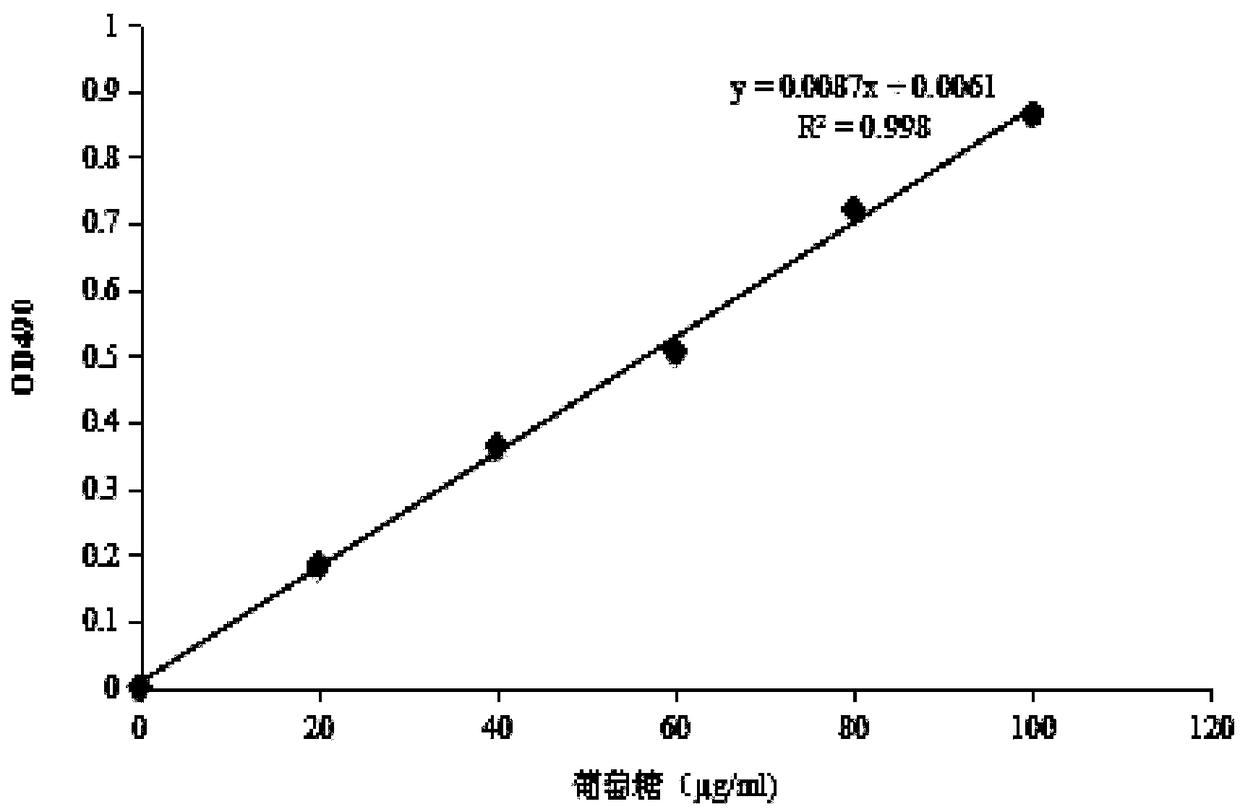
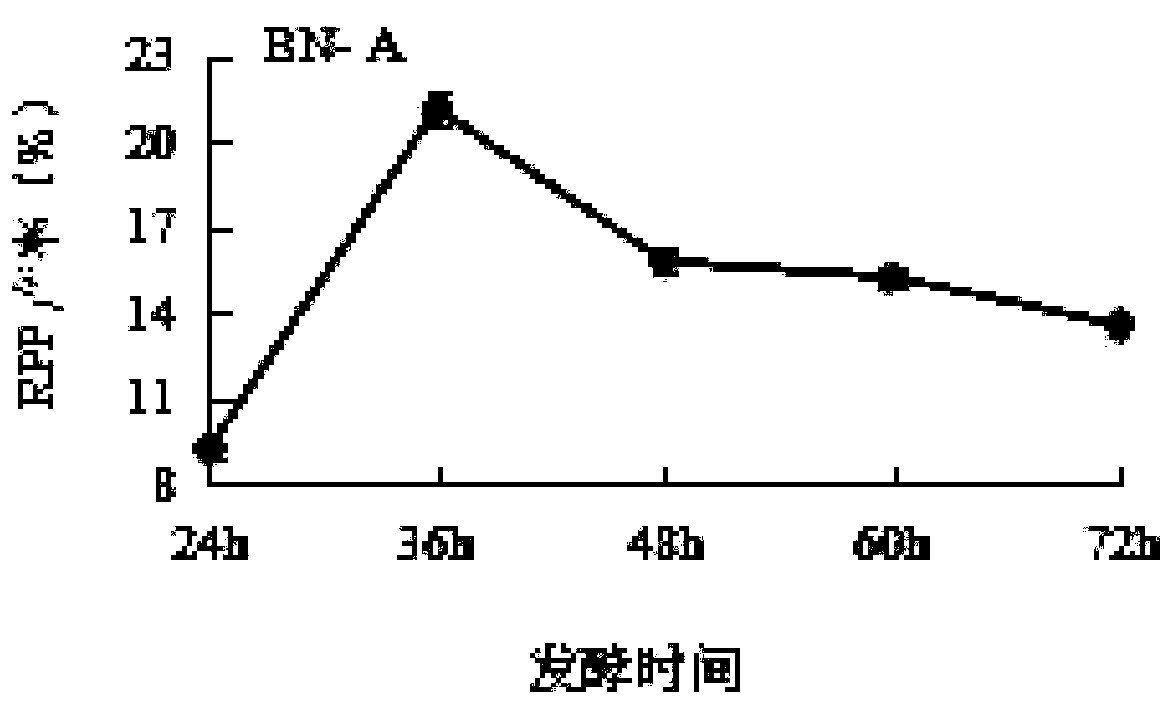
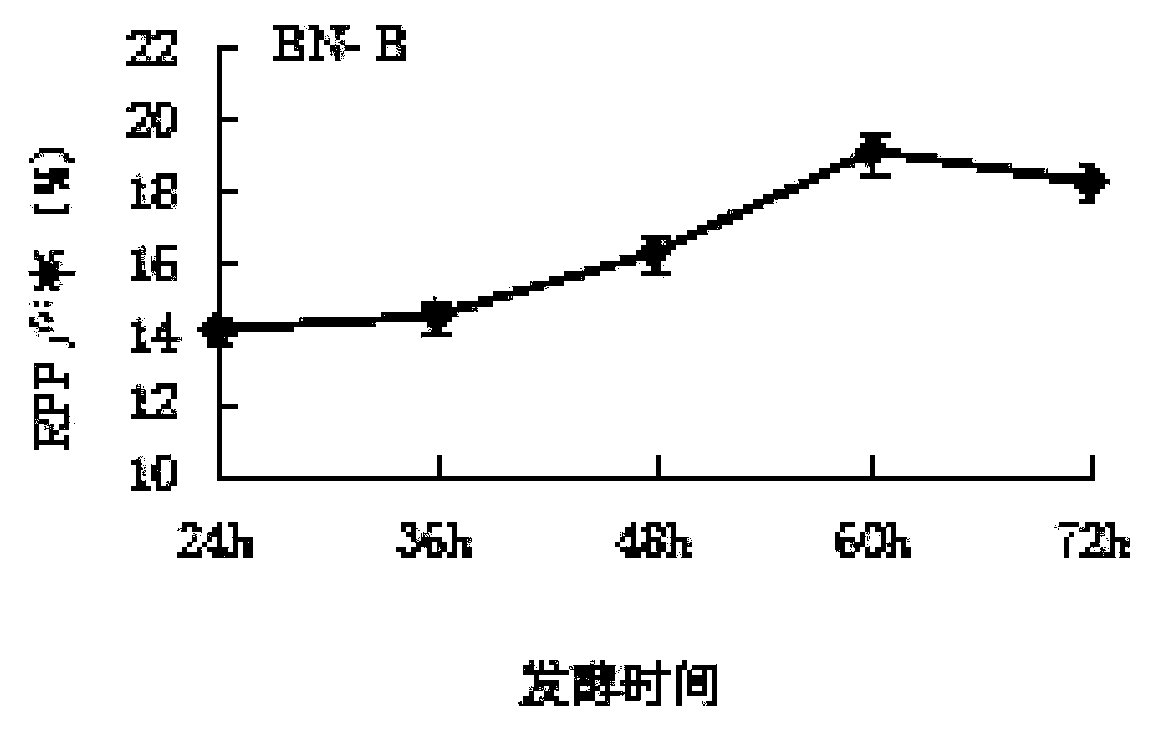
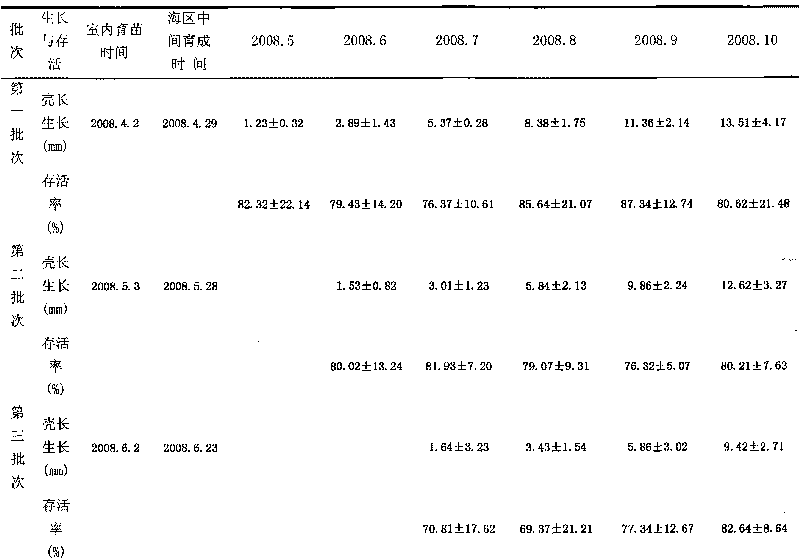
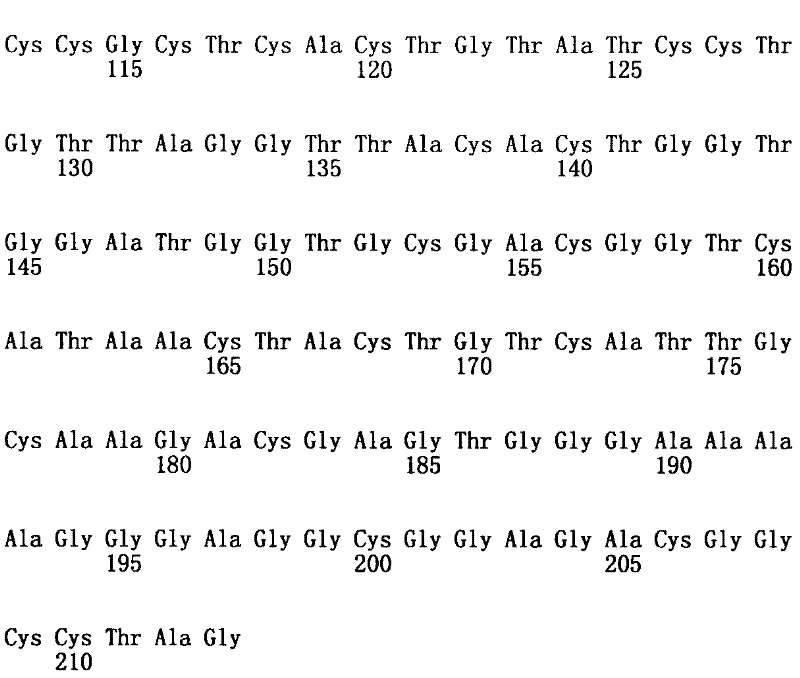Patents
Literature
100 results about "Ruditapes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ruditapes is a genus of marine bivalve molluscs, in the family Veneridae.
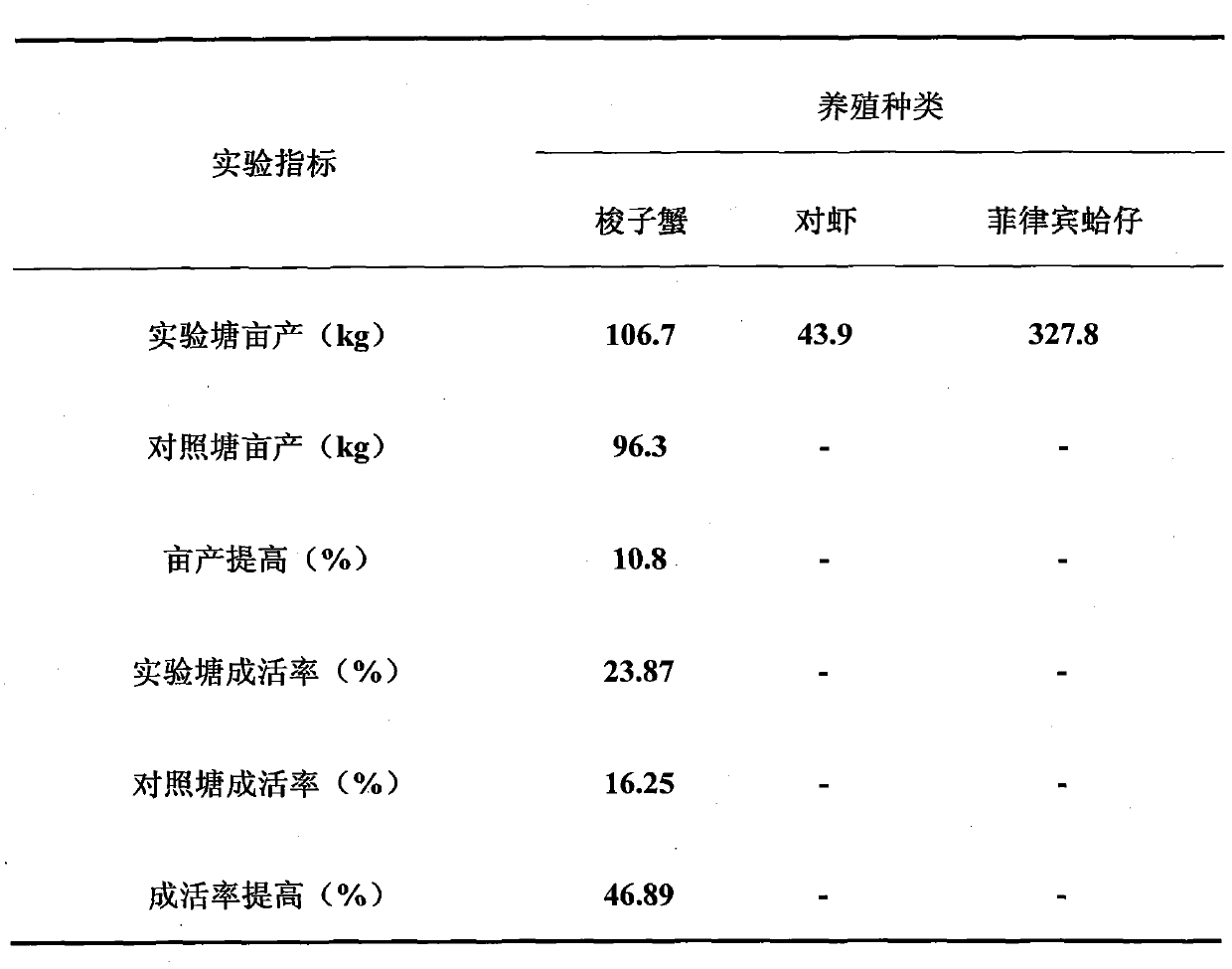
High-efficient ecological seedling-raising method of blue crabs
ActiveCN102613126AReasonable collocationPromote healthy developmentClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseEcological environment
The invention provides a high-efficient ecological seedling-raising method of blue crabs. The high-efficient ecological seedling-raising method comprises the following steps of: selecting parent crabs after artificial breeding, adopting circulating water to keep the water temperature in an overwintering pond, feeding clam worms, ruditapes philippinarum, squid and other baits for performing intensive culture on the parent crabs, utilizing a single-crab and single-pond mode to perform pond arrangement, and laying disinfection sea mud at the bottom of a larval rearing tank for simulating a sea natural ecological environment. By using the method disclosed by the invention, vertical transmission of diseases can be avoided, the use of coal is reduced, and energy conservation and emission reduction are realized; and the baits can be reasonably matched for promoting the healthy development of embryos, and self-mutilation of larvae can be reduced for improving the yield and the quality of seedlings. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the yield of the seedlings of the blue crabs can be improved by 30-50%, the outdoor farming survival rate can be improved by 10-15%, and the method can be widely applied to offshore sea waters and has significant economic benefits.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for realizing ecological larval culture on rapana venosa
InactiveCN102160529AIncrease emergenceReduce manufacturing costClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffWater qualityOrganism
