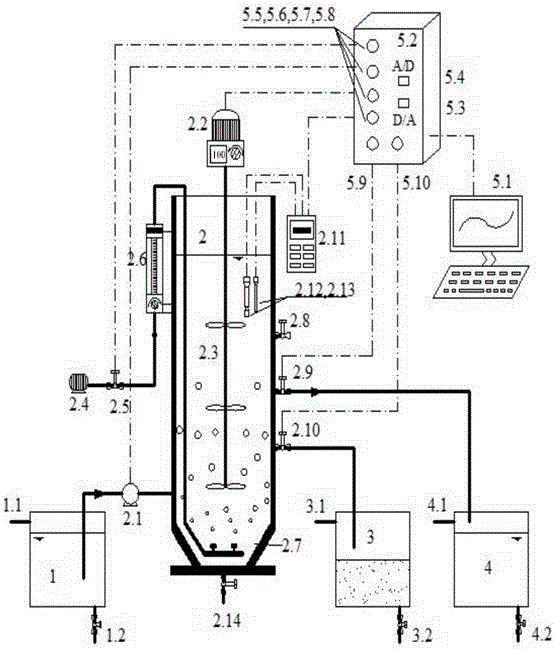
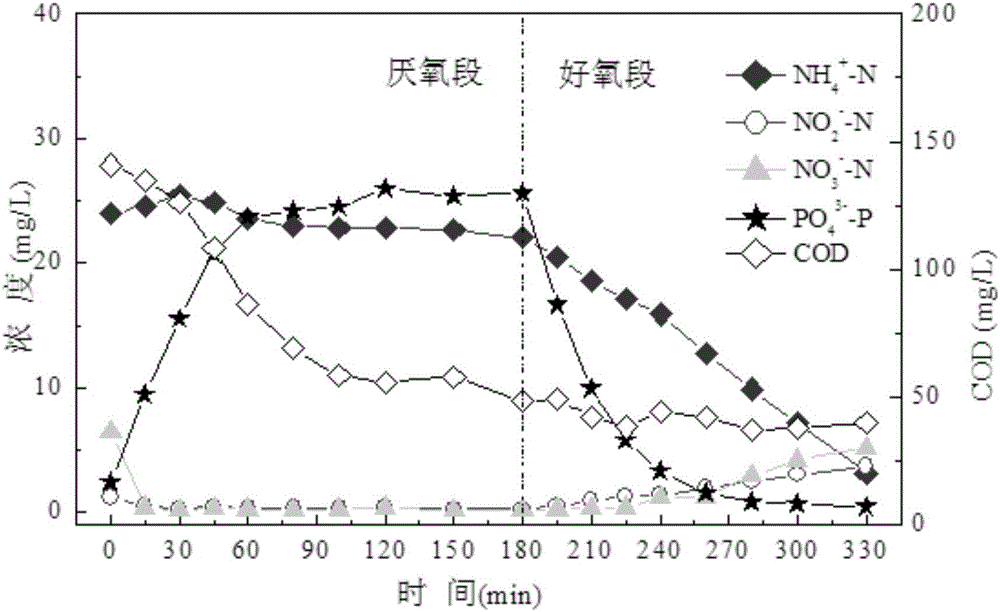
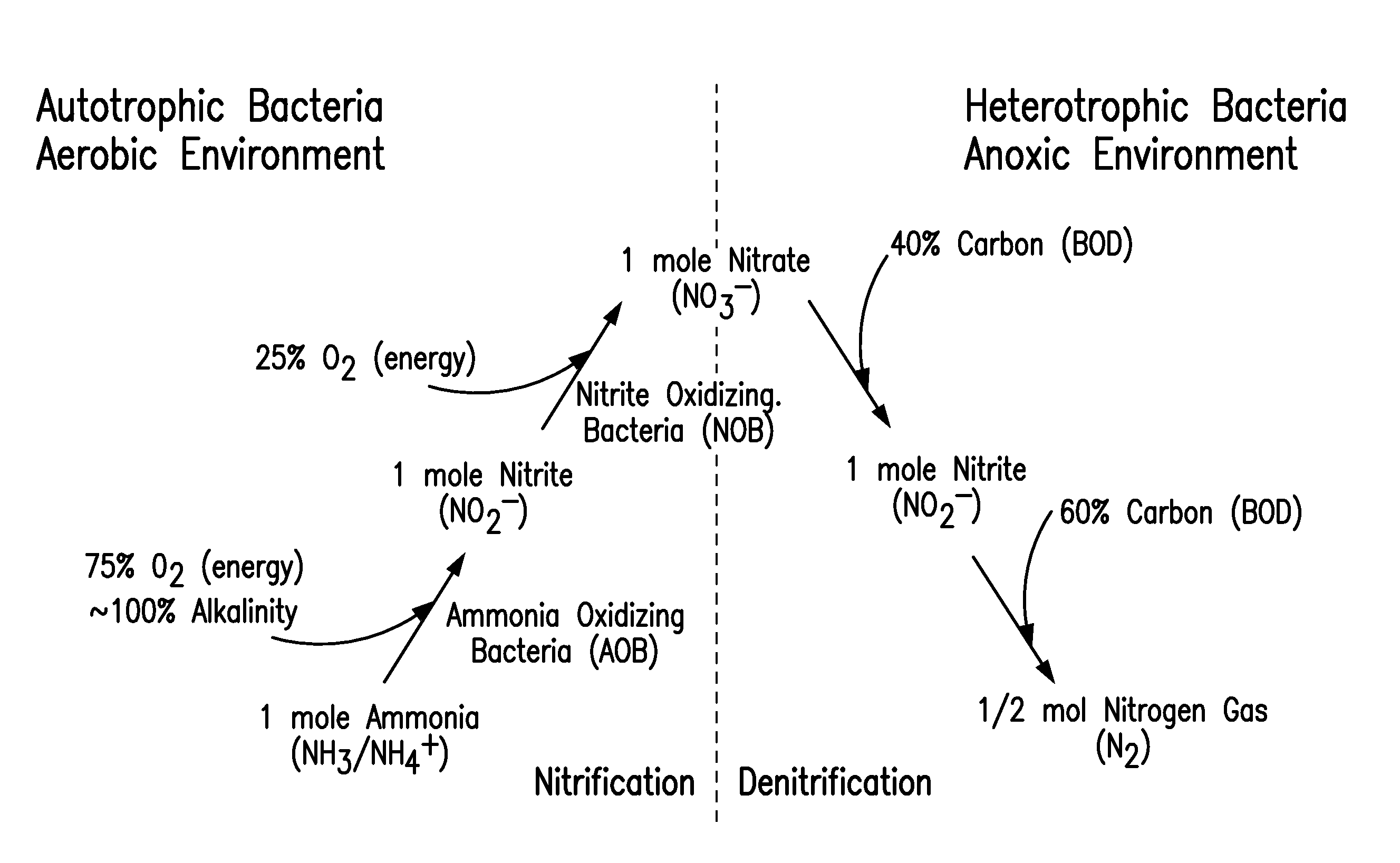
Patents
Literature
487 results about "Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
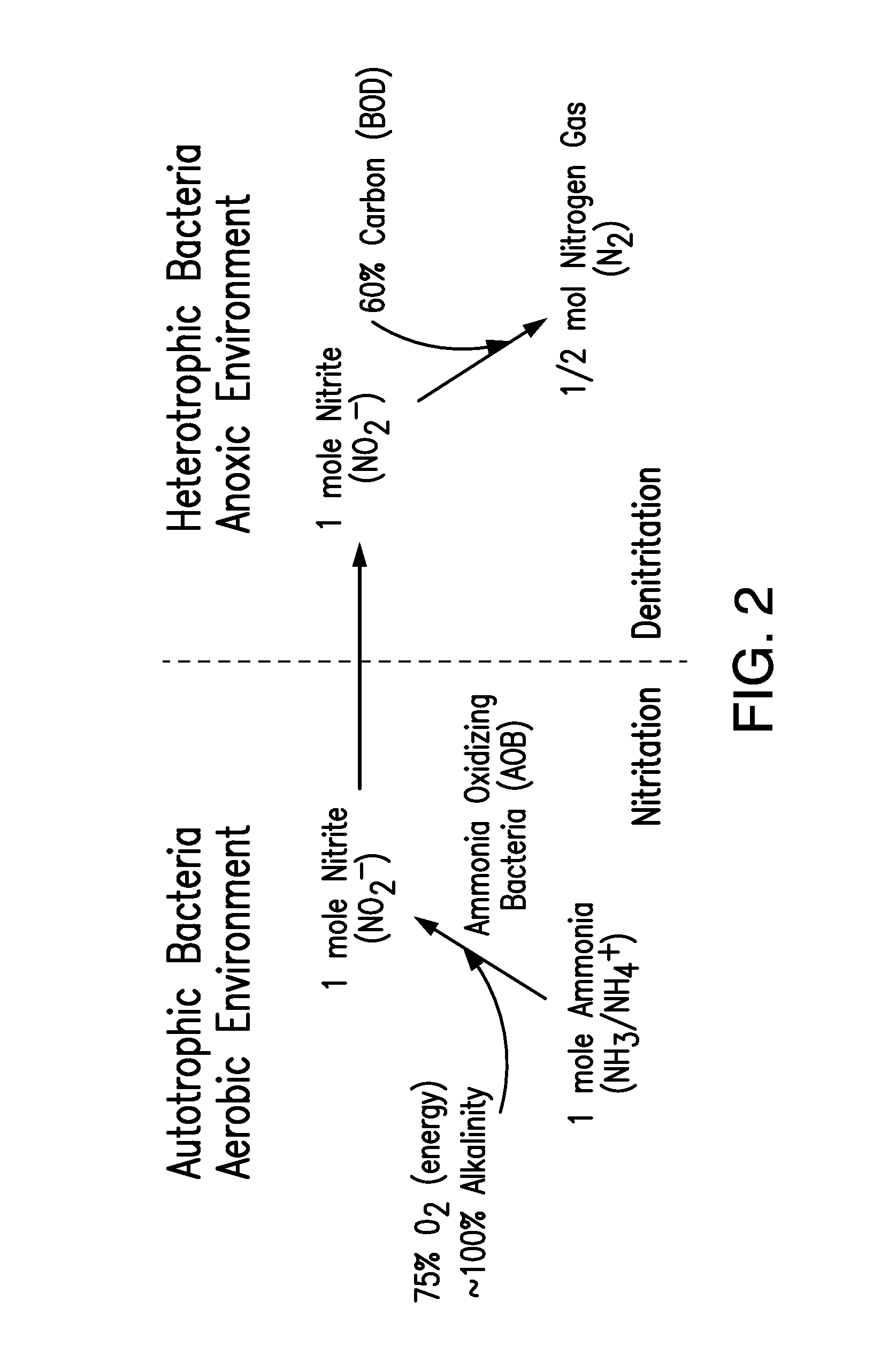
Nitrifying bacteria are chemolithotrophic organisms that include species of the genera Nitrosomonas, Nitrosococcus, Nitrobacter and Nitrococcus. These bacteria get their energy by the oxidation of inorganic nitrogen compounds. Types include ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB).
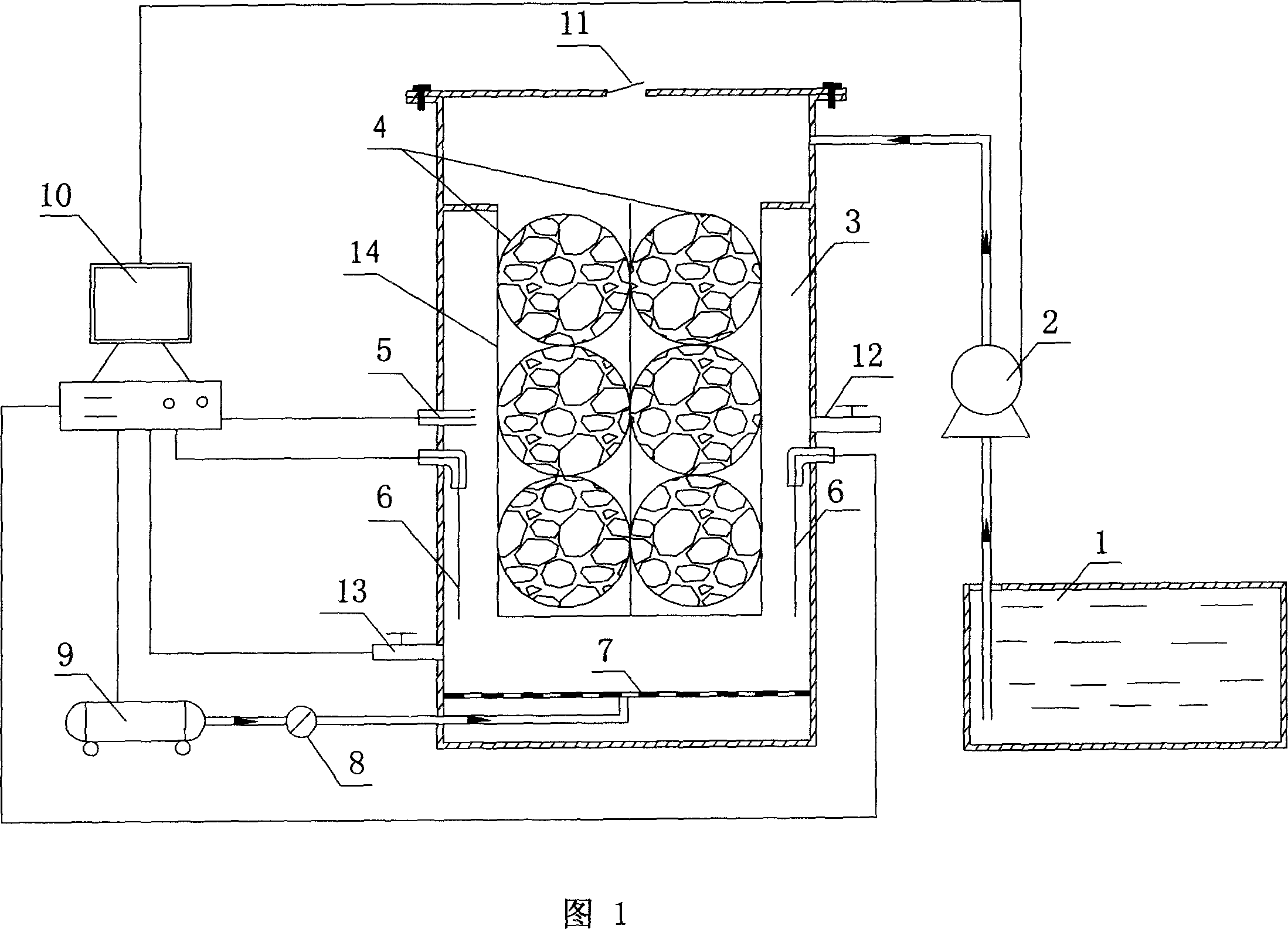
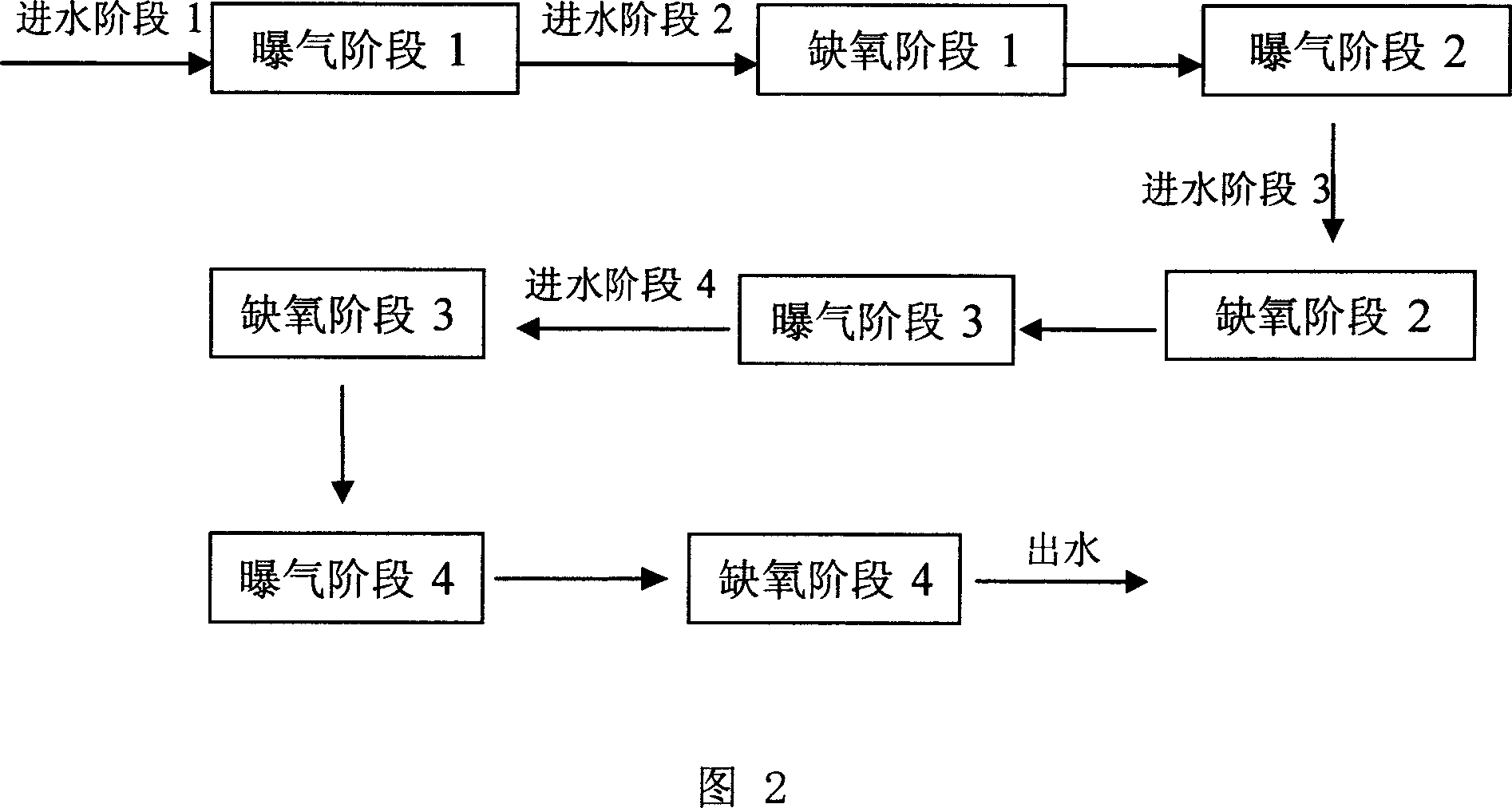
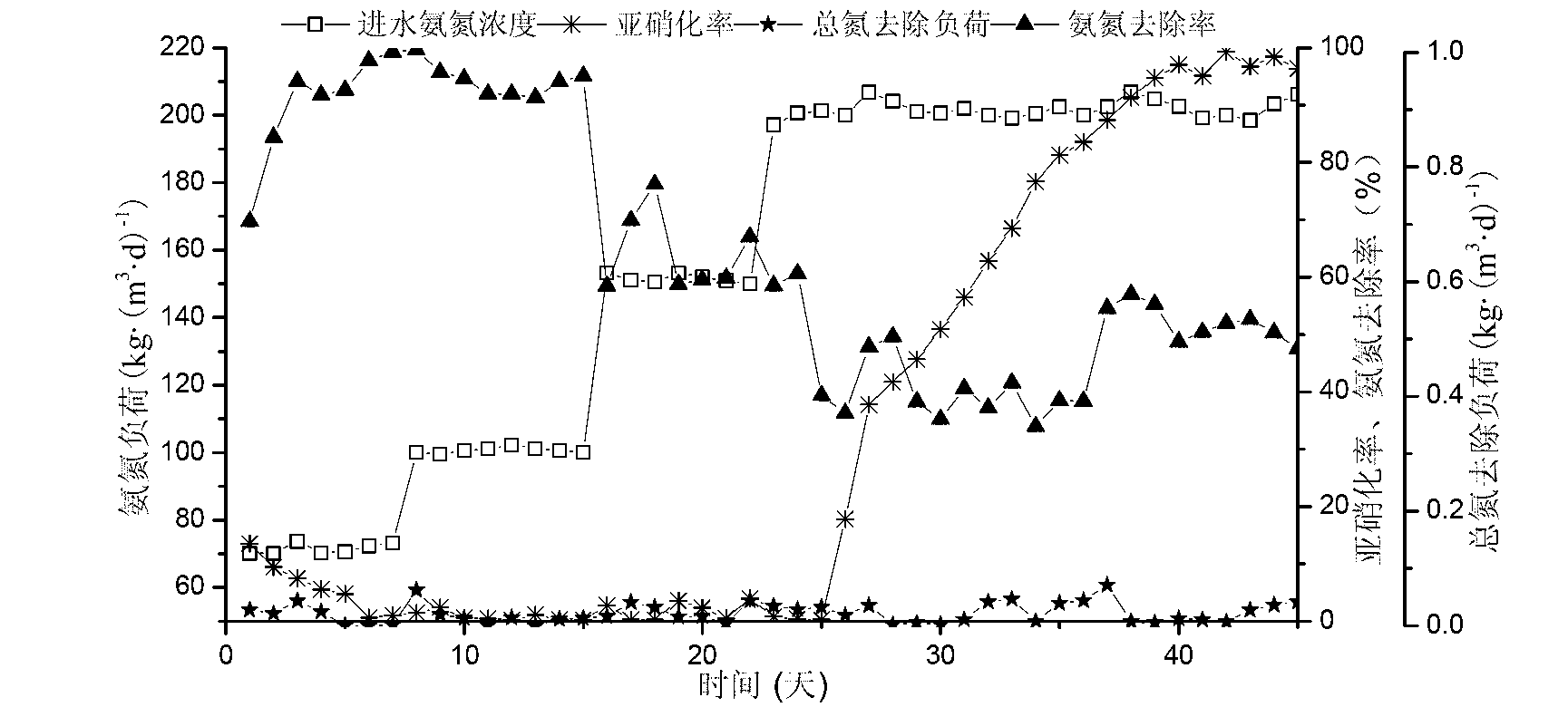
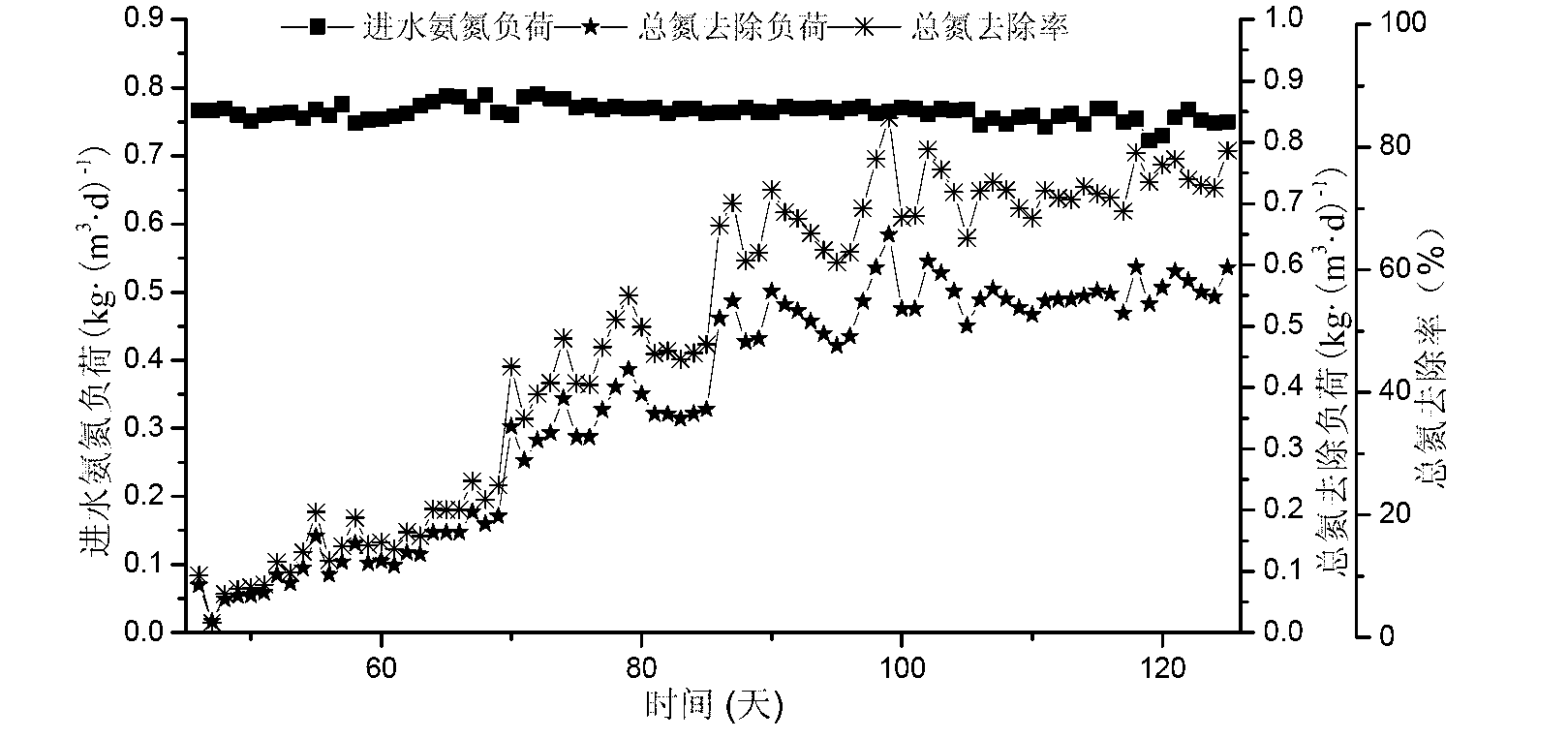
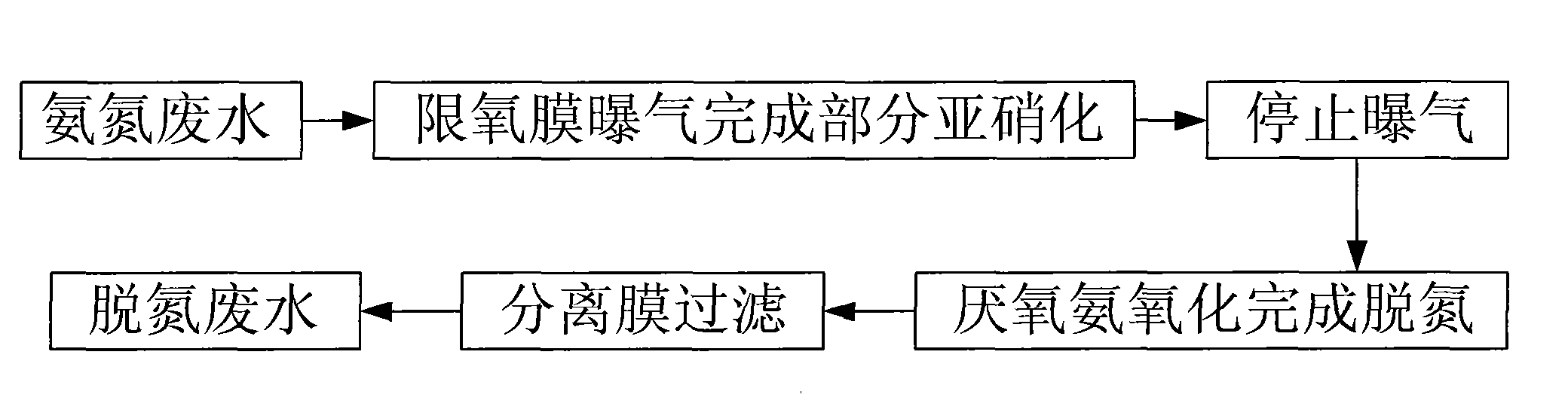
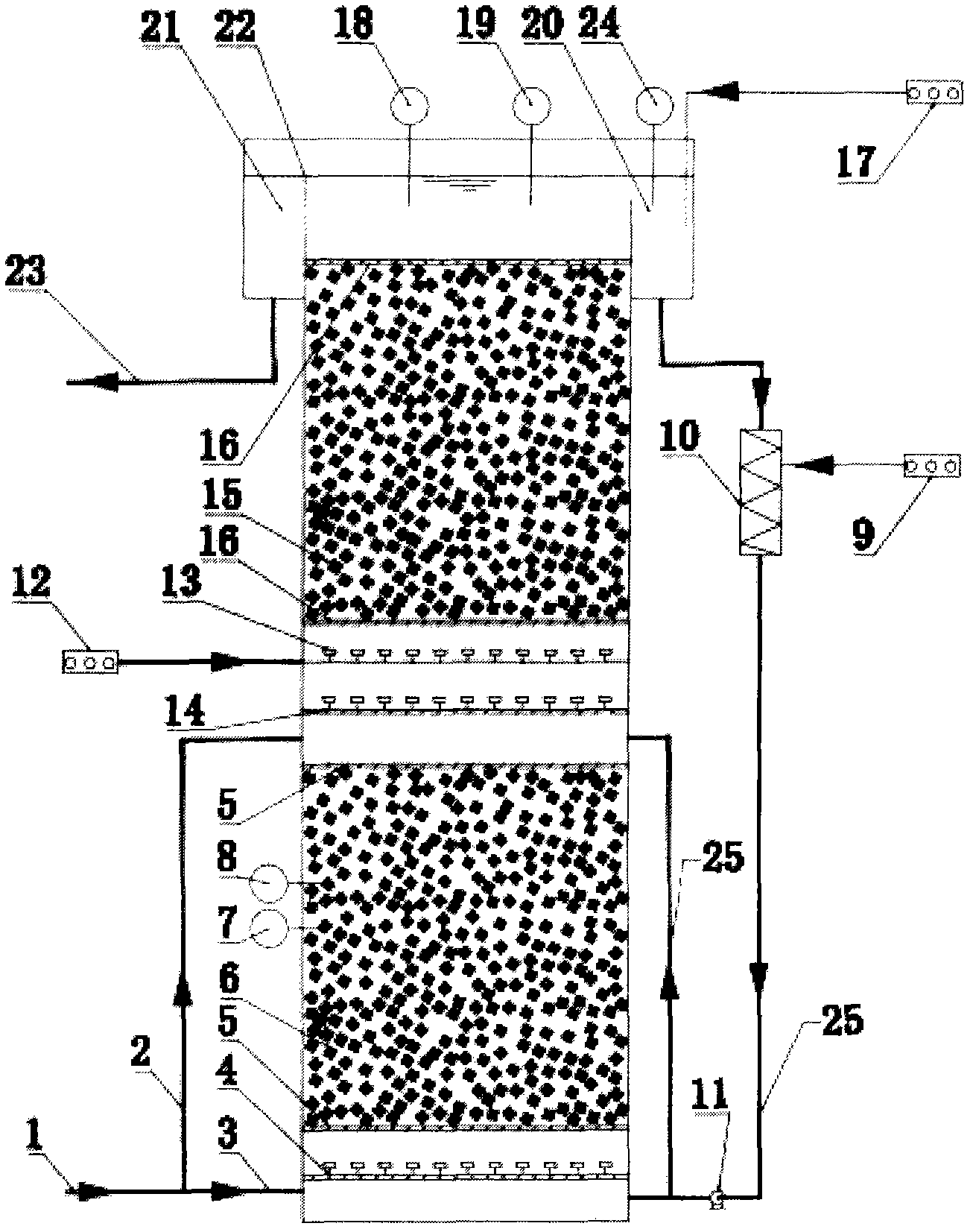
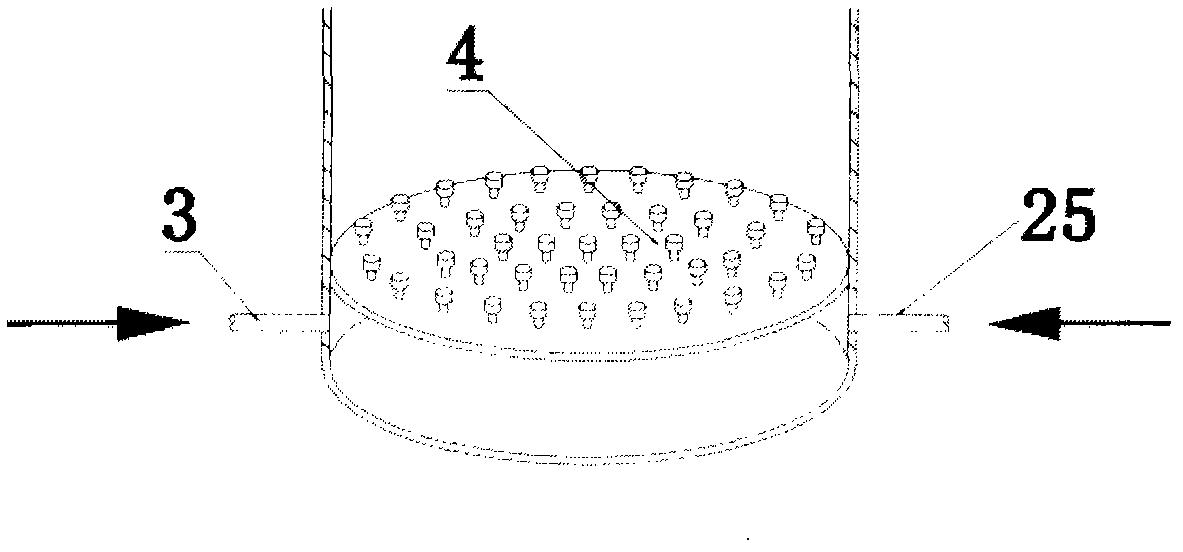
Operation mode and apparatus of short distance nitration-anaerobic ammoxidation batched biomembrane denitrogenation
InactiveCN1927739AToxic reductionControl the maximum cumulative concentrationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeElectron donor
One kind of short range nitrifying-anaerobic aminoxidizing sequencing batch type denitrifying biomembrane mode and plant is disclosed. The limited aerating mode with real-time control of the sewage temperature inside the reactor and high frequency alternation between aeration and anaeration can inhibit the growth of nitrite oxidizing bacteria and denitrifying bacteria so that the aminoxidizing bacteria and the anaerobic aminoxidizing bacteria become the dominant bacteria in the nitrifying and denitrifying stages. In the nitrifying stage, nitrification is stopped in the nitrite step; and in the denitrifying stage, ammonia nitrogen acts as the direct electron donor to reduce nitrite. The plant is provided with fixed spherical composite stuffing with spherical shell of polypropylene and filled inside biological composite material. Sectional discrete water feeding mode is adopted to feed the sewage to be treated in four stages into the reactor.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Autotrophic nitrogen removal method for biological phosphorus removal of urban sewage based on short-cut denitrification for providing nitrite
ActiveCN104556376AReduced oxygen demandReduce operating energy consumptionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention discloses an autotrophic nitrogen removal method for biological phosphorus removal of urban sewage based on short-cut denitrification for providing nitrite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly feeding urban sewage into an anaerobic zone of a biological phosphorus removal nitrogen removal reactor, wherein short-cut denitrification is firstly carried out on denitrifying bacteria on a biological membrane so as to reduce nitrate nitrogen in return sludge to nitrite nitrogen, anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria on the biological membrane further convert nitrite nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen while anaerobic phosphorus release is carried out on phosphorus-accumulating bacteria in floc sludge; then feeding the sewage into the anaerobic zone again, wherein short-cut denitrification is carried out on the denitrifying bacteria on the biological membrane so as to reduce nitrate nitrogen in return sludge to nitrite nitrogen, and anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria on the biological membrane further convert nitrite nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen; then feeding the sewage into an aerobic zone and ammonia oxidizing bacteria and nitrite oxidizing bacteria in the floc sludge oxidize residual ammonia nitrogen in the sludge to nitrate nitrogen; and finally, implementing residual phosphorus removal and autotrophic nitrogen removal of urban sewage of a continuous flow, wherein the treatment energy consumption of an urban sewage plant is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Rapid starting method of membrane bioreactor completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology
