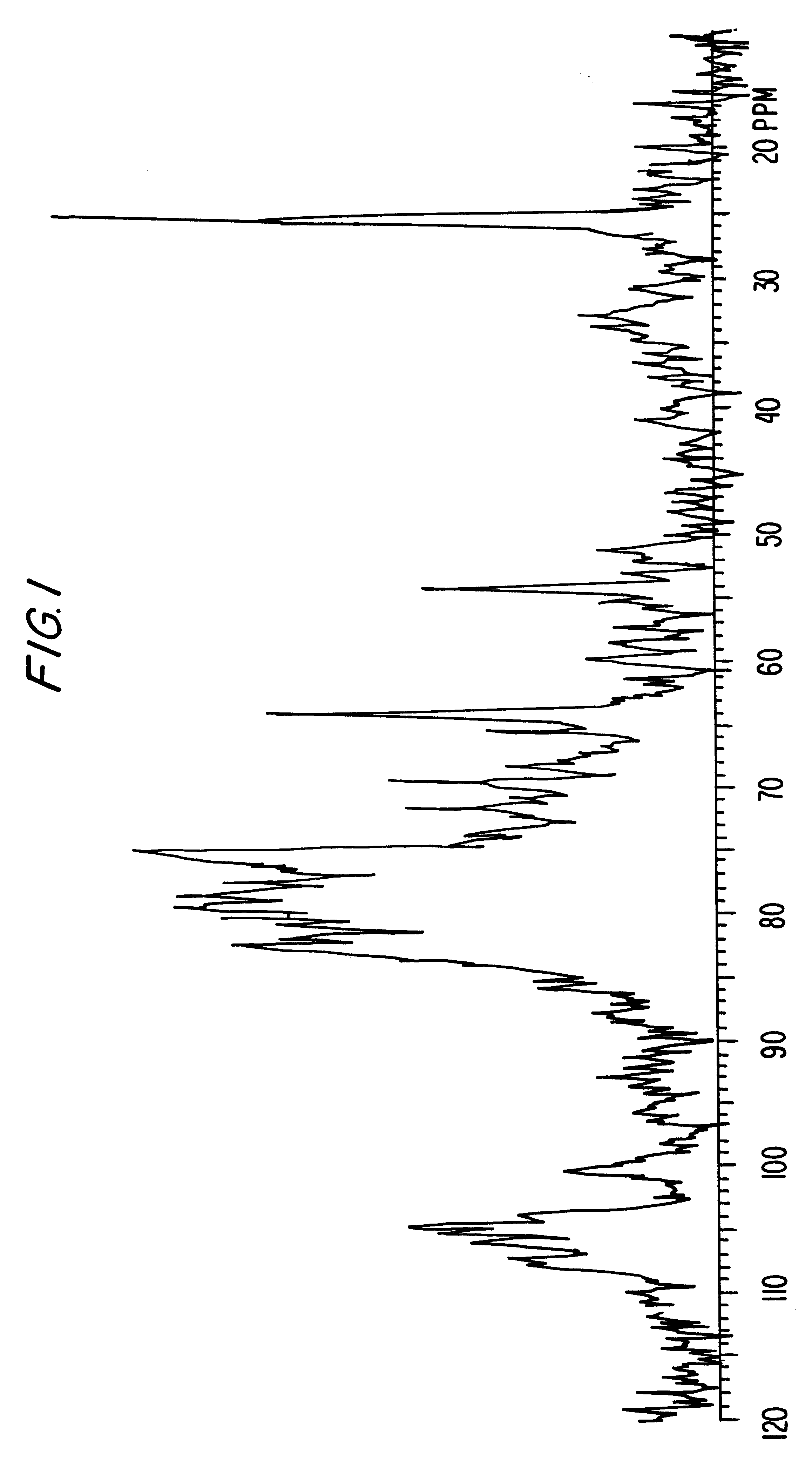
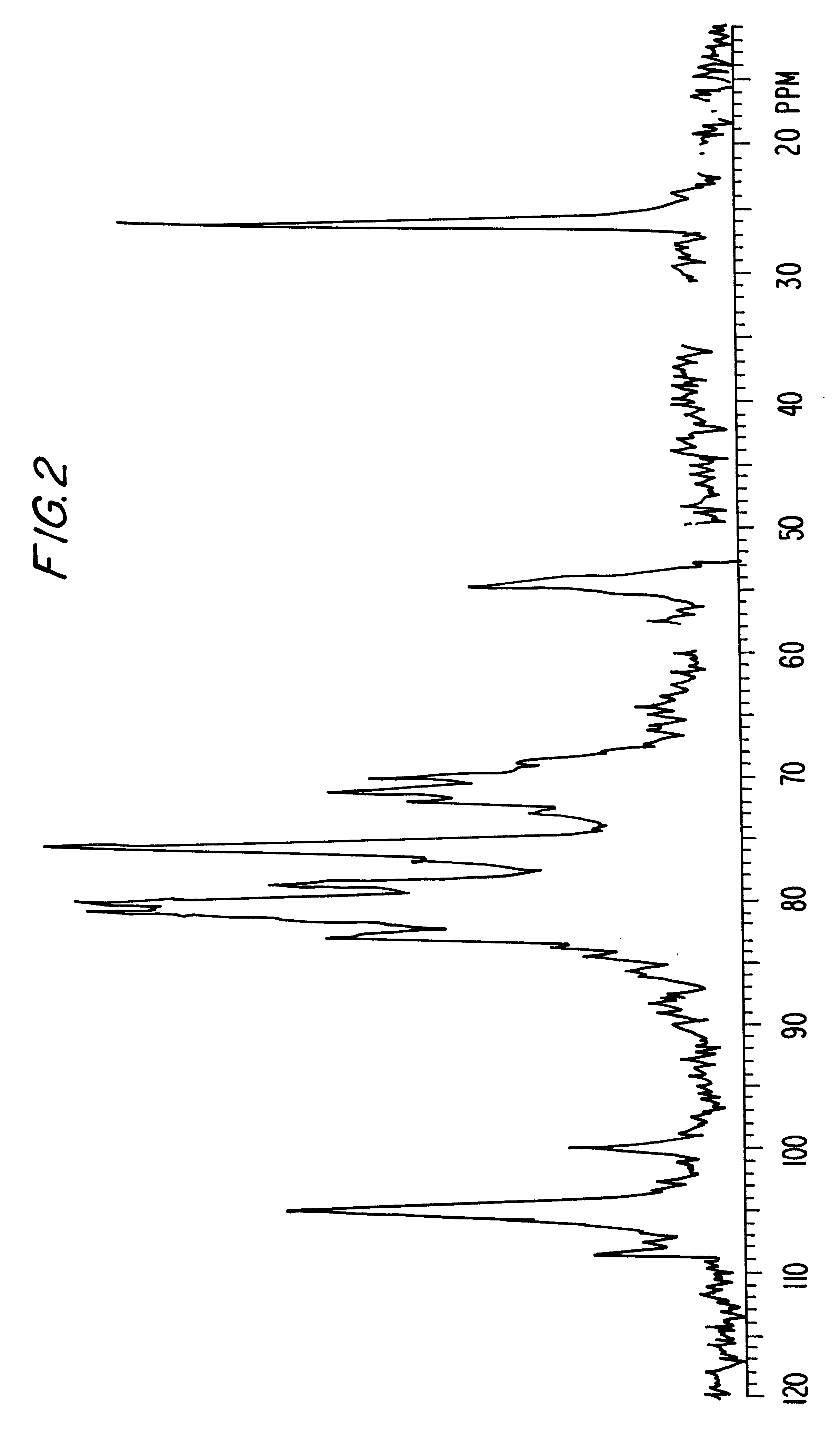
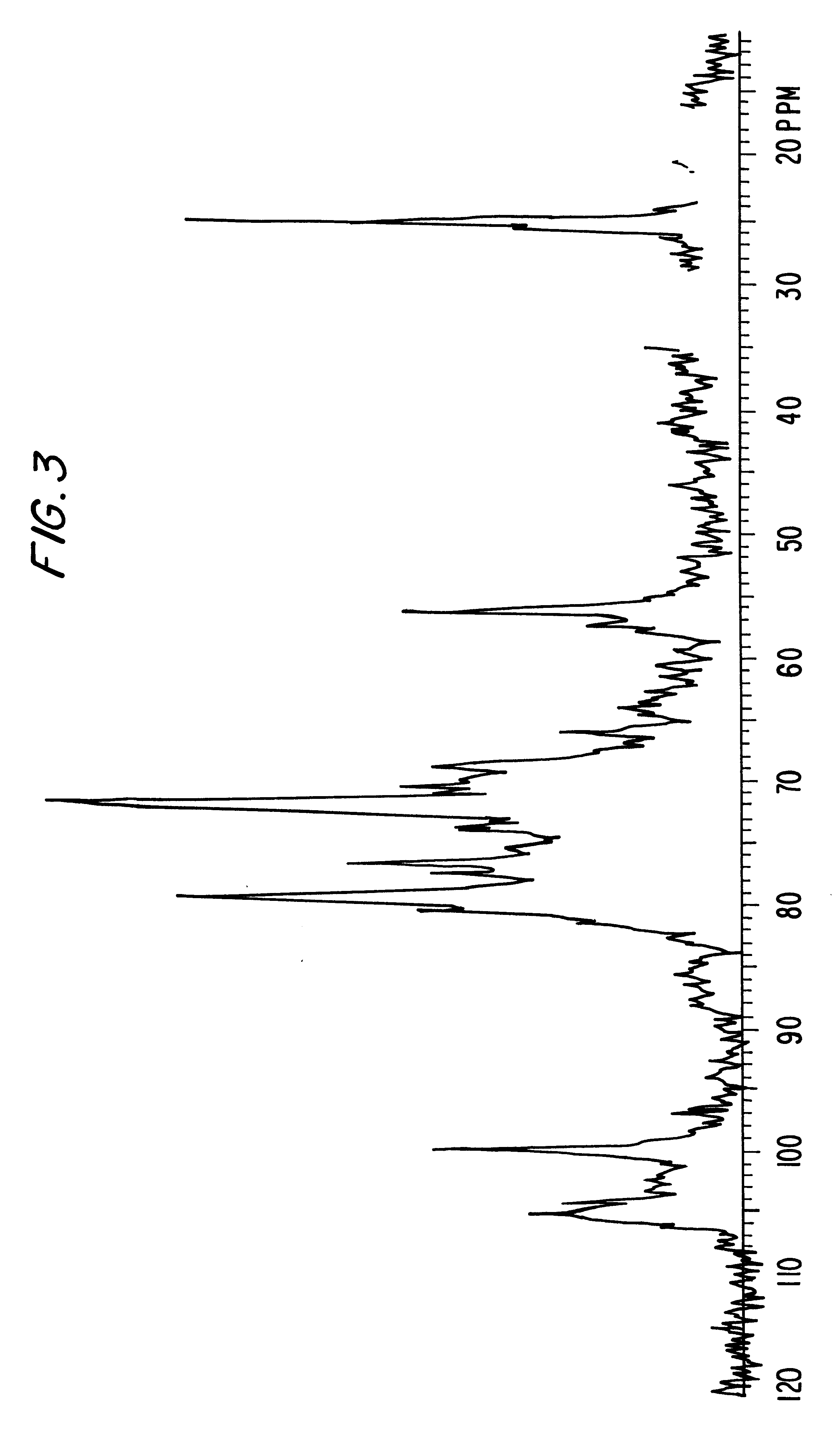
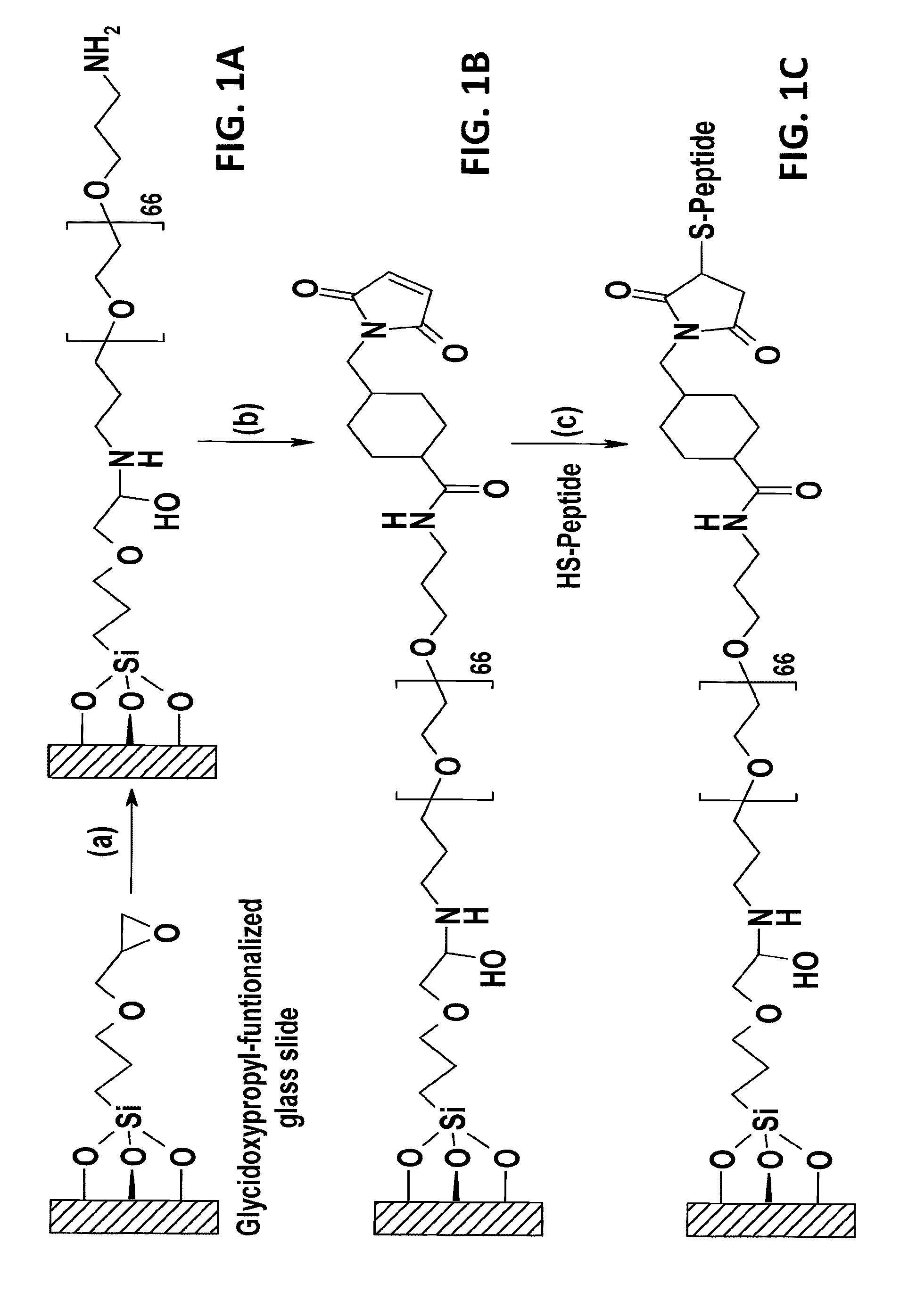
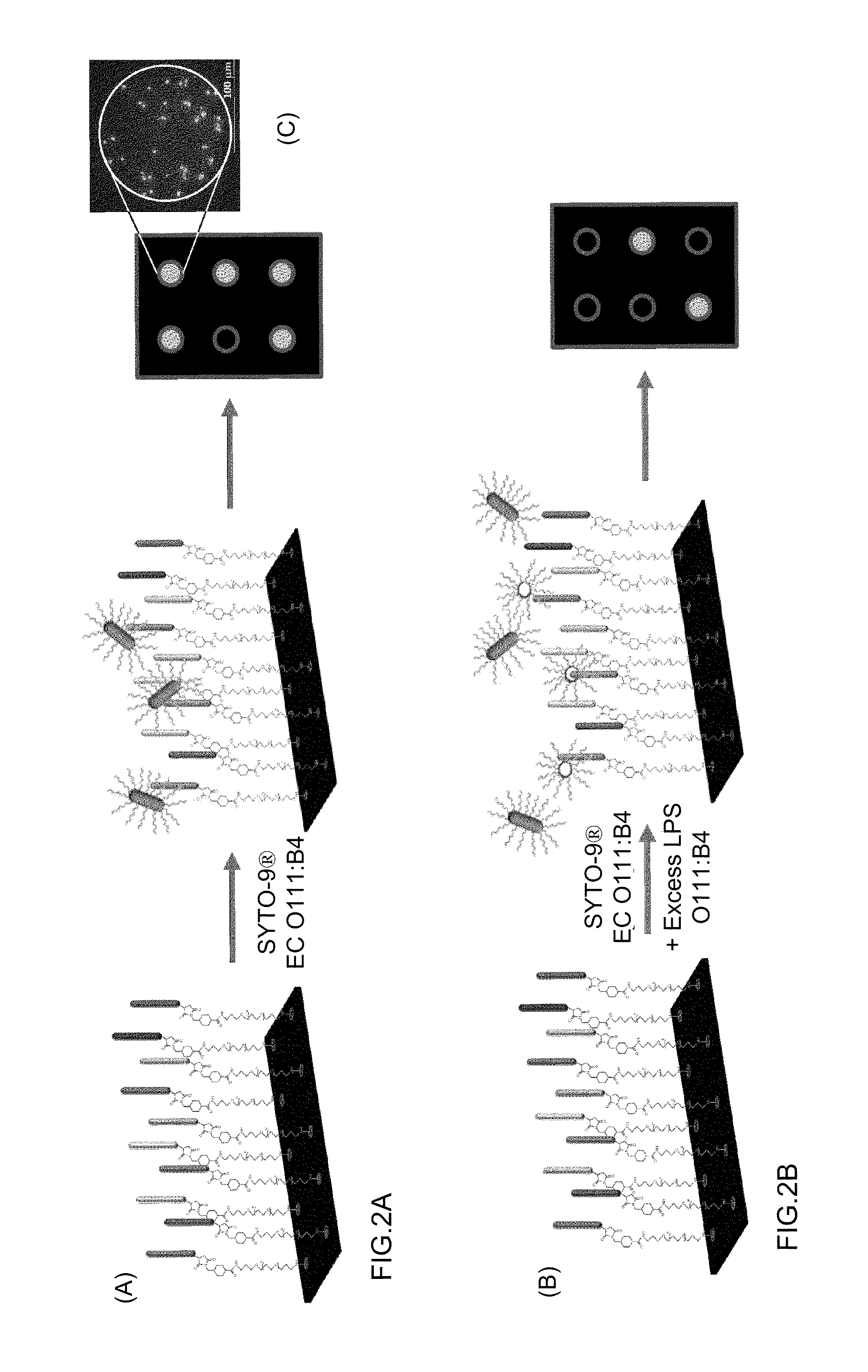
Patents
Literature
855 results about "Microbacterium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbacterium is a genus of bacteria in the family Microbacteriaceae.
