Patents
Literature
53 results about "Microbial cellulose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microbial cellulose, sometimes called bacterial cellulose, is a form of cellulose that is produced by bacteria. It is widely used in the traditional Filipino dessert Nata de coco. Microbial cellulose was first confirmed as cellulose in 1886.
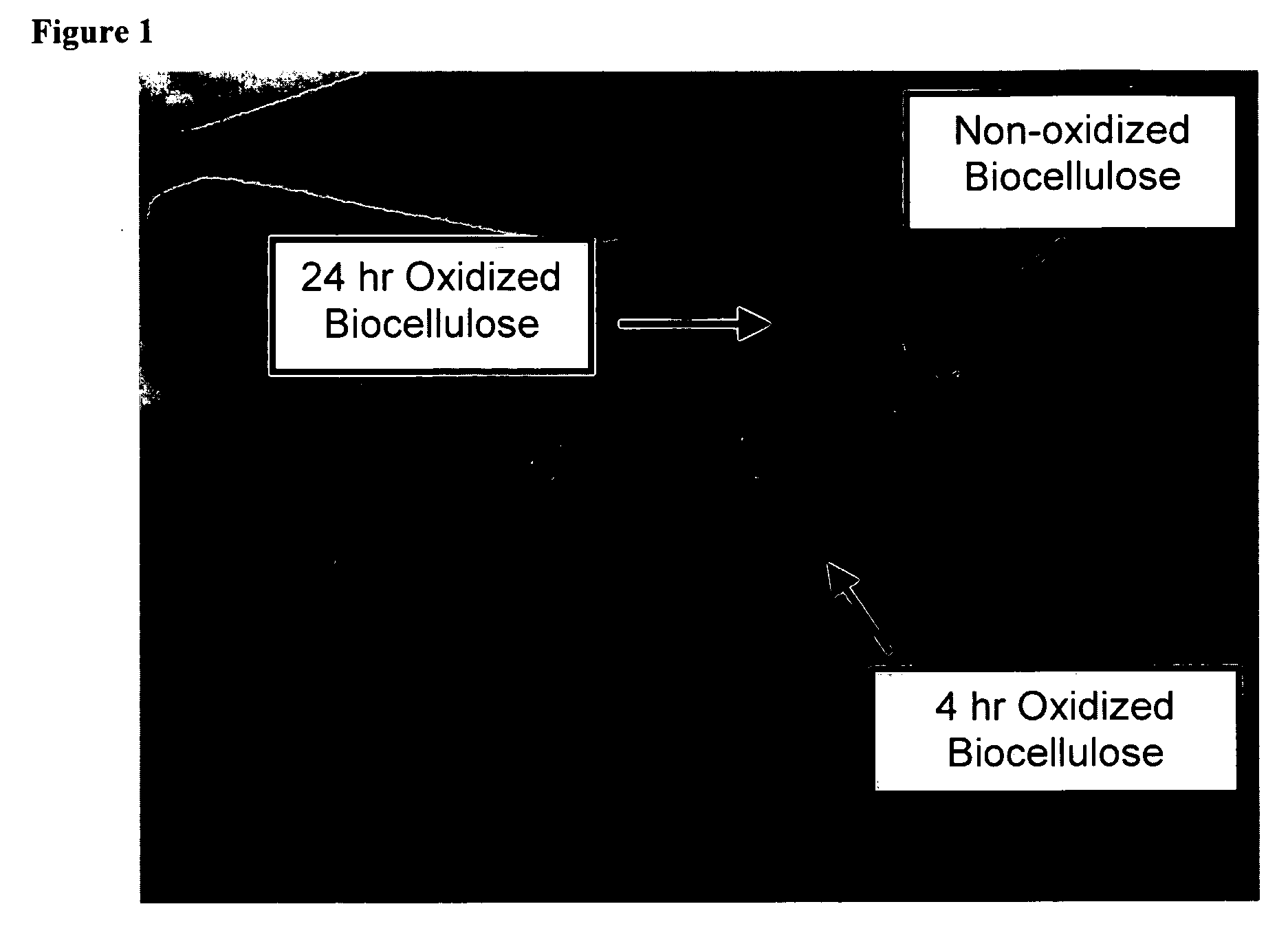
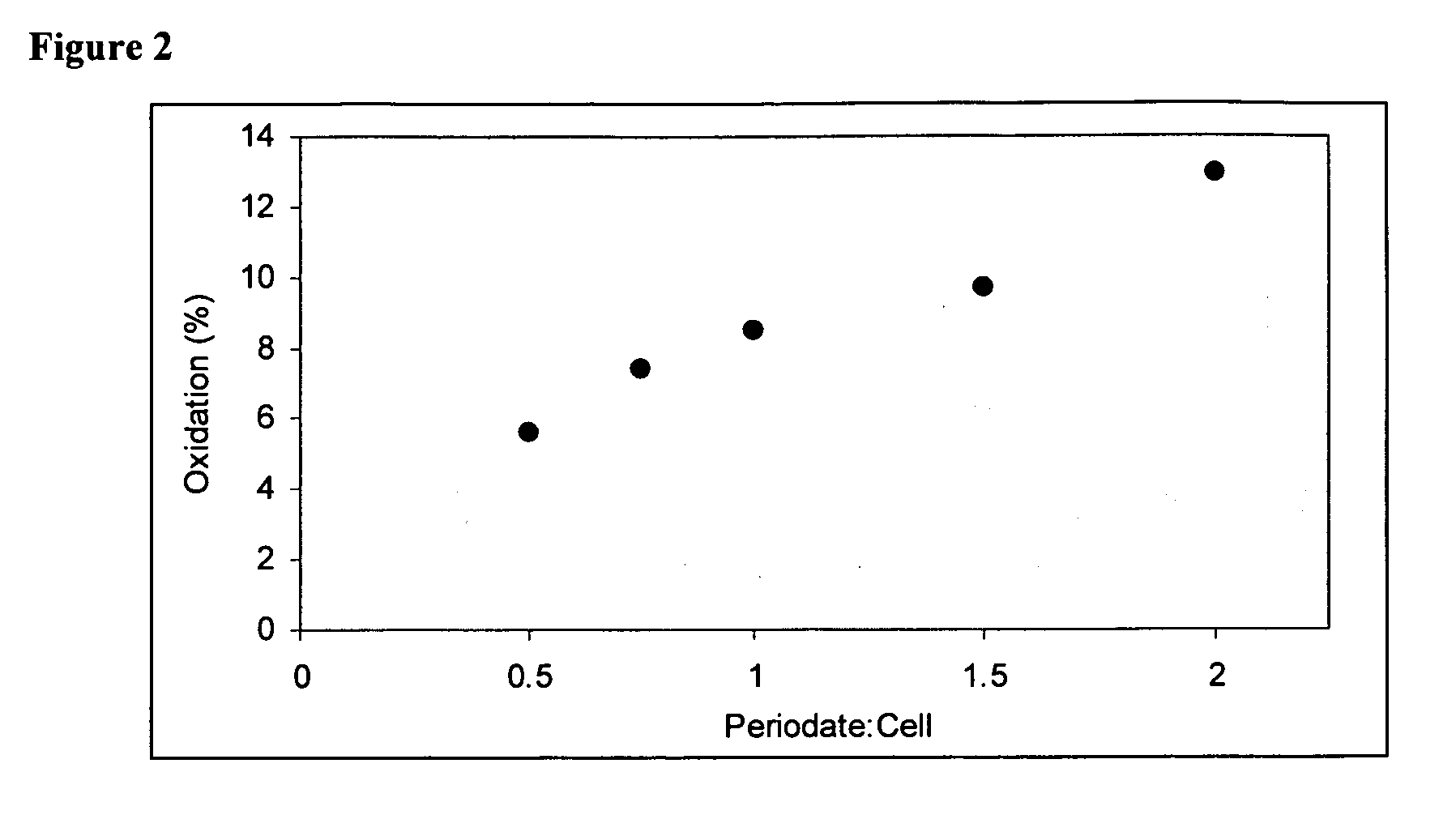
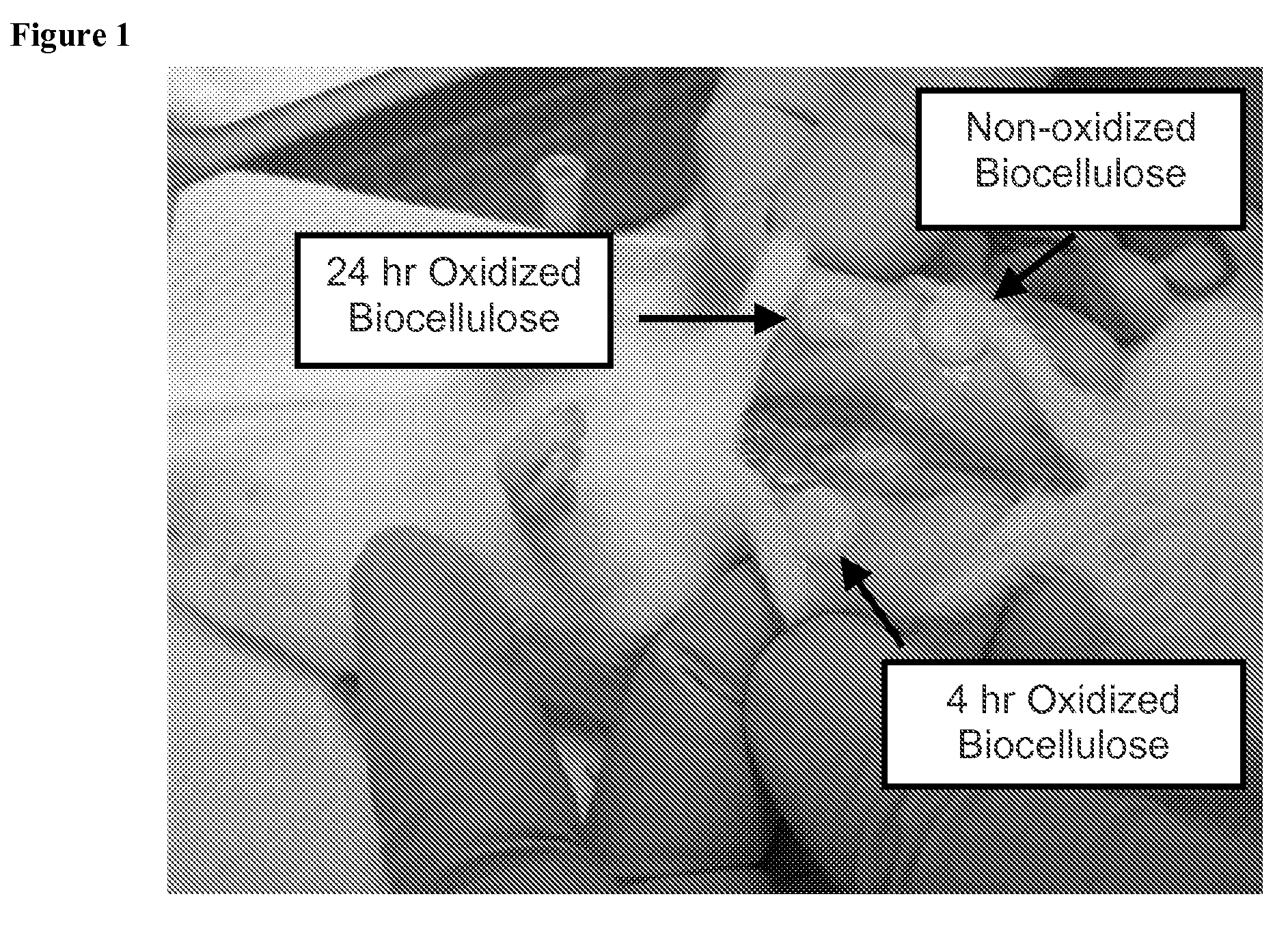
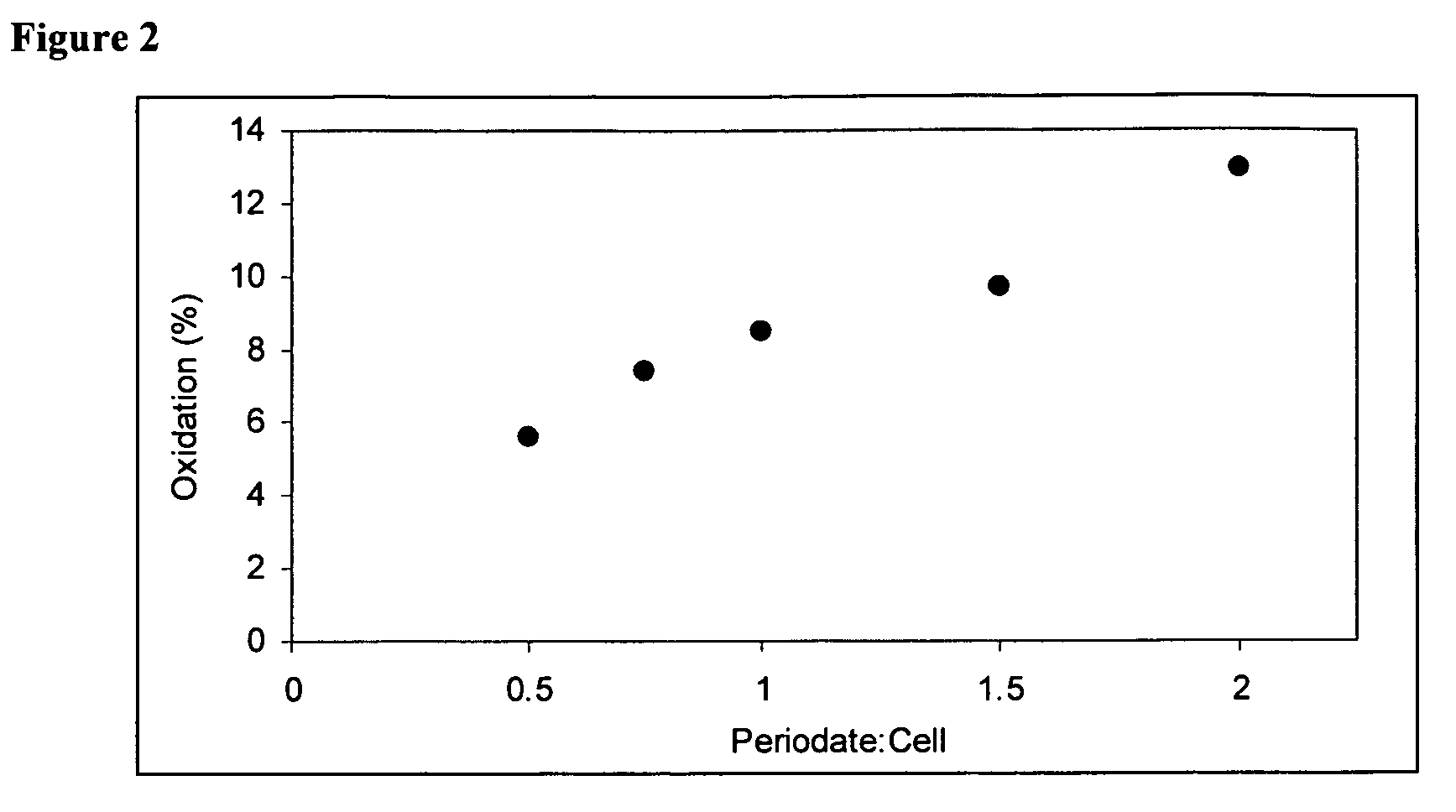
Oxidized microbial cellulose and use thereof
This application describes a bioresorbable biocellulose suitable for medical and surgical applications. In particular, the invention describes periodate oxidized microbial cellulose that can be produced to have any mechanical and degradation profile, depending on the desired application of the oxidized cellulose.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
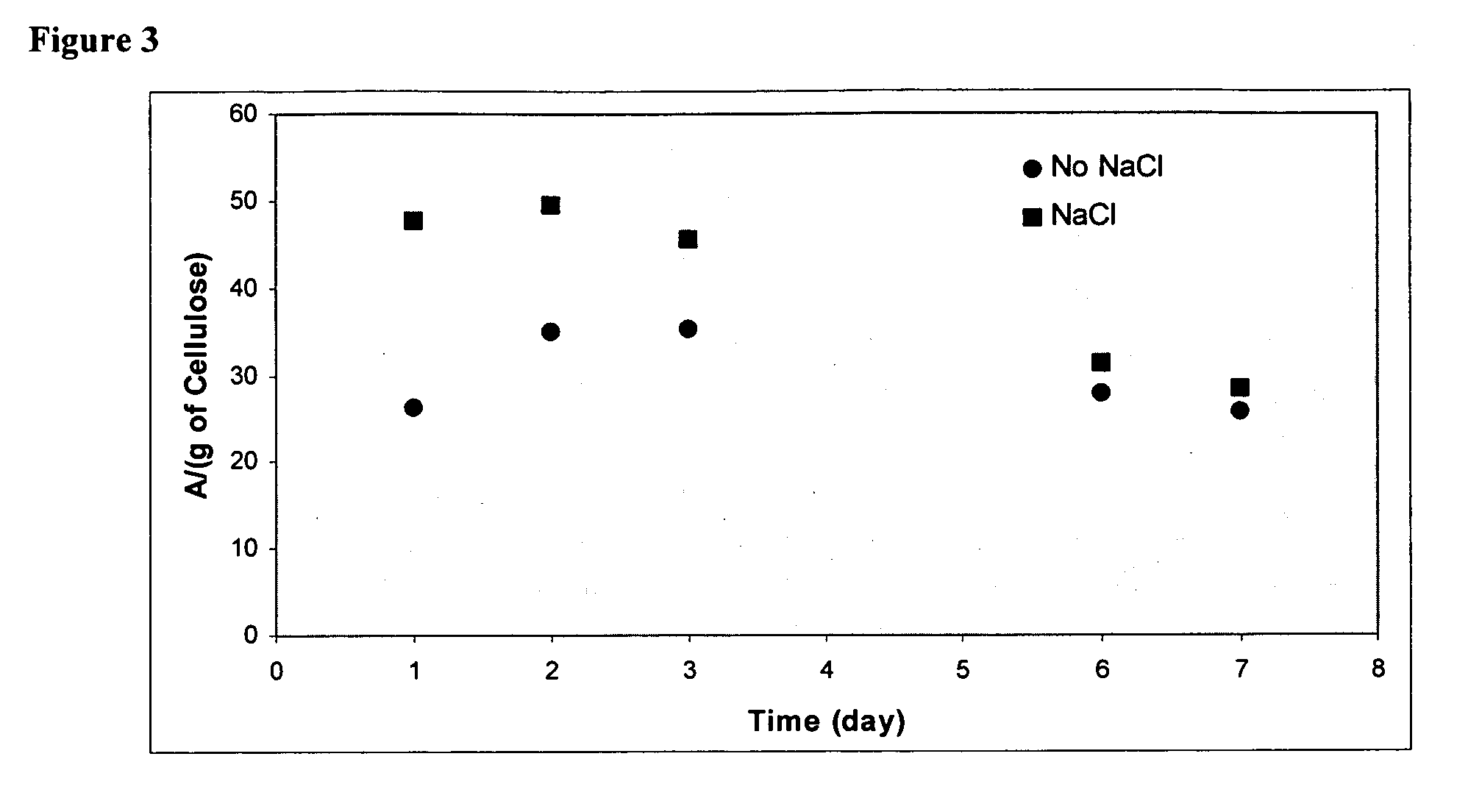
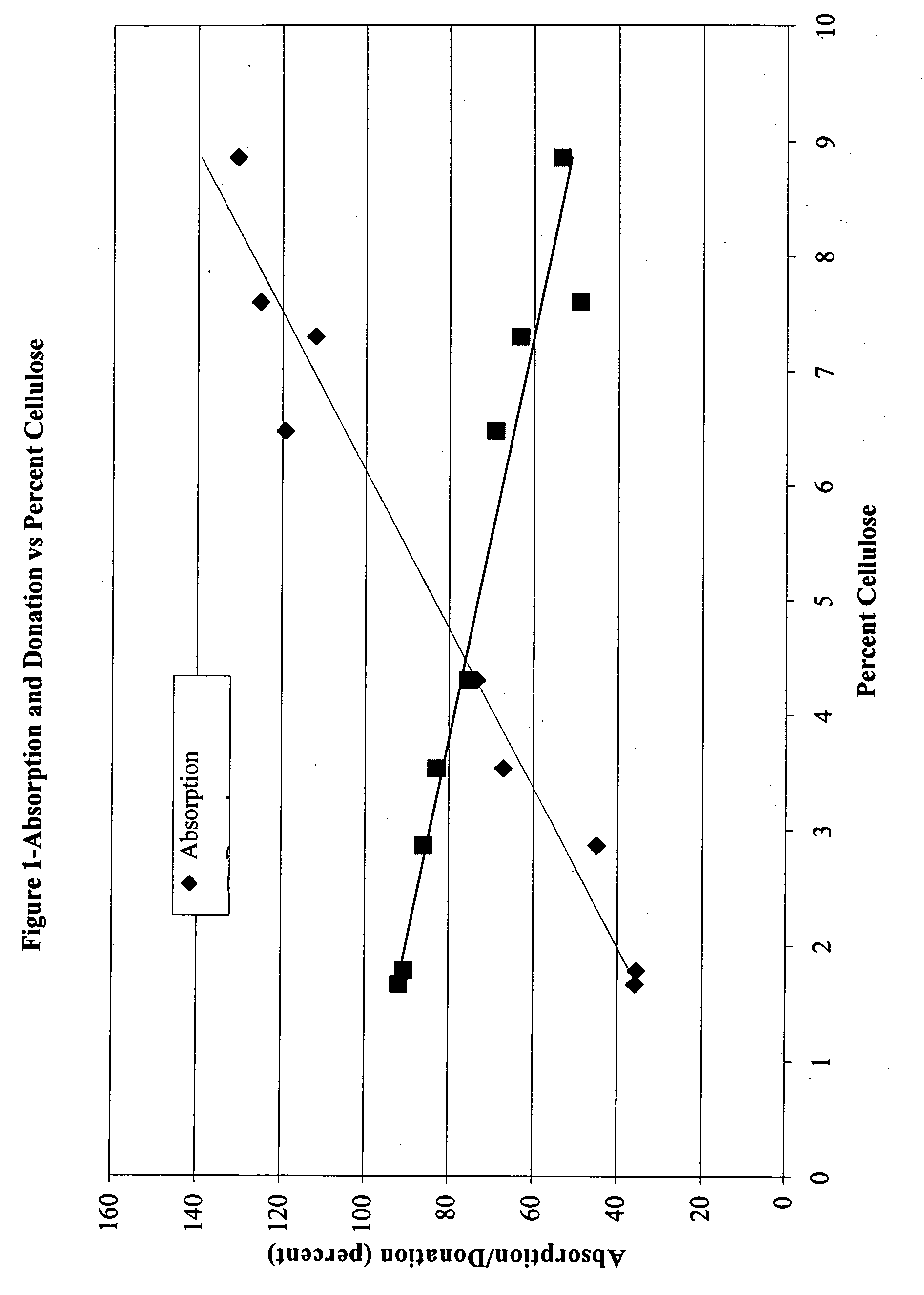
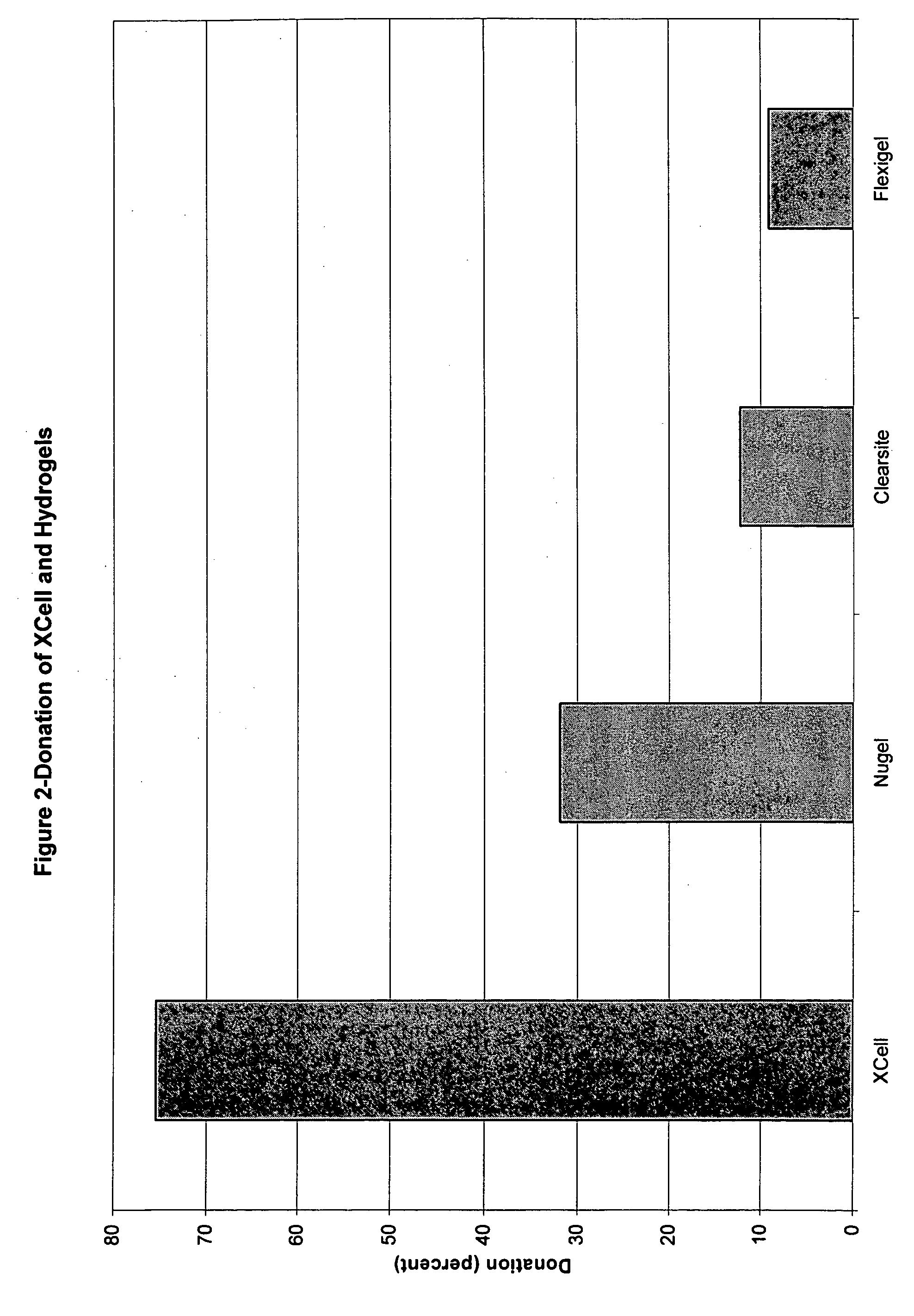
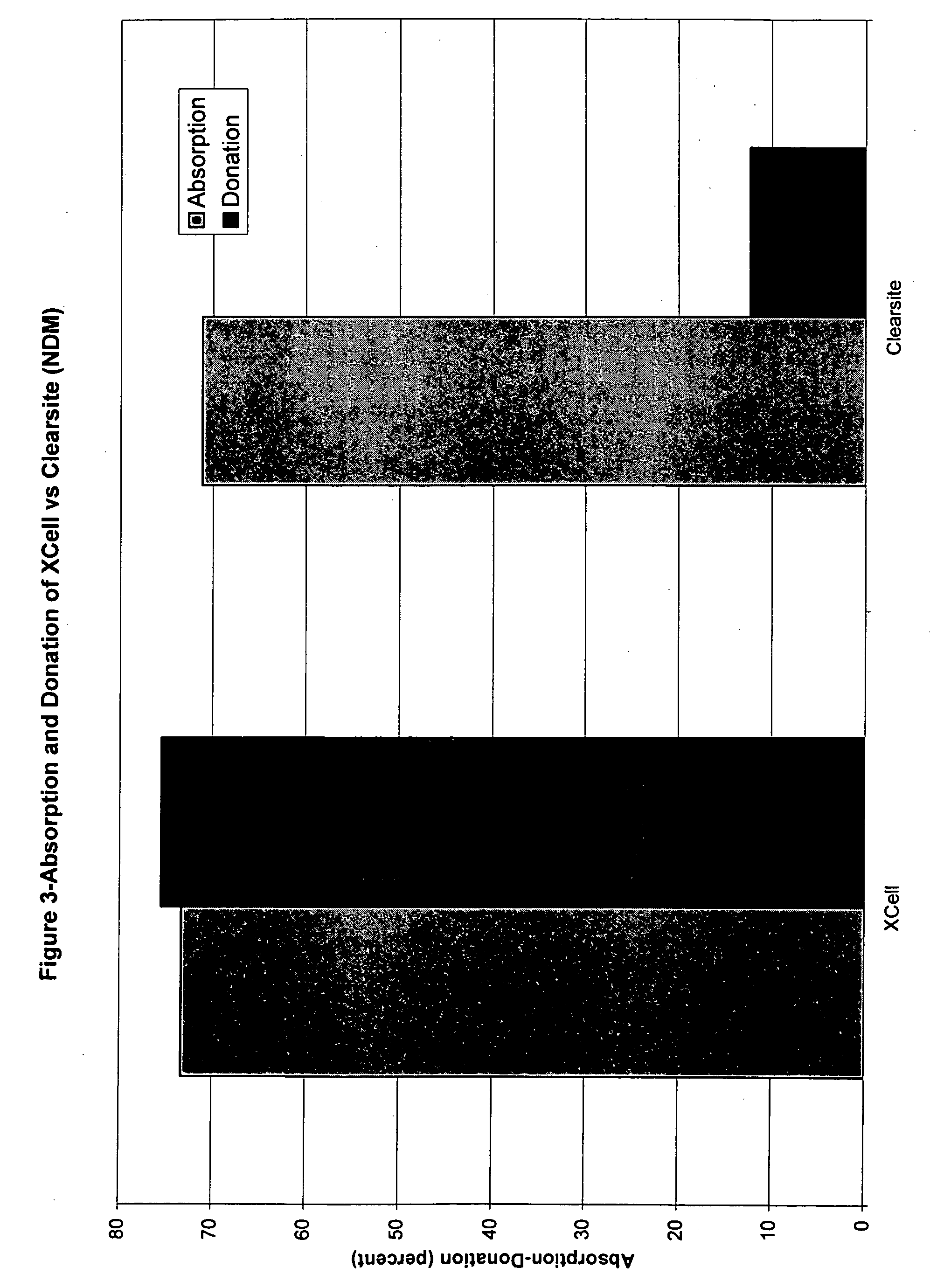
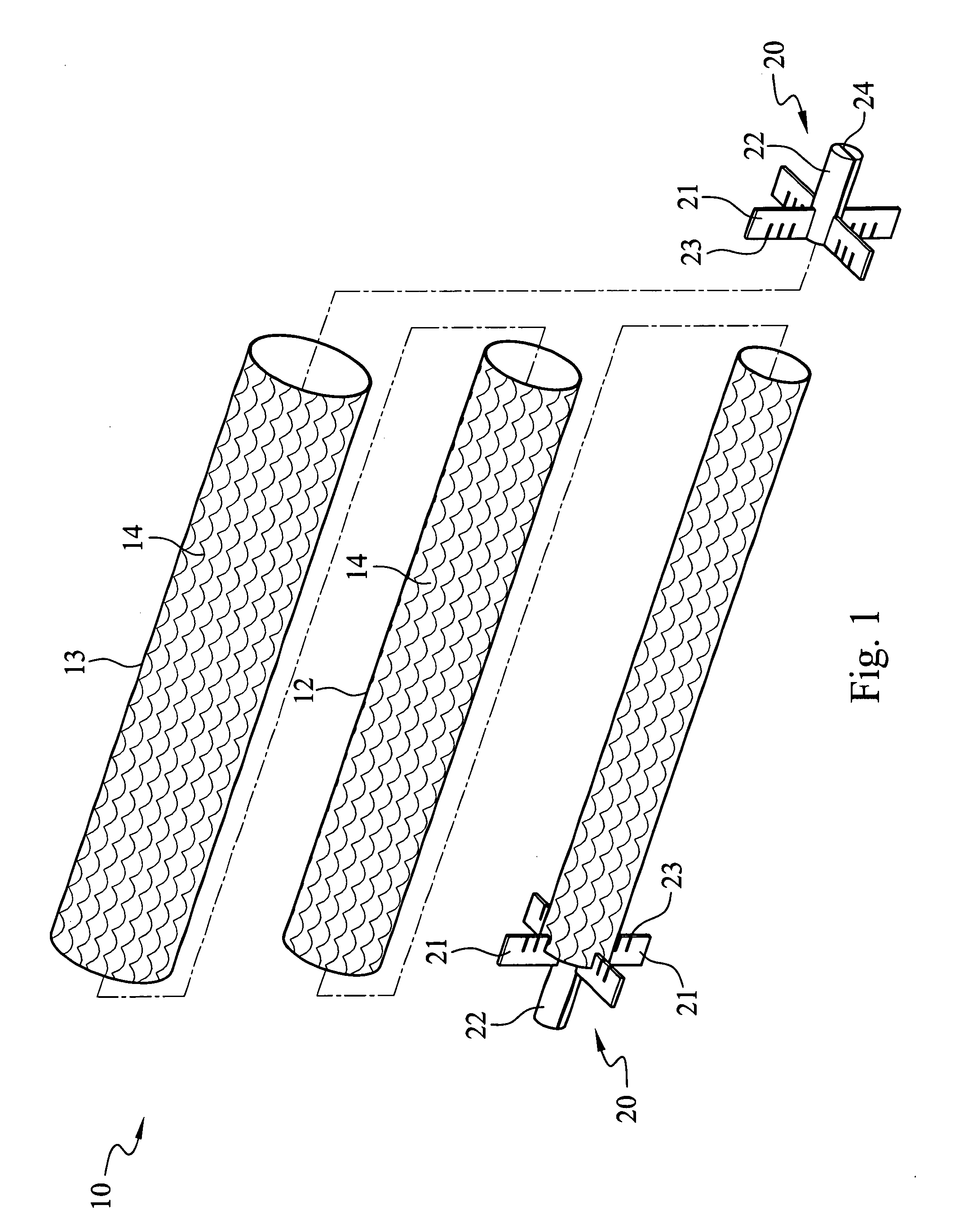
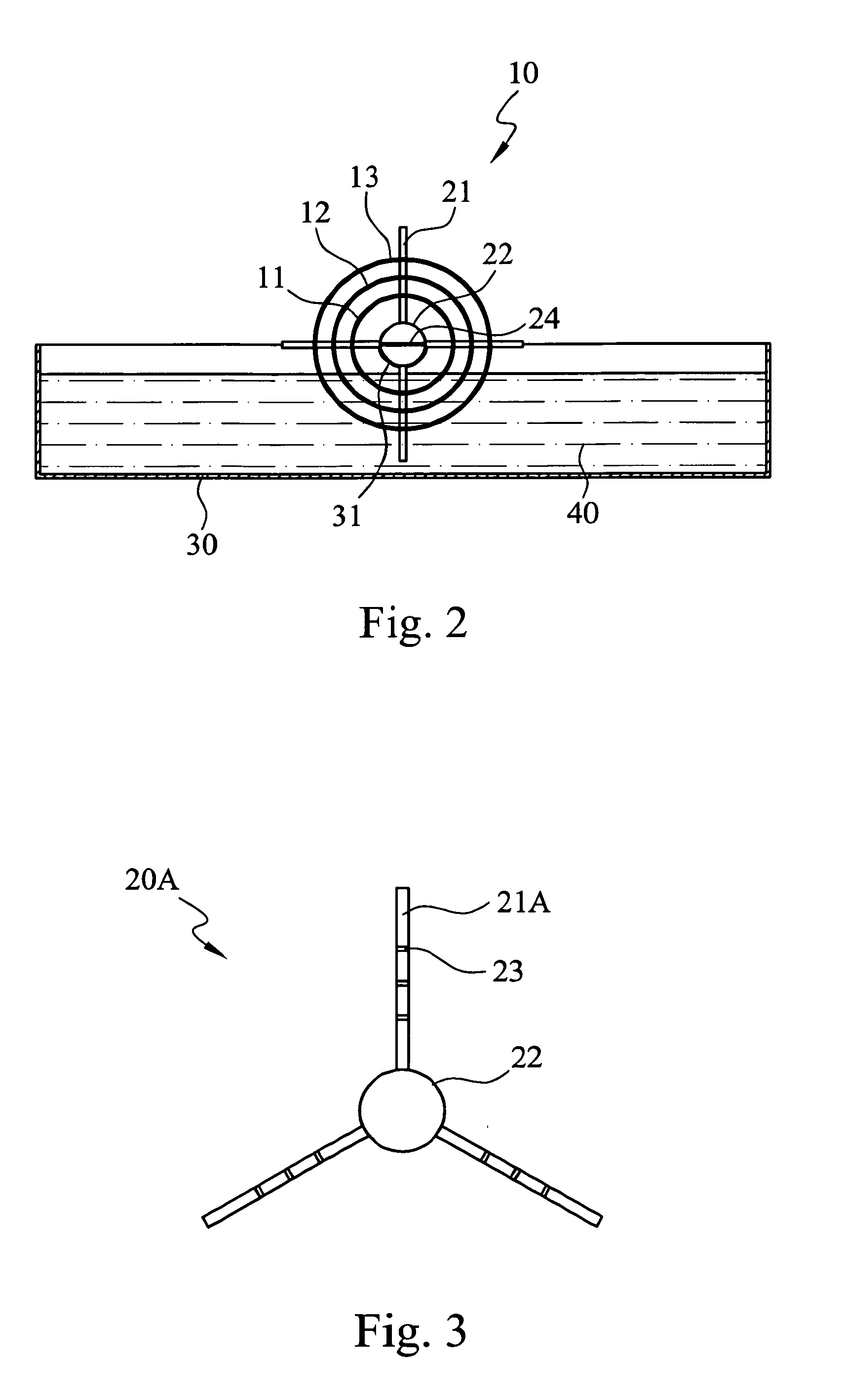
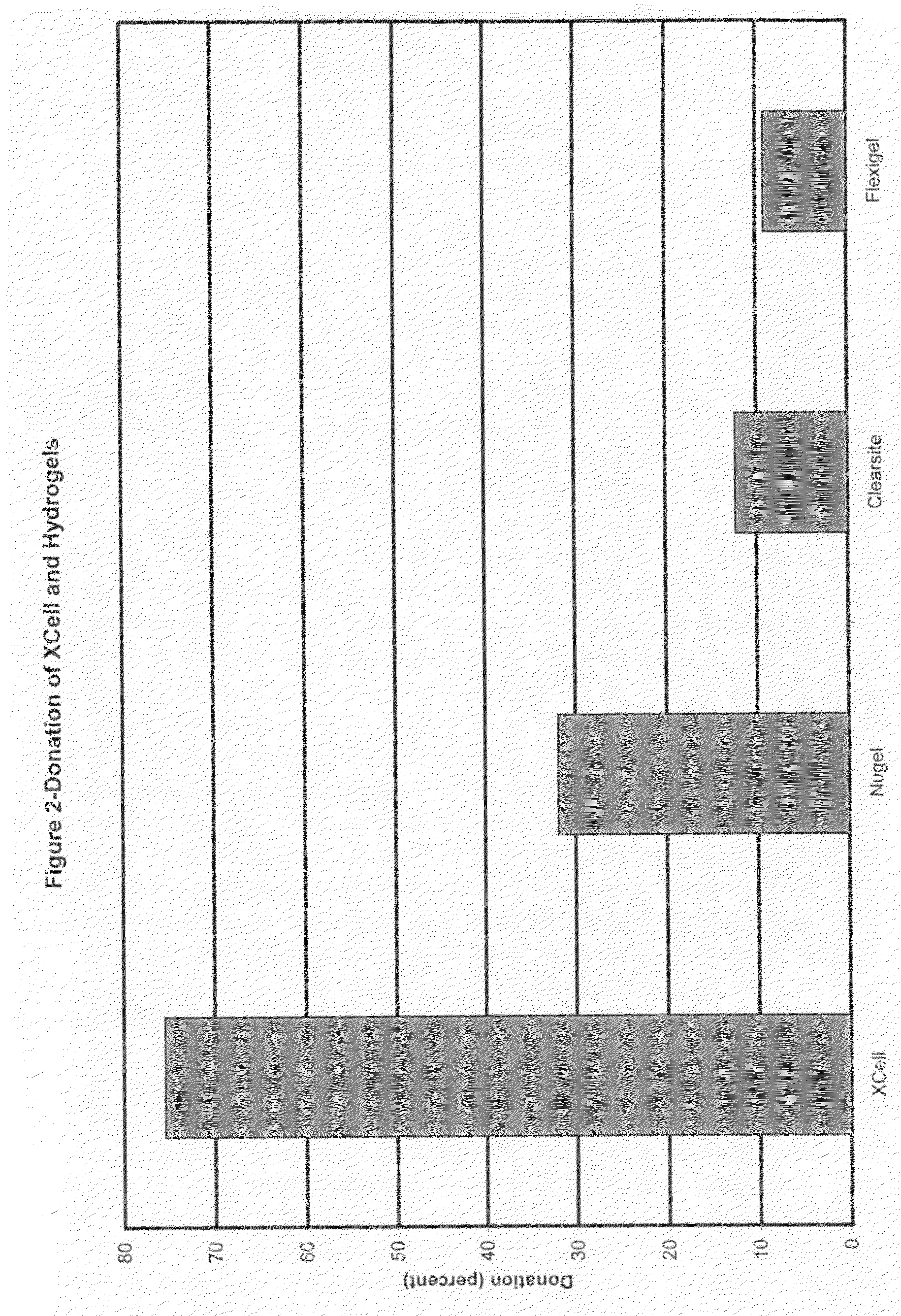
Microbial cellulose wound dressing for treating chronic wounds
InactiveUS20050019380A1Optimal tissue healingPromote improvementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAbsorbent padsWound dressingMicrobial cellulose
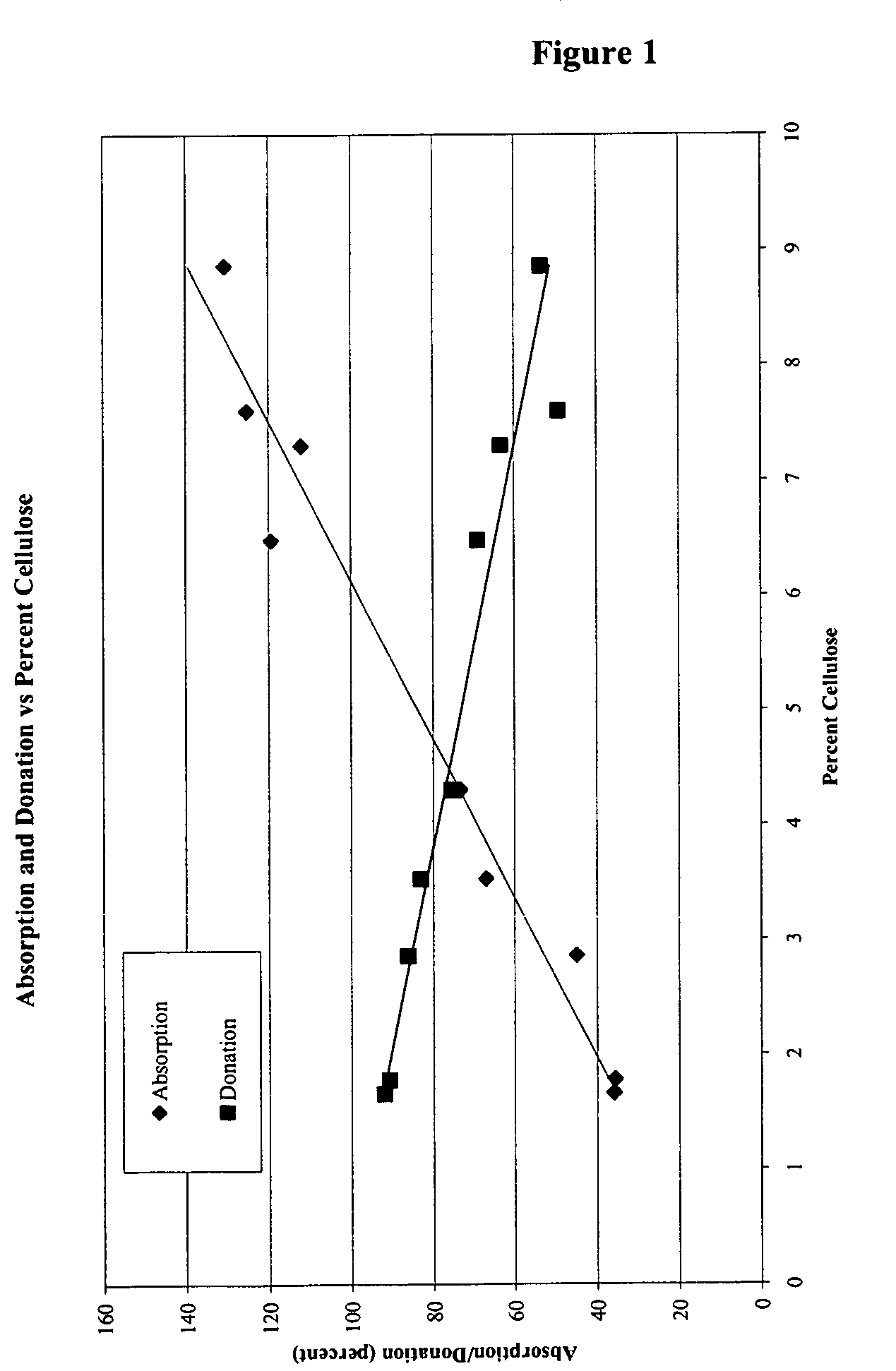
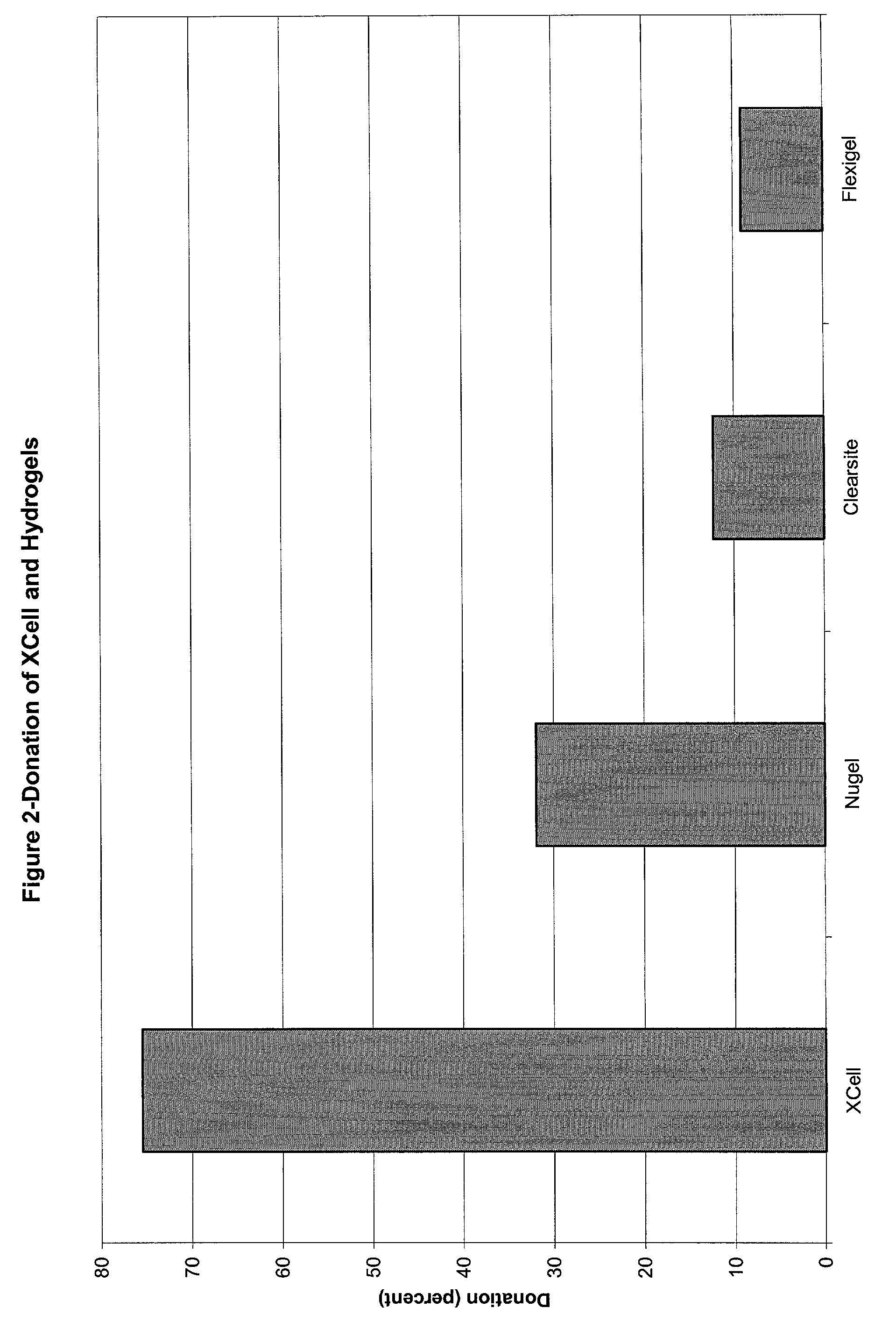
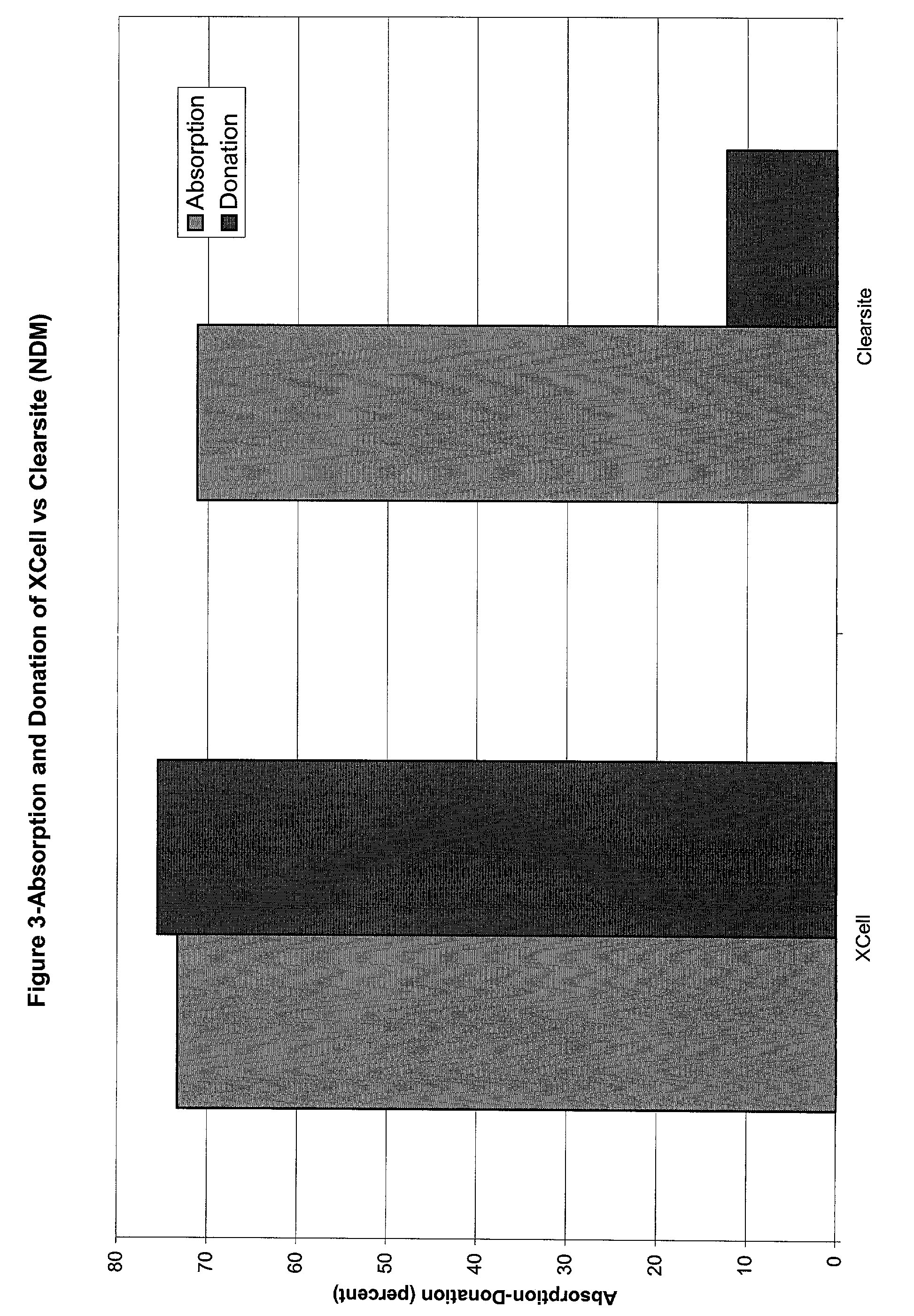
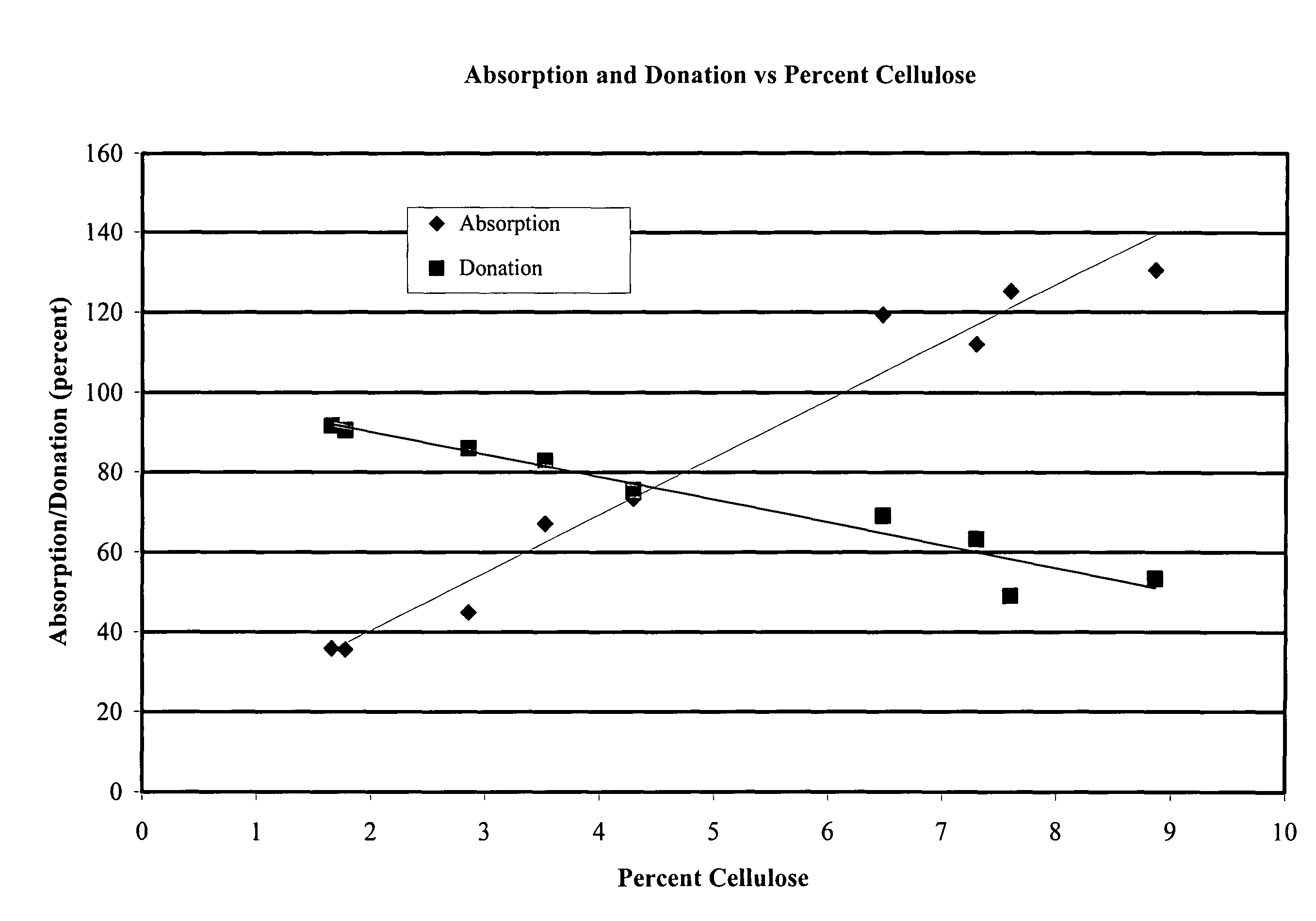
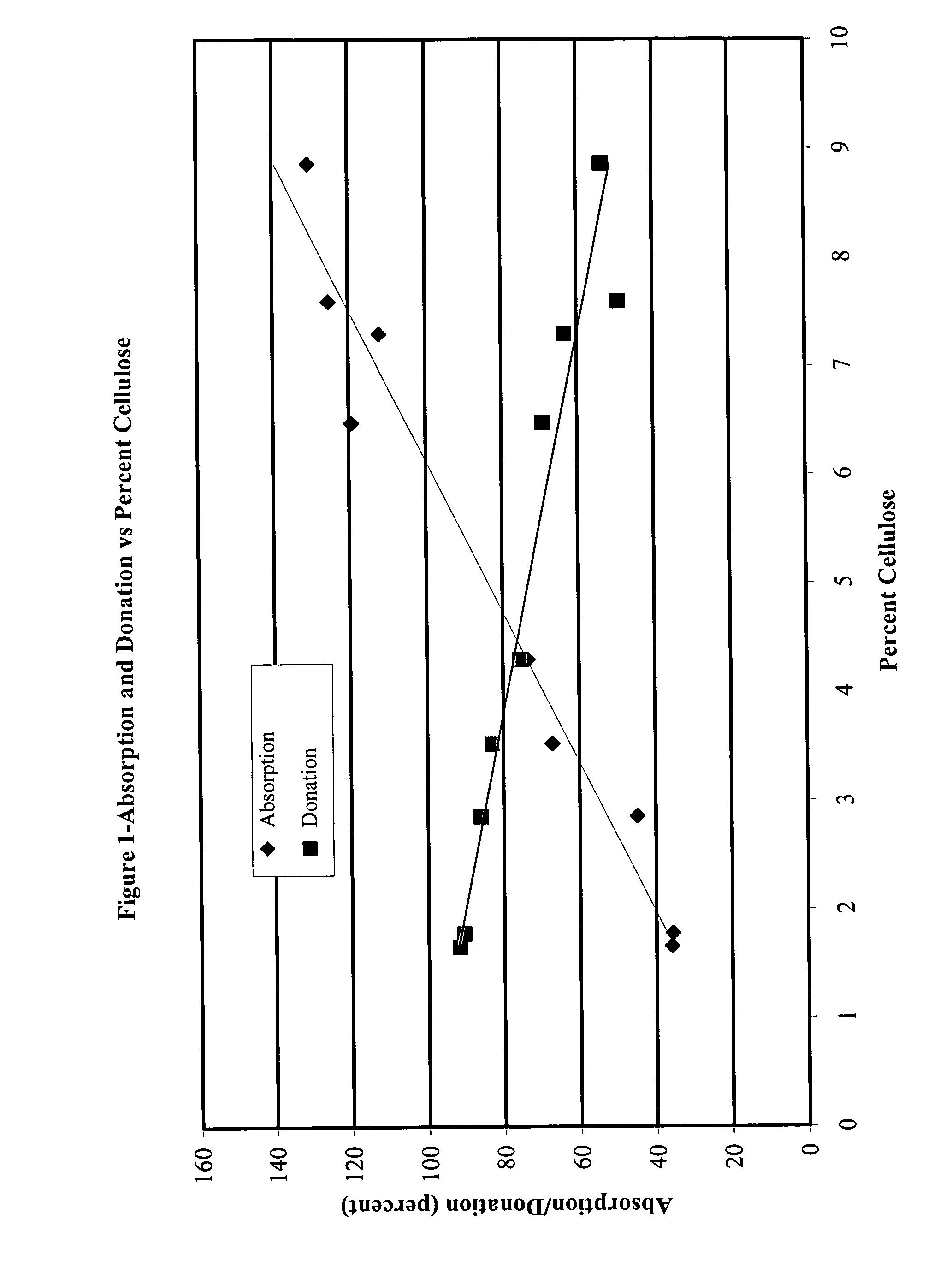
The invention relates to a dressing comprised of microbial-derived cellulose for aesthetic application The dressing is capable of donating liquid to dry substrates and is also capable of absorbing exudating wounds. Delivery of various medicaments using the dressing is possible. Positive clinical outcomes including reduced pain and discomfort, faster epithelialization, and healing were observed with use of the dressing.
Owner:LOHMANN & RAUSCHER
Oxidized microbial cellulose and use thereof
This application describes a bioresorbable biocellulose suitable for medical and surgical applications. In particular, the invention describes periodate oxidized microbial cellulose that can be produced to have any mechanical and degradation profile, depending on the desired application of the oxidized cellulose.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Microbial strains and processes for the manufacture of biomaterials
InactiveUS20090226962A1Increase enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCell culture media
