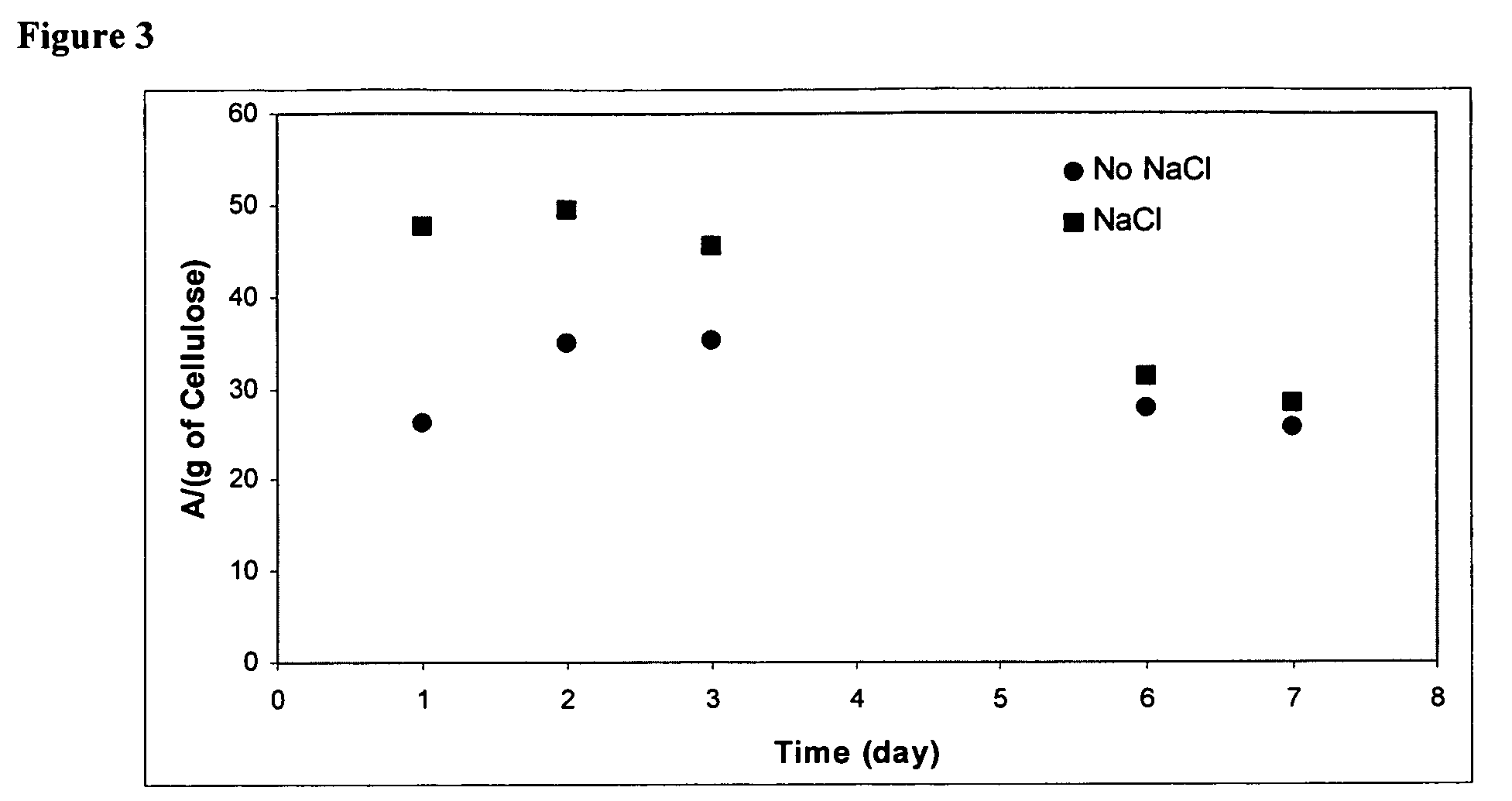
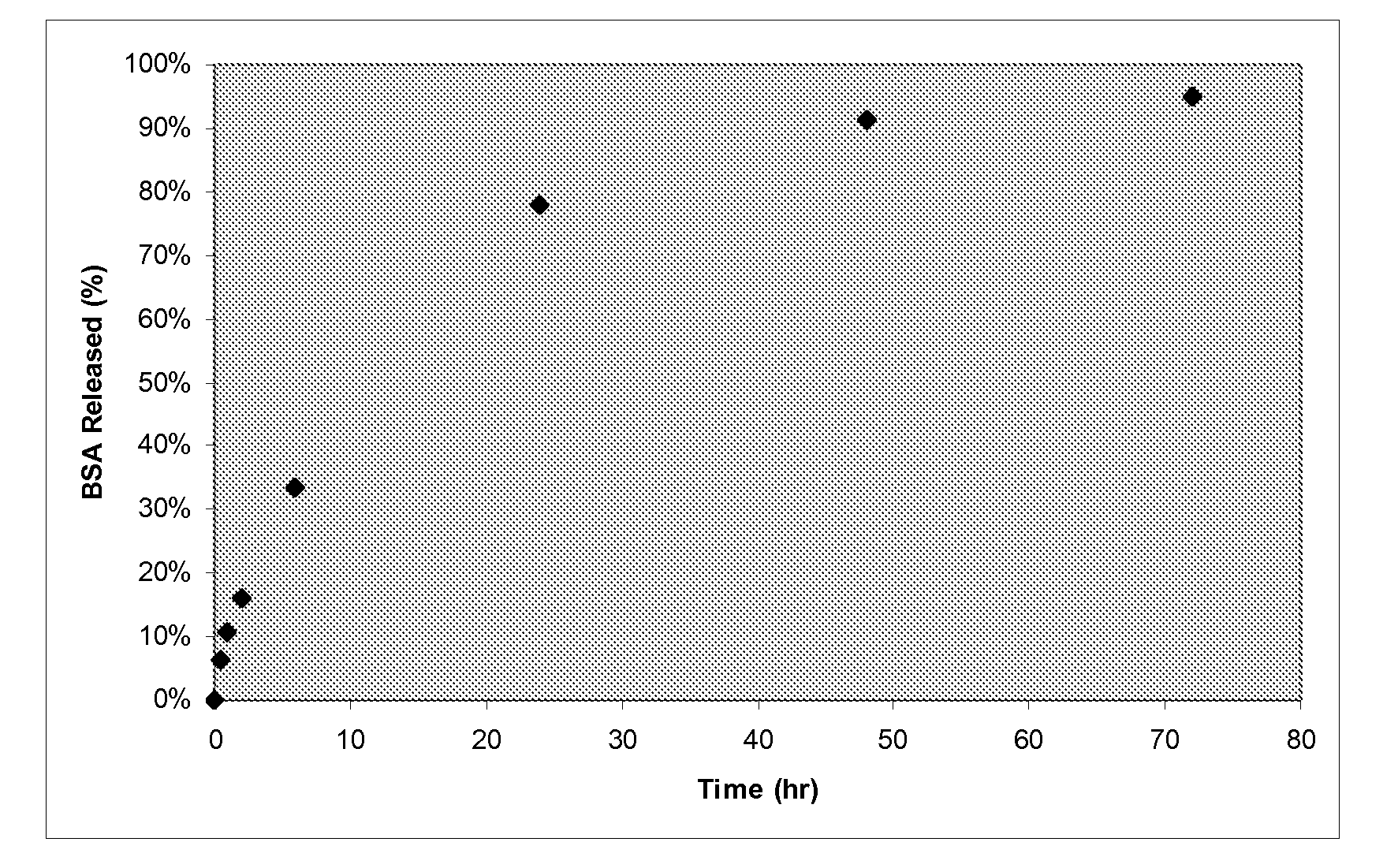
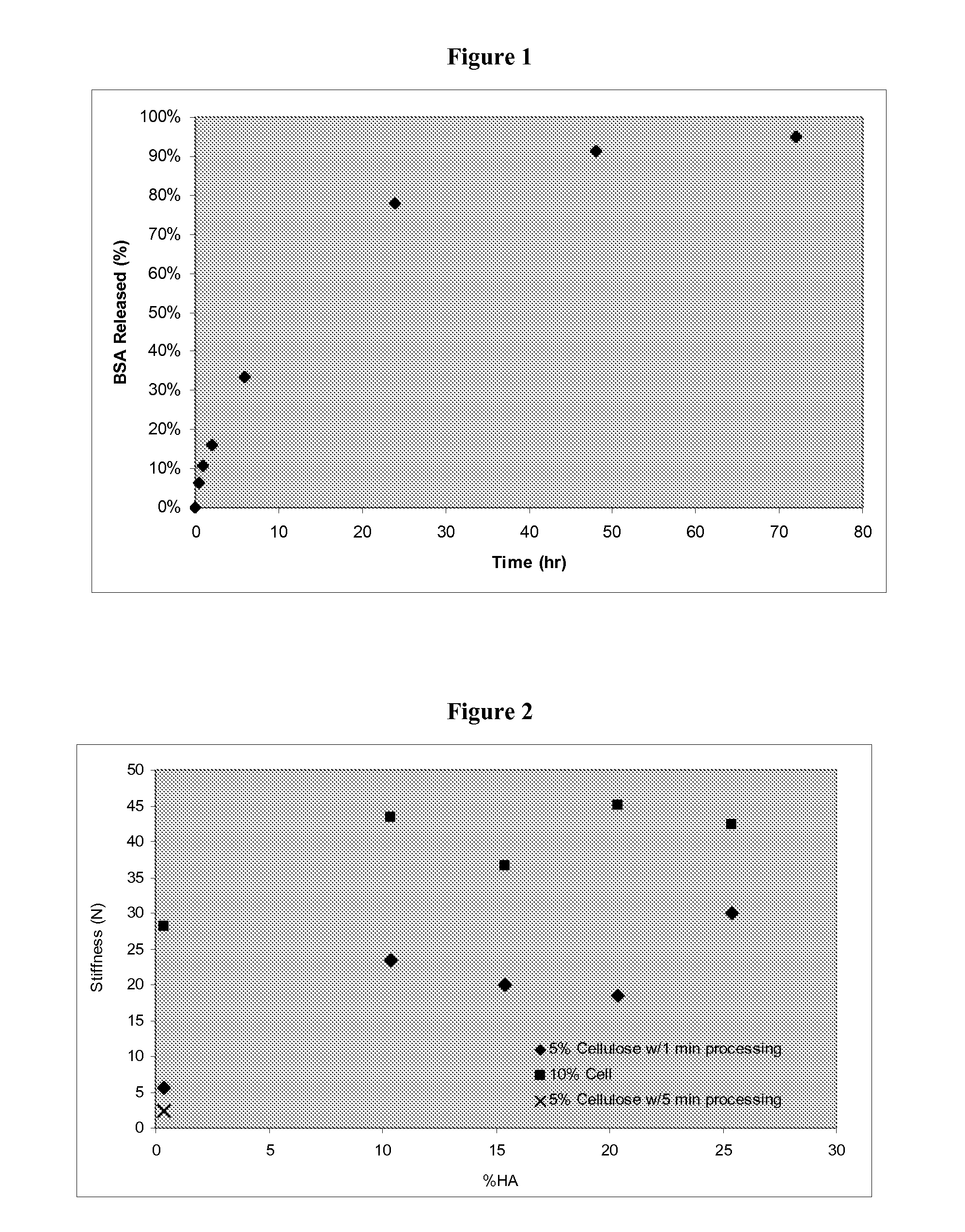
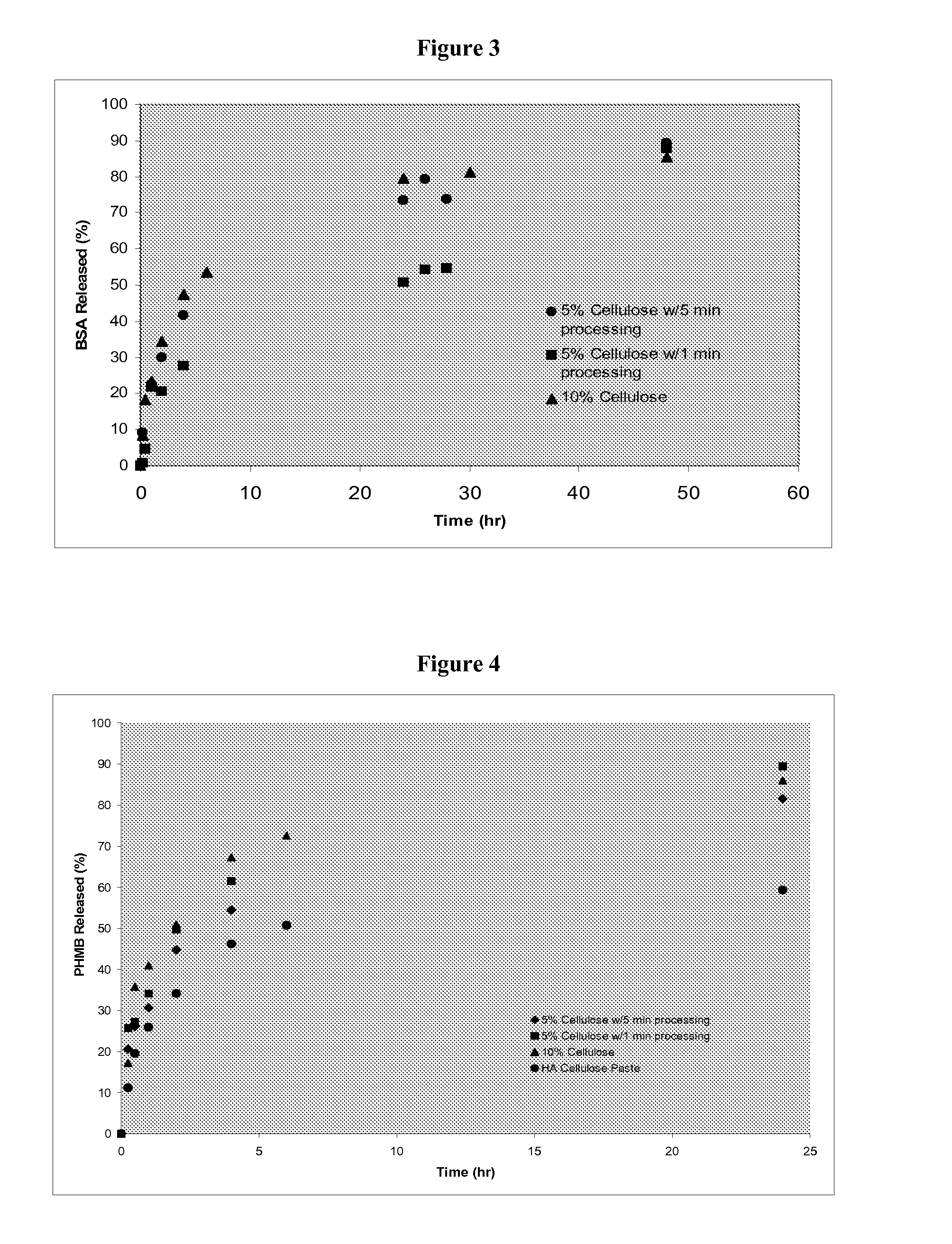
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Gluconacetobacter xylinum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
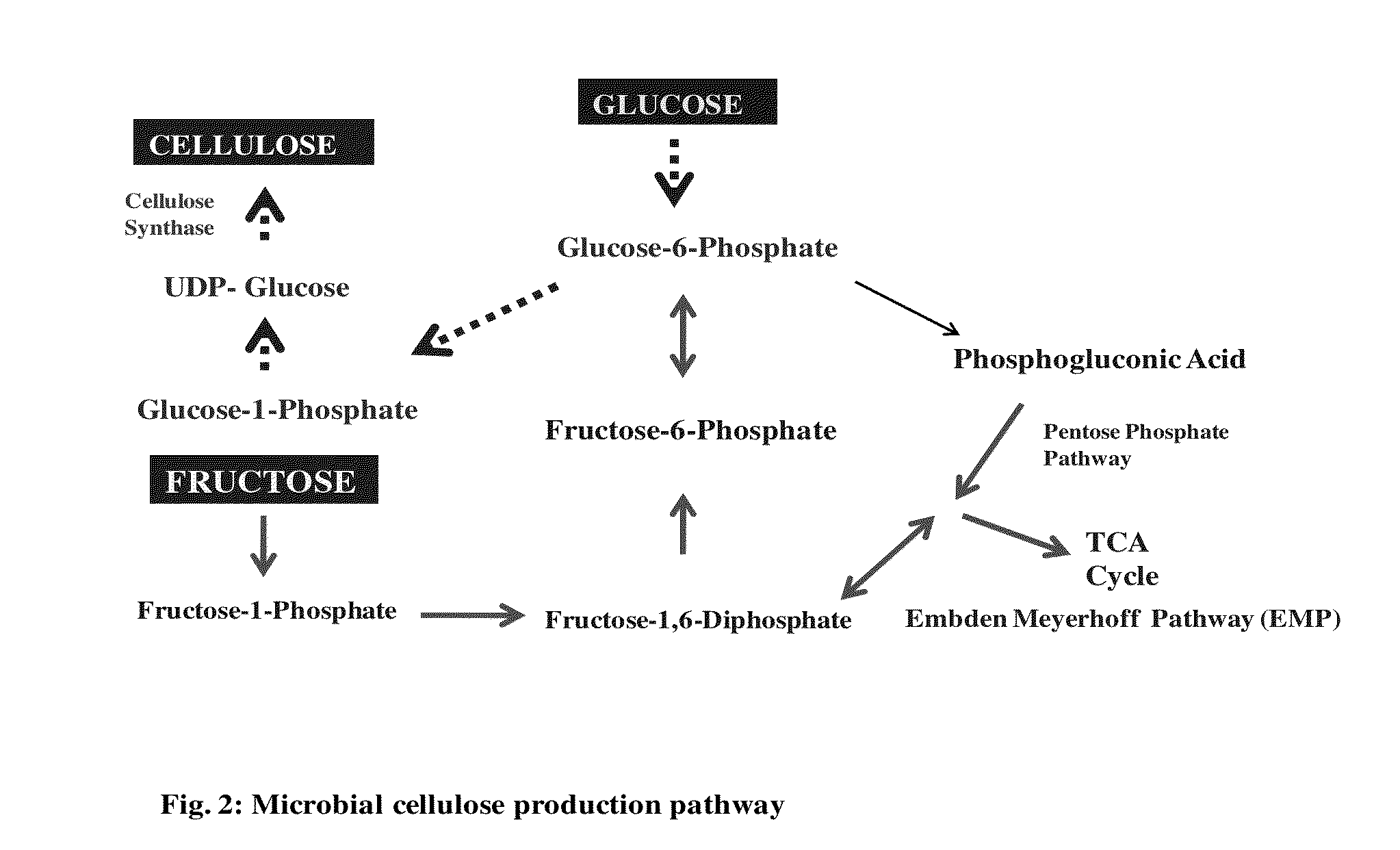
One continuing mystery surrounding microbial cellulose is its exact biological function. A. xylinus, since been renamed as Gluconacetobacter xylinus and more recently as Komagataeibacter xylinus, is a successful and prevalent bacterium in nature, frequently finding a home in rotting fruits and sweetened liquids.
