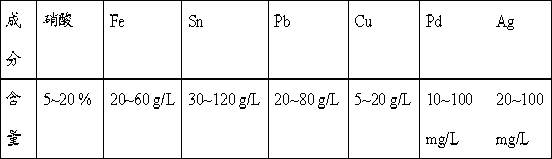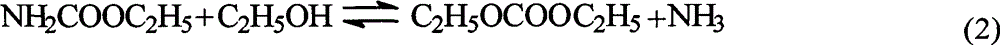Patents
Literature
227 results about "Lead chloride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lead chloride may refer to: Lead chloride, mineral name: cotunnite. Lead chloride
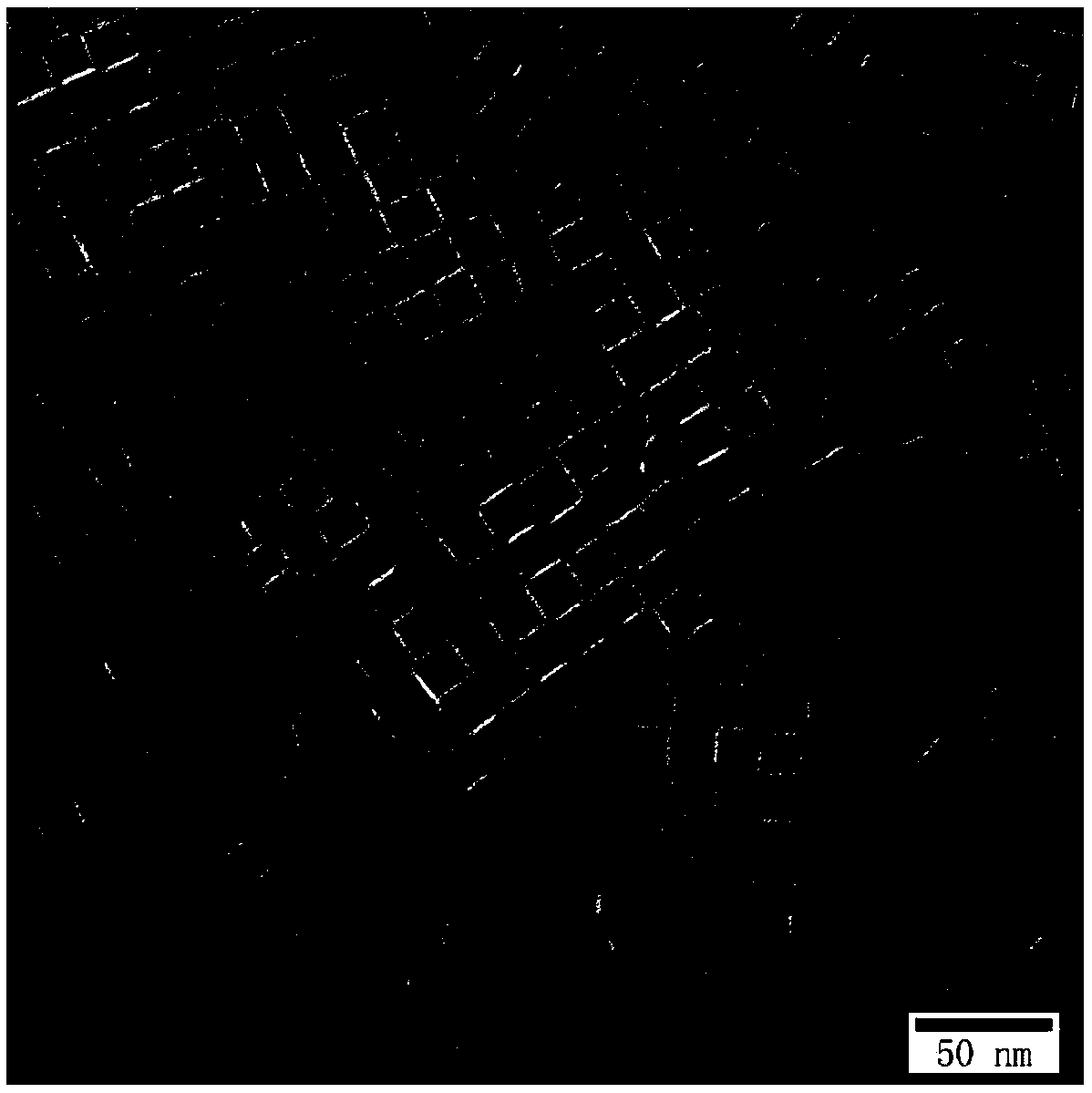
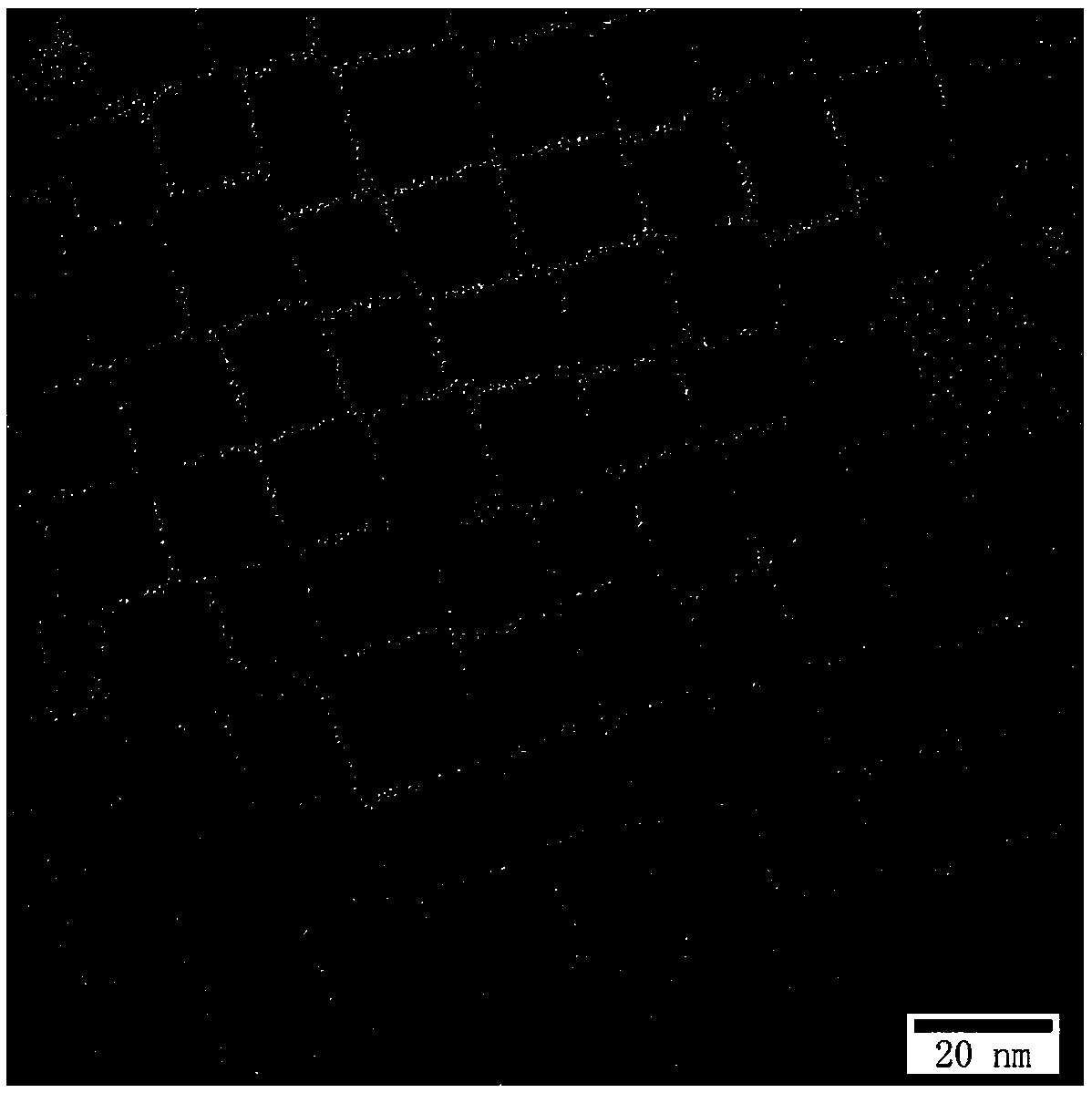
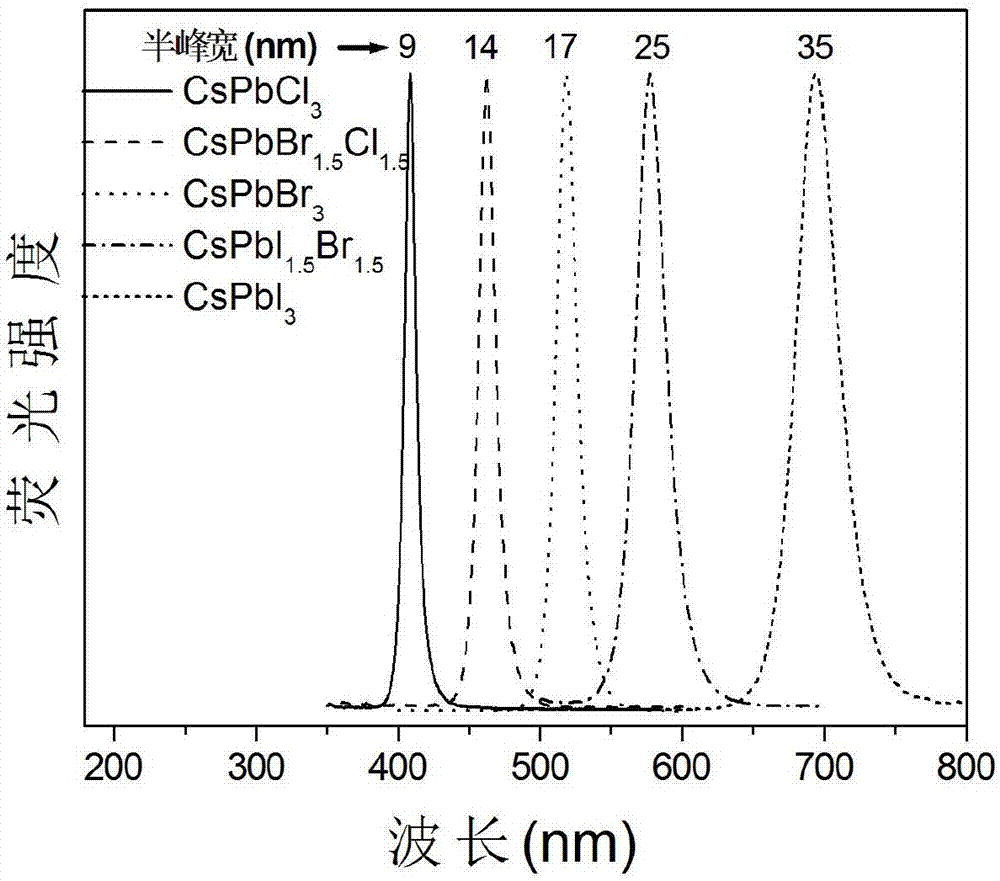
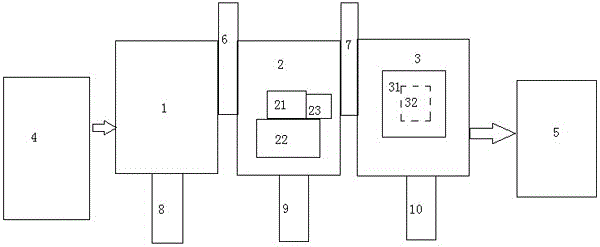
Single-size CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystalline preparation method
InactiveCN105523581AEasy to adjust sizeEasy to operateLead compounds preparationLead halidesCarboxylic saltLead chloride
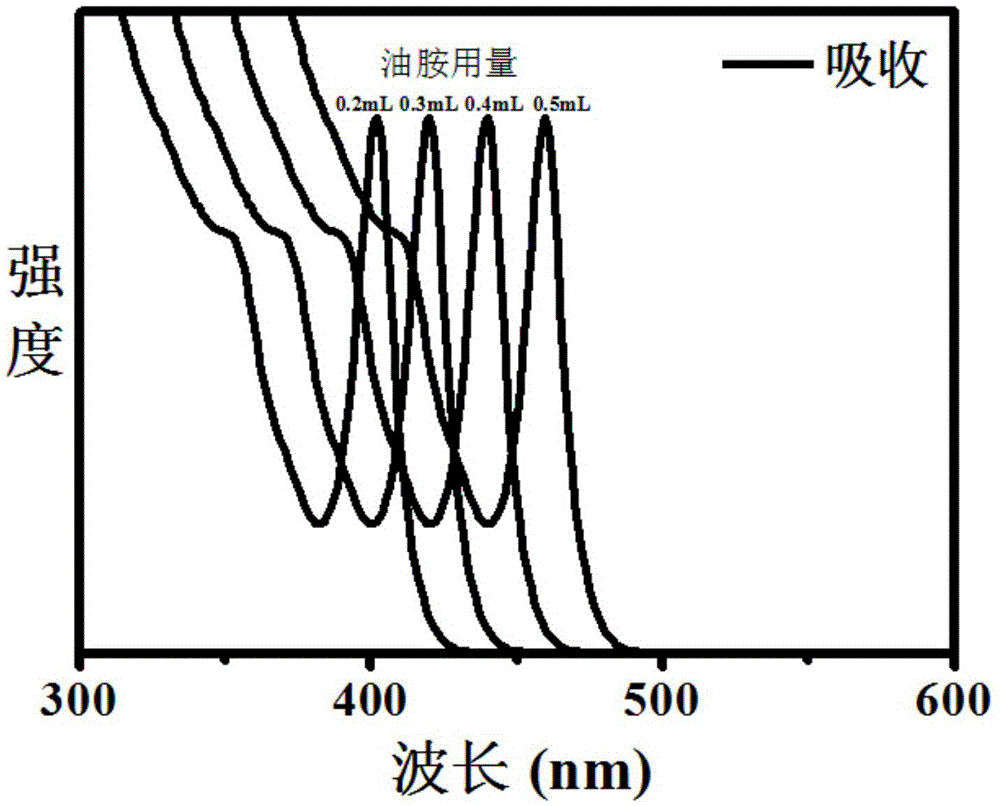
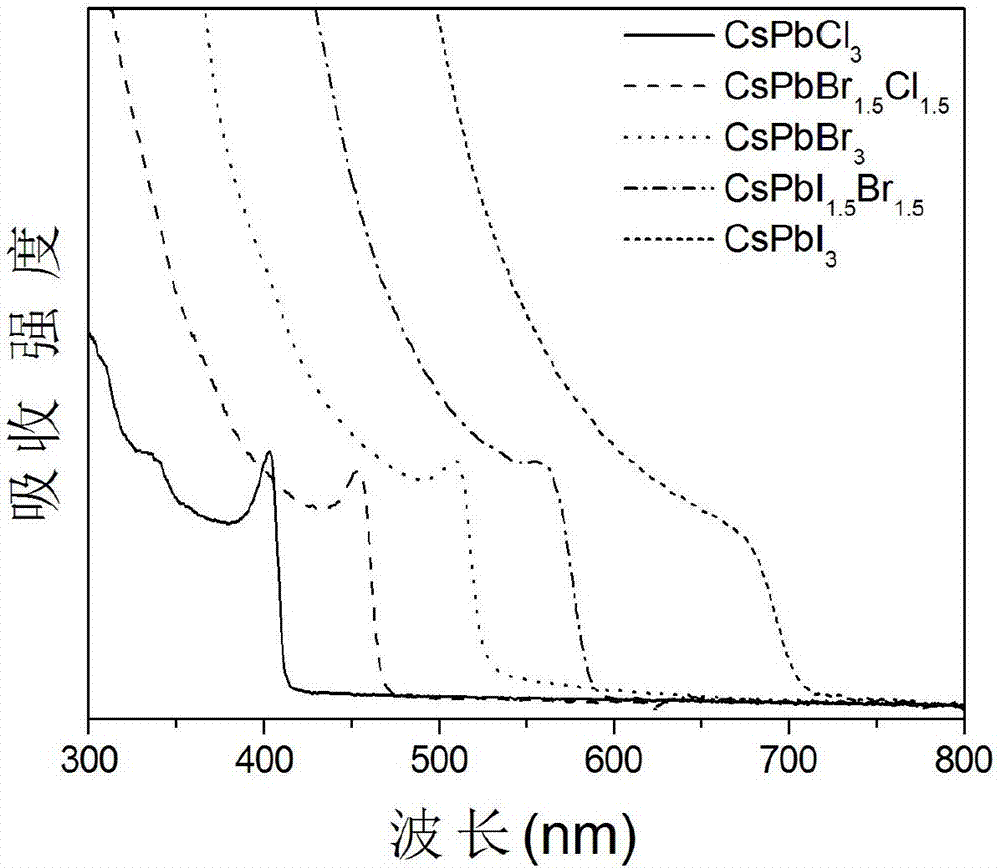
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of semiconductor nanomaterials and discloses a single-size CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystalline preparation method. The method includes: adding cesium carboxylate solution into N2 protected lead bromide solution to realize reaction for obtaining single-size CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystalline; scattering the single-size CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystalline into normal hexane, and gradually adding lead chloride solution or lead iodide solution drop by drop to realize reaction for obtaining single-size CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystalline. The single-size CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystalline preparation method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, easiness in size adjustment of products, component controllability and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Preparation method of perovskite quantum dots
InactiveCN107500345AGuaranteed stabilityGuaranteed fluorescence quantum efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceComputational chemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of perovskite quantum dots. The preparation method comprises steps as follows: A), Cs2CO3, oleic acid and octadecene are mixed and subjected to a heating reaction under the condition of protective atmosphere, and a cesium oleate precursor solution is obtained; B), lead halide and octadecene are mixed and subjected to heating and heat preservation under the condition of protective atmosphere, after an oleic acid and oleylamine mixed solution is added and heated to 170-190 DEG C, an obtained mixed solution is mixed and reacts with the cesium oleate precursor solution, and the perovskite quantum dots are obtained, wherein the lead halide is selected from one or more of lead chloride, lead bromide and lead iodide. According to the preparation method, the coordination effect of surface ligands of the perovskite quantum dots of different halide ions directly synthesized at a higher temperature is more remarkable, so that stability and fluorescence quantum efficiency of the synthesized perovskite quantum dots are both guaranteed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
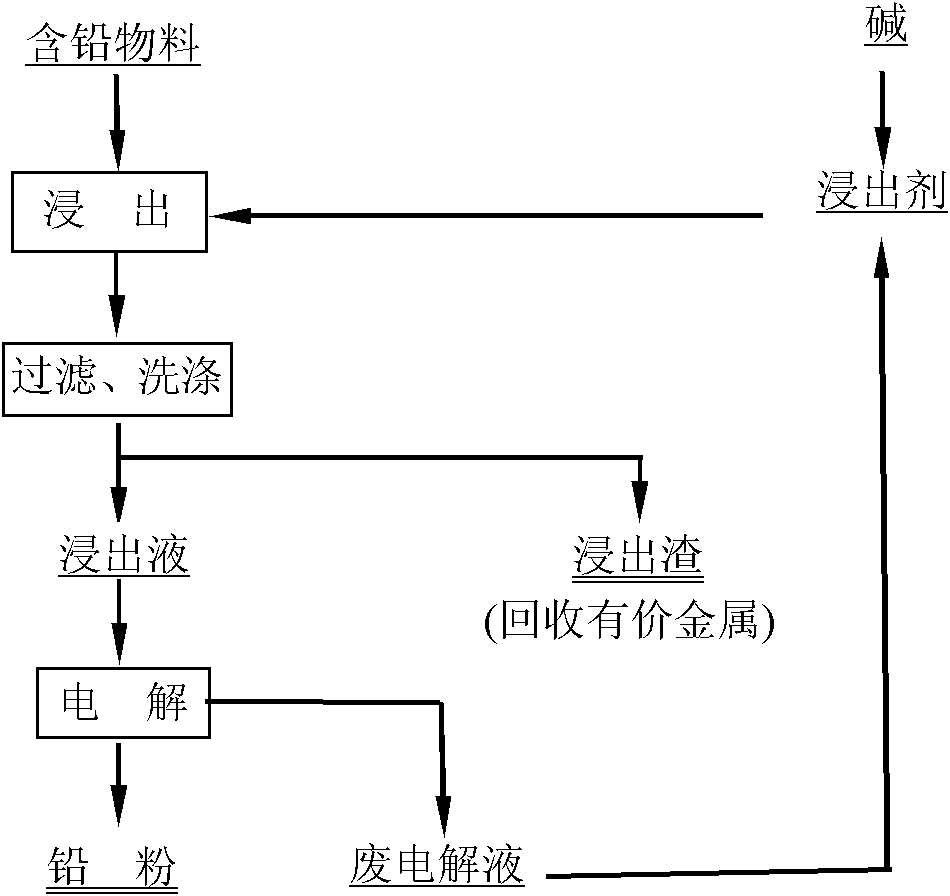
Method for recovering lead from lead-containing material by matching leaching-electrowinning method