ActiveCN103224284AEasy to interceptSolve the problem of difficult sourceSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentNitrogen removalAeration rate
A rapid starting method of a membrane bioreactor completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology belongs to the municipal sewage processing and recycling fields. The starting method of a completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology in a membrane bioreactor (MBR) comprises the following steps: inoculating nitrated sludge of the aeration tank of a municipal sewage plant, and recovering the activities of sludge at normal temperature under low ammonia nitrogen of inlet water; reducing the aeration rate and gradually increasing the ammonia nitrogen concentration to successfully enrich ammonia oxidizing bacteria; and reducing the aeration rate, reducing DO, and inducing anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria to successfully start the completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology. Problems comprising slow starting and strict sludge inoculation requirement of a completely-autotrophic nitrogen removal technology are solved in the invention, and the rapid starting method of the shortcut nitration in the MBR realizes the efficient ammonia nitrogen removal, and provides a way for the long-term efficient and stable running of the shortcut nitration in the MBR.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for quickly starting oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing biofilter
InactiveCN101830569AQuick changeLow running costBiological water/sewage treatmentHydroxylamineSludge
The invention relates to a method for quickly starting an oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing biofilter, and relates to a method for biological denitrification of waste water, which comprises the following steps of: (1) inoculating an anaerobic denitrification biomembrane biofilter, and after a denitrification biomembrane is cultured, converting the anaerobic denitrification biomembrane biofilter into an oxygen-poor environment for cultivating oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing bacteria; (2) taking inorganic carbon NaHCO3 as a carbon source, taking NH4Cl as a nitrogen source of ammonia nitrogen, taking NaNO2 as the nitrogen source of nitrite nitrogen, taking KH2PO4 as a phosphorus source, and controlling the pH value to be alkalescent, wherein the concentration is low-matrix, and the temperature is room temperature; adding hydroxylamine, and inducing and inoculating sludge to be converted towards an oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing biomembrane; and (3) taking the biofilter as a reactor, and taking ceramsite as filter materials. In the method, the oxygen-poor ammonia oxidizing bacteria are applied to the sewage denitrifying technology to realize the shortest denitrification of nitrogen, so the problems of a large number of required carbon sources and neutralizers, large energy consumption and large sludge producing amount in the conventional biological denitrifying technology are solved.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Device and method for realizing partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation by adding hydroxylamine
