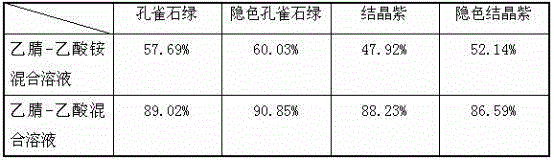
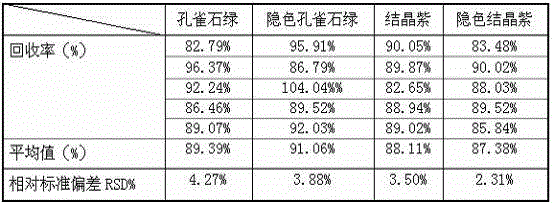
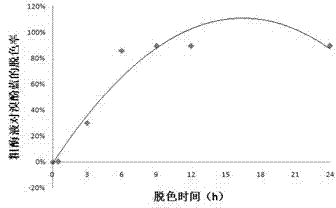
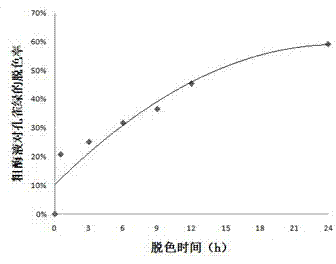
Patents
Literature
468 results about "Malachite green" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
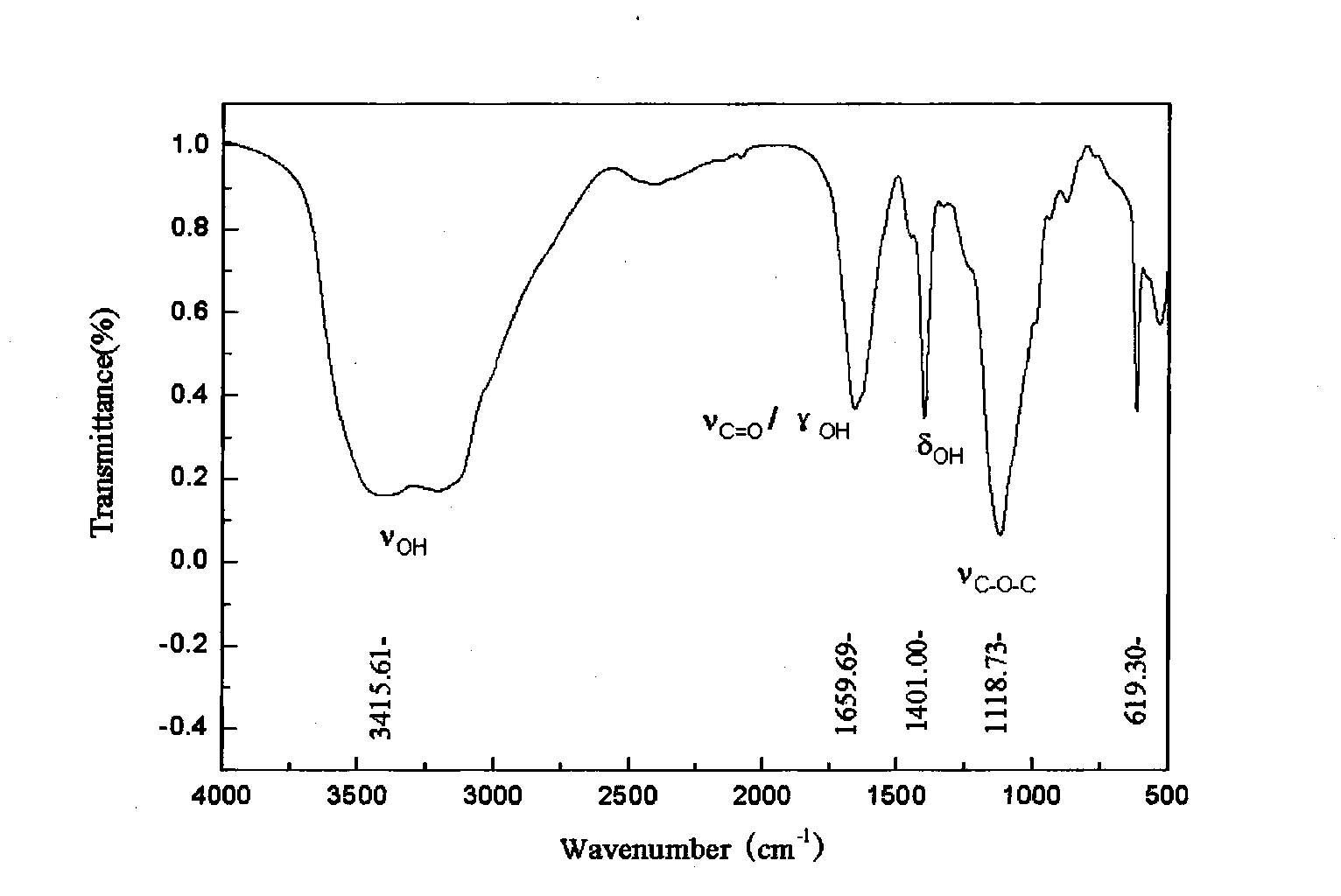
Malachite green is an organic compound that is used as a dyestuff and controversially as an antimicrobial in aquaculture. Malachite green is traditionally used as a dye for materials such as silk, leather, and paper. Despite its name the dye is not prepared from the mineral malachite, and the name just comes from the similarity of color.
Preparation method and application of graphene oxide-polyurethane foam material
InactiveCN103408718AImprove adsorption capacityGood removal effectOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMalachite greenPolymer science
The invention belongs to the field of high polymer material synthesis, and relates to preparation of a graphene oxide-polyurethane foam material, in particular to a preparation method and application of the graphene oxide-polyurethane foam material. The preparation method of the graphene oxide-polyurethane foam material comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing graphene oxide by adopting an improved Hummers method, then mixing and stirring graphene oxide, polyether glycol NJ-330, foaming agent, foam stabilizer and catalyst at room temperature, adding isophorone diisocyanate, and finally, foaming further to obtain the graphene oxide-polyurethane foam material. The graphene oxide-polyurethane foam material prepared through the method can be applied to absorption of coloring matters or heavy metal ions in waste water, and has better absorption and removal effects as shown in a test by taking a solution containing malachite green and Cd (II) as the absorption object. The application of the foam material to treatment of the coloring matters and the heavy metal ions in sewage has the characteristics of simplicity in operation and high absorption rate, and has a certain practical value.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Preparation method and application of graphene/cellulose/titanium dioxide composite material
InactiveCN105251453AGood adsorption and removal effectEasy to operateOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionMalachite greenCellulose
The invention belongs to the field of synthesis of nano materials, relates to the preparation of graphene / mesoporous oxide series of nano composite material, and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of graphene / cellulose / titanium dioxide composite material. The graphene / cellulose / titanium dioxide composite material is prepared by preparing graphite oxide by utilizing an improved Hummers method, carrying out ultrasound to obtain graphene oxide, reducing graphene oxide into graphene by using sodium borohydride; and finally uniformly mixing cellulose, titanium dioxide, a surface active agent (hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) and grephene. According to the invention, the synthesis method is simple, the prepared graphene / cellulose / titanium dioxide composite material is taken as an adsorbent, and a malachite green dye solution is taken as an adsorption object, the experiment shows that the composite material has an excellent adsorption removal effect. The composite material is applied to the treatment of dyes in sewage water, has the advantages of simplicity in operation, convenience, easiness in availability, high adsorption rate and the like, and has good industrially practical value.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Indirect competitive ELISA kit for detecting malachite green in aquatic product
