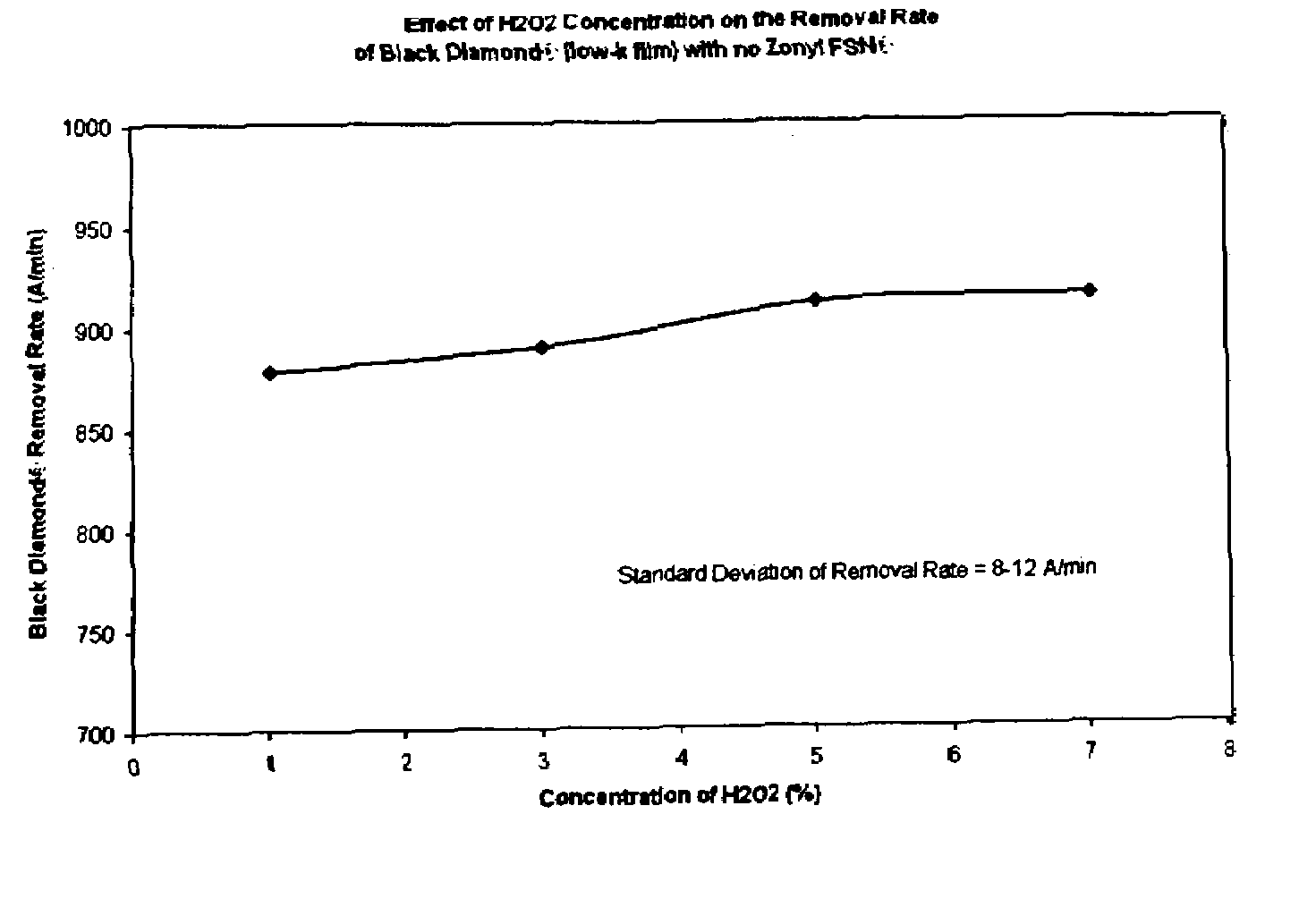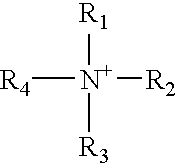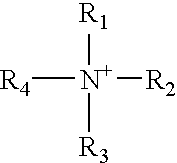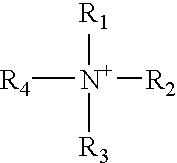Patents
Literature
218results about How to "Reduce removal rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
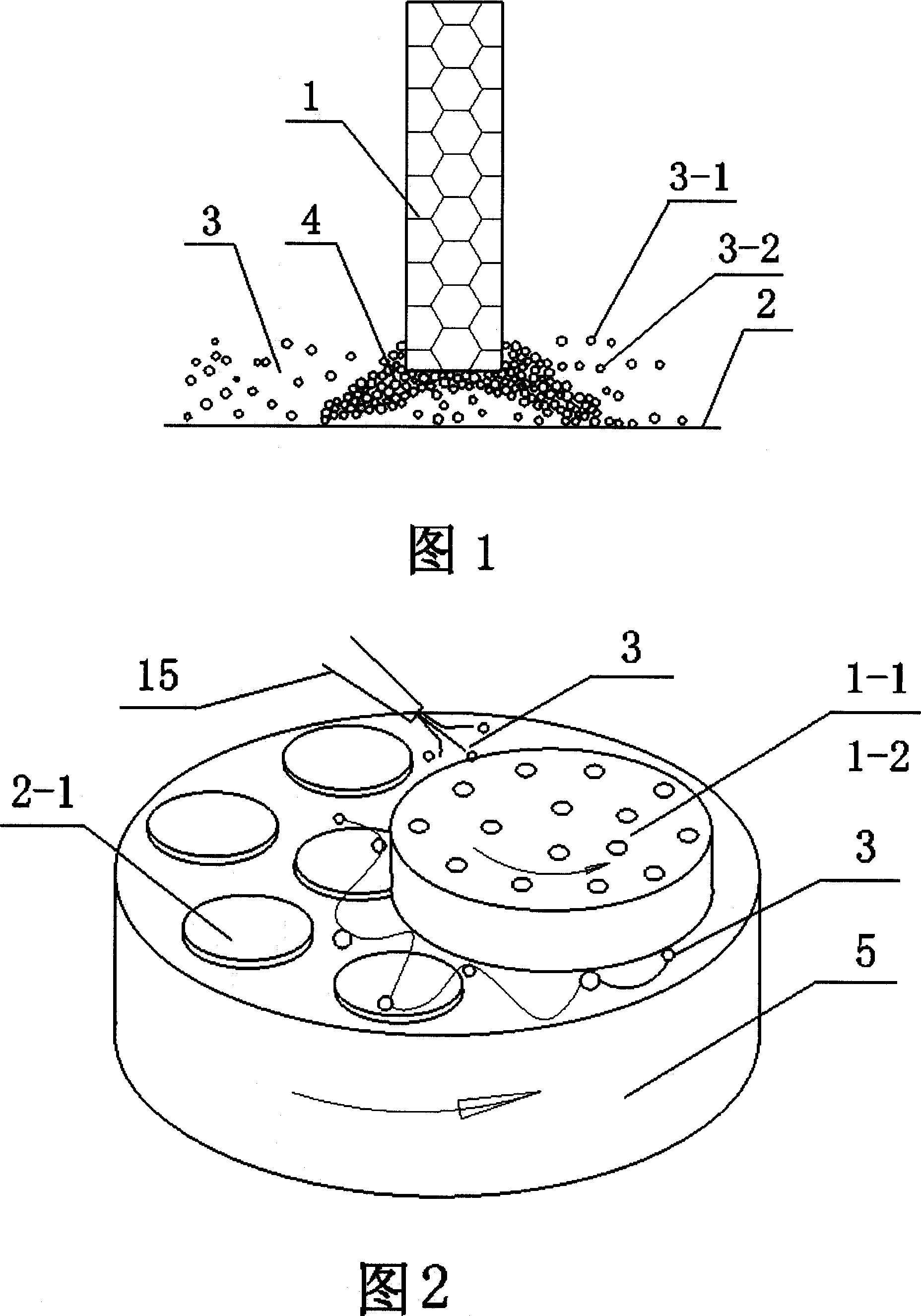
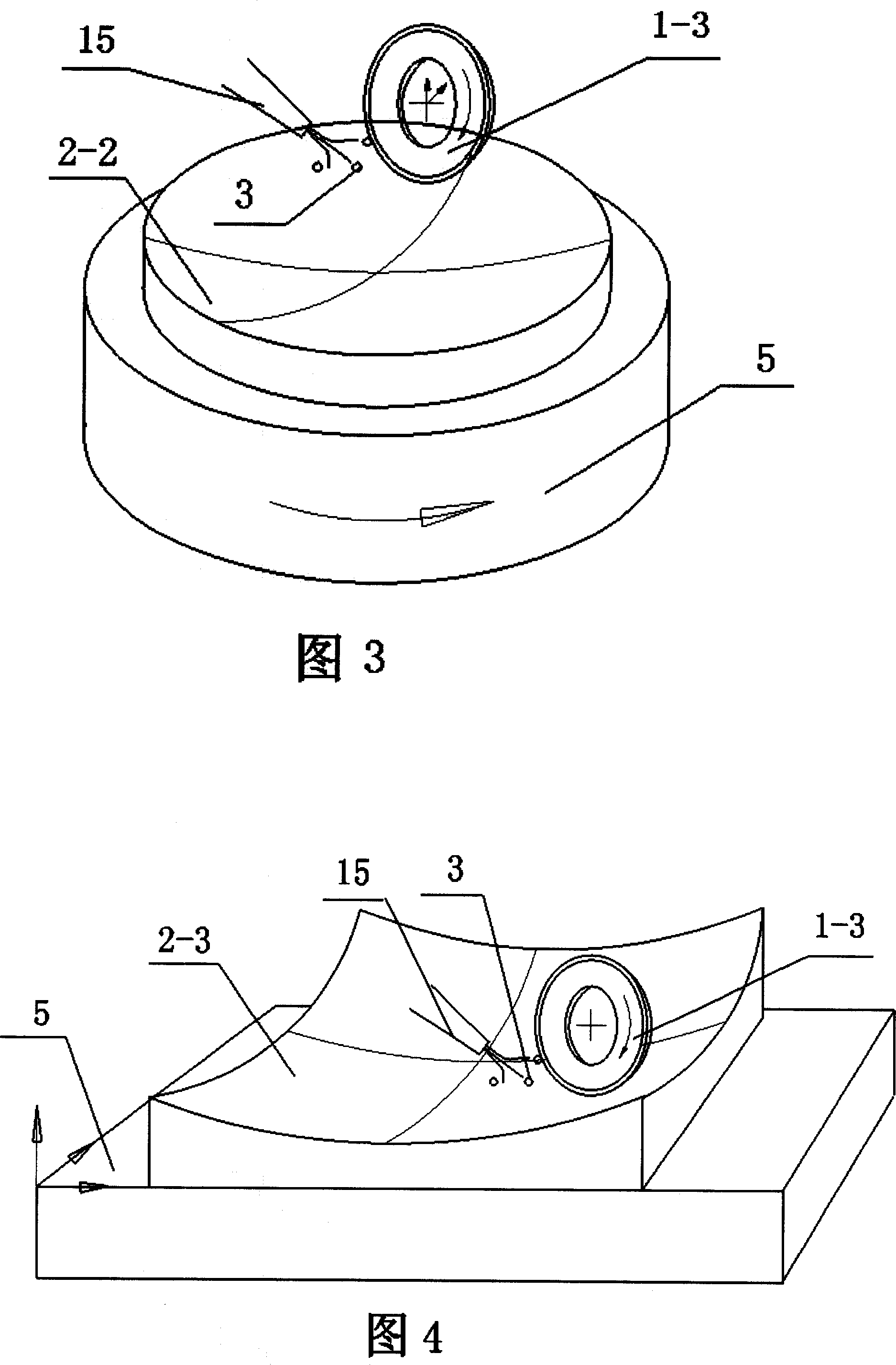
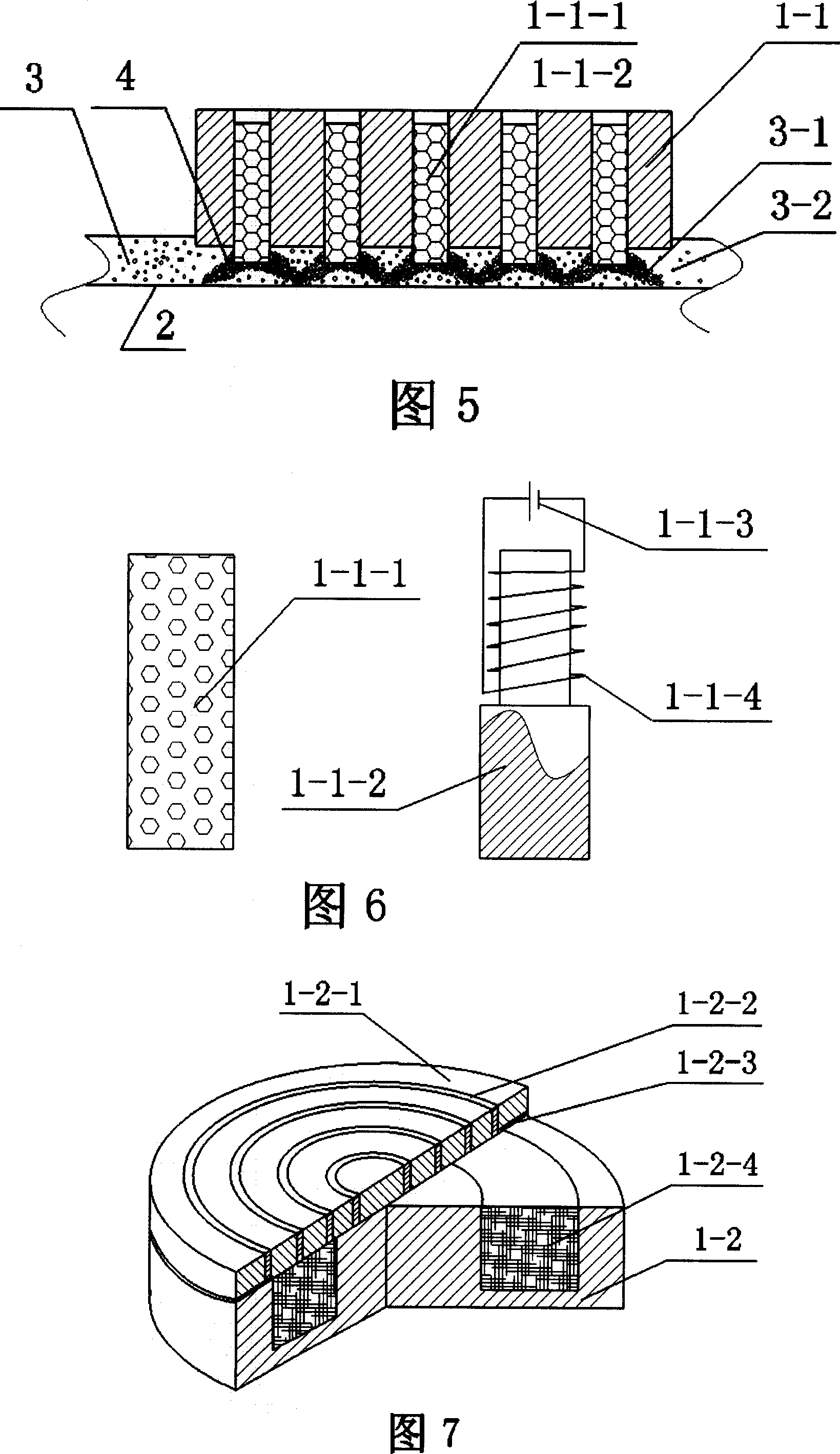
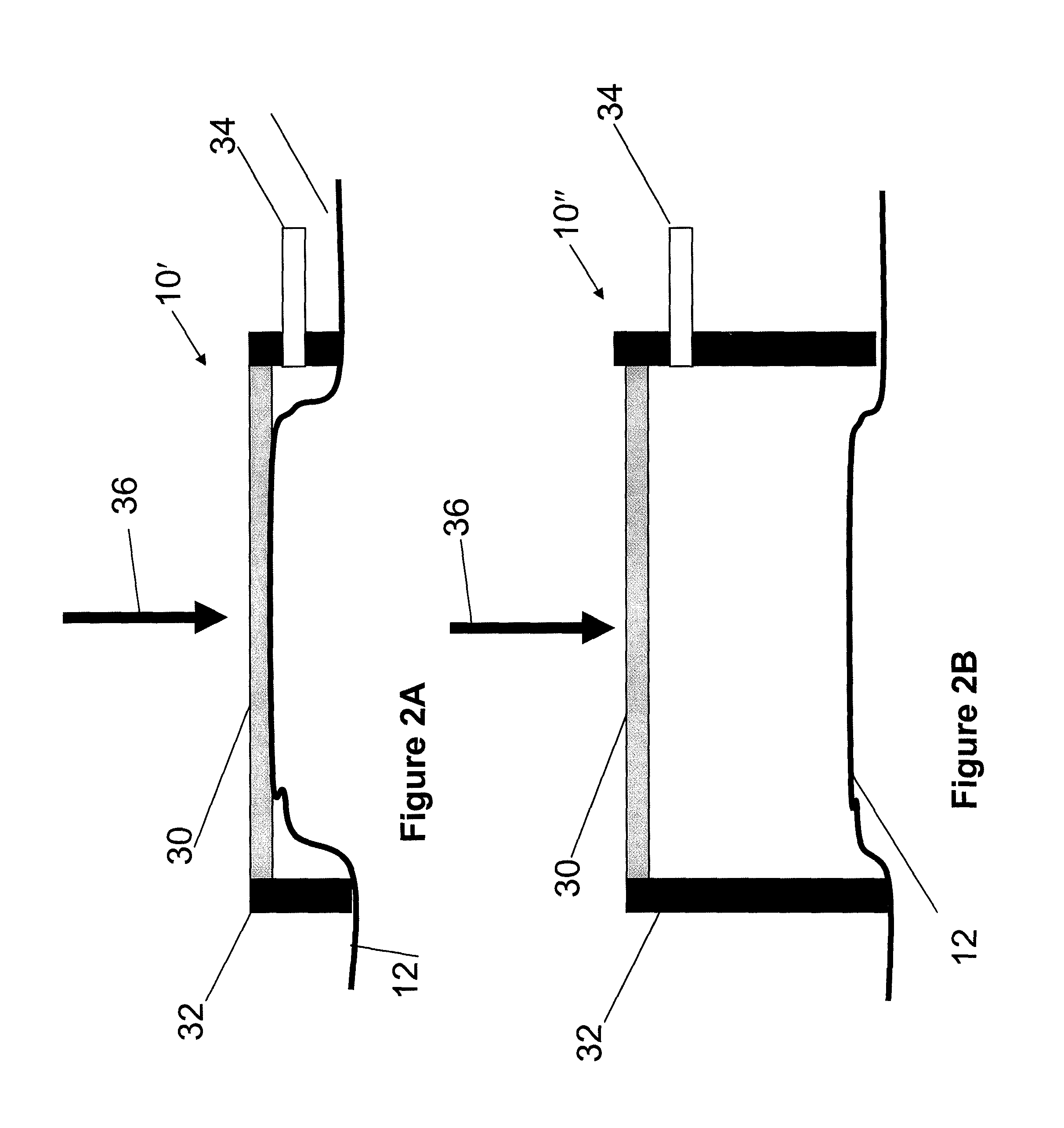
Grinding polishing method based on magnetic rheology effect and its polishing device
InactiveCN100999061AReduce removal rateReduce machining accuracyPolishing machinesPolishing compositions with abrasivesMagnetorheological fluidMaterials science
The present invention discloses a grinding-polishing method based on magnetorheological effect. Said method is characterized by that in the magnetorheological fluid a kind of free abrasive material is added, used as grinding-polishing liquor and injected into the between of magnetic body and workpiece surface, under the action of magnetic field the ferromagnetic particles in the magnetorheological fluid can be arranged by strings to cover the abrasive material pacticles and can be constrained in the end face of magnetic body to form magnetic grinding brush, said magnetic grinding brush can be used for grinding-polishing workpiece surface. Said invention also provides a grinding-polishing device for implementing said grinding-polishing method. Said device includes grinding tool mounted on main shaft connected with motor and working table for mounting workpiece.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Downhole filter
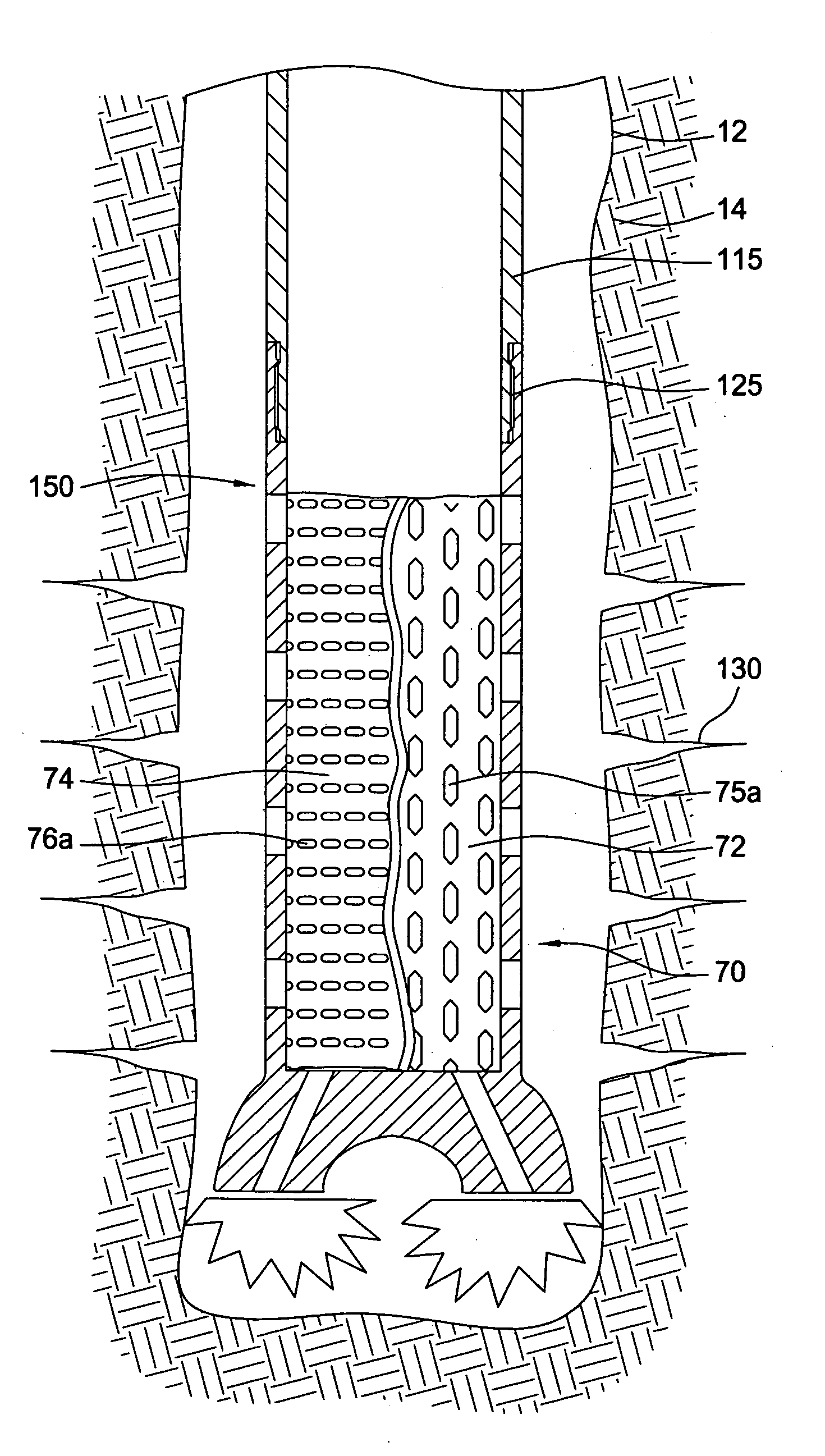
InactiveUS7188687B2Without complexityWithout expenseDrilling rodsConstructionsParticulatesEngineering