DNA constructs and genetically engineered microbial strains constructed using these DNA constructs, which produce a nuclease enzyme with specificity for DNA and / or RNA, are provided. These strains secrete nuclease into the periplasm or growth medium in an amount effective to enhance productivity and / or recovery of polymer, and are particularly suited for use in high cell density fermentation processes. These constructs are useful for modifying microbial strains to improve production and recovery processes for polymers such as intracellular proteins, such as enzymes, growth factors, and cytokines; for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates; and for producing extracellular polysaccharides, such as xanthan gum, alginates, gellan gum, zooglan, hyaluronic acid and microbial cellulose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Implantable microbial cellulose materials for hard tissue repair and regeneration
This invention relates to polysaccharide materials and more particularly to microbial cellulose containing materials having suitable implantation properties for repair or replacement of hard tissue. The invention also relates to the use of the implantable microbial cellulose as a bone void filler and as a carrier vehicle for active agent delivery for repair or regeneration of hard tissue.
Owner:SYNTHES USA PROD
Microbial cellulose wound dressing for treating chronic wounds
ActiveUS7390499B2Promote wound healingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMicrobial celluloseEngineering
The invention relates to a wound dressing comprising a microbial-derived cellulose for treatment of specific types of chronic wounds, including pressure sores, venous and diabetic ulcers. The wound dressing is capable of donating liquid to dry substrates is also capable of absorbing exudating wounds.
Owner:LOHMANN & RAUSCHER
Preparation of hollow cellulose vessels
InactiveUS20100042197A1Good mechanical resistanceIncrease burst pressureEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsHollow fibreLymphatic vessel
The present invention relates to an improved method for the preparation of hollow cellulose vessels produced by a microorganism, and hollow cellulose vessels prepared by this method. The method is characterized by the culturing of the cellulose-producing microorganisms being performed on the outer surface of a hollow carrier, and providing an oxygen containing gas on the inner side of the hollow carrier, the oxygen containing gas having an oxygen level higher than atmospheric oxygen. The hollow microbial cellulose vessels of the present invention are characterized by improved mechanical properties and can be used in surgical procedures to replace or repair an internal hollow organ such as the urethra, ureter, the trachea, a digestive tract, a lymphatic vessel or a blood vessel
Owner:ARTERION AB
Separator including microbial cellulose, method of producing the separator, and use of the separator
Provided is a separator including microbial cellulose, a battery comprising the separator, and a method of producing the separator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
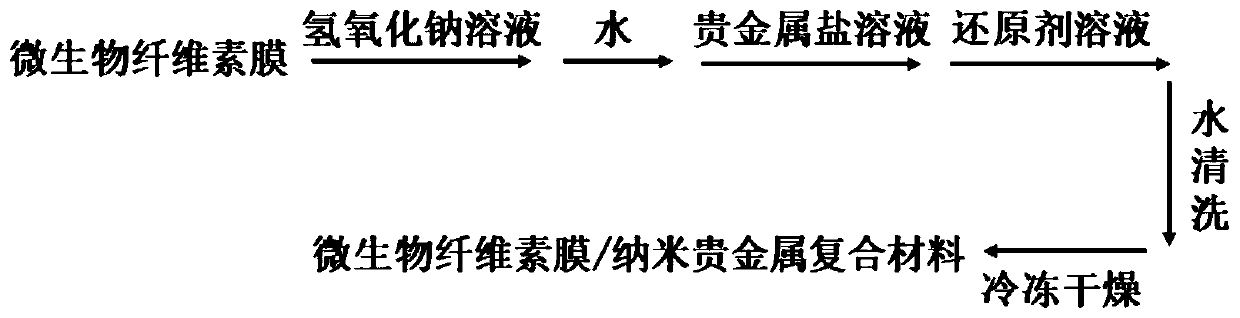
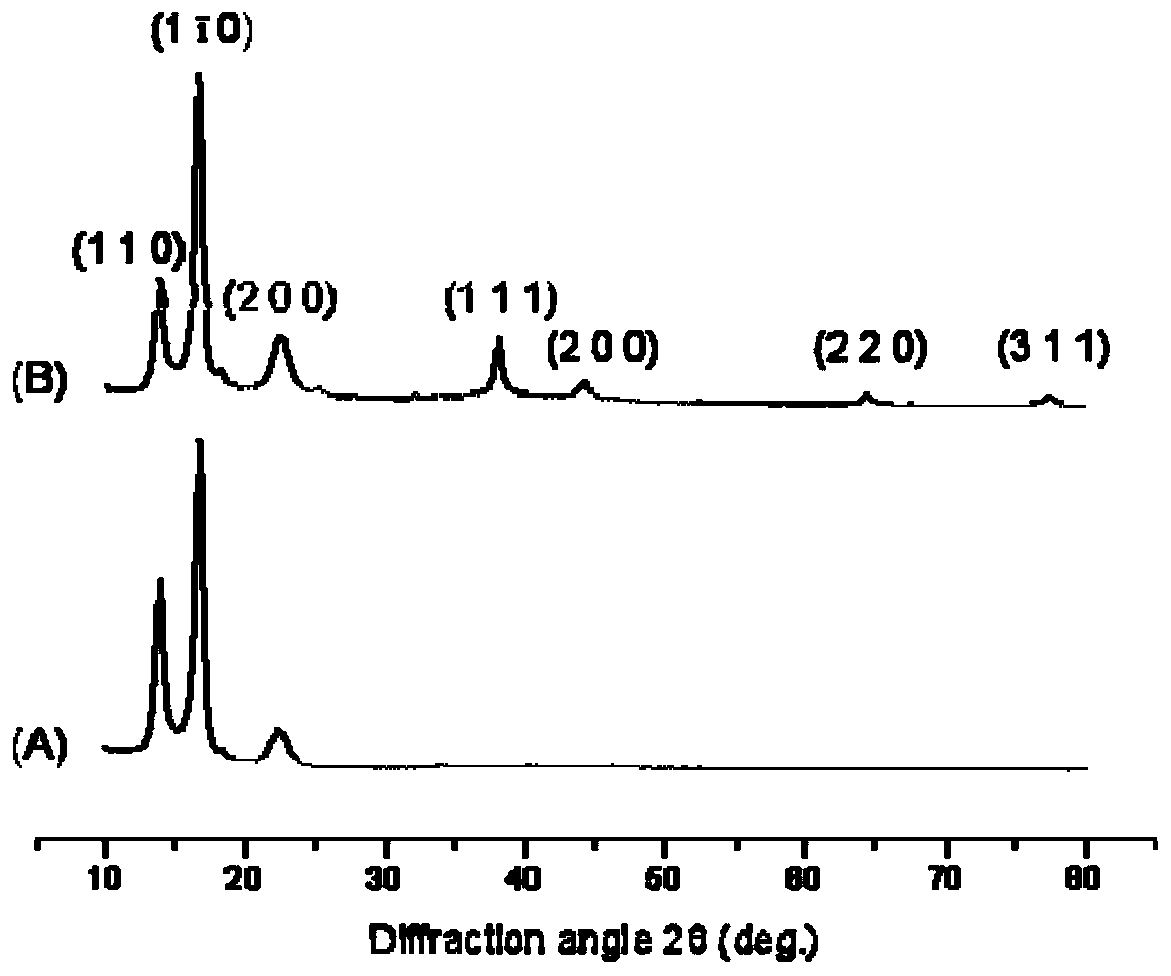
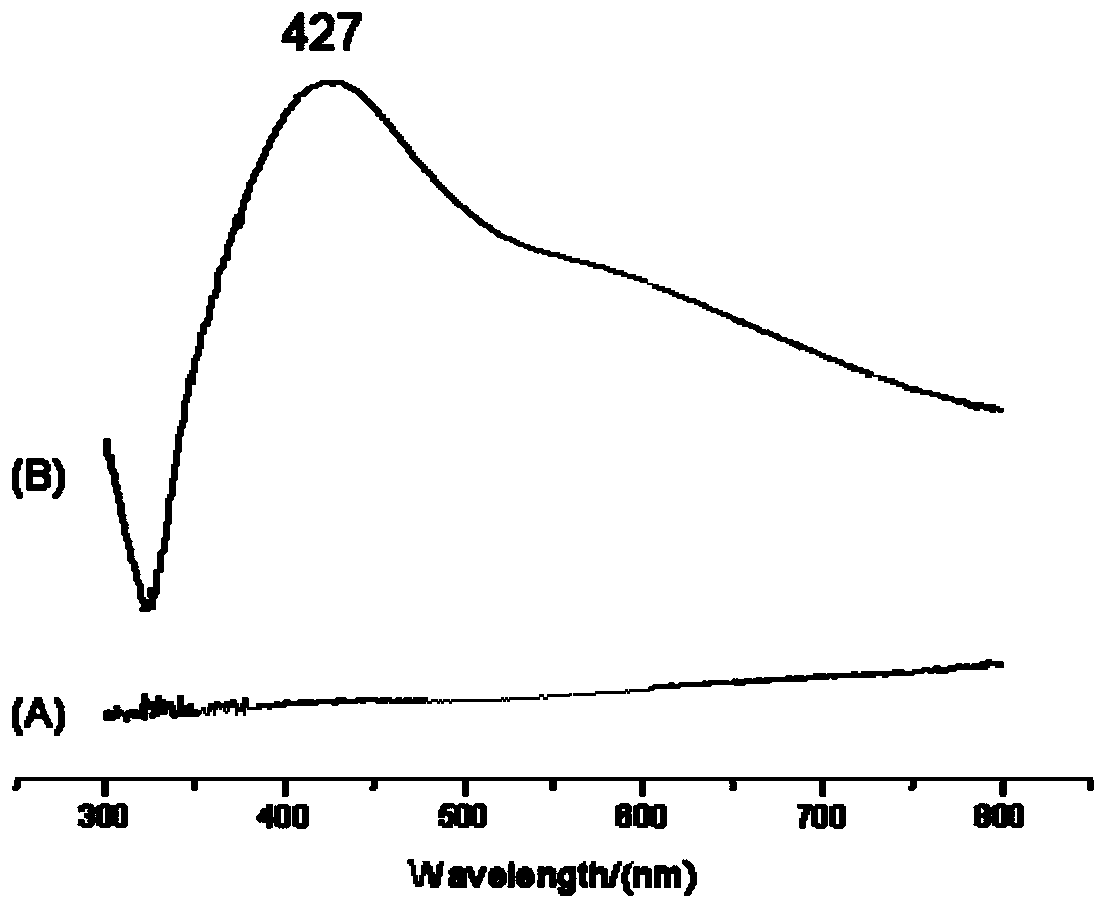
Microbial cellulose membrane/nanometer noble metal composite material, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN110669241ARestrict growthGood Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering EffectRaman scatteringFiber bundleSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