The invention relates to a method for realizing ecological larval culture on rapana venosa. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly selecting a pond which is convenient in water exchange, takes lithoherm and stone bottom as a substrate and is in the size of 2-5Mu; then placing mature rapana venosa with the length of 7-10cm into the pond in the quantity of 100kg per Mu, mating and spawning after the rapana venosa eats ruditapes and mussel for 2-3 days, when enough oocysts are obtained, removing the rapana venosa away, incubating the oocysts for 20-22 days at the water temperature of 20-25 DEG C to obtain planktonic larva, growing the planktonic larva by eating the planktonic larva in the pond, starting to throwing polyethylene corrugated plate adherence ortile under the condition that the water temperature is 22-25 DEG C after 15-16 days, sticking benthic diatom and the planktonic larva onto the polyethylene corrugated plate or tile, transfigurating the planktonic larva of the rapana venosa into young spiral shell after 5-6 days, growing the transfigurated young spiral shell by eating the planktonic larva and benthic diatom on the corrugated plate, wherein the survival rate of the transfigurated young spiral shell on the corrugated plate can reach more than 50%, and feeding small low-value bivalve to the young spiral shell with the length morethan or equal to 3mm. By applying the method provided by the invention, the defects that the survival rate is low and the larval yield is low as bait conversion is difficult and water is polluted when carnivorous fish mice are used as feed in indoor artificial larval culture can be overcome, and the larval yield is improved by more than 50% compared with the indoor artificial larval culture. Meanwhile, the production cost is saved as no bait is thrown into the pond, thus the method is environment-friendly, and the produced larval is strong.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for continuously breeding artificially-collected larvae of ruditapes philippinarum
InactiveCN104304137AFast supplyGrow fastClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaZoologySeawater
The invention discloses a method for continuously breeding artificially-collected larvae of ruditapes philippinarum. The method mainly includes the following steps: (1) a natural sea beach is selected to serve as a continuous breeding field; (2) a breeding beach range is separated from the periphery through plastic boards to prevent the ruditapes philippinarum from escaping and facilitate feeding; (3) pre-disinfection treatment is carried out on the breeding beach; (4) the collected or purchased larvae of the ruditapes philippinarum are evenly put into the breeding field in a