Patents
Literature
3106 results about "Liquid ammonia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
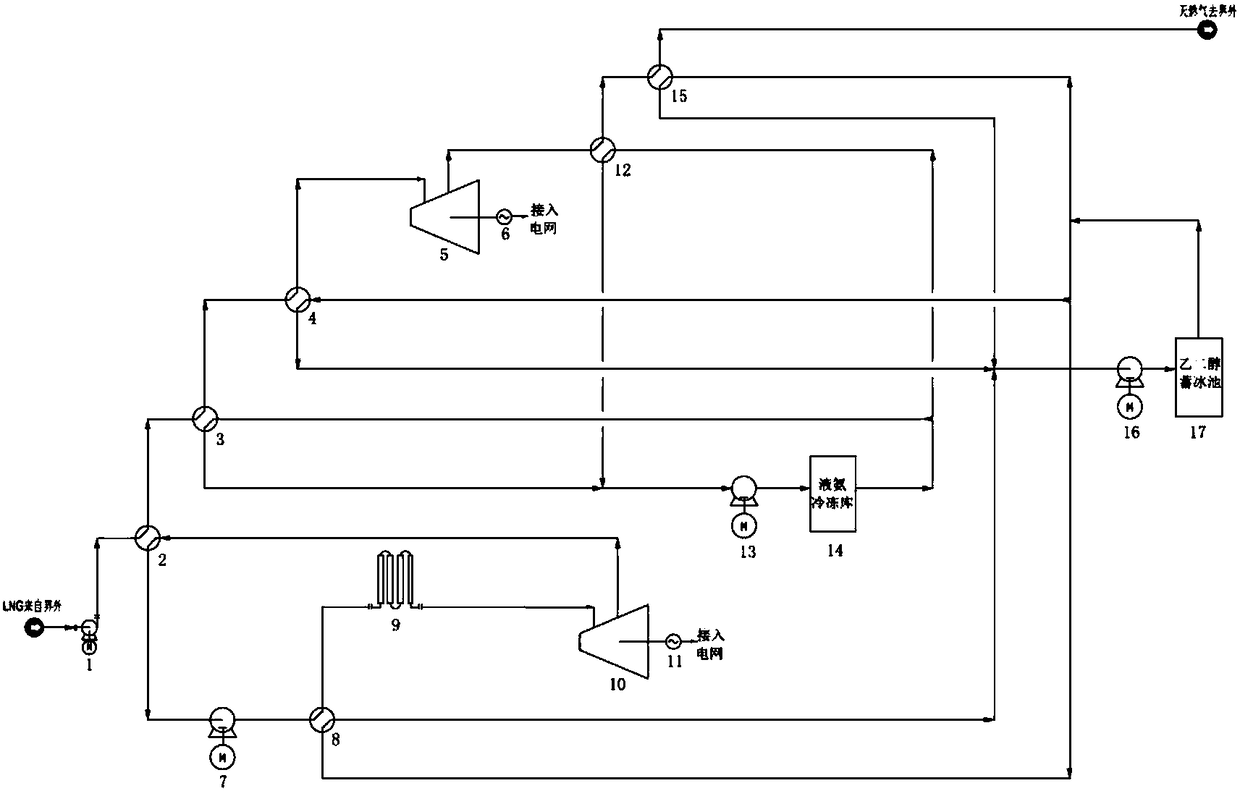
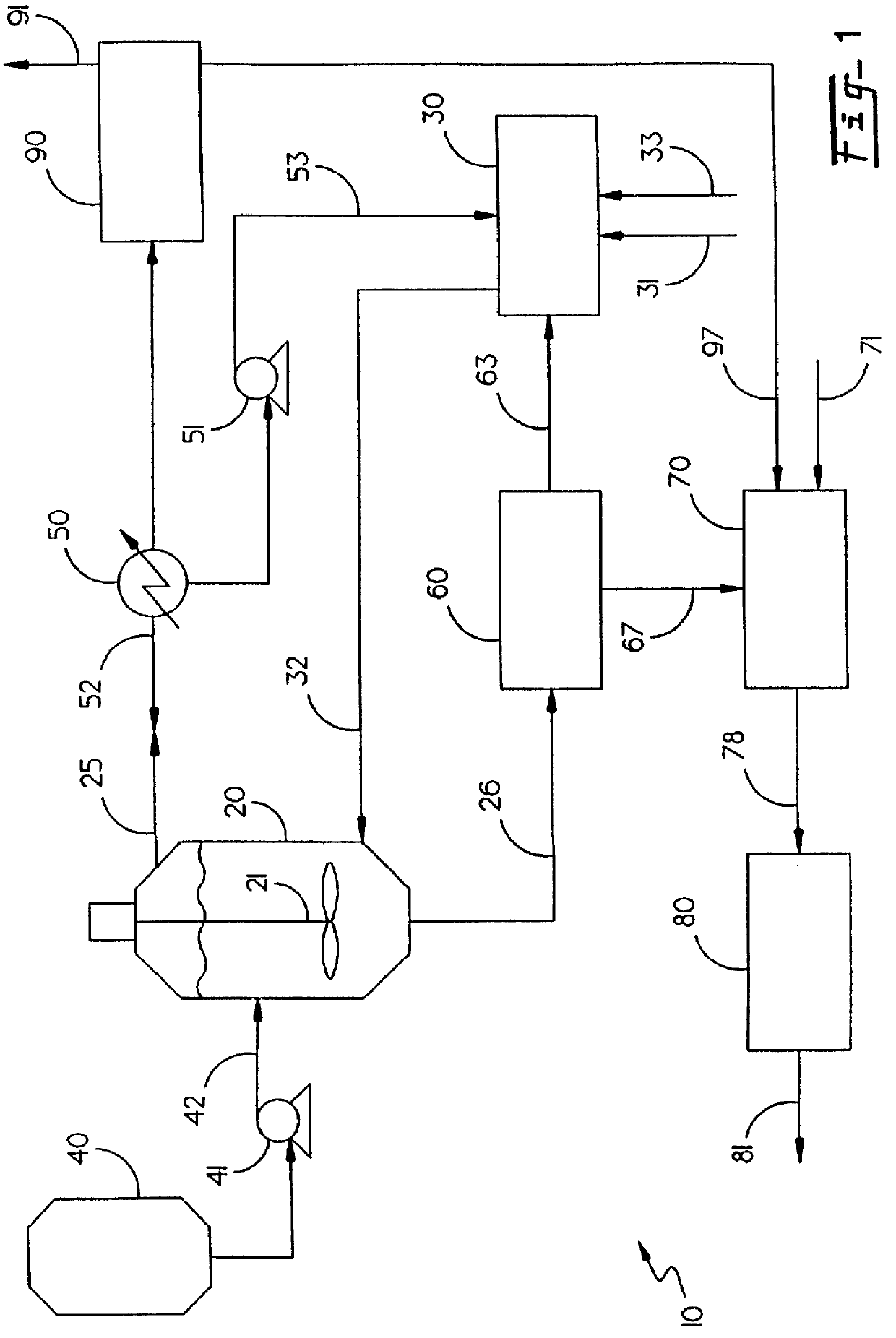
System for comprehensively utilizing LNG cold energy for power generation and cold supply
ActiveCN108087050AImprove utilization efficiencyClimate change adaptationCompression machines with several condensersIce storageRefrigeration
The invention relates to a system for comprehensively utilizing LNG cold energy for power generation and cold supply. The system comprises a LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation system, a mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation system, a liquid ammonia refrigeration house cold supply system and an ethylene glycol ice storage bath air conditioner cold supplycirculation system. The cold energy released in the LNG gasification process is utilized; high-grade electric energy is generated through LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation and mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation; cold is supplied to a refrigeration house through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ammonia recycling; and cold is supplied to an air conditioner through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ethylene glycol ice storage bath recycling. By means of the system, gradient utilization of the LNG cold energy is achieved, and the cold energy utilization efficiency is high.
Owner:SICHUAN HENGRI GAS ENG CO LTD
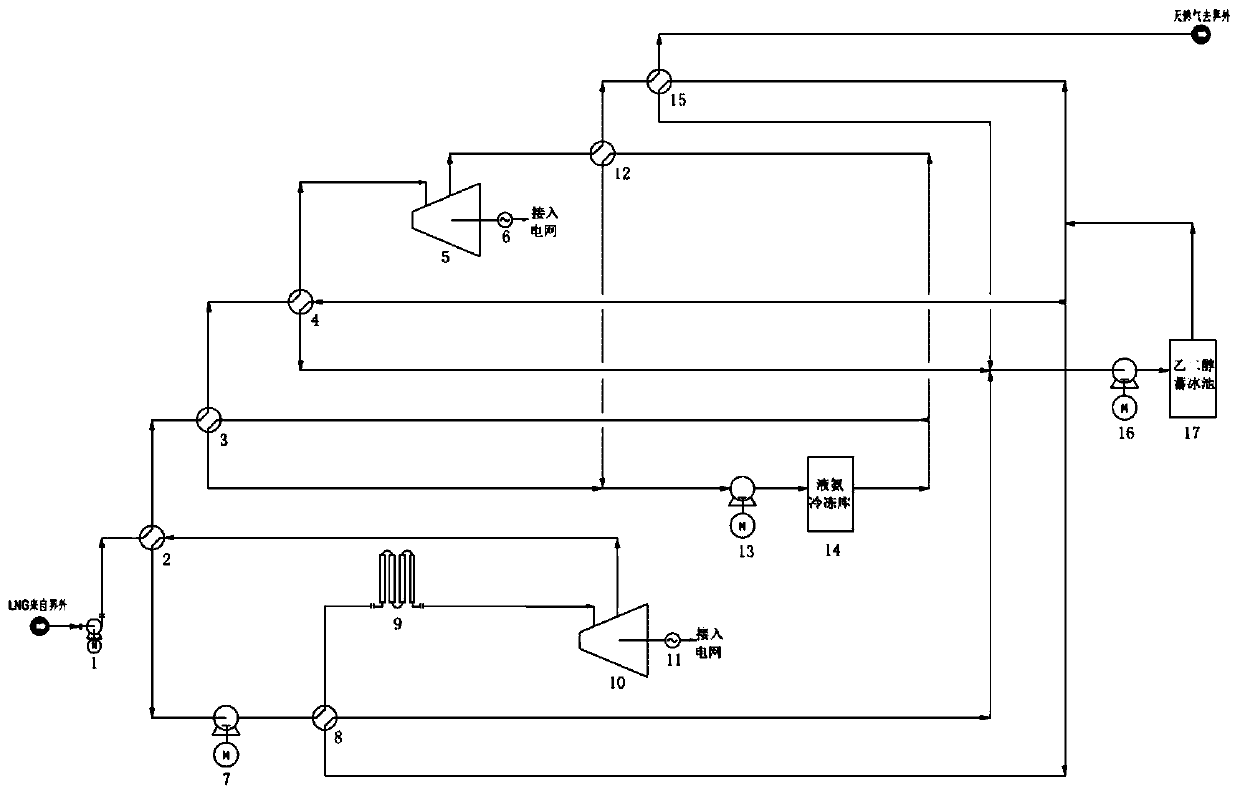
A system for comprehensive utilization of lng cold energy for power generation and cooling
ActiveCN108087050BImprove utilization efficiencyClimate change adaptationCompression machines with several condensersIce storageEngineering
The invention relates to a system for comprehensively utilizing LNG cold energy for power generation and cold supply. The system comprises a LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation system, a mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation system, a liquid ammonia refrigeration house cold supply system and an ethylene glycol ice storage bath air conditioner cold supplycirculation system. The cold energy released in the LNG gasification process is utilized; high-grade electric energy is generated through LNG supercharging gasification direct expansion power generation and mixed working medium Rankine cycle power generation; cold is supplied to a refrigeration house through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ammonia recycling; and cold is supplied to an air conditioner through the cold energy released in the LNG gasification process for ethylene glycol ice storage bath recycling. By means of the system, gradient utilization of the LNG cold energy is achieved, and the cold energy utilization efficiency is high.
