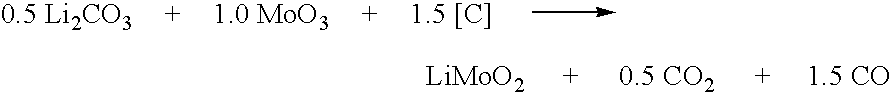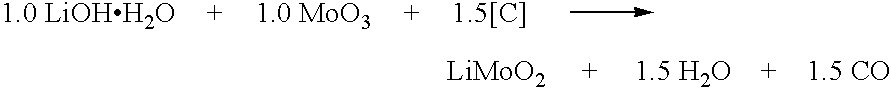Patents
Literature
1175results about "Vanadium compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
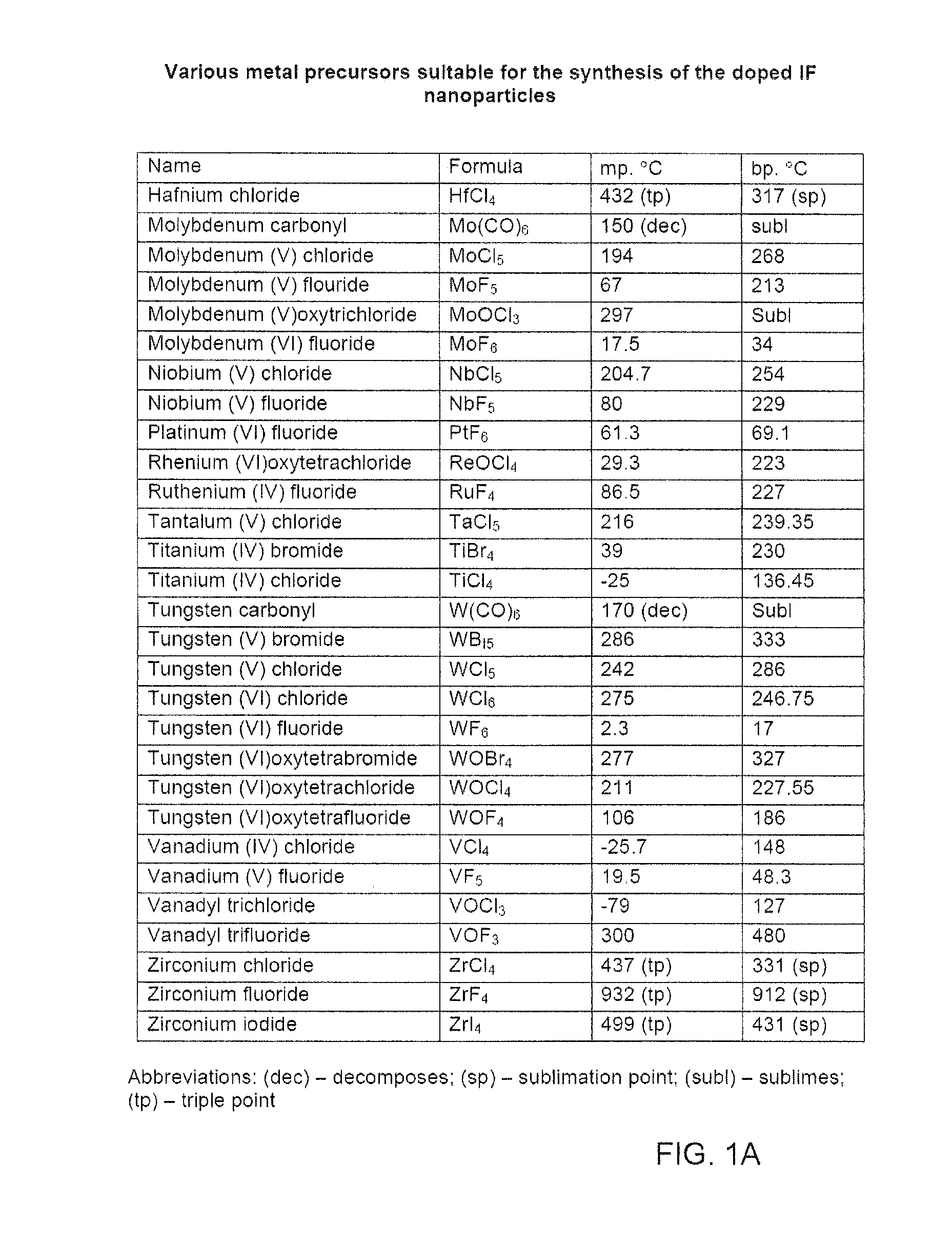
Synthesis of nanoparticles
InactiveUS20030032192A1High sensitivityIncreasing efficiency of collectorOptical radiation measurementMaterial nanotechnologyDopantOrganic solvent
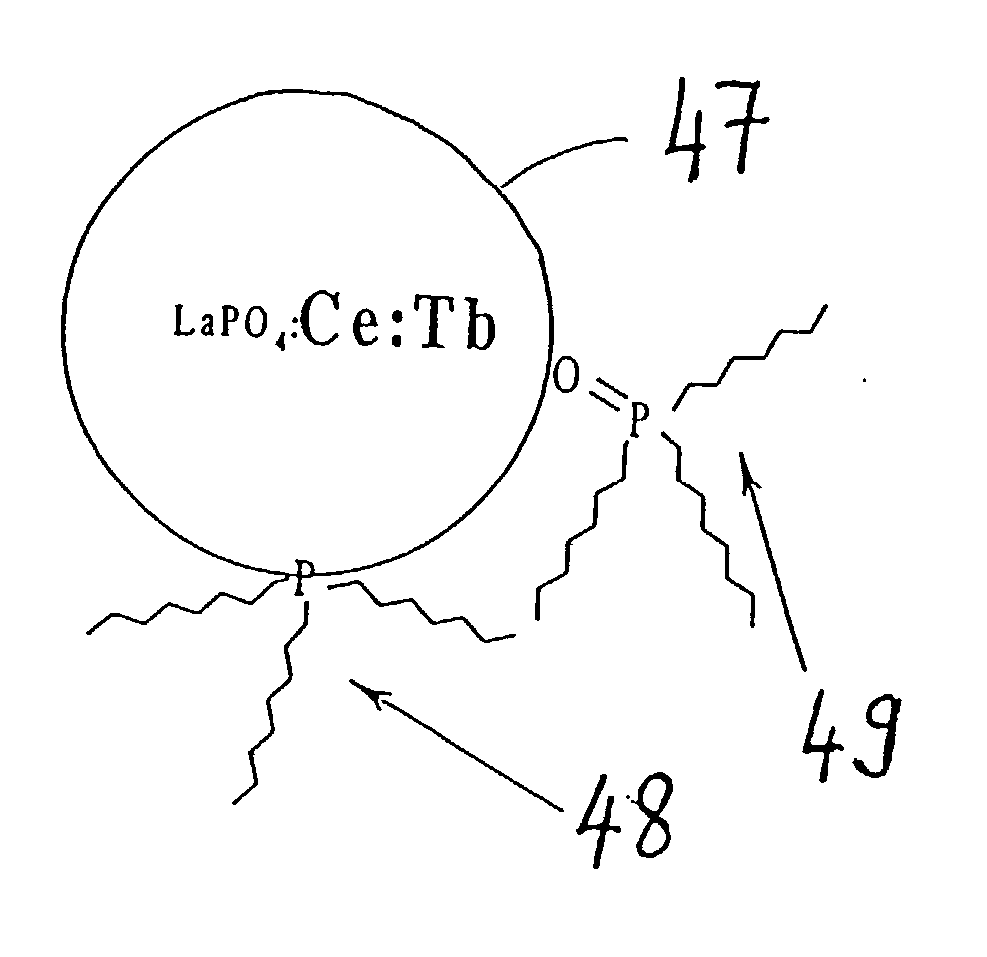
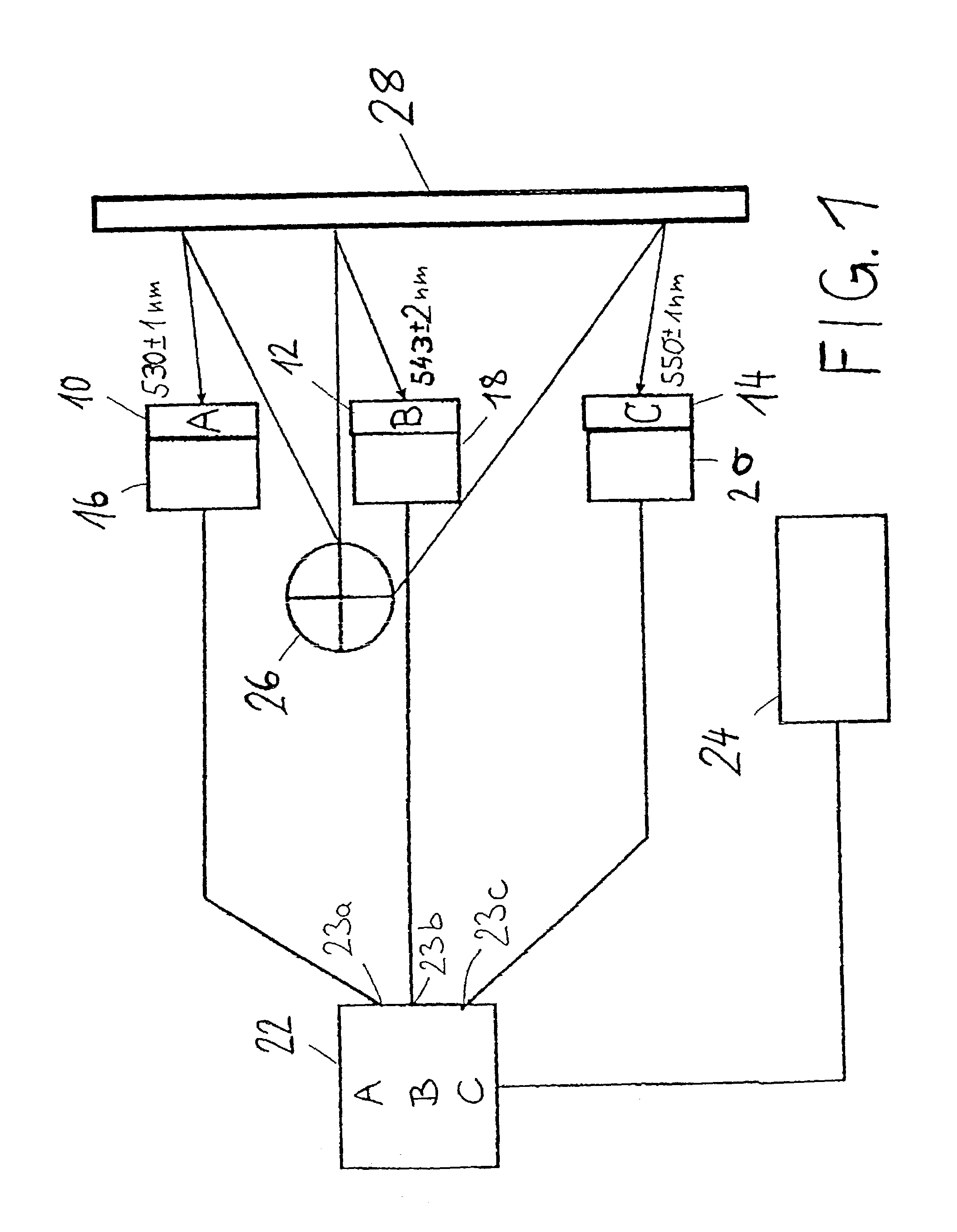
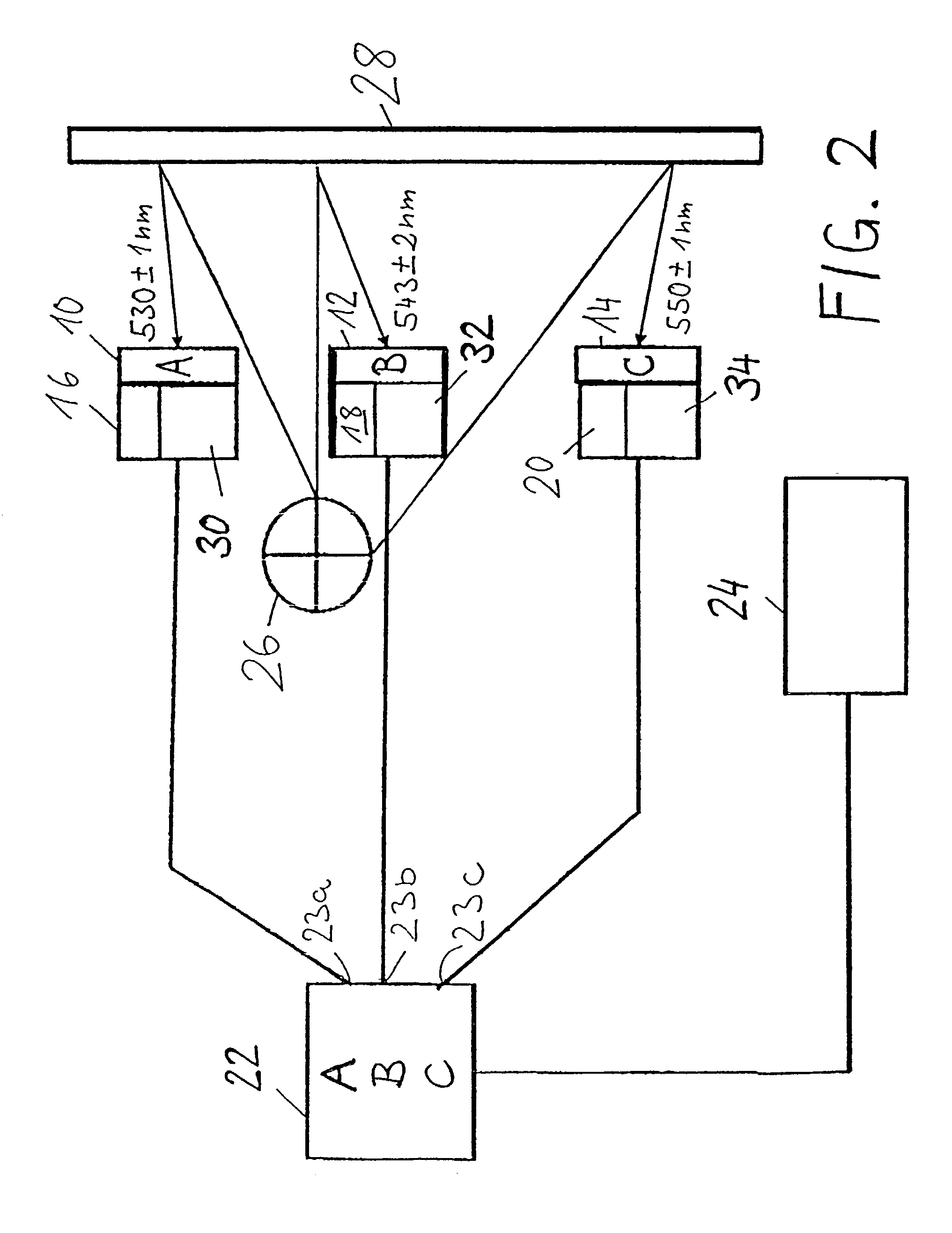
The present invention relates to methods for the preparation of inorganic nanoparticles capable of fluorescence, wherein the nanoparticles consist of a host material that comprises at least one dopant. The synthesis of the invention in organic solvents allows to gain a considerably higher yield compared to the prior art synthesis in water. All kinds of objects can advantageously be marked and reliably authenticated by using an automated method on the basis of a characteristic emission. Further, the size distribution of the prepared nanoparticles is narrower which renders a subsequent size-selected separation process superfluous.
