Patents
Literature
396 results about "Copper anode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A copper anode is a node that allows an electrical current to flow into an electrical device. It is usually, but not always, the positive terminal of an electrochemical cell where anions, negatively charged ions, are concentrated.
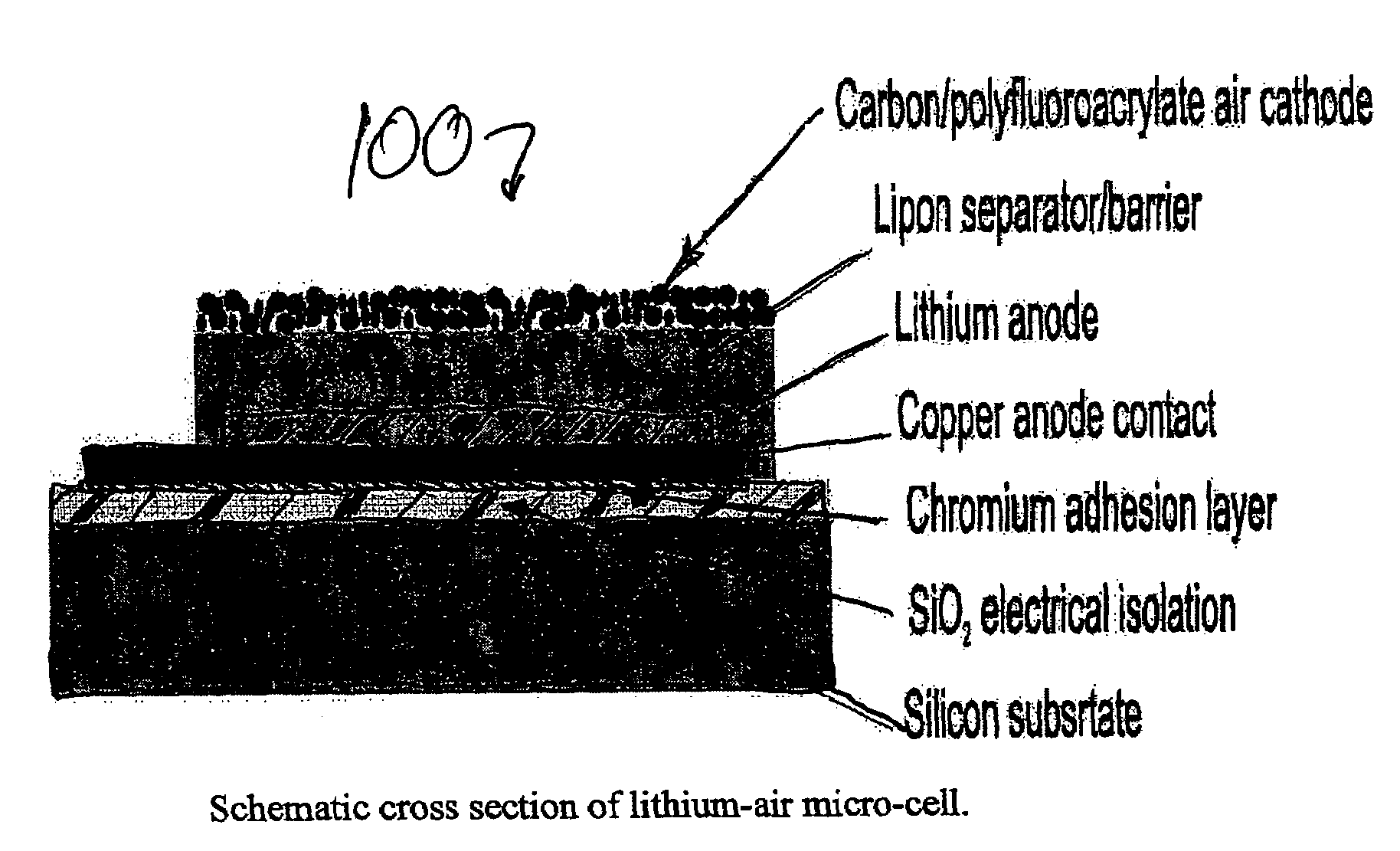
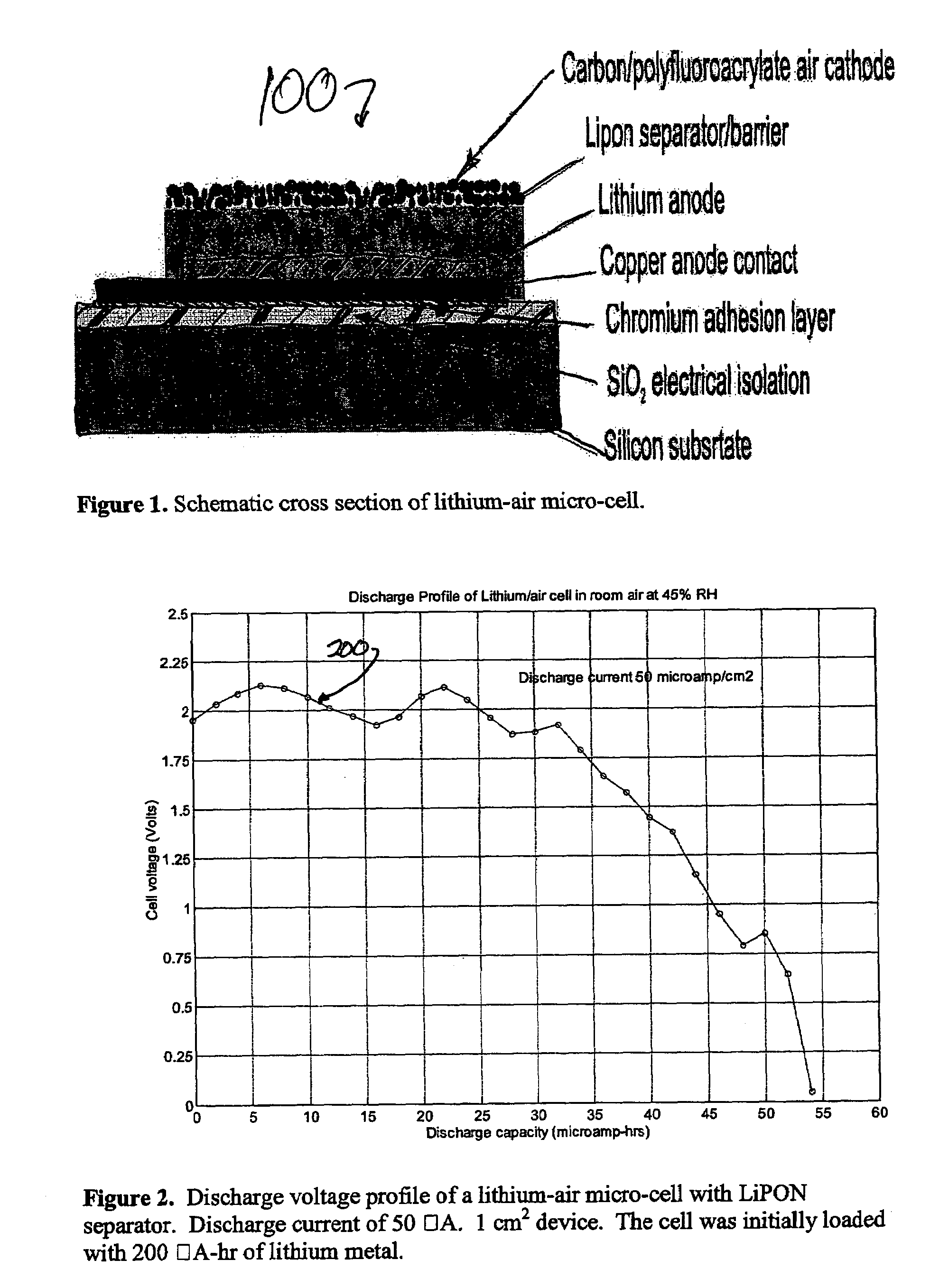
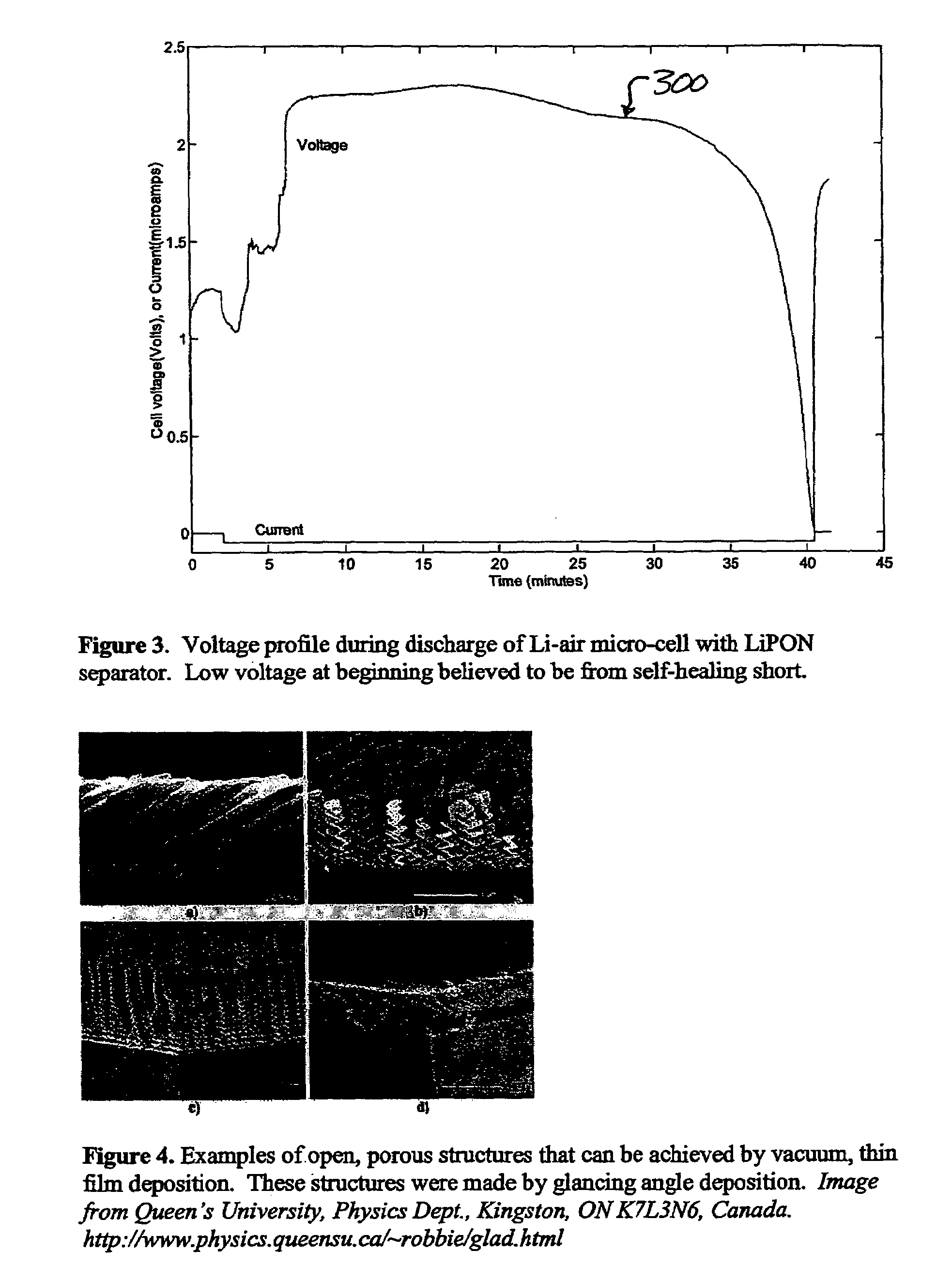
Lithium/air batteries with LiPON as separator and protective barrier and method
A method and apparatus for making lithium / air batteries with LiPON as separator and protective barrier, and the resulting cell(s) and / or battery(s). Some embodiments include an apparatus that includes a lithium anode; a polymer-air cathode; and a LiPON separator between the anode and cathode. In some embodiments, the polymer-air cathode includes a carbon-polyfluoroacrylate material. In some embodiments, the anode overlays a copper anode contact.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
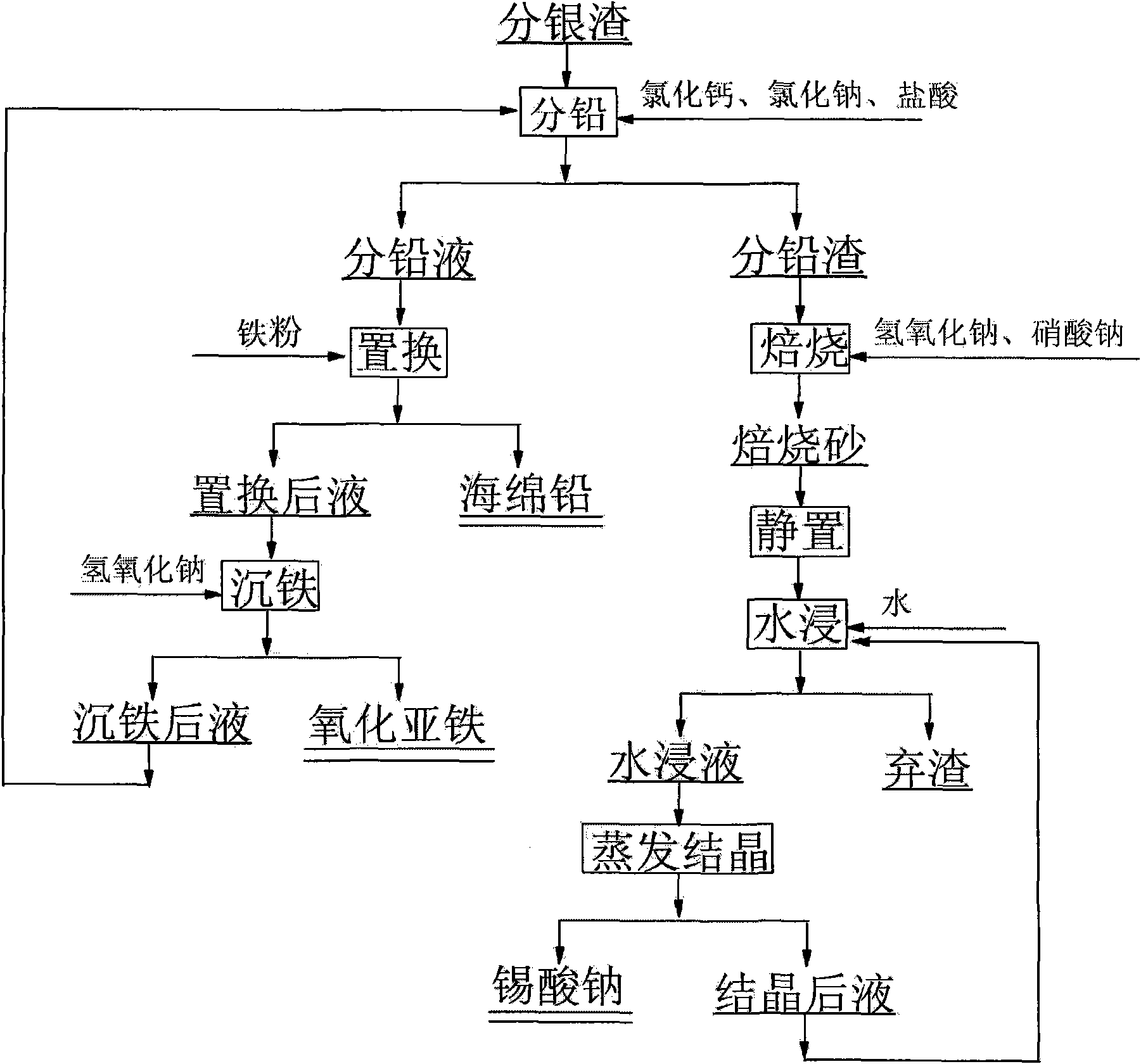
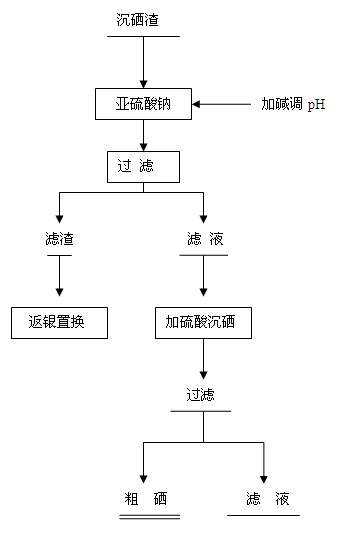
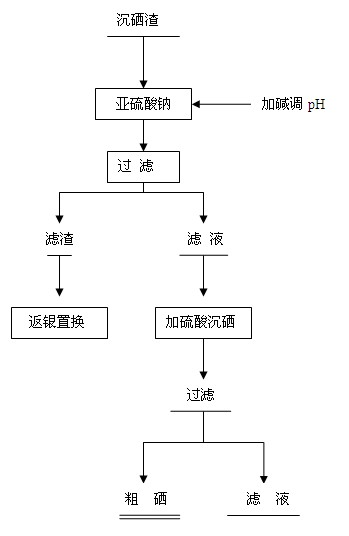
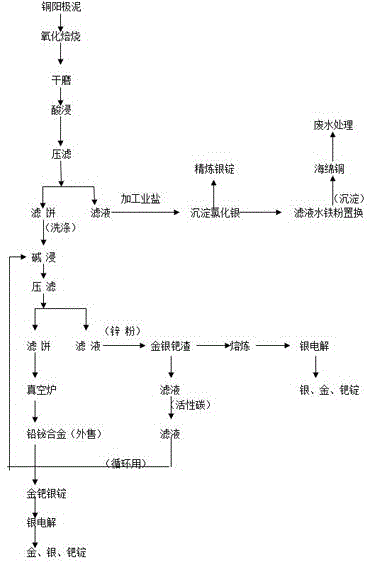
Method for recycling lead-tin in silver separating residue of copper anode slime of circuit board
ActiveCN101555550AReduce generationEmission reductionProcess efficiency improvementIron powderWastewater
The invention discloses a method for recycling lead-tin in silver separating residue of copper anode slime of a circuit board and relates to a method for recycling silver separating residue of copper anode slime of the circuit board by a wetting method. The method comprises the following steps of: stirring silver separating residue, water, hydrochloric acid, calcium chloride and sodium chloride for 0.5 to 2.0h under proper temperature according to requirements, filtering and obtaining lead separating liquid and lead separating residue; carrying out displacement to the lead separating liquid by using excess iron powder, filtering and obtaining spongy lead and displaced liquid; using sodium hydroxide to adjust pH value of the displaced liquid till the precipitate is not generated; and returning lead separating procedure after the iron is precipitated. The lead separating residue, the sodium hydroxide and sodium nitrate are mixed evenly to carry out roasting with the temperature of 350 