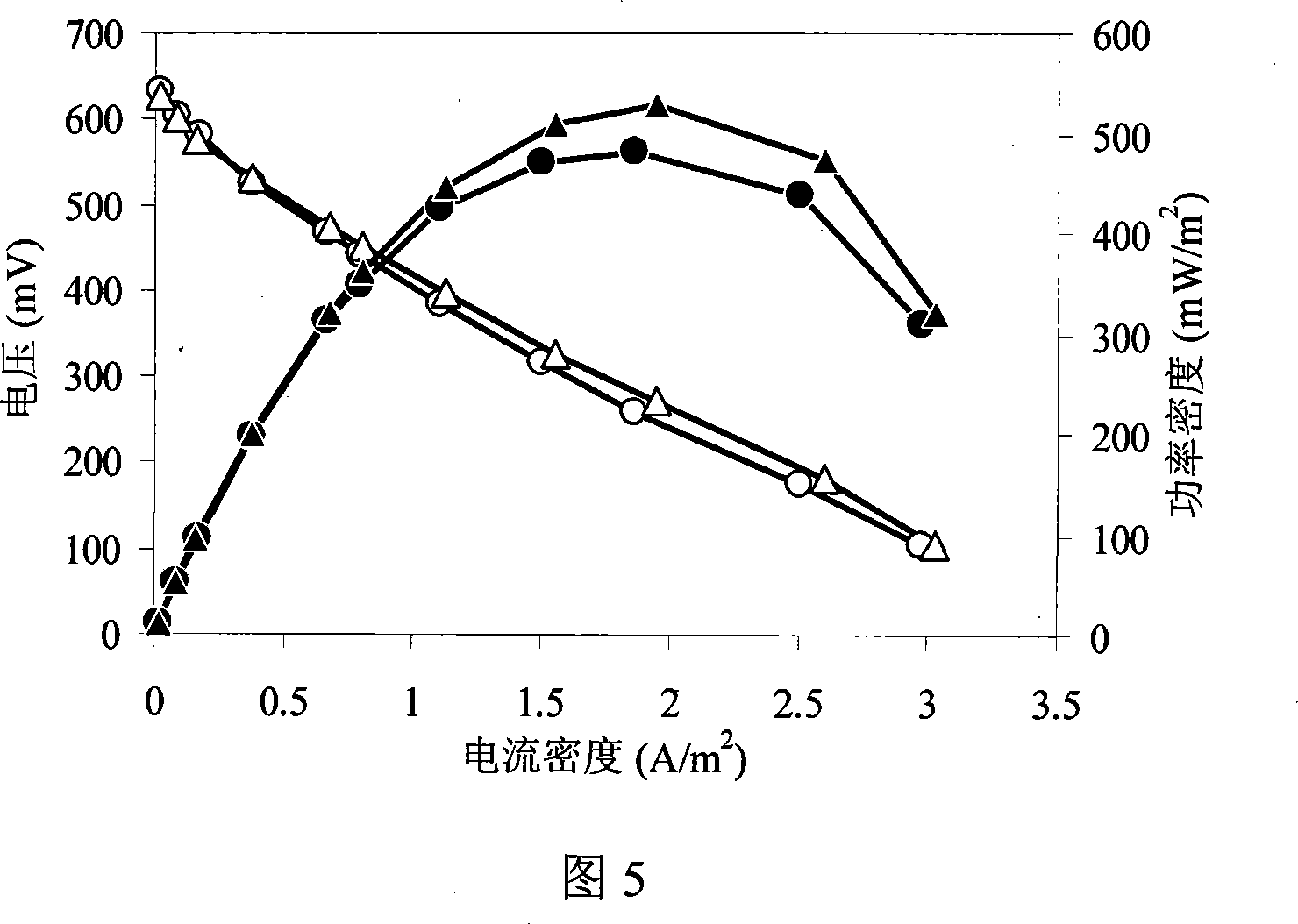
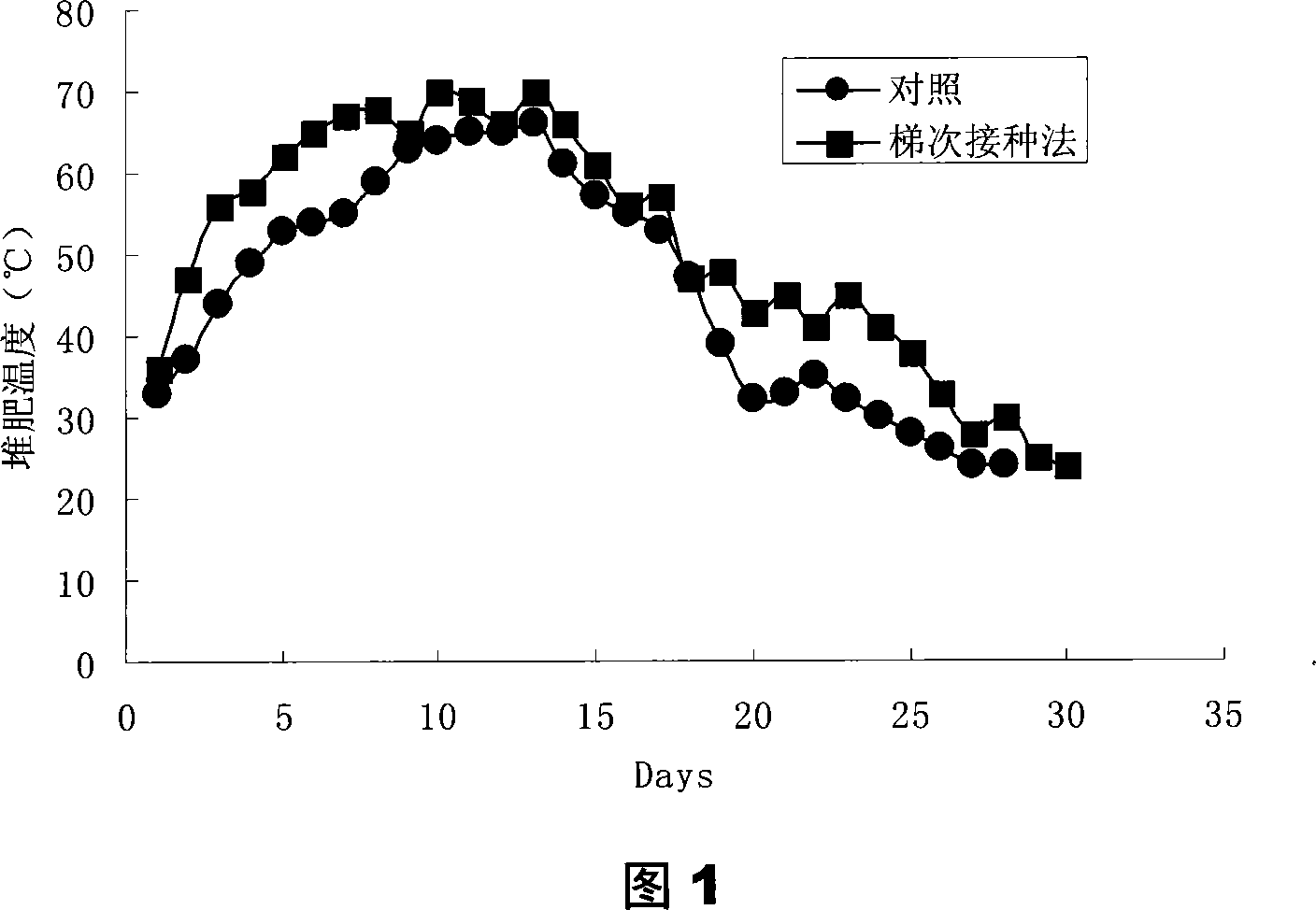
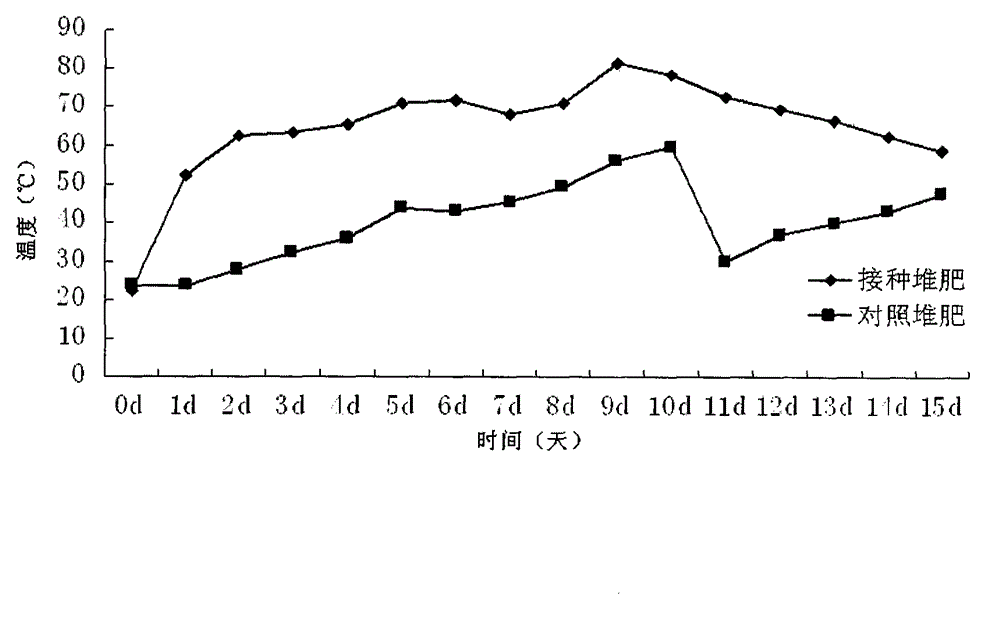
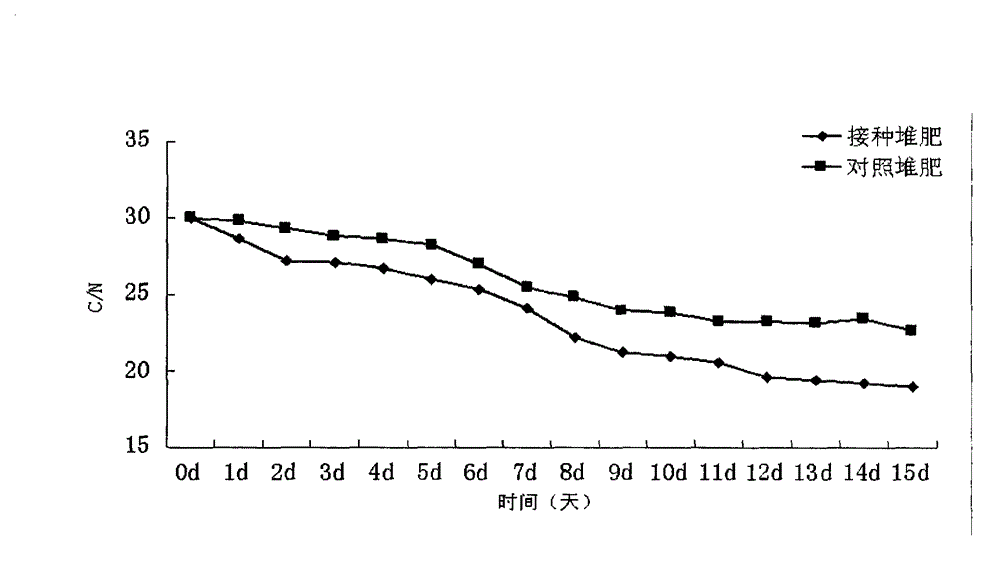
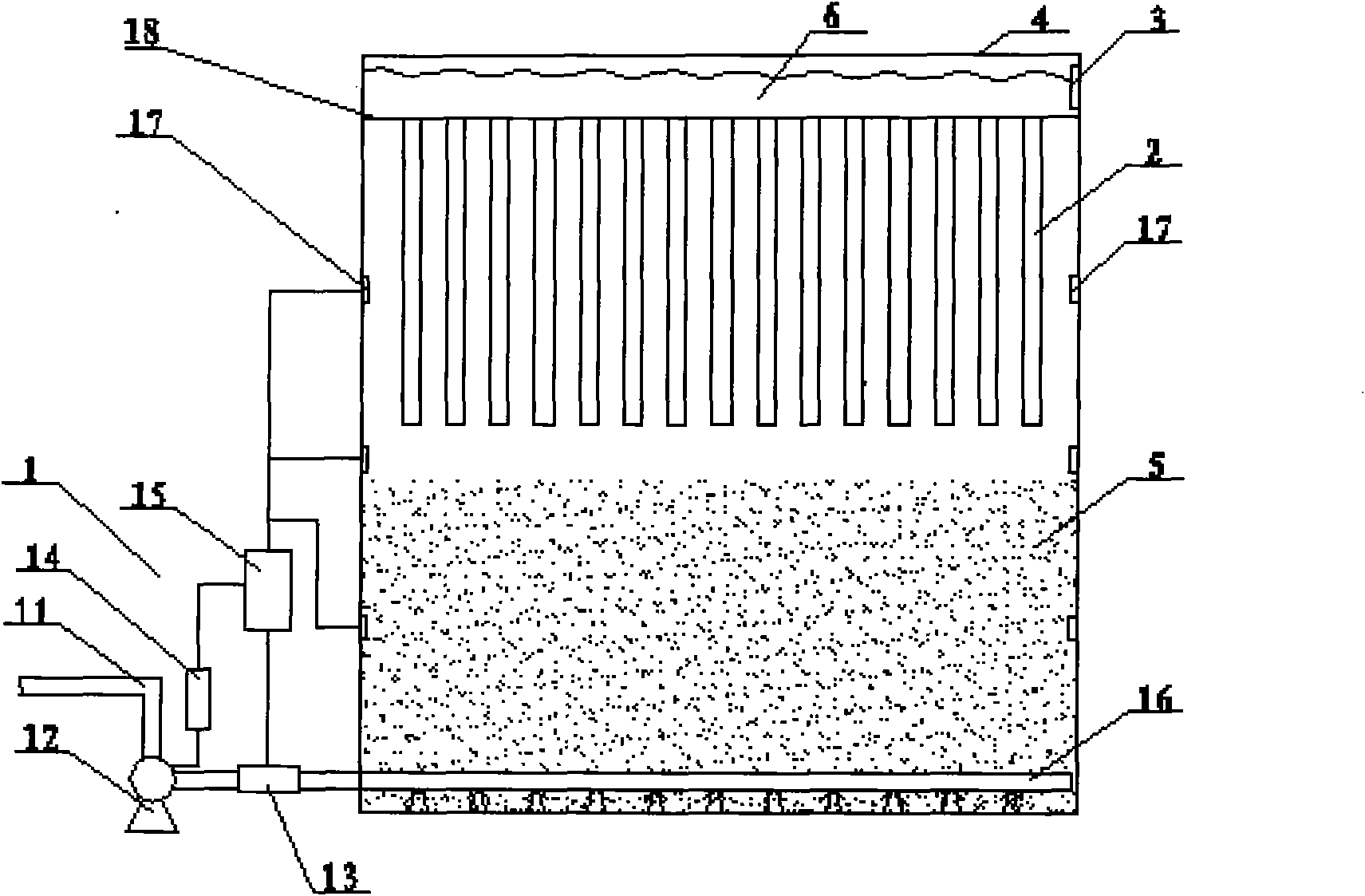
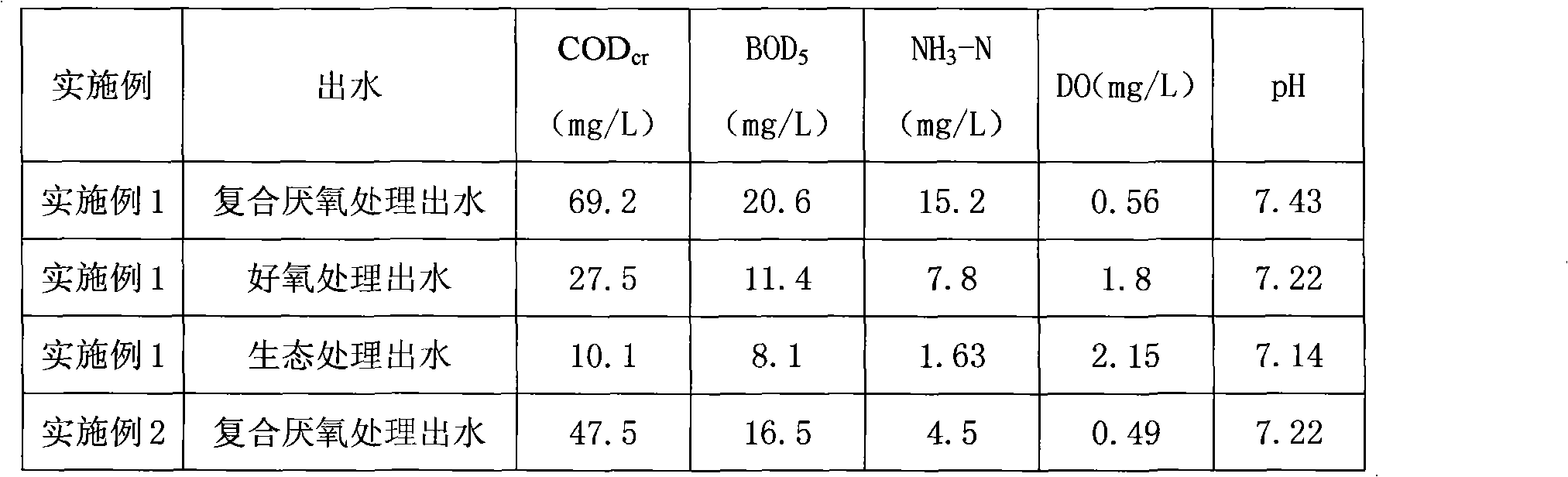
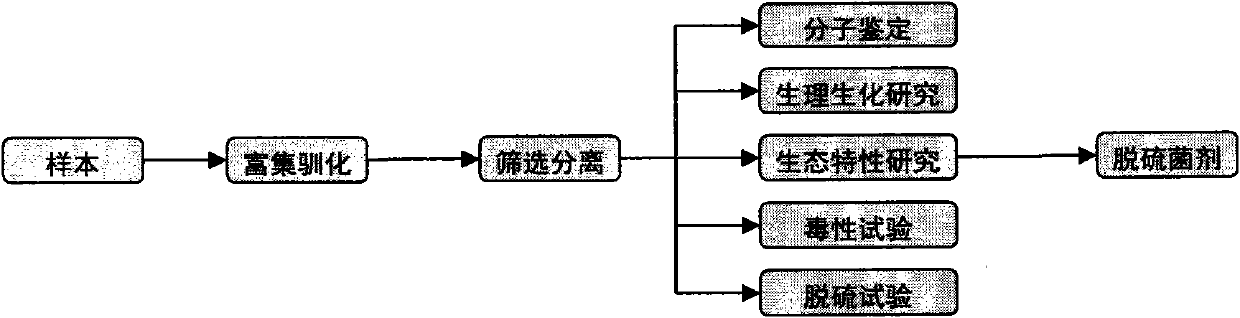
Patents
Literature
376 results about "Indigenous microorganisms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term “indigenous microorganisms” refers to a group of beneficial microbes that are native to the area, thus the name indigenous (locally existing, or not imported); EMs or effective microorganisms on the other hand is a laboratory-cultured mixture of microorganisms.
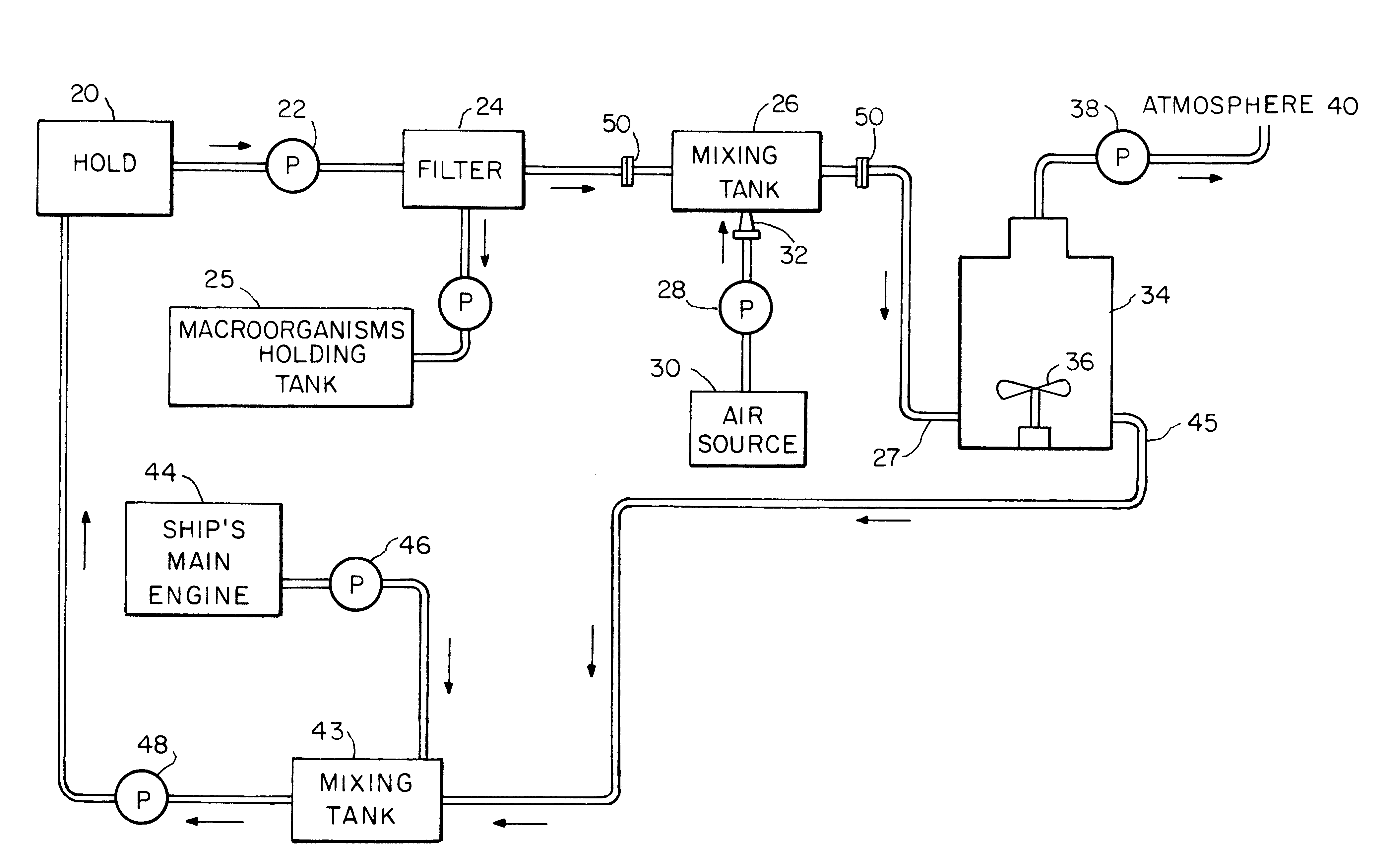
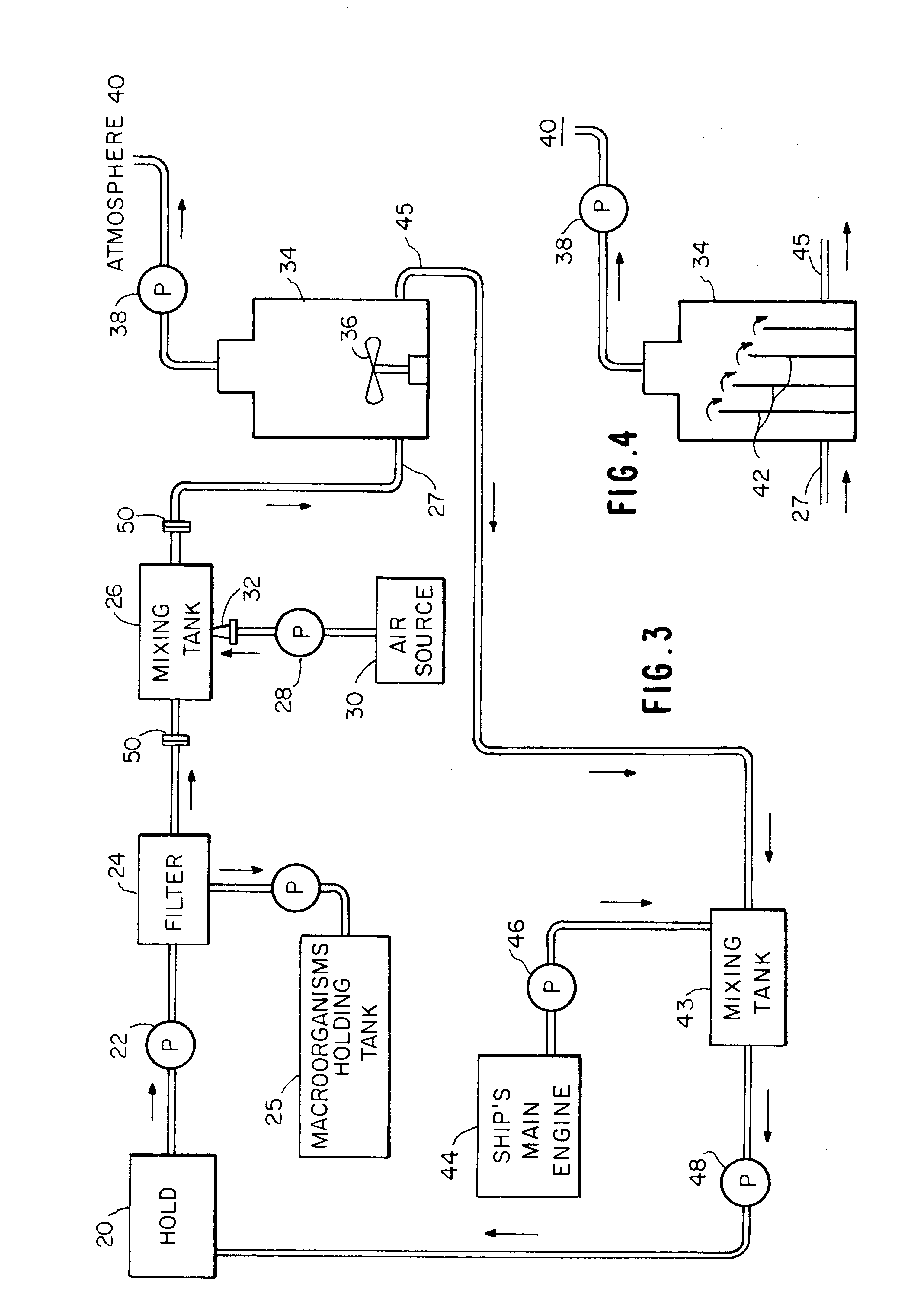
Method and apparatus for killing microorganisms in ship ballast water
InactiveUS6171508B1Rapidly reduce the DOTime requiredHull interior subdivisionWater treatment parameter controlOxygenAnaerobic microorganisms
A method and apparatus for treating ship ballast water before it is discharged into coastal waters. The ballast water may contain a generalized and diverse species population of harmful non-indigenous microorganisms. Before discharge, the ballast water is oxygenated and deoxygenated to reduce the populations of anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms, respectively. If anaerobic microorganisms are of no concern, the oxygenation step can be eliminated. Also, a method and apparatus for treating large volumes of any water, to reduce the population of a wide spectrum of diverse species of microorganisms wherein the water is deoxygenated, and then held in a sealed space for a period of time until the aerobic population has been reduced.