Novel Ethanologenic Clostridium species, Clostridium coskatii
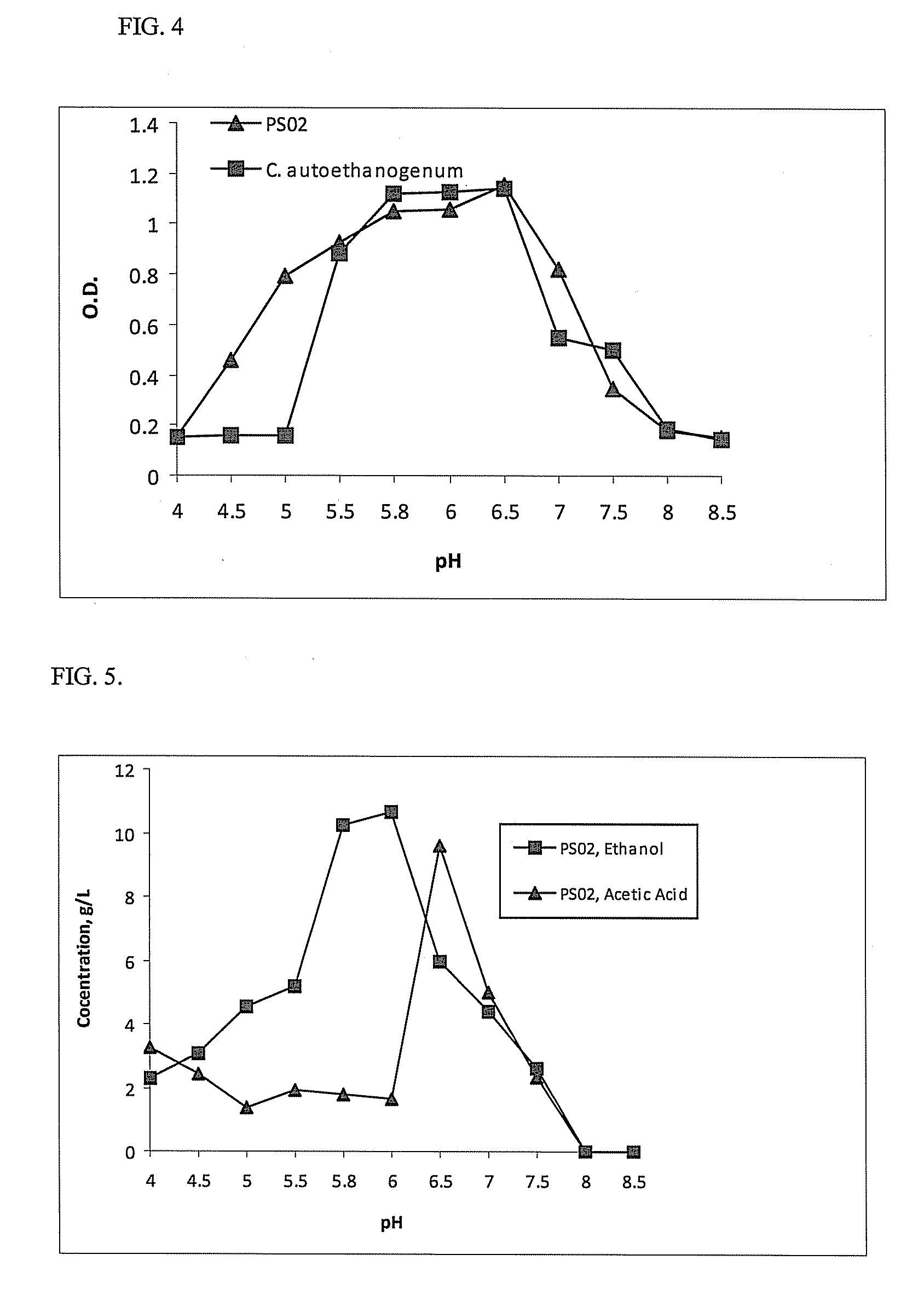
A novel clostridia bacterial species (Clostridium coskatii ATCC No. PTA-10522, “PS02”) is provided. Under anaerobic conditions C. coskatii can convert CO and / or H2 and / or CO2 to ethanol or acetate. Thus, this novel bacterium is capable of transforming waste gases (e.g. syngas and refinery wastes) into useful products.
Owner:SYNATA BIO INC
Microbial production of nuclease resistant DNA, RNA, and oligo mixtures
Owner:FRAYNE CONSULTANTS
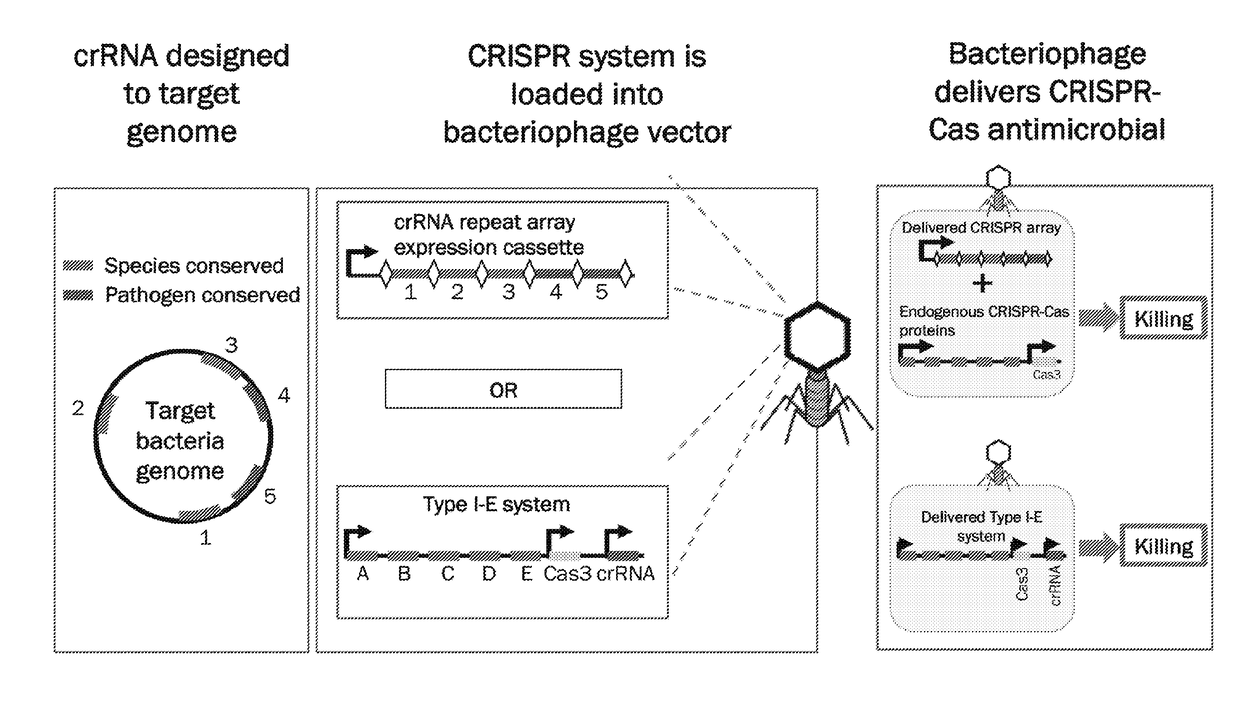
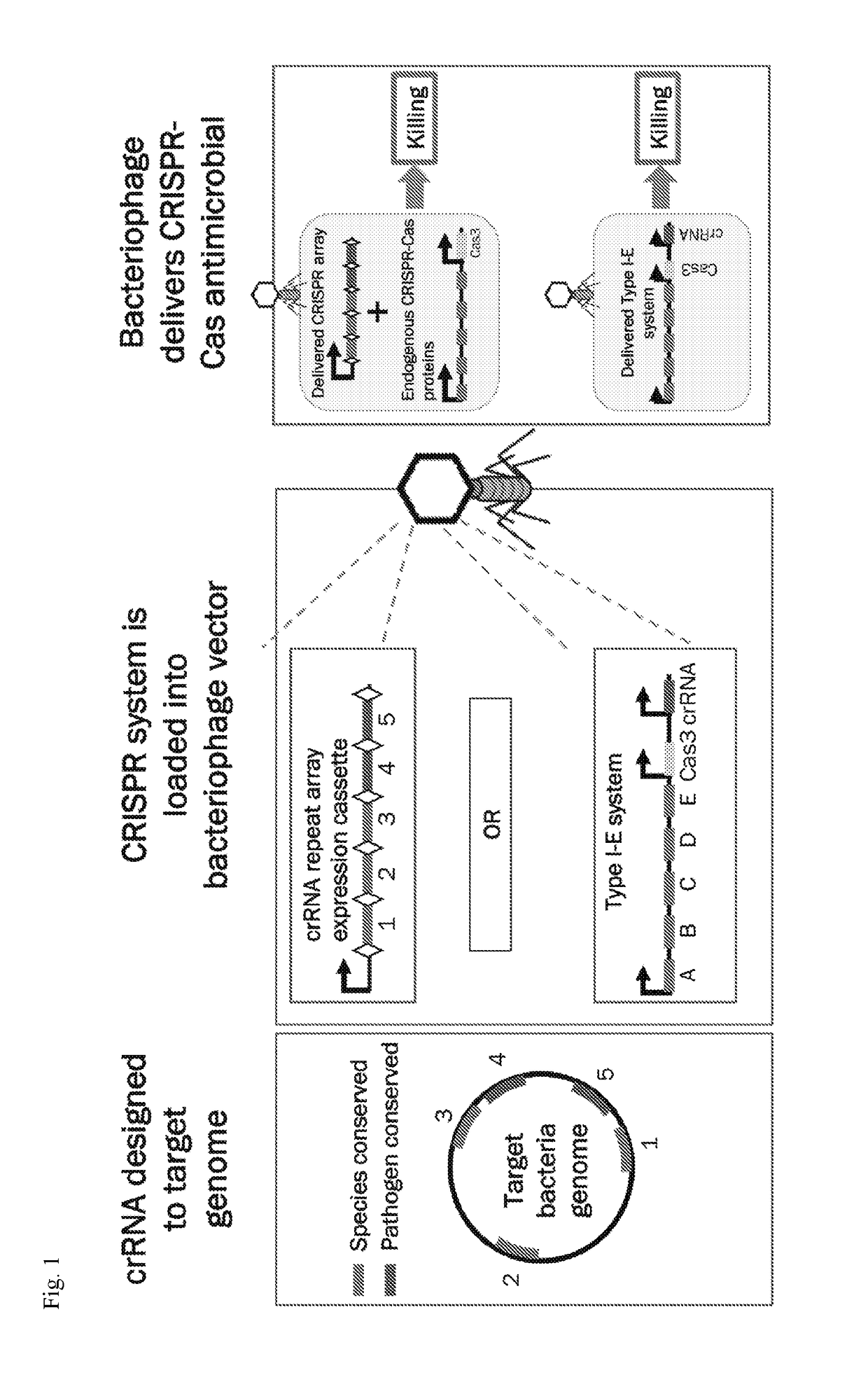
Methods and compositions for efficient delivery of nucleic acids and rna-based antimicrobials
ActiveUS20180155729A1Improve efficiencyAlters activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicrobial agentAntimicrobial
The invention relates to the methods for modifying the methylation pattern of bacteriophage DNA and phagemid DNA and to methods for selective killing of bacteria using lysogenic bacteriophages comprising bacteriophage DNA or phagemid DNA comprising components of an engineered CRISPR-Cas system.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain, and gene deletion vaccine strain thereof and applications thereof
ActiveCN102994458AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsRabiesMicrobacterium
The invention discloses a porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain, and a gene deletion vaccine strain thereof and applications thereof. The porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain is named as HeN1, the microbial preservation number of the porcine pseudorabies virus virulent strain is CGMCC NO.6656, the deleted gE gene obtaines the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ on the basis of the virulent strain HeN1, and the microbial preservation number is CGMCC NO.6657. The virulent strain can be prepared into inactivated vaccine (single vaccine or combined vaccine), the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ can be prepared into activated vaccine or inactivated vaccine (single vaccine or combined vaccine) and the like, so that porcine pseudorabies can be effectively prevented or cured, or the gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ can be prepared into a diagnosis reagent for diagnosing the porcine pseudorabies. The gene deletion vaccine strain rPRV-gE-EGFP+ has the advantages of being good in safety, high in protection efficiency, beneficial to differential diagnosis.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
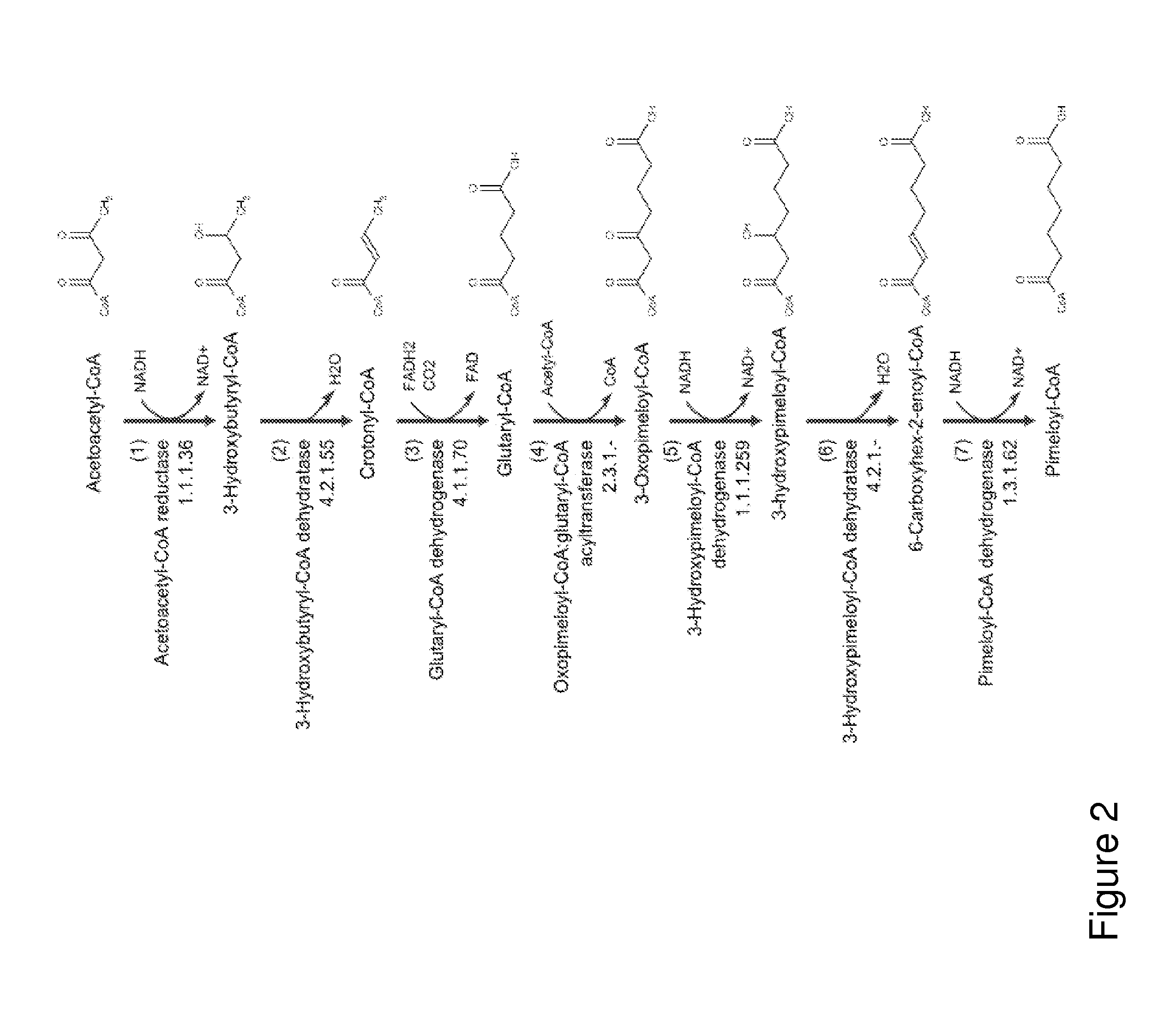
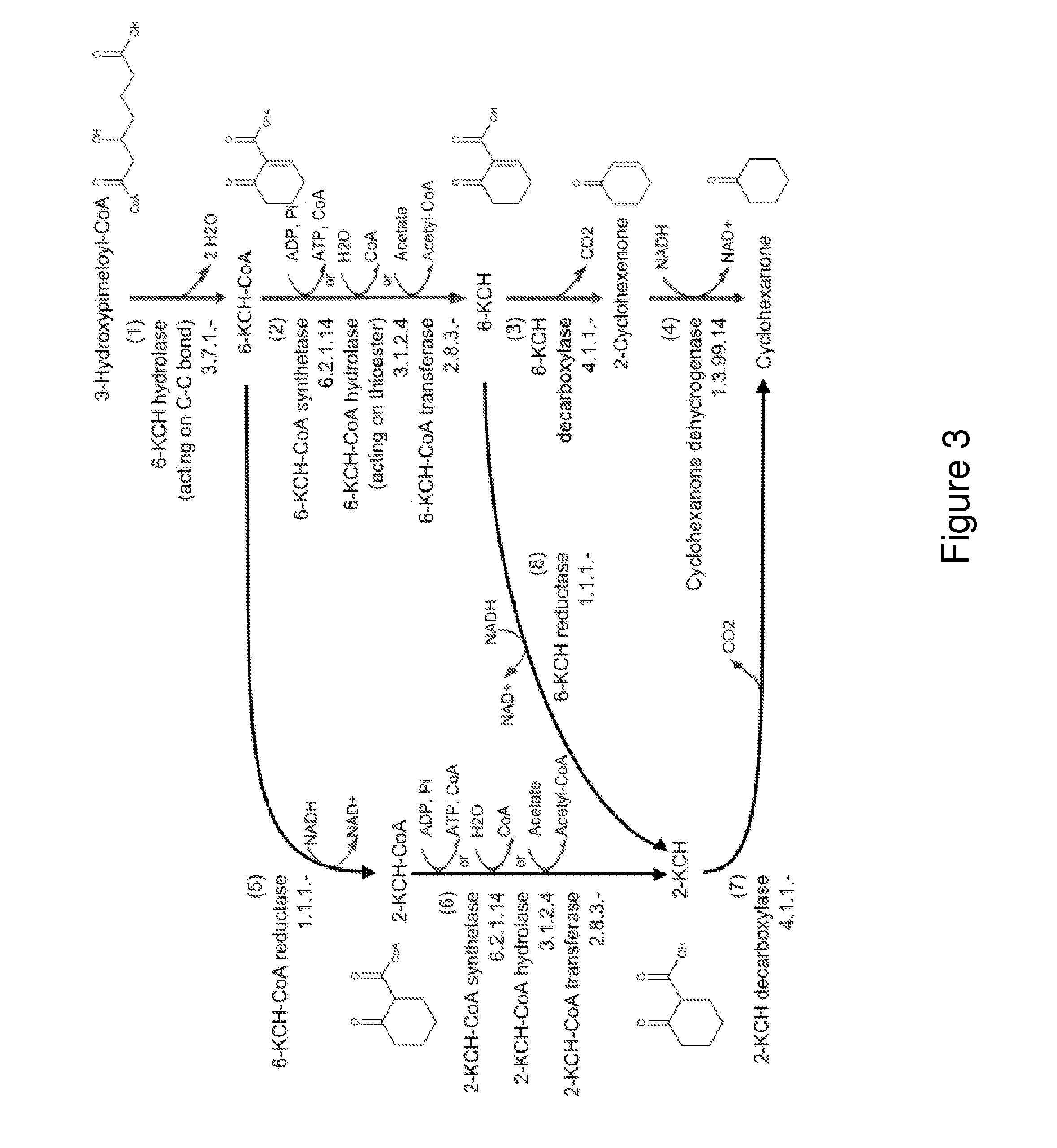
Organisms for the production of cyclohexanone