to 500 DEG C, and then are added with water and filtered, thus obtaining the sodium stannate. Compared with the prior art, due to the adoption of a full-wetting process, the method reduces a large amount of waste gas and dusts in the process of pyrometallurgical treatment; the liquid after the iron is precipitated contains the main compositions of hydrochloric acid and sodium chloride; and the method can return acid pickling procedure, reduce discharge of waste water and lower cost, and is characterized by simple technique, no pollution and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
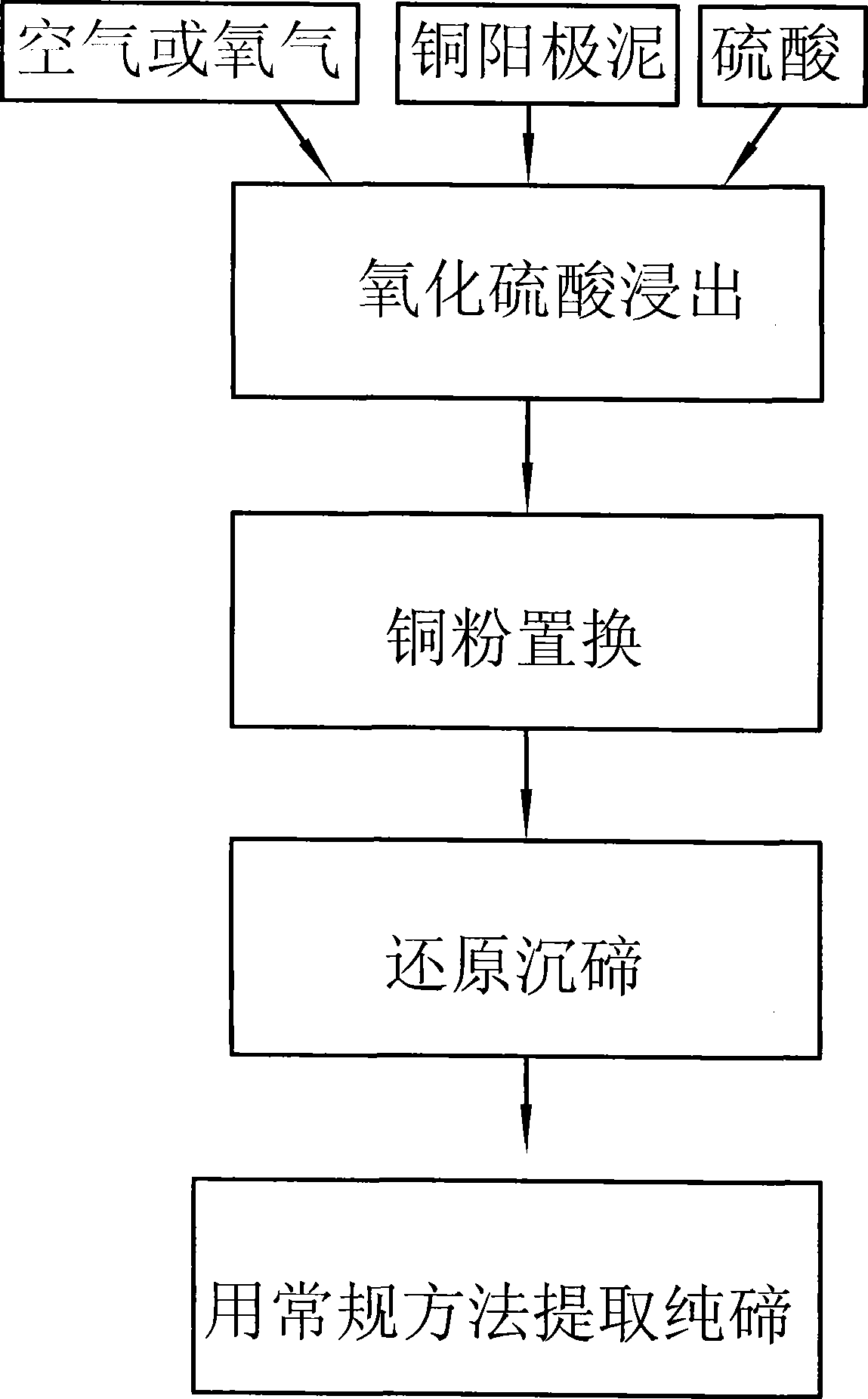
Process for extracting tellurium from copper anode mud
ActiveCN101434385AReduce consumptionEasy to separateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumTe elementOxygen
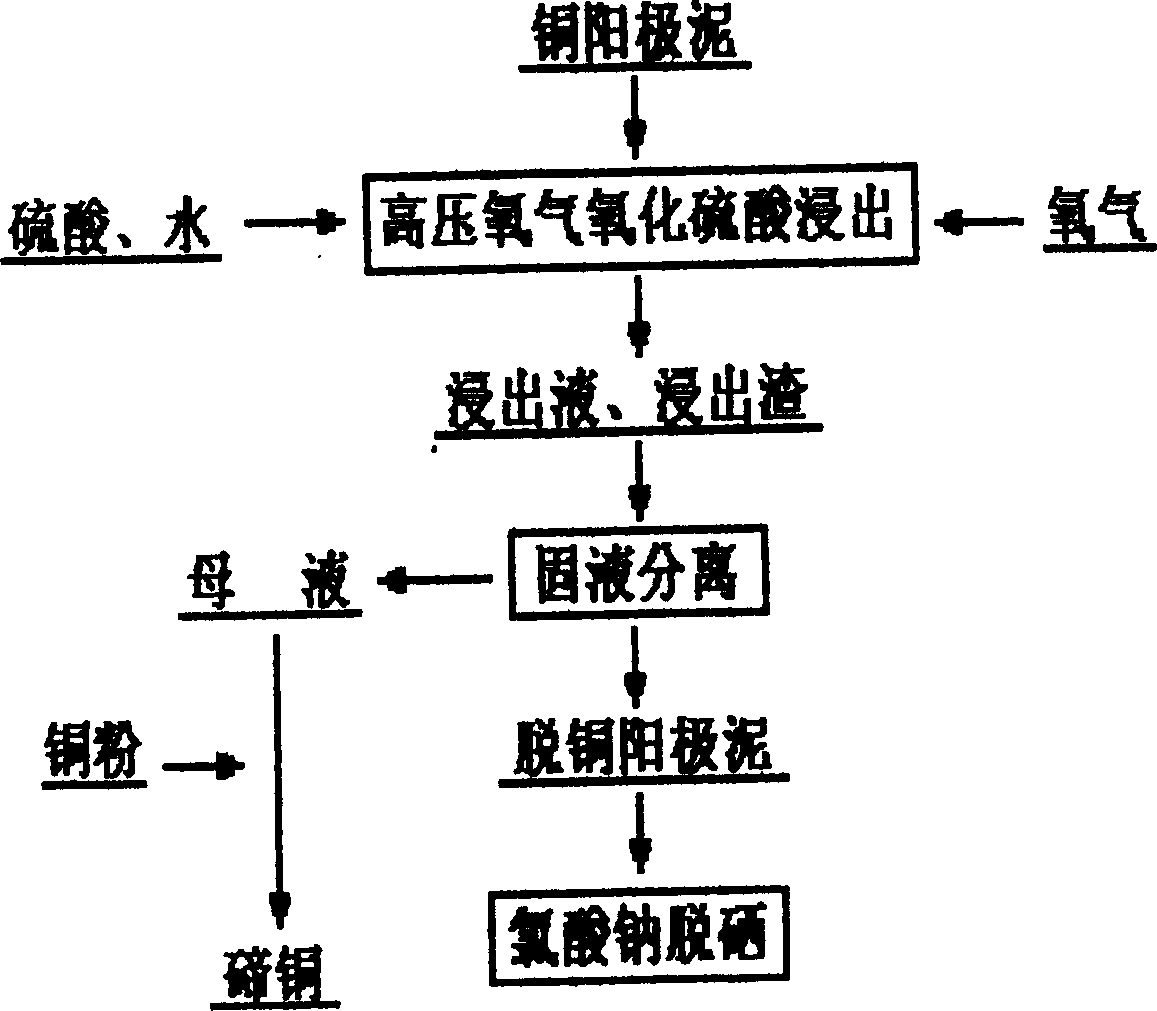
The invention discloses a technology for extracting tellurium from copper anode slime, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) the copper anode slime is put into a sulfuric acid solution, oxygen is introduced into the sulfuric acid solution for oxidation sulfuric acid leaching; solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain leachate containing copper and tellurium; and the leaching process being finished in a closed high-pressure device; (2) copper powder is added into the leachate to remove silver or selenium in the leachate by substitution, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out; (3) sulfur dioxide is introduced into the leachate obtained from the step (2) to precipitate the tellurium by reduction, and the solid-liquid separation is carried out to obtain crude tellurium; and (4) the crude tellurium is processed according to a conventional method to extract pure tellurium. The technology adopts one-section oxidation acid leaching to leach the copper and tellurium out, copper powder to remove the impurities of silver, selenium and the like by substitution, and sulfur dioxide to precipitate the tellurium by reduction (obtaining tellurium dioxide), and the tellurium dioxide precipitation is alkali-dissolved and then electrolyzed to obtain the tellurium, therefore, the flow is simple, the consumption of the copper powder is remarkably reduced, and the simplification of the technology is beneficial to improve the recovery ratio of the tellurium, which can achieve more than 90 percent.
