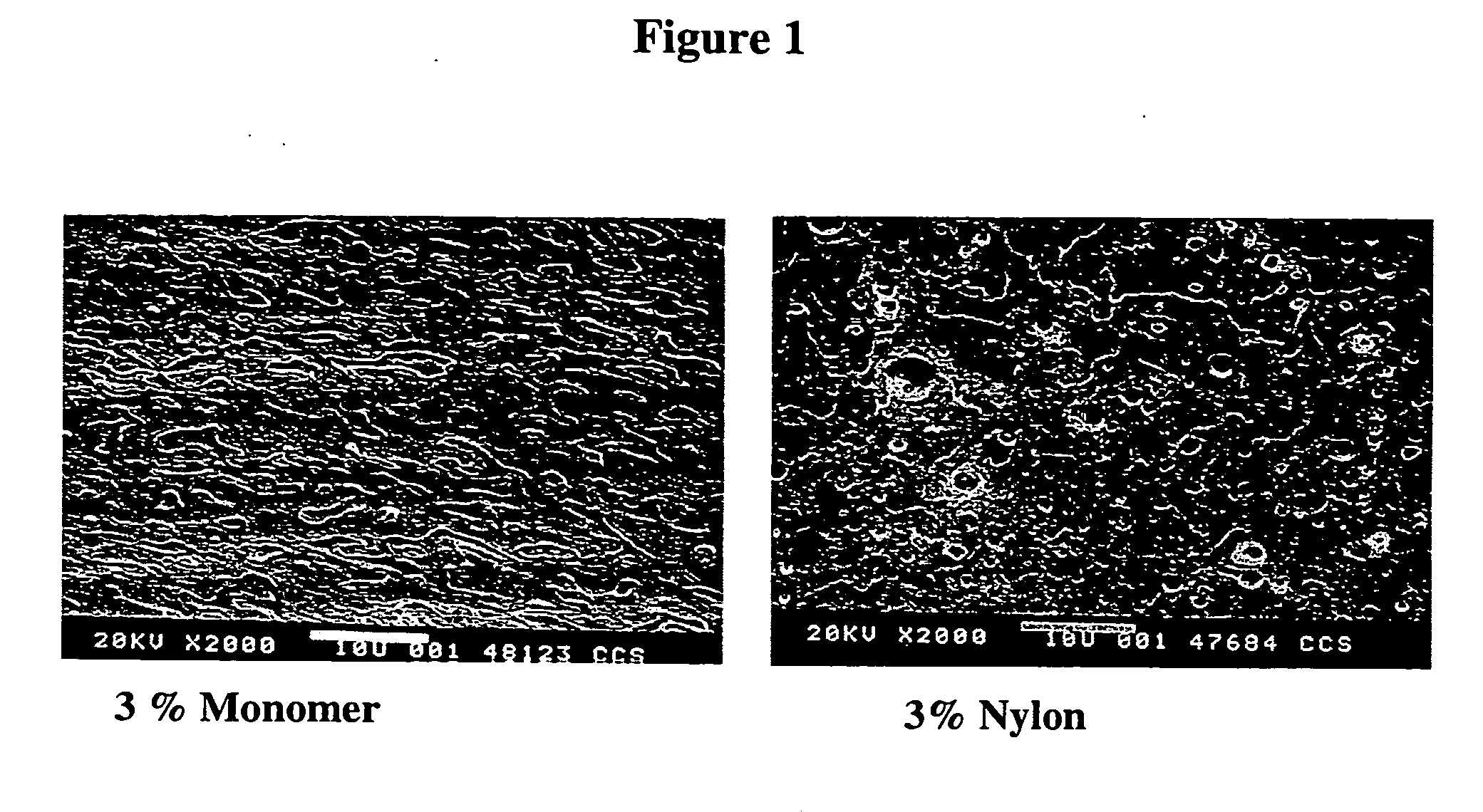
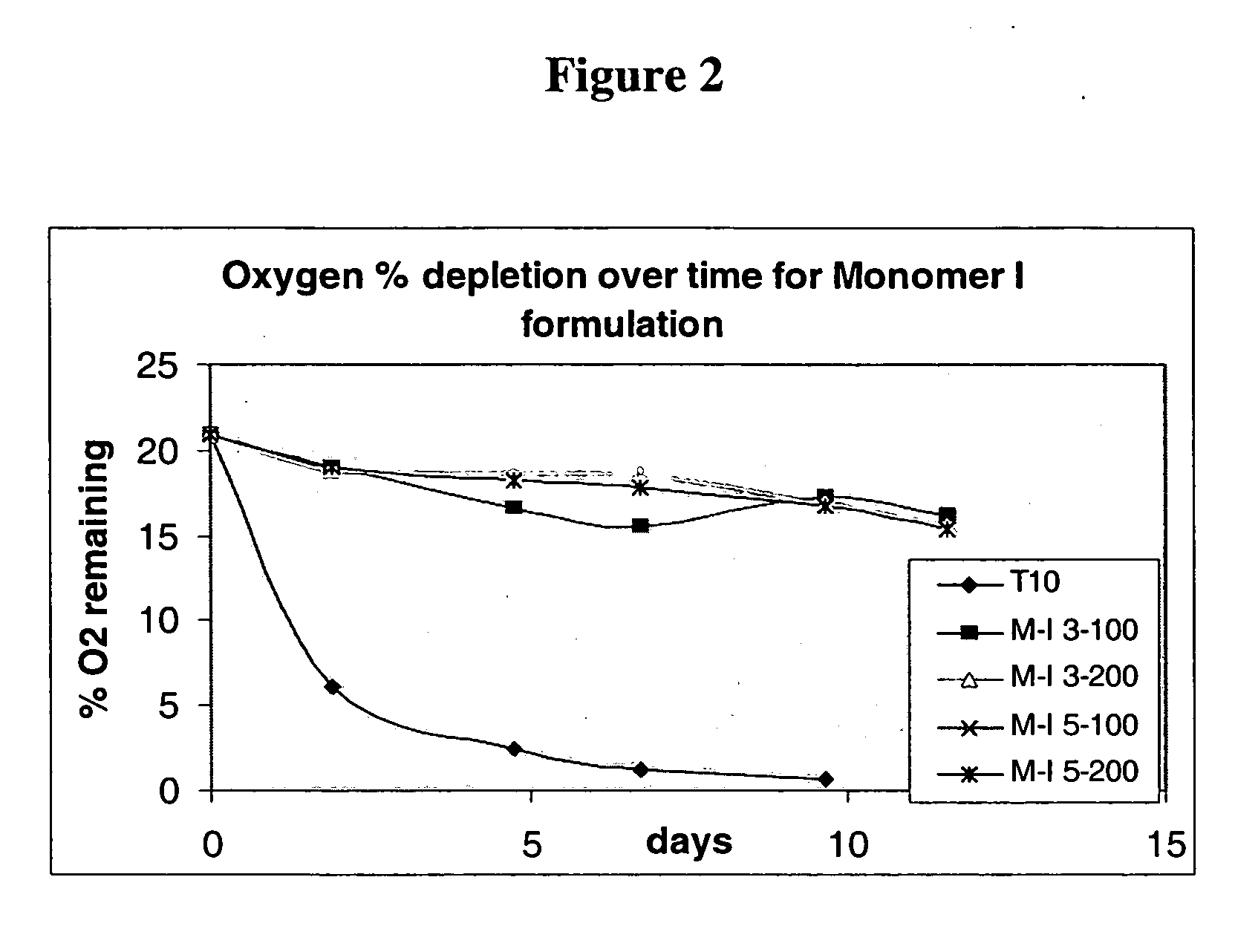
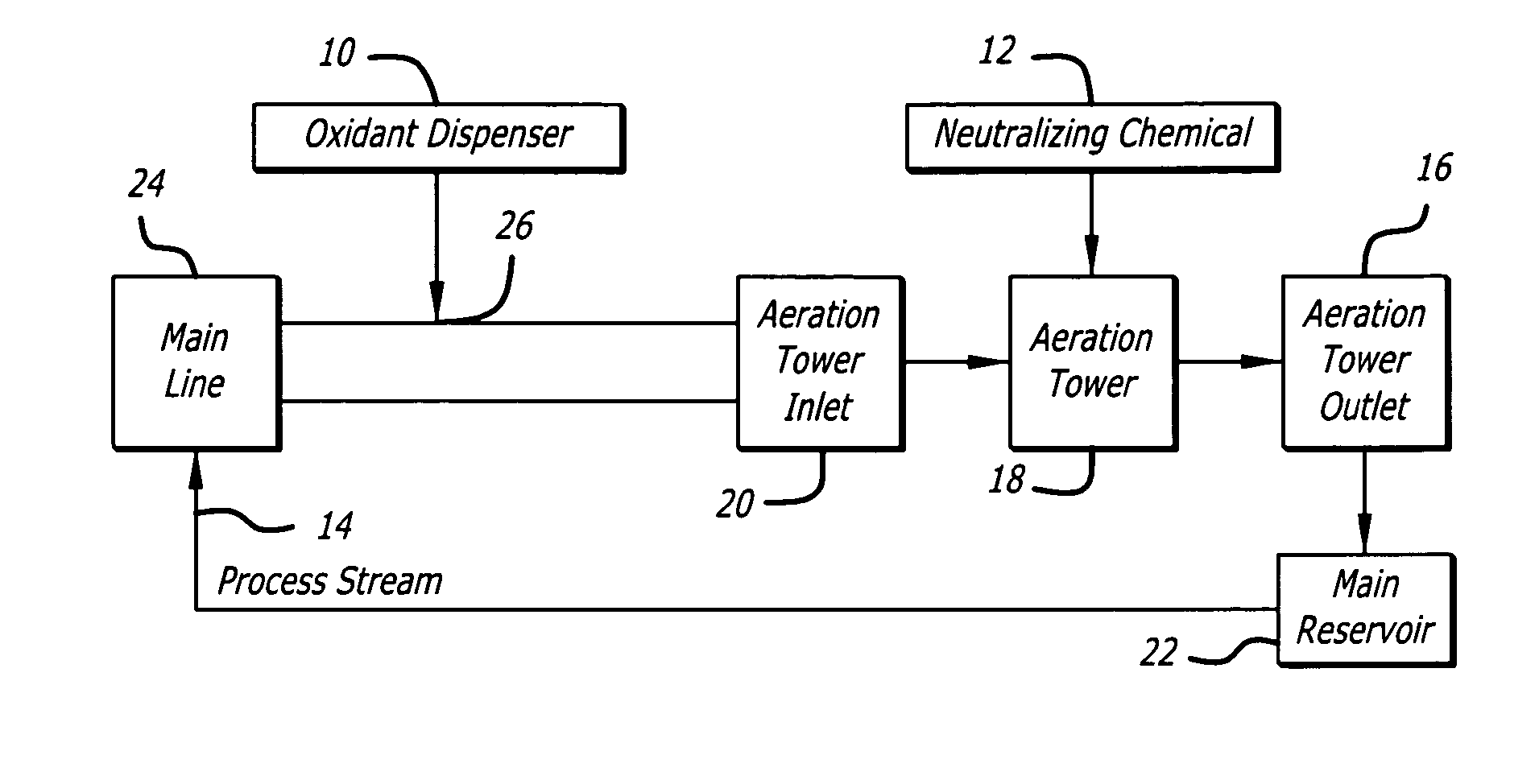
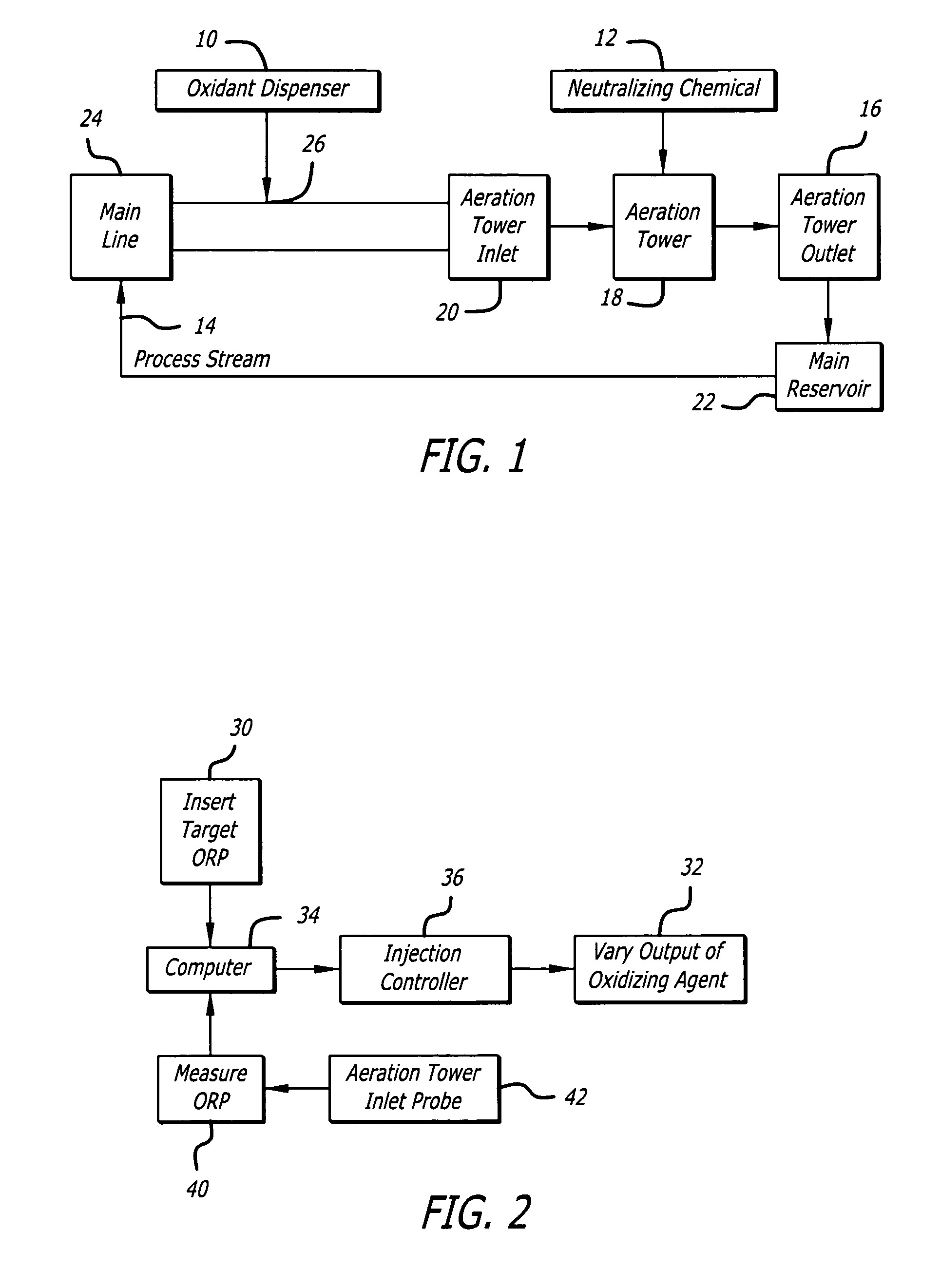
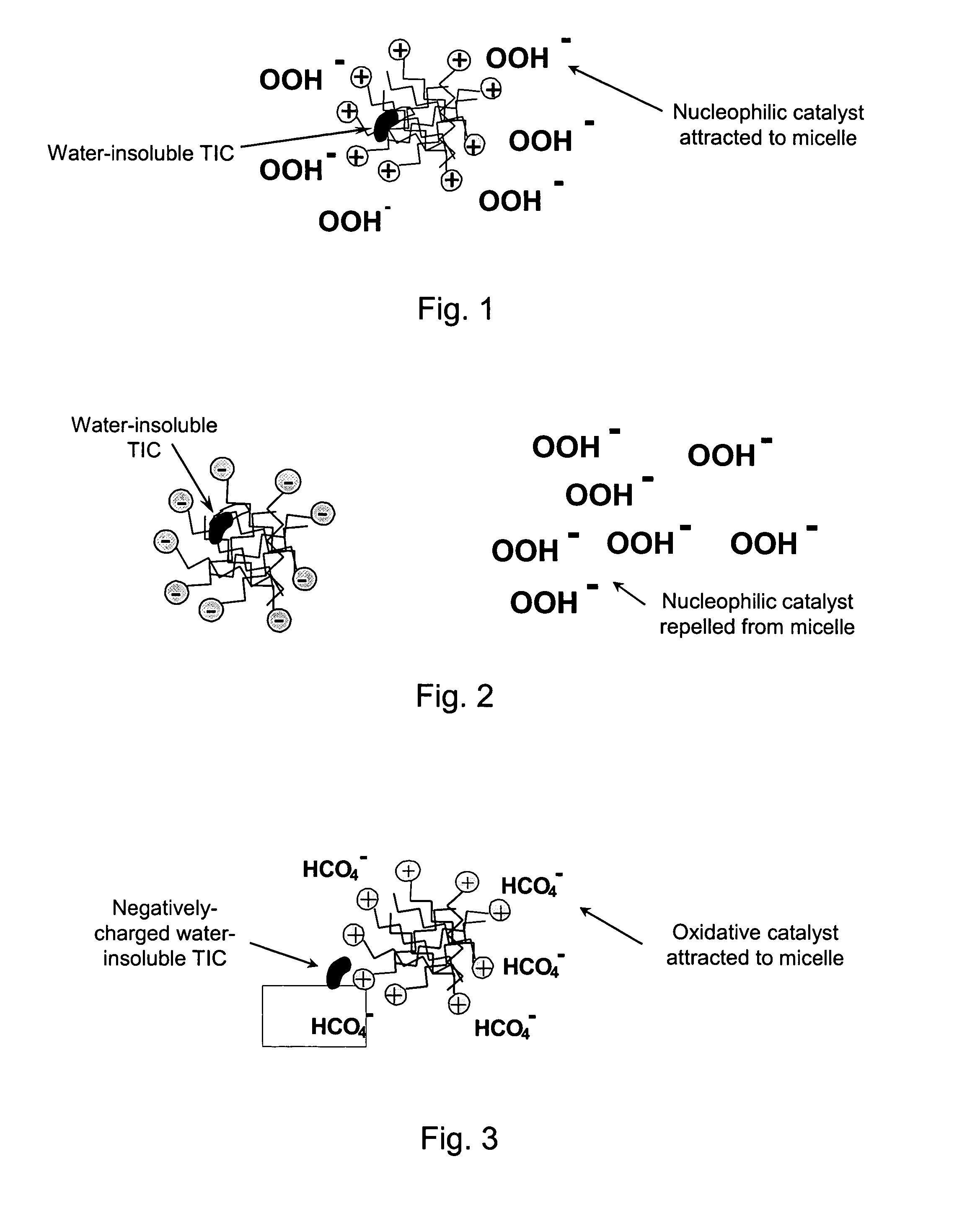
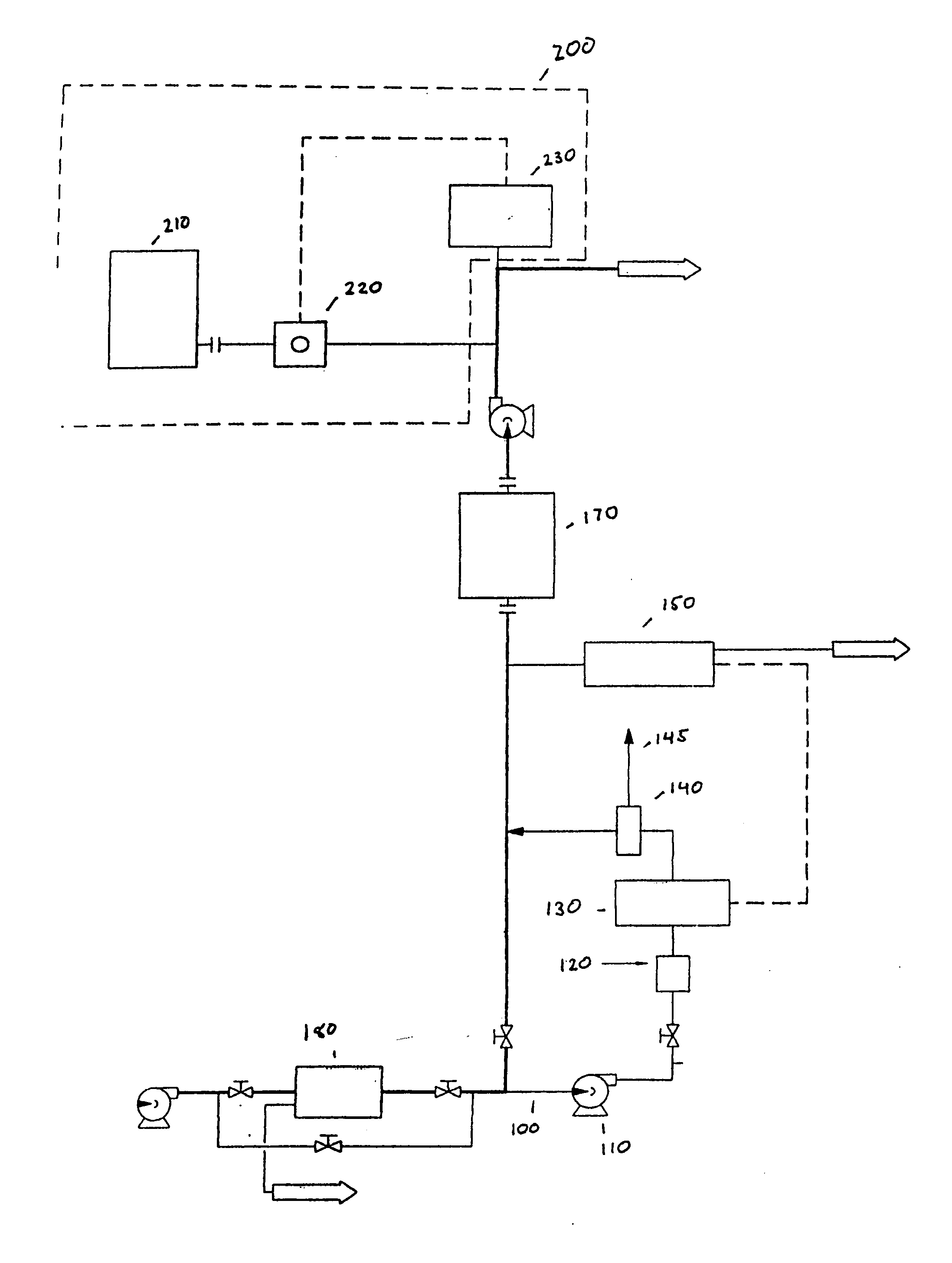
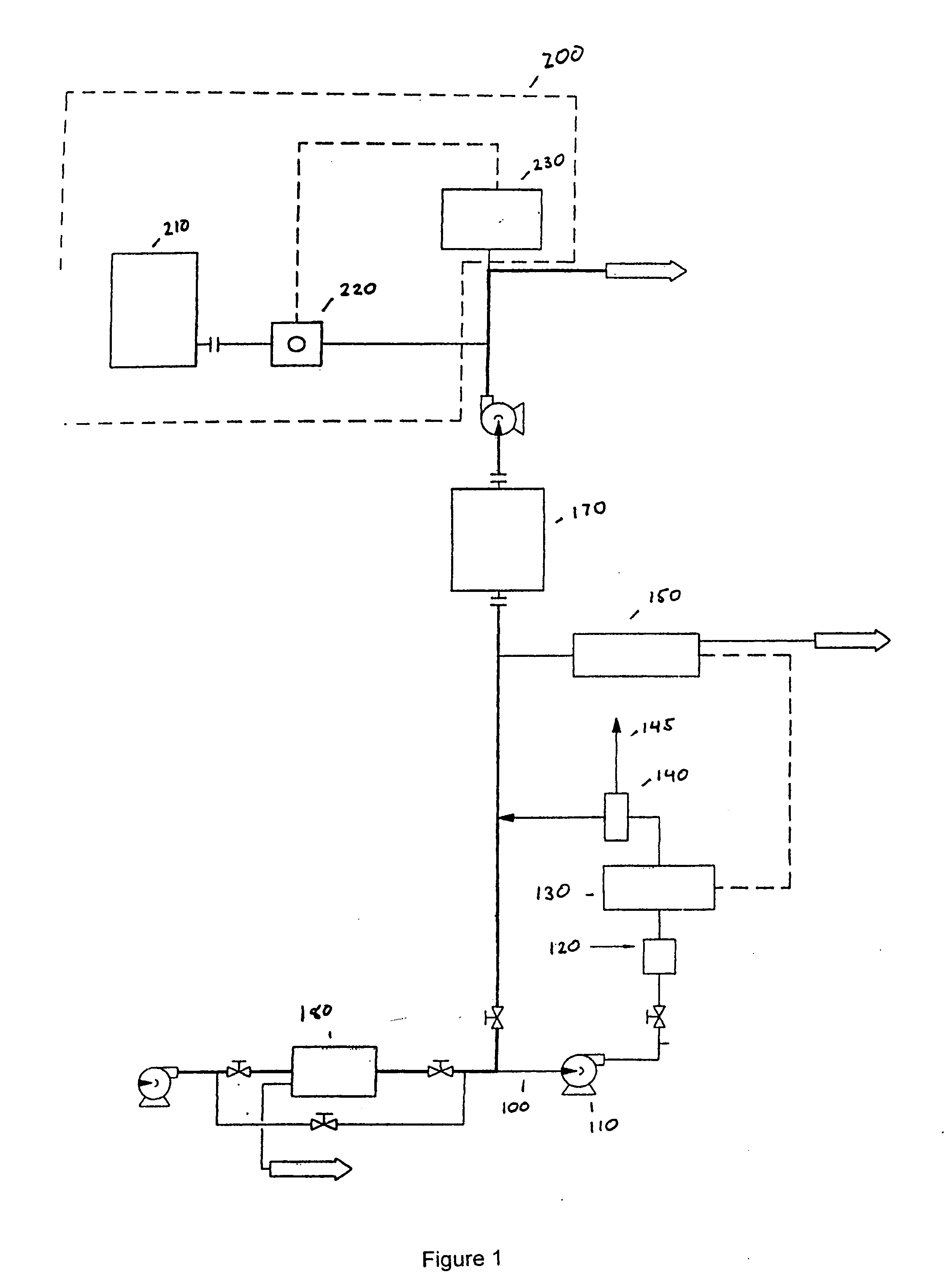
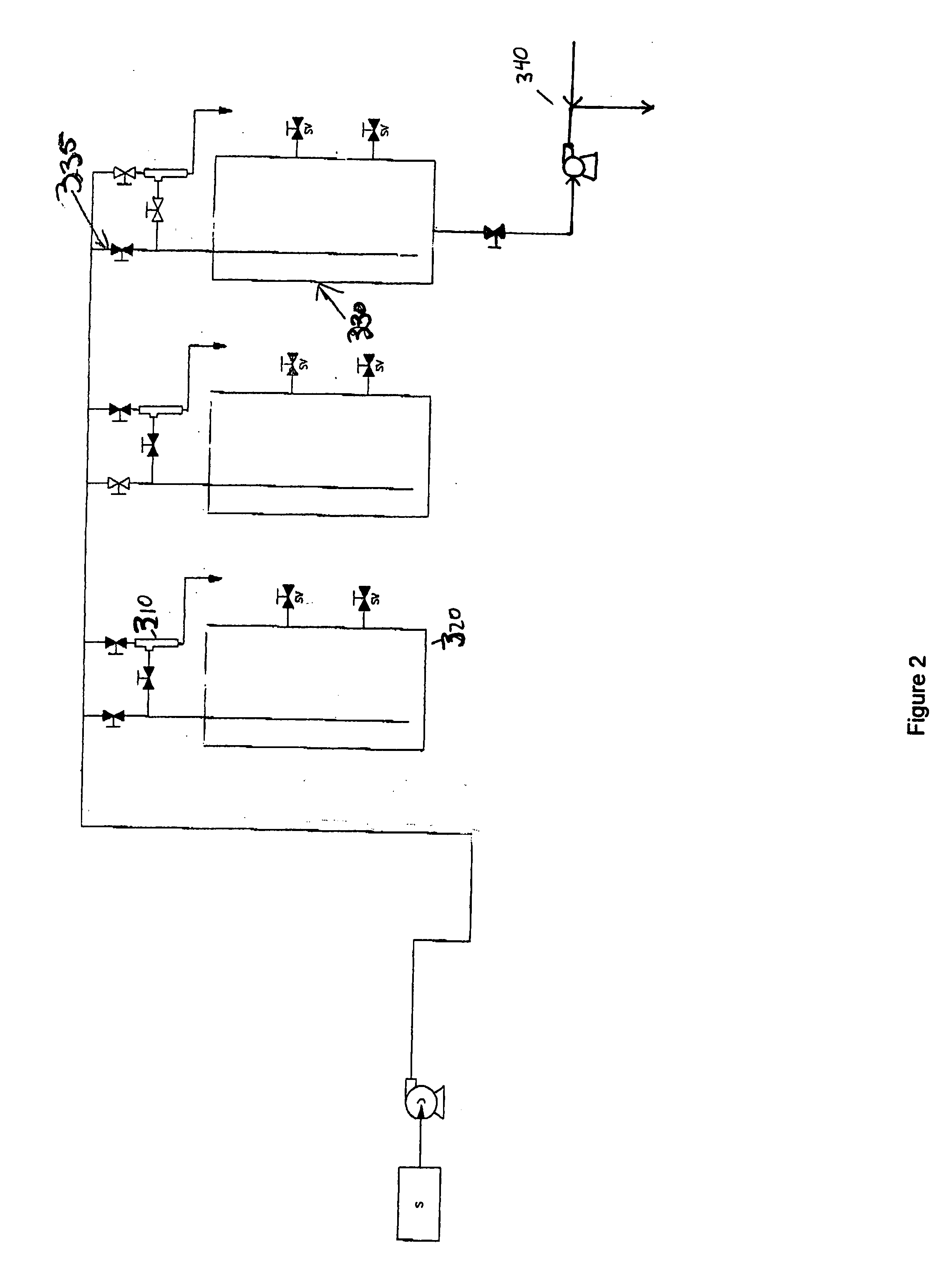
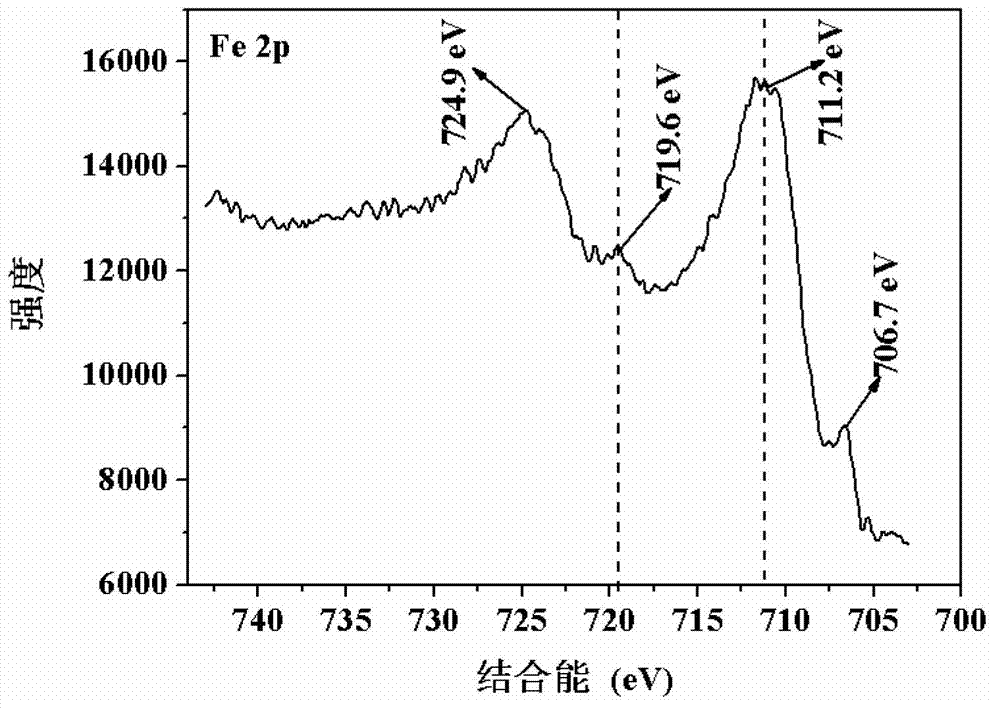
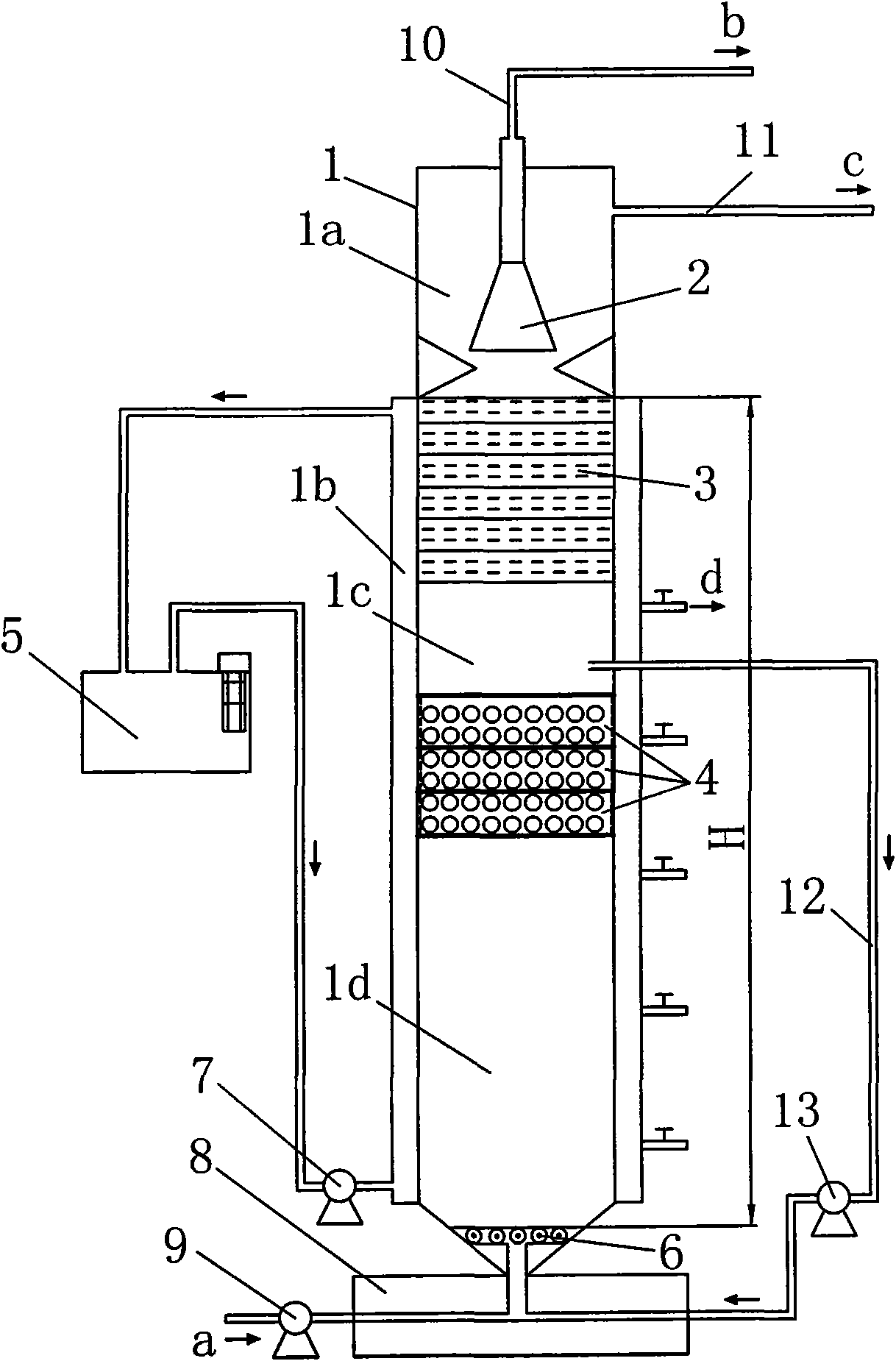
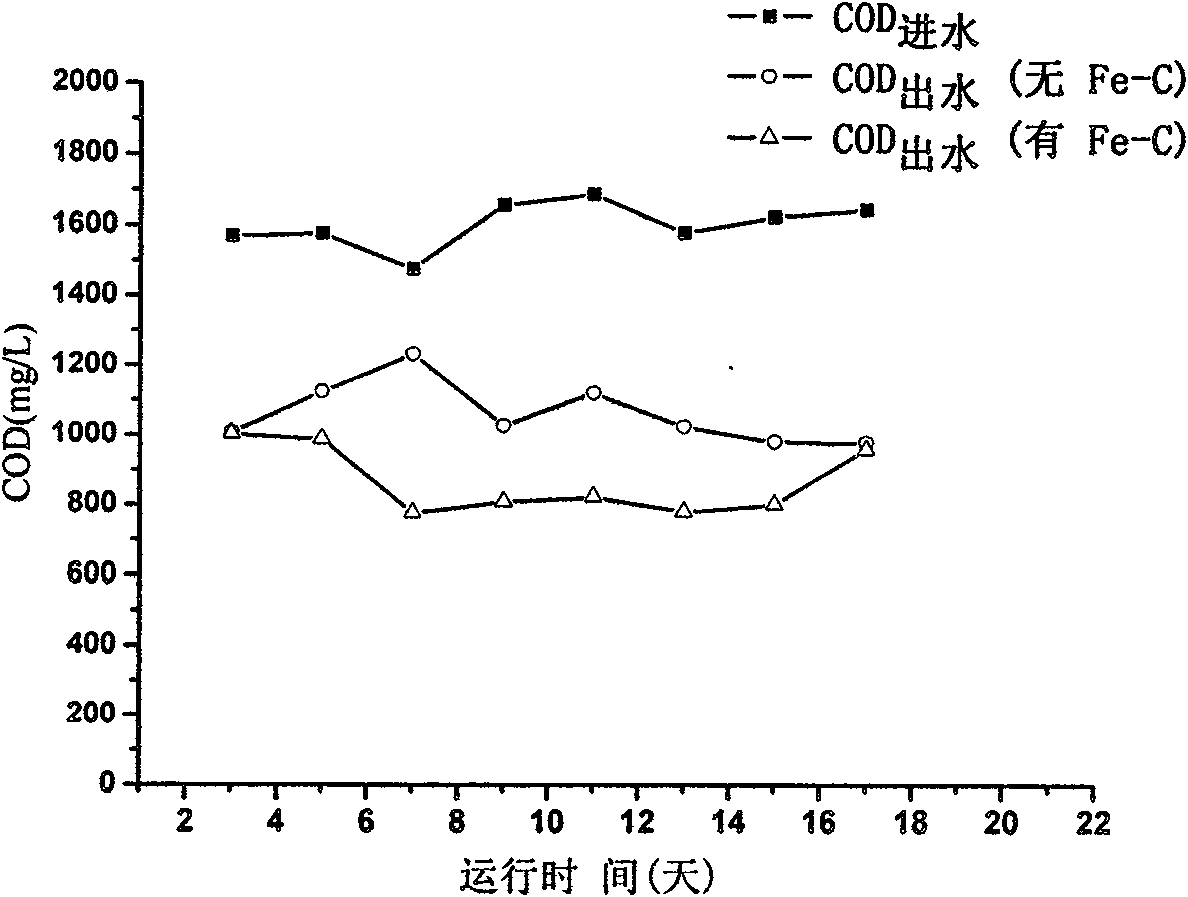
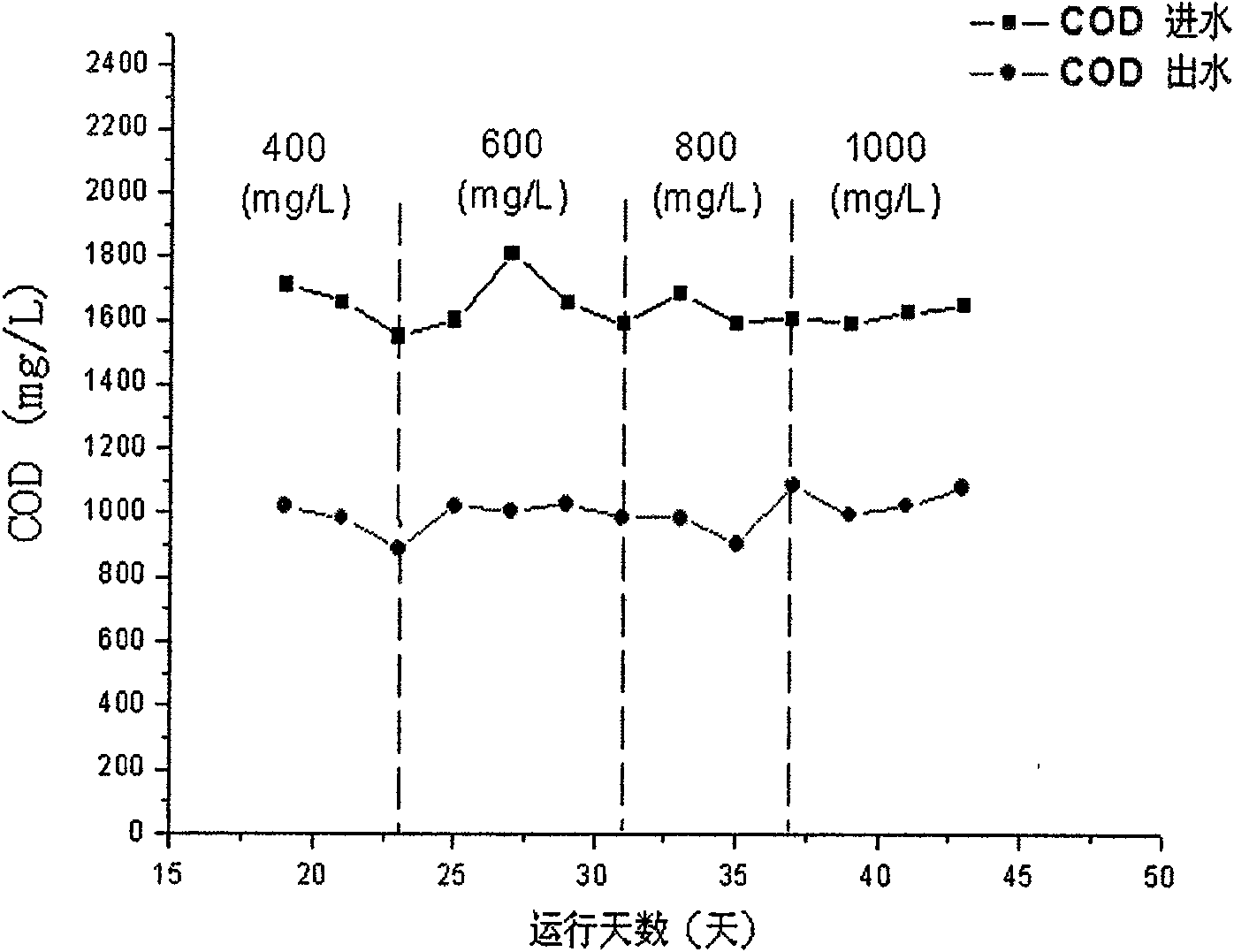
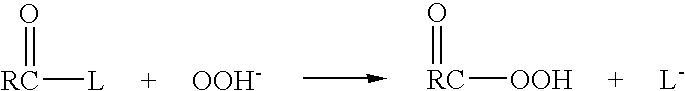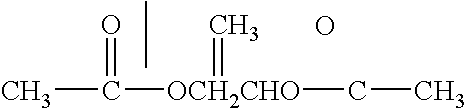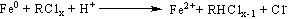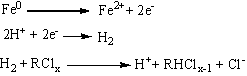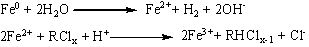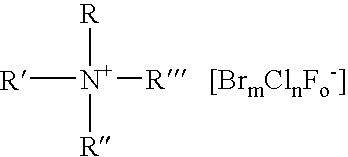Patents
Literature
3673results about "Water/sewage treatment by reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
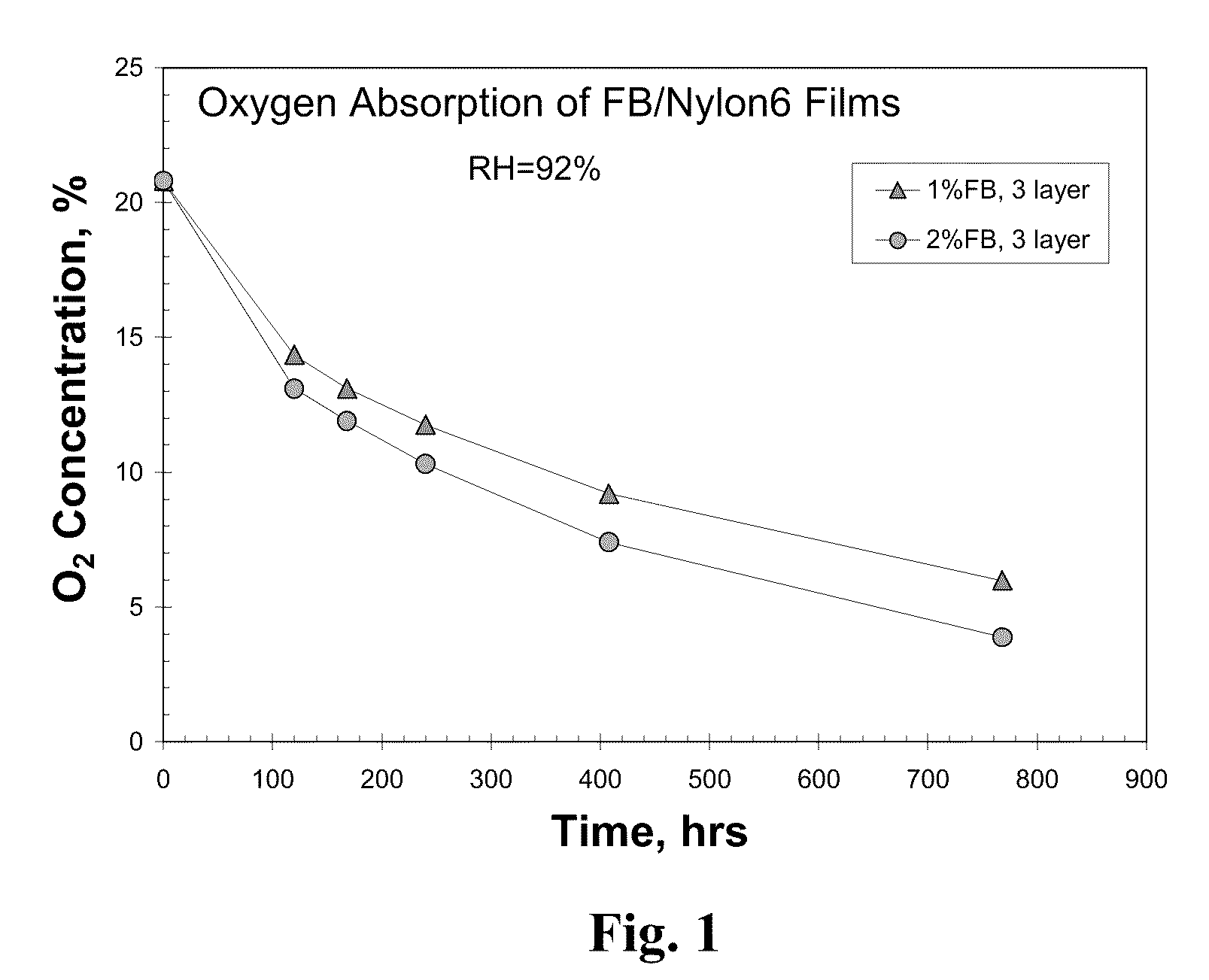
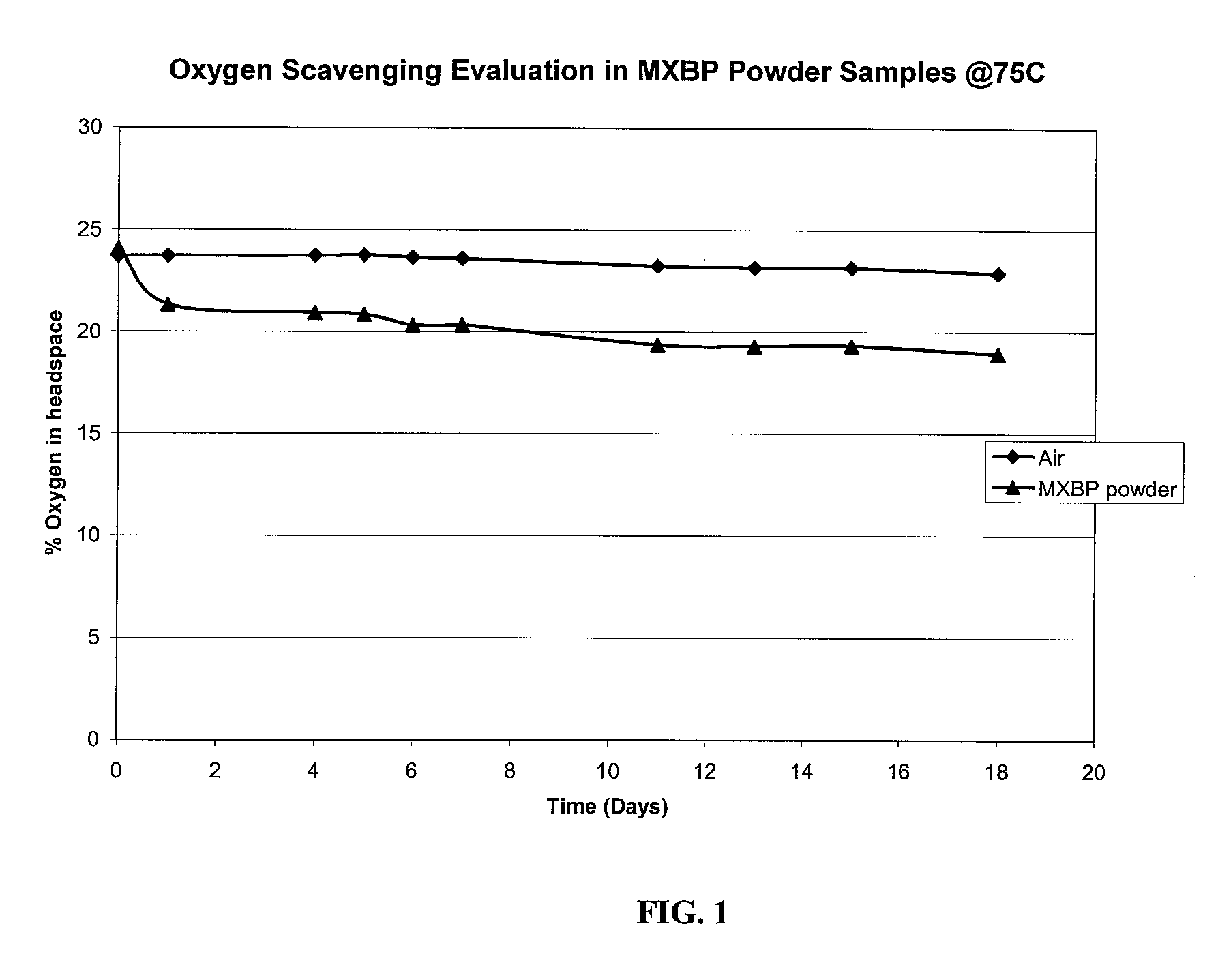
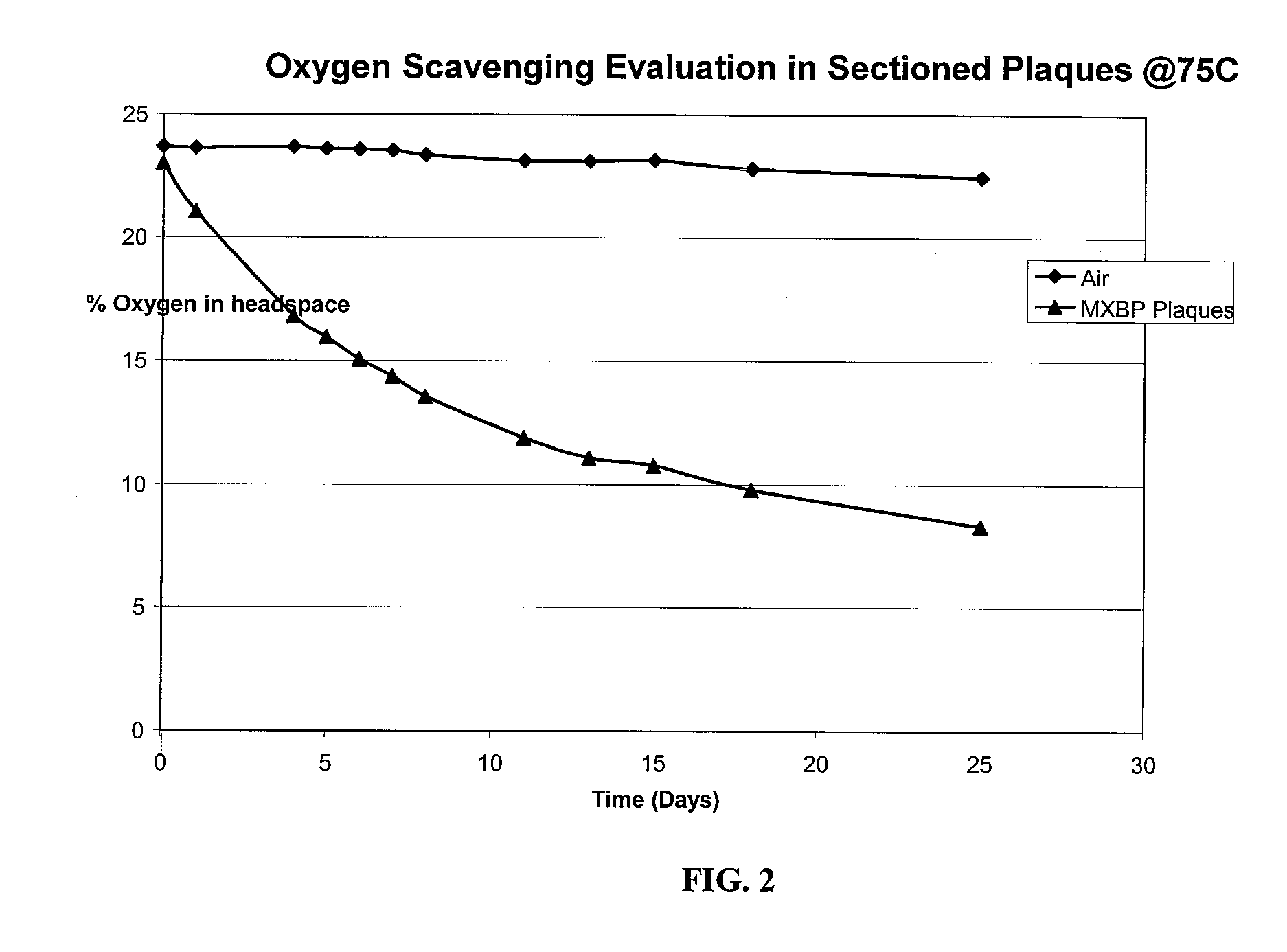
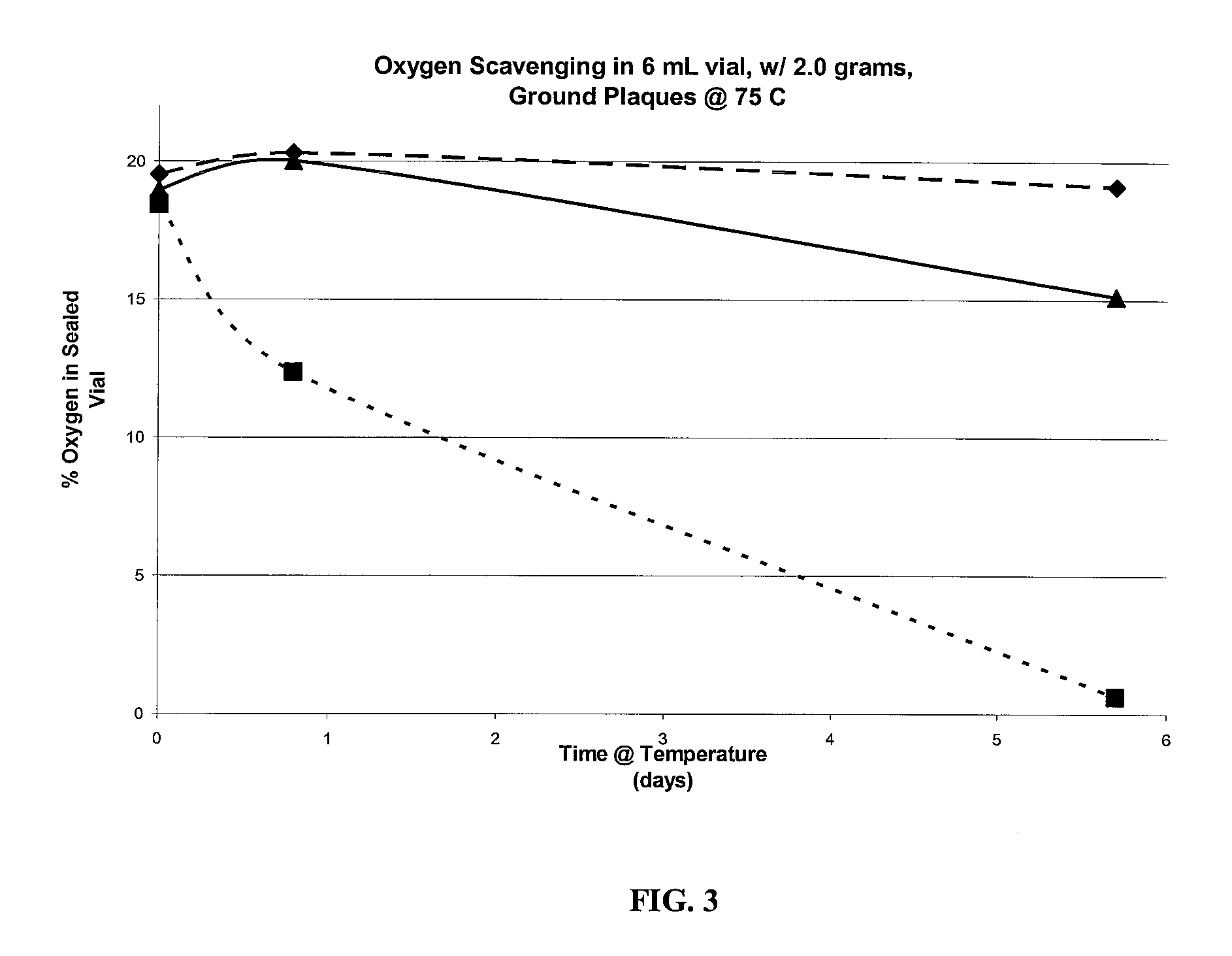
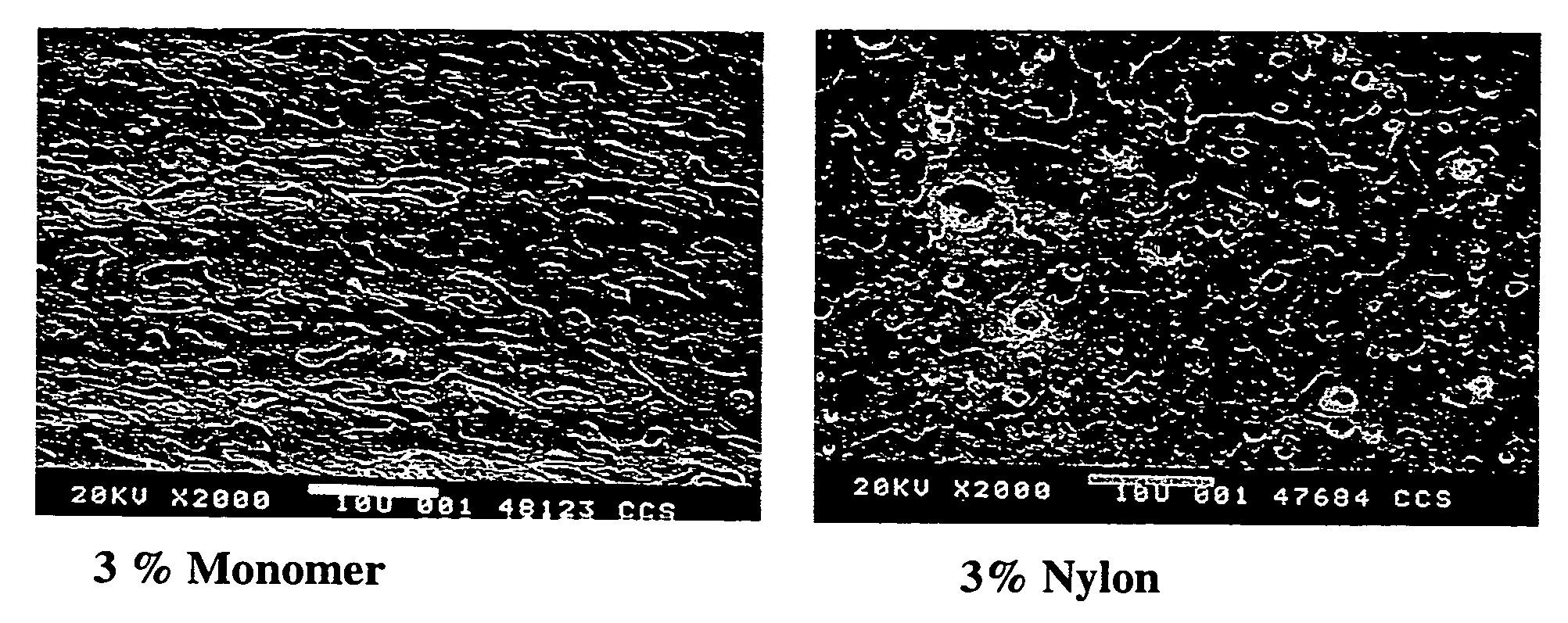
Oxygen scavenging films
InactiveUS20100255231A1Metal-working apparatusGlass/slag layered productsParticulatesAlkaline earth metal
