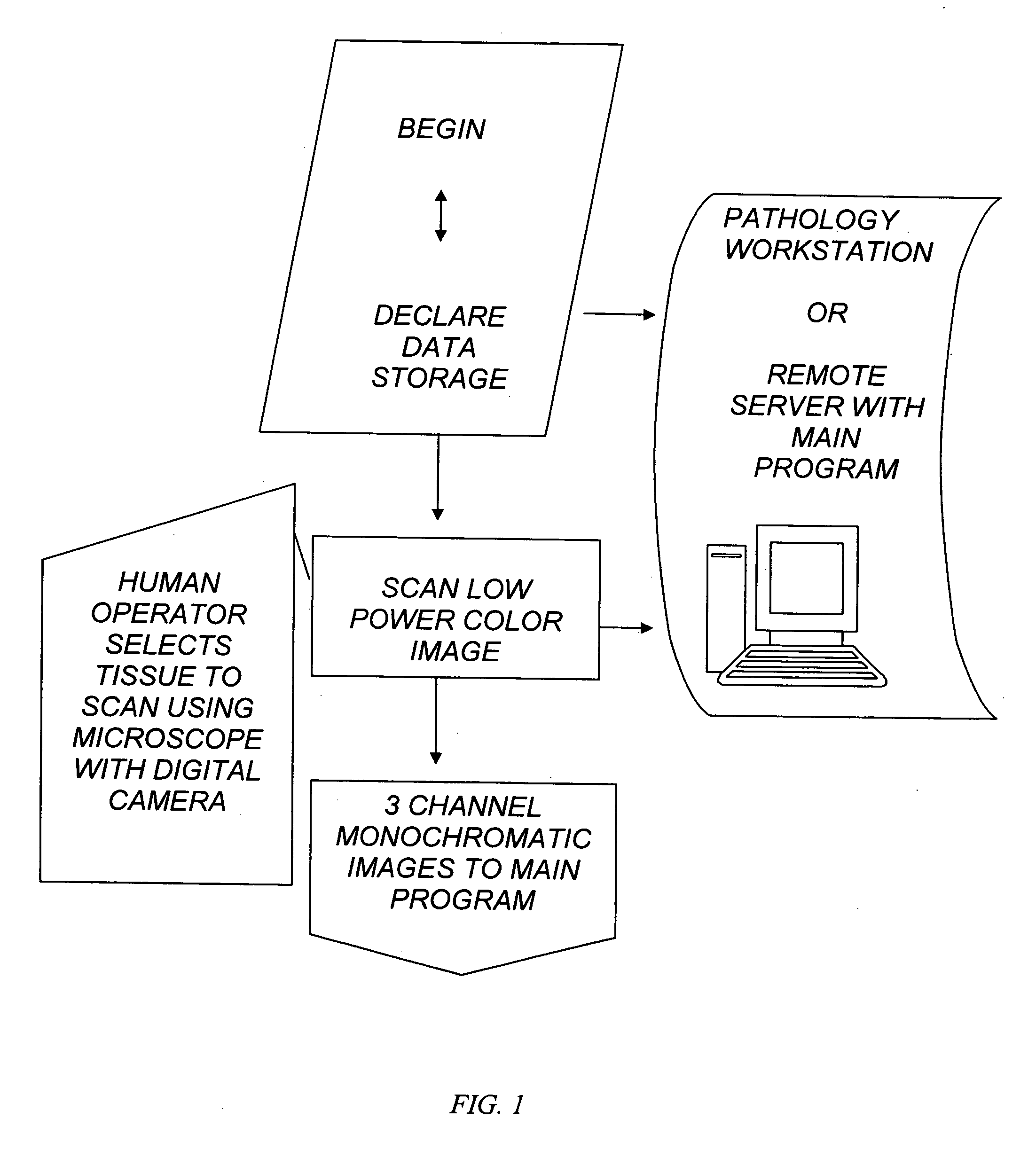
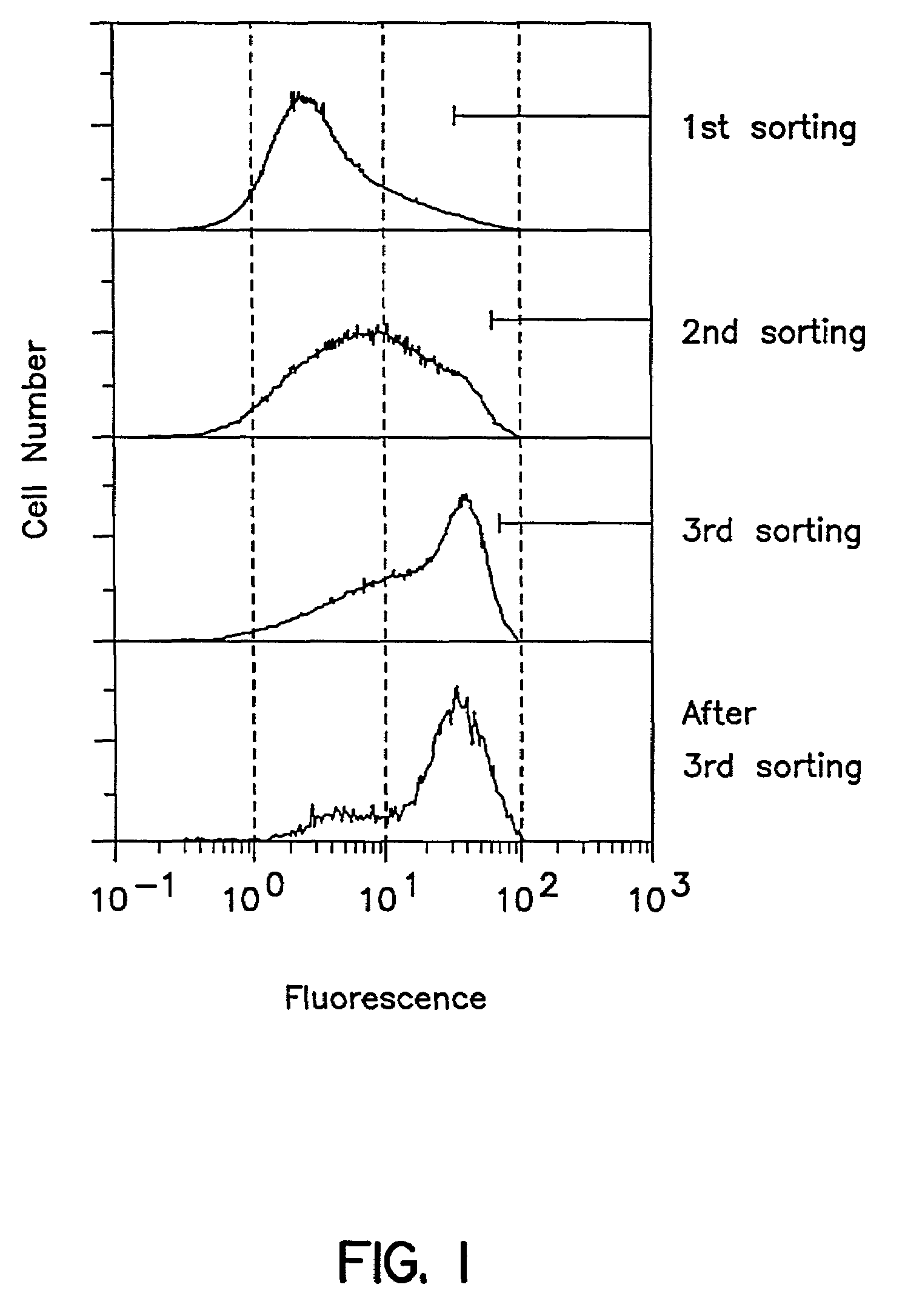
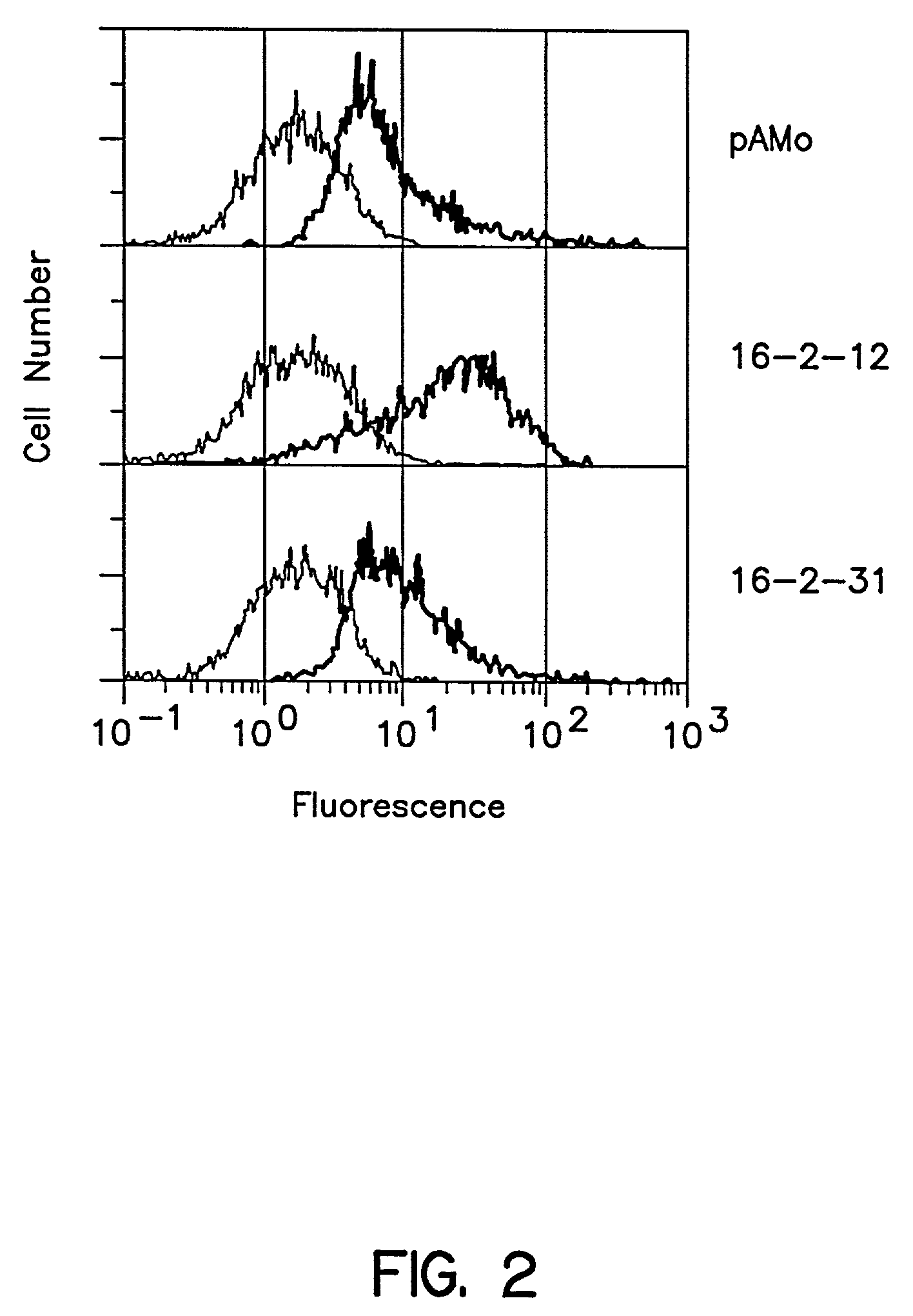
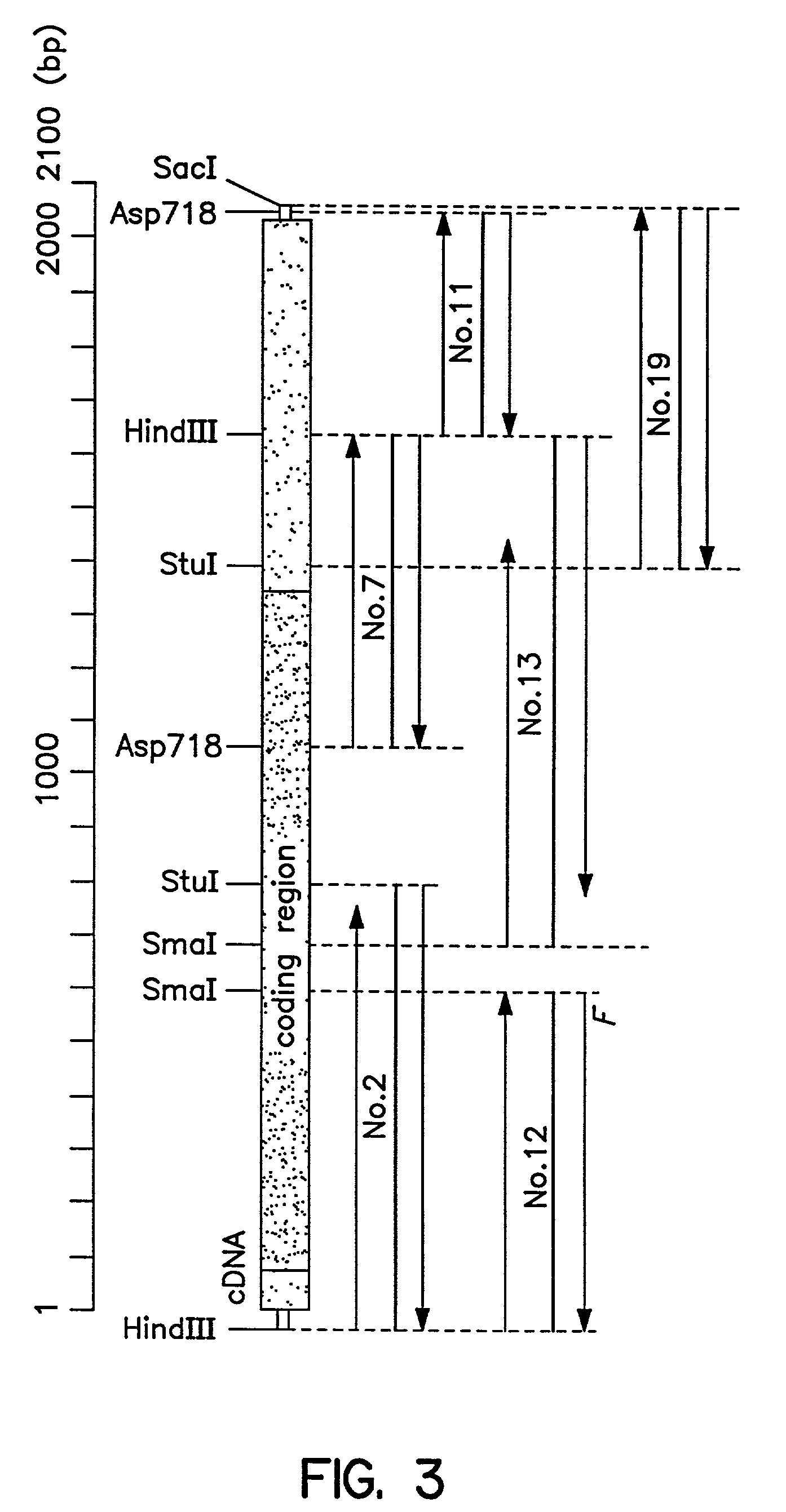
Patents
Literature
107 results about "Immunostaining" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods.
Cell enriching, separating and extracting method and instrument and single cell analysis method
ActiveCN102690786AEnrichment reachedEfficient collectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomass after-treatmentImmunofluorescence stainingMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a method and an automatic instrument device for enriching and extracting target cells and separating single cells by using a positive magnetic bead method and performing immunity and molecular biology identification and analysis on single cells. By the method and the instrument device, the on / off of a capture magnet and a release magnet is controlled by various methods to complete target cell searching, capturing, cleaning and releasing operation once or for multiple times, so that the target cell detection sensitivity and stability are improved. When the capture magnet searches and captures the target cells, the search line is circular, square, comb-shaped, S-shaped or U-shaped. In addition, the captured substances are filtered, most free micro magnetic beads are removed, the purity of the product is further improved and the product can be used as a good experimental material. By combining a special filter and the adsorption of the capture magnet, more than 95 percent of free micro magnetic beads can be effectively removed. Meanwhile, the types of the single cells are identified and biological characteristics of the single cells are analyzed by an immunofluorescence staining method and a method in molecular biology, and effective biological indexes are provided for clinical diagnosis and treatment of cancers.
Owner:GD TECH INC
Virtual flow cytometry on immunostained tissue-tissue cytometer
InactiveUS20070020697A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStainingCancers diagnosis
The invention provides an automated method of single cell image analysis which determines cell population statistic, applicable in the field of pathology, disease or cancer diagnosis, in a greatly improved manner over manual or prior art scoring techniques. By combining the scientific advantages of computerized automation and the invented method, as well as the greatly increased speed with which population can be evaluated, the invention is a major improvement over methods currently available. The single cells are identified and displayed in an easy to read format on the computer monitor, printer output or other display means, with cell parameter such as cell size and staining distribution at a glance. These output data is an objective transformation of the subjective visible image that the pathologist or scientist relies upon for diagnosis, prognosis, or monitoring therapeutic perturbations. Using our novel proposed technology, we combine the advantages provided by the clinical standard tool of flow cytometry in quantifying single cells and also retain the advantages of microscopy in retaining the capability of visualizing the immunoreactive cells. Unlike flow cytometry however, the invention uses commonly available formalin fixed immunostained tissue and not fresh viable cells. To accomplish this aim, we resort to new and improved advanced image analysis using a unique, useful, and adaptive process as described herein. The method uses multi-stage thresholding and segmentation algorithm based on multiple color channels in RGB and HS I spaces and uses auto-thresholding on red and blue channels in RGB to get the raw working image of all cells, then refines the working image with thresholding on hue and intensity channels in HS I using an adaptive parameter epsilon in entropy mode, and further separates different groups of cells within the same class, by auto-thresholding within the working image region. The Immunohistochemistry Flow cytometry (IHCFLOW) combination results in a new paradigm that is both useful, novel, and provides objective tangible result from a complex color image of tissue.
Owner:CUALING HERNANI D
Non-invasive prenatal genetic diagnosis using transcervical cells
InactiveUS20050181429A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPrenatal diagnosisStaining
A non-invasive, risk-free method of prenatal diagnosis is provided. According to the method of the present invention transcervical specimens are subjected to trophoblast-specific immuno-staining followed by FISH, PRINS, Q-FISH and / or MCB analyses and / or other DNA-based genetic analysis in order to determine fetal gender and / or identify chromosomal and / or DNA abnormalities in a fetus. Also provided is a method of in situ chromosomal, DNA and / or RNA analysis of a prestained specimen by incubating the prestained specimen in ammonium hydroxide. Also provided is a method of identifying embryonic cells according to a nucleus / cytoplasm ratio of at least 1:1 and the presence of at least variably condensed chromatin.
Owner:MONALIZA MEDICAL
Antibodies and their use
InactiveUS6113897APeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLymphatic SpreadUrokinase Plasminogen Activator
A monoclonal or polyclonal antibody directed against urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (u-PAR), or a subsequence, analogue or glycosylation variant thereof. Antibodies are disclosed which react with free u-PAR or with complexes between u-PA and u-PAR and which are capable of 1) catching u-PAR in ELISA, or 2) detecting u-PAR, e.g. in blotting, or 3) in radioimmunoprecipitation assay precipitate purified u-PAR in intact or fragment form, or 4) is useful for immunohistochemical detection of u-PAR, e.g. in immunostaining of cancer cells, such as in tissue sections at the invasive front, or 5) inhibits the binding of pro-u-PA and active u-PA and thereby inhibits cell surface plasminogen activation. Methods are disclosed 1) for detecting or quantifying u-PAR, 2) for targeting a diagnostic to a cell containing a u-PAR on the surface, 3) for preventing or counteracting proteolytic activity in a mammal. Methods for for selecting a substance suitable for inhibiting u-PA / u-PAR interaction, for preventing or counteracting localized proteolytical activity in a mammal, for inhibiting the invasion and / or metastasis comprise the use of the antibodies and of nude mice inoculated with human cancer cells which are known to invade and / or metastasize in mice and having a distinct color, f.x. obtained by means of an enzyme and a chromogenic substrate for the enzyme, the color being different from the cells of the mouse.
