Patents
Literature
4990 results about "Submersible pump" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
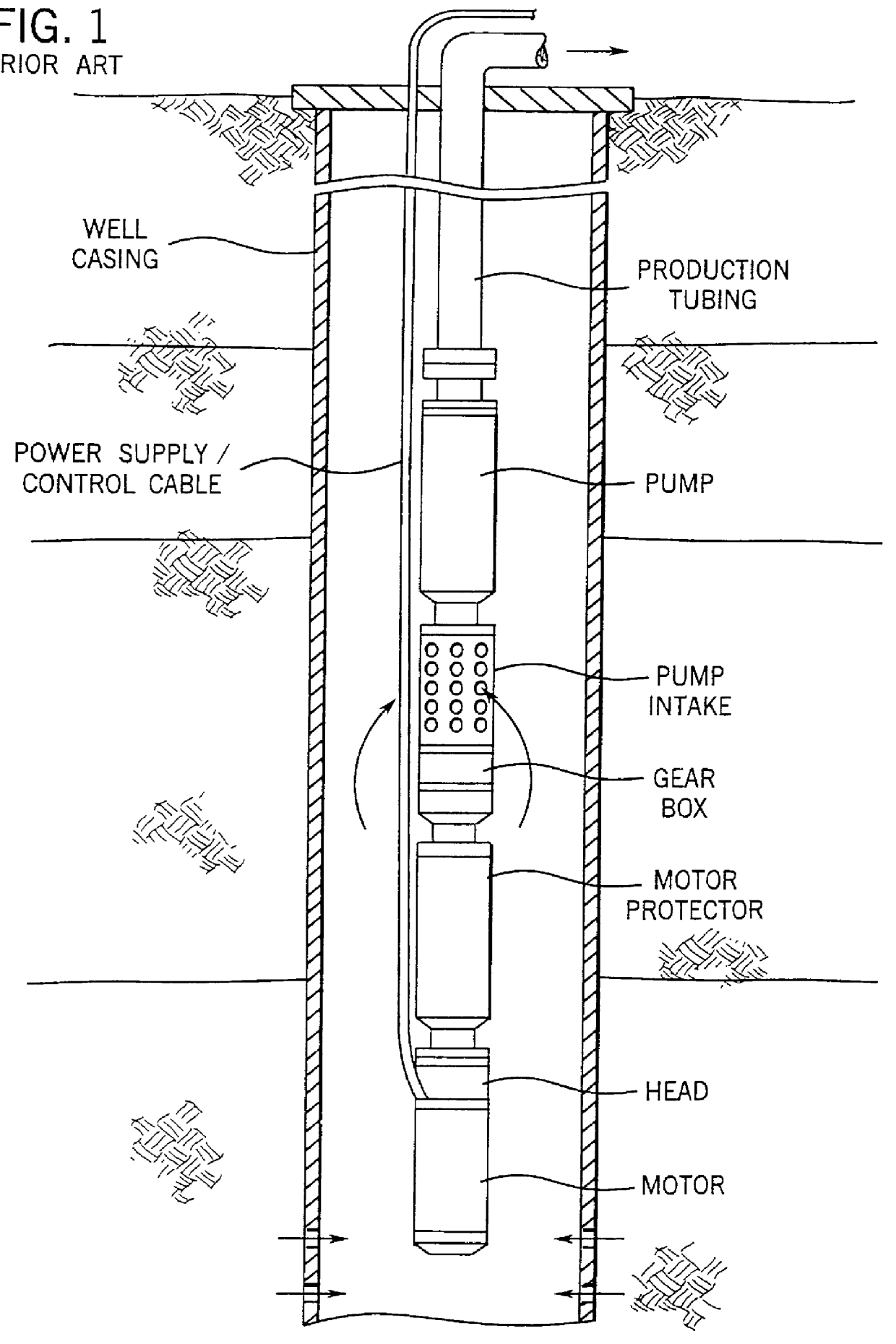
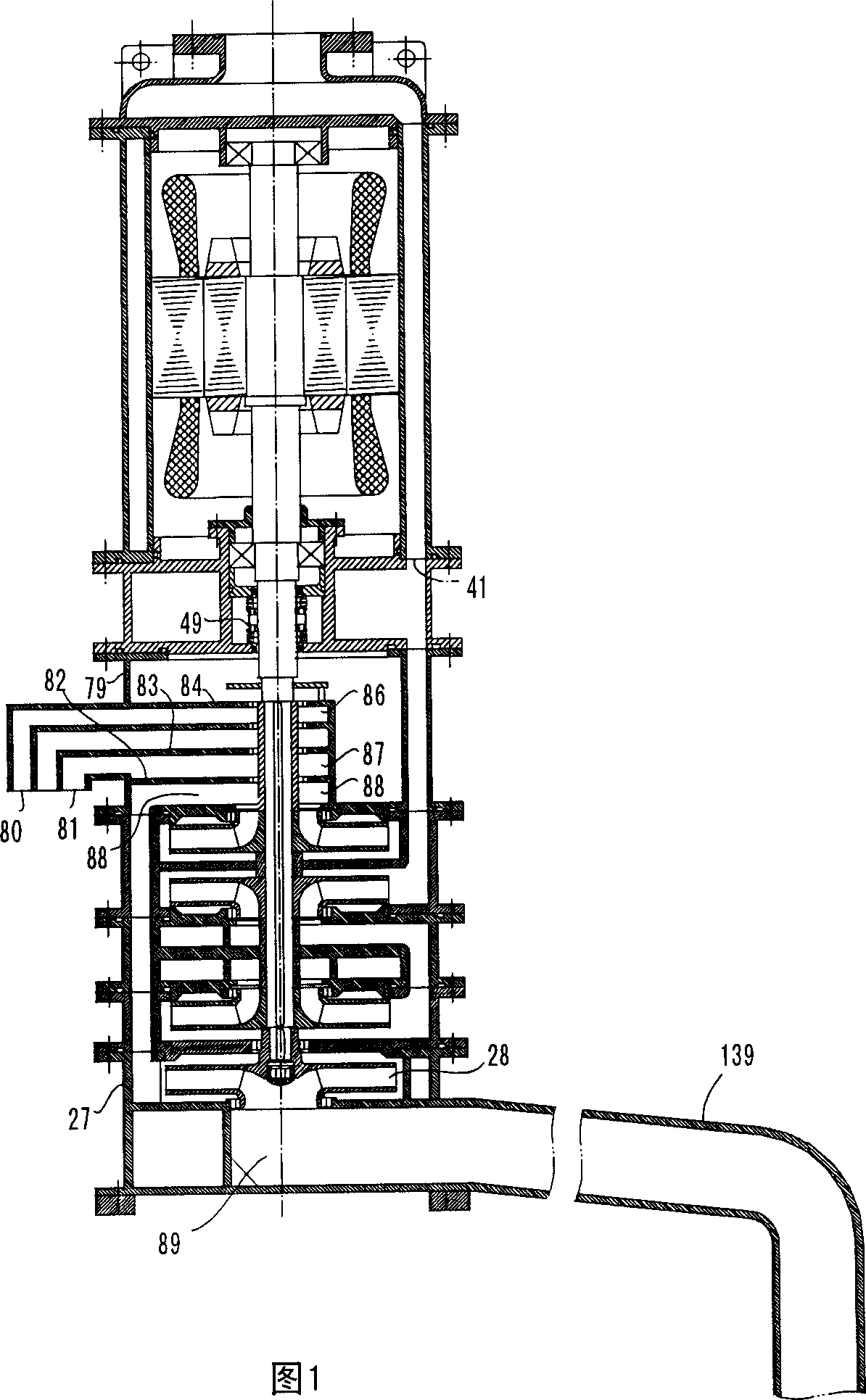
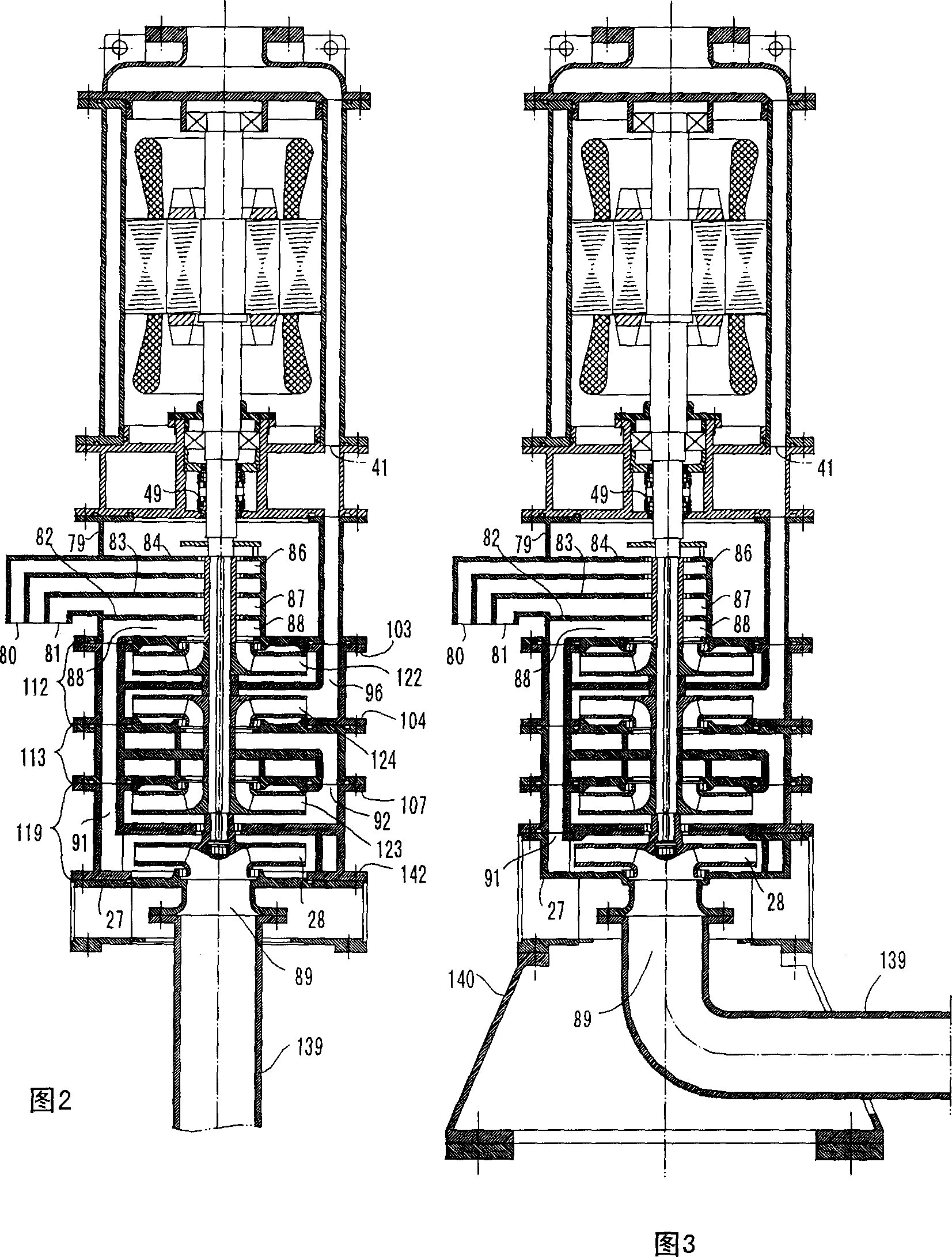
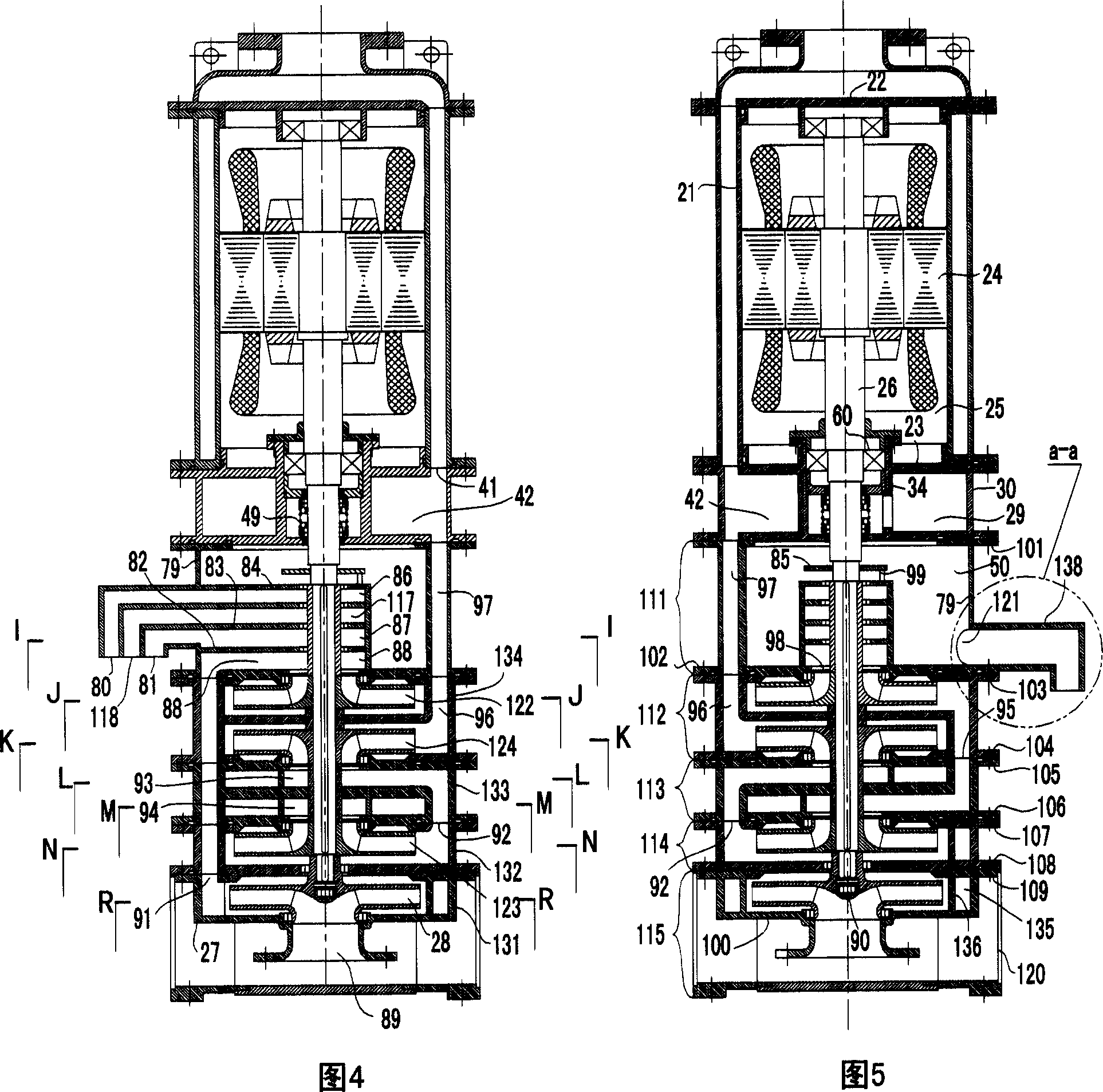
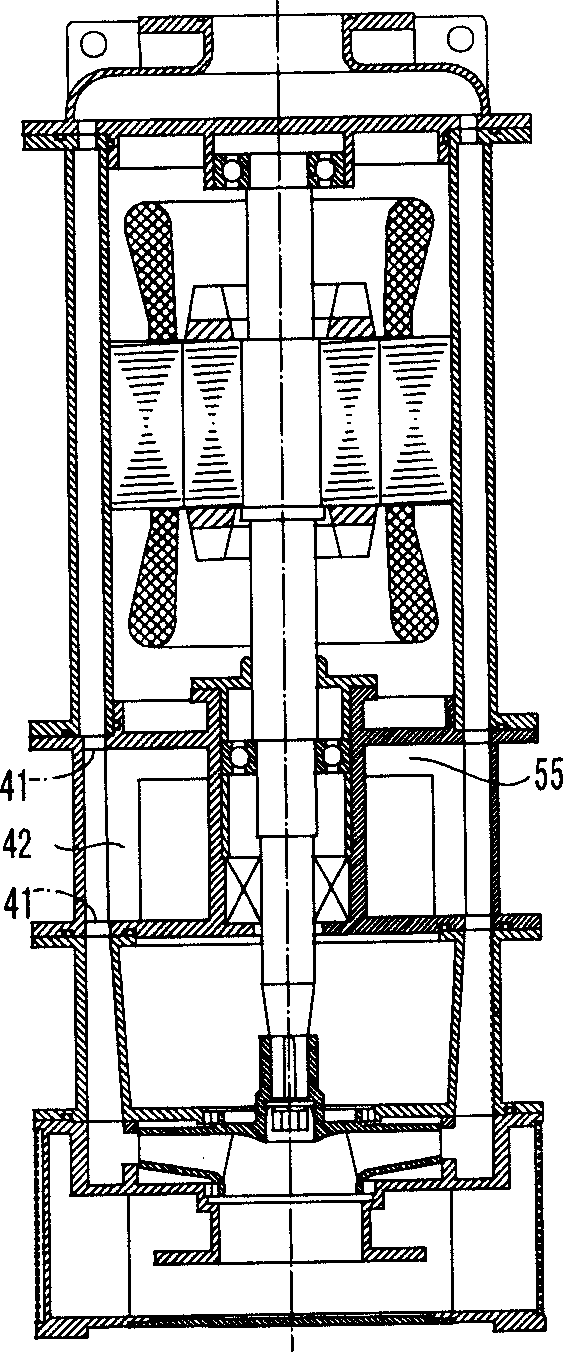
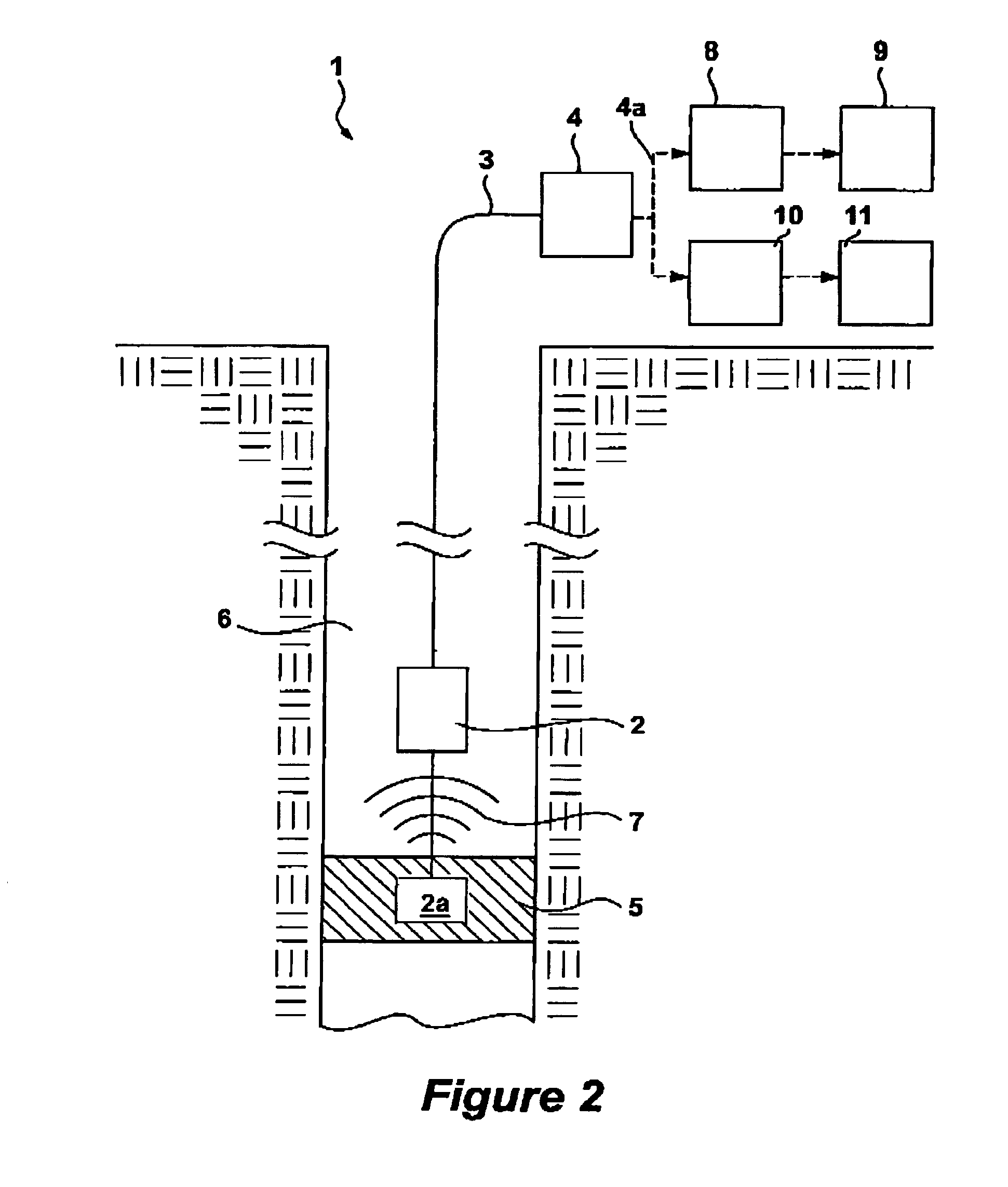
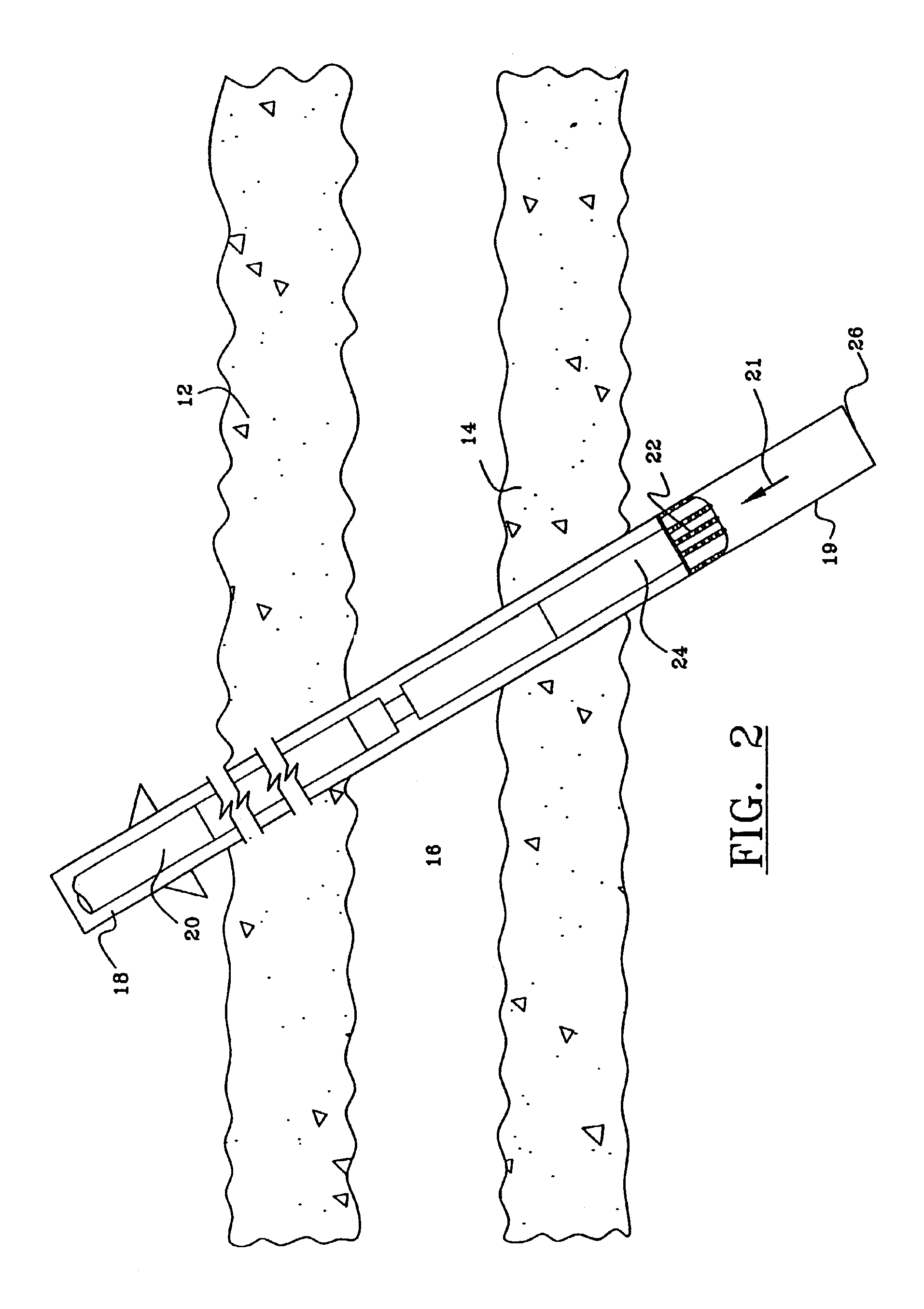
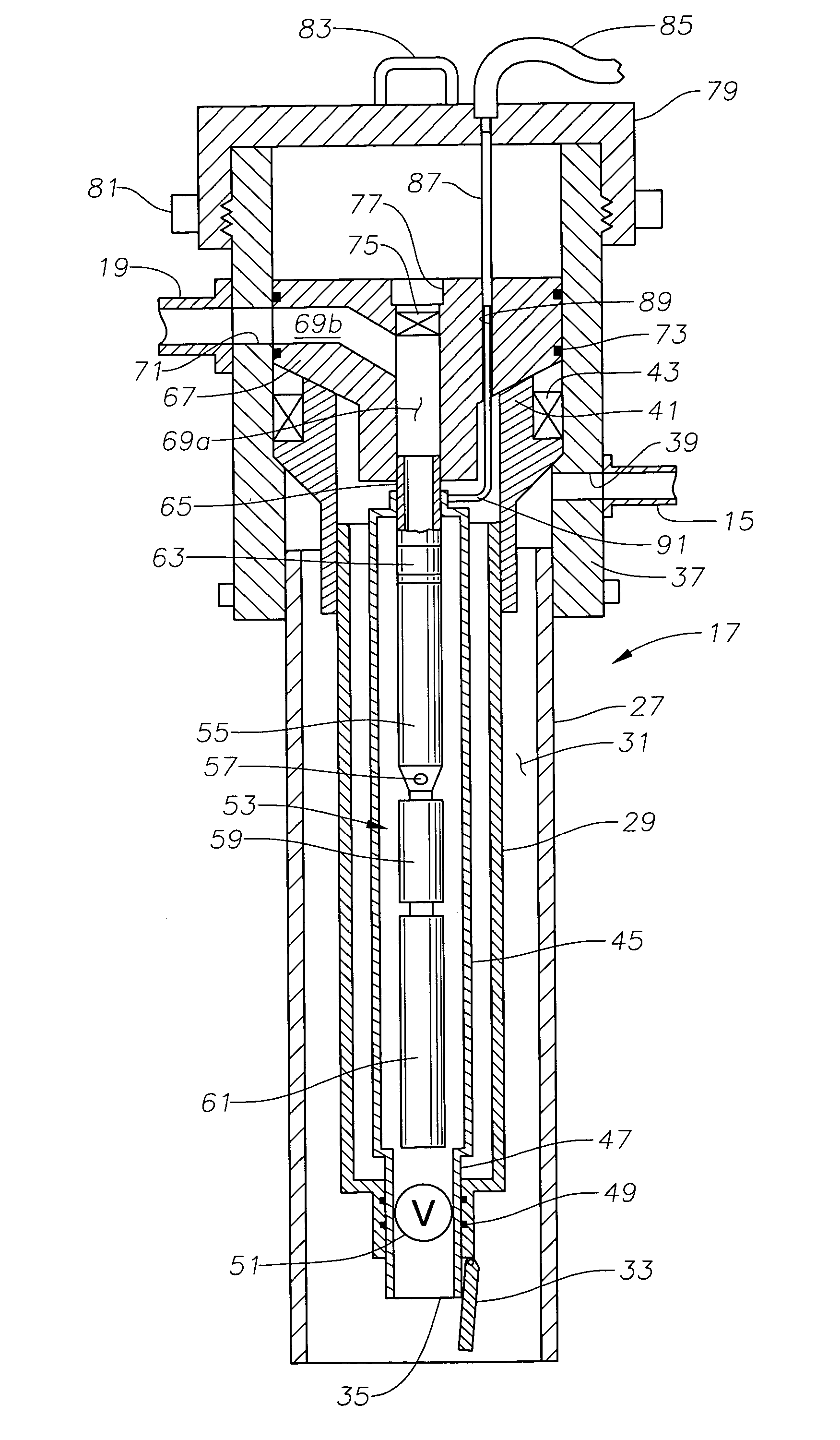
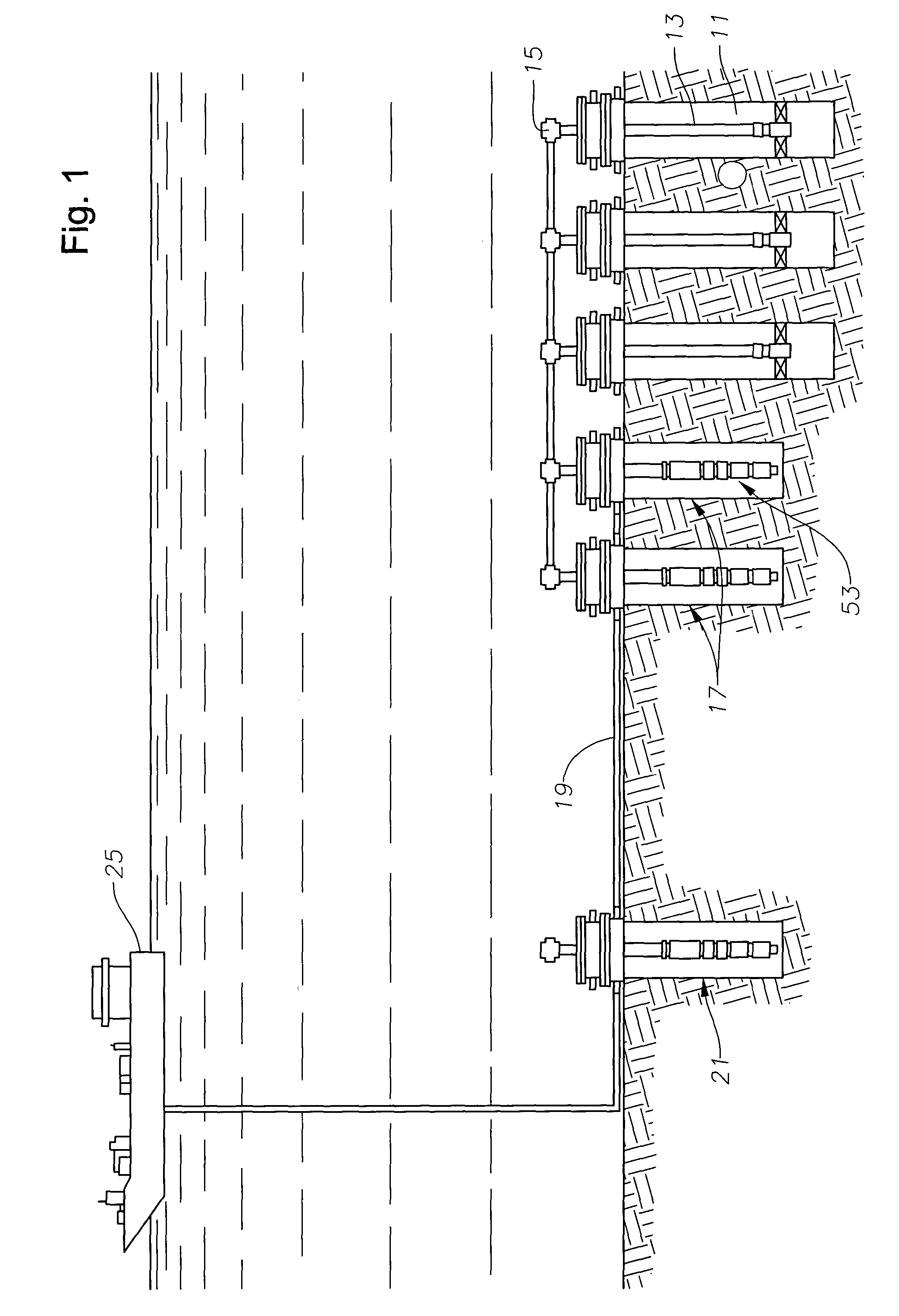
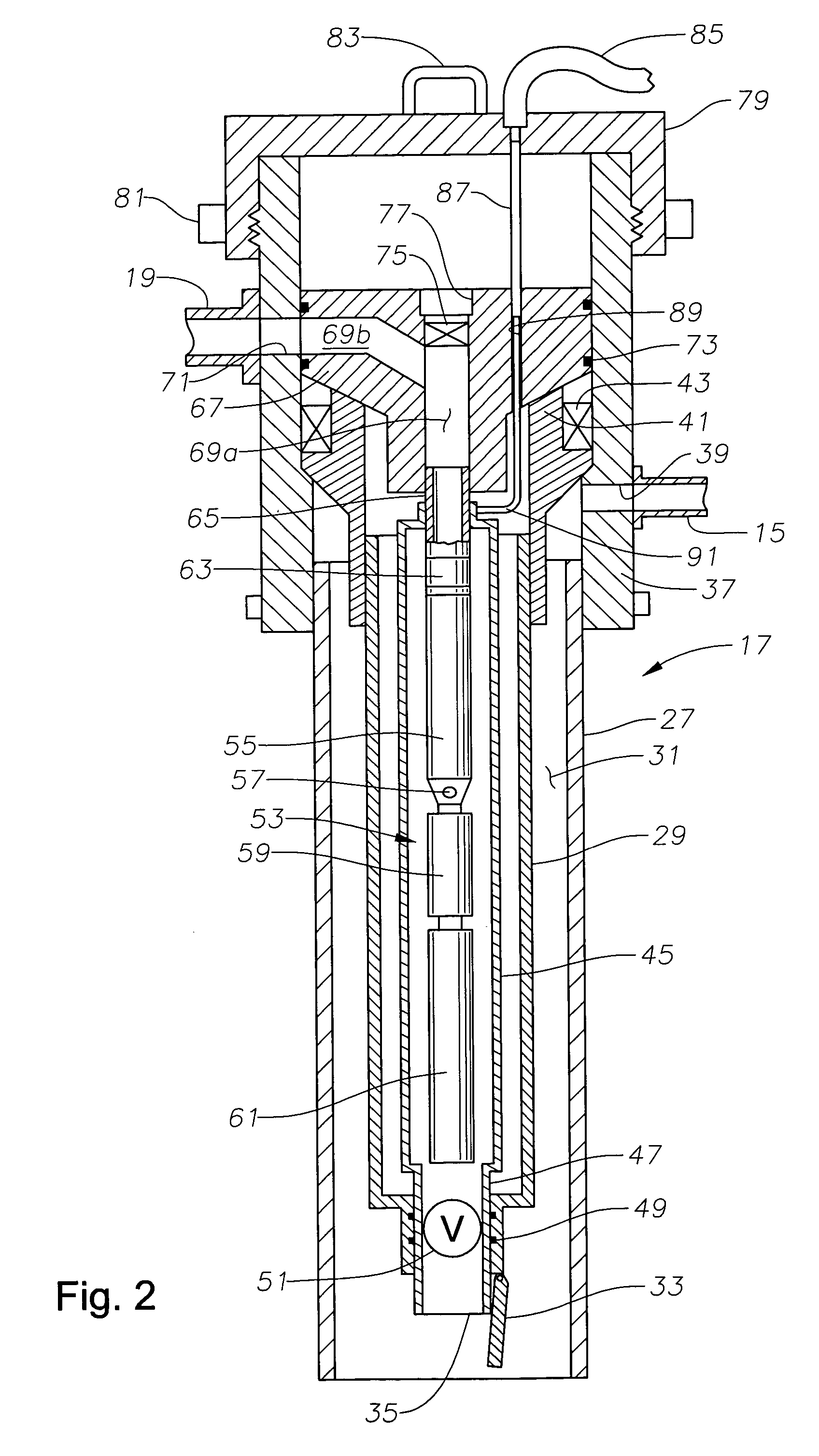
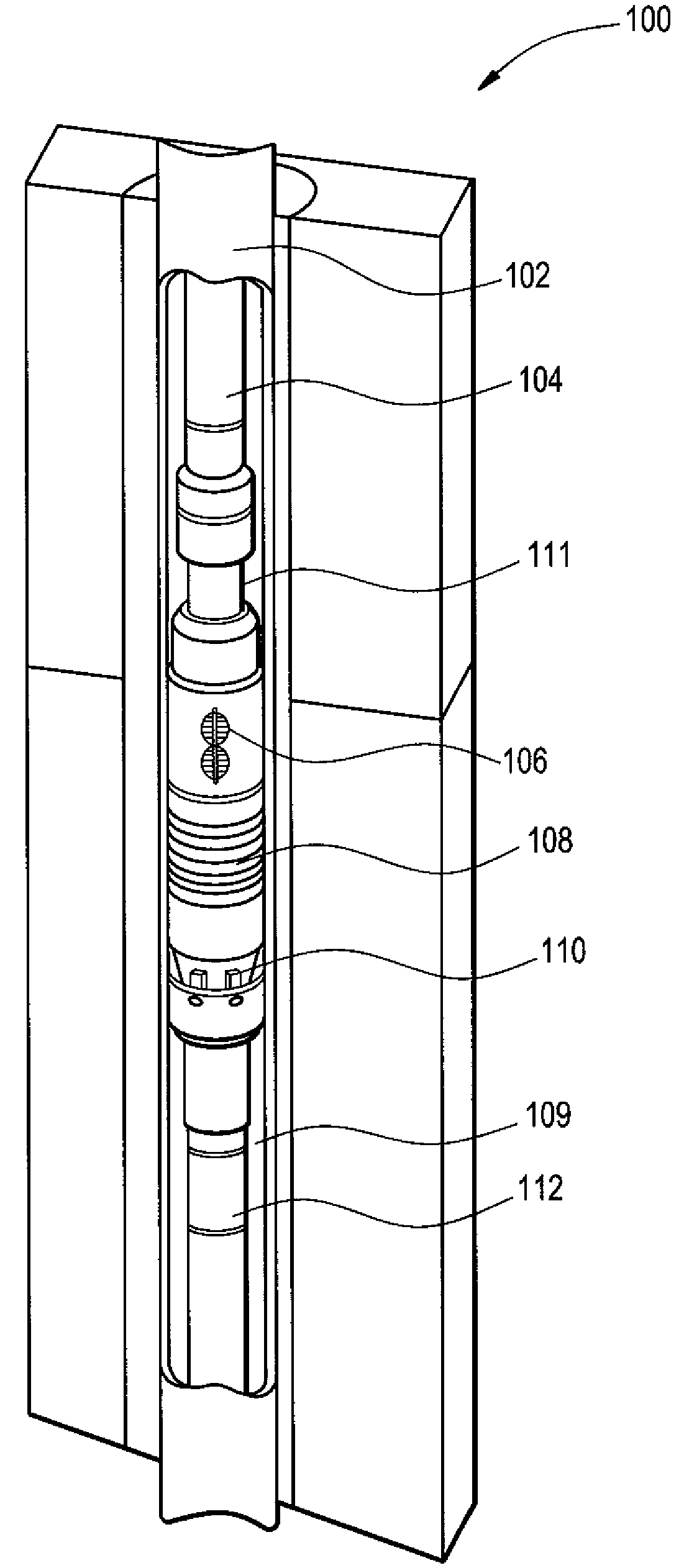
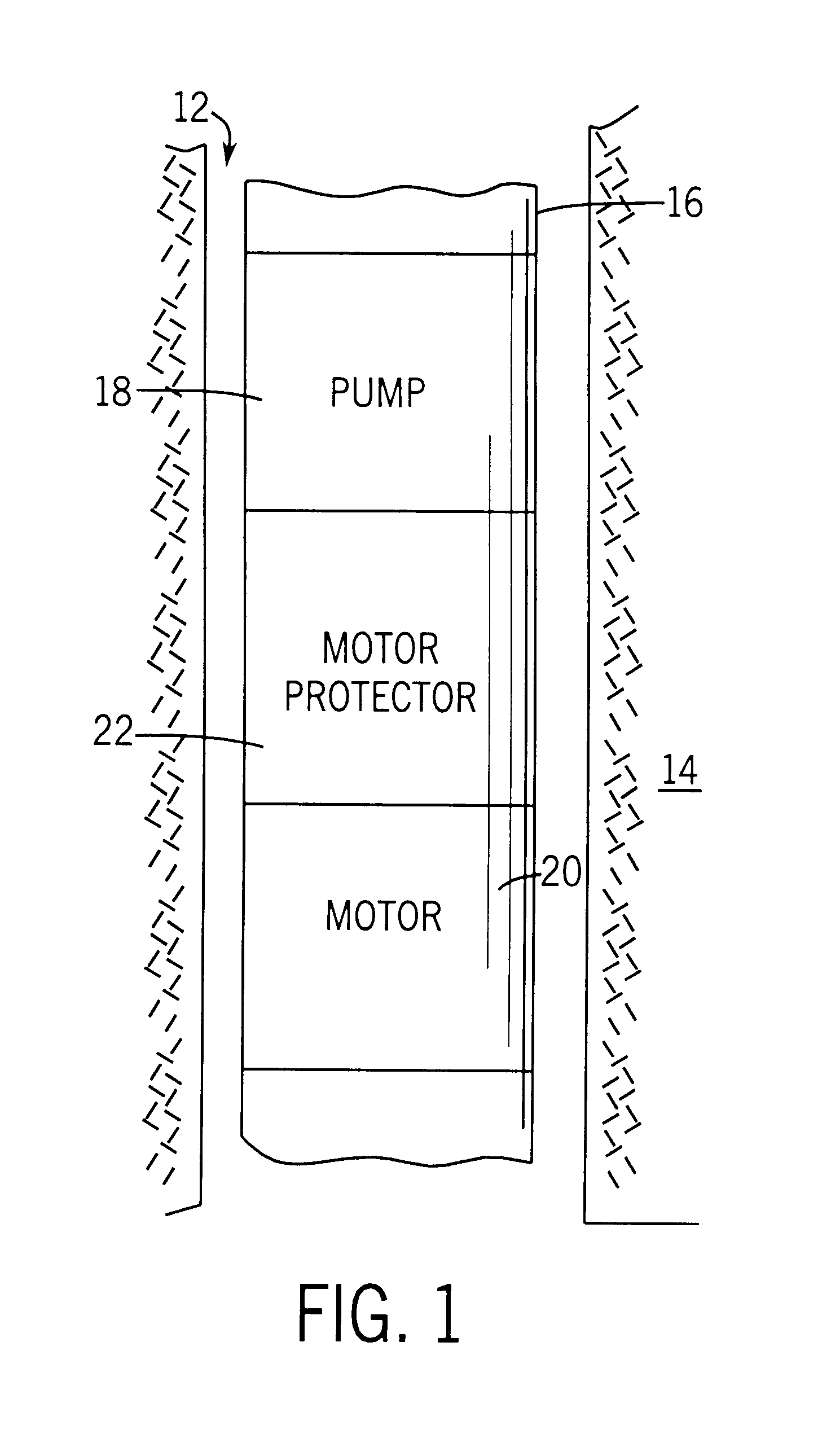
A submersible pump (or sub pump, electric submersible pump (ESP)) is a device which has a hermetically sealed motor close-coupled to the pump body. The whole assembly is submerged in the fluid to be pumped. The main advantage of this type of pump is that it prevents pump cavitation, a problem associated with a high elevation difference between pump and the fluid surface. Submersible pumps push fluid to the surface as opposed to jet pumps which create a vacuum and rely upon atmospheric pressure. Submersibles are more efficient than jet pumps. Hydraulic submersible pumps (HSP's) use pressurised fluid from the surface to drive a hydraulic motor downhole, rather than an electric motor, and are used in heavy oil applications with heated water as the motive fluid.
