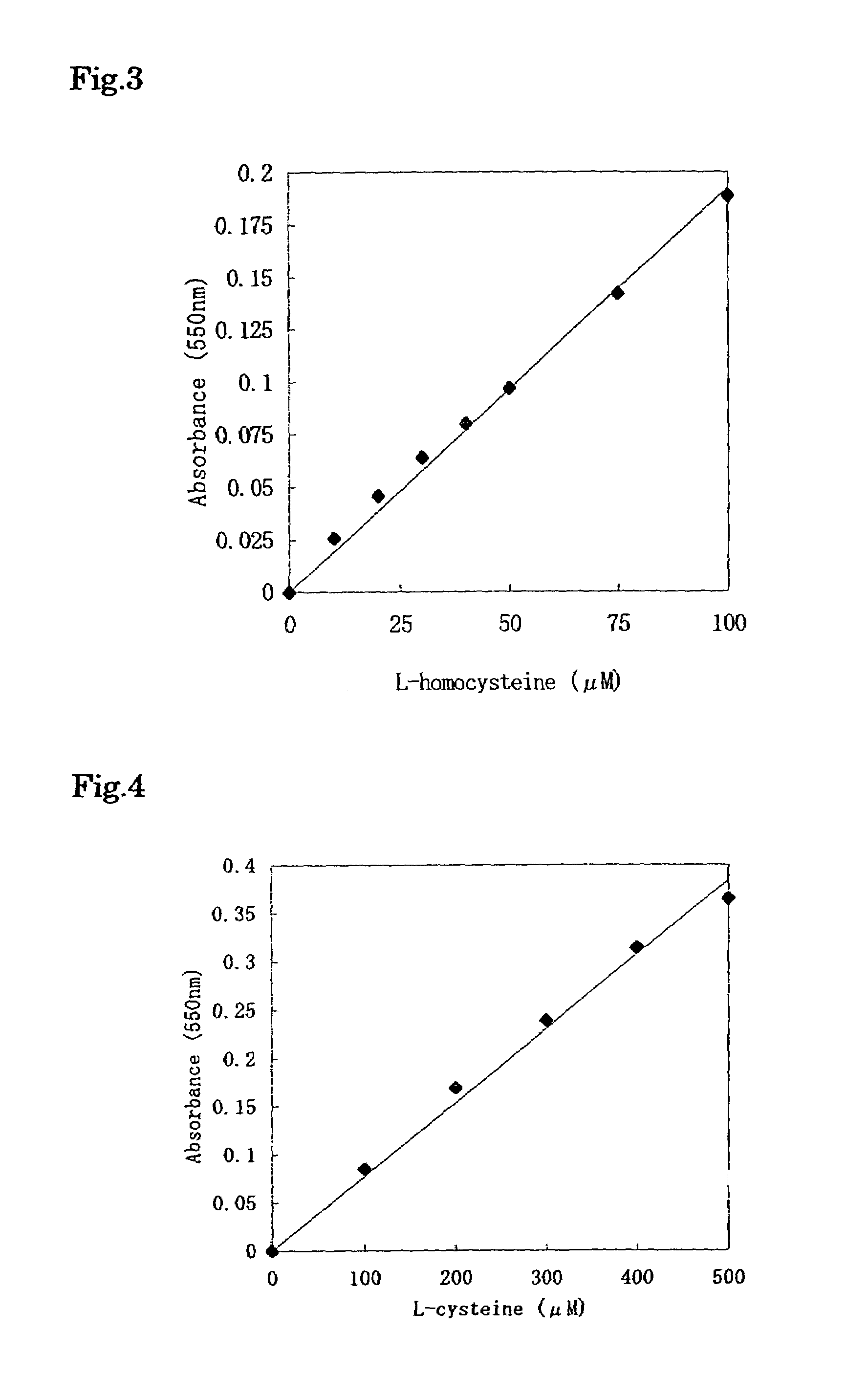
Method for determination of hydrogen sulfide or sulfide ion and method for determination of specific substance utilizing said method
InactiveUS6969613B1High sensitivityConveniently determinedMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionSulfide ionsHydrogen sulfide
The present invention provides a method for quantitatively determining hydrogen sulfide or sulfide ions conveniently with high sensitivity, which comprises adding to a sample containing hydrogen sulfide or sulfide ions, metal ions or a compound which liberates said metal ions and a metal indicator which reacts with the metal ions and resultingly undergoes color development, wherein the color development is accelerated or inhibited by the hydrogen sulfide or sulfide ions; and measuring the degree of color development of the metal indicator. The present invention further provides a method for quantitatively determining a specific substance, which comprises adding to a sample containing a specific substance, a component which acts on the specific substance so that the specific substance forms hydrogen sulfide or sulfide ions, metal ions or a compound which liberates said metal ions, and a metal indicator which reacts with the metal ions and resultingly undergoes color development, wherein the color development is accelerated or inhibited by the hydrogen sulfide or sulfide ions; and measuring the degree of color development of the metal indicator.
Owner:SEKISUI MEDICAL CO LTD
Method for preparing trace element fertilizer containing organic titanium through microwave chelating process
The invention relates to a method for preparing a trace element fertilizer containing organic titanium through a microwave chelating process. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a newly precipitated metatitanic acid which does not contain chloride and sulfide ions and can be dissolved in citric acid by neutralizing an iced solution of a titanium salt with an alkali; using the newly precipitated metatitanic acid which does not contain the chloride and sulfide ions and can be dissolved in the citric acid to substitute chlorides and sulfates of titanium for being used as a raw material for synthesizing citric acid titanium without the chloride and sulfide ions; taking the newly precipitated metatitanic acid which does not contain the chloride and sulfide ions and can be dissolved in the citric acid as a titanium source, taking citric acid as an acid solvent and a chelating agent, and synthesizing the citric acid titanium without the chloride and sulfide ions through a microwave hot-melting chelating process; and preparing the trace element fertilizer containing the organic titanium by performing microwave hot-melting (dissolving) chelating on the acidic citric acid titanium and basic salts of copper, zinc, iron, manganese and molybdenum. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a titanium element can be used for promoting the absorption of trace elements and the operation of crops, promoting the growth of the crops and improving the yield and quality of the crops, and all the advantages and effects of the trace elements can be fully played.
