Method for separating copper from lead matte and comprehensively utilizing lead matte
A lead matte and copper-rich technology, applied in the field of lead matte, can solve the problems of long process flow, inconvenient operation, high temperature and high pressure, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
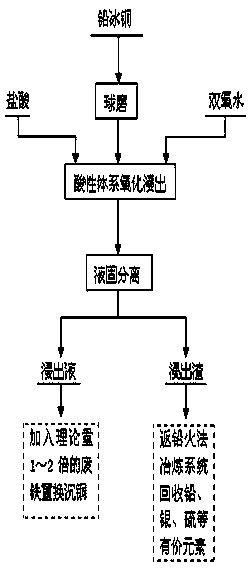
[0012] Break 1kg of lead matte material (Pb 16.58%, Cu 31.94%, S 19.88%, Ag 0.7253%, Fe 18.53%), ball mill to a particle size below 100 mesh, send the ball milled lead matte to the leaching tank, add hydrochloric acid successively Leaching with hydrogen peroxide, the leaching conditions: HCl concentration 3 mol / L, hydrogen peroxide concentration 1.5 mol / L, liquid-solid ratio 3:1, temperature 60°C, stirring speed 300 r / min, reaction time 1h. The leaching rate of copper is 98.5%, while the lead remains in the slag in the form of lead sulfate and lead chloride; the leaching solution is reduced with iron filings, and the reduction conditions are: pH=1, temperature 25°C, and the amount of added iron filings is 2% of the theoretical amount. times, time 1h. The copper reduction rate is 97%, and the purity of sponge copper is 95%.
Embodiment 2
[0014] Break 1kg of lead matte material (Pb 18.82%, Cu 29.09%, S 18.28%, Ag 0.8823%, Fe 20.53%), ball mill to a particle size below 80 mesh, send the ball milled lead matte to the leaching tank, add hydrochloric acid successively Leaching with hydrogen peroxide, the leaching conditions: HCl concentration 4 mol / L, hydrogen peroxide concentration 2 mol / L, liquid-solid ratio 4:1, temperature 80°C, stirring speed 500 r / min, reaction time 2h. The leaching rate of copper is 98%, while the lead remains in the slag in the form of lead sulfate and lead chloride; the leaching solution is reduced with iron filings, and the reduction conditions are: pH=1.5, temperature 25°C, and the amount of iron filings added is 1.5 of the theoretical amount times, time 2h. The copper reduction rate is 97.5%, and the purity of sponge copper is 92.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0016] 1kg of lead matte material (Pb 19..12%, Cu 34.96%, S 17.68%, Ag 0.9614%, Fe 17.53%) is crushed and ball milled to a particle size below 100 mesh, and the ball milled lead matte is sent to the leaching tank. Add hydrochloric acid and hydrogen peroxide successively for leaching, the leaching conditions: HCl concentration 3 mol / L, hydrogen peroxide concentration 2.5 mol / L, liquid-solid ratio 8:1, temperature 70°C, stirring speed 500 r / min, reaction time 2h. The leaching rate of copper is 95.5%, while the lead remains in the slag in the form of lead sulfate and lead chloride; the leaching solution is reduced with iron filings, and the reduction conditions are: pH=1, temperature 25°C, and the amount of added iron filings is 2% of the theoretical amount. times, time 2h. The copper reduction rate is 97%, and the purity of sponge copper is 94.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com