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has cyclohexanone pathways that include at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a cyclohexanone pathway enzyme. A pathway includes a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase and an enzyme selected from a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, and a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase. A pathway includes an enzyme selected from a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on C—C bond), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxyl-CoA reductase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, a 6-ketocyclohex-1-ene-1-carboxylate reductase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA synthetase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA transferase, a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), a 2-ketocyclohexane-1-carboxylate decarboxylase, and a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase. A pathway includes an adipate semialdehyde dehydratase, a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydrogenase, and a cyclohexane-1,2-diol dehydratase. A pathway includes a 3-oxopimelate decarboxylase, a 4-acetylbutyrate dehydratase, a 3-hydroxycyclohexanone dehydrogenase, a 2-cyclohexenone hydratase, a cyclohexanone dehydrogenase and an enzyme selected from a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA synthetase, a 3-oxopimeloyl-CoA hydrolase (acting on thioester), and a 3-oxopimeloyl-coA transferase. Each these pathways can include a PEP carboxykinase. A method for producing cyclohexanone includes culturing these non-naturally occurring microbial organisms.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
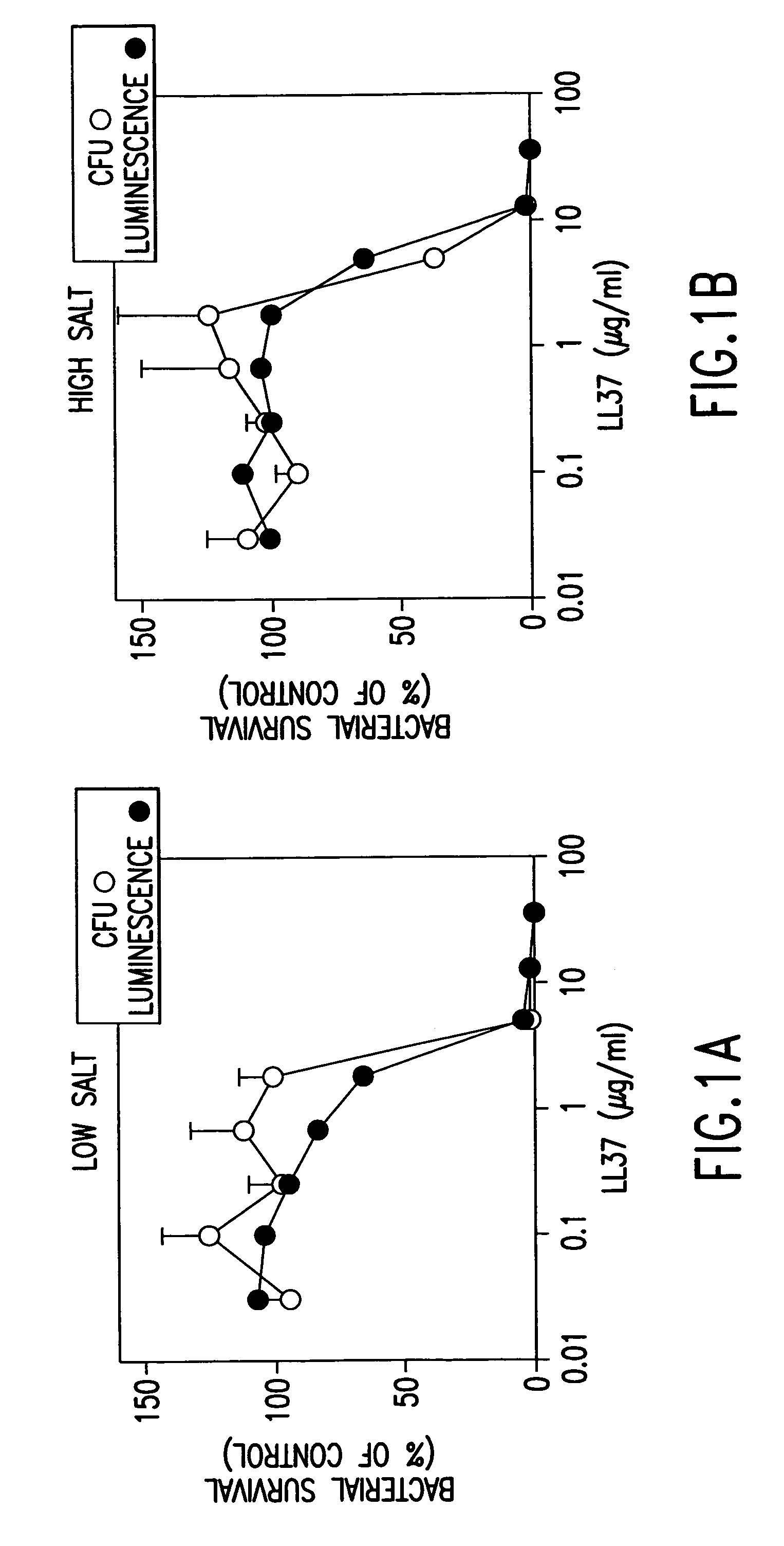
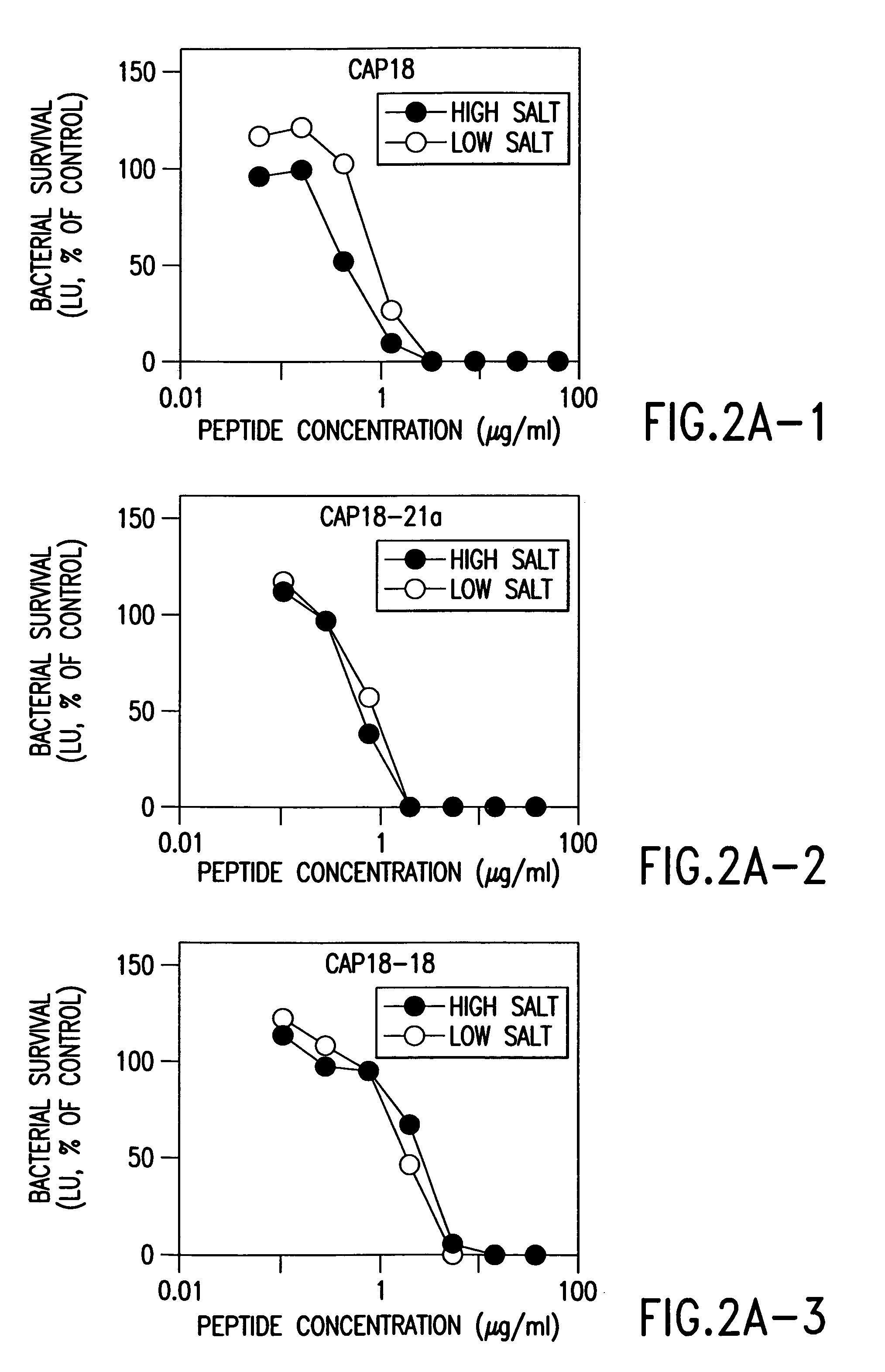
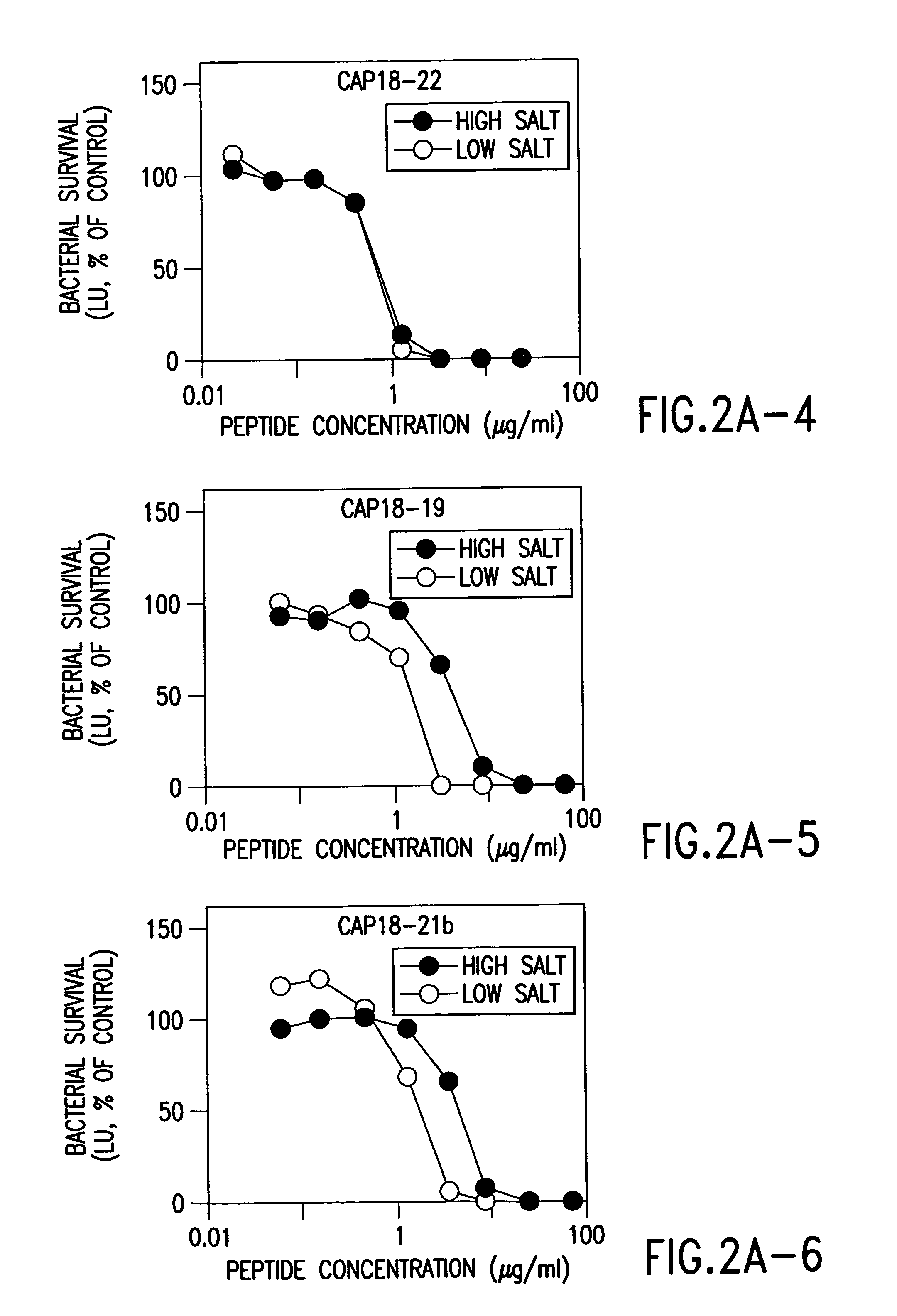
Alpha helical peptides with broad spectrum antimicrobial activity that are insensitive to salt
InactiveUS7071293B1Enhanced microbialEnhanced bacterial killingPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesMicroorganismAntimicrobial peptides
The present invention relates to the use of antimicrobial peptides in the inhibition of microbial growth and proliferation. Novel antimicrobial truncated peptides are disclosed which are based upon SMAP 29 and RCAP 18, but which contain a lesser number of amino acid residues yet still retain bactericidal activity. In addition, synthetic peptides based upon the SMAP 29 protein are disclosed which have fewer amino acid residues and include substitutions yet retain substantial activity. The invention also relates to a method of inhibiting microbial growth by administering an effective amount of a peptide in accordance with the invention, or by combining the peptides with other antimicrobial agents or antibiotics.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
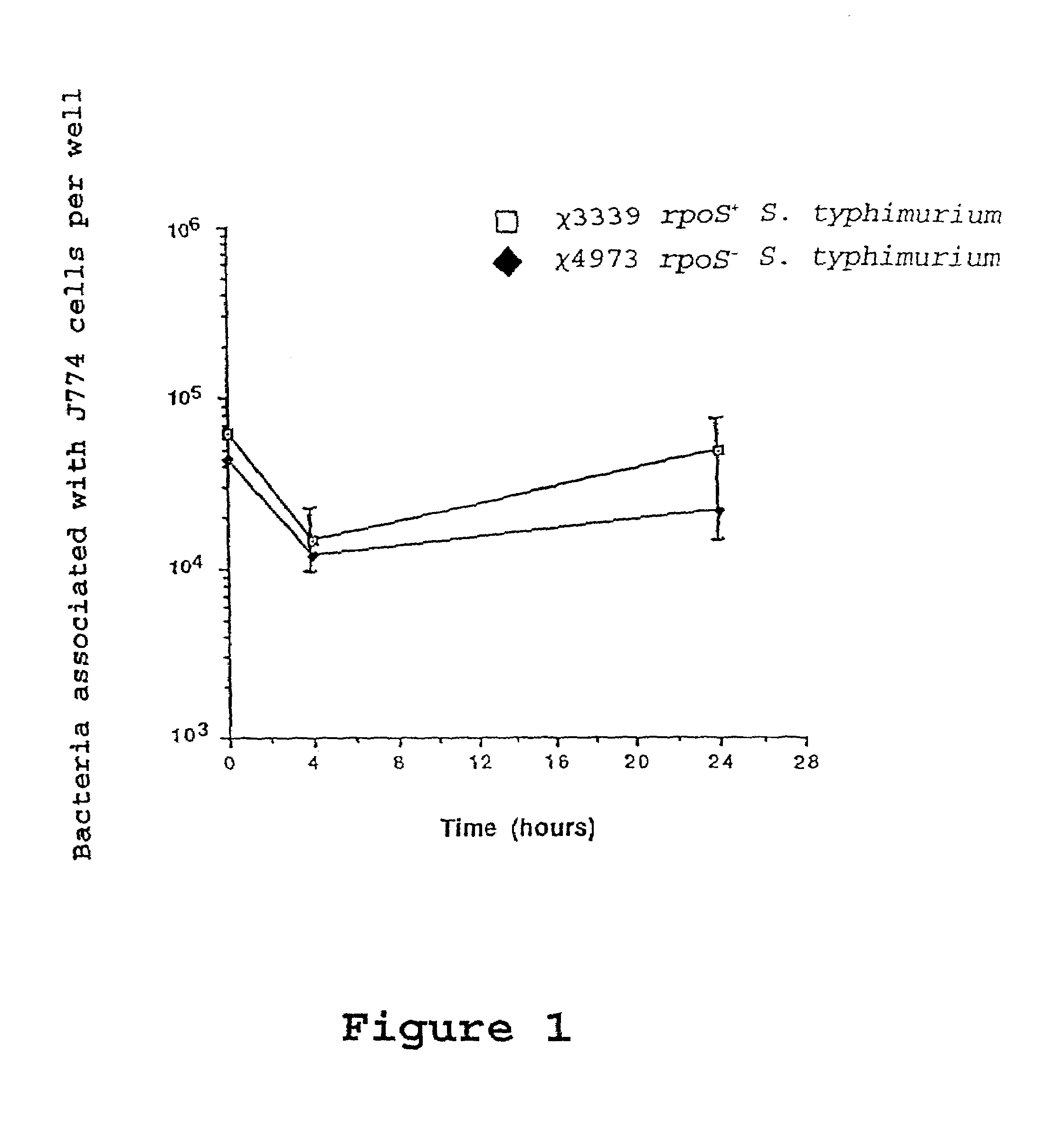
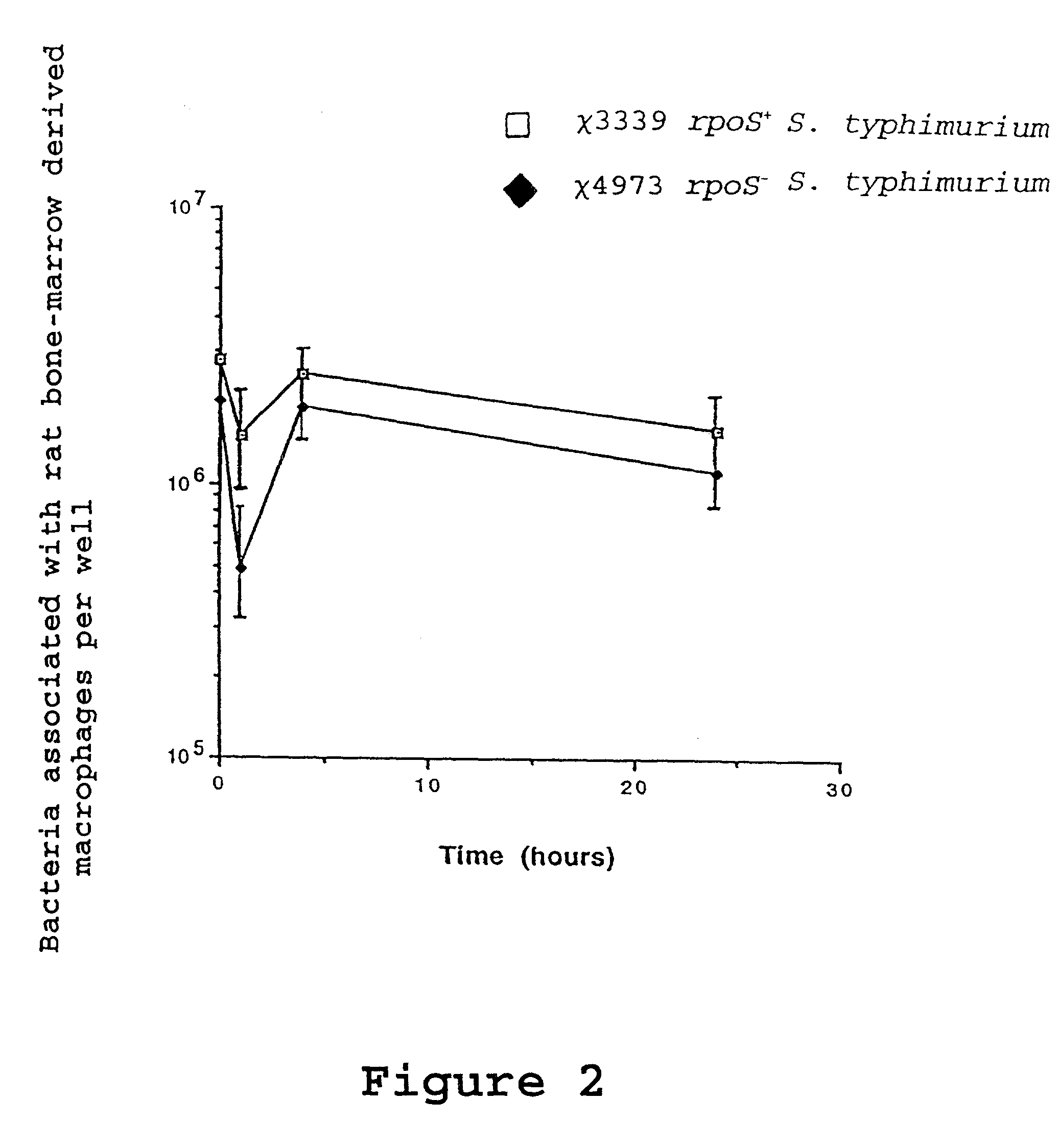
Recombinant vaccines comprising immunogenic attenuated bacteria having RpoS positive phenotype