Owner:FUJIAN CHAODA GROUP
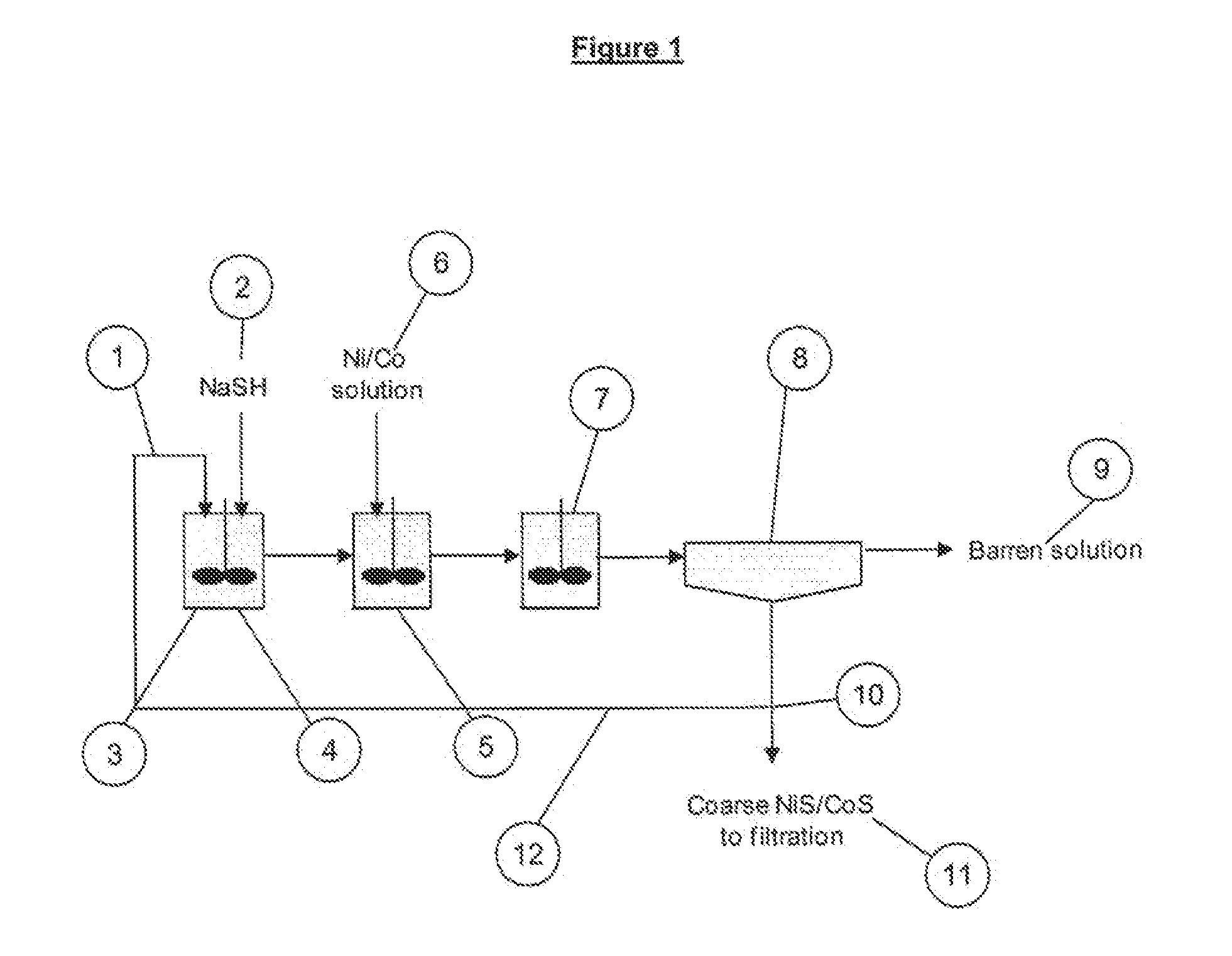
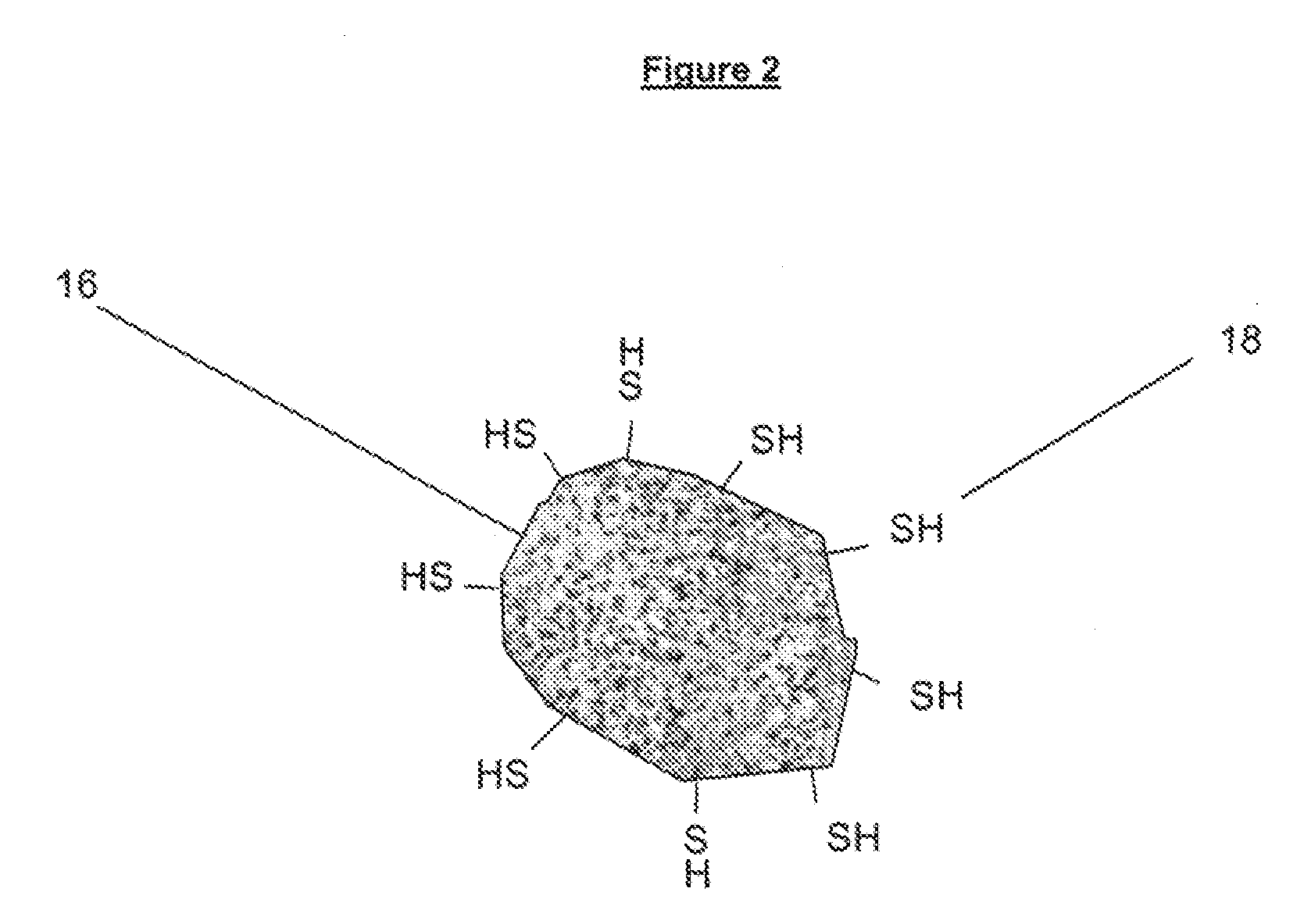
Method for recovering valuable metals
Owner:METSO OUTOTEC (FINLAND) OY
Process for treatment of a fluid comprising an oxidizable containment
ActiveUS10131557B2Increase ratingsConvenient treatmentWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsBenzeneWastewater
There is described a process for treatment of a fluid comprising an oxidizable contaminant. The process comprises the step of contacting the wastewater with a combination of: (i) a sulfide, (ii) a complex of Fe(III) and a chelating agent, and (iii) an oxidant. It has been discovered that of treatment of a fluid containing an oxidizable contaminant employing iron(III)-chelates as the Fenton catalyst may be significantly improved by including a sulfide in the reaction scheme. As described herein, by employing sulfide ion, the present inventors have been able to: (i) increase the rate of iron recycling from minutes or hours to a few seconds, and (ii) destroy benzene in an oil and gas refinery (OGR) wastewater in less than one minute. It is believed that these findings in OGR wastewater can be extended to other fluids containing other oxidizable contaminants.