Owner:CENT FUR ANGEWANDTE NANOTECH
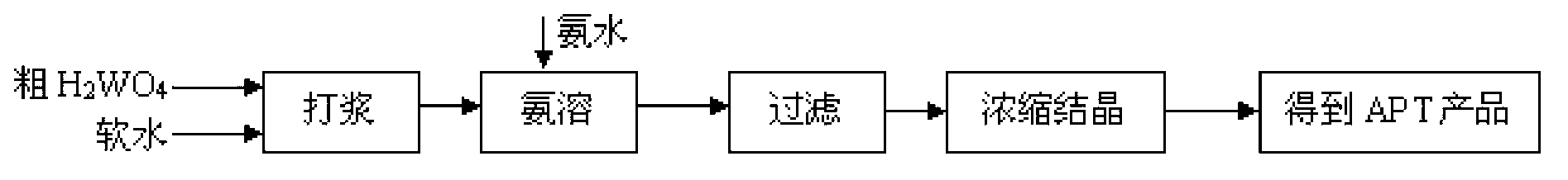
Recovery process of honeycomb type selective catalytic reduction (SCR) waste catalyst containing tungsten, vanadium and titanium
InactiveCN102936039AHigh purityHigh recovery rateTitanium dioxideVanadium compoundsHigh concentrationAmmonium paratungstate
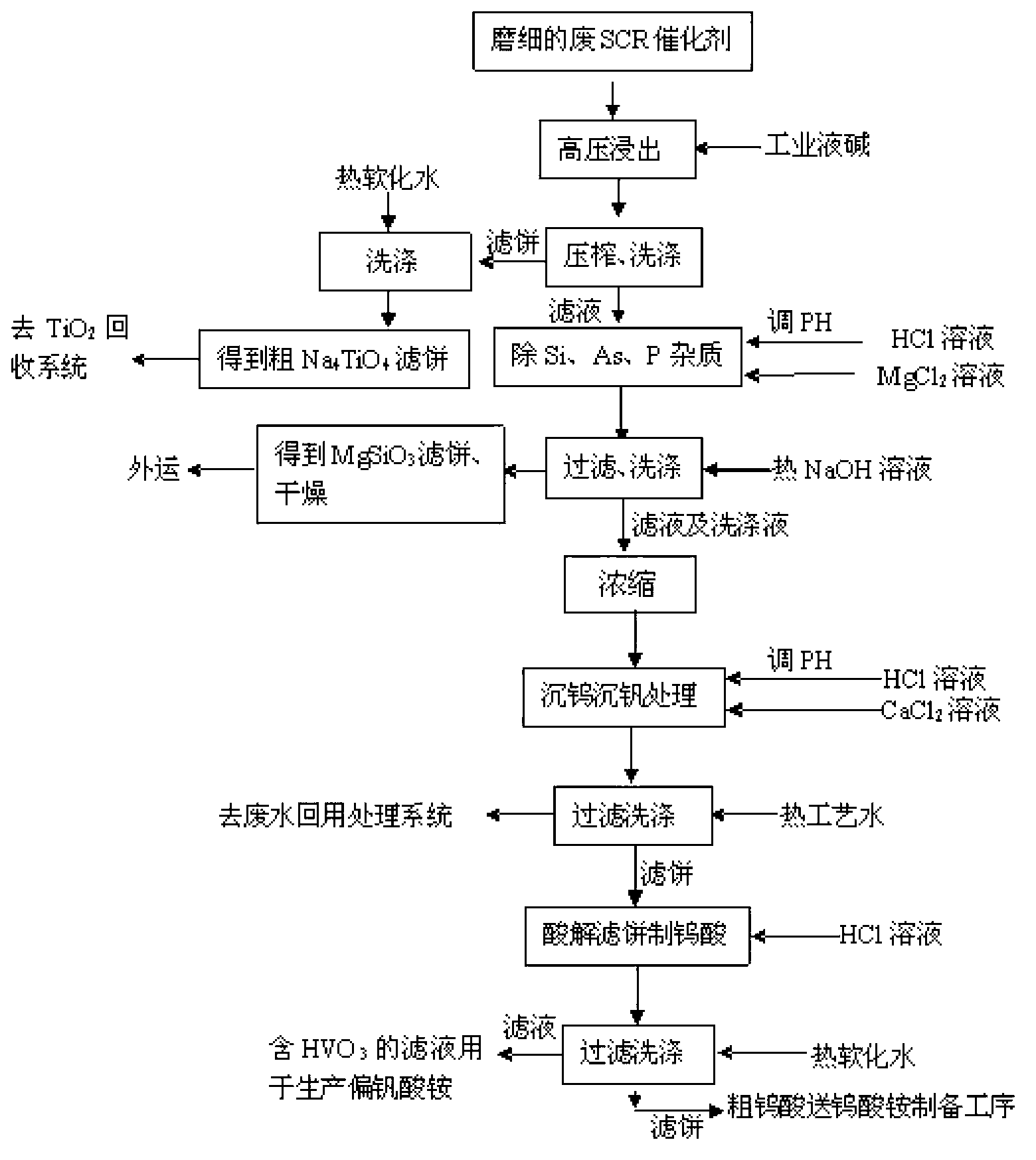
The invention discloses recovery process of honeycomb type selective catalytic reduction (SCR) waste catalyst. The process includes the following steps: a, preprocessing the SCR waste catalyst and leaching at the high temperature and under high pressure; b, adding hydrochloric acid into leaching liquid, adjusting pH, and removing impurities; c, adding hydrochloric acid into the leaching liquid, reacting, calcining and preparing rutile titanium dioxide; d, preparing ammonium paratungstate; e, preparing ammonium metavanadate; and f, recycling and treating waste water. Main products of ammonium paratungstate, ammonium metavanadate and rutile titanium dioxide obtained in the process are high in purity and recovery rate. By-products of silicon magnesium slags, salty mud, high-concentration sodium chloride liquid and barium sulfate dregs are high-purity harmless useful goods. The process is free of harmful secondary pollutant emission, environment-friendly and capable of circulating, has high economical and social benefit and is practicable.
Owner:曾瑞
Electrode (anode and cathode) performance enhancement by composite formation with graphene oxide
ActiveUS20120100402A1Low and reduced matrix contentHigh matrix conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyBatteries circuit arrangementsFiberPerformance enhancement
Described is an electrode comprising and preferably consisting of electronically active material (EAM) in nanoparticulate form and a matrix, said matrix consisting of a pyrolization product with therein incorporated graphene flakes and optionally an ionic lithium source. Also described are methods for producing a particle based, especially a fiber based, electrode material comprising a matrix formed from pyrolized material incorporating graphene flakes and rechargeable batteries comprising such electrodes.
Owner:BELENOS CLEAN POWER HLDG
Nano-sized particles, processes of making, compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070140951A1Economical and efficientQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyToilet preparationsSolventPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention describes methods for preparing high quality nanoparticles, i.e., metal oxide based nanoparticles of uniform size and monodispersity. The nanoparticles advantageously comprise organic alkyl chain capping groups and are stable in air and in nonpolar solvents. The methods of the invention provide a simple and reproducible procedure for forming transition metal oxide nanocrystals, with yields over 80%. The highly crystalline and monodisperse nanocrystals are obtained directly without further size selection; particle size can be easily and fractionally increased by the methods. The resulting nanoparticles can exhibit magnetic and / or optical properties. These properties result from the methods used to prepare them. Also advantageously, the nanoparticles of this invention are well suited for use in a variety of industrial applications, including cosmetic and pharmaceutical formulations and compositions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery,a method of preparing the same, and a rechargeable lithium battery including the same
ActiveUS20080118834A1Improve stabilityImprove cycle lifeElectrode manufacturing processesMolybdeum compoundsArylHigh rate
A negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery includes a core including an active material being capable of performing reversible electrochemical oxidation and reduction, and a coating layer on the surface of the core. The coating layer includes a reticular structure including —O-M-O— wherein M is selected Si, Ti, Zr, Al, or combinations thereof and an organic functional group linked to the M as a side chain. The organic functional group is selected from the group consisting of an alkyl group, a haloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, and combinations thereof. The negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery according to the present invention can be applied along with an aqueous binder, and improve high capacity, good cycle-life, and particularly high capacity during charge and discharge at a high rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Hydromethanation of a carbonaceous feedstock with vanadium recovery
ActiveUS20110262323A1Easy to understandSolvent extractionOrganic compound preparationMaterials scienceHydromethanation
Owner:SURE CHAMPION INVESTMENT LTD
Method for recovering tungsten trioxide and ammonium metavanadate from selective catalytic reduction (SCR) denitration catalyst
ActiveCN102557142AEmission reductionTungsten oxides/hydroxidesDispersed particle separationWarm waterAmmonium paratungstate
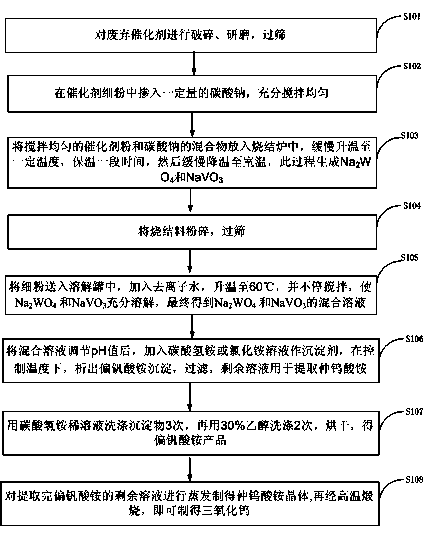
The invention relates to a method for recovering tungsten trioxide and ammonium metavanadate from a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) denitration catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing the SCR denitration catalyst, sieving to obtain catalyst powder, mixing with sodium carbonate, and stirring fully and uniformly; putting the mixed powder into a sintering furnace, and sintering to obtain a sintered material; keeping temperature for 1 hour, and sieving to obtain sintered material powder; pouring warm water, so that Na2WO4 and NaVO3 in the sintered material powder are dissolved fully, filtering, and removing precipitates to obtain a mixed solution of Na2WO4 and NaVO3; regulating the pH value to be 6.5-7.5, adding an ammonium bicarbonate solution or an ammonium chloride solution, and precipitating ammonium metavanadate precipitate; filtering, washing by using a diluted ammonium bicarbonate solution for 2 to 3 times, washing by using 30 percent ethanol for 1 to 2 times, and drying to obtain an ammonium metavanadate finished product; and converting the Na2WO4 in the residual solution into ammonium paratungstate, evaporating the residual solution to obtain ammonium paratungstate crystals, and calcining to obtain the tungsten trioxide. By the method, the ammonium metavanadate and the tungsten trioxide can be recovered, and the discharge of pollutants is reduced.
Owner:江苏万德环保科技有限公司
Methods of making lithium metal cathode active materials
The invention provides a novel method for making lithium mixed metal materials in electrochemical cells. The lithium mixed metal materials comprise lithium and at least one other metal besides lithium. The invention involves the reaction of a metal compound, a phosphate compound, with a reducing agent to reduce the metal and form a metal phosphate. The invention also includes methods of making lithium metal oxides involving reaction of a lithium compound, a metal oxide with a reducing agent.
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV
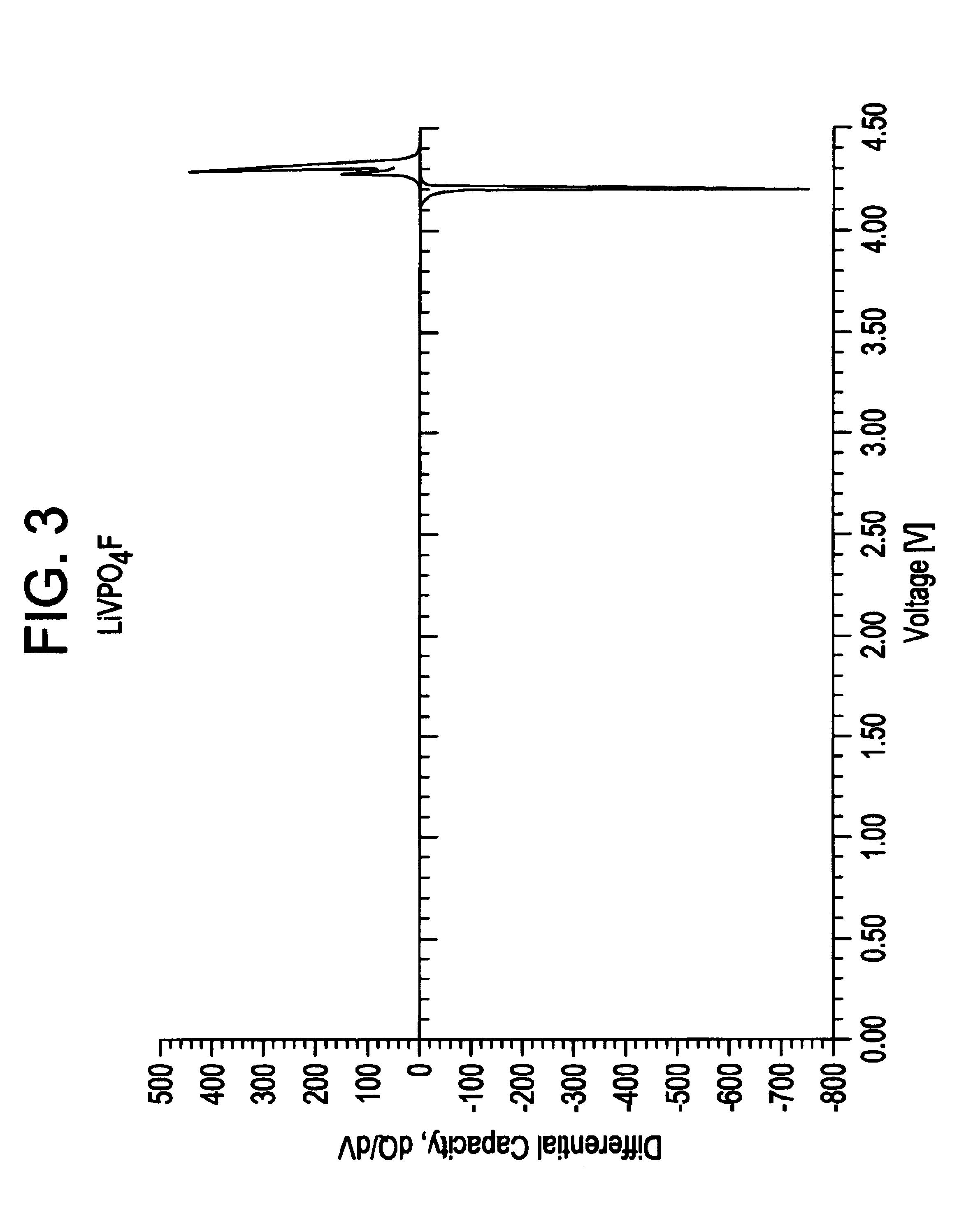
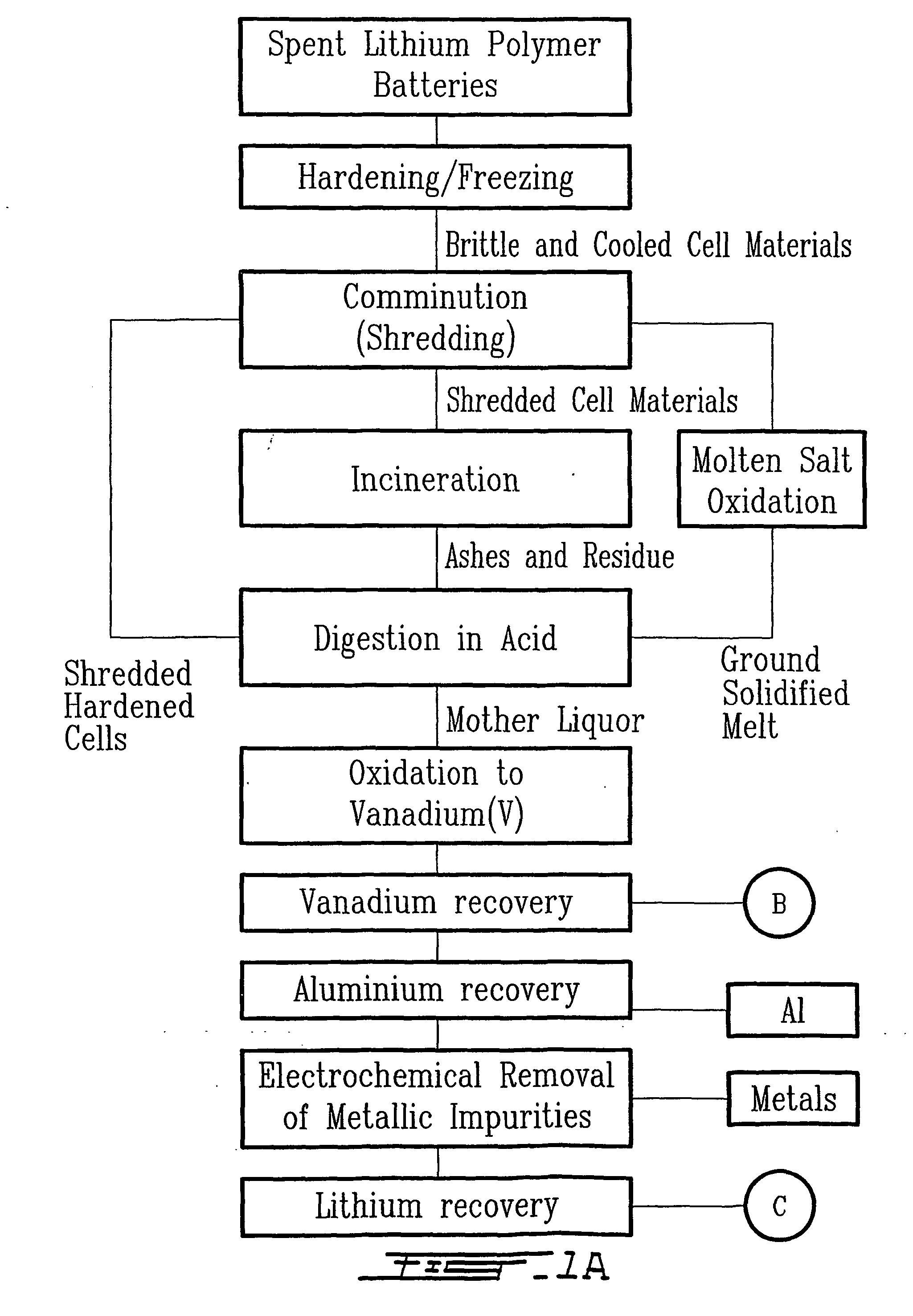
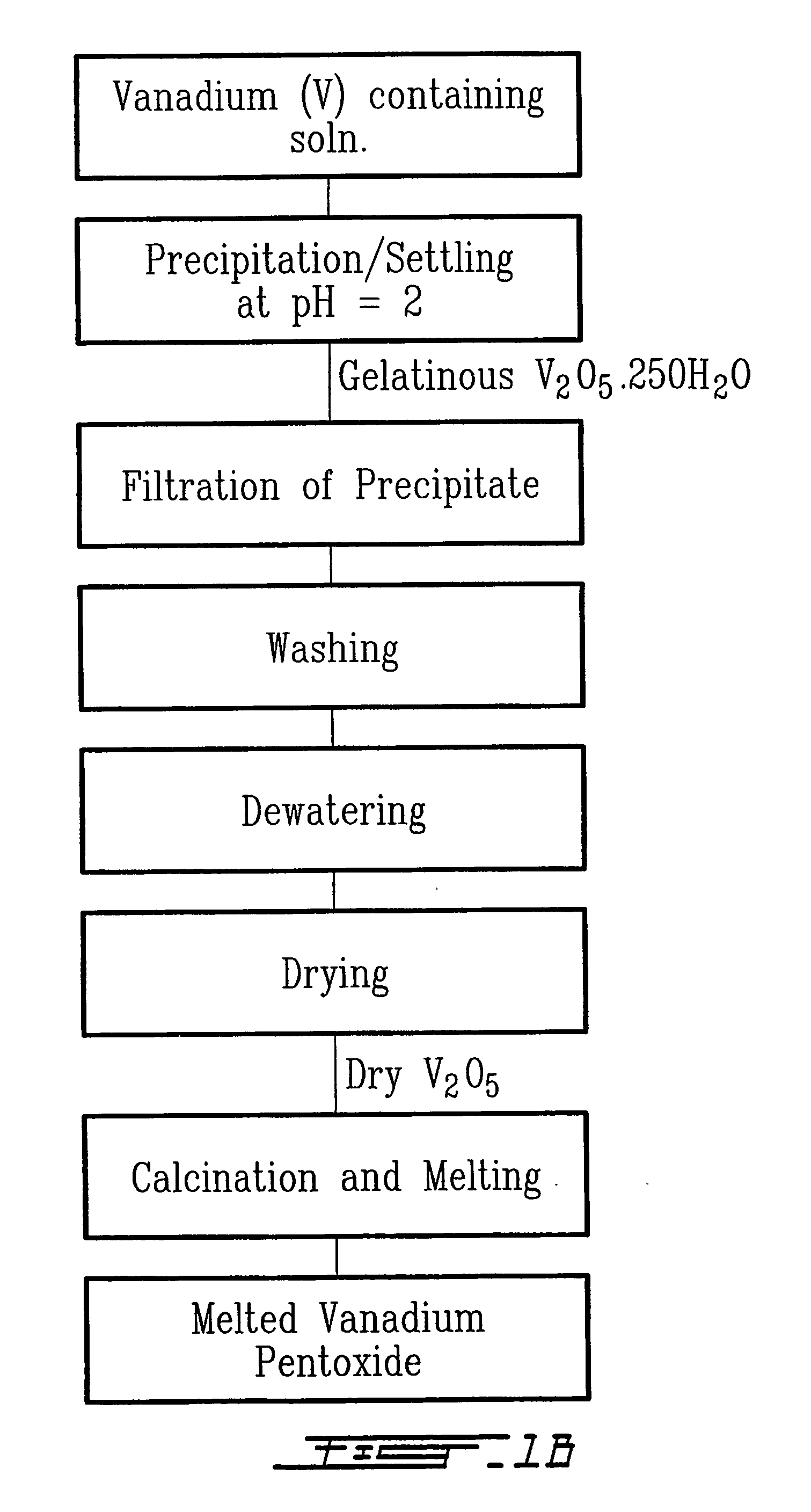
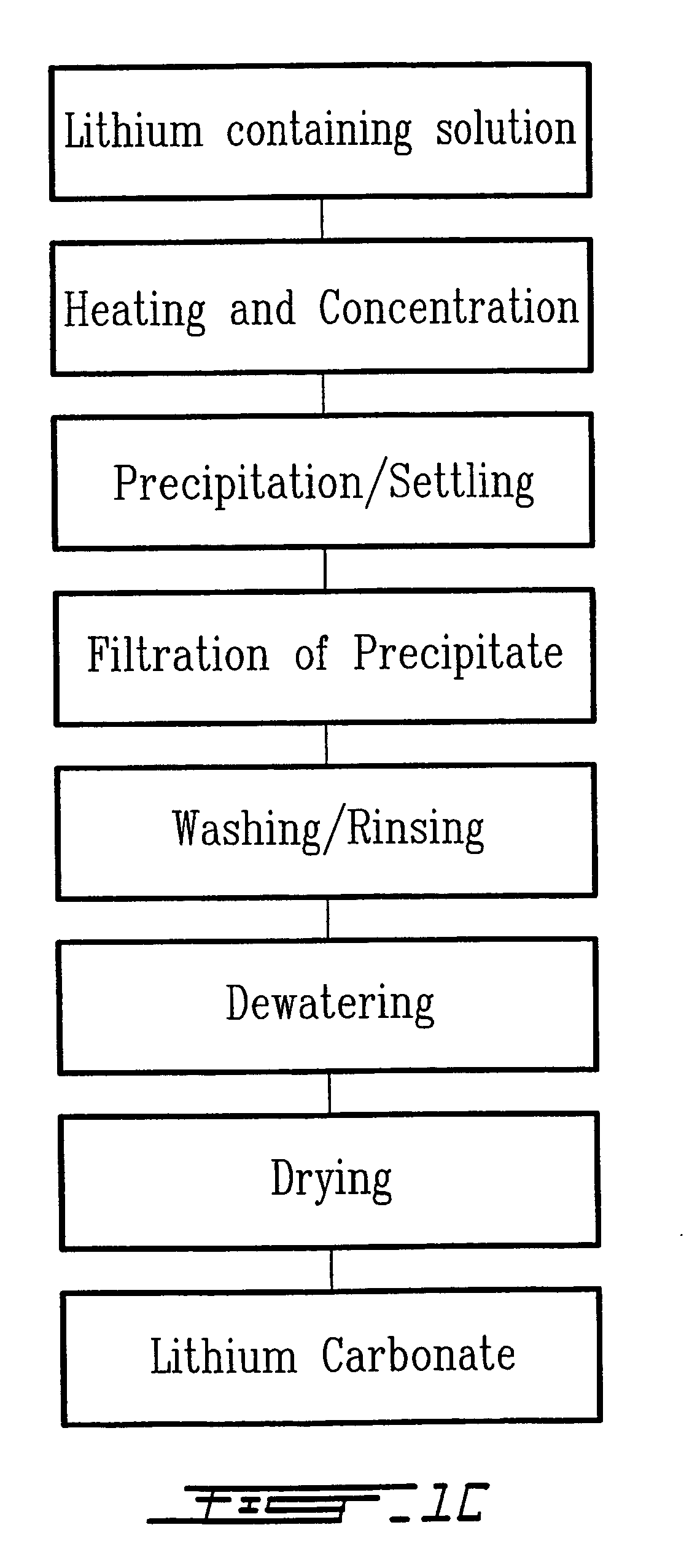
Method for recycling spent lithium metal polymer rechargeable batteries and related materials
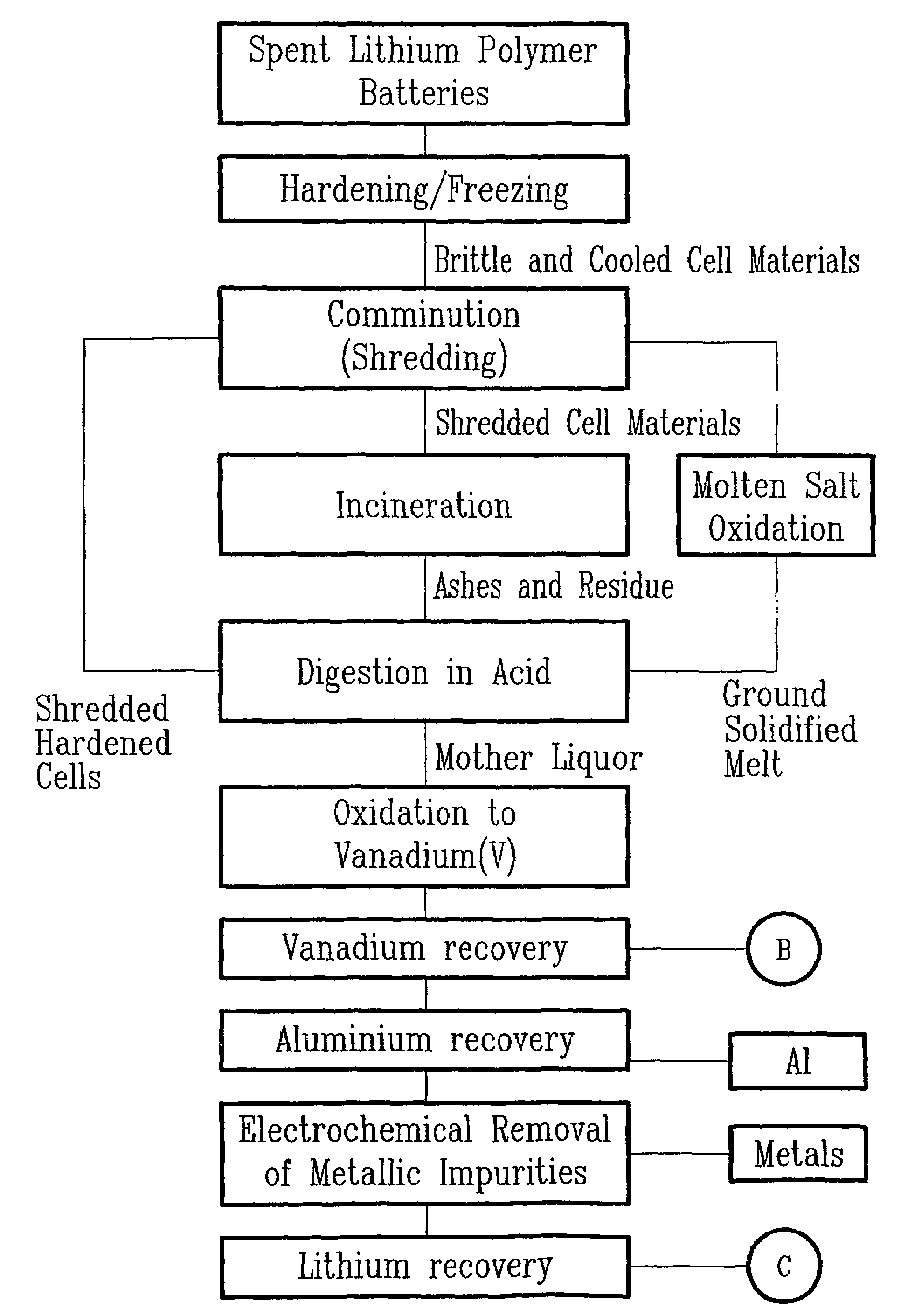
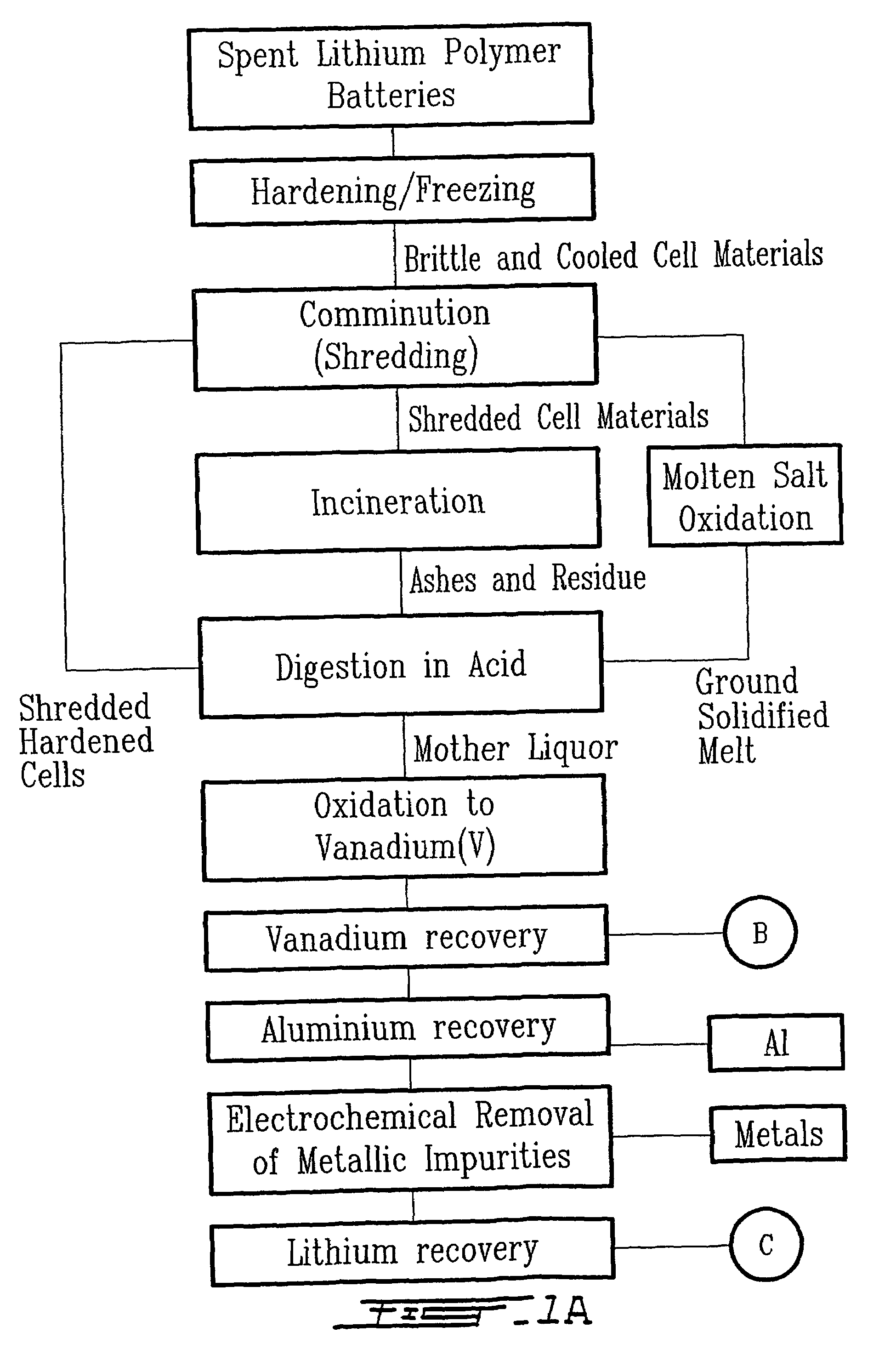
The method relates to a pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical process for the recovery and recycling of lithium and vanadium compounds from a material comprising spent rechargeable lithium batteries, particularly lithium metal gel and solid polymer electrolyte rechargeable batteries. The method involves providing a mass of the material, hardening it by cooling at a temperature below room temperature, comminuting the mass of cooled and hardened material, digesting with an acid its ashes obtained by incineration, or its solidified salts obtained by molten salt oxidation, or the comminuted mass itself, to give a mother liquor, extracting vanadium compounds from the mother liquor, separating heavy metals and aluminium therefrom, and precipitating lithium carbonate from the remaining solution.