A well dispersed oxygen scavenging particulate compounded in a polymer matrix. The oxygen scavenging formulation consists of iron powder with a mean particle sizes within 1-25 um and pre-coated with at least one or more activating and acidifying powdered compounds, usually in the form of solid organic and inorganic salts of alkaline and alkaline earth metals such as sodium chloride and sodium bisulfate. The pre-coated iron particulate is dispersed into a polymer resin by using a conventional melt processing method such as twin-screw extrusion. The oxygen scavenging compound is mixed with polymer pellets in the solid state prior to melting. The polymer resin pellets and the coated iron powder are preferably treated with a surfactant in the dry state to help dispersing the iron / salt powder with the resin pellets. The melt extruded compounds are pelletized and kept in the dry state to prevent premature activation.
Owner:MULTISORB TECH INC
Oxygen scavenging pharmaceutical package and methods for making same
The present invention relates generally to a pharmaceutical packaging for increasing the product shelf life, reducing discoloration, and reducing degradation of pharmaceuticals by reducing the oxygen level present in the pharmaceutical package. The pharmaceutical package comprises a substantially oxygen impermeable container, at least one oxygen scavenging element disposed in the container, and at least one packaged pharmaceutical product disposed in the oxygen impermeable container.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Oxygen Scavenging Molecules, Articles Containing Same, And Methods Of Their Use
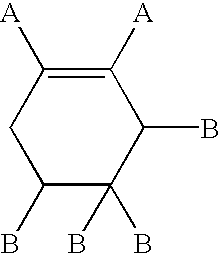
The invention relates to compounds of the structure of formula I and II:where X is selected from the group consisting of O, S and NH; Y, A and B are independently selected from the group consisting of N and CH; D, E and F are independently selected from the group consisting of CH, N, O and S; the symbol — represents a single or a double bond; and R1, R2 and R3 are independently selected from the group consisting of H, electron withdrawing groups and electron releasing groups. In other embodiments, the compounds are used as oxygen scavengers and in barrier compositions and articles.