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
Regenerated acidic etching solution, copper recycling method and special device thereof
InactiveCN101768742ARealize recyclingEmission reductionPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementAlloyElectrochemistry
The invention discloses regenerated acidic etching solution, a copper recycling method and a special device thereof, belonging to the field of electrochemically recycling waste solution and nonferrous metal. An electrolytic tank in electrochemical treatment is divided into an anode chamber, an intermediate chamber and a cathode chamber. Dilute sulfuric acid solution is contained in the anode chamber, and a lead-tin-calcium alloy plate is adopted as an anode electrolytic plate. Waste acidic etching solution is contained in the intermediate chamber. Copper sulfate solution is contained in the cathode chamber, and a stainless steel plate is adopted as a cathode electrolytic plate. Under the function of an electric field, copper is dissolved out from a copper sulfate system. Water in the anode chamber is oxidized to generate oxygen gas and hydrogen ions. When the concentration of the copper ions is reduced to 1g or lower than 1g, the etching solution can be used anew. The method greatly reduces the production cost and causes no atmospheric pollution at the same time as realizing the recycling.
Owner:青海复绿生态科技有限公司
All-wet process pretreatment method for copper anode mud
InactiveCN103966450AReduce processingHigh enrichment rateProcess efficiency improvementPretreatment methodHydrometallurgy
The invention relates to a wet-process metallurgy technology in the metallurgical field and particularly relates to an all-wet process pretreatment method for copper anode mud. The all-wet process pretreatment method is as follows: firstly, carrying out hot acid leaching onto copper anode mud, leaching metals such as copper, selenium, sliver, barium, and the like and adding in liquor, leaving gold, tellurium, tin, platinum and platinum-family metals in leaching residue; by virtue of alkali leaching of hot acid leaching residue, leaching and enriching metals such as tellurium, lead, arsenic, and the like in liquor; carrying out chlorination on the obtained tellurium-separating residue for separating gold, enriching the gold, the platinum and the platinum-family metals in the liquor, enriching the tin and the antimony in residue; diluting the hot acid leaching liquor by water, enriching the copper and the selenium in diluted liquor, dissolving obtained precipitates by nitric acid, and filtering to obtain barium sulfate molten slag and sliver nitrate liquor. The all-wet process pretreatment method disclosed by the invention cancels a sulfating and roasting process which is high in energy consumption and great in pollution in the conventional copper anode mud treatment method, removes and openly recycles barium by the hot acid leaching before extracting the gold and the sliver, reduces treatment amount of the copper anode mud, and improves recovery rate of gold and sliver.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
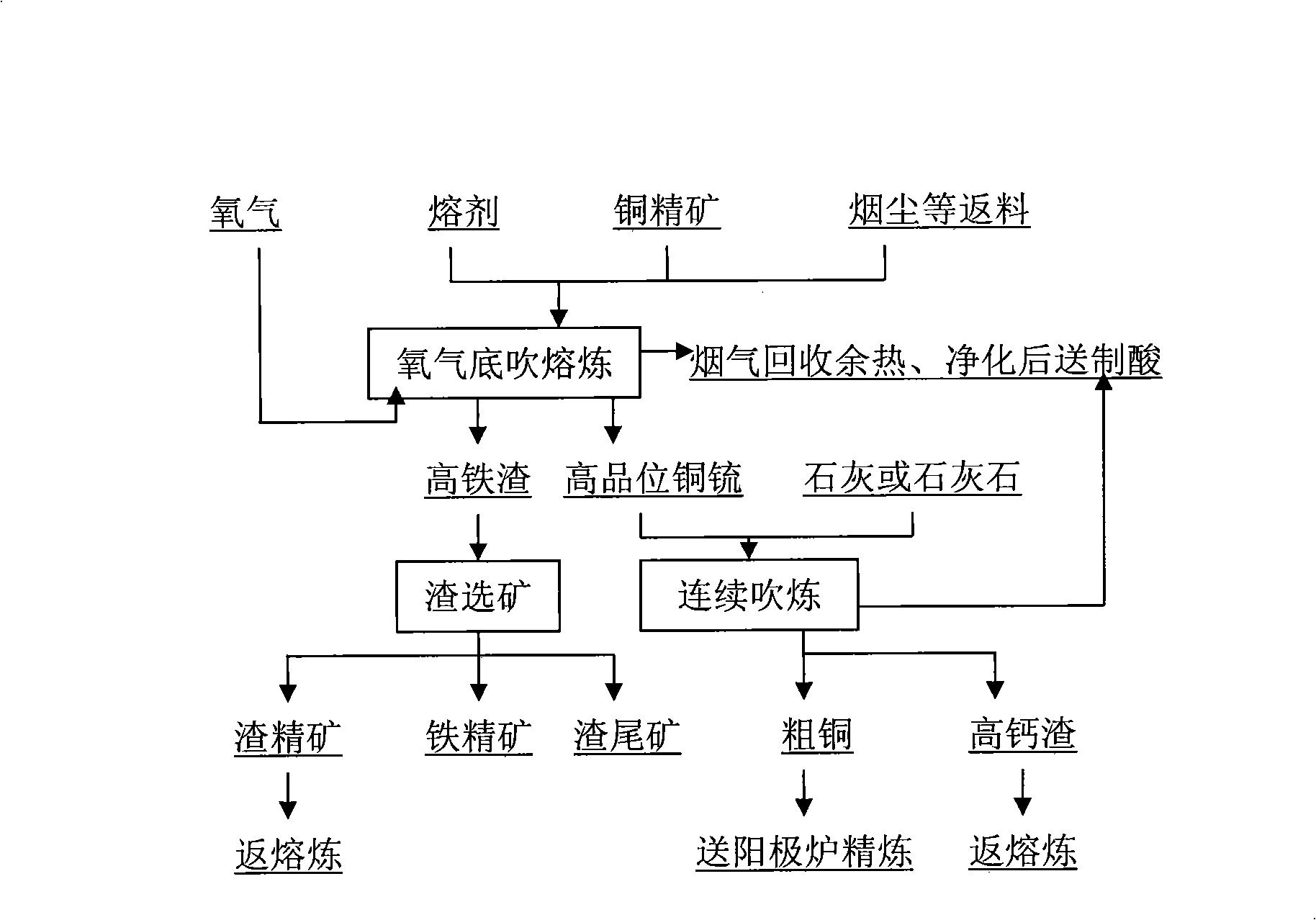
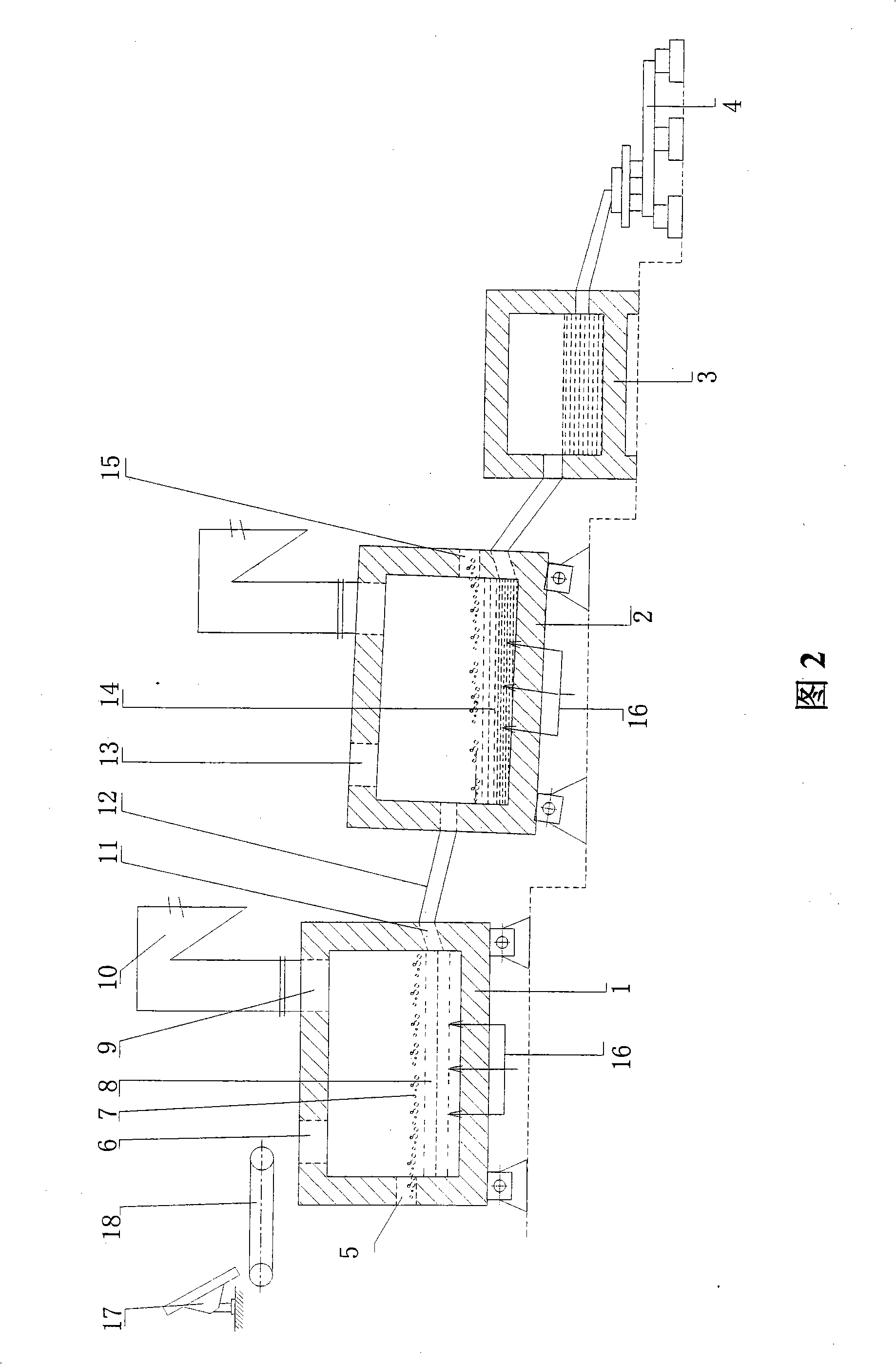
Oxygen bottom blowing continuous copper smelting apparatus
InactiveCN101328543ALess slagHigh yieldRotary drum furnacesCrucible furnacesSmelting processLiquid copper
The invention provides an oxygen bottom blowing continual copper smelting device used in the continual copper smelting process. The device is characterized in that the device comprises an oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace, an oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace, an anode furnace and an anode plate casting machine, wherein the oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace and the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace are connected by a first chute, so that liquid copper matte smelted by the oxygen bottom blowing smelting furnace can be continuously injected into the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace through the first chute to obtain coarse copper by the continuous converting of the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace; the oxygen bottom blowing converting furnace and the anode furnace are connected by a second chute, so that the coarse copper can flow in the anode furnace through the second chute and is subjected to refining by the anode furnace to obtain anode copper; and the anode furnace and the anode plate casting machine are connected by a third chute, so that the anode copper can flow into the anode plate casting machine through the third chute and is subjected to casting by the anode plate casting machine to obtain the copper anode plate.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Method for extracting selenium from selenium-contained material
ActiveCN102086029AHigh purityImprove pass rateElemental selenium/telluriumSulfite saltSodium sulfites
The invention relates to a method for extracting selenium from selenium-deposited residue. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving selenium-deposited residue to an alkaline sodium sulfite solution, generating water-soluble seleno sodium sulfate through a reaction between elemental selenium and the sodium sulfite solution; fully reacting the seleno sodium sulfate under the acidification of sulfuric acid to obtain a selenium elemental precipitate; and washing and drying to obtain coarse selenium with the purity of about 90 percent. The invention realizes separation of copper, silver and selenium in the selenium residue, and the separated selenium can be directly refined due to higher purity, therefore, the process flow of selenium recovery is shortened, the recovery rate is increased, and the production cost is decreased; the trouble of high copper content of an anode plate in silver electrolysis in the gold and silver refining process is solved and the pass rate of primary silver powder electrolysis is increased. The invention can be applied to recovering and extracting selenium from materials, such as selenium-contained residue generated in the technical process by using a wet method for treatment or selenium-contained acid mud generated in the production process of the copper anode slime by using a pyrogenic method for treatment and can also be applied to the production of high-purity selenium products by directly purifying a coarse selenium raw material.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for extracting platinum-palladium out of copper anode mud
ActiveCN103305699ASimple configurationEasy to operateProcess efficiency improvementPlatinumProcess equipment
The invention discloses a method for extracting platinum-palladium out of copper anode mud. The method is characterized in that the platinum-palladium is extracted by employing a secondary gold dust chlorination gold leaching liquid, and the method comprises the following process steps of: firstly, carrying out sulfation roasting on the copper anode mud, carrying out primary chlorination gold leaching, carrying out sulfur dioxide gas reduction so as to obtain a primary reduction liquid, and subsequently carrying out zinc powder replacement so as to enrich gold, silver, platinum and palladium into secondary gold powder; secondly, dissolving the secondary gold powder, removing the impurities, filtering the obtained filtered residue, carrying out secondary chlorination gold leaching, adding ammonium chloride and a reduction inhibitor sodium chlorate into the filtered liquid, and reacting so as to obtain platinum and palladium precipitate; and finally reducing the filtered liquid by using a liquid sulfur dioxide to leach the gold. The method is simple in process equipment arrangement and convenient to operate; the recycling rate of the gold in the copper anode mud is increased; and meanwhile the platinum-palladium is effectively enriched in platinum-palladium concentrate.