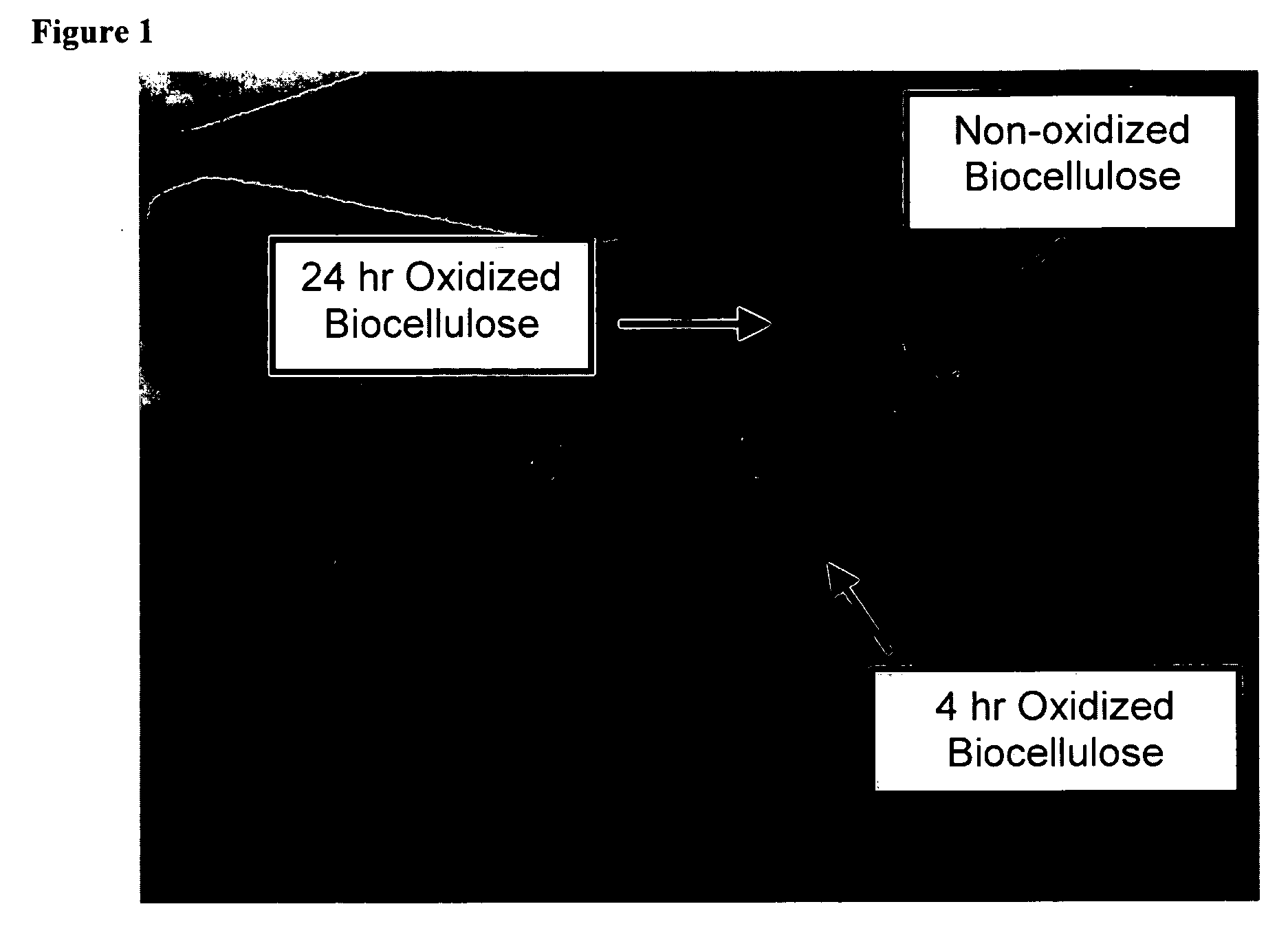
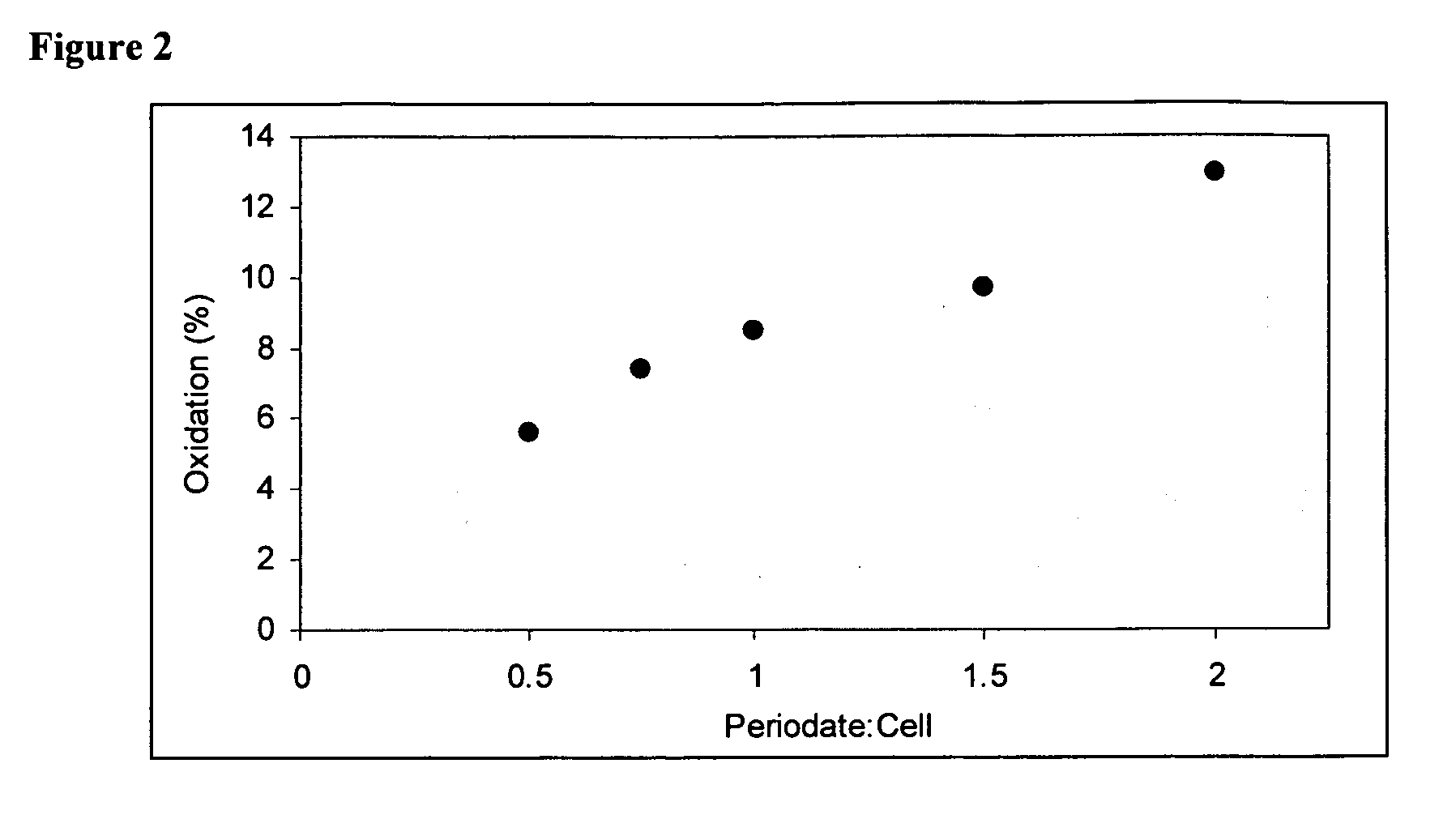
Oxidized microbial cellulose and use thereof
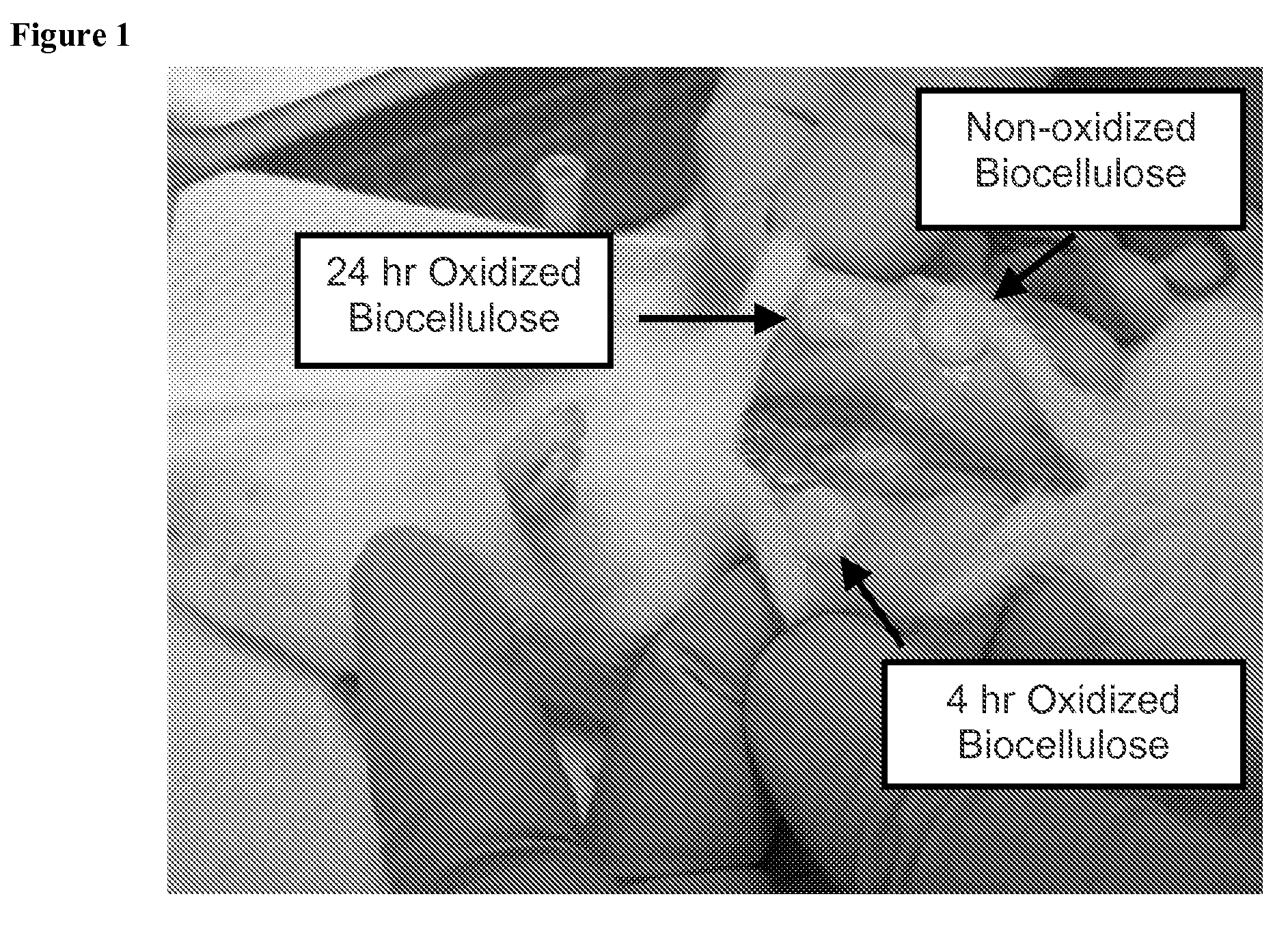
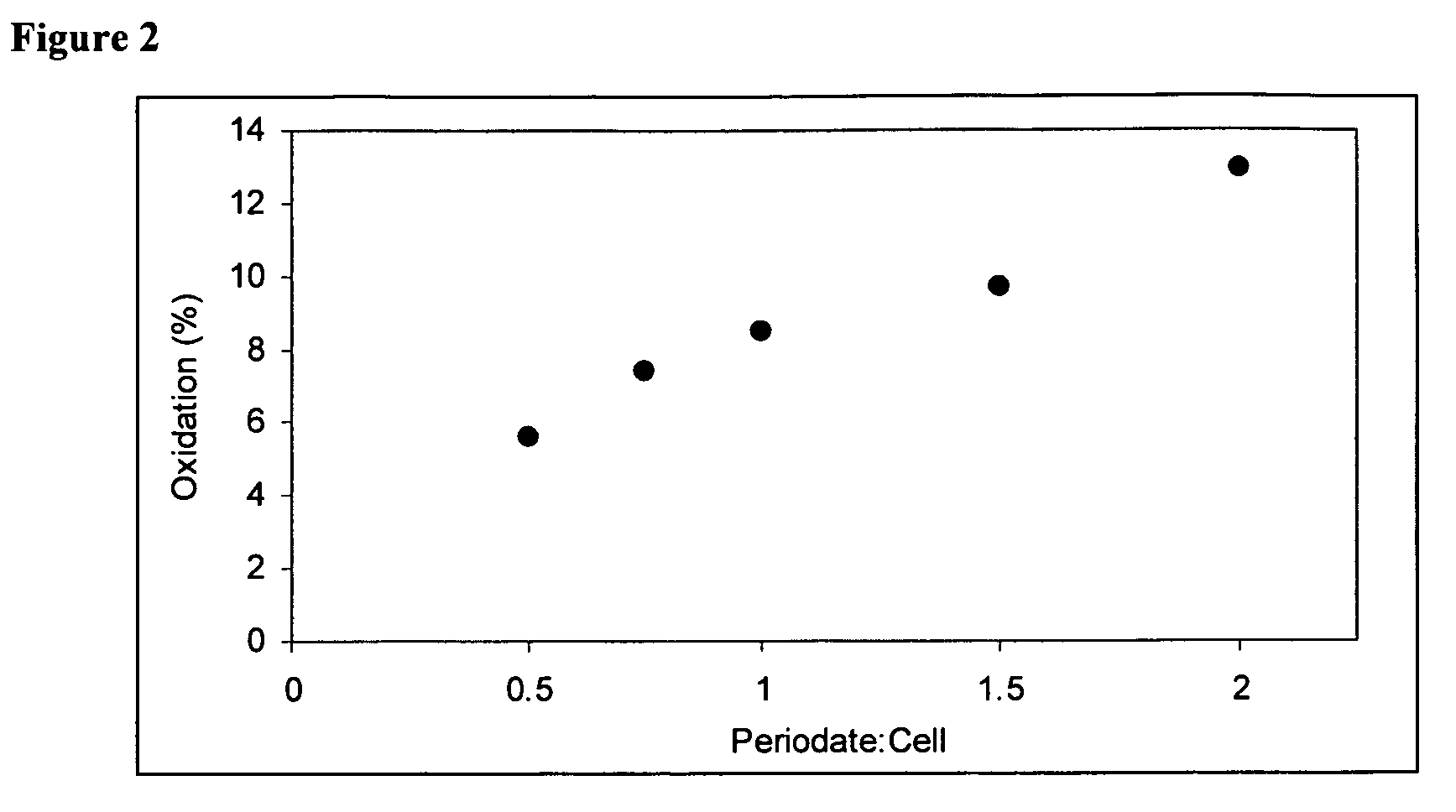
This application describes a bioresorbable biocellulose suitable for medical and surgical applications. In particular, the invention describes periodate oxidized microbial cellulose that can be produced to have any mechanical and degradation profile, depending on the desired application of the oxidized cellulose.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
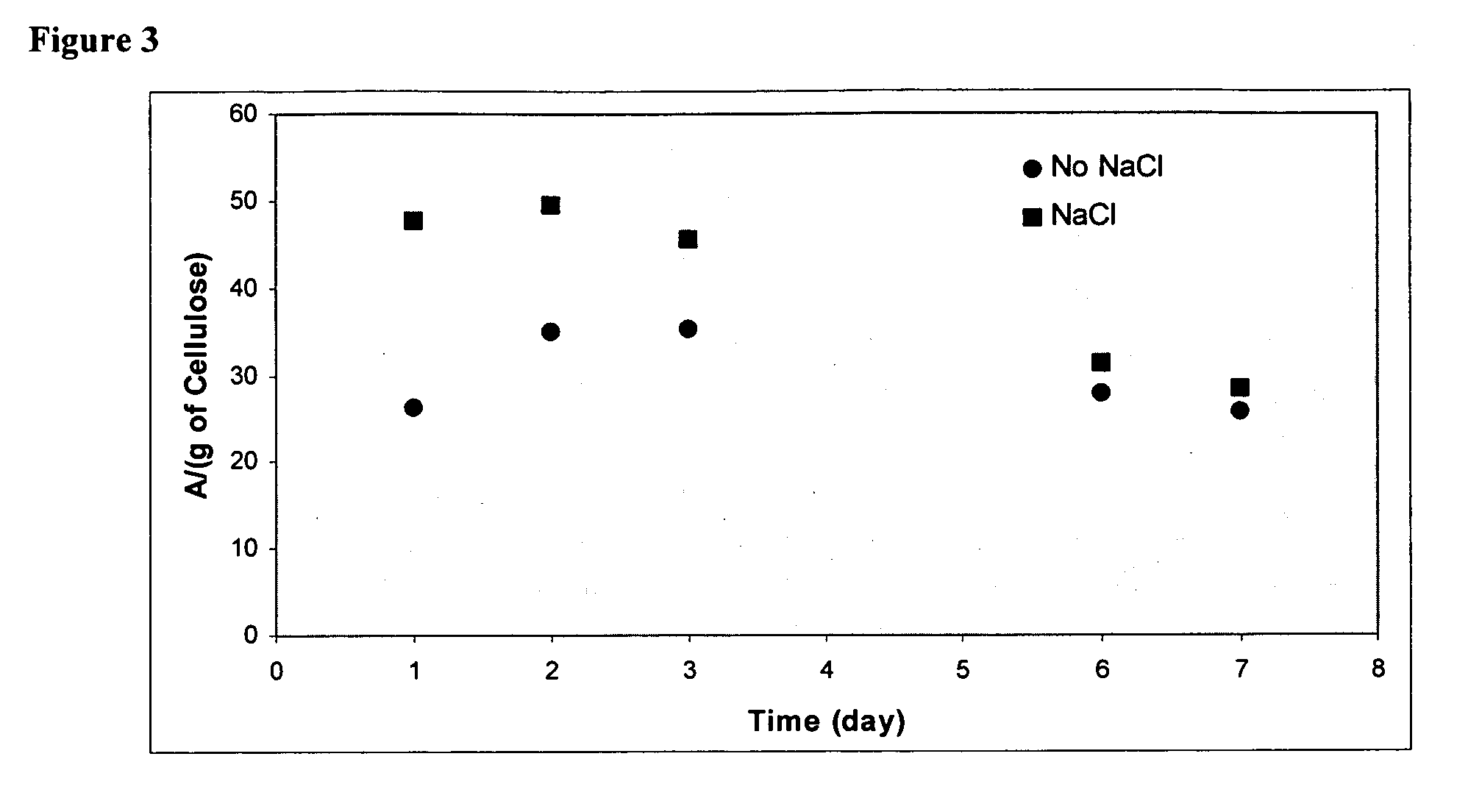
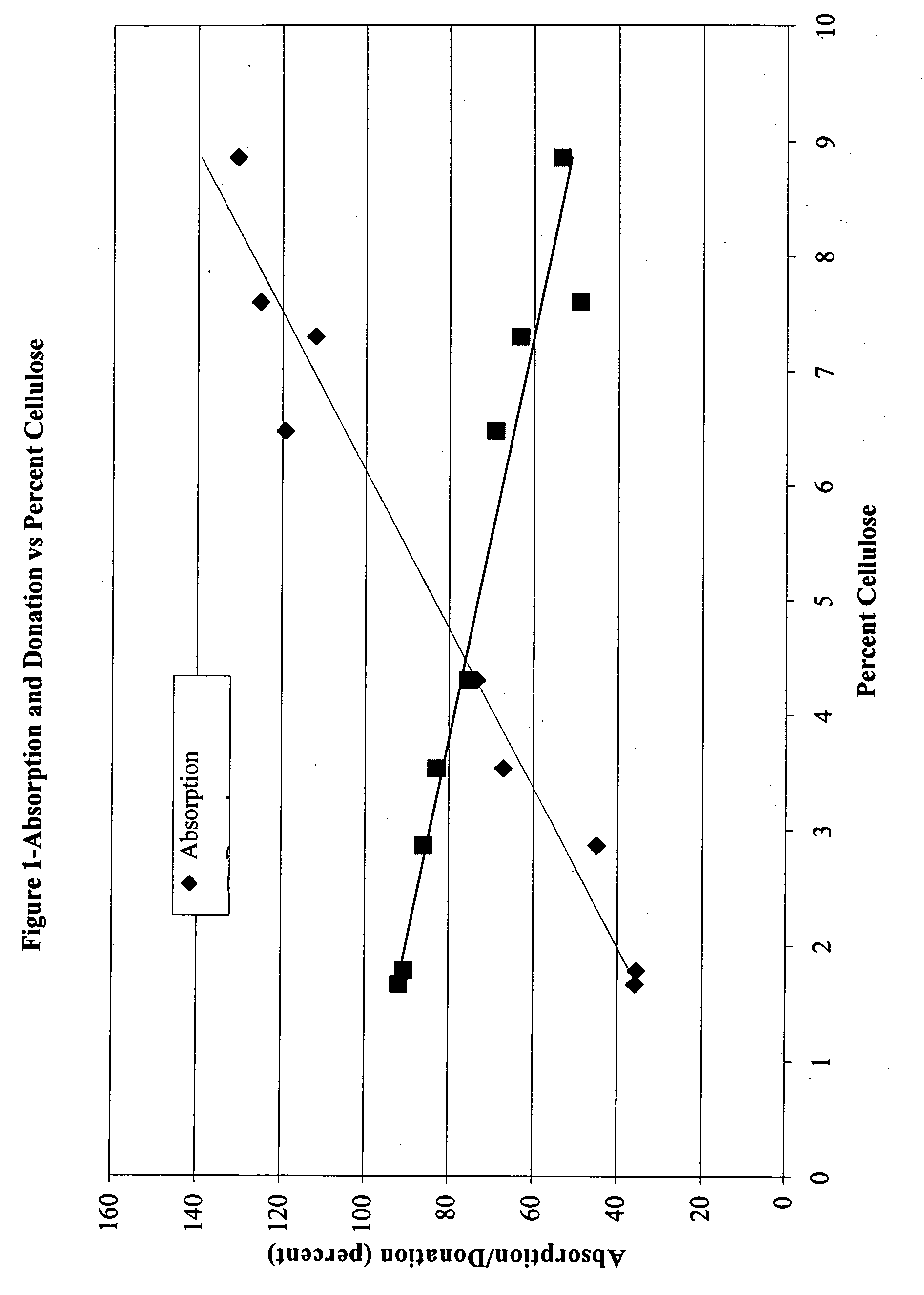
Microbial cellulose wound dressing for treating chronic wounds
InactiveUS20050019380A1Optimal tissue healingPromote improvementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesAbsorbent padsWound dressingMicrobial cellulose