The invention discloses a microbial cellulose membrane / nanometer noble metal composite material, a preparation method and applications thereof. According to the invention, nanometer noble metal particles grow in situ in the nano-fiber network structure of a microbial cellulose membrane through a noble metal salt and a reducing agent, the growth of the noble metal particles is limited by utilizingthe superfine three-dimensional network-like structure of the microbial cellulose membrane to uniformly distribute the formed nanometer noble metal particles in the nano-scale holes of the microbial cellulose membrane and adhere the nanometer noble metal particles to the fiber bundles, and finally dehydrating drying treatment is performed to obtain the surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrate with good surface-enhanced Raman spectrum scattering effect; the preparation method has characteristics of simple preparation process, mild conditions, simple operation and inexpensive raw materials; and the prepared material can be used as the surface enhanced Raman substrate for rapid detection of protein biomacromolecules, and has good application prospects.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A nano microbeam cellulose, method for preparing the same and use thereof
InactiveCN1464047ABacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsMicrobial celluloseGluconacetobacter xylinum
The present invention relates to one kind of nano microbial cellulose and the nano microbial cellulose features the size range of 10-1000 nm. The present invention also relates to the preparation process of the nano microbial cellulose. On the other hand, the present invention also relates to the use of the nano microbial cellulose in preparing medicine composition.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
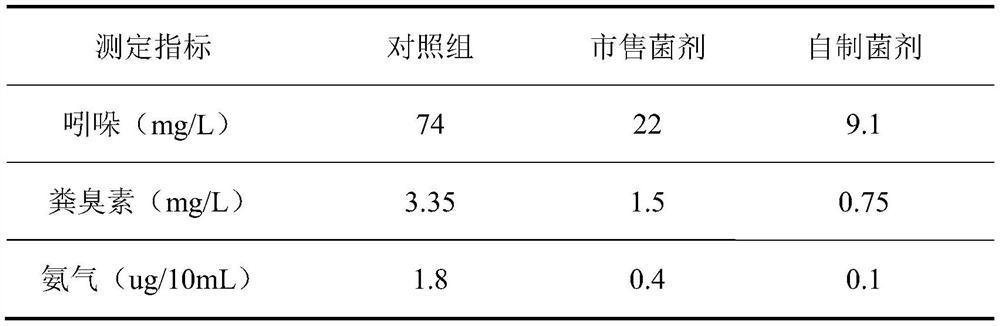
Livestock and poultry manure deodorizing microbial agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111876358AFully degradedSolve the problem of bad smellFungiBacteriaBacillus ginsengihumiMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a livestock and poultry manure deodorizing microbial agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The microbial agent is prepared by uniformly mixing a protein degradation strain with a starch degradation strain and a cellulose degradation strain, wherein the protein degradation strain is one or two of bacillus subtilis and Pakistan lysine bacillus; the starch degradation strain is one or two of aspergillus niger and lysine borate bacillus; and the cellulose degradation strain is one or two of botrytis fungi and panax ginseng bacillus. Screened proteindegradation microorganisms, starch degradation microorganisms and cellulose degradation microorganisms are adopted to prepare a complex microbial inoculant, the problem of stink is solved by using the complex microbial inoculant as a feed additive or directly using the complex microbial inoculant for stink excrement and the like. The livestock and poultry manure deodorizing microbial agent is simple in use method, remarkable in effect, low in cost, and is safe and environment-friendly.