Owner:PLASTIPAK PACKAGING
Oxygen-scavenging filled polymer blend for food packaging applications
InactiveUS6037022AOxygen transmission propertyLow oxygenDomestic containersThin material handlingPaperboardFood packaging
The specification discloses a polymer blend especially well-suited for coating paperboard substrates used in food packaging, particularly acidic or acid-generating foods such as fruit and vegetable juices. The blend contains an acid-activatable oxygen scavenger dispersed in a film-forming synthetic polymer such as an EVOH copolymer. When placed as a film or layer on the side of the substrate inside the container in contact with the food the blend is effective to reduce the oxygen in the container over time to a very low concentration, replacing the same with carbon dioxide, for an excellent preservative effect.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Oxygen scavenging compositions and packaging comprising said compositions
InactiveUS20060180790A1Removing hazeRecord information storageOrganic/inorganic per-compounds compounding agentsOxidation stateCompound (substance)
The instant invention concerns a composition comprising a base polymer, at least one compound of the formula E-(L-E)x wherein: E is and L is a linking group; and at least one transition metal in a positive oxidation state. The invention also concerns packages containing walls comprising such compositions, methods of forming such packages, and methods of packaging an oxygen-sensitive item within such a package
Owner:PLASTIPAK PACKAGING
Cellulosic composite
Provided is a cellulosic composite comprised of cellulosic material and a binder. The binder comprises a reaction product of an amine and a reactant in the form of an amino-amide intermediate. To the amino-amide is added an aldehyde or ketone to form a curable binder composition. The composition when mixed with cellulosic material and cured forms a cellulosic composite.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
Process control oxidation
InactiveUS20060006122A1Reduce pointsSeawater treatmentSolid sorbent liquid separationProcess controlChemistry
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC
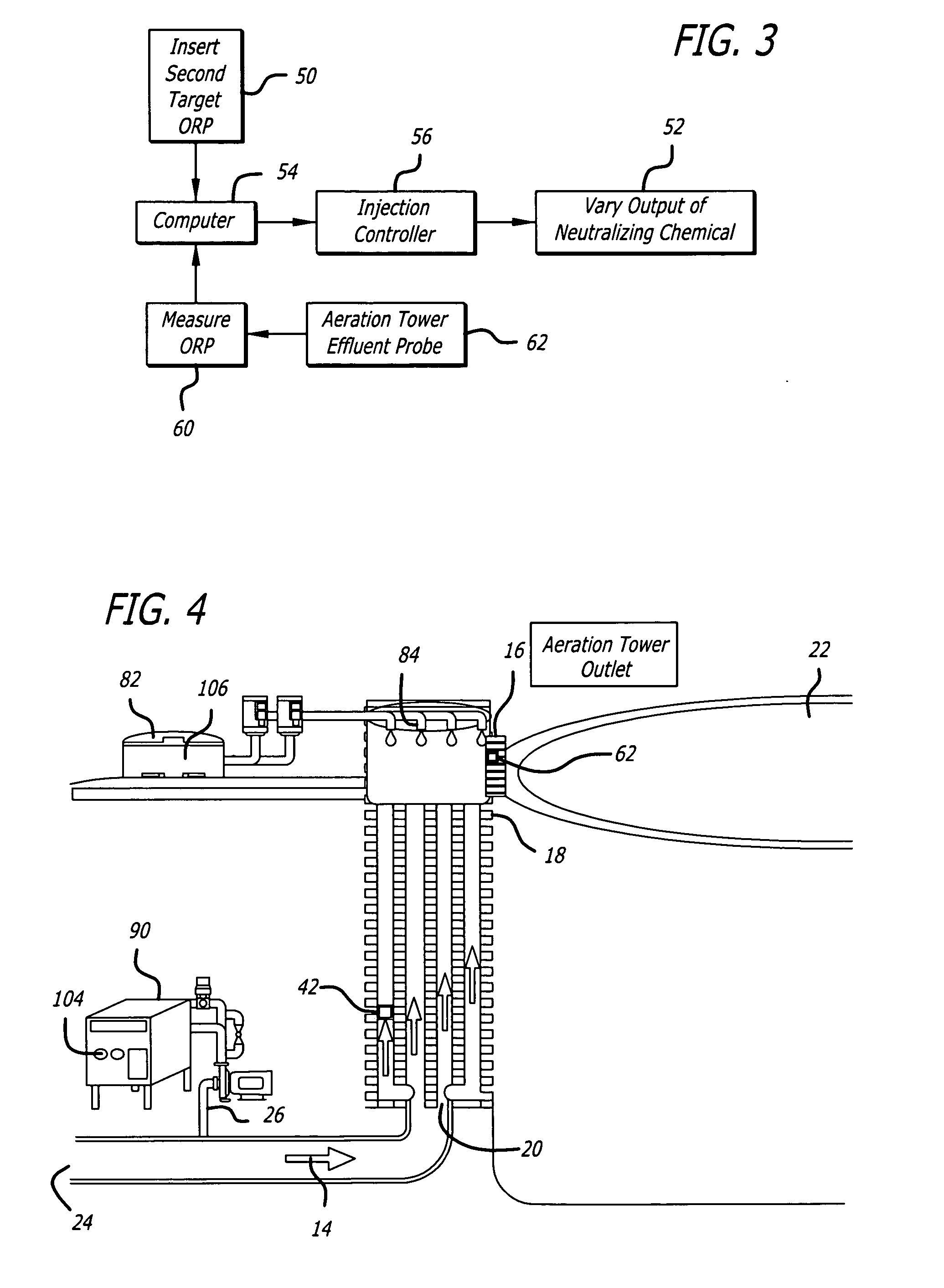
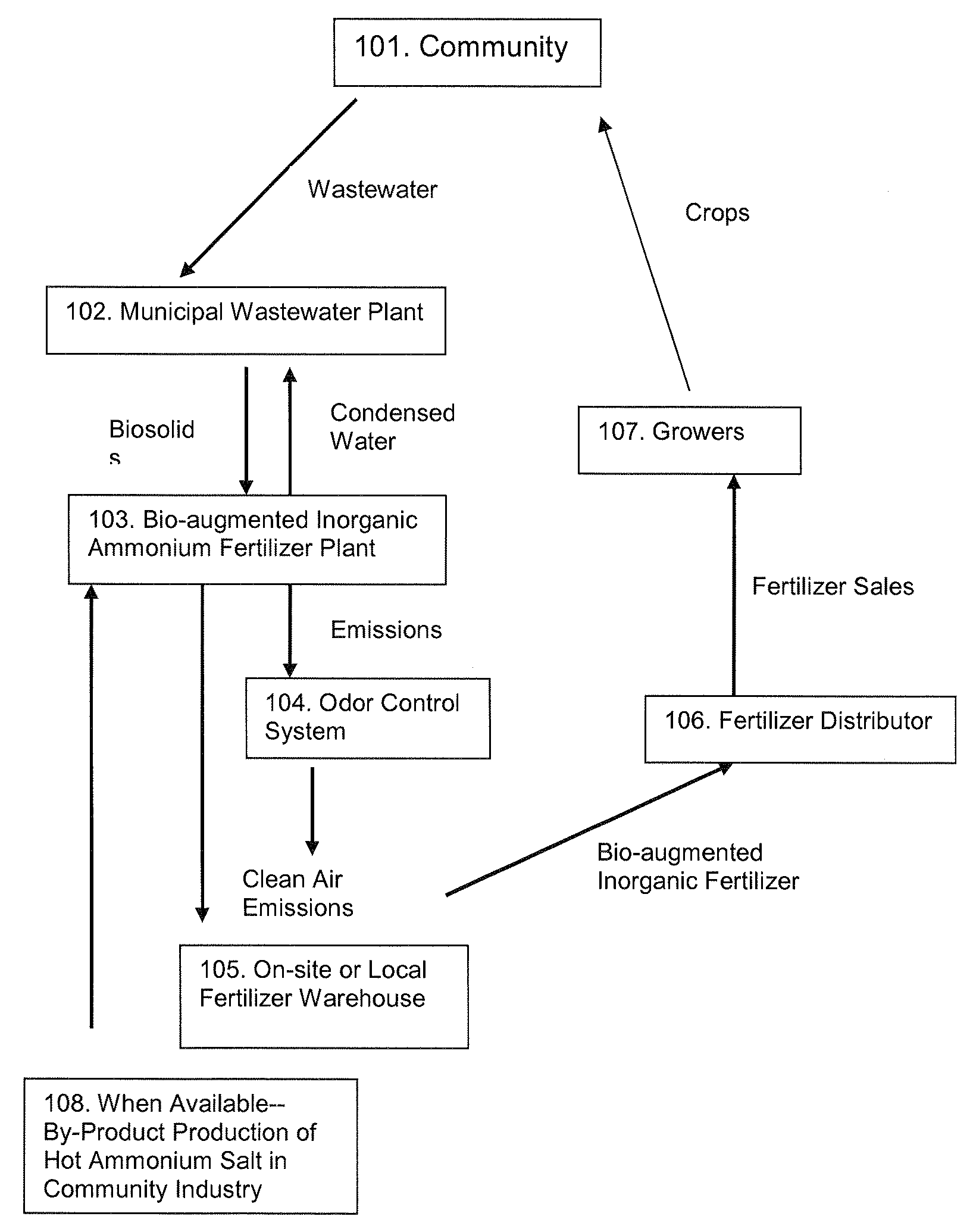
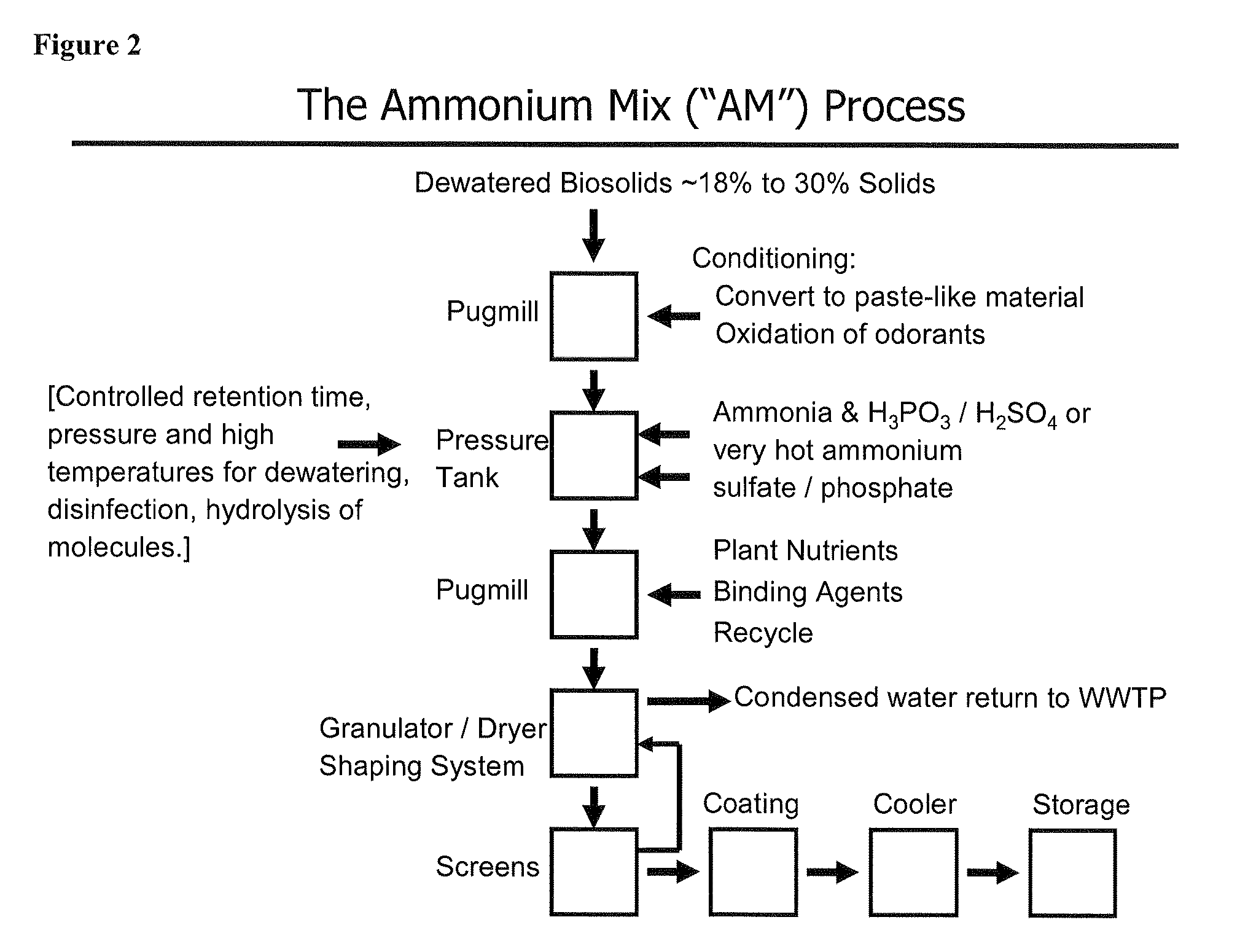
Process for treating sludge and manufacturing bioorganically-augmented high nitrogen-containing inorganic fertilizer
ActiveUS20080230484A1Reduce logisticsReduces liabilityByproduct vaporizationExcrement fertilisersPhosphateRetention time
The invention describes a new method for treating sludge, which can result in the production of high nitrogen organically-augmented inorganic fertilizer that incorporates municipal sludges or biosolids or organic sludges that can compete with traditional fertilizers such as ammonium phosphate, ammonium sulfate and urea on the commodity fertilizer marketplace. The method takes advantage of the thixotropic property of dewatered biosolids or organic sludge to create a pumpable paste-like material from the biosolids or organic sludge that is then treated with an oxidizer to reduce odorant effects and an acid. This mix is then interacted with concentrated sulfuric and or phosphoric acids and an ammonia source or alternatively a hot or molten melt or salt of ammonium sulfate / phosphate to form a fertilizer mix. The present invention controls the heat, atmospheric pressure and retention time of the fertilizer mix in the reaction vessel. When a fertilizer melt is formed ammoniation is subsequently completed by the specific use of vaporized ammonia. The invention can also be an add-on to commercial production of ammonium salts. The fertilizer produced by the present invention contains more than 8 wt. % nitrogen and preferably 15 wt. % nitrogen. The invention is oriented to be tailored to the biosolids production for individual municipal waste treatment plants in order to keep the fertilizer manufacturing plants of the present invention small with a minimization of logistics and liability.
Owner:GENERATE LENDING LLC +1
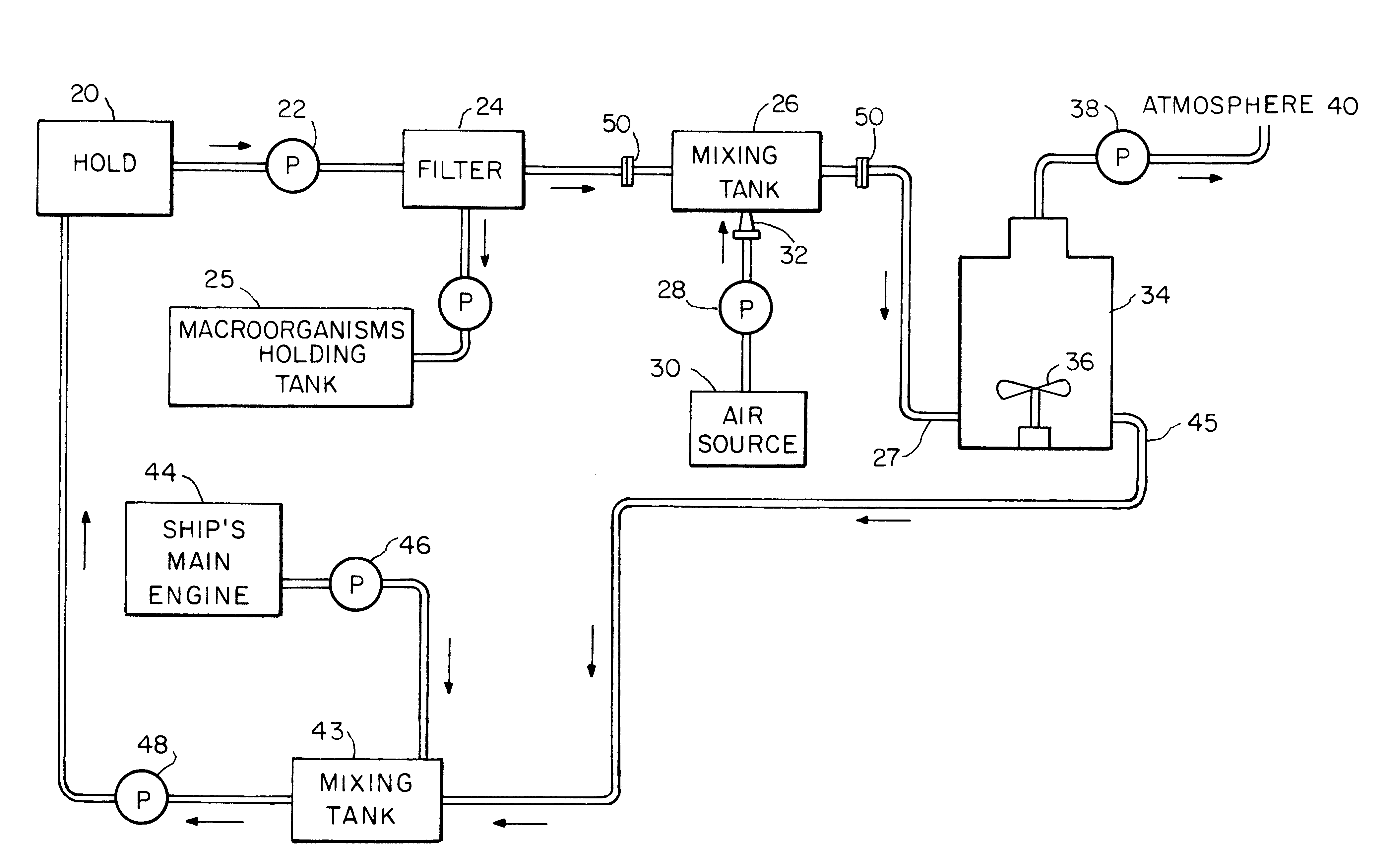
Method and apparatus for killing microorganisms in ship ballast water
InactiveUS6171508B1Rapidly reduce the DOTime requiredHull interior subdivisionWater treatment parameter controlOxygenAnaerobic microorganisms
A method and apparatus for treating ship ballast water before it is discharged into coastal waters. The ballast water may contain a generalized and diverse species population of harmful non-indigenous microorganisms. Before discharge, the ballast water is oxygenated and deoxygenated to reduce the populations of anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms, respectively. If anaerobic microorganisms are of no concern, the oxygenation step can be eliminated. Also, a method and apparatus for treating large volumes of any water, to reduce the population of a wide spectrum of diverse species of microorganisms wherein the water is deoxygenated, and then held in a sealed space for a period of time until the aerobic population has been reduced.