InactiveCN102206750AEasy to separateImprove the efficiency of follow-up operationsPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSlagLead sulfate
The invention discloses a method for recovering lead from a lead-containing material by matching a leaching-electrowinning method. The method comprises the following steps of: selectively leaching the lead from the lead-containing material at the temperature of -95DEG C by using a mixture of 0.005-0.5M ethylenediaminotetraacetateedetate and 0.05-1.0M alkali as a leaching agent, and filtering and separating to obtain a lead-containing solution; and separating out metal lead powder from the solution by using an electrowinning method, blending electrowinning waste liquor, and returning to the leaching step. By leaching lead from secondary zinc oxide soot, the grade of zinc in secondary zinc oxide and the leaching rate of subsequent leaching can be improved, and subsequent treatment is facilitated; and by leaching lead from low-grade lead slag containing lead oxide, lead sulfate or lead chloride, the leached sewage in the slag piling process never contains lead or contains little lead, environment is not affected, the waste is changed into treasure, and the lead can be recovered from the lead slag. The method has the advantages of simple flow, simple operation, low energy consumption and the like, and can be widely used for treating lead-containing secondary zinc oxide materials and low-grade lead slag.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
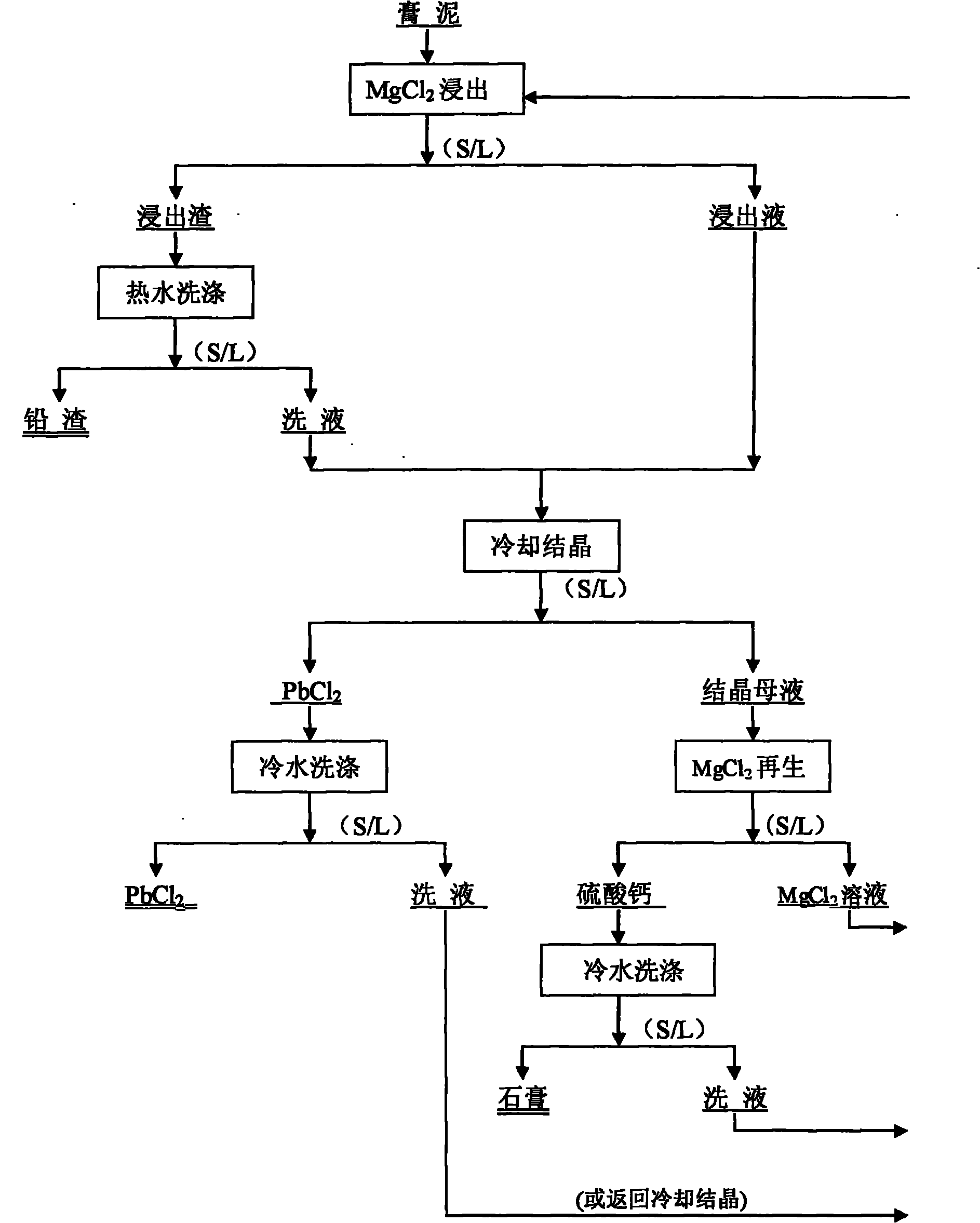
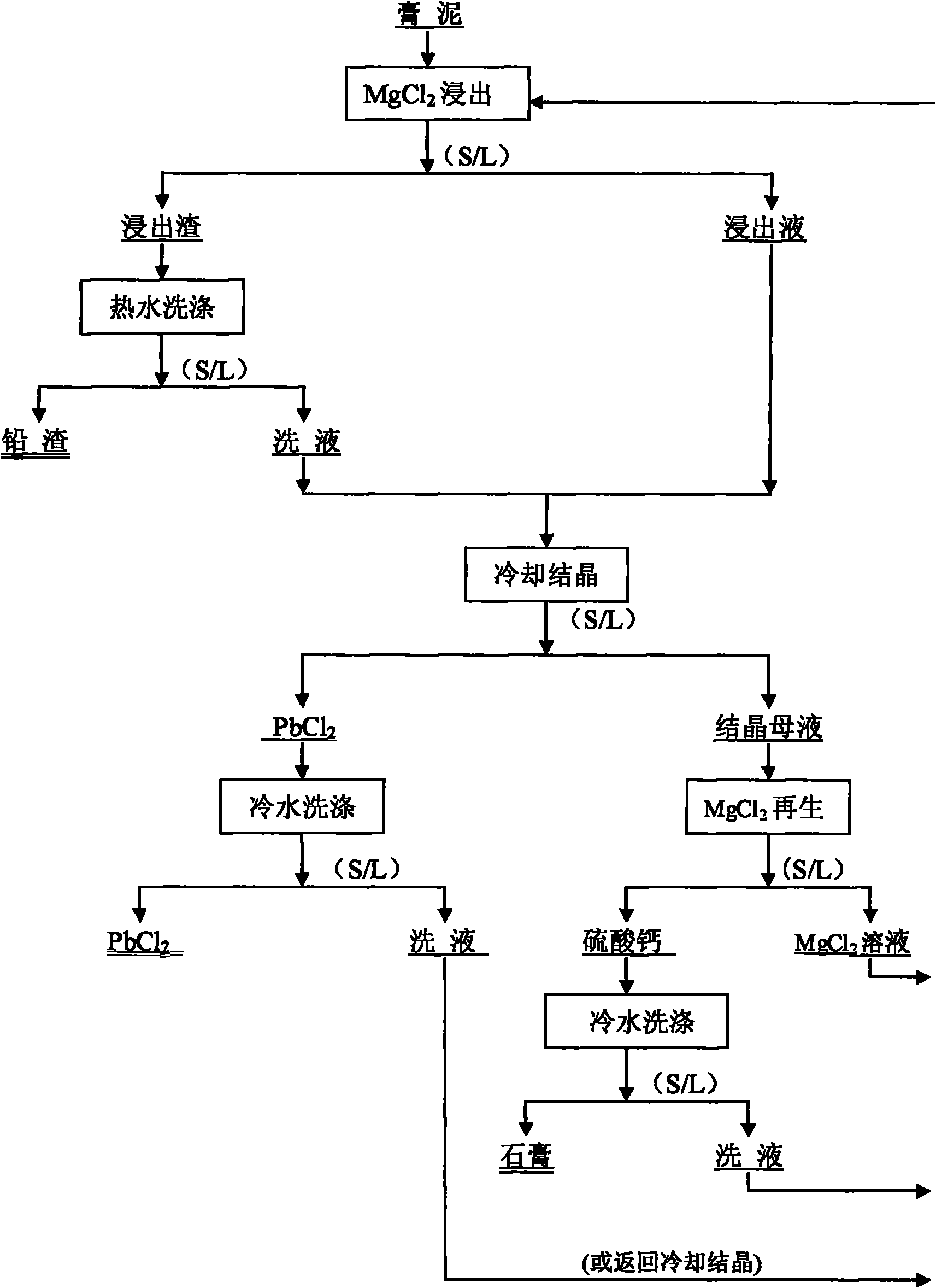
Method for removing sulfur from waste lead-acid storage battery gypsum mud by using magnesium chloride
The invention relates to a method for removing sulfur from waste lead-acid storage battery gypsum mud by using magnesium chloride, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, decomposing a waste lead storage battery subjected to acid pouring to obtain the gypsum mud, and entering the next process for later treatment; then leaching the gypsum mud by using a magnesium chloride solution, converting lead sulfate in the gypsum mud into lead chloride entering into the solution, leaving other oxides of lead in leached slag, carrying out liquid-solid separation after leaching is ended, and smelting the leached slag at the low temperature to produce wet lead; cooling to crystallize a leachate to obtain solid lead chloride and crystallized mother liquor, smelting the solid lead chloride at low temperature to produce the wet lead, carrying out regeneration treatment on the crystallized mother liquor by using the crystallized mother liquor and then returning to the step of desulfurizing and leaching the gypsum mud; and finally, adding calcium chloride to the crystallized mother liquor to regenerate the magnesium chloride as a desulfurizing agent and simultaneously produce calcium sulfate as a byproduct. The invention has good desulfurizing effect, and the magnesium chloride as the desulfurizing agent has low price, is easy to regenerate and can be recycled. The invention does not have high requirement on production equipment, greatly reduces the production cost and has obvious advantages.
