Patents
Literature
570 results about "ELISA unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
ELISA is a popular format of wet-lab type analytic biochemistry assay that uses a solid-phase enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence of a substance, usually an antigen, in a liquid sample or wet sample.
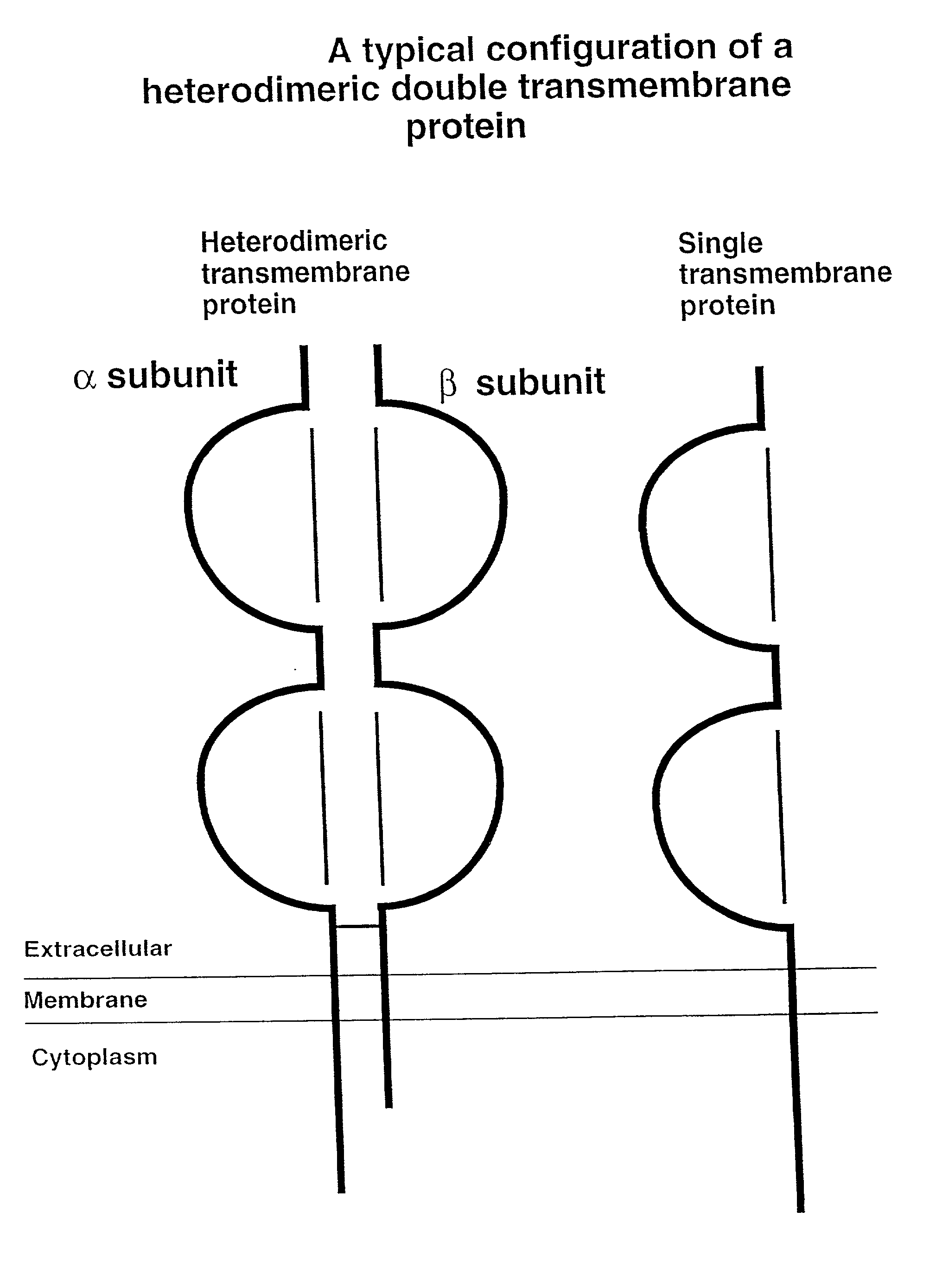
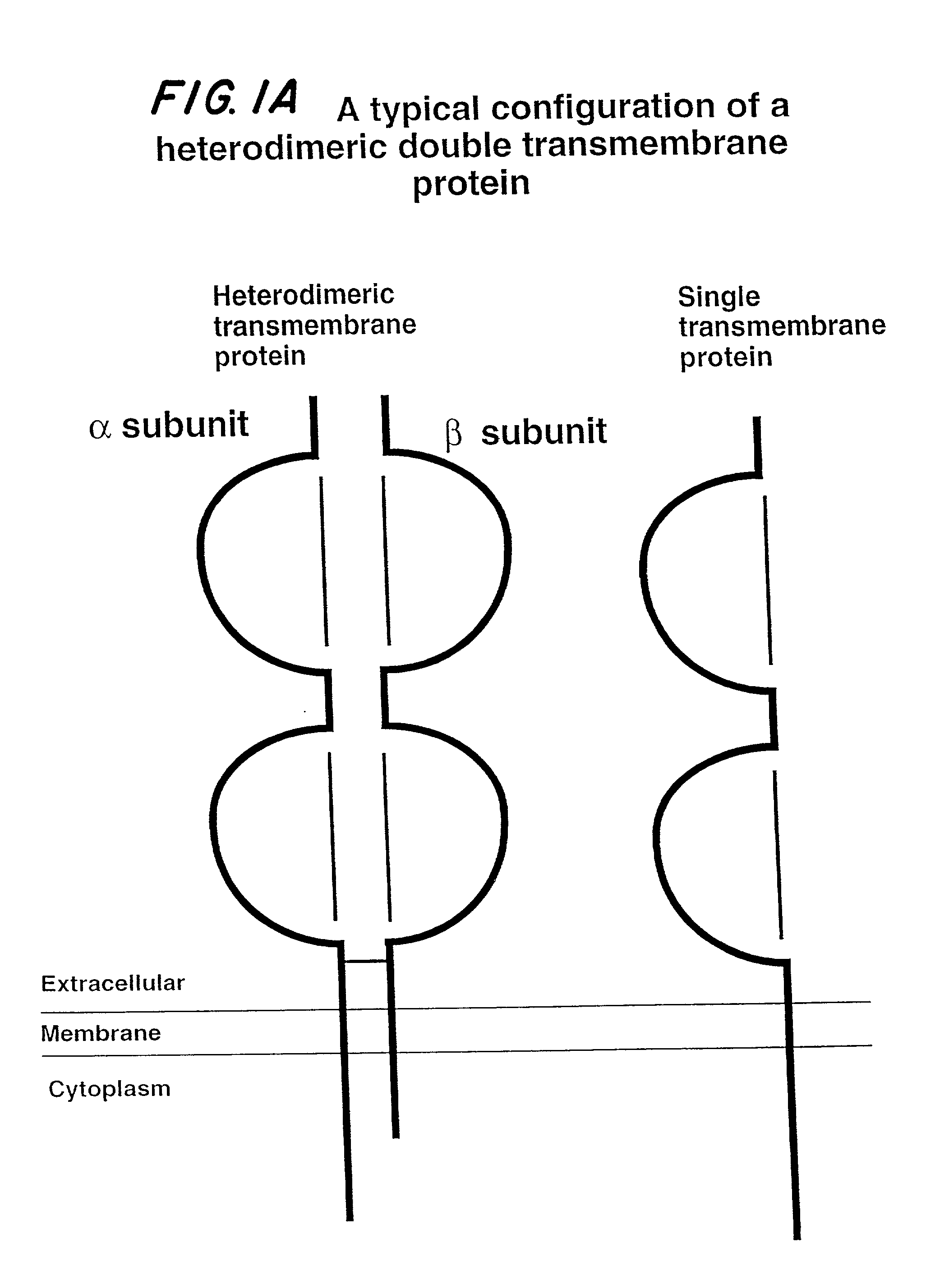
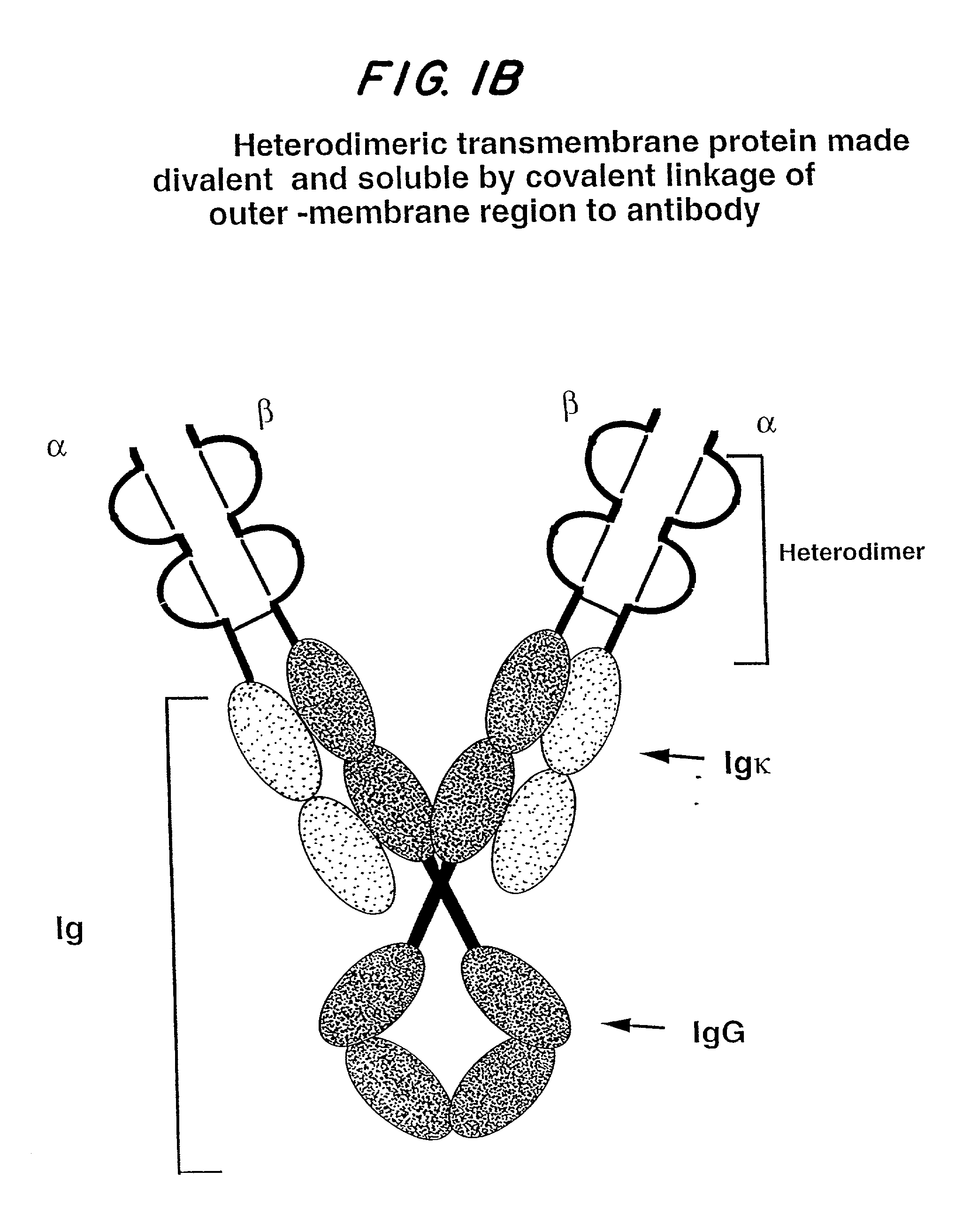
Soluble divalent and multivalent heterodimeric analogs of proteins
InactiveUS20020127231A1Well representedHigh affinityVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsSpecific immunity
Specificity in immune responses is in part controlled by the selective interaction of T cell receptors with their cognate ligands, peptide / MHC molecules. The discriminating nature of this interaction makes these molecules, in soluble form, good candidates for selectively regulating immune responses. Attempts to exploit soluble analogs of these proteins has been hampered by the intrinsic low avidity of these molecules for their ligands. To increase the avidity of soluble analogs for their cognates to biologically relevant levels, divalent peptide / MHC complexes or T cell receptors (superdimers) were constructed. Using a recombinant DNA strategy, DNA encoding either the MHC class II / peptide or TCR heterodimers was ligated to DNA coding for murine Ig heavy and light chains. These constructs were subsequently expressed in a baculovirus expression system. Enzyme-linked immunosorbant assays (ELISA) specific for the Ig and polymorphic determinants of either the TCR or MHC fraction of the molecule indicated that infected insect cells secreted approximately 1 .mu.g / ml of soluble, conformnationally intact chimeric superdimers. SDS PAGE gel analysis of purified protein showed that expected molecular weight species. The results of flow cytometry demonstrated that the TCR and class II chimeras bound specifically with high avidity to cells bearing their cognate receptors. These superdimers will be useful for studying TCR / MHC interactions, lymphocyte tracking, identifying new antigens, and have possible uses as specific regulators of immune responses.
Owner:SCHNECK JONATHAN +1
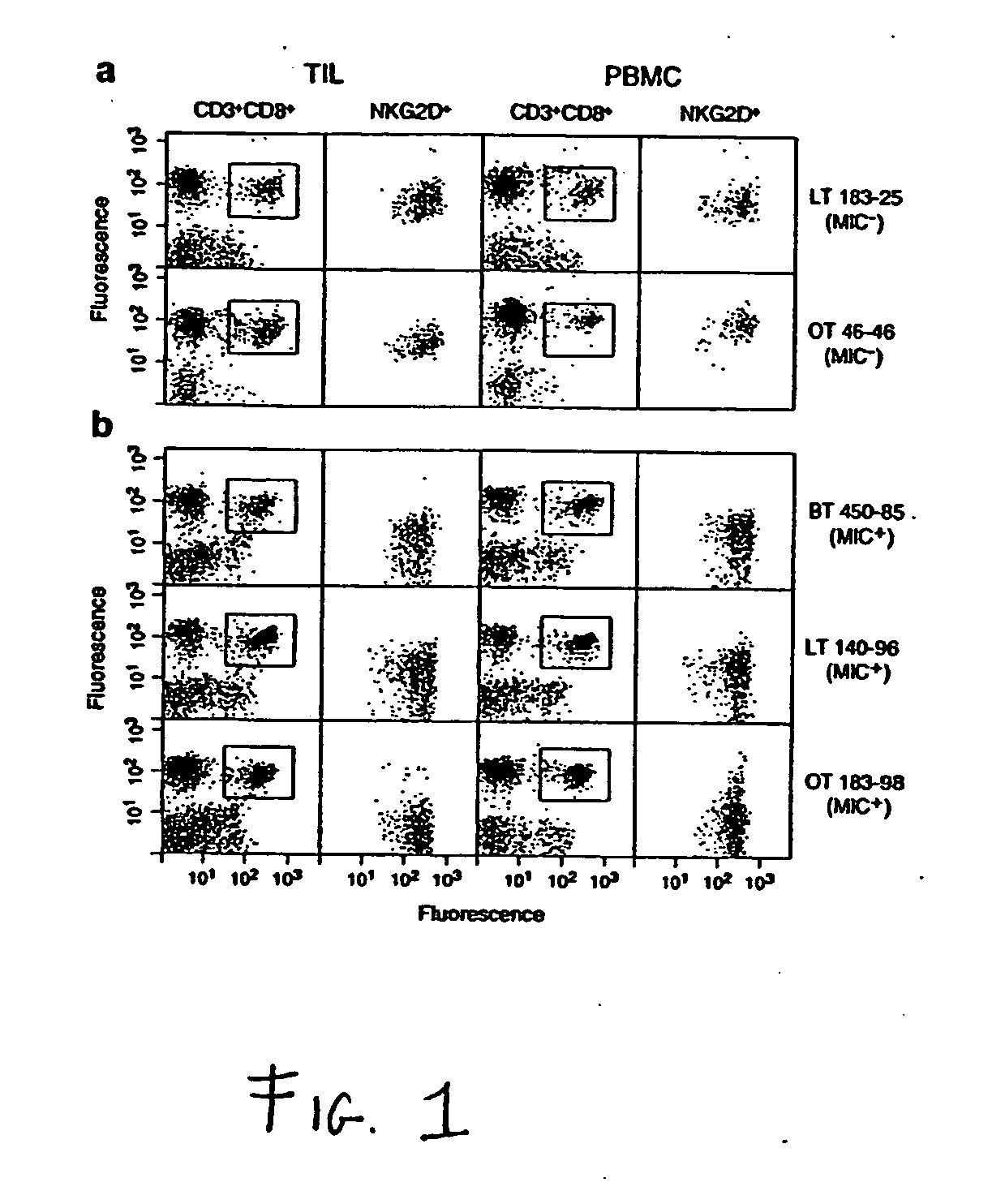
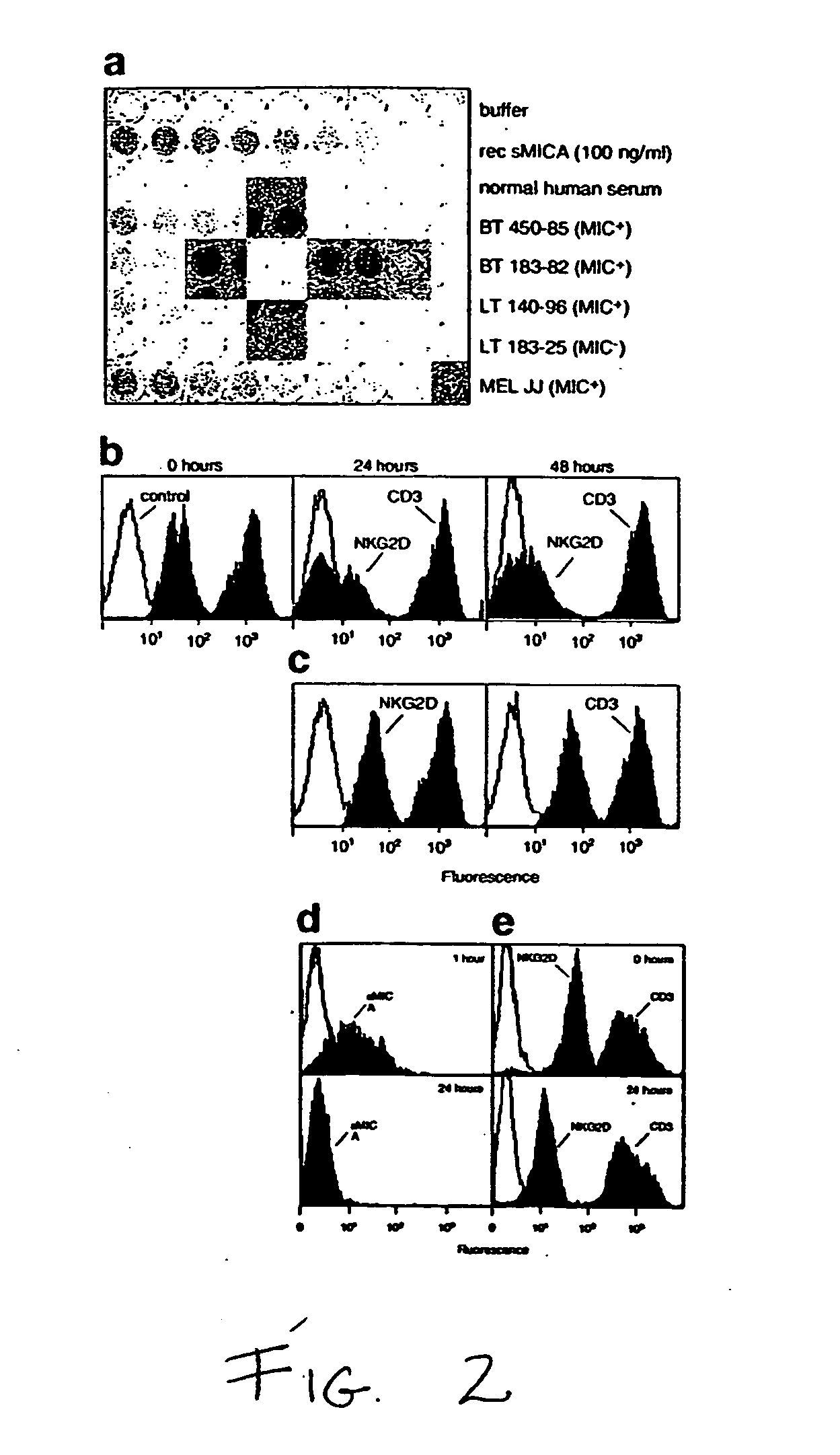
Soluble mic polypeptides as markers for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases or conditions
ActiveUS20050233391A1Lower Level RequirementsSkeletal disorderAntibody ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides prognostic and diagnostic methods for cancer, as well as methods for monitoring or staging cancer. Methods involve assaying for tumor-derived soluble MIC polypeptide—either MICA or MICB or both—in a sample from a subject. Assays can be implemented with a MIC polypeptide binding agent such as a MIC polypeptide antibody or recombinant NKG2D. An ELISA sandwich assay is employed in some embodiments of the invention to identify a soluble MIC polypeptide. In additional embodiments, a sample is assayed for tumor cell-surface bound MIC in addition to assaying for soluble MIC. The invention also provides methods of cancer therapy involving detecting cancer in the subject by assaying for soluble MIC polypeptide and then administering a cancer therapy.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
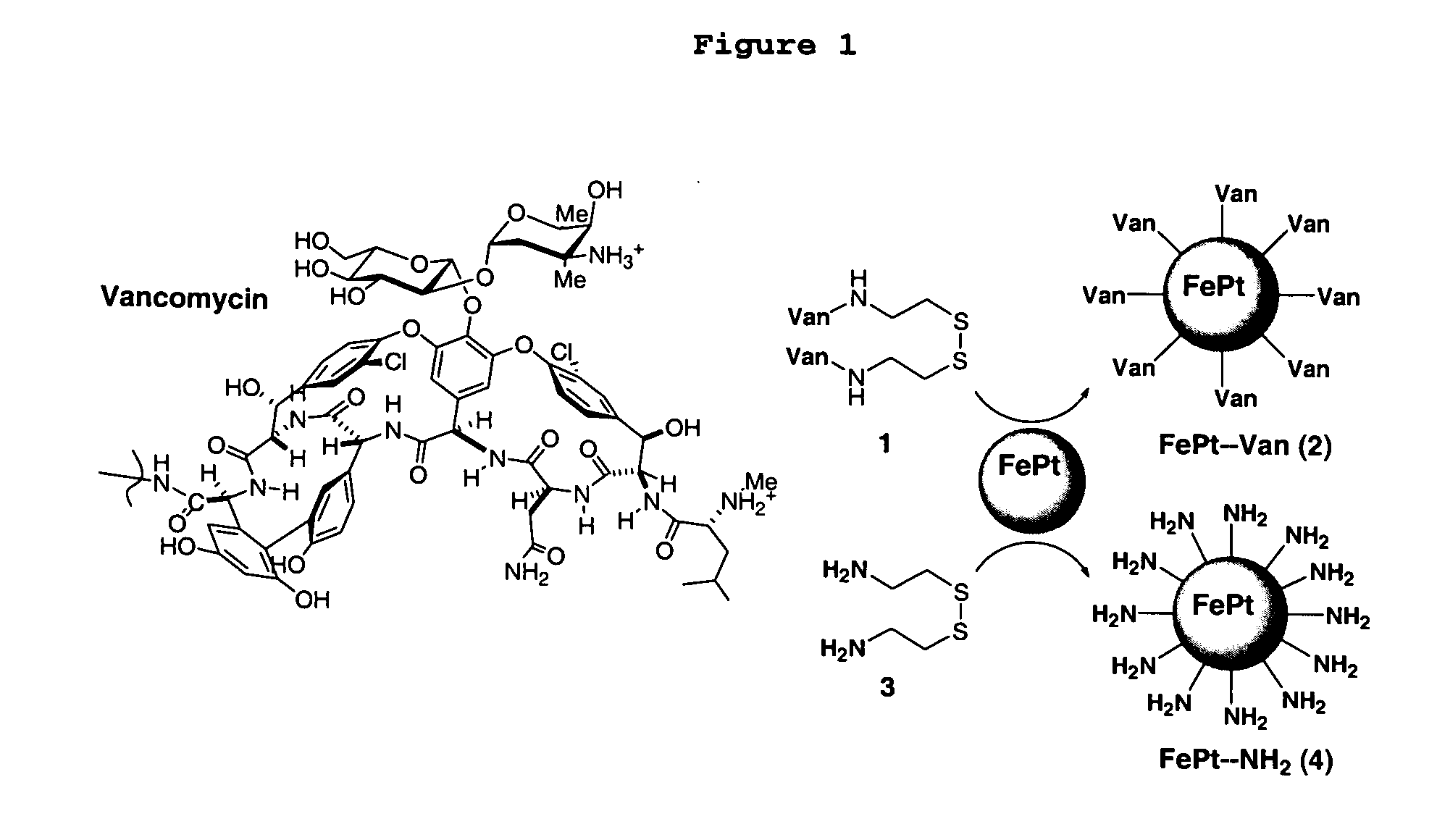
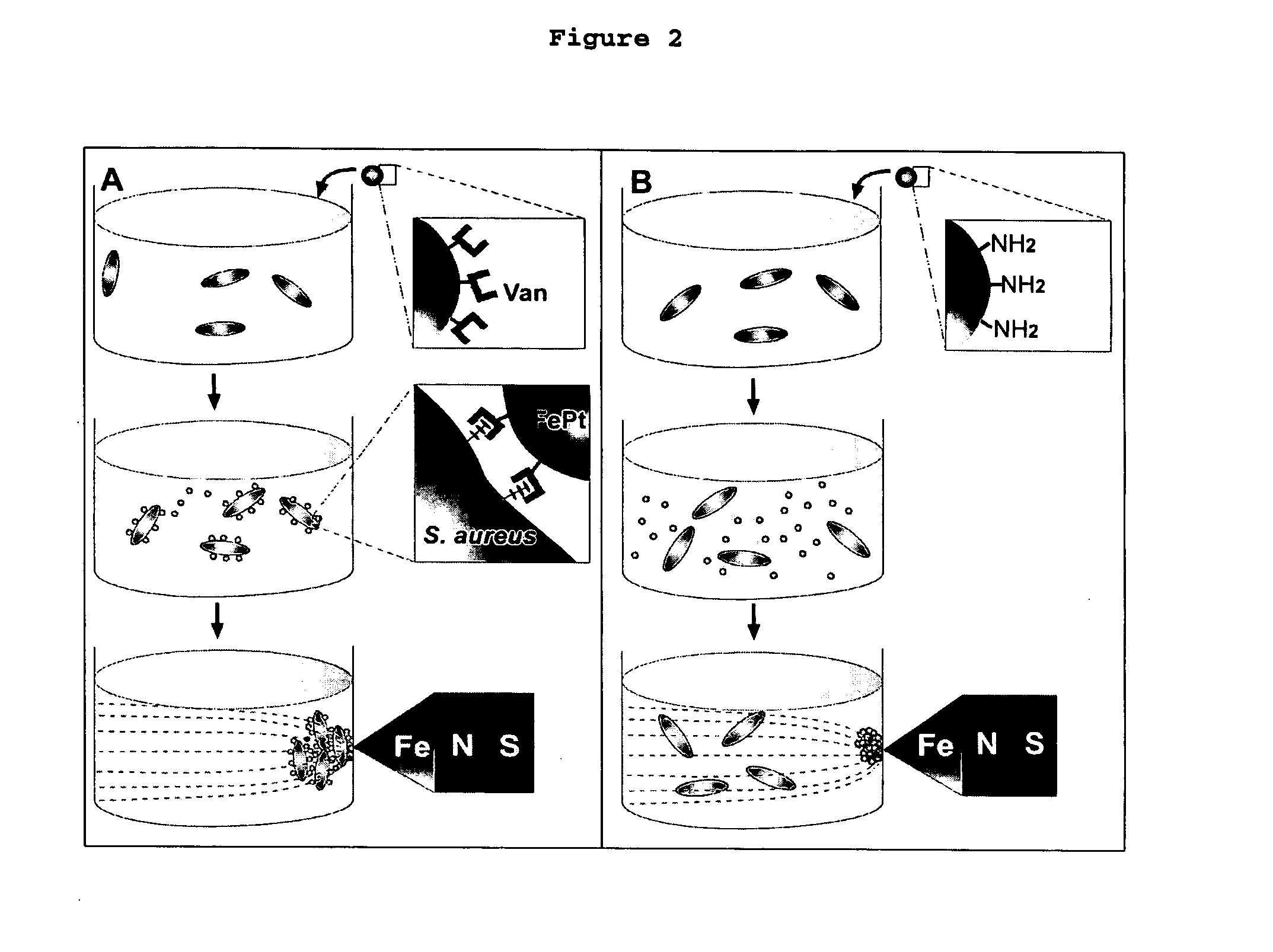
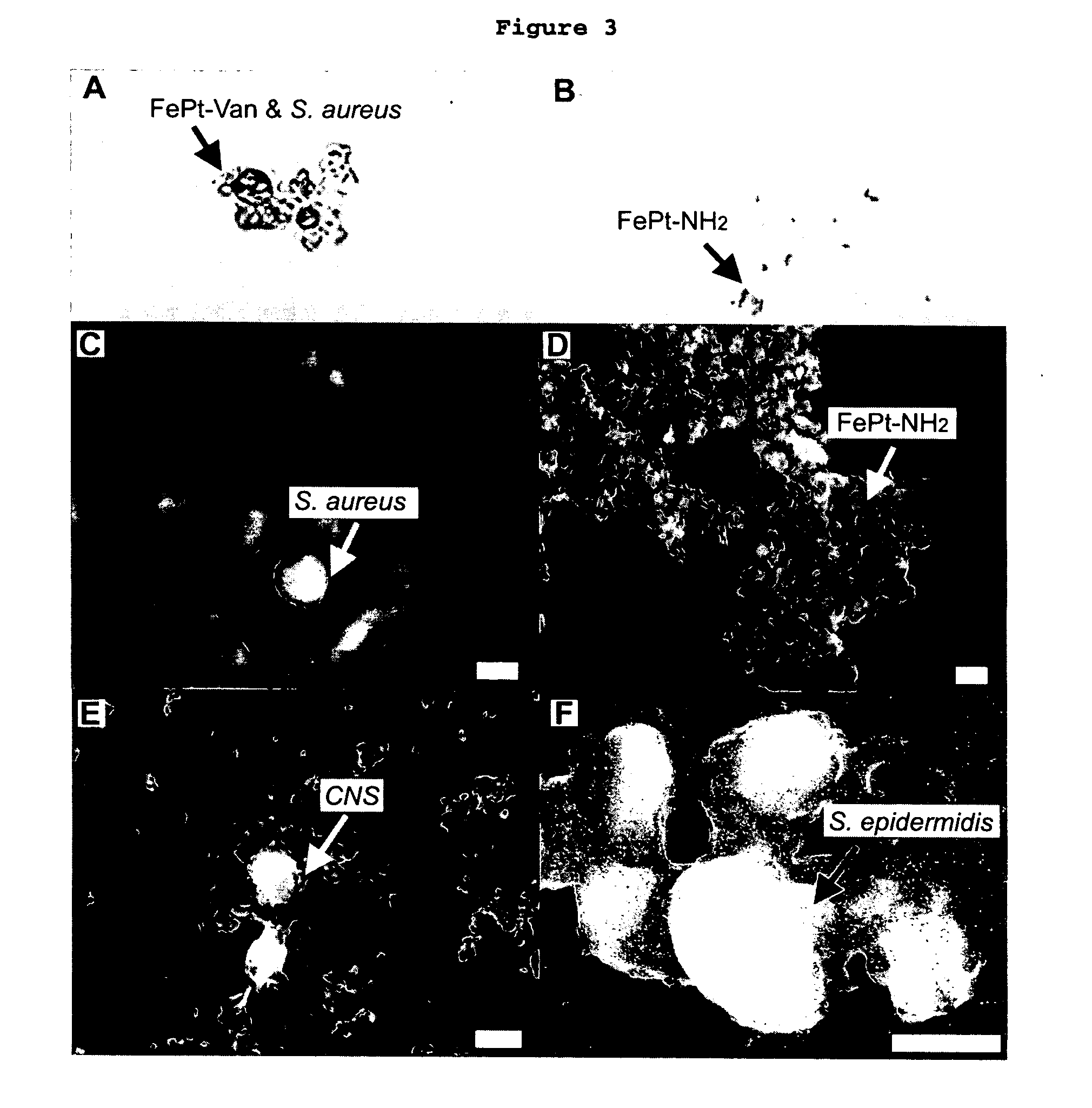
Biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles for pathogen detection
InactiveUS20060292555A1High sensitivityEasy to reportNanotechMicrobiological testing/measurementMagnetite NanoparticlesBiology