A downhole filter comprises a tubular member having a wall defining a plurality of openings. The openings have an outer width less than an inner width. The parts of the opening defining the smaller width are defined by radially outer parts of the openings, such that particulates or sand prevented from passing through the openings will tend to be retained to the outside of the tubular member. A method comprises providing a tubular string having a non-porous tubular portion and a porous tubular portion, and installing the tubular string within a wellbore such that the porous tubular portion is located adjacent a fluid-producing formation within the wellbore. In another embodiment, an apparatus comprises a drill string comprising a non-porous tubular portion and a porous tubular portion, and an earth removal member operatively connected to a lower end of the drill string.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Vacuum assisted treatment of the skin
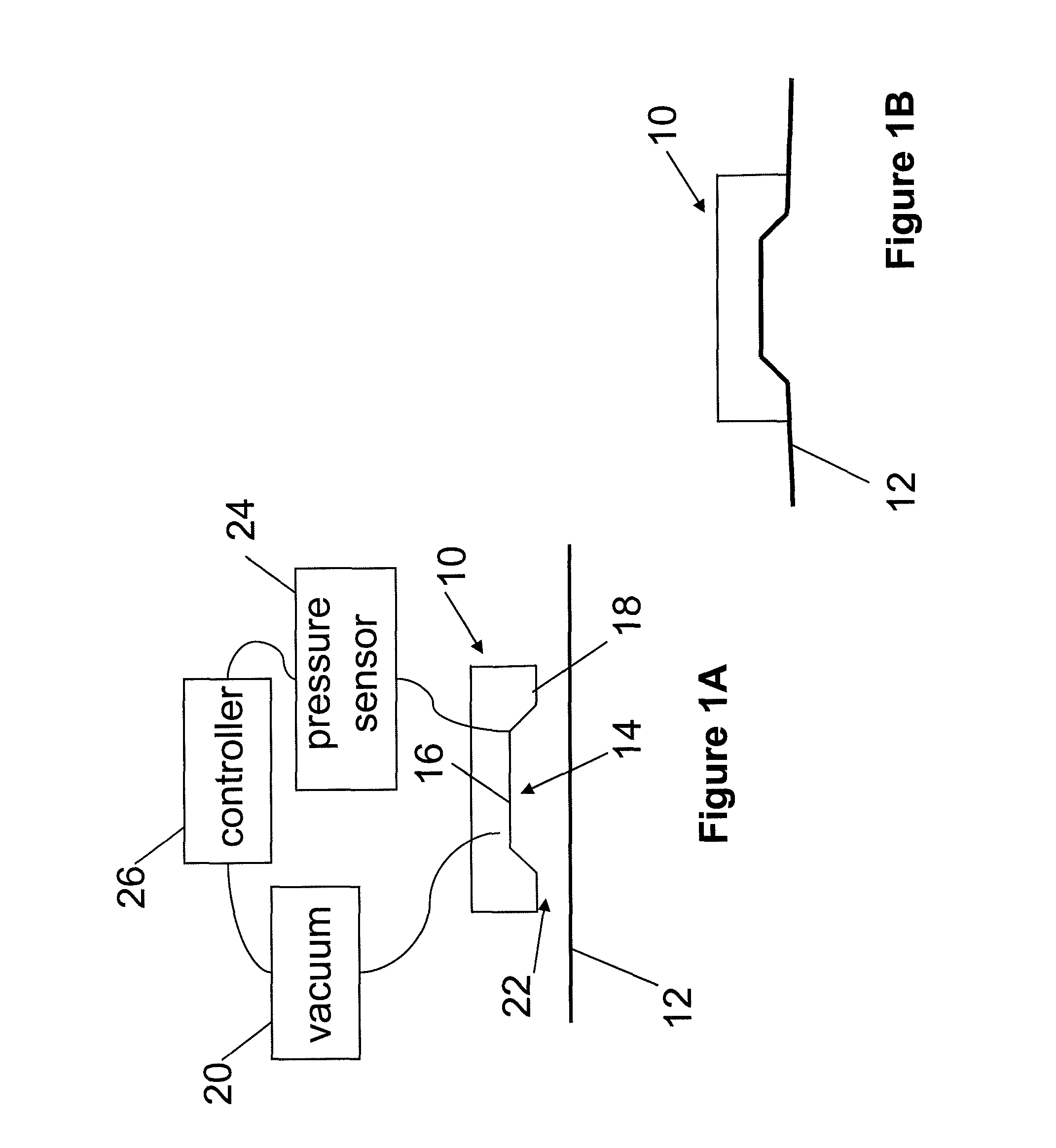
InactiveUS20090088823A1Easily and rapidly movedEasy to installElectrotherapyDiagnosticsVacuum assistedSkin surface
An apparatus for treating skin includes a chamber defined by a surface and a rim extending from the surface. A source of vacuum is capable of removing air from inside the chamber so that air outside the chamber flows into the chamber. Impedance of the air flowing between the rim of the chamber positioned adjacent the skin surface causes the pressure inside the chamber to decrease relative to ambient. A pressure sensor can determine when the pressure inside the chamber decreases to a threshold value. A controller can receive a signal from the pressure sensor when the threshold value is reached, which causes the rate of removal of the air from inside the chamber by the source of vacuum to be increased. The rim of the chamber forms a substantially fluid tight seal with the skin. The skin is drawn toward an inner surface of the chamber.
Owner:CANDELA CORP
Porous chemical mechanical polishing pads
ActiveUS20170203406A1Enhancing positive zeta potentialIncrease ratingsAdditive manufacturing apparatusAbrasion apparatusAdditive layer manufacturing3D printing
