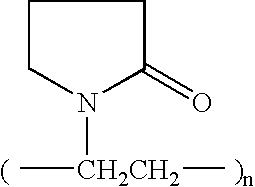
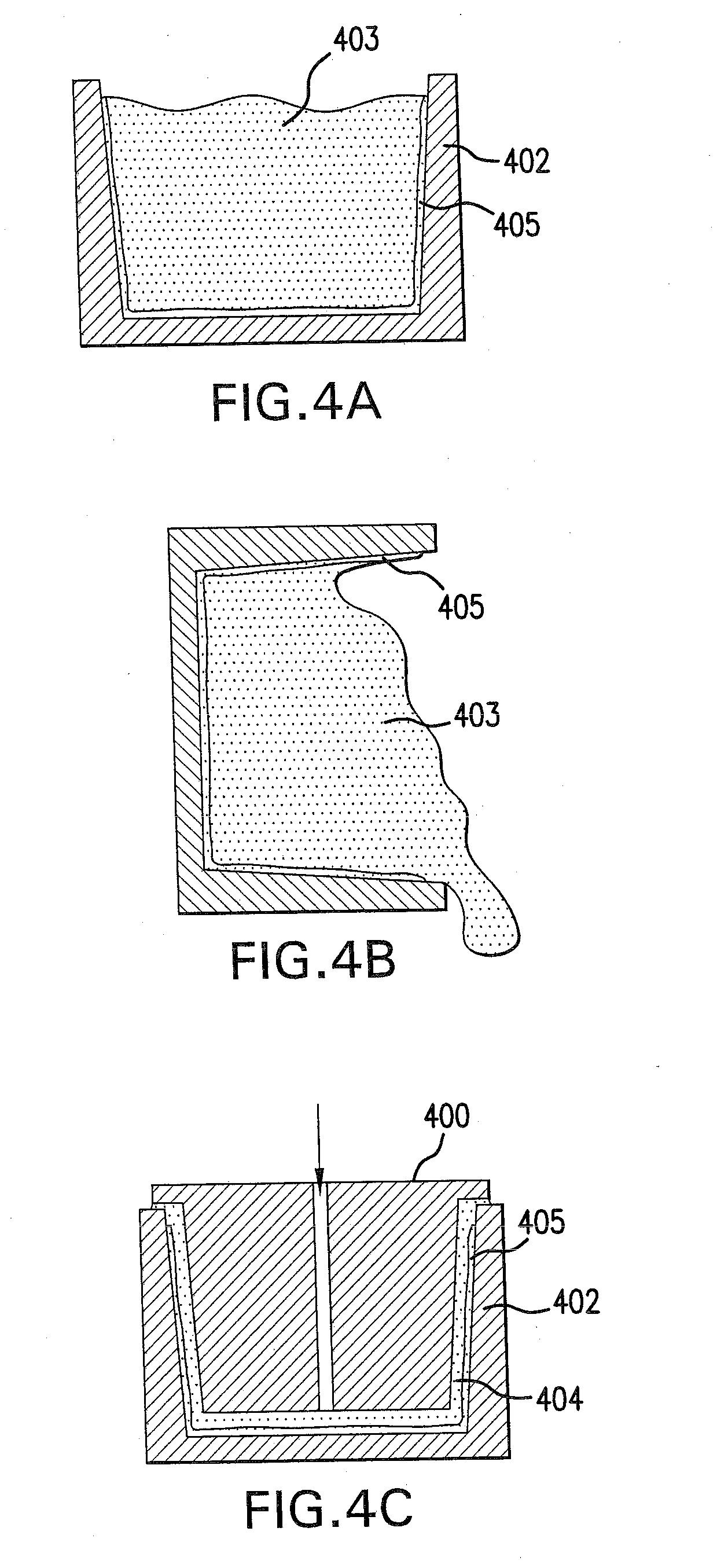
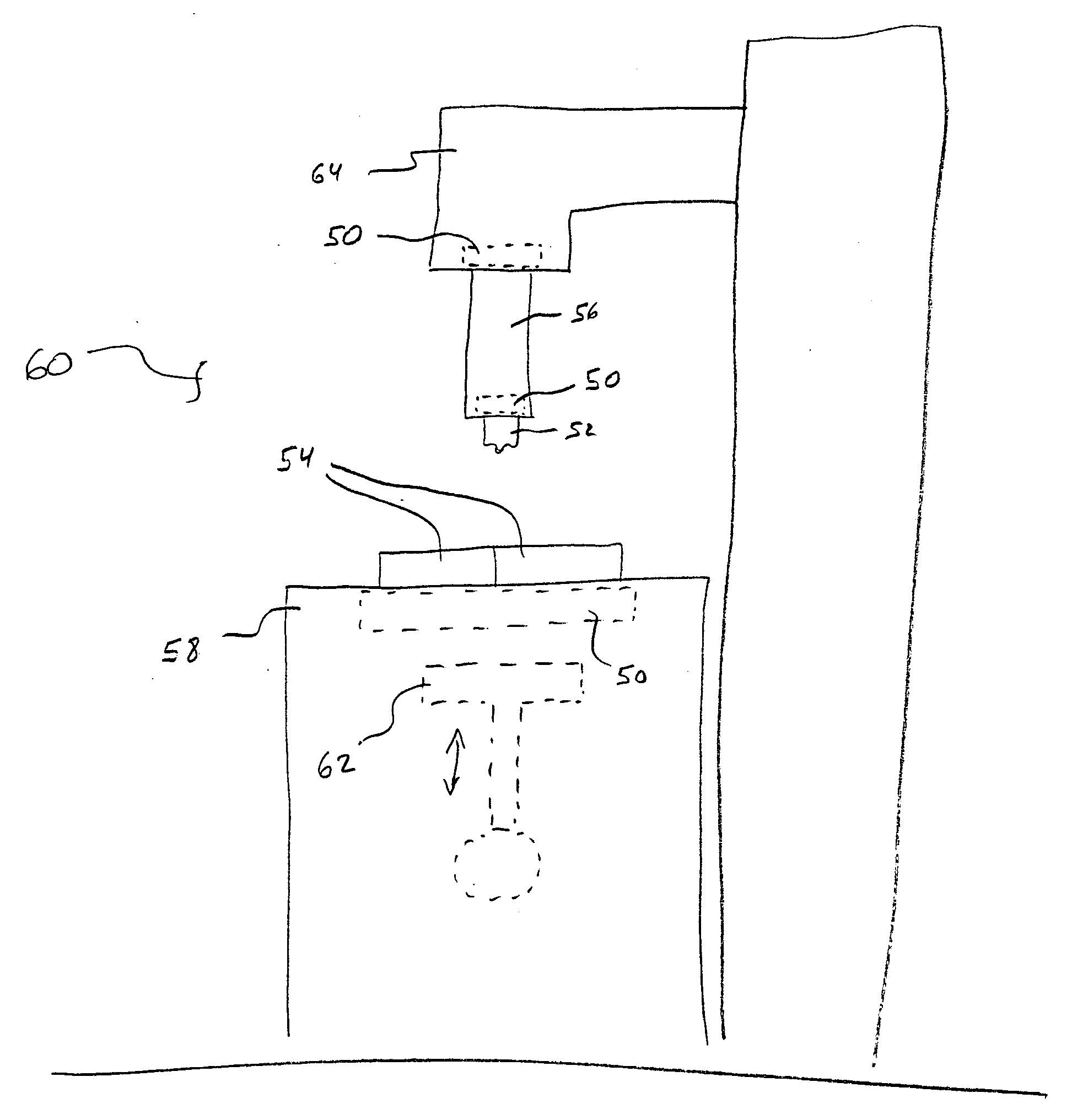
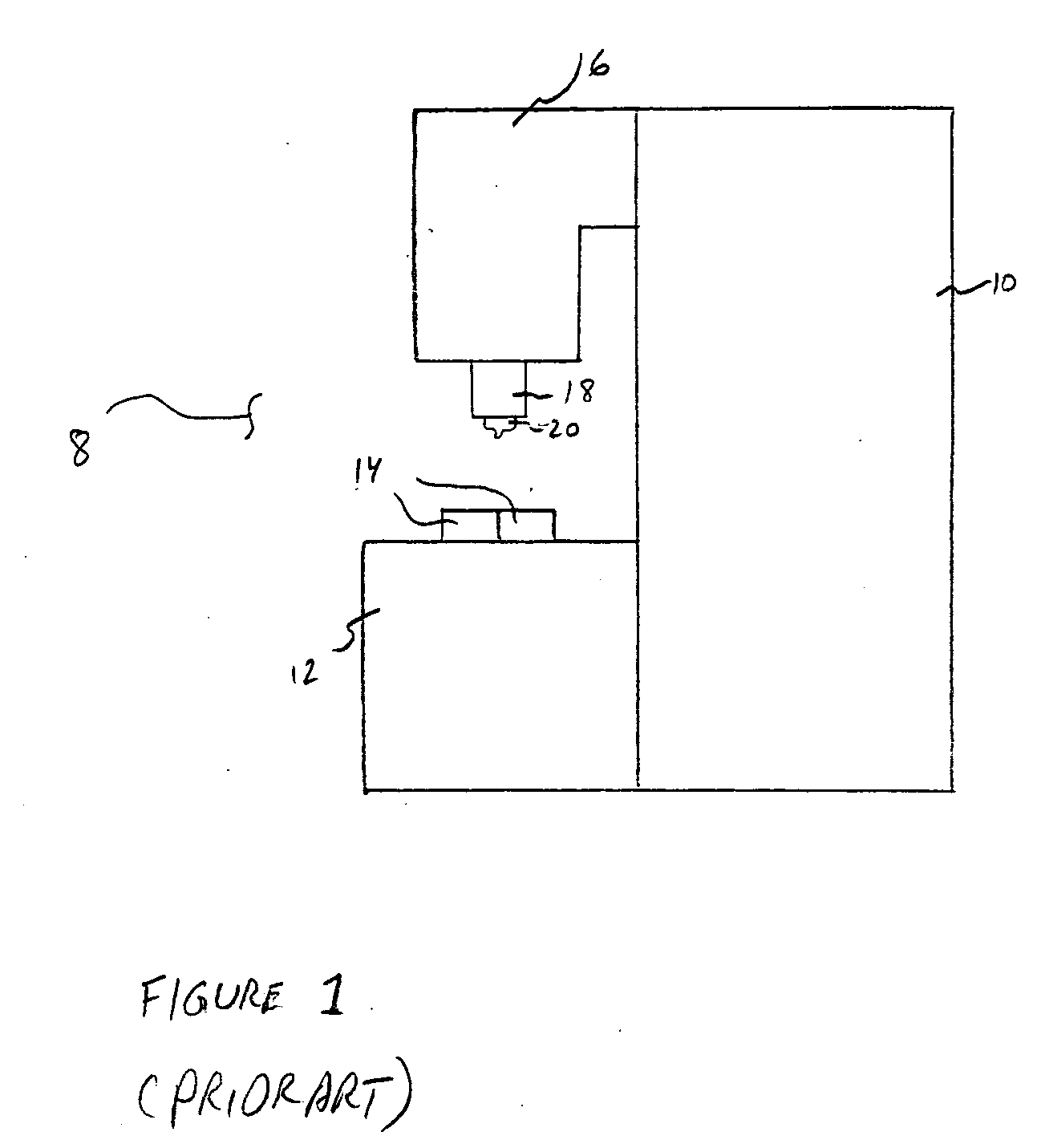
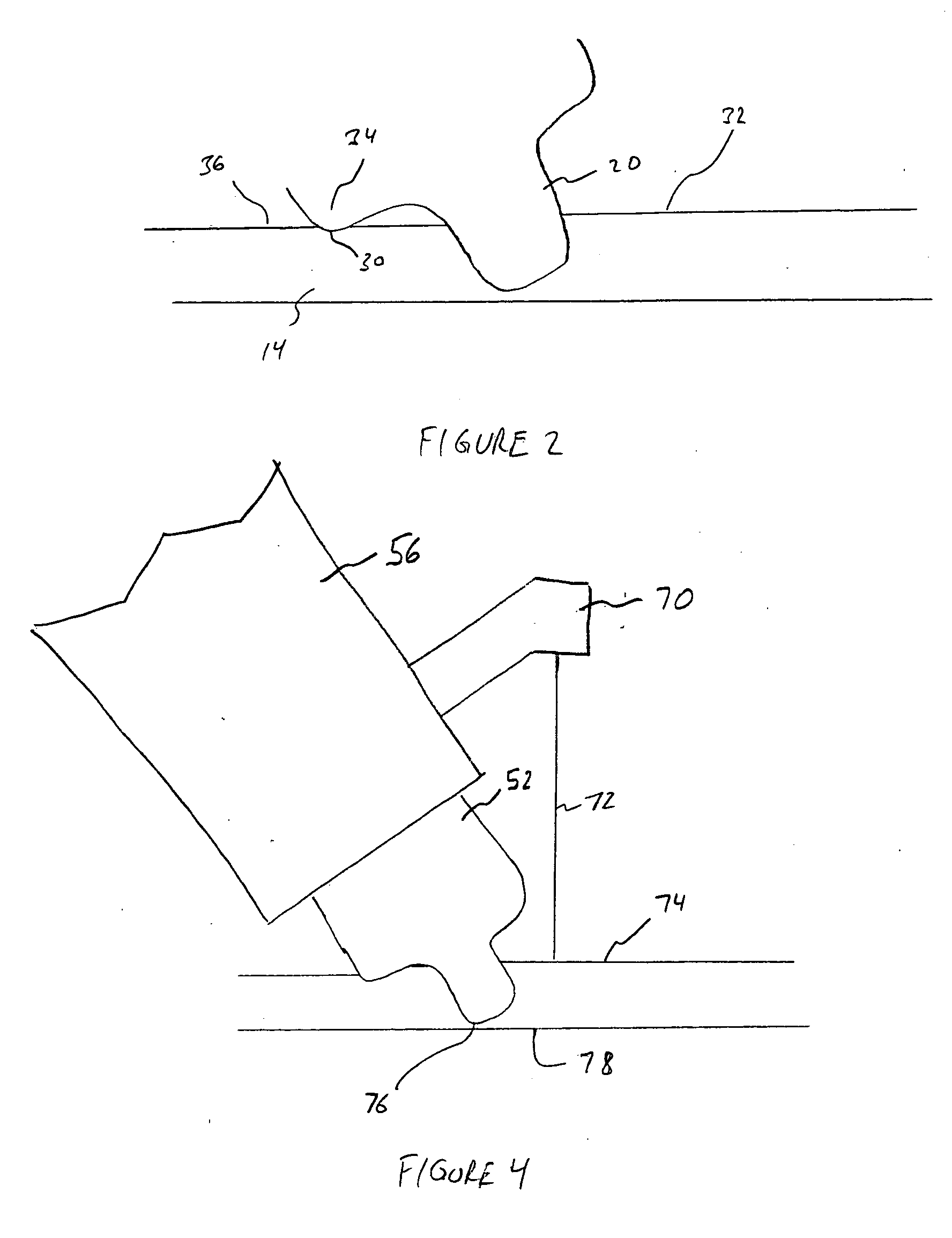
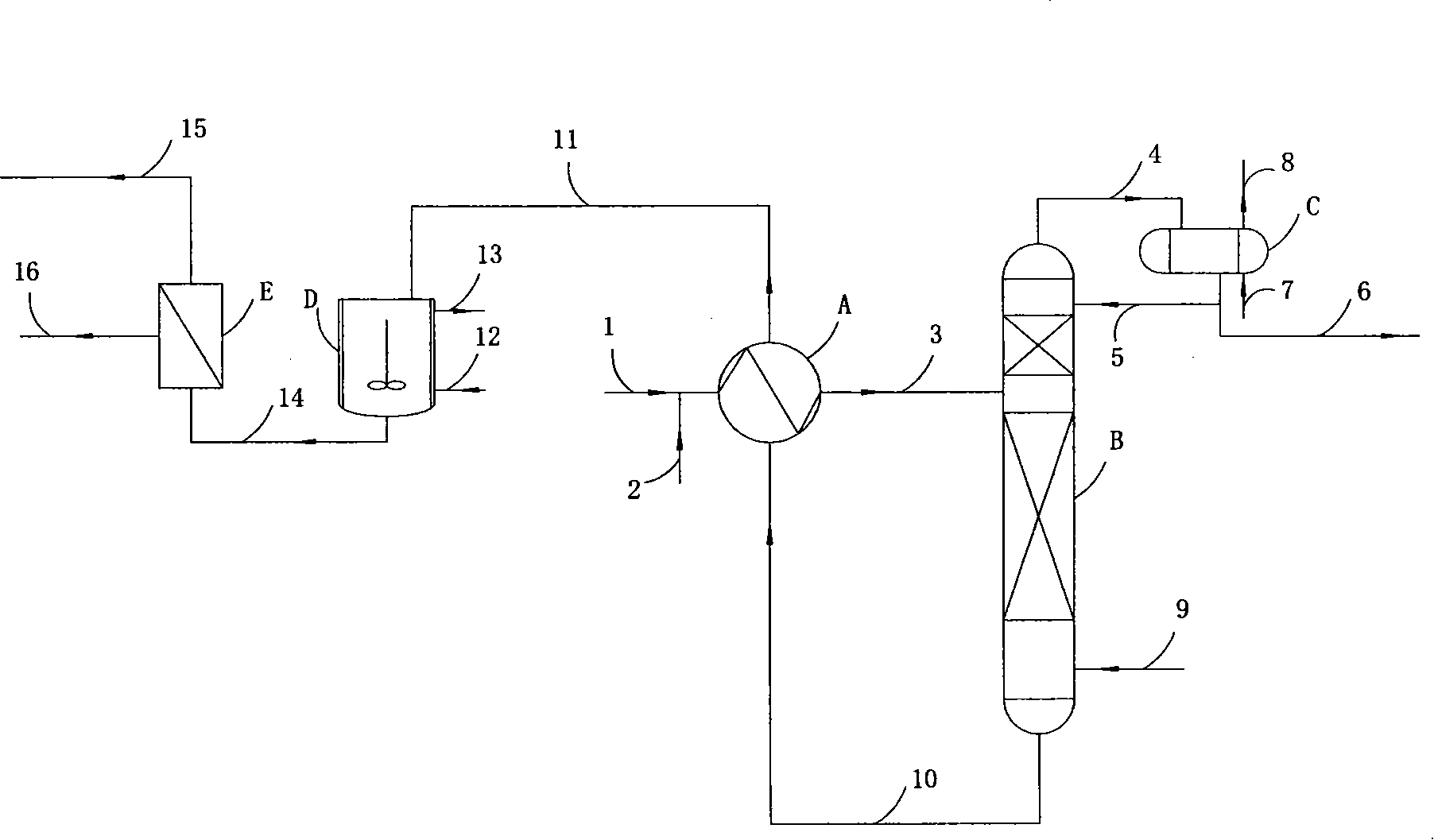
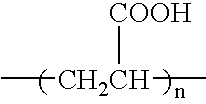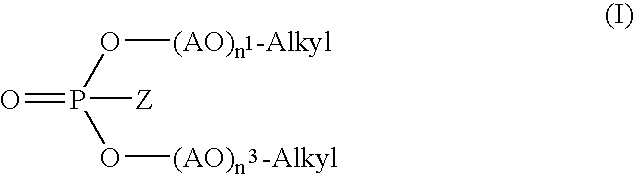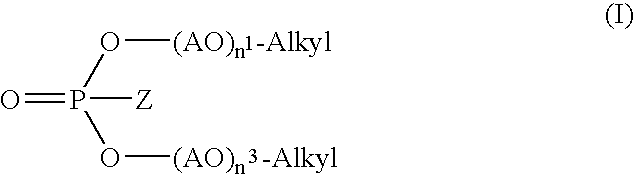Patents
Literature
2385 results about "Non-ferrous metal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
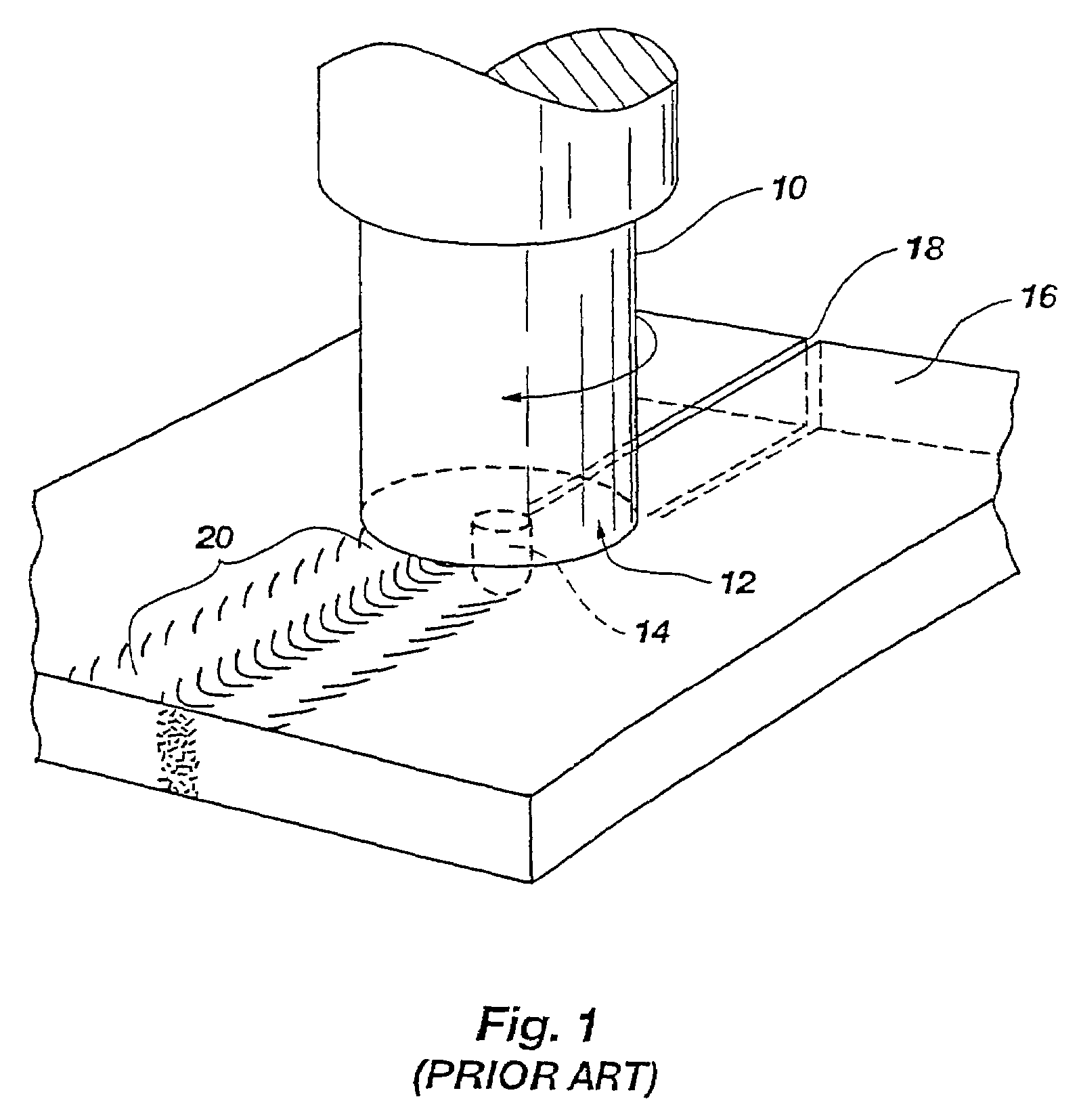
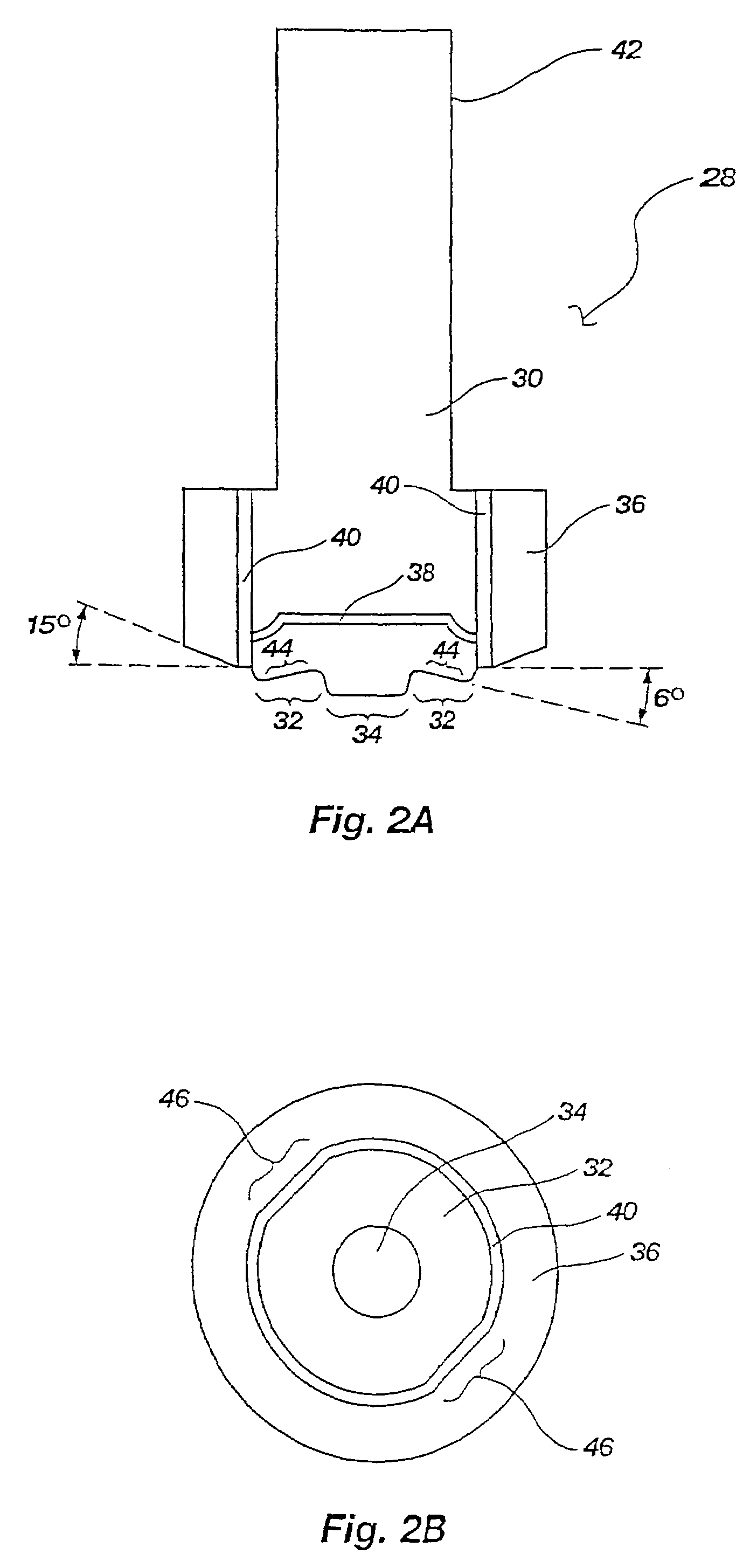
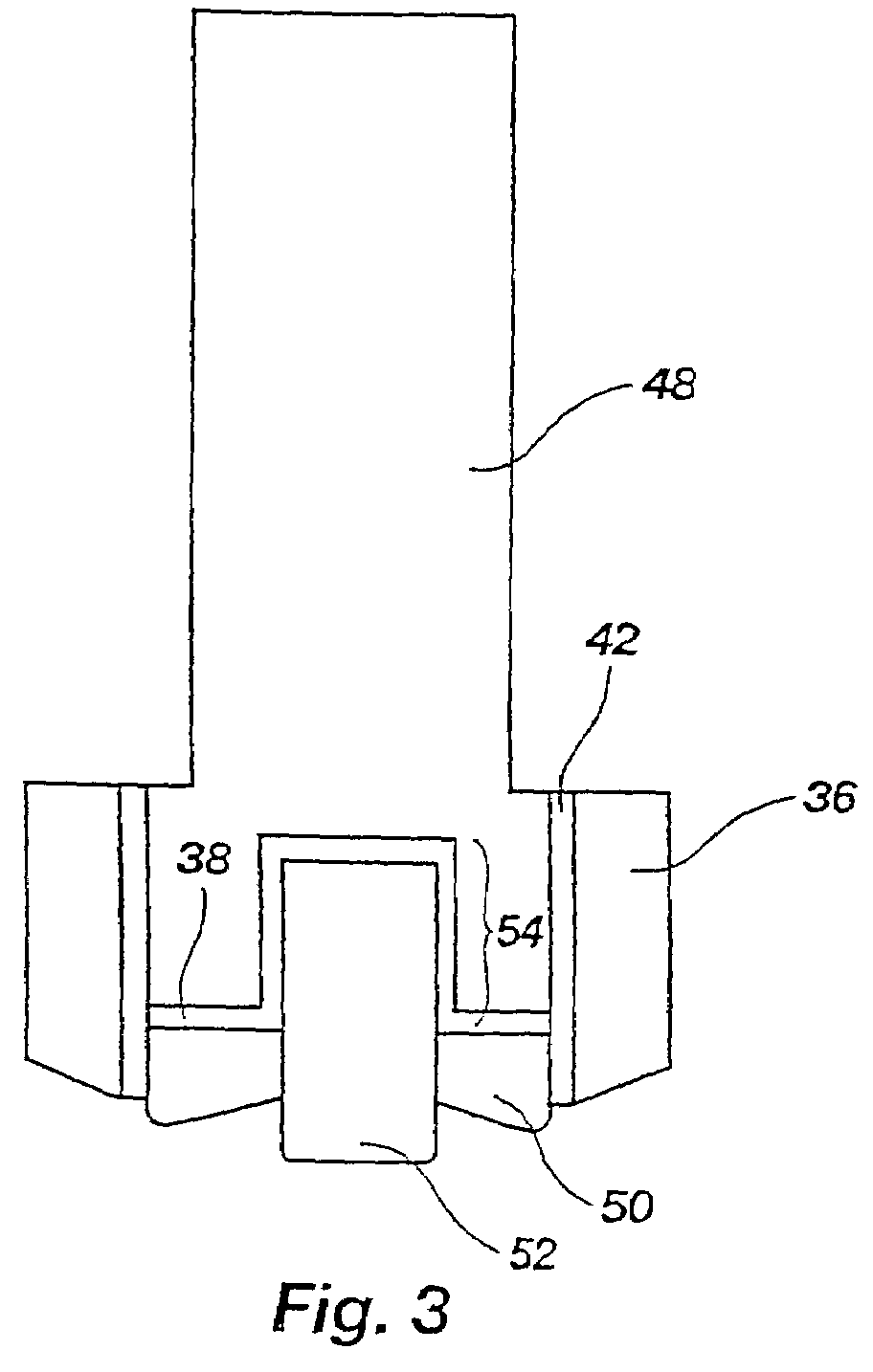
In metallurgy, a non-ferrous metal is a metal, including alloys, that does not contain iron (ferrite) in appreciable amounts. Generally more costly than ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals are used because of desirable properties such as low weight (e.g. aluminium), higher conductivity (e.g. copper), non-magnetic property or resistance to corrosion (e.g. zinc). Some non-ferrous materials are also used in the iron and steel industries. For example, bauxite is used as flux for blast furnaces, while others such as wolframite, pyrolusite and chromite are used in making ferrous alloys.
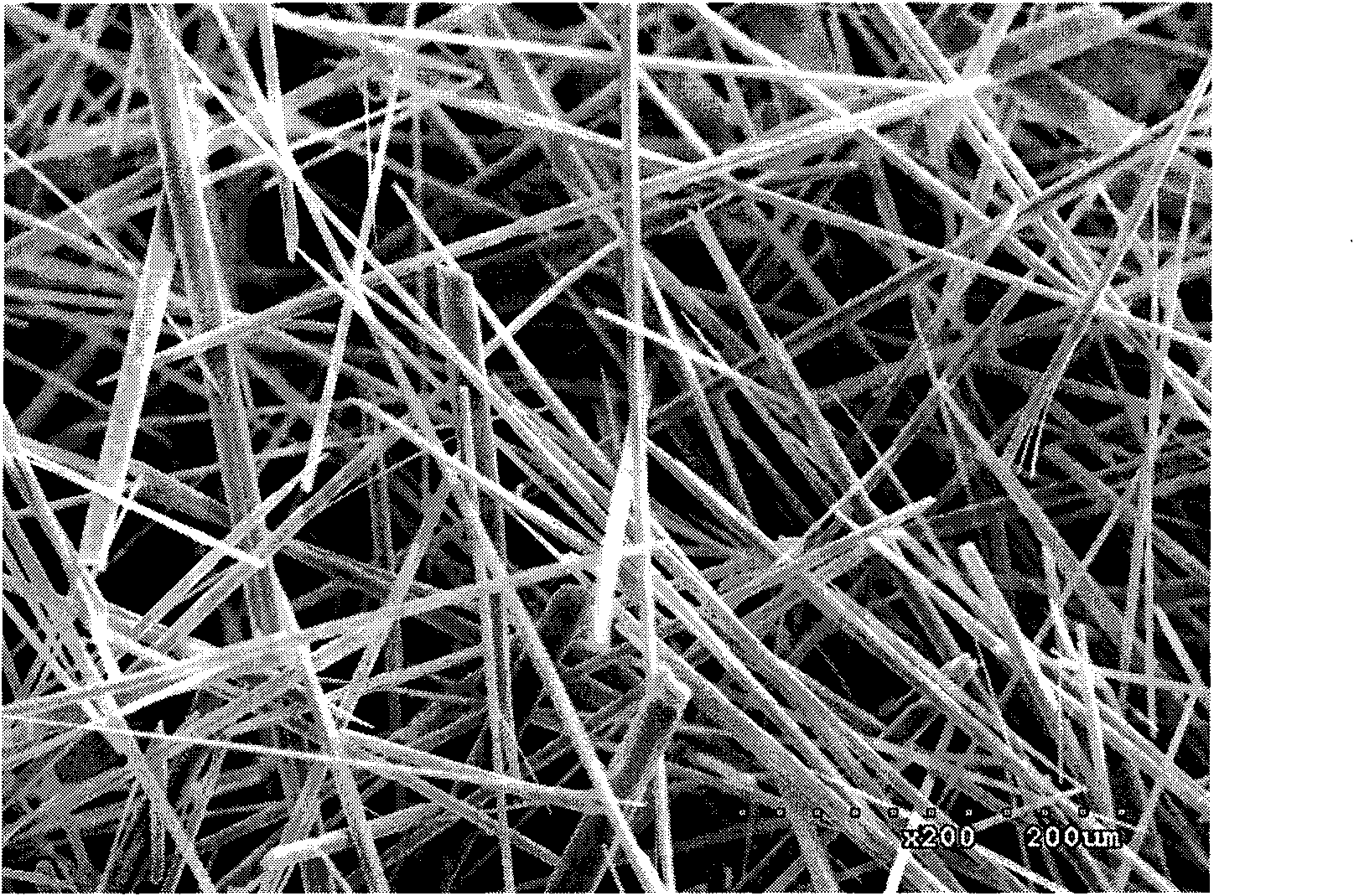
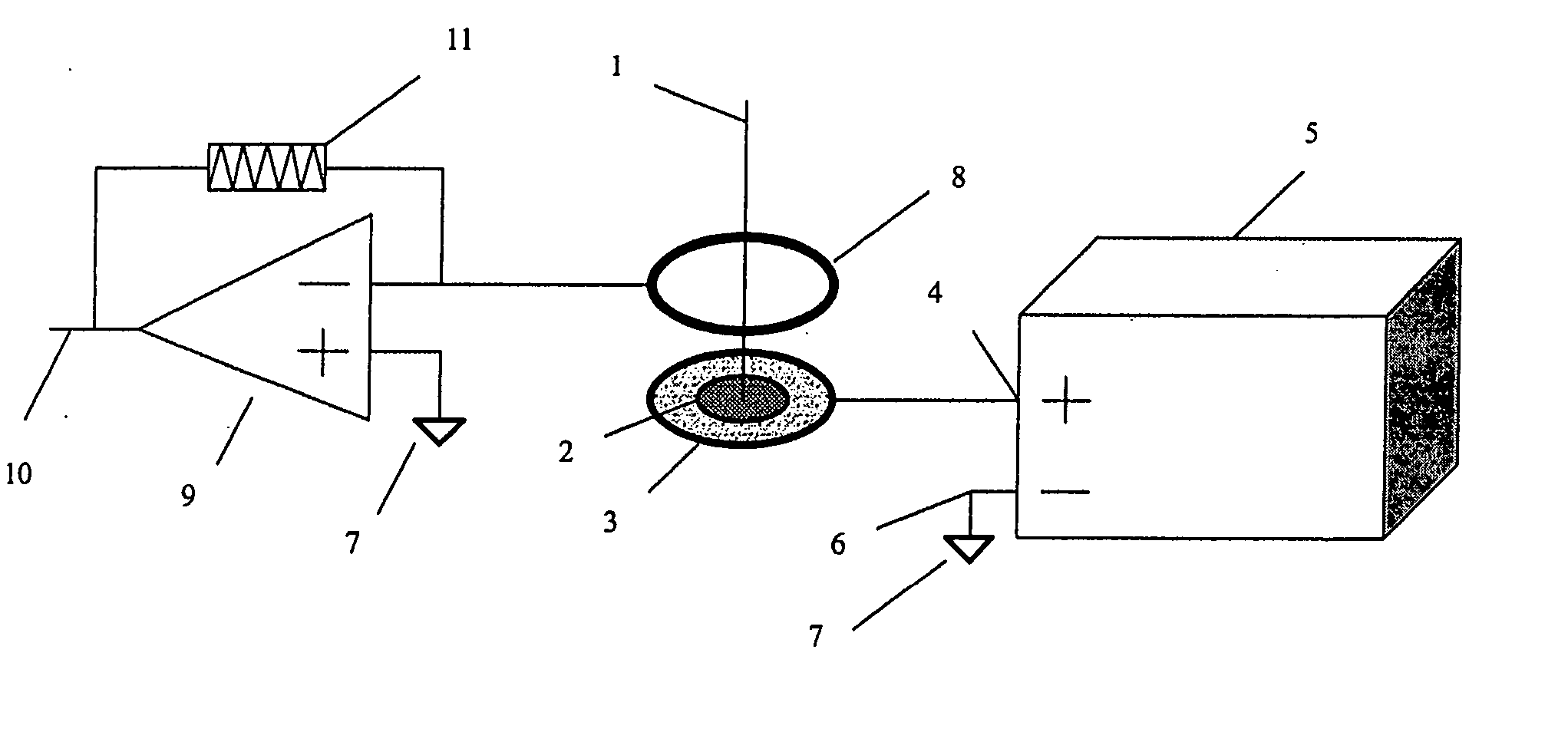
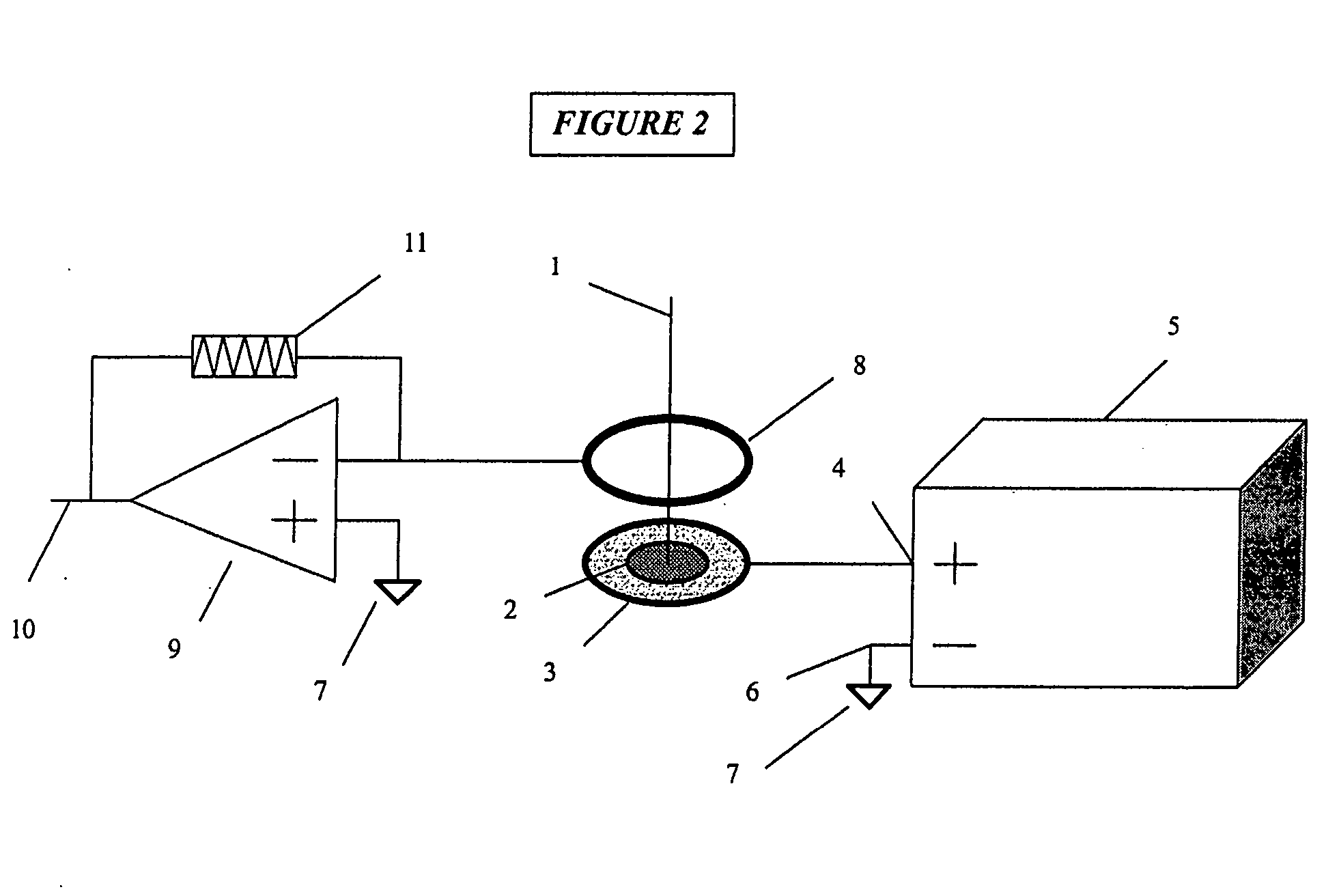
Laser ablation feedback spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050061779A1Precise depth controlReduce the amount requiredWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusMass spectrometryAblation plasma
Methods, for use with a laser ablation or drilling process, which achieve depth-controlled removal of composite-layered work-piece material by real-time feedback of ablation plasma spectral features. The methods employ the use of electric, magnetic or combined fields in the region of the laser ablation plume to direct the ablated material. Specifically, the electric, magnetic or combined fields cause the ablated material to be widely dispersed, concentrated in a target region, or accelerated along a selected axis for optical or physical sampling, analysis and laser feedback control. The methods may be used with any laser drilling, welding or marking process and are particularly applicable to laser micro-machining. The described methods may be effectively used with ferrous and non-ferrous metals and non-metallic work-pieces. The two primary benefits of these methods are the ability to drill or ablate to a controlled depth, and to provide controlled removal of ablation debris from the ablation site. An ancillary benefit of the described methods is that they facilitate ablated materials analysis and characterization by optical and / or mass spectroscopy.