Owner:SICHUAN HENGRI GAS ENG CO LTD
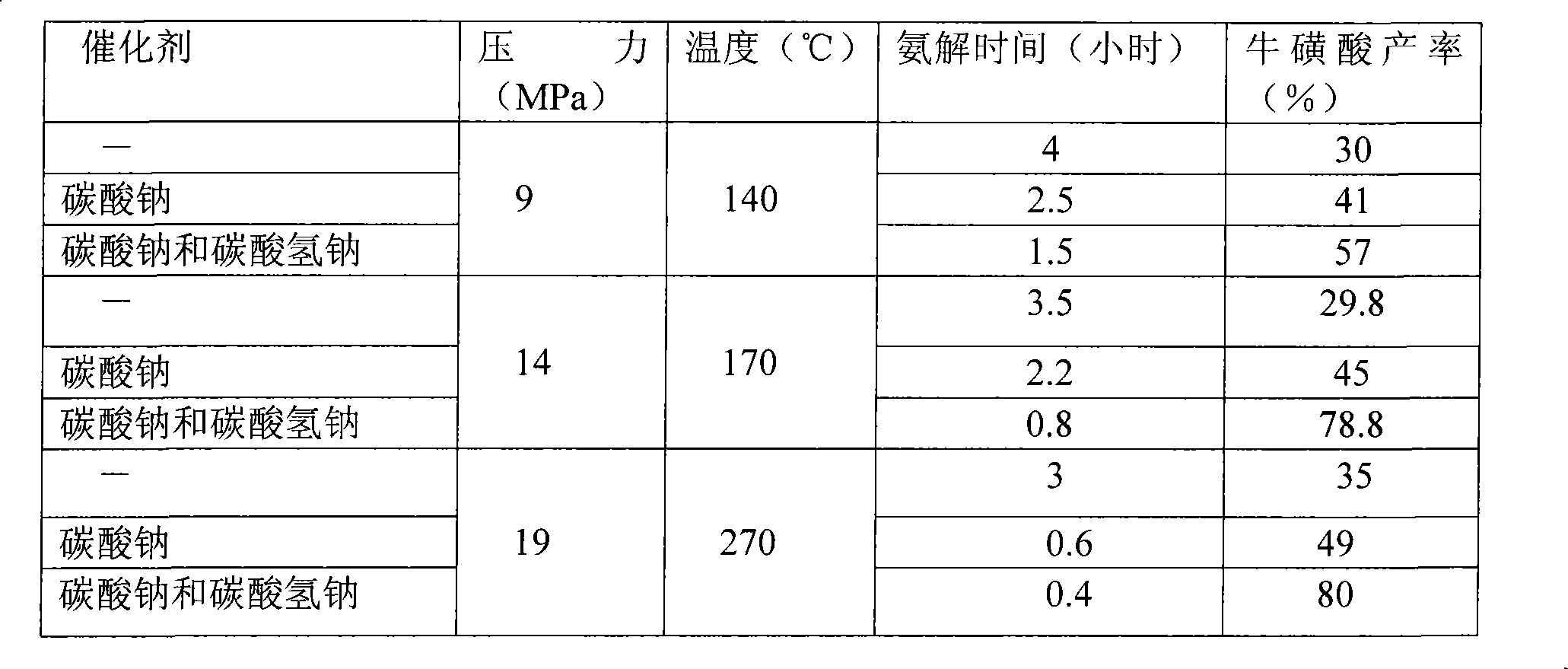
Synthesis of taurine
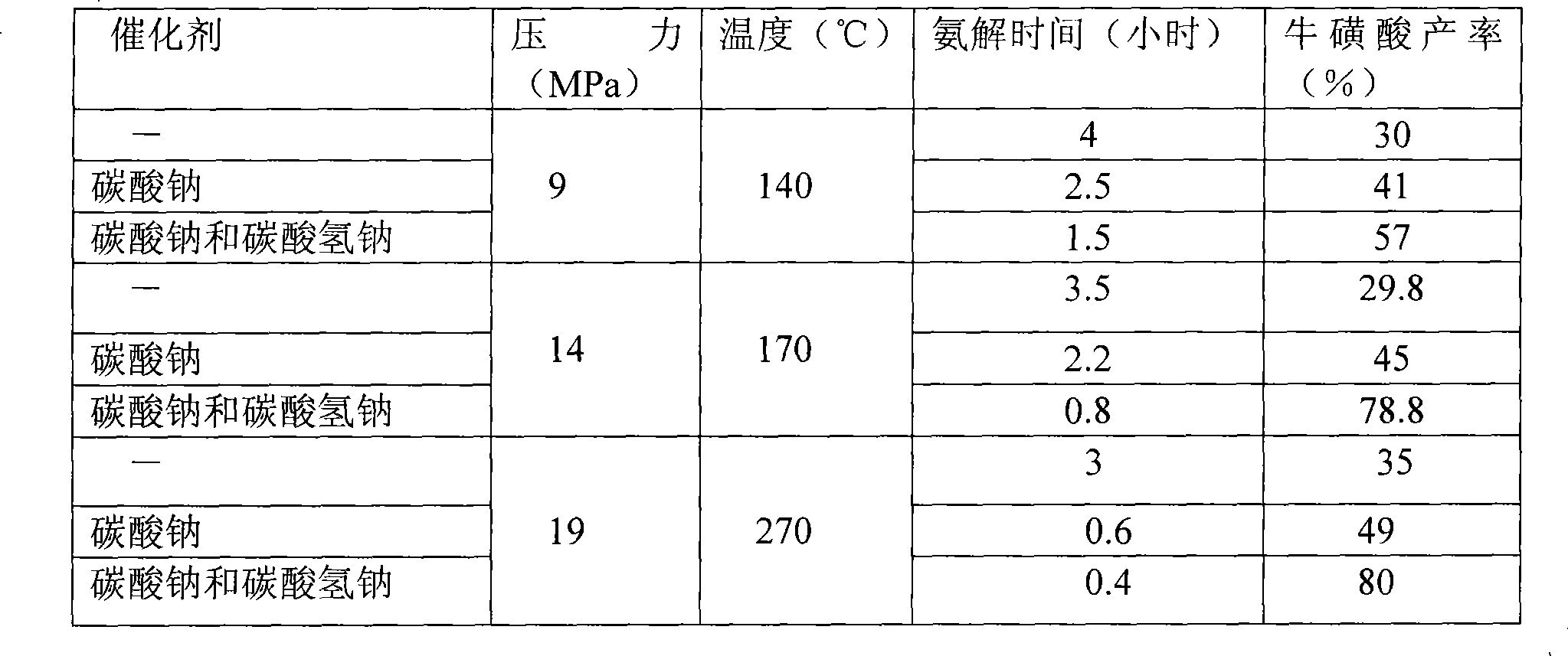
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing taurine, comprising the following steps: (1) according to the amount ratio of materials of 1:1 to 1:1.2, epoxy ethane and sodium bisulfite are subjected to addition reaction under 0.05 to 0.1MPa, with pH value of 6.5 to 7.5 and at a temperature between 75 and 85 DEG C to form hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate; (2) the hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate and liquid ammonia are subjected to ammonolysis reaction under 14 to 21MPa and at a temperature between 160 and 280 DEG C to generate sodium taurate, and the mass concentration of ammonia in the reaction liquid is 20 to 30 percent; and (3) neutralization: namely, the sodium taurate is neutralized by sulphuric acid to generate the taurine. The method for synthesizing the taurine has the advantages of short time, high yield and lower cost, and is easy for industrialized production.
Owner:王代龙 +1
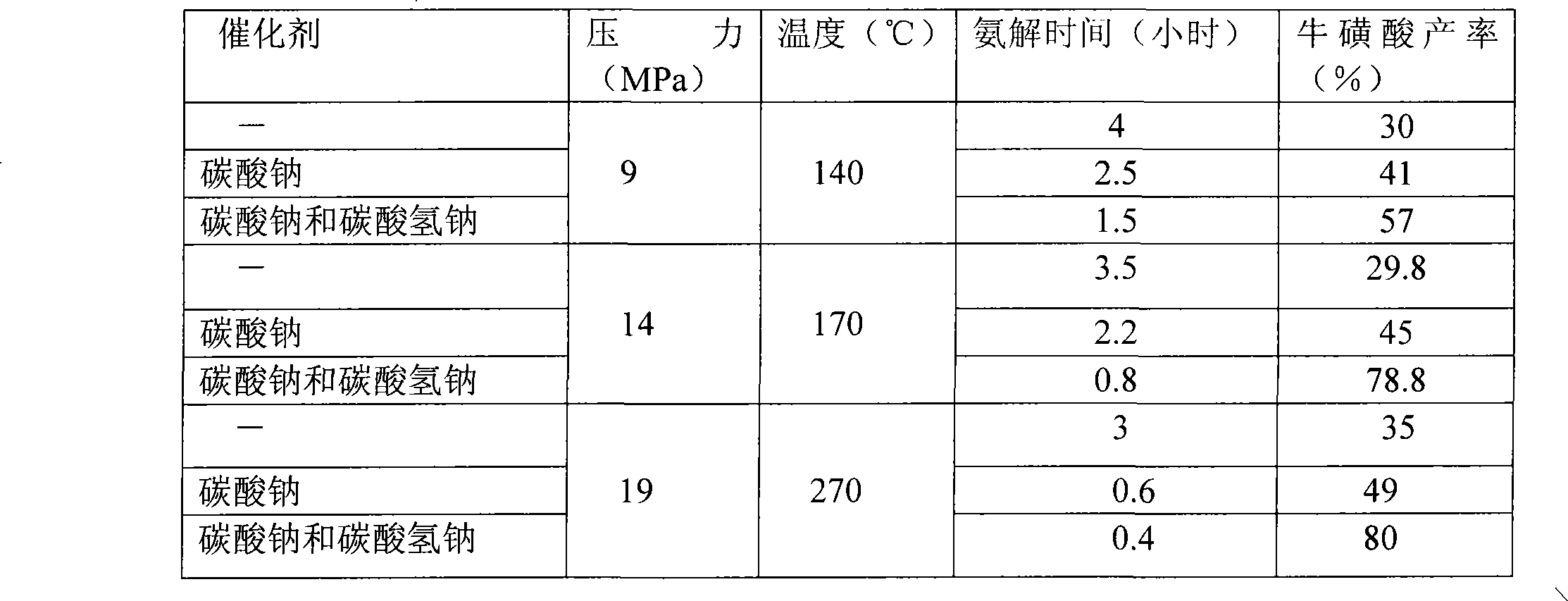
Method for preparing taurine
The invention relates to a method for preparing taurine, comprising the following steps: epoxy ethane and sodium bisulfite are reacted under 0.05 to 0.1MPa, with pH value of 6.5 to 7.5 and at a temperature between 75 and 85 DEG C to form hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate; the hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate and liquid ammonia are subjected to ammonolysis reaction at under 14 to 21MPa and at a temperature between 160 and 280 DEG C to form ammonolysis solution containing sodium taurate; and the ammonolysis solution is evaporated to remove ammonia, neutralized by sulphuric acid, concentrated, crystallized, separated, pre-dried in a boiling drying device or a vibration fluidization drying device, and then added into a microwave drying device to be dried and sterilized to obtain the taurine. The method for synthesizing the taurine has the advantages of short time, high yield and lower cost, and is easy for industrialized production. The water content of a taurine wet product can be reduced to below 0.30 percent through combined application of pre-drying of the boiling drying device or the vibration fluidization drying device and microwave drying, and simultaneously the device has the function of sterilizing.
Owner:王代龙 +1
Method of preparing taurine
The invention relates to method for preparing taurine, comprising the following steps: (1) reacting epoxy ethane with sodium sulfite under 0.05 to 0.1MPa, with pH value of 6.5 to 7.5 and at temperature between 75 and 85 DEG C to obtain hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate; (2) carrying out ammonolysis reaction on the hydroxyethyl sodium sulfonate and liquid ammonia under 14 to 21MPa and at temperature between 160 and 280 DEG C to obtain ammonolysis solution containing sodium taurate; (3) introducing the ammonolysis solution into a single flash evaporator for primary flash evaporating at a temperature between 160 and 200 DEG C and under 1.3 to 2.0MPa; introducing the flash evaporated liquid into a secondary flash evaporating and falling film evaporator, using the primary flash vapor as a heating medium to carry out flash evaporating and falling film evaporating on the primary flash evaporated liquid in the secondary flash evaporating and falling film evaporator at a temperature between 110 and 140 DEG C and at 0.1 to 0.6MPa; evaporating and concentrating the flash evaporated liquid subjected to secondary flash evaporating and falling film evaporating with flash vapor and steam as heating media in a multi-effect flash evaporating and falling film evaporator; and (4) neutralizing the sodium taurate by sulphuric acid to obtain the taurine. The method for preparing the taurine has the advantages of short time, high yield and low cost, and is easy for industrialized production. In addition, by primary flash evaporating and secondary flash evaporating processes, almost all the ammonia and 40% to 60% of water in the flash evaporated liquid can be removed, thus having double effects of removing ammonia and condensing.