Owner:SHENYANG RES INST OF NONFERROUS METALS
Perovskite base thin film solar cell and manufacturing method thereof
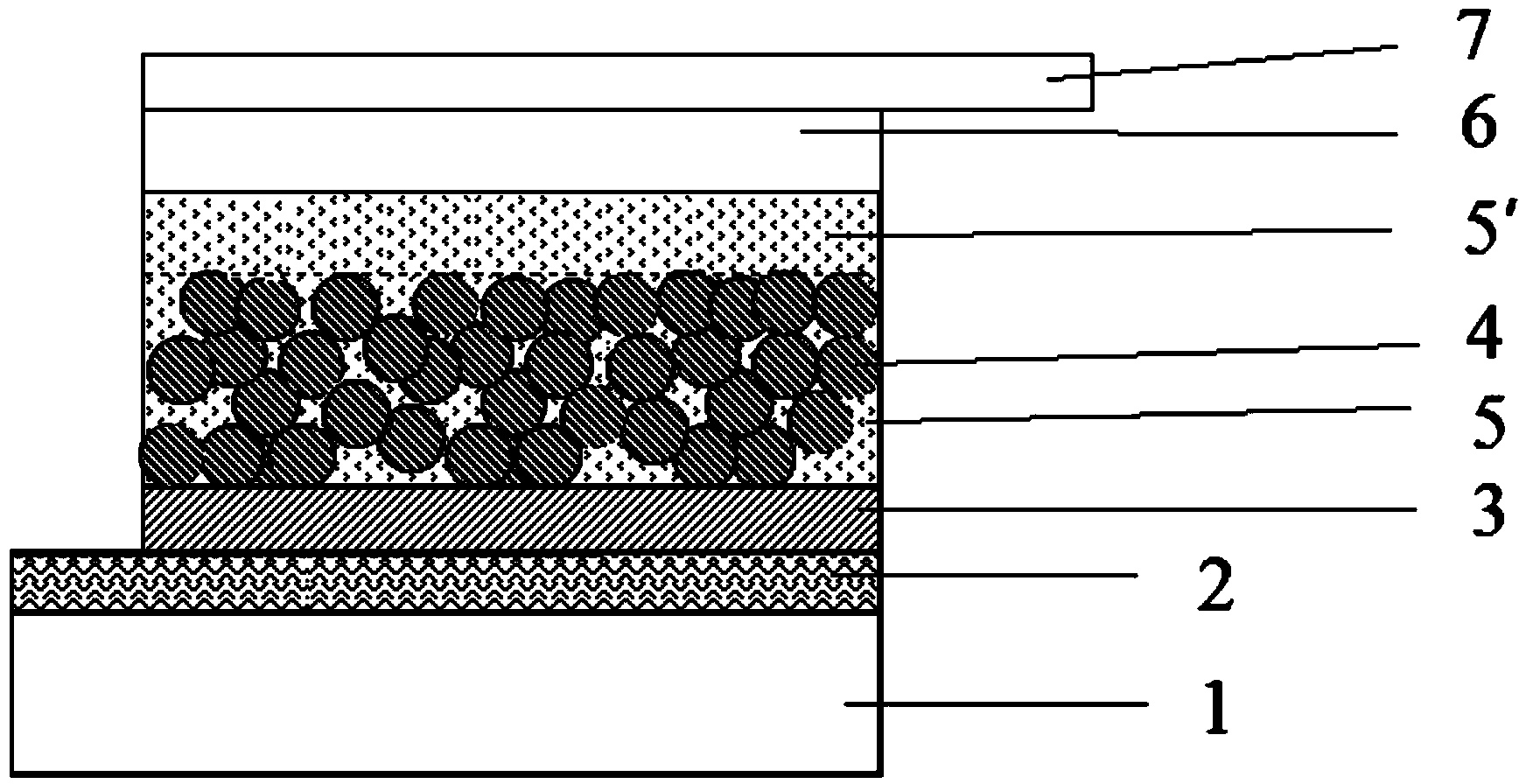
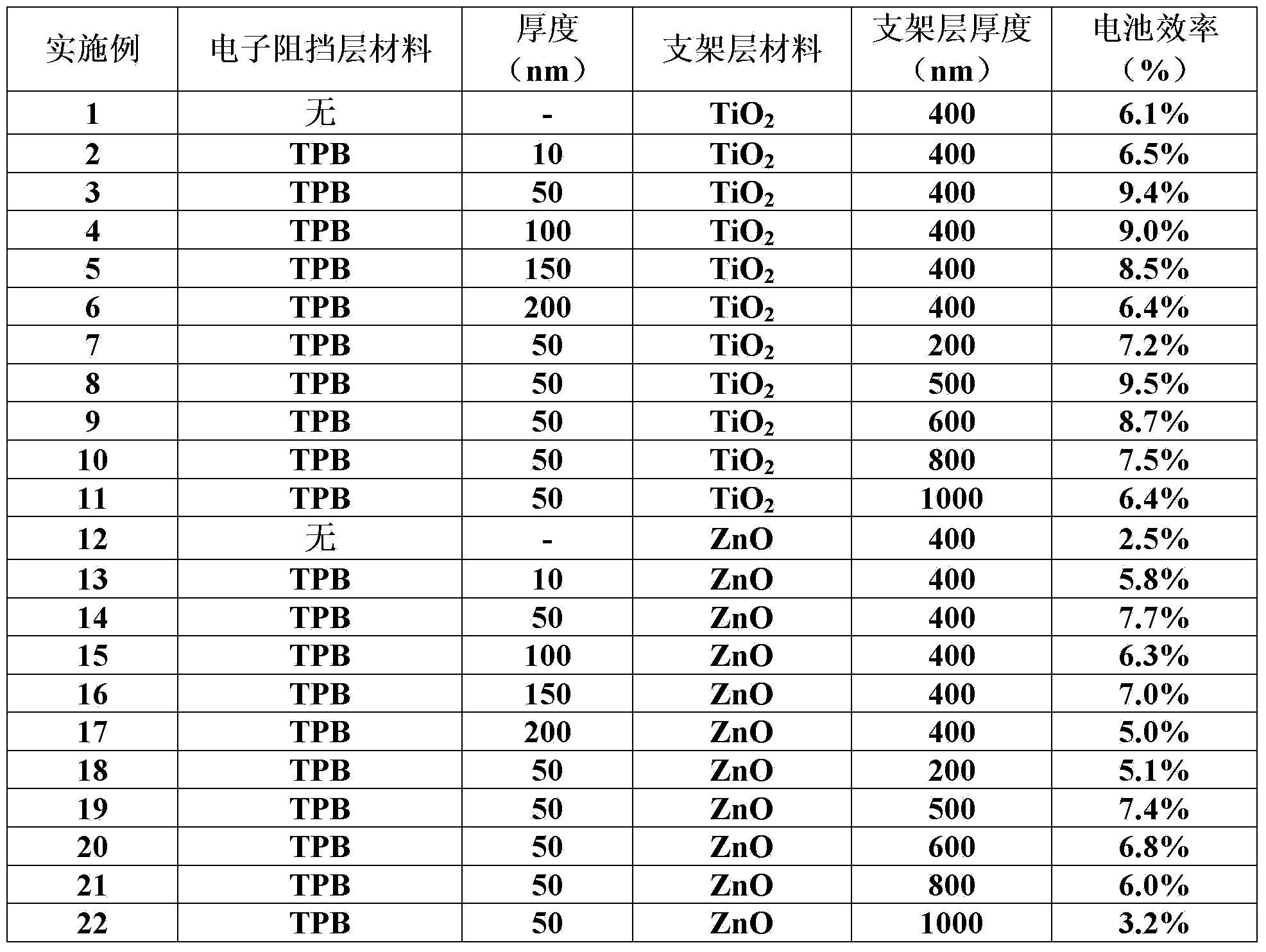
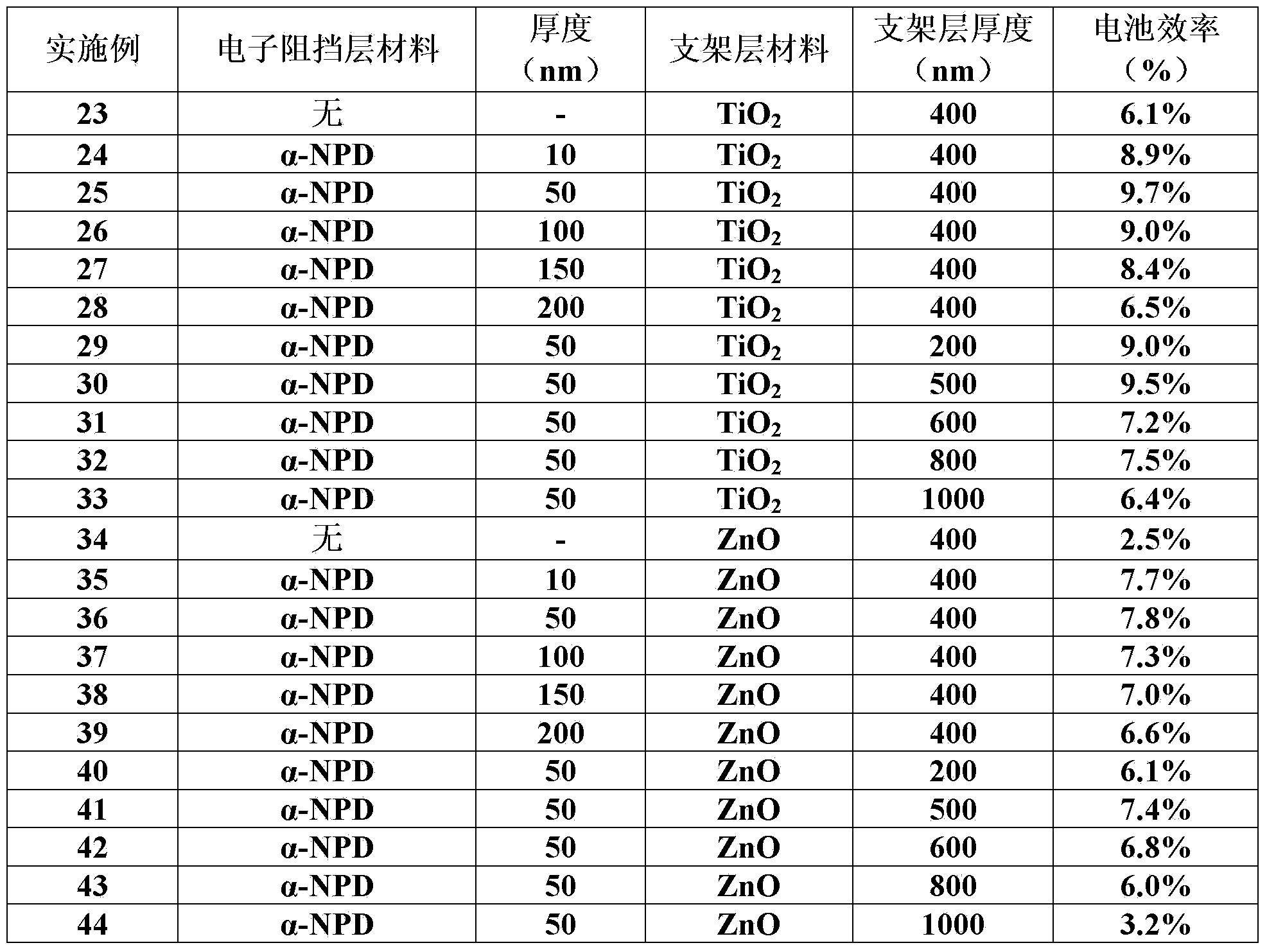
ActiveCN103762315AAvoid heavy dopingGood back contactSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOhmic contactLead chloride
The present invention provides a perovskite base thin film solar cell and a manufacturing method of the perovskite base thin film solar cell. The perovskite base thin film solar cell comprises an organic metal semiconductor light absorption layer of a perovskite structure, an electronic barrier layer formed on the organic metal semiconductor light absorption layer, and metal counter electrodes formed on the electronic barrier layer, wherein the electronic barrier layer is made of organic electronic barrier materials. According to the perovskite base thin film solar cell, ohmic contact between the counter electrodes and perovskite-type organic lead chloride materials is achieved due to the arrangement of the electronic barrier layer, good back contact can be achieved without further doping, high-difficulty heavy doping on the perovskite-type organic lead chloride materials is avoided, and the high-efficiency perovskite base thin film solar cell is obtained.
Owner:深圳市华物光能技术有限公司
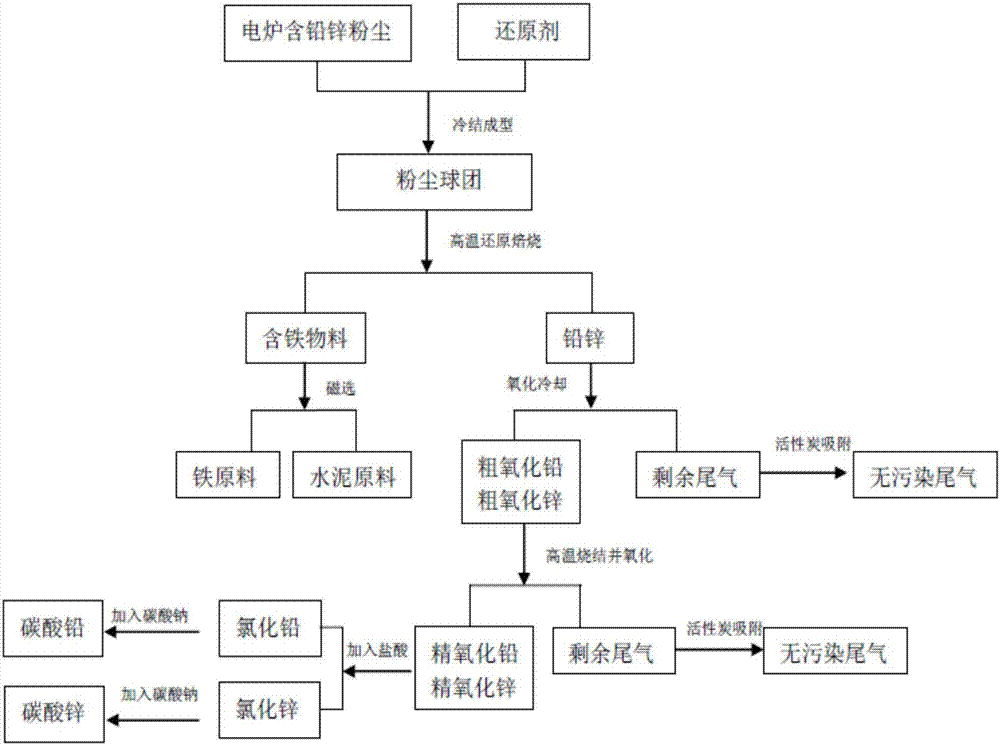
Comprehensive recycling method of electric steel making lead and zinc-contained dust
ActiveCN107460327AWide variety of sourcesLow priceRotary drum furnacesProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingCarbonate
The invention provides a comprehensive recycling method of electric steel making lead and zinc-contained dust. The comprehensive recycling method comprises the following steps: lead and zinc-contained dust is prepared as pellets for reduction roasting at high temperature; lead and zinc are reduced as simple substances for volatilization in a gas-state form; iron-contained materials are formed to molten blocks, and are separated from lead and zinc; lead and zinc-contained gas and dust are collected, and are oxidized and cooled to obtain rough oxidized lead powder and rough oxidized zinc powder; the iron-contained materials without lead and zinc are collected for quick cooling, crushing and magnetic separation to obtain iron raw materials; the rough oxidized lead powder and the rough oxidized zinc powder are put in a rotary kiln again for high-temperature sintering, and are oxidized and cooled to obtain high-purity finish oxidized lead powder and finish oxidized zinc powder; the finish oxidized lead powder and the finish oxidized zinc powder are firstly reacted with hydrochloric acid to obtain lead chloride and zinc chloride; and lead chloride and zinc chloride are reacted with sodium carbonate to finally obtain lead carbonate and zinc carbonate. The comprehensive recycling method is simple in process, high in lead and zinc recovery rate and high overall resource recycling rate.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
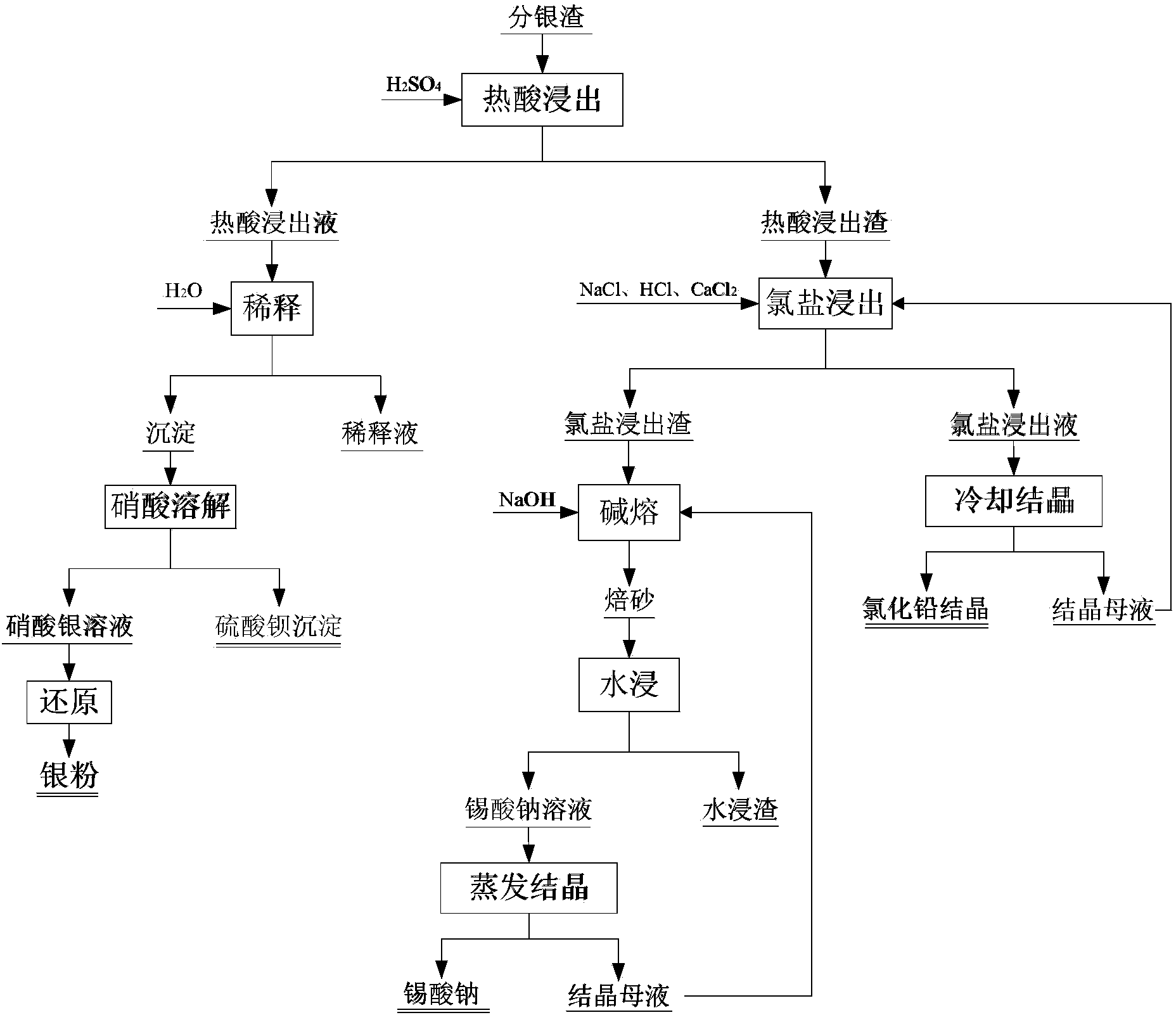
Method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from copper anode sludge silver separating slag
The invention relates to a copper anode sludge silver separating slag reutilization technique, particularly a method for comprehensively recovering valuable metals from copper anode sludge silver separating slag. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out hot acid leaching on silver separating slag, filtering to obtain a hot acid leaching solution containing silver and barium and hot acid leaching slag containing tin and lead; diluting the hot acid leaching solution with water, filtering to obtain a precipitate, dissolving the precipitate with nitric acid, and filtering to obtain a barium sulfate precipitate and a silver nitrate solution; reducing the solution to obtain silver powder; leaching the hot acid leaching slag with acidic chlorine salt, filtering to obtain a chlorine salt leaching solution and chlorine salt leaching slag; cooling the chlorine salt leaching solution to crystallize and precipitate lead chloride; and carrying out alkali fusion, water immersion and evaporation crystallization on the chlorine salt leaching slag to obtain sodium stannate. The method can effectively recover all the valuable metals with higher content in the silver separating slag, and the recovery rates of the lead, silver, tin and barium are respectively up to higher than 97%, 92%, 90% and 95%. The method has the characteristics of simple technique, no emission of three wastes, high metal recovery rate and the like, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing luminescent band gap tunable double-light emitting manganese doping perovskite nano-crystal
InactiveCN108865126ALuminous color continuous tuningHigh photoluminescence efficiencyNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsTrioctylphosphineIon exchange