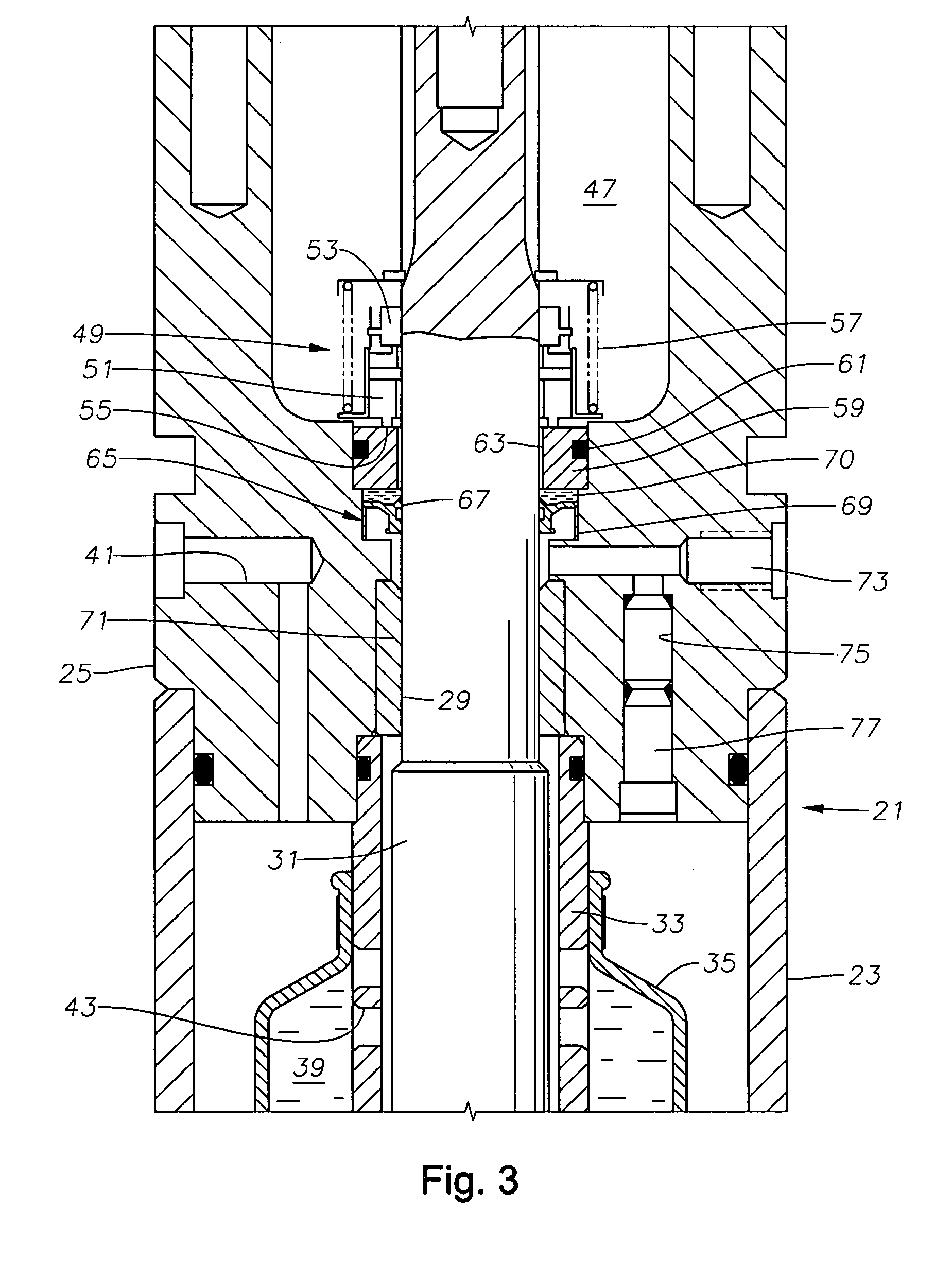
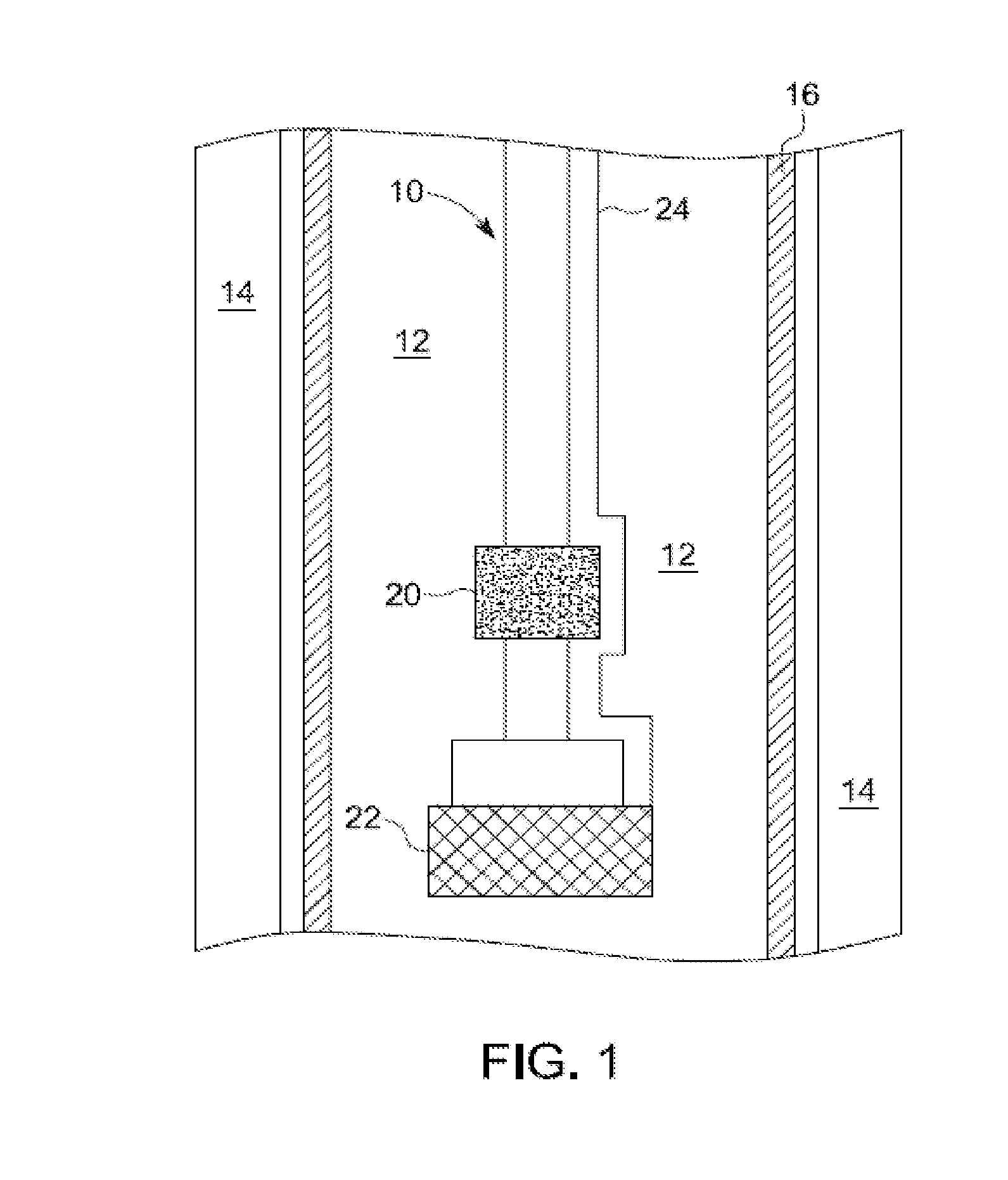
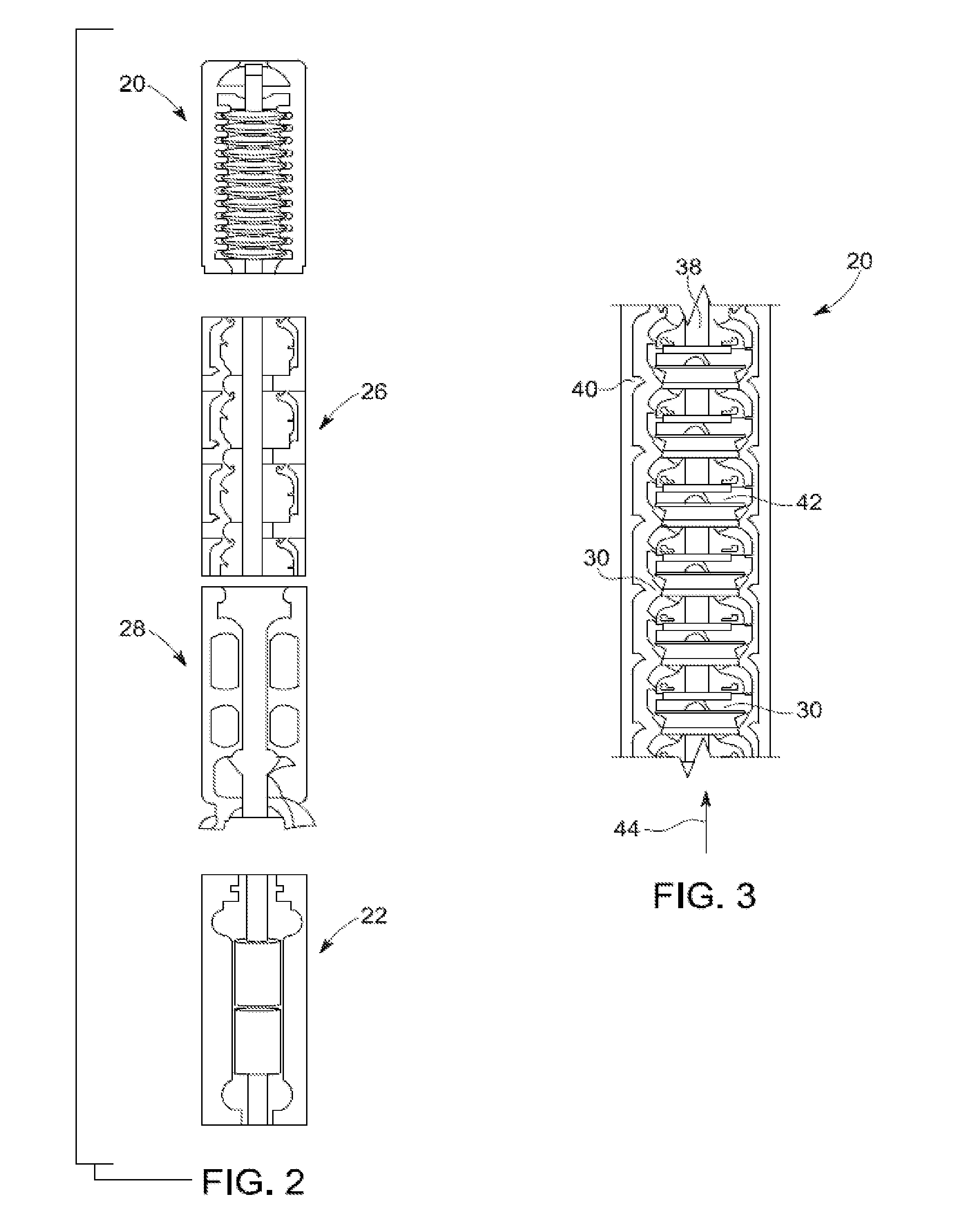
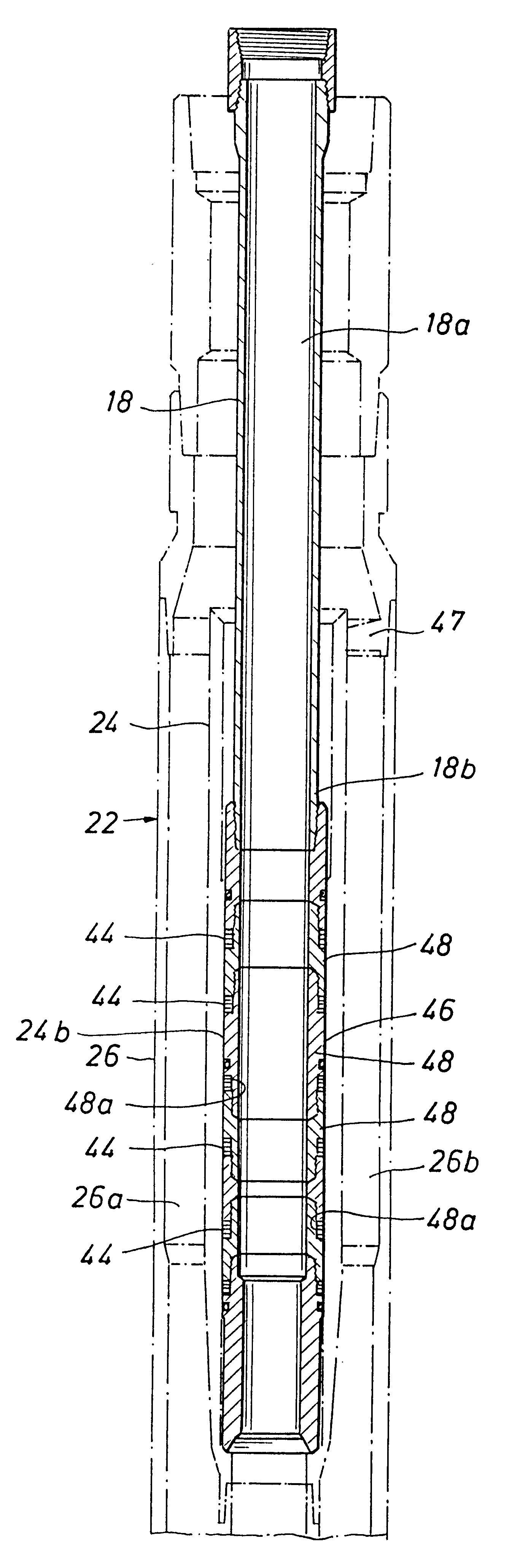
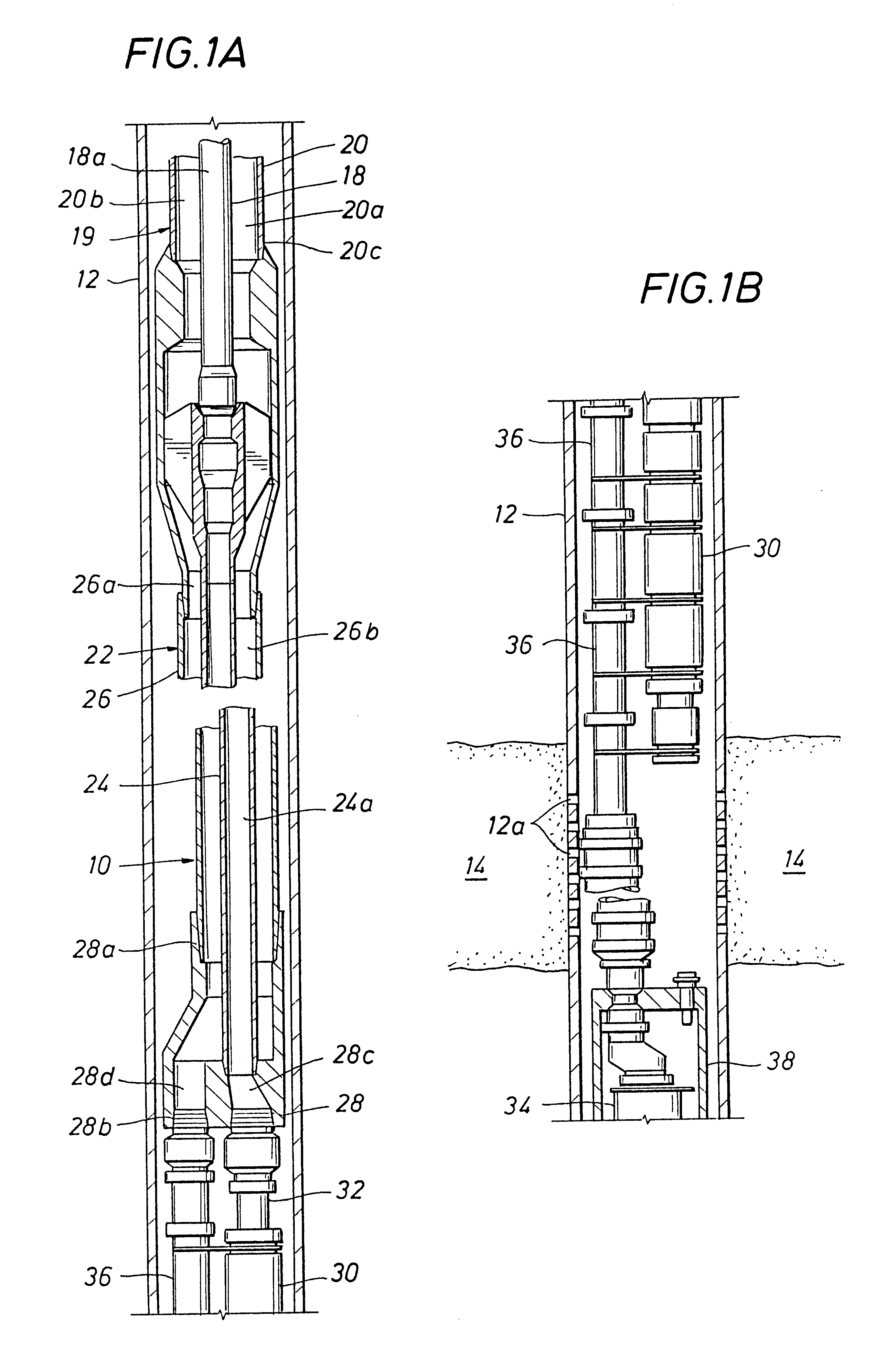
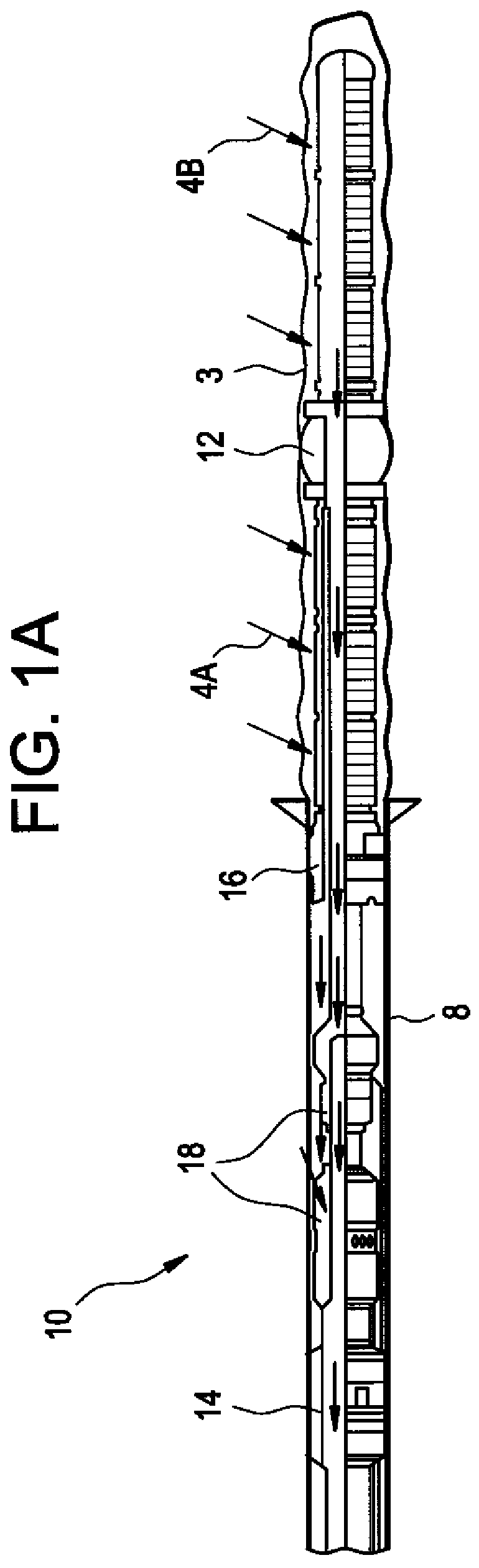
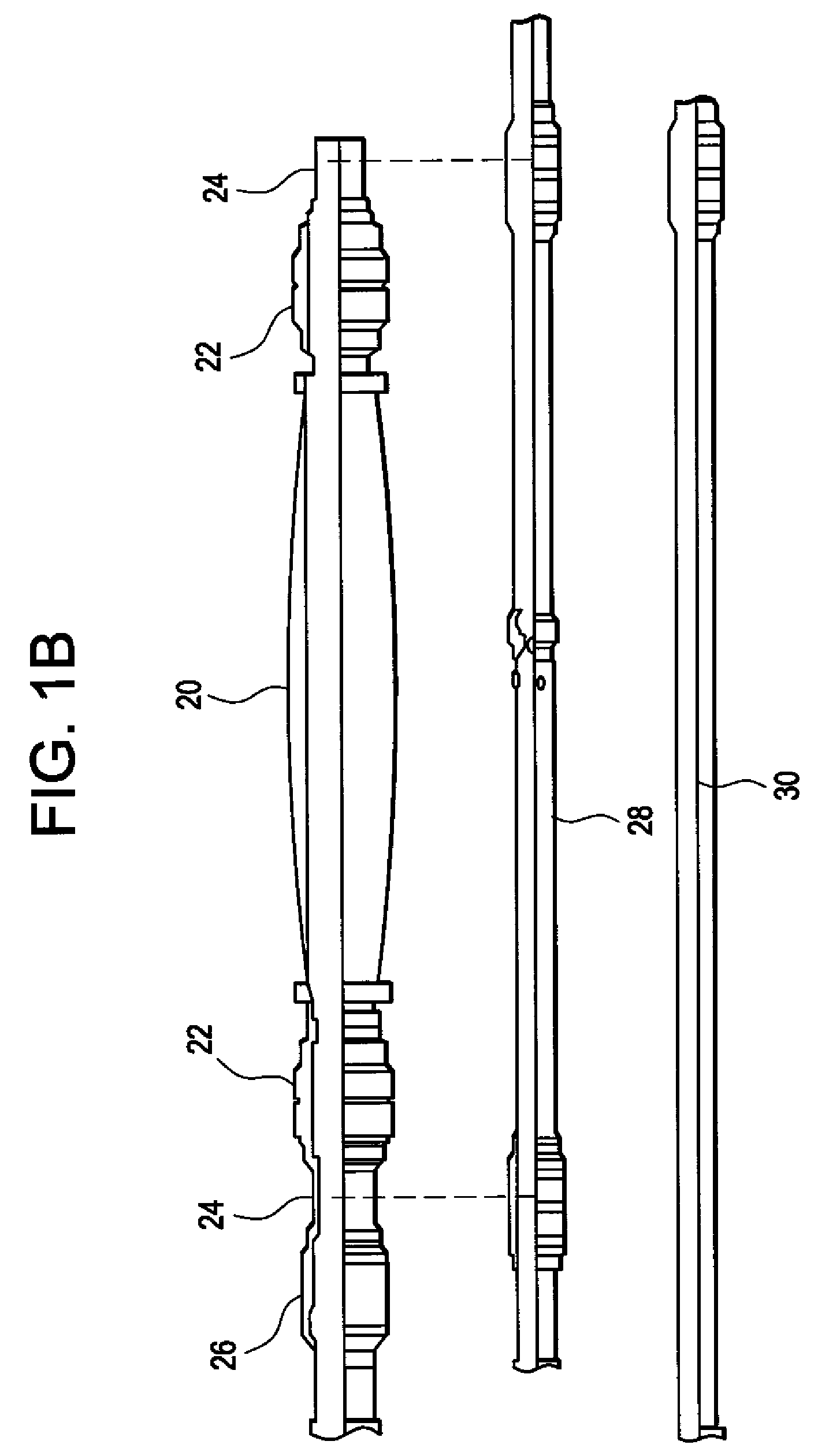
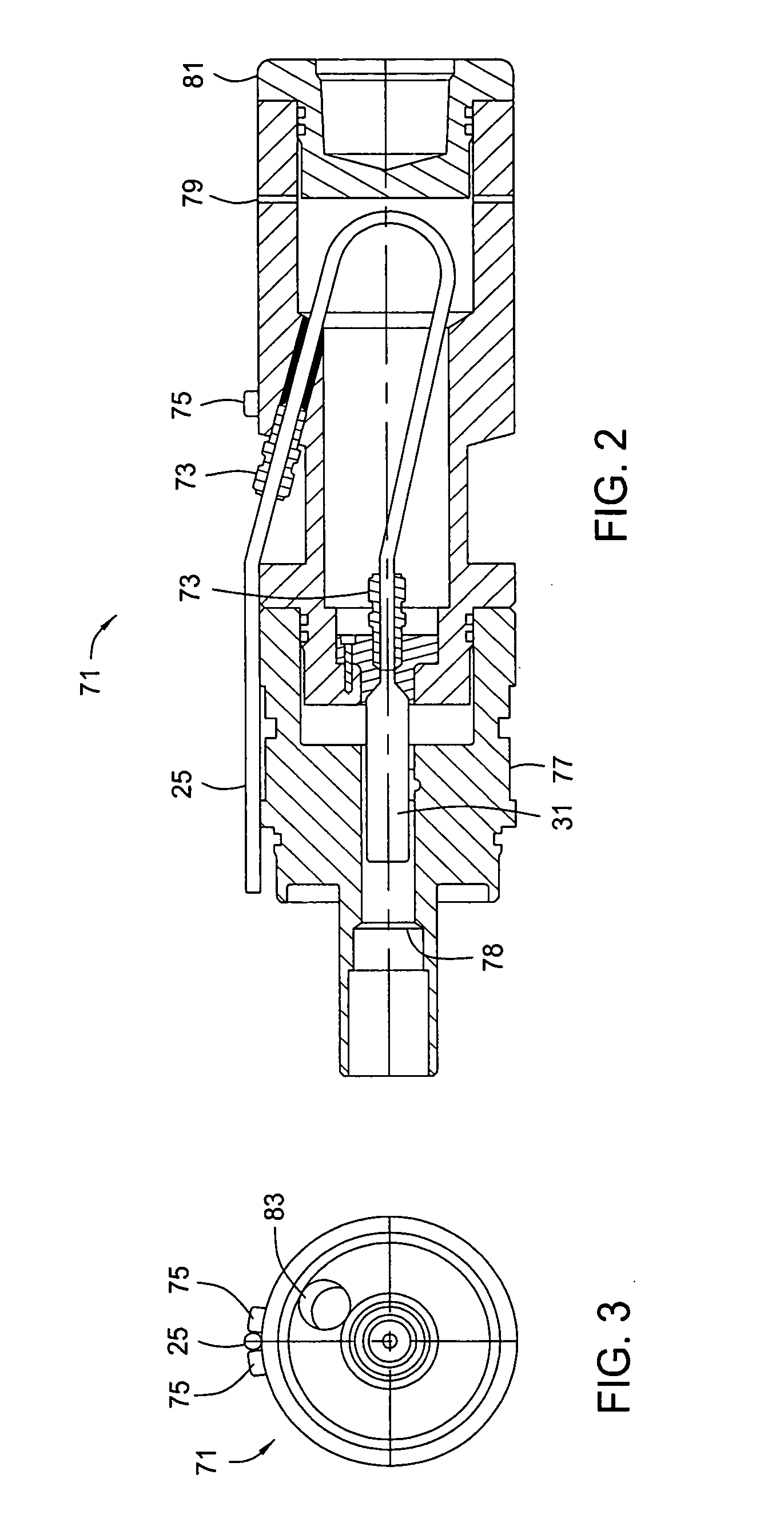
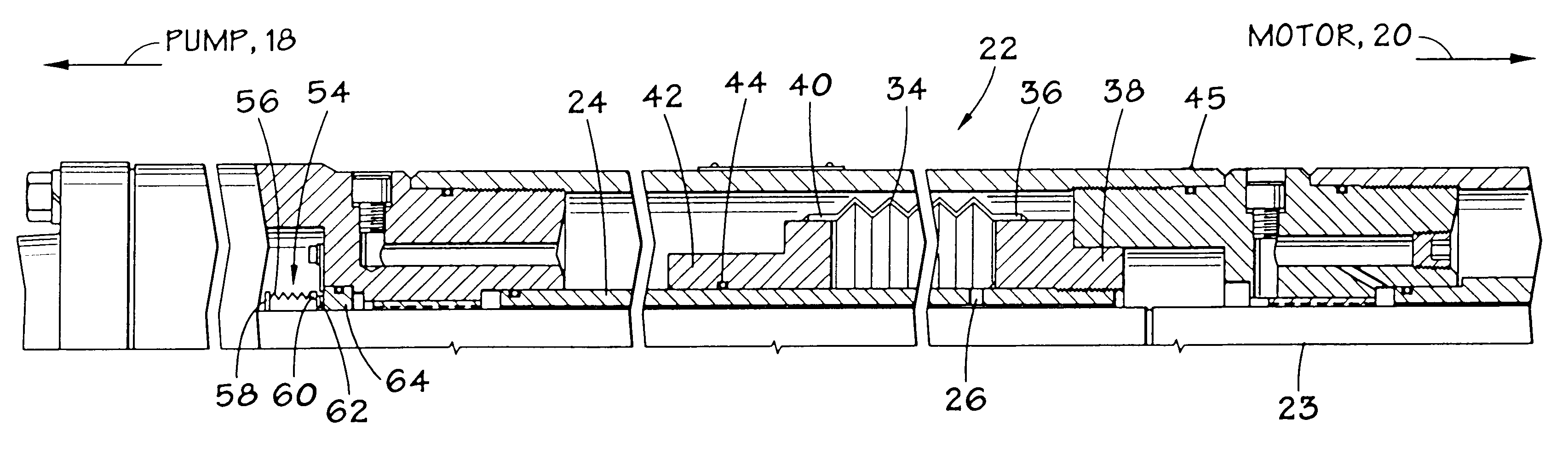
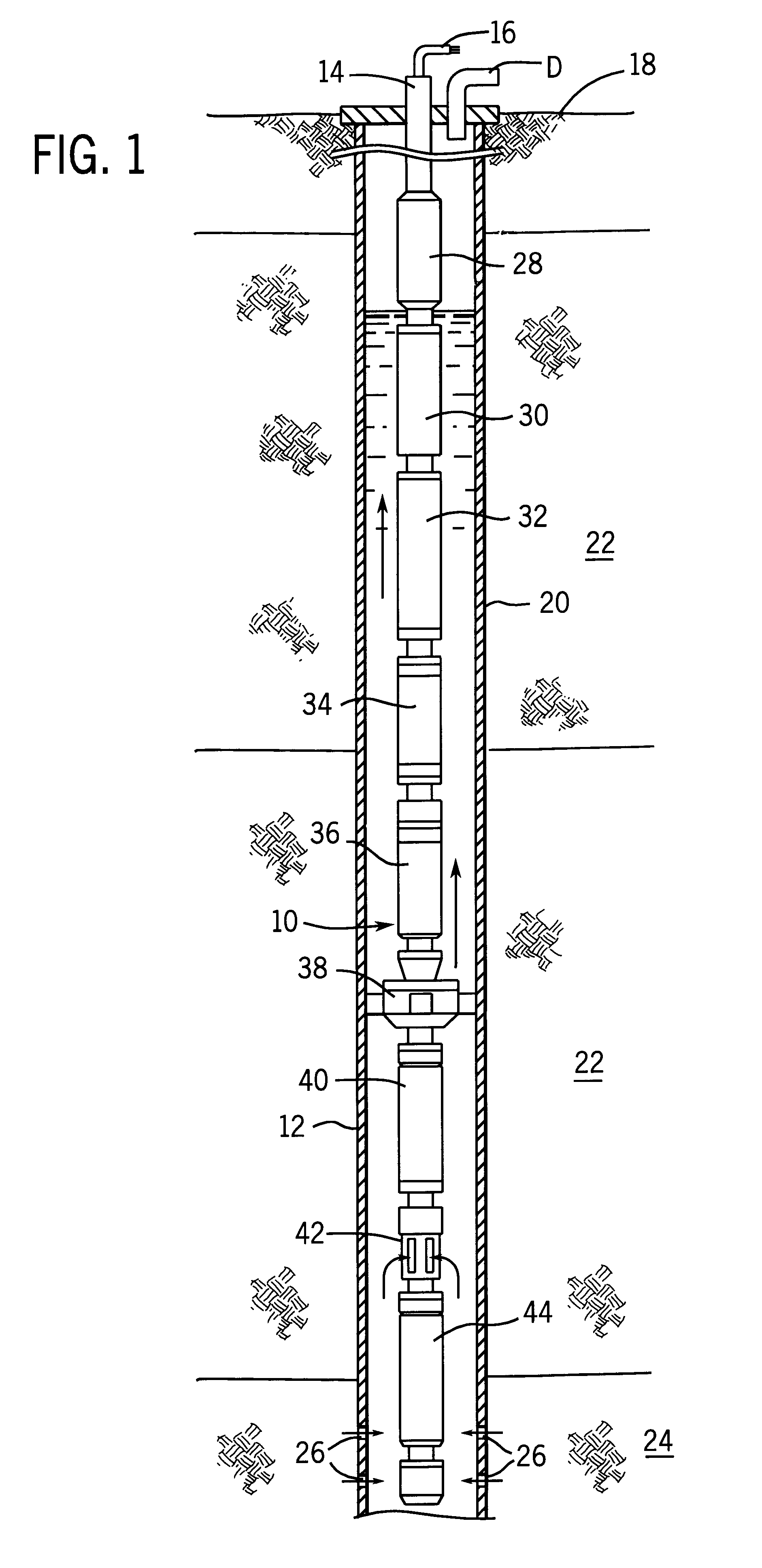
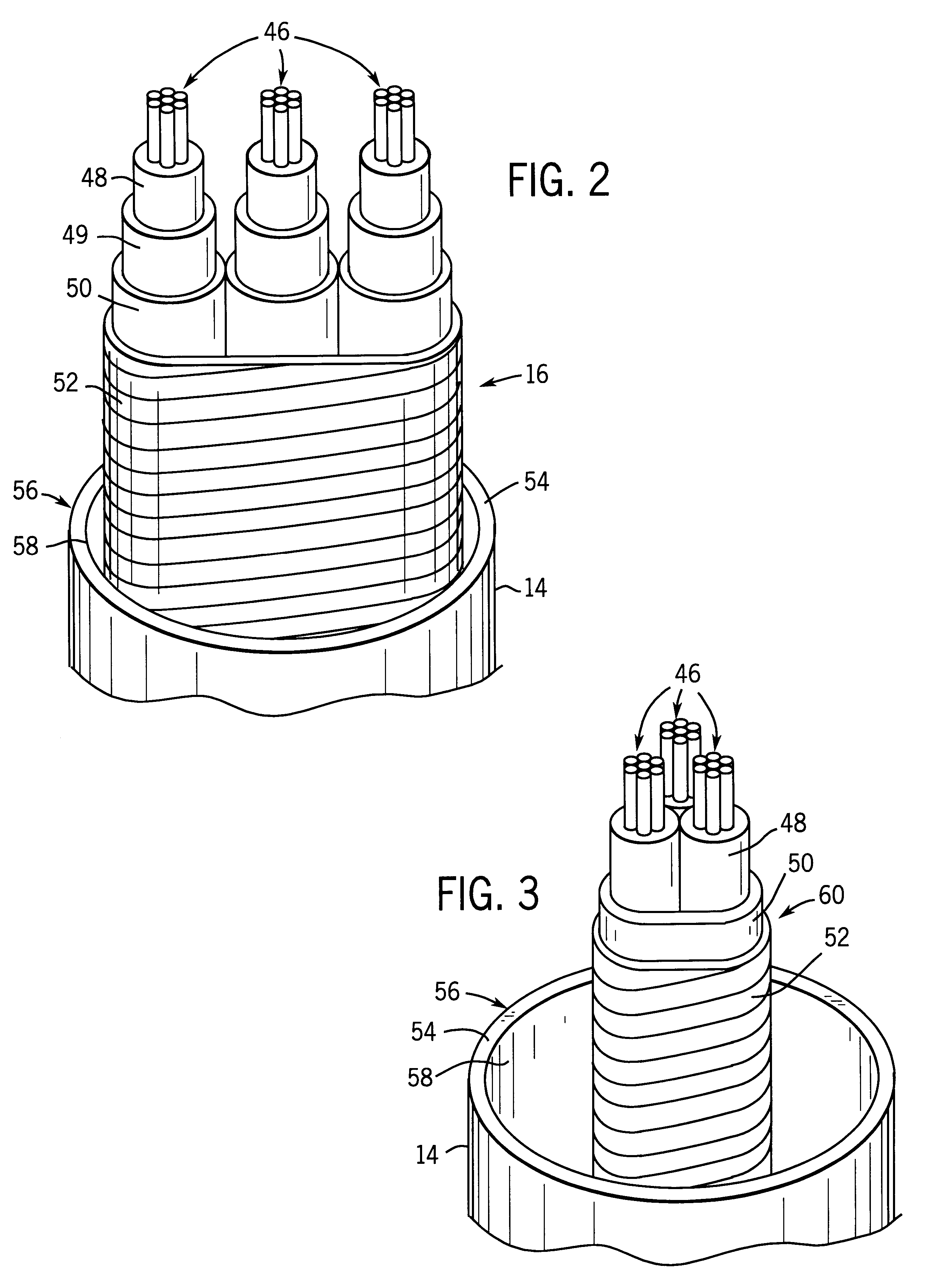
Stress control cones for downhole electrical power system tubing encapsulated power cables
ActiveUS20190089143A1Reduce electrical stressElectrically conductive connectionsDrilling rodsInsulation layerPower cable
A stress cone for reducing electrical stresses is disclosed for use on terminated ends of tubing encapsulated power cable used in surface applications in a subsurface well power system employing electric submersible pumps (ESPs). The stress cone comprises an annular section about a longitudinal axis for receiving a terminated end of the TEPC in its first end and for abutting the terminated metal TEPC end against a metal shoulder at its second end therein, and an insulation chamber axially aligned with and connected to the annular section. The chamber comprises a metal interior surface symmetrical about the axis. The insulated TEPC core (without outer metal sheath) passes through the insulation chamber along the axis and then exits. The ID of the TEPC metal sheath and the inside metal surface of the chamber form a smooth ground plane transition surface. Insulation material surrounds the TEPC insulation layer within the insulation chamber.
