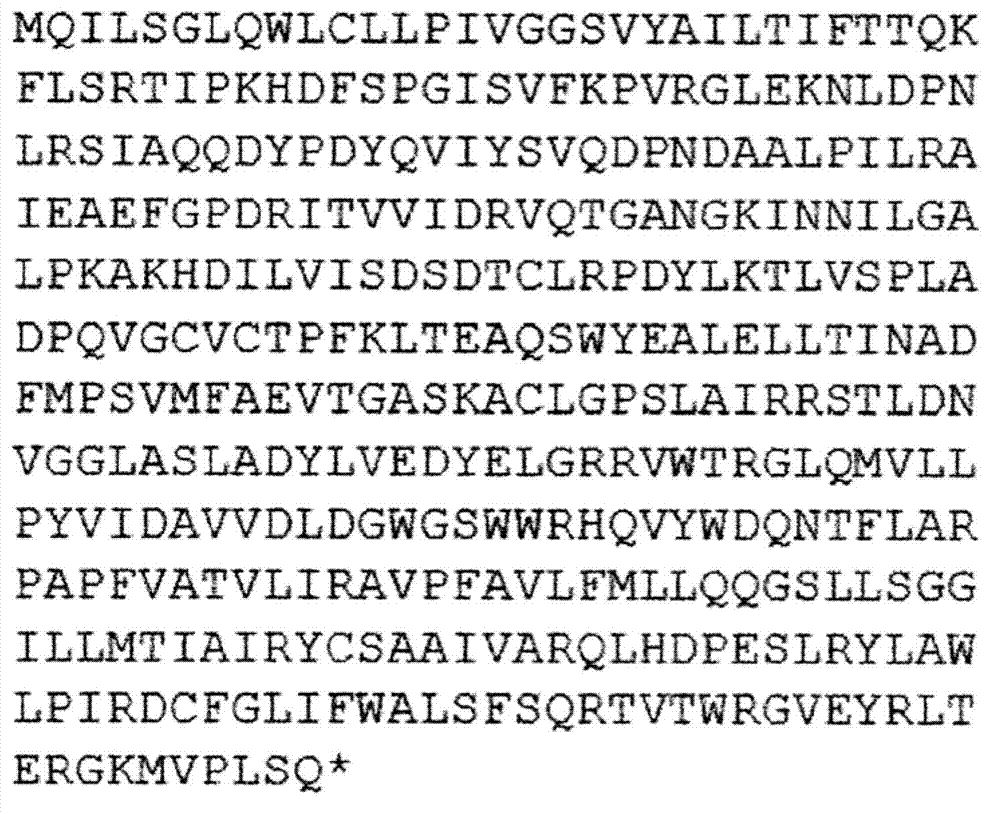Patents
Literature
67 results about "Synechocystis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synechocystis is a genus of unicellular, freshwater cyanobacteria in the family Merismopediaceae. It includes a strain, Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, which is a well studied model organism.
Method for improving content of fatty acid in synechocystis PCC6803
InactiveCN103014037AStrong low temperature toleranceIncrease total fatty acid contentUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesPolymerase chain reactionSynechocystis
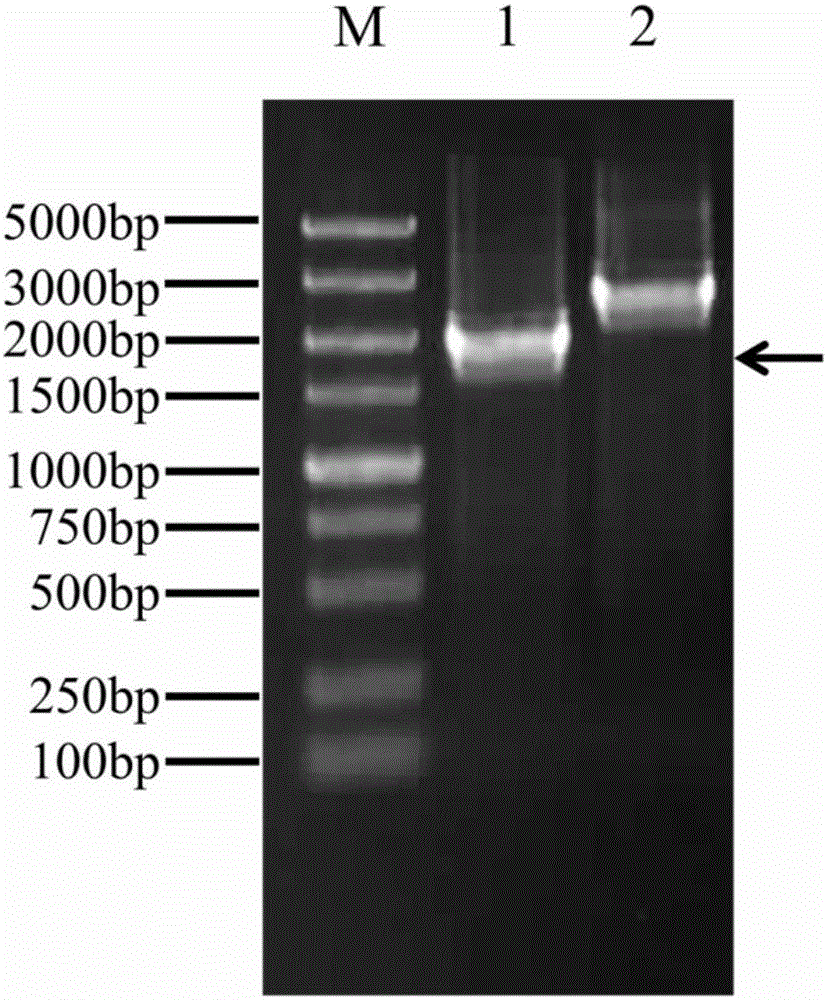
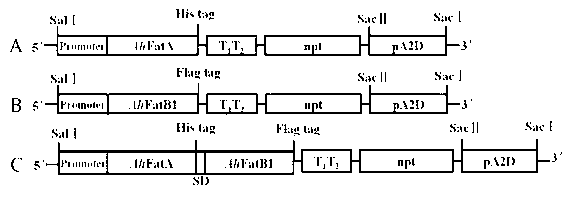
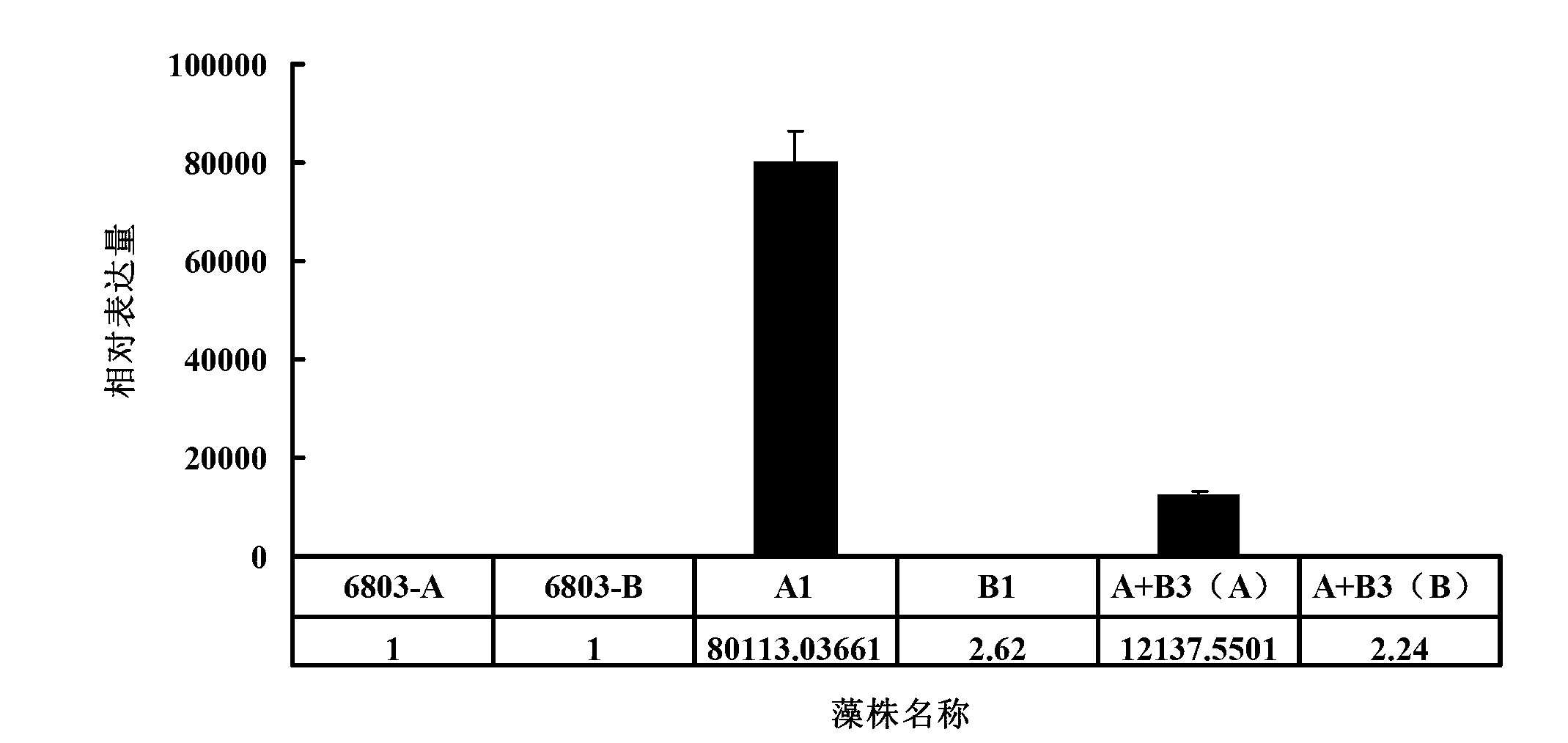
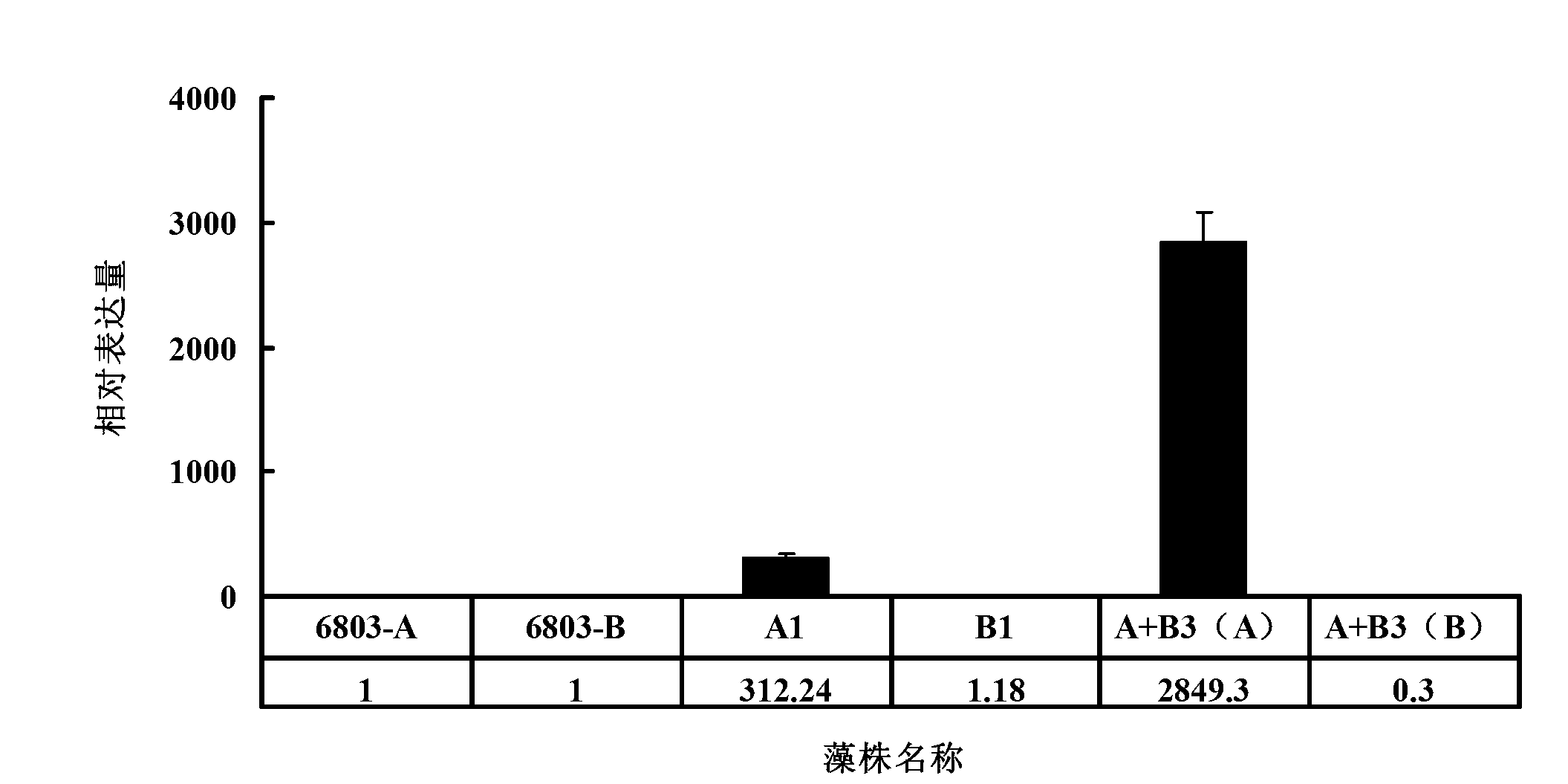
The invention relates to a method for improving the content of fatty acid in synechocystis PCC6803. The steps are as follows: I, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on psbA2 promoters and peanut sulfur lipase genes AhFatA and AhFatB1; II, fusing PCR, Promotor+AhFatA and Promotor+AhFatB1; III, preparing Promotor+AhFatA+AhFatB1 through fusing PCR amplification; IV, inserting into plasmids to prepare a recombinant vector; V, preparing transgenosis synechocystis through transforming; and VI, culturing under the condition with the temperature of 30 DEG C to prepare synechocystis PCC6803 with high content of fatty acid. According to the invention, the content of linoleic acid of transgenosis synechocystis obtained by the method and transformed into AhFatA gene-positive synechocystis PCC6803 under the mixed culturing condition with the temperature of 30 DEG C is obviously increased, so that the method for improving the content of fatty acid in synechocystis PCC6803 has broad application prospect.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
Synechocystis efficient double homologous recombinant vector as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103014053AIncrease contentIncrease total fatty acid contentUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesStearidonic acidNucleotide sequencing
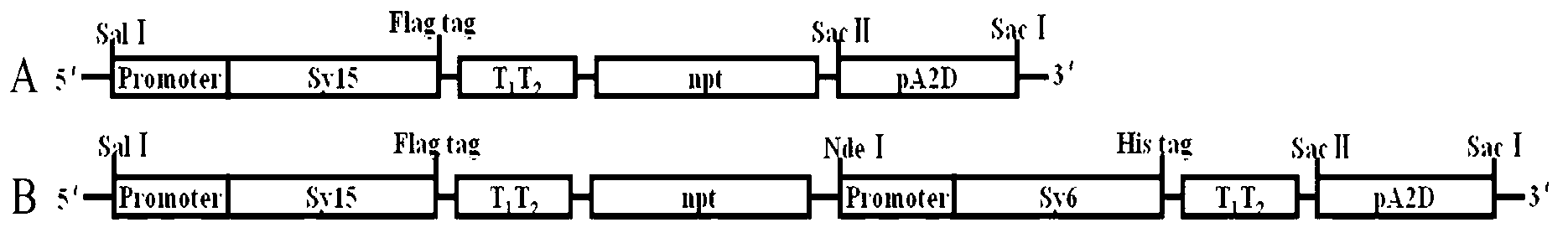
The invention particularly relates to synechocystis efficient double homologous recombinant vector as well as a construction method and the application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the synechocystis efficient double homologous recombinant vector is shown as SEQ ID NO.8 or SEQ ID NO.9. The invention also discloses the construction method and the application of the synechocystis efficient double homologous recombinant vector. The synechocystis efficient double homologous recombinant vector expresses synechocystis PCC6803Delta 15, Delta 15 and Delta 6 fatty acid desaturase gene in synechocystis PCC6803, and can obviously increase the content of therapic acid in synechocystis.