high-density mode; (5) feed is immediately put after the ebb, and a thin water layer is kept for five hours; (6) inner-field surface residuals should be completely washed away through seawater; (7) when the adult ruditapes philippinarum is harvested, the ruditapes philippinarum in the sizes meeting the requirement is screened through a screen, and larvae, with the number the same as the number of the screened-out adult ruditapes philippinarum, of the ruditapes philippinarum are additionally put into the field. By means of the method for continuously breeding the artificially-collected larvae of the ruditapes philippinarum, continuous breeding is carried out through the artificially-collected larvae, the natural larvae of the ruditapes philippinarum can obtain sufficient feed and the natural environment, growing is rapid, the breeding time is greatly shortened, and the ruditapes philippinarum can be rapidly supplied to the market.
Owner:毛艳玲
Seed production method of Philippines little clam breeding lines
InactiveCN101288387AGrow fastStrong stress resistanceClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffZoologyPearl white
The invention relates to a method of preparation seeds of breeding lines of ruditapes philippinarum. The qualitative character of shell color is used as the marker, and ruditapes philippinarums with different shell colors are used as raw material, and then the breeding lines with advanced characters are obtained by directive breeding of successive generations. More particularly, the shell colors and lines include two-red-strip, two-white-strip, black onyx, oceanic red, pearl white, zebra clam and ripple clam; due to directive purity of a plurality of generations, the lines of pearl white, oceanic red and two-red-strip which grow fast and the lines of zebra clam with strong stress resistance are screened out. The breeding lines of the invention has the characteristics of fast growth or high livability, thus establishing certain foundation for the hybridization of shell color and lines of ruditapes philippinarum as well as breed improvement.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
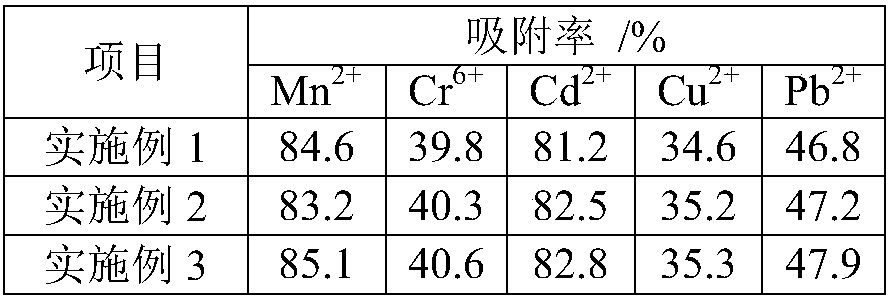
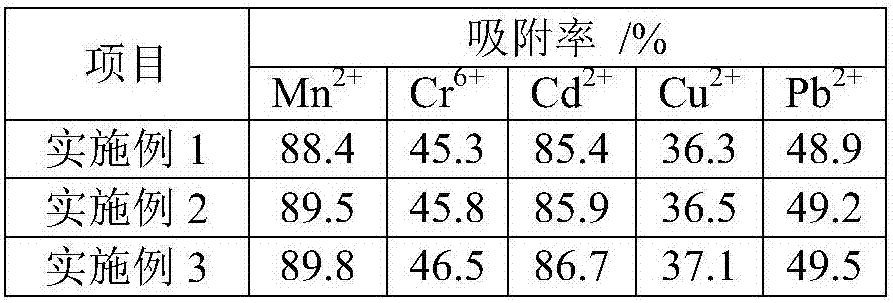
Method for preparation of heavy metal adsorbent from marine Psychrobacter strain
ActiveCN107626285AImprove adsorption capacityImprove adsorption efficiencyOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSludgePsychrobacter sp.