Implementations disclosed herein generally relate to polishing articles and methods for manufacturing polishing articles used in polishing processes. More specifically, implementations disclosed herein relate to porous polishing pads produced by processes that yield improved polishing pad properties and performance, including tunable performance. Additive manufacturing processes, such as three-dimensional printing processes provides the ability to make porous polishing pads with unique properties and attributes.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Ruthenium-barrier polishing slurry
InactiveUS20080148649A1Reduce removal rateOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricEthylene oxide
The polishing slurry is useful for removing ruthenium layers from patterned semiconductor substrates in the presence of at least one nonferrous interconnect metal and a dielectric. The polishing slurry includes 0.001 to 10 weight percent periodic acid or salt, at least 0.0001 weight percent inhibitor for reducing removal rate of the nonferrous interconnect metals, 0.00001 to 5 weight percent organic additive for reducing dielectric removal rate, the organic additive being selected from at least one of water soluble polymers and surfactants, the organic additive containing an ethylene oxide group or an amide group, 0.1 to 50 weight percent abrasive and balance water; and the slurry having a pH of greater than 8 to 12.
Owner:LIU ZHENDONG
Low friction planarizing/polishing pads and use thereof
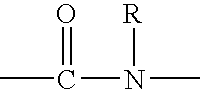
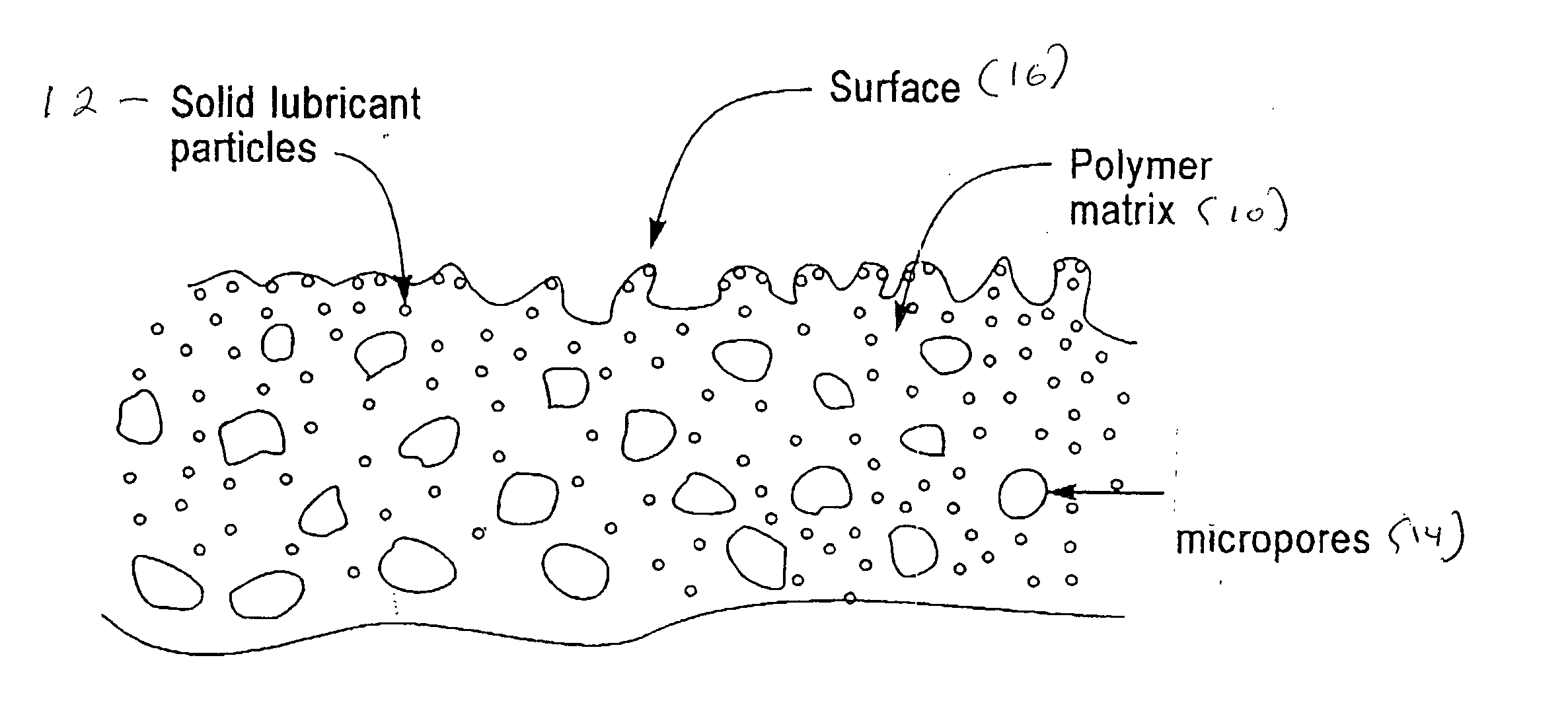
InactiveUS20050042976A1Slight frictionReduced removal rateAbrasion apparatusLapping machinesEngineeringLubricant
A polishing pad comprising a polymeric matrix and solid lubricant particles is useful for planarizing surfaces, and preventing delamination and scratches.