Owner:TIDEWATER BALLAST SOLUTIONS LLC
Method for manufacturing livestock cultivation fermentation bed and swine production method
InactiveCN101779608AEliminate hazardsEasy to useAnimal feeding stuffAnimal housingAnimal scienceDigestion
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a fermentation bed for livestock cultivation and a method for breeding pigs on the fermentation bed. The livestock cultivation fermentation bed is characterized by being manufactured by paving a loess layer on a foundation layer of an organic gasket and sprinkling sodium chloride, brown sugar and strains consisting of compound microbial inoculants where effective microorganisms and indigenous microorganisms coexist, rice bran and wheat bran on the loess layer. Green feed serves as main feed for the pigs on the fermentation bed, and energy feed and supplementary feed consisting of Chinese medicaments having the functions of benefiting gastrointestinal health, facilitating digestion and expelling toxin to improve the immunity of the pigs also can be fed to the pigs. Compared with the prior art, the livestock cultivation fermentation bed has the advantages that the pigs bred on the bed have strong immunity, need no vaccines and antibiotic and can be fed with the green feed for bulls and sheep; and the meat of the bred pigs has the same pleasant taste as wild pigs.
Owner:刘英宁 +2
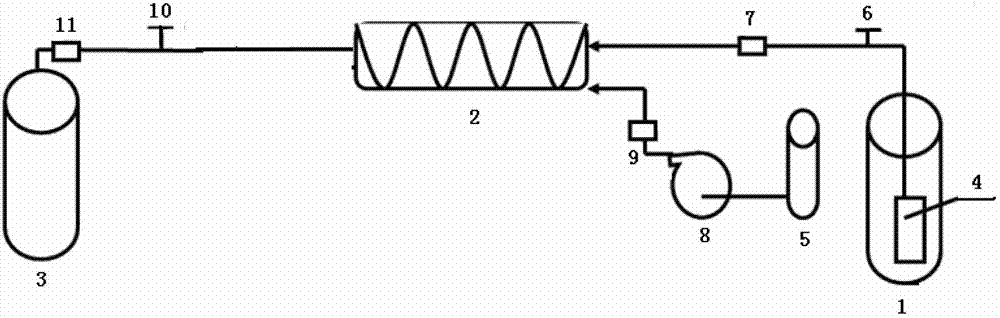
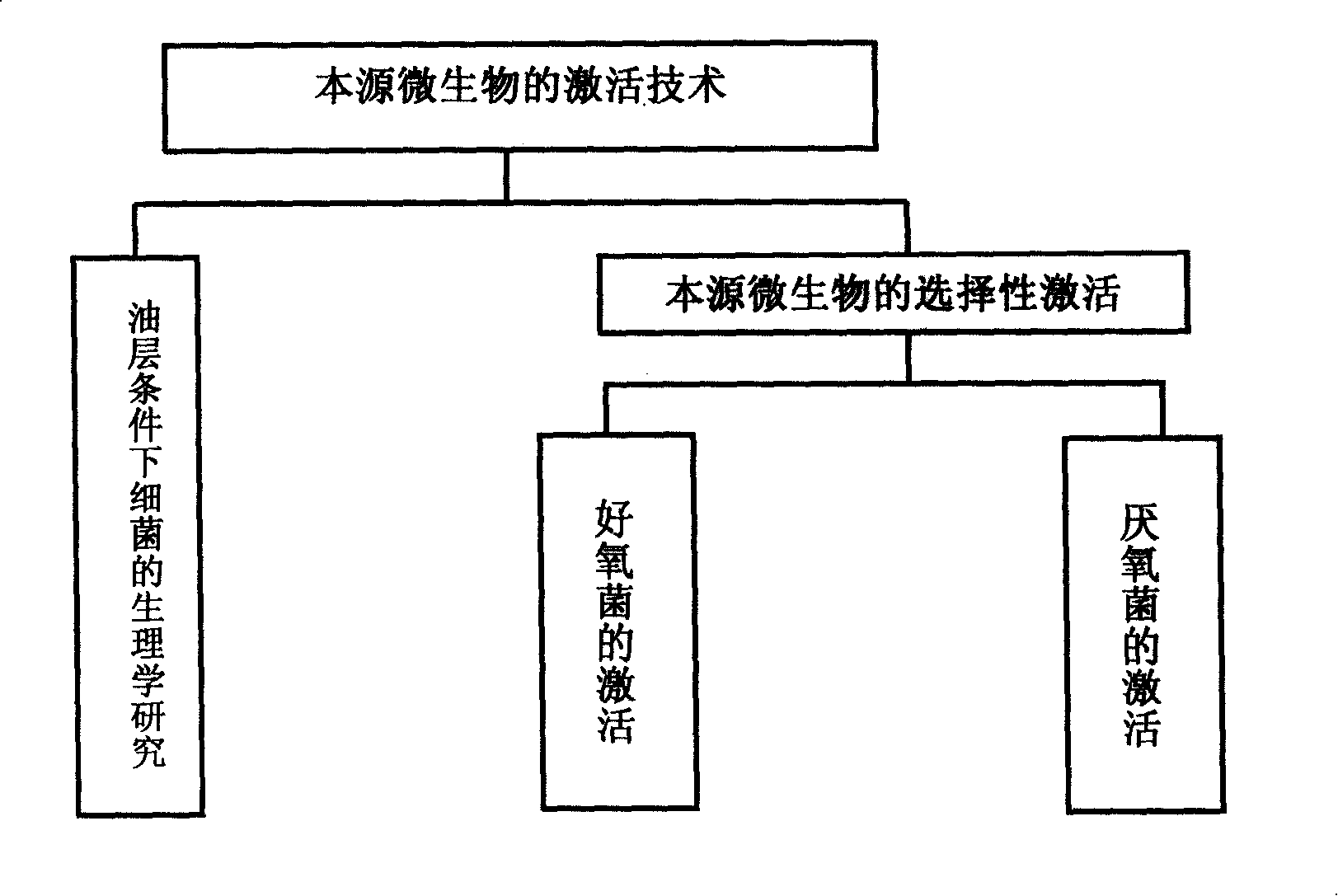
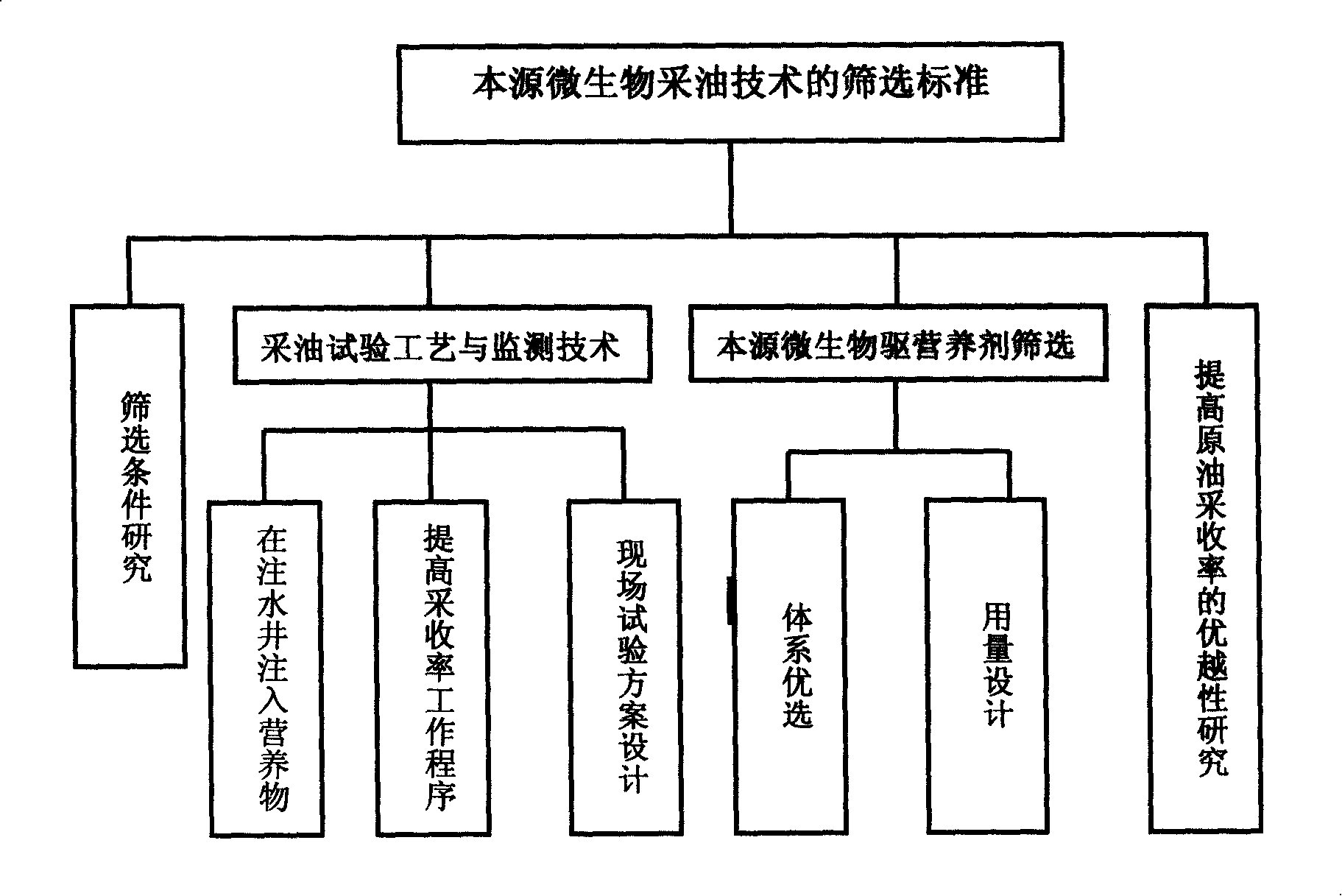
Method for improving oil well yields by means of oil pool indigenous microorganisms
ActiveCN103291267ASave on-site testing costsStrong targetingFluid removalDrilling compositionRecovery methodInjection rate
The invention relates to a microorganism enhanced oil recovery method, in particular to a method for improving oil well yields by means of oil pool indigenous microorganisms. The method includes the following steps of (1) screening of a test oil well, (2) screening of activating agents, (3) confirming of the injection rate of the activating agents, (4) confirming of well closing time and (5) on-site testing. By means of the indigenous microorganisms existing in the activated oil well, on-site test cost is thereby saved, different formulas of the activating agents are chosen according to the different indigenous microorganisms, activating effects and on-site test effects are effectively improved, the stratum cannot be damaged and the environment cannot be polluted when nutrient substances are injected, and therefore the method can be widely used for microorganism enhanced oil recovery.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Combined type ecological floating bed water purifying device
InactiveCN101851024AFavorable for attachment growthAvoid the disadvantages of churnBiological water/sewage treatmentEutrophicationWater quality
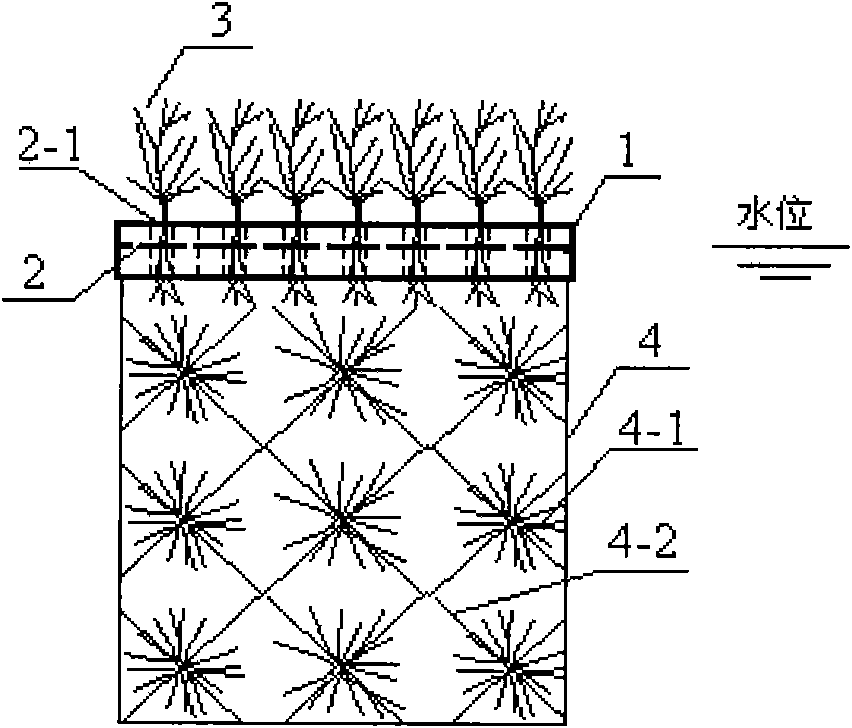
The invention relates to a combined type ecological floating bed water purifying device used for in-situ purification treatment of polluted water in rivers and lakes. A floating body frame of a floating bed is provided with a grid-like bamboo charcoal floating bed main board made of bamboo charcoal pieces which are processed intensely by a compound enzyme biological promoter before being used, and when the bamboo charcoal pieces are used, the bamboo charcoal pieces can quite well adsorb nitrogen and phosphorus in the water and effectively promote the attached growth of indigenous microorganisms in the water; grid holes on the bamboo charcoal floating bed main board are used as planting holes of plants, and various aquatic plants or economic plants with water purification function can be mixedly planted; and biological fillers are arranged on the lower part of the floating bed, and biomass-based materials which are natural vegetable fibers are used by biofilm formation of microorganisms. The device can greatly improve the capability of removing nitrogen, phosphorus and organic matters from the eutrophication water of the ecological floating bed device and has the characteristics of simple structure, convenient mounting and control, high water flow impact resistance and the like, so that the device is quite suitable to be used for the in-situ purification treatment of water in natural rives, lakes and reservoirs and scenic water.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Animalcule fuel battery and its method for processing beer waste water
ActiveCN101145620ALow costHandling is smallBiochemical fuel cellsBiological water/sewage treatmentWater useDecomposition
The invention provides a microbiological fuel cell and a method for treating beer waste water using the same, which belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment. The invention solves the problems of the prior beer waste water method, such as large influence of temperature on treatment efficiency, high cost and high COD of discharged water. The inventive microbiological fuel cell has an opened end and a sealed end, comprises a cathode fixed at the opened end, an anode fixed at the sealed end, and a fuel chamber formed between the cathode / anode and a barrel shell (1), without any cation exchange membrane being added between the cathode and the anode. The invention utilizes the indigenous microorganisms in the beer waste water as a bacterial source, after starting a reactor, to degrade organic substances and simultaneously generate power energy by using microbial decomposition. In the invention, the COD removal rate of the beer waste water is above 85 percent (up to 98 percent), the COD content in the discharge water is less than 450mg / L (minimum 20mg / L). The invention has the advantages of simple process and equipment structure, low cost, high efficiency, and less influence of temperature on the treatment effect and power yield; and is suitable for the large-scale promotion and application.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing microbial fertilizer, nutrient solution, fodder and pesticide and for fermentation bed cultivation by utilizing indigenous microorganism probiotics
InactiveCN106831238AAchieve healthActivate reproductionBiocideBio-organic fraction processingFecesAmino acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing a microbial fertilizer, a nutrient solution, a fodder and a pesticide and for fermentation bed cultivation by utilizing indigenous microorganism probiotics. The microorganism probiotics are formed by fermenting eight pure natural materials, including indigenous bacteria, green juice, fresh fish amino acid, enzyme alcohol, Chinese prescription nutrient solution, lactic acid bacteria, natural calcium and water-soluble calcium phosphate potassium; the microorganism probiotics contain the mixed flock of various beneficial bacteria, such as, lactic acid bacteria, photosynthetic bacteria, bacillus and yeast; the fertilizer can be used for fertilizing and loosening soil; the agricultural products are free from residue, taste nice and are high in yield; the fodder can be used for guaranteeing no residue on the cultured animal meat product; the meat is tender and free from smell; after the microorganism nutrient solution is used, the microorganism pesticide can prevent and treat insect diseases; the chemical pesticide and the fertilizer residue can be eliminated and decomposed; when the fermentation bed is used for culturing, the excrement cleaning is not required; the animal excrement is decomposed by the fermented padding while beneficial mycoprotein is formed; the fodder can be eaten by the animals; the microbial fertilizer is odorless, zero-emission, environment-friendly, pollution-free to environment and beneficial to the health of human and animals.