Owner:CANCERFORSKNINGSFONDEN AF 1989 FONDEN TIL FREMME
Novel fluorinated rhodamines as photostable fluorescent dyes for labelling and imaging techniques
ActiveUS20120135459A1High fluorescence quantum yieldLow rateSugar derivativesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceStimulated emissionCombinatorial chemistry
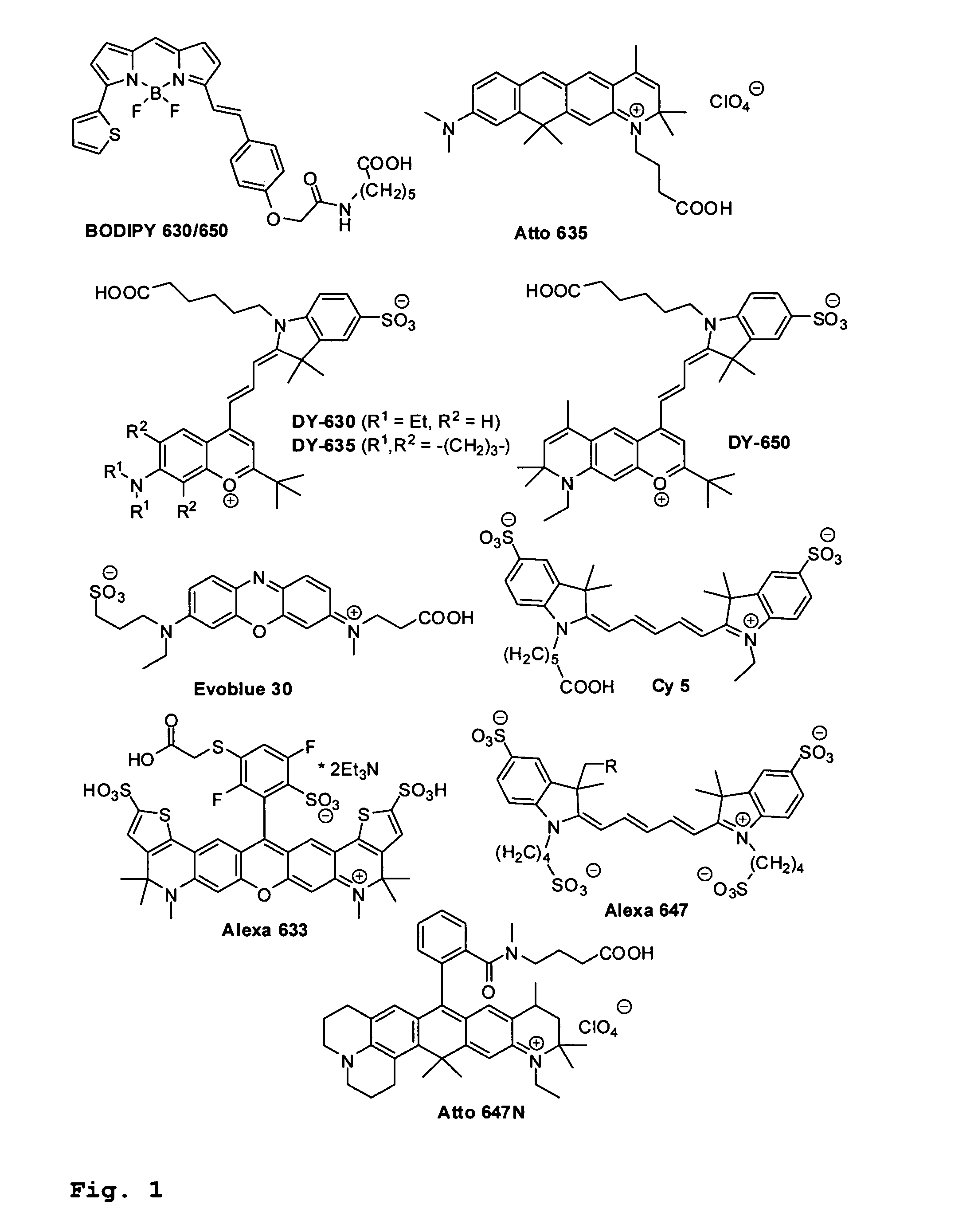
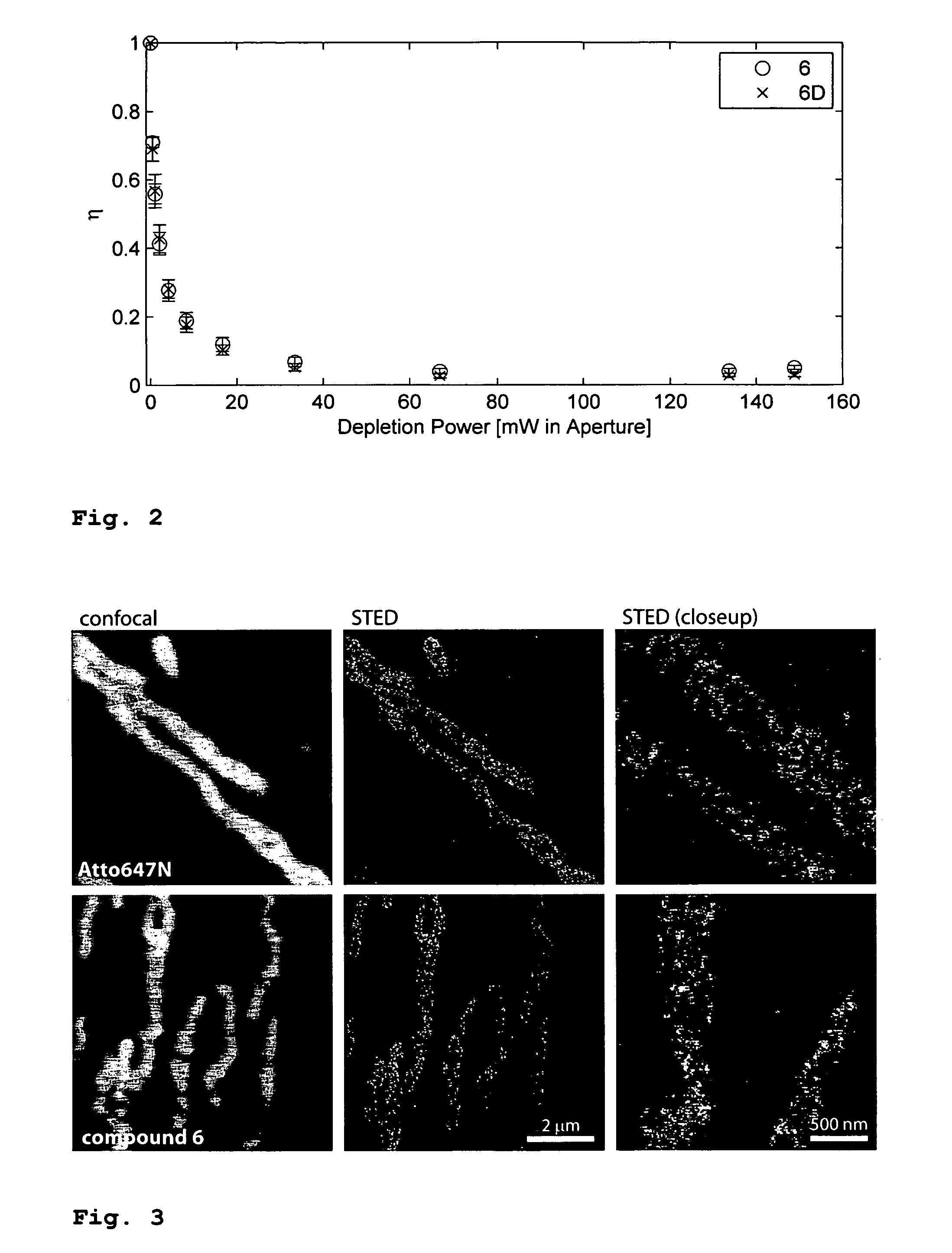
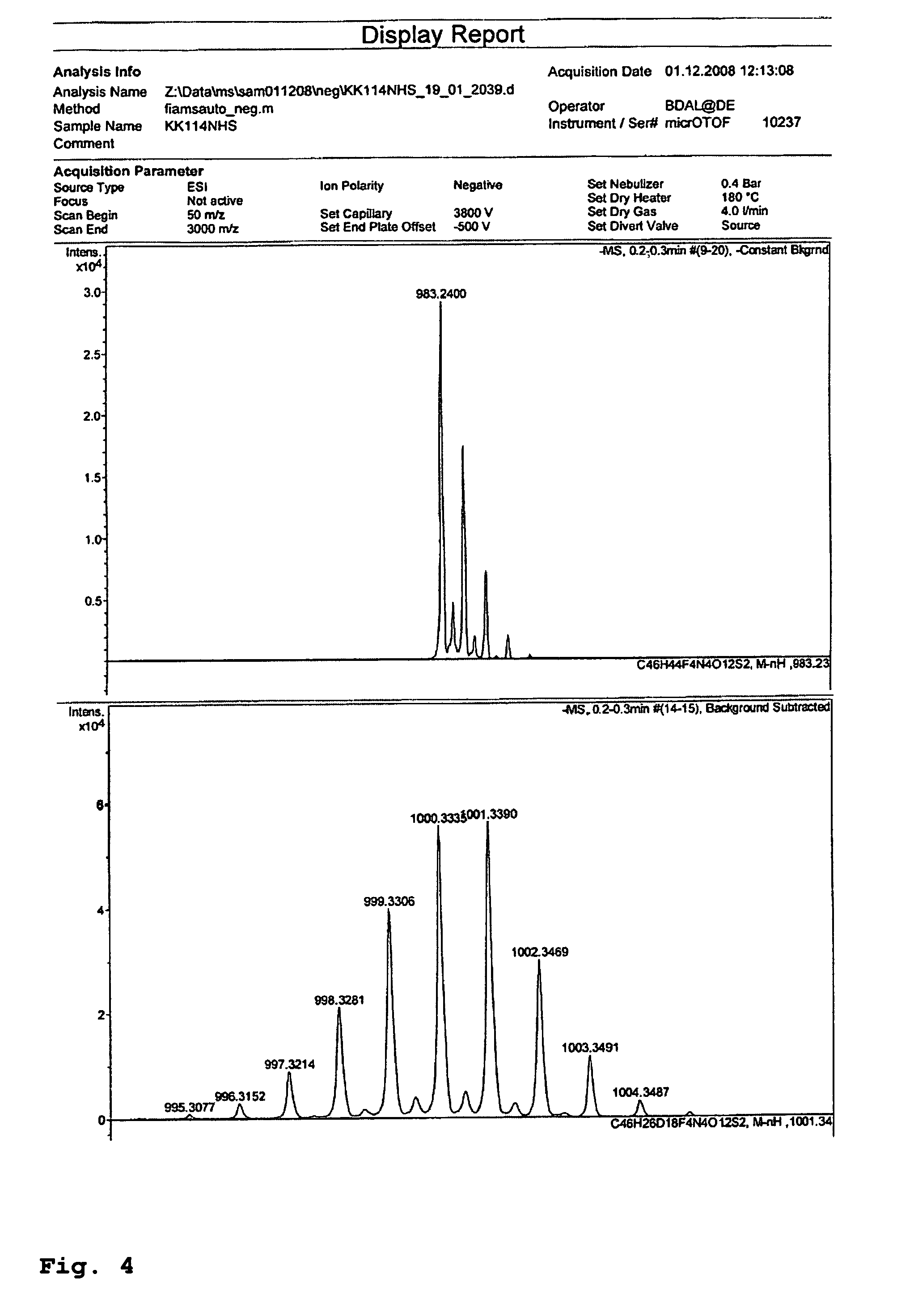
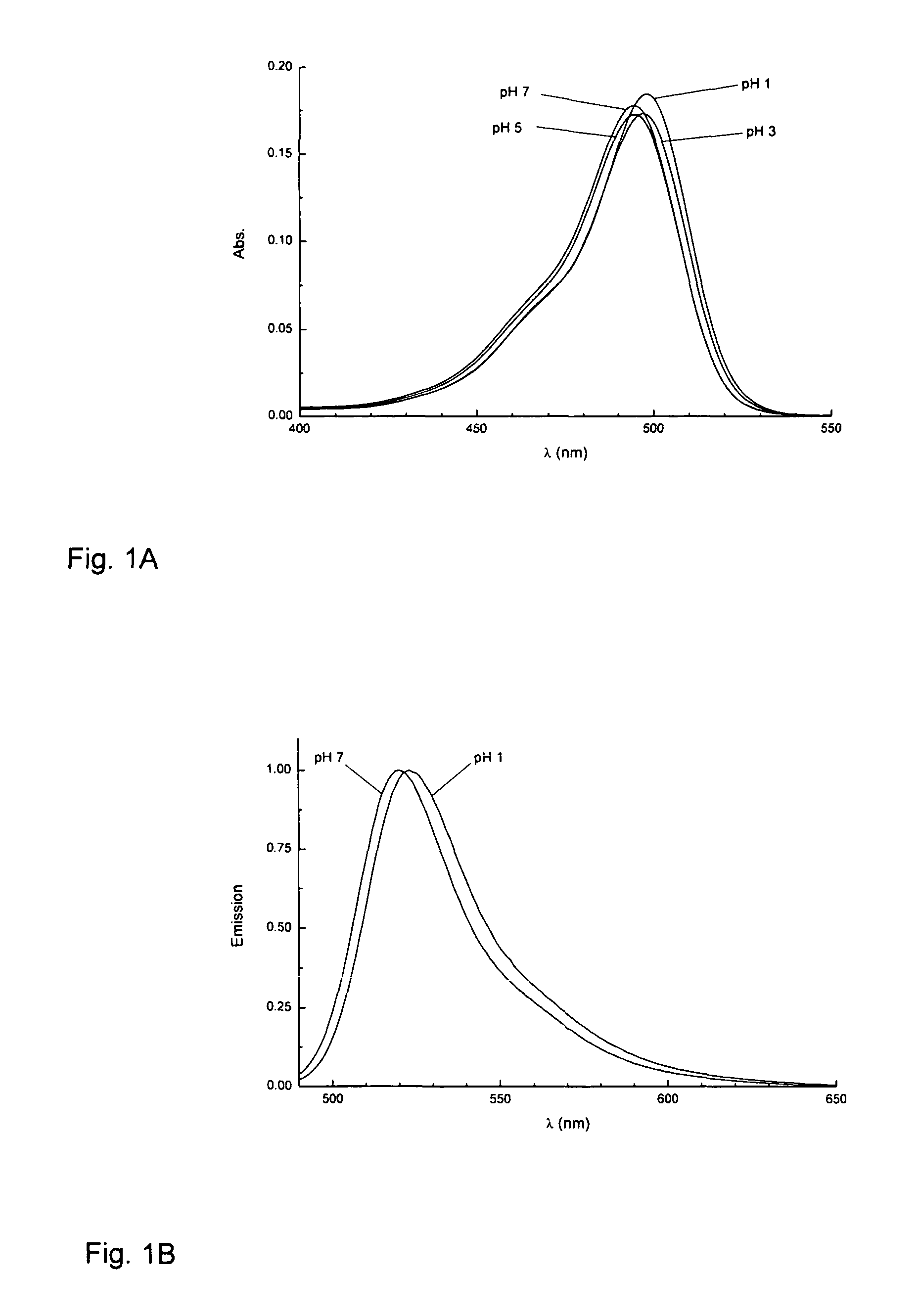
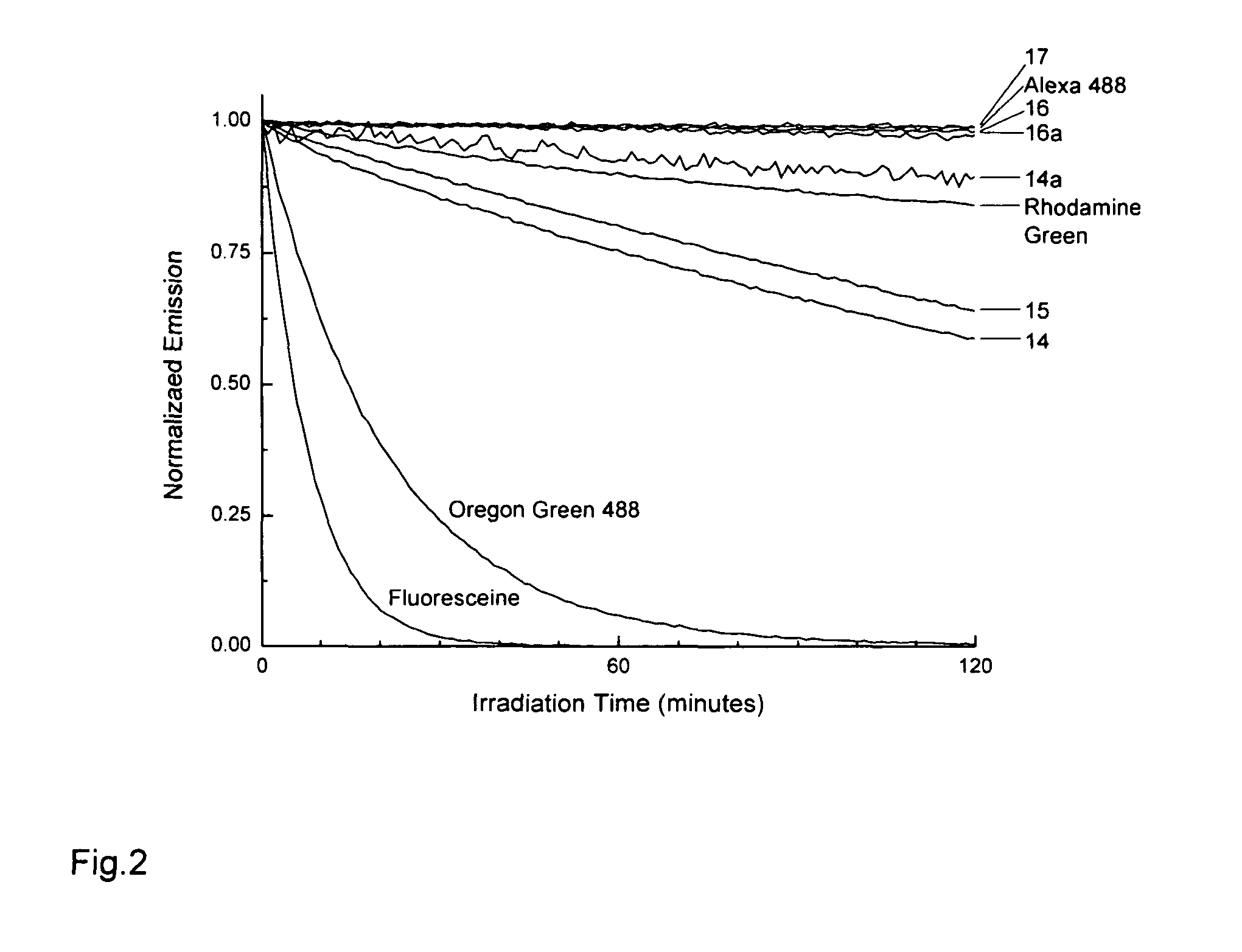
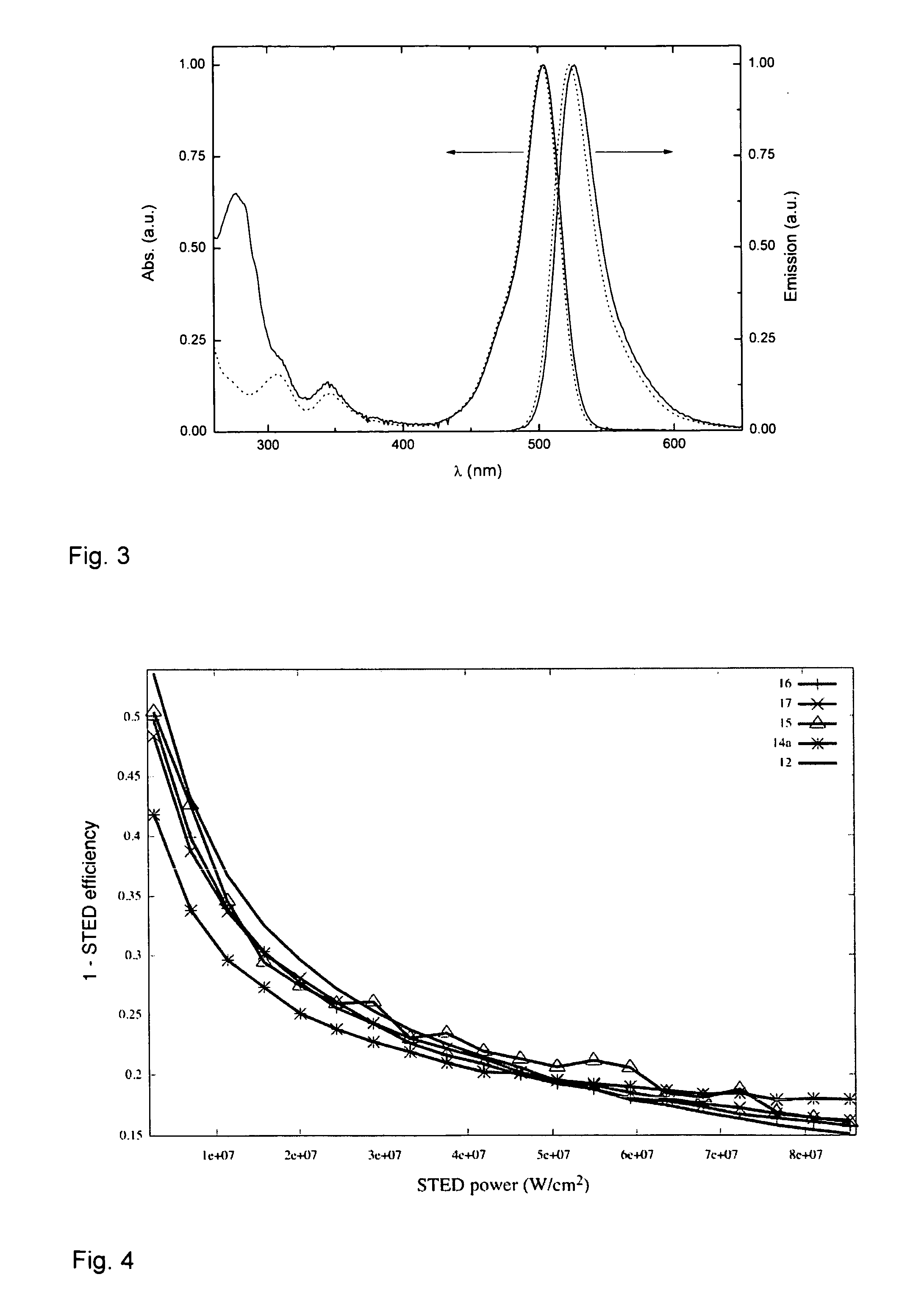
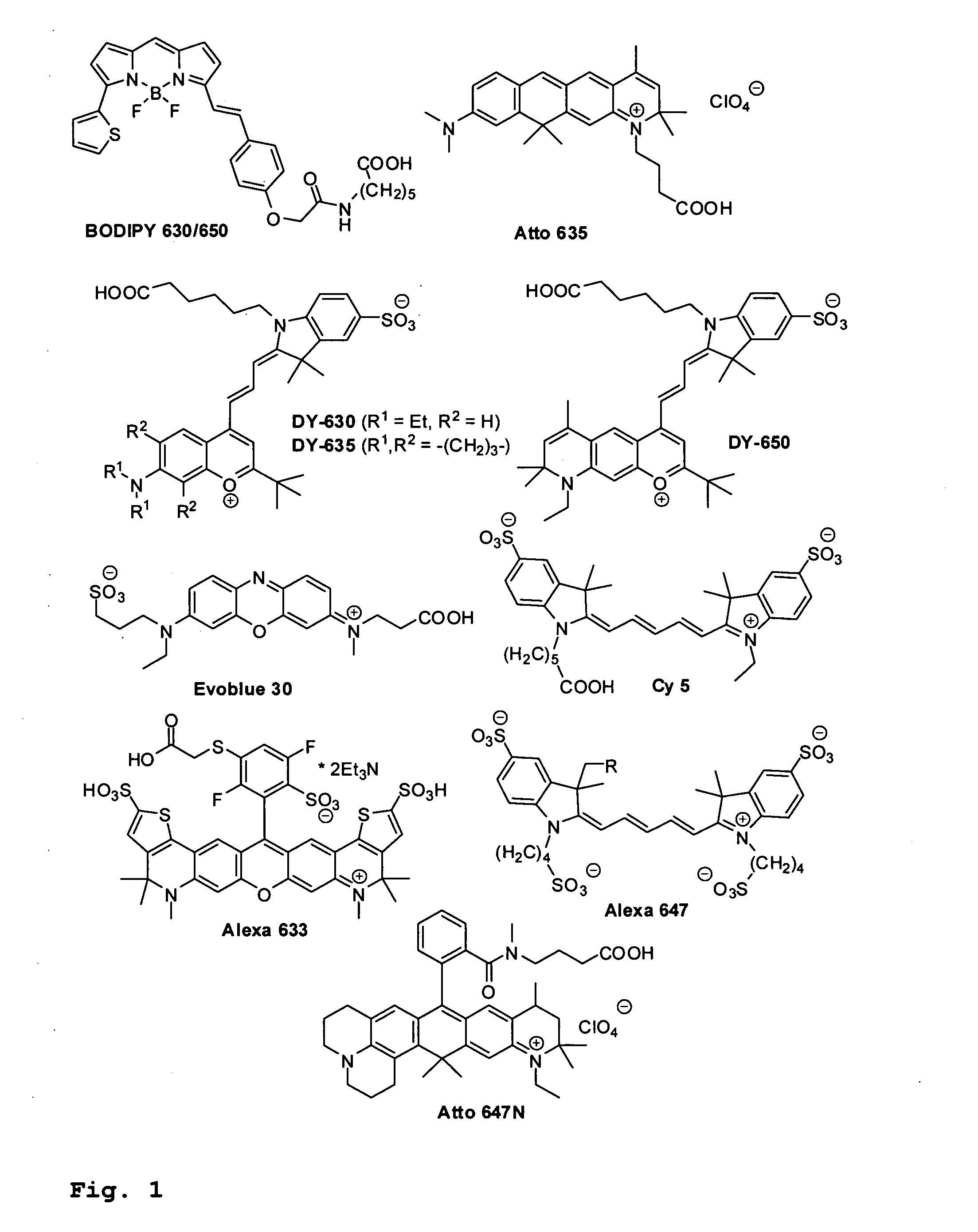
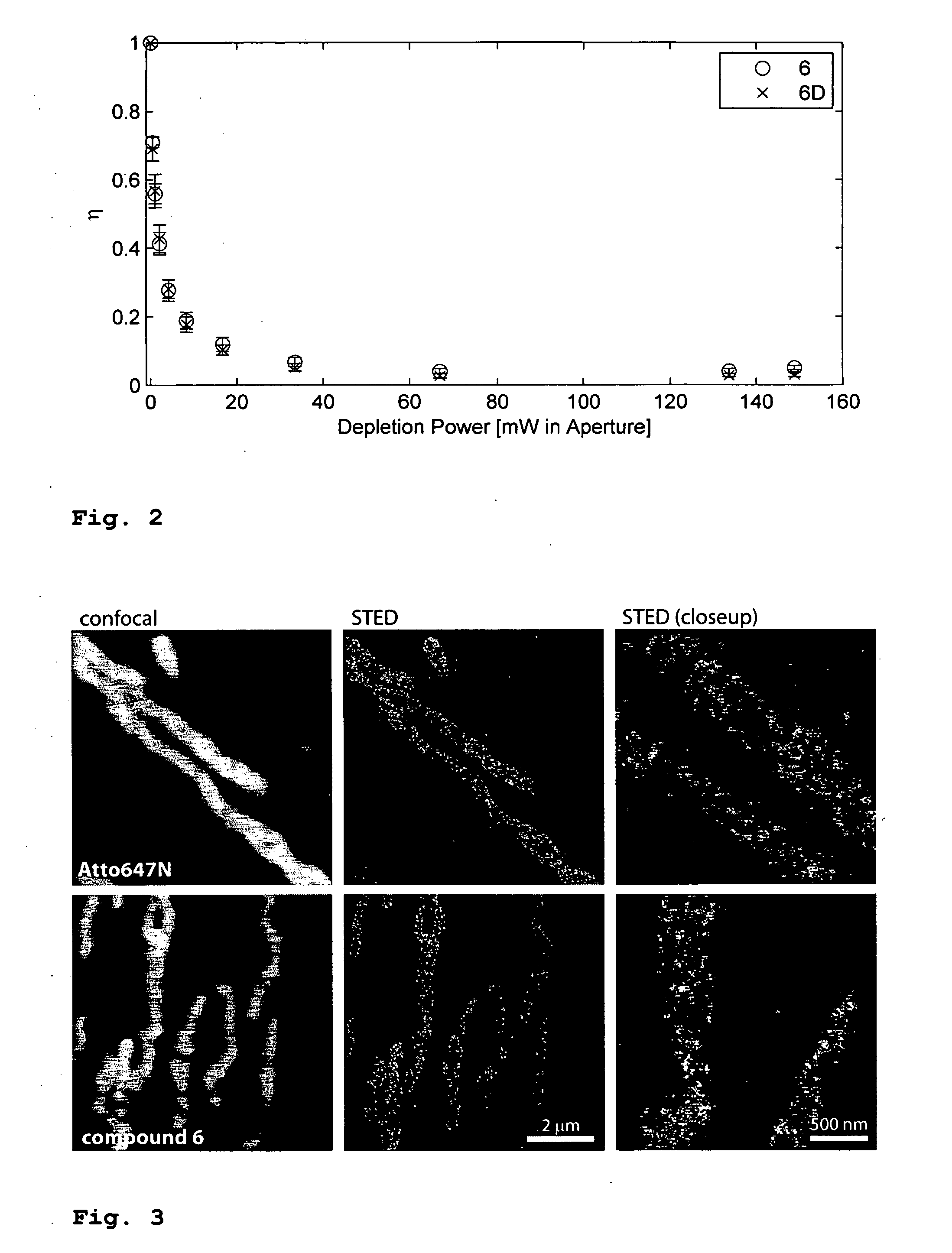
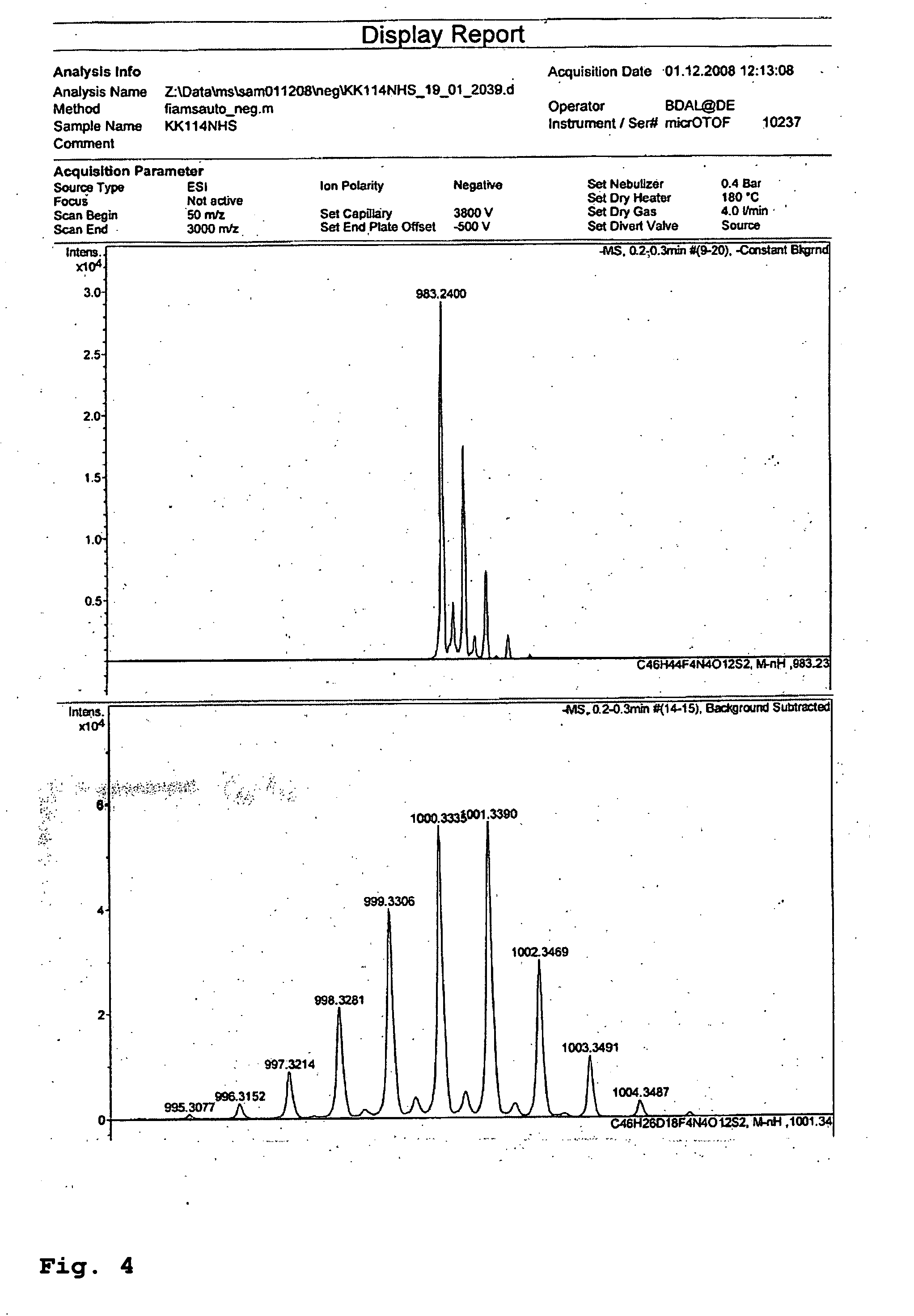
The present invention relates to novel fluorinated 3,6-diaminoxanthene compounds derived from the basic structural formula (I) and to their uses as photostable fluorescent dyes, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional microscopy, stimulated emission depletion (STED) reversible saturable optically linear fluorescent transitions (RESOLFT) microscopy, and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The claimed compounds are also useful as molecular probes in various spectroscopic applications.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
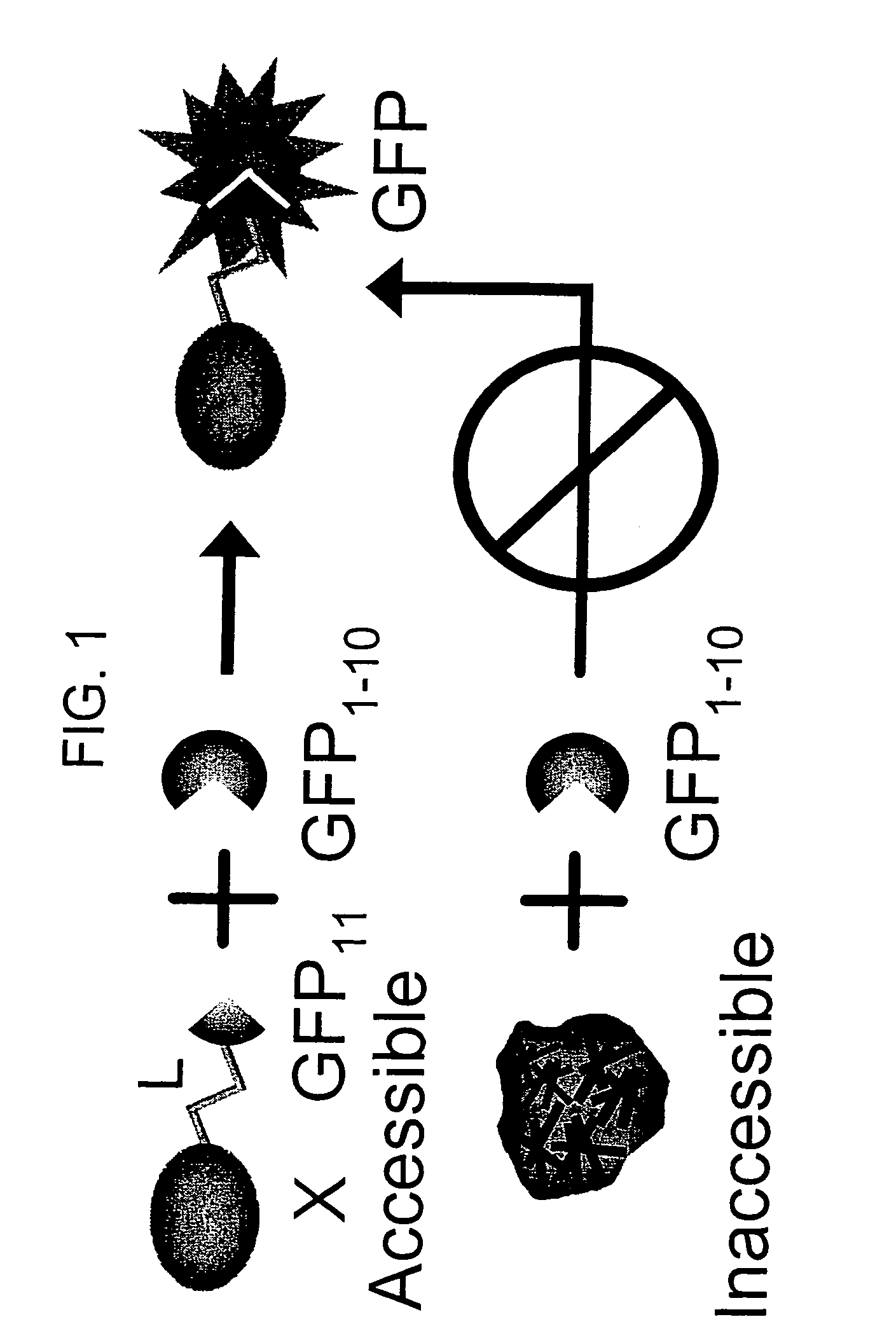
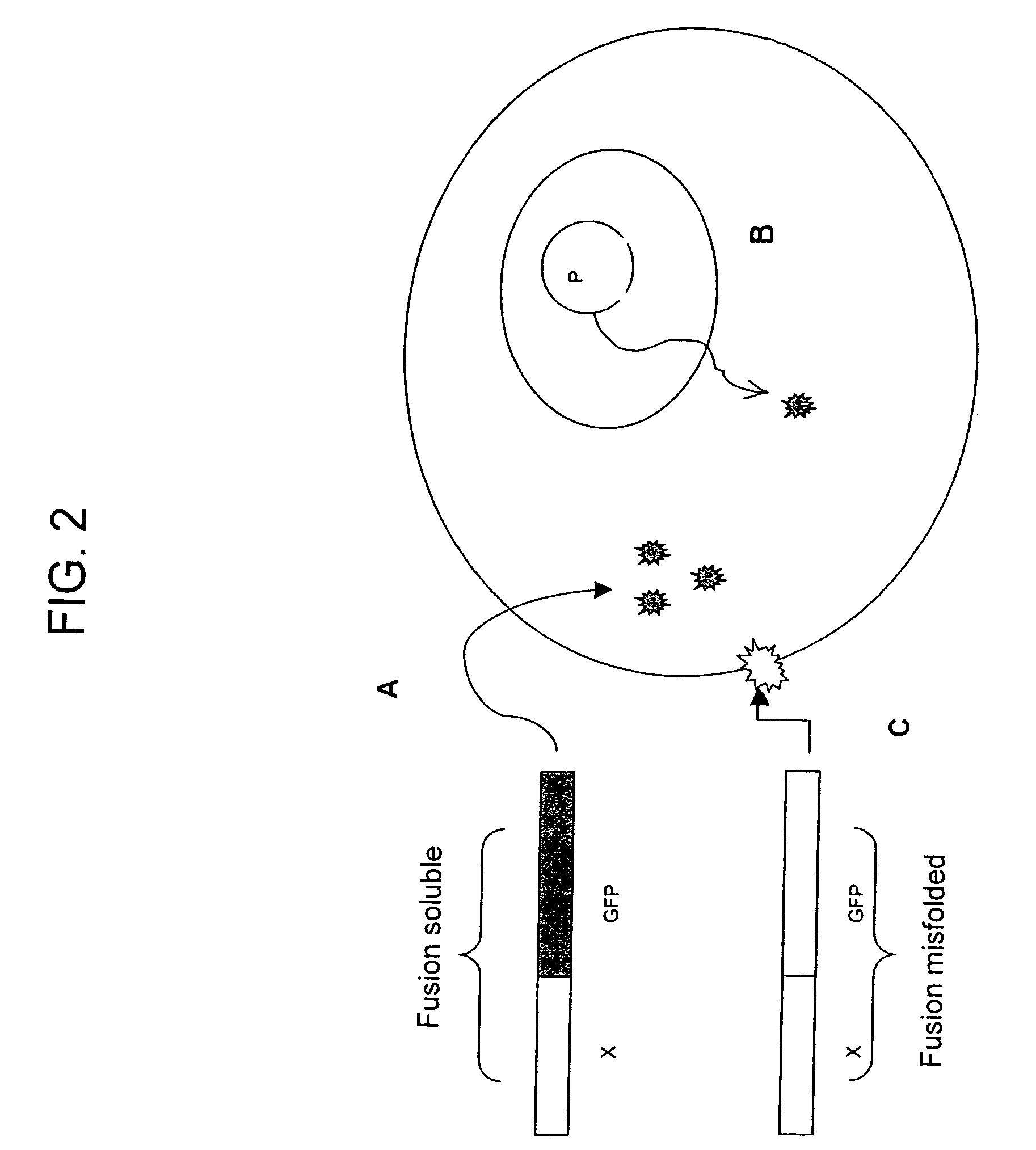
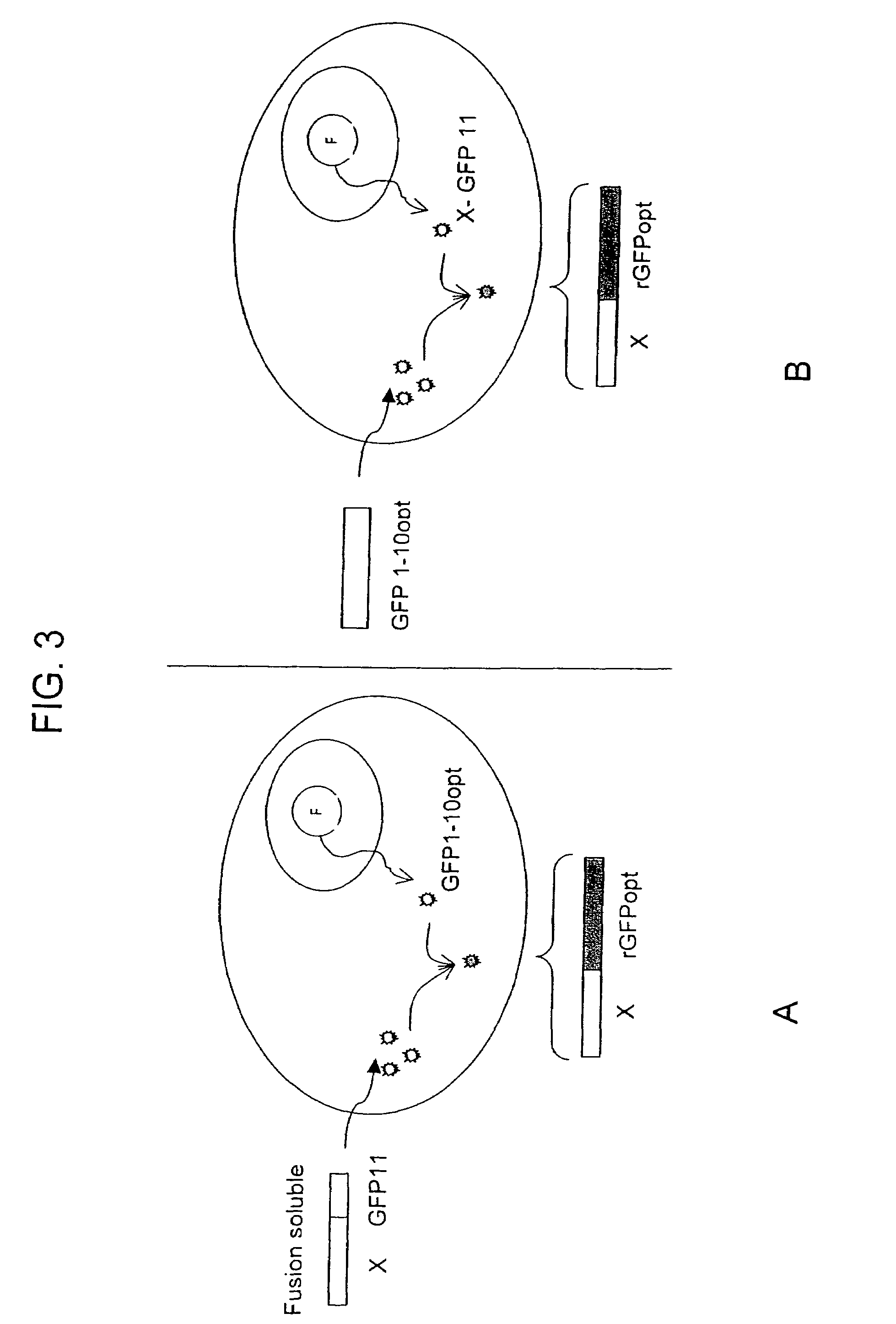
Protein subcellular localization assays using split fluorescent proteins
ActiveUS20060257942A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceDirect observation
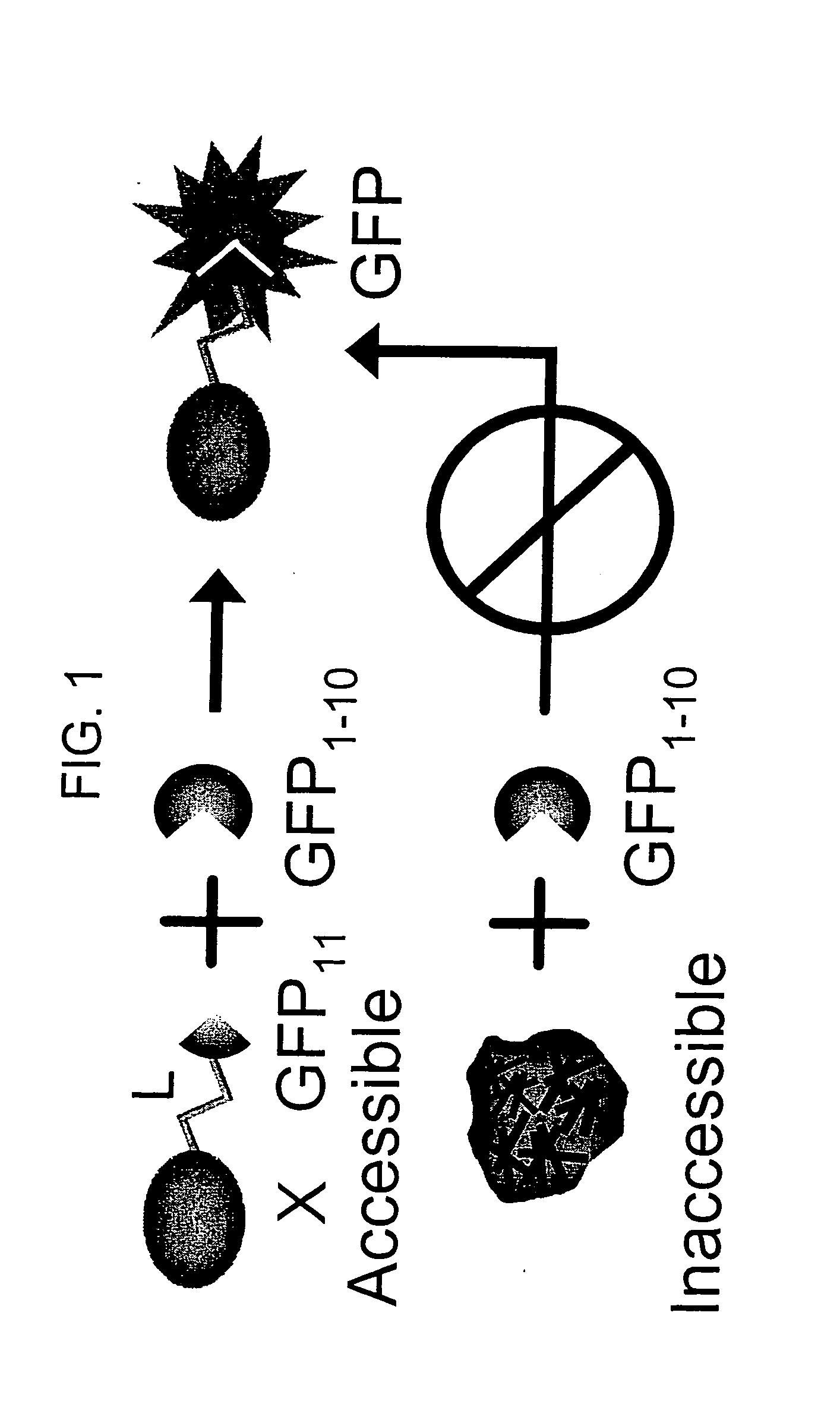
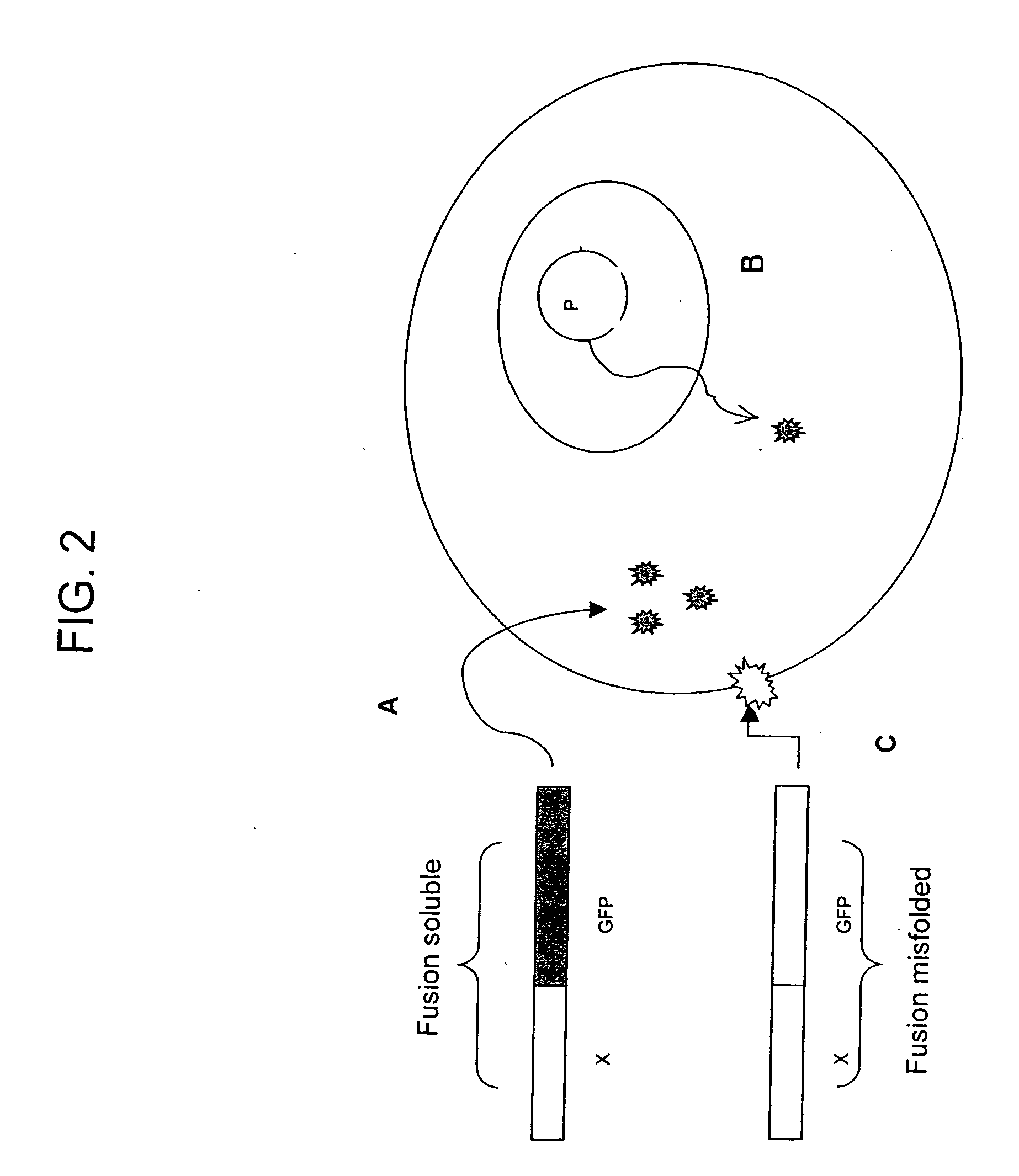
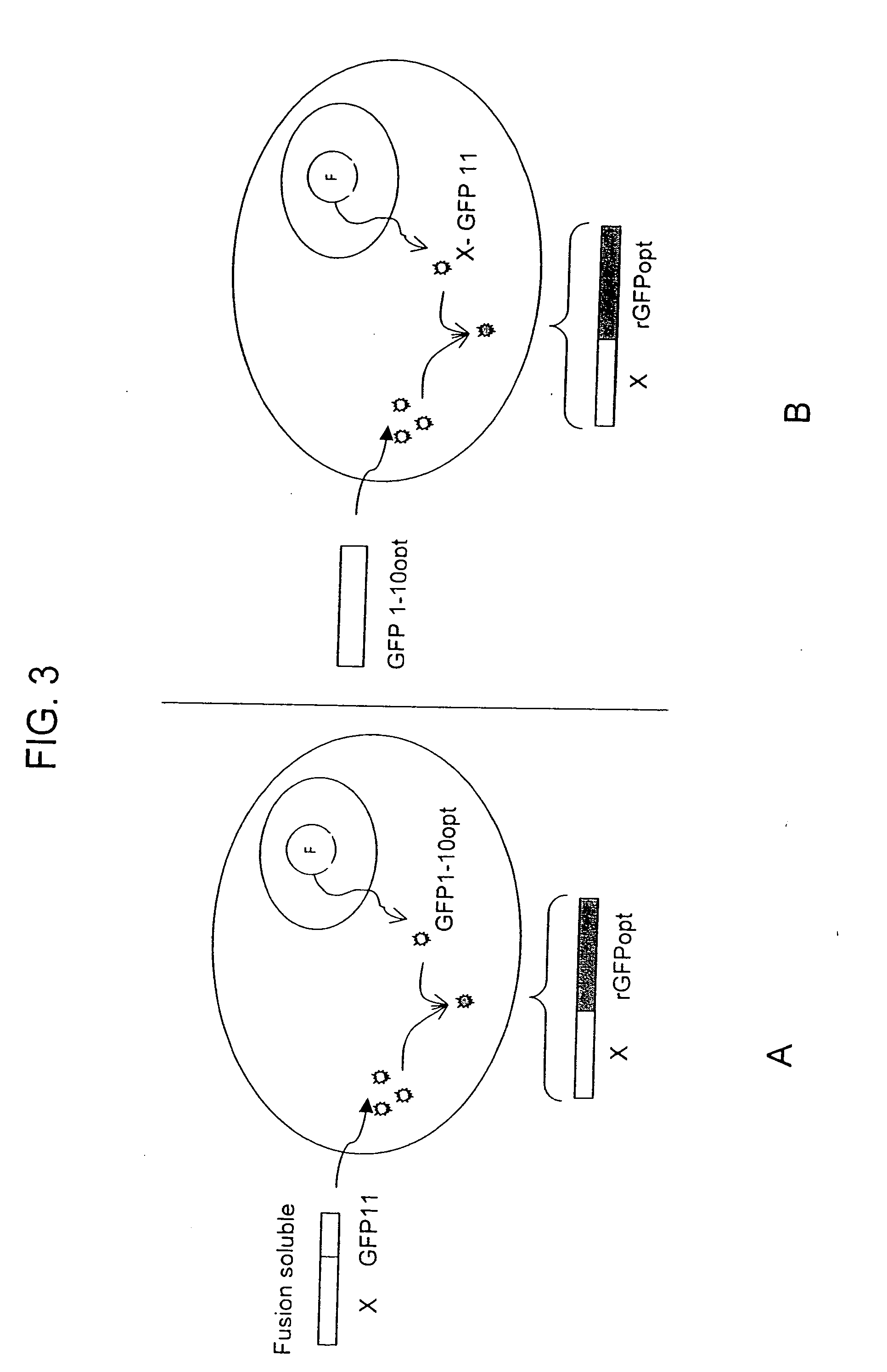
The invention provides protein subcellular localization assays using split fluorescent protein systems. The assays are conducted in living cells, do not require fixation and washing steps inherent in existing immunostaining and related techniques, and permit rapid, non-invasive, direct visualization of protein localization in living cells. The split fluorescent protein systems used in the practice of the invention generally comprise two or more self-complementing fragments of a fluorescent protein, such as GFP, wherein one or more of the fragments correspond to one or more beta-strand microdomains and are used to “tag” proteins of interest, and a complementary “assay” fragment of the fluorescent protein. Either or both of the fragments may be functionalized with a subcellular targeting sequence enabling it to be expressed in or directed to a particular subcellular compartment (i.e., the nucleus).