InactiveUS7083794B2Improve balanceImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSalmonella entericaSalmonella serotype typhi
Attenuated immunogenic bacteria having an RpoS+ phenotype, in particular, Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi having an RpoS+ phenotype and methods therefor are disclosed. The Salmonella have in addition to an RpoS+ phenotype, an inactivating mutation in one or more genes which render the microbe attenuated, and a recombinant gene capable of expressing a desired protein. The Salmonella are attenuated and have high immunogenicity so that they can be used in vaccines and as delivery vehicles for genes and gene products. Also disclosed are methods for preparing the vaccine delivery vehicles.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Microbial strains and processes for the manufacture of biomaterials
InactiveUS20090226962A1Increase enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCell culture media
DNA constructs and genetically engineered microbial strains constructed using these DNA constructs, which produce a nuclease enzyme with specificity for DNA and / or RNA, are provided. These strains secrete nuclease into the periplasm or growth medium in an amount effective to enhance productivity and / or recovery of polymer, and are particularly suited for use in high cell density fermentation processes. These constructs are useful for modifying microbial strains to improve production and recovery processes for polymers such as intracellular proteins, such as enzymes, growth factors, and cytokines; for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates; and for producing extracellular polysaccharides, such as xanthan gum, alginates, gellan gum, zooglan, hyaluronic acid and microbial cellulose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain
Owner:NOVOZYMES BIOLOGICALS
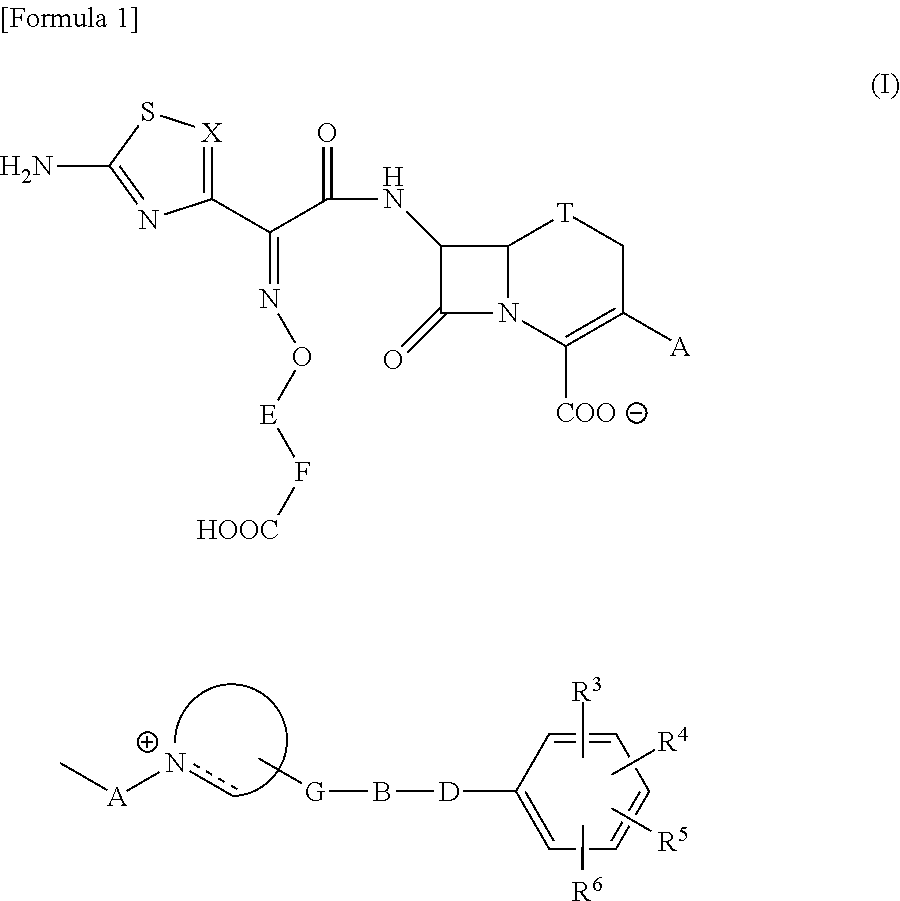
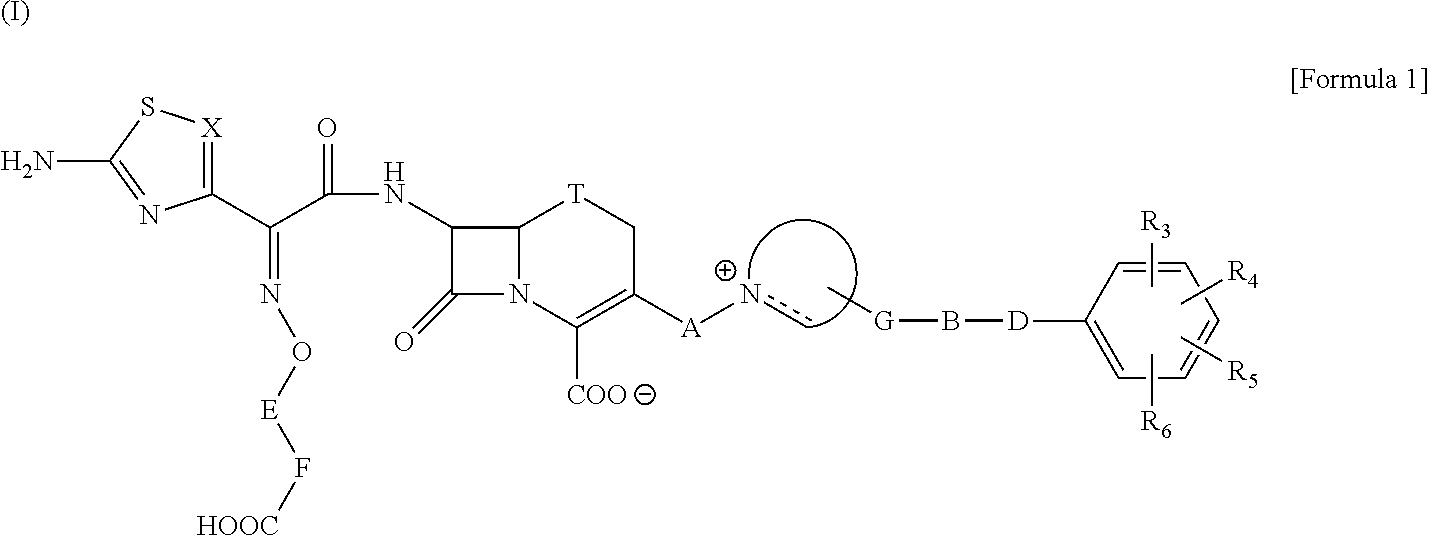
Cephalosporin having catechol group
ActiveUS20110190254A1Potent antimicrobial spectrumHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide chainPharmaceutical medicine
The present invention provides Cephem compounds which have a wide antimicrobial spectrum and have potent antimicrobial activity against beta-lactamase producing Gram negative bacteria as follows:A compound of the formula:wherein,X is N, CH or C—Cl;T is S or the like;A and G are lower alkylene or the like;B is a single bond or the like;D is a single bond, —NR7—, —CO—, —CO—NR7—, —NR7—CO—, —NR7—CO—NR7—, or the like;E is optionally substituted lower alkylene;F is a single bond or optionally substituted phenylene;R3, R4, R5 and R6 each is independently hydrogen, halogene, nitrile, or the like;or an ester, a compound protected at the amino on the ring in the 7-side chain, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, or a solvate thereof.
