Patents
Literature
264 results about "Tellurium dioxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tellurium dioxide (TeO₂) is a solid oxide of tellurium. It is encountered in two different forms, the yellow orthorhombic mineral tellurite, β-TeO₂, and the synthetic, colourless tetragonal (paratellurite), α-TeO₂. Most of the information regarding reaction chemistry has been obtained in studies involving paratellurite, α-TeO₂.
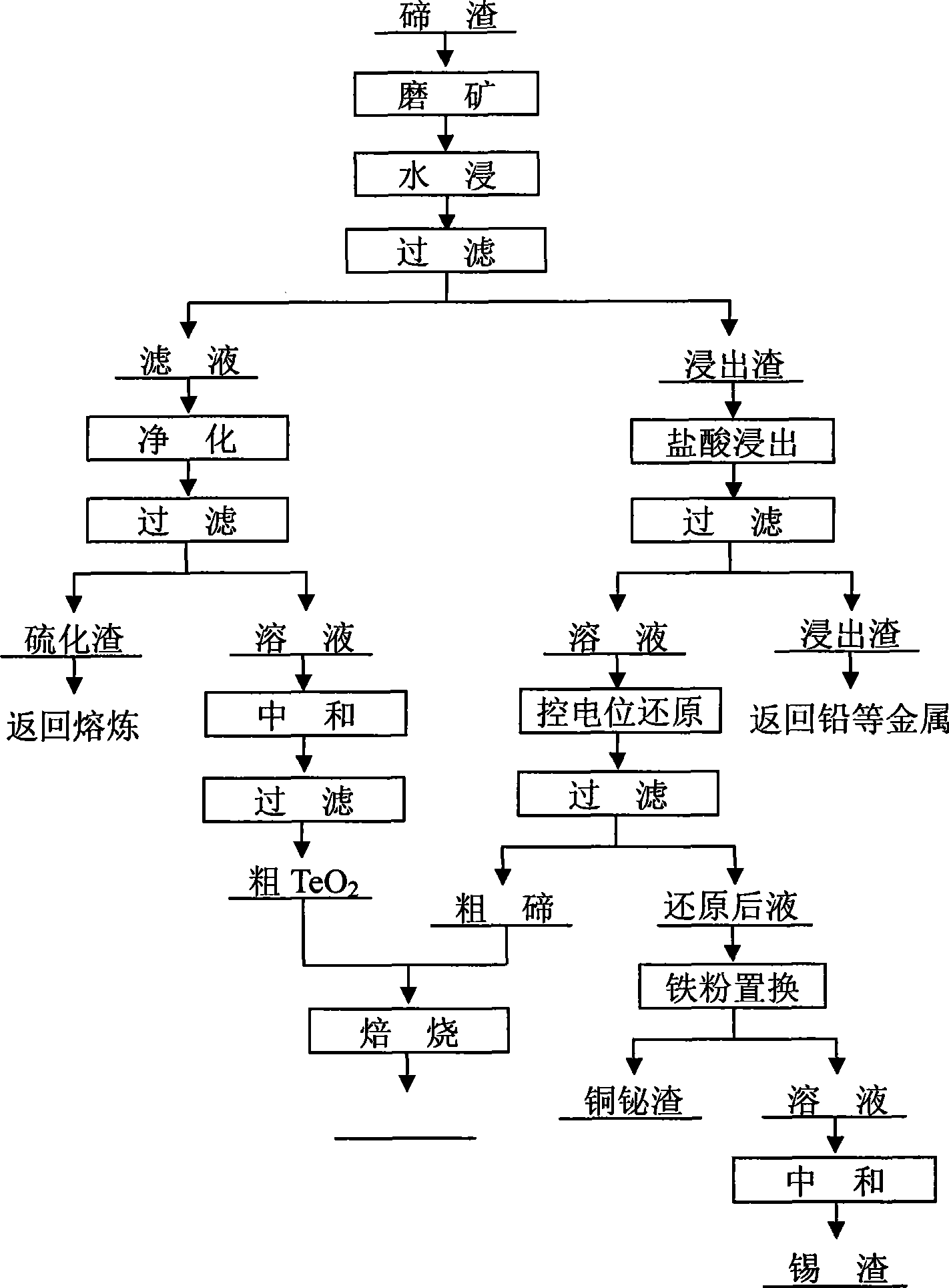
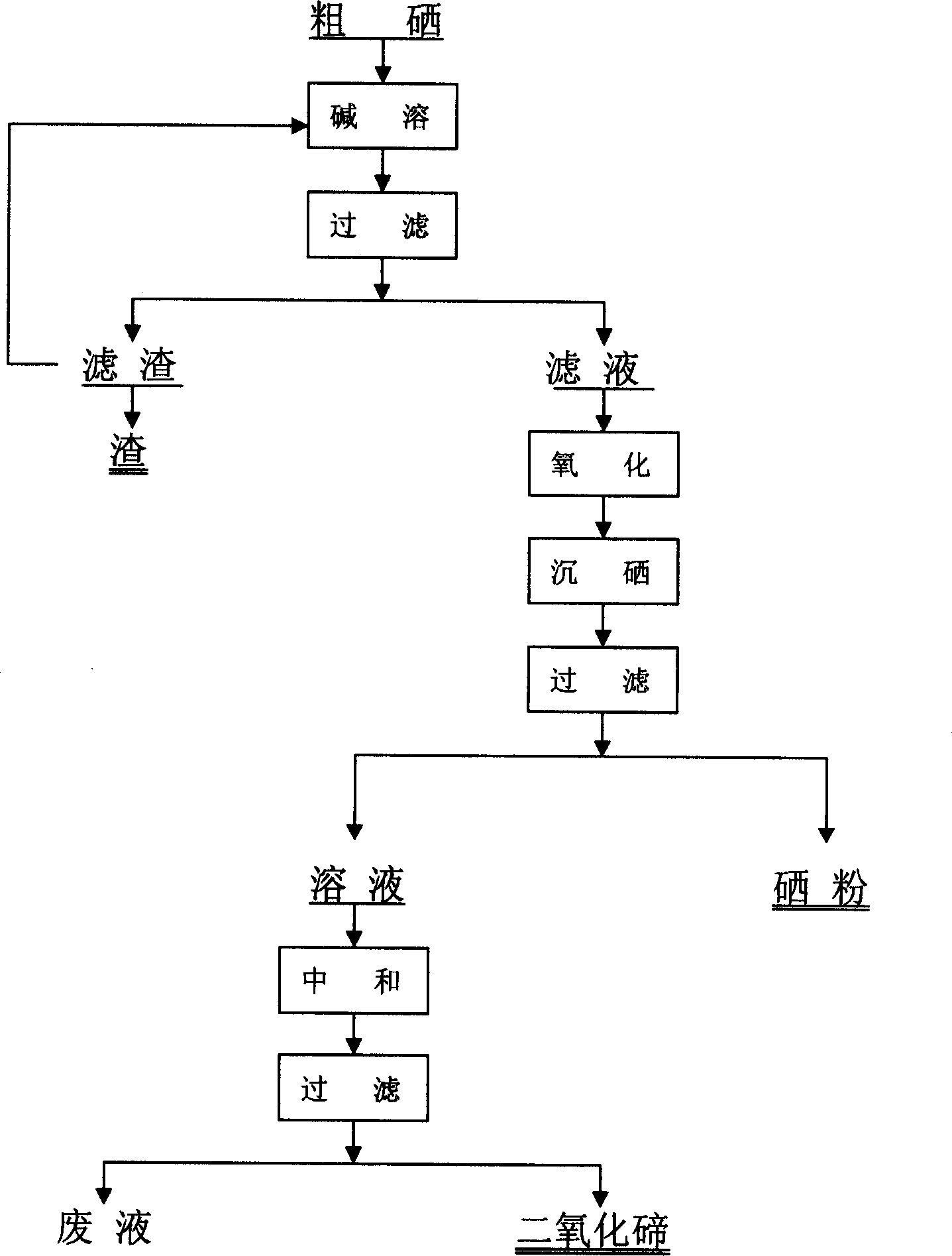
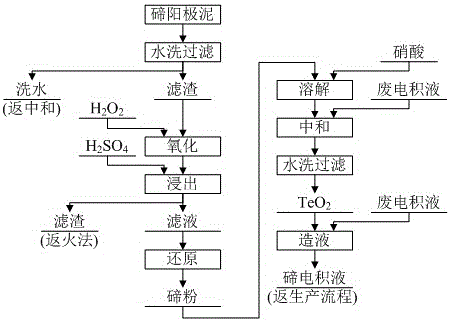
Method for separating tellurium from tellurium slag
InactiveCN101508426APrecisely control the amount addedImprove solubilityElemental selenium/telluriumSludgeSlag
The invention relates to a method for separating tellurium from tellurium slag, which comprises the following steps: firstly, grinding the tellurium slag, leaching out the obtained product in an aqueous solution, purifying and neutralizing a water leaching solution, and producing tellurium dioxide; secondly, performing hydrochloric acid leaching on water leaching residue in a hydrochloric acid system, cooling and filtering an acid leaching solution, and returning acid leaching residue to an anode sludge treatment process; thirdly, performing controlled potential reduction on the acid leaching solution to produce coarse tellurium, and performing roasting and impurity removal on the coarse tellurium and the tellurium dioxide produced by neutralization to obtain pure tellurium dioxide; and fourthly, using the conventional method to reclaim valuable metals such as copper, bismuth, tin, and the like from a reduced solution respectively. The total tellurium leaching rate of the method is as high as more than 98 percent, and the produced coarse tellurium has the advantages of low content of impurity elements, small amount of return slag, small modification amplitude of equipment, short treatment time, and low treatment cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
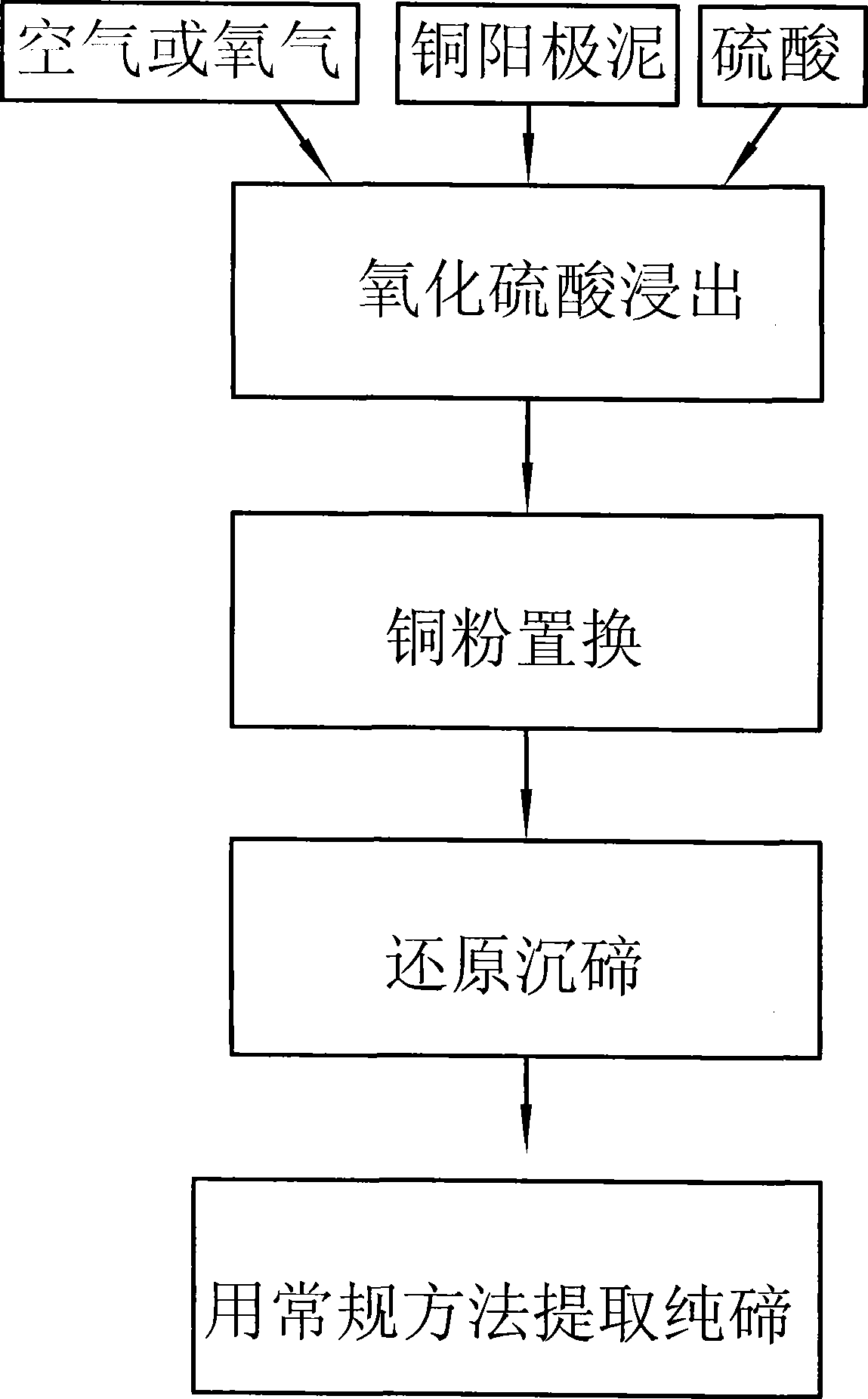
Process for extracting tellurium from copper anode mud
ActiveCN101434385AReduce consumptionEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumTe elementOxygen