This invention provides a method of detecting pathogens comprising the steps of: (a) contacting a sufficient amount of biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles with an appropriate sample for an appropriate period of time to permit the formation of complexes between the pathogens in the sample and the nanoparticles; (b) using a magnetic field to aggregate said complexes; and (c) detecting said complexes. The method may further comprise the additional step of removing said complexes. The biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles are preferably a conjugate of vancomycin and FePt. The pathogens may be bacteria or viruses, and the sample may be a solid, liquid, or gas. Detection may involve conventional fluorescence assay, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), optical microscope, electron microscope, or a combination thereof. The sensitivity of detection for the method is at least as low as 10 colony forming units (cfu) of the pathogens in one milliliter of solution within one hour.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Anti-Sars Monoclonal Antibodies
ActiveUS20080081047A1Sugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsDrug biological activityWestern immunoblot
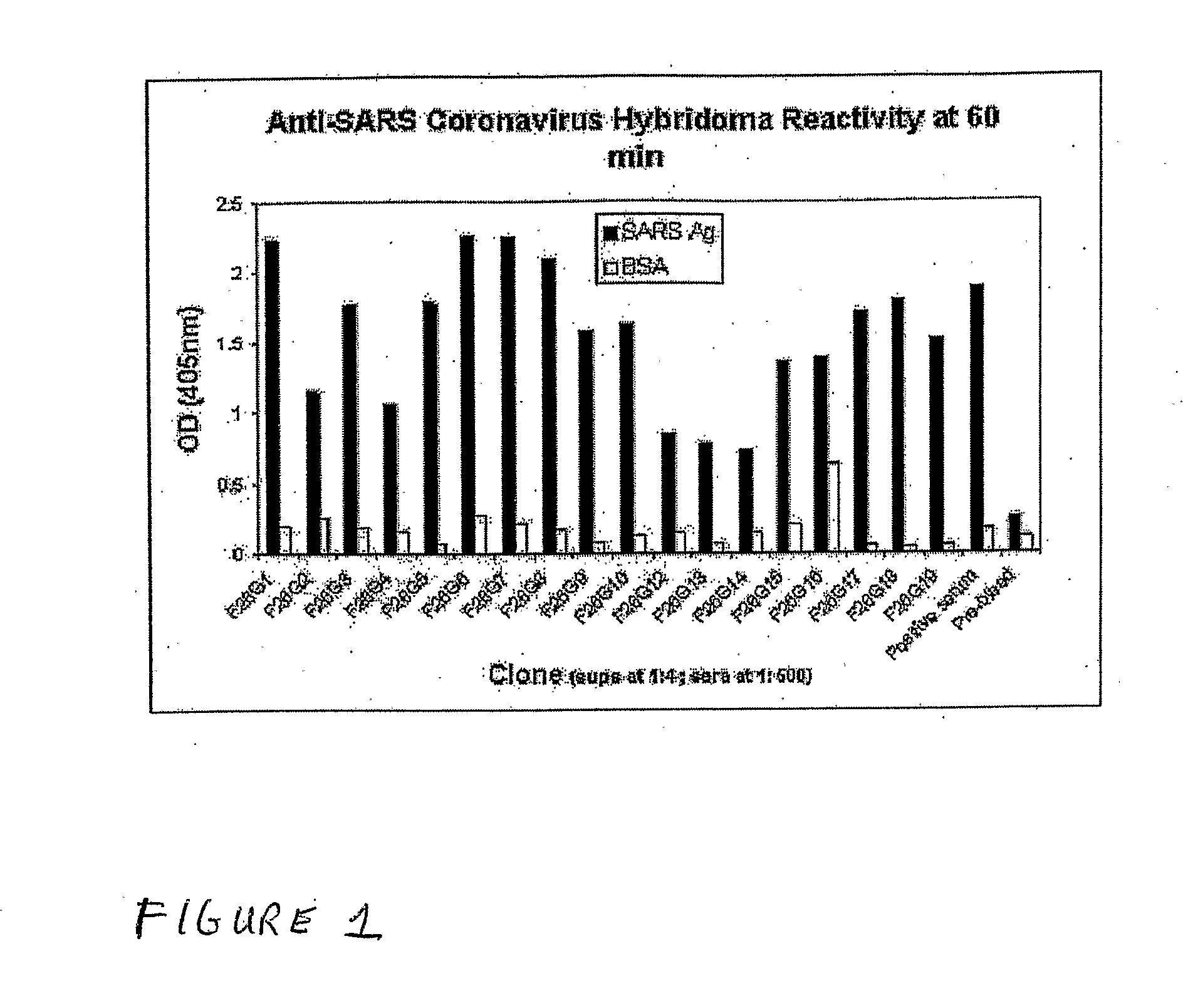
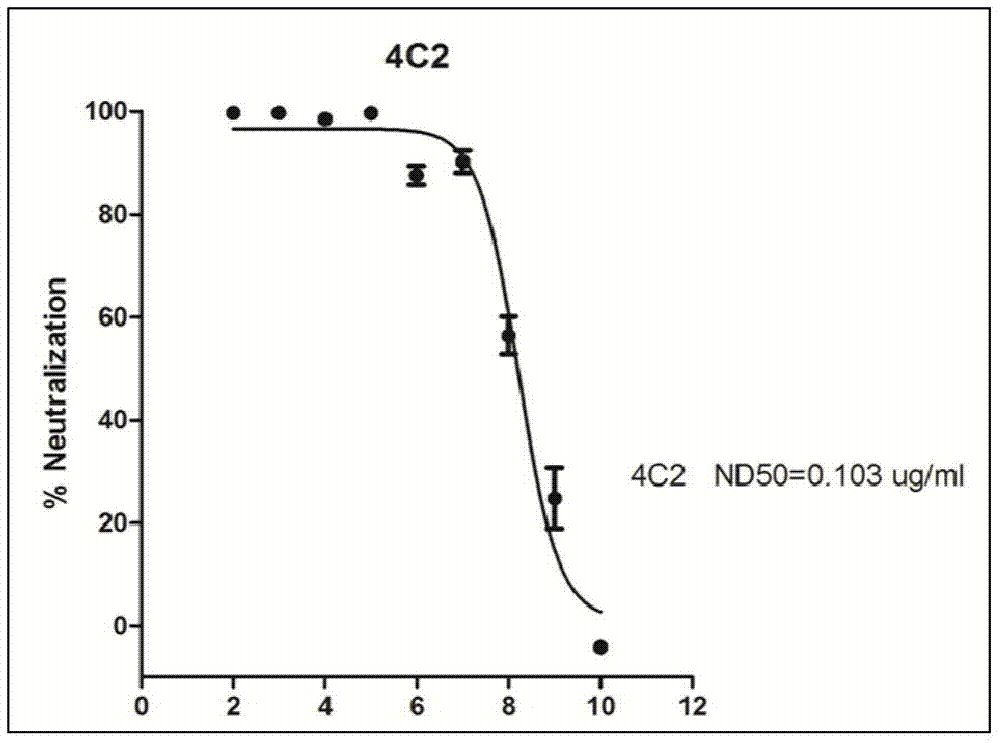
Monoclonal antibody reagents that recognize the SARS-coronavirus (SARS-HCoV) are needed urgently. In this report we describe the development and immunochemical characterisation of mAbs against the SARS-HCoV based upon their specificity, binding requirements, and biological activity. Initial screening by ELISA, using highly purified virus as the coating antigen, resulted in the selection of seventeen mAbs. Five mAbs exhibited Western immunoblot reactivity with the denatured spike protein, of which two demonstrated the ability to neutralize SARS-HCoV in vitro. Another four Western immunoblot-negative mAbs also neutralize the virus. These antibodies will be useful for the development of diagnostic tests, pathogenicity and vaccine studies.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
Antibodies and their use
InactiveUS6113897APeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLymphatic SpreadUrokinase Plasminogen Activator
A monoclonal or polyclonal antibody directed against urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (u-PAR), or a subsequence, analogue or glycosylation variant thereof. Antibodies are disclosed which react with free u-PAR or with complexes between u-PA and u-PAR and which are capable of 1) catching u-PAR in ELISA, or 2) detecting u-PAR, e.g. in blotting, or 3) in radioimmunoprecipitation assay precipitate purified u-PAR in intact or fragment form, or 4) is useful for immunohistochemical detection of u-PAR, e.g. in immunostaining of cancer cells, such as in tissue sections at the invasive front, or 5) inhibits the binding of pro-u-PA and active u-PA and thereby inhibits cell surface plasminogen activation. Methods are disclosed 1) for detecting or quantifying u-PAR, 2) for targeting a diagnostic to a cell containing a u-PAR on the surface, 3) for preventing or counteracting proteolytic activity in a mammal. Methods for for selecting a substance suitable for inhibiting u-PA / u-PAR interaction, for preventing or counteracting localized proteolytical activity in a mammal, for inhibiting the invasion and / or metastasis comprise the use of the antibodies and of nude mice inoculated with human cancer cells which are known to invade and / or metastasize in mice and having a distinct color, f.x. obtained by means of an enzyme and a chromogenic substrate for the enzyme, the color being different from the cells of the mouse.