InactiveCN1766623AEasy to operateStrong specificityTesting medicinal preparationsMalachite greenElisa kit
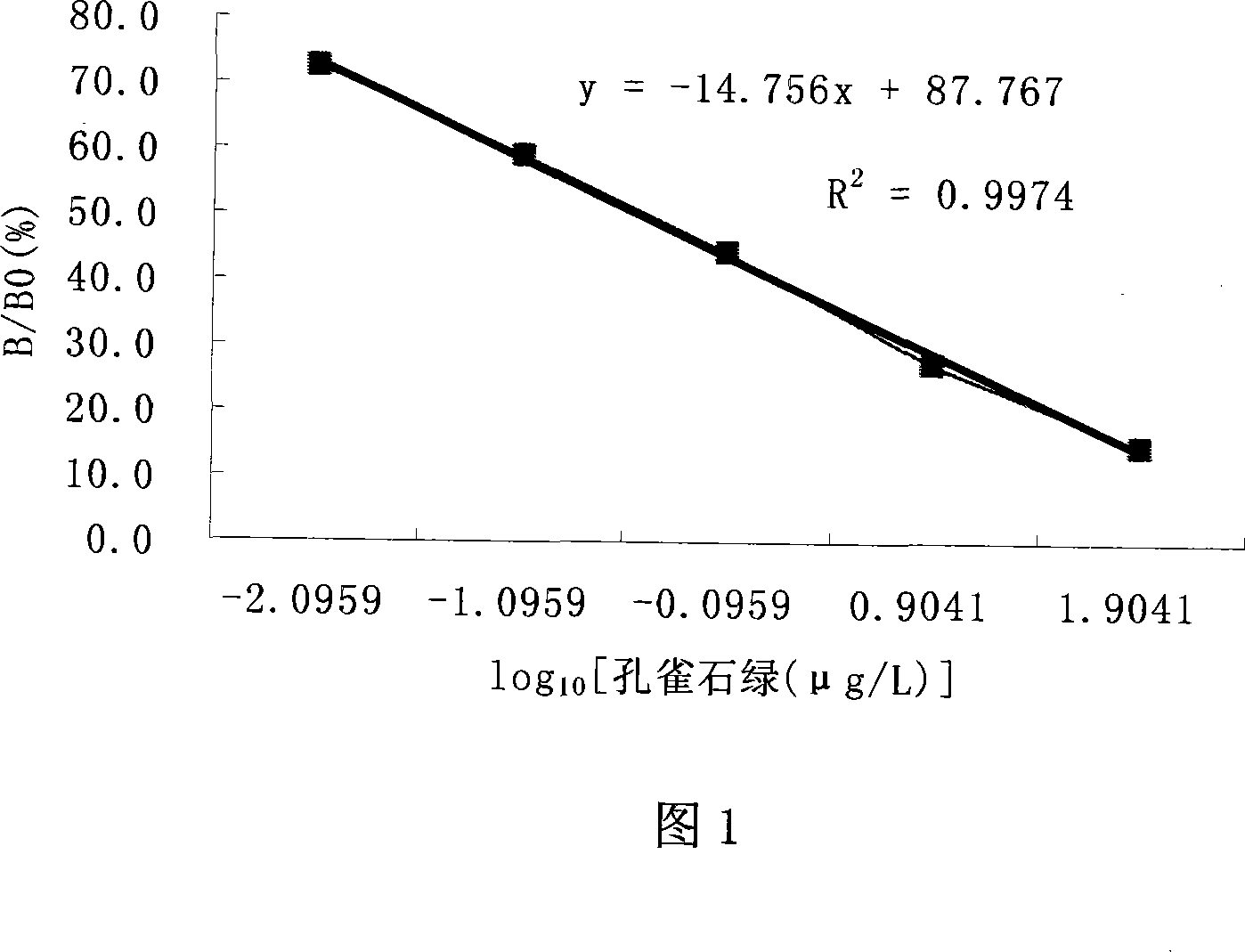
The invention relates to a colorless green malachite green indirect compete ELISA test agent box of an aquatic product. The test plate of the agent box is a split 96 holes enzyme mark plate which coats colorless green malachite green and albumin coupling material; the anti-colorless green malachite green antibody is a monoclonal antibody which is prepared by the colorless green malachite green and the albumin coupling material immune mouse; the tested sample uses ethyl hexoate and cyclohexane to extract after uniform and adjusts PH value for detecting. The quoting standard of the sample detecting is that it is a regression curve which uses the logarithm value of the sample density as abscissa and uses the degradation rate as ordinate. We could read the density of the corresponding sample from the degradation rate of each sample. The sensibility of the test method is 0.0023ª–g / ml; the test range is 0.0016-1ª–g / ml.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU OF P R C +1
Malachite green vestigial ELISA detection kit and usage method thereof
The invention discloses an enzyme immunoassay of testing the bice green residues in animal derived food, which comprises an enzyme label plate covering bice green antigen, enzyme label bice green antibody working solution, bice green standard solution, substrate solution, substrate buffer solution, reaction termination solution, concentration washing liquid and sample dilute solution. The invention further discloses a method for using the immunoassay to test bice green residues, which comprises sample pretreatment, testing via the immunoassay, processing and analyzing result. The inventive immunoassay of bice green test uses direct competition enzyme-linked immunoassay adsorption analysis technique, with high sensitivity, high stability, simplified operation, reduced reaction time, reduced error caused by complex operation, reduced cost, wide application for testing samples and high practicality.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
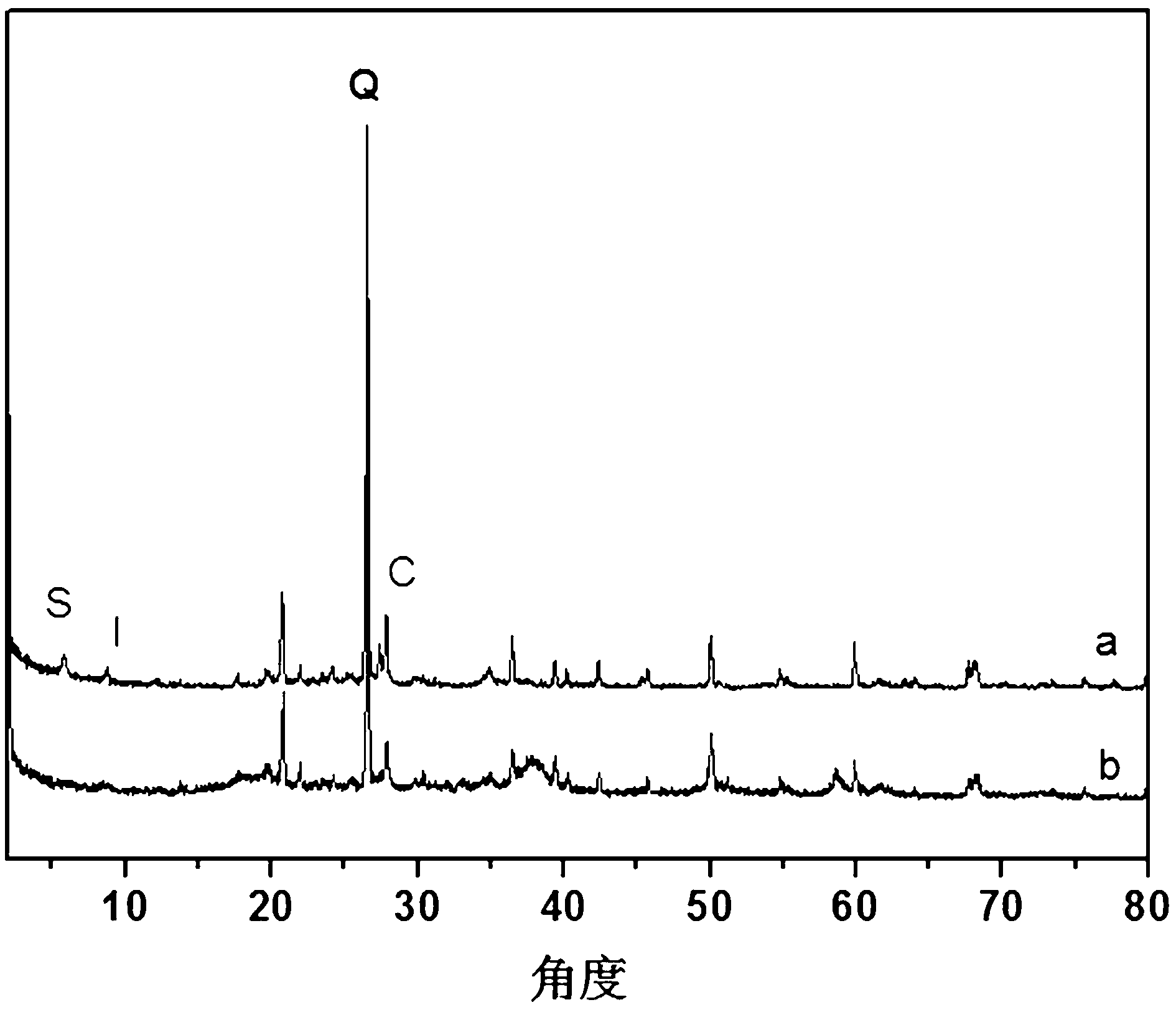
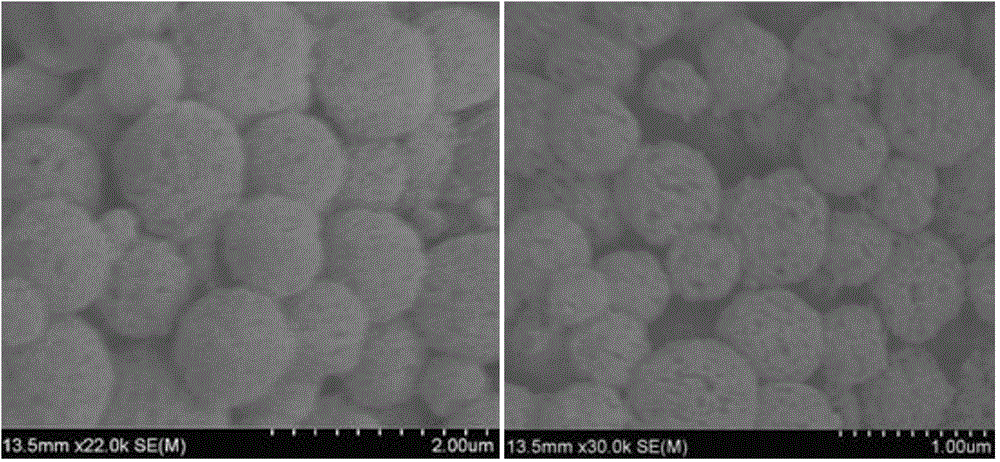
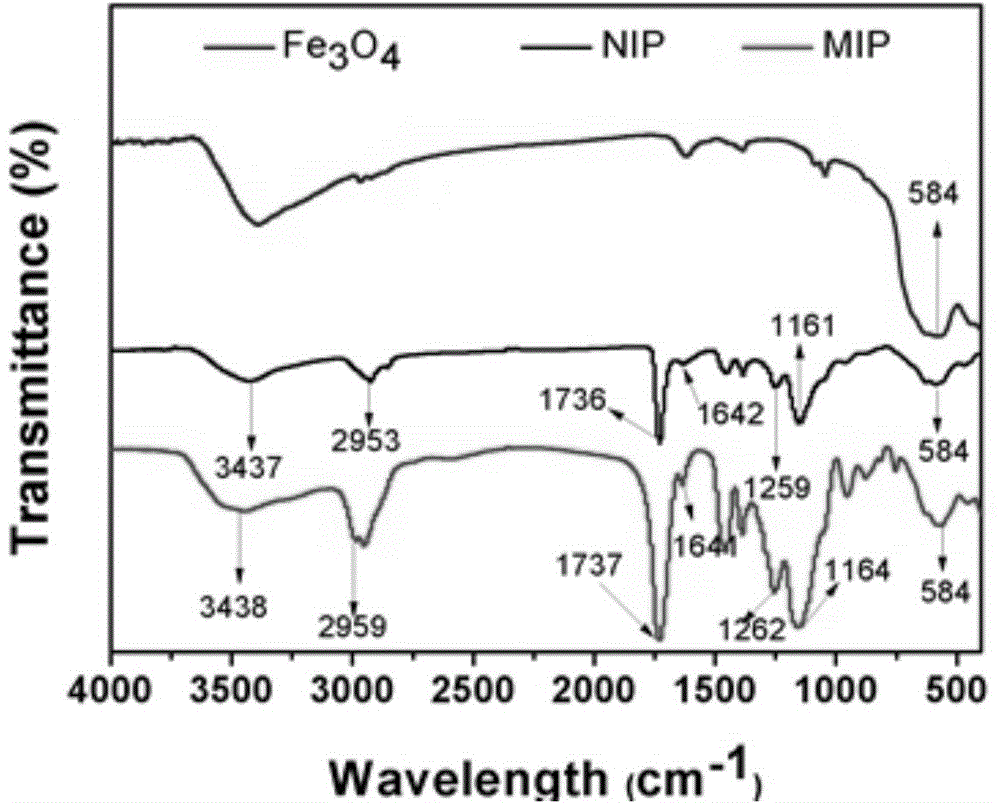
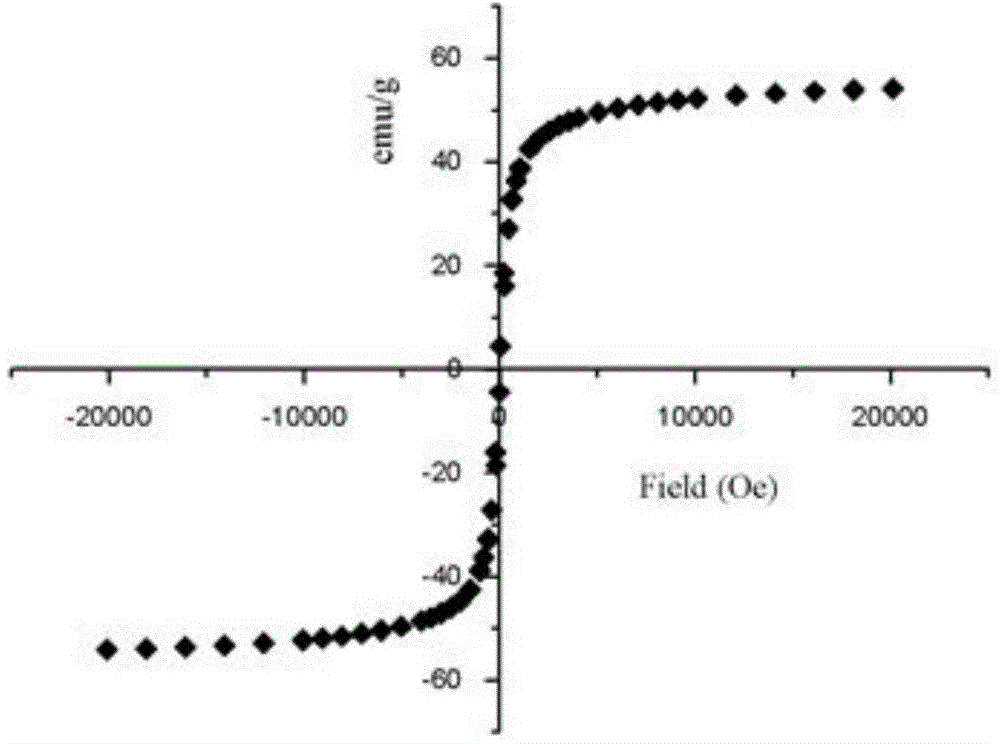
Molecular blotting polymer microsphere for detecting malachite green
InactiveCN101216464ASimple processGood reproducibilityOther chemical processesComponent separationMalachite greenFunctional monomer
The invention provides a molecular imprinted polymer microsphere for fast detecting malachite green in aquatic products, which is prepared by mixing two functional monomers at a certain ratio, mixing a malachite green template with the monitor at a certain ratio, sequentially adding a crosslinking agent, an initiator, an emulsifying agent and a lipophilic solvent, and preparing the molecular imprinted polymer microsphere. The invention further provides a method for detecting the malachite green in a sample, which comprises the following steps of: identifying, adsorbing and concentrating a processed aquatic product, and determining the concentration of the malachite green by spectrophotometry. Additionally, the sample can be concentrated to lower the detection limit, so that the method is especially suitable for detection of low-content samples.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for treating malachite green dye waste water