The invention provides a method for preparing luminescent band gap tunable double-light emitting manganese-doping perovskite nano-crystal, and belongs to the technical field of material preparation. The method comprises: firstly mixing cesium carbonate, oleic acid, and octadecene, obtaining a cesium oleate precursor solution; mixing lead bromide, oleylamine, oleic acid and octadecene, obtaining alead bromide precursor solution; mixing lead chloride, manganese chloride, and octadecene, obtaining a first mixed solution; adding oleylamine, oleic acid, and tri-n-octylphosphine to the first mixedsolution, obtaining a second mixed solution; adding the cesium oleate precursor solution to the second mixed solution, to obtain Mn:CsPbCl3 nano-crystal solution; injecting the lead bromide precursorsolution to the Mn:CsPbCl3 nano-crystal solution, and stirring, preparing Mn:CsPbCl3-xBrx nano-crystals, wherein X is greater than 0 but less than 3. By adopting the method provided by the invention,the luminescent band gap of the manganese-doping perovskite nanocrystals and continuous tuning of the corresponding illuminating color are realized through anion exchange.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
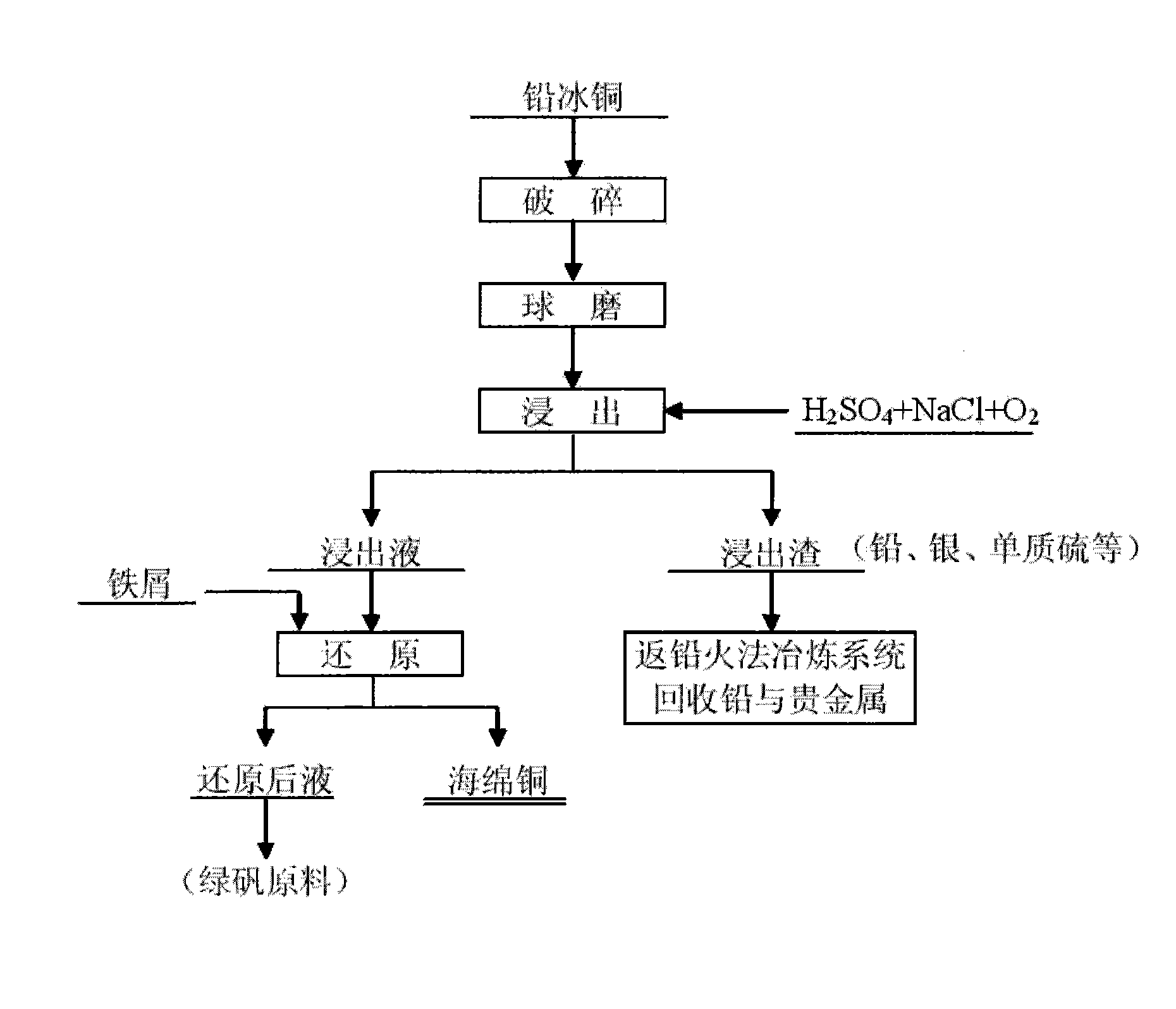
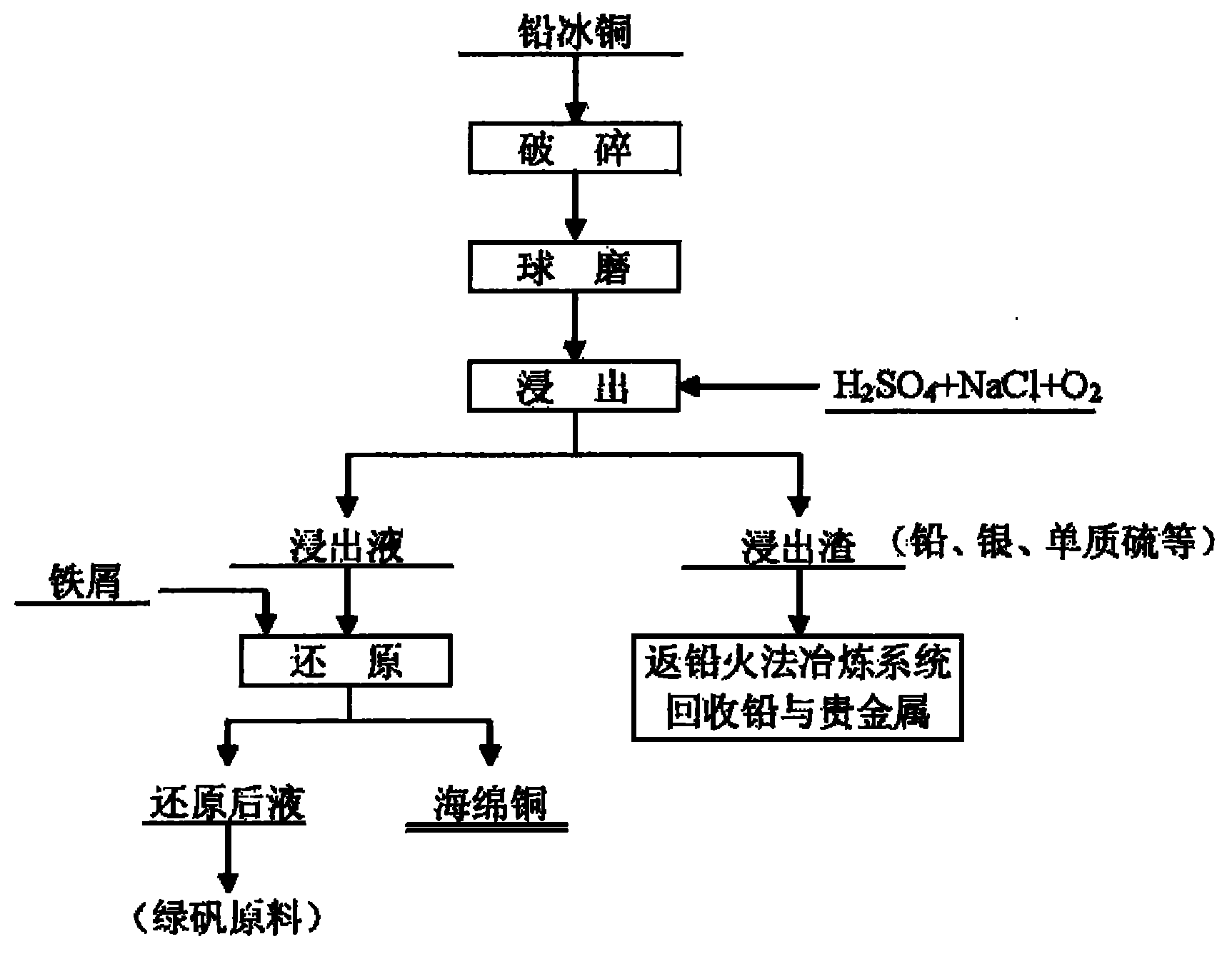
Wet process for treating lead copper matte
The invention relates to a wet process for treating lead copper matte, and belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal hydro-metallurgy. In the process, the lead copper matte is treated by a normal-pressure leaching wet process; and the lead copper matte is leached by sulfuric acid and sodium oxide, and oxygen is continuously introduced in the leaching process, wherein copper is leached, and the lead in forms of lead sulfate and lead chloride is retained in residue. After the leaching process is finished, liquid-solid separation is carried out and primary separation of metals is implemented; copper-containing leachate is reduced by scrap iron to form copper sponge, and solution after reduction serves as a raw material for recycling iron; and the leaching residue returns to a lead pyrometallurgy system, and valuable elements such as lead, silver, simple sulfur substance and the like are recycled. In the wet process, solution is not discharged, the environment is protected, and the wet process belongs to clean metallurgy; the process is simple and practicable, and is convenient to operate; and the cost is low and the comprehensive recoverability is high.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Preparation method of dimension-controllable CsPbX3 perovskite nanometer crystals
InactiveCN108101102AAdjustable absorption peakEasy to adjust sizeNanotechnologyLead compoundsCarboxylic saltLead chloride
The present invention relates to a preparation method of dimension-controllable CsPbX3 perovskite nanometer crystals, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of a semiconductor nanomaterial.The method comprises: firstly, adding a cesium carboxylate solution to a lead bromide solution in N2 protection for a reaction, thereby obtaining CsPbBr3 perovskite nanometer crystal seeds; then, dispersing CsPbBr3 perovskite nanometer crystal seeds in hexane, injecting the obtained product to octadecene at different temperature to obtain CsPbBr3 perovskite nanometer crystals with different sizes; and finally, dispersing CsPbBr3 perovskite nanometer crystals in hexane, and gradually adding a lead chloride solution or a lead iodide solution drop by drop for a reaction to obtain other CsPbX3 (X=Cl, Ir) perovskite nanometer crystals. The method is simple to operate, the size of products is easy to adjust, and the components are controllable.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
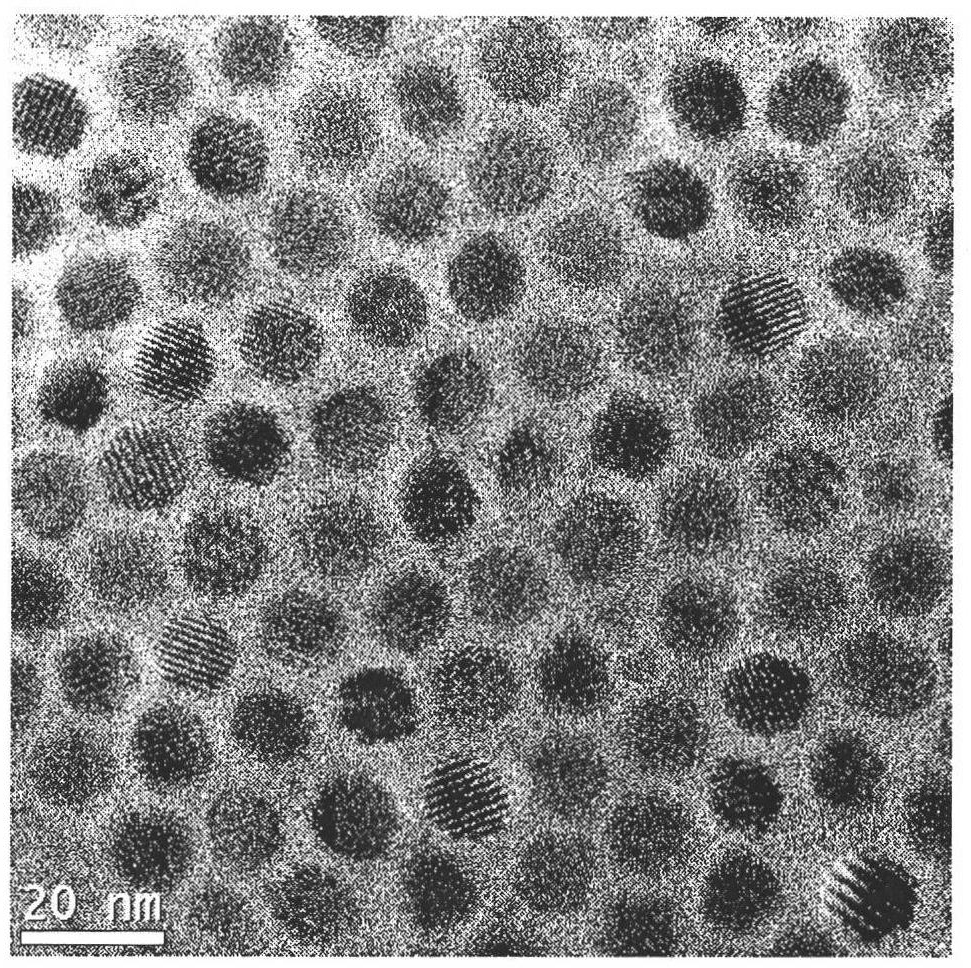
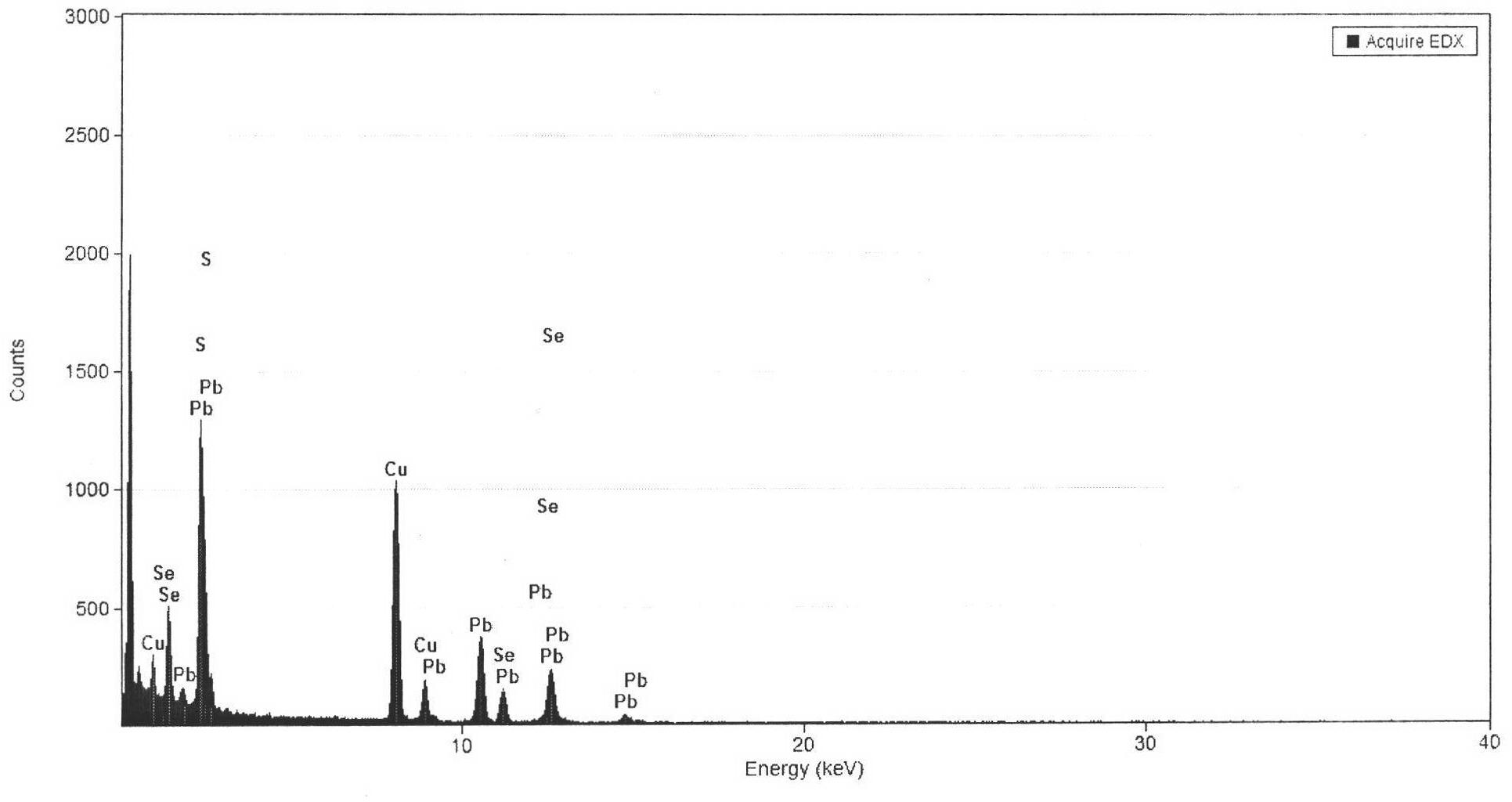
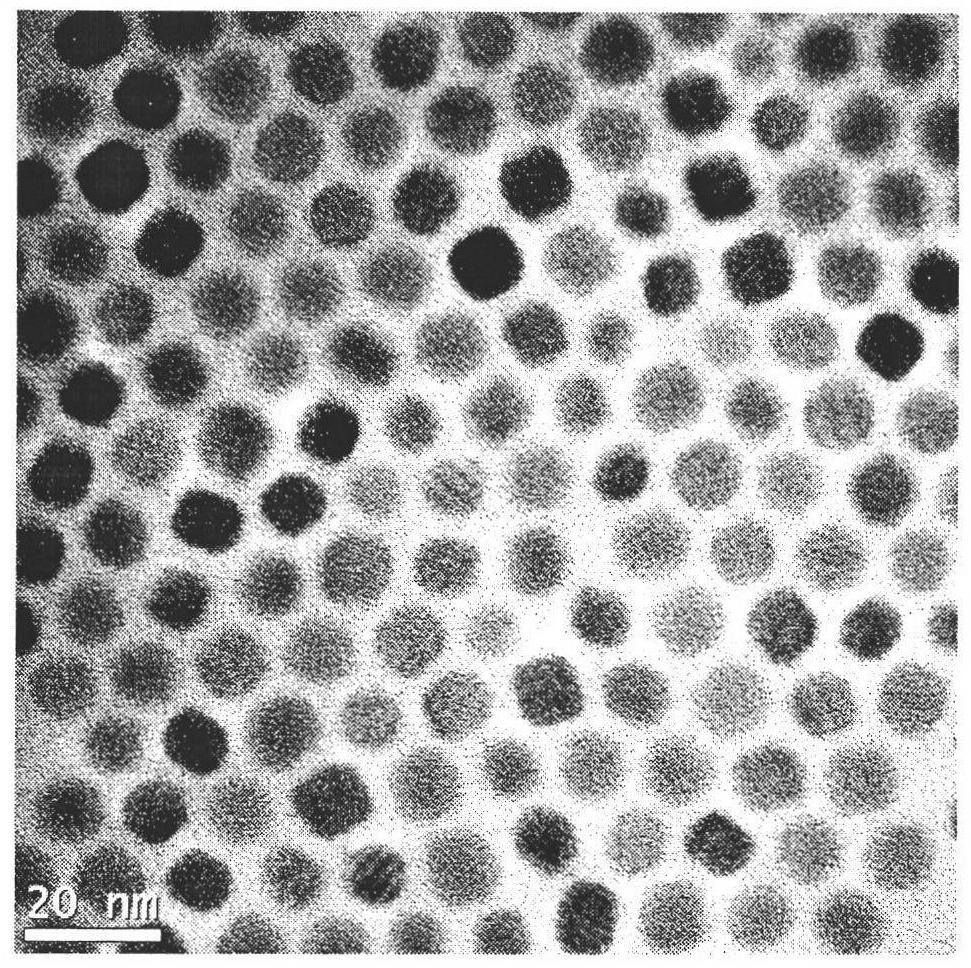
Preparation method of PbSxSe1-x ternary nanocrystal
InactiveCN102633239ASimple methodEasy to operateSelenium/tellurium compundsEnergy inputEthyl ChlorideEthanol
The invention discloses a preparation method of PbSxSe1-x ternary nanocrystal. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: mixing selenium powder and sulfur powder according to a certain proportion, slowly adding alkylamine which has long chain and has boiling point more than 180 DEG C, sufficiently stirring, heating (the selenium powder and the sulfur powder) amine mixed liquor into 180-260 DEG C, forming into settled solution at constant temperature, and adding the alkylamine which is dissolved with lead chloride and has the long chain and the boiling point more than 180 DEG C, so that a system is naturally cooled into room temperature after being sufficiently reacted, adding 10mL of chloroform into the system, and adding ethanol of which the volume is twice as high as the volume of the reaction solution into the reaction system, so that PbSxSe1-x ternary nanocrystal particle precipitate is separated out, therefore, the PbSxSe1-x ternary nanocrystal particle can be obtained.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
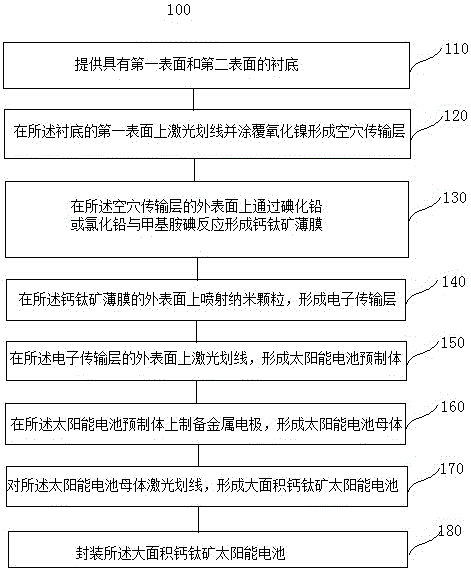
Manufacturing method and system of large-area perovskite solar cell
ActiveCN106252460AImprove uniformityIncrease speedFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionEngineering
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a large-area perovskite solar cell. The method comprises the steps of making a line on FTO glasses by laser, preparing a cavity transmission layer, preparing lead iodide or lead chloride in a first evaporating chamber, preparing methyl amine iodine in a second evaporating chamber, forming a perovskite film through reaction, preparing an electronic transmission layer by a spray method, making a line P2 by laser, preparing a metal electrode, and making a line P3 by laser to form a large-area perovskite component. The invention also provides a manufacturing system of a large-area perovskite solar cell. The system comprises a sample introduction chamber, the first evaporating chamber, the second evaporating chamber, a cavity transmission layer preparation room, and a metal electrode preparation room. The large-area uniformity and preparation rate of the perovskite solar cell can be greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