Owner:BLUMENFELD WALTER +2
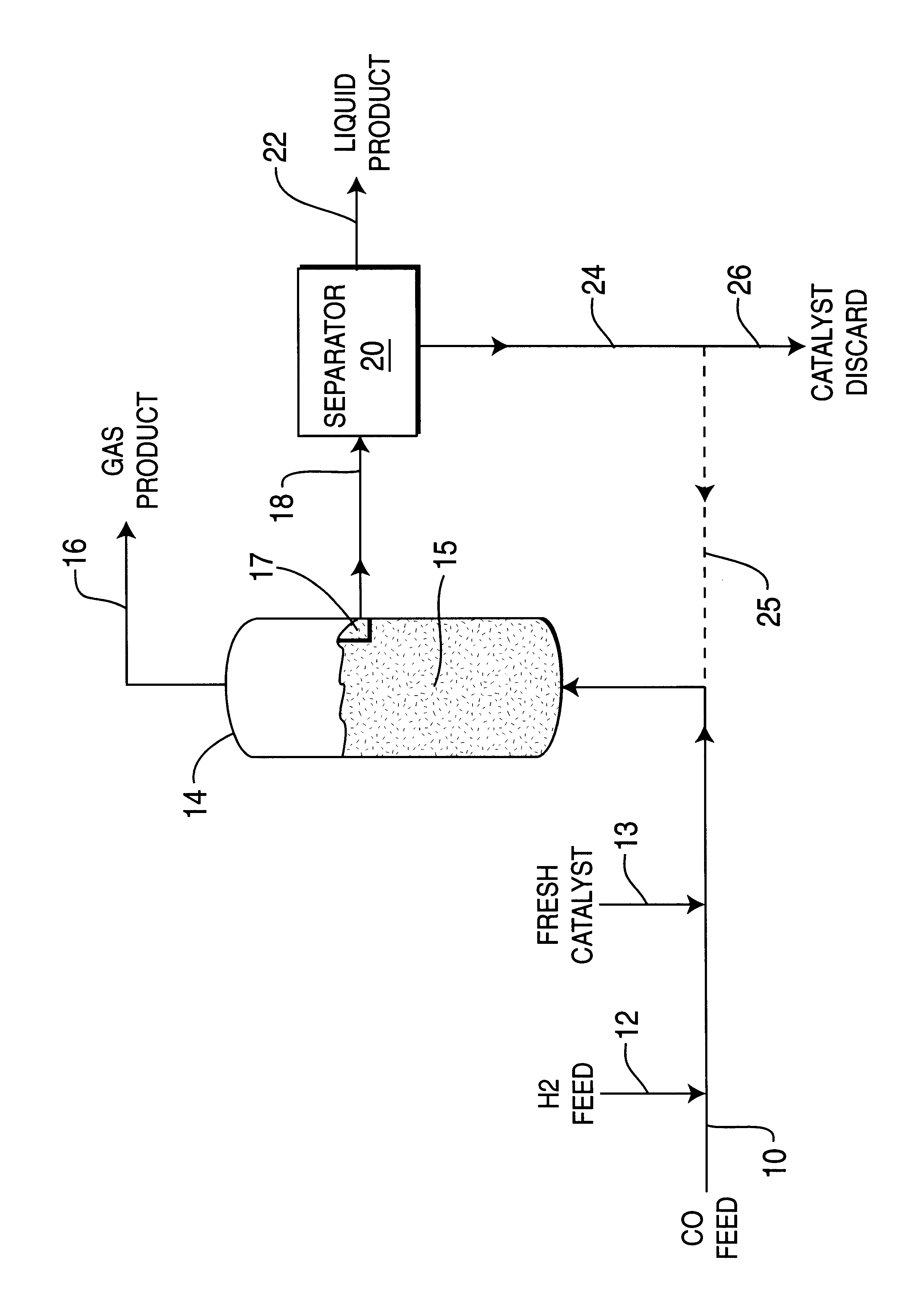
Skeletal iron catalyst having improved attrition resistance and product selectivity in slurry-phase synthesis processes
InactiveUS6277895B1High particle strengthGood attristion resistanceHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesOrganic compound preparationFixed bedSlurry
Particulate skeletal iron catalyst is provided which contain at least about 50 wt. % iron with the remainder being a minor portion of a suitable non-ferrous metal and having characteristics of 0.062-1.0 mm particle size, 20-100 m2 / g surface area, and 10-40 nm average pore diameter. Such skeletal iron catalysts are prepared and utilized for producing synthetic hydrocarbon products from CO and H2 feeds by Fischer-Tropsch synthesis process. Iron powder is mixed with non-ferrous powder selected from aluminum, antimony, silicon, tin or zinc powder to provide 20-80 wt. % iron content and melted together to form an iron alloy, then cooled to room temperature and pulverized to provide 0.1-10 mm iron alloy catalyst precursor particles. The iron alloy pulverized particles are treated with NaOH or KOH caustic solution at 30-95° C. temperature to extract and / or leach out most of the non-ferrous metal portion, and then screened and treated by drying and reducing with hydrogen and to provide the smaller size skeletal iron catalyst material. Such skeletal iron catalyst is utilized with CO+H2 feedstream for Fischer-Tropsch reactions in either a fixed bed or slurry bed type reactor at 180-350° C. temperature, 0.5-3.0 mPa pressure and gas hourly space velocity of 0.5-3.0 L / g Fe / hr to produce desired hydrocarbon products.
Owner:INST OF COAL CHEM ICCCHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
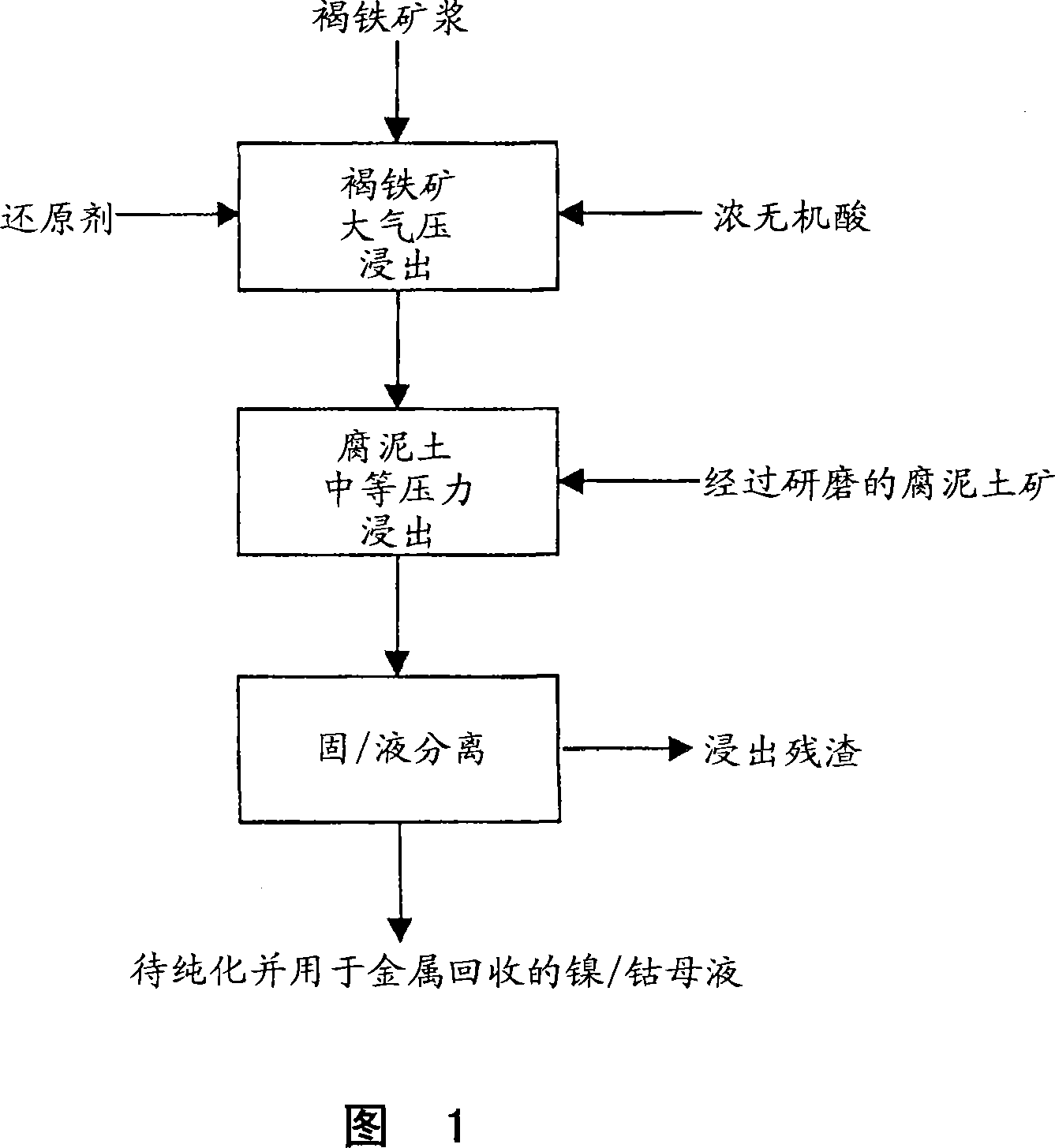
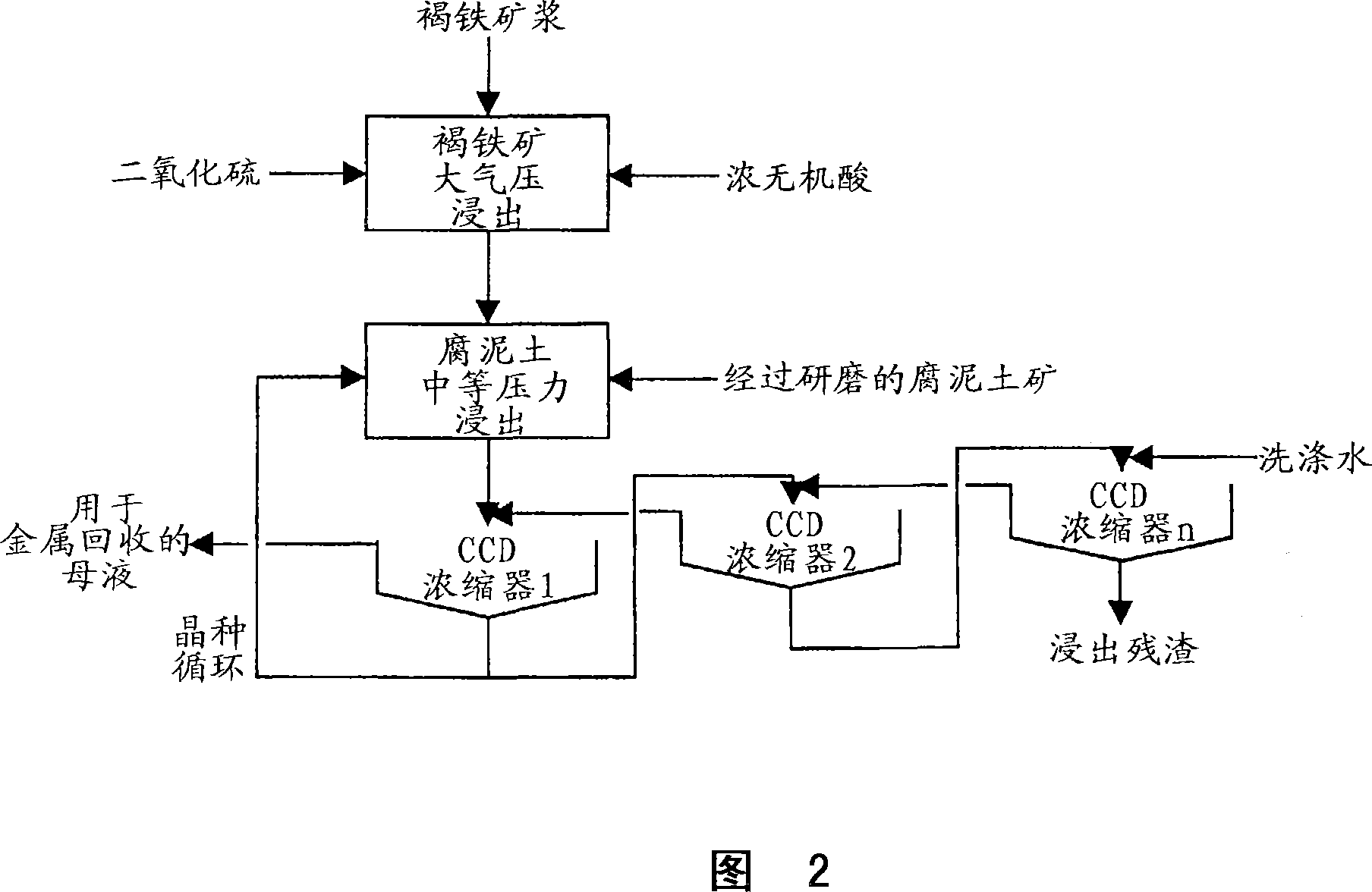
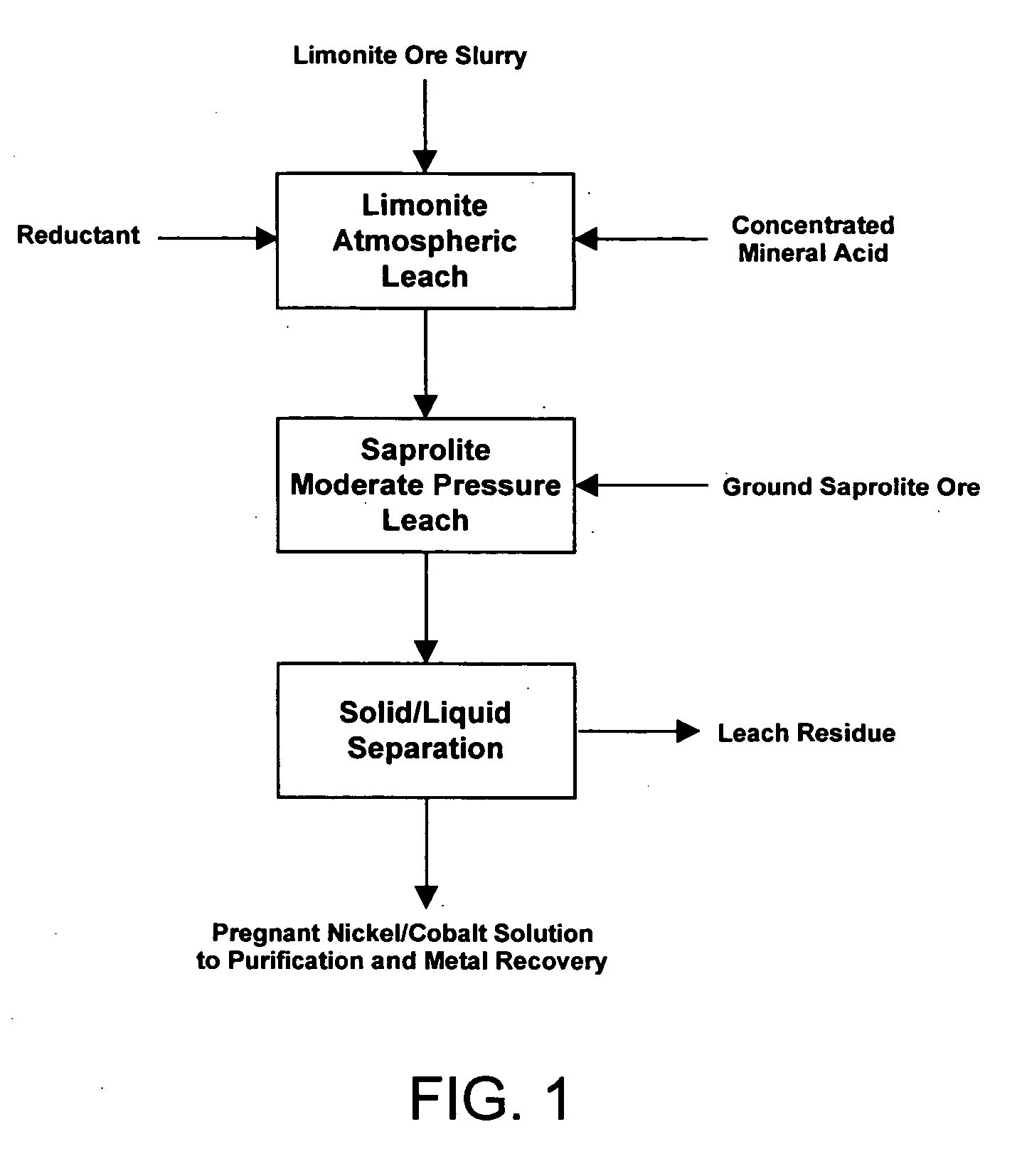
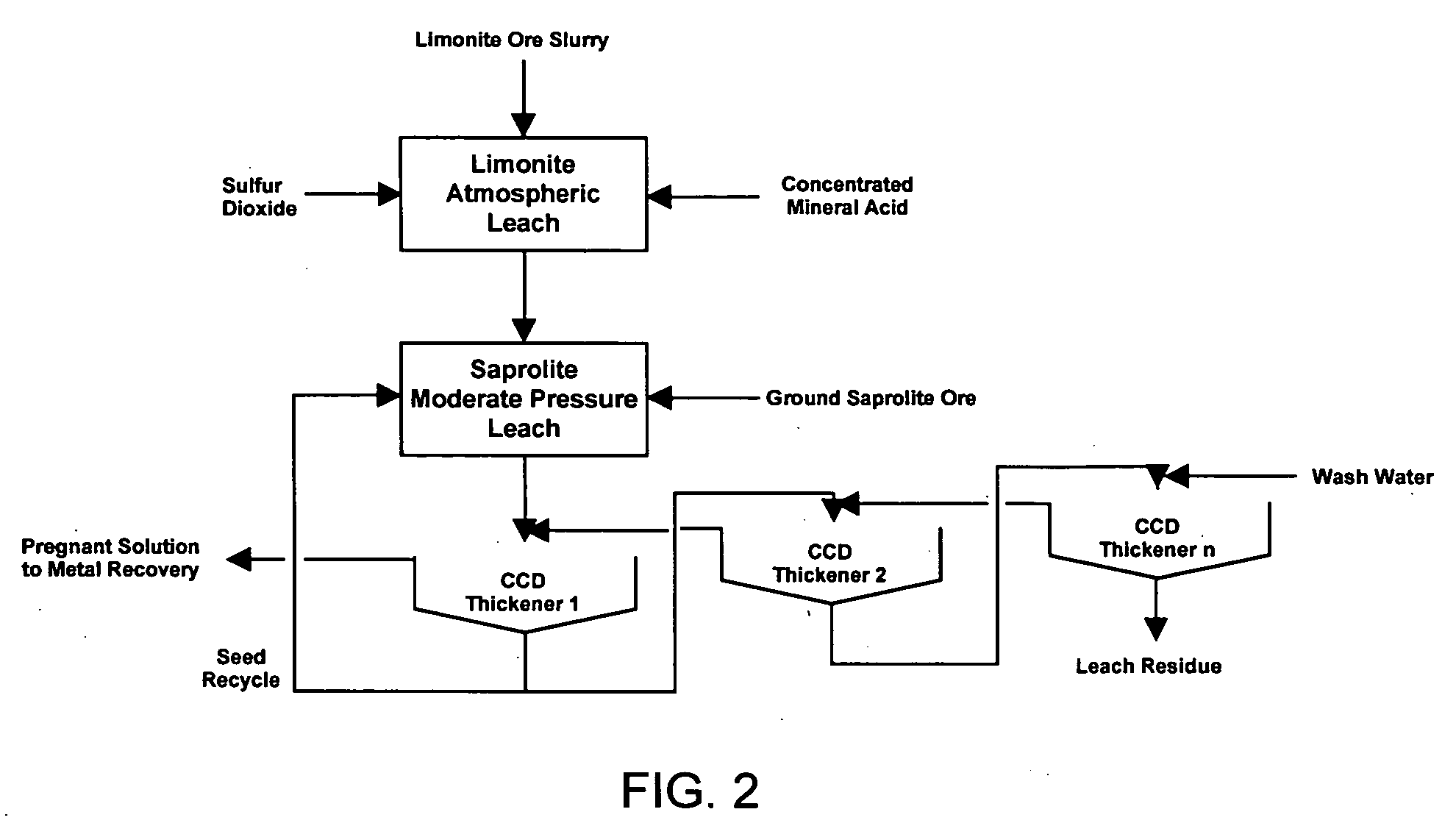
Method for nickel and cobalt recovery from laterite ores by combination of atmospheric and moderate pressure leaching
InactiveCN101001964AHigh extraction rateAvoid environmental unfriendlinessProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodIon exchange
A process for leaching laterite ores containing limonite and saprolite. Sufficient mineral acid is added to a slurry of limonite which is leached at atmospheric pressure to dissolve most of the soluble non-ferrous metals and soluble iron. After adding saprolite the slurry is further leached at a temperature above the normal boiling point and at a pressure above atmospheric pressure for a time sufficient to leach most of the contained nickel in the saprolite and to precipitate most of the iron in solution. The pressure of the slurry is then reduced, and nickel and / or cobalt is subsequently recovered from the leach solution by solvent extraction, resin-in-pulp or other ion exchange, sulfide or hydroxide precipitation, or other recovery method.
Owner:SKYE RESOURCES
Treatment method of nickel-cobalt material
The invention provides a treatment method of a cobalt-containing material, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metal smelting. In the treatment method, through six steps such as peroxidation roasting, sulfuric acid leaching, N902 extraction of copper, chemical iron calcium magnesium removal, P204 extraction and impurity removal, P507 extraction and separation of nickel-cobalt, nickel,cobalt and copper in the nickel-cobalt material are extracted in high recovery, and impurities such as iron, zinc, manganese, calcium, magnesium and the like in the nickel-cobalt material are removed, thereby achieving nickel-cobalt-copper separation and resource comprehensive utilization. According to the treatment method provided by the invention, the process is simple and production cost is relatively low; the adaptability of the method on raw materials is strong and can be used for treating the nickel-cobalt material with complicated components and high copper-zinc-magnesium contents.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Flame retardant coatings