InactiveCN101973640ASignificant progressSignificant positive effectNature of treatment waterBiological water/sewage treatmentMalachite greenMicroorganism
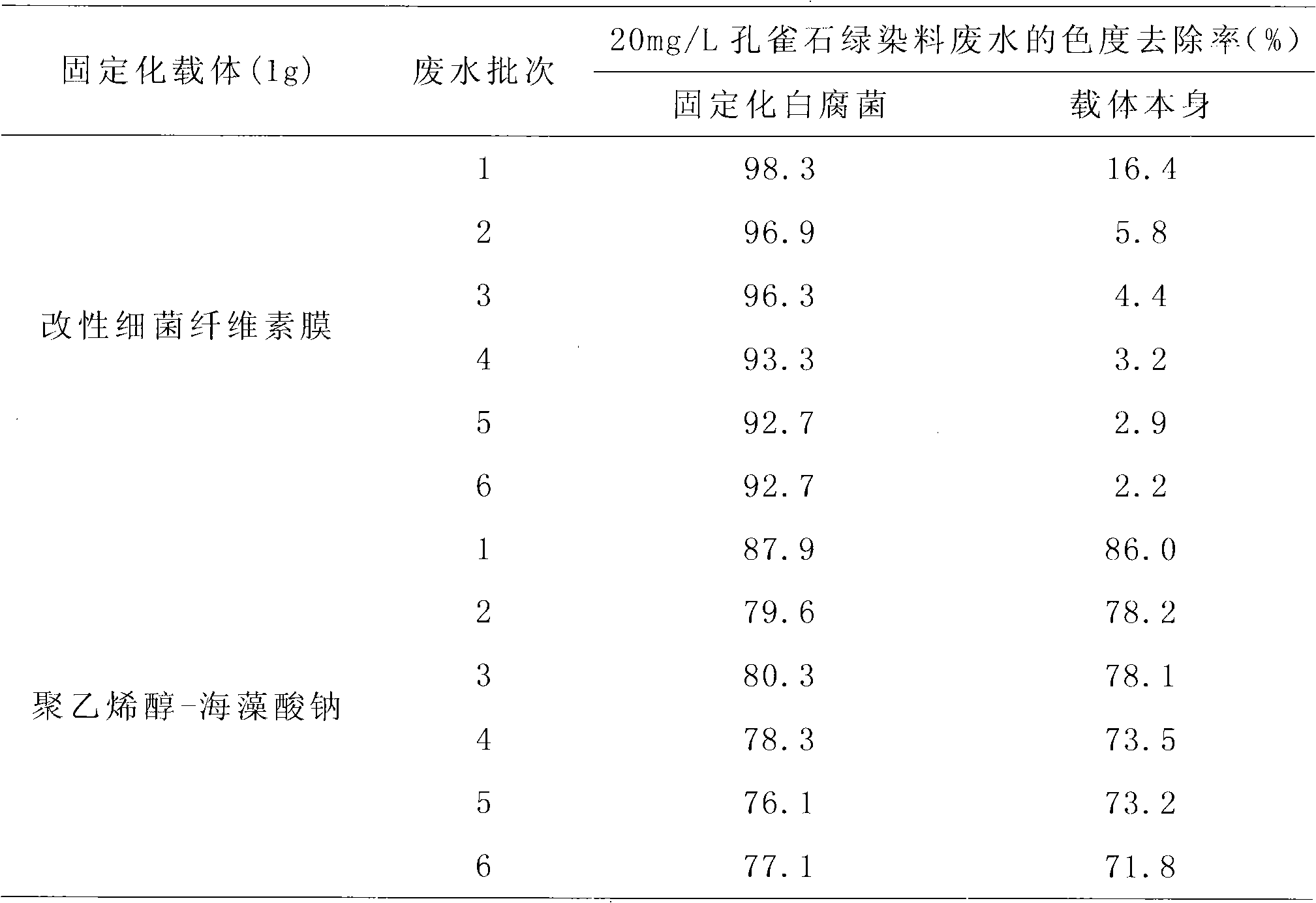
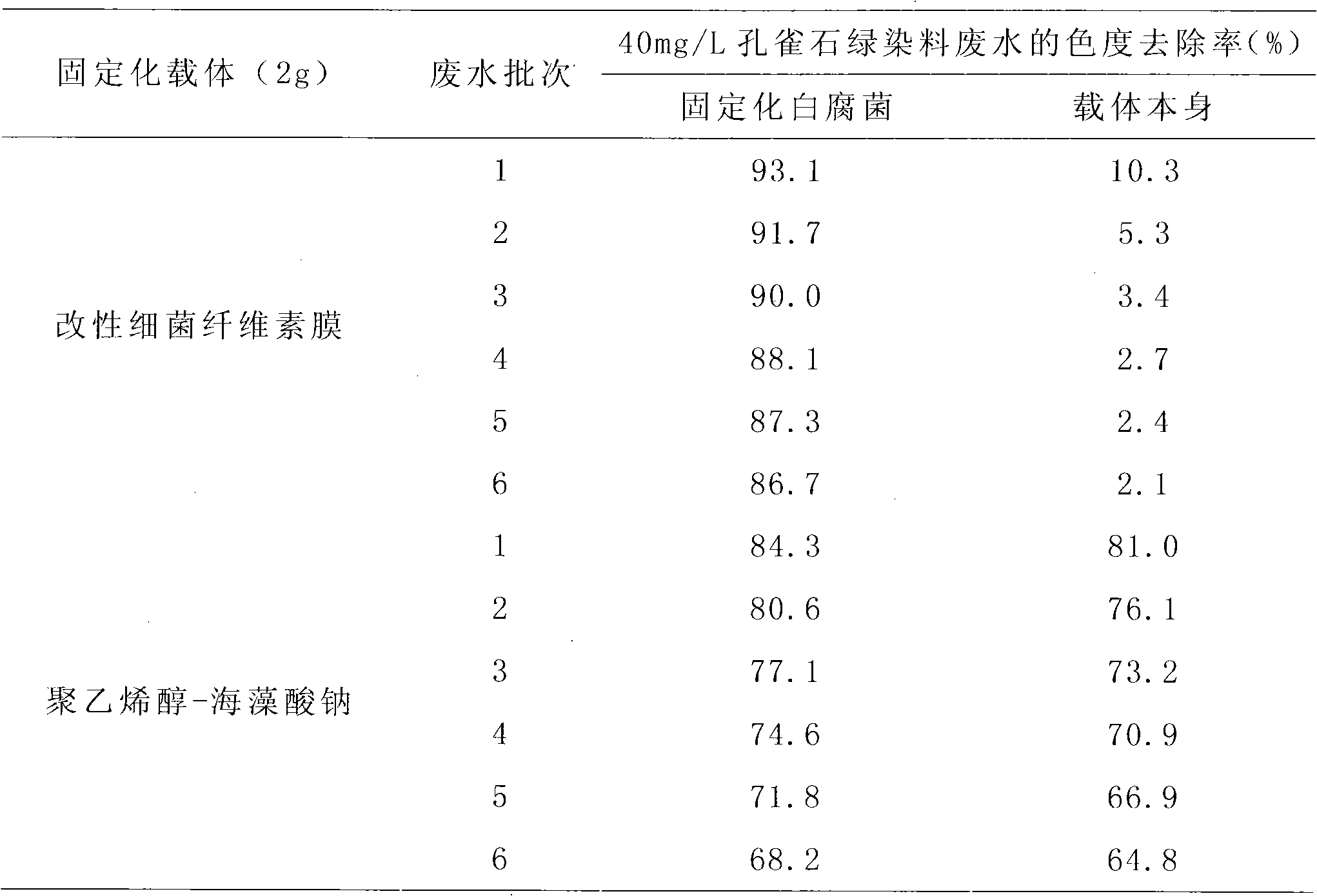
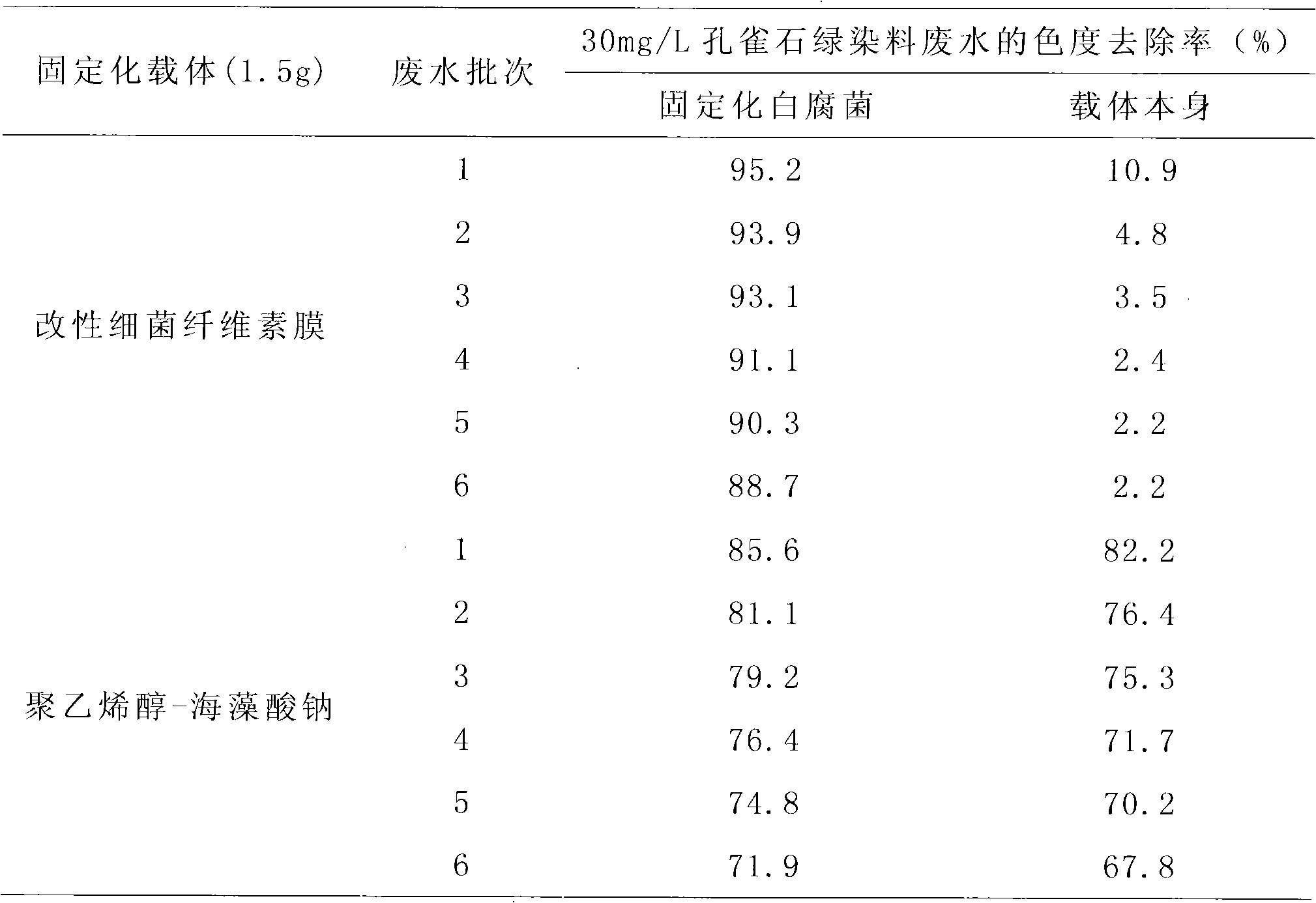
The invention discloses a method for treating malachite green dye waste water, which comprises the following steps of: preparing a bacterial cellulose membrane; modifying the bacterial cellulose membrane; immobilizing white rot fungi by using the modified bacterial cellulose membrane; adding the obtained immobilized white rot fungi modified bacterial cellulose membrane into 50 mL of the malachite green dye waste water; dissolving 20 to 40 mg of malachite green into 1 L of white rot fungi liquid restrictive culture medium; treating the waste water on a gas bath constant-temperature shaking table at a speed of 120 rpm for 5 days at 28 DEG C, and measuring the chroma of the waste water at intervals of 24 hours; 5 days later, discarding the treated waste water, and retaining the immobilized fungi; adding 50 mL of newly-prepared dye waste water with the same concentration, treating the waste water under the same condition, and measuring the chroma of the waste water at intervals of 24 hours; and taking 5 days as a cycle, and repeating the steps for 5 times, wherein the removal rate of the chroma of the waste water is always over 86 percent. In the method, the referred bacillus xylinus and the white rot fungi are purchased from the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center.
Owner:NORTHEAST DIANLI UNIVERSITY +1
Water body, method for rapidly detecting residue of malachite green and colorless malachite green in aquatic product and detection box therewith
ActiveCN101566574AEasy to operateFew stepsComponent separationMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMalachite greenLead dioxide
The invention relates to a water body, a method for rapidly detecting the residue of malachite green and colorless malachite green in an aquatic product, belonging to the technical field of residue detection in a water body and an aquatic product. The method comprises the following steps: oscillating and mixing a sample to be detected and an extractant I uniformly; adding an extractant II, oscillating and mixing and then standing still; taking and adding an supernatant to an enrichment column; observing color change of a chromogenic reagent on the lowest layer; and determining that the sample contains the malachite green and colorless malachite green if a green circular strap is formed. The extractant I is a mixed solution of acetonitrile, dichloromethane, n-hexane and paratoluenesulfonic acid, the extractant II is a mixture of lead dioxide and acid alumina, and the sample to be detected is a water body sample to be detected or an aquatic product sample to be detected. The invention has the advantages of simple operation and fewer steps, does not need expensive instruments and equipment and can embody the convenience and the flexibility to on-site detection.