The invention discloses a technology for extracting tellurium from copper anode slime, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) the copper anode slime is put into a sulfuric acid solution, oxygen is introduced into the sulfuric acid solution for oxidation sulfuric acid leaching; solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain leachate containing copper and tellurium; and the leaching process being finished in a closed high-pressure device; (2) copper powder is added into the leachate to remove silver or selenium in the leachate by substitution, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out; (3) sulfur dioxide is introduced into the leachate obtained from the step (2) to precipitate the tellurium by reduction, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain crude tellurium; and (4) the crude tellurium is processed according to a conventional method to extract pure tellurium. The technology adopts one-section oxidation acid leaching to leach the copper and tellurium out, copper powder to remove the impurities of silver, selenium and the like by substitution, and sulfur dioxide to precipitate the tellurium by reduction (obtaining tellurium dioxide), and the tellurium dioxide precipitation is alkali-dissolved and then electrolyzed to obtain the tellurium, therefore, the flow is simple, the consumption of the copper powder is remarkably reduced, and the simplification of the technology is beneficial to improve the recovery ratio of the tellurium, which can achieve more than 90 percent.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
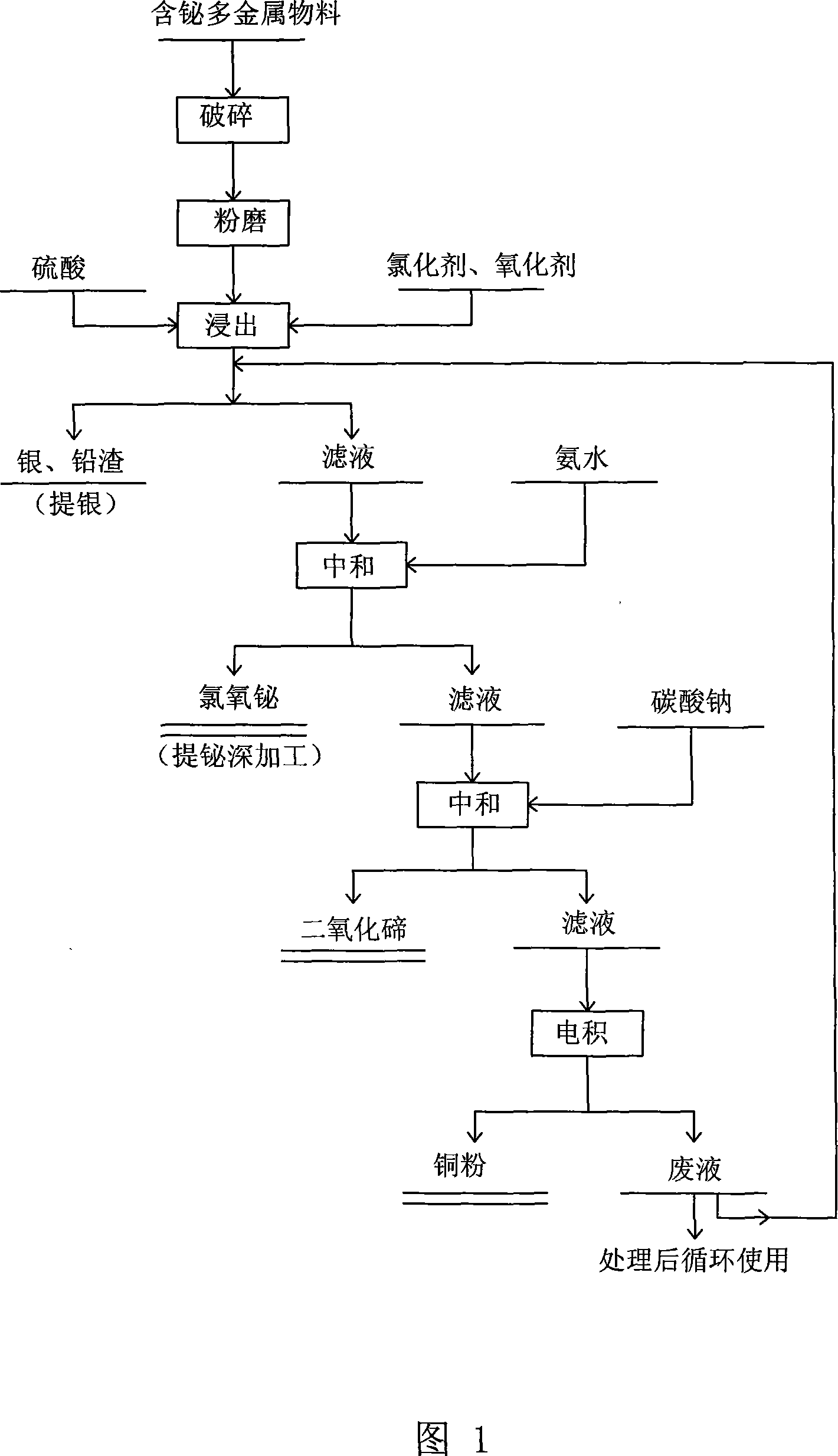
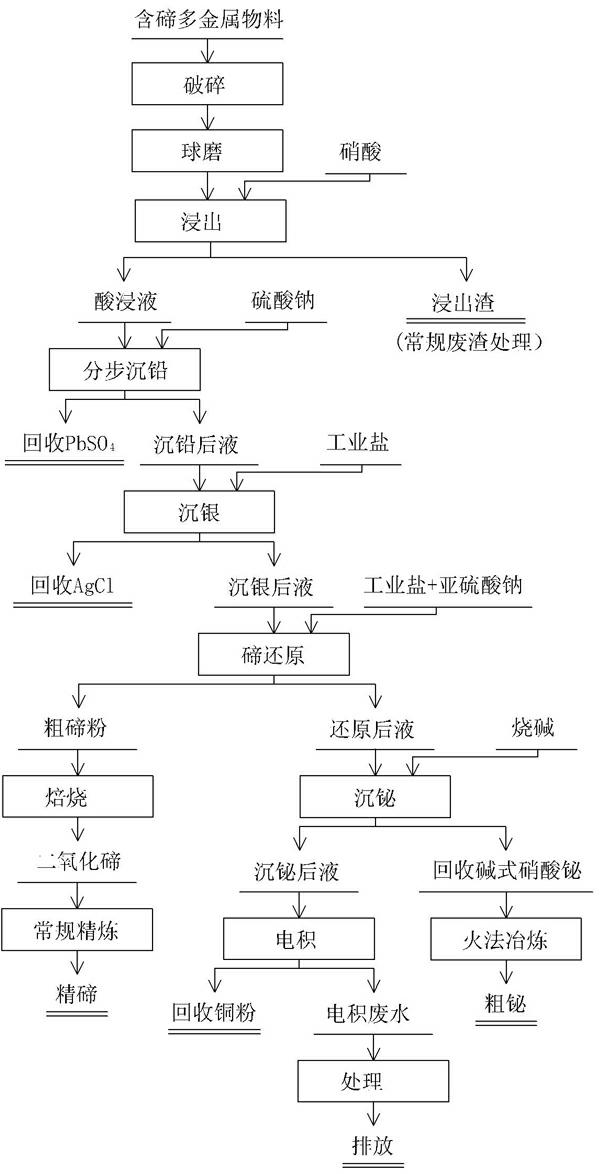
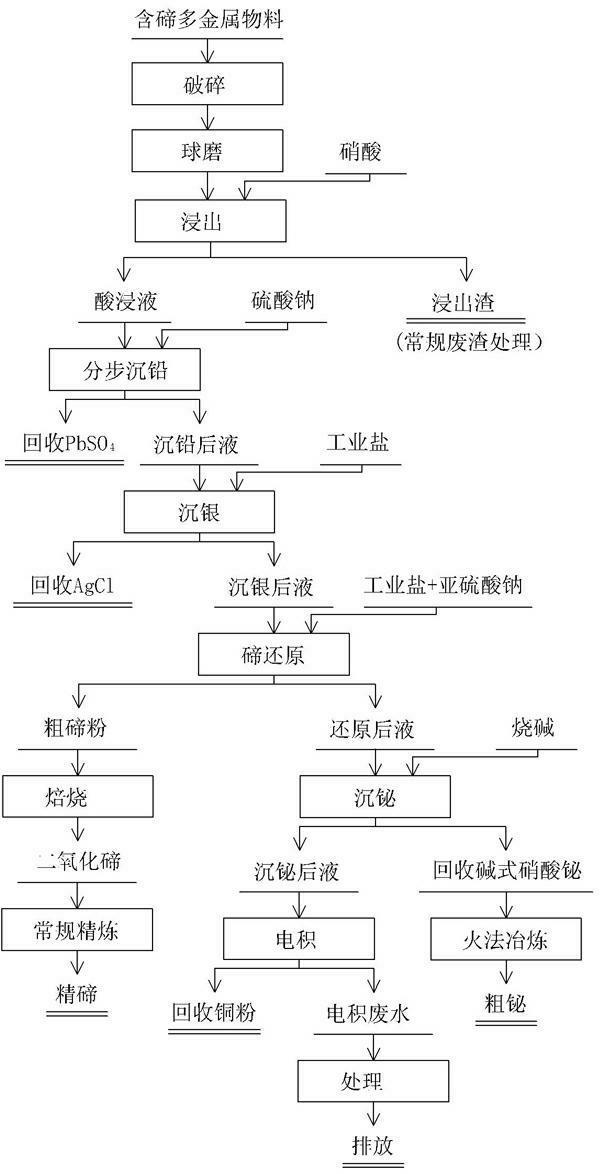
Comprehensive extraction of valent metal from bismuth-containing polymetallic material
InactiveCN101029353AHigh recovery rateImprove product added valuePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSesquioxideTe element
A method for extracting metal from bismuth-contained multi-metal material is carried out by leaching out copper and tellurium from bismuth-contained multi-metal by sulfuric acid, adding into chlorinating agent and oxidant to leach out metal bismuth, extracting silver from leaching-out slag with AgCl, PbSO4 and PbC12, adding ammonia water into leaching-out liquid, adjusting pH value to 1.5 to obtain bismuth oxychloride slag with 70% bismuth content, smelting into coarse bismuth by firing method or machining to obtain high-purity bismuth sesquioxide, adjusting pH value to 4.5 by Na2CO3, depositing tellurium to obtain tellurium dioxide and copper-contained solution, and electrically depositing to obtain copper powder with copper-contained content90%. It adopts wetting and firing metallurgical technology, has higher metal recovery rate and excellent leaching-out separation effect and effluent circulating utilization and no environmental pollution.