Owner:CANCERFORSKNINGSFONDEN AF 1989 FONDEN TIL FREMME
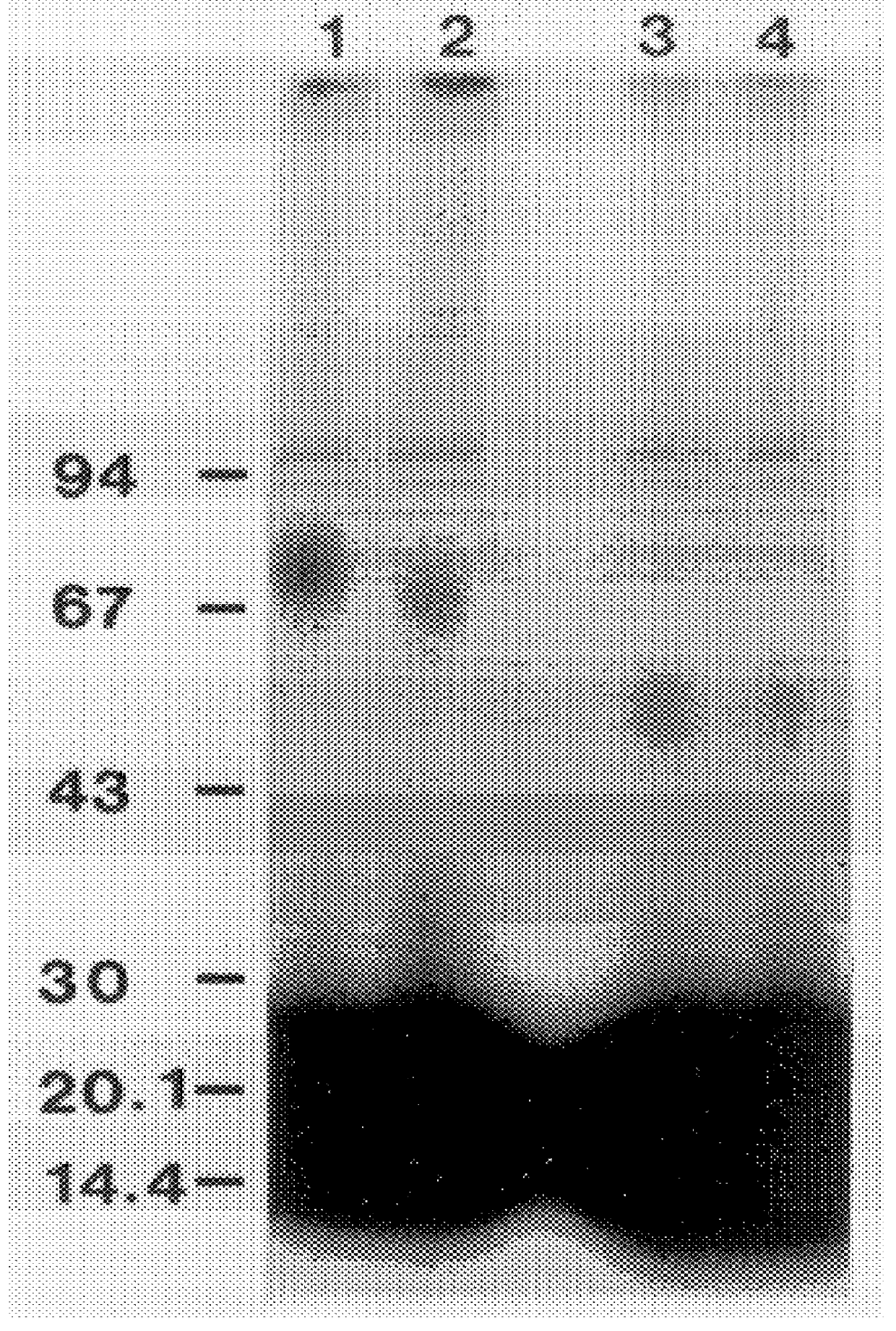
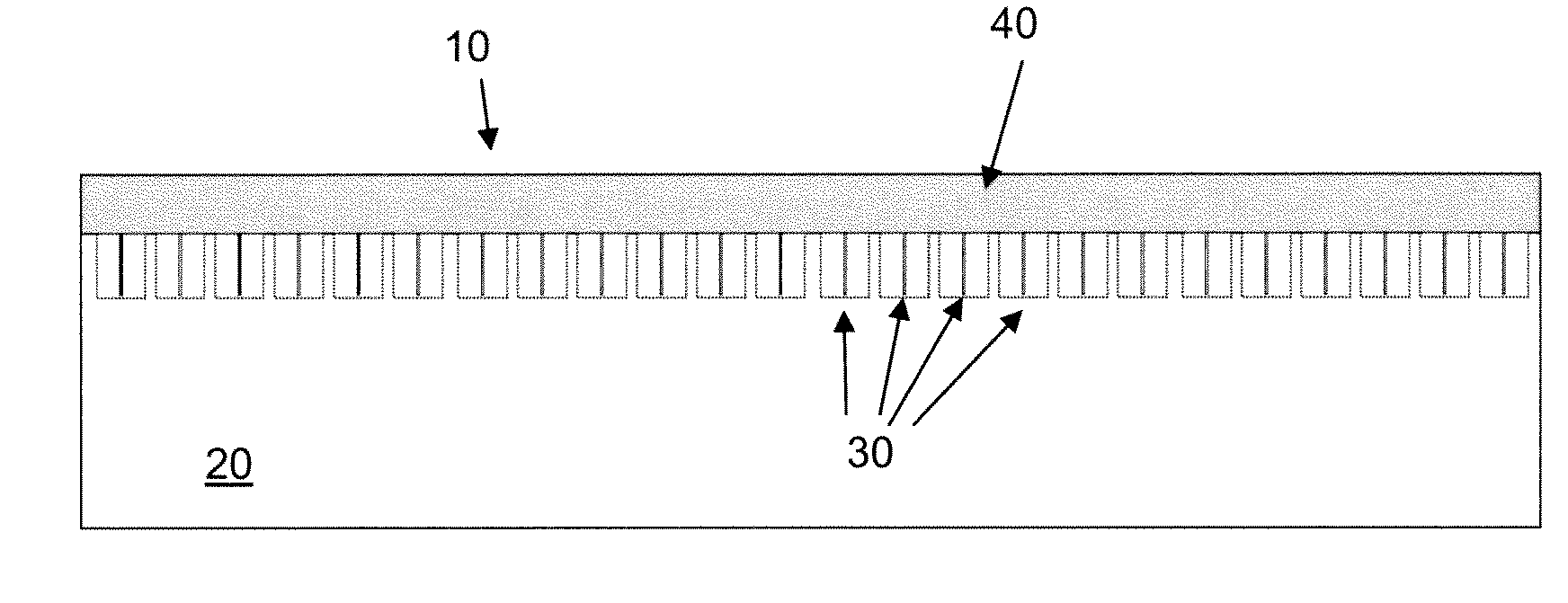
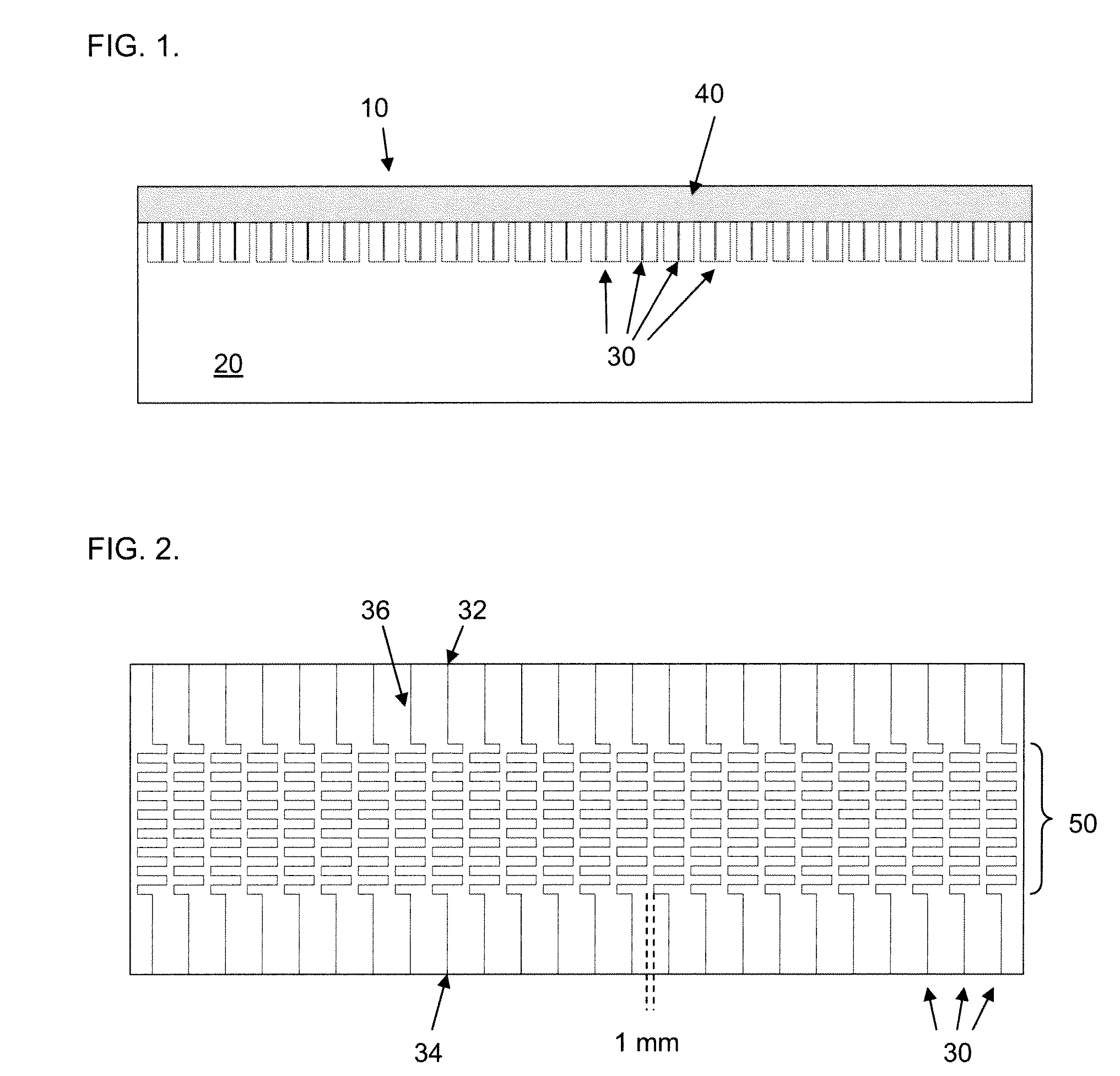
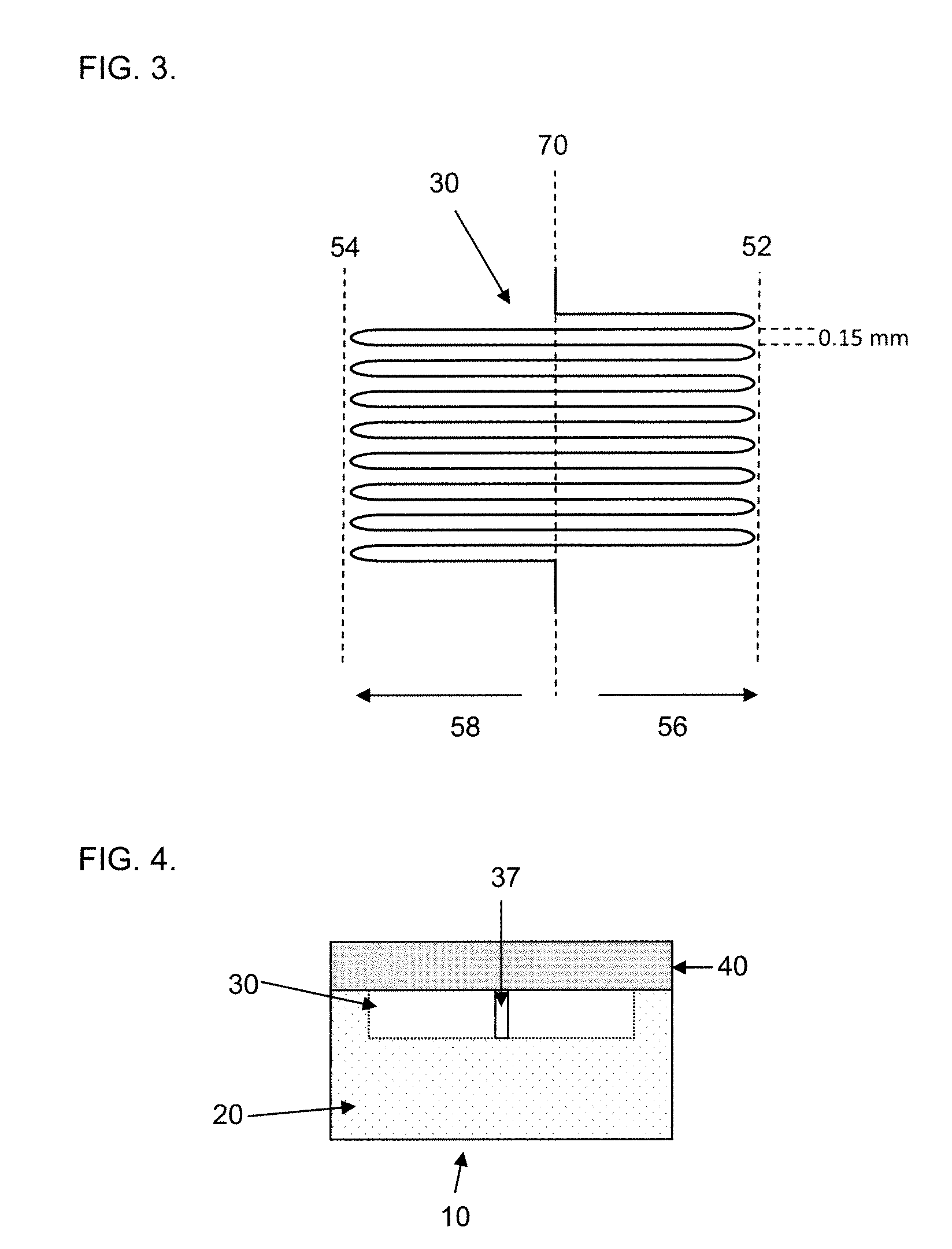
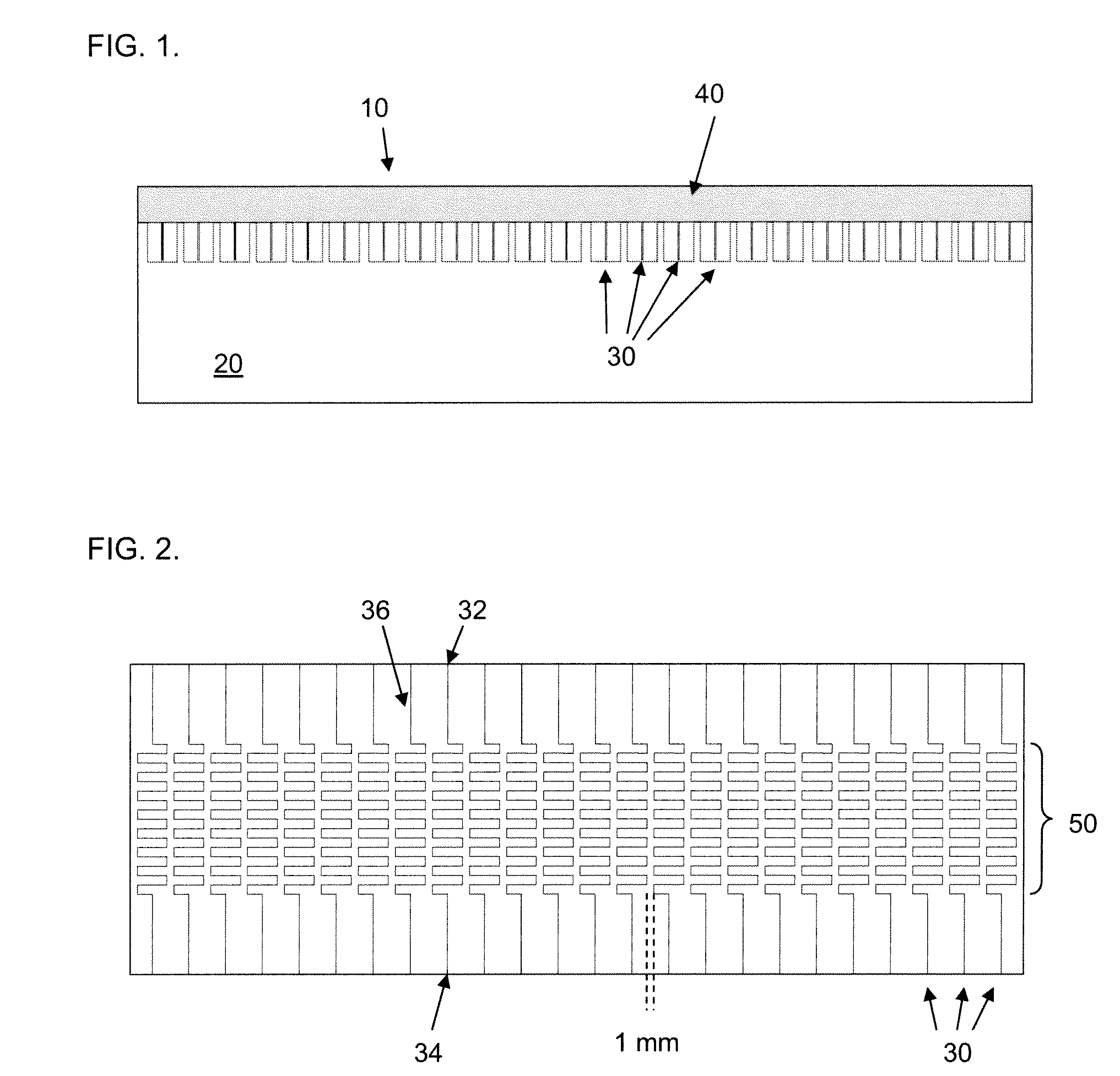
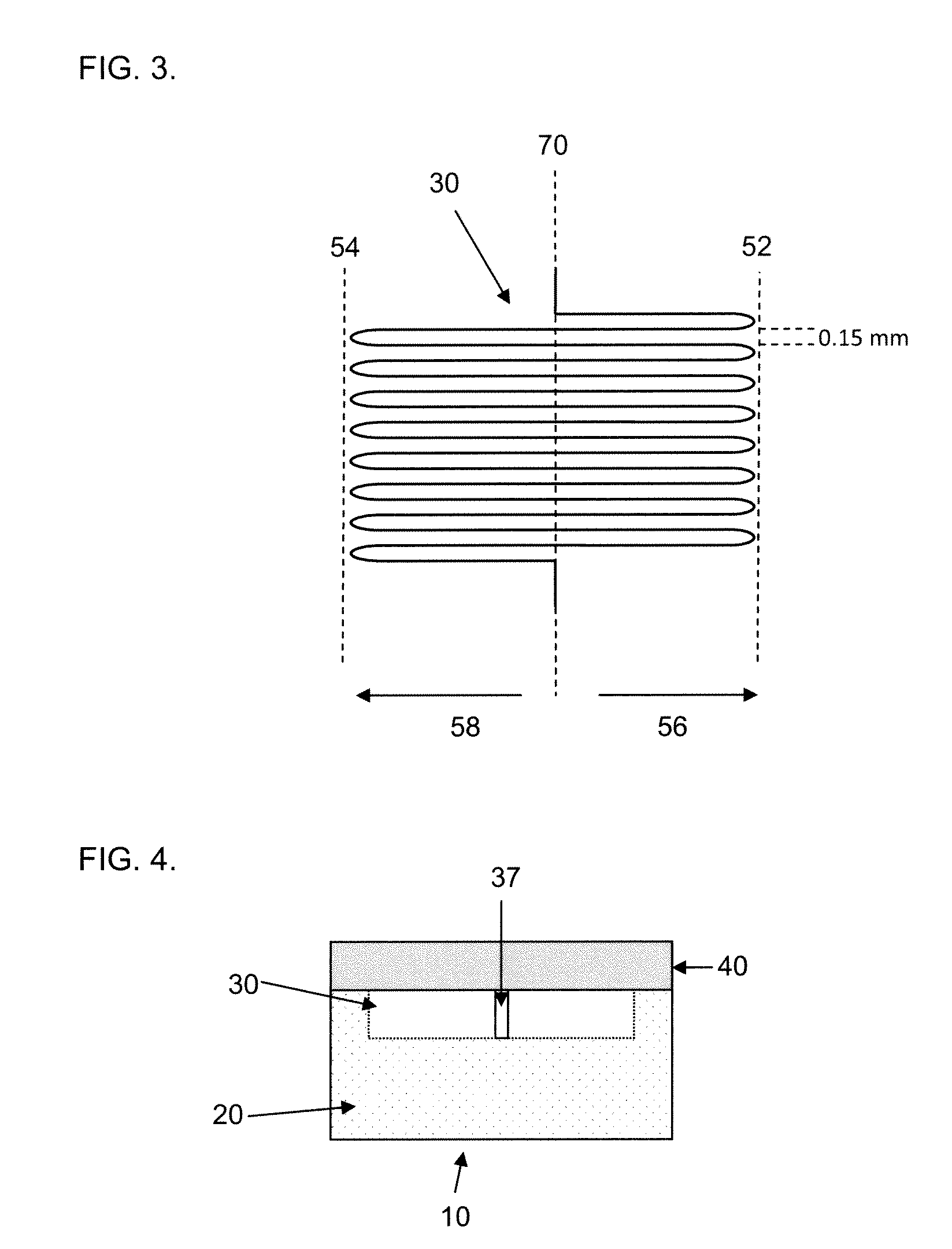
Microfluidic chips for rapid multiplex elisa
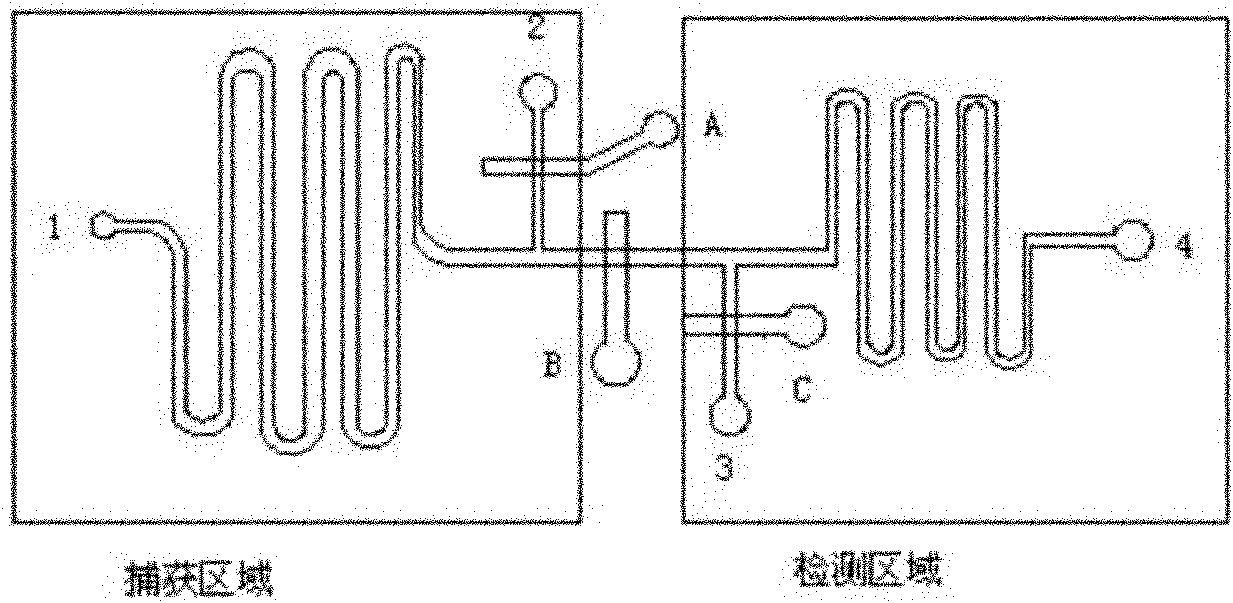
ActiveUS20090123336A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteELISA unit
A microfluidic chip comprises a substrate and a channel or multiple channels in the substrate. Each channel includes a tortuous path section or multiple tortuous path sections. A receptor for the detection of an analyte can be immobilized in a tortuous path section, for example by adsorption. Different receptors can be immobilized in different tortuous path sections of each channel or in different channels for simultaneous detection of multiple analytes. The chip is especially useful for running immunoassays, particularly ELISA.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
Anti-viral compositions comprising heterocyclic substituted phenyl furans and related compounds
InactiveUS20060287319A1Potent anti-HIV activityInhibit HIV replicationBiocideAntiviralsFuranFluorescence
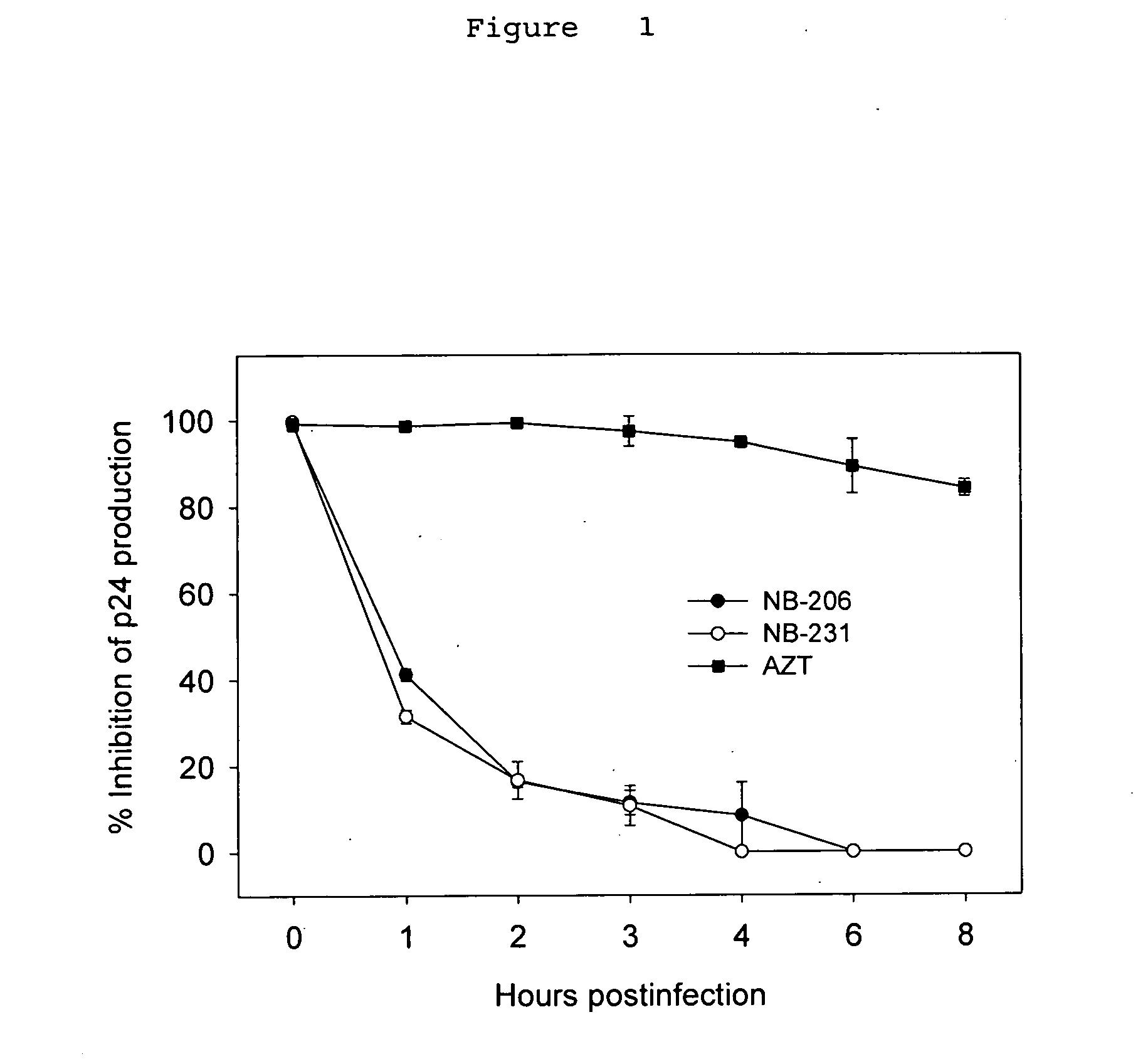
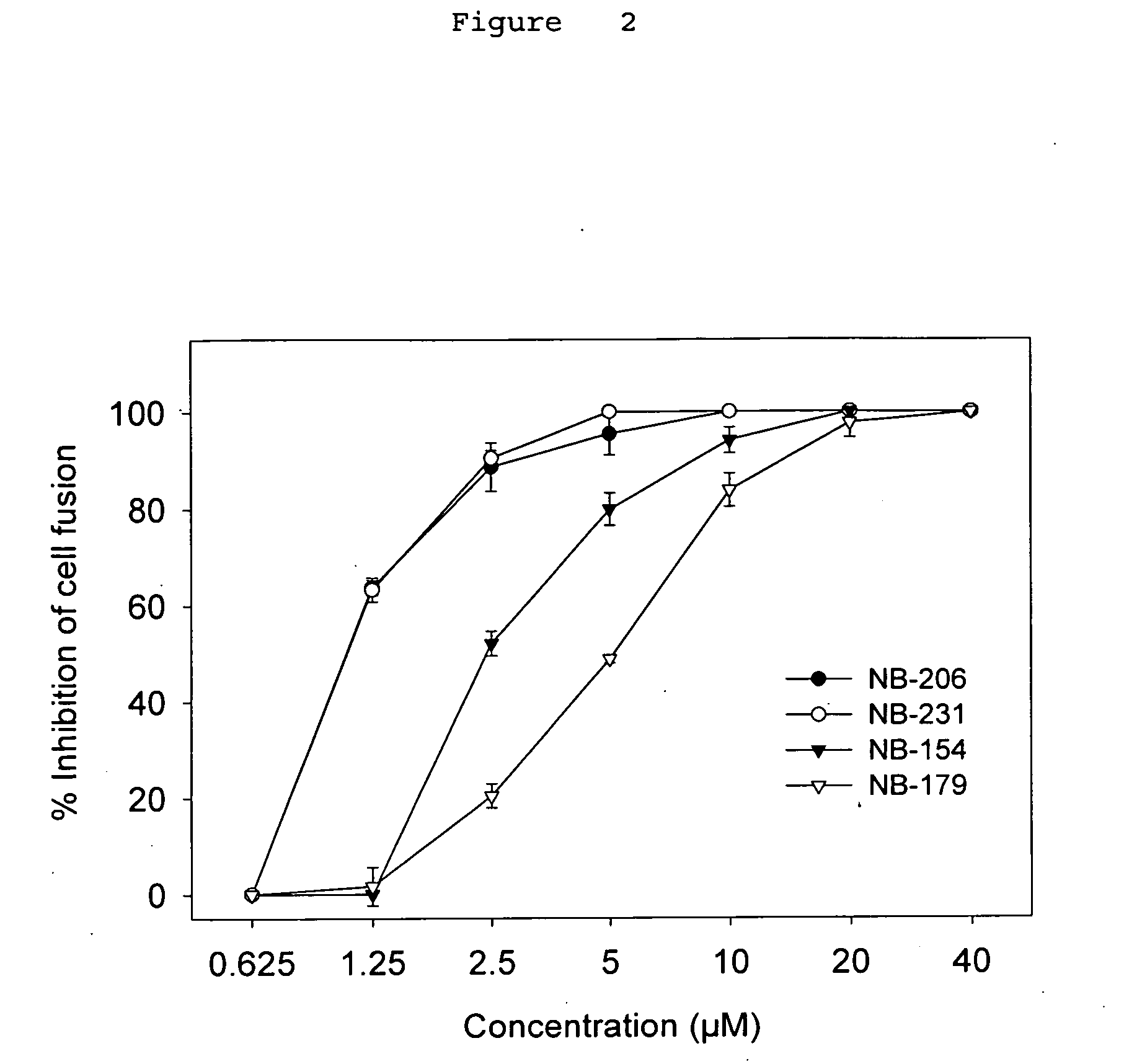
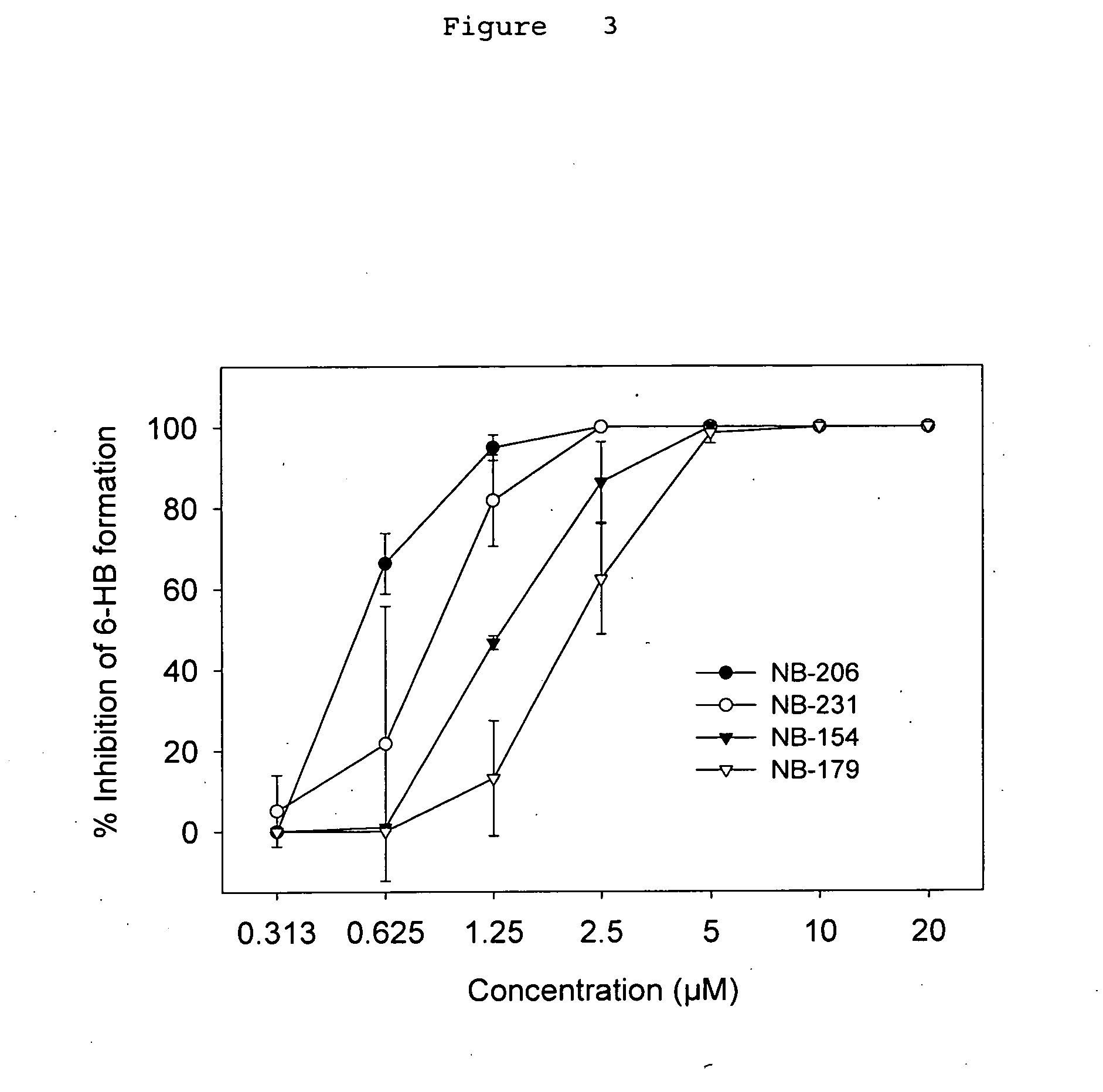
A group of compounds that inhibit HIV replication by blocking HIV entry was identified. One representative compound, designated NB-206, and its analogs inhibited HIV replication (p24 production) with IC50 values at nanomolar levels. It was proved that NB-206 and its analogs are HIV entry inhibitors by targeting the HIV gp41 since: 1) they inhibited HIV-mediated cell fusion; 2) they inhibited HIV replication only when they were added to the cells less than one hour after virus addition; 3) they blocked the