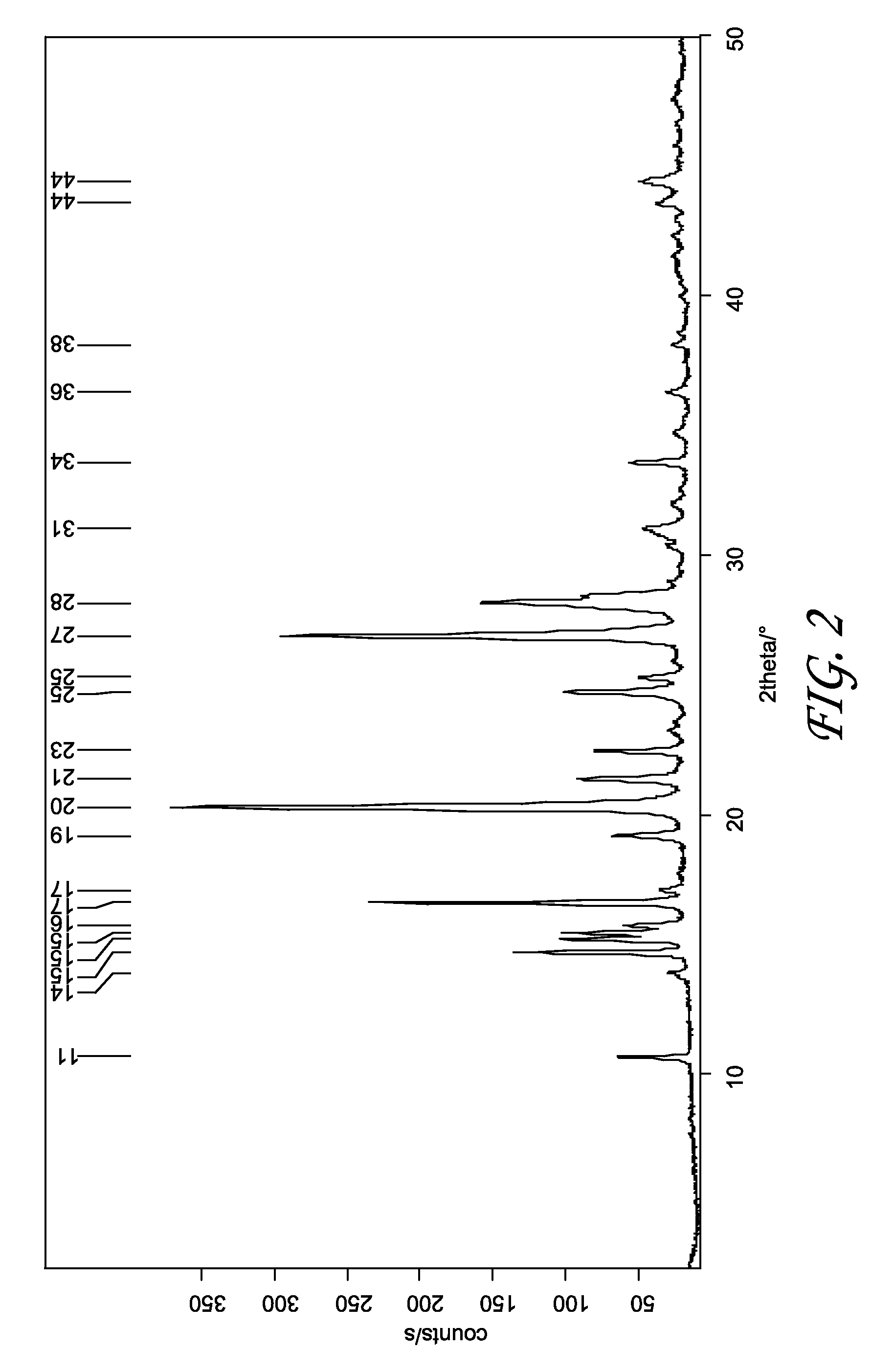
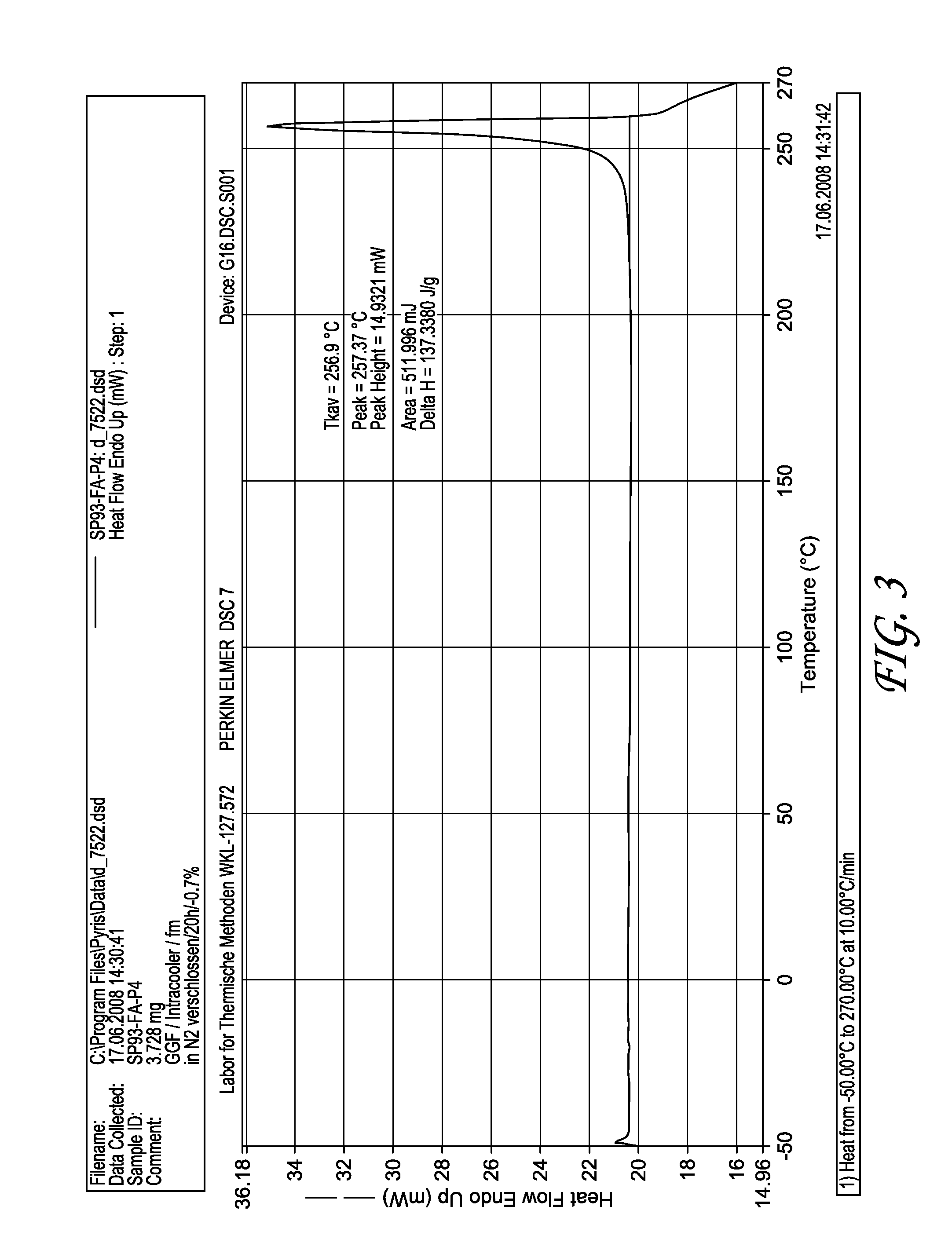
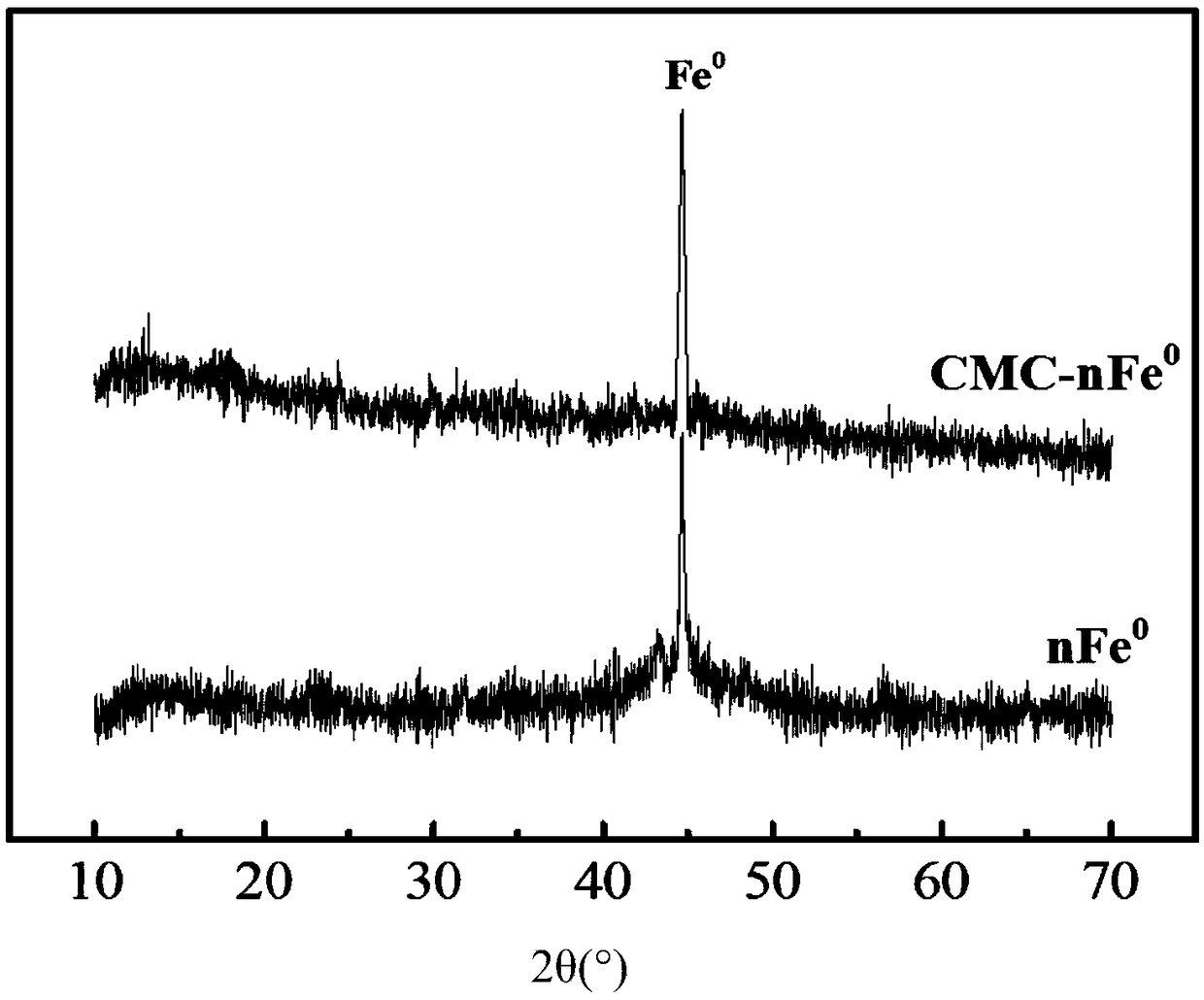
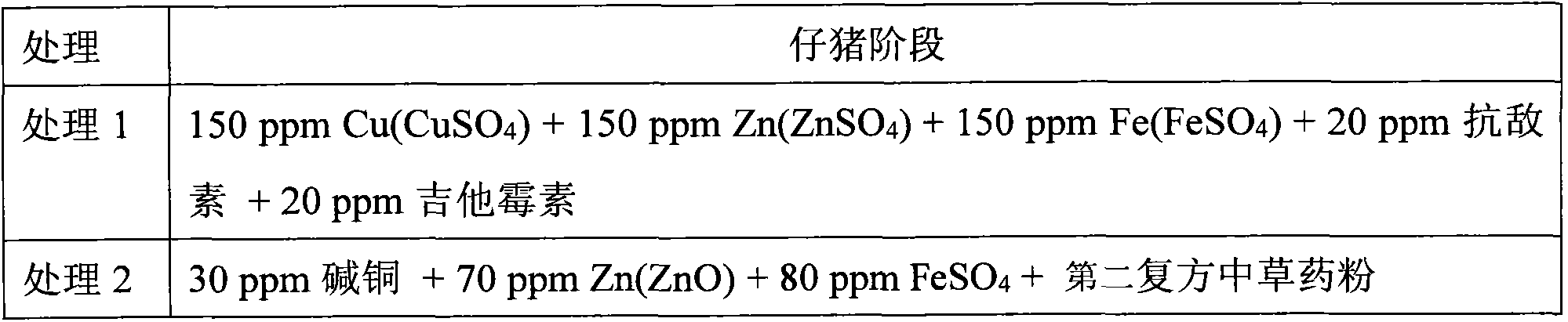
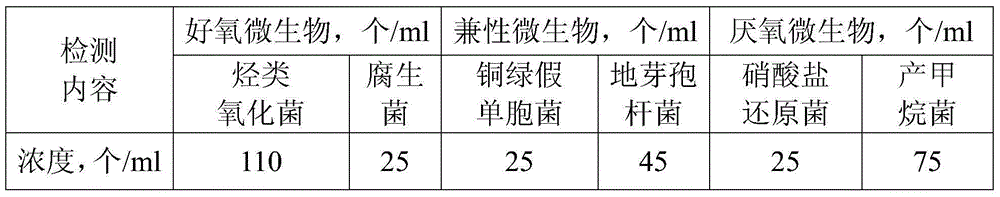
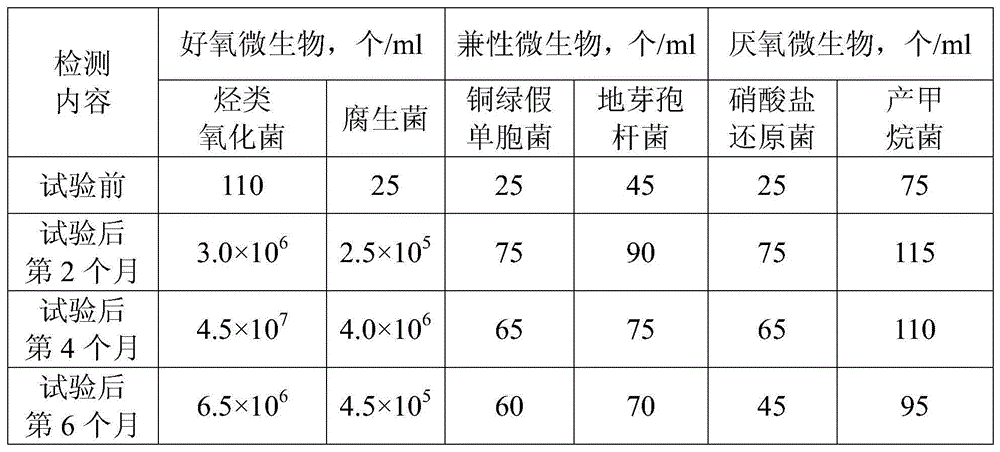
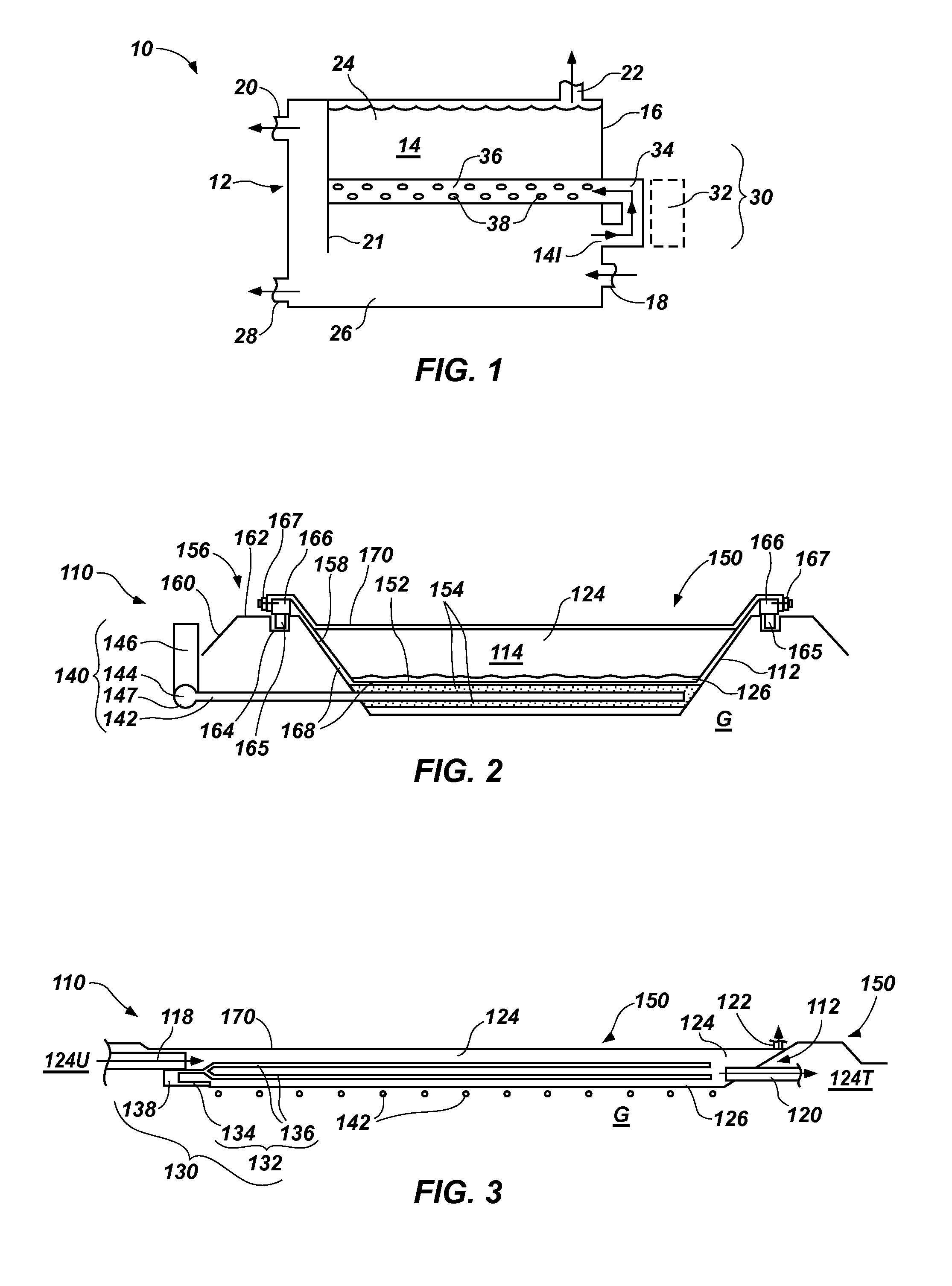
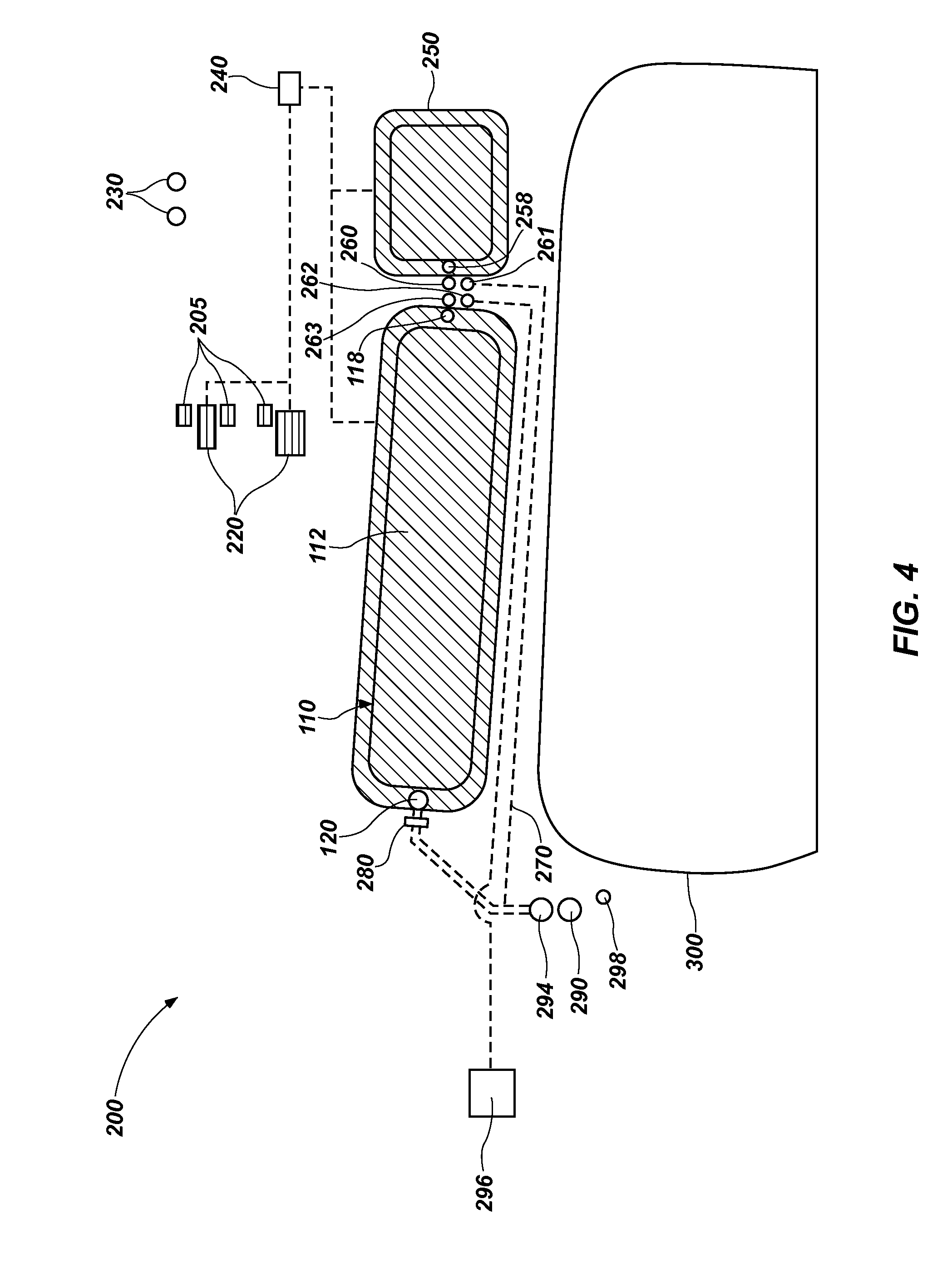
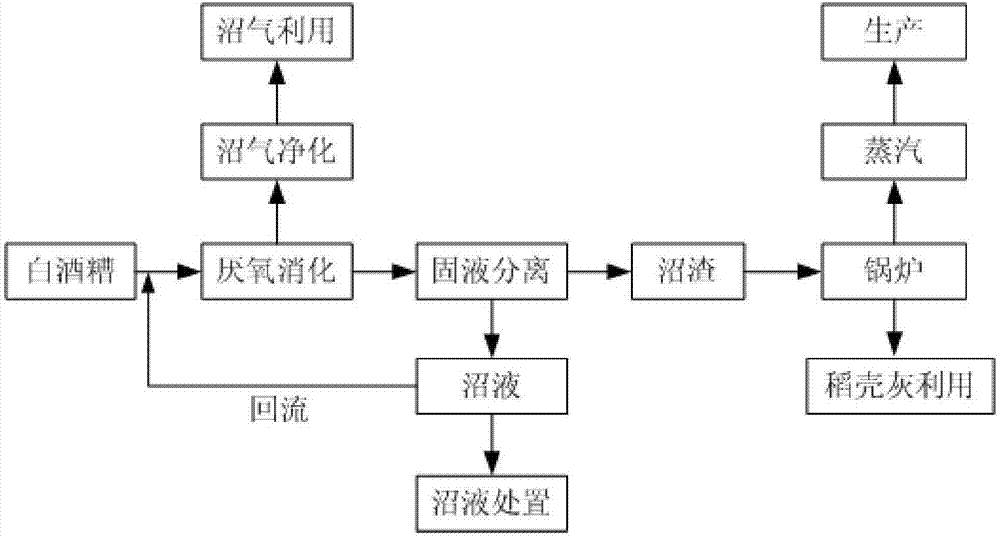
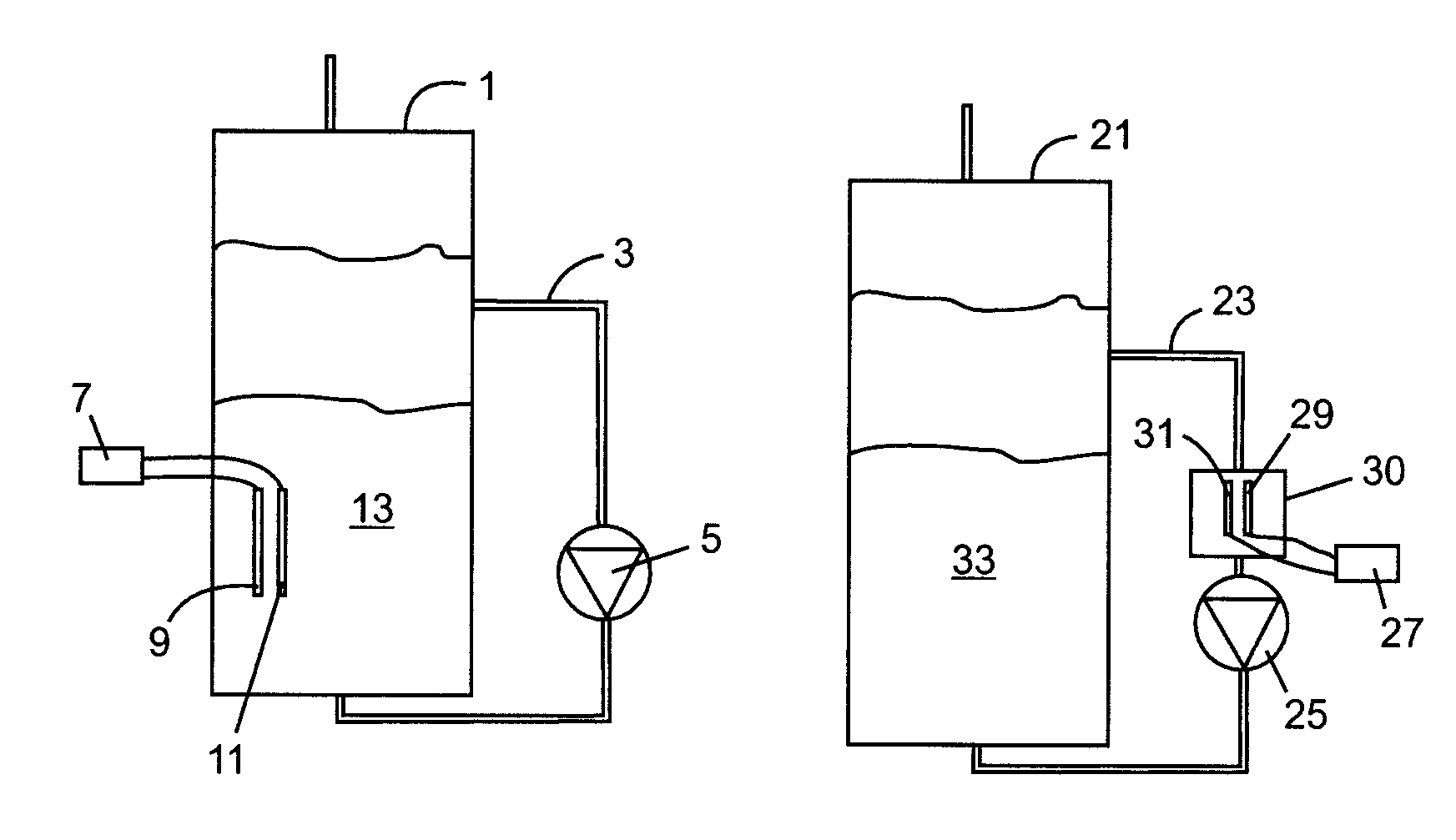
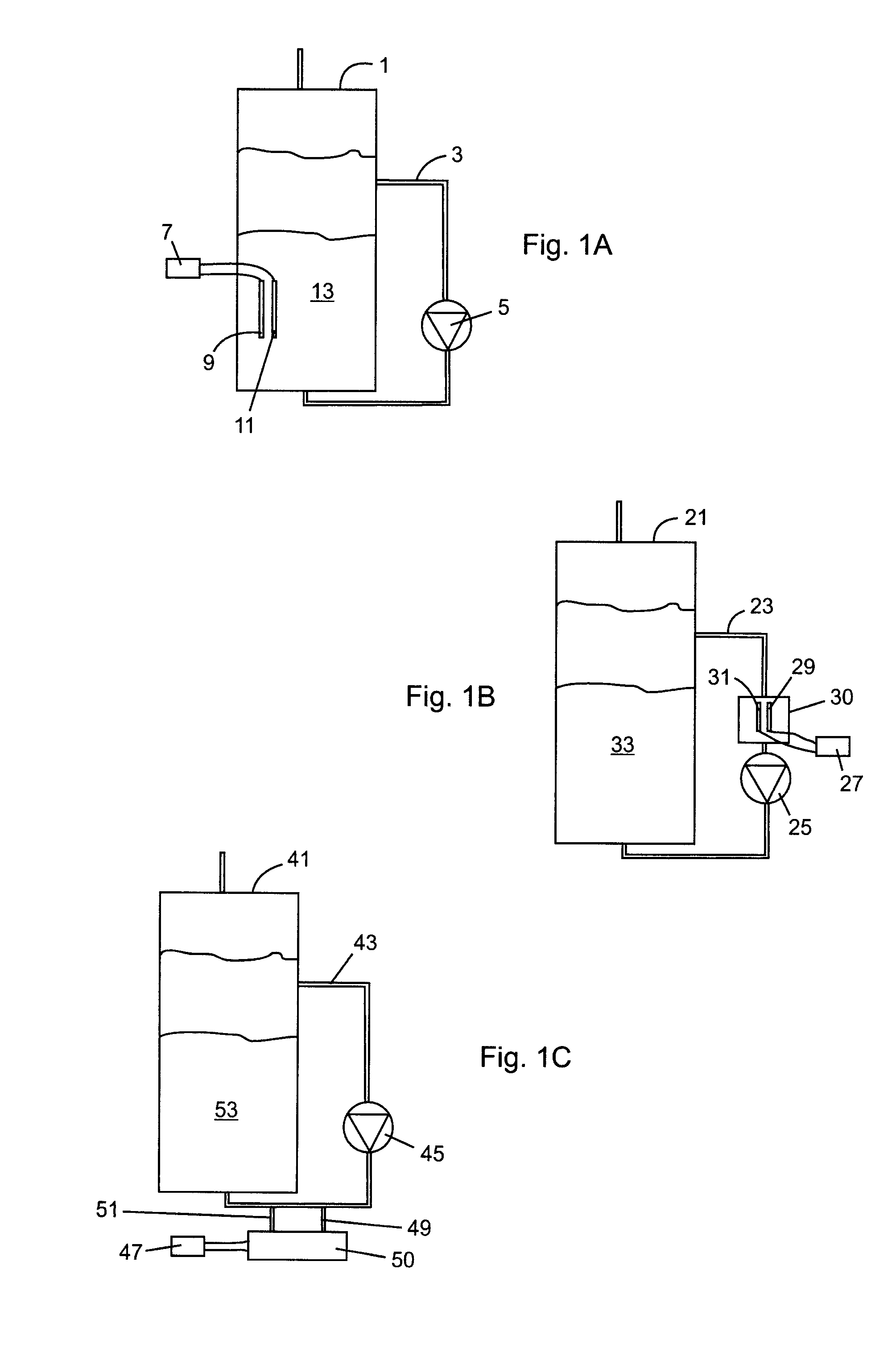
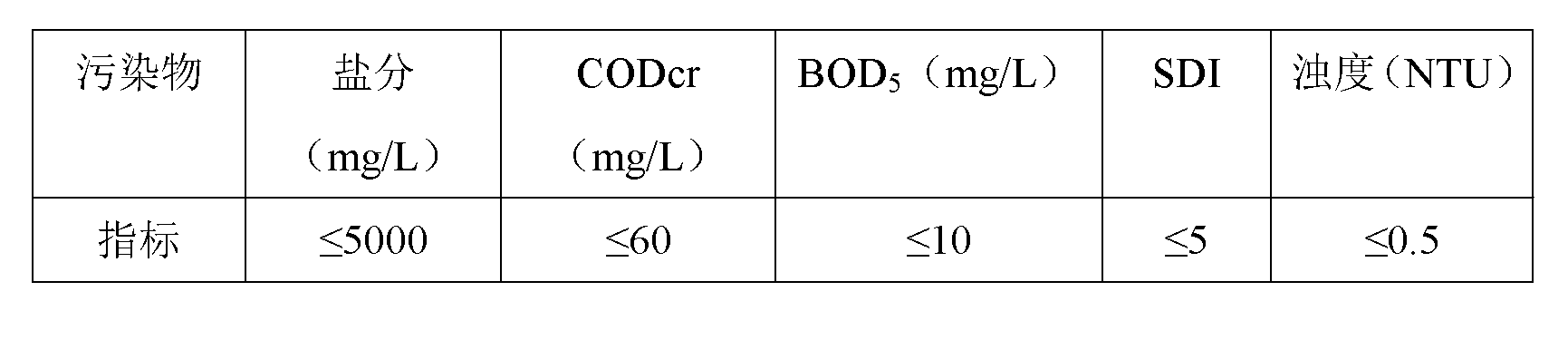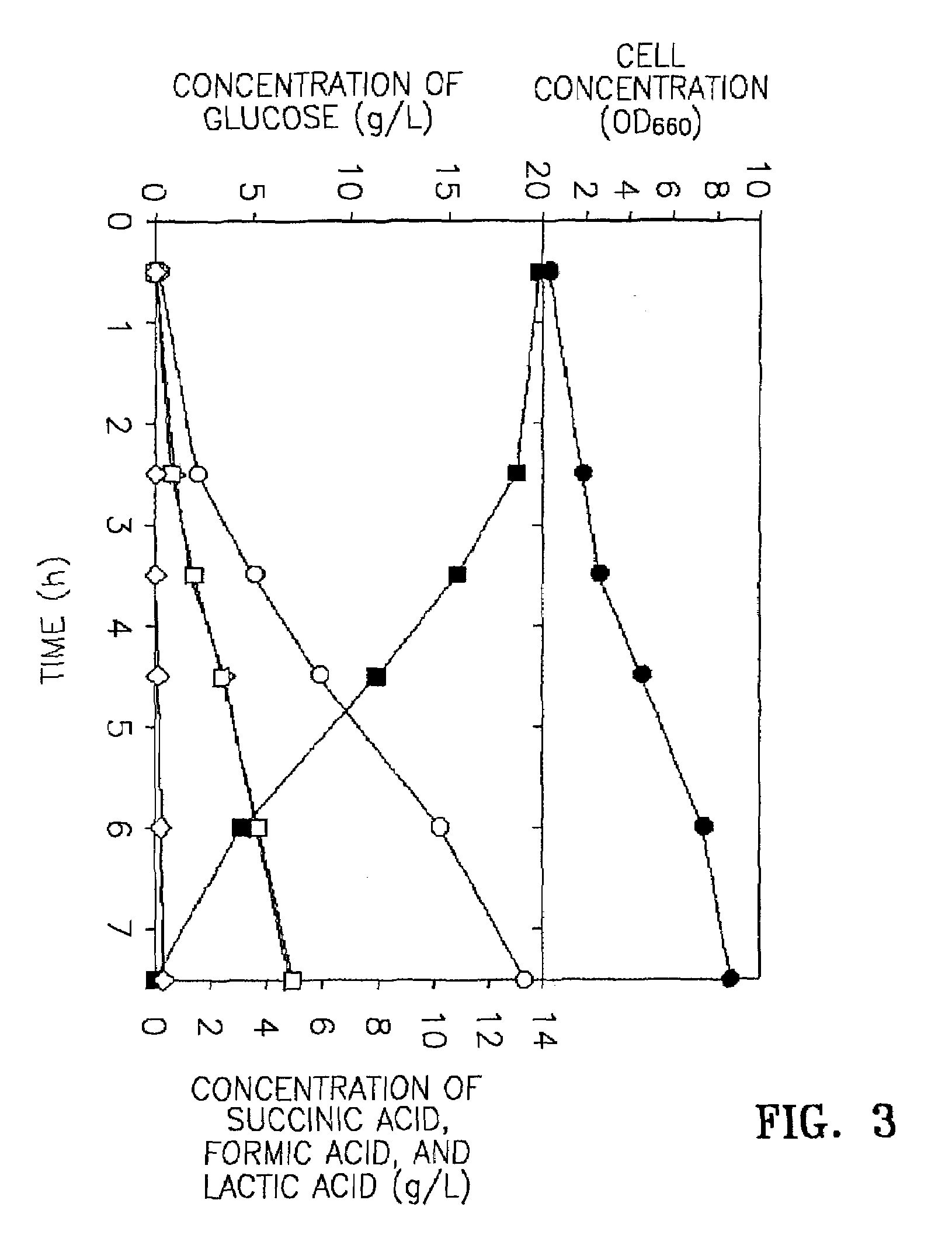Patents
Literature
457 results about "Anaerobic microorganisms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbial culture liquors containing microorganisms differing in characteristics and living in symbiosis and metabolites thereof, carriers and adsorbents containing the active components of the culture liquors and utilization of the same
Solutions containing microorganisms differing in characteristics from each other and living in symbiosis with each other and enzymes characterized by containing aerobic microorganisms, anaerobic microorganisms and at least one basidiomycete belonging to the family Pleurotaceae living in symbiosis, metabolites thereof and enzymes; carriers obtained by adsorbing the components of the above solutions onto finely ground carbonaceous materials; and porous materials obtained by adsorbing the components of the above solutions onto porous materials. Because of having various effects of absorbing, adsorbing and decomposing harmful matters, deodorizing, decolorizing, etc., these materials are applicable to various uses in the fields of agriculture and environment.