Owner:IBM CORP
Non-polymeric organic particles for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS20050005525A1Reduce defectsHigh selectivityPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesSoft waterSURFACTANT BLEND
An abrasive composition comprising non-polymeric organic particles that is useful for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), and which can widely be used in the semiconductor industry. The inventive compositions preferably comprise soft water in combination with 0.001-20 w / w % of non-polymeric organic particles, 0.1-10 w / w % of an oxidizing agent, 0.05-10 w / w % of a chelating agent, 0.01-10 w / w % of a surfactant, and 0-10 w / w % of a passivation agent at a pH in the range of 2-12, wherein said percentages are w / w (weight / weight) percentages, based on the total weight of said compositions. The abrasive compositions provide an efficient polishing rate, excellent selectivity and good surface quality when utilized as a new abrasive composition in CMP applications.
Owner:DYNEA AUSTRIA
Barrier polishing solution
ActiveUS20050236601A1Reduces removal rateReduce removal rateInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOther chemical processesAqueous solutionDielectric
The polishing solution is useful for preferentially removing barrier materials in the presence of nonferrous interconnect metals with limited erosion of dielectrics. The polishing solution comprises 0 to 20 weight percent oxidizer, at least 0.001 weight percent inhibitor for reducing removal rate of the nonferrous interconnect metals, 10 ppb to 4 weight percent complexing agent, 0 to 50 weight percent abrasive and balance water; and the solution having a pH of less than 7.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Composition for polishing pad and polishing pad using the same
InactiveUS20020010232A1Reduce removal rateSuture equipmentsNon-fibrous pulp additionWater insolubleCrosslinked polymers
An object of the invention is to provide a polishing pad having the excellent slurry retaining properties and the large removal rate and a composition for a polishing pad which can form such the polishing pad. A composition for polishing pad of the invention is comprising a water-insoluble matrix material containing a crosslinked polymer and a water-soluble particle dispersed in the water-insoluble matrix material. The elongation remaining after breaking is 100% or less when a test piece comprising the water-insoluble matrix material is broken at 80° C. according to JIS K 6251. A polishing pad of the invention is that at least a part of the polishing pad comprises the composition for polishing pad.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Method of using COX-2 inhibitors in the treatment and prevention of ocular COX-2 mediated disorders
Owner:PHARMACIA CORP
Non-polymeric organic particles for chemical mechanical planarization
InactiveUS7037351B2High selectivitySacrificing removal ratePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesMetallurgyActive agent
An abrasive composition comprising non-polymeric organic particles that is useful for chemical mechanical planarization (CMP), and which can widely be used in the semiconductor industry. The inventive compositions preferably comprise soft water in combination with 0.001–20 w / w % of non-polymeric organic particles, 0.1–10 w / w % of an oxidizing agent, 0.05–10 w / w % of a chelating agent, 0.01–10 w / w % of a surfactant, and 0–10 w / w % of a passivation agent at a pH in the range of 2–12, wherein said percentages are w / w (weight / weight) percentages, based on the total weight of said compositions. The abrasive compositions provide an efficient polishing rate, excellent selectivity and good surface quality when utilized as a new abrasive composition in CMP applications.
Owner:DYNEA AUSTRIA
Supercritical water oxidization treatment system for high-salinity organic waste water
InactiveCN102642947AGuaranteed heat transfer coefficientAvoid cloggingSolidificationLiquefactionCycloneReaction temperature
The invention discloses a supercritical water oxidization treatment system for high-salinity organic waste water. The high-salinity waste water is subjected to cooling crystallization through cold energy of liquid oxygen to reduce mass concentration of inorganic salt in the waste water; a large amount of solid salt grains separated out from the waste water are removed by using a hydraulic cyclone device under a supercritical water condition to effectively prevent a subsequent pipeline and a reactor of the hydraulic cyclone device from plugging; and a desalting device is arranged at the lower part of the hydraulic cyclone device to continuously remove the inorganic salt from the system. In addition, excessive oxygen and CO2 product gas are recovered through a separation recovery part; the reaction time and the reaction temperature of supercritical water oxidization are reduced through arranging a simple subsequent treatment unit; and the system recovers heat energy of the reacted high-temperature fluid in a steam mode through the arrangement of a water softening device, so that the operation cost of the system is reduced. The system can be widely applied to the innocent treatment process of the high-salinity organic waste water.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Method and slurry for tuning low-k versus copper removal rates during chemical mechanical polishing
InactiveUS20080149884A1Efficiency tuningRemoval rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPeroxideHydrogen peroxide
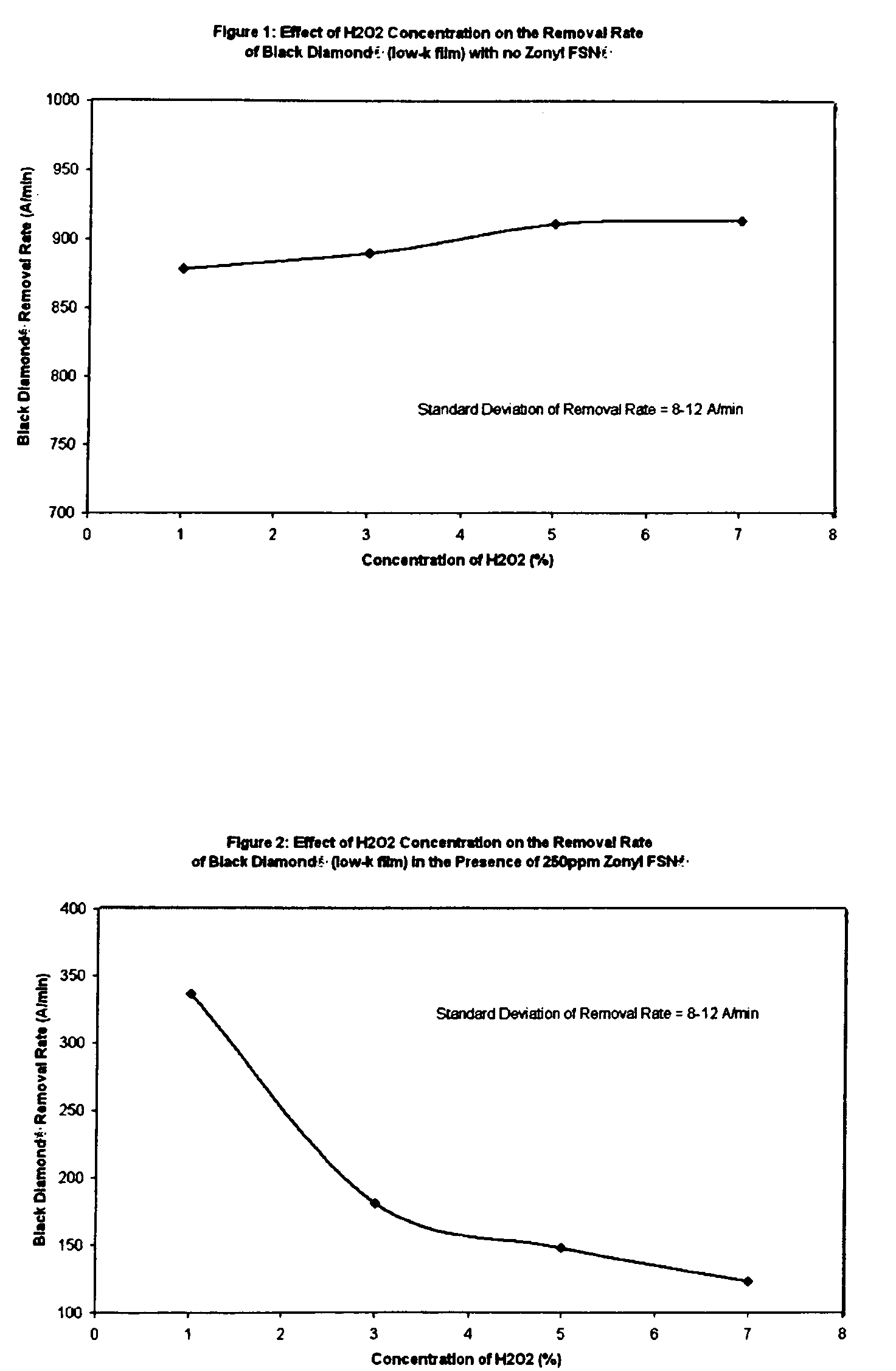
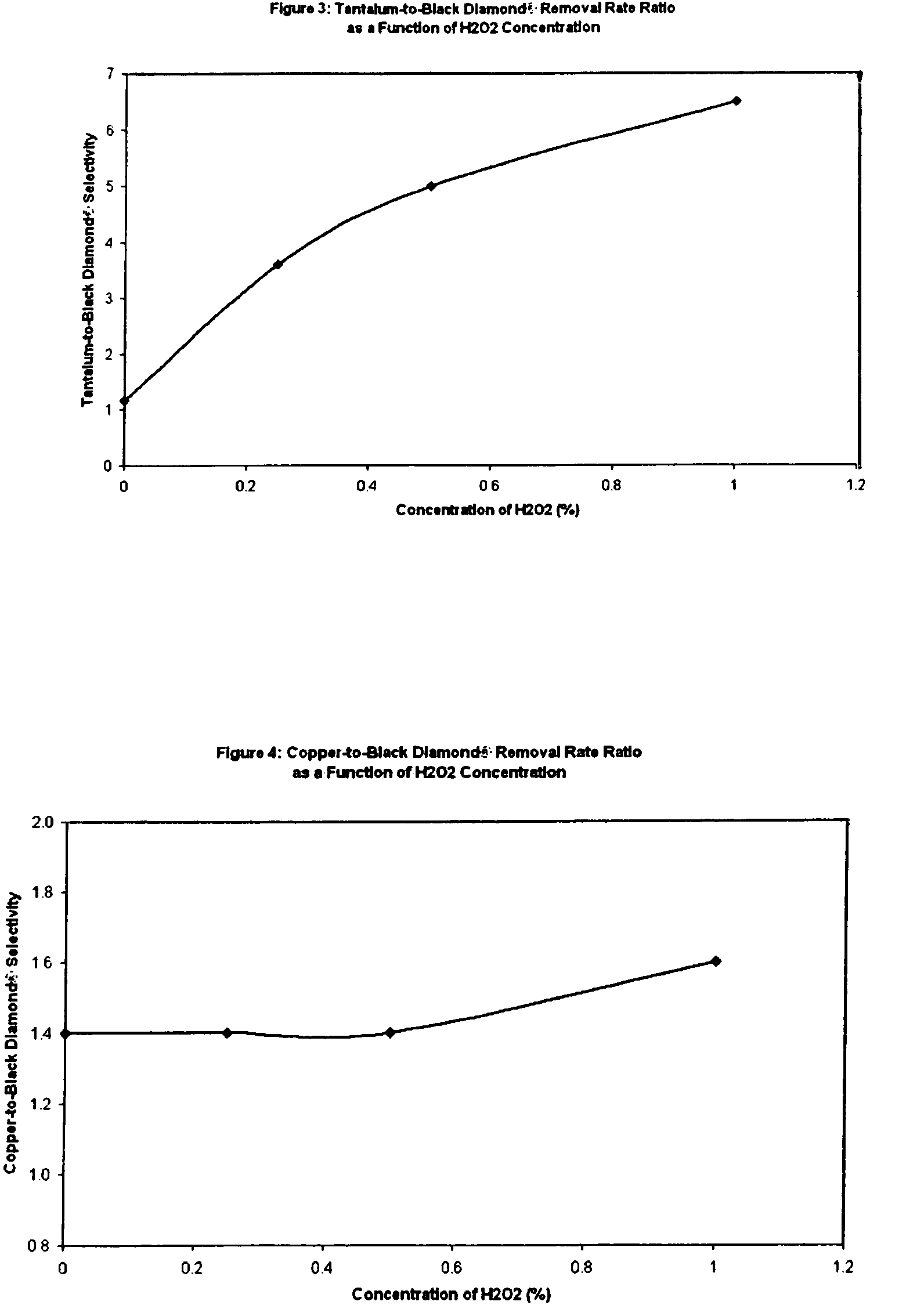
A composition and associated method for the chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) of metal substrates on semiconductor wafers are described. The composition contains a nonionic fluorocarbon surfactant and a per-type oxidizer (e.g., hydrogen peroxide). The composition and associated method are effective in controlling removal rates of low-k films during copper CMP and provide for tune-ability in removal rates of low-k films in relation to removal rates of copper, tantalum, and oxide films.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Anionic abrasive particles treated with positively charged polyelectrolytes for CMP
InactiveUS7306637B2Increase chanceReduce reunionPigmenting treatmentPolishing machinesPolyelectrolyteChemistry
The invention provides chemical-mechanical polishing systems, and methods of polishing a substrate using the polishing systems, comprising (a) an abrasive, (b) a liquid carrier, and (c) a positively charged polyelectrolyte with a molecular weight of about 15,000 or more, wherein the abrasive comprises particles that are electrostatically associated with the positively charged polyelectrolyte.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Vacuum assisted treatment of the skin
InactiveUS7740651B2Easily and rapidly movedEasy to installElectrotherapyDiagnosticsEngineeringSurgery
An apparatus for treating skin includes a chamber defined by a surface and a rim extending from the surface. A source of vacuum is capable of removing air from inside the chamber so that air outside the chamber flows into the chamber. Impedance of the air flowing between the rim of the chamber positioned adjacent the skin surface causes the pressure inside the chamber to decrease relative to ambient. A pressure sensor can determine when the pressure inside the chamber decreases to a threshold value. A controller can receive a signal from the pressure sensor when the threshold value is reached, which causes the rate of removal of the air from inside the chamber by the source of vacuum to be increased. The rim of the chamber forms a substantially fluid tight seal with the skin. The skin is drawn toward an inner surface of the chamber.