Owner:TIDEWATER BALLAST SOLUTIONS LLC
System and method for dissolving gases in liquids
ActiveUS7255332B2Improve solubilityFlow mixersTransportation and packagingSuspended particlesDissolution
Apparatus and methods for dissolving a gas into a liquid comprises a saturation tank, a high pressure liquid pump in fluid communication with the tank, and a pressurized gas source in communication with a regulated gas head space of the saturation tank. The saturation tank comprises a pressure vessel for containing the liquid and has a regulated gas head space above the liquid, contains at least one liquid spray nozzle that permits passage of liquid into the pressure vessel, and an outlet for the liquid containing dissolved gas. Upon passing the gas-containing liquid into a second fluid, the gas is released in the form of microbubbles. The microbubbles aid in flocculation of suspended particles and promote dissolution of the gas in the second fluid. Preferred gases for use with the apparatus are oxygen, air, and ozone. Anticipated uses include treatment of rivers, streams, and ponds in natural or industrial settings, as well as smaller scale applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
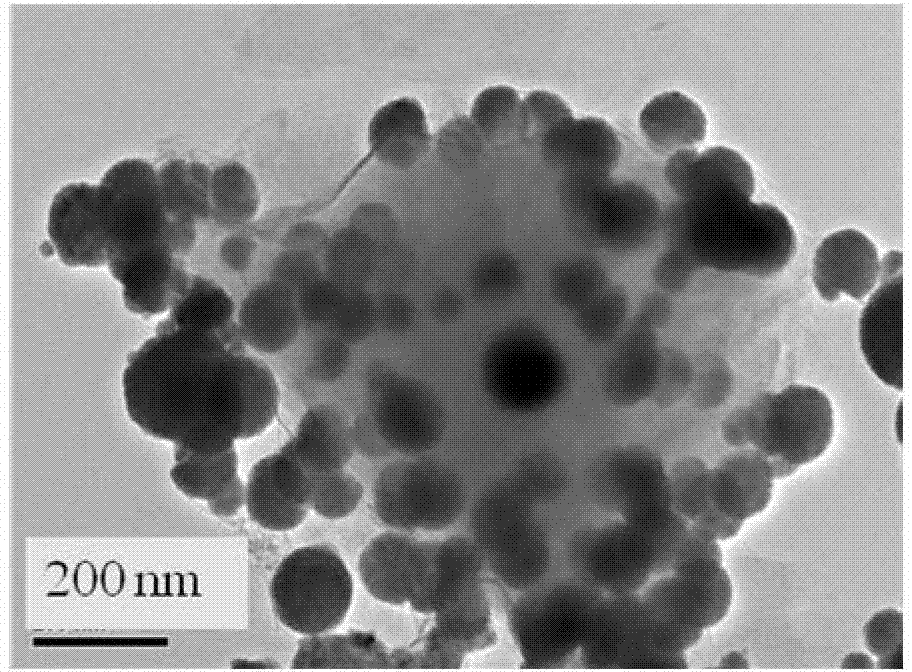
In Situ Remediation of Inorganic Contaminants Using Stabilized Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070256985A1Low costProcess environmental protectionMaterial nanotechnologyWater treatment compoundsCelluloseMaterials science
A method for preparing highly stabilized and dispersible zero valent iron nanoparticles and using the nanoparticles as a remediation technology against inorganic chemical toxins in contaminated sites. The method employs a composition containing select polysaccharides (starch or cellulose) as a stabilizer for the iron nanoparticles in a liquid carrier, and results in suspensions of iron nanoparticles of desired size and mobility in water, brine, soils or sediments. The stabilizer facilitates controlling the dispersibility of the iron nanoparticles in the liquid carrier. An effective amount of the composition is delivered to a contaminated site so that the zero valent iron nanoparticles can remediate one or more toxins such as an arsenate, a nitrate, a chromate, or a perchlorate in the contaminated site.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Chemical cleaning for membranes
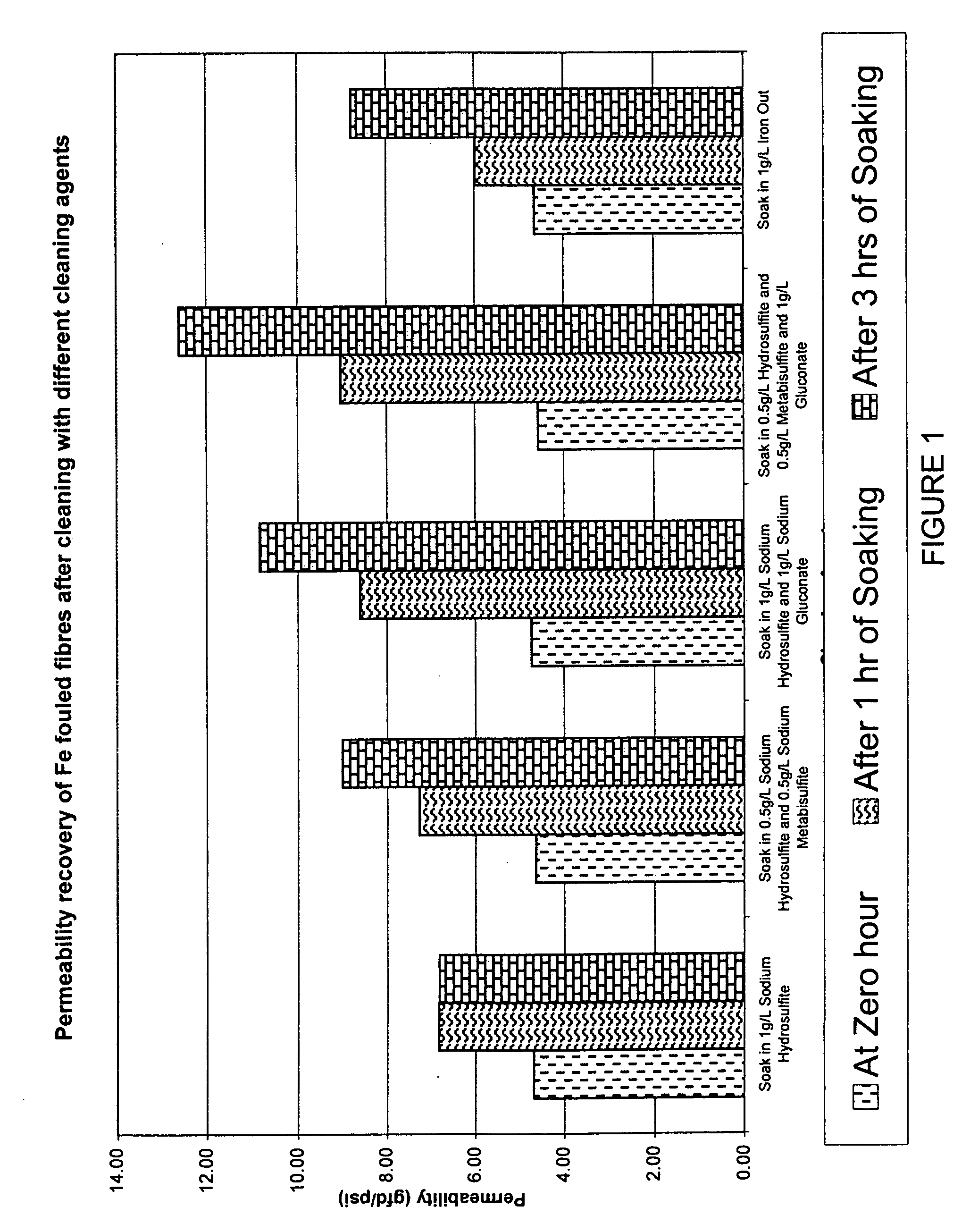
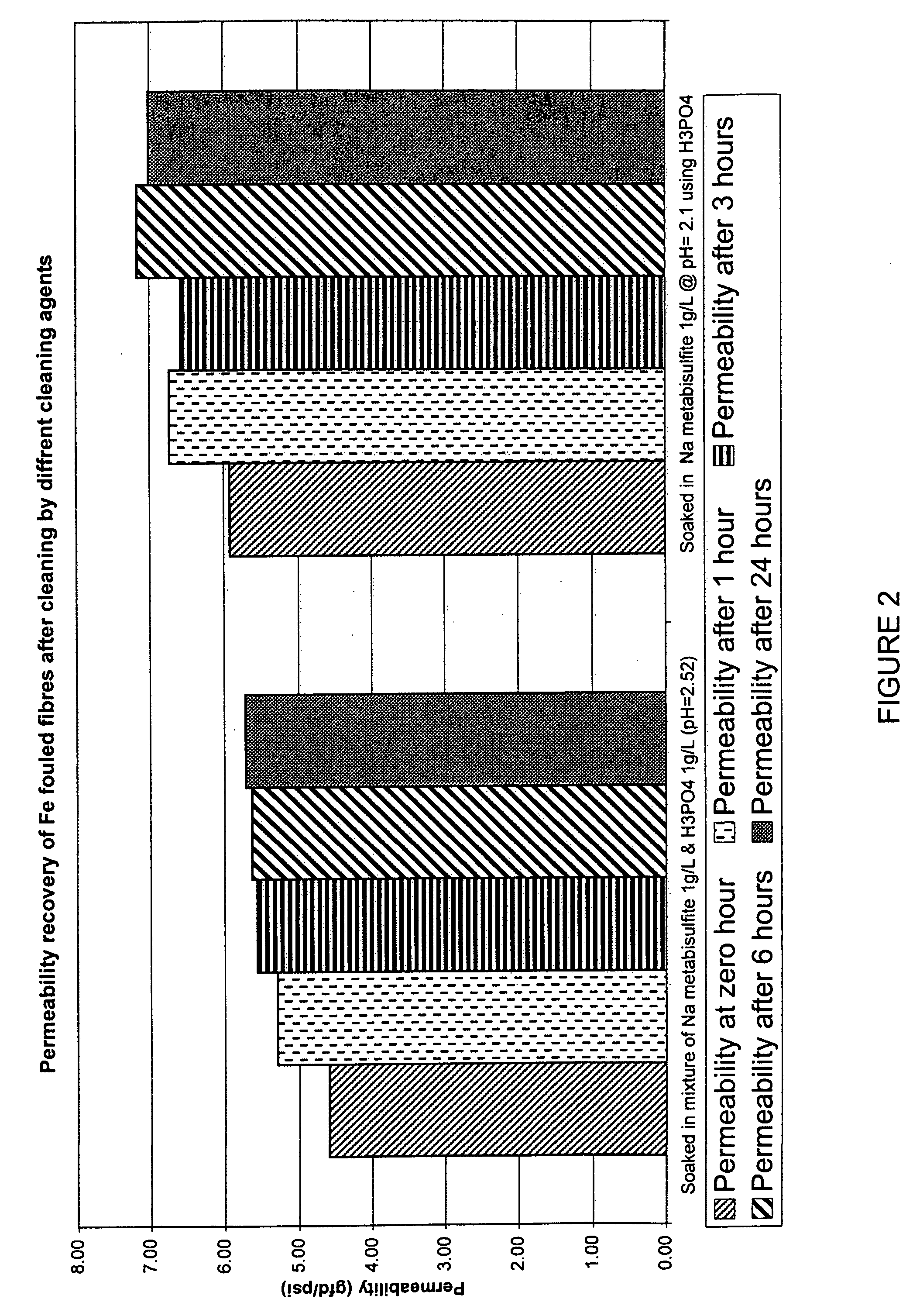
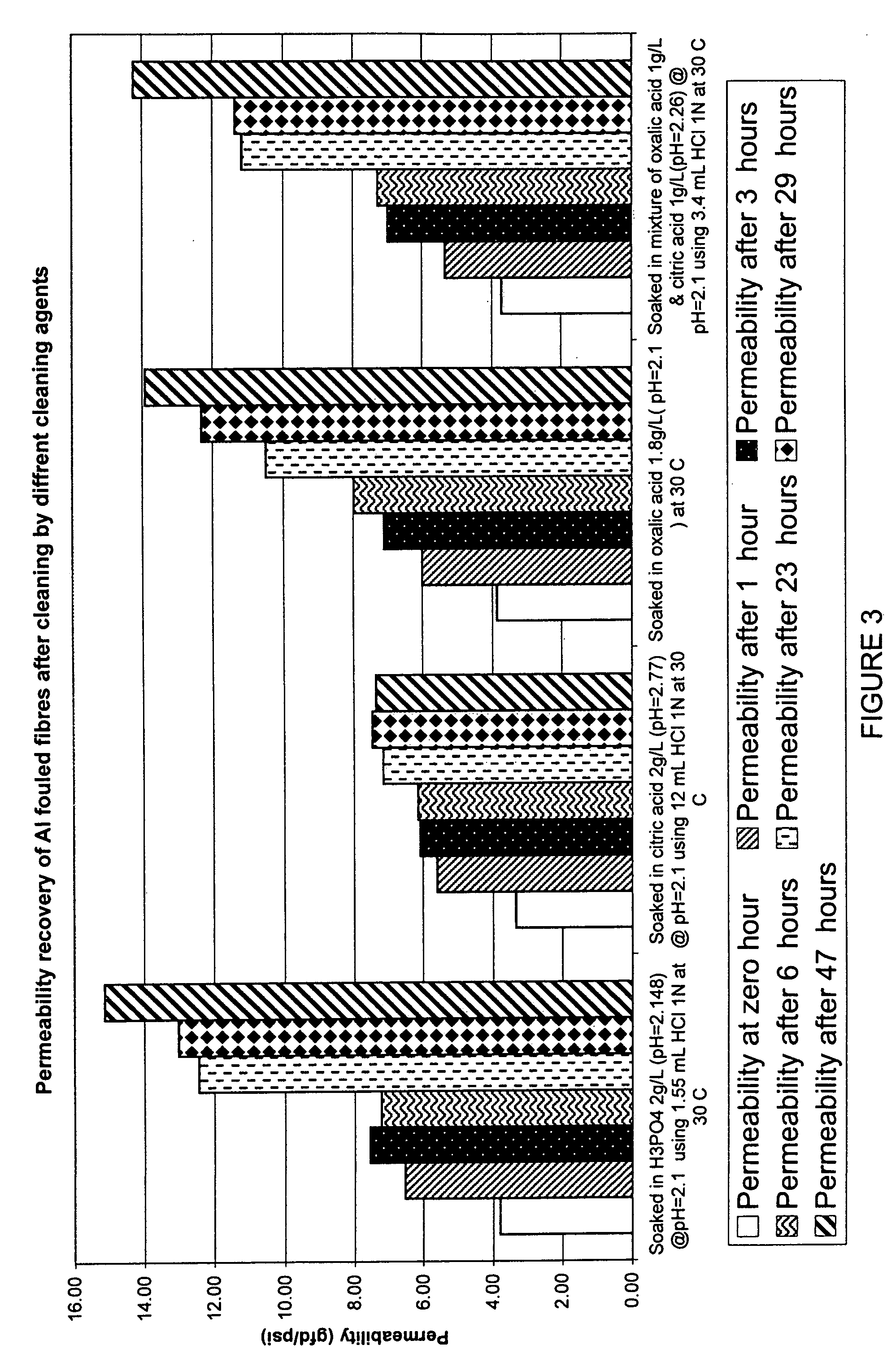
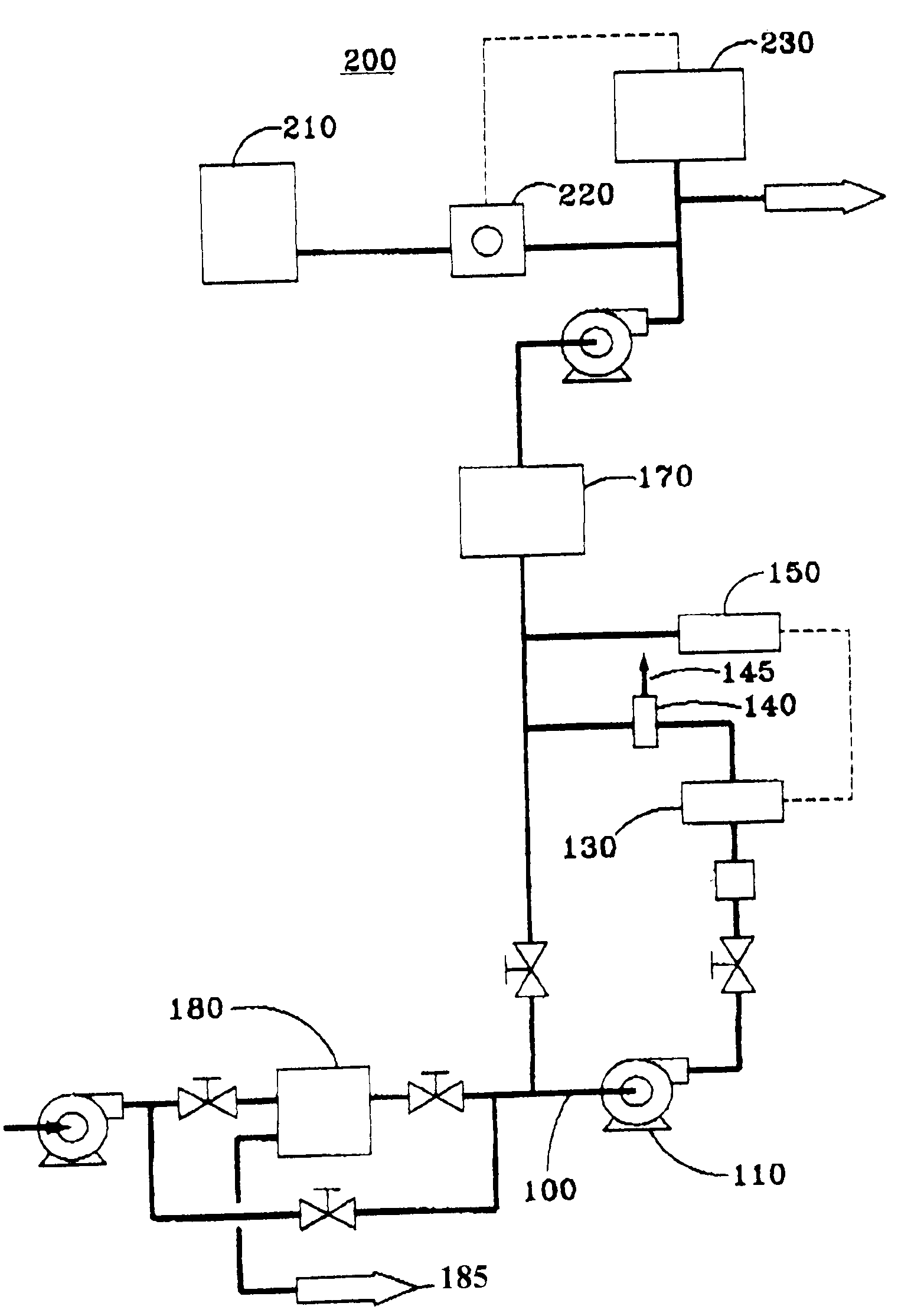
Membranes, for example immersed polymeric ultrafiltration or microfiltration membranes, are cleaned by contacting them with a chemical cleaner comprising one or more of a gluconate, a hydrosulfite, a metabisulfite or an acid, for example phosphoric acid. The membranes may have been exposed to organic or inorganic foulants, some of which may have resulted from pretreatment involving adding coagulants, for example coagulants containing iron or aluminum, to water to be treated. Methods for treating a waste cleaning solution were described.
Owner:SYED MURTUZA ALI +3
System and Process for Treatment and De-halogenation of Ballast Water
A system and process for de-halogenating ballast water before releasing the ballast water from the vessel. In one embodiment, the system comprises a means for measuring the halogen content of the ballast water, a reducing agent source in fluid communication with the ballast water, and a means for controlling the amount of reducing agent supplied to the ballast water. In one aspect, the means for measuring the halogen content comprises one or more oxidation / reduction potential analyzers. In another embodiment, the system comprises one or more hypochlorite electrolytic cells for generating hypochlorite to treat the ballast water.One embodiment of the process for de-halogenating ballast water comprises measuring the oxidation / reduction potential of the ballast water and adding one or more reducing agents to the ballast water to de-halogenate the ballast water in response to the measured oxidation / reduction potential. In one aspect, the oxidation / reduction potential is modulated so that excess reducing agent is present in the ballast water.
Owner:DE NORA WATER TECH
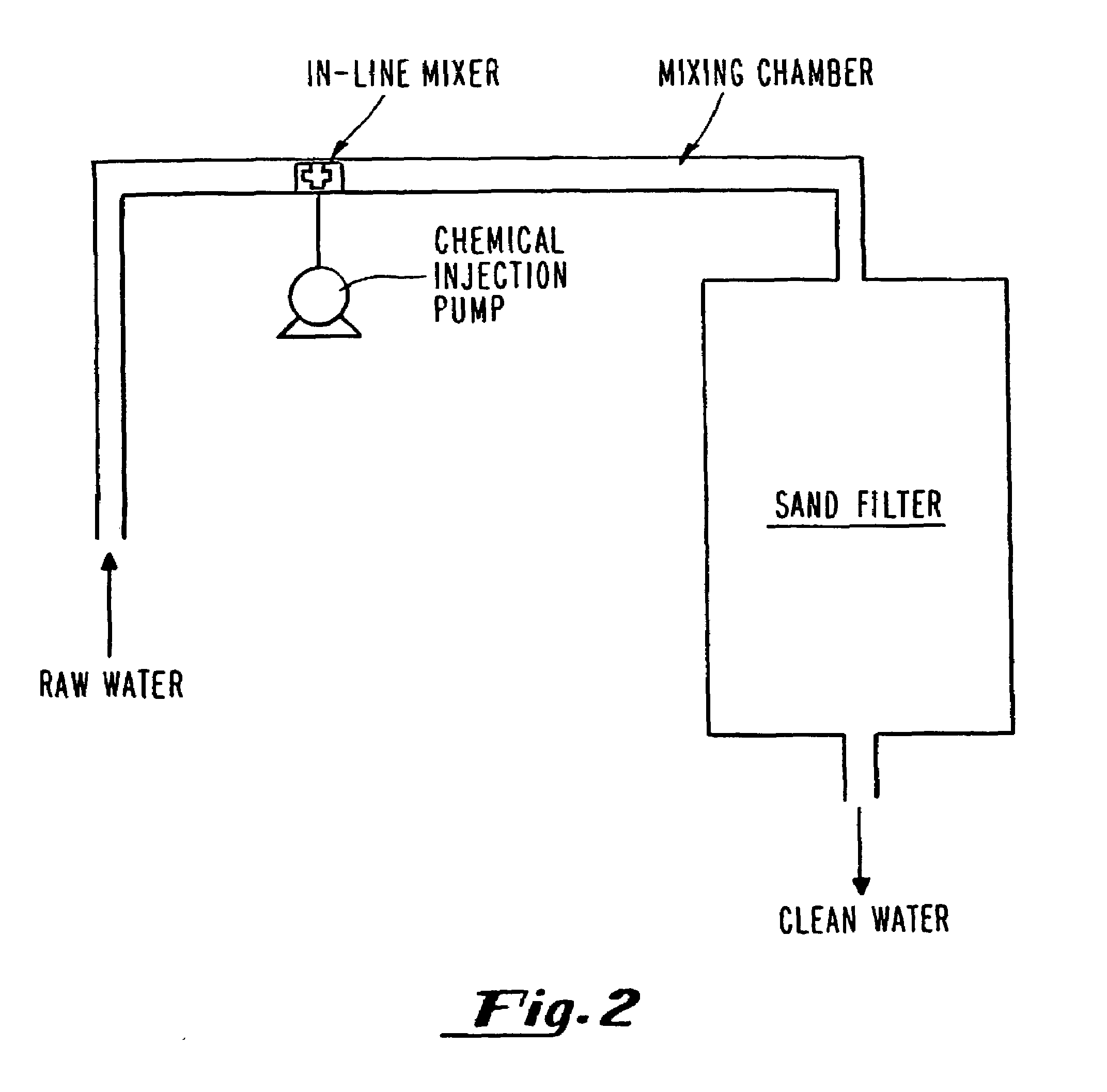
Iron powder and sand filtration process for treatment of water contaminated with heavy metals and organic compounds
InactiveUS6942807B1Improve efficiencyGood removal effectSolid sorbent liquid separationSedimentation separationIron powderFiltration
A water filtration device (3) and method which removes heavy metals and organic compounds from raw water is provided.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Reactive formulations for a neutralization of toxic industrial chemicals
InactiveUS7125497B1Efficiently neutralizedHydrogen peroxideLiquid degasificationBoron trichlorideMalathion
Decontamination formulations for neutralization of toxic industrial chemicals, and methods of making and using same. The formulations are effective for neutralizing malathion, hydrogen cyanide, sodium cyanide, butyl isocyanate, carbon disulfide, phosgene gas, capsaicin in commercial pepper spray, chlorine gas, anhydrous ammonia gas; and may be effective at neutralizing hydrogen sulfide, sulfur dioxide, formaldehyde, ethylene oxide, methyl bromide, boron trichloride, fluorine, tetraethyl pyrophosphate, phosphorous trichloride, arsine, and tungsten hexafluoride.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Carbon material loaded nano zero valence metal catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103191742AGood dispersionImprove stabilityWater contaminantsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActivated carbonPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a carbon material loaded nano zero valence metal catalyst which comprises a nano zero valence metal and a carbon material, wherein the nano zero valence metal is uniformly dispersed in the carbon material; the loading quantity of the nano zero valence metal is 5-15mg / g; the nano zero valence metal is iron, copper, zinc or nickel; and the carbon material is a carbon nano tube, graphene or nano activated carbon. The invention further discloses the preparation and an allocation and application of the catalyst. The nano zero valence metal is loaded to the carbon material, so that the agglomeration of the zero valence metal is prevented, the stability of the catalyst is improved, and the specific surface area of the catalyst is remarkably increased; the catalyst is high efficient, cheap and stable in performance; a chlorine-containing organic pollutant can be rapidly and efficiently absorbed and enriched; and meanwhile the excellent electronic transmission capability of the nano carbon material can greatly accelerate the catalytic degradation speed of the pollutant, so that the pollutant can be more rapidly and effectively removed, so that the carbon material loaded nano zero valence metal catalyst is safe and economical.