Owner:TROJAN TECH
Application of non-porous diaphragm in lithium sulfur secondary battery
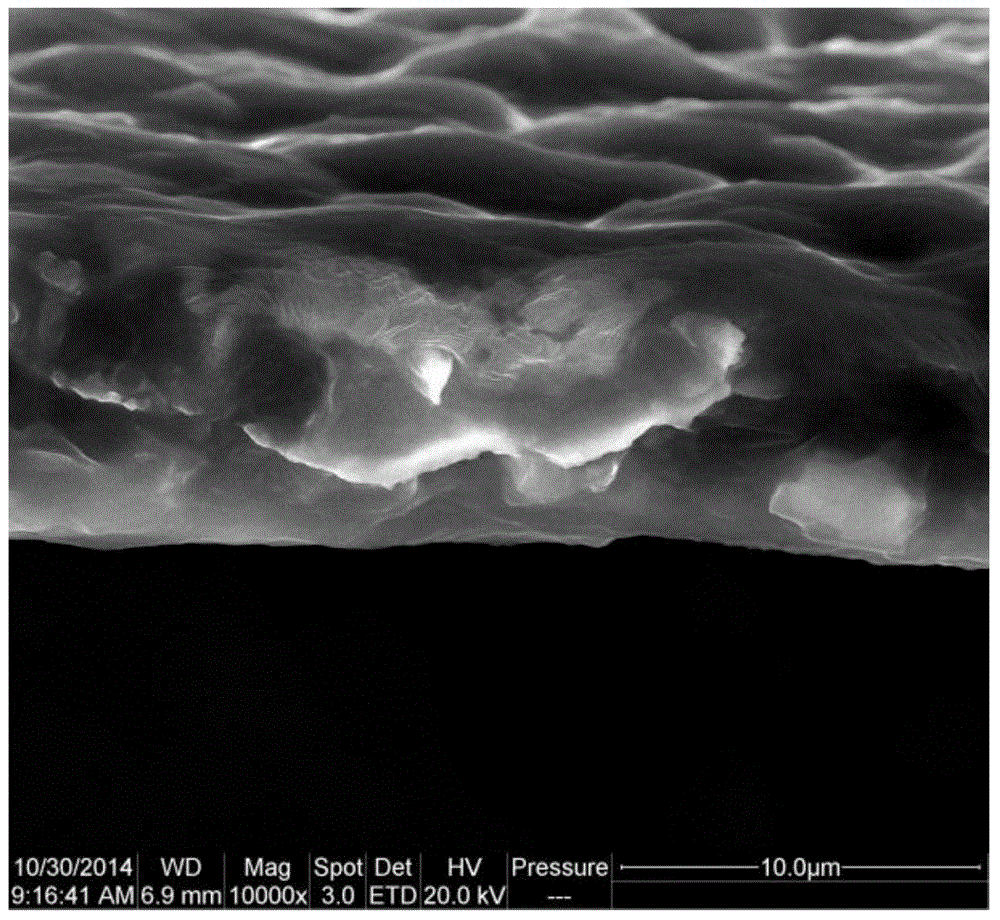
InactiveCN105742547APreserve ion permeation selectivityAchieve separationLi-accumulatorsCell component detailsLithium sulfurIon exchange
The invention discloses application of a non-porous diaphragm in a lithium sulfur secondary battery. The non-porous diaphragm is prepared according to the step of taking polyvinylidene fluoride organic high-molecular resin as a raw material by a casting film formation method, and the thickness of the non-porous diaphragm is 5-10 micrometers. By such diaphragm, the separation of poly-sulfide ions and lithium ions can be effectively achieved, the ion transmittance selectivity of the diaphragm is maintained, and ion transfer and poly-sulfide ion blocking can be achieved in no need of dependence on an ion exchange group and a particular lattice structure. The diaphragm material is simple in preparation method and low in cost, and mass production can be easily realized, and the processing method and the selection range of the diaphragm material of the lithium sulfur secondary battery are expanded.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Concentration measuring apparatus for hydrogen sulfide in gas flow, and method for determining sulfide ion
ActiveUS8709820B2High selectivityEasy to adjustComponent separationMaterial heat developmentGaseous hydrogenHollow fiber membrane