Owner:HUNAN JINWANG BISMUTH
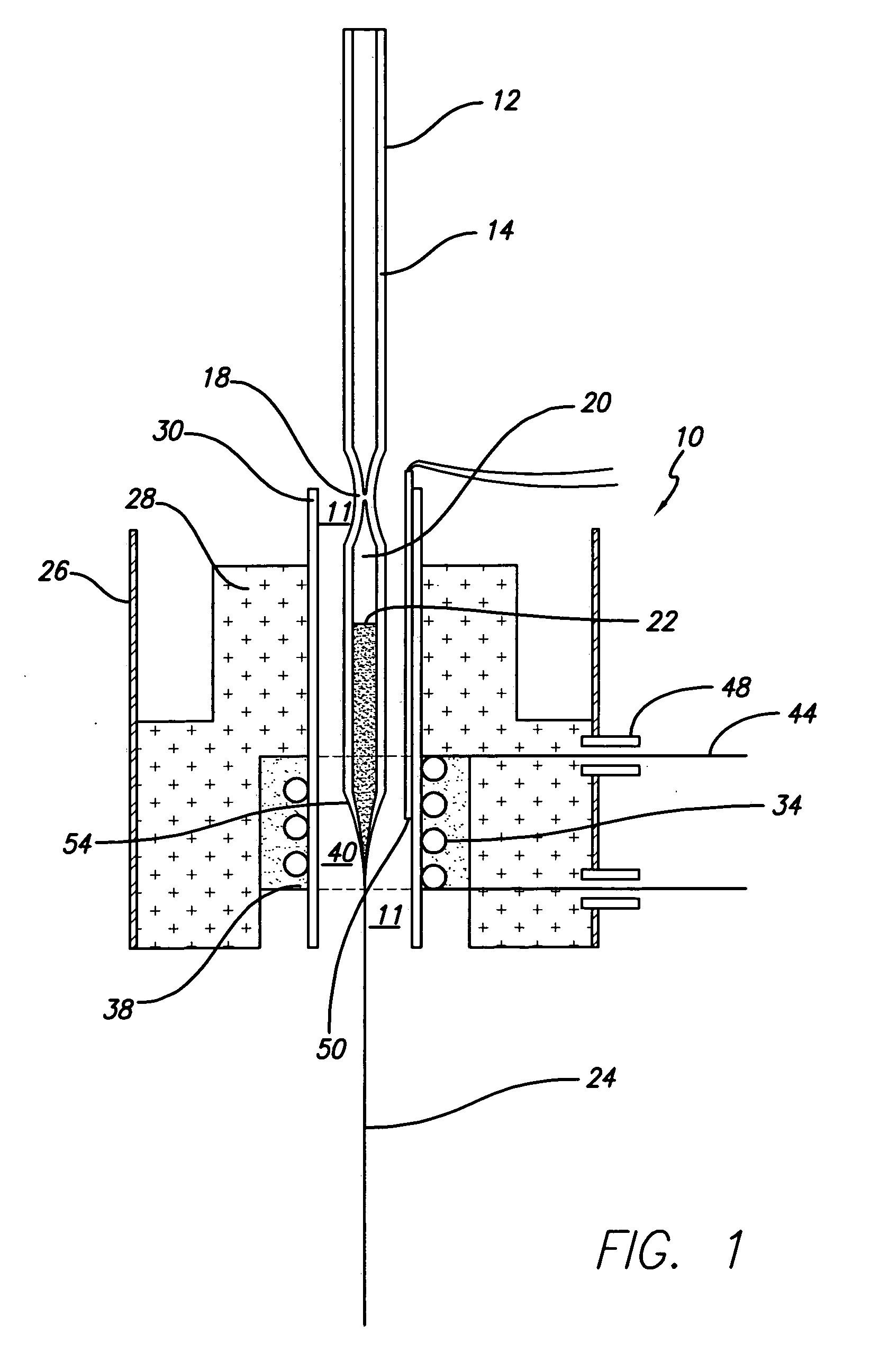
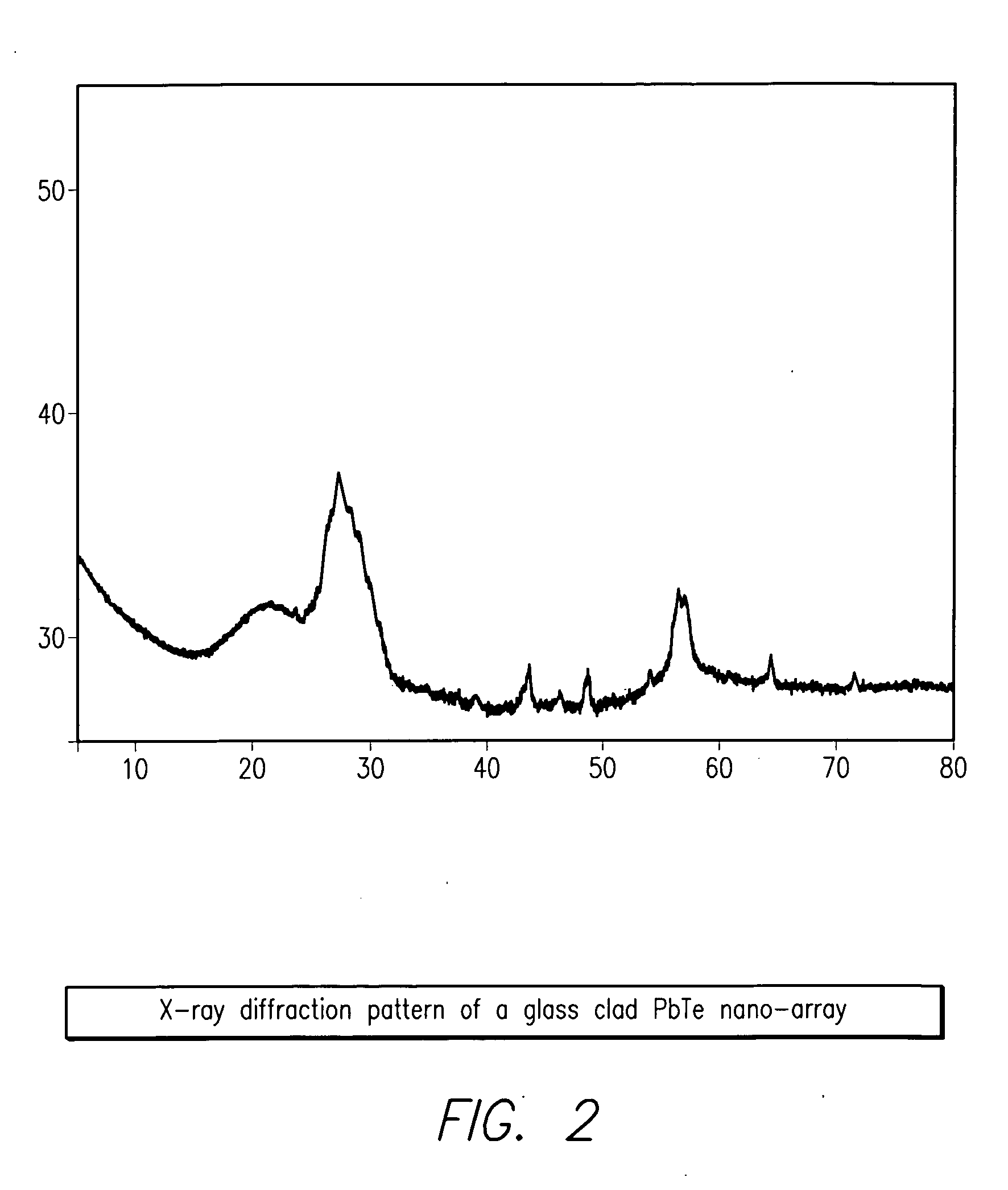
High density nanowire arrays in glassy matrix
InactiveUS20070131269A1Cost-effectivelySmall footprintThermoelectric device detailsThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsFiber
The present invention provides high density nanowire arrays in a glassy matrix comprising one or more thermoelectric fibers embedded in an electrically insulating material such that the thermoelectric material exhibits quantum confinement. According to the preferred embodiment of the invention, the thermoelectric material comprises PbTe and the glassy matrix comprises an electrically insulating material comprising a binary, ternary or higher component glass such as pyrex, borosilcate, aluminosilicate, quartz. The glass may also be formed from multiple constituents but not limited to lead oxide, tellurium dioxide and silicon dioxide, alumina, calcium oxide etc.
Owner:ZT3 TECH INC
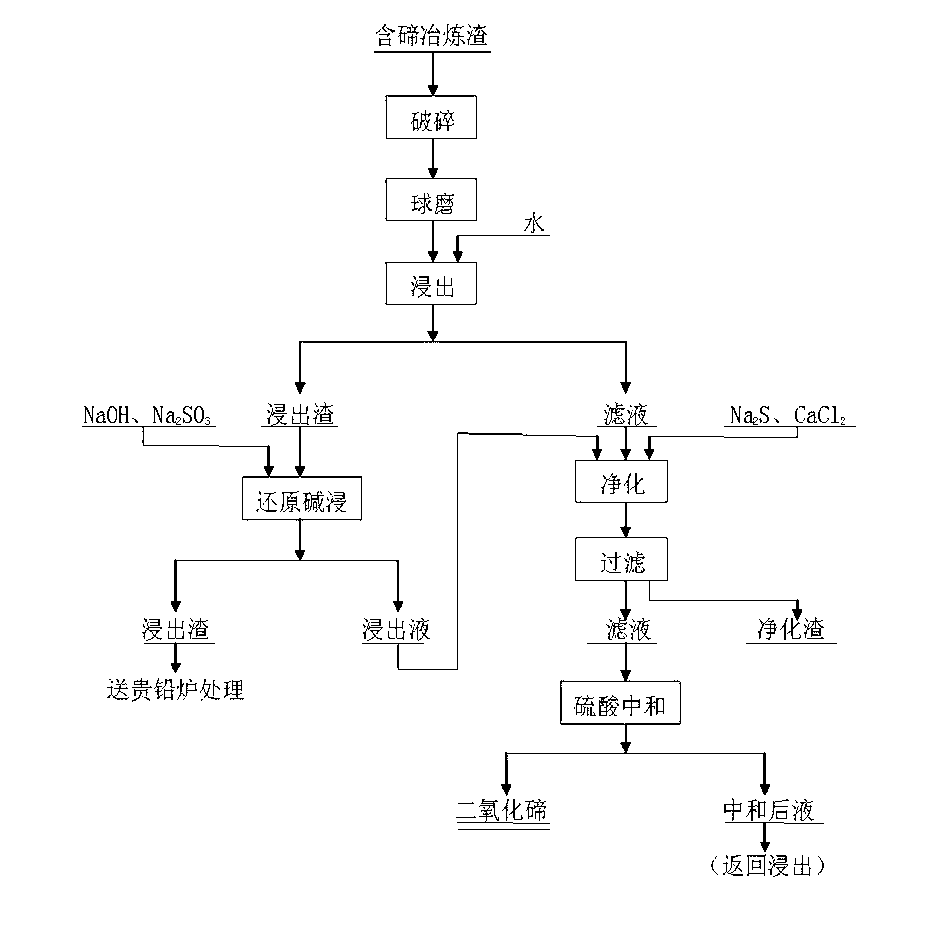
Technology for extracting tellurium dioxide from tellurium-containing smelting slag
ActiveCN102992280AImprove leaching rateReduce dosageWaste processingSolid waste disposalSlagMaterials science
The invention relates to a technology for extracting tellurium dioxide from tellurium-containing smelting slag. The technology comprises the following steps: ball-milling tellurium slag, leaching by water, carrying out reduction alkali leaching, vulcanizing, carrying out silicon removal purification, and neutralizing to precipitate tellurium. The method has the advantages of tellurium leaching rate improvement, reduction of the alkali application amount in the leaching operation, and production cost reduction. The method is characterized in that sodium hydrosulphite is adopted as a transition agent to transit insoluble high-valence tellurium to low-valence tellurium, so the leaching rate leaching rate is increased. The total tellurium leaching rate can reach above 90% under a suitable technological condition; and after recovering tellurium through neutralizing, the TeO2 grade of the smelting slag can reach above 50%, and the content of tellurium in the waste liquid obtained after the neutralizing is 0.1-0.3g / L. The method also has the advantages of further enrichment of copper, lead, bismuth, antimony and precious metals in the leaching slag, realization of the resource reuse, production cost reduction, and energy saving, and is of great importance to the resource recovery and the environmental protection.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
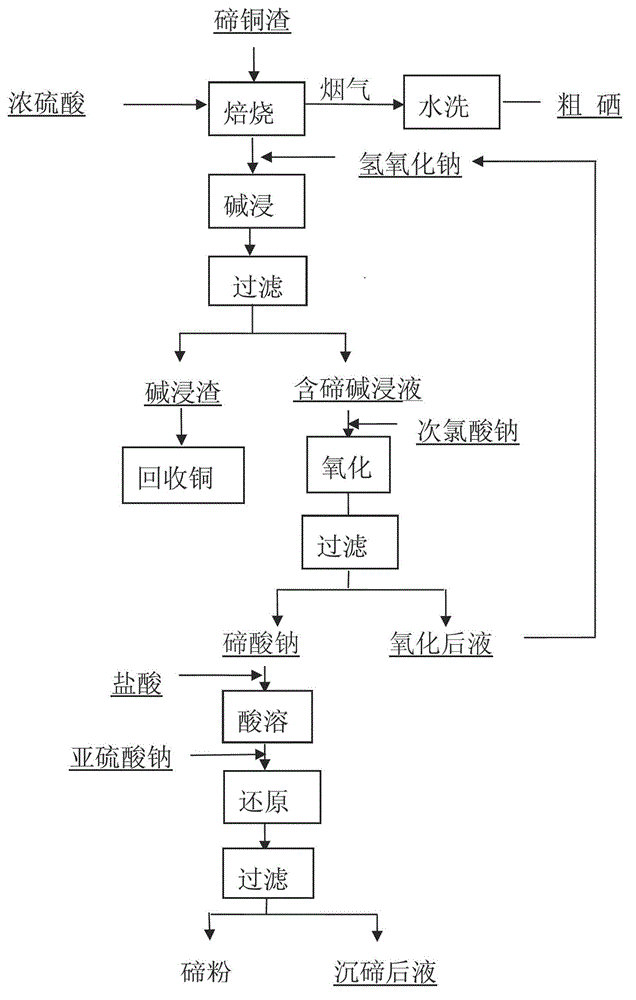
Method for extracting tellurium from tellurium copper slags
ActiveCN102745657AEasy to separateAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumAcid dissolutionCalcination
The invention provides a method for extracting tellurium from tellurium copper slags. The method includes the following steps of (1) sulfating calcination at a high temperature, grinding the tellurium copper slags, mixing ground tellurium copper slags with a concentrated sulfuric acid to calcine, enabling the mass ratio between the concentrated sulfuric acid and the tellurium copper slags to be (1.2-1.5):1, maintaining the calcination temperature in a range from 450 DEG C to 600 DEG C and maintaining the calcination time in a range from 3 hours to 5 hours; (2) alkaline leaching to separate the tellurium, leaching obtained calcination slags by a sodium hydroxide alkaline liquor, and then filtering to obtain a tellurium containing alkali leaching liquid and alkali leaching slags; (3) oxidizing the alkali leaching liquid, oxidizing the tellurium containing alkali leaching liquid by sodium hypochlorite of an oxidant and then filtering to obtain sodium tellurate filtered slags; and (4) acid dissolution reduction, dissolving the sodium tellurate filtered slags by a chloridion containing acidic system, adding a reducing agent to achieve reduction and then filtering to obtain tellurium powders. According to the method for extracting the tellurium from the tellurium copper slags, a complete separation of copper, selenium and tellurium can be fully achieved, a comprehensive recovery of the copper, selenium and tellurium can be achieved, the technological process is simple, tellurium dioxide of an intermediate product is not required, the tellurium powders with a high purity can be directly produced, and the tellurium powders can serve as raw materials of 6N high purity tellurium.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
Method for preparing radioactive <124>I ions
ActiveCN103771341ANo leaksImprove radiation effectIodineAlkali metal iodidesAngle of incidenceDistillation
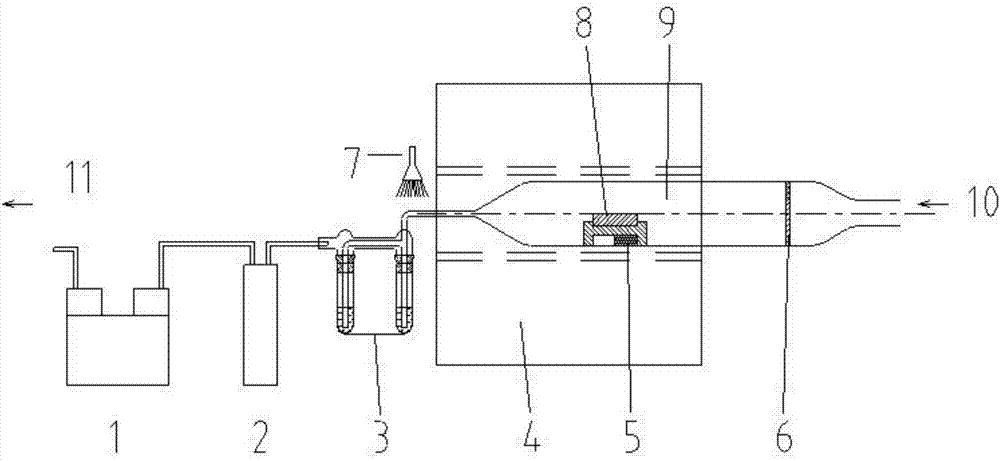
The invention discloses a method for preparing radioactive <124>I ions. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a, taking aluminium oxide powder and tellurium dioxide powder in a mass ratio of 1:18-22, uniformly mixing the powder, and pressing the obtained mixture into a tellurium target with a thickness of 50-60 mg / cm<2>; b, placing the prepared tellurium target in a circular accelerator, and irradiating the tellurium target 2-3 h by Te (p, n) <124>I, wherein the incident p particle beam intensity is 18-20 mu A, the energy is 18.5-20 MeV, and the angle of incidence is 6-10 DEG; meanwhile, cooling the tellurium target by using water in the process of irradiating, and after the irradiating is completed, placing the tellurium target to cool 4-6 h; c, placing the tellurium target in a quartz distillation tube of a destructive distillation device to distill, meanwhile, controlling the temperature to 750 DEG C so as to heat the tellurium target, so that radioactive <124>I ions are escaped, and collecting the radioactive <124>I ions. The problems that radionuclide <124>I prepared in the prior art is low in yield and low in recovery rate are solved.
