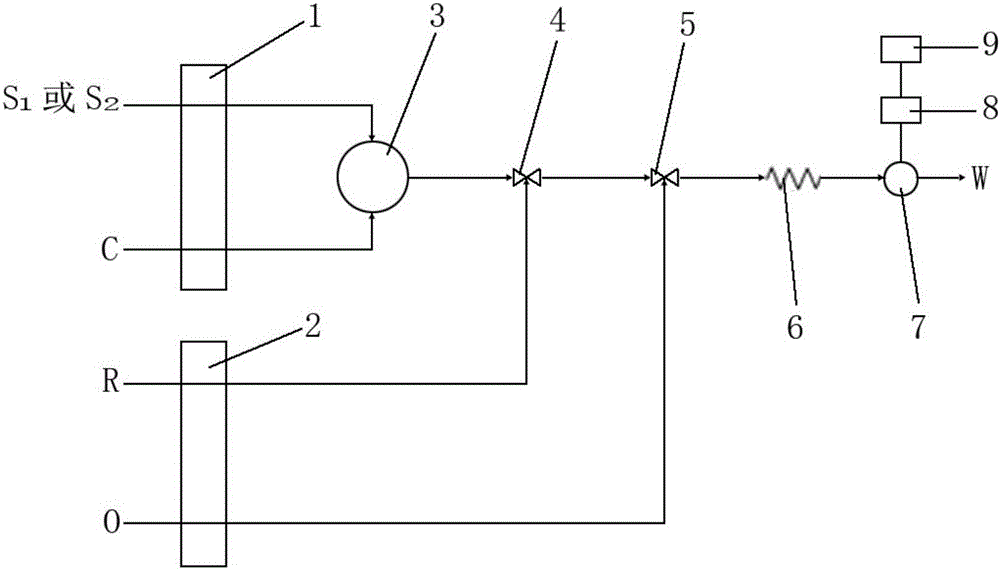
Preservation method and automatic analysis method of trace divalent sulfide ions in water sample
An automatic analysis, divalent sulfur technology, applied in the analysis of materials, material analysis by observing the impact on chemical indicators, preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problem of low automation, large errors, and short life of ion electrodes Selectivity and other issues, to achieve the effect of simple and fast preservation method and simplified preservation conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
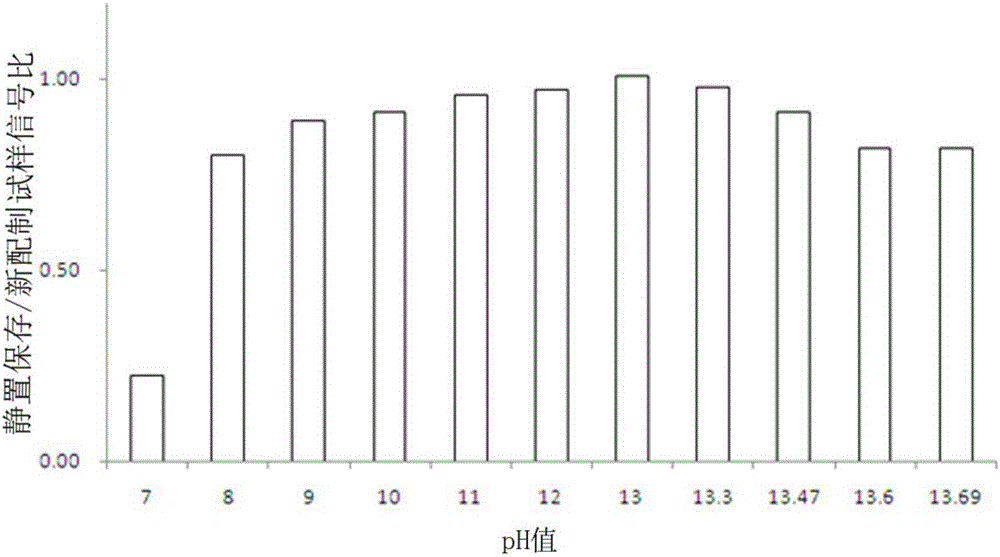
[0031] In this implementation, the stability of divalent sulfide ions under different pH conditions is investigated, and the storage method of divalent sulfide ions in water samples is determined.
[0032] 1. Specimen Preparation
[0033] (1) Static divalent sulfide ion sample: 0.75gNa 2 S·9H 2 Dissolve O in deionized deionized water, dilute to 100mL volumetric flask with deoxygenated deionized water to obtain the mother liquor, and place it in a refrigerator at 4°C to refrigerate; dilute the newly prepared mother liquor with deionized water, and adjust the pH value with sodium hydroxide standard solution , to obtain pH values of 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 13.3, 13.47, 13.6, 13.69 and a concentration of 0.5 mg / L divalent sulfide ion solution, respectively recorded as 1 # ~ 11 # test Samples were tested at room temperature for 24 hours.