formation of the gp41 core that is detected by sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using a conformation-specific MAb NC-1; and 4) they inhibited the formation of the gp41 six-helix bundle revealed by fluorescence native-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (FN-PAGE). These results suggested that NB-206 and its analogs may interact with the hydrophobic cavity and block the formation of the fusion-active gp41 coiled coil domain, resulting in inhibition of HIV-1 mediated membrane fusion and virus entry.
Owner:NEW YORK BLOOD CENT
Microfluidic chips for rapid multiplex ELISA
ActiveUS8075854B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteEngineering
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND +1
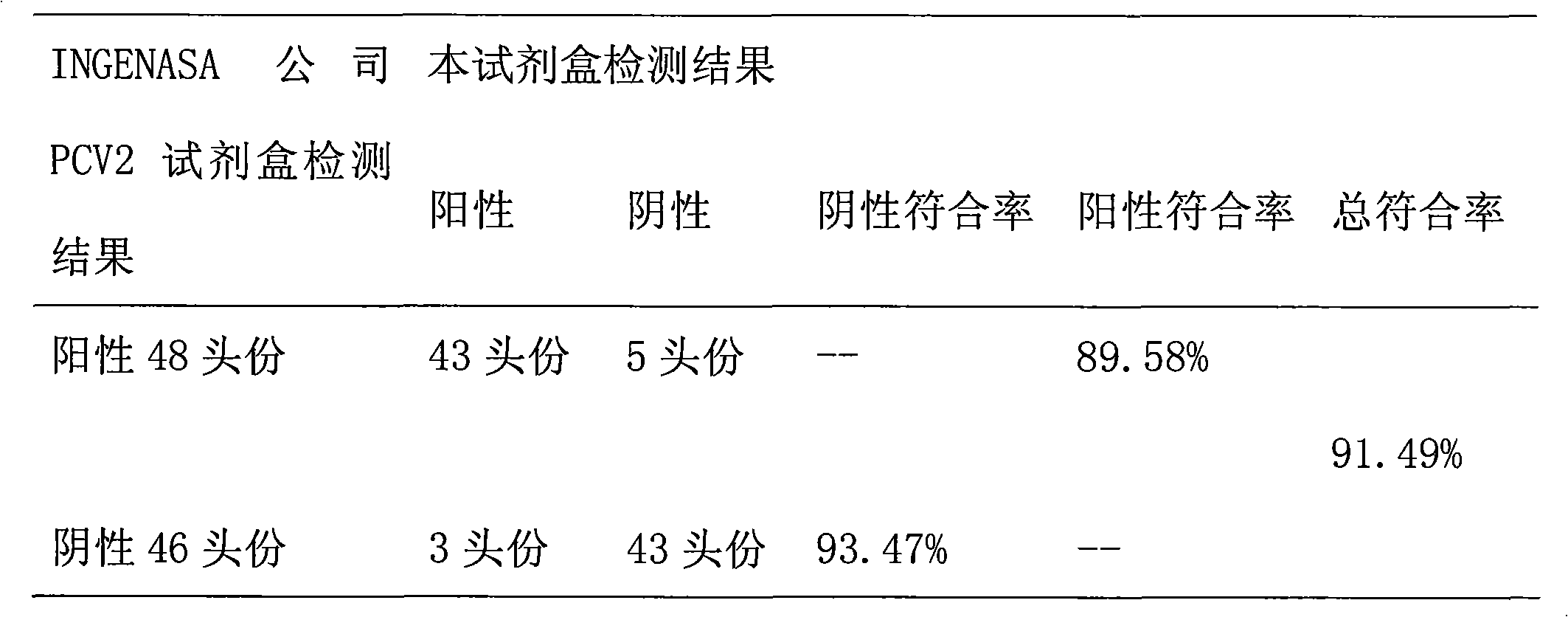
ELISA kit for detecting porcine circovirus antibody II
ActiveCN101629956ASimilar sensitivityStrong specificityMicroorganism based processesBiological testingSerum igeElisa kit
The invention relates to an ELISA kit for detecting porcine circovirus antibodies II, wherein, the kit is developed according to the double antigen sandwich ELISA principle. The ELISA kit comprises a prepacked ELISA antigen plate bar, a cleaning solution, 100 times concentrated enzyme labeled antigen, an enzyme labeled dilution, a zymolyte coloration, a stopping solution, standard PCV2 negative sera, and standard PCV2 positive sera. The kit replaces enzyme labeled anti-antibodies with the enzyme labeled antigen. The enzyme labeled antigen can not combine with antibodies absorbed with ELSA plate without specificity. Meanwhile, the serum specimen to be detected does not need to be pre-diluted, and the serum specimen can be directly mixed with the enzyme labeled antigen with working concentration to be directly used for determination. The ELISA kit has the advantages of simple operation and shorter detecting time.