Owner:王代龙 +1
Process of producing small molecular weight polyether amine by continuous method
ActiveCN104119239AReduce the impactThe process steps are simpleOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationHydrogenMetal catalyst
The invention relates to a process of producing small molecular weight polyether amine by a continuous method. A continuous method fixed bed process is adopted, polyether, liquid ammonia and hydrogen are used as raw materials, 2-6 reactors which are fixed bed reactors or tubular reactors are connected in series and each reactor is internally filled by a Raney metal catalyst or a supported metal catalyst, respectively; under the reaction condition of certain temperature, pressure and molar proportion, the raw materials are sequentially reacted through the reactors to obtain polyether amine, the molecular weight of which is 100-1000. The process provided by the invention is simple in step. Multiple reactors and a compound catalyst system are adopted, so that the influence of generated water in the reaction to the catalyst efficiency is effectively reduced, and the yield and the conversion ratio of reaction are improved.
Owner:WUXI ACRYL TECH
Method for treating coal gasification wastewater by single-tower pressurization stripping and device therefor
InactiveCN1884150AHigh removal rateReduce crystallizationFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesMultistage water/sewage treatmentCoal gasification wastewaterOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a gasification wastewater disposing method and device through single-tower pressurizing stripping, which comprises the following steps: entering the extracted of acid gas or ammonia gas of cold and hot coal gasification wastewater from band lateral line in the stripping tower from top and upper top; blending gas; dividing phases; washing; separating light oil and acid gas; preparing liquid ammonia through two-grade concreting and refining; separating crude phenol and organic solvent from bottom of tower through inversed-extracting autoclave liquid and organic solvent; recycling organic solvent through stripping. The gasification disposing device contains oil acid gas / ammonia stripping tower, extracting tower, acid gas washing tower, solvent stripping tower, solvent recycling tower, oil-water separator, dephlegmator, pump and reservoir.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for destroying energetic materials
InactiveUS6121506AAffect environmentSafely, simply and economicallyAmmunitionHalogenated hydrocarbon separation/purificationChemical reactionSolvation
Energetic materials, such as nitrocellulose, TNT, RDX, and combinations thereof, optionally in combination with chemical warfare agents, such as mustard gas, Lewisite, Tabun, Sarin, Toman, VX, and combinations thereof, are destroyed when chemically reacted according to the method of the invention. The method comprises reacting the energetic materials and chemical warfare agents, of present, with solvated electrons which are preferably produced by dissolving an active metal such as sodium in a nitrogenous base such as anhydrous liquid ammonia.
Owner:MILFORD CAPITAL & MANAGEMENT
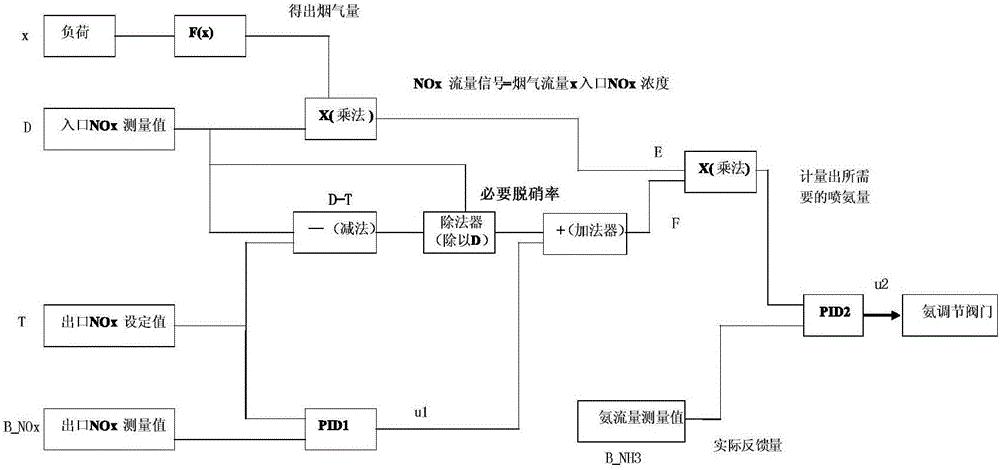
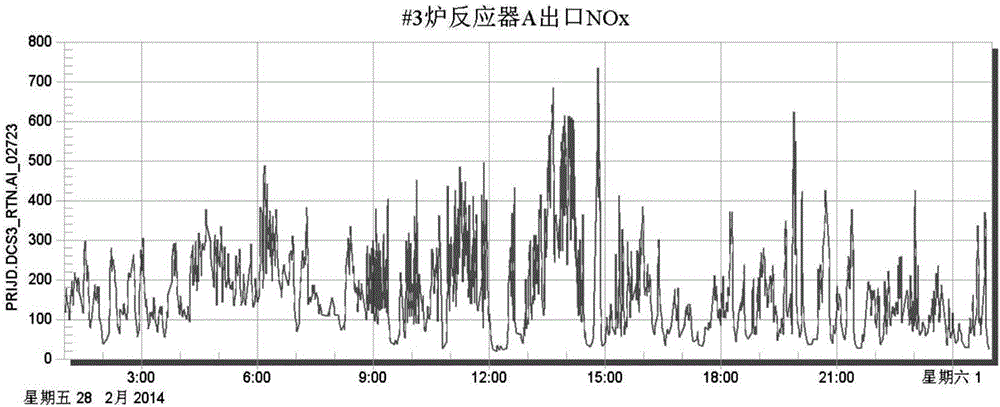
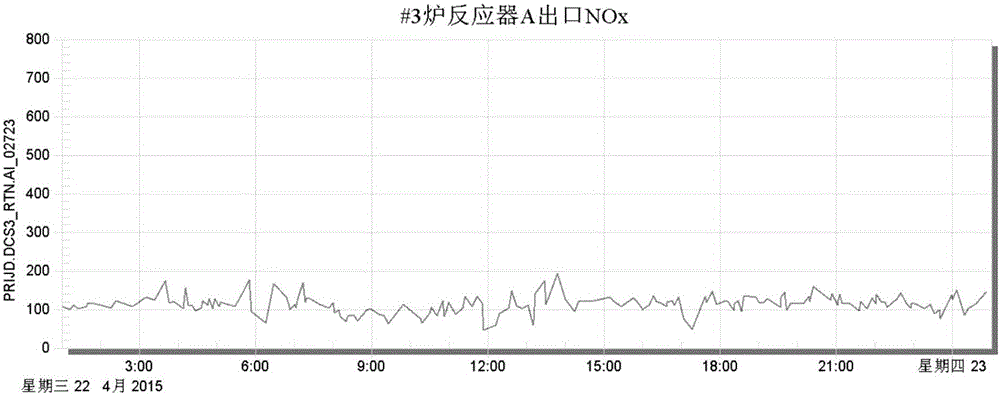
Boiler denitration control method based on outlet NOx content control and system thereof
InactiveCN105045089AEnsuring that environmental protection meets emission standardsAvoid corrosionDispersed particle separationControllers with particular characteristicsFlue gasControl engineering
The invention discloses a boiler denitration control method based on outlet NOx content control and a system thereof. Two PID controllers are used to adjust an ammonia spraying amount so as to finally control a NOx content of a boiler outlet. During a control process, an inlet flue gas NOx flow E needs to be determined in real time and the E satisfies the following equation: E=DFGA*D, wherein the D is the NOx content (concentration) of the boiler inlet; the DFGA is an inlet flue gas amount; and the DFGA satisfies the following equation: DFGA=x*F(x). An output signal of a second PID controller is u2. The u2 expresses an opening degree of an ammonia spraying regulating valve. The opening degree of the ammonia spraying regulating valve is adjusted according to the u2 and the boiler denitration control is realized. The boiler denitration control method based on the outlet NOx content control and the system are easy to perform. Liquid ammonia consumption and a chimney NOx concentration can be greatly reduced.
Owner:DATANG HUAYIN ELECTRIC POWER
Liquid ammonia modified method of cotton fibriia and yarn
InactiveCN101413213AGood flexibilityImprove curling effectLiquid/gas/vapor removal by centrifugal forceTextile treatment by pouringYarnVegetable fibers
The invention provides a method for modifying cotton and long vegetable fiber or yarn by ammonia liquid, which comprises the following steps: firstly, drying pre-treatment of raw materials; secondly, ammonia leaching of the raw materials in a hermetical treatment tank; thirdly, spin-drying of the raw materials subjected to ammonia leaching when a creel is twirled; fourthly, drying of the raw materials subjected to spin-drying by ammonia flow when the creel rotates slowly; fifthly, flushing of the raw materials which are dried by the ammonia flow by airflow when the creel rotates slowly; and so on. The method keeps the inherent advantages of the cotton, the long vegetable fiber and the yarn, overcomes the defects of the cotton, the long vegetable fiber and the yarn, increases softness, crimp tendency and fluffiness of the cotton, the long vegetable fiber and the yarn, improves the dye-uptake rate, the leveling property and the showy dye level, and further solves the problems of energy conservation, efficiency improvement and environmental protection.
Owner:上海业安纺织科技有限责任公司
A method for resource processing non-ferro metals processing wastewater containing ammonia and sulfate radical
ActiveCN101161596AHigh practical valueEliminate pollutionWater contaminantsWaste water treatment from metallurgical processSulfate radicalsSodium sulfate
The invention relates to a novel process for recycling treatment for waste water which contains ammonia and sulfate radicals and is produced in the process of non-ferrous metal processing. The invention is characterized in that: sodium hydroxide is added into the waste water to convert ammonium ions in the waste water into molecular ammonia; then the waste water is heated by heat resource in a rectification tower; the ammonia in the waste water enters into a condenser in the form of gas from the top of the tower to be cooled into liquid ammonia and partial liquid ammonia returns, thus the remainder becomes the product; the water removed of ammonia exchanges heat with the waste water to be treated and then continues to be cooled, thus sodium sulfate crystals are obtained; the water removed of sodium sulfate removed is removed also sulfate radicals and ammonia, and can directly return to a production plant. The invention has a combined process of ammonia rectification recycle and sodium sulfate cooling crystallization, ensures the recycling use of the water as the ammonia in the water is reclaimed in the form of liquid ammonia or ammonia water as well as the sulfate radicals are reclaimed in the form of sodium sulfate, retains valuable metal ions in the water, and improves the recycling rate of the resource. In a word, the process can realize the recycling utilization of ammonia-nitrogen waste water produced by non-ferrous metal processing, has a simple process flow, is suitable for large-scale industrial production, and has both economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:BEIJING CYCLE COLUMBUS ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH
Novel production method for glutamic acid
ActiveCN102703537AReduce lossesLess waste waterOrganic compound preparationMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationFluidized bed drying
The invention discloses a novel production method for glutamic acid, belonging to the technical field of the production of amino acid. The novel production method for the glutamic acid comprises the following steps of: removing thalli and insolubles by means of high-speed disc separation; evaporating and concentrating separated glutamic acid material liquid through a multi-effect plate type evaporator at low temperature, wherein the generated secondary steam condensed water is used for fermentation ingredients of the glutamic acid; performing continuous isoelectric extraction on the glutamic acid in the evaporated glutamic acid concentrated solution; absorbing the glutamic acid by making supernatant fluid pass through ion exchange columns; performing isoelectric reextraction on the analyzed glutamic acid; inputting high-concentration wastewater into a fertilizer workshop for producing fertilizer; squeezing heavy phase (mycoprotein) through a plate frame, and granulating; and drying through a fluid bed, and thus producing high-protein feed. The novel production method for the glutamic acid has the advantages of low unit consumption of liquid ammonia and sulfuric acid, high extraction yield of the glutamic acid, less ion exchange investment and the like; and meanwhile, the purity of the extracted glutamic acid is high, sodium glutamate can be produced without crystalloblast, resources are fully used in the whole process, the aims of energy conservation and consumption reduction are achieved, and the novel production method for the glutamic acid has a wide application prospect.