ActiveCN106865773AAddress serious problemsNo swellingTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesHydroxylamineAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention discloses a device and a method for realizing partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation by adding hydroxylamine, and belongs to the field of urban domestic sewage biological treatment. For two-stage partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation, the stable operation of the short-range nitrification is crucial to a process; the short-range nitrification is very difficult to start and maintain stably only through process parameter control; a very good nitrite accumulating effect can be achieved by adding the hydroxylamine in the patent; partial short-range nitrification reactors can be started and high nitrite accumulation can be maintained within a short time. The hydroxylamine serves as an intermediate product in a nitrifying process, is a reducing agent of ammonia monooxygenase and a stimulating agent of AOB (Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria) and can improve the cell yield of the AOB; meanwhile, the hydroxylamine is an inhibiting agent of NOB (Nitrite Oxidizing Bacteria) and can elutriate the NOB. Compared with a conventional denitrogenation process, a partial short-range nitrification-anaerobic ammonia oxidation process can save aeration quantity and carbon source, and is particularly suitable for urban domestic sewage with low C / N.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
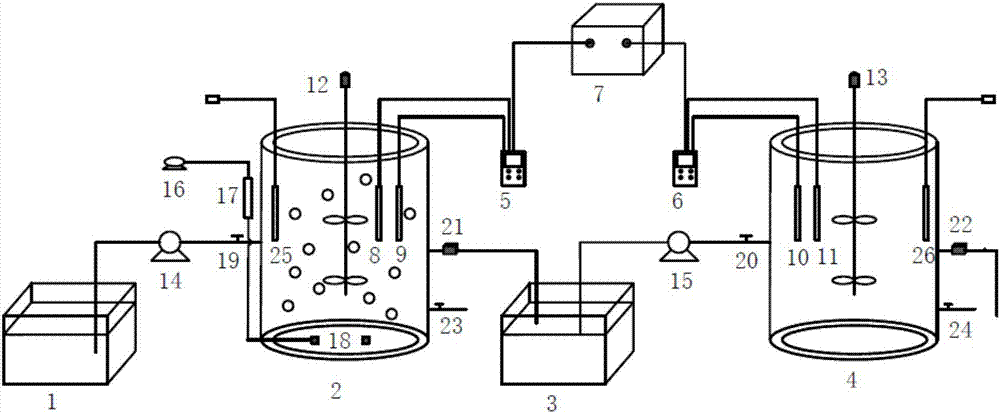
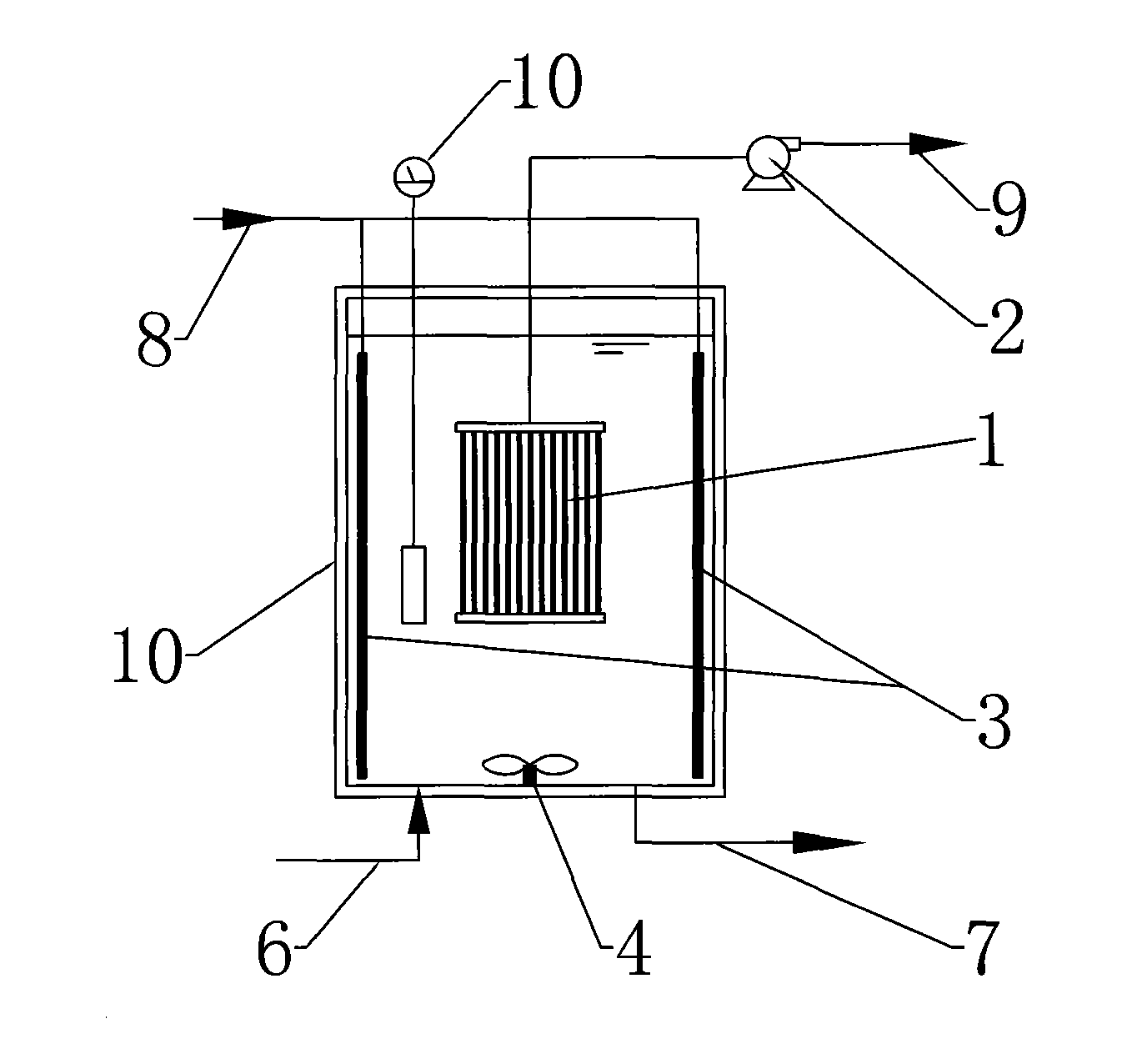
Single-stage whole process autotrophic denitrification sewage treatment device and technique thereof
InactiveCN101671094AAchieve enrichmentAchieve short-cut nitrificationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSingle stageAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention discloses a single-stage whole process autotrophic denitrification sewage treatment device and a technique thereof. The device comprises a reactor, a water outlet pump, a stirrer, a separation membrane component and an aeration membrane component, wherein the separation membrane component is arranged at the central part inside the reactor; the aeration membrane component consists ofa membrane tube which is wound on the inner wall of the reactor; and an air inlet pipe is connected with the aeration membrane component, and a water inlet of a water outlet pump is connected with theseparation membrane component by a pipeline. The method mainly comprises: the dissolved oxygen is controlled to be about 0.5-1.0mg / L, and partial short-cut nitrification is carried out on ammonia nitrogen under the action of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria; and then, aeration is stopped, denitrification is completed by anaerobic ammonium oxidation, and clean outlet water can be obtained by membrane separation. The invention leads the aeration membrane and the separation membrane to be arranged inside the same reactor to form a membrane aeration separating reactor, thus coupling bubble-free aeration, membrane separation and biological degradation. By utilizing the characteristics of high efficiency and easy control of membrane aeration, the good short-cut nitrification of nitrogenous effluent can be realized.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
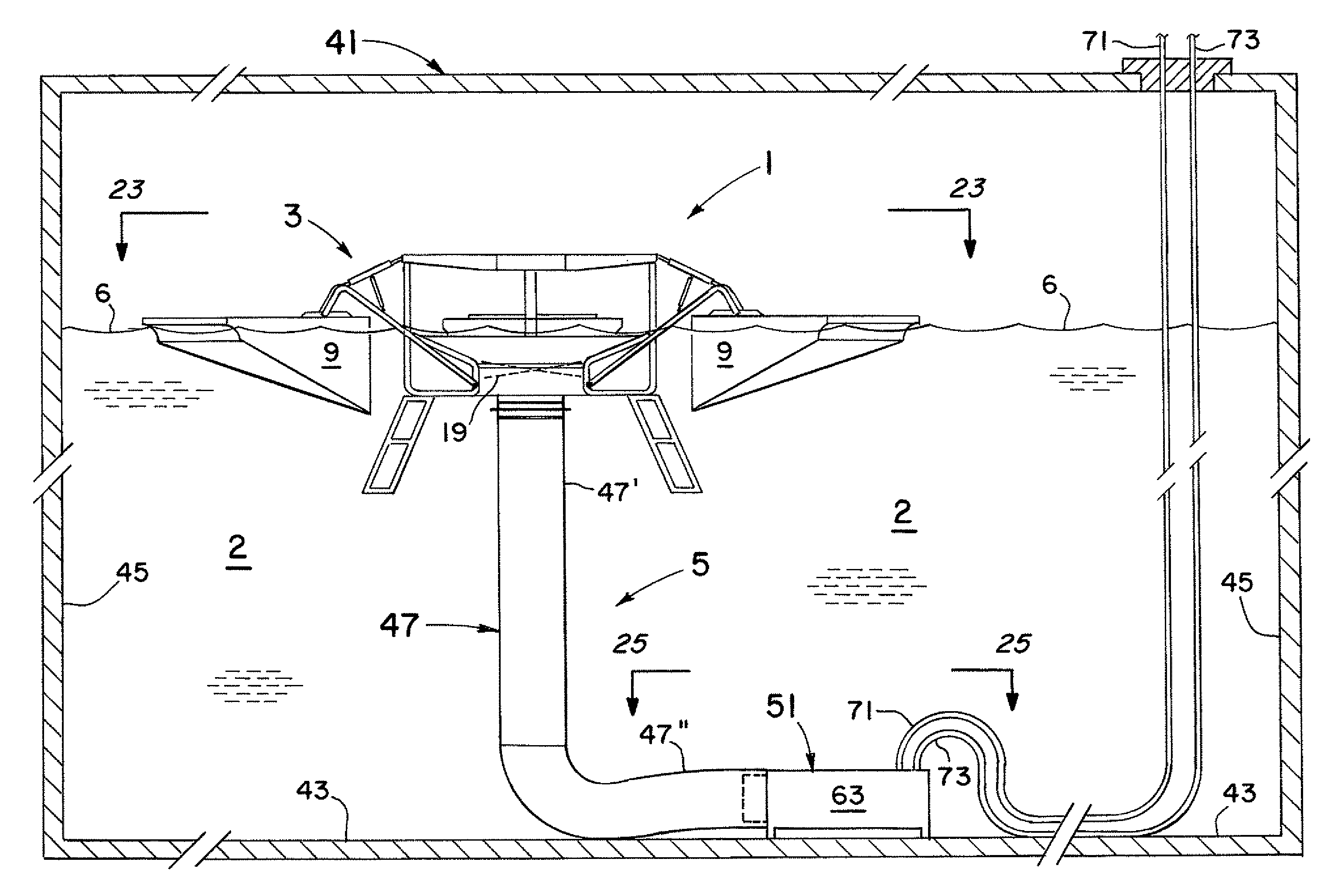
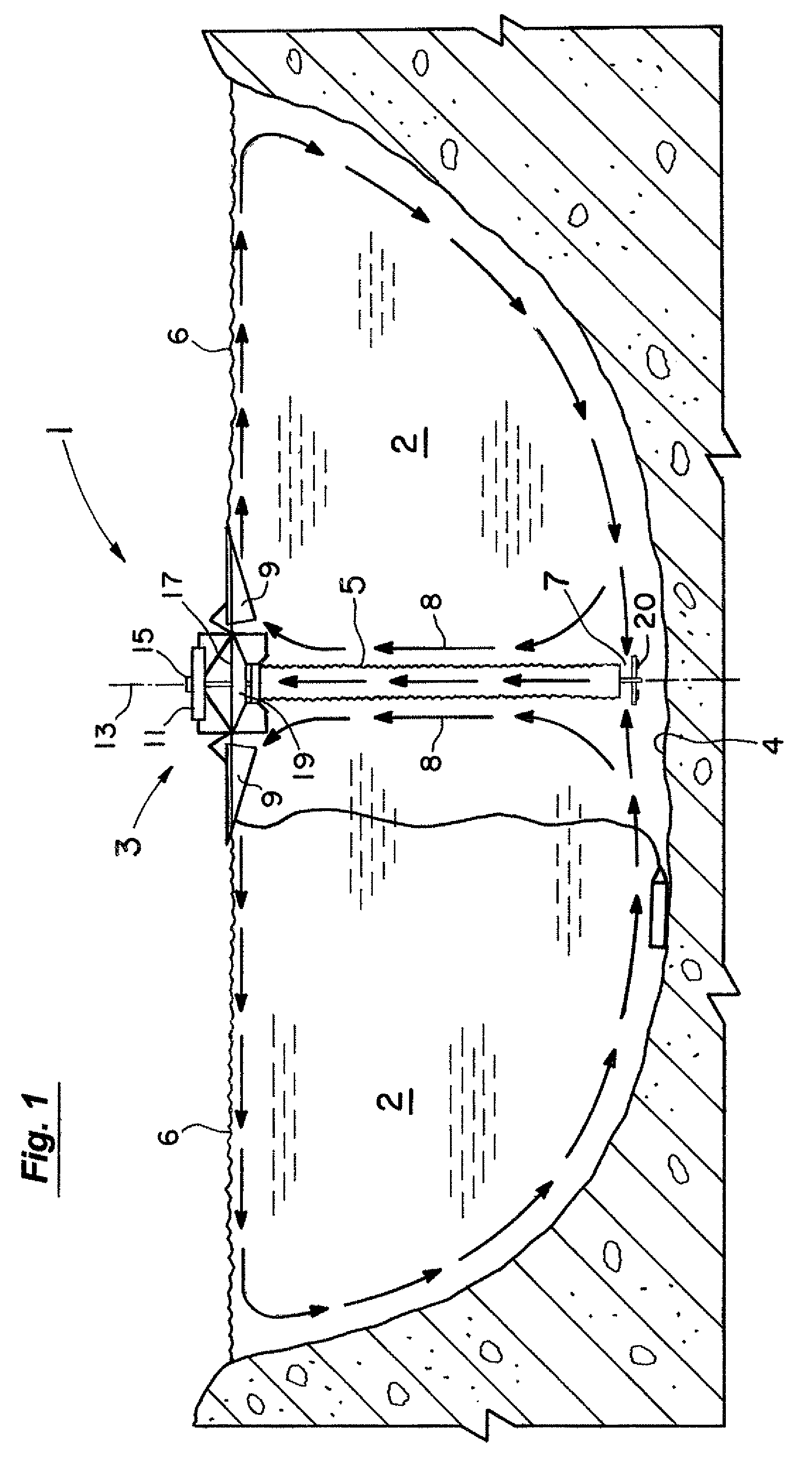
Water circulation systems for ponds, lakes, municipal tanks, and other bodies of water
ActiveUS7517460B2Damage to flotationDamage to partsTreatment using aerobic processesFlow mixersAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaWater cycling
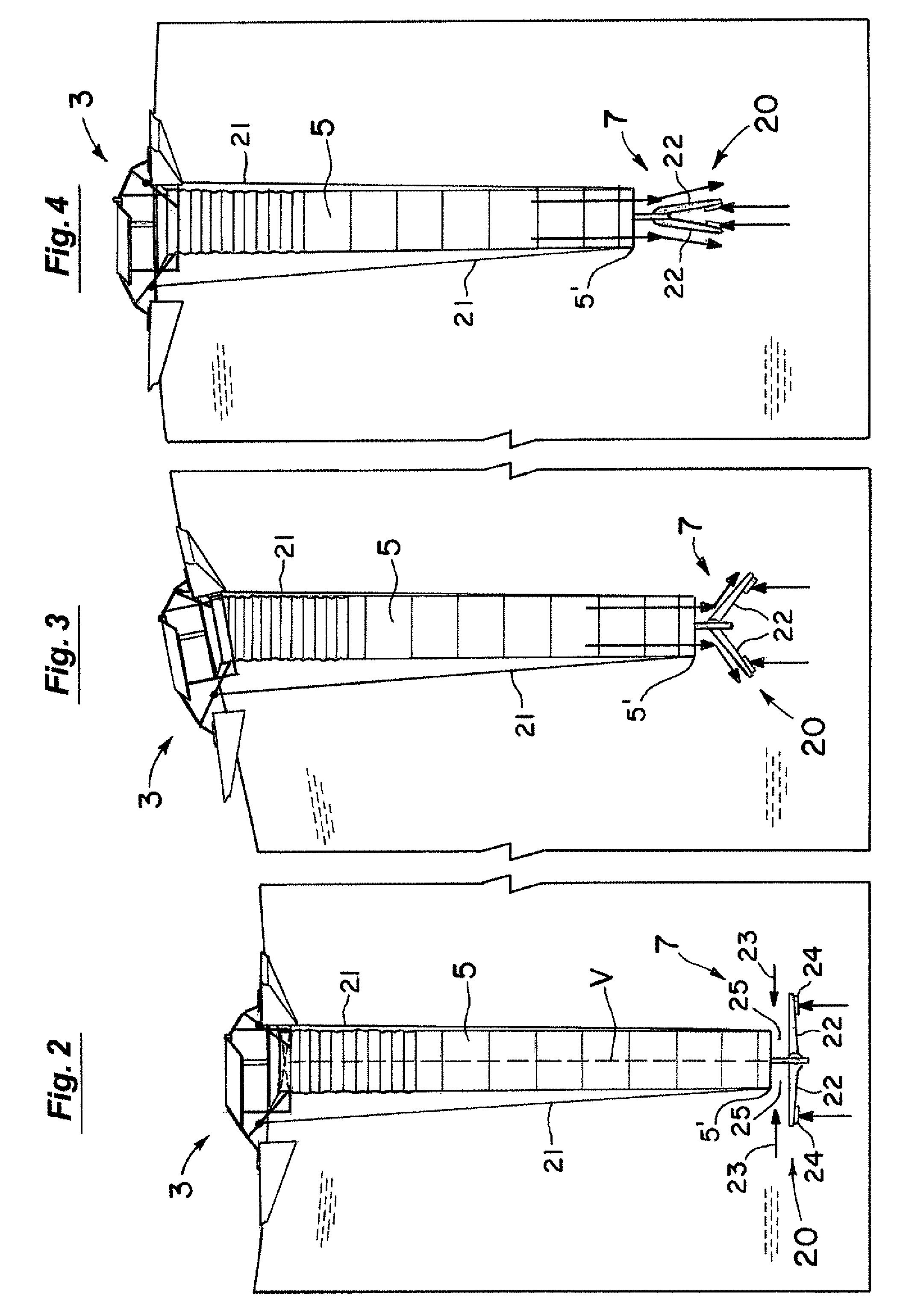
A circulation system for bodies of water. In one set of embodiments for larger bodies of water, modified horizontal plate designs are provided at the entrance of the draft hose. The plate designs have sections that pivot downwardly as the flotation platform and depending draft hose are rapidly raised in high wave conditions to let the water escape downwardly out of the hose. Adaptations to the floats for the elongated arms of the platform are also made to essentially eliminate the creation of any damaging torques on them from high waves. Another set of embodiments are particularly adapted for smaller systems in municipal water tanks for thorough mixing of the water and treatment to kill undesirable ammonia oxidizing bacteria and prevent or at least inhibit their return.