Owner:陕西均良土壤环境技术有限责任公司
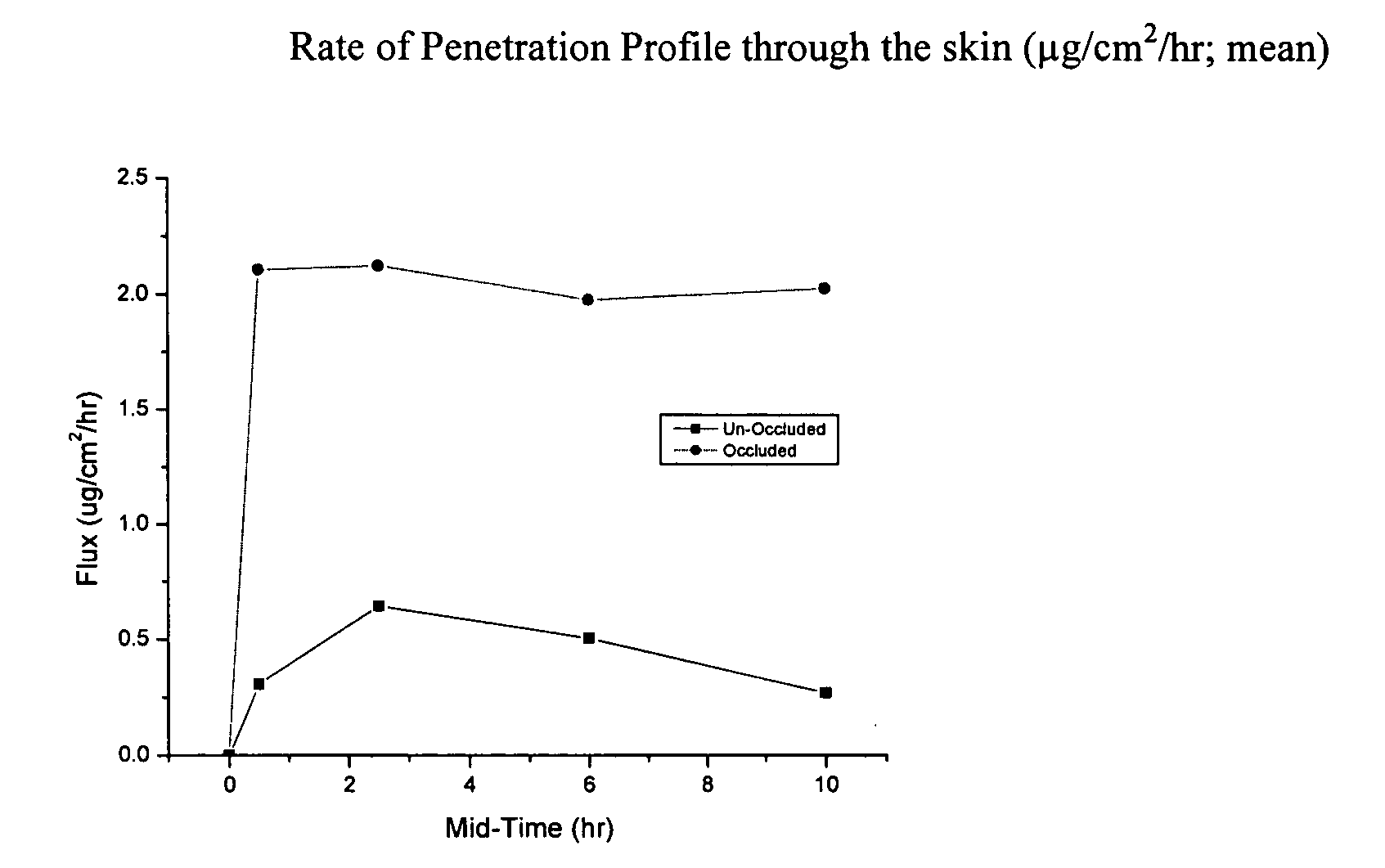
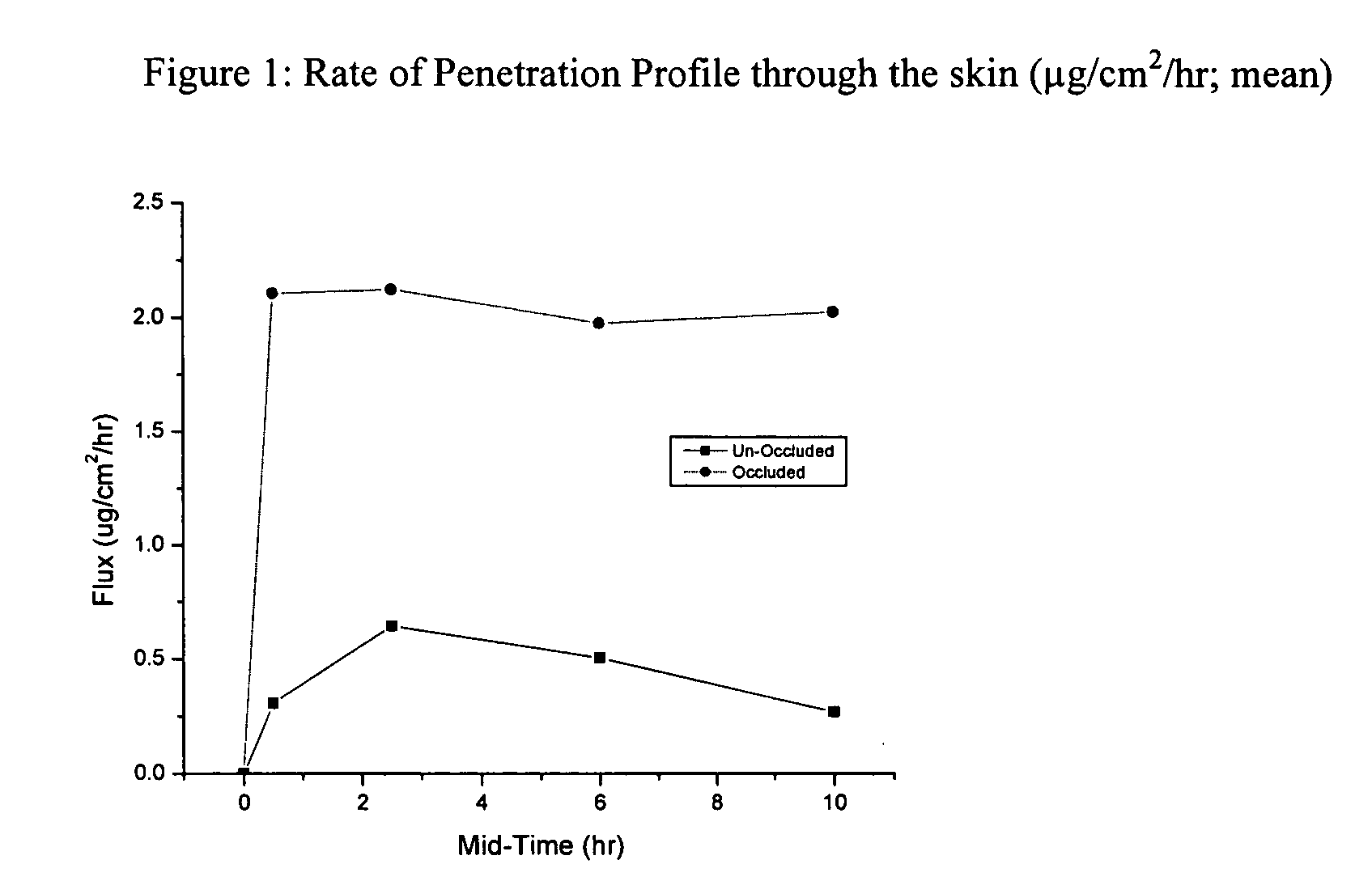
Microbial cellulose materials for use in transdermal drug delivery systems, method of manufacture and use
A method for transdermally delivering a biologically active agent to a subject in need thereof, comprising topically applying a composition comprising insoluble microbial cellulose, water, and a therapeutically effective amount of the biologically active agent, wherein the biologically active agent penetrates through the subject's stratum corneum at a substantially constant rate.
Owner:XYLOS CORP
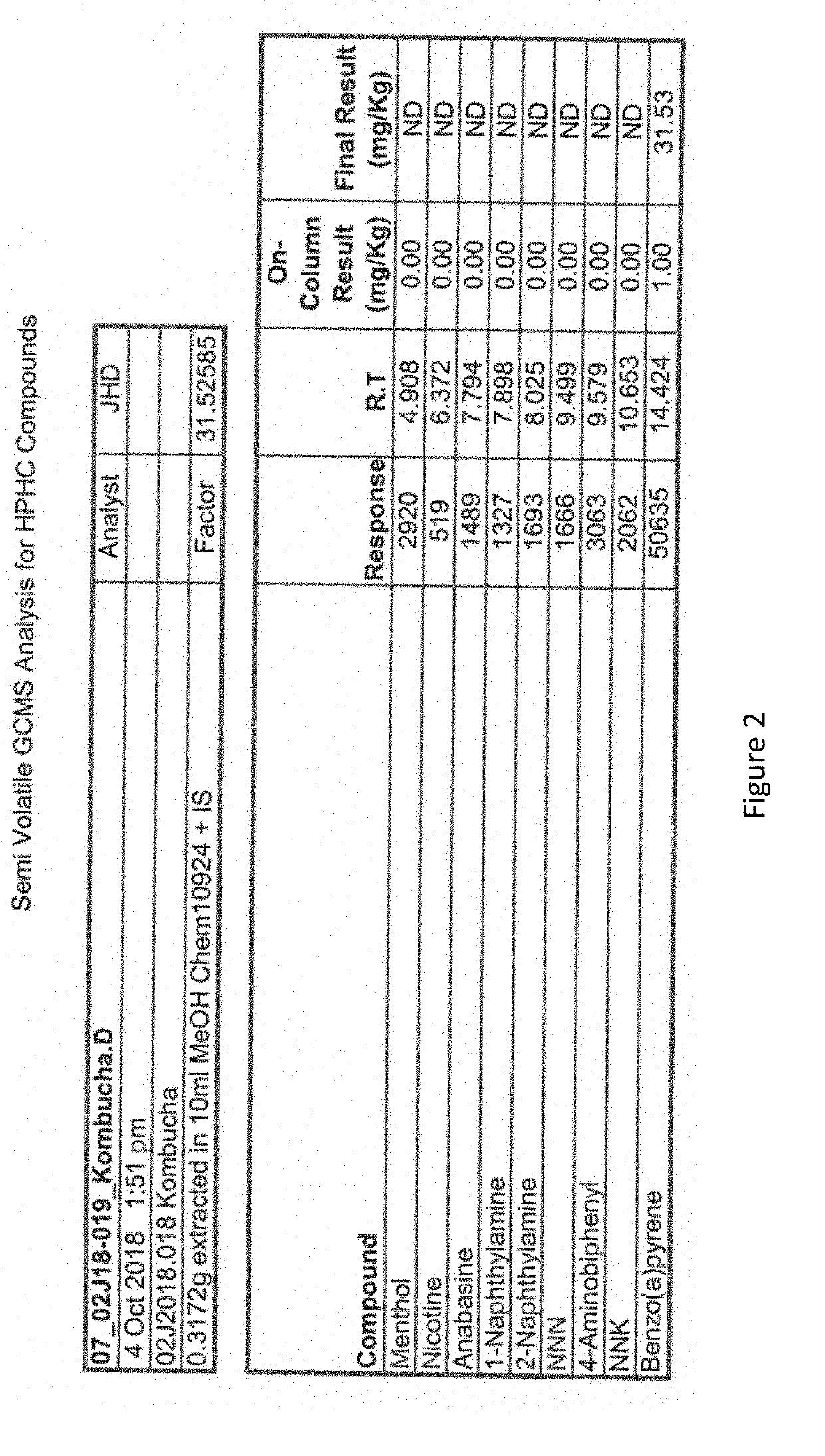
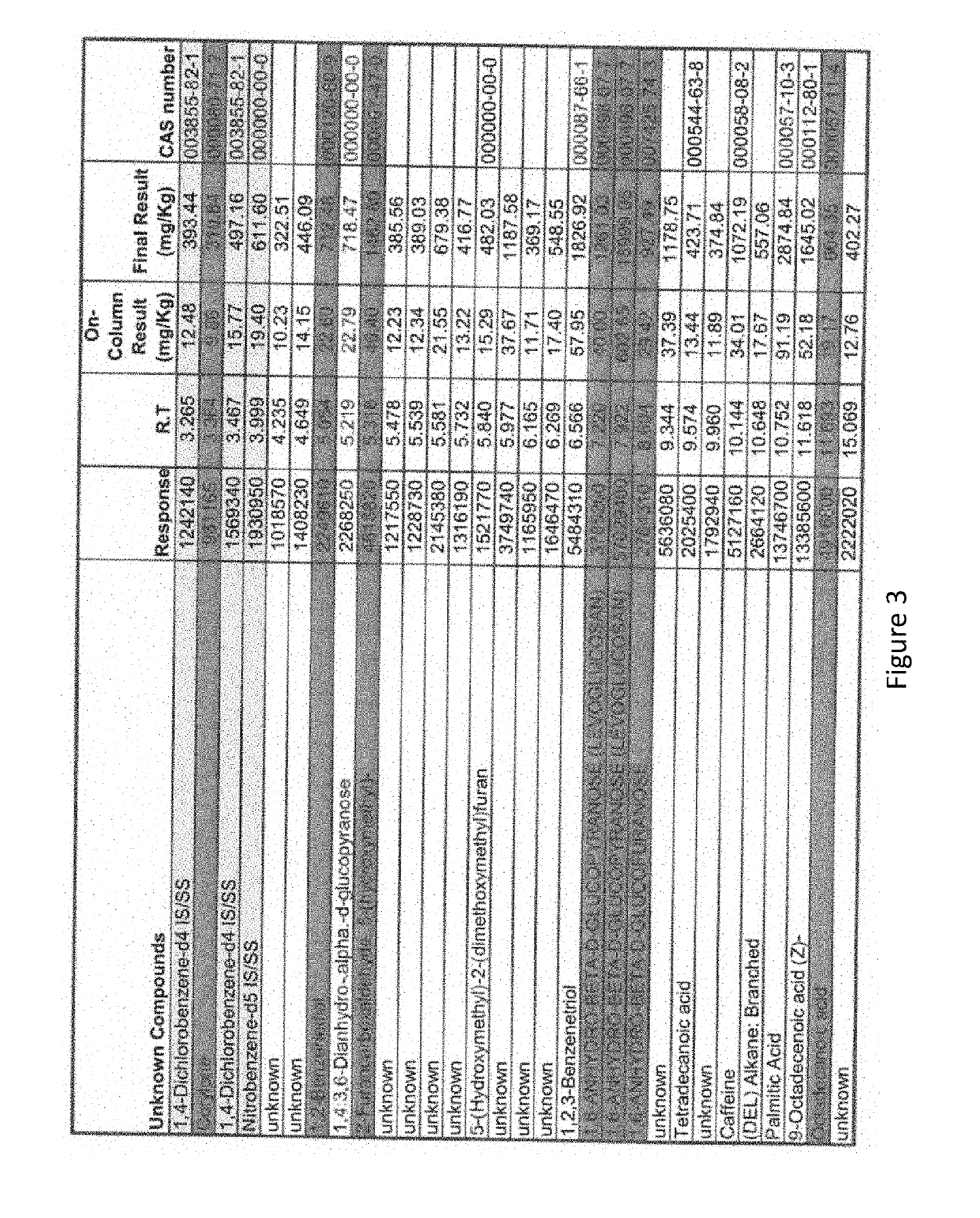
Cigarette rolling papers formed from kombucha biofilms
ActiveUS20190174815A1Unique propertyLacking and neededCigar manufacturePaper/cardboard layered productsBiofilmMicroorganism
Rolling papers formed from fermented microbial cellulose derivatives (e.g., Kombucha fermentation biofilms) and methods of manufacture are described.
Owner:KOMBUCHA BIOMATERIALS LLC
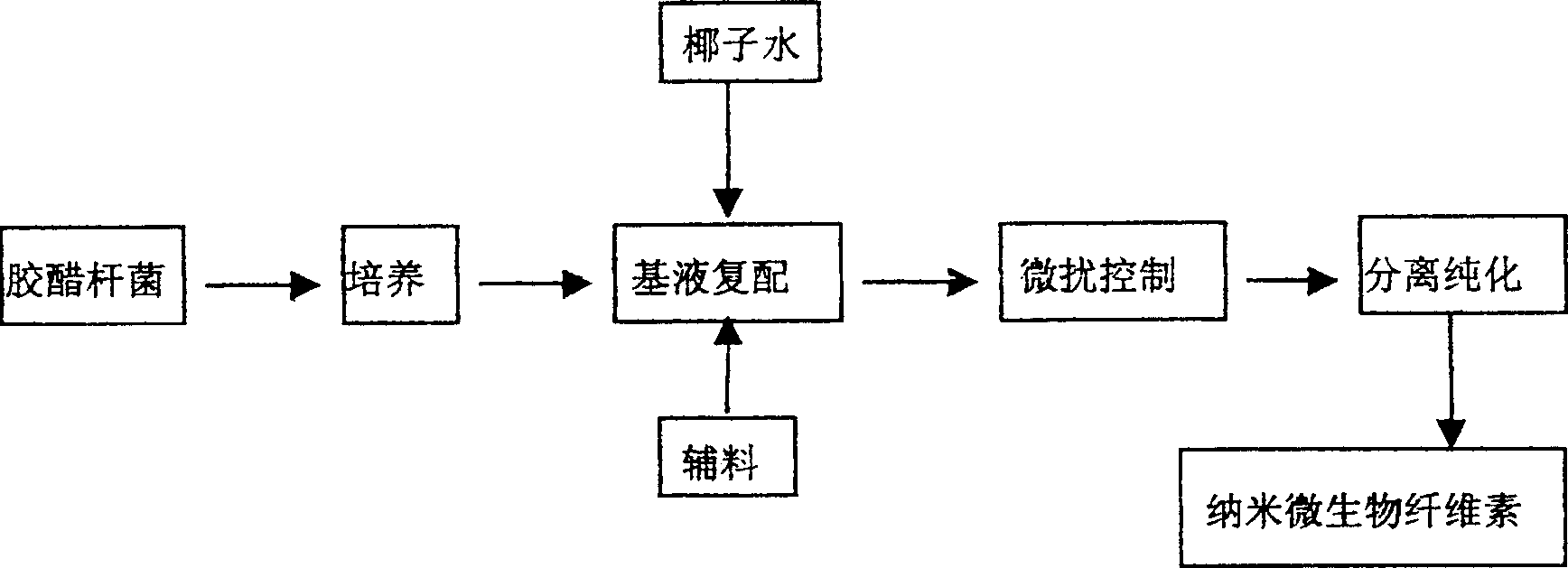
Fermentation compounding device for microbial cellulose and base material and technology of fermentation compounding device
InactiveCN106010965AUniform deposition thicknessClosely connectedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyYarn
The invention provides a fermentation compounding device for microbial cellulose and a base material. The fermentation compounding device is provided with a base material unwinding device, an introducing roller, a fermentation compounding box, clamping rollers, a drying inactivation device and a compound coil winding device in sequence in the base material walking direction. Mixed paste of a microbial strain and cellulose stoste is stored in the fermentation compounding box, the base material is pulled to pass through the mixed paste in the fermentation compounding box, and microbial cellulose filaments excreted by microorganisms are uniformly deposited on the surface of the base material to form a compound product. The base material is paper made of plant long fibers or cotton or hemp or chemical fiber yarns or non-woven cloth or woven cloth made of cotton or hemp or chemical fiber yarns. The compounding box is connected with a temperature control device, a vibration device and the like. The microbial cellulose is densely deposited on the base material with a uniform deposition thickness, and the fermentation compounding device is suitable for large-scale production work. The obtained product has excellent mechanical properties, elasticity and water resistance.