Owner:HULUNBEIER NORTHEAST FUFENG BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
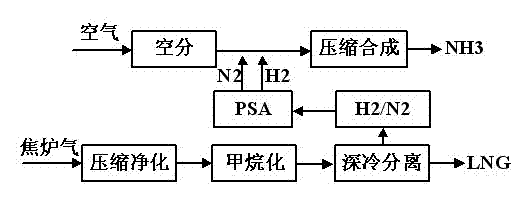
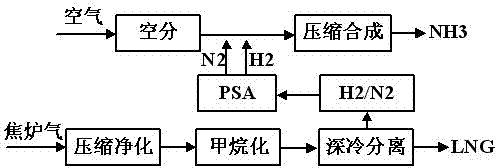
Technology for preparing liquefied natural gas and liquid ammonia by using coke oven gas
InactiveCN102517108AIncrease added valueReduce in quantityGaseous fuelsBulk chemical productionMethanationCoke oven
The invention discloses a technology for preparing liquefied natural gas and liquid ammonia by using coke oven gas. The coke oven gas is subjected to the steps of compression, purification, methanation, cryogenic separation and liquefaction of synthetic natural gas, variable pressure adsorptive separation and liquid ammonia preparation with hydrogen rich gas, so that the liquefied natural gas (LNG) of which methane purity is more than 99 percent and the liquid ammonia reaching national first level standard are obtained. By the technology, the hydrogen byproduct of the coke oven gas for preparing the LNG is fully utilized; effective ingredients of the coke oven gas such as H2, N2, CH4, CO and CO2 are furthest utilized; the CO and the CO2 are methanated, so that the yield of the CH4 is improved by about 1 / 3; the liquefied CH4 is used as the LNG and sold; and the rest nitrogen-containing hydrogen-rich gas is used as a raw material for synthesizing ammonia, so that the additional value of the coke oven gas is improved, and reliable raw material guarantee is provided for developing downstream products with high additional values and prolonging the product chain.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES & DESIGN INST OF CHEM IND
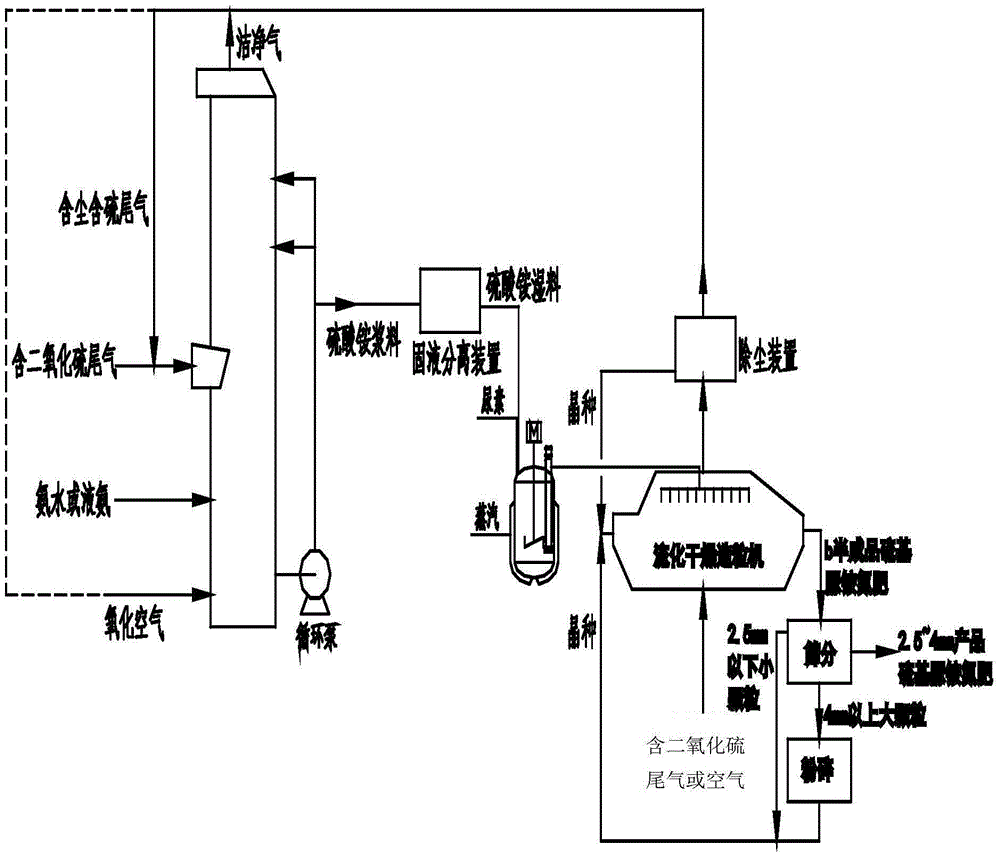
Method used for producing sulfur-based urea compound fertilizer from ammonia desulphurization by-products
The invention discloses a method used for producing sulfur-based urea compound fertilizer from ammonia desulphurization by-products. The method comprises following steps: sulfur dioxide-containing tail gas is delivered into a desulfurizing tower; ammonium hydroxide or liquid ammonia is sprayed so as to absorb sulfur dioxide, ammonium sulfite is oxidized with air, and an obtained product is subjected to concentration so as to obtain an ammonium sulfate slurry, and the ammonium sulfate slurry is subjected to solid-liquid separation so as to obtain an ammonium sulfate wet material; the ammonium sulfate wet material is delivered into a molten urea groove via a conveyor, solid urea is delivered into the molten urea groove via another hopper, and an obtained mixture is subjected to heating melting, or liquid urea is added directly; fluidization granulation is carried out, wherein dried seed crystal is delivered into a fluidized bed through one end, and is driven to flow to the other end of the fluidized bed in the fluidized bed; a mixed ammonium sulfate-urea composite solution is pumped into the fluidized bed, and multistage spraying is carried out; the sulfur dioxide-containing tail gas is delivered into the fluidized bed or / and fluidized drying with hot air is carried out, and semi-finished product sulfur-based urea compound fertilizer is obtained via seed crystal growth; and a obtained fluidization tail gas is subjected to dust separation, and is delivered into an ammonia desulphurization tower. According to the method, ammonium sulfate low in additional value is changed into sulfur-based urea high in additional value at low investment and operation cost.
Owner:JIANGSU NEW CENTURY JIANGNAN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Suppressing and slowing method of coking in ethylene cracking furnace tube
InactiveCN1546609AReduce coking rateExtended service lifeThermal non-catalytic crackingAdhesiveDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for suppressing and slowing coking in ethylene cracking furnace tube comprising the steps of, (1) atmosphere processing, using the gaseous mixture produced from liquid ammonia decomposition as reducing gas to process the boiler tube atmosphere, (2) alloying treatment, preparing the alloy powder and adhesive into pulp, coating onto the surface of the processed furnace tube, drying and solidifying at 50-120 deg. C, placing into heating-furnace for diffusion treatment, cooling the furnace tube after the completion of the treatment, and removing the alloy powder coating on the furnace tube surface.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
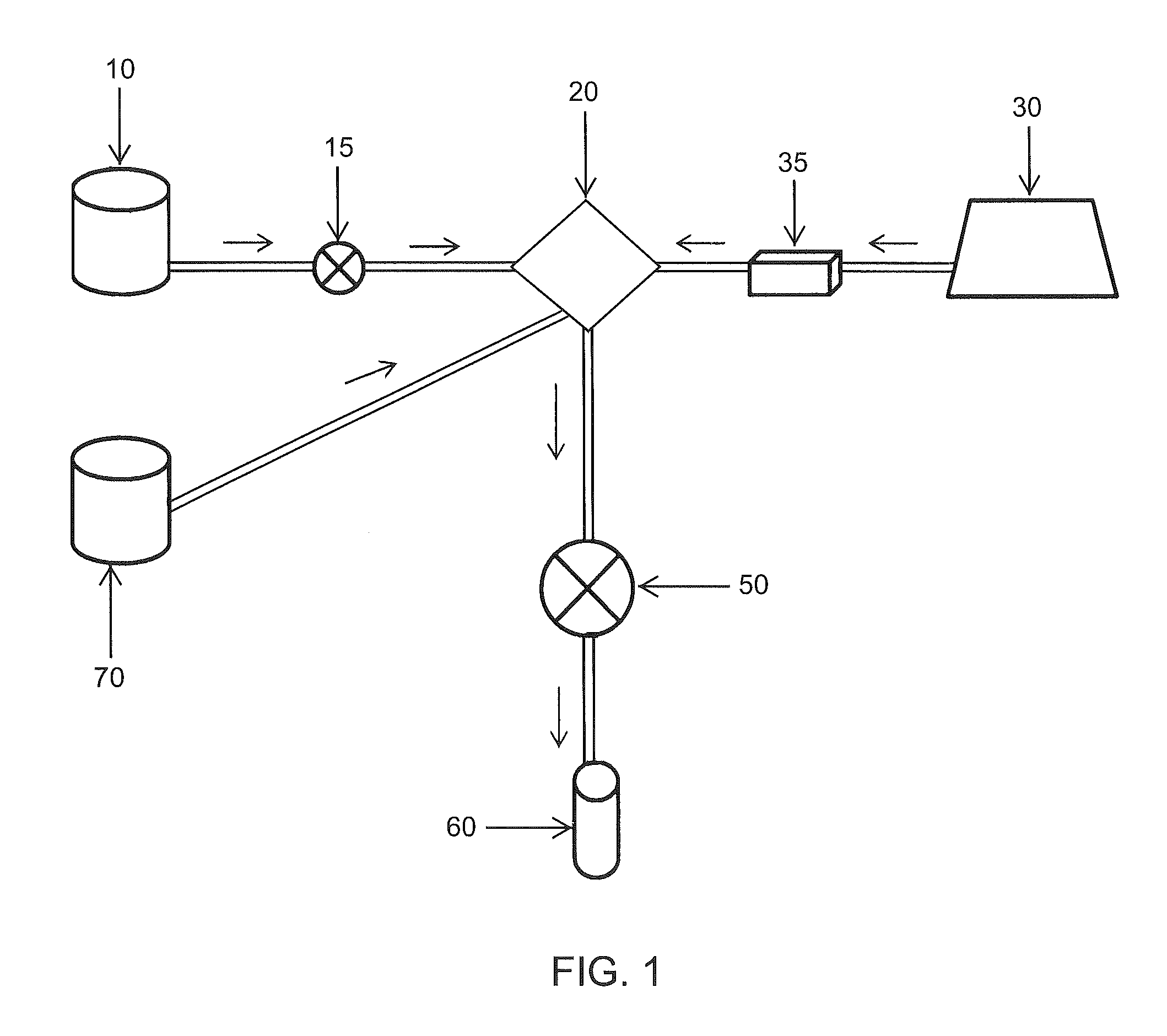
Purification and transfilling of ammonia
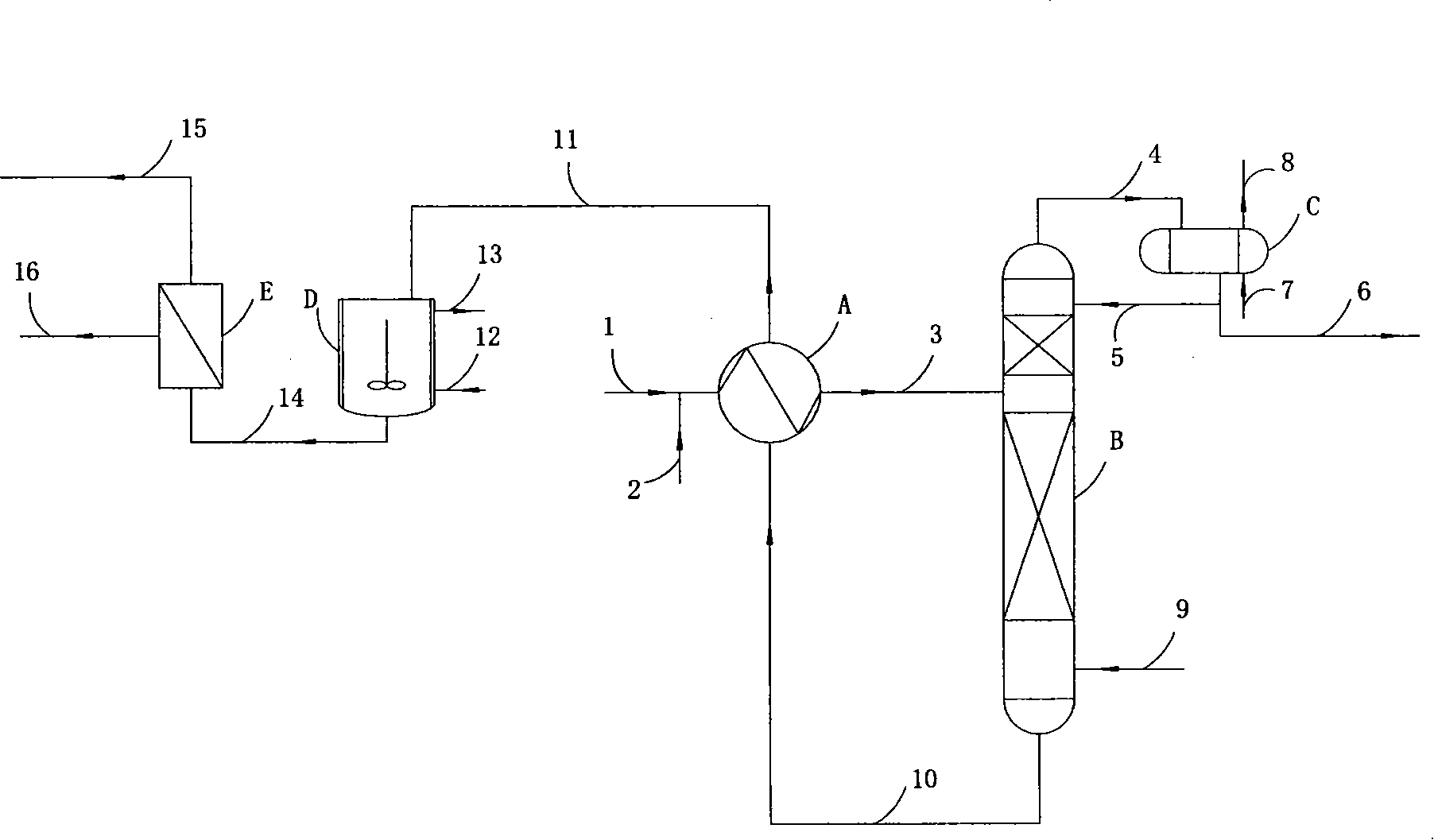
InactiveUS7297181B2Ultra-high purity levelsEfficient and economicalSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnGaseous ammonia
An ammonia purification system includes a hydrocarbon removal station that removes hydrocarbons from gaseous ammonia via adsorption, a moisture removal station that removes water from gaseous ammonia via adsorption, and a distillation station including a distillation column connected with a condenser to facilitate removal of impurities from ammonia and condensation of gaseous ammonia to form a purified liquid ammonia product. The system further includes a storage tank to receive purified ammonia, a remote station connected with the storage tank, and a vaporizer connected with the storage tank. The vaporizer is configured to receive and vaporize liquid ammonia from the storage tank and deliver gaseous ammonia back to the storage tank so as to facilitate pumping of the ammonia to the remote station based upon a vapor pressure established within the storage tank.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Fracturing process using liquid ammonia
A fracturing fluid that includes the combination of liquid ammonia and a proppant, and a method for fracturing an underground formation by pumping this fracturing fluid into a wellbore that extends to the formation. The process includes generating pressure in the wellbore, creating fractures in the formation using the liquid or gelled ammonia and proppant slurry, and releasing pressure from the wellbore. The ammonia released from the liquid or gelled ammonia helps stabilize clays in the formation and the proppant helps to maintain the fractures in the formation.