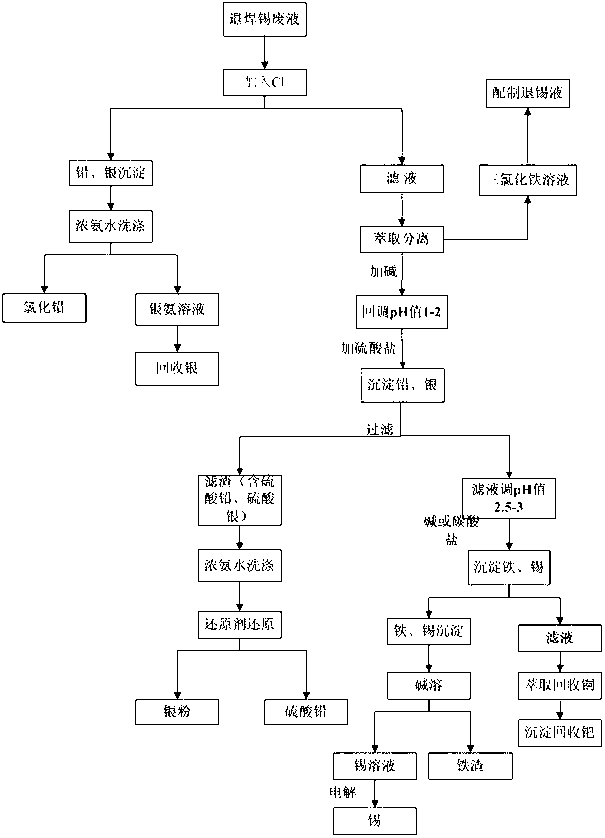
Processing method for waste liquid from stripping tin scolding
ActiveCN103031437AReduce wasteReduce pollutionLead halidesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater chlorinationLead(II) sulfate
The invention provides a processing method for waste liquid from stripping tin scolding, which comprises the following steps: in the waste liquid from stripping tin scolding, adding a chlorate for reacting, then filtering the solution, washing the filter residue by a concentrated ammonia liquor for dissolving the silver chloride sediment, recovering silver by a washing lotion to acquire pure lead chloride, extracting a filtrate by an extractant to obtain ferric iron, wherein a strip liquor is a ferric trichloride solution which can be prepared to a tin stripping liquid, adding sulfate for depositing lead and silver, wherein the reacted filter residue is a mixed sediment of lead sulphate and silver sulfate, washing by the concentrated ammonia liquor, reducing to obtain a silver powder and lead sulphate; filtering and depositing lead and silver, depositing tin and iron, filtering to obtain the sediment and dissolving by alkali, and then electrolyzing to obtain tin, electrolyzing the residual filtrate to recovery copper, and depositing palladium in the solution to obtain the sediment for recovering palladium. The processing method has reasonable and useful process flow, and performs comprehensive recovery and utilization on valuable metal in the waste liquid from stripping tin scolding, the resource waste is reduced, and the environmental pollution is reduced.
Owner:JIANGXI GREEN ECO MFG RESOURCE CYCLE
Preparation method of cathode and anode-modified perovskite solar cell
InactiveCN105489769ASpeed up extractionIncrease currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterials processingChemistry
The invention provides a preparation method of a cathode and anode-modified perovskite solar cell. The method comprises the following preparation steps: dissolving methyl ammonium iodide and lead chloride into dimethyl formamide to prepare a perovskite precursor solution; dissolving metal nano-particles into ethanol, mutually dissolving with PEDOT:PSS, carrying out processing on a substrate and then carrying out annealing to obtain a cured anode modifying layer; processing the perovskite precursor solution on the anode modifying layer, and then carrying out annealing to obtain a curved photosensitive layer; processing [6,6]-phenyl-C61-methyl butyrate on the photosensitive layer to obtain an electron transport layer; processing an organic material on the electron transport layer to obtain a cathode modifying layer; and processing a cathode electrode on the cathode modifying layer to obtain the cathode and anode-modified perovskite solar cell. The prepared cathode and anode-modified perovskite solar cell is high in energy conversion efficiency and good in photovoltaic characteristics.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Preparation method for processing wastewater adsorbing material containing lead
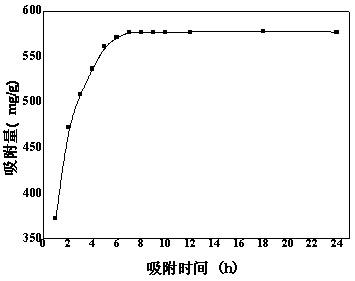
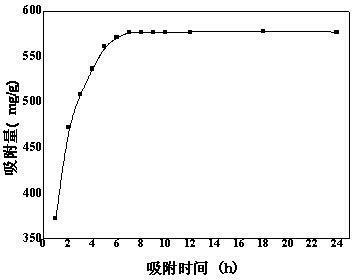
InactiveCN102688751AIncrease the areaHigh porosityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCrosslinked chitosanSpinning
The invention belongs to the field of high polymer material and environmental protection technology, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a lead ion imprinting crosslinking chitosan nanofiber adsorbing material applied to the wastewater containing lead. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing spinning solution by mixing the solution of chitosan and lead chloride and the solution of trifluoroacetic acid and dichloromethane according to a certain proportion; preparing the chitosan nanofiber adsorbing material by using an electrospinning process;and removing chelate ions by crosslinking agent crosslinking and solution washing treatments to obtain the lead ion imprinting crosslinking chitosan nanofiber adsorbing material. Lead ion adsorption experiments show that the adsorption amount of the adsorbing material for lead ions in the wastewater containing lead can reach 500-700mg / g, and the adsorption amount is far better than that of the traditional adsorbing material; and the preparation method of the absorbing material is simple and practical and has good promotional value.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for recovering tin, antimony and lead and enriching indium from tin residue
InactiveCN101660053ASolve the problem of comprehensive collection and recyclingAvoid circulation lossProcess efficiency improvementIndiumArsenic oxide
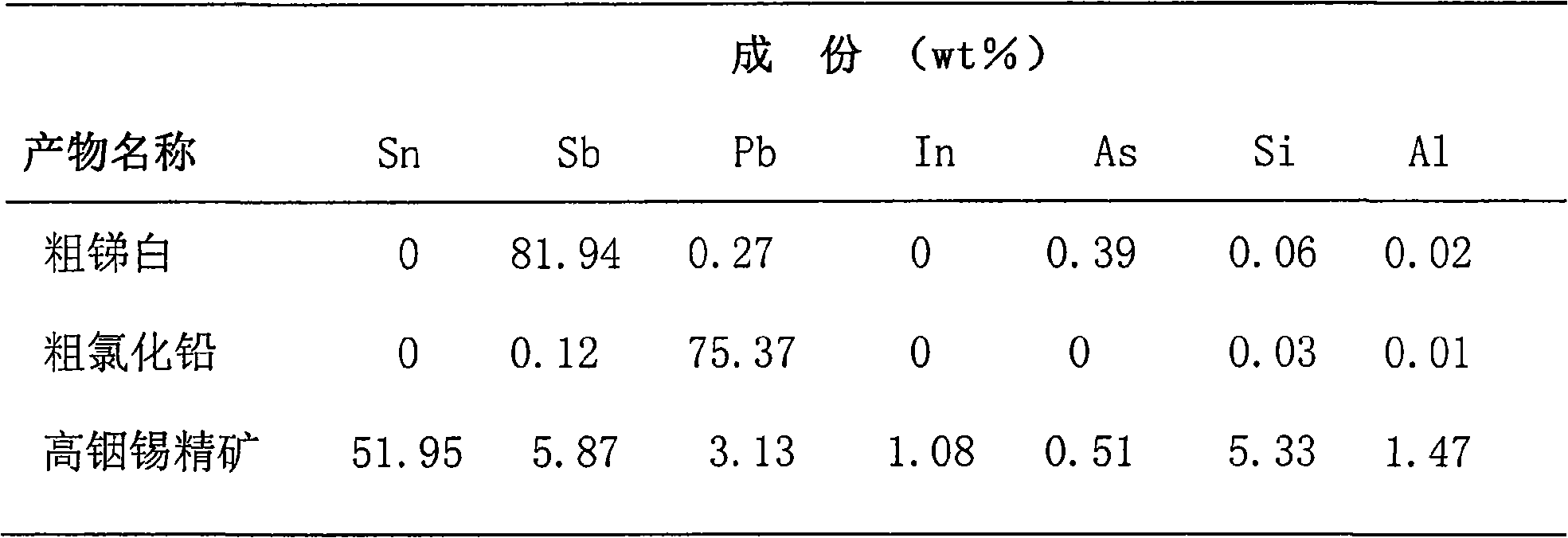
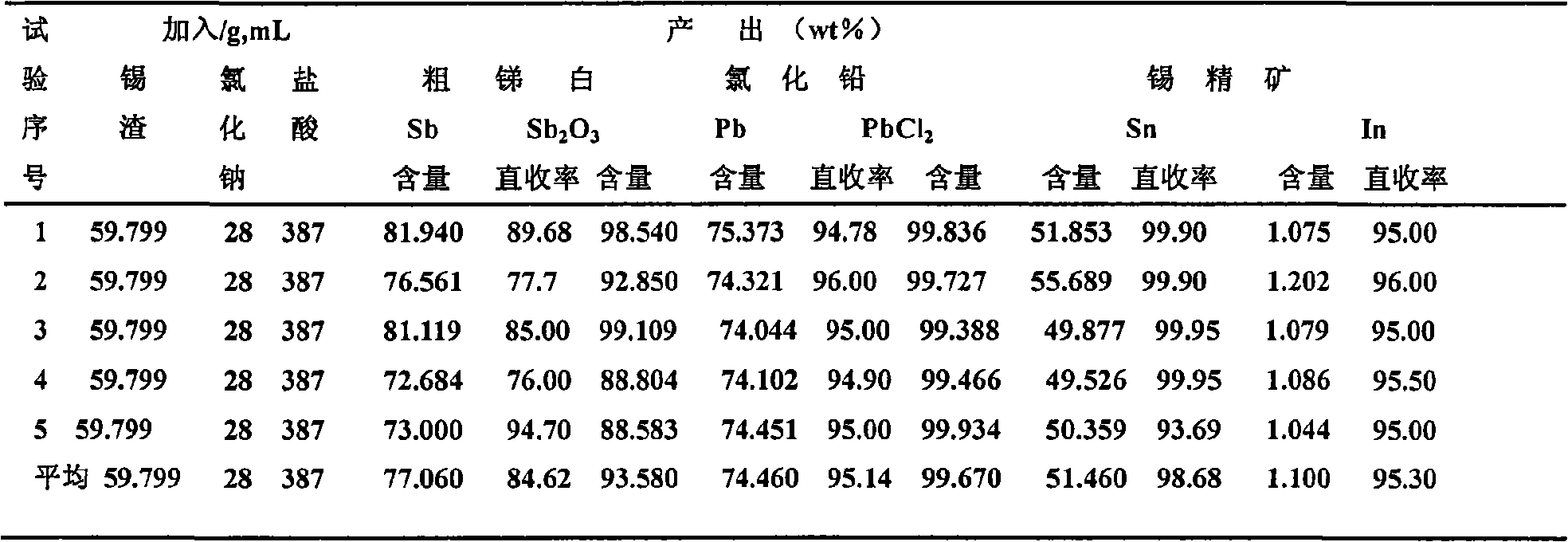