Owner:刘富金
Echelon circulation inoculation temperature-control compost method
ActiveCN101186537AReduce composting costsAchieve balance optimizationBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationTemperature controlBiotechnology
The invention relates to a method of temperature controlled compost for echelon circulation inoculation. Among three different stages in the composting process, three different degradation facilitating microbial inocula are added respectively according to composting temperature. In each stage of fermentation and compost, a part of raw materials are taken out to serve as the functional microbial inoculum which is used as composting inoculation next time. Since a new microbial inoculum is unnecessary to be inoculated in each fermentation process, compost cost is obviously reduced and circulation inoculation can effectively overcome the antagonism problem between external connection microorganism and indigenous microorganism, thus fully developing the positive effect of the indigenous microorganism and achieving the effect of accomplishing twice the result with half the effort.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of aerobic high-temperature static compost by using corrosion-promoting compost composite fermentation bacteria agent
ActiveCN102942395AWell mixedIncrease temperatureBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationDecompositionMicrobiology
The invention relates to a preparation method of aerobic high-temperature static compost and discloses a preparation method of the aerobic high-temperature static compost by using corrosion-promoting compost composite fermentation bacteria inoculants. The preparation method includes that an indigenous microorganism strain indigenous bacteria agent and thermophilic bacteria thermophilic fat bacilli are combined to be prepared into composite microbial inoculants, temperature of a pile rises rapidly more than 55 DEG C in early access of a compost substrate, previous time of pile fermentation is shortened, activity of substrate microorganism is enhanced, and the compost enters a high-temperature stage in a shortest time. Through activity of thermophilic bacteria and oxygen leading in the pile, rapid decomposition is achieved, and therefore compost quality is improved.
Owner:甘肃兰太环境治理科技有限责任公司
Method for activating oil reservoir indigenous microorganisms to produce object surface active agents
InactiveCN103628851AImprove accuracyStrong targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrobial enhanced oil recoveryActive agent
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial enhanced oil recovery, and particularly relates to a method for selectively activating water-drive oil reservoir indigenous microorganisms to produce object surface active agents so as to improve the crude oil recovery efficiency. The method includes the following steps of firstly, conducting sampling on site, analyzing the microorganisms which are contained in an oil reservoir sample and produce the object surface active agents, and analyzing the oil-water physicochemical property; secondly, determining dominant population capable of producing the object surface active agents and key metabolic substrates of the dominant population, and designing an active agent formula system; thirdly, optimizing an active agent formula; fourthly, optimizing the active agent on-site injection technology; fifthly, conducting a test on site. The method has the advantages of being high in pertinence and reliability, wide in oil reservoir application range, simple in method, high in operability, good in on-site implementing effect and the like, and therefore the method can be widely applied to microorganism oil displacement on-site tests.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for remedying contaminated site through combination of nanoscale zero-valent iron and reducing microorganisms
ActiveCN104801540AAvoid reunionPromote degradationContaminated soil reclamationSite RemediationsInjection well
The invention relates to a contaminated site remediation method, in particular to utilization of nanoscale zero-valent iron particles and orthotopic injection of microbial bacteria in a site, namely, a contaminated site remediation technology adopting nanoscale zero-valent iron and a microorganism remediation technology. The method for remedying the contaminated site through combination of the nanoscale zero-valent iron and reducing microorganisms comprises steps as follows: a nanoscale zero-valent iron injection is injected to contaminated soil through an injection well, and the nanoscale zero-valent iron in the injection is coated with an organic polymer coating layer. The method is characterized in that after the nanoscale zero-valent iron injection coated with the organic polymer coating layer is injected and the nanoscale zero-valent iron in the injection is completely oxidized, a reducing bacterium solution is injected into the contaminated soil for microorganism remediation. The organic polymer layer on the surface of the nanoscale zero-valent iron can stop agglomeration of the nanoscale zero-valent iron, can promote growth of indigenous microorganisms and accelerates pollutant degradation. According to the remediation method, the synergistic effect for the nanoscale zero-valent iron remediation technology and the microorganism remediation technology for the contaminated site remediation is realized.
Owner:山东冽泉环保工程咨询有限公司
River sediment in-situ remediation method
InactiveCN101224940ALow costConstruction is progressing rapidlySludge processingBiological sludge treatmentIn situ remediationSelf purification
The invention discloses an in-situ remediation method of sediment in rivers, which comprises the steps that: (1) aboriginal microorganism liquid, biological growth stimulation liquid and biological detoxification liquid are fully mixed according to a weight ratio of 8-10: 0.8-1.5: 0.8-1.2; (2) a spray hopper gun or an injection method is adopted to inject the mixed liquid obtained in step (1) to the bottom of the sediment in rivers and the concentration of the aboriginal microorganism liquid is 0.010 multiplied by 10<-6>- 0.015 multiplied by 10<-6>g / m<3>; (3) after 5-7 days, the biological growth stimulation liquid is injected into the sediment in rivers each day and the weight of the biological growth stimulation liquid is the same with the weight of the mixed liquid in step (1); then the biological growth stimulation liquid is injected in a halved amount each day for 25-30 days. The method of the invention has good treatment and remediation effect, simple operation and little influence on normal municipal administration and the life of residents. A river flow aerobic self-purification ecological system established can keep persistent good state; good conditions are created for the establishment of the river flow aerobic self-purification ecological system so as to completely eliminate malodorous black river.