Owner:IXOM OPERATIONS
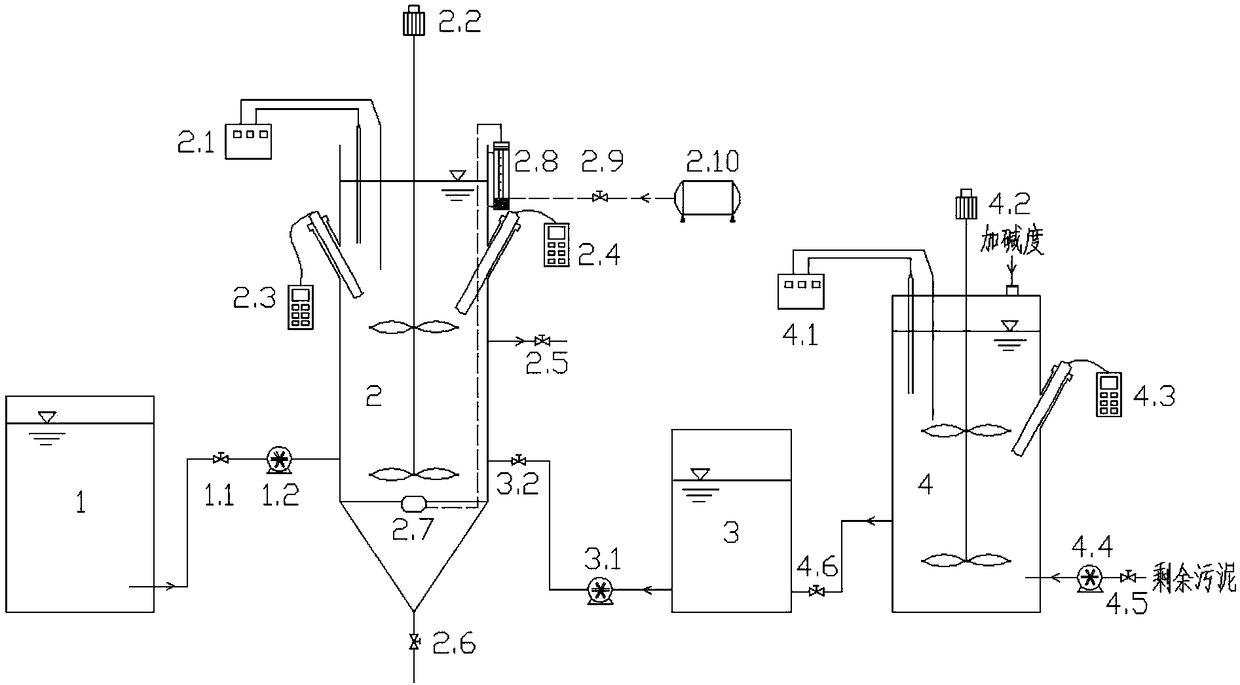
Method for achieving partial short-cut nitrification-Anammox/denitrification of sewage by using sludge fermentation materials
ActiveCN108439595ARealize deep denitrificationAchieve reductionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaNitrogen gas
The invention provides a method for achieving partial short-cut nitrification-Anammox / denitrification of sewage by using sludge fermentation materials, and belongs to the field of treatment of sewagesludge. A device used by the method comprises a raw water tank, an SBR reactor, a sludge fermentation material storage tank and a residual sludge fermentation tank. The method comprises mixing residual sludge fermentation materials with domestic sewage for treating, and achieving the short-cut nitrification by using the sludge fermentation materials, wherein the inhibition of the sludge fermentation materials on nitrite oxidizing bacteria is far greater than the inhibition of the sludge fermentation materials on ammonia oxidizing bacteria. The method is specifically characterized in that in ananaerobic phase, polyphosphate accumulating bacteria are used for releasing phosphorus by using the sludge fermentation materials and carbon sources in raw water, and storing the inner carbon sources, in an aerobic phase, the partial short-cut nitrification is achieved through real-time control on DO and pH, in an anoxic phase, anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria are used for converting ammonianitrogen and nitrite nitrogen into nitrogen and nitric nitrogen, and heterotrophic bacteria are used for reducing residual nitrite nitrogen and the generated nitric nitrogen into nitrogen by using theinner carbon sources. Through the method, the aeration intensity is reduced; meanwhile, the deep denitrification of the domestic sewage with a low C / N ratio and the reduction of exogenous sludge areachieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for enriching and culturing anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria by using membrane bioreactor
InactiveCN102061281AGuaranteed uptimeRapid enrichmentBacteriaTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention discloses a method for enriching and culturing anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria by using a membrane bioreactor, relating to a method for enriching and culturing anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria and solving the problems of long enriching time and low enriching efficiency of the anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria in the traditional anaerobic ammonia oxidation process. The method for enriching and culturing the anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria by using the membrane bioreactor as an enriching reactor comprises the steps of: inoculating activated sludge of a sewage plant in the membrane bioreactor; and 2, enriching and culturing after inoculating. Compared with the traditional enriching method, the method for enriching and culturing the anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria by using the membrane bioreactor realizes rapid enrichment of the anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria, ensures that the enriching efficiency of the anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria is improved by 80-95 percent, and can be widely applied to the biological denitrification technical field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
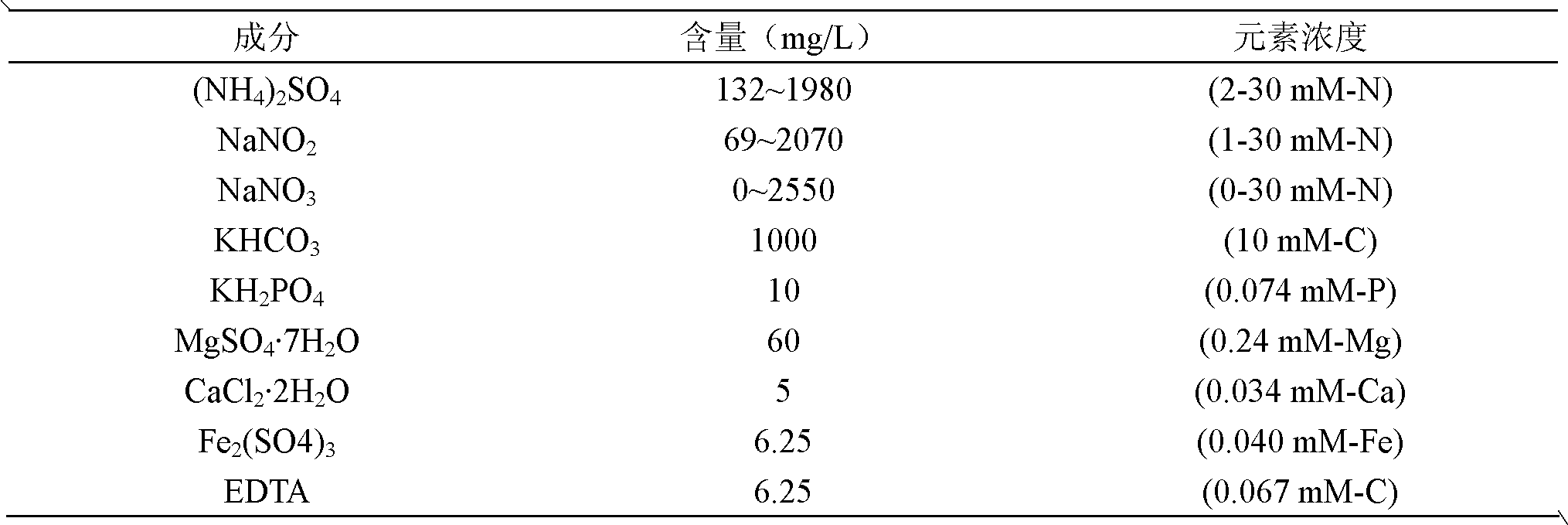
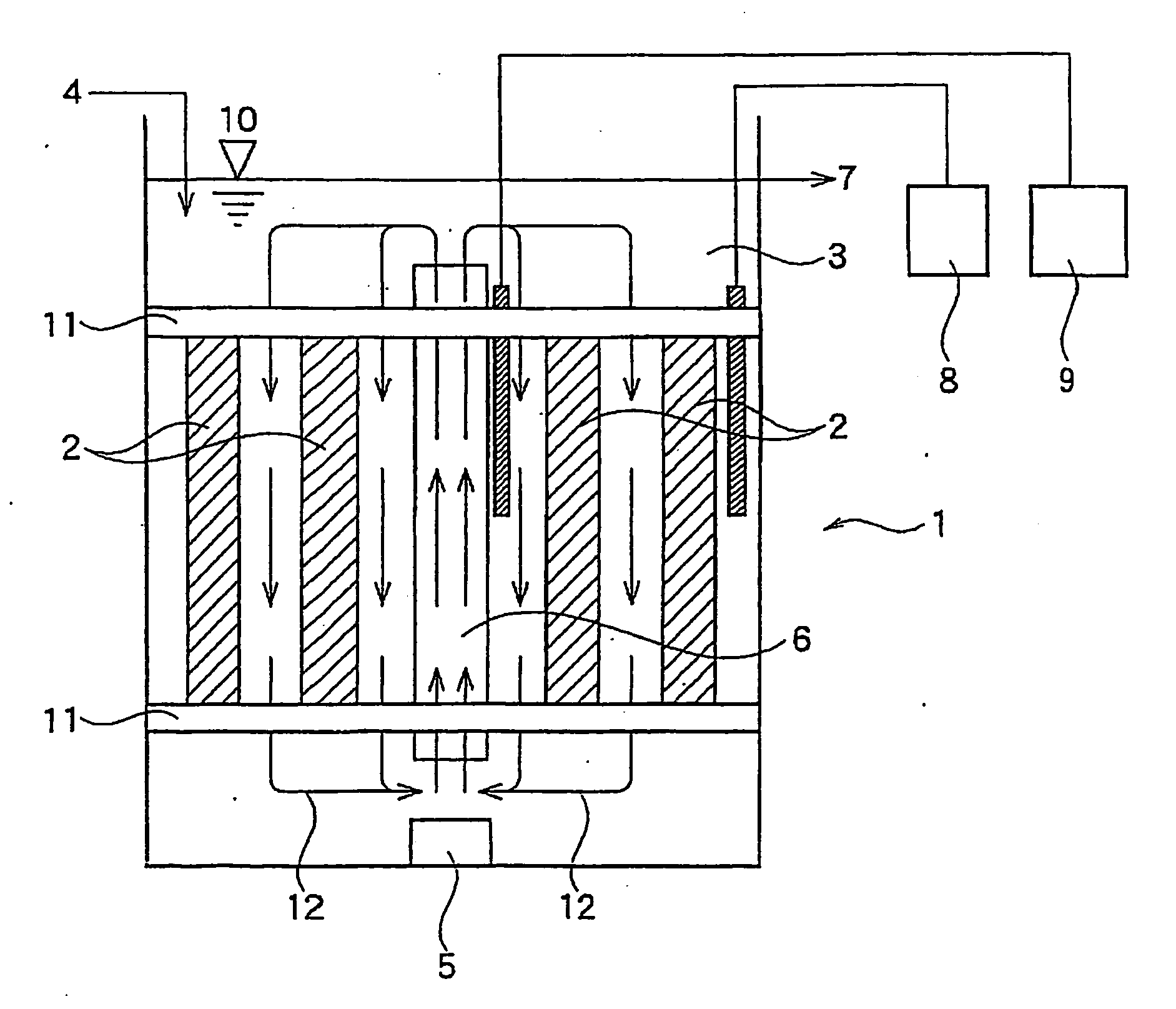
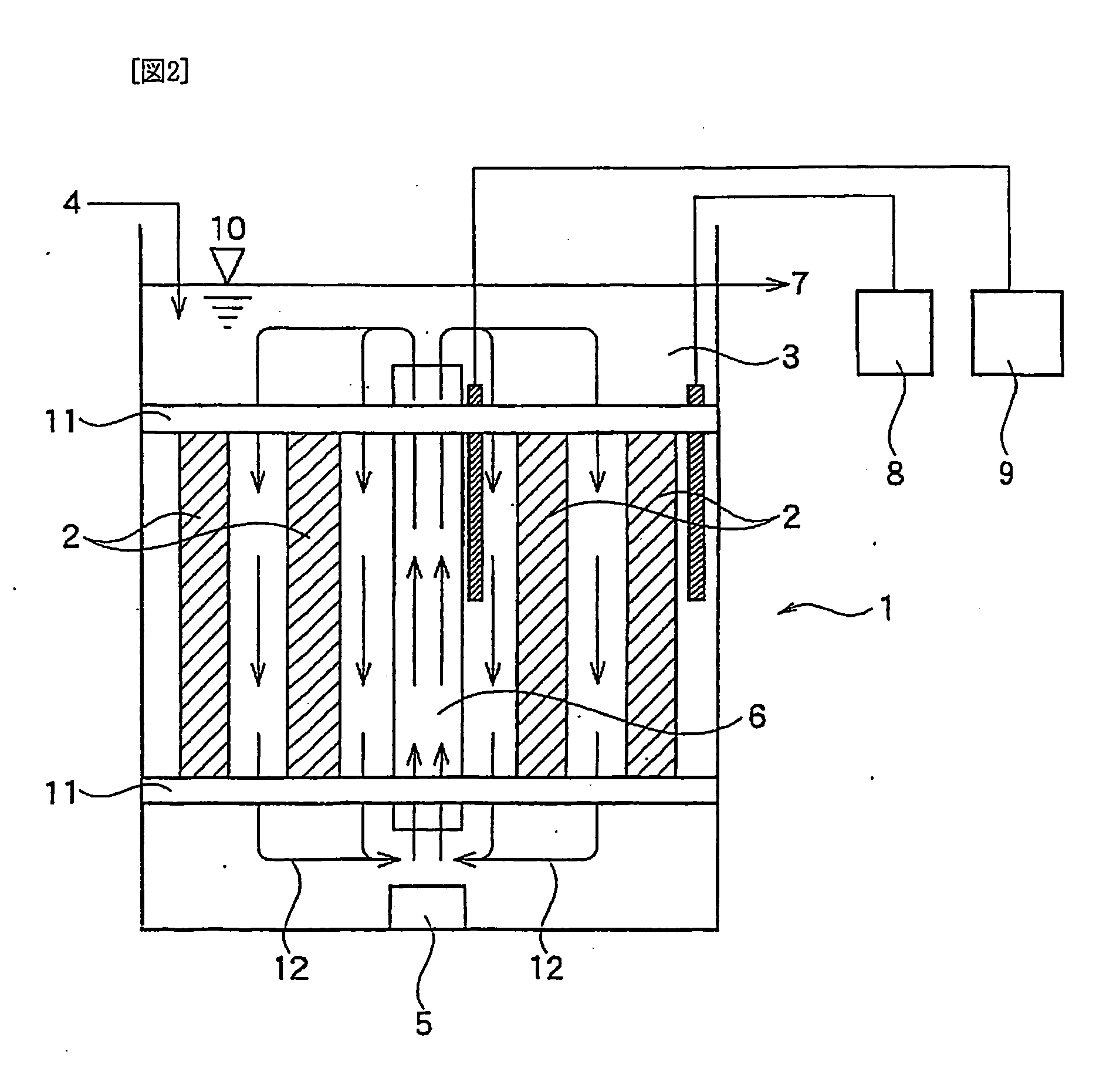
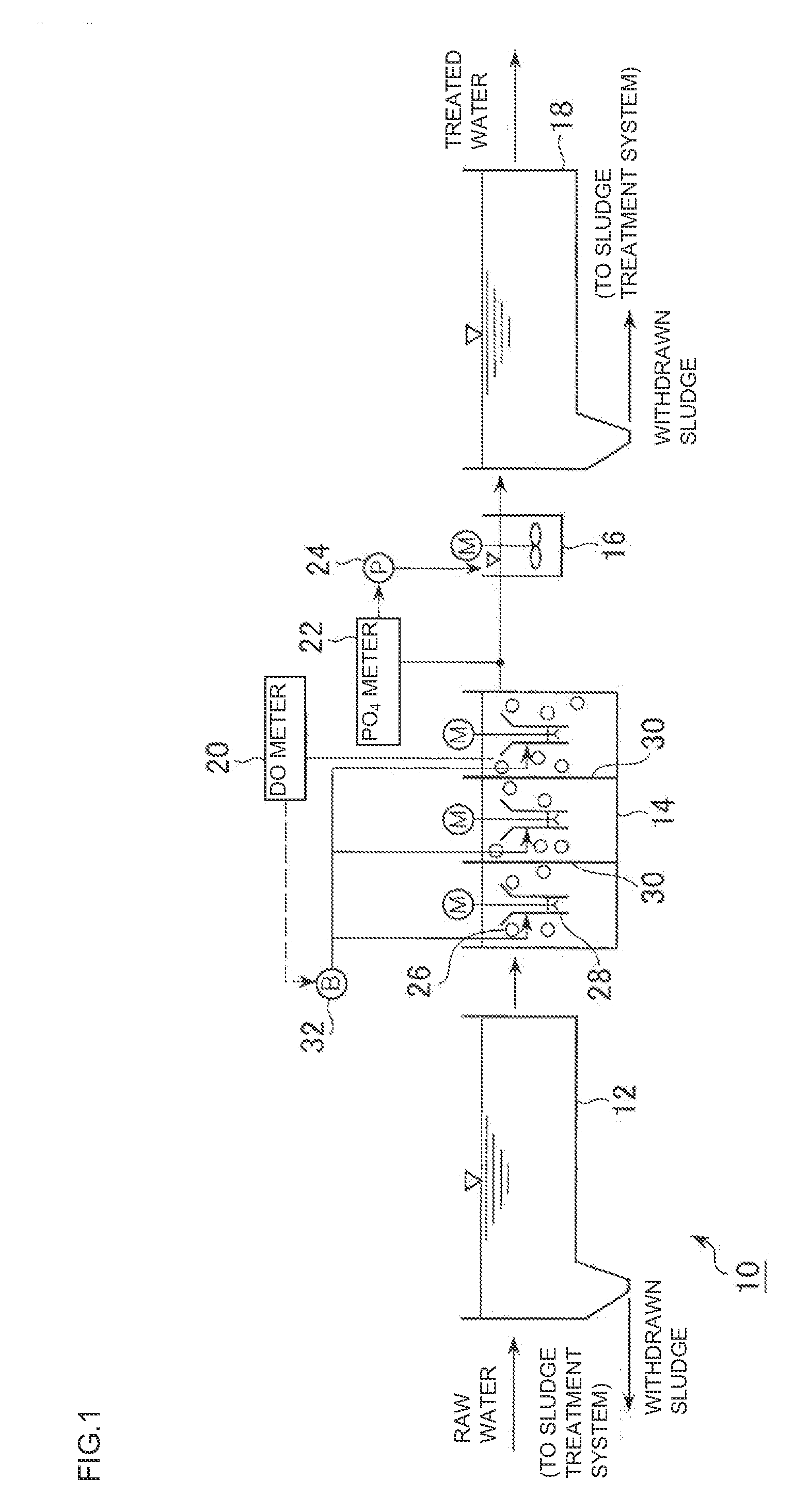
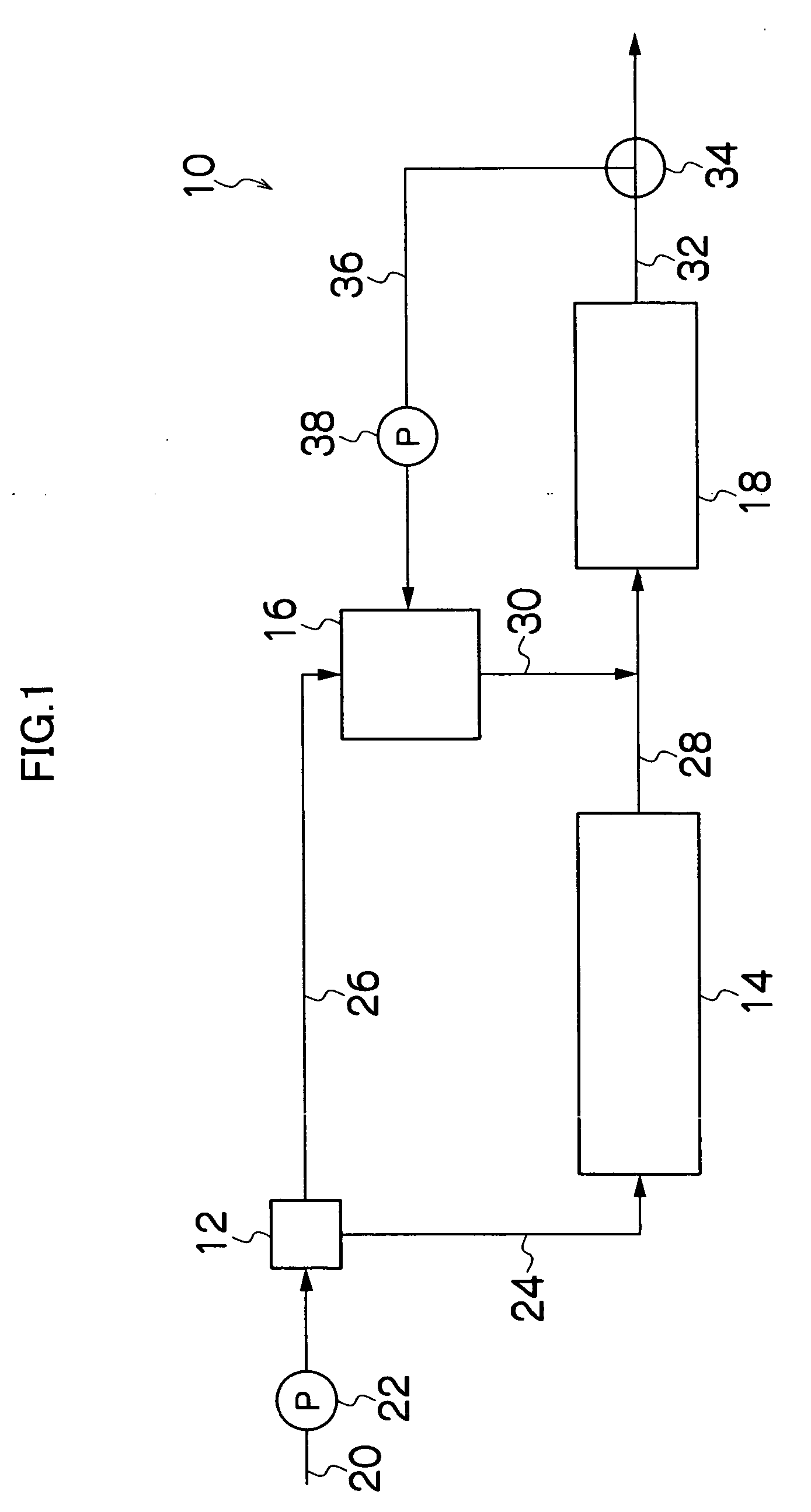
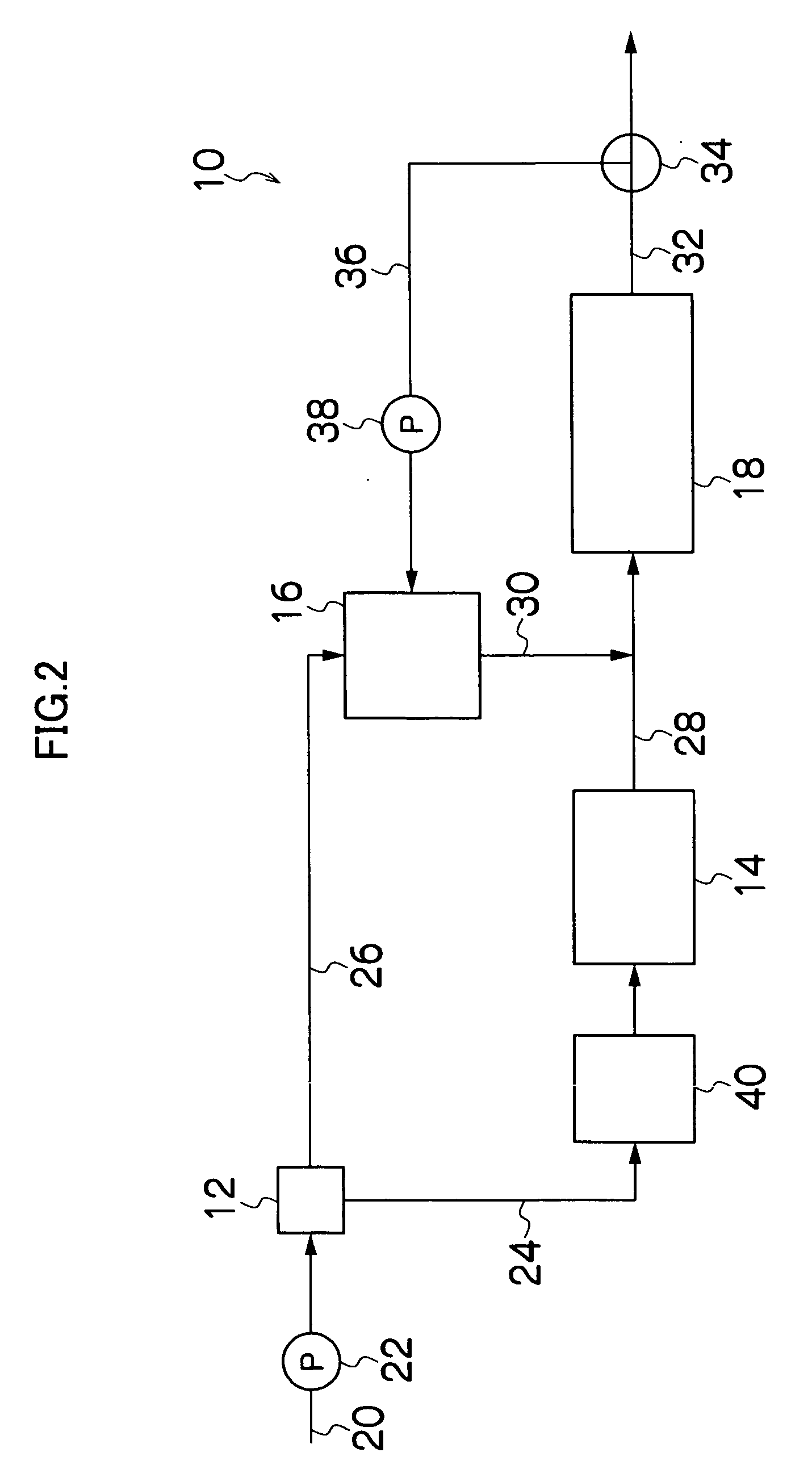
Method For Treating Ammonia-Containing Wastewater
A process for treating ammonia containing wastewater includes bringing an ammonia-treating material and ammonia containing wastewater into contact with each other to remove ammonia in the wastewater continuously as nitrogen gas, the ammonia-treating material including a long carrier and complex bacterial sludge attached and immobilized on the biomass carrier, the carrier including a net, a nonwoven fabric or a woven fabric of fibers or filaments, the carrier being attached to a support, the complex bacterial sludge containing bacterial sludge including autotrophic anammox bacteria and bacterial sludge including autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, the ammonia containing wastewater containing dissolved oxygen at a concentration of not less than 0.5 mg / l. The process for treating ammonia containing wastewater uses the treating material in which the bacterial sludge are attached and immobilized, and nitritation and anammox reaction can take place efficiently and economically even when the wastewater contains dissolved oxygen at a high concentration.