Owner:济南市供排水监测中心
Method of sterilizing and initiating a scavenging reaction in an article
InactiveUS6875400B2Effective sterilizationScale removal and water softeningPackage sterilisationScavengerAlternative methods
A method includes providing an article including an oxygen scavenger; forming the article into a container; placing an oxygen sensitive product into the container; and exposing the container to actinic radiation at a dosage effective to sterilize the container, and trigger the oxygen scavenger in the article. Alternative methods are also disclosed. A package includes a container, the container including an activated oxygen scavenger; wherein the container is sterilized; and wherein an oxygen sensitive product is disposed in the container.
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
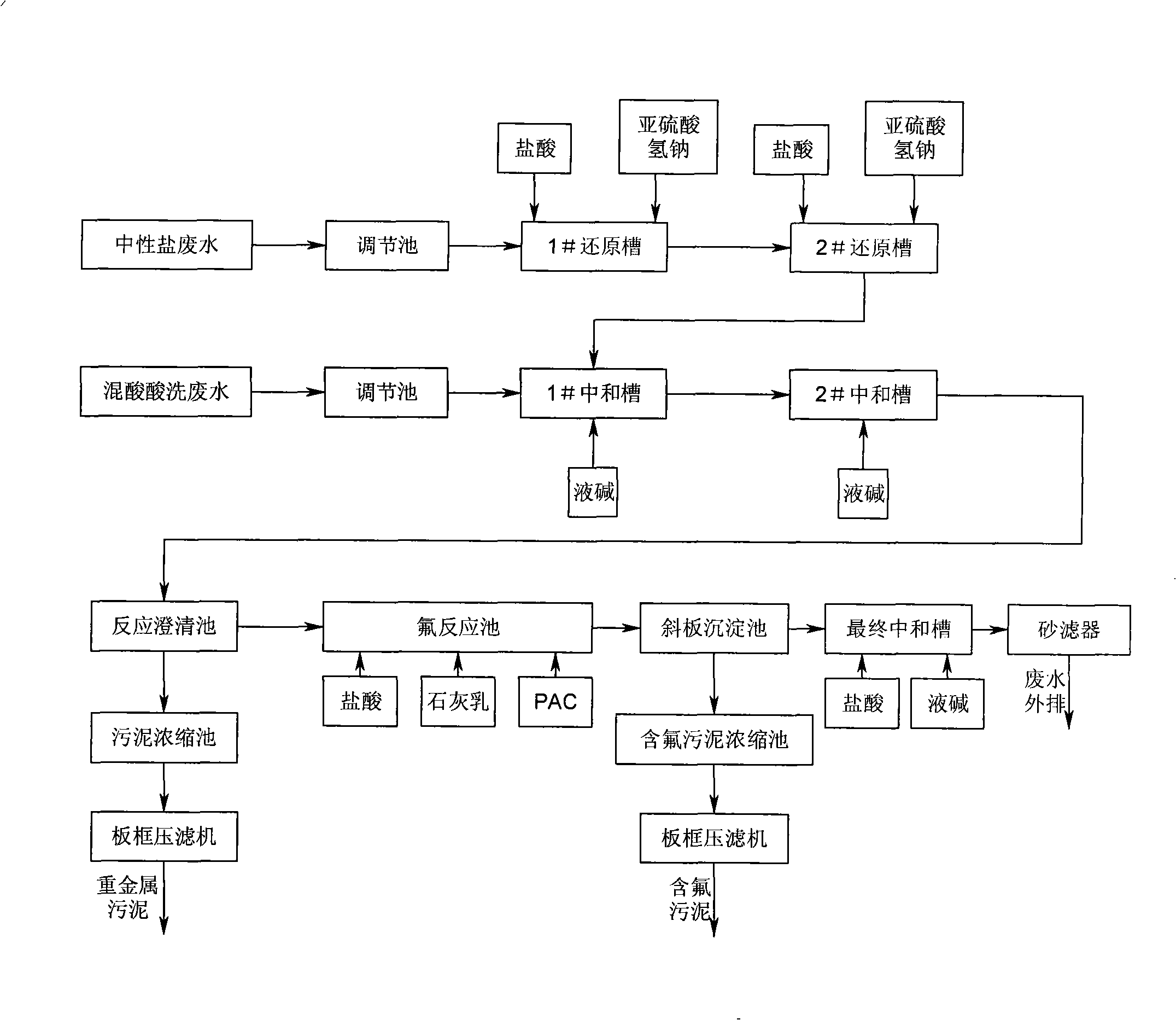
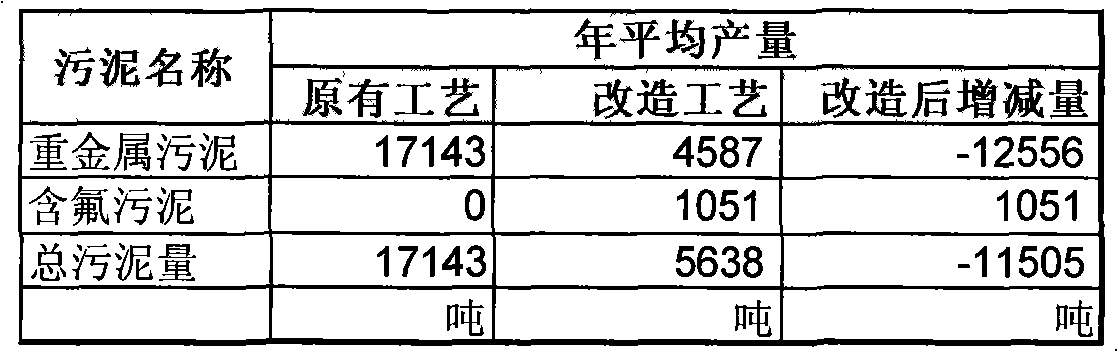
Processing method for stainless steel acid cleaning waste water and liquid
InactiveCN101269889AMeet emission compliance requirementsMeet compliance requirementsSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningIron oxides/hydroxidesLiquid wasteSludge
The invention relates to a processing method of stainless steel pickling waste liquid, which is characterized in that the processing method includes the steps that: neutral salt wastewater flows into a neutral reduction cell, and mixed acid pickling waste waters flow into a neutralizing tank; reducing agent is added into the neutral reduction cell, and then the reduced wastewater liquid is put into the neutralizing tank and is mixed with the adjusted mixed acid pickling waste waters, and liquid alkali is added into the neutralizing tank; the separated clear waste liquid removes fluorin ions in a settlement tank; neutralizing liquid is added into a final neutralizing tank to cause the pH value of treatment liquid to adjust to be neutralized wastewater liquid which passes through a sand filter to be discharged. The processing method has the advantages that metal ions and fluorin ions are performed the subsection treatment, and neutralizing agent is changed into the liquid alkali from lime cream, the requirement of reaching the standard of the waste liquid emission is not only achieved, but also the mud quantity produced by a mass of lime cream is greatly reduced, heavy metal mud of a retention pond only contains heavy metal compound, the salts of calcium fluoride and calcium sulphate, etc. are separated from the inclined plate settlement tank during the fluoridation stage, thereby the treatment cost is effectively lowered.
Owner:NINGBO BAOXIN STAINLESS STEEL
Cellulosic composite
Provided is a cellulosic composite comprised of cellulosic material and a binder. The binder comprises a reaction product of an amine and a reactant in the form of an amino-amide intermediate. To the amino-amide is added an aldehyde or ketone to form a curable binder composition. The composition when mixed with cellulosic material and cured forms a cellulosic composite.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE CORP
System and method for treatment of ballast water
ActiveUS20060113257A1Prevent outbreakLiquid separation by electricityAuxillariesHypochloriteHydrogen
A system and method for treating ballast water within an ocean going vessel by generating hypochlorite for treating the ballast water. The system comprises one or more hypochlorite electrolytic cells in fluid communication with a stream of ballast water. A chlorine analyzer is positioned downstream from the electrolytic cells to determine the chlorine concentration of the treated ballast water. A hydrogen separator is connected to the hypochlorite electrolytic cells for venting hydrogen. In the method of this invention, water is taken aboard the ship for ballast in one port. A treatment stream is separated from the ballast water stream and piped to hypochlorite electrolytic cells. Hypochlorite is generated into the treatment stream and the hydrogen byproduct is separated by the hydrogen separators. The treatment stream is then reintroduced to the ballast water to eliminate marine species and pathogenic bacteria from ballast water. The ballast water undergoes de-chlorination prior to being discharged into a new port.
Owner:DE NORA WATER TECH
Treatment of swimming pool water
InactiveUS6146539AEasy to controlReduction of unpleasant chloraminesSeparation devicesSedimentation separationAlgal growthPhosphate
Methods and compositions are disclosed for treating swimming pool waters in order to remove one or more nutrients necessary for algal growth and to accelerate the breakdown of objectionable chloramines within chlorinated pool waters. The target nutrients of preference are those containing phosphorus or nitrogen. Phosphorus nutrients are preferably removed by ion-exchange with finely divided lanthanum carbonate, or by direct precipitation in the pool with liquid lanthanum chloride. Nitrogen nutrients (including, in particular, chloramines) may be removed (possibly with the aid of catalysts and in separate reactors). The same reagents used to scavenge phosphates are useful in this regard, the nitrogen being released from the pool water as a nitrogenous gas. To allow the fine lanthanum carbonates to be conveniently handled in the pool environment, they may be linked to larger carrier particles, such as those of diatomaceous earth, or they may be embedded within porous beads formed from polymers or gels. In this form the reagent can be either added to, retained within and backwashed from pool filters, or added directly to pools (with or without a flocculating agent) and sucked to waste after settling. A variety of formulations for these purposes is disclosed.
Owner:NATURAL CHEM
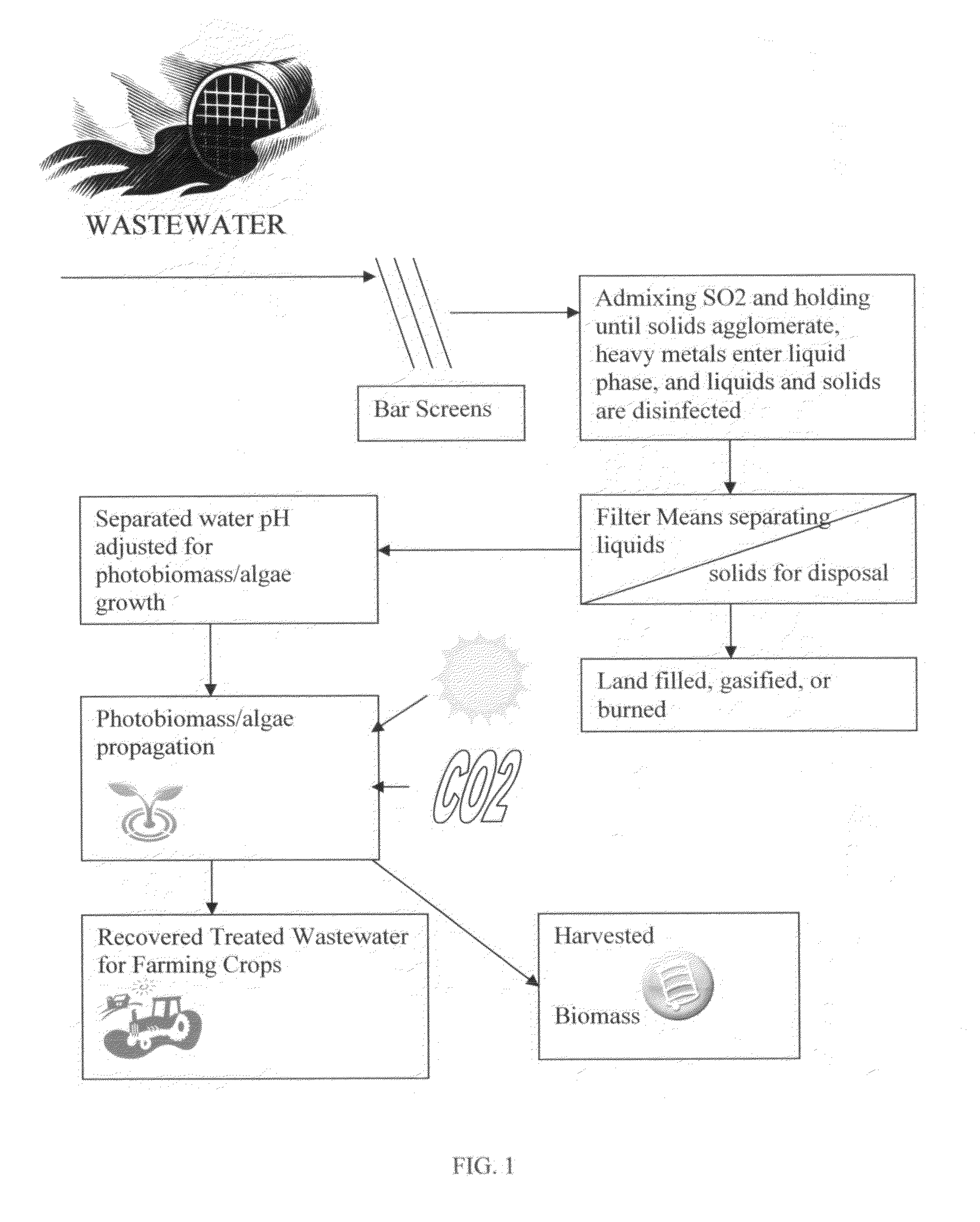
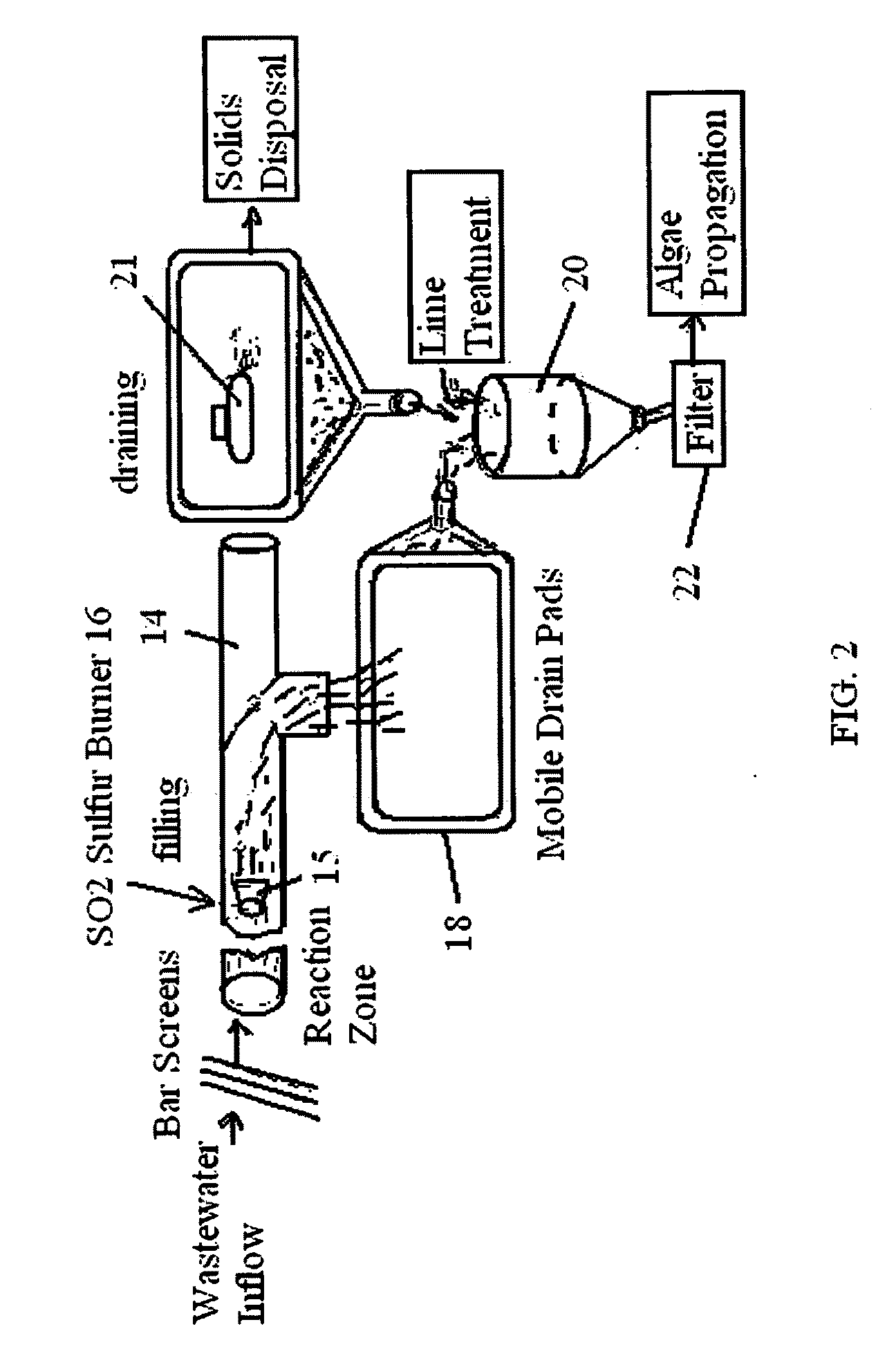
Wastewater photo biomass/algae treatment method
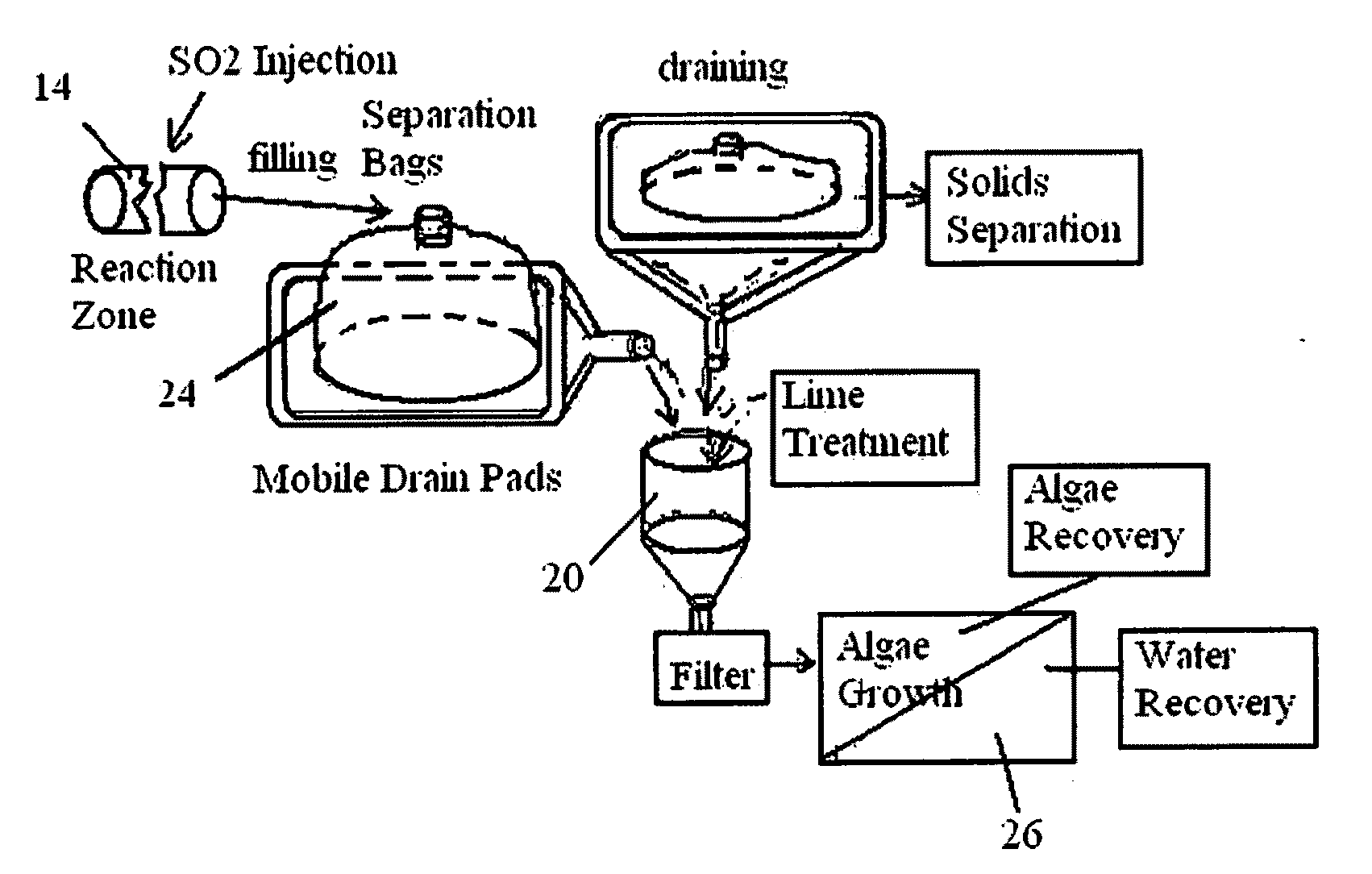
ActiveUS20090294354A1Minimizing stream eutrophicationPrevent eutrophicationUnicellular algaeEnergy based wastewater treatmentCarbon creditBiofuel feedstock
A treatment method for wastewater employing sulfur dioxide and lime chemical dewatering technology in conjunction with an environmental photo biomass / algae biological treatment system growing photo biomass / algae to reduce dissolved solids, heavy metals, and ammonia in the wastewater to produce recovered treated wastewater for vegetation consumption, biofuel feedstock, and biofuel and carbon credits.