Owner:ORIENT GREEN
Media supplements and methods to culture human gastrointestinal anaerobic microorganisms
InactiveUS20140342438A1Enhance their axenic growthAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroidesAnaerobic bacteria
A media supplement for culturing anaerobic bacteria is provided which comprises a filtrate of effluent from a chemostat vessel in which a target bacterial ecosystem has been cultured. Methods of using the supplement for culturing or isolating anaerobic microbial strains or communities, particularly anaerobic bacteria from the human gut, are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
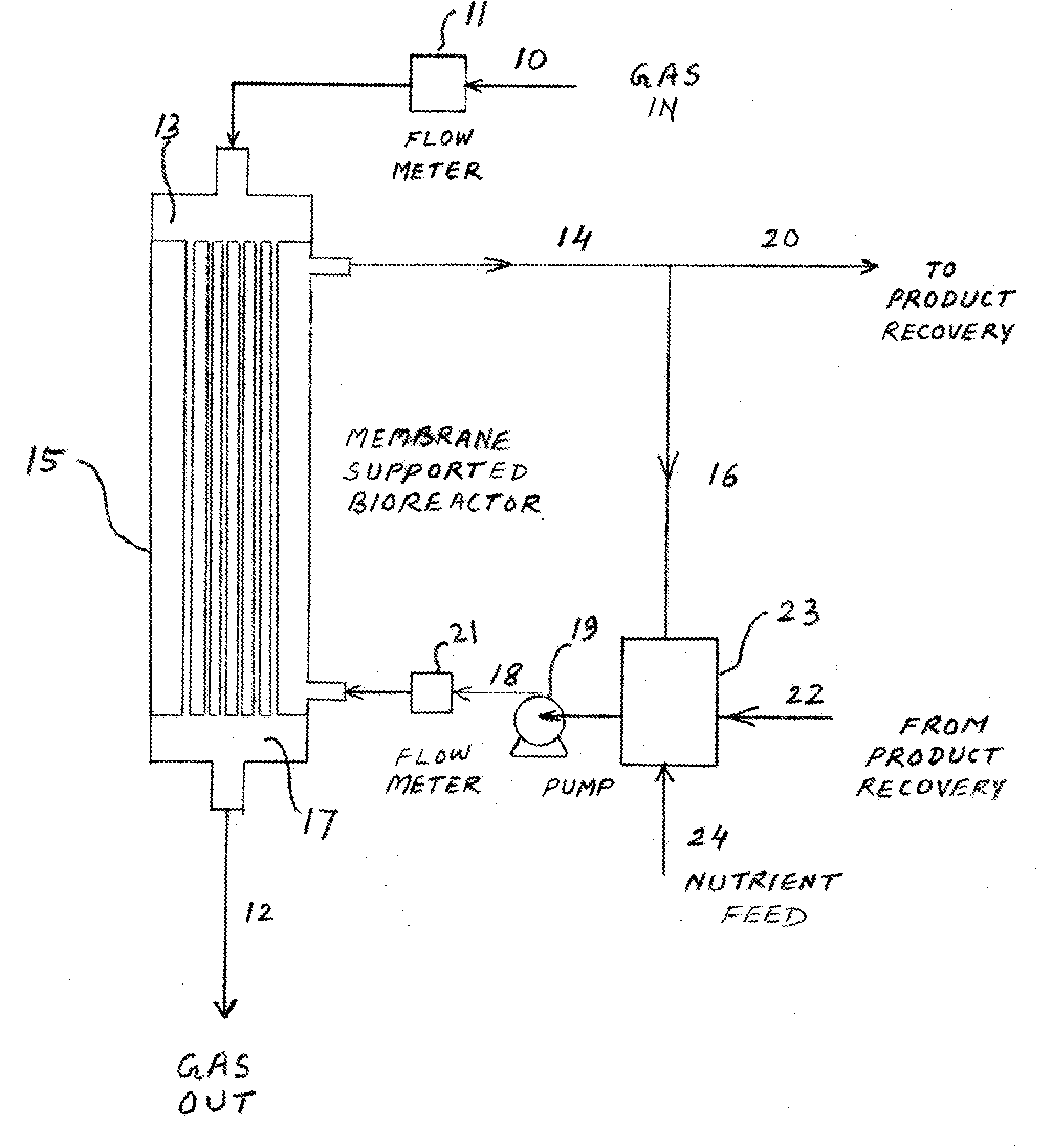
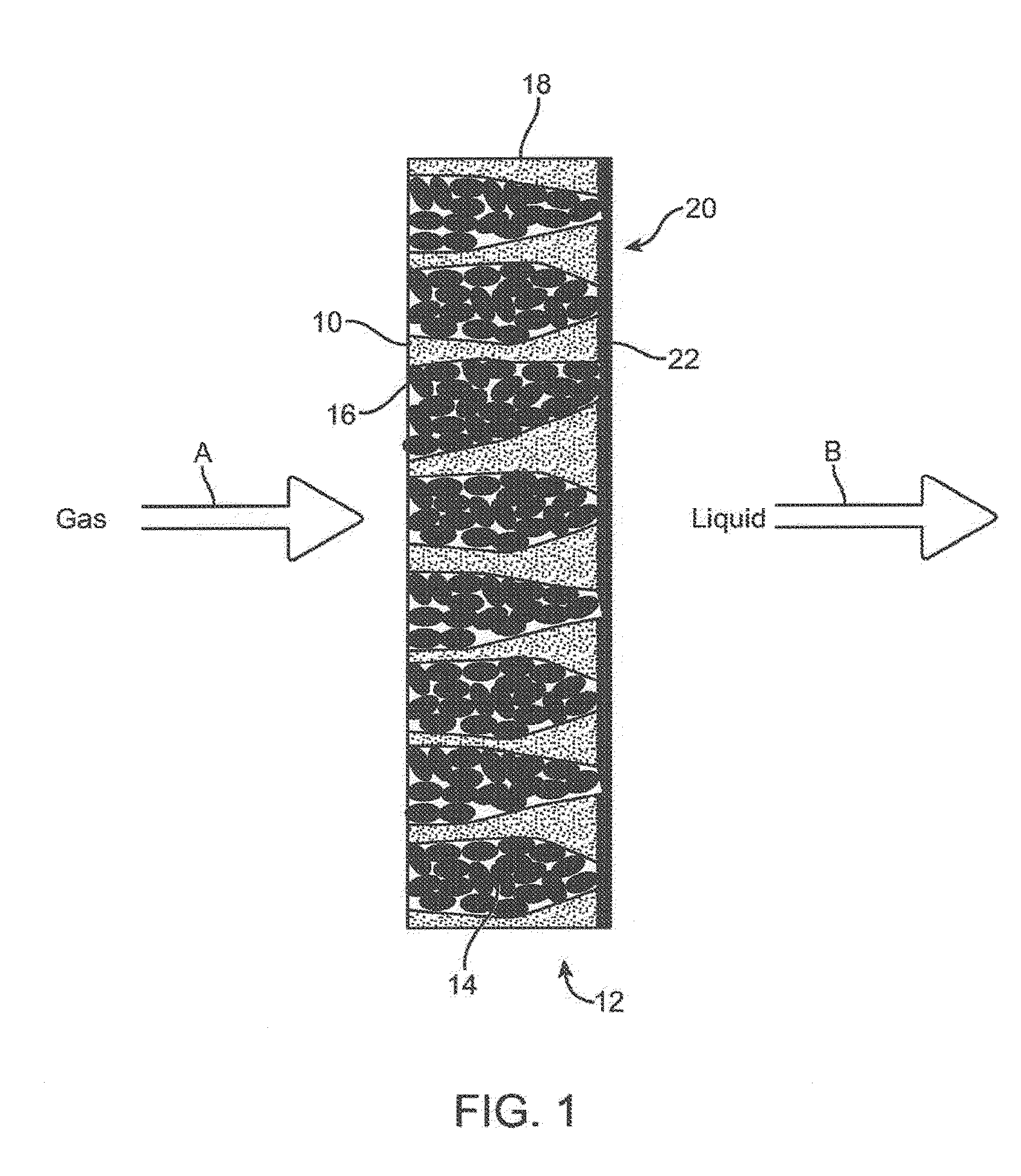
Membrane supported bioreactor for conversion of syngas components to liquid products
InactiveUS20080305539A1Guaranteed economic efficiencyEasy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid productBiofilm
Ethanol and other liquid products are produced by contacting syngas components such as CO or a mixture of CO2 and H2 with a surface of a membrane and transferring these components in contact with a biofilm on the opposite side of the membrane. These steps provide a stable system for producing liquid products such as ethanol, butanol and other chemicals. The gas fed on the membrane's gas contact side transports through the membrane to form a biofilm of anaerobic microorganisms that converted the syngas to desired liquid products. The system can sustain production with a variety of microorganisms and membrane configurations.