Owner:KUMAMOTO TECH & IND FOUND
Device and method capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from sewage in low C/N ratio by coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification
ActiveCN105923772AHigh degree of enrichmentAerobic phosphorus uptakeWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaLow oxygen
The invention discloses a device and a method capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from sewage in a low C / N ratio by coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. After entering an SBR coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification, sewage is first subjected to anaerobic stirring, and GAOs (glycogen-accumulating organisms) and PAOs (phosphorus-accumulating organisms) absorb organic carbon sources from the sewage and synthesize an internal carbon source PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) to be stored in bodies; then the sewage is subjected to low-oxygen aeration stirring, AOB (ammonia oxidizing bacteria) play a role in shortcut nitrification to convert ammonia nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen, and the PAOs decompose the PHA for aerobic phosphorus accumulation so as to create a hypoxic microenvironment beneficial to that the GAOs and the PAOs use the nitrite nitrogen produced during shortcut nitrification for endogenous denitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal respectively. The method coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and endogenous denitrification is capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from the sewage in the low C / N ratio without addition of a carbon source, so that oxygen consumption and energy consumption are reduced and urban sewage treatment costs are saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
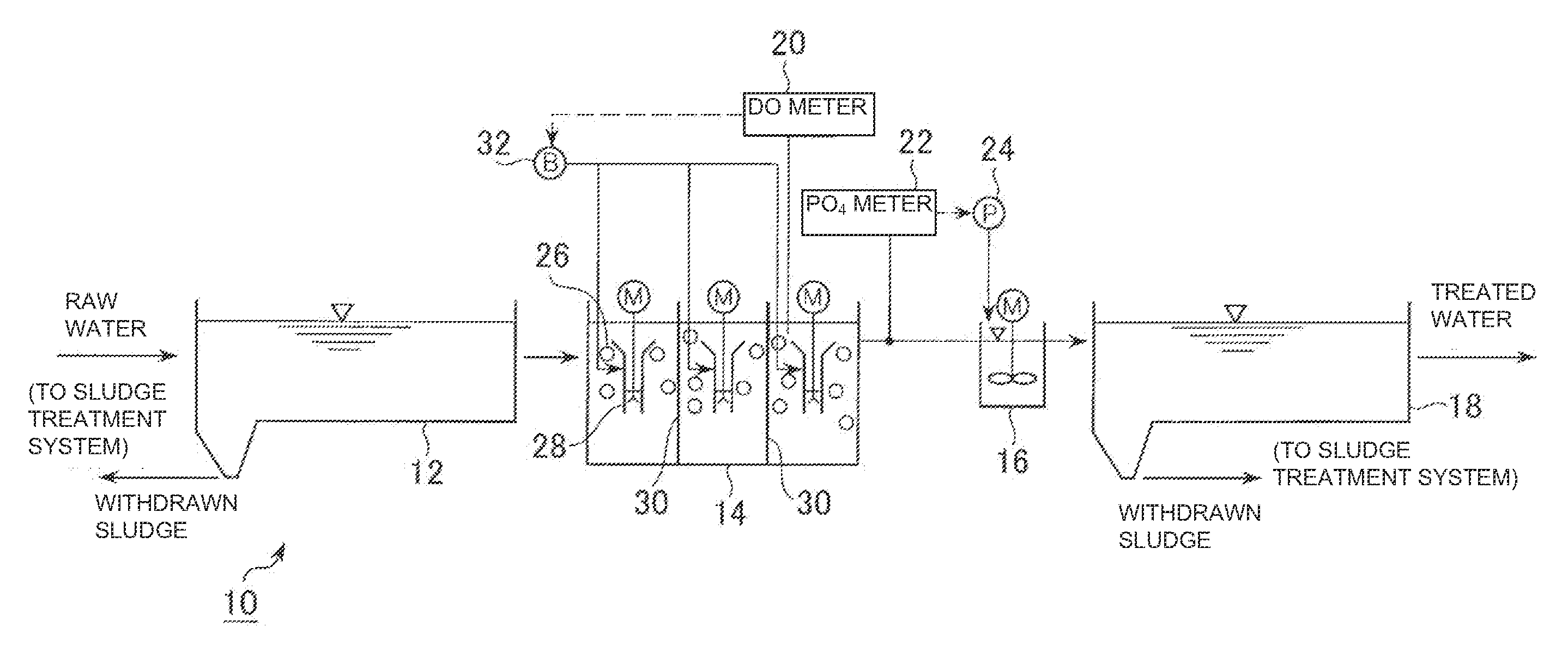
Method and apparatus for nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment
ActiveUS20140069863A1Easy to controlSemi-permeable membranesWater treatment parameter controlNitrogen removalAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
A reactor and control method thereof for nitrogen removal in wastewater treatment achieves a measured control of maintaining high ammonia oxidizing bacteria (AOB) oxidation rates while achieving nitrite oxidizing bacteria (NOB) repression, using various control strategies, including: 1) ammonia and the use of ammonia setpoints, 2) operational DO and the proper use of DO setpoints, 3) bioaugmentation of a lighter flocculant AOB fraction, and 4) proper implementation of transient anoxia within a wide range of reactor configurations and operating conditions.
Owner:D C WATER & SEWER AUTHORITY +1
Integrative bioreactor for treating refuse leachate
InactiveCN1769211ANo need to addImprove nitrogen removal efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectron donorAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention relates to an integral bioreactor for garbage percolating liquid treatment, belonging to environment protection art. The bioreactor comprises of two biological reaction zones and an adjustment zone, and each biological reaction zone is filled with biological filler to make up aerobic and anaerobic zone. In the aerobic zone, the organics is degraded by aerobic heterotrophic bacteria to organic carbon and controls the ammonia nitrogen nitration in hitrosation stage, 50% ammonia nitrogen is oxygenated to nitrite, and the water outlet in the aerobic zone is mixed uniformly in the adjustment zone with PH modifier and then flows into the anaerobic zone. In the anaerobic zone, anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria reduces nitrite with ammonia nitrogen as electron donor and oxygenizes ammonia nitrogen with nitrite as electron acceptor, ammonia nitrogen and nitrous nitrogen transit into nitrogen, some organics is absorbed or degraded by other anaerobic microorganism. It can clear ammonia nitrogen and organics in the water quality of low carbon-nitrogen ratio of garbage percolating liquid, and adjust the water quality of garbage percolating liquid and the impact load of water, and the operation is effective and stable.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for removing the contamination of c,n utilizing heterotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
ActiveUS20100314311A1Reduce unnecessary power consumptionEasy to useWater treatment compoundsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNitrogen removalAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
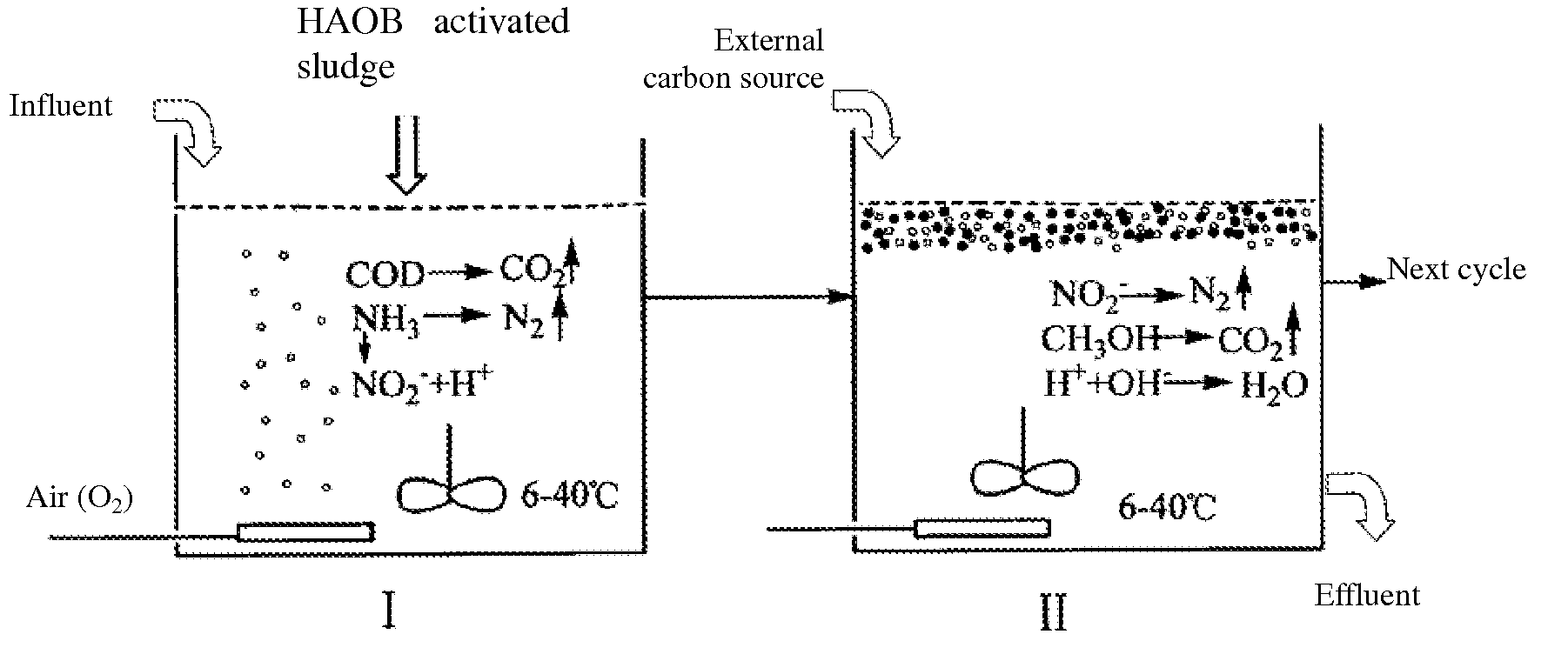
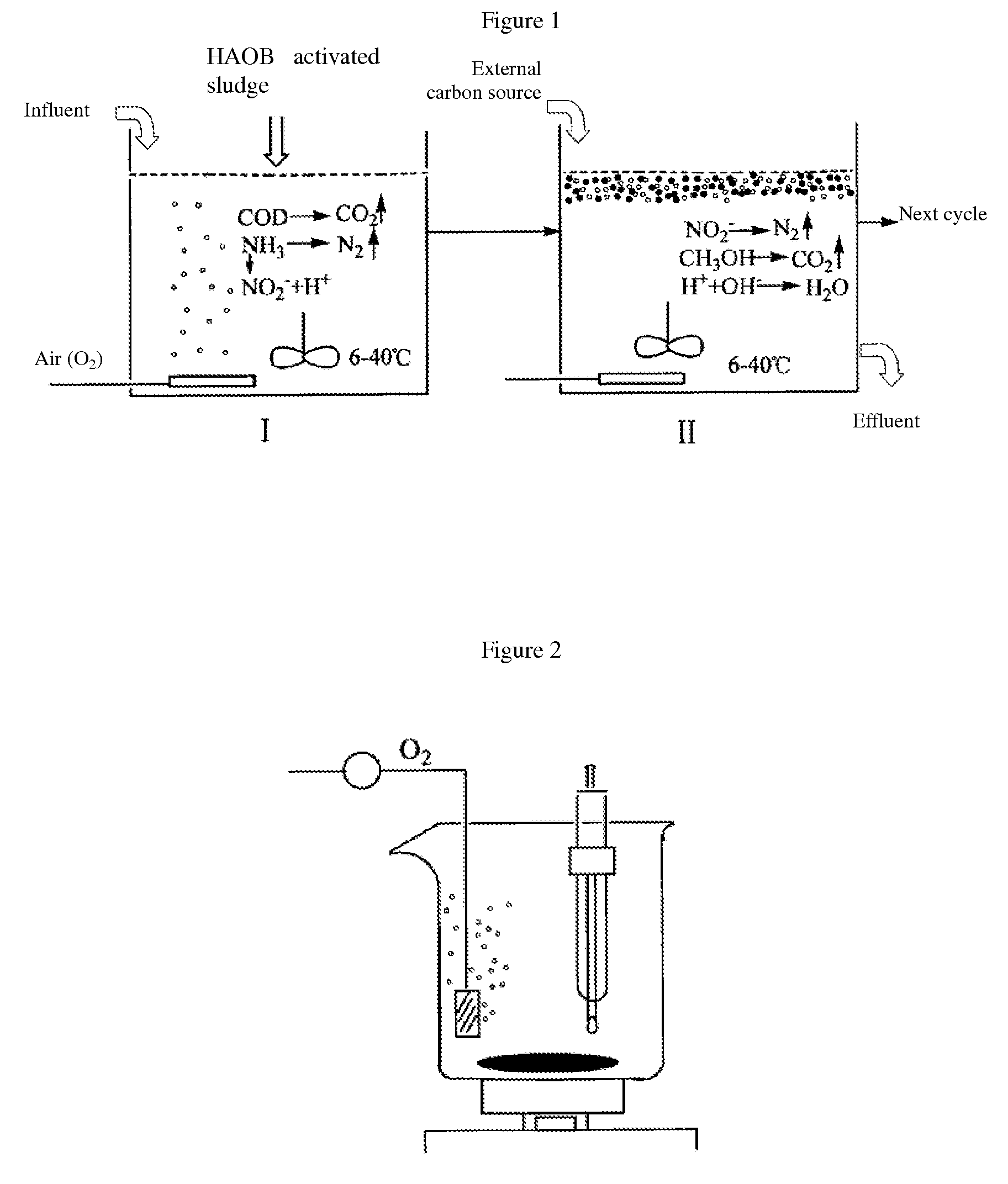
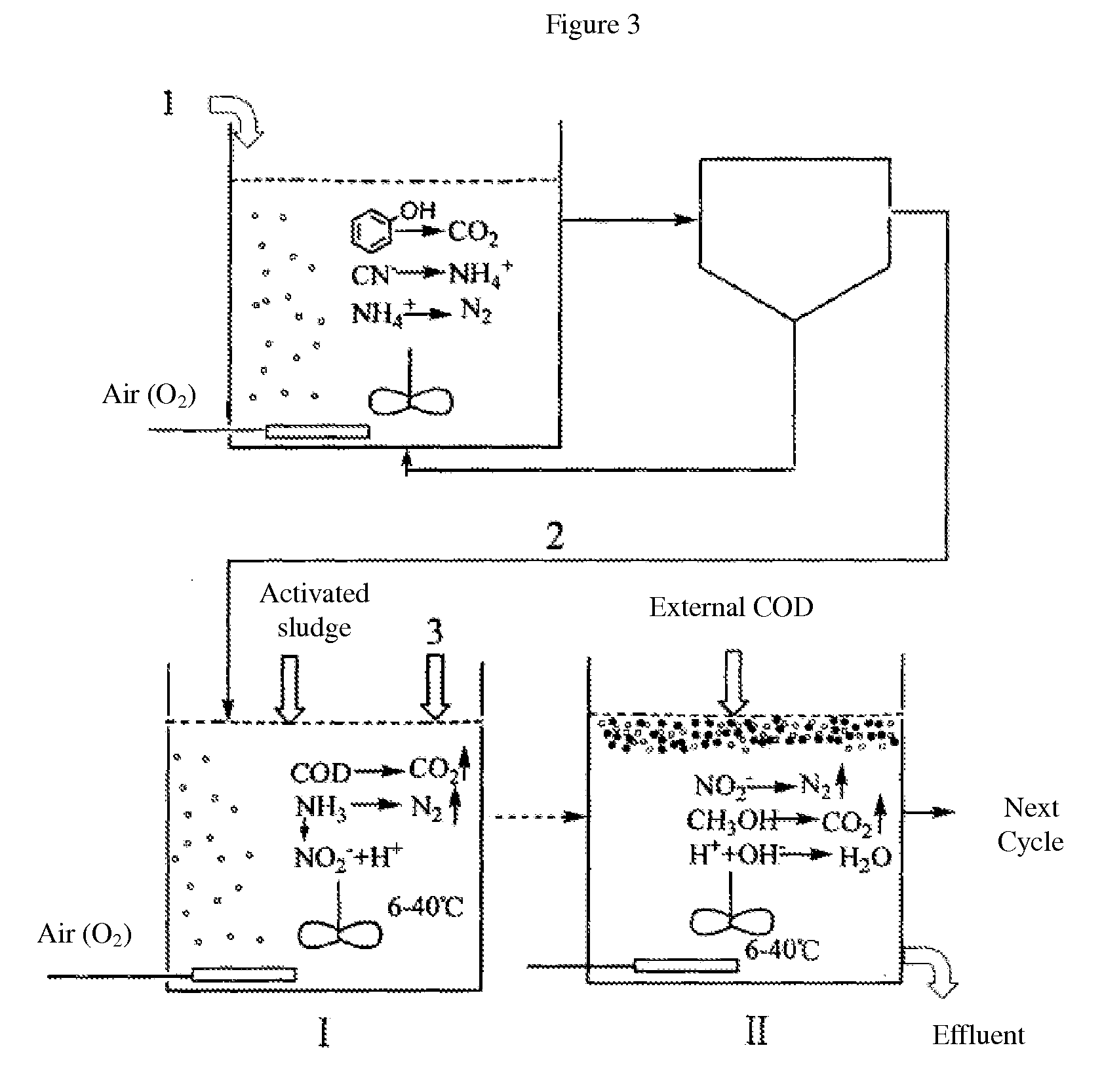
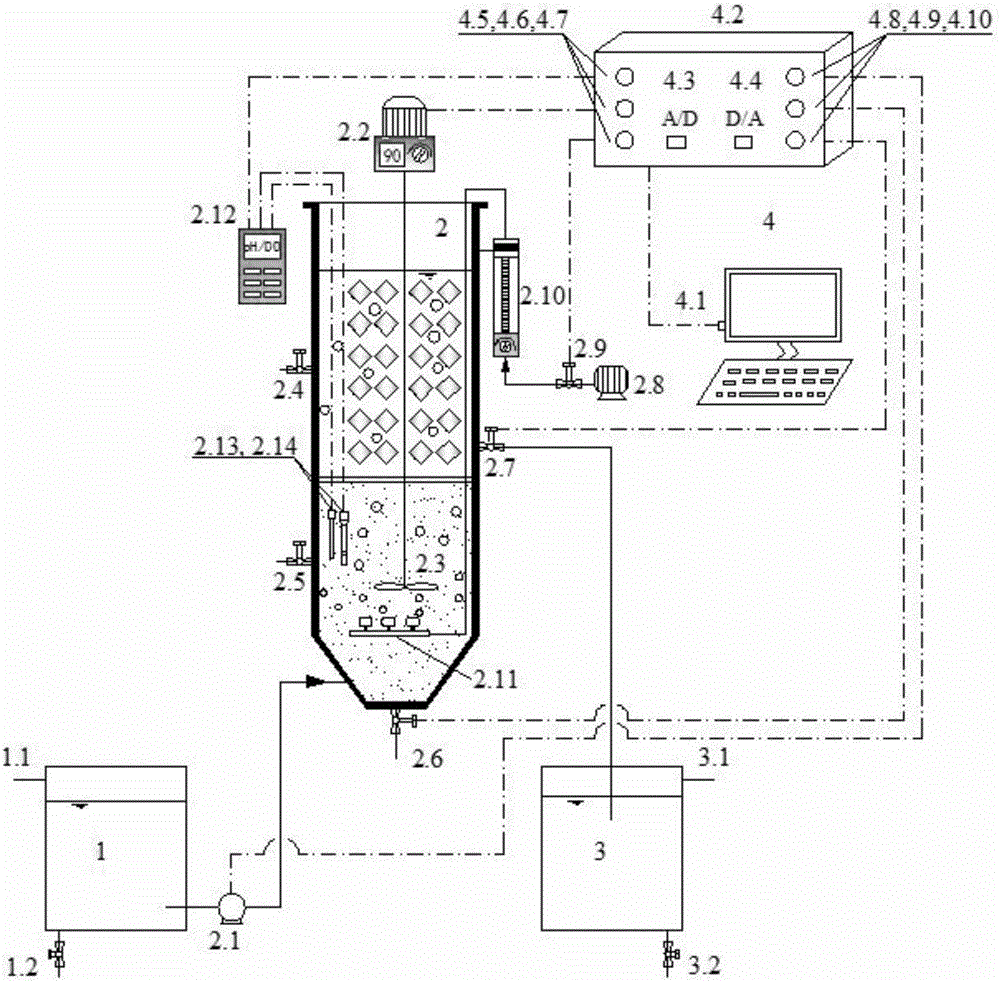
This invention relates to a method that uses heterothrophic ammonia oxidation bacteria (HAOB) to remove carbon and nitrogen pollutants in wastewater. The method includes the cultivation of the heterotropic bacteria in an activated sludge environment and the removal of carbon and nitrogen from the wastewater. According to the physiological characteristics of HAOB and the principles of combined oxidation of carbon and nitrogen, the method is able to achieve simultaneous removal of carbon and nitrogen under the condition that the cells do not grow. The process is able to be carried out in the temperature range of 6-40° C. No excess sludge is produced in the process. The invention is able to control the process and product composition of anaerobic ammonia oxidation through the control of organic carbon source, and is able to realize zero-accumulation of NO3−N in the nitrification process. The invention can fully utilize existing activated sludge systems to remove carbon and nitrogen. Therefore there is no need to build new facilities, and all carbon and nitrogen removal processes can be finished in a single reactor.