Owner:TRAVIS GARY LEE
Pure cotton bleached thermal smelting adhesive lining with extremely low washing shrinkage and production method thereof
ActiveCN101942728AEnvironmental protection is goodEasy to operateDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesBleaching apparatusDry heatHot melt
The invention discloses a pure cotton bleached thermal smelting adhesive lining with extremely low washing shrinkage. The adhesive lining is characterized in that the warp-wise and zonal washing dimensional change rate is larger than or equal to minus 0.5%; the quantity of the formaldehyde released by the interlining is less than or equal to 35mg / kg; and the peeling strength is larger than or equal to 12N; the warp-wise and zonal dry heat dimensional change rate is larger than or equal to minus 0.8%. The production method of the invention comprises the following steps in sequence: overedging,singeing, bleaching, stoving, re-bleaching, liquid ammonia finishing, shrink resistant finishing, powder point coating and compressive shrinkage. The invention has the following advantages: the warp-wise and zonal washing dimensional change rate is large; the peeling strength is high; the environmental-friendly performance is good; and the production method can be easily operated.
Owner:曹平
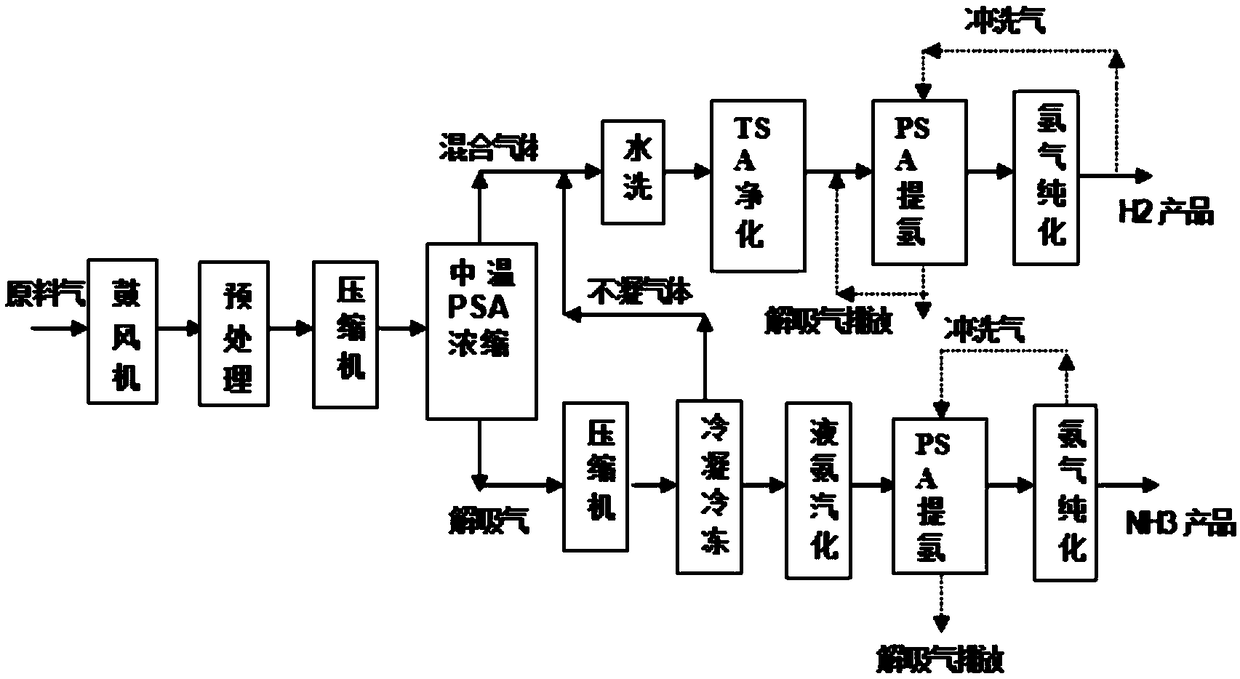
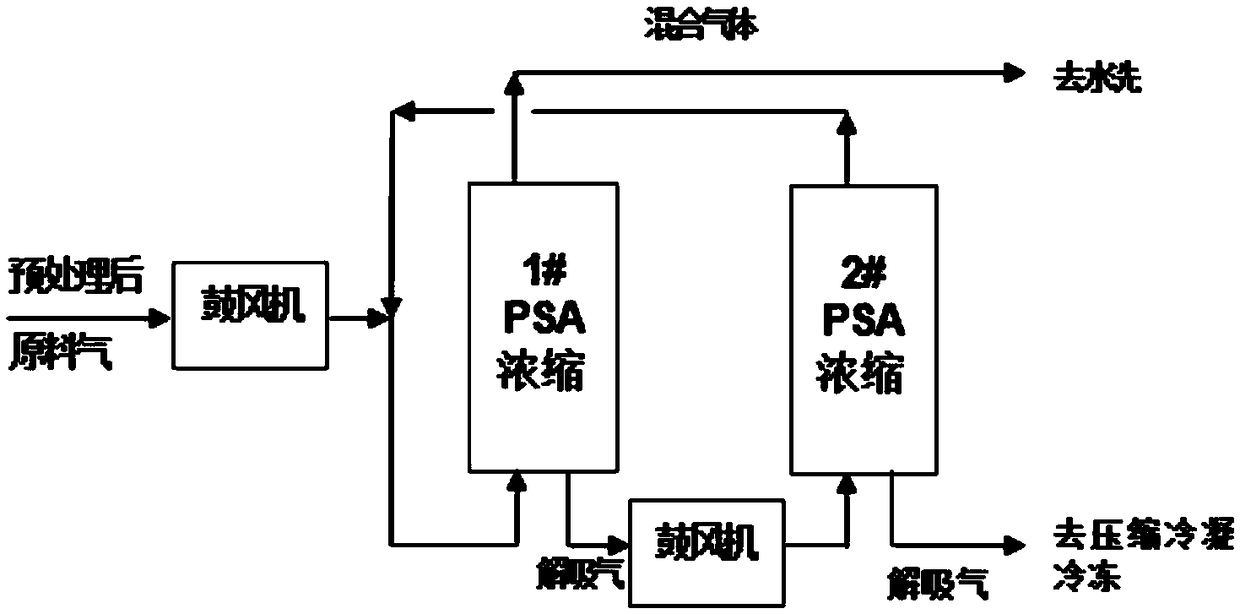
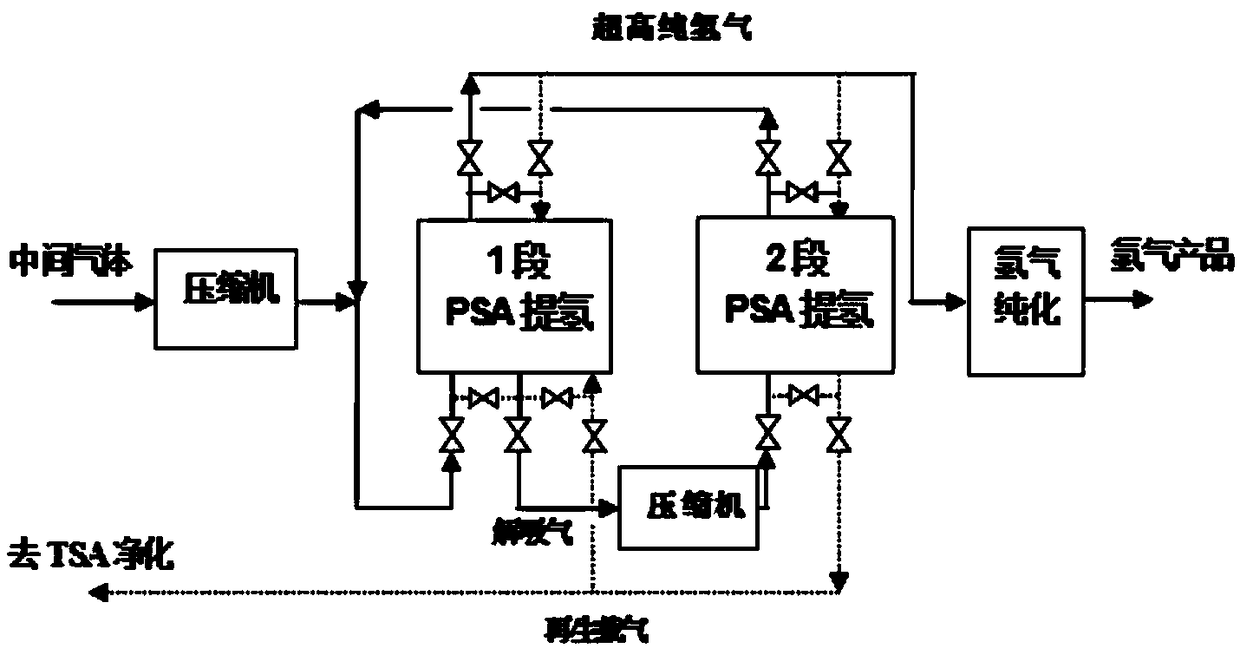
Method for recycling and reusing all components of LED-MOCVD (Light Emitting Diode-Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition) preparation process tail gas through pressure swing adsorption in whole temperature process
ActiveCN108658042ARealize the recycling and reuse of all componentsEmission reductionHydrogen separation using solid contactDispersed particle separationDistillationLight-emitting diode
The invention discloses a method for recycling and reusing all components of an LED-MOCVD (Light Emitting Diode-Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition) preparation process tail gas through pressure swing adsorption in a whole temperature process. The method comprises procedures of pretreatment, medium-temperature pressure swing adsorption concentration, variable-temperature adsorption purification, pressure swing adsorption (PSA) hydrogen refining, hydrogen purification, condensation, freezing or ammonia gas distillation, liquid ammonia gasification, pressure swing adsorption ammonia extraction and ammonia gas purification, and hydrogen or ammonia-containing waste gases of the LED-MOCVD preparation process are purified till standards of electron-scale hydrogen (of which the purity is greater than or equal to 99.99999%v / v) and an electron-scale ammonia gas (of which the purity is greater than or equal to 99.99999%v / v) used in the LED-MOCVD preparation process, then recycling and reuseof waste gases are achieved, the hydrogen yield is greater than or equal to 75-86%, and the ammonia gas yield is greater than or equal to 70-85%. By adopting the method, the technical difficulty thata normal-pressure or low-pressure waste gas in the LED-MOCVD preparation process cannot be recycled or reused in the LED-MOCVD preparation process can be solved, and blanks of green and circular economic development of the LED industry can be made up.