Owner:COSKATA INC
Method and apparatus for killing microorganisms in ship ballast water
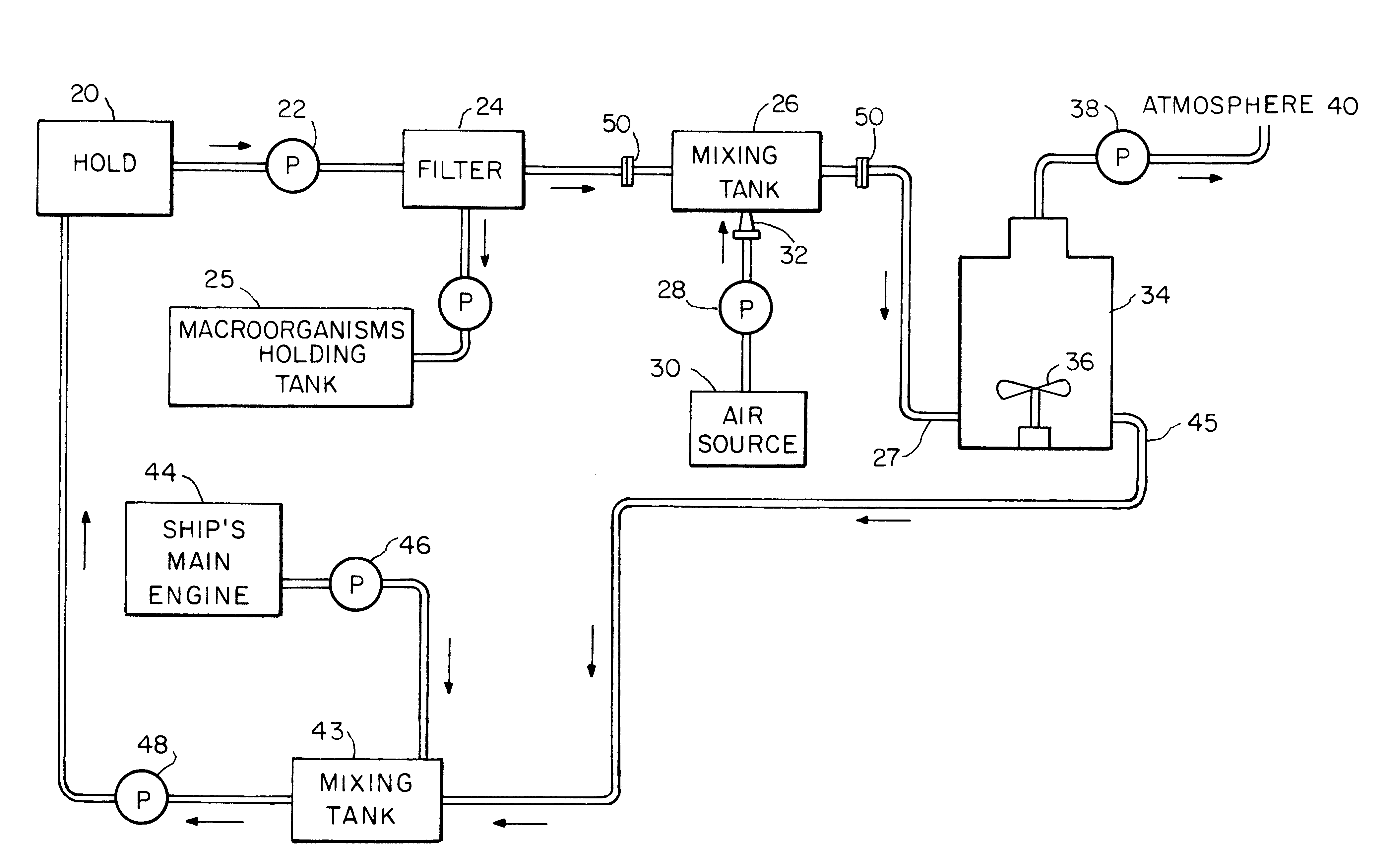
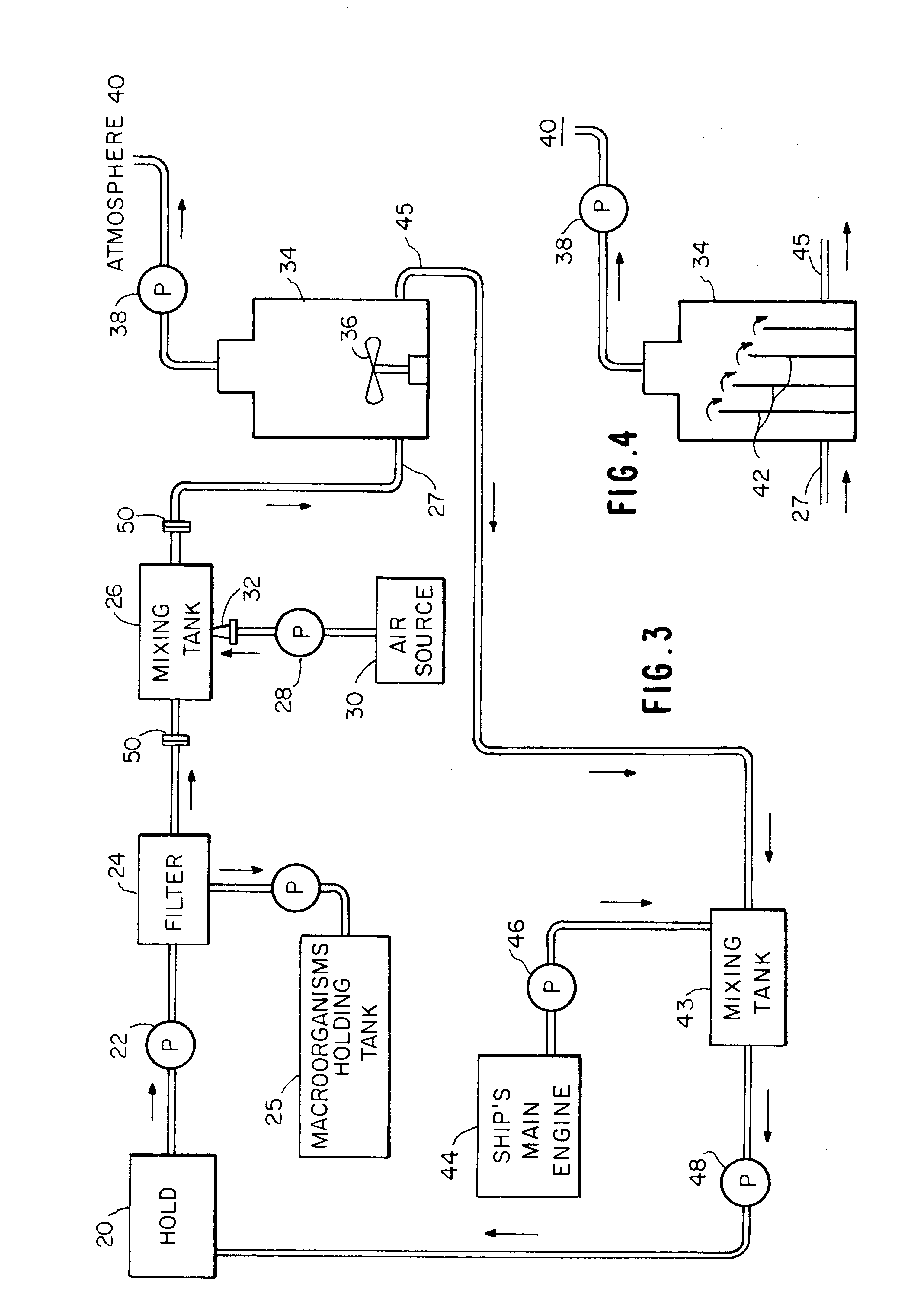
InactiveUS6171508B1Rapidly reduce the DOTime requiredHull interior subdivisionWater treatment parameter controlOxygenAnaerobic microorganisms
A method and apparatus for treating ship ballast water before it is discharged into coastal waters. The ballast water may contain a generalized and diverse species population of harmful non-indigenous microorganisms. Before discharge, the ballast water is oxygenated and deoxygenated to reduce the populations of anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms, respectively. If anaerobic microorganisms are of no concern, the oxygenation step can be eliminated. Also, a method and apparatus for treating large volumes of any water, to reduce the population of a wide spectrum of diverse species of microorganisms wherein the water is deoxygenated, and then held in a sealed space for a period of time until the aerobic population has been reduced.
Owner:TIDEWATER BALLAST SOLUTIONS LLC
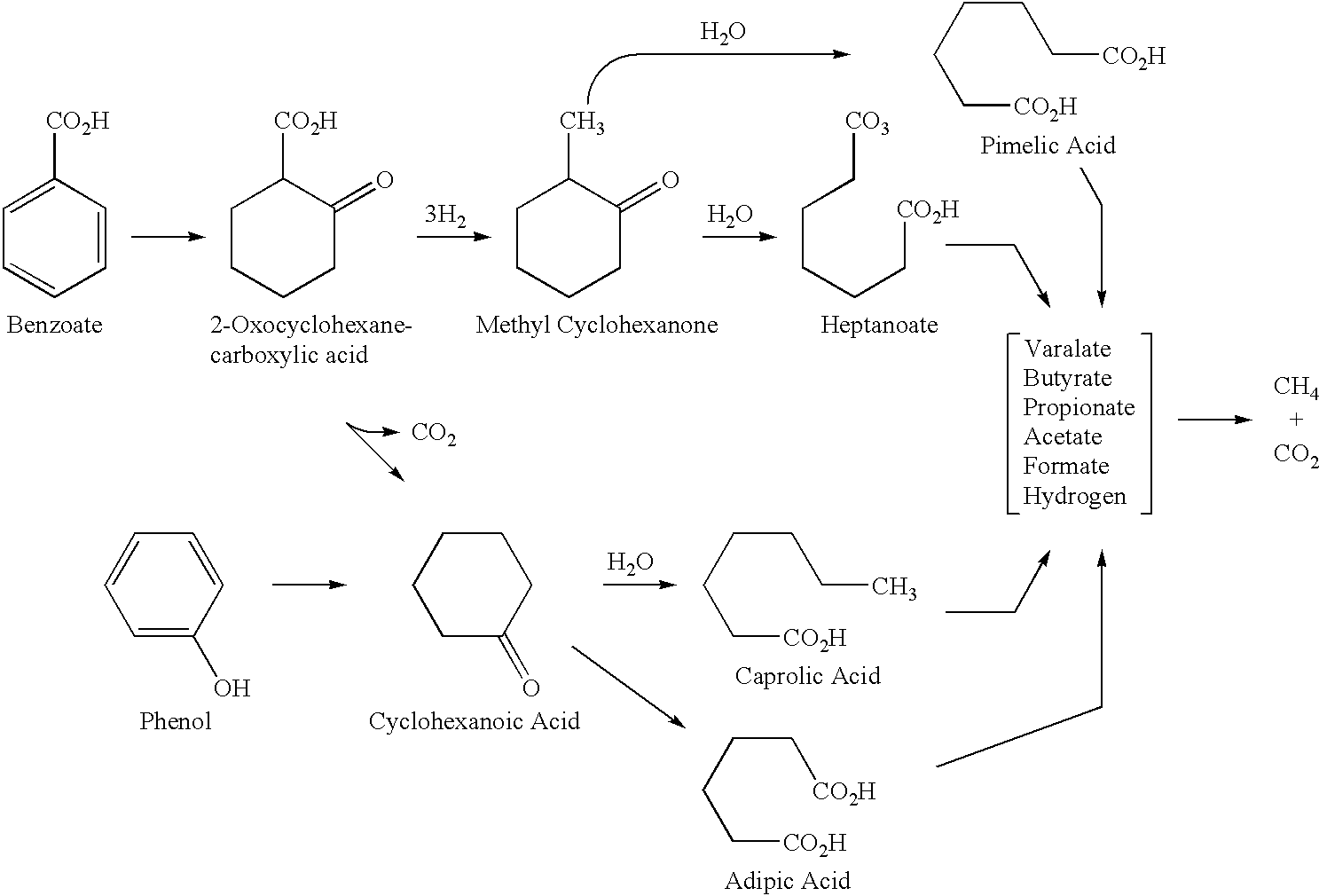
Analysis and enhancement of metabolic pathways for methanogenesis
InactiveUS20100035309A1Enhancing biogenic productionReliable informationWaste based fuelFermentationHydrogenMethanogenesis
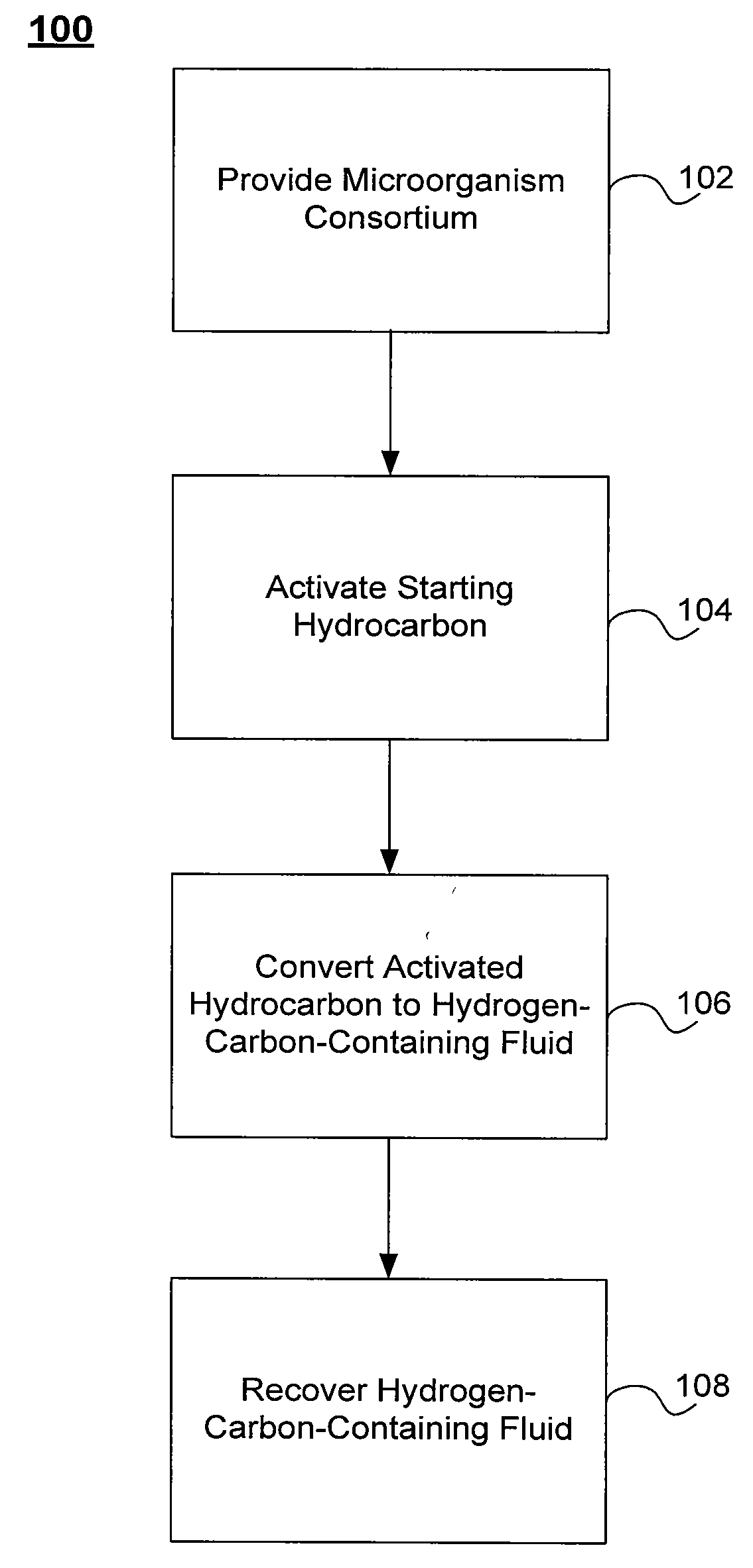
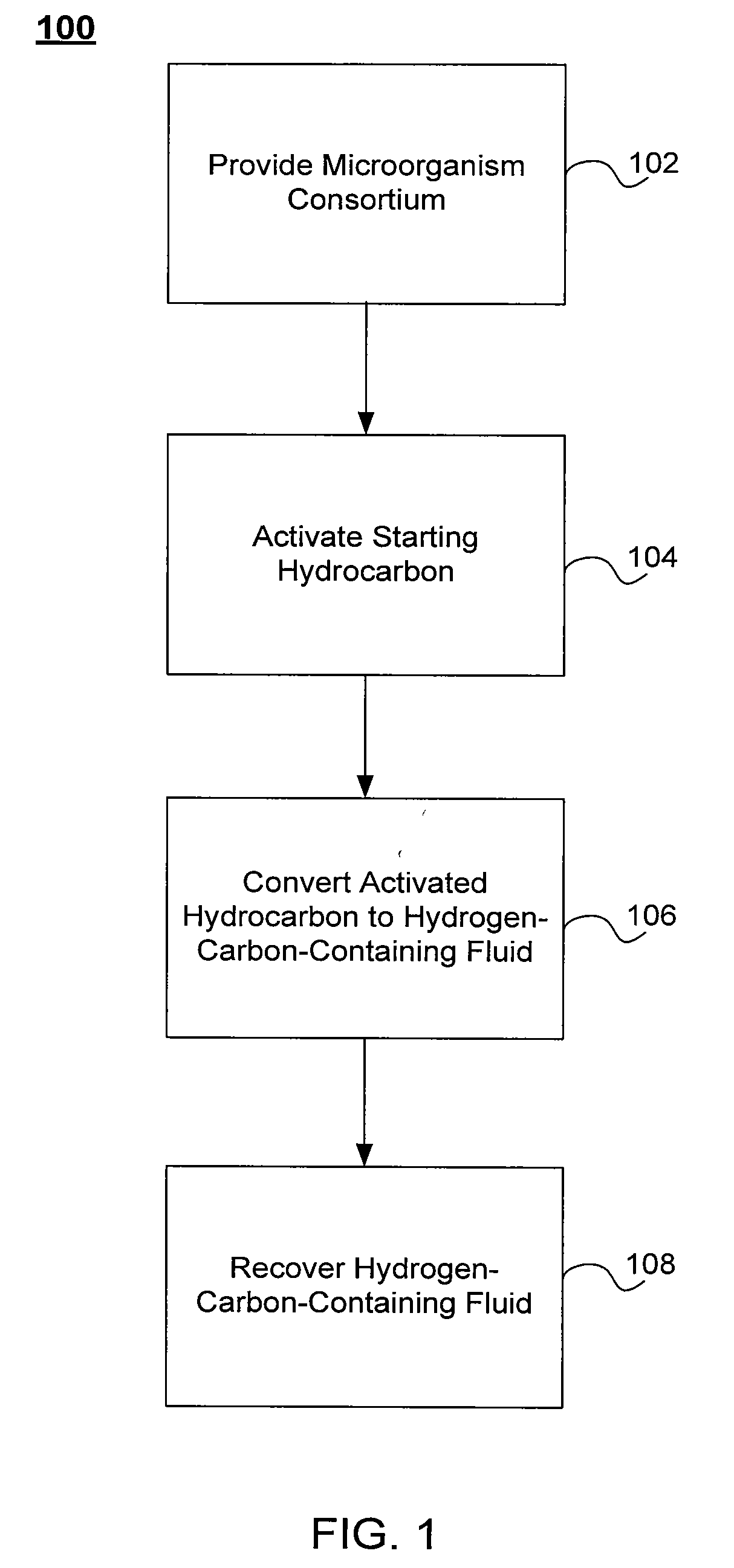
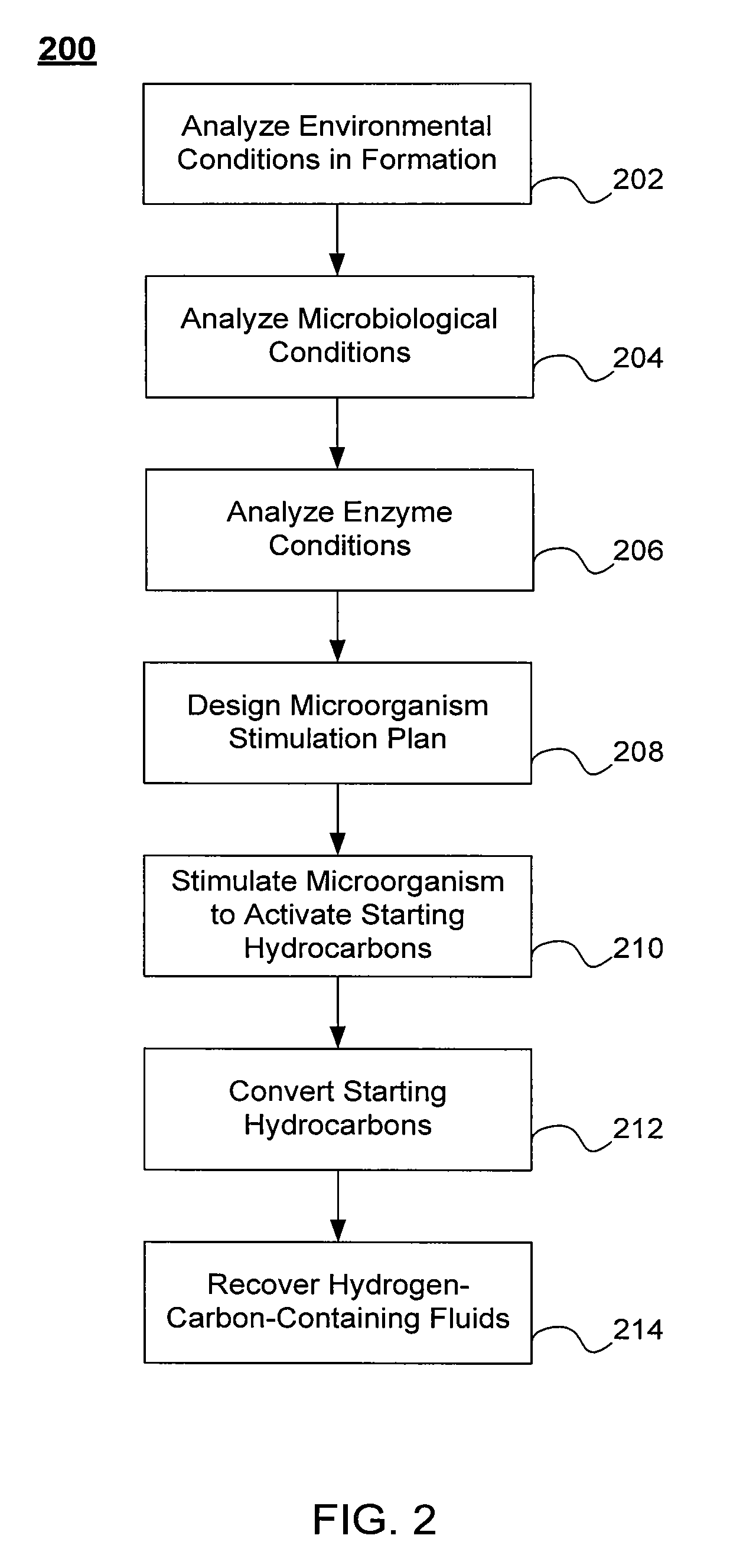
Processes for biogenic production of a hydrogen-carbon-containing fluid from a hydrocarbon containing formation are described. The processes may include providing in the formation an anaerobic microorganism consortium containing one or more enzymes to activate a starting hydrocarbon by an addition of a chemical group to the hydrocarbon. The processes may further include converting the activated hydrocarbon into the hydrogen-carbon-containing fluid through one or more intermediate hydrocarbons, and recovering the hydrogen-carbon-containing fluid from the formation.