Owner:SHANDONG HUMON SMELTING
Preparing method for ultra-fine high-purity Ti2AlNb alloy powder
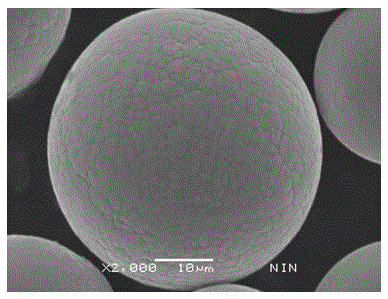
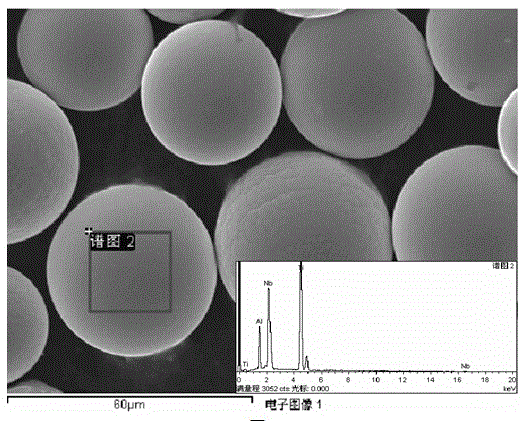
ActiveCN105537603AHigh purityHigh sphericityTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusAlloyUltra fine
The invention provides a preparing method for ultra-fine high-purity Ti2AlNb alloy powder. The preparing method comprises the following steps that 1, components of a Ti2AlNb base alloy are used as ingredients and smelted into a Ti2AlNb alloy bar; 2, finish turning is carried out on the smelted Ti2AlNb alloy bar, the diameter of a processed electrode bar ranges from 10 mm to 100 mm, and the length ranges from 100 mm to 1000 mm; 3, the electrode bar is loaded into a reaction chamber, the reaction chamber is vacuumized, and helium or argon or helium and argon mixed gas is introduced into the reaction chamber; 4, plasma gun powder of PREP powder manufacturing equipment ranges from 100 kW to 300 kW, a plasma torch comprises a tungsten cathode and a copper anode, the electrode bar is not used as an electrode, the end of the electrode bar is heated to be melted uniformly, atomized drops are tossed out from the end of the electrode bar, the drops are cooled fast in an inert gas environment to form spherical particles, and the spherical particles drop into a bottom collector of the reaction chamber; 5, prepared Ti2AlNb alloy powder is screened and packaged in the inert gas protection environment; 6, the Ti2AlNb alloy powder prepared through the method has the advantages of being ultra-fine, high in purity, high in spherical degree and low in oxygen content.
Owner:SINO EURO MATERIALS TECH OF XIAN CO LTD
Method for processing copper anode slime in total wet manner
ActiveCN102965501ABig investmentHigh separation recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumRaffinateTin
The invention discloses a method for processing copper anode slime in a total wet manner, relating to a total wet production process for recycling rare and precious metals from the copper anode slime in nonferrous metallurgy. The method comprises the steps of pressurizing the copper anode slime by a chloride medium at a high temperature and leaching to directly separate out valuable metals such as copper, stibium, bismuth, tellurium, and tin; and recycling tellurium, stibium, tin, bismuth, copper and the like from a pressurized lixivium in stages. The method is further characterized in that a selective extraction method is adopted to separate gold in a gold selenium chloride solution and the selenium is recycled from a gold raffinate. According to the method, the sulfating roasting with serious pollution and huge investment is avoided, but the sulfating roasting is carried out firstly for the copper anode slime in the conventional wet method or (pyrometallurgical process); the separation recovery rate of the metals is high, but the separation effect of tellurium, stibium, tin and bismuth in the conventional process is far from ideal; by adopting the method, the leaching problems of above metals can be solved in a single process and above metals can be recycled respectively from the lixivium; the recovery rate of the metals is 90-99% respectively; the copper separation and the tellurium separation can be simplified; and the operation flow is optimized in a better manner.
Owner:JIANGXI COPPER
Method for extracting silver from silver slag
The invention discloses a method for extracting silver from silver separated residue, which relates to a method for recycling silver from the solid residue of copper anode sludge after the metal such as Se, Cu, Te, Au, and Ag is separated and extracted. The invention is characterized in that the invention comprises the steps that firstly, the silver separated residue is pulped, industrial H2SO4 is adopted to adjust the acidity of the solution, the oxidizing agent NaClO3 is added to control oxidation reduction potential of the solution to perform oxidizing pretreatment, Ag2O, Ag2SO4, Ag2S, and simple substance Ag in the silver separated residue which can be hardly leached are changed into AgCl which can be easily leached by Na2SO3, and the AgCl is reduced into coarse Ag powder through CH2O under the alkalinity condition. The method of the invention has the advantages that the equipment is simple, the process flow is simple, the silver recovery ratio is high, the loss of the noble metal such as Pt and Pd, etc. in the silver separated residue can not be caused, and the invention is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Method for extracting tellurium from copper anode sludge
InactiveCN102220489AEasy to separateRaise the gradePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSludge
The invention discloses a method for extracting tellurium from copper anode sludge and relates to the method for recovering the tellurium from copper-containing tellurium material, in particular to the method for extracting the tellurium from the copper anode sludge. The method is characterized in that the process sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) performing oxygenation, pressurization and sulfuric acid leaching on the copper anode sludge for leaching copper, the tellurium and part of selenium; (2) introducing sulfur dioxide gas into leachate, and precipitating and separating the selenium; (3) performing electrodeposition on a solution after removing the selenium by precipitation and separation, and separating the copper; and (4) introducing the sulfur dioxide gas into the solution after removing the copper by electrodeposition and separation for performing reduction reaction so as to get the deposited crude tellurium. In the method, the selenium deposition and tellurium deposition technology by sulfur dioxide step-by-step reduction is adopted, no copper powder is consumed during the process, the effect of separating the selenium, the tellurium and the copper is good, the grades of the crude tellurium and crude selenium are high, the production cost can be greatly reduce, the process flow is simplified, and convenient conditions are provided for preparing follow-up fine tellurium.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