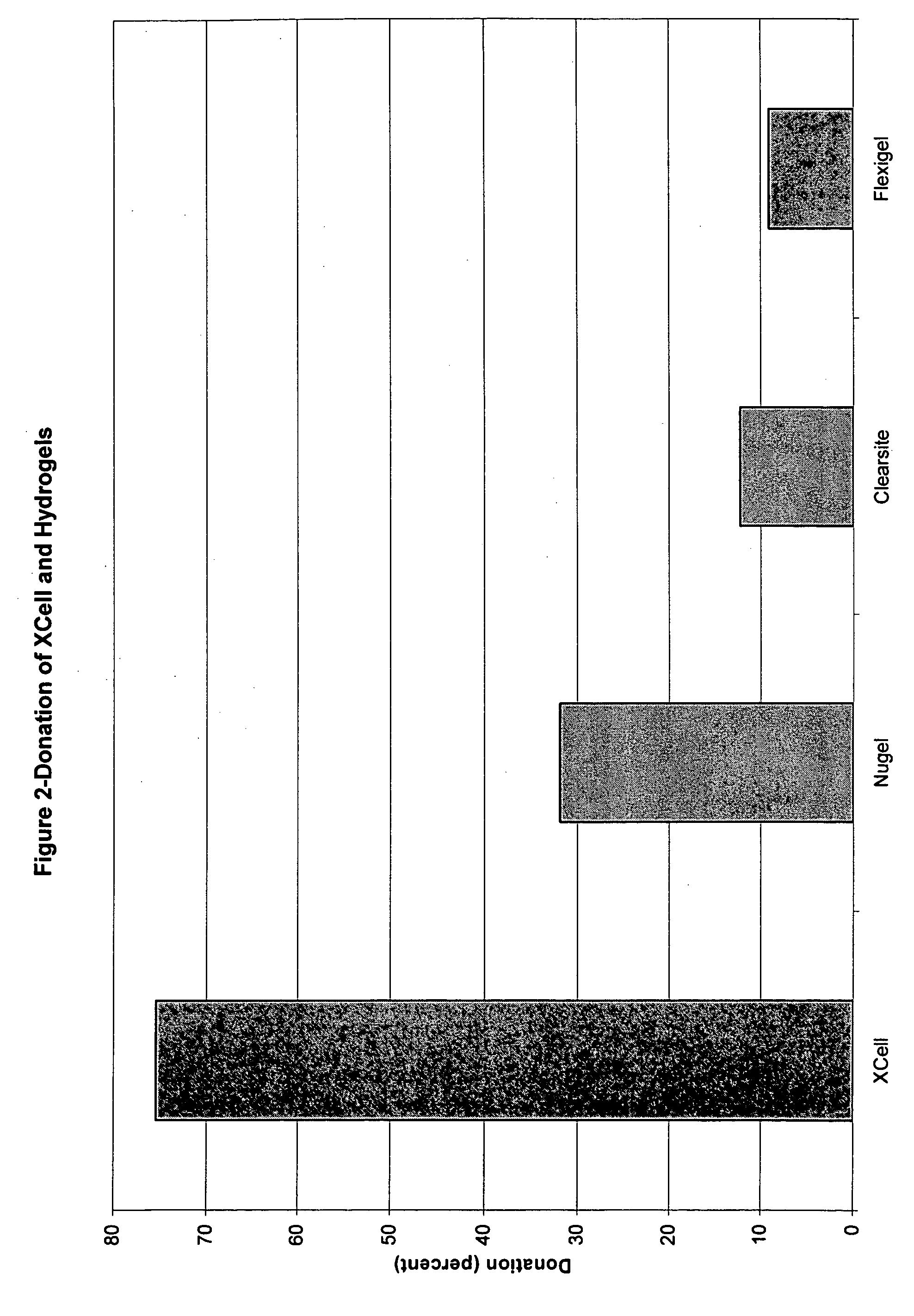
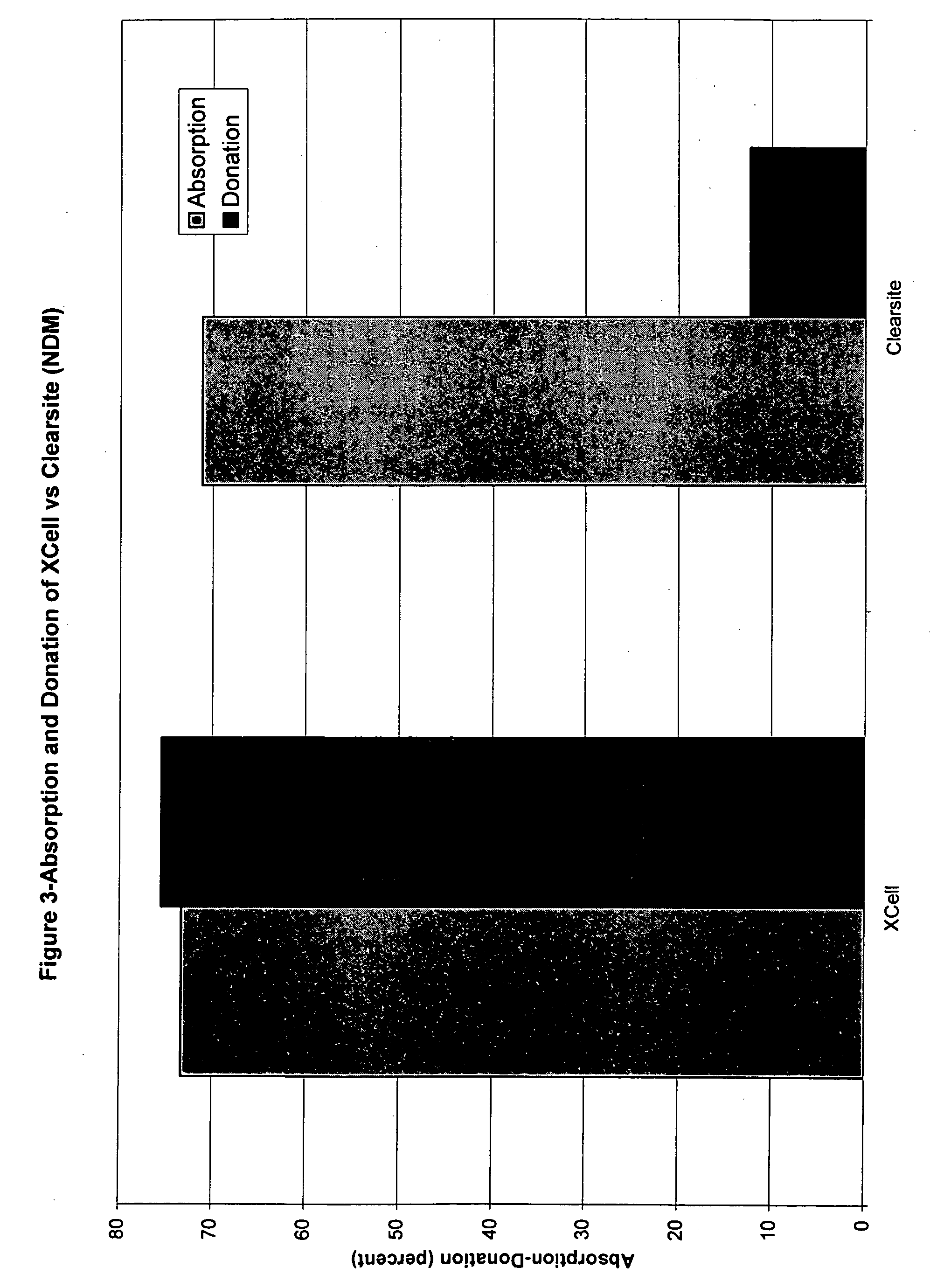
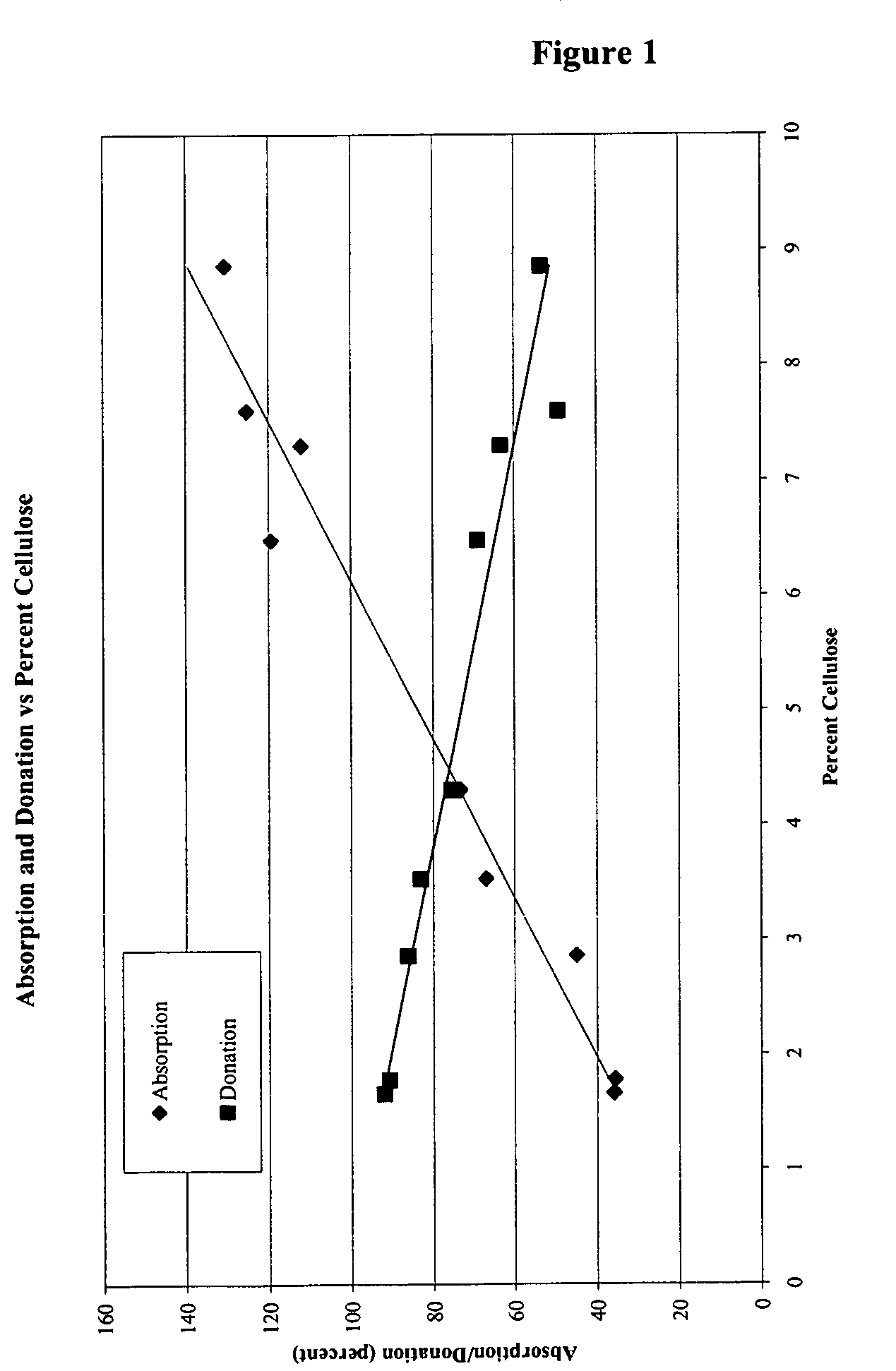
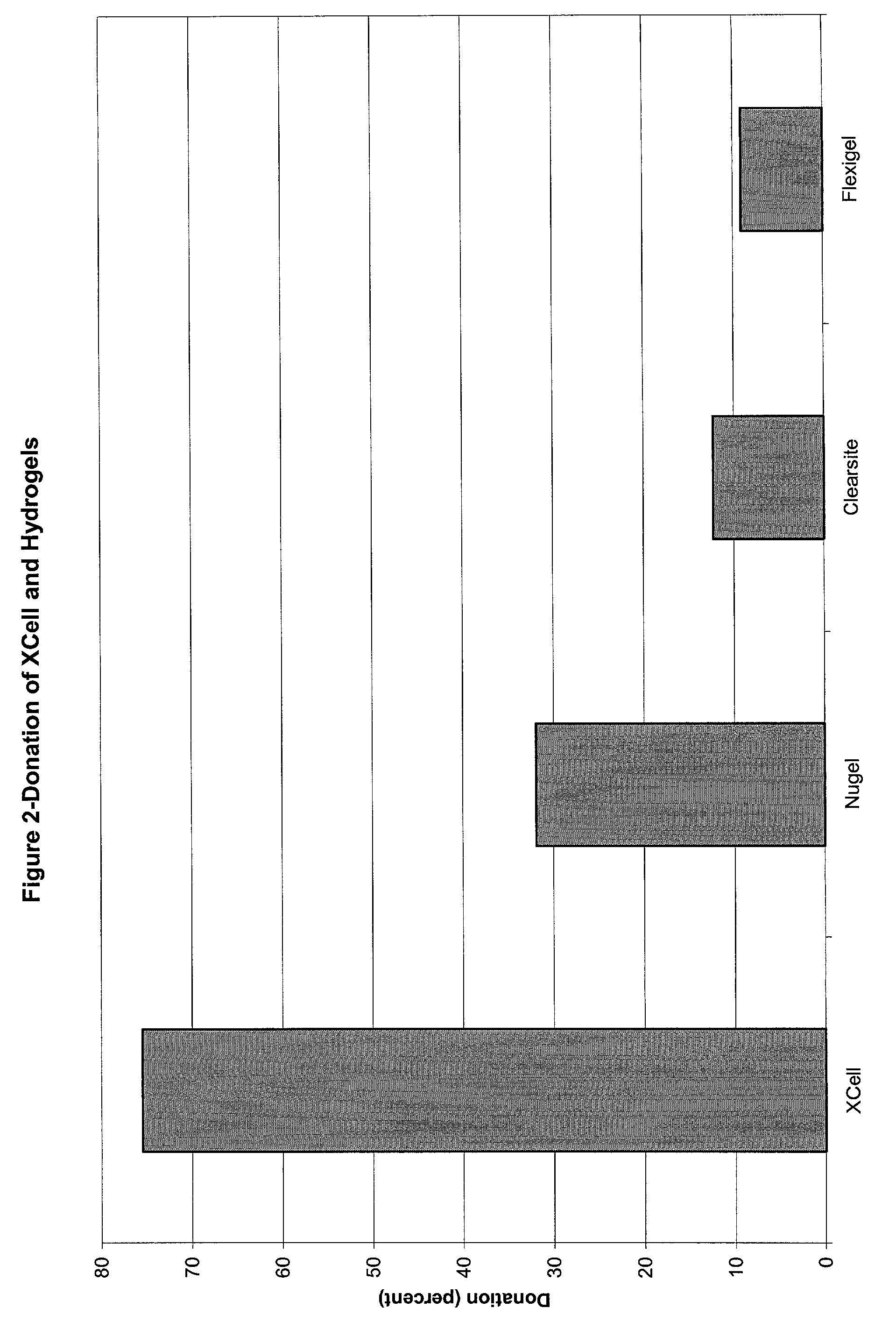
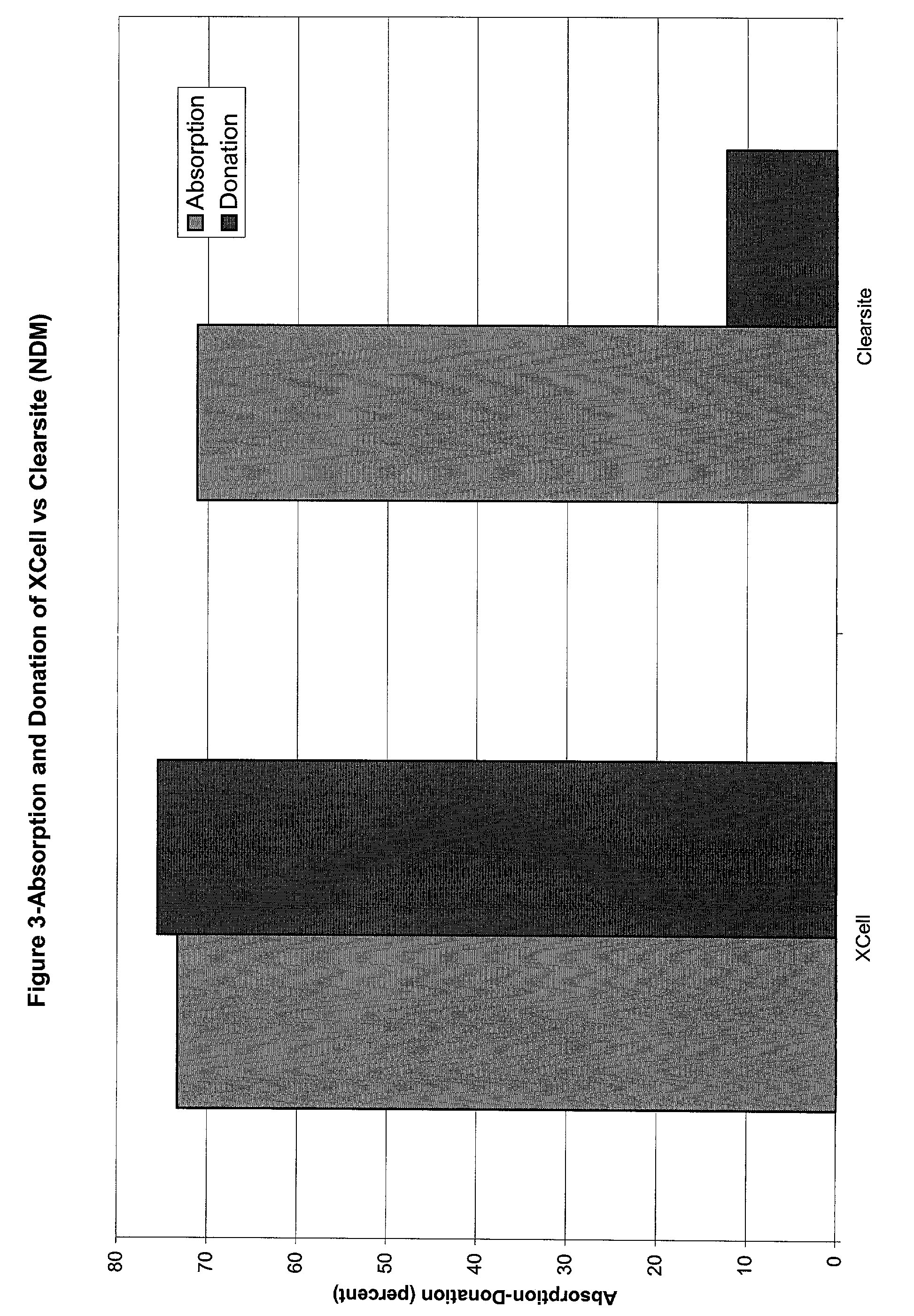
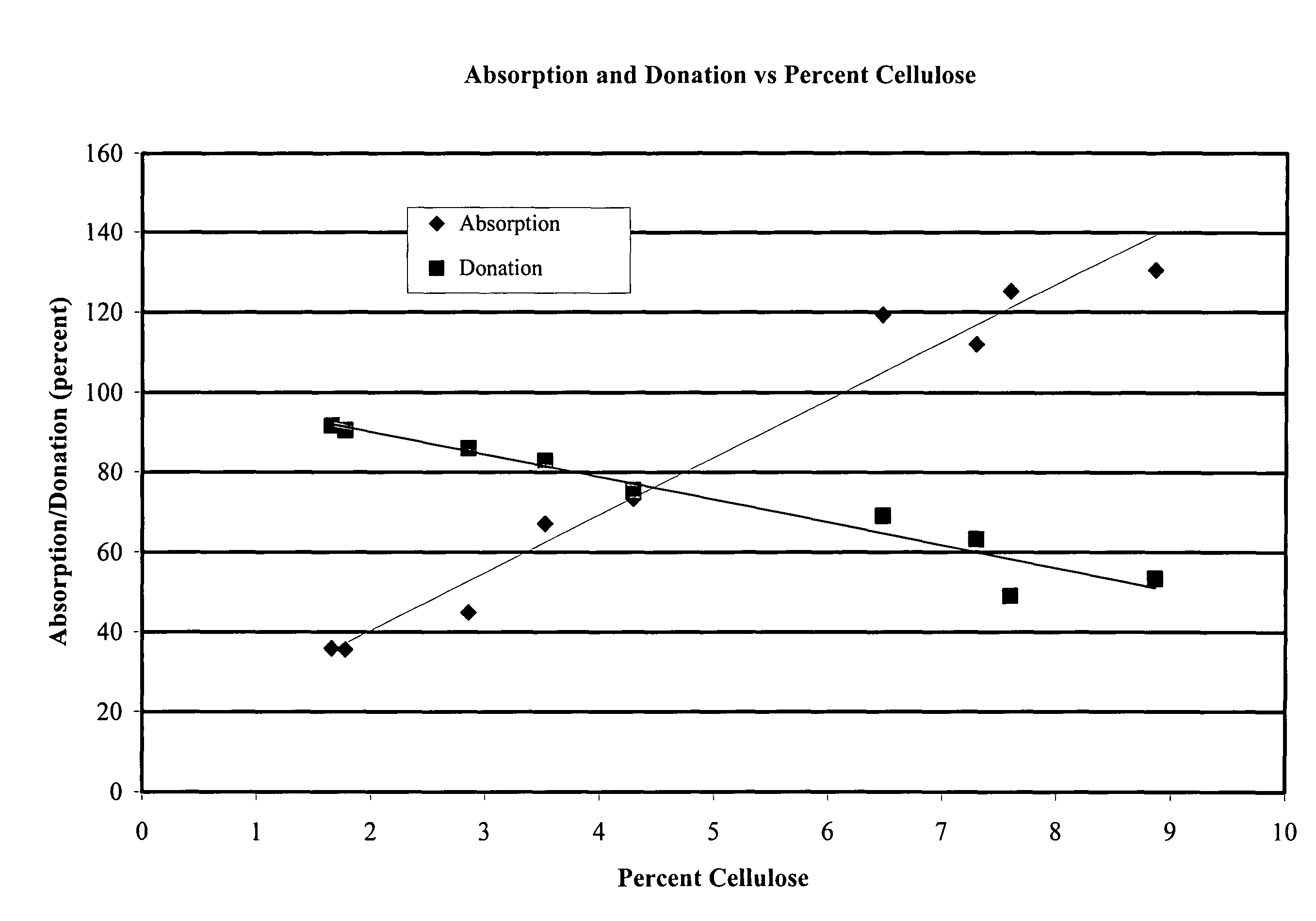
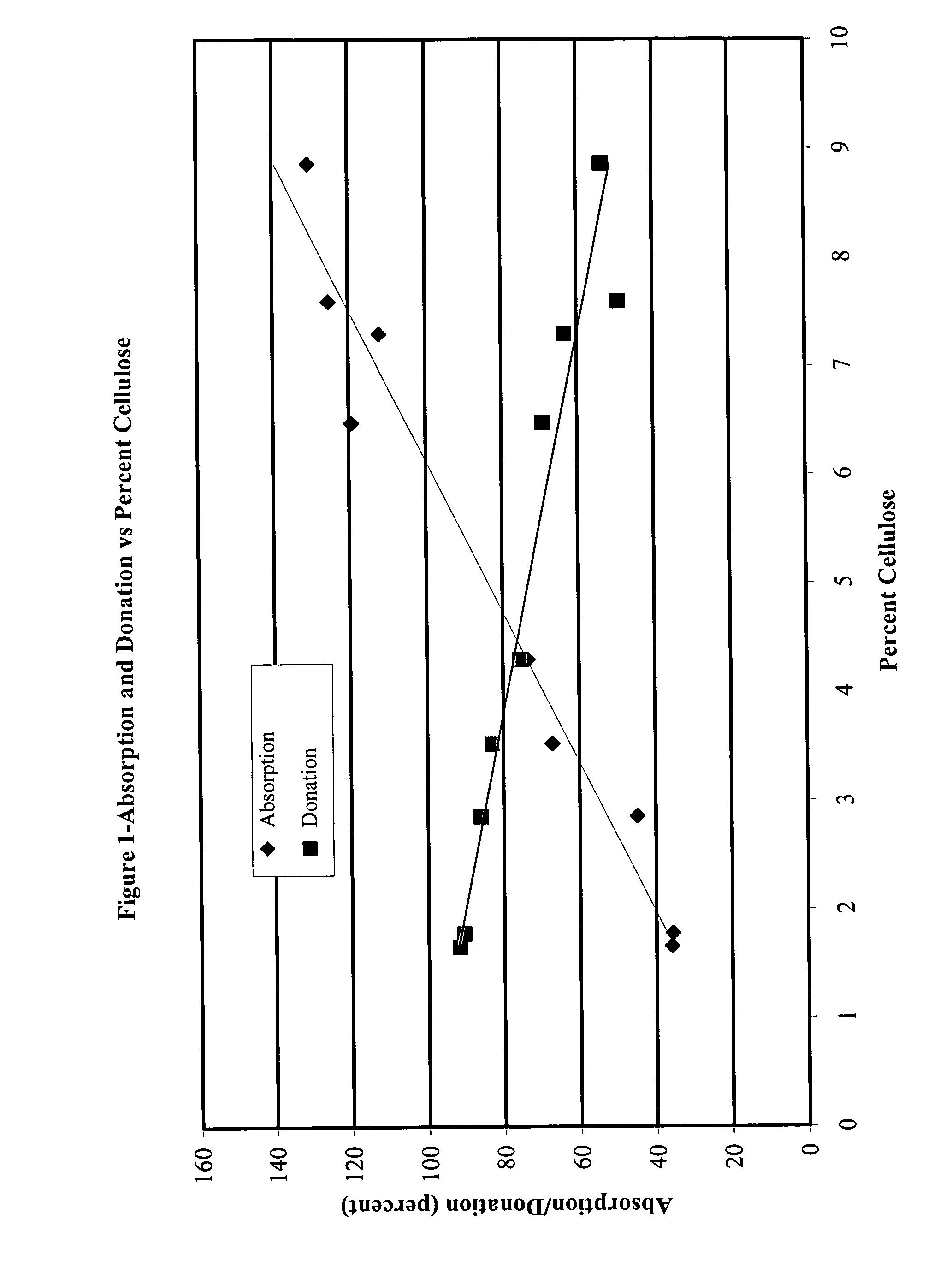
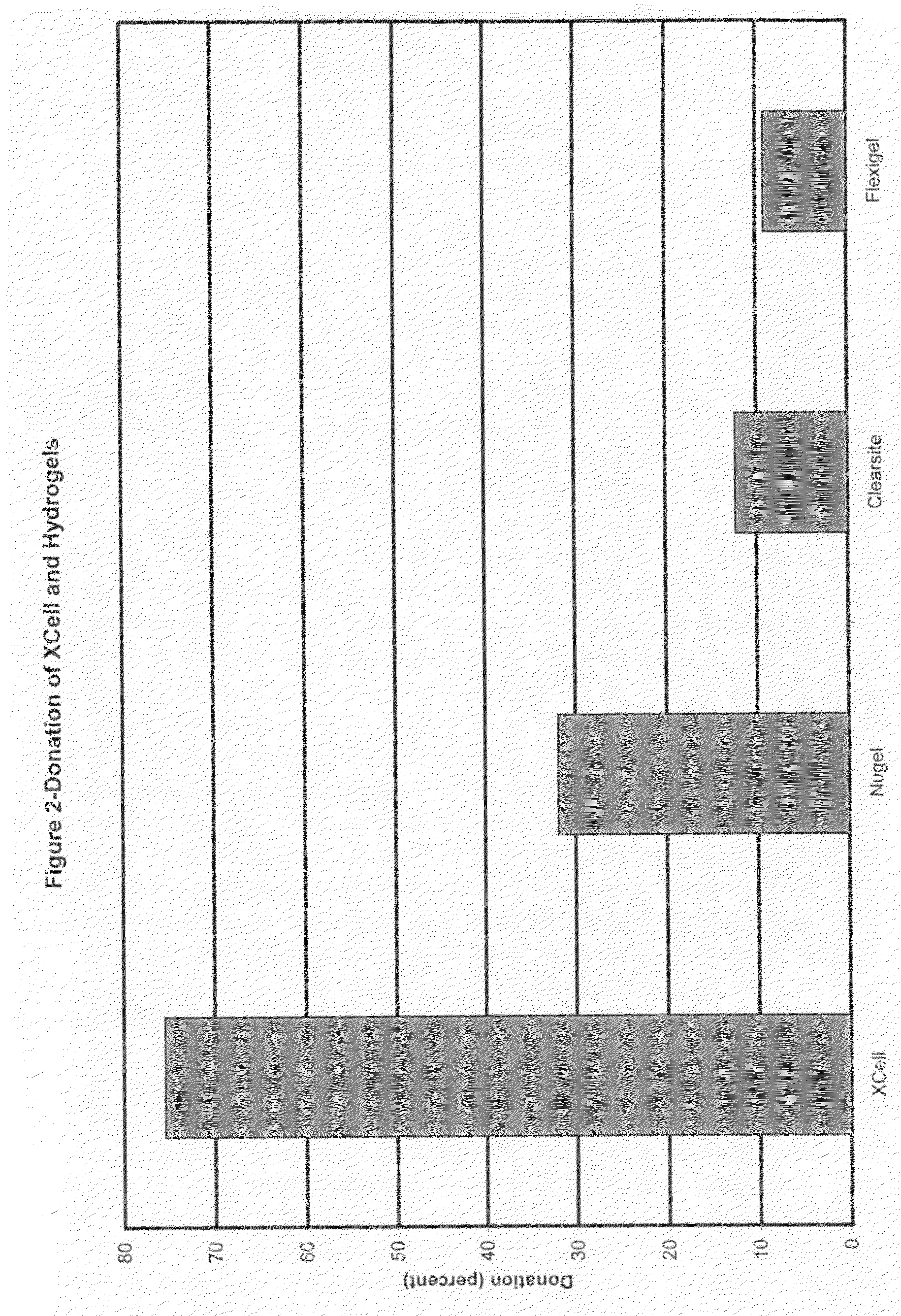
The invention relates to a dressing comprised of microbial-derived cellulose for aesthetic application The dressing is capable of donating liquid to dry substrates and is also capable of absorbing exudating wounds. Delivery of various medicaments using the dressing is possible. Positive clinical outcomes including reduced pain and discomfort, faster epithelialization, and healing were observed with use of the dressing.