Owner:广州市净水有限公司
Biotechnological process for hydrocarbon recovery in low permeability porous media
ActiveUS20110146973A1Enhanced overall recoveryImprove mobilityFluid removalDrilling compositionMetaboliteAPI gravity
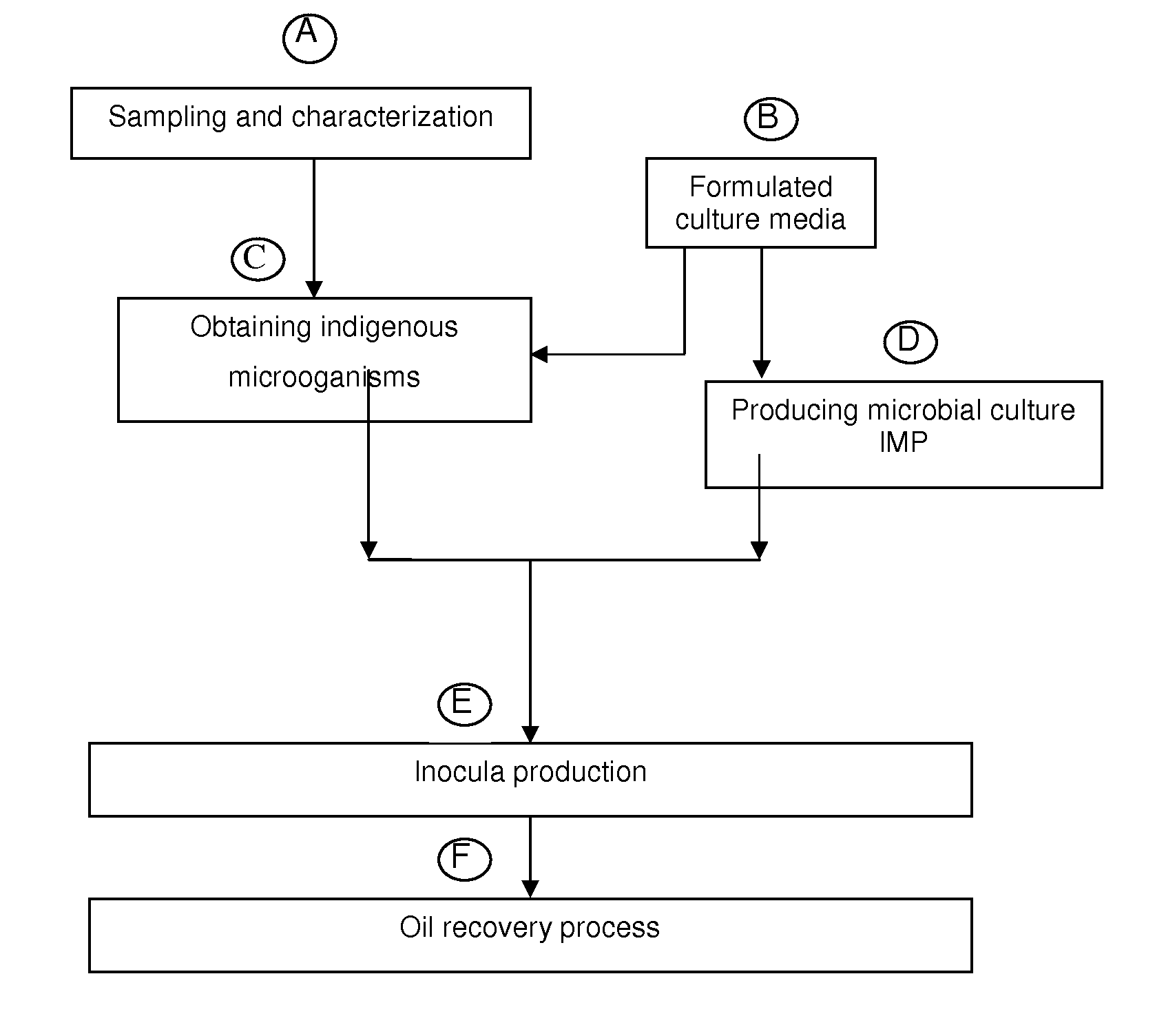
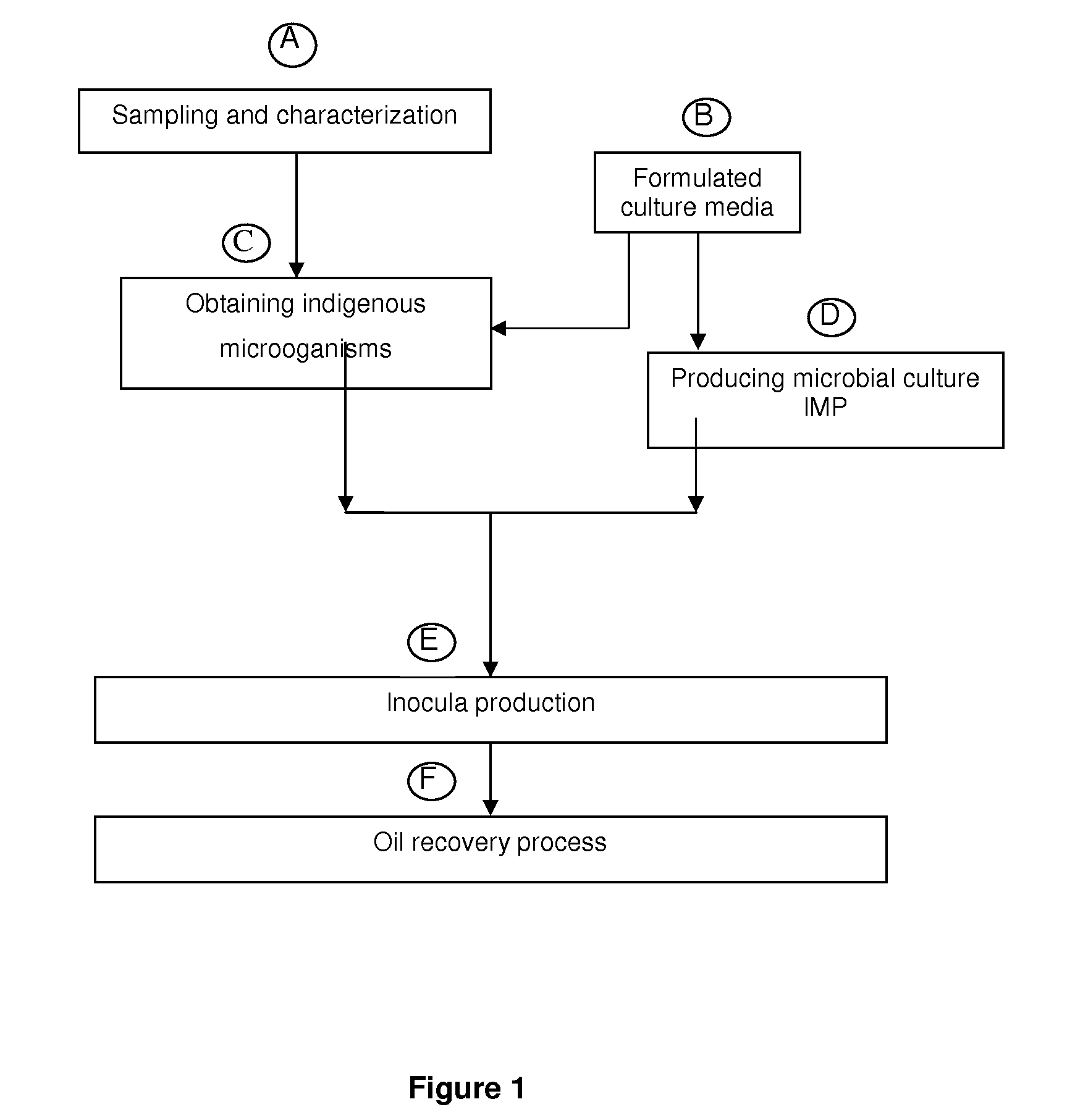
The present invention refers to a biotechnological process that enhances oil recovery of a 14 to 25 API Gravity oil contained in carbonate-containing and / or clayey sandstone porous rock systems with low permeability (7 to 100 mD), thus focused to petroleum wells associated to zones with low recovery factor. The process utilizes the indigenous extremophile microorganisms activity from the oil reservoir and an IMP culture, as well as its metabolites (gases, acids, solvents and surfactants), which improve oil mobility and are able to develop at 60 to 95° C. temperatures, 7 to 154.6 Kg / cm2 (100 to 2,200 psi) pressures and NaCl content from 5,000 to 45,000 ppm, in anaerobic conditions. The biotechnological process of the present invention includes: indigenous microorganisms sampling, collecting and characterization from the reservoir; formulation of culture media; selection, enrichment, activation and preservation of such microorganisms, as well as biostimulation (indigenous microorganisms) and bioaugmentation (IMP culture) to increase the metabolite production, useful for oil recovery in a porous media impregnated with oil in carbonate-containing and / or clayey sandstone porous systems, with one or several cycles and confinement periods from 5 to 10 days, to increase oil recovery. Experimental tests show that the biotechnological process of the present invention supplies an oil recovery increase up to 30%, additional to that obtained in secondary recovery processes.
Owner:INST MEXICANO DEL GASOLINEEO
Ex-situ bioremediation method of soil contaminated by organic matters
InactiveCN103008336AEliminate the step of screening reinforcementLow costContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentNutrition
The invention relates to an ex-situ bioremediation method of soil contaminated by organic matters. The ex-situ bioremediation method comprises the following steps of: crushing and mixing the soil and mushroom residues; adding fertilizers to the soil to regulate the content of organic carbon and mineral nutrition of the soil and keep the soil moist; establishing a biological heap after the pH value of the soil is regulated; and simultaneously monitoring the temperature, humidity and oxygen content of the biological heap, and carrying out active aeration and passive aeration on the biological heap. According to the ex-situ bioremediation method of the soil contaminated by the organic matters, indigenous microorganisms of the soil are adopted to degrade organic pollutants of the soil, the steps of screening and strengthening of microorganisms are eliminated, the cost is low, the ex-situ bioremediation method is easily implemented and can be applied to small-scale industrial application, the labor investment is reduced, and the production efficiency is improved; the mushroom residues, which are generated in the production of edible mushrooms, are adequately utilized and recycled, so that not only is the pressure to the ecological environment from the mushroom residues relieved, but also the mushroom residues are adopted to accelerate the degradation of the organic pollutants of the soil and contribute to the protection of the ecological environment; and tests show that after the method is carried out for a cycle, the degradation rate of the biological degradation method on nitrobenzene reaches 99.1%, and the concentrations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons such as phenanthrene, acenaphthene and naphthalene decrease below limit of detection.
Owner:南京市生态环境保护科学研究院
In-situ repair system for treating pollution of underground water
InactiveCN102774965AGood processing effectEasy accessTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesAutomatic controlSide effect
The invention provides an in-situ repair system for treating the pollution of underground water. The in-situ repair system comprises a water pumping well, a static mixer and a water injecting well; the water pumping well is internally provided with a submersible pump, and a water outlet of the submersible pump is connected with a water inlet of the static mixer; the other inlet of the static mixer is connected with a drug jar, and the drug jar internally accommodates carbon source drug; the underground water and the carbon source drug pumped out of the water pumping well are evenly mixed with each other by the static mixer; and an outlet of the static mixer is connected with an inlet of the water injecting well. The system puts repairing agent by the injecting well, the water pumping well is used for pumping water to accelerate the spread of the drug in an underground water pollution region, and the indigenous microorganism can be activated to promote the denitrification effect by putting the nutrient carbon source, so that the nitrate nitrogen in the water can be converted into the gas to be removed. The system is small in occupied land area, the facility is easy to install, the system is high in automatic control degree, and a water treating facility does not need to be built on the ground. The put carbon source is easy to obtain, and low in price, and the system is good in underground water treating effect, and free from the secondary pollution and other side effects.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF WATER +1
Indigenous microorganism oil flooding method
An oil extraction method driven by substrate microorganism, the first stage: aerobic fermentation stage, oxybiontic hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacterium and facultative anaerobe of hydrocarbon-oxidizing bacterium are activated at the near zone of the water injection well. Because of being partial oxidation of hydrocarbons, it produces alcohol, fatty acid, surfactant, CO2, biological polysaccharide and other product; on one hand these substance is base oil releaser, on the other hand it is as nutrient source of anaerobe including methanogen; The second stage: anaerobic fermentation stage, methanogen is activated in the deep part of anoxic oil pool, producing CO4, CO2 and other matter which increases oil fluid and increases recovery after the matter dissolving in water; In the process, the proportion between isotope light methane produced by biology and general methane is increased.