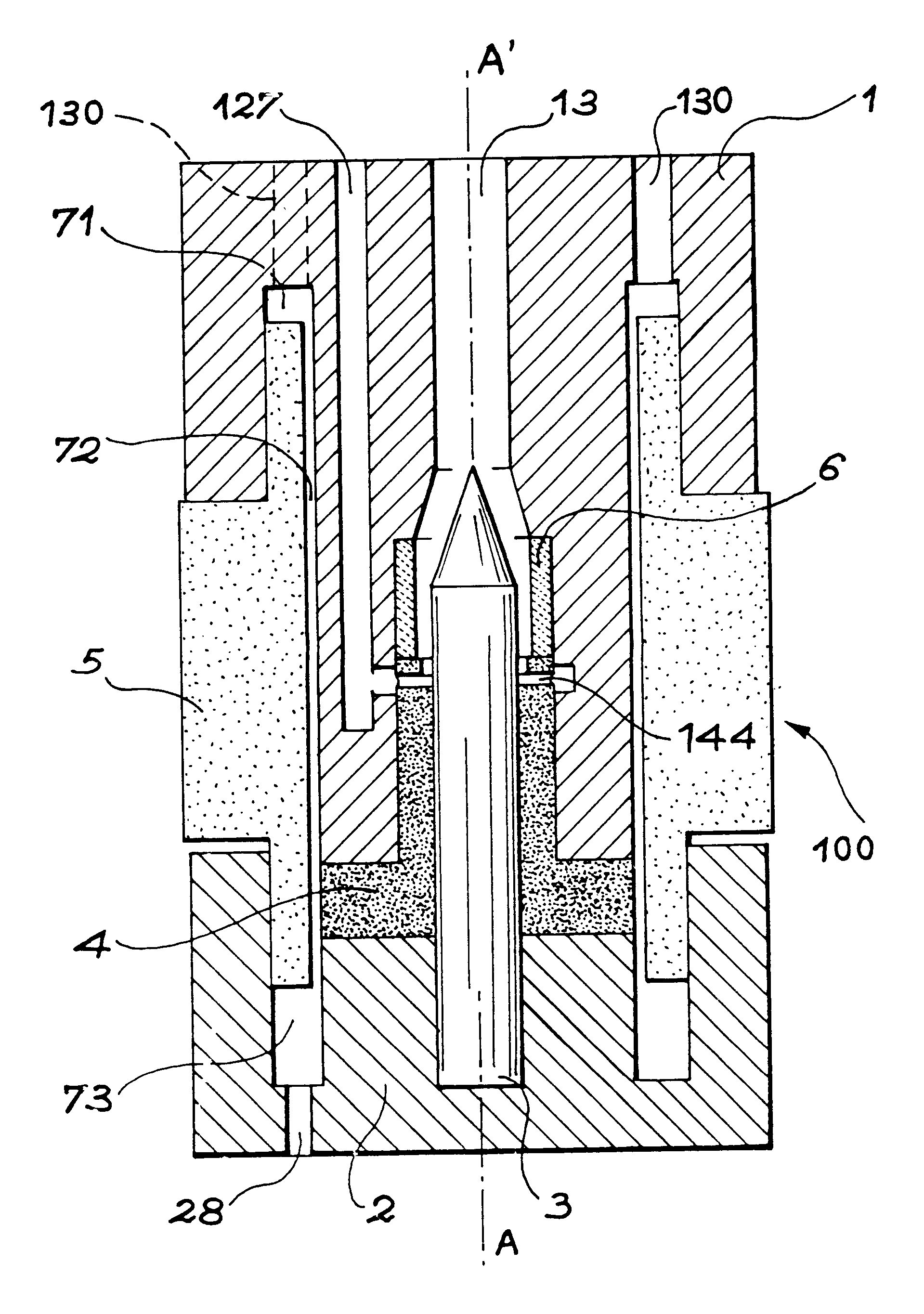
Plasma torch cartridge and plasma torch equipped therewith
InactiveUS6515252B1Simplify workShort timePlasma welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsForming gasMetallurgy
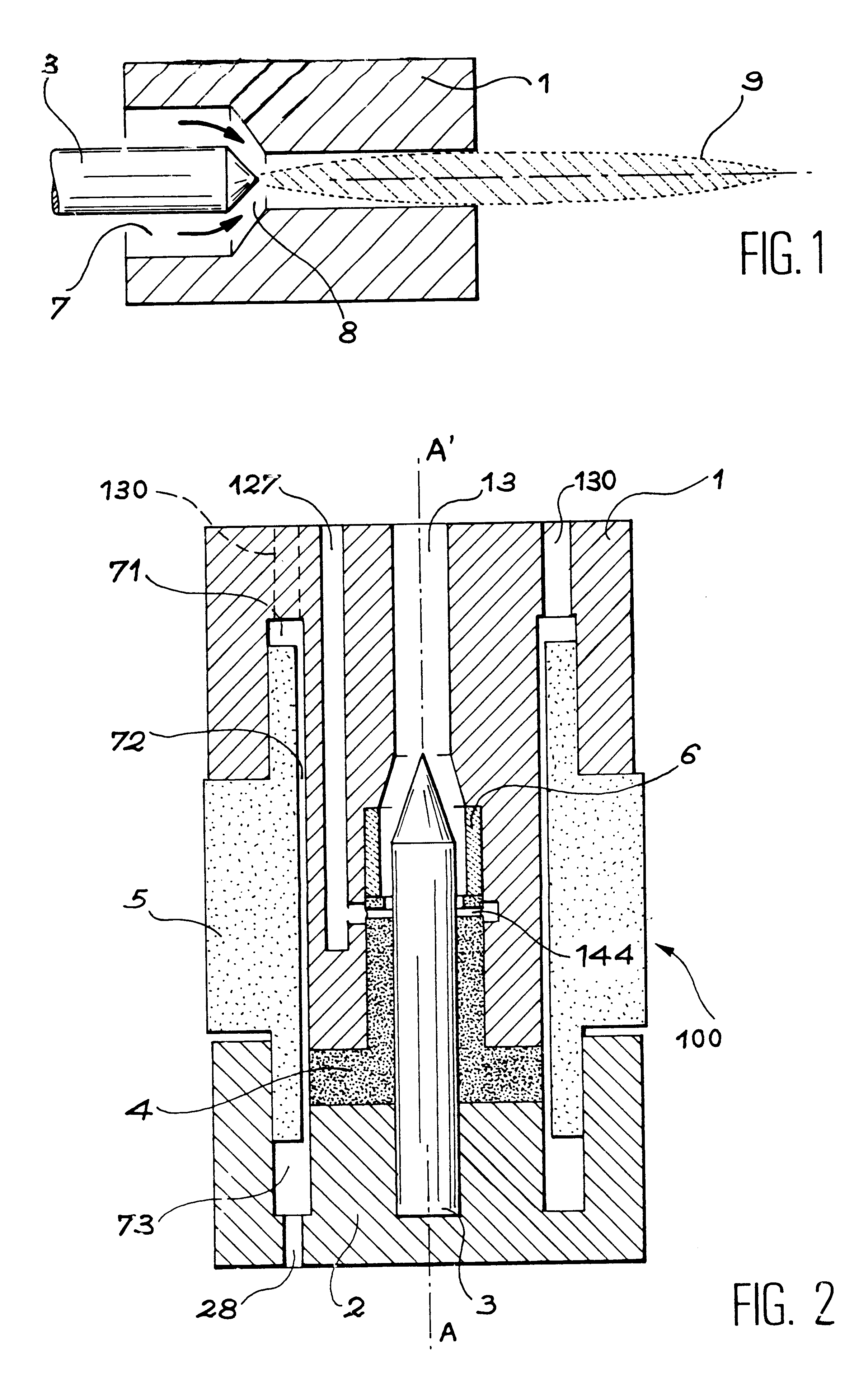
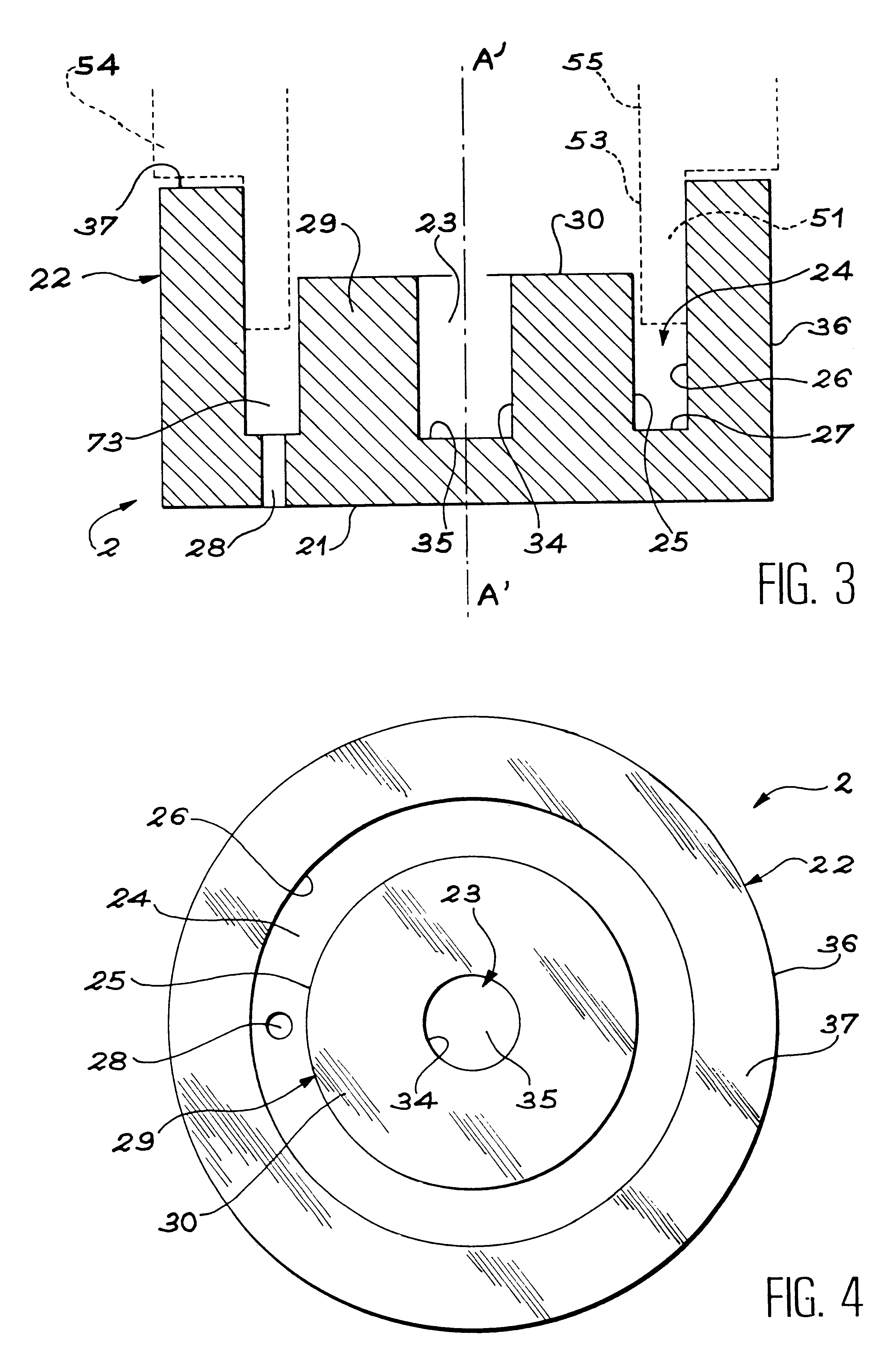
The invention concerns a plasma torch comprising an interchangeable cartridge (100) consisting of six components only: an electroplating copper anode nozzle (1); an electroplating cathode support (2); a doped tungsten cathode (3); a plastic cathode diffusing-centring device (4); a plastic assembling device (5); a ceramic insert (6). Said components are assembled by pressing and the assembly of the components form volumes (71, 72, 73) constituting the anode cooling circuit and the plasma forming gas intake conduits (127, 44). The intake and discharge of fluid are provided by a connecting and maintaining structure designed for the easy mounting of the cartridge (100).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method of producing chip copper interconnection high-purity copper sulfate electroplate liquid
A method for producing a chip copper interconnection high-purity copper sulfate electroplating solution of the present invention firstly includes an electrolysis step: in the process of electrolysis, an electrolytic cell is used, and an anode and a cathode are arranged in the electrolytic cell, the anode adopts an electrolytic copper plate, and the cathode Platinum plates are used, separated by a one-way membrane between the cathode and the anode, sulfuric acid is used as the electrolyte in the electrolytic cell, and metallic copper is dissolved by electrochemical methods; secondly, a superfiltration purification step is included to obtain a total amount of metal impurities less than 10PPM, high-purity copper sulfate mixed plating solution with organic impurities less than 10PPM. The present invention adopts a purification method combining electrochemistry and membrane technology. By adjusting process parameters and combining semiconductor ultra-purification and ultrafiltration technology, other indicators of the product can be controlled, and the product can be purified without evaporation and crystallization, and the qualified product can be directly produced. High-purity copper sulfate electroplating solution for copper interconnection.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINYANG SEMICON MATERIALS
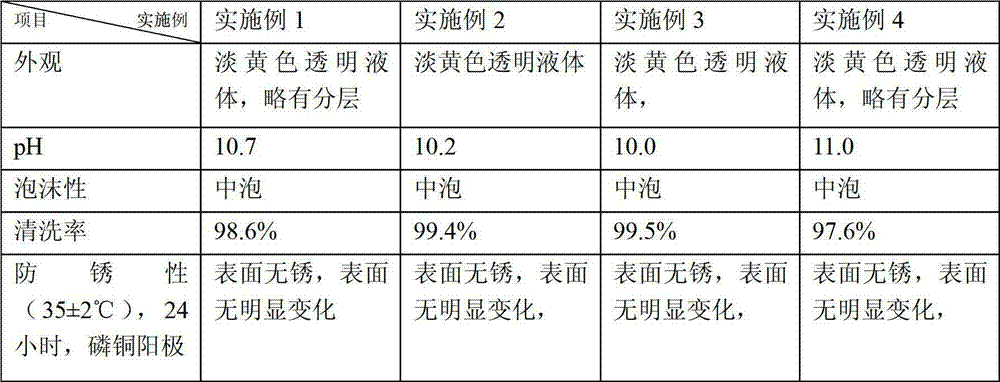
Water-based phosphor copper anode cleaning agent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a water-base phosphor copper anode cleaning agent and a preparation method thereof. The phosphor copper anode cleaning agent comprises, by weight, 25.5-28% of a mixed surfactant, 2.5-5% of rust-proof constituents, 0.5-2% of a chelating agent, 10-15% of an inorganic assistant, and the balance water. The mixed surfactant consists of a nonionic surfactant and an anionic surfactant, and AEO-9, polyoxyethylene sorbitan fatty acid ester-80 (tween-80), triethanolamine oleate and a JFC are mixed to form the nonionic surfactant. Under the common action of the surfactant, the inorganic assistant and a rust-proof agent, the cleaning agent can be cleaned at a normal temperature, dirts on the surface of a phosphor copper anode can be removed quickly, the cleanliness is high, no residual organic matter exists on the surface, the cleaned phosphor copper anode can be used for electrofacing of a circuit board directly, and no activating treatment is required. Besides, no phosphate or biological degradation-resistant surfactant are contained, and no ecological pollution is caused.
Owner:佛山市承安集团股份有限公司 +1
Preparation method of superfine high-grade spherical EP741NP alloy powder
The invention relates to a preparation method of superfine high-grade spherical EP741NP alloy powder. The method comprises the following steps: 1) proportionally preparing materials according to the EP741NP alloy composition, and smelting to obtain an EP741NP alloy bar; 2) processing the smelted EP741NP alloy bar into an electrode bar; 3) installing the electrode bar into a reaction chamber, vacuumizing the reaction chamber, and proportionally charging inert gas into the reaction chamber; 4) heating the end of an electrode bar to uniformly melt the end, throwing atomized liquid drops from the end of the electrode bar so that the liquid drops are quickly cooled into spherical particles in an inert gas atmosphere and fall into a collector, wherein a plasma torch comprises a tungsten cathode and a copper anode, and the electrode bar is not used as an electrode; and 5) carrying out electrostatic separation on the prepared EP741NP alloy powder in an inert gas protective atmosphere, screening, sampling and packaging. The EP741NP alloy powder prepared by the method is superfine, and has the characteristics of high purity, high-grade sphericity and no hollow powder or satellite powder.