Owner:SICHUAN TECHAIRS
Ammonia absorption type refrigerating apparatus utilizing waste heat of exhaust
InactiveCN1766462AEfficient use ofImprove waste heat utilizationBoilers/analysersEnergy efficient heating/coolingAmmonium hydroxideProcess engineering
The invention discloses an ammonia absorption refrigerating device of tail gas residual heat, which consists of ammonia solution circulation loop and ammonia circulation loop, wherein the pumped cooling high concentrated ammonia solution is given back to the residual heat generator to heat, which utilizes the heat of heat regenerator, finestiller coiler, generation-absorption heat exchanger and the combination body of exhausting device and heat regenerator; the cooling quantity of low-temperature ammonia steam from evaporator and liquid ammonia from condenser is withdrawn to improve the refrigeration coefficient. The invention adapts the tail gas to heat directly, which can be used in other non residual heat occasions.
Owner:ほう啓東
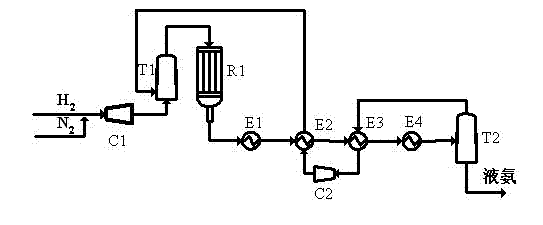
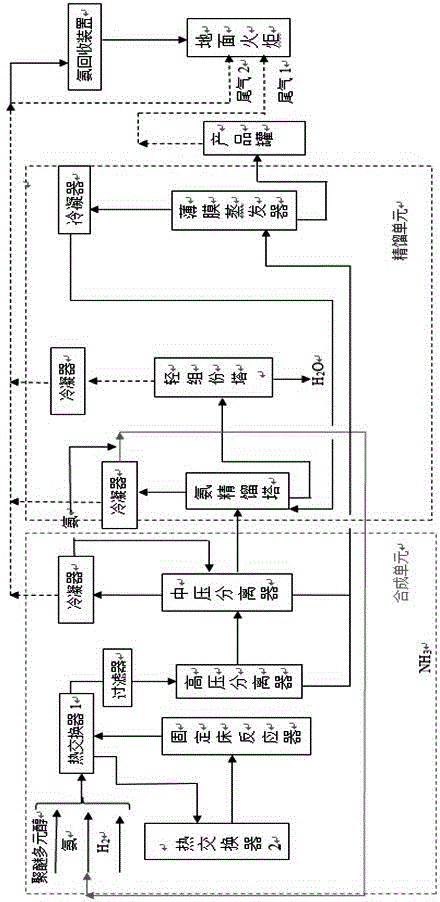
Process for coproducing liquefied natural gas (LNG) and synthetic ammonia
ActiveCN102533365ATake advantage ofOmit the step of separating nitrogenSolidificationLiquefactionMethanationNitrogen
The invention belongs to the technical field of coal chemical industry and particularly relates to a process for coproducing gasified synthetic ammonia and liquefied natural gas (LNG). The invention provides a method and equipment for coproducing the LNG and the synthetic ammonia by using raw coal gas generated by a high-temperature entrained bed; the desulphurization and the decarbonization are carried out by using a mature and advanced physical and chemical absorption process, methane is obtained by using an advanced methanation conversion technology, then, a deep cooling technology is adopted to produce liquid methane and hydrogen through staged cooling and washing separation, the produced liquid methane is outputted as a product, i.e. the LNG, meanwhile, the produced hydrogen is mixed with nitrogen to form a synthetic gas, and the synthetic gas is conveyed to an ammonia synthesizer for the production of the synthetic ammonia after the cold energy is recovered. The coproduction of natural gas and liquid ammonia is achieved, the equipment has corresponding capability for load adjustment, and the emission of vent gas in synthesis is not needed, so that the raw coal gas is maximally used in the production of products.
Owner:CHANGZHENG ENG
Non-iron finish method for pure cotton or polyester fabrics
ActiveCN102828393AImprove gross effectImproves easy-care performanceDry-cleaning apparatus for textilesVegetal fibresCarboxymethyl celluloseFiber
The invention provides a non-iron finish method for pure cotton or polyester fabrics. The non-iron finish method for pure cotton or polyester fabrics is characterized in that the technological processes sequentially include fabric preparing, liquid ammonia finishing, acid washing, pre-softening, preshrinking, moist crosslinking agent applying through a foaming machine, storage reacting, washing, tentering and forming, preshrinking and inspecting and packaging; the concentration of an acid catalyst MC1 in auxiliaries for the acid washing process is 50g / l, the pH valve of a cloth cover is controlled to be 4-5, and the cloth cover is then subjected to alkaline neutralization to control the pH value to be 6-7; and the foaming machine is used to apply a moist crosslinking agent, the moist crosslinking agent comprises the following components according to weight ratio: 220-260g / l of resin carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), 110-130g / l of catalyst MC1, 20-30g / l of fiber protective agent HDP, 10-30g / l of softening agent RPU-N, 1-2g / l of hydrochloric acid and the balance of water, the temperature of a drying room is controlled between 80-100 DEG C, the temperature of the cloth cover is controlled between 35-40 DEG C, the humidity of a doffing is between 6-8%, and finally, the fabrics are wound on the doffing.
Owner:鲁丰织染有限公司
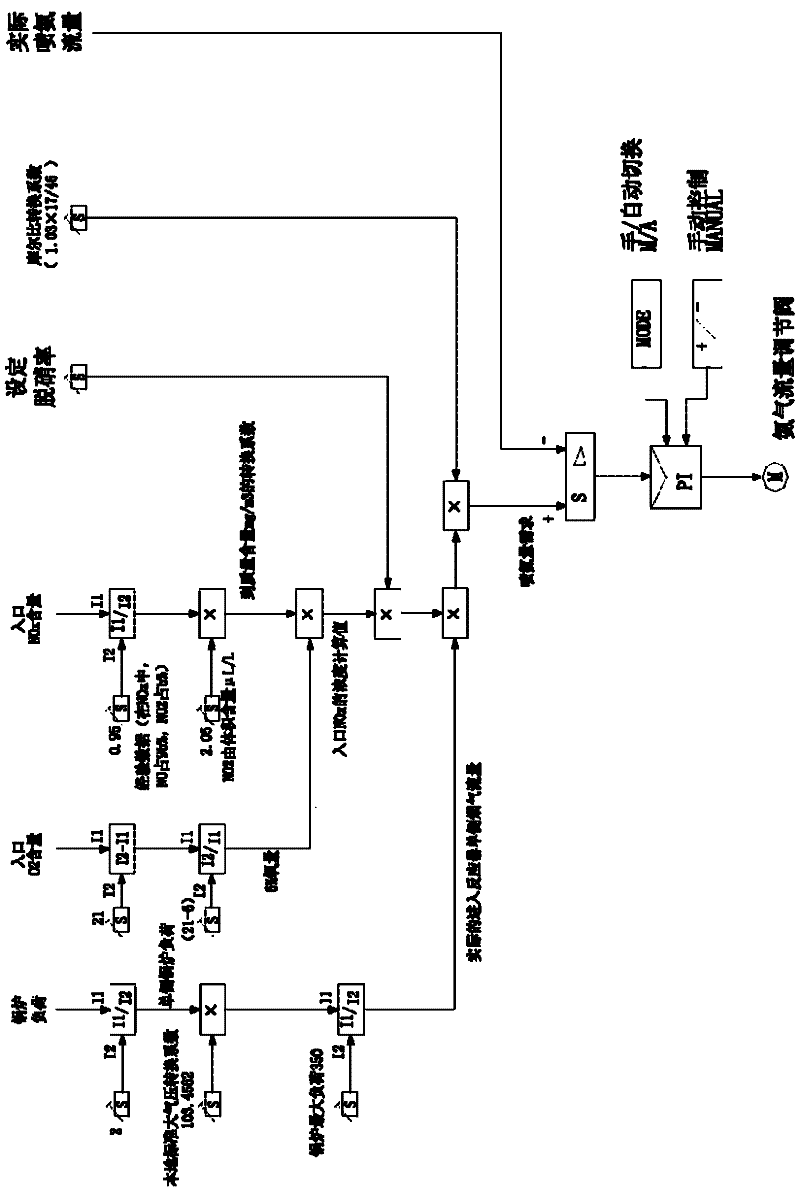
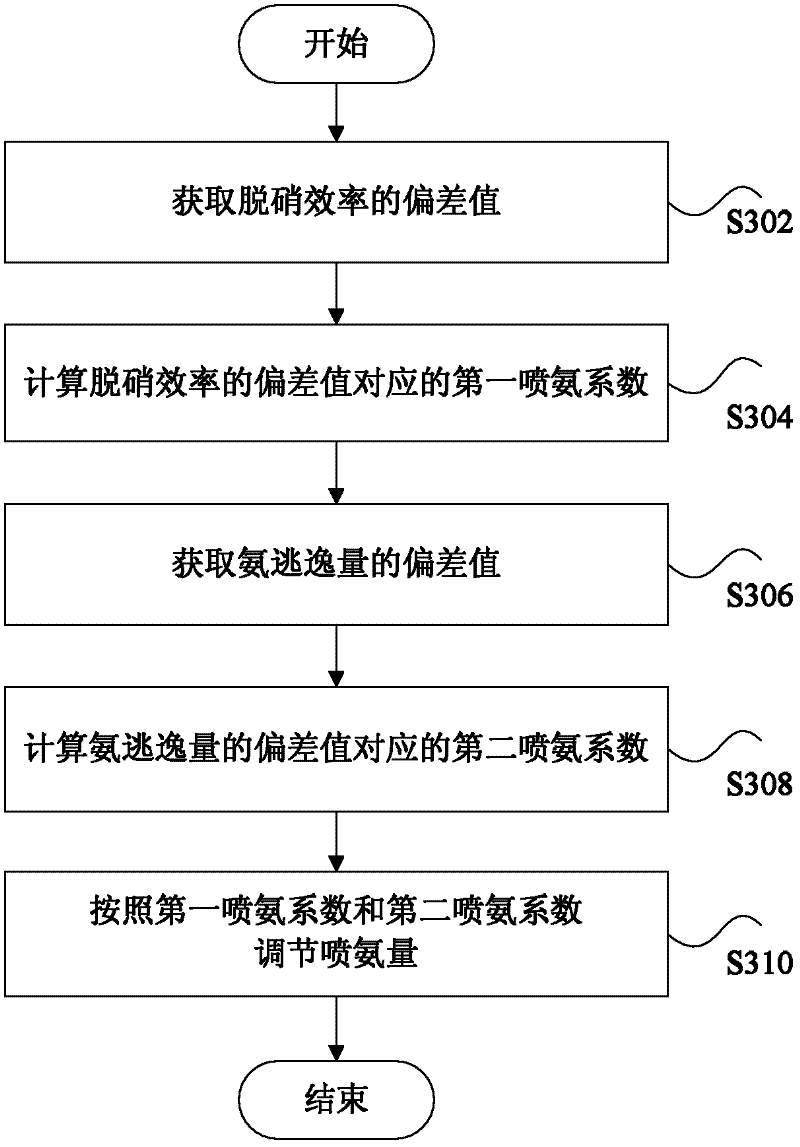
Smoke denitration ammonia injection amount control method and device
ActiveCN102654776AImprove accuracyHigh precisionControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsDispersed particle separationPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a smoke denitration ammonia injection amount control method and device. The smoke denitration ammonia injection amount control method comprises the following steps of: obtaining an offset value of denitration efficiency; calculating a first ammonia injection coefficient corresponding to the offset value of the denitration efficiency; obtaining an offset value of an ammonia escape amount; calculating a second ammonia injection coefficient corresponding to the offset value of the ammonia escape amount; and regulating the ammonia injection amount according to the first ammonia injection coefficient and the second ammonia injection coefficient. Through the smoke denitration ammonia injection amount control method and device, disclosed by the invention, a problem of the ammonia injection amount required by smoke denitration can not be exactly controlled is solved, thus the accuracy of liquid ammonia amount required by the smoke denitration and an effect of the precision are reached, and an effect of diagnosing whether the activity and the operation parameter of a catalyst are reasonable or not is also realized at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING HUANENG XINRUI CONTROL TECH
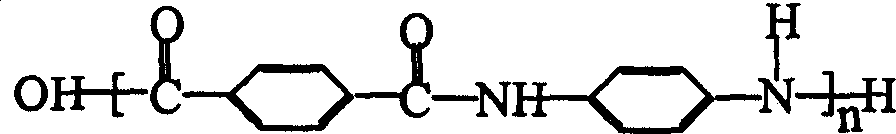
Semi-continuous preparation method of poly p-phenylene terephthalamide resin
The invention discloses a semi-continuous preparation method of poly p-phenylene terephthalamide resin which comprises the steps of, proceeding pre-polycondensation to p-phenylene diamine and part of the paraphthaloyl chloride into the dissolvent architecture of solvent and assisting solvent, charging in pre-polymerization member and the remaining paraphthaloyl chloride powder into double bolt extrusion machine, letting in dried liquid ammonia to neutralize the hydrogen chloride gas produced in the reaction, and charging macromolecular addictive polyvinylpyrrolidone into the double bolt extrusion machine to obtain the polymer.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Production method for continuously synthesizing polyether amine through static bed
ActiveCN104693434AZero pollutionEasy to implement automation controlOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationHydrogenPolyol
The invention provides a production method for continuously synthesizing polyether amine through a static bed, and relates to the technical field of gydrogenated (amination) ammoniation of polyether polyol, long-chain fatty alcohol or aromatic alcohol compounds. The method comprises the steps of carrying out uniform spray mixing on polyether polyol and liquid ammonia and then mixing the mixture with hydrogen; carrying out hydrogen-present ammoniation reaction on a static bed reactor containing nickel / copper / lanthanum-loaded activated framework catalyst at the temperature 130 DEG C-280 DEG C and at the pressure of 3.0MPa-15.0MPa; and carrying out gas-liquid separation on reactants, dehydrating and deaminating a liquid material by virtue of an evaporator, continuously discharging, thereby obtaining polyether amine. The production method disclosed by the invention is a production method for continuous synthesis of polyether amine, which easily realize automation control.