Owner:EARTH RENAISSANCE TECH
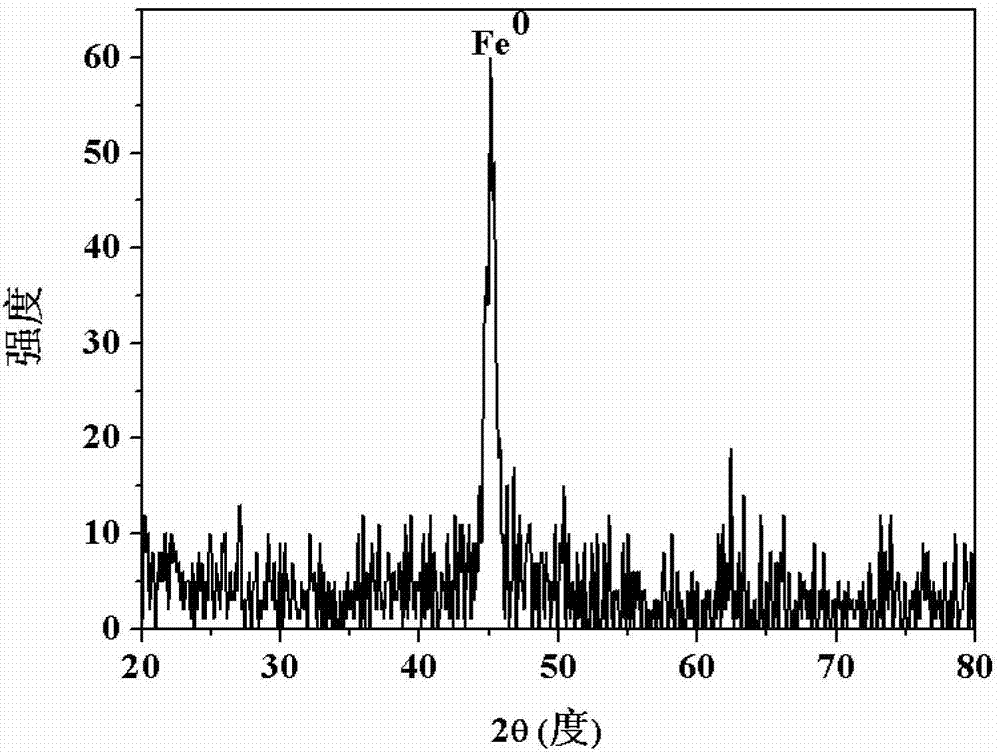
Nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as carrier, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102923835AReduce aggregationHigh activityWater/sewage treatment by sorptionWater/sewage treatment by reductionPotassium borohydrideMontmorillonite
The invention provides nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as a carrier, and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the steps of dissolving ferrous sulfate, adding soluble starch and montmorillonite particles into the ferrous sulfate solution in proportion, and obtaining mixed liquid; stirring after performing ultrasound treatment to the obtained mixed liquid, and obtaining precursor solution; adding the obtained precursor solution into sodium borohydride or potassium borohydride solution in proportion under the conditions of continuous stirring, continuing stirring for a period of time, performing solid-liquid separation, and obtaining the solid which is the nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as the carrier. According to the prepared nano zero-valent iron with montmorillonite serving as the carrier, interlayer and surface spaces of montmorillonite can be fully utilized, the activity and the stability are high, polymerization of the nano zero-valent iron can be reduced, and the nano zero-valent iron has remarkable effect when used for treating waste water containing hexavalent chromium.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Anaerobic zero-valent iron sewage treatment method
ActiveCN101624250AImprove responseAvoid formingWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesAnaerobic reactorDyeing wastewater
The invention relates to an anaerobic zero-valent iron sewage treatment method, belonging to the sewage treatment technical field. The anaerobic zero-valent iron sewage treatment places zero-valent iron in an anaerobic reactor and utilizes the environmental conditions of the anaerobic isolated air to largely reduce the formation rate of the rust of zero-valent iron and avoid the formation of hardening; meanwhile, the method uses the reducing action of metal iron to increase the anaerobic reductive atmosphere, balance the pH and increase the effect of the anaerobic organism. A circulating pump is adopted for sewage backflow so as to increase the overflow load of an iron / activated carbon layer and the reaction effect of zero-valent iron, improve the fluidization effect of sludge to increase the anaerobic process efficiency. In a sewage treatment system, ferrous iron contained in the discharged sewage is oxidized to Fe(OH)3 with the air and the coagulation generated in the process can further purify the sewage. Long-term experiment research shows that the decolorizing rate of the sewage treatment method for dye wastewater can teach 85%-95%, the COD can be reduced by more than 50% and the biodegradability can be increased to more than 0.3.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
pH-adjusting compositions in water-soluble pouches
InactiveUS20080185347A1Other chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationWater solubleNuclear chemistry
A composition comprising a pre-measured amount of an acid component and an alkaline component in a sealed water-soluble pouch, said composition when contacted with water generating effervescence and neutralizing the pH of the water is disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
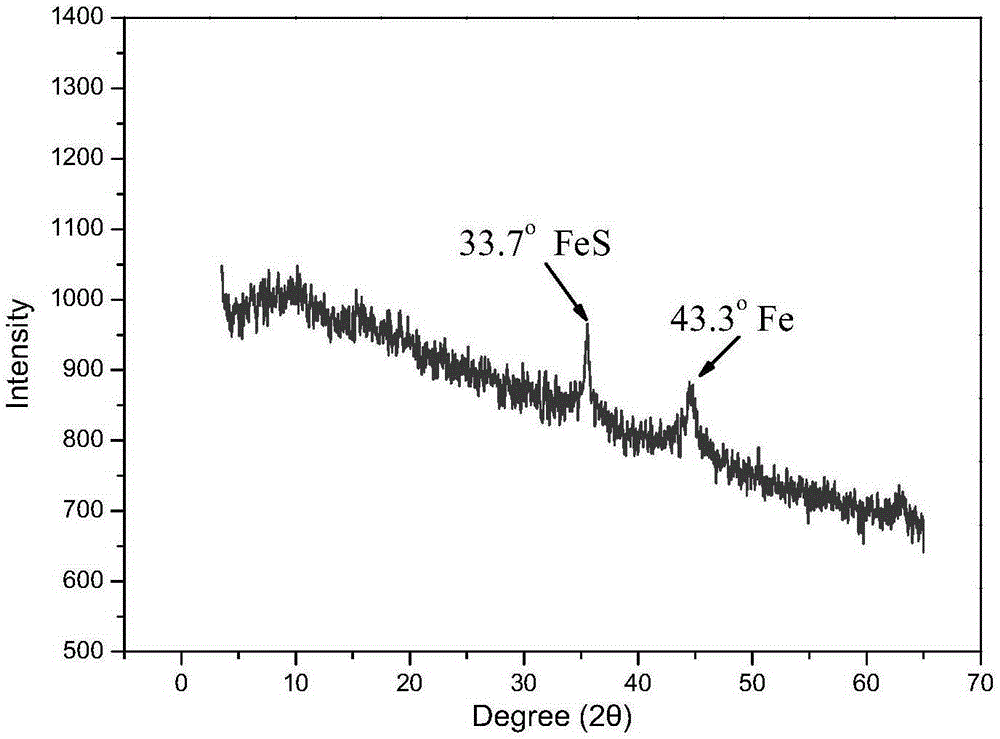
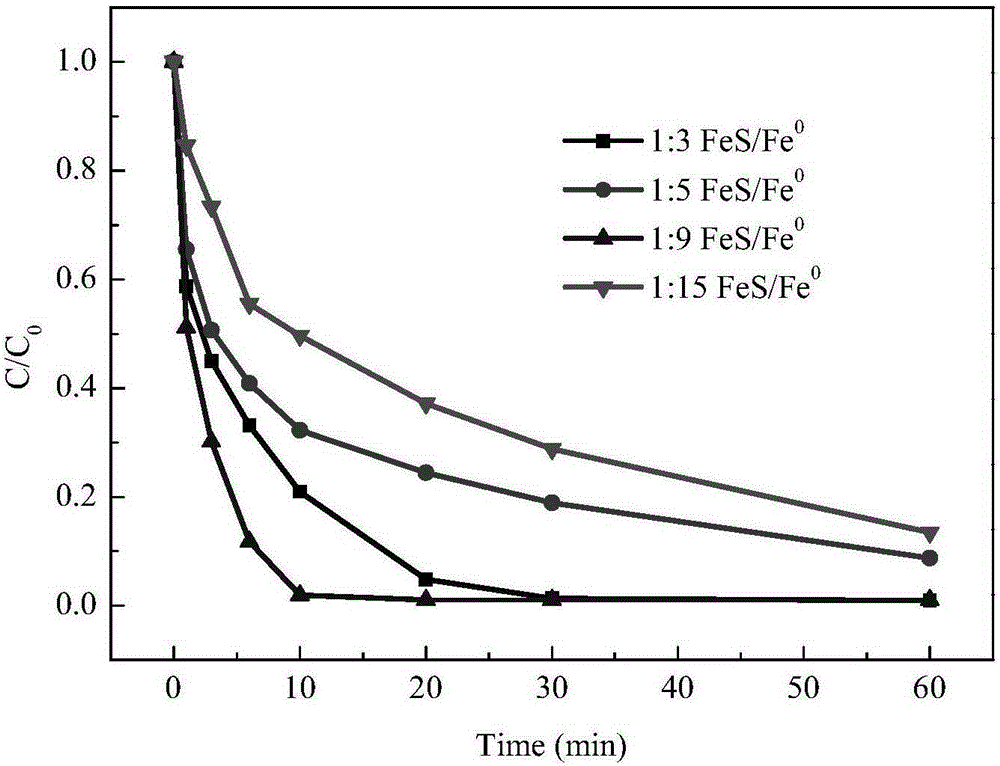
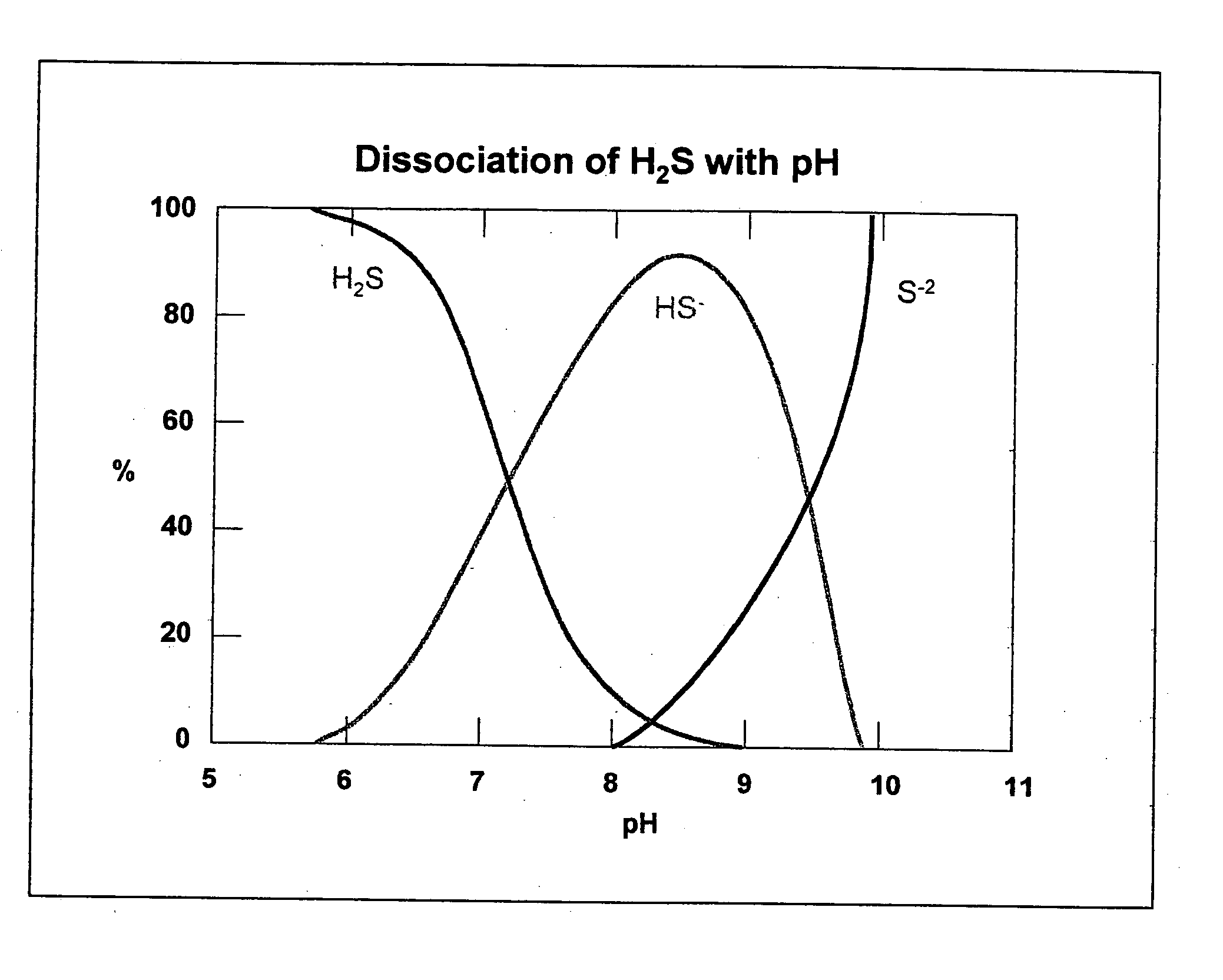
FeS and Fe0 composite and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105174414AEfficient degradationHigh reactivityIron sulfidesWater/sewage treatment by reductionWastewaterSurface water
The invention belongs to the field of chemical materials, and particularly relates to a FeS and Fe0 composite and a preparation method and application thereof. The FeS and Fe0 composite is formed by compositing nano FeS and nano Fe0, the surface of the nano Fe0 is coated with the nano FeS, and the molar ratio of the nano FeS to the nano Fe0 is 2:1 to 15:1. According to the FeS and Fe0 composite and the preparation method and application thereof, the preparation process is simple, convenient, environmentally friendly and feasible, the prepared FeS and Fe0 composite is high in reaction activity, capable of efficiently and rapidly reducing and adsorbing heavy metal ions in waste water within a wider temperature range, a pH value range and a dissolved oxygen content range and further capable of rapidly and efficiently activating hydrogen peroxide and persulfate to make a system generate hydroxyl free radicals and sulfate free radicals to degrade and mineralize organic pollutants, and therefore the FeS and Fe0 composite can be widely applied to degradation of the organic pollutants in surface water and underground water.