Owner:SINO EURO MATERIALS TECH OF XIAN CO LTD
Efficient enrichment method for precious metal secondary resources
InactiveCN105886770AAdaptableSimple processProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisEnrichment methods
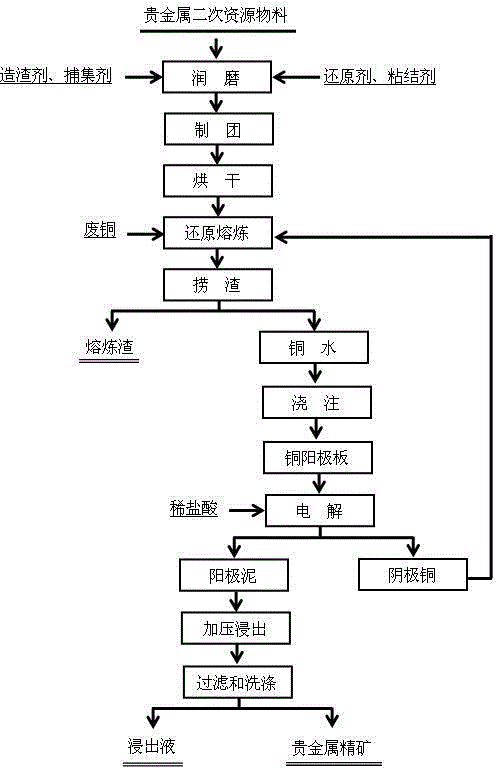
The invention discloses an efficient enrichment method for precious metal secondary resources. The method comprises the steps that precious metal secondary resource materials, a copper collecting agent, a reducing agent, a slag forming constituent, a binding agent and water are subjected to full wet-grinding in a ball mill, and are mixed evenly and manufactured into pellets through a ball forming machine, and the pellets are dried to obtain composite pellets; after waste copper is molten in an intermediate-frequency furnace, the composite pellets are added into the intermediate-frequency furnace in batches and are subjected to mixing smelting for a period of time, smelting slag is fished out, and molten copper is poured into a casting mold to form a copper anode plate; cathode copper is obtained through an electrolysis method, precious metals enter anode mud, and electrolytic residual anodes return to conduct smelting and pouring on the anode plate and conduct electrolysis again; the anode mud is subjected to pressure acid leaching, filtering and washing to obtain precious metal concentrate, and accordingly precious metal enrichment is realized. By means of the method, the process is simple, the raw materials are high in adaptability, high efficiency and environmental friendliness are achieved, the enrichment ratio is high, cost is low, and industrialization is facilitated.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY COLLEGE
Process for preparing cathode copper by one-step electrolysis of raw red copper
InactiveCN1390983AHigh recovery rateNo pollution in the processPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementInsulation layerElectrolysis
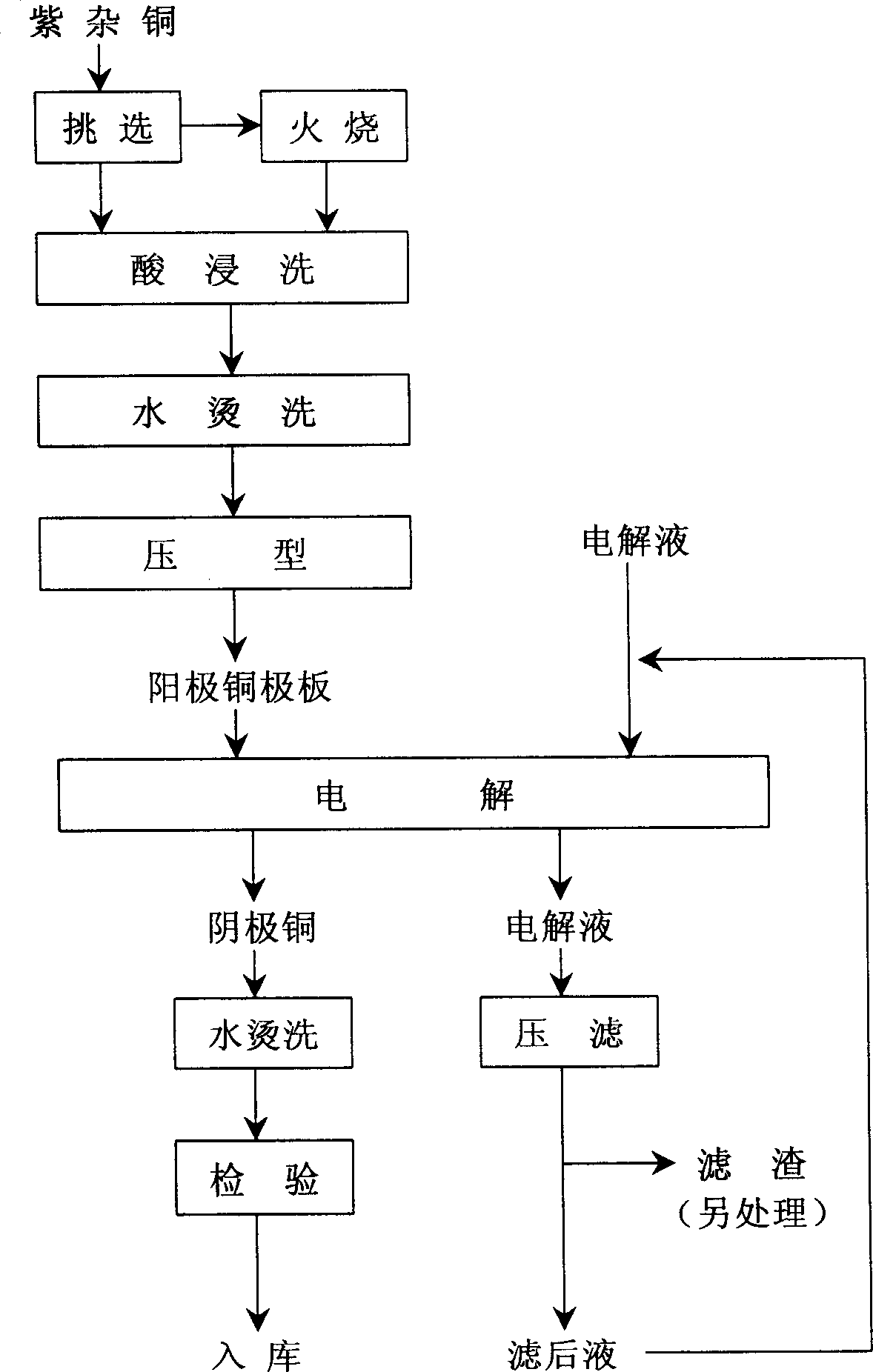
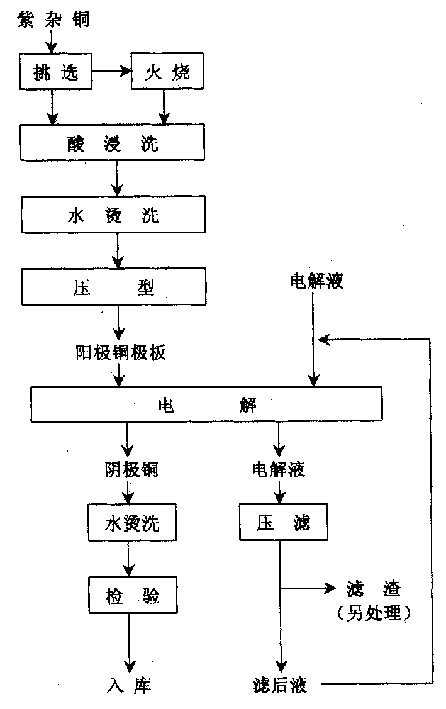
A process for preparing cathode copper from raw red copper by one-step electrolysis includes such steps as removing impurity, firing to remove insulation layer, pickling to remove oxidized layer, washing with hot water, die pressing to obtain copper anode, wapping it in acid-resistant porous cloth bag, suspending in electrolyte, electrolyzing to obtain cathode copper and washing with hot water. Its advantages are simple process, high recovery rate of copper, high quality, low cost and no environmental pollution.
Owner:HONGZHI IND DEV JILIN CITY
Casting trough and method for casting copper anodes
InactiveCN1938113AImprove abilitiesSmall fluctuationMelt-holding vesselsMolten metal pouring equipmentsCasting moldCopper
The invention is a casting trough and method for pouring molten metal in a casting mold. Owing to the design and trajectory of the casting trough, there is achieved an even and rapid pouring from the casting trough to the casting mold. The spout of the casting trough comprises a curved pouring edge and a downwardly directed curved pouring surface. The mass flow rate of the molten metal is controlled by means of a choke element fitted in the casting trough. The direction and magnitude of the kinetic energy of the molten metal are affected by the design of the spout of the casting trough and by a suitably chosen trajectory of the pouring motion.
Owner:OUTOTEC OYJ
Method for separating and recovering valuable metals from copper anode slime
ActiveCN105543485ALess investmentShorten the timeProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumPregnant leach solutionLead bismuth
The invention discloses a method for separating and recovering valuable metals from copper anode slime. The method comprises the following steps: (1) the copper anode slime is subjected to oxidizing roasting, and primary dust and a roasting product are obtained; selenium is recovered from the primary dust, and secondary dust and crude selenium powder are obtained; (2) the roasting product is broken and added to a reactor, acid is added for acid leaching, an oxidizing agent is added continuously in an acid leaching process, acid leached residues and an acid leached liquid are obtained, and silver and copper are recovered from the acid leached liquid; (3) alkali is added to the acid leached residues for alkaline leaching, sodium cyanide and an ore selecting agent are added simultaneously, alkaline leached residues and an alkaline leached liquid are obtained, the valuable metals are recovered from the alkaline leached liquid, and a lead bismuth alloy and heavy metals are recovered from the alkaline leached residues. The method has the advantages of short process flow, low investment, short time, fast effect taking, high comprehensive recovery rate, high technical-economic indicators and high metal recovery rate.