A concentration measuring apparatus for hydrogen sulfide includes an absorbing liquid that can absorb gaseous hydrogen sulfide as sulfide ion; a hollow fiber membrane contactor that contacts a gas flow with a flow of the absorbing liquid through a membrane, so that the absorbing liquid absorbs gaseous hydrogen sulfide in the gas flow as sulfide ion; a pump for a first channel that feeds the absorbing liquid to the hollow fiber membrane contactor; an oxidizer that exothermically reacts with sulfide ion; a pump for a second channel that feeds the oxidizer to the absorbing liquid; a first thermometer that measures a temperature of the absorbing liquid before the sulfide ion that the absorbing liquid has absorbed exothermically reacts with the oxidizer; and a second thermometer that measures the temperature of the absorbing liquid after the sulfide ion that the absorbing liquid has absorbed exothermically reacts with the oxidizer.
Owner:JAPAN COOPERATION CENT +1
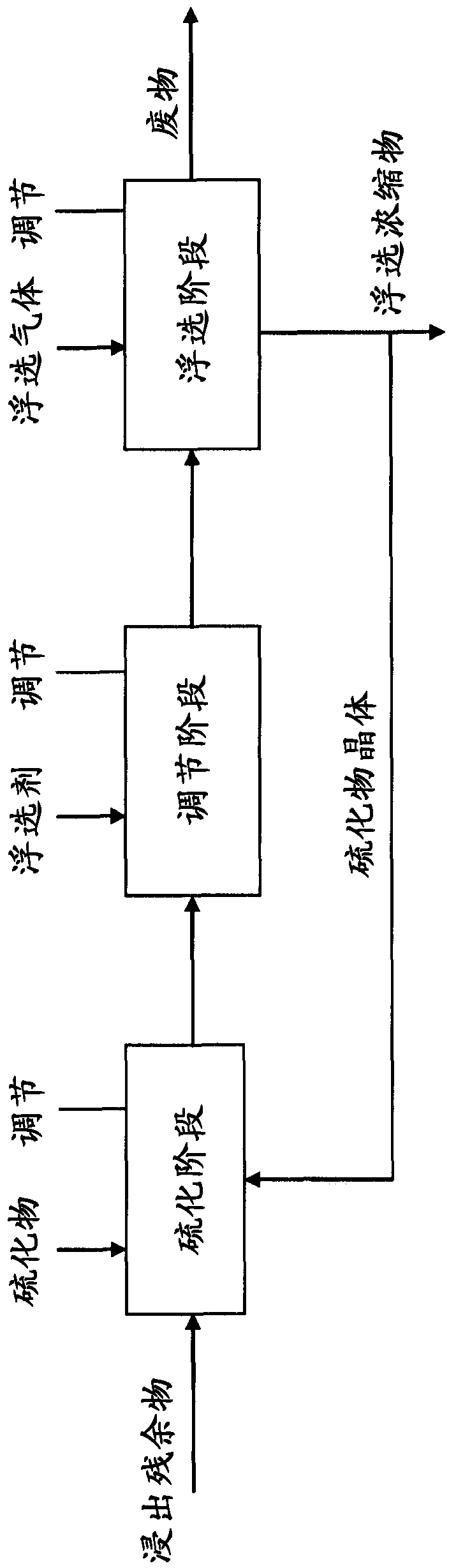
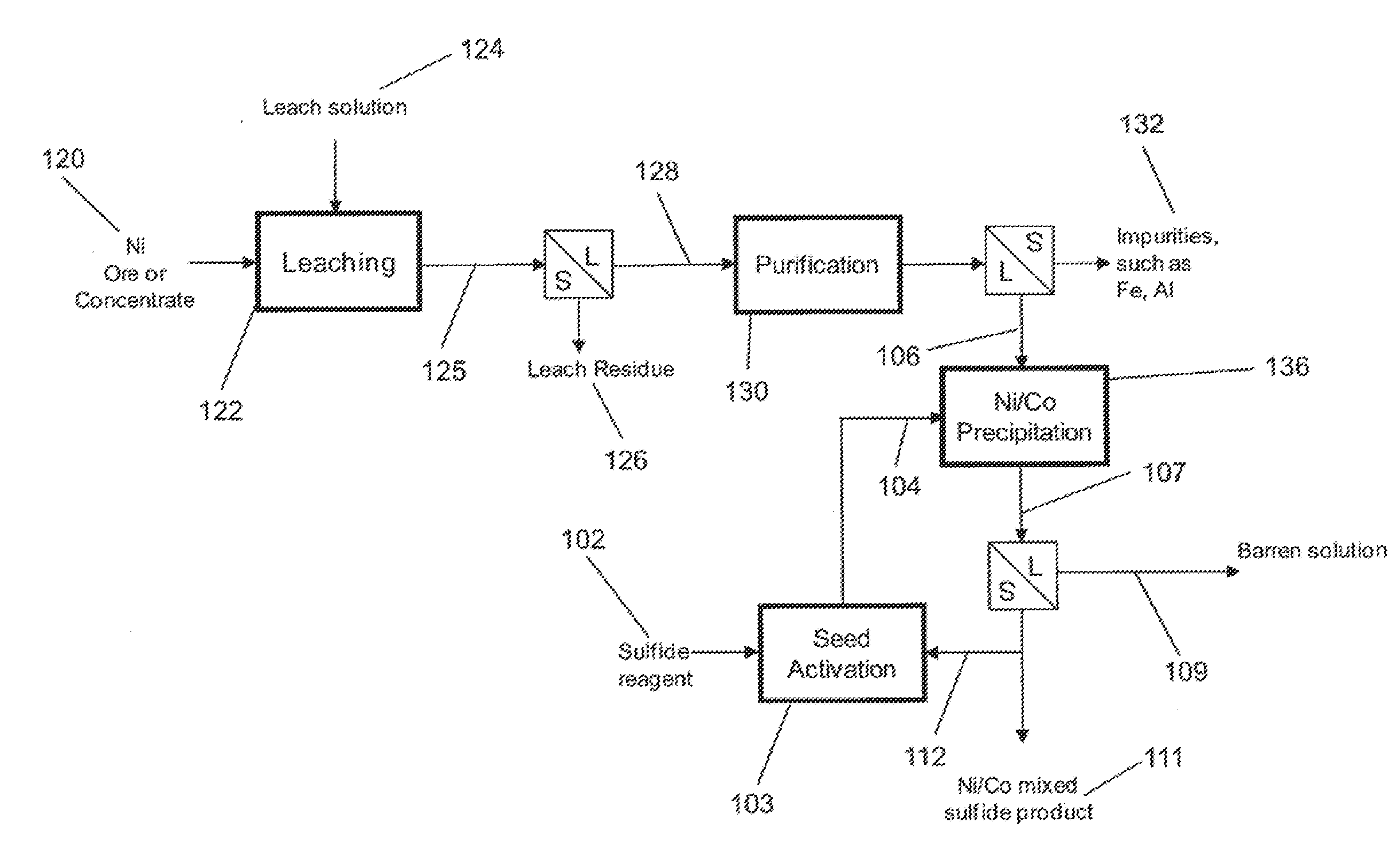
Process for Forming High Density Sulfides
InactiveUS20110123418A1Increased settling densityReduce overflowAluminium compoundsCobalt sulfidesHigh densityMetallic sulfide
A process for the recovery of a metal sulfide from a metal ion containing solution, including the steps of: a) providing a slurry containing seed panicles of said metal sulfide; h) adding a sulfide ion containing solution to said slurry to form an activated seed slurry; c) mixing said activated seed slurry with said metal ion containing solution to thereby form a metal sulfide precipitate; and d) recovering said metal sulfide precipitate.
Owner:BHP BILLITON SSM TECH PTY LTD
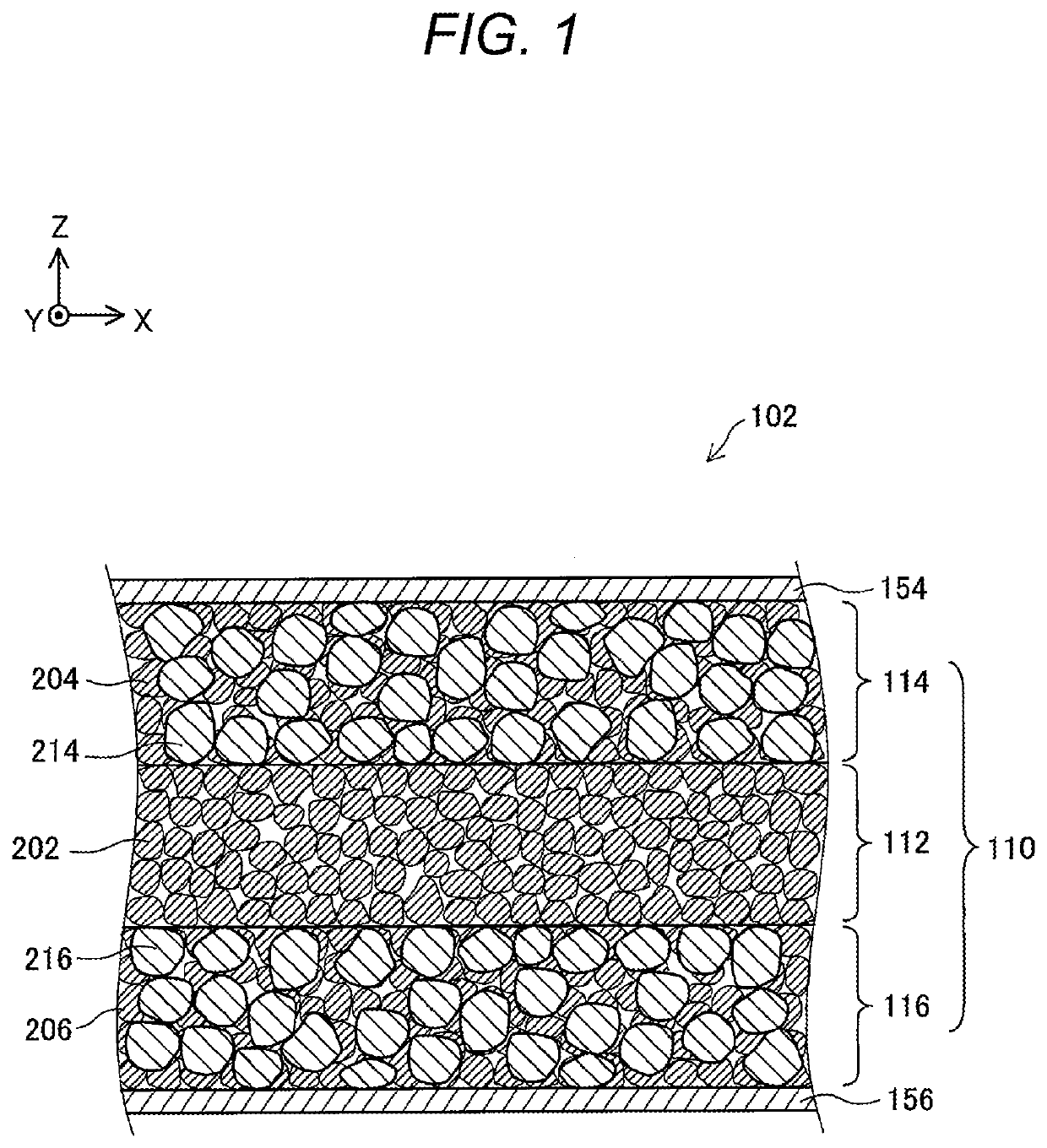
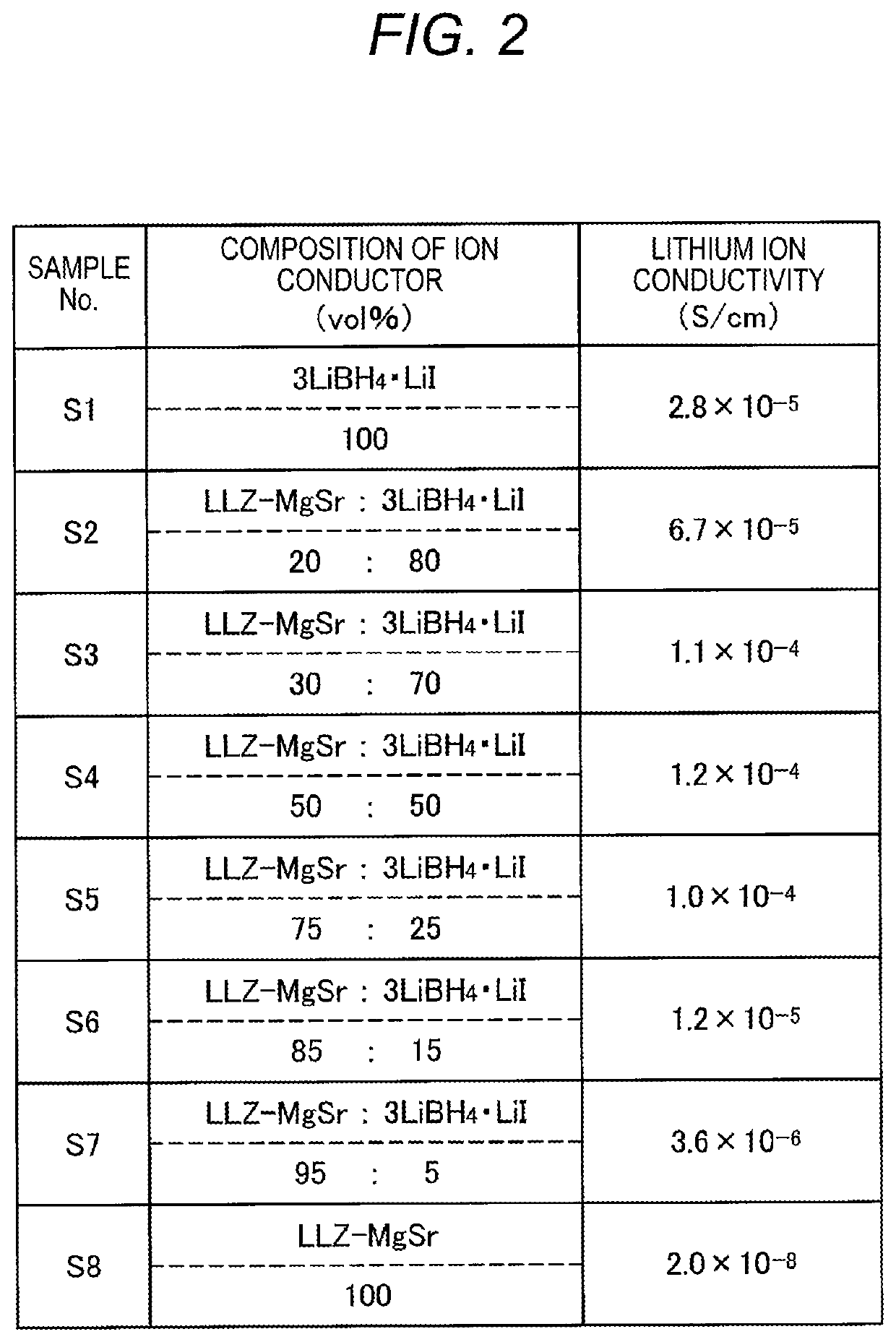