Owner:北京金诺百泰生物技术有限公司
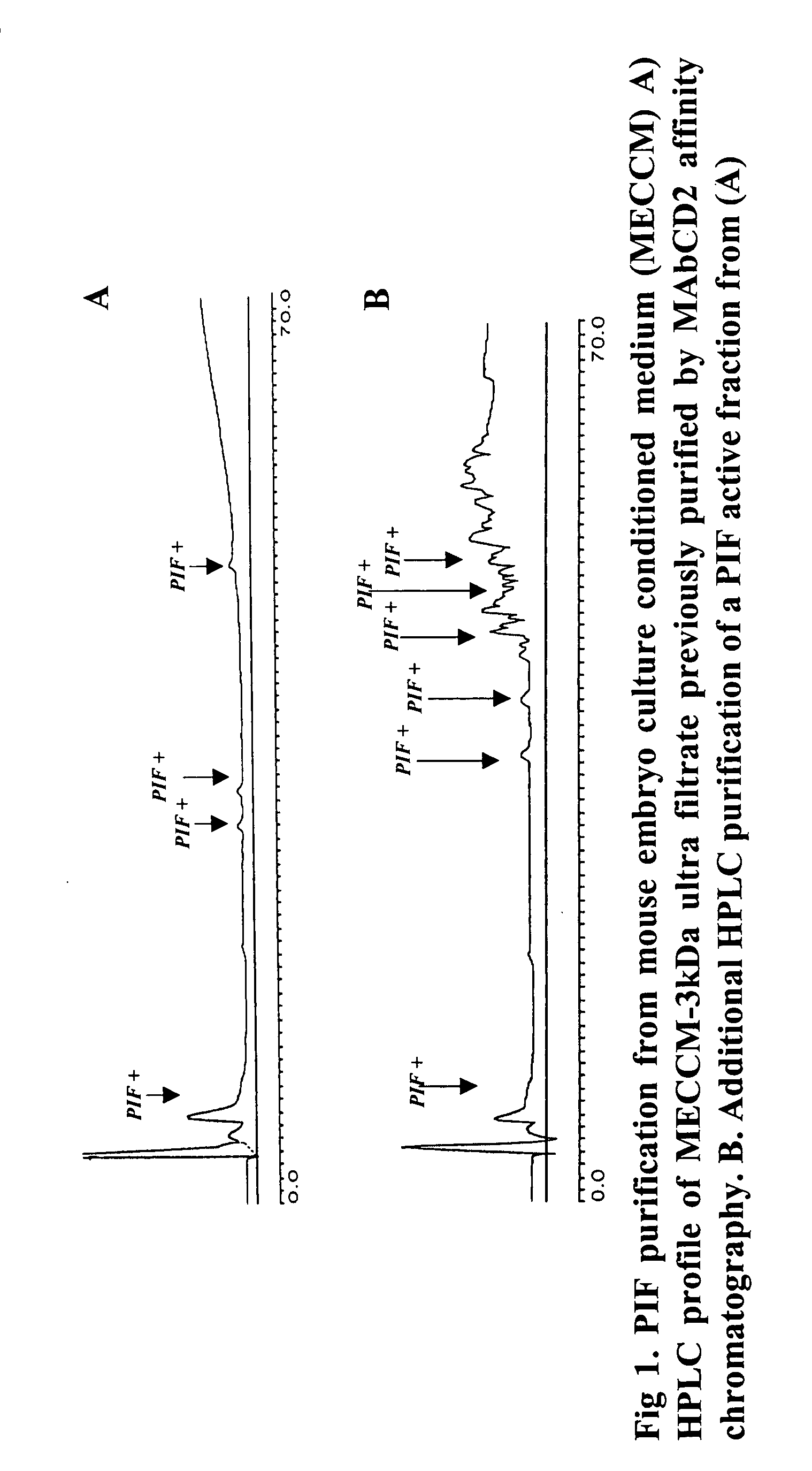
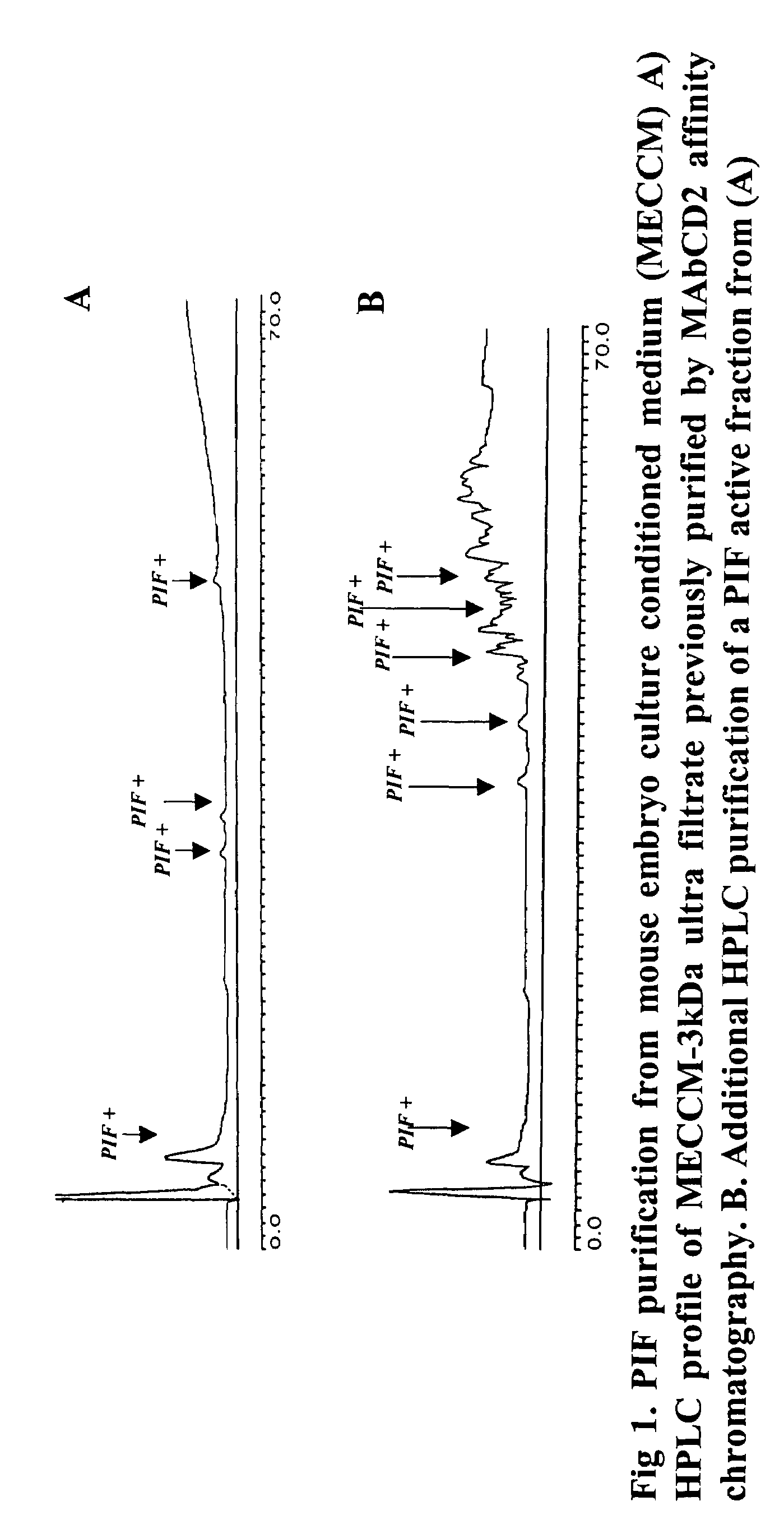
New assays for preimplantation factor and preimplantation factor peptides
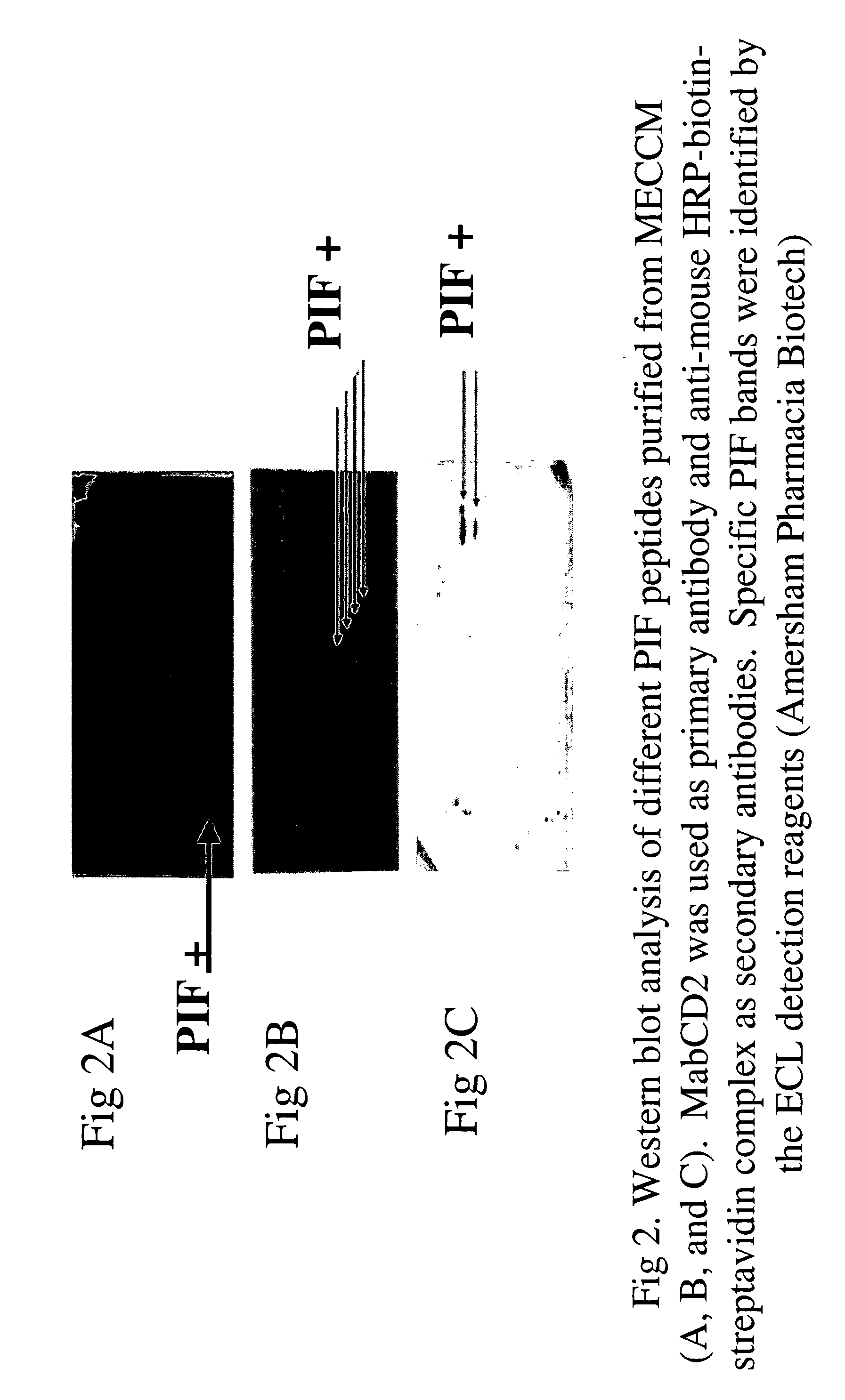
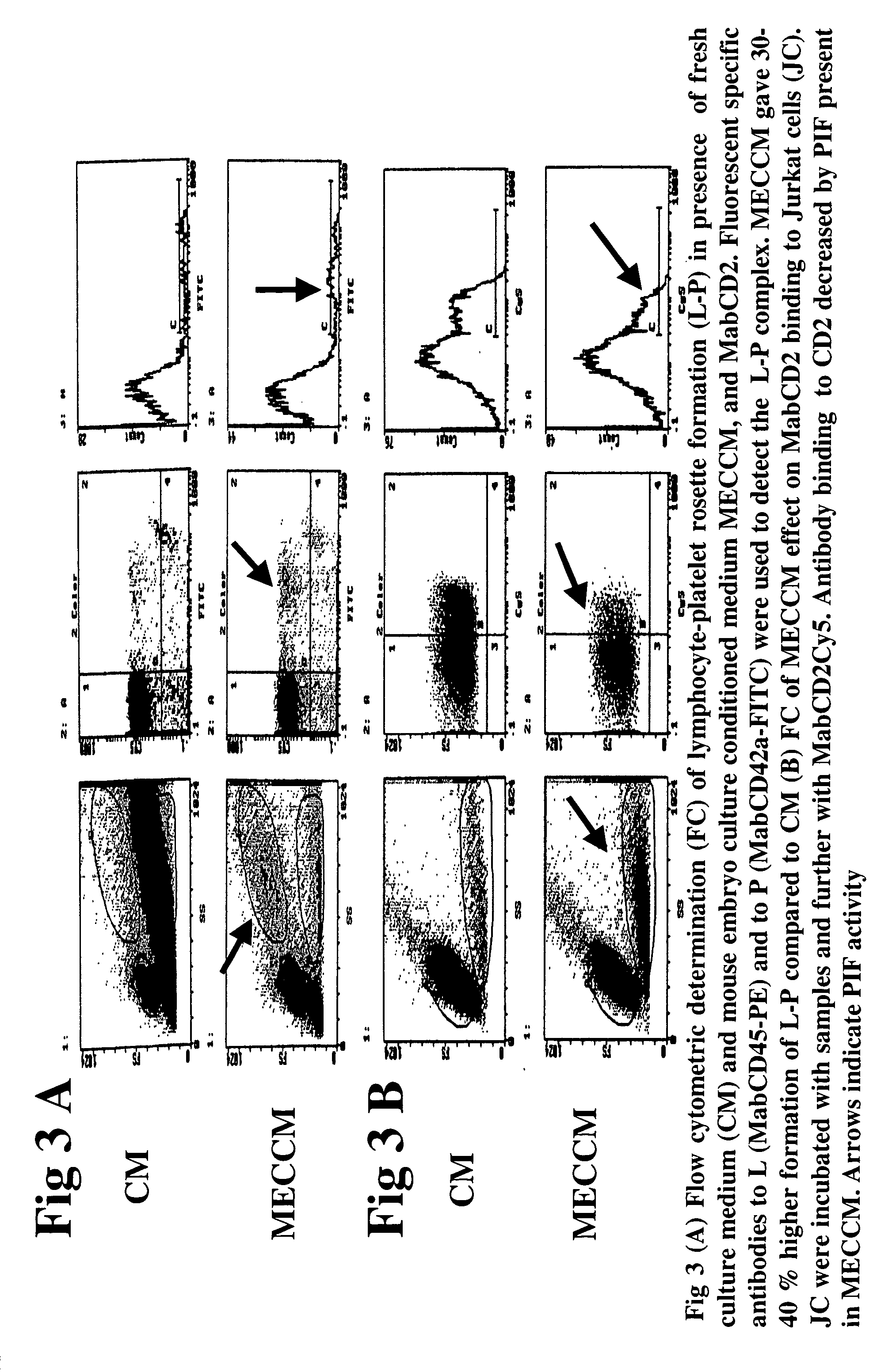
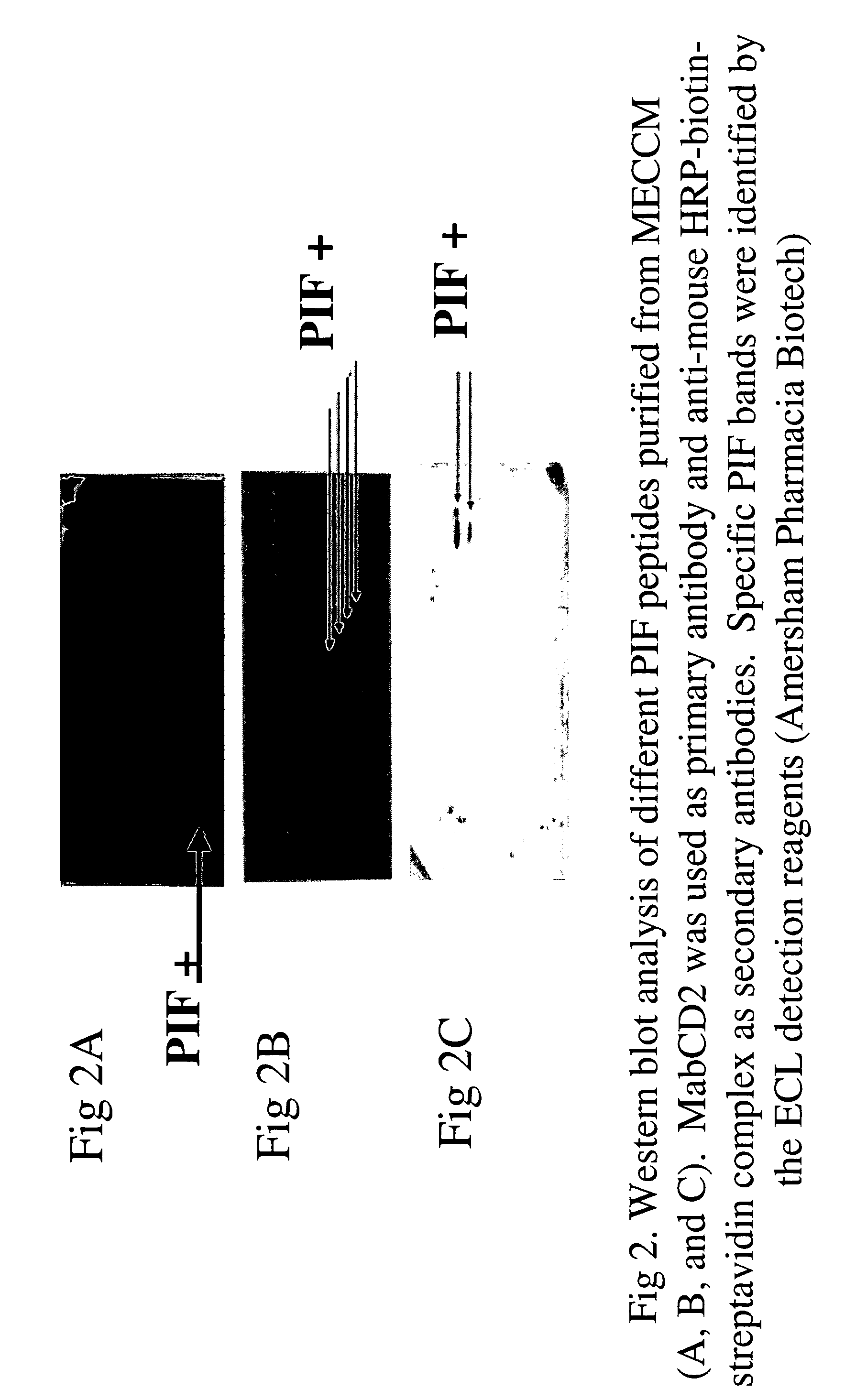
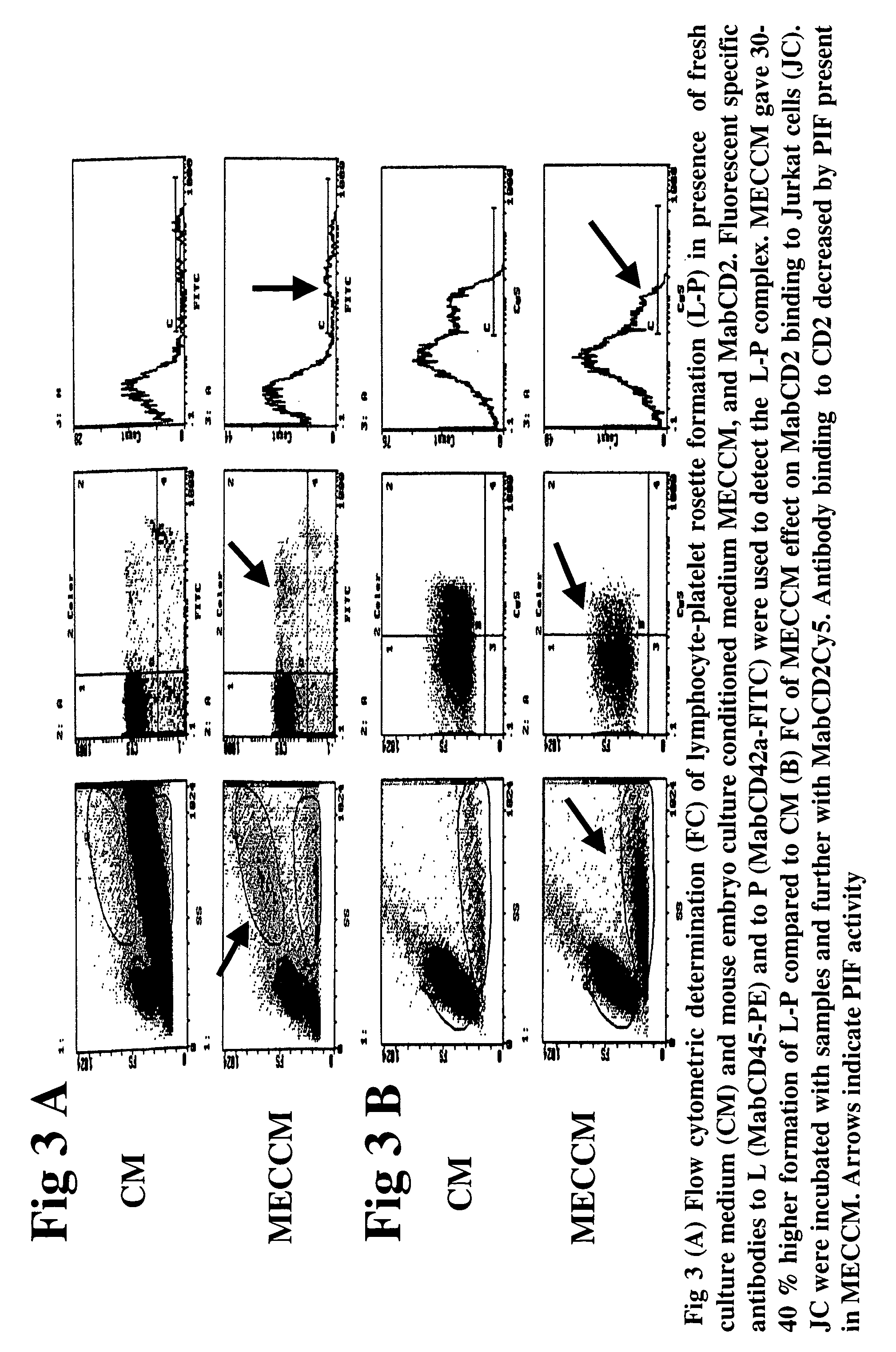
InactiveUS20050064520A1High expressionReduce cell viabilityBiological material analysisBiological testingPIF peptideFluorescence
The present invention relates to assay methods used for detecting the presence of PIF, and to PIF peptides identified using this assay. In particular, the present invention relates to flow cytomery assays for detecting PIF. It is based, at least in part, on the observation that flow cytometry using fluorescently labeled antilymphocyte and anti-platelet antibodies demonstrated an increase in rosette formation in the presence of PIF. It is further based on the observation that flow cytometry demonstrated that monoclonal antibody binding to CD2 decreased in the presence of PIF. The present invention further relates to PIF peptides which, when added to Jurkat cell cultures, have been observed to either (I) decrease binding of anti-CD2 antibody to Jurkat cells; (ii) increase expression of CD2 in Jurkat cells; or (iii) decrease Jurkat cell viability. In additional embodiments, the present invention provides for ELISA assays which detect PIF by determining the effect of a test sample on the binding of anti-CD2 antibody to a CD2 substrate.
Owner:BIOLNCEPT INC
Middle east and respiratory syndrome coronavirus antibody and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103864924APrevent intrusionHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsMiddle East respiratory syndromeBaculovirus expression vector system
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
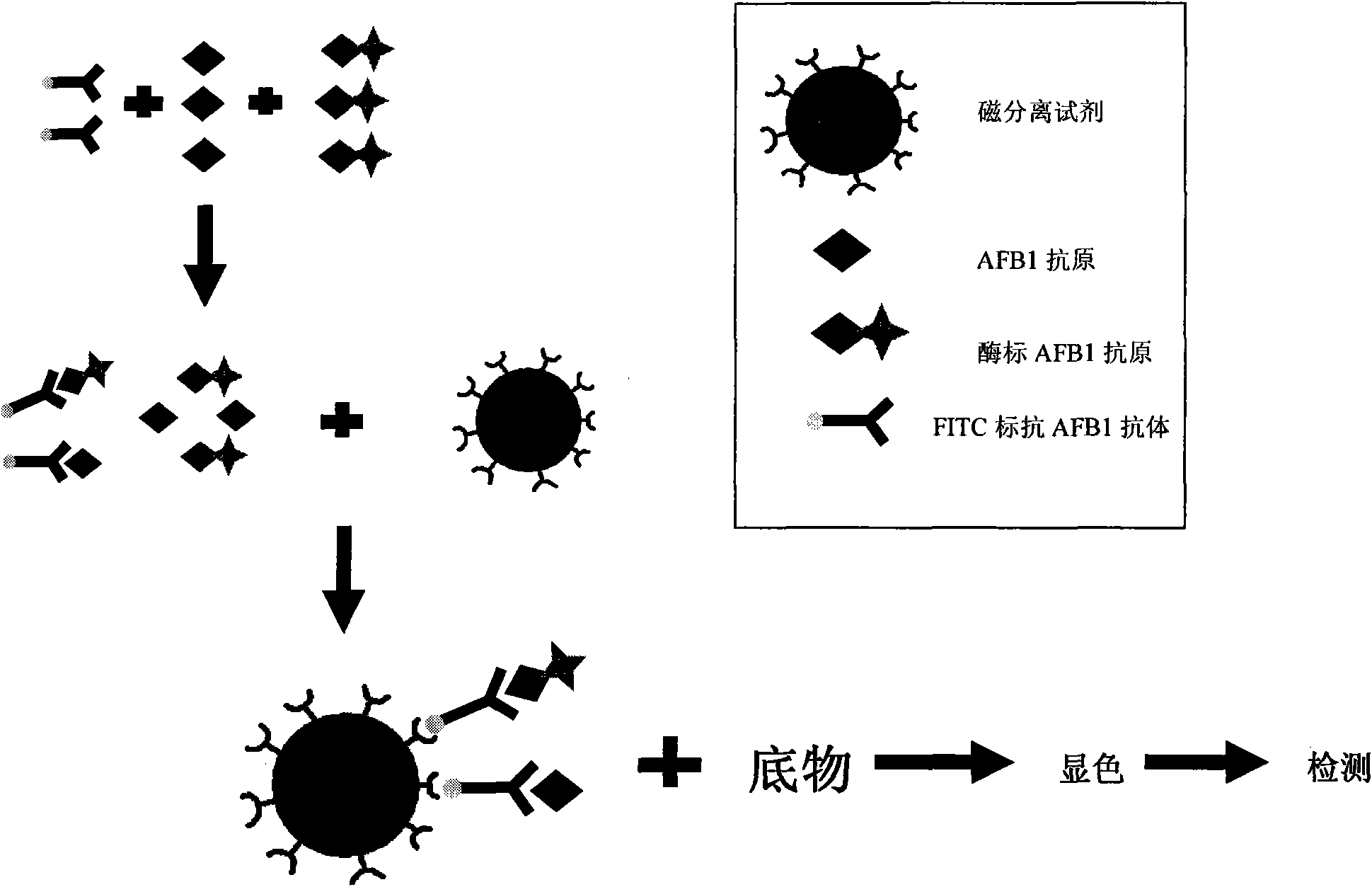
Aflatoxin B1 magnetic particle separation enzyme-linked immunoassay
InactiveCN101661036ASimple processing methodHigh detection sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSorbentFluorescein isothiocyanate
The invention provides an aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) magnetic separation enzyme-linked immunity quantitative detection method, belonging to the field of food safety immunoassay technique. The method adopts the immuno-detection principle of competition law; and AFB1 is connected with biological enzyme to prepare enzyme-labeled antigen reagent, anti-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) antibody is absorbed onthe surfaces of magnetic particles to prepare magnetic separation reagent, and the FITC is connected with the AFB1 antibody to prepare anti-reagent. In a sample, the AFB1 competes with the enzyme-labeled AFB1 and is combined with a small amount of FITC-labeled anti-AFB1 antibody, so that antigen-antibody complex can be formed. After the magnetic separation reagent is added, the complex is caughtonto the surfaces of the magnetic particles by the anti-FITC antibody connected on the surfaces of the magnetic particles. After being washed, the product is finally added with substrate and detected.The method has the advantages that (1) the magnetic particles are used for replacing the traditional enzyme-labeled plate to be taken as a solid-phase carrier, so that immunoreaction is carried out under the approximate liquid phase condition; and the reaction is more complete and rapid, and has the characteristics of high specificity and good repeatability compared with the traditional enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA); furthermore, (2) by adopting one-step competition law principle, the time used for detection is short.