Owner:MITRO BIOTECH CO LTD
Preparation method of high purity tellurium
InactiveCN102153054AReduce manufacturing costElemental selenium/telluriumSemiconductor materialsPurification methods
The invention discloses a preparation method of high purity tellurium. In the method, industrial tellurium of which purity is 99% is used as a raw material and the chemical and physical methods are combined to prepare high purity tellurium. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving the raw material in nitric acid, stirring, heating, filtering, adding the obtained tellurium dioxide in hydrochloric acid, introducing hydrogen peroxide, filtering after dissolving; adding sodium sulfite solution in the filtrate to reduce and obtain 3N-4N of fine tellurium; and dissolving at 400-450 DEG C in hydrogen atmosphere, and adopting the Czochralski purification method to treat fine tellurium and obtain 5N-6N of high purity tellurium. The method has low preparation cost; and the high purity tellurium can be used in the semiconductor material fields such as solar cell, light-emitting diode (LED), thermoelectricity and infrared field.
Owner:JIAXING DAZE PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Method for preparing tellurium dioxide by using crude tellurium as raw material
InactiveCN101648702AReduce pollutionReduce harmBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsTe elementOxidizing agent
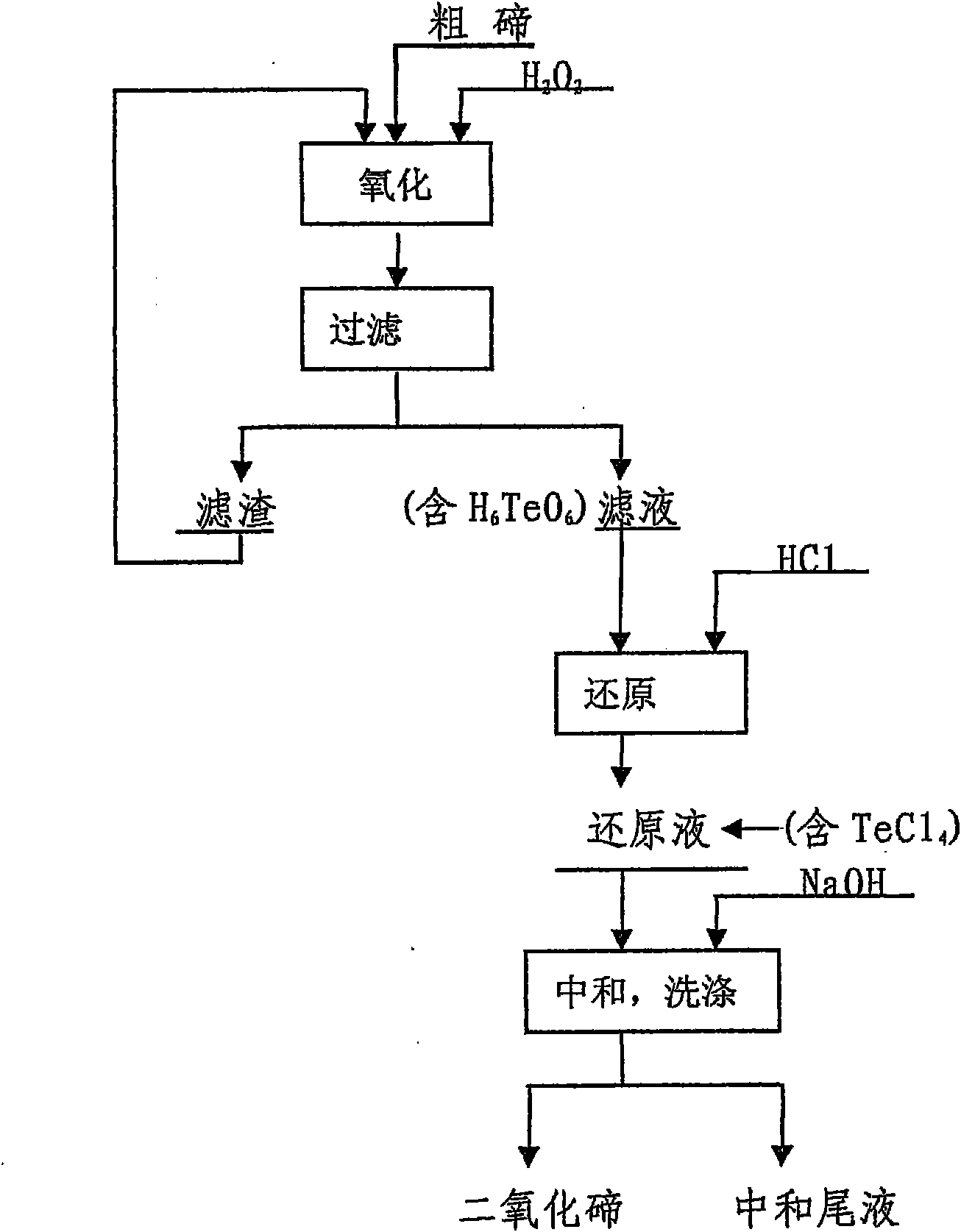
The invention discloses a method for preparing tellurium dioxide by using crude tellurium as the raw material, which is characterized in that hydrogen peroxide is used as an oxidizer for oxidizing thecrude tellurium, hydrochloric acid is used as a reducer to reduce the oxidized sexivalent tellurium into quadrivalent tellurium, and at last alkali is used for neutralization to obtain tellurium dioxide. The invention does not produce toxic or harm gases, greatly reduces environmental pollution and damage to human bodies, and is good for industrial production.
Owner:SICHUAN XINJU MINERAL RESOURCE DEV CO LTD
Conductive paste and method for manufacturing same
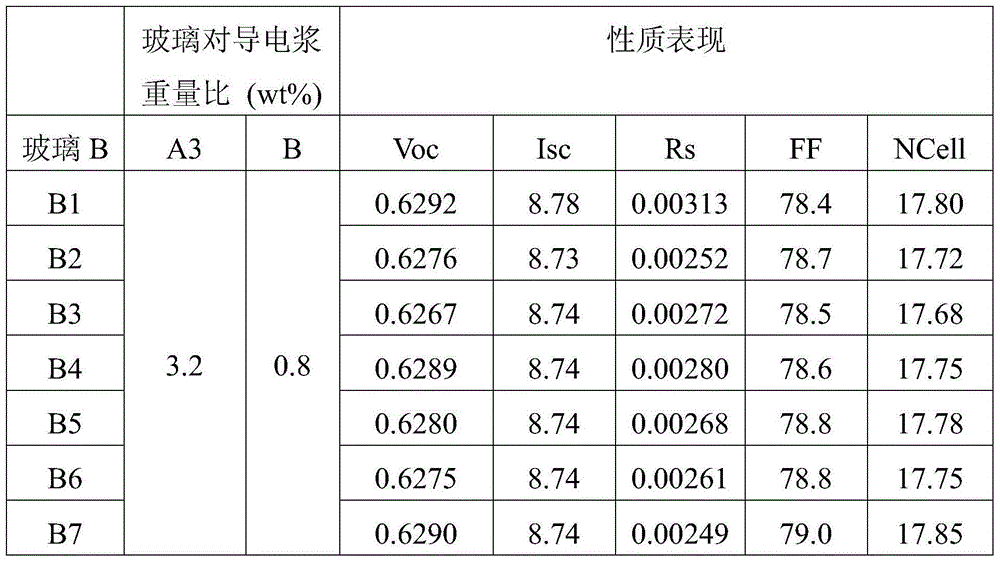
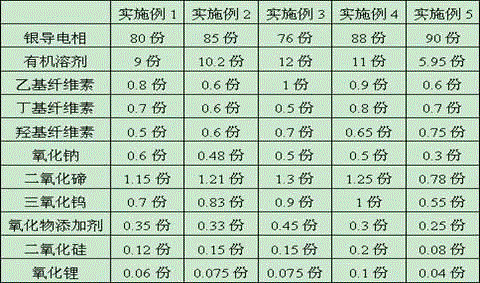
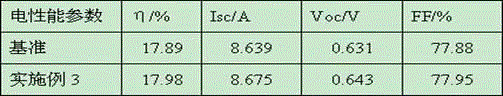
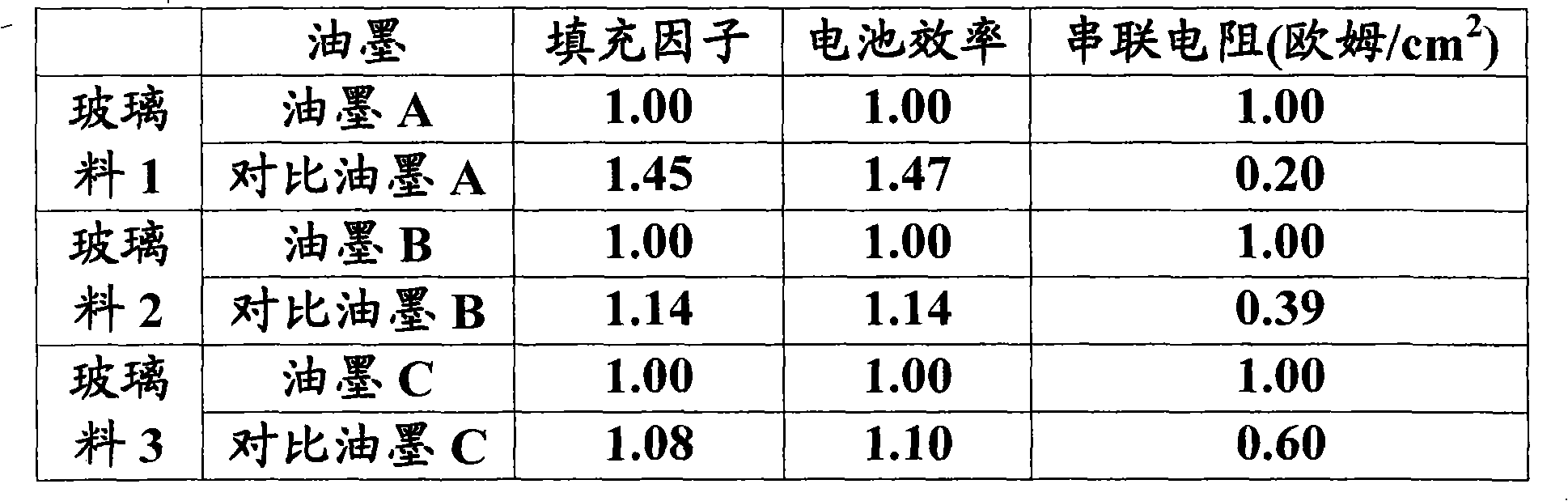
ActiveCN104575661ATo achieve the effect of energy savingImprove conversion efficiencyNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialPhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon oxideSilicon dioxide
Owner:GIGA SOLAR MATERIALS
Conductive Paste for Solar Cell and the Method Thereof
InactiveUS20150115207A1Enhance performance of conversion efficiencyImprove conversion efficiencyConductive materialNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialSilicon oxideTellurium dioxide
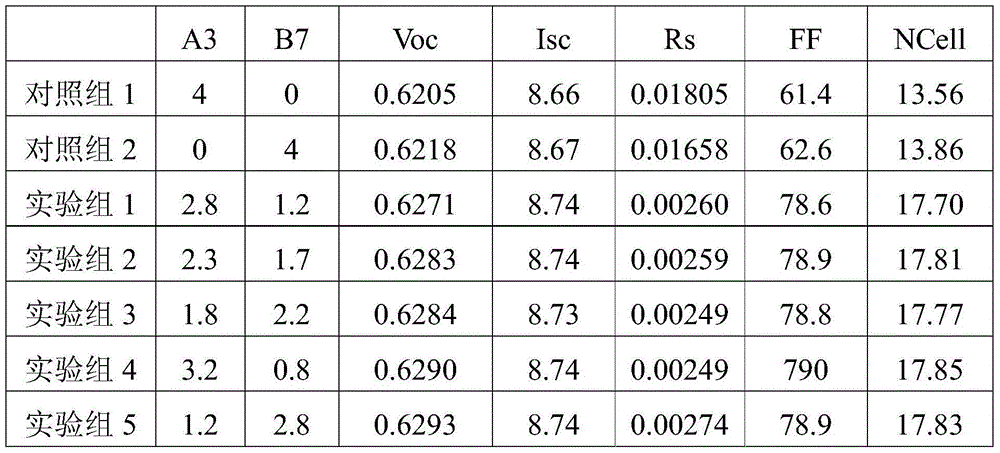
The present invention discloses a conductive paste for solar cell, including the following composition: silver particle and two glass frits. A glass frit (I) comprises bismuth oxide, tellurium oxide, tungsten oxide, silicon oxide, and zinc oxide; and a glass frit (II) comprises lead oxide, tellurium oxide, and zinc oxide. The conductive paste is utilized to form the electrode of the substrate for solar cell to enhance the performance of Ohmic contact, fill factor and conversion efficiency of the solar cell, after sintering.