Provided are flame retardant coating compositions and articles coated therewith, which compositions comprise (A) a coating and (B) an effective flame retarding amount of a mixture of (i) at least one compound selected from the group consisting of the (a) sterically hindered nitroxyl stabilizers, (b) sterically hindered hydroxylamine stabilizers and (c) sterically hindered alkoxyamine stabilizers and (ii) at least one conventional flame retardant selected from the group consisting of (d) organohalogen flame retardants, (e) organophosphorus flame retardants, (f) isocyanurate flame retardants and (g) melamine based flame retardants. The coated articles are for example iron, steel, stainless steel, aluminum and other non-ferrous metals, wood, plywood, paper, cardboard, chip board, particle board, plastics, thermoplastics, epoxies, neoprene, rubber, composites, fiberglass reinforced composites, polyesters, polymeric foam, masonry, fabric or textiles, wire and cable constructions and circuit boards.
Owner:TROUTMAN MALISA +3
Ruthenium-barrier polishing slurry
InactiveUS20080148649A1Reduce removal rateOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricEthylene oxide
The polishing slurry is useful for removing ruthenium layers from patterned semiconductor substrates in the presence of at least one nonferrous interconnect metal and a dielectric. The polishing slurry includes 0.001 to 10 weight percent periodic acid or salt, at least 0.0001 weight percent inhibitor for reducing removal rate of the nonferrous interconnect metals, 0.00001 to 5 weight percent organic additive for reducing dielectric removal rate, the organic additive being selected from at least one of water soluble polymers and surfactants, the organic additive containing an ethylene oxide group or an amide group, 0.1 to 50 weight percent abrasive and balance water; and the slurry having a pH of greater than 8 to 12.
Owner:LIU ZHENDONG
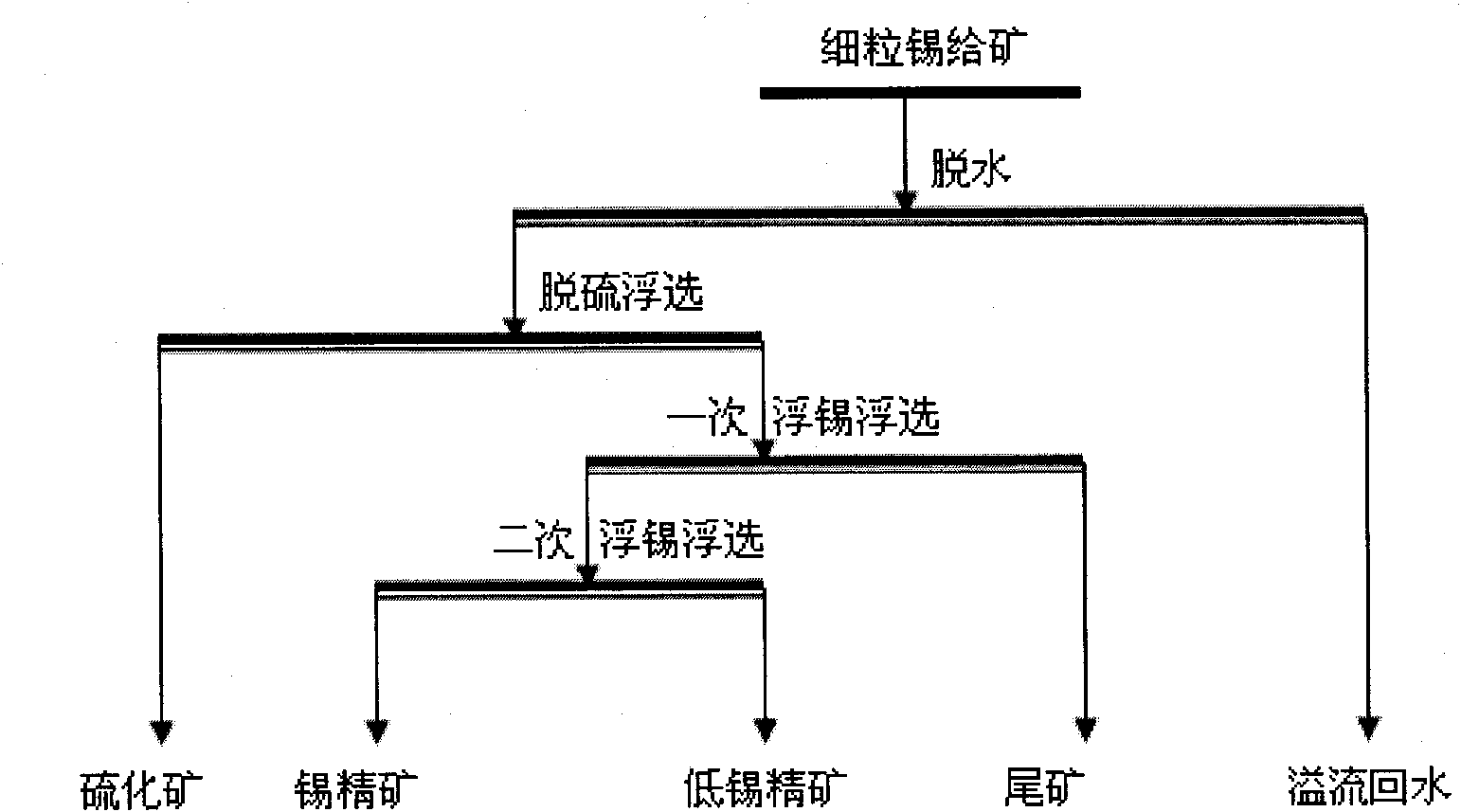
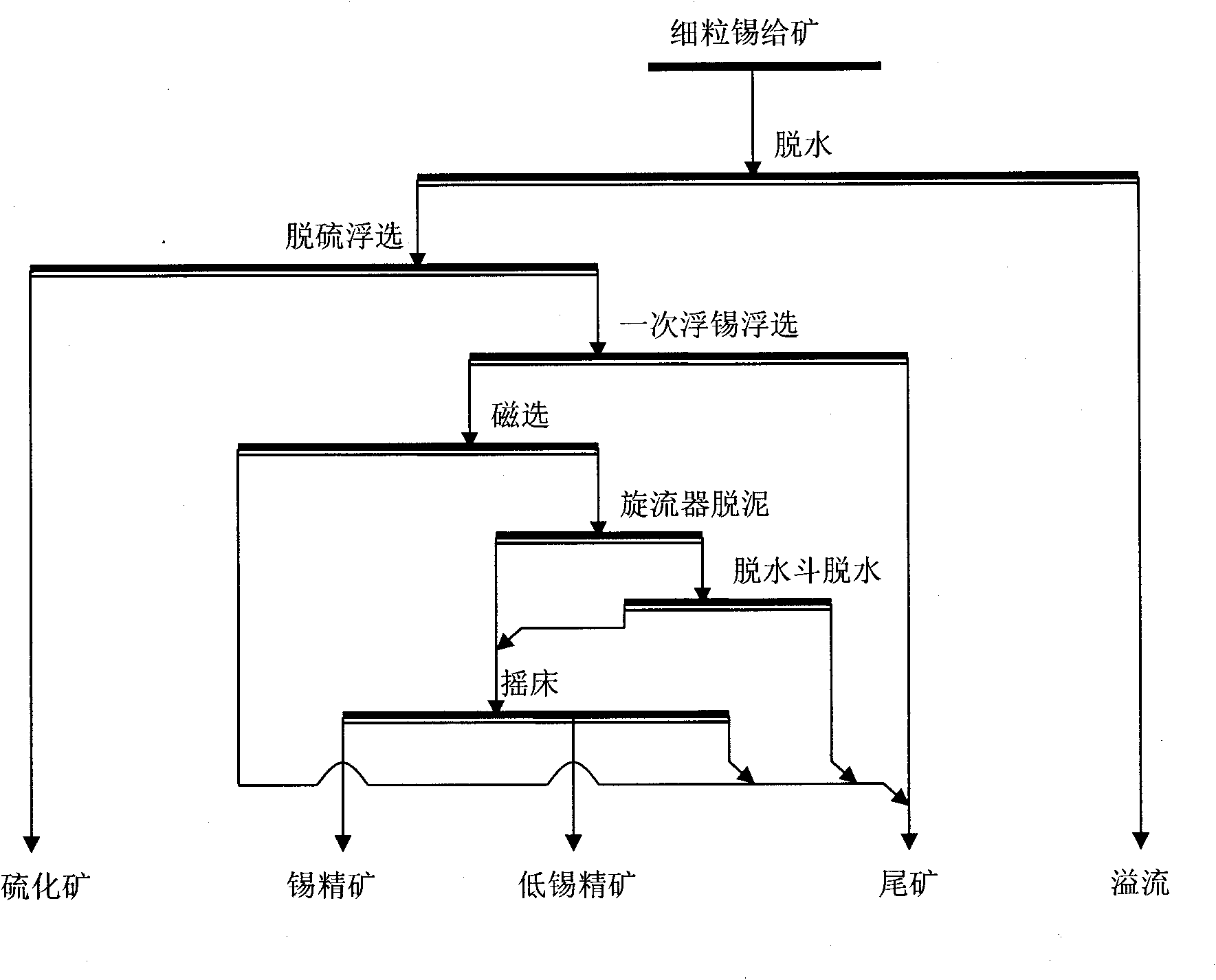
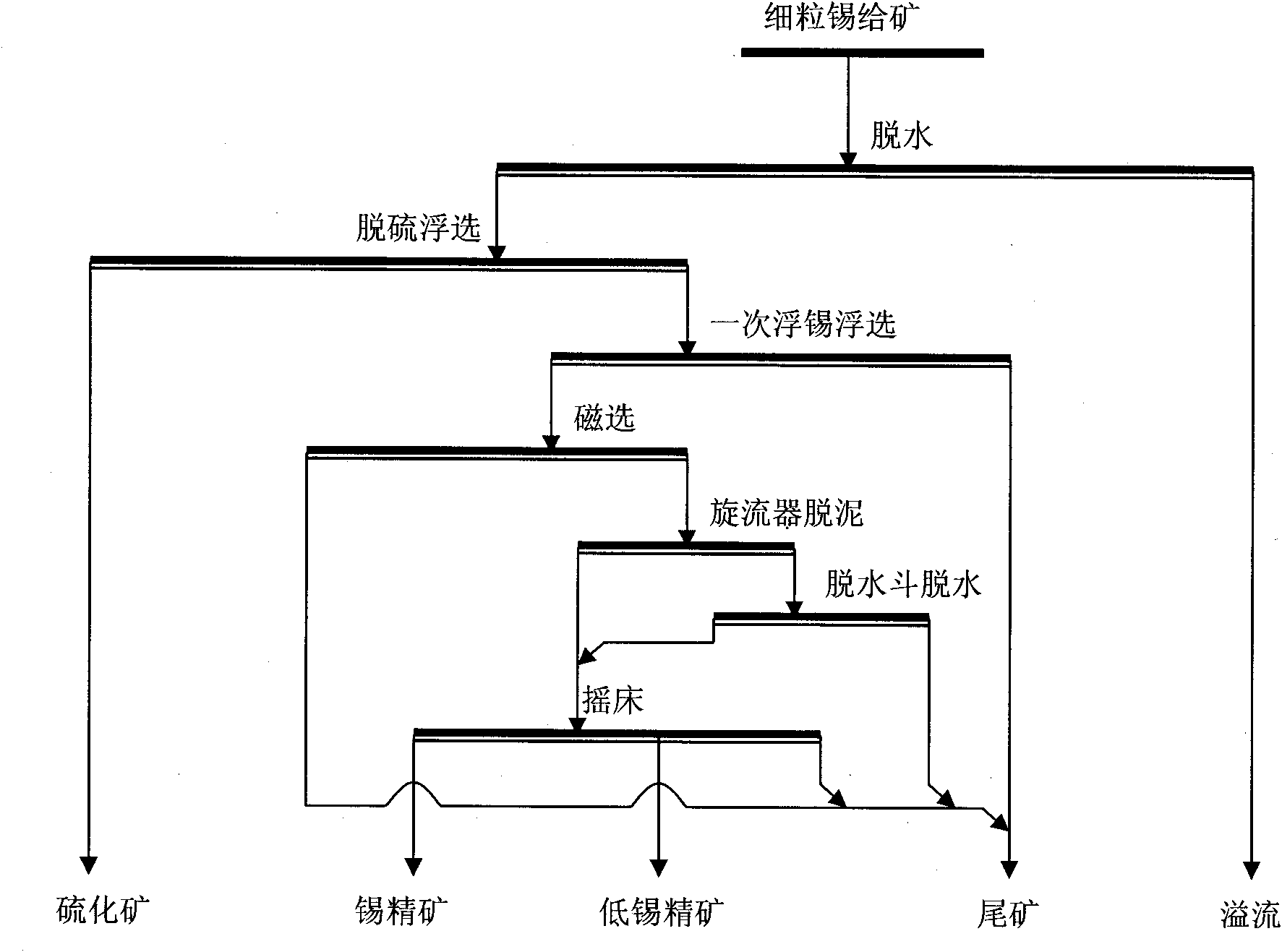
Combined mineral dressing technology of fine grain and micro grain cassiterite
ActiveCN101884951AAchieve separationAvoid interferenceFlotationWet separationNiobiumConcentration ratio
The invention relates to a combined mineral dressing method of fine grain and micro grain cassiterite, which gives up the single mineral dressing method of fine grain and micro grain cassiterite for years. The invention adopts the effective combination of two-time flotation operation, magnetic separation operation, desliming and dewatering operation and reselection operation, provides a new mineral dressing model for selecting grain and micro grain cassiterite which has the size of 10-37 micrometers and has complex mineral property, high impurity content and big mineral dressing difficulty, and improves the cassiterite concentration ratio and cassiterite operation recovery rate; cassiterite concentration ratio can reach 5-10, the cassiterite operation recovery rate can be above 70%, and the tin-containing grade of tin concentrate products can be above 50%. The method also can be used for the mineral dressing of fine grains and micro grains of non-ferrous metal, such as tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum, niobium and the like and has favorable economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:广西华锡矿业有限公司铜坑矿业分公司
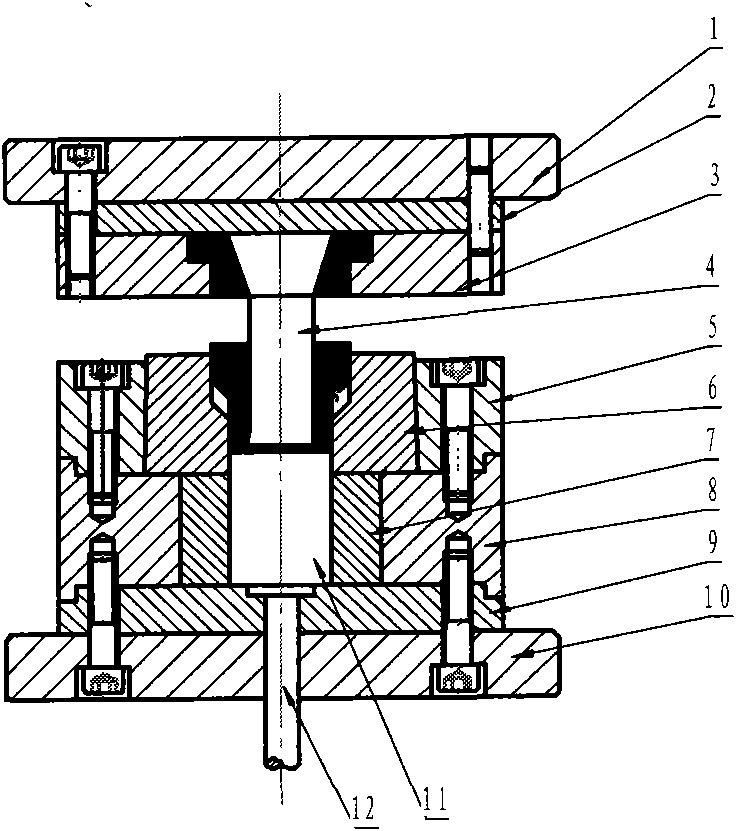
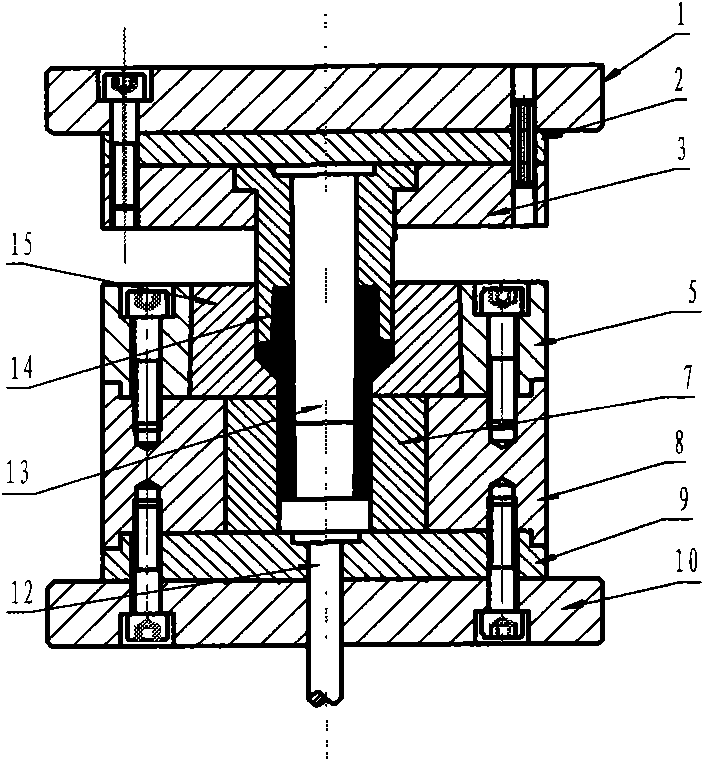
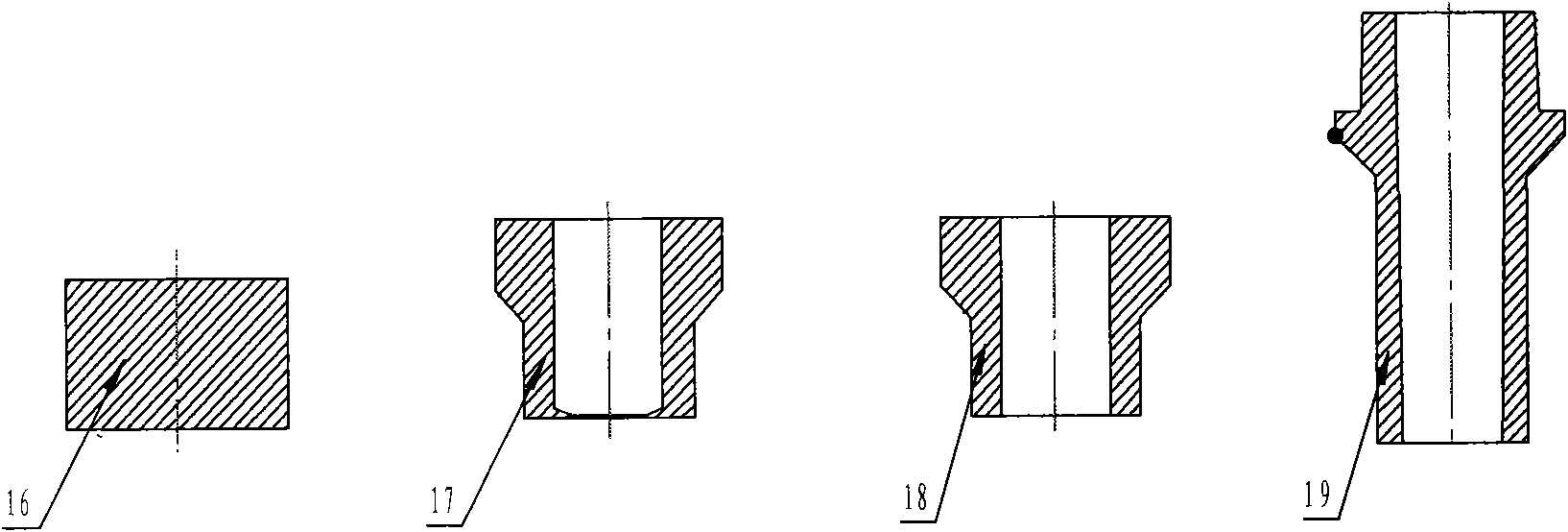
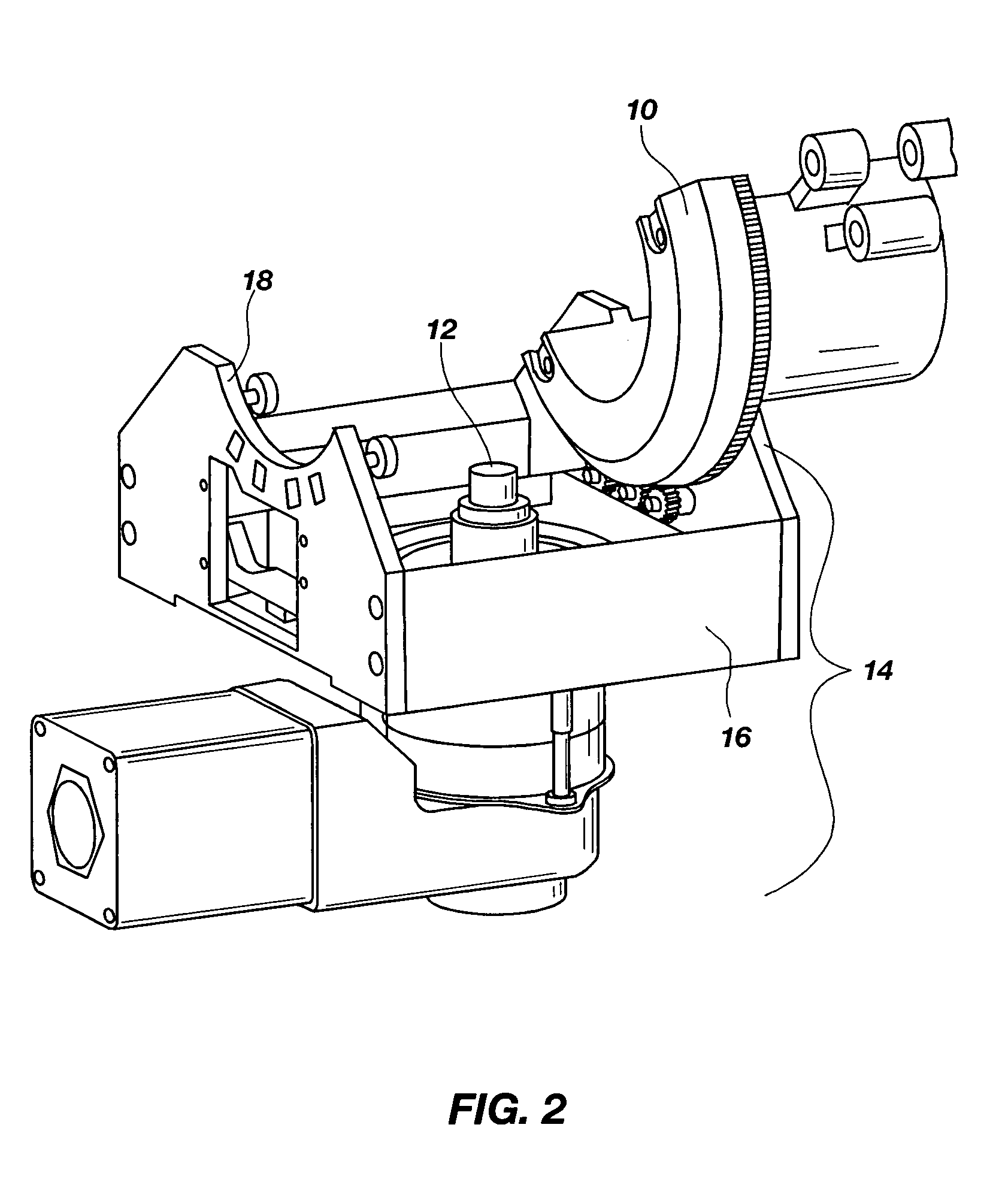
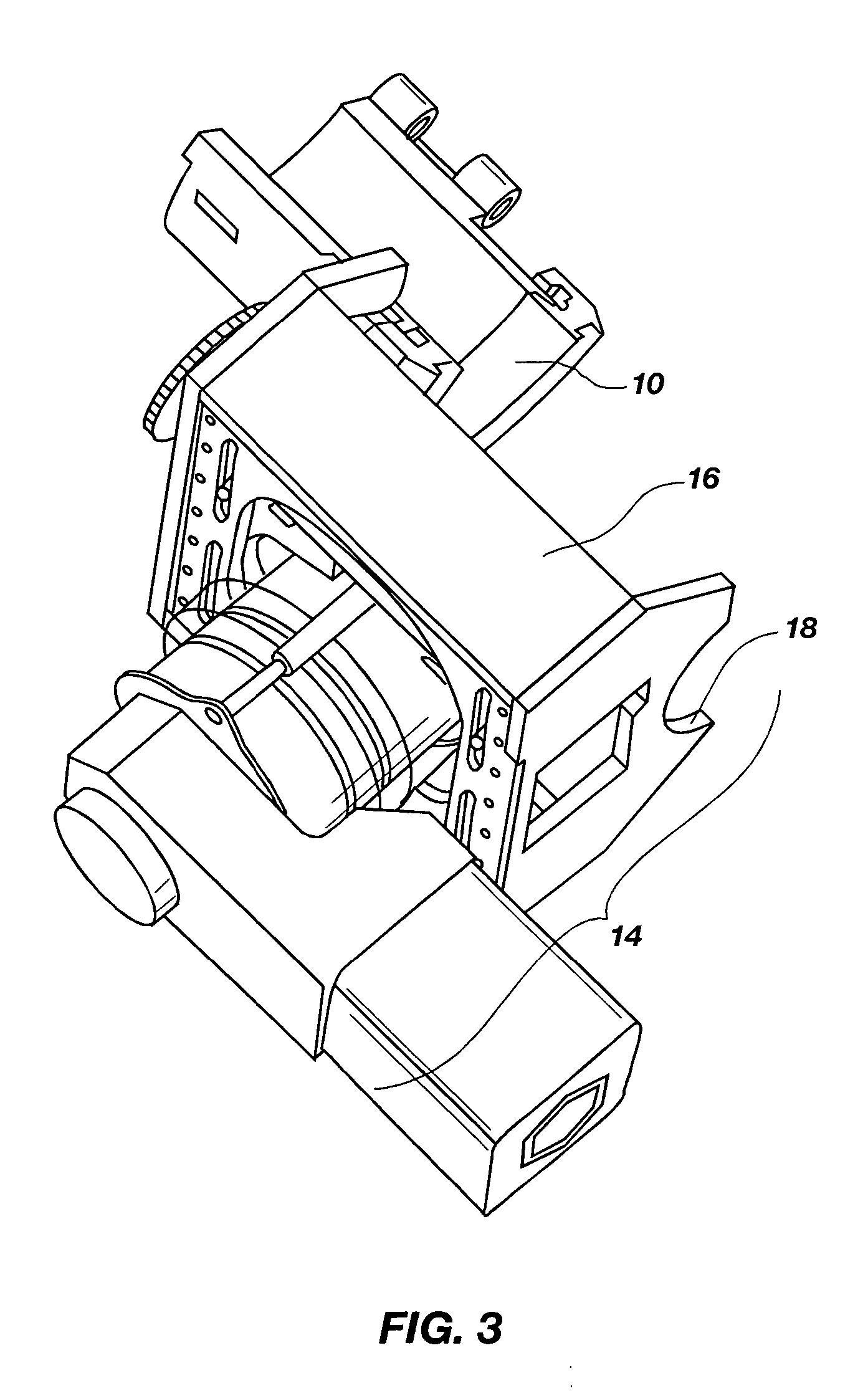
Extrusion forming process of thin-wall long pipe-shaped part blank with flange and mould
InactiveCN101829698AImprove internal qualityHigh dimensional accuracyExtrusion diesMaterials scienceForming processes
The invention belongs to extrusion forming technologies for non-ferrous metal materials and relates to a precise extrusion forming process of a thin-wall long pipe-shaped part blank with a flange. The forming process comprises two steps of primary backward extrusion and secondary forward extrusion, wherein in the step of primary backward extrusion, a primary backward extrusion convex mould (6) is utilized to match with a primary backward extrusion concave mould to together with a piece pusher (11) as an auxiliary for obtaining a primary backward extrusion pipe blank (17) with a web; a secondary forward extrusion convex mould consisting of a forward extrusion convex mould (14) and a mandrel (13) and a secondary forward extrusion concave mould (15) are utilized to carry out the secondary forward extrusion; and the secondary forward extrusion convex mould is placed into a primary backward extrusion pipe blank (18) and moves downwards to extrude the primary backward extrusion pipe blank (18) to obtain a secondary forward extrusion pipe blank (19) so as to finish a secondary forward extrusion process. The internal quality, the size precision and the material utilization rate of the produced thin-wall long pipe-shaped part blank with the flange are greatly improved; and meanwhile, the production efficiency is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for recovering vanadium, tungsten and titanium from waste vanadium-tungsten-titanium-based denitration catalyst