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to a method for preparation of a heavy metal adsorbent from a marine Psychrobacter strain. The selected marine Psychrobacter strain Psychrobacter sp.GHF2 is separated from the sludge liquid spit by ruditapes philippinarum, the strain is subjected to enlarged culture to prepare a strain solution, and fermentation cultureis carried out to produce abundant exopolysaccharide, then the fermented strain solution is dialyzed to remove part of medium components, and centrifugation is conducted to obtain supernatant, ethanol precipitation purification is carried out twice to obtain a refined extraction product of exopolysaccharide, and the refined extraction product of exopolysaccharide is mixed with agar and starch toprepare the heavy metal adsorbent. The heavy metal adsorbent has high adsorption efficiency, can be used directly in drinking water, and is safe and harmless.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
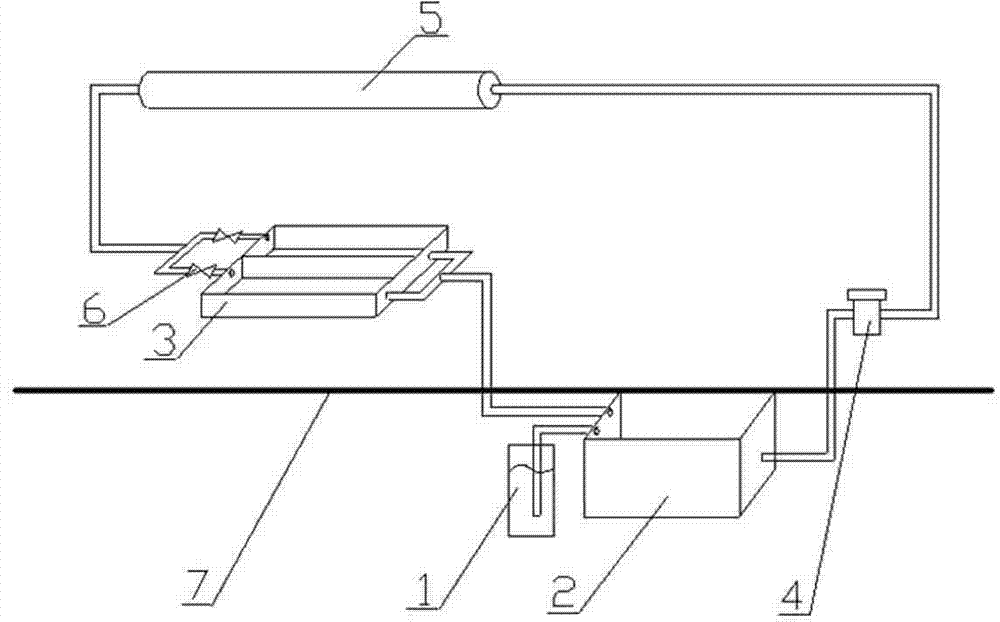
Processing technology for purifying pollutant in hard-shelled seawater shellfish
InactiveCN102823530AGood removal effectNo secondary pollutionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSeawater treatmentUltravioletHygienic quality
The invention discloses a processing technology for purifying pollutants in four kinds of hard-shelled seawater shellfish by adopting an ultraviolet seawater treatment technique, wherein the four kinds of hard-shelled seawater shellfish include Ruditapes philippinarum, Meretrix meretrix Linnaeus, Cyclina sinensis and Tegillarca granosa. The technology provided by the invention adopts a semi-closed circulating system and the processing is conducted in a room with environmental temperature capable of being regulated. The technology is implemented through the following six steps of: selecting shellfish, cleaning the shellfish, containing the shellfish in a basket and placing the basket into a purifying pond; pumping deep-well seawater with seawater quality which satisfies the requirement into a circulating water pond; pumping the deep-well seawater into an ultraviolet sterilizer for sterilization through a water pump; spraying the sterilized seawater into the purifying pond to purify the shellfish according to technological parameters; draining return water into the circulating water pond for recirculation; and completing the purification technological process of one batch till the hygienic quality standard on the shellfish is met or after the minimum purification time which is 24 hours. The processing technology has the advantages that the pollutant removing effect is remarkable, the vitality of the shellfish after purification is strong, the technology is simple, the investment is small and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
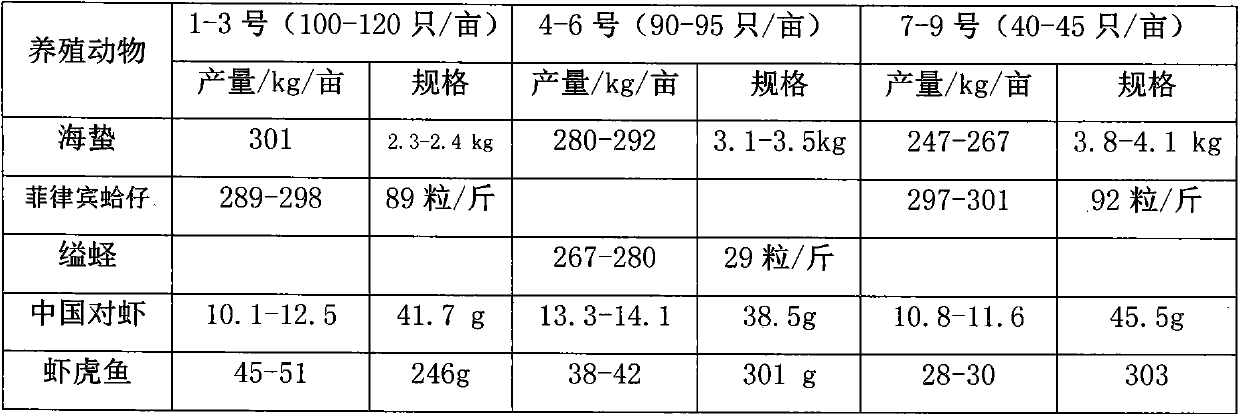
Jellyfish breeding method
ActiveCN104186393AIncrease the amount of feedingFeed amount increasedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMixed cultureWater quality
The invention discloses a jellyfish breeding method including subjecting jellyfishes to mixed culture with ruditapes philippinarum, sinonovacula constrictas, penaeus chinensis, penaeus monodons and goby; controlling ecological breeding technologies including a stocking system based on breeding species and density, a feeding system based on a match between the species and number and a water quality control system based on a principle that firstly applying fertilizer into water, secondly maintaining fertilizer content and thirdly controlling the water quality. In this way, the jellyfishes and other species are rapid to grow and high in output and economic benefit. By the use of the jellyfish breeding method, the jellyfish output reaches 200-400kg / mu, the outputs of the ruditapes philippinarum and the sinonovacula constrictas reach 200-300kg / mu, and the outputs of the penaeus chinensis and the penaeus monodons reach 10-30kg / mu, and the goby output reaches 20-30kg / mu.
Owner:辽宁每日农业集团有限公司
Artificial cultivation method of hemifusus termatamus
InactiveCN101843225AImprove the breeding environmentImprove farming efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLaminaria japonicaWater source
The invention discloses an artificial cultivation method of hemifusus termatamus and relates to shellfish cultivation. The invention provides the artificial cultivation method of hemifusus termatamus, which can effectively reduce cultivation cost and labor intensity, is convenient for daily inspection and has convenient operation and management. The method comprises the following steps: selecting cultivation facilities and water sources; before stocking young hemifusus termatamus, sterilizing, when using a land cultivation pond, laying attaching base at the bottom of the pool for the young hemifusus termatamus to attach, and cleaning the bottom and sucking sewage regularly after stocking the young hemifusus termatamus; after starting to cultivate the young hemifusus termatamus, feeding with bait every day, wherein the bait comprises the following ingredients according to mass ratio: 50-70 of sinonovacula constricta, 30-60 of ruditapes philippinarum, 40-70 of trash fish and 10-30 of laminaria japonica; when cultivating the hemifusus termatamus, cleaning residual bait at the bottom of the pool, on the attaching base or in the cultivation cage every day, when the shell length of the young hemifusus termatamus reaches 1-3cm, the stocking density is 300-600 / m2, when the shell length reaches more than 5cm, carrying out division, and controlling the stocking density of the young hemifusus termatamus to be within 30-60 / m2.