Owner:LOHMANN & RAUSCHER
Oxidized microbial cellulose and use thereof
This application describes a bioresorbable biocellulose suitable for medical and surgical applications. In particular, the invention describes periodate oxidized microbial cellulose that can be produced to have any mechanical and degradation profile, depending on the desired application of the oxidized cellulose.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Microbial strains and processes for the manufacture of biomaterials
InactiveUS20090226962A1Increase enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyCell culture media
DNA constructs and genetically engineered microbial strains constructed using these DNA constructs, which produce a nuclease enzyme with specificity for DNA and / or RNA, are provided. These strains secrete nuclease into the periplasm or growth medium in an amount effective to enhance productivity and / or recovery of polymer, and are particularly suited for use in high cell density fermentation processes. These constructs are useful for modifying microbial strains to improve production and recovery processes for polymers such as intracellular proteins, such as enzymes, growth factors, and cytokines; for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates; and for producing extracellular polysaccharides, such as xanthan gum, alginates, gellan gum, zooglan, hyaluronic acid and microbial cellulose.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Moisturizing eye mask prepared from bacterial cellulose
InactiveCN102784071AReliable hardnessGood flexibilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyMembrane surface
The invention discloses a moisturizing eye mask prepared from bacterial cellulose. The method for preparing a moisturizing eye mask from bacterial cellulose comprises: inoculating 1-2 rings of activated inclined seed Gluconacetobacter xylinum into a medium, and conducting oscillating culture to obtain a seed solution; then inoculating the seed solution into the medium, fully oscillating the bacterial solution obtained by mixing the seed solution and the medium to make them mixed uniformly, then conducting stationary culture, thus generating a bacterial cellulose membrane floating on the solution surface, flushing the generated bacterial cellulose membrane with water to remove the medium and impurities on the membrane surface, then immersing the membrane in an alkali solution to remove thalli and residual medium from the membrane, and finally flushing the membrane with distilled water till the pH value of the membrane is measured up to 7-7.2, thus obtaining a bacterial cellulose wet membrane, which is then cut into an eye mask. The eye mask has the advantages of good moisturizing property and biological tissue compatibility, no toxicity, harmlessness, and simple material processing technology.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Gluconacetobacter oboediens strain and method for breeding and producing bacteria cellulose thereof
ActiveCN101608167AReduce manufacturing costAvoid pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRoom temperature
The invention provides a gluconacetobacter xylinums strain and a method for breeding and producing bacteria cellulose thereof. The strain is collected in a common microorganism center in the China type microorganism culture collection committee on July 12th 2004, and the collection registering number is CGMCCNO.1186, the name is gluconacetobacter xylinum 323, and the classification name is gluconacetobacter xylinum. The method for breading and producing bacteria cellulose comprises the following steps: sieving gluconacetobacter xylinum producing thick cellulose membrane with strong activity under room temperature; cooling and culturing then sieving; cooling and culturing, and sieving the gluconacetobacter xylinums strain which can produce the bacteria cellulose at 10-20 DEG C. the method for producing the bacteria cellulose comprises the following steps: strain expanding culture, culture medium preparation, culture medium panning and inoculation fermentation. The strain can break through the limit of the temperature, lowers the production cost, and effectively prevents living contaminants during the production, thereby improving the yield.
Owner:HAINAN YEGUO FOODS
Method for preparing Fe3O4 magnetotactic bacterial cellulose spheres
InactiveCN101979633AEvenly distributedControllable diameterMicroorganism based processesFermentationSuperparamagnetismCoprecipitation
The invention relates to a method for preparing Fe3O4 magnetotactic bacterial cellulose spheres. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing nanoscale Fe3O4 (with superparamagnetism) by a coprecipitation method; sterilizing the nanoscale Fe3O4 and a fermentation culture medium respectively and mixing; inoculating gluconacetobacter xylinum (CGMCC No. 2955); controlling the rotate speed of a shaker and culture time to obtain magnetotactic cellulose spheres with different diameters; immersing and washing the magnetotactic cellulose spheres in flowing water for one hour to remove the residual thalli and the culture medium; and washing by using deionized water for five times (the using amount of deionized water every time is 500 milliliters). Due to inconsistent diameters of the magnetotactic bacterial cellulose spheres formed by fermentation, the magnetotactic bacterial cellulose spheres with required diameters can be screened out by using a screen plate with a certain bore diameter, and Fe3O4 particles are distributed uniformly and wrapped in the bacterial cellulose spheres layer by layer along with the biosynthesis and secretion of bacterial cellulose (BC). The magnetotactic bacterial cellulose spheres can be used as a vector of immobilized enzyme or cells, and have the advantage that: after a reaction is finished, the magnetotactic bacterial cellulose spheres are separated by a magnetic field, and can be used repeatedly after the magnetic field is removed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Implantable microbial cellulose materials for hard tissue repair and regeneration
This invention relates to polysaccharide materials and more particularly to microbial cellulose containing materials having suitable implantation properties for repair or replacement of hard tissue. The invention also relates to the use of the implantable microbial cellulose as a bone void filler and as a carrier vehicle for active agent delivery for repair or regeneration of hard tissue.
Owner:SYNTHES USA PROD
Bacterial cellulose fermentation medium made from apple pomace and method for producing bacterial cellulose by utilizing medium
ActiveCN104031956AImprove solubilityReduce degradationMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateSugar
The invention discloses a bacterial cellulose fermentation medium made from apple pomace and a method for producing the bacterial cellulose by utilizing the medium, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The bacterial cellulose fermentation medium comprises cane sugar, beef extract, disodium hydrogen phosphate, citric acid, ethanol and apple pomace hydrolysate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) activating and propagating gluconacetobacter xylinum to obtain gluconacetobacter xylinum seed solution, incubating the gluconacetobacter xylinum seed solution into a bacterial cellulose fermenting medium for fermenting to obtain bacterial cellulose fermenting solution; and (2) treating a bacterial cellulose in the bacterial medium fermenting solution to obtain bacterial cellulose. The method has the advantages of low cost, simple process and the like, is convenient for industrial production, is good in stability and reproducibility, and is suitable for large-scale production, wherein the yield of the fermented bacterial cellulose is more than 15g / L.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Microbial cellulose wound dressing for treating chronic wounds
ActiveUS7390499B2Promote wound healingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMicrobial celluloseEngineering
The invention relates to a wound dressing comprising a microbial-derived cellulose for treatment of specific types of chronic wounds, including pressure sores, venous and diabetic ulcers. The wound dressing is capable of donating liquid to dry substrates is also capable of absorbing exudating wounds.
Owner:LOHMANN & RAUSCHER
Preparation of hollow cellulose vessels
InactiveUS20100042197A1Good mechanical resistanceIncrease burst pressureEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsHollow fibreLymphatic vessel
The present invention relates to an improved method for the preparation of hollow cellulose vessels produced by a microorganism, and hollow cellulose vessels prepared by this method. The method is characterized by the culturing of the cellulose-producing microorganisms being performed on the outer surface of a hollow carrier, and providing an oxygen containing gas on the inner side of the hollow carrier, the oxygen containing gas having an oxygen level higher than atmospheric oxygen. The hollow microbial cellulose vessels of the present invention are characterized by improved mechanical properties and can be used in surgical procedures to replace or repair an internal hollow organ such as the urethra, ureter, the trachea, a digestive tract, a lymphatic vessel or a blood vessel
Owner:ARTERION AB
Preparation of bacteria cellulose special-shaped product by microbial fermentation direct biosynthesis
InactiveCN101487033AImprove tensile propertiesGood biocompatibilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiocompatibility TestingPack material
The invention discloses a preparation method of modified bacterial cellulose products that are directly obtained by biosynthesis with microbial fermentation, belongs to the field of biology, and relates to preparation methods of modified bacterial cellulose products that are directly obtained by biosynthesis with microbial fermentation, in particular to the preparation of modified bacterial cellulose products that adopts the raw materials including a Gluconacetobacter xylinum with the preservation number of CGMCC No.1.1812, a mould that is a material with oxygen permeability function and a culture medium as well as the steps of strain cultivation, fermentation, washing and drying. The preparation method of the invention has simple techniques, achieves direct synthesis of the products with different shapes by utilizing microbial techniques, and has low production cost. The modified bacterial cellulose products that are prepared by the method have controllable shapes and thicknesses as well as good tensile property and biocompatibility, not only can be used as food package materials but also can be used as tissue engineering scaffold materials, and have good application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Separator including microbial cellulose, method of producing the separator, and use of the separator
Provided is a separator including microbial cellulose, a battery comprising the separator, and a method of producing the separator.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
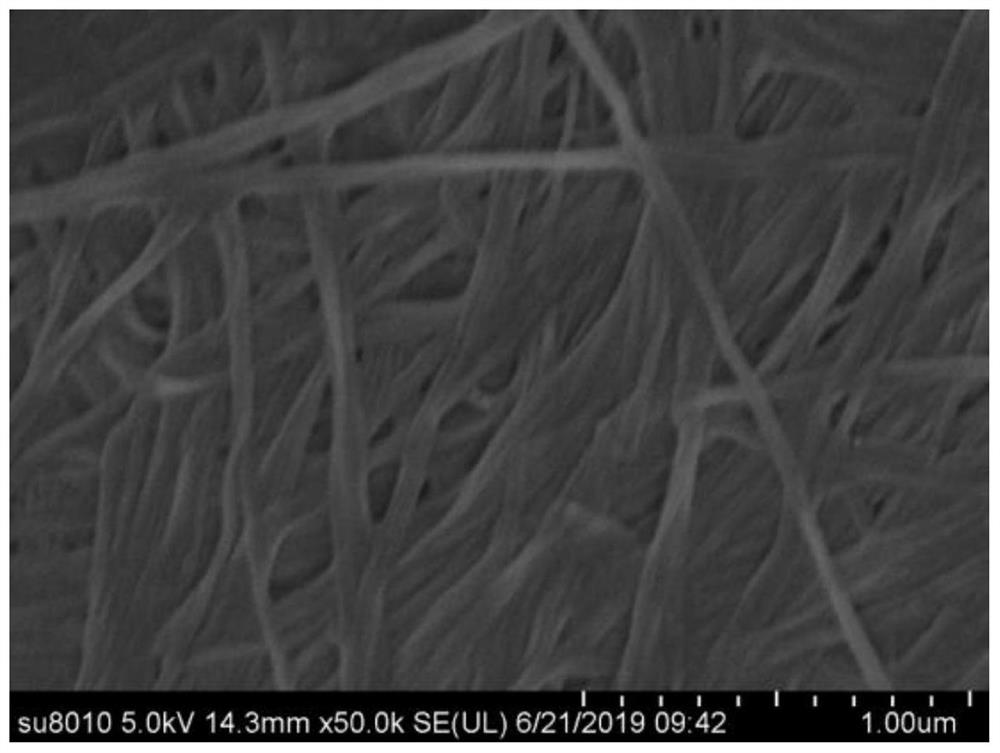
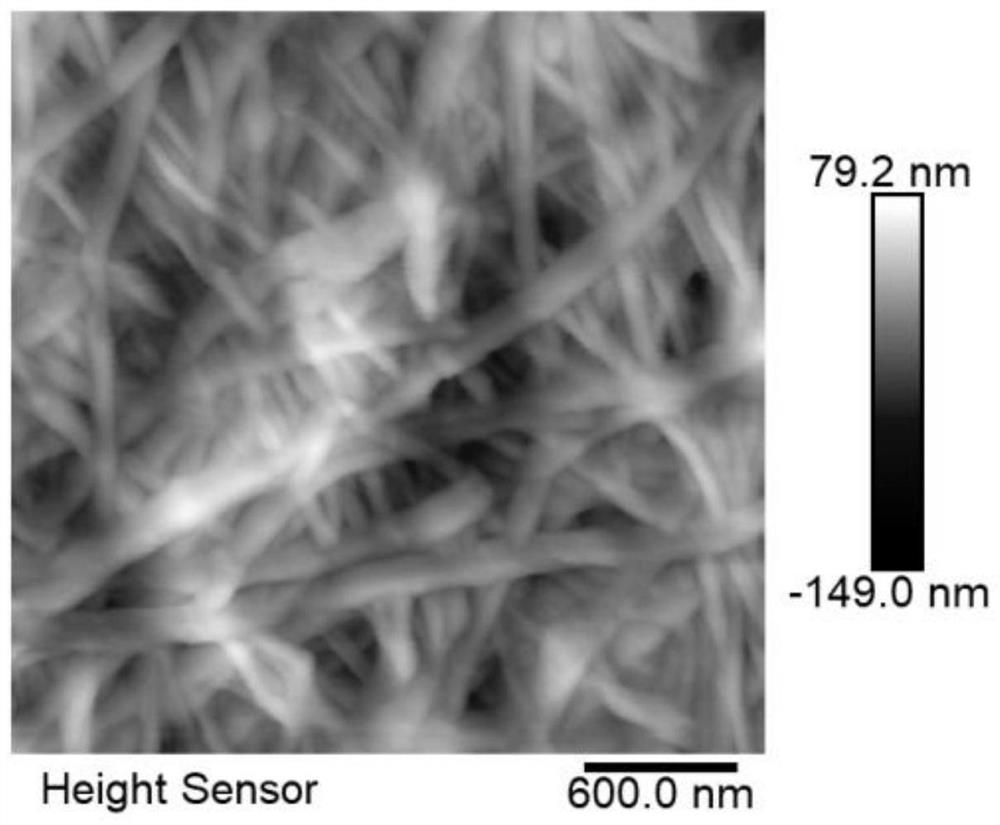
A nano microbeam cellulose, method for preparing the same and use thereof
InactiveCN1464047ABacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsMicrobial celluloseGluconacetobacter xylinum
The present invention relates to one kind of nano microbial cellulose and the nano microbial cellulose features the size range of 10-1000 nm. The present invention also relates to the preparation process of the nano microbial cellulose. On the other hand, the present invention also relates to the use of the nano microbial cellulose in preparing medicine composition.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Method of preparing nano level bacterial cellulose from waste food
InactiveCN105647988AAvoid pollutionLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationCulture fluidEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method of comprehensively preparing bacterial cellulose from waste liquor of candied date. The bacterial cellulose is used to produce textiles, medical dressing, and filtering materials. The method comprises the following steps: directly using waste liquor of candied date as the culture medium to culture bacterial cellulose, adding the following components: glucose, ammonium citrate, Na2HPO4, and amino acid, which respectively account for 2%, 0.1%, 0.5%, and 0.01-0.1% of the weight of waste liquor of candied date to prepare the culture medium; sterilizing the culture medium, adding 6 to 10% of Gluconacetobacter xylinum CGMCC No.2955 culture liquid, allowing the culture medium to stand still, and culturing for 5 to 10 days at a temperature of 25 to 30 DEG C to obtain the bacterial cellulose. The invention provides a novel method for comprehensively utilizing waste food. At the same time, the production cost of bacterial cellulose is reduced, the biological resources are fully utilized, the raw material are cheap and easily available, the generation of wastes is reduced, and more economic benefits are generated.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
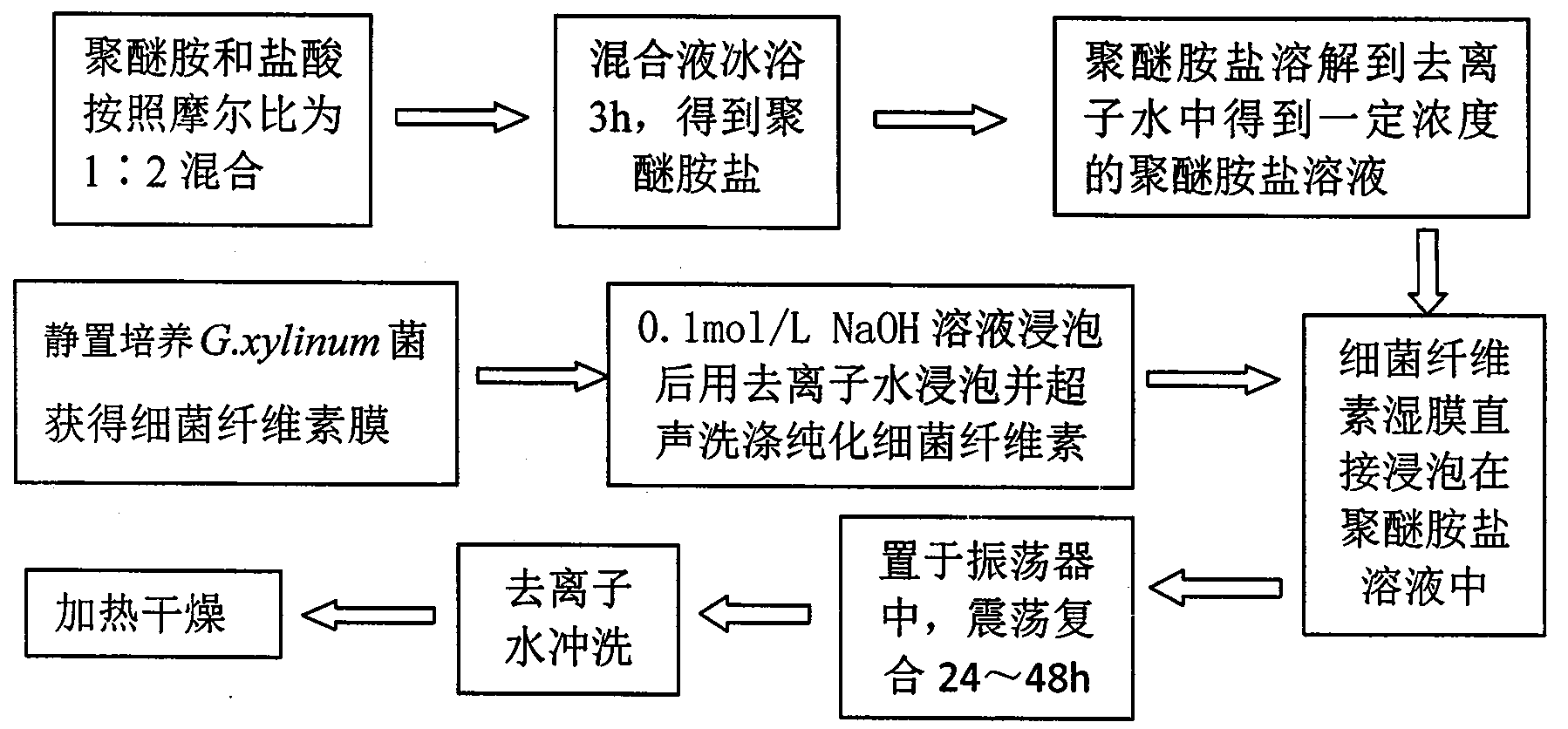
Method for improving plasticity and flexibility of bacterial cellulose membrane
ActiveCN104262662AGood flexibilityLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberRoom temperature
The invention relates to a method for improving the plasticity and flexibility of a bacterial cellulose membrane. Microbial Gluconacetobacter xylinum is cultured by static culture so as to obtain an initial bacterial cellulose wet membrane sample, and after the sample is soaked in alkaline liquor and then soaked and purified in deionized water, the purified bacterial cellulose membrane is soaked into polyether amine salt solutions with different concentrations (1-5.2wt%) firstly, the obtained object is put into an oscillator to oscillate and compound for 24h at room temperature, and then the compounded bacterial cellulose membrane / polyether amide membrane, after being washed by using deionized water, is dried at certain temperature, the plasticity of the obtained final bacterial cellulose / polyether amine compounded membrane is 45.8%, compared with the plasticity 4% of a bacterial cellulose membrane before compounding, the plasticity of the compounded cellulose membrane is increased by 11.45 times, so that the bacterial cellulose is applied more widely to the fields of chemical engineering, paper making and biomedicine; and in addition, the method is low in production and operation costs, less in equipment investment, and high in feasibility.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
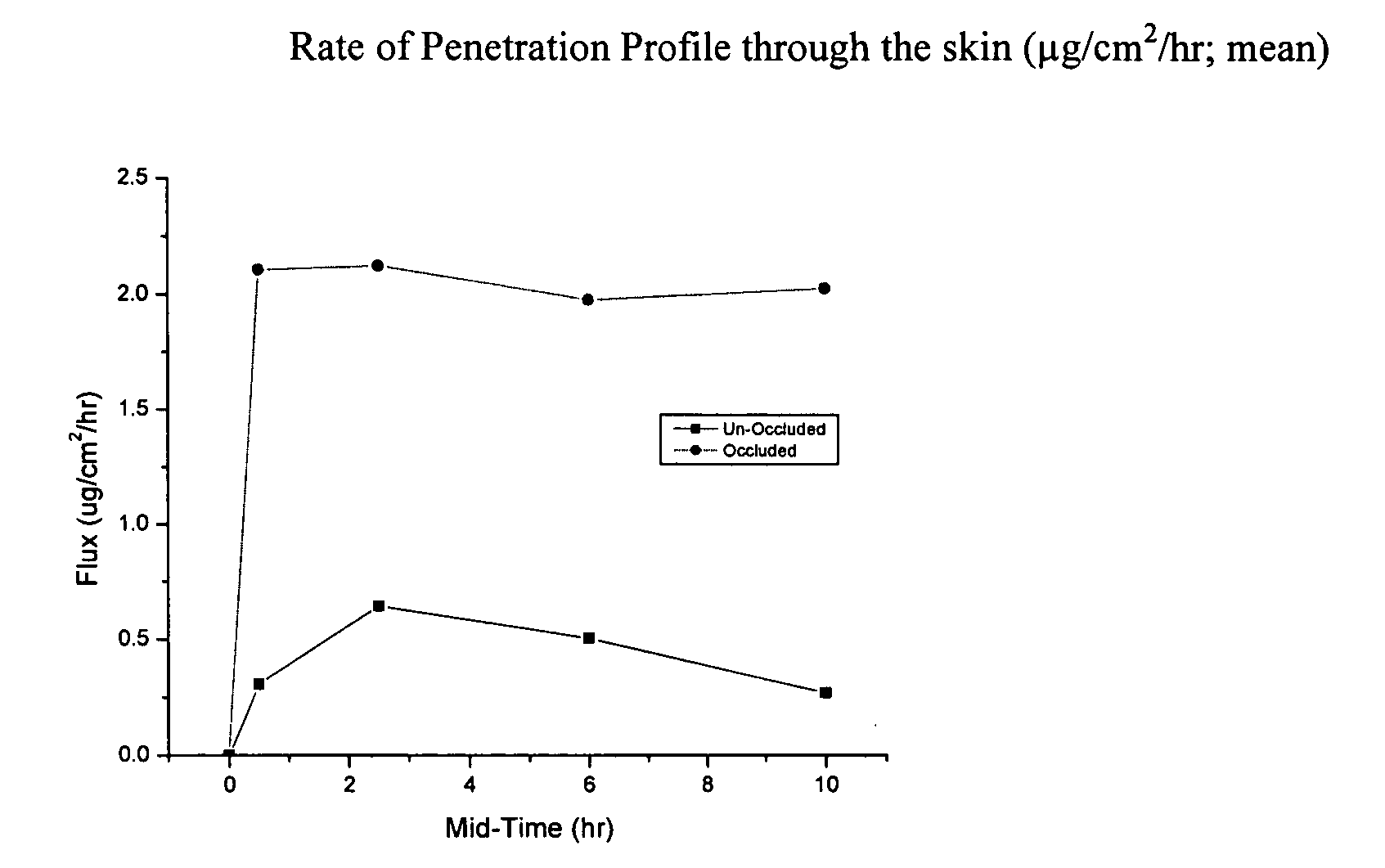
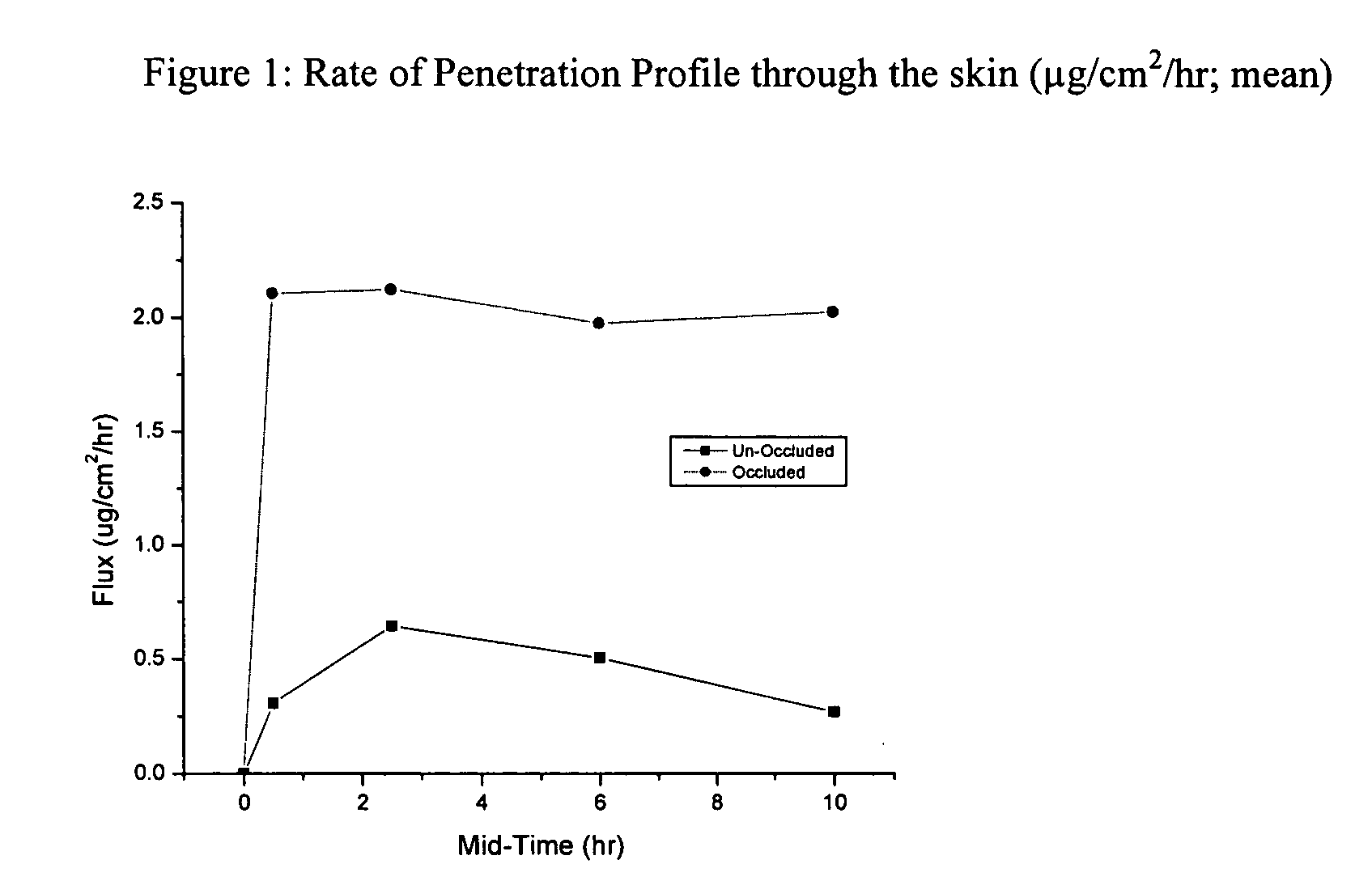
Microbial cellulose materials for use in transdermal drug delivery systems, method of manufacture and use
A method for transdermally delivering a biologically active agent to a subject in need thereof, comprising topically applying a composition comprising insoluble microbial cellulose, water, and a therapeutically effective amount of the biologically active agent, wherein the biologically active agent penetrates through the subject's stratum corneum at a substantially constant rate.