Owner:扬州晨化新材料股份有限公司
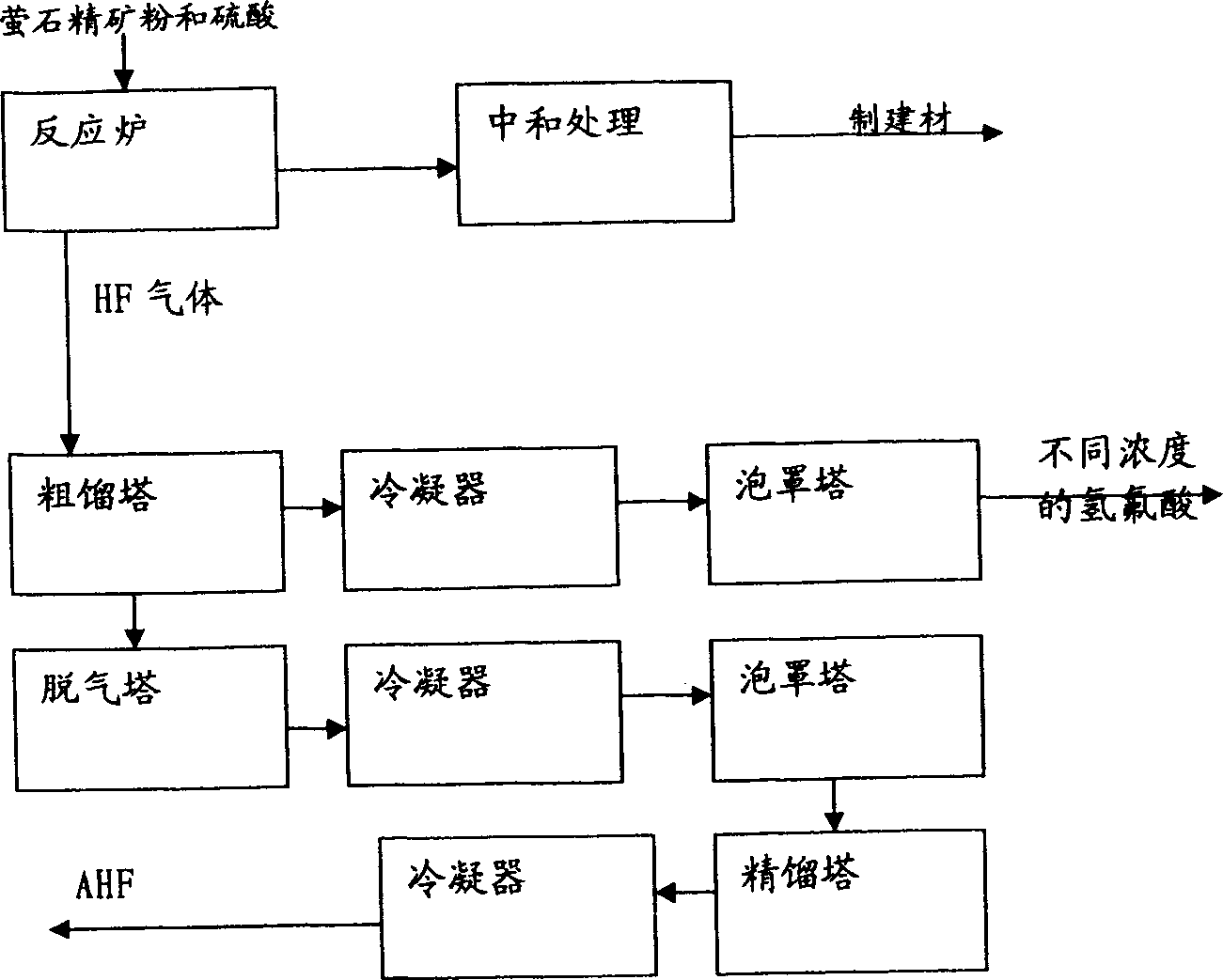
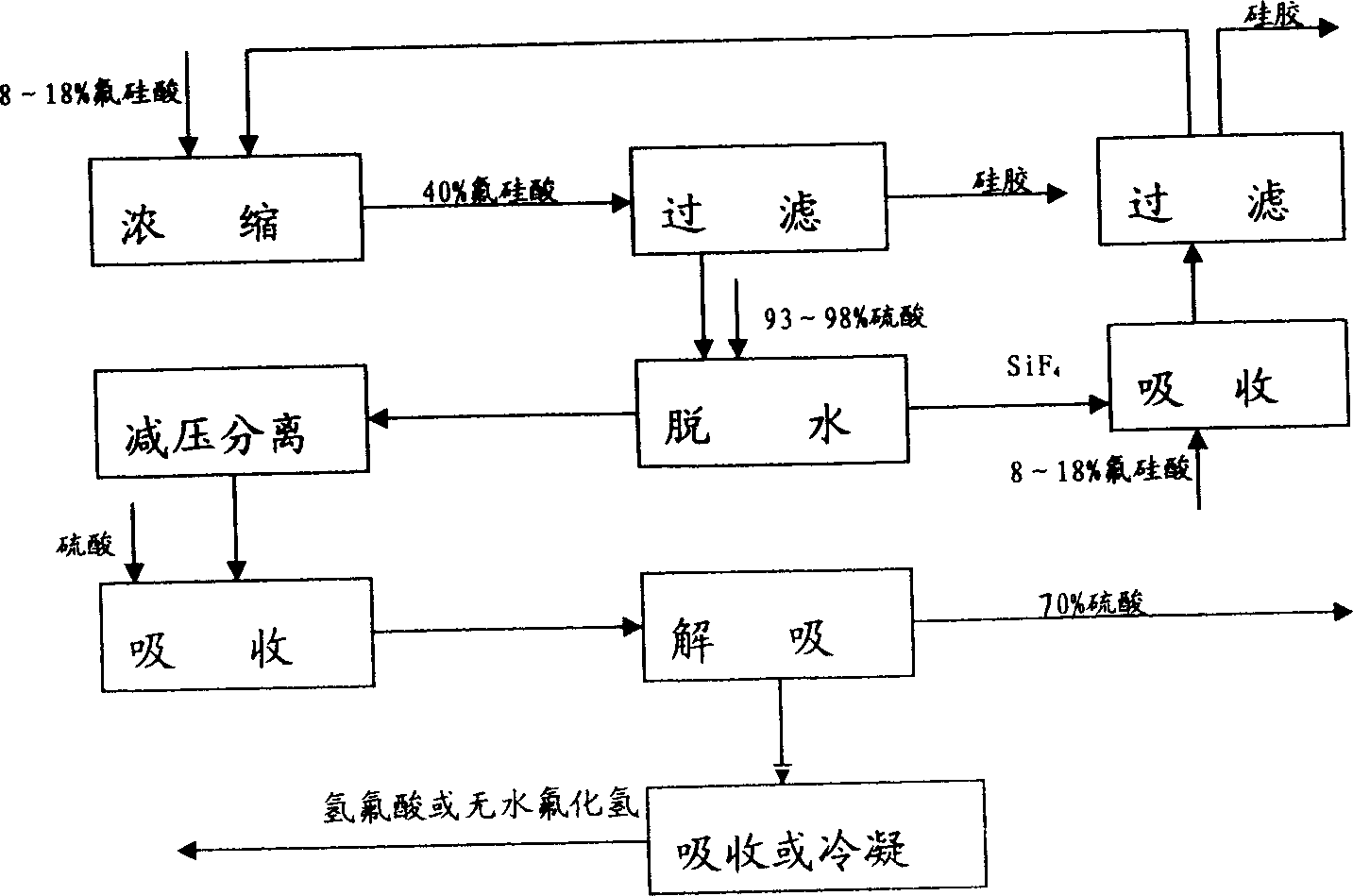
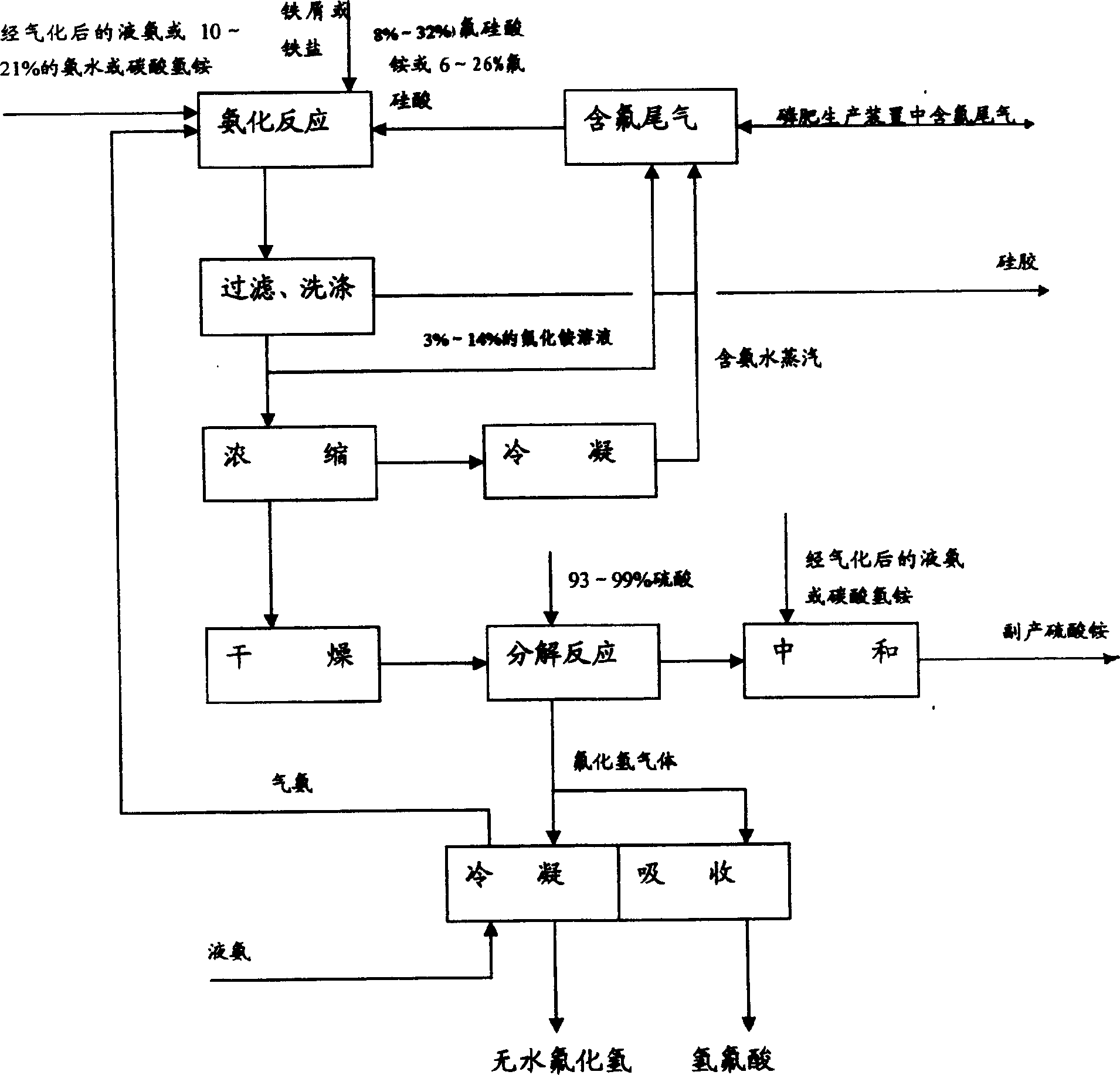
Method for comprehensively utilizing phosphate fertilizer by-product
InactiveCN1554570AReasonable designReduce material requirementsSolid waste disposalFluorine/hydrogen-fluorideIron saltsAmmonium fluorosilicate
The method of comprehensively utilizing phosphate fertilizer by-product includes utilizing ammonium fluoride solution of 3-14% concentration to absorb side product fluorine containing tail gas ammonium fluorosilicate solution; adding iron scrap or iron salt to fluorosilicic acid as one other by-product to eliminate phosphorus; adding liquid ammonia, ammonia water or ammonium bicarbonate; filtering, washing, and eliminating silica precipitate; returning ammonium fluoride solution to phosphate fertilizer absorbing system, concentration and drying to obtain ammonium hydrogen fluoride; reacting solid ammonium hydrogen fluoride and sulfuric acid at high temperature to obtain HF gas, absorbing HF gas to obtain hydrofluoric acid, purification and condensation to obtain anhydrous HF; and mixing the mixture of ammonium sulfate and ammonium bisulfate with ammonium bicarbonate or ammonia in a mixer, curing and crushing to ammonium sulfate fertilizer.
Owner:云南三环化工有限公司 +1
Method for producing o-chloroaniline
InactiveCN101333169AHigh yieldLow costOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationEthylenediamineO-nitrochlorobenzene
An o-chloroaniline production method takes o-nitrochlorobenzene as raw material and is characterized in that the o-nitrochlorobenzene is dissolved in alcohol solvent in the presence of catalyst and additive and reacted with hydrogen at 10-120 DEG C and under 0.3-4.0 MPa; the reaction process is continuous reaction; after the completion of the reaction, the o-chloroaniline is obtained through treatment, wherein, the catalyst can be selected from one of the following: Ni / Al2O3, Raney Ni, Pt / C and Pd / C; while the additive can be selected from one, or two, or three of the following compounds: cyclohexylamine, ethylenediamine, ethanolamine, diethanolamine, triethanolamine, pyridine, liquid ammonia, ammonium bicarbonate, ammonium carbonate, sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, potassium bicarbonate, potassium carbonate, potassium hydrogen phosphate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, sodium hydrogen phosphate and sodium dihydrogen phosphate; the dosage of the catalyst takes up 0.05% to 20% of the mass of the o-nitrochlorobenzene; the dosage of the additive takes up 0. 5% to 20% of the mass of the o-nitrochlorobenzene; the alcohol can be methanol or ethanol; the dosage of alcohol takes up 30% to 150% of the dosage of the o-nitrochlorobenzene; the continuous reaction is realized through 1 to 6 tank reactors which are connected in series.
Owner:淮安嘉诚高新化工股份有限公司
Method for preparing bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide metal salt
InactiveCN101456832ANo pollution in the processHigh puritySecondary cellsSulfonic acid amide preparationImideAlkali metal oxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide metallic salt. The method comprises the following steps: trifluoromethane halogenated sulfonyl, liquid ammonia and organic amine alkali as raw materials are used to generate a mixture solvent containing bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide quaternary ammonium salt by a nonpolar inert solvent; the mixture containing the bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide quaternary ammonium salt is distilled to reclaim the solvent so as to obtain a bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide quaternary ammonium salt solid; the bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide quaternary ammonium salt solid reacts with alkali metal oxide in an aqueous solution to generate a mixture of the bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide metallic salt; and finally, the target product is prepared by the obtained mixture of the bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide metallic salt through decompressed dehydrating, decompressed drying and other steps. The process has a simple route, and does not pollute the environment. The purity of the bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide metallic salt prepared by the method is more than 99 percent, and the yield is over 90 percent.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG HUASHENG CHEM CO LTD
