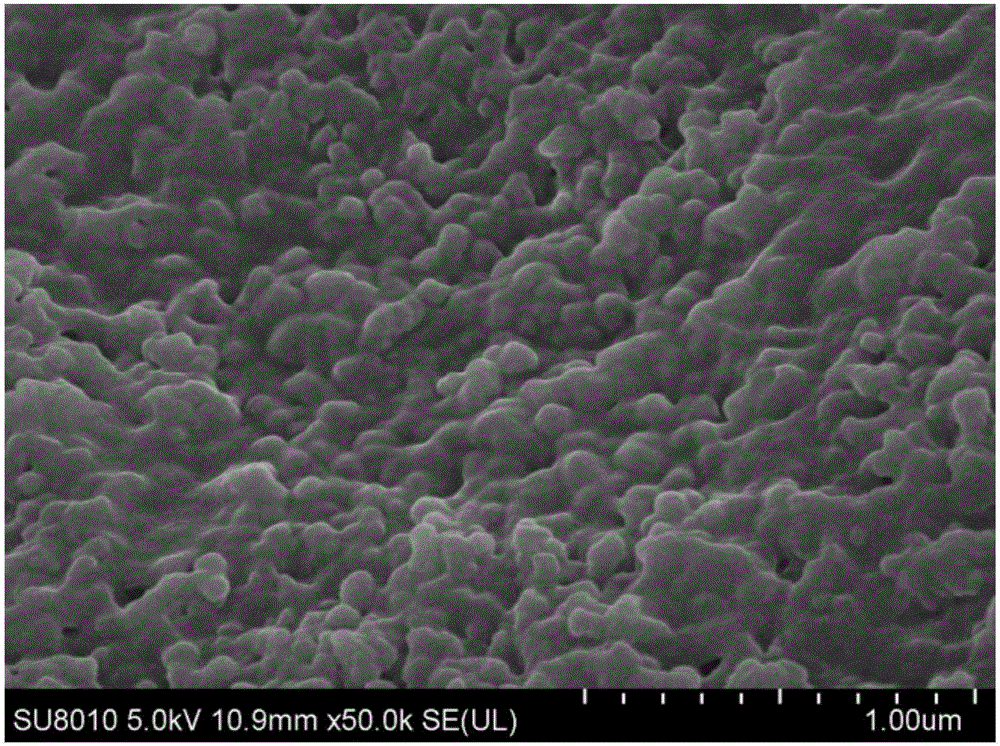
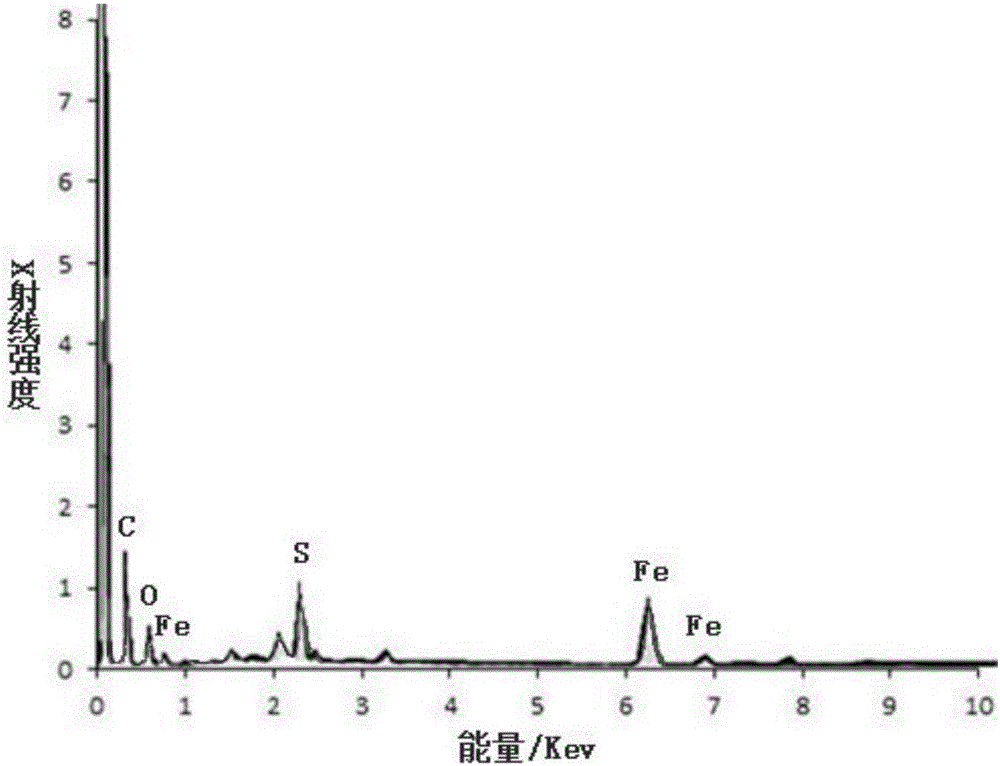
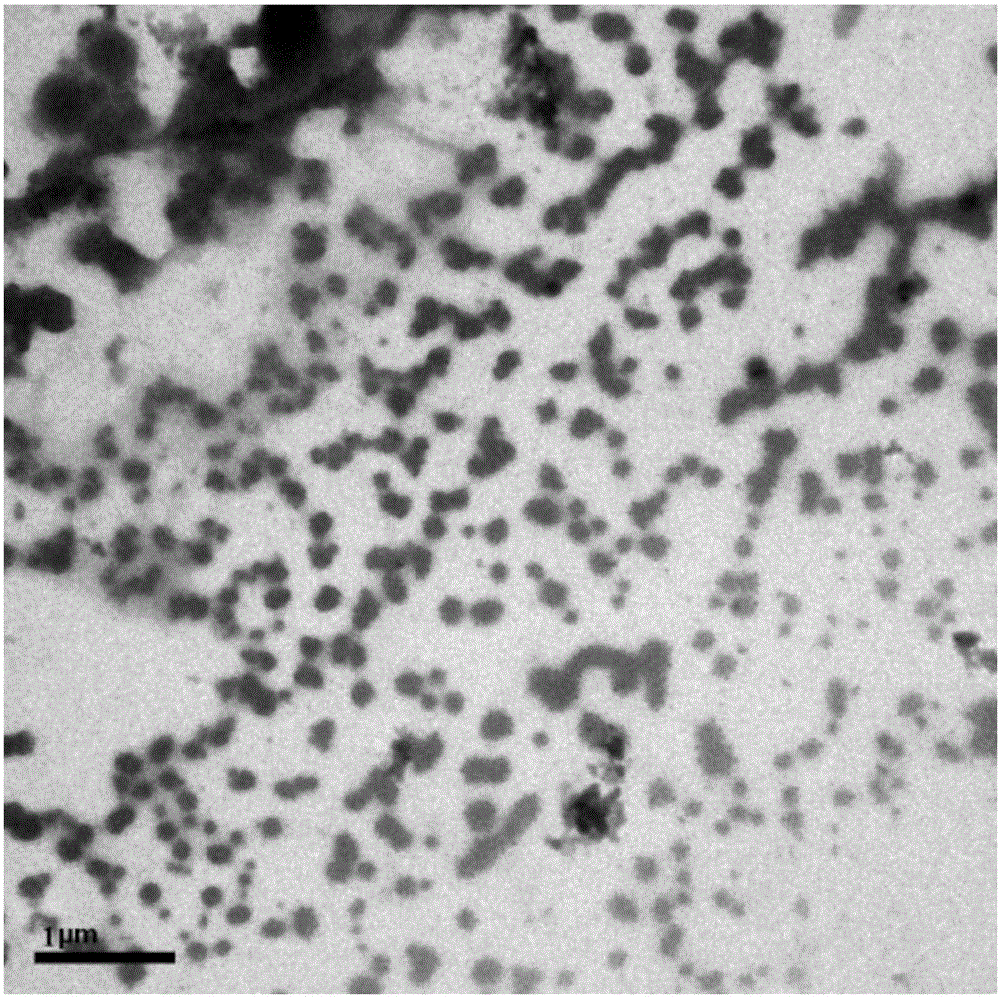
Application of nano-iron synthesized by tea leaves in p,p'-DDT removal
A tea leaf and nano-iron technology, applied in nanotechnology, restoration of polluted soil, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high toxicity accumulation, restricting the feasibility of animal restoration, and long restoration period, etc. Achieve the effect of low technical requirements, good application prospects and improved degradation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] (1) Collection and processing of tea leaves
[0054] The tea tree leaves used in the present invention are all collected from Qianchuan Town, Lin'an City, Zhejiang Province. The tea tree leaves collected are not young leaves for drinking, but non-drinkable leaves located near the roots and with a long growth cycle. After the tea tree leaves that have been washed off the surface impurities are naturally dried, they are ground and passed through a 140-mesh standard sieve, and sealed in bags for later use.
[0055] (2) Preparation of plant extract
[0056] Select 10g of plant powder and 200ml of ultrapure water and add them to a conical flask at a mass-to-volume ratio of 1:20 for mixing. Seal the conical flask and heat and stir in a water bath at 80°C for 2 hours on a magnetic stirrer. Then the plant mixture was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes, and passed through a 0.45 μm organic phase needle filter to obtain tea tree leaf extract.
[0057] (3) Synthesis of green ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] (1) Collection and processing of tea leaves