Owner:ARTIFICIAL ELEVATOR
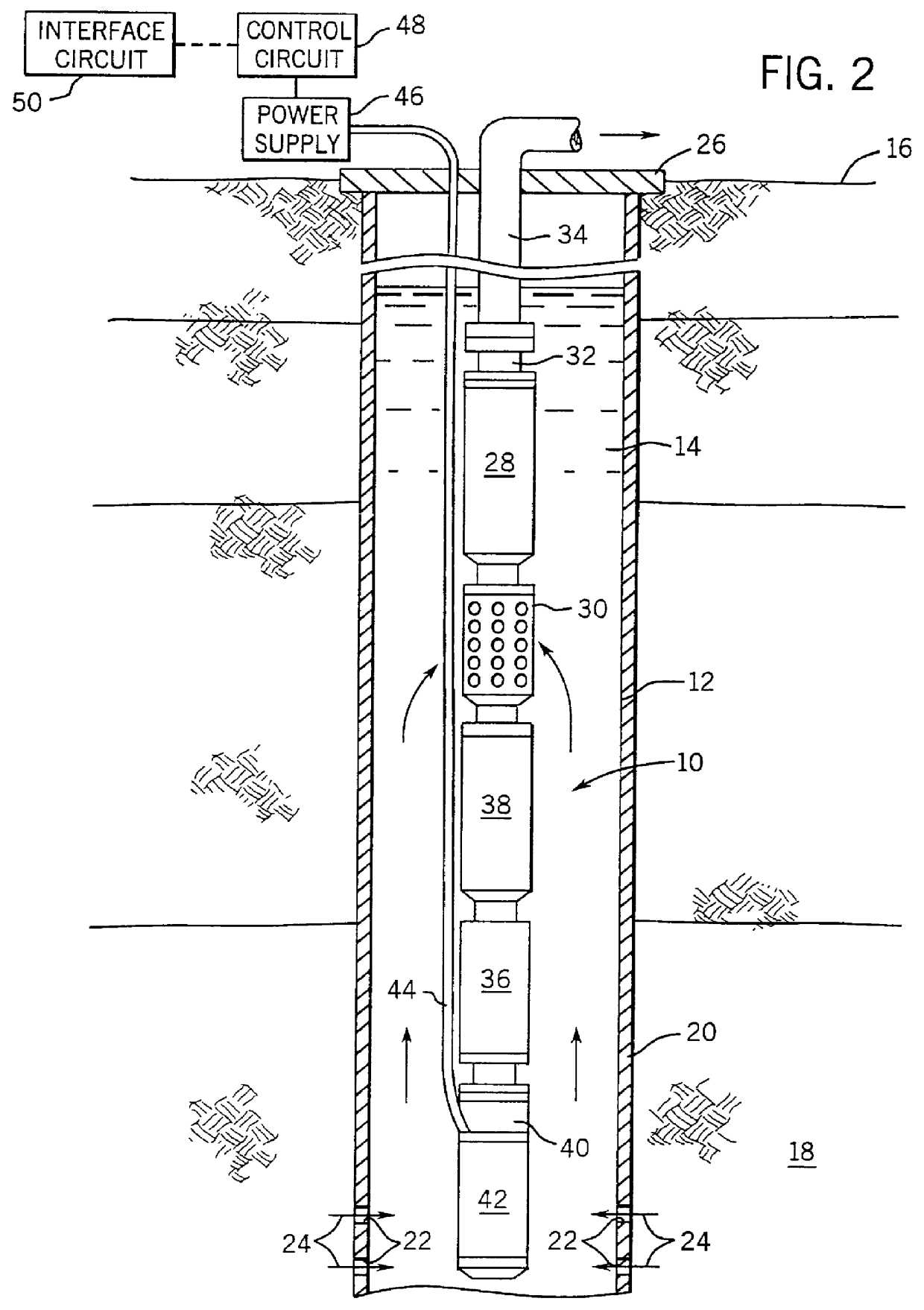
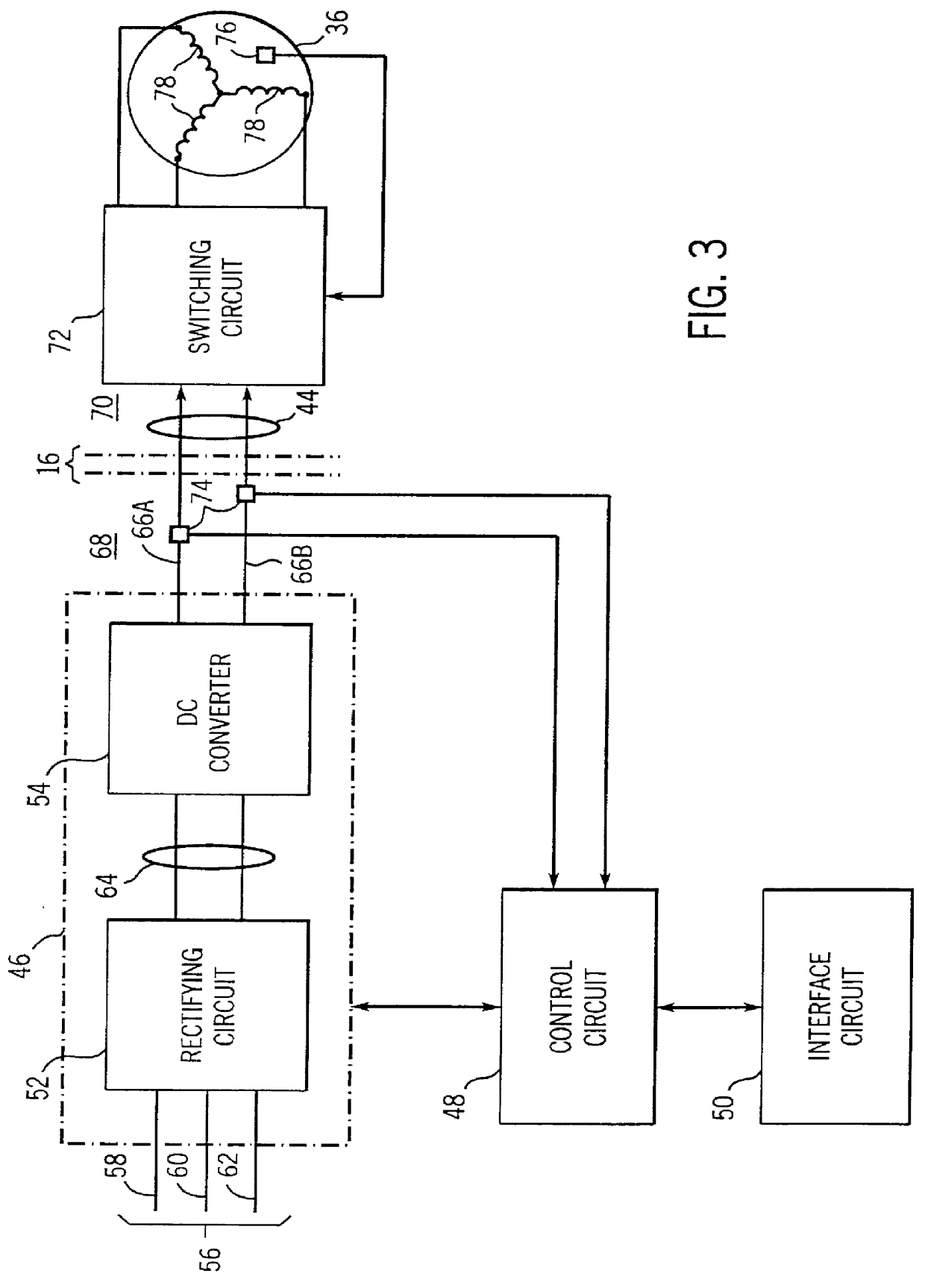
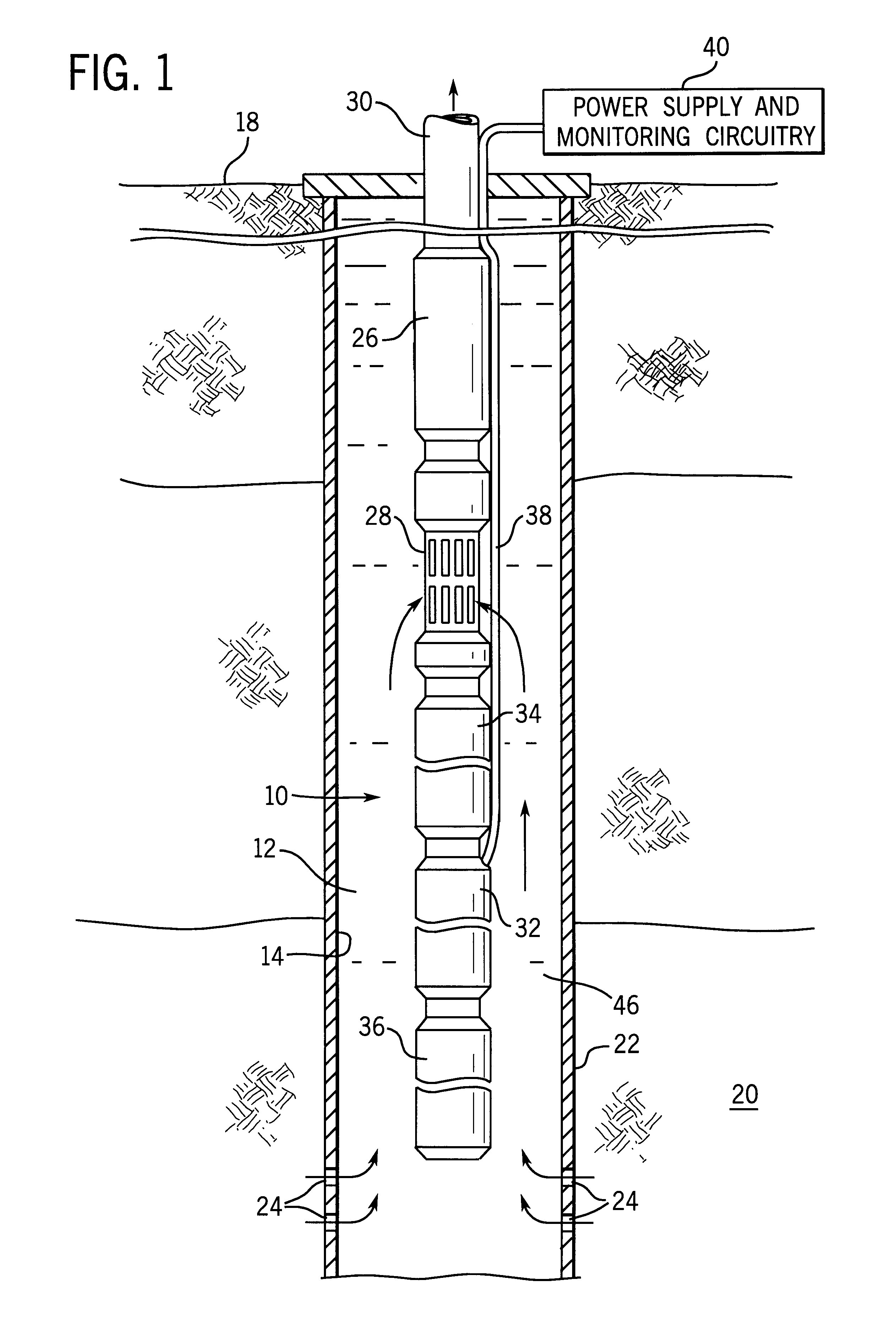
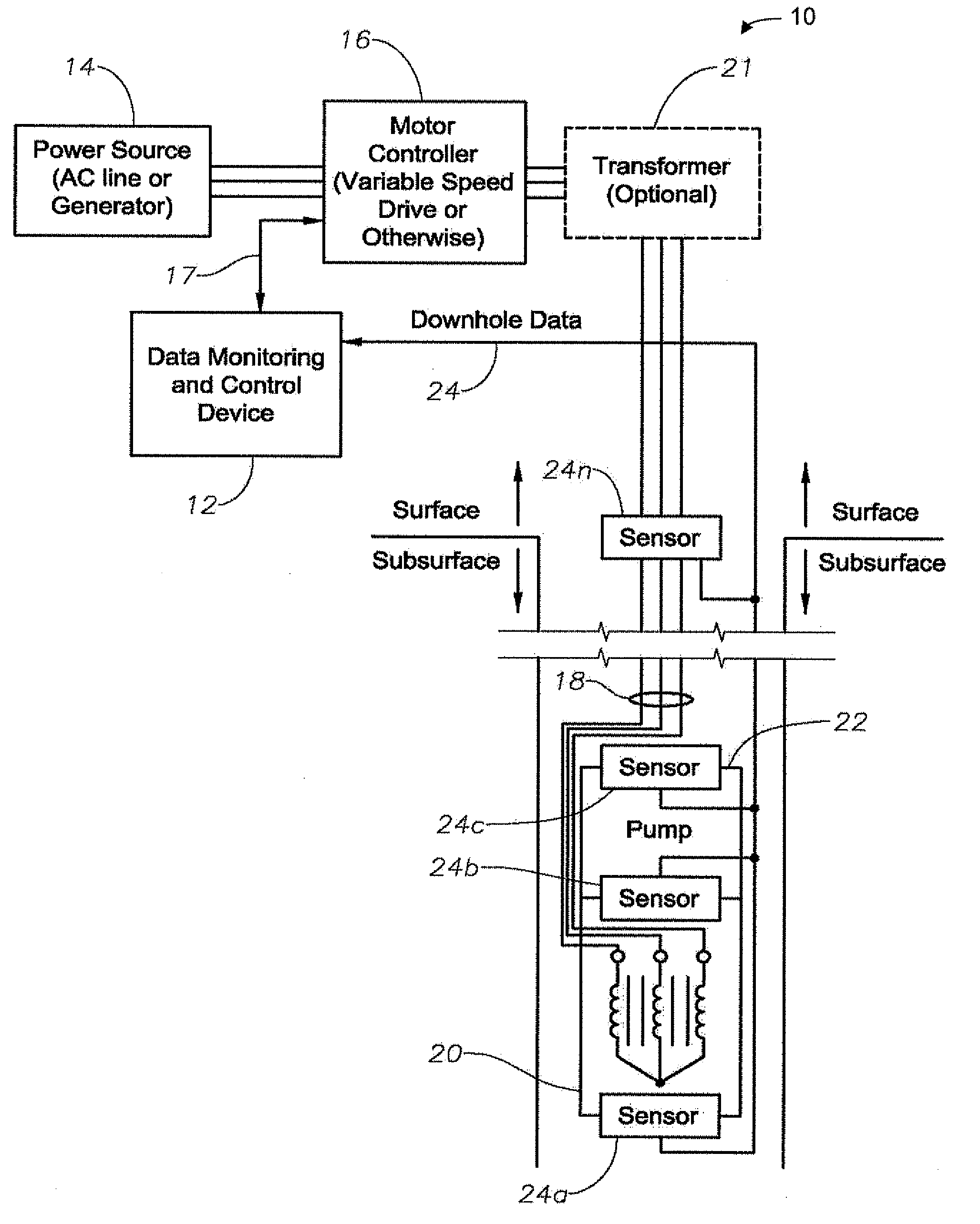
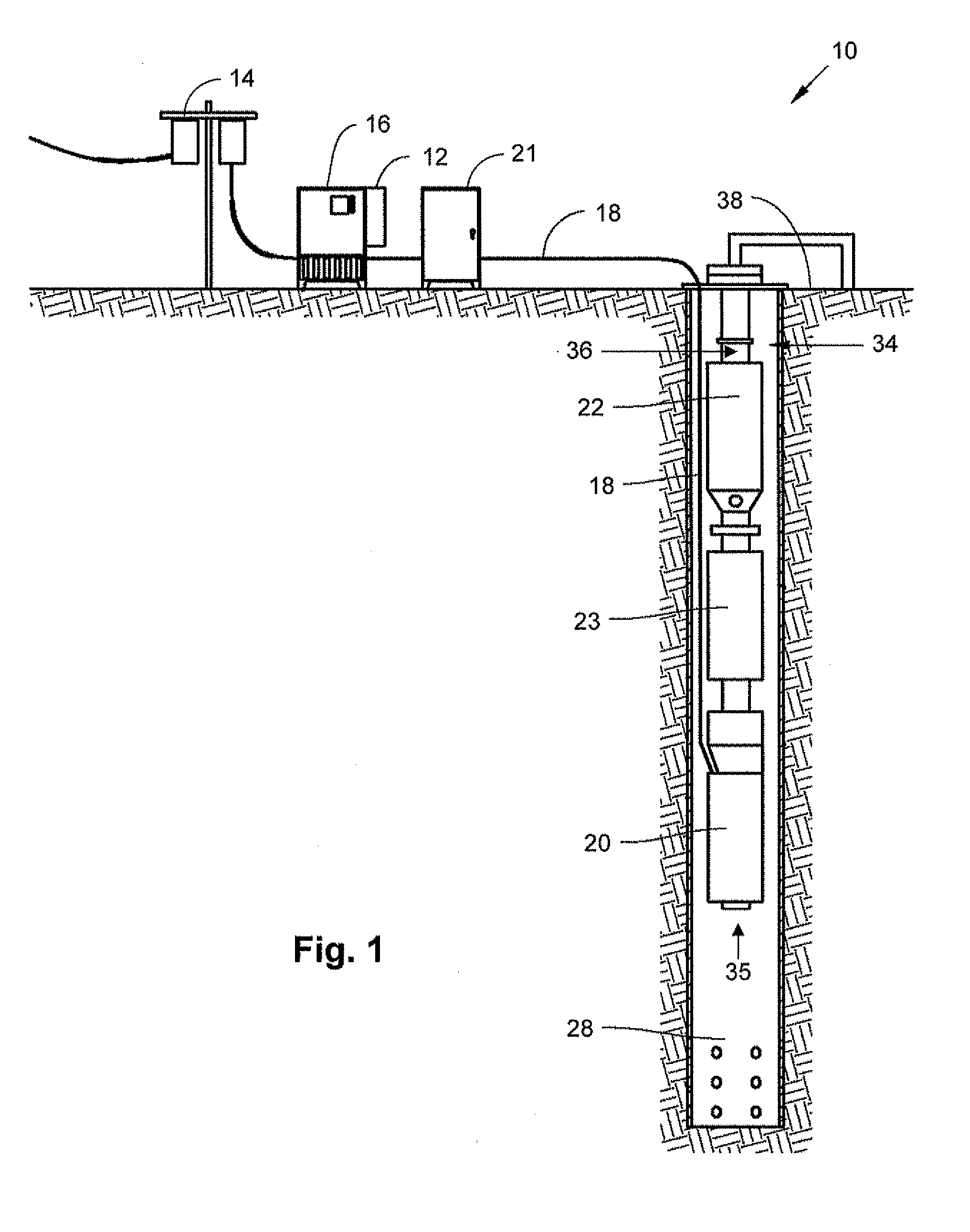
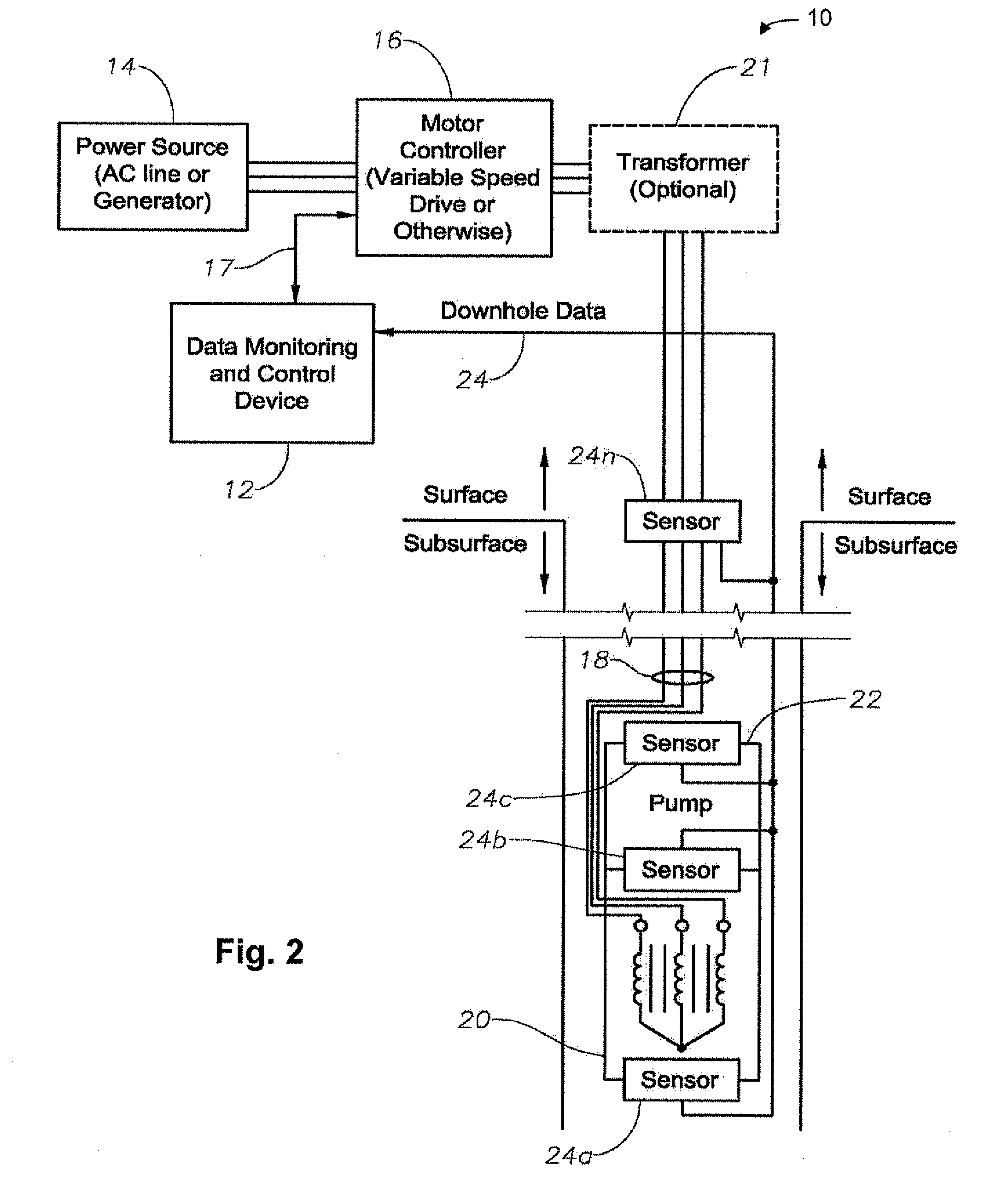
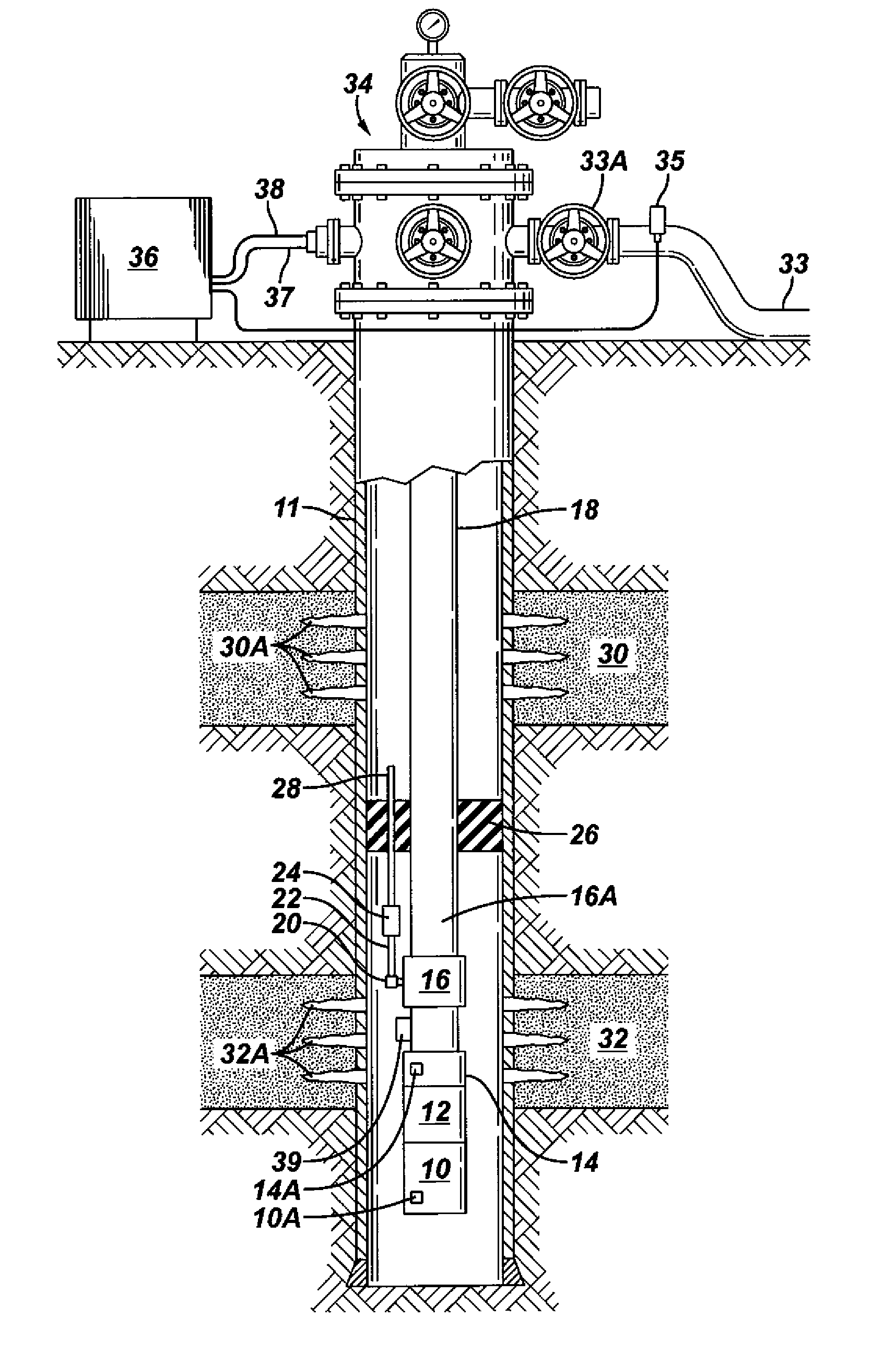
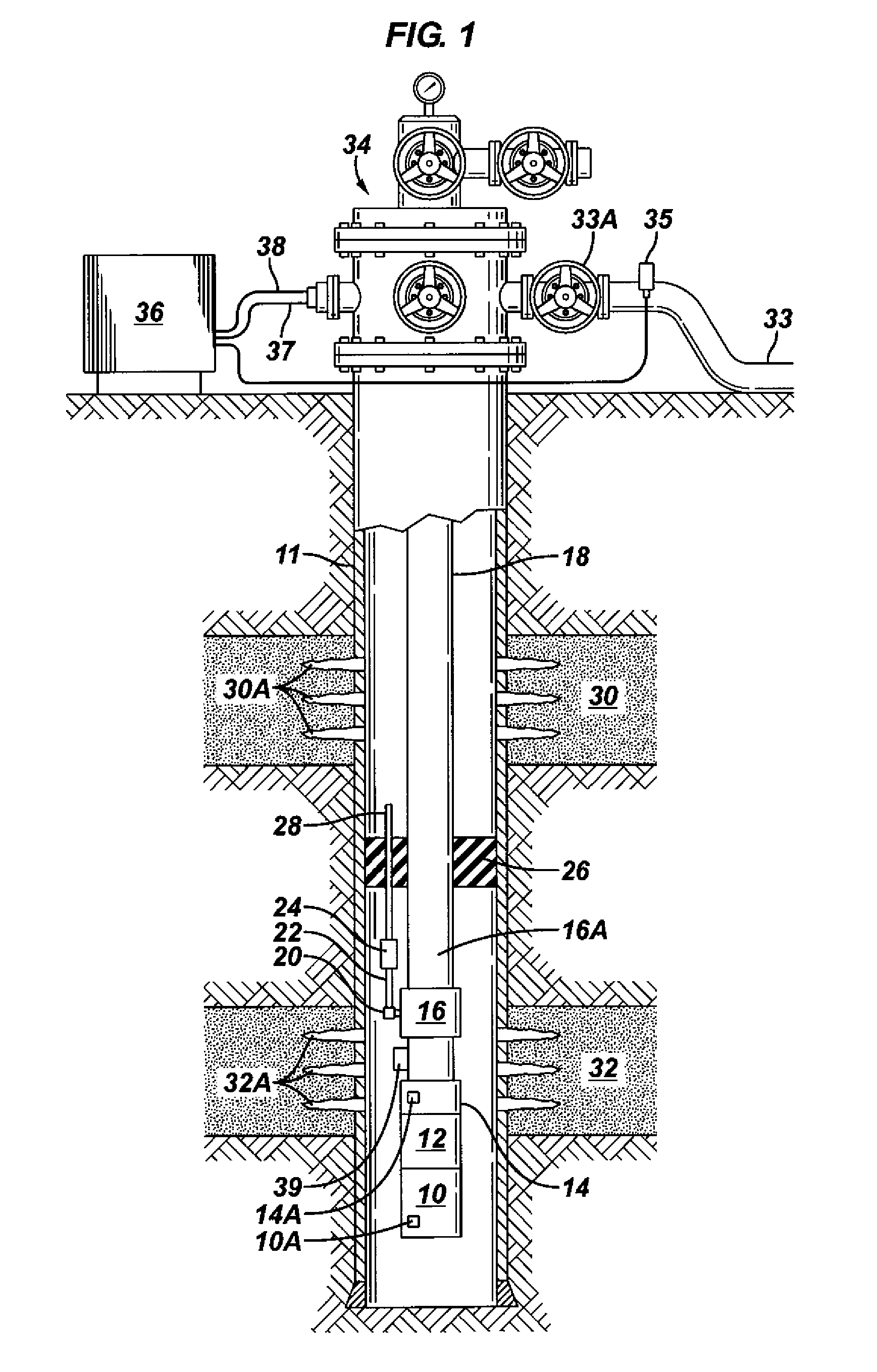
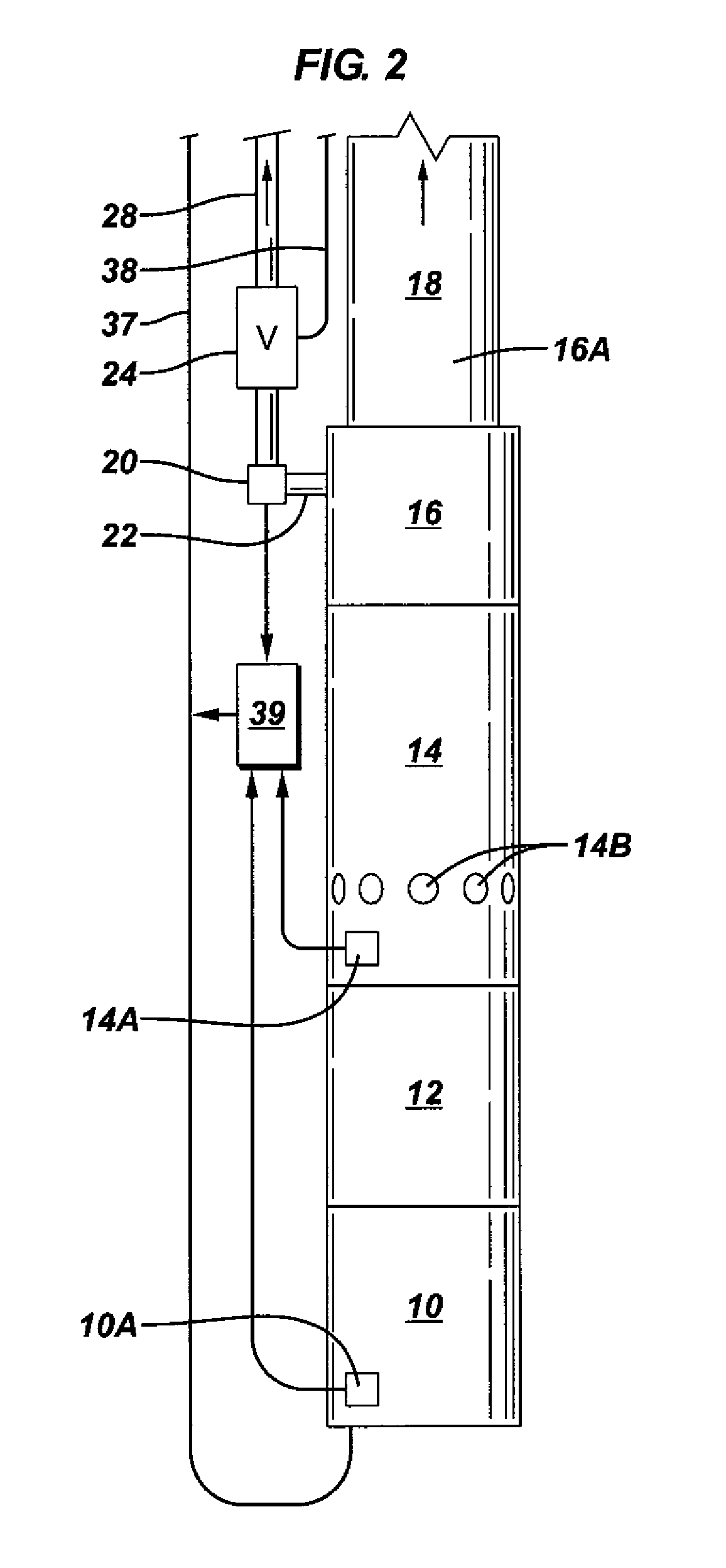
Method and apparatus for controlling a submergible pumping system
A submergible pumping unit for raising viscous fluids from a well is driven by an electronic drive and control system, a first portion of which is located above the well, and a second portion of which is coupled to the submergible pumping unit. The drive and control system includes a power supply circuit located above the well for converting AC power from a source to DC power having current and voltage levels. The DC power is transmitted to the pumping unit via a two-conductor DC bus cable. The pumping unit includes a switching circuit which receives the DC power for driving a submergible motor, such as a permanent magnet brushless motor. The speed of the motor, and of a pump coupled thereto, is proportional to the voltage of the DC power applied to the pumping unit. The pump is preferably a progressive cavity pump, and the drive and control circuitry provides sufficient torque to start the pump from a static condition. A control circuit is provided for transmitting configuration and desired flow rate and speed data to the power supply.