Owner:XYLOS CORP
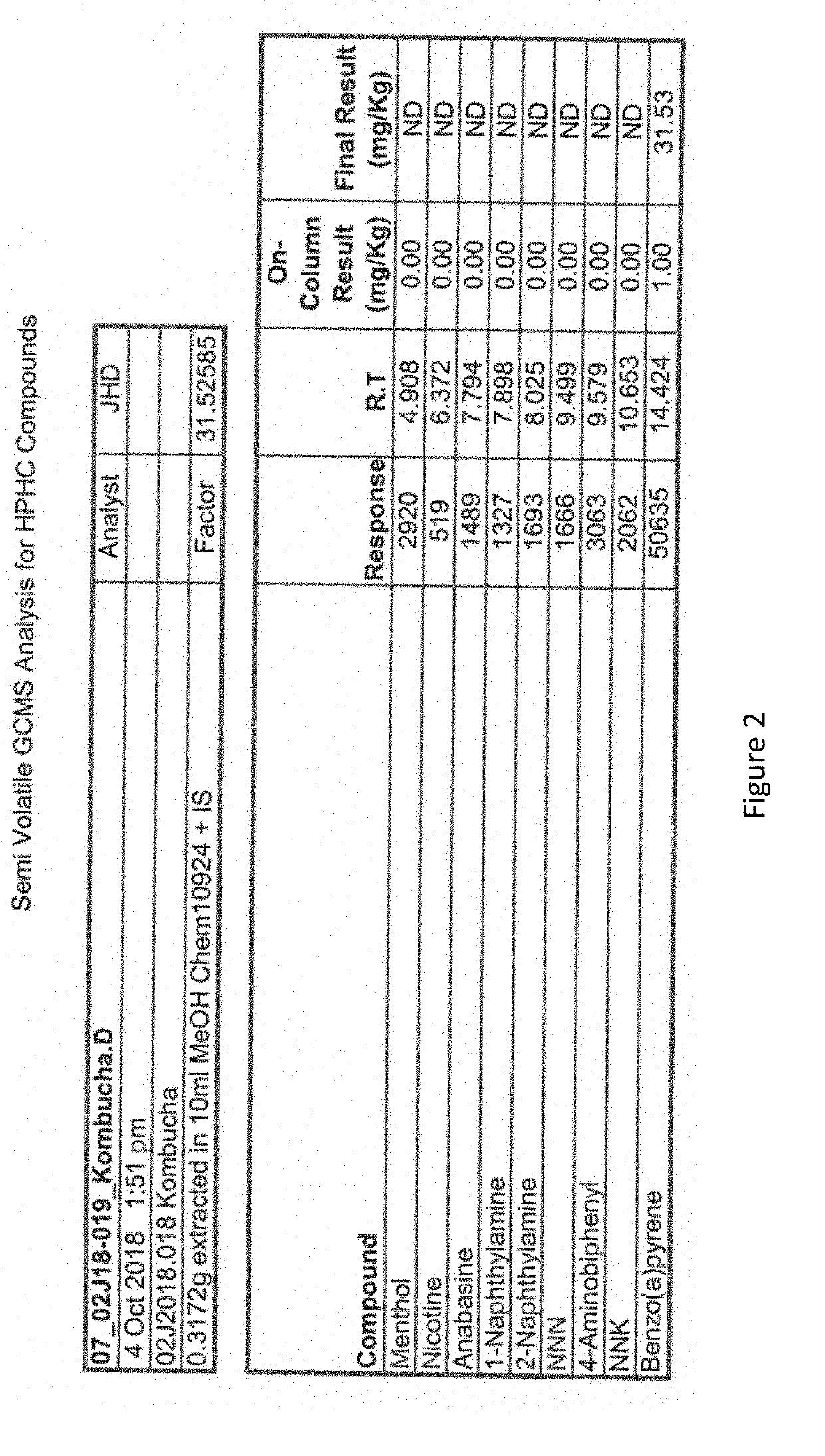
Cigarette rolling papers formed from kombucha biofilms
ActiveUS20190174815A1Unique propertyLacking and neededCigar manufacturePaper/cardboard layered productsBiofilmMicroorganism
Rolling papers formed from fermented microbial cellulose derivatives (e.g., Kombucha fermentation biofilms) and methods of manufacture are described.
Owner:KOMBUCHA BIOMATERIALS LLC
Completely degradable tissue engineering skin scaffold material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111001042APromote growthDoes not affect biocompatibilityElectro-spinningNon-woven fabricsFiberMicrosphere
The invention discloses a completely degradable tissue engineering skin scaffold material which comprises two parts, namely, a bacterial cellulose / chitosan nanofiber layer and a large-aperture array micron fiber scaffold. The bacterial cellulose / chitosan nanofiber layer is an upper layer, the upper part of the large-aperture array micron fiber scaffold is a lower layer, and the layers are crosslinked and combined through glutaraldehyde. The bacterial cellulose / chitosan nanofiber layer is formed by in-situ synthesis of gluconacetobacter xylinum, and cellulase is fixed on the surface of the bacterial cellulose / chitosan nanofiber layer. The large-aperture array micron fiber scaffold is a scaffold formed by arranging electrostatic spinning lactic acid / hyaluronic acid / fibroin micro-nano fibersin an orderly manner, and the surface of the large-aperture array micron fiber scaffold is modified with polylactic acid-glycolic acid growth factor sustained-release microspheres. The used raw materials are non-toxic and harmless, the fiber property is stable, and good biocompatibility is achieved. The scaffold material can be completely degraded in vivo. The pore diameter of the lower-layer scaffold is close to the cell size, and cells can enter the scaffold. Growth factors can be stably released, and skin tissue regeneration is facilitated.
Owner:广州市拜沃思生物科技有限公司
Bioreactor and method for producing microbial cellulose
InactiveUS20100317066A1Improve production efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismLiquid medium
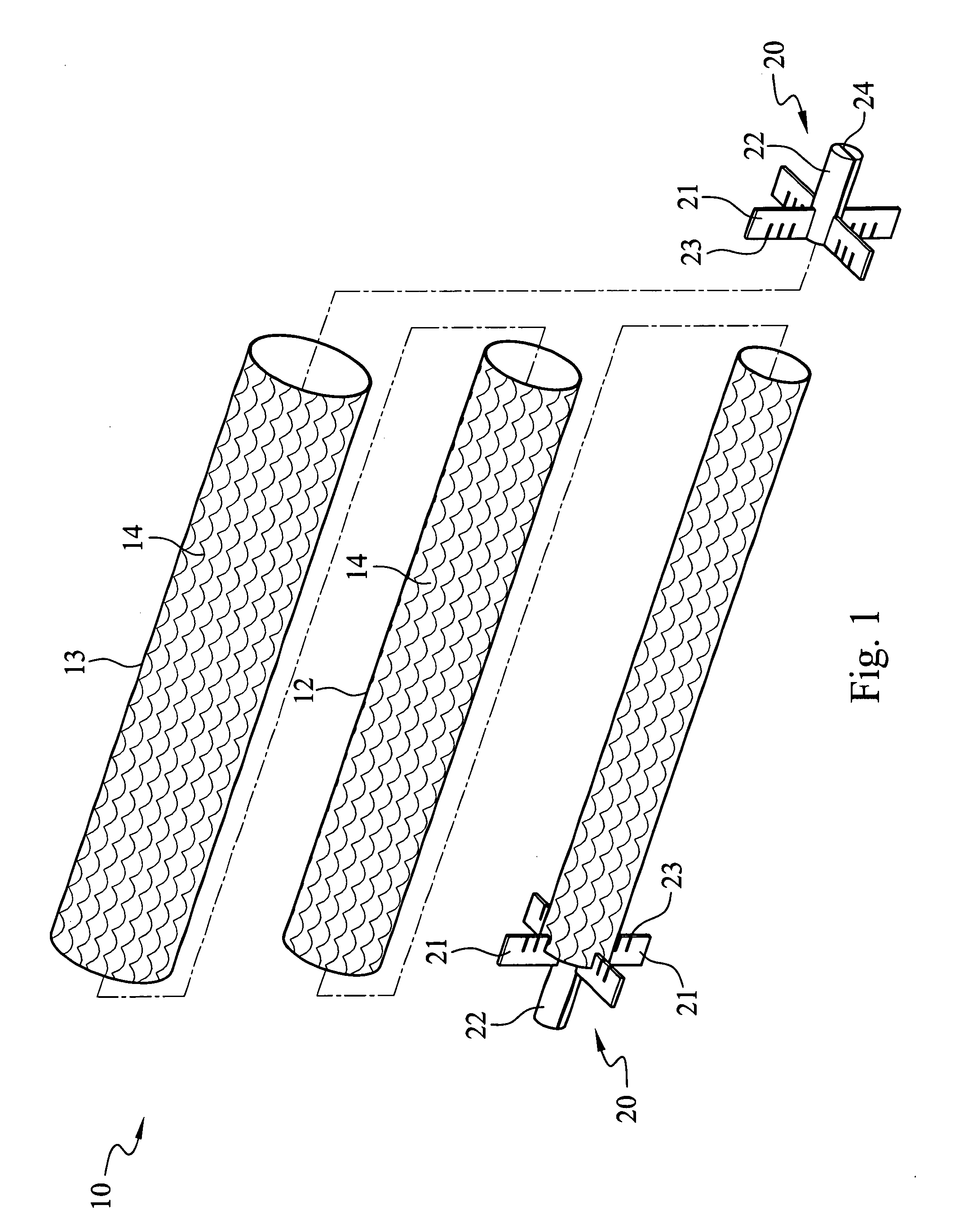
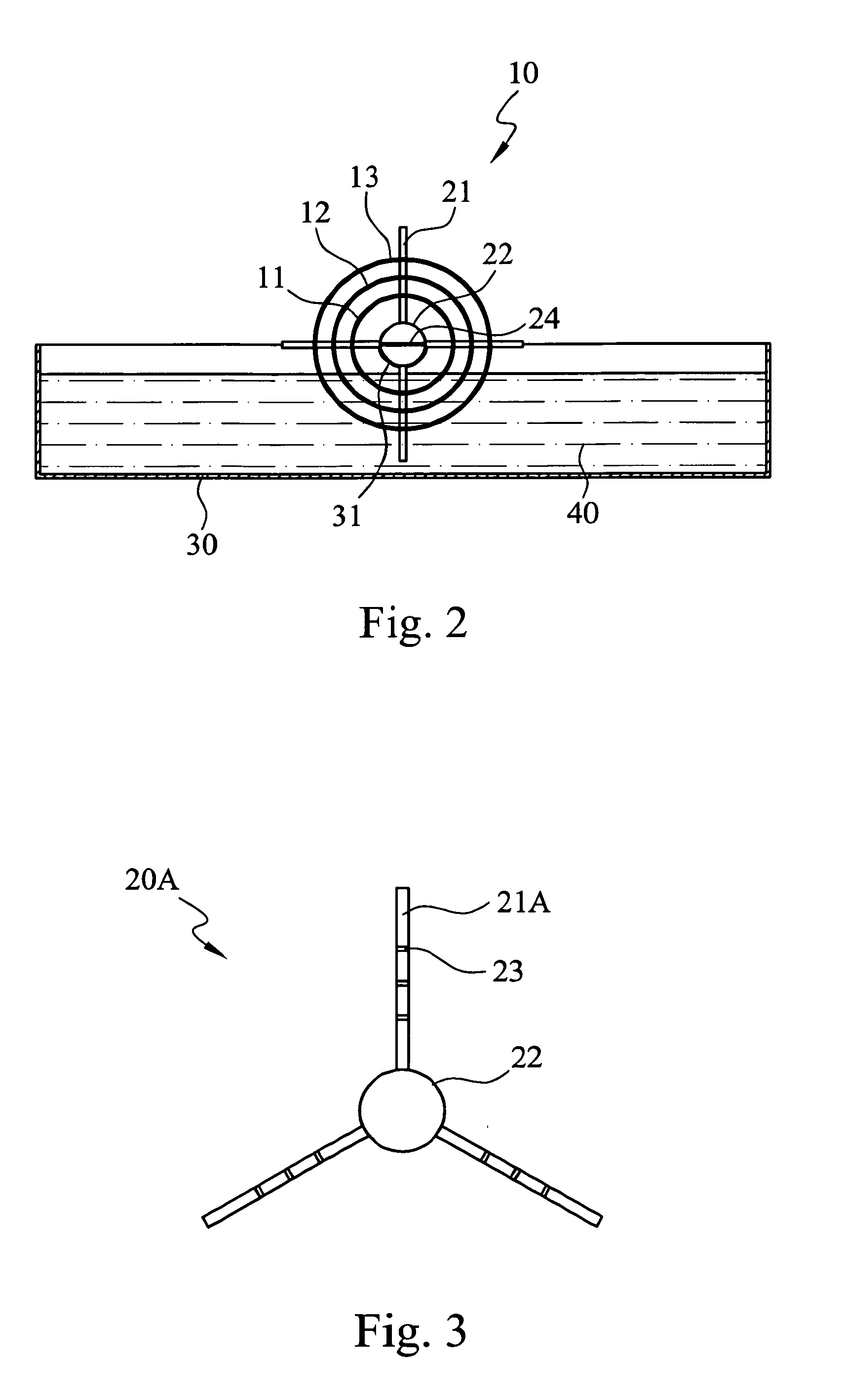
A technique for producing microbial cellulose is provided, including: preparing a liquid medium for microbial cultivation in a container; horizontally rotating multiple hollow tubes that are fitted together or separated from one another, so that each of the hollow tubes is alternately partially immersed in the liquid medium and partially exposed above the horizontal surface of the liquid medium; wherein each of the hollow tubes has a rough outer surface and a smooth inner surface, so as to allow microorganisms to form microbial cellulose on the outer surface of each hollow tube, as well as forming sheets of microbial cellulose on the horizontal surface of the liquid medium not being disturbed by the hollow tubes, and removing the microbial cellulose from the outer surfaces of the hollow tubes in order to obtain tubular microbial cellulose. In addition, the sheets of microbial cellulose are also harvested from the liquid medium.
Owner:FOOD IND RES & DEV INST
Synechococcus engineering bacterium capable of improving yield of cellulose, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102242065AShorten the growth cycleNo pollution problemUnicellular algaeBiofuelsDry weightSynechococcus sp.
The invention discloses a synechococcus engineering bacterium and a preparation method and application thereof. The synechococcus engineering bacterium is a cesA gene-deficient Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 mutant; the plasmid or genome of the mutant is integrated with 7 cellulose synthesis related genes (cmcase, ccp, acsA, acsB, acsC, acsD and bglxA) of Gluconacetobacter xylinum ATCC 53582; and the 7 genes are started and expressed by a promoter PcpcBA of a cpcBA gene of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 or Synechocystis sp. PCC6803. The cellulose content of the engineering bacterium accounts for about 13% of the dry weight of the cell wall; and simultaneously, the cellulose produced by the synechococcus engineering bacterium has a short growth cycle and does not have the pollution problem of lignin in wood, the extraction and purification processes can be greatly simplified, and the degree of pollution to the environment can also be greatly reduced correspondingly, thus the synechococcus engineering bacterium is an ideal biological engineering bacterium for producing cellulose and is further used as a raw material for producing biological ethanol.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Microbial cellulose wound dressing for treating chronic wounds
InactiveUS7709021B2Promote wound healingRelieve painOrganic active ingredientsBiocideVeinWound dressing
The invention relates to a wound dressing comprising a microbial-derived cellulose for treatment of specific types of chronic wounds, including pressure sores, venous and diabetic ulcers. The wound dressing is capable of donating liquid to dry substrates is also capable of absorbing exudating wounds.