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Hydrophilic and lipophilic rhodamines for labelling and imaging
ActiveUS8580579B2High fluorescence quantum yieldLow rateSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhoto stabilityMass spectrometry
The invention relates to novel and improved photostable rhodamine dyes of the general structural formulae I or II and their uses as fluorescent markers, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional and stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The partially deuterated analogues are useful as molecular mass distribution tags in mass spectroscopic applications, wherein R1=an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group; R2=H, an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group, or an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group, or any combination of such groups; X=CH2, C═O, C═NORa, C═NNRaNRb, CH(ORa), O, S, SO, SO2, or any other derivatives of these groups, with Ra and Rb independently being H or an organic residue, in particular an unsubstituted or substituted (cyclo)alkyl group or heterocycloalkyl group, an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group; Z=a negatively charged group with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 charges per anion.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Production of Differentiated Enteroendocrine Cells and Insulin Producing Cells
ActiveUS20170349884A1Promote cell differentiationHigh expressionGastrointestinal cellsAntipyreticHistone methylationWnt inhibitor
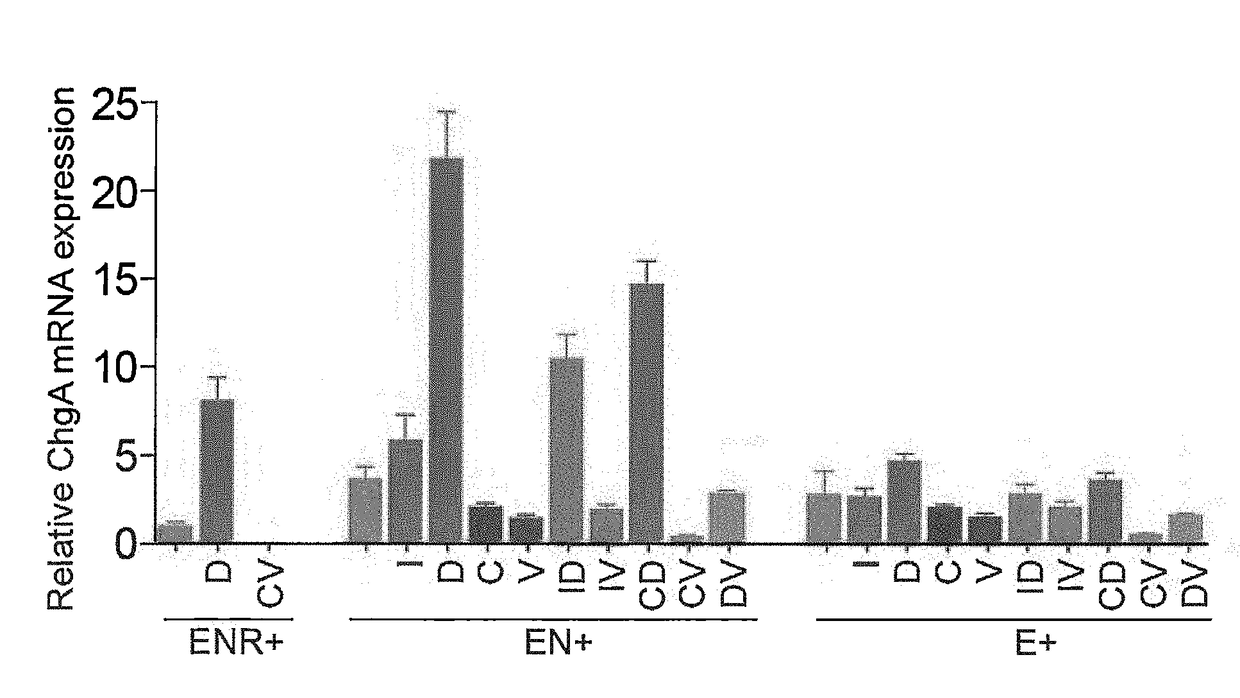
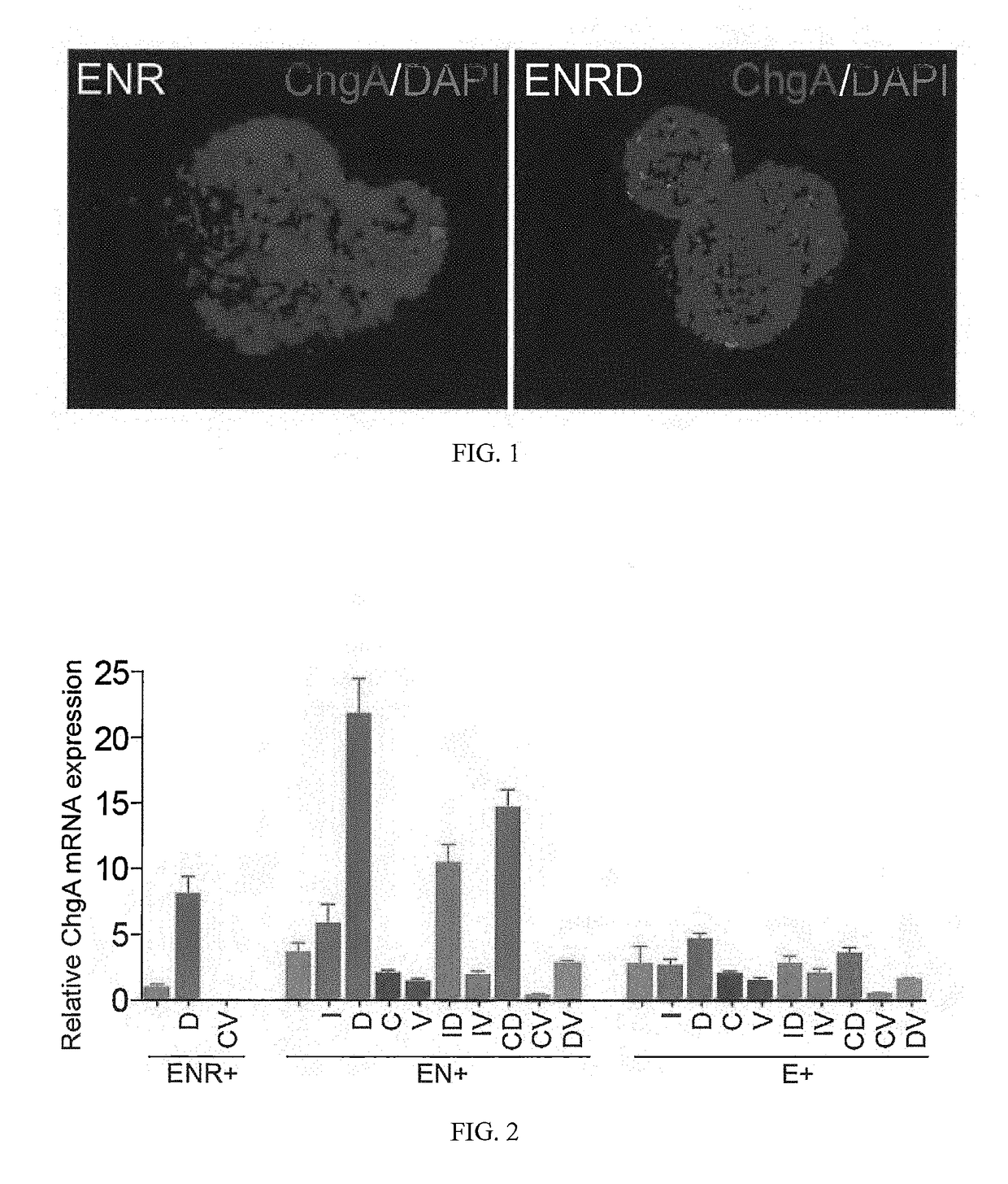
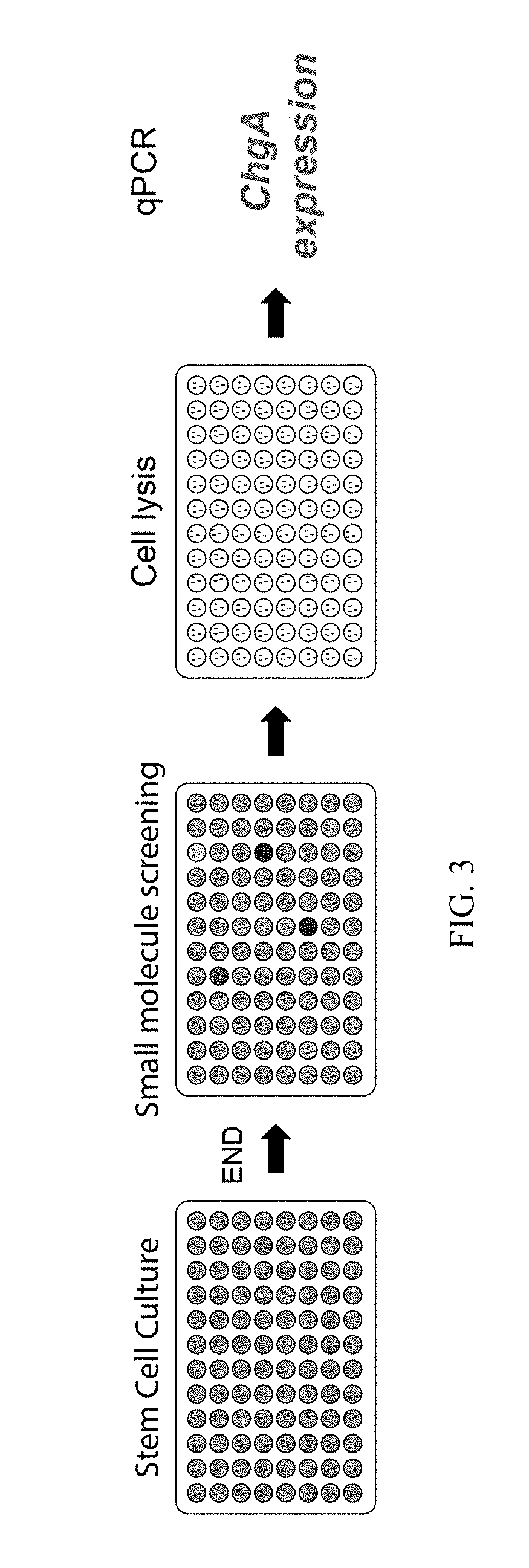