Owner:CAMCO INT
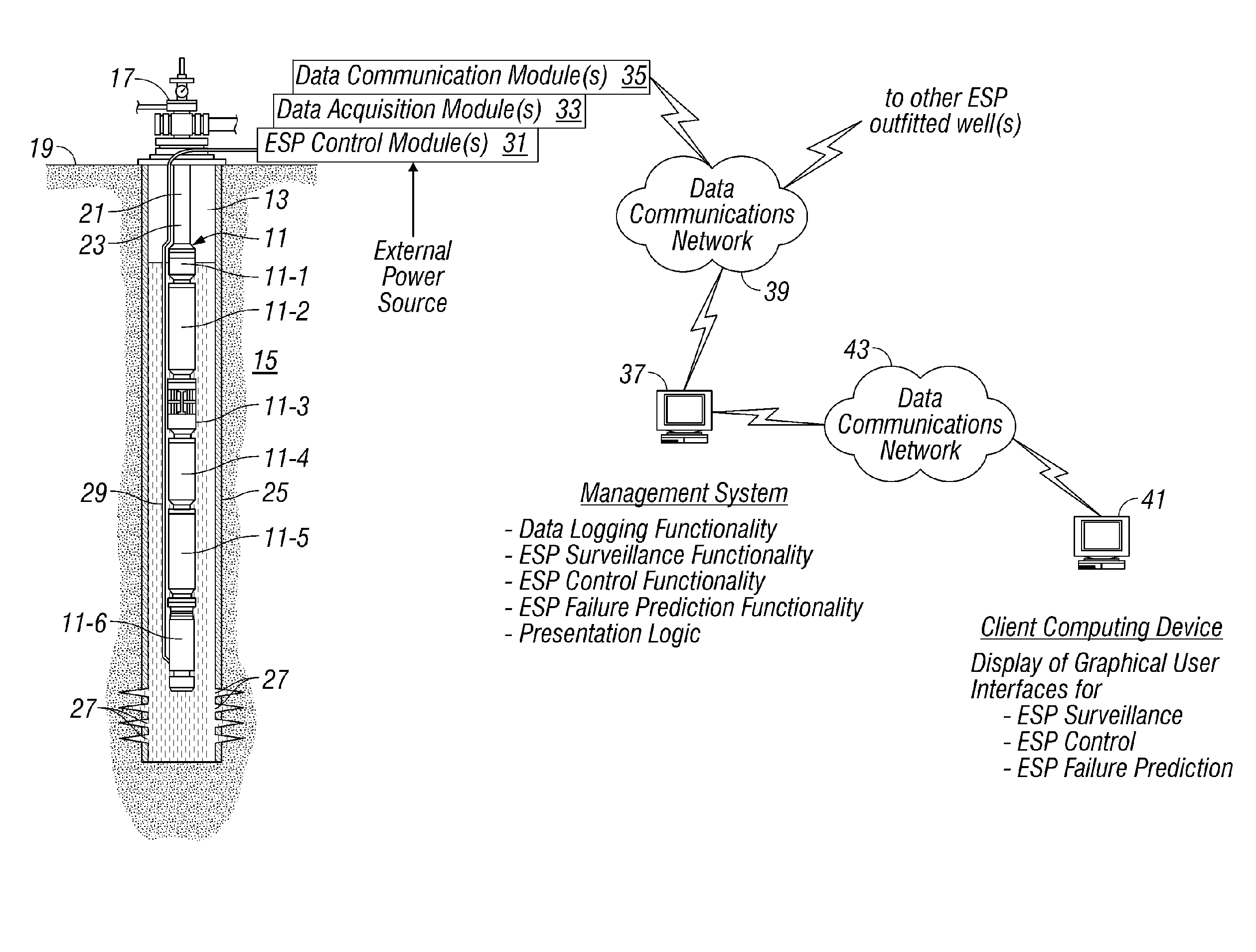
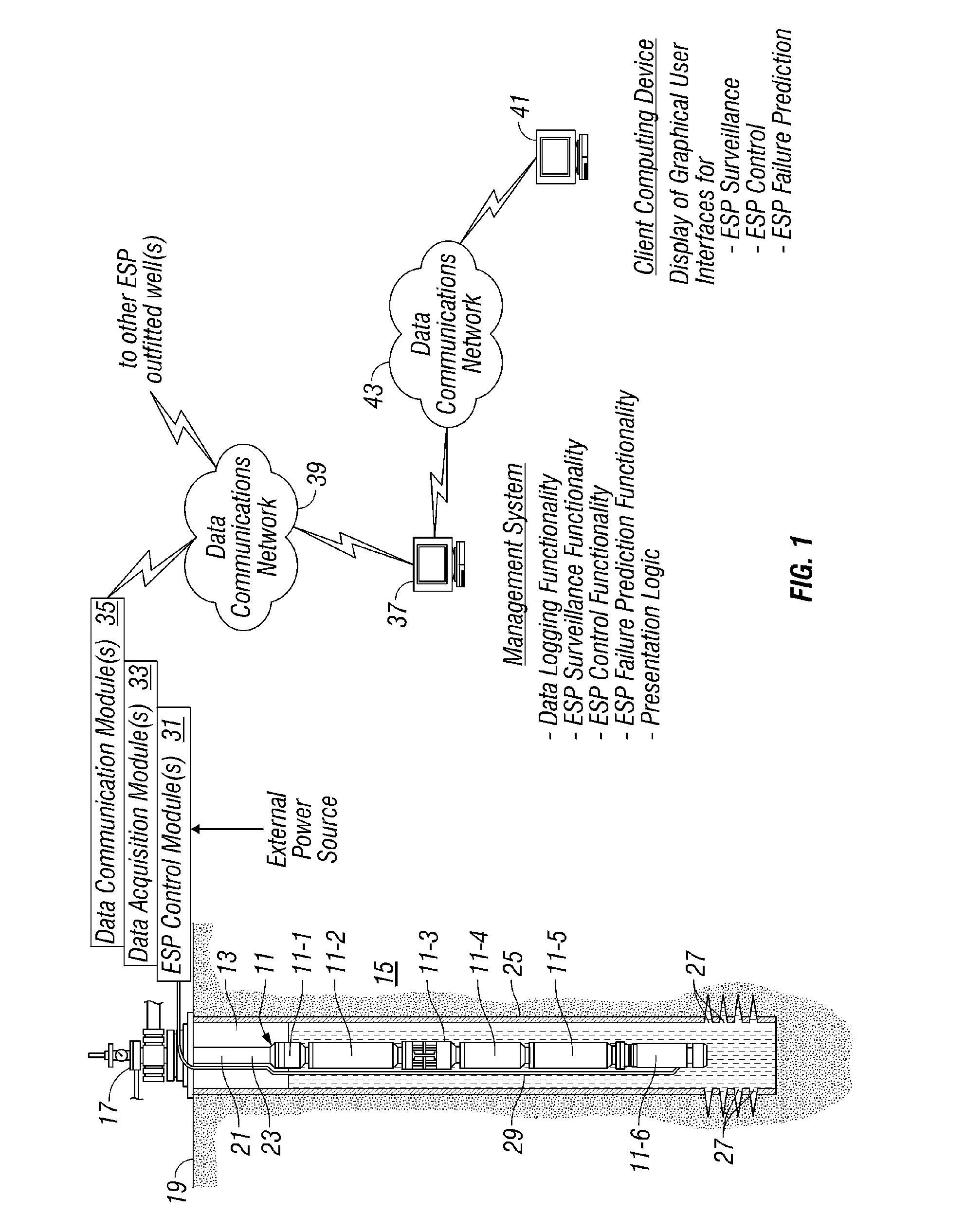
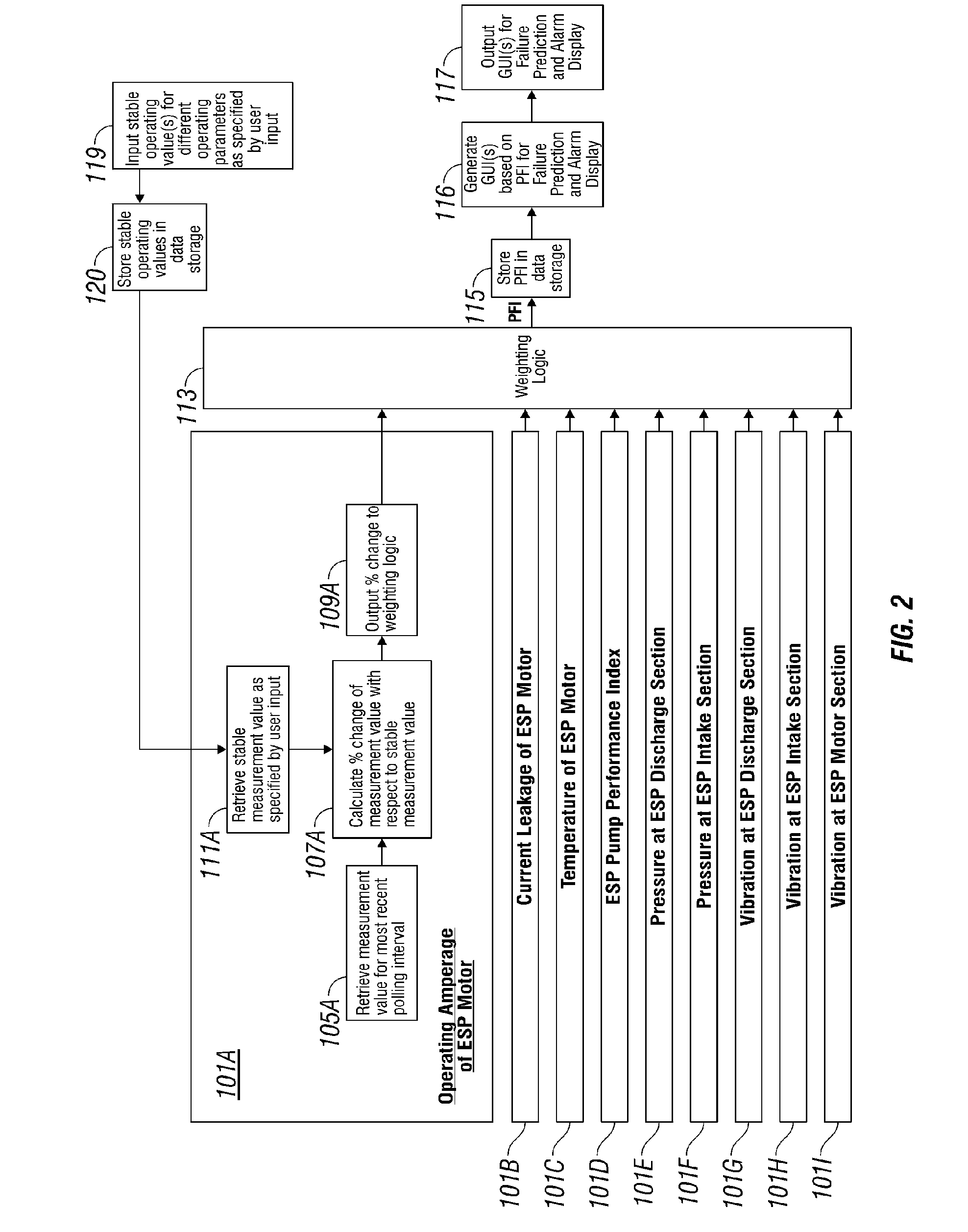
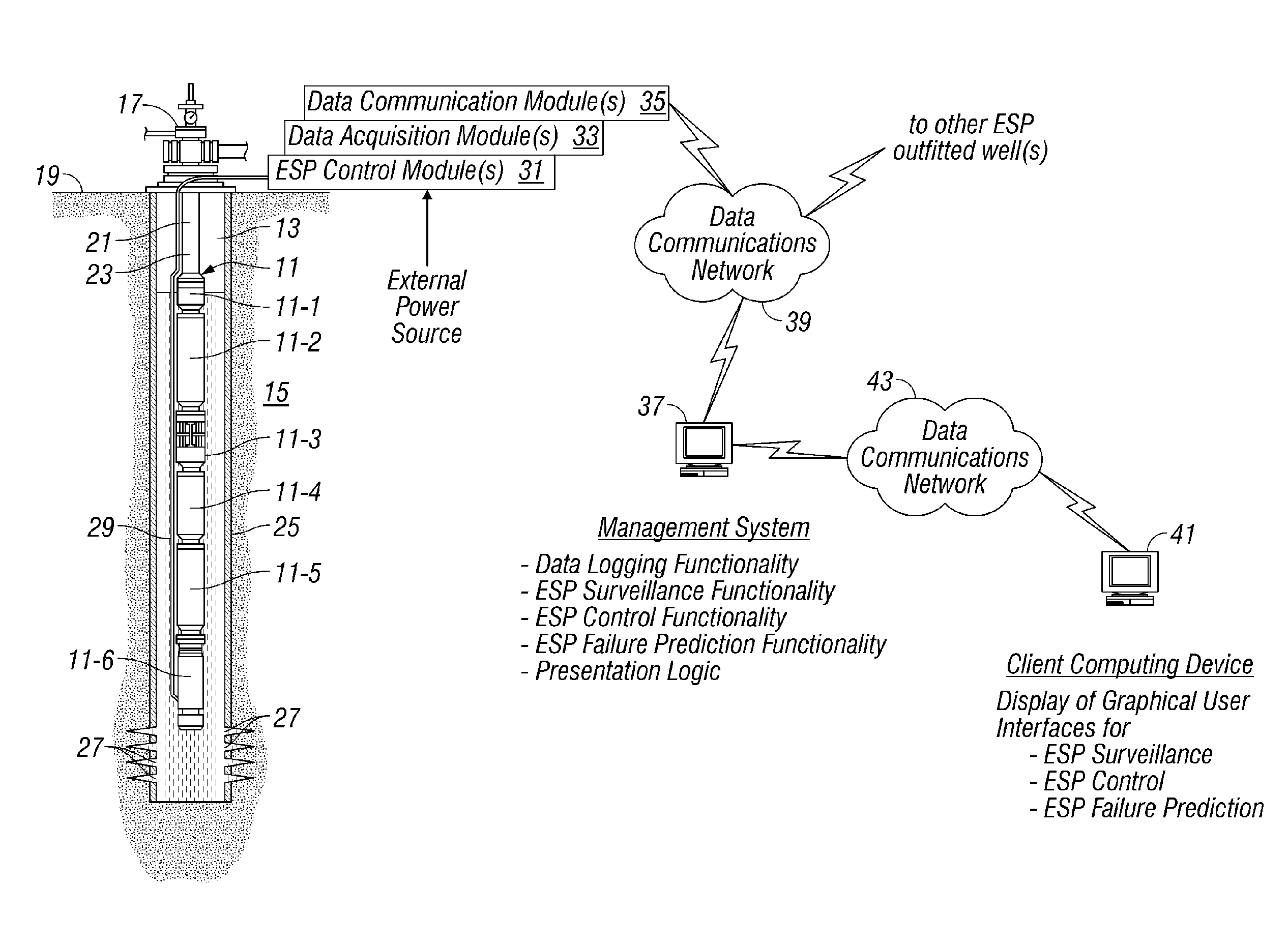
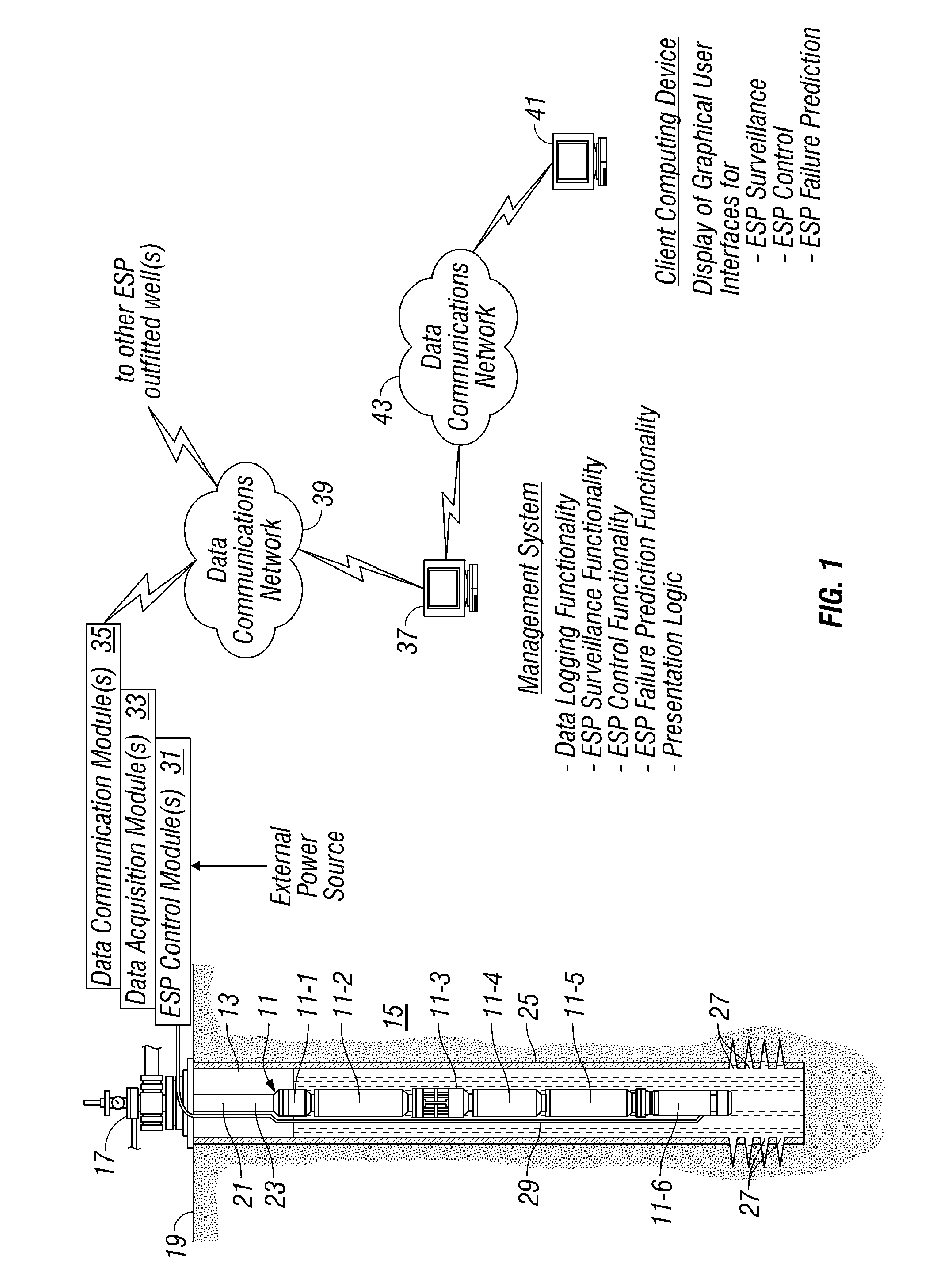
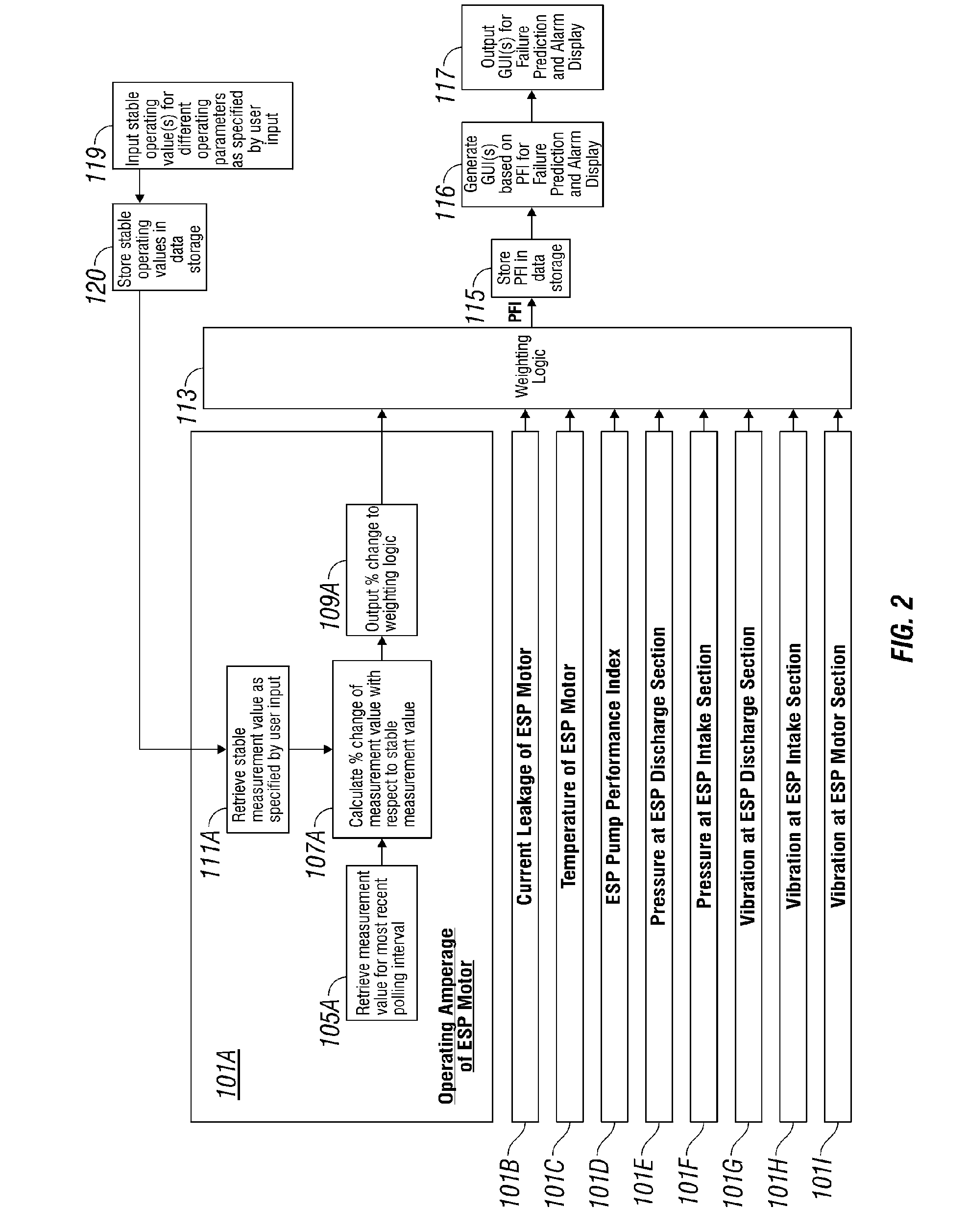
System and Method for Real-Time Monitoring and Failure Prediction of Electrical Submersible Pumps
ActiveUS20070252717A1Simple and user-friendly mechanismFail to accuratelyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsReliability engineeringSubmersible pump
A system and method for real-time monitoring and failure prediction of electrical submersible pumps.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
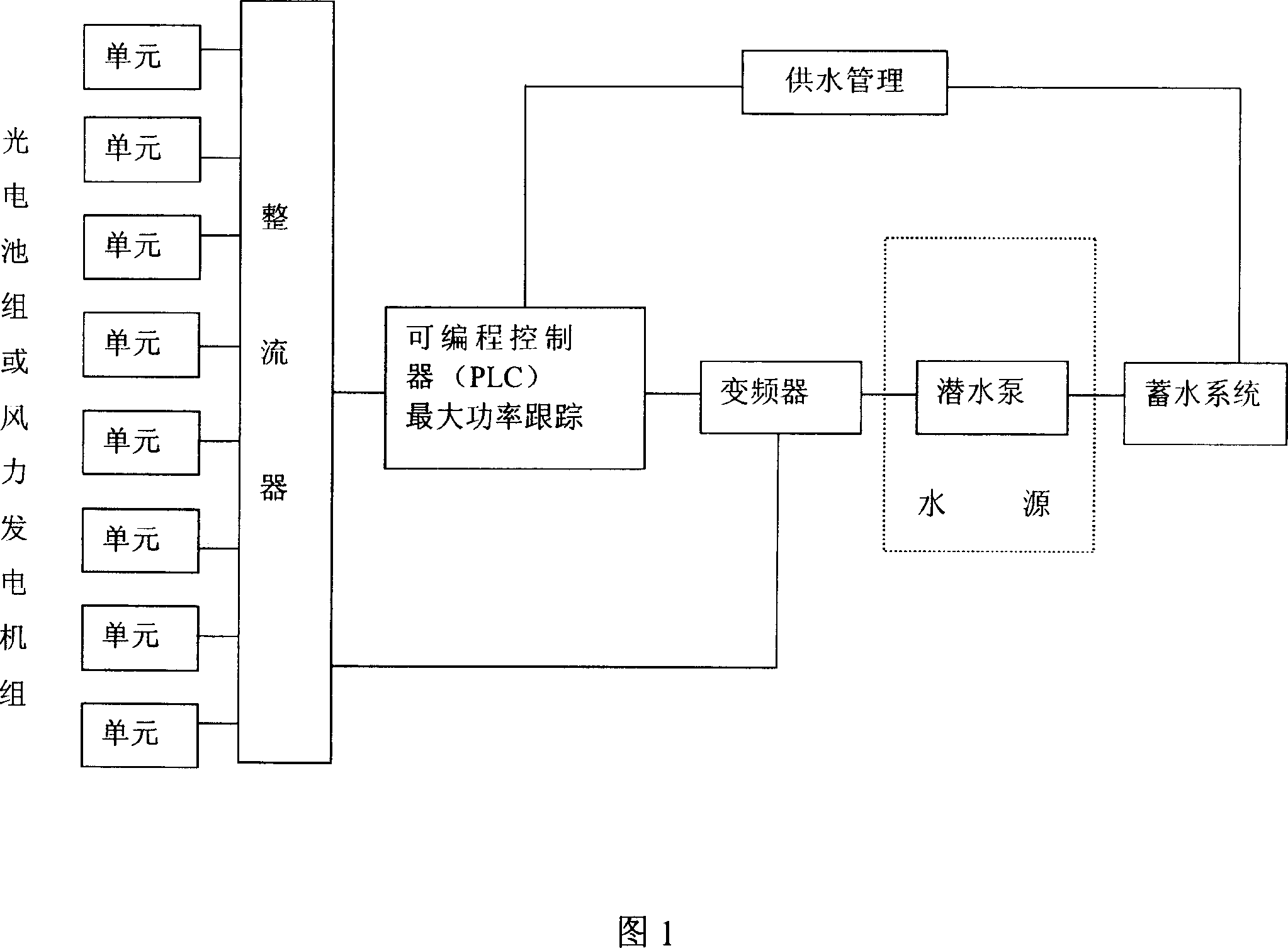
Multiple fan parallel type wind-light complementary water pumping system
InactiveCN101050770ALow costImprove efficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsAC motor controlWind drivenWater level
The present invention relates to a several wind mills parallelly-connected type wind energy and optical energy complementary water elevation system. Said system includes the following several portions: wind-driven power generator unit, solar cell component, intelligent controller and submersible pump. The described intelligent controller can be used for controlling, managing and tracking said system.