Owner:GIGA SOLAR MATERIALS
Method for preparing tellurium dioxide from tellurium slag
InactiveCN102390819AMain grade improvedSave resourcesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention relates to a method for preparing tellurium dioxide from tellurium slag. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of: adding tellurium slag to sulfuric acid solution, stirring at normal temperature, adding 10% oxydol at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C, and then heating to 80-90 DEG C, and leaching under normal pressure; adding copper powder to leachate, carrying out replacement reaction at the temperature of 90-95 DEG C for 2 hours, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain copper telluride slag; adding copper telluride slag to sulfuricacid solution, adding 10% oxydol, stirring at the temperature of 90 DEG C for 1 hour, and filtering; adding sodium carbonate to filtrate for neutralizing the filtrate till pH of the filtrate is 3, and filtering; adding NaOH to filter residue, carrying out alkali leaching and stirring at the temperature of 85-95 DEG C for 1 hour, and filtering; and adding H2SO4 to filtrate for neutralizing the filtrate till pH of the filtrate is 6-7, filtering, washing and drying to obtain a product. The method has the characteristics that: low-grade tellurium-containing material discarded by a copper anode mud production enterprise is used as a raw material to produce high-purity tellurium dioxide, the process is reasonable and pollution-free, and the recovery rate of tellurium is high.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for comprehensively extracting valuable metals from tellurium-containing polymetallic materials
InactiveCN102690946AEasy to separateReduce manufacturing costProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumSulfite saltSlag
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively extracting valuable metals from tellurium-containing polymetallic materials, and belongs to hydrometallurgy. The method comprises the steps of carrying out ball milling on the tellurium-containing polymetallic materials, carrying out oxidation leaching by using nitric acid, adding sodium sulfate to separate lead from the solution in a form of lead sulfate; adding industrial salt to precipitate silver in a form of silver chloride; reducing tellurium ions to crude tellurium powder by using sodium sulfite and the industrial salt and obtaining refined tellurium by using an electrolytic deposition method; and depositing bismuth by using caustic soda and depositing copper by using the electrolytic deposition method in the tellurium reduced solution, so as to realize the comprehensive recovery. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high tellurium recovery rate, has good separating effect of copper, lead, bismuth, tellurium and silver, has no return slag and is suitable for treating low-grade tellurium-containing polymetallic materials.
Owner:HUNAN JINWANG BISMUTH
Method of recycling tellurium from anode mud
ActiveCN105905874ASimple methodEasy to operateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumPotassiumSodium hydroxide
A method of recycling tellurium from anode mud comprises the following steps: a) roasting; b) copper separation; c) gold separation; d) bismuth separation; and e) platinum and palladium separation: mixing bismuth separation residue in the step d) with sulfuric acid, controlling liquid-solid ratio to be 2:1-3:1 and the content of sulfuric acid in the liquid to be 190-210 g / L, stirring the mixture, and adding sodium chlorate to the bismuth separation residue until the bismuth separation residue is white after the bismuth separation residue is pulped, performing solid liquid separation to obtain a platinum and palladium separation residue and a platinum and palladium separation liquid, adding potassium chloride to the platinum and palladium separation liquid, controlling the content of the potassium chloride to be 45-55 g / L, and feeding chlorine to generate potassium chloroplatinate and potassium chloropalladite respectively from the platinum and palladium; and f) tellurium recovery: mixing the platinum and palladium separation residue in the step e) with water, controlling liquid-solid ratio to be 2:1-3:1, adding sodium hydroxide until the pH is 10-11, filtering the liquid, adding diluted sulfuric acid to a filtrate, controlling the pH to be 4.5-5.5 to generate tellurium dioxide, and reducing the tellurium dioxide to prepare tellurium. The method is simple and convenient, and is high in recovery rate and recovery purity of the tellurium.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YADONG IND CO LTD
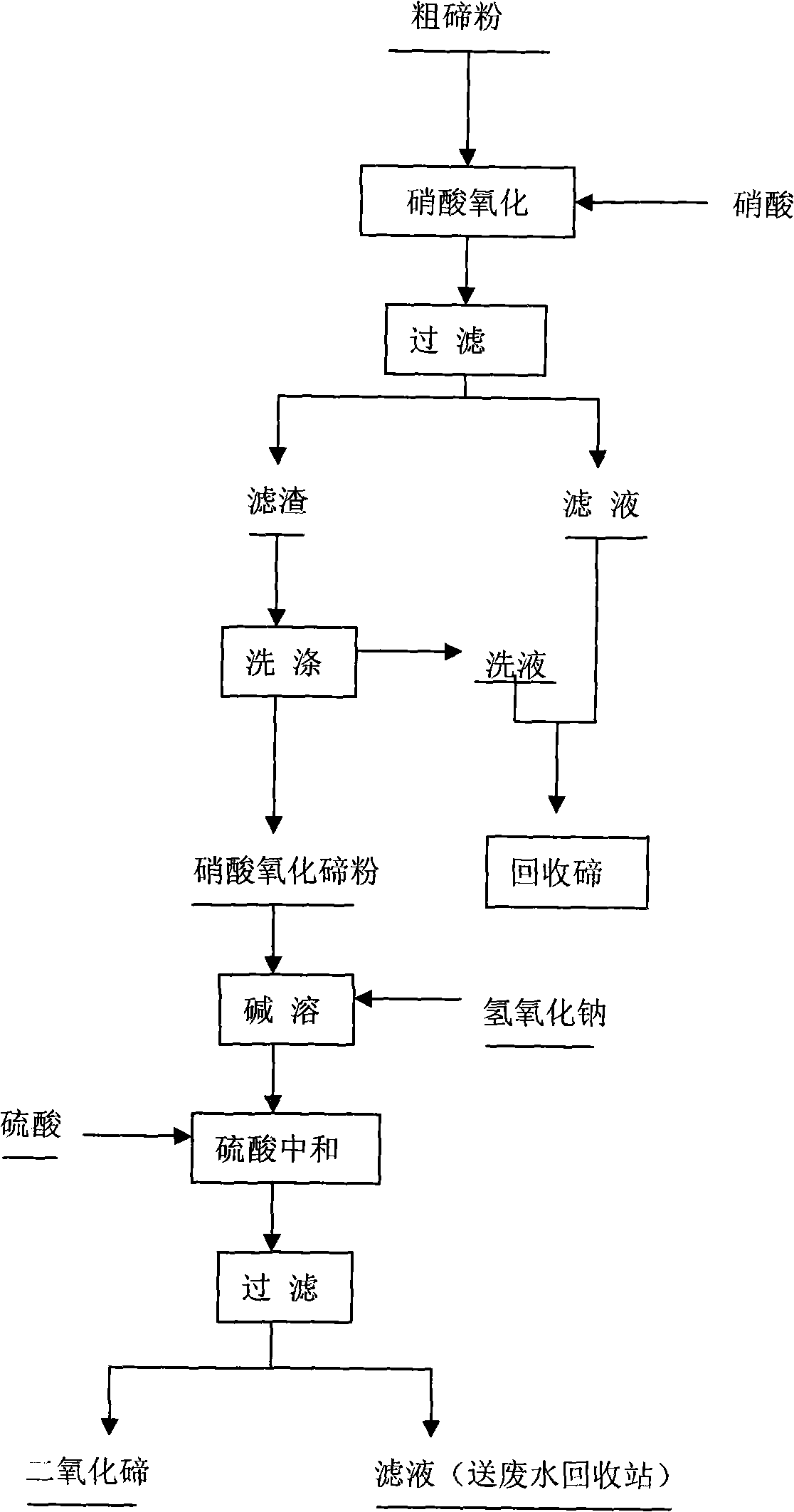
Deep impurity-removing method for crude tellurium powder
InactiveCN101259956ASimple processReduce labor intensityElemental selenium/telluriumNitrateTe element
The invention provides a method for removing deep impurities of coarse tellurium powders, relating to a method for removing deep impurities in the coarse tellurium powders which are recovered from copper anode slimes. The invention is characterized in that in the process of impurity removal, coarse tellurium powders react with nitric acids, which makes the tellurium in the coarse tellurium powders oxidized into the tellurium dioxide and makes impurity elements in the coarse tellurium powders form nitrates to be dissolved into the solution, and after filtering and separation, impurity nitrates are removed; after being washed, filter slimes are dissolved by sodium hydroxide, and solid impurities are obtained by filtering and separation; and the filtrate is added with sulphuric acids for neutralization, and tellurium dioxide powders are obtained after filtering. The method of the invention adopts the nitric acid oxidation impurity removal process, thereby major impurity elements in the coarse tellurium powders can be removed; moreover, the purity of tellurium dioxide powders obtained by the method is more than 99.9 percent.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metal from copper tellurium slag
InactiveCN102994766AReduce the impactReduce pollutionProcess efficiency improvementBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsFractional PrecipitationSlag
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metal from copper tellurium slag. The copper tellurium slag is dissolved by using nitric acid, so that silver, copper and bismuth in the copper tellurium slag are basically dissolved in a solution; tellurium is oxidized into tellurium oxide, thereby entering undissolved slag. Silver, copper and bismuth are separated and recovered via fractional precipitation of the solution; and tellurium is separated and recovered via alkaline leaching of the undissolved slag. The method solves the problems that cost of a conventional process is high, copper recovery rate and tellurium recovery rate are not high, and that silver and bismuth cannot be recovered in the conventional process; influences on the environment of the production process are reduced; a whole process is simple; and pollutions toward the environment is small. The method is simple in the whole production process, low in cost and small pollutions toward the environment, has high comprehensive recovery rate, and realizes complete separation of silver, copper, bismuth and tellurium. The obtained products have high purity; and the recovery rate of silver, copper, bismuth and tellurium is higher than 99%.