Ionic conductor and electricity storage device
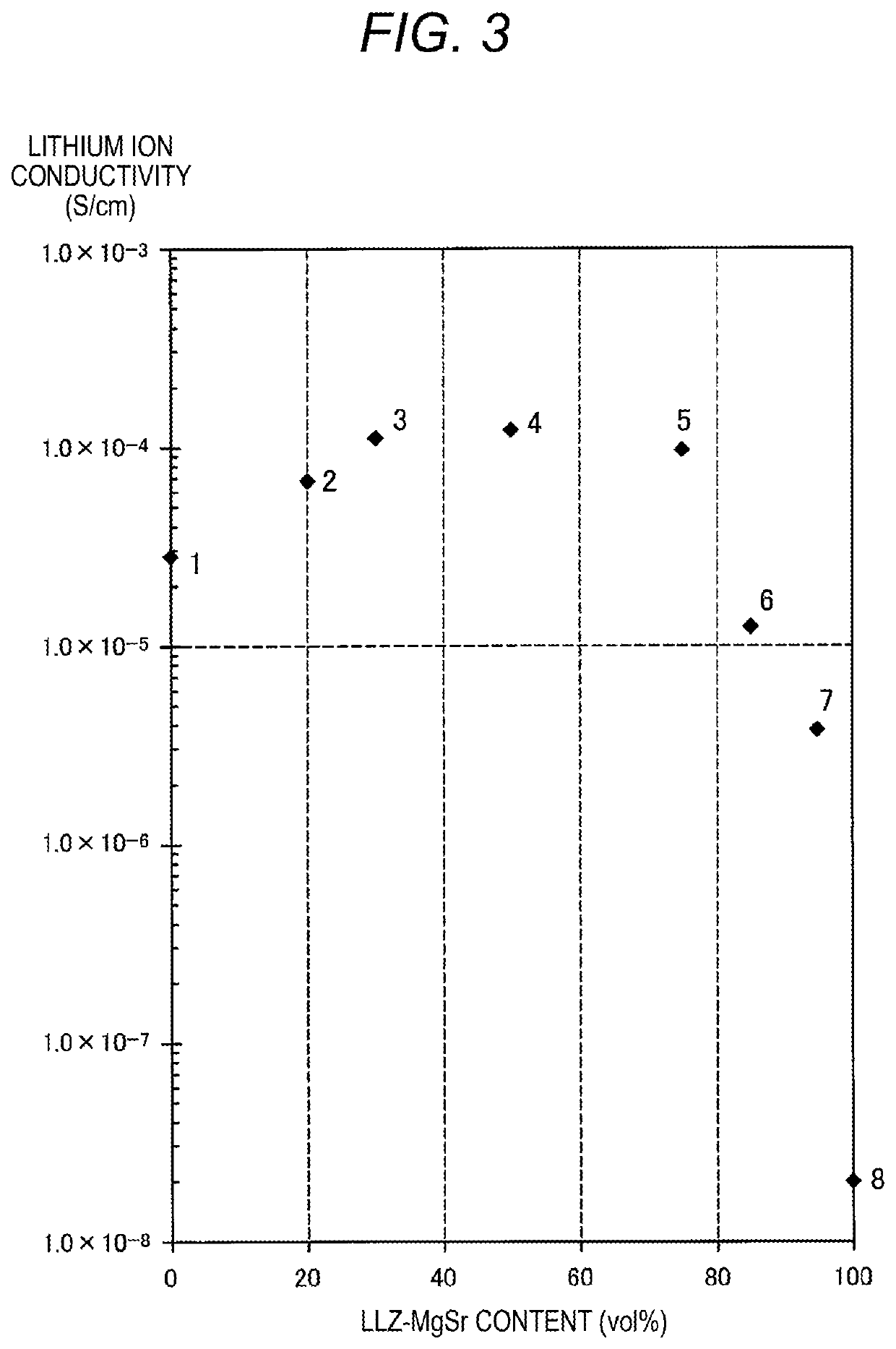
PendingUS20210104776A1Improve lithium ion conductivityClose contactHybrid capacitor electrolytesFuel and secondary cellsElectrical conductorEngineering
Provided is an ionic conductor with which adhesion between particles can be enhanced simply by pressure-molding a powder without using sulfide ionic conductors and without performing firing or vapor deposition, and which can exhibit a high lithium ionic conductivity. This ionic conductor contains, in addition to an oxide lithium ionic conductor, a complex hydride.
Owner:NGK SPARK PLUG CO LTD
Hydrogen sulfide removal process by use of a sulfur dye catalyst
A process is presented where a feed stream containing a hydrogen sulfide and another feed component is introduced into an absorber that the feed stream flows upward from the bottom of the absorber andcontacts a liquid treatment solution, where the liquid treatment solution contains a sulfur dye catalyst. The hydrogen sulfide is absorbed into the liquid treatment solution and converted into sulfide ions. The other feed component is removed from the absorber vessel substantially free of the hydrogen sulfide and a spent treatment solution is also removed from the absorber vessel and fed to an oxidation vessel where it is contacted with an oxygen containing gas causing the sulfide ions to oxidize to thiosulfate and converting the spent sulfur dye catalyst to regenerated sulfur dye catalyst. The thiosulfate is recovered, and the regenerated sulfur dye catalyst can be recycled as part of the liquid treatment solution.