Owner:JIANGSU TRIGIANT TECH
Beta-cyclodextrin polymer and preparation method as well as method for treating cationic dye wastewater by using beta-cyclodextrin polymer
InactiveCN108554387ALarge specific surface areaLow costOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMalachite greenMethyl violet
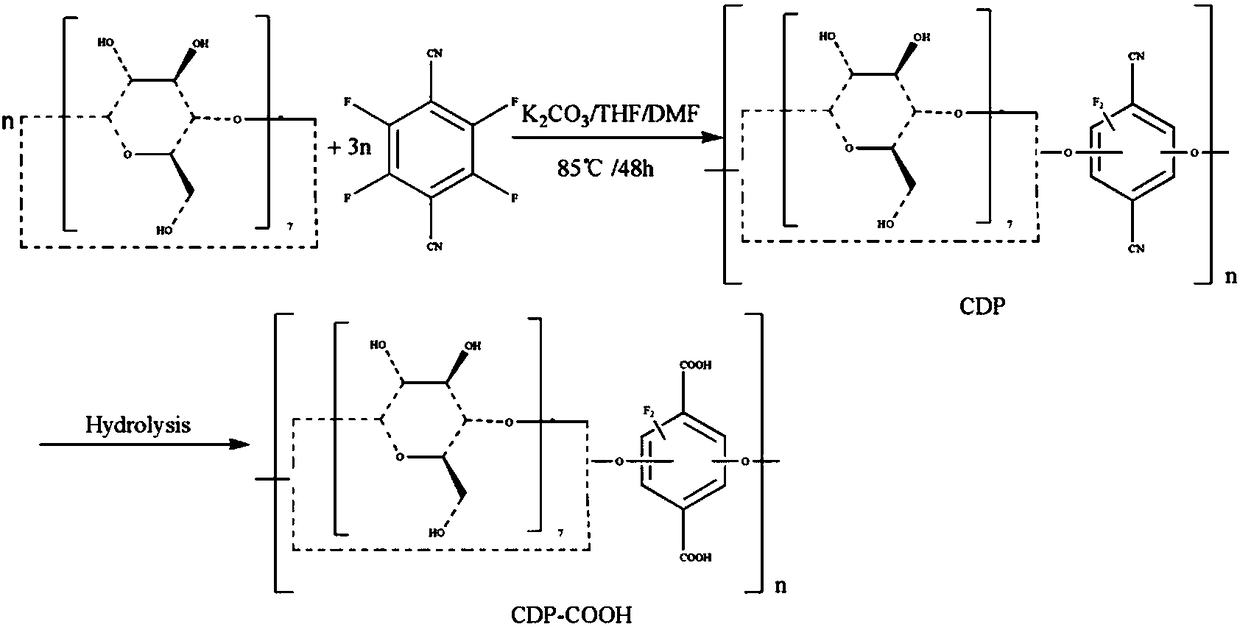
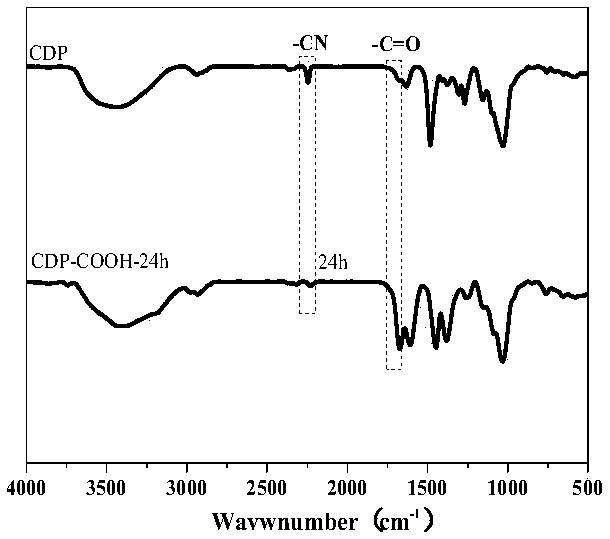
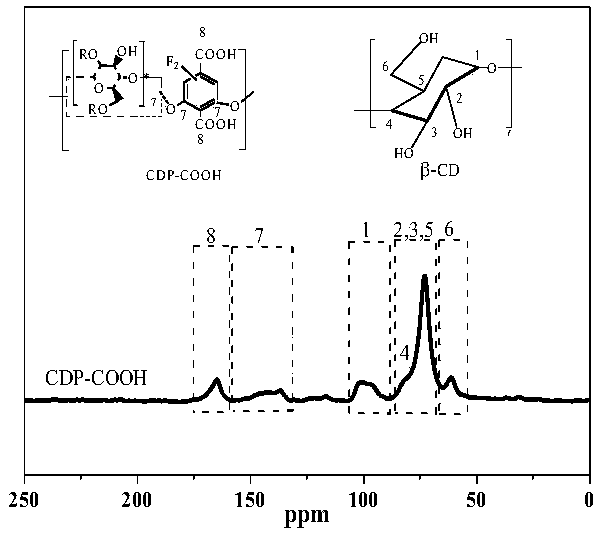
The invention discloses a beta-cyclodextrin polymer and a preparation method thereof as well as a method for treating cationic dye wastewater by using the beta-cyclodextrin polymer. The preparation method of the beta-cyclodextrin polymer comprises the following steps: carrying out polymerization reaction on beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD), a crosslinking agent (tetrafluoroterephthalonitrile TFPN) anda basic salt compound into an organic solvent in the inert atmosphere; reacting the obtained polymer with sodium hydroxide, thereby obtaining a reaction product, namely a porous beta-cyclodextrin polymer (CDP-COOH). The porous beta-cyclodextrin polymer prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly removing cationic dye contaminants such as methylene blue, malachite green, basic fuchsin, methyl violet and alkaline blackish green in water, and the adsorption rate of the beta-cyclodextrin polymer is greater than that of an activated carbon material. Besides, the polymer can be regenerated for multiple times under mild conditions, and the adsorption performance loss is smaller.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Natural pyrite based photocatalysis method for synergic removal of heavy metal-organic pollutants from water
ActiveCN105060455AReduce concentrationRelieve pressureWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsMalachite greenMalachite green stain
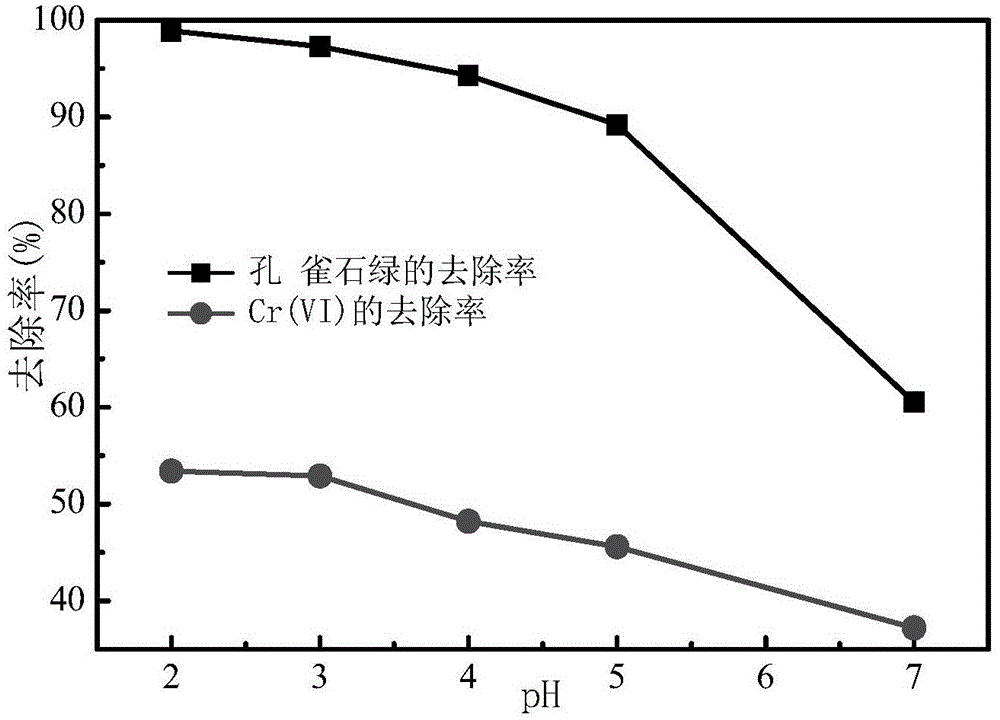
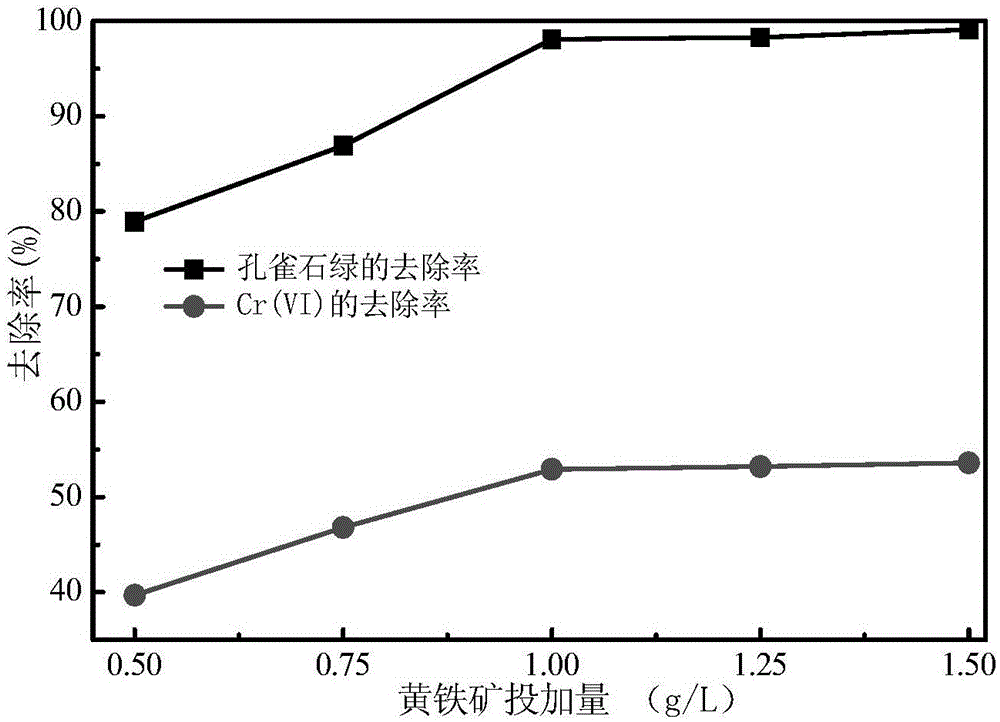
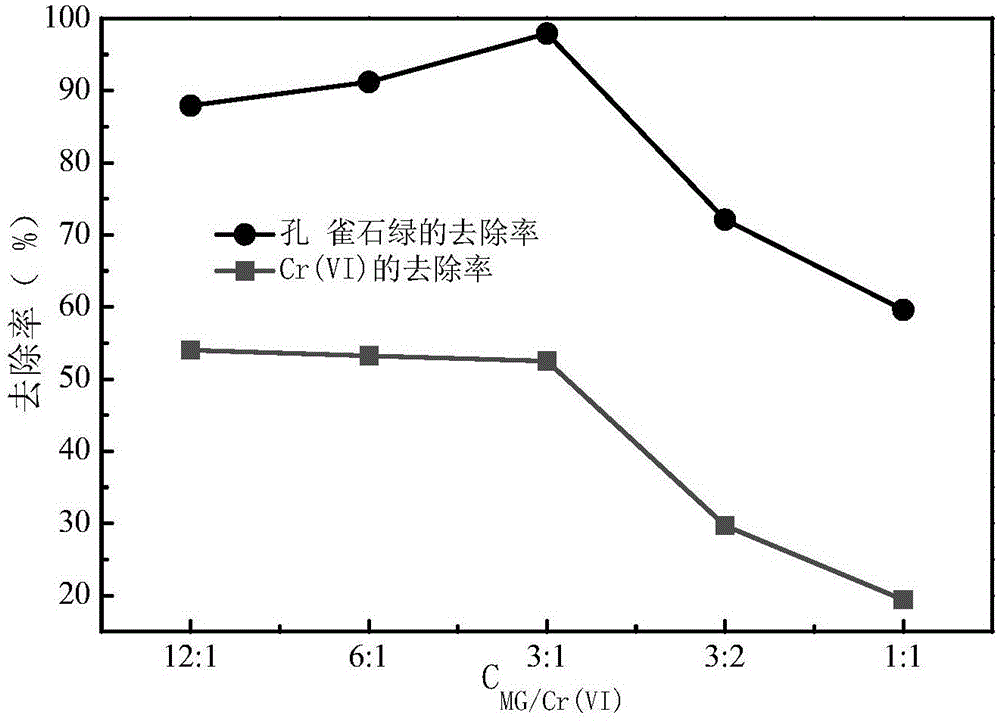
The invention discloses a natural pyrite based photocatalysis method for synergic removal of heavy metal-organic pollutants from water. The catalyst pyrite involved in the photocatalysis system is crushed, ground and sieved, and then composes a pyrite photocatalysis system together with ultraviolet. The pyrite photocatalysis technology involved in the invention can be applied to synergic removal of heavy metal Cr (VI) and organic matter malachite green from water. Under ultraviolet irradiation, the removal rates of malachite green and Cr (VI) can respectively reach 97% and 52%. The pyrite photocatalyst has good repeated use performance, can maintain good reaction activity after five times of repeated use, and is fully used. The catalytic reaction operation conditions involved in the reaction are simple, and the catalyst raw materials are cheap and easily available. Based on the pollution treatment concept of using waste to treat waste, the method provided by the invention has good application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
ELISA adsorption analysis method for measuring gross amount of malachite green and colorless malachite green in water sample and aquatic products
InactiveCN101482559AHigh sensitivityEasy to handleComponent separationBiological testingMalachite greenMalachite green stain
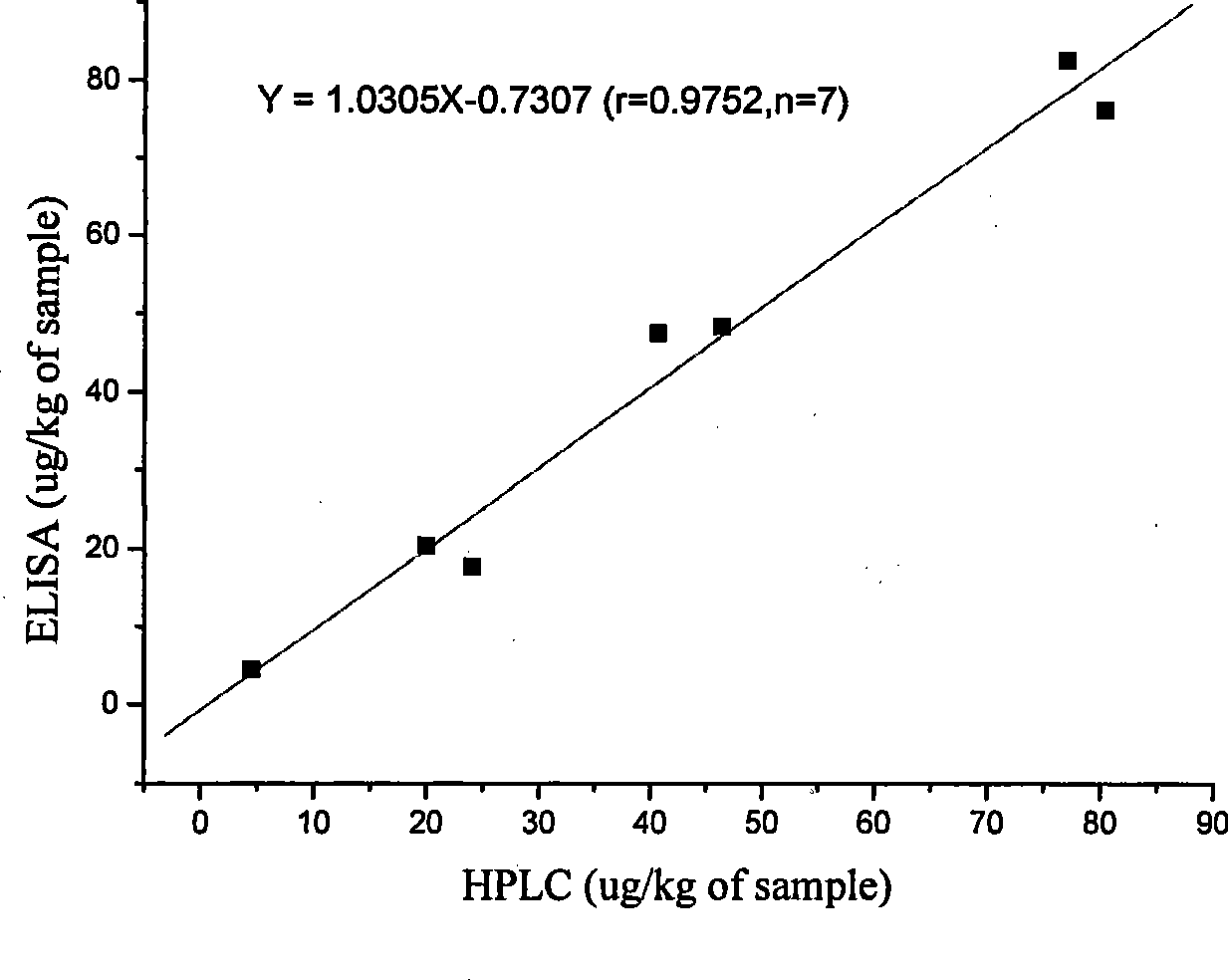
The invention discloses an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay method (ELISA) for detecting the total amount of diamond green and blank diamond green in measurement water sample and aquatic products, characterized in that: the modified compound of amido blank diamond green is synthesized and linked with the protein to produce immunogen and envelope antigen, and the polyclonal antibody of rabbit-anti colorless diamond green is obtained by immuning animal and the concentration range of ELISA standard curve is 0.1-100ng / mL, IC50 is 0.9-2.6ng / mL and the recovery of standard addition is 76.2-95%, the correlation coefficient of ELISA and HPLC is 0.975, n=7; because the cross-reaction rates of the prepared antibody and diamond green are respectively 95.25%, the ELISA can be used for measuring the total amount of the diamond green and blank diamond green without any oxidation step.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Phosphorus nitrogen boron lumber combustion inhibitor