Owner:SIHUI CITY HONGMING PRECIOUS METALS
Method for recycling tellurium from copper anode slime
ActiveCN103112833AImprove leaching rateReduce contentBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsSlagTe element
The invention relates to a method for recycling tellurium from copper anode slime. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-treating copper anode slime in a mixed solution of sodium chloride, hydrochloric acid and sulphuric acid to remove impurities after ore-grinding; obtaining pre-treated solution and pre-treated slag after solid-liquid separation; carrying out sulfating roasting on the pre-treated slag; removing the copper from the roasted pre-treated slag by adopting a sodium chloride solution; obtaining copper-containing lixivium and copper-removed slag after the solid-liquid separation; separating tellurium from the copper-removed slag and obtaining the tellurium-containing lixivium and tellurium-removed slag after the solid-liquid separation; adding concentrated sulphuric acid to the tellurium-containing lixivium to control the final pH to 6-8; and obtaining the crude tellurium dioxide after neutralizing the tellurium-containing lixivium. In the conventional sodium hydroxide tellurium-leaching process, the tellurium leaching rate is lower than 60wt% and the tellurium content of the leached residue is bigger than 2.00%; and in the tellurium separating process disclosed by the invention, the tellurium leaching rate is higher than 83wt% and the tellurium content of the leached residue is lower than 1.10%, and so the tellurium leaching rate is high, the production period is short, the process is simple and the treatment cost is low.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for recovering tellurium from bismuth telluride base semiconductor refrigeration material
InactiveCN1994869AImprove applicabilityReduce loadSelenium/tellurium compundsBismuth tellurideTe element
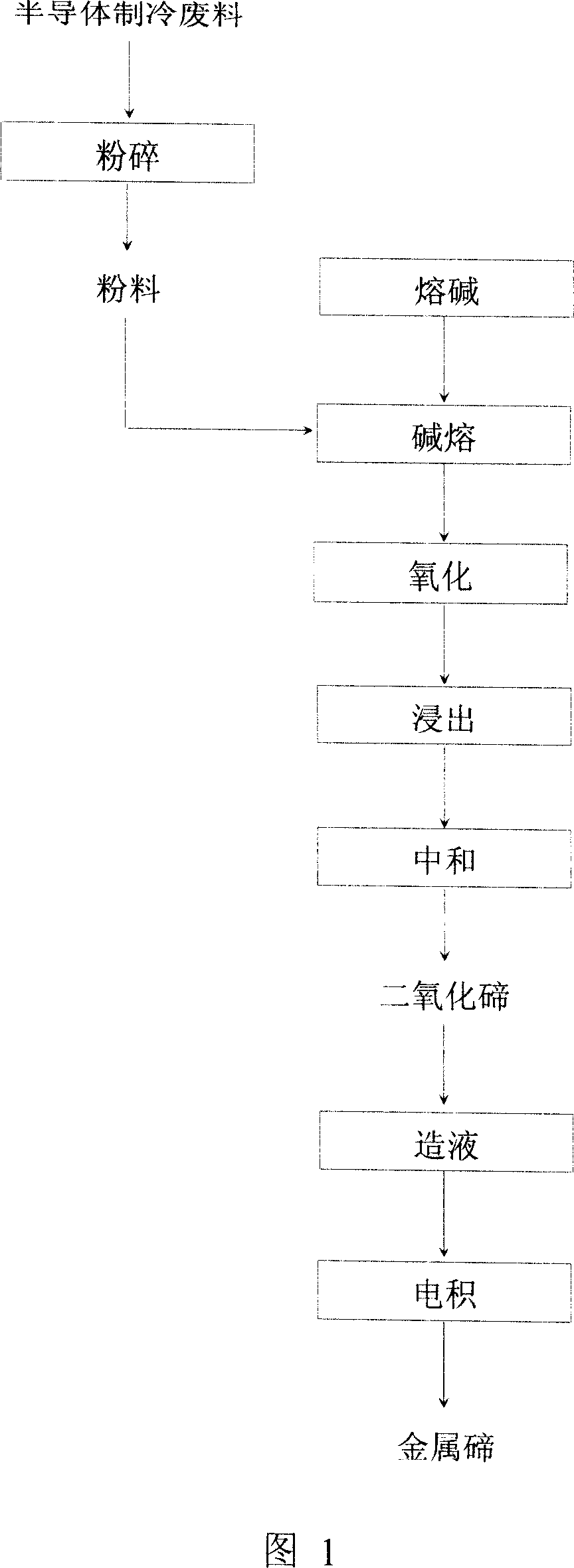
The invention discloses a recycling method of tellurium in the refrigeration material of bismuth telluride based semiconductor, which comprises the following steps: adding broken and grinded material into fused alkali metal hydroxide or compound of other alkali metal carbonate; proceeding alkali fusing at 640-720 deg. c; adding oxidant; leaching molten substance through water once or twice; neutralizing the leached solution through acid until the pH value is 5-6; obtaining tellurium dioxide; dissolving tellurium dioxide through alkali; obtaining sodium tellurate solution; electrodepositing to obtain the metal tellurium.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
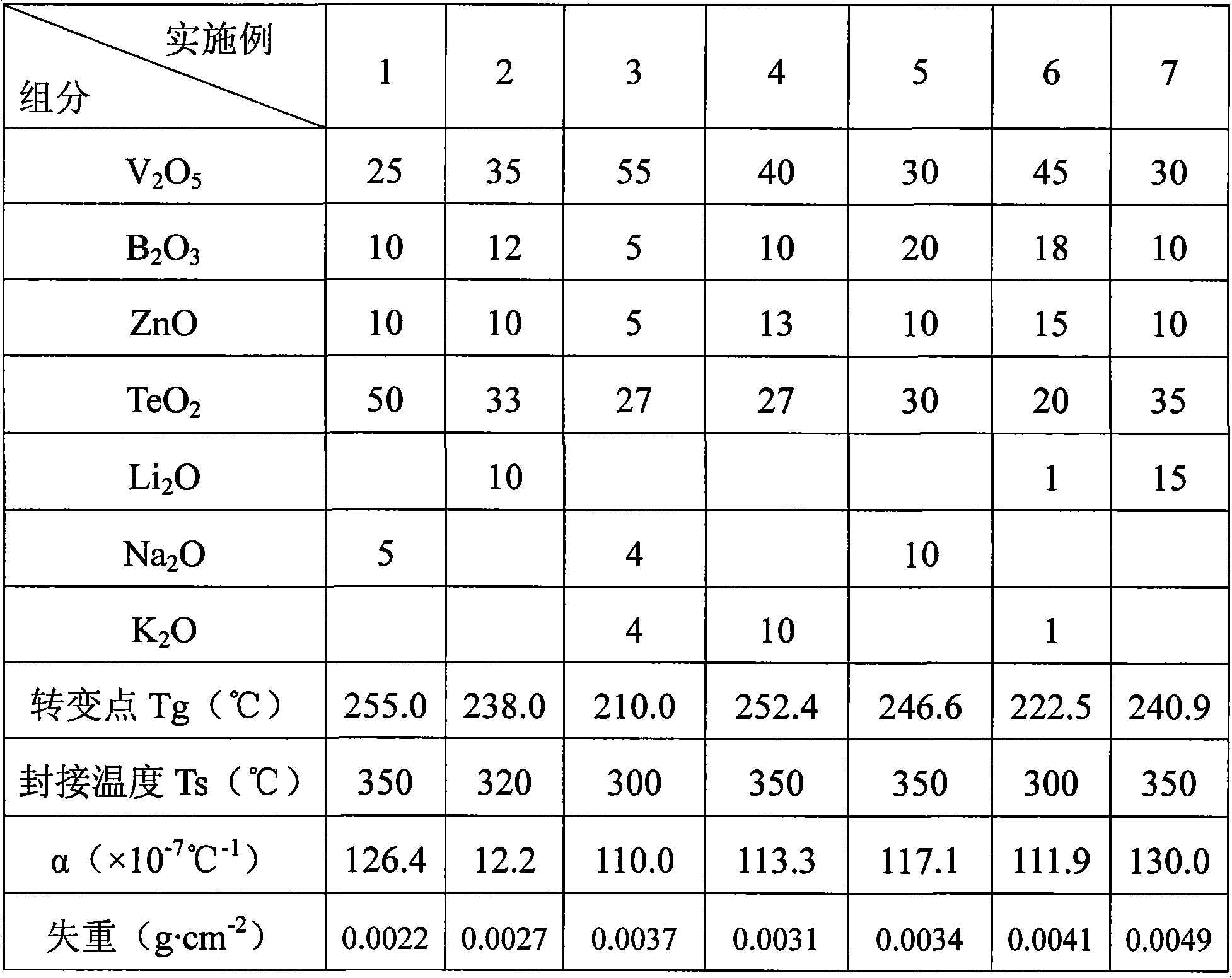
Vanadates leadless low-temperature sealing glass material and method for preparing same
The invention relates to a vanadate-system lead-free low temperature sealing glass material and a preparation method thereof. The components of the sealing glass material by mol percentage are as follows: 25 percent to 55 percent of V2O5, 5 percent to 20 percent of B2O3, 5 percent to15 percent of ZnO, 20 percent to 50 percent of TeO2 and 2 percent to 15 percent of an alkali metal oxide R2O. The preparation method of the invention comprises the steps that vanadium pentoxide, boric acid, zinc oxide, tellurium dioxide and alkali metal carbonate are adopted as raw materials; the weight percentages of the raw materials are calculated according to the mol percentage of each component of the sealing glass; the raw materials are then weighted and evenly mixed to be placed in a corundum crucible and fused under the temperature of 800 to 900 DEG C; molten glass is then cast for formation or ground into powder after being treated with water quenching and the powder is then filtered by a 200-mesh sieve. The sealing glass material of the invention contains no toxic and harmful substances such as lead, cadmium, thallium, and the like, and has the advantages of low temperature for sealing, the minimum temperature reaching 300 DEG C, and good chemical stability, and is especially applicable to the sealing of electronic components.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Terylene air-jet textured yarn fabric with high color fastness