A population of enteroendocrine cells (EEC) is obtained from a mammalian post-natal cell population, such as a population including post-natal stem cells, by treating the population with a plurality of small molecules that upregulate ChgA and promote differentiation of the cells to form the enteroendocrine cells. The upregulation of ChgA is such that the fraction of cells expressing CGA in the obtained cell population, as measured by a ChgA Immunostaining Assay, is at least about 1.5%. Small molecules that can be used to differentiate the post-natal cells into the enteroendocrine cells can include at least one of a Wnt activator, a Notch inhibitor, a Wnt inhibitor, a MEK / ERK inhibitor, a growth factor, a HDAC inhibitor, a Histone Methylation Inhibitor, a Tgf-β inhibitor, and a NeuroD1 activator. Also, the insulin expression of a population of mammalian cells is increased by treating the population with a plurality of small molecules that increase the insulin expression.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Collection and Concentration System for Biologic Substance of Interest and Use Thereof
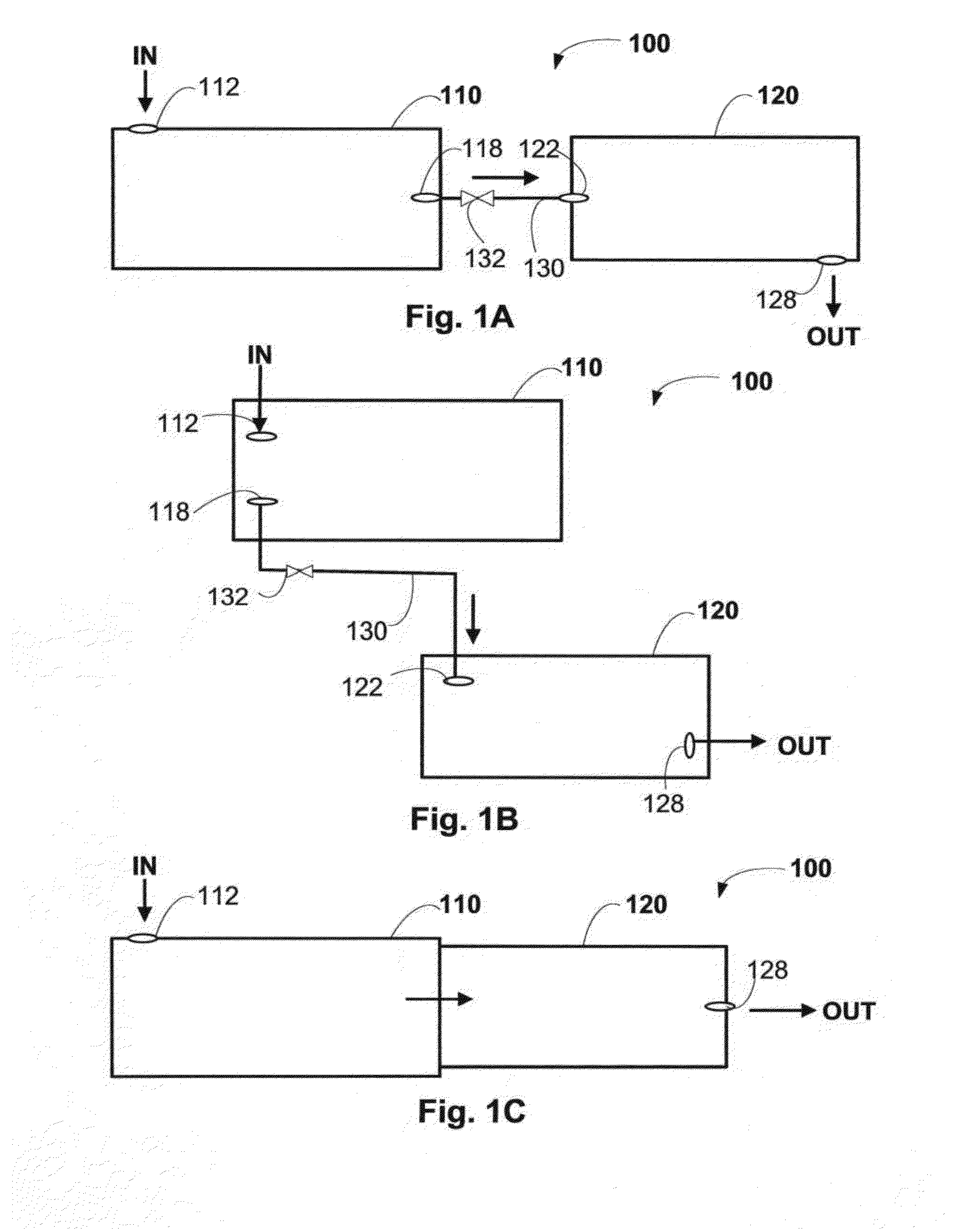
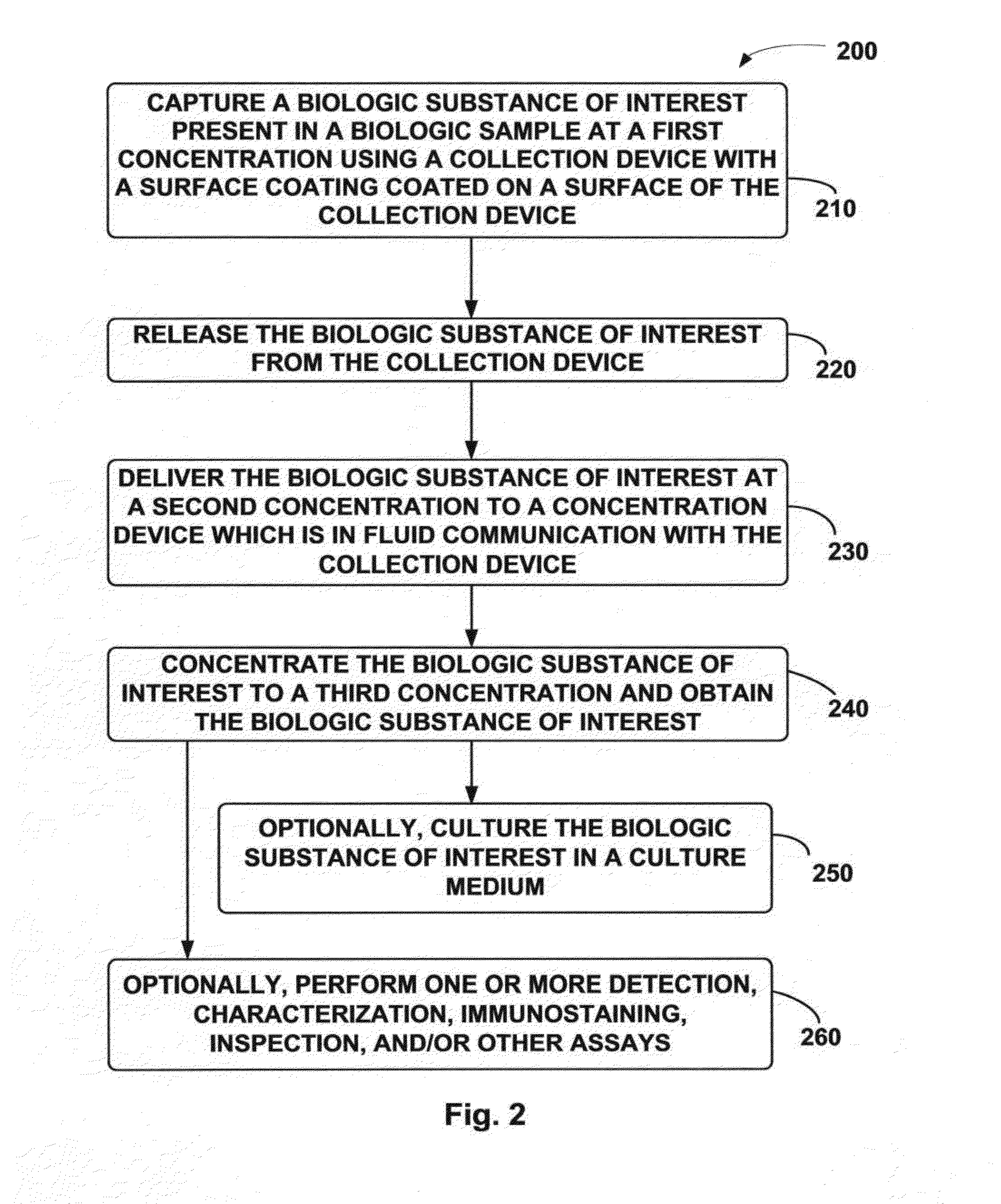
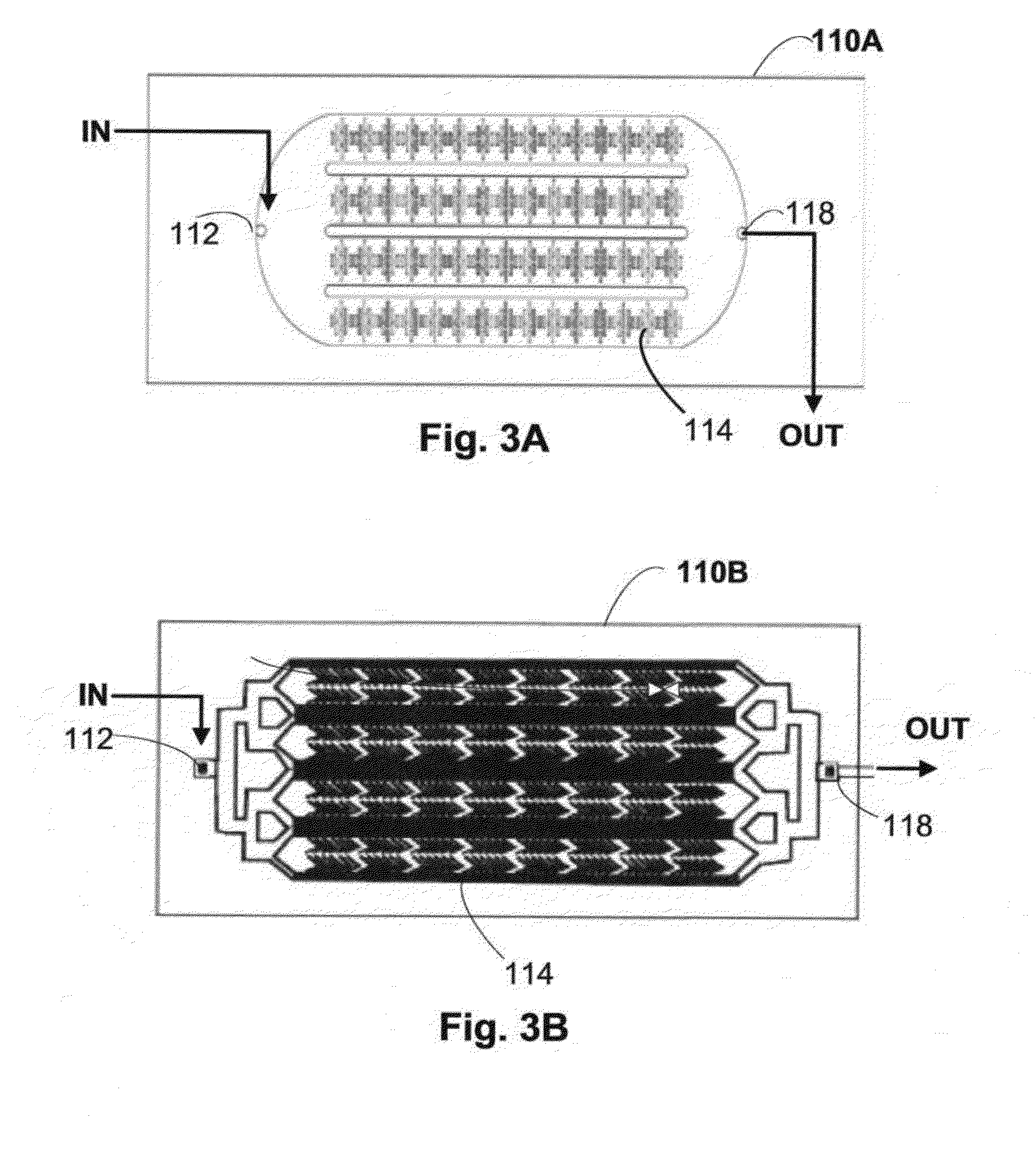
ActiveUS20140120537A1Improve concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMolecular analysisBiochemistry
A system and method thereof for collecting and concentrating a biologic substance of interest is provided. The biologic of interest obtained from a biologic sample present at an initial low concentration (or low number counts) can be captured and released through a collection device of the system to an intermediate second concentration, and further recovered through a concentration device of the system to a third concentration, thereby facilitating subsequent detection, characterization, enumeration, immunostaining, inspection, imaging, culturing, molecular analysis, and / or other assays.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Methods for phenotyping of intact whole tissues
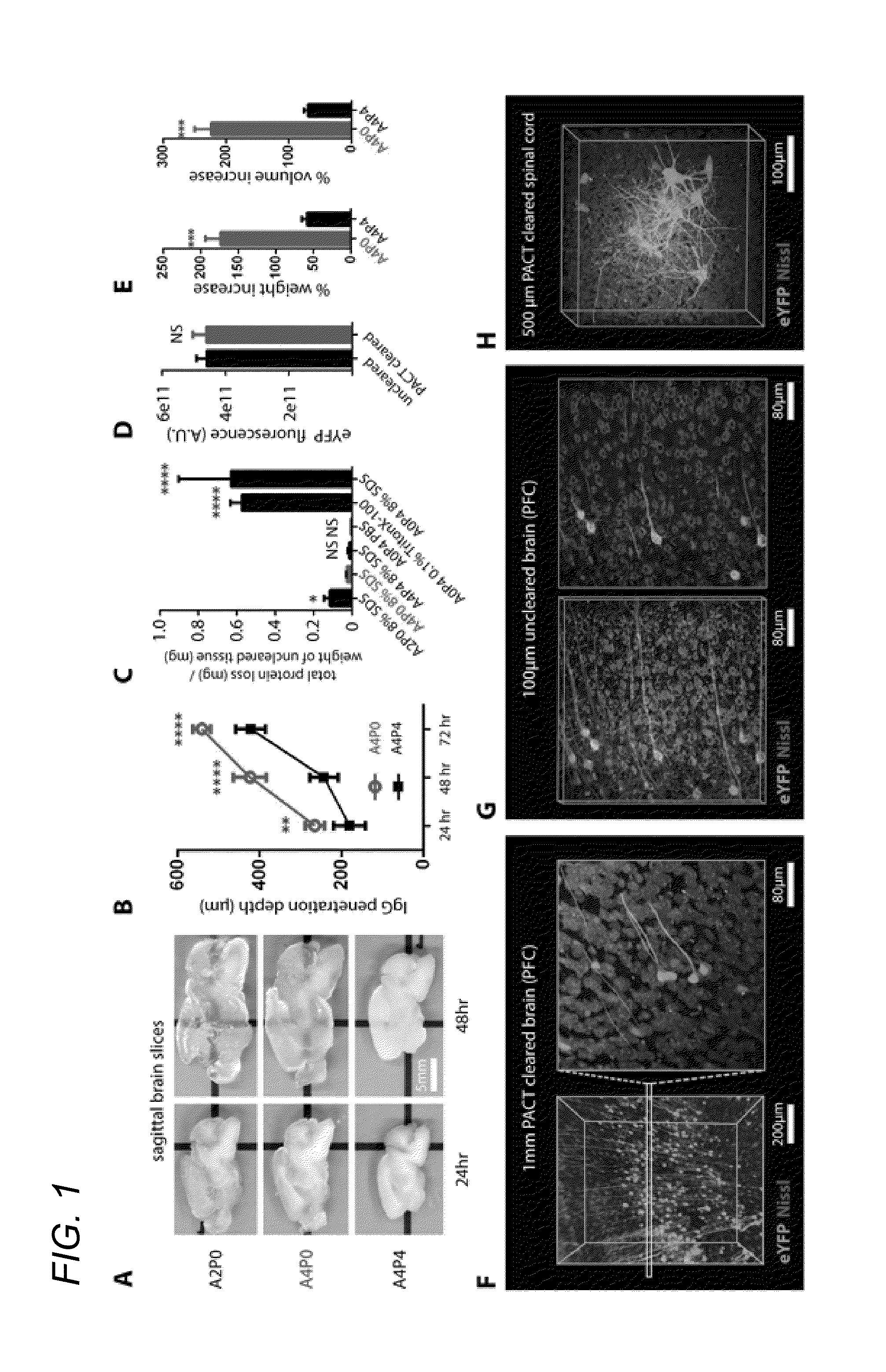
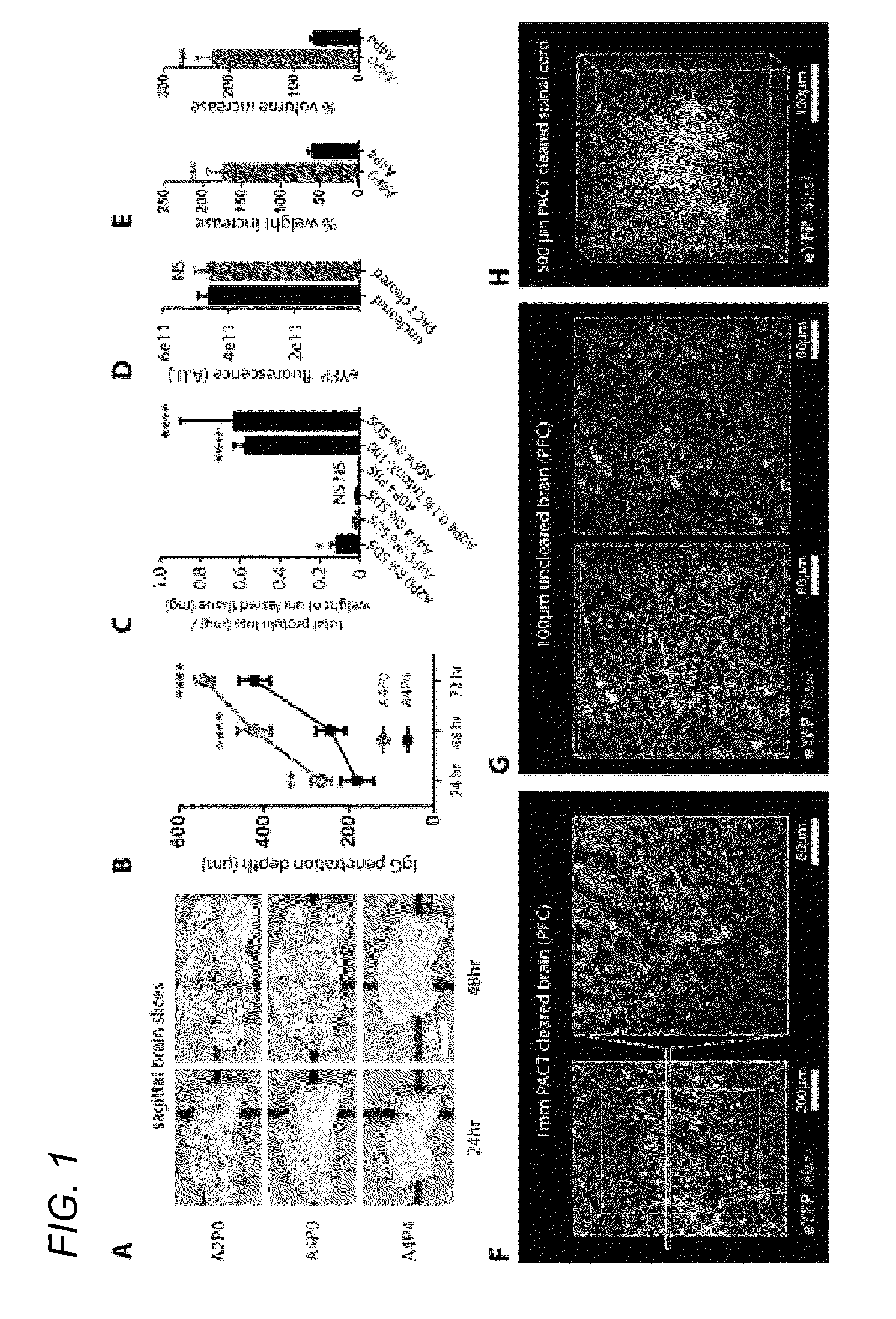
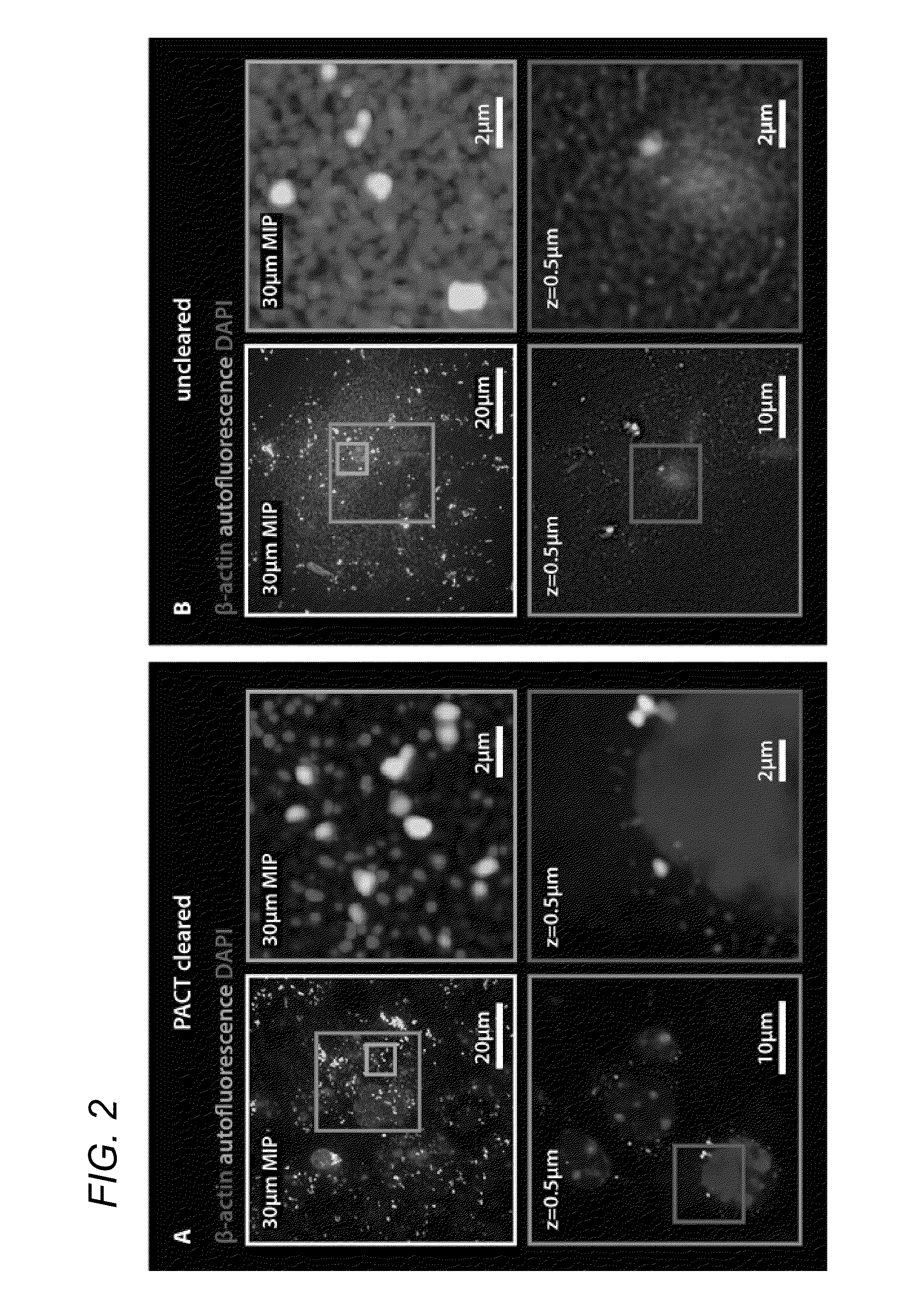
ActiveUS20150087001A1Reduced feature requirementsPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingWhole bodyTissue clearing