ActiveCN103484678ASimultaneous recoveryLow recovery rateTitanium compoundsVanadium compoundsTungstateAmmonium metavanadate
The invention relates to a method for recovering non-ferrous metals from waste denitration catalysts, particularly relates to a method for recovering vanadium, tungsten and titanium from a waste vanadium-tungsten-titanium-based denitration catalyst, belonging to the field of non-ferrous metal recovery technologies. The method mainly comprises the steps of preparing the catalyst into powder with the grain size being smaller than 100 meshes, and adding concentrated alkali liquor; heating to react vanadium, tungsten and titanium with alkali, so as to produce slightly-soluble titanate, water-soluble vanadate and tungstate; filtrating to obtain a titanate filter cake, wherein titanate or titanic acid can be prepared from the filter cake; adding ammonium salt into a filtrate so as to precipitate ammonium metavanadate, and filtrating to obtain ammonium metavanadate and a new filtrate; adding concentrated acid into the new filtrate, thereby preparing solid tungstic acid. The method has the advantages of simple process, low energy consumption, good solid-liquid reaction contact, high vanadium, tungsten and titanium recovery rate, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for producing dehydrated calcium sulfate whisker
InactiveCN101550585ANo emissionsReduce manufacturing costPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsAnhydrous Calcium SulfateLixiviant
The invention provides a method for producing dehydrated calcium sulfate whisker, comprising: using copper, lead, zinc, aluminium, nickel, cobalt, stannum, non-ferrous metal secondary resource cycle utilizing, calcium nitrate solution produced in treating process of electroplating waste, calcium chloride solution, or mixed water solution of calcium nitrate and calcium chloride as raw material, using sulfuric acid as calcium ion precipitant, adding whisker shape regulating agent, controlling reaction condition, regenerating aqua fortis or hydrochloric acid lixiviant, and simultaneously producing ultralong and big length to diameter ratio calcium sulphate dihydrate whisker. After calcium sulphate dihydrate whisker is deposited from calcium nitrate solution, calcium chloride solution or the mixed solution of calcium nitrate and calcium chloride are deposited, the water solution is translated to be nitric acid solution, hydrochloric acid solution or a mixed solution of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, returning back to leaching out or treating process for processing non-ferrous metal mineral substance, non-ferrous metal secondary resource or electroplating remove. The calcium sulphate dihydrate whisker is treated by microwave heating, forming calcium sulfate hemihydrate or anhydrous sulphate of calcium after dehydration.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Green multifunctional detergent and its prepn process
InactiveCN1847381AHigh decontamination efficiencyOperational securityOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsSemiconductor materialsLiquid-crystal display
The present invention discloses one kind of green multifunctional detergent comprising surfactants, detergency promoter, permeating agent, chelating agent, defoaming agent and water in certain weight proportion. The green multifunctional detergent is used in cleaning ferrous metals, non-ferrous metals and stainless steel, as well as semiconductor material and device, LCD glass plate, coated glass, LCD box and electronic circuit board. The present invention has the advantages of compounding and use at normal temperature, powerful detergency, high cleaning efficiency, no ODS matter contained, no phosphate contained, no inflammability, no explosion, no pollution, and direct exhaust and reuse of used waste liquid.