Owner:LOHMANN & RAUSCHER
High-cellulose functional red date fermented beverage and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105995330AImprove the bactericidal effectImprove actual functionsPre-extraction tea treatmentYeast food ingredientsYeastFiber
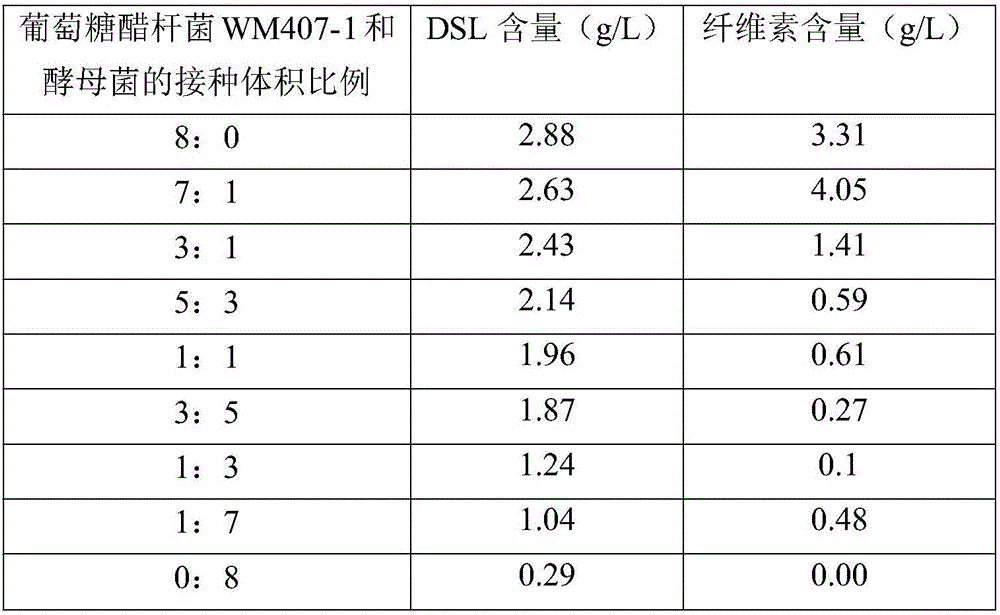
The invention discloses a high-cellulose functional red date fermented beverage and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of preparation of functional beverages. The red date fermented beverage with high dietary fibers and high lactone content is produced through crushing, carrying out enzymolysis, extracting, filtering and clarifying, inoculating gluconacetobacter xylinum WM407-1 yeast according to a certain ratio and fermenting. In a process of preparing the compound red date fermented beverage, other substances are not added and the content of high sugar in a red date extracting solution is greatly reduced in an extracting process. The high-cellulose functional red date fermented beverage is low in sugar and high in dietary fibers so that the beverage is suitable for a diet trend of modern people and has a very good application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Multi-function emergency bandage
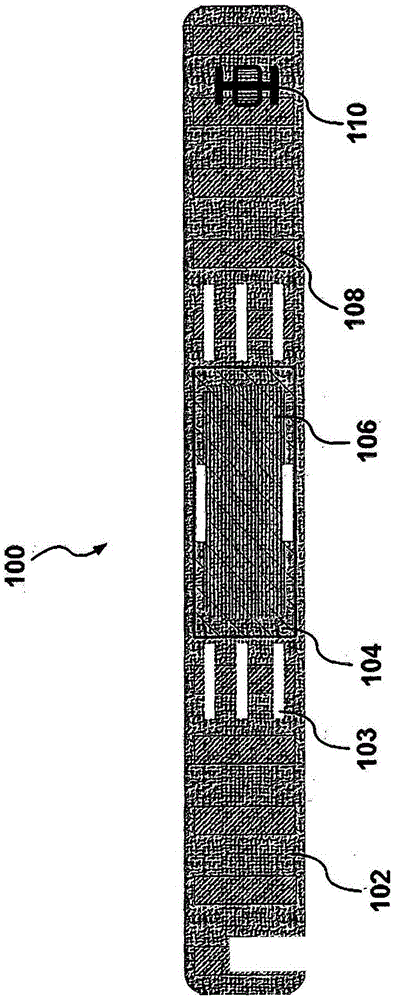
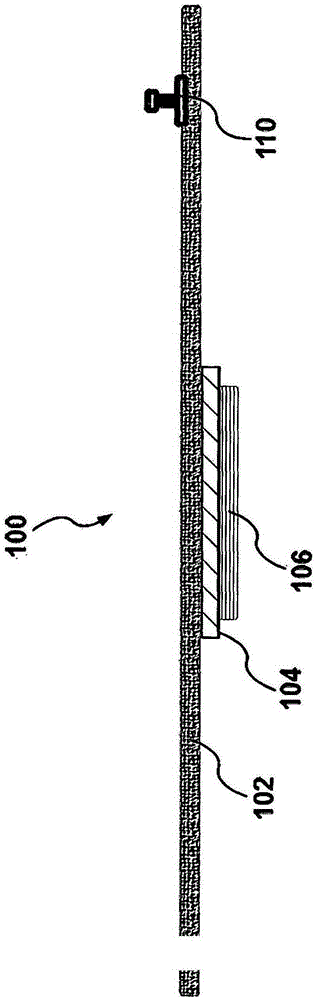
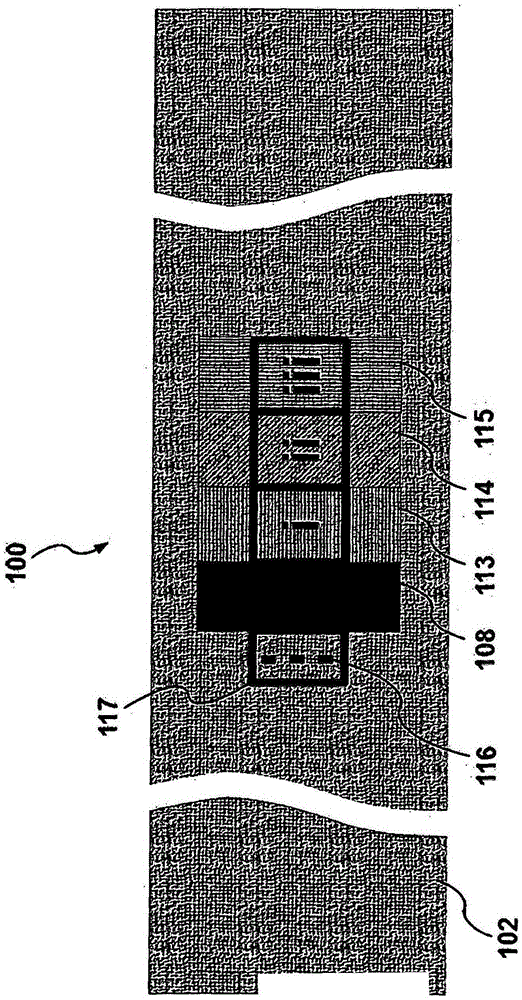
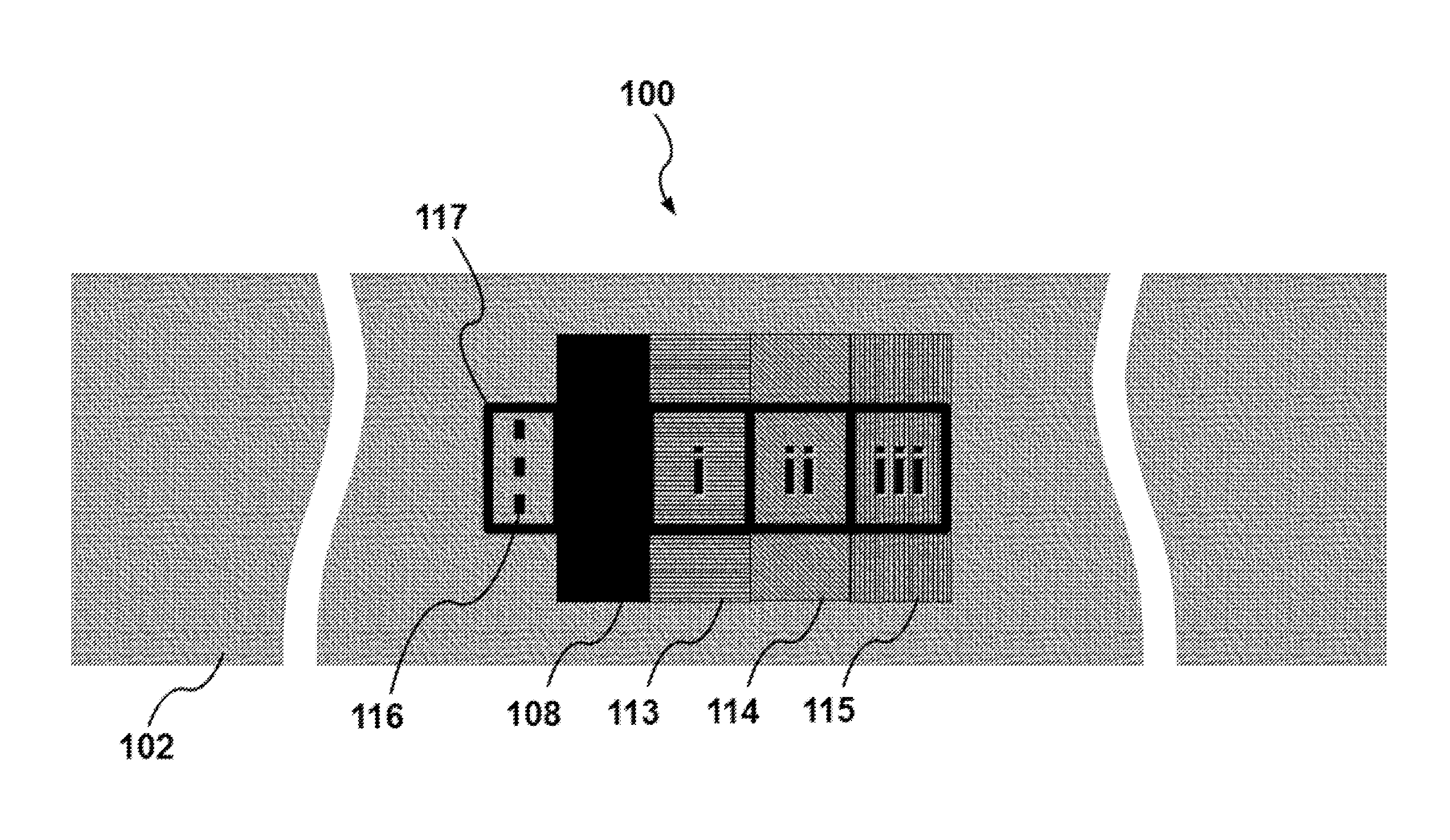
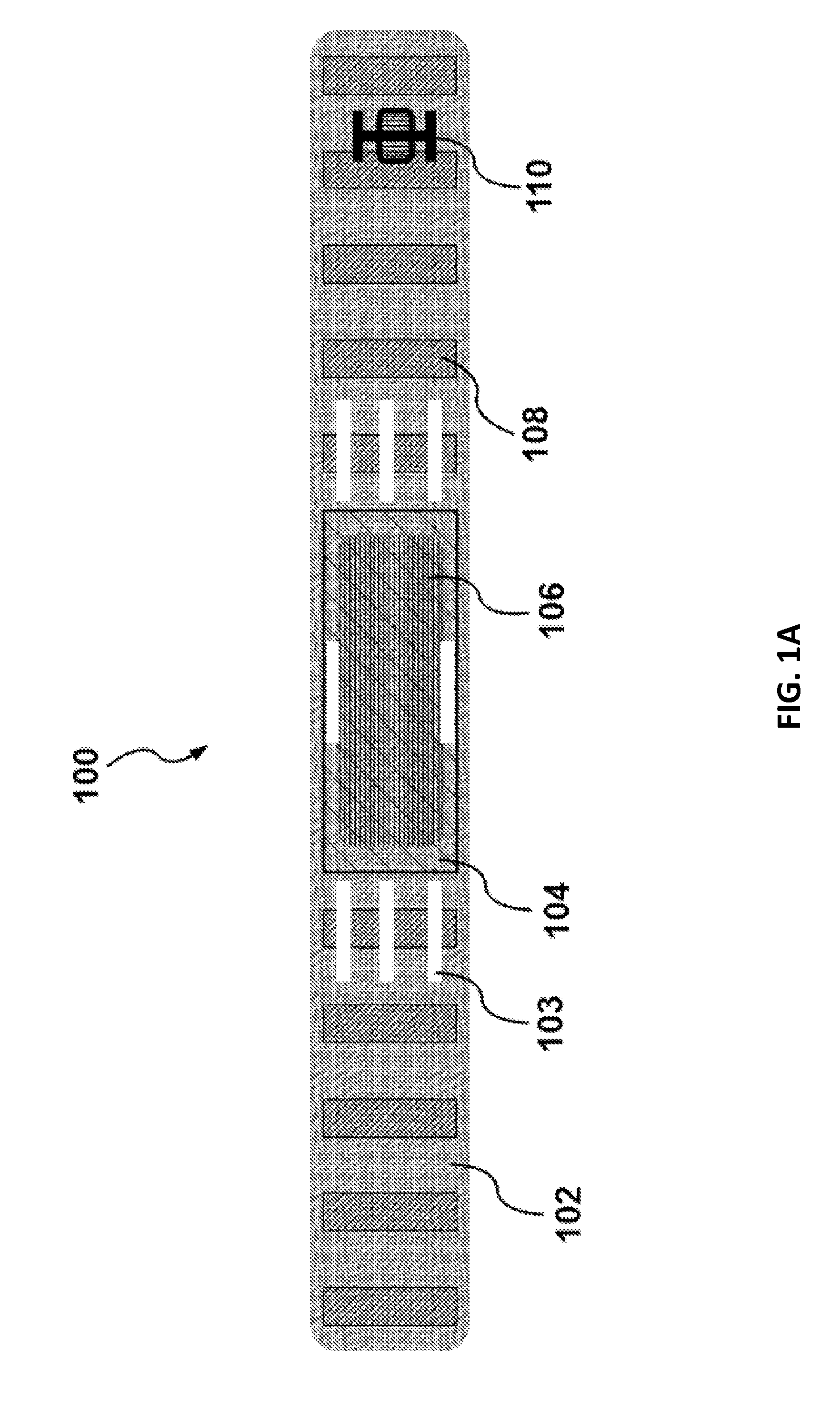
A unique multi-functional emergency bandage is introduced, wherein bleeding is stopped by: (1) optimizing mechanical properties and preventing ischemia and / or necrosis while applying enough pressure to help stop bleeding, and (2) incorporating inorganic anti-bleeding nano-structures (embedded within a gauze and / or microbial cellulose) with almost infinite life-time. Additionally, pathogen passage through the bandage is prohibited (via an intermediate filter layer). Together with the overall anti- microbial character of the bandage, the unique multi-functional bandage offers all these vital features within a single design. The unique bandage can be applied by using a single hand and bandaging direction can be changed using a unique binding apparatus. Visual aids, such as printed rectangles, on the final fabric provides the user with an indication of how to control the amount of stretch, as vertical rectangles would turn into horizontal rectangles when stretched too much, whereas rectangles turn to squares around the optimum region of the stress-strain curve.
Owner:SANKO TEKSTIL ISLETMELERI SANAYI & TICARET A S
Multi-Function Emergency Bandage
ActiveUS20140371650A1Avoid ischemiaAvoid necrosisNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersMicrobial celluloseEngineering
A unique multi-functional emergency bandage is introduced, wherein bleeding is stopped by: (1) optimizing mechanical properties and preventing ischemia and / or necrosis while applying enough pressure to help stop bleeding, and (2) incorporating inorganic anti-bleeding nano-structures (embedded within a gauze and / or microbial cellulose) with almost infinite life-time. Additionally, pathogen passage through the bandage is prohibited (via an intermediate filter layer). Together with the overall anti-microbial character of the bandage, the unique multi-functional bandage offers all these vital features within a single design. The unique bandage can be applied by using a single hand and bandaging direction can be changed using a unique binding apparatus. Visual aids, such as printed rectangles, on the final fabric provides the user with an indication of how to control the amount of stretch, as vertical rectangles would turn into horizontal rectangles when stretched too much, whereas rectangles turn to squares around the optimum region of the stress-strain curve.
Owner:SANKO TEKSTIL ISLETMELERI SANAYI & TICARET A S
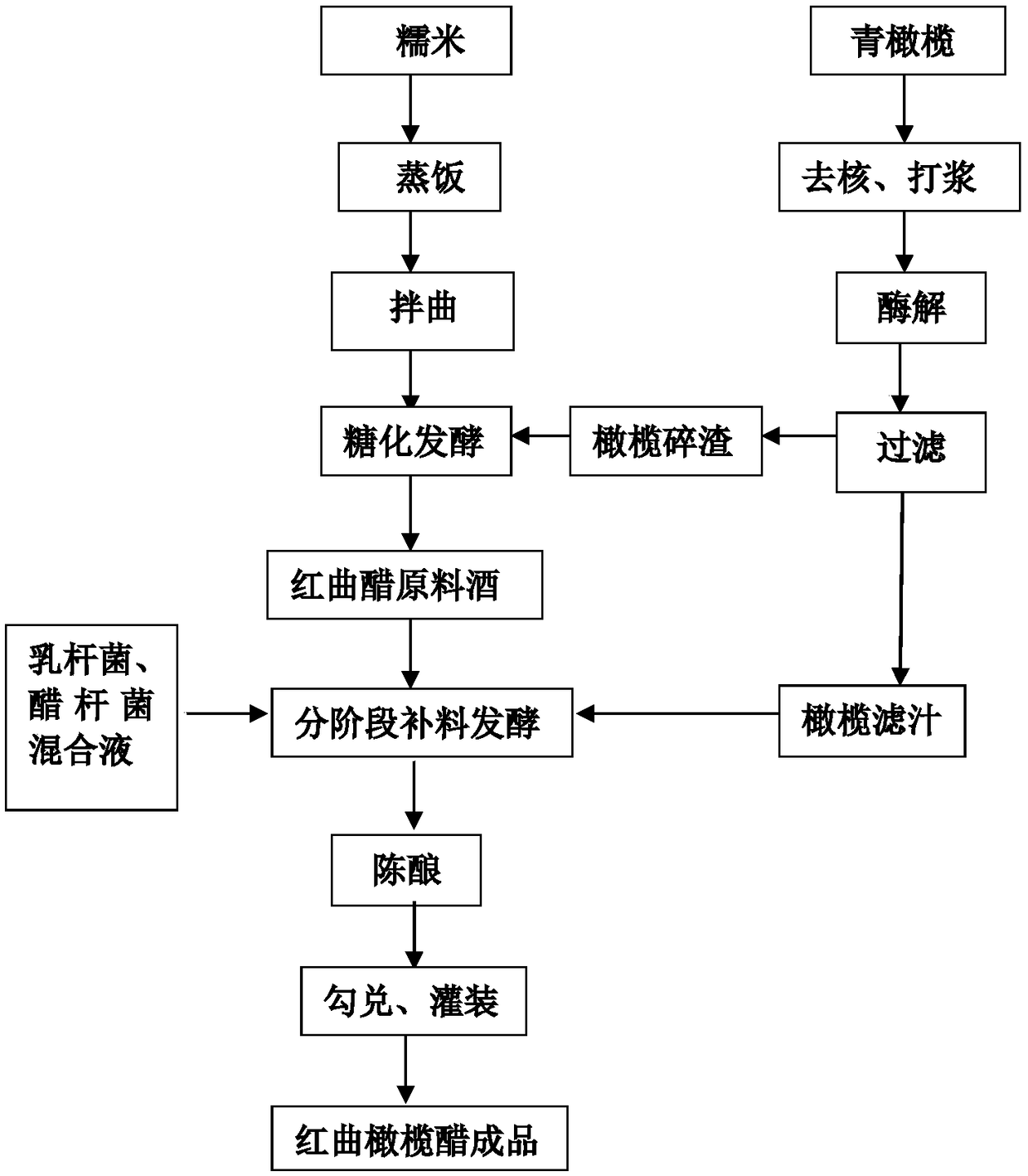
Preparation method of monascus purpureus olive vinegar
The invention belongs to the technical field of functional fermented food processing, and particularly relates to a preparation method of monascus purpureus olive vinegar. The preparation method comprises the following steps: removing and crushing olive fruit kernels, adding water for pulping, and adding compound enzymes for enzymolysis to obtain filtered olive juice and crushed olive residues; soaking sticky rice and then steaming rice to obtain glutinous rice; adding aspergillus candidus, monascus purpureus and the crushed olive residues in the glutinous rice to perform diastatic fermentation to obtain mature fermented mash; performing squeezing separating and blending to obtain monascus purpureus vinegar raw wine; and adding the mixed solution of the monascus purpureus vinegar raw wine,the filtered olive juice, bacterium lacticum and gluconacetobacter xylinum in an acetic acid tank for staged fed-batch fermentation, and ageing to obtain the monascus purpureus olive vinegar. The monascus purpureus olive vinegar is prepared by adopting an olive whole fruit fermentation method, medical components of olive fruit are effectively extracted and used, and the monascus purpureus olive vinegar has faint scent of olive fruit and strong olive flavor.