In various embodiments, the present application teaches methods and compositions for tissue clearing in which whole organs and bodies are rendered macromolecule-permeable and optically-transparent, thereby exposing their cellular structure with intact connectivity. In some embodiments, the present application teaches PACT, a protocol for passive tissue clearing and immunostaining of intact organs. In other embodiments, the present application teaches RIMS, a refractive index matching media for imaging thick tissue. In yet other embodiments, the application teaches PARS, a method for whole-body clearing and immunolabeling.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Fluorinated rhodamines as photostable fluorescent dyes for labelling and imaging techniques
ActiveUS8735444B2High fluorescence quantum yieldLow rateBiocideChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceStimulated emissionCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention relates to novel fluorinated 3,6-diaminoxanthene compounds derived from the basic structural formula (I) and to their uses as photostable fluorescent dyes, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional microscopy, stimulated emission depletion (STED) reversible saturable optically linear fluorescent transitions (RESOLFT) microscopy, and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The claimed compounds are also useful as molecular probes in various spectroscopic applications.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Protein subcellular localization assays using split fluorescent proteins
ActiveUS7585636B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein subcellular localization predictionProtein subcellular location
The invention provides protein subcellular localization assays using split fluorescent protein systems. The assays are conducted in living cells, do not require fixation and washing steps inherent in existing immunostaining and related techniques, and permit rapid, non-invasive, direct visualization of protein localization in living cells. The split fluorescent protein systems used in the practice of the invention generally comprise two or more self-complementing fragments of a fluorescent protein, such as GFP, wherein one or more of the fragments correspond to one or more beta-strand microdomains and are used to “tag” proteins of interest, and a complementary “assay” fragment of the fluorescent protein. Either or both of the fragments may be functionalized with a subcellular targeting sequence enabling it to be expressed in or directed to a particular subcellular compartment (i.e., the nucleus).