Cellulose fiber liquid ammonia dyeing method
InactiveCN103225218ASolve the problem of energy consumptionSolve pollutionFibre treatmentDyeing processAcid washingCellulose fiber
The invention provides a cellulose fiber liquid ammonia dyeing method, which concretely comprises: adopting a cation modification agent and NaOH to treat cellulose fibers, sequentially carrying out hot water washing, cold water washing and acid washing, carrying out water washing to achieve a neutral state, and drying to obtain cationization cellulose fibers; and dissolving a dye capable of being dissolved in liquid ammonia in liquid ammonia, and immersing the prepared cationization cellulose fibers into the liquid ammonia dyeing solution to dye under a certain condition to obtain the dyed subject, wherein the condition comprises that a dye use amount is more than or equal to 10% (o.m.f), a bath ratio is more than or equal to 1:20, and a dyeing time is more than or equal to 20 seconds. With the present invention, problems of high production process energy consumption and heavy water pollution in the existing cellulose fiber dyeing are solved, a dye uptake rate and a color fixation rate of the dye in liquid ammonia dyeing are increased, a dye use amount is saved, advantages of less dyeing process steps, short dyeing time, recycling of dyed dye, environmental pollution reduction, and the like are provided, and waterless dyeing requirements during a fiber dyeing process can be achieved.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
Ammonian remover used for treating highly concentrated ammonian wastewater and treatment method
InactiveCN101555076AEasy to makeEasy to handleMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationPhosphateMagnesium salt
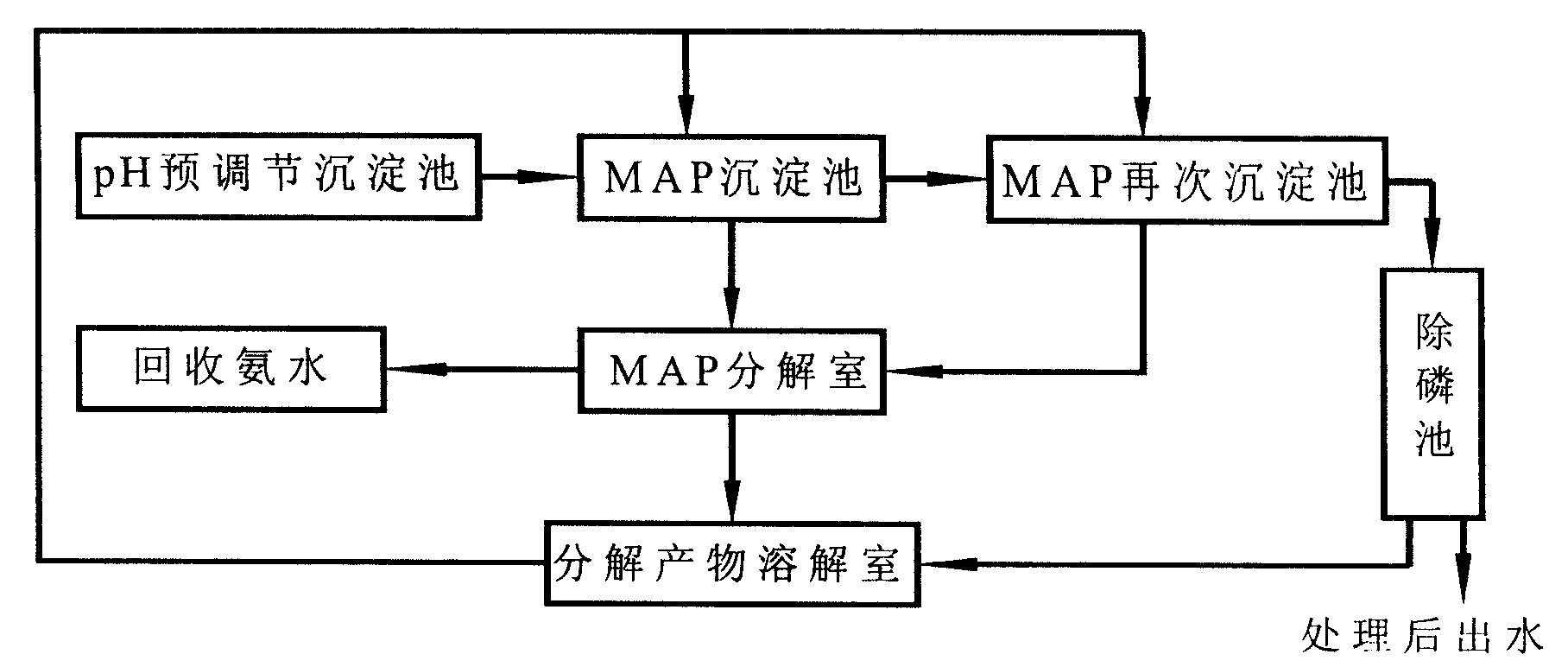
The invention relates to an ammonian remover used for treating highly concentrated ammonian wastewater and a treatment method, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The ammonian remover is prepared in such a way that magnesium salts and phosphates are added into the ammonian wastewater with set quantity according to a rule of Mg:NH4:PO4=1.4-1.6:1:1.4-1.6 for reaction to generate precipitate, the precipitate is decompounded in an MAP decomposition chamber, and decomposed products are dissolved by hydrochloric acid and is evenly mixed to be of slime shape. The treatment method using the ammonian remover is characterized by comprises the following steps: the ammonian wastewater with set quantity primarily enters a pH pre-adjusting precipitation tank and enters an MAP precipitation tank later, the ammonian remover is added for reacting with the ammonian wastewater and the ammonian wastewater enters an MAP secondary precipitation tank or not according to the ammonian concentration of supernatant fluid, at last the ammonian wastewater enters a phosphorus removing tank for removing phosphorus; generated MAP is sent to the MAP decomposition chamber for being decompounded, and decomposed products and precipitate produced in the phosphorus removing tank are sent to a decomposed product dissolving chamber for dissolving. The treatment method has low cost of wastewater treatment without secondary pollution or environment factor interference; and ammonian and surplus phosphorus concentration in treated wastewater reaches national wastewater primary emission standard.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF GEOCHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com