Owner:TIANJIN JINDA GASOLINEEUM NEW TECH
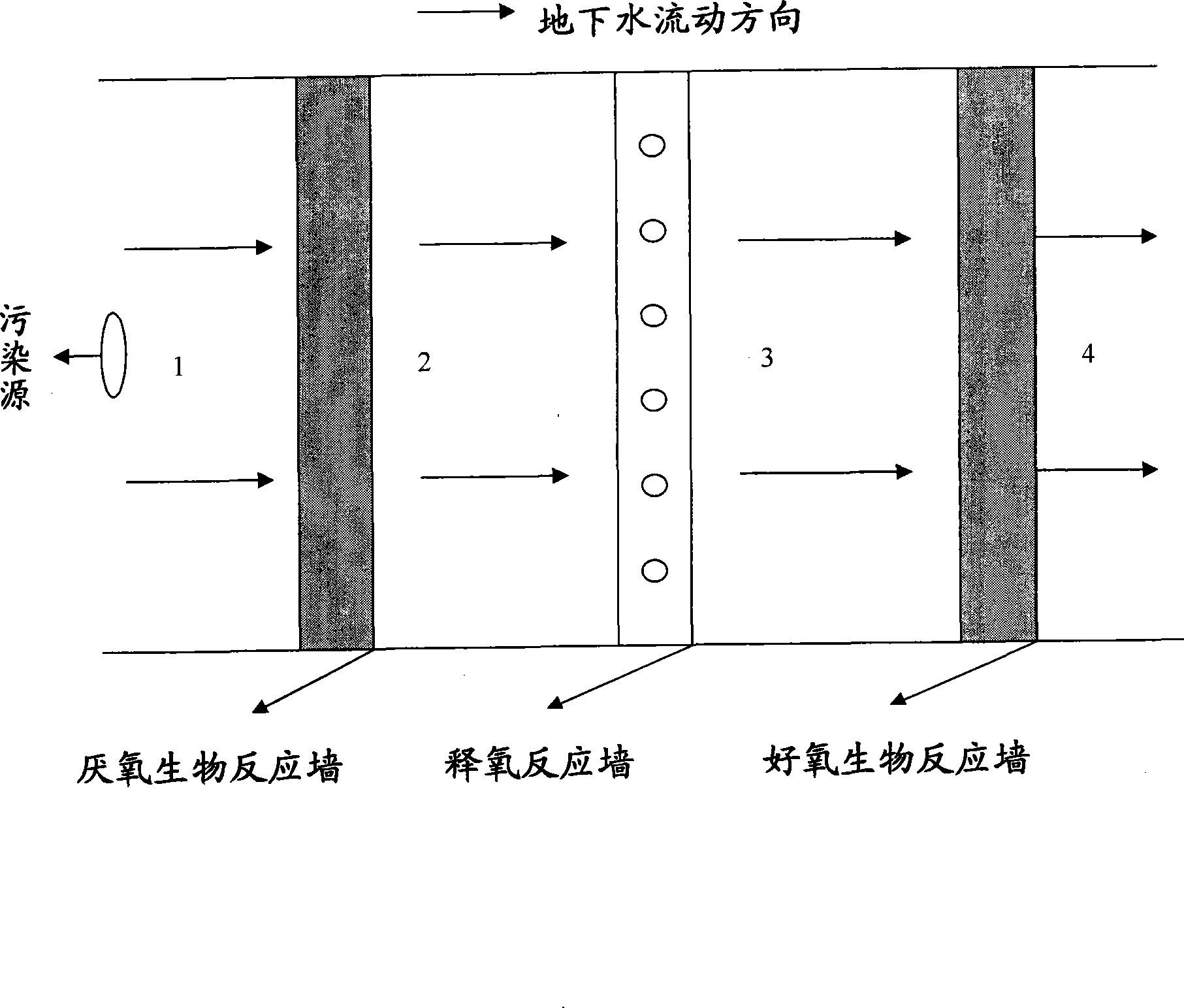
System and method for restoring triclene polluted groundwater
InactiveCN101428906AHigh activityImprove biodegradation efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeBioremediation
The invention relates to a repair system and a repair method for underground water polluted by trichloroethylene. The repair system for the underground water polluted by the trichloroethylene consists of an anaerobe reaction wall, an oxygen release reaction wall and an aerobe reaction wall, and is built and assembled according to the order of the anaerobe reaction wall, the oxygen release reaction wall and the aerobe reaction wall. The invention establishes the multifunctional biological permeable reaction wall system for in situ repair of the underground water polluted by the trichloroethylene, wherein an oxygen release agent provides sufficient oxygen for indigenous microorganisms, and three substances, namely residual activated sludge, immobilized trichloroethylene aerobic degrading bacteria and biological enzyme preparation related to trichloroethylene metabolism, are added respectively, so that the microorganism action is strengthened and the trichloroethylene biodegradation efficiency is improved. The invention provides an ideal and high-efficiency biological repair system which has wide application prospect for the underground water polluted by the trichloroethylene through stepped combination of the anaerobe action, the oxygen release action and the aerobe action.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
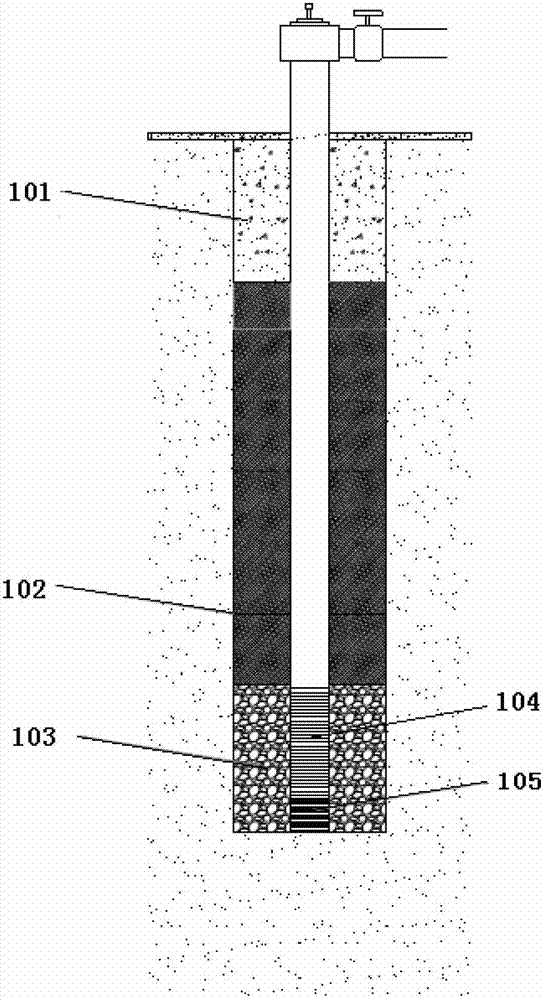
In situ precipitation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) by indigenous microorganisms to improve mechanical properties of a geomaterial
A method for increasing the concentration of calcium carbonate in a geomaterial that contains indigenous microorganisms capable of hydrolyzing urea to ammonia, which method includes enriching the geomaterial with a source of nutrients, adding urea to the geomaterial which is hydrolyzed to ammonia and which raises the pH of the geomaterial, and adding a source of calcium ions to the geomaterial. Carbonate ions obtained by the hydrolysis of the urea combine with calcium ions to form calcium carbonate.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF IDAHO
Method for preparing solid repair agent by using protein peptide and repairing soil by using soil repair agent
ActiveCN102580998AAchieve fixPlant heightContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonLight pollution
The invention provides a method for preparing a solid repair agent by using protein peptide and repairing soil by using the soil repair agent. The method comprises the steps of: preparing the protein peptide prepared by using a method in the patent ZL200610019063.7 or the protein peptide prepared by using protein-containing waste according to the following formula in site, wherein the formula comprises 1) 5-10 percent of protein peptide, 2-6 percent of molasses and the balance of water; 2) 5-10 percent of protein peptide, 0.5-1.0 percent of laccase crude product, 1-2 percent of laccase strain and the balance of water; and 3), 5-10 percent of protein peptide and the balance of water. The formula 1 is suitable for the soil in which plants are planted and which is seriously polluted by heavy metal ions; the formula 2 is suitable for the soil in which plants are planted and which is seriously polluted by heavy metal ions and is polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon; and the formula 3 is suitable for directly acting on conventional polluted soil with light pollution. The protein peptide soil repair agent can be used as a nutrient in which a microorganism or indigenous microorganism for promoting the enrichment of the plants to the heavy metal ions, so that the polluted soil is repaired. The soil repair agent has low price, high efficiency and good effect.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
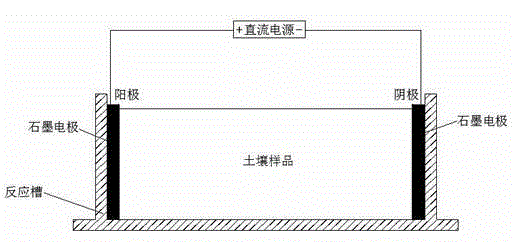
Electric-microbial combined remediation method for heavy metal contaminated soil
The invention relates to an electric-microbial combined remediation method and an electric-microbial combined remediation device for heavy metal contaminated soil. The electric-microbial combined remediation device comprises a pretreatment system, a direct current stabilized power supply, an electric electrode and an aftertreatment system; a cathode and anode electrolytic tank is arranged on the electric-microbial combined remediation device, the electrode is directly inserted into soil, so that the technology is relatively close to reality, and the direct current stabilized power supply is directly connected with a graphite plate in the electrode; an electric pretreatment system comprises indigenous microorganism cultivation and acclimation. The electric-microbial soil remediation technology can effectively and quickly solve the problems that the conventional soil remediation technology is high in processing cost and can easily cause secondary pollution.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Microbial enhanced oil recovery method
ActiveCN105201471AEnhanced overall recoveryHigh yieldFluid removalRecovery methodMicrobial enhanced oil recovery
The invention discloses a microbial enhanced oil recovery method and belongs to the technical field of tertiary oil recovery. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1, conducting displacement of reservoir oil through biosurfactant; 2, adjusting injection-production patterns; 3, conducting displacement of reservoir oil through indigenous microorganisms; 4, conducting oil recovery through microorganism single well huff-and-puff. According to the method, firstly, the biosurfactant is injected, so that the displacement efficiency of a water-driven oil reservoir is improved; then through adjustment of the injection-production patterns, the swept volume, in the oil reservoir, of the indigenous microorganisms is expanded; finally, through the microorganism single well huff-and-puff treatment, crude oil in the immediate vicinity of an oil well is displaced out, and thereby the purpose of further raising the recovery ratio of the oil reservoir is achieved finally. The method has the advantages that activator has the advantages of being wide in source, low in price and harmless to strata; the method is wide in oil reservoir application range and particularly suitable for an oil reservoir which is exploited in a water-driven mode and is medium and high in permeability; the process is simple, and the pertinence and operability are great; the field test effect is good, and the enhanced oil recovery rate is testified by field tests to be larger than 15.0%. Therefore, the method can be widely applied to the technical field of microbial enhanced oil recovery.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method and system for remediation and treatment of polluted river water
ActiveCN102464404AHighly stable controlControl altitudeWater resource protectionTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesAnaerobic treatmentInoculation
The invention discloses a method and a system for remediation and treatment of polluted river water. The method comprises the following steps that a river way is separated so that a composite anaerobic treatment segment is formed; a sediment stirring device is installed in the composite anaerobic treatment segment; a filling material is arranged at an upper part of the composite anaerobic treatment segment; river sediment is stirred by the sediment stirring device, then suspends and fully contacts with polluted river water from a lower part of the composite anaerobic treatment segment, wherein original indigenous microorganisms in the river sediment can effectively degrade pollutants in the polluted river water; the polluted river water with a part of the river sediment flows upstream, contacts with the filling material, and then is subjected to inoculation enrichment on the filling material so that a biomembrane is formed; the polluted river water is subjected to further treatment to form product water; and product water obtained by the method can be subjected to further aerobic and ecological remediation treatment and is discharged. The method and the system for remediation and treatment of polluted river water can obviously decrease a river sediment amount, can realize effective degradation of various pollutants in river water, and have the advantages of environmental friendliness, safety and good effectiveness.