Owner:PENG GUANGHAO
Device and method for treating low-carbon domestic sewage through single-stage SBBR short-range synchronous nitration, denitration and dephosphorization coupled anaerobic ammonia oxidation
ActiveCN105776538ACarbon savingSave energyWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSingle stageAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
The invention relates to a device and method for treating low-carbon domestic sewage through single-stage SBBR short-range synchronous nitration, denitration and dephosphorization coupled anaerobic ammonia oxidation and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. The domestic sewage enters a short-range synchronous nitration, denitration and dephosphorization coupled anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor through a water feed pump. In the short-range synchronous nitration, denitration and dephosphorization coupled anaerobic ammonia oxidation reactor, phosphorus accumulating bacteria achieve anaerobic phosphorus release by making full use of an organic carbon source in raw water; part of NH4<+>-N in the raw water is converted into NO2<->-N by ammonia oxidizing bacteria, one part of the NO2<->-N and the NH4<+>-N remaining in the raw water are subjected to an anaerobic ammonia oxidation action so as to achieve autotrophic denitrification, and the other part of NO2<->-N and a small amount of NO3<->-N resulting from the anaerobic ammonia oxidation action are utilized by denitration phosphorus accumulating bacteria so as to achieve synchronous deep denitrification and dephosphorization. According to the method, short-range nitration, anaerobic ammonia oxidation and denitration dephosphorization are applied to the biological treatment on the domestic sewage in a coupled manner, so that the synchronous deep denitrification and dephosphorization of the domestic sewage can be achieved on the basis of saving energy and making full use of the carbon source.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
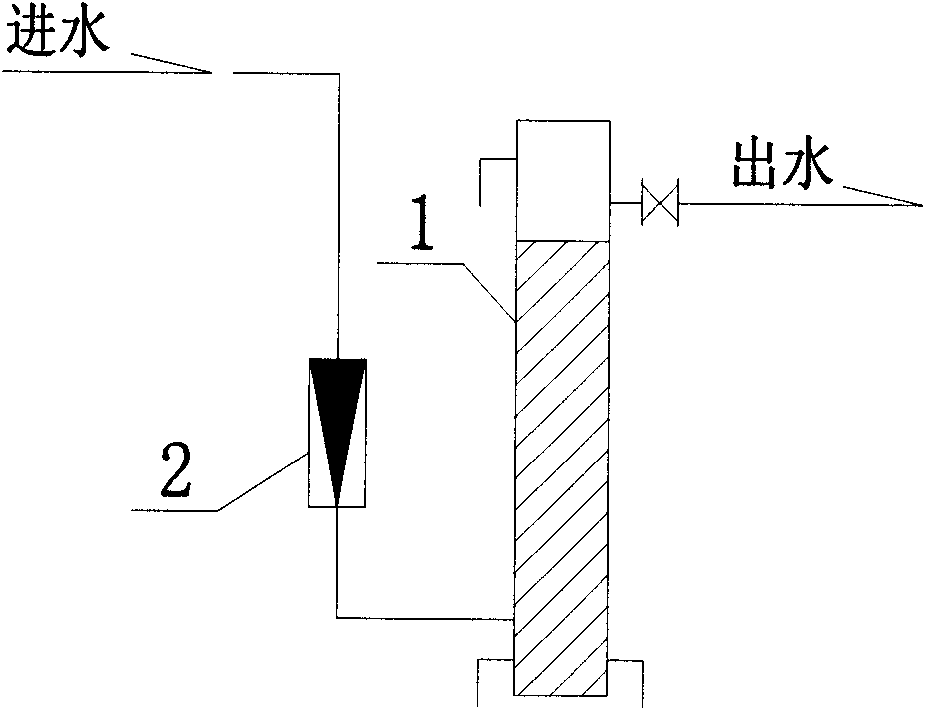
Two-segment aerobic-anaerobic ammonia oxidization reactor
InactiveCN102557353AEvenly distributedIncrease contactTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentLoad resistanceGrating
The invention discloses a two-segment aerobic-anaerobic ammonia oxidization reactor. The reactor comprises an anaerobic segment water distribution disc, anaerobic segment biological filler grating plates, an anaerobic segment biological filler, an aerobic segment water distribution disc, an aerobic segment biological filler, and aerobic segment biological filler grating plates. The reactor is characterized in that the reactor which is cylindrical in shape has an upper segment and lower segment integration structure, the upper segment is the aerobic segment, the lower segment is the anaerobic segment, the anaerobic segment water distribution disc is arranged in the bottom of the anaerobic segment, the anaerobic segment biological filler grating plates are symmetrically arranged in the middle part of the anaerobic segment, the anaerobic segment biological filler is arranged among the anaerobic segment biological filler grating plates, the aerobic segment water distribution disc is arranged between the anaerobic segment and the aerobic segment, the aerobic segment biological filler grating plates are symmetrically arranged in the middle part of the aerobic segment, and the aerobic segment biological filler is arranged among the aerobic segment biological filler grating plates. The reactor which allows the rapid screening of ammonia oxidizing bacteria by a biological system to be guaranteed has the advantages of benefiting of the high efficiency interception of the ammonia oxidizing bacteria, removal efficiency improvement, mass transfer effect improvement, water dilution, andimpact load resistance improvement, and is suitable for high ammonia nitrogen and low C / N ratio wastewater processing.
Owner:马文臣
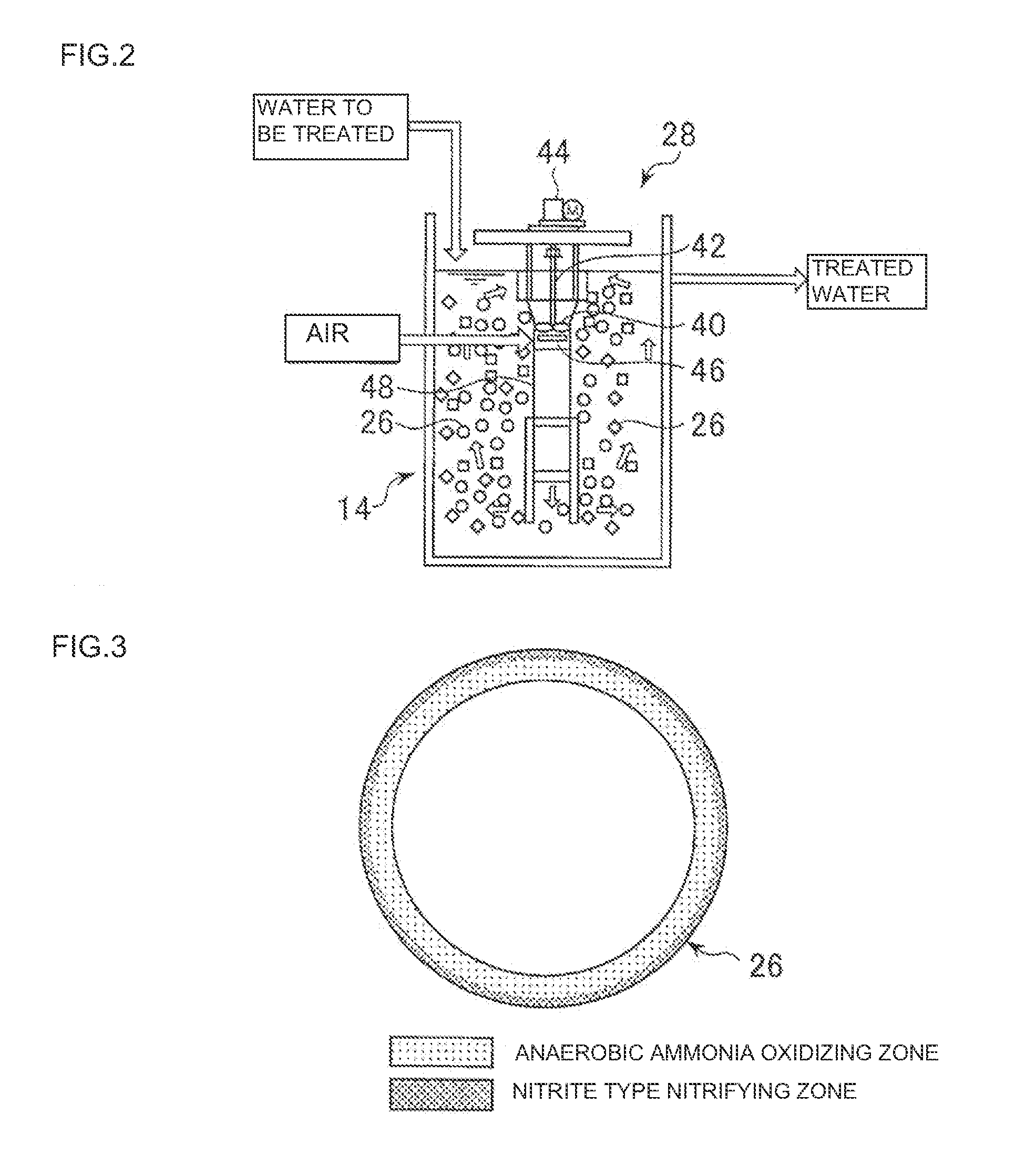
Method and device for removing biological nitrogen and support therefor
ActiveUS20110253625A1Secure denitrification efficiencyWater treatment parameter controlBacteriaNitrogen removalAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
Provided is a biological nitrogen removal method which includes, causing to flow a support having, on the surface portion thereof, a two-layered microbial film which holes, in the outer layer, nitrite type nitrifying bacteria or aerobic bacteria and nitrite type nitrifying bacteria as a dominant species and, in the inner layer, anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria as a dominant species while being surrounded with the nitrite type nitrifying bacteria; and thereby carrying out denitrification of the water to be treated by making use of the anaerobic ammonia oxidation reaction. In the biological nitrogen removal method, a feed rate of the support (total surface area of the support per unit capacity of the reaction tank) is adjusted so that an amount of nitrous acid produced by the nitrite type nitrification reaction through the action of the nitrite type nitrifying bacteria reaches a level to inhibit a nitrate type nitrification reaction.