The invention relates to a method for recovering tin, antimony and lead and enriching indium from tin residue, which comprises the following steps: tin residue powder containing tin, antimony, lead, indium and arsenic oxide uses mixed liquor of hydrochloric acid, sodium chloride and hydrazine hydrate as a leaching agent, carries out electric potential control and two step countercurrent to recoverleached antimony, one-step leaching agent is neutralized and hydrolyzed to output crude antimony oxide, lead can be leached by sodium chloride solution in two-step leaching residue; after lead is leached, the liquor is cooled and crystallized to obtain lead chloride; after lead is leached, sodium is washed out in residue to obtain high indium tin concentrate containing 49.52-55.69wt% of tin and 1.04-1.2wt% of indium. The purities of crude antimony oxide and crude lead chloride are respectively 93.58wt% and 99.67wt%; the recovery efficiencies of tin, antimony, lead and indium respectively reach up to 98.68wt%, 84.616wt%, 95.136wt%, and 95.3wt%. The method has the advantages of short flow, good separation effect and good working conditions.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
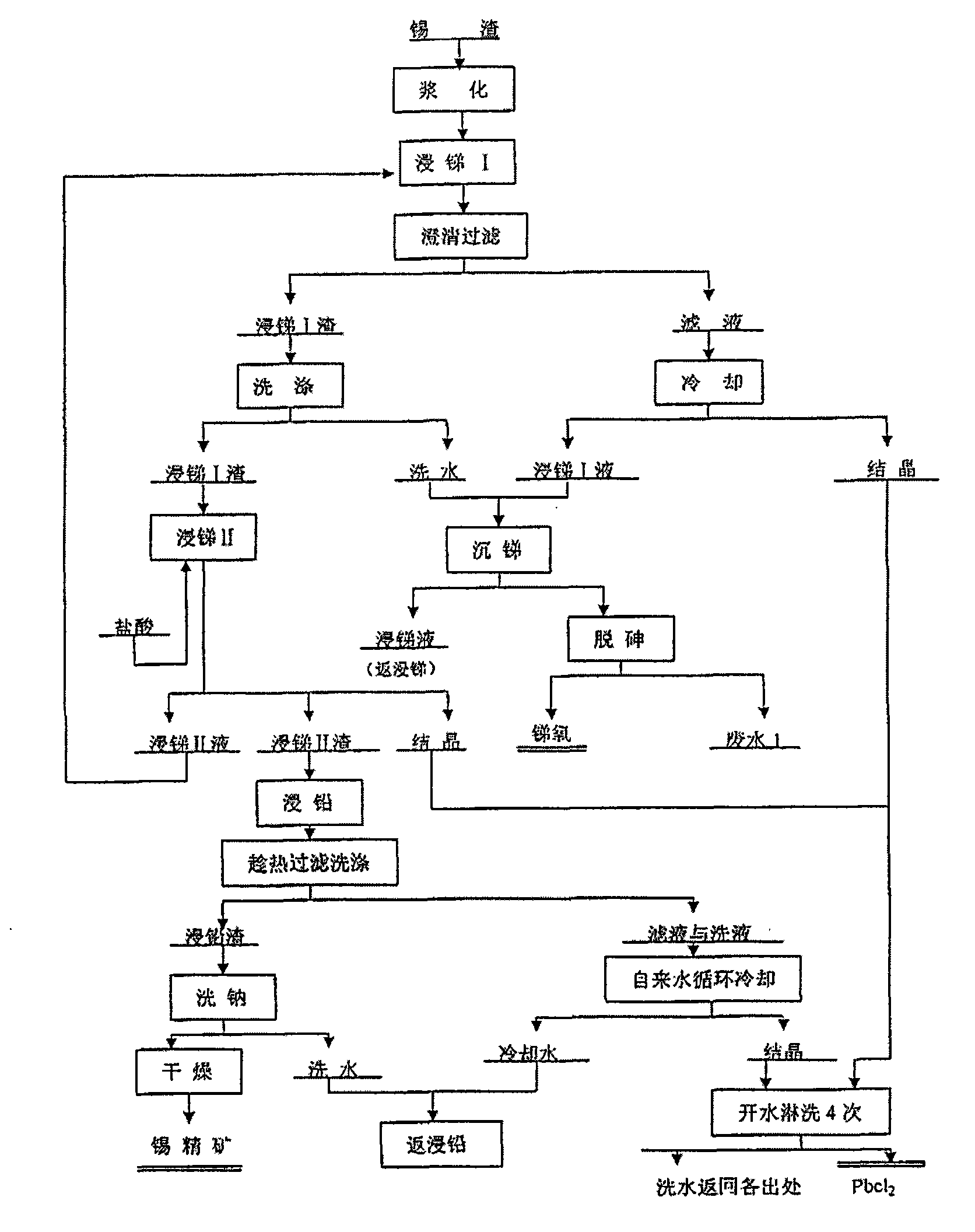
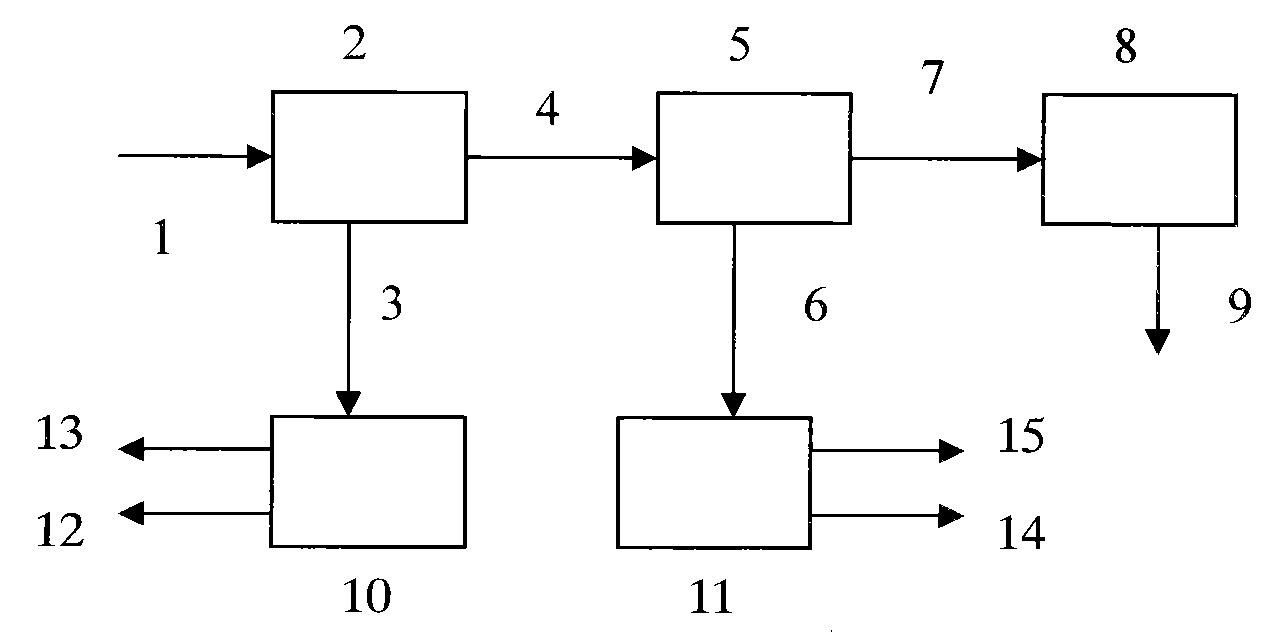
Method for recovering lead chloride from sintered ashes and preparing lead monoxide
ActiveCN101723439AExtended service lifeReduce the shutdown rateLead monoxideLead halidesLead chlorideSlurry
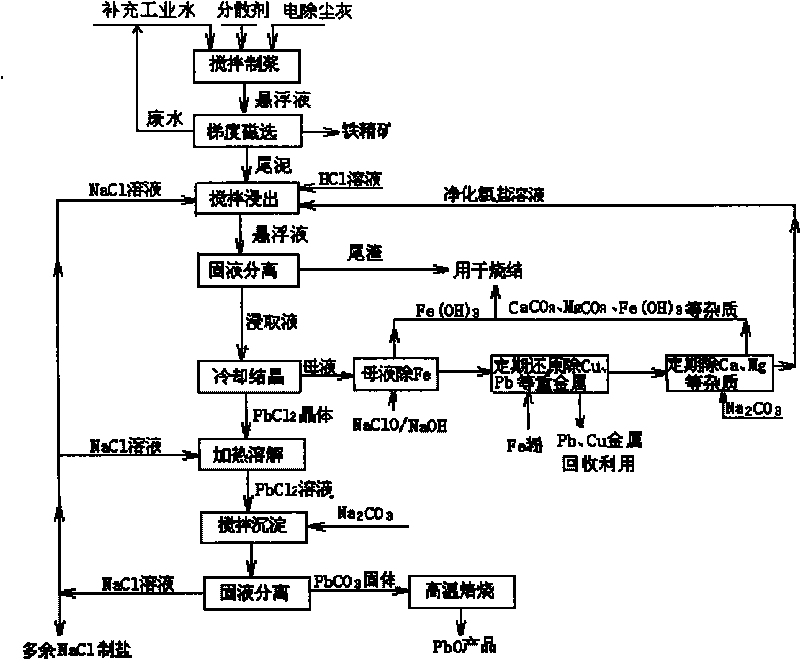
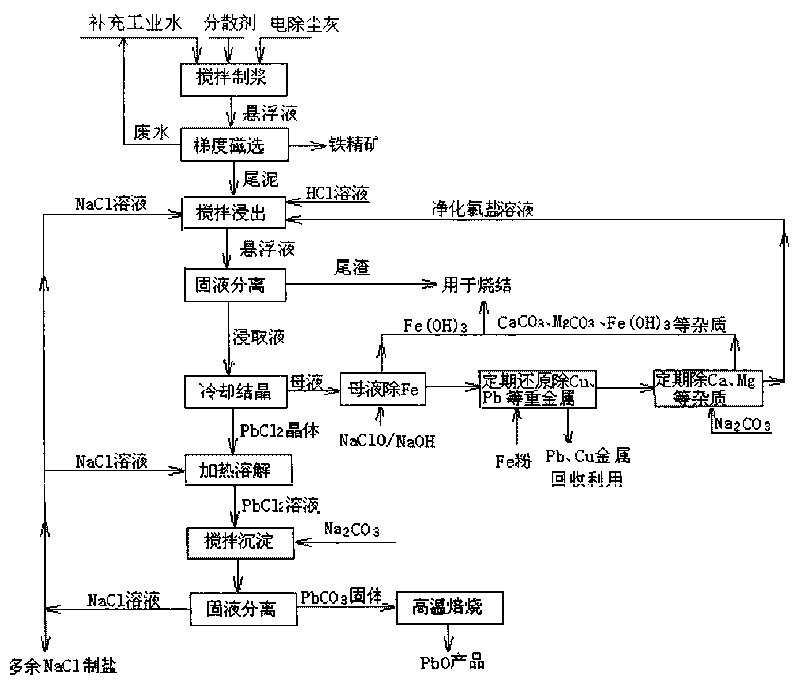
The invention discloses a method for recovering lead chloride from sintered ashes and preparing lead monoxide, which mainly comprises the following steps of: (A) adding the sintered ashes into industrial water while stirring to prepare into suspension slurry, and carrying out two-stage gradient magnetic concentration consisting of a weak magnetic concentration and strong magnetic concentration on the suspension slurry of the sintered ashes; (B) adding tail mud obtained from the magnetic concentration in to a NaCl solution, and recovering lead in the tail mud by adopting a chlorination extraction mode of hydrochloric acid and NaCl; and (C) dissolving PbCl2 crystal in a NaCl water solution, adding Na2CO3 into the solution for complete precipitation reaction, centrifugally filtering and washing the suspension solution, and drying and roasting the obtained solid to obtain a lead monoxide produce. The invention can not only completely remove corrosion and damages of elements of lead, copper and the like on a blast furnace when the sintered ashes are directly recycled during iron and steel melting, but also recover and comprehensively utilize the valuable elements.
Owner:HUNAN VALIN XIANGTAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
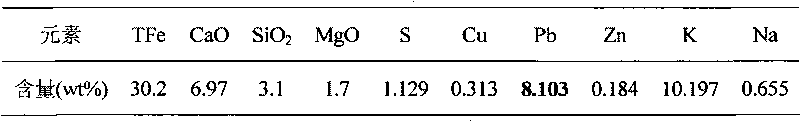
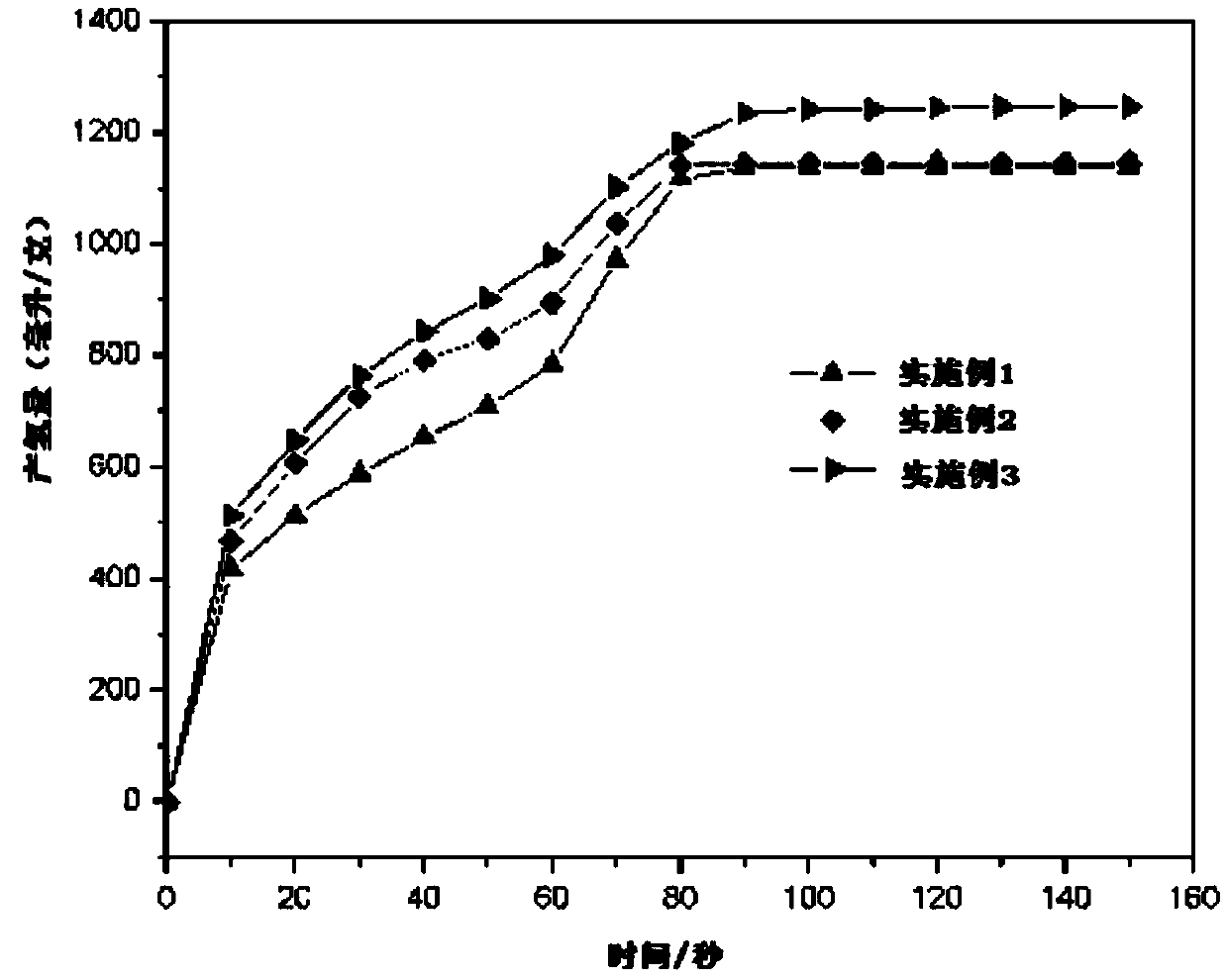
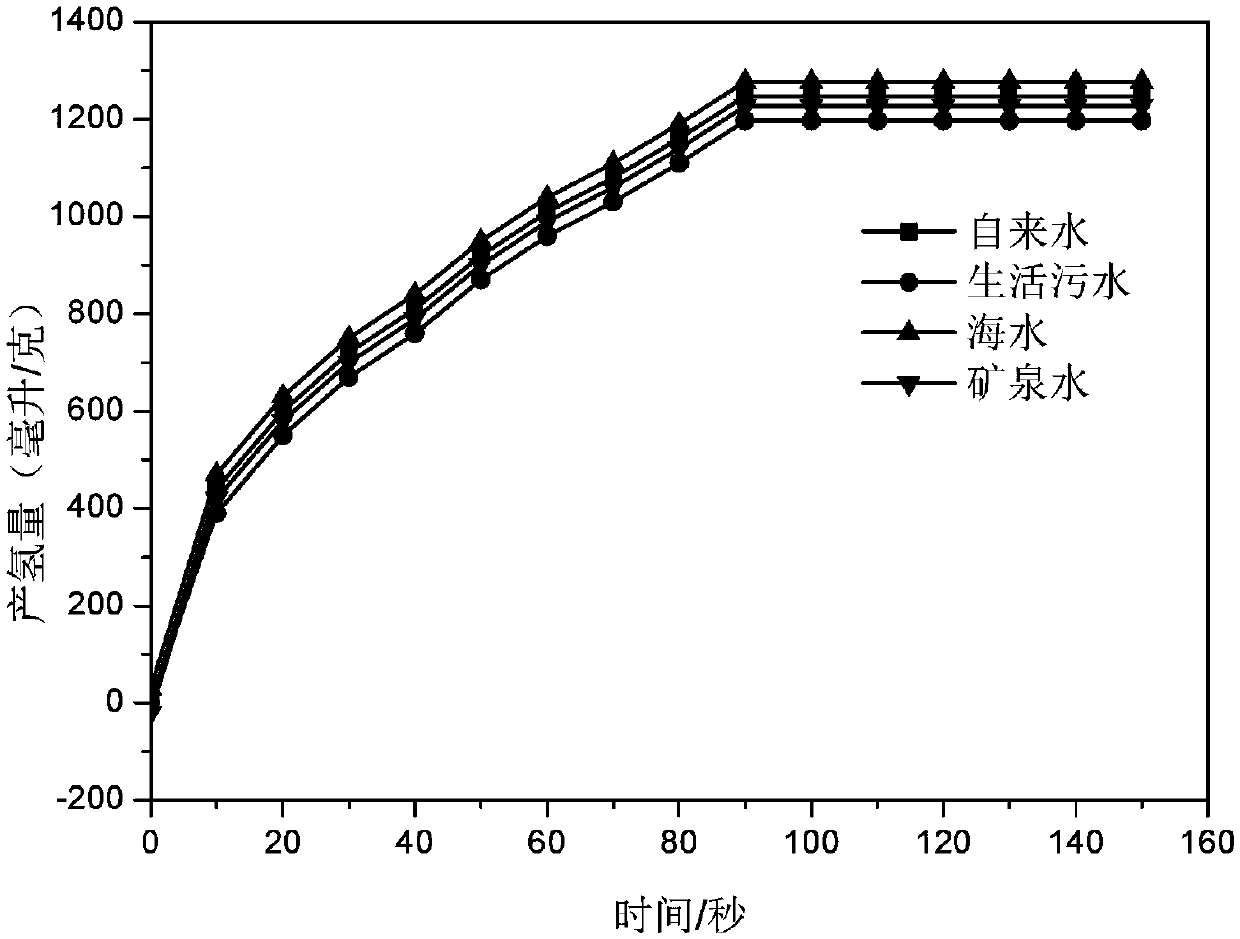
Hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy, preparing method thereof and application
InactiveCN109652684AHigh activityImprove the performance of hydrogen production by hydrolysisHydrogen productionPotassiumCadmium Cation
The invention discloses a hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy. The hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy comprises raw materials including, by mass percent, 90 to 95% of Al and 5 to10% of an additive. The additive is one or multiple of a metal element, metallic oxide and metal chloride, the metal element comprises one or multiple of magnesium, antimony, zinc, lead, cadmium, bismuth, tin, potassium and sodium, the metallic oxide comprises one or multiple of magnesium oxide, antimony oxide, zinc oxide, lead oxide, cadmium oxide, bismuth oxide, tin oxide, potassium oxide and sodium oxide, and the metal chloride comprises one or multiple of magnesium chloride, antimony chloride, zinc chloride, lead chloride, cadmium chloride, bismuth chloride, tin chloride, potassium chloride and sodium chloride. In the hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy, the cost of hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy is greatly reduced while hydrogen production is ensured. The invention further provides a preparing method of the hydrolysis hydrogen production aluminum alloy and application.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for extracting heavy metals from secondary flying ash generated during burning wastes
The invention discloses a method for extracting heavy metals from secondary flying ash generated during burning wastes, which comprises the following steps of: adding secondary flying ash generated during burning wastes into water under the condition that the ratio of the secondary flying ash to the water is 1:2-3; stirring and washing with water at 60-80 DEG C for 30-90 minutes; naturally precipitating for 2-4 hours, and separating supernatant liquid from residues; adding an isometric concentrated hydrochloric acid solution into the residues, stirring, refluxing and extracting at 60-80 DEG C for 30 minutes, and centrifugally separating solids from liquid to obtain extraction liquid and residual solid residues; evaporating the supernatant liquid at 100 DEG C to obtain mixed solid powder of CuCl2 and ZnCl2, and condensing the evaporated water vapor for recycling; carrying out vacuum evaporation on the extraction liquid at 60-80 DEG C to obtain PbCl2 powder, and simultaneously, recovering the hydrochloric acid; and adding lime of which the weight concentration is 10% into the residual solid residues for stirring uniformly to form inert solid wastes. In the invention, copper chloride and zinc chloride are separated by heating and water washing firstly, and lead chloride is obtained by adding the concentrated hydrochloric acid for heating, refluxing and extracting secondly, thereby realizing the purpose of recovering heavy metals.