The invention relates to a phosphorus-nitrogen-boron wood flame retardant, which is characterized in that the range of each component name and weight percentage of the compositions comprises: 70 to 80 percent of 8-sodium diborate and 18 to 30 percent of one or two of inorganic phosphorus-nitrogen compound and water soluble ammonium polyphosphate, wherein the inorganic phosphorus-nitrogen compound is one or more of ammonium phosphate, diammonium phosphate and monoammonium phosphate. A germicide with the weight percentage of between 0.7 and 3 percent or / and a staining agent with the weight percentage of between 0.7 and 7 percent can be added to the phosphorus-nitrogen-boron wood flame retardant, wherein the germicide is one or more of chlorothalonil, sanmate and tebuconazol; and the staining agent is one or more of malachite green, alkali red, alkali blue, alkali yellow and alkali black. The phosphorus-nitrogen-boron wood flame retardant can be dissolved in water and the concentration of the wood flame retardant is less than or equal to 20 percent. Wood subjected to treatment through the phosphorus-nitrogen-boron wood flame retardant has the effects of good flame retardant effect, small hygroscopicity, corrosion resistance, insect prevention, mildew prevention, more color change and so on. The phosphorus-nitrogen-boron wood flame retardant has the advantages of low toxicity, no chlorine and lower cost.
Owner:GUANGDONG ACAD OF FORESTRY +1
Pretreatment method of detection on malachite green, crystal violet and residues of malachite green and crystal violet in eels
The invention provides a pretreatment method of detection on malachite green, crystal violet and residues of malachite green and crystal violet in eels, belonging to the field of analytical chemistry. The method comprises the operations of weighing of a sample to be detected, homogenization, solid phase extraction, elution and the like; instruments used in the method comprise a constant temperature oscillator, a high speed dispersing homogenizer, a centrifugal machine and the like. A sample solution prepared by using the pretreatment method can be directly detected by using a liquid chromatogram-tandem mass spectrometry method; compared with the prior art, the pretreatment method has the advantages of simple and effective operation, less time consumption, low cost, good reproducibility and the like, and has very strong operability, so that the pretreatment method has the hope to be widely popularized and applied in a large scale in industries such as environment protection, commodity inspection, entry and exit inspection and quarantine and the like, with significant economic benefits.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for treating dye waste water by enzyme production through mixed biomass fermenting
InactiveCN102583769ASimple methodEasy to operateWaste water treatment from textile industryBiological water/sewage treatmentMalachite greenCongo red
The invention discloses a method for treating dye waste water by enzyme production through mixed biomass fermenting. In the method, white rot fungi which can generate a lignin degrading enzyme system are used as a fermenting enzyme-production strain; a solid and liquid culture method is adopted, a cottonseed hull and / or paddy straw are / is used as a fermentation substrate, and lignin degrading enzyme is induced to obtain an optimal lignin degrading enzyme system; and finally, crude enzyme liquid is extracted, separated and prepared and can be used for decoloring treatment of waste water of commonly-used synthetic dye, such as Congo red, phenol red, bromophenol blue, crystal violet, malachite green and the like so as to obtain the optimal decoloring effect of dye sewage. The method is simple and is easy to operate. The enzyme system induced by the method disclosed by the invention has high enzymolysis efficiency, and the optimal decoloring effect can be achieved by adopting the enzyme system to treat the dye waste water.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Indirectly racing ELISA kit for detecting leuco malachite green
ActiveCN101451999AJudgment concentration rangeQuick analysisMaterial analysisMalachite greenElisa kit
The invention discloses an ELISA kit for detecting recessive malachite green, comprising recessive malachite green polyclonal antibody, recessive malachite green hapten and complete antigen and enzyme-labelled antigen. The inventive ELISA kit is sensitive, fast and accurate, mainly used for screening of mass samples. Mainly reagent in the kit is provided in the form of work liquid, with the advantages of convenient usage, high specificity, high accuracy, high exactness and the like, for fast detecting recessive malachite green residual in the aquatic products.