Owner:山东省农业科学院高新技术研究中心
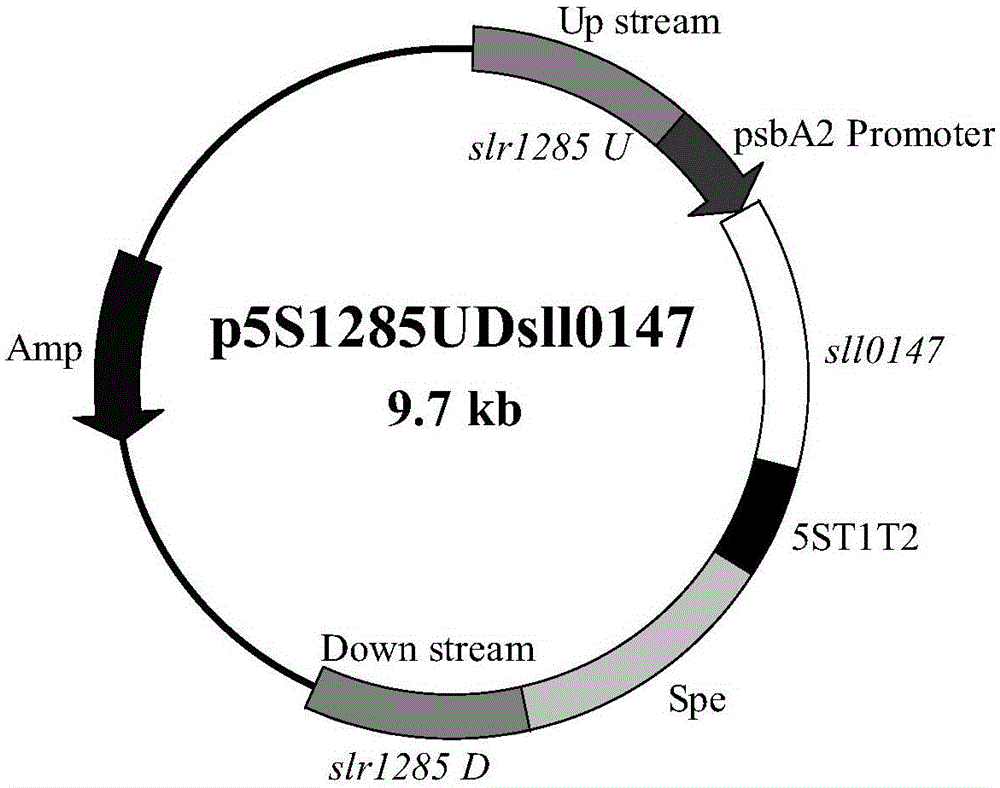
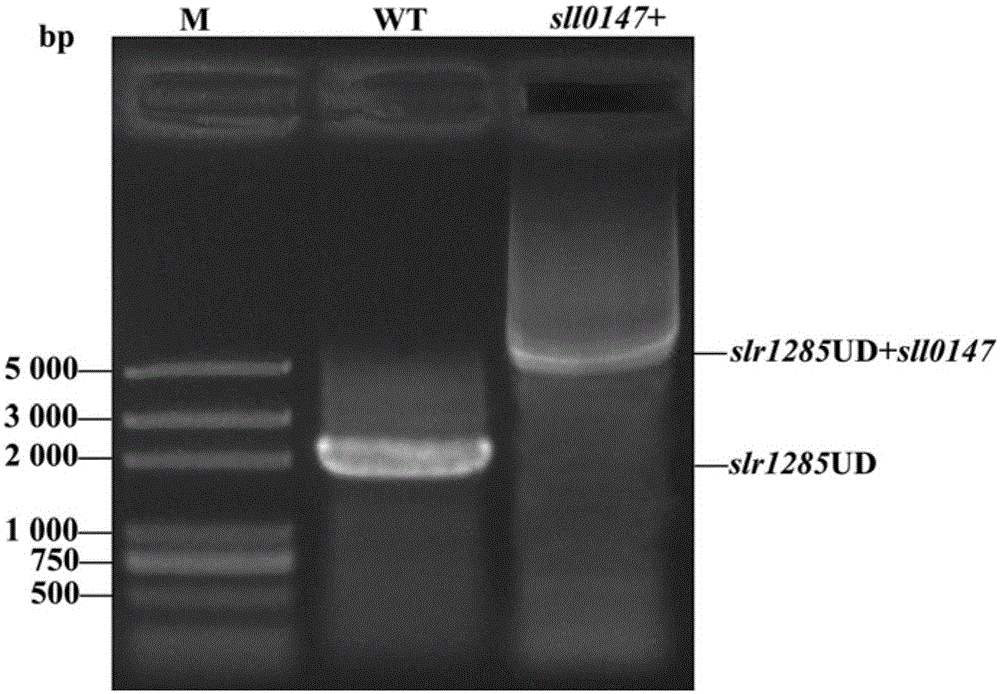
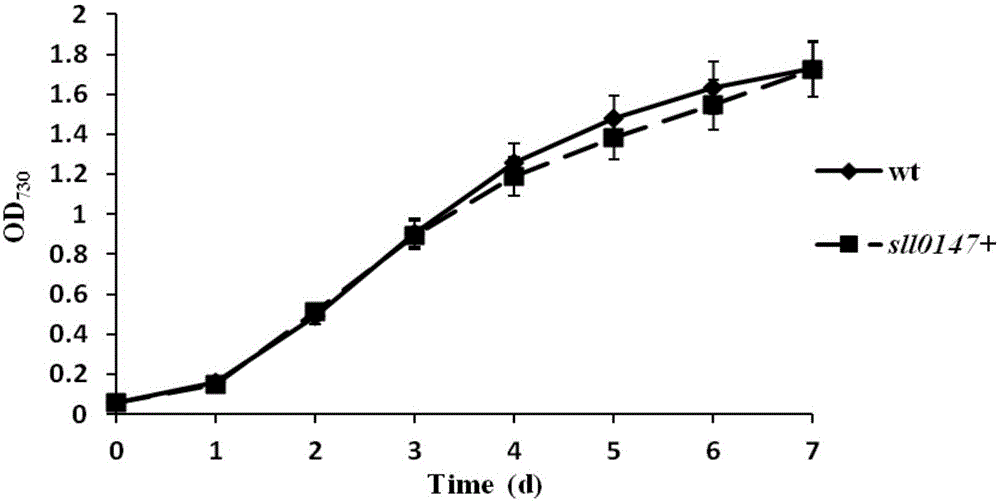
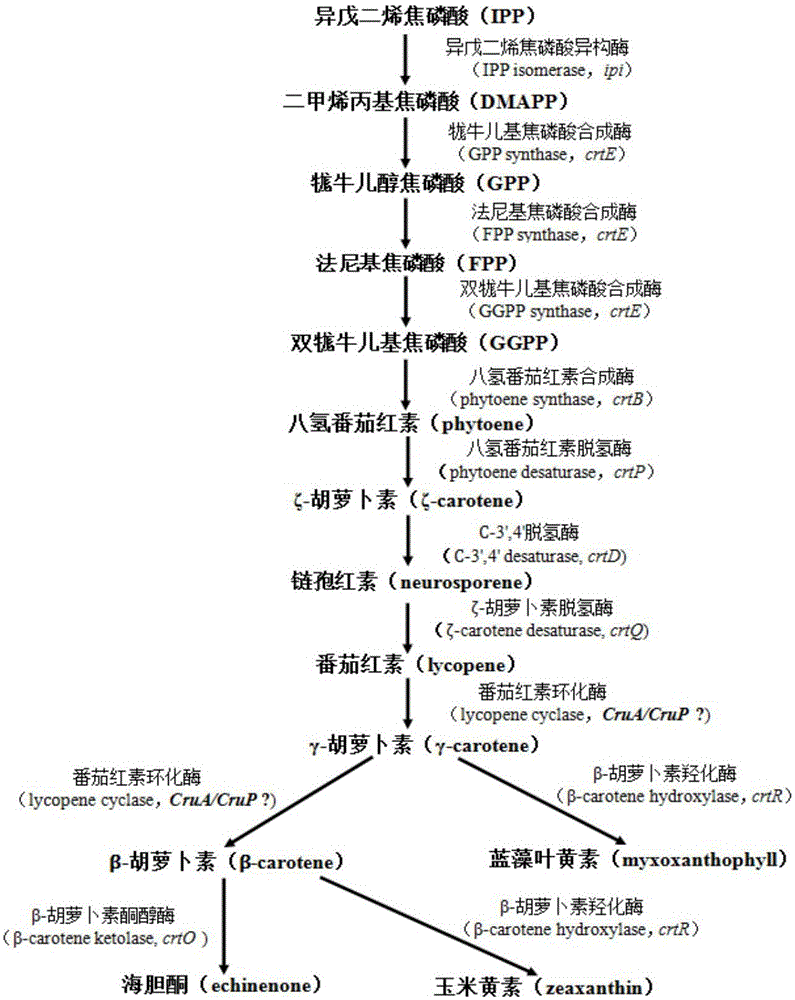
Application of sll0147 gene in synthesizing synechocystis carotenoids
ActiveCN105087604AIncrease contentReduce contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBeta-CaroteneNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to an application of a sll0147 gene in synthesizing synechocystis carotenoids, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the sll0147 gene in the application is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. For the first time, the invention discloses the important effect of the sll0147 gene of synechocystis PCC6803 in synthetising carotenoids; by increasing the expression of the sll0147 gene in the synechocystis PCC 6803 through an overexpression method by the applicant, the percentage composition of the carotenoid component in a mutant strain is obviously changed, wherein the content of myxoxanthophyll is increased by 47.4%, the content of zeaxanthine is increased by 93.8%, while the content of echinenone is reduced by 60.9%, and the content of beta-carotene is reduced by 15.9%.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
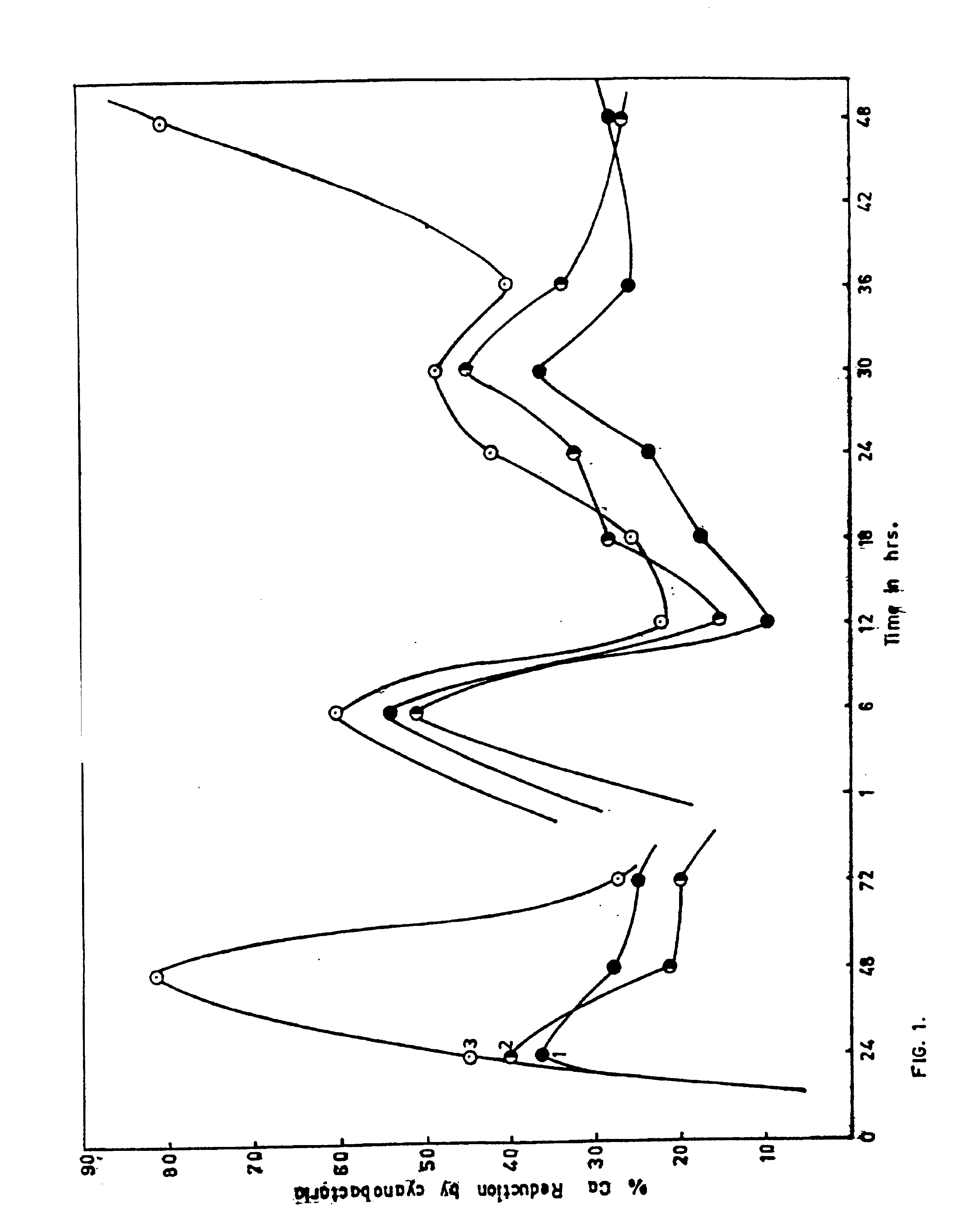
Process for the removal of calcium ions from the brine by marine cyanobacteria
InactiveUS6812011B2Economical simplePractical and convenientFungiBacteriaMicrobiologySynechocystis sp.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
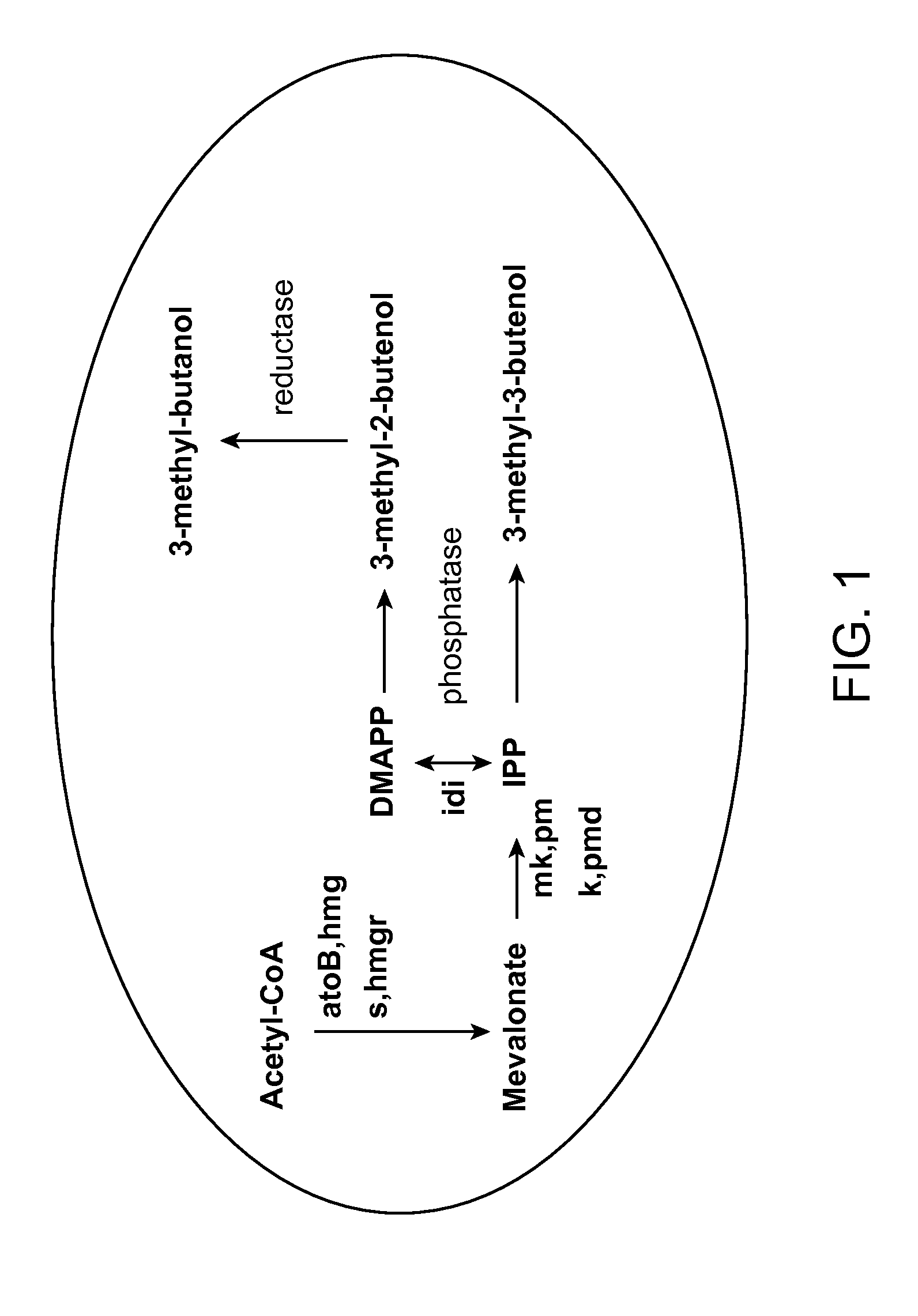
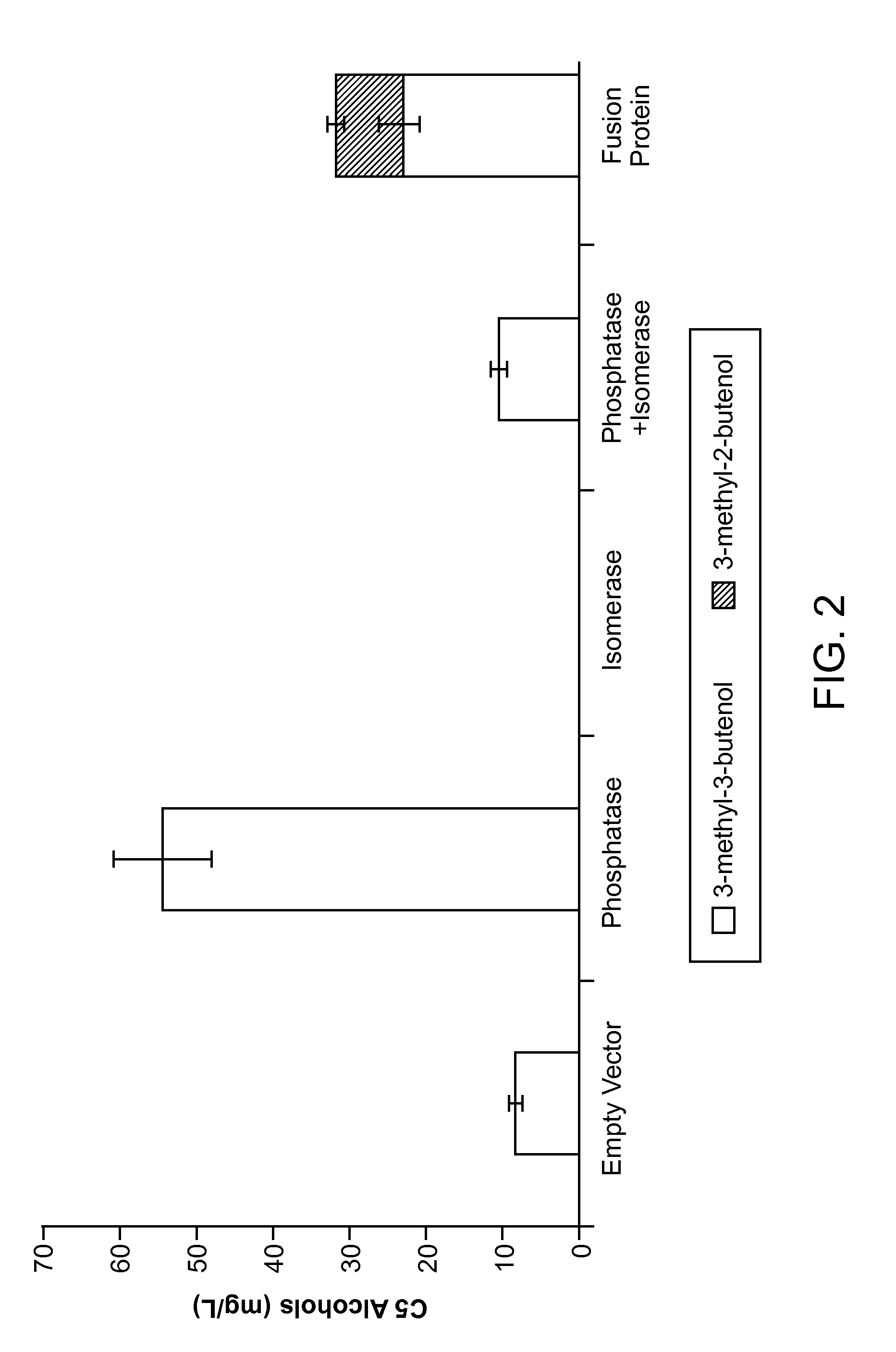
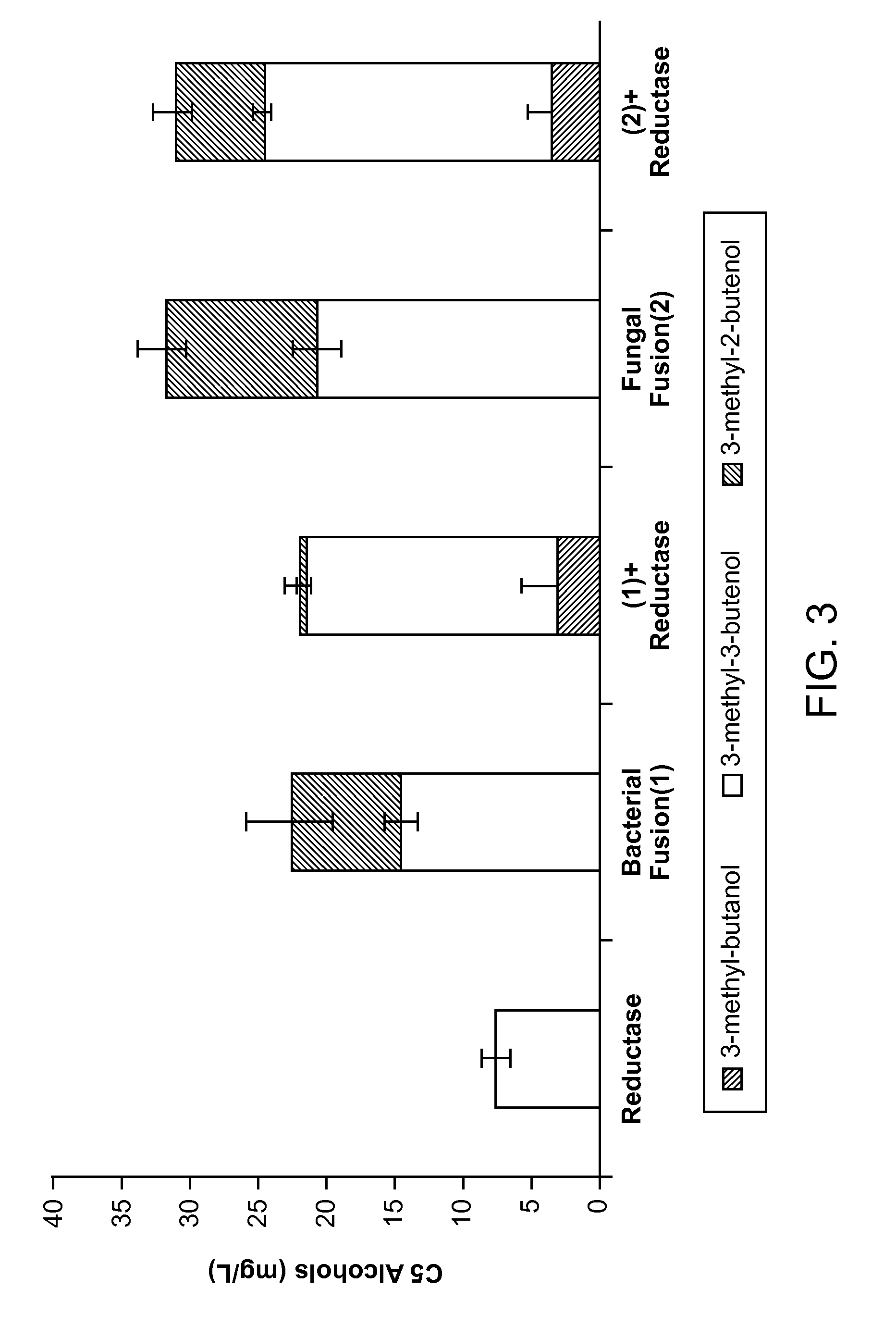
Methods for increasing production of 3-methyl-2-butenol using fusion proteins
The invention relates, in part, to nucleic acid constructs, genetically modified host cells and methods employing such constructs and host cells to increase the production of 3-methyl-2-butenol from IPP. Thus, in some aspects, the invention provides a genetically modified host cell transformed with a nucleic acid construct encoding a fusion protein comprising a phosphatase capable of catalyzing the dephosphorylation of dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) linked to an IPP isomerase capable of converting IPP to DMAPP, wherein the nucleic acid construct is operably linked to a promoter. In some embodiments, the genetically modified host cell 5 further comprises a nucleic acid encoding a reductase that is capable of converting 3-methyl-2-butenol to 3-methyl-butanol. In some embodiments, the reductase is encoded by a nucleic acid construct introduced into the cell. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type I isomerase. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is a Type II isomerase. In some embodiments, the host cell is selected from a group of taxonimcal classes consisting of 20 Escherichia, Enterobacter, Azotobacter, Erwinia, Bacillus, Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia, Shigella, Rhizobia, Vitreoscilla, Synechococcus, Synechocystis, and Paracoccus taxonomical classes. In some embodiments, the host cell is an Escherichia coli cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is a fungal cell, such as a yeast cell. In some embodiments, the yeast cell is a Saccharomyces sp. cell. In some embodiments, the host cell is an algal, insect or mammalian cell line. In some embodiments, the phosphatase is nudB from E. coli. In some embodiments, the IPP isomerase is encoded by an idi gene from E. coli or idil gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
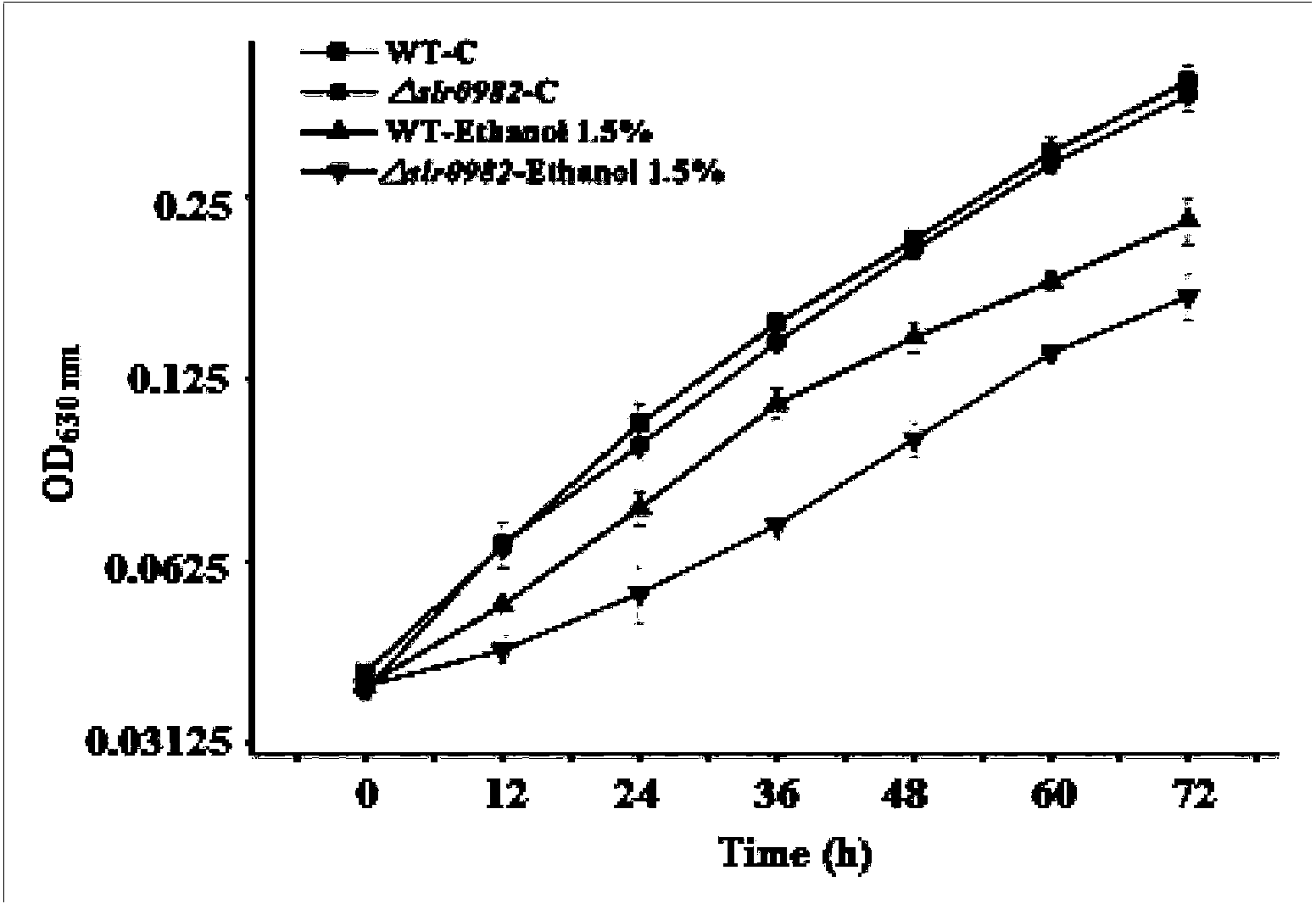
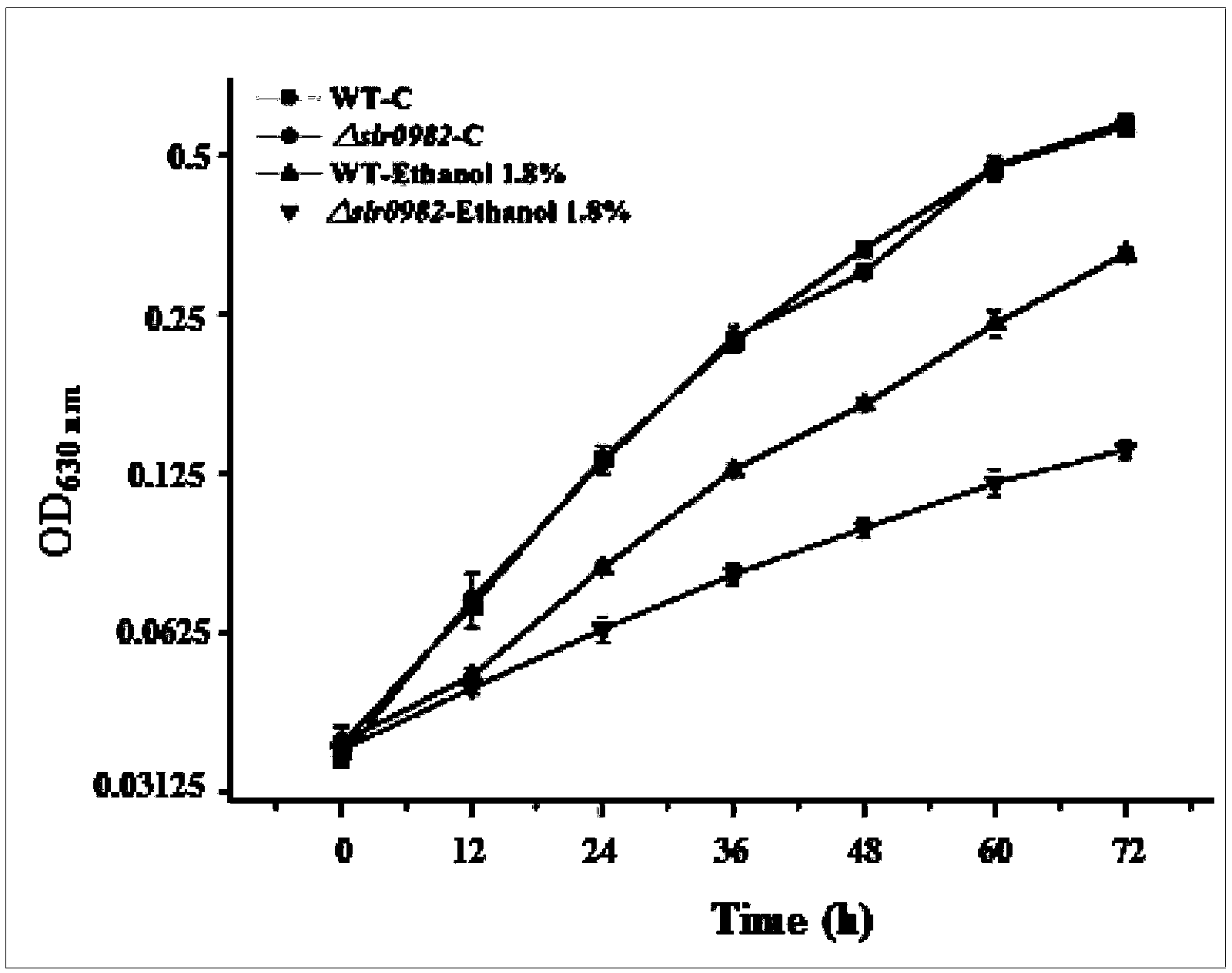