Owner:北京倍爱康生物技术有限公司
Peptide-based diagnostic reagents for SARS
InactiveUS20050100883A1Improve quality controlBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseSARS coronavirusAssay
The present invention is directed to antigenic peptides and peptide compositions selected from the Membrane glycoprotein (M), the Spike glycoprotein (S), and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein antigens of the SARS coronavirus (SCoV). The present invention is also directed to methods of use of the peptides of the invention, e.g., for the detection of SARS-associated antibodies. Detection methods include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or other immunoassay procedures.
Owner:UNITED BIOMEDICAL INC
Hybridoma cell line 3G1 and anti-alfatoxin B1 monoclonal antibody produced by the same
ActiveCN102747043AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityBiological material analysisTissue cultureAflatoxin BELISA unit
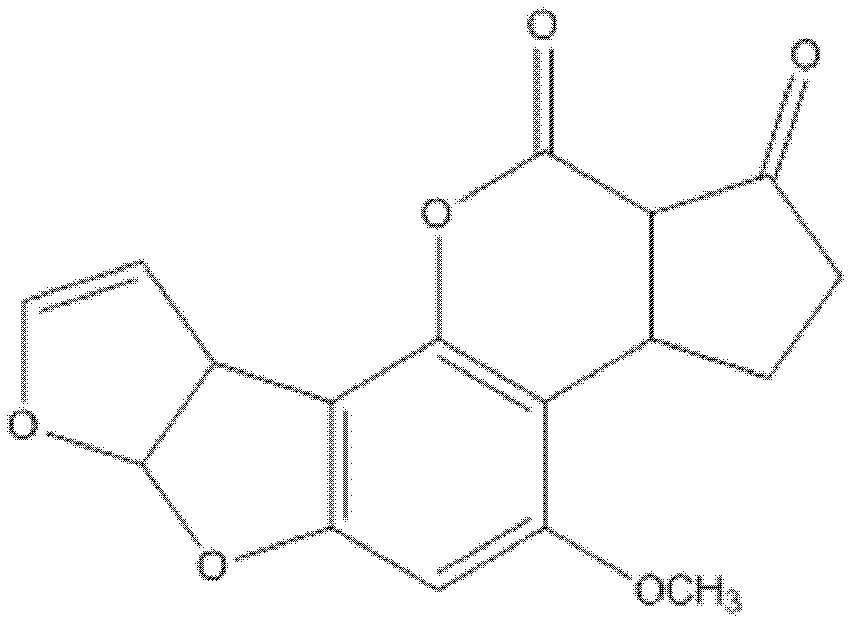
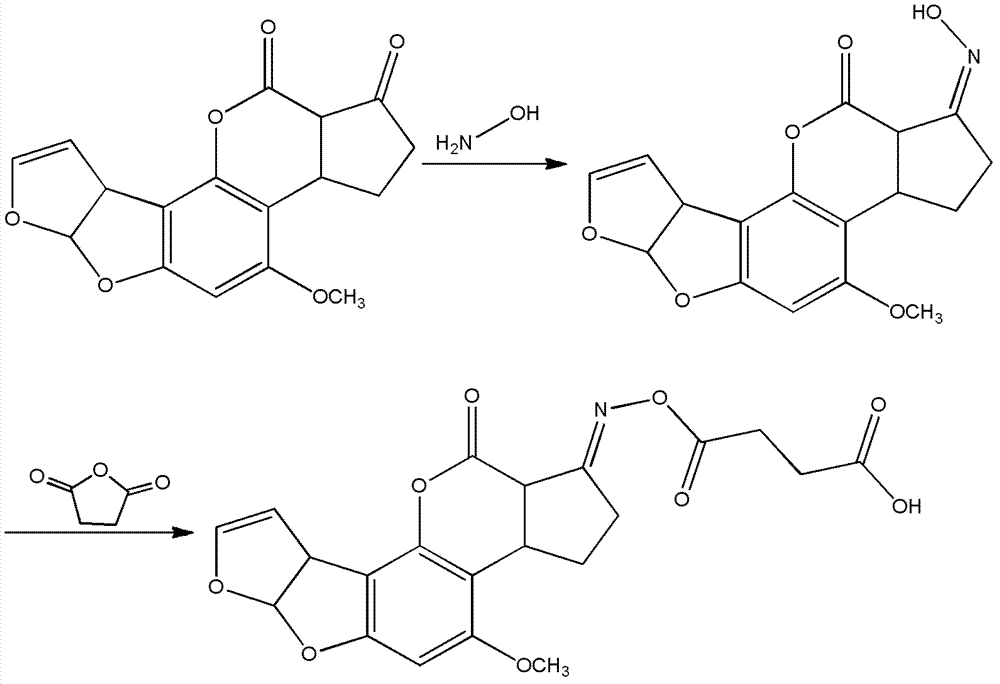
The present invention relates to a hybridoma cell line 3G1 and an anti-alfatoxin B1 monoclonal antibody produced by the hybridoma cell line 3G1. The hybridoma cell line 3G1 (CCTCCNO.C201014) can be used for preparation of a high titer anti-aflatoxin B1 monoclonal antibody, wherein an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method is adopted to determine a titer, and the titer is 6.40*10<6>. The anti-aflatoxin B1 monoclonal antibody of the present invention has characteristics of high sensitivity and good specificity, wherein 50% inhibiting concentration on aflatoxin B1 by the monoclonal antibody is 1.6 ng / mL, cross reaction rate with aflatoxin B2 is 6.4%, and cross reaction rates with aflatoxin G1 and G2 are less than 1%. In addition, the anti-aflatoxin B1 monoclonal antibody of the present invention can be used for determination of aflatoxin B1.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rapid method for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
InactiveUS6498016B1Fast wayRapid diagnosis of diseaseDielectric heatingOptical radiation measurementAntigenFood technology
This invention relates to a rapid and efficient method for carrying out enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of minute quantities of biomolecules such as antigen, antibody etc. This invention particularly relates to microwave mediated immobilization of antigen or antibody on to the activated surface followed by performing subsequent steps of ELISA by controlled microwave irradiation. The invented procedure has dramatically reduced the total time required for ELISA to less than 10 minutes from hours to days. The invented ELISA procedure is rapid, economical, reproducible and simple and can be automated. The invented procedure is useful for carrying out ELISA in clinical diagnostics, molecular biology, agriculture, sericulture, food technology, environmental science, biomedical research and other related fields.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
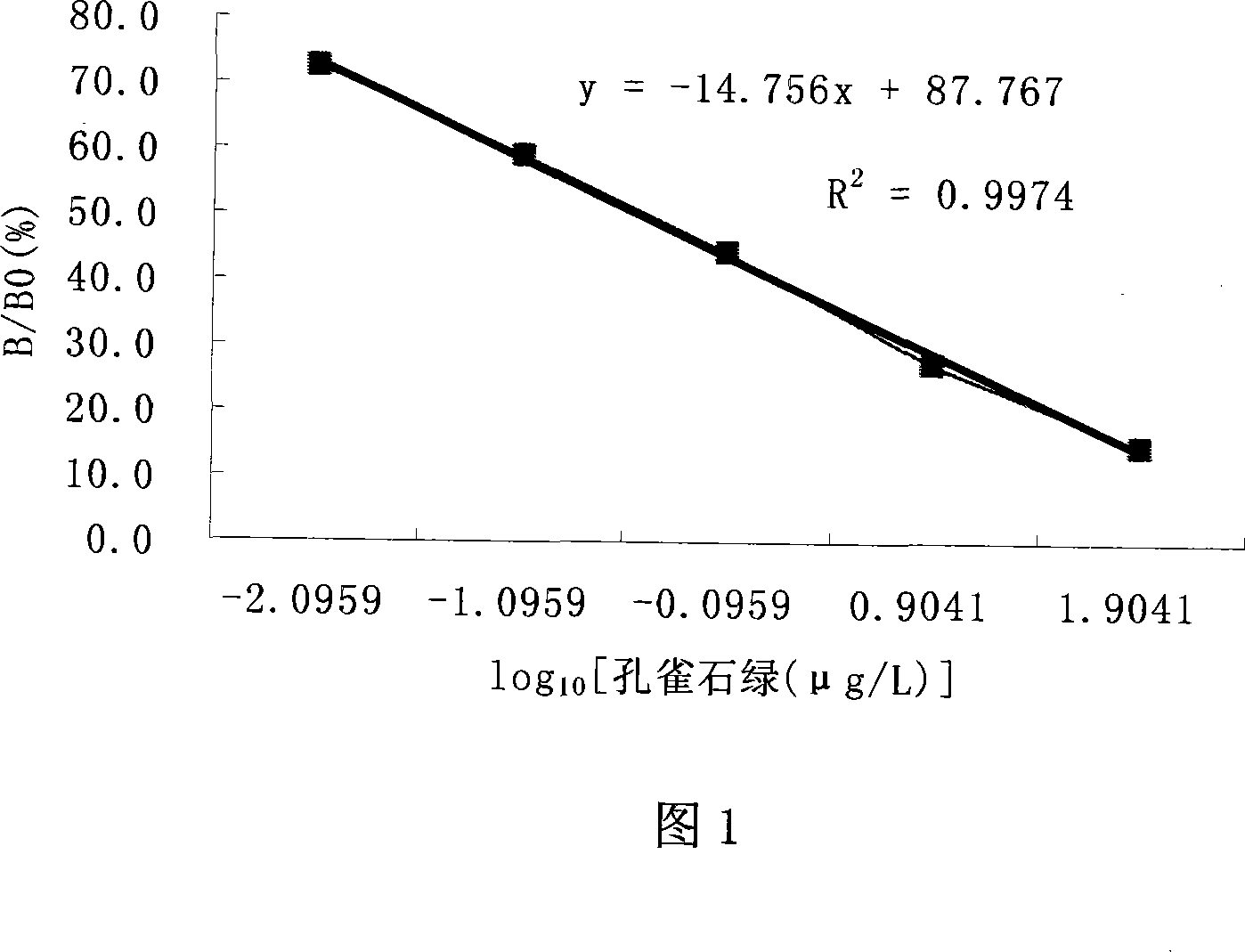
Malachite green vestigial ELISA detection kit and usage method thereof
The invention discloses an enzyme immunoassay of testing the bice green residues in animal derived food, which comprises an enzyme label plate covering bice green antigen, enzyme label bice green antibody working solution, bice green standard solution, substrate solution, substrate buffer solution, reaction termination solution, concentration washing liquid and sample dilute solution. The invention further discloses a method for using the immunoassay to test bice green residues, which comprises sample pretreatment, testing via the immunoassay, processing and analyzing result. The inventive immunoassay of bice green test uses direct competition enzyme-linked immunoassay adsorption analysis technique, with high sensitivity, high stability, simplified operation, reduced reaction time, reduced error caused by complex operation, reduced cost, wide application for testing samples and high practicality.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nano probe based method for detecting trace proteins by using microfluidic chip
InactiveCN102147414AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresDecorative surface effectsBiological testingAntigenProtein target
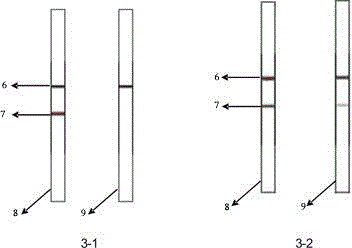
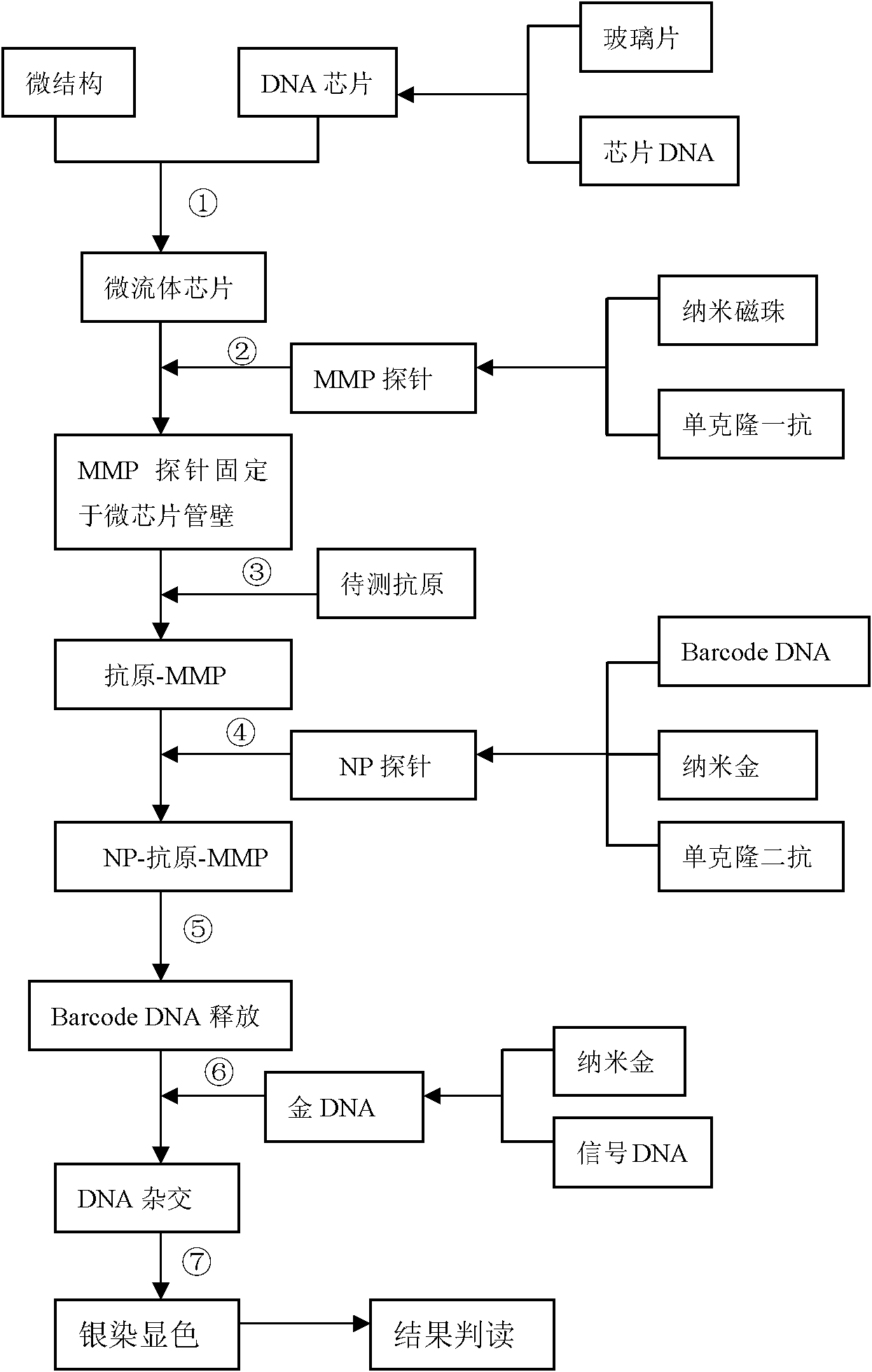
The invention relates to a nano probe based method for detecting trace proteins by using a microfluidic chip, which is characterized by comprising the steps: manufacturing a microstructure by using a standard photoetching process, and sealing a glass sheet (spotted with a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) probe) and the microstructure to prepare a required microfluidic chip; simultaneously labeling a monoclonal secondary antibody and a Barcode DNA with a signal amplification function on a nano gold particle, and labeling a monoclonal primary antibody on a magnetic bead; and detecting the trace target proteins in a microfluidic chip channel by means of immunoreaction of antigens and antibodies as well as gradual amplification and silver staining development of signals. The nano probe based method provided by the invention integrates the procedures of enrichment, separation and detection of biological samples, has the characteristics of specificity, rapidness and high sensitivity, and is expected to be applied to the diagnosis and detection of trace proteins (the antigens or antibodies) in clinical laboratory medicine. The sensitivity can reach a pg / ml level and is improved by 1000 times compared with the common ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method in clinical application.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
ELISA reagent box for determining antibody and antigen of swine circular virus II
InactiveCN1584597AEasy to operateSuit one's needsColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingPositive controlAntigen testing
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Assays for preimplantation factor and preimplantation factor peptides
The present invention relates to assay methods used for detecting the presence of PIF, and to PIF peptides identified using this assay. In particular, the present invention relates to flow cytomery assays for detecting PIF. It is based, at least in part, on the observation that flow cytometry using fluorescently labeled antilymphocyte and anti-platelet antibodies demonstrated an increase in rosette formation in the presence of PIF. It is further based on the observation that flow cytometry demonstrated that monoclonal antibody binding to CD2 decreased in the presence of PIF. The present invention further relates to PIF peptides which, when added to Jurkat cell cultures, have been observed to either (I) decrease binding of anti-CD2 antibody to Jurkat cells; (ii) increase expression of CD2 in Jurkat cells; or (iii) decrease Jurkat cell viability. In additional embodiments, the present invention provides for ELISA assays which detect PIF by determining the effect of a test sample on the binding of anti-CD2 antibody to a CD2 substrate.