Owner:刘阳生 +1
Method for preparing lead chloride and calcium sulfate from lead plasters of waste lead accumulators by wet process
InactiveCN101885510AAchieve recyclingEfficient removalCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesLead halidesSulfurSulfate
The invention discloses a method for preparing lead chloride and calcium sulfate from lead plasters of waste lead accumulators by a wet process. The lead plasters of the waste lead accumulators are taken as a raw material, and the method comprises the following steps of: leaching the lead plasters in an HCl-NaCl system; cooling the leach solution to separate out crystals; and separating, washing and drying. The method is characterized in that: a sulfur resource is recovered from cooling crystallization filtrate, and the cooling crystallization filtrate is in a closed cycle; the cooling crystallization filtrate is added with calcium chloride to form a calcium sulfate precipitate; the calcium sulfate precipitate is separated, washed and dried to form a calcium sulfate product; and the filtrate is used for preparing saturated NaCl solution which returns to the leaching process. Through the method, the lead chloride is obtained, and the industrial gypsum with the purity of over 97 percent is also obtained, so the sulfur resource is recycled, the cooling crystallization filtrate is circularly used, the lead recovery rate is over 96 percent after four times of circulation, and the waste of the lead resource and the lead pollution are avoided.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH +1
Preparation method of cross-linked fullerene bulk heterojunction perovskite solar cell
ActiveCN105470403AImprove performanceReduce performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCross-linkHeterojunction
The invention provides a preparation method of a cross-linked fullerene bulk heterojunction perovskite solar cell. The method comprises the following preparation steps: dissolving methyl ammonium iodide, lead chloride and [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric styryl dendron ester into dimethyl formamide to prepare 30wt% of perovskite dimethyl formamide solution; processing a PEDOT:PSS solution on a substrate to form cured anode modifying layer; processing the perovskite dimethyl formamide solution on the anode modifying layer to obtain a uniformly cured bulk heterojunction photosensitive layer; processing [6,6]-phenyl-C61-methyl butyrate on the bulk heterojunction photosensitive layer to obtain a uniform electron transport layer; and processing a cathode electrode on the electron transport layer, so as to obtain the cross-linked fullerene bulk heterojunction perovskite solar cell. The perovskite solar cell prepared by the method has the advantages of high energy conversion efficiency and good photovoltaic characteristic.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Manufacturing method for perovskite solar cell with compound electronic transmission layer structure
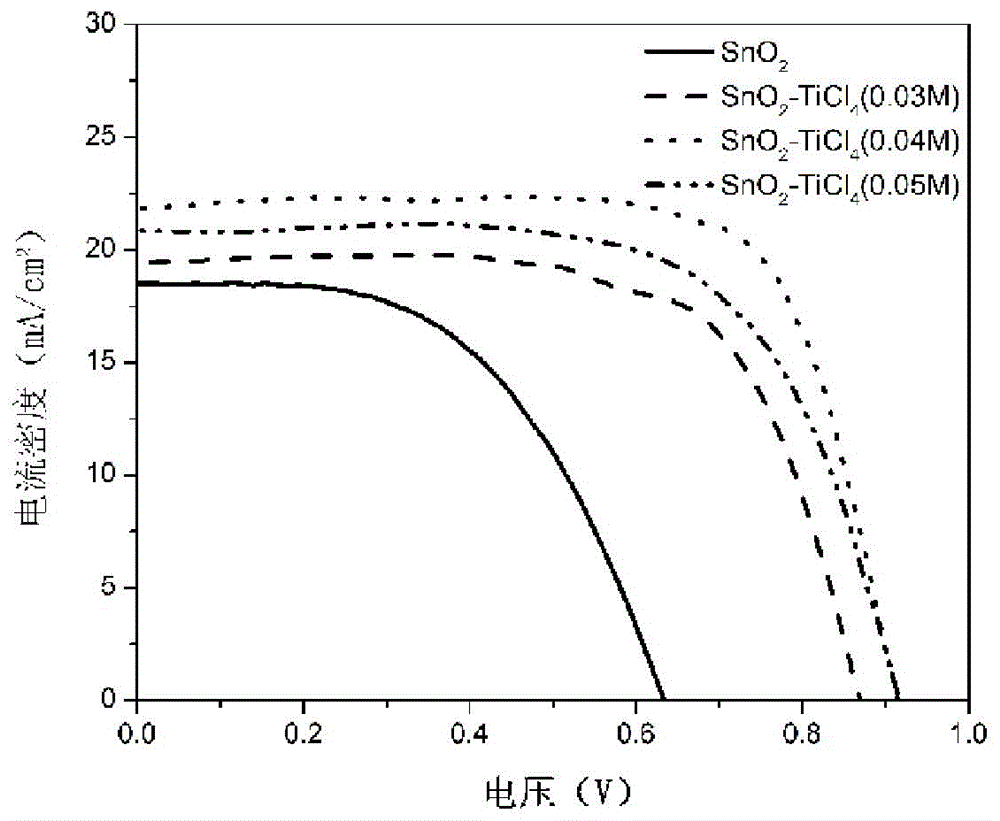
InactiveCN106299141ARaise the conduction band energy levelImprove efficiencyFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesElectronic transmissionEvaporation
The invention provides a manufacturing method for a perovskite solar cell with a compound electronic transmission layer structure. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) spin-coating a SnO2 compact layer on a conductive glass layer and then putting into a muffle furnace for burning for 1h at 180 DEG C; (2) dissolving iodine methylamine and lead chloride at mole ratio of (5:1)-(1:1) into N,N-dimethyl formamide, forming a solution, using a gluing machine for depositing the solution on the SnO2 compact layer, controlling the temperature at 70-150 DEG C and crystallizing, thereby acquiring a methylamine lead iodine polycrystalline film; (3) uniformly coating the organic solution of a hole-transport material onto the methylamine lead iodine polycrystalline film, thereby forming a hole-transport material layer; (4) adopting an evaporation method for evaporating a silver electrode layer on the hole-transport material layer. The cell produced according to the method provided by the invention has higher photovoltaic conversion efficiency; the compounding technique is simpler; the prepared SnO2 compound electronic transmission material is performed under lower temperature below 180 DEG C; the energy consumption of the cell is reduced; the cost is saved.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Preparation method of color-adjustable small-size Mn: CsPbCl3 nanocrystal
InactiveCN108585030AFeed lessGood monodispersityNanoopticsLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceTrioctylphosphine
The invention discloses a preparation method of a color-adjustable small-size Mn: CsPbCl3 nanocrystal and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor nanomaterial preparation. The preparation method comprises weighing lead chloride, oleic acid, oleylamine and octadecene, putting the materials into a three-necked flask, carrying out vacuum-pumping at 120 DEG C, adding trioetylphosphine into thematerials in the nitrogen gas protective atmosphere at 150 DEG C to obtain a mixed solution, cooling the mixed solution to the room temperature, pouring a cesium oleate solution into the mixed solution for a reaction at the room temperature for 1h to obtain a CsPbCl3 nanocrystal seed, preparing lead bismuth chloride perovskite with different sizes from the CsPbCl3 nanocrystal seed, carrying out purification, adding a manganese salt into the perovskite, and carrying out grinding to obtain Mn: CsPbCl3 nanocrystals in different colors. The preparation method can adjust the amaranth of the Mn: CsPbCl3 nanocrystal to red color. The color-adjustable small-size Mn: CsPbCl3 nanocrystal has the controllable size and high fluorescence efficiency. The preparation method has simple processes, utilizes easily available raw materials, realizes large-scale synthesis and has a wide product application prospect.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for preparing alkali lead chloride micro-nano structure crystal
ActiveCN108807986AGood dispersionHigh crystallinityCell electrodesSecondary cellsEnvironmental resistanceMicro nano
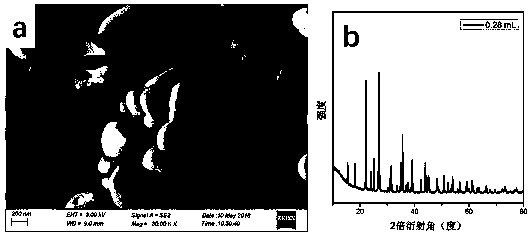
The invention discloses a method for preparing an alkali lead chloride micro-nano structure crystal and belongs to the technical field of micro-nano material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving lead chloride with deionized water, and adding triethylamine to carry out a reaction under a heating condition, thereby obtaining the alkali lead chloride micro-nano structurecrystal. Through suction filtration and drying, powder of the alkali lead chloride micro-nano structure crystal can be made. The prepared alkali lead chloride micro-nano structure crystal takes the shape of a rod, has a length range about 300-1600n m and a thickness range about 30-400 nm, and has the advantages of being simple in synthesis process, good in repeatability, low in cost, safe, and environmentally friendly. On the basis of the characteristics, the crystal has very high values in both laboratory investigation and industrial application.
Owner:HENAN INST OF ENG
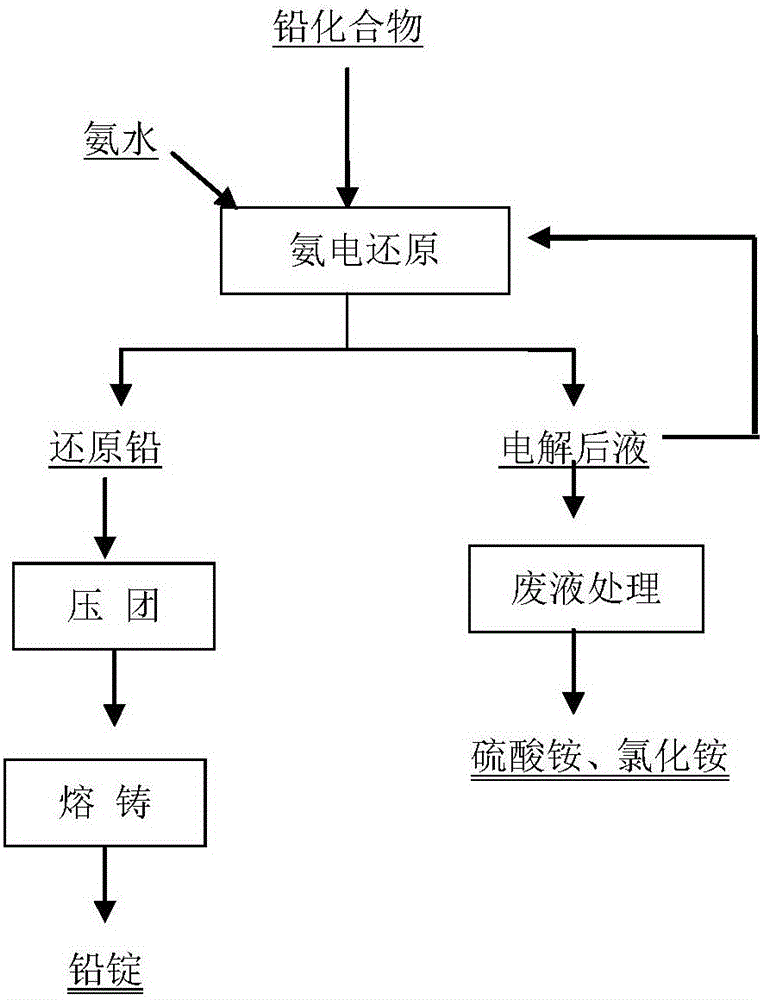
Process for preparing lead by ammonium sulfate through ammonia power reduction
ActiveCN106065485ANo pollution in the processShort processPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsLead dioxideAmmonia production
The invention belongs to a wet metallurgy process, and relates to a process for reducing a lead compound as metal lead in ammonium sulfate water solution. Ammonium sulfate water solution is used as electrolyte; the lead compound is used as a raw material; titanium is used as an anode; stainless steel or lead is used as a cathode; a direct-current electric field is applied in an electrolytic cell; the lead compound obtains electrons at the cathode to reduce as the metal lead; ammonia is oxidized as nitrogen for emission at the anode, and meanwhile, H+ ions are generated; sulfates and chlorine ions in the compound enter the solution to generate ammonium sulfate and ammonium chloride with added ammonia water; lead monoxide and lead dioxide in the lead compound are reduced as the metal lead; and meanwhile, H+ ion combination generation water generated by OH+ and the anode is released. The lead compound includes such materials as lead sulfate, lead monoxide, lead dioxide, lead chloride and mixtures thereof as waste lead accumulator paste. The process is different from traditional electrolysis and electrodeposition process; electrolyte contains no lead; and the lead compound is directly reduced as the metal lead at the cathode.