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Method for combining immunostaining and fish using covalently binding fluorophores
InactiveUS20070243545A1High sequence similarityImage analysisMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorophoreStain
Among embodiments is disclosed a process for immunostaining a sample such that the stain is stable under FISH conditions
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Microfluidic Cytochemical Staining System
ActiveUS20120230886A1Accurate disease diagnosisGood curative effectSamplingLaboratory glasswaresCytochemistryDisease
The present invention provides devices and associated methods to facilitate multiplexed staining on a slide. The use of multiplexed staining on a single slide allows for more accurate disease diagnosis while also conserving sample. A PDMS based cytology overlay was created that is capable of coupling on-chip morphological, cytochemical, and immunological staining. Morphological and cytochemical staining of blood smears, along with immunostaining of lymph node imprints, was carried out to demonstrate the application of this microfluidic cytology chip (μCC) device.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for positioning immune tissues of growth hormone for malus plants and application thereof
ActiveCN102147417AEliminates effects prone to non-specific stainingEliminate the effects of non-specific stainingPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingPlant tissueWoody plant
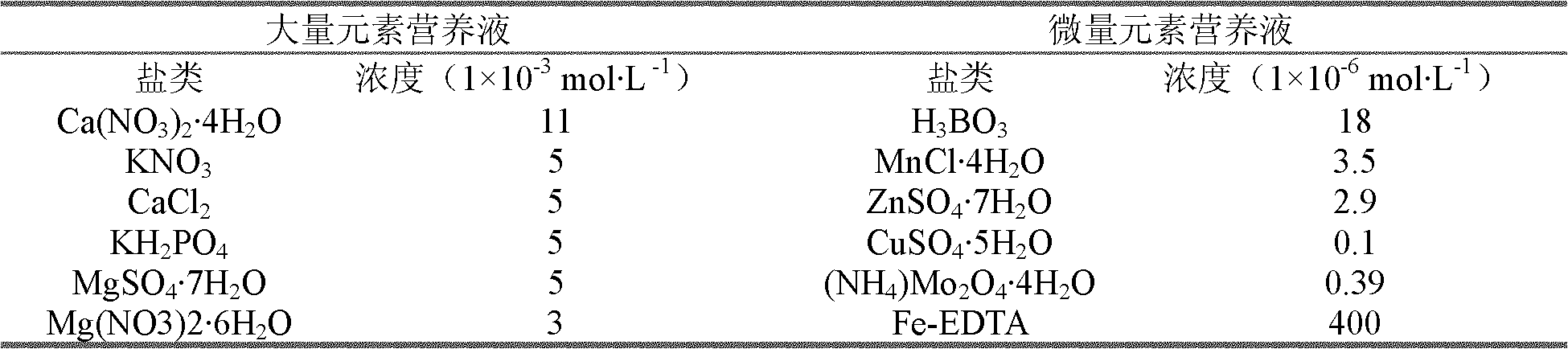
The invention discloses a method for positioning immune tissues of growth hormone for malus plants and application thereof. The method for positioning immune tissues of growth hormone for malus plants comprises the following steps of: (1) fixing plant tissues to obtain fixed plant tissues; (2) carrying out slice making on the fixed plant tissues on the basis of the step (1) to obtain a plant tissue slice; and (3) immunostaining the obtained plant tissue slice on the basis of the step (2), and determining the distribution condition of hormone in the plant tissues through observing a position of a positive signal. The method for positioning immune tissues of growth hormone for malus plants can eliminate the easily caused influence of nonspecific staining of woody plant tissues, and can identify the positive signal clearly. The method for positioning immune tissues of growth hormone for malus plants verifies that the growth hormone has tissue specificity when being distributed in the tissues of a stem tip or a root tip of an apple tree in a condition of iron deficiency.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Beta-amyloid plaque recognition and measurement method based on image processing
ActiveCN107561264AAutomatic measurement quantityAutomatic size measurementImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionStatistical analysis
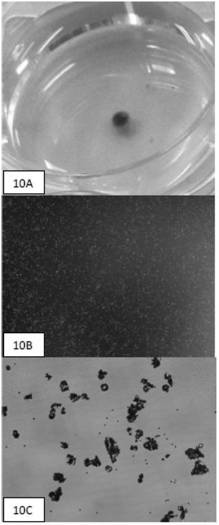
The invention provides a beta-amyloid plaque recognition and measurement method based on image processing, and belongs to the technical field of biological image processing. The method comprises the following concrete steps that a model organism brain slice is subjected to immunostaining by a beta-amyloid protein monoclonal antibody; after the immune dying, the extracellular beta-amyloid plaque ofthe model organism brain slice shows bright plaque in a fluorescence microscope; a fluorescence microscope is used for shooting a picture of the fluorescence microscope subjected to immunostaining; the picture is processed to recognize the located bright plaque region of the beta-amyloid plaque; through the image processing, the beta-amyloid plaque indicated by the bright plaque is subjected to automatic quantity statistics and feature calculation to obtain the statistics data; the statistics data is matched with feature information of the model organism for statistics analysis. The deposition condition of the beta-amyloid plaque is quantificationally reflected by a method of recognizing and measuring the bright plaque in the pictures shot by the fluorescence microscope.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Differential staining method for inner cell mass cells and trophoblastic cells of cattle blastulae
InactiveCN102426126APromote research progressPreparing sample for investigationFluorescent stainingMonoclonal antibody
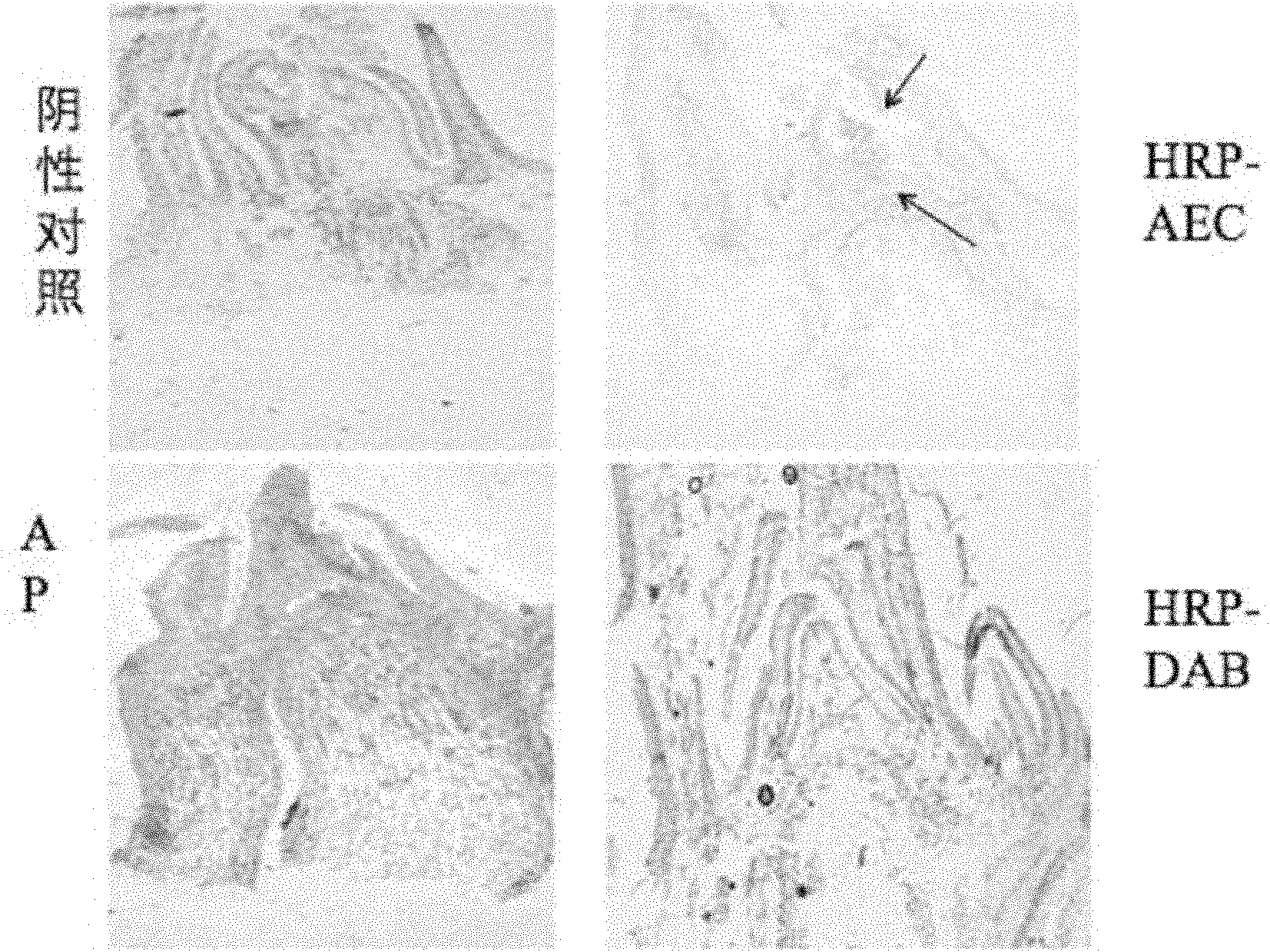
The invention discloses a differential staining method for inner cell mass cells and trophoblastic cells of cattle blastulae. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out immune combination on an anti-CDX2 monoclonal antibody which is adopted as a primary antibody and CDX2 molecules which are specifically expressed in the trophoblastic cells of the cattle blastulae through an immunostaining process; 2, the cattle blastulae which are cleaned and are combined with the primary antibody are immunostained with an antibody which is labeled by red fluorescence and can combine with the anti-CDX2 monoclonal antibody as a secondary antibody through the immunostaining process; and 3, whole nuclei of the cattle blastulae are subjected to fluorescent staining after completing the immunostaining to form the differential staining. On the basis of a case that CDX2 proteins specifically express in the trophoblastic cells and do not express in the inner cell mass cells, the method of the invention allows the differential staining to be carried out based on the red immunostaining of the CDX2 molecules and the blue staining of DAPI nuclei, so the accuracy is 100%, and obtained pictures are intelligible and beautiful.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
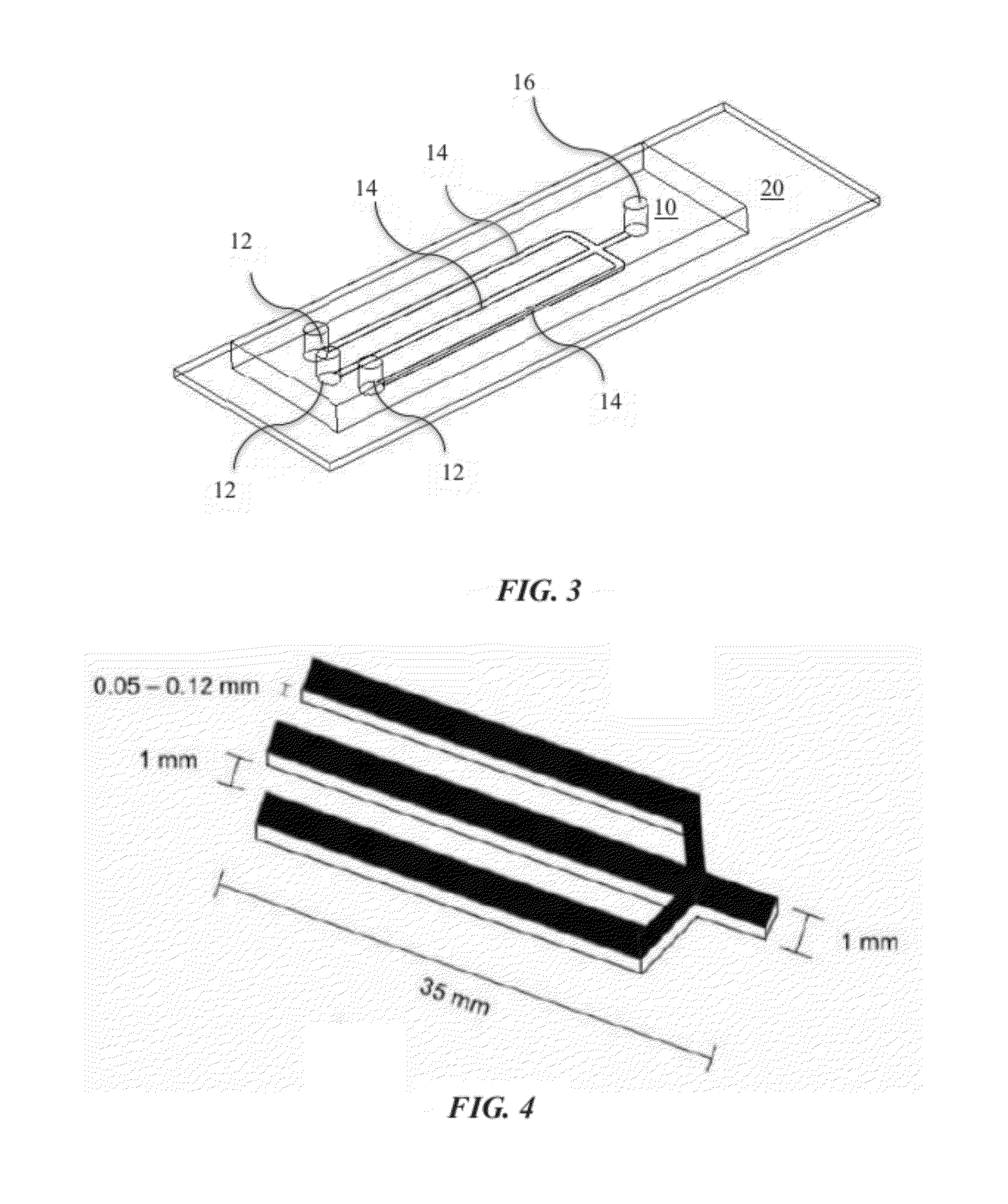
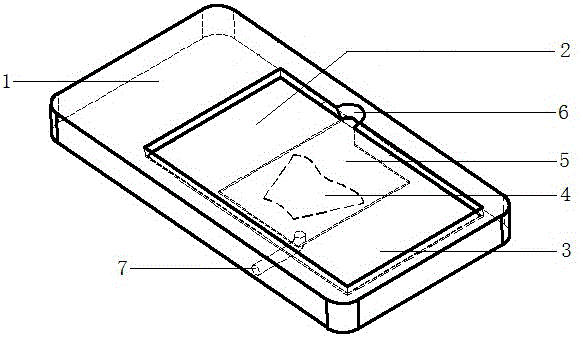
Device and method for repeated immunostaining of same tissue section
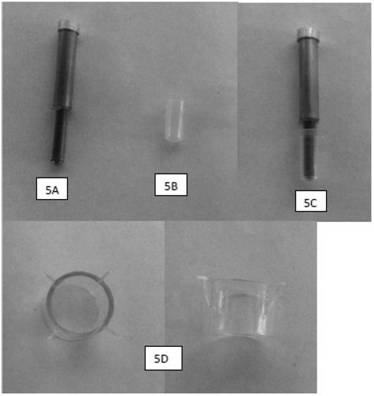
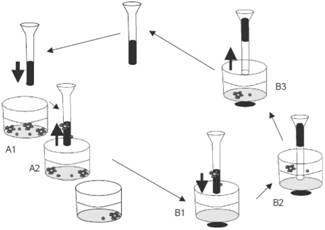
The invention discloses a device and method for repeated immunostaining of the same tissue section in order to realize repeated immunostaining of the same tissue section and save tissue samples and meet diagnosis needs, including a tissue section bearing device and an application method thereof. The tissue section bearing device comprises a glass slide with a groove and a cover glass. The tissue section bearing device is adopted for repeated staining of sequentially circulating staining, photographing, cleaning, staining again, photographing again and cleaning again of the same tissue section; and through comparative analysis of pictures taken after the repeated staining, the antigen expression profile of each cell on the tissue section can be obtained.