Owner:METAWATER CO LTD
Novel Anammox Bacterium Isolate
ActiveUS20110180476A1Ammonia reductionReduce ammonia levelsBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesMicrobacterium
Disclosed is an isolated bacterial strain Candidatus Brocadia caroliniensis strain, having Accession Deposit Number NRRL B-50286. The strain is capable of oxidizing ammonium and releasing di-nitrogen gas.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Method for quickly starting short-cut nitrification and denitrification of ammonia-containing wastewater
ActiveCN105621611AGrow fastAdapt quicklyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeHydroxylamine
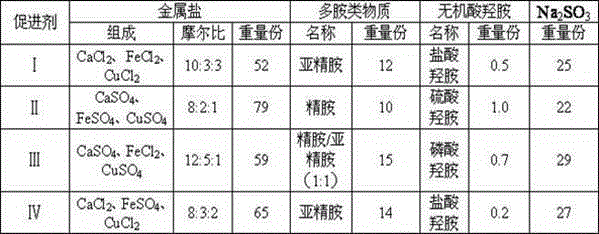
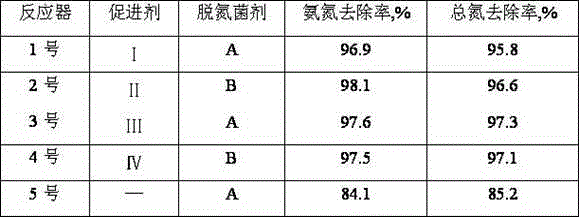
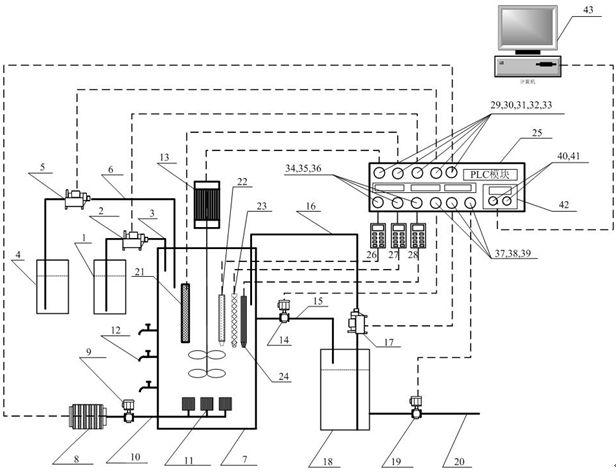
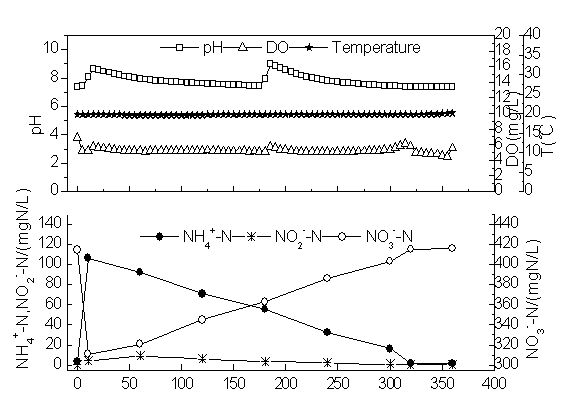
The invention discloses a method for quickly starting short-cut nitrification and denitrification of ammonia-containing wastewater. The method includes the steps: (1) putting denitrified activated sludge into a bioreactor; and (2) starting by a way of batch water feeding and gradual increase of the fed water ammonia-nitrogen concentration, and adding an ammonia oxidizing bacteria growth promoter, wherein the ammonia oxidizing bacteria growth accelerator includes 40 to 100 parts by weight of metal salts, 5 to 30 parts by weight of a polyamine substance, 0.05 to 1.5 parts by weight of inorganic acid hydroxylamine and 10 to 40 parts by weight of Na2SO3, the metal salts comprise a calcium salt, a ferrous salt and a copper salt, and the molar ratio of Ca<2+> to Fe<2+> to Cu<2+> is (5-15) to (1-8) to (0.5-5); and (3) when the fed water ammonia-nitrogen concentration reaches 400 to 700 mg / L, changing the mode into a mode of continuous water feeding, continuing to add the growth promoter, and when the ammonia-nitrogen removal rate is more than 90% and the nitrosation rate reaches 80%, starting to add a denitrification inoculum. The method can quickly start short-cut nitrification and denitrification process in a short time, and has the advantages of short starting time and high total nitrogen removal rate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method and device for quickly enriching ammonia oxidizing bacteria
ActiveCN102559489AGrowth inhibitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologySequencing batch reactor
The invention provides a method and a device for quickly enriching ammonia oxidizing bacteria. The ammonia oxidizing bacteria are enriched by a sequencing batch reactor, a method of gradually increasing ammonia nitrogen concentration in a culture solution and a pH process controlling method; and the adopted culture solution for enriching comprises the inorganic salt used as a main component, and a trace element culture solution, a buffer solution and ammonia carbonate; and the concentration of dissolved oxygen in the culture process is maintained more than 5mg / L by a process controlling device, pH is maintained 7.0 to 8.5, and temperature is maintained 20 to 25 DEG C. By the scheme, the growth of heterotrophic bacteria in activated sludge can be inhibited obviously, and the enriched ammonia oxidizing bacteria are 60 to 65 percent of the total number of microorganism bacteria in the activated sludge, and are tolerant to high ammonia nitrogen concentration; and finally high-ammonia-nitrogen wastewater of which the concentration can reach 500mg / L can be treated, and high-concentration ammonia nitrogen in the wastewater can be reduced to less than 1.0mg / L.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
An/O type composite artificial wetland system for enhanced treatment of low-C/N ratio wastewater
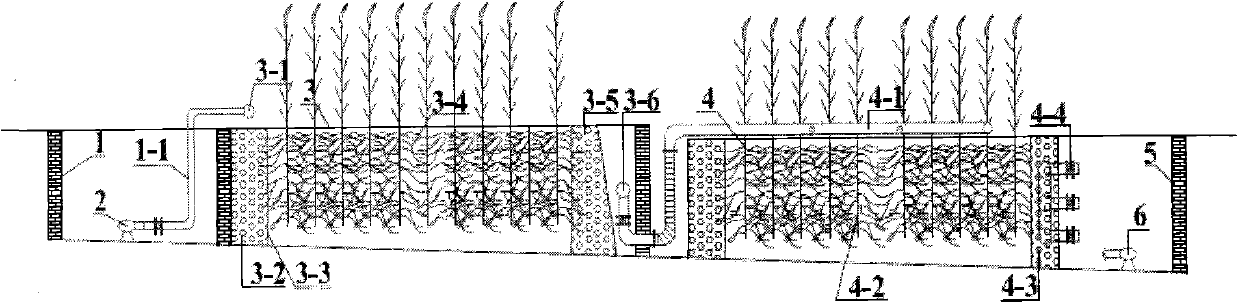
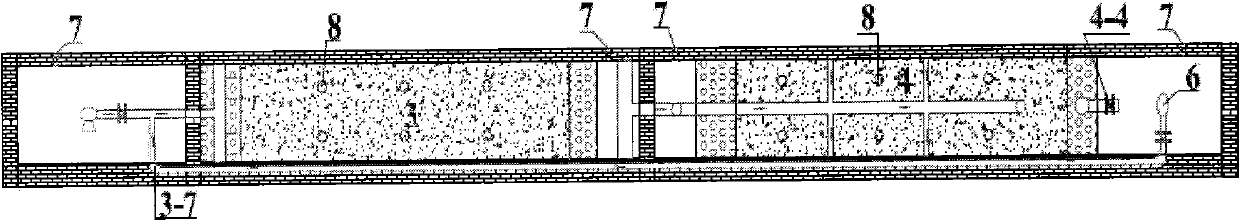
InactiveCN102557330AHigh removal rateReduce consumptionMultistage water/sewage treatmentPorosityConstructed wetland
The invention relates to an An / O type composite artificial wetland system for the enhanced treatment of low-C / N ratio wastewater. The invention relates to a wastewater treatment apparatus, which is a land treatment apparatus suitable for treating low-C / N ratio wastewater and recycling treated water. According to the An / O type composite artificial wetland system, wastewater sequentially flows through a horizontal subsurface flow wetland and a vertical subsurface flow wetland, effluent water part then flows back into the horizontal subsurface flow wetland, and a dissolved oxygen (DO) gradient is utilized to couple aerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) and anammox in the vertical subsurface flow wetland by means of effluent water level regulation in order to enhance the low-C / N ratio wastewater denitrification efficiency of the An / O type composite artificial wetland system. Broken bricks, oyster shells and other packing with large specific surface area, high porosity and good adsorbability are filled in the composite artificial wetland system, consequently, the amount of organisms held by the system is greatly increased, and high phosphorus-and-nitrogen-removing efficiency is guaranteed. The An / O type composite artificial wetland system has the advantages of simple structure, multiple functions, high efficiency, low cost and the like, is easy to operate and manage, can stably operate, and can synchronously remove carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, the treated effluent water can be directly recycled, landscape plants can be planted on the ground surface, and the An / O type composite artificial wetland system can be combined with ecological construction and city and town greening functions.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wastewater advanced denitrification apparatus and method employing single-stage SBBR (sequencing batch biofilm reactor) short-cut nitrification anammox coupled endogenous denitrification
ActiveCN106348439AAchieving synergistic couplingEfficient deep denitrification processWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsBiofilmNitrogen removal
A wastewater advanced denitrification apparatus and method employing single-stage SBBR (sequencing batch biofilm reactor) short-cut nitrification anammox coupling with endogenous denitrification belong to the field of wastewater bio-treatment. Wastewater enters a single-stage SBBR short-cut nitrification coupled endogenous denitrification reactor through a water pump; in anaerobic stirring phase, phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and glycogen accumulating organisms make use of an inorganic carbon source in raw water to store internal carbon sources; in hypoxic aeration stirring phase, ammonia oxidizing bacteria convert partial NH4<+>-N in the raw water into NO2<->-H, part of NO2<->-H is subjected to autotrophic nitrogen removal with the rest NH4<+>-N in the raw water via anammox effect, and the other part of NO2<->-H and little NO3<->-H produced in anammox are utilized by the phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and glycogen accumulating organisms in the subsequent anoxic stirring phase to provide endogenous denitrification. According to the method, by coupled application of short-cut nitrification, anammox and endogenous denitrification to wastewater bio-treatment, it is possible to provide wastewater advanced denitrification based on energy saving, and full utilization of carbon sources.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for treating low-temperature high-ammonia nitrogen wastewater by use of constant magnetic field
ActiveCN104909468APromote enrichmentHigh activitySustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentHydroxylamineReaction rate
The invention discloses a device and a method for treating low-temperature high-ammonia nitrogen wastewater by use of a constant magnetic field. The device mainly comprises a shortcut nitrification SBR reactor, magnetic field intensifying devices symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the reactor, an online shortcut nitrification monitoring system and a feedback control system. According to the device and the method, the magnetic biological effect is thoroughly utilized, and the active sites of proteins in the ammonia monooxygenase and the hydroxylamine oxidase of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria are affected by use of the magnetic field, and therefore, the activity of the enzymes is improved, the ammoxidation reaction rate is increased and the enrichment of the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria is promoted, and especially, the influence of the temperature to the activity of the enzyme can be compensated under a low temperature condition; besides, the speed of movement of charged particles is increased by use of the action of the magnetic field force, and furthermore, the mass transfer efficiency is improved, the defects of unstable operation of the reactor, low ammonia nitrogen degradation rate and the like in existing low-temperature wastewater treatment are made up, and meanwhile, efficient nitrosation is realized in the reactor under the low-temperature condition by controlling dissolved oxygen, pH, hydraulic retention time and sludge age; and as a result, the sewage retention time is shortened and the cost and the energy consumption are reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
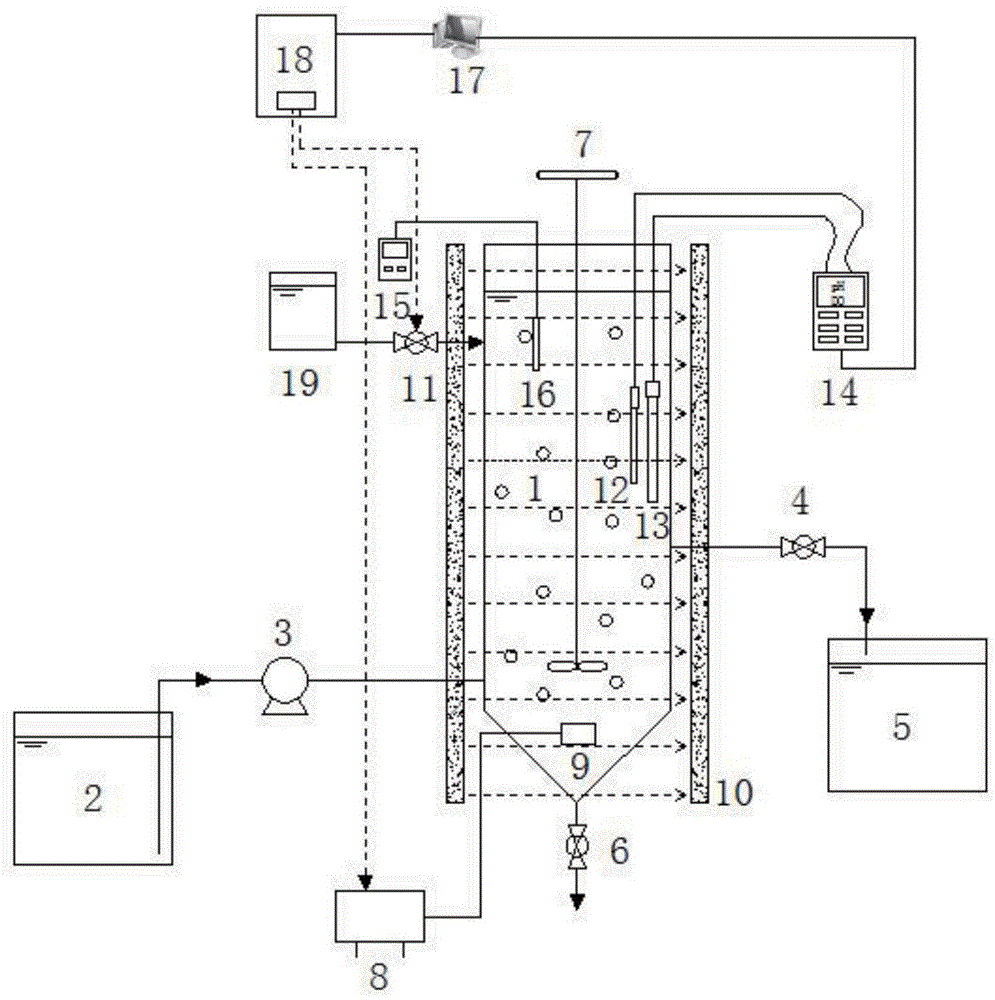
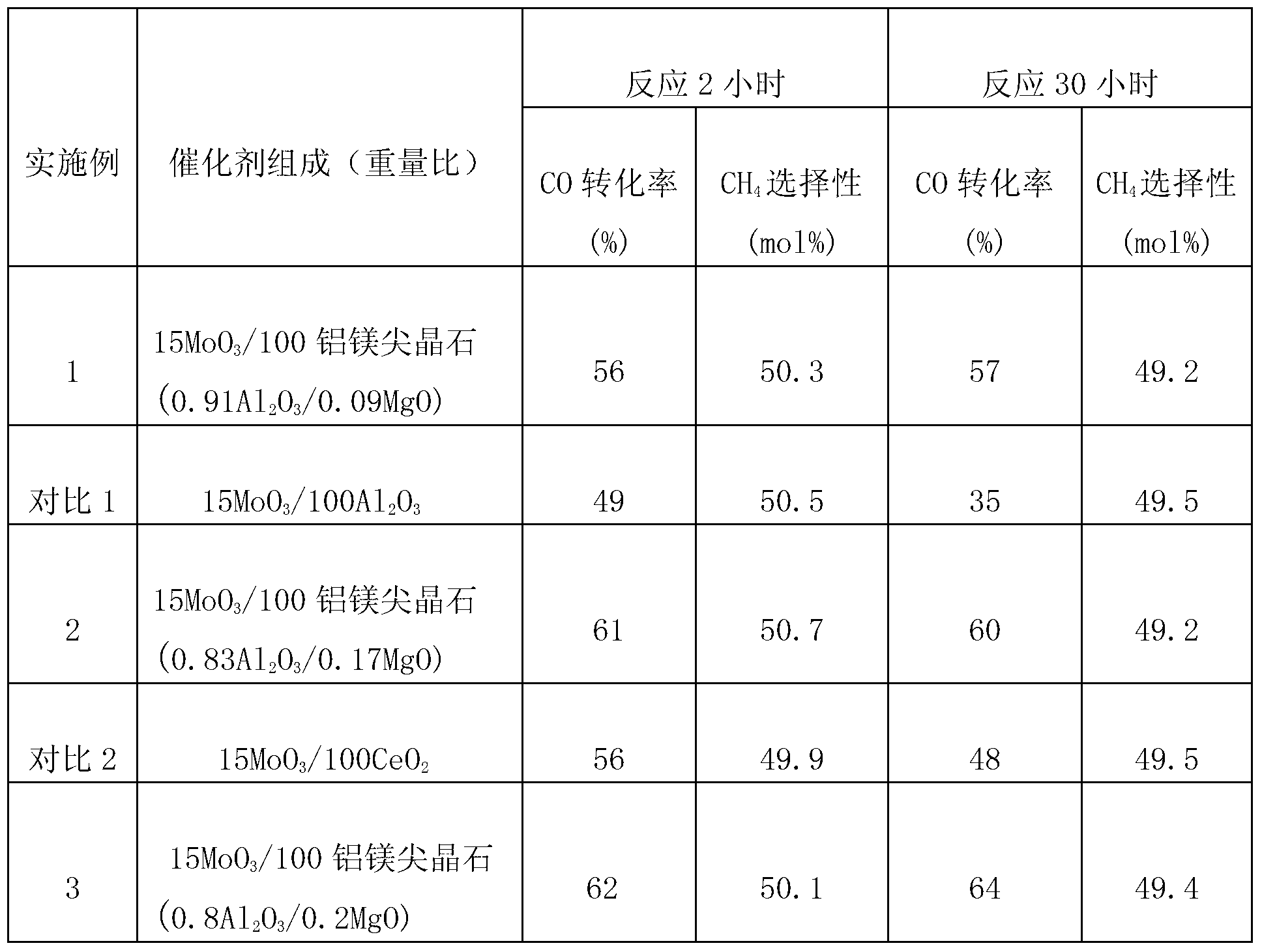
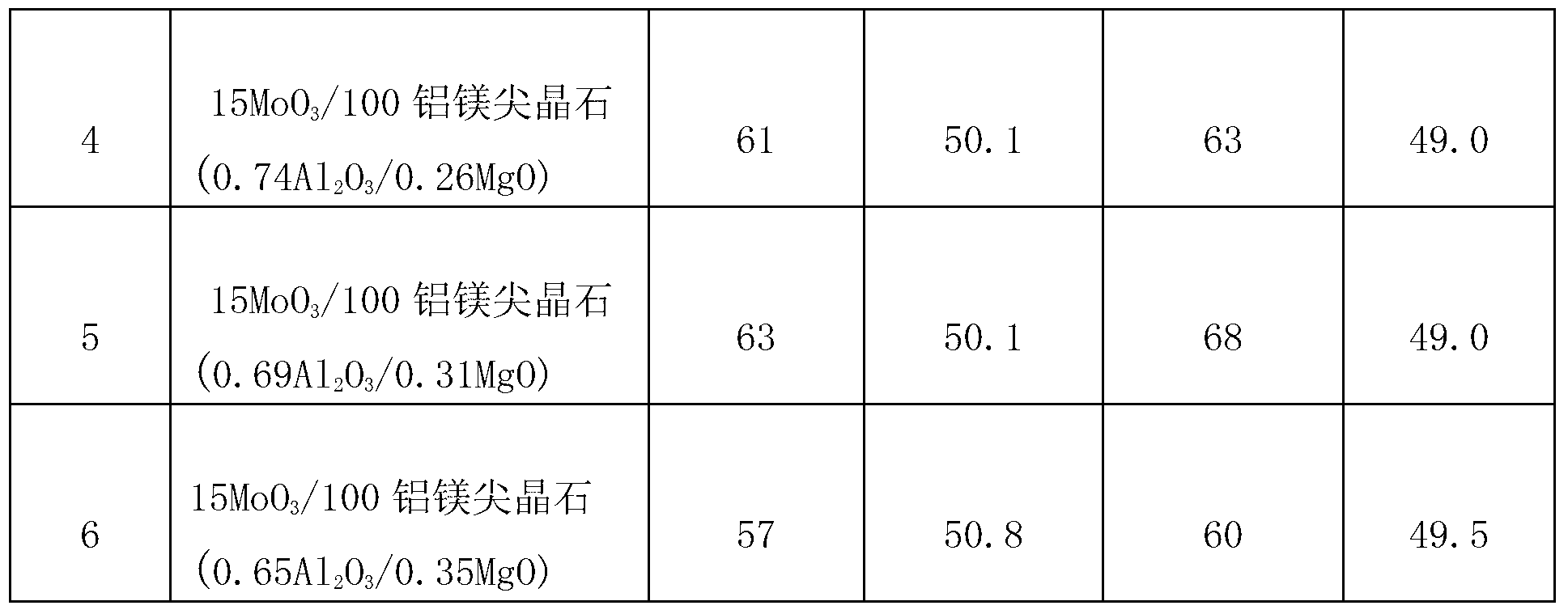
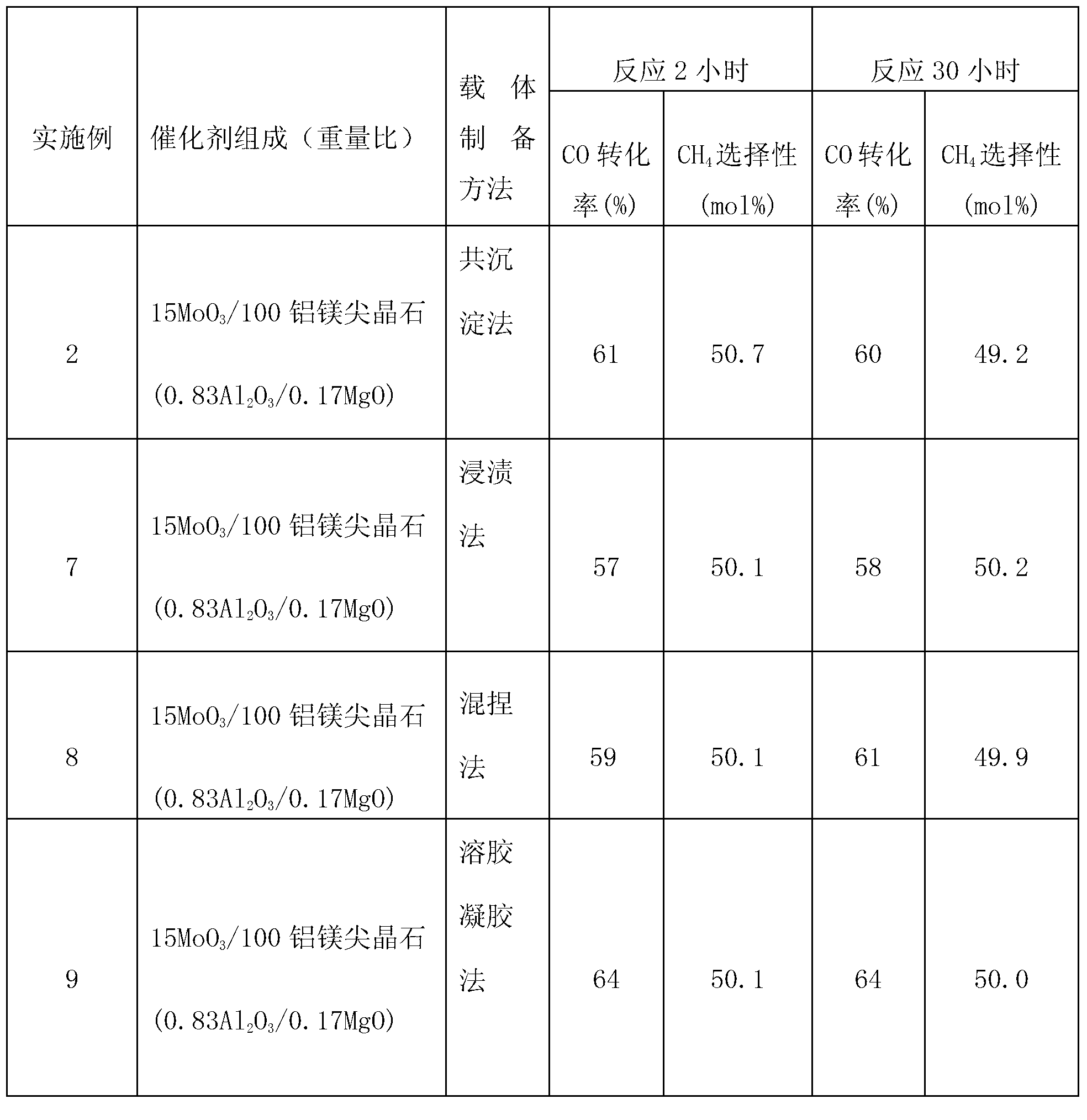
Magnesium aluminate spinel-supported sulphur-tolerant methanation catalyst
ActiveCN103191720AHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsChemical oxygen demandActive component
The invention discloses a magnesium aluminate spinel-supported sulphur-tolerant methanation catalyst. The magnesium aluminate spinel-supported sulphur-tolerant methanation catalyst comprises 0-20 parts (by weight) of catalyst auxiliary (M1) AOB (ammonia oxidizing bacteria), 5-90 parts (by weight) of catalyst active component (M2) COD (chemical oxygen demand), 5-90 parts (by weight) of support modifier (M3) EOF (electroosmotic flow), and 100 parts (by weight) of porous support-magnesium aluminate spinel, wherein M1 is Co, Ni, La and / or K; M2 is Mo, W and / or V; and M3 is Ce, Zr, Ti and / or Si.