Owner:福建吉百年食品有限公司
Novel isolated bacterial strain of gluconacetobacter oboediens and an optimized economic process for microbial cellulose production therefrom
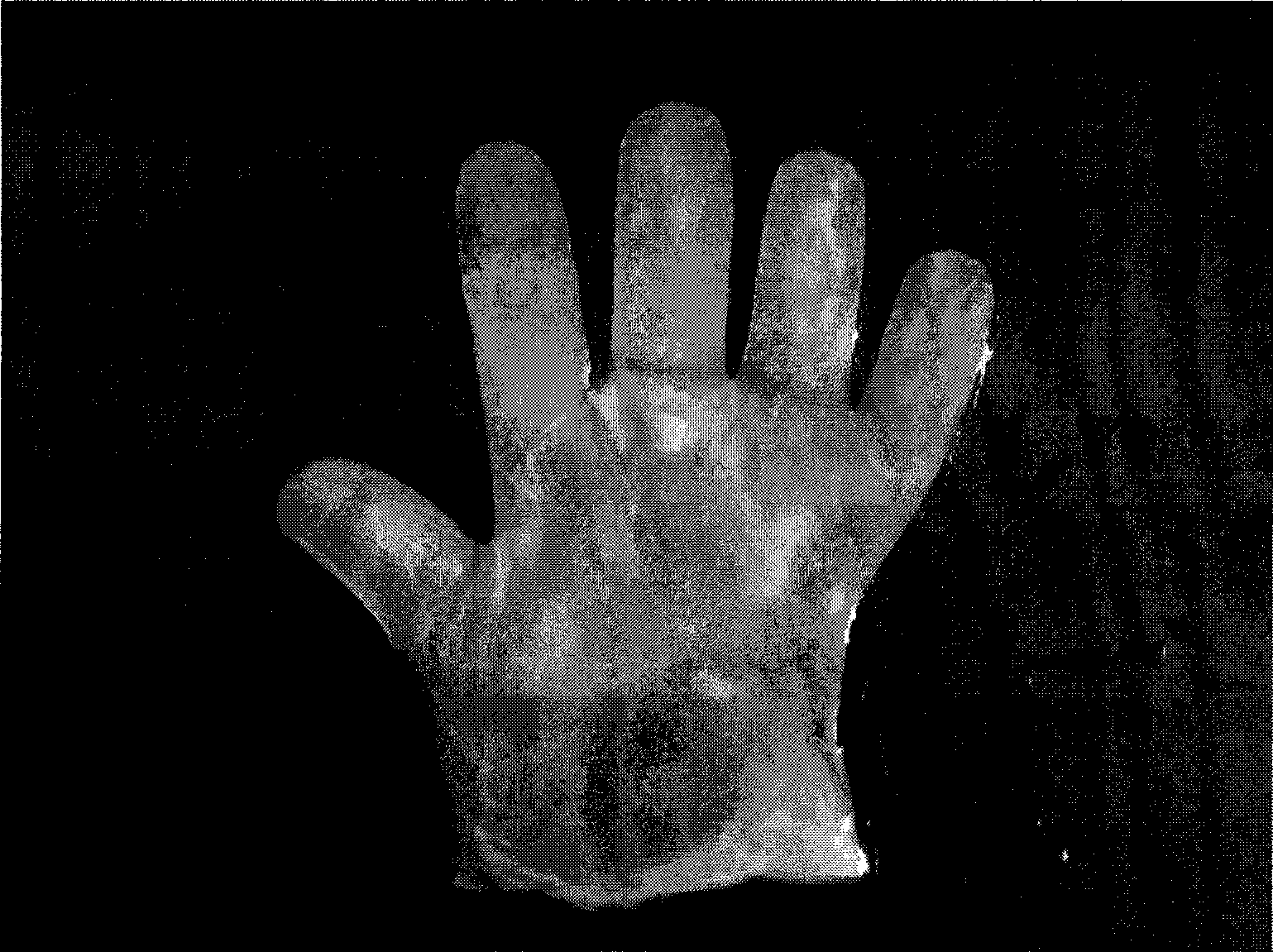
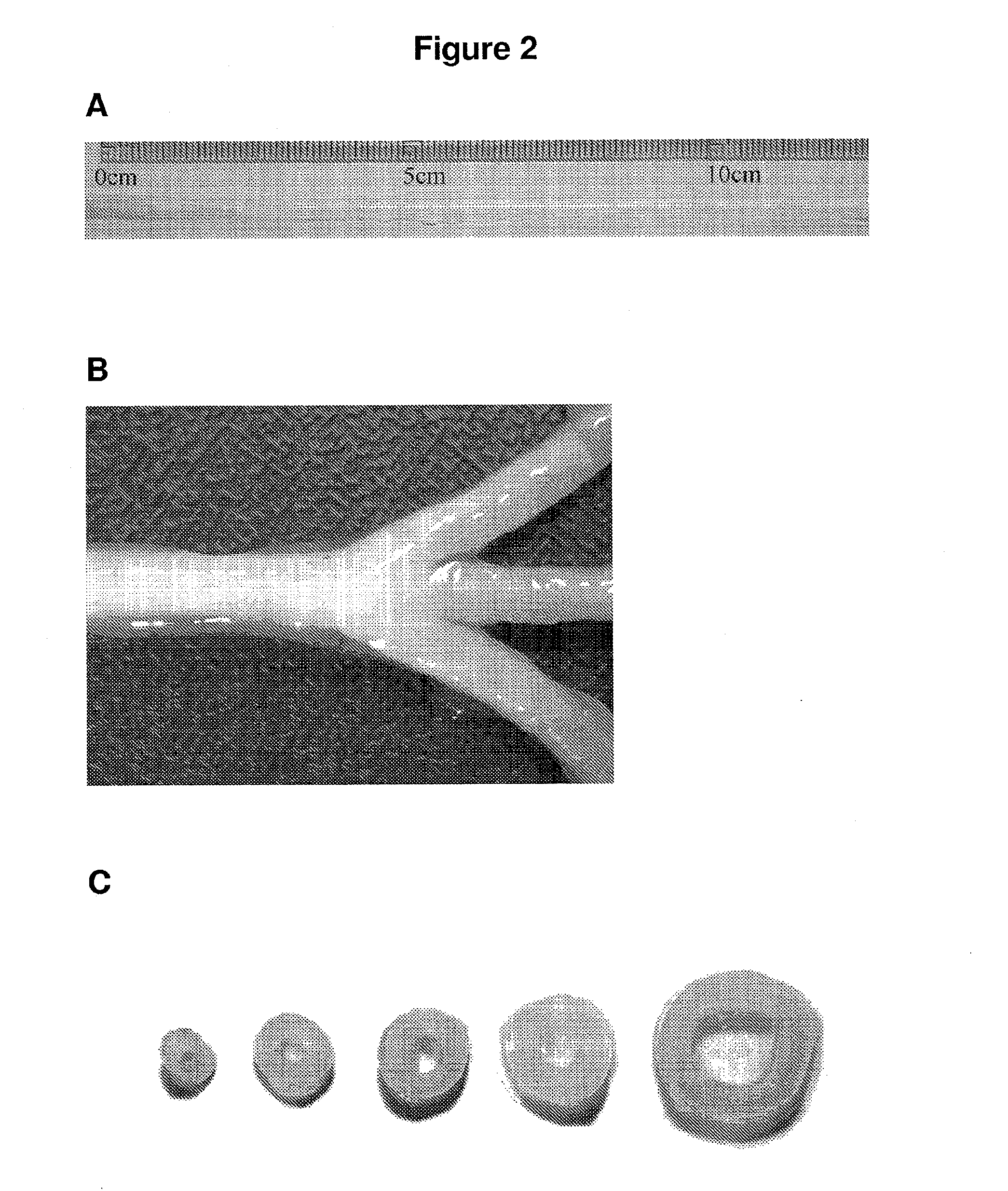
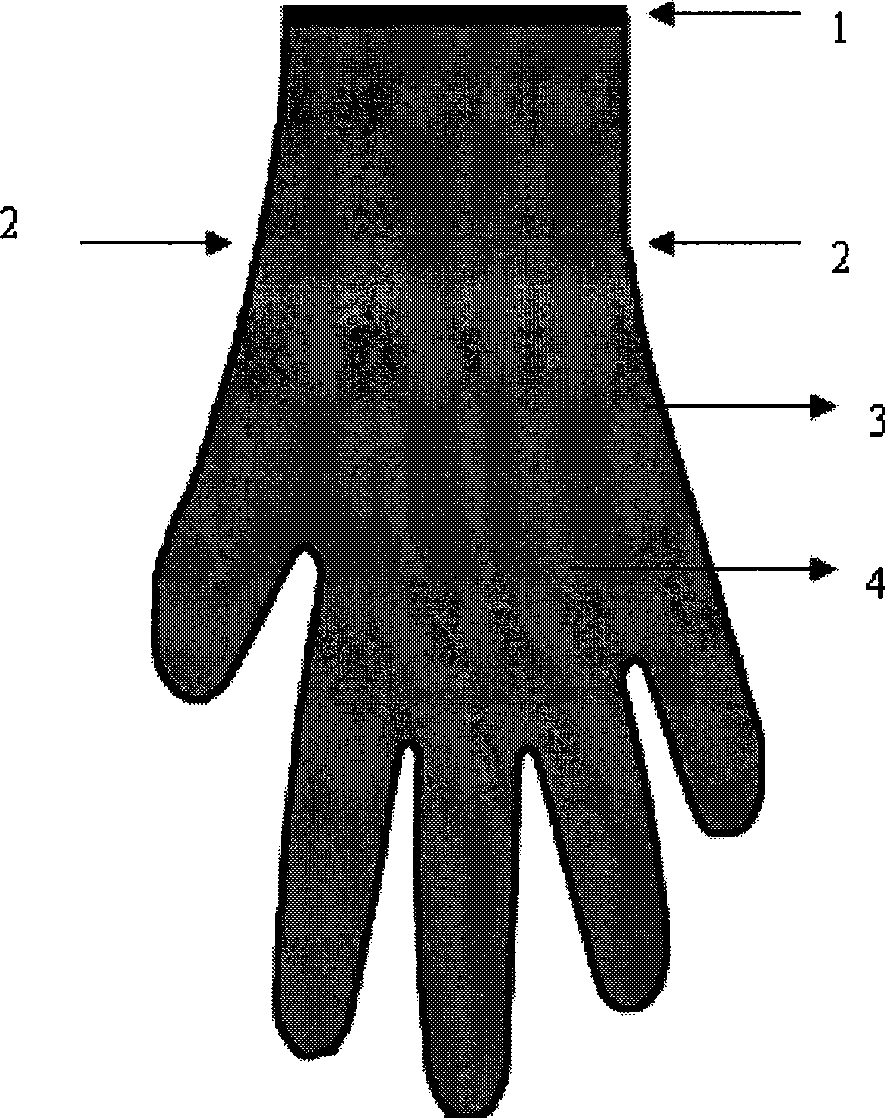
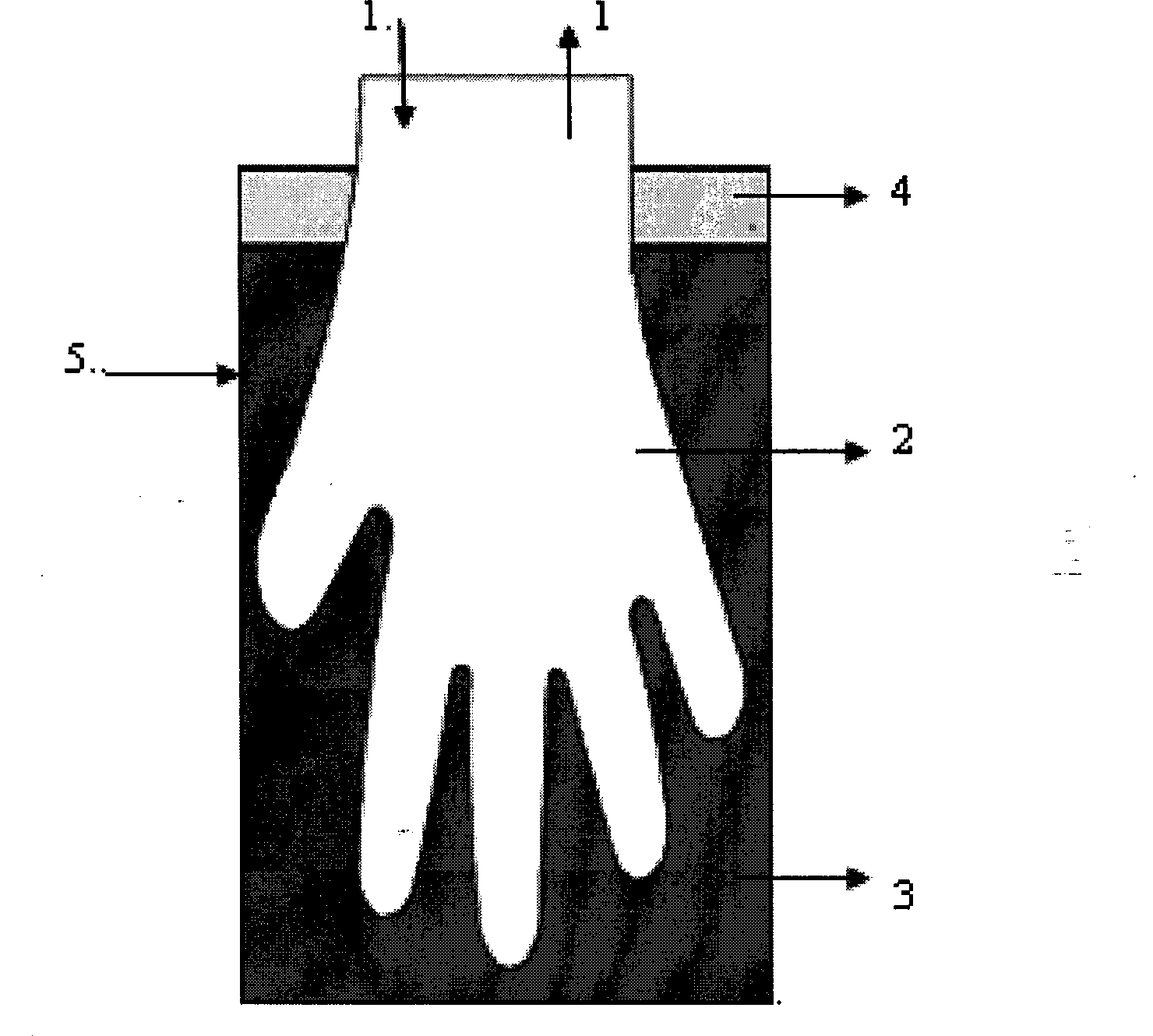
The present invention provides a novel and potent cellulose producing bacterial species, Gluconacetobacter oboediens which was isolated from mixed fruit residue deposited at MTCC, IMTECH, Chandigarh under the deposition number MTCC 5610. The process for the production of microbial cellulose by this bacterium was optimized and thus, an efficient and economic process for producing high titres of microbial cellulose was developed. Further, a novel and improved method for drying of microbial cellulose has been developed wherein the microbial cellulose mats were dried using a wooden plank and porous fabric as a base at room temperature. The microbial cellulose production was successfully scaled up to 5 liters volume of production medium in trays. The present invention also recites the production and optimization of microbial cellulose in different shapes and sizes (gloves and vessels) which will be of great help for burn and injured persons / patients.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method and device for producing shaped microbial cellulose for use as biomaterial especially for microsurgery
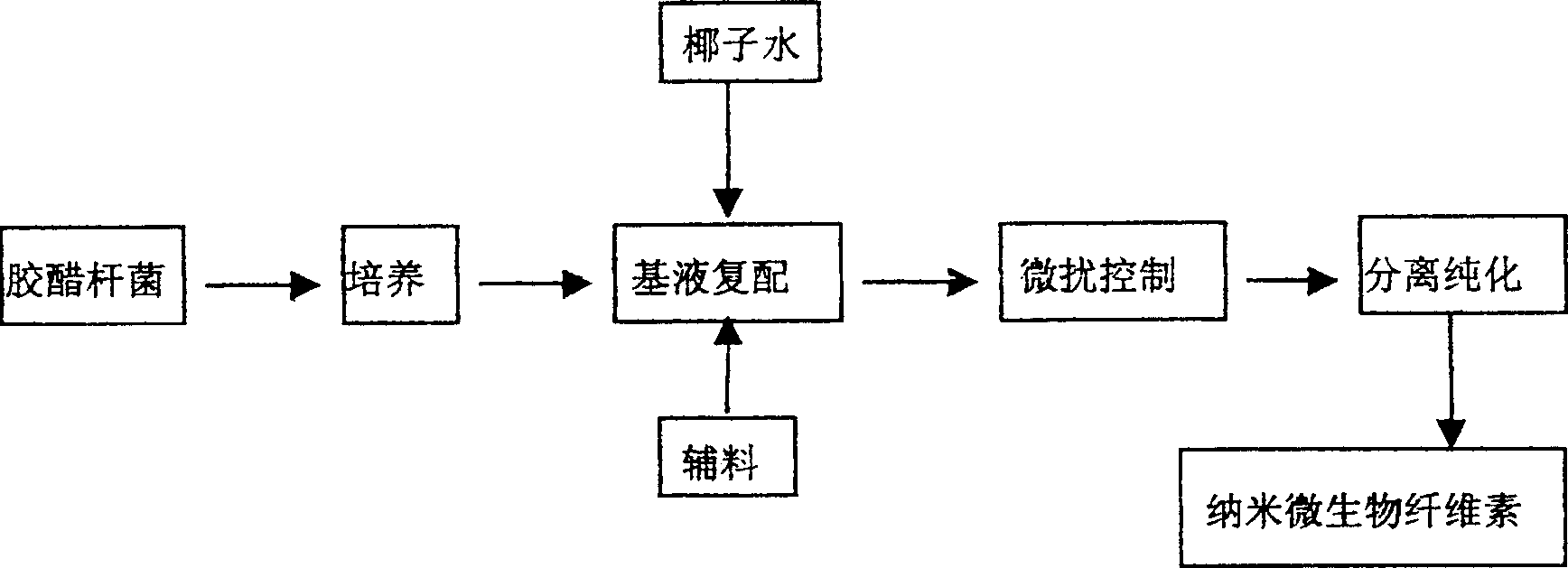
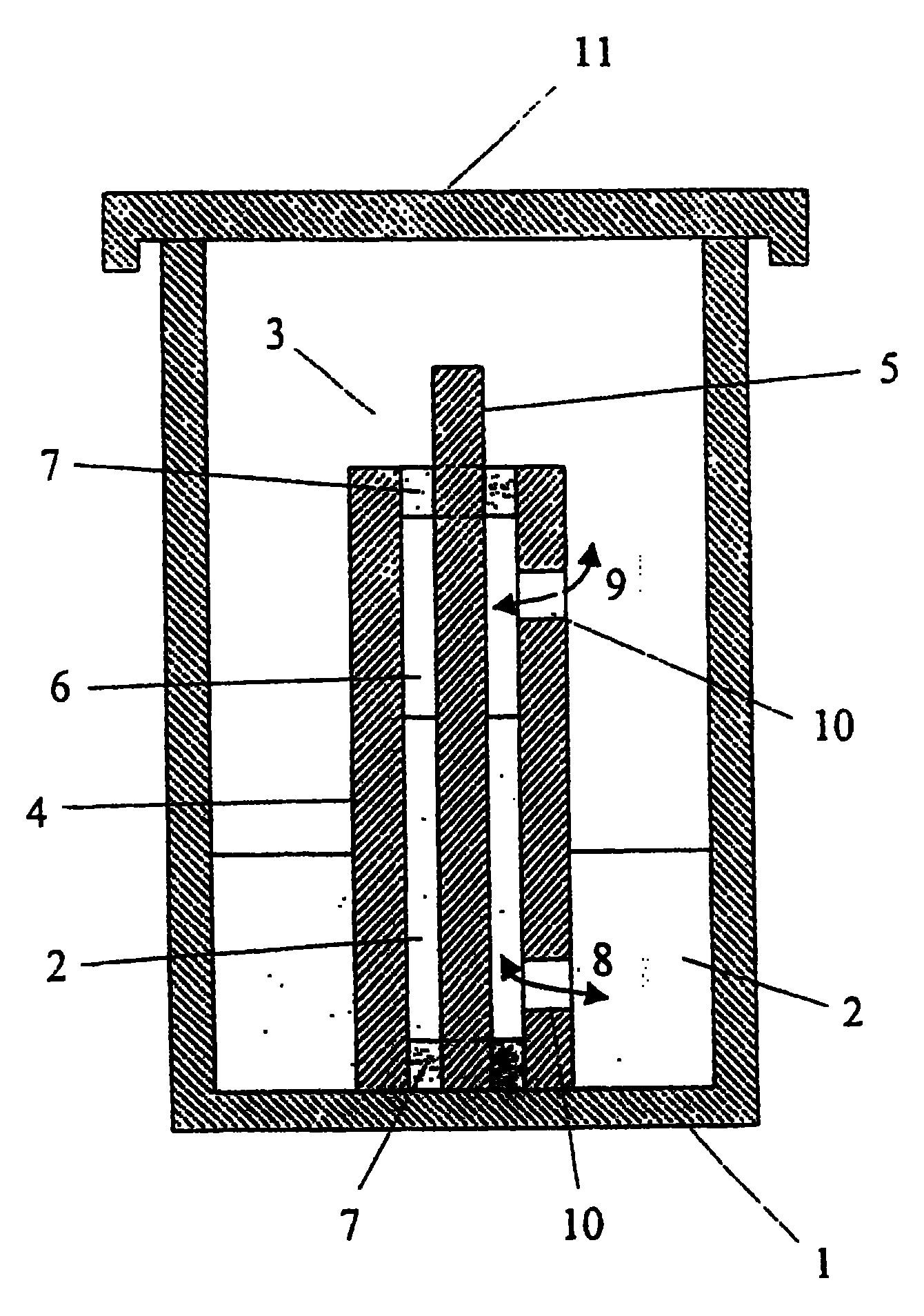
InactiveCN100451125CQuality improvementReproducible qualitySuture equipmentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCulture fluidMicrobial cellulose
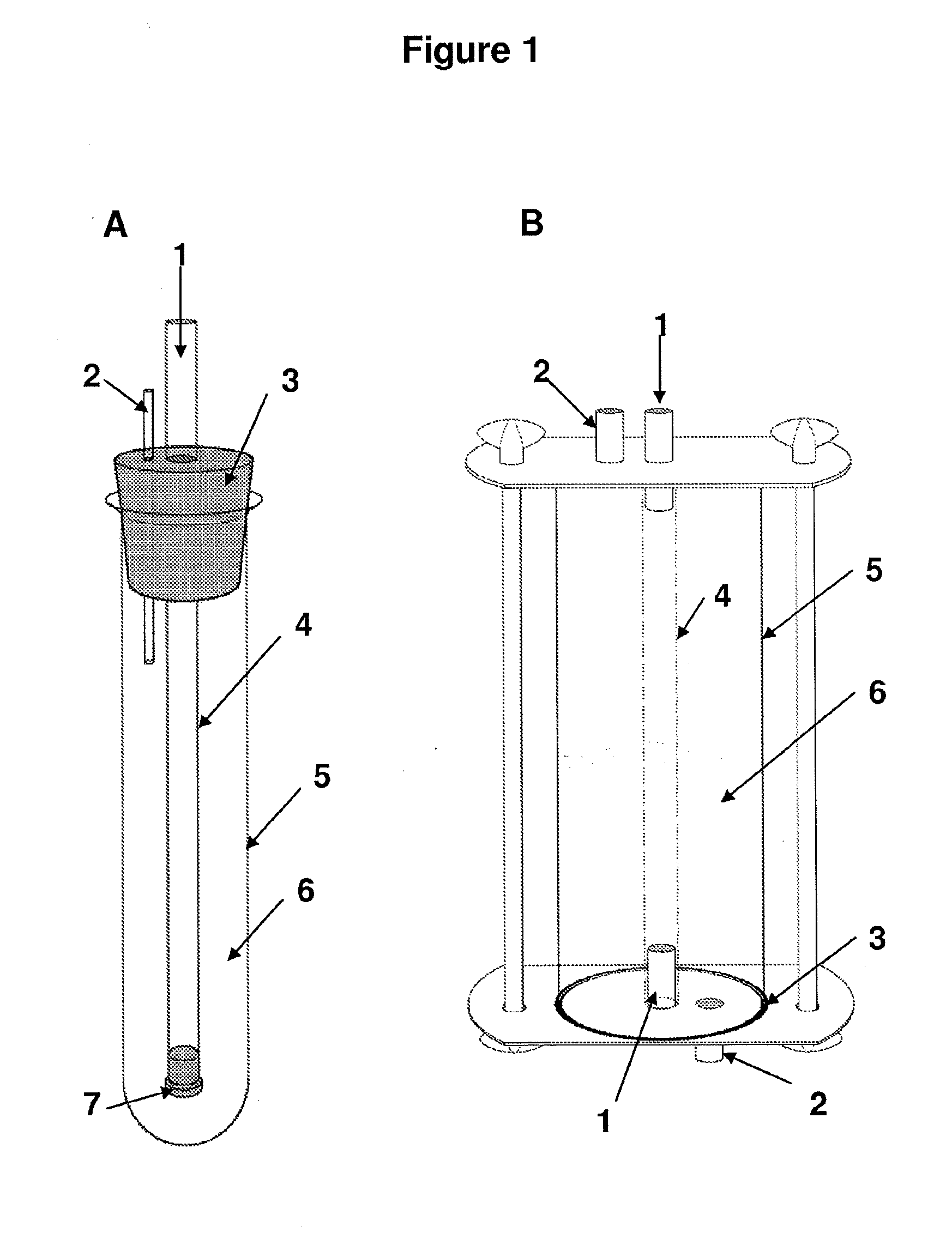
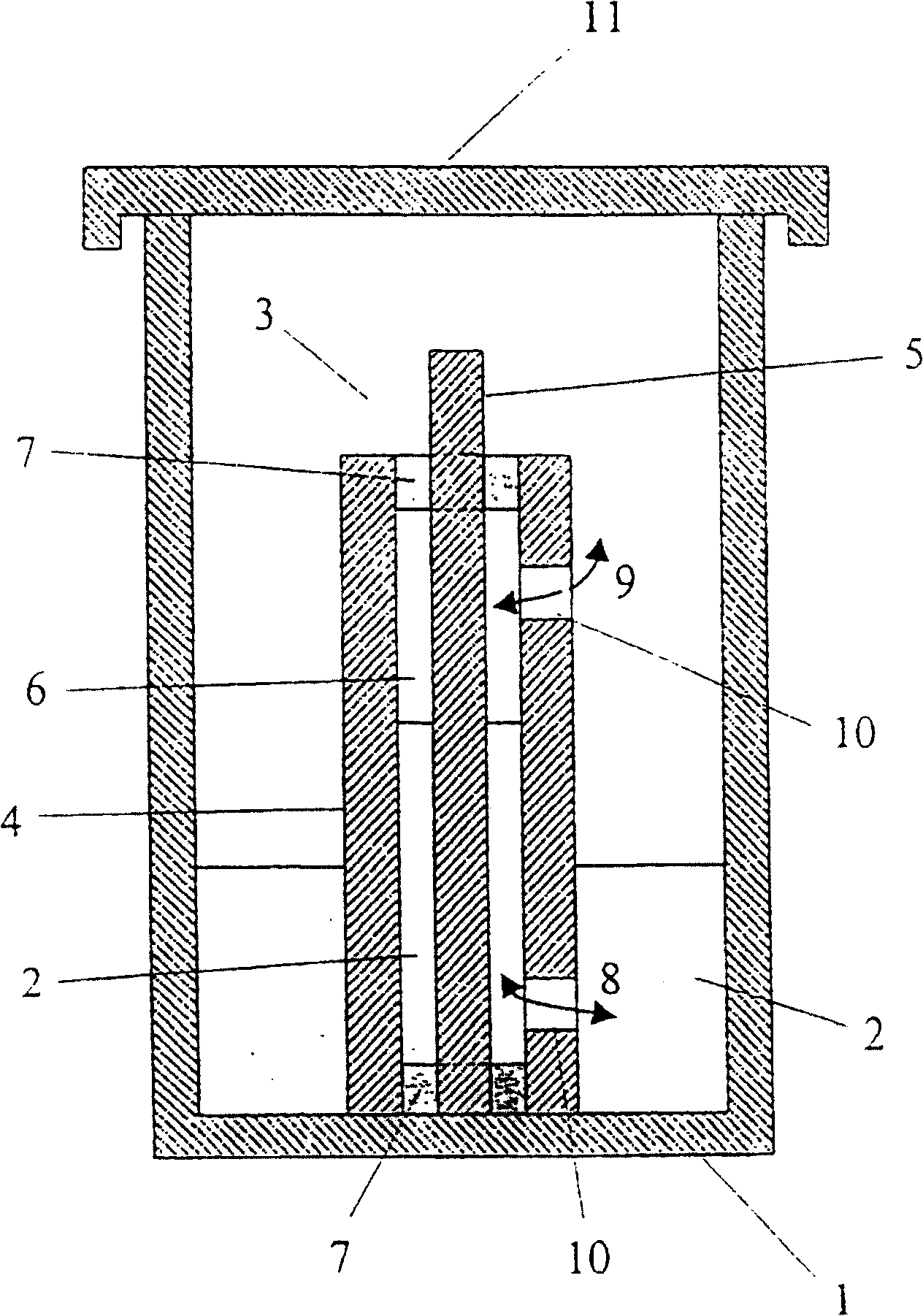
The use of exogenic materials for replacing blood vessels carries the risk of thrombosis and is therefore particularly unsuitable for microsurgical applications (inner vessel diameters of 1-3 mm and less), or only suitable under certain conditions. Replacements of blood vessels with a very small lumen in particular require biomaterials which guarantee that the surfaces of the prosthesis that come into contact with the blood are of a very high quality, and which reliably avoid this kind of thrombosis adhesion. The biomaterial is produced by immersing shaped body walls, especially of a glass matrix consisting of a glass tube and glass body, in a container of an inoculated nutrient solution so that the inoculated nutrient solution is drawn into the area between the walls of the shaped body and cultivation takes place in a moist, aerobic environment. In each subsequent cultivation process, an unused shaped body (glass body) is used as the shaped body wall for shaping the surface of the prosthesis material that is to come into contact with the blood when the biomaterial is used. This is the only sure way of reproducing the high surface quality of the vessel prosthesis and hereby reliably preventing thrombosis adhesion on the biomaterial used. The inventive method is particularly suitable for microsurgical applications, especially for replacing blood vessels and other internal hollow organs or as a cuff for covering nerve fibres, etc.