Owner:LUCA TECH
Anaerobic biological wastewater treatment system and process
ActiveUS20060131231A1Improve volume efficiencyLower initial installation costsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAnaerobic microorganismsTreatment system
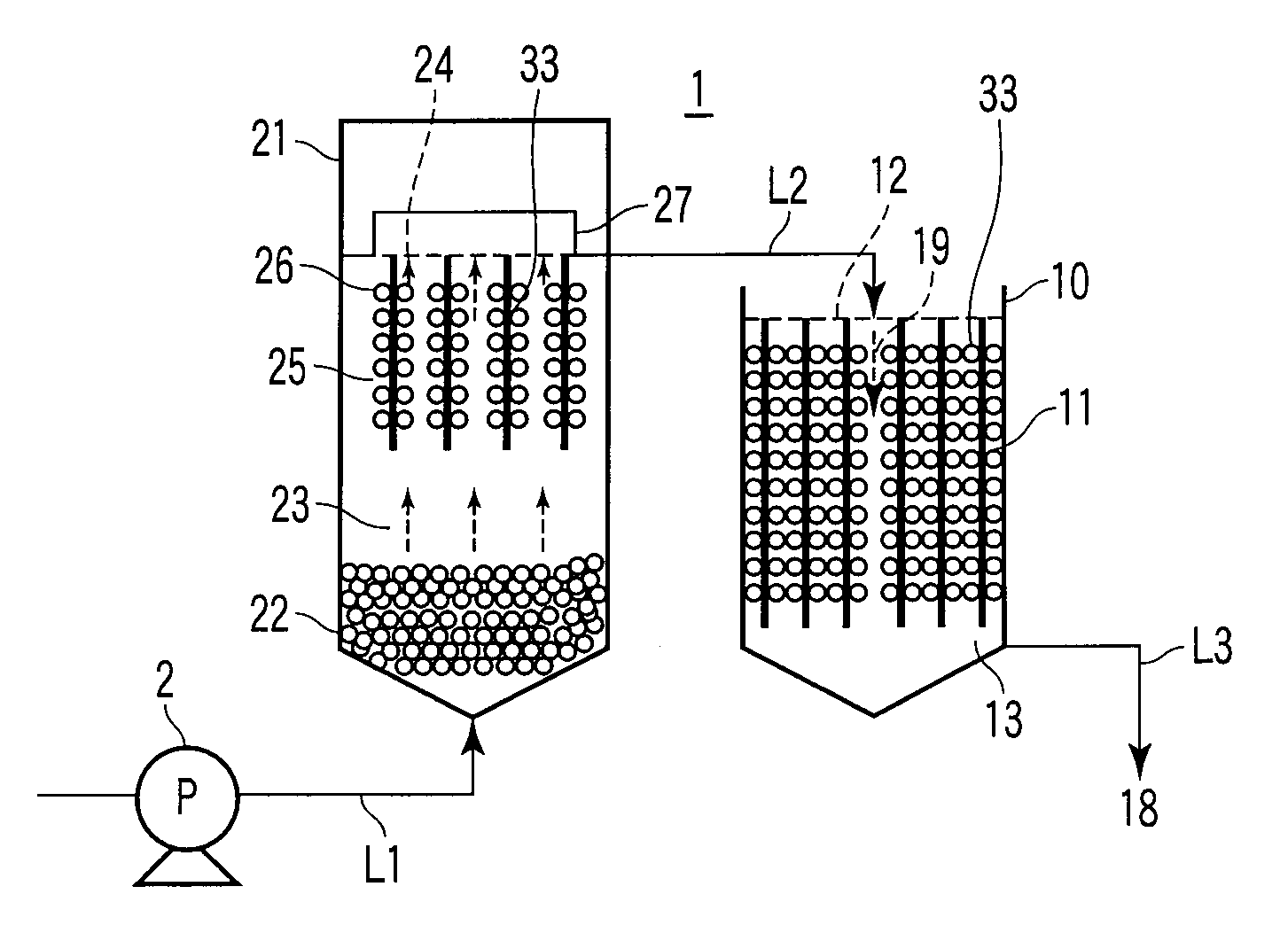
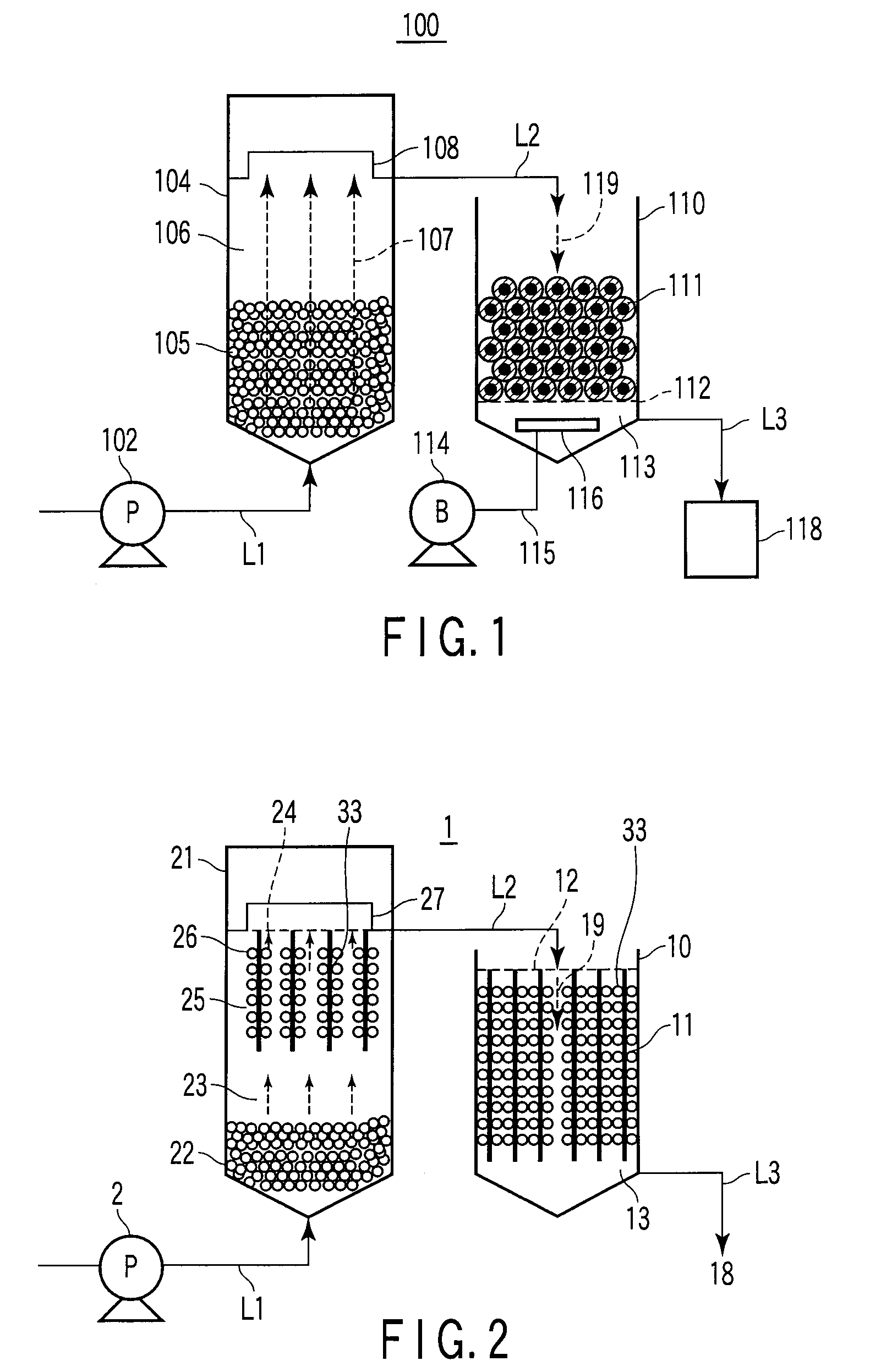
The present invention discloses an anaerobic biological wastewater treatment system for treating wastewater containing organic contaminants, which includes an anaerobic sludge bed reactor and a dissolved-air flotation tank. The anaerobic sludge bed reactor is used to decompose organic contaminants by way of an anaerobic biological treatment. The dissolved-air flotation tank is used to carry out liquid-solid separation on effluent from the anaerobic sludge bed reactor, so that anaerobic microorganisms entrained in the effluent can be recovered and recycled to the anaerobic sludge bed reactor, thereby enhancing the hydraulic loading of the anaerobic sludge bed reactor.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Siderite-based nitrogen and phosphorus removal material and application method thereof
ActiveCN103801254AWith strengthHigh porosityOther chemical processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesPorosityPhosphate
The invention discloses a preparation method and applications of a siderite-based nitrogen and phosphorus removal material. The preparation method is implemented through steps of crushing siderite ores, enabling the obtained ores to pass through a 40-mesh sieve, and adding a foaming agent into siderite ore powder in an appropriate proportion of the siderite ore powder, a binder and a pore-foaming agent or in an appropriate proportion of the siderite ore powder and a binder so as to obtain a porous granular material taking the siderite ore powder as a main body; and the porous granular material has the characteristics of high particle strength, high porosity, large specific surface area, large microbial load, and the like. The material is a microbial carrier, an anaerobic microorganism electron donor and a phosphorus removal adsorbent. The material is fed in a fixed bed to treat wastewater by way of filtering, and vaccinates nitrate-depended iron-oxidizing-bacteria-based anaerobic strain liquid, and under anaerobic conditions, microorganisms reduce nitrates into nitrogen by taking ferrous irons in siderite as electron donors, and the adsorption effect on phosphorus is enhanced. The material is mainly used for synchronously removing nitrate nitrogen and phosphates in wastewater.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Devices for culturing anaerobic microorganisms and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20050239200A1Eliminates the cumbersome, time consuming and costly stepsMinimize flowBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOxygenAnaerobic microorganisms
Culture devices for promoting the growth of microorganisms, especially anaerobic microorganisms, are disclosed. The culture devices include an oxygen scavenging material. In one aspect, the culture device includes a supporting substrate and a cover sheet affixed to at least one edge of the supporting substrate. At least one of the supporting substrate and cover sheet includes the oxygen scavenging material. In another aspect, the culture device is an article that includes a container, e.g. a pouch, including a film having an oxygen scavenging material, with a culture media placed within the container.
Owner:CRYOVAC ILLC
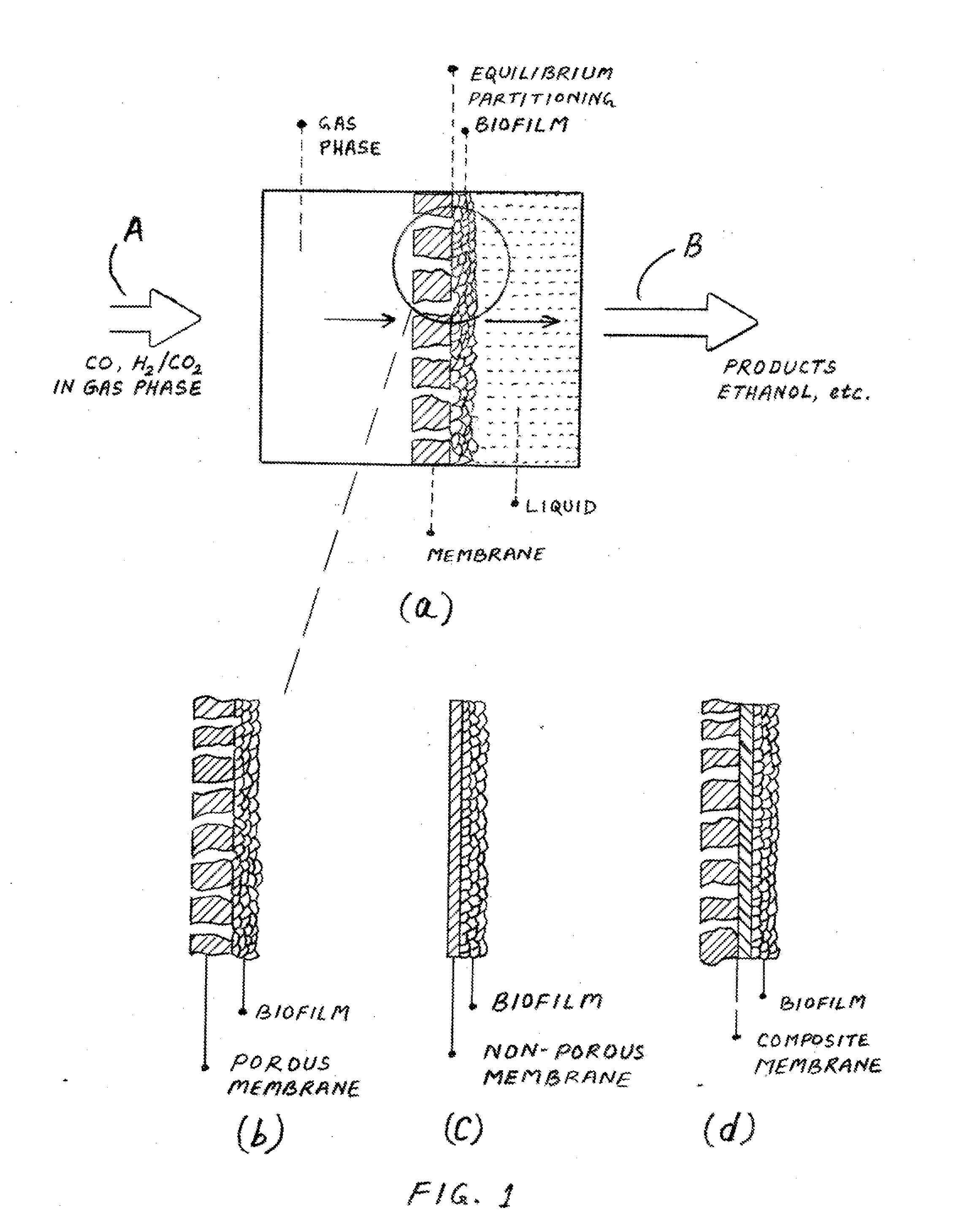
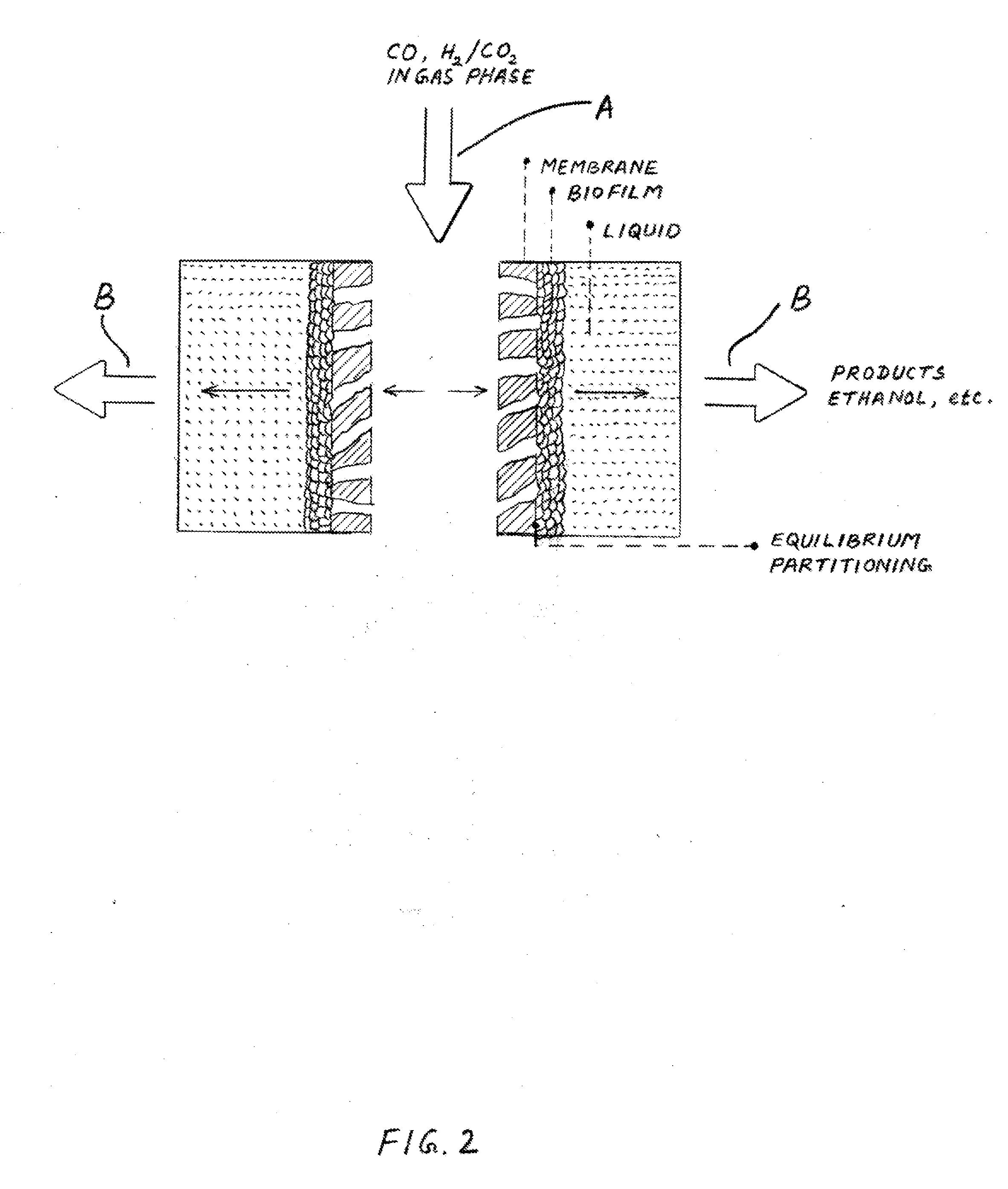
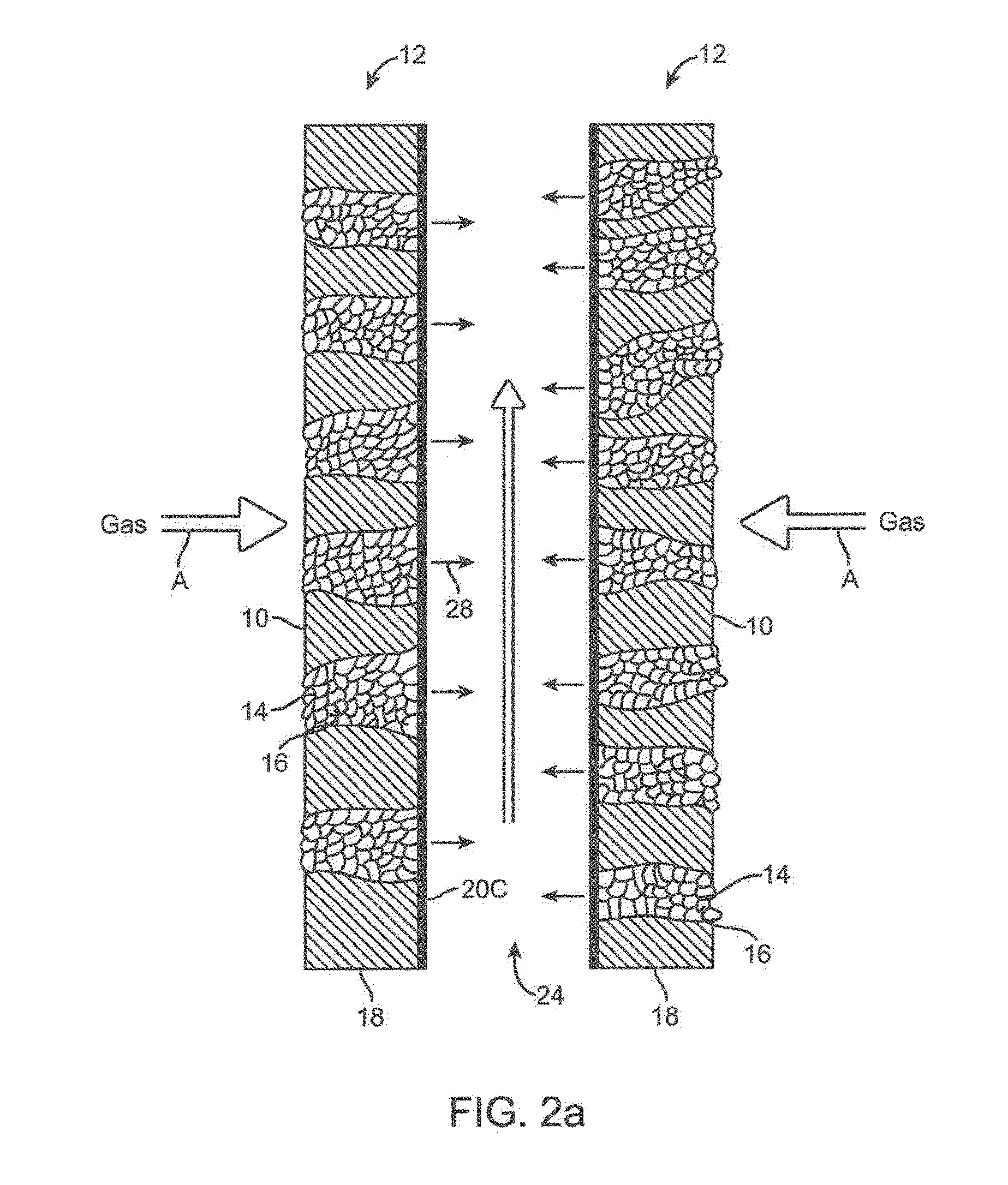
Syngas conversion system using asymmetric membrane and anaerobic microorganism
InactiveUS20090215163A1Increase productionLess permeabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid productMetabolite