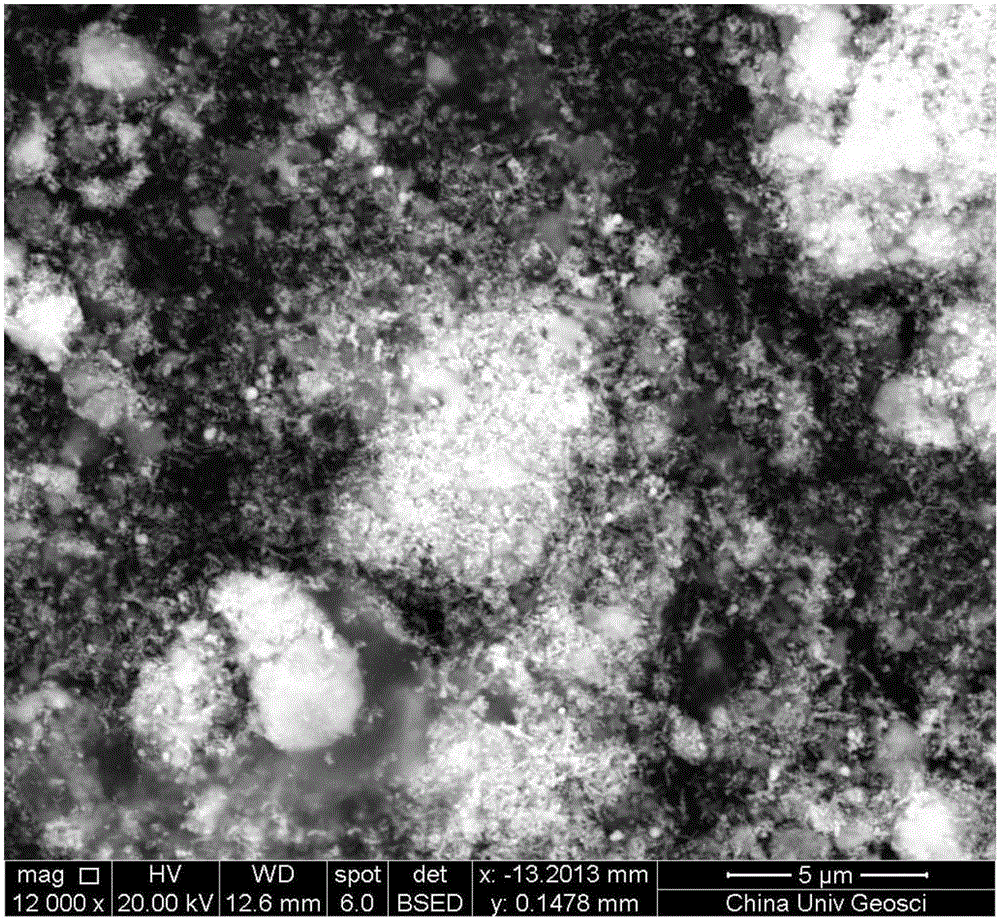
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Composition for odor control
ActiveUS20050115895A1Promote growthInhibition productionSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsSpecific enzymeWaste stream
A synergistic composition is provided for controlling odor from waste products. The composition comprises a combination of nitrate salt, sulfide-consuming compound, pH-elevating compound, sulfide-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria, and sulfide-oxidizing enzyme. The method includes adding a sufficient amount of the composition to a waste stream to provide sufficient sulfide-consuming compound to effect immediate removal of sulfide. The composition incorporates a pH elevating compound, which both decreases the amount of gaseous H2S and puts the aqueous phase into a pH range where naturally occurring bacteria can more easily metabolize the sulfide. The composition also includes one or more nitrate salts which will accomplish longer term prevention of odors. Specific bacteria are incorporated into the formulation to insure that the nitrate has the right type and amount of bacteria present to prevent formation of and / or consume sulfide. Specific enzymes are incorporated into the formulation to promote oxidation of sulfide.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Composition for the production of chlorine dioxide using non-iodo interhalides or polyhalides and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS7087190B2Reduce microbial countQuick buildBiocideLiquid degasificationChlorine dioxideCHLORITE ION
A composition for the generation of chlorine dioxide including at least one non-iodo interhalide, polyhalide or salt thereof having the formulaBrmClnFoXpwherein m=0–3, n=0–4, o=0–3, p=0–2, X is a cationic moiety and with the provisos that m+n+o cannot be zero; if m+n+p<2, or mixtures thereof, and at least one source of chlorite ions.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Methods for the on-line, on-demand preparation of sterile, water-for-injection grade water
InactiveUS6745903B2Low costLower Level RequirementsOrganic anion exchangersDialysis systemsSpecific adsorptionFiltration
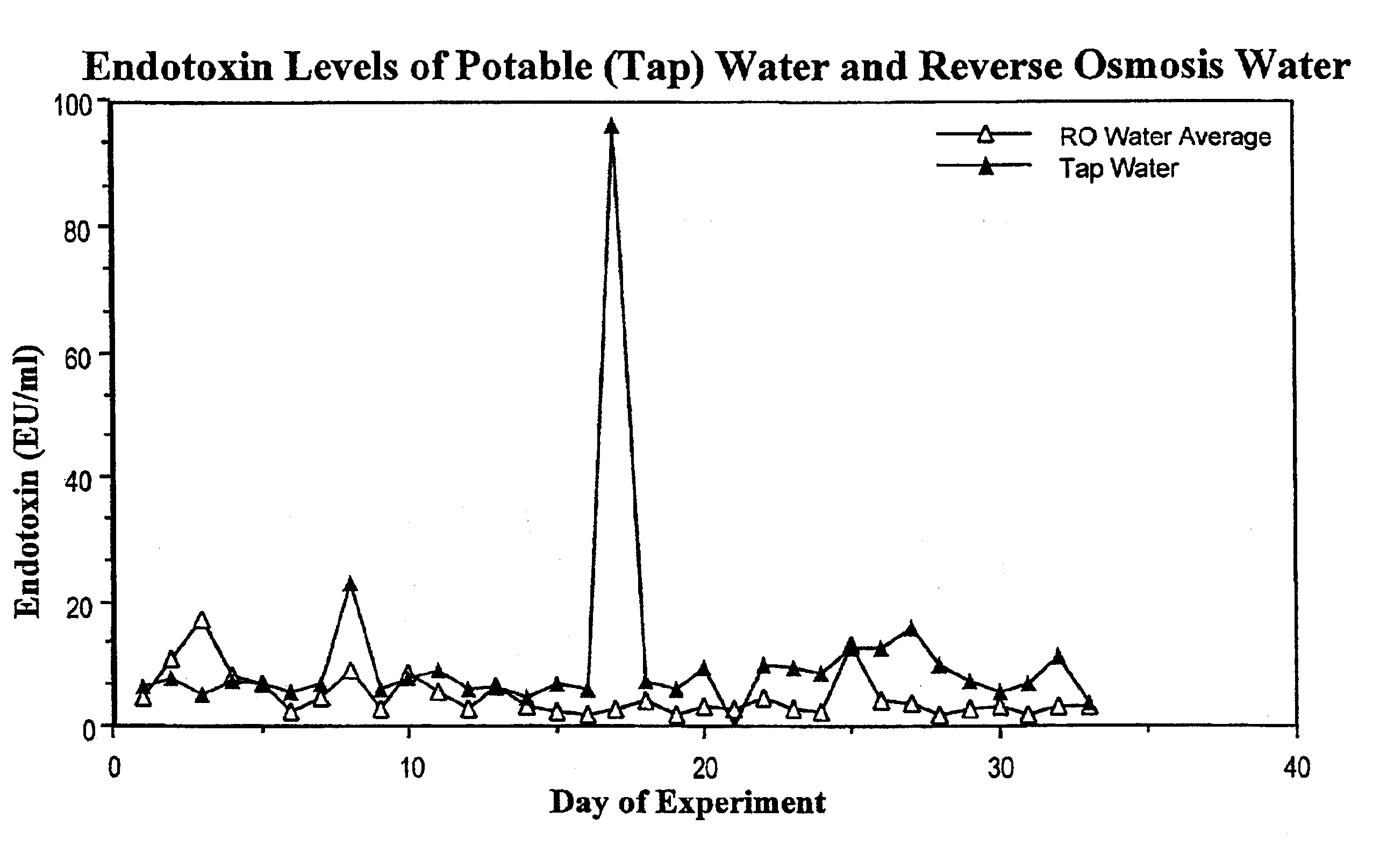
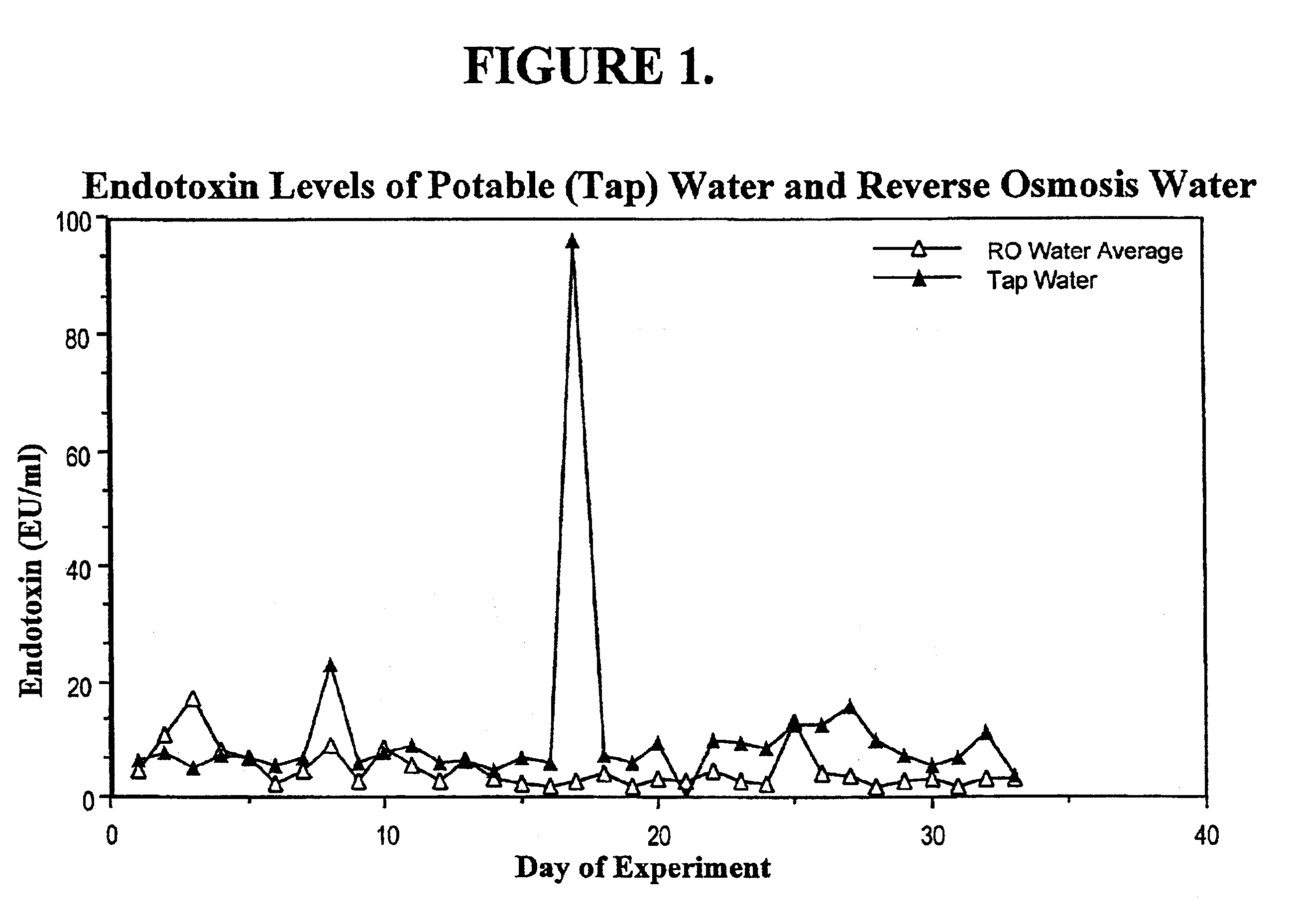
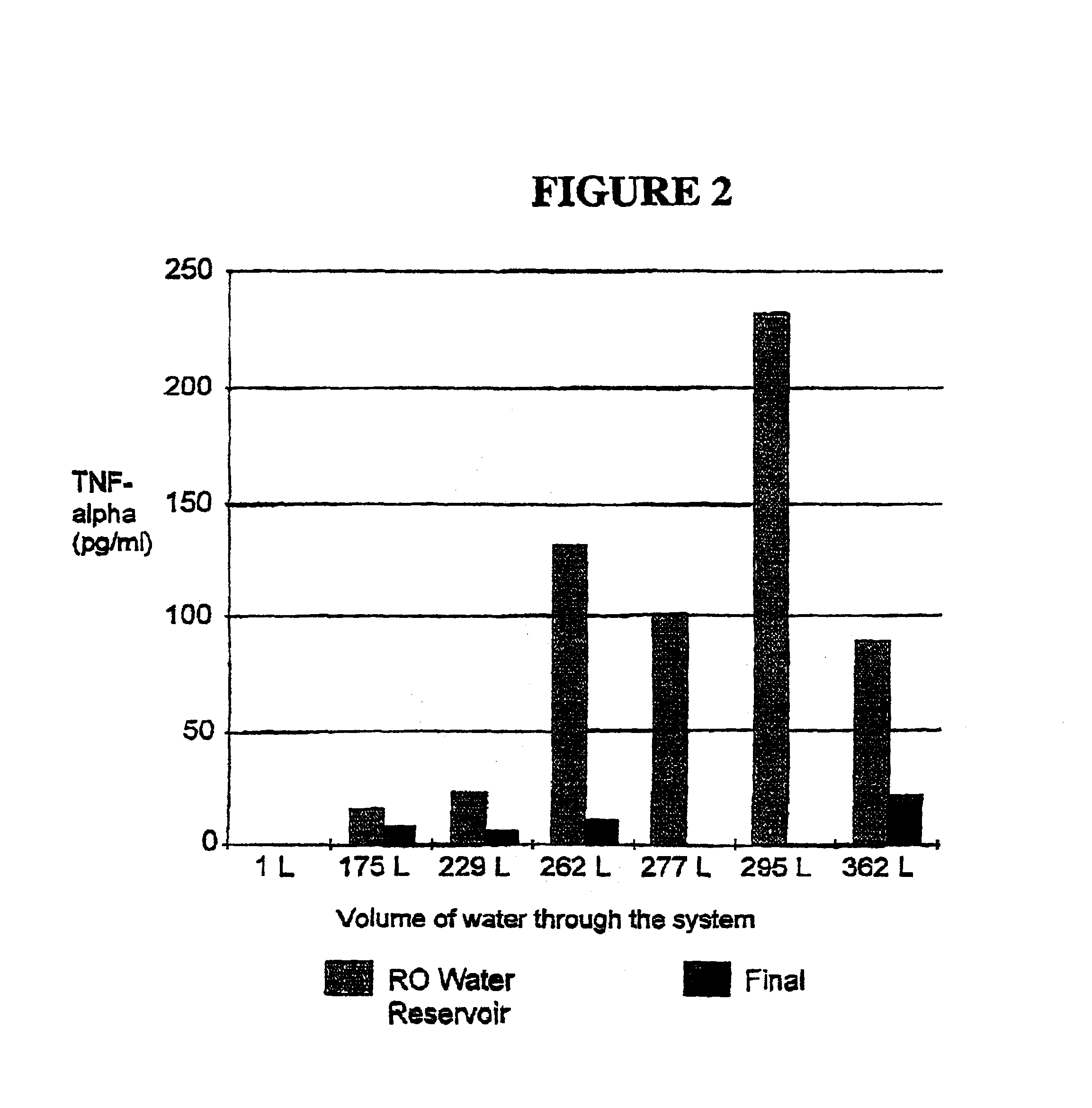
A new method is described to produce large volumes of low cost sterile, Water-for-Injection (WFI) grade water on-line, on-demand from potable water in order to meet the needs of dialysis therapies and other biological applications for sterile, injectable grade water. The source water is processed by a combination of membrane and column chromatographic methods including reverse osmosis, chemical sterilization, reduction of iodine sterilant to iodide, deionization, endotoxin-specific adsorption and polishing filtration in order to reduce contaminant levels below those specified by the US Pharmacopoeia.
Owner:GRANDICS PETER
Nanocomposite materials based on metal oxides having multi-functional properties
InactiveUS20140187413A1Improved gas and vapour, flame retardant, mechanical and thermal propertiesLimit fixationPigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyAntioxidantActive agent
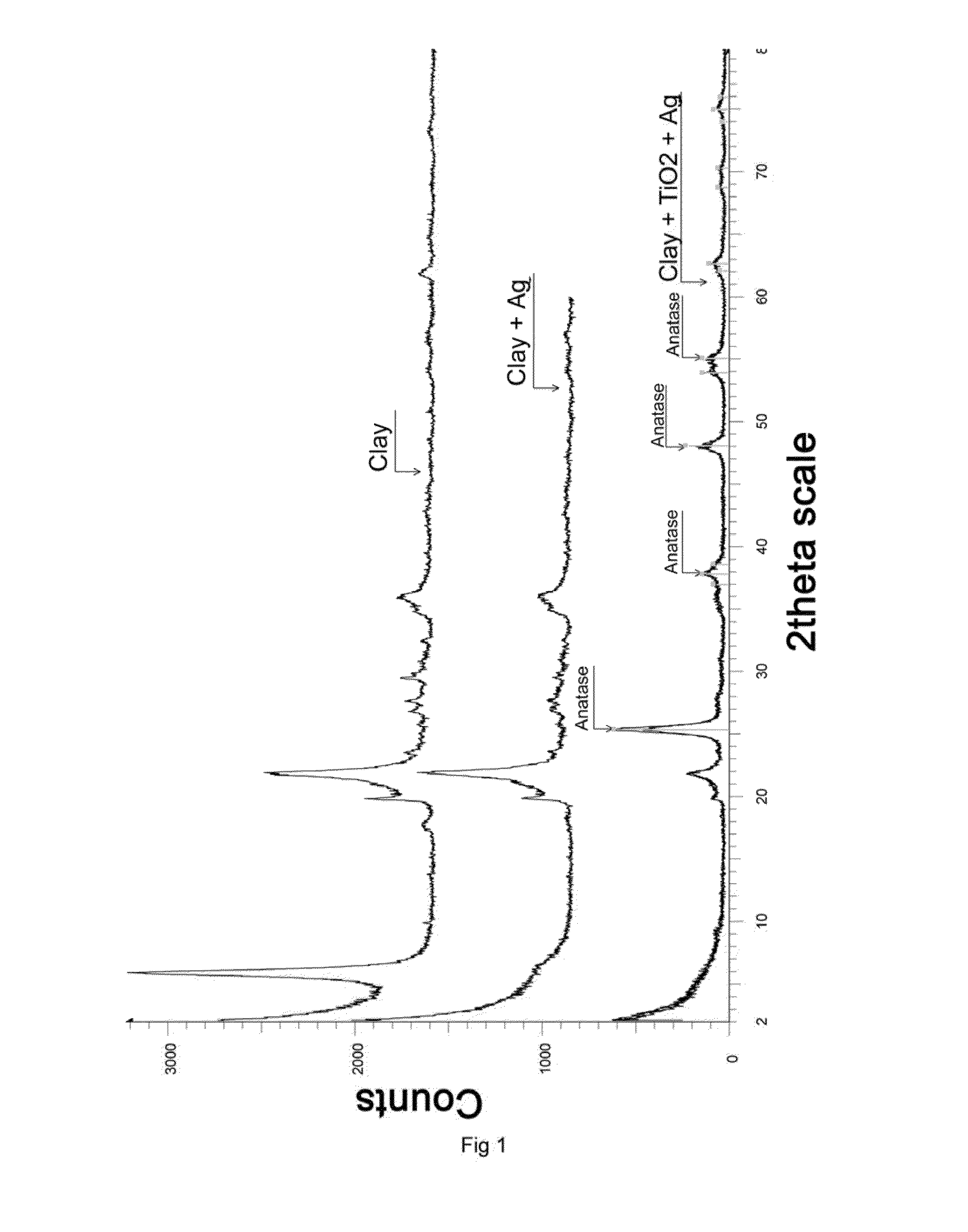
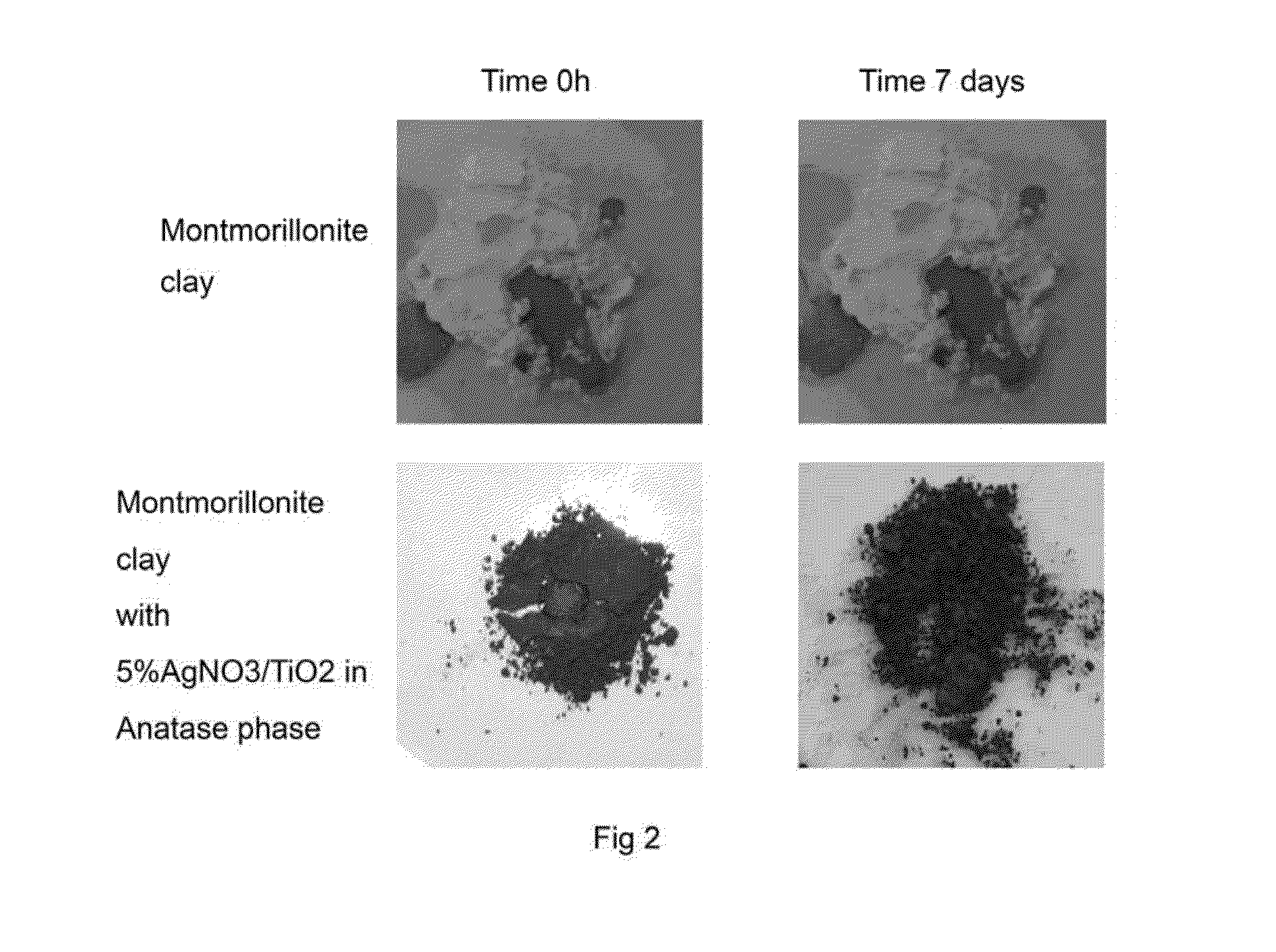
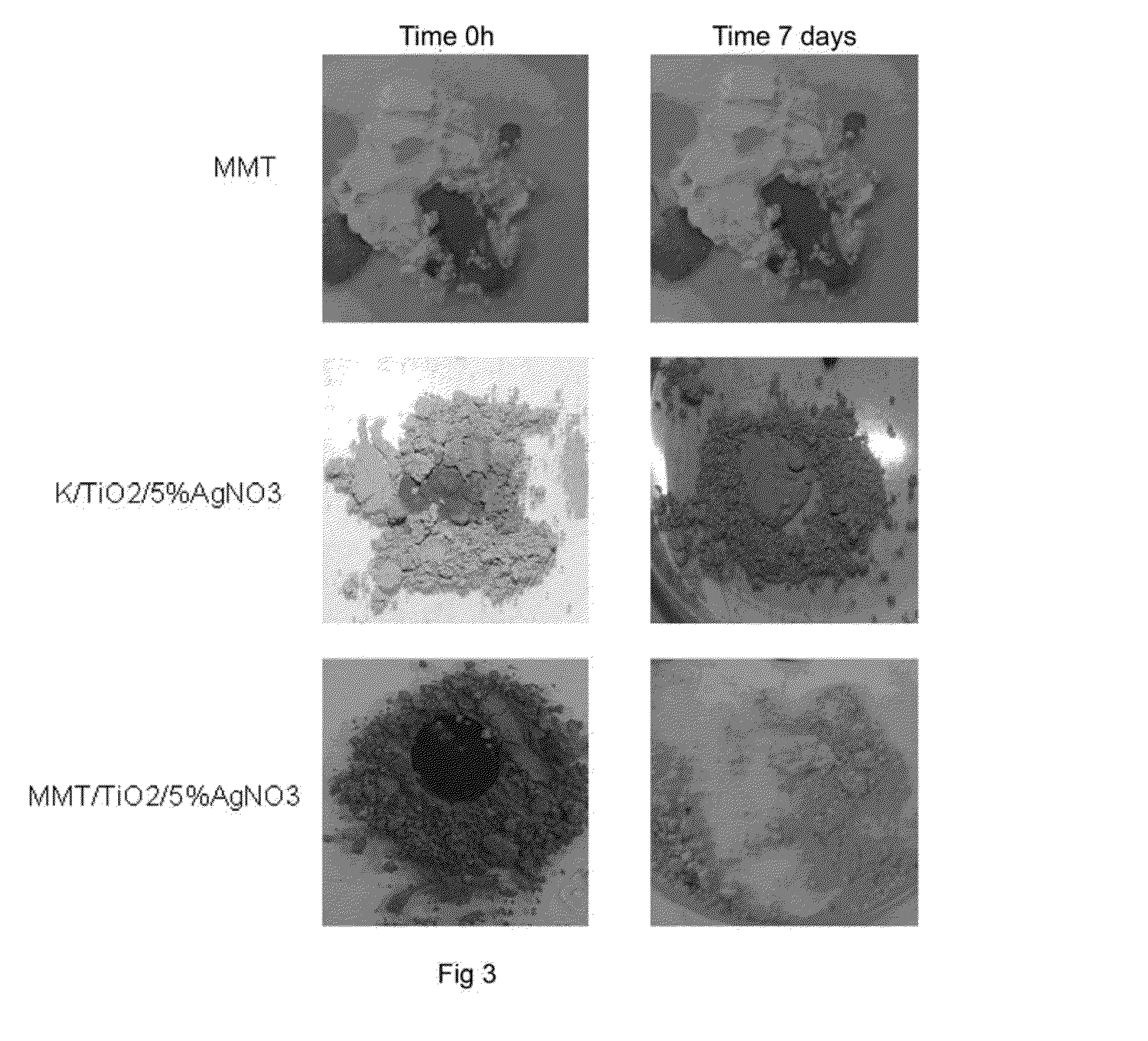
The present invention relates to nanocomposite materials comprising nanoclays as support of metal oxide particles which give the materials multi-functional properties. Said properties are obtained through the formulation of a specific type of additives based on layers of natural and / or synthetic clays which are intercalated with metal oxides with antimicrobial and / or oxygen sequestrating and / or catalytic and / or self-cleaning and / or anti-abrasive capacity; and which may optionally contain other organic, metal, inorganic compounds or combination thereof which may exercise a role of compatibilization and / or dispersion and / or increase in the functionality of the metal oxides and / or providing new functionalities, both passive of physical strengthening and active such as biocide character, antioxidant and chemical-species absorbers.Furthermore, the present invention discloses the use of said materials for multi-sector applications.
Owner:NANOBIOMATTERS RES & DEV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com