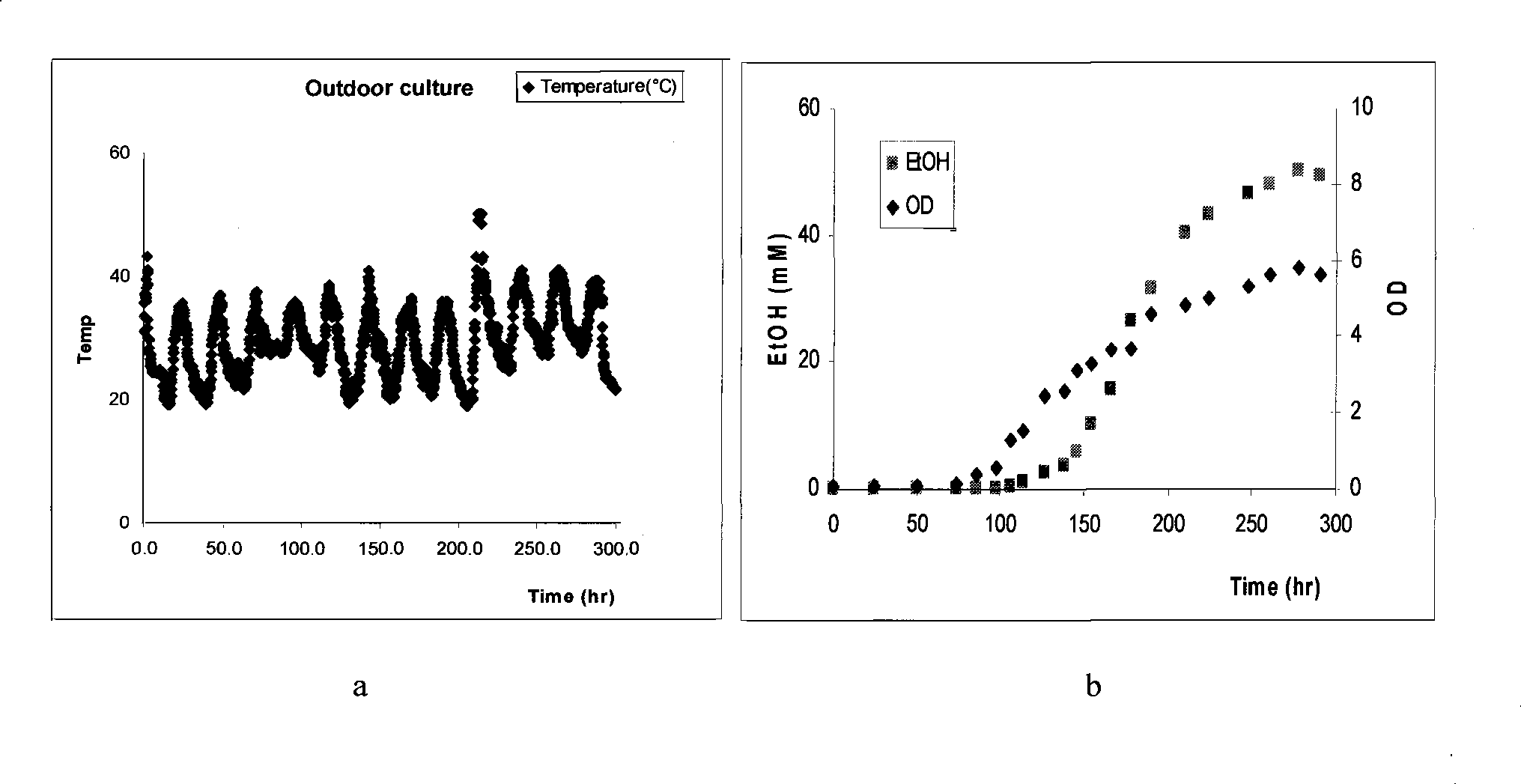
Ethanol-tolerant related gene slr0982 of synechocystis 6803 and applications of gene
InactiveCN104293803AHigh ethanol toleranceImprove toleranceBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses an ethanol-tolerant related gene slr0982 of synechocystis 6803and applications of the gene. The gene is shown in SEQ ID No.5. The gene is applied to construction of engineering bacteria for fermenting to produce ethanol. The ethanol-tolerant related gene is identified through constructing mutant strain slr0982 of synechocystis 6803, which has important theoretical and practical significance for improvement of microorganism ethanol tolerance and plays an important role in the fermentation of microorganism; the gene has a wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for improving ethanol tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803 and application
ActiveCN106399114APromote growthImprove toleranceUnicellular algaeBiofuelsMicroorganismEthanol stress
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving ammonium salt tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803 and application
ActiveCN109022285APromote growthImprove toleranceUnicellular algaeStable introduction of DNAMicroorganismHigh concentration
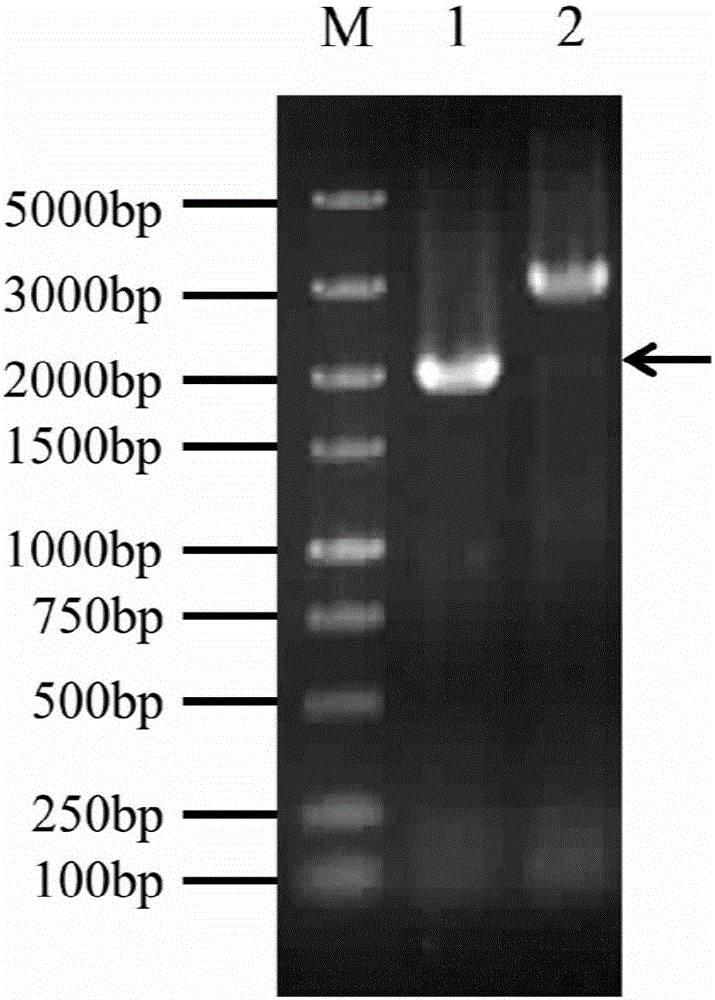
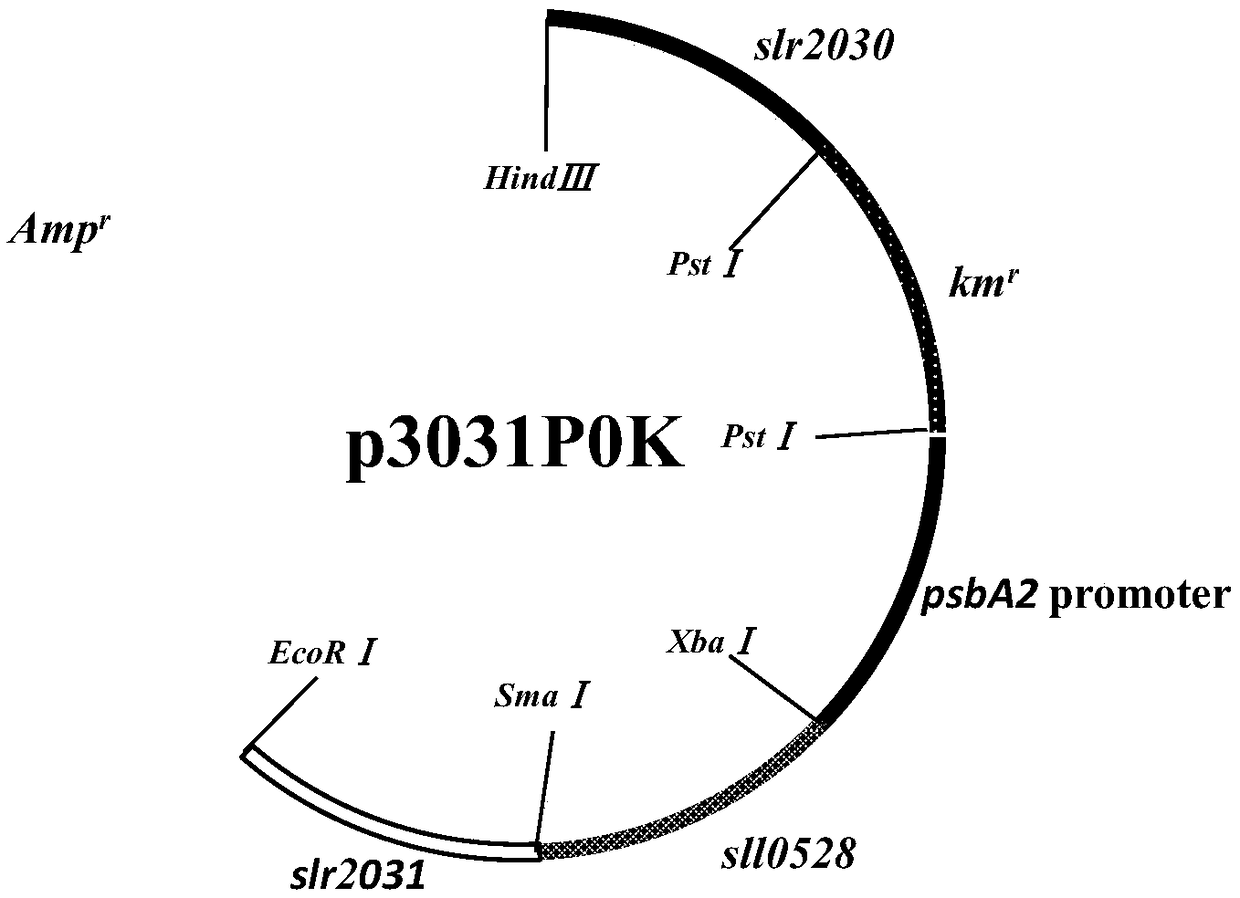
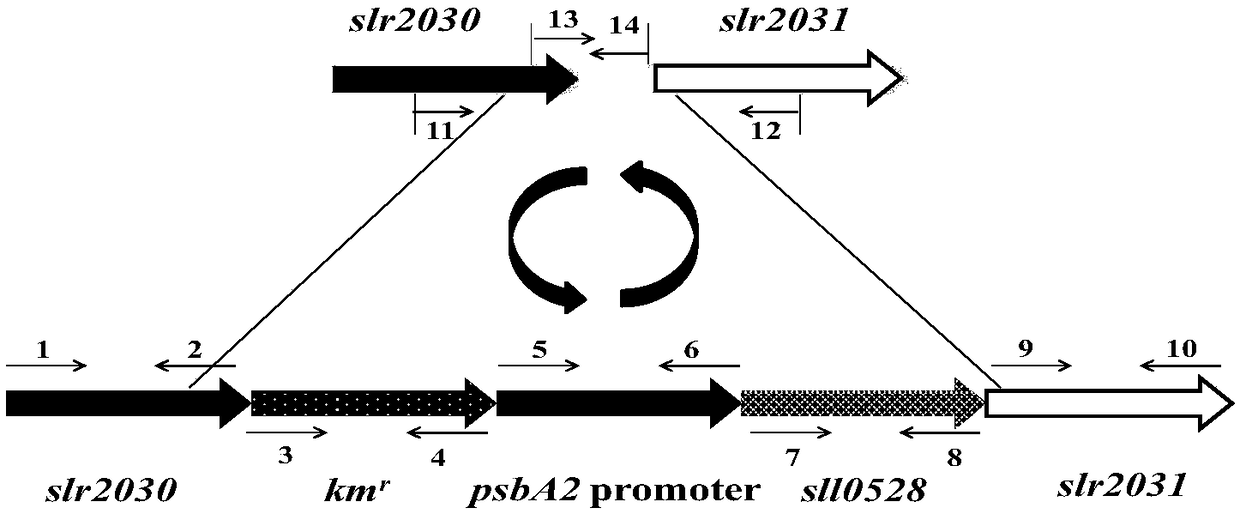
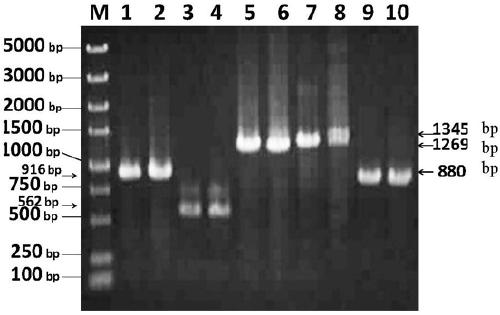
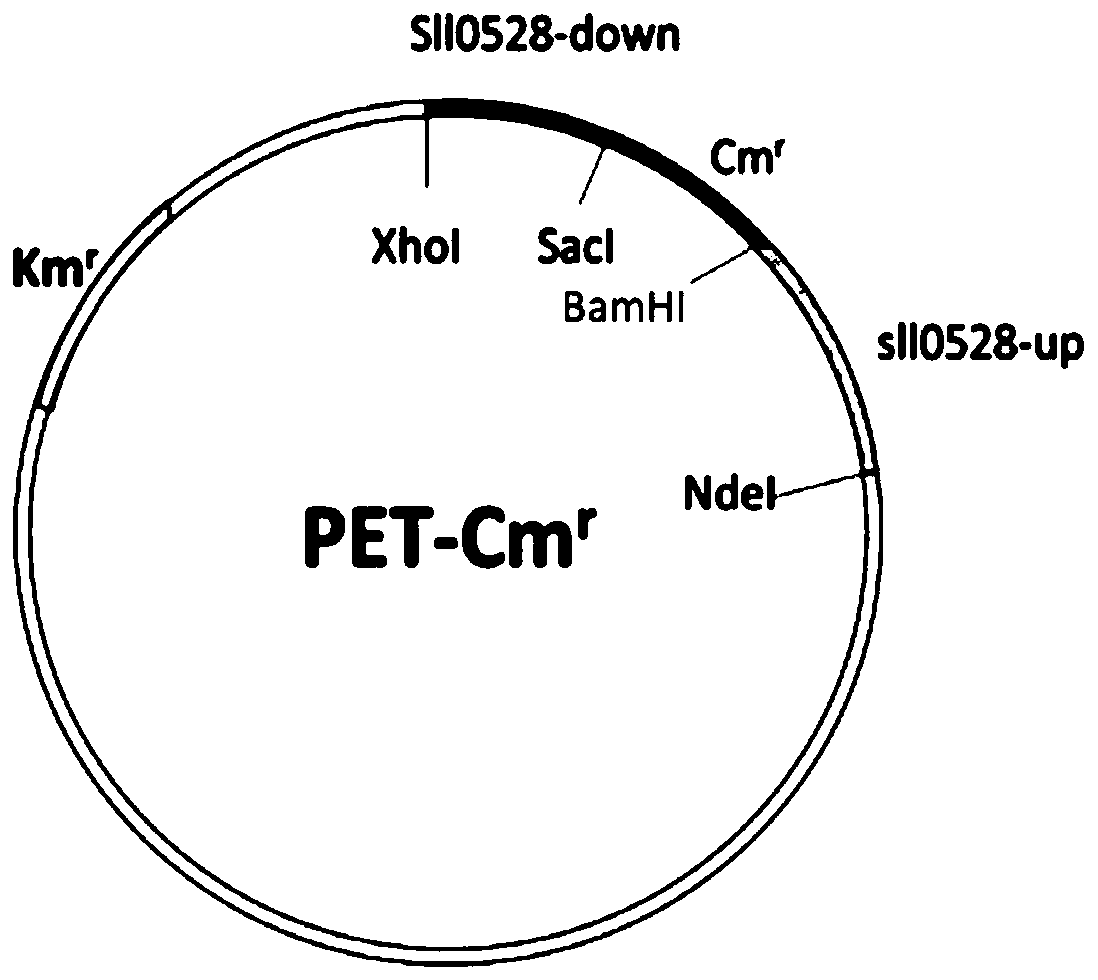
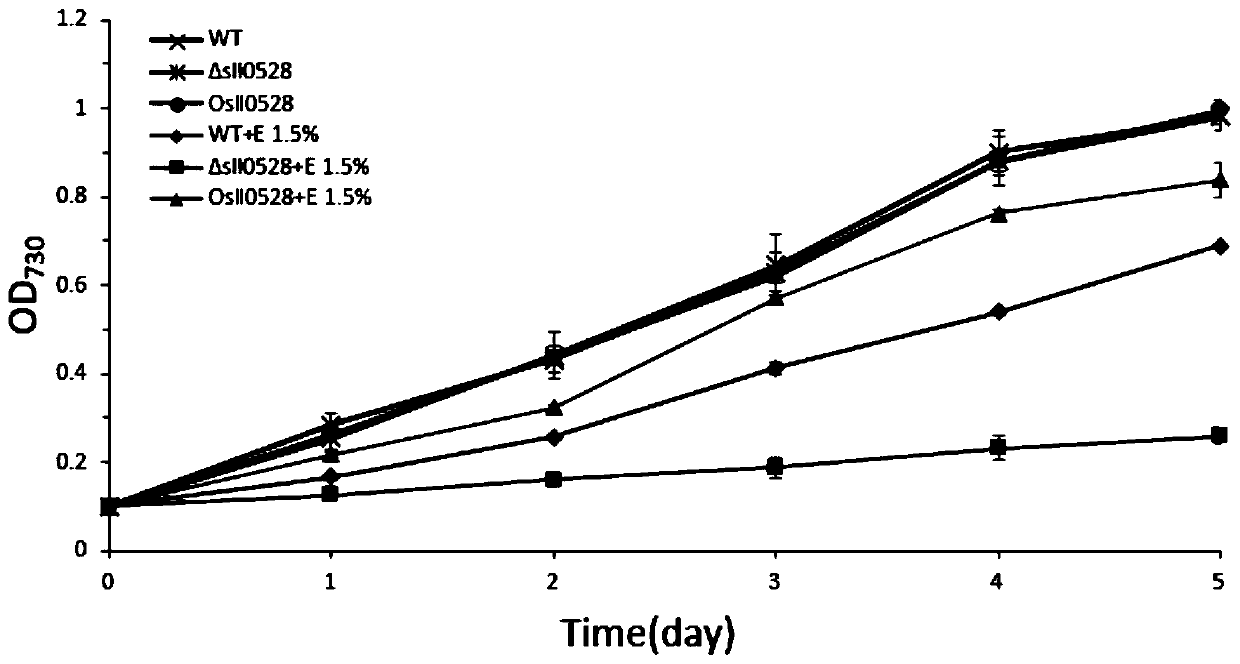
Belonging to the field of industrial microorganisms, the invention discloses a method for improving the ammonium salt tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803 and application. By means of the method, a synechocystis PCC6803 overexpression strain OE0528 with significantly improved ammonium salt tolerance can be obtained. The algal strain can be used for construction of a high concentration ammonium saltwastewater purified genetic engineering strain. By overexpression of the sll0528 gene in synechocystis PCC6803, the synechocystis PCC6803 overexpression strain OE0528 has significantly improved ammonium salt tolerance. Under 180-210mM ammonium salt stress, the growth status of the overexpression algal strain is obviously superior that of the wild type. The ammonium salt tolerant overexpression algal strain obtained by the invention has important theoretical and practical significance for further construction and utilization of genetic engineering bacteria of high concentration ammonium salt, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Cyanobacterial nucleic acid fragments encoding proteins useful for controlling plant traits via nuclear or plastome transformation
InactiveUS7285701B2Improve methodEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
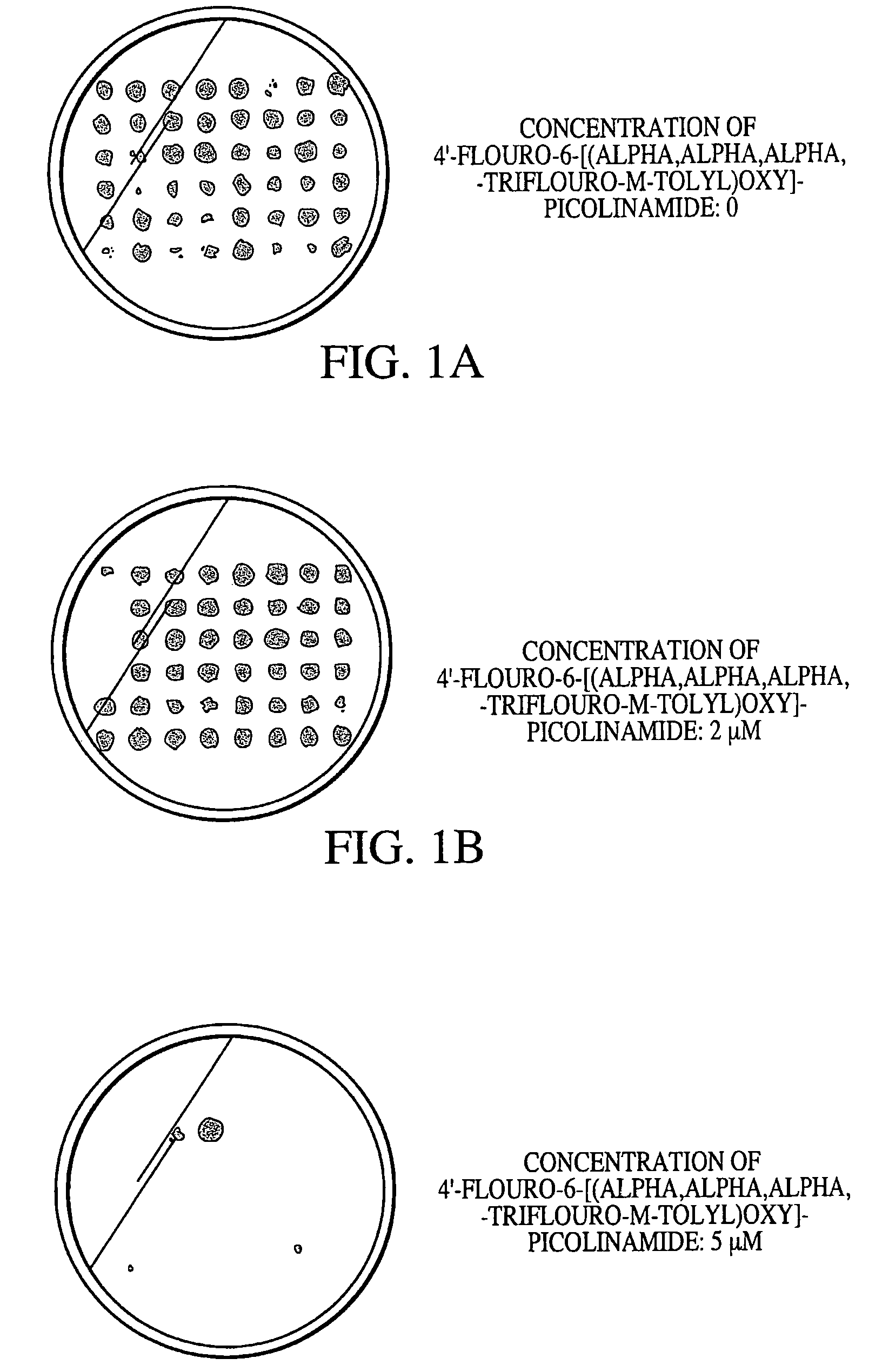
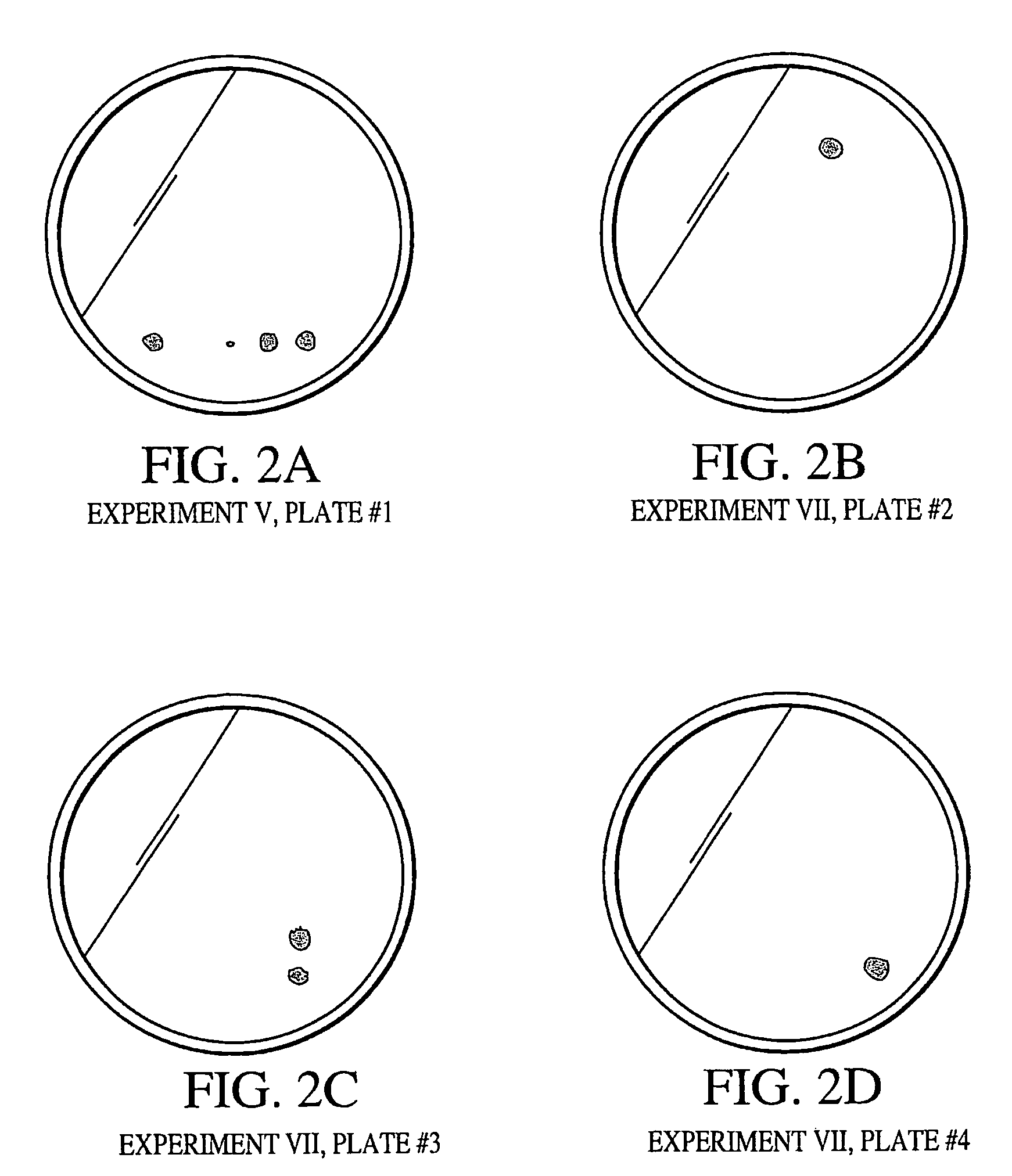
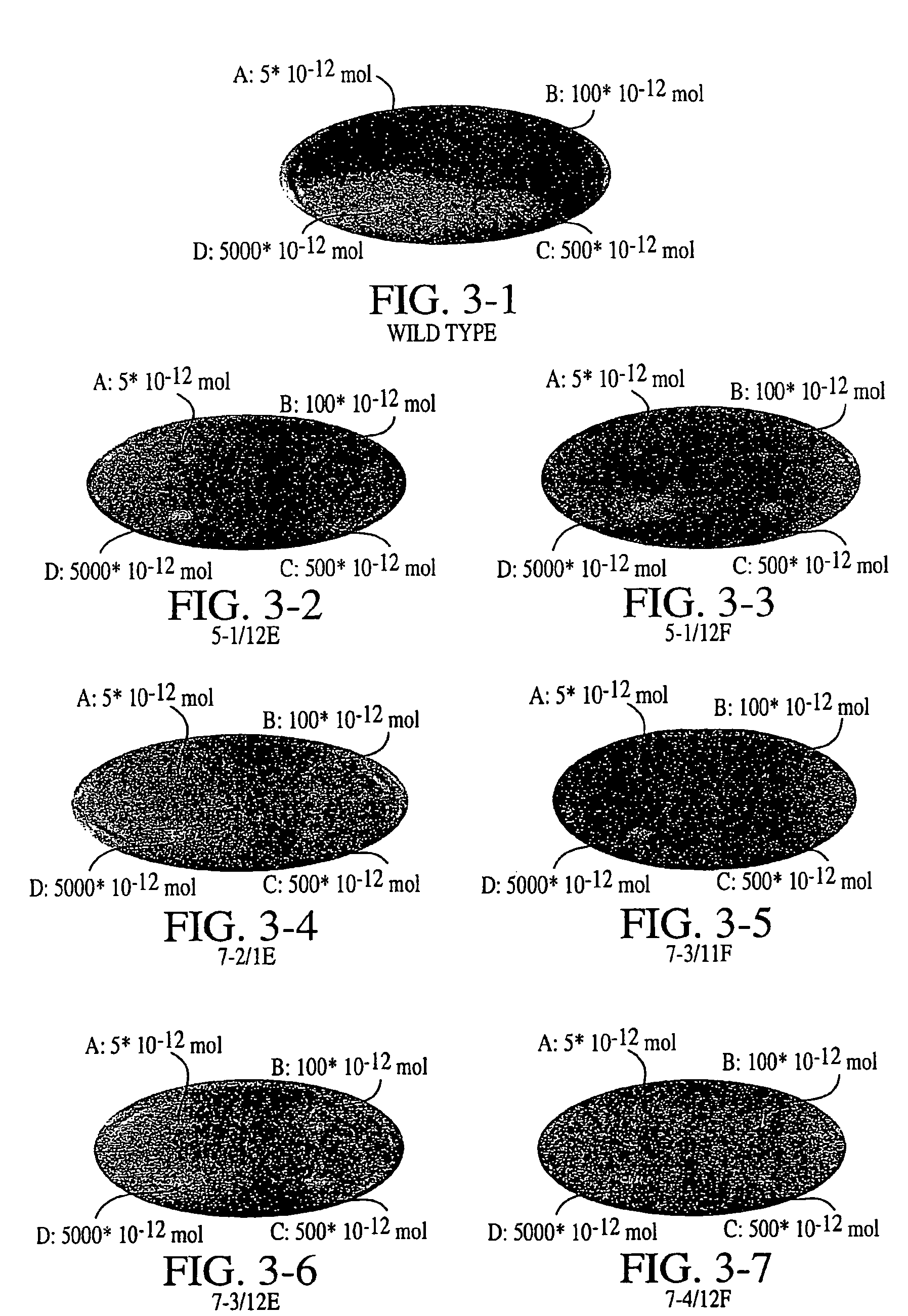
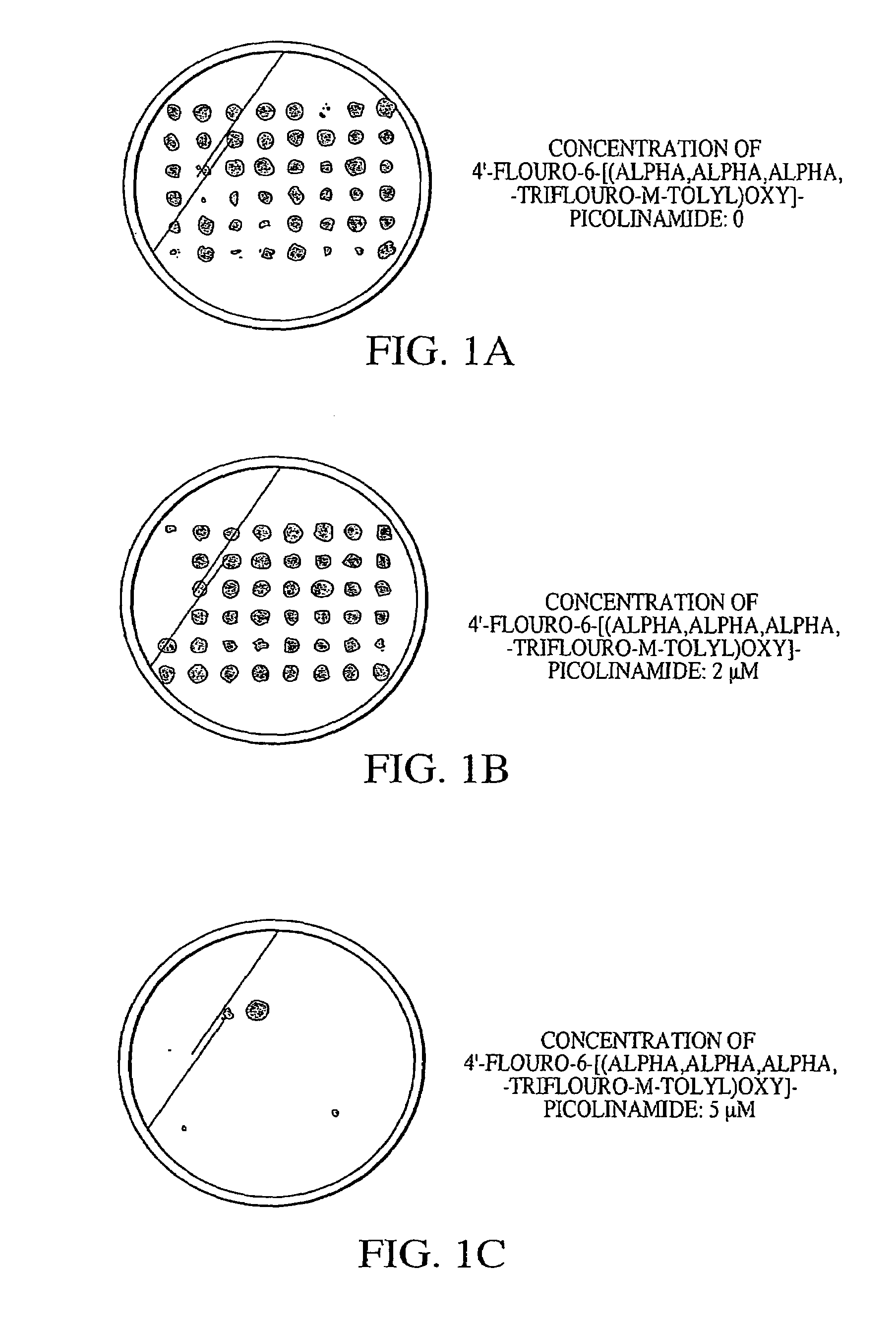
This invention provides cyanobacteria as an alternative source of ahas and pds genes for plant transformations and for selectable markers. In particular, it provides for cyanobacteria, for example, Synechocystis, as a source of genes encoding herbicide insensitive proteins, and elements of genes for control of expression in plastids. Nucleic acid fragments, both the acetolactate synthase (ahas) large subunit and the ahas small subunit, were found to provide herbicide resistance. Also, the present invention provides novel Synechocystis mutant phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene conferring resistance to 4′-fluoro-6[(alpha,alpha,alpha,-trifluoro-m-tolyl)oxy]-picolinamide, a bleaching herbicide. The present invention provides improvements to method involving cyanobacteria for the screening of compounds, including a new high-through-put protocol that is a rapid and cost effective way to identify target site genes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Sewage treatment apparatus with Synechocystis-Bacillus blend system and method of using same