Owner:SHIONOGI & CO LTD
Extraction method of soil microbe genome DNA and total RNA
The invention provides a method for effectively extracting crop rhizosphere soil microbe genome DNA and total RNA, which comprises the following steps: firstly, removing humus and other impurities which severely disturb nucleic acid extraction in soil samples by aluminum sulfate; further crushing soil microbe cells by glass beads; adding sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS) and LiCl solutions for cracking cells and dissociating nucleic acids; adding the mixture of phenol, chloroform and isoamylol for extracting; and then, depositing the extraction solution by isopropanol and sodium acetate to finally acquire the soil microbe metagenome DNA and total RNA. The method is suitable for extraction of the DNA and total RNA of soil in different regions. The invention establishes an extraction technology which has the advantages of simple and easy operation processes and higher purity of the prepared sample, and can provide an important basis for the research of soil metagenomics.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Pine endosymbiotic bacterium-new burkholderia cenocepacia NSM-05 and application thereof
InactiveCN102191201AImprove growth performanceGood antibacterial effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBacteroidesDisease
The invention discloses a pine endosymbiotic bacterium which is classified and named after a new burkholderia cenocepacia NSM-05 and is stored in the China typical culture collection center with the storage number of CCTCC NO: M2011015 and the storage data of January 11, 2011. The invention also discloses application of the new burkholderia cenocepacia NSM-05 to the preventing and treating pine shoot dieback diseases and promoting the growth of pines. The invention also discloses an antagonistic inoculant for preventing and treating the pine shoot dieback diseases; the antagonistic inoculant is obtained by inoculating NSM-05 bacterium strains in a culture medium. The NSM-05 bacterium strain provided by the invention is the pine endosymbiotic bacterium, has strong bacteriostasis on the pine shoot dieback diseases, has the antagonism effect on multiple woods and crop pathogenic bacteria and road-spectrum antibacterial activity, is safe and non-toxic to people, livestock and plants and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Feed additive composition
InactiveUS20150216203A1Improve performanceImprove feed conversionMilk preparationBiocideAlglucerasePentagalacturonic acid
A feed additive composition comprising a direct fed microbial (DFM), in combination with a xylanase (e.g. endo-1,4-β-d-xylanase) and a β-glucanase (and optionally a further fibre degrading enzyme), wherein the DFM is selected from the group consisting of an enzyme producing strain; a C5 sugar-fermenting strain; a short-chain fatty acid-producing strain; a fibrolytic, endogenous microflora-promoting strain; or combinations thereof. The DFM may be selected from the group consisting of: Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS3BP5, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS442, B. subtilis AGTP BS521, B. subtilis AGTP BS918, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS1013, B. subtilis AGTP BS1069, B. subtilis AGTP 944, B. pumilus AGTP BS 1068 or B. pumilus KX11-1, Enterococcus faecium ID7, Propionibacterium acidipropionici P169, Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM-1-3698, Lactobacillus farciminis CNCM-1-3699, a strain having all the characteristics thereof, any derivative or variant thereof, and combinations thereof and the further fibre degrading enzyme may be selected from the group consisting of a cellobiohydrolase (E.C. 3.2.1.176 and E.C. 3.2.1.91), a β-glucosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.21), a β-xylosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.37), a feruloyl esterase (E.C. 3.1.1.73), an α-arabinofuranosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.55), a pectinase (e.g. an endopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.15), an exopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.67) or a pectate lyase (E.C. 4.2.2.2)), or combinations thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
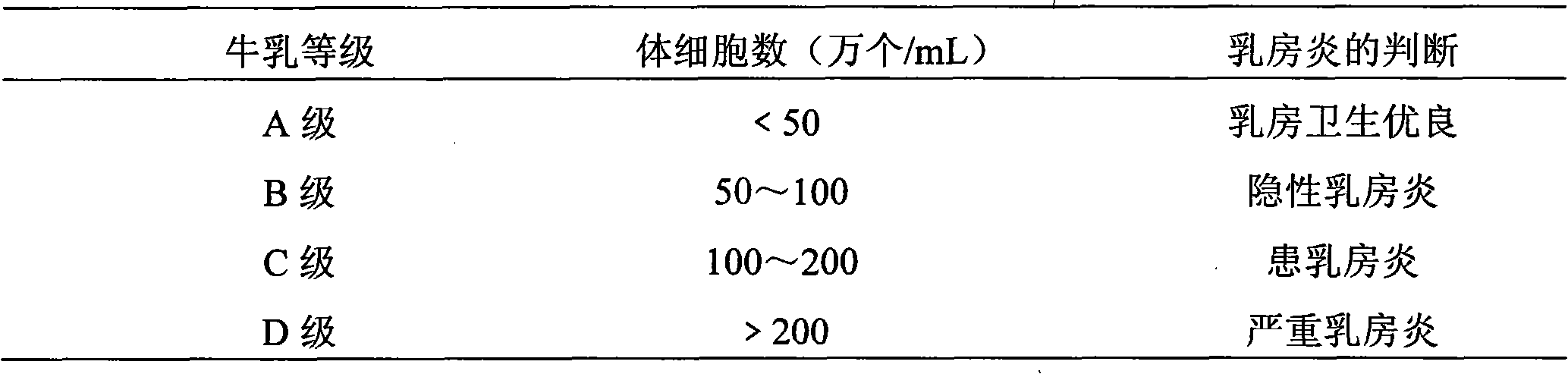
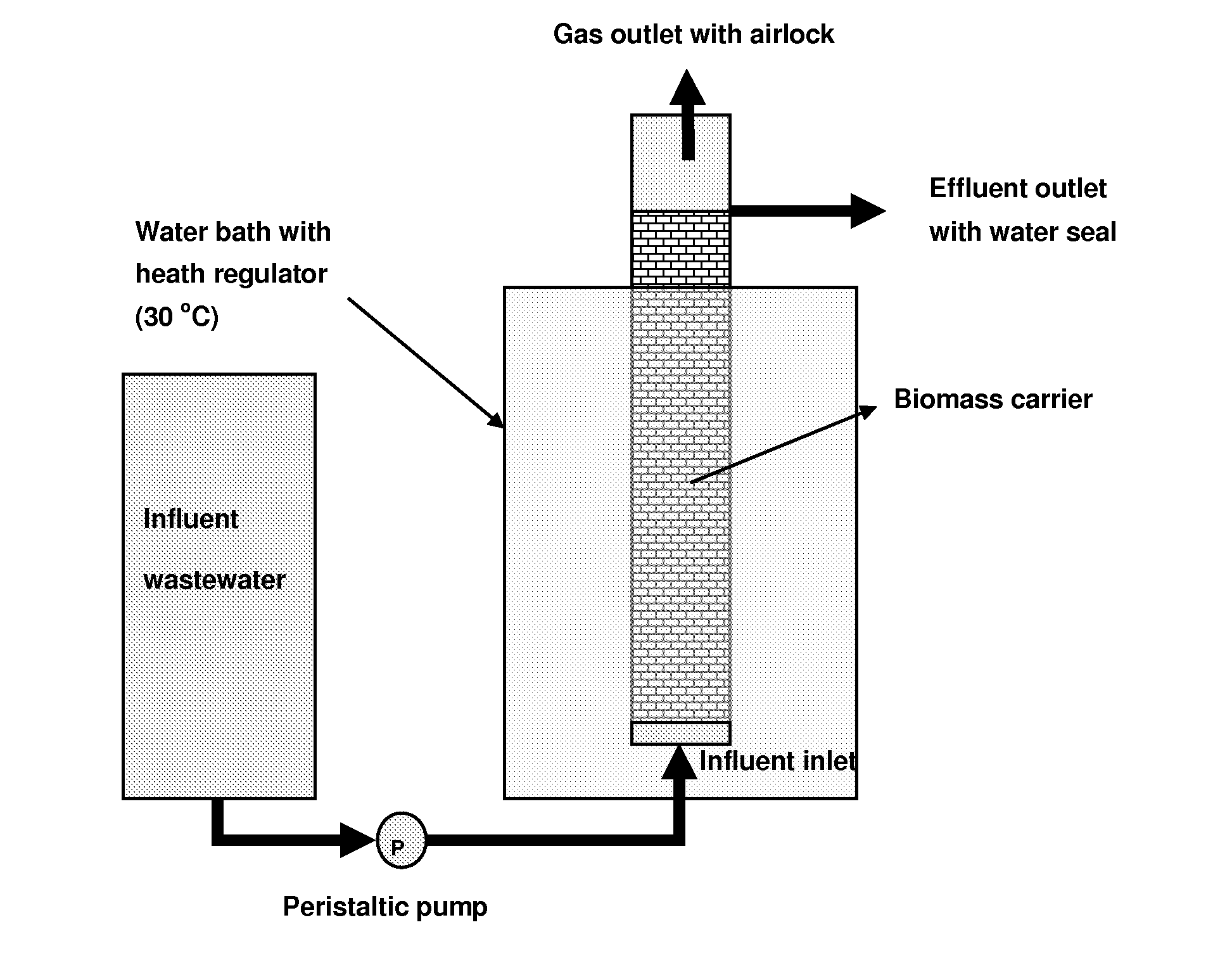
Bdellovibrio strain for preventing and treating mastitis and applications thereof
The invention discloses a Bdellovibrio strain for preventing and treating mastitis and applications thereof. A Bdellovibrio BDS01 is obtained by separation, and is unicellular, arced and 0.9-0.25 micrometer in size; the end of the Bdellovibrio BDS01 has flagellum which is 4 micrometers long. When cultured by a two-layer plating method at 28 DEG C for four days, the Bdellovibrio BDS01 can form transparent round plaques with the diameter of 1-2 mm. The microbial preparation prepared by using the Bdellovibrio BDS01 plastid has favorable effects for preventing cow mastitis. Compared with the telotroch, the plastid has the characteristics of convenient preparation and storage, strong environmental resistance, slightly slow sterilization action, longer sterilization action time, and the like, and does not have toxic or side effect on cows. Therefore, the microbial preparation containing the Bdellovibrio BDS01 plastid is suitable for large-size factory culture of cows, and a novel method forgreen processing and production of milk and for preventing and treating mastitis can be provided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel Anammox Bacterium Isolate
ActiveUS20110180476A1Ammonia reductionReduce ammonia levelsBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesMicrobacterium
Disclosed is an isolated bacterial strain Candidatus Brocadia caroliniensis strain, having Accession Deposit Number NRRL B-50286. The strain is capable of oxidizing ammonium and releasing di-nitrogen gas.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
O-sulfated bacterial polysaccharides
InactiveUS6288044B1Interesting anti-angiogenetic and antiviral as well as anticoagulant activityPrevention of hair falling outOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBacteroidesChlorosulfuric acid
Process for the preparation of O-sulfated K4, K5 and K40 polysaccharides useful for the treatment of tumoral, HIV-1 and coagulation pathologies and in cosmetic preparations, wherein the K4, K5 or K40 polysaccharide in the form of sodium salt is suspended in an aprotic solvent and directly submitted to the reaction of O-sulfation with a pyridine-sulphur trioxide or trimetylamine-sulphur trioxide adduct or with chlorosulfonic acid.
Owner:INALCO SPA
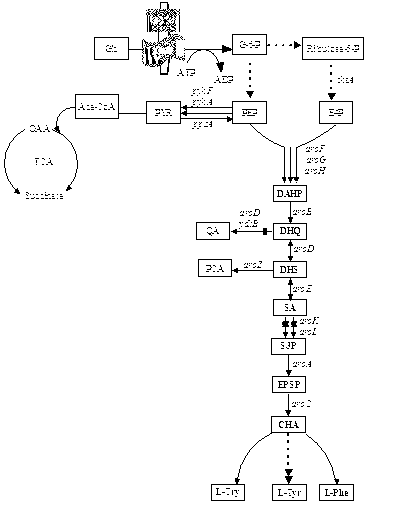
Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102994439AEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliShikimate kinase
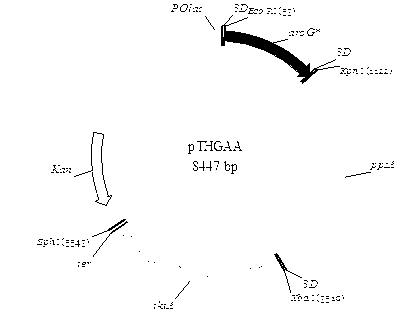
An Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and a construction method and application thereof belong to the technical field of microbial gene engineering. The invention firstly utilizes a molecular biology technique to delete shikimic acid kinase I gene (aroK) and shikimic acid kinase II gene (aroL) of Escherichia coli CICIMB0013, and a gene (ptsG) of a key protein EIIBC<Glc> and a quinin acid / shikimic acid dehydrogenase gene (ydiB) of a glucose phosphotransferase system to obtain an Escherichia coli mutant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 (delta aroK, delta aroL, delta ptsG, delta ydiB). The invention also constructs a recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA containing key genes comprising aroG*,ppsA and tktA in a metabolic pathway of shikimic acid; and the recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA is transferred into the recombinant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 to obtain a recombinant Escherichia coli B0013 (SA4 / pTHGAA) capable of producing shikimic acid efficiently. The Escherichia coli recombinant strain provided by the invention can realize efficient accumulation of shikimic acid in a fermentation process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Identification and application of biocontrol bacillus strain
InactiveCN108641981APromote safe productionGood control effectBiocideBacteriaBacteroidesBiotechnology
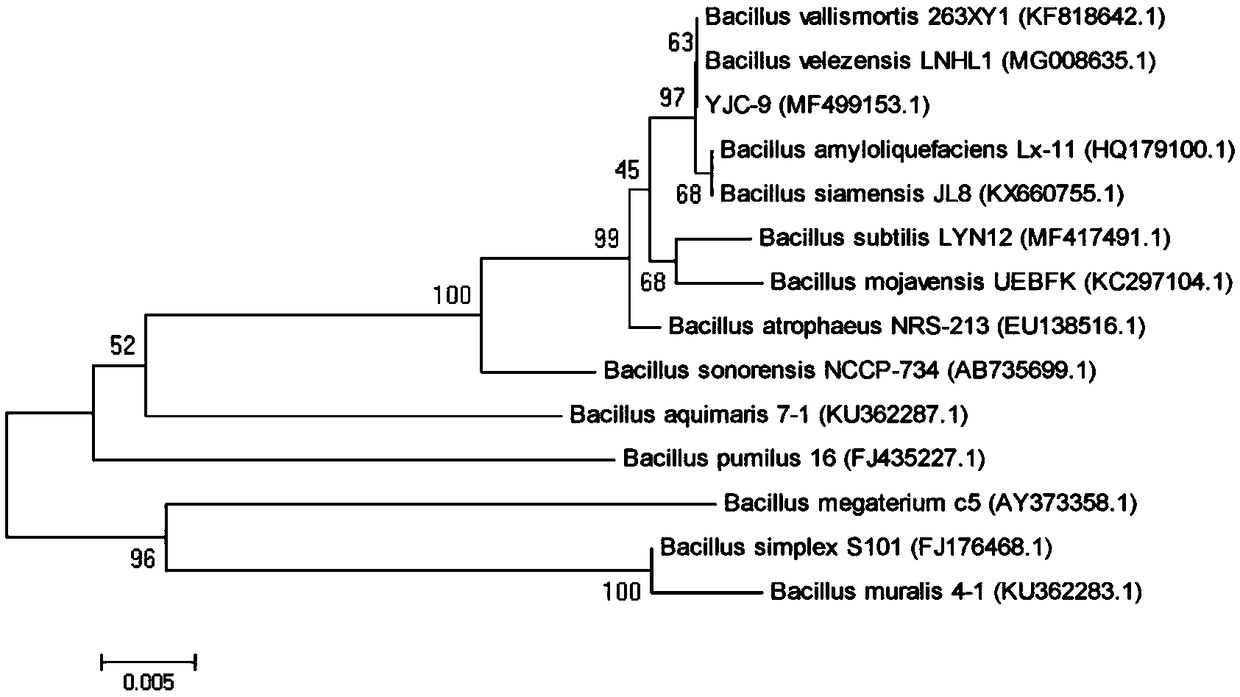
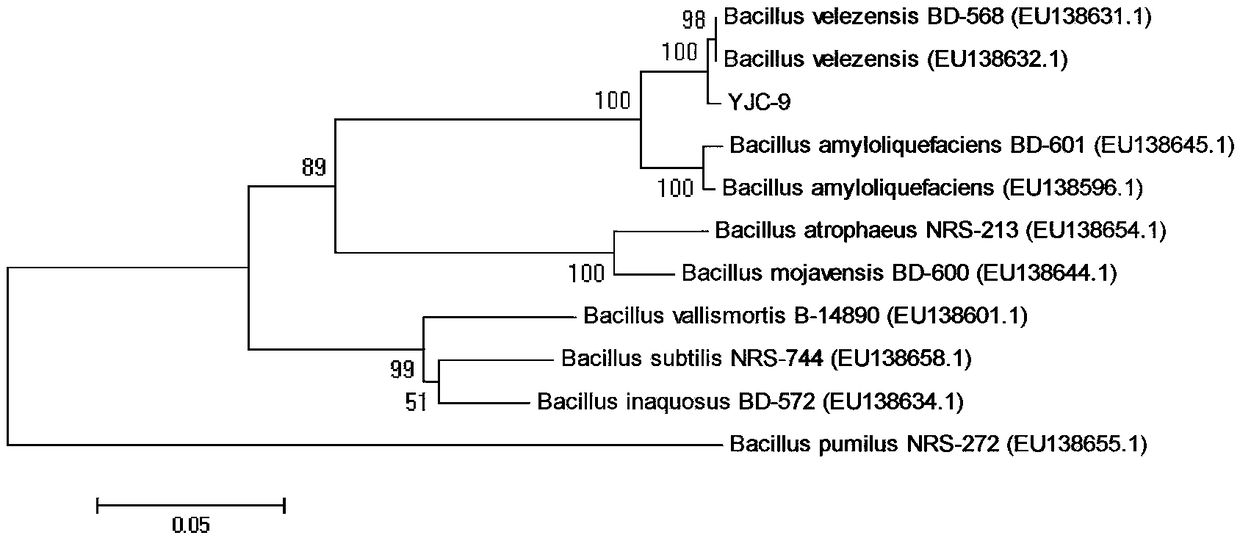
The invention discloses identification and application of a biocontrol bacillus strain, and belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms. Biocontrol bacillus is bacillus velezensis YJC-9, the strain is already reserved in The China Typical Culture Collection Center of Wuhan university at 11thApril in 2018, and the preservation serial number of the strain is CCTCC NO.M 2018196. Thebiocontrol bacillus strain can prevent and control wheat sharp eyespot, wheat scab, sclerotinia rot of colza, gray mold of strawberries, pepper root rot, kidney bean blight and tobacco alternariaalternata, is a biocontrol bacterium having broad-spectrum resistance, and has good application prospects in agricultural disease prevention and control.