Owner:MERICHEM CO
A kind of composite material based on silica metal sulfide and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN112490018BReduce corrosionEasy and quick passHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceManganese
The invention discloses a silica-based metal sulfide composite material, which uses a two-step hydrothermal method to grow a nano-flower structure of manganese disulfide and cobalt disulfide on the outer surface of the template agent silica, and at the same time through the vulcanization reaction, Silicon dioxide is etched by hydroxide, so that part of the silicon dioxide is released from the hydrolysis of sulfide ions, and the internal silicon dioxide template is etched into certain holes to facilitate ion migration to obtain a silicon dioxide-based layered nanometal sulfide composites. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1. preparation of composite metal oxide precursor; 2. preparation of silicon dioxide-based metal sulfide composite material. As an electrode material for supercapacitors, it is charged / discharged in the range of 0‑0.55 V, and the specific capacitance is 1150‑1160 F / g when the discharge current density is 1 A / g. It has excellent material stability and excellent ion transmission ability.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
A preparation method of high-efficiency visible light degradation agent nanosheet in2.77s4
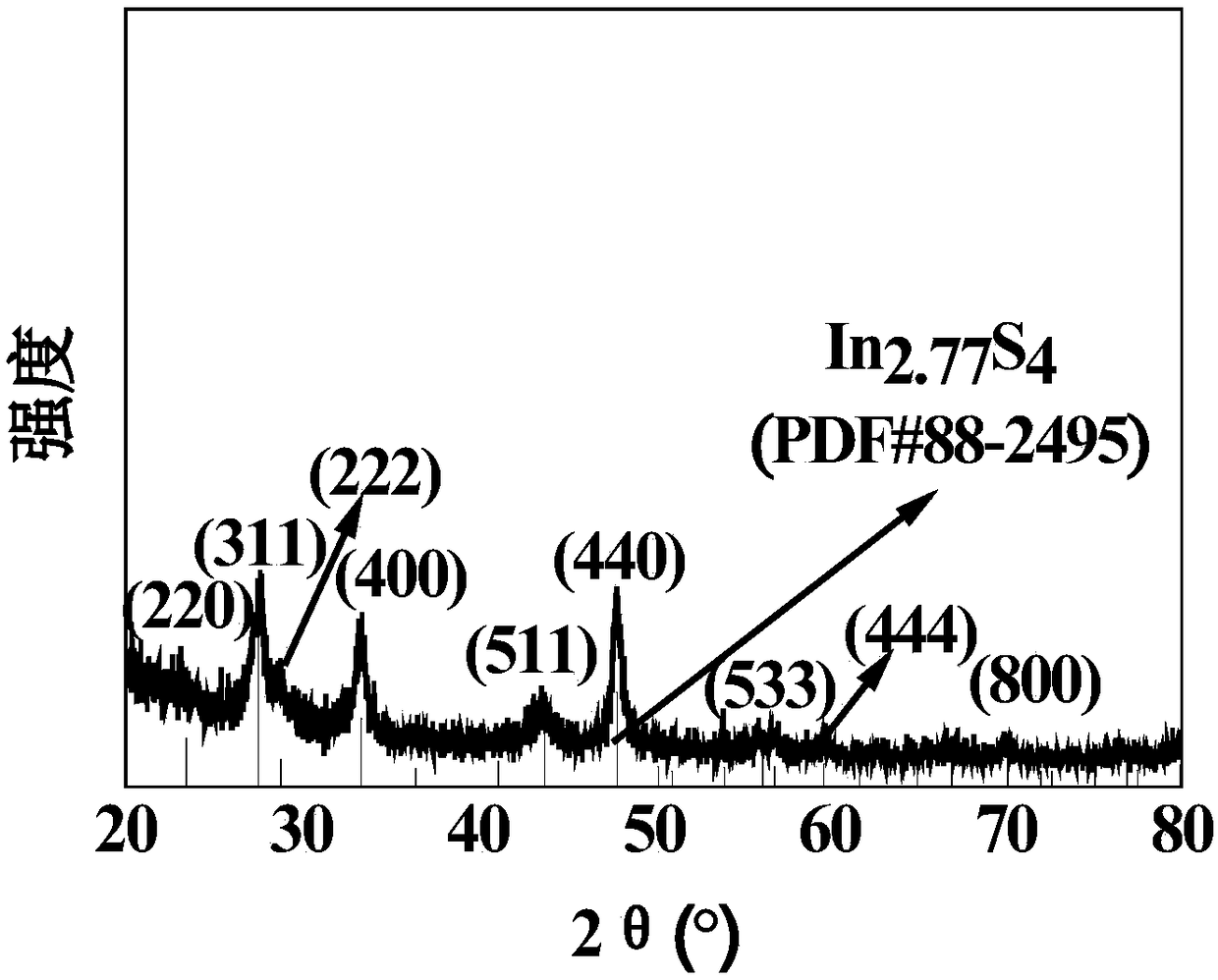
InactiveCN106345494BImprove degradation efficiencyPromote degradationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsIndiumMeth-