ActiveCN106145389AMeet processing needsPromote growthBiological treatment apparatusMultistage water/sewage treatmentBacillus sp. ETSewage
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Synechocystis-6803 genetically engineered bacterium capable of producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN104789516ABacteriaMicroorganism based processes3-Hydroxypropionic acidMalonyl-coenzyme A reductase
The invention discloses a synechocystis-6803 genetically engineered bacterium capable of producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid, and a construction method and application thereof. The construction method is as follows: a malonyl coenzyme A reductase gene in orange chloroflexus is cloned into synechocystis 6803; and acetylcoenzyme A carboxylase, biotin acylase and an NAD(P) transhydrogenase gene in the synechocystis 6803 are expressed. The synechocystis 6803 is transformed through a synthetic biology method to obtain the synechocystis-6803 genetically engineered bacterium capable of producing the 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The experiments prove that the final yield of the 3-HP (3-hydroxypropionic acid) of the genetically engineered bacterium is up to 837.18mg / L, which is of great theoretical and practical significances for the production of the 3-HP through photosynthetic microorganisms.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
A method for enzymatic protein cyclization
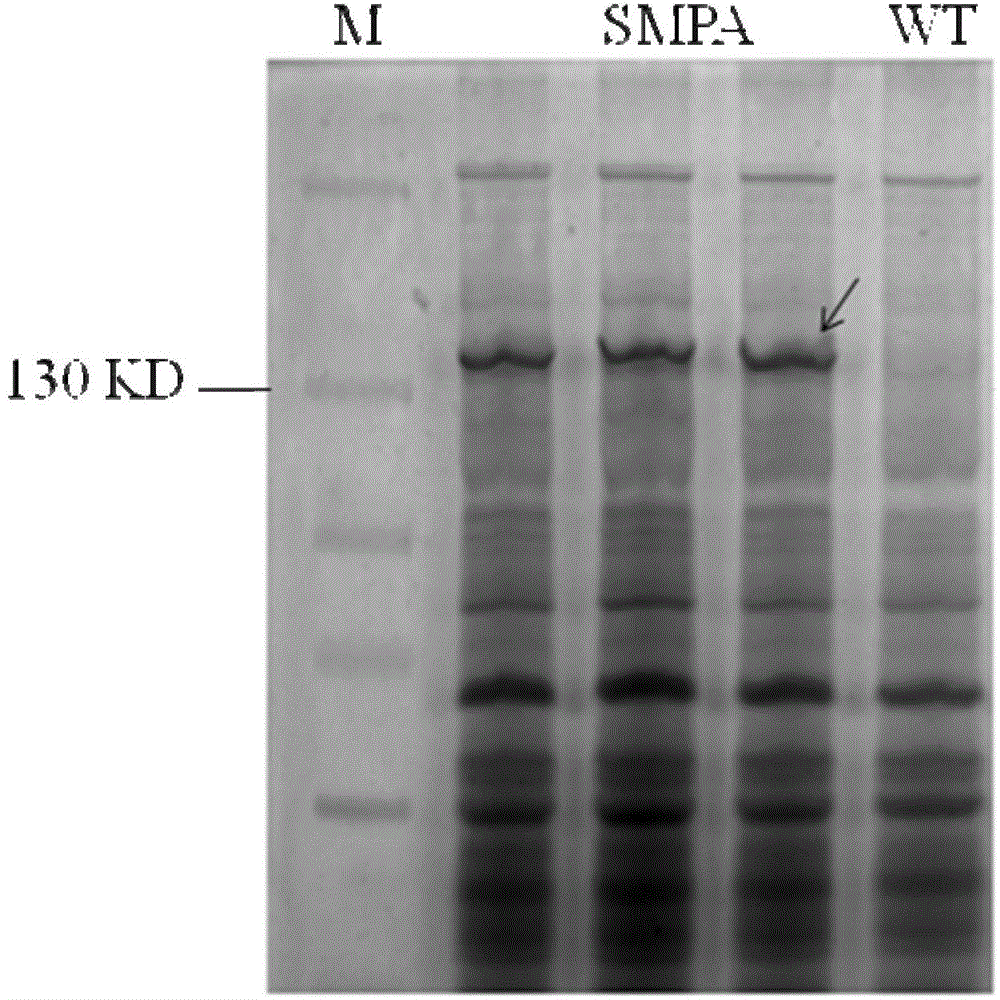
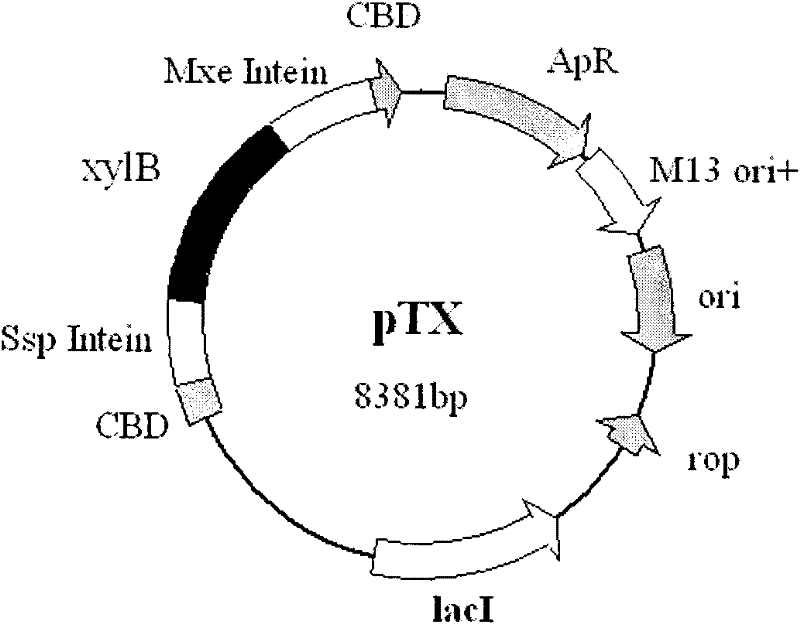
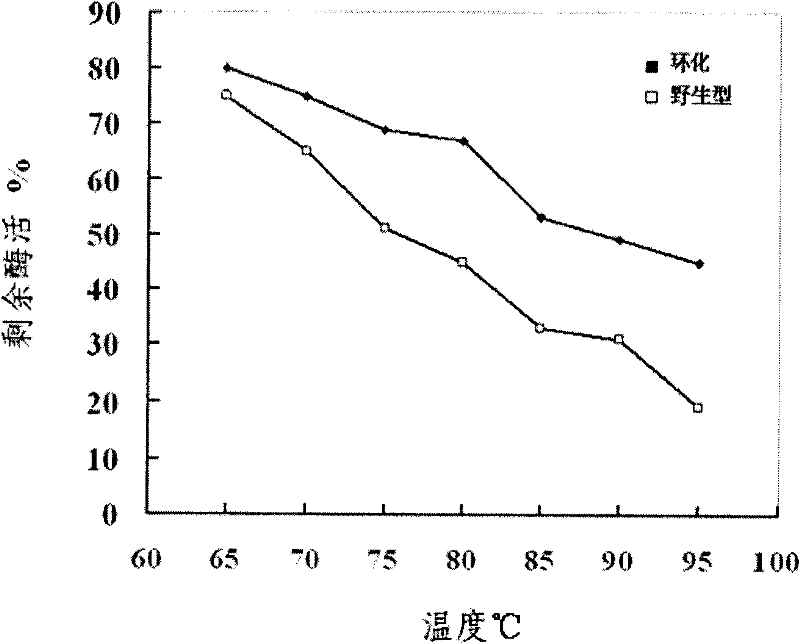
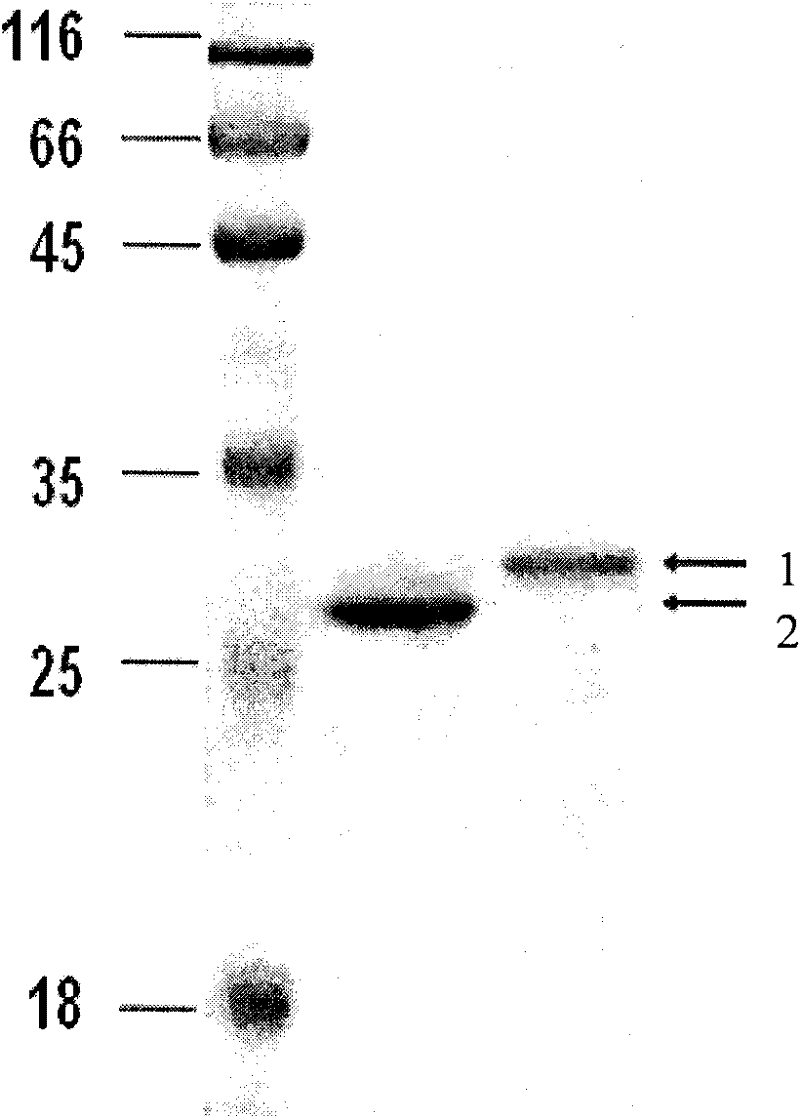
The invention relates to a method for cyclizing an enzyme protein. The cyclase protein is mediated by Synechocystis Ssp DnaB intein and Mycobacterium xenopus Mxe GyrA intein, and the N and C of the enzyme protein are cyclized by natural peptide bonds. Link both ends. The present invention obtains the cyclized xylanase with enhanced thermostability by the above method.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Biological mothballing system suitable for synechococcus elongatus, and construction method and application of biological mothballing system
ActiveCN110438053AAvoid Biosafety ConcernsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhylum CyanobacteriaSynechococcus elongatus
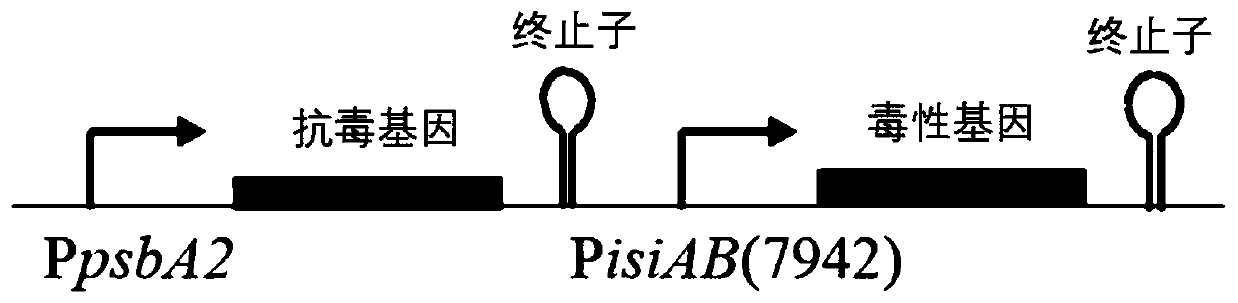
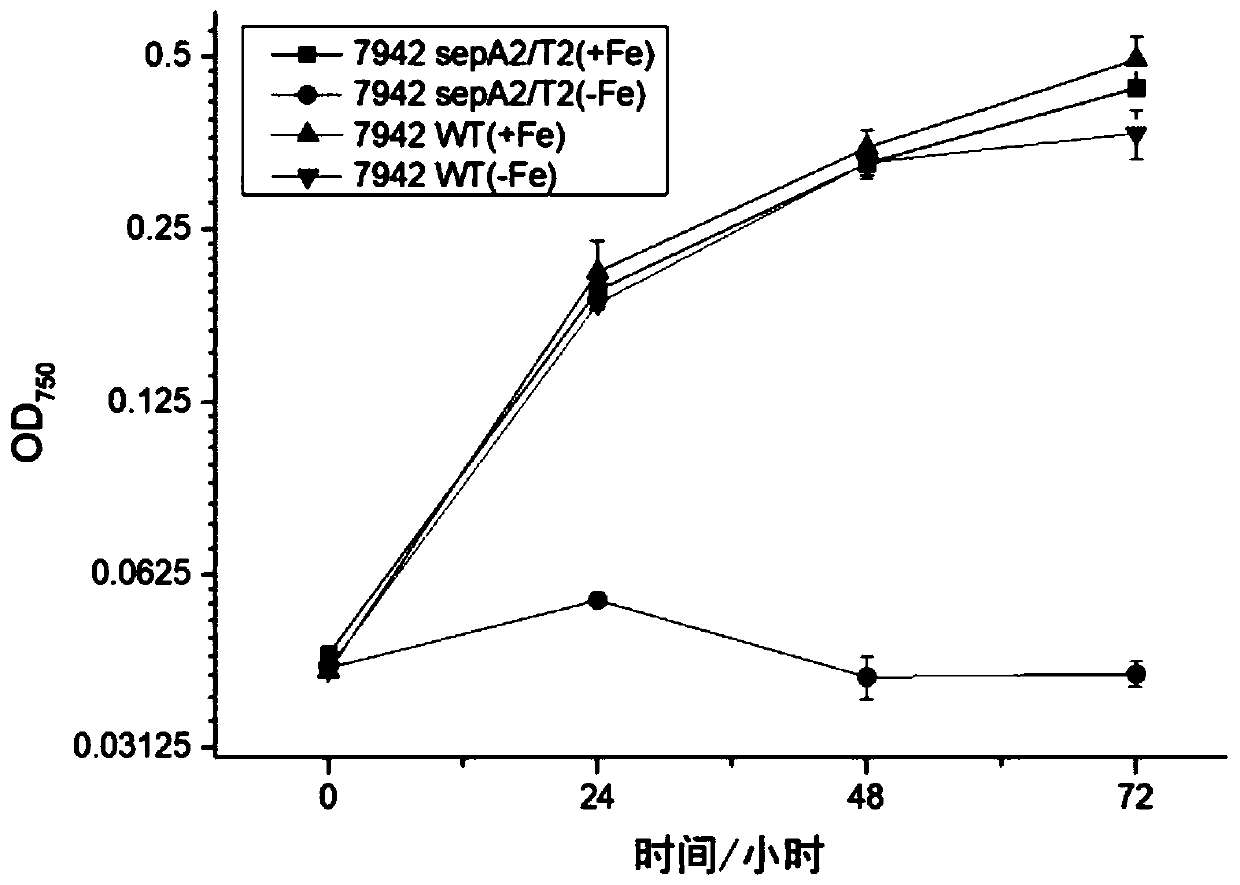
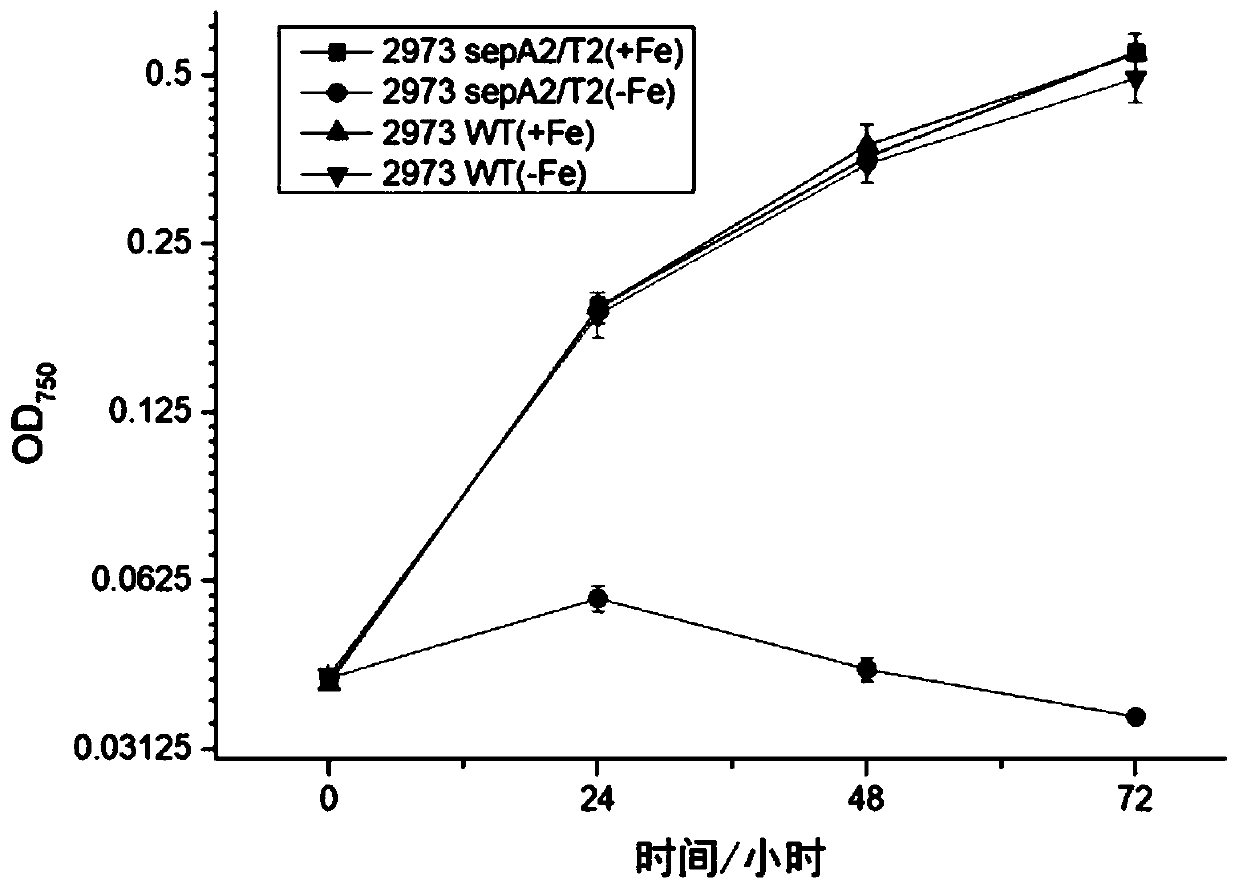
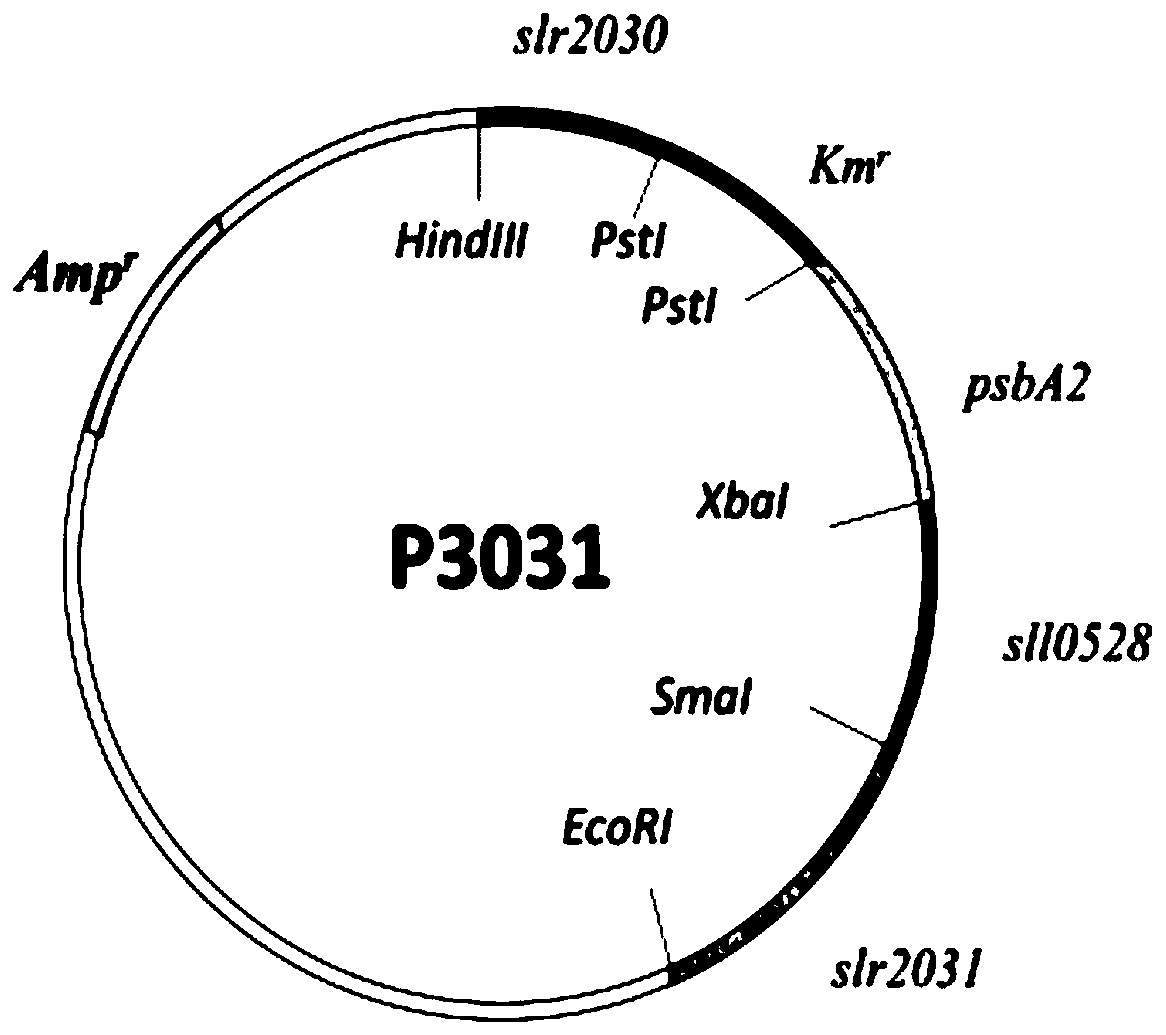
The invention discloses a biological mothballing system suitable for synechococcus elongatus, and a construction method and application of the biological mothballing system. The construction method comprises the steps that a virulent gene sepT2, an antitoxic gene sepA2 and an iron-deficiency inducible promoter PisiAB are obtained from the synechococcus elongatus 7942, and a promoter PpsbA2 is obtained from synechocystis 6803; a terminator Trbcl is obtained from integrative plasmid pBA3031 through amplification; pBR322 is taken as a carrier, the virulent gene sepT2 is expressed with the iron-deficiency inducible promoter PisiAB, and the terminator Trbcl is used for terminating transcription; and the antitoxic gene sepA2 is expressed with the promoter PpsbA2, and plasmid is constructed and transferred into the synechococcus elongatus. According to the system, the synechococcus elongatus grows normally under the non-inducing situation and rapidly dies after being induced. The important theoretical and practical significance for development and optimization of the biological mothballing system of the synechococcus elongatus is achieved, and reference is also provided for solving the bio-safety problem of other cyanobacteria.