Owner:CANDELA CORP
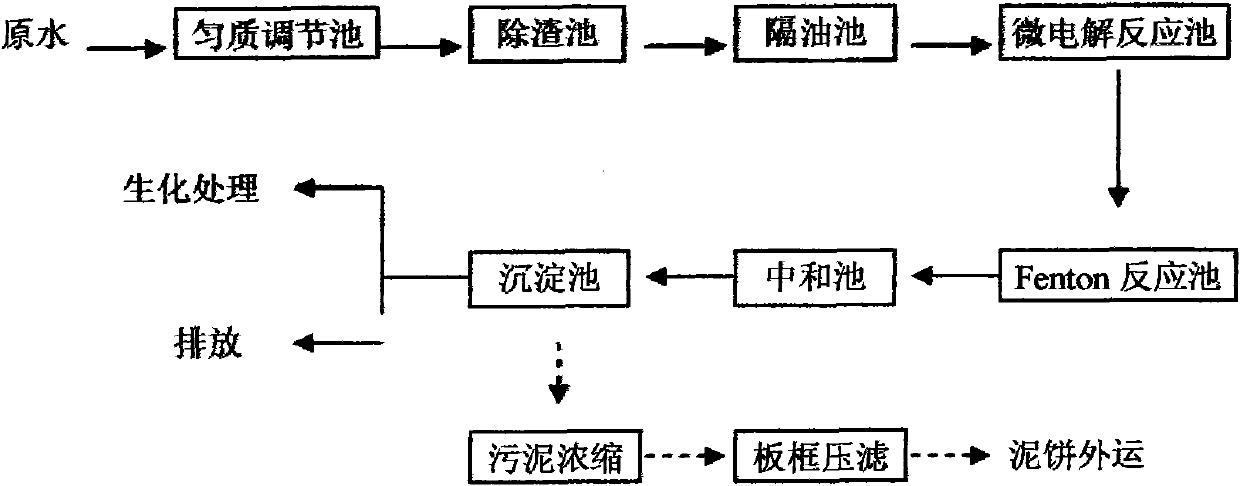
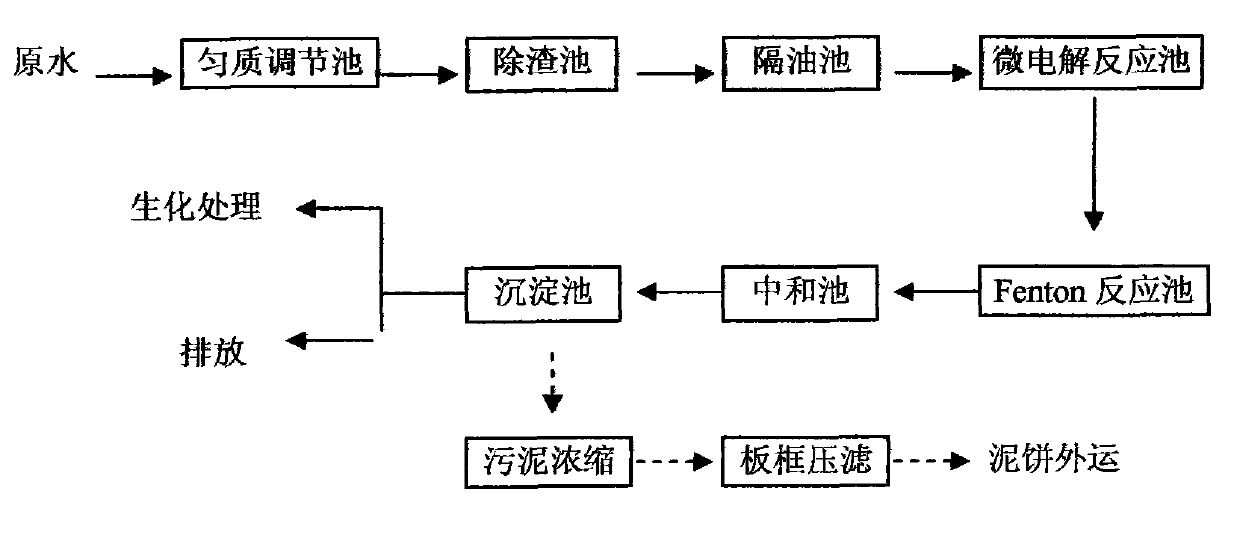
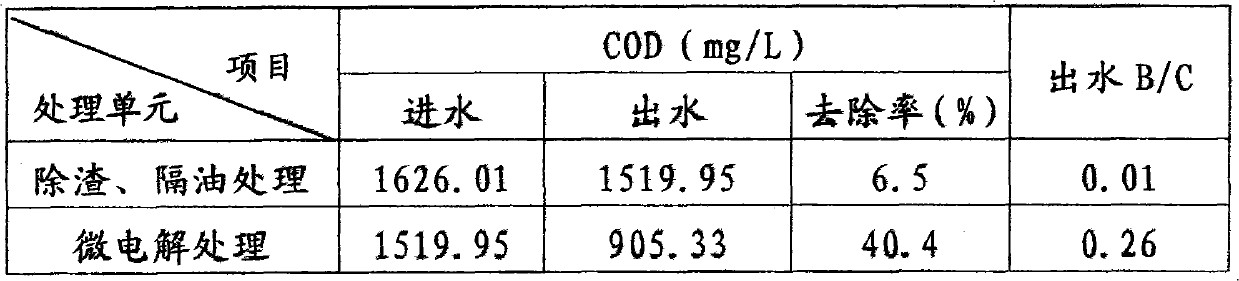
Pretreatment process of organic silicon wastewater
InactiveCN102001775AReduce loadReduce effluent CODMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemistryStrong acids
The invention discloses a pretreatment process of organic silicon wastewater, comprising the steps of homogeneous treatment, slag removal, oil removal, iron-carbon micro-electrolysis process, Fenton process, neutralization deposition and overflow and discharge of supernate. Aiming at the strong acid characteristic of the organic silicon wastewater, the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis can be directly carried out after the homogeneous impurity removal; partial COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) can be degraded while the biochemical quality of the wastewater is improved and the pH value is improved; then hydrogen peroxide is directly added to form a Fenton system; a strong oxidant is formed to damage the structure of organic matters and chromophonic groups in the wastewater and effectively oxidize so as to remove the organic matters which are difficult to degrade and cannot be removed by the traditional wastewater treatment technology, and thereby the aims of further reducing the COD and improving the biodegradability of the wastewater can be improved. The organic silicon wastewater can reach the national third-grade discharge standard after being subjected to neutralization and the precipitation and reach the national first-grade discharge standard after being subjected to biochemical treatment. The pretreatment process has the advantages of low cost and stable treatment effect and is simple for operation.