Owner:SURA CHEM GMBH
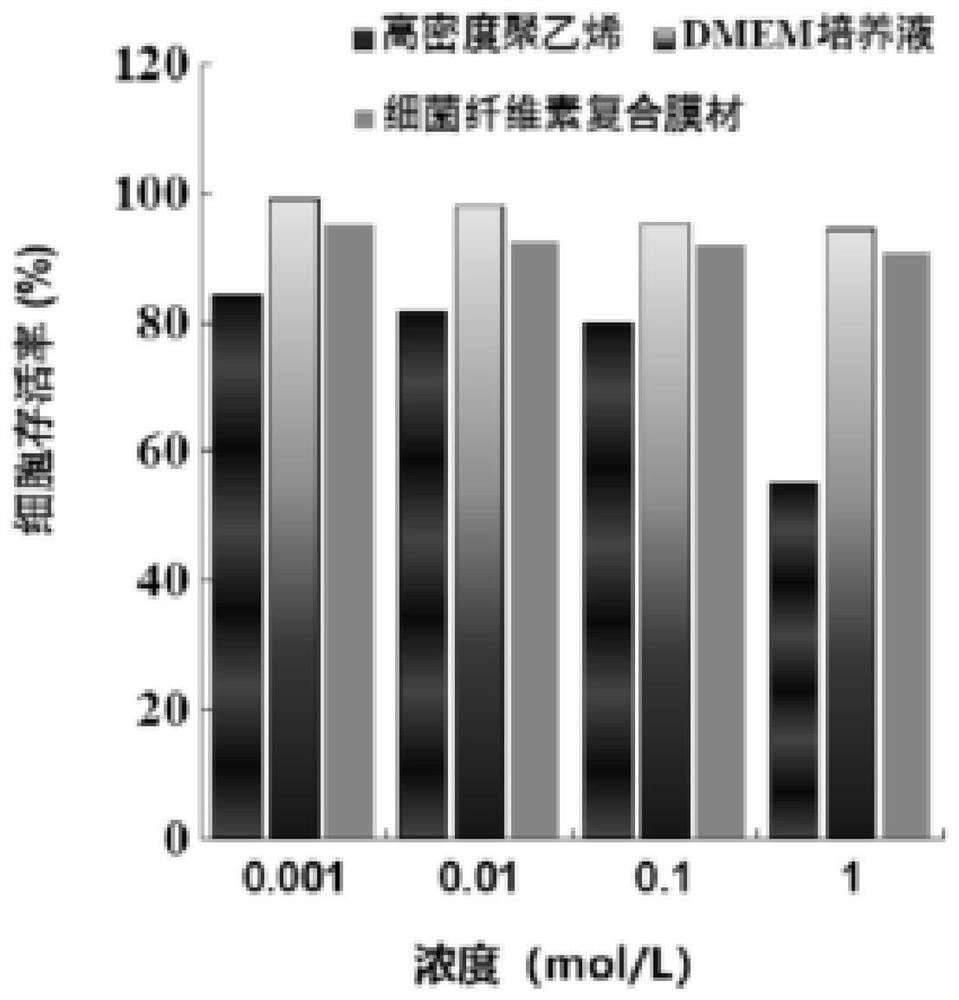
Preparation method of bacterial cellulose, bacterial cellulose-chitosan composite gel skincare mask and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112877384AHigh mechanical strengthGood value for moneyCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBiotechnologyAcetobacter
The invention discloses a preparation method of bacterial cellulose. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a soybean residue biological fermentation culture medium by using soybean residues as a basic raw material, namely soybean residues for short, adding 10-18% of a gluconacetobacter xylinum seed solution and amygdalin into the soybean residue biological fermentation culture medium, adding 12-25 mL of a gluconacetobacter xylinum seed solution into every 100 mL of the soybean residue biological fermentation culture medium, wherein the pH is 4.8-6.0, the culture temperature is 28-35 DEG C, the culture time is 12-18 days, the use amount of amygdalin is 150-450 U / mL, and obtaining a bacterial cellulose membrane material. The invention further discloses a bacterial cellulose-chitosan composite gel skin care mask and a preparation method thereof. The mask is good in tensile strength and high in mechanical strength, has a certain inhibition effect on bacteria and fungi, and is good in biocompatibility.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
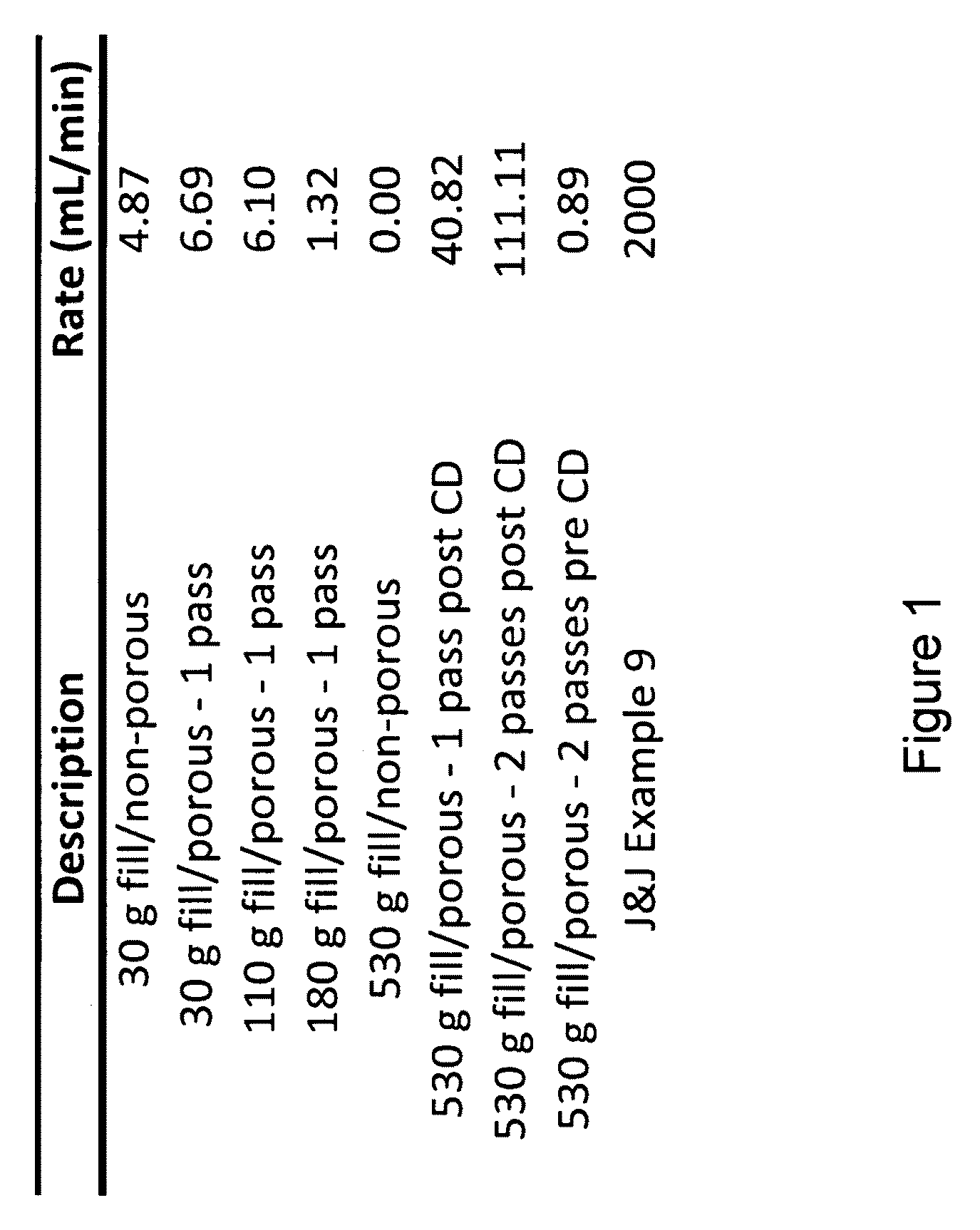
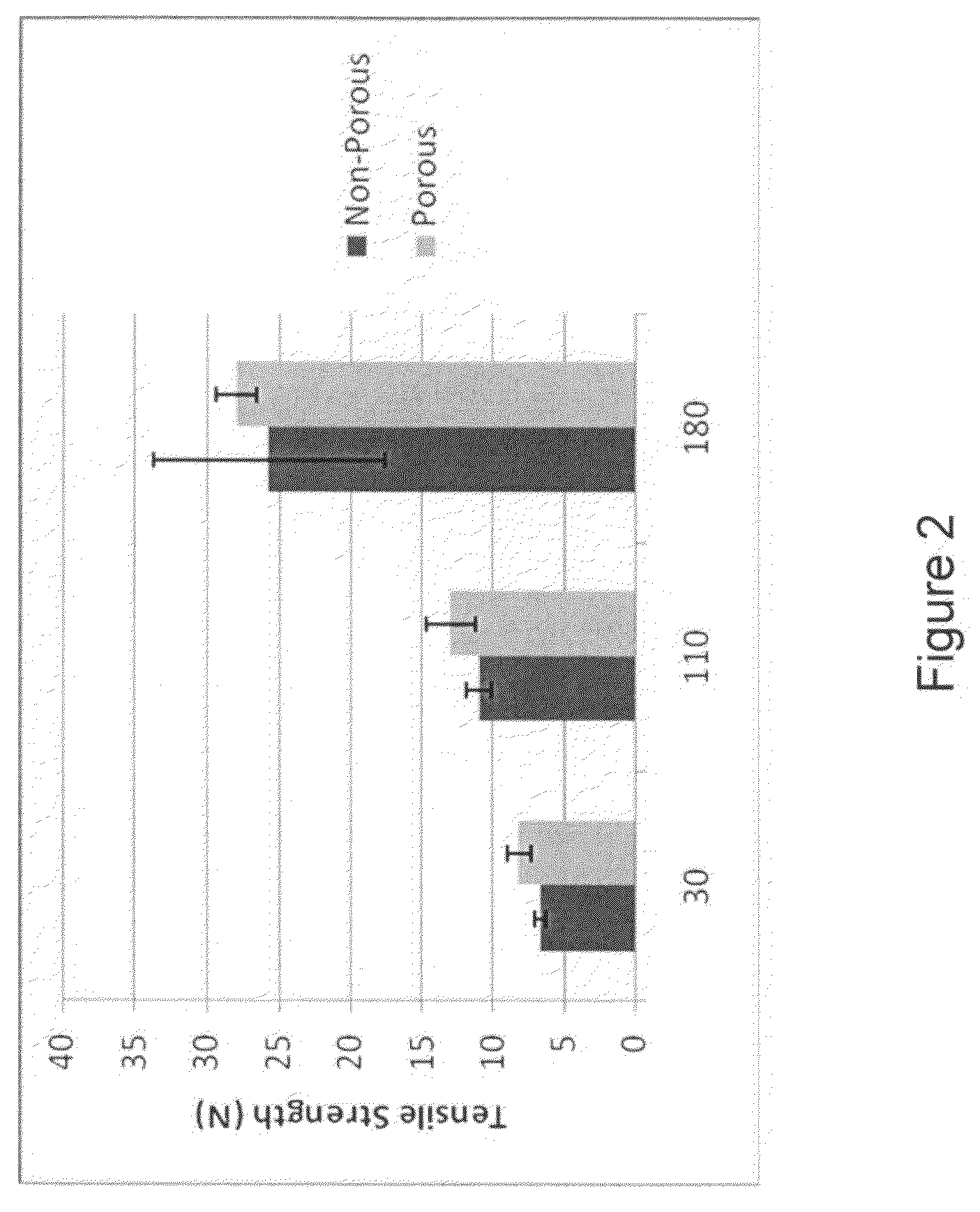
Porous structures of microbial-derived cellulose for in vivo implantation
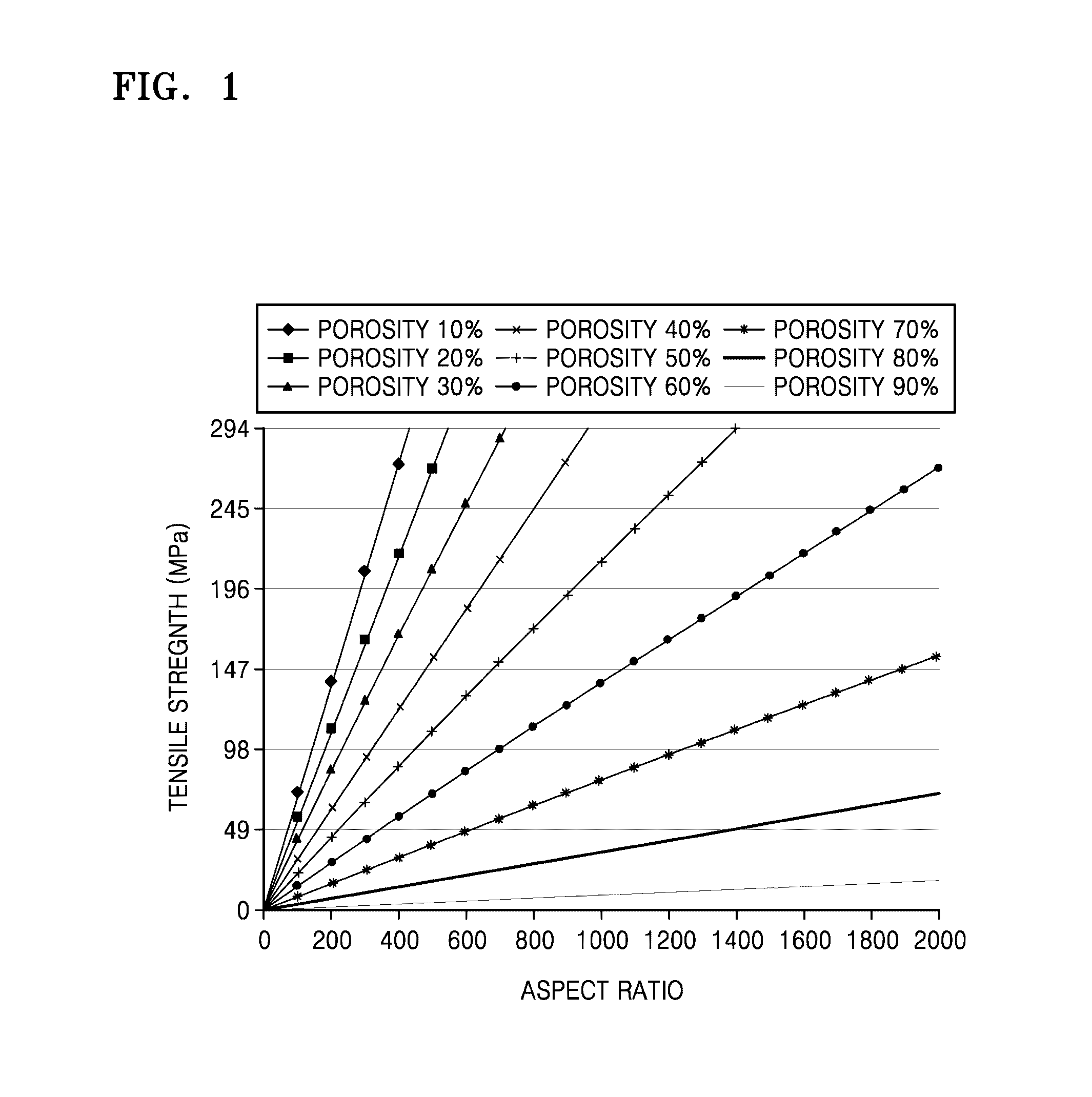
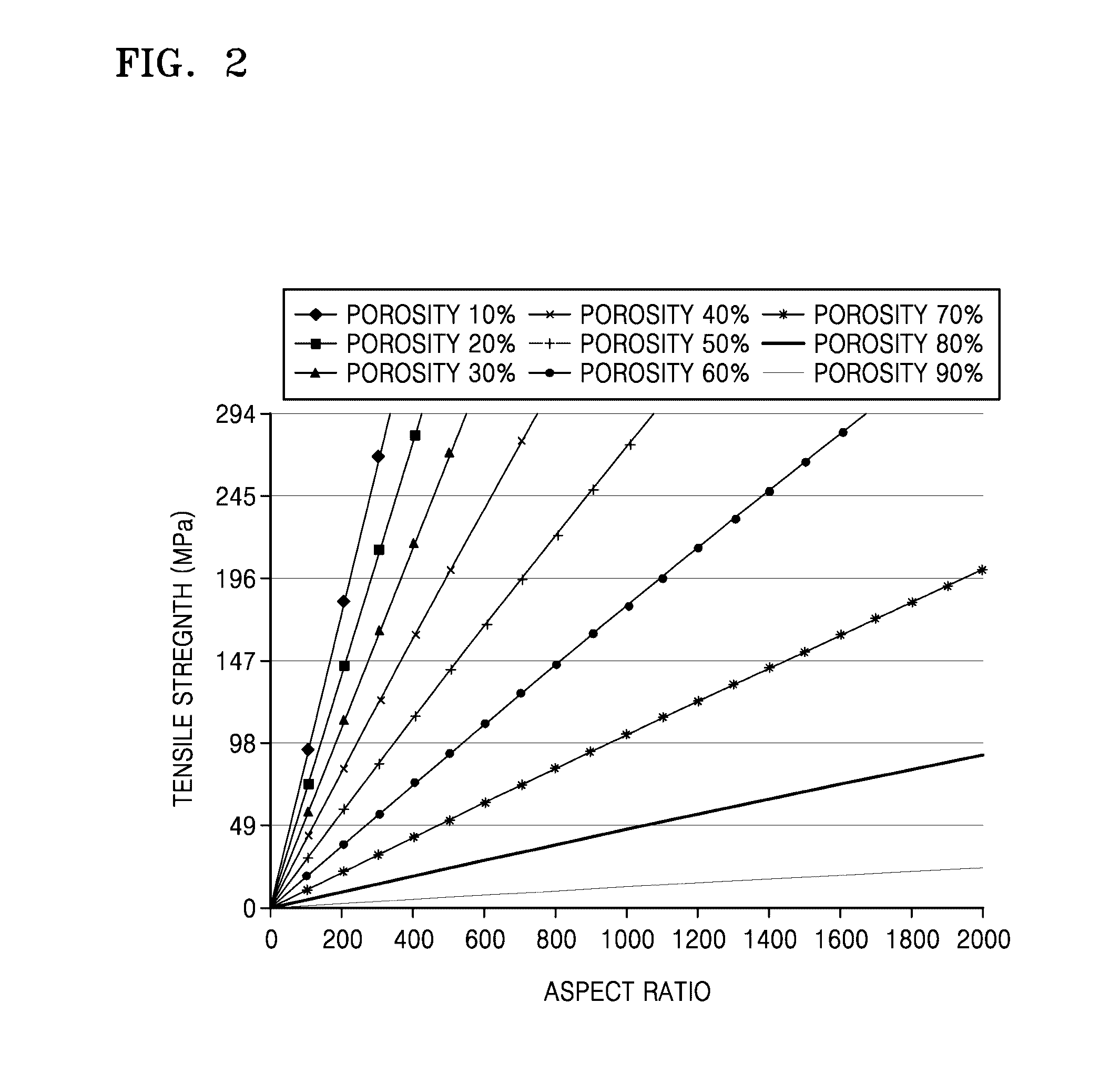
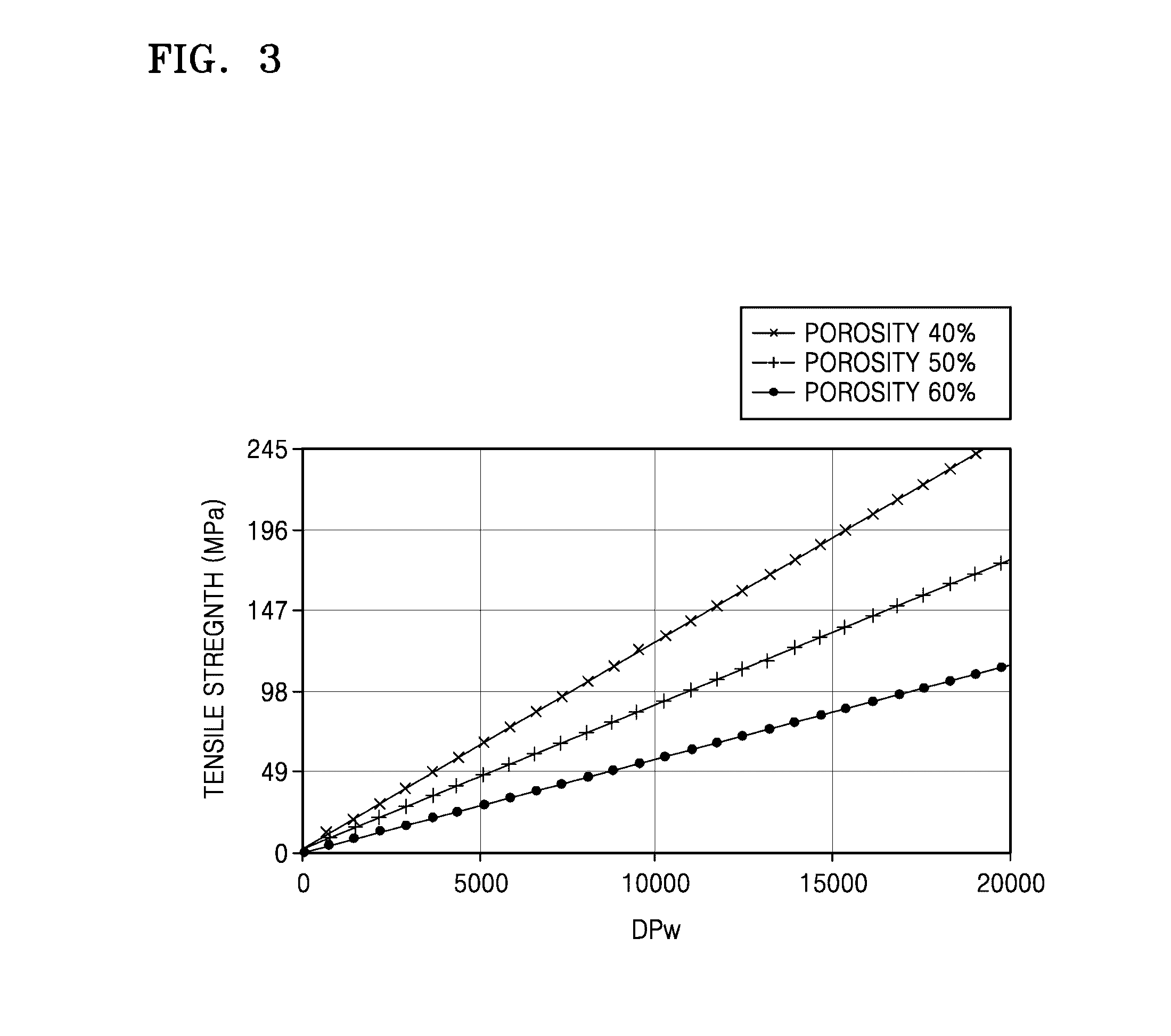
This invention relates to polysaccharide materials and more particularly to microbial-derived cellulose having the porosity and containing pores of the desired size making it suitable for cellular infiltration during implantation and other desirable properties for medical and surgical applications. The invention also relates to the use of porous microbial-derived cellulose as tissue engineering matrices, human tissue substitutes, and reinforcing scaffolds for regenerating injured tissues and augmenting surgical procedures. The invention outlines various methods during and after fermentation to create porous microbial cellulose capable of allowing cell infiltration while preserving the physical properties of the microbial-cellulose.
Owner:SYNTHES USA PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com