Owner:SHANGHAI WANDE WIND POWER
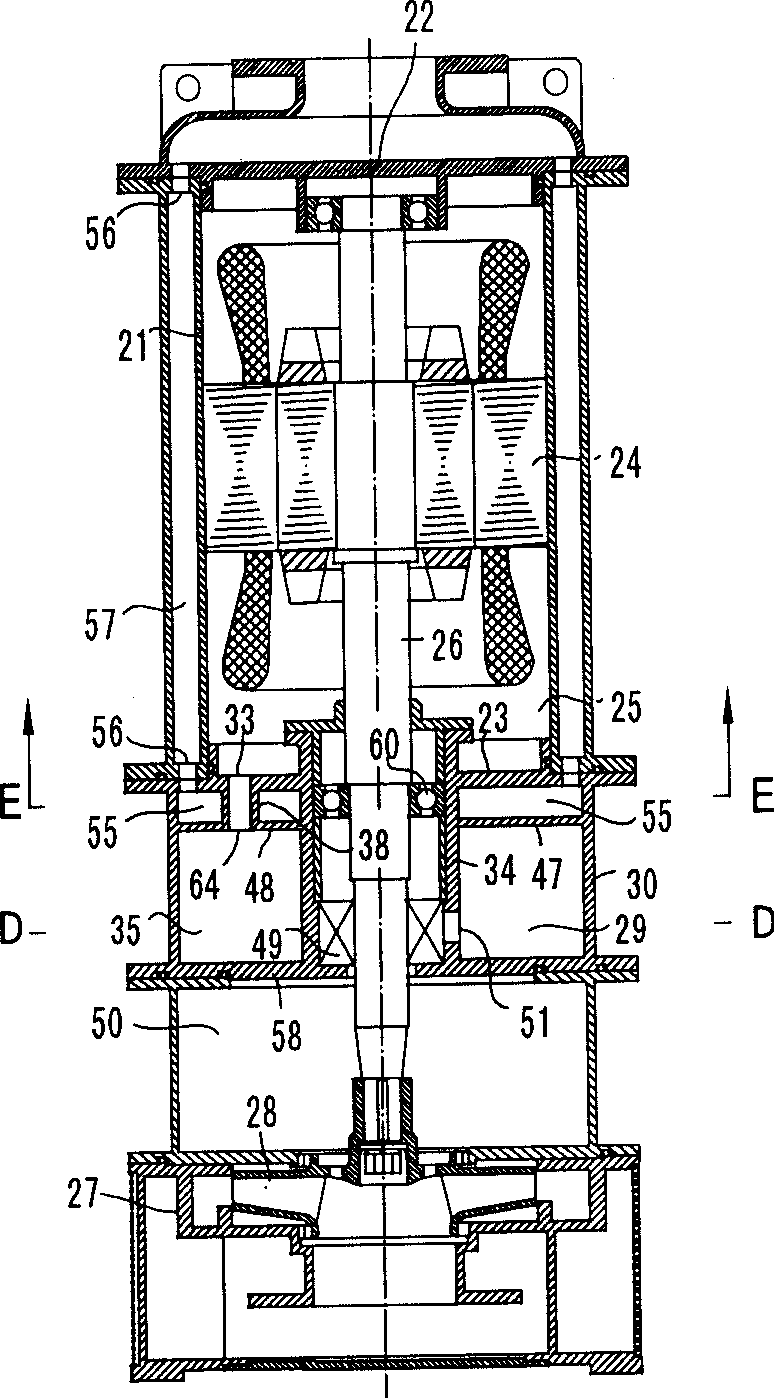
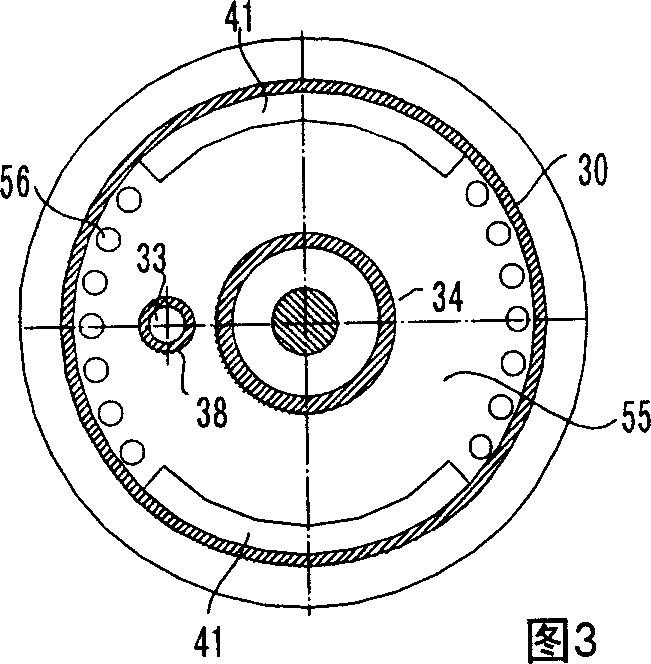
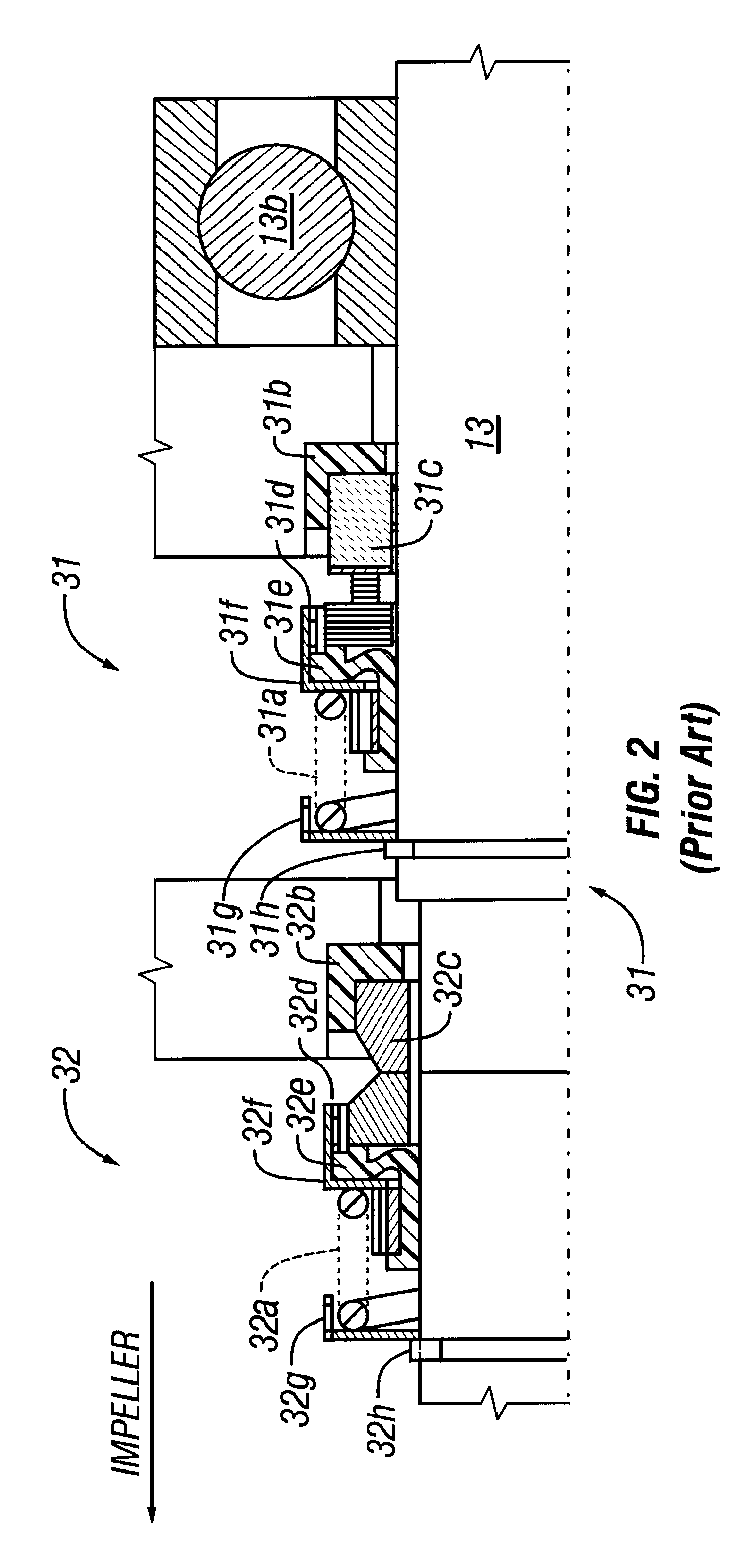
Self-centering rotor bearing assembly for submersible pump motors
The invention provides a submersible pumping system which includes a motor containing self-centering rotor bearing assemblies. Each rotor bearing assembly in accordance with the present invention includes a sleeve, a journal, and at least two seals. The journal is preferably disposed about the sleeve which is keyed to the power transmission shaft of the motor. The journal has a peripheral surface which is configured to have at least two circumferential support regions which are spaced apart from one another. Each of these circumferential support regions supports a corresponding seal. Each seal includes an interface member and an activating member. When in place in a rotor section of a submersible pump motor, the seals frictionally engage the inner surface of the stator and exert a centering force against the journal and thus against the bearing sleeve and the power transmission shaft. The seals also exert a force against the inner surface of the stator which prevents rotation of the journal when the power transmission shaft is rotating.
Owner:CAMCO INT
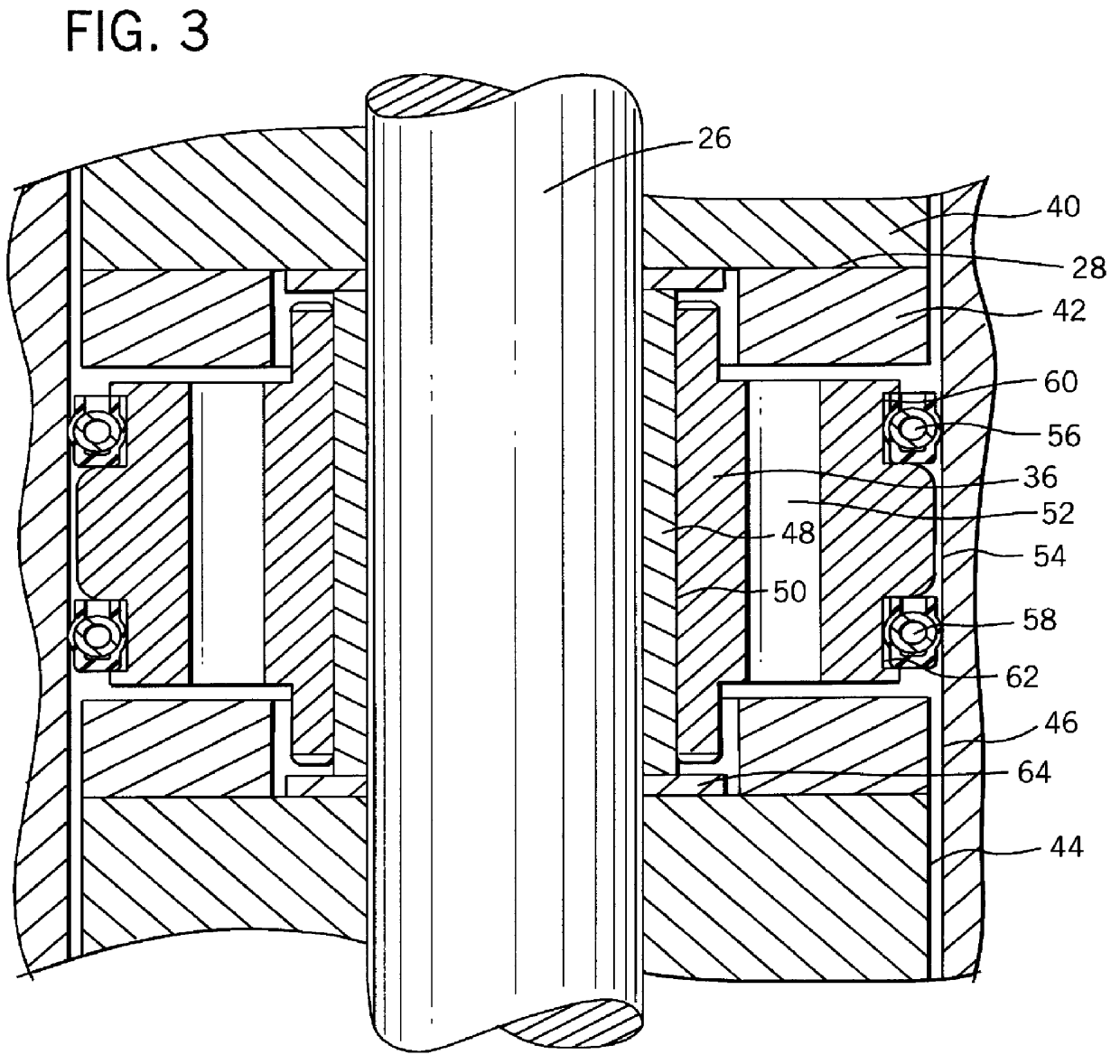
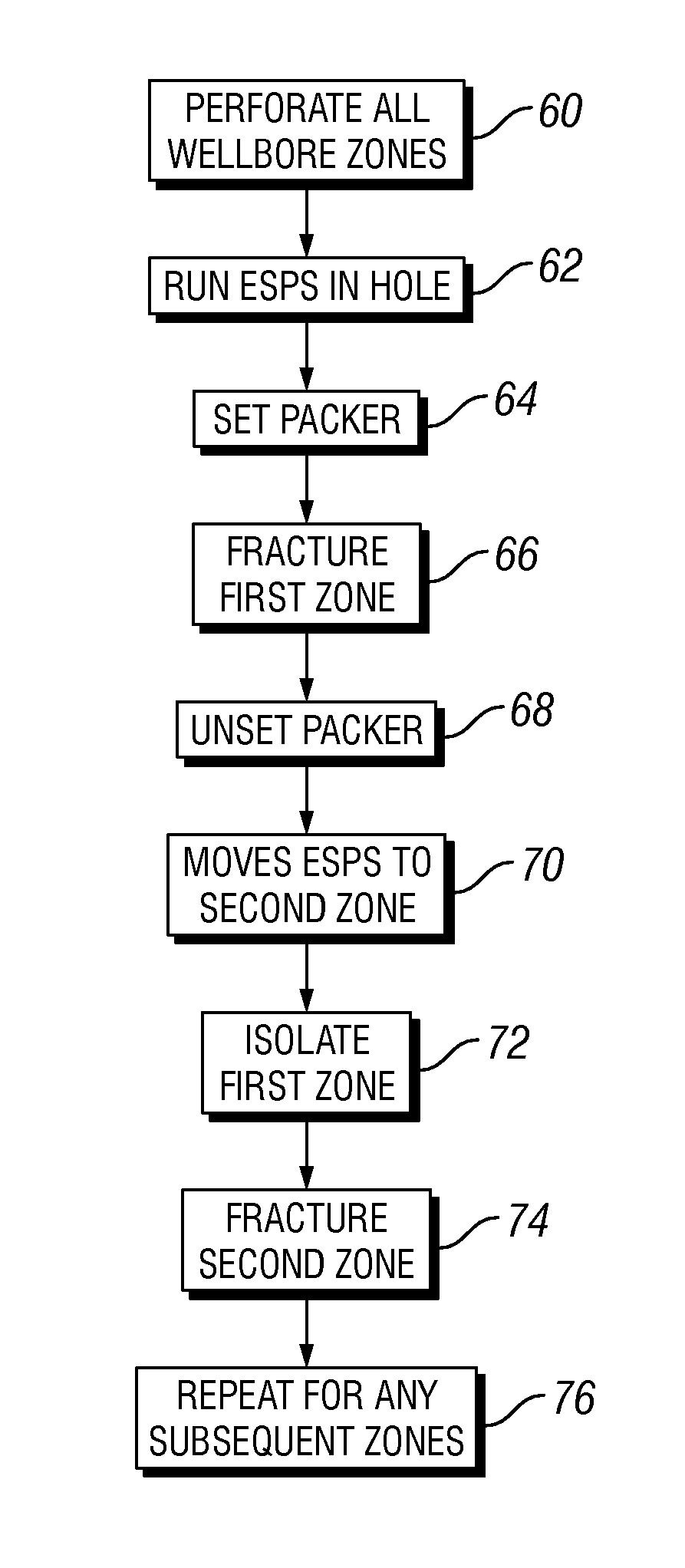
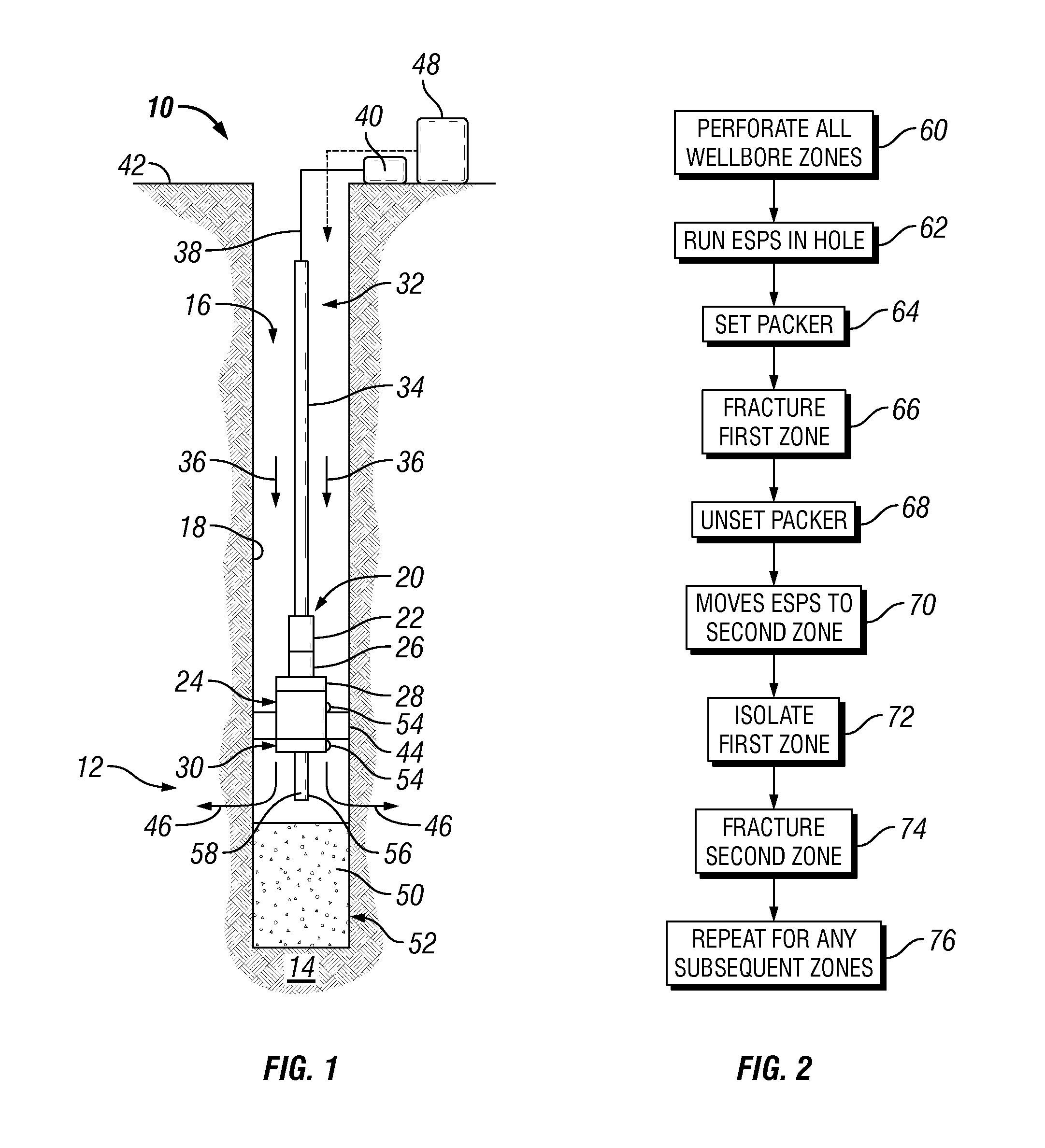
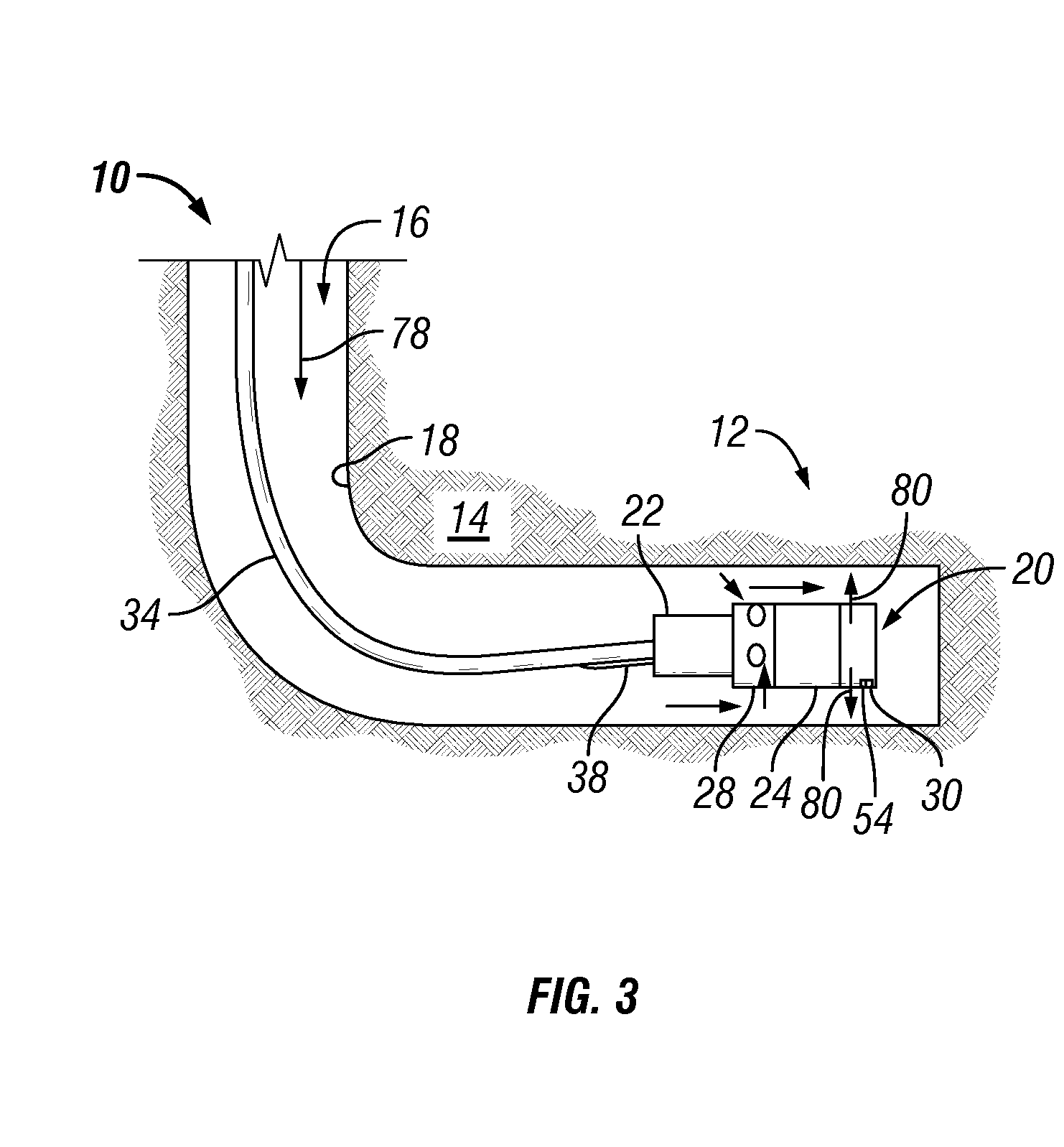
Well treatment using electric submersible pumping system
InactiveUS20080264640A1Convenient treatmentFacilitates well treatmentFluid removalSealing/packingElectricityHydrology
A technique provides an electric submersible pumping system to facilitate a well treatment, such as a hydraulic fracturing well treatment. The electric submersible pumping system is positioned downhole and oriented to intake a fluid delivered downhole for use in the well treatment. Once the fluid is delivered downhole, the electric submersible pumping system pumps, pressurizes and discharges this fluid to perform the well treatment, e.g. the hydraulic fracturing treatment. The pumping system reduces the pressure at which the treatment fluid must be delivered downhole.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
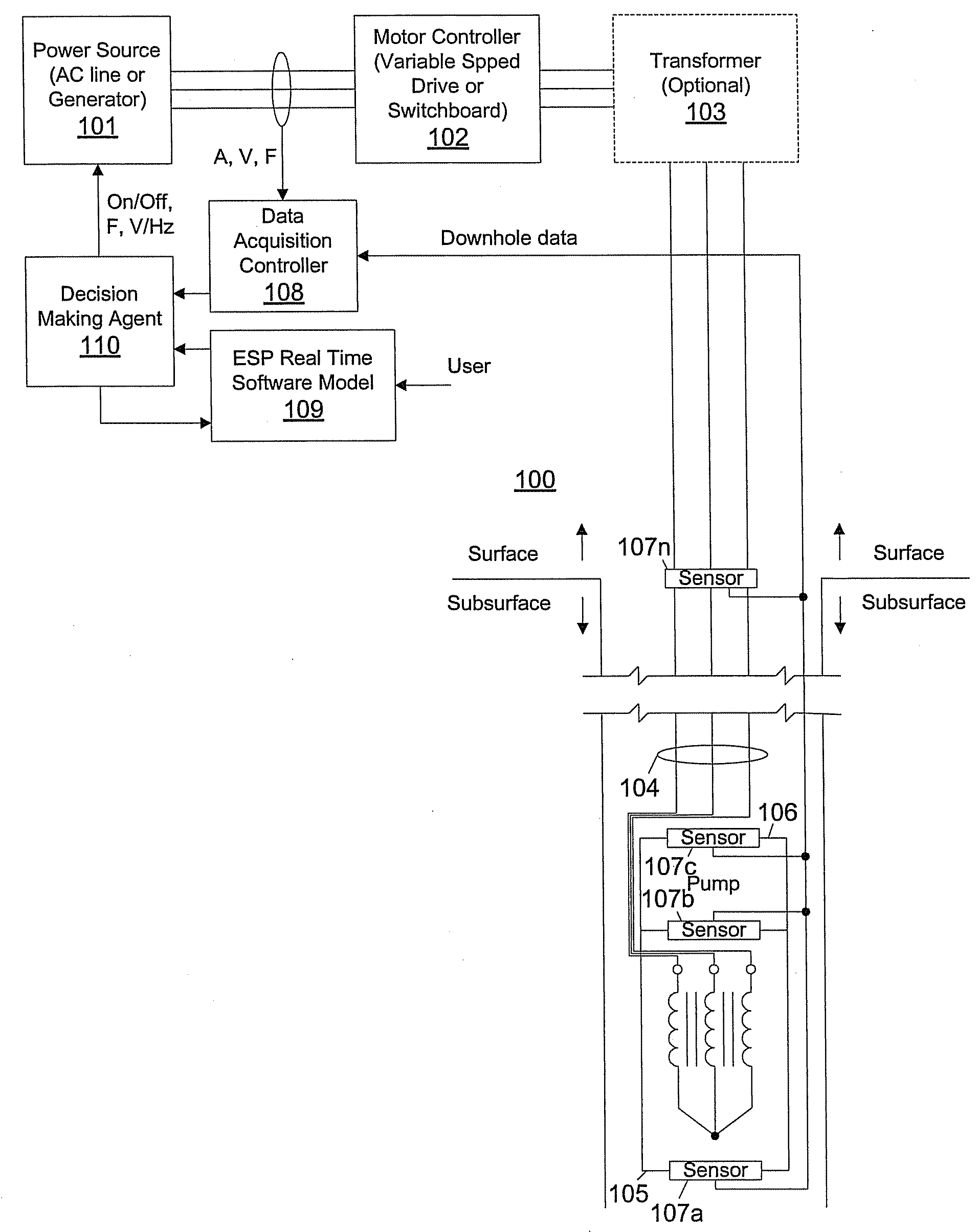
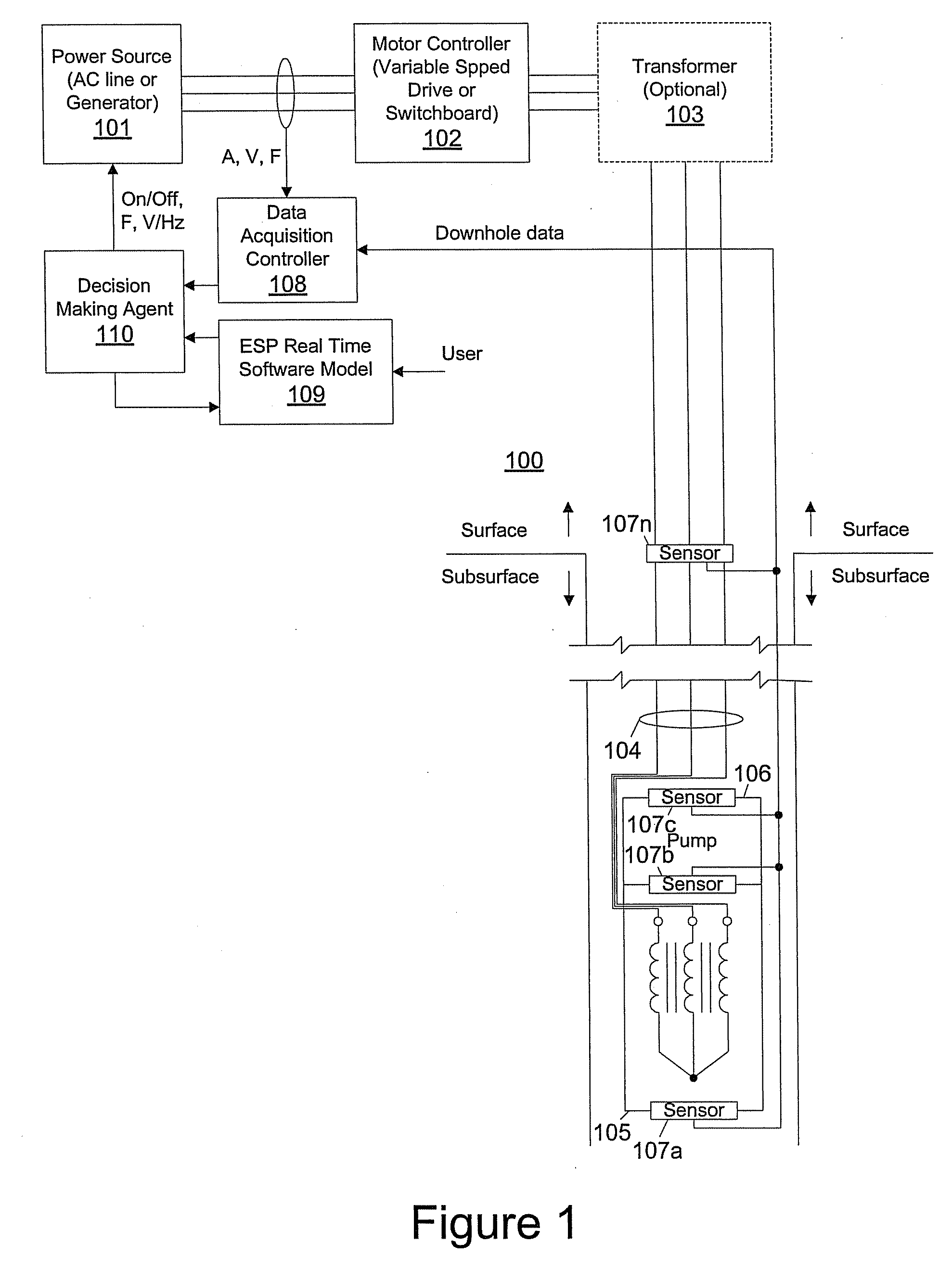
Smart motor controller for an electrical submersible pump
A motor controller for an electrical submersible pump production system is coupled to a real-time software model using known correlations and algorithms to model the performance of the production system, including the production equipment and the well, and executes separately from any modeling used to compute operating parameters from downhole measurements for use by the motor controller. The real-time software model receives operating parameter measurements from a data acquisition subsystem and compares the measurements with projected operating parameter values according to the model. Differences between measured and projected values are analyzed to identify operating problems or non-optimal operating conditions, with automatic corrections and / or notifications being triggered.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