Owner:中广信(福建)环保投资有限公司
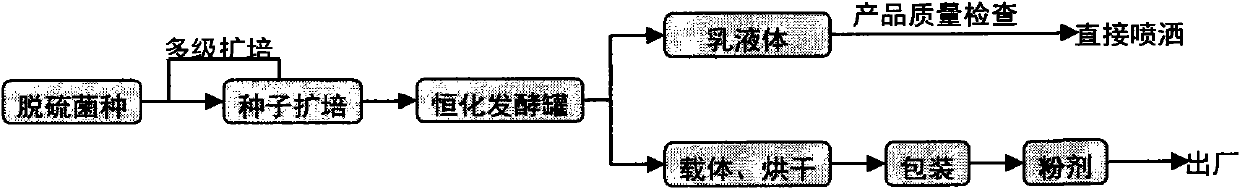
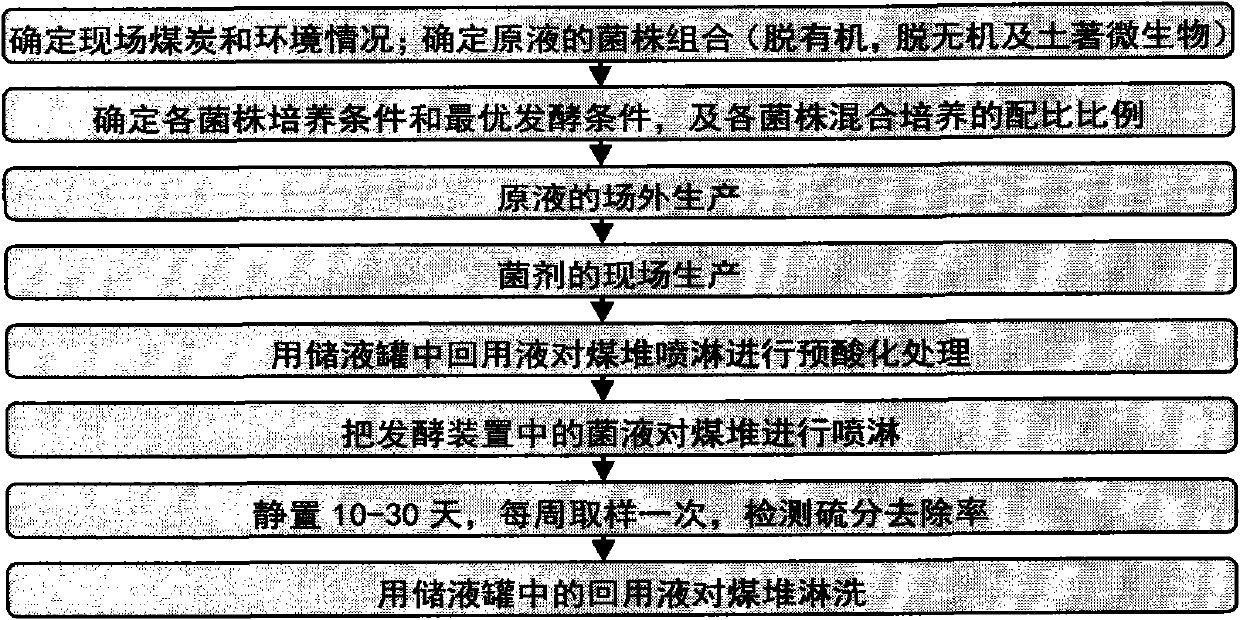
Combined microbial desulfurization method and its technology for coal
A combined desulfurization idea and process for coal removal, including the combination of high-efficiency core desulfurization bacteria agent and indigenous bacteria agent, as well as the combination of inorganic sulfur removal and organic sulfur removal technology, perfects the type and level of desulfurization, and can improve the desulfurization speed and efficiency. This invention considers and analyzes the differences in the state and content of sulfur in different coals, screens the indigenous microbial communities in the treated coal, and increases the local microbial populations’ influence on the core desulfurizing bacteria when the desulfurizing agents are expanded and applied in batches. Ecological support to form a combined desulfurization bacteria agent that is really suitable for the coal to be treated; at the same time, through the design and transformation of the traditional heap leaching method, the inorganic sulfur (mainly pyrite sulfur and elemental sulfur) and organic sulfur ( Dibenzothiophenes) are oxidized and decomposed into sulfuric acid by stage microorganisms and collected, so as to achieve the purpose of desulfurization. The combined microbial desulfurization method adopted in the present invention is a new technology pioneered at home and abroad.
Owner:上海彤微环保科技有限公司
Composite bio-energizer used for in-situ ecological remediation of polluted river sediment
InactiveCN102815794ACause ecological riskImprove repair effectWater resource protectionBiological water/sewage treatmentMicroecosystemSludge
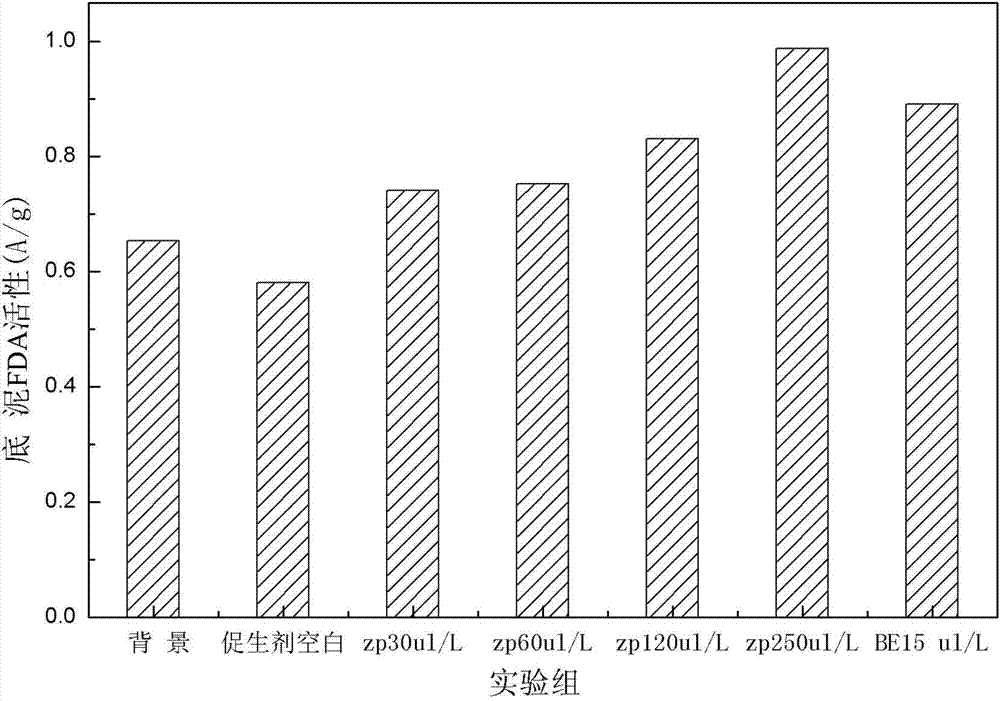
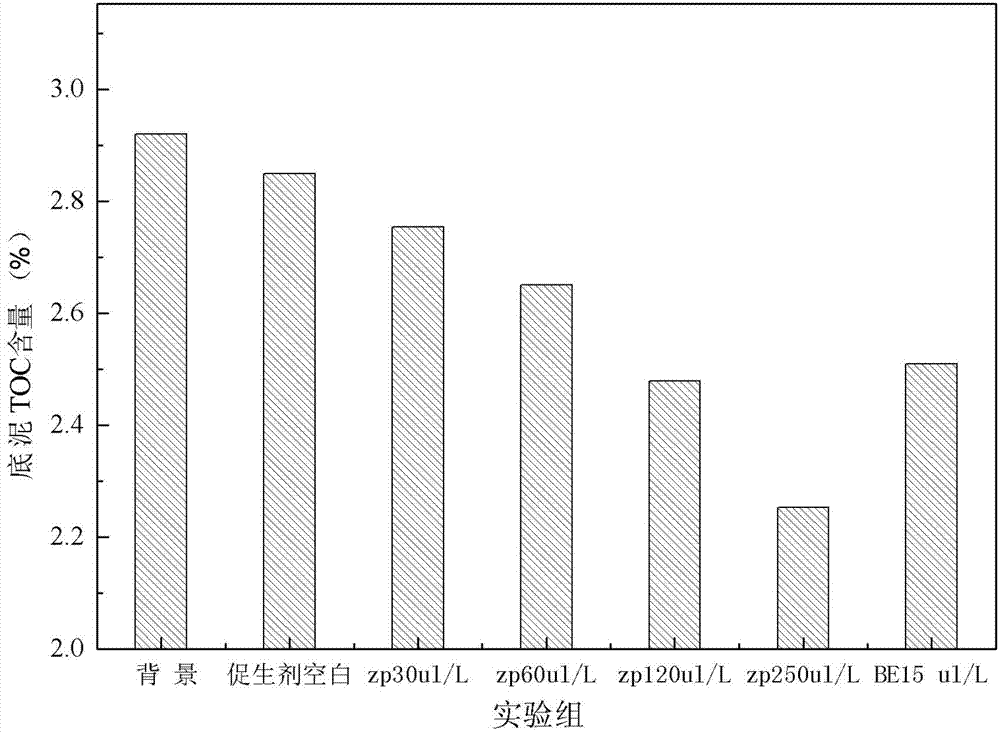
The invention discloses composite bio-energizer used for in-situ ecological remediation of polluted river sediment. The composite bio-energizer comprises oxidant and bio-energizer. The oxidant is one or two of calcium peroxide or calcium nitrate. The bio-energizer comprises amino acid, micro-molecular organic acid, vitamin, inorganic salt and microelement. According to the characteristics of bottom sludge in a river, oxidant and bio-energizer compositions are obtained by screening, matching quality of the oxidant can be adjusted according to pollution level of the bottom sludge in the river, and ecological risk cannot be caused to the bottom sludge due to absence of microorganism. In addition, growth and reproduction of indigenous microorganism are achieved by stimulating the bottom sludge, a pollution-resistant bottom sludge micro-ecosystem is established, and remediation effect of the bottom sludge can be kept excellent for a long term. An experimental research shows that by the use of the composite bio-energizer, content of TOC (total organic carbon) in the bottom sludge can be reduced, and diversity and activity of microorganisms are increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MEP
Microbial restoration agent for heavy metal contaminated soil and restoration method
ActiveCN107413841AEasy to trainLow costContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersRestoration methodBioremediation
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil microbial restoration, and particularly relates to a microbial restoration agent for heavy metal contaminated soil and a restoration method. The restoration method mainly comprises the two steps of preparation of the microbial restoration agent and spraying restoration of the soil. Treatment is conducted on the metal contaminated soil by adopting the microbial restoration agent for the heavy metal contaminated soil and the restoration method, the content of heavy metal in the soil can be rapidly reduced, and the restoration effect is good. The restoration method is simple in operation and low in cost, the restoration method is low in project investment, the dosage of the microbial restoration agent can be adjusted according to practical conditions, when a plurality of metal elements exist in the contaminated soil, treatment can be conducted by mixing and matching different thalli to prepare a microbial restoration agent according to needs. The soil fertility is not damaged and indigenous microorganisms are not harmed when restoration is conducted on the soil by adopting the restoration method, secondary pollution does not exist, the microbial restoration agent and the restoration method are safe and environmentally friendly, and suitable for restoration of a large area of heavy metal contaminated soil, is good in practical application effect, and can be used in a large scale.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
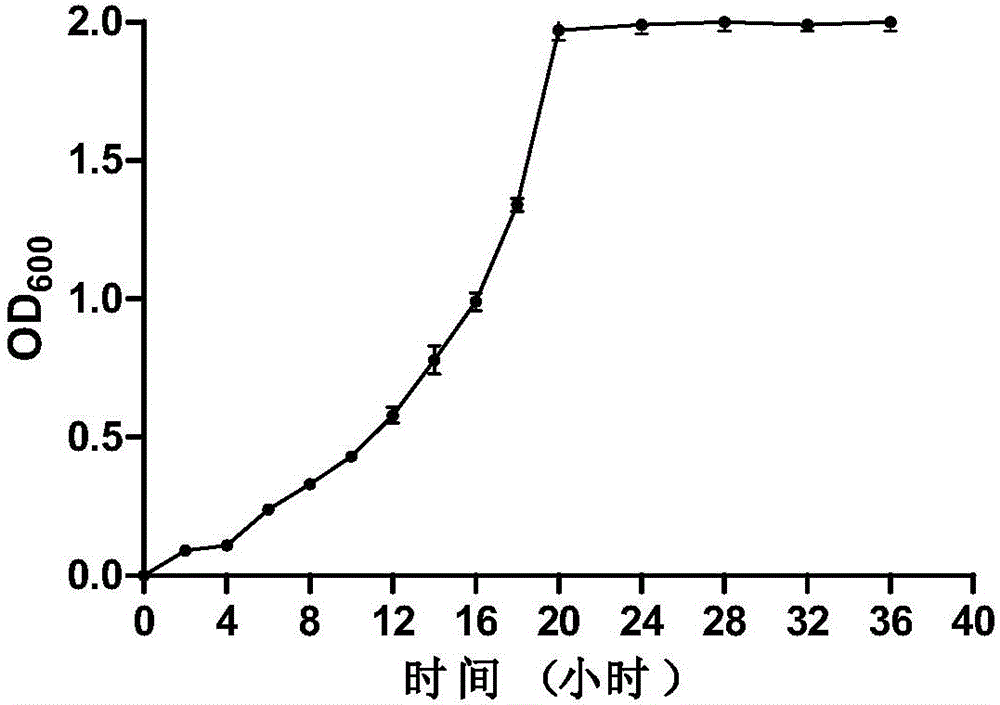
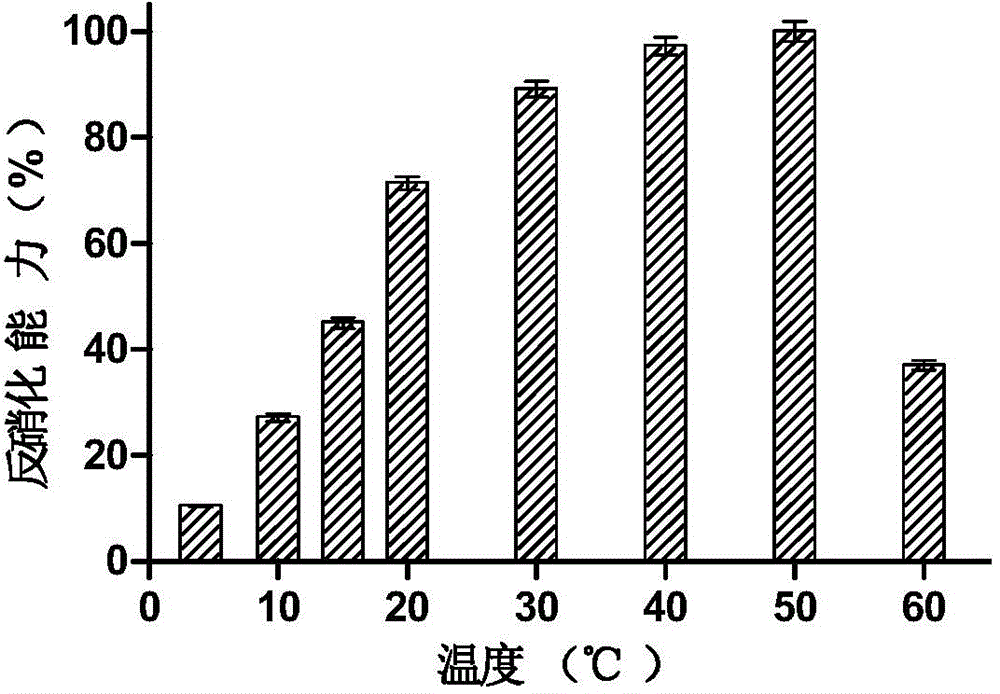
High-temperature-resistant aerobic denitrification bacteria and application of same
InactiveCN104830710AReduce accumulationAvoid environmental incompatibilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEutrophicationPollution
The invention belongs to the field of environmental microorganisms and discloses a high-temperature-resistant aerobic denitrification bacteria, of which the classification name is pseudomonas stutzeri sp., wherein the strain has been preserved at China center for type culture collection at 2015 Jan.9 and has been assigned the accession number CCTCC NO: M2015027. The invention also discloses an application of the high-temperature-resistant aerobic denitrification bacteria. The strain grows well at 50 DEG C, has strong denitrification performance, is very less in accumulation of nitrite during denitrification and is free of secondary pollution. In the invention, the high-efficient aerobic denitrification bacteria are obtained through screening from a eutrophic lake water body, when being subjected to enlarged cultivation, the bacteria strain can be directly used for denitrification on lake water and can avoid environmental inadaptability of non-indigenous microorganisms. The bacteria strain can achieve huge economic benefit when being used in treatment of industrial waste.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for quantifying microorganisms for producing lipopeptide surfactant in microbial flooding reservoir
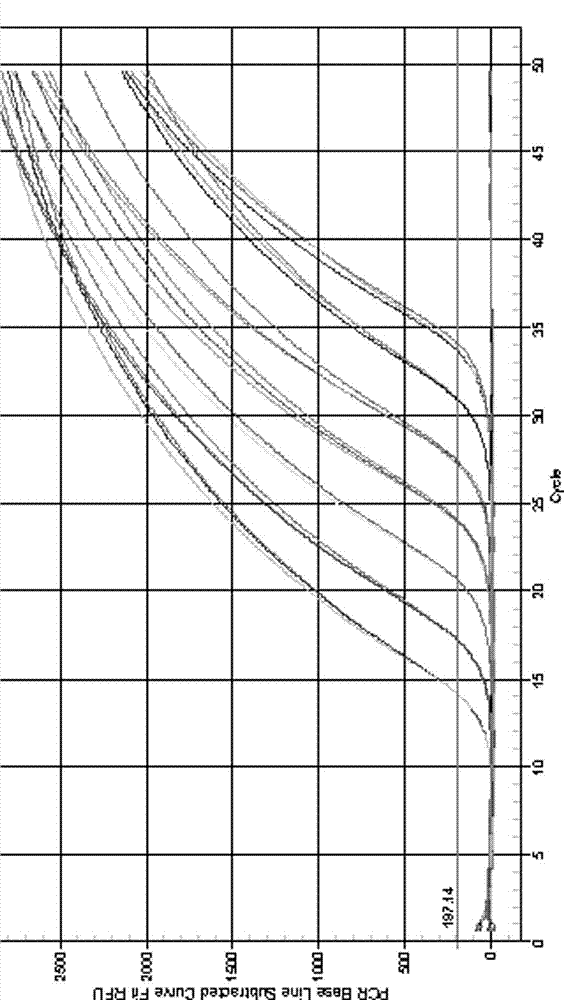
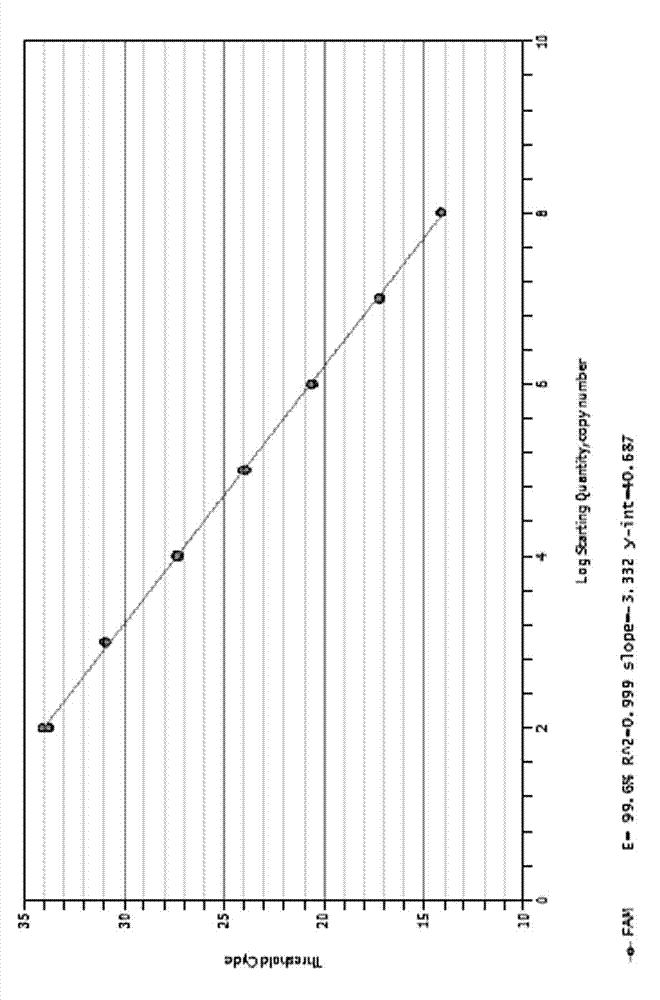
ActiveCN102925563AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicrobial enhanced oil recoveryLinear relationship