Owner:WUXI ZODOLABS BIOTECH
Method for cultivating and artificial breeding plateau saline-alkali water area northern pike
The invention relates to a method for cultivating and artificial breeding plateau saline-alkali water area northern pike, aiming at providing a technology suitable for cultivating and artificial breeding the northern pike in the plateau saline-alkali water area. The method adopts first filial generation fingerling bred by wild northern pike to be cultivated into parent fish. The method is characterized in that before the northern pike fingerling is put into a pond, forage fish can be cultivated by an original pond, the northern pike fingerling with the length of 5cm is put into the pond aftertwo weeks, and the polyculture proportion between the northern pike fingerling and the forage fish is 1:200-300; when the temperature of the pond reaches to 7-8 DEG C, parent fish roe of the northernpike can be selected for semidry method artificial fertilization for 5min, and talc powder is used for abhesion after fertilization; oosperm is sterilized by malachite green solution and then enters into an incubator to be incubated; by controlling the speed and the flow rate of the water flow, the dead oosperm of the northern pike can be promoted to be discharged from a drain pipe; deep well water which contains 7-9mg / L of dissolved oxygen and has the water temperature of 12DEG C can be continuously pumped into the bottom of the incubator, and running water incubation can be carried out underthe dim light; and when the fingerling flatly swim to intake the exogenous nutrition, the fish can be fed by fish bait in time.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Malachite green fast detecting method and fast detecting kit
InactiveCN101067619ADoes not affect observationLow costComponent separationMalachite greenMalachite green stain
The invention discloses a fast testing process of malachite green, which settles after mixed the measured sample and withdraw medicinal preparation, take the supernatant into the chromatography column, observes most lower level absorbent color change in the chromatography column, if forms the green clitellum, might judges that malachite green contains in the sample; the withdraw medicinal preparation is the mixture of acetonitrile and ethyl acetate solution and the acidic aluminum oxide, of which the volume ratio of the acetonitrile and ethyl acetate is 1: 15-30, the quality of the states measured sample and the mixture solution of acetonitrile and ethyl acetate volume ratio is 1:3; the quality ratio of the measured sample and the acidic aluminum oxide is 2:1. The invention used acetonitrile-ethyl acetate solution to withdraw the malachite green more completely and remarkably reduce the toxicity which is used in the reagent, also had stronger service ability to a fat product with higher content.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Preparation method and applications of aptamer electrochemical sensor for detecting malachite green (MG)
InactiveCN103713026AImprove conductivityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerMalachite green
The invention provides an aptamer electrochemical sensor for detecting malachite green (MG). A preparation method for the electrochemical sensor comprises the steps of: the prepared graphene-chitosan compound and nanogold are modified on an electrode surface, an aptamer is connected on the nanogold through chemical action, a target object is bound onto the electrode surface through the specific binding action of the aptamer and the target and then connected with an antibody of the target object, thus constructing the biosensor with a sandwich structure. When the detected solution contains the target object, a certain amount of target objects and corresponding antibodies can be fixed on the electrode surface, so that a sensing structure is formed. Horseradish peroxidase (HRP) is modified on the antibodies, and the hydrogen peroxide can be catalyzed to be decomposed, so that the change of an electrochemical signal can be generated, and the detection on the MG can be realized through the change of the electrochemical signal. The prepared aptamer electrochemical sensor is strong in selectivity, high in sensitivity, simple and fast to operate, and suitable for detection on the MG of aquatic products.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Laccase gene as well as encoded protein and application thereof
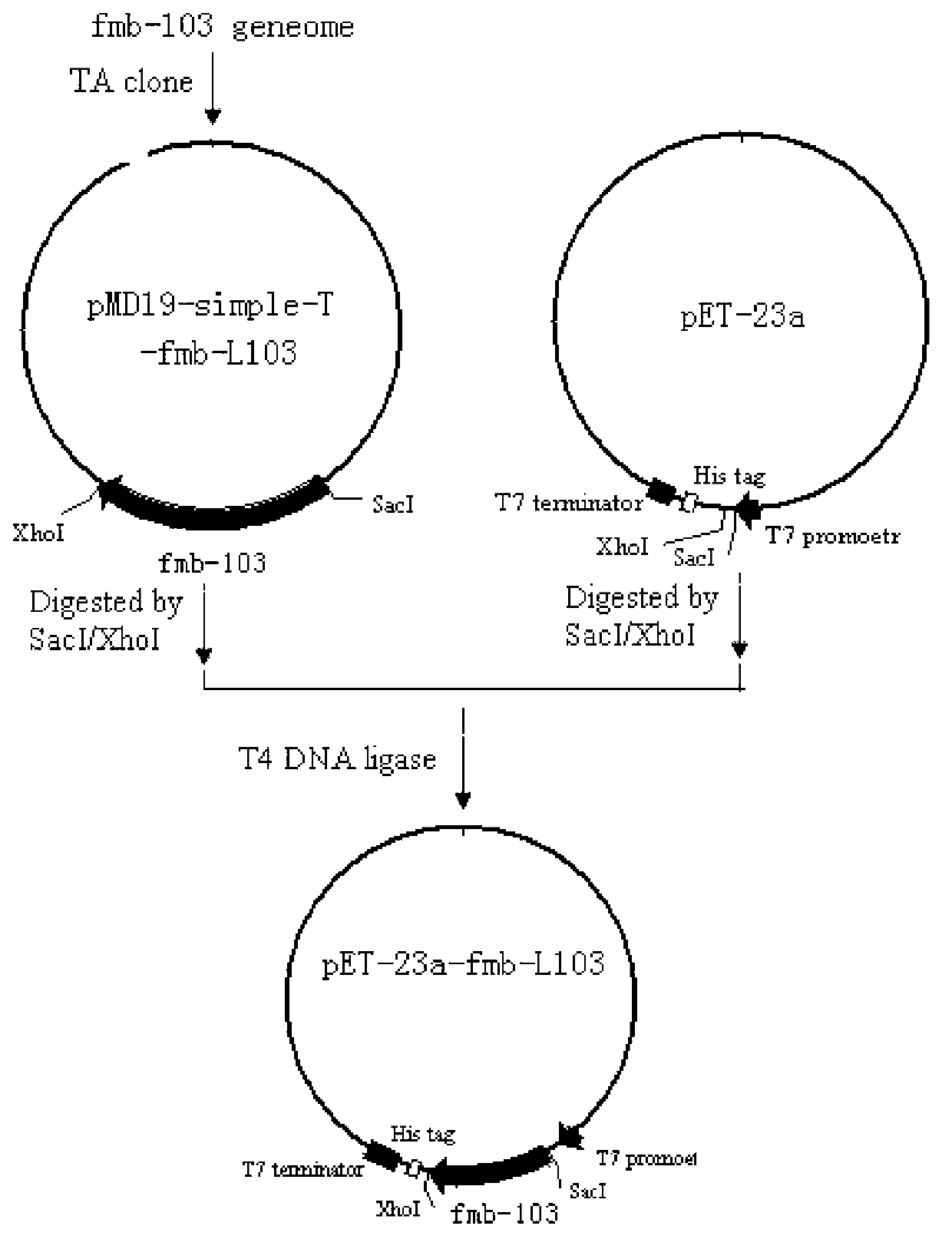
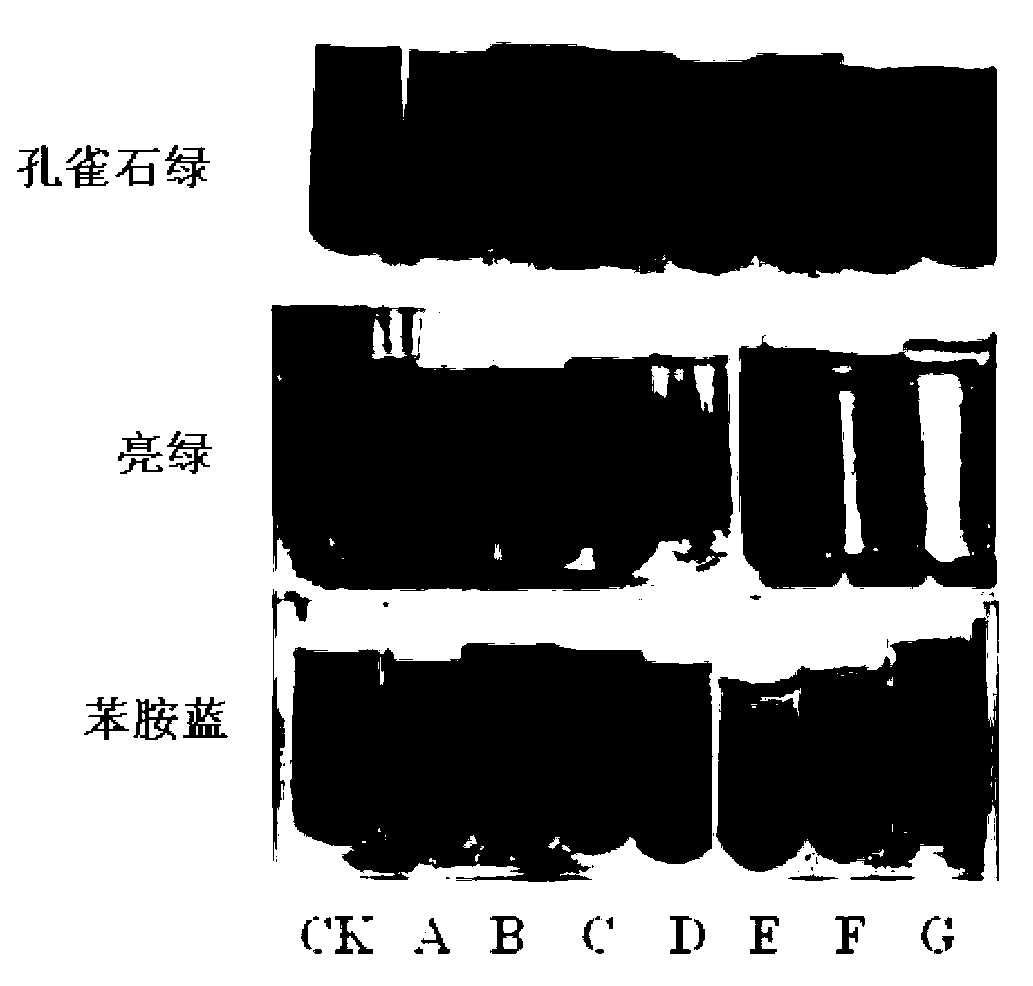
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a laccase gene as well as an encoded protein and an application thereof. The open reading frame sequence of the laccase gene fmb-L103 is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the laccase gene fmb-L103 disclosed by the invention is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The laccase gene fmb-L103 disclosed by the invention is applied to decoloration for triphenlmethane dyes. The inventor clones from the selected dead bacillus vallismortis fmb-L103 with a spore laccase activity to obtain a novel prokaryotic laccase gene fmb-L103, and realizes the heterologous efficient expression of escherichia colli expression host bacteria. The recombinase fmb-L103 can be used for efficiently catalyzing the degradation of the triphenlmethane dyes of malachite green, brilliant green and aniline blue.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Fiber natural polymeric adsorbent and application thereof
InactiveCN103100376AGood biocompatibilityImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionCelluloseSodium bicarbonate
The invention provides a fiber natural polymeric adsorbent, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The fiber natural polymer uses bean dregs as a fiber source. Fresh bean dregs are successively treated by distilled water, ethanol solution and sodium bicarbonate solution for processing, so as to remove water-soluble substances and small molecular substances; and then the bean dregs are subjected to drying, crushing and sieving through a 100 mesh screen. Adsorption tests prove that the fiber natural polymer adsorbent has excellent adsorption performance on wastewater containing heavy metal lead ions and copper ions, a dye methylene blue, malachite green, basic fuchsin and organic pollutant naphthol. Therefore, the fiber natural polymeric adsorbent can be used for industrial treatment on wastewater containing heavy metal ion, dyes and organics. At the same time, the adsorbent mainly comprises components including cellulose, lignin and a small amount of glycoprotein, and is a non-toxic, pollution-free edible natural polymer with good compatibility; therefore, the adsorbent can also be used as a rapid antidote for heavy metal poisoning.