Owner:十堰市农业科学院
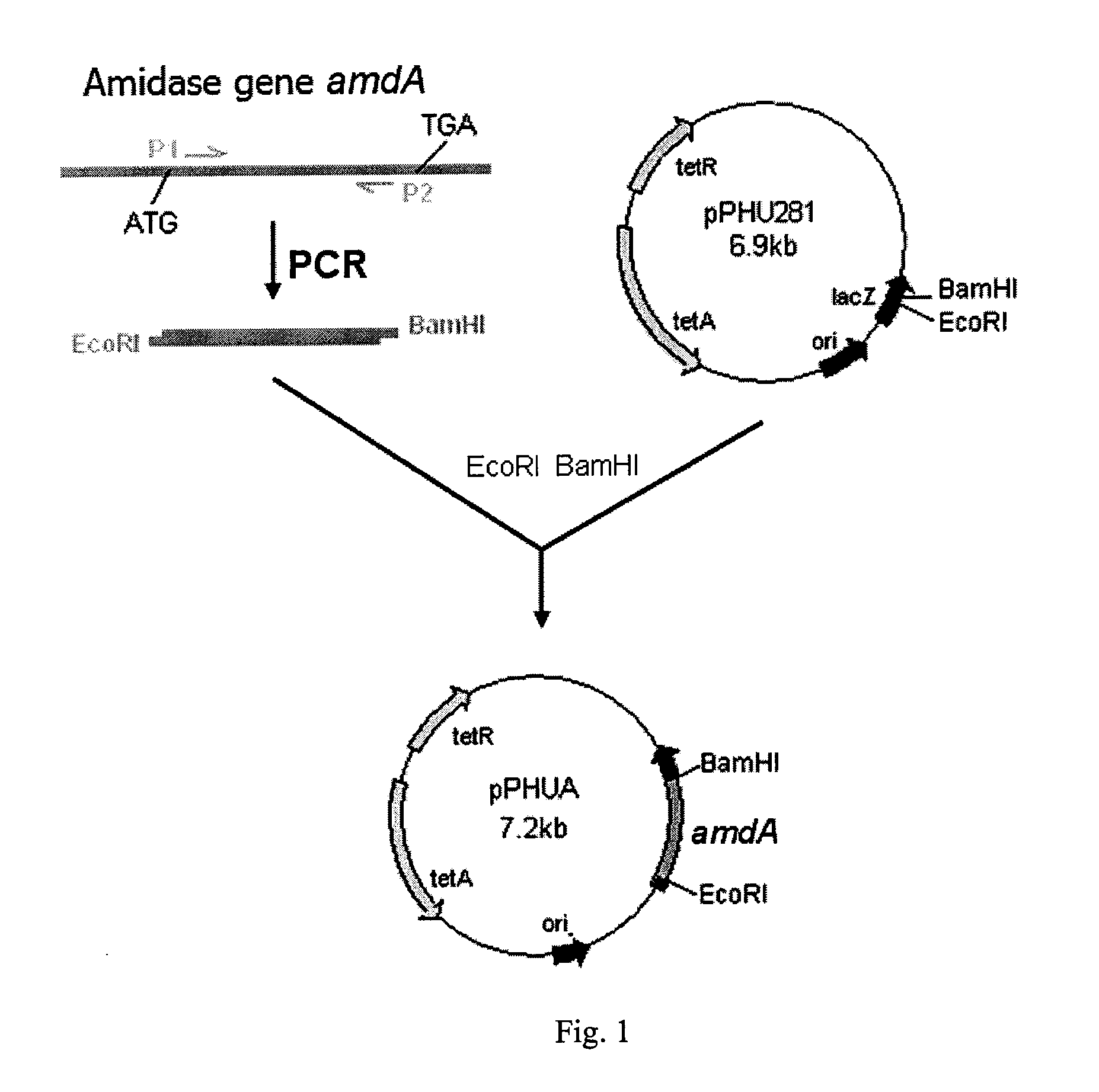
Engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium with amidase gene koucked-out, the construction and the use thereof
ActiveUS20110104690A1Inhibit expressionNot affect performance of strainBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesLarge fragment
An engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium and its construction method as well as its applications, wherein the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium is a mutant strain of an original nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium strain obtained by knocking-out or inhibiting the amidase gene in the original strain. The construction method of the engineered bacterium is to block the expression of the amidase gene by inserting the large fragment of a recombinant suicide plasmid carrying an amidase gene fragment into a wild-type strain through the homologous recombination between the recombinant suicide plasmid and the amidase gene of the wild-type strain. Compared to the corresponding wild-type bacterium strain, both the cell growth and the nitrile hydratase expression of the engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium according to the invention are increased. In the process of catalyzing the hydration of acrylonitrile to produce acrylamide, the yield of the product, acrylamide, is significantly increased, while the yield of the by-product acrylic acid is significantly decreased. The engineered nitrile hydratase-producing bacterium of the present invention has wide application prospect in the production of acrylamide by microbiological process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
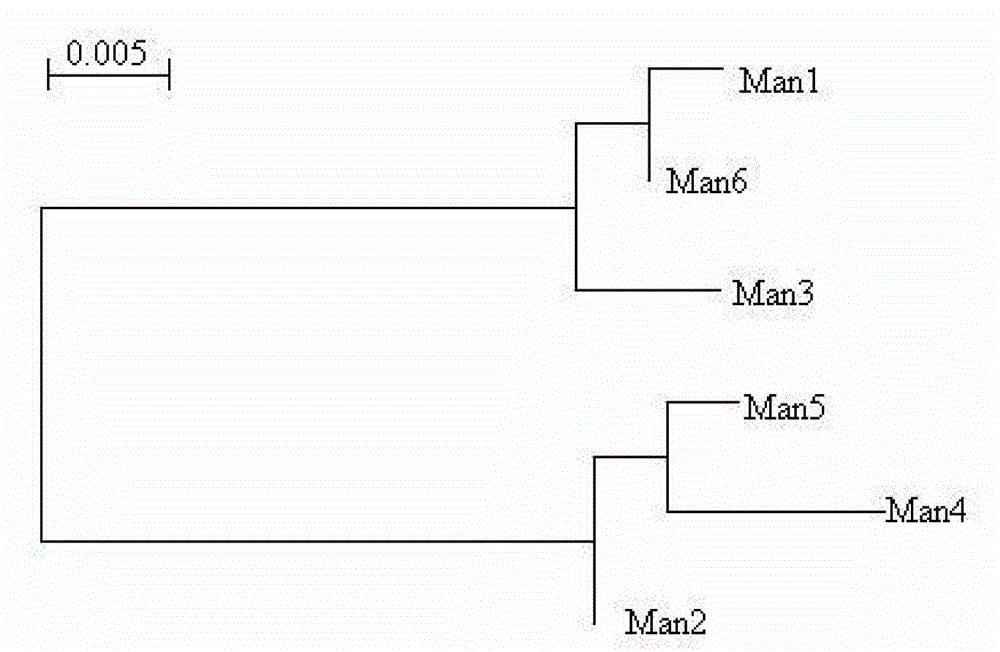
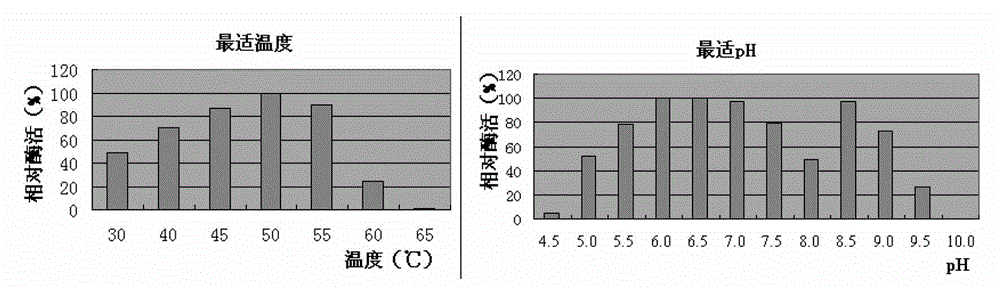
Mannase and mutants thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering and provides mannase with a high enzyme activity and mutants thereof. According to the mannase and the mutants thereof, six mannase genes obtained by cloning different strains of Bacillus licheniformis and encoded mannase of the mannase genes, difference and genetic relationships among the six mutants are analyzed by bioinformatics. The mannose has the high enzyme activity in a neutral pH condition, and can be used as a feed enzyme preparation in an optimum temperature.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
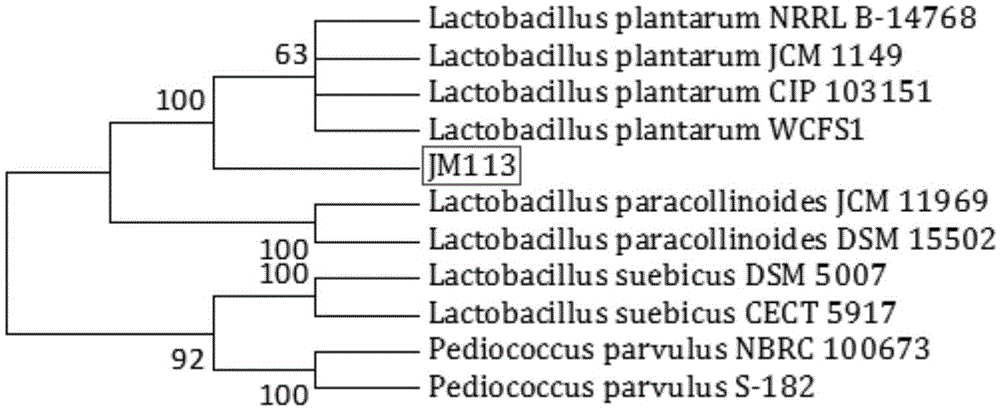
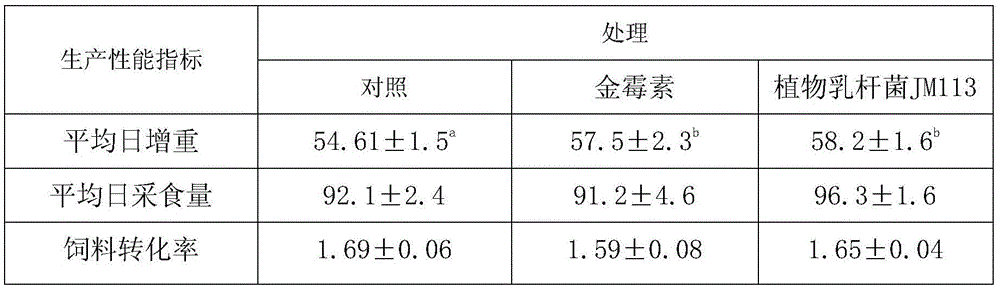
Lactobacillus plantarum JM113 and application thereof
InactiveCN105543126AEnhanced inhibitory effectIncrease production capacityBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBacteroidesMicrobacterium
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum JM113, wherein a strain JM113 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTC) on November 18th, 2015 with a preservation number of CCTC M2015680, and is called simply the JM113. The lactobacillus plantarum JM113 disclosed by the invention can better tolerate factors such as acid and cholate which are unbeneficial to bacterial growth in a gastrointestinal tract and has a good inhibiting action for enteropathogetic bacteria; the lactobacillus plantarum JM113 has better fermentability and potential for mass production. The lactobacillus plantarum JM113 disclosed by the invention is prepared into lactococus lactis powder which is added into broiler diet, so that the production performance of broilers can be remarkably improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Inhibition of RNA function
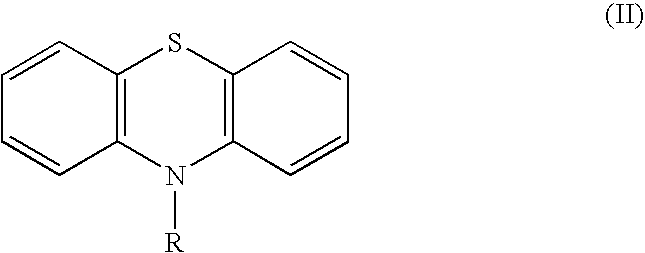
Inhibition of RNA function, and treatment or control of diseases or conditions, e.g. infectious diseases such as viruses and viral infections (including HIV) and microbial infections, by the contacting of the RNA with a compound having a central or core structure comprising three fused rings containing from 12 to 15 ring atoms, the central ring including at least one heteroatom selected from nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur, the atoms of the three-ring core structure being optionally substituted with substituents such as halogens, cyano, and / or various substituted or unsubstituted aliphatic and / or heteroaliphatic moieties, or contacting the RNA with yohimbine, usnic acid or N-{4-[2,5-Dioxo-1-(4-trifluoromethoxy-phenyl)-pyrrolidin-3-yl]-phenyl}-2,2,2-trifluoro-acetamide. Preferred compounds are various phenothiazines, including both known and novel compounds.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof
ActiveCN103540545AImprove acid resistanceGood resistance to bile saltsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyStaining
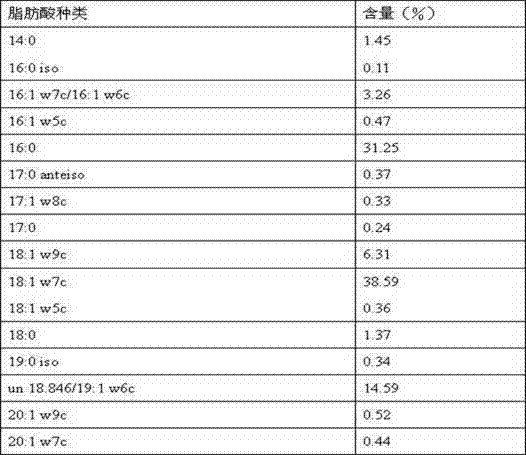
The invention discloses pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof. The Latin name of the pediococcus pentosaceus is Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05, and the pediococcus pentosaceus is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7049. The pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention has the morphological characteristics that the thallus is rod-shaped, dose not generate spores, does not have motility, and has masculine Gram staining. The whole-cell fatty acid of the pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention comprises the following main components in percentage by weight: about 1.45% of 14:0, about 3.26% of 16:1w7c / 16:1w6c, about 31.25% of 16:0, about 6.31% of 18:1w9c, about 38.59% of 18:1w7c, about 1.37% of 18:0 and about 14.59% of un18.846 / 19:1w6c. The invention also discloses a complete sequence of 16S ribosome DNA (16SrDNA) of the pediococcus pentosaceus. The pediococcus pentosaceus and a preparation thereof disclosed by the invention can be used for adjusting the micro-ecological balance of intestinal tracts of human or animals, promoting digestive absorption and slowing down the happening and development of liver failure of experimental animals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Molecular and bioinformatics methods for direct sequencing
InactiveUS20160180018A1Fast and accurate methodMinimize degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisBiotechnologyRNA - Ribonucleic acid
The present invention relates to methods for preparing an isolated biological sample containing at least one of DNA and RNA, such that the DNA and / or RNA is preserved in the sample at ambient temperatures for at least thirty days, the method comprising: contacting the isolated biological sample with a composition comprising a chaotropic agent, and subjecting the contacted sample to microbial cell lysis; and optionally, contacting the lysed biological sample with a slurry of size-selected silicon dioxide to form at least one of DNA-silicon dioxide complexes or RNA-silicon dioxide complexes in the sample; isolating at least one of DNA-silicon dioxide complexes or RNA-silicon dioxide complexes from the sample; and, separating at least one of DNA and RNA from the silicon dioxide and collecting at least one of the DNA and RNA.The present invention further relates to methods for preparing an isolated biological sample, the method comprising, separating the components in an isolated biological sample according to their size, wherein the components are at least one of DNA and RNA; purifying and isolating SSU rRNA from the biological sample using a composition comprising a ribonuclease inhibitor and a deoxyribonuclease to remove DNA from the sample, reverse transcribing the SSU rRNA into ds cDNA using random primers for SSU rRNA.The present invention also relates to computer implemented methods comprising, receiving an isolated sample prepared according to the methods of the invention, sequencing the sample, and providing the sequence with a sequence identifier (ID), the sequence comprising a plurality of groups of k-mers, each group of k-mers defining a node in a multi-level hierarchy which defines the relationship between the groups of k-mers; providing each group of k-mers with a respective group identifier (ID), determining the frequency of the k-mers in each group; generating a group signature array for each group of k-mers, each group signature array comprising the k-mers in each group that have the most increased frequency compared with the sibling k-mers; generating a signature map comprising each group signature array and at least one of the identifiers, the identifier of at least one parent group and the identifier of at least one child group; and outputting the signature map to be used to classify the sequence.