Owner:BIOLNCEPT INC
Supersensitive immunoassays
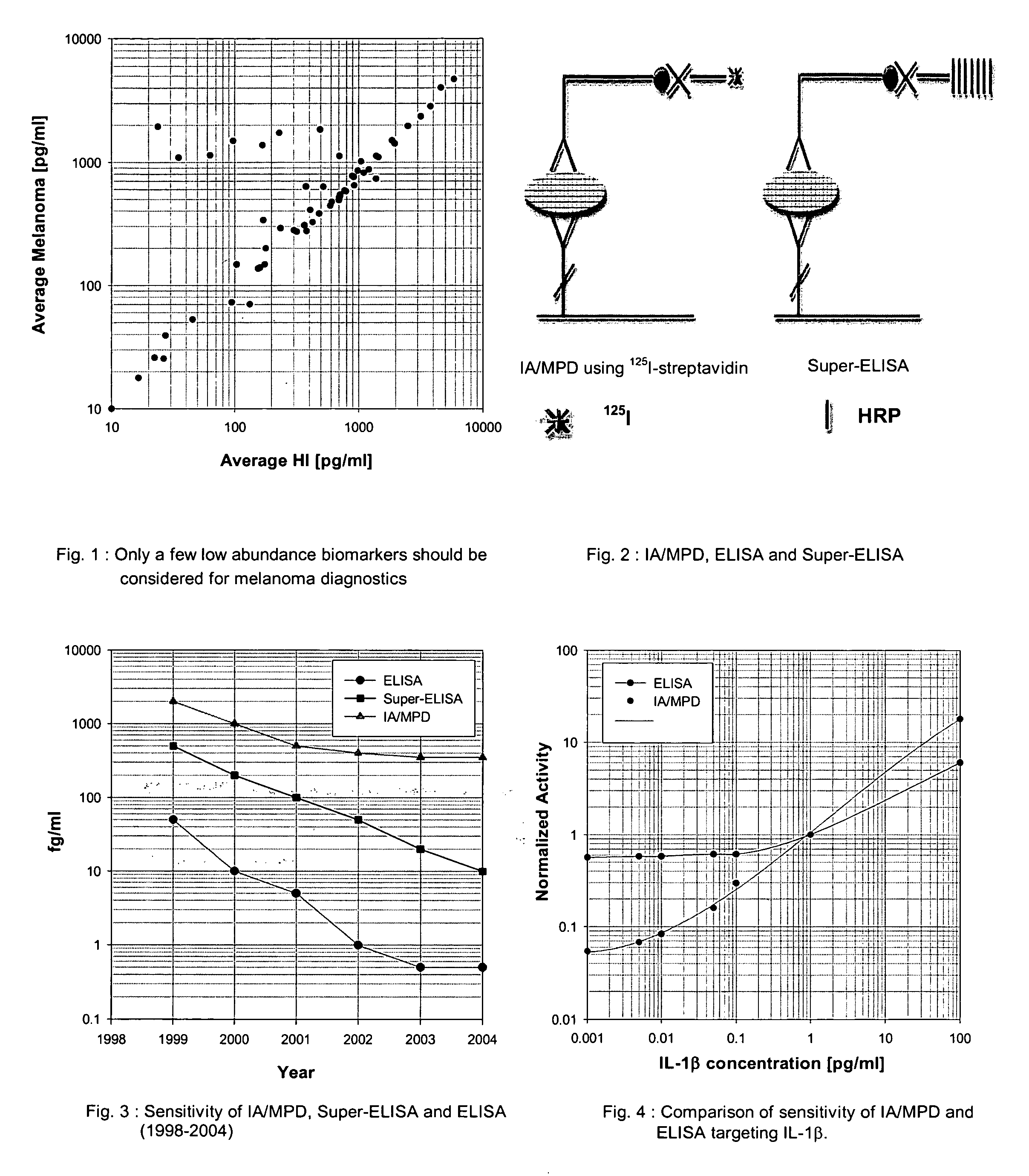
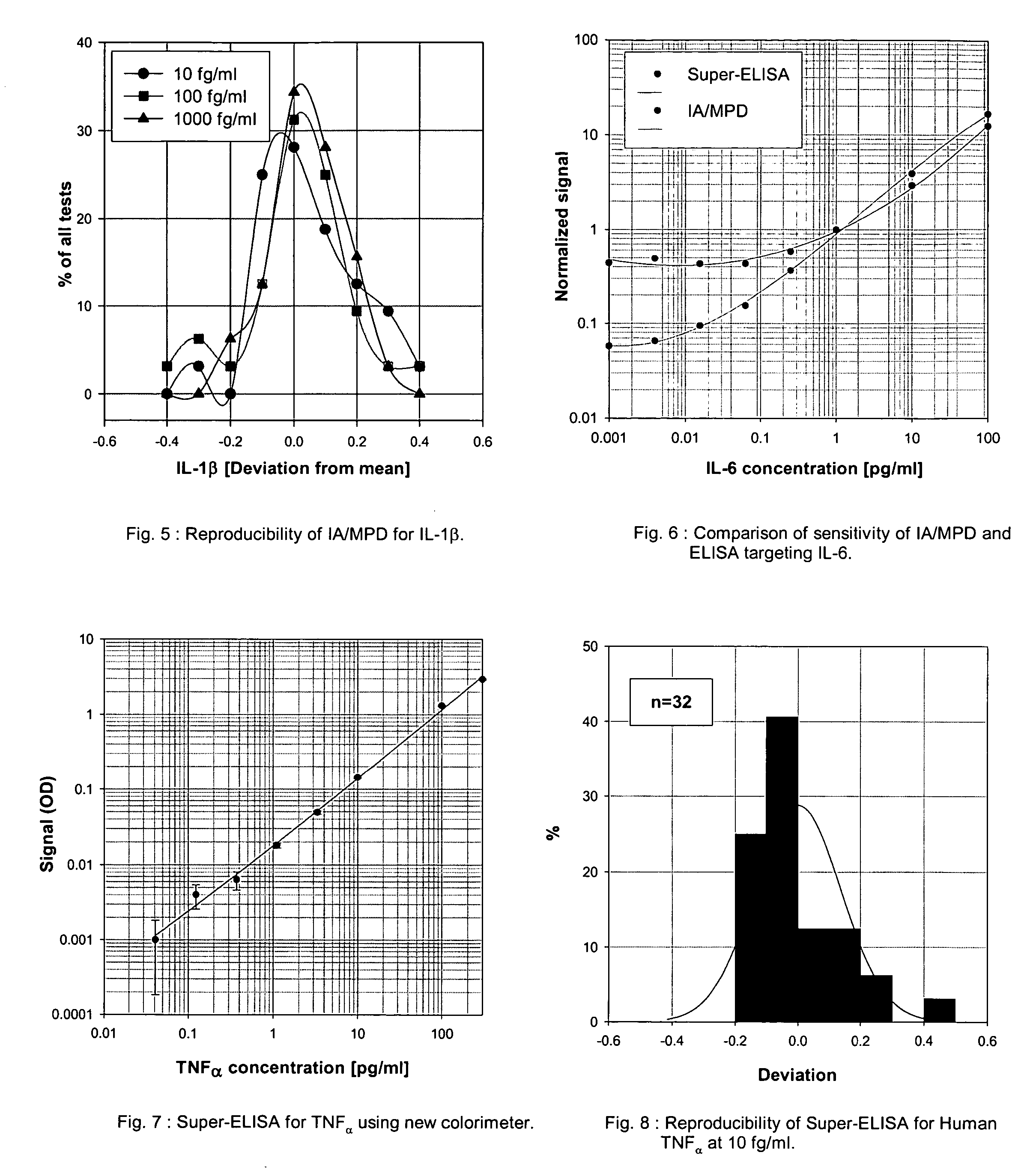
InactiveUS20050272110A1Improve reliabilityStrong specificityBiological testingImmunoassaysMedicineProstate cancer
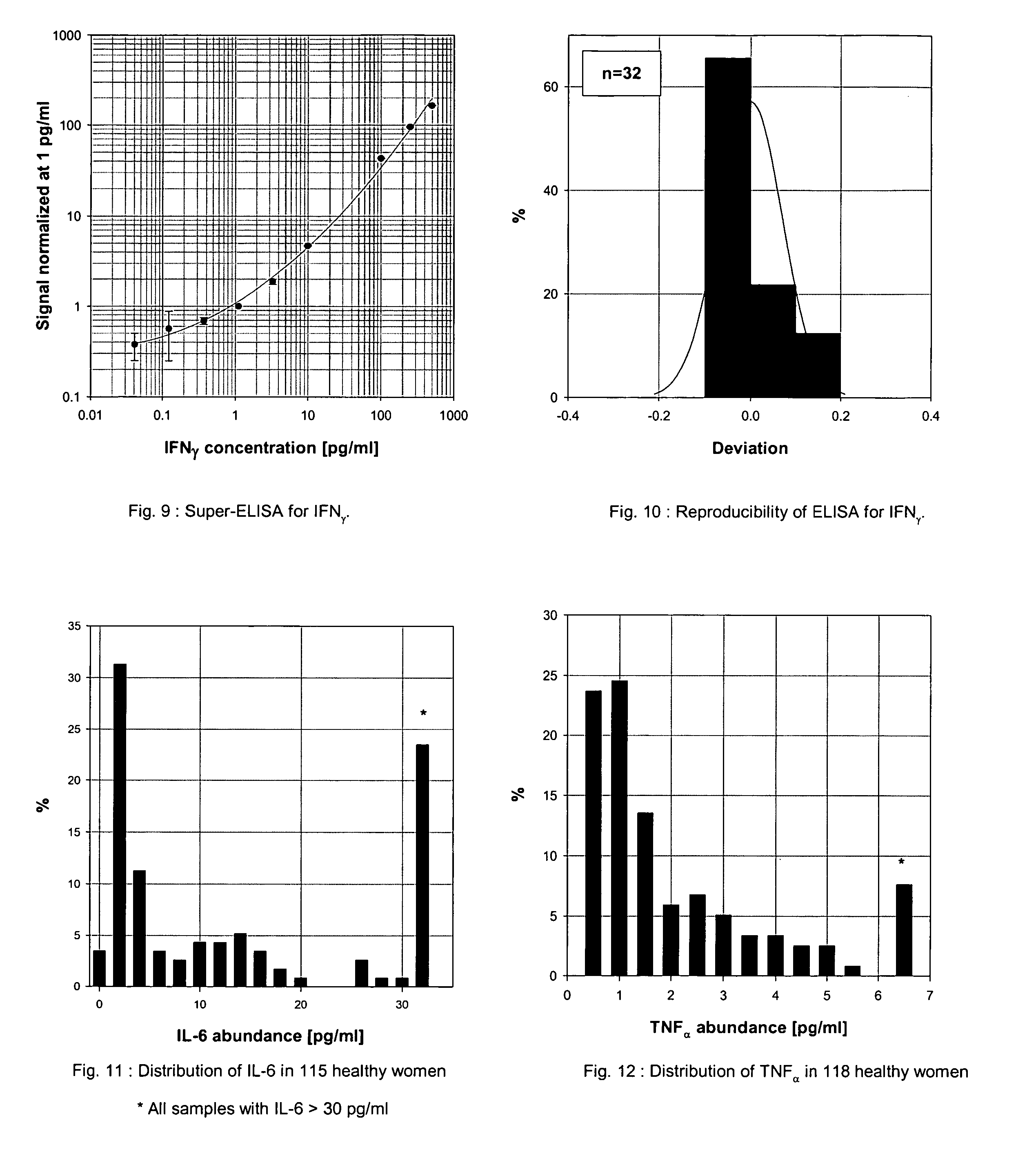
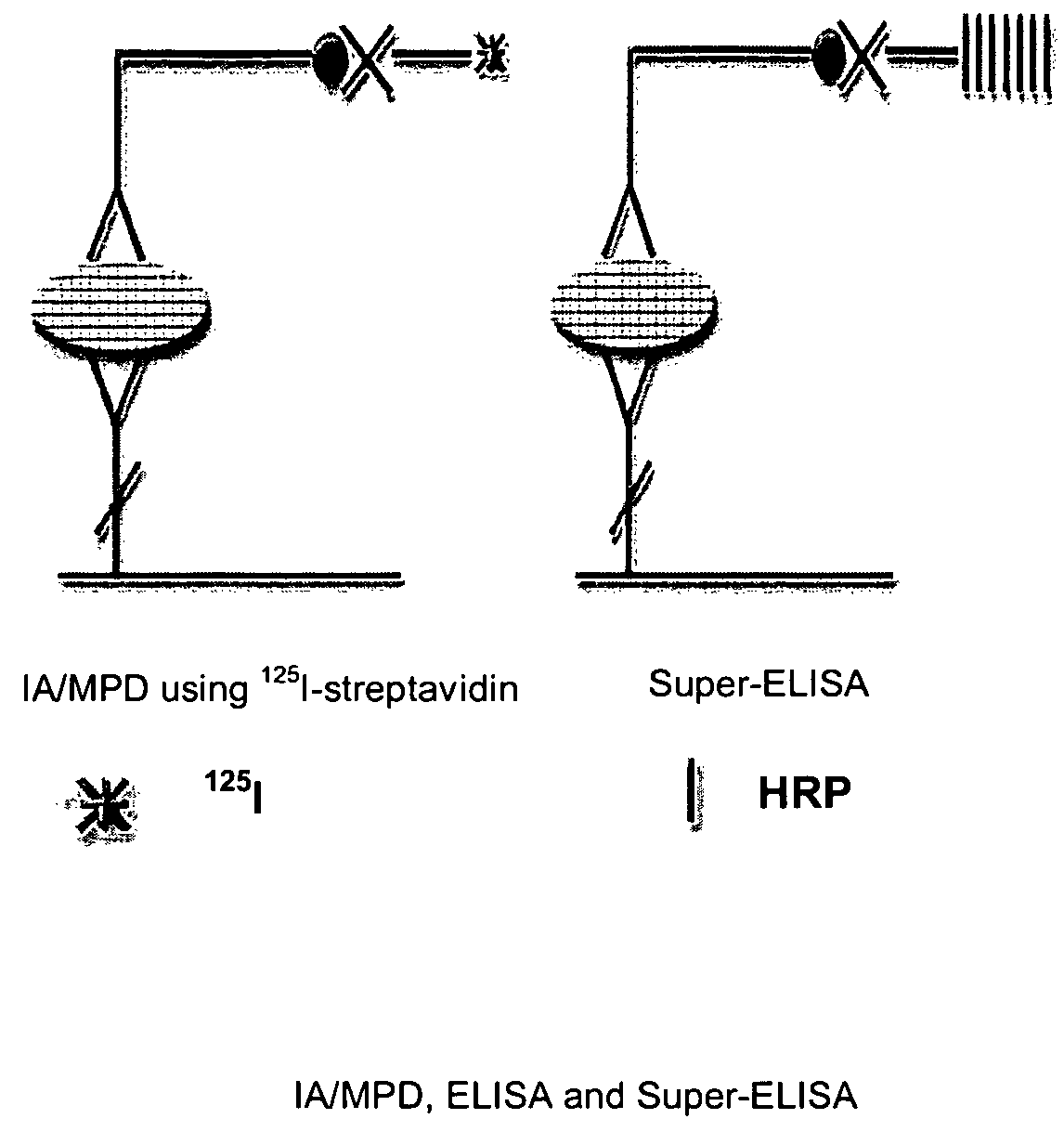
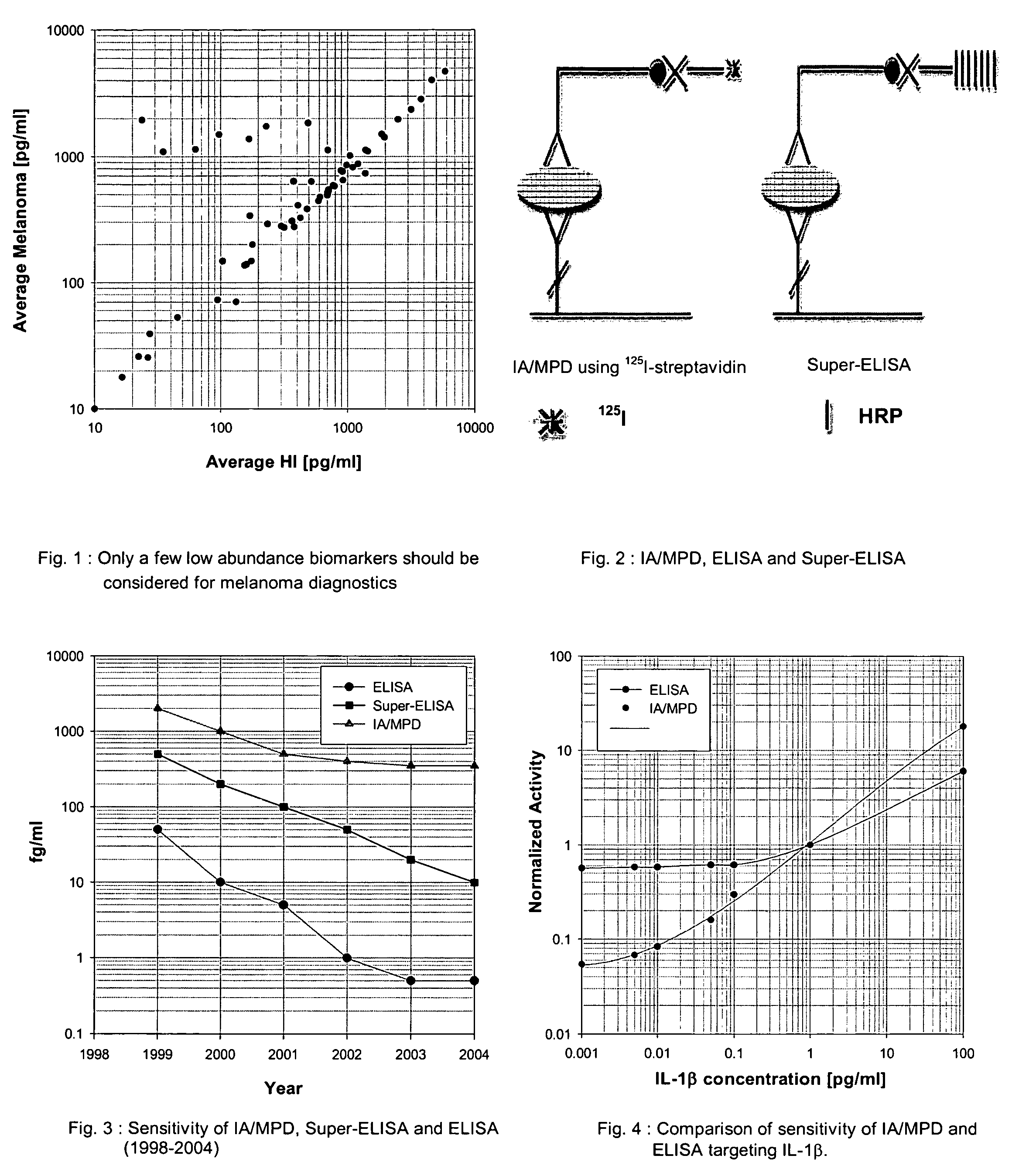
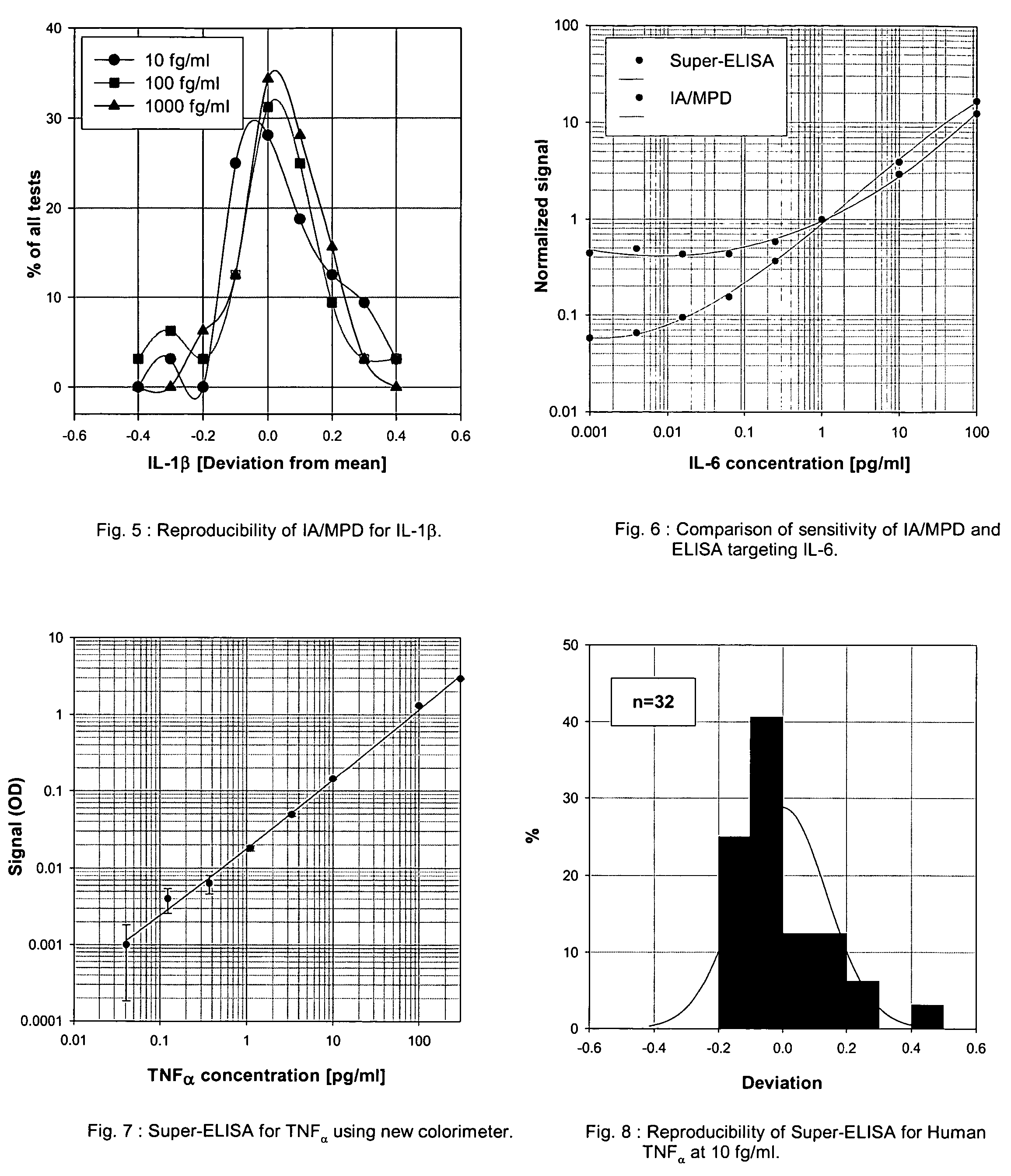
An assay exhibiting improved sensitivity for achieving a factor of ten times (10×) better sensitivity than current sensitivity levels achieved by prior-art immunoassays, as exemplified by ELISA. Three main implementations are described: IA / MPD, Super-ELISA and Reverse Geometry Immunoassay, including specific panel biomarker relationships for the early detection and recognition patterns of breast and prostate cancers. More sensitive immunoassays are achieved through a better understanding of sources of biological background, and by the rejection of particular sources thereof. Super-sensitive immunoassays permit measurement of blood sample biomarkers, and show distribution of low abundance proteins included relationships between cytokine non-Gaussian distributions, very large dynamic ranges and strong age dependence, and including new algorithms based on 2D correlations of studied biomarkers.
Owner:BIOTRACES
PCV2 (porcine circovirus 2) ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) antigen detection kit as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103033622AImprove expression efficiencyImproving immunogenicityMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringSorbentMonoclonal antibody
The invention relates to a PCV2 (porcine circovirus 2) ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) antigen detection kit as well as a preparation method and applications thereof, wherein the detection kit comprises an elisa plate of a polyclonal antibody of peridium anti-PCV2-Cap (nucleocapsid) protein, seal liquids, sample diluent, an antigen standard product, a second antibody of a monoclonal antibody of HRP marked anti-PCV2-Cap protein, a concentrated washing liquid, an enzyme substrate solution A, an enzyme substrate solution B and a stop solution, wherein the antigen standard product is purified reconstructed PCV2-Cap protein. The specificity of the kit provided by the invention achieves 100%, and the sensitivity is as high as 4ng / ml, and the kit can be used for swinery PCV2 antigen detection and PCV2 vaccine product quantitative detection.
Owner:WUHAN CHOPPER BIOLOGY
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting aflatoxin B1-containing medicine and application for same
The invention provides an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit for detecting an aflatoxin B1-containing medicine and an application for the same. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit comprises an ELISA plate coated with a coating antigen, an enzyme label, aflatoxin B1 specific antibody working solution (contained in the case that the coating antigen on the ELISA plate and the enzyme label are enzyme-labelled antibodies or enzyme-labelled antigens), aflatoxin B1 standard substance solution, substrate developing solution, stopping solution, concentrated washing solution and concentrated compound solution. The method for detecting aflatoxin B1 by virtue of the kit provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: performing sample pre-treatment at first, and then detecting by virtue of the kit, and finally analysing the detected result. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit provided by the invention can be used for detecting the residual amount of aflatoxin B1 in samples such as oil, peanuts and grains, as well as is simple and convenient to operate, low in expense, high in sensitivity, capable of being monitored in the field, and suitable for screening lots of samples.
Owner:BEIJING KWINBON BIOTECH
Method for detecting pig plague virus specific antibody and its ELISA reagent kit
InactiveCN101144818AGuaranteed specificityGuaranteed Differential DiagnosisMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorElisa kitSwine Fever Virus
The invention discloses a method for detecting the specific antibody of classical swine fever virus and a special ELISA kit thereof. The kit includes a classical swine fever virus antigen and an enzyme-labeled classical swine fever virus single-epitope specific antibody; the said swine fever virus antigen is a polypeptide containing one or more than one amino acid residue sequence described in sequence 1. The detection reagent of the classical swine fever virus specific antibody of the present invention can carry out effective detection to the classical swine fever virus specific antibody by solid-phase antigen competition ELISA (blocking method); The B cell epitope ensures the differential diagnosis, and the high degree of conservation of the epitope among various strains ensures the specificity of detection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
Method and device for detecting and separating HP (helicobacter pylori) ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay)
InactiveCN103278628AOvercoming Abundant MedicineOvercoming demandsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting and separating HP ELISA. According to the method, a prepared magnetic bead provided with HP, an enzyme-labeled antibody, an enzyme reaction substrate, a gastric juice sample and a cleaning fluid are placed in different liquid storage tanks on a micro-fluidic chip by the aid of an electric fluid force, and flow of liquids in the different liquid storage tanks is electrically controlled , so that ELISA is fully and automatically detected; and a detected fluorescence signal is taken as a trigger signal, so that an HP sample is fully and automatically separated. The device comprises a platform structure, the micro-fluidic chip and an electric cabinet, wherein the micro-fluidic chip comprises a glass sheet, a PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) square plate and a driving electrode, a micro channel, a mixed channel and a detection area are formed in the surface of the PDMS square plate in a photoetching manner by the aid of a soft lithography technology, and the liquid storage tanks are arranged on the PDMS square plate. The device for detecting and separating the HP ELISA has the advantages as follows: the device is small in size, light in weight, convenient to carry and operate and low in construction cost and can be handheld for field detection, thereby facilitating popularization and application.