Owner:GANSU TIPTOP PLANT TECH CORP
Preparation of xanthated loess adsorbent and application of xanthated loess adsorbent to waste water treatment
InactiveCN103071461ALoose surface structureLarge specific surface areaOther chemical processesWater contaminantsMalachite greenMalachite green stain
The invention provides a preparation method of a xanthated loess adsorbent. The method comprises the following steps of: dispersing loess into a sodium hydrate solution to form a suspension; dropwise adding carbon bisulfide into a system, and stirring for reacting to generate a xanthated loess sodium salt; adding a soluble sodium salt into the system, and stirring for reacting to generate a xanthated loess magnesium salt; and washing, drying in vacuum, and grinding into powder to obtain the xanthated loess adsorbent. As proved by a large quantity of experiments, the xanthated loess adsorbent disclosed by the invention has a looser surface structure than that of natural loess, has a large specific surface area, has very high adsorption performance on heavy metal copper ions and malachite green in waste water, has a high adsorption capability and a large adsorption volume when applied to treatment of waste water containing heavy metal copper ions and a malachite green dye, and can be used for treating waste water containing the heavy metal copper ions and the malachite green dye.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
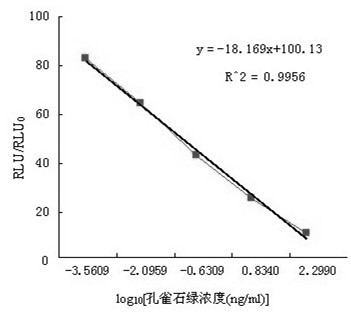
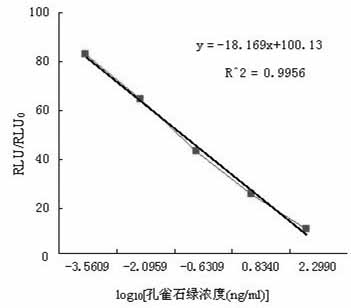
Magnetic molecular imprinting bionic ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) detecting method of malachite green
The invention discloses a magnetic molecular imprinting bionic ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) detecting method. The magnetic molecular imprinting bionic ELISA detecting method includes steps of preparing magnetic molecular imprinted polymer and setting up a direct-competition ELISA method. By the detecting method, uniform-particle MG-MMIPs (malachite green-magnetic molecular imprinted polymers) are prepared by an emulsion polymerization method, adsorption performance is investigated, the MG-MMIPs is used as bionic antibody, and the directly-competitive ELISA detecting method is established by means of competitive adsorption to MG antigen and enzyme labeling MG antigen. Under the optimum reaction conditions, the standard curve sensitivity is 20.14 ugL-1, and the minimum detection limit is 0.12 ugL-1 and is lower than detection limit of 2 ppb (ng / g) of a MG rapid-detection card. Meanwhile, the method has high selectivity for MG, and cross reaction rates for two structural analogues (methyl violet and brilliant green) of the MG are 7.4% and 3.9% respectively.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
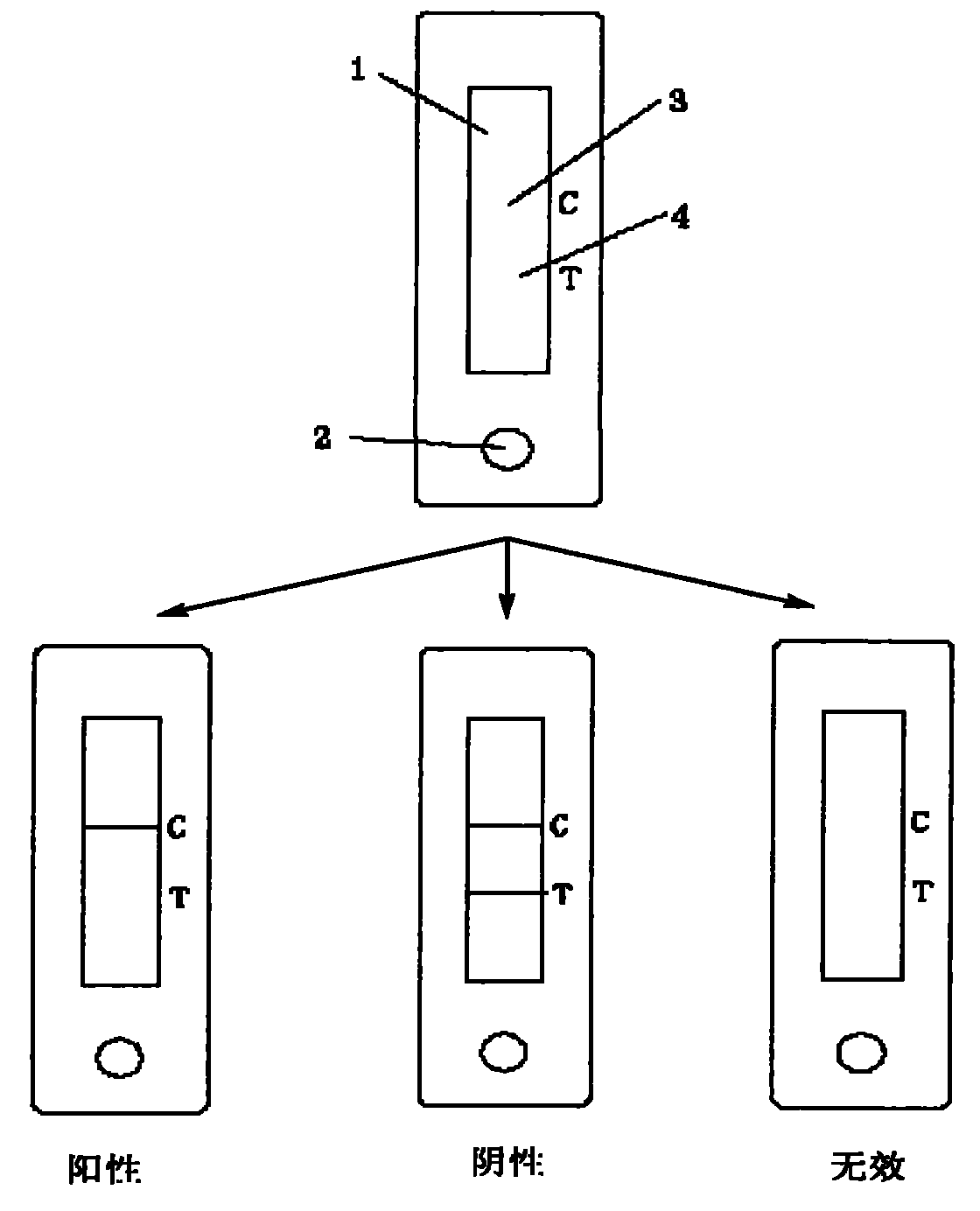
Immunochromatographic test strip for detecting malachite green (MG) and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN102353775ARapid and Sensitive AssayRealize objective measurementMaterial analysisCelluloseMalachite green
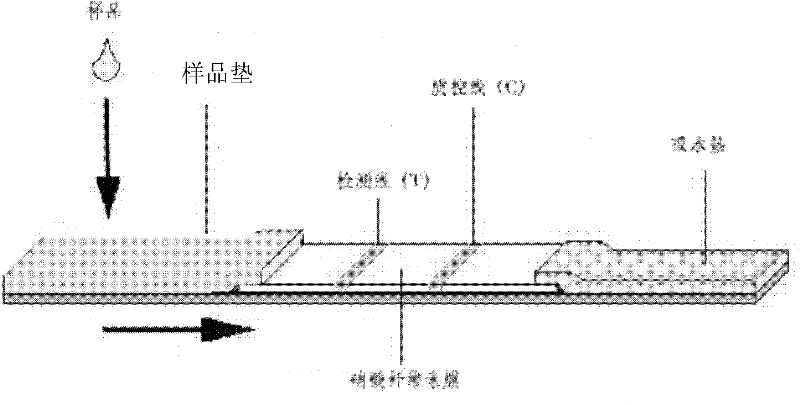
The invention discloses an immunochromatographic test strip for detecting MG and a preparation process thereof. The immunochromatographic test strip for detecting MG provided in the invention comprises a sample pad containing MG antibodies marked by superparamagnetic composite particles, a cellulose nitrate membrane connected with one end of the sample pad and an absorbent connected with another end of the cellulose nitrate membrane; the cellulose nitrate membrane is coated by mutually separated detection lines and quality control lines, wherein, the detection lines contain MG antigens, and the quality control lines contain antiantibodies which can specifically bind to the MG antibodies. Experiments in the invention prove that the test strip provided in the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, strong specificity, rapidness, simpleness and capability of realizing objective detection when is used for detecting MG.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
ELISA reagent for detecting malachite green and method
InactiveCN101424686ASimple and fast operationThe pre-processing process is simpleMaterial analysisMalachite greenMalachite green stain
The invention discloses an Elisa agent for detecting malachite green and a method thereof. The Elisa agent comprises a malachite green antigen or antibody coated Elisa plate, an enzyme label, a malachite green specific antibody, a malachite green standard solution, a substrate developing solution, a stop solution, a concentrated cleaning solution, enzyme label diluents and a concentrated combined solution. The Elisa agent is used for the quantitative detection of the content of the malachite green in fishes, shrimps and water samples and has the advantages of high specificity and sensitivity, easy sample pretreatment, short detection time, large sample detection amount, and the like.
Owner:深圳市绿诗源生物技术有限公司
Method for treating malachite green wastewater and recycling resources
InactiveCN101786737AEfficient governanceWide range of concentration adaptationMethine/polymethine dyesMultistage water/sewage treatmentMalachite greenHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for treating malachite green wastewater and recycling resources, which comprises the following steps: adjusting pH to be between 3.5 and 7 by adding diluted alkaline into the malachite green wastewater, filtering the malachite green wastewater to obtain filtrate and making the malachite green wastewater flow through an adsorption column or an absorption tower filled with activated carbon fibers, so that malachite green is absorbed onto the activated carbon fibers; directly discharging absorption effluent when the pH of the effluent is 6 to 7, and if the pH of the absorption effluent is lower than 6, rationally adding the diluted alkaline into the absorption effluent until the pH is adjusted to be between 6 and 7 and then discharging the absorption effluent; taking the solution of hydrochloric acid and ethanol as a desorbent and performing desorption and regeneration on the activated carbon fibers absorbing the malachite green; distilling a desorption solution containing high-concentration malachite green, recycling the desorbent and taking the desorbent as the desorbent of a next batch and separating malachite green solids out from residual liquid at the bottom of a kettle so as to recycle the malachite green; and taking the desorption solution containing low-concentration malachite green as a starting desorbent of the desorbent of the next batch. The malachite green wastewater treated by the method has the removing rate of the malachite green approximate to 100 percent, and desorption rate of the malachite green over 97 percent. In respect of the treatment on the malachite green wastewater and the purification of low-concentration malachite green water bodies, the method is of greater application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
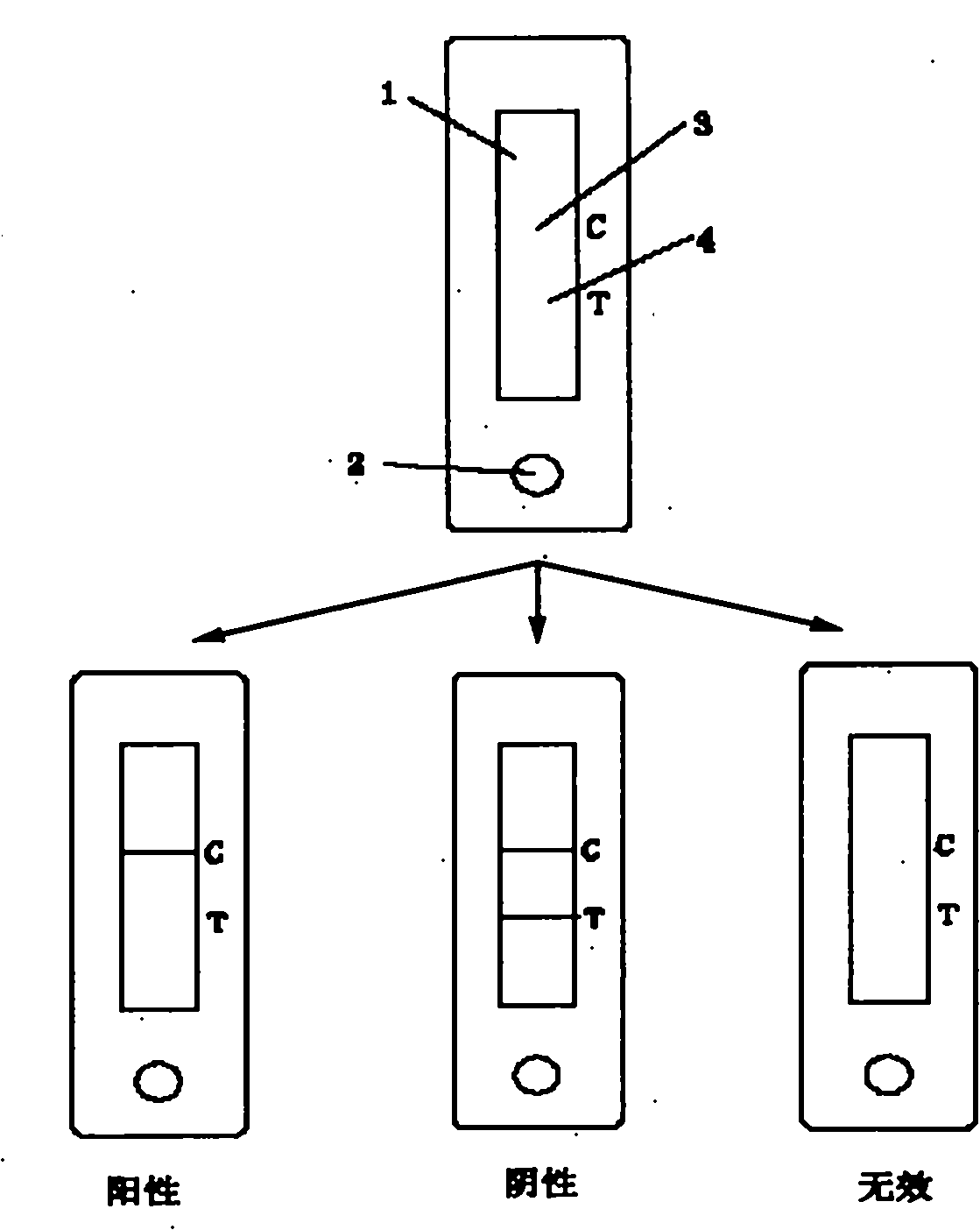
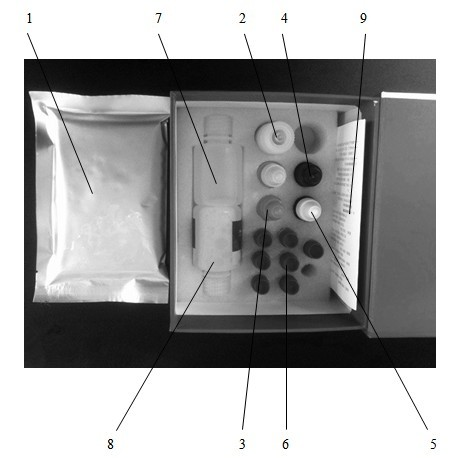
Malachite green collaurum detection card and production and application methods thereof
ActiveCN101995467AMeet the testing requirementsLow priceOvalbuminSerum albuminMalachite greenNitrocellulose
The invention relates to a malachite green collaurum detection card and production and application methods thereof, belonging to the technical field of immunology. The rapid diagnosis card comprises a case and a test strip; wherein the case is opened with a sample injecting hole and an observation window, the test strip is arranged in the case, the middle part of a PVC liner plate is superposed with a nitrocellulose membrane, the two ends are respectively superposed with an absorbent pad and a sample pad, the nitrocellulose membrane is overlapped and connected with the absorbent pad and the sample pad, a membrane containing malachite green monoclonal antibody immune collaurum compound is coated on a sample region, and a detection strip containing malachite green envelop antigen and a quality control strip containing goat anti mouse IgG are arranged on the nitrocellulose membrane. The invention is a rapid, accurate and sensitive diagnosis card, requires no special apparatus, has simple operation and can meet the detection requirements of food safety, fishery and detection mechanism.