Owner:惠安县山霞友兴鲍鱼场
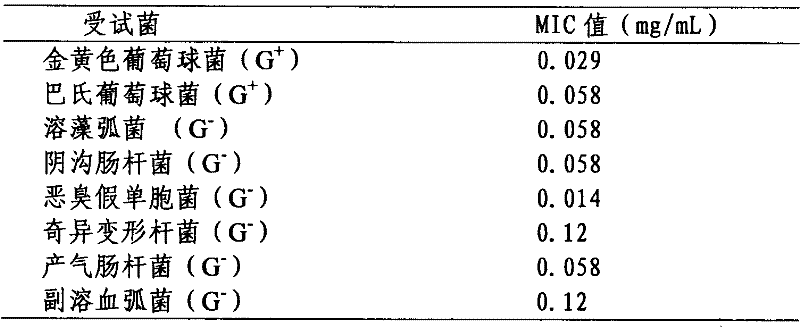
Ruditapes philippinarum Defensin B gene, its recombinant protein and application
InactiveCN102363784AStrong inhibitory activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsGramRuditapes
The invention relates to antibacterial peptide, more specifically to a Ruditapes philippinarum Defensin B gene, its recombinant protein, a construction method and an application. The Defensin B gene is as shown in a base sequence in a sequence table SEQ ID NO.1. The gene recombinant protein is as shown in an amino acid sequence in a sequence table SEQ ID NO.2. The Defensin B provided by the invention is Ruditapes philippinarum antibacterial peptide, has a strong inhibitory activity of a plurality of marine Gram-positive and negative pathogenic organisms and has application values of being developed into broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs, genetic breeding, feed additives and the like.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for breeding ruditapes philippinarum
ActiveCN103828746ANo pollution in the processImprove fertilization rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOosporeSexual maturity
The invention discloses a method for breeding ruditapes philippinarum. The method includes steps of selecting individuals with full gonads as parents in ruditapes philippinarum sexual maturity periods; taking gonad samples of the parents; performing microscope examination on the gonad samples in fresh seawater; selecting first certain individuals as female parents and selecting second certain individuals as male parents; placing acquired egg liquid in fresh seawater for 15-45min; activating the egg liquid; placing sperms in the successfully activated egg liquid, performing fertilization in the successfully activated egg liquid, specifically, placing 3-5 sperms around each egg and performing fertilization in a stirring mode; hatching the eggs in a slight inflation manner; cultivating offspring according to a convention process for cultivating the ruditapes philippinarum to acquire large quantities of juvenile mollusks and adults. The first certain individuals have eggs which are microscopically perfectly circular, the eggs are gray black and have complete egg envelopes, the diameters of the eggs are consistent, the diameters of the eggs of northern colonies of the first certain individuals are 70.0+ / -0.5 micrometers, and the diameters of the eggs of southern colonies of the first certain individuals are 60.0+ / -0.5 micrometers. The second certain individuals have the sperms all of which jump microscopically. The method has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, easiness in popularization and the like.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV +1
Breeding boar feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104206810ARich in proteinIncrease appetiteFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceBOAR
The invention discloses a breeding boar feed and a preparation method thereof. The feed is prepared from following raw materials including, by weight, 35-45 parts of wheat, 15-20 parts of corn, 8-16 parts of soybean meal, 4-7 parts of fish meal, 3-5 parts of shells of ruditapes philippinarum, 5-8 parts of dried sheep manure, 3-6 parts of male silkworm moth powder, 2.5-4.5 parts of powder of cotyledon of sesbania cannabina, 2-3 parts of cell-disrupted yeast powder, 1.5-2.5 parts of MACA powder, 2-3 parts of ocimum basilcum, 3-4 parts of fish sauce, 2-3 parts of a smoking solution, 0.4-0.8 parts of red yeast powder, 5-10 parts of powder and residue of canna edulis, 4-8 parts of dried peels of persimmon, 3-6 parts of crushed tea dust, 5-10 parts of waste bacteria sticks of lentinula edodes and 2.5-4.5 parts of modified limestone powder. The feed is rich in high-quality proteins, vitamins and minerals, can provide energy required in growth, generation of sperm, hybridization activation and the like of breeding boars, is good in palatability, is easy to digest, can enable the breeding boars to have good appetite and sexual desire and can improve sperm quality and breeding capability of the breeding boars.
Owner:安徽金源农牧股份有限公司
Nucleoside ingredient obtained from ocean low-value shellfish through separation and purification and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106018582ALiver protectionImprove antioxidant capacityComponent separationColor/spectral properties measurementsSurf clamAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying a nucleoside chemical ingredient from ocean low-value shellfish (such as mactra veneriformis, ruditapes philippinarum, meretrix lusoria, anadara subcrenata, cyclina sinensis, solen and surf clam shell). The method comprises the first step of preparation of shellfish water extract and alcohol precipitate supernate, the second step of macroreticular resin column rough separation and the third step of separation and purification of cation exchange resin. The method for separating and purifying the nucleoside chemical ingredient from the ocean low-value shellfish is reasonable in technological design, strong in operability, short in production period, low in cost and high in environmental protection; the prepared nucleoside chemical ingredient is high in purity and has the good effect of protecting liver; mactra veneriformis, ruditapes philippinarum, meretrix lusoria and other low-value shellfish resources can be sufficiently utilized, and the important economic value is obtained.
Owner:浙江海富海洋生物科技有限公司
Method for solving problem of biological deposition of sand-bottom stichopus japonicus aquaculture pond by aid of biological functions
InactiveCN103053456AMaintain ecological balanceReduce disease incidenceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSinonovaculaOrganism
The invention discloses a method for solving the problem of biological deposition of a sand-bottom stichopus japonicus aquaculture pond by the aid of biological functions. The method can solve problems that an effect for improving biological deposition of a sand-bottom stichopus japonicus aquaculture pond is poor in the prior art, a sedimentary environment of the stichopus japonicus aquaculture pond cannot be effectively improved, diseases of stichopus japonicus cannot be prevented and the like. The method is characterized in that certain quantities of penaeus japonicus, fenneropenaeus chinensiss, ruditapes philippinarum and sinonovacula constricta are fed into the stichopus japonicus aquaculture pond, an effect of loosening the bottom of the pond is realized owing to sand diving functions of the penaeus japonicus, the fenneropenaeus chinensiss, the ruditapes philippinarum and the sinonovacula constricta, organisms such as nereid and copepoda in the aquaculture pond are ingested by the penaeus japonicus and the fenneropenaeus chinensiss, and residual feeds, organic detritus, humus, fungi and the like are subjected to filter-feeding by the ruditapes philippinarum and the sinonovacula constricta. Accordingly, the method has the advantages that the purpose of improving a sedimentary environment of the aquaculture pond is achieved, and the problem of biological deposition of the aquaculture pond is solved.
Owner:MARICULTURE INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Seedling production method for Philippines cockle young hybridization series
InactiveCN101292635AIncrease productionGrow fastClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffHigh survival rateBiology
The invention provides a breeding method of a hybridization line of Ruditapes philippinarum. By utilizing qualitative character of shell color as tag, the method takes Ruditapes philippinarum with different shell colors as material, the hybridization line with excellent properties are obtained by monomer hybridization and colony hybridization. In particular, the invention adopts two red lines of pearl white and ocean red which grow rapidly, and zebra clam line with strong stress resistance as material to establish the hybridization line so as to obtain the hybridization line of white zebra and red zebra with the properties of rapid growth speed and strong stress resistances. The hybridization line obtained by the invention is characterized by fast growth speed and high survival rate, thereby effectively improving the yield of Ruditapes philippinarum and laying a solid foundation for breed modification of Ruditapes philippinarum.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Aerobic active marine bacteria and preparation method of decolorizing flocculant of aerobic active marine bacteria
ActiveCN107460144AGood decolorization effectHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMalachite green
The invention discloses aerobic active marine bacteria and a preparation method of a decolorizing flocculant of the aerobic active marine bacteria. The aerobic active marine bacteria is formed by performing isolation and screening on mud disgorged by ruditapes philippinarum bred in a sea farm in a Zhujiajian, Zhoushan, Zhejiang in China, and is authenticated to be pseudoalteromonas ((i) Pseudoalteromonas ( / i)sp.). The decolorizing flocculant has the beneficial effects that the formed adecolorizing flocculant has good decoloration effect, and the flocculation rate of the decolorizing flocculant to kaolin reaches greater than 90 percent; the decolorizing flocculant has high activity for performing decoloration on high-concentration waste water, and the flocculation rate of the decolorizing flocculant to methylene blue, malachite green and crystal violet reaches greater than 92 percent, 99 percent and 98 percent; the decolorizing flocculant does not have potential toxicity for organisms, and is green and healthy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Ecological polyculture method for portunus trituberculatus mainly cultured in pond
InactiveCN101919361AConducive to controlling the spreadPromote growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPolycultureFenneropenaeus chinensis
The invention discloses an ecological polyculture method for portunus trituberculatus mainly cultured in a pond. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of cleaning the pond, culturing ruditapes philippinarum, fenneropenaeus chinensis and the portunus trituberculatus, feeding bait and the like. By using ecological complementarity of the ruditapes philippinarum, the fenneropenaeus chinensis and the portunus trituberculatus for polyculture, the method of the invention fully utilizes the natural bait, increases the spatial stratification of the ecological structure of the culture pond, improves the stability of the environment of the culture pond and solves the problems of cannibalism of the portunus trituberculatus, insufficient bait, diseases, degradation of water quality and the like during the culturing, so that the technical effects of high yield, high efficiency and environmental protection are realized.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Method for preparing heavy metal high-efficiency adsorbent by utilizing compound bacterial agent
ActiveCN107574219AVigorousIncrease productionOther chemical processesWater contaminantsSorbentSludge
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a heavy metal high-efficiency adsorbent by utilizing a compound bacterial agent. The compound bacterial agent comprises marine salt monoucleosis strains Halomonas sp.GHF11 and marine psychrobacter psychrophilus strains Psychrobacter sp .GHF2; the two types of strains are both obtained by separating and purifying sludge liquid which is spit by ruditapes philippinarum; the two types of the strains are compounded and fermented after being subjected to enlarged cultivation respectively; the two types of the strains are synergic to strengthen each other in fermenting and cultivating processes; the activity of the strains is high; the yield of produced exopolysaccharide is high; the exopolysaccharide is separated by dialyzing a fermented fermenting bacteria liquid, removing part of culture medium components, performing centrifuging and performing ethanol precipitation twice, and then is prepared into the heavy metal adsorbent by curing through agar and starch; the heavy metal adsorbent is good in adsorption effect, high in adsorption efficiency and stable in performance, is safe and harmless, and can be directly added into drinking water.