Owner:CHNA ENERGY INVESTMENT CORP LTD +1
Method for enriching anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria from common activated sludge
InactiveCN103159325AShorten the timeHigh activityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeActivated carbon
The invention relates to the field of water treatment, and particularly relates to a method for enriching anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria by performing nitration treatment on common activated sludge. The method is characterized in that nitration treatment is performed on the common activated sludge, thus increasing the quantity of aerobiotic ammonium oxidation bacteria (AOB) in the sludge; some AOB are facultative anaerobes and capable of performing similar anaerobic ammonium oxidation in an oxygen-free condition; additionally, AOB generate hydroxylamine oxidoreductase which is beneficial to enrichment for the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria; and activated carbon is poured in an activity enhancement phase to improve the attachment environment for the anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, and the competitions of other bacteria and Anammox bacteria for the attachment environment of activated carbon can also be reduced. The invention provides a time-saving and efficient method for enriching anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for cultivating aerobic short-cut nitrification granular sludge for treating domestic sewage
ActiveCN101531983AGuaranteed uptimeCompact structureBacteriaSustainable biological treatmentHigh concentrationSludge
The invention relates to a method for cultivating aerobic short-cut nitrification granular sludge for treating domestic sewage, which is characterized in that an SBR reactor adopts ratio of height to diameter of 1.8-10 and volume exchange rate of 50-67%; the sedimentation time is 30-50min, which is gradually shortened to 3min, or the sedimentation time is set as 5-8min. In the process of biochemical reaction, dissolved oxygen (DO) and pH value are regarded as real-time control parameters; aeration time is controlled according to the fuzzy control rule; nitrification is controlled to stop on the short-cut nitrification stage. The method can increase the content of ammonia oxidizing bacteria and volume load, shorten nitration reaction time, improve the sedimentation property of the sludge by a wide margin, shorten sedimentation time, narrow the floor area of the reactor and solve the problems of low operating efficiency and unstable nitrosification caused by time program control of the sewage treatment system. The aerobic short-cut nitrification granular sludge prepared by the invention is suitable for treating high-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater with low COD and is a biological wastewater treatment technology with broad market prospect.
Owner:BEIJING DRAINAGE GRP CO LTD
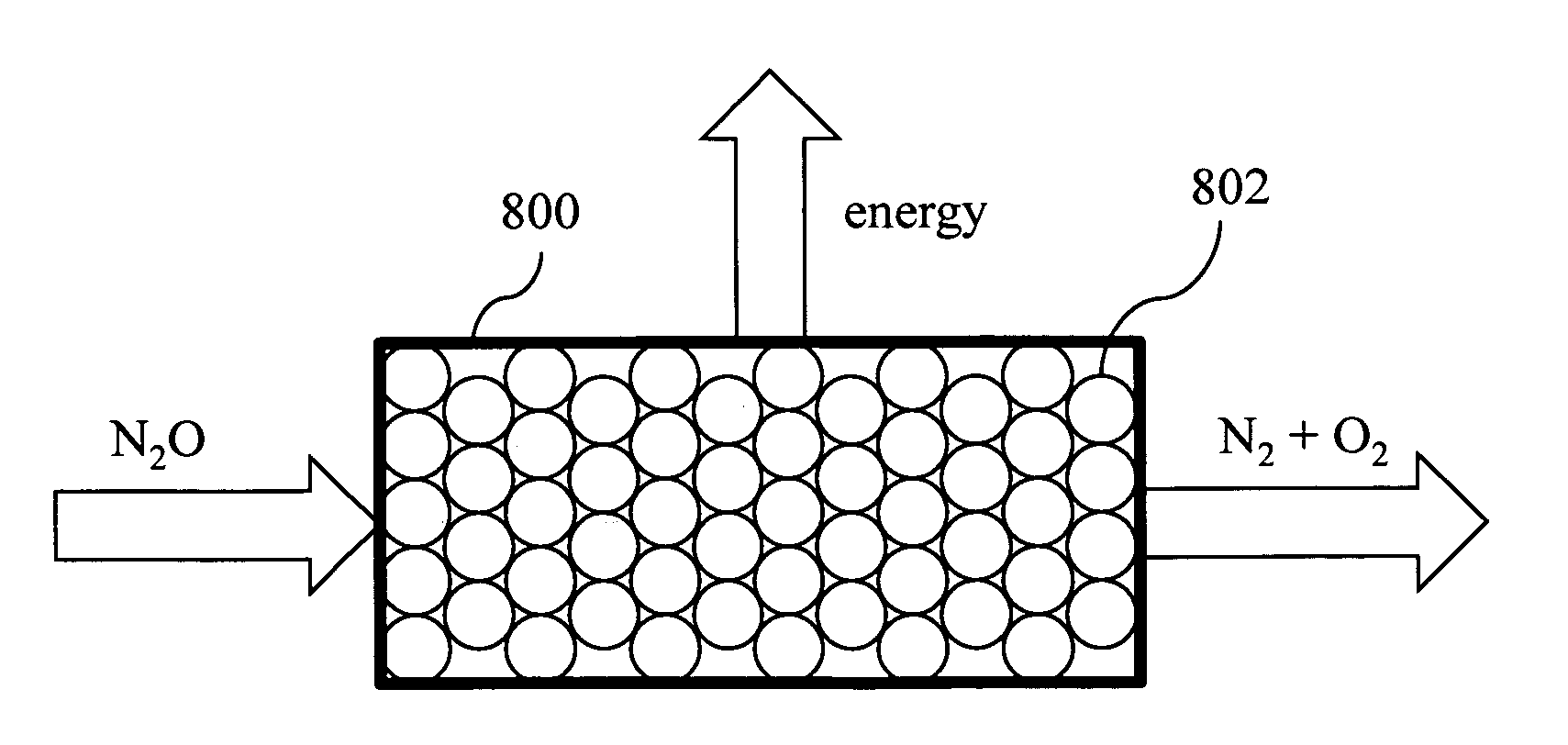
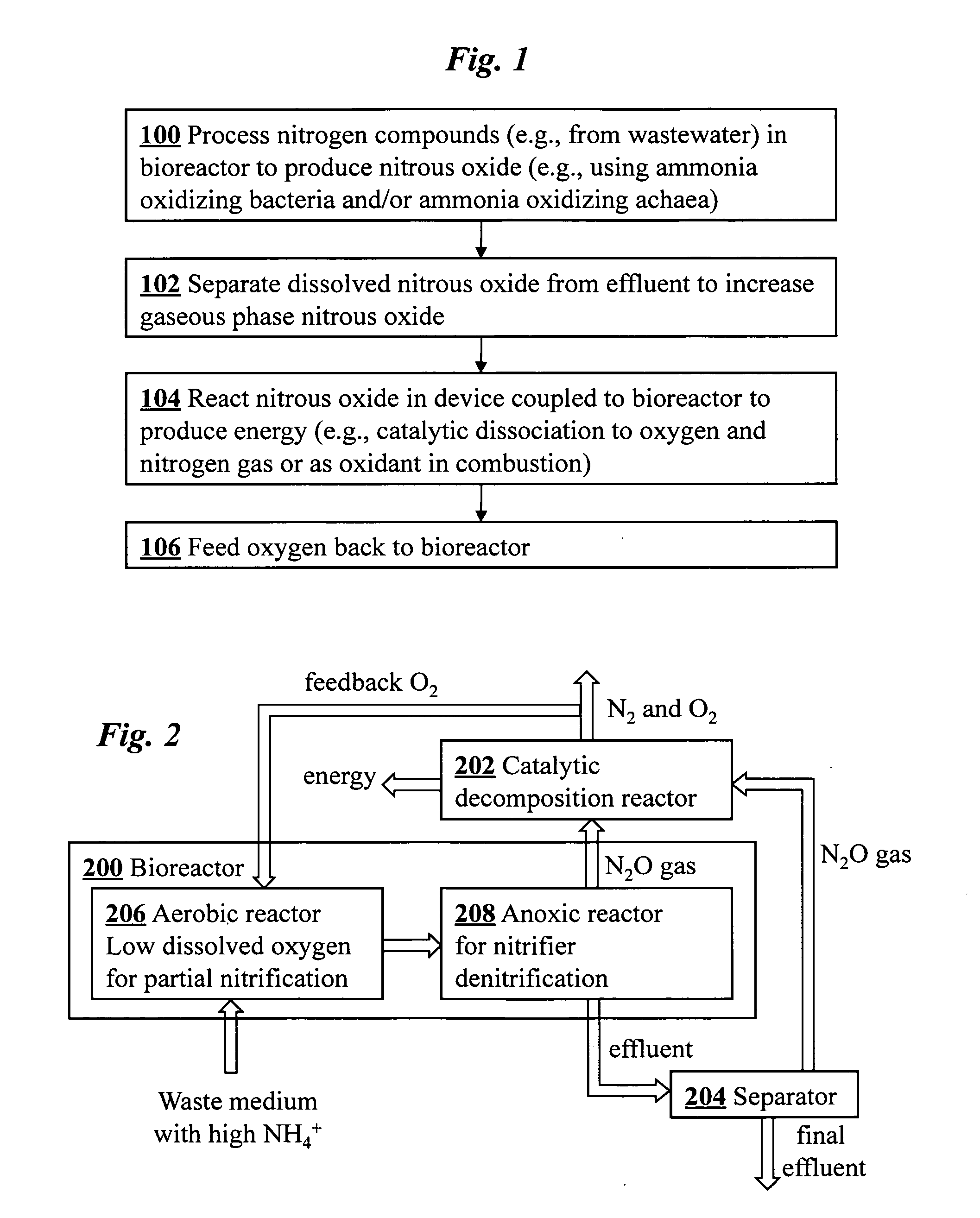
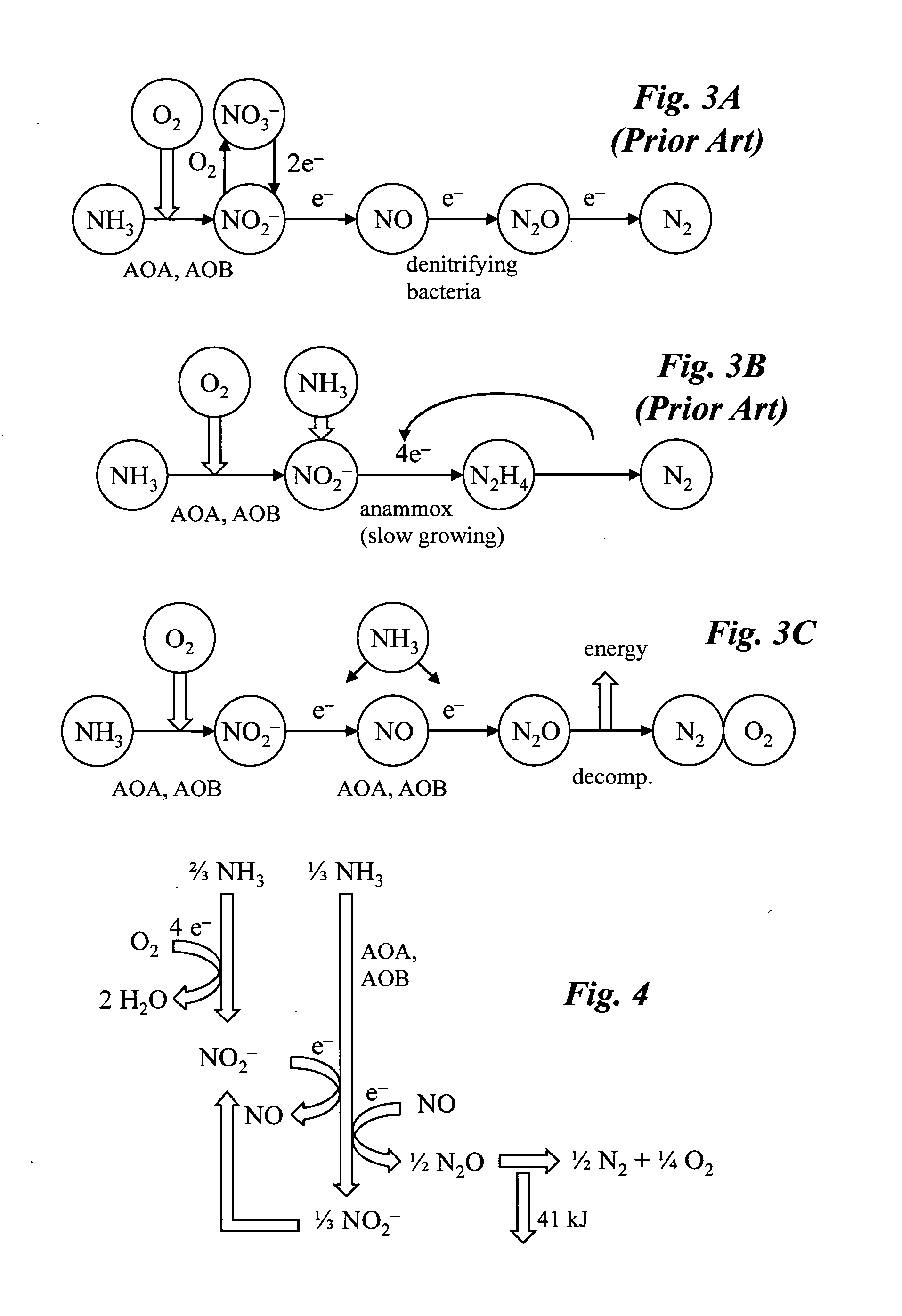
Microbial production of nitrous oxide coupled with chemical reaction of gaseous nitrous oxide
InactiveUS20100272626A1Minimize N2O productionProducer of clean energyWater treatment parameter controlOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideChemical reactionAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
A bioreactor designed to produce N2O from organic nitrogen and / or reactive nitrogen in waste is coupled to a hardware reactor device in which the N2O is consumed in a gas phase chemical reaction, e.g., catalytic decomposition to form oxygen and nitrogen gas. Heat from the exothermic reaction may be used to generate power. The bioreactor may use communities of autotrophic microorganisms such as those capable of nitrifier denitrification, ammonia oxidizing bacteria, and / or ammonia oxidizing archaea. A portion of the N2O dissolved in aqueous effluent from the bioreactor may be separated to increase the amount of gas phase N2O product. The amount of the gas phase N2O in a gas stream may also be concentrated prior to undergoing the chemical reaction. The N2O may alternatively be used as an oxidant or co-oxidant in a combustion reaction, e.g., in the combustion of methane.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Device and method for strengthening sludge fermentation by FNA and realizing short-distance nitrogen and phosphorus removal of wastewater
ActiveCN108217950AComplex structureStrong impact resistanceWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaOxygen
The invention discloses a device and a method for strengthening sludge fermentation by FNA and realizing short-distance nitrogen and phosphorus removal of wastewater, and belongs to the field of wastewater and sludge treatment. The device comprises a raw water tank, an SBR reactor, an intermediate water tank, a UASB reactor, a sludge treatment reactor, and a sludge fermentation tank. According tothe method, FNA is used for inhibiting nitrite oxidizing bacteria to achieve short-cut nitrification and taken as sludge fermentation pretreatment step to promote the combination of hydrolysis and acidification, a part of sludge discharged by a short-range nitrification reactor is returned after being treated by FNA, and the other part of the sludge enters into the sludge fermentation tank. The SBR reactor firstly performs anoxic denitrification to remove excessive nitrite in the upper cycle, then anaerobic phosphorus release, aerobic phosphorus absorption and partial short-range nitrification, effluent enters UASB together with sludge fermentation broth, a part of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite are subjected to autotrophic nitrogen removal through anaerobic ammonia oxidizing bacteria, and residual nitrite and produced nitrate nitrogen are removed by denitrification of organic matters in the sludge fermentation broth. According to the invention, FNA is used for promoting the developmentof an internal carbon sources and realizing nitrogen and phosphorus removal of municipal wastewater, and the amount of the sludge is reduced, and the energy consumption of wastewater treatment is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Process comprising anammox bacteria on biofilm carriers for removing ammonium from a wastewater stream
A process that utilizes ammonium oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and anaerobic ammonium oxidizing (ANAMMOX) bacteria to remove ammonium from a wastewater stream. Sludge separated from the wastewater in a mainstream is processed in a sidestream that includes an anaerobic digester, a dewatering system, and a biofilm reactor. The anaerobic digester produces digested sludge that is dewatered, producing reject water that includes a relatively high ammonium concentration and a relatively low organic carbon concentration and a relatively high temperature. The reject water is treated in a sidestream deammonification biofilm reactor that includes biofilm carriers seeded with AOB and ANAMMOX bacteria that are effective to remove ammonium from the reject water. AOB and ANAMMOX bacteria on the media carriers is utilized to contact the wastewater in the mainstream and to remove ammonium therefrom.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Method and apparatus of removing nitrogen
InactiveUS20050211629A1Nitrite nitrogen concentration can be decreasedImprove performanceTreatment using aerobic processesWater contaminantsDecompositionAmmonia-oxidizing bacteria
A method of removing nitrogen, in which the nitrogen is removed from wastewater containing a BOD component and ammonium nitrogen by anaerobic ammonium oxidation, comprising the steps of: distributing the wastewater into two portions which are a nitrification vessel and a denitrification vessel at a predetermined distribution ratio; mixing first treated water which is nitrified by ammonium oxidizing bacteria from ammonia to nitrite in the nitrification vessel, with second treated water which is denitrified by denitrification bacteria in the denitrification vessel; and feeding the mixed water to an anaerobic ammonium oxidation vessel to simultaneously denitrify ammonia and nitrite by ammonium oxidizing bacteria, thereby obtaining a third treated water treated in the anaerobic ammonium oxidation vessel, which is then fed back to the denitrification vessel for denitrification and BOD decomposition.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com