Owner:NANTONG HONGTONG BIO TECH
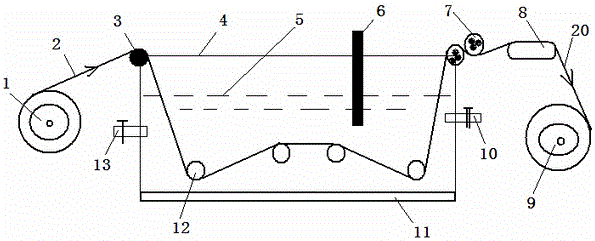
Bioreactor and method for producing microbial cellulose
InactiveUS20100317066A1Improve production efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismLiquid medium
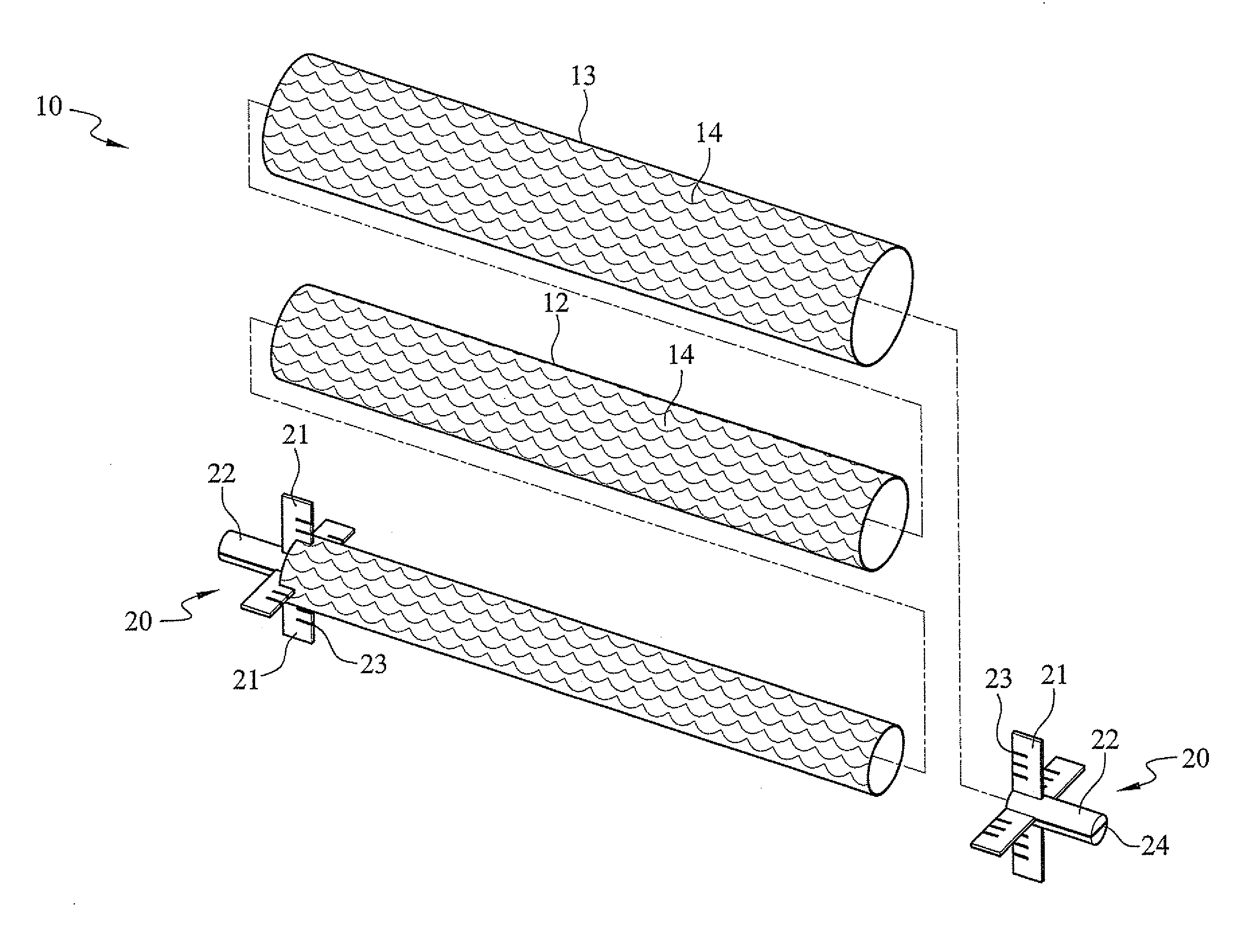
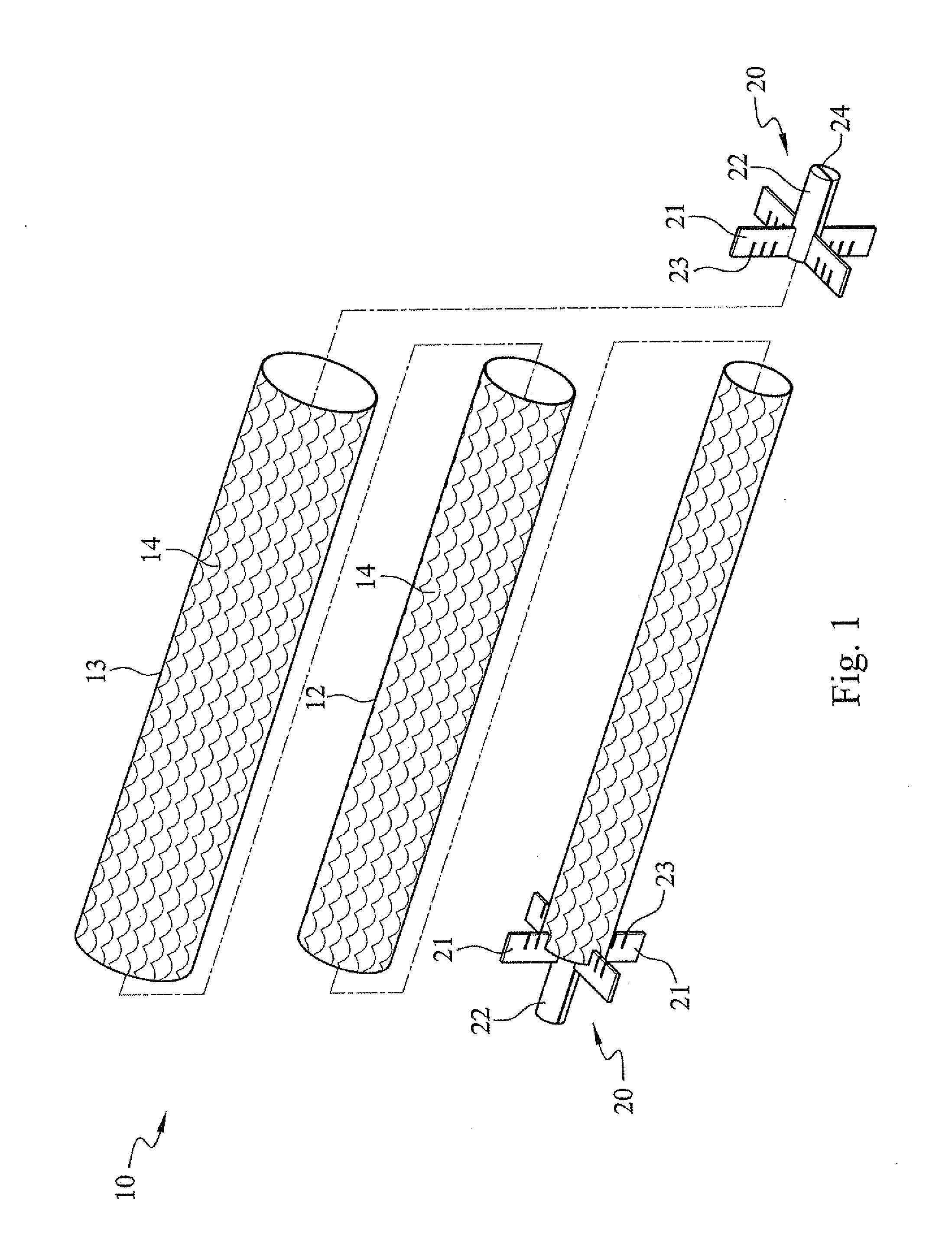
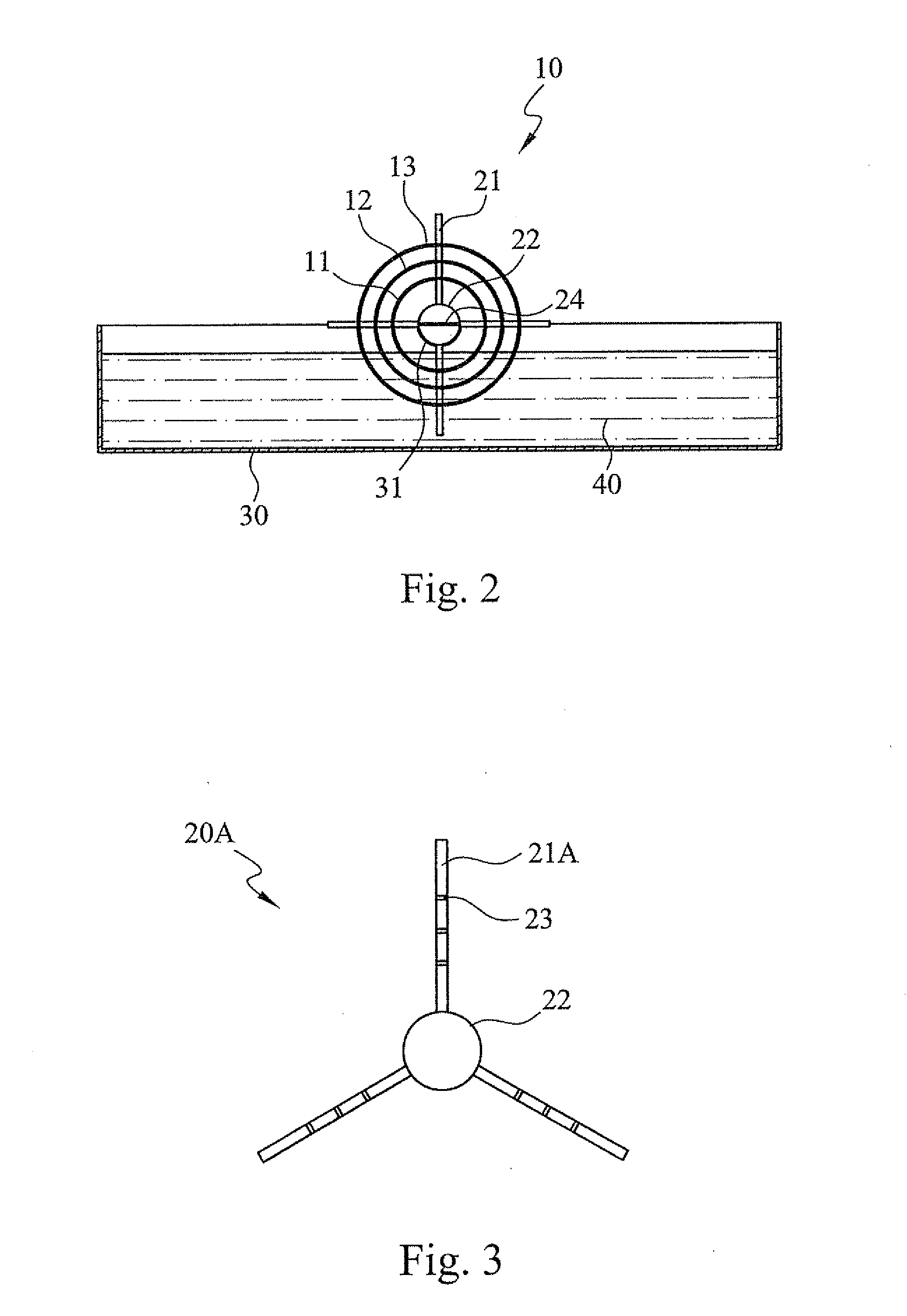
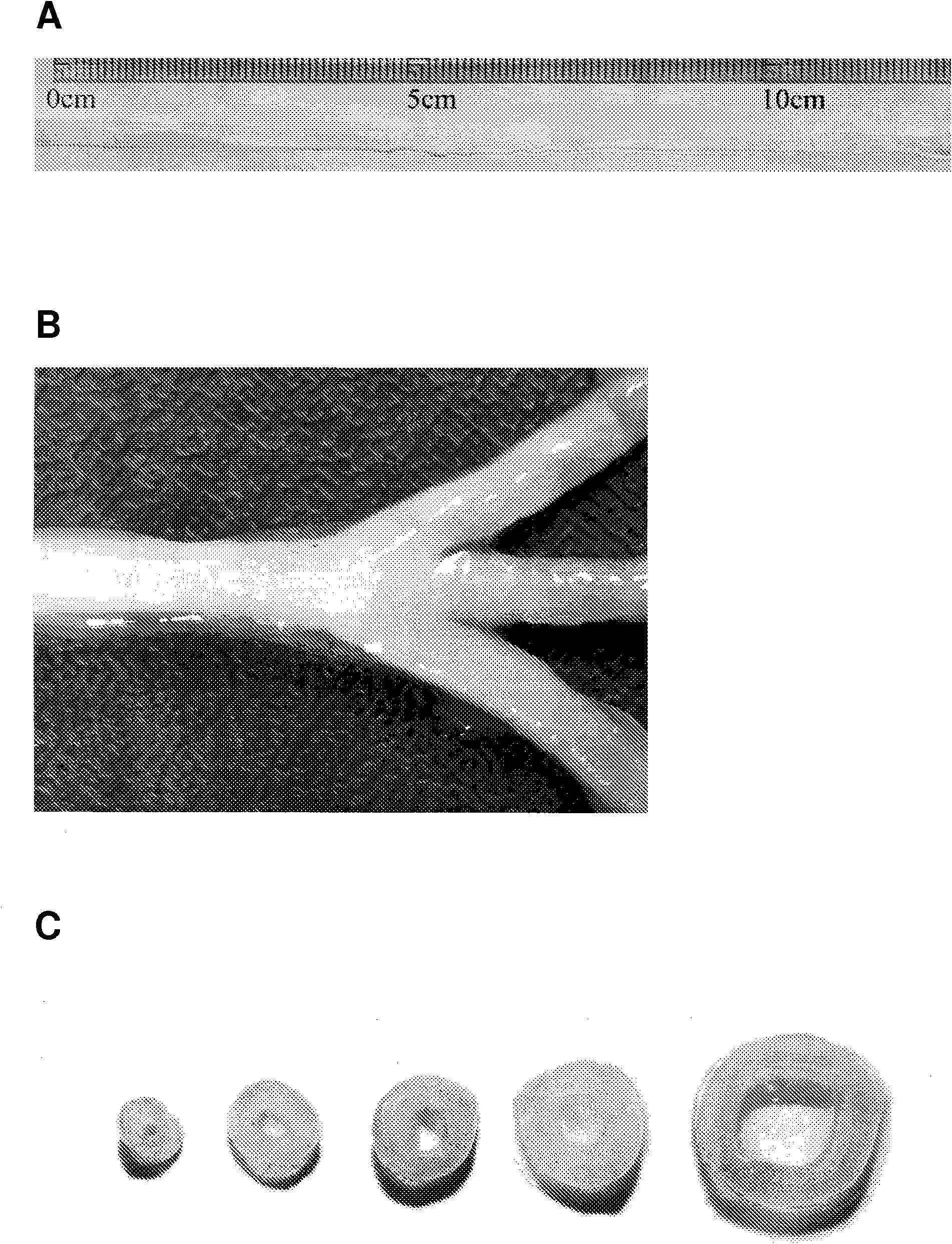
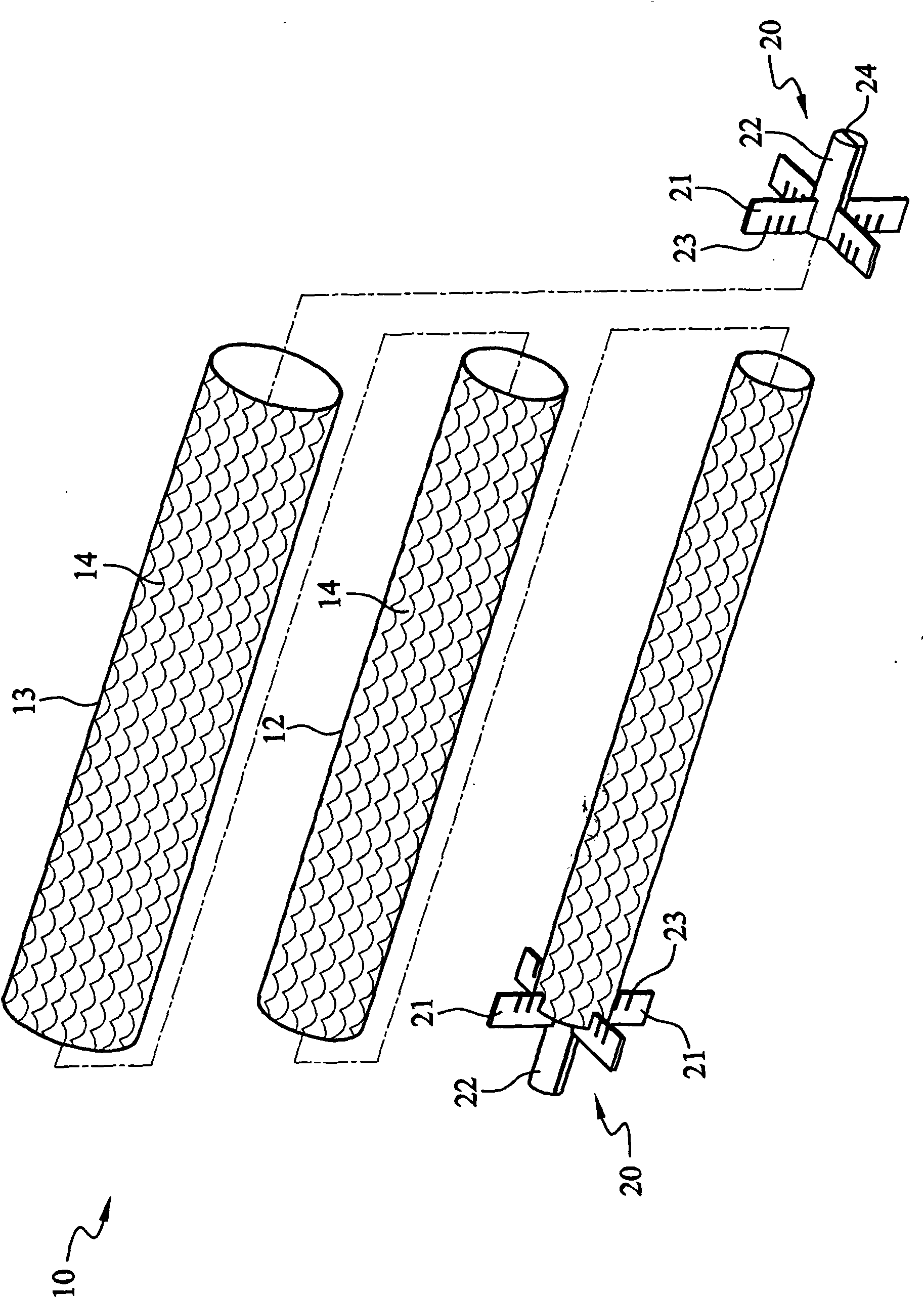
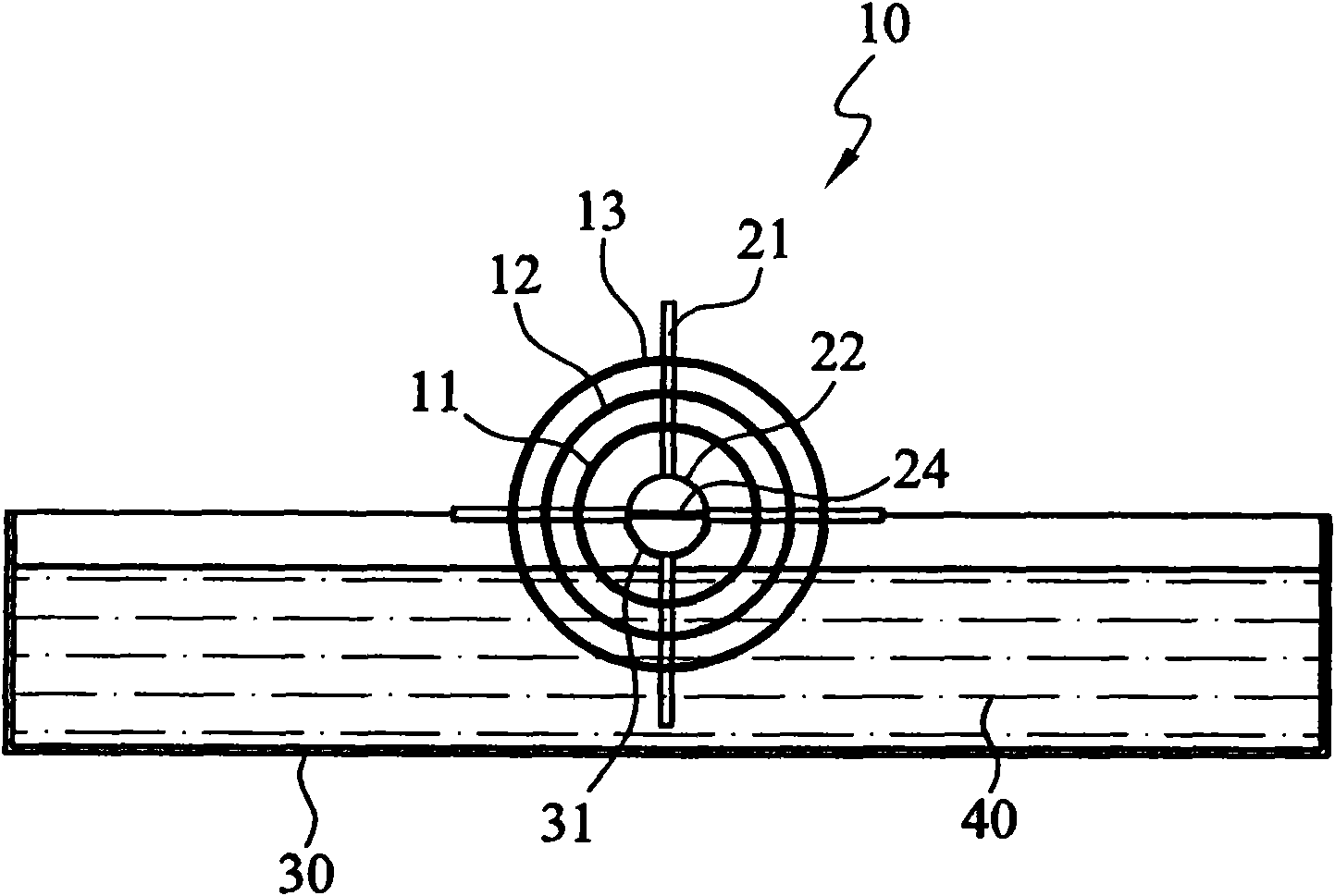
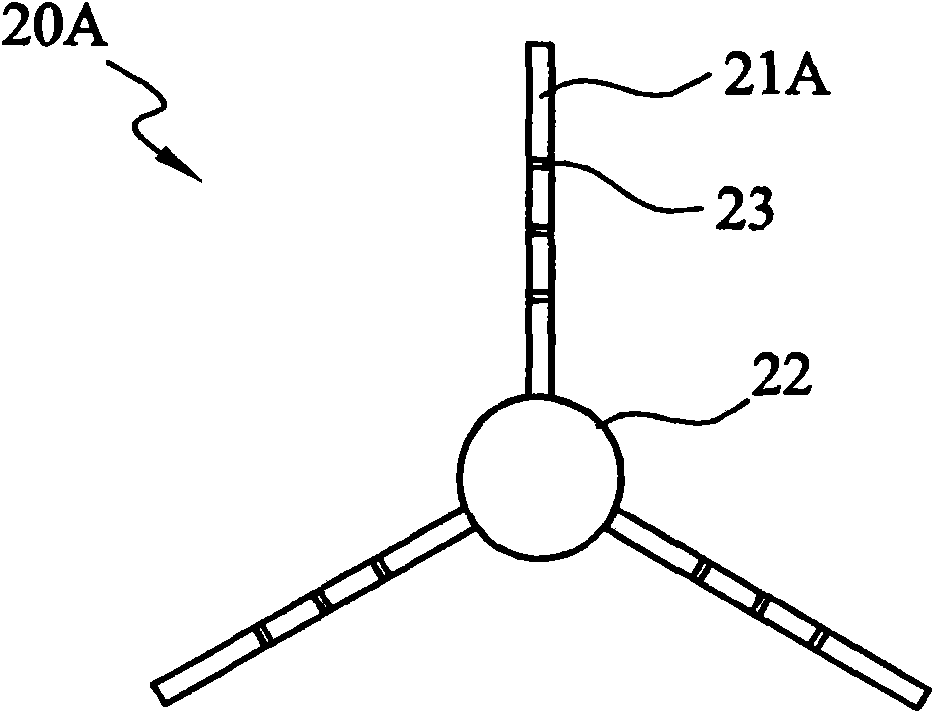
A technique for producing microbial cellulose is provided, including: preparing a liquid medium for microbial cultivation in a container; horizontally rotating multiple hollow tubes that are fitted together or separated from one another, so that each of the hollow tubes is alternately partially immersed in the liquid medium and partially exposed above the horizontal surface of the liquid medium; wherein each of the hollow tubes has a rough outer surface and a smooth inner surface, so as to allow microorganisms to form microbial cellulose on the outer surface of each hollow tube, as well as forming sheets of microbial cellulose on the horizontal surface of the liquid medium not being disturbed by the hollow tubes, and removing the microbial cellulose from the outer surfaces of the hollow tubes in order to obtain tubular microbial cellulose. In addition, the sheets of microbial cellulose are also harvested from the liquid medium.
Owner:FOOD IND RES & DEV INST
Microbial cellulose wound dressing for treating chronic wounds
InactiveUS7709021B2Promote wound healingRelieve painOrganic active ingredientsBiocideVeinWound dressing
The invention relates to a wound dressing comprising a microbial-derived cellulose for treatment of specific types of chronic wounds, including pressure sores, venous and diabetic ulcers. The wound dressing is capable of donating liquid to dry substrates is also capable of absorbing exudating wounds.
Owner:LOHMANN & RAUSCHER
Multi-function emergency bandage
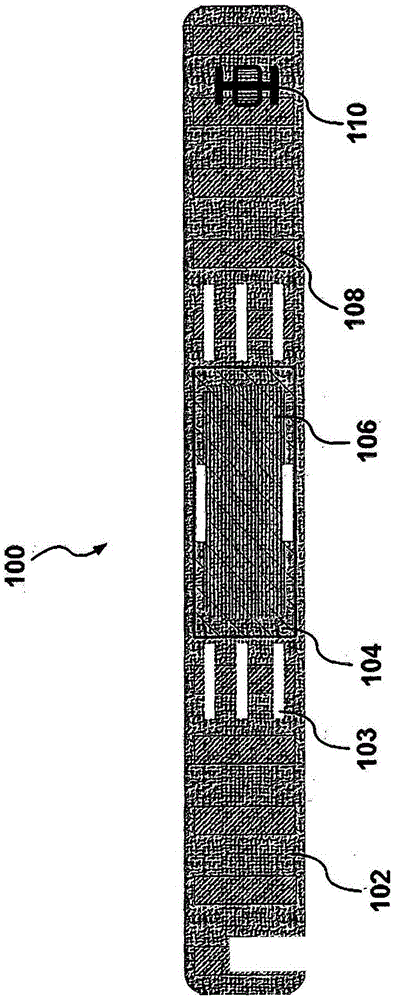
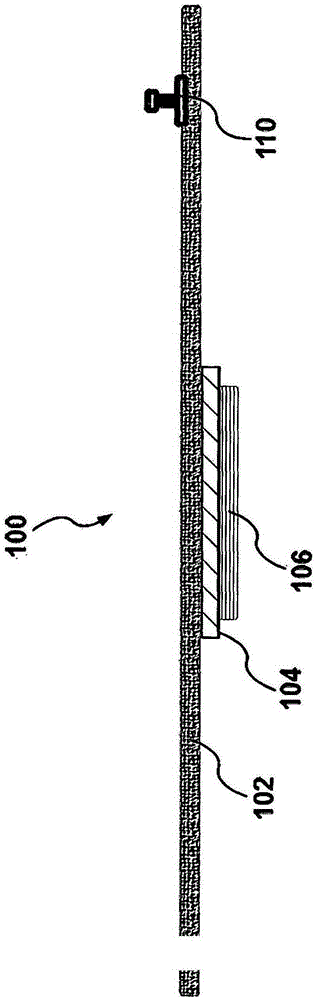
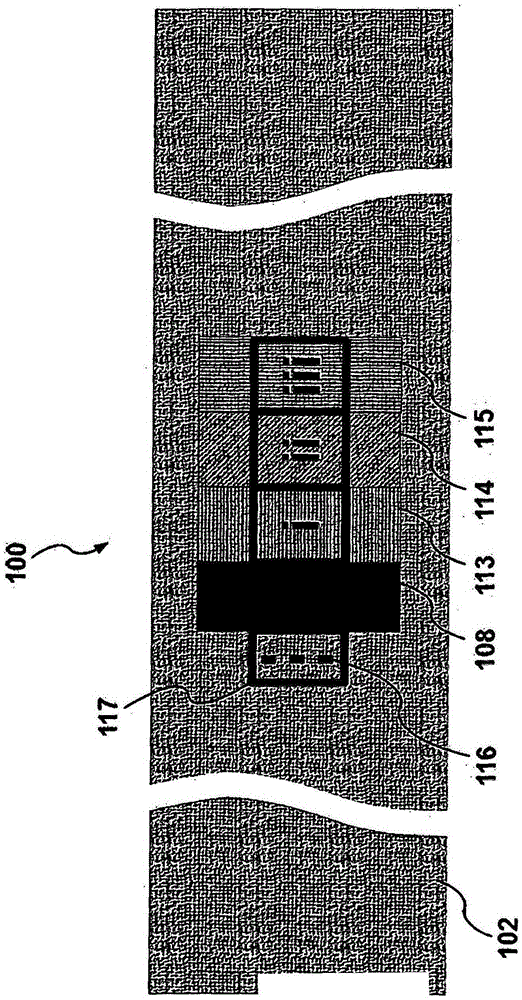
A unique multi-functional emergency bandage is introduced, wherein bleeding is stopped by: (1) optimizing mechanical properties and preventing ischemia and / or necrosis while applying enough pressure to help stop bleeding, and (2) incorporating inorganic anti-bleeding nano-structures (embedded within a gauze and / or microbial cellulose) with almost infinite life-time. Additionally, pathogen passage through the bandage is prohibited (via an intermediate filter layer). Together with the overall anti- microbial character of the bandage, the unique multi-functional bandage offers all these vital features within a single design. The unique bandage can be applied by using a single hand and bandaging direction can be changed using a unique binding apparatus. Visual aids, such as printed rectangles, on the final fabric provides the user with an indication of how to control the amount of stretch, as vertical rectangles would turn into horizontal rectangles when stretched too much, whereas rectangles turn to squares around the optimum region of the stress-strain curve.
Owner:SANKO TEKSTIL ISLETMELERI SANAYI & TICARET A S
Multi-Function Emergency Bandage
ActiveUS20140371650A1Avoid ischemiaAvoid necrosisNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersMicrobial celluloseEngineering
A unique multi-functional emergency bandage is introduced, wherein bleeding is stopped by: (1) optimizing mechanical properties and preventing ischemia and / or necrosis while applying enough pressure to help stop bleeding, and (2) incorporating inorganic anti-bleeding nano-structures (embedded within a gauze and / or microbial cellulose) with almost infinite life-time. Additionally, pathogen passage through the bandage is prohibited (via an intermediate filter layer). Together with the overall anti-microbial character of the bandage, the unique multi-functional bandage offers all these vital features within a single design. The unique bandage can be applied by using a single hand and bandaging direction can be changed using a unique binding apparatus. Visual aids, such as printed rectangles, on the final fabric provides the user with an indication of how to control the amount of stretch, as vertical rectangles would turn into horizontal rectangles when stretched too much, whereas rectangles turn to squares around the optimum region of the stress-strain curve.