Owner:北京美胜同创科技发展有限公司
Psychrobacter aquimaris and method for preparing flocculating agent by psychrobacter aquimaris
ActiveCN107619802AImprove flocculation abilityAccelerated settlementBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcoholPsychrobacter sp.
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to psychrobacter aquimaris and a method for preparing a flocculating agent by the psychrobacter aquimaris. The psychrobacter aquimaris Psychrobacter sp. GHF2 is separated and purified from sludge liquor spit by ruditapes philippinarum, a strain of the psychrobacter aquimaris is subjected to enlarging cultivation to prepare strain liquid, the strain liquid is fermented and cultivated to prepare fermented liquid, a flocculating carrier is added into the fermented liquid in a fermentation late period, and the flocculating carrier and added ethyl alcohol are mutually reinforced, so that extracellular polysaccharide in the fermented liquid is safely settled. The extracellular polysaccharide secreted by the screened psychrobacter aquimaris Psychrobacter sp. GHF2 has strong flocculating effects, the flocculating carrier is added in the fermentation late period, so that bacterial cells are clumped on the flocculating carrier, settling of the extracellular polysaccharide is promoted, use of the ethyl alcohol is reduced, and the obtained flocculating agent is strong in flocculating capacity and stable in performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Aquatic feed for promoting weight of giant salamanders to quickly gain
InactiveCN104543560AIn line with feeding habitsMeet nutritional needs for growthAnimal feeding stuffRuditapesWhey protein
The invention discloses aquatic feed for promoting weight of giant salamanders to quickly gain. The aquatic feed is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-50 parts of water fleas, 20-40 parts of silkworm chrysalis, 10-15 parts of slugs, 15-25 parts of grandling, 30-38 parts of black carps, 10-15 parts of grass carps, 10-15 parts of carps, 5-10 parts of yellow croakers, 20-25 parts of krill, 20-25 parts of pond crayfishes, 10-20 parts of black tiger shrimps, 5-10 parts of ruditapes philippinarum, 10-15 parts of freshwater mussels, 5-10 parts of razor clams, 2-5 parts of stone crabs, 10-15 parts of extruded corns, 30-40 parts of soybean milk powder, 10-15 parts of fermented rapeseed meal, 8-12 parts of casein, 10-15 parts of whey protein, 3-9 parts of potato protein, 2-4 parts of lactic acid, 5-8 parts of guar gum, 1-3 parts of polysaccharide derivatives, 2-5 parts of tea-seed oil, 1-3 parts of composite vitamin, 0.5-0.8 part of composite mineral substances, 1-2 parts of a probiotics preparation, 4-8 parts of hawthorn fruits, and 8-12 parts of isatis roots.
Owner:无为县清源特种水产养殖专业合作社
Method for ruditapes philippinarums aquiculture in shallow sea of subtidal zone
InactiveCN103688886AStrong ability to resist harsh environmentExpand the breeding spaceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaTerrainGram
The invention discloses a method for ruditapes philippinarums aquiculture in the shallow sea of a subtidal zone. The method comprises the following steps: before ruditapes philippinarums seedling sowing, removing harmful bionts from the shallow sea of the subtidal zone, which has the salinity of 25-32, has a non-polluted substrate and a flat terrain, does not have fresh water injection and serves as a bottom sowing aquiculture area; taking young shellfishes as aquiculture seedlings, wherein the specifications of the young shellfishes are that the lengths are 7-20mm, the density is 600-7000 pieces per 500 grams, the shell color is white, the specifications are uniform, the activity is high and the young shellfishes are not broken; in mid-to-late April, sowing the seedlings into a 10-meter isobath by a wet sowing method, and scattering the seedlings within the range of the aquiculture area in a concentrated manner according to the density of 3,000-5,000 pieces per square meter, wherein the seedling sowing operation is required to be executed at the time of slack water, the specification of the seedlings is equal to or larger than 7mm, and the harmful bionts are regularly removed from the aquiculture area in an aquiculture process; after half a year to two years of aquiculture, the ruditapes philippinarums can be harvested when the ruditapes philippinarums shellfishes grow to be equal to or longer than 4cm and are individually equal to or heavier than 8 grams.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV +1
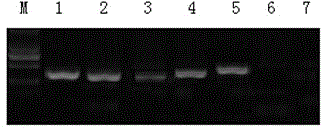
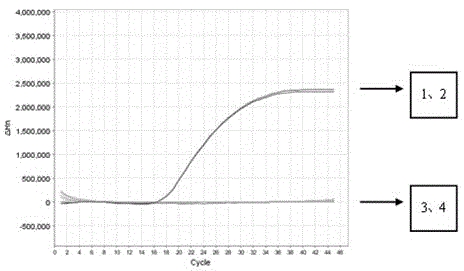
Ruditapes philippinarum species real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) specific detection system and application thereof
InactiveCN104962660AReasonable designHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific detectionFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a Ruditapes philippinarum species real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) specific detection system and application thereof. The sequences of the primers and probe are as follows: 5'-ggttgaacagtctaccctcc-3' (forward); 5'-gctaacatactactacgcaaaa-3' (reverse); and 5'-tctcttcacgtaggtggtgtctcttcaatt-3' (probe). After the Ruditapes philippinarum species specific detection primers and probe are adopted to perform real-time fluorescent PCR amplification on CoxI gene of Ruditapes philippinarum, a specific amplification curve can be generated, thereby performing specific identification on the Ruditapes philippinarum components. The specific primers and probe are reasonably designed, and have the advantages of favorable specificity and high detection sensitivity when being used for Ruditapes philippinarum species detection. The fluorescent PCR analysis can be performed to accurately identify the Ruditapes philippinarum components, thereby having favorable specificity.
Owner:刘淑艳 +3
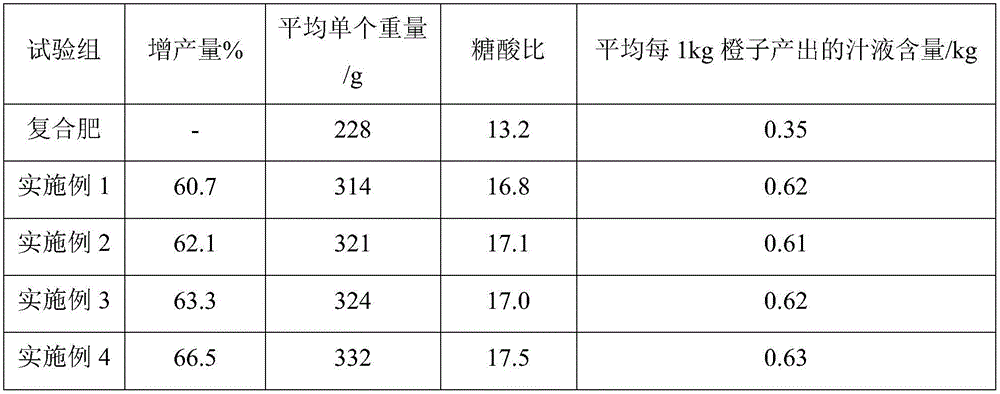
Special fertilizer for improving disease resistance and yield of navel orange and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106064982AGood fertilizer effectWith detoxification and insecticideAnimal corpse fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersDiseasePotassium
The invention discloses a special fertilizer for improving disease resistance and yield of navel orange and a preparation method thereof. The fertilizer comprises the following raw materials by weight: 50-58 parts of mixed enzyme, 20-25 parts of molasses alcohol waste liquid, 12-16 parts of Astragalus adsurgens Pall., 26-30 parts of pine and cypress ash, 12-15 parts of a Chinese medicine, 5-7 parts of a shrimp powder, 8-10 parts of a walnut kernel shell powder, 12-15 parts of Ruditapes philippinarum powder, 2-4 parts of dandelion pollen, 0.8-1.0 part of ammonium molybdate, 1.6-2.2 parts of potassium citrate, 3.2-3.6 parts of sodium lignosulfonate, 0.5-0.8 part of selenium-enriched yeast, 0.5-0.8 part of actinomyces, 0.3-0.5 parts of potassium bacteria, and 1.2-1.6 parts of Bacillus. The special fertilizer can improve the structure of soil for orange cultivation, increases the yield of navel orange planting; the navel orange is juicy and delicious; the invention greatly improves the economic benefit of farmers planting navel orange.