A stable system for producing liquid products such as ethanol, butanol and other chemicals from syngas components contacts CO or a mixture of CO2 and H2 with a highly porous side of an asymmetric membrane under anaerobic conditions and transferring these components into contact with microorganisms contained within bio-pores of the membrane. The membrane side of the membrane utilizes a dense layer to control hydration of the bio-pores with a liquid phase. The gas feed directly contacts the microorganisms in the bio-pores and maximizes their utilization of the syngas. Metabolic products produced by the microorganisms leave the membrane through the side opposite the entering syngas. This system and method establishes a unitary direction across the membrane for the supply of the primary feed source to the microorganisms and the withdrawal of metabolically produced products. The feed and product flow improves productivity and performance of the microorganism and the membrane.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Baffle-board reactor and method for treating sewage by using it
InactiveCN1850655APromote degradationRemove eutrophication effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeCoupling
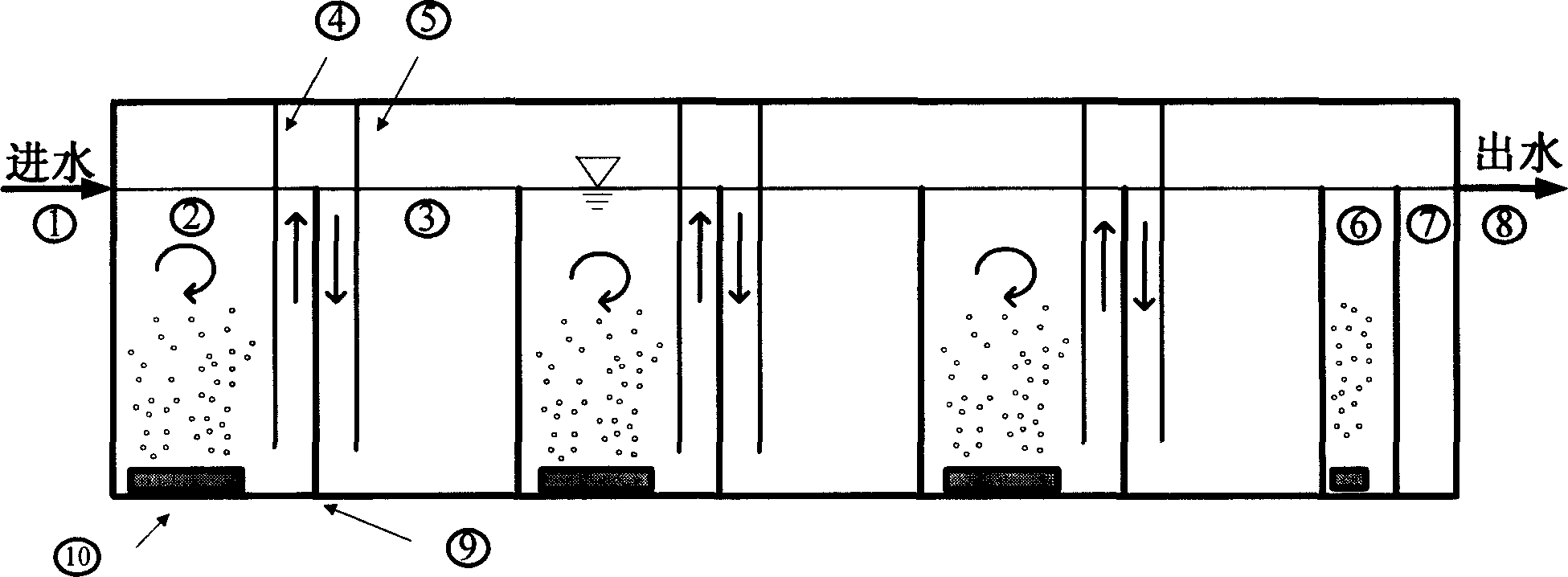
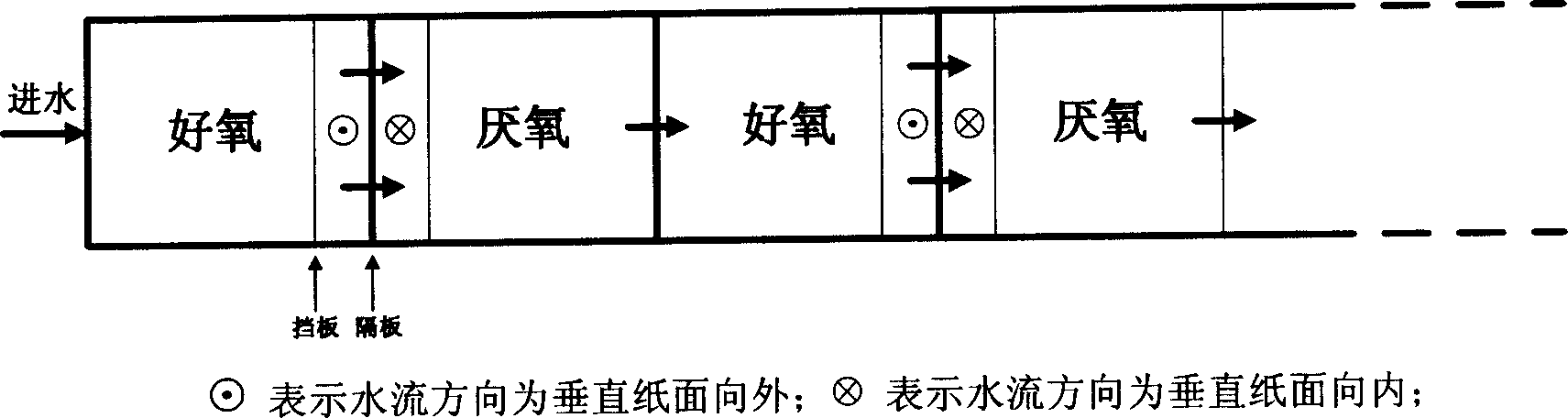
The invention relates to a flow turning plate reactor and a method for implementing aerobic-anaerobic microbe repeated coupling sewage water processing by it, and it comprises cuboid, aeration device, isolation baffles, flow guide baffles, where one end of it is provided with water inlet and the other end is provided with water outlet, several vertical isolation baffles and flow guide baffles are arranged at the cuboid in the direction of water flow; and thus it implements repeated occurrence of aerobic unit with aeration device and anaerobic unit without aeration device in the direction of the water flow. And the sewage water enters from the water inlet into the reactor and goes through several aerobic-anaerobic unit couplings in the flow turning mode and finally is drained out of the reactor through the water outlet, thus the sewage is processed. And the invention can remove organic matters and nitrogen from the sewage water and save foundation construction and operation expenses.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for purifying matter contaminated with halogenated organic compounds
InactiveUS6303367B1Excessive decoloration of contaminated matterImprove responseSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationChemical reactionSilicon alloy
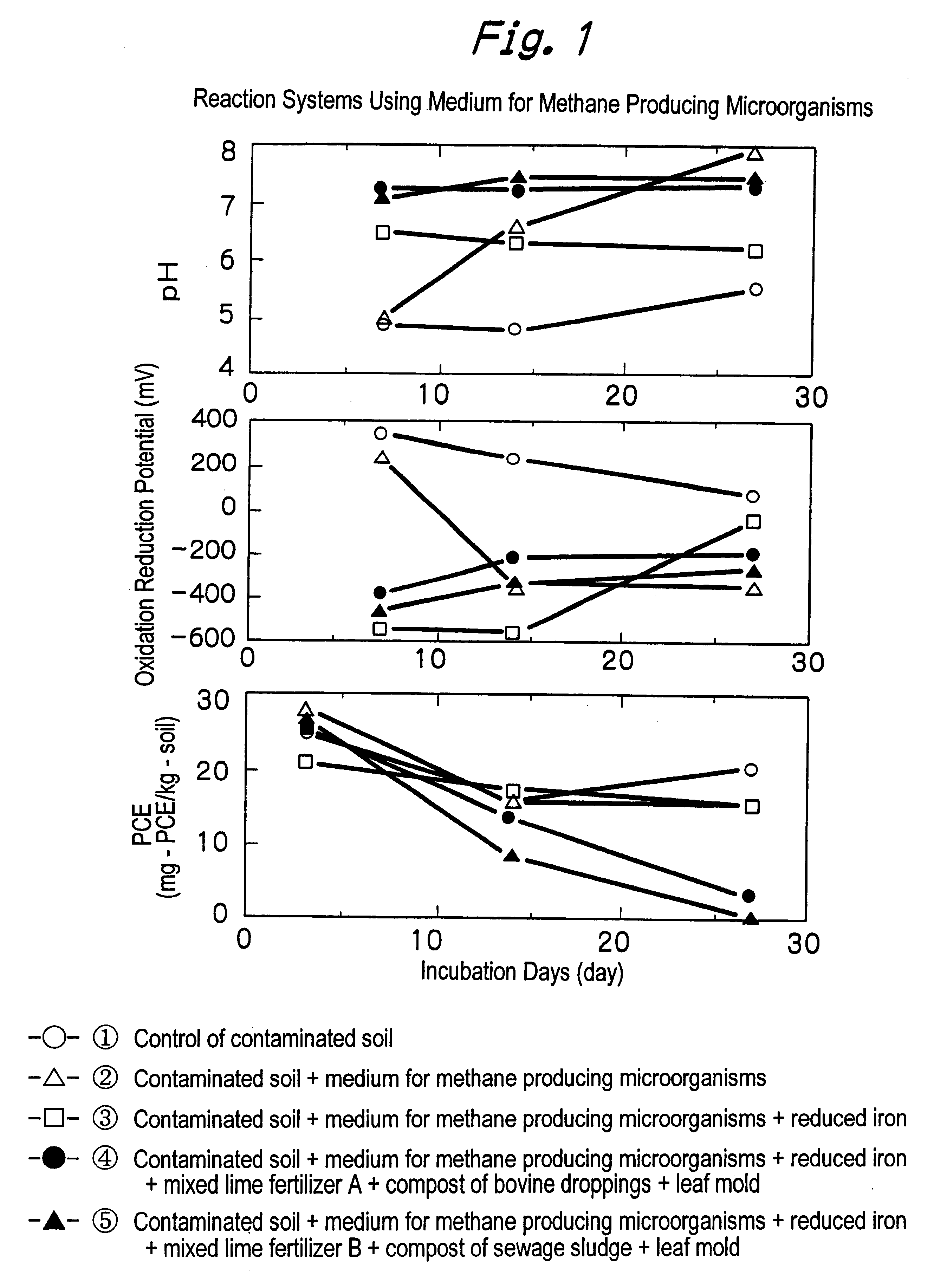
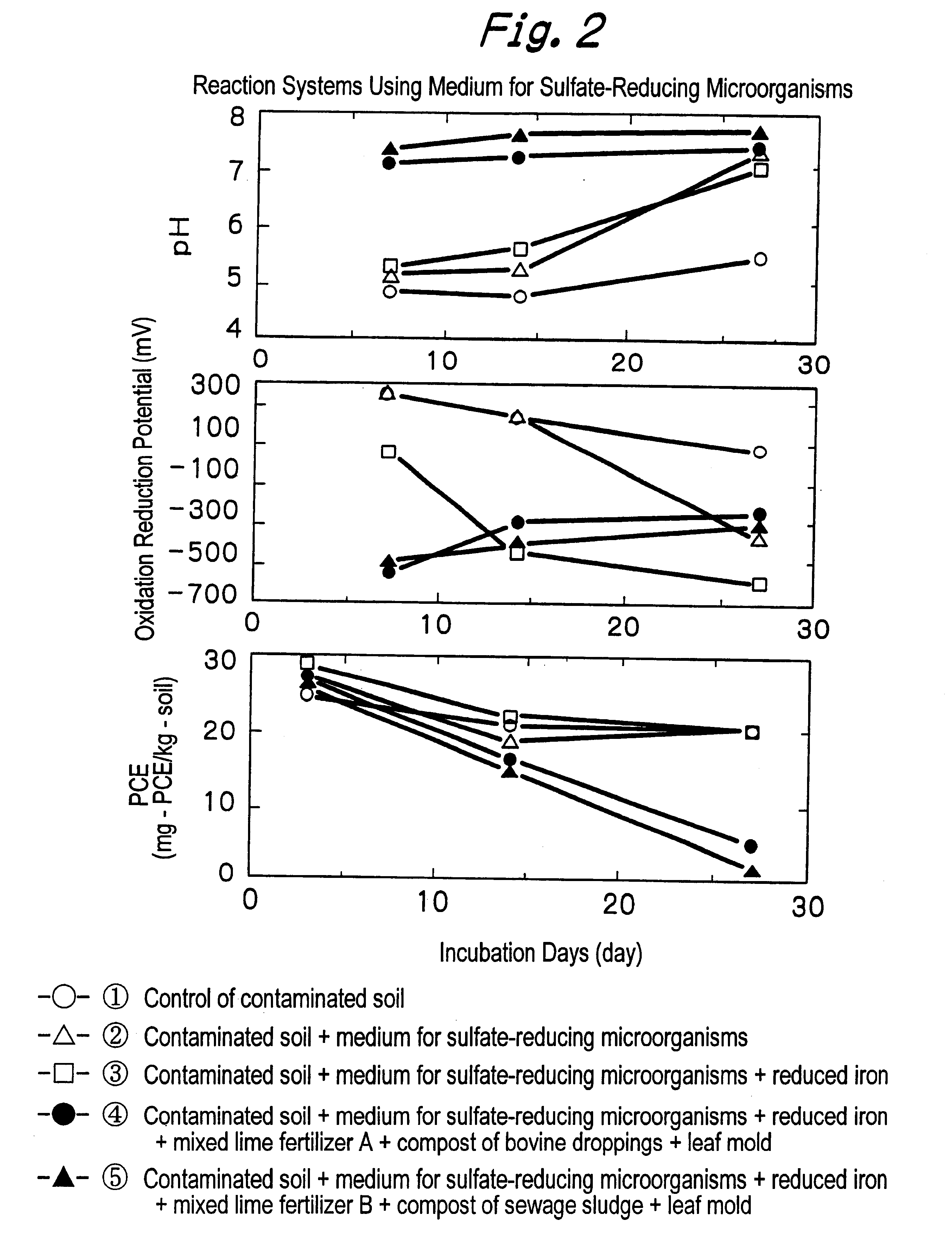
A method for purifying matter contaminated with a halogenated organic compound is disclosed. The method includes the step of adding a reducing agent and a nutritional source for a heterotrophic anaerobic microorganism to the contaminated matter. The reducing agent is reduced iron, cast iron, iron-silicon alloy and so on, or a water soluble compound. A combination of chemical reactions with microorganisms allows to decompose the halogenated organic compound. The nutritional source including an organic carbon and 20 to 50 percent by weight of an oxidized form of nitrogen is added, thereby preventing by products of the decomposition such as generation of noxious gases and decoloration of soil. A method includes the steps of mixing a reducing agent and a nutritional liquid with the contaminated matter, wherein the mixing step including a step of adjusting the contaminated matter at pH ranging from 4.5 to 9.0; and keeping the mixture in a condition that air hardly penetrates through a matrix, thereby allowing to uniformly mix a large amount of the contaminated matter.