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-efficiency visible light degradation agent nanosheet In2.77S4, which includes the following steps: A. Material preparation: In(NO3)3·4.5H2O and thioacetamide are fully dissolved in deionized water, wherein, The indium ion concentration is 0.05mol / L, the molar ratio of indium ions and sulfide ions is 1:3-1:5, and then placed in a hydrothermal reactor lined with polytetrafluoroethylene; B. Reaction: control hydrothermal The reaction temperature is 180°C, and the reaction time is 14-16 hours. After the reaction is completed, the reaction kettle is naturally cooled to room temperature; C. Post-processing: Take out the product in the reaction kettle, wash it repeatedly with deionized water, and filter it until neutral After drying, flake In2.77S4 is obtained. The method of the invention is simple, has mild reaction conditions, short technological process and high preparation efficiency. The obtained product has high degradation efficiency of rhodamine B, methyl orange and potassium dichromate under visible light.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG TIEDAO UNIV
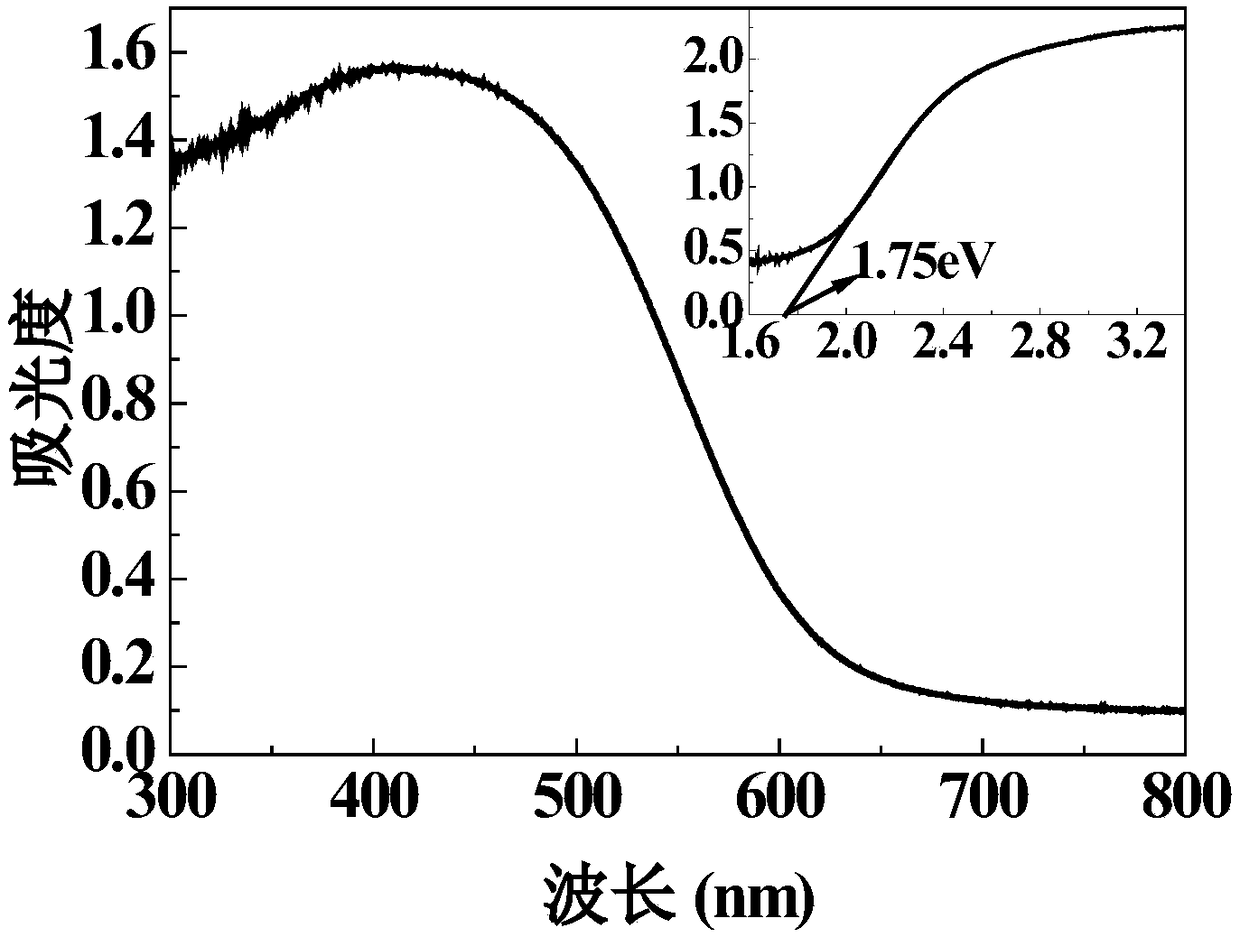
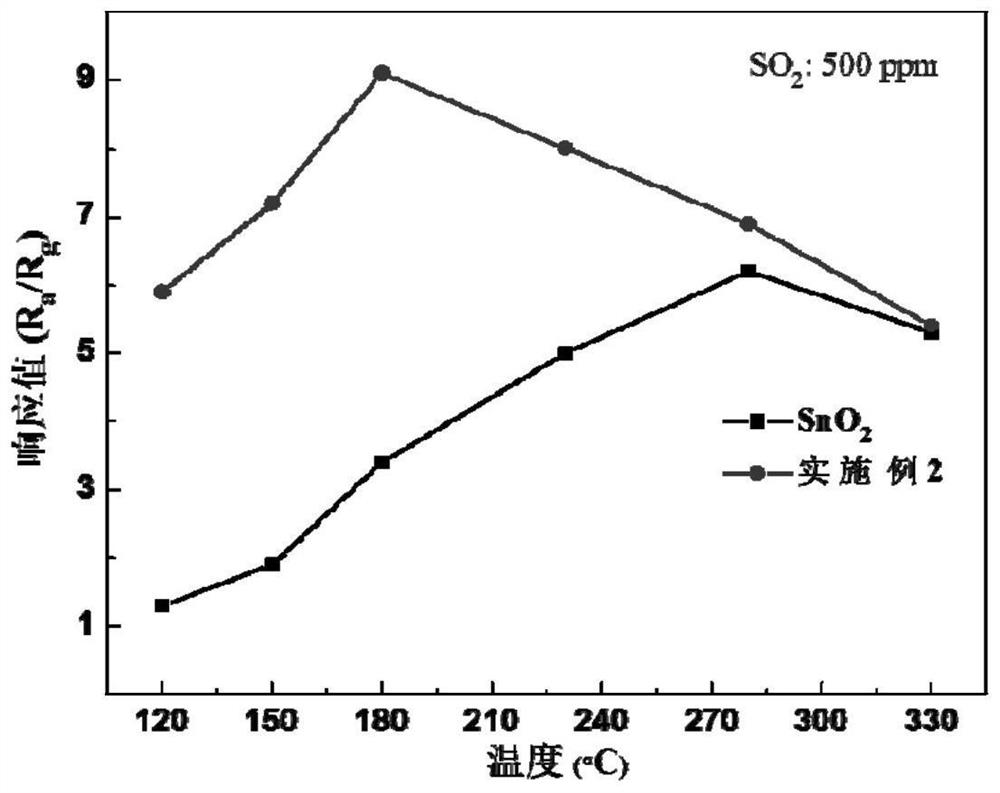
A sulfide ion-modified sno 2 base low temperature so 2 Sensitive material and preparation method thereof
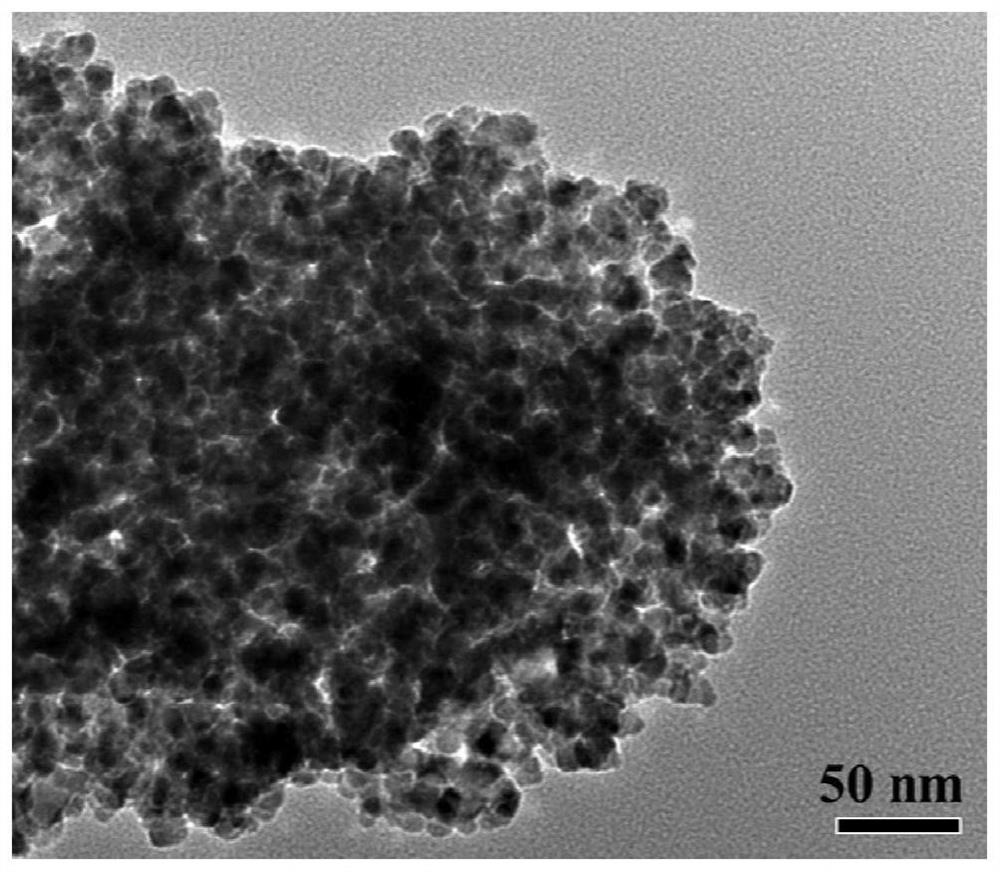
ActiveCN110243879BSmall granularityGood dispersionMaterial nanotechnologyNanosensorsNanoparticleSulfide ions