Owner:BEIJING XINLI MACHINERY
Friction stir welding improvements for metal matrix composites, ferrous alloys, non-ferrous alloys, and superalloys using a superabrasive tool
InactiveUS20050082342A1Improves friction stir weldingImprove featuresWelding/cutting auxillary devicesPipe elementsMetal alloyEngineering
A friction stir welding system that enables clamping of a pipe to enable friction stir welding around the pipe OD, a movable mandrel that provides a counter-force to the pressure exerted on the outside of a pipe by a tool, and a system for providing friction stir welding and repair inside a nuclear vessel in an underwater environment.
Owner:MAZAK CORP +1
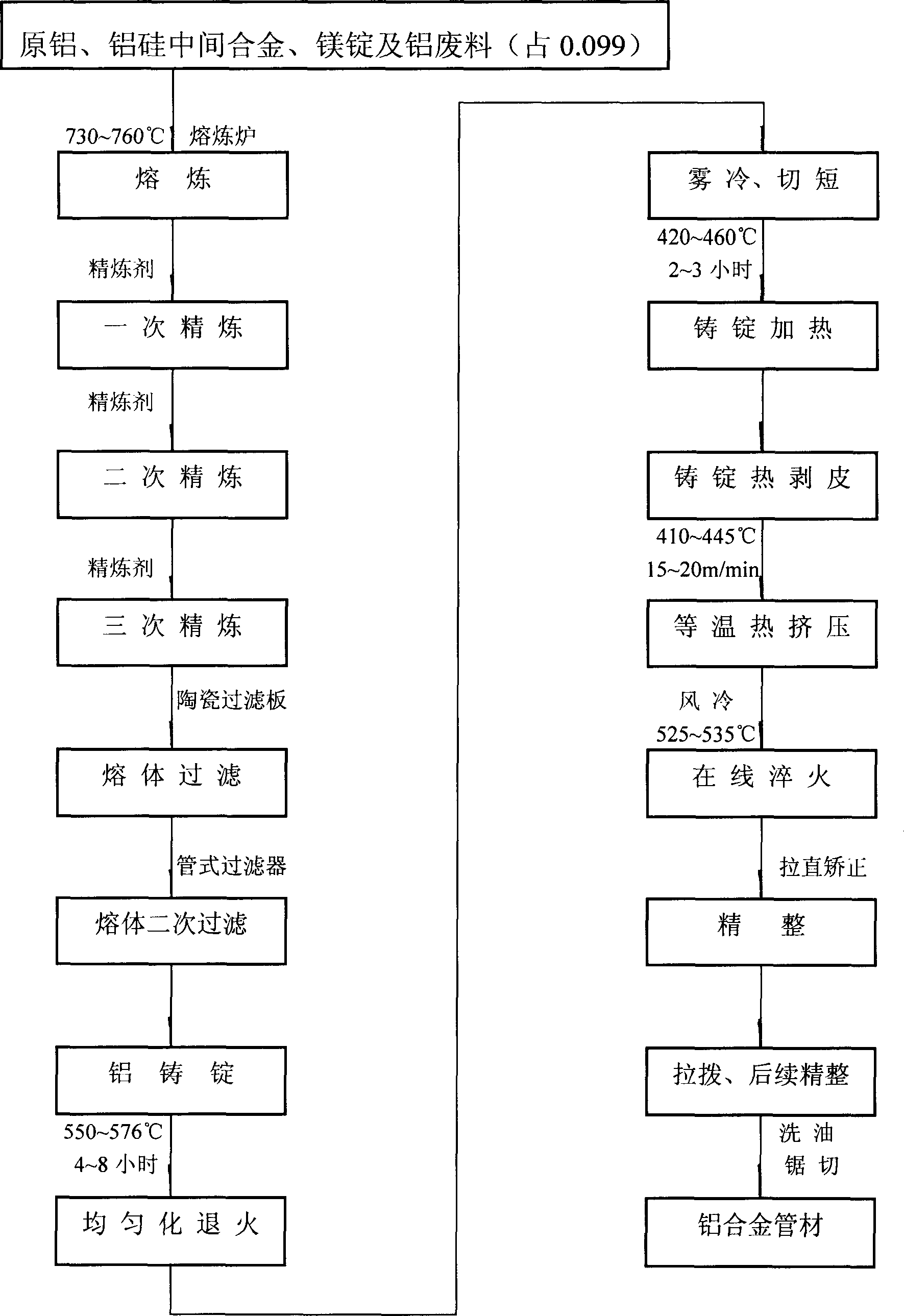
Aluminum alloy pipe for high purity and high precision light sensitive drum base material and producing method
The present invention is a kind of aluminum alloy pipe for making photosensitive drum and belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal pipe manufacture. The aluminum alloy pipe is made of material comprising Si 0.20-0.23 weight portion, Mg 0.45-0.50 weight portion, Fe 0.01-0.15 weight portion, impurity elements S and P 0.00-0.01 weight portion and Al 99.34-99.11 weight portions. It is produced through smelting, refining, in-situ fining, in-situ deairing, filtering, casting to form ingot, annealing, heating ingot to peel, extruding breakdown, quenching, finishing, drawing, post-finishing and other steps. The aluminum alloy pipe has low impurity content, and is suitable for manufacturing high purity and high precision photosensitive drum and similar products.
Owner:GUANGDONG HOSHION IND ALUMINUM CO LTD
Process for preparing metallic titanium and titanium master alloy
The invention relates to the non-ferrous metal metallurgy fused salt electrolysis field, a method mainly comprises the steps of: preparing titanium dioxide, titanium tetrachloride, titanium dichloride and fluotitanate as raw materials, electrolyzing one or a plurality of combinations of TiO2, TiC14 and the fluotitanate in an electrolysis bath, preparing metallic titanium or titanium-based master alloy through an electrolysis method or a thermal reduction-electrolysis combined method, performing the TiO2 and connecting direct current to deoxidize or adopting metal (or metallic compound) for heat reducing the TiO2 beforehand, preparing the metallic titanium which contains oxygen (O) with certain concentration, and then electrolyzing aluminium, alkali metal, alkaline earth, rare earth metal, metallic copper, metallic zinc or metallic lead to deoxidize finally in the electrolysis bath. The purpose of the method is to reduce the production cost of the metallic titanium, simplify the production procedures and lower the environmental pollution in the production process, especially the titanium dioxide taken as the raw materials, the production flow is shortened, the storage and the transportation are convenient, none chlorine gas takes part in the reaction, and green metallurgy of the metallic titanium can be realized.
Owner:曹大力 +1
Friction stir welding of metal matrix composites, ferrous alloys, non-ferrous alloys, and superalloys using a superabrasive tool
InactiveUS7124929B2Improve wear characteristicsWelding/cutting auxillary devicesVacuum evaporation coatingHeat flowSuperalloy
Owner:MAZAK CORP
Cleaning and Corrosion Inhibition System and Composition for Surfaces of Aluminum or Colored Metals and Alloys Thereof Under Alkaline Conditions
InactiveUS20080108539A1Inhibit and reduce of surfaceReliably inhibit reduce corrosionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsAlkaline earth metalPharmaceutical industry
The present invention relates to corrosion inhibitor systems, in particular to cleaning and corrosion inhibiting compositions for surfaces of aluminum or colored metals and alloys thereof under alkaline conditions, especially in the food and pharmaceutical industries. The cleaning and corrosion inhibiting compositions comprise as a corrosion inhibitor at least one alkyleneoxy alkylphosphate di- or triester having the general formula (I) where Z is either —O—M or —O—(AO)n2— Alkyl wherein M is an ammonium, alkali metal or alkaline earth metal cation, Alkyl is a C5-C22 alkyl or alkylaryl group, AO is a C2-4-alkylene oxide unit and n1, n2 and n3 each are integers from 2 to 10.
Owner:JOHNSONDIVERSEY INC
Quartz glass body, method and casting mold for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20080153688A1Low purityLow impurity contentAfter-treatment apparatusFinal product manufacturePorosityVitreous Bodies
The invention includes an improved quartz glass body, especially an improved quartz glass crucible for melting non-metals, non-ferrous metals, or silicon, and a method and casting mold for making it The quartz glass body is made by a method in which a quartz glass-water mixture is supplied to a casting mold comprising an outer part and an inner part, dried in the mold, and put under an overpressure during the drying. Later a resulting green glass body is removed from the mold. At least a portion of the shaping surfaces of the inner part of the mold are surfaces of a water-impermeable substance. The method provides a cast body with a reduced tendency to crack and with a smaller open porosity.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Control system for friction stir welding of metal matrix composites, ferrous alloys, non-ferrous alloys, and superalloys
InactiveUS20050051602A1Precise speed controlEasy to controlWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesControl systemSuperalloy
A control system and method of use that enables friction stir welding of metal matrix composites, ferrous alloys, non-ferrous alloys, and superalloys when using a superabrasive tool, wherein the control system and method enables control of various operational aspects of a friction stir welding mill in order to make it possible to perform friction stir welding that is repeatable, reliable, and results in a superior finished workpiece.
Owner:SII MEGADIAMOND +3
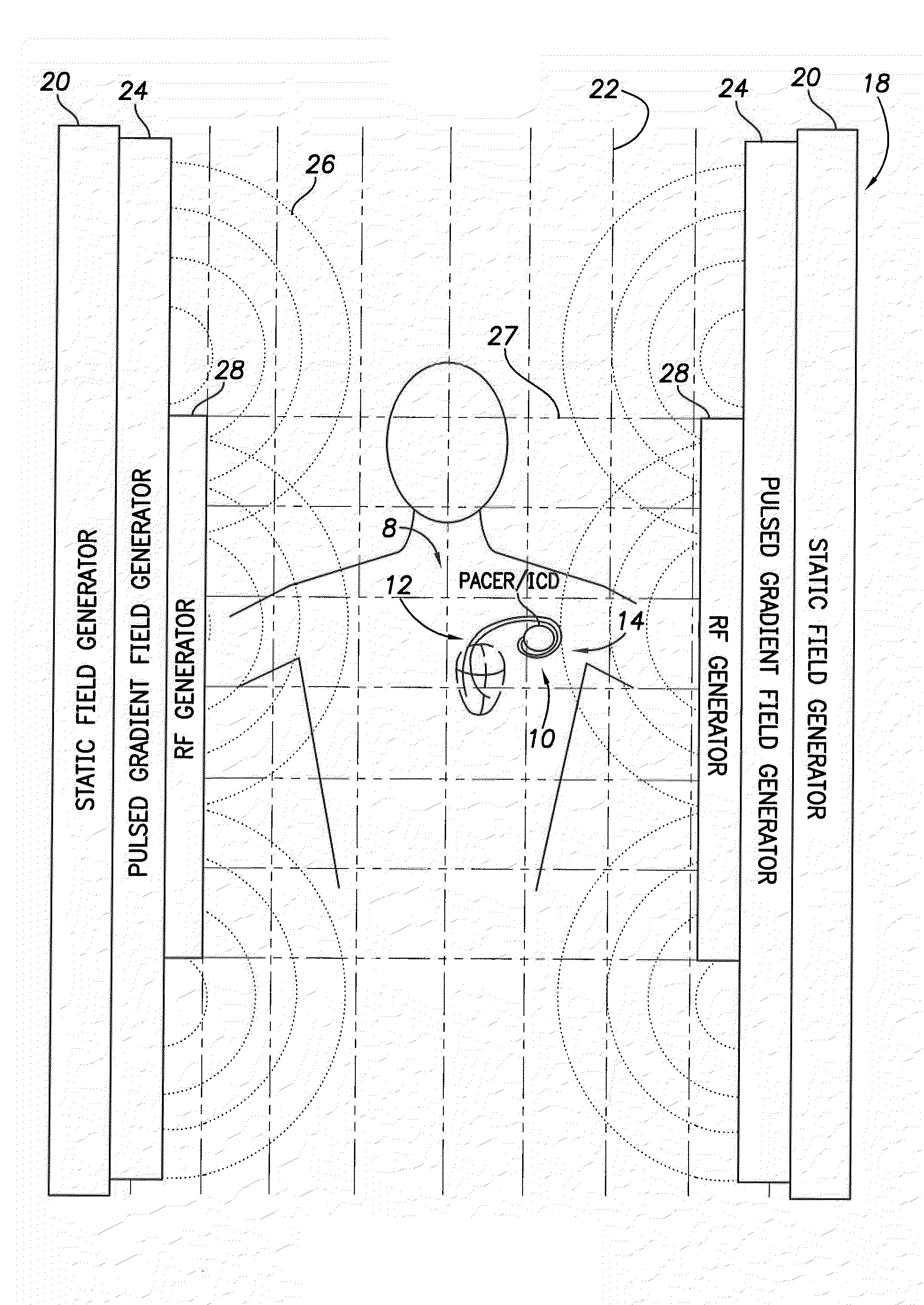
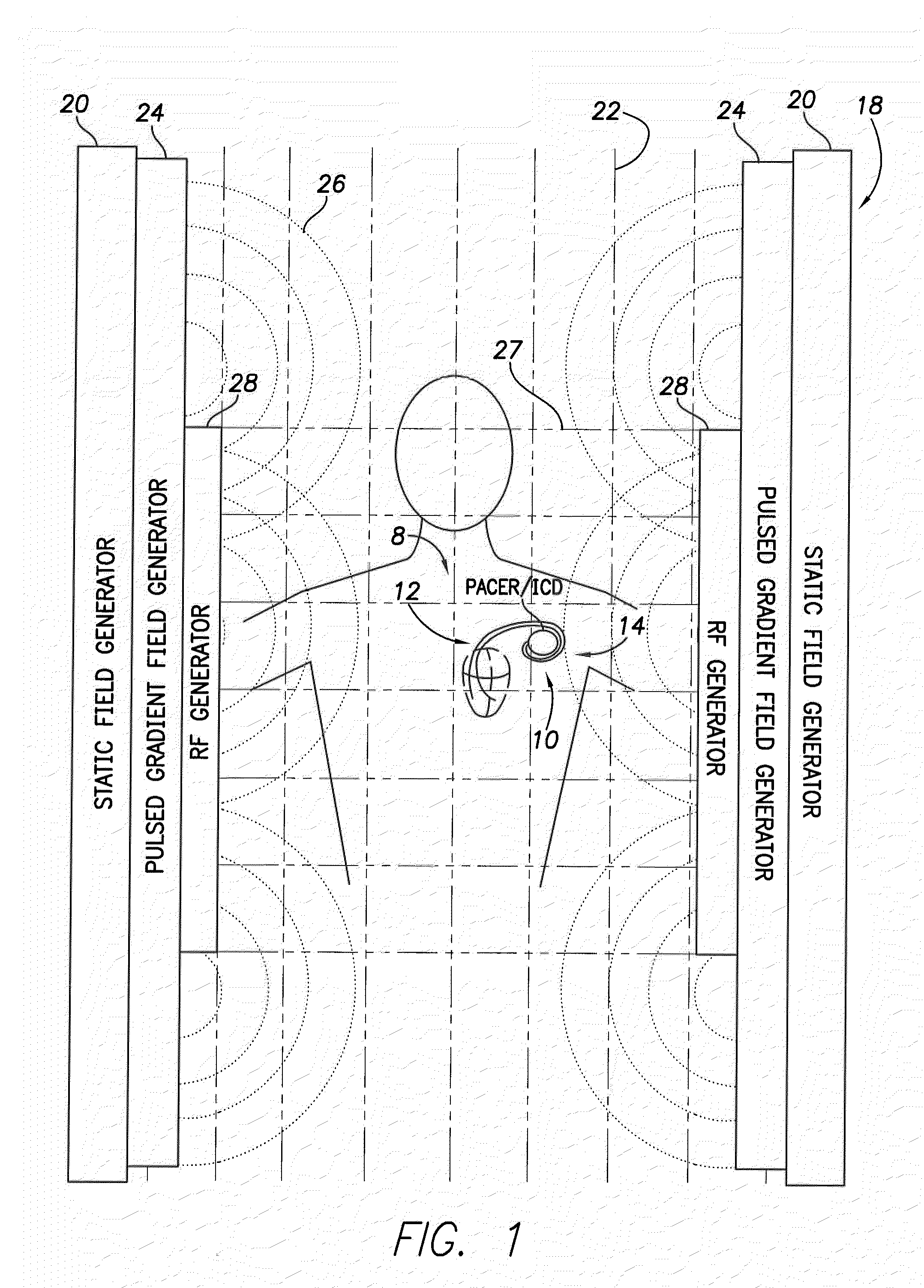
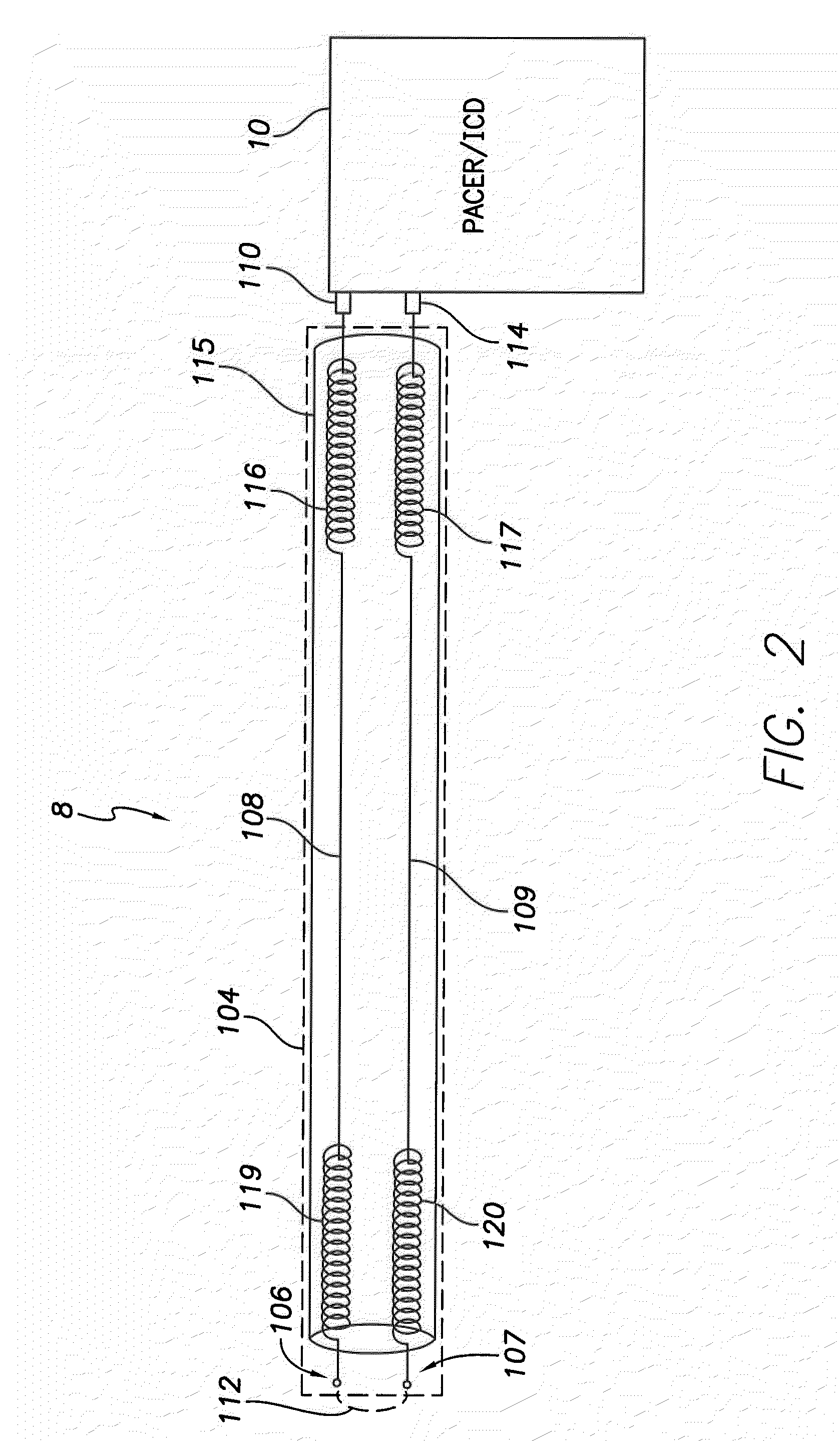
Implantable medical device lead incorporating a conductive sheath surrounding insulated coils to reduce lead heating during MRI
InactiveUS20110034983A1Reduce couplingReduce heatInternal electrodesExternal electrodesDevice implantConductive polymer