Owner:广西宁明百事康生物工程有限公司
Method for preparing ecological bionic microbial flocculant from leftovers of marine products
InactiveCN107089712ALow costGood flocculation effectWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationMicroorganismFlocculation
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ecological bionic microbial flocculant from leftovers of marine products. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating sludge suspension spat out by ruditapes philippinarum into a liquid culture base prepared from the leftovers of marine products and culturing, and then naturally settling or centrifugally separating precipitates and freeze-drying. According to the invention, the cost of the culture medium can be greatly reduced, the flocculation effect is excellent, pollutants and suspension particles in water can be effectively removed and the excellent settling property is guaranteed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
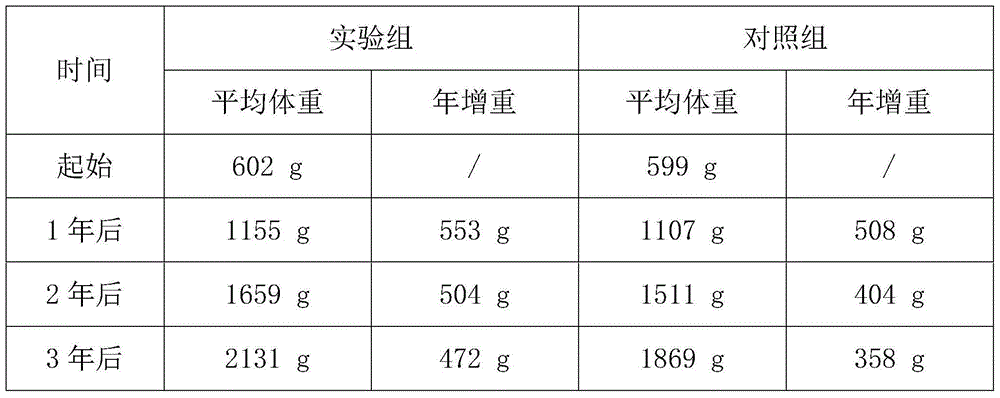
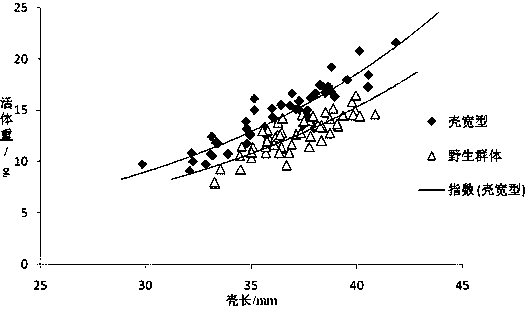
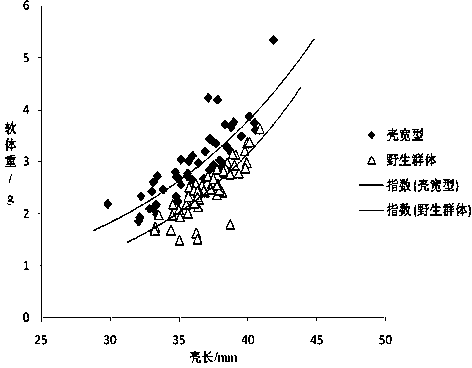
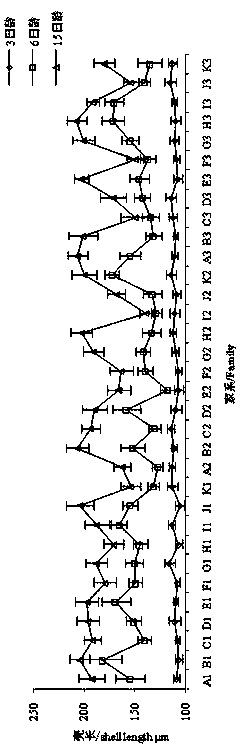
Seed production method for new lines of wide-shell-type ruditapes philippinarum
ActiveCN104855311AImprove survival rateIncrease egg productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMethod selectionArtificial insemination
The invention discloses a seed production method for new lines of wide-shell-type ruditapes philippinarum. The seed production method comprises following steps: collecting multiple ruditapes philippinarum out of natural population, measuring width and length of a shell of each one of ruditapes philippinarum, arraying ruditapes philippinarum in the manner from large to small according to ratios among shell widths and shell lengths, selecting individuals ranking the top 10% thereof as the first generation of spats, utilizing the first generation of spats to set up multiple wide-shell-type families, utilizing a multi-trait Blup breeding method to select families with breeding values ranking the top 20% of families, selecting individuals with ratios among shell widths and shell lengths ranking the top 10% as the second generation of spats in accordance with the above mode in these families and breeding the second generation of spats, hastening parturition and carrying out artificial insemination and the like in order to obtain the line of wide-shell-type ruditapes philippinarum.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
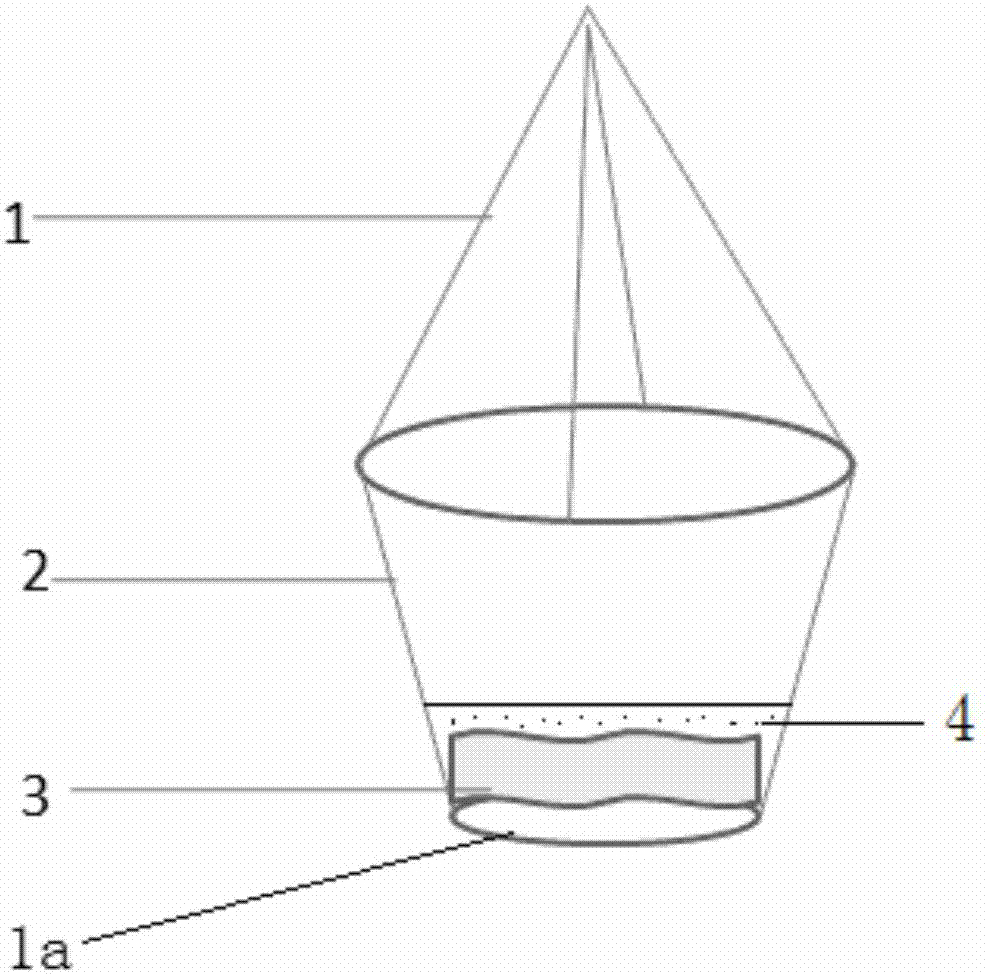
Method for solen grandis spat rearing
InactiveCN107182869AReduce concentrationImprove water qualityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPretreatment methodFiltration
The invention relates to the field of solen grandis spat rearing, in particular to a method for solen grandis spat rearing. In the aspect of a water pretreatment method for spat rearing, biological secondary purification is conducted on seawater obtained after sand filtration by using ruditapes variegate, toxic and harmful substances in the seawater can be further removed, and a good water quality condition is provided for the production of spat. In the aspect of an oviposition method, an oviposition barrel is used for oviposition, movable operation of the parent shellfish is achieved, and the problems that the oviposition density of the solen grandis is too large and the number of sperms is too large, and accordingly egg membrane dissolution or fertilized egg development malformation is caused can be solved. In the aspect of a fertilized egg hatching method, a method for hatching fertilized eggs in an original oviposition pond is used, so that the problems that the fertilized eggs are damaged due to water flow impact, friction and extrusion in the fertilized egg collection process, the fertilized eggs cannot be completely collected, and waste is caused are solved. In the aspect of selection and application of adhering substrates, the two materials including sea mud and fine sand serve as the adhering substrates in different juvenile shellfish stages, harmful organisms are removed easily, and the growth speed and the survival rate of juvenile shellfishes are increased.