Owner:深圳市三方圆生物科技股份有限公司
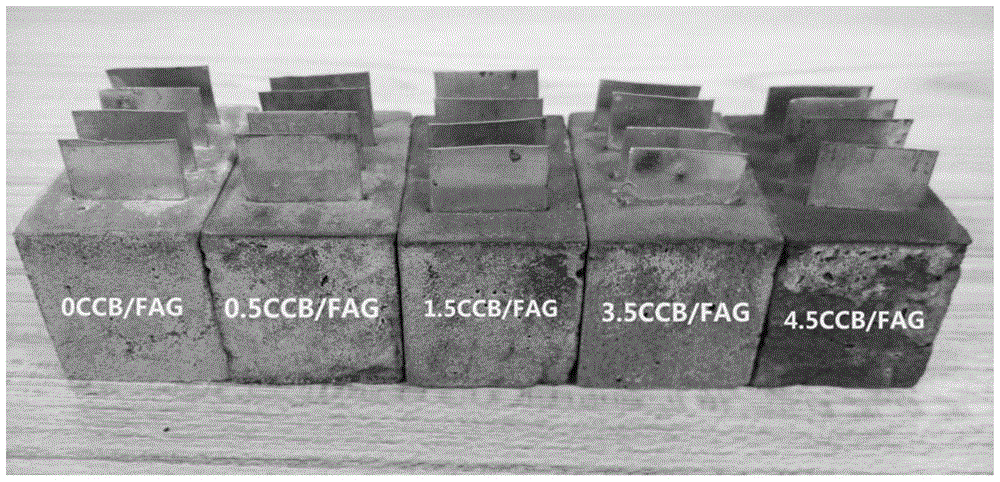
Preparation and application of conductivity-controllable fly ash-based geopolymer material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a conductivity-controllable fly ash-based geopolymer semiconductor material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: putting fly ash, carbon black, sodium silicate nonahydrate and an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide into a stirring device and mixing; and forming with a mould and curing to obtain the conductivity-controllable fly ash-based geopolymer semiconductor material, wherein the dosage of the sodium silicate nonahydrate, potassium hydroxide, carbon black and water accounts for 15%, 7%, 0.5-4.5% and 30-40% of the fly ash mass respectively; the stable conductivity of the prepared fly ash-based geopolymer semiconductor material can be controlled in a range from 0.00025 to 0.65 (S / m) in a curing age of 28 days; and when the prepared conductivity-controllable fly ash-based geopolymer semiconductor material is used as a novel photocatalyst for degrading malachite green organic dye, a change law that the conductivity of the material is directly proportional to the degradation rate of the dye is discovered. The preparation technology is simple, the cost is low, the discharge of three wastes is avoided in the preparation process, and the conductivity-controllable fly ash-based geopolymer semiconductor material can be used as a dye degrading high-activity catalyst.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation process of complex photocatalyst with multiwalled carbon nanotube loading silver/silver phosphate core-shell structure
InactiveCN105148955AUniform sizeSimple structureMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsMalachite greenOrganic dye
The invention relates to a preparation process of a complex photocatalyst with a multiwalled carbon nanotube loading silver / silver phosphate core-shell structure. The preparation process comprises the following steps of performing pretreatment on a carbon nanotube and preparing the complex photocatalyst with the multiwalled carbon nanotube loading silver / silver phosphate core-shell structure by an in-situ glycol reduction method. The preparation process disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that a sample of the complex photocatalyst with the multiwalled carbon nanotube loading silver / silver phosphate core-shell structure has a regular morphology, a comparatively uniform particle size and better particle dispersibility; experiment raw materials have wide sources; the preparation steps are simpler; the condition is mild; the production cycle is shorter, and the obtained composite has a better structure; the nano-composite photocatalyst has an efficient degradating effect on the organic dye malachite green under visible light radiation, can be applied to the photocatalytic oxidation technology, and is capable of effectively removing organic pollutants in water environments.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN101580550AHigh flocculation activityMicroorganism based processesSustainable biological treatmentBiotechnologyActivated sludge
The invention relates to an extra-cellular polysaccharide of aerobic Ruthia sp. strain metabolin and preparation and application thereof. An aerobic strain ZHT4-13 is separated from adhesive sludge of wild Ruditapes philippinarums in the Bohai sea offshore of China and is identified as a Ruthia sp. The aerobic strain is treated by seed culture and amplification culture, and a fermentation broth of the aerobic strain is precipitated with ethanol and separated centrifugally to obtain the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13. The extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 is measured to have high flocculation activity, the FR value to kaolin reaches over 80 percent, and the removal rate to hexavalent chromium ions reaches 69.3 percent; the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 has high activity to decolorize high-concentration wastewater, and the decolorization ratios to methylene blue, ink blue, malachite green and crystal violet reach 86.11 percent, 99.49 percent and 97.84 percent; and the extra-cellular polysaccharide MBF4-13 plays a role of obviously improving the performance and the structure of activated sludge. The extra-cellular polysaccharide has potential value of developing a novel microbial flocculant.
Owner:DALIAN JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Malachite chemiluminescence ELISA detection method and kit
ActiveCN102661946AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceELISA unitImmuno detection
The invention discloses a malachite chemiluminescence ELISA detection method and a kit. According to the invention, it is the first time to discuss chemiluminescence ELISA mechanism of malachite, a malachitechemiluminescence ELISA detection system and a detection method are successively established, and perfect combination of high sensitivity and high specificity is realized. The kit provided by the invention has high sensitivity, accuracy, precision and stability, is used to simplify operation steps and reaction time and reduce errors caused by complex operation, is very suitable for trace analysis and batch detection of malachite residues, and is of great practical application significance.
Owner:广州万联生物科技有限公司
Application of echinacoside in anti-tumor medicaments
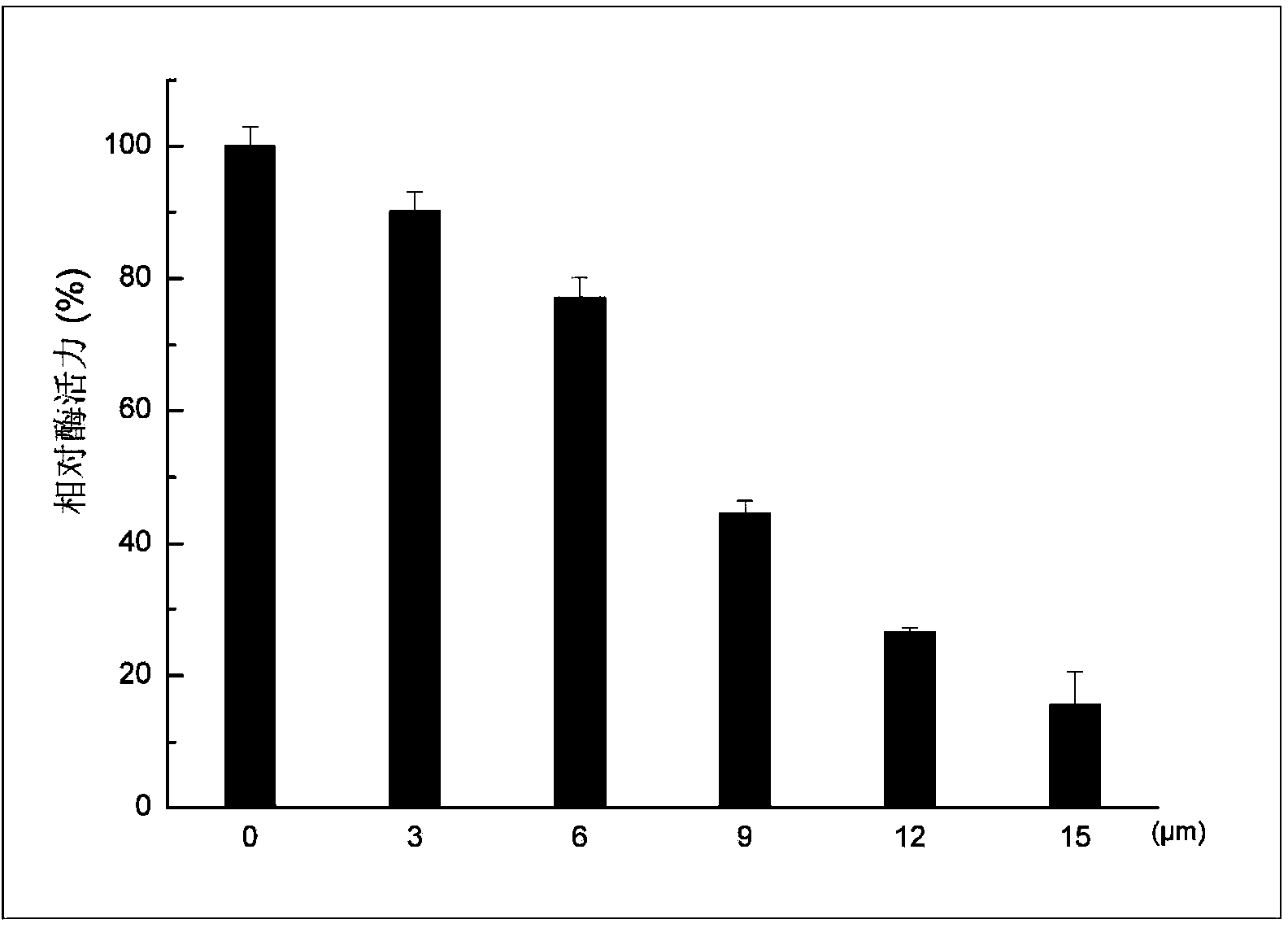
ActiveCN104288170AInhibitory activityBlock scavenging oxidationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMalachite greenCancer cell
The invention relates to application of echinacoside in anti-tumor medicaments. The application provided by the invention is as follows: firstly adding MTH1, inorganic pyrophosphatase and dGTP into a reaction solution (100mM pH 8.0 Tris-acetic acid, 40mM NaCl, 10mM magnesium acetate, 0.005% Tween 20 and 1mM DTT), incubating an enzyme and a substrate at room temperature for 1h, then adding 25 mu l of malachite green solution to terminate reaction and performing absorbance detection at 630nm by using an iMark microplate reader, wherein results show that echinacoside has a significant effect of inhibiting enzyme activity of MTH1; and secondly detecting the effects of echinacoside against tumor cells at the cellular level by an MTT experiment, wherein the results show that echinacoside can obviously inhibit the growth of SW480 colon cancer cells and U2OS human osteosarcoma cells. According to the application provided by the invention, echinacoside is used for inhibiting specific enzyme MTH1 for maintaining survival in the tumor cells, and oxidized nucleotide is mixed into DNA, thereby resulting in fatal DNA double-strand break in the cancer cells, producing an anti-tumor effect, finding a new medical use of echinacoside and laying a foundation for future development of the new anti-tumor medicaments.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com