Owner:蓝星环境工程有限公司
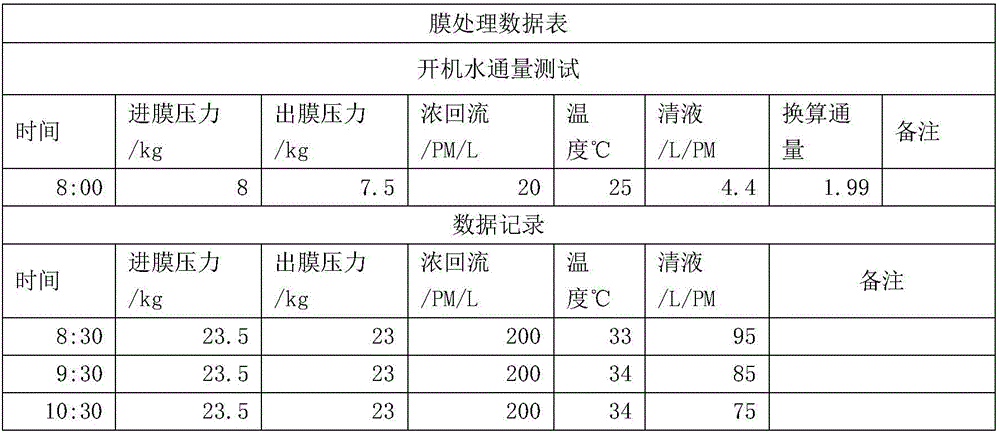
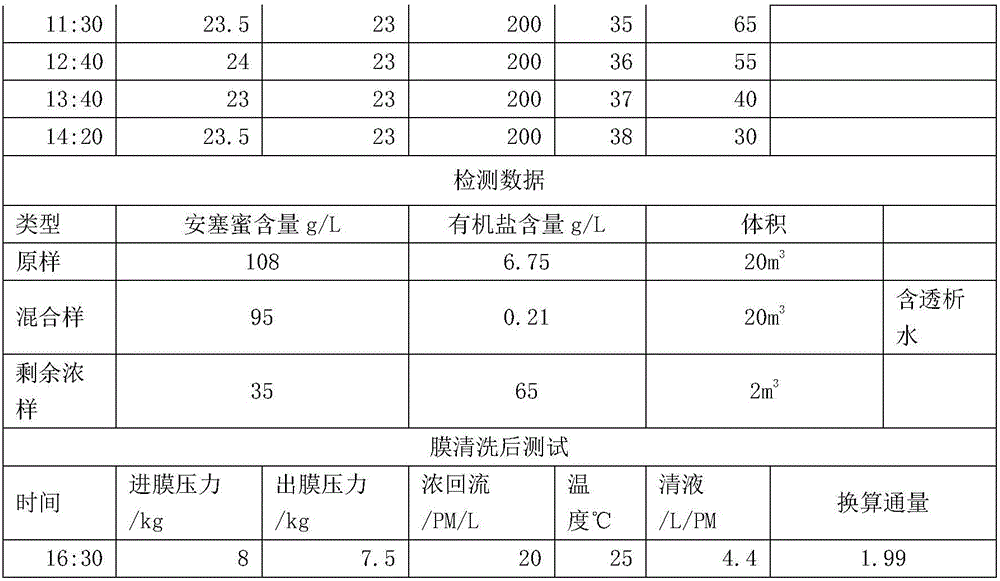
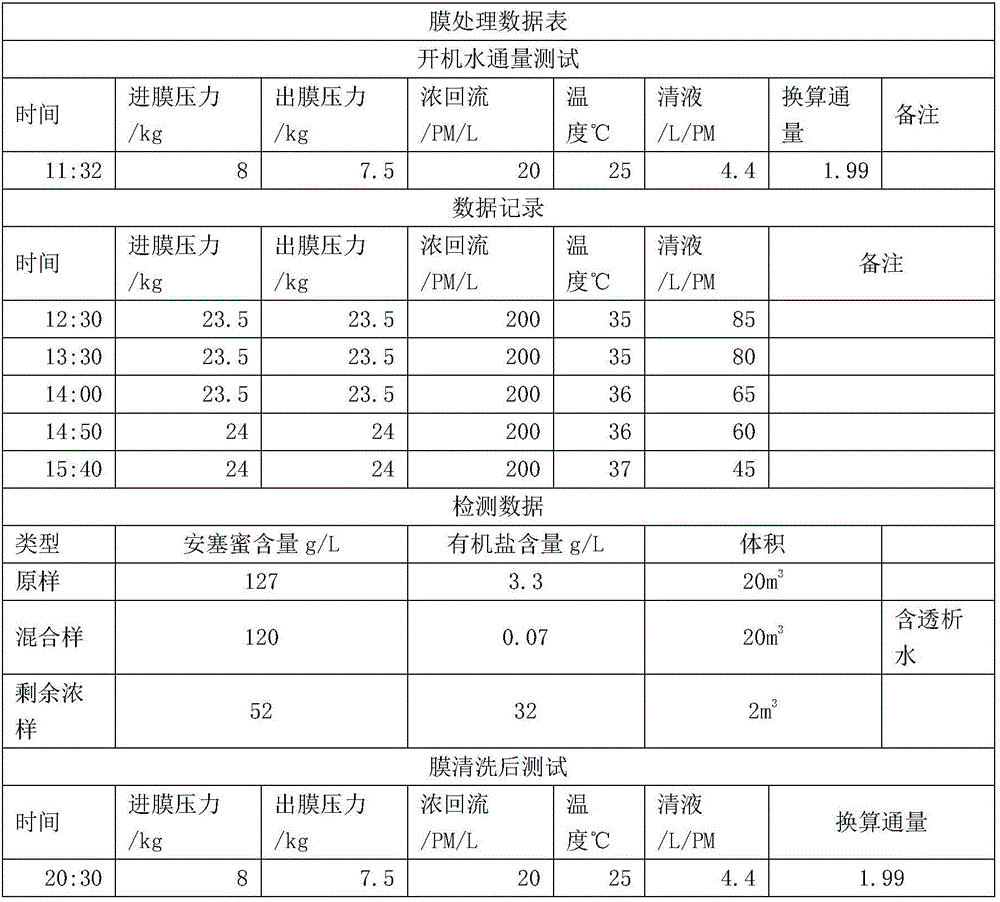
Method for equivalent dialysis through directly adopting membrane treatment
InactiveCN106262665AReduce energy consumptionReduce removal rateSemi-permeable membranesFood membrane processLiquid wasteLiquid storage tank
The invention discloses a method for equivalent dialysis through directly adopting membrane treatment. The method comprises the following steps: S1: storing the filtrate of Acesulfame in a filtrate storage tank, which is taken as a stock solution; S2: adopting a hot water circulation system to increase the temperature of the stock solution in the filtrate storage tank, setting membrane ingress pressure and membrane egress pressure simultaneously, and through transmission and concentration of an organic membrane, allowing a clear membrane liquid to flow to a clear membrane liquid storage tank for recycle; S3: when the clear membrane liquid flux in the clear membrane liquid storage tank drops to 20-60L / PM, using the same amount of water to dialyze, and dialyzing the Acesulfame out and recycling; S4: discharging the residual liquid in a circulation tank to a liquid waste disposing center directly so as to have liquid waste disposal; and S5: washing and detecting membrane equipment. The method disclosed by the invention adopts the hot water circulation system for heating and omits the concentration treating and recycling process, so that the energy consumption is saved, the concentration temperature is low, the material is difficult to break down, the purposes of liquid decoloration and organic salt treatment are realized, the product obtained can be recycled directly, and the equipment has a simple structure and a low treatment cost.
Owner:ANHUI WEIDUO FOOD INGREDIENTS CO LTD
CMP slurry for forming aluminum film, CMP method using the slurry, and method for forming aluminum wiring using the CMP method
ActiveUS20050112894A1Reduces removal rateRemoval rateDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDefect preventionCorrosion
A first chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) slurry includes a polishing agent, an oxidant, a pH control additive, and an oxide film removal retarder which reduces a removal rate of the silicon oxide film. A second chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) slurry includes a polishing agent, an oxidant, a pH control additive, an oxide film removal retarder which reduces a removal rate of silicon oxide, and a defect prevention agent which inhibits scratch defects and / or corrosion defects at a surface of an aluminum film. In a one-step CMP process, either of the first or second slurry is used throughout CMP of an aluminum layer until an upper surface of an underlying silicon oxide layer is exposed. In a two-step CMP process, the first slurry is used in an initial CMP of the aluminum layer, and then the second slurry is used in a subsequent CMP until the upper surface of the underlying silicon layer is exposed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Endotoxin adsorption material for curing endotoxemia
InactiveCN101157018AStable physical and chemical propertiesGood blood compatibilityOther chemical processesHaemofiltrationBlood plasmaToxin
The invention relates to endotoxin adsorbing material for curing endotoxemia in the bioseparation and the biomedical engineering fields. The adsorbing material which takes sepharose gel as a carrier is coupled with spacer arm molecules through the activating reaction, and then is coupled with two groups of quarternary ammonium salt cations and dewatering molecules as functional groups to be prepared. The adsorbing material is simultaneously coupled with the two groups of functional groups mutually effected with endotoxin, and further the adsorbing selectivity of the adsorbing material to the endotoxin is improved. The physicochemical property of the adsorbing material is steady, and the adsorbing material has good blood compatibility, thereby being able to used for removing the endotoxin in blood plasma, and curing the endotoxemia. The preparation process of the adsorbing material is simple, the preparation cost is low, and the adsorbing material belongs to the novel endotoxin adsorbing material.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Multi-component barrier polishing solution
ActiveUS20070184661A1Reduced removal rateControl erosionOther chemical processesDecorative surface effectsDielectricSURFACTANT BLEND
The polishing solution is useful for removing barrier materials in the presence of at least one nonferrous interconnect metal with limited erosion of dielectrics. The solution contains 0 to 20 weight percent oxidizer, at least 0.001 weight percent inhibitor for reducing removal rate of the nonferrous interconnect metals, 1 ppm to 4 weight percent organic-containing ammonium cationic salt formed with a quantenary ammonium structure, 1 ppm to 4 weight percent anionic surfactant, the anionic surfactant having 4 to 25 carbon atoms and the total carbon atoms in of the ammonium cationic salt plus the anionic surfactant being 6 to 40 carbon atoms, 0 to 50 weight percent abrasive and balance water; and the solution having a pH of less than 7.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Simple method for loading ultrafine nano zero-valent iron on porous material
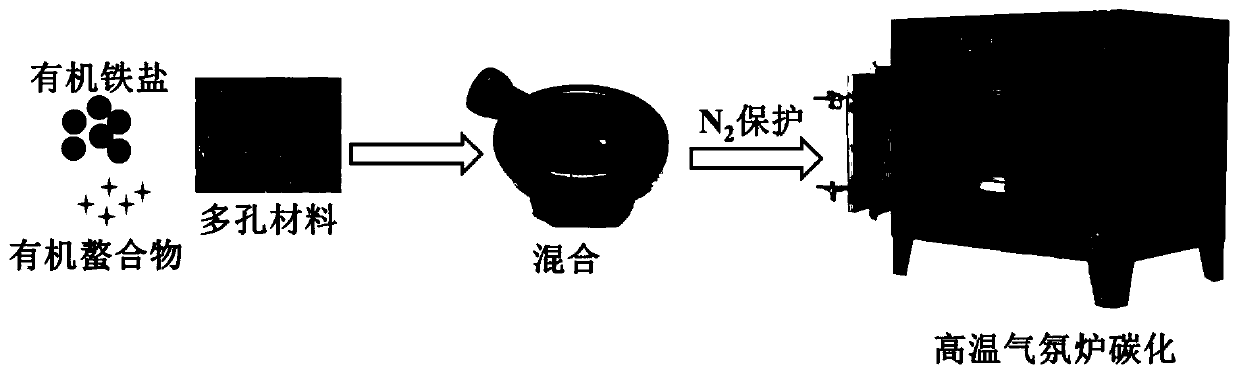
ActiveCN111097414AEasy accessPrevent oxidationOther chemical processesWater contaminantsIron saltsPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-toxicity pollutant treatment, and relates to a simple and convenient method for loading superfine nano zero-valent iron on a porous material and application of the porous material as an adsorbent and a heterogeneous Fenton catalyst for degrading and removing pollutants. The organic iron salt, the organic ligand and the porous material only needto be simply mixed and then are subjected to high-temperature carbonization under the protection of inert gas, so that the superfine zero-valent iron can be uniformly loaded on the inner and outer surfaces and pore passages of the porous material. According to the method, a complex, time-consuming and harsh liquid-phase impregnation process in a conventional liquid-phase reduction method is omitted, no solvent or dispersing agent is needed, and the utilization rate of raw materials is high. The obtained zero-valent iron is large in loading capacity, good in crystallinity and small in particlesize. The porous material loaded with the superfine nanoscale zero-valent iron can be used as an adsorbent and a catalyst, and high-toxicity inorganic and organic pollutants in a water body are removed by utilizing adsorption, an Fe-C micro-electrolysis technology and a Fenton oxidation technology.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for treating waste salt dregs containing cyanogen
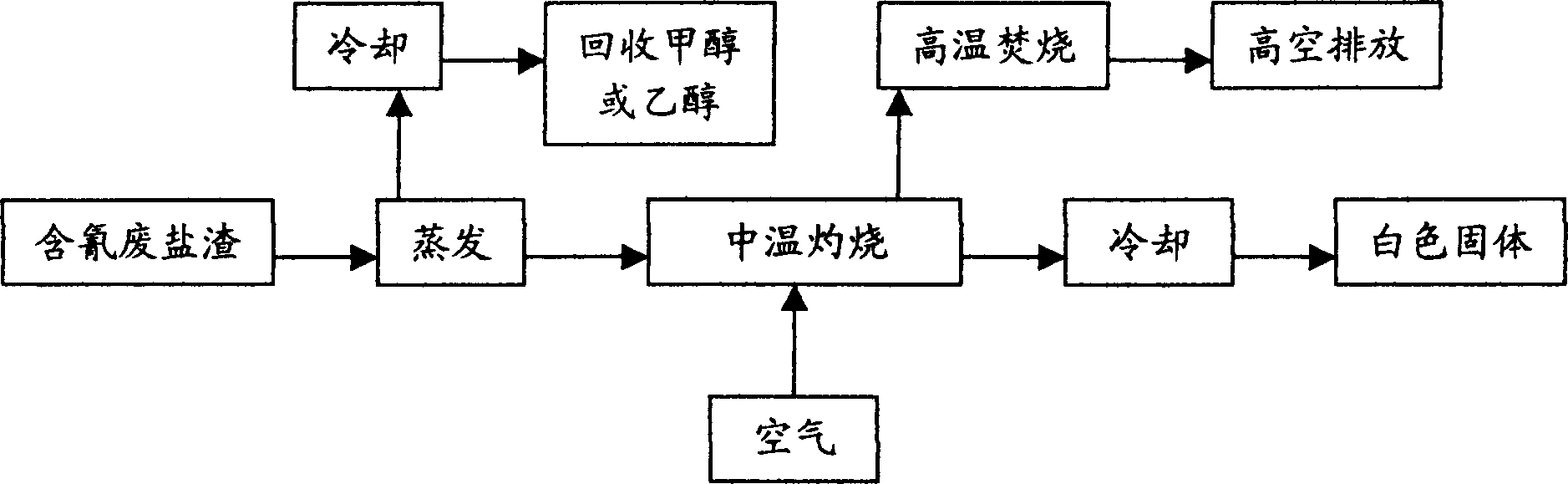
The invention relates to a processing method for cyanogens contained waste salt dredge, the process steps are: the cyanogens contained waste salt dredge is put into the drier to be heated; the heating temperature is controlled with 60-120deg.C, the carbinol and the alcohol volatilize from the dredge, the carbinol and the alcohol are reclaimed with high purity after beings cooled in the condenser; the cyanogens contained waste salt dredge without carbinol and alcohol is baked in oxygen condition, the oxide in the dredge is fully oxidized, the organic is oxidized or volatilized off, thus eliminates the cyanogens and organic in the salt dredge; the gas generated in the baking process is transmitted to the burning furnace, the temperature is not lower than 1100deg.C, thus the tail gas may accord the discharging standard.