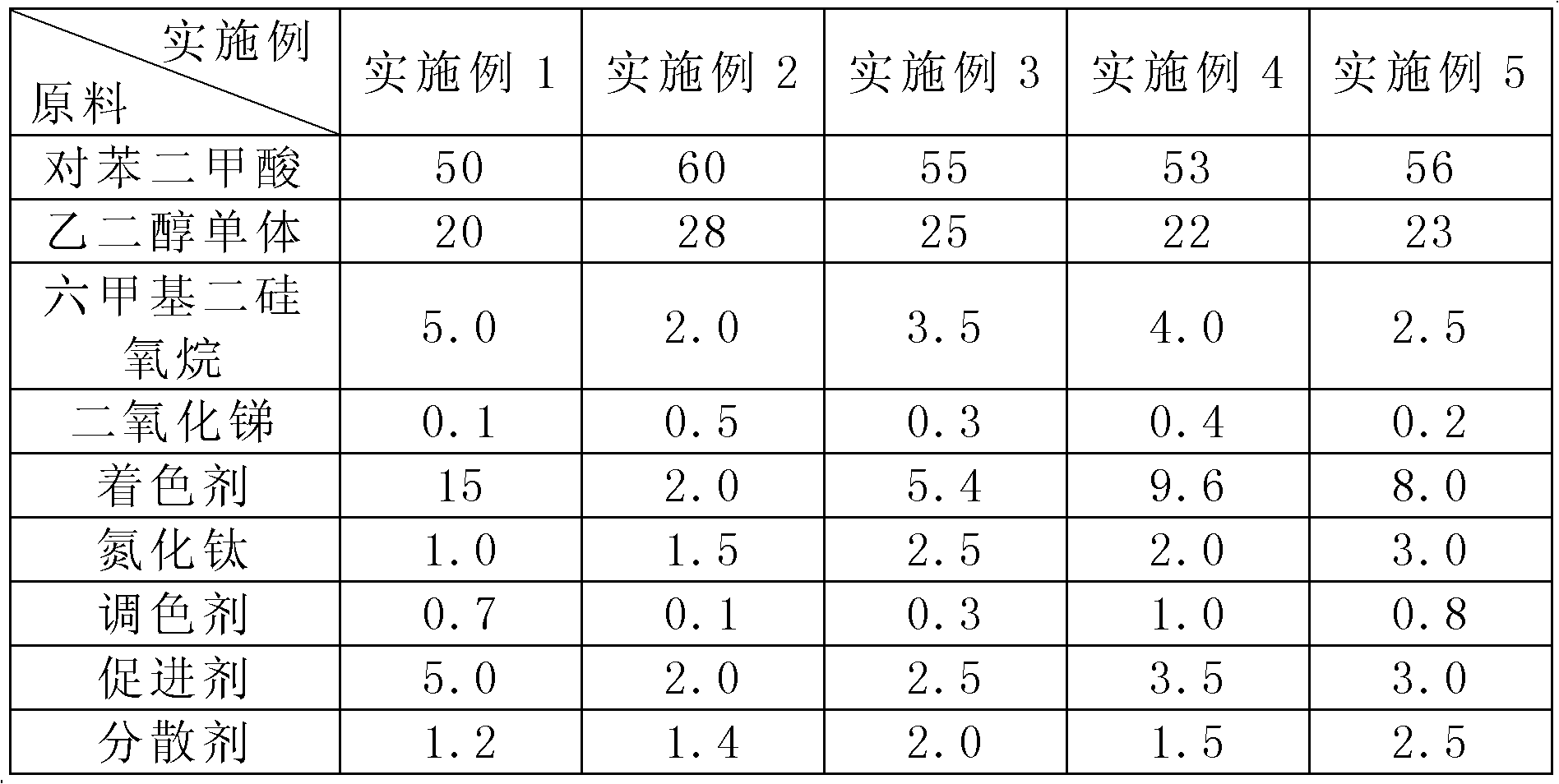
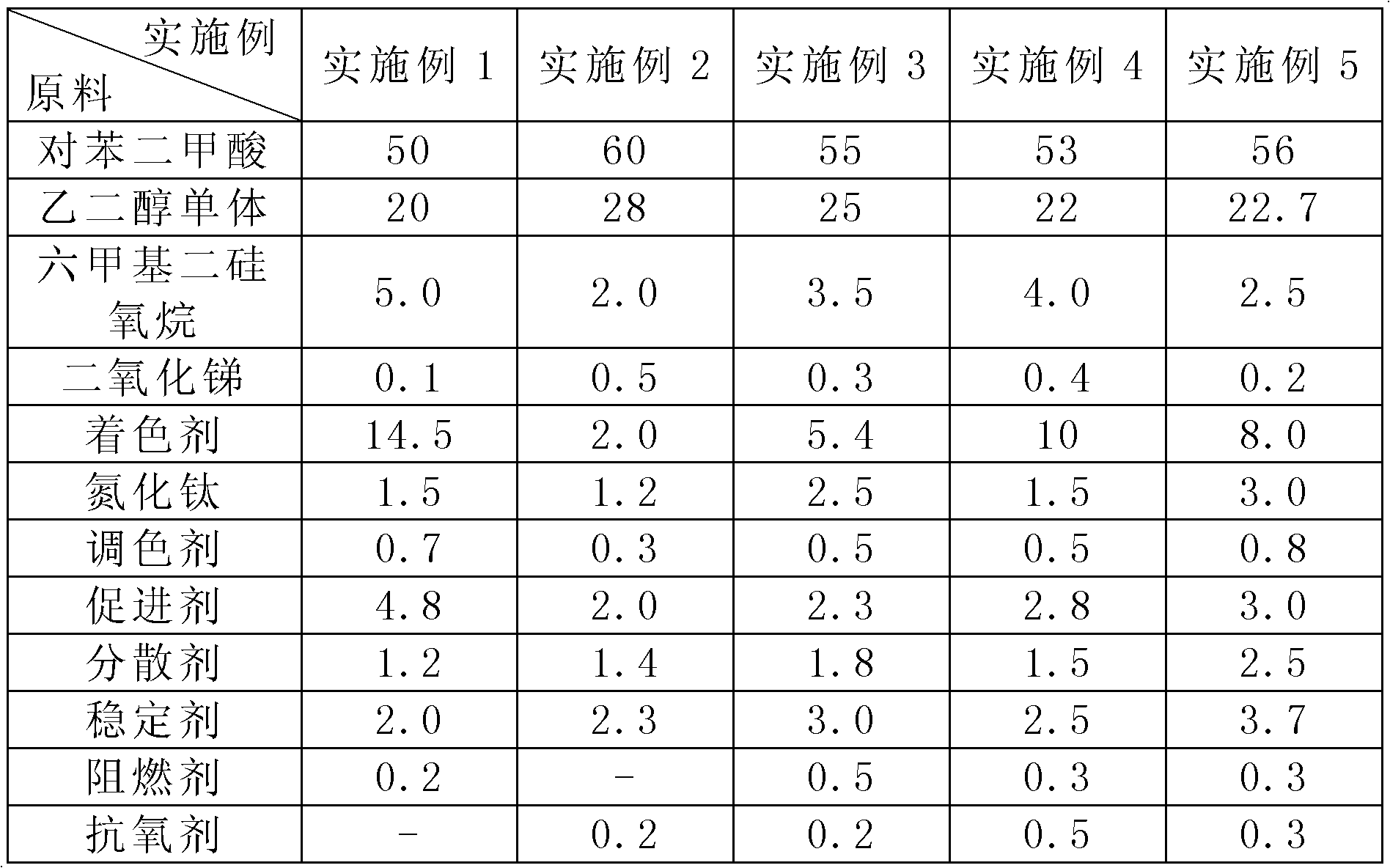
ActiveCN102628194AGuaranteed color brightnessHigh color fastnessMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentYarnTitanium nitride
The present invention relates to a terylene air-jet textured yarn fabric with high color fastness and belongs to the technical field of textile. In order to solve a problem of poor color fastness of a fabric in the existing technology, the invention provides terylene air-jet textured yarn fabric with high color fastness. The fabric is mainly weaved from terylene air-jet textured yarn, wherein the terylene air-jet textured yarn is mainly prepared from raw materials of terephthalic acid, glycol monomer, hexamethyldisiloxane, tellurium dioxide, colouring agent, titanium nitride, toner, promoter, dispersant and stabilizer, and the raw materials can also be added with fire retardant or antioxidant. The invention has advantages of high color fastness, uniform coloring and good brightness, and reaches washing resisting color fastness of grade 4-5 , sweat resisting color fastness of grade 4-5 and light resisting color fastness of higher than grade 7; and the raw materials of the invention do not need dyeing after spinning to realize the reduction of environmental pollution, reduction of high temperature dyeing process, and improvement of the strength property of the yarn.
Owner:台州东海翔织造有限公司
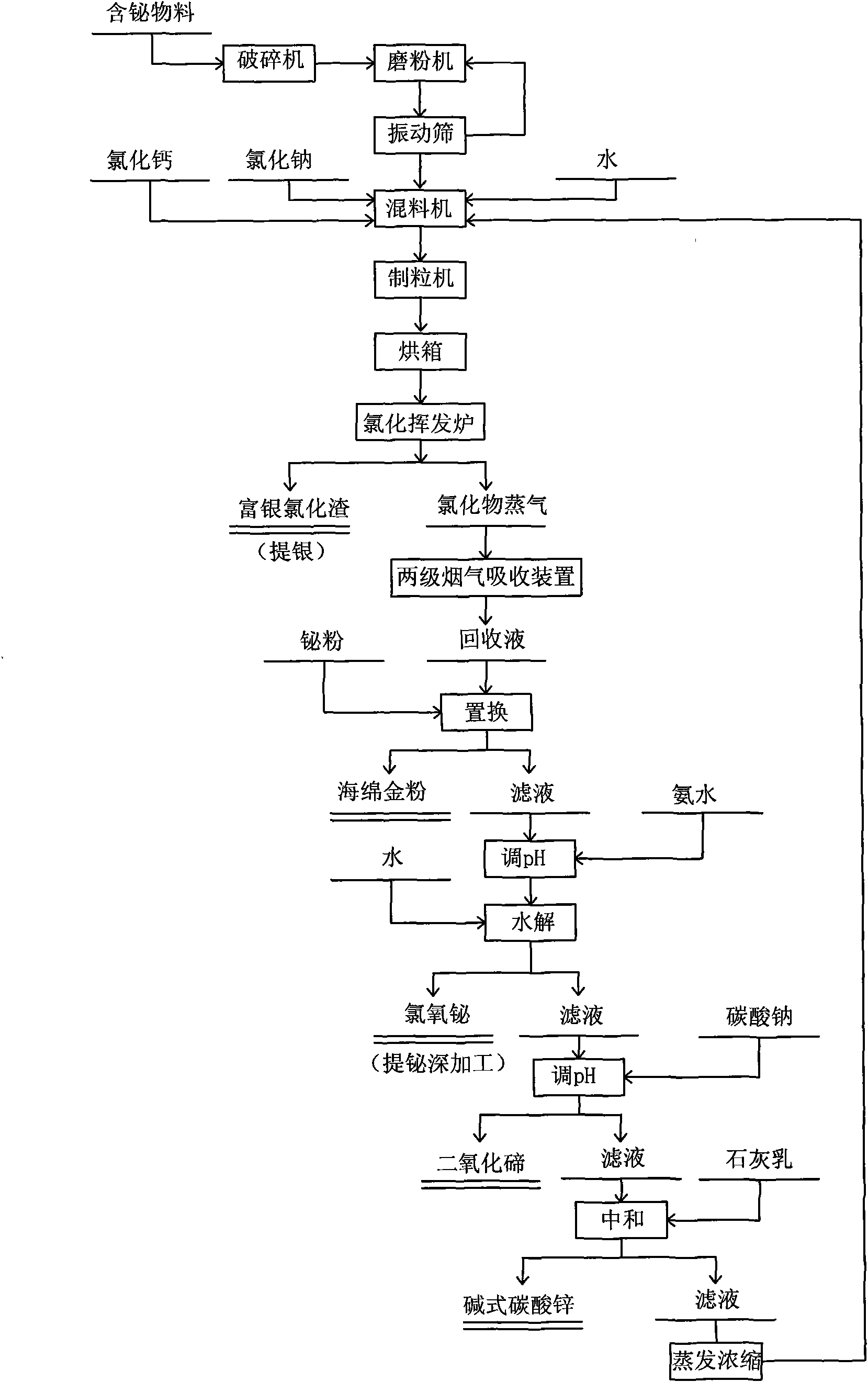
Process for recovering valuable metals in bismuth-containing material by selective chloride volatilizing method
ActiveCN101570832ALower requirementFaster turnaroundSelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationSlag
The invention relates to a process for recovering valuable metals in a bismuth-containing material by a selective chloride volatilizing method, and belongs to the technical field of colored metallurgy. The process comprises the following steps of: mixing bismuth-containing powder prepared from the bismuth-containing material, calcium chloride, sodium chloride and water in a ratio of 100:3-6:5-8:7-9, and pelletizing the mixture to obtain dry material balls; carrying out chlorination and volatilization roasting to the dry material balls in a chloridizing volatilization furnace at a temperature of between 600 and 900 DEG C, and desilvering a silver-rich chloride slag after roasting; condensing and absorbing chloride steam generated by the roasting by water or a thin hydrochloric acid solution to obtain a recovery solution; adding bismuth powder in the recovery solution to displace, and obtaining sponge gold powder by filtration; then introducing ammonia and water into a filtrate for hydrolysis to obtain a bismuth chloride oxide, and carrying out de-bismuth further process to the bismuth chloride oxide; adding Na2Co3 in a raffinate to precipitate tellurium to obtain tellurium dioxide; adding a lime cream in a later filtrate generated by the tellurium precipitation and filtration, and stirring and filtering the mixture to obtain basic zinc carbonate; and finally, evaporating and concentrating the filtrate into a concentrated solution to return for mixture pelletizing. The method has the advantages of low requirement on the processed bismuth-containing material, strong adaptability, low cost, simple operation, high recovery rate and the like.