A conducting sheath is provided along at least a portion of an implantable medical device lead, and preferably along substantially its entire length, for mitigating heating problems arising during magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedures, particularly problems arising due to a problem described herein as the “coiling effect.” During device implant, the clinician may elect to wrap or coil excess proximal portions of leads around or under the medical device being implanted. Thereafter, during MRI procedures, shunt capacitance may develop between the housing of the implantable device and insulated coils within the proximal portions of the lead that are near the device, resulting in greater lead heating during the MRI. The conducting sheath helps suppress induced currents and also reduces or eliminates shunt capacitance. The conducting sheath may be, for example, formed using a metal mesh or a conducting polymer tube incorporating non-ferrous metal powders. The sheath may be formed in ¼ wavelength segments.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
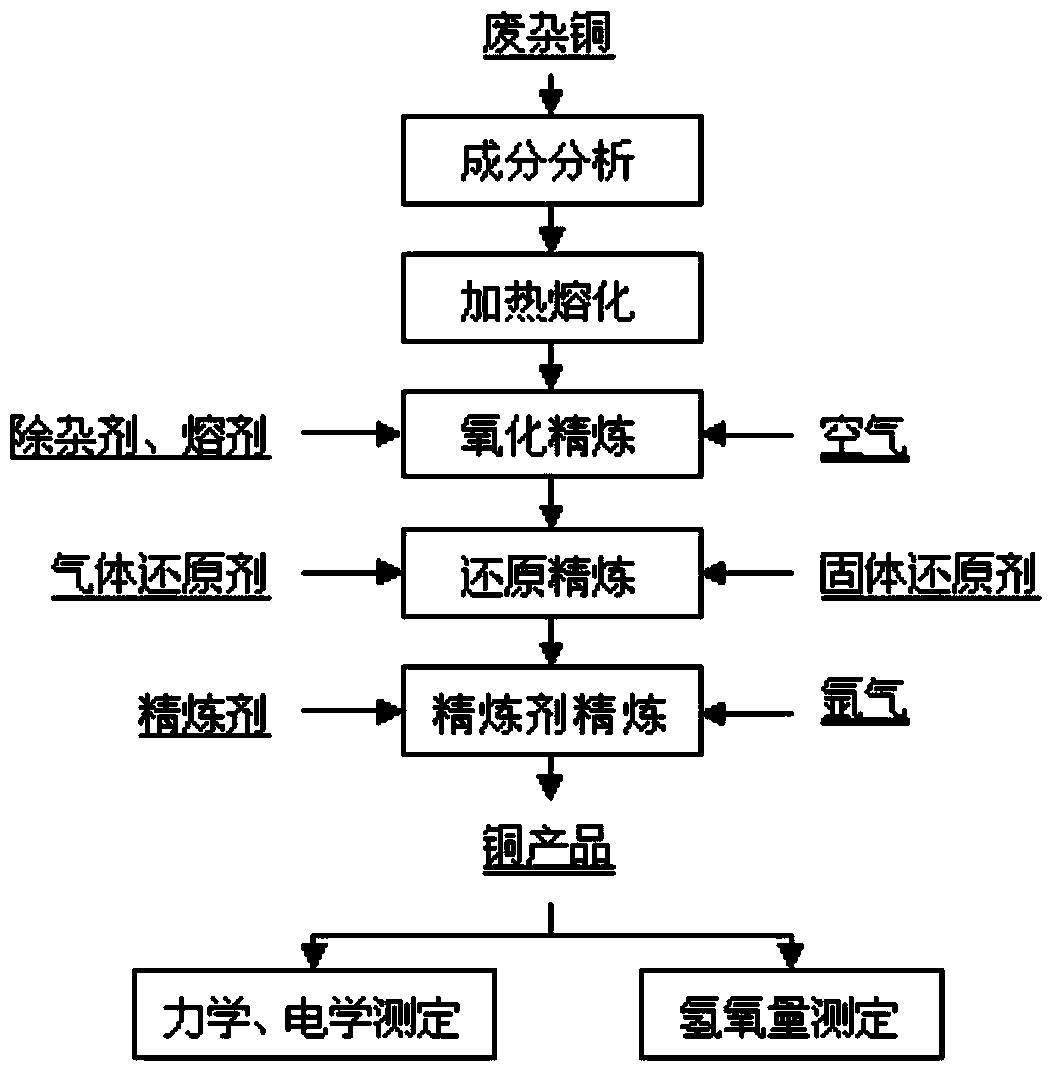
Method for directly producing high-purity oxygen-free copper by pyrogenic process continuous refining of scrap copper
ActiveCN103725897AOptimizing Process ParametersReduce manufacturing costProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisCopper wire
The invention relates to a method for directly producing high-purity oxygen-free copper by pyrogenic process continuous refining of scrap copper, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: by taking scrap copper as a raw material; analyzing the component characteristics of each batch of raw material, and then preparing into a mixture, wherein the mass percent of a copper element in the mixture is greater than or equal to 93%; adding metaphosphate or phosphorus pentoxide and flux to the mixture; refining by oxidation; stewing and drossing after oxidation is finished, and then orderly carrying out reduction refining and refining agent refining under an agitation state, so as to obtain the high-purity oxygen-free copper of which the copper content is greater than or equal to 99.95% and the oxygen content is smaller than 0.003%, wherein the electrical resistivity of the obtained copper wire after drawing is below 0.017241omega / (mm), and the relative electrical conductivity is over 100% of International annealed copper standard (IACS). The method is strong in flexibility, significant in refining effect, and applicable to different components of scrap copper materials; the scrap copper can be used for directly making a rod after being refined. Compared with the traditional pyrogenic process smelting-electrolytic refining-copper cathode purification process, the method disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the flow is shortened, the cost is reduced, the energy is saved, and continuous operation is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for nickel and cobalt recovery from laterite ores by combination of atmospheric and moderate pressure leaching
InactiveUS20060024224A1Efficient leachingEfficient separationIron compoundsCobalt compoundsRecovery methodIon exchange
A process for leaching laterite ores containing limonite and saprolite. Sufficient mineral acid is added to a slurry of limonite which is leached at atmospheric pressure to dissolve most of the soluble non-ferrous metals and soluble iron. After adding saprolite the slurry is further leached at a temperature above the normal boiling point and at a pressure above atmospheric pressure for a time sufficient to leach most of the contained nickel in the saprolite and to precipitate most of the iron in solution. The pressure of the slurry is then reduced, and nickel and / or cobalt is subsequently recovered from the leach solution by solvent extraction, resin-in-pulp or other ion exchange, sulfide or hydroxide precipitation, or other recovery method.
Owner:SKYE RESOURCES
Disk shearing blade and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101177765AImprove wear resistanceHigh strengthShearing machinesFurnace typesHigh intensityWear resistance
A disc scissors blade and its manufacturing method, the composition weight percentage of the material of the disc scissors blade is: C: 0.40-0.70%, Si: 0.50-1.2%, Mn: 0.20-0.50%, Ni: 1.00-1.50% %, Cr: 4.00-6.00%, Mo: 0.50-2.00%, V: 0.30-1.50%, Nb: 0.10-0.80%, P≤0.02%, S≤0.02%. The method introduces an electroslag remelting process into a common manufacturing method of disc shears, and increases the temperature of quenching and tempering heat treatment and final heat treatment. The disc scissors have good wear resistance and deformation resistance, and are suitable for slitting or trimming hot-rolled high-strength thick steel plates. In addition, the disc shear blade of the present invention also has a good use effect on disc shears in other similar working conditions, and can also be applied to disc shears for stripping or edge trimming of cold-rolled strip steel, and also has a promotional effect on non-ferrous metal disc shears. value and application prospects.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD +1
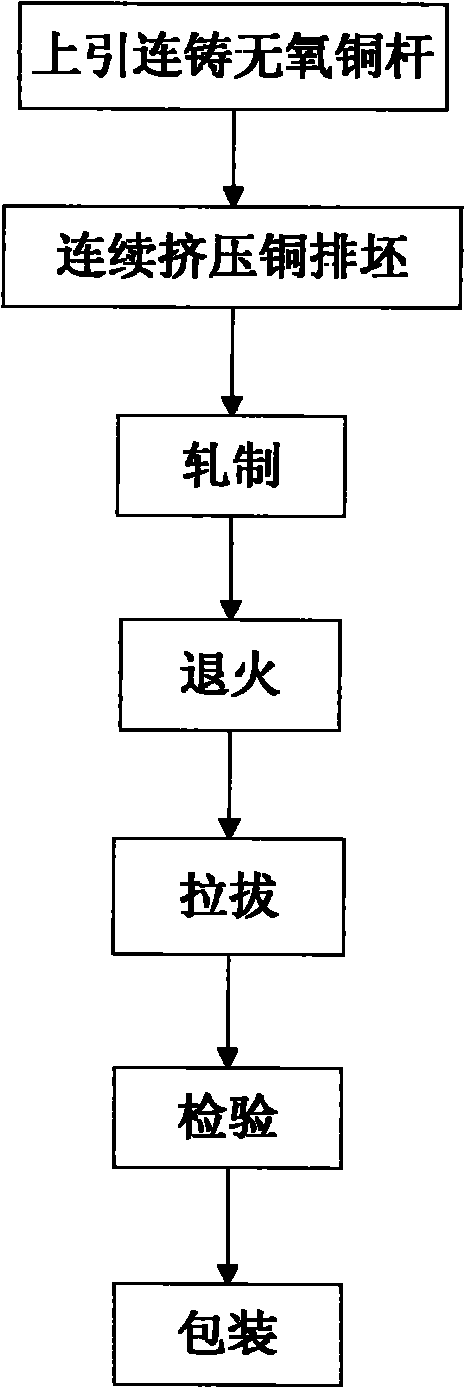
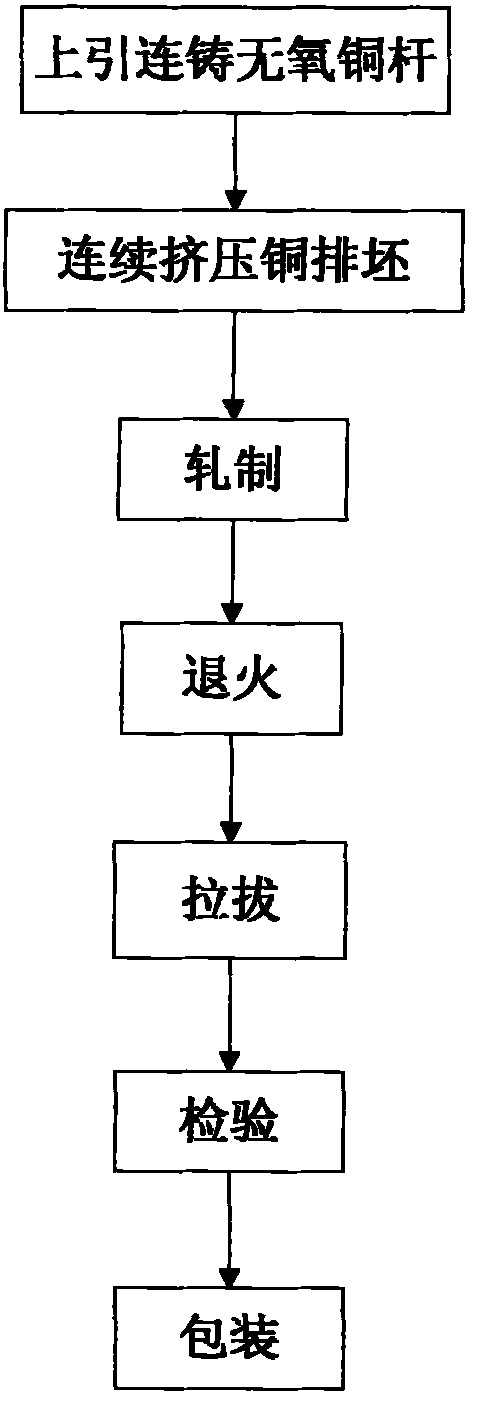
Production method of conducting copper bars for bus duct with large flakiness ratio
InactiveCN101916624AAvoid picklingImprove working environmentOpen bus-bar installationsCable/conductor manufactureLow oxygenHigh conductivity
The invention discloses a production method of conducting copper bars for a bus duct with a large flakiness ratio, belonging to the technical field of processing of non-ferrous metals. The production method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: upward continuously casting oxygen-free copper bars, continuously extruding copper bar billets, rolling, annealing, drawing, checking and packaging. By adopting the continuous extrusion technology to produce the copper bar billets, the continuous production can be realized, and the weight of each roll of copper bar billets can reach more than 3 tons. Moreover, because the copper bar billets are produced in a roll shape, the defect of cutting the head and the tail of each copper bar in the traditional production process is avoided, and the yield of the product reaches more than 90%. Meanwhile, by reasonably setting continuous extrusion process parameters, rolling rate and the like, the invention effectively improves the quality of the product and has the advantages of high purity, low oxygen content, high conductivity, excellent surface quality and the like. The product is detected to show that the content of Cu and Ag is greater than or equal to 99.97%, the content of O is less than or equal to 10ppm, and the conductivity is 98-101% according to the IACS.