Owner:郴州百一环保高新材料有限公司
Method for preparing tellurium dioxide from tellurium slag
InactiveCN102390819AMain grade improvedSave resourcesBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsPregnant leach solutionSlag
The invention relates to a method for preparing tellurium dioxide from tellurium slag. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps of: adding tellurium slag to sulfuric acid solution, stirring at normal temperature, adding 10% oxydol at the temperature of 30-40 DEG C, and then heating to 80-90 DEG C, and leaching under normal pressure; adding copper powder to leachate, carrying out replacement reaction at the temperature of 90-95 DEG C for 2 hours, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain copper telluride slag; adding copper telluride slag to sulfuricacid solution, adding 10% oxydol, stirring at the temperature of 90 DEG C for 1 hour, and filtering; adding sodium carbonate to filtrate for neutralizing the filtrate till pH of the filtrate is 3, and filtering; adding NaOH to filter residue, carrying out alkali leaching and stirring at the temperature of 85-95 DEG C for 1 hour, and filtering; and adding H2SO4 to filtrate for neutralizing the filtrate till pH of the filtrate is 6-7, filtering, washing and drying to obtain a product. The method has the characteristics that: low-grade tellurium-containing material discarded by a copper anode mud production enterprise is used as a raw material to produce high-purity tellurium dioxide, the process is reasonable and pollution-free, and the recovery rate of tellurium is high.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Super-high heat-conductive diamond-copper composite package material and production method
InactiveCN101070461ASolve the problem of high thermal resistanceSolution volumeOther chemical processesLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectrolysisPhosphate
The invention discloses a diamond-copper composite-encapsulation material and its manufacturing method. The matrix-material is copper. The granular mass of diamond is 2-60%,and the particle diameter is about 1-150um. The adjunct is copper or silver which granular mass is 0.1-10%. Gild the adjunct on the surface of the diamond powder granola in a way of chemical plating. The steps as follows: (1). Gild the adjunct o the surface of the diamond powder granola in a way of chemical plating, and form a coat of 0.1-5%um. Around. (2). Put the granola on the metallic mold dispersive, and then put the mold into electrolysis bath. (3). Make the metallic mold cathode, the copper anode, and cupric phosphate solution bath composition. Then separate out the copper on the mold, until it covers the diamond. (4). Take out the sample and wash it carefully, then cut it according to the needed size. The material of the invention has the advantages of high thermal coefficient and low thermal expansion coefficient.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
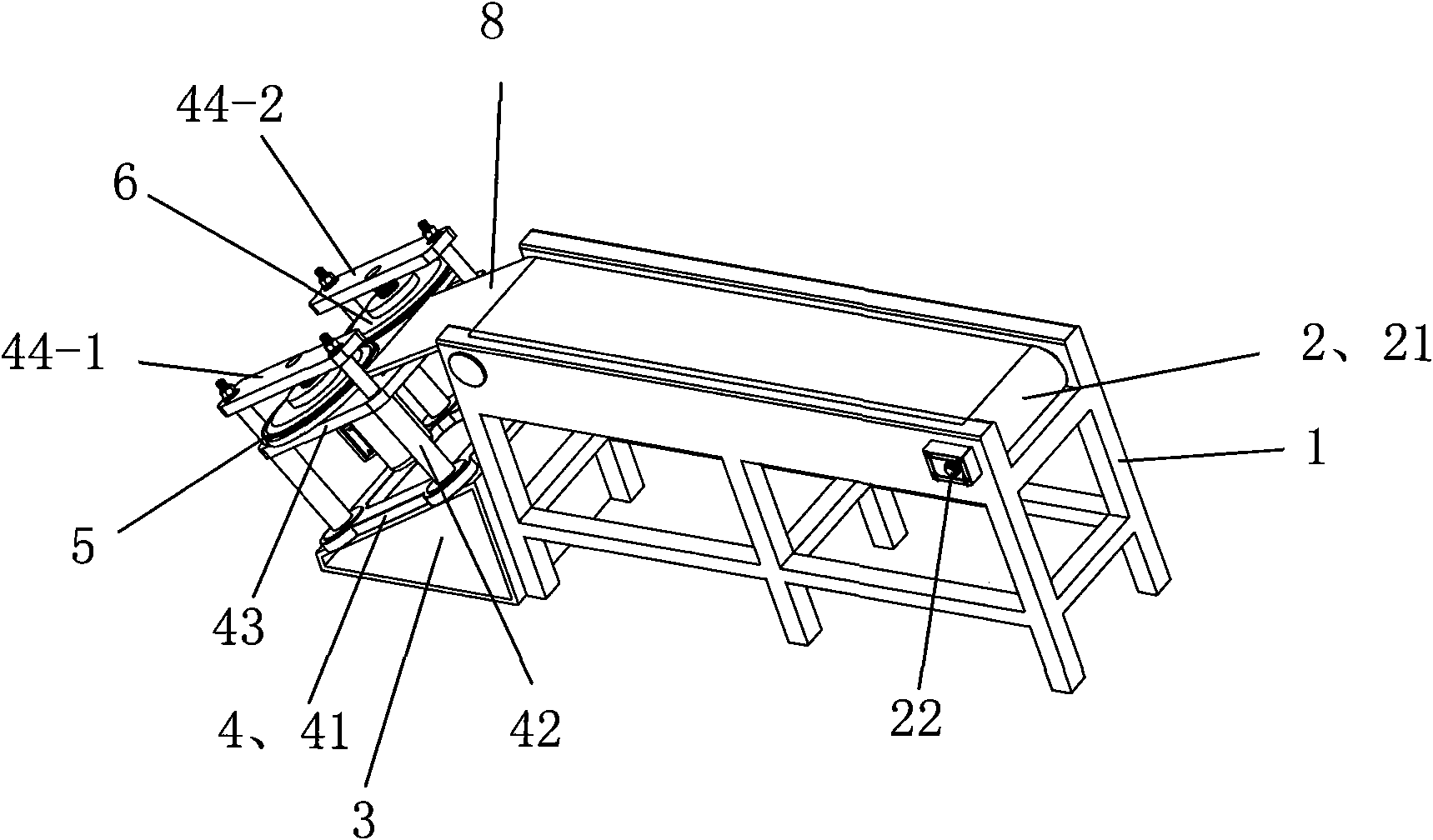
Novel process for all-component high-added-value clean utilization of waste circuit boards
InactiveCN101569889AHigh purityHigh recovery rateWaste processingSolid waste disposalEngineeringAlloy
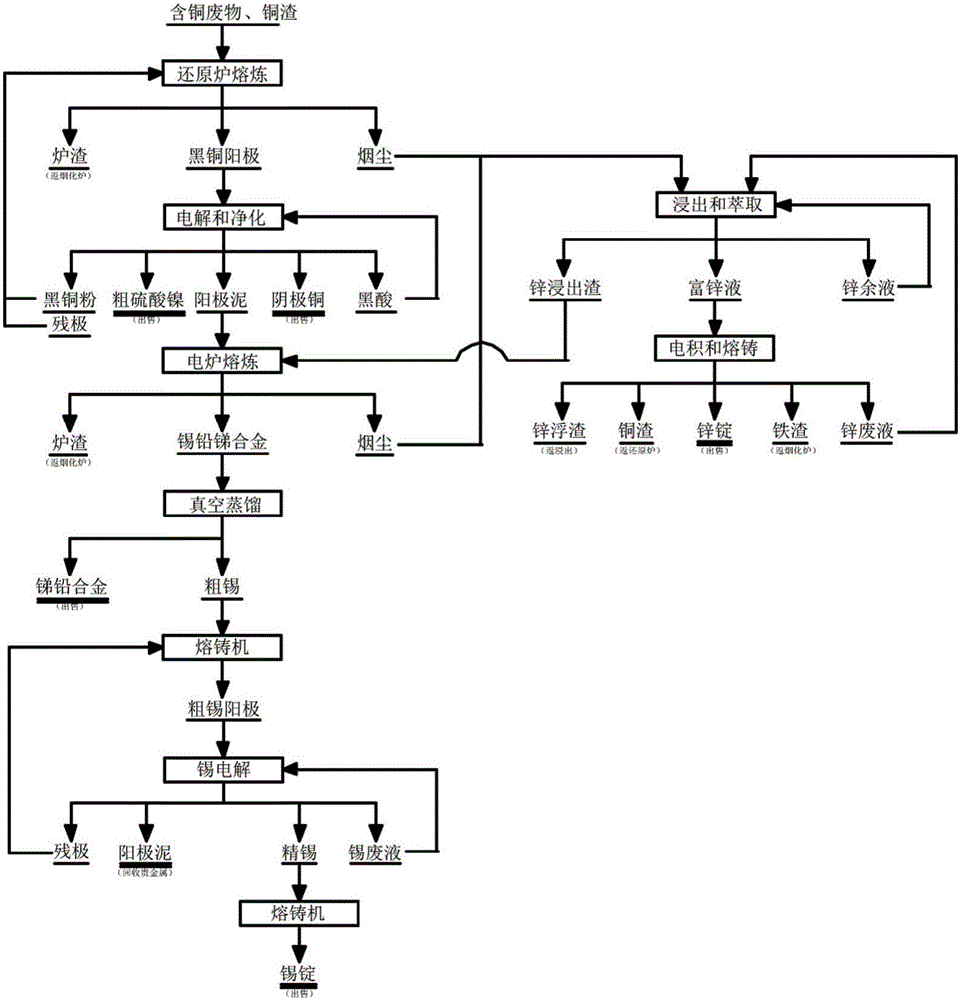
The invention relates to a novel process for all-component high-added-value clean utilization of waste circuit boards, which comprises the steps: a) automatically disassembling and separating the waste circuit boards, crushing separated electronic components and then taking the crushed electronic components as a unit raw material for deep processing of precious metals; b) crushing the separated circuit boards by a crushing machine, and then obtaining a metal concentrate and nonmetal powder through air separation; c) sending the metal concentrate into a rotary incinerator for incineration, removing resin organic substances, and separating low melting point metals such as lead, tin and the like to form alloy recovery; d) sending an incineration material into an anode furnace, and casting melt subjected to oxidation reduction refining to obtain a copper anode plate; e) electrolyzing the copper anode plate to obtain a copper cathode plate and anode mud, and taking the anode mud as a unit raw material for the deep processing of the precious metals; and f) treating the unit raw materials for the deep processing of the precious metals to obtain the precious metals such as gold, silver and the like. The process mainly adopts a combined flow of automatic disassembly classification, a pyrogenic process and a wet process to treat the waste circuit boards; and the process has the advantages of high recovery rate, small energy consumption and less pollution on the environment.
Owner:JIANGSU TEACHERS UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from copper anode sludge silver separating slag
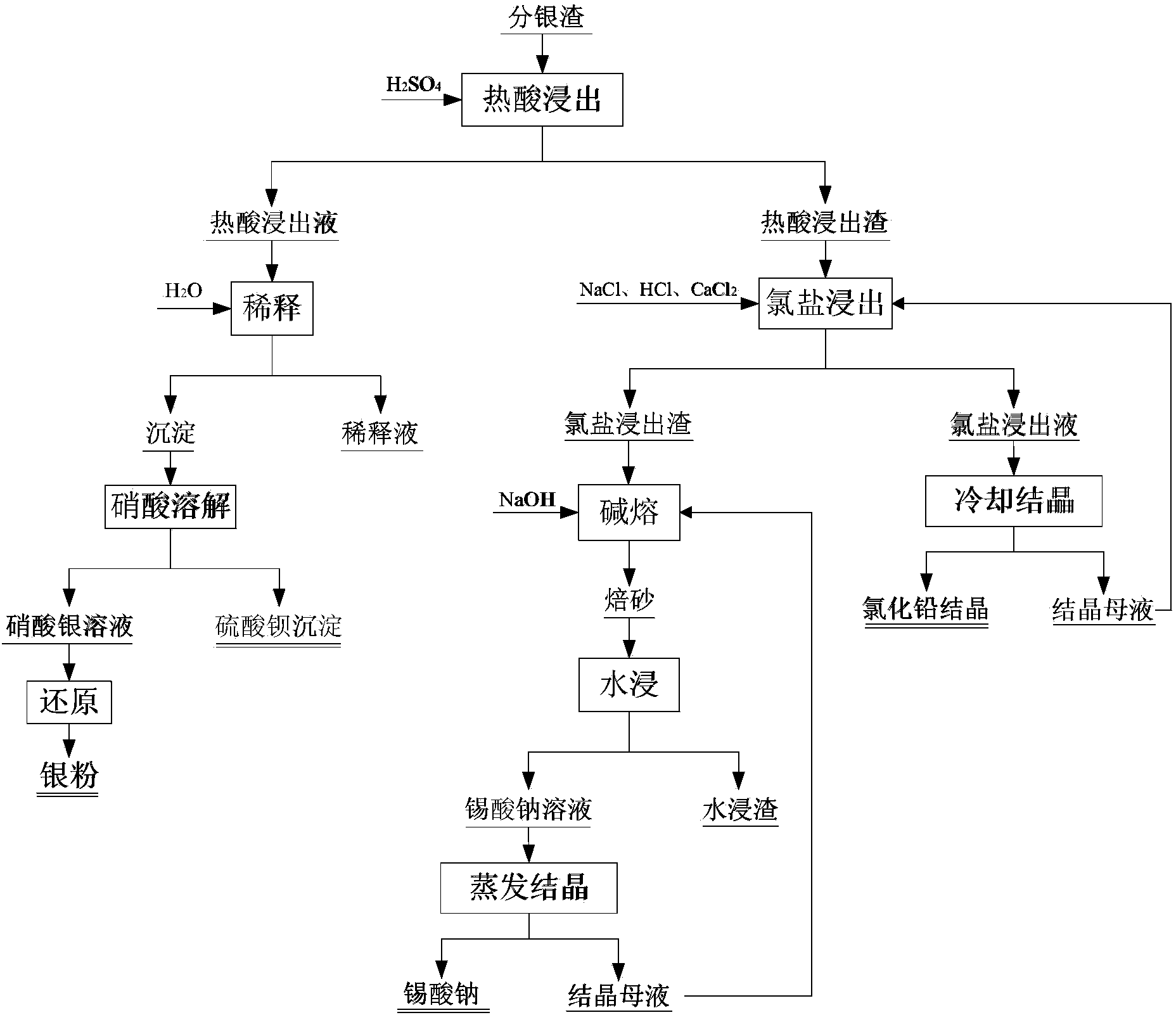
The invention relates to a copper anode sludge silver separating slag reutilization technique, particularly a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from copper anode sludge silver separating slag. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out hot acid leaching on silver separating slag, filtering to obtain a hot acid leaching solution containing silver and barium and hot acid leaching slag containing tin and lead; diluting the hot acid leaching solution with water, filtering to obtain a precipitate, dissolving the precipitate with nitric acid, and filtering to obtain a barium sulfate precipitate and a silver nitrate solution; reducing the solution to obtain silver powder; leaching the hot acid leaching slag with acidic chlorine salt, filtering to obtain a chlorine salt leaching solution and chlorine salt leaching slag; cooling the chlorine salt leaching solution to crystallize and precipitate lead chloride; and carrying out alkali fusion, water immersion and evaporation crystallization on the chlorine salt leaching slag to obtain sodium stannate. The method can effectively recover all the valuable metals with higher content in the silver separating slag, and the recovery rates of the lead, silver, tin and barium are respectively up to higher than 97%, 92%, 90% and 95%. The method has the characteristics of simple technique, no emission of three wastes, high metal recovery rate and the like, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Full-path full-valence separation method for multifarious metal
ActiveCN105695744AInnovative technologyHigh recycling valuePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementAntimonyRaw material
The invention discloses a full-path full-valence separation method for multifarious metal. Low-grade waste containing copper and copper slag serves as a raw material. The separation method comprises the following main steps that 1, the raw material is subjected to reduction smelting through a regeneration reduction furnace so that a black copper anode can be obtained, the raw material is subjected to electrolytic refining so that a metal cathode copper product and a crude nickel sulfate product can be obtained, and thus copper and nickel in the raw material are separated and recycled; 2, slag is leached out of copper anode mud and zinc and is subjected to reduction smelting through an electric furnace so that tin-lead-antimony alloy can be obtained, the tin-lead-antimony alloy is smelted through a vacuum furnace to be separated so that a antimony-lead alloy product and crude tin can be obtained, the crude tin is subjected to electrolytic refining so that refined tin can be obtained, that is, a tin ingot product is obtained, and hence tin, lead and antimony are separated and recycled; 3, a zinc ingot product is obtained by recycling smelting fume through a 'leaching- extraction- electrodeposition' method, so that the zinc, the tin and the lead are separated, and the zinc is recycled; and 4, tin anode mud is sent to a precious metal recycling factory as a precious metal enrichment material. According to the full-path full-valence separation method for the multifarious metal, the multifarious metal is completely separated, and remarkable economic benefits, environmental benefits and social benefits are achieved.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