Owner:郴州雄风环保科技有限公司
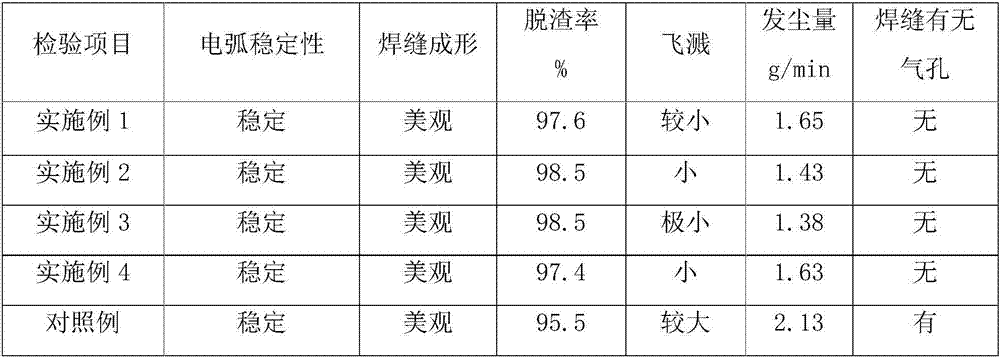
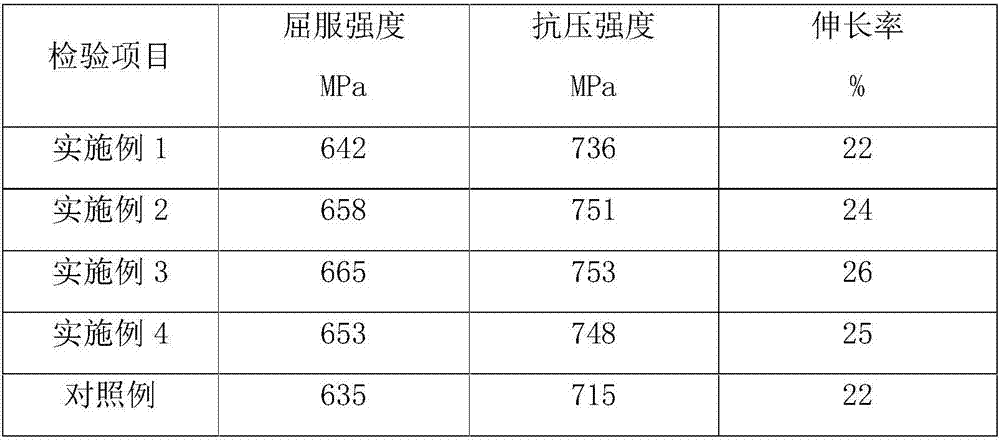
Stainless steel flux-cored wire and production method thereof
ActiveCN107877035AImprove wear resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaCrack resistanceSlag
The invention relates to a stainless steel flux-cored wire and a production method thereof. The stainless steel flux-cored wire is characterized in that the stainless steel flux-cored wire is composedof a flux-core and a stainless steel belt, wherein the flux-core is wrapped with the stainless steel belt; the weight of the flux-core accounts for 18-28% of the total weight of the flux-cored wire;and the flux-core comprises, by mass, 15-20% of chromium powder, 10-15% of rutile powder, 5-10% of nickel powder, 4-8% of manganese powder, 4-8% of feldspar powder, 2-4% of aluminum-magnesium alloy powder, 2-4% of molybdenum iron powder, 2-4% of complex nitride, 0.5-2% of complex fluoride, 0.5-1% of bismuth oxide, 0.1-1% of tellurium dioxide, 0.1-1% of cerium oxide, and the balance iron powder, and the sum of the mass percents of the components is 100%. The stainless steel flux-cored wire has the advantages that weld joint forming is attractive, slag removal is easy, splashing is low, an electric arc is stable, no small air hole exists in a weld joint, the amount of fumes in the welding process is small, and meanwhile, the weld joint microstructure further has excellent abrasion resistance, corrosion resistance, crack resistance and fatigue resistance.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF AEROSPACE TECH
Preparation method of water-soluble CdTe quantum dot
InactiveCN102634342AReduce in quantityHigh quantum yieldLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldQuantum dot
The invention discloses a preparation method of a water-soluble CdTe quantum dot, which includes: using cadmium salt as a cadmium source, tellurium dioxide as a tellurium source and sulfhydryl compound as stabilizer, and performing one-step preparation in a water phase system to directly synthetize high-fluorescence and water-soluble CdTe quantum dot. The preparation method has simple steps, used reagents are few, cost is low and the method is easy to implement. The whole production process meets the green and chemical requirements and is safe and environment-friendly. The prepared CdTe quantum dot has high quantum yield and high stability.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Preparation process for lead-free front electrode silver paste of solar cell
ActiveCN105118578AImprove glass propertiesHigh viscosityNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureLithium oxideCellulose
The invention discloses a preparation process for the lead-free front electrode silver paste of a solar cell. The process comprises the steps of 1, placing sodium oxide, tellurium dioxide, tungsten trioxide, silicon dioxide, lithium oxide, and oxide additives in a blender mixer to uniformly mix up the materials, placing the above materials in a muffle furnace to fully melt and adulterate the materials, and subjecting the materials to the water-quenching and annealing treatment to obtain the water-quenched glass frit; 2, grinding the water-quenched glass frit obtained in the step 1 in an alcohol system in a planet type grinding machine to obtain glass powder; 3, stirring an organic solvent, ethyl cellulose, butyl cellulose and hydroxy cellulose to obtain a carrier; uniformly mixing up a silver conductive phase, the glass powder obtained in the step 2 and the carrier obtained in the step 3, stirring, grinding and filtering the mixture to obtain the lead-free front electrode silver paste of the solar cell. According to the invention, the performances in the prior art are maintained, while the glass is low in viscosity and good in wettability with other components. After the printing and sintering process of the paste, the paste is good in contractility and does not easily diffuse. Therefore, the fineness of printed graphics is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU ISILVER MATERIALS
Waste gas denitration composite catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107456981AImprove catalytic reduction abilityImprove adsorption capacityDispersed particle separationCatalyst activation/preparationCordieriteWater resistant
The invention relates to a waste gas denitration composite catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The waste gas denitration composite catalyst is prepared from a perovskite type catalyst, a catalyst promoter and a catalyst carrier, wherein the formula of the perovskite type catalyst is ABO3, the site A represents a mixture of rare earth metals La (lanthanum) and Y (yttrium), and the site B represents one or a mixture of transition metals Cr (chromium), Mn (manganese), Fe (iron) and Co (cobalt); the catalyst promoter is selected from one or a mixture of SeO2 (selenium dioxide), TeO2 (tellurium dioxide) and PtO2 (platinum dioxide), so as to prevent the deactivation caused by the fact that oxygen atoms in the perovskite type catalyst ABO3 is replaced by sulfur atoms in waste gas; the catalyst carrier is selected from one of TiO2 (titanium dioxide), ZrO2 (zirconium dioxide), SiO2 (silicon dioxide), SnO2 (tin dioxide), Al2O3 (aluminium oxide), zeolite and cordierite; 10g of waste gas denitration composite catalyst is loaded into a fixed bed catalyzing reactor, the NO (nitric oxide)-containing waste gas produced by burning the volatile organic matter is treated at the temperature of 300 DEG C, and the removal rate of NO is 92.9% to 95.8%. The waste gas denitration composite catalyst has the advantages that the water-resistant and sulfur pollution-resistant properties are good, the service life is long, and the running cost is low.
Owner:TIANJIN VOCATIONAL INST
Conductive inks with metallo-organic modifiers
A conductive ink having a glass frit, an organic medium a conductive species and one or more metallo- organic components which form metal oxides upon firing and reduce series resistance to a same or greater degree a ink that do not include metallo-organic components, is provided. Embodiments of conductive ink include metallo-organic components that include a bismuth metallo-organic component and glass frits comprising one or more of bismuth oxide, silica, boron oxide, tellurium dioxide, and combinations thereof. Embodiments of photovoltaic cells with an anti-reflection coating, gridlines formed from conductive ink incorporating one or more metallo-organic components, are also provided.
Owner:BASF AG
Preparation method of high-purity tellurium dioxide powder
InactiveCN103803510AIncrease contact areaReduce decreaseBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsTe elementEnergy consumption
The invention provides a preparation method of high-purity tellurium dioxide powder. The preparation method comprises the following steps: grinding a raw material tellurium powder, oxidizing the tellurium powder with concentrated nitric acid under a heating condition, cleaning the precipitate with deionized water and adjusting the pH value, and calcining after high-temperature dehydration to obtain the high-purity tellurium dioxide, next, putting the thoroughly calcined material in a pulverizer for pulverizing, and finally, sieving the powder with a 200-mesh stainless steel vibrating screen to obtain the high-purity tellurium dioxide powder having the grain size ranging from 75 to 150 microns. The preparation method is reduced in tellurium dioxide preparation steps and used chemical reagents, lowered in energy consumption and improved in efficiency; the preparation method is simplified in process flow, simple in equipment, and beneficial to industrial production and environmental conservation.
Owner:张家港绿能新材料科技有限公司
Method for removing tellurium from coarse selenium
The present invention relates to a method for removing tellurium from crude selenium. Said method is characterized by that it includes the following steps: adding crude selenium into sodium hydroxide solution to make reaction, then making dilution and filtration, introducing air or oxygen gas into the filtrate to make oxidation, using dilute sulfuric acid to regulate pH of solution so as to obtain selenium powder precipitate, filtering, washing and drying so as to obtain selenium powder. The selenium percent recovery can be up to above 95%, purity of selenuim is 95-99% and tellurium content is less than or equal to 0.5%.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
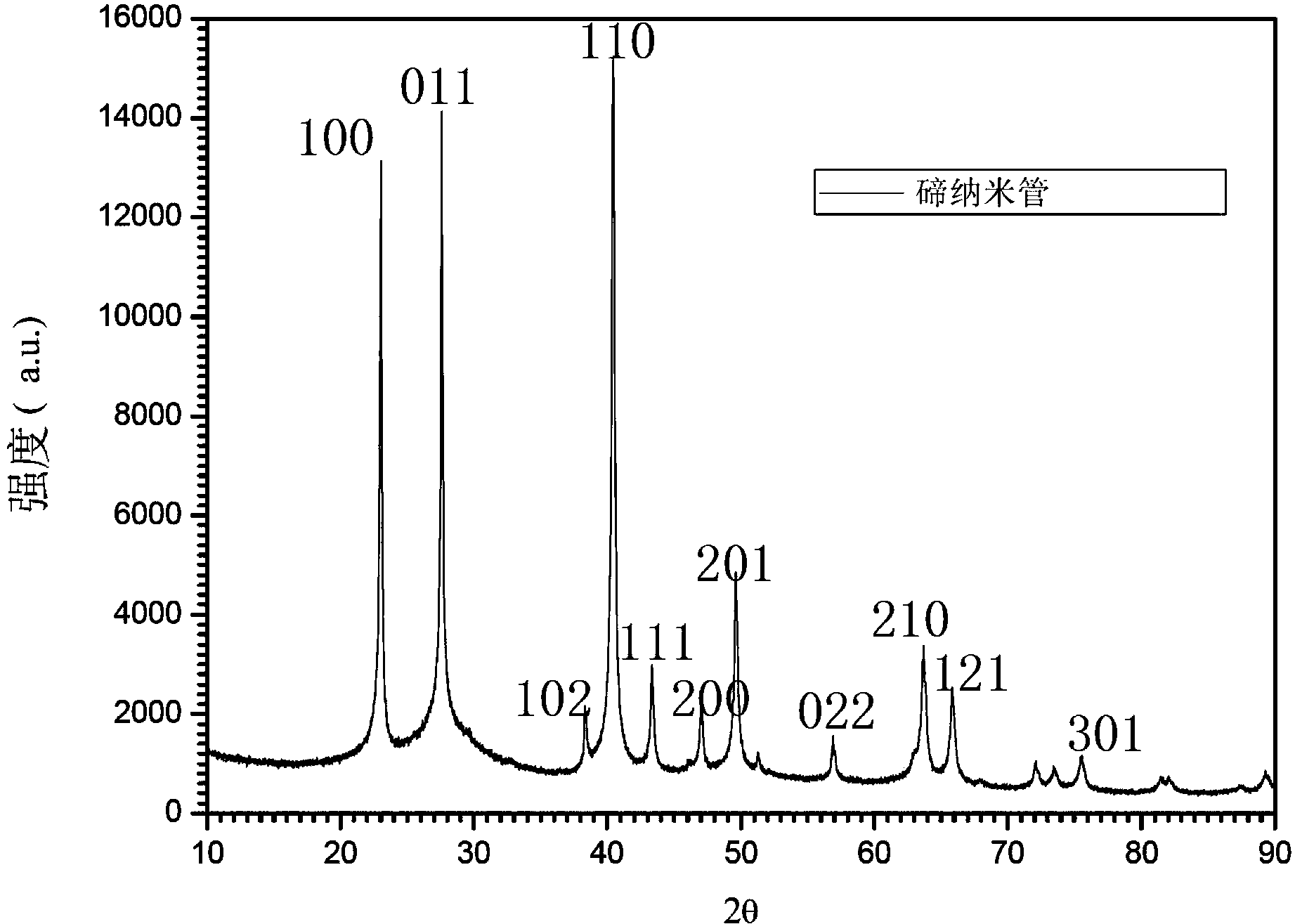
Single-crystal tellurium nanotube and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103350988ANo pollution in the processIncrease productionMaterial nanotechnologyElemental selenium/telluriumSingle crystalEthylene glycol
The invention relates to a single-crystal tellurium nanotube and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the single-crystal tellurium nanotube comprises the steps as follows: adding tellurium dioxide and poly vinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) into a glycol solution; agitating and heating the mixture till clarification; continuously heating the mixture to 180-230 DEG C; adding sodium hydroxide into the mixture and agitating for 5-60 minutes at the temperature of 180-230 DEG C to obtain the tellurium nanotube, wherein the weight ratio of the tellurium dioxide, the poly vinyl pyrrolidone (PVP), glycol and the sodium hydroxide is (0.16-0.64):(0.2-0.8):(55-112):(0.05-0.8). The prepared single-crystal tellurium nanotube is 170-460 nanometers in diameter, about 5.0-9.0 microns in length and 30-40 nanometers in wall thickness. The single-crystal tellurium nanotube can service as an in-situ template for compounding PbTe pyroelectricity nanotubes, Bi2Te3 pyroelectricity nanotubes and Sb2Te3 pyroelectricity nanotubes.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Method for recycling tellurium from tellurium anode slime
ActiveCN106006572AHigh recovery rateImprove utilization efficiencyElectrolysis componentsElemental selenium/telluriumLiquid wastePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a method for recycling tellurium from tellurium anode slime. By adopting the technical scheme, the method comprises the steps that firstly, distilled water is used for washing tellurium anode slime, hydrogen peroxide is used for completely oxidizing uncleaned Na2TeO3 into Na2TeO4, then, sulfuric acid is slowly added into the tellurium anode slime to leach out tellurium, filtering is performed to obtain a tellurium leaching agent, Na2SO3 is used for reducing Te6+ into crude tellurium powder, then, a saltpeter solution is adopted for dissolving the crude tellurium powder, tellurium electrodeposition regularly-discharged liquid waste or tellurium anode mud washing water is added into the solution for neutralization, the pH value of the reaction endpoint is controlled to 5-6, tellurium is totally converted into tellurium dioxide, impurities are removed from the neutralized solution, finally, the tellurium dioxide is dissolved through the tellurium electrodeposition liquid waste, the solution composition is adjusted to meet the requirement of electrodeposition new liquid compositions, and the solution is returned to the electrodeposition process to produce refined tellurium. Tellurium in anode mud produced by tellurium electrodeposition can be supplemented in time for performing process production tellurium refining, the resource utilization efficiency is improved, the technology is reasonable, operation and implementation are easy, and the tellurium recovery rate is high.
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG RESOURCE COMPREHENSIVE UTILIZATION CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com