Owner:SANKO TEKSTIL ISLETMELERI SANAYI & TICARET A S
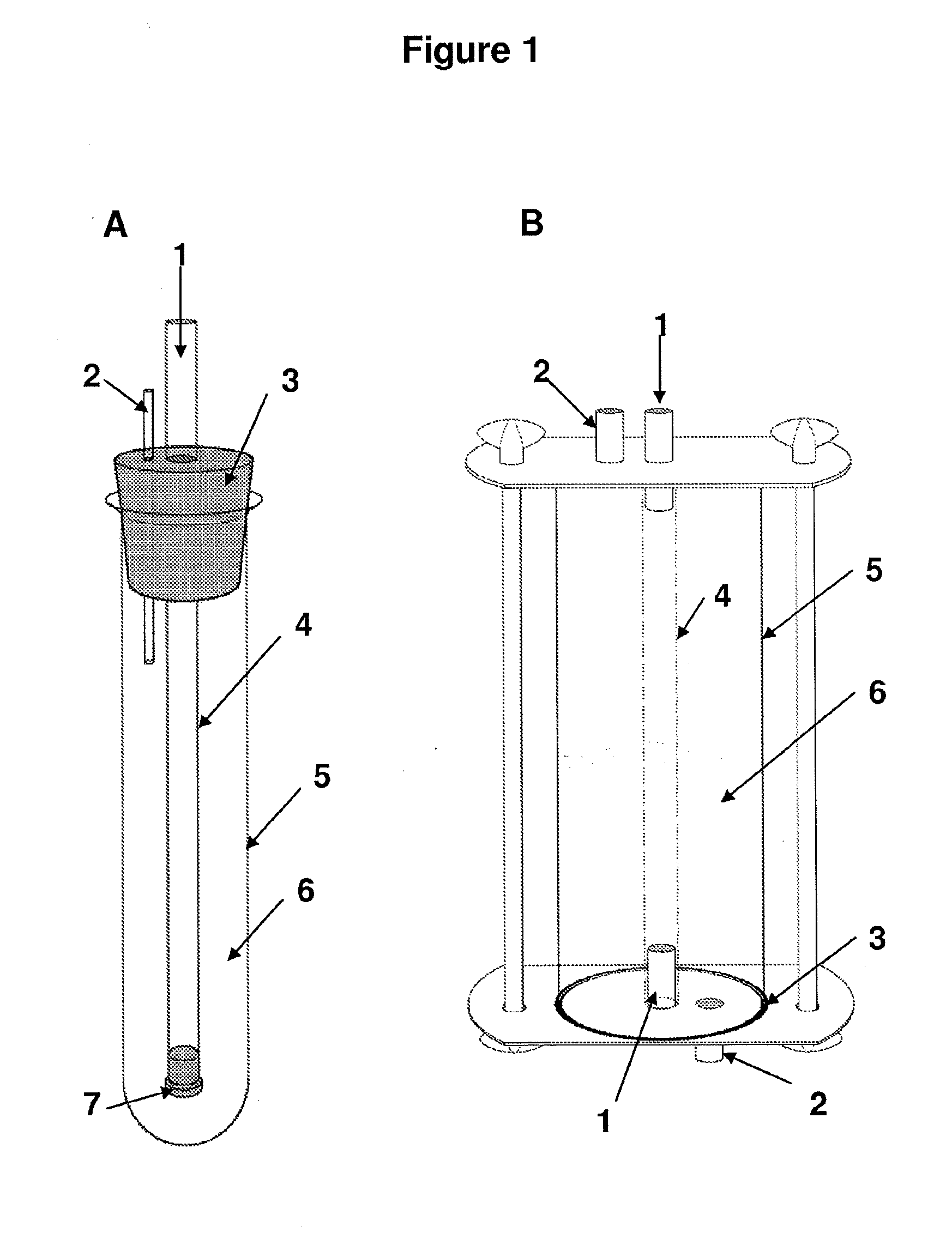
Method and device for producing shaped microbial cellulose for use as biomaterial especially for microsurgery
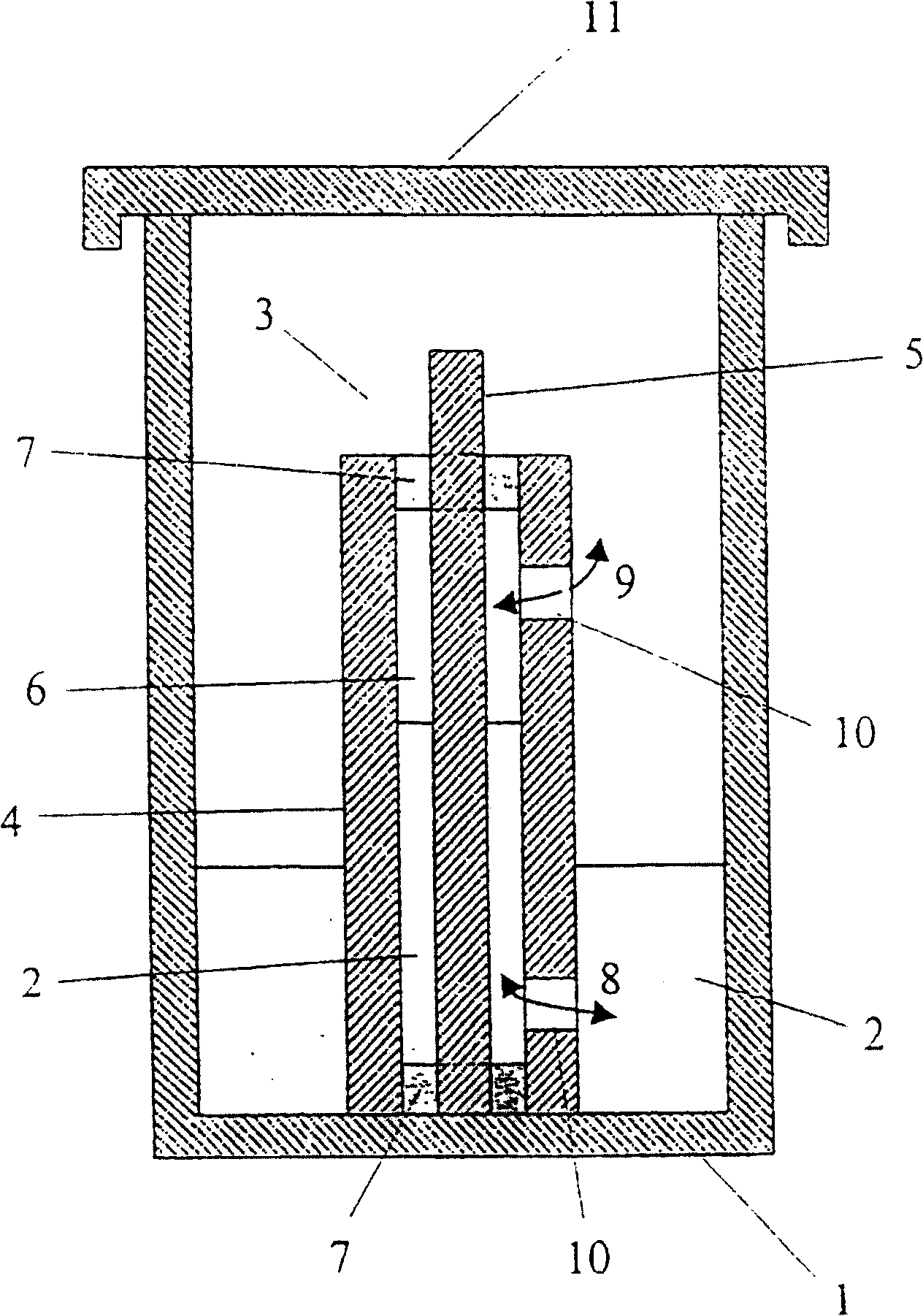
InactiveCN100451125CQuality improvementReproducible qualitySuture equipmentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCulture fluidMicrobial cellulose
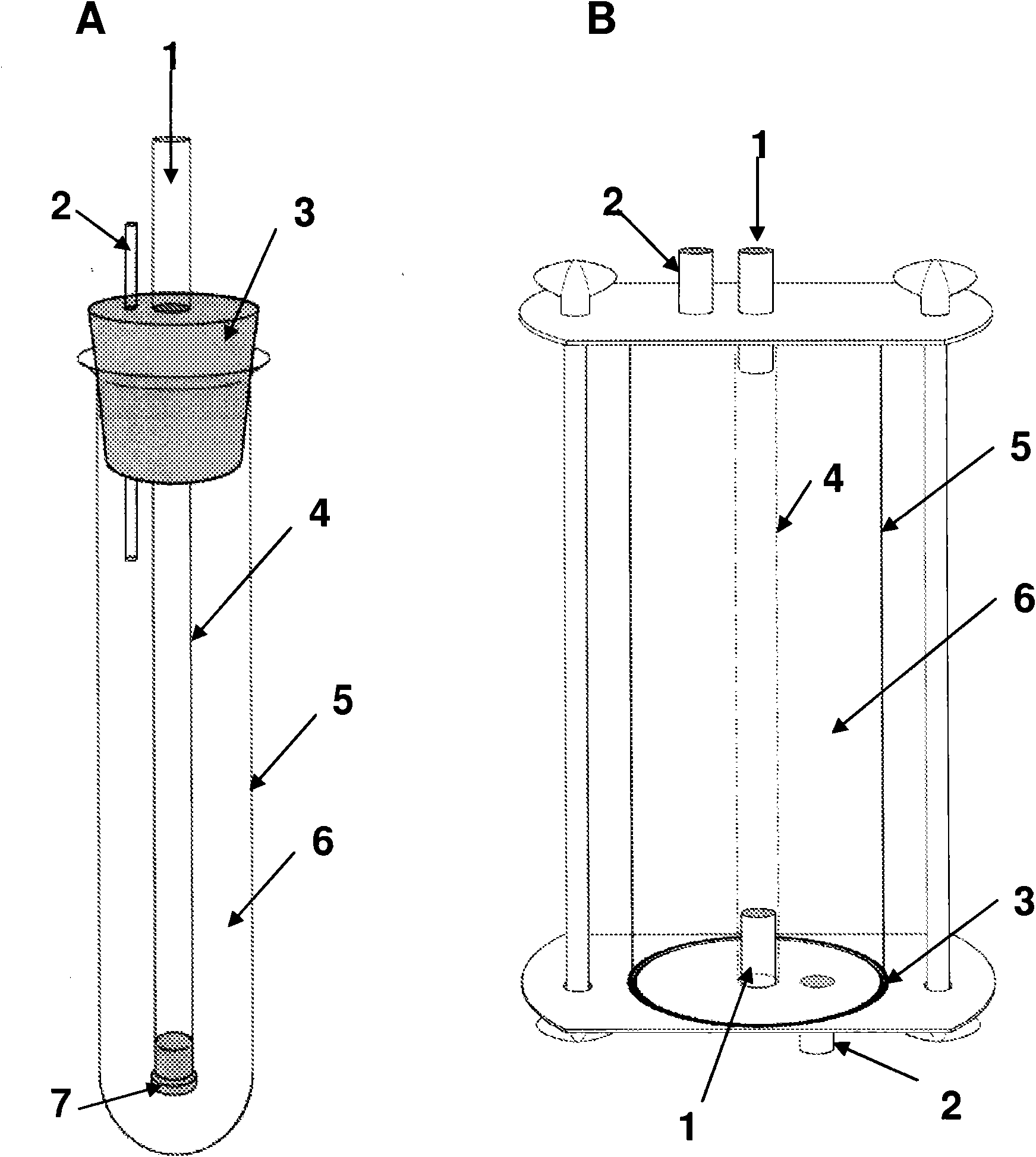
The use of exogenic materials for replacing blood vessels carries the risk of thrombosis and is therefore particularly unsuitable for microsurgical applications (inner vessel diameters of 1-3 mm and less), or only suitable under certain conditions. Replacements of blood vessels with a very small lumen in particular require biomaterials which guarantee that the surfaces of the prosthesis that come into contact with the blood are of a very high quality, and which reliably avoid this kind of thrombosis adhesion. The biomaterial is produced by immersing shaped body walls, especially of a glass matrix consisting of a glass tube and glass body, in a container of an inoculated nutrient solution so that the inoculated nutrient solution is drawn into the area between the walls of the shaped body and cultivation takes place in a moist, aerobic environment. In each subsequent cultivation process, an unused shaped body (glass body) is used as the shaped body wall for shaping the surface of the prosthesis material that is to come into contact with the blood when the biomaterial is used. This is the only sure way of reproducing the high surface quality of the vessel prosthesis and hereby reliably preventing thrombosis adhesion on the biomaterial used. The inventive method is particularly suitable for microsurgical applications, especially for replacing blood vessels and other internal hollow organs or as a cuff for covering nerve fibres, etc.
Owner:SURA CHEM GMBH
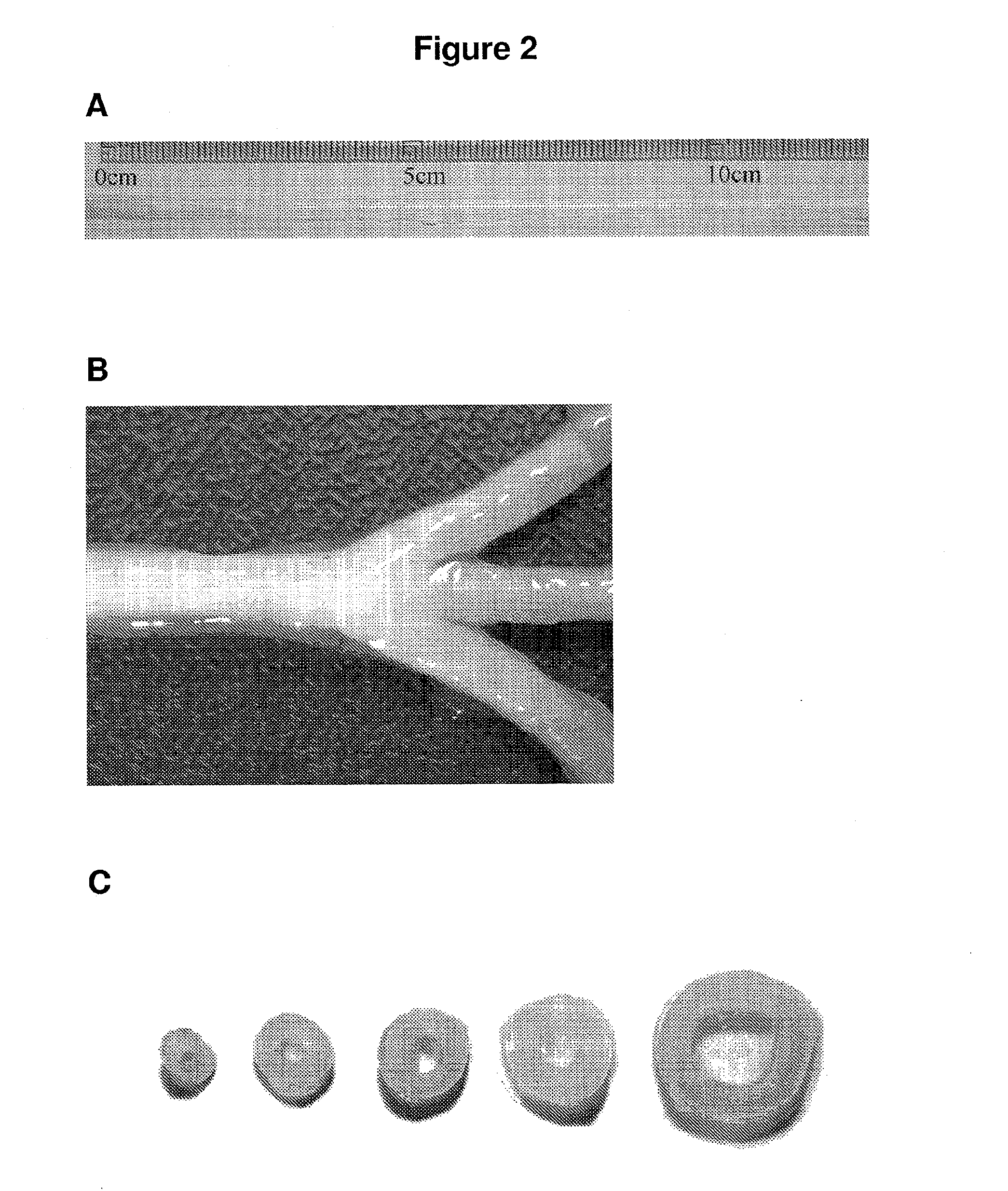
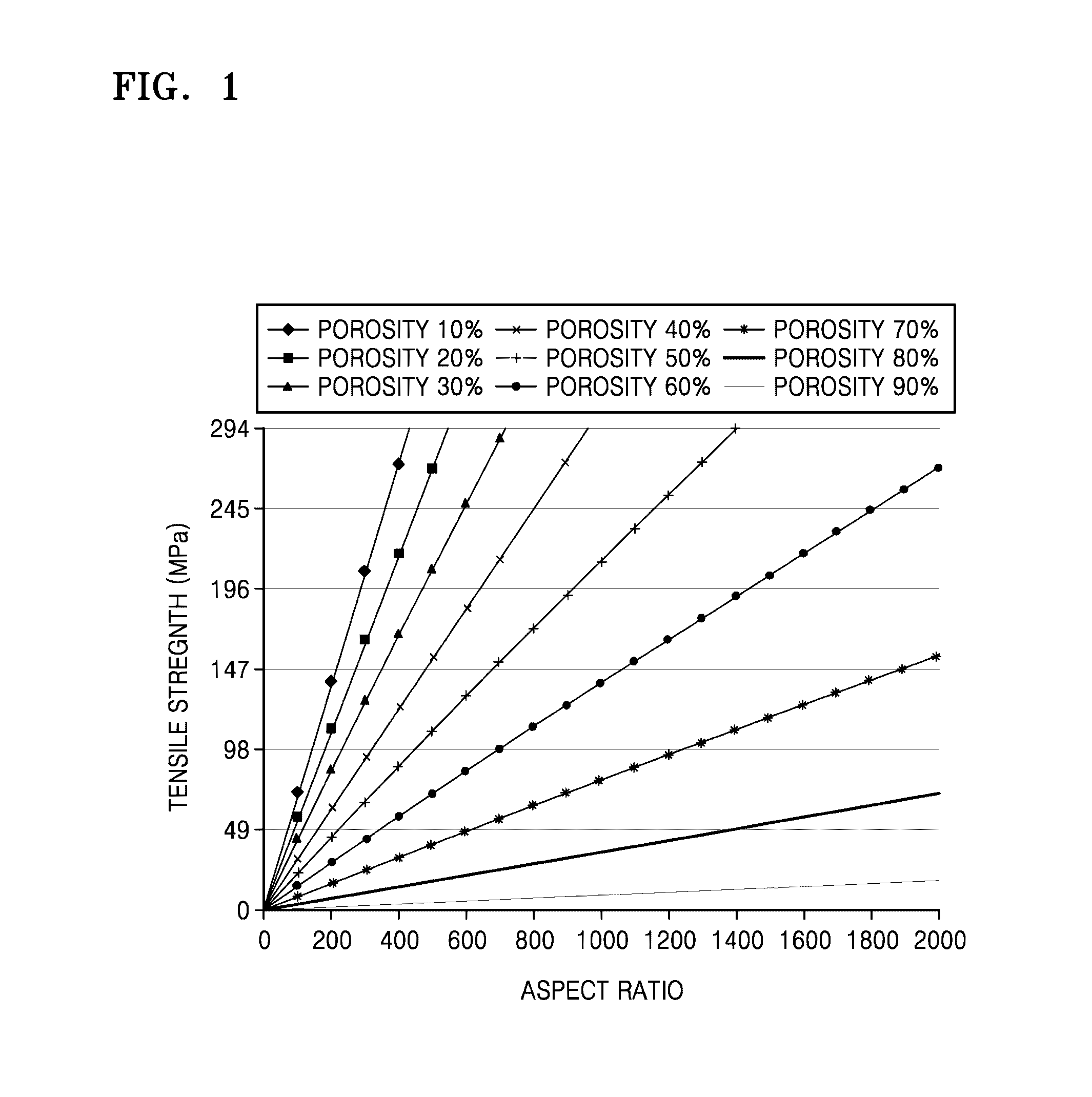
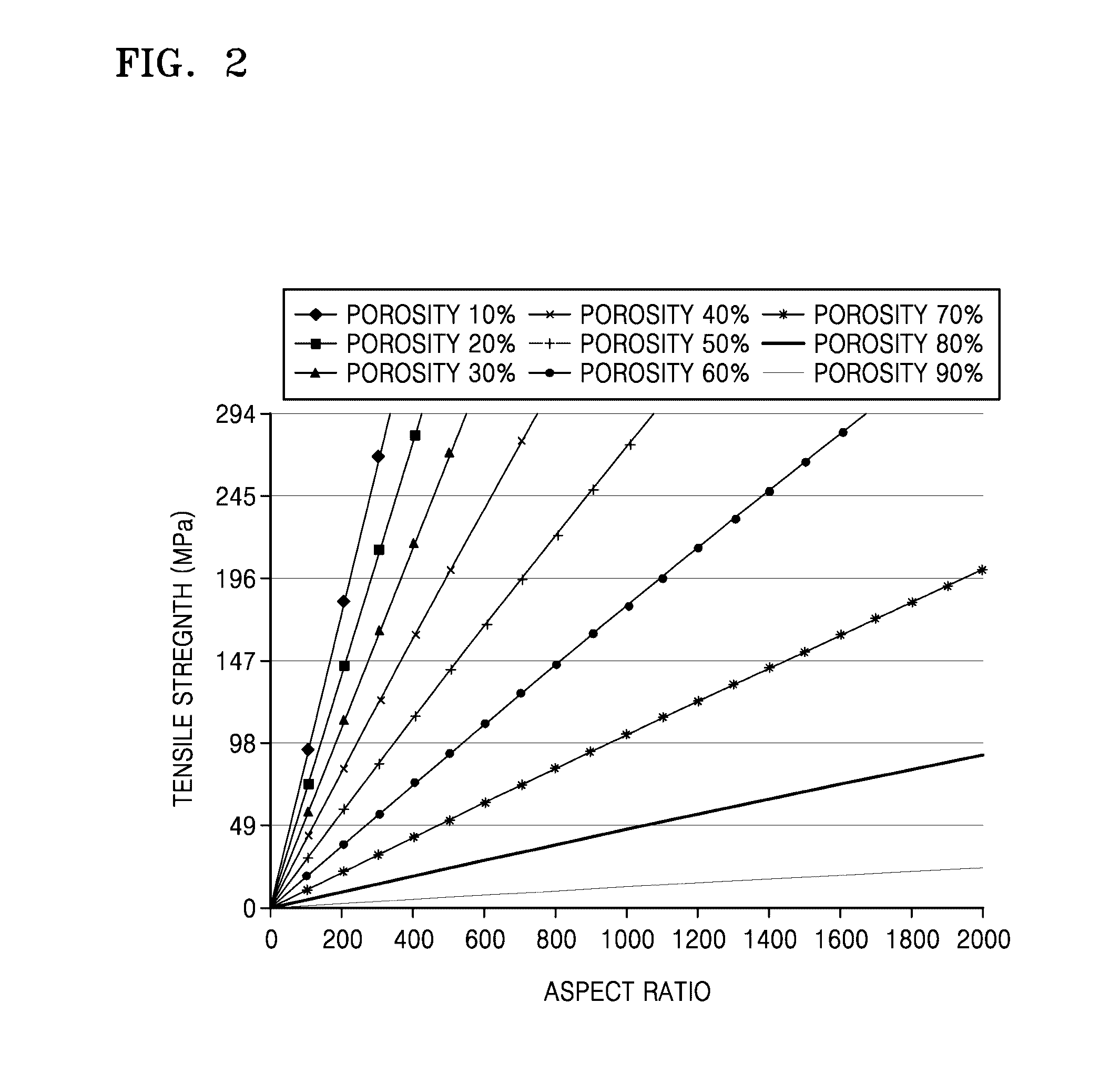
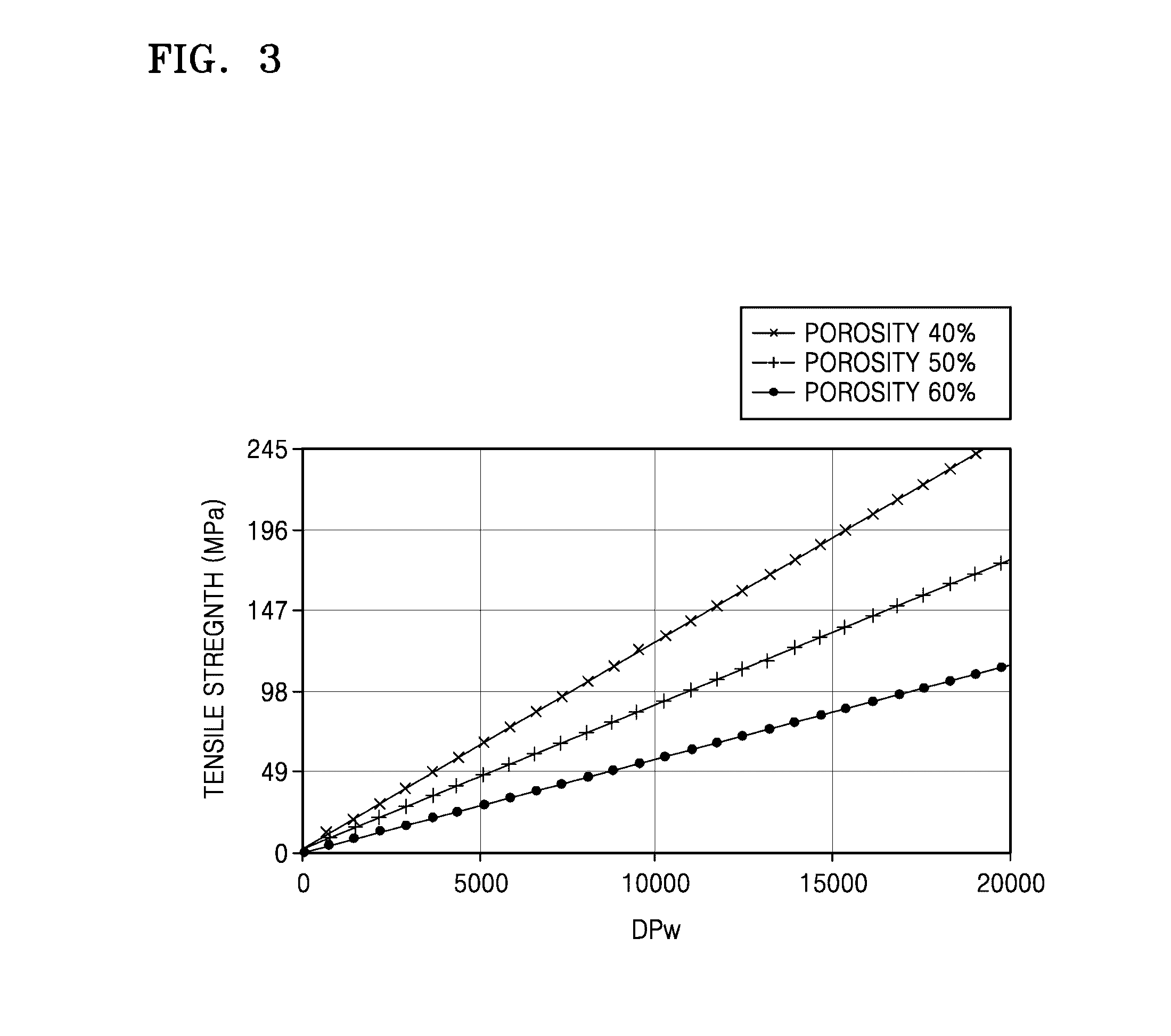
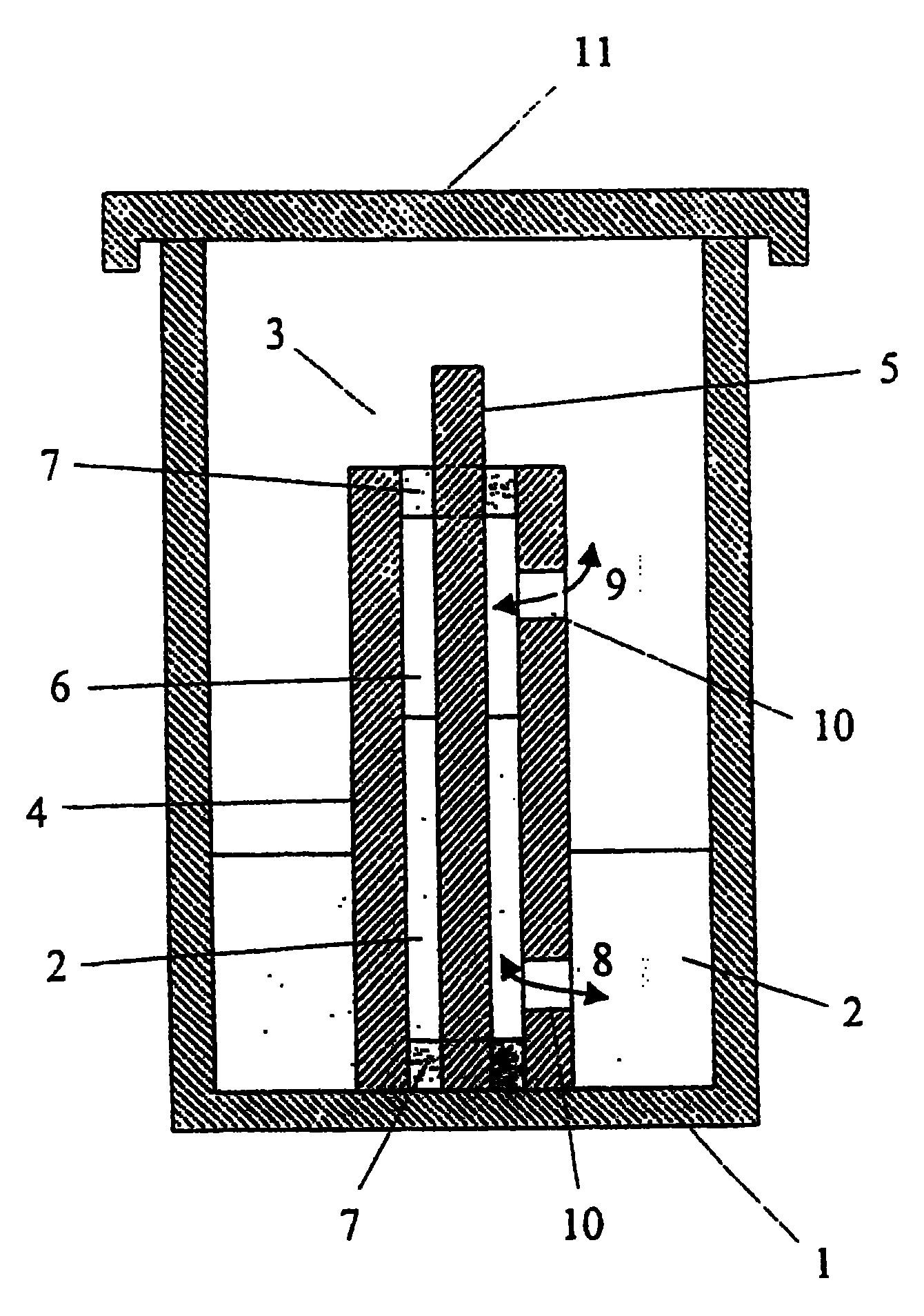
Porous structures of microbial-derived cellulose for in vivo implantation
This invention relates to polysaccharide materials and more particularly to microbial-derived cellulose having the porosity and containing pores of the desired size making it suitable for cellular infiltration during implantation and other desirable properties for medical and surgical applications. The invention also relates to the use of porous microbial-derived cellulose as tissue engineering matrices, human tissue substitutes, and reinforcing scaffolds for regenerating injured tissues and augmenting surgical procedures. The invention outlines various methods during and after fermentation to create porous microbial cellulose capable of allowing cell infiltration while preserving the physical properties of the microbial-cellulose.