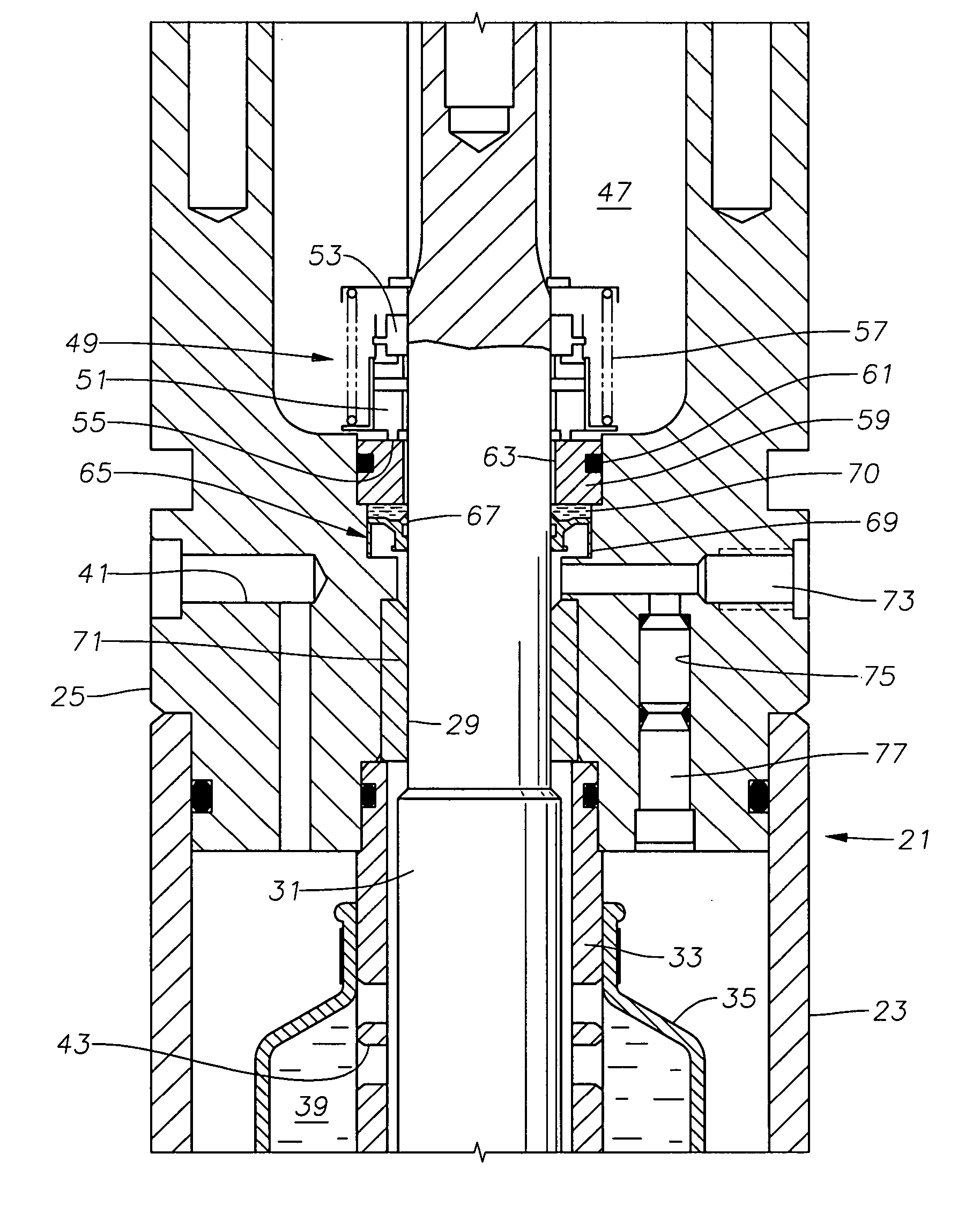
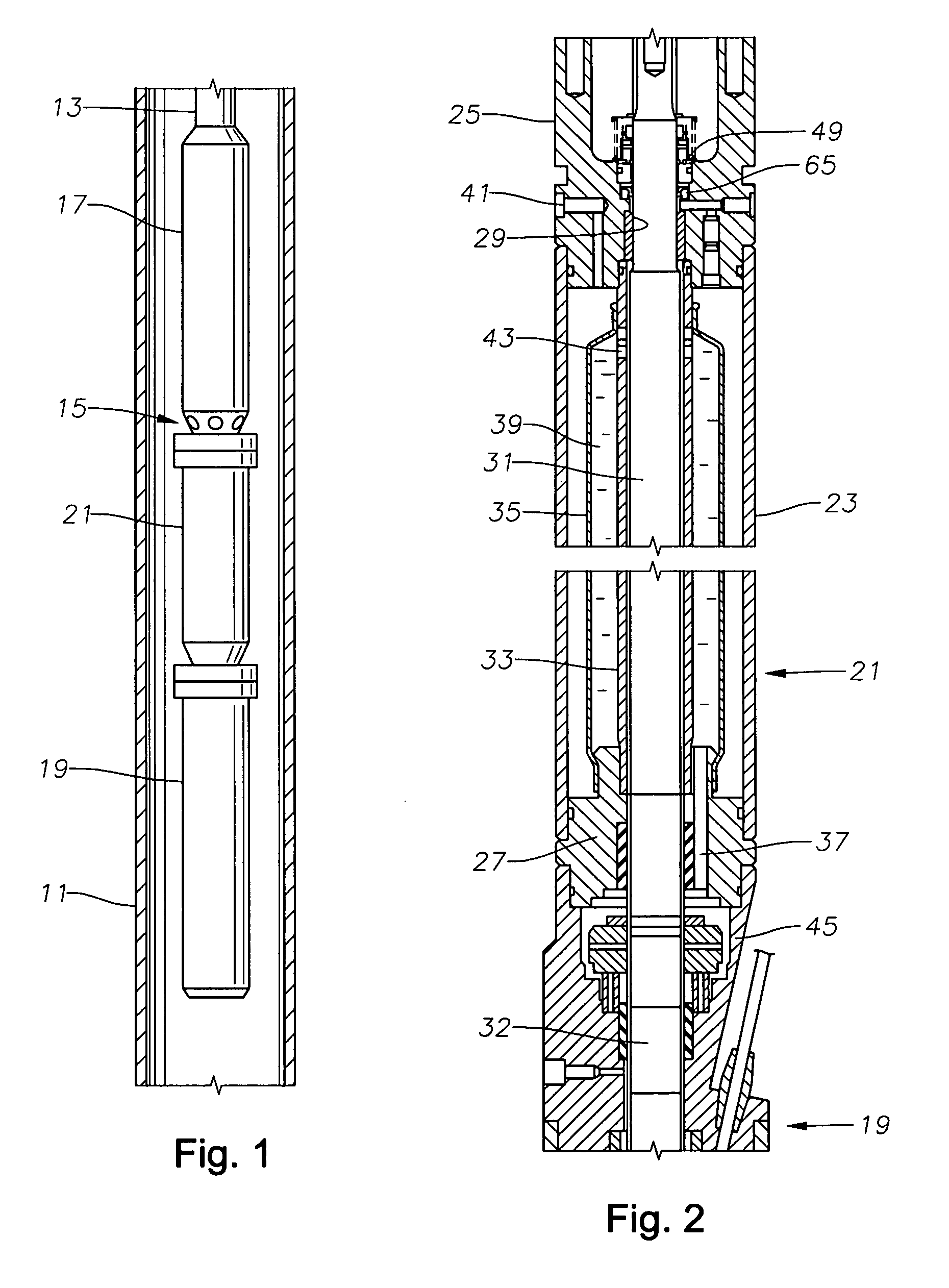
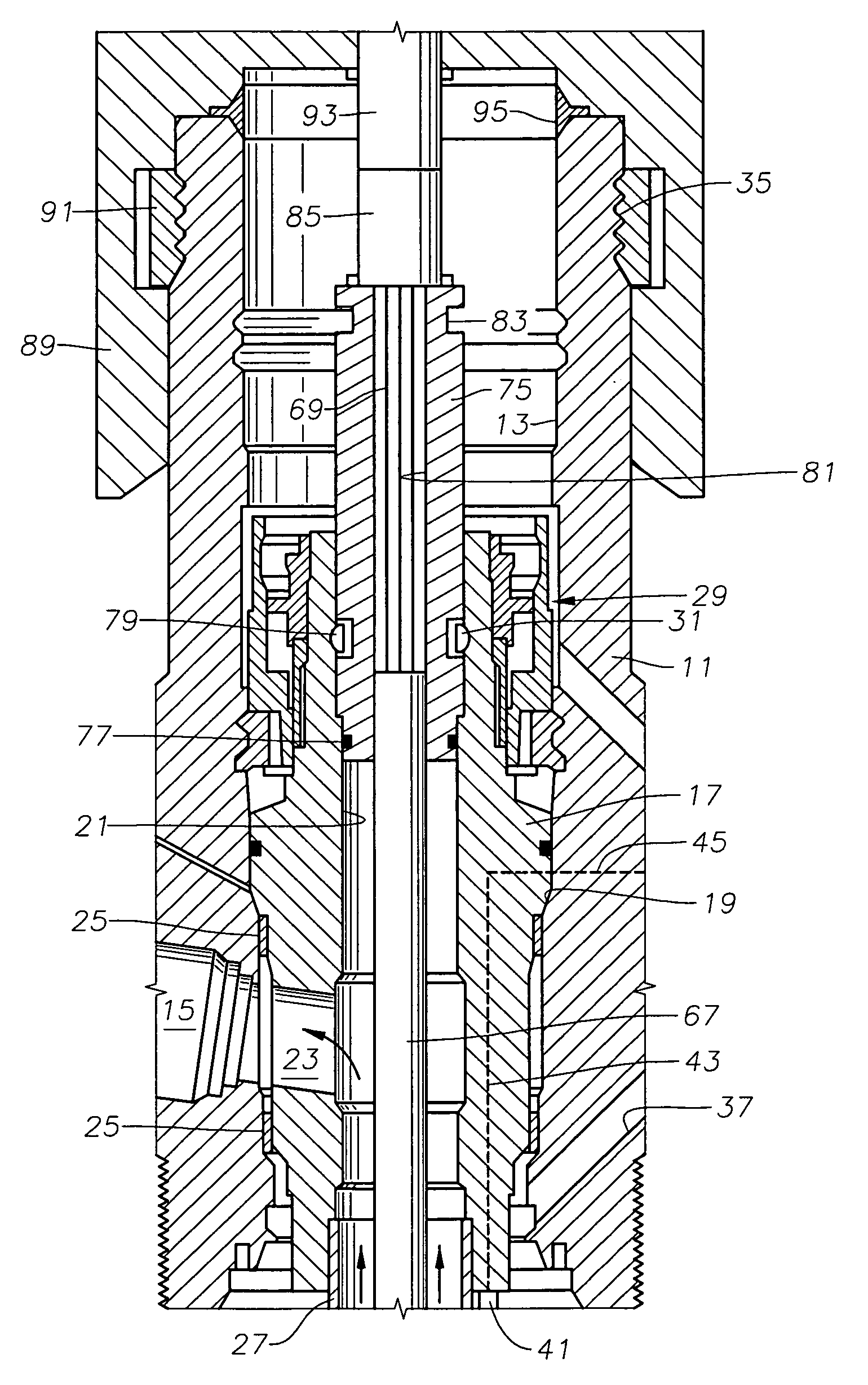
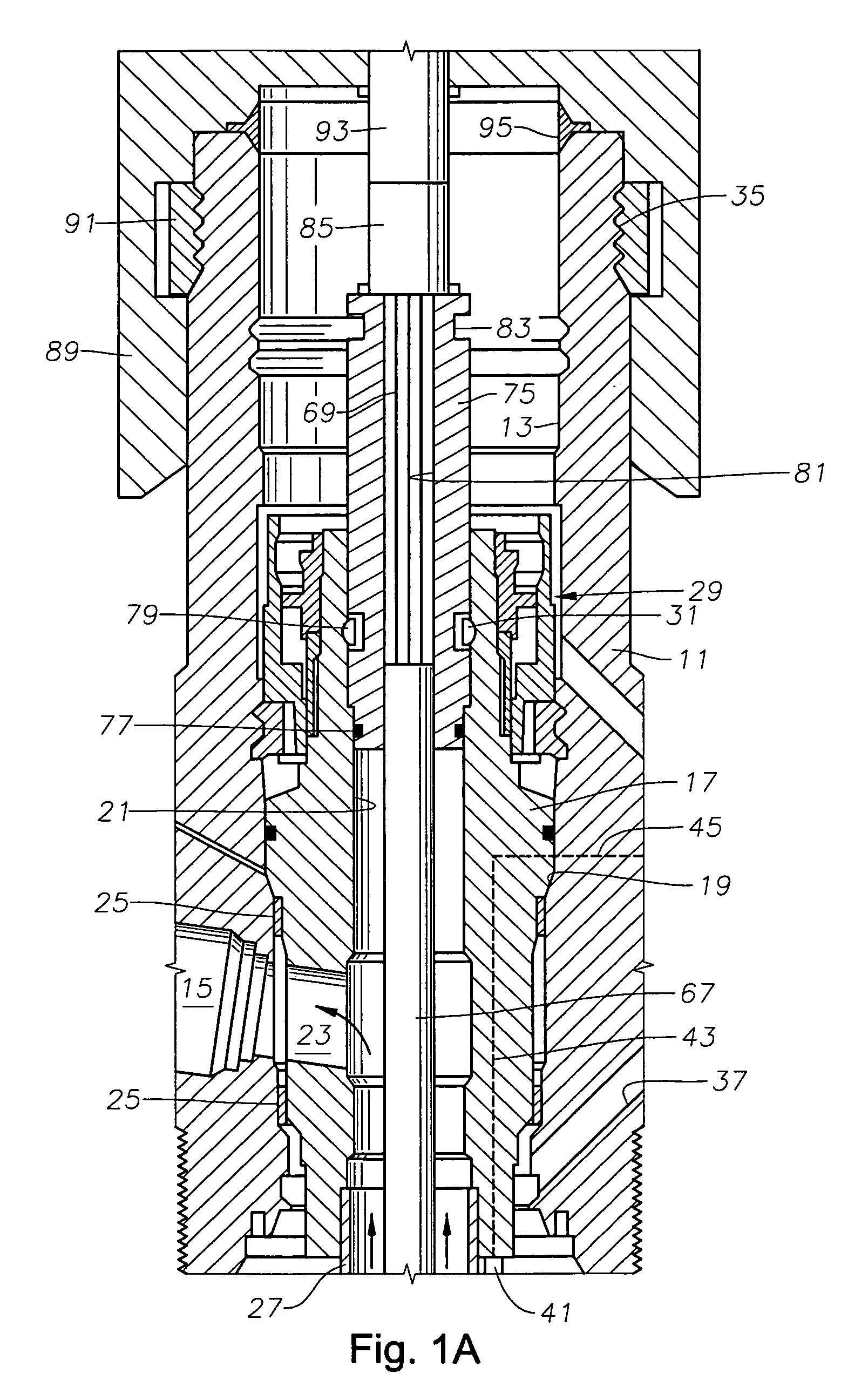
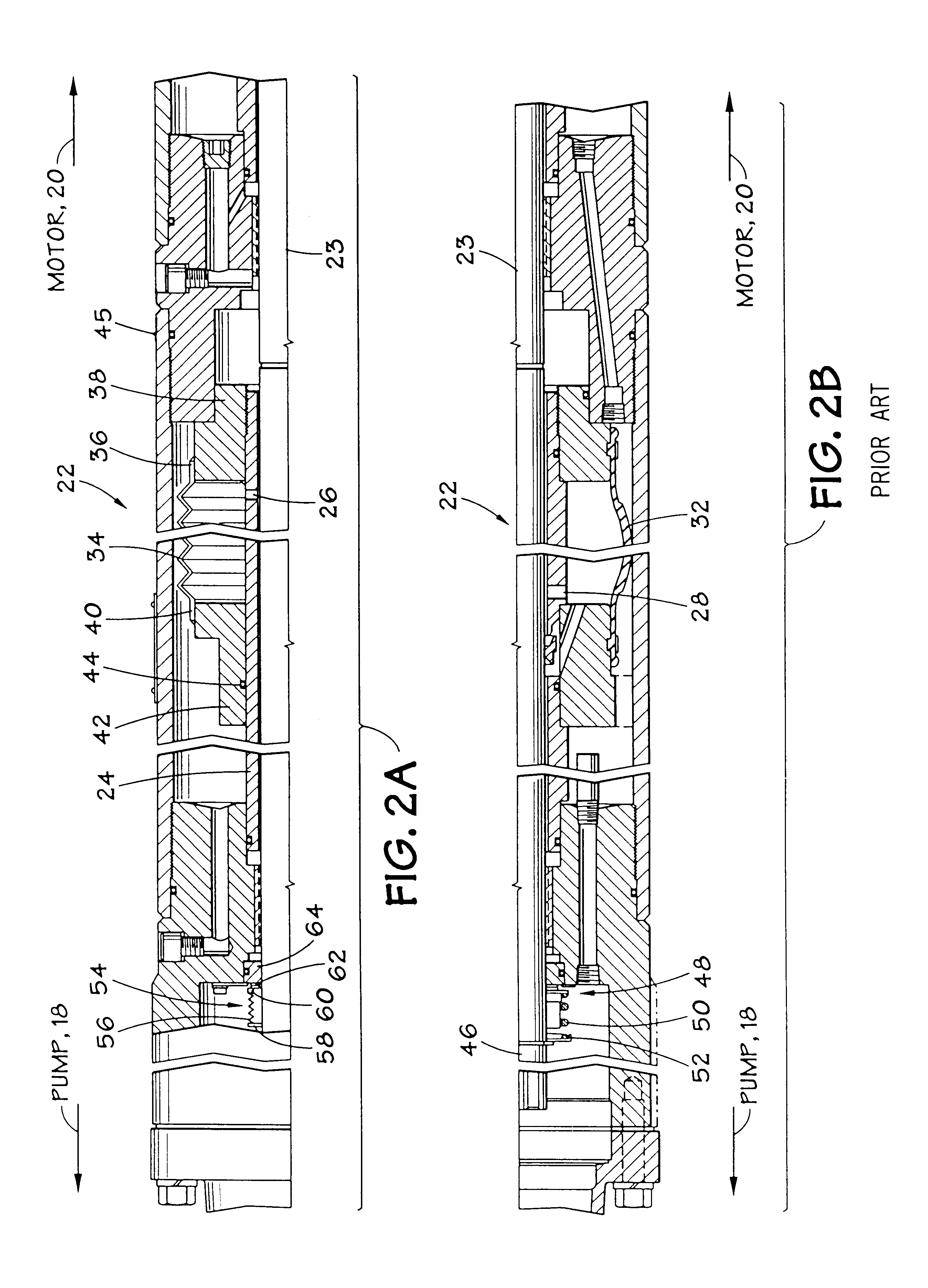
Seal section oil seal for submersible pump assembly
InactiveUS20070140876A1Prolongs the entry of well bore fluidMore resistant to demulsifying with waterPump componentsFluid removalRotary pumpPressure balance
A seal section for location between a submersible rotary pump and motor has a primary mechanical seal and a secondary oil seal at the pump end of the seal section. The mechanical seal has rigid seal faces that slide in engagement with each other. The secondary seal has an inner portion that seals against the shaft of the seal section and an outer portion that seals against the housing. The seal section has a pressure equalizing device for equalizing pressure of motor lubricant with well bore pressure.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Vertical pump for mine
ActiveCN1752453ASimple structureEasy to manufacturePump componentsPump installationsEngineeringSafety valve
The invention is a mine vertical pump being as a self-explosion-proof sand-discharging submersible pump. A safety valve with the one-way discharge hole is disposed in the cavity of the motor chamber or in the mechanical sealed outer oil chamber of the axle hole. It's better for the safety valve to have a sheath. At one end of the safety valve a sleeve with the explosion-proof assembly can be put.
Owner:王庆武
Vertical pump for mine
ActiveCN1752452ASimple structureEasy to manufacturePump installationsNon-positive displacement fluid enginesEngineeringSubmersible pump
The invention is a mine vertical pump being as light welded sand-discharging submersible pump. In the invention there are several diaphragms in the space between the pump casing and the fluid-guiding plate. In the space divided by the diaphragms there is a channel grid with the channel opening on the casing end cover plate and a stifling grid enclosed by the casing end cover plate.
Owner:王庆武
Vertical pump for mine
ActiveCN1752454ASimple structureEasy to manufacturePump componentsPump installationsThree-dimensional spaceEngineering
The invention is a mine vertical pump being as a light sand-discharging submersible pump in which are assembled a lower bearing, a mechanical sealed outer oil chamber outside the barrel, oil-passing hole in communication with the mechanical seal inside the barrel. The openings of the overflow pipe and the long sleeve are both disposed in the middle of the three-dimensional space in the outer cavity.