Owner:NANCHANG DEMANDUO TECH CO LTD
Quantification of single target molecules in histological samples
ActiveUS20140038169A1Possible to determineMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisBiochemistryBiomedical engineering
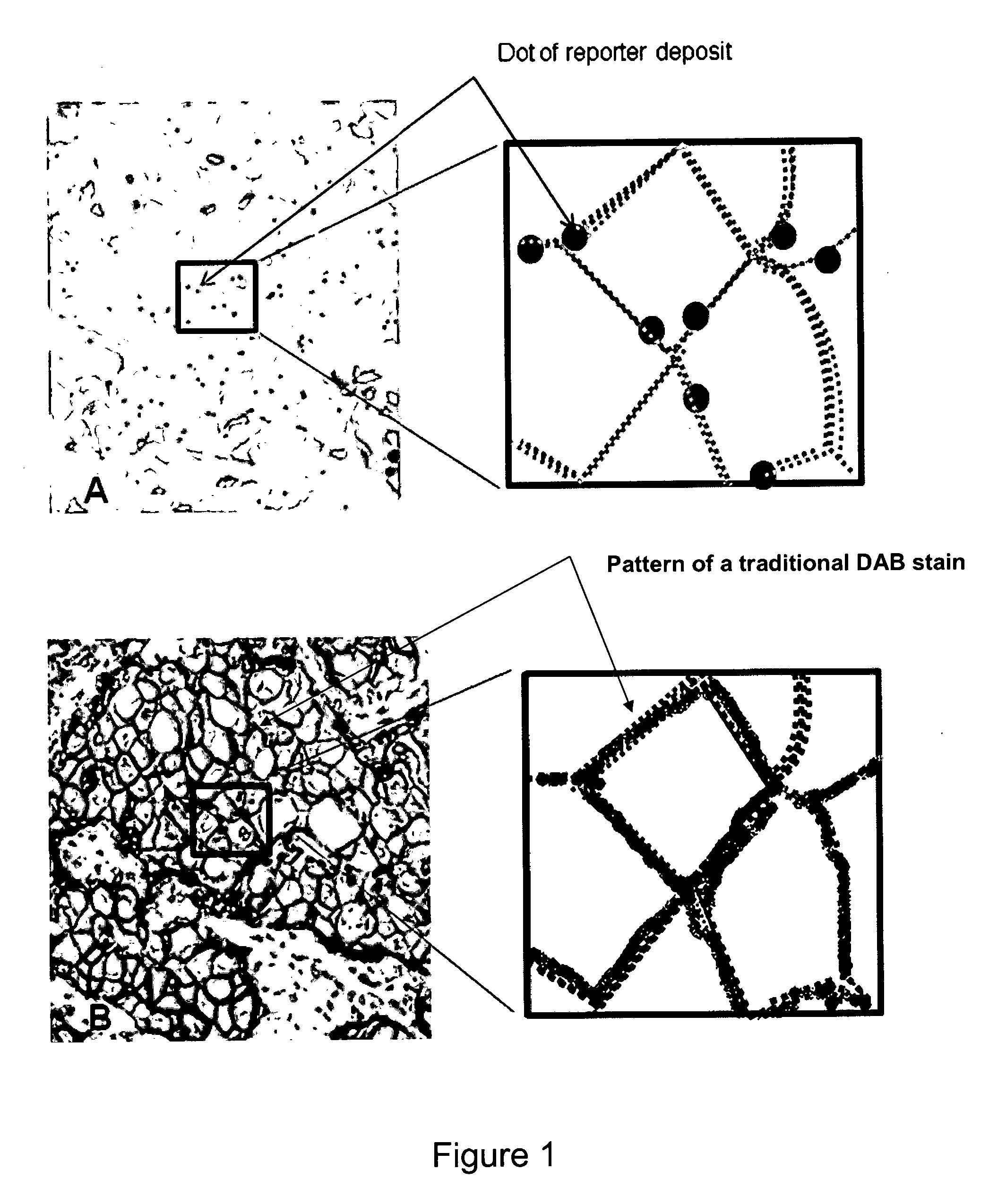
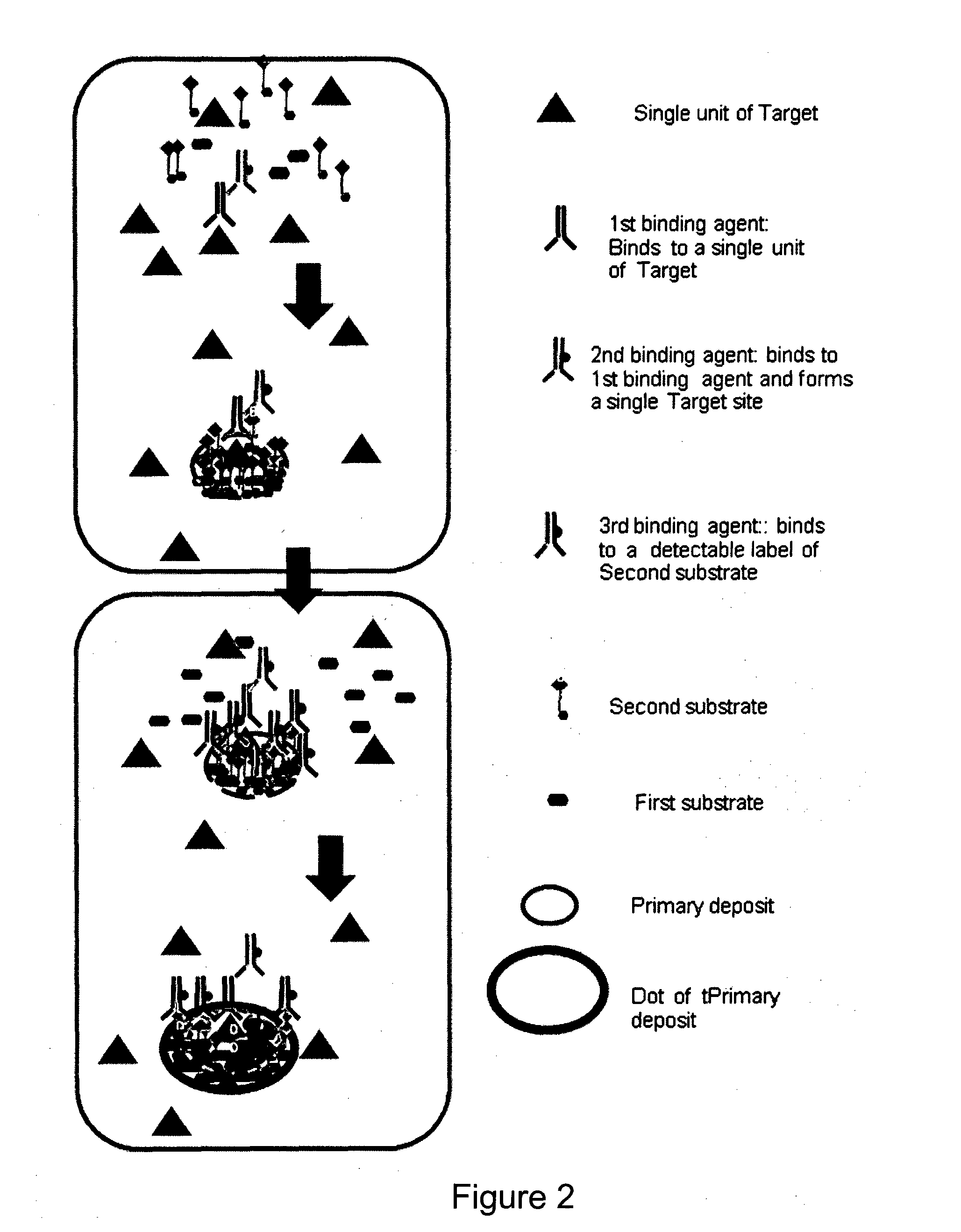
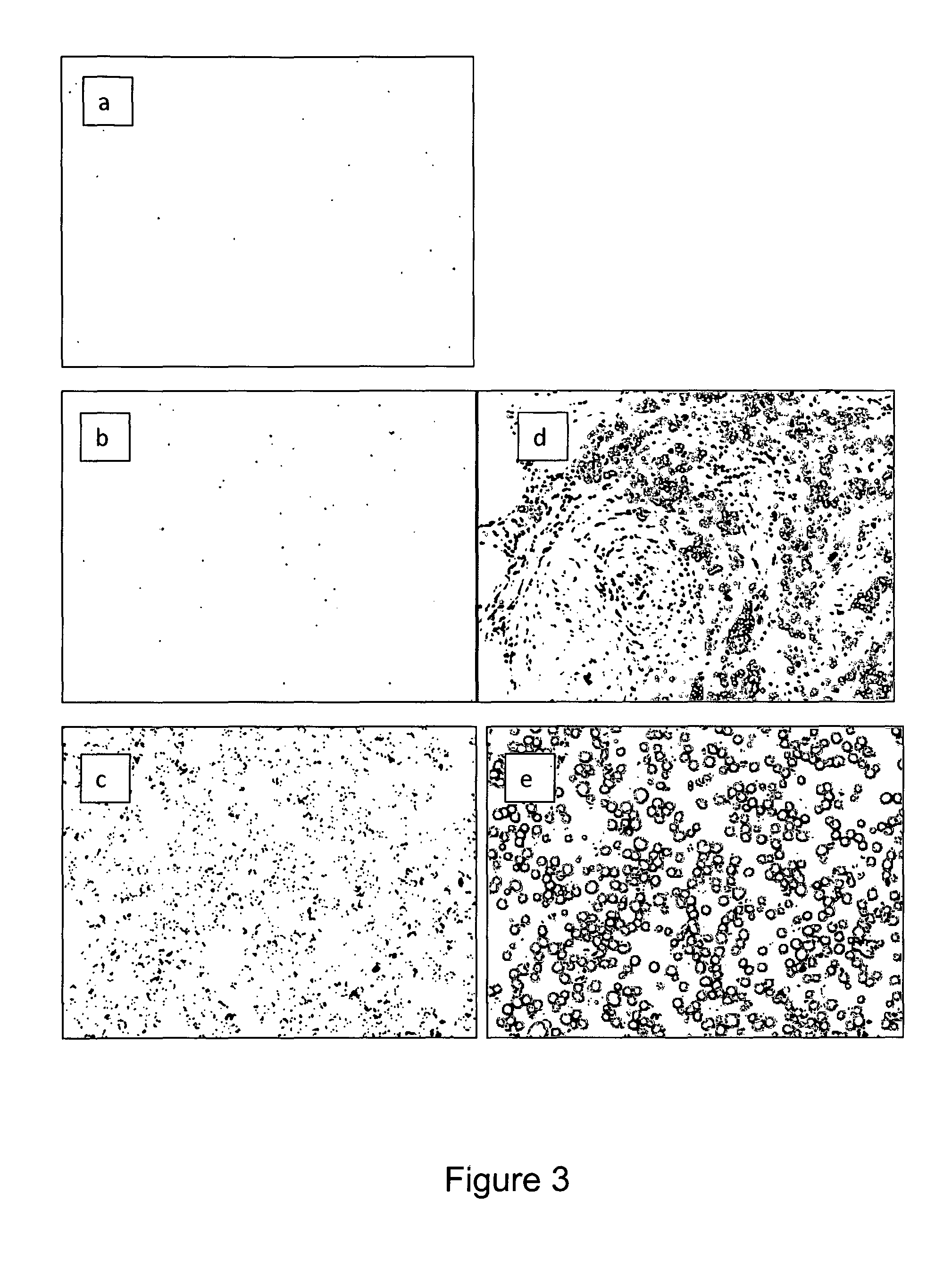
The present invention lies in the field of visualization and quantification of immobilized targets in samples using immunochemical means. The methods of the invention utilize an immunostaining system allowing visualizing single target units in samples as distinct dots. In particular, the invention relates to methods and reagents for visualization and quantification of molecular targets immunostained in histological samples and use of said method and reagents in medical diagnostic. However, the visualization and quantification methods of the invention are applicable to a variety of targets in different samples and allow precise quantifying both relative and absolute amounts thereof.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Circulating tumor cell in-vivo capturing device and circulating tumor cell in-vivo capturing method on basis of indwelling needles
InactiveCN103908306AHigh selectivityNo extra damageSurgical needlesInfusion needlesCirculating cancer cellIn vivo
The invention discloses a circulating tumor cell in-vivo capturing device on the basis of indwelling needles. The circulating tumor cell in-vivo capturing device comprises the indwelling needles. Materials capable of adsorbing proteins wrap the outer surfaces of the indwelling needles, and epithelial cell specific antibodies which are used for recognizing specificity and capturing circulating tumor cells are adsorbed on the materials capable of adsorbing the proteins. The invention further discloses a method for capturing the circulating tumor cells by the aid of the capturing device. The circulating tumor cell in-vivo capturing device and the method have the advantages that patients are transfused through the indwelling needles, so that the circulating tumor cells in the blood vessels of the patients can be captured by the modified specific antibodies on the indwelling needles during transfusion; the indwelling needles are pulled out of the patients after the transfusion is completed, so that the captured circulating tumor cells can be removed from the bodies of the patients, and are eluted by eluent; the eluted cells can be observed and counted under microscopes, or immunostaining can be carried out on target molecules to be tested in the cells, and the target molecules to be tested in the cells can be observed through confocal microscopes; the circulating tumor cell in-vivo capturing method is simple in operation, and the target cells can be efficiently and selectively captured by the aid of the circulating tumor cell in-vivo capturing method.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
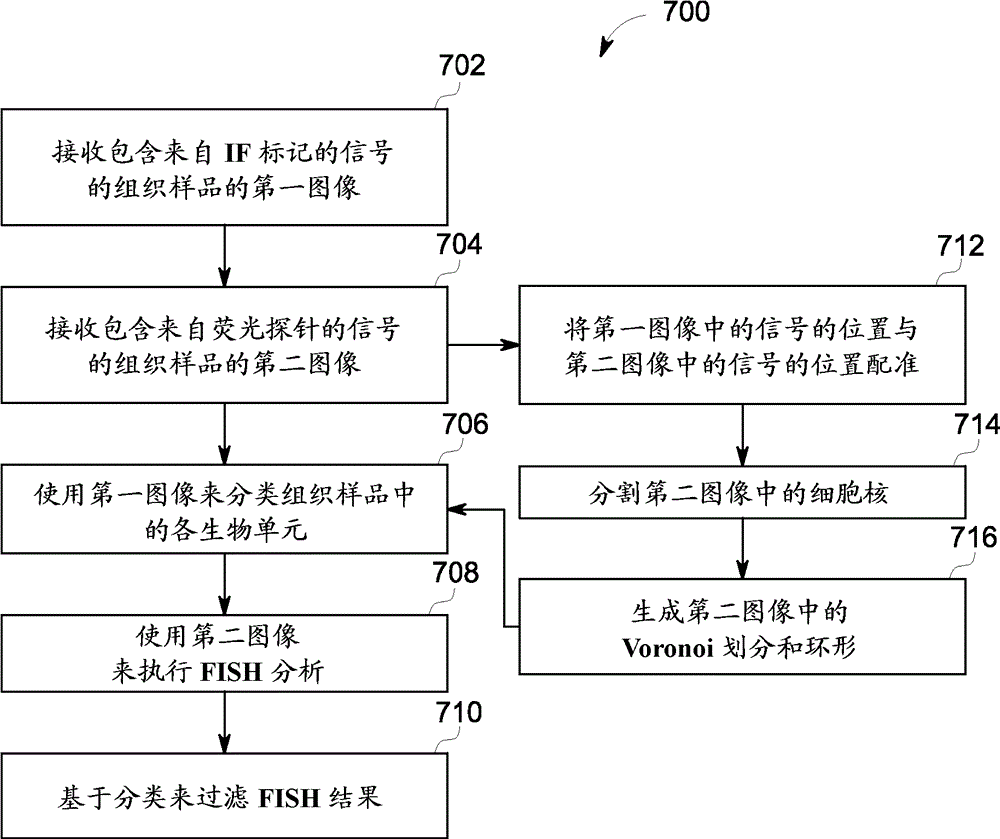
Systems and methods for using immunostaining mask to selectively refine ISH analysis results
A computer-implemented method of processing image data representing biological units in a tissue sample includes receiving a first image of the tissue sample containing signals from an immunofluorescent (IF) morphological marker, wherein the tissue sample is stained with the IF morphological marker, and receiving a second image of the same tissue sample containing signals from a fluorescent probe, wherein the tissue sample is hybridized in situ with the fluorescent probe. The method further includes classifying each biological unit in the tissue sample into one of at least two classes based on a mean intensity of the signals from the IF morphological marker in the first image, performing a fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis of the tissue sample in the second image to obtain results therefrom, and filtering the results of the FISH analysis to produce a subset of the results pertaining to biological units classified in one class.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Novel hydrophilic and lipophilic rhodamines for labelling and imaging
The invention relates to novel and improved photostable rhodamine dyes of the general structural formulae I or II and their uses as fluorescent markers, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional and stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The partially deuterated analogues are useful as molecular mass distribution tags in mass spectroscopic applications. wherein R1=an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group; R2═H, an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group, or an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group, or any combination of such groups; X═CH2, C═O, C═NORa, C═NNRaNRb, CH(ORa), O, S, SO, SO2, or any other derivatives of these groups, with Ra and Rb independently being H or an organic residue, in particular an unsubstituted or substituted (cyclo) alkyl group or heterocycloalkyl group, an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group; Z=a negatively charged group with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 charges per anion.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Methods for phenotyping of intact whole tissues
ActiveUS20160123854A1Reduced feature requirementsPreparing sample for investigationBiological testingWhole bodyTissue clearing
In various embodiments, the present application teaches methods and compositions for tissue clearing in which whole organs and bodies are rendered macromolecule-permeable and optically-transparent, thereby exposing their cellular structure with intact connectivity. In some embodiments, the present application teaches PACT, a protocol for passive tissue clearing and immunostaining of intact organs. In other embodiments, the present application teaches RIMS, a refractive index matching media for imaging thick tissue. In yet other embodiments, the application teaches PARS, a method for whole-body clearing and immunolabeling.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for quantifying immune cells in tumoral tissues and its applications
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
Polypeptides
The present invention provides pharmaceutical preparations for anti-inflammation, anti-infection, inhibition of cancer metastasis etc., foods such as dairy products etc., and a method for improving proteins, as well as a method for diagnosis of inflammatory diseases and cancer malignancy. According to the present invention, there can be provided a polypeptide having poly-N-acetyllactosamine sugar chains synthesis-related activity, a process for producing the polypeptide, DNA coding for the polypeptide, a process for producing the DNA, a recombinant vector having the DNA integrated therein, a transformant carrying the recombinant vector, an antibody recognizing the polypeptide, a process for producing poly-N-acetyllactosamine sugar chains by use of the DNA or the polypeptide, diagnosis and treatment of diseases such as inflammations, cancers etc. by use of the DNA, the polypeptide or the antibody, determination and immunostaining of the polypeptide of the present invention by use of the antibody, a method for screening a compound varying the expression of a gene coding for the polypeptide, and a method for screening a substance varying the activity of the polypeptide.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