Owner:EBARA ENG SERVICE
Microbially-mediated method for synthesis of non-oxide semiconductor nanoparticles
ActiveUS20100193752A1Non-prohibitive costWide rangeConductive materialSulfide conductorsElectron donorNanoparticle
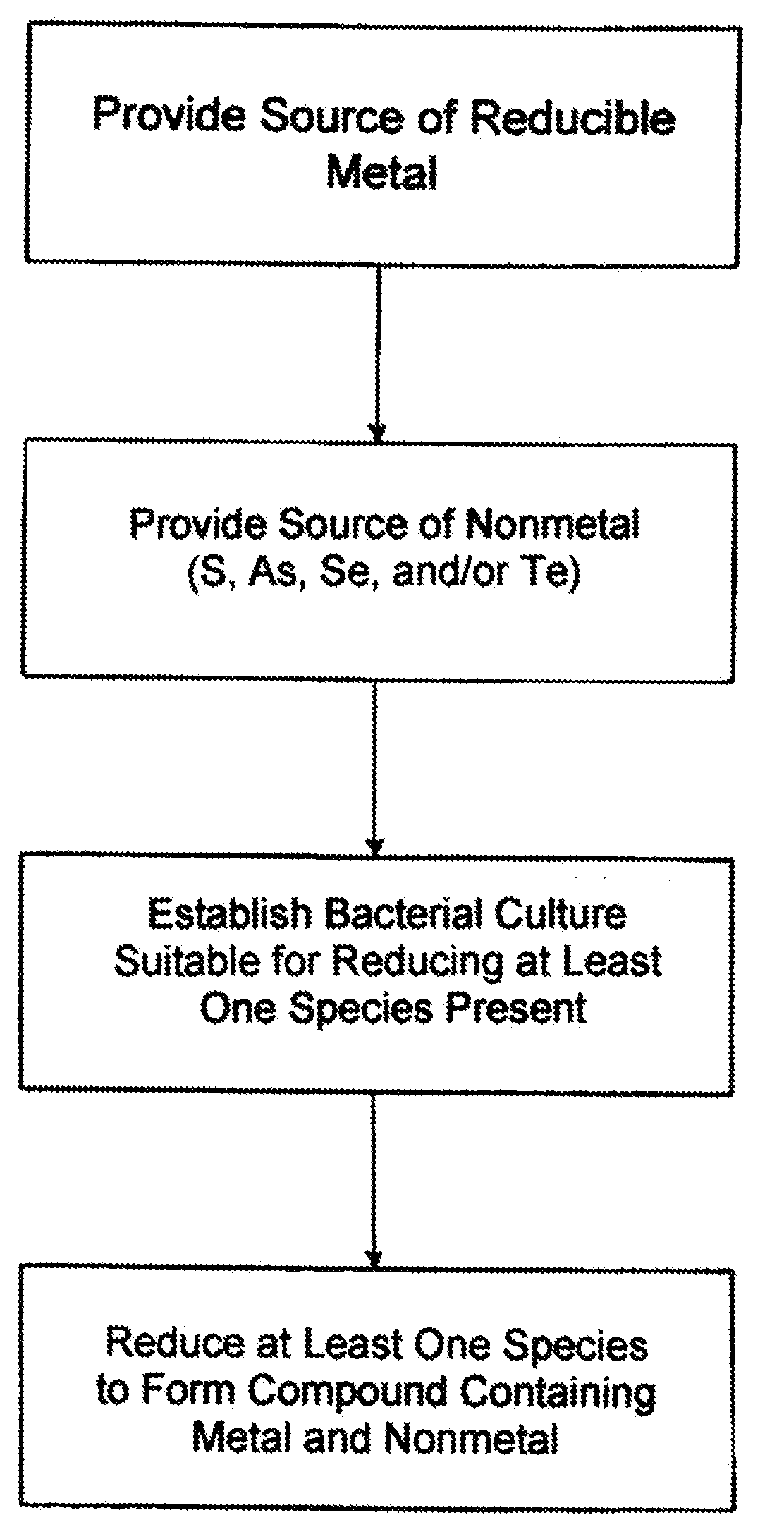
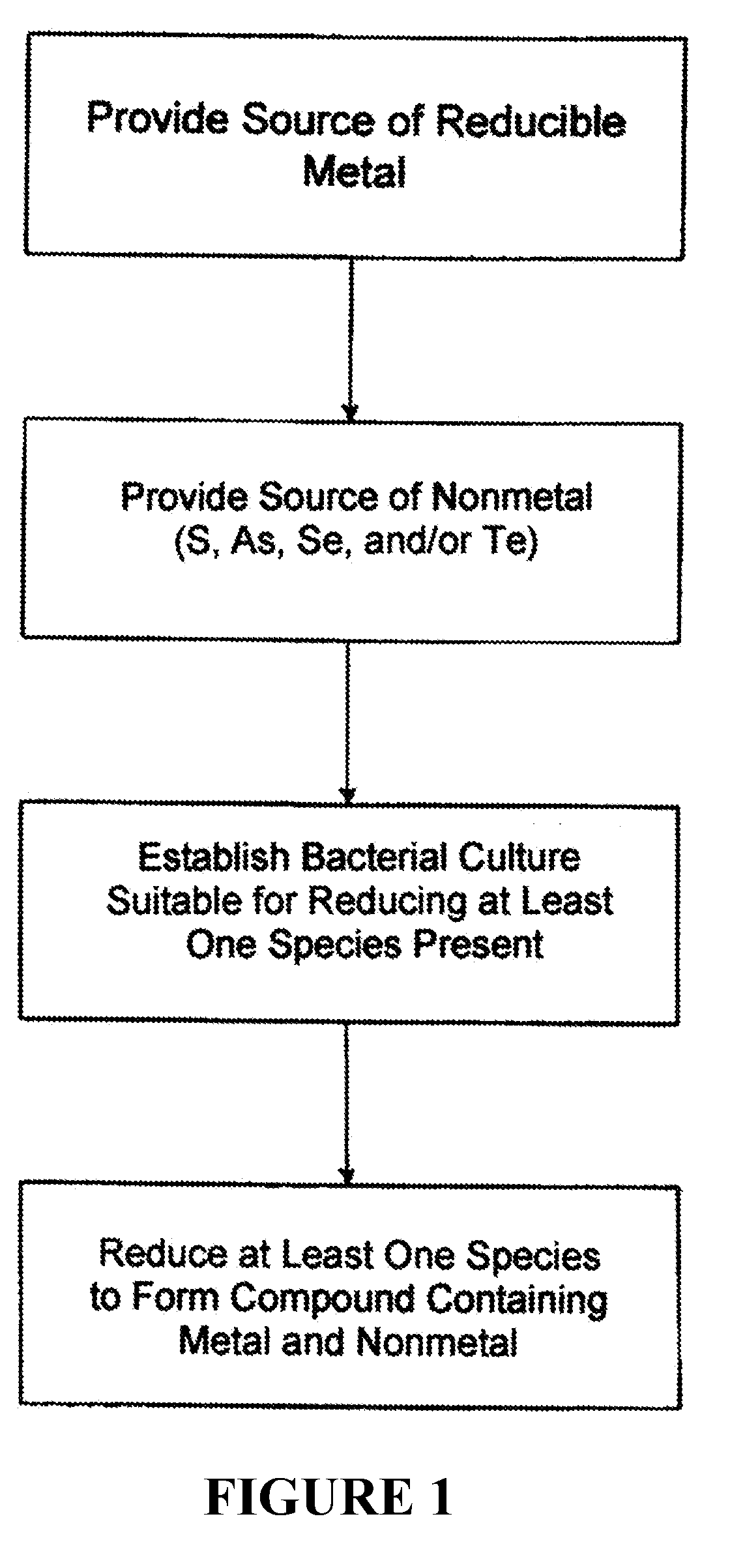
The invention is directed to a method for producing non-oxide semiconductor nanoparticles, the method comprising: (a) subjecting a combination of reaction components to conditions conducive to microbially-mediated formation of non-oxide semiconductor nanoparticles, wherein said combination of reaction components comprises i) anaerobic microbes, ii) a culture medium suitable for sustaining said anaerobic microbes, iii) a metal component comprising at least one type of metal ion, iv) a non-metal component containing at least one non-metal selected from the group consisting of S, Se, Te, and As, and v) one or more electron donors that provide donatable electrons to said anaerobic microbes during consumption of the electron donor by said anaerobic microbes; and (b) isolating said non-oxide semiconductor nanoparticles, which contain at least one of said metal ions and at least one of said non-metals. The invention is also directed to non-oxide semiconductor nanoparticle compositions produced as above and having distinctive properties.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
Crystalline form of r)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)pyridin- 5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate
ActiveUS20100227839A1Reduce filter timeImprove usabilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsPhosphateAntibacterial activity
A crystalline form of crystalline (R)-3-(4-(2-(2-methyltetrazol-5-yl)-pyridin-5-yl)-3-fluorophenyl)-5-hydroxymethyl oxazolidin-2-one dihydrogen phosphate, methods of making the crystalline form and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the crystalline form are useful antibiotics. Further, the derivatives of the present invention may exert potent antibacterial activity versus various human and animal pathogens, including Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococi, Enterococci and Streptococi, anaerobic microorganisms such as Bacteroides and Clostridia, and acid-resistant microorganisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium. Accordingly, the compositions comprising the crystalline form may be used in antibiotics.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Method for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil by modified nanoscale zero-valent iron synergizing with microorganisms
InactiveCN108723073AGood dispersionImprove antioxidant capacityContaminated soil reclamationAnaerobic microorganismsHigh activity
The invention belongs to the technical field of heavy metal contaminated soil repair, and discloses a method for repairing heavy metal contaminated soil by modified nanoscale zero-valent iron synergizing with microorganisms. The method comprises the following steps that (1) carboxymethyl cellulose is used as a modifier, a liquid phase reduction method is adopted, and a water-soluble salt containing Fe is subjected to reduction by using a reducing agent to obtain carboxymethyl cellulose modified nanoscale zero-valent iron; and (2) the carboxymethyl cellulose modified nanoscale zero-valent iron,anaerobic microorganisms, water and the heavy metal contaminated soil are uniformly mixed and stood for reaction, and the repair of the heavy metal contaminated soil is completed. The modified nanoscale zero-valent iron has high dispersibility and oxidation resistance, corrosion of the zero-valent iron is accelerated and high-activity minerals are generated through the synergistic effect with themicroorganisms, and the effect of the modified nanoscale zero-valent iron on repairing the heavy metal contaminated soil is further improved. The method for repairing the heavy metal contaminated soil by the modified nanoscale zero-valent iron synergizing with the microorganisms has the advantages of high processing efficiency, simple process conditions, less secondary pollution and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Ecological cultivation method with health care fermented feed matched with probiotic fermentation bed
InactiveCN103891674AReduce dosageSave resourcesBio-organic fraction processingFood processingWater sourceWater quality
The invention relates to an ecological cultivation method with health care fermented feed matched with a probiotic fermentation bed. The method includes the steps that first, probiotic fermentation is carried out, wherein the probiotic fermentation comprises anaerobic fermentation of anaerobes and aerobic fermentation of aerobic microorganisms; second, the probiotic fermentation bed is prepared, wherein various raw materials for preparing the material of the fermentation bed are evenly mixed so as to obtain organic bedding, bacterium solution is inoculated for fermentation, and the organic bedding contains saw dust, rice husks, bran and first compound Chinese herbal medicine; third, the fermented feed contains corn, bean pulp, vitamins, microelements, mineral substances, amino acids, other additives, second compound Chinese herbal medicine and the like, and microorganisms are added into the feed components for fermentation. The ecological cultivation method has the advantages that water can be purified, and hidden danger to health of hogs caused by a water source is blocked; the using amount of the microelements is reduced, resources are saved, emissions are reduced, and the environment is protected; no antibiotics or residue exists, and food safety and human health are guaranteed; the Chinese herbal medicines have the functions of being resistant to disease and promoting growth and can replace antibiotics.
Owner:BEIJING HUAMU GREAT EXPLOIT SCI & TECH
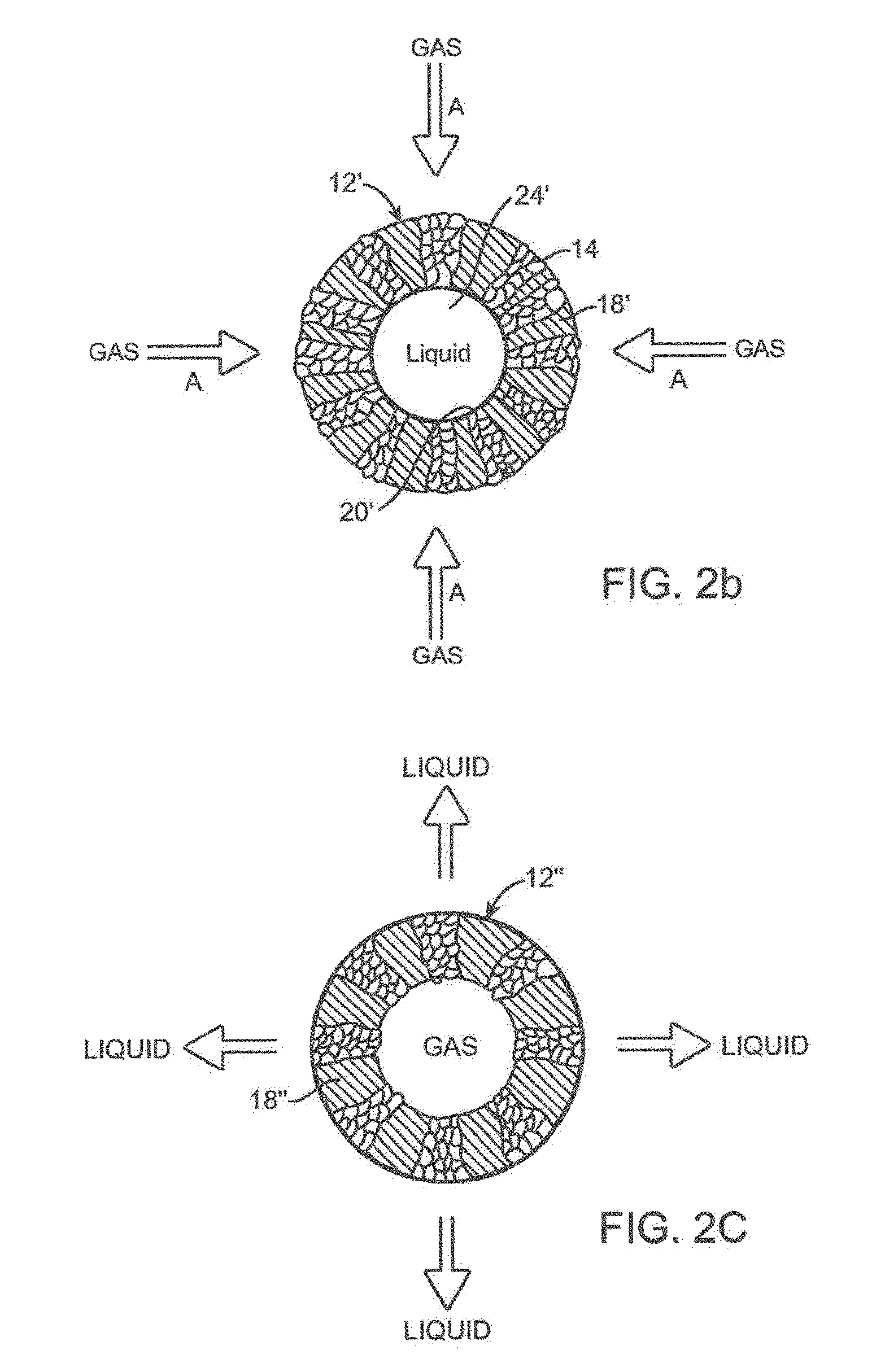
Syngas conversion method using asymmetric membrane and anaerobic microorganism
InactiveUS20120009638A1Increase productionLess permeabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid productProduction rate
A stable method for producing liquid products such as ethanol, propanol, butanol and other chemicals from syngas components that contacts CO or a mixture of CO2 and H2 with a highly porous side of an asymmetric membrane under anaerobic conditions and transfers these components into contact with microorganisms contained within bio-pores of the membrane. A liquid contacting side of the membrane utilizes a dense layer to control hydration of the bio-pores with a liquid phase. The gas feed directly contacts the microorganisms in the bio-pores and maximizes their utilization of the syngas. Metabolic products produced by the microorganisms leave the membrane through the side opposite the entering syngas. This method establishes a unitary direction across the membrane for the supply of the primary feed source to the microorganisms and the withdrawal of metabolically produced products. The feed and product flow improves productivity and performance of the microorganism and the membrane.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Integrative bioreactor for treating refuse leachate
InactiveCN1769211ANo need to addImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectron donorAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention relates to an integral bioreactor for garbage percolating liquid treatment, belonging to environment protection art. The bioreactor comprises of two biological reaction zones and an adjustment zone, and each biological reaction zone is filled with biological filler to make up aerobic and anaerobic zone. In the aerobic zone, the organics is degraded by aerobic heterotrophic bacteria to organic carbon and controls the ammonia nitrogen nitration in hitrosation stage, 50% ammonia nitrogen is oxygenated to nitrite, and the water outlet in the aerobic zone is mixed uniformly in the adjustment zone with PH modifier and then flows into the anaerobic zone. In the anaerobic zone, anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria reduces nitrite with ammonia nitrogen as electron donor and oxygenizes ammonia nitrogen with nitrite as electron acceptor, ammonia nitrogen and nitrous nitrogen transit into nitrogen, some organics is absorbed or degraded by other anaerobic microorganism. It can clear ammonia nitrogen and organics in the water quality of low carbon-nitrogen ratio of garbage percolating liquid, and adjust the water quality of garbage percolating liquid and the impact load of water, and the operation is effective and stable.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for improving oil recovery efficiency through microbial oil displacement
The invention discloses a method for improving oil recovery efficiency through microbial oil replacement and belongs to the technical field of microbial oil recovery. The method specifically comprises the following steps of performing in-situ sampling on a test site and detecting indigenous microorganisms, wherein the detected indigenous microorganisms are composed of aerobic, facultative and anaerobic microorganisms; performing oil displacement on oil reservoir through the aerobic microorganisms, filling the aerobic microorganisms or the activator of the aerobic microorganisms and air into the oil reservoir, and detecting the aerobic microorganisms inside the output liquid of the oil reservoir; performing oil displacement on oil reservoir through the facultative microorganisms, filling the facultative microorganisms or the activator of the facultative microorganisms and air into the oil reservoir, and detecting the facultative microorganisms inside the output liquid of the oil reservoir; performing oil displacement on oil reservoir through the anaerobic microorganisms and filling the anaerobic microorganisms or the activator of the anaerobic microorganisms and air into the oil reservoir. According to the method for improving the oil recovery efficiency through the microbial oil replacement, the activators are abundant in sources, low in price and free from damage to stratums. The method for improving the oil recovery efficiency through the microbial oil replacement is simple in process, high in pertinence and operability and good in in-situ testing effects and improves the recovery efficiency of in-situ tests by larger than 10.0%, thereby being capable of being widely applied to in-situ tests for improving the recovery efficiency through microorganisms.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Aeration-less water treatment apparatus
InactiveUS20090032451A1Quality improvementTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesSewageWater contact
An aeration-less water treatment apparatus including an anaerobic reactor which receives sewage to cause the sewage to flow as an upward stream, and an aerobic reactor which receives treated water from the anaerobic reactor to cause the water to flow as a downward stream so that the water contacts aerobic microorganisms and air to aerobically treat the polluted matter in the water, the apparatus further including a suspended sludge section located in a lower part of the anaerobic reactor and in which the anaerobic microorganisms are suspended in the sewage, and a carrier section located in an upper part of the anaerobic reactor and having carriers to which the anaerobic microorganisms are attached, the anaerobic microorganisms having flowed from the suspended sludge section being further attached to the carriers.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Fine chemical wastewater treatment and reuse method
InactiveCN103159381AAchieve reductionEasy to handleMultistage water/sewage treatmentAerobic treatment systemChemical treatment
The invention discloses a chemical treatment method and specifically relates to a fine chemical wastewater treatment and reuse method based on a membrane bioreactor (MBR)-reverse osmosis (RO) combination technology. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: performing oil separation, air floatation and coagulative precipitation on wastewater drained from a production workshop, then performing decomposition through an extracellular enzyme of anaerobic microorganisms in a hydrolysis treatment system, further entering an aerobic treatment system with aerobic microorganisms, further enabling the wastewater from the aerobic treatment system to enter an MBR system to perform further aerobic treatment, simultaneously performing mud-water separation, directly enabling water from the MBR system to enter an RO system, reusing the water produced by the RO system in production, and draining concentrated water into a pipeline network in a park. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of combining MBR with RO, improving the biochemical treatment effect of the system, further improving the recovery rate of the RO system, increasing the yield of pure water and reducing the discharge amount of the wastewater. The method has the advantages of short process flow of the system, high degree of automation, simplicity and convenience in operation and stability in operation.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Process and apparatus for treating wastewater from pulping papermaking
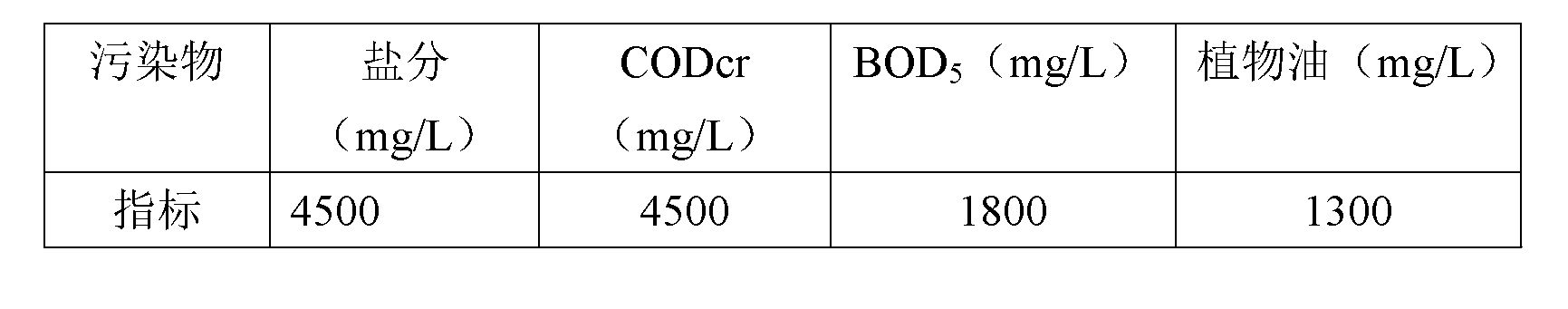
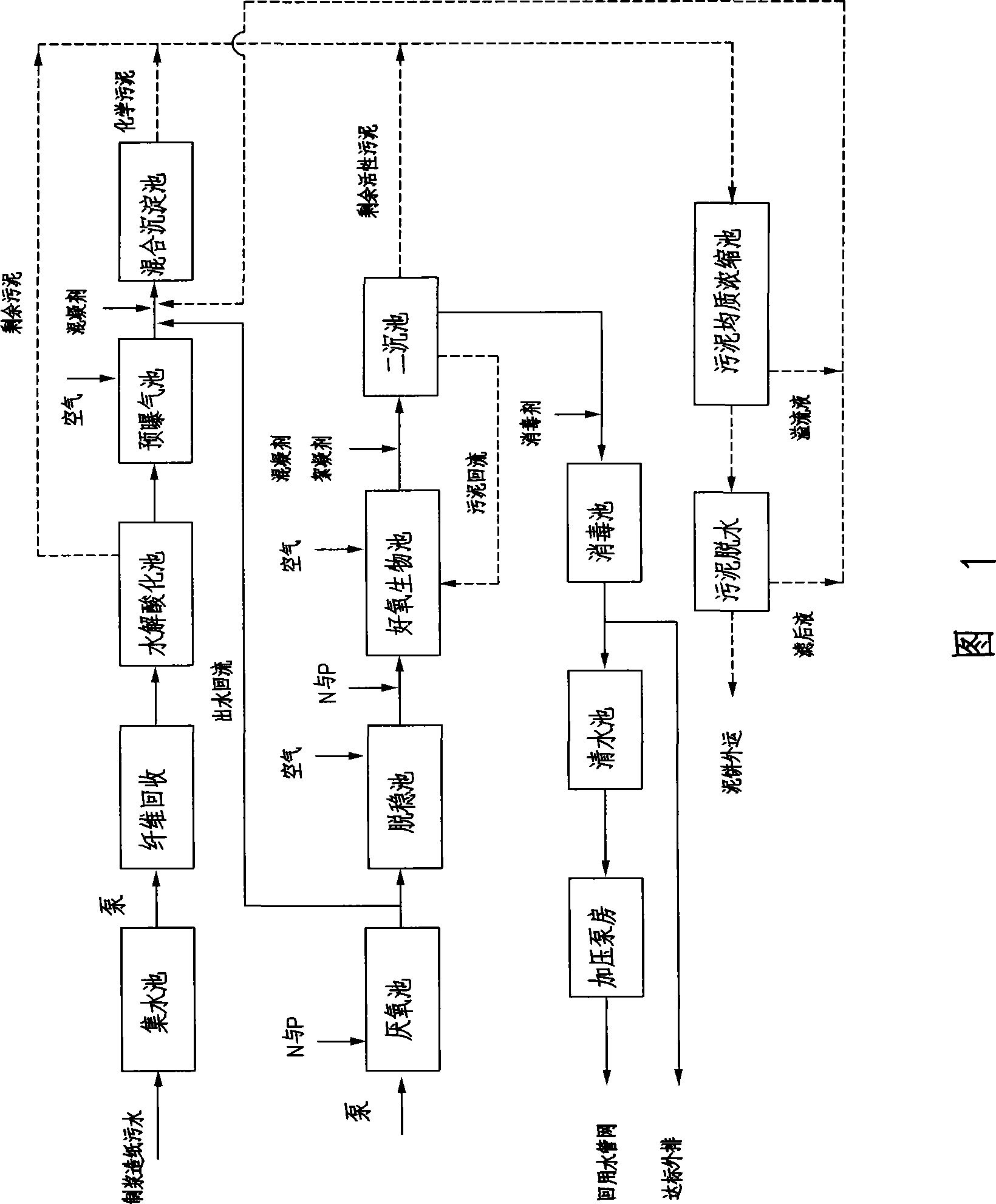
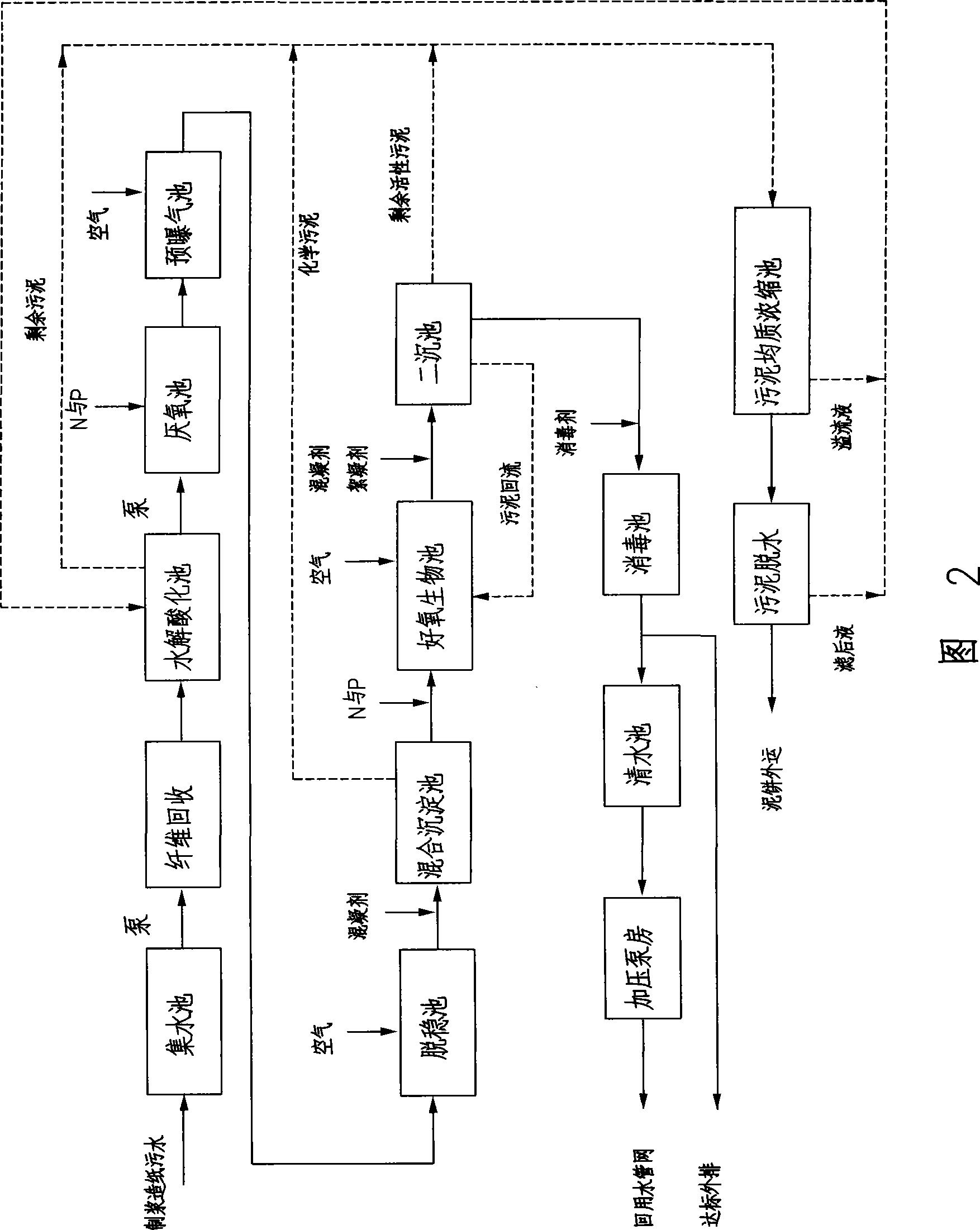
ActiveCN101428941AEasy to handleIncrease destabilization processTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentFiberSludge
The invention discloses a process for treating paper-making sewage, which comprises the following steps: 1. sewage in a water collecting pond is lifted to a fiber recovering tank for fiber recovery; 2. the discharged water is guided in a hydrolysis acidification tank for hydrolysis acidification reaction; 3. the discharged water is pretreated; 4. the sewage after pretreatment is guided in an anaerobic tank to degrade organic pollutants by anaerobic microorganism; 5. the discharged water at the step 4 is guided in a destabilization tank for improving biodegradability of the sewage; 6. the discharged water is guided in an aerobic biological tank for treatment; 7. the discharged water is guided in a secondary sedimentation tank for mud-water separation; and 8. the discharged water is sterilized and disinfected to meet the discharge standard and discharge into a clean water tank, and pressurized by a water pump and sent to a reuse water pipe network. The process has simple process and lower cost, and the discharged water directly meets the new standards, and the treating capabilities of the anaerobic tank and the aerobic biological tank are greatly improved simultaneously; moreover, the process only uses a small quantity of medicaments, and generates relatively less sludge.