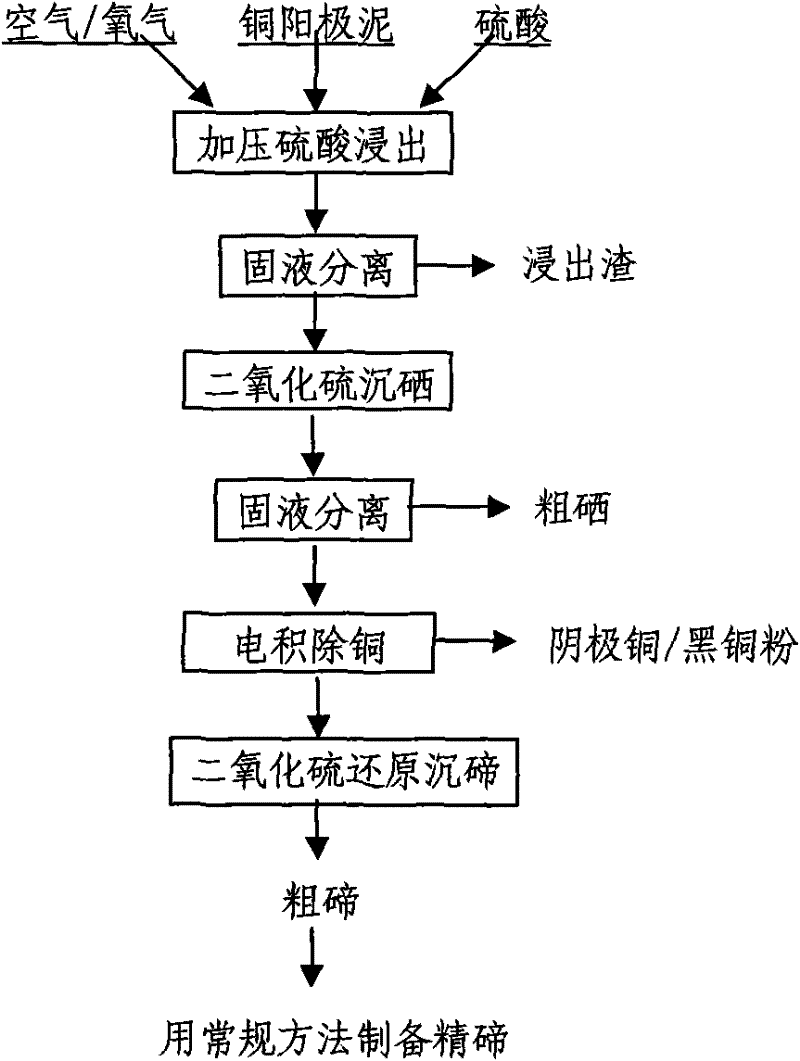
Method for leaching tellurium from copper anode mud using pressurized acid leaching process
InactiveCN1821060AEfficient leachingImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumPregnant leach solutionTe element
The present invention relates to pressurizing and acid leaching process for leaching out tellurium from copper anode mud, and belongs to the field of wet metallurgical technology of rare dispersion element. The process includes the following steps: mixing water and anode mud in 1-40 wt% to prepare slurry, filtering to eliminate large grain and sand, mixing with sulfuric acid solution of 70-300 g / L concentration, heating in a high pressure reactor at 100-180 deg.c, introducing gaseous oxidizing medium, regulating and maintaining the pressure at 0.5-1.6 MPa for direct acid leaching reaction for 60-120 min, solid-liquid separation to obtain the tellurium leachate. The present invention has simple technological process, less needed apparatus, reinforced process, short leaching period and high tellurium leaching rate.
Owner:YUNNAN METALLURGICAL GROUP
Method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings
InactiveCN105483384ASettle the lossHigh removal rateSelenium/tellurium compundsProcess efficiency improvementSootAntimony
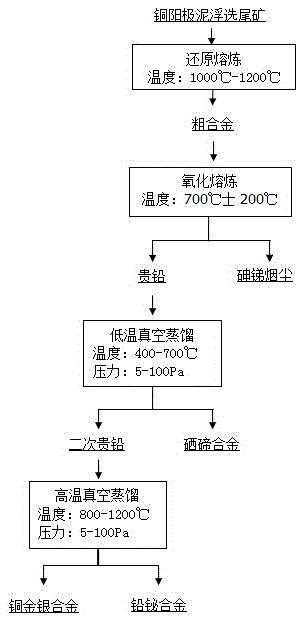
The invention relates to a method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings and belongs to the technical field of thermometallurgy. The method comprises: firstly, performing retailoring on the copper anode mud flotation tailings to obtain a reduction product, and then performing oxidative blowing on the reduction product to obtain rich lead and arsenic and antimony containing soot; first-stage low-temperature vacuum distillation: performing primary low-temperature vacuum distillation on the obtained rich lead under the conditions of a temperature of 400-700 DEG C and a pressure of 1-100Pa for 1-3h, thereby obtaining secondary rich lead and a selenium-tellurium alloy; and second-stage high-temperature vacuum distillation: performing primary high-temperature vacuum distillation on the obtained secondary rich lead under the conditions of a temperature of 800-1200 DEG C and a pressure of 1-100Pa for 1-3h, thereby obtaining a lead-bismuth and a copper-gold-silver alloy. The method for recovering valuable metals from copper anode mud flotation tailings is safe and controllable in whole process flow, simple and convenient to operate, simple in equipment needed, free from three-waste emissions, and environment-friendly.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for potential-controlled separation and enrichment of tellurium in copper anode slime
ActiveCN107447105AEfficient enrichmentReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementElemental selenium/telluriumTe elementCopper anode
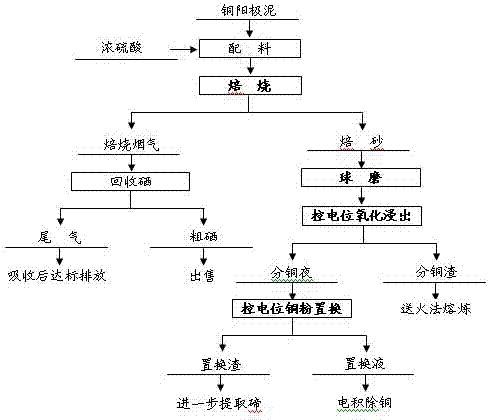
The invention discloses a method for potential-controlled separation and enrichment of tellurium in copper anode slime. The method comprises the steps of stirring and mixing the copper anode slime and concentrated sulfuric acid according to a center ratio, roasting under different temperature gradients, carrying out ball milling on the roasted product to a required particle size, adding hydrogen peroxide and carrying out oxidation leaching in a dilute sulfuric acid solution in the potential controlling way, adding copper powder to a copper leaching liquid and replacing in the potential controlling way, enriching the tellurium in the replacement residue and recycling copper through carrying out electrodeposition on the replaced liquid. The essence of method disclosed by the invention is that the purposes that the oxidation leaching process and the copper powder replacing process are adjustable and controllable are respectively realized in the potential controlling way; the leaching rates of the copper and the tellurium are respectively up to above 99.0% and above 80.0% in the potential-controlled oxidation leaching process; and the replacement rate of the tellurium in the potential-controlled replacing process is up to above 99.0%. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the technical index in the technical processes is stable; the labour intensity is low; the production cost is low and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for recycling gold and silver from silver separating residues of copper anode slime
ActiveCN102943180AImprove leaching rateSimple processProcess efficiency improvementPhysical chemistryCopper
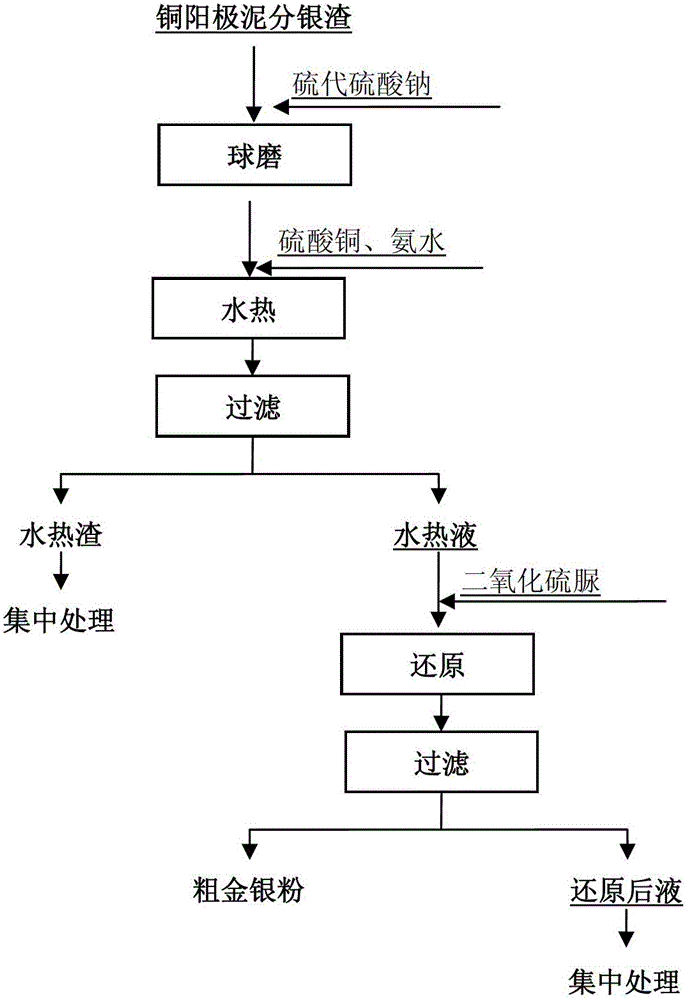
The invention relates to a method for recycling gold and silver from waste residues and particularly relates to a method for recycling gold and silver from silver separating residues of copper anode slime. The method specifically includes that the silver separating residues of the copper anode slime and sodium thiosulfate are subjected to mixing and ball-milling to obtain a ball-milling material; the ball-milling material and a reaction solvent are filled in a hydrothermal reaction still for hydrothermal reaction; and thiourea dioxide is added into a hydrothermal solution obtained by filtering a hydrothermal product for reduction reaction to obtain coarse gold and silver powders. Compared with methods in prior art, the method has the advantages that by means of the ball-milling and the hydrothermal reaction, leaching rates of the gold and the silver are greatly improved, the process is simple and easy to achieve, and raw materials are common, cheap and pollution-free.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Method for recovery of selenium from copper anode mud
InactiveCN106379870AHigh recovery rateReduce recycling costsElemental selenium/telluriumSeleninic acidPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for recovery of selenium from copper anode mud. The method consists of: pre-sulfating copper anode mud containing impurities, then performing roasting to generate gaseous selenium dioxide and sulfur dioxide, sending the mixed gas of selenium dioxide and sulfur dioxide into a lead absorption tower through a pipeline so as to obtain a part of elemental selenium and a part of seleninic acid, recovering absorption liquid with residual seleninic acid into a vacuum circulation jet pump barrel filled with excessive sulfur dioxide, and performing reduction to obtain elemental selenium. The method increases the recovery rate of selenium in copper anode mud from 90%-95% of the conventional process to 99.5% or more, lowers the selenium recovery cost, alleviates the environmental protection pressure, and reduces emission of sulfur dioxide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YADONG IND CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com