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Application of sll0528 genes to improvement of ethanol tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803
The invention discloses an application of sll0528 genes to improvement of ethanol tolerance of synechocystis PCC6803, and belongs to the field of industrial microorganisms. Through a homologous reorganization method, the sll0528 genes in the synechocystis PCC6803 are knocked out and overexpressed, so that a synechocystis PCC6803 algae strain Osll0528 with notable improvement of ethanol tolerance is obtained. In a BG11 culture medium of ethanol of different concentrations (1.5%, 2.0%, 2.5% and 3.0%v / v), the growth state of the algae strain is obviously higher than that of wild algae strains. The obtained algae strains being tolerant to ethanol have important theory and actual significance in genetic engineering bacteria for producing ethanol as fuel, and have broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Synechocystis PCC6803 alga for achieving remarkable improvement of tolerance to ethyl alcohol and construction method thereof
ActiveCN106086055APromote growthHigh ethanol toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAlcohol
The invention discloses synechocystis PCC6803 alga for achieving remarkable improvement of tolerance to ethyl alcohol and a construction method thereof and belongs to the field of industrial microorganisms. Sll0687 genes in synechocystis PCC6803 are knocked out through a homologous recombination method, and the synechocystis PCC6803 alga ISm5 for remarkably improving tolerance to ethyl alcohol is obtained. Under stress of 1.5% (v / v) ethyl alcohol, the growth state of the alga is obviously superior to that of wild alga. The obtained ethyl-alcohol-tolerant alga has important theoretical and practical significance for constructing genetically engineered bacteria for producing fuel ethanol and has wide application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Cyanobacterial nucleic acid fragments encoding proteins useful for controlling plant traits via nuclear or plastome transformation
InactiveUS7083967B1Easy to identifyImprove methodBacteriaTransferasesPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
This invention provides an alternative source of ahas and pds nucleic acids for plant transformation and selection. In particular, the invention provides ahas and pds nucleic acids from cyanobacteria, for example, Synechocystis, and expression elements of these genes for control of expression in plastids. The invention further provides nucleic acids encoding the acetolactate synthase (ahas) large subunit and the ahas small subunit which were found to provide herbicide resistance to plants. The present invention also provides a novel Synechocystis mutant phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene conferring resistance to 4′-fluoro-6-[(alpha, alpha, alpha,-trfluoro-m-tolyl)oxy]-picolinamide, a bleaching herbicide. The present invention provides improved methods involving cyanobacteria for the screening of compounds, including a new high throughput protocol that is a rapid and cost effective way to identify target site genes.