Owner:SYNTHES USA PROD
Multi-function emergency bandage
ActiveUS9861531B2Increase coefficient of frictionPrevent ischemia and necrosisNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersNano structuringMicrobial cellulose
Owner:SANKO TEKSTIL ISLETMELERI SANAYI & TICARET A S
Preparation method of microbial cellulose
InactiveCN102191296ADoes not affect tasteImprove water retentionMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesWater bathsMycoprotein
The invention provides a preparation method of microbial cellulose. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a fermentation medium, namely sterilizing 5 percent of corn hydrolyzing sugar, 0.5 percent of ammonium sulfate, 0.5 percent of NaCl, 0.2 percent of magnesium sulfate, 0.1 percent of acetic acid and 0.15 percent of lactate for 10 to 30 minutes at the temperature of between 110 and 150 DEG C, cooling the mixture to 30 DEG C, and inoculating 4 percent of ultraviolet mutagenesis acetobacter aceti seed liquor onto the mixture, and culturing the mixture for 120 hours in a shake bed; after centrifuging the fermentation liquor for 20 minutes at the speed of 3,000r / min in a high-speed centrifugal machine, pouring the supernatant fluid; heating the centrifugal precipitate for 30 minutes in a boiling water bath of which the temperature is 100 DEG C by using 4 percent of Na OH solution, to remove mycoprotein; centrifuging the solution, adding a proper amount of neutral detergent solution into the precipitate, and heating the precipitate for 1 hour in the boiling water bath of which the temperature is 100 DEG C to remove impurities, such as impure sugars, lipoids and the like from the precipitate; repeatedly washing the precipitate with deionized water and 0.5 percent of acetic acid; and drying the precipitate for 24 hours at the temperature of 80 DEG C to obtain the microbial cellulose.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG PROV LIGHT INDAL SCI RES ACAD
Method for preparing micro organism cellulose
InactiveCN101358221ADoes not affect tasteImprove water retentionMicroorganism based processesFermentationWater bathsMycoprotein
The invention provides a preparation method for microbe cellulose. Firstly, fermentation medium is prepared: 5 percent of corn hydrolysis sugar, 0.5 percent of ammonium sulfate, 0.5 percent of NaCl, 0.2 percent of magnesium sulfate, 0.1 percent of acetic acid and 0.15 percent of lactate are sterilized under the temperature of 110 to 150 DEG C for 10 to 30 minutes and cooled under the temperature of 30 DEG C, are inoculated with 4 percent of ultraviolet to mutagenize MC-5 Acetobacter xylinum seed liquid, and are cultured by a shaking table for 120 hours; then the fermentation liquid is centrifugated in a high speed of 3000r / min for 20 minutes in a high-speed centrifuger, supernatant fluid is poured away, centrifuged sentiments are taken and heated in boiling water bath with the temperature of 100 DEG C for 30 minutes by 4 percent NaOH solution to remove mycoprotein and then are centrifuged; sediments are taken and added with neutral detergent solution to be heated in 100 DEG C water bath for one hour to remove the impurities such as saccharide, lipid and the like in the sentiments, then are repeatedly washed by de-ionized water and 0.5 percent acetic acid, and finally are dried under the temperature of 80 DEG C for 24 hours to obtain bacterial cellulose.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG PROV LIGHT INDAL SCI RES ACAD
Bioreactor and method for producing microbial cellulose
ActiveUS20120094334A1Improve production efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismLiquid medium
A technique for producing microbial cellulose is provided, including: preparing a liquid medium for microbial cultivation in a container; horizontally rotating multiple hollow tubes that are fitted together or separated from one another, so that each of the hollow tubes is alternately partially immersed in the liquid medium and partially exposed above the horizontal surface of the liquid medium; wherein each of the hollow tubes has a rough outer surface and a smooth inner surface, so as to allow microorganisms to form microbial cellulose on the outer surface of each hollow tube, as well as forming sheets of microbial cellulose on the horizontal surface of the liquid medium not being disturbed by the hollow tubes, and removing the microbial cellulose from the outer surfaces of the hollow tubes in order to obtain tubular microbial cellulose. In addition, the sheets of microbial cellulose are also harvested from the liquid medium.
Owner:FOOD IND RES & DEV INST
Process for the preparation of hollow cellulose vessels by culturing cellulose- producing microorganisms on the surface of a hollow carrier and providing a gas having an oxygen level of at least 35%
InactiveCN101595225AIncreased mechanical resistanceIncrease burst pressureChemical recyclingFermentationHollow fibreLymphatic vessel
Owner:ARTERION AB
Bioreactor for producing microbial cellulose and method thereof
ActiveCN101921701AImprove utilization efficiencyIncrease productivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismLiquid medium