Owner:丹东市水产技术推广总站
Mixed overwintering farming method of Portunus trituberculatus, Takifugu rubripes and Ruditapes philippinarum
ActiveCN109548719AAvoid predationPrevent outflowClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaVolumetric Mass DensityTakifugu rubripes
The invention discloses a mixed overwintering farming method of Portunus trituberculatus, Takifugu rubripes and Ruditapes philippinarum and belongs to the field of aquaculture. By making use of differences of ecological niches of species, Portunus trituberculatus, Takifugu rubripes and Ruditapes philippinarum are comprehensively overwintered and farmed in an indoor overwintering pond. It is prevented that Portunus trituberculatus preys on Ruditapes philippinarum; a protective net is used in a Ruditapes philippinarum farming zone, can prevent sand in the farming pond from flowing out during water changing and can also protect Ruditapes philippinarum. Ruditapes philippinarum is farmed in the 20% of the farming pond under the farming density of 100 individuals per m<2>; stocking density of Portunus trituberculatus is 5 individuals per m<2>; stocking density of Takifugu rubripes is 10 individuals per m<2>; when daily quantity of feed which is fresh trash fishes accounts for 5% of the weight of Portunus trituberculatus, ecological balance is exactly achieved for the three species in the farming pond; the feed is made full use, little water is changed, and resources are saved.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Bacillus natto and application thereof to fermenting ruditapes philippinarum to prepare active polysaccharides
ActiveCN108410767AHigh activityIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaRuditapesBacillus natto
The invention discloses Bacillus subtilis subsp. natto PS-I-HepG2. The Bacillus subtilis subsp. natto PS-I-HepG2 is used for fermenting ruditapes philippinarum to prepare active polysaccharides. The preparation method of the active polysaccharides comprises pretreatment of ruditapes philippinarum, preparation of bacterium suspension, fermentation, extraction, alcohol precipitation, deproteinization, ultra-filtration and freeze-drying to obtain ruditapes philippinarum polysaccharide powder. According to the Bacillus subtilis subsp. natto PS-I-HepG2, hepatoma carcinoma cell in vitro activity inhibiting experiments prove that the polysaccharides prepared by fermenting the ruditapes philippinarum through the Bacillus subtilis subsp. natto PS-I-HepG2 have significant anti-cancer activity and achieve a three-fold yield compared those produced before the ruditapes philippinarum is fermented. The active polysaccharides obtained through the Bacillus subtilis subsp. natto PS-I-HepG2 via the preparation method can be applied to preventing and treating solid tumors such as lung cancer and liver cancer.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Method for cultivating large-scale Ruditapes philippinarum white spats in sea area
ActiveCN105075937AImprove survival rateIncrease productionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaObserved SurvivalAquaculture
The invention discloses a method for cultivating large-scale Ruditapes philippinarum white spats in a sea area, and belongs to the field of aquaculture. The method comprises the following steps of choosing a white spat cultivation sea area, cleaning a sea area, sowing sand spats, preventing from natural enemies and harvesting the spats. By adopting the above technical scheme, the yield is 2.6 to 3.2 million white spats per mu, the size is 8000 to 15000 white spats per kilometer, the survival rate of the white spat cultivation in the sea area is 26 to 30 %. The method for cultivating large-scale Ruditapes philippinarum white spats can be popularized and applied to a large-scale coastal area in our country, the Ruditapes philippinarum white spats can be industrially cultivated, so the method provides spat guarantee for development of Ruditapes philippinarum cultivation.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST OF FUJIAN +1
Sea area intermediate breeding method applicable to Ruditapes philippinarum seedlings
ActiveCN101715750AIncrease productionThe process steps are simpleClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater flowSalinity
The invention discloses a sea area intermediate breeding method applicable to Ruditapes philippinarum seedlings, comprising the following steps: preparing an intermediate breeding tool of Ruditapes philippinarum seedlings; collecting seedlings with a mesh bag and hanging at sea for breeding; keeping normal water temperature, salinity and pH hydration index during intermediate breeding management at sea, brushing the bag every seven days, cleaning fluid mud and removing attachment to ensure smooth water flow of the mesh bag; after the size of the Ruditapes philippinarum seedlings reaches 1mm, selecting a mesh bag with 20 meshes and transferring on the sea according to the density of 5000 granules / bag, and temporarily breeding once again according to the above sea area hung breeding way; and after the size the Ruditapes philippinarum seedlings reaches 2mm, selecting a mesh bag with 10 meshes and transferring on the sea according to the density of 2000 granules / bag, and then hanging for breeding once again according to the above sea area hung breeding way. The method has the characteristics of simple process steps, easy operation and control and low cost, and improves the yield of unit water body.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Low-cost nutrition-balanced giant salamander aquatic feed
InactiveCN104543559AIn line with feeding habitsMeet nutritional needs for growthAnimal feeding stuffGiant salamanderPeanut meal
The invention discloses low-cost nutrition-balanced giant salamander aquatic feed. The low-cost nutrition-balanced giant salamander aquatic feed comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 50-60 parts of earthworms, 30-40 parts of silkworm chrysalis, 20-25 parts of water earthworms, 5-10 parts of wigglers, 10-15 parts of diplopods, 14-18 parts of pelteobagrus fulvidraco, 5-10 parts of parabramis pekinensis, 15-20 parts of snakeheads, 20-25 parts of silver carps, 20-25 parts of bighead carps, 5-10 parts of basses, 5-10 parts of mantis shrimps, 10-20 parts of black tiger shrimps, 2-5 parts of small-sized shrimps, 10-20 parts of ruditapes philippinarum, 15-20 parts of field snails, 10-20 parts of corbicula fluminea, 10-20 parts of extruded soybeans, 10-20 parts of fermented peanut meal, 30-40 parts of corn protein powder, 20-30 parts of skim milk powder, 10-15 parts of egg white, 5-10 parts of malic acid, 3-6 parts of locust bean gum, 5-8 parts of gelatin, 2-5 parts of grape seed oil, 1-3 parts of composite vitamin, 1.5-2 parts of composite minerals, and 1-2 parts of a probiotic preparation. According to the low-cost nutrition-balanced giant salamander aquatic feed, the cost is reduced, and the nutrition is comprehensive, rich and balanced.
Owner:无为县清源特种水产养殖专业合作社
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com