[0065] The tea tree leaves used in the present invention are all collected from Qianchuan Town, Lin'an City, Zhejiang Province. The tea tree leaves collected are not young leaves for drinking, but non-drinkable leaves located near the roots and with a long growth cycle. After the tea tree leaves that have been washed off the surface impurities are naturally dried, they are ground and passed through a 140-mesh standard sieve, and sealed in bags for later use.
[0066] (2) Preparation of plant extract
[0067] Plant powder and ultrapure water were selected and added to a conical flask at a mass-to-volume ratio of 1:20 for mixing. The conical flask was sealed and heated and stirred in a water bath at 80°C for 2 hours on a magnetic stirrer. Then the plant mixture was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes, and passed through a 0.45 μm organic phase needle filter to obtain tea tree leaf extract.
[0068] (3) Synthesis of green n...
Embodiment 3
[0074] (1) Collection and processing of tea leaves
[0075] The tea tree leaves used in the present invention are all collected from Qianchuan Town, Lin'an City, Zhejiang Province. The tea tree leaves collected are not young leaves for drinking, but non-drinkable leaves located near the roots and with a long growth cycle. After the tea tree leaves that have been washed off the surface impurities are naturally dried, they are ground and passed through a 140-mesh standard sieve, and sealed in bags for later use.
[0076] (2) Preparation of plant extract
[0077] Select 10g of plant powder and 20ml of ultrapure water and add them into a conical flask at a mass-to-volume ratio of 1:20 for mixing. Seal the conical flask and heat and stir in a water bath at 80°C for 2 hours on a magnetic stirrer. Then the plant mixture was centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes, and passed through a 0.45 μm organic phase needle filter to obtain tea tree leaf extract.
[0078] (3) Synthesis of green...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com