The invention relates to a method for quantifying indigenous microorganisms for producing lipopeptide surfactant in microbial flooding reservoir. Primers are designed according to lipopeptide synthetase genes of microorganisms for producing lipopeptide surfactant, and fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is performed. In optimized reaction procedures and reaction system, the lipopeptide synthetase genes obtained from a standard lipopeptide-producing strain is connected with a carrier to construct a recombinant plasmid used as a standard sample for real-time quantitative PCR; the standard sample is subjected to 10-time gradient dilution and used as a template for fluorescent quantitative PCR, and a standard curve is drawn; a microbial flooding reservoir sample is subjected to simple treatment and used as a template for fluorescent quantitative PCR; and whether data of replicate samples are identical and whether initial templates having different numbers of copies have the same amplification efficiency are judged according to linear relationship R2 and amplification efficiency E. When being used for detecting microorganisms for producing lipopeptide surfactant in reservoir under optimized reaction conditions, the lipopeptide synthetase specific primers have higher stability and sensitivity, thereby being widely used in the field of microbial enhanced oil recovery.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process and equipment for preparing marsh gas by solid fermentation
InactiveCN101717794AReasonable workmanshipReasonable equipment designBiological substance pretreatmentsGas production bioreactorsChemistryIndigenous microorganisms
The invention belongs to the field of marsh gas preparation, and relates to a process and equipment for preparing marsh gas by solid fermentation of animal wastes and crop straws. The process and the equipment are characterized in that the equipment comprises a system for preparing the marsh gas by solid fermentation, wherein the system consists of at least one group or more groups of marsh gas fermentation units; and the process comprises a pretreatment step of marsh gas raw materials. Generally, the process adopts a sequential solid fermentation process, which comprises the following steps: firstly, tearing the crop straws, and naturally heaping the crop straws for 3 to 7 days for fermentation to obtain a raw material 1; heaping and acidifying dry and fresh waste in the animal wastes for 3 to 5 days for fermentation to obtain a raw material 2; and then mixing the raw material 1 and the raw material 2 in a proper carbon-nitrogen ratio to obtain a mixed fermentation raw material, and inoculating a proper amount of sludge in a marsh gas pool or a sewage treatment plant with the mixed raw material so as to promote the production of the marsh gas through indigenous microbes. The equipment of the invention generally consists of 26 independent and intercommunicated fermentation devices, traveling transport devices, feeding devices, discharging devices, marsh gas solution delivering devices, marsh gas solution reflux devices and marsh gas collection devices. The process and the equipment provide new technology for low-carbon economy.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Bacillus cereus TH-35 capable of activating heavy metal cadmium in soil and application thereof
Belonging to the technical field of soil pollution biological treatment, the invention in particular discloses a Bacillus cereus TH-35 strain capable of activating heavy metal cadmium in soil. The strain is preserved in Guangdong microbiology culture center (GDMCC) on June 13, 2016, and the preservation number is GDMCC No.60044. According to the invention, an indigenous microorganism with efficient cadmium activation function is screened out from farmland soil, and is utilized to activate soil mineral nutrients at the rhizosphere and promote plant growth, at the same time, the indigenous microorganism also can effectively dissolve soil carbonate bounded forms, phosphate bounded forms and other major bounded forms of cadmium, thus effectively improving the efficiency of remediation of soil heavy metal cadmium by hyperaccumulator plants. In the process of activating soil heavy metal cadmium with the strain, no emission pollutant unfriendly to the environment is generated, therefore the Bacillus cereus TH-35 strain has great application prospects in preparation of environment friendly soil conditioners.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Composite micro-ecological preparation for treating black stink water in rivers, pits and ponds and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110438046AReduce CODImprove water purification efficiencyFungiBacteriaBacillus megateriumVesuvianite
The invention discloses a composite micro-ecological preparation for treating black stink water in rivers, pits and ponds and a preparation method thereof. The composite microbial preparation comprises indigenous microorganism, functional strain and carrier matrix which are separated from a black stink water body to be treated and have a repairing function. The indigenous microorganism is at leastone of nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria and bacillus subtilis, the functional strain is at least one of photosynthetic bacteria, candida utilis, bacillus megaterium, lactic acid bacteria and actinomycetes, and the carrier matrix is at least one of crocalite, green zeolite, ceramsite, quartz sand, vesuvianite and vermiculite. The black stink water body includes black stink surface waterof black stink rivers, black stink lakes or polluted ground. According to the invention, the composite micro-ecological preparation is formed by immobilizing the indigenous microorganism, the functional strain and the carrier matrix, has remarkable effects of degrading the pollutants such as COD, NH3-N, TP and the like in the black stink water. The preparation method disclosed by the invention haswide applicability to black stink surface water of various black stink rivers, black stink lakes or polluted ground.
Owner:江西清瀞自然环境科技有限公司
Method for deeply treating micro-polluted source water through in-situ enrichment, immobilization and acclimatization of indigenous microorganisms
ActiveCN105417727AAvoid introducingNo ecological riskImmobilised enzymesMicroorganism separationStart timeWater quality
The invention provides a method for deeply treating micro-polluted source water through in-situ enrichment, immobilization and acclimatization of indigenous microorganisms. In-situ enrichment and immobilization of the indigenous microorganisms are carried out in a stuffy aeration manner under an appropriate aeration condition by inoculating underwater bed sediment to be treated and water to be treated and adding nutrient elements; then, the immobilized microorganisms are gradually adapted to the water quality to be treated by arranging automatic water intake / discharge, gradually reducing the concentration of the nutrient elements in intake water and increasing the amount of intake / discharged water. The method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages: 1) under the stuffy aeration condition, loss of the microorganisms is avoided, multiplication of the indigenous functional microorganisms is accelerated, and the start time of the process is greatly shortened; 2) the multiplication of autotrophic nitrobacteria flora is preferably promoted by inoculating the underwater bed sediment having nitrobacteria flora of high abundance, adding ammonia nitrogen and reducing a carbon nitrogen ratio, and the diversity of the inoculated nitrobacteria flora is ensured by inoculating the underwater bed sediment having an appropriate depth, and therefore the operation stability of a system is promoted.
Owner:NANJING FRONTIER ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com