The invention provides a sulfide ion surface modified SnO 2 Preparation of low-temperature SO 2 As for the synthesis method of sensitive materials, the present invention first prepares SnO2 nanoparticles by the sol-gel method. The prepared SnO 2 Nanoparticles have small particle size (10-20nm) and good dispersion. Later, in this patent, the prepared nano-SnO 2 Surface modifications were made. Using hydrothermal method in SnO 2 The surface of the nanoparticles was doped with sulfur ions to prepare SnO surface-modified with sulfur ions. 2 sensitive materials. Able to implement SO 2 For low-temperature detection, the optimal detection temperature is determined by pure SnO 2 of 280℃ reduced to 180℃. And improve the SO 2 The response value of the gas shows good stability and response-recovery characteristics.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
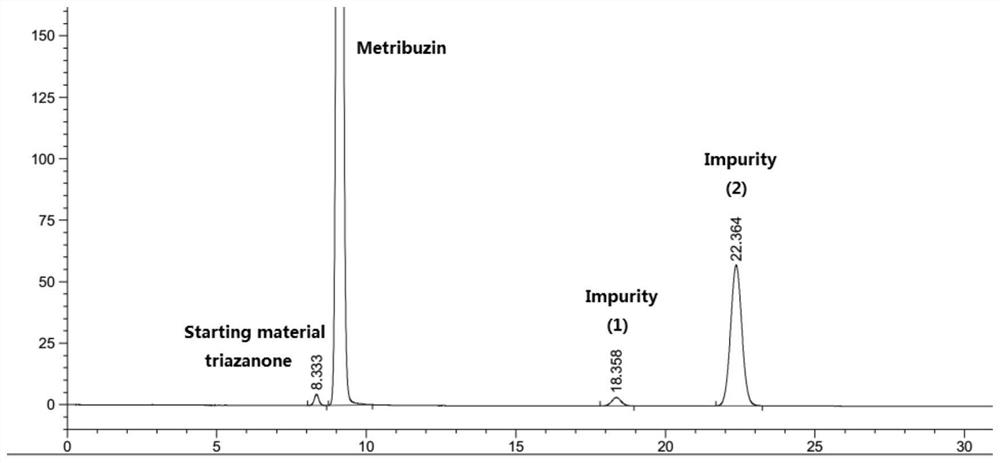
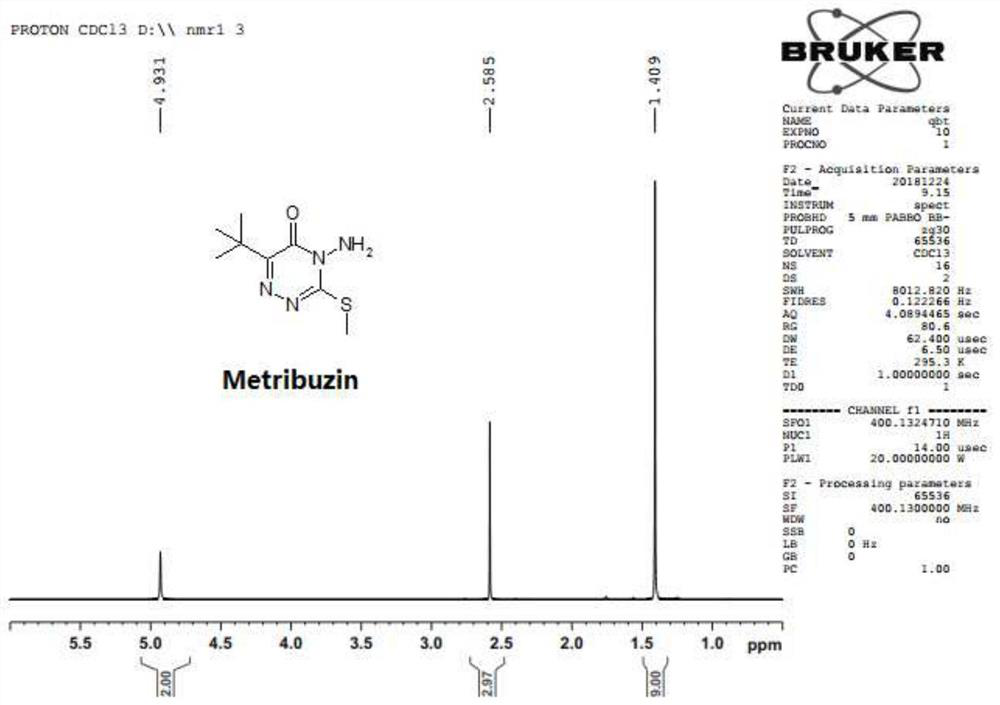
The preparation method of azimidone
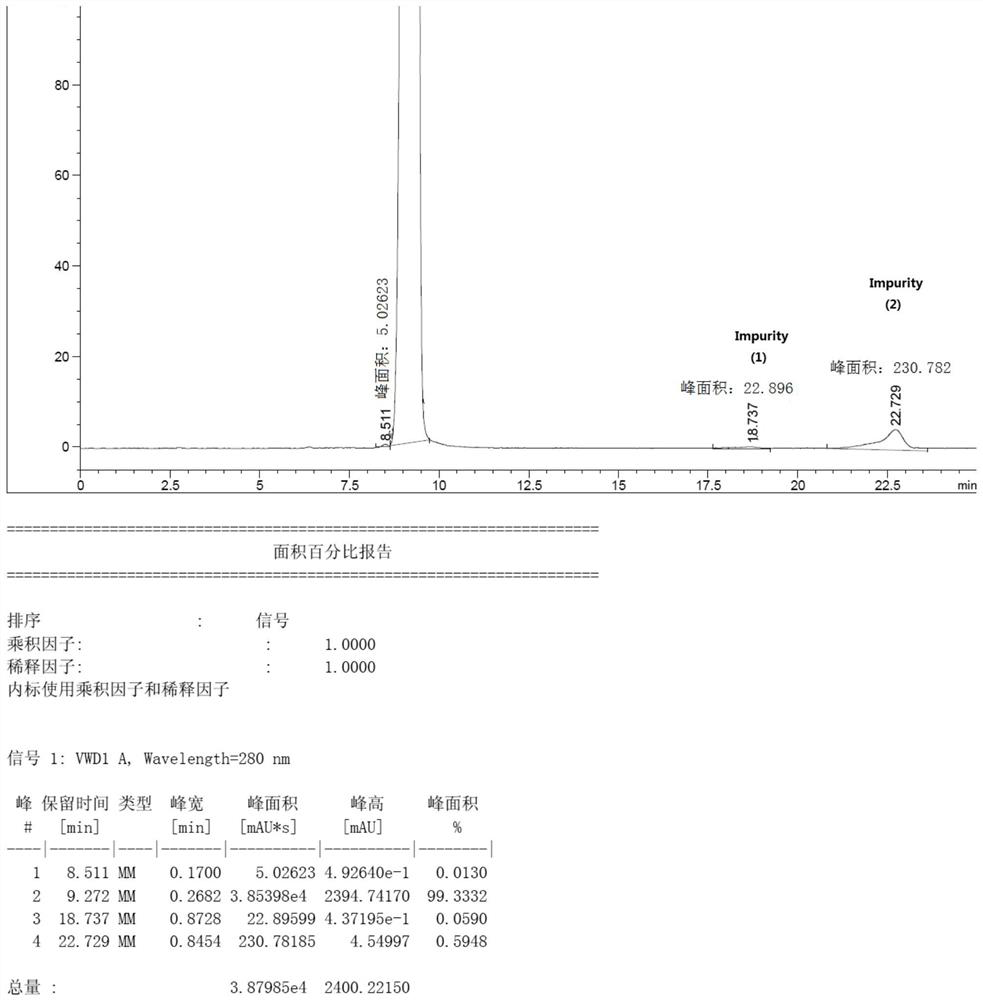
The invention discloses a method for preparing metrizone. Using methanol-water as a solvent, in the presence of pH 11.5-12.5 and lithium ions, triazinone and methyl halide react at 5°C-20°C to three Azinones disappear completely. The present invention adds lithium ions to the reaction system during the preparation of mecitrione, which improves the selectivity of the reaction to produce mecitrione. The addition of lithium ions improves the ability of triazinone to exist in the form of thiols, thereby increasing the concentration and reactivity of sulfide anions in the reaction system, and the generated products are mainly S-methylated products, reducing impurities N-methyl Therefore, there is basically no impurity in the product, and the purity of mecitrione is more than 99%.
Owner:JIANGSU REPONT PESTICIDE FACTORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com