Owner:AVESTOR
Negative active material for a lithium secondary battery, a method of preparing the same, and a lithium secondary battery comprising the same
InactiveUS20050164090A1Increase chanceElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsLithiumHigh rate
The present invention relates to a negative active material for a lithium secondary battery which includes a metal oxide-based core material and a carbon material disposed on the surface of the core material, a method of preparing the same, and a lithium secondary battery including the negative active material. According to the present invention, a negative active material for a lithium secondary battery is prepared by coating a core material having good energy density per unit volume with a carbon material, thereby improving the cycle life and charge-discharge characteristics of a lithium secondary battery at a high rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Thermoelectric material and thermoelectric converting element using the same
Compounds are expressed by general formula of AxBC2-y where 0<=x<=2 and 0<=y<1, and have CdI2 analogous layer structures; A-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, Hf, Ta, W, Re, Ir, Pt, Au, Sc, rare earth elements containing Y, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Sn, Pb and Bi; B-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W, Ir, and Sn; C-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of S, Se and Te; the compounds exhibit large figure of merit so as to be preferable for thermoelectric generator / refrigerator.
Owner:NEC CORP
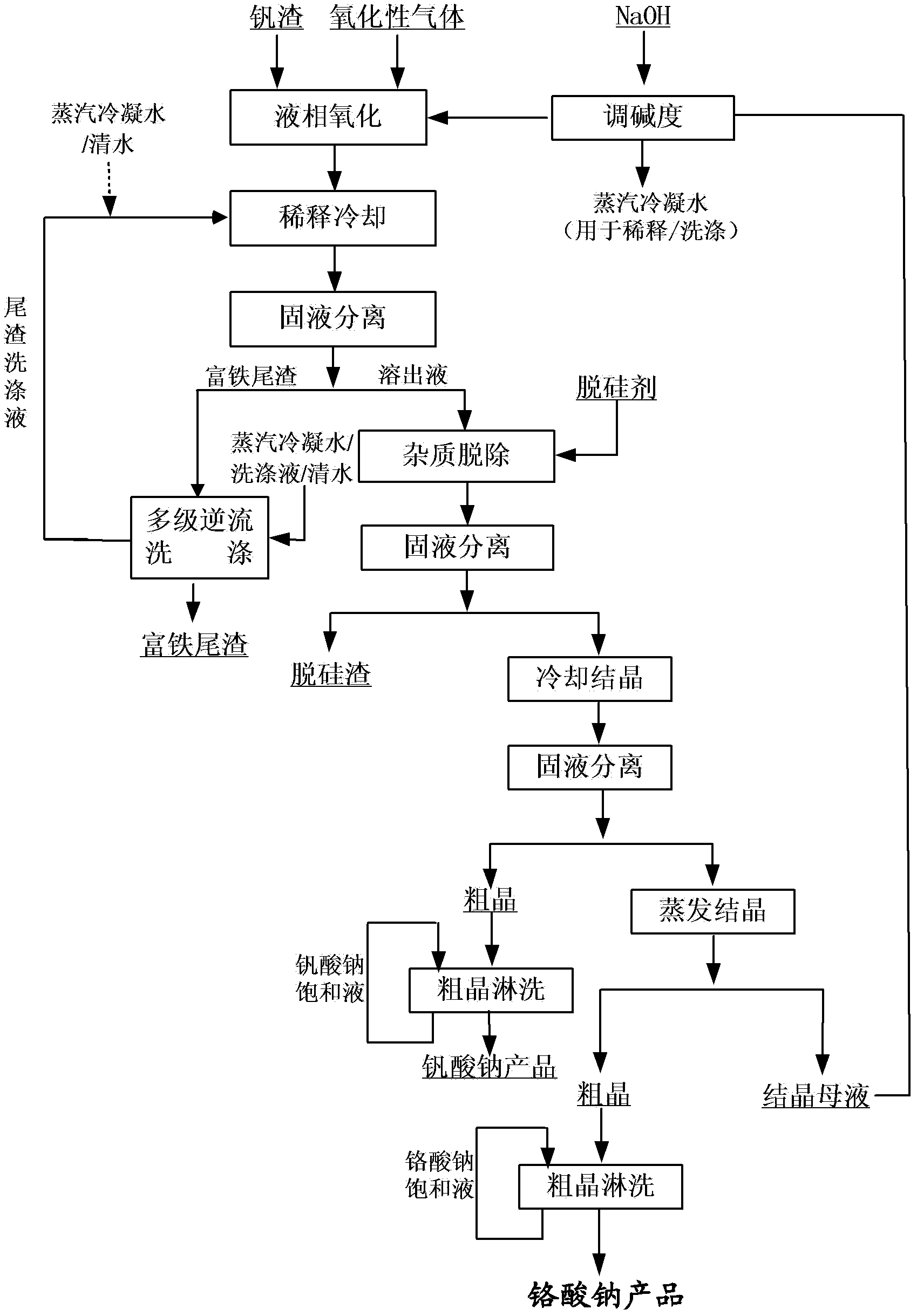
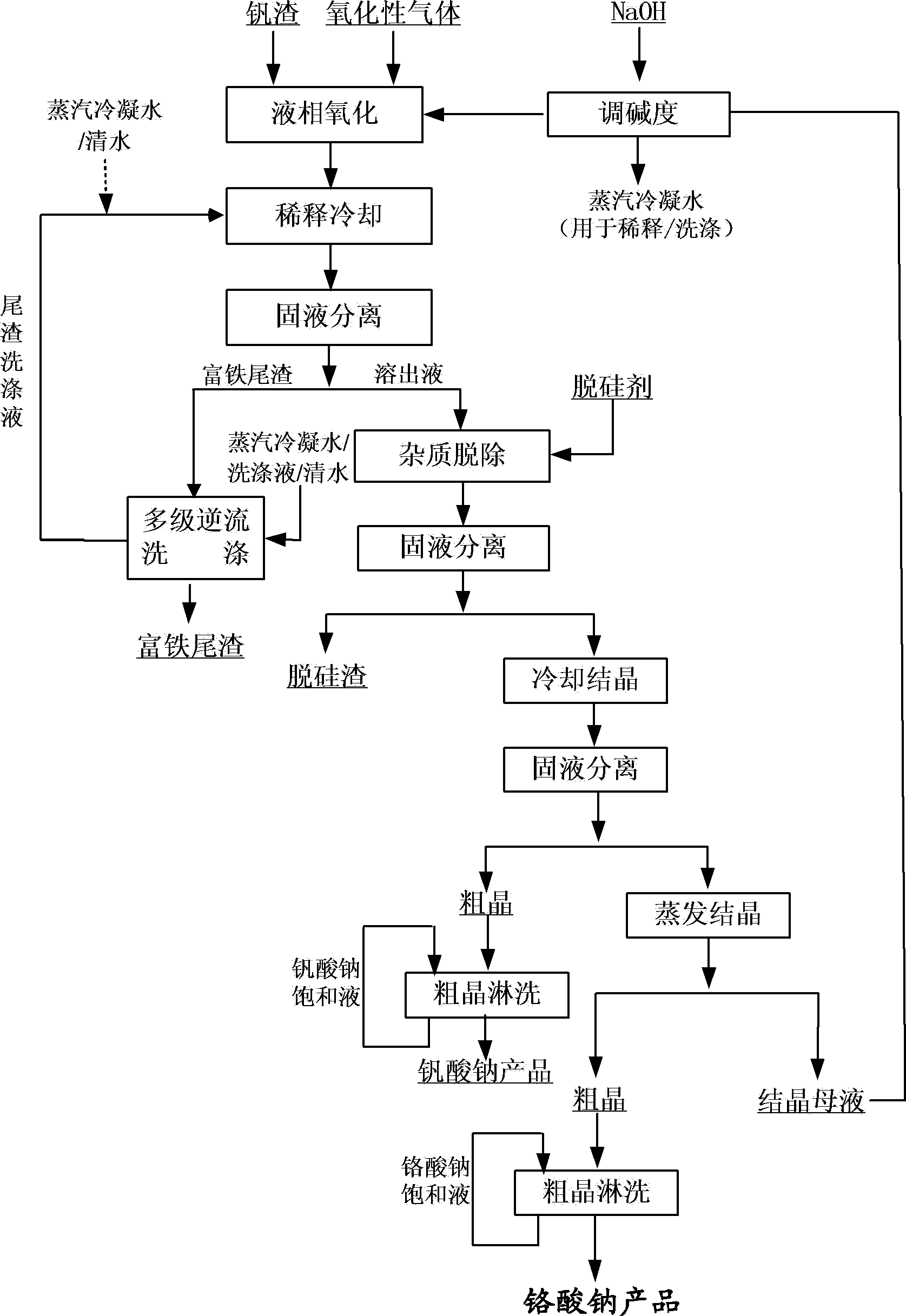
Method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag
ActiveCN102531056ASimple ingredientsAchieve separationChromates/bichromatesVanadium compoundsSlagSlurry
The invention relates to a method for cleaner production of sodium vanadate and sodium chromate by pressure leaching of vanadium slag. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) mixing materials, namely mixing the vanadium slag and a solution of NaOH to obtain a reaction material; (2) reacting, namely performing oxidization reaction on the vanadium slag and oxidizing gas in the solution of NaOH under high pressure to obtain solid-liquid mixed slurry of a solution containing NaOH, Na3VO4, Na2CrO4 and water-soluble impurity components, and iron-rich tailings; (3) performing solid-liquid separation; (4) removing impurities; (5) crystallizing sodium vanadate; and (6) crystallizing sodium chromate. The method is easy to operate and is high in safety; and the operating temperature is greatly lower than the temperature of the traditional vanadium extraction process, energy consumption is low, the high-efficiency co-extraction of vanadium and chromium is realized, and the extraction rate of vanadium and chromium is over 95 percent.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alkali metal electrochemical cell having an improved cathode activated with a nonaqueous electrolyte having a carbonate additive
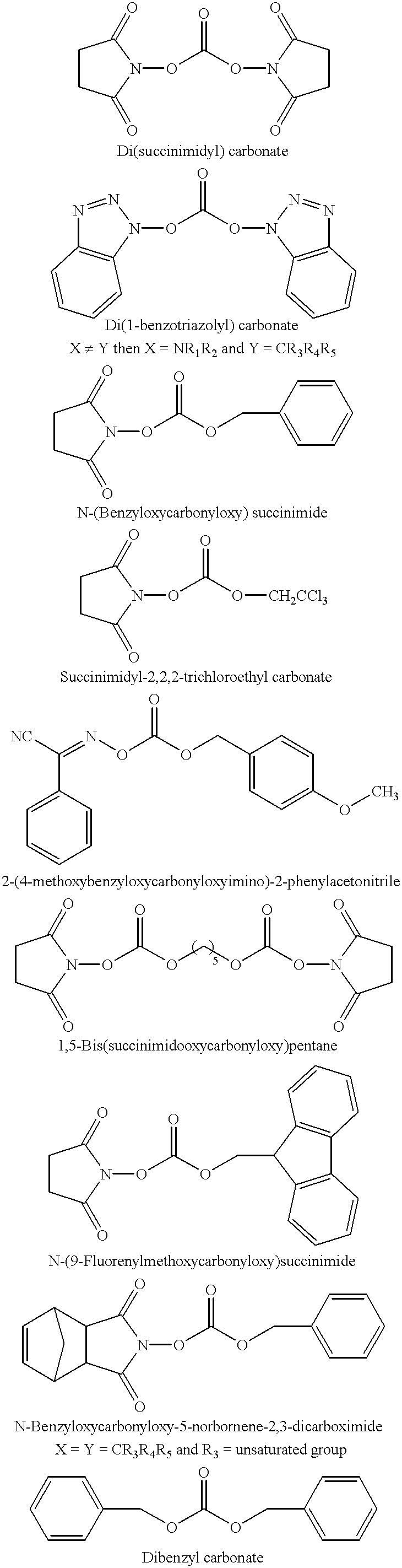
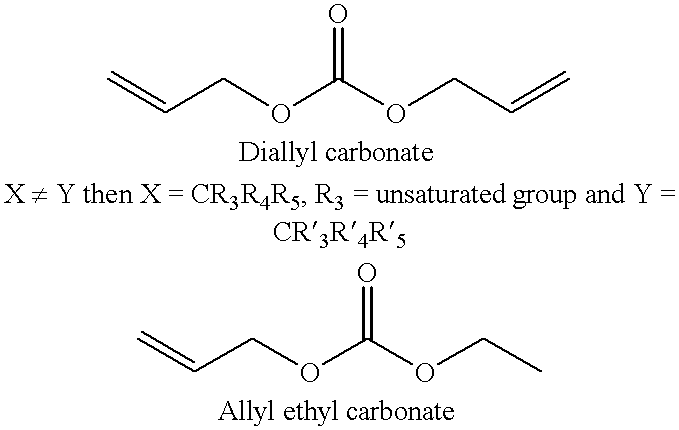
The present invention is directed to an unexpected benefit in a lithium cell derived from using a combination of silver vanadium oxide prepared in a temperature range of about 450° C. to about 500° C. activated with a nonaqueous electrolyte having a passivation inhibitor additive selected from a nitrite, a nitrate, a carbonate, a dicarbonate, a phosphonate, a phosphate, a sulfate and hydrogen fluoride, and mixtures thereof. The benefits include additional battery life resulting from a reduction in voltage delay and RDC build-up. A preferred electrolyte is 1M LiAsF6 in a 50:50 mixture, by volume, of PC and DME having dibenzyl carbonate added therein.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
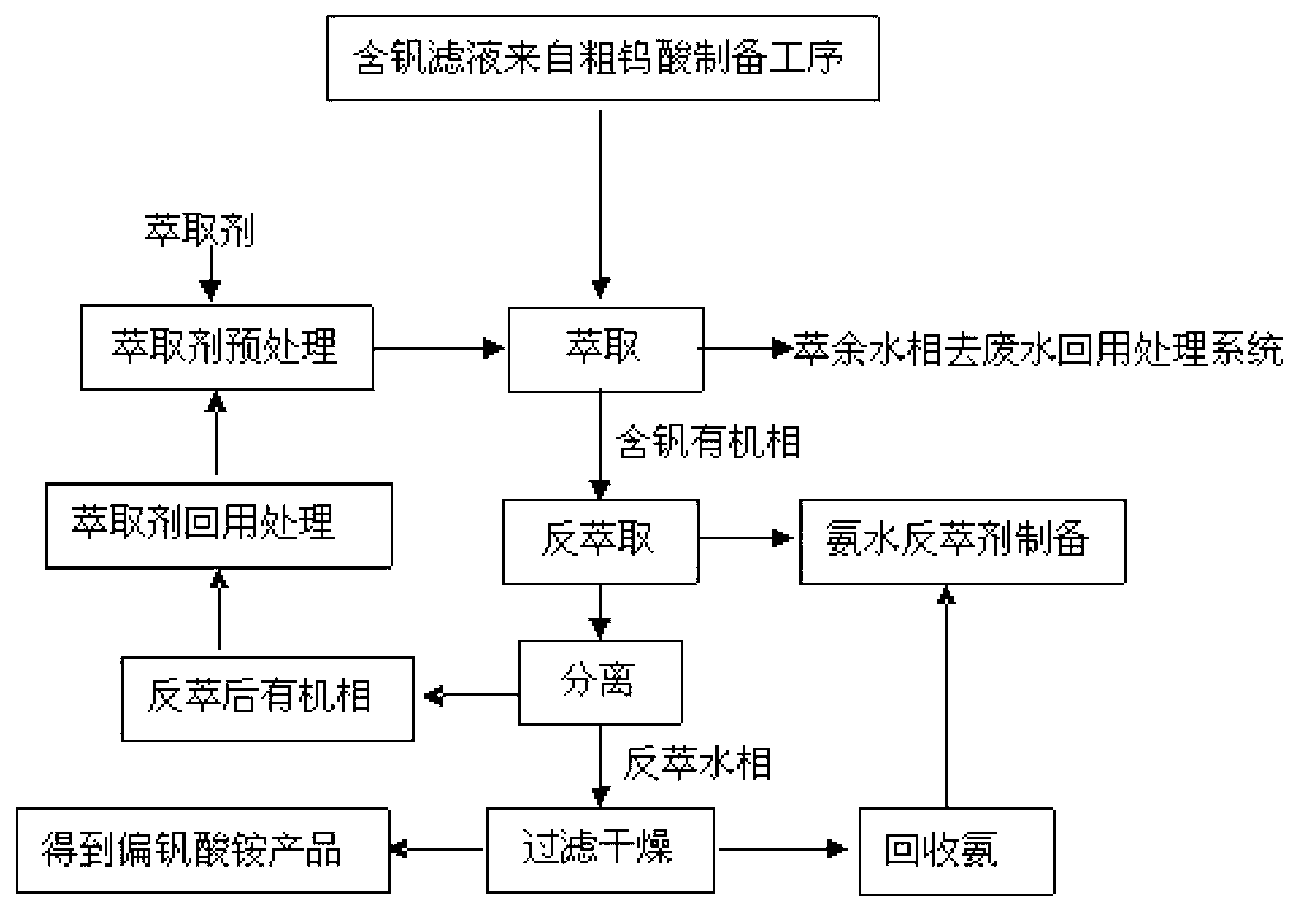
Method for recovering vanadium, tungsten and titanium from waste vanadium-tungsten-titanium-based denitration catalyst
ActiveCN103484678ASimultaneous recoveryLow recovery rateTitanium compoundsVanadium compoundsTungstateAmmonium metavanadate
The invention relates to a method for recovering non-ferrous metals from waste denitration catalysts, particularly relates to a method for recovering vanadium, tungsten and titanium from a waste vanadium-tungsten-titanium-based denitration catalyst, belonging to the field of non-ferrous metal recovery technologies. The method mainly comprises the steps of preparing the catalyst into powder with the grain size being smaller than 100 meshes, and adding concentrated alkali liquor; heating to react vanadium, tungsten and titanium with alkali, so as to produce slightly-soluble titanate, water-soluble vanadate and tungstate; filtrating to obtain a titanate filter cake, wherein titanate or titanic acid can be prepared from the filter cake; adding ammonium salt into a filtrate so as to precipitate ammonium metavanadate, and filtrating to obtain ammonium metavanadate and a new filtrate; adding concentrated acid into the new filtrate, thereby preparing solid tungstic acid. The method has the advantages of simple process, low energy consumption, good solid-liquid reaction contact, high vanadium, tungsten and titanium recovery rate, and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for regeneration and resource utilization of waste honeycombed denitrification catalyst