Owner:邱滔 +1
Sewage advanced treatment and recycling method capable of substantially raising economy
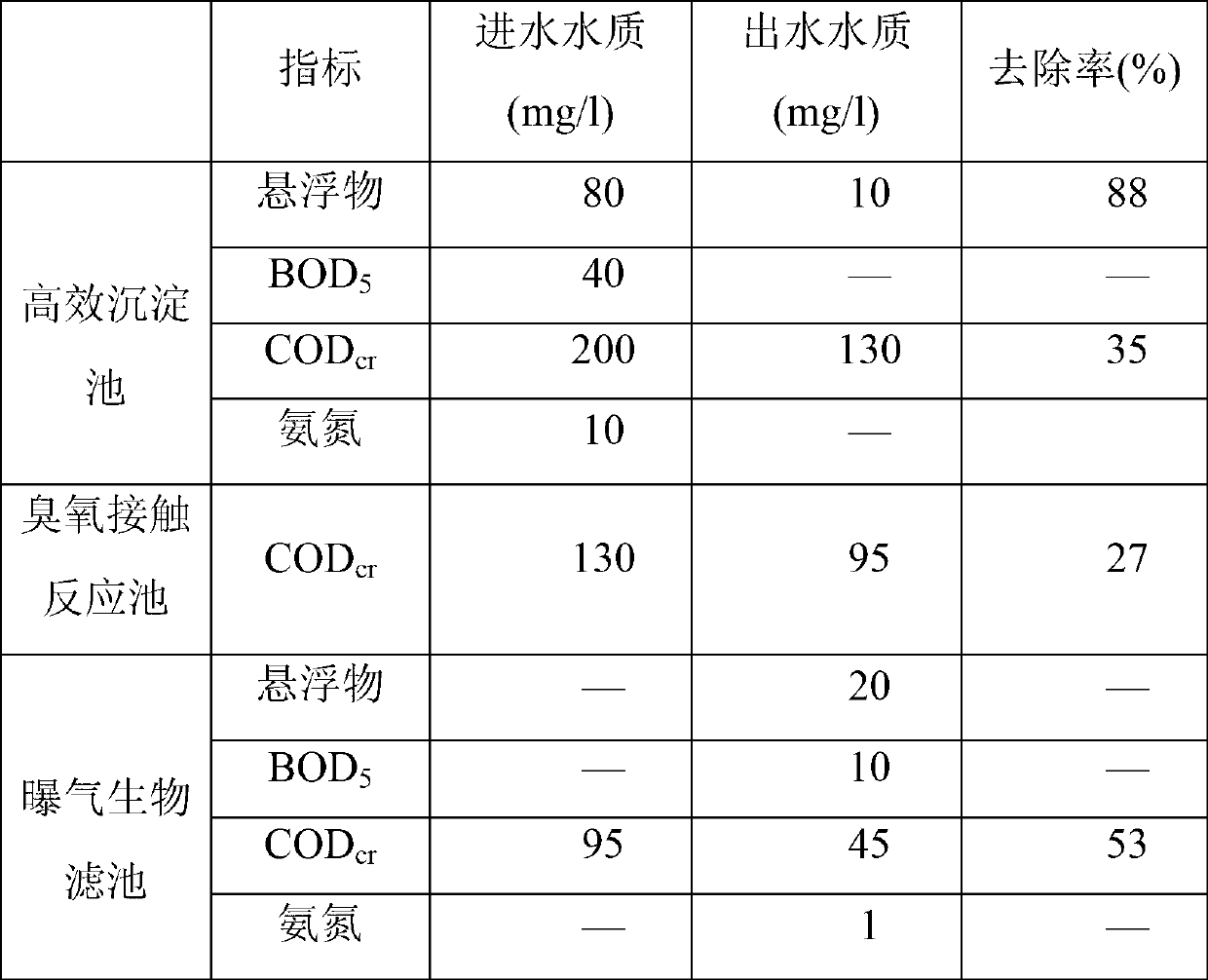
InactiveCN103214141AReduce removal rateLow recycling rateMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationFlocculationFiltration
The invention provides a sewage advanced treatment and recycling method capable of substantially raising economy, comprising processes of high efficiency coagulation deposition, ozone oxidation and biochemical treatment, wherein the method is characterized in that a coagulation deposition stage integrates coagulation, flocculation, deposition and sludge backflow, a forced sludge outer circulation backflow mode is utilized, sludge concentration in a flocculation reaction is increased, contact flocculation and deposition net capturing effects of backflow sludge is fully utilized, and a removal rate of COD suspensions is raised, thereby substantially reducing a subsequent additive amount of ozone. In an ozone oxidation stage, COD in sewage id further removed by adding ozone, and biodegradability of sewage is raised. Ozone tail gas generated in the stage is converted into pure oxygen, which is collected and conveyed to a front biochemical stage for providing oxygen required for aeration, thereby reducing operation cost. Biochemical degraded COD generated in the ozone oxidation stage is removed by an aeration biological filtration pool in the biochemical treatment process.
Owner:北京翰祺环境技术有限公司
Repairing method for cadmium and zinc heavy metal contaminated soil
ActiveCN105583222AGood removal efficiencyGood removal effectContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersContaminated soilsSodium silicate
The invention discloses a repairing method for cadmium and zinc heavy metal contaminated soil. The method includes the following steps that firstly, a repairing agent is prepared, wherein zeolite powder, coal ash, zinc oxide, sodium silicate, hydroxyapatite, sugarcane ash, fowl manure, selenium oxide, cyclodextrin, nano-nickel powder, potassium citrate and portland cement are mixed and then ground; secondly, the contaminated soil is flatly laid on a plate, one third of the total weight of the repairing agent is scattered on the contaminated soil, vertical ploughing is conducted, and water is sprayed; thirdly, one third of the total weight of the repairing agent is scattered on the contaminated soil, vertical ploughing is conducted, a phosphoric acid aqueous solution is sprayed, and ploughing is conducted after standing; fourthly, the rest of the repairing agent is scattered on the contaminated soil; and fifthly, the upper surface of the contaminated soil is covered with a layer of protection film finally for repairing. After the repairing method is used for repairing for 10 hours, the removing rate of cadmium ions in the soil is higher than 89.3%, the removing rate of zinc ions is higher than 90.5%, and high removing efficiency and a good removing effect are shown.