Owner:中冶生态环保集团有限公司
Compound microorganism oil extraction method for low permeability oilfield
InactiveCN102852497AImprove mobility ratioIncrease the spread areaFluid removalSurface-active agentsAnaerobic microorganisms
The invention discloses a compound microorganism oil extraction method for a low permeability oilfield. The compound microorganism oil extraction method comprises the following steps of (1) cultivating pseudomonas aeruginosa YM4 strains and pseudomonas stutzeri DP1 strains in an indoor shaking flask respectively, and obtaining fermentation broth of high-activity pseudomonas aeruginosa YM4 strains and fermentation broth of polymer produced strains through first-stage and second-stage seeding tank amplification and fermentation production of a production tank; (2) mixing surface active agent produced strains and the pseudomonas stutzeri DP1 strains fermented and produced in the step (1) according to volume ratio of 1:1; and (3) enabling compound microorganism bacterium liquid obtained in the step (2) to serve as an oil-displacing agent to inject in an oil layer directly through a water injection well, and obtaining crude oil from a producing well. The YM4 strains and the DP1 strains are both facultative anaerobic microorganisms and can both grow and breed in a ground layer, polymers produced by the DP1 strains can improve mobility ratio, increases water injection affecting area, and the product surface active agent of the YM4 strains can reduce oil-water interfacial tension and improve oil recovery.
Owner:RES INST OF SHAANXI YANCHANG PETROLEUM GRP
Methods for treating wastewater from exploration for and production of oil and gas
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as BTEX methanol and other non-phase separable hydrocarbons may be removed from wastewater obtained from oil or gas exploration or production operations by way of a bioreactor. The bioreactor may employ anaerobic microorganisms that metabolize various VOCs. In some embodiments, such a bioreactor may be configured to treat process flow rates of thousands of barrels of wastewater per hour. Such a bioreactor may comprise a large vessel at a larger water treatment site.
Owner:R N IND
In-situ remediation method for nitrate pollutions in groundwater
ActiveCN104129850AReduce solubilityDoes not change the compositionTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesContaminated groundwater/leachate treatmentParticulatesAnaerobic microorganisms
The invention discloses an in-situ remediation method for nitrate pollutions in groundwater, which is characterized by comprising the steps of crushing low-grade siderite ores, and screening the obtained object so as to obtain particles with a particle size of 0.1-1 mm; excavating a groove in an aquifer perpendicular to the flow direction of groundwater, and filling the siderite particles into the groove so as to build an underground permeable wall; and injecting nitrate-dependent iron oxidizing bacteria liquid for oxidizing siderites and reducing nitrates in the presence of iron oxidizing bacteria of anaerobic microorganism depended nitrates. New iron oxides also have a function of absorbing other pollutants in purified water.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
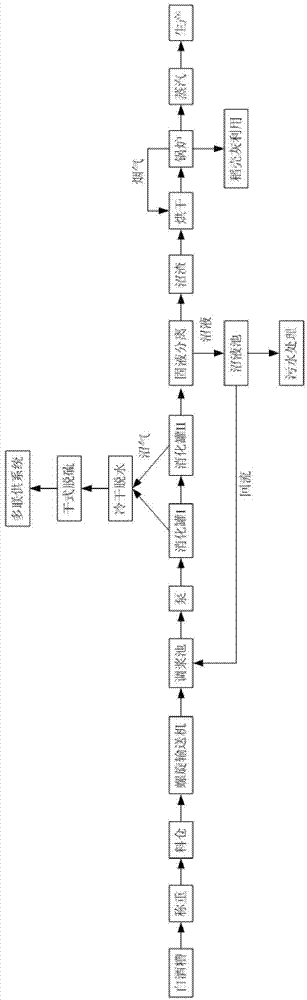
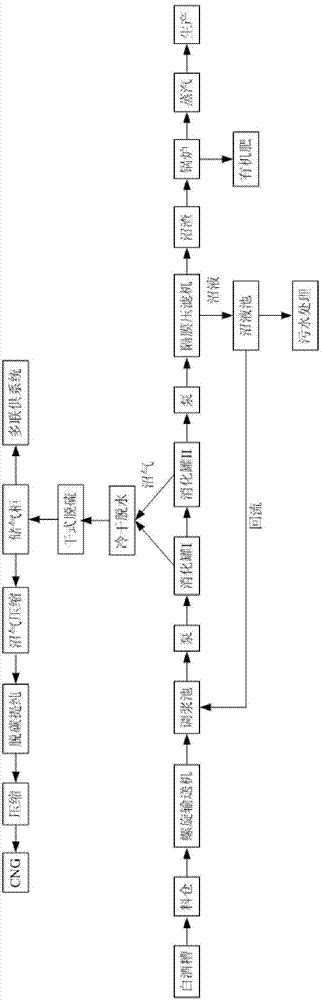
Distillate spirit vinasse spot comprehensive utilization method
ActiveCN102921700AReduce consumptionPromote sustainable developmentWaste processingSolid waste disposalAnaerobic microorganismsVinasse
The invention relates to a distillate spirit vinasse spot comprehensive utilization method. Distillate spirit vinasse is fed into an anaerobic digestor, anaerobic microorganisms are used for conducting fermentation treatment, degradable organisms are converted to biogas, the biogas serves as fuel of a boiler and a multiply combined cooling heating and power system and is purified to natural gas, a biogas fluid is subjected to solid-liquid separation, the biogas fluid and a biogas residue are obtained, the biogas fluid is refluxed and serves as an anaerobic digestor germ, redundant biogas fluid is discharged into a spirit factory sewage disposal system or serves as liquid fertilizer, the dried biogas residue serves as the fuel of the boiler, the produced steam is used for production, rice hull ash is used for agricultural production or production of other high value-added products, and the biogas residue can be processed to organic fertilizer and is used for agricultural production. By the aid of the method, the distillate spirit vinasse can be subjected to spot treatment in the spirit factory, raw materials cannot be transported for a long distance, water and chemical medicines are not required to be added during the production and treatment process, products can be applied in the spirit factory completely and are not affected by seasons and market requirements, and the system energy utilization efficient is high.
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
Organic acid producing microorganism and process for preparing organic acids employing the same
A novel microorganism capable of producing organic acids, Mannheimia sp. 55E, and a process for producing organic acid through anaerobic and aerobic incubation using the novel microorganism are provided. The method of producing an organic acid using the microorganism involves incubating Mannheimia sp. 55E with Accession Number KCTC 0769BP in a medium under anaerobic or aerobic conditions and obtaining an organic acid from the medium. Mannheimia sp. 55E produces succinic acid, lactic acid, and formic acid under anaerobic conditions saturated with CO2, and succinic acid, lactic acid, acetic acid, and formic acid under aerobic or N2 anaerobic conditions. Mannheimia sp. 55E is a facultative anaerobe tolerant of oxygen. Thus, the use of Mannheimia sp. 55E in producing organic acids can eliminate a problem of process instability, which would occur by the presence of oxygen in a fermentation process of producing organic acids using an obligate anaerobic microorganism.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for accelerating anaerobic fermentation of residual sludge by utilizing zero-valent iron technology
ActiveCN103288319APromote reductionHigh yieldWaste based fuelBiological sludge treatmentTemperature controlAnaerobic microorganisms