Owner:BASF CORP
Laccase gene slr1573 derived from synechocystis and application thereof in dye decolorization
PendingCN110295182AEfficient decolorizationEfficient catalytic decolorizationWater contaminantsMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMalachite green
The invention relates to a laccase gene slr1573 derived from synechocystis 6803 and application thereof in dye decolorization and belongs to the technical field of biology. The DNA sequence of the laccase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and an amino acid sequence of an encoded protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. A prokaryotic expression vector of the synechocystis laccase gene slr1573 is constructed, an escherichia coli expression strain BL21 (DE3) is transformed, the strain expressing the recombinant Slr1573 is successfully obtained, and the enzymatic property of crude recombinant laccase liquid is detected. The obtained slr1573 laccase gene is efficiently expressed, and the recombinant laccase can efficiently catalyze decolorization of dyes such as malachite green.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
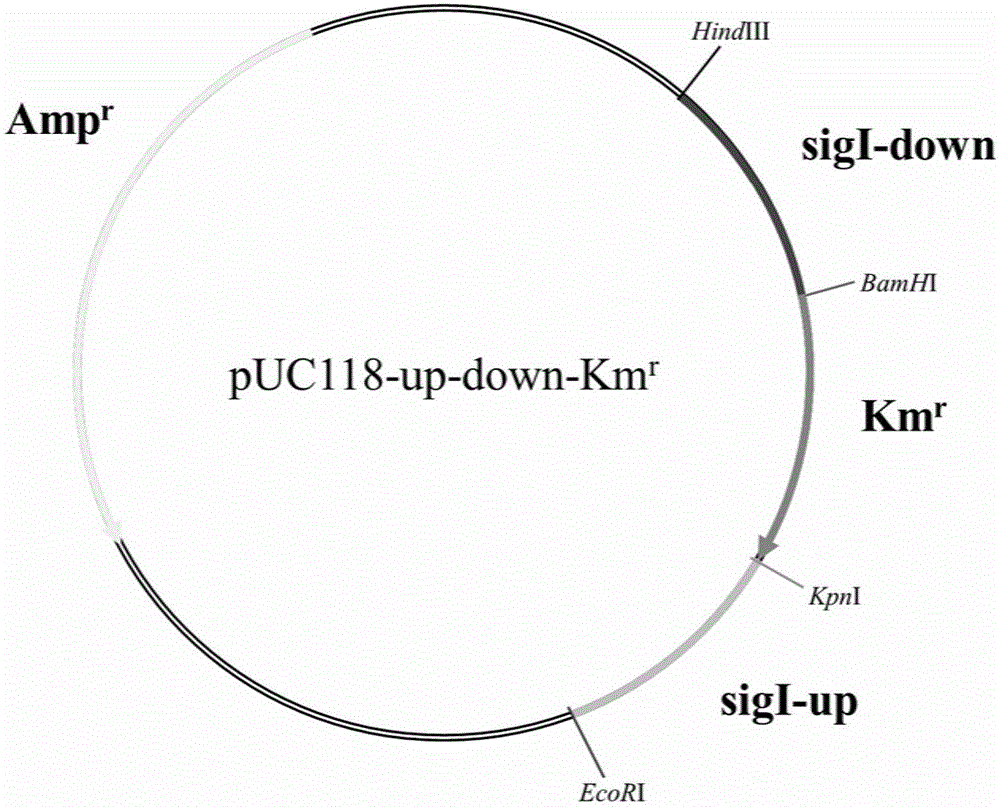
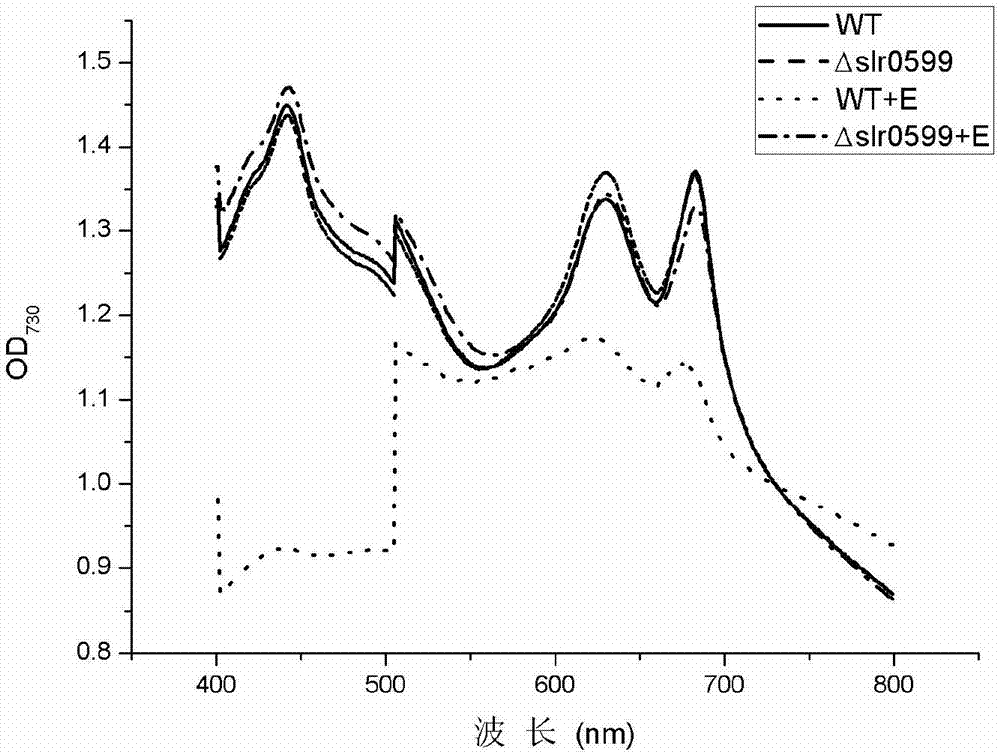
Mutant strain of synechocystis PCC6803 and application thereof
Belonging to the field of industrial microorganisms, the invention in particular relates to a synechocystis PCC6803 mutant strain with significantly improved ethanol tolerance and application thereof. The ethanol tolerance related gene is slr0599, and the base sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.7. The mutant strain PCC 6803Deltaslr0599 is preserved on August 4, 2017 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) located at No.3, 1st yard, Beichen west road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the preservation number is CGMCC14333, and the strain is named as Synechocystis sp. by taxonomy. The synechocystis mutant strain is an ethanol tolerant mutant strain, and under 1.5% (v / v) ethanol stress, the growth state of the algal strain is obviously superior to that of wild algal strains. The ethanol tolerant algal strain obtained by the invention has important application value and referential significance for production of biofuel ethanol with synechocystis, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cyanobacteria modified by gene engineering and use thereof for producing ethanol
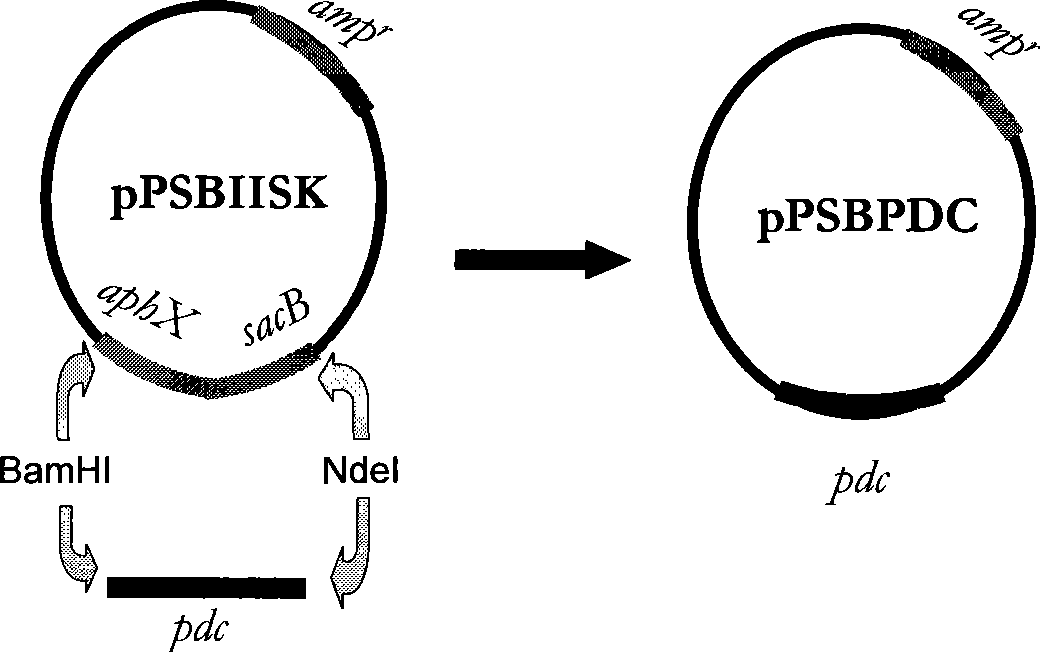
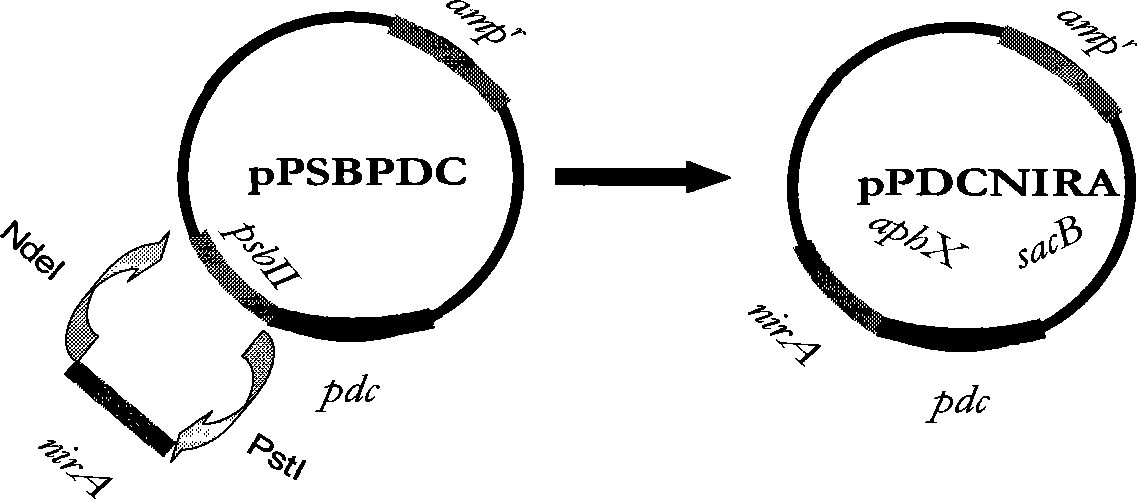
InactiveCN101372669AStrong heat and ethanol resistanceUnicellular algaeBiofuelsPhylum CyanobacteriaKetoacid decarboxylase
The invention relates to the technical field of biological energy source, in particular to a cyanobacteria synechocystis mutant, a method for screening the synechocystis mutant, a plasmid expression vector introduced with a promoter sequence which is encoded with pyruvate decarboxylase polynucleotide and / or is inducted by nitrate, the synechocystis mutant introduced with the promoter sequence which is encoded with the pyruvate decarboxylase polynucleotide and / or is inducted by the nitrate, and the application of the mutant to prepare ethanol.