Owner:16S TECH INC
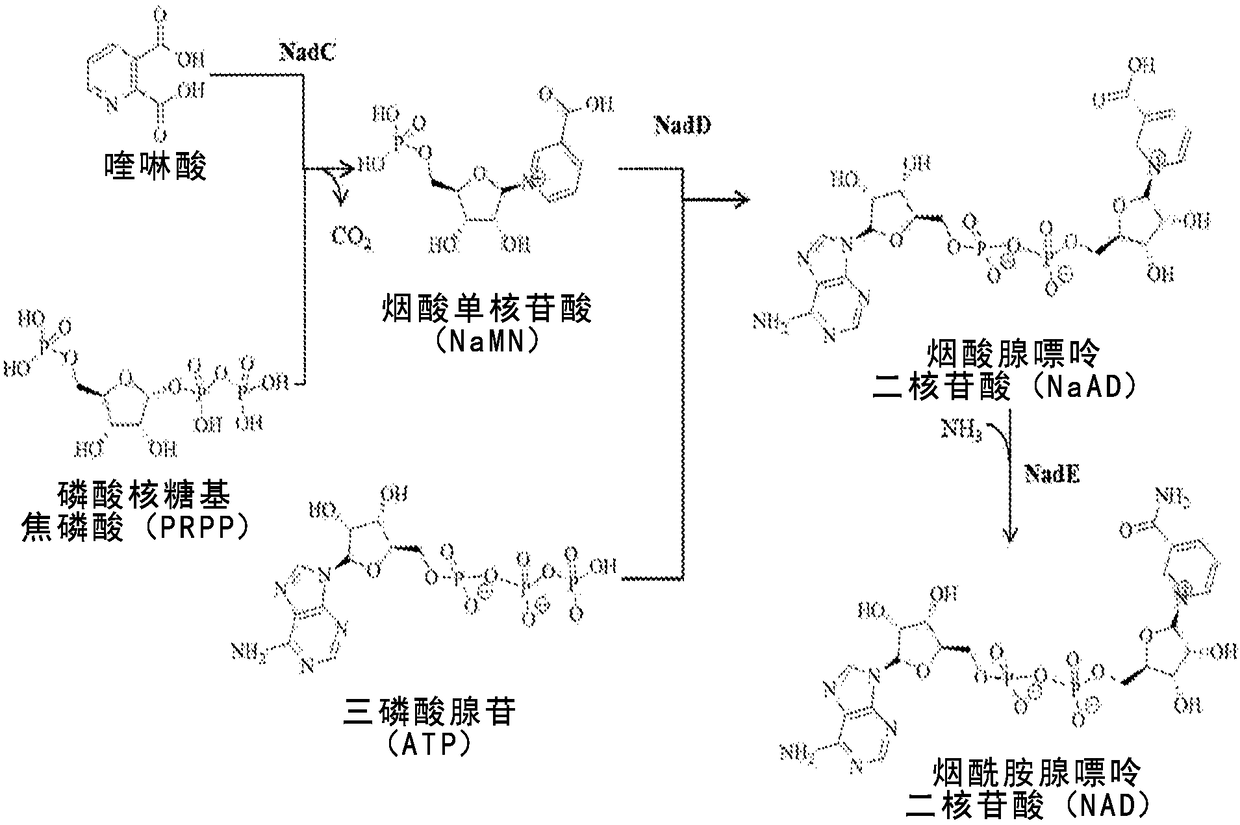
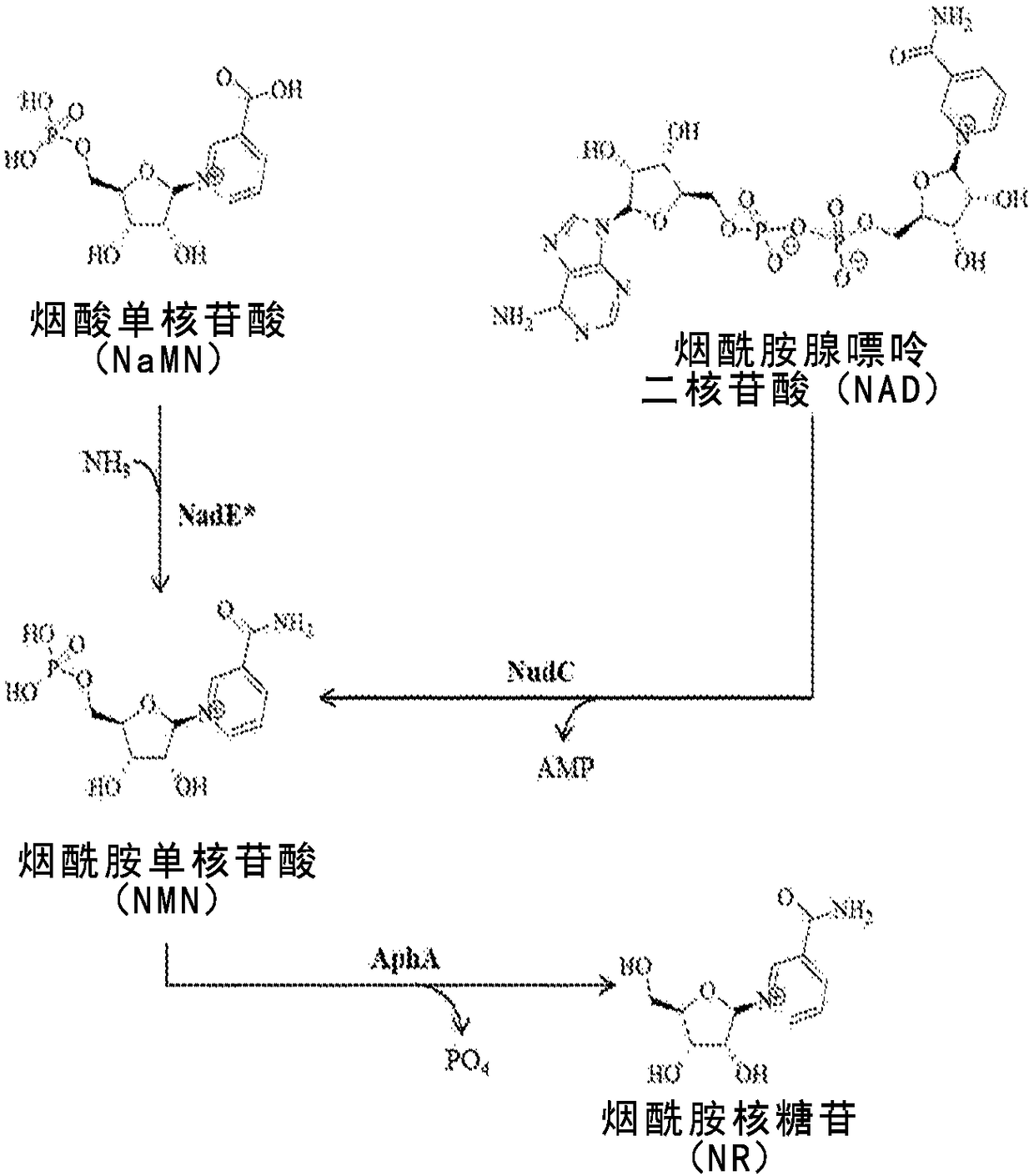
Microbial production of nicotinamide riboside
The disclosure relates to a novel method, expression vectors, and host cells for producing nicotinamide riboside by regulating the pathways that lead to the production of nicotinamide riboside.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
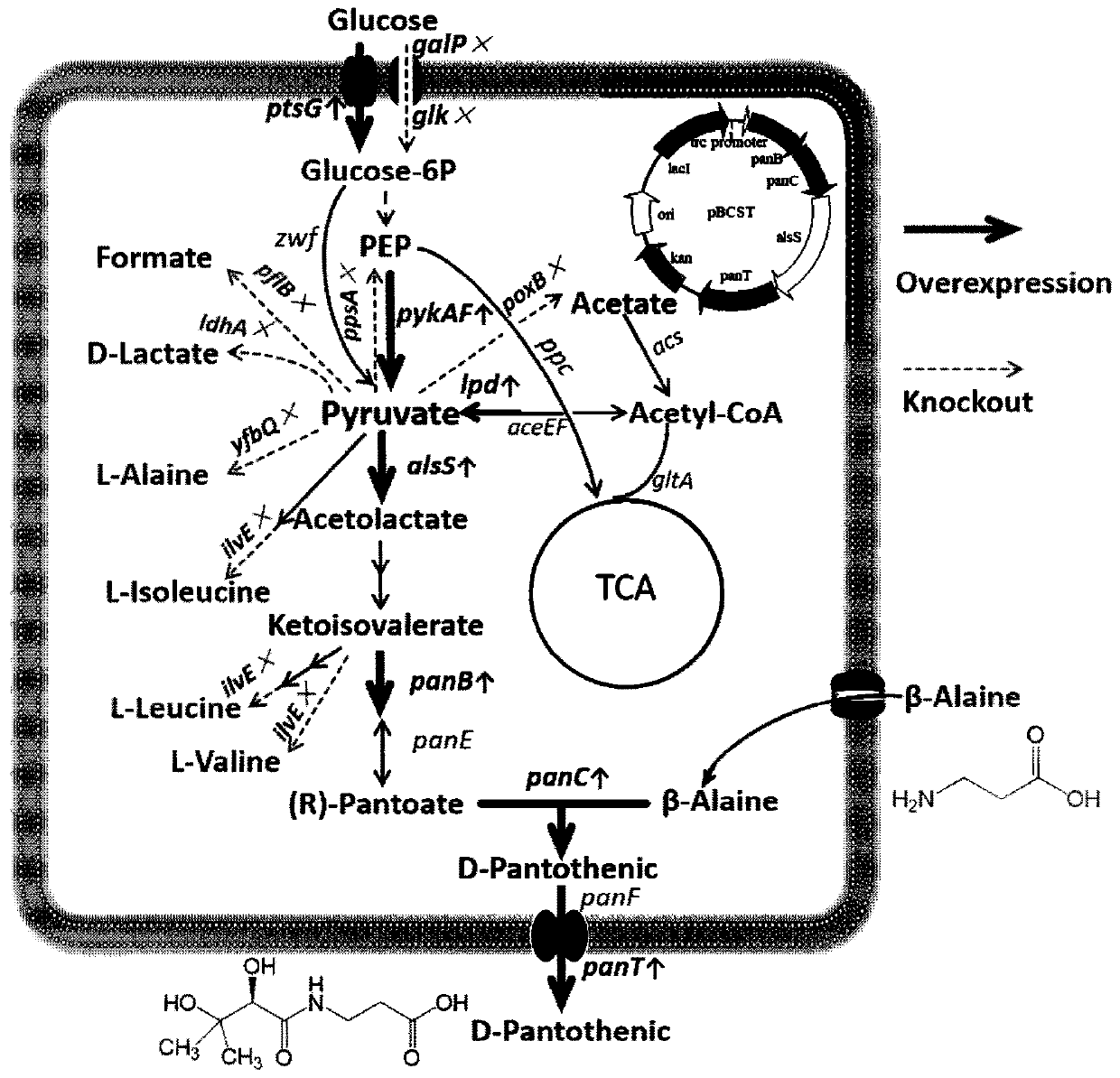
Construction method of high-yield pantothenic-acid genetically engineered bacterium and bacterium strain
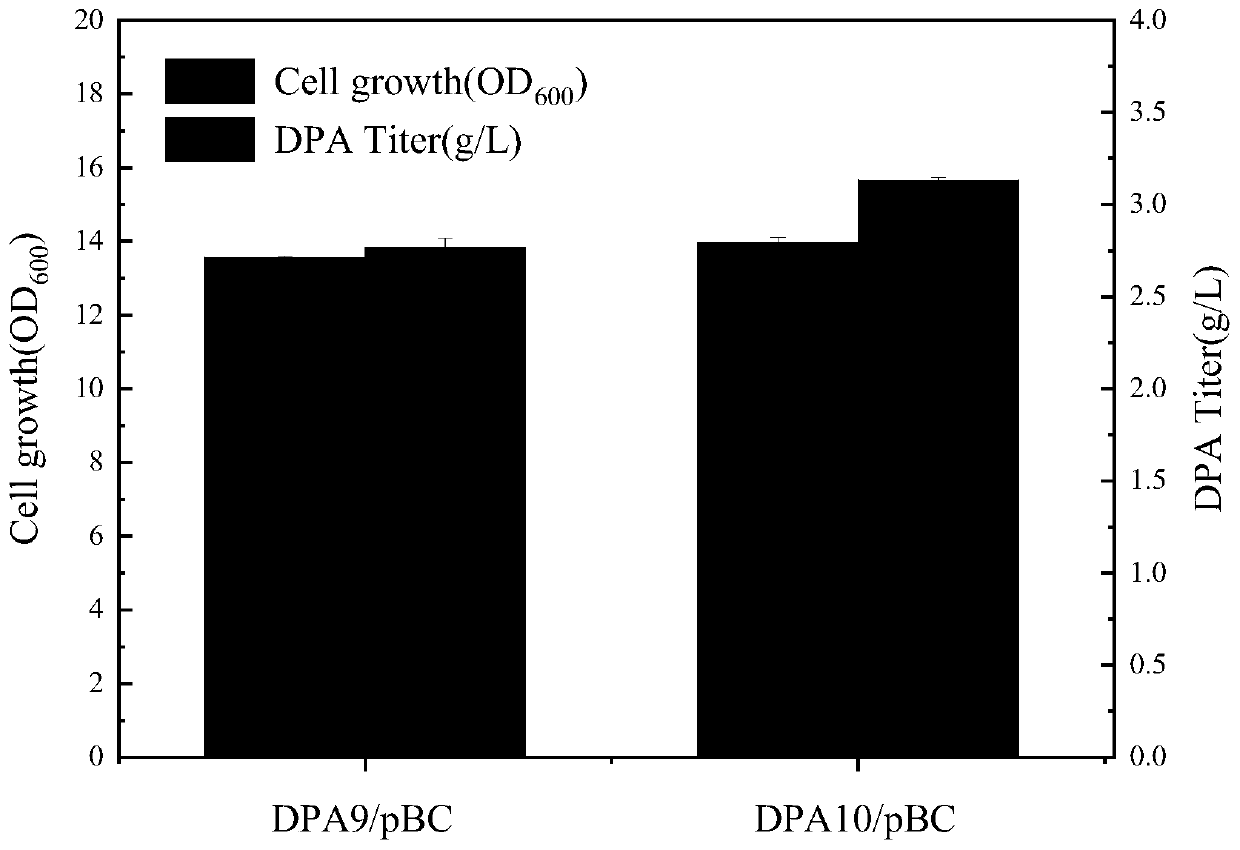
ActiveCN111100834APromote accumulationGuaranteed supplyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The present invention relates to a construction method of high-yield pantothenic-acid genetically engineered bacterium and the bacterium strain, and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium in preparation of D-pantothenic acid by microbial fermentation. The construction method is as follows: (1) enhancing expression of lpd gene; (2) knocking out glk and galP, destroying a glucose non-PTS transport system, enhancing expression of ptsG gene and enhancing a glucose PTS transport system; (3) knocking out yfbQ and ppsA genes; (4) knocking out poxB, pflB and ldhA genes; (4) knocking out ilvE gene; (5) introducing heterologous acetolactate synthase gene alsS; and (6) introducing heterologous pantothenic-acid transporter panT into plasmids and finally obtaining the optimal D-pantothenic acid high-yield escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium strain. D-pantothenic acid potency increases from 2.76 g / L to 6.33 g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
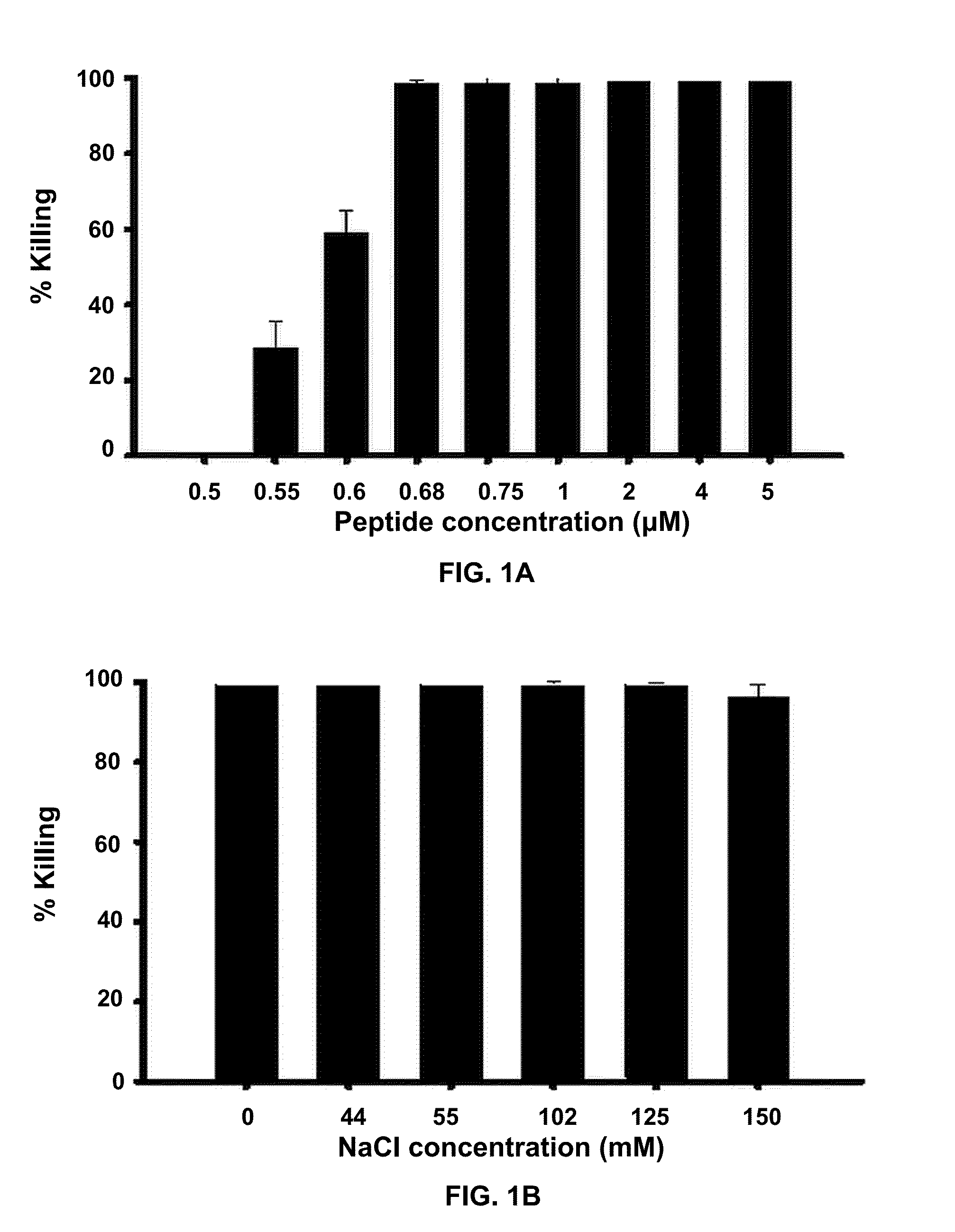
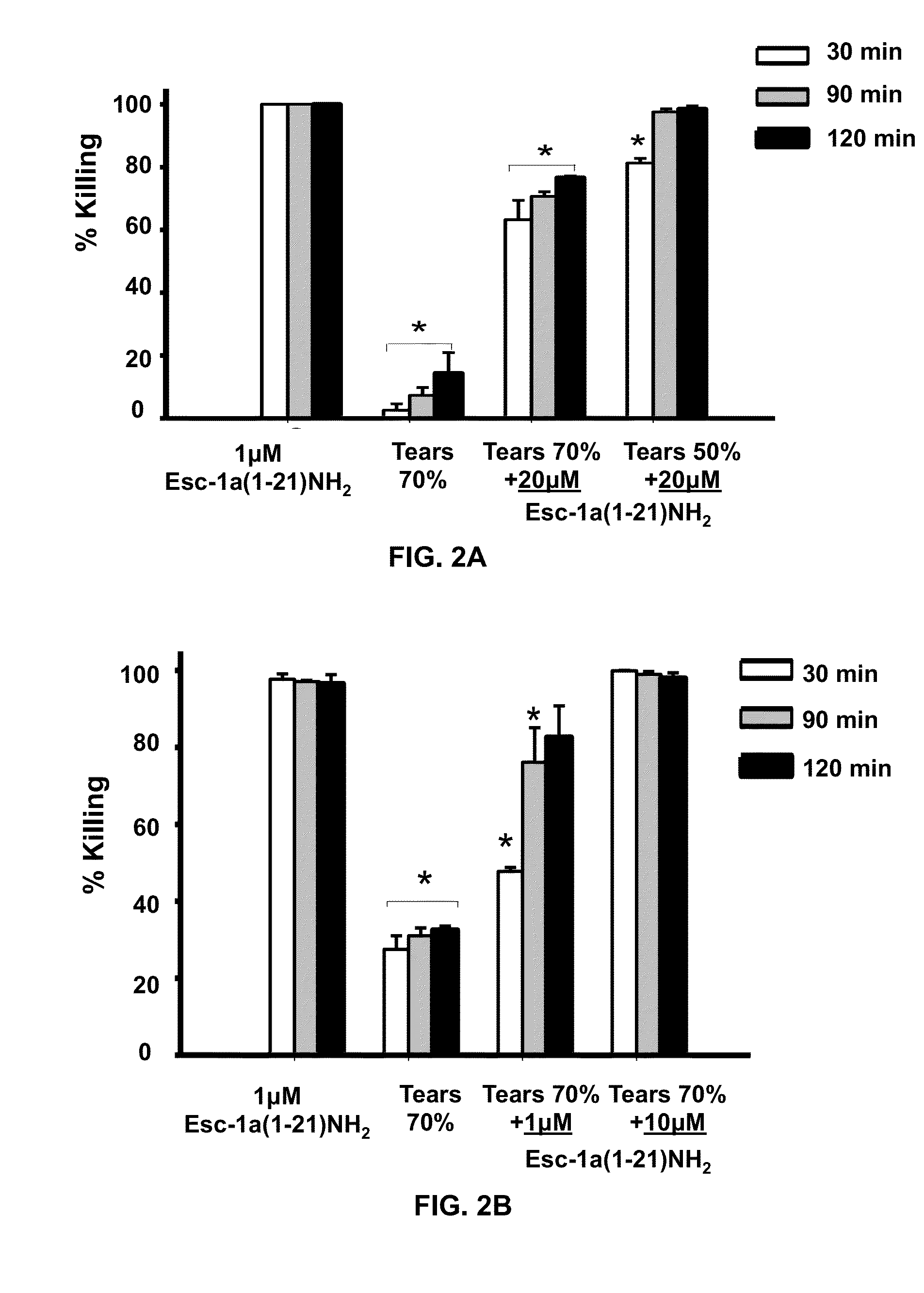
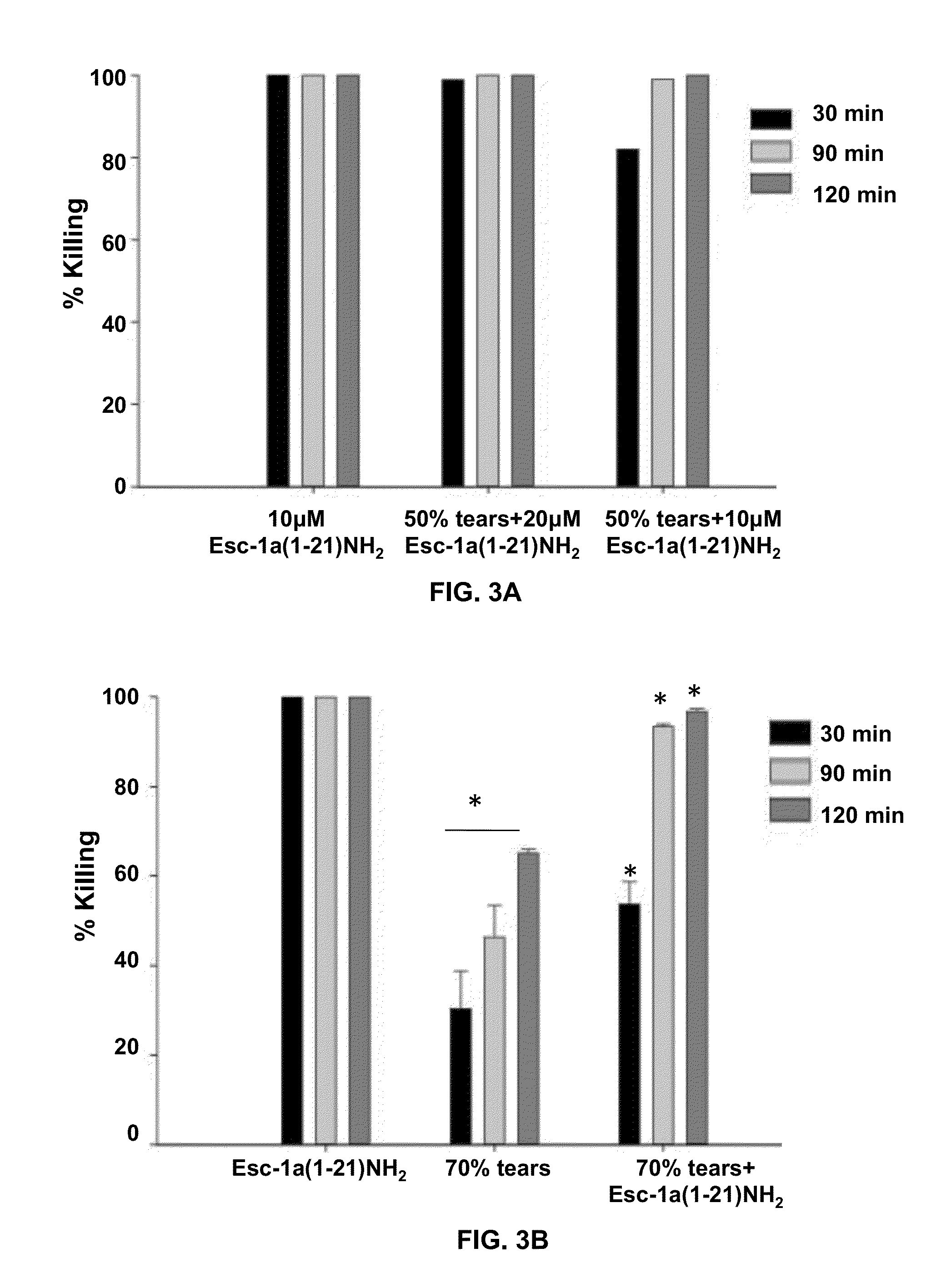
Esculentin 1a Derivatives and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20150104492A1Anti-microbial activity can be reducedCompromise antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideWound healingMedicine
The present invention provides synthetic antibacterial peptides comprising a sequence at least 80% identical to a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 or the diastereomer thereof with a sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 3 or pharmaceutical compositions thereof. Also provided are methods for reducing the severity of microbe-induced inflammation and for stimulating wound healing via the synthetic antibacterial peptides. Further provided is a device having a surface with a coating comprising the synthetic antibacterial peptides.
Owner:UNIV DEGLI STUDI DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA +1
Compositions and methods for rapid selection of pathogen binding agents
InactiveUS20110136727A1Improve abilitiesIncrease pressureAntibacterial agentsBiocideSyndecan bindingMicrometer