A method for accelerating anaerobic fermentation of residual sludge by utilizing a zero-valent iron technology comprises the following steps: mixing a high solid sludge with a solid ratio of less than 10% and iron scraps, putting the mixture into an anaerobic fermentation reactor, and inoculating with anaerobic microorganisms; undergoing the anaerobic fermentation in the reactor with stirring, and collecting methane generated during the fermentation process; having requirements of the stirring speed, the pH value in the reactor, the temperature control during the stirring process; after finishing fermentation, discharging the sludge, wherein the residual iron scraps remaining in the anaerobic fermentation reactor are used for next batch of the sludge fermentation. With the method for accelerating the anaerobic fermentation of the residual sludge by utilizing the zero-valent iron technology, the following technical effects are achieved: reduction of the high solid sludge is promoted after the anaerobic fermentation, and at the same time, the methane generation amount during the fermentation process is improved. The method has low investment cost, simple technical operation, and strong processing ability, and can be applied to upgrade reconstruction of new built sludge anaerobic fermentation equipment or existing equipment.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
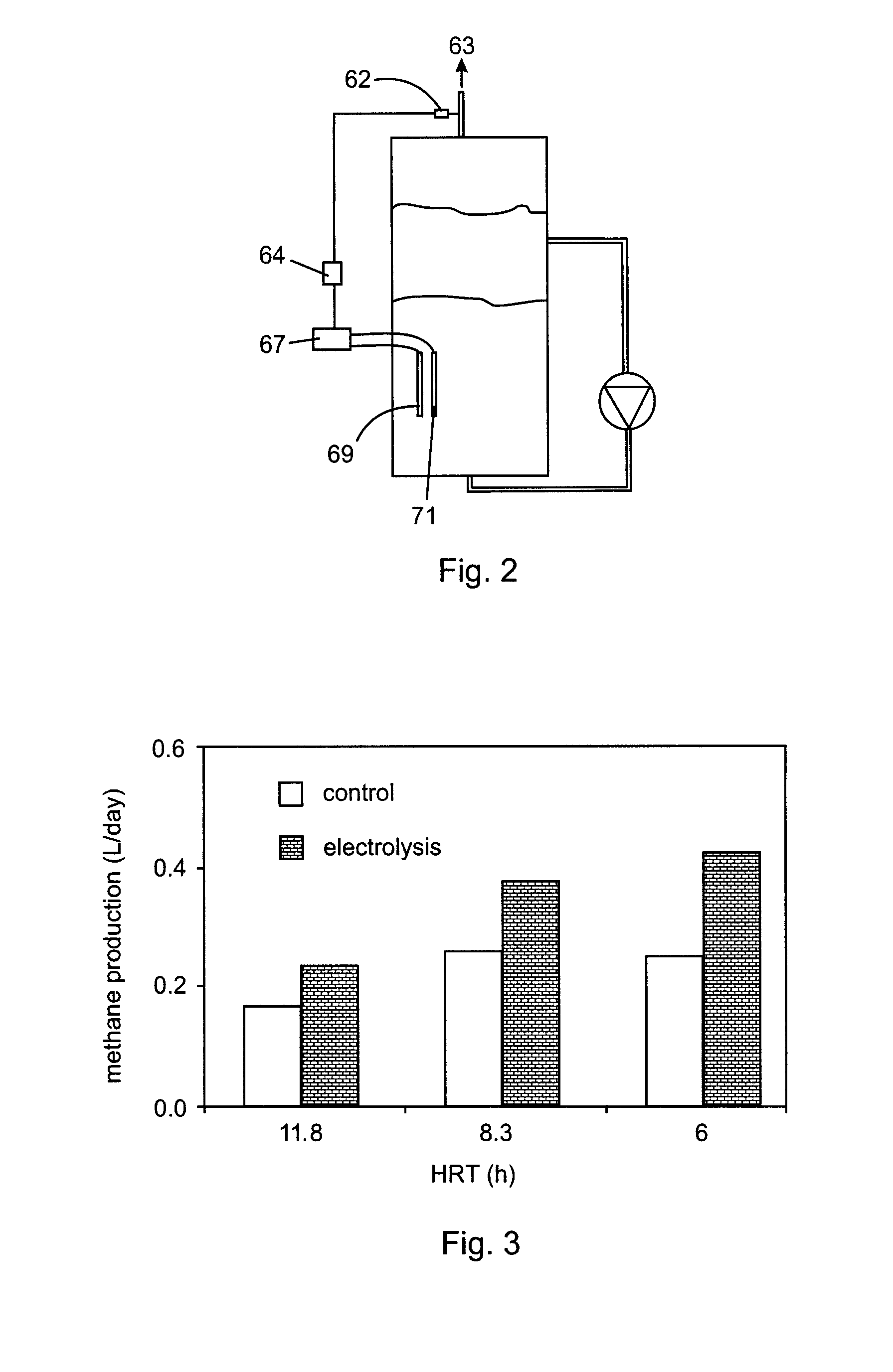
Microbially-assisted water electrolysis for improving biomethane production
InactiveUS20120100590A1Increase surface areaReduce the amount requiredBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsElectrochemistryAnaerobic microorganisms
A method of producing in a bioreactor a biogas rich in methane involves electrolyzing water in an aqueous medium at a voltage in a range of from 1.8 V to 12 V in the presence of electrochemically active anaerobic microorganisms that biocatalyze production of hydrogen gas, and, contacting a species of hydrogenotrophic methanogenic microorganisms with the hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide to produce methane. Volumetric power consumption is in a range of from 0.03 Wh / LR to 0.3 Wh / LR. Current density is 0.01 A / cmE2 or lower. The voltage is sufficient to electrolyze water without destroying microbial growth. Such a method results in improved electrolysis efficiency while avoiding the use of noble metal catalysts. Further, a combination of water electrolysis with anaerobic degradation of organic matter results in increased biogas quality and in increased biogas quantity and yield. Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide contributes to the increased quality, while an increase in the rate of organic matter hydrolysis and an increase in the production of methane from hydrogen contributes to the increased quantity and yield.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
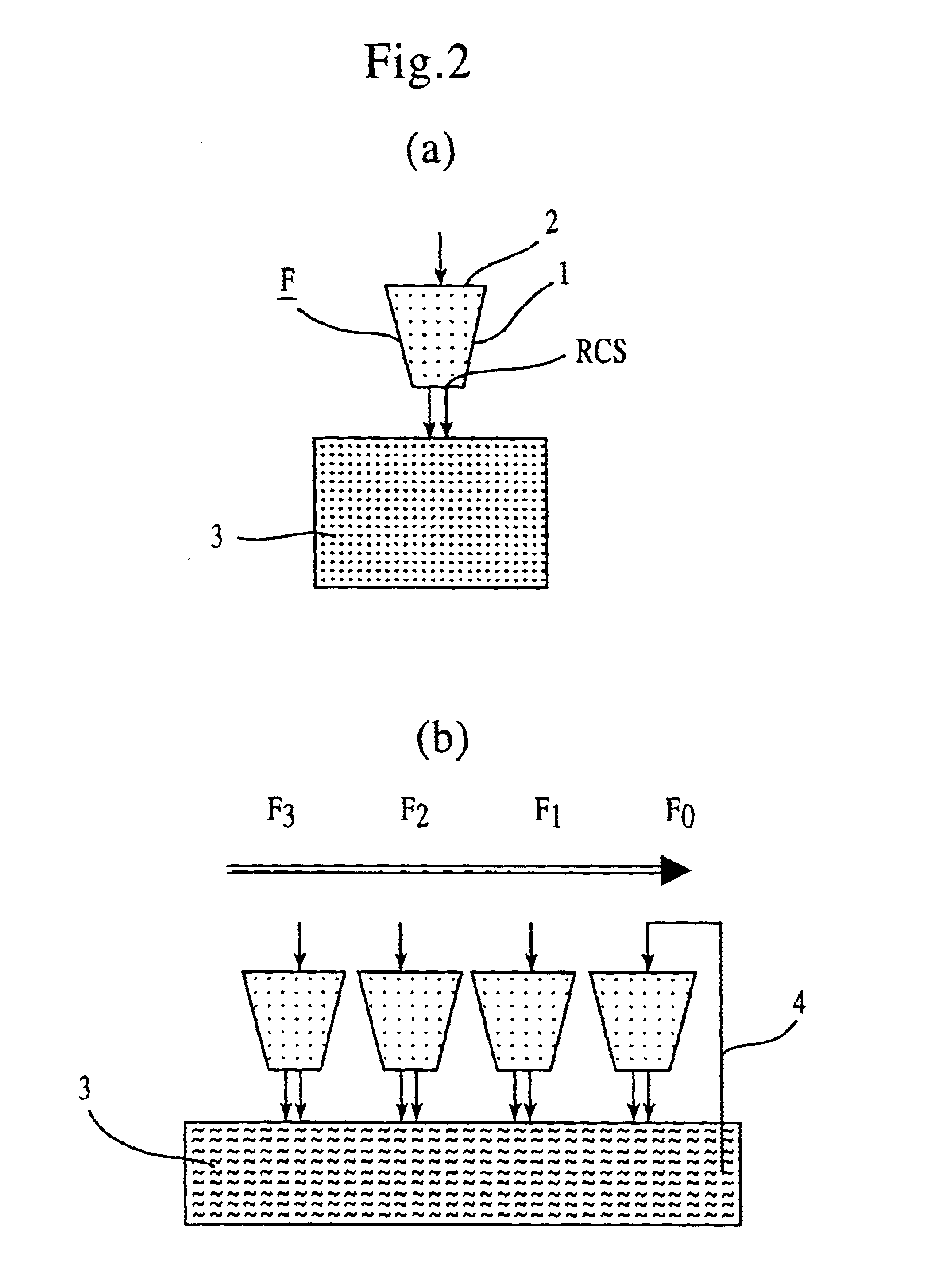
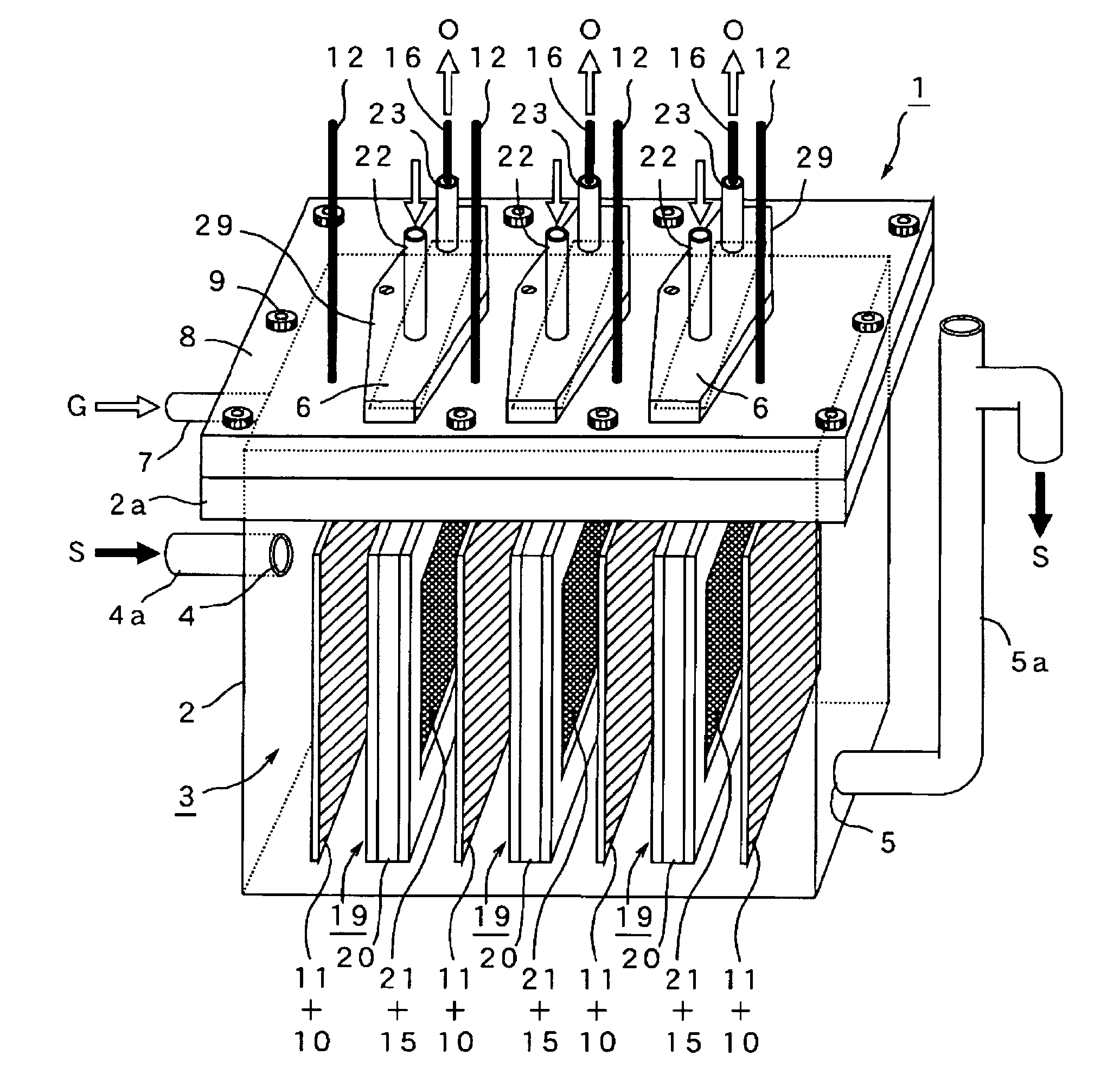
Microbial fuel cell and membrane cassette for microbial fuel cells
InactiveUS20120003504A1Efficient degradationReduce harmFuel cell auxillariesBiochemical fuel cellsMicrobial fuel cellFuel cells
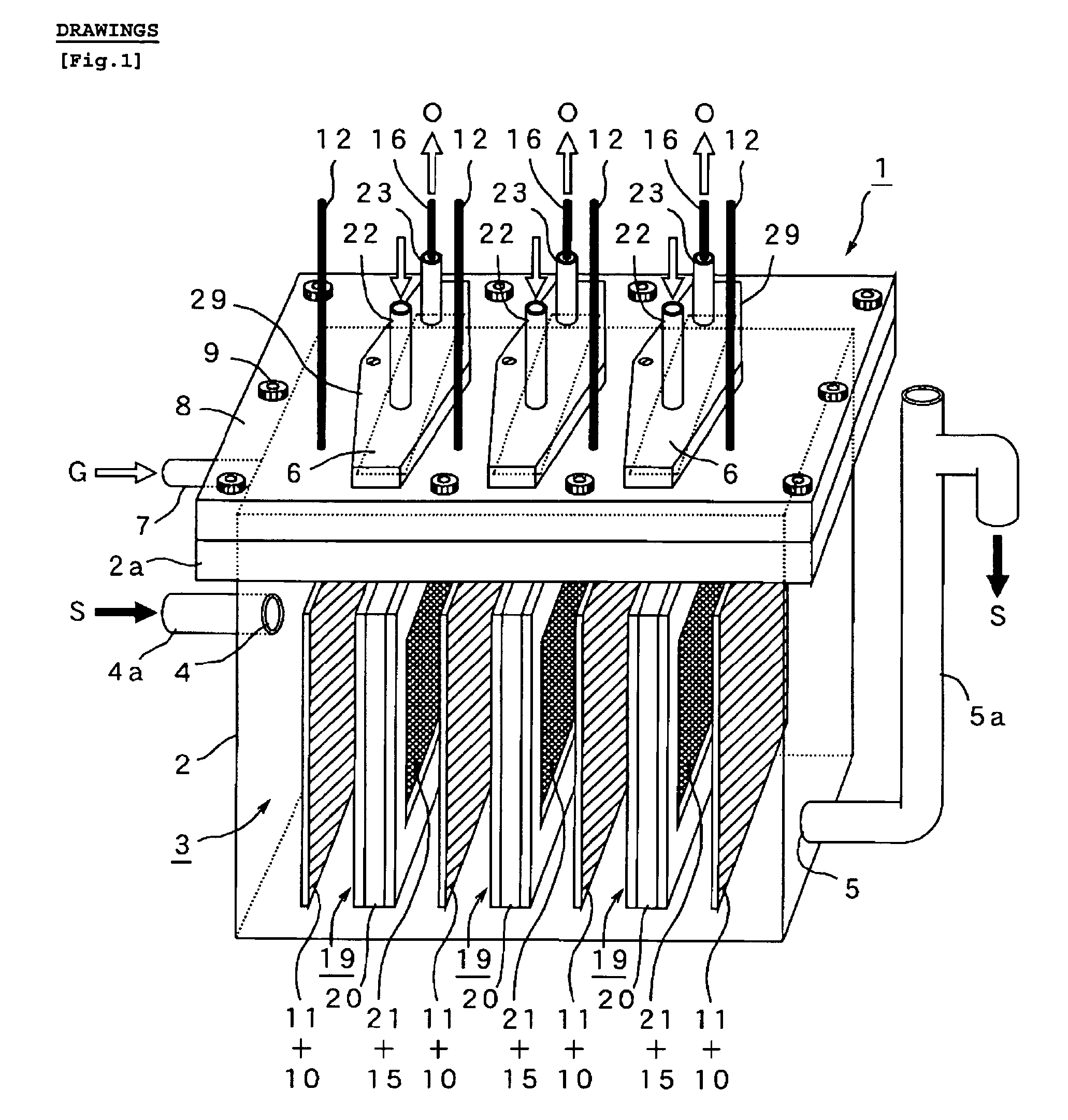
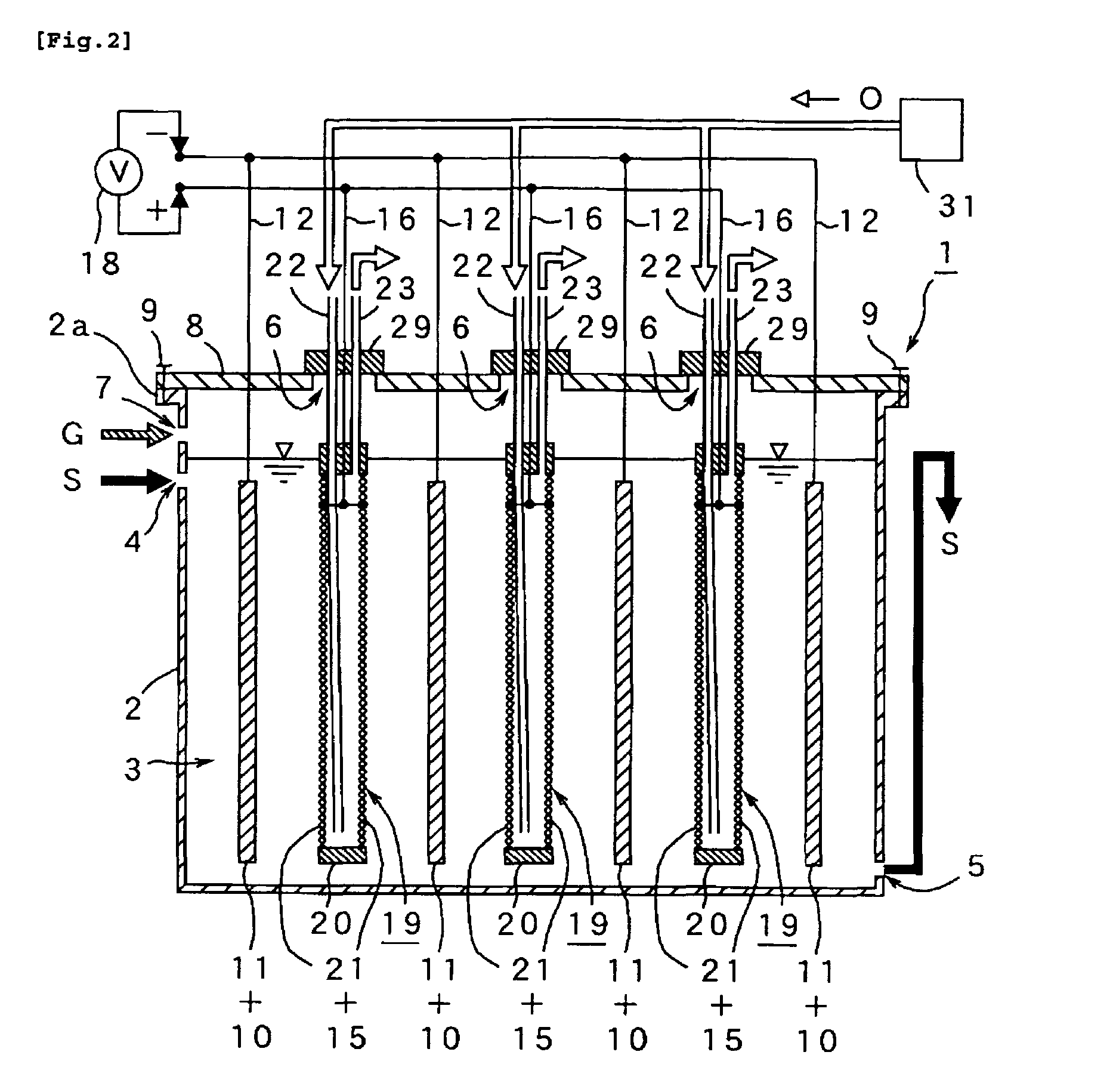
[PROBLEMS] To provide a microbial fuel cell whose parts can be replaced without lowering the energy recovery efficiency and a membrane cassette for microbial fuel cells. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] A negative electrode (10) supporting anaerobic microorganisms (11) is immersed in an organic substrate (S). A positive electrode (15) sealed together with an electrolyte (D) in a closed hollow cassette (20) having an outer shell (25) at least a part of which is formed of an ion-permeable membrane (21), an inlet (22), and an outlet (23) or connected to the inner side of an ion-permeable membrane (21) is inserted into the organic substrate (S). While oxygen (O) is supplied into the cassette (20) through the inlet (22) and the outlet (23), electricity is taken out through a circuit (18) electrically interconnecting the negative and positive electrodes (10, 15). Preferably, the outer shell (25) of the closed hollow cassette (20) is a hollow outer shell frame (25) having an opening (26) which is closed by stretching an ion-permeable membrane (21), an inlet (22), and an outlet (23), and the ion-permeable membrane (21) is a membrane / electrode assembly (MEA) formed integrally with the positive electrode (15).
Owner:KAJIMA CORP
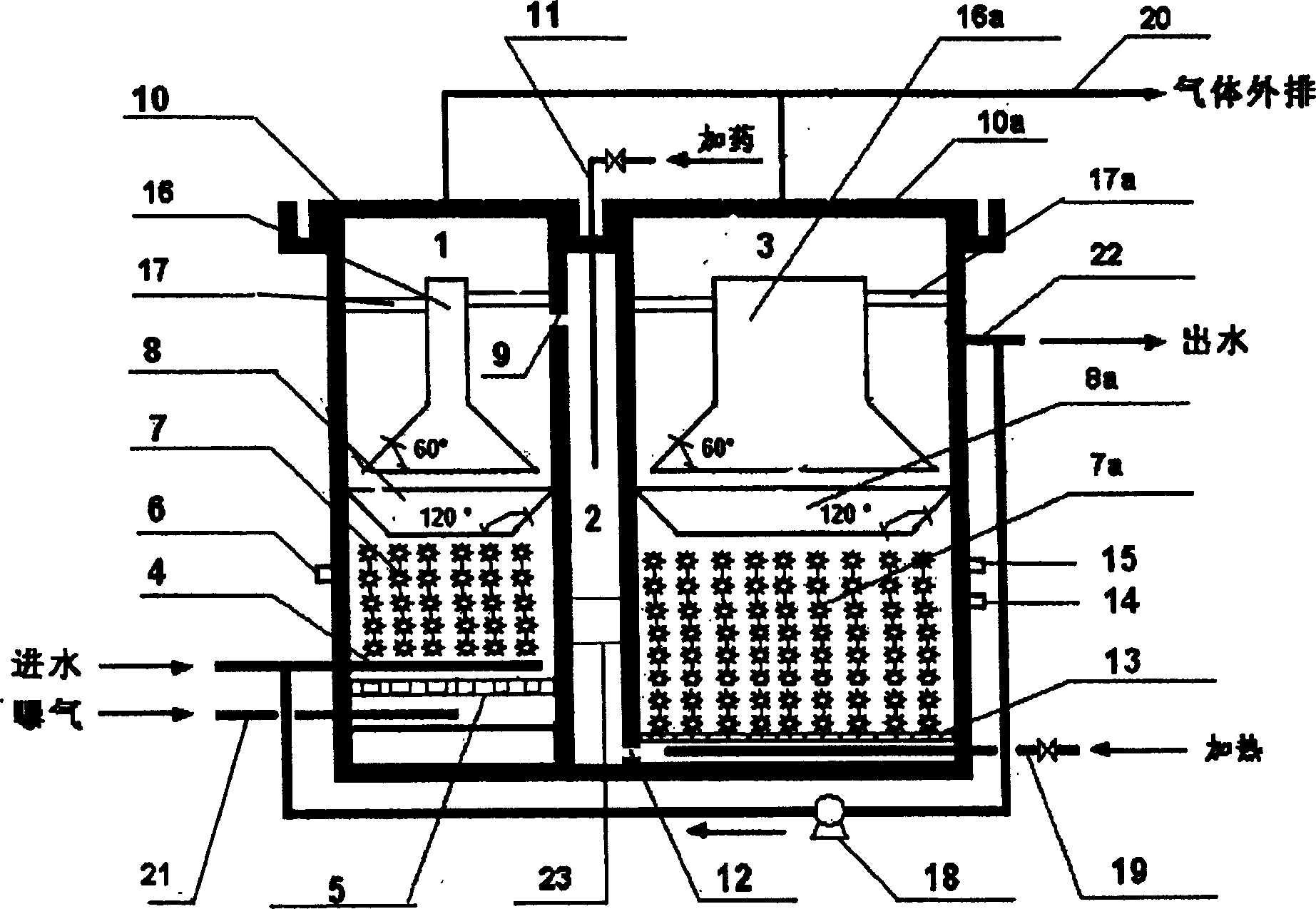
Sewage treatment system
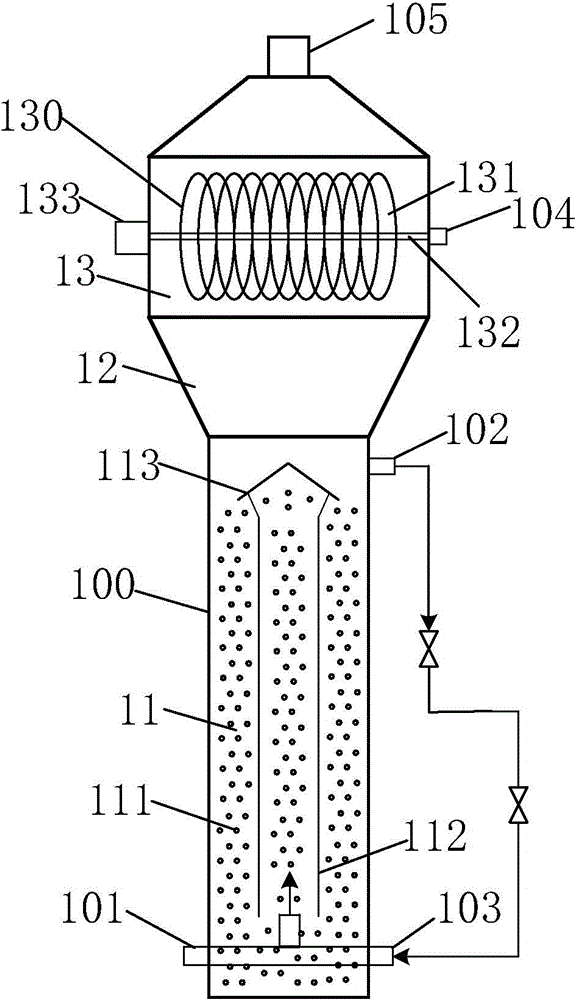
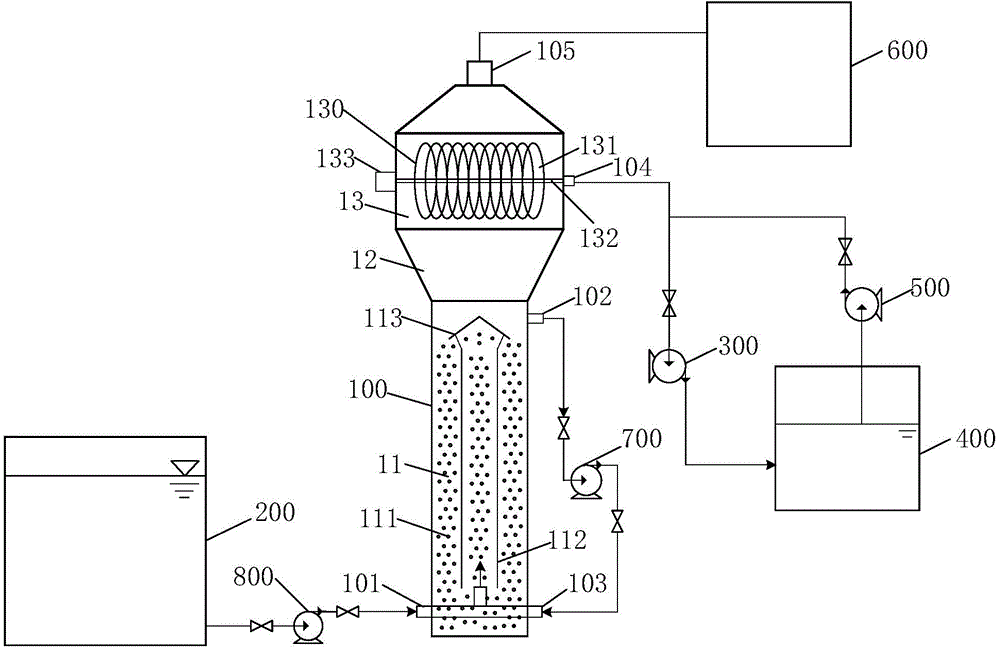
ActiveCN104556369AImprove processing efficiencyReduce energy consumptionWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesFluidized bedProduct gas
The invention discloses a sewage treatment system comprising a treatment tower body, a muddy water outlet, a muddy water outlet, a muddy water inlet, a clean water outlet and a biogas outlet, wherein an anaerobic fluidized bed reaction zone, a sludge settling zone and a membrane separation zone are sequentially defined in the treatment tower body from bottom to top; carrier particles attached with anaerobic microorganisms are contained in the anaerobic fluidized bed reaction zone which is provided with a vertical flow guide cylinder; a solid-liquid separator is arranged at the upper end of the flow guide cylinder; the membrane separation zone is provided with a rotary membrane component; the sewage inlet is formed in the lower part positioned on the side wall of the anaerobic fluidized bed reaction zone; the muddy water outlet is formed in the upper part positioned on the side wall of the anaerobic fluidized bed reaction zone; the muddy water inlet is formed in the lower part positioned on the side wall of the anaerobic fluidized bed reaction zone and is communicated with the flow guide cylinder; the clean water outlet is formed in a side wall positioned in the membrane separation zone; and the biogas outlet is formed in the top part positioned in the membrane separation zone. The system not only can realize purification of sewage but also can generate a lot of high-caloric-value biogas, and is compact in structure and low in running cost.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com