Owner:旭利尔生物技术有限公司
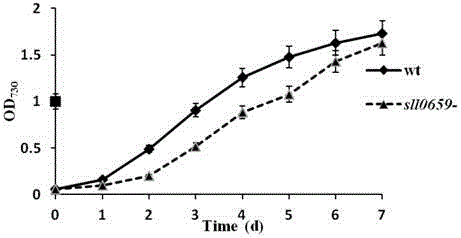
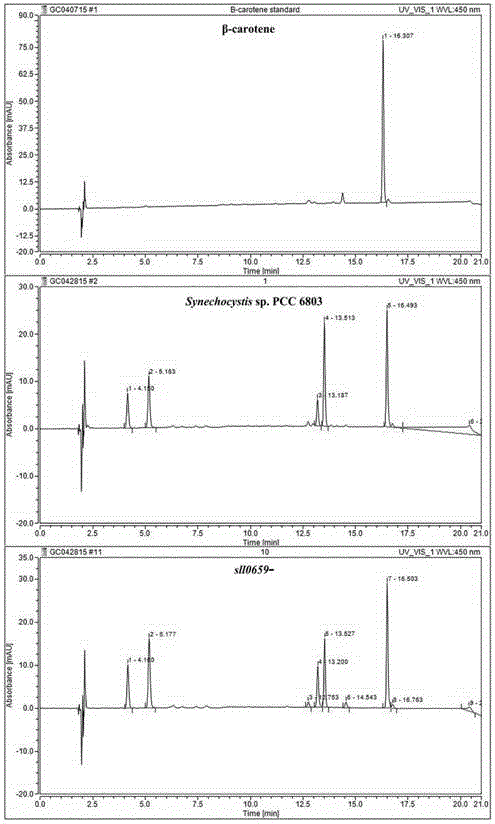
Application of sll0659 gene to synthesis of synechocystis carotenoids
ActiveCN105087627AIncrease Lutein ContentReduce percentageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBeta-CaroteneAlpha-Carotene
The invention relates to application of a sll0659 gene to synthesis of synechocystis carotenoids. The nucleotide sequence of the sll0659 gene is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The invention provides application of the sll0659 gene in synechocystis PCC6803, which has an important effect on synthesis of synechocystis PCC6803 beta-carotene. By knocking out the sll0659 gene in synechocystis PCC6803, the lutein content of the synechocystis PCC6803 is increased by 22.3%, zeaxanthin content is increased by 31.3%, the echinenone content is reduced by 34.3%, and the percentage content of beta-carotene is reduced by 1.3%. Meanwhile, HPLC detection results show when synechocystis PCC6803 involved in the invention is compared with wild synechocystis PCC6803, an obvious peak exists in the carotenoid components in the sll0659 gene knockout mutant, and the obvious peak is determined to be alpha-carotene by contrasting the obvious peak with a standard product and detecting.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
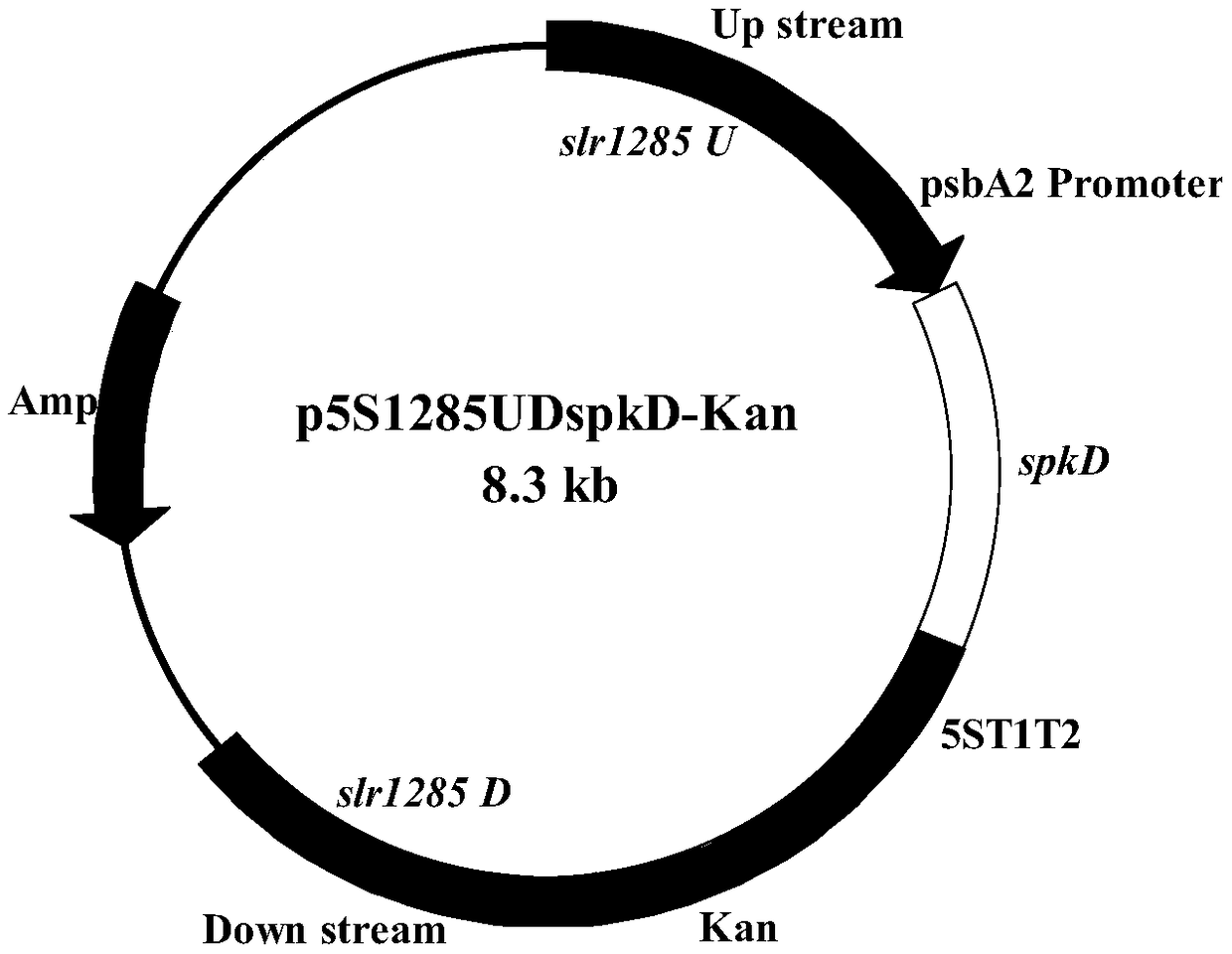
Application of gene spkD for regulating growth rate of Synechocystis
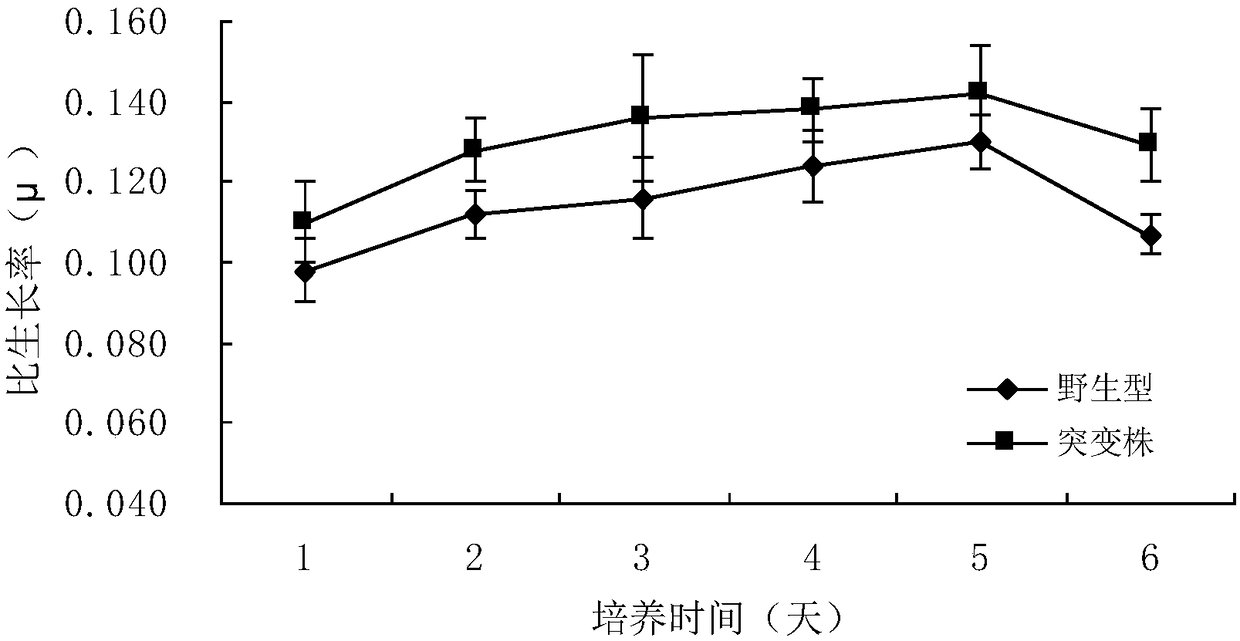
ActiveCN109234300AIncrease growth rateIncrease specific growth rateBacteria peptidesFermentationWild typeRecovery stage
The invention relates to the application of a gene spkD for regulating growth rate of Synechocystis. Application of the gene spkD regulating the growth rate of Synechocystis in increasing the growth rate of Synechocystis and / or restoring the growth rate after light stress; The nucleotide sequence of the gene spkD is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The invention discloses for the first time the important role of spkD gene of Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806 in improving the growth rate of Synechocystis. The average specific growth rate of the transgenic Synechocystis sp. Increased by 13.97% compared withthe wild type in 6 days under normal culture conditions, However, both mutants overexpressing spkD gene and wild type exhibited overcompensatory growth performance in the light recovery stage (6 daysculture stage) after light limitation stress, and the specific growth rate of mutants increased by 7.13% compared with wild type in the overcompensatory growth stage.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE +1
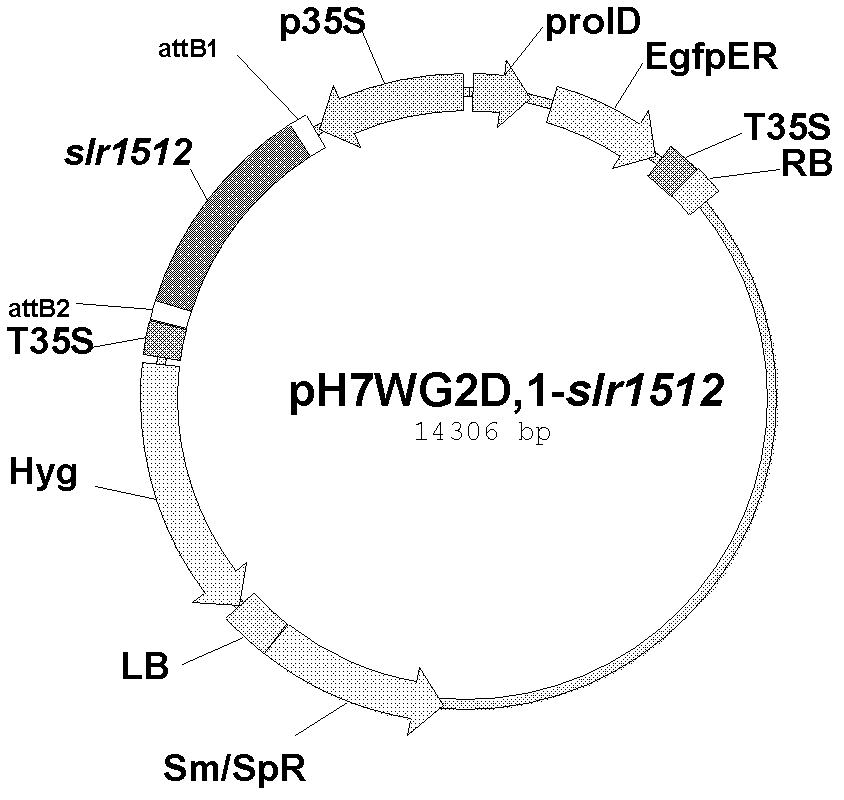
New use of synechocystis protein in paddy rice property improvement
The invention discloses a new use of a synechocystis protein in paddy rice property improvement, provides an application of a protein having a structure represented by sequence 2 in a sequence table in the improvement of the plant chlorophyll content and / or the plant heading rate, and also provides an application of a gene encoded by the protein having a structure represented by the sequence 2 in the sequence table in the improvement of the plant chlorophyll content and / or the plant heading rate. Transgenic experiments that an slr1512 gene is introduced into paddy rice prove that the chlorophyll content and the heading rate of the slr1512 gene transferred paddy rice are obviously improved, so the slr1512 gene and products encoded thereby are of great theoretical and practical significance to the cultivation of photosynthesis enhanced new species of crops, and can be used for cultivating agricultural high-yield plant varieties.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
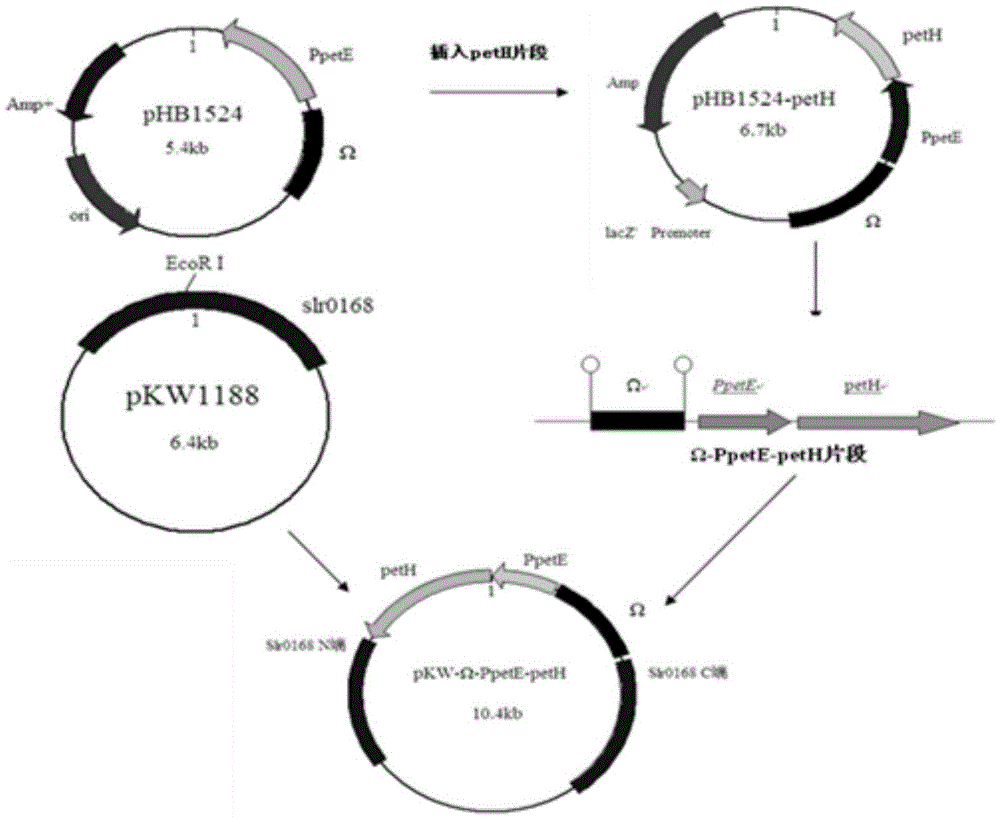
Genetic engineering synechocystis capable of promoting regeneration of intracellular coenzyme NADPH and application of synechocystis
InactiveCN105567621APromote regenerationImprove regeneration efficiencyBacteriaFermentationFerredoxin—NADP(+) reductaseIntracellular
The invention discloses engineering synechocystis PCC6803 capable of promoting regeneration of an intracellular coenzyme NADPH and a construction method and application of the synechocystis. Homologous recombination is performed on a gene petH of ferredoxin-NADP reductase (FNR) which can catalyze regeneration of the coenzyme NADPH to obtain recombinant plasmids pKW-omega-PpetE-petH, the recombinant plasmids are transformed into the synechocystis PCC6803, the FNR gene is integrated in chromosomal DNA of the synechocystis through homologous recombination, and high-strength expression of the FNR can be regulated and controlled according to the concentration of Cu<2+>. The engineering synechocystis constructed through the method can promote overexpression of the FNR, improve the total enzyme activity of the intracellular FNR and greatly promote the regeneration efficiency of the intracellular coenzyme NADPH. The synechocystis obtained through the method can be applied to the biological catalysis and conversion process which has the large quantity demand on the coenzyme and the biotechnology field by promoting regeneration of the intracellular coenzyme NADPH of microalgae and has the wide application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
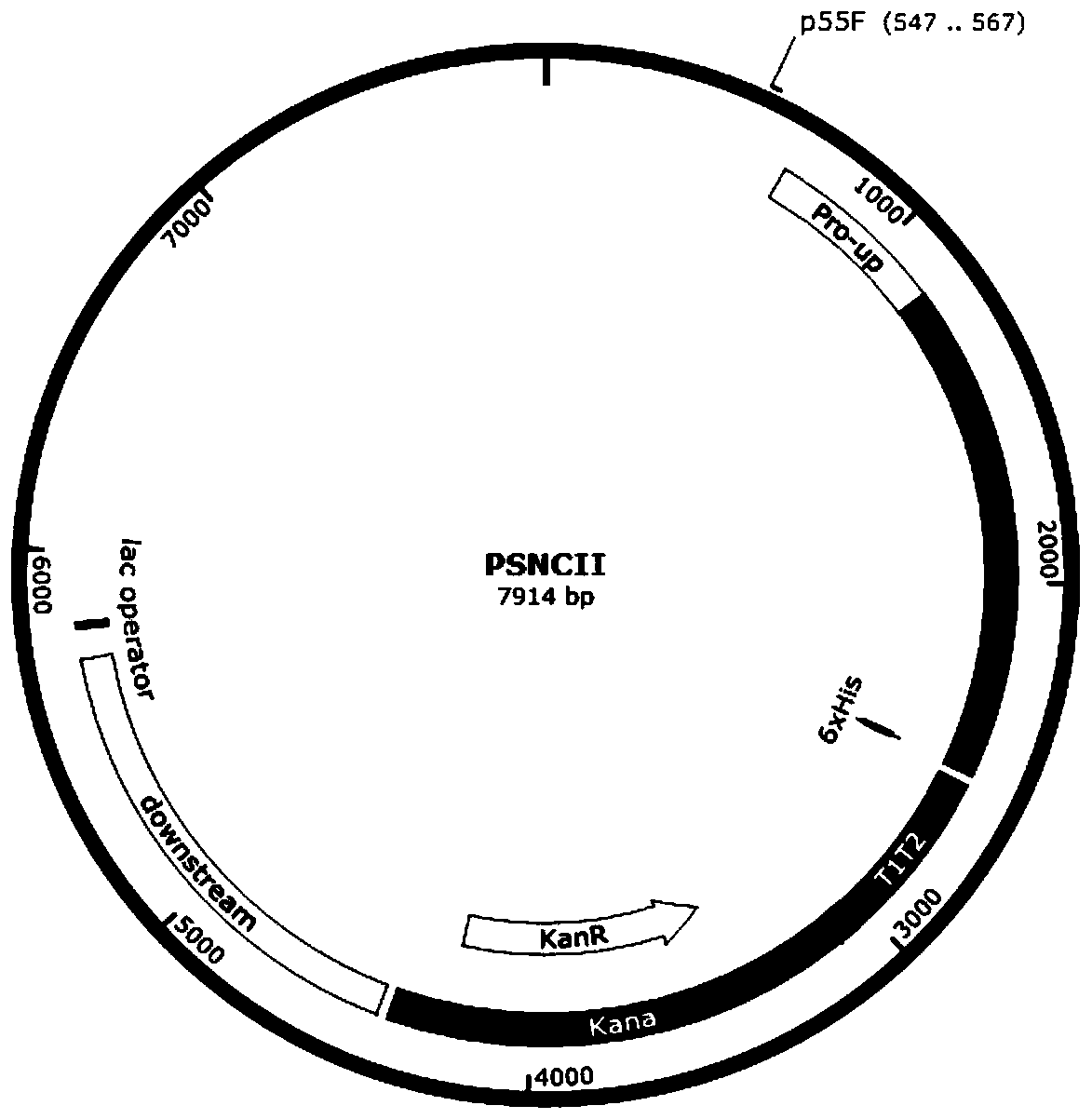
Genetically engineered algae strain of synechocystisPCC6803 producing cellulase and construction method thereof
InactiveCN110684704AA method for realizing the expression of exogenous cellulaseIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a genetically engineered algae strain of synechocystisPCC6803 producing cellulase and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of industrial microorganisms. According to the genetically engineered algae strain of synechocystisPCC6803 producing cellulase and the construction method thereof, through the method of homologous recombination, an exogenous cellulaseexcision enzyme CBHII gene is integrated into the genome of the synechocyst is PCC6803 to obtain an algae strain SPSNCII of the synechocystisPCC6803.Under the same culture condition, the activity ofthe produced cellulase is significantly better than that of the wild synechocystis strain. According to the genetically engineered algae strain of the synechocystisPCC6803 producing the cellulase andthe construction method thereof, a novel way of obtaining the cellulase by using inorganic salt and carbon dioxide through photosynthetic organism-synechocystis is opened up, the genetically engineered algae strain of the synechocystisPCC6803 producing the cellulase and the construction method thereof are of great significance to reducing the consumption of an organic carbon source in the processof enzyme production and reducing the release of the greenhouse gases in the process of producing the cellulase, and the application prospect is broad.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