Owner:浙江力博实业股份有限公司
High-formability and high-strength aluminum alloy material as well as preparation method and application of the high-formability and high-strength aluminum alloy material
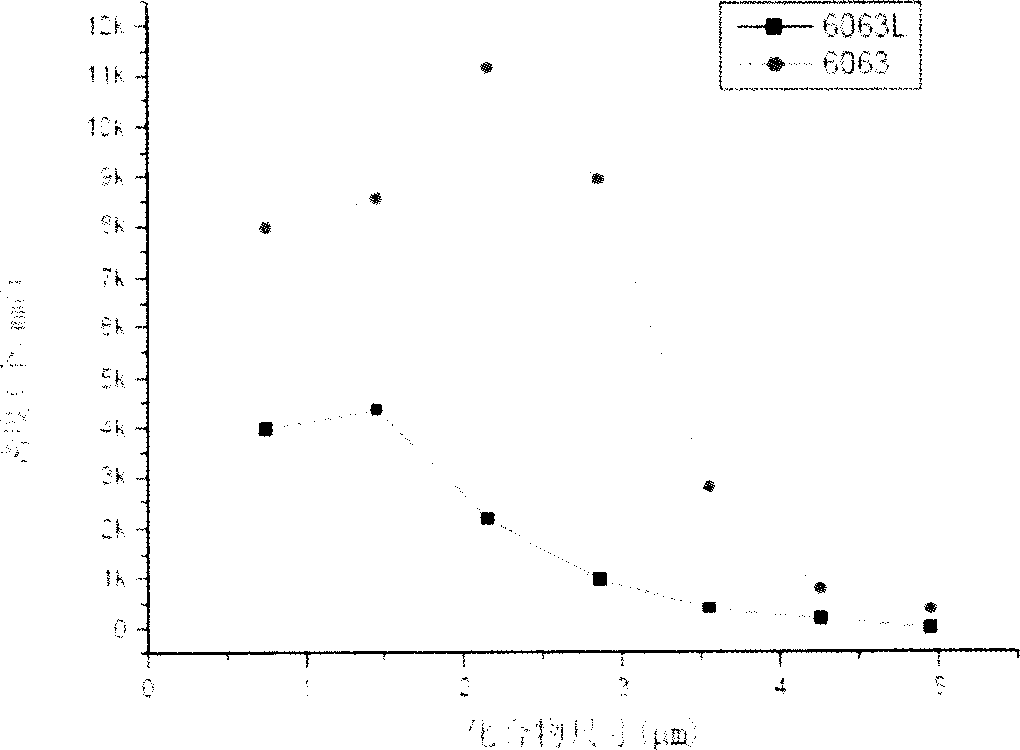
The invention relates to an aluminum alloy material, in particular to a high-formability and high-strength aluminum alloy material as well as a preparation method and application of the high-formability and high-strength aluminum alloy material, belonging to the field of non-ferrous metal materials. The high-formability and high-strength aluminum alloy material contains the following components in mass percent: 0.40-0.50% of Mg, 0.35-0.70% of Si, 0.01-0.06% of Sr, 0.06-0.10% of Mn, and the balance of Al and unavoidable impurities. Compared with the mechanical properties of 6063-T5, the tensile strength of the aluminum alloy material is improved to 220Mpa from 160Mpa, the yield strength is improved to 180Mpa from 110Mpa, and the elongation is improved to above 12% from 8%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LEXIANG ALUMINUM
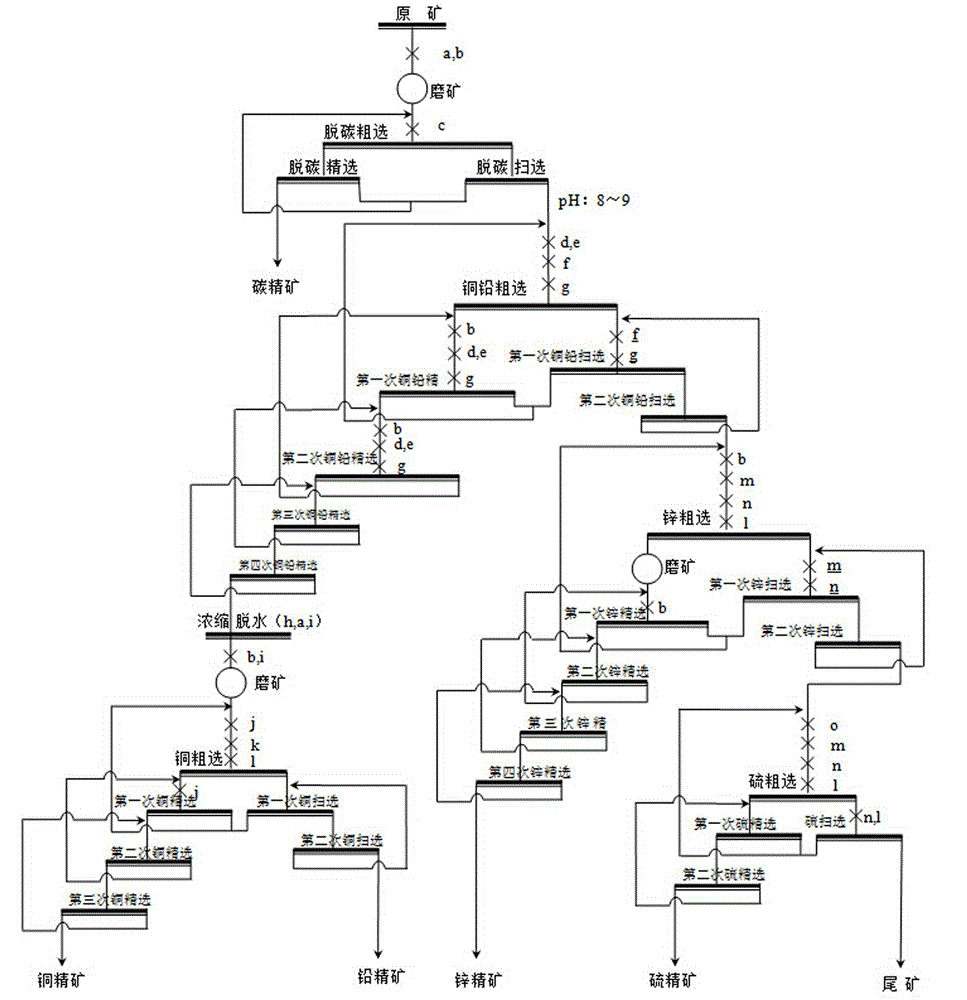
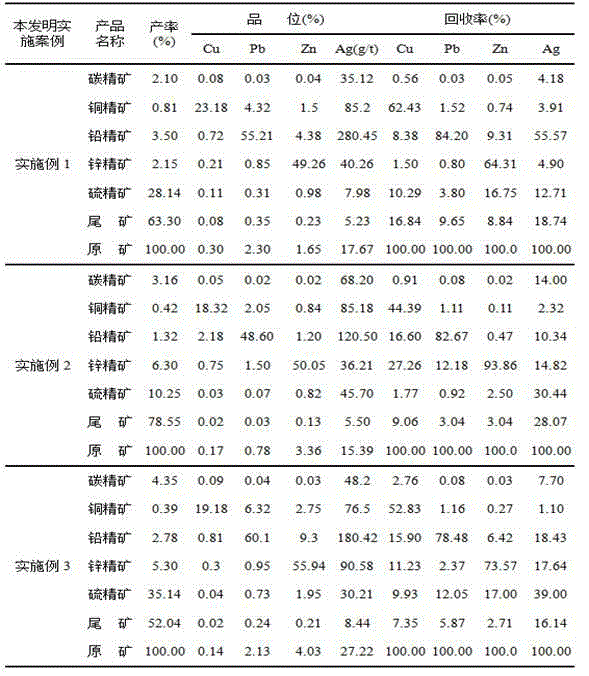
Beneficiation method for cu-pb-zn polymetallic ores
The invention discloses a beneficiation method for cu-pb-zn polymetallic ores, and belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal beneficiation. According to the technical scheme, the characteristic of complex cu-pb-zn-sulfur polymetallic ores with embedded fine-grained carbon level is utilized, a technological process of carbon-removing, cu-pb partial bulk flotation, cu-pb separation and zn-and-sulfur choosing in tailings is adopted, a concentration and fine grinding mode is adopted to achieve deep reagent removal, the influence of slurry on flotation is effectively eliminated, efficient collectors A8 and depressors T721 for cu-pb separation are used in the cu-pb partial bulk flotation process, separation and recovery of copper, lead, zinc and sulfur are effectively achieved, and concentrate mixing is obviously lowered.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
Method for recycling vanadium pentoxide in waste SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration catalyst
ActiveCN104195342ASolve pollutionAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementEconomic benefitsOxidizing agent
The invention belongs to the field of non-ferrous metal recycling, and in particular relates to a method for separating and recycling vanadium pentoxide in a waste SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) denitration catalyst according to a reduction acid leaching method. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, reducing pentavalent vanadium in the catalyst by using a reducing agent in an acidic solution to tetravalent vanadium which is more soluble, then oxidizing the tetravalent vanadium in the acidic solution to the pentavalent vanadium by using an antioxidant, fully hydrolyzing the pentavalent vanadium under certain conditions for precipitation by adjusting the pH value of the solution, collecting the precipitation, roasting the precipitation and then obtaining the vanadium pentoxide with high purity. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process, higher in operability, and suitable for large-scale production. The recovery rate of the vanadium pentoxide can be ensured to reach above 95%, and the purity of the obtained vanadium pentoxide is high (higher than 98%), so that the vanadium pentoxide can be directly used for preparing raw materials of the SCR denitration catalyst; the method disclosed by the invention can not only turn wastes into useful resources, and harm into benefits, but also solve a series of potential environmental pollution problems to bring considerable economic benefits and environmental benefits.
Owner:无锡华骏宏科技有限公司
A method for resource processing non-ferro metals processing wastewater containing ammonia and sulfate radical
ActiveCN101161596AHigh practical valueEliminate pollutionWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processSulfate radicalsSodium sulfate
The invention relates to a novel process for recycling treatment for waste water which contains ammonia and sulfate radicals and is produced in the process of non-ferrous metal processing. The invention is characterized in that: sodium hydroxide is added into the waste water to convert ammonium ions in the waste water into molecular ammonia; then the waste water is heated by heat resource in a rectification tower; the ammonia in the waste water enters into a condenser in the form of gas from the top of the tower to be cooled into liquid ammonia and partial liquid ammonia returns, thus the remainder becomes the product; the water removed of ammonia exchanges heat with the waste water to be treated and then continues to be cooled, thus sodium sulfate crystals are obtained; the water removed of sodium sulfate removed is removed also sulfate radicals and ammonia, and can directly return to a production plant. The invention has a combined process of ammonia rectification recycle and sodium sulfate cooling crystallization, ensures the recycling use of the water as the ammonia in the water is reclaimed in the form of liquid ammonia or ammonia water as well as the sulfate radicals are reclaimed in the form of sodium sulfate, retains valuable metal ions in the water, and improves the recycling rate of the resource. In a word, the process can realize the recycling utilization of ammonia-nitrogen waste water produced by non-ferrous metal processing, has a simple process flow, is suitable for large-scale industrial production, and has both economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:BEIJING CYCLE COLUMBUS ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
Short-flow preparation method of minor-caliber nickel-based alloy thin-wall tubes
InactiveCN102463272AIncrease productivityShort labor intensityExtrusion control devicesAlloyMaterials science
The invention relates to a short-flow preparation method of minor-caliber nickel-based alloy thin-wall tubes, belonging to the technical field of processing non-ferrous metal material tubes, mainly comprising the following steps that: (1) centrifugal casting technology is carried out to prepare nickel-based alloy tube billets, wherein, the ratio of outer diameters and inner diameters of the tube billets is 0.4-0.6; (2) the hot extrusion temperature of nickel-based alloy tubes is 1000-1250 DEG C, and the extrusion ratio is 5-16; (3) LG / LD and other series of cold pilger mills or drawing machines are used for carrying out multi-pass cold processing to reduce the tube diameter and reduce the wall thickness, so as to obtain thin-wall tubes; and (4) intermediate annealing, final annealing and final tube straightening are carried out. The method has the advantages of short flow, low labor intensity, laborsaving shaping, low cost, and high production efficiency. The prepared minor-caliber nickel-based alloy thin-wall tubes have high additional values. The method is suitable for large scale production, and has remarkable economic benefits and social benefits.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
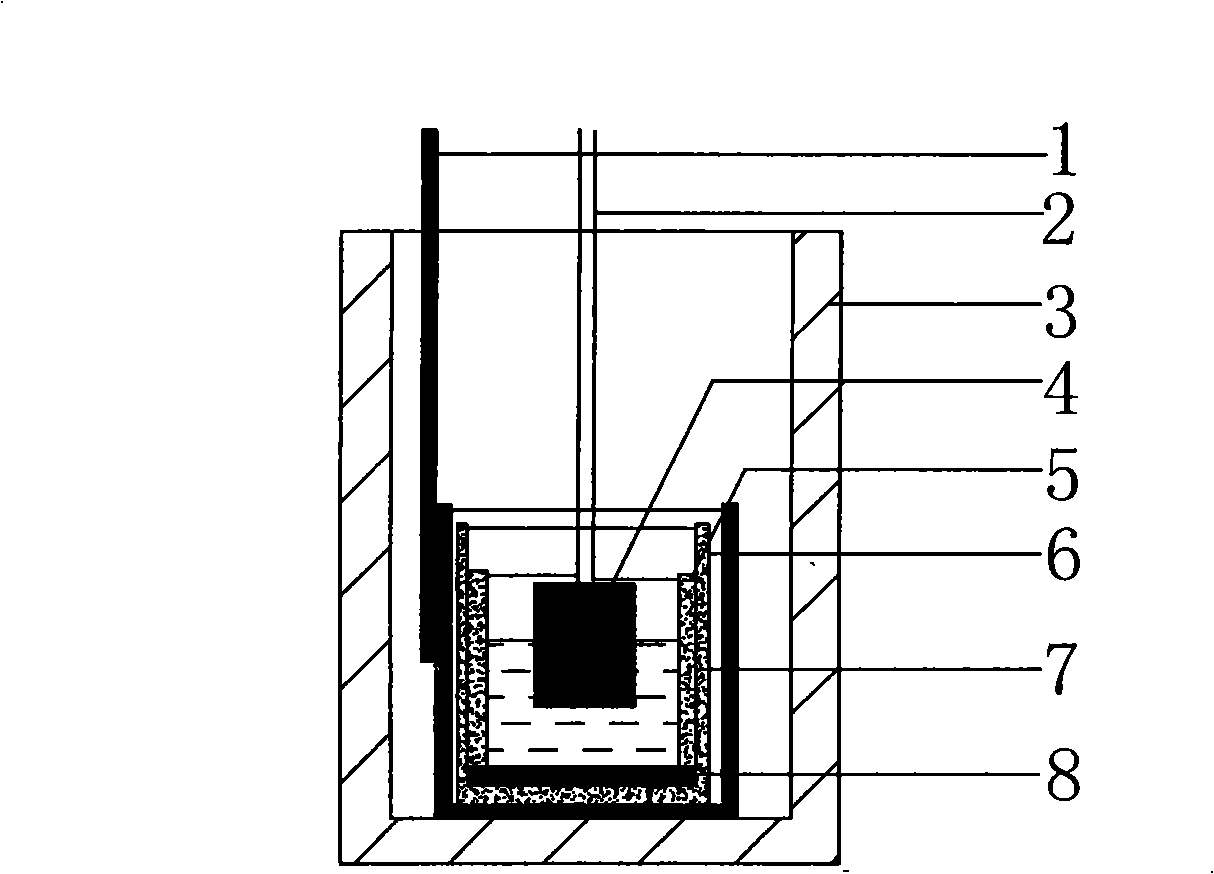
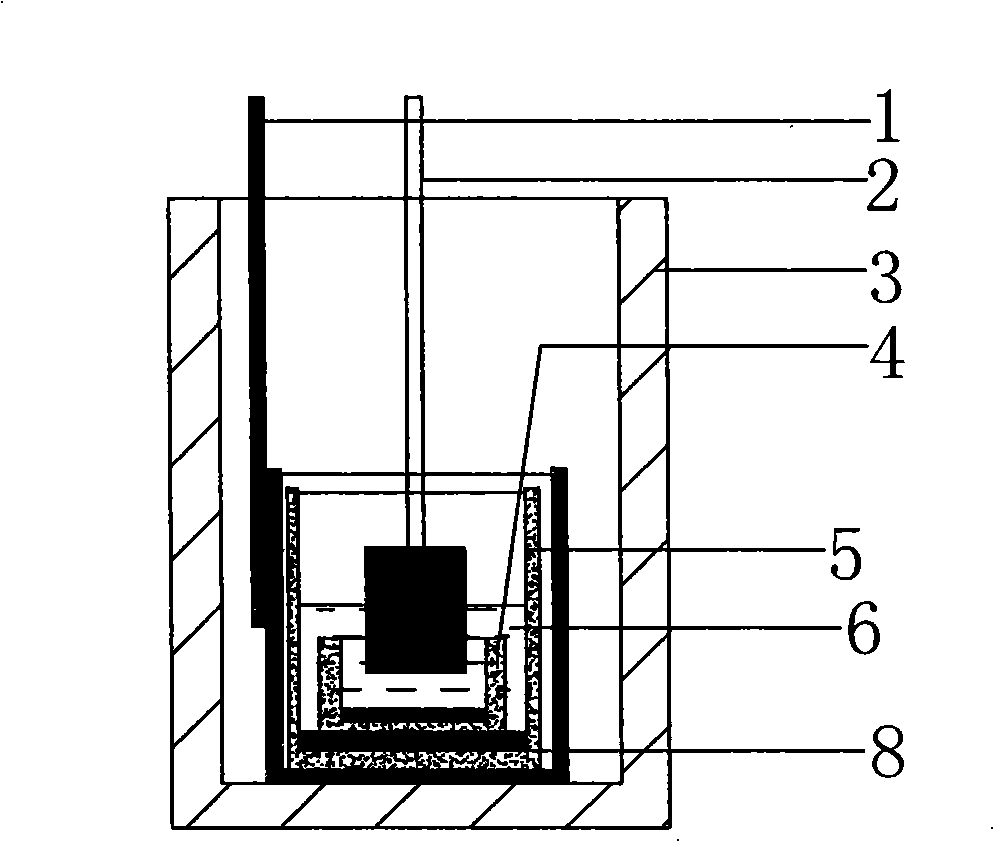
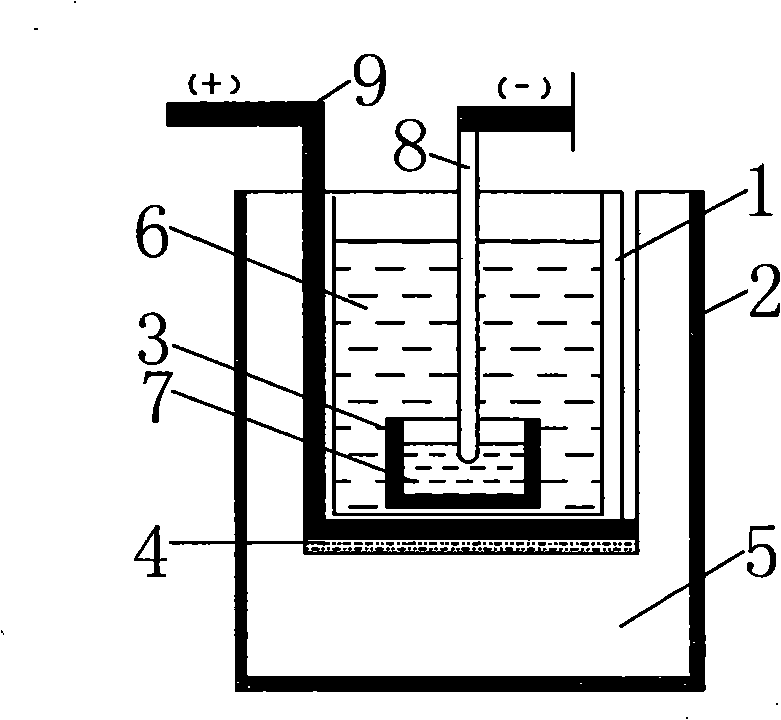
Electropolishing preparation method of sample for EBSD (Electron Back-Scattered Diffraction) analysis of titanium-aluminum alloy
InactiveCN107402150AIncrease the areaEasy and flexible operationPreparing sample for investigationElectrolysisHigh rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of non-ferrous metal analysis and particularly relates to an electropolishing preparation method of a sample for EBSD (Electron Back-Scattered Diffraction) analysis of a titanium-aluminum alloy. The electropolishing preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out earlier stage treatment on the sample: determining the size of the sample to be smaller than 7mm*6mm*4mm, and carrying out standard metallographic treatment and mechanical polishing on the testing surface; secondly, setting up a portable device: connecting the sample with a positive pole of a power supply, connecting a stainless steel plate with a negative pole of the power supply and matching the bottom end of electrolyte with a magnetic stirrer; thirdly, preparing the electrolyte: selecting 4 to 12 percent of perchloric acid, 55 to 65 percent of methyl alcohol and the balance of n-butyl alcohol according to the volume ratio, wherein the total amount of the electrolyte is 700ml; putting the electrolyte into a beaker with the volume of 1L; fourthly, carrying out electrolysis treatment, washing and drying: controlling the temperature to be 30 DEG C below zero to 20 DEG C below zero, controlling the voltage to be 25 to 35V and controlling the polishing time to be 40 to 55 seconds. The electropolishing preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of large surface area for treating the sample and suitability for preparing titanium-aluminum alloy samples with various components and various test purposes, which are prepared by different processing method. In addition, the electropolishing preparation method has the advantages of easiness and flexibility in operation, no restriction from site facilities and the like, good polishing effect and high rate of finished products; the device has the characteristics of high mobility, low cost, easiness in promotion and wide application prospect.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Anti-incrustation corrosion inhibitor for circulating water system with high concentration time and high chloride ion content
InactiveCN101759301AReduce corrosionShorten speedTreatment using complexing/solubilising chemicalsHigh concentrationIon content
The invention relates to an anti-incrustation corrosion inhibitor for a circulating water system with a high concentration time and a high chloride ion content. The anti-incrustation corrosion inhibitor comprises the following components in parts by weight: 1-100 parts of phosphoric acid and salt thereof, 1-500 parts of organic phosphonic acid and salt thereof, 5-1,000 parts of acrylic copolymer, 1-20 parts of zinc salt, 10-200 parts of anode corrosion inhibitor and 0.5-5 parts of imidazoline non-ferrous metal corrosion inhibitor. Compared with the prior art, the invention can effectively suppress under-deposit corrosion and point corrosion caused by low pH value and high chloride ion content.
Owner:上海淼清水处理有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com