Isolated glycan binding peptide complex comprise two or more glycan binding peptides operatively coupled to each other. These are bacterial binding peptide conjugates (e.g., glycan binding peptides) to a multivalent polymer (e.g., a multivalent PEG molecule) or to the surface of particles that create multimeric constructs that inhibit growth and aggregation of microbes. Included is a method of evaluating a substance for the presence of a microbe comprising contacting the substance with a peptide microarray or a peptide complex comprising a plurality glycan binding peptide operatively coupled to a substrate or multivalent linker, wherein the glycan binding peptide is coupled to an array by a linker that is at least 0.5 micrometers in length.
Owner:SVAROVSKY SERGEI
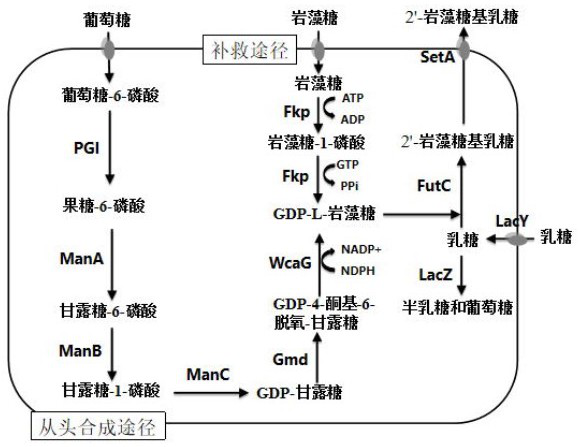
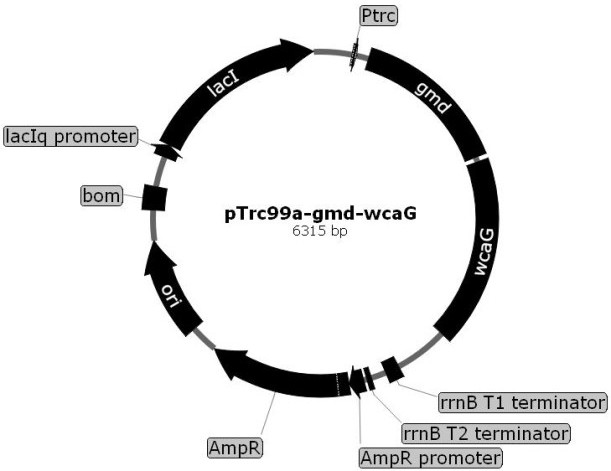
Escherichia coli for producing 2'-fucosyllactose and application thereof
The invention relates to recombinant escherichia coli for producing 2'-fucosyllactose and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbial metabolic engineering. According to a regulation and control strategy for the expression level of 2'-fucosyllactose de novo synthesis route key enzyme, different enzymes are subjected to regulation and control of genome overexpression or plasmid overexpression, the efficiency of a metabolic pathway can be greatly improved, compared with the prior art, the efficiency of a genetic engineering strain constructed through related strategies is improvedby 13 times or above, and a foundation is laid for industrial production of the 2'-fucosyllactose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for producing extracellular pullulanase by applying auto-induction culture medium and dual-temperature control strategy
ActiveCN102676480AImprove abilitiesIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for producing extracellular pullulanase by applying an auto-induction culture medium and a dual-temperature control strategy, belonging to the technical field of pullulanase production through microbial fermentation. The method has the following beneficial effects: pullulanase coding genes from Klebsiella variicola CCTCC M2012108 are inserted into an expression vector pET28a(+) to construct recombinant plasmids and E.coli is converted to obtain a recombination strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pulA containing the target pullulanase gene; the auto-induction culture medium is utilized to culture the recombinant E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pulA and ferment the recombinant E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pulA to generate enzyme by adopting the dual-temperature control mode of firstly culturing at 37 DEG C for 2-4 hours and then continuing culture at 25 DEG C for 48-72 hours; and after adopting the optimized fermentation conditions of the auto-induction culturemedium and dual-temperature, the extracellular pullulanase activity can reach 60-70U / mL. The method provides an effective strategy for producing extracellular pullulanase with recombinant E.coli and has great significance in the production process for developing novel recombinant pullulanase in future and application value of pullulanase.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com