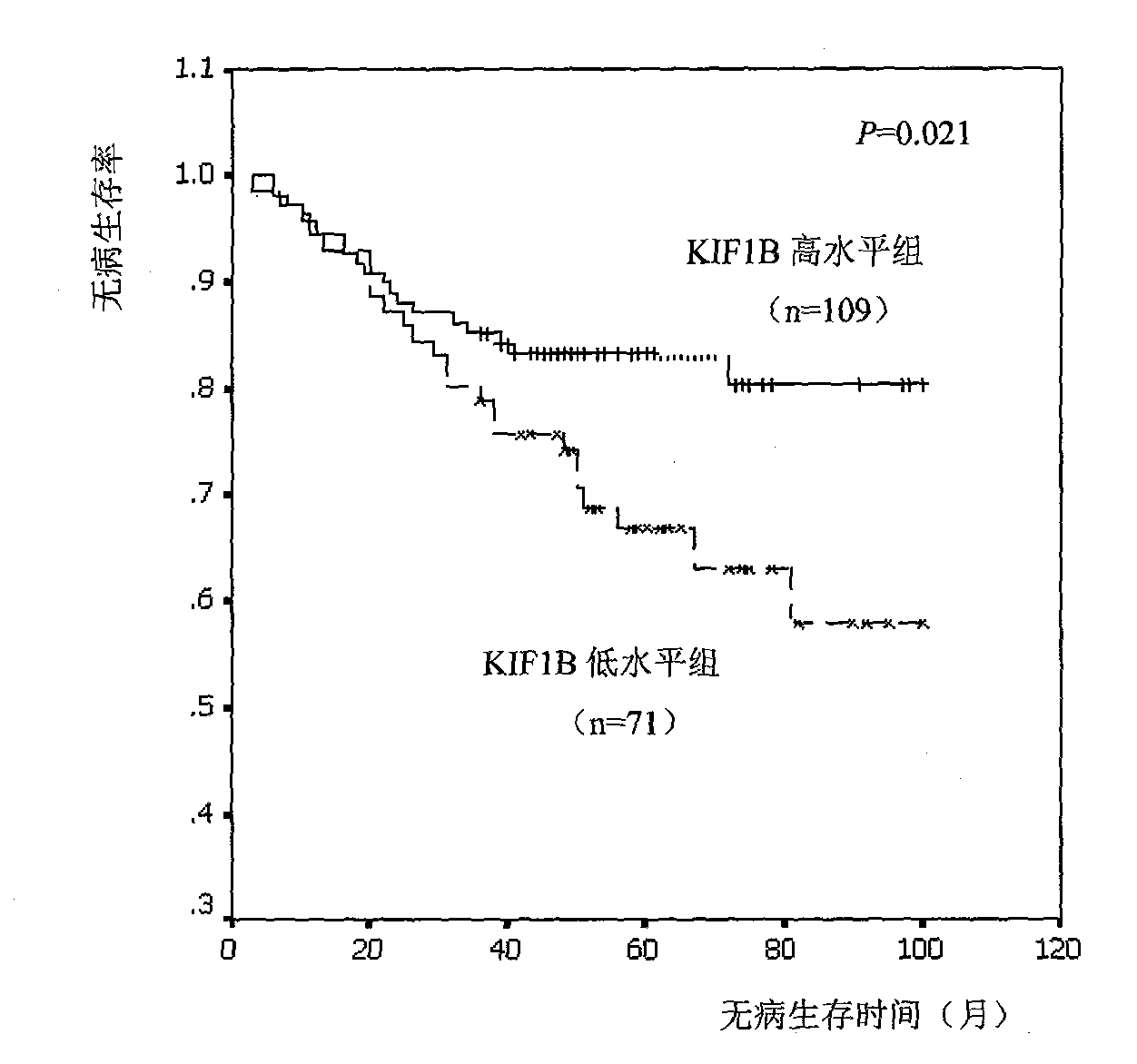
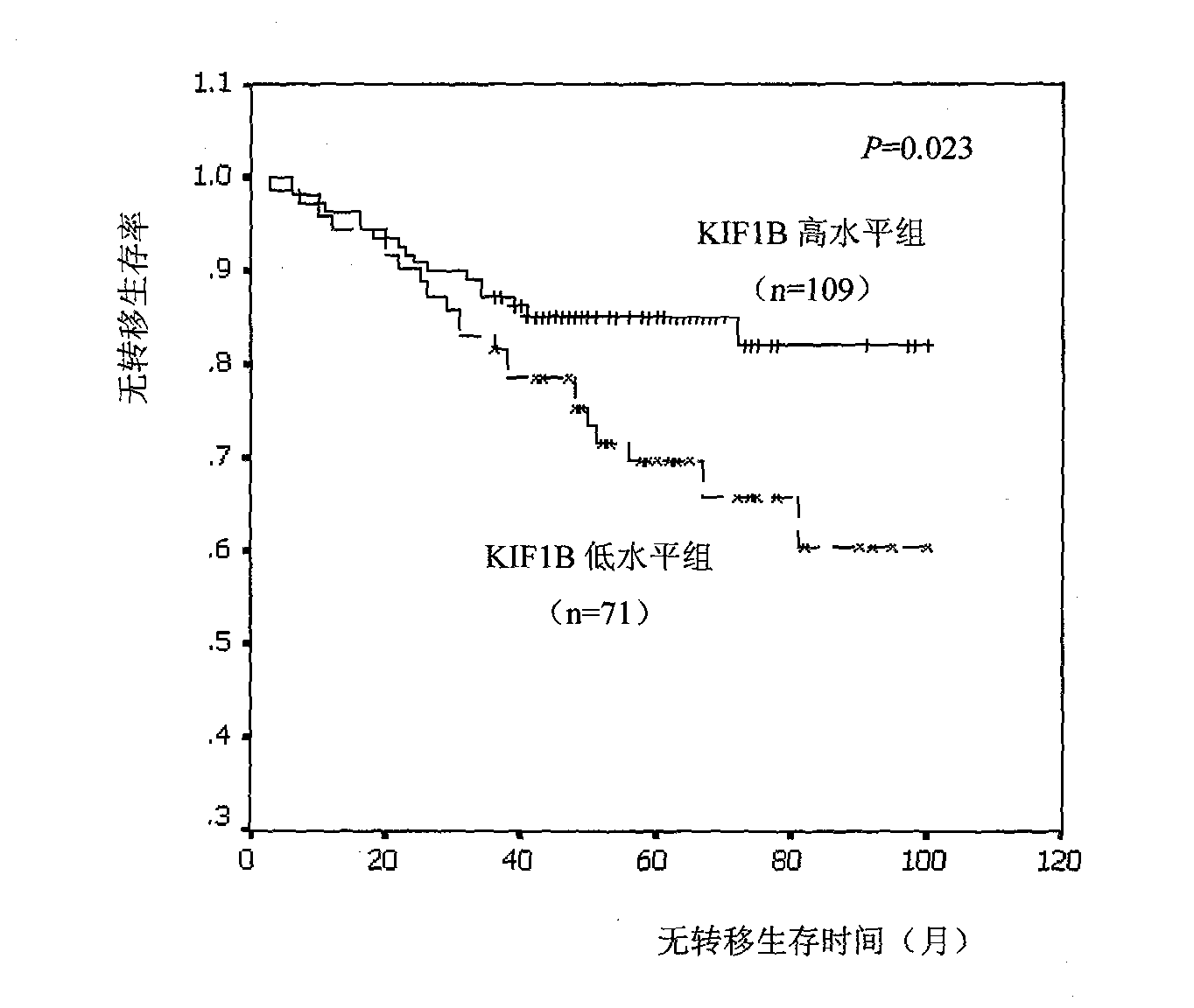
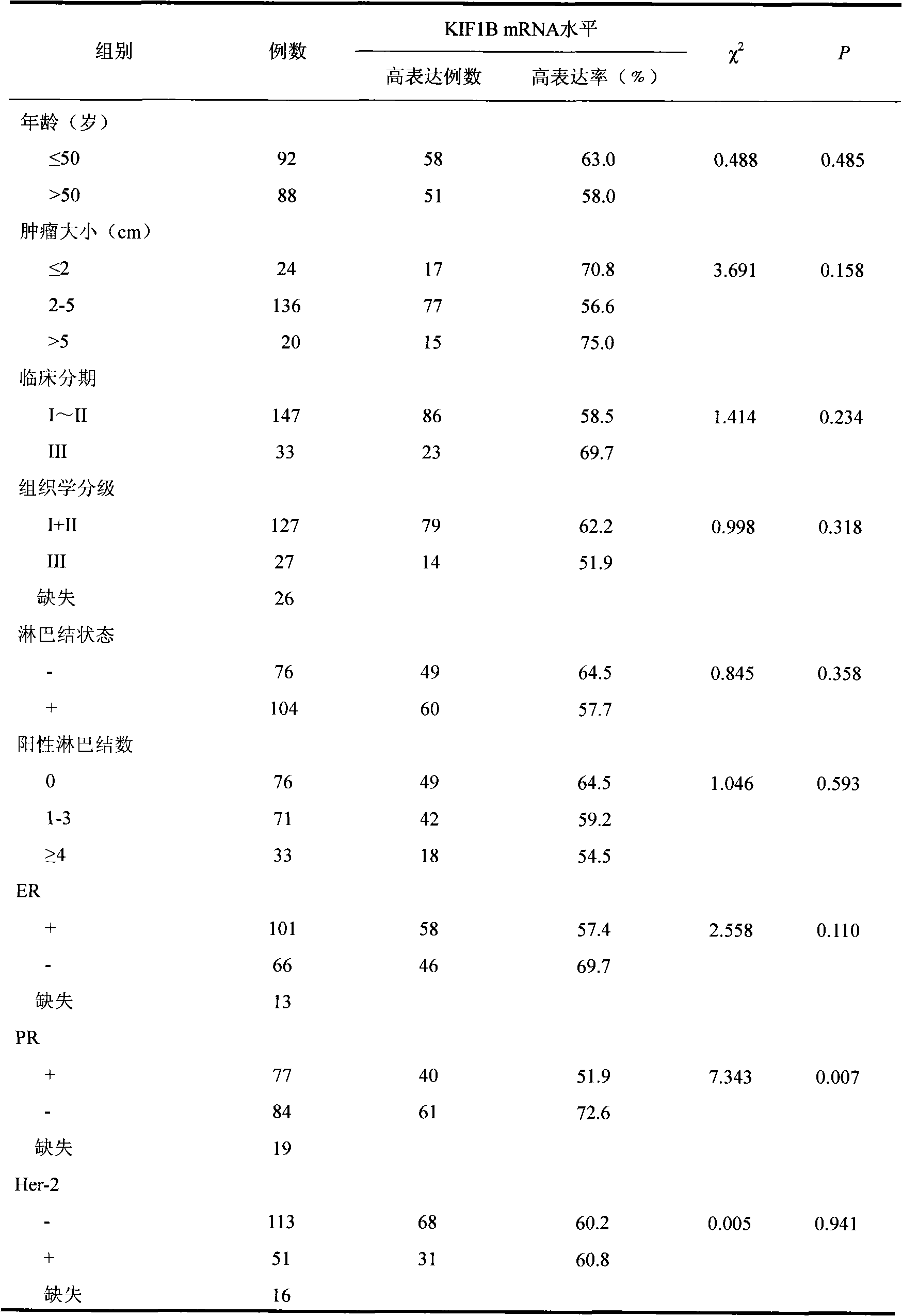
Relative transferring function of kinesin family member KIF1B, landmark application thereof in predicting tumor patient prognosis and application method thereof
The invention discloses a relative transferring function of kinesin family member KIF1B, a landmark application thereof in predicting tumor patient prognosis and an application method thereof, belonging to the technical field of tumor molecular biology. The invention discloses a relative transferring function of kinesin family member KIF1B, a landmark application of KIF1B expression level in predicting tumor patient prognosis and a detection and application method based on the KIF1B expression level in predicting tumor patient prognosis. In the method, real-time quantitative RT-PCR is carried out to detect the method for KIF1B mRNA expression level; quantitative PCR amplification comprises relative quantitative PCR amplification and absolute quantitative PCR amplification; the KIF1B expression level detection can also adopt a molecular hybridization method to detect the KIF1B mRNA expression level; an immunostaining method and / or immunoblotting method can be adopted to detect the KIF1B protein expression level; a critical value for prognosis judgment is determined according to the KIF1B gene or protein expression level in the primary cancer tissues of recurrent and metastatic positive cases and recurrent and metastatic negative cases of tumor patients; and the patient the critical value of whom is higher than the threshold value has favorable prognosis, and the patient the critical value of whom is lower than the threshold value has poor prognosis.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV CANCER HOSPITAL
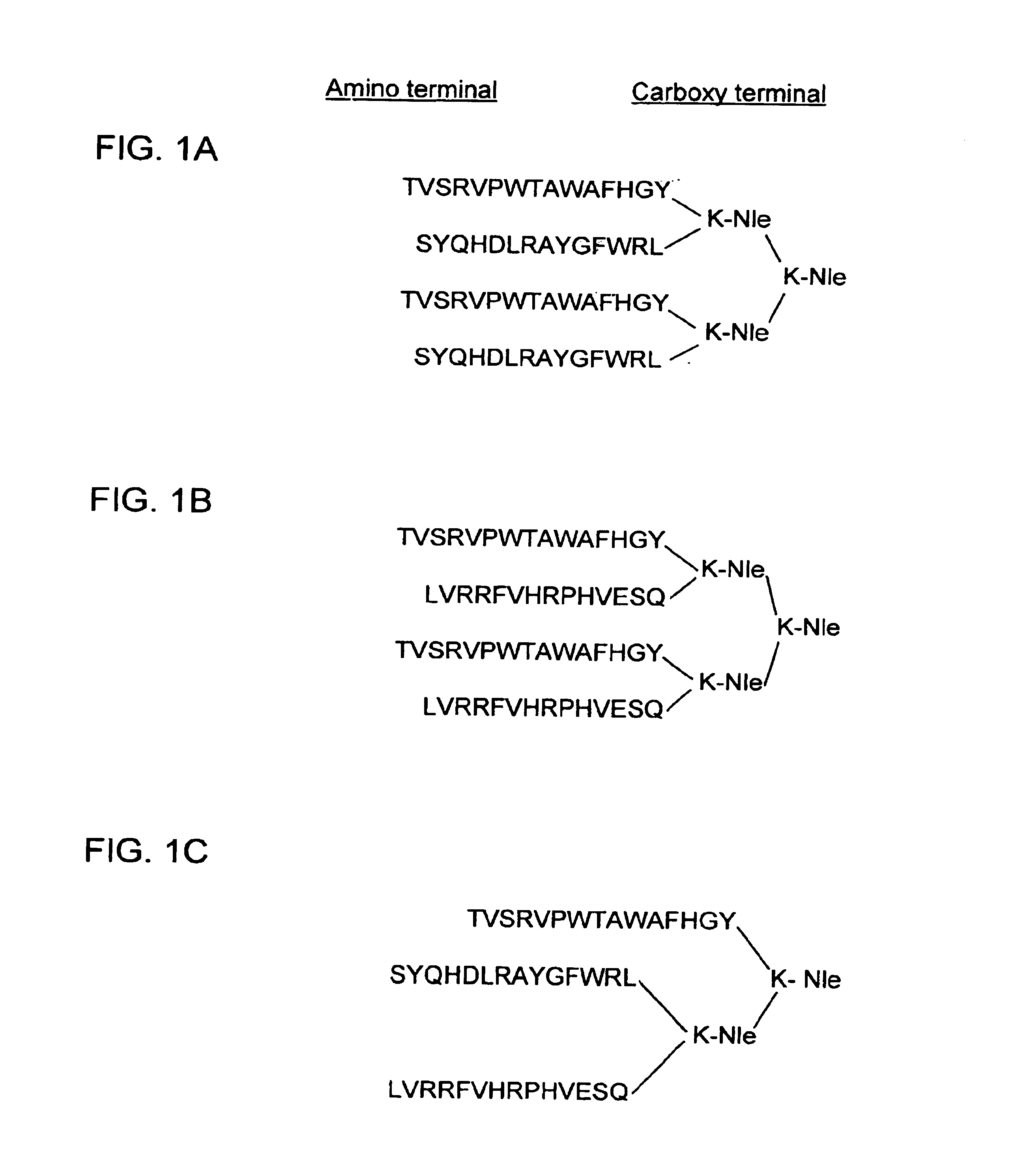
Multiple antigenic peptides immunogenic against Streptococcus pneumonia
InactiveUS6903184B1Effectively eliciting production of antibodyBacterial antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsStreptococcus pneumoniaeMonoclonal antibody
The invention provides a nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa pneumococcal surface adhesion A protein (PsaA) from Streptococcus pneumoniae. The invention also provides purified polypeptides encoded by the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein from and the nucleic acids comprising unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. Additionally, multiple antigenic peptides that provide protection against S. pneumoniae challenge are provided. These multiple antigen peptides comprise the peptides that immunospecifically bind to the monoclonal antibodies. Also provided are vaccines comprising such immunogenic peptides, and methods of conferring protective immunity against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection by administering therapeutic composition comprising the immunogenic peptides of the invention. Also provided are methods of detecting the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a sample using antibodies or antigens and methods of preventing and treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in a subject.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES REPRESENTED BY THE SEC CDC
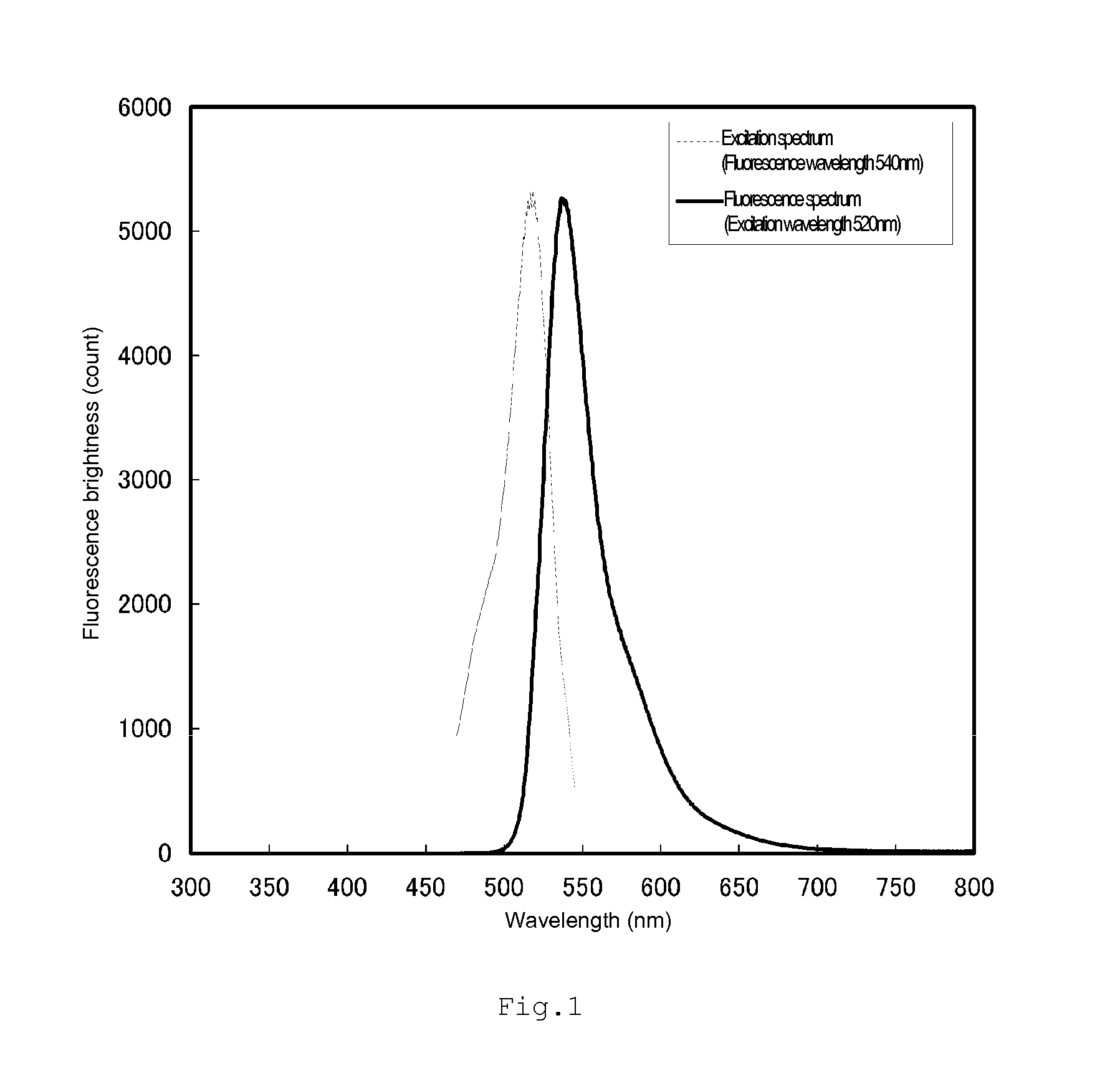
Fluorescent label for biological substance detection method
ActiveUS20140186857A1The result is accurateBiological material analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansCross-linkHalide
The present invention provides a fluorescent label that can be used for carrying out a biological substance detection method for specifically detecting a biological substance from a pathological specimen, by which method, when immunostaining using a fluorescent label and staining for morphological observation using a staining agent for morphological observation are simultaneously performed, the results of fluorescence observation and immunostaining can be assessed properly even if the fluorescent label and / or the staining agent is / are deteriorated by irradiation with an excitation light. The fluorescent label is a fluorescent dye-containing nanoparticle in which the parent material is a cross-linked polymer and the fluorescent dye is an aromatic ring-based dye molecule. The cross-linked polymer is suitably a melamine resin or a styrene resin. The aromatic ring-based dye molecule is suitably a perylene and more suitably a perylene diimide. The dye molecule can have a polar group such as sulfonic acid group or its acid halide.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Anti-human clcp1 antibody and use thereof
The present invention provides novel antibodies that recognize the extracellular domain of a human CLCP1 antigen; nucleic acids encoding the antibodies; vectors carrying the nucleic acids in an expressible manner; transformed cells containing the vectors; methods for producing the antibodies; diagnostic methods for cancer or prognosis of cancer, immunohistological or immunocytological assay methods, and kits for determining the expression level of CLCP1 in cells or tissues, all of which use the antibodies; pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies; agents for treating or preventing CLCP1-expressing cancer; agents for inhibiting growth, migration, invasion, or metastasis of CLCP1-expressing cancer cells; immunostaining agents for staining CLCP1-expressing cancer cells; and agents for treating or preventing CLCP1-expressing tumor. The present invention also provides methods of screening for candidate substances that inhibit cancer cell growth, invasion, migration, or metastasis, or candidate substances having cytotoxicity against cancer cells.
Owner:MEDICAL & BIOLOGICAL LAB CO LTD
Device used for repeated immunostaining of same tissue slice
PendingCN106289923APrevent disengagementEasy to dyePreparing sample for investigationTissue sampleTissue specimen
In order to implement repeated immunostaining of a same tissue slice to save a tissue sample and meet the diagnosis requirement, the invention discloses a device for repeated immunostaining of the same tissue slice. The device is characterized by comprising a slide glass groove and a cover glass; the slide glass groove is provided with an upper groove and a lower groove which are mutually continued, and the size and the shape of the upper groove are matched with the size and the shape of the cover glass; the lower groove is located in the center of the bottom part of the upper groove, and the bottom part is flat; one face, facing downwards, of the cover glass is attached with the tissue slice; the tissue slice is located in a space formed by the cover glass and the lower groove. By using the device, the same tissue slice is subjected to repeated immunostaining and pictures are taken for the same tissue slice.
Owner:NANCHANG DEMANDUO TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com