Owner:杨云婷
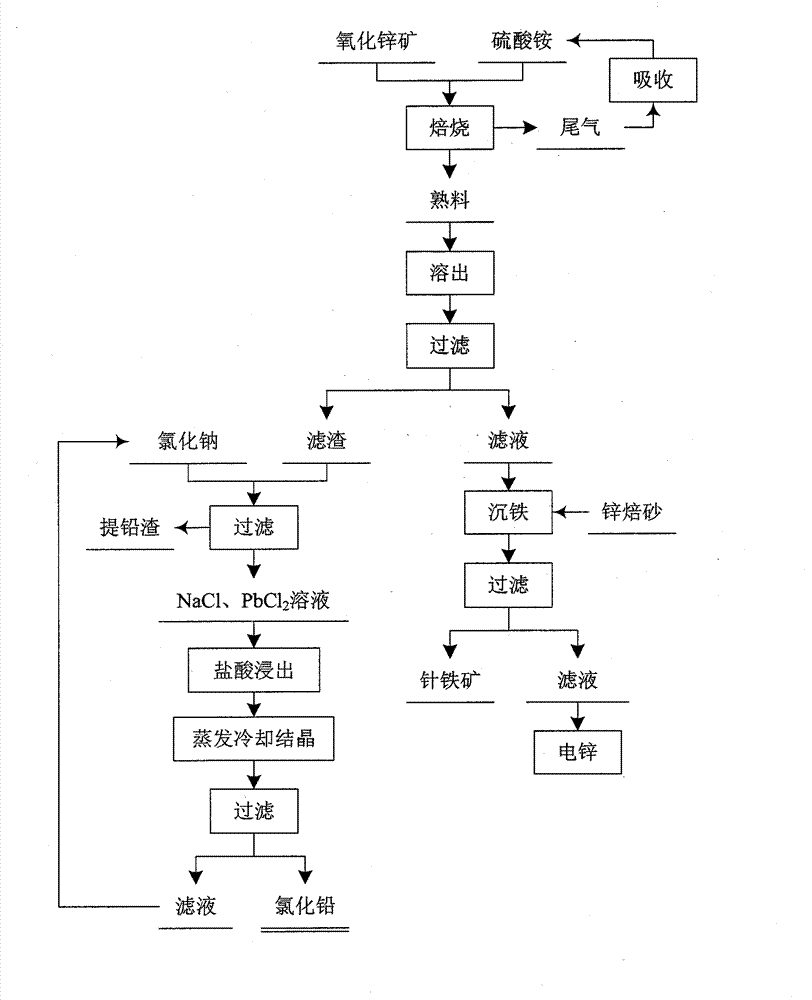
Method for preparing lead chloride and zinc sulfate by using mid low grade zinc oxide ores and zinc oxide-lead oxide paragenetic ores
The invention discloses a method for preparing lead chloride and zinc sulfate by using mid low grade zinc oxide ores and zinc oxide-lead oxide paragenetic ores, comprising the following steps: (1) crushing zinc ores and levigating, then mixing the levigated zinc ores with ammonium sulfate and roasting; (2) dissolving out clinkers obtained by roasting, carrying out iron precipitation and aluminium precipitation on the obtained filtrate, and further separating lead from the residues of zinc extraction; (3) boiling down a zinc sulfate solution obtained after iron precipitation and aluminium precipitation for electrolysis; and (4) leaching the residues of zinc extraction with an NaCl solution to obtain a filtrate, condensing the filtrate, cooling down and crystallizing out PbCl2 crystals, and returning the NaCl solution to the leaching process. According to the invention, circulation utilization is realized.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for separating copper from lead matte and comprehensively utilizing lead matte
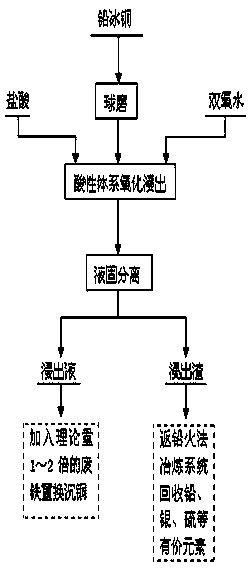
InactiveCN104004907AReduce pollutionLow equipment requirementsProcess efficiency improvementSulfate radicalsRefining (metallurgy)
The invention relates to a method for separating copper from lead matte and comprehensively utilizing lead matte, and belongs to the field of wet metallurgy of non-ferrous metals. The process is characterized by adding hydrogen peroxide under a hydrochloric acid system for oxidization leaching. The method is as follows: ball-milling lead matte blocks until grain size is lower than 100 meshes, and feeding the ball-milled lead matte into a leaching slot for carrying out oxidization leaching, wherein HCl concentration is controlled to 1mol / L-6mol / L, concentration of hydrogen peroxide is controlled to 0.5mol / L-3.5mol / L, a liquid-solid ratio is controlled to (3-10):1, a temperature is controlled to 60-90 DEG C and reaction time is controlled to 1-2 hours. Under a hydrochloric acid condition, hydrogen peroxide is utilized and used as an oxidant for leaching sulfide; in the oxidization leaching process, sulfur in the lead matte is oxidized into elemental sulfur or sulfate radical, copper is oxidized to enter liquor in the form of ion, and lead is left in slag with gold and sliver in the form of lead chloride or lead sulfate. After the leaching process is completed, solid-liquid separation is carried out to realize preliminary separation of copper and lead. Copper-rich leachate can replace deposited copper by adding scrap iron, and leaching residue is returned to a pyrogenic process lead refining system for recycling valuable elements such as lead, sliver, elemental sulfur, and the like.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
Polymer-perovskite films, devices, and methods
ActiveUS9905765B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolymer scienceSpin casting
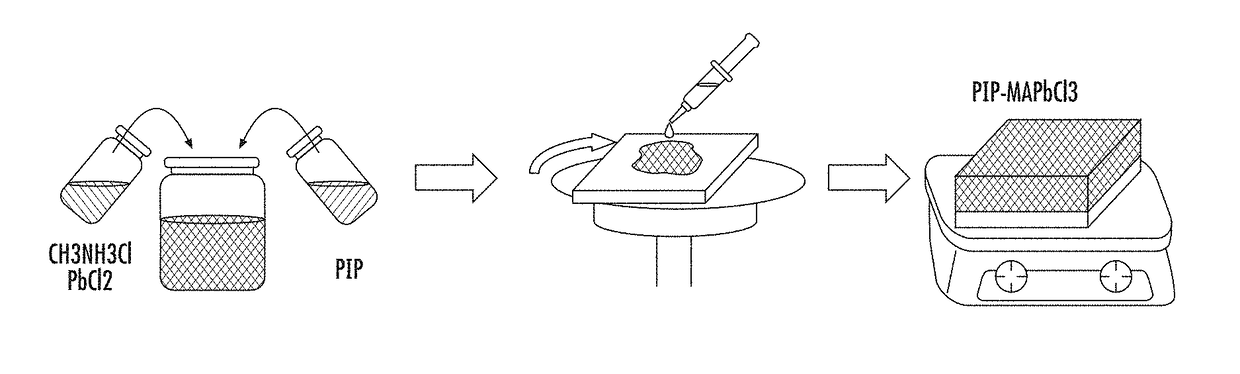
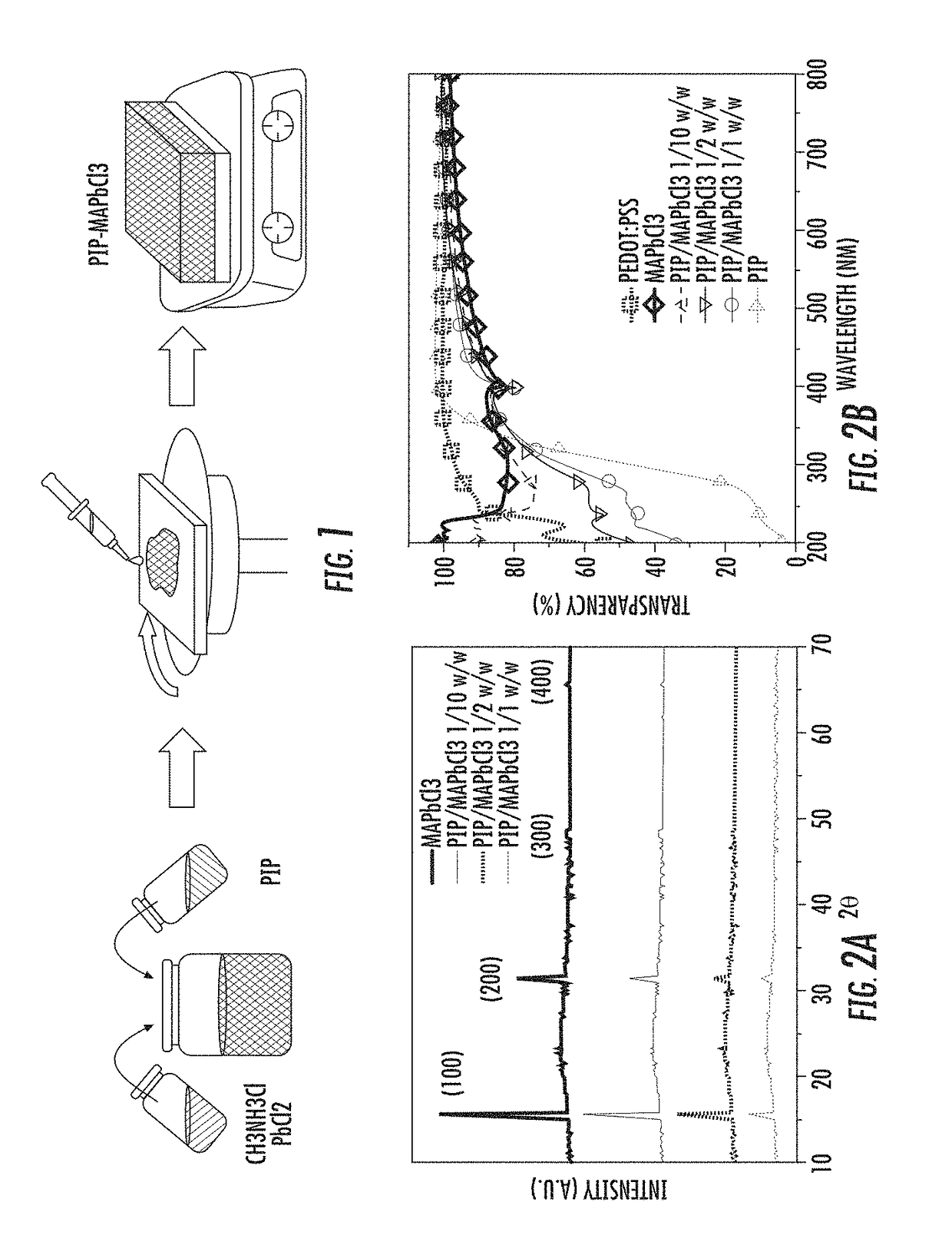
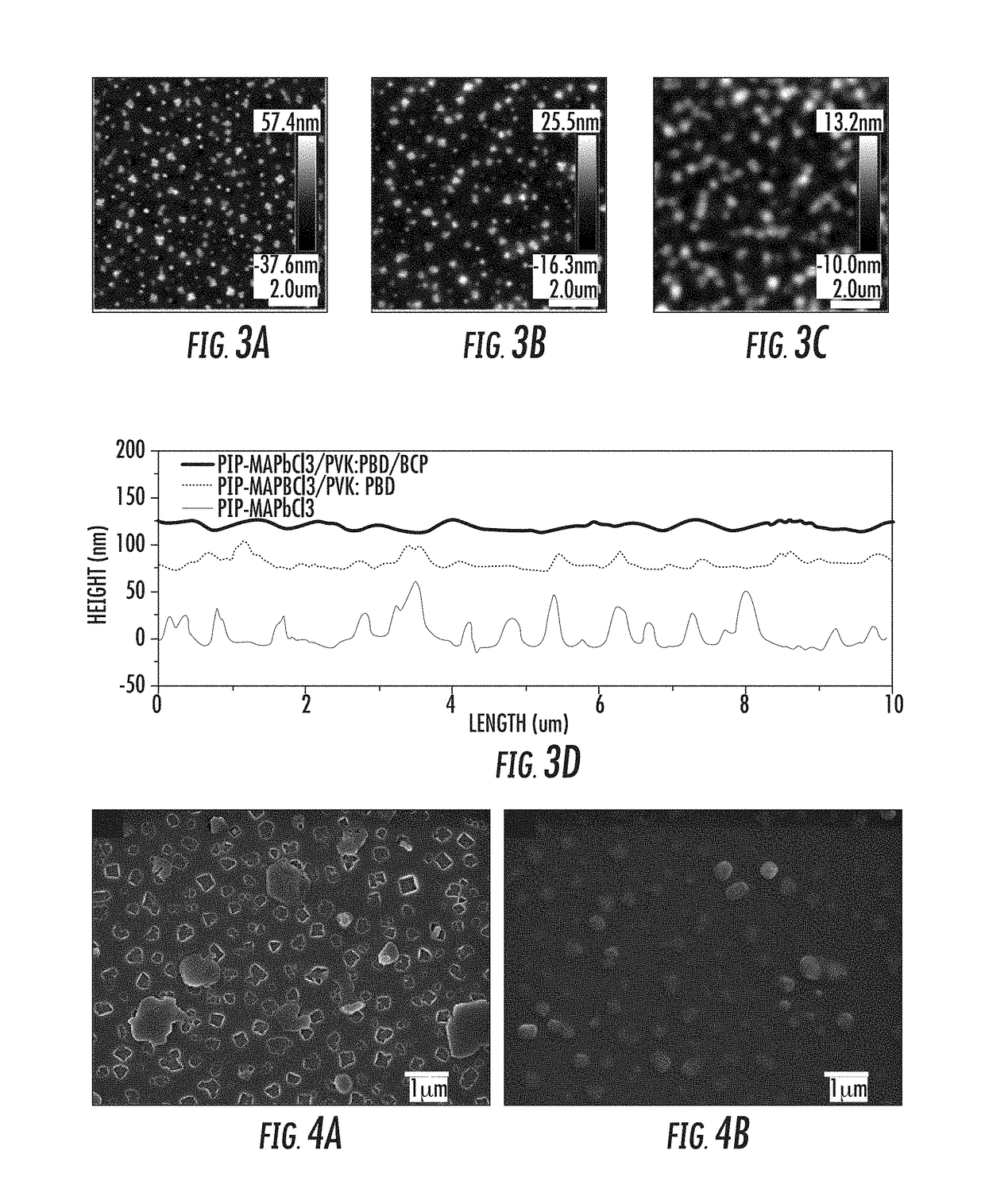
Provided herein are perovskite-polymer films, methods of forming polymer-perovskite films, and devices including polymer-perovskite films. The polymer-perovskite films may include a plurality of methylammonium lead chloride (CH3NH3PbCl3) nanopillar crystals embedded in a polymer matrix. The devices can be optoelectronic devices, such as light emitting diodes, which include polymer-perovskite films. The polymer-perovskite films of the devices can be hole transport layers in the devices. The methods of making films may include spin casting a precursor solution followed by thermal annealing.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
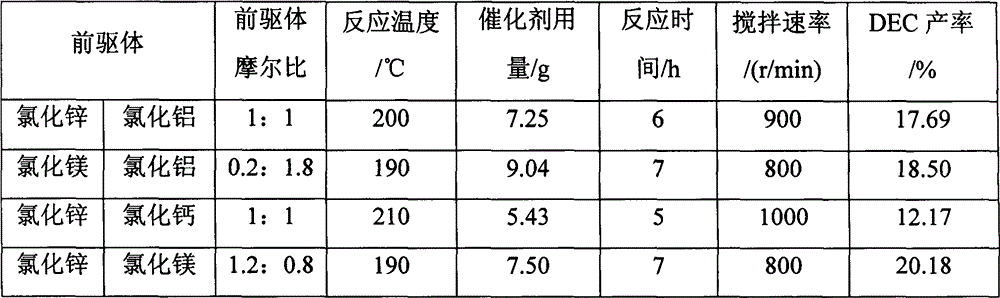
Ion liquid catalyst for synthesizing diethyl carbonate by urea alcoholysis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102909076ARaw materials are easy to getLow priceOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsReaction temperature1-Methylimidazole
The invention provides a process for synthesizing diethyl carbonate by urea alcoholysis through an ion liquid catalyst. The catalyst is imidazole metal salts ion liquid. The method comprises the steps of adding absolute ethyl alcohol, urea and the catalyst into a high-pressure reaction kettle, wherein the agitation speed is 700-1000 r / min, the mol ratio of the absolute ethyl alcohol to the urea ranges from 5: 1 to 15: 1; the reaction temperature is 160-230 DEG C, the reaction time is 4-10 hours and the use amount of the ion liquid catalyst is 1-10% of the mass of raw materials; cooling to room temperature and separating to obtain a product; enabling 1-methylimidazole and n-chlorobutane (in a mol ratio of 1: 1) to react to synthesize an intermediate chlorinated 1-butyl-3-methylimidazole (BMIMCl); and further enabling the BMIMCl to react with a metal chloride to obtain a product. The added metal chloride is Lewis acid of zinc chloride, magnesium chloride, aluminum chloride, lead chloride, calcium chloride and the like, and is prepared by adding one or more of the Lewis acid to react according to a certain ratio. The method has the advantages of green environmental friendliness, high repeated utilization rate, simple process, no corrosion, selectivity of close to 100%, high yield (which is close to 30% to the greatest extent) and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
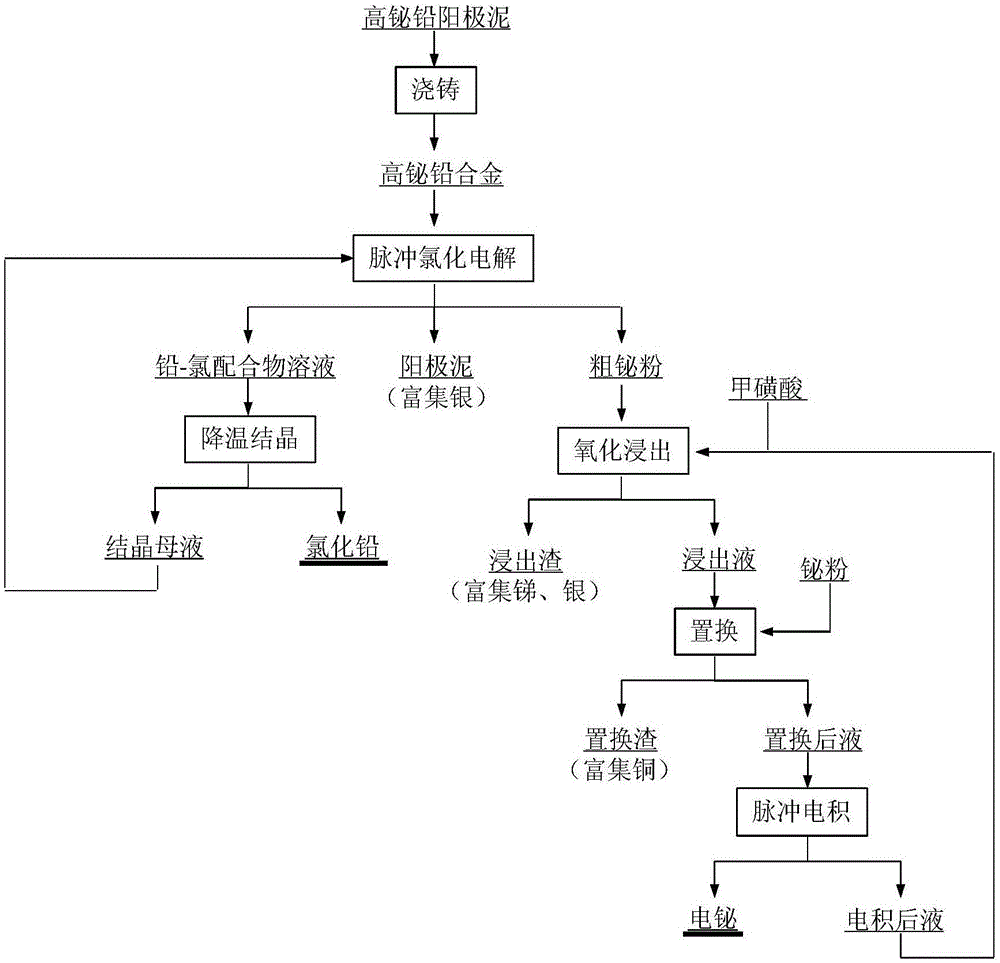
Process for separating lead and bismuth from high bismuth lead alloy
ActiveCN107177865ATo achieve full enrichmentElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisSlag
The invention discloses a process for separating lead and bismuth from a high bismuth lead alloy; and the process uses an alloy formed by casting high bismuth lead anode mud as an anode; and the alloy is fed in an anode bag for pulse chlorination electrolysis in a hydrochloric acid-chlorine salt system. Insoluble matters of the anode fall into the anode bag to form anode mud during electrolyzing; lead is dissolved in solution in a lead-chlorine complex form; and bismuth is separated out from a cathode in a rough bismuth powder form. The anode mud, lead chloride complex solution and rough bismuth powder are respectively obtained after electrolysis. The lead chloride solution is cooled for crystallization to obtain lead chloride; and crystallization mother liquor is returned to prepare electrolyte. The oxidation leaching is performed on the rough bismuth powder by adopting methane sulfonic acid to respectively obtain leaching liquid and leaching slag enriched with antimony and silver. The leaching liquid is replaced and purified for pulse electrodeposition to obtain electric bismuth; and electrodeposition back liquid is returned to leaching of the rough bismuth powder. The process can perform classified extraction on lead and bismuth in the high bismuth lead alloy; silver is enriched; the closed cycle of the technological process is realized; and the process has the advantages of simple technological process, high yield of valuable elements, cleanness and environmental protection.
Owner:YIYANG SHENGLI CHEM IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com