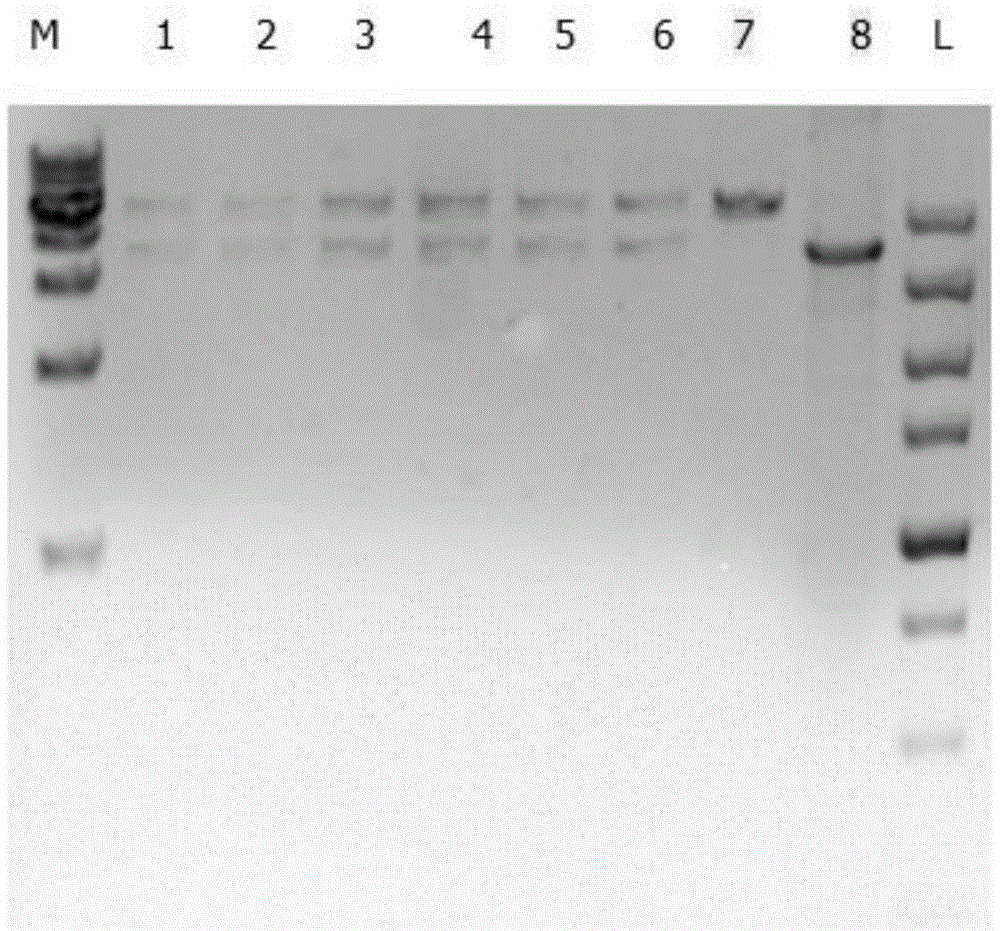
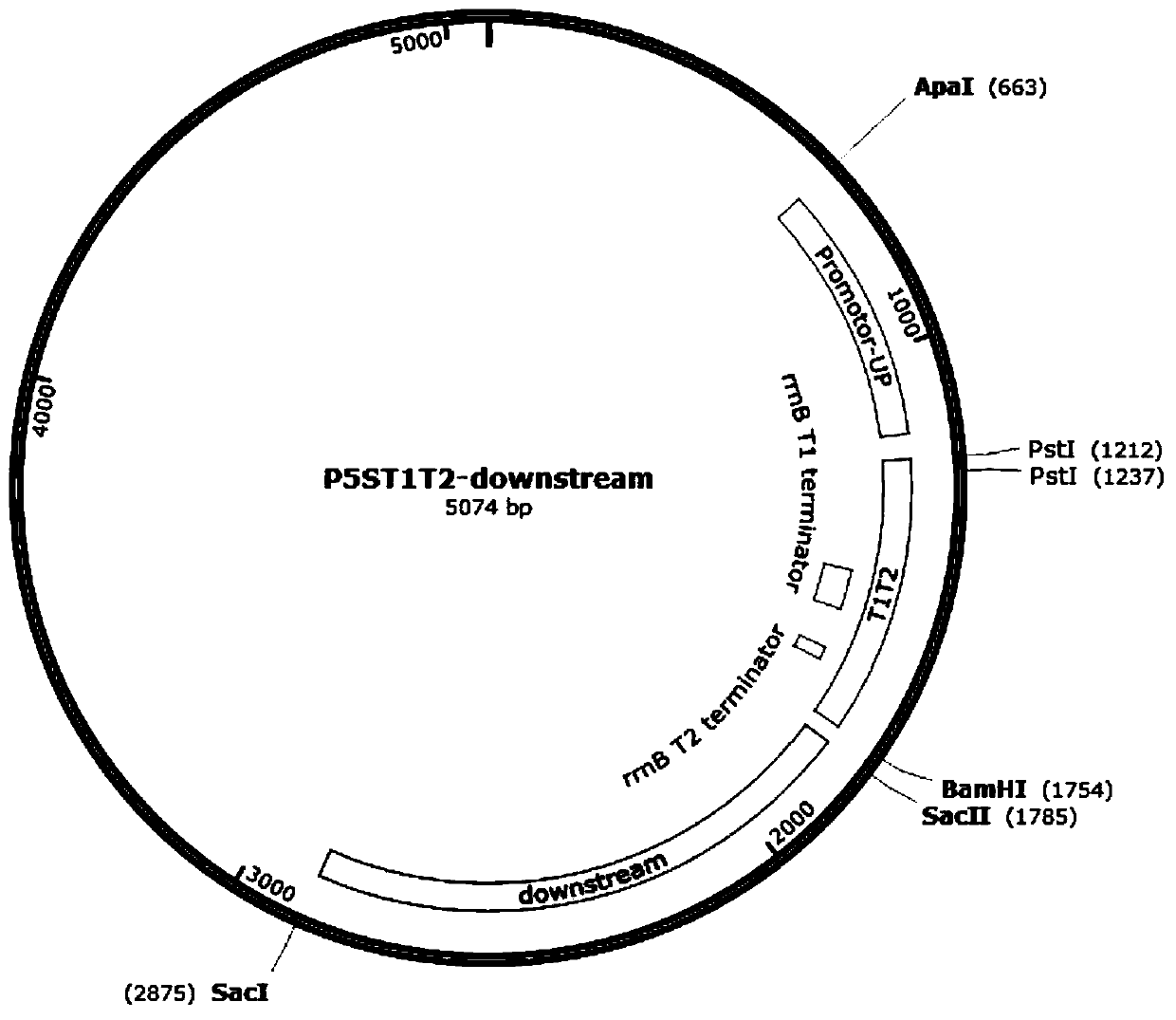
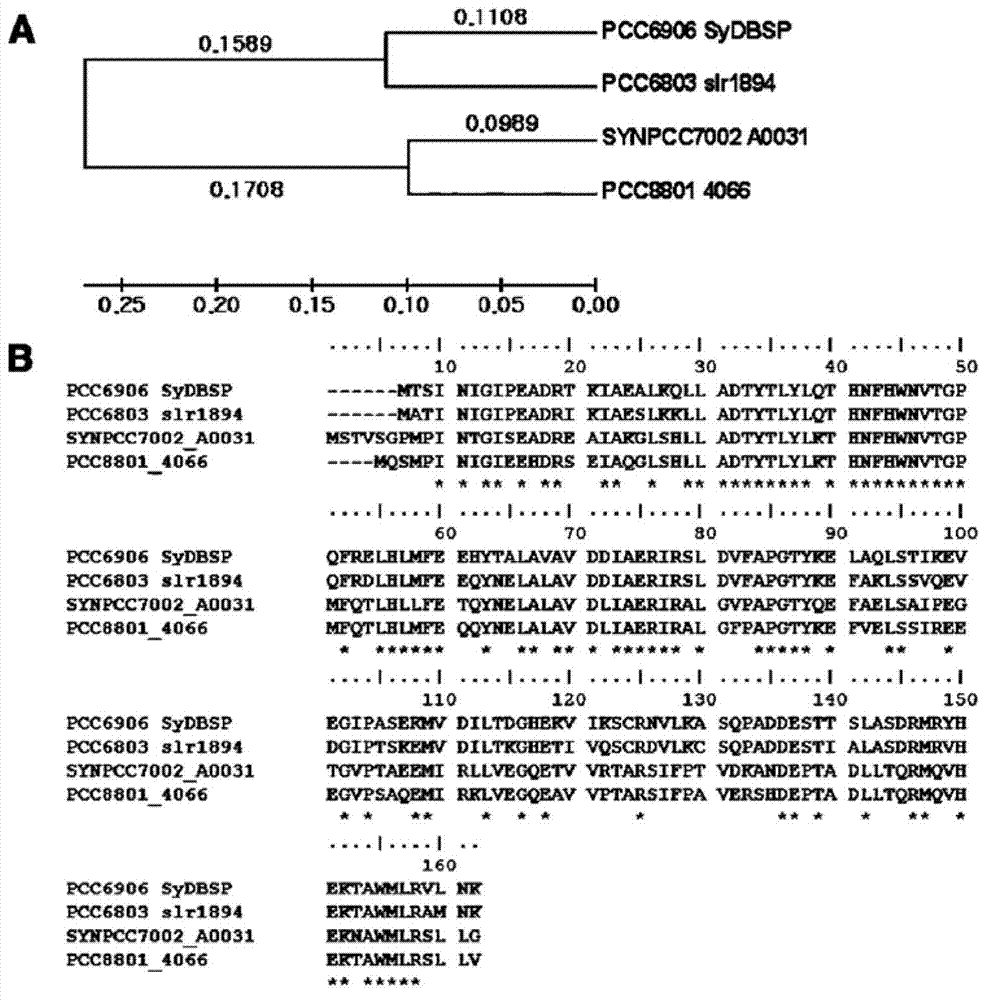
Salt tolerance SyDBSP gene derived from synechocystis, and uses thereof
InactiveCN103200814AImprove salt toleranceImprove the possibility of applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyPlant cell
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
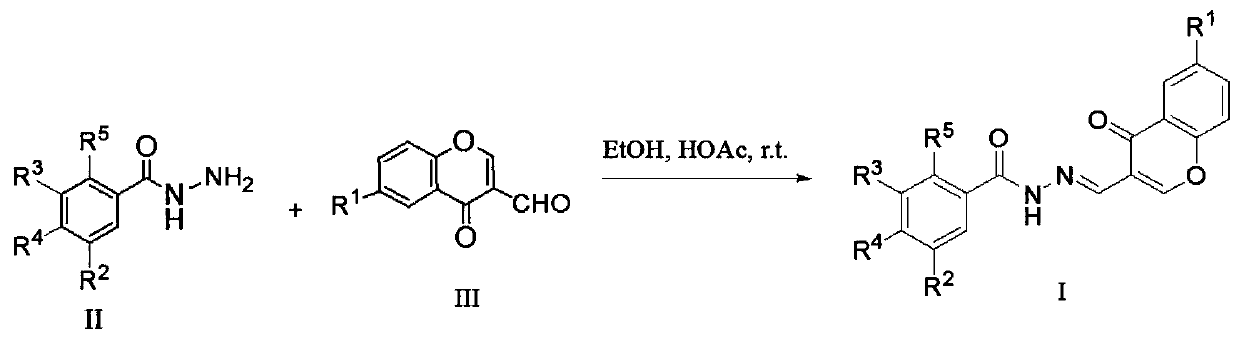
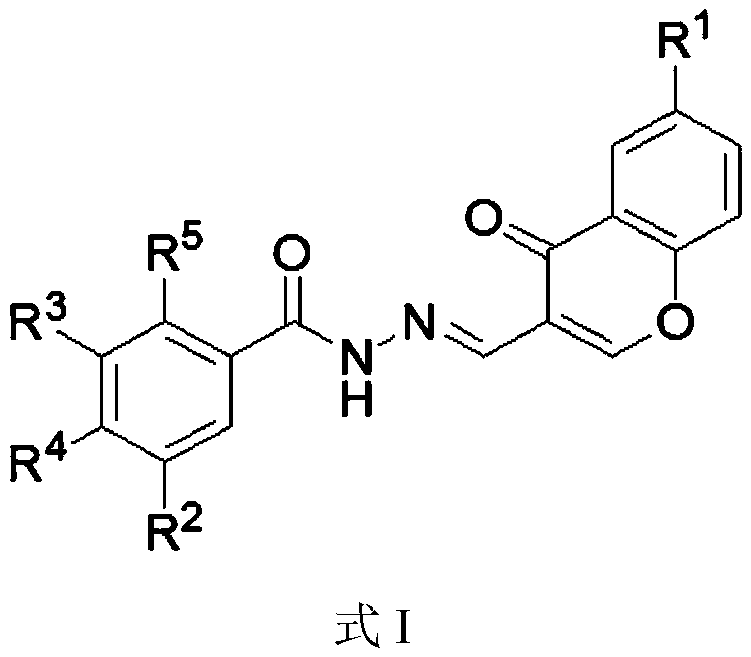
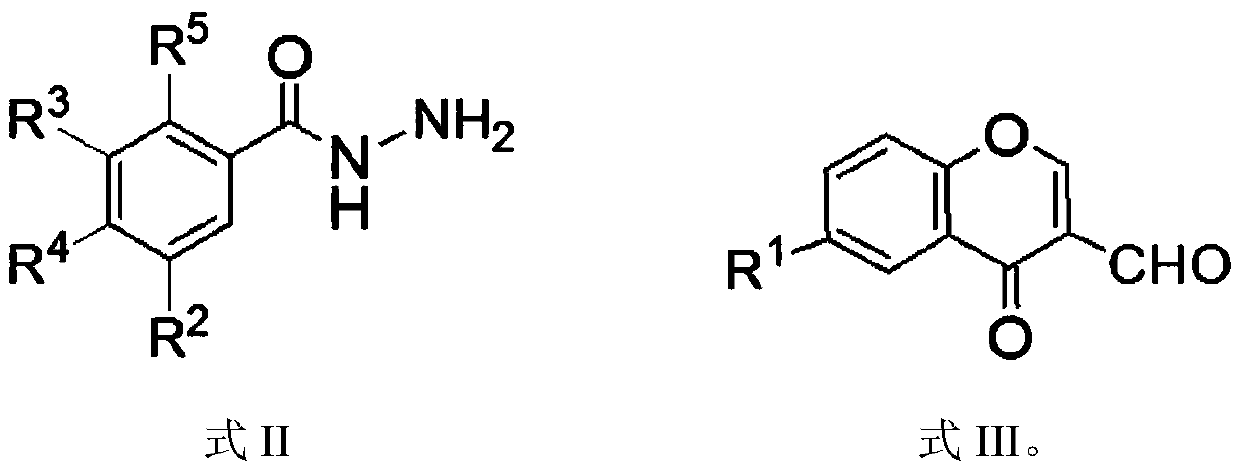
Chromone-containing benzoyl hydrazone compound with inhibiting effect on growth of synechocystis PCC6803 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111548338AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh activityBiocideOrganic chemistryCarboxyl radicalChromone
The invention provides a chromone-containing benzoyl hydrazone compound with an inhibiting effect on growth of synechocystis PCC6803 and a preparation method thereof. The molecular structure of the compound is shown as a formula I, wherein R1 is selected from hydrogen, halogen, nitro, hydroxyl, carboxyl and C1-C4 alkyl; R2 is selected from hydrogen, bromine, hydroxyl or nitro; R3 is selected fromhydrogen or hydroxyl; R4 is selected from hydrogen, halogen, nitro, trifluoromethyl or hydroxyl; and R5 is selected from hydrogen or hydroxyl. The invention further provides a preparation method of the compound. According to the preparation method, benzoyl hydrazine or a substituent thereof reacts with 3-formyl chromone or a substituent thereof in an ethanol environment containing acetic acid to generate the compound. The compound has a good effect on inhibiting the growth of synechocystis PCC6803, the EC50 value is within a range of 0.8-29.8 [mu]M, and the compound can be used for preparing related algistat products.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Cultivation method of heat-resistant zooxanthellae
InactiveCN110373329AImprove heat resistanceUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesHeat shockAnimal science
The invention belongs to the technical field of alga cultivation and particularly discloses a cultivation method of heat-resistant zooxanthellae. The cultivation method specifically includes the stepsof firstly, inoculating, to be more specific, inoculating healthy zooxanthellae into a photobioreactor set; secondly, culturing, to be more specific, inoculating healthy zooxanthellae obtained in thefirst step into a photobioreactor set to perform independent culturing; thirdly, performing directed evolution; fourthly, repeating the steps above, and gradually increasing temperature and heat shock time at the same time to allow synechocystis mutant strains to be able to normally grow at the temperature larger than 45 DEG C. The cultivation method has the advantages that the directed evolutionis used to modify the zooxanthellae, the obtained synechocystis mutant strains can normally grow at the temperature larger than 45 DEG C, and the zooxanthellae is good in heat resistance.
Owner:浙江山诺生物科技有限公司
In-situ restoration method for large water area pollution based on microbial strains
InactiveCN109179689AQuickly restore balanceQuick recovery of self-cleaning functionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsRestoration methodSelf purification
The invention relates to an in-situ restoration method for large water area pollution based on microbial strains. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing first mixed bacterial strain in a polluted water area; wherein the first mixed bacterial strain comprises synechocystis, lactic streptococci and actinomyces; after 20 to 30 hours, placing second mixed bacterial strain in thepolluted water area; wherein the second mixed bacterial strain comprises synechocystis, denitrifying bacteria, streptomyces jingyangensis and thiobacillus oxidans; after 10 to 15 hours, placing a third mixed bacterial strain in the polluted water area; wherein the third mixed bacterial strain comprises synechocystis, rhodopseudomonas palustris, alcaligenes and aspergillus oryzae; and salvaging and collecting flocculates on the surface of polluted water area to purify the water in the water area. The in-situ restoration method can rapidly degrade pollutants such as nitrogen and phosphorus in the polluted water area, can rapidly decompose and convert toxic and harmful substances such as ammonia, nitrite and hydrogen sulfide in the water, and quickly restore the ecological balance and self-purification function of the water area.
Owner:四川晴川环境治理有限公司
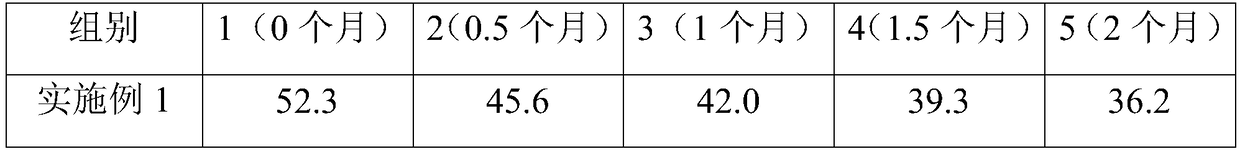
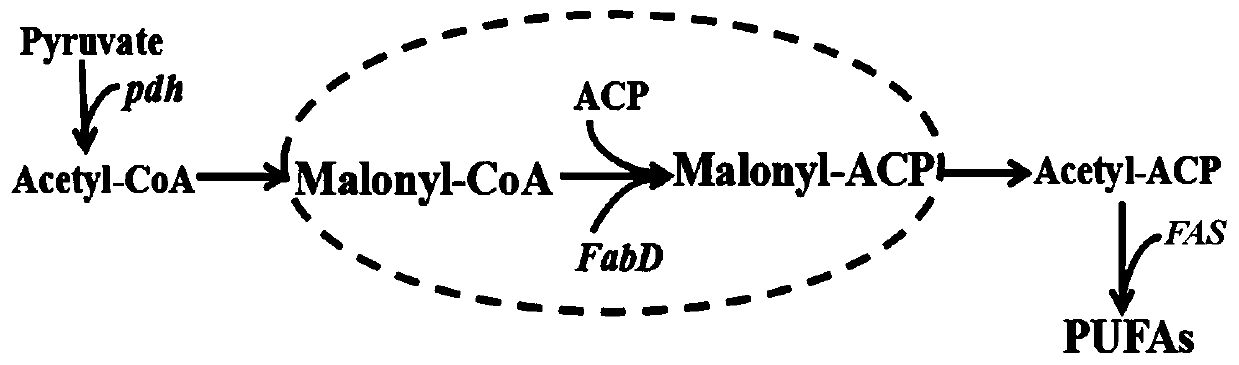
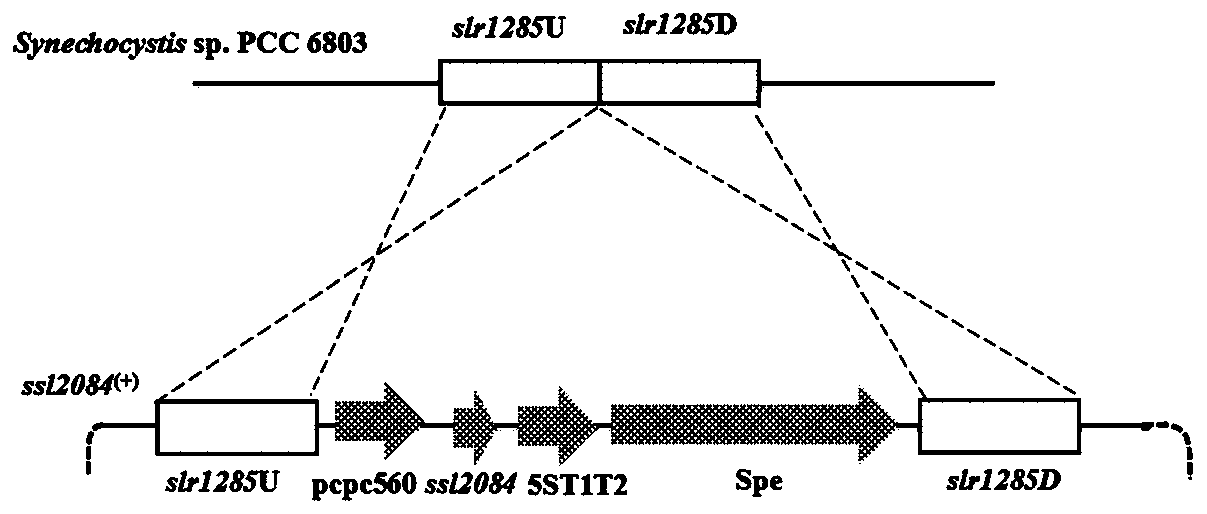
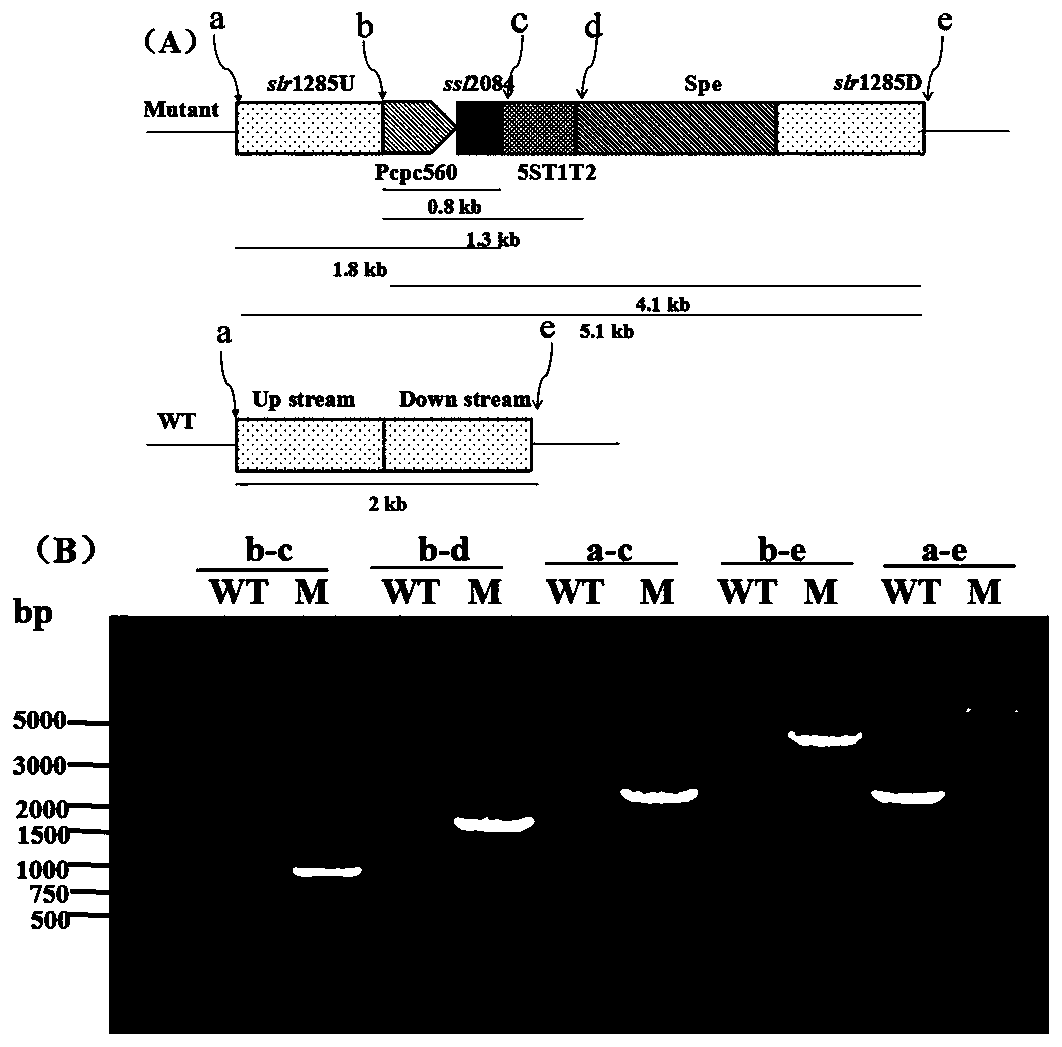
Application of ssl2084 gene in synthesis of medium and long chain fatty acids
ActiveCN110950941AIncrease contentUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesLong chain fatty acidProteinogenic amino acid
The invention relates to application of ssl2084 gene in synthesis of medium and long chain fatty acids. The ssl2084 is a protein capable of promoting synthesis of the medium and long chain fatty acidsin synechocystis, and has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention further relates to application of the ssl2084 gene in synthesis of medium and long chain saturated fatty acids ofthe synechocystis. For the first time, the invention discloses an important role of the ssl2084 gene of the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 in synthesis of the medium and long chain saturated fatty acidsat low temperature. By increasing expression of the ssl2084 gene in the synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 by utilizing an overexpression method, contents of C12:0, C16:0 and C18:0 in mutant strains are significantly increased; and moreover, the contents of the C12:0, the C16:0 and the C18:0 in the mutant strains are further increased after low-temperature treatment, so that the recognition that it is easy to synthesize unsaturated fatty acids at low temperature in the field is changed.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Salt tolerance SyGT gene derived from synechocystis, and uses thereof
InactiveCN103200813AImprove salt toleranceImprove the possibility of applicationMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationHalotolerancePlant cell
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF BIOSCI & BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com