The invention relates to a bioreactor for producing microbial cellulose and a method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a microbial culture liquid medium in a container; horizontally rotating a plurality of hollow tubes which are alternately sheathed together or separated from each other so that each part of each of the hollow tubes is immersed in the liquid medium held in the container and exposed on a horizontal plane of the liquid medium in turn, wherein, each hollow tube is provided with a rough outer surface and a smooth inner surface, so a microbe forms the microbial cellulose on the outer surface of each hollow tube and forms the flaky microbial cellulose on the horizontal plane part of the liquid medium which is not disturbed by the plurality of the hollow tubes in the container; and removing the microbial cellulose from the outer surface of each hollow tube to obtain the tubular microbial cellulose, and obtaining the flaky microbial cellulose from the liquid medium.
Owner:FOOD IND RES & DEV INST
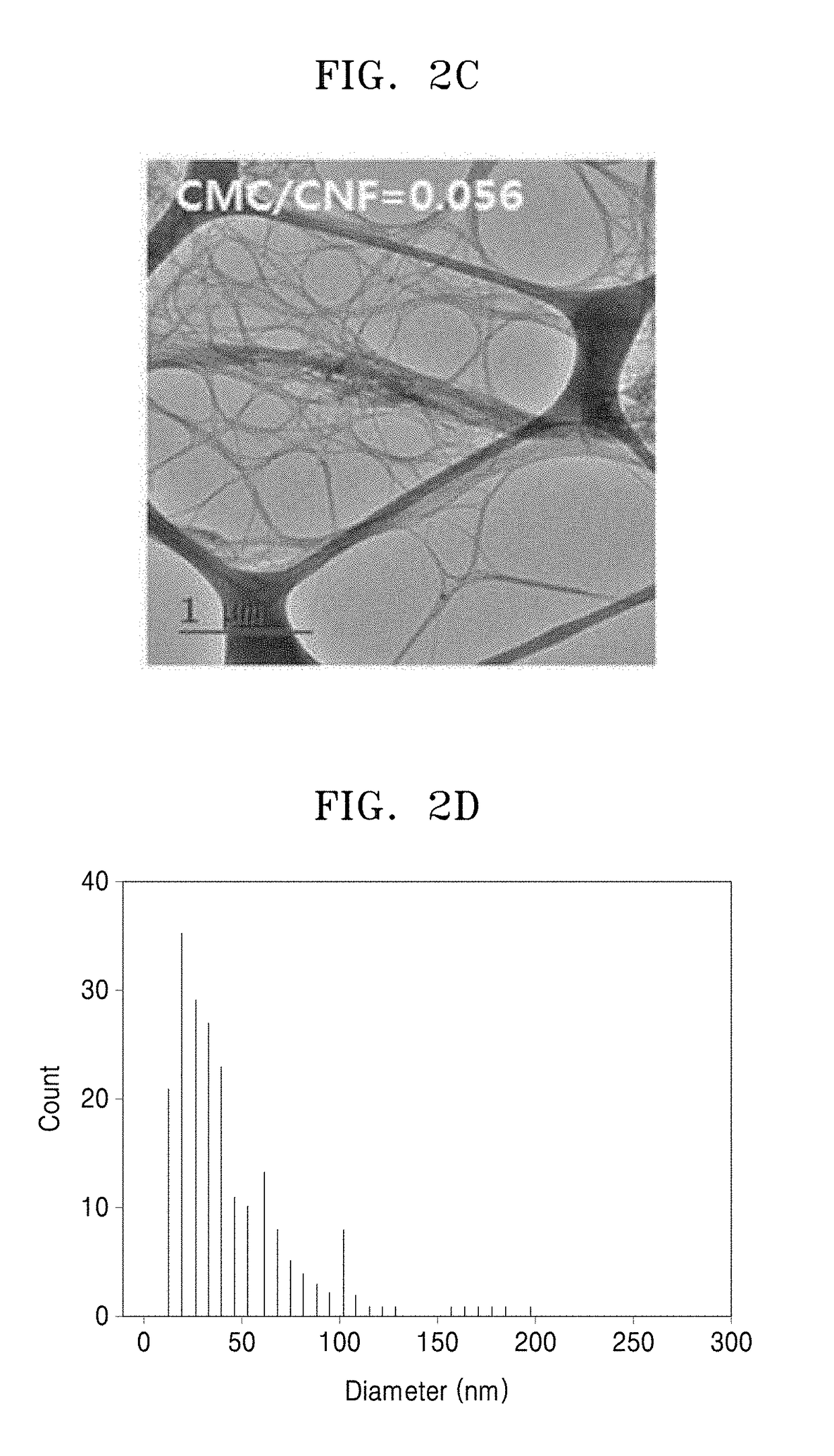
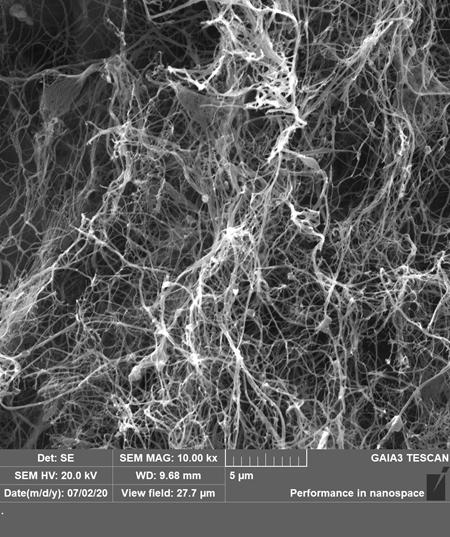
Method of producing cellulose nonwoven fabric, cellulose nonwoven fabric produced thereby, and secondary ion battery including the same
A method of producing a cellulose nonwoven fabric, a cellulose nonwoven fabric produced thereby, and a secondary ion battery including the same, wherein the method includes passing a cellulose suspension with microbial cellulose and a water-soluble cellulose disintegrating agent in a medium through an orifice of a high-pressure homogenizer to obtain a cellulose dispersion and removing the medium from the obtained cellulose dispersion to form the nonwoven fabric.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Preparation method of cellulose aerogel-based efficient air filtering membrane
ActiveCN112876713AImprove mechanical propertiesSimple processHuman health protectionSemi-permeable membranesAir filtrationFreeze-drying
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
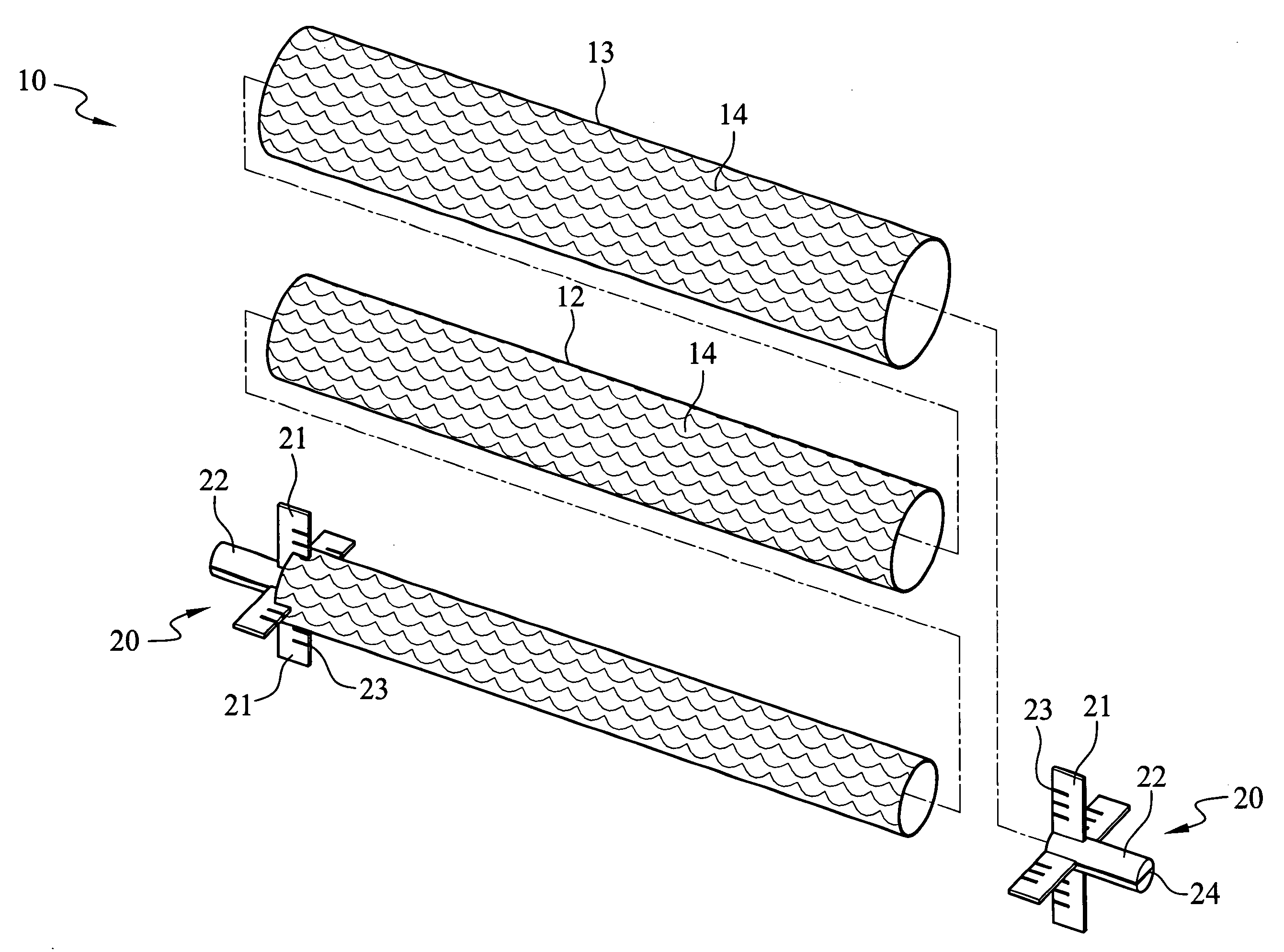
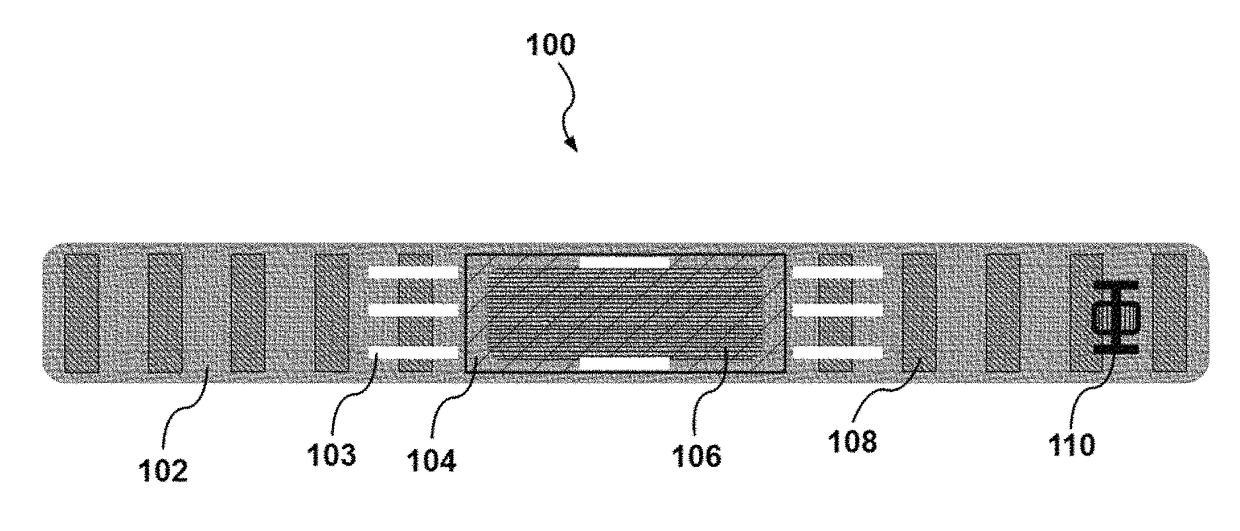
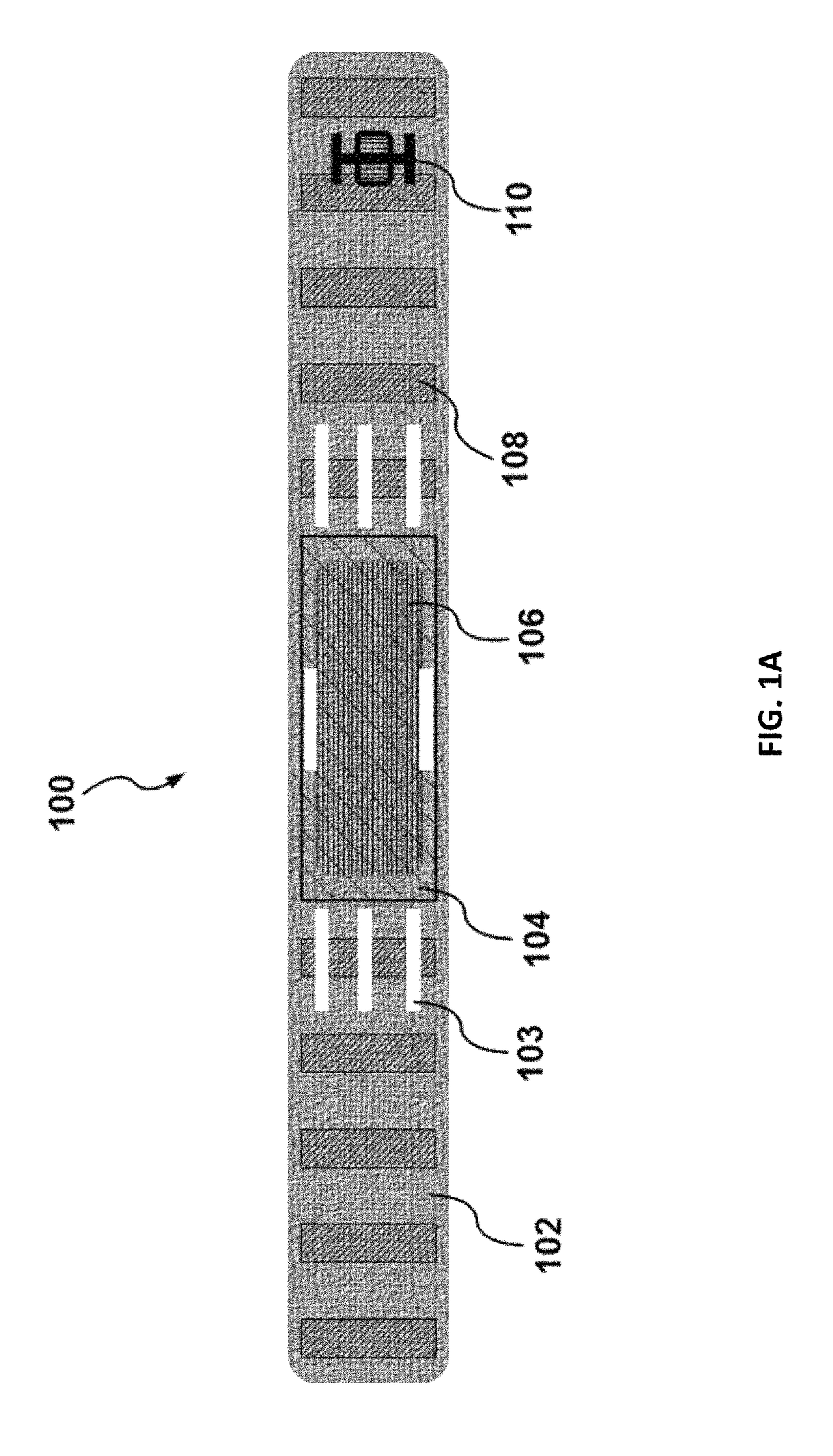
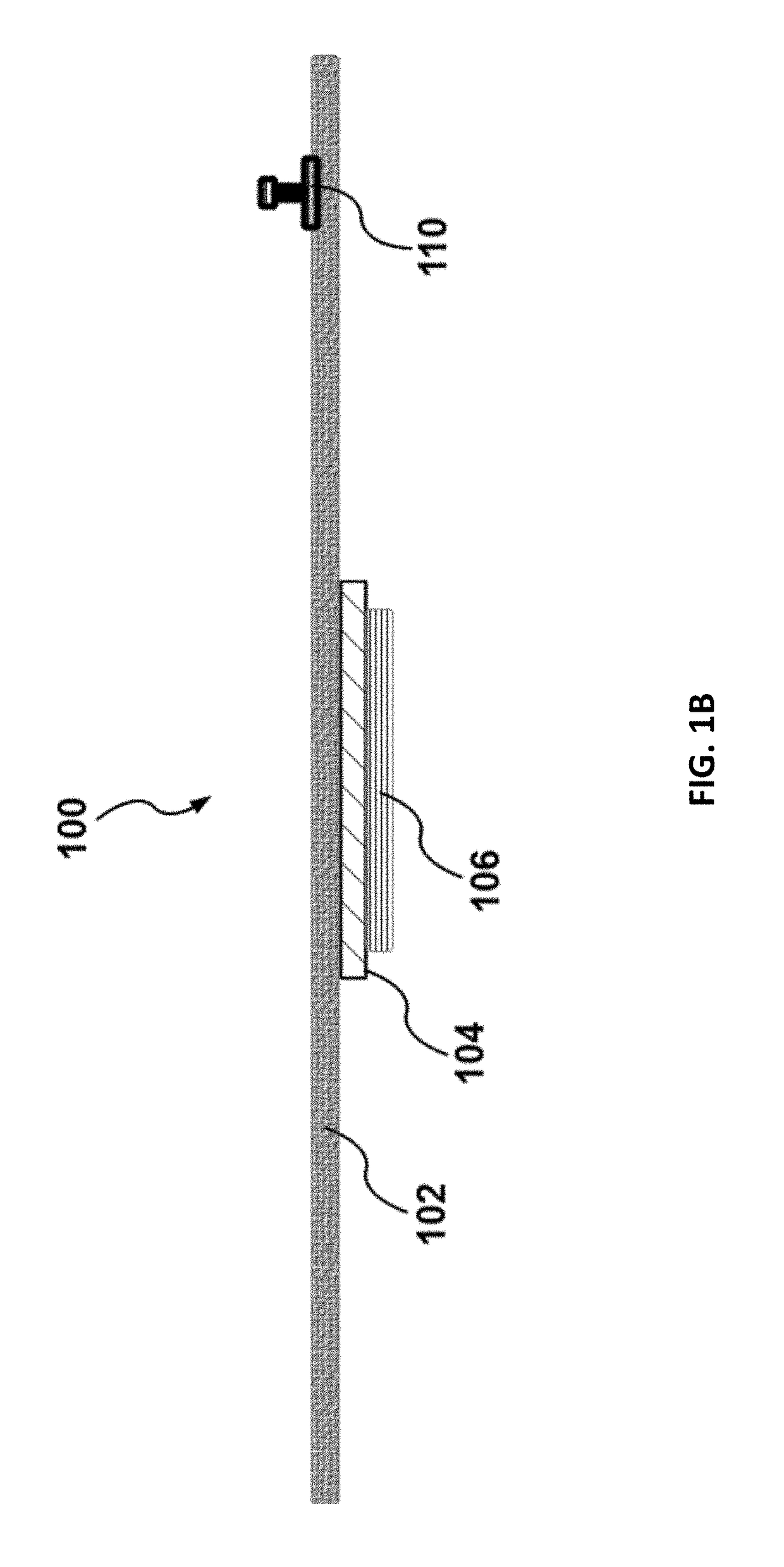
Medical implant based on nanocellulose
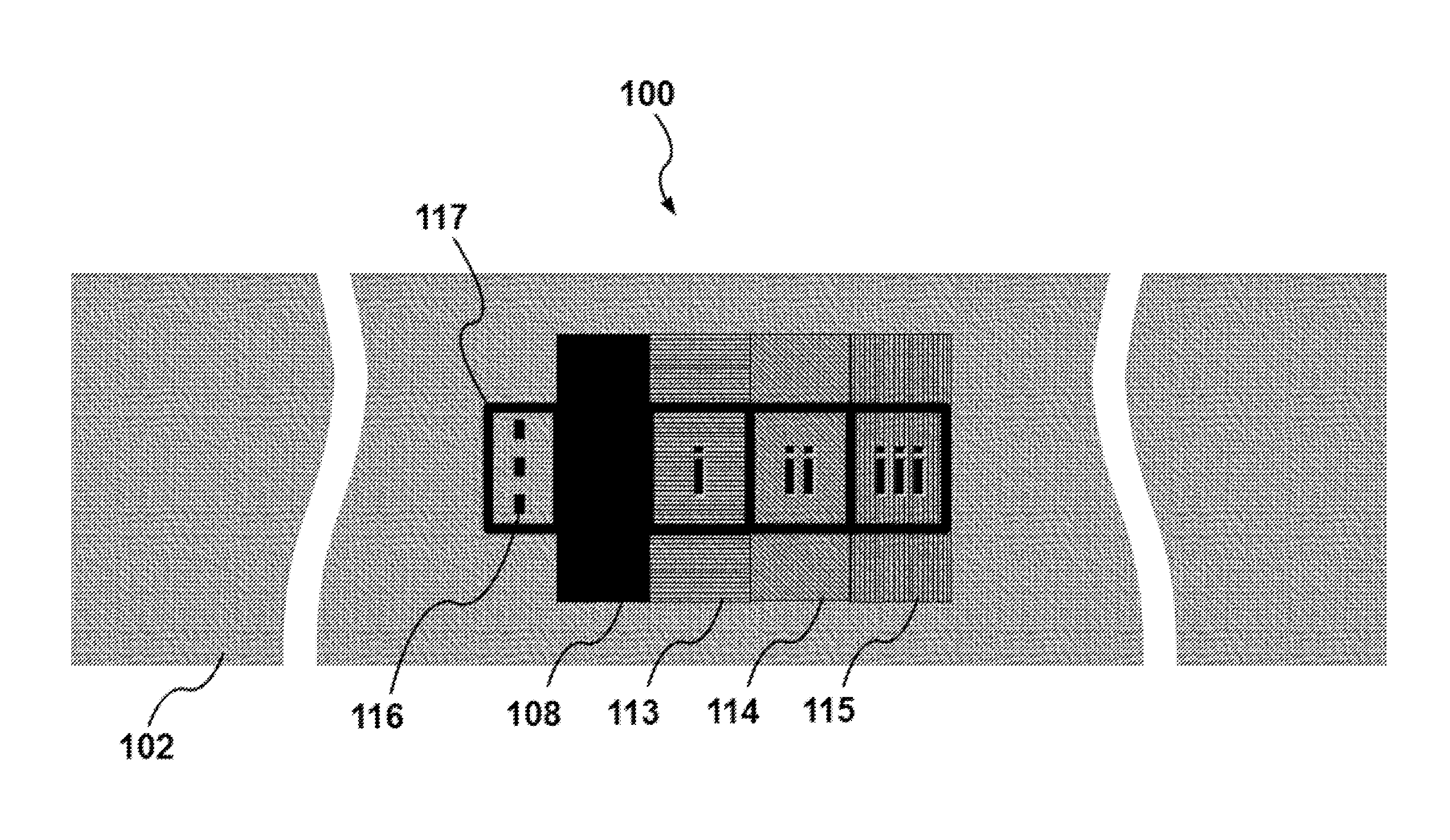
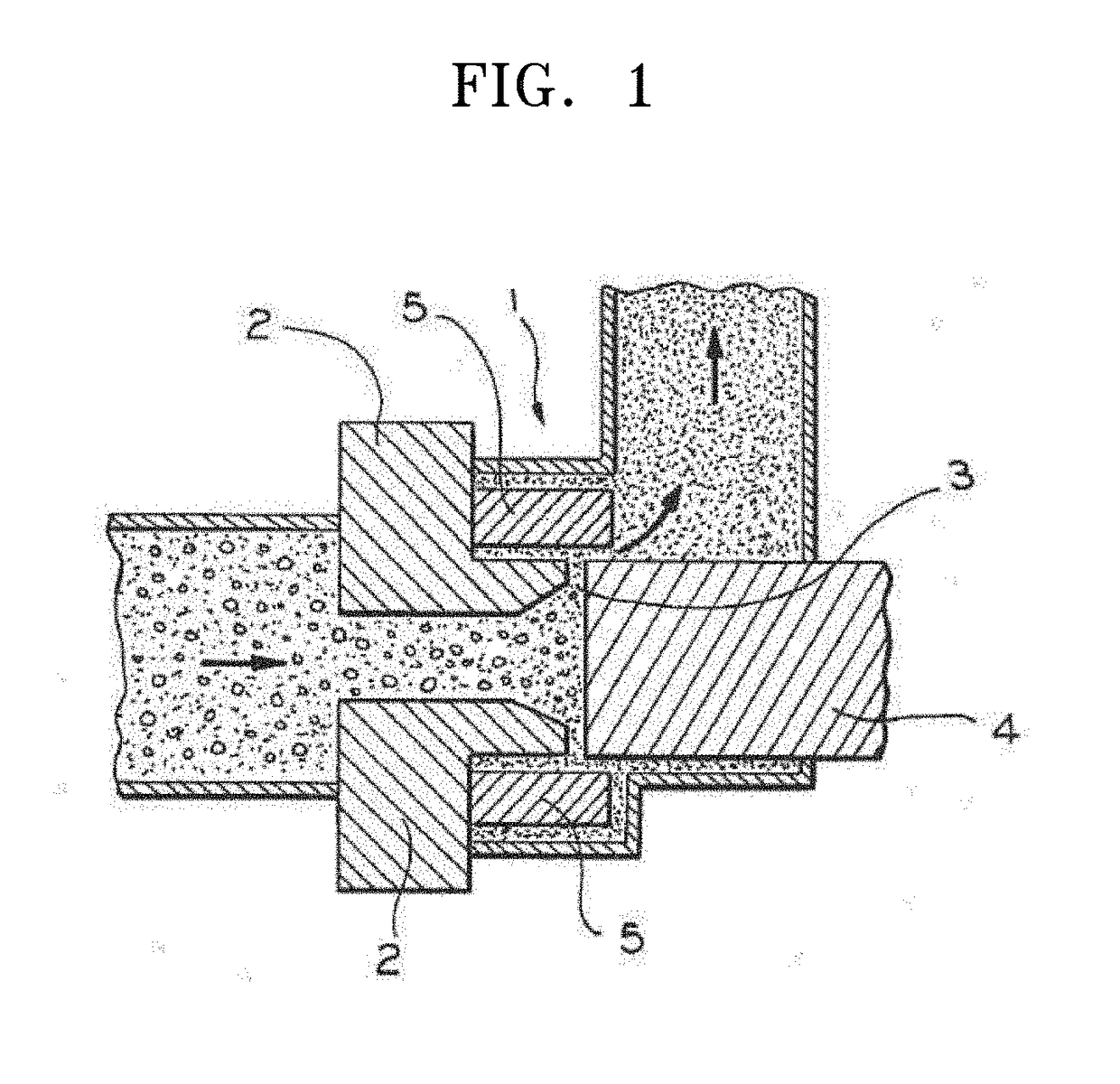
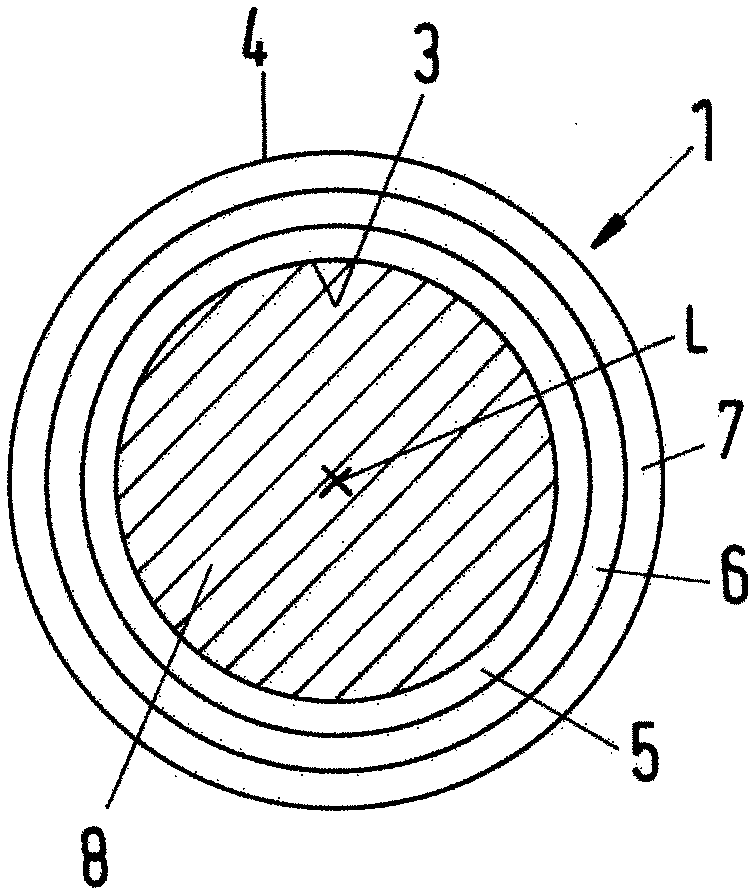
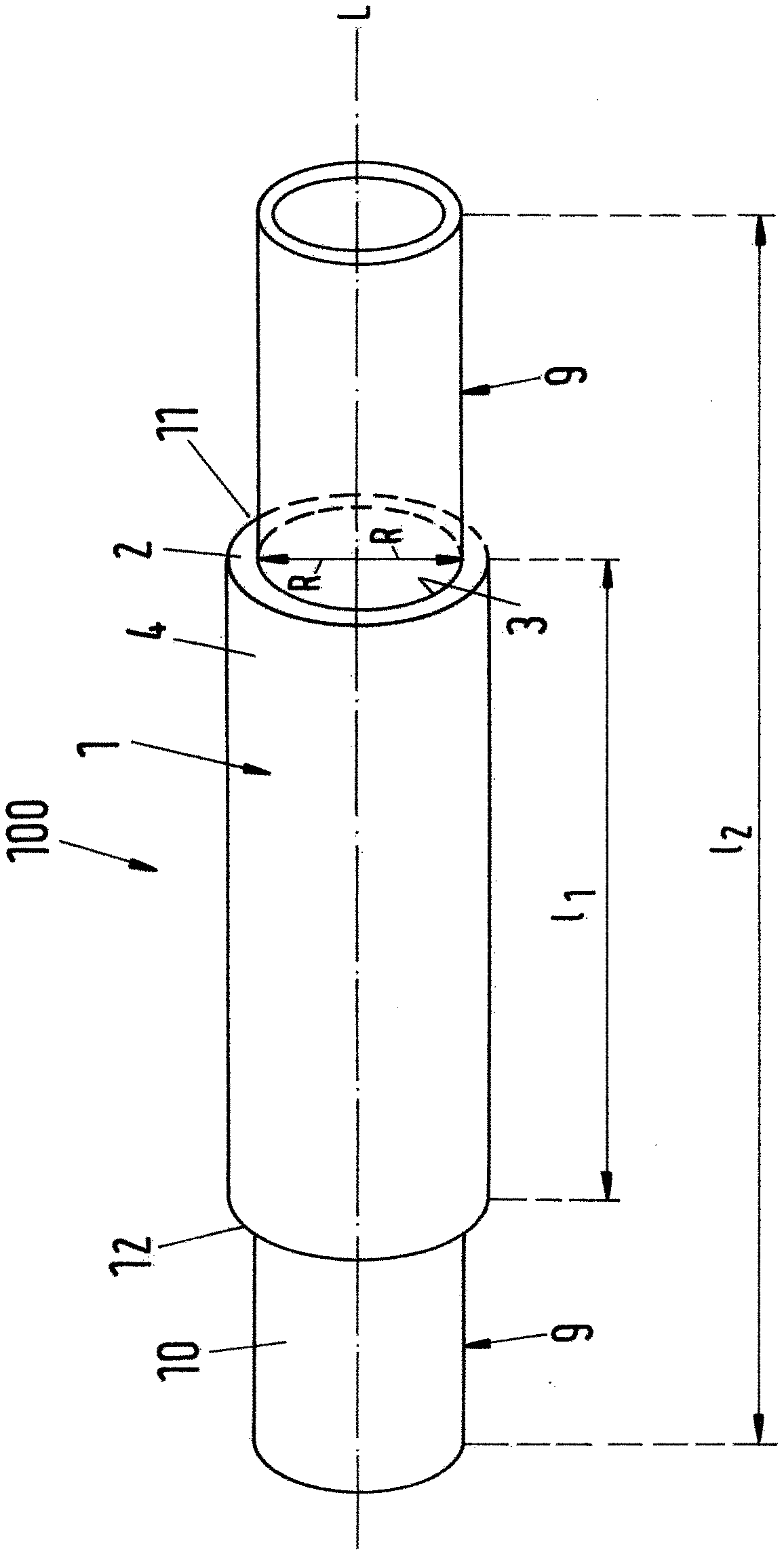
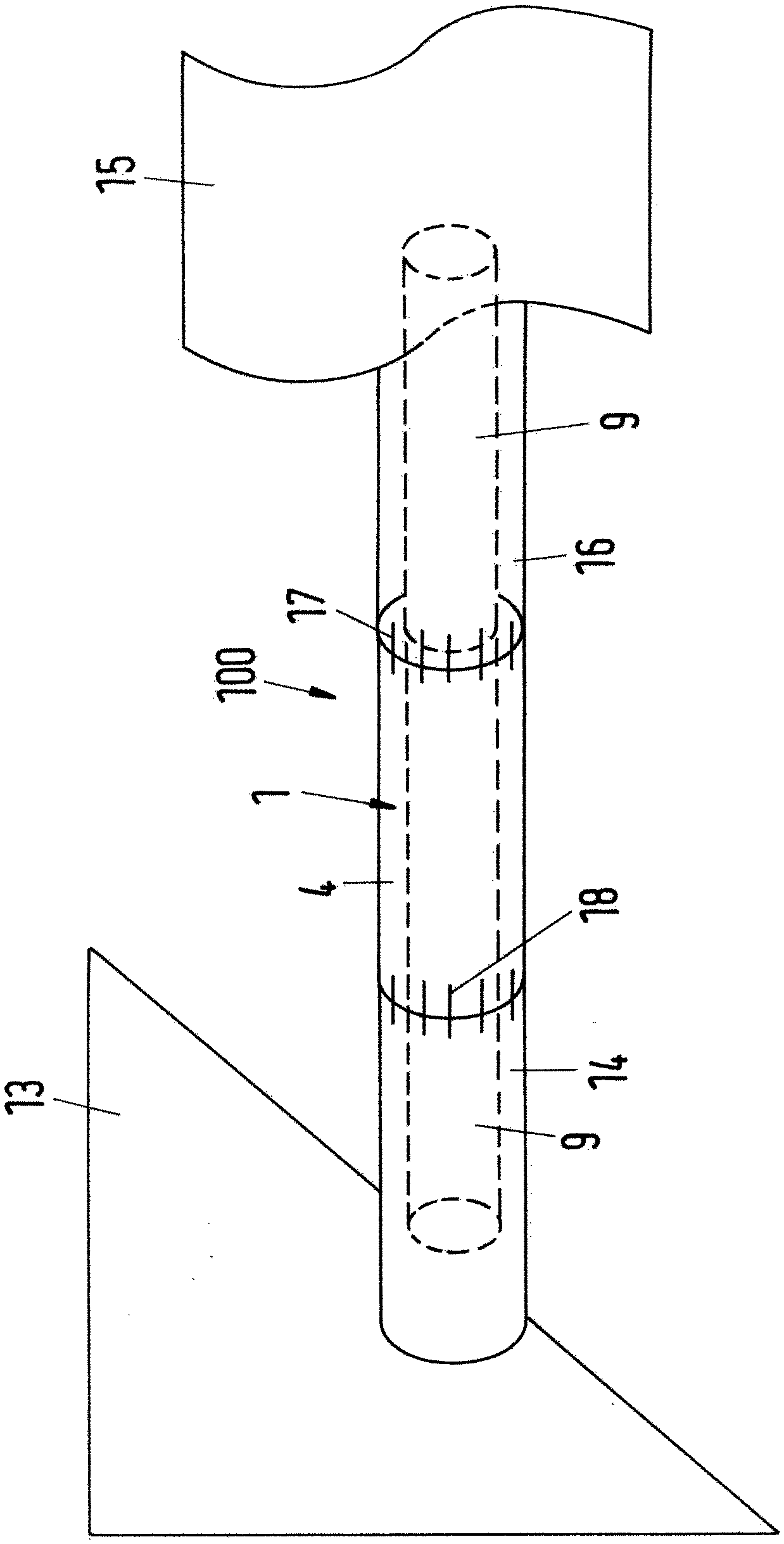
The present invention provides a medical Implant (100). The medical Implant (100) comprises: a microbial cellulose tube (1) comprising a wall (2) having an inner surface (3) and an outer surface (4),wherein the wall comprises several layers (5, 6, 7) of microbial cellulose, the layers are concentric or substantially concentric to a longitudinal axis (L) of the tube; and a stent (9) which placed inside of the microbial cellulose tube (1), wherein an outer surface (10) of the stent contacts the inner surface (3) of the microbial cellulose tube (1), and method for producing such implant. The implant can be covered with newly created bile duct epithelium, thereby creating a new bile duct from body cells. The implant can be removed after completion of creation of the new bile duct. So, the implant as suitable as a temporary implant. The implant can be used for surgery, such as surgery of gall bladder, bile duct and / or liver, e.g. gall bladder removal, hepatobiliary malignancy surgery or liver transplantation. The implant can particularly be used for repairing or regeneration of bile duct. Further fields of use are the use as esophagus implant or urether implant.
Owner:耶拿大学综合医院
Straw fermented feed and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111084277AIncrease appetiteImprove the immunityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyMicrobial cellulose
The invention belongs to the technical field of feed processing, and discloses a straw fermented feed and a preparation method thereof. The straw fermented feed comprises the following raw materials:green straw, traditional Chinese medicines, white carbon black, fumaric acid, montmorillonite powder, compound microorganisms and cellulase. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) harvesting the green straws, removing impurities, cutting the green straws into small sections with a length of 3-4 cm by using a chopping machine, and regulating moisture so as to obtain a silage rawmaterial; (2) respectively diluting the compound microorganisms and the cellulase with water, uniformly mixing the diluted compound microorganisms and cellulase with the silage raw material, loading an obtained mixture into a clean bag in a layered manner, treading and compacting the mixture once when the bag is filled with the mixture with a thickness of 25-35 cm, exhausting air, and tightening abag opening by using a rope; and (3) putting a material obtained in the step (2) into a fermentation tank for anaerobic fermentation, taking a fermented material out of the fermentation tank, addingthe white carbon black, the fumaric acid and the montmorillonite powder in proportion, and performing uniform mixing so as to obtain the straw feed. The straw feed disclosed by the invention takes thegreen straws and the Chinese herbal medicines as main raw materials, has the effects of strengthening the spleen and stomach, improving the appetite of livestock and enhancing the resistance of the livestock, and increases the weight of the livestock.
Owner:绵阳市隆豪农业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com