Owner:QIQIHAR MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measuring heavy metal mercury
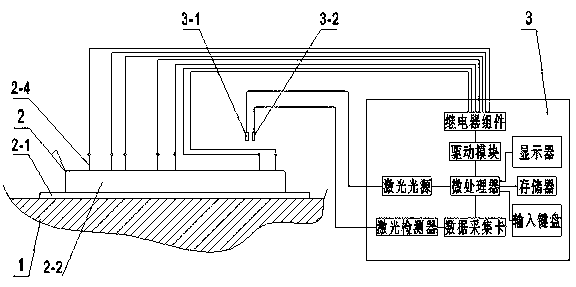
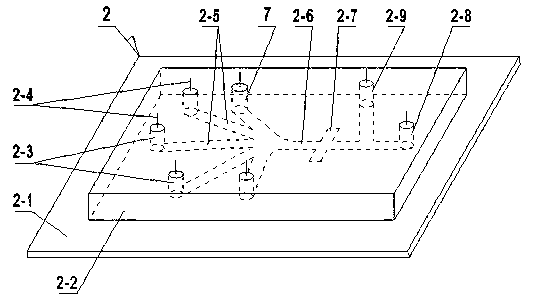
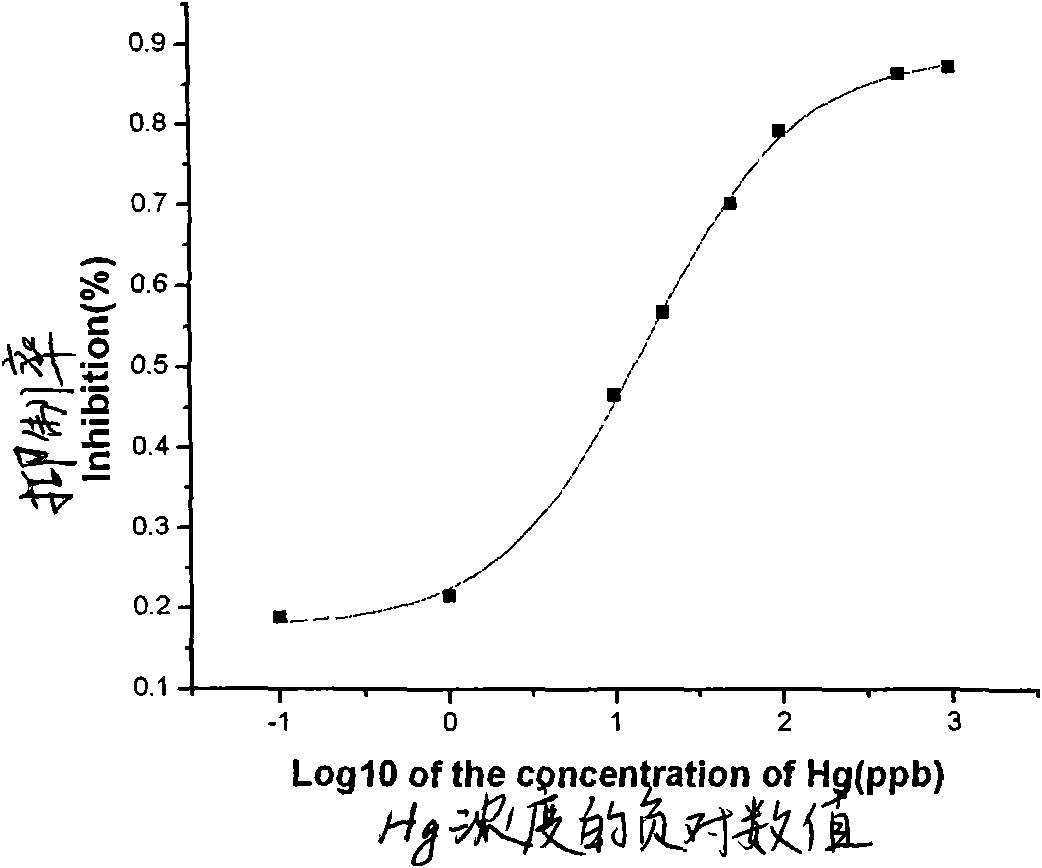
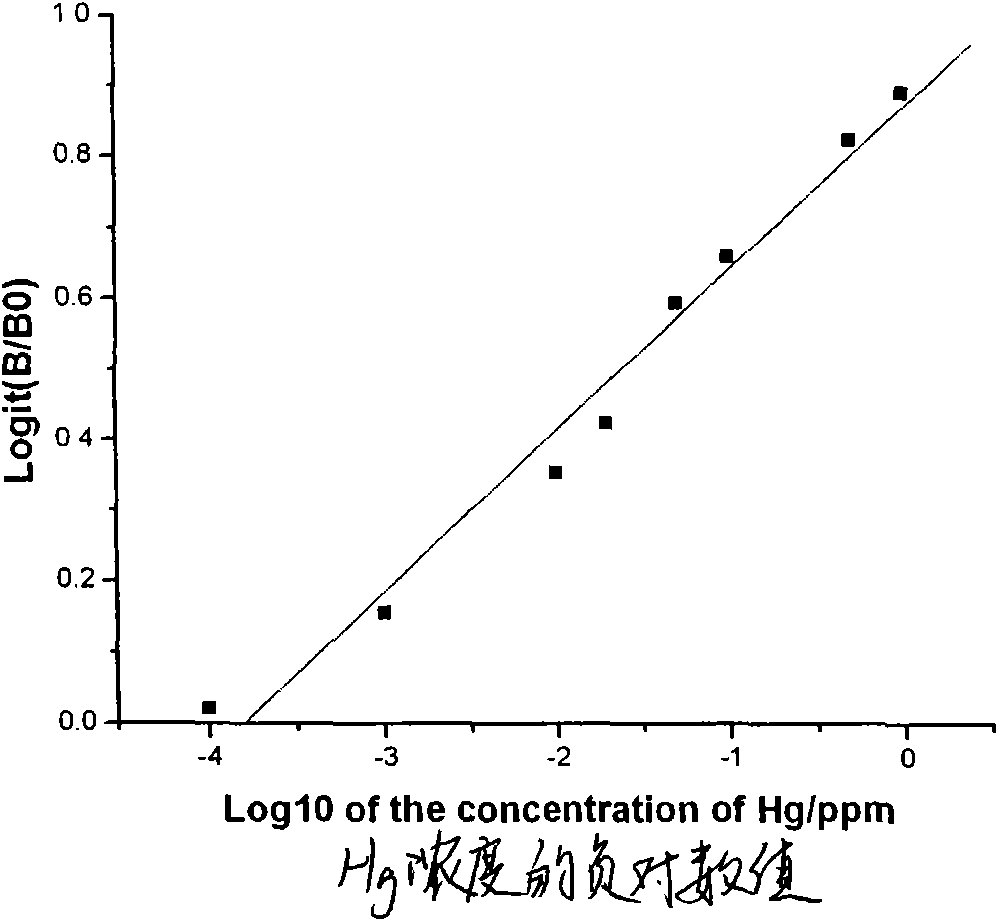
The invention discloses an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for measuring heavy metal mercury, belonging to a method for measuring heavy metal mercury in an environment water sample. The method comprises the following steps: taking a monoclonal antibody for specially identifying mercury-chelating agent EDTA compound Hg-EDTA as the base, coating the coated antigen mercury-chelating agent-albumen on a 96-hole ELISA plate; incubating at 4 DEG C over night and then sealing by phosphate buffer solution PBS including 1% of gelatin, after washing the ELISA plate, addinga mixing solution of the specificity mercury monoclonal antibody and samples to be measured, incubating at 37 DEG C and then washing the plate, adding an ELISA secondary antibody, incubating at 37 DEGC, adding an enzyme reaction substrate after washing the plate, and adding a reaction stop solution for stopping the reaction after the incubation, and then measuring the absorbance value of each hole by an ELISA reader; obtaining a standard competitive inhibit curve, then executing Logit transition on the curve, and drawing the standard curve of the mercury in the sample to carry out the quantitative analysis. The method is suitable for the measurement of trace mercury in an environment water sample, simultaneously provides the technical support for the fast scene measurement of heavy metalpollution emergency in order to remedy the pollution accident and go back to work in time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Soluble MIC polypeptides as markers for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer and autoimmune diseases or conditions
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
Supersensitive immunoassays
InactiveUS7604956B2Improve reliabilityStrong specificityBiological testingImmunoassaysMedicineProstate cancer
An assay exhibiting improved sensitivity for achieving a factor of ten times (10×) better sensitivity than current sensitivity levels achieved by prior-art immunoassays, as exemplified by ELISA. Three main implementations are described: IA / MPD, Super-ELISA and Reverse Geometry Immunoassay, including specific panel biomarker relationships for the early detection and recognition patterns of breast and prostate cancers. More sensitive immunoassays are achieved through a better understanding of sources of biological background, and by the rejection of particular sources thereof. Super-sensitive immunoassays permit measurement of blood sample biomarkers, and show distribution of low abundance proteins included relationships between cytokine non-Gaussian distributions, very large dynamic ranges and strong age dependence, and including new algorithms based on 2D correlations of studied biomarkers.
Owner:BIOTRACES
Biologically safe Africa swine fever antigen multifactorial serum for ELISA diagnosis
The invention relates to a biologically safe Africa swine fever antigen multifactorial serum for ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) diagnosis. A technical scheme adopted in the invention includes: adopting gene-expressed structural protein P72, K205R, P54, and A104R, conducting chemical purification, carrying out coating with a Freund's incomplete adjuvant, performing intramuscular immunization on laboratory swine in three batches, collecting swine blood after one month, separating serum, implementing serological testing, and conducting subpackaging and preservation. The serum is subpackaged into ELISA kits to undergo test according to conventional ELISA test methods.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HEALTH & EPIDEMIOLOGY CENT
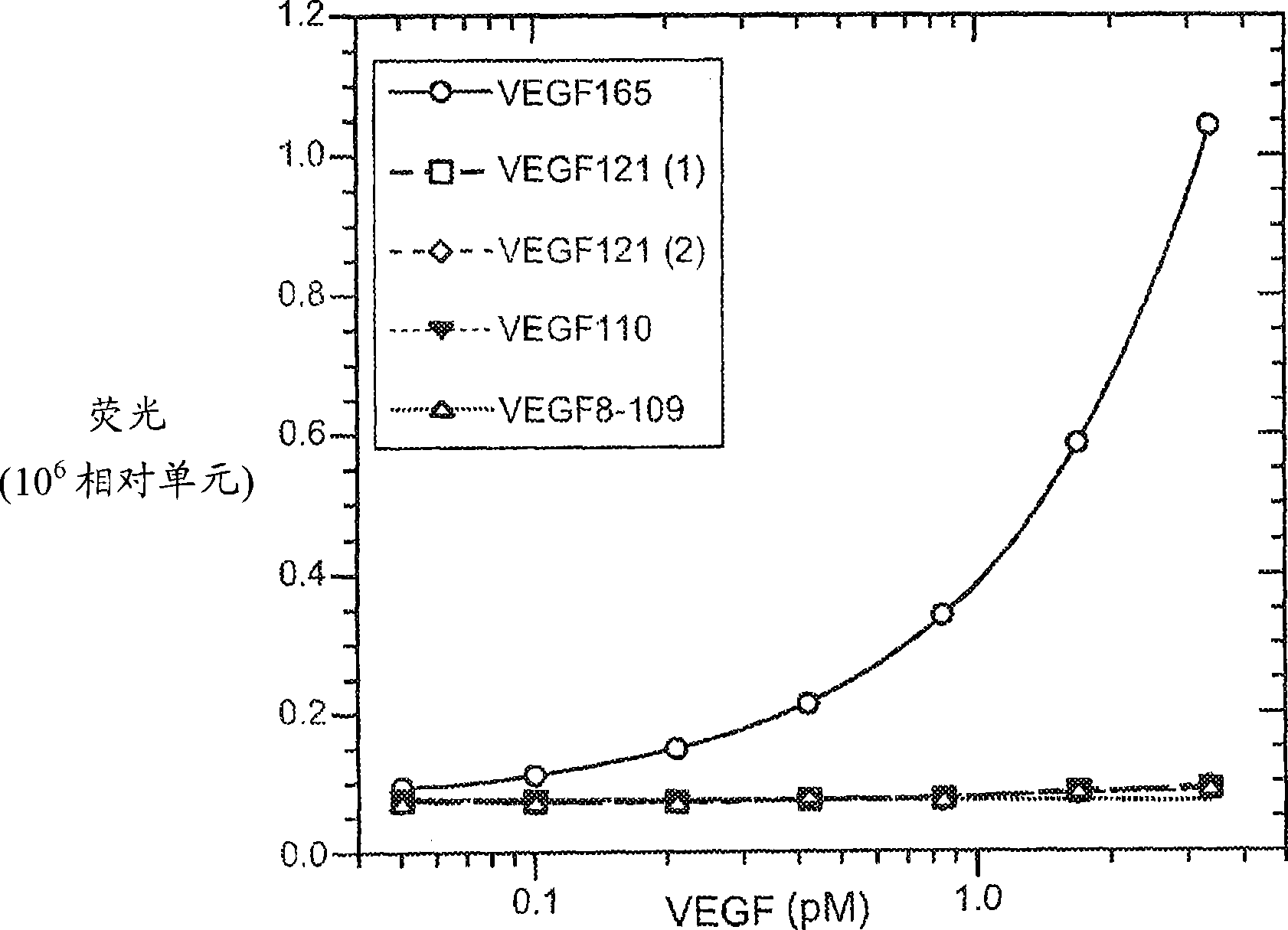
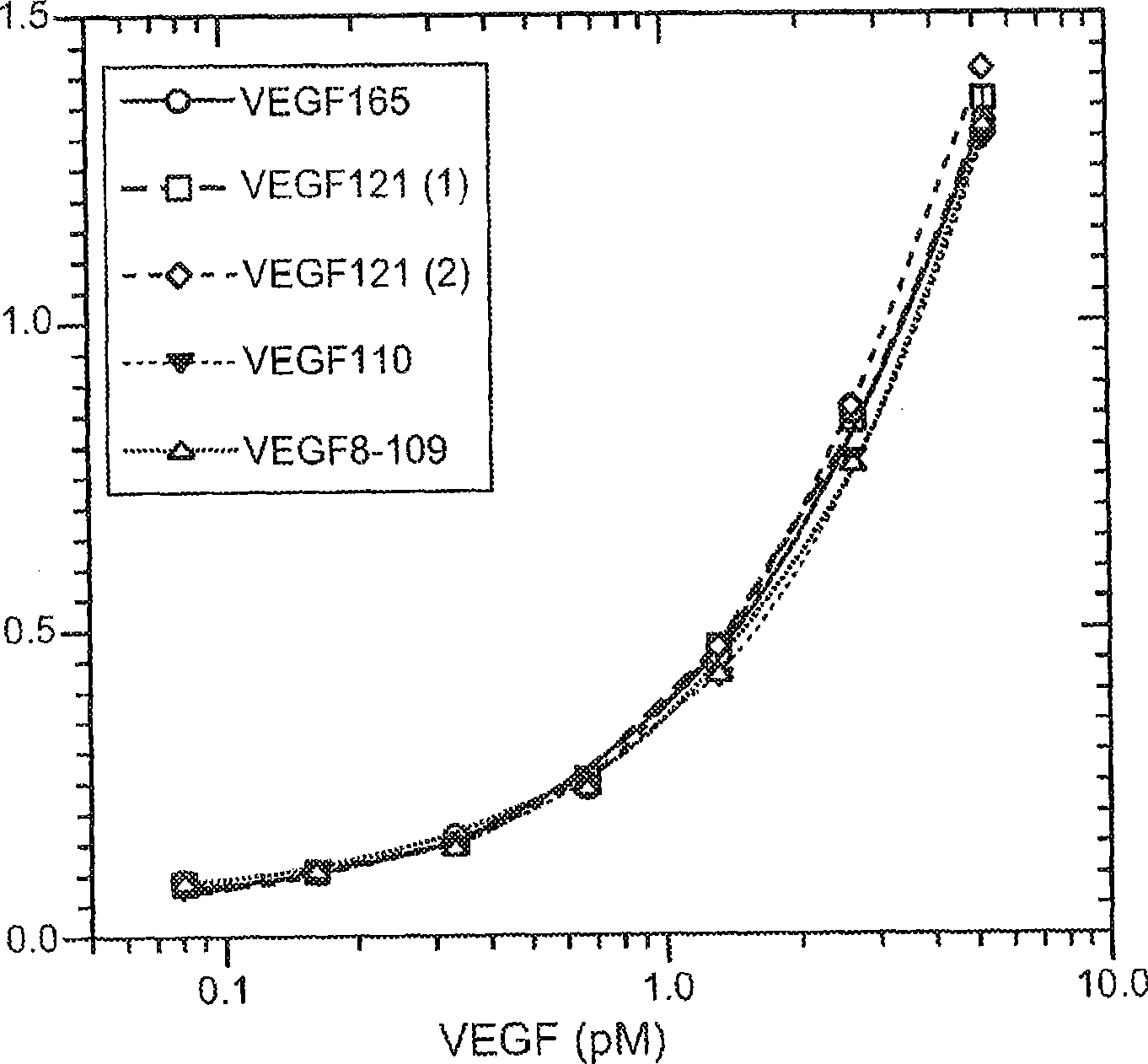
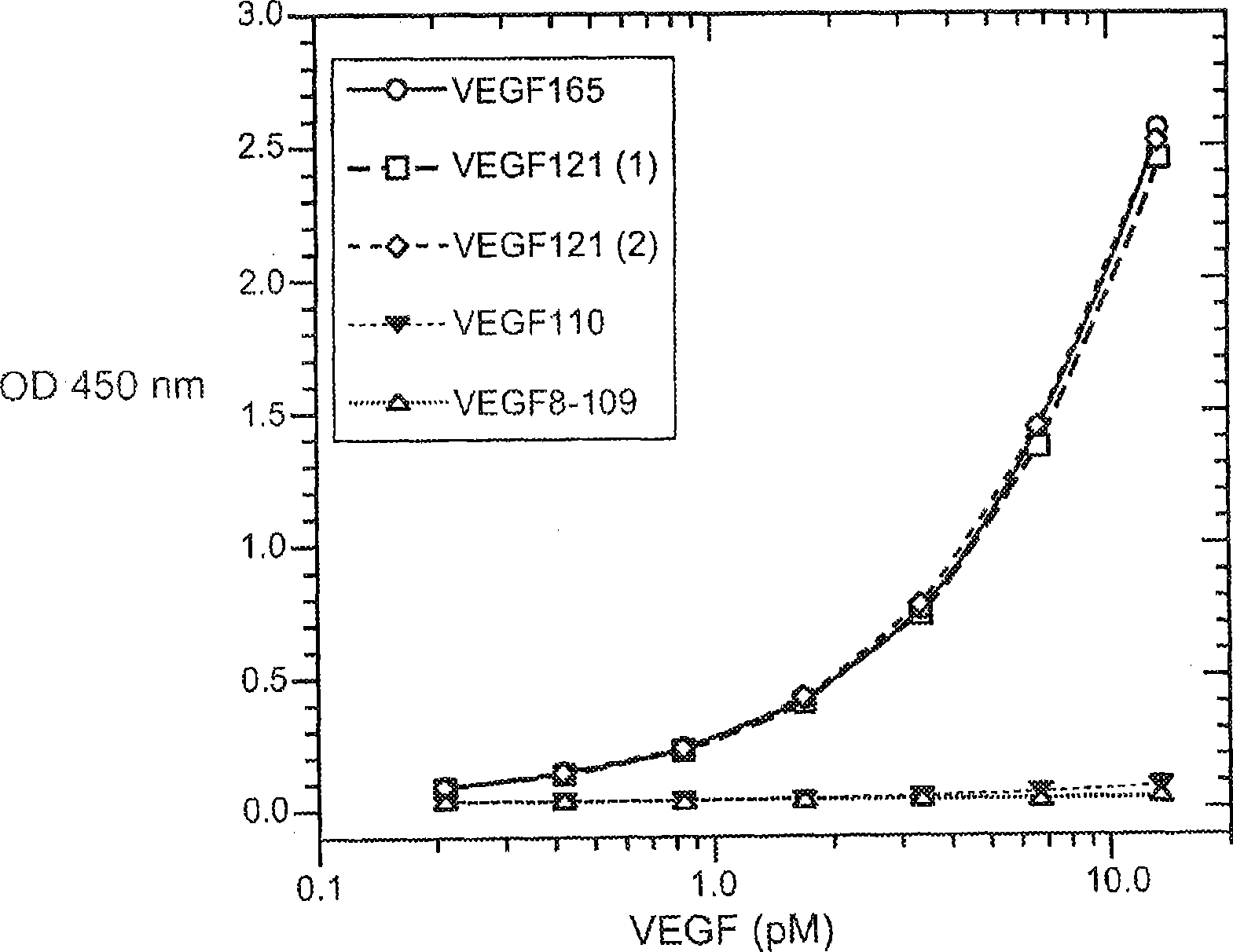
ELISA for VEGF
ActiveCN101523220ABiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntigenDiabetes mellitus
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) activity in a patient's bloodstream or other biological sample can serve as a diagnostic and prognostic index for cancer, diabetes, heart conditions, and other pathologies. Antibody-sandwich ELISA methods and kits for VEGF as an antigen are provided to detect types of VEGF levels in biological samples from animal models and human patients and can be used as a diagnostic / prognostic index.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Korean novel duck hepatitis viral antibody ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detection kit
InactiveCN102127531ASolve the difficulty of purificationImprove securityRecombinant DNA-technologyFermentationDuck hepatitis A virusViral antibody
The invention discloses a Korean novel duck hepatitis viral antibody ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detection kit. The detection kit contains an ELISA board coated by Korean novel duck hepatitis VP1 (Phenotypic Variance1) recombination protein, a sample diluent, concentrated washing liquid, an enzyme conjugate working solution, a chromogenic reagent (A), a chromogenic reagent (B), a stopping solution, a positive contrast solution and a negative contrast solution. The VP1 recombination protein is obtained by using the following method: using Korean novel duck hepatitis viruses as a material, augmenting and cloning the VP1 gene through an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction) method to obtain recombinant expression plasmid pMD (physical medium dependent)-VP1; then, directionally inserting to an expression vector pET-32a (+) and screening to obtain recombinant expression plasmid pET-32a(+)-VP1; and inducing, expressing and purifying by ITPG (Isopropyl beta-D-Thiogalactopyranoside) to obtain VP1 recombination protein. The detection kit is used for detecting the Korean novel duck hepatitis and has strong specificity, high sensitivity, simplicity of operation, easiness of popularization and application in a large-area range and wide market prospects.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com