Owner:王庆武
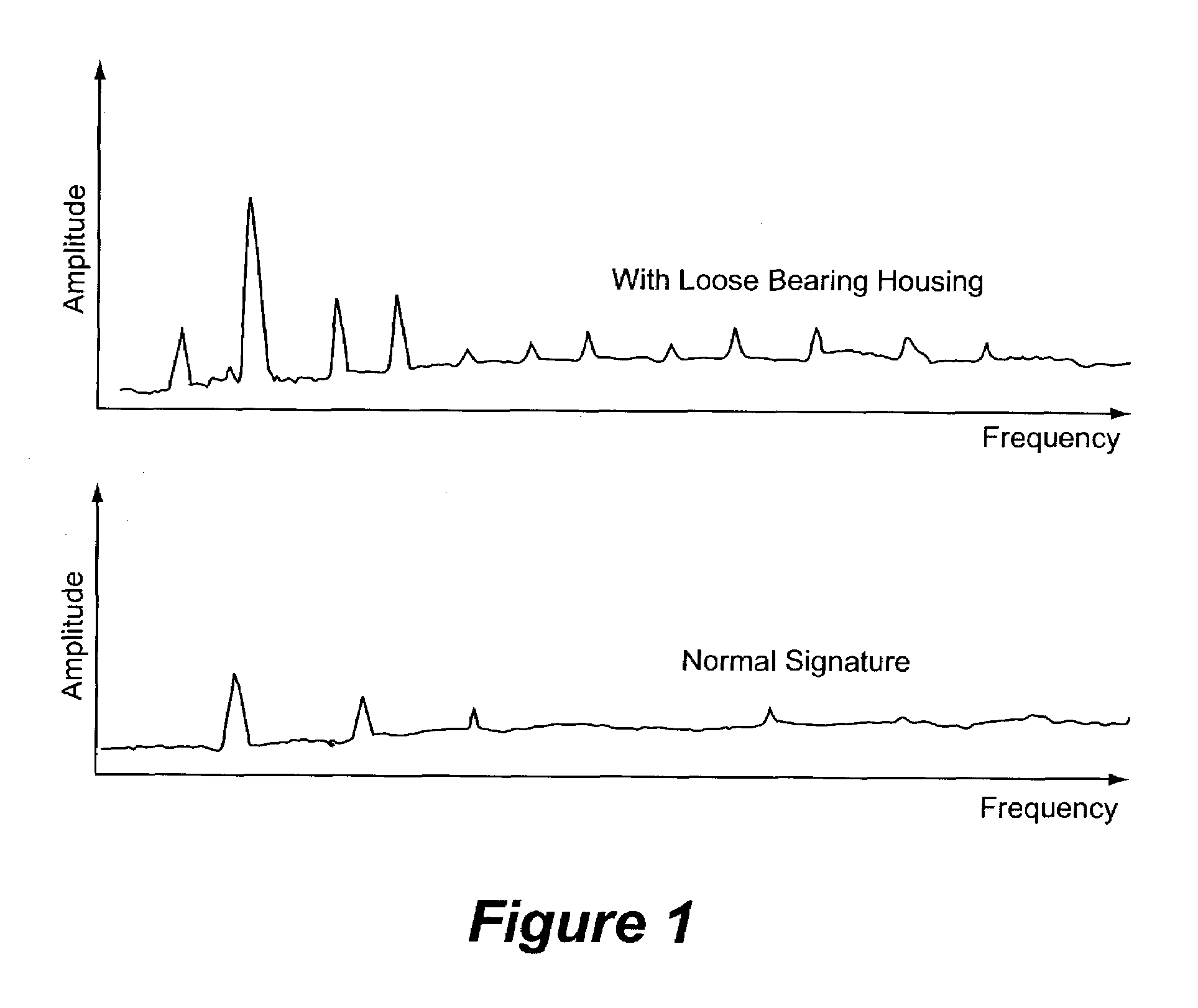
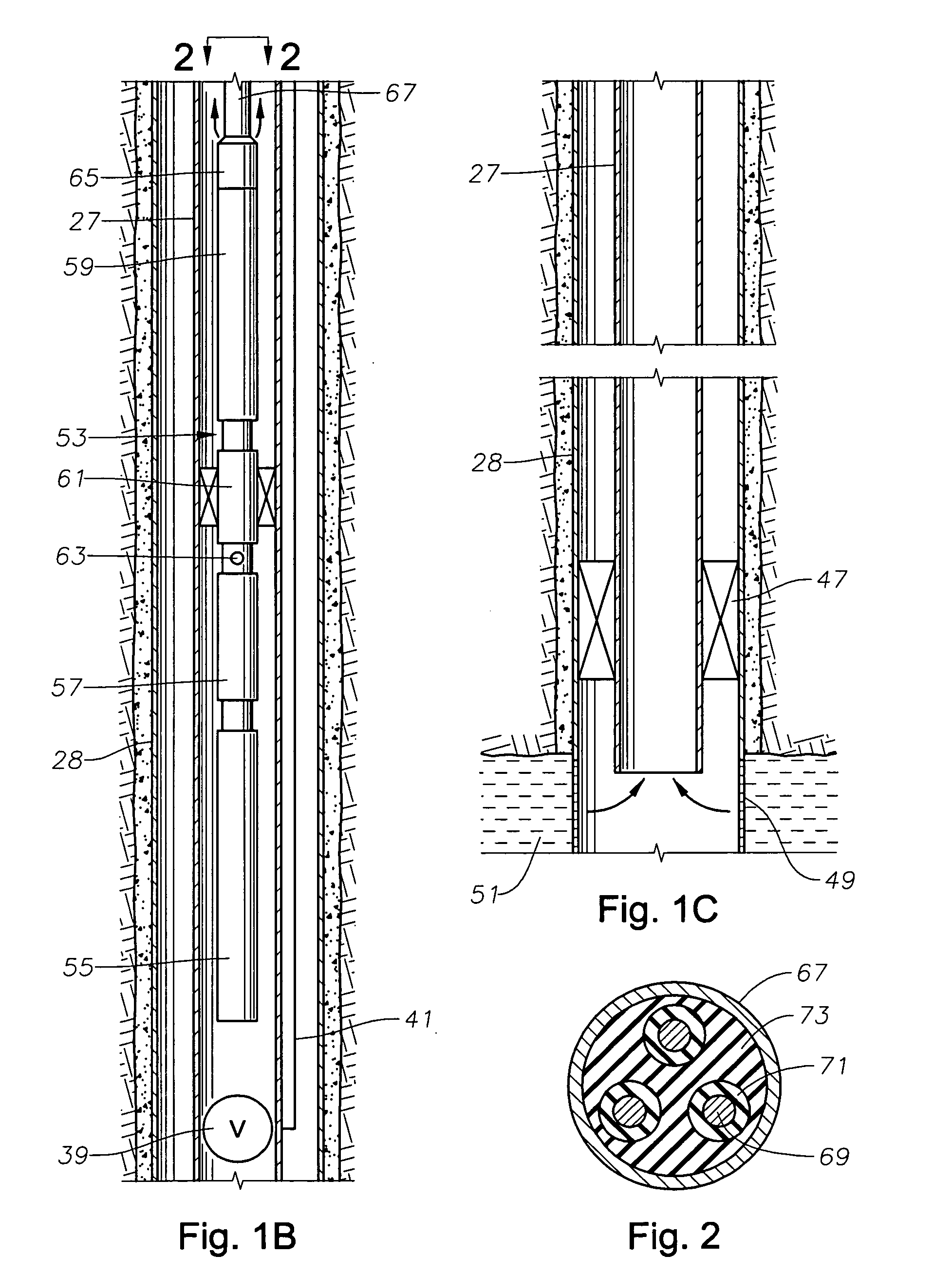
System and method for monitoring performance of downhole equipment using fiber optic based sensors
A method and system for monitoring the operation of downhole equipment, such as electrical submersible pumps, is disclosed. The method and system rely on the use of coiled fiber optic sensors, such as hydrophones, accelerometers, and / or flow meters. These sensors are either coupled to or placed in proximity to the equipment being monitored. As the sensor is perturbed by acoustic pressure disturbances emitted from the equipment, the length of the sensing coil changes, enabling the creation of a pressure versus time signal. This signal is converted into a frequency spectrum indicative of the acoustics emissions of the equipment, which can then be manually or automatedly monitored to see if the equipment is functioning normally or abnormally, and which allows the operator to take necessary corrective actions.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
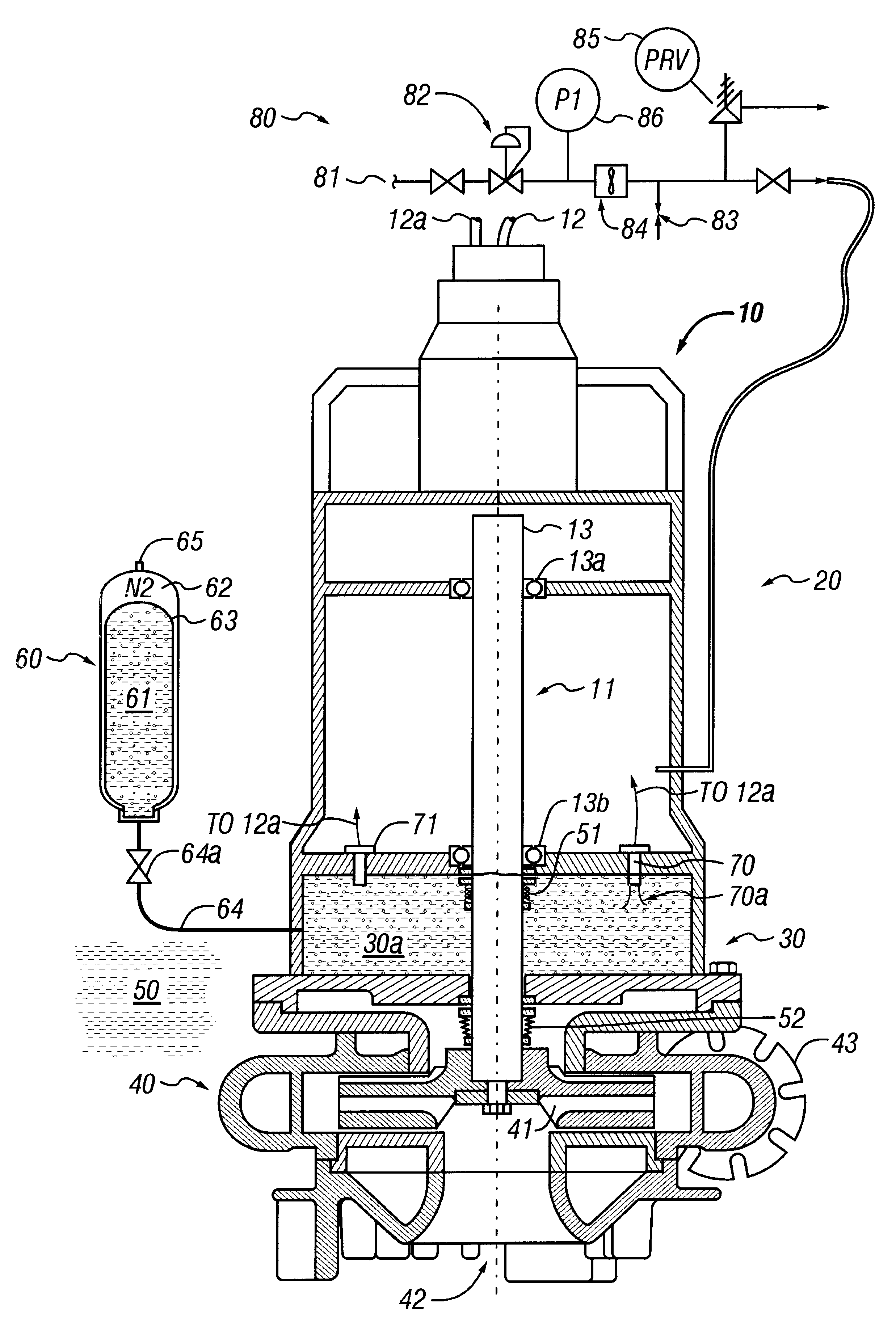
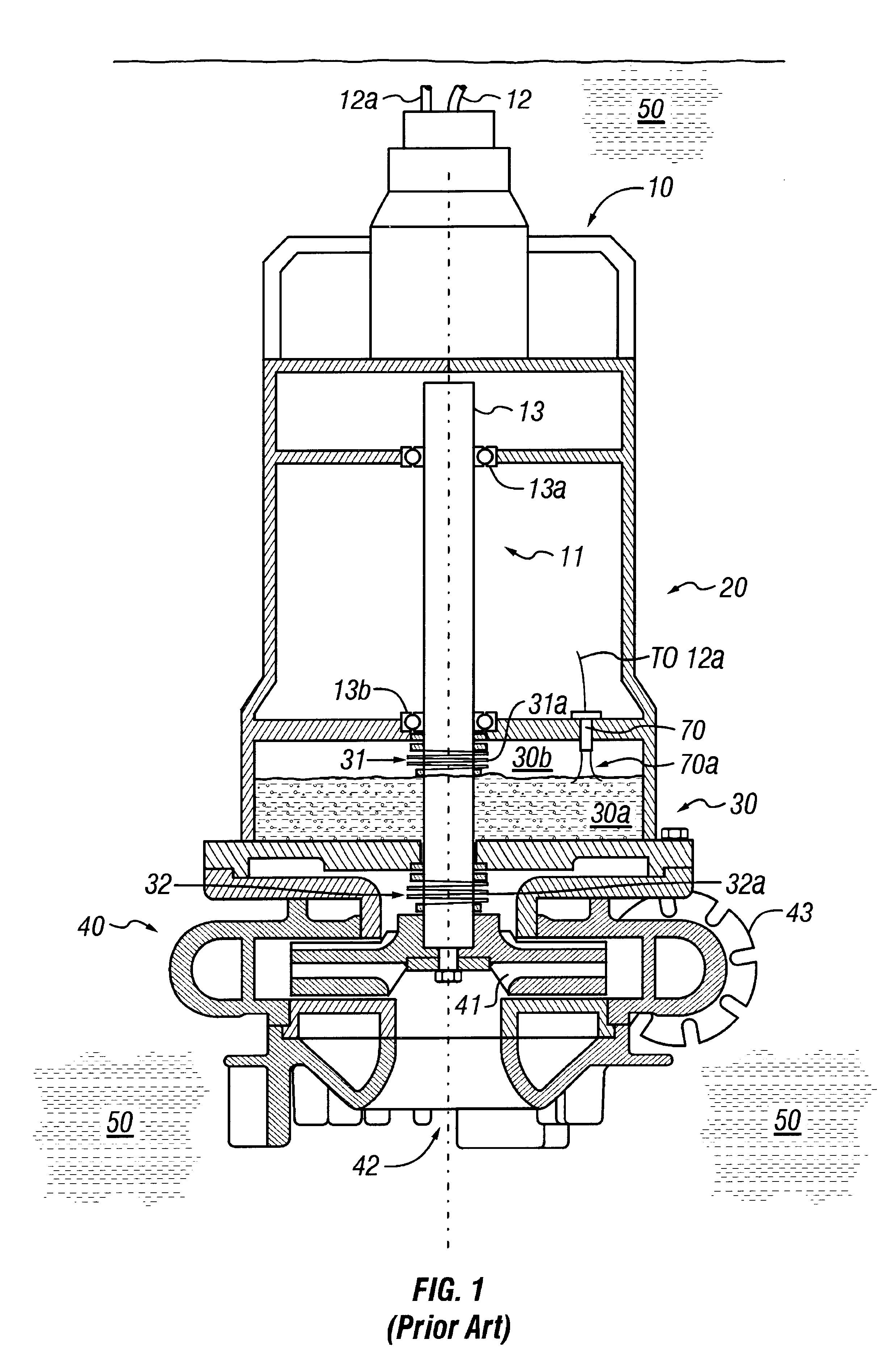
Pressurized seal for submersible pumps
A submersible pump employs a sealed, oil-filled chamber with a moisture-sensing probe to detect the presence of any pumpage, such as water, which has leaked into the chamber. If contamination is detected, the pump may be shut down for repairs before it fails. Two mechanical seals are installed the lower seal is located between the pump and the oil chamber and an upper seal is located between the oil chamber and the motor. The improvement disclosed herein combines a pressurized oil accumulator with the pump oil chamber described above. The accumulator is divided into two compartments separated by a bladder, one compartment being connected to the reservoir of the pump and filled with oil for providing make-up oil to the reservoir and for accepting surplus (expansion) oil from the reservoir. The second compartment is pressurized and applies pressure to the bladder that, in turn, transfers the pressure to the oil in the first compartment and to the oil-filled chamber. The purpose is to pressurize the pump oil chamber in order to equalize pressure across the seals and thereby prevent failure of the seals or, at least, extend their life. The invention also includes apparatus for purging the motor casing with air and a pressure transducer for detecting a decrease in reservoir oil pressure.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Pothead with pressure energized lip seals
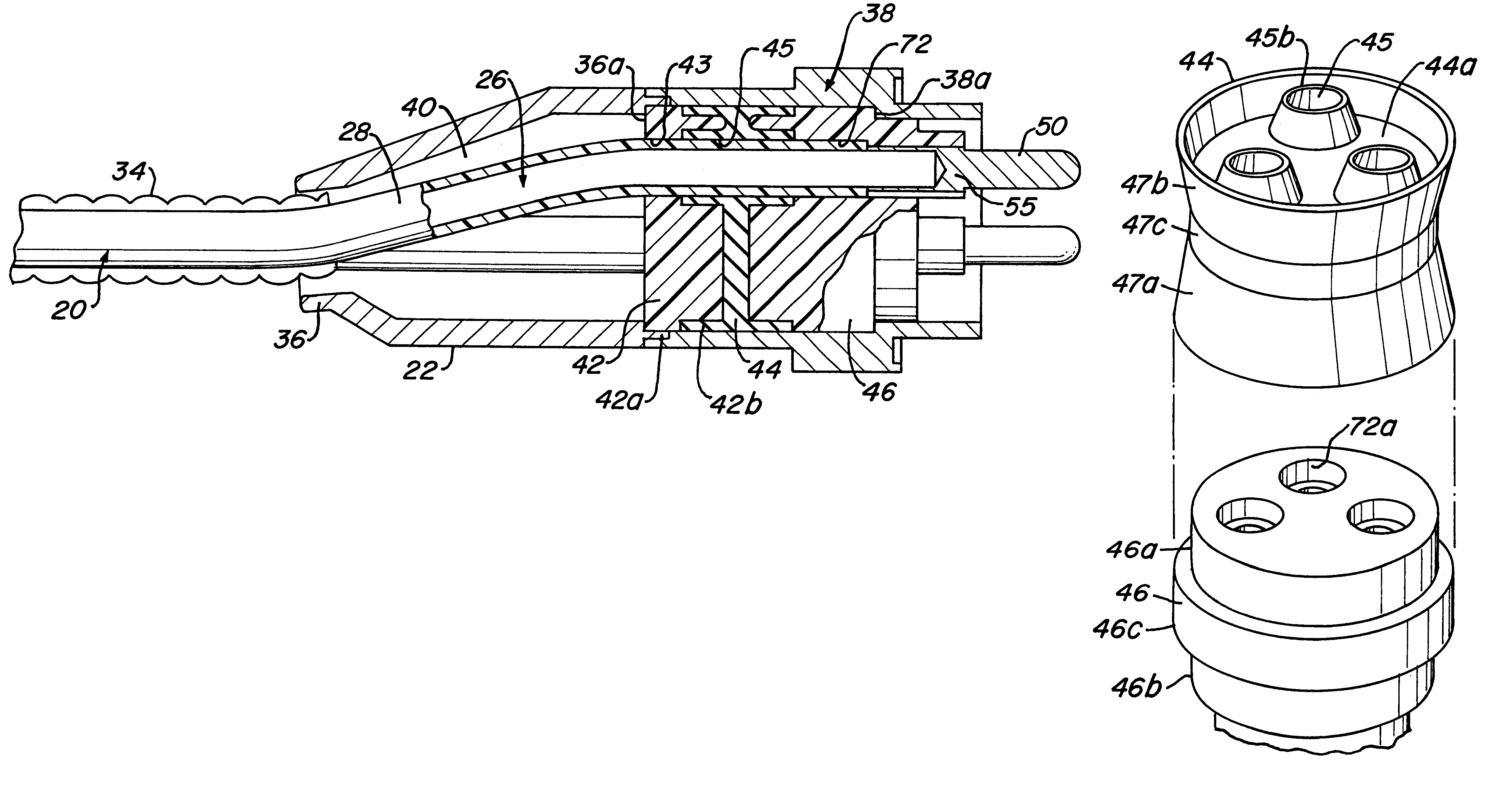
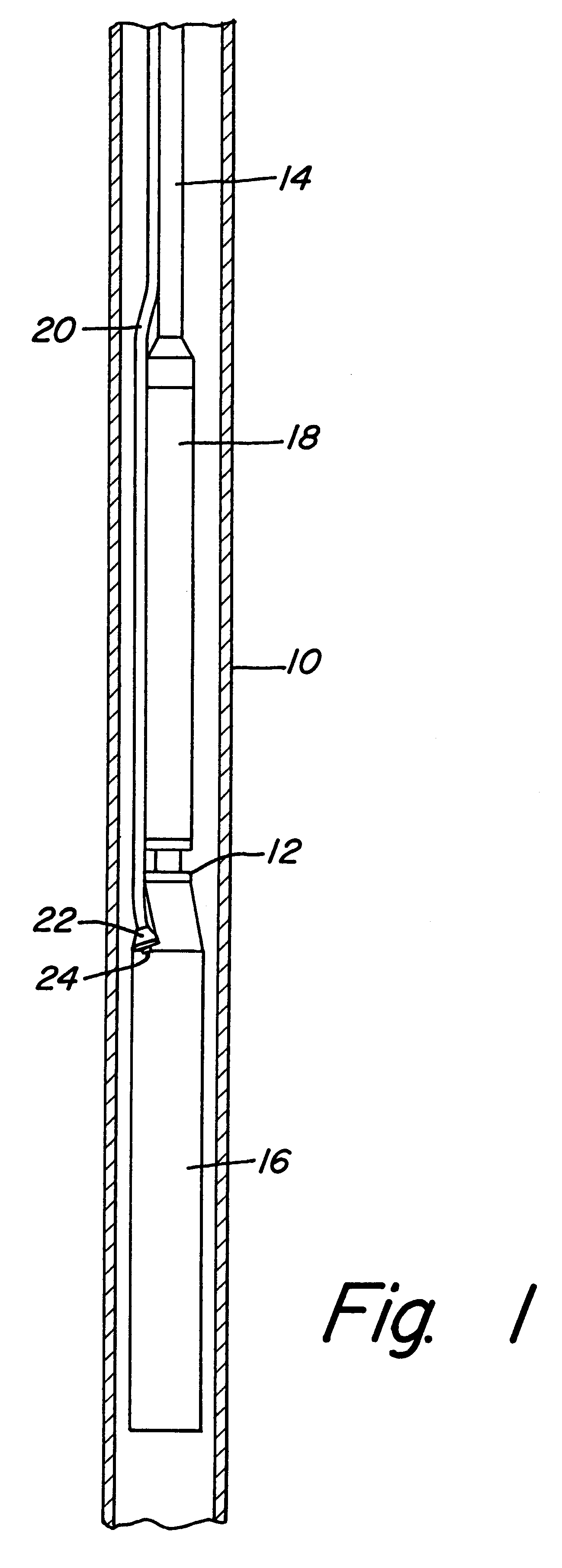
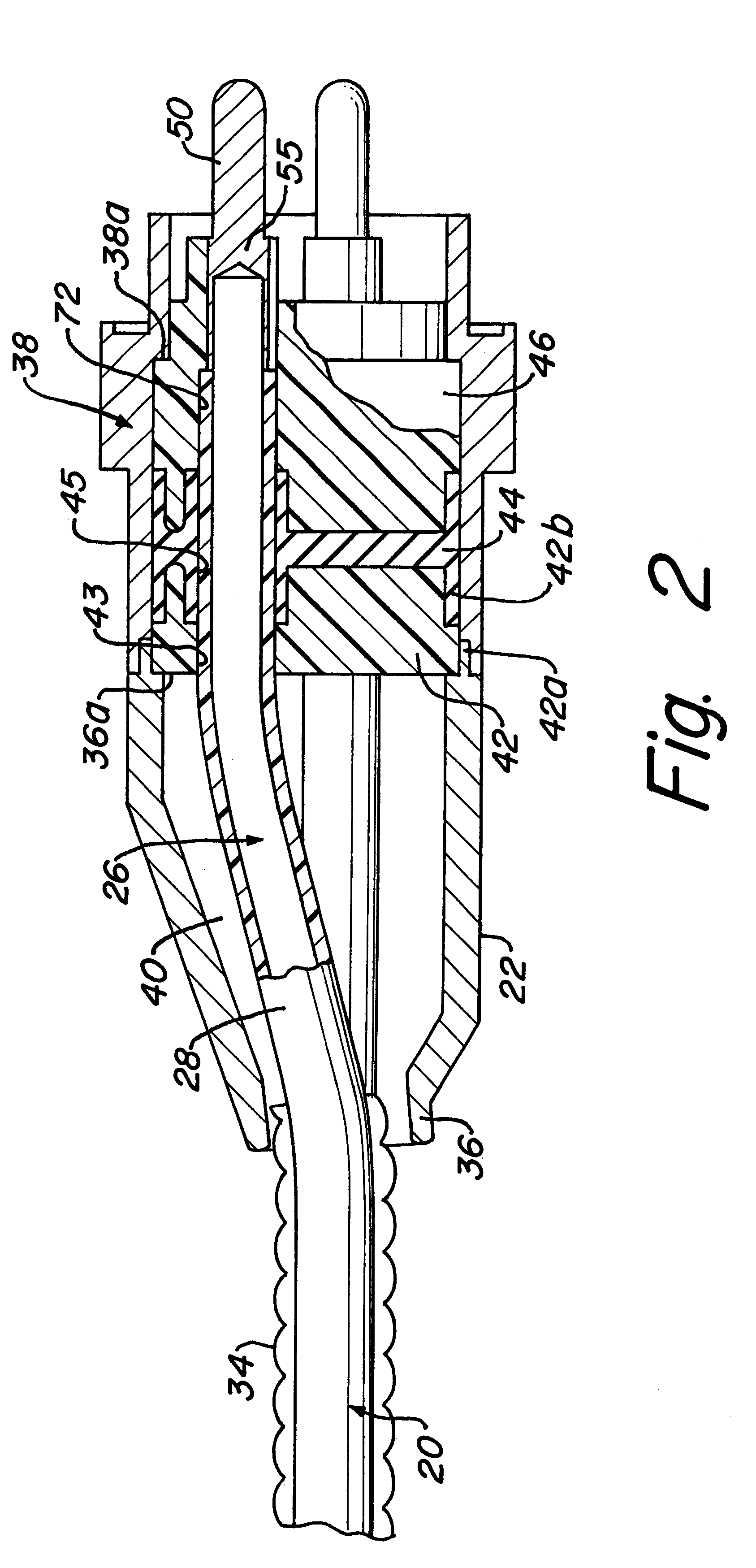
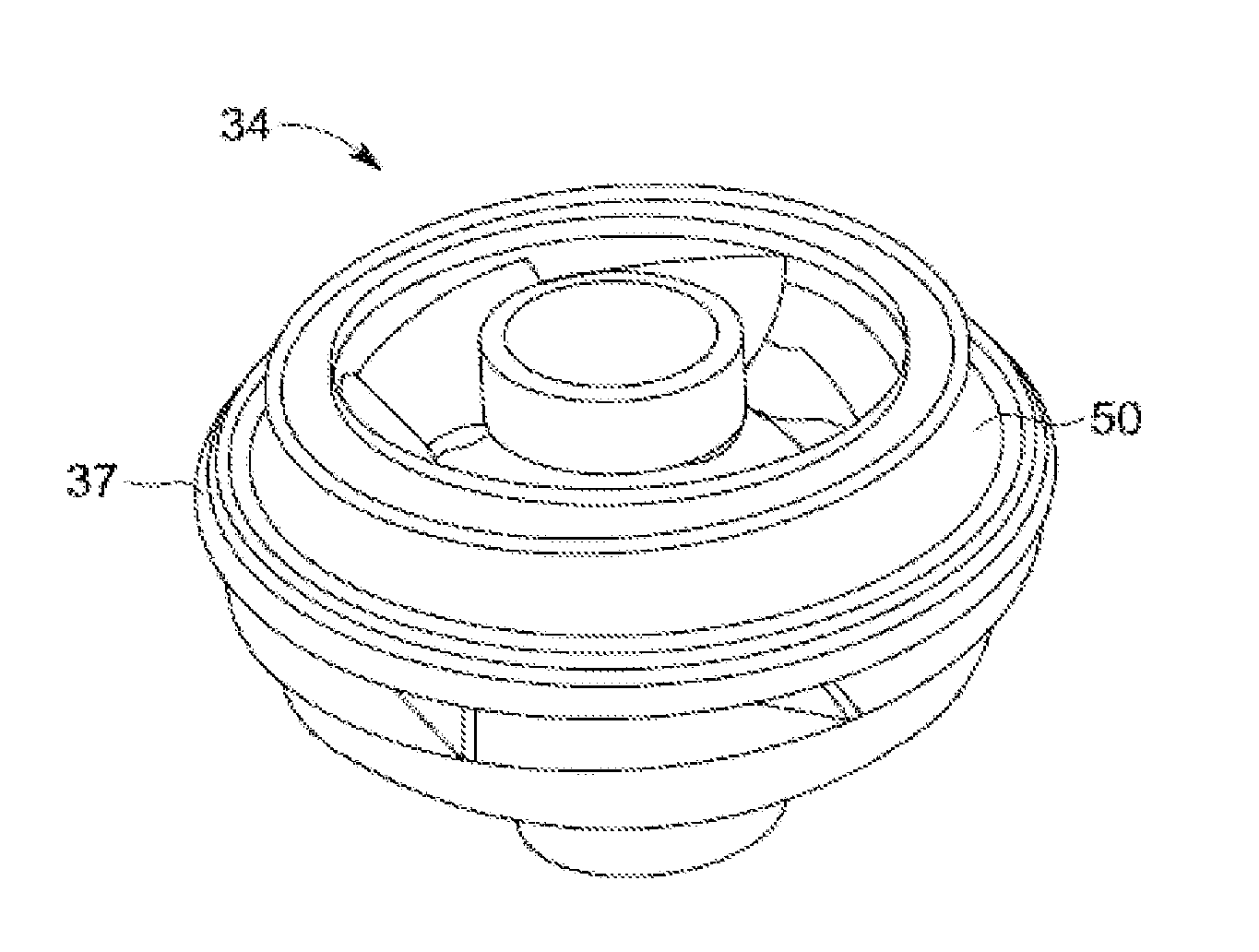
InactiveUS6361342B1Sleeve/socket jointsFluid pressure sealed jointsElectrical conductorInsulation layer
An electric submersible pump is provided having a pothead connector for use to connect a downhole cable to an electric motor of the submersible pump. The pothead connector has a housing having an upper and a lower end. The downhole cable has electrical conductors which are separately covered by insulation layers. The downhole cable extends through the upper end and into the housing, and then is electrically connected to the electric motor through the lower end of the housing. Two insulating blocks are provided in the lower end of the housing for separating electrical conductors in alignment for mating with a connector mounted to the electric motor. A conductor pin is secured to the insulating block and to each of the conductors. An elastic sealing ring is disposed within the housing, intermediately between the two insulating blocks. An epoxy layer are disposed within the upper end of the housing.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Electrical submersible pump and pump system including additively manufactured structures and method of manufacture
An electric submersible pump and pump system including additively manufactures structures and method of manufacture are disclosed. The pump system including the electric submersible pump and an electric motor configured to operate the electric submersible pump. The electric submersible pump including a housing, at least one impeller and at least one diffuser disposed within the housing in cooperative engagement. The housing, the at least one impeller, and the at least one diffuser defining an internal volume configured to receive a fluid. At least one of the at least one impeller and the at least one diffuser configured as a monolithic additively manufactured structure comprised of a metal matrix composite. Also provided is an electric submersible pump including an impeller and a diffuser, wherein at least one of the impeller and the diffuser is configured as a monolithic additively manufactured structure comprised of a tungsten carbide (WC) dispersed in a metal matrix.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
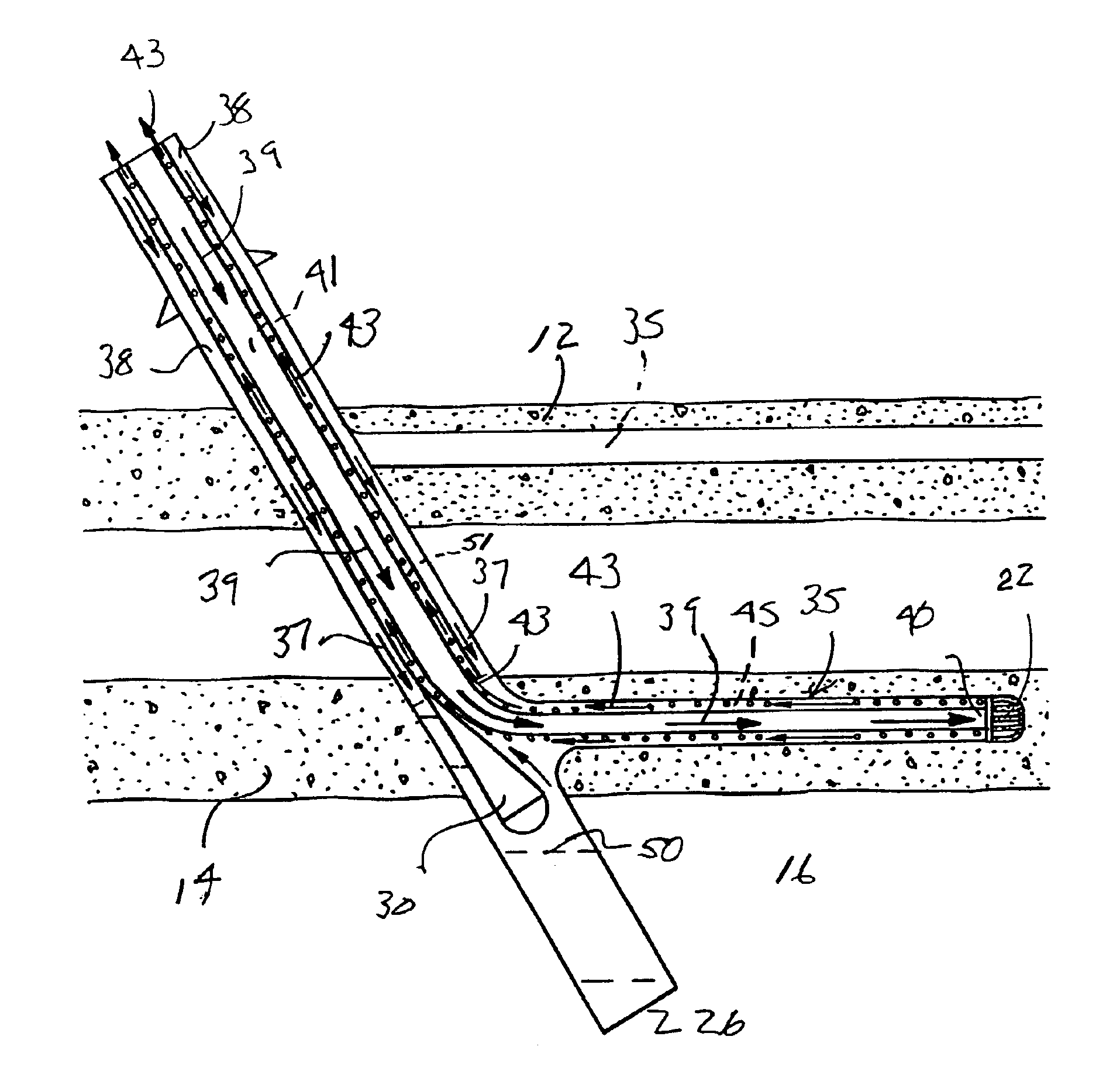
Artificial lift, concentric tubing production system for wells and method of using same
An artificial lift, concentric tubing production system for a well and method of using same. The system including an upper concentric tubing string portion comprising an inner production tubing string positioned within an outer production tubing string. A flow crossover assembly is connected to the upper concentric tubing string portion. The flow crossover assembly has first and second passageways. The inner production tubing string is in fluid communication with the first passageway and the outer production tubing string in fluid communication with the second passageway. An upper transducer is in fluid communication with one of the passageways of the flow crossover assembly and a lower apparatus is in fluid communication with the other of the passageways of the flow crossover assembly. The upper transducer may be a pump such as an electric submersible pump or a progressive cavity pump. The lower apparatus may be a pump, including an electric submersible pump, or a liquid / gas separator.
Owner:YPF INT
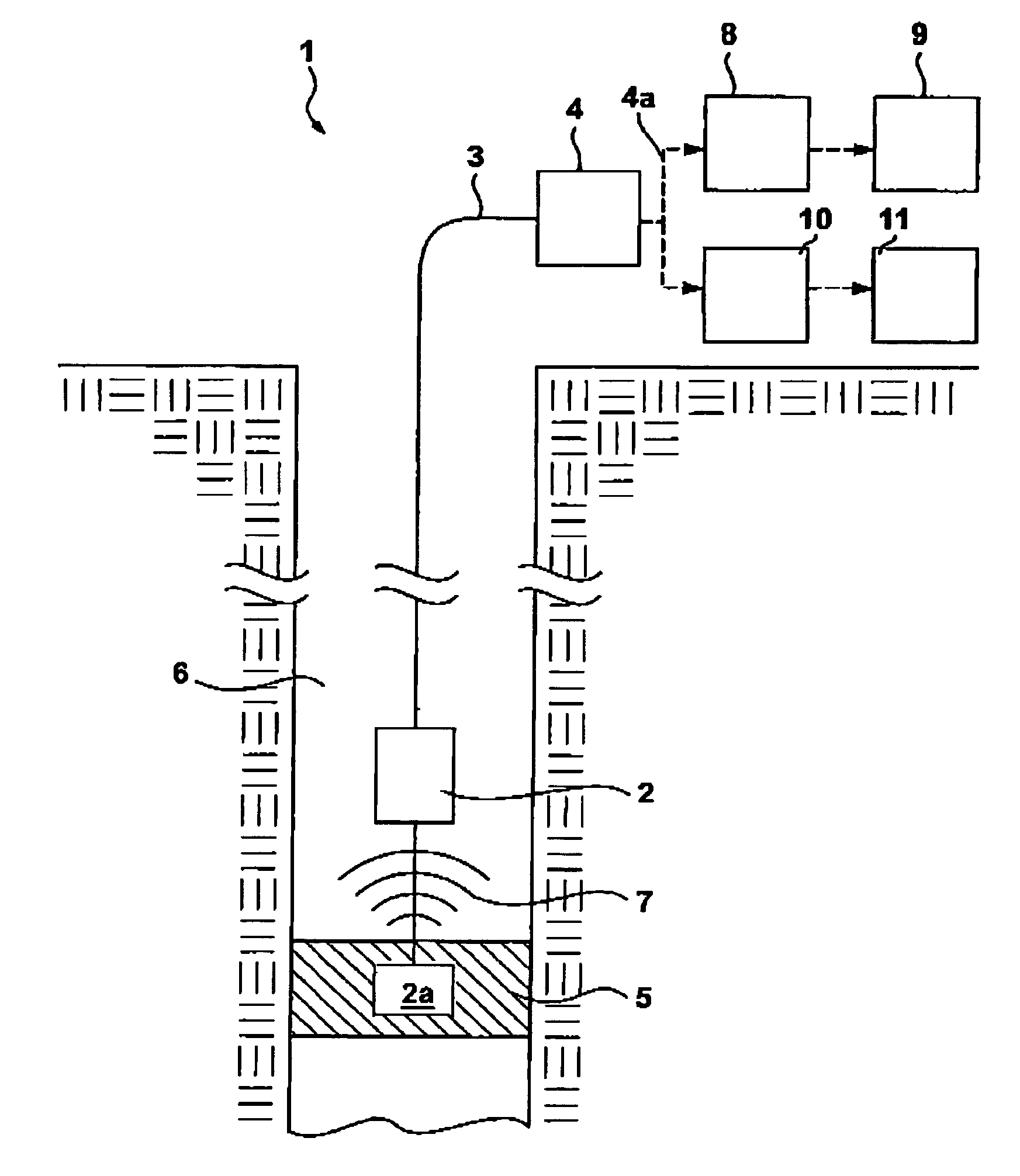
Natural gas hydrate water discharge gas production exploitation device and exploitation method of natural gas hydrate water discharge gas production exploitation device
ActiveCN103410488ASpeed up decompositionReduce moisture contentConstructionsFluid removalElectricityVapor–liquid separator
The invention provides a natural gas hydrate water discharge gas production exploitation device and an exploitation method of the natural gas hydrate water discharge gas production exploitation device, and belongs to the technical field of natural gas hydrate exploitation. A feeding cavity (12) communicated with a natural gas hydrate layer (29) is connected with an in-well gas-liquid separator (7), an exhaust cavity (8) of the in-well gas-liquid separator (7) is communicated with a gas production sleeve pipe (17), and a water discharge opening of the in-well gas-liquid separator (7) is communicated with a liquid storage cavity (2) arranged at the lower part. According to the exploitation method adopting the device, the natural gas hydrate layer (29) is firstly heated, the in-well gas-liquid separator (7) is utilized for separating gas-water mixture generated in the natural gas hydrate decomposition process, meanwhile, a liquid level monitoring device is utilized for regulating the water discharge speed of an electric submersible pump (4), and the decomposition speed of the natural gas hydrate is controlled. The device and the method have the advantages that the natural gas hydrate exploitation well liquid accumulation can be effectively prevented, the gas production efficiency is improved, the work is safe and reliable, the environment is protected, the service life is long, and the like.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
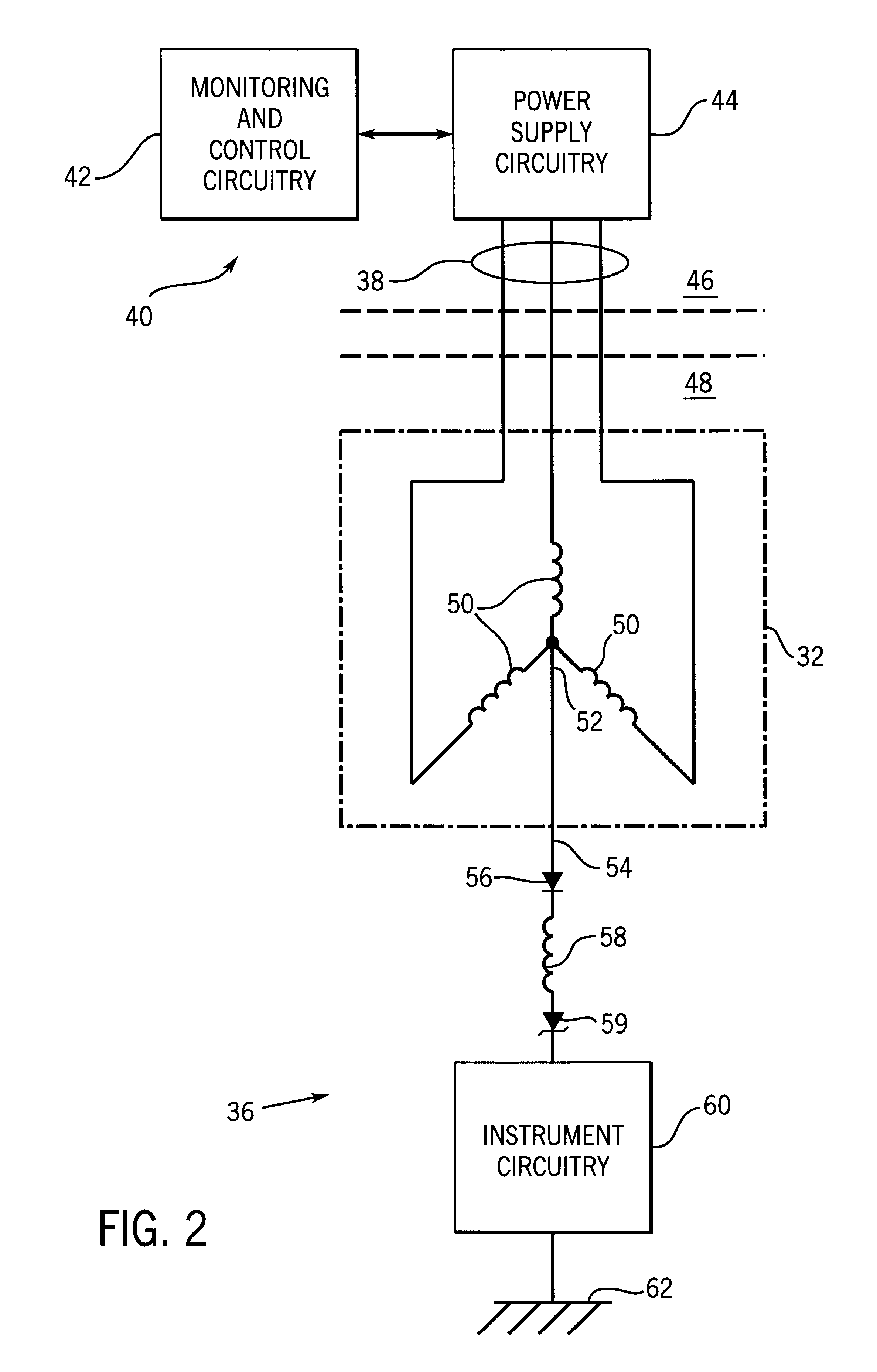
Inductor system for a submersible pumping system
InactiveUS6176308B1Transformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionTransformers/inductances casingsElectricityWave shape
An inductor assembly is disclosed for protecting electronic circuitry in a downhole equipment string. The inductor assembly includes a plurality of modular inductors coupled to one another in series to provide the desired inductance. The modular inductors are supported by a support structure in a protective housing, such as in a common housing with the electronic circuitry. The inductor assembly is electrically isolated from the housing. The support structure may include insulative end members and rail members extending between the end members to which the inductors are secured. One or more insulative covers are provided around the inductors to further isolate the inductors from the housing. The inductor assembly dissipates energy in the event of certain failure modes of power supply circuitry or lines extending from the earth's surface. The inductor may be secured electrically between a neutral node in a Y-wound motor to prevent high voltage ac waveforms from damaging the electronic circuitry. Insulation of the inductors inhibits arcing with the housing, thereby inhibiting damage to the inductors or the electronic circuitry during such failure modes.