Owner:JIANGSU GAIYA ENVIRONMENTAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
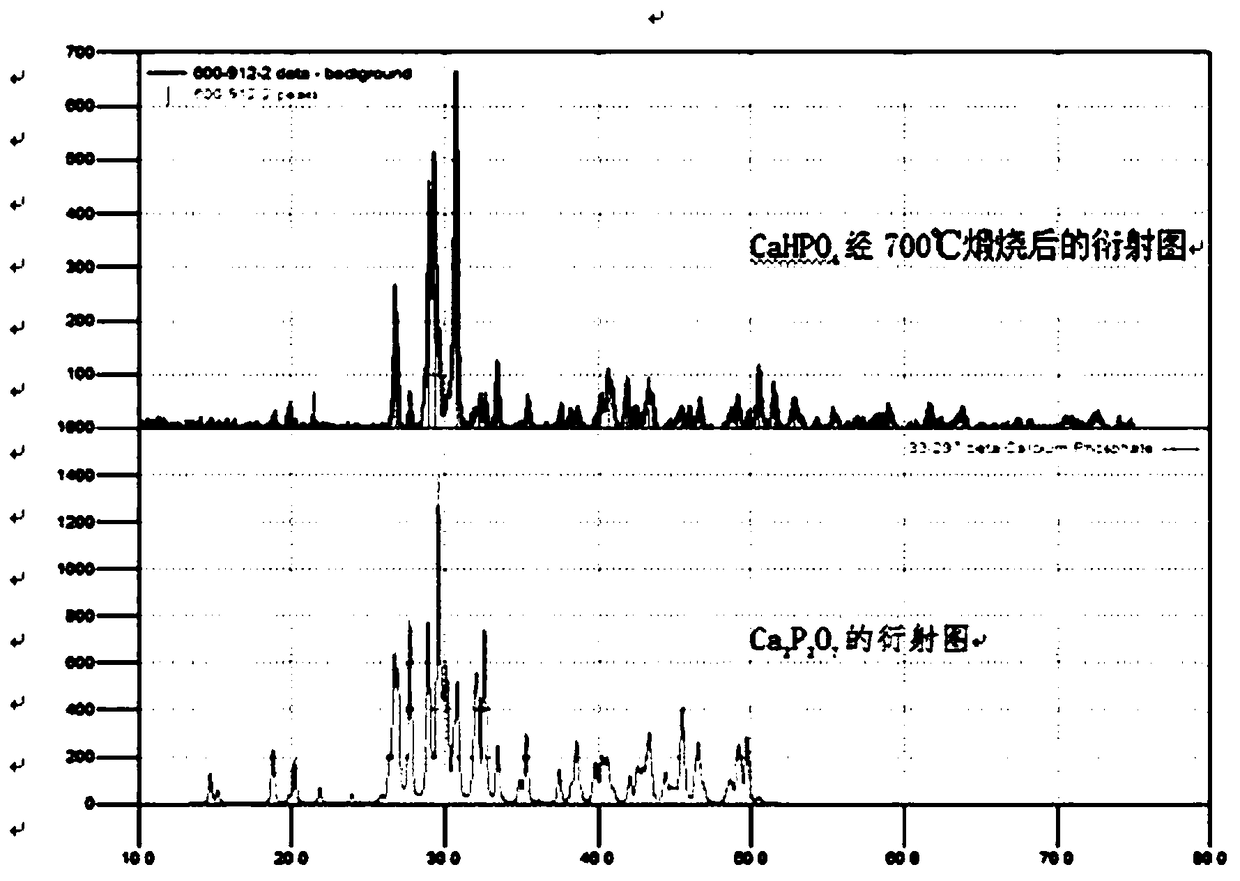
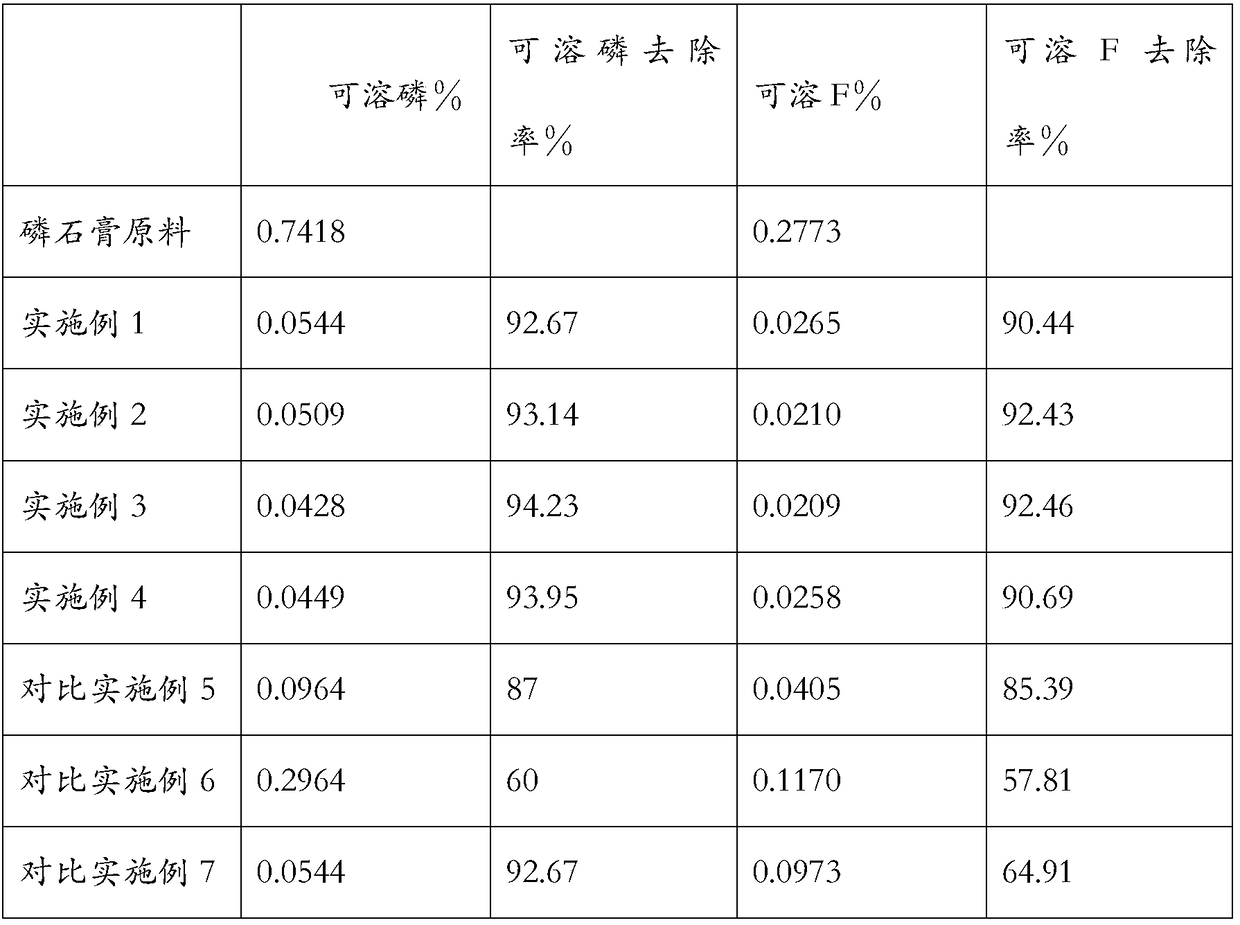
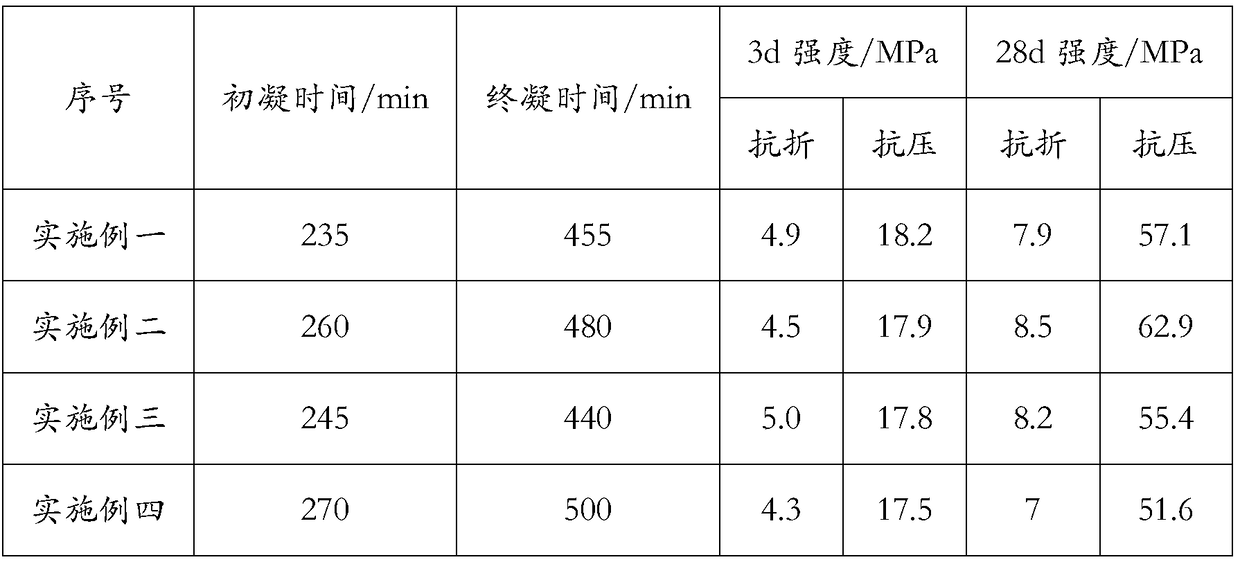
Ardealite supersulfated cement and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an ardealite supersulfated cement and a preparation method thereof. The ardealite supersulfated cement disclosed by the invention contains the following components by weight percent: 50%-80% of superfine slag powder, 10%-40% of modified ardealite, 0%-10% of mineral admixture, 1%-8% of alkaline excitant and 0.1%-0.5% of early strength agent. The preparation method disclosedby the invention comprises the following steps: (1) modifying ardealite: neutralizing by doping calcium hydroxide or calcium carbonate into ardealite, performing high-temperature calcinations on the neutralized ardealite, cooling and then milling till the specific area is not less than 400m2 / kg, thereby acquiring the modified ardealite; (2) mixing superfine slag powder, modified ardealite, mineraladmixture, alkaline excitant and early strength agent in parts by weight, and then uniformly stirring, thereby acquiring the ardealite supersulfated cement. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the influence of harmful elements in ardealite can be effectively eliminated and the ardealite is fully utilized.
Owner:JIANGSU EFFUL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Downhole filter
InactiveUS20050121232A1Least riskEasy to manufactureDrilling rodsConstructionsParticulatesEngineering
In one aspect, a downhole filter comprises a tubular member having a wall defining a plurality of openings. The openings have an outer width less than an inner width. The parts of the opening defining the smaller width are defined by radially outer parts of the openings, such that particulates or sand prevented from passing through the openings will tend to be retained to the outside of the tubular member. In another aspect, a method comprises providing a tubular string having a non-porous tubular portion and a porous tubular portion, and installing the tubular string within a wellbore such that the porous tubular portion is located adjacent a fluid-producing formation within the wellbore. In yet another aspect, an apparatus comprises a drill string comprising a non-porous tubular portion and a porous tubular portion, and an earth removal member operatively connected to a lower end of the drill string.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Oil field visous crude sewage silicone-removing and cleaning process
InactiveCN1412128ANon-fouling benefitsReduce dosageSedimentation separationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationHigh concentrationSludge
The oil field viscous crude sewage silicone-removing cleaning technological process is characterized by that in the course ore moving silicone it has no need of regulating pH value of sewage, the active magnesium oxide can be directly added into the pretreated sewage, and after the sewage is passed through the vortex reactor and reacted, the inorganic aluminium salt anjd organic floccultant can be added in the discharge water, then fed into sludge reactor, said sludge reactor can provide high-concentration sludge, and said sludge can be fully reacted with feeding water, then fed into precipitation clearing device to implement sludge and water separation so as to obtain silicone dioxide and treated water in which the suspended matter content is lower.
Owner:LIAONING HUAFU ENVIRONMENTAL ENG
Application of nano-iron synthesized by tea leaves in p,p'-DDT removal
InactiveCN105945299ALow costLow technical requirementsWater contaminantsContaminated soil reclamationFiltrationCentrifugation
The invention discloses the application of nano-iron synthesized by tea leaves in p,p'-DDT removal. According to the application, tea powder which is located near the root and has long growth cycle is mixed with ultrapure water according to the proportion of 1g:10-40 mL, and centrifugation and filtration are conducted, so that a tea leaf extracting solution is obtained; and the tea leaf extracting solution and an FeSO4 solution with the concentration being 0.1 mol / L are mixed according to the volume ratio of 2:1, and oscillation is conducted for 30 min under the conditions that the temperature is 25 DEG C and the rotating speed is 250 rpm, so that green nano-iron turbid liquid is obtained. The application of the nano-iron synthesized by tea leaves in p,p'-DDT removal has the advantages that equipment is simple, the application can be conducted at the normal temperature and pressure, the cost is low, and environmental friendliness is achieved; and in addition, the application belongs to waste utilization, the requirements for the technical conditions are low, the time efficiency is high, and industrial production can be achieved hopefully. The p,p'-DDT degradation efficiency of the obtained nano-iron is remarkably improved, and the nano-iron has good application prospects in the field of organic pollutant degradation.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Barrier polishing solution
ActiveUS7253111B2Reduce removal rateControl erosionInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOther chemical processesDielectricOxidizing agent
The polishing solution is useful for preferentially removing barrier materials in the presence of nonferrous interconnect metals with limited erosion of dielectrics. The polishing solution comprises 0 to 20 weight percent oxidizer, at least 0.001 weight percent inhibitor for reducing removal rate of the nonferrous interconnect metals, 10 ppb to 4 weight percent complexing agent, 0 to 50 weight percent abrasive and balance water; and the solution having a pH of less than 7.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Porous chemical mechanical polishing pads
InactiveUS20190224809A1Enhancing positive zeta potentialIncrease ratingsAdditive manufacturing apparatusAbrasion apparatusAdditive layer manufacturing3D printing
Implementations disclosed herein generally relate to polishing articles and methods for manufacturing polishing articles used in polishing processes. More specifically, implementations disclosed herein relate to porous polishing pads produced by processes that yield improved polishing pad properties and performance, including tunable performance. Additive manufacturing processes, such as three-dimensional printing processes provides the ability to make porous polishing pads with unique properties and attributes.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com