InactiveCN103508491ALow costRestore activityTungsten oxides/hydroxidesDispersed particle separationResource utilizationAmmonium paratungstate
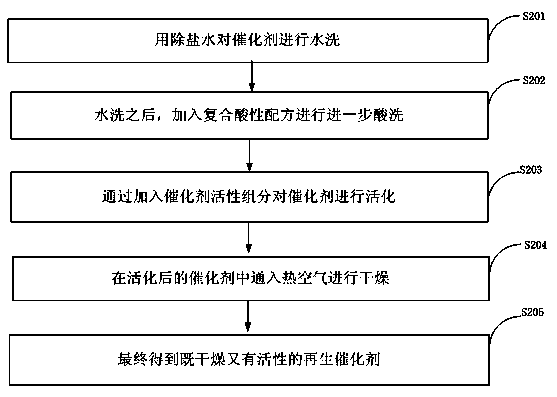
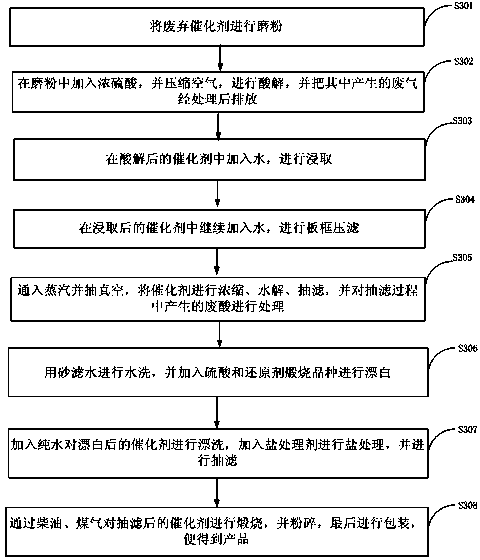
The invention discloses a method for regeneration and resource utilization of a waste honeycombed denitrification catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing, grinding and sieving the waste catalyst; loading a mixture of the powdered catalyst and sodium carbonate into a sintering furnace to produce Na2WO4 and NaVO3, dissolving completely, adjusting the pH value to separate ammonium metavanadate precipitates, filtering, applying the remaining liquid to ammonium paratungstate extraction, washing the precipitates and oven-drying to obtain ammonium metavanadate, and making ammonium paratungstate crystals and tungsten trioxide. The regeneration method of the SCR catalyst comprises the following steps of: performing water-washing, pickling, activation and drying on the catalyst. The method for producing titanium pigment from the waste catalyst as raw material comprises the following steps of: performing pulverization, acidolysis and extraction on the waste catalyst, performing plate-frame pressure filtration; performing concentration, hydrolysis and suction-filtration on the catalyst, washing and blanching with sand leaching water, calcining, grinding and packaging. The method disclosed by the invention can effectively restore the activity of a deactivated catalyst and prolong the service life of the deactivated catalyst, which not only reduce the operating cost of a thermal power plant but also save the valuable rare earth resources.
Owner:YIXING YIGANG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG & MATERIALS
Bismuth vanadate powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101318700AHigh activityImprove visible light absorptionVanadium compoundsBismuth compoundsBismuth vanadateIon exchange
The invention discloses bismuth vanadate powder and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, bismuth-bearing compounds and vanadium-bearing compounds are respectively dissolved in a nitric acid, mixed and then added with a hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide solution, the mol ratio of bismuth to vanadium to the nitric acid to hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide is 1 to 1 to 2.5 to 0.025, and the mixture is stirred for 1 to 2 hours by magnetic force so as to form a bismuth vanadate precursor; the bismuth vanadate precursor is placed in a reaction kettle, undergoes hydrothermal treatment for 70 to 75 hours at a temperature of between 80 and 200 DEG C, cooled, centrifugally separated, and then added with a saturated sodium chloride solution of anhydrous ethanol and deionized water; ion-exchange is performed after the bismuth vanadate precursor is completely immersed, and then centrifugal separation is performed; and finally the bismuth vanadate precursor is washed for 3 to 5 times by mixture of the deionized water and ethanol, then the bismuth vanadate powder with microspheric and / or micro-flaky particles is prepared. The method has simple operation and mild conditions; and bismuth vanadate powder particles prepared are uniform, have large specific surface area, have the characteristics of good visible light response and high photocatalytic activity, and are suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparation method for vanadyl sulfate electrolyte of all-vanadium flow battery
ActiveCN102683733AAchieve mass productionSimple processRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium compoundsAlkaline earth metalKerosene
The invention discloses a preparation method for vanadyl sulfate electrolyte of an all-vanadium flow battery. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: adjusting pH value of vanadyl sulfate solution obtained from leaching vanadium slag and stone coal, back extracting and resin-analyzing treatments by using oxide or hydroxide of alkali metal or alkaline earth; adding an inorganic reducing agent; performing multi-grade counter-current extraction by using P204 or P507: TBP: sulfonated kerosene extracting agent; after the two-phase separation, washing the vanadium-loaded organic phase; performing 2-5 grades of multi-grade counter-current back extraction on the vanadium-loaded organic phase by using sulfuric acid solution to obtain the back extracting liquid of vanadyl sulfate; adjusting the pH value of the back extracting liquid of vanadyl sulfate, adding the organic reducing agent to adjust the potential value of the solution; extracting the solution by using the extracting agent; after the two-phase separation, washing the vanadium-loaded organic phase by using the sulfuric acid solution; performing multi-grade counter-current back extraction by using the sulfuric acid solution to obtain the vanadyl sulfate solution; and distilling until the concentration required for all-vanadium flow battery. The method provided by the invention can improve the purity, simplify the preparation procedure and reduce the cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF RARE METALS
Negative active material for rechargeable lithium battery, method of preparing thereof, and rechargeable lithium battery including the same
ActiveUS20080118840A1Improve stabilityExcellent charge and discharge efficiency and cycle-lifeMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdeum compoundsDischarge efficiencyVanadium oxide
A negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery of the present invention includes a lithium-vanadium oxide core material being capable of performing reversible electrochemical oxidation and reduction, and an inorganic oxide coating layer disposed on the surface of the core material. The negative active material can improve stability at the interface between a negative electrode and an electrolyte, charge and discharge efficiency, and cycle-life, and can be applied along with all kinds of aqueous and non-aqueous binders.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
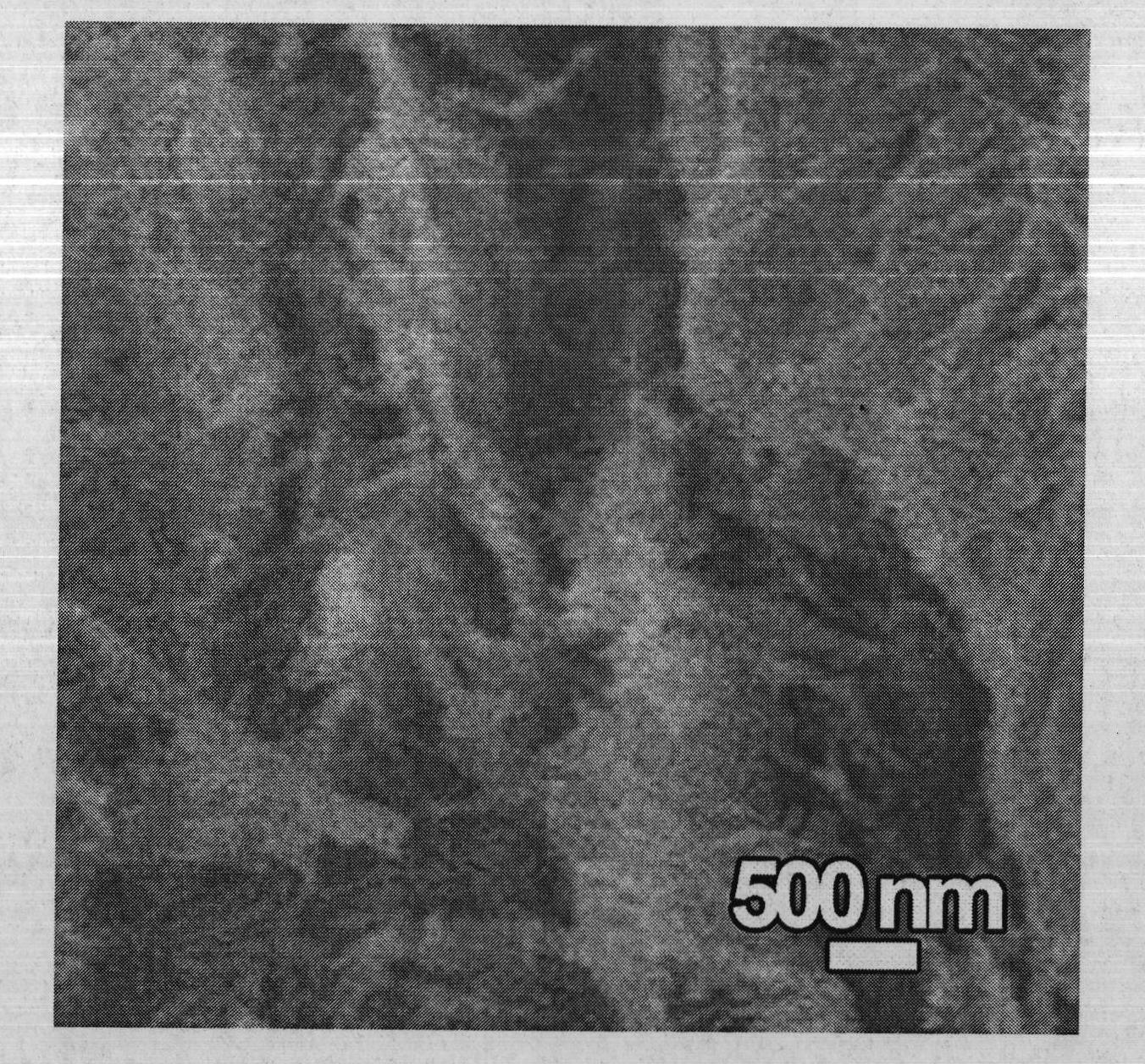
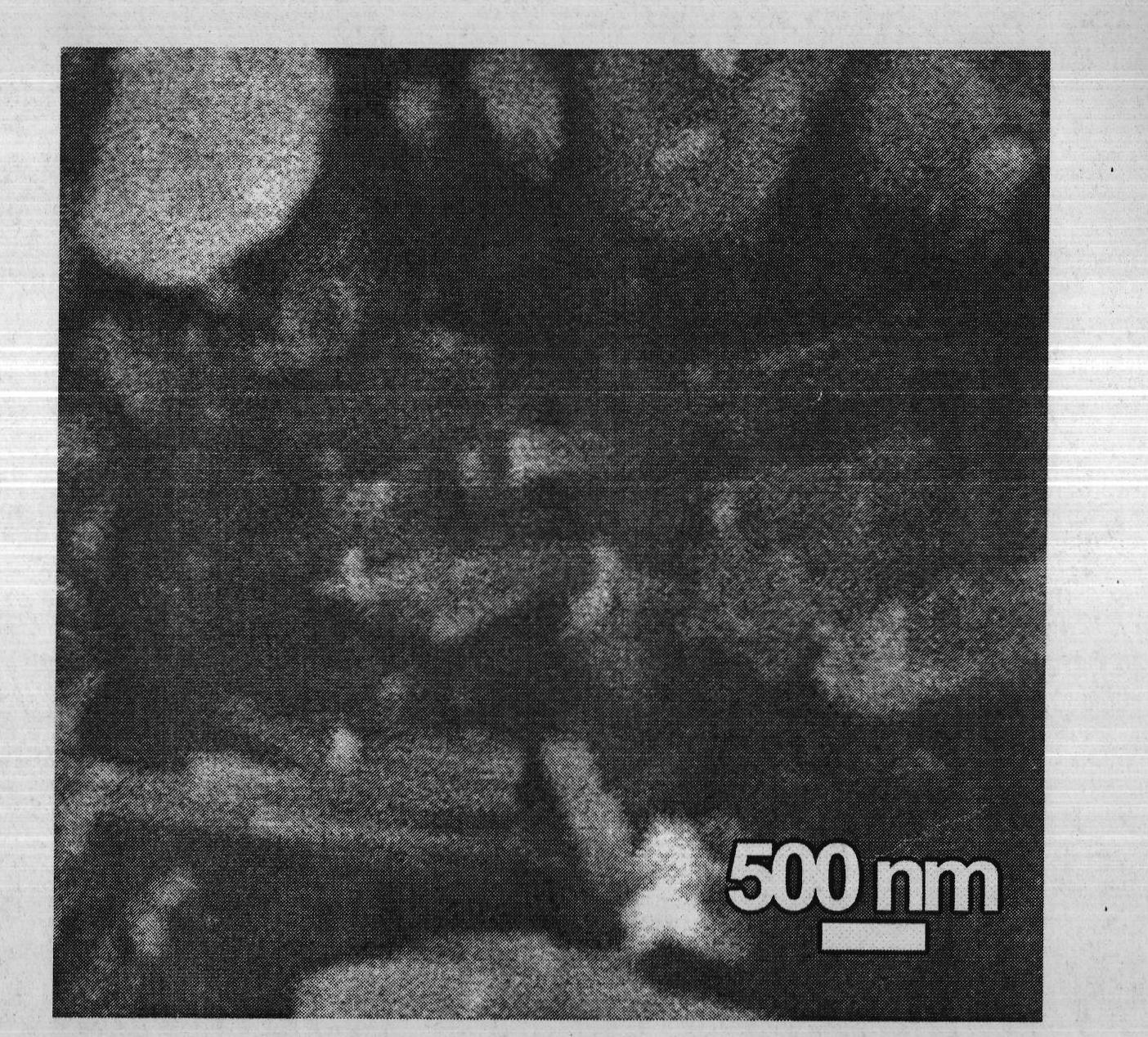
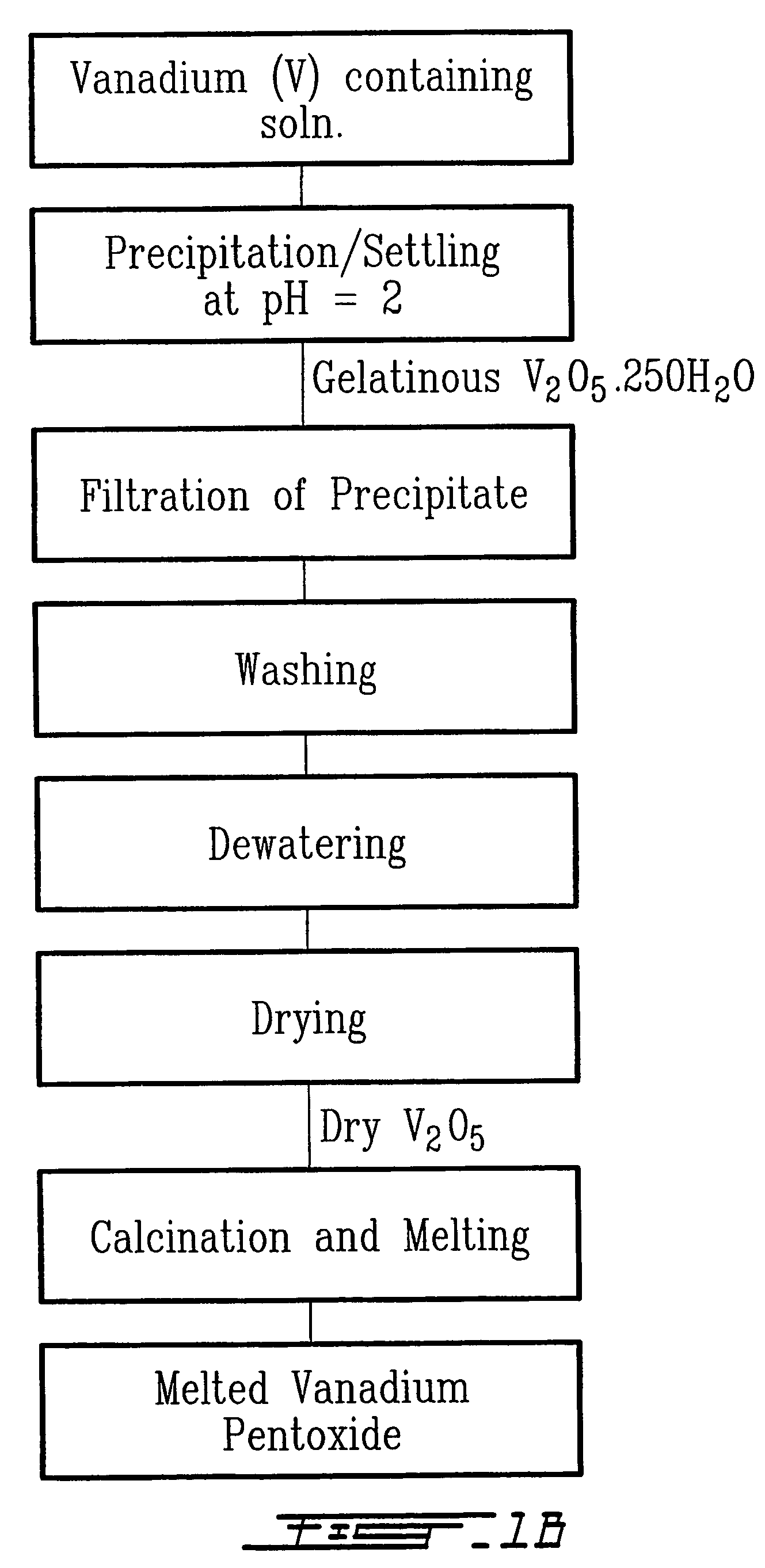
Synthesis of nanoparticles
Owner:CENT FUR ANGEWANDTE NANOTECH
Method for synthesizing vanadium acid zinc micro/nanowire material by adopting hydrothermal method
InactiveCN102140691AEasy to operateExperimental conditions are easy to controlPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsNanowirePhotoluminescence
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a vanadium acid zinc micro / nanowire material by adopting a hydrothermal method. In the method, ammonium metavanadate and zinc nitrate are used as reaction materials, distilled water is used as a solvent, a surfactant is used for controlling a microstructure, and the vanadium acid zinc micro / nanowire material with a regular appearance can be prepared under a hydro-thermal condition. The technology has the advantages of simplicity in operation, feasibility, controllable experimental condition, good repeatability, suitability for mass production and the like; and the synthesized material can play an important and positive role in multiple fields such as electrode material, photoluminescence, gas sensing and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing vanadium disulphide nano powder
InactiveCN102010004AHigh purityLow costNanotechnologyVanadium compoundsHigh volume manufacturingCentrifugation
The invention provides a method for preparing vanadium disulphide nano powder. The method comprises the following steps: a) sulphur source is added into a hydrothermal device filled with a vanadium source aqueous solution; b) the obtained mixed solution be subjected to is kept at the temperature of 40-300 DEG C; and c) after reaction is completed, natural cooling is carried out, and the product is washed and collected by centrifugation, thus obtaining the vanadium disulphide nano powder. In the invention, the vanadium disulphide nano powder is prepared by hydrothermal synthesis at lower temperature, the vanadium source and the sulphur source react according to the reaction principle of oxidoreduction, fixing of quadrivalence of vanadium is realized, no large-scale equipment and extreme conditions are required, raw materials are cheap and easily available, the cost is low, the process is simple, the yield is high, the purity of the prepared vanadium disulphide nano powder is high, the system is clean, and mass production is easy to realize.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method and application of rare earth metal hydroxide or vanadate nano material
InactiveCN101624206AEffective control compositionEffective control structureVanadium compoundsRare earth metal compoundsNanowireRare earth
The invention provides a controllable preparation method and an application of rare earth metal hydroxide or vanadate nano material by using an ionic liquid assisted hydrothermal method. The preparation method comprises the following steps of taking rare earth metal salt, metavanadate and sodium hydroxide as raw materials, mixing evenly, adding deionized water to form precipitate, adding mixed solution of imidazolium ionic liquid and anhydrous ethyl alcohol, stirring for 10-30 min, transferring into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, carrying out hydrothermal reaction for 1-8h under the temperature of 100-220 DEG C and obtaining rare earth metal hydroxide nano particles, nano rods or nano-wire materials. If the reaction time is prolonged to 16-148h, rare earth vanadate one-dimensional nano-wire and two-dimensional nanoflake materials can be prepared. The method provided by the invention can effectively adjust and control phases and features of rare earth metal hydroxide and vanadate nano materials, and has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, simple technique, low cost, high yield and the like, thus being hopeful to be widely applied in the fields such as luminescent devices, electrocatalytic components, permanent magnets, biological and medical industry and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for preparing super-fine vanadic-acid bismuth-yellow pigment
InactiveCN101070435AMild reaction conditionsReduce manufacturing costPigmenting treatmentVanadium compoundsBismuth vanadateGranularity
The invention discloses the methods of preparation for a superfine bismuth vanadate yellow pigment, the characteristics of its bismuth nitrate, partial vanadate or vanadate are the main raw material. Through controlling of its appropriate pH and temperature to get the Ultra-fine particles,which composed of bismuth vanadate yellow pigments.well by adding surfactant or changing vanadium source, itcan further control particle morphology, which were prepared by a diameter of 50-150 nm spherical particles, 100-200 nanometer length, width 50-100 nanometers Flake Vanadate Bismuth or length of 200-300 nm rod bismuth vanadate. The preparation of this invention is a simple process, and can be controlled morphology, the bismuth vanadate can meet the needs of different occasions, which can be widely used in the automotive topcoat, ink, paint and other requirements for a higher size area.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY +1
Preparation method of ammonium poly-vanadate
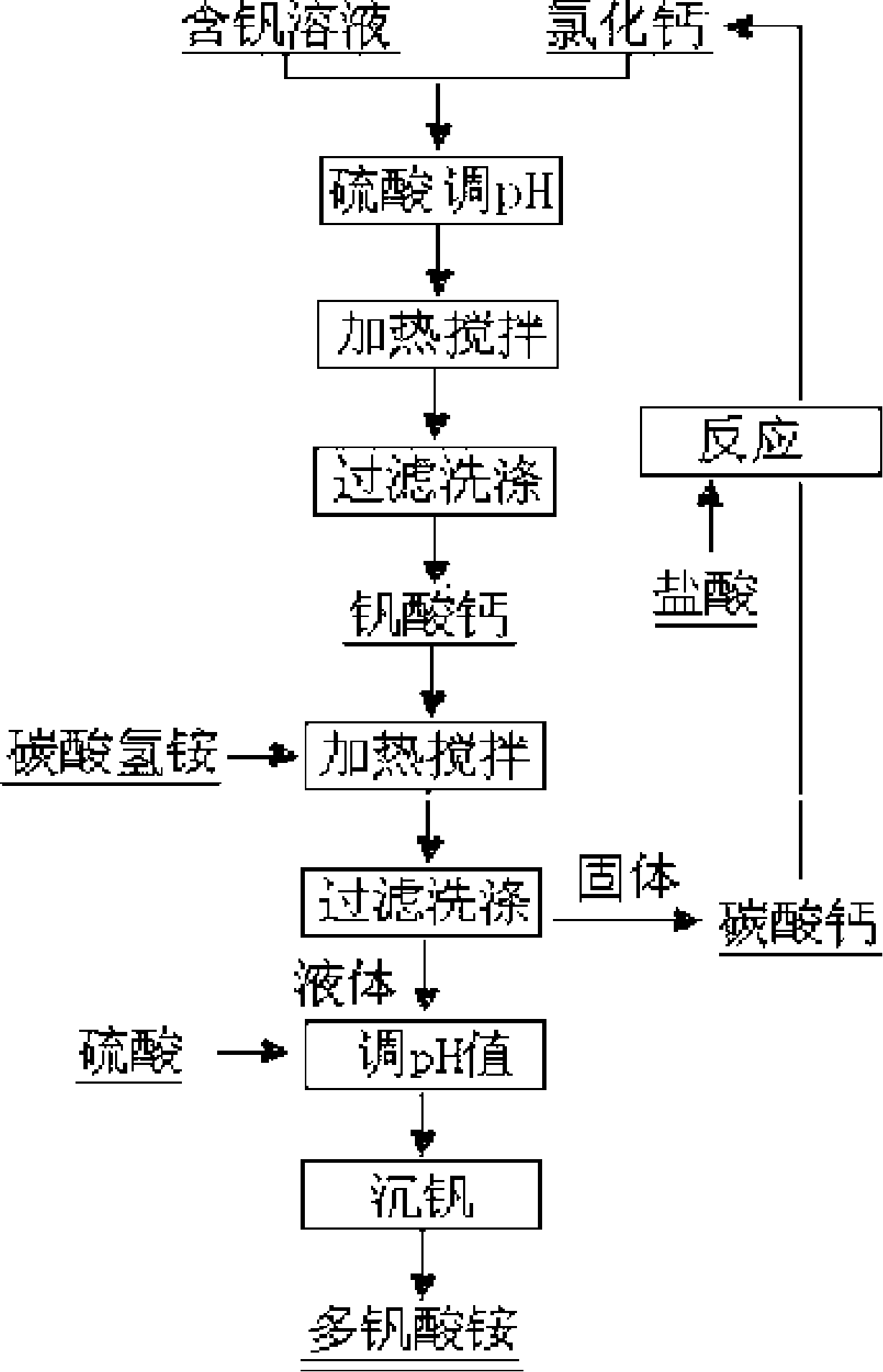
The invention belongs to the chemical engineering field, in particular relates to a method for preparing ammonium polyvandata with vanadium-containing solution. The method uses the vanadium-containing solution produced with the traditional sodium roasting-water immersing technology as the raw material. First, vanadium combines with added calcium compounds and produces calcium vanadate, which reacts with ammonium bicarbonate and transfers vanadium into the solution but transforms calcium into more insoluble calcium carbonate; the ammonium polyvandata is produced with the separated solution under appropriate pH and heating conditions. After redissolution of calcium vandata, the ammonium bicarbonate containing less than 0.1percent of SUM (Na2O+K2 O) can be obtained. The ammonium bicarbonate can be used for production of vanadium trioxide and vanadium pentoxide with exceedingly low contents of potassium and sodium; and the ammonia content of vanadium-precipitation waste water is only 60percent to 75 percent of vanadium-extraction waste water in traditional technologies. The invention has very promising application prospect.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
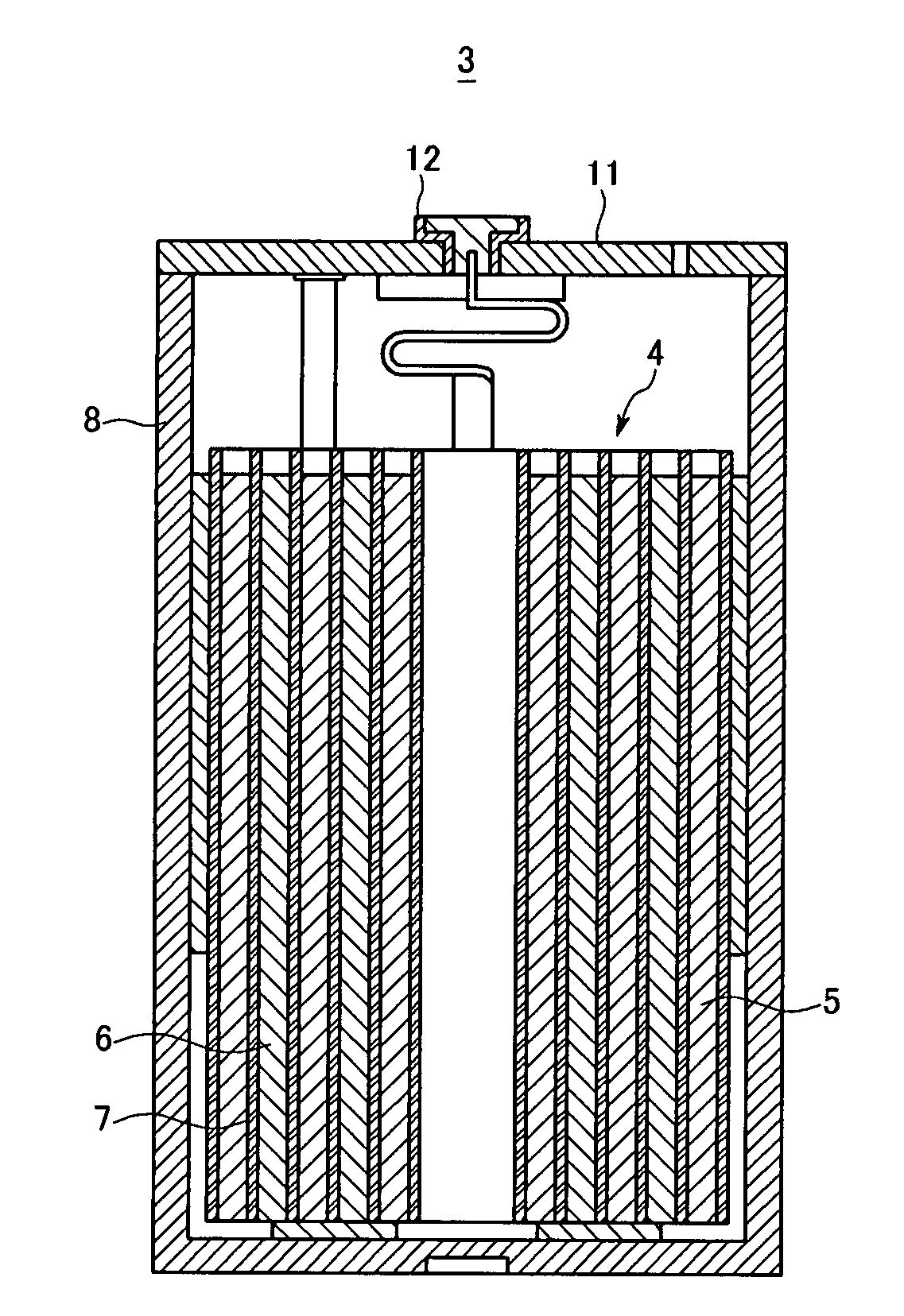
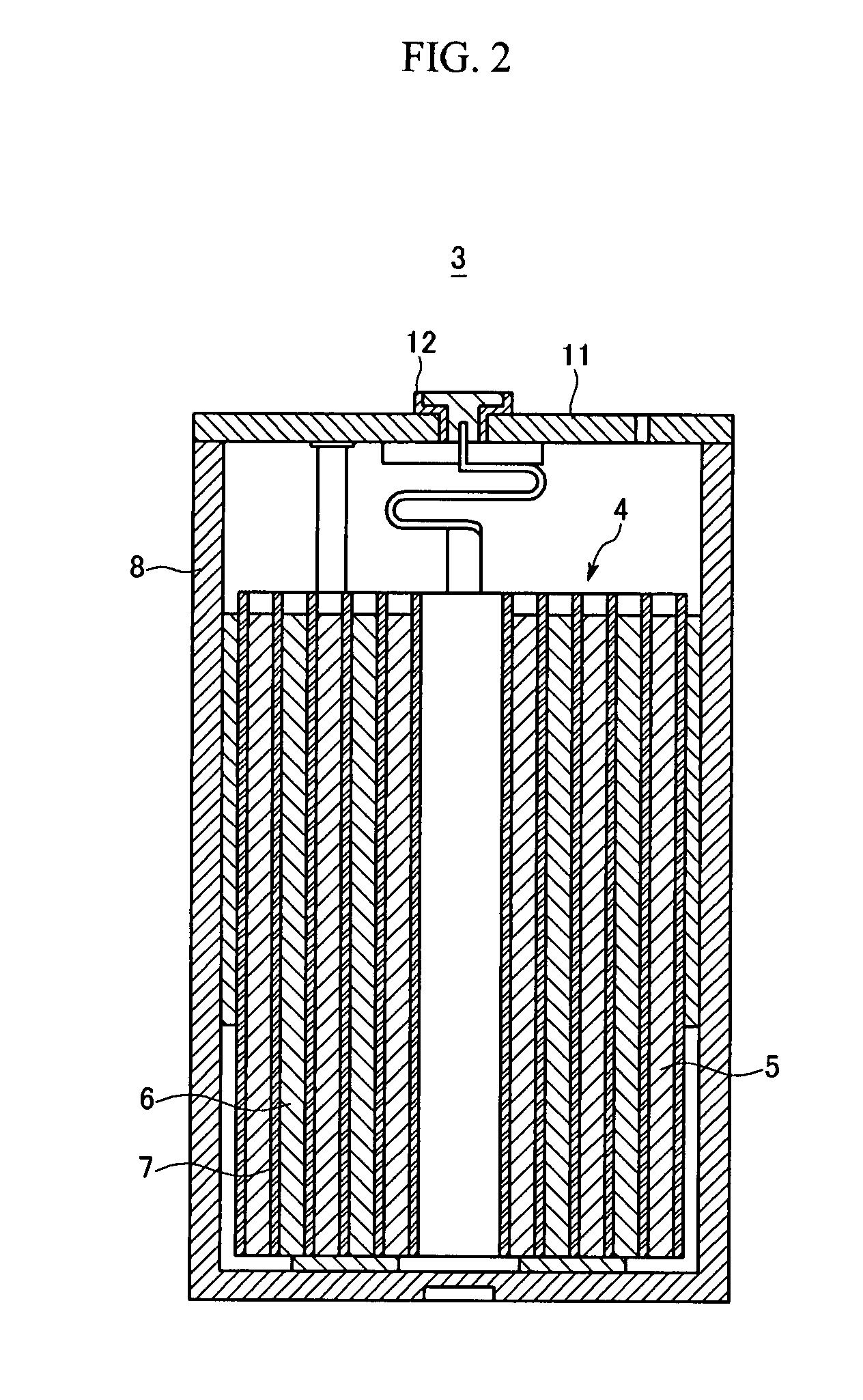
Compact steam reformer
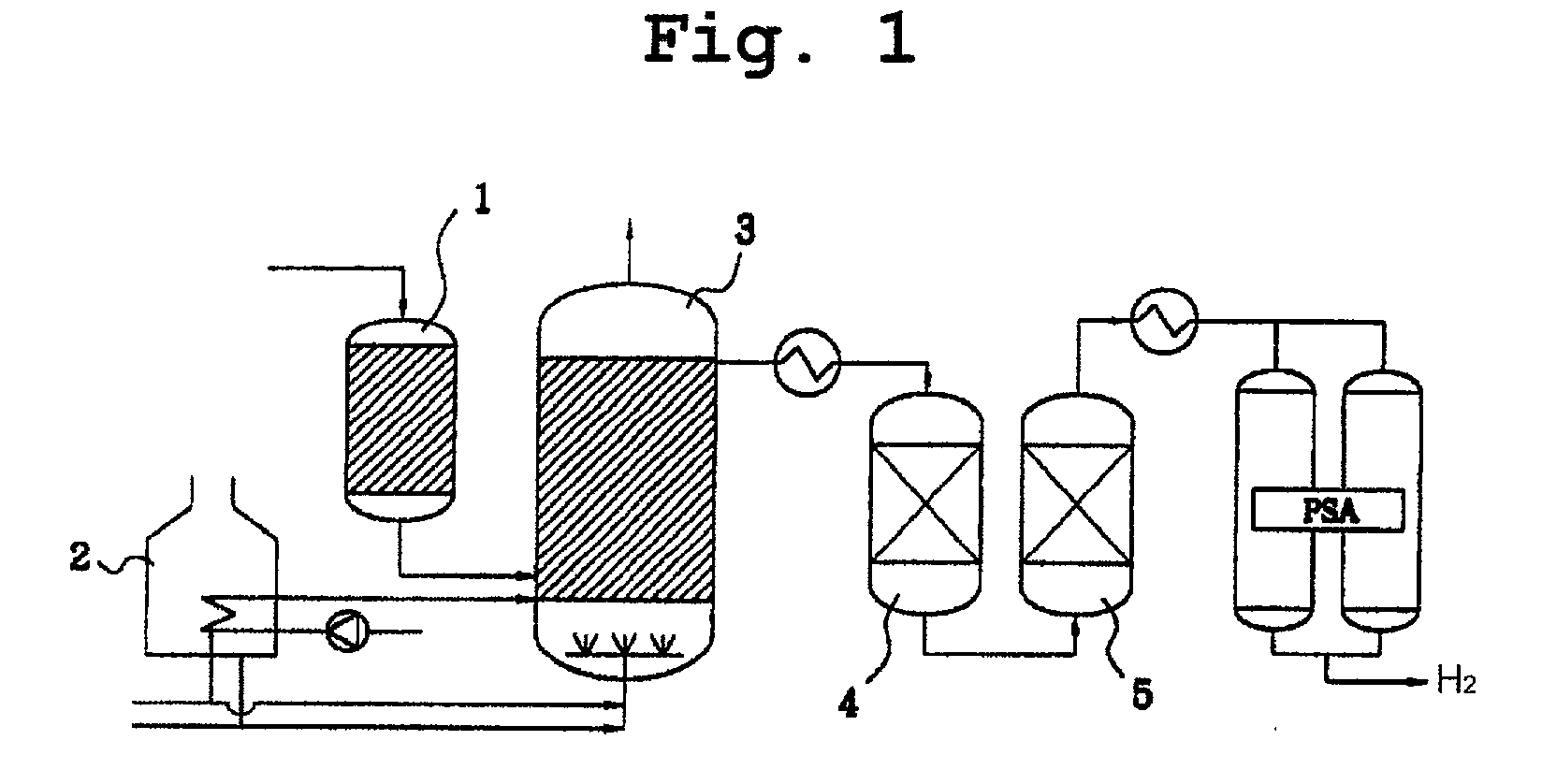
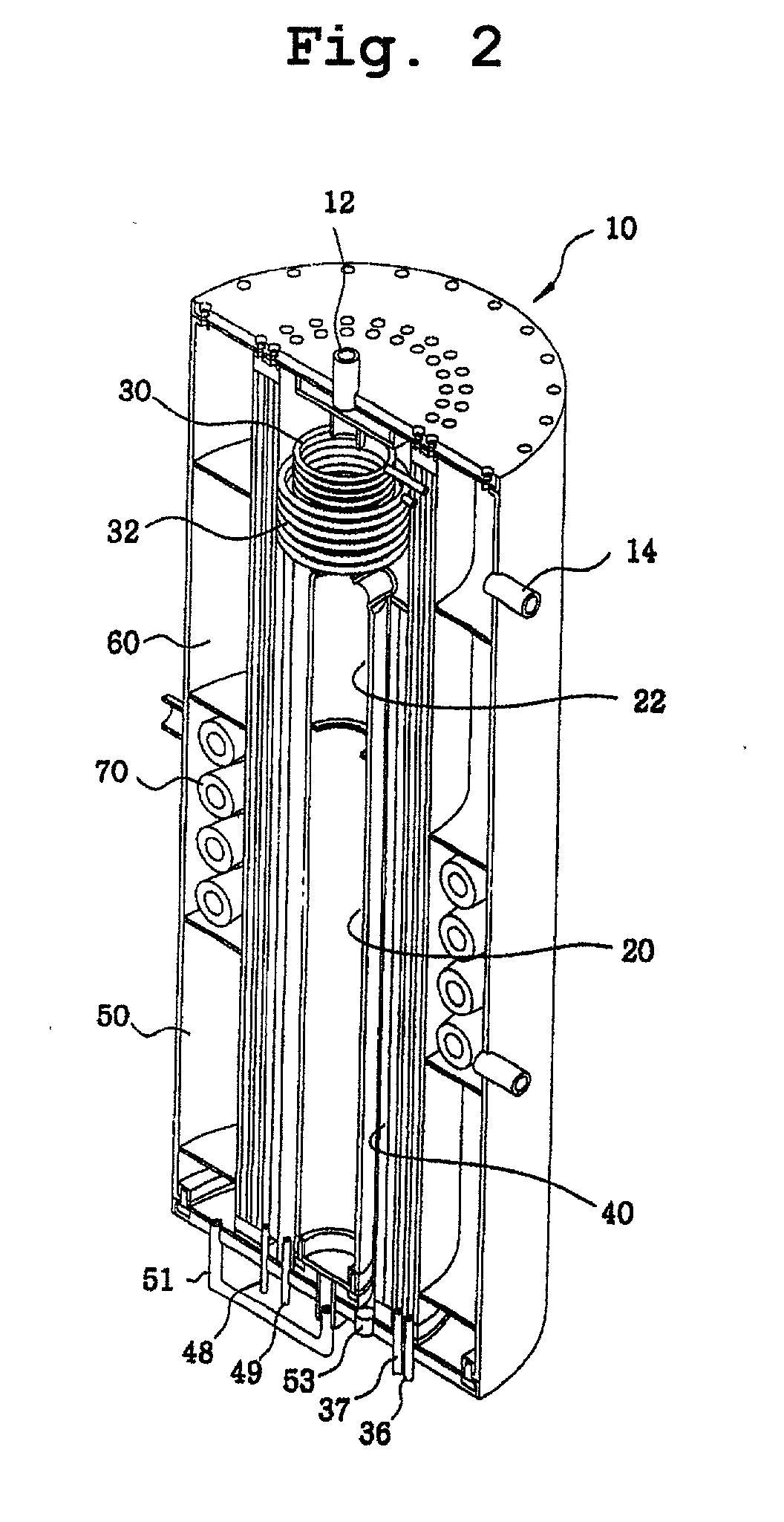
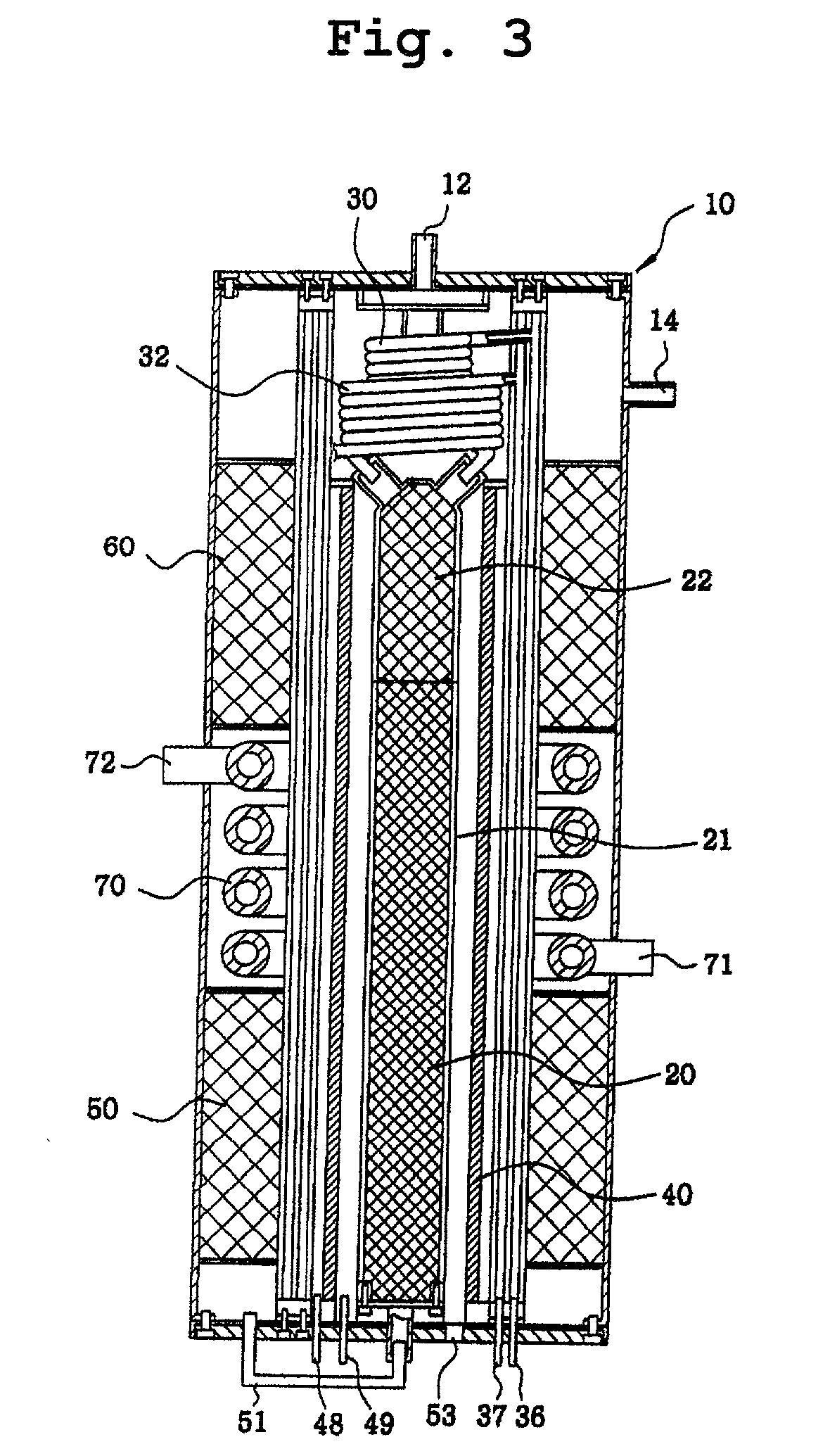
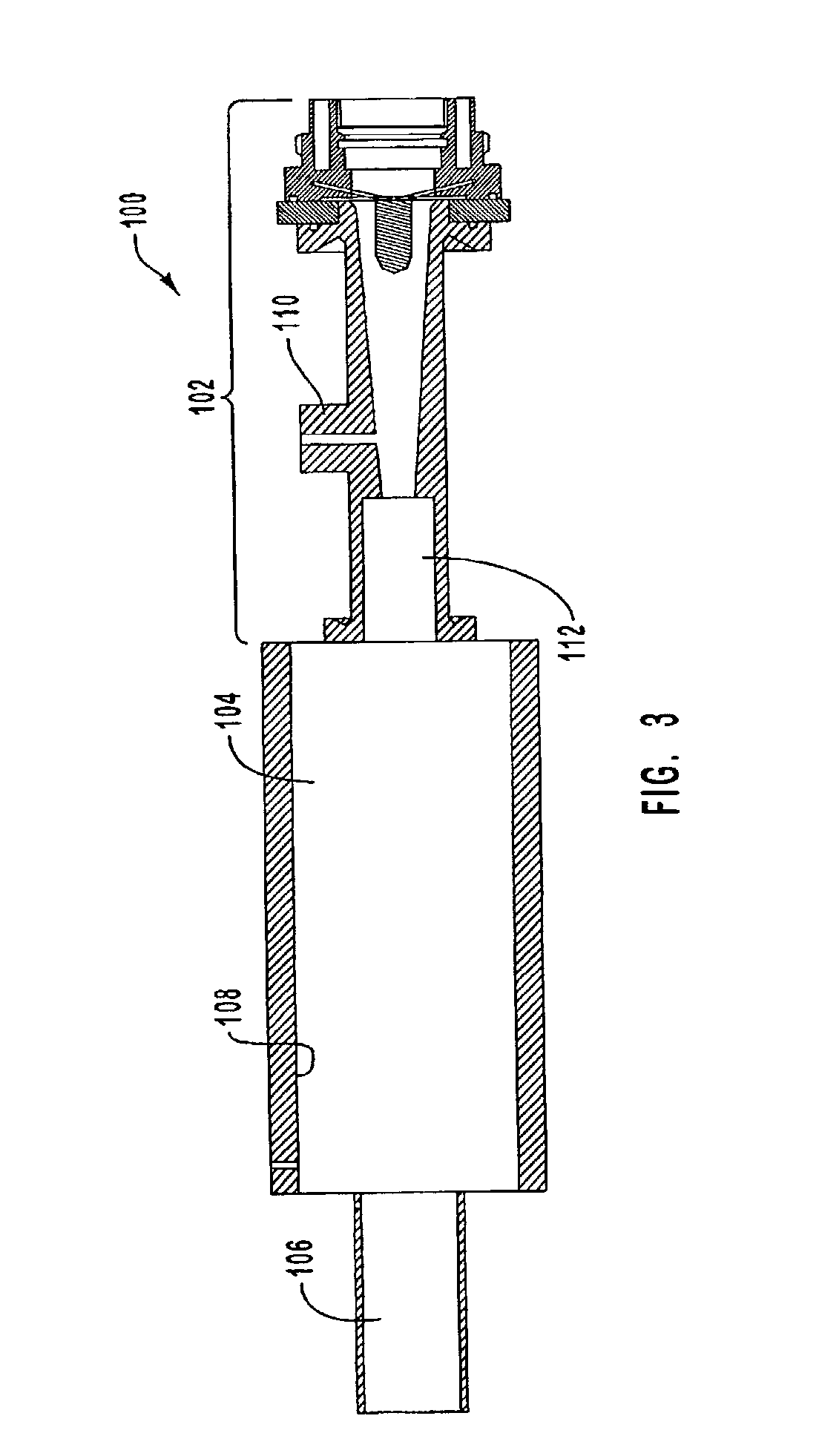
Disclosed is a compact steam reformer which integrally comprises a housing; a reforming reactor having an upper mixing compartment for mixing natural gas and steam and a lower compartment for accommodating a catalyst bed; a natural gas feeding coiled pipe through which natural gas is introduced while being heated; a steam generating coiled pipe in which pure water is converted to steam by the exhaust; a metal fiber burner for heating the reforming reactor; a high-temperature converter for primarily removing carbon monoxide from a synthetic gas; a low-temperature converter for secondarily reducing the carbon monoxide level of the synthetic gas; and a heat exchanger, provided between the high-temperature converter and the low-temperature converter, for cooling the gas effluent from the high-temperature converter. The steam reformer enjoys the advantage of being easy to install in situ and being fabricated at low cost. Also, the cylindrical metal fiber burner can provide heat uniformly over the reforming reactor without a temperature gradient, thereby maximizing the reforming efficiency. The reformer has such a structure as to utilize the heat of the burner exhaust in generating steam, bringing about an effect of reducing the cost of the reformer because no additional steam generators are required.
Owner:KOREA GAS CORPORATION +2
Synthesis of Metal Compounds Under Carbothermal Conditions
InactiveUS20050255026A1Economical and convenient processLower capability requirementsPhosphatesLithium compoundsOxidation stateGraphite
Active materials of the invention contain at least one alkali metal and at least one other metal capable of being oxidized to a higher oxidation state. Preferred other metals are accordingly selected from the group consisting of transition metals (defined as Groups 4-11 of the periodic table), as well as certain other non-transition metals such as tin, bismuth, and lead. The active materials may be synthesized in single step reactions or in multi-step reactions. In at least one of the steps of the synthesis reaction, reducing carbon is used as a starting material. In one aspect, the reducing carbon is provided by elemental carbon, preferably in particulate form such as graphites, amorphous carbon, carbon blacks and the like. In another aspect, reducing carbon may also be provided by an organic precursor material, or by a mixture of elemental carbon and organic precursor material.
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV +1
Method for recycling spent lithium metal polymer rechargeable batteries and related materials
The method relates to a pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical process for the recovery and recycling of lithium and vanadium compounds from a material comprising spent rechargeable lithium batteries, particularly lithium metal gel and solid polymer electrolyte rechargeable batteries. The method involves providing a mass of the material, hardening it by cooling at a temperature below room temperature, comminuting the mass of cooled and hardened material, digesting with an acid its ashes obtained by incineration, or its solidified salts obtained by molten salt oxidation, or the comminuted mass itself, to give a mother liquor, extracting vanadium compounds from the mother liquor, separating heavy metals and aluminium therefrom, and precipitating lithium carbonate from the remaining solution.
Owner:AVESTOR
Fullerene-like nanostructures, their use and process for their production
ActiveUS20100227782A1Improve conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialAlloyElectronic properties
A nanostructure, being either an Inorganic Fullerene-like (IF) nanostructure or an Inorganic Nanotube (INT), having the formula A1−x-Bx-chalcognide are described. A being a metal or transition metal or an alloy of metals and / or transition metals, B being a metal or transition metal B different from that of A and x being ≦0.3. A process for their manufacture and their use for modifying the electronic character of A-chalcognide are described.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Thermal synthesis apparatus and process
InactiveUS20030021746A1Improve efficiencyHigh yieldTantalum compoundsIndirect heat exchangersNuclear engineeringReaction zone
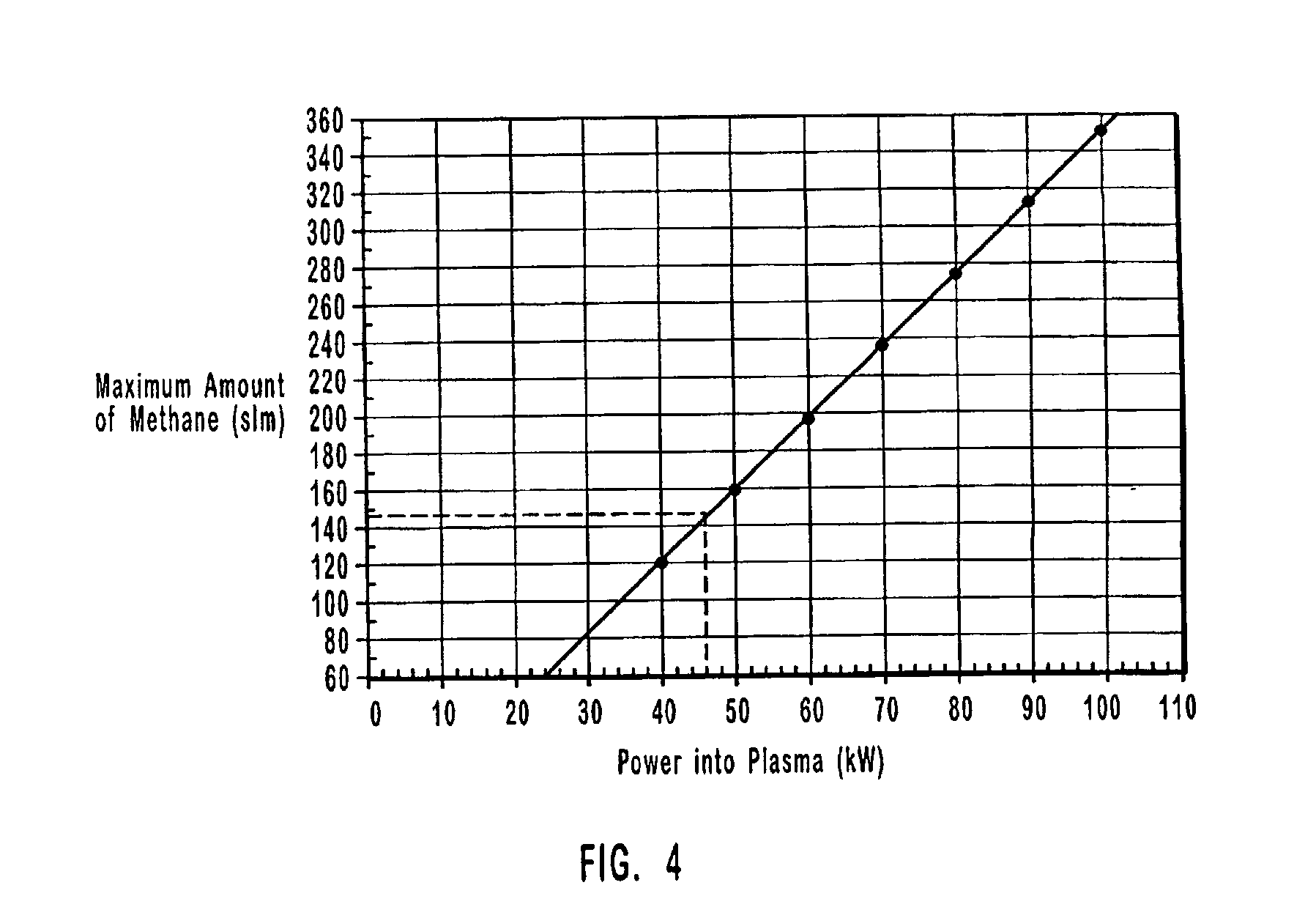
An apparatus for thermal conversion of one or more reactants to desired end products includes an insulated reactor chamber having a high temperature heater such as a plasma torch at its inlet end and, optionally, a restrictive convergent-divergent nozzle at its outlet end. In a thermal conversion method, reactants are injected upstream from the reactor chamber and thoroughly mixed with the plasma stream before entering the reactor chamber. The reactor chamber has a reaction zone that is maintained at a substantially uniform temperature. The resulting heated gaseous stream is then rapidly cooled by passage through the nozzle, which "freezes" the desired end product(s) in the heated equilibrium reaction stage, or is discharged through an outlet pipe without the convergent-divergent nozzle. The desired end products are then separated from the gaseous stream.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Process for preparinbg vanadylic sulfate and use
The preparation process of vanadylic sulfate includes adding V2O3 and V2O5 into sulfuric acid, filtering and evaporating the filtrate, eliminating crystalline water to obtain light blue VOSO4 powder. Compared with available technological path, the said technological process of the present invention has less steps, mild reaction condition, simple technological process, low cost and stable product quality. The filtrate may be used as the material as electrolyte in vanadium cell.
Owner:攀枝花钢铁有限责任公司钢铁研究院
Popular searches
Nanostructure manufacture Alkaline-earth metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparation Wood layered products Natural mineral layered products Phosphorus compounds Metal layered products Peroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonides Gallium/indium/thallium compounds Calcium/strontium/barium sulfates Synthetic resin layered products
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com