Owner:CAMCO INT
Multi seam coal bed/methane dewatering and depressurizing production system
InactiveUS6923275B2Minimal environmental impactEliminate infrastructure long-term maintenance and environmental impactFluid removalDirectional drillingWell drillingProduct gas
A process for underbalanced drilling into multiple coal and shale formations, and dewatering the drilled formations, which includes drilling a first borehole through several coal seams to a certain depth, defined as a cased borehole; lowering an upstock on the end of a carrier string to the depth of the upper coal seam; lowering a drill string in the carrier string, and angling off of the upstock, to drill a lateral or horizontal borehole within the coal seam; repeating the process for the second coal seam; setting a packer in place above the first coal seam in the annulus between the cased borehole and the carrier string; forming perforations in the wall of the carrier string below the packer; retrieving the upstock from the carrier string; lowering an electrical submersible pump to the bottom of the principal borehole, defined as a sump portion of the borehole; collecting methane gas from the two coal seams through the annulus between the second drill string and the carrier string to the surface; pumping water from the sump portion to the surface within the annulus of the second drill string, while gas within the annulus between the carrier string and the outer casing enters the plurality of perforations in the carrier string to be carried up to the surface.
Owner:GARDES ROBERT
Subsea well with electrical submersible pump above downhole safety valve
A subsea well production system has a natural drive mode and a lift-assist mode using a submersible pump. The submersible pump can be installed while the well is live. The well system has a downhole safety valve in the production tubing. The operator closes the downhole safety valve and lowers an electrical submersible pump assembly into the production tubing. Once landed, the valve is opened and the pump assembly placed in operation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
ROV retrievable sea floor pump
A subsea pumping assembly locates on a seafloor for pumping well fluid from subsea wells to the level. The pumping assembly has a tubular outer housing that is at least partially embedded in the seafloor. A tubular primary housing locates in the outer housing and has a lower end with a receptacle. An annular space surrounds the primary housing within the outer housing for delivering fluid to a receptacle at the lower end of the primary housing. A capsule is lowered in and retrieved from the primary housing. The capsule sealingly engages the receptacle for receiving well fluid from the annular space. A submersible pump is located inside the capsule. The pump has an intake that receives well fluid and a discharge that discharges the well fluid exterior of this capsule. The capsule has a valve in its inlet that when closed prevents leakage of well fluid from the capsule. The capsule may be retrieved through open sea without a riser.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Oilfield apparatus comprising swellable elastomers having nanosensors therein and methods of using same in oilfield application
An oilfield apparatus has a swellable elastomeric composition that includes a swellable elastomer and one or more nanosensors dispersed therein. An oilfield assembly for exploring for, drilling for, testing for, or producing hydrocarbons includes various oilfield elements such as tubing, jointed pipe, sucker rods, submersible pump motor protector bags, packer elements, blow out preventer elements, zonal isolation tool elements, etc; and one or more of the oilfield elements has a swellable elastomeric composition that includes a swellable elastomer and one or more nanosensors dispersed therein. A method of selecting one or more oilfield elements has a component of an elastomeric composition that includes a swellable elastomer and one or more nanosensors dispersed therein; and a method of using the one or more oilfield elements in an oilfield operation, thus exposing the oilfield element to an oilfield environment.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System, method, and apparatus for downhole submersible pump having fiber optic communications
A downhole submersible pump system, method, and apparatus utilizes fiber optic sensors and distributed temperature sensors below the submersible pump to monitor pump discharge pressure and temperature, intake pressure and temperature, and motor temperature. In addition, distributed temperature sensors are used below the pump to monitor the perforations within the well bore.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Device and Method For Gas Lock Detection In An Electrical Submersible Pump Assembly
ActiveUS20090250210A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyElectricityDifferential pressure
A device and method can detect, and also break, an occurrence of gas lock in an electrical submersible pump assembly in a well bore based upon surface or downhole data without the need for operator intervention. To detect an occurrence of gas lock, an instantaneous value is monitored using a sensor. Then a controller compares the instantaneous value to a threshold value over a predetermined duration to thereby detect the occurrence of gas lock in the electrical submersible pump assembly. Sensors can include, for example, a differential pressure gauge, a pressure gage located in a pump stage located toward the inlet, a fluid temperature sensor located toward the discharge, a free gas detector located near the pump discharge, an electrical resistivity gage, a flow meter located within surface production tubing, and a vibration sensor attached to a tubing string to measure a vibration signature.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Monitoring and automatic control of operating parameters for a downhole oil/water separation system
A method for operating a downhole oil water separator and electric submersible pump includes measuring fluid pressure proximate one of the pump intake, separator intake and a bottom of a wellbore. At least one of flow rate and pressure is measured at the separator water outlet. Pump and a water outlet restriction are controlled to maintain an optimum fluid pumping rate and an optimum injection rate of separated water. A flow control system includes a controllable valve disposed in a water outlet of the separator. At least one of a pressure sensor and a flowmeter is operatively coupled to the water outlet. A controller is in signal communication with the at least one of a pressure sensor and flowmeter and in operative communication with the valve. The controller operates the valve to maintain at a selected pressure and / or a selected flow rate through the water outlet.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Automatic sampler of water quality sampling UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle)
ActiveCN105571904AReduce weightImprove performanceWithdrawing sample devicesUncrewed vehicleWater quality
The invention discloses an automatic sampler of a water quality sampling UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle). The automatic sampler comprises a main body support, a fixed height sensor, a water sample collecting device, a lifting device, a sample dividing device, a sample storage device and a control circuit board, wherein the water sample collecting device comprises a submersible pump, a pressure and liquid level sensor, a flexible water pipe and a flow sensor and is capable of completing fixed-depth sampling; the lifting device comprises a servo motor, a magnetic encoder, a reduction gear, a slip ring, a bearing, a proximity switch, a telescopic rod and a ceramic eye component and is capable of realizing retracing and releasing functions of the water sample collecting device; the sample storage device is formed by three layers of detachable plastic bottles. According to the automatic sampler disclosed by the invention, the weight of the automatic sampler can be effectively reduced, and the performance of the whole water quality sampling UAV is increased; meanwhile, the fixed-depth sampling is realized through the lifting device and the pressure and liquid level sensor which is additionally arranged in a sampling opening, the water quality collecting device can be retracted during a flying process of the water quality sampling UAV, and the safety during the flying process of the water quality sampling UAV is increased.
Owner:WUHAN BOGAN SPACE TECH CO LTD
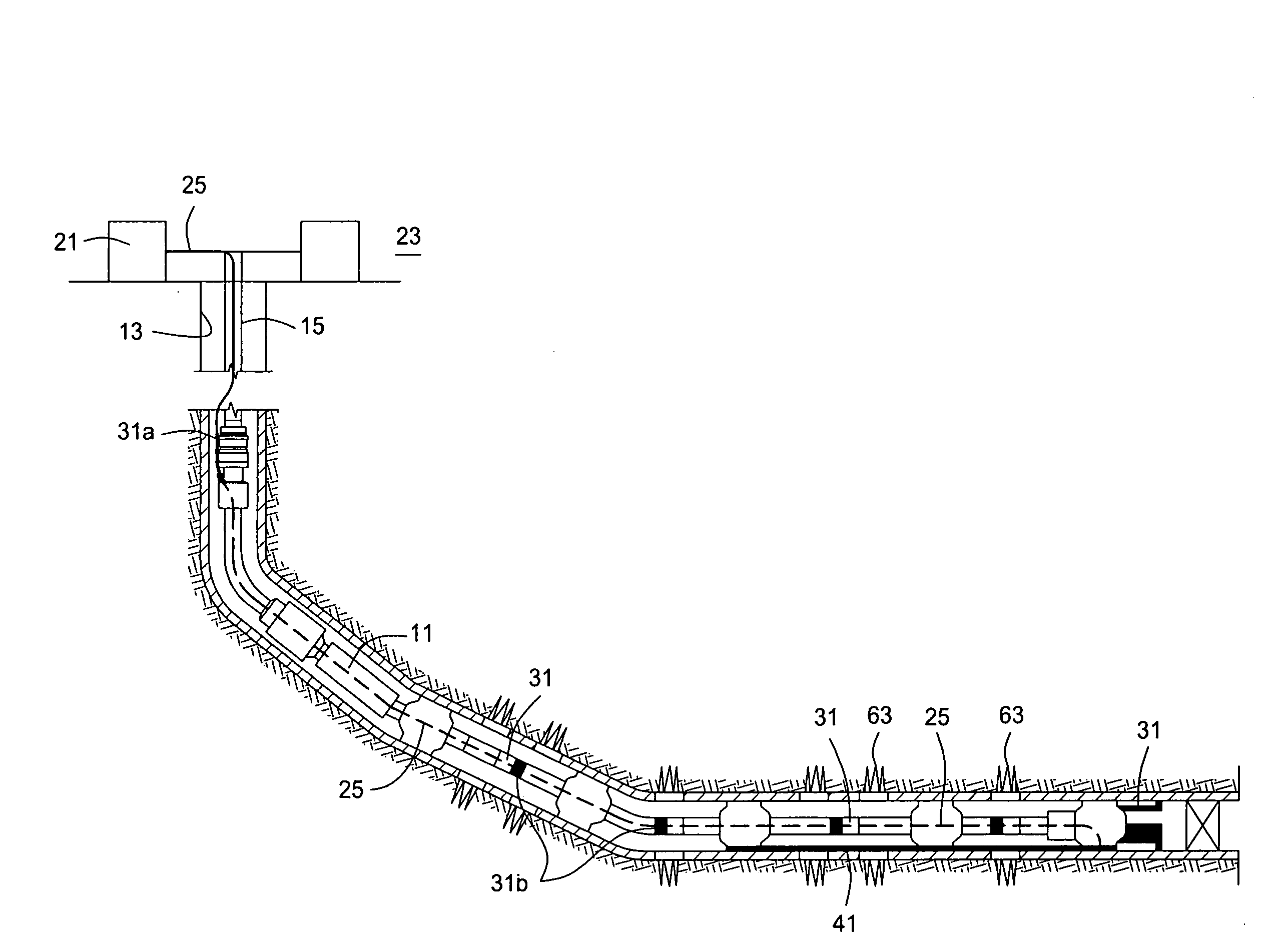
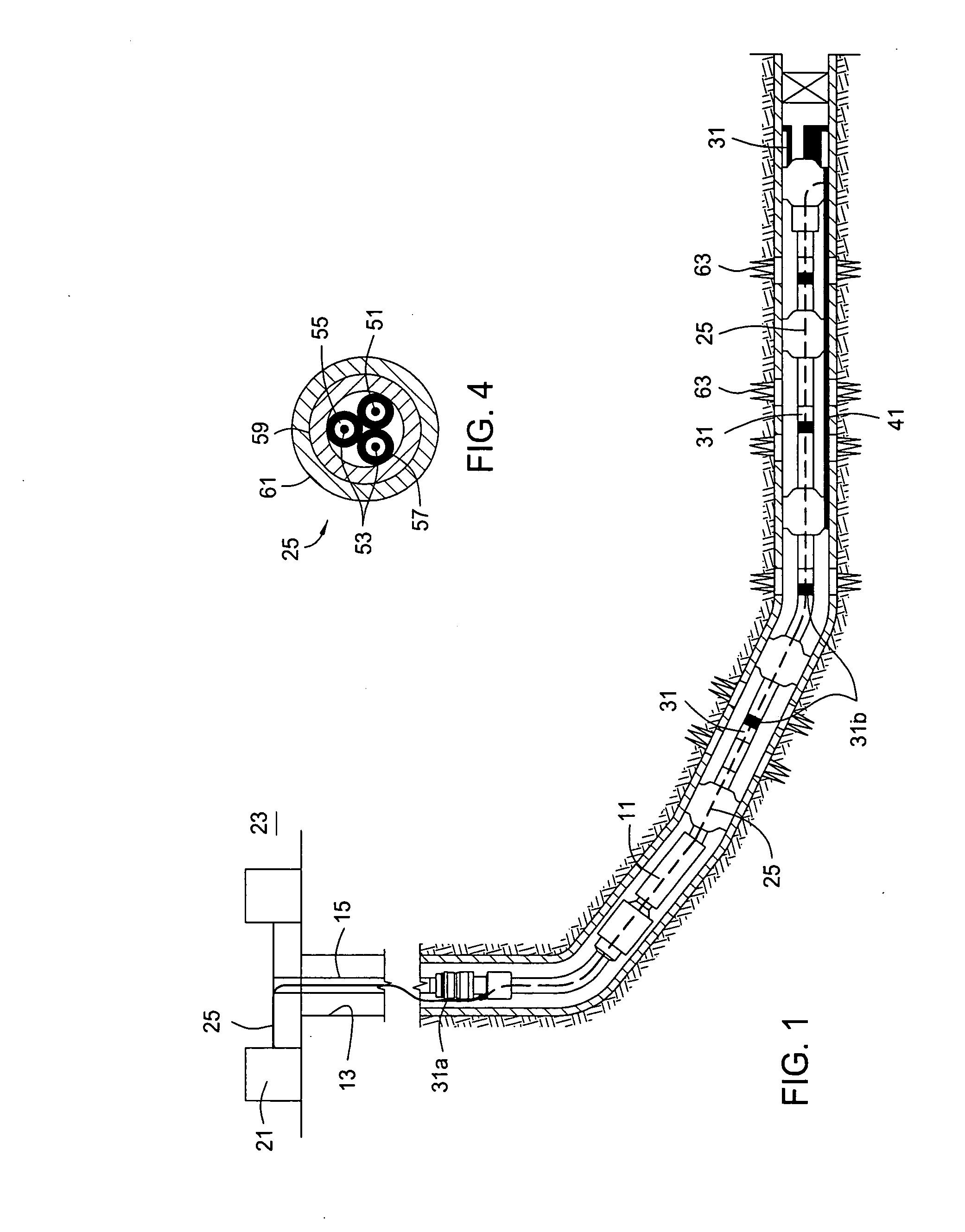
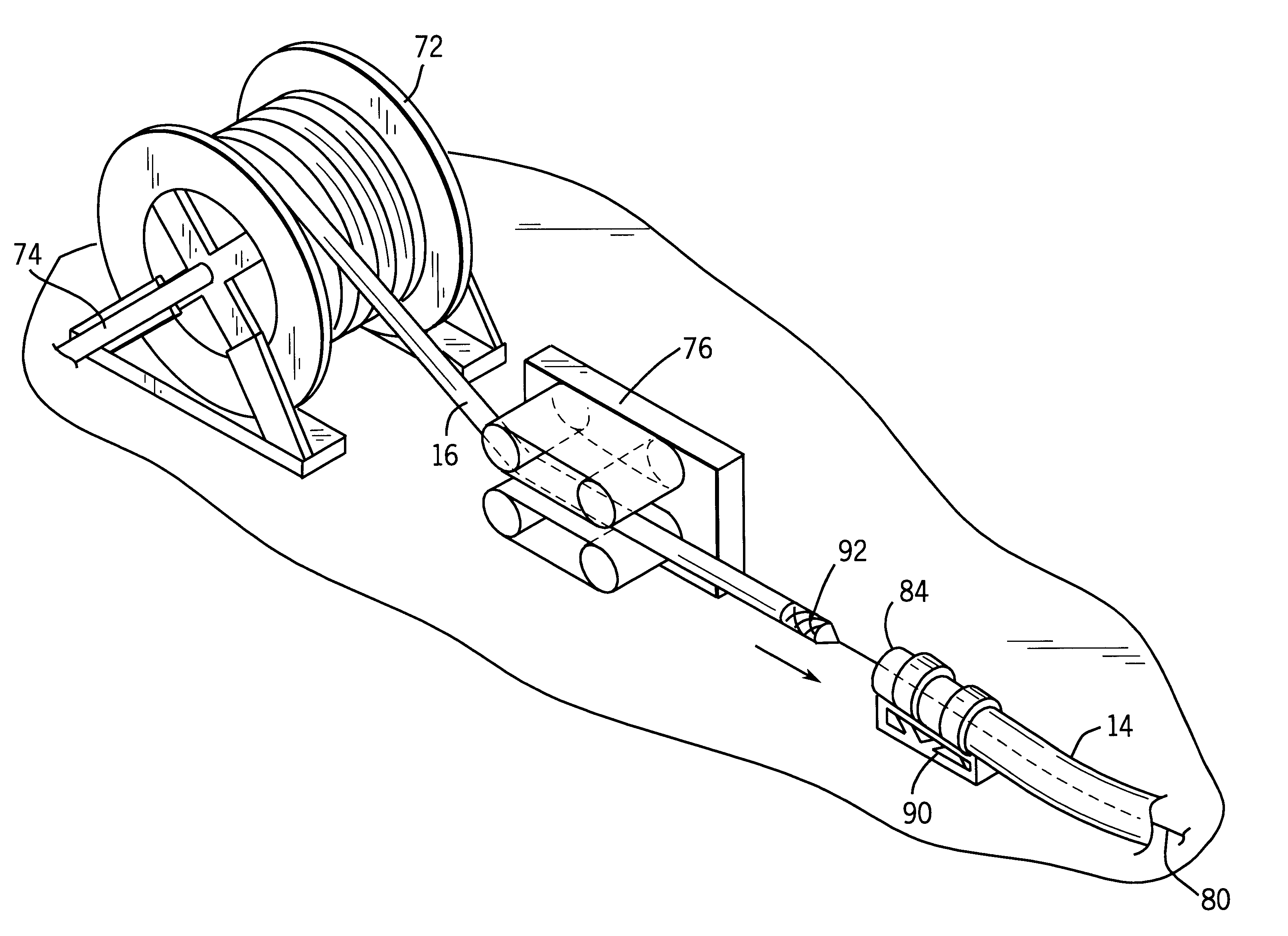
Method and apparatus for installing a cable into coiled tubing
A technique for installing a length of cable assembly and coiled tubing includes application of both compressive and tensile forces on the cable assembly. The compressive forces are applied to the cable assembly in a compression station at an entry end of the coiled tubing. Tensile forces are applied to the cable assembly by a wire line or a similar structure situated at an exit end of the coiled tubing. Following installation of the cable assembly in the coiled tubing, the coiled tubing may be transported to an application site, and coupled to equipment, such as a submersible pumping system. The submersible pumping system may then be deployed by extension of the coiled tubing and cable assembly. Additional lengths may be obtained by joining subassemblies formed by the tensile and compressive force technique. The technique reduces residual elongation or strain in the cable assembly as compared to conventional methods.
Owner:CAMCO INT
System and method for real-time monitoring and failure prediction of electrical submersible pumps
InactiveUS7979240B2Efficient use ofFail to accuratelyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsManagement systemReliability engineering
The present application relates to a system and method for real-time monitoring and failure prediction of electrical submersible pumps. The design includes generating a failure prediction value with a management system by calculating a percentage change of the respective first measurement values and the corresponding user-supplied stable operating values, the failure prediction value representing likelihood of failure of the electrical submersible pump.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Apparatus, system and method for treatment of an electric submersible pump power cable
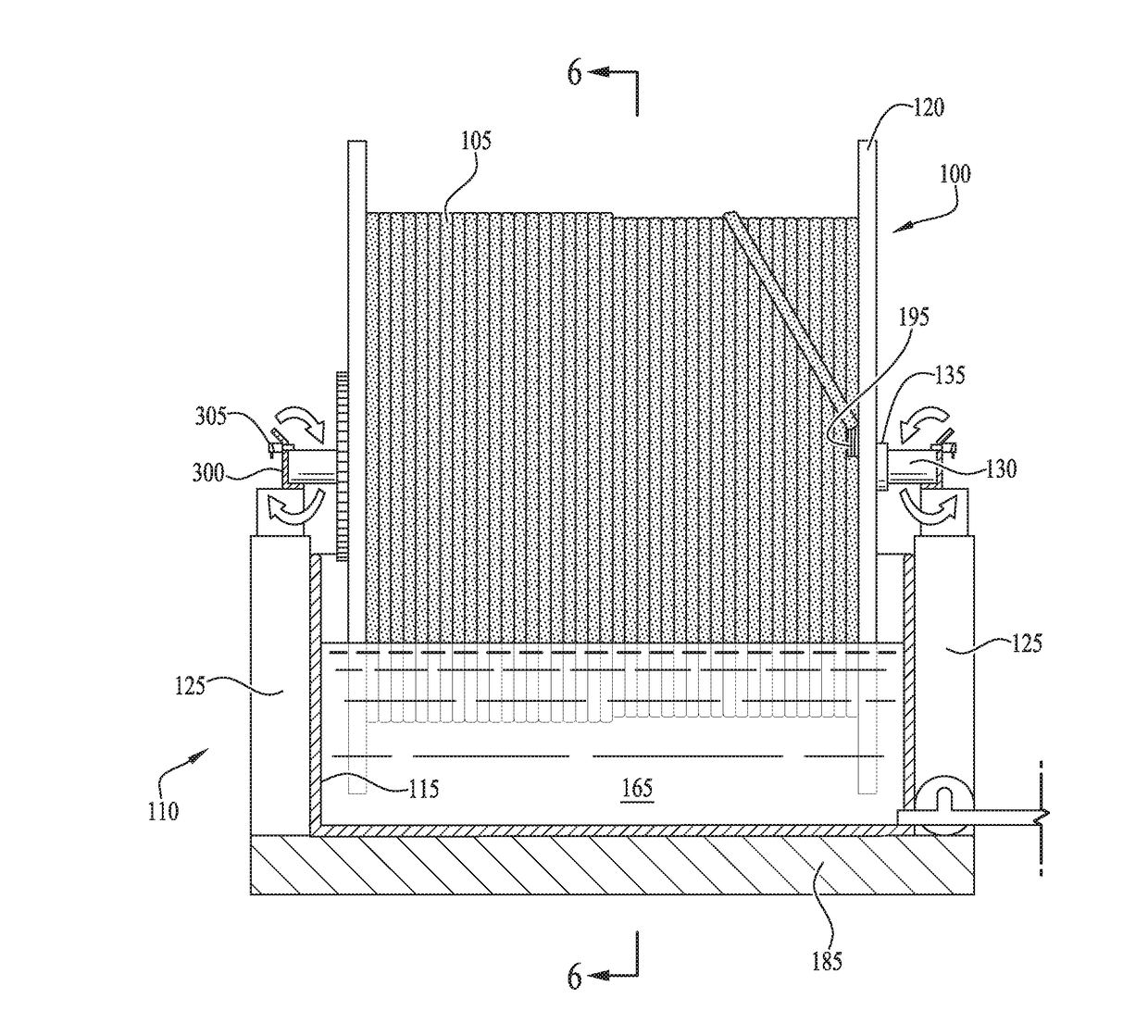
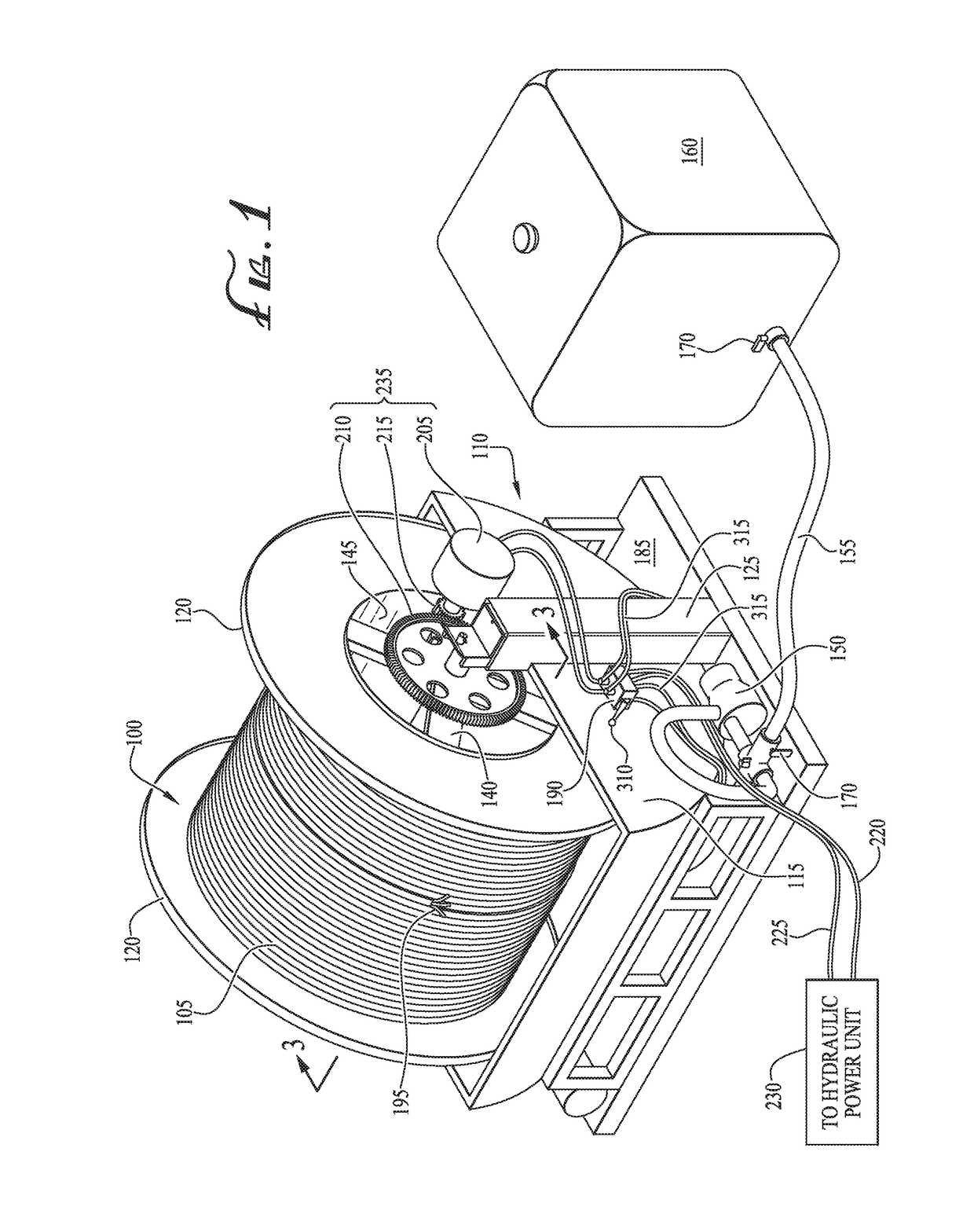
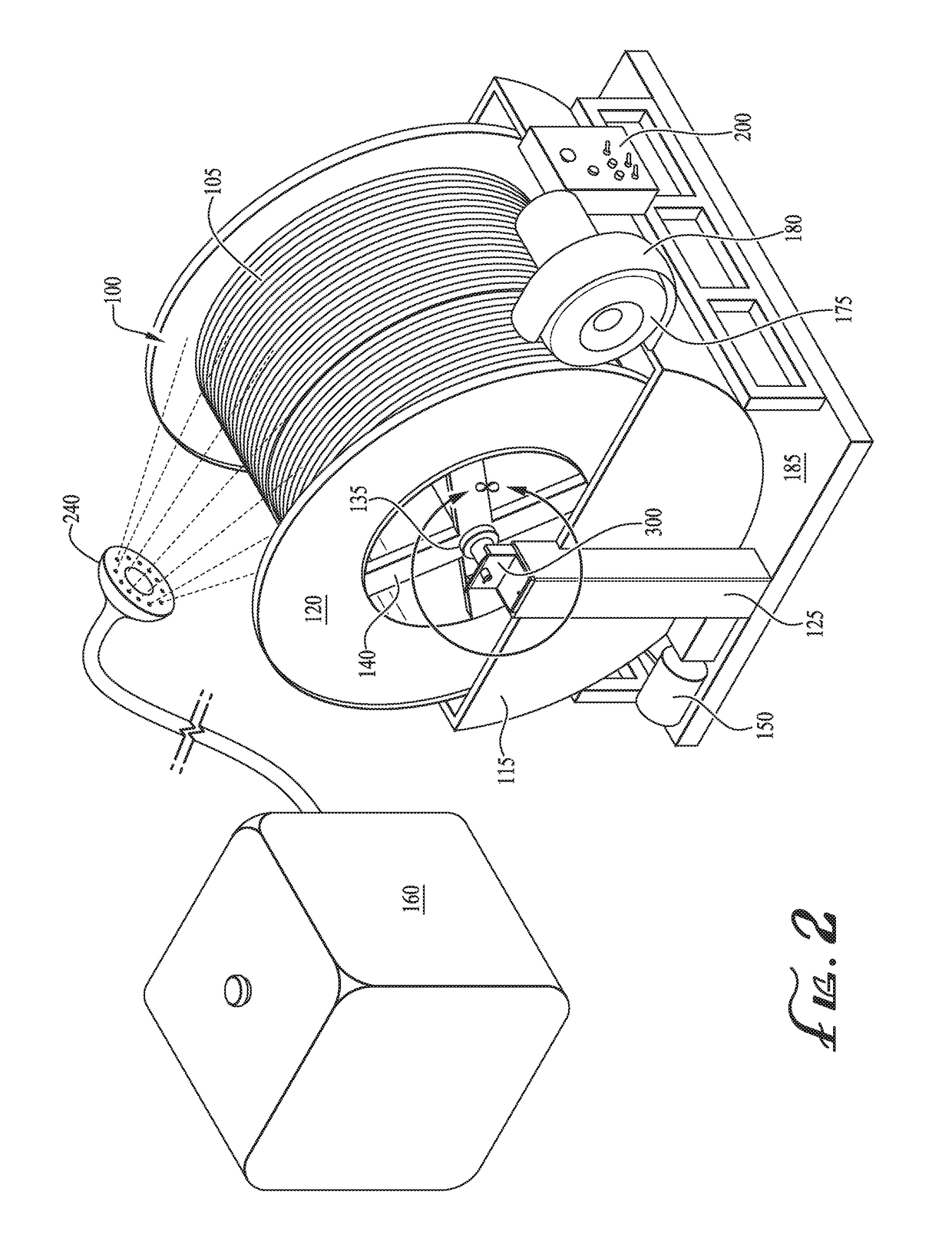
An apparatus, system and method for treatment of an electric submersible pump (ESP) power cable is described. A method of treating an ESP power cable includes wrapping an ESP power cable around a reel as the cable is removed from a production well to form cable layers, supporting the cable-wrapped reel horizontally above a tank, the reel supported on a shaft extending between actuatable support members, pumping treatment fluid into the tank, lowering the cable-wrapped reel partially into the tank by activating the actuatable support members such that a lower portion of the reel is submerged in the treatment fluid and an inner diameter of the cable-wrapped reel is fluidly coupled to the treatment fluid, rotating the reel around its central axis such that each portion of an outermost layer of the cable is submerged in the treatment fluid at least once to coat the ESP power cable.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com