[0034] (2) Newly prepared divalent sulfide ion sample: add 0.75gNa 2 S·9H 2 O was dissolved in deoxygenated deionized water, and the vol...
Embodiment 2
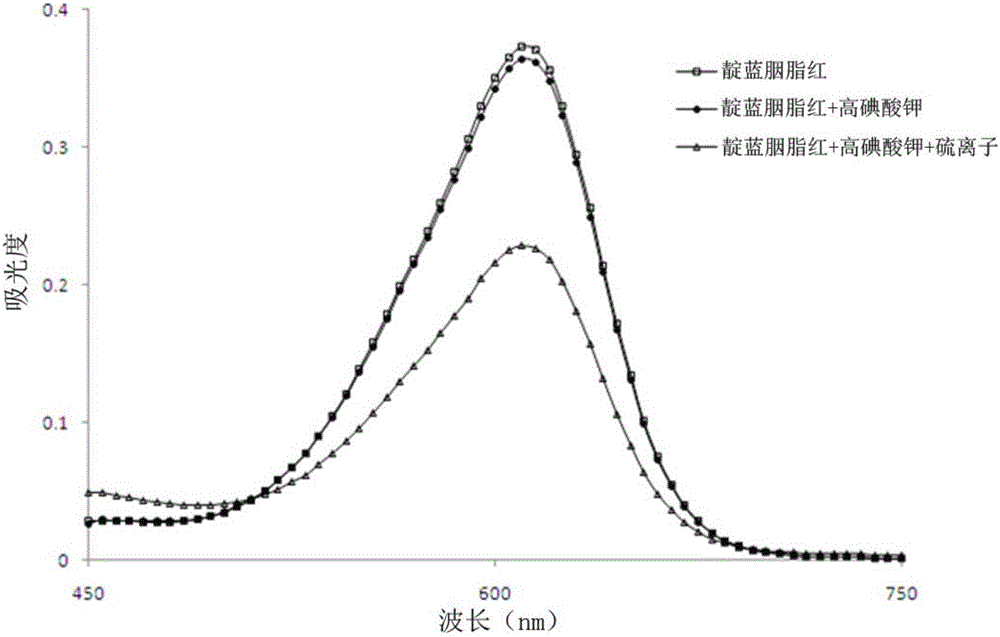
[0046] In this implementation, investigate the catalytic ability of divalent sulfide ion to potassium periodate oxidation indigo carmine, the steps are as follows:
[0047] 1. Preparation of sample solution
[0048] (1) Preparation of divalent sulfur standard sample: 0.75gNa 2 S·9H 2 O was dissolved in deoxygenated deionized water, then sodium hydroxide was added to a concentration of 0.1mol / L, and the mother liquor was obtained by distilling the volume into a 100mL volumetric flask with deoxygenated deionized water, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use; the mother liquor was deoxygenated with Dilute with deionized water, add sodium hydroxide to a final concentration of 0.1mol / L, and prepare a standard sample with a divalent sulfide ion concentration of 0.5mg / L.
[0049] (2) 10mmol / LKIO 4 Solution preparation: 2.23gKIO 4 Dissolve in deionized water and dilute to the mark of the 1000mL volumetric flask.
[0050] (3) Preparation of 5mmol / L indigo carmine soluti...
Embodiment 3
[0058] In this embodiment, the standard sample is tested to investigate the influence of different inorganic acids on the oxidation of indigo carmine catalyzed by potassium periodate with divalent sulfur ions. The steps are as follows:
[0059] 1. Preparation of standard samples
[0060] (1) Add 0.75gNa 2 S·9H 2 Dissolve O in deoxygenated deionized water, then add sodium hydroxide to a concentration of 0.1 mol / L, dilute to 100mL volumetric flask with deoxygenated deionized water to obtain the mother liquor, and store it in a refrigerator at 4°C for later use;
[0061] (2) Dilute the mother liquor with deoxygenated deionized water, add sodium hydroxide to a final concentration of 0.1mol / L, and prepare a standard sample with a divalent sulfide ion concentration of 0.5mg / L.
[0062] 2. Preparation of oxidizing solution O
[0063] Take KIO with a concentration of 0.01mol / L 4 120mL aqueous solution, the final concentration acidity